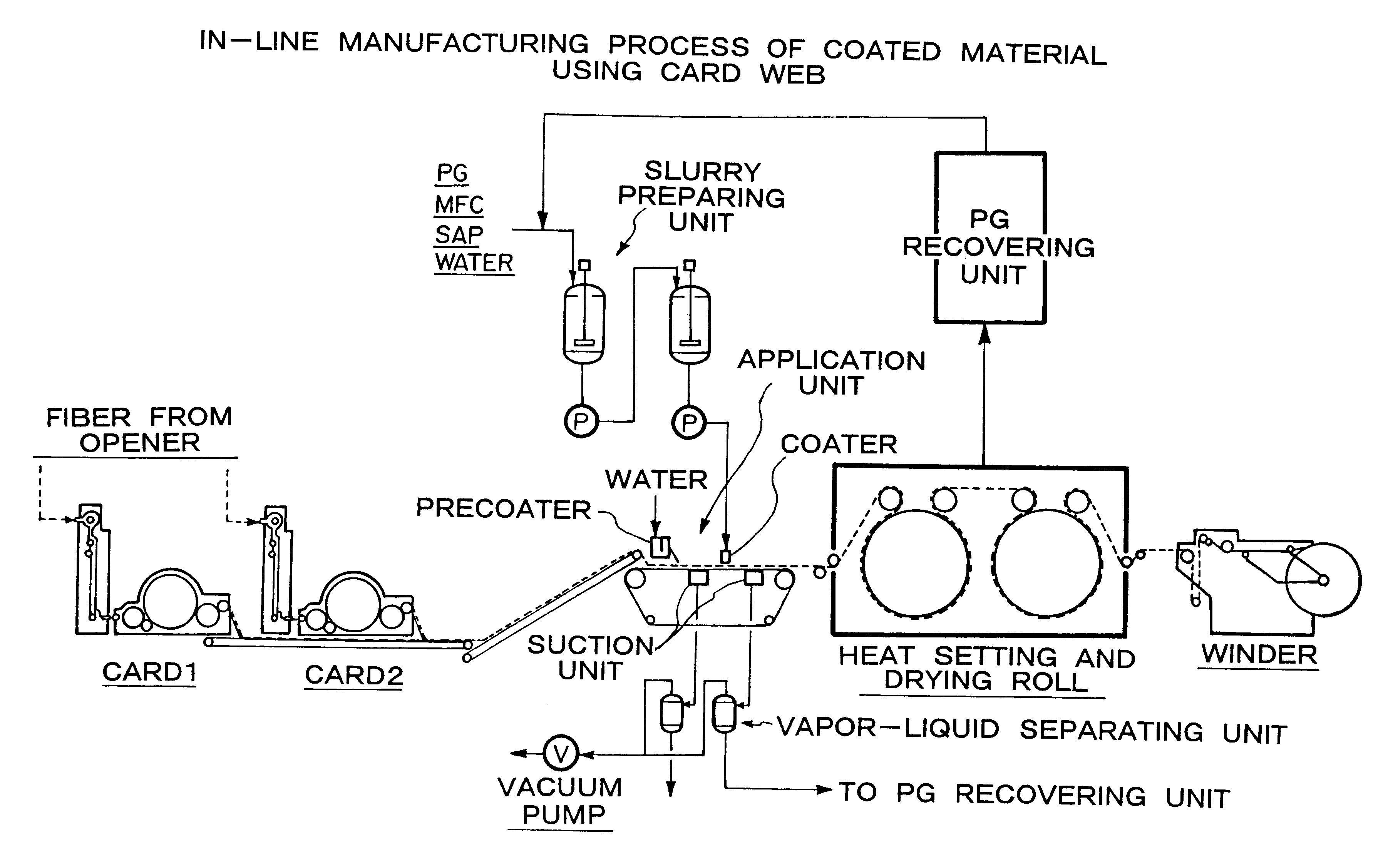
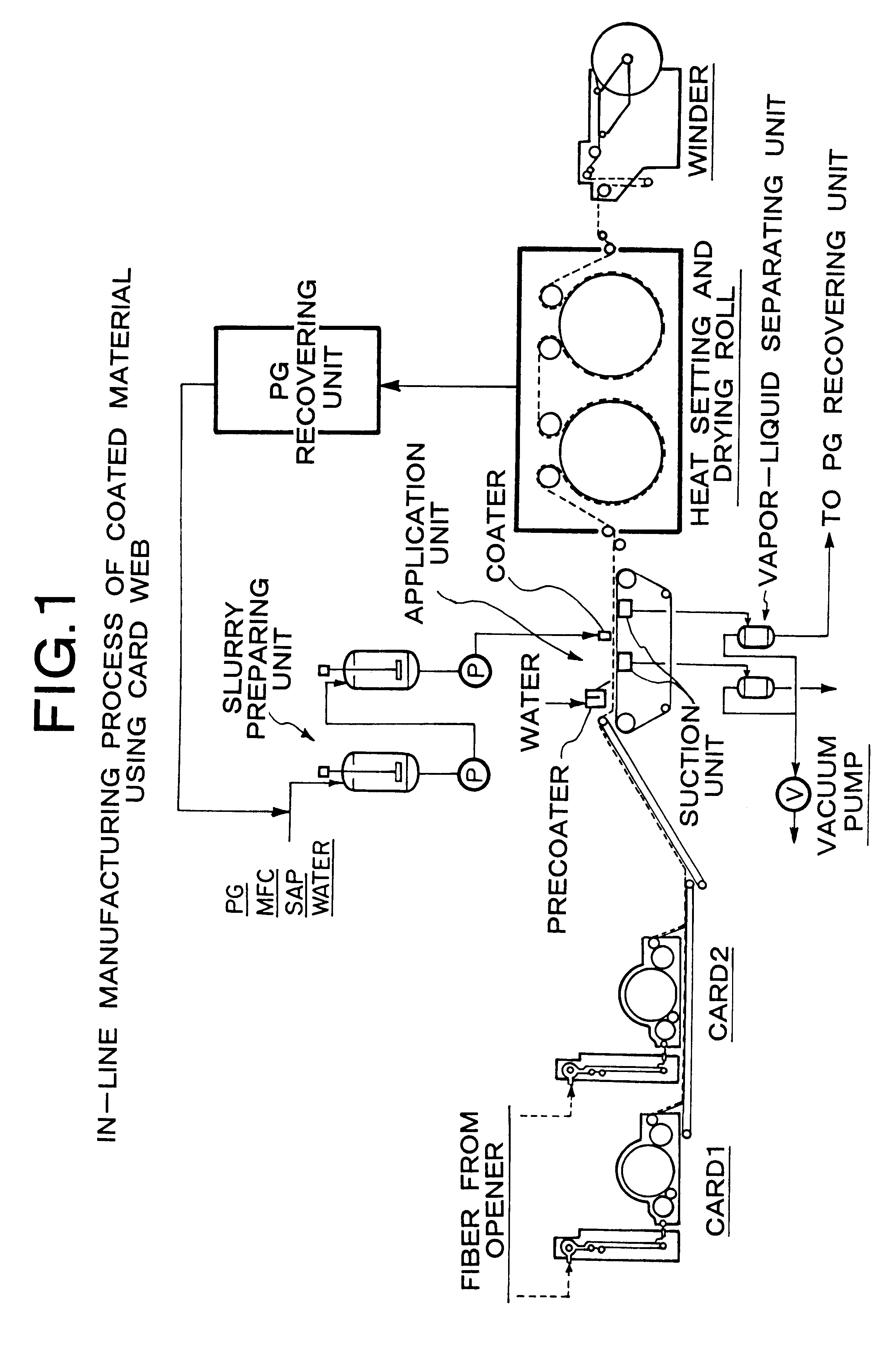
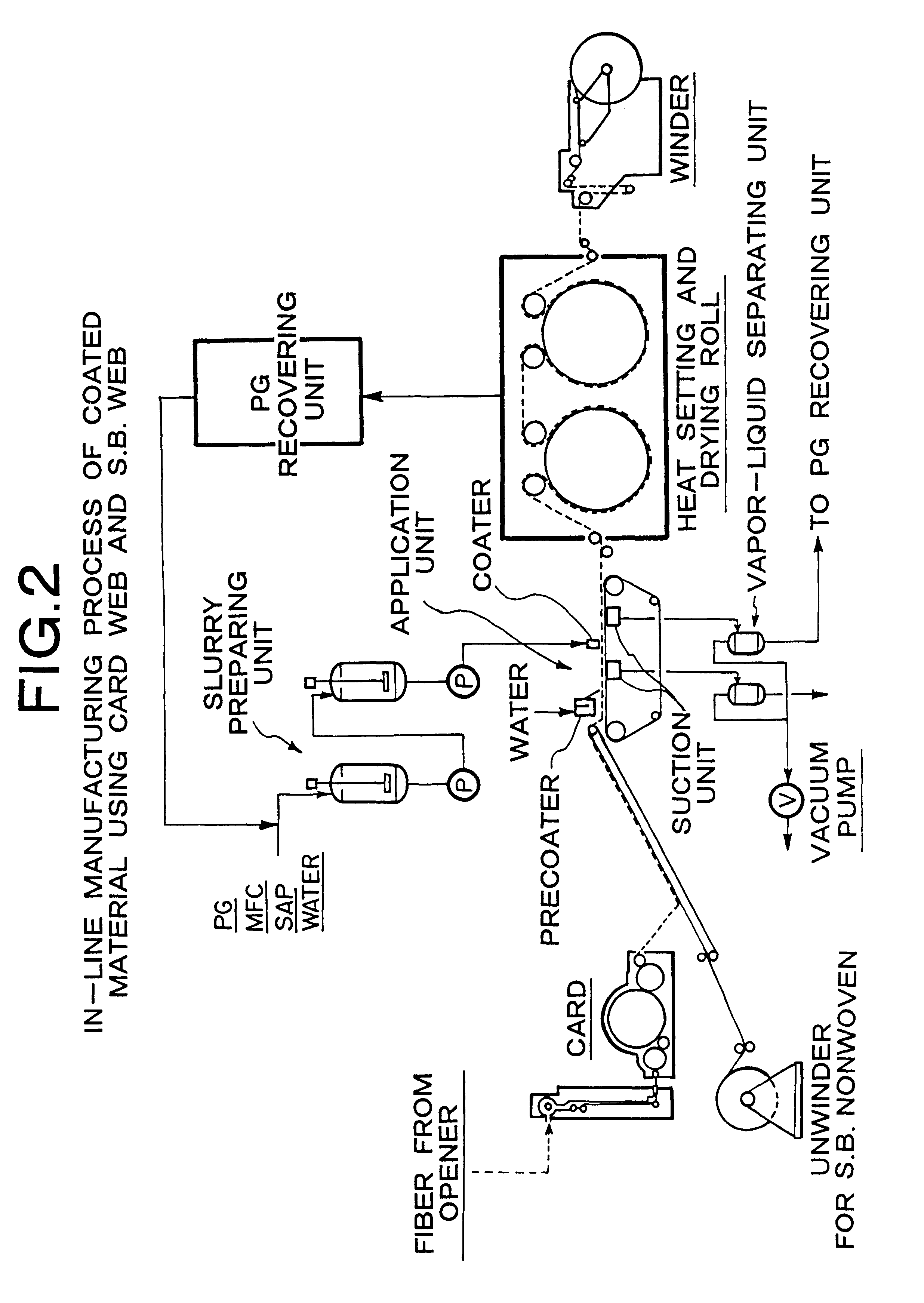
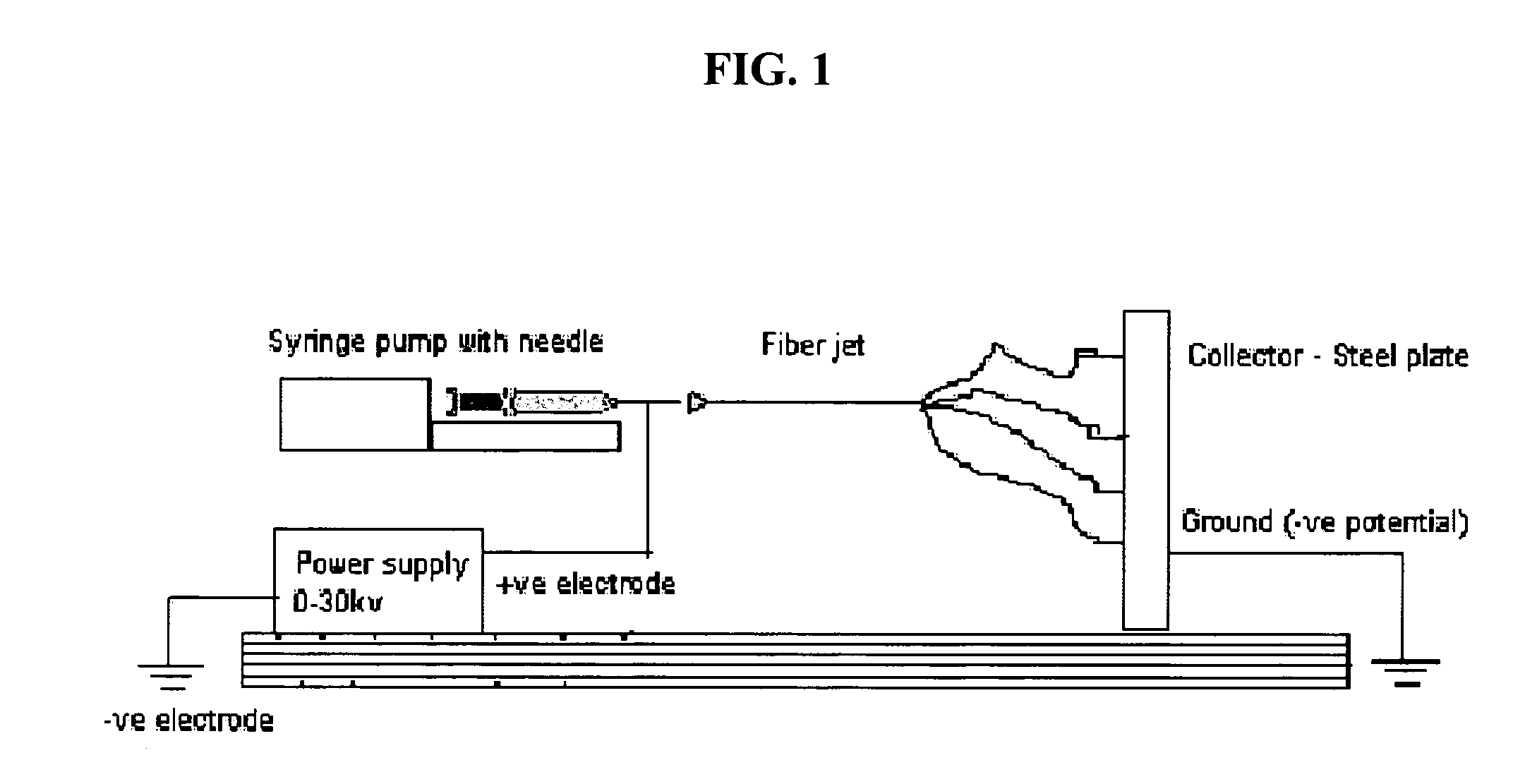
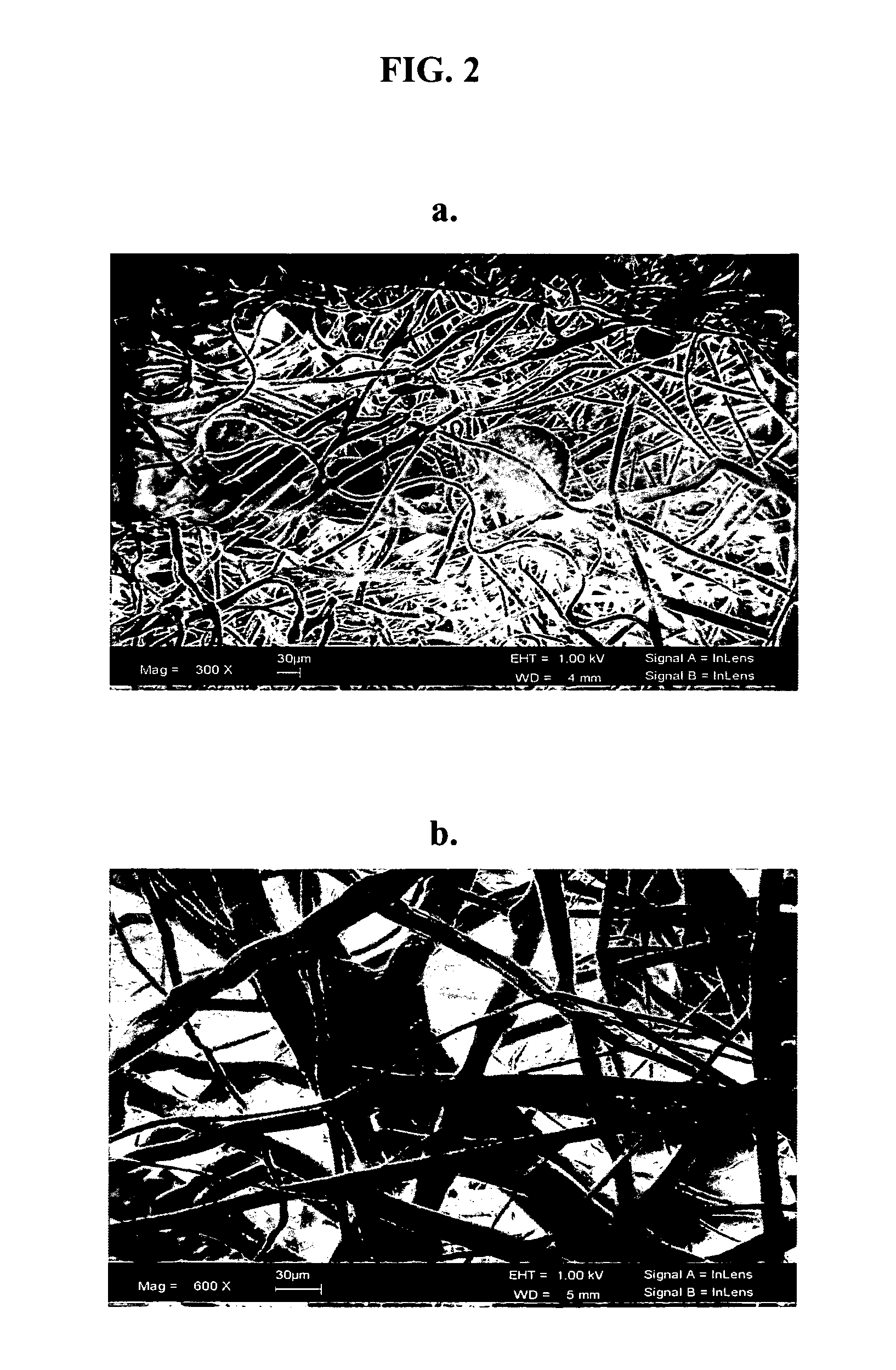
Patents
Literature
501 results about "Fiber matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
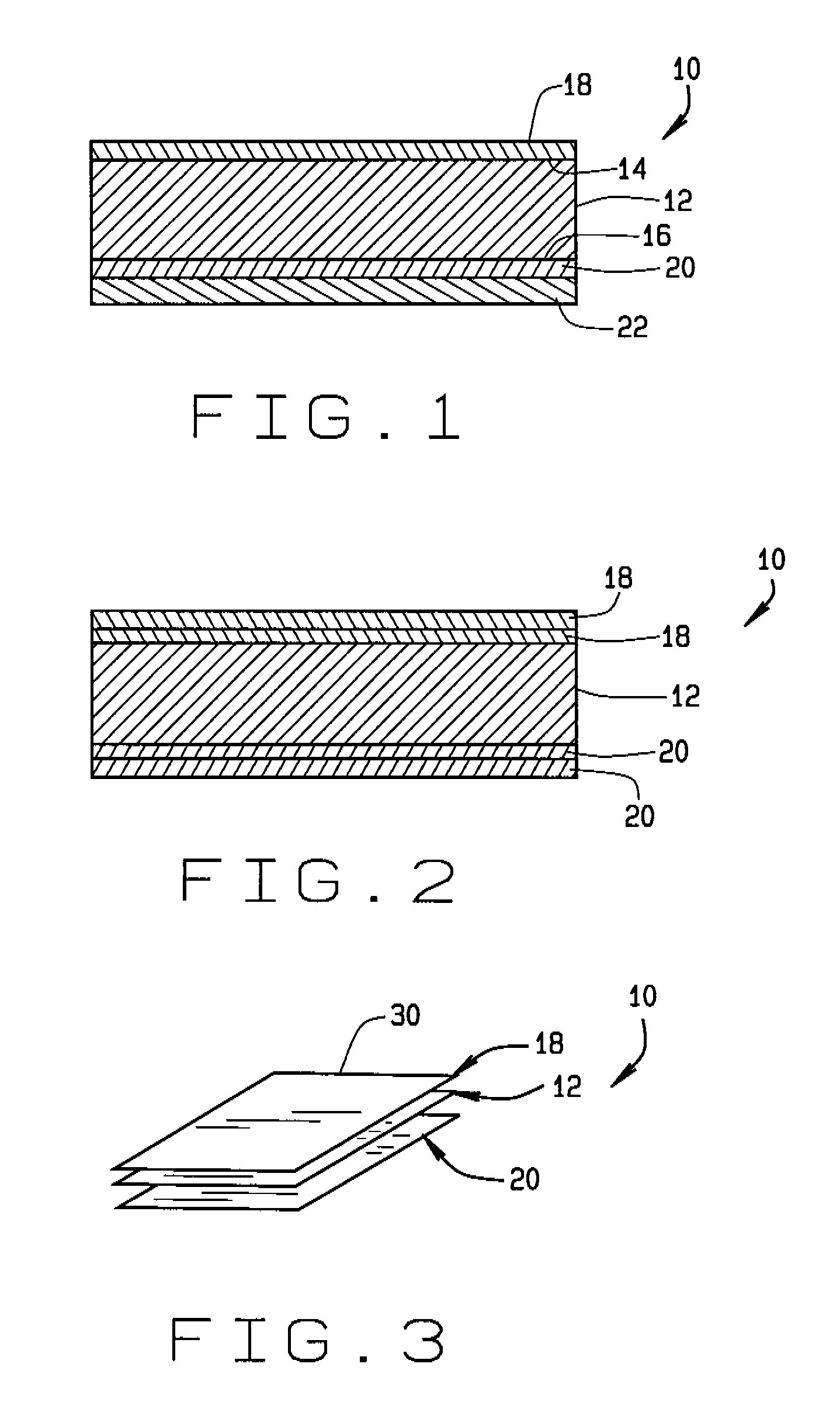
TheraCell has developed a proprietary patented process to make fibers from demineralized bone and with those fibers, using textile processes to make a range of unique products. The TheraFuze DBF™ demineralized bone fibers in TheraCell's Fiber Matrix™ products are osteoinductive and osteoconductive and can be formed into a number of shapes.
Medical articles incorporating surface capillary fiber
Medical devices are described that comprise surface capillary (SCF) fibers, which can impart desirable properties to the devices. For example, implantable prostheses are described comprising SCF fibers. In other embodiments, catheters are described having SCF fibers along the surface of the catheters. In addition, SCF fibers can be useful for the delivery of bioactive agents in association with the fibers. Due to the fluid flow capabilities of the fibers, medical devices are described that incorporate fiber matrices to facilitate blood delivery to cells within the structure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
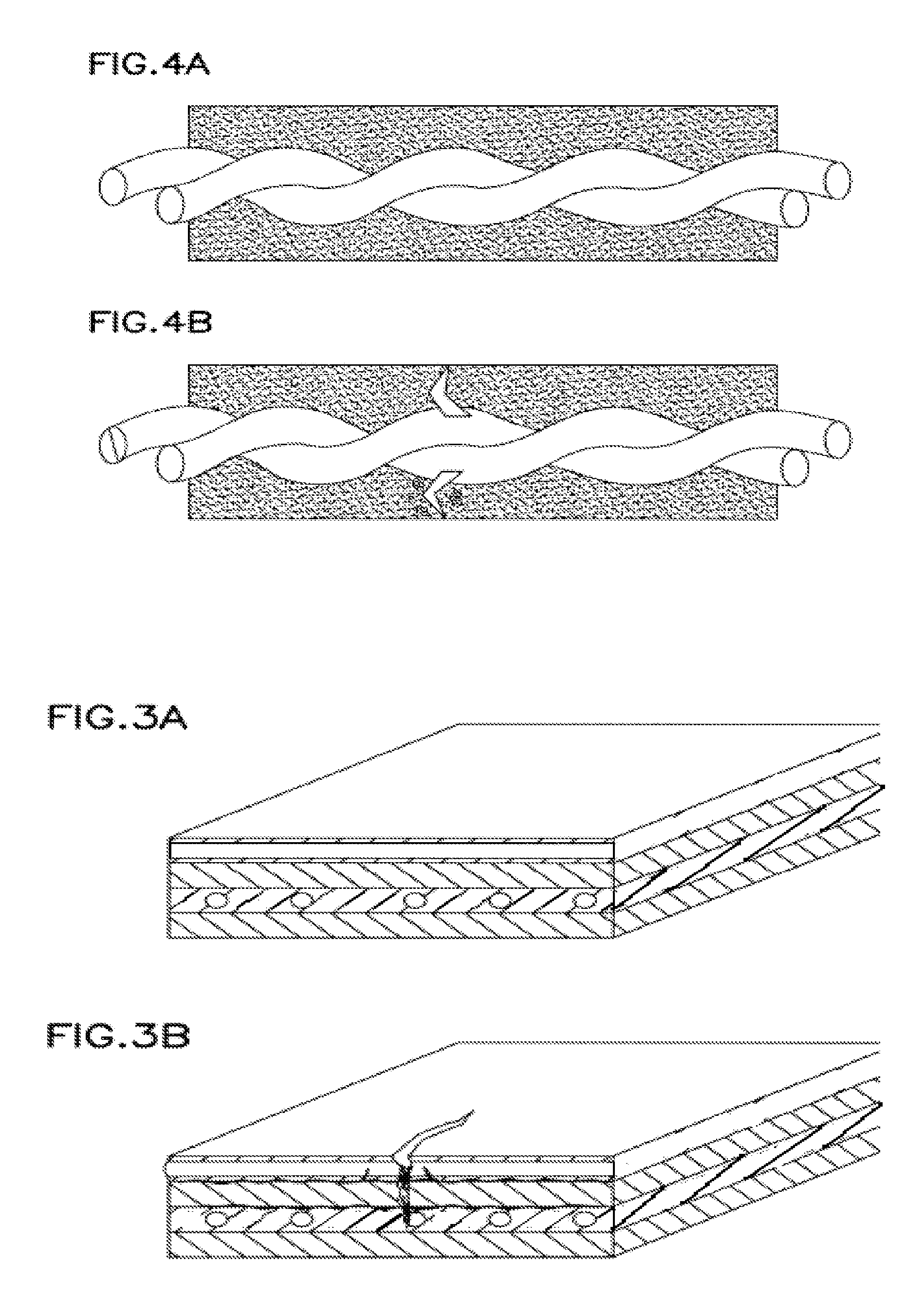
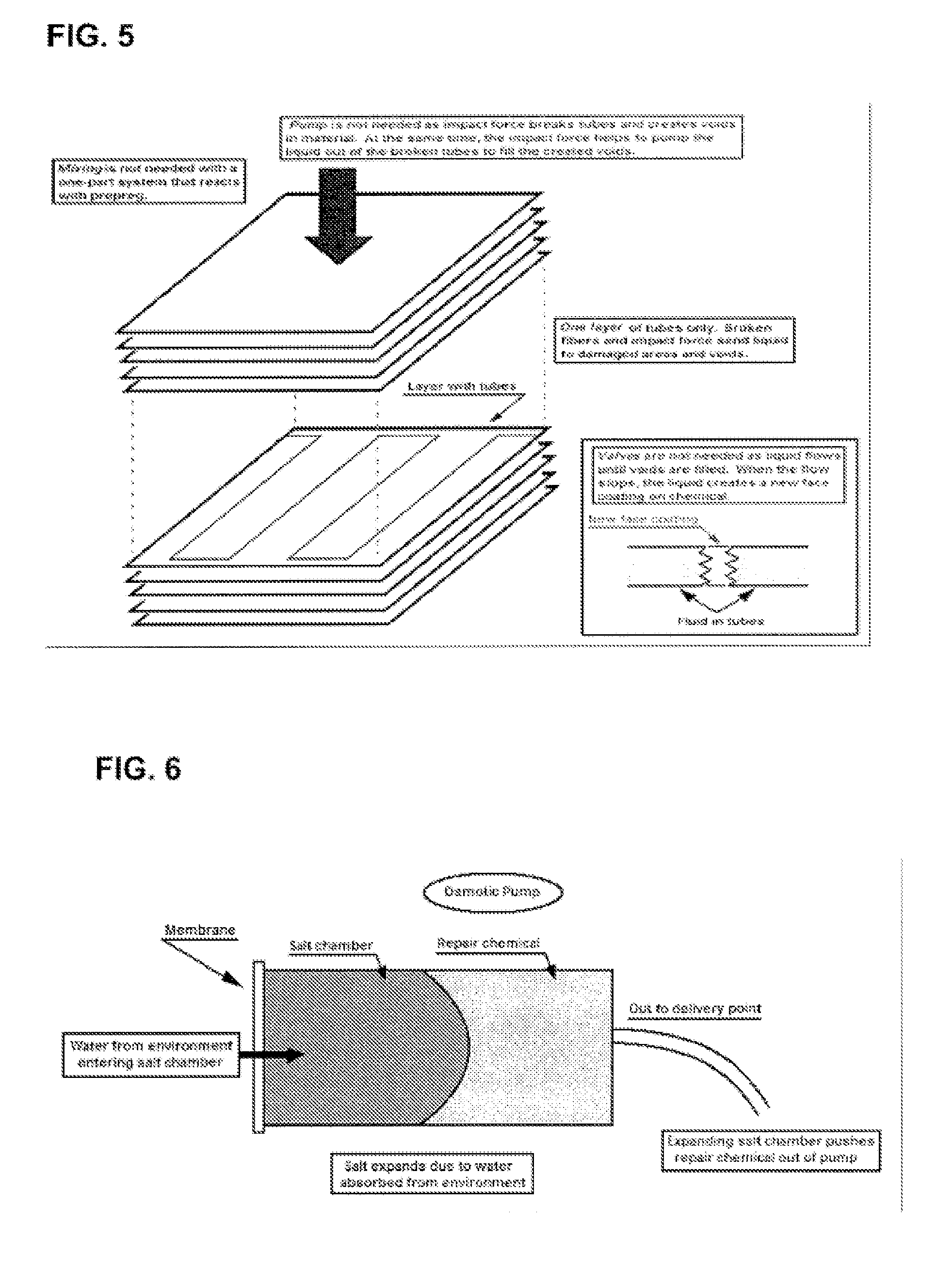
Multiple function, self-repairing composites with special adhesives
InactiveUS20070087198A1Fast chemical reactionExtended shelf lifeLayered productsConstructions elementsFiber matrixChemical substance
A system for self-repairing matrices such as concrete or cementitous matrices, polymeric matrices, and / or fibrous matrices, including laminates thereof. The system includes repair agents retained in and / or on vessels, such as hollow fibers, within the matrix. Upon impact, the vessel rupture, releasing the chemicals. For multi-layer laminates, the systems provides a total dynamic energetic circulation system that functions as an in situ fluidic system in at least one layer or area. The energy from the impact ruptures the vessels to release the chemical(s), and mixes the chemical(s) and pushes the chemical(s) and / or resulting compound through the matrix. The repair agents can withstand high temperatures, such as the heat of processing of many laminates, e.g., 250-350° F.
Owner:DRY CAROLYN
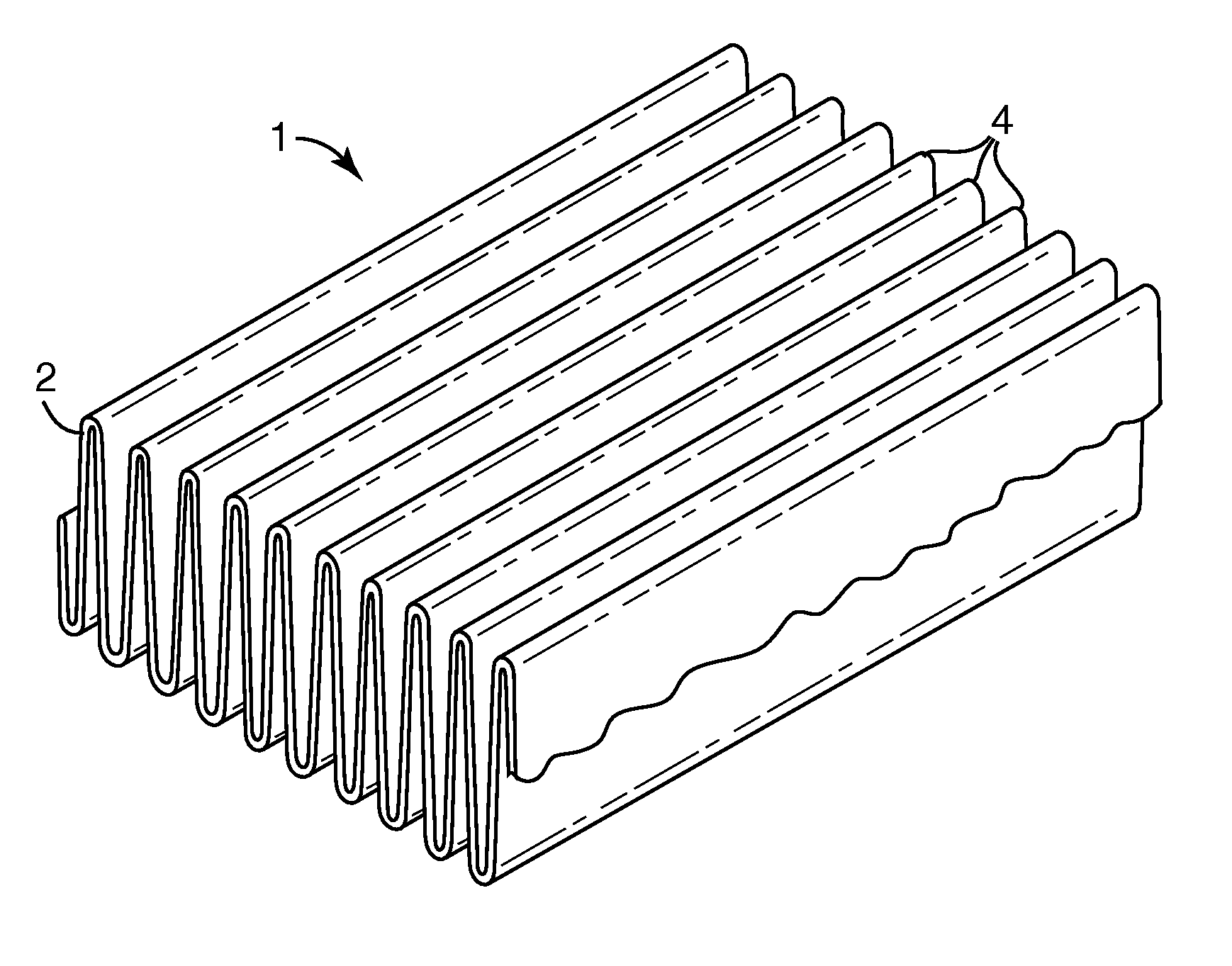
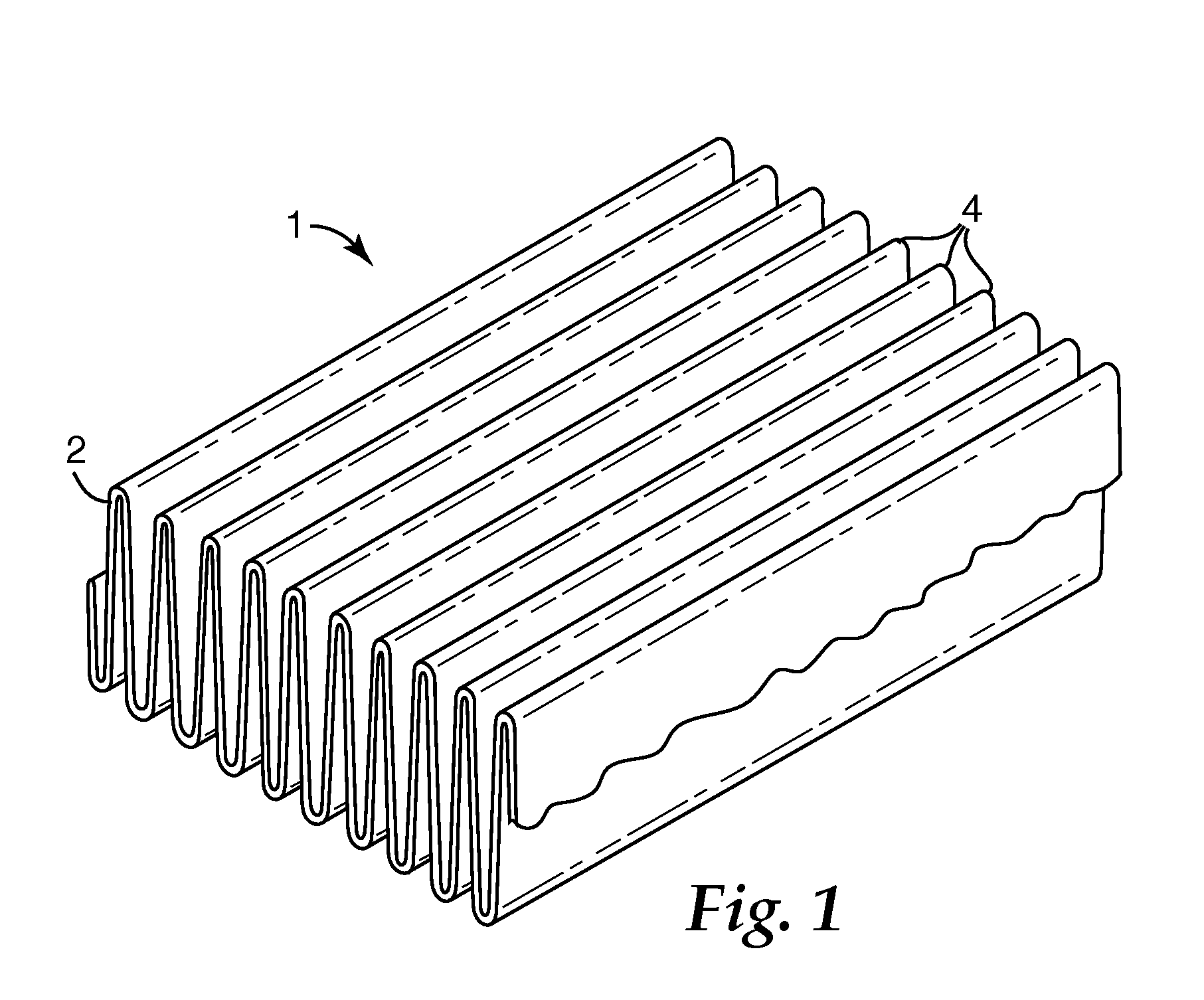
Pleated filter with bimodal monolayer monocomponent media
InactiveUS20080022643A1Improve filtering effectIncrease fiber surface areaDispersed particle filtrationLoose filtering material filtersPolymer scienceFilter media
A pleated filter is made from a monocomponent monolayer nonwoven web containing a bimodal mass fraction / fiber size mixture of intermingled larger size and smaller size continuous monocomponent polymeric fibers of the same polymeric composition. Rows of pleats are formed in the nonwoven web, and the pleated web is cut to a desired size and shape to provide a filter element containing a self-supporting porous monocomponent monolayer matrix of fibers bonded to one another at at least some points of fiber intersection and having an average initial submicron efficiency of at least 15% at a 1.52 meters / sec face velocity. The filter element is deformation resistant without requiring stiffening layers, bicomponent fibers or other reinforcing measures in the filter media layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Cell storage and delivery system
Cell storage and delivery systems and methods for storing and delivering viable cells to a mammal are disclosed. The cell storage and delivery systems include a biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fibrous matrix physically associated with viable cells to contain and release the cells at a controlled rate. The biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable matrix can be formed by electrospinning fibers of biodegradable and / or bioabsorbable fiberizable material. The methods include methods for storing viable cells and for delivering viable cells to a mammal using the cell storage and delivery system.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Super water-absorbent composite and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS6540853B1Low costBenefit is optimisedNon-fibrous pulp additionWood working apparatusFiberPolymer science
An absorbent composite sheet mainly consisting of a fibrous substrate web, a super absorbent polymer, and a bonding component bonding both of them with each other, wherein (a) the fibrous substrate web is a non-bonded web with a few of the constituent fibers bonded with each other, (b) a liquid mixture system is used of a medium mainly consisting of the super absorbent polymer and the bonding component, (c) a composite web is formed by adding the liquid mixture system to the fibrous substrate web, and (d) a liquid component is separated from the composite web so that fixing of the super absorbent polymer to the fibrous substrate web and bonding of the webs of the fibrous substrate web with one another are carried out at the same time. Methods of manufacturing such absorbent composite sheets are also provided.
Owner:DSG INT LTD
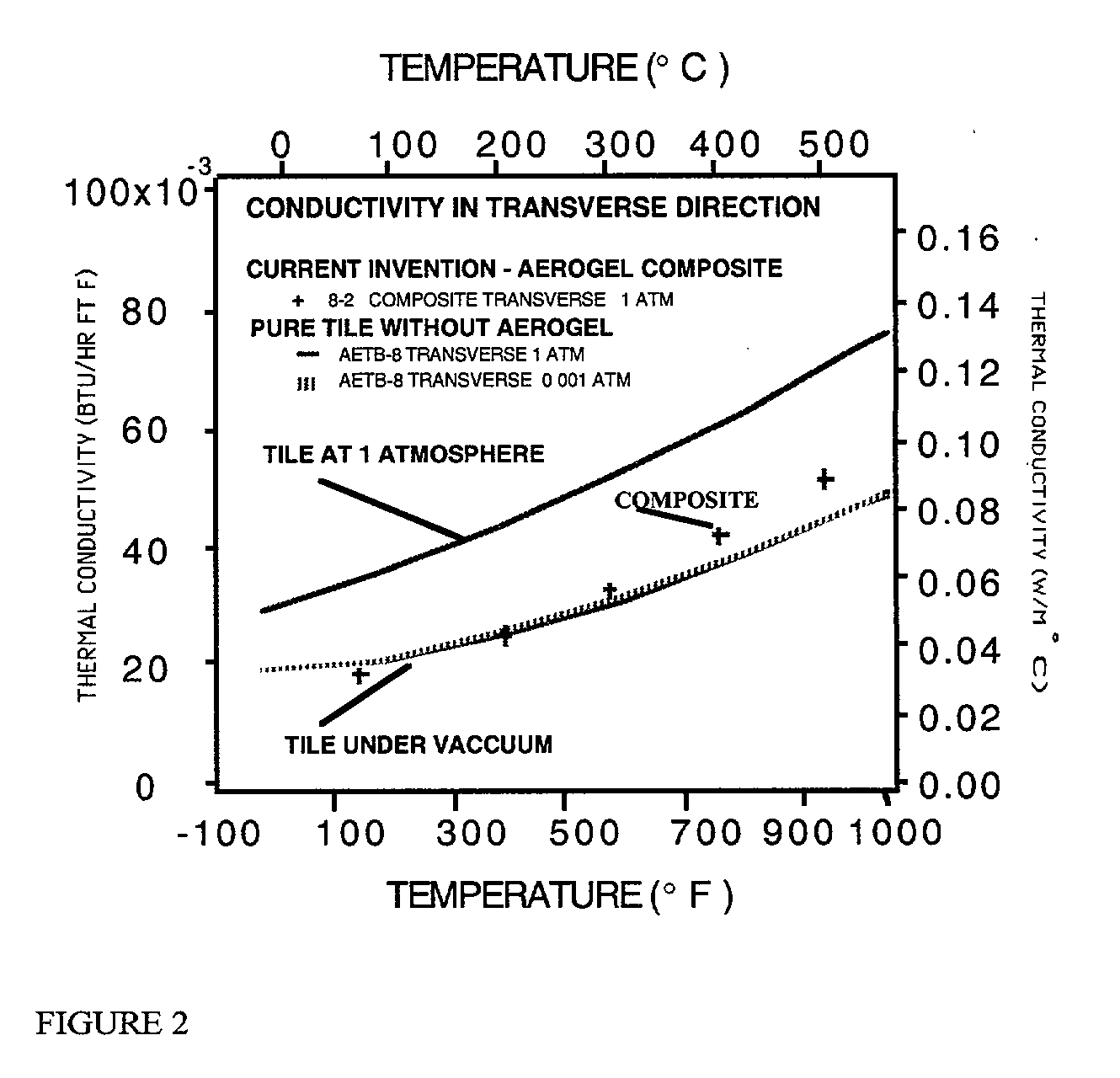
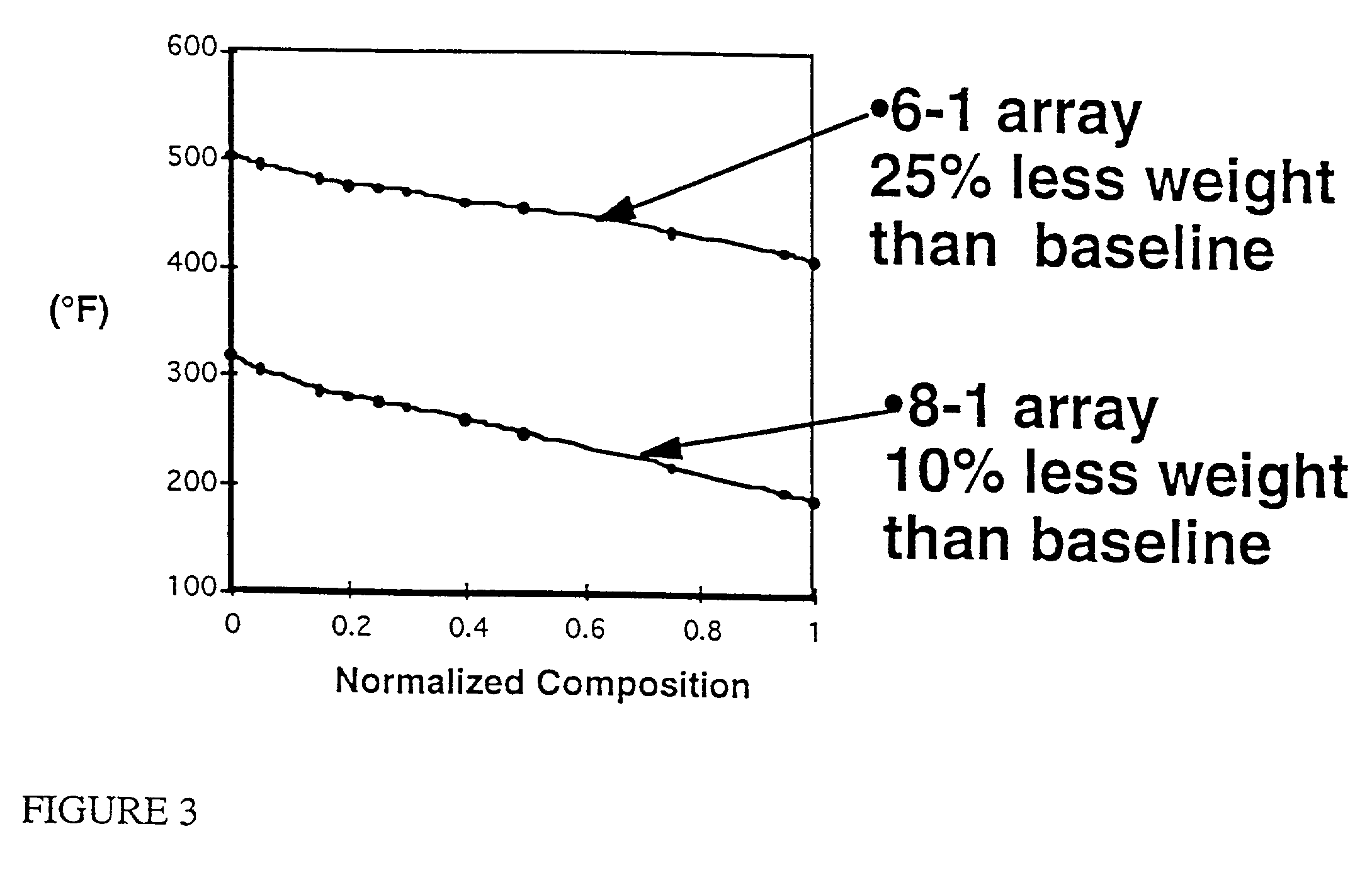
Aerogel loaded tile composite material
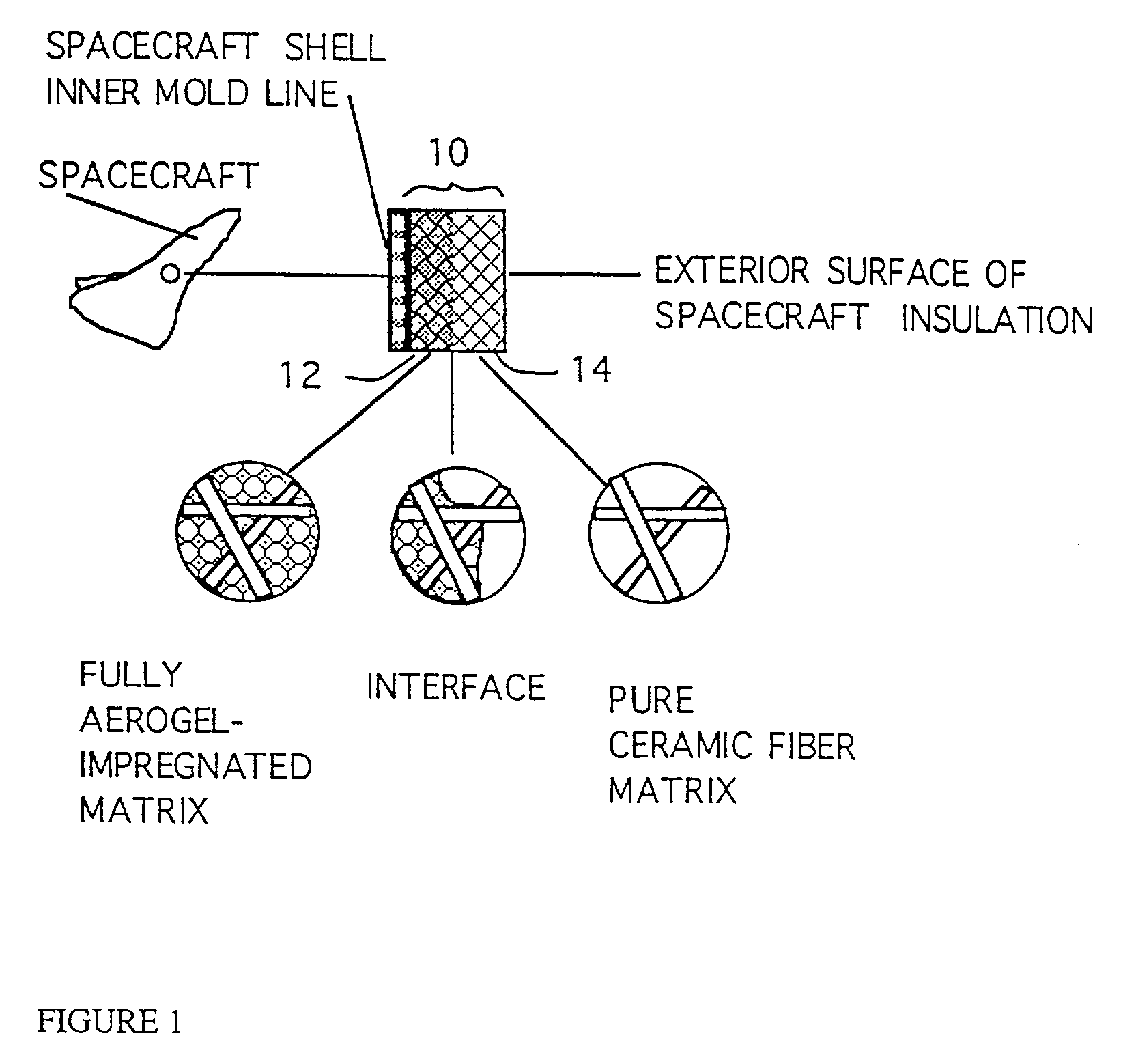
InactiveUS20020061396A1Avoid condensationImprove insulation performanceSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic layered productsTotal thicknessFiber matrix
A composite material having a preferably rigid preformed ceramic fiber matrix at least partially impregnated with an aerogel and forming a multi-layered material. The matrix is impregnated with an aerogel material which forms a layer having a total thickness r where r is less than t or equal to t, where t is the thickness of the matrix, thus forming a single or multilayered composite material. The material may be formed with numerous layers s1, s2, S3, . . . snn where r=SIGMAsn and r is less than or equal to t. Thus, a multi-layered material is formed. Alternatively, the aerogel / fiber matrix composite has channels devoid of aerogel.
Owner:NASA
Inflatable heating device for in-situ repair of conduit and method for repairing conduit
InactiveUS7052567B1Extend the life cycleRobust and heatingConfectionerySweetmeatsElastomerResin matrix
The apparatus of the present invention is generally characterized by a heating / inflation module having pressurizable interior and an attached heat curable pre-preg. In particular, an elastomeric, seamless composite is provided that includes a heating element disposed within a thermoset resin matrix. The composite adapted to maintain a consistent temperature profile and an internal air pressure. A first end piece is attached to a first end of the composite and has an air port for communication with a compressed air source, a vacuum port for communication with a vacuum supply source and at least one electrical cable port for communication with a power supply source. A second end piece attached to a second end of the composite. The apparatus further includes a pre-preg removably attached to an outer surface of the composite. The pre-preg includes a structural fiber matrix supporting a heat curable resin. The composite is constructed by applying a liquid silicone matrix to at least one layer of braided or wound and / or tape fibers, wherein a portion of the fibers are electrically conductive. The layer of braided fibers is introduced into a mold, and a removable, expandable inner bladder is then loaded into the mold. The inner bladder is inflated to conform the layer of braided fibers to an interior surface of the mold. An electric current is caused to flow to the conductive fibers to cure the silicone matrix into a stable, elastomeric state. The composite is removed from the mold. A method for repairing a damaged section of a conduit is also disclosed.
Owner:EMS USA HLDG I +1
Pleated filter with monolayer monocomponent meltspun media
ActiveUS20080022642A1Good molding effectReduce lossesDispersed particle filtrationLaminationFilter mediaEngineering
A pleated filter is made from a monocomponent monolayer nonwoven web of continuous monocomponent meltspun partially crystalline and partially amorphous oriented fibers of the same polymeric composition that are bonded to form a coherent and handleable web having a Gurley Stiffness of at least 100 mg and which further may be softened while retaining orientation and fiber structure. Rows of pleats are formed in the nonwoven web, and the web is cut to a desired size and shape to provide a pleated filter element containing a self-supporting porous monocomponent monolayer matrix of fibers bonded to one another at at least some points of fiber intersection and having an average initial submicron efficiency of at least 15% at a 1.52 meters / sec face velocity. The filter element is deformation resistant without requiring stiffening layers, bicomponent fibers, adhesive or other reinforcement in the filter media layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Carbon-carbon composite article manufactured with needled fibers
InactiveUS20060177663A1Manufacturing EaseReduce layeringLayered productsTextiles and paperCarbon compositesCarbon fibers
Method of making a carbon-carbon composite article such as an aircraft brake disc. The method includes: selecting carbon fiber precursors, having limited shrinkage in the axial direction when carbonized, in the form of individualized chopped or cut fibers; placing the selected chopped or cut carbon fiber precursors into a preform mold configured in the form of a brake disc to form a fibrous matrix; and then needling the molded fibrous matrix to provide it with three-dimensional structural integrity and to reduce layering. The carbon fiber precursor matrix may subsequently be infused with liquid carbon matrix precursor, the impregnated matrix may be carbonized; e.g., at 600-1800° C. for 1-10 hours to provide a preform having a density of at least about 1.1 g / cc, and the carbonized preform may be further densified to a density of at least about 1.6 g / cc by known liquid resin infiltration techniques and / or by conventional CVI / CVD processing.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Substrate recognition by differentiable human mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS20060128012A1Effective therapyPulse automatic controlFilament/thread formingFiberNanofiber
The invention described herein provides a structure for growing isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, which includes a three-dimensional matrix of fibers. The matrix serves as an implantable scaffolding for delivery of differentiable human mesenchymal cells in tissue engineering. The invention further provides compositions that contain the three-dimensional matrix of fibers seeded with isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, wherein the matrix forms a supporting scaffold for growing the isolated differentiable human mesenchymal cells, and wherein the differentiable human mesenchymal cells differentiate into a mature cell phenotype. The invention further provides methods of preparing the implantable nanofiber matrix scaffolding seeded with differentiable human mesenchymal cells for use in tissue engineering.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Carbon composite materials comprising particles of metal carbides dispersed therein and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20070166546A1Excellent abrasion resistanceReduce weightLayered productsBraking discsCarbon compositesCarbon fibers
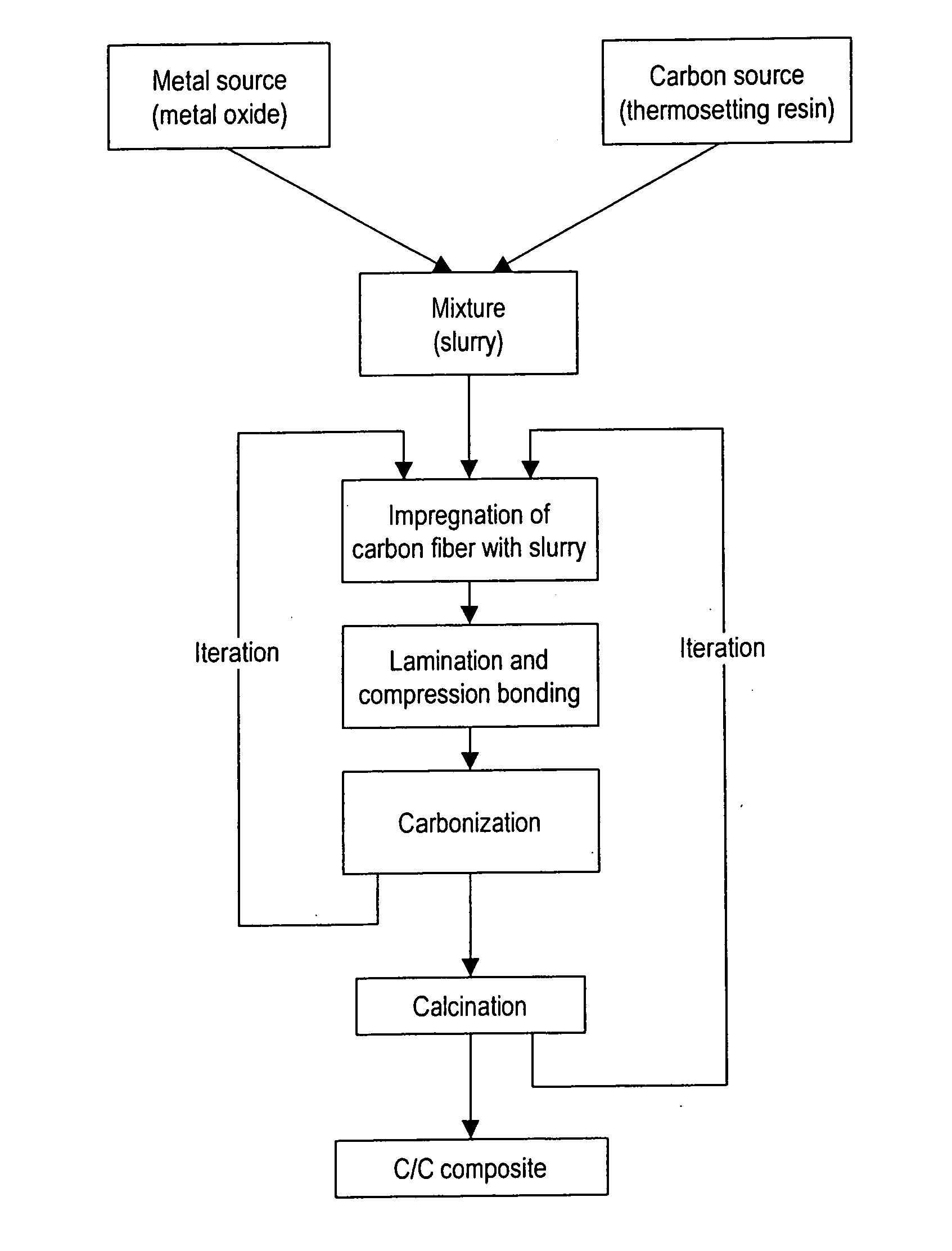
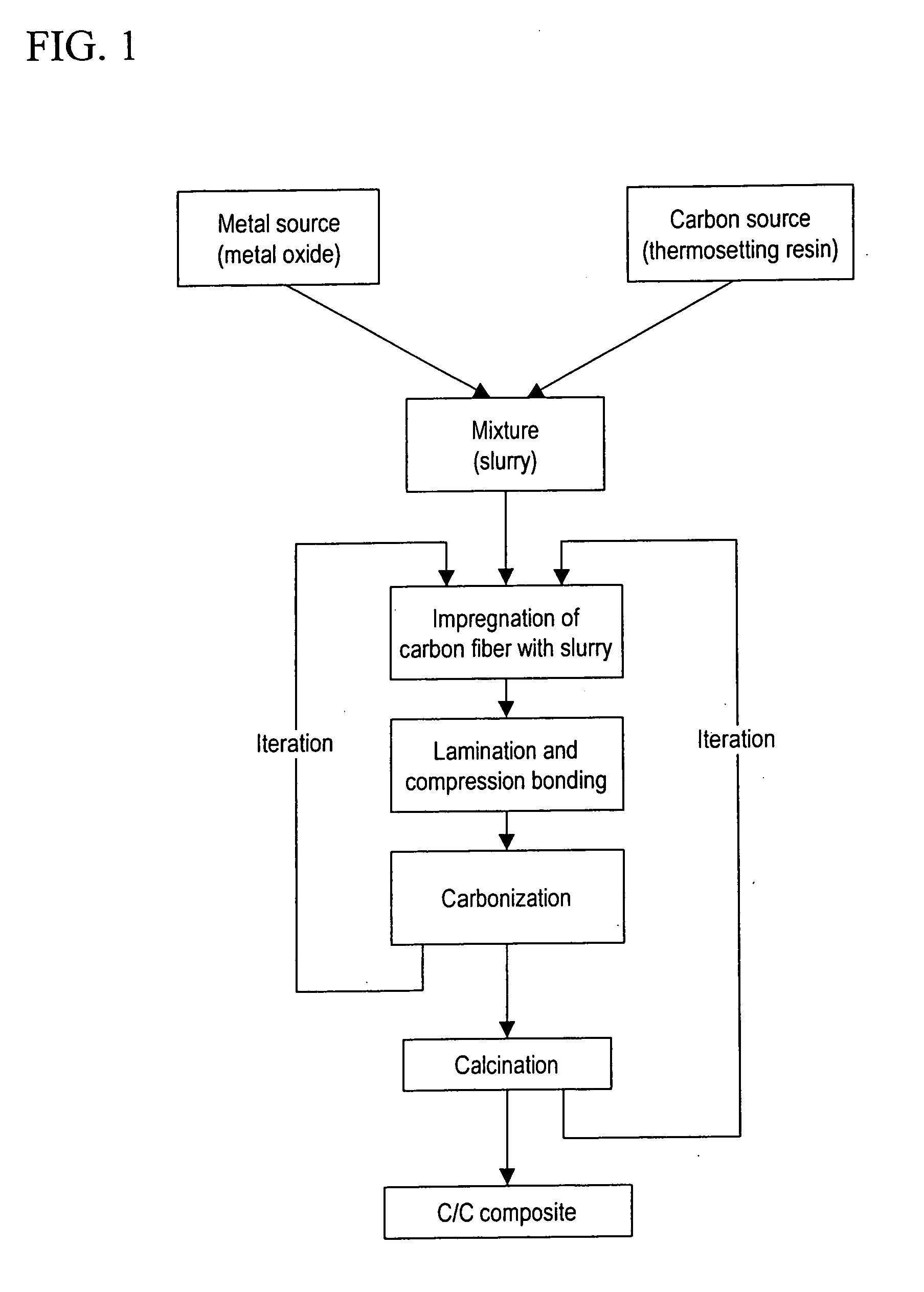
This invention provides carbon composite materials, which comprise metal carbide particles, at least the particle surfaces or the entirety of which are metal carbides, synthesized in situ from a metal source, i.e., at least one member selected from the group comprising metal particles, metal oxide particles, and composite metal oxide particles, and a carbon source, i.e., a thermosetting resin, dispersed in a carbon, carbon fiber, or carbon / carbon fiber matrix, and contain no free metal particles. This invention also provides a method for producing such composite carbon materials, which enables the production of carbon composite materials having a high coefficient of friction, high thermostability, and abrasion resistance.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
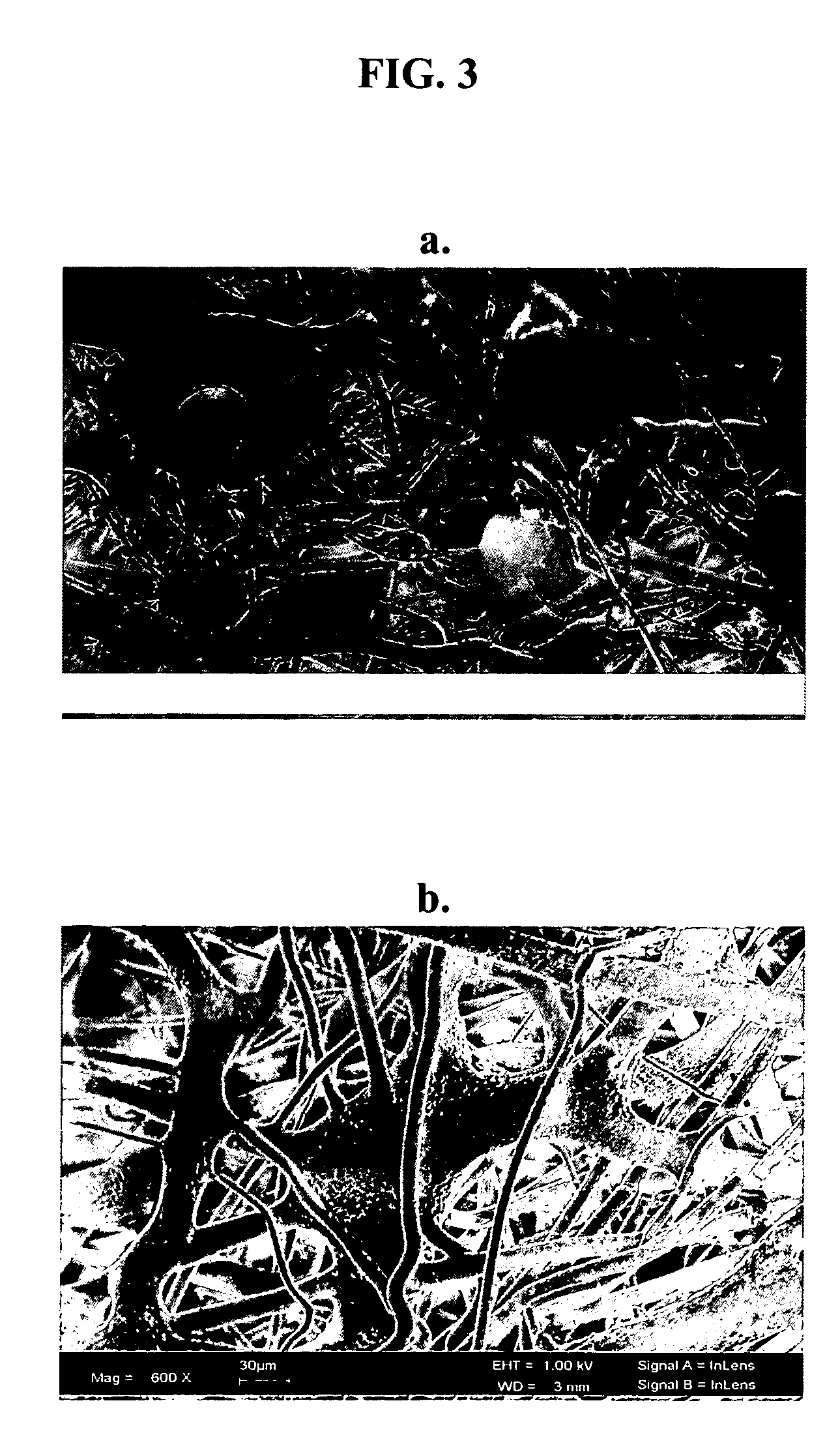
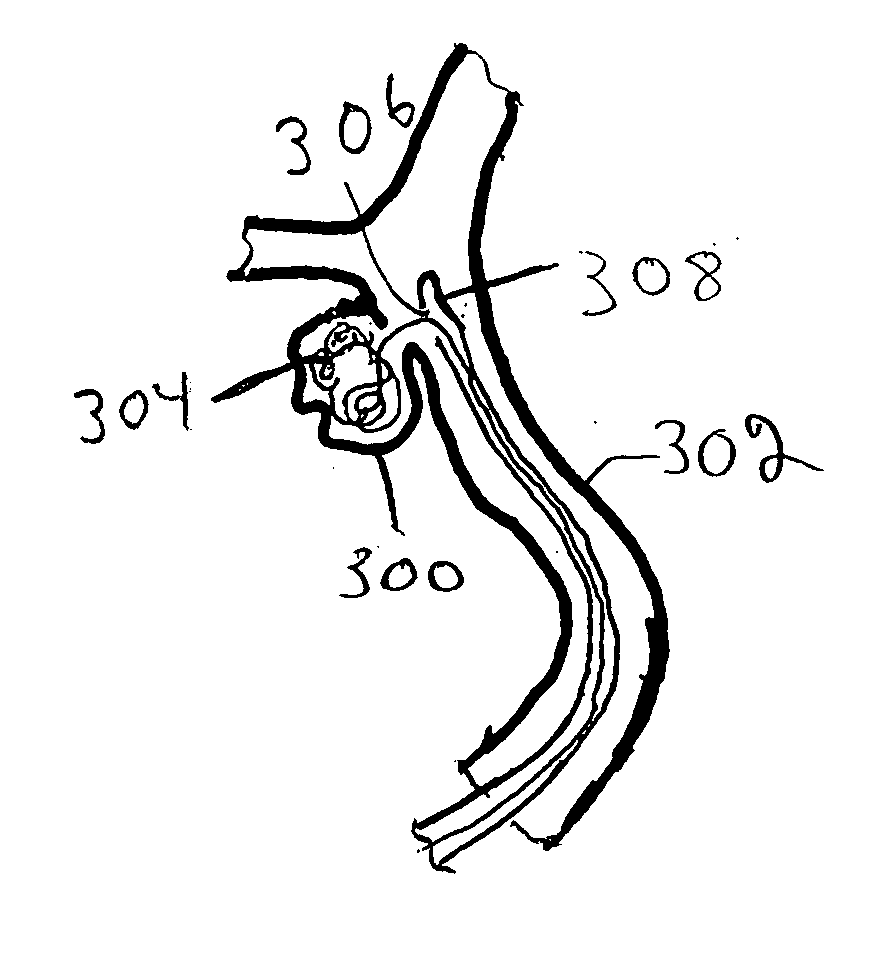
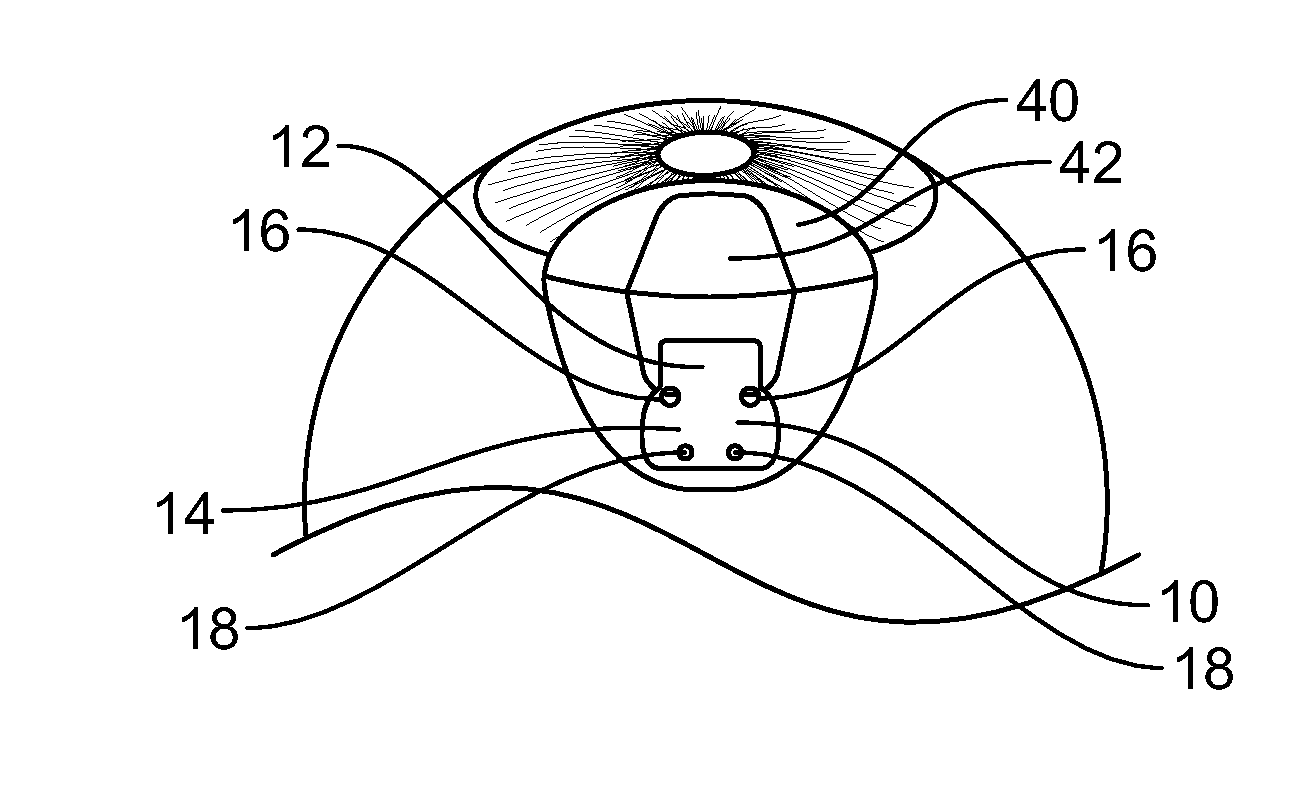
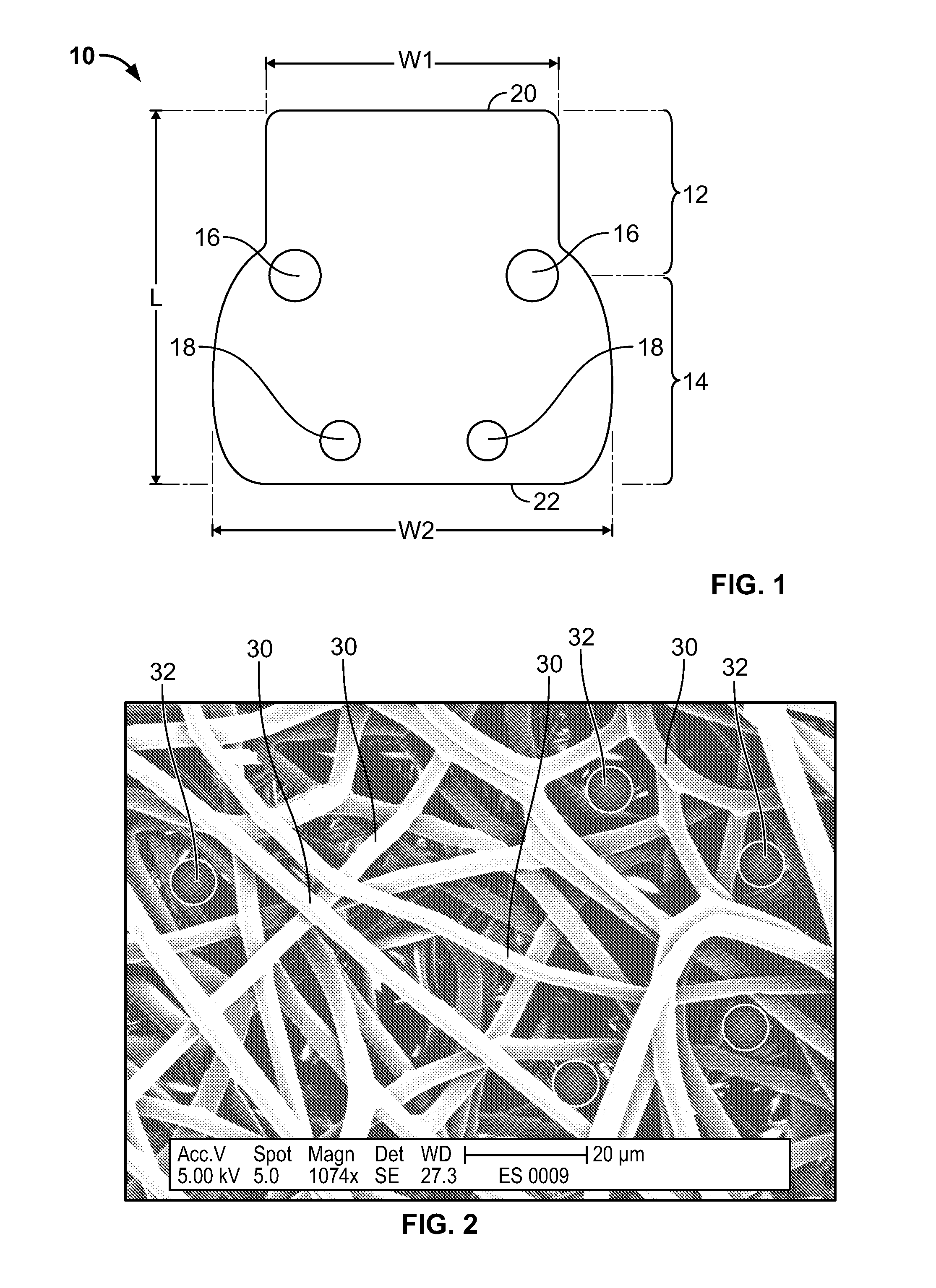
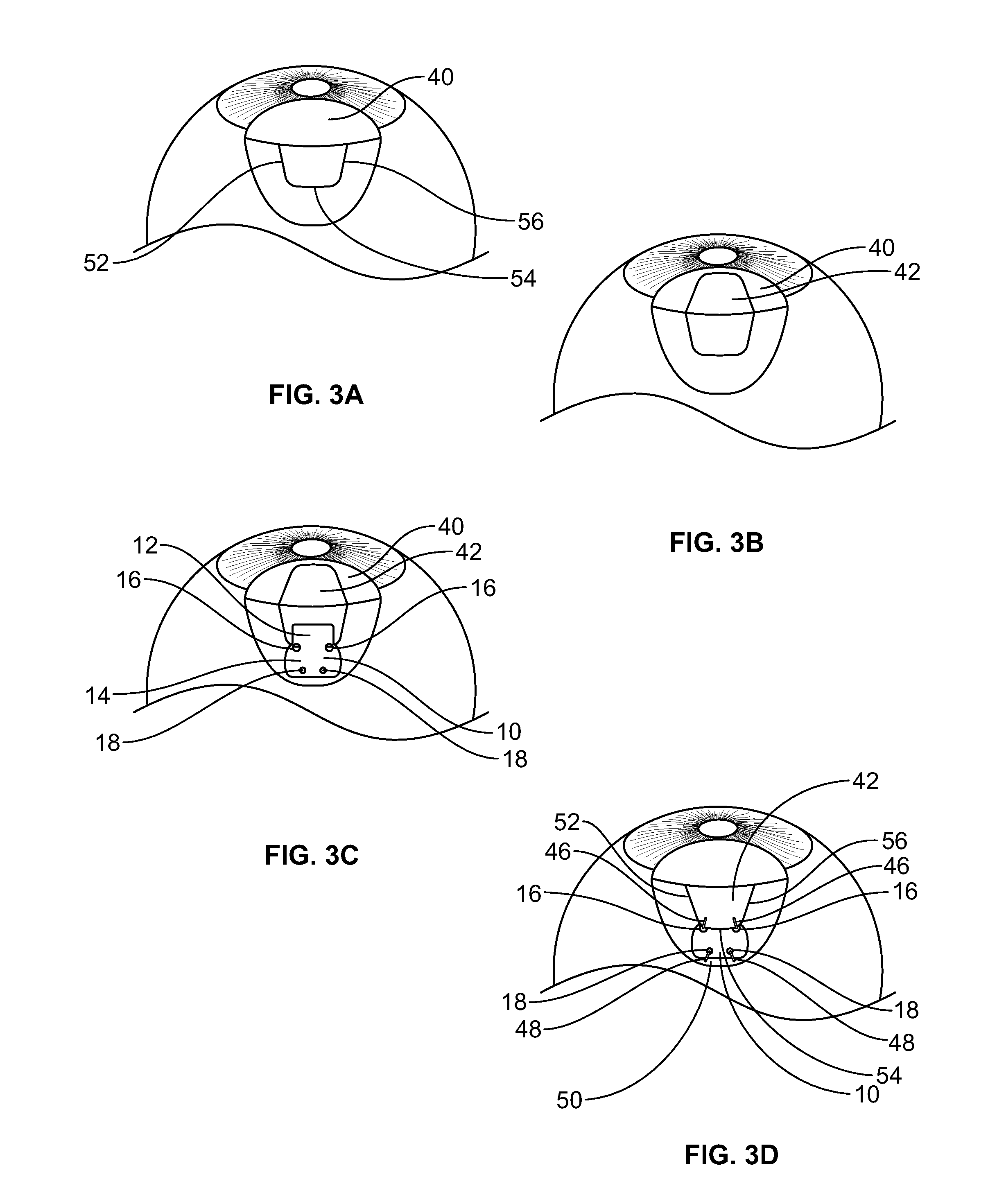
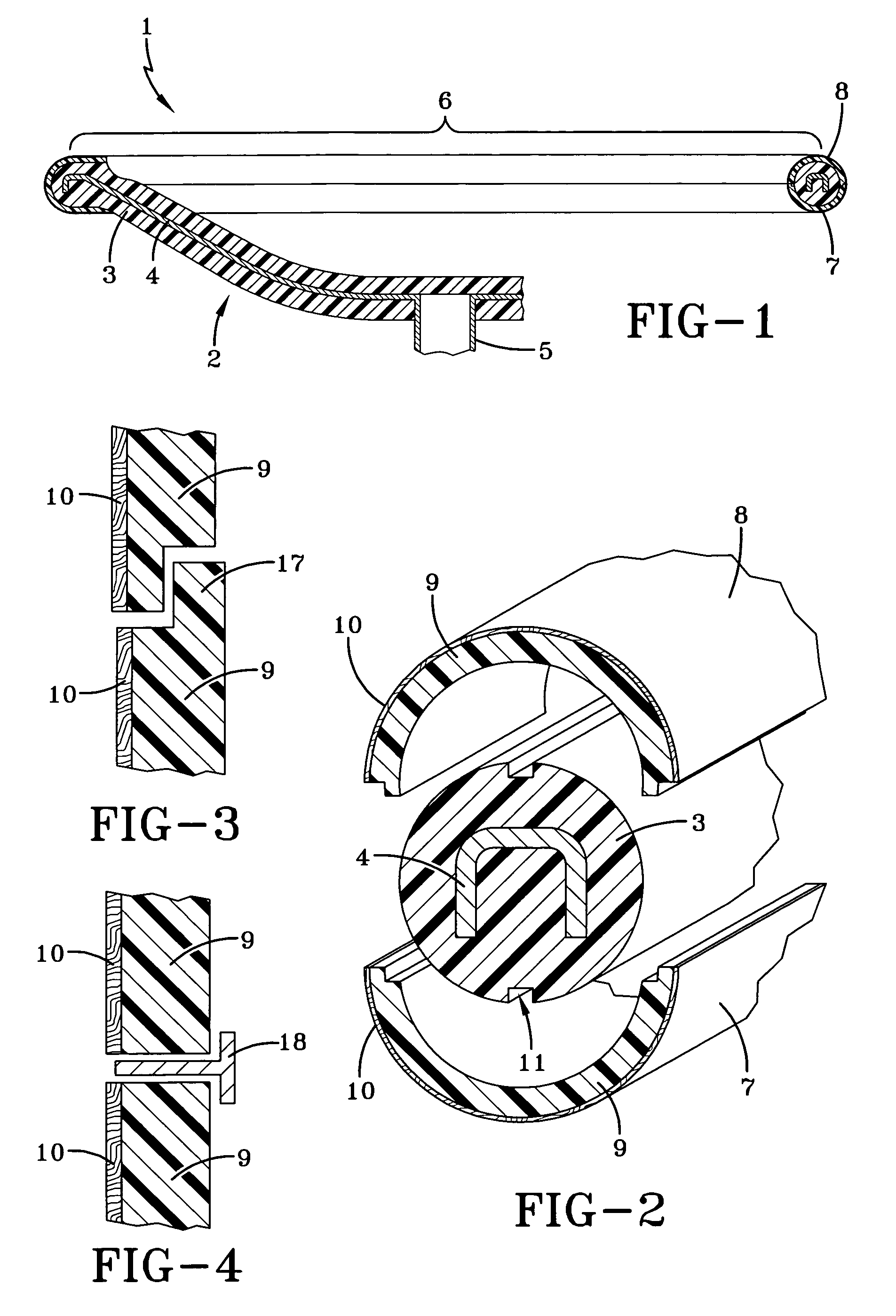
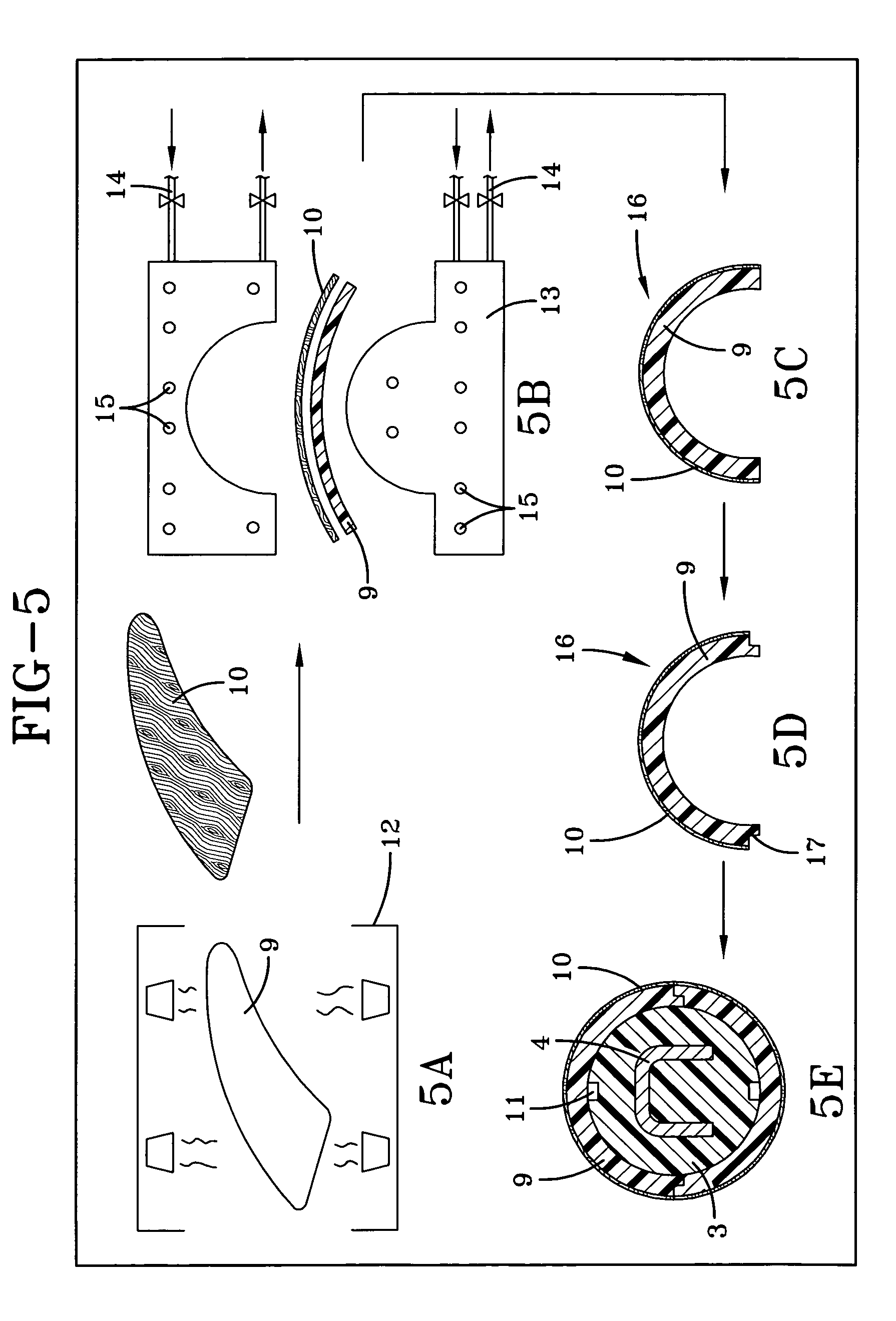
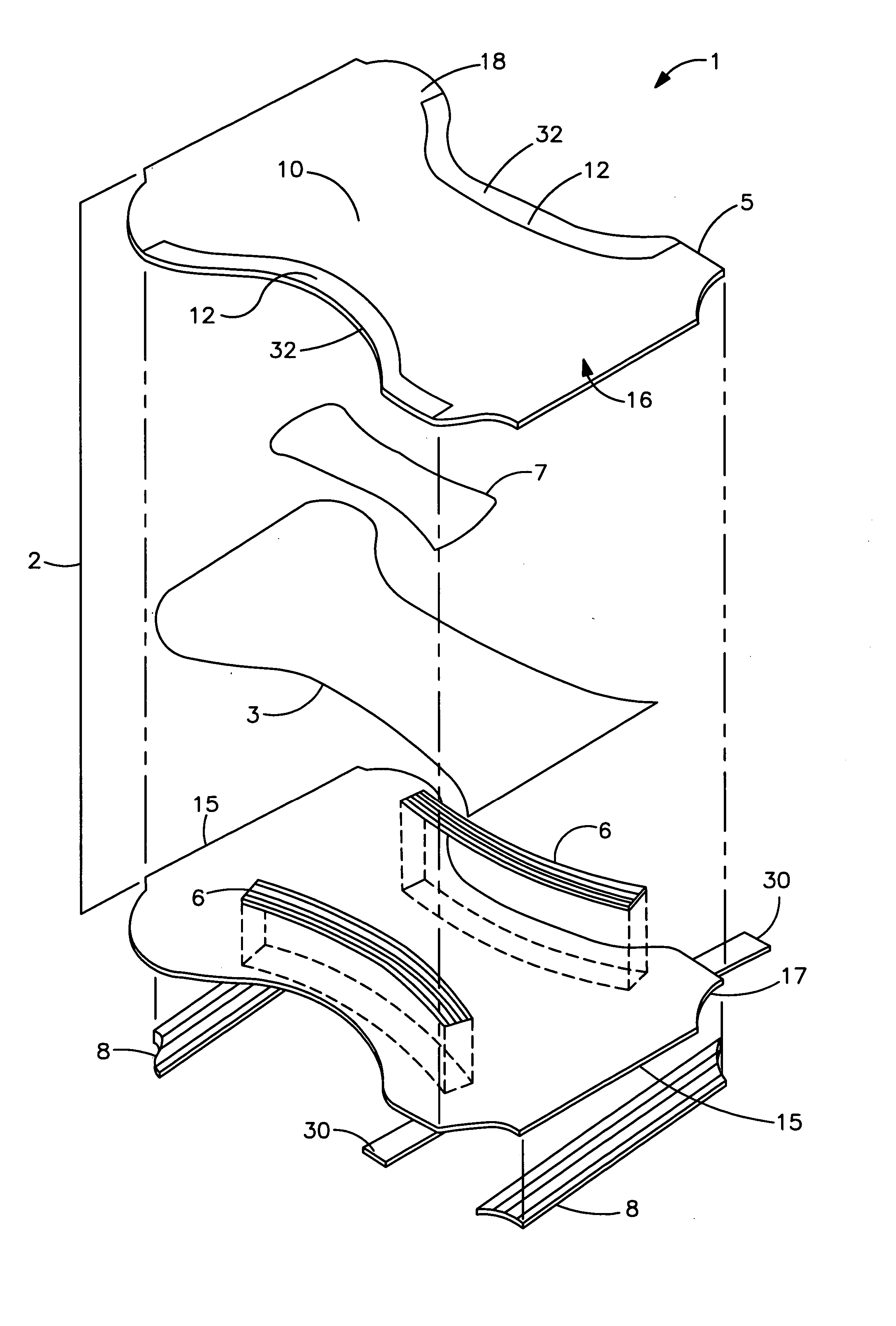
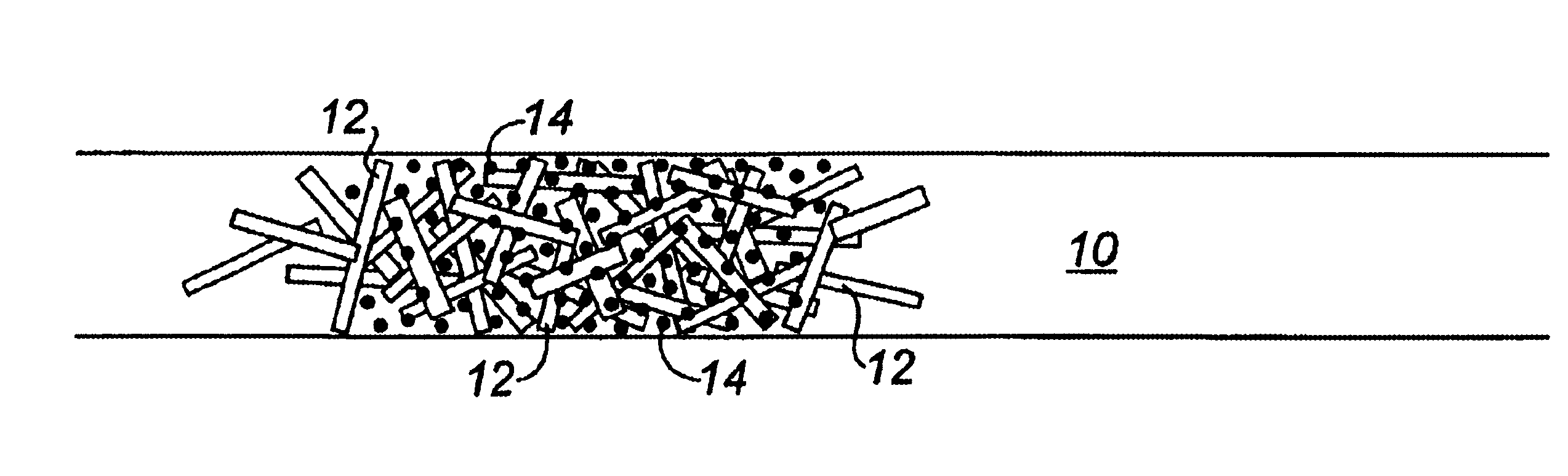
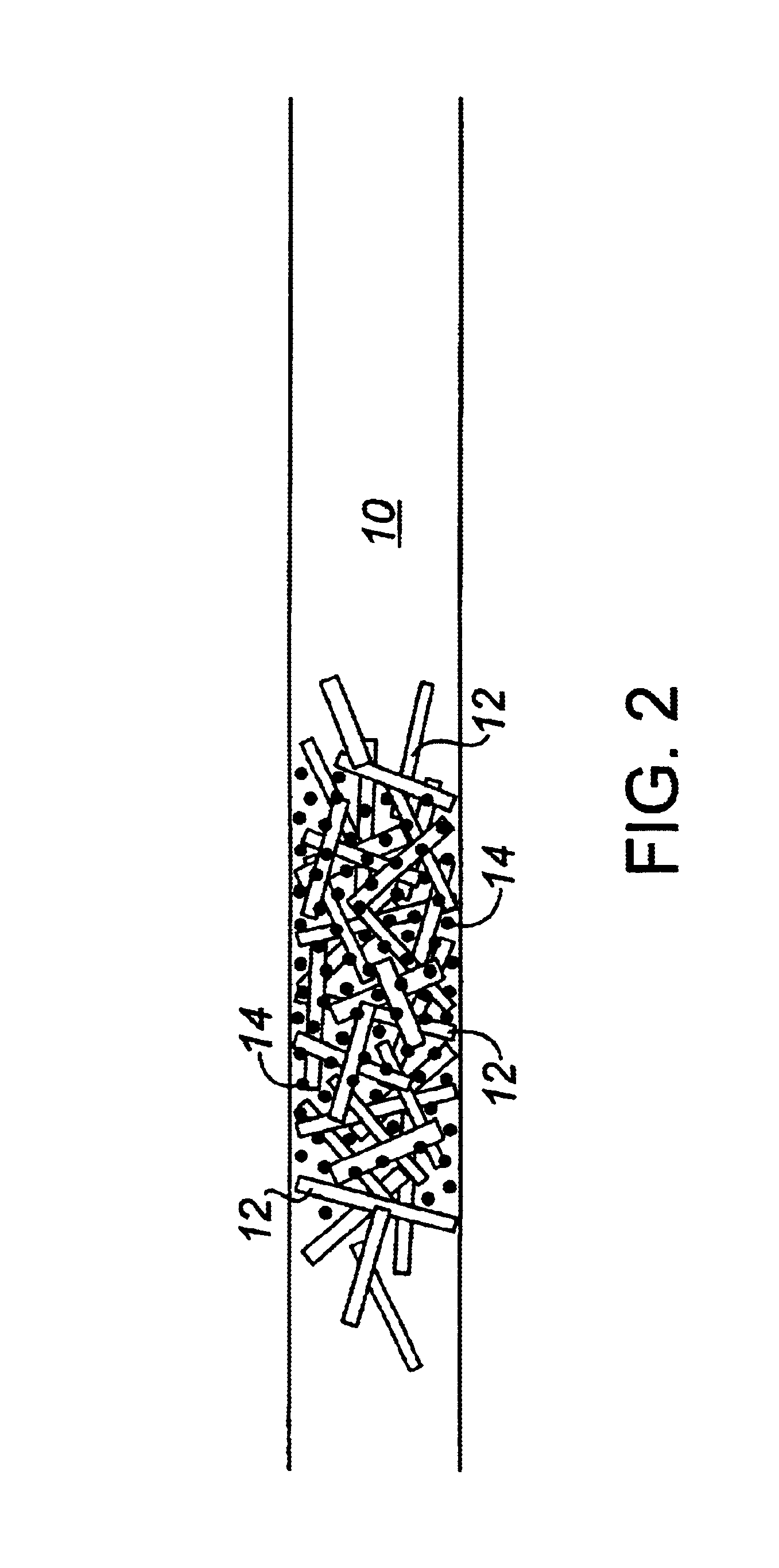
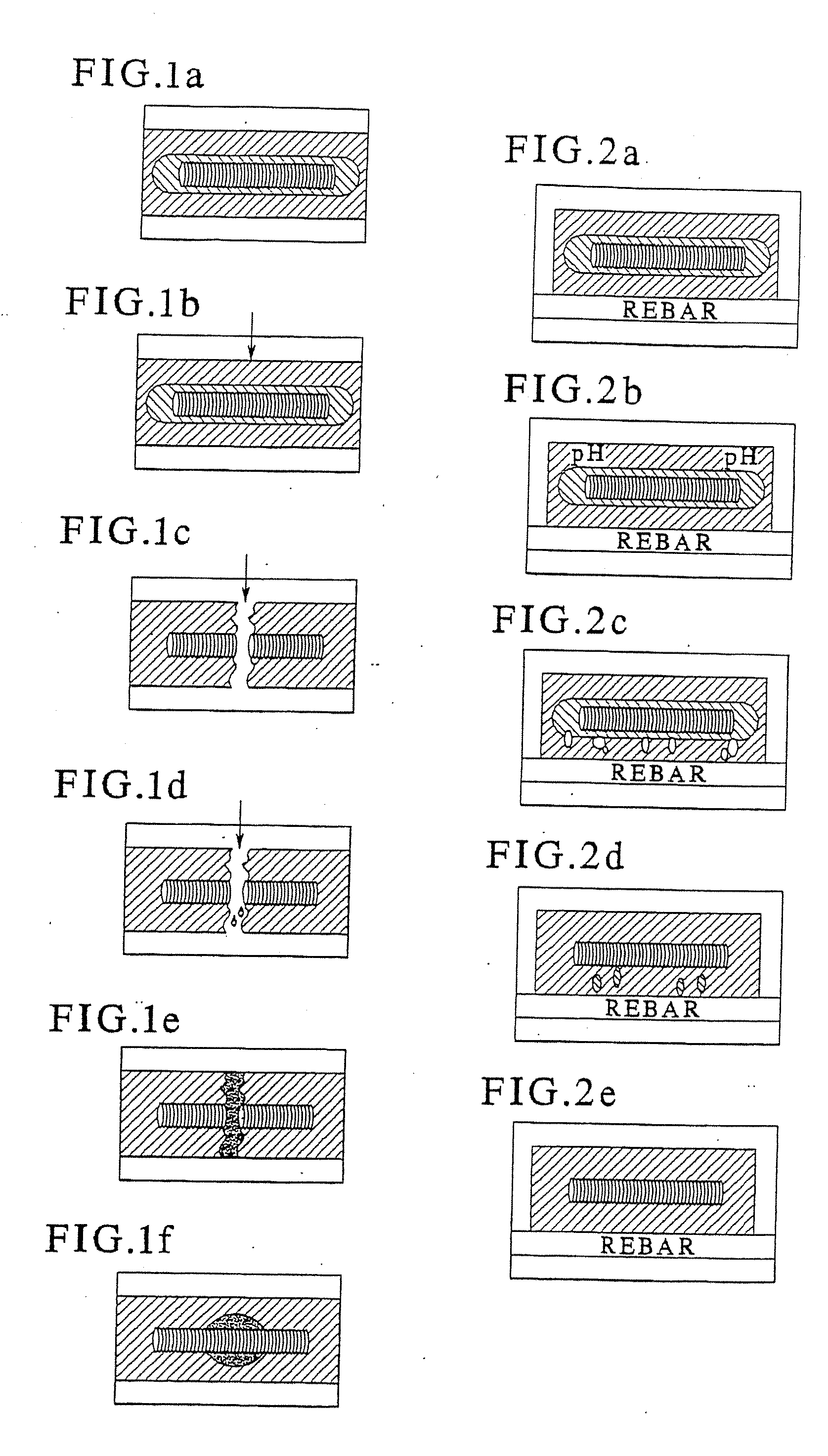
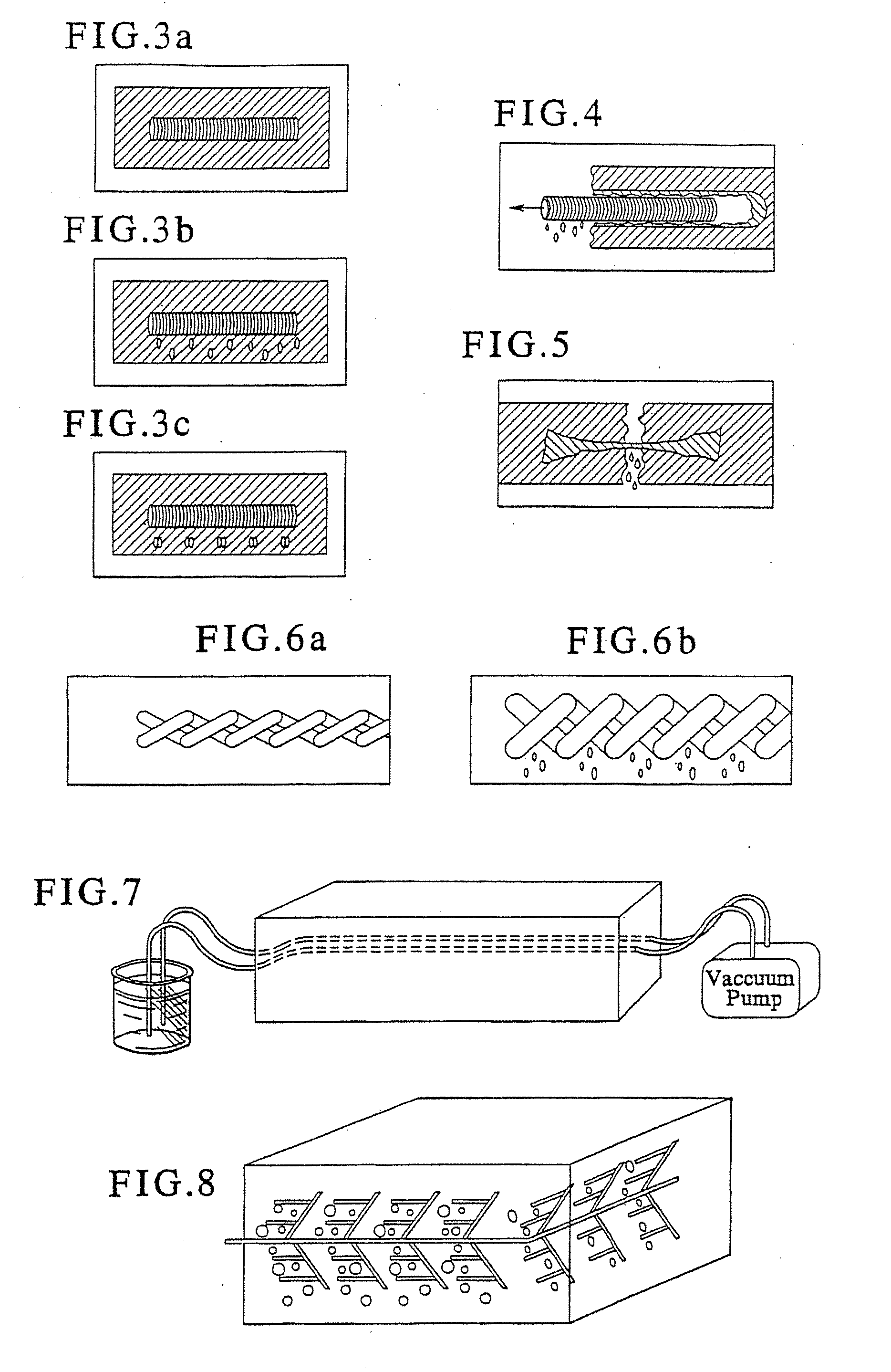
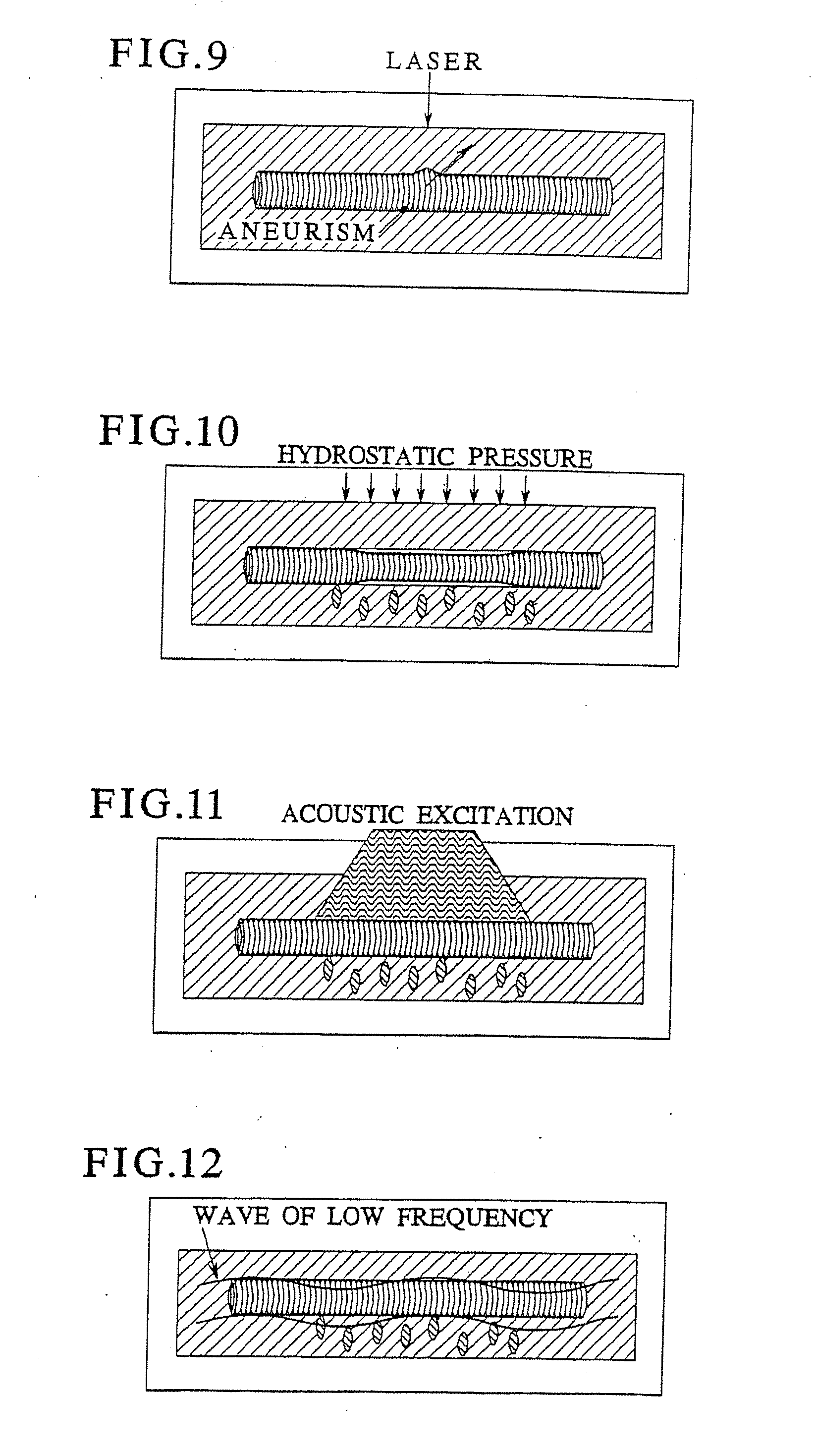
Fiber matrix for maintaining space in soft tissues
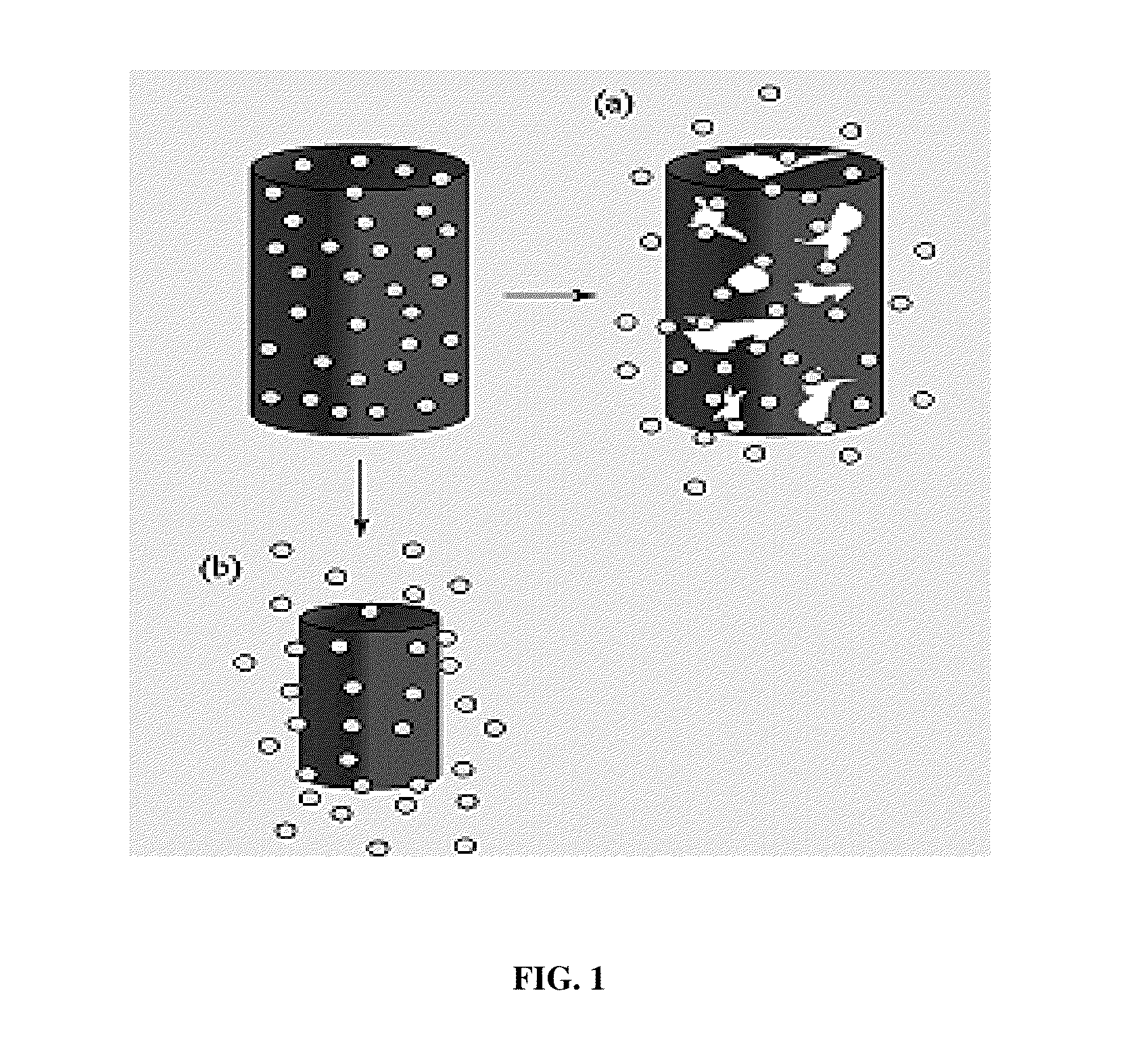
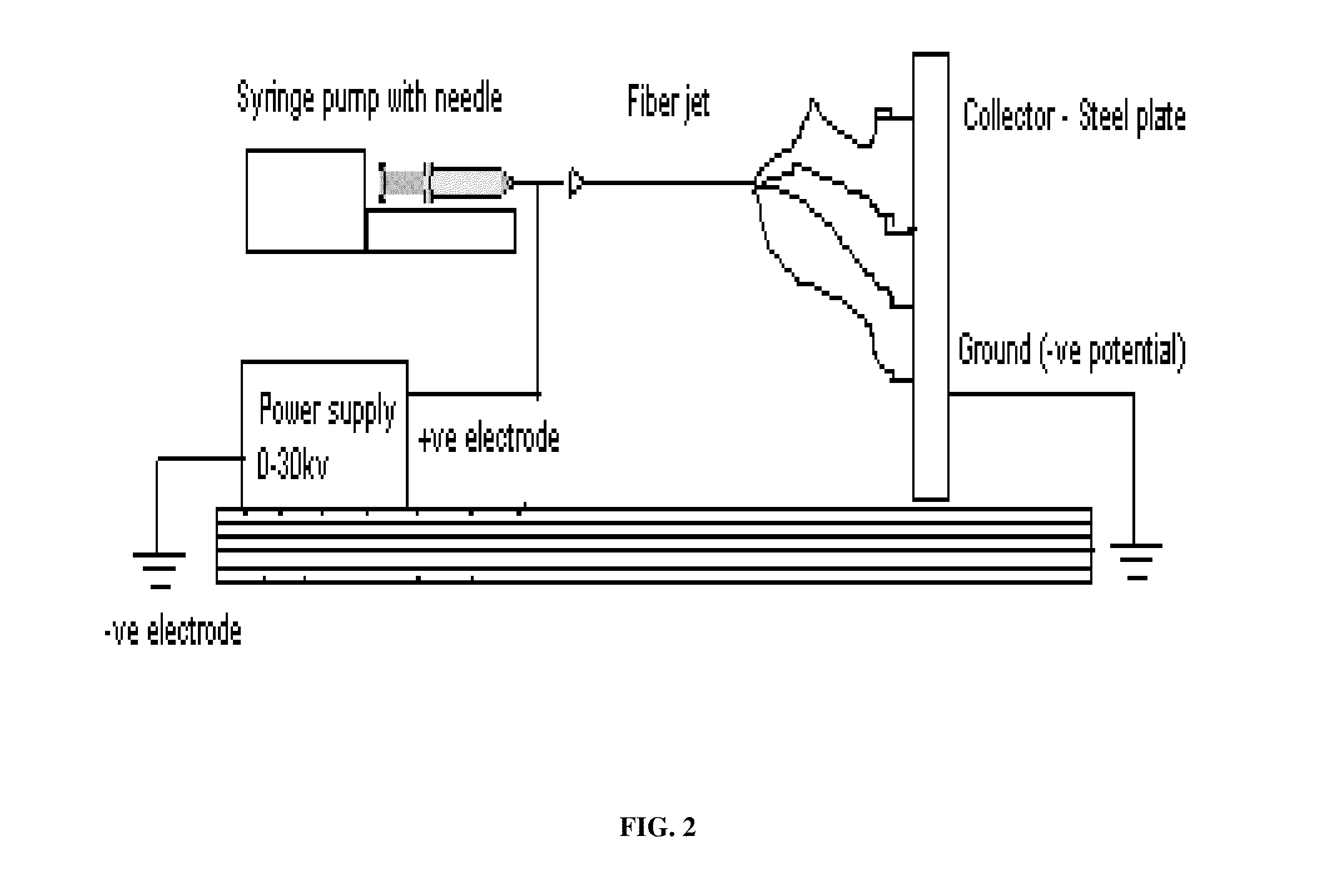
A fiber matrix is provided for maintaining space in soft tissue, for example for use in procedures for assisting drainage of aqueous humor from an eye to treat glaucoma. The fiber matrix comprises a plurality of crossing fibers forming a mesh with a plurality of void spaces. The fibers and void spaces are sized and arranged so as to permit passage of fluid through the fiber matrix and to inhibit formation of scar tissue through the fiber matrix. The fibers may comprise a polymeric material, and the fiber matrix may be manufactured by electrospinning. The fibers may comprise a biostable and / or a biodegradable material. In one method of using a fiber matrix, the fiber matrix is positioned under a scleral flap, with at least part of the fiber matrix under the scleral flap.
Owner:ALCON INC
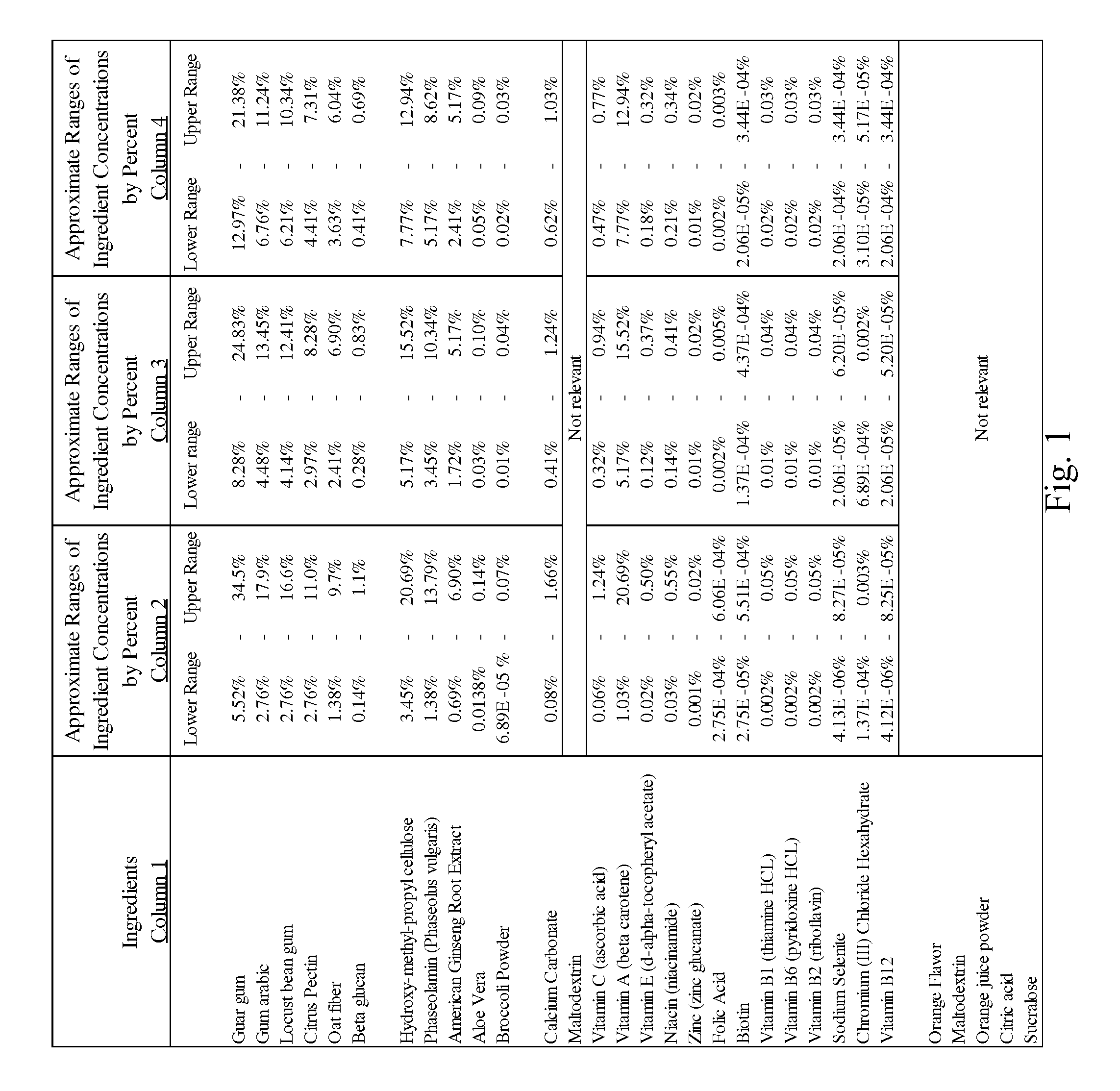
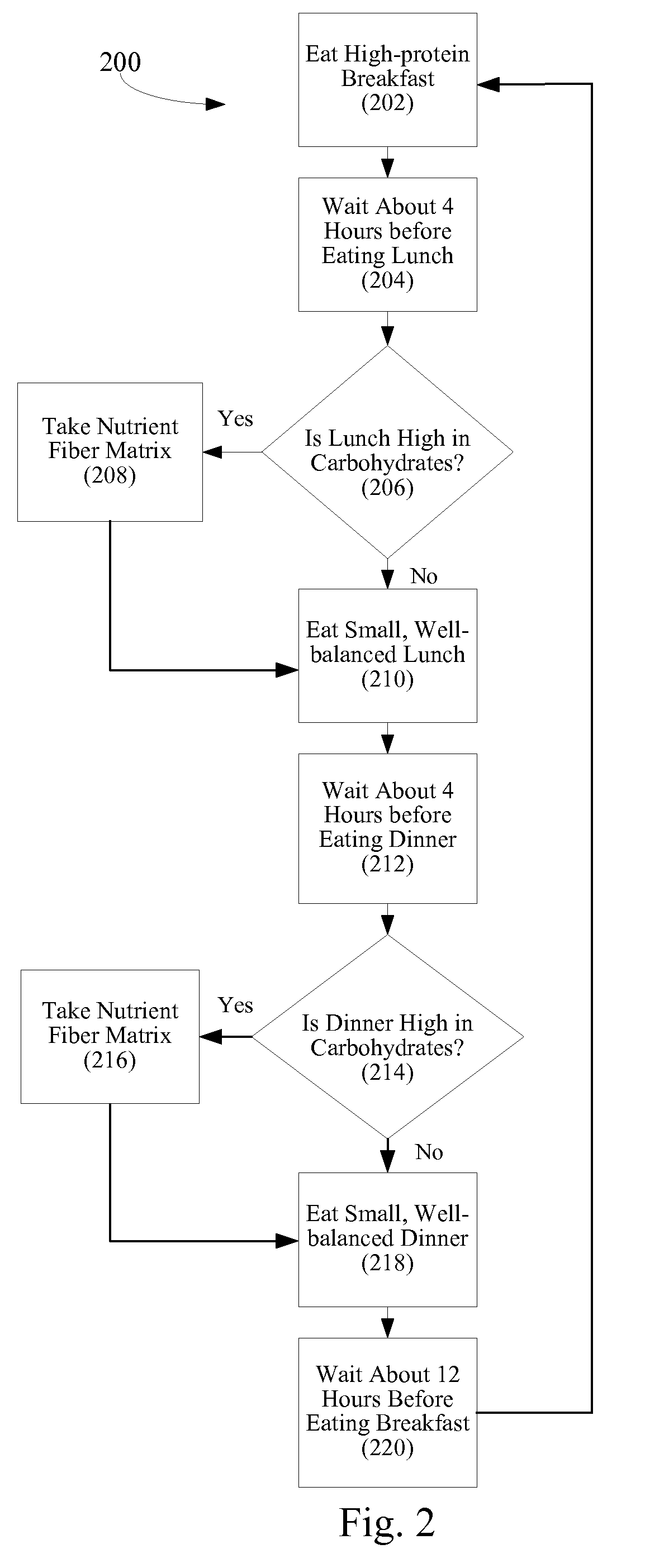
Method of controlling blood sugar levels, insulin levels, cholesterol levels, body fat levels, and body weight by administering a nutrient fiber matrix
InactiveUS20100074969A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce rateOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCholesterolLevel insulin
A nutrient fiber matrix and associated methods that help control blood sugar levels is described. The matrix can control blood sugar in a variety of ways. In one possible example, the matrix blocks carbohydrates in a manner that reduces the body's ability to take the carbohydrates into its cells. In another example, the matrix acts to increase a person's energy level and feelings of satiety. Thus, the matrix can reduce the person's desire to consume more food and, thereby, help the person to keep from increasing his or her blood sugar levels by eating more. In still another example, the fiber matrix helps sugars to be absorbed over a longer period of time so as to smooth out and prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
Owner:UNICITY INTERNATIONAL
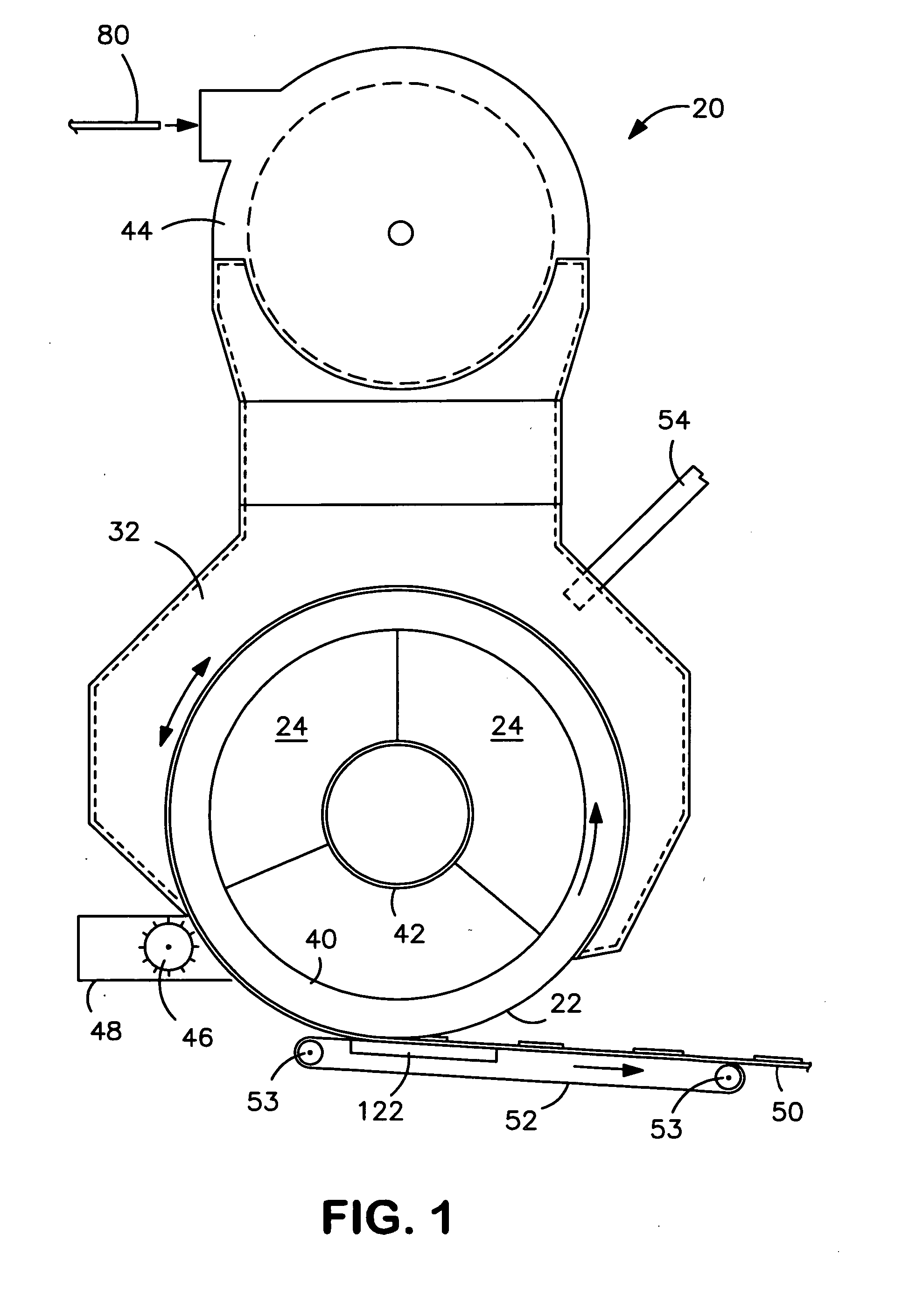
Rotating element sheet material with generalized containment structure
The present invention relates to rotating element sheet material with a generalized containment structure and methods of fabricating such rotating element sheet material, where the rotating element sheet material comprises a fibrous matrix, a plurality of rotatable elements, and an enabling fluid, and where the plurality of rotatable elements are disposed within the fibrous matrix and are in contact with the enabling fluid. In addition, rotating element sheet material with a generalized containment structure, and methods of fabricating such rotating element sheet material, includes rotating element sheet material which comprises a fibrous matrix and a plurality of micro-capsules, and where the micro-capsules define a hollow space therein, and the hollow space contains a subset of a plurality of rotatable elements and an enabling fluid, and where the plurality of micro-cavities are disposed within the fibrous matrix.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Process for producing a fibre compositions
InactiveUS20070143932A1Eliminate the problemGood componentSpecial paperPaper after-treatmentPolymer scienceFibre composition
The present invention relates to fibre compositions. In particular, the present invention concerns a process for producing a fibre composition comprising a lignocellulosic fibre material and a synthetic, electrically conductive polymer formed by polymerized monomers. The invention provides for good adhesion between the fibre matrix and the polymer, because the monomer is polymerized directly on the fibre. The conductivity of the polymer is improved and the electrical properties and conductivity levels of the modified fibre can be adjusted by changing the amounts of the electrically conductive polymer.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
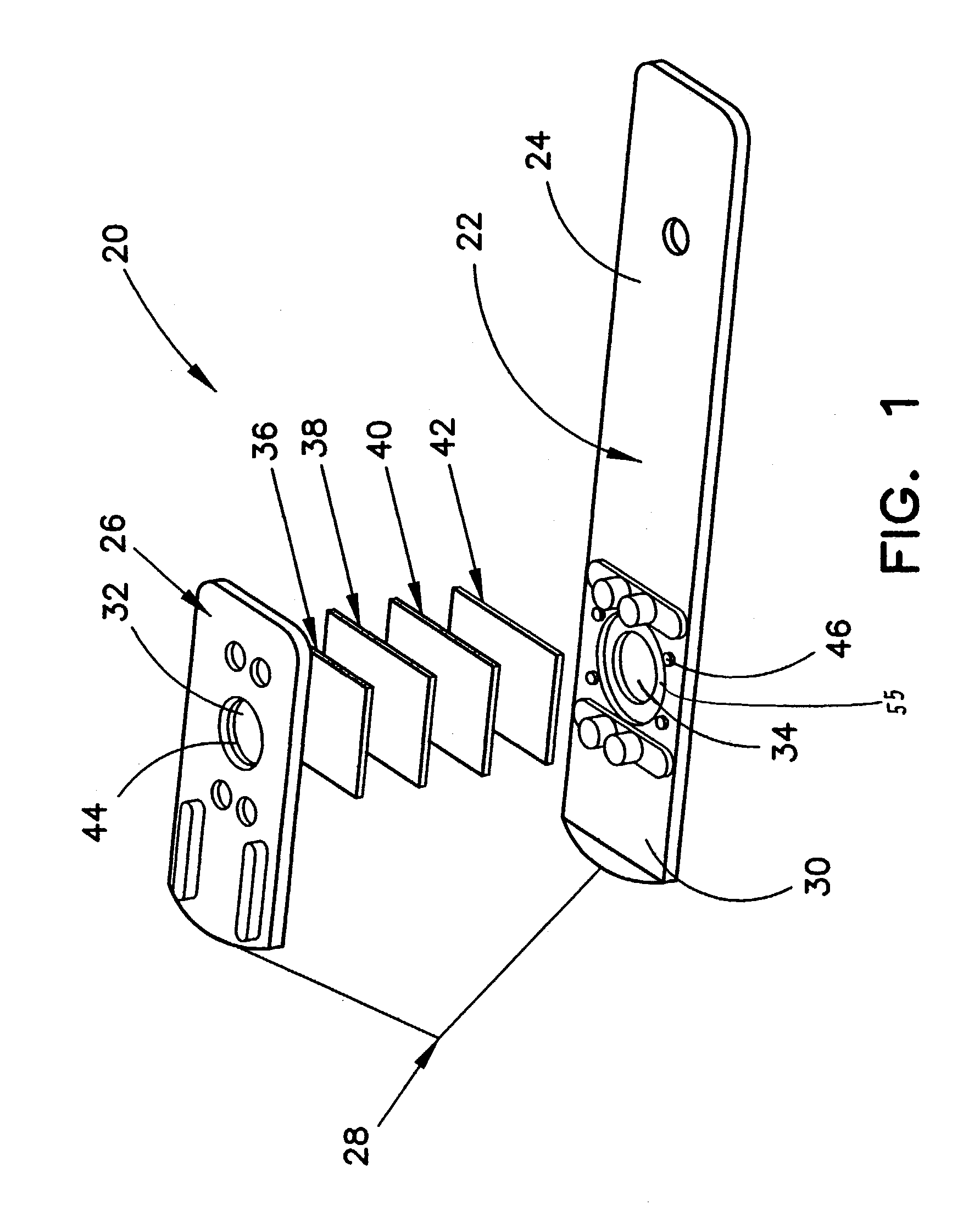
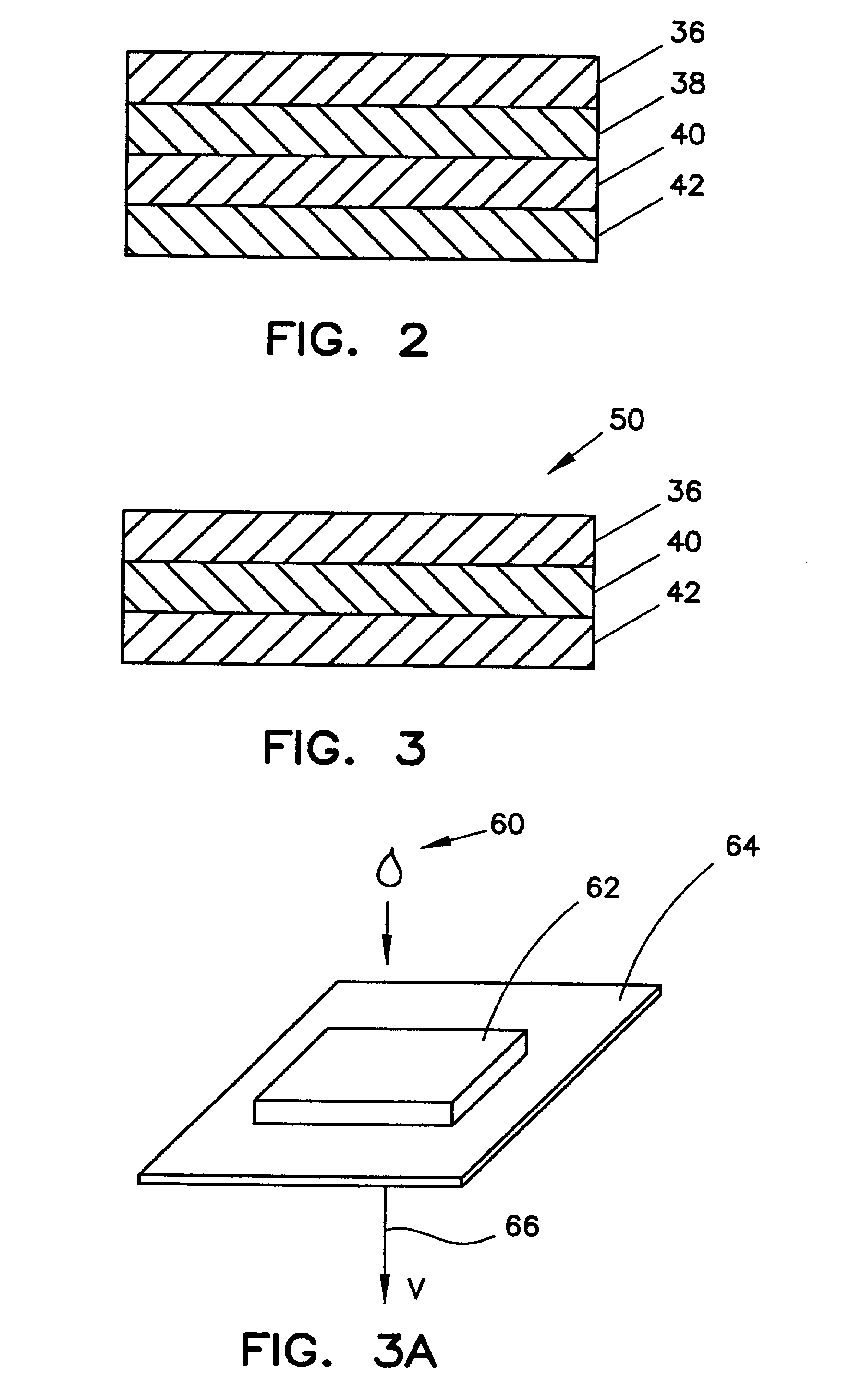
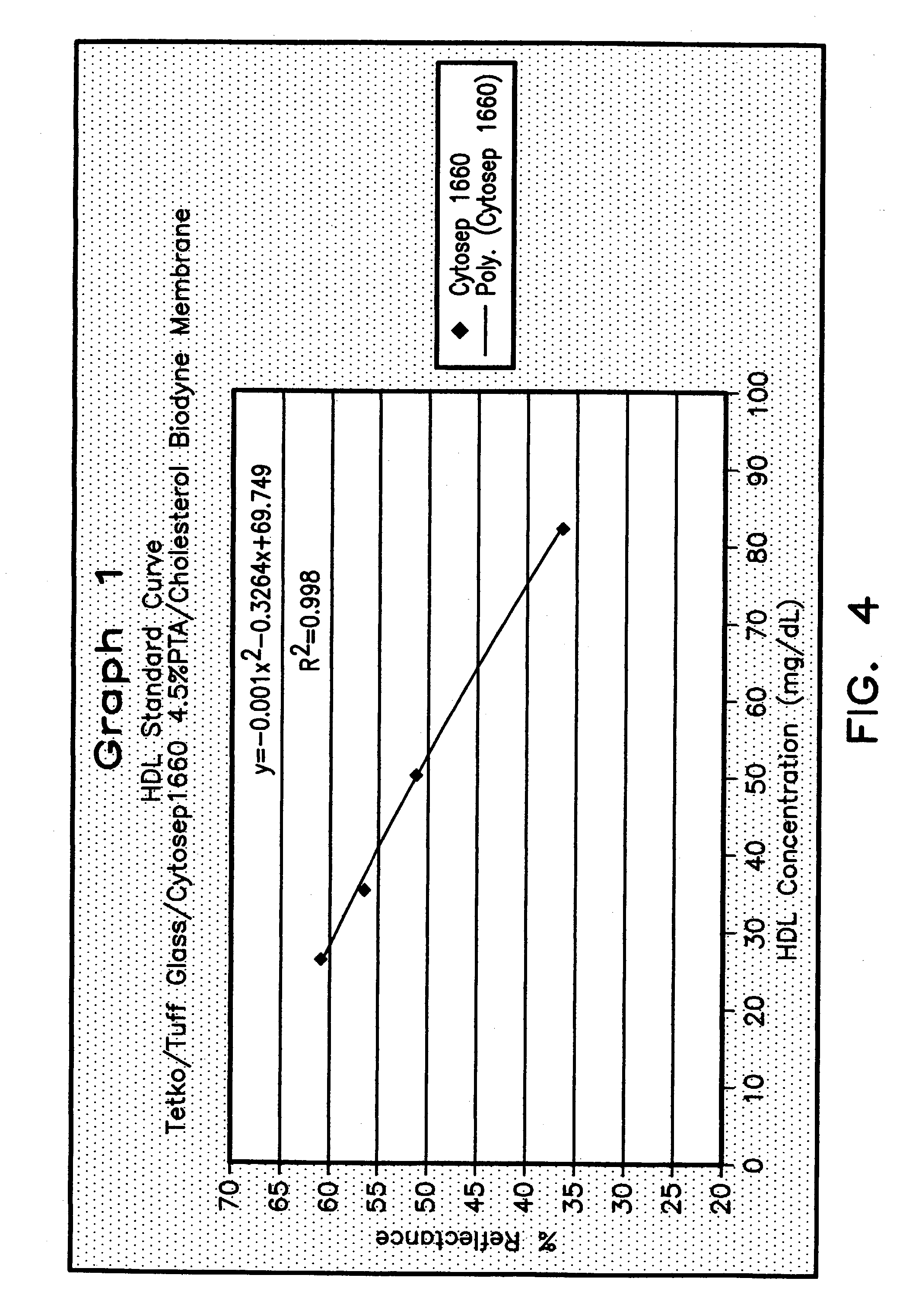
Method for determining HDL concentration from whole blood or plasma
ActiveUS7087397B2Avoid flowEasy and fast assemblyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementReaction layerCholesterol
A multilayer test strip and method of using the test strip for determining concentration of HDL cholesterol in a whole blood sample. The inventive test strip includes a two-stage blood separation mechanism, including a first glass fiber matrix which separates most of the blood cells and an adjacent, second matrix preferably also containing glass fibers that separates the remainder of the blood cells. The second layer also precipates and retains non-HDL cholesterol, thereby providing plasma that is substantially free of red blood cells and substantially free of non-HDL cholesterol to a reaction layer. Precipitation and retention on non-HDLs takes place by a vertical or dead-end filtration in a single layer. The reaction layer produces a color, the intensity of which is proportional to the concentration of HDL cholesterol in the blood sample which is applied to the test strip. Advantageously, the inventive test strip is a vertical flow device, which can be made more compact and operates more efficiently than a lateral flow device.
Owner:POLYMER TECH SYST
System and method for electrospun drug loaded biodegradable chemotherapy applications
InactiveUS20110038936A1Good coagulationImprove adhesionPowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsBiomedical engineeringPolymer
Biodegradable resorbable drug delivery systems characterized by an electrospun biodegradable resorbable polymeric fiber matrix with at least one therapeutic agent incorporated into the fibers of the matrix, wherein the fiber matrix has an interfibrillar space of at least 65% by volume. Therapeutic methods for delivering a chemotherapeutic agent to body cavities from which a tumor has been excised and for strengthening weakened blood vessel walls are also disclosed.
Owner:GRISWOLD KIMBERLY A +1
Treated textile substrate and method for making a textile substrate
Owner:MILLIKEN & CO
Coform Nonwoven Web Formed from Propylene/Alpha-Olefin Meltblown Fibers
A coform nonwoven web that contains a matrix of meltblown fibers and an absorbent material is provided. The meltblown fibers are formed from a thermoplastic composition that contains at least one propylene / α-olefin copolymer of a certain monomer content, density, melt flow rate, etc. The selection of a specific type of propylene / α-olefin copolymer provides the resulting composition with improved thermal properties for forming a coform web. For example, the thermoplastic composition crystallizes at a relatively slow rate, thereby allowing the fibers to remain slightly tacky during formation. This tackiness may provide a variety of benefits, such as enhancing the ability of the meltblown fibers to adhere to the absorbent material during formation of the coform web. In certain embodiments, the coform web may also be imparted with texture using a three-dimensional forming surface. In such embodiments, the slow crystallization rate of the meltblown fibers may increase their ability to conform to the contours of the three-dimensional forming surface. Once the fibers crystallize, however, the meltblown fibers may achieve a degree of stiffness similar to conventional polypropylene, thereby allowing them to retain their three-dimensional shape and form a highly textured surface on the coform web.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Containment case and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20130153456A1Increased shear strengthLower resistanceBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesIn planeUltimate tensile strength
A containment case comprises a composite core, with an inner and outer surface, at least one puncture resistant layer bonded to the inner surface of the composite core and at least one energy capture layer bonded to the outer surface of the composite core. The puncture resistant layer having a high through-thickness shear strength and high interlaminar toughness at impact. The energy capture layer having a high in-plane tensile strength and low resistance to delamination and fiber-matrix debonding at impact. A method of fabricating a containment case includes the steps of disposing one or more layers of a puncture resistant material on a layup mandrel, disposing one more layers of a structural composite material on an exterior surface of the puncture resistant material, disposing one or more layers of an energy capture material on an exterior surface of the structural material and curing a resin in the plurality of layers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Water-repellent and soil-resistant finish for textiles
InactiveUS6855772B2Improve wear resistanceGood water solubilityPretreated surfacesOrganic dyesYarnEmulsion
The present invention is directed to polymeric treatment preparations for textiles and other fibrous substrates that impart water and oil repellency to fibers, yarns, textiles, or other fibrous substrates. More particularly, this invention comprises an aqueous solution, emulsion or suspension of (a) a fluorinated polymer that contains reactive groups that can complex with metal atoms that have a formal charge of 2 or greater, and (b) one or more metal atoms that have a formal charge of 2 or greater. The invention is further directed to the process for treating fibrous substrates with textile preparations in one step that provide water / soil repellency that is durable to repeated cleanings and to abrasion. This invention is further directed to the yarns, fibers, fabrics, textiles, webs, finished goods, or nonwovens (encompassed herein under the terms “textiles” and “fibrous substrates”) treated with the textile-reactive water- and soil-resistant preparation of the invention. Such fibrous substrates exhibit a greatly improved, durable water and soil repellency or resistance, even after multiple launderings.
Owner:NANO TEX
Steering wheel with thermoplastic composites
ActiveUS7143663B2Less timeImprove product qualityControlling membersMechanical apparatusSteering wheelEngineering
A steering wheel or other component for motor vehicle interiors, is produced by pressure thermoforming an external layer of decorative material, together with an internal structural layer of support material that includes a matrix of thermoplastic material and a plurality of reinforcing fibers for the thermoplastic matrix. The matrix may be of polymer that impregnates the fabric or made of fabrics that are interwoven or mixed with the reinforcing fibers.
Owner:KEY SAFETY SYST
Absorbent articles with improved odor control
A technique for incorporating odor control agent particles into an absorbent article is provided. More specifically, the odor control particles are “homogenously” distributed (e.g., in a substantially uniform manner) within an airformed fiber matrix of an absorbent core of an absorbent article. An absorbent core containing such a homogeneously distributed odor control particles may possess a greater surface area for contacting malodorous compounds, thereby increasing the likelihood of odor reduction.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Nutrient solution for plants
The invention discloses a nutrient solution for plants. The nutrient solution is prepared by taking macroelements, microelements, vitamins, fiber matrix substances and water as main raw materials, can be used for culturing, planting and cultivating various plants such as cucumbers, tomatoes, kidney beans, flowers and plants and the like, and has the characteristics of abundant nutrition, benefit for growth of the plants and low cost.
Owner:邯郸市垚岸农业科技有限公司
2ª–m band light-emitting oxyhalide tellurite glasses
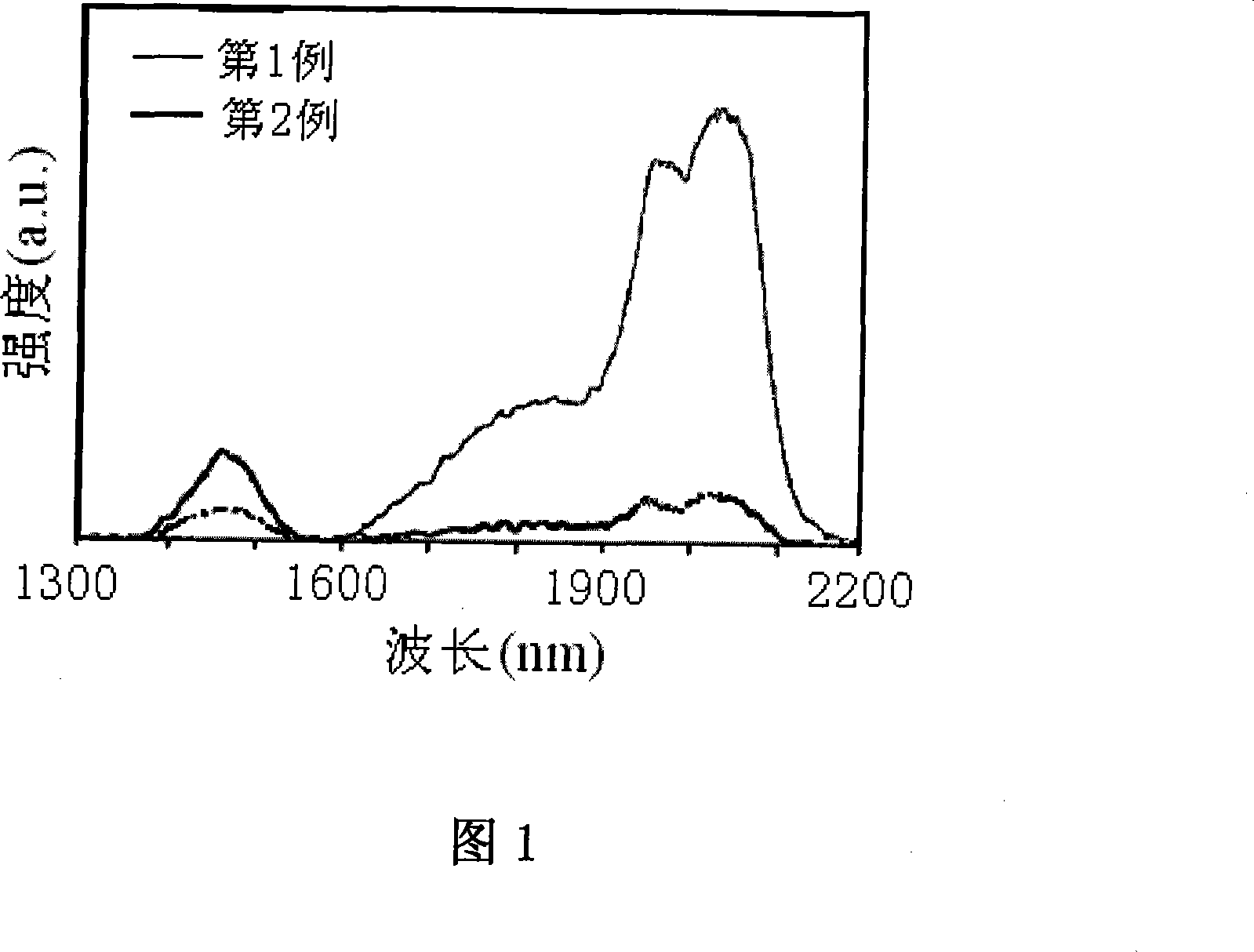
The invention relates to a piece of luminous oxyhalide tellurate glass with 2 Mum wave band, the glass compositions and mole percentages are as follows: TeO2: 40-85, PbO: 0-15; PbF2 plus ZnF2: 5-30; ZnO: 0-15; GeO2: 0-10; Nb2O5: 0-10; WO3: 0-10; Li2O plus Na2O plus K2O: 3-10; Tm2O3 plus Ho2O3 plus Er2O3 plus Yb2O3: 2-7, wherein, at least one of the Tm2O3 and the Ho2O3 is not equal to zero. The glass is prepared through a common melting method. The oxyhalide tellurate glass of the invention has the advantages of high infrared transmittance, transparence, no crystallization, no bubbles and stripes, excellent pinhole test, high luminous efficiency at the 2 Mum wave band, etc. The preparation technique is simple, can be operated easily and has lower cost. The materials of the invention are applicable to infrared laser optical lenses at the 2 Mum wave band or infrared special fiber matrix materials at the 2 Mum wave band.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High temperature gas seals
InactiveUS6902798B2Improve sealingMaximum sealing performanceNatural cellulose pulp/paperEngine sealsAlcoholFuel cells
A flexible seal for use in a solid oxide fuel cell stack is formed from a fiber matrix impregnated with a plurality of solid particles. The fibers and particles are preferably ceramic and may be formed from alumina or zirconia. The seal may be formed by dipping the fiber matrix into a slurry of the particles in an alcohol, drying the seal and precompressing prior to installation in the fuel cell stack.
Owner:VERSA POWER SYST
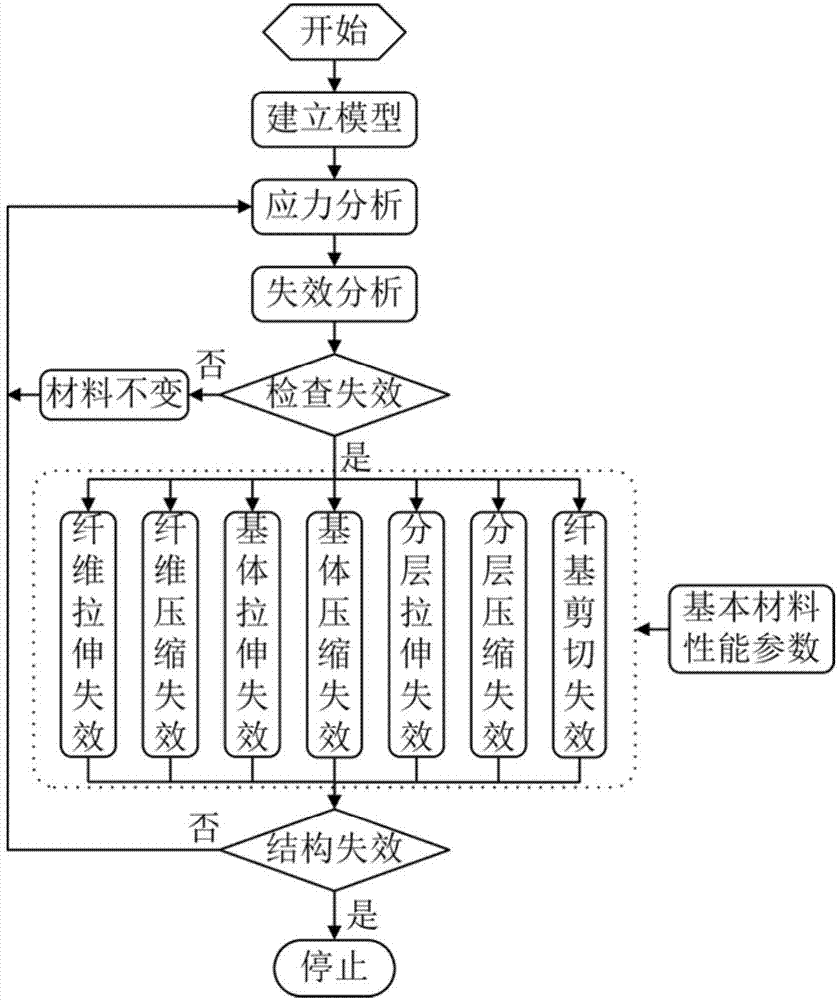
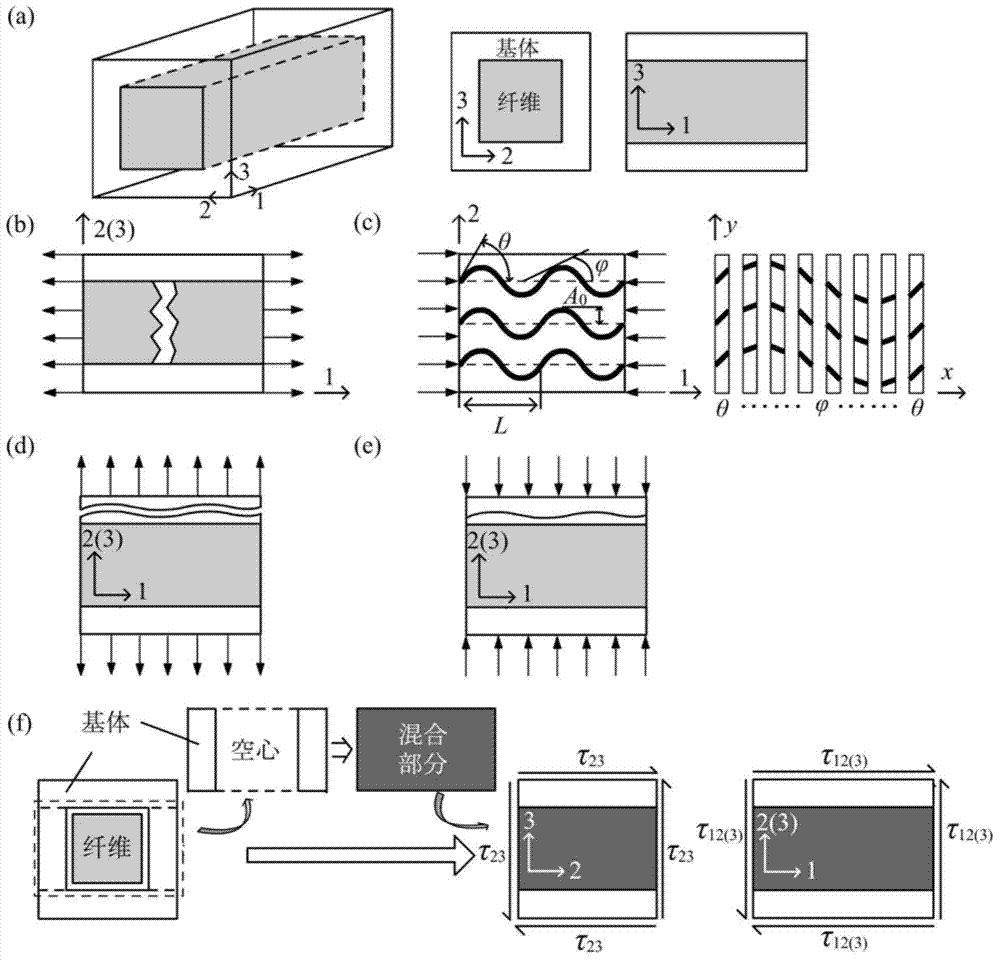
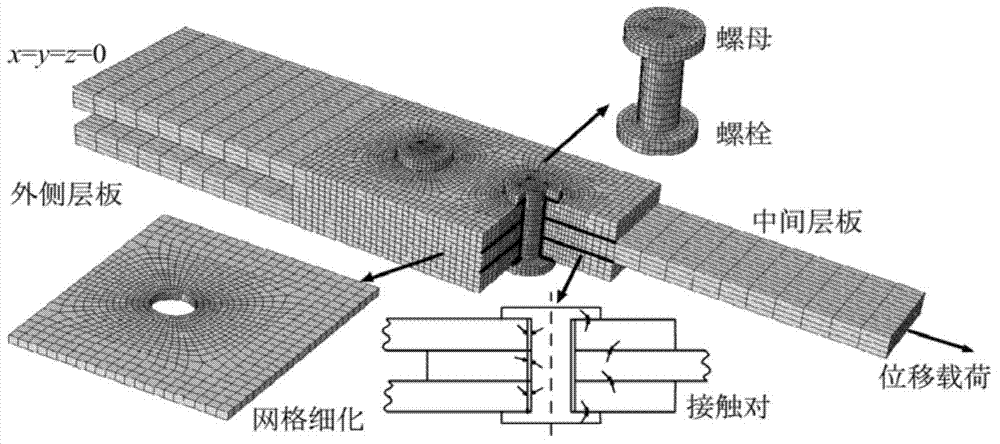
Composite material structure failure analysis method based on mesomechanics degradation model
InactiveCN103698199AAvoid time costReduce testing costsSpecial data processing applicationsStrength propertiesMaterial DegradationFailure analysis
The invention relates to a composite material structure failure analysis method based on mesomechanics degradation model, and three dimensional basic material performances of the composite material are input parameters, and material performances of the composite material after damage are obtained by mesomechanics calculating method, and seven common failure modes are taken into consideration, which comprise: fiber stretch, fiber compression, matrix stretch, matrix compression, fiber-matrix shearing, layered stretch and layered compression, and finally the material degradation mode in composite material progressive damage analysis is obtained for carrying out failure analysis of the composite material structure; the invention not only can accurately predict structure failure, but also can predict failure mode and position of the structure. According to the composite material structure failure analysis method based on mesomechanics degradation model provided by the invention, the material degradation model is obtained by theory analysis, thereby connecting macroscopic failure and microscomic mechanism of composite material, and compared to the present material degradation model based on experience or test, time and test cost are substantially reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Self-repairing, reinforced matrix materials
InactiveUS20060169180A1Long-term durabilityIncreased durabilityMaterial nanotechnologyAuxillary shaping apparatusMaterials sciencePolymer
Self-repairing, fiber reinforced matrix materials include a matrix material including inorganic as well as organic matrices. Disposed within the matrix are hollow fibers having a selectively releasable modifying agent contained therein. The hollow fibers may be inorganic or organic and of any desired length, wall thickness or cross-sectional configuration. The modifying agent is selected from materials capable of beneficially modifying the matrix fiber composite after curing. The modifying agents are selectively released into the surrounding matrix in use in response to a predetermined stimulus be it internal or externally applied. The hollow fibers may be closed off or even coated to provide a way to keep the modifying agent in the fibers until the appropriate time for selective release occurs. Self-repair, smart fiber matrix composite materials capable of repairing microcracks, releasing corrosion inhibitors or permeability modifiers are described as preferred embodiments in concrete and polymer based shaped articles.
Owner:DRY CAROLYN M
Lightweight composite thermoplastic sheets including reinforcing skins
A multi-layered fiber reinforced sheet for automotive vehicle interior structural components includes, in an exemplary embodiment, a permeable fiber reinforced thermoplastic core layer having a first surface and a second surface. The core layer includes a plurality of reinforcing fibers bonded together with a thermoplastic resin, and has a density of about 0.1 gm / cc to about 1.8 gm / cc. The multi-layered fiber reinforced sheet also includes at least one first reinforcing skin applied to the first surface of the core layer, and at least one second reinforcing skin applied to the second surface of the core layer. Each first and second reinforcing skin includes a matrix of reinforcing fibers and a thermoplastic resin wherein the matrix of reinforcing fibers applied to the first surface are arranged in a bi-directional orientation and the matrix of reinforcing fibers applied to the second surface are arranged in a bi-directional orientation.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
Heat conduction type aramid nano insulation paper and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108978328AHigh strengthImprove insulation performancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperNanofiberDiameter ratio
The invention discloses heat conduction type aramid nano insulation paper and a preparation method thereof. According to the heat conduction type aramid nano insulation paper and the preparation method thereof, disclosed by the invention, aramid nano fiber with high strength, high modulus, high length-diameter ratio, good temperature resistance and good insulativity is utilized as a matrix, and good mechanical performance, good insulativity, good temperature resistance and good flexibility are given to aramid nano insulation paper; hydroxylated nano boron nitride is used as heat conduction filler and is dispersed in the aramid nano fiber matrix so as to be used for a main carrier for heat conduction, so that interface bonding is optimized, interface thermal resistance is reduced, high heatconductivity is given to the aramid nano insulation paper, and meanwhile, the insulavitity of the aramid nano insulation paper cannot be influenced; the problems that since the heat conductivity of aramid insulation paper at present is low, electrical insulation equipment is poor in heat dissipation and short in service life are solved; meanwhile, the problems that since a heat conduction composite resin impregnation technology is utilized, insulation paper is hard and crispy, the technology is complicated and the like are avoided.
Owner:宝鸡科达特种纸业有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com