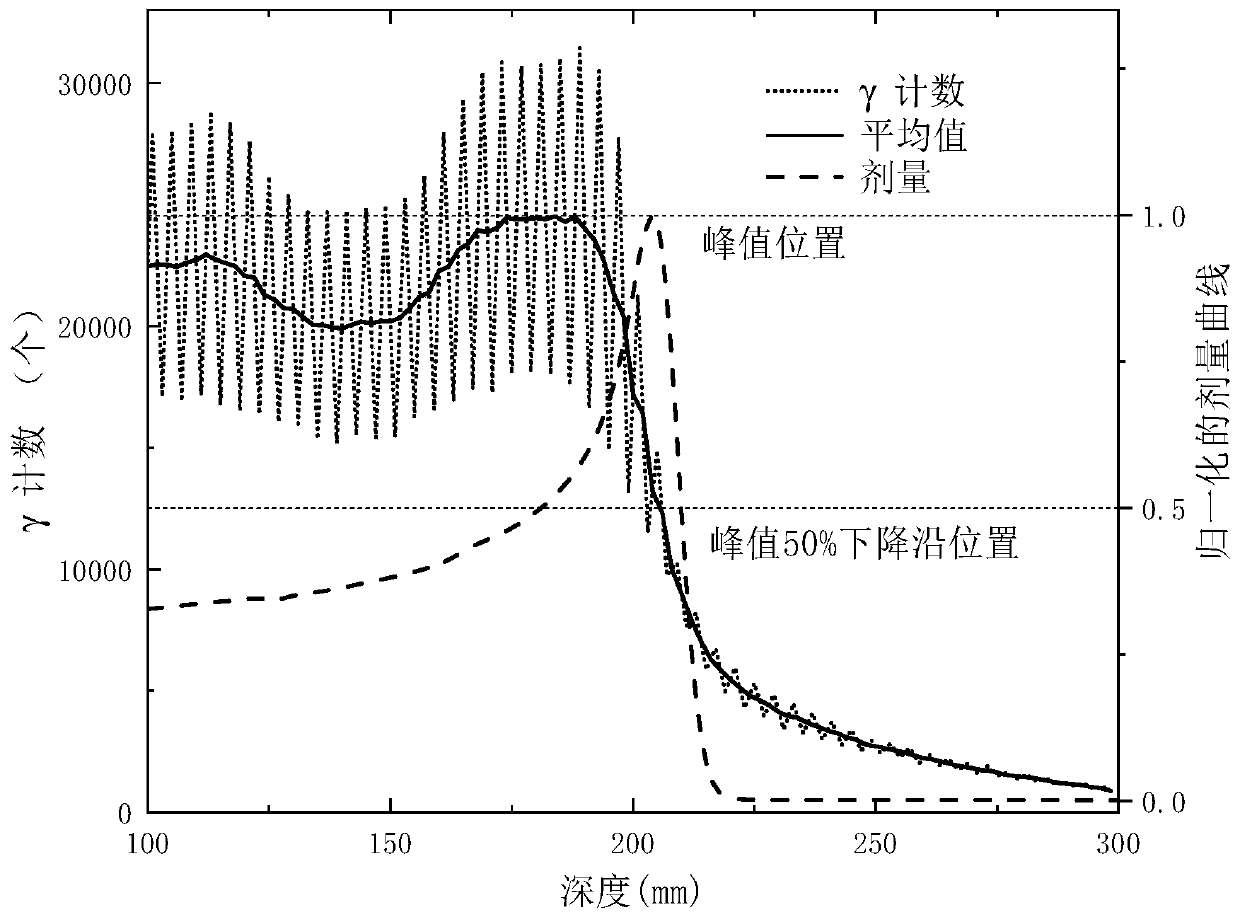
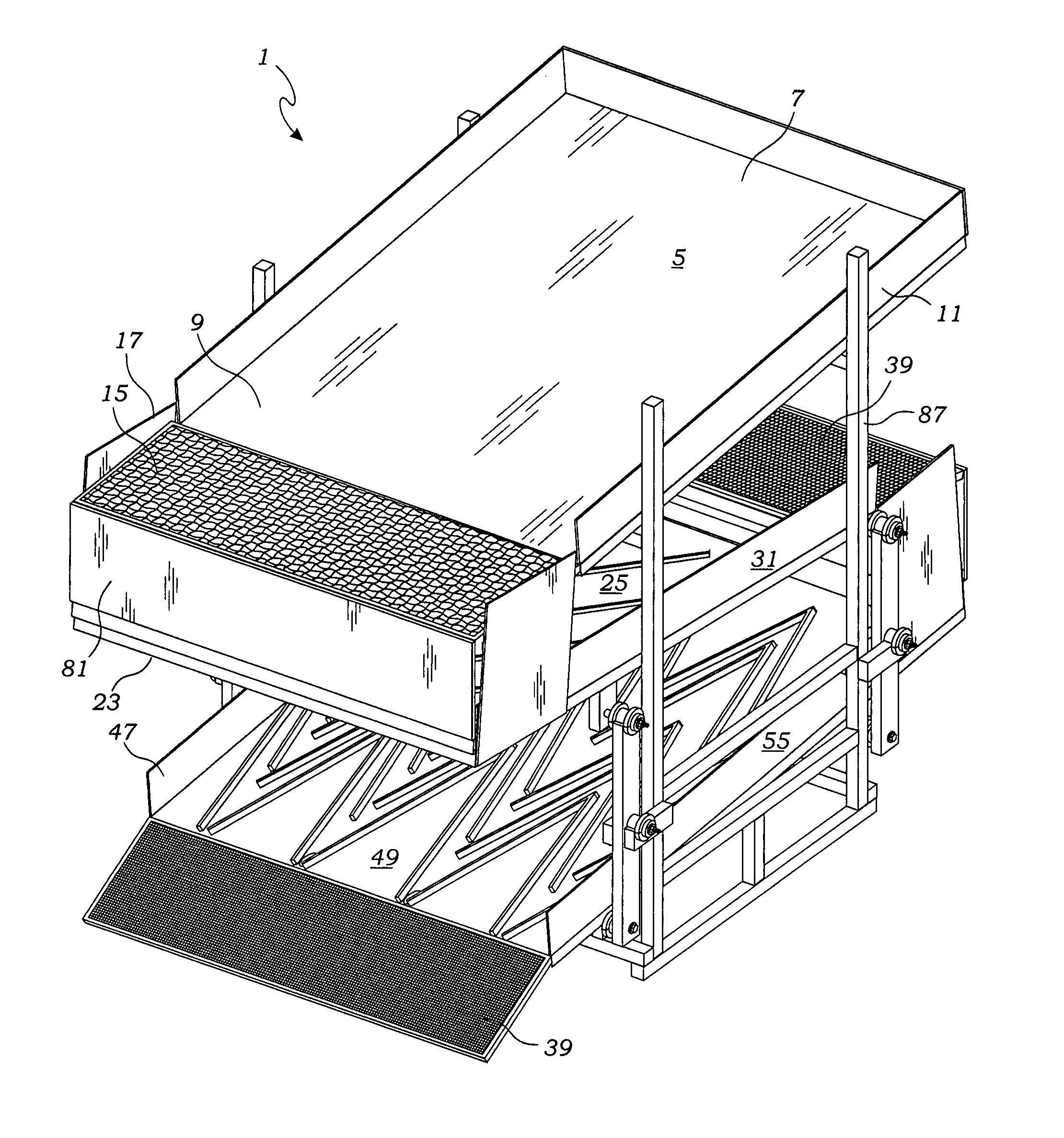
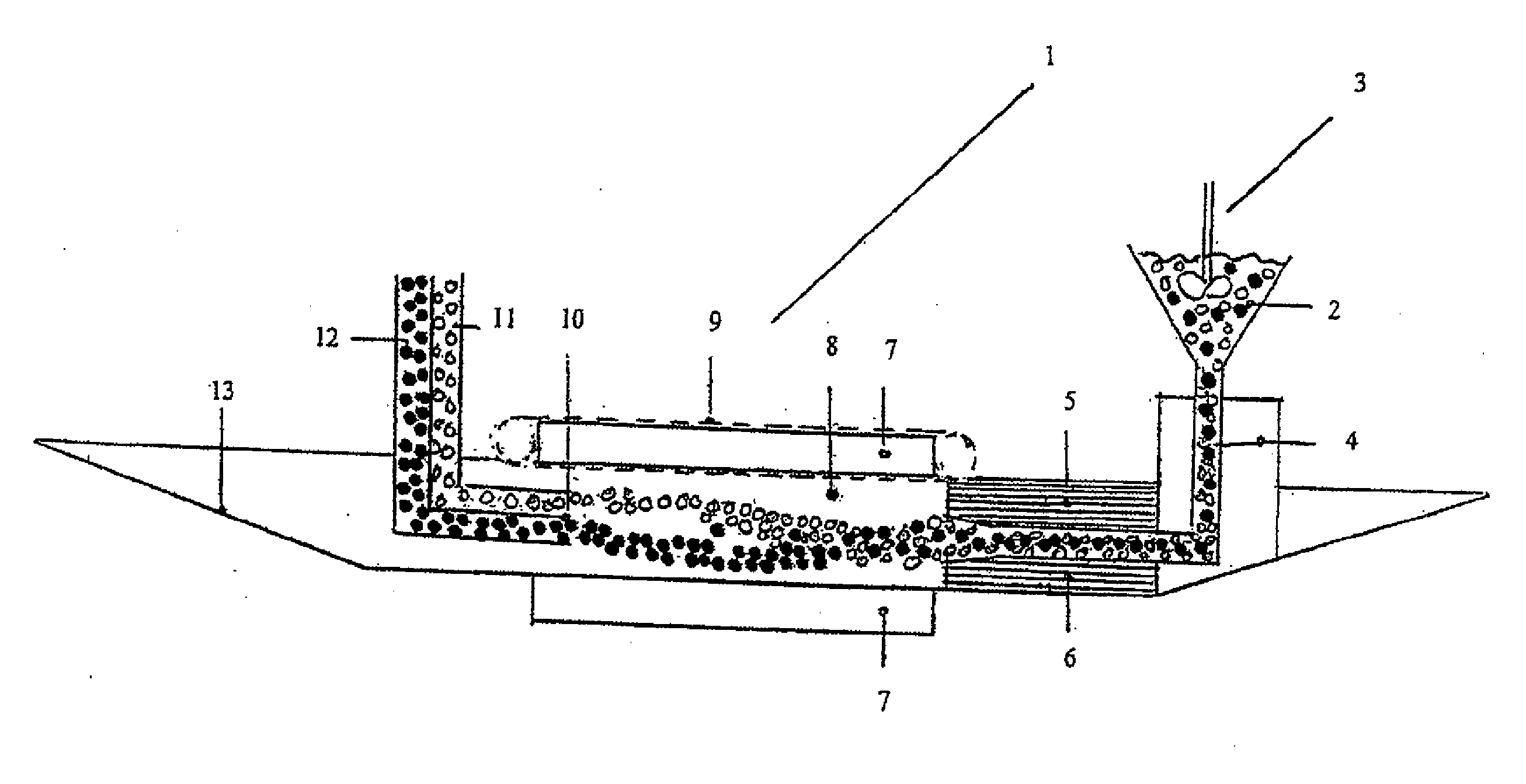
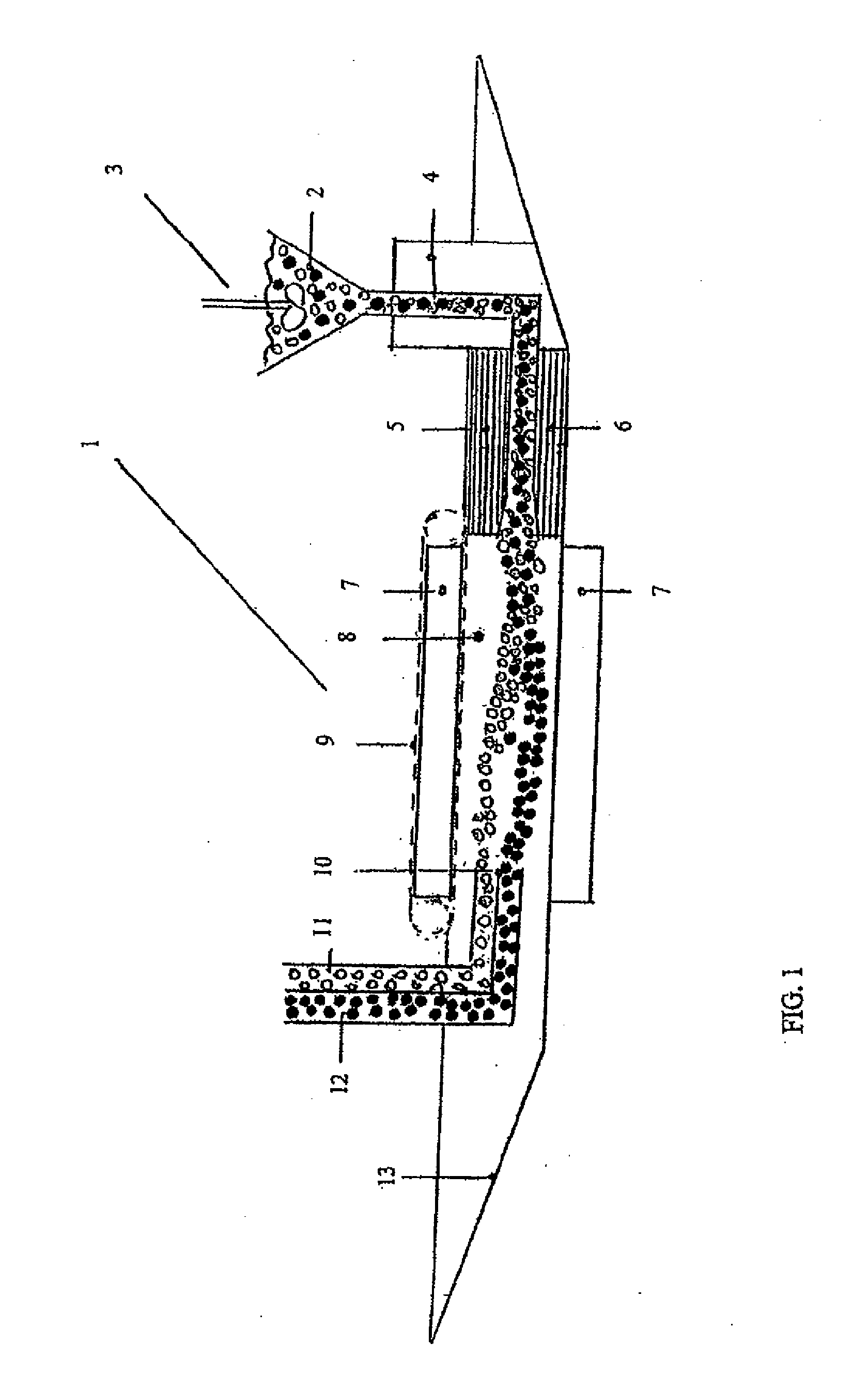
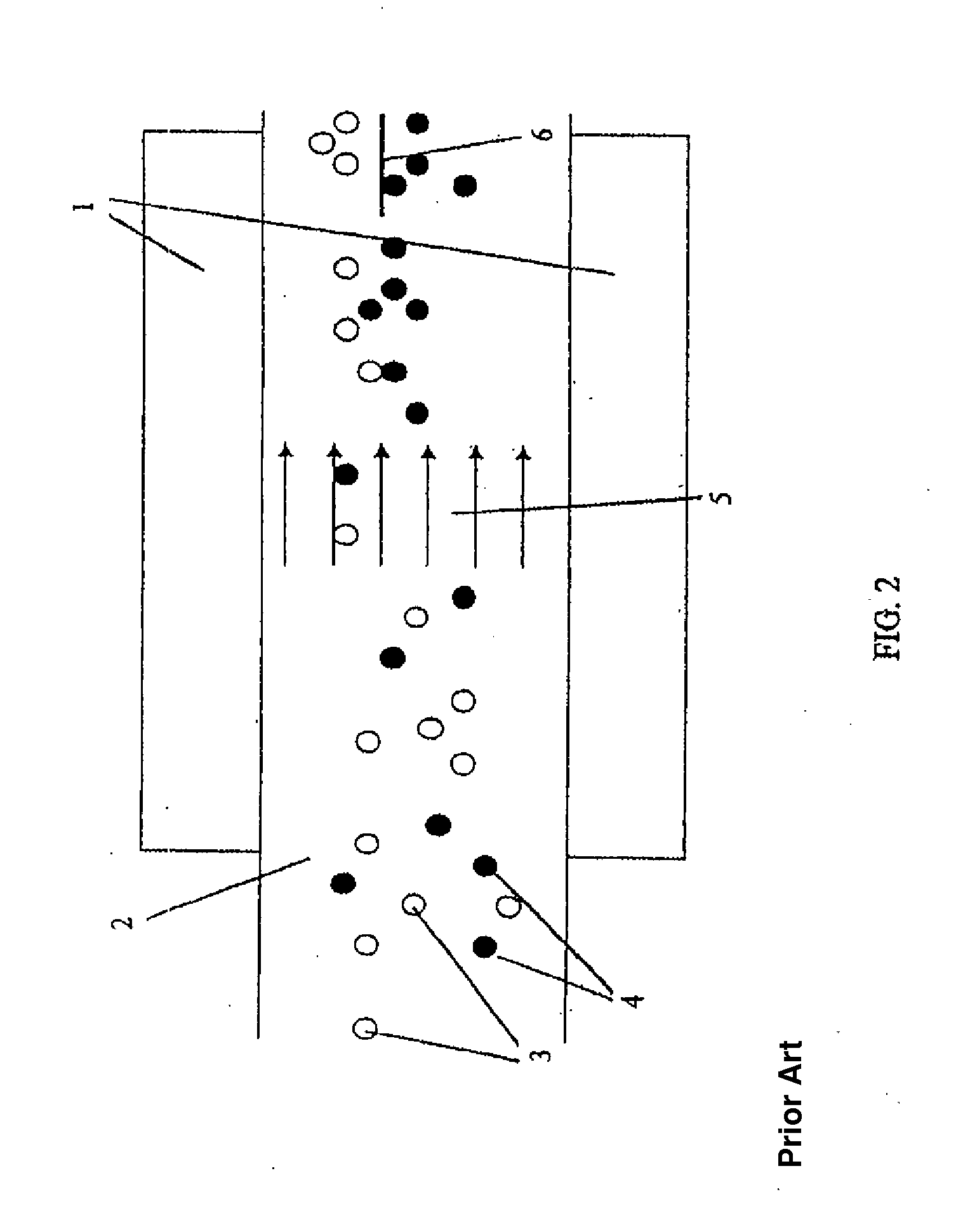
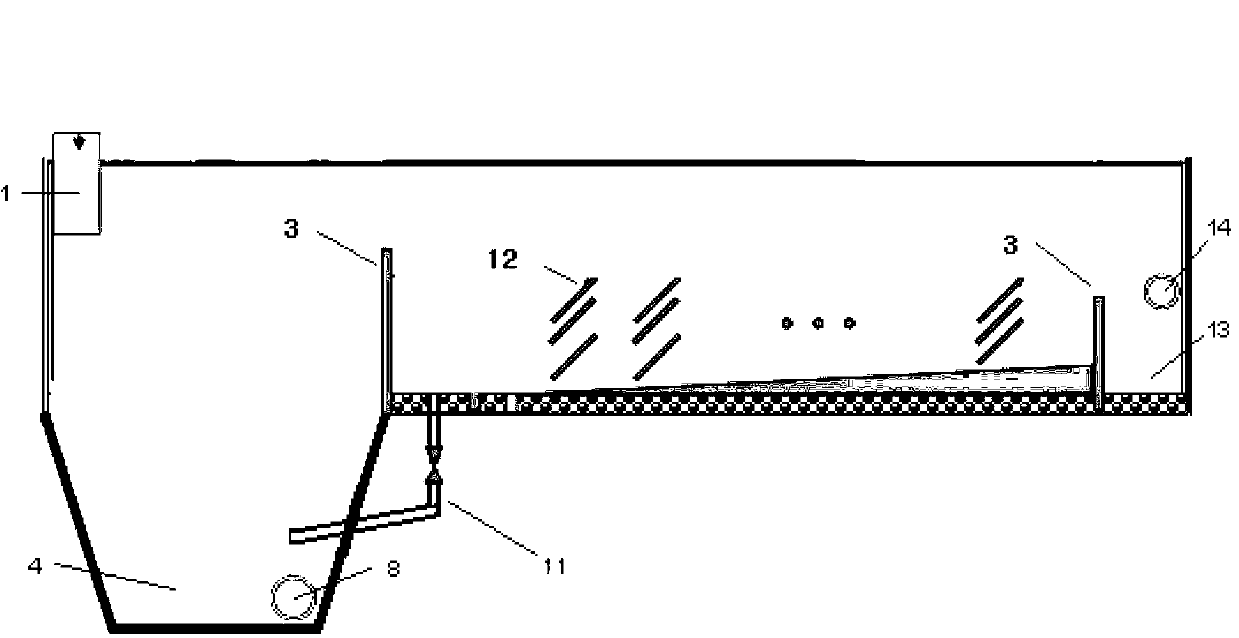
Patents
Literature
150 results about "Heavy particle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term heavy charged particle refers to those energetic particles whose mass is one atomic mass unit or greater. This category includes alpha particles, together with protons, deuterons, fission fragments, and other energetic heavy particles often produced in accelerators. These particles carry….
Golf club and other structures, and novel methods for making such structures
InactiveUS6723279B1Overcome deficienciesImprove performanceMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingFiberHeavy particle
Golf club structures, including club heads and shafts, composed of composites comprised of a matrix of metal, such as an aluminum alloy, or a plastic material and a fiber such as graphite or a ceramic, which may be whiskerized, and which may also be selectively weighted as in the toe and heel of a club head, with heavy particles such as tungsten metal. The club structure may also be surface hardened by applying a coating of fullerenes to a metal club structure and heat treating it to produce a hard coating of metal carbide, preferably by coating a titanium golf club structure with fullerenes and heat treating the coated structure to produce a titanium carbide surface.
Owner:MATERIALS & ELECTROCHEM RES
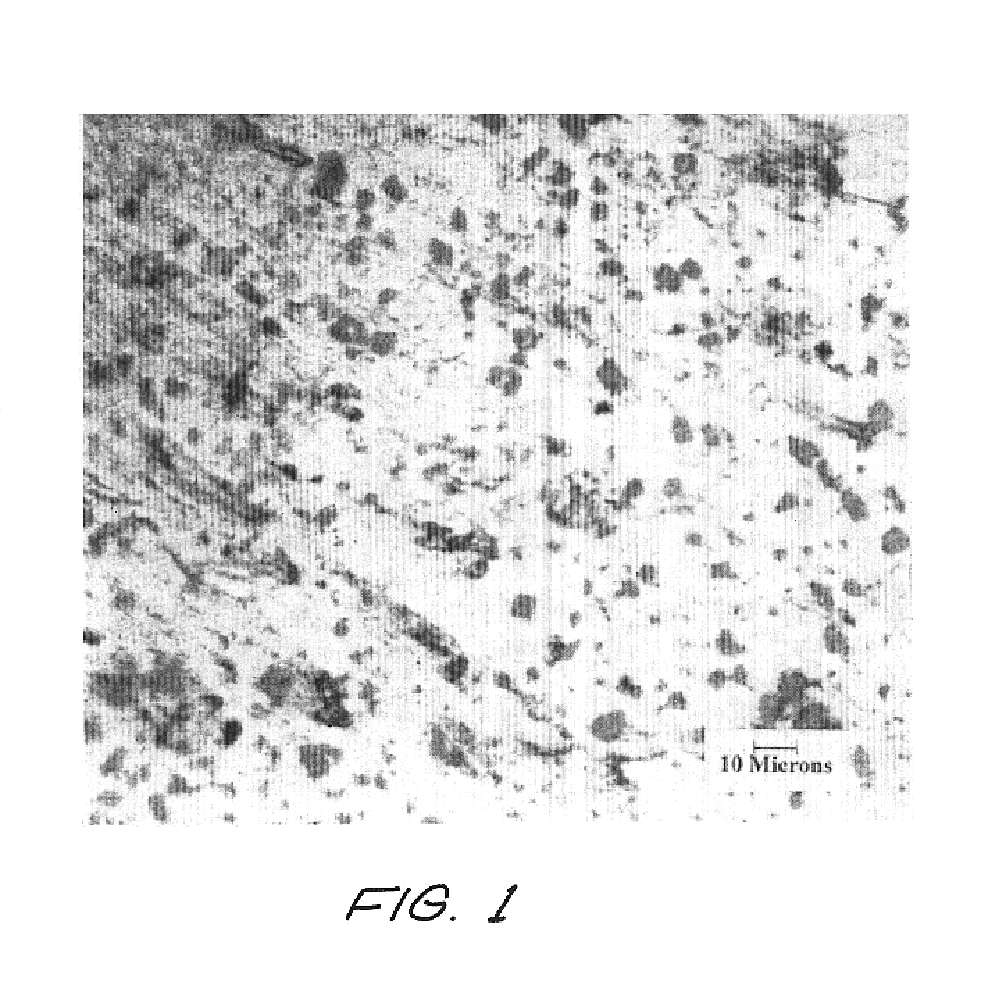
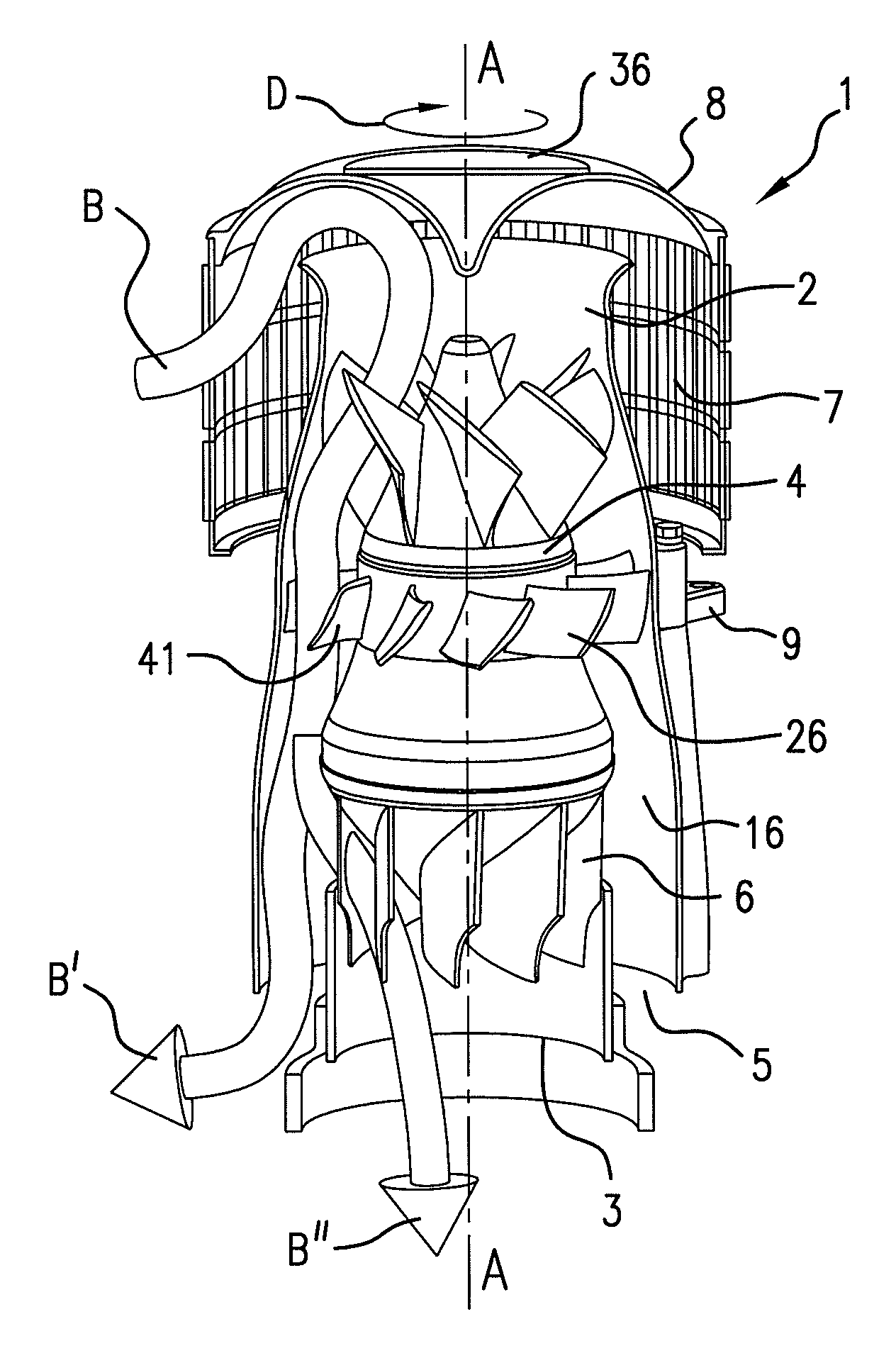
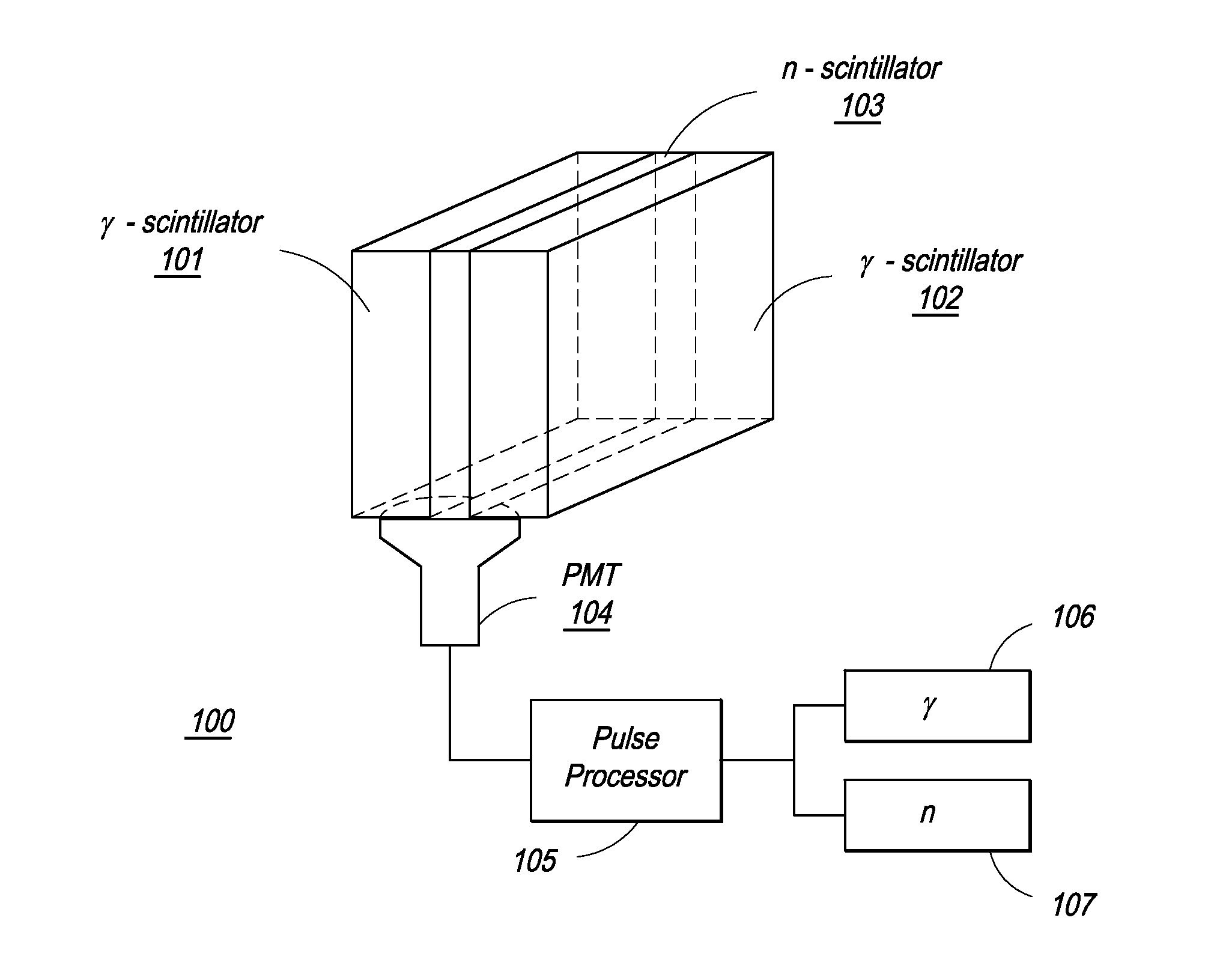
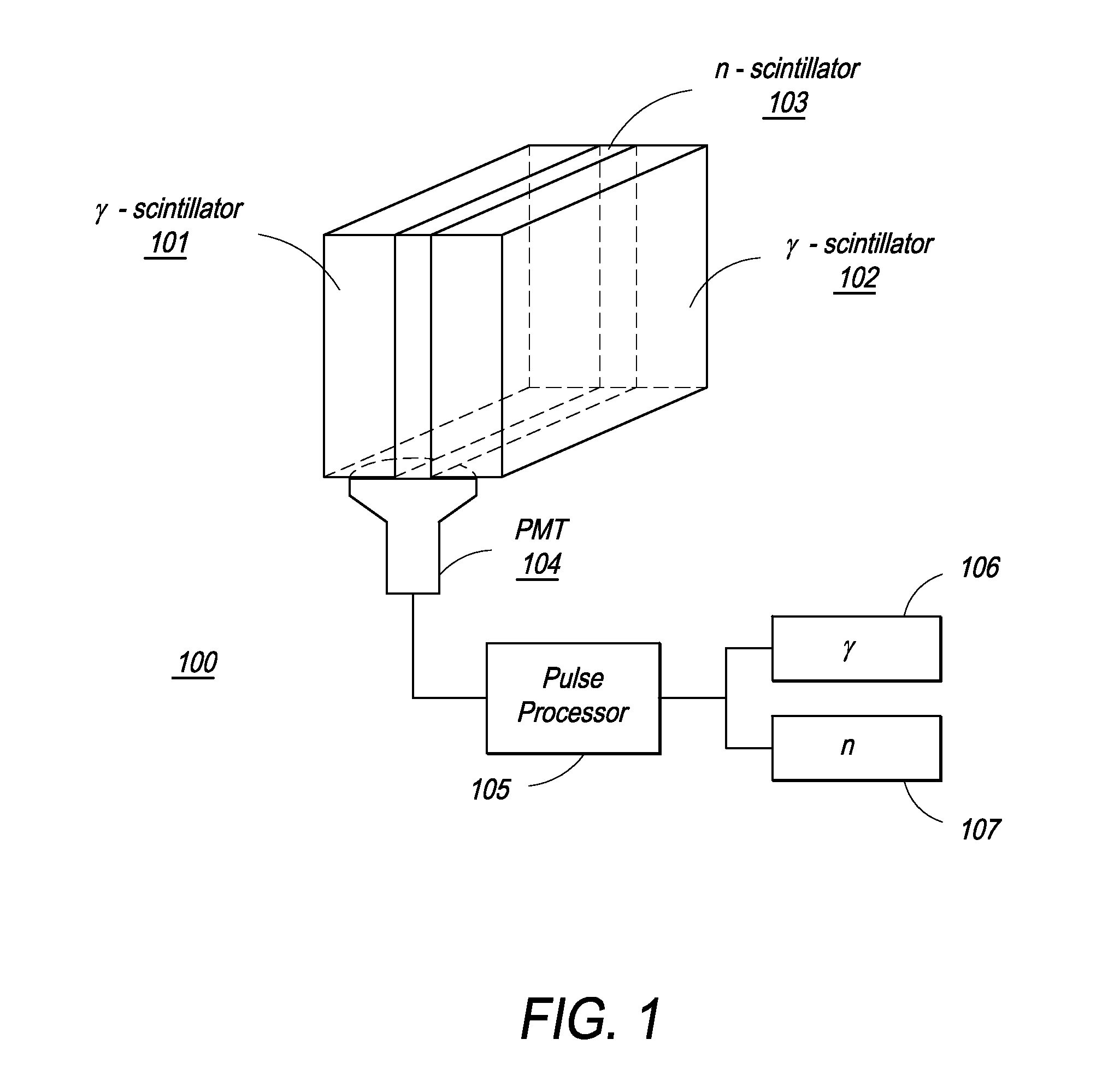
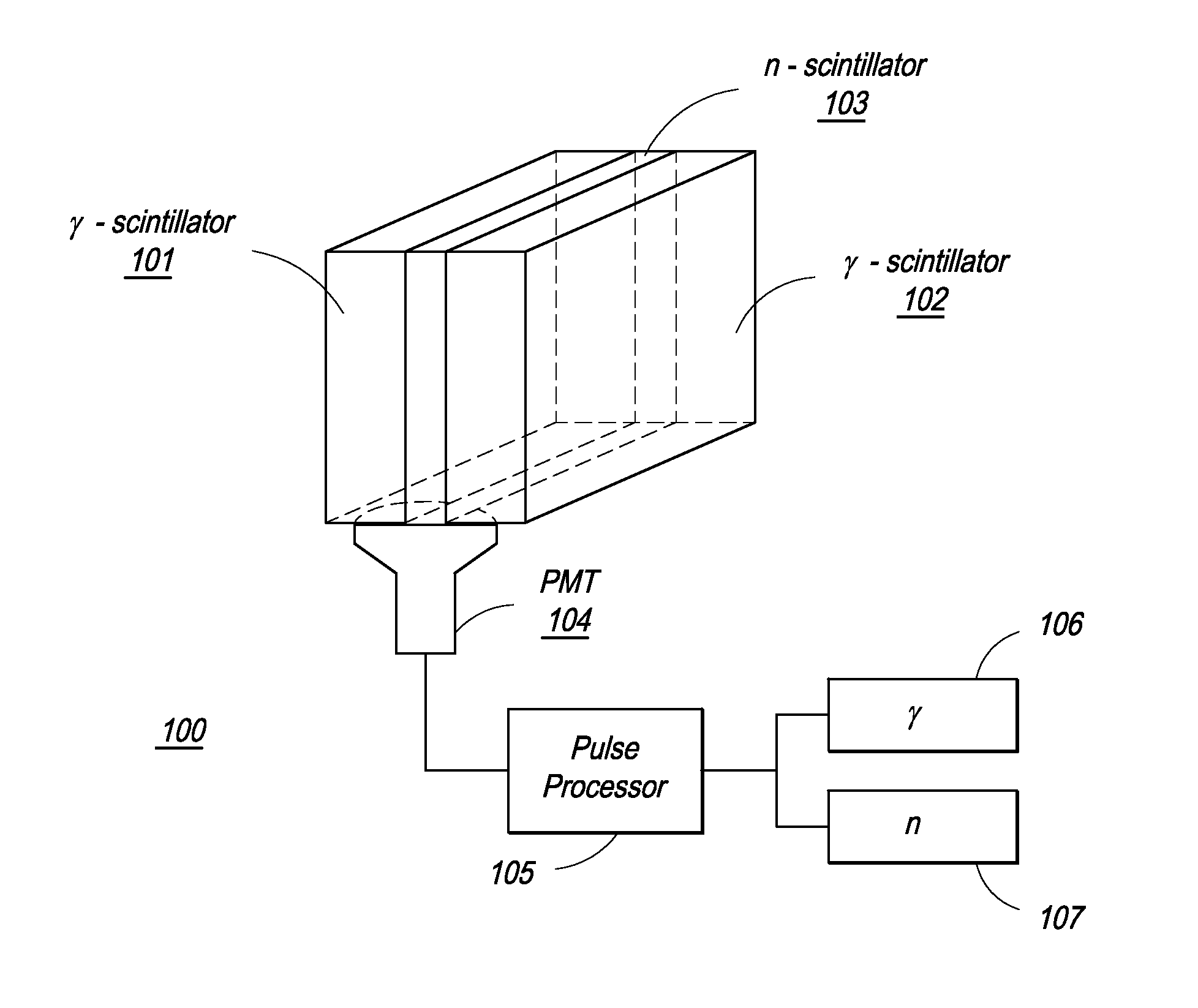
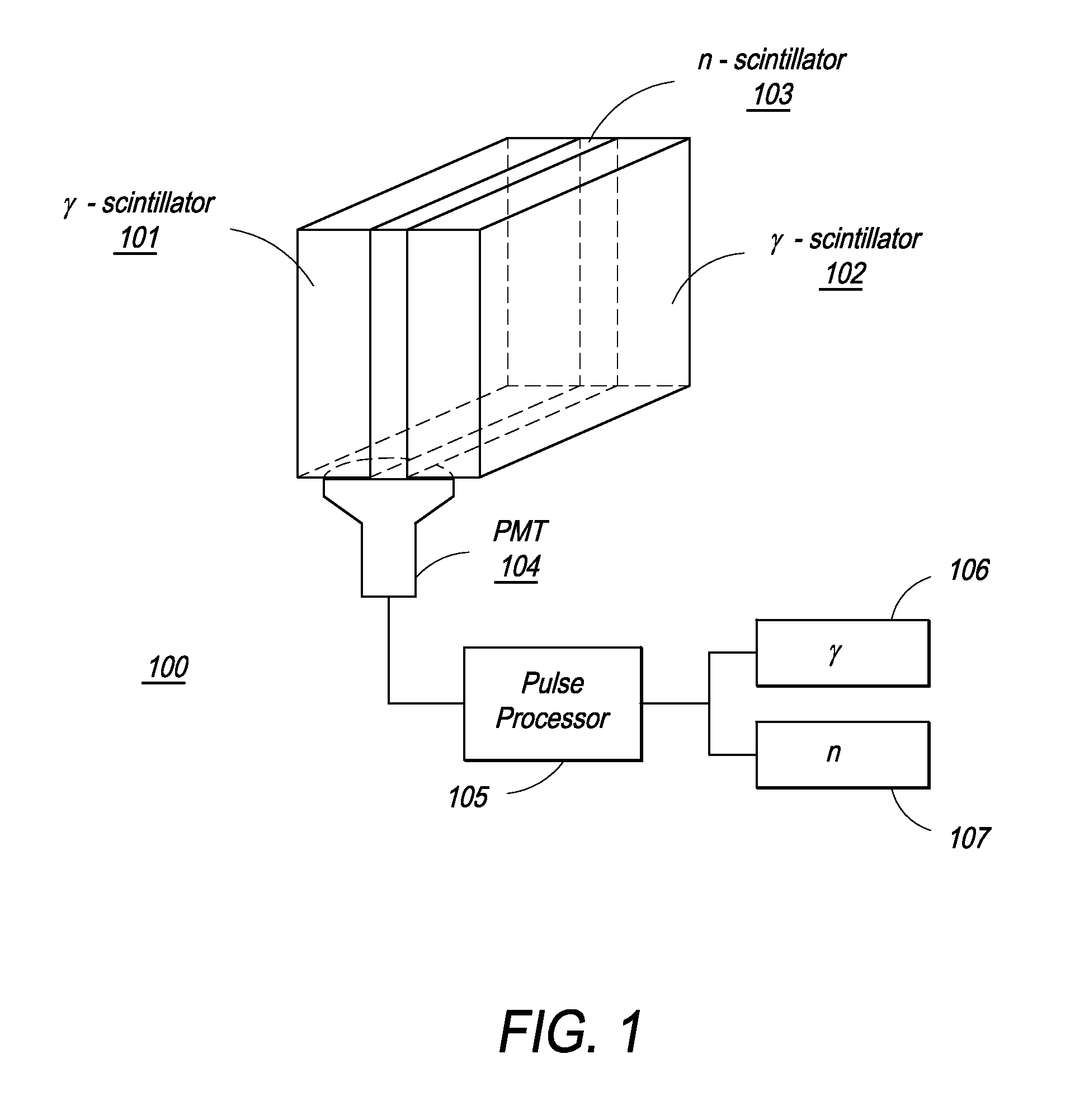
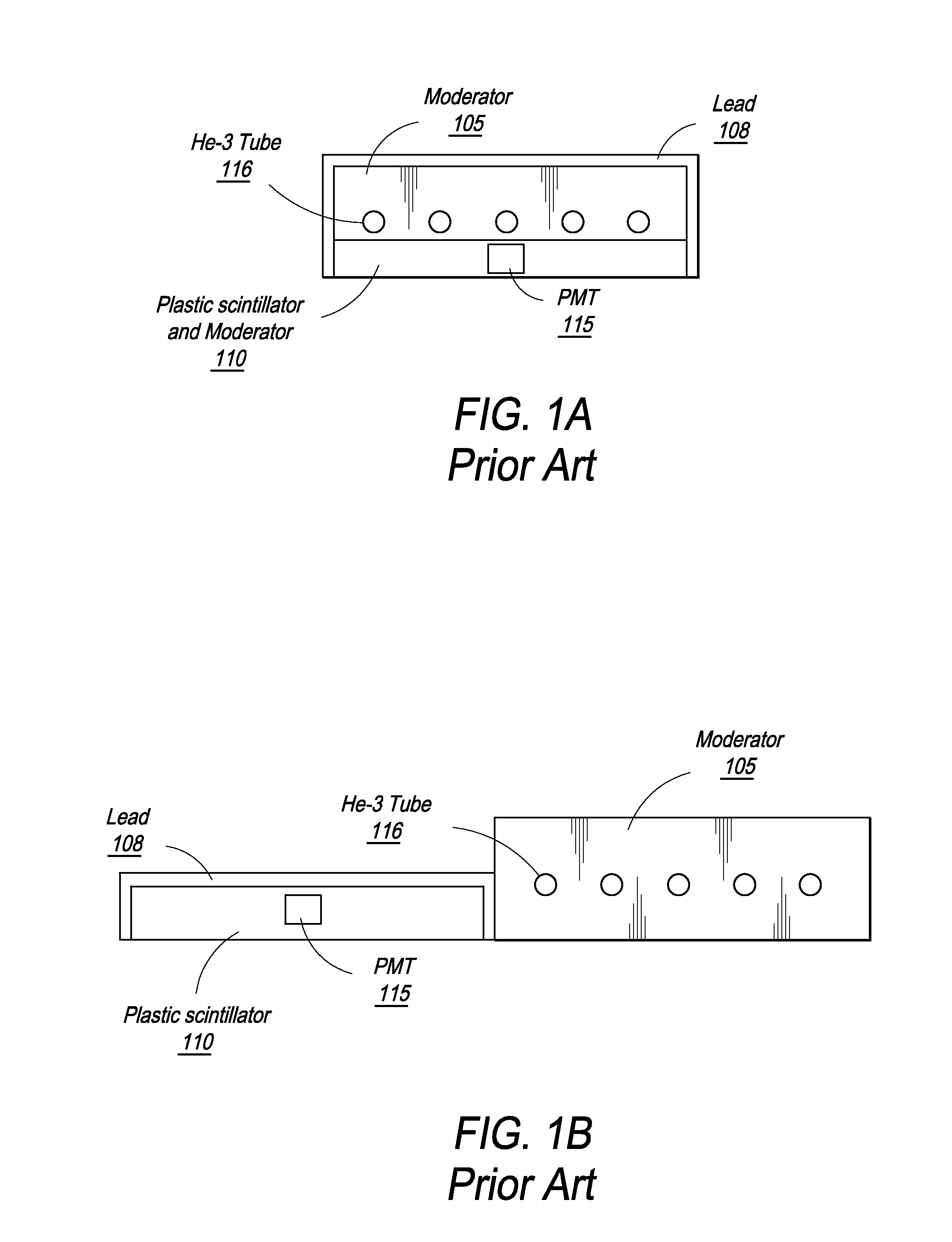
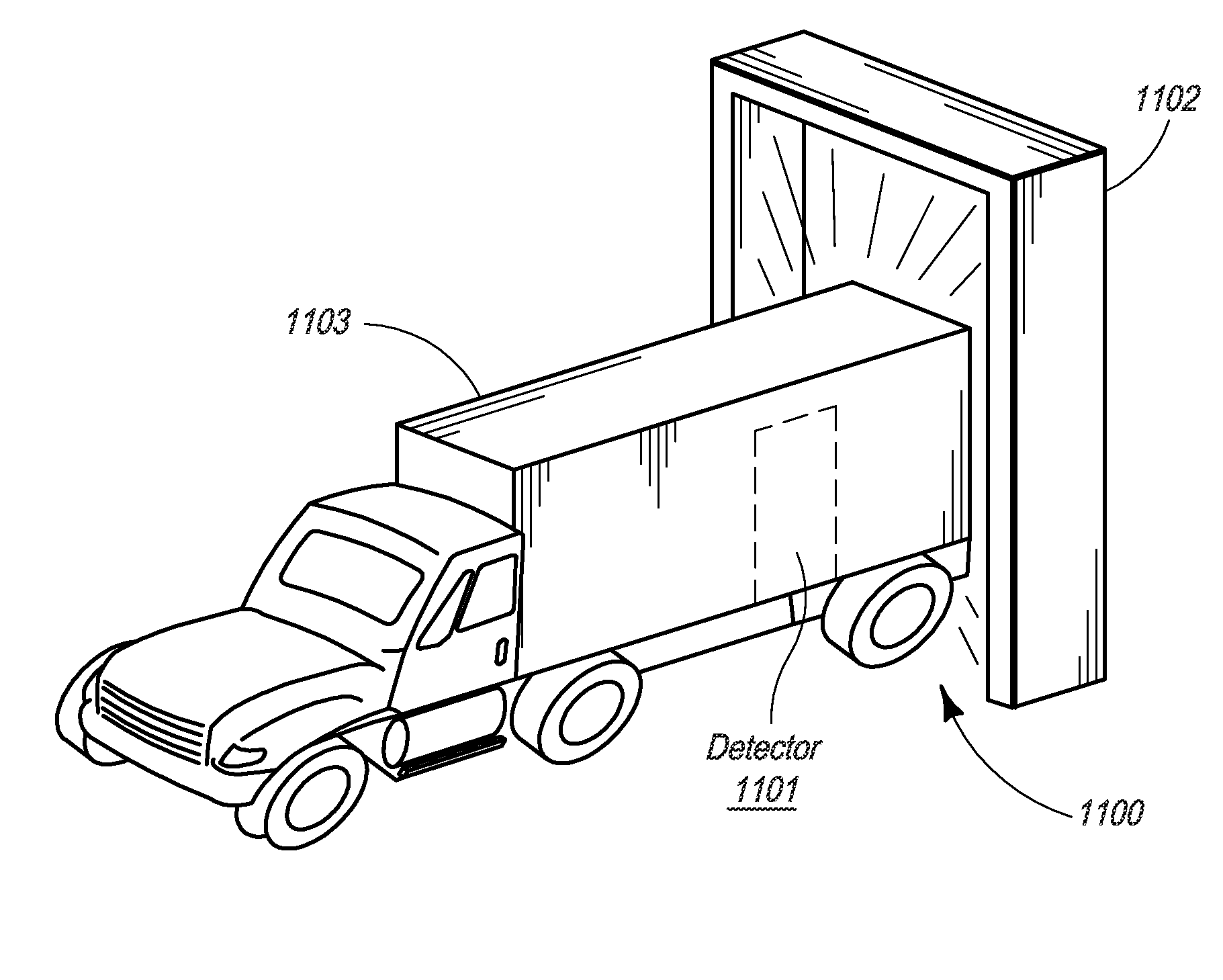
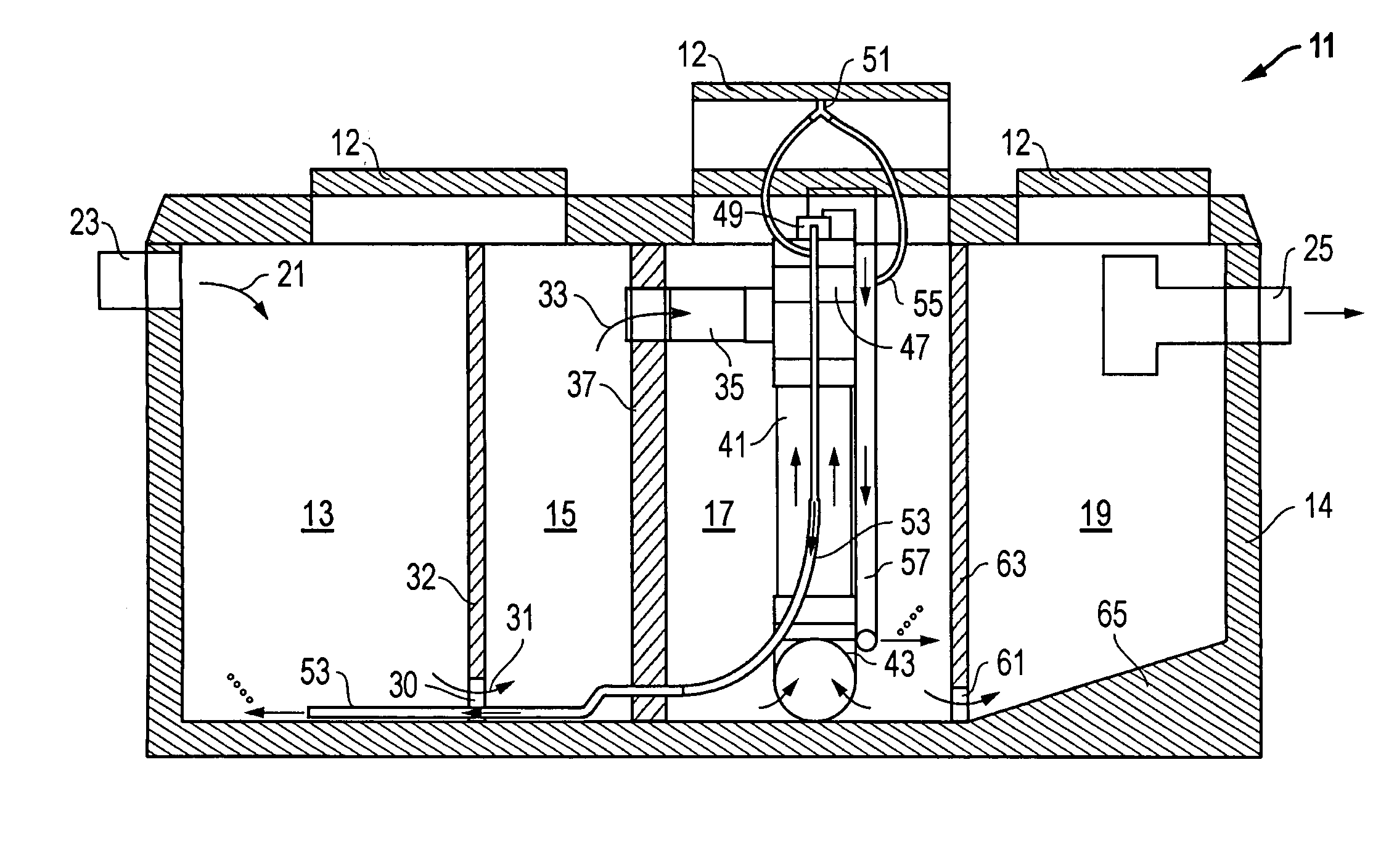
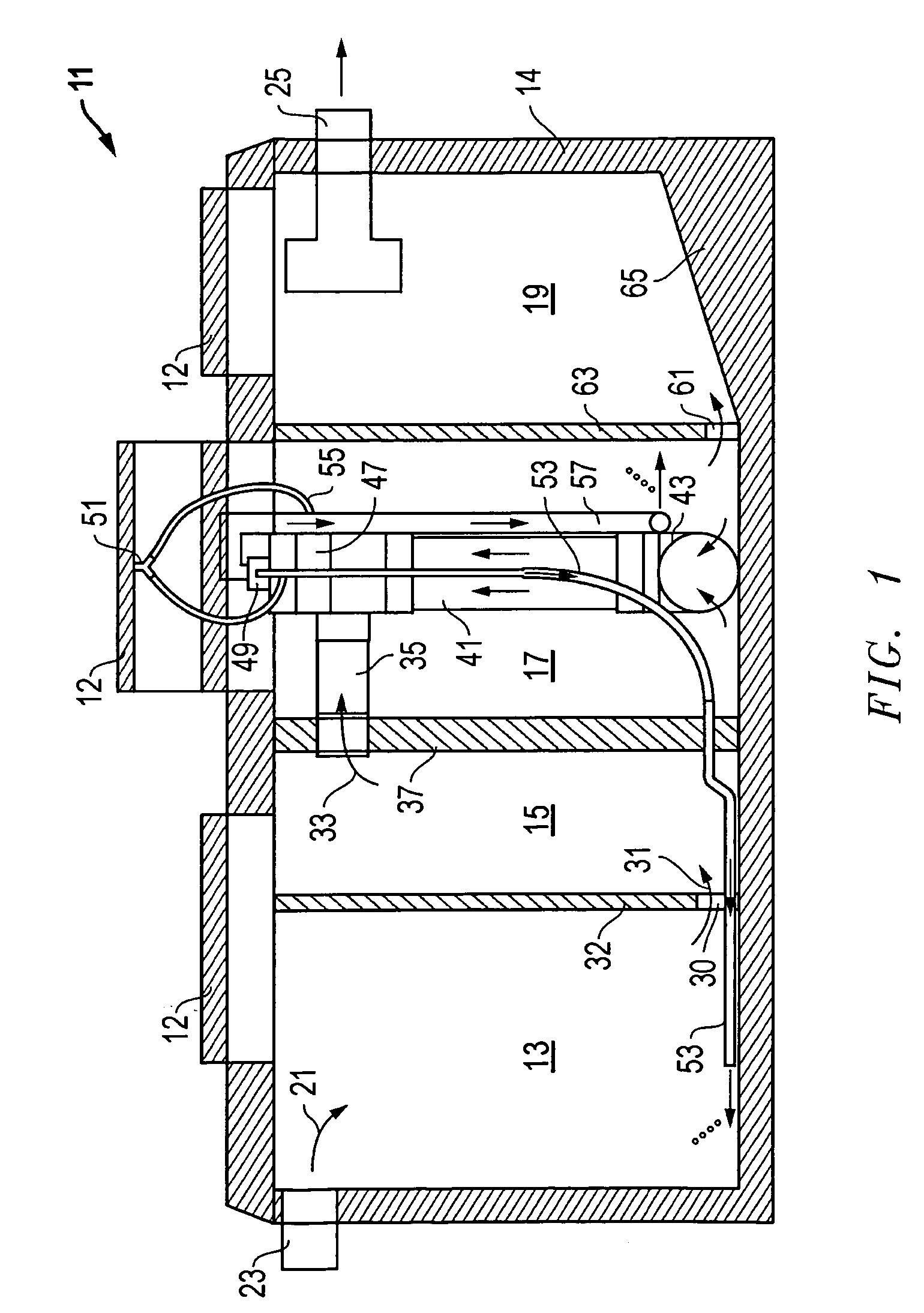
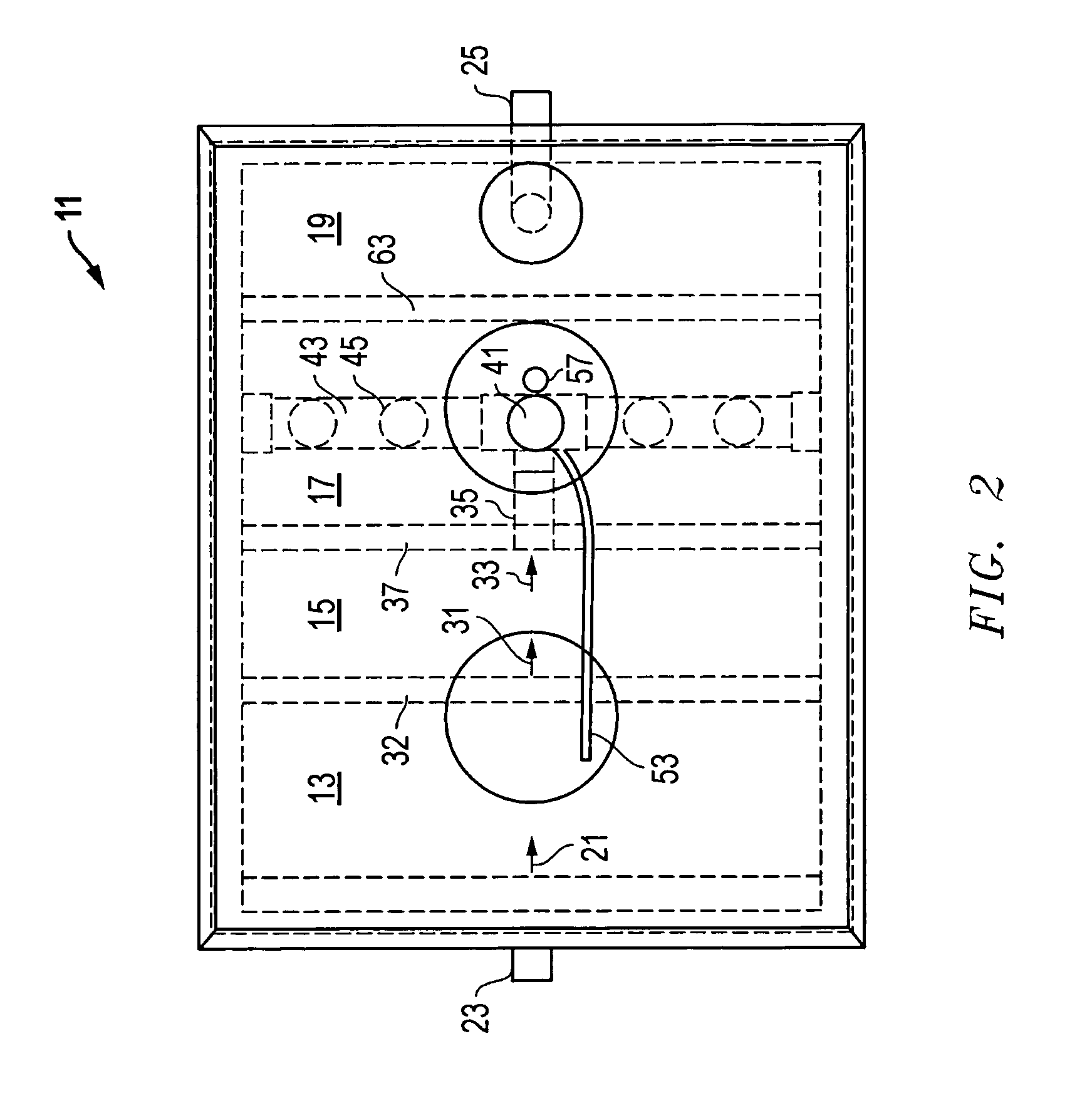
Composite Gamma-Neutron Detection System
ActiveUS20110204243A1Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
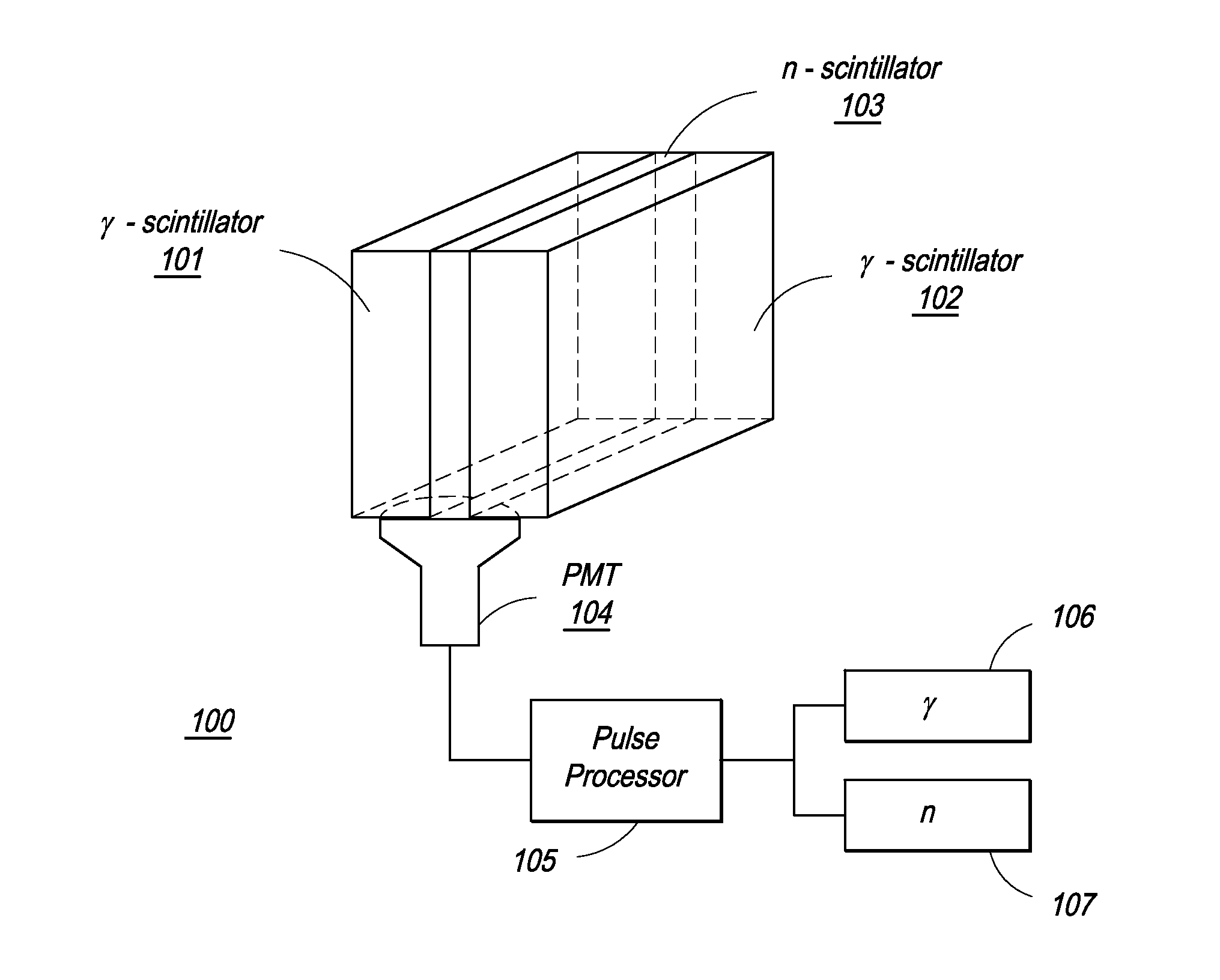
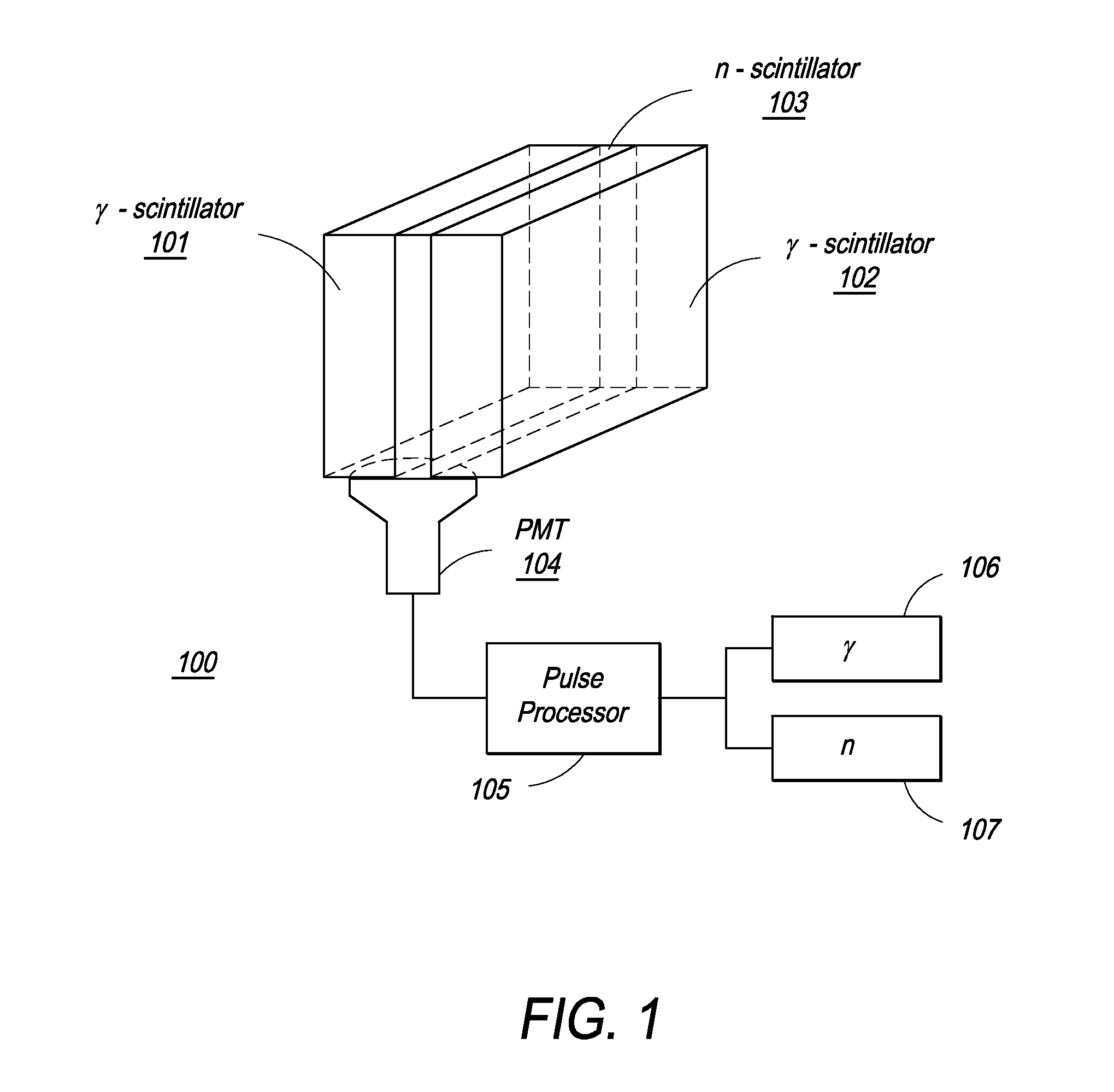
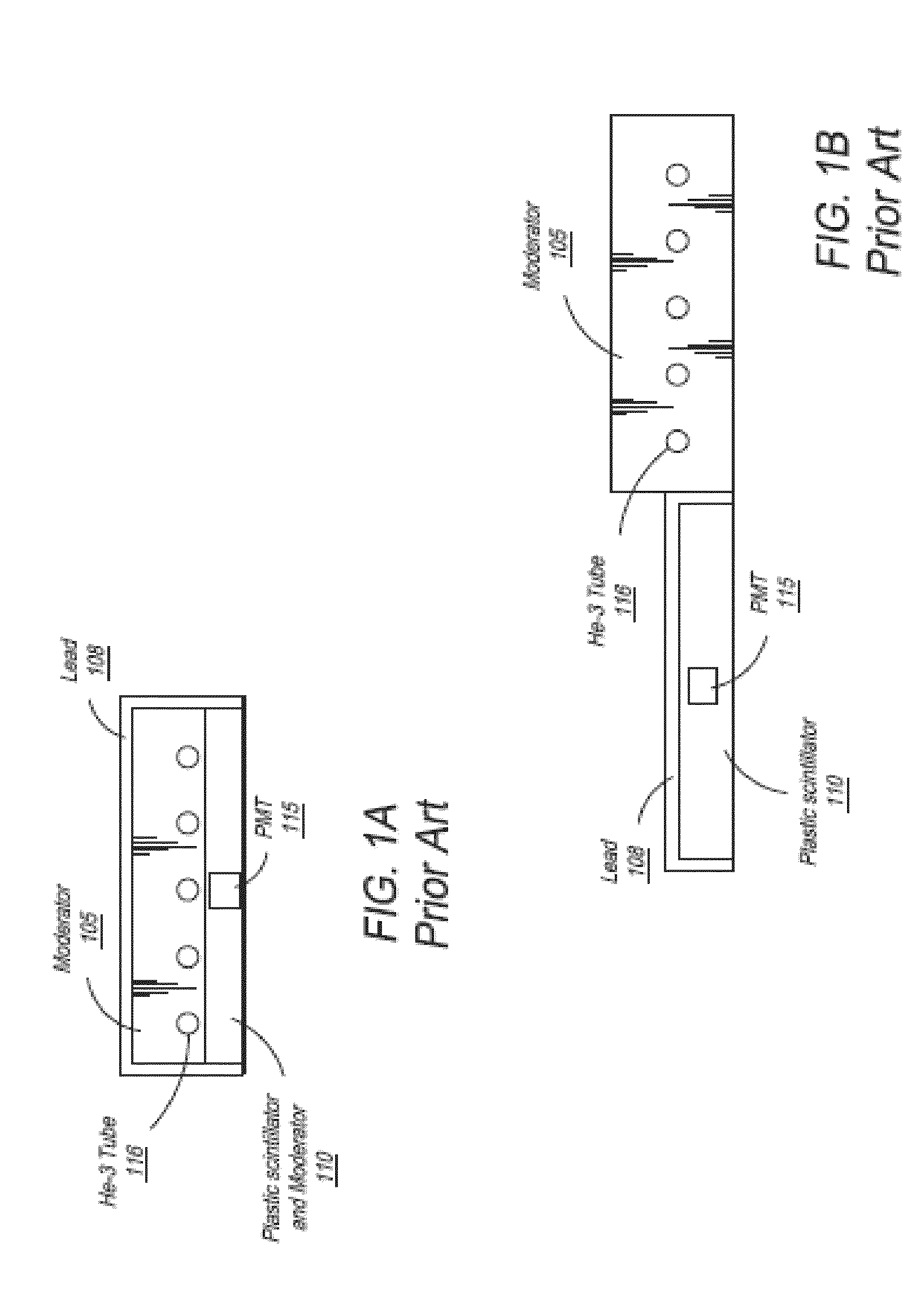
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Powered air cleaning system and air cleaning method
InactiveUS7056368B2Efficient removalAvoids and reduces problemCombination devicesLiquid degasificationParticulate debrisHeavy particle
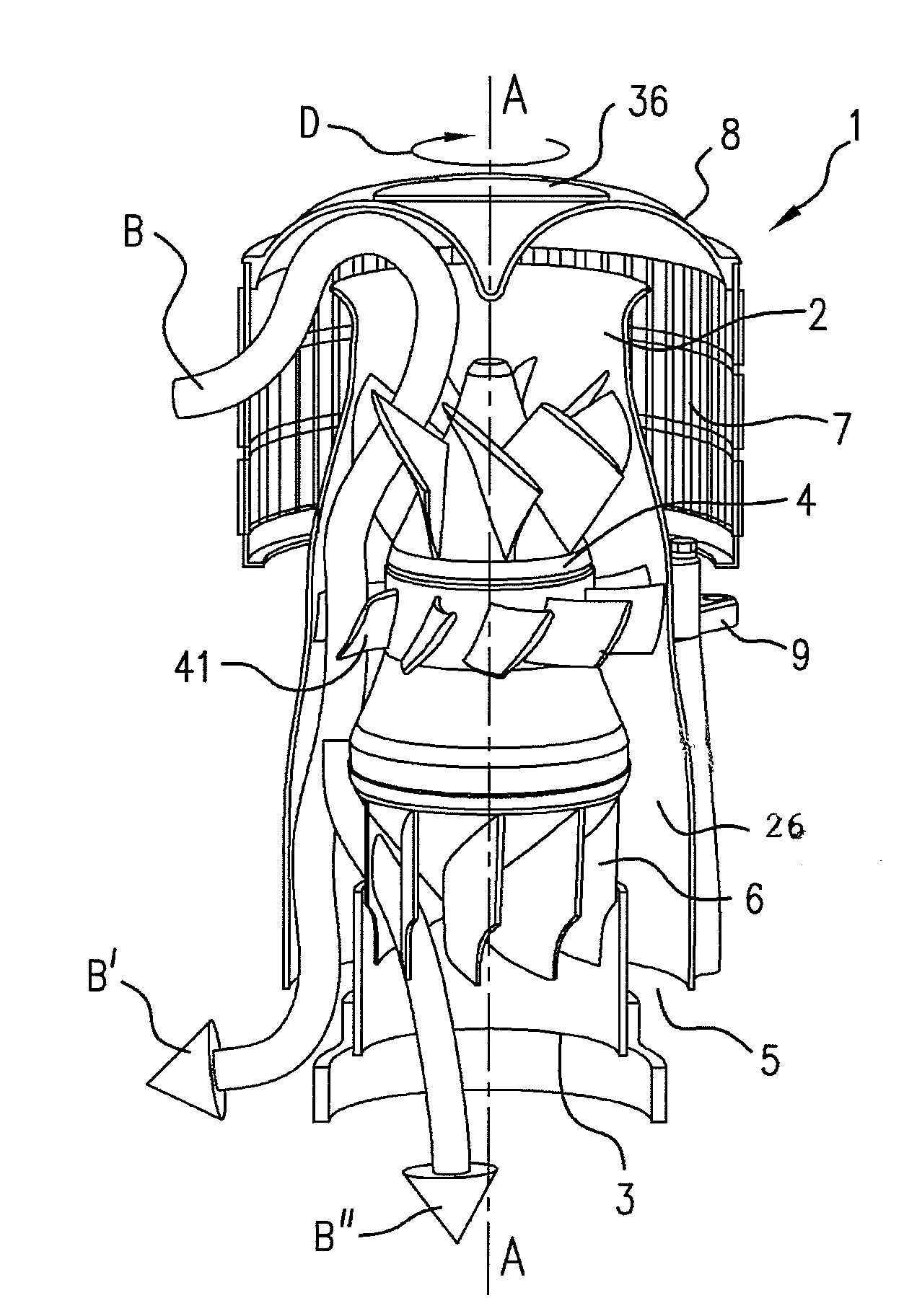
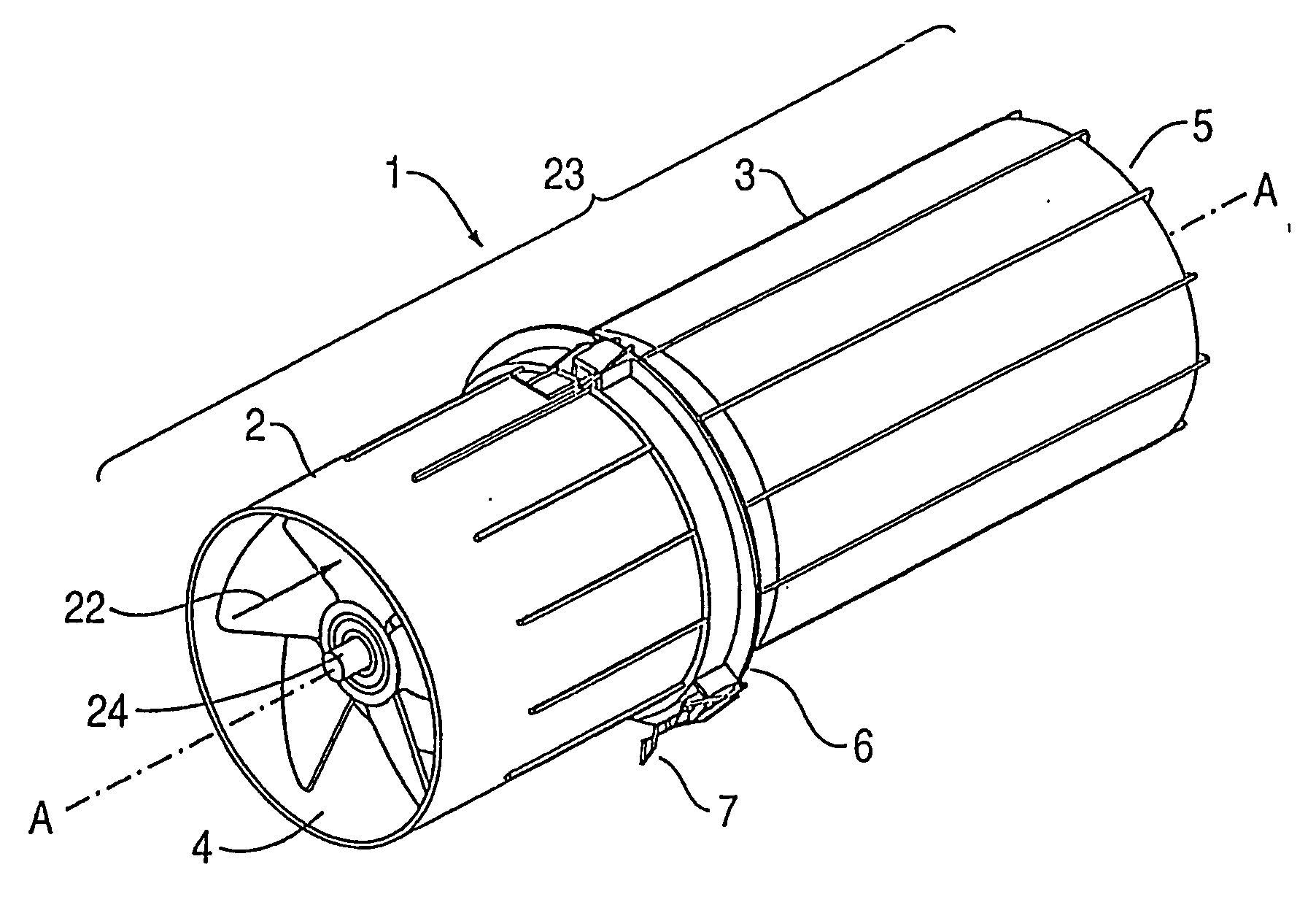
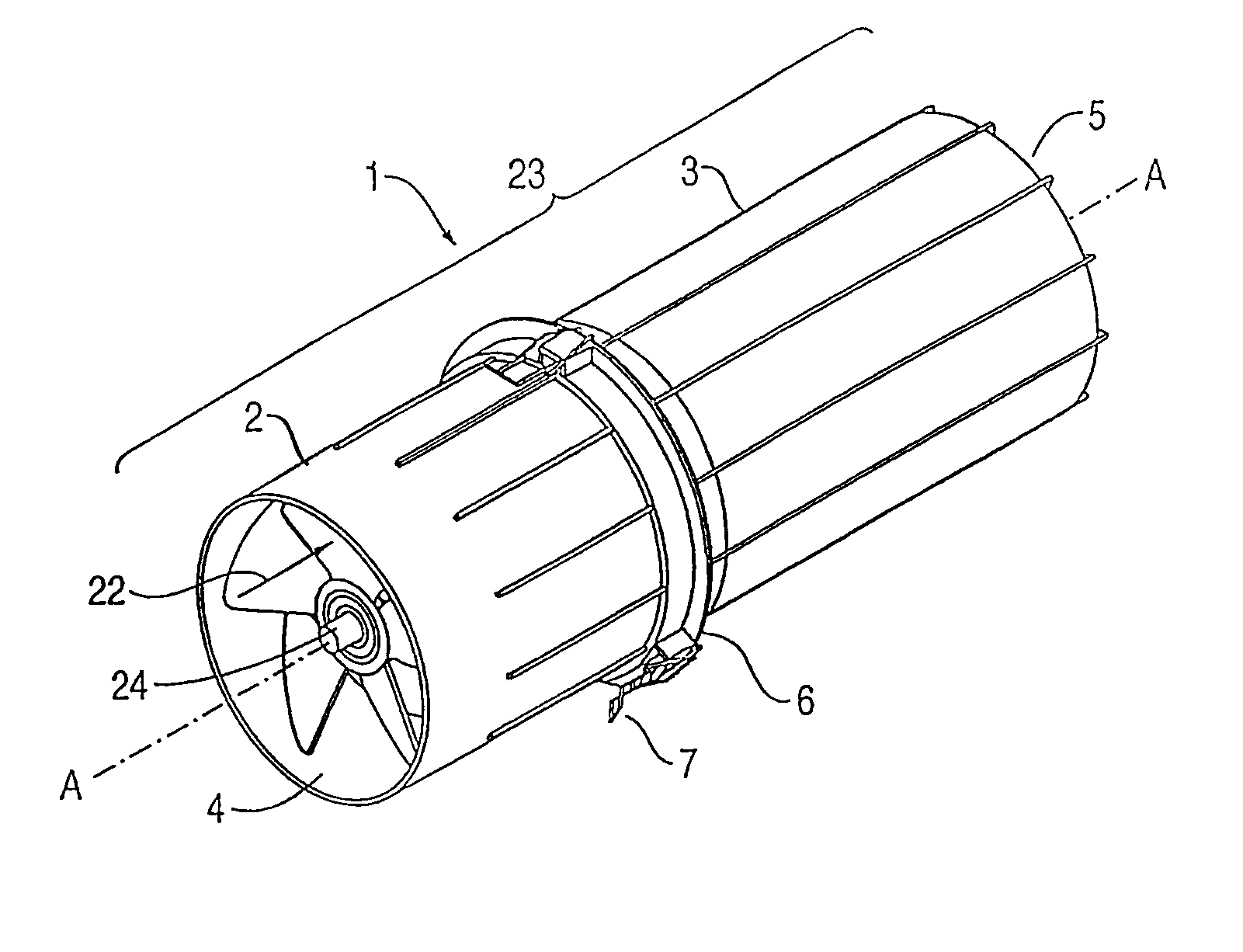
A powered air cleaning system (1) and air cleaning method are disclosed. The system has a flow path (22) extending through the system from an air inlet (4) to a clean air outlet (5). A motor-driven fan (24) located along the flow path draws particulate debris laden air into the inlet and rotates it about an axis (A—A) to form a rotating flow that stratifies the debris laden air with the heaviest particles in the outermost orbits of the rotating flow. An ejector port (25) is provided for ejecting particulate debris laden air from the stratified rotating flow in the system to the environment. An air filter (9) located within the rotating flow and across the flow path upstream of the outlet filters air from the innermost orbits of the stratified rotating flow. The motor-driven fan is operated to maintain a positive air pressure in the system on the filter even with cyclic air flow demands so that the rotating air flow continually sweeps the outside surface of the air filter to minimize buildup of debris on the filter.
Owner:SY KLONE
Powered air cleaning system and air cleaning method
ActiveUS20090101013A1Reduction in operation performanceHigh operating costsCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulate debrisMotor drive
A powered air cleaning system has a flow path extending through the system from an inlet to an outlet. A motor-driven fan is located along the flow path to draw particulate debris laden air into the inlet and rotate it about an axis to form a rotating flow that stratifies the debris laden air with the heaviest particles in the outermost orbits of the rotating flow. An ejector port ejects particulate debris laden air from the stratified rotating flow in the system. At least one de-swirl component located within the rotating flow aerodynamically redirects clean air from the innermost orbits of the stratified rotating flow toward the outlet to provide a positive airflow pressure out of the outlet. The system has a variable speed fan motor and an integrated controller for adjusting the speed of the motor and thereby the flow rate of clean air through the outlet of the system. The controller receives a signal that is a function of airflow requirements of a device supplied with clean air by the system. The system can be mounted above or below a hood housing an engine to be supplied with clean air.
Owner:SY KLONE
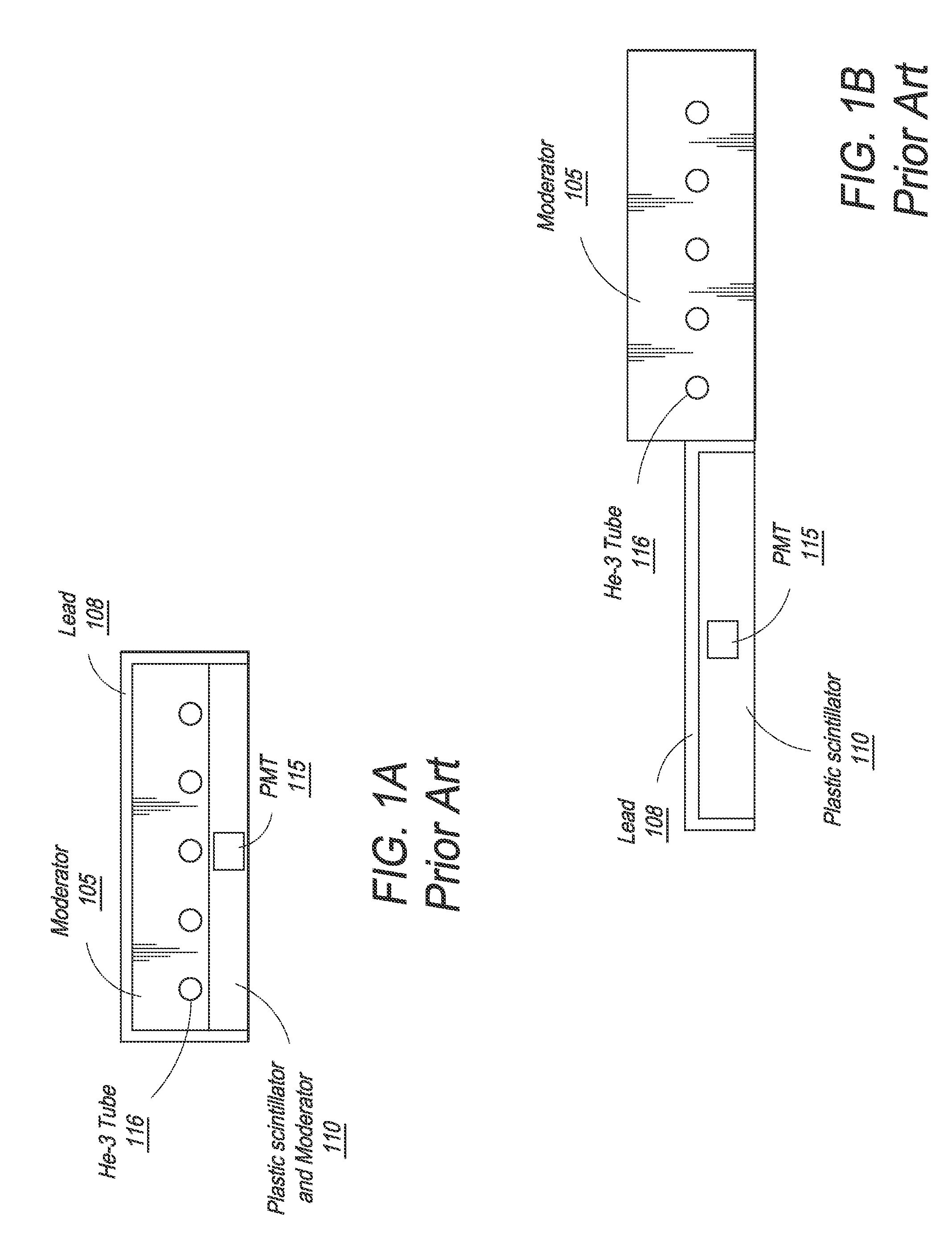
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
ActiveUS8389941B2Avoid cross contaminationMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Composite gamma-neutron detection system
InactiveUS20140197321A1Avoid cross contaminationMeasurement with scintillation detectorsPhotometryHeavy particleLight guide
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. The detector consists of one or more thin screens embedded in transparent hydrogenous light guides, which also serve as a neutron moderator. The emitted particles interact with the scintillator screen and produce a high light output, which is collected by the light guides into a photomultiplier tube and produces a signal from which the neutrons are counted. Simultaneous gamma-ray detection is provided by replacing the light guide material with a plastic scintillator. The plastic scintillator serves as the gamma-ray detector, moderator and light guide. The neutrons and gamma-ray events are separated employing Pulse-Shape Discrimination (PSD). The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:BENDAHAN JOSEPH +1
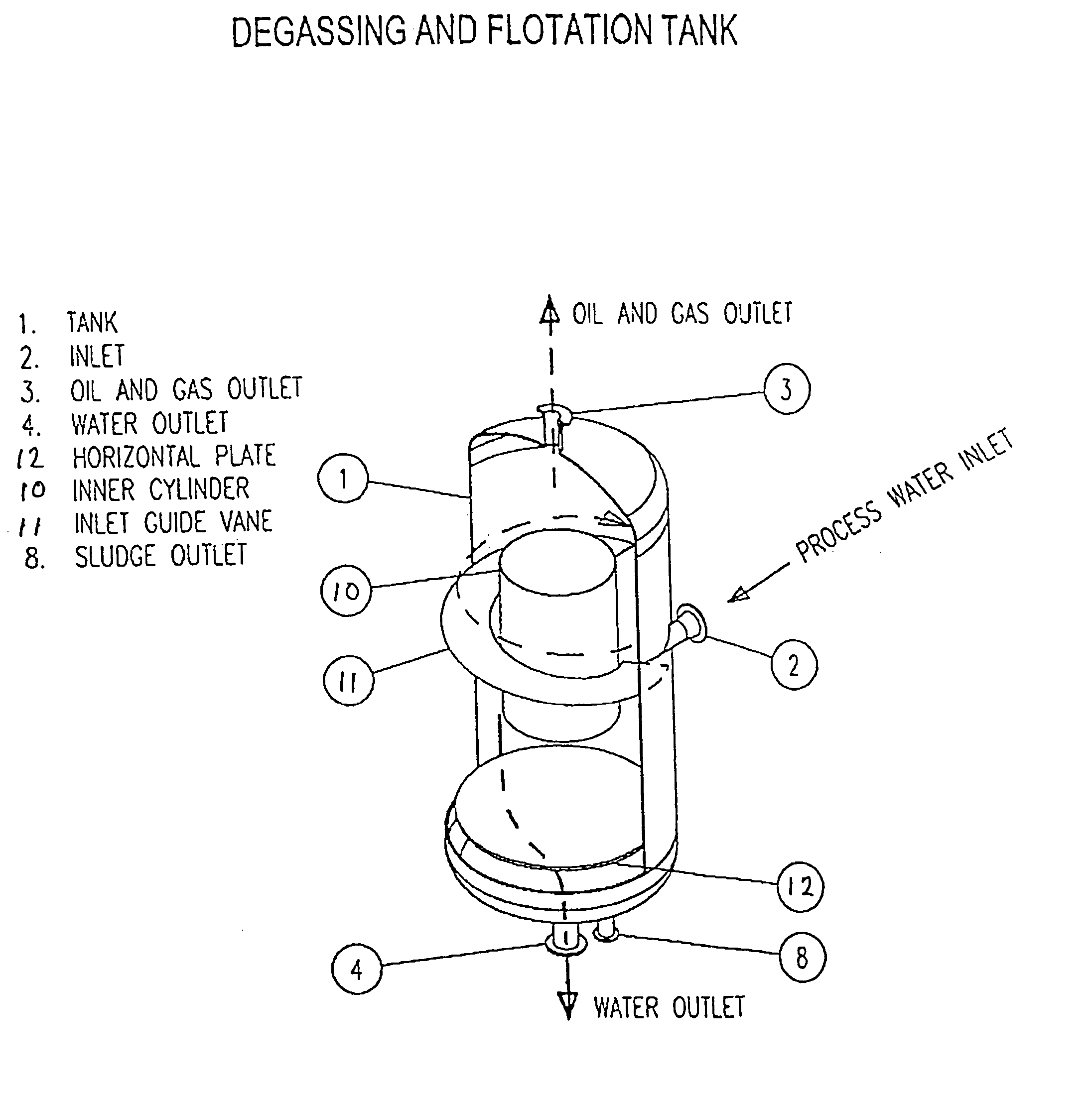
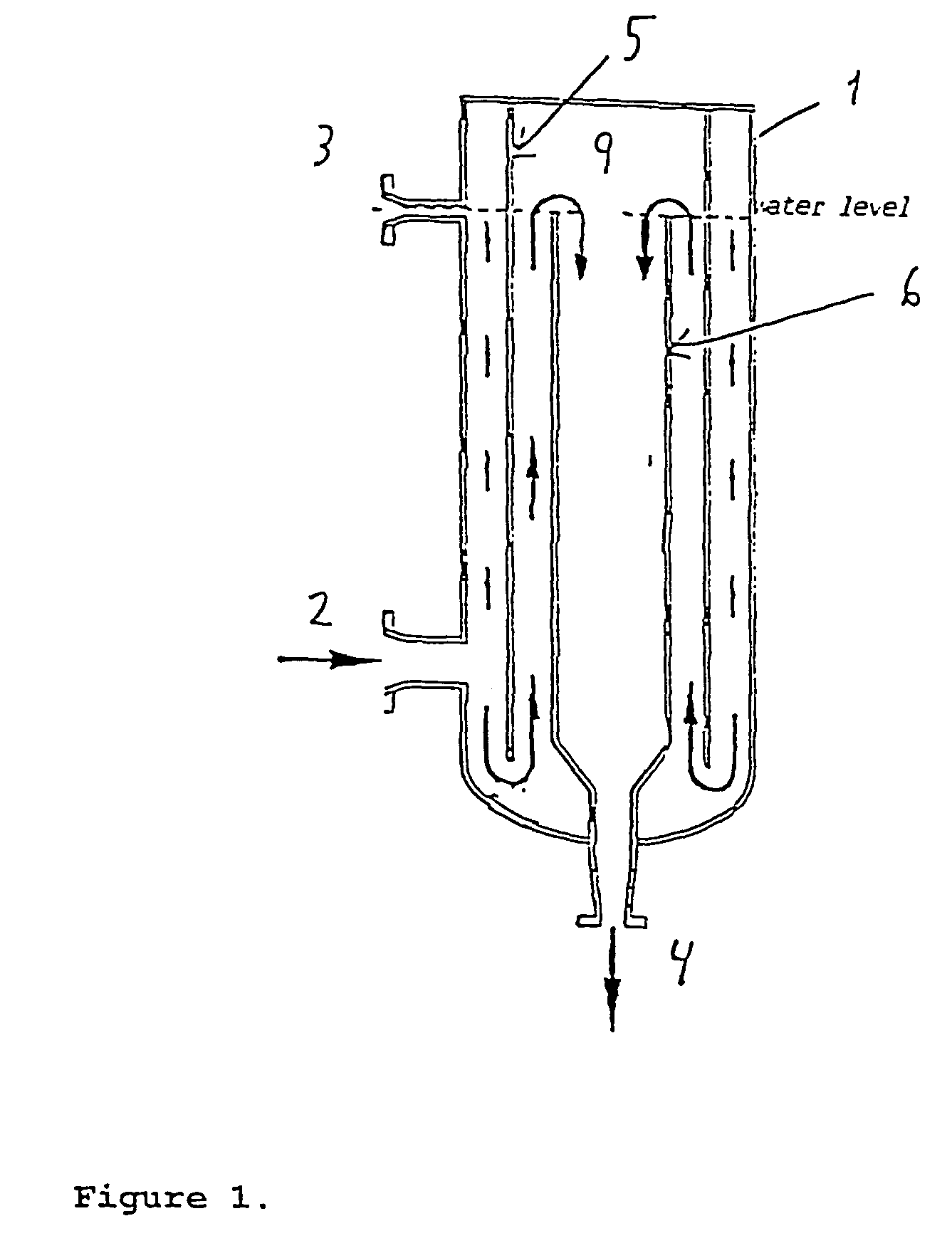
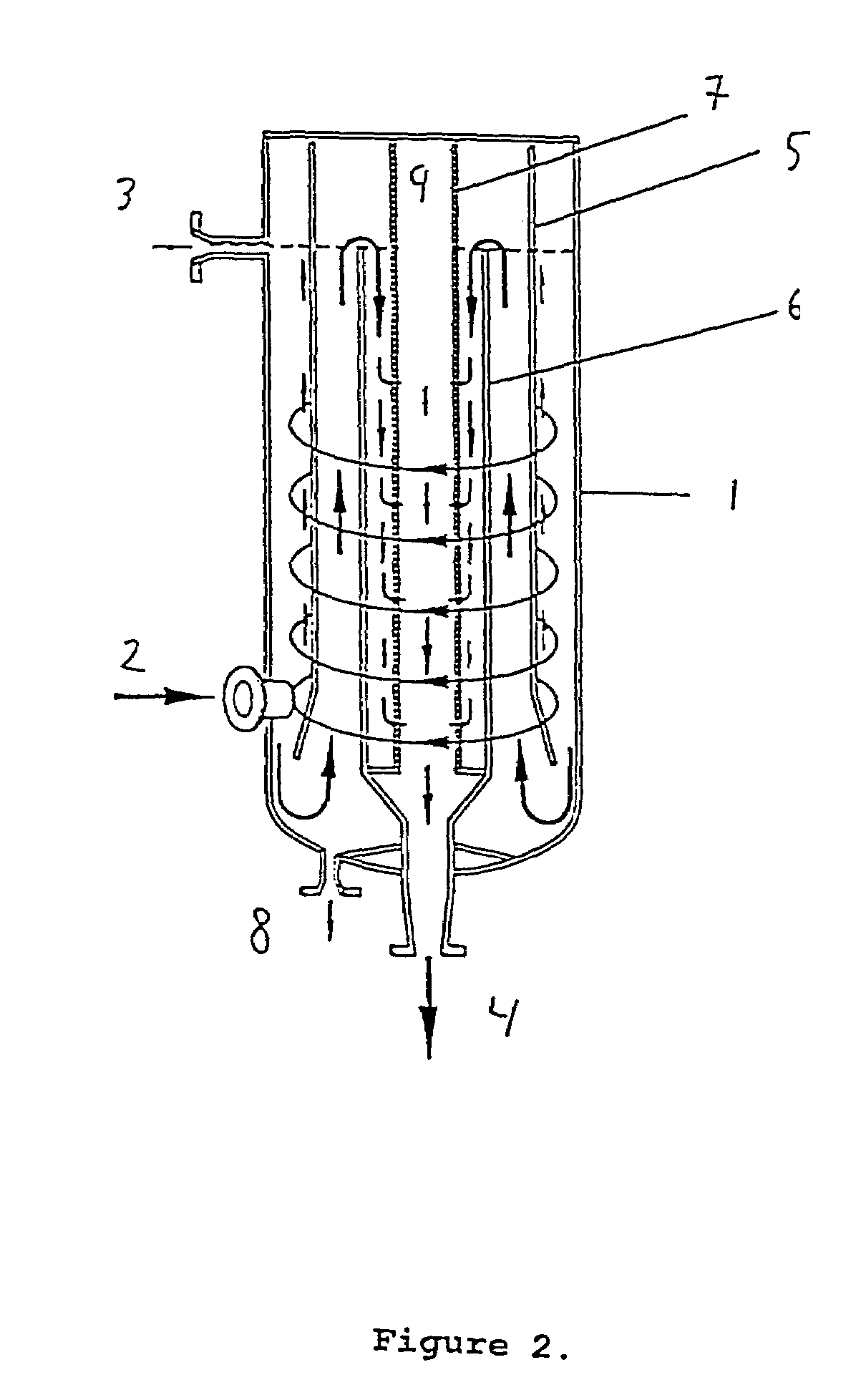
Combined degassing and flotation tank
InactiveUS7144503B2Improve efficiencyImprove throughputCombination devicesLiquid degasificationHeavy particleSludge
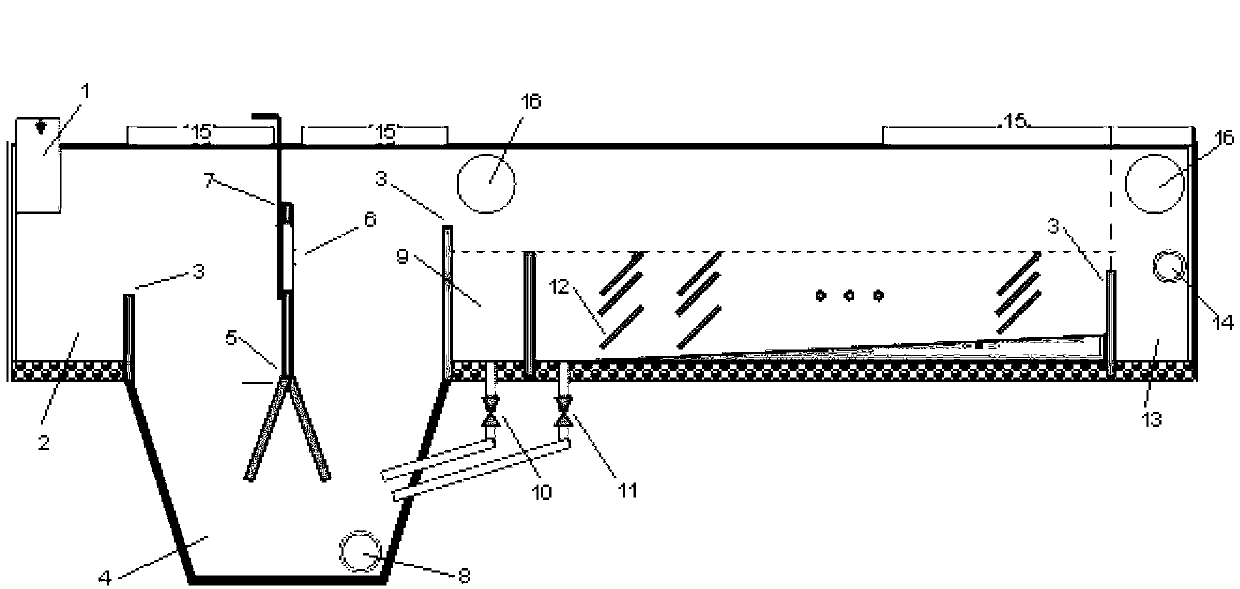
A combined degassing and flotation tank for separation of a water influent containing considerable amounts of oil and gas. A rotational flow is created in the tank which forces the lighter components such as oil and gas droplets towards an inner concentric cylindrical wall where they coalesce and rise to the surface of the liquid and are removed via the outlet (3) whereas the heavier parts are forced down where the heavy particles sink to the lower part where they may be removed as a sludge. The water is discharged via an outlet in the lower part of the tank. The combined degassing and flotation tank is particular suited for use in oil production at sea for removal of oil and gasses from water streams before the water is returned to the sea.
Owner:SHCLUMBERGER NORGE AS
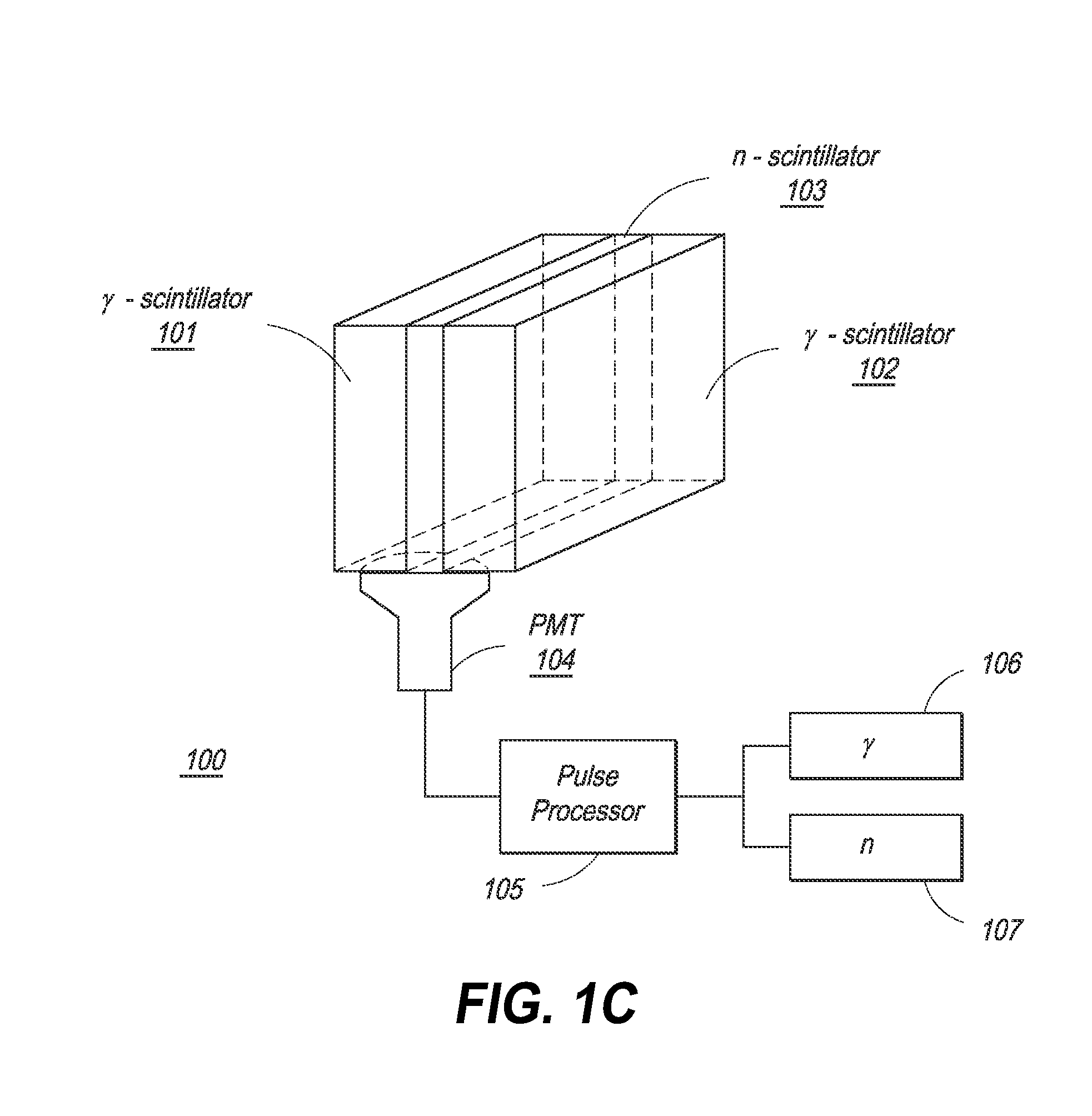
Composite Gamma-Neutron Detection System
ActiveUS20140042330A1Improve efficiencyEasy constructionMultiplier cathode arrangementsMeasurement with scintillation detectorsHeavy particlePhotomultiplier
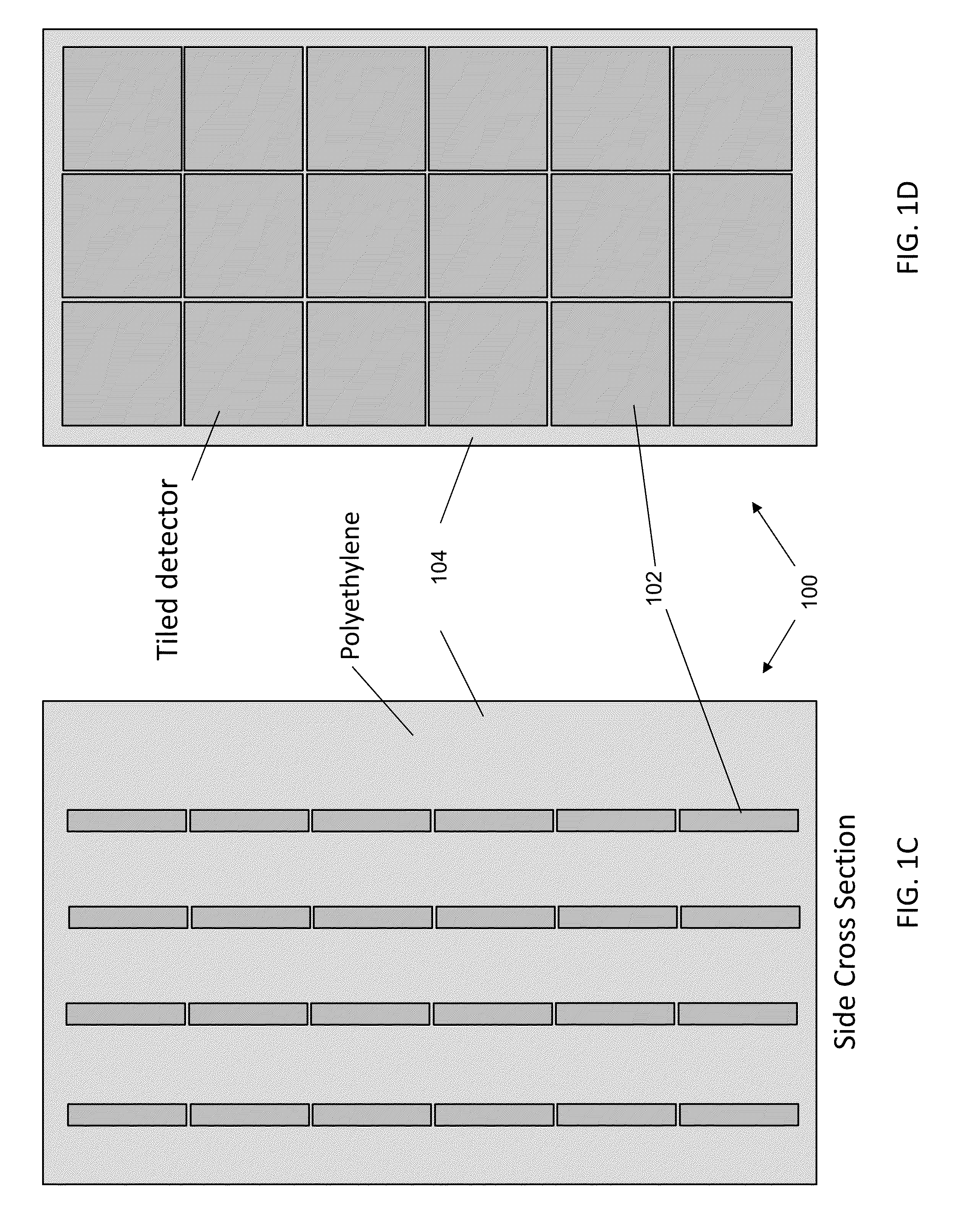
The present invention provides a gamma-neutron detector based on mixtures of thermal neutron absorbers that produce heavy-particle emission following thermal capture. In one configuration, B-10 based detector is used in a parallel electrode plate geometry that integrates neutron moderating sheets, such as polyethylene, on the back of the electrode plates to thermalize the neutrons and then detect them with high efficiency. The moderator can also be replaced with plastic scintillator sheets viewed with a large area photomultiplier tube to detect gamma-rays as well. The detector can be used in several scanning configurations including portal, drive-through, drive-by, handheld and backpack, etc.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Apparatus and method for separating and filtering particles and organisms from flowing liquids
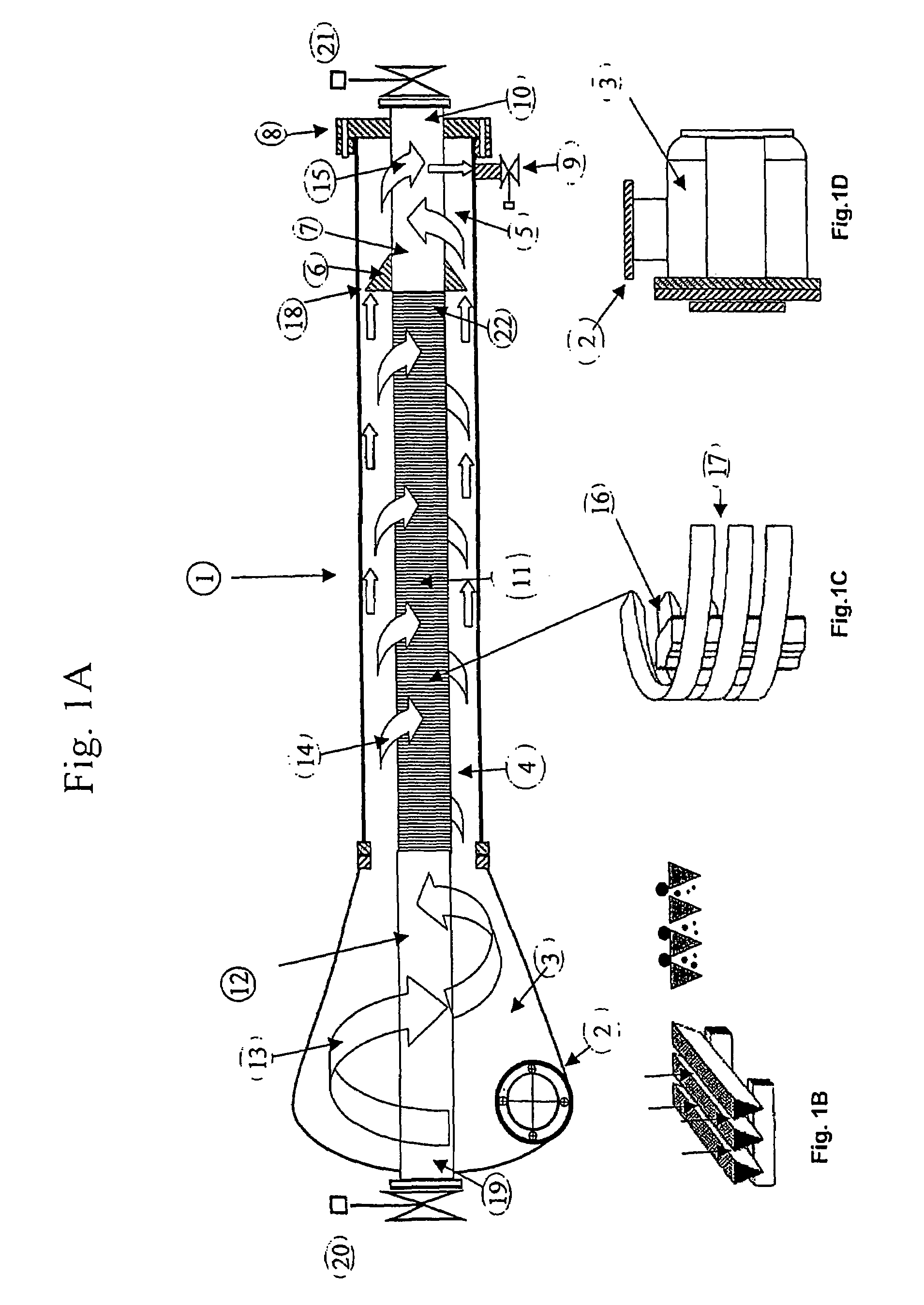
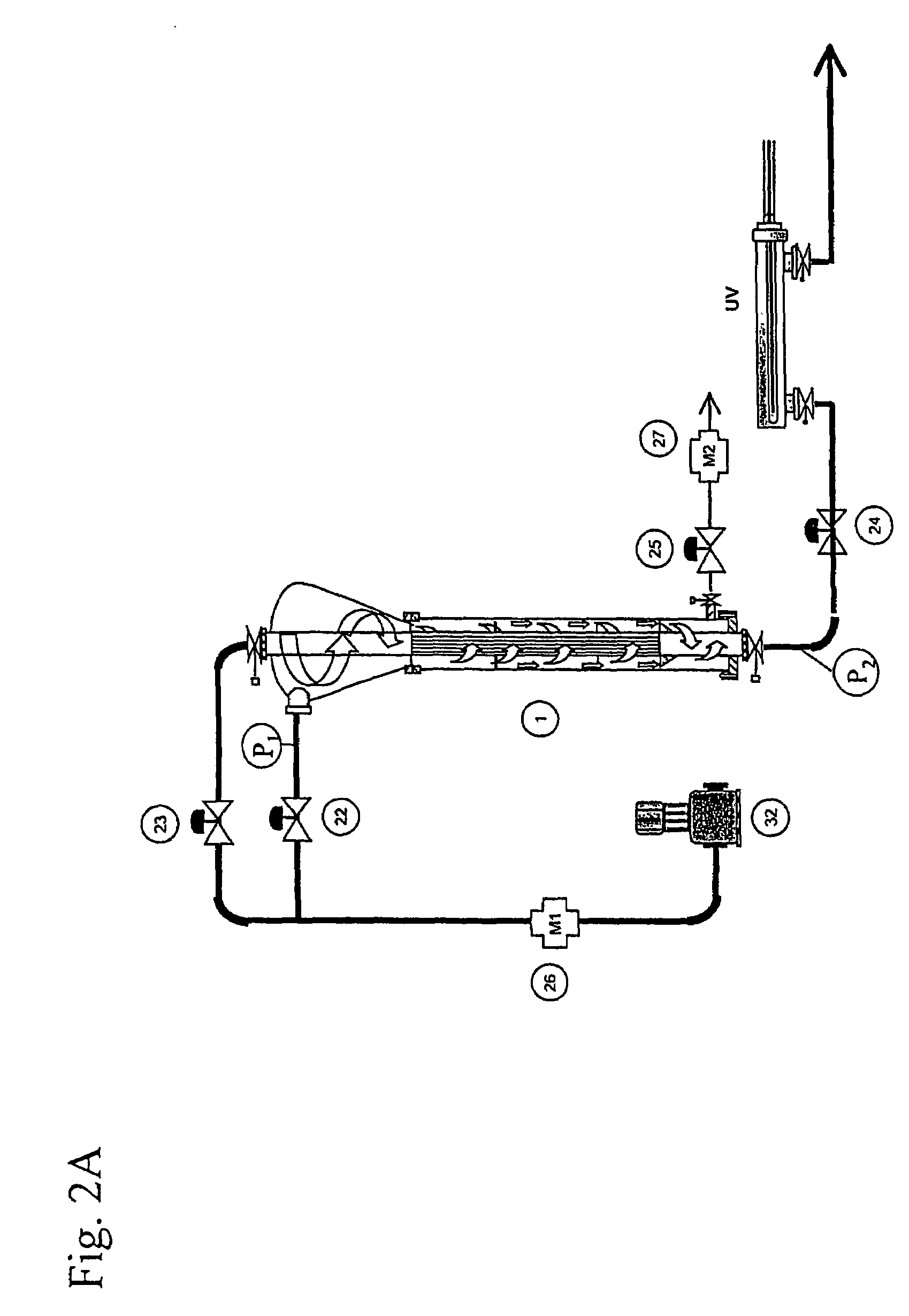
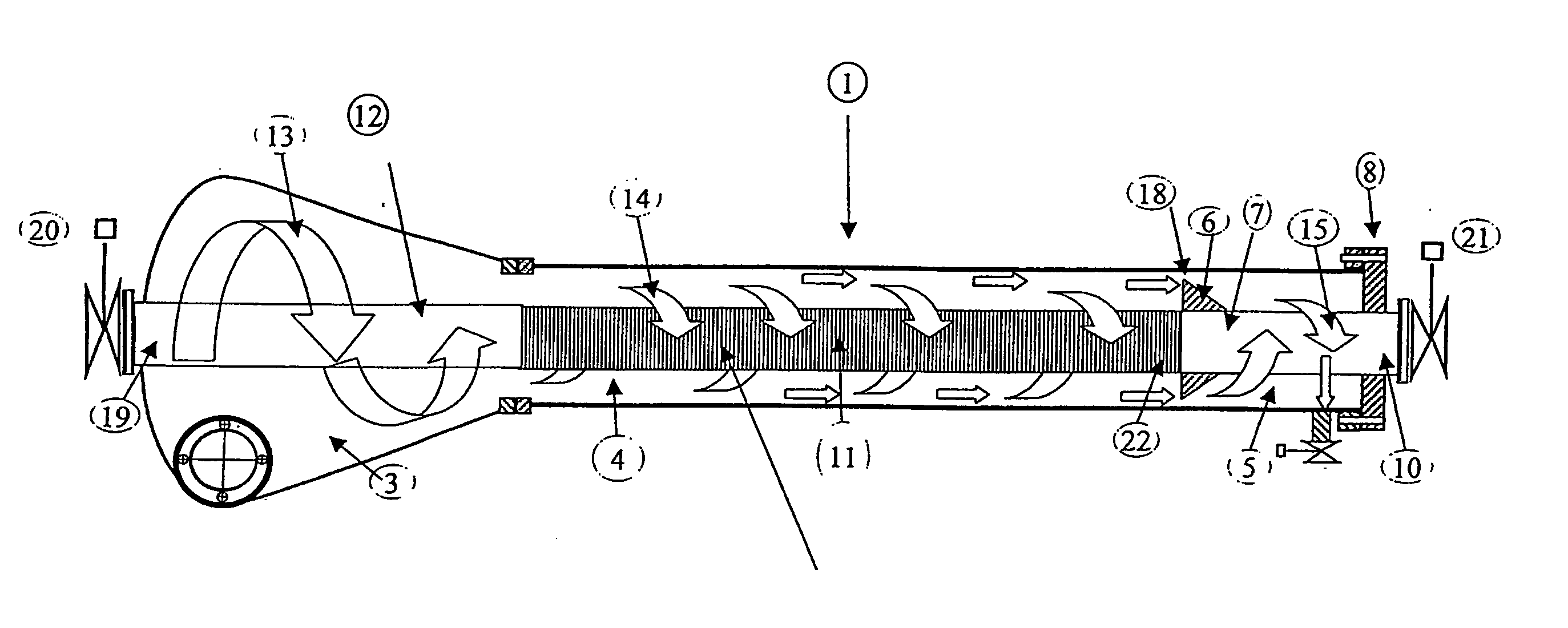
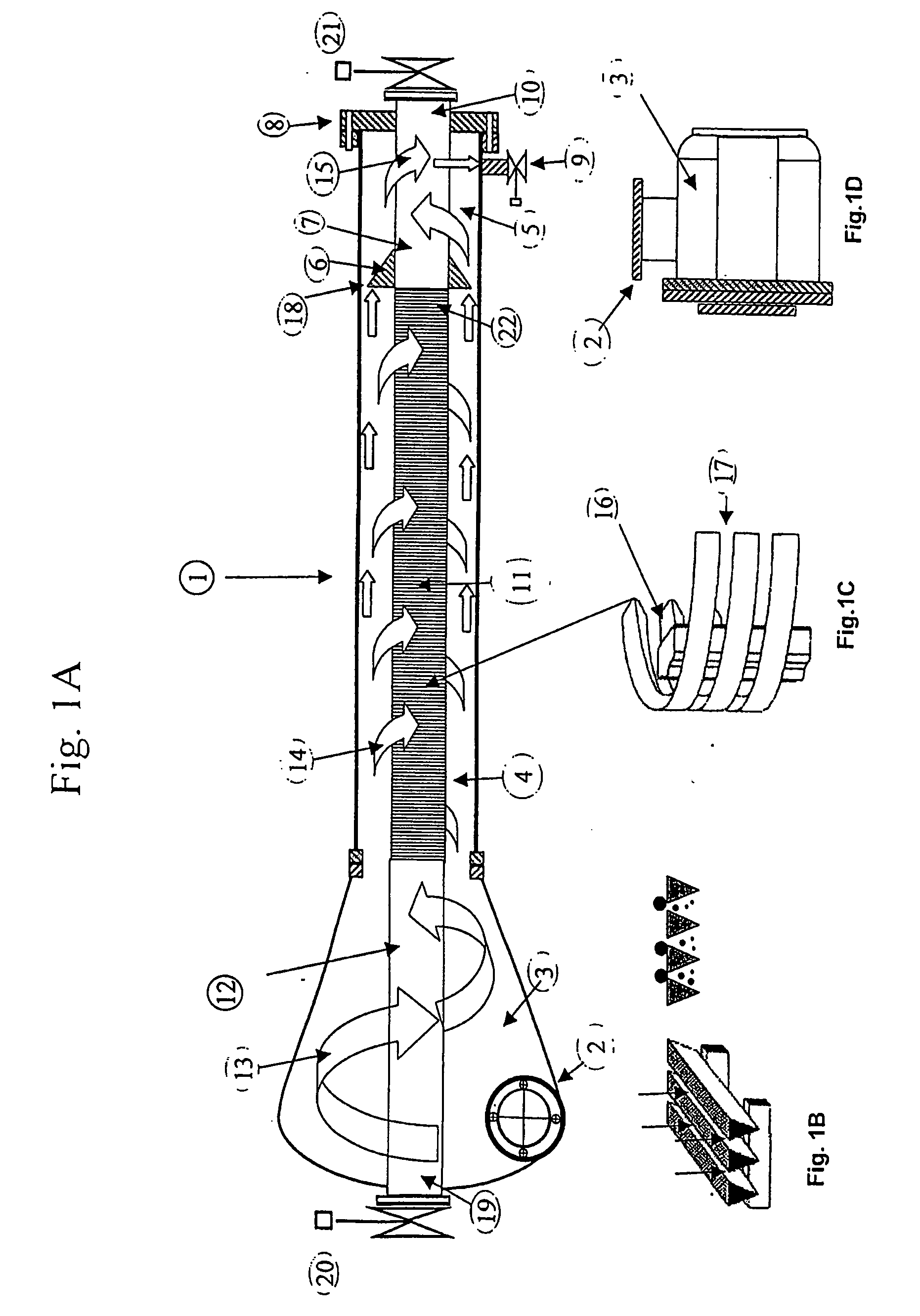
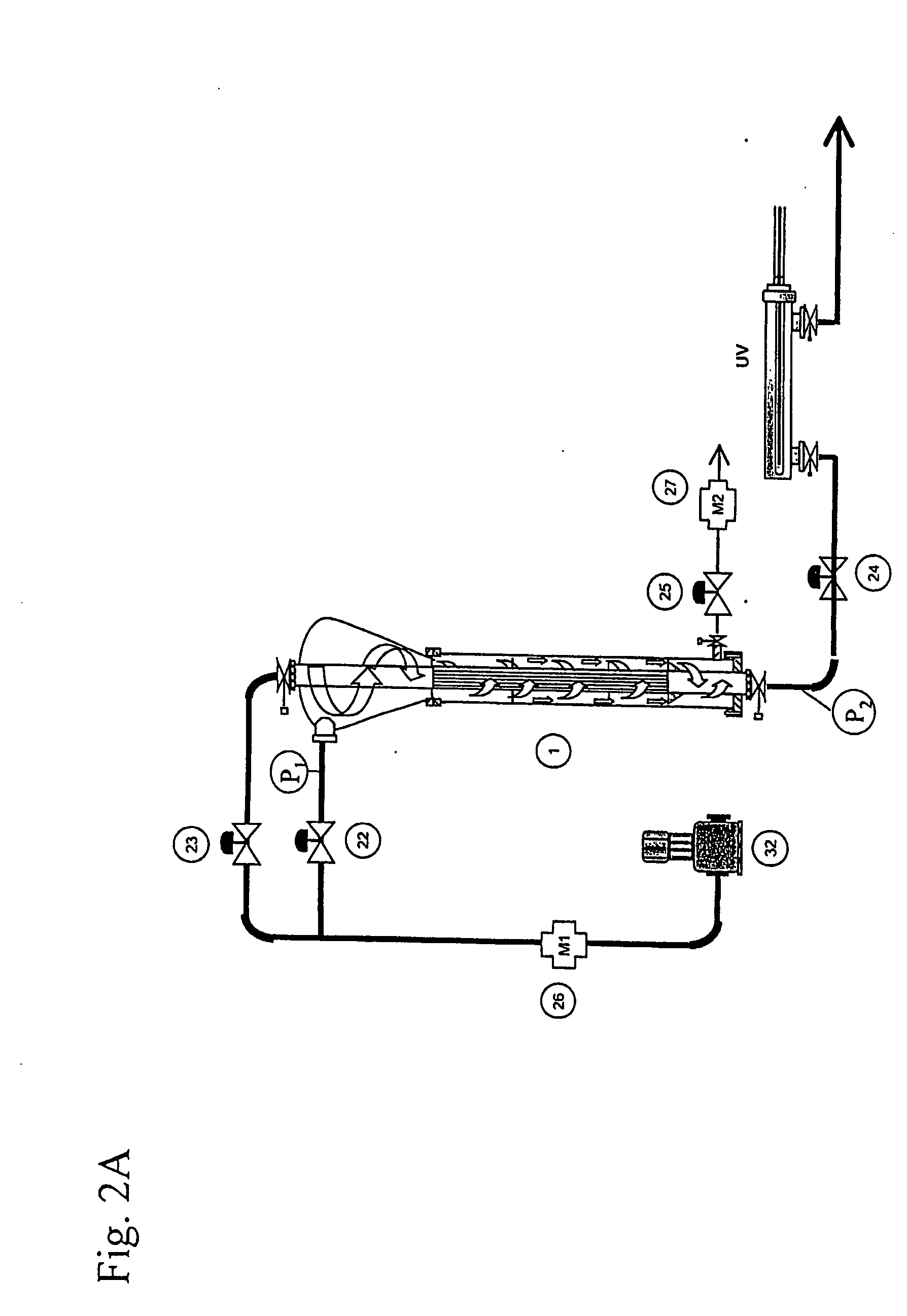
InactiveUS7166230B2Reduce weight and sizeEasy to operateReversed direction vortexTreatment involving filtrationHeavy particleUltraviolet lights
A device (1) for separating and filtering particles and organisms from a high volume flowing liquid operating under low pressure. The device (1) includes a conical or cylindrical shape inlet chamber (3) were liquids enter tangentially creating a circular flow without creating a vortex, the liquids accelerate into a separation and filter chamber (14) where the liquids spin around a longitudinally disposed filter element (11) in the center of the chamber (14), with the centrifugal forces separating out larger and heavier particles towards the perimeter of the separation and filter chamber (14), and where smaller particles having a specific gravity closer to that of the liquid are filtered when the liquid penetrates through the filter element wall into the center of the filter element and flows out one of the longitudinal outlets of the unit. Ultraviolet light irreparably damages bacteria, microorganisms and pathogens contained in processed ballast water and may be incorporated as part of the system.
Owner:NILSEN HALVOR +1
Apparatus and method for separating and filtering particles and organisms from flowing liquids
InactiveUS20050040091A1Small sizeReduce weightReversed direction vortexTreatment involving filtrationBiological bodyHeavy particle
A device (1) for separating and filtering particles and organisms from a high volume flowing liquid operating under low pressure. The device (1) includes a conical or cylindrical shape inlet chamber (3) were liquids enter tangentially creating a circular flow without creating a vortex, the liquids accelerate into a separation and filter chamber (14) where the liquids spin around a longitudinally disposed filter element (11) in the center of the chamber (14), with the centrifugal forces separating out larger and heavier particles towards the perimeter of the separation and filter chamber (14), and where smaller particles having a specific gravity closer to that of the liquid are filtered when the liquid penetrates through the filter element wall into the center of the filter element and flows out one of the longitudinal outlets of the unit. Ultraviolet light irreparably damages bacteria, microorganisms and pathogens contained in processed ballast water and may be incorporated as part of the system.
Owner:NILSEN HALVOR +1
Powered air cleaning system and method of making same
Owner:SY KLONE
Powered air cleaning system and air cleaning method
ActiveUS8007565B2Lower performance requirementsImprove performanceCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulate debrisMotor drive
A powered air cleaning system has a flow path extending through the system from an inlet to an outlet. A motor-driven fan is located along the flow path to draw particulate debris laden air into the inlet and rotate it about an axis to form a rotating flow that stratifies the debris laden air with the heaviest particles in the outermost orbits of the rotating flow. An ejector port ejects particulate debris laden air from the stratified rotating flow in the system. At least one de-swirl component located within the rotating flow aerodynamically redirects clean air from the innermost orbits of the stratified rotating flow toward the outlet to provide a positive airflow pressure out of the outlet. The system has a variable speed fan motor and an integrated controller for adjusting the speed of the motor and thereby the flow rate of clean air through the outlet of the system. The controller receives a signal that is a function of airflow requirements of a device supplied with clean air by the system. The system can be mounted above or below a hood housing an engine to be supplied with clean air.
Owner:SY KLONE
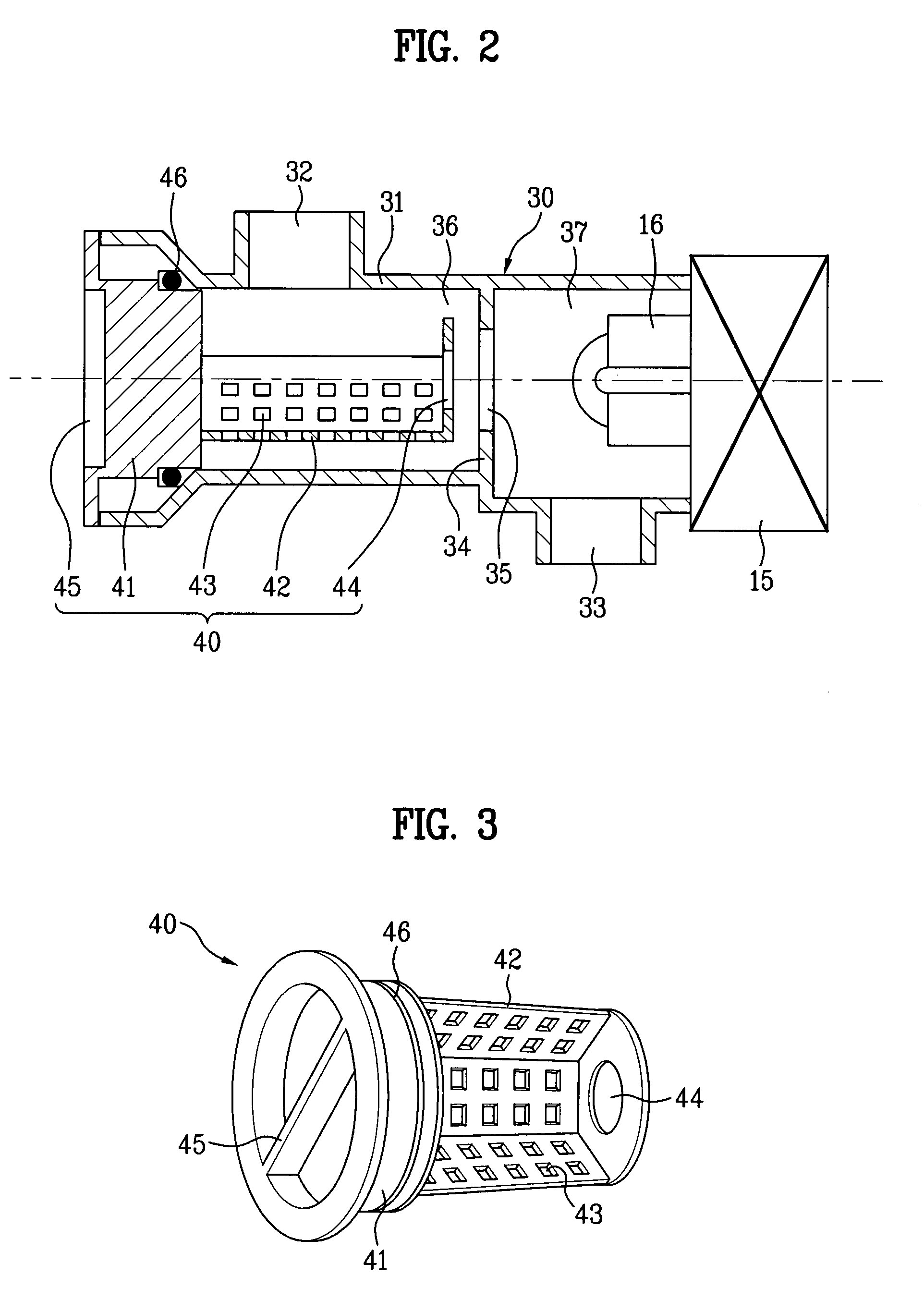
Powered air cleaning system and method of making same
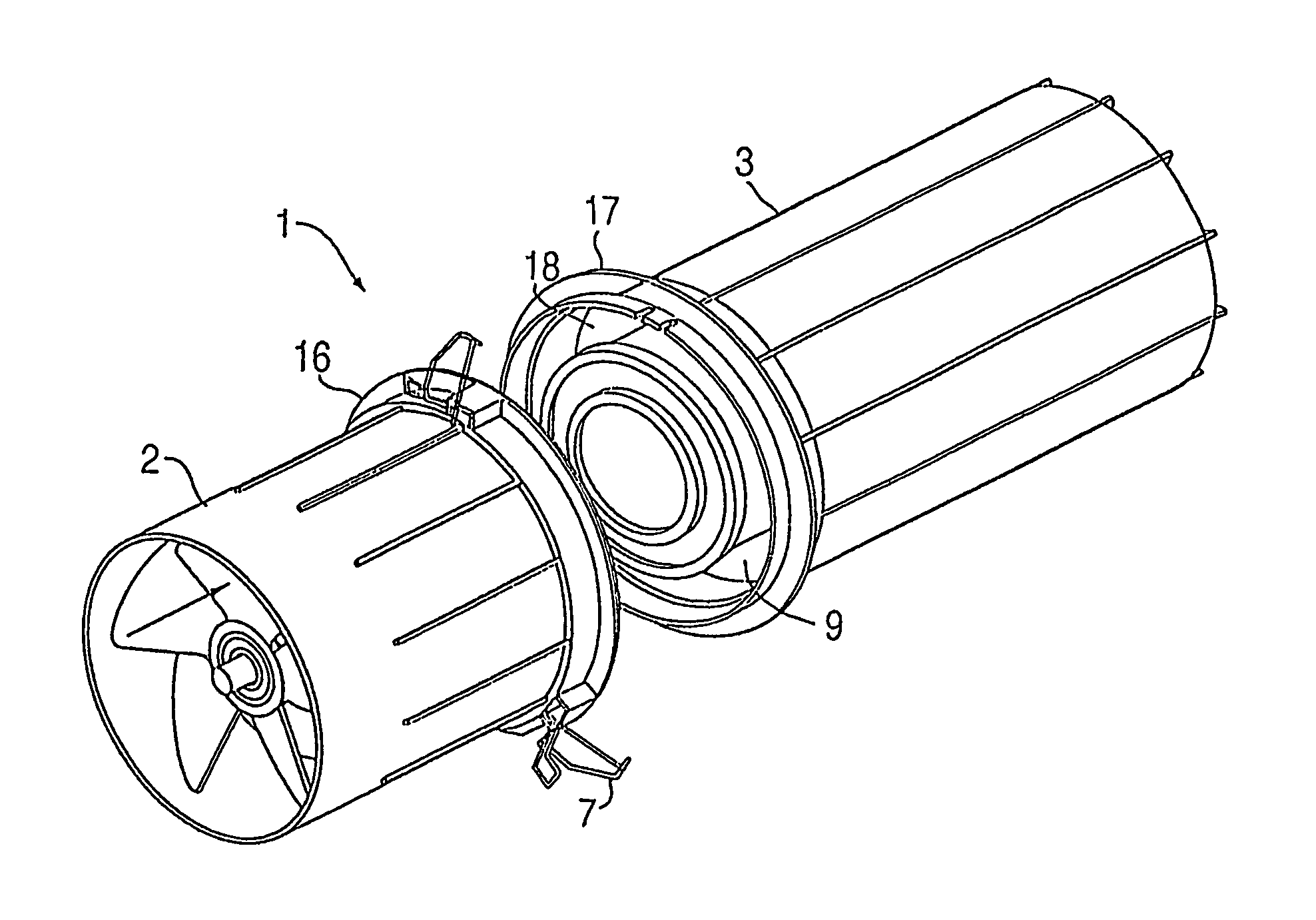
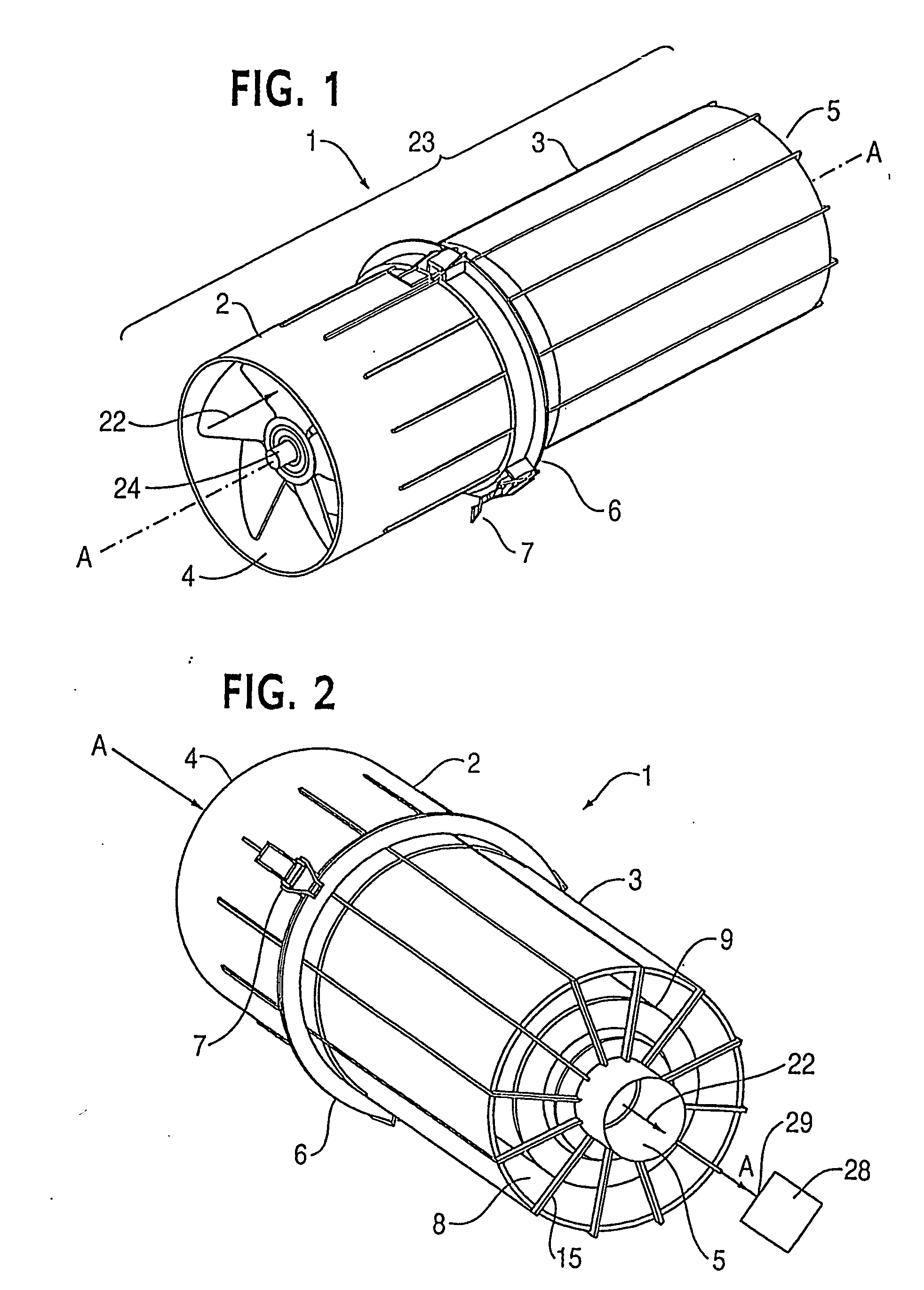
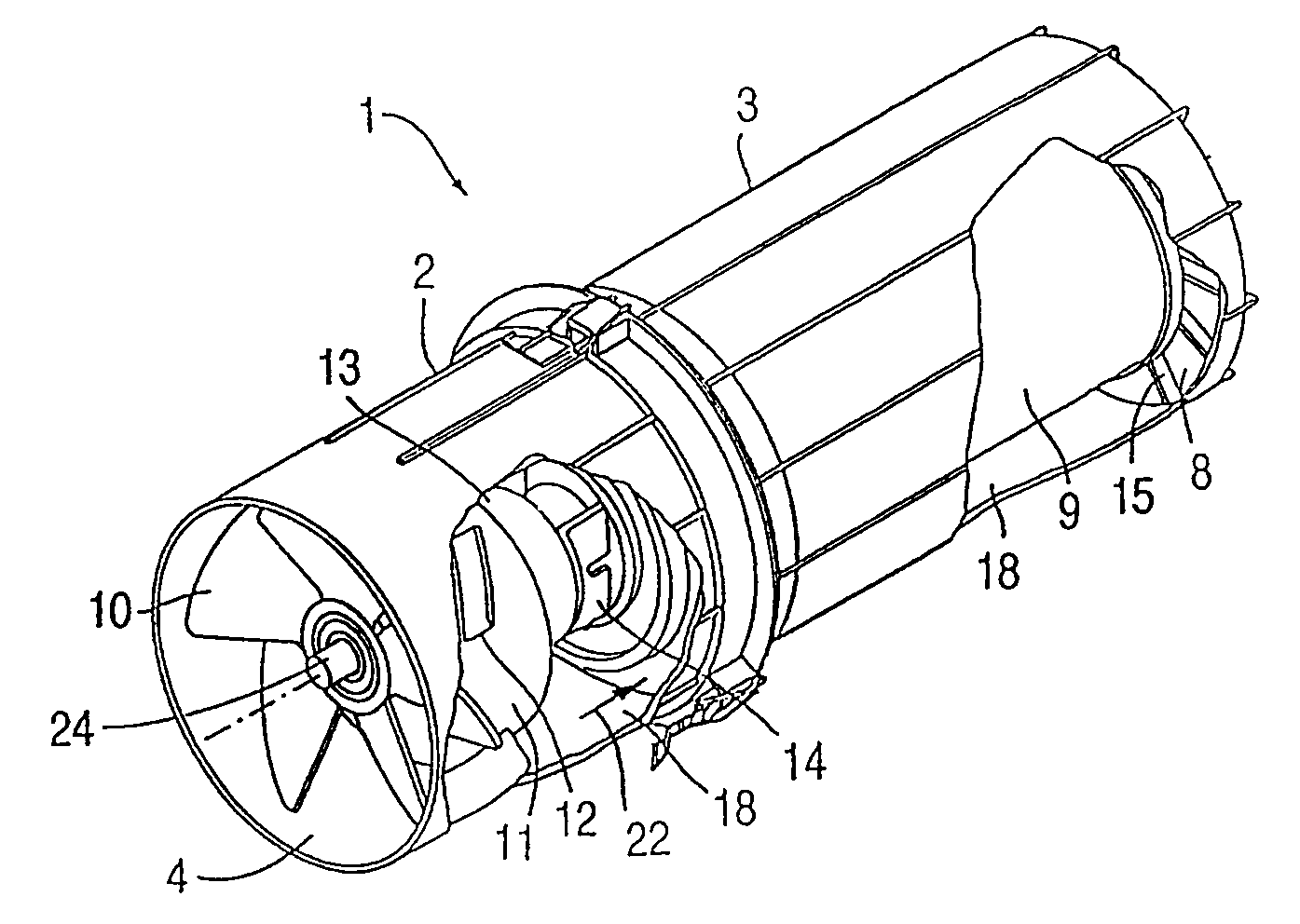
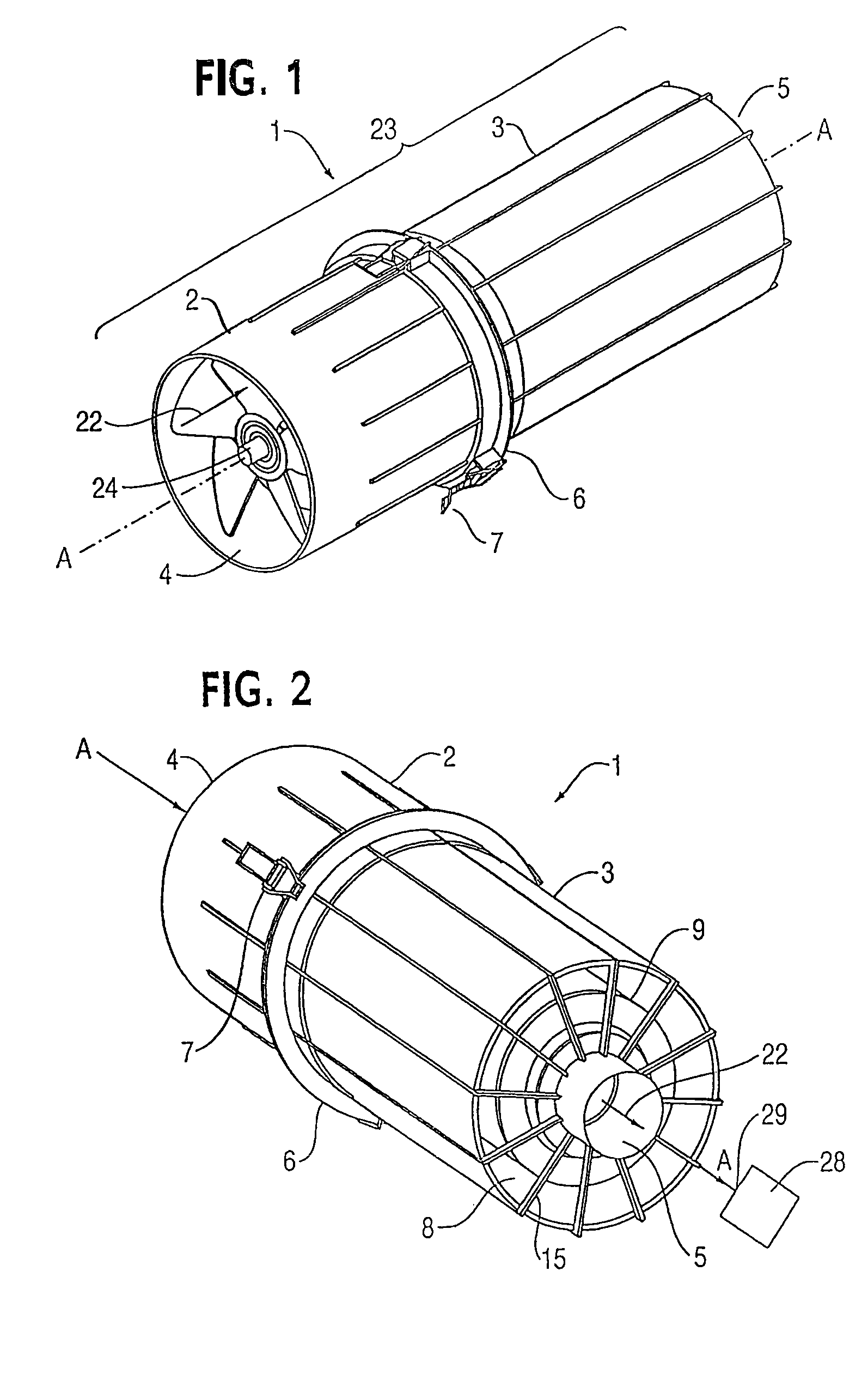
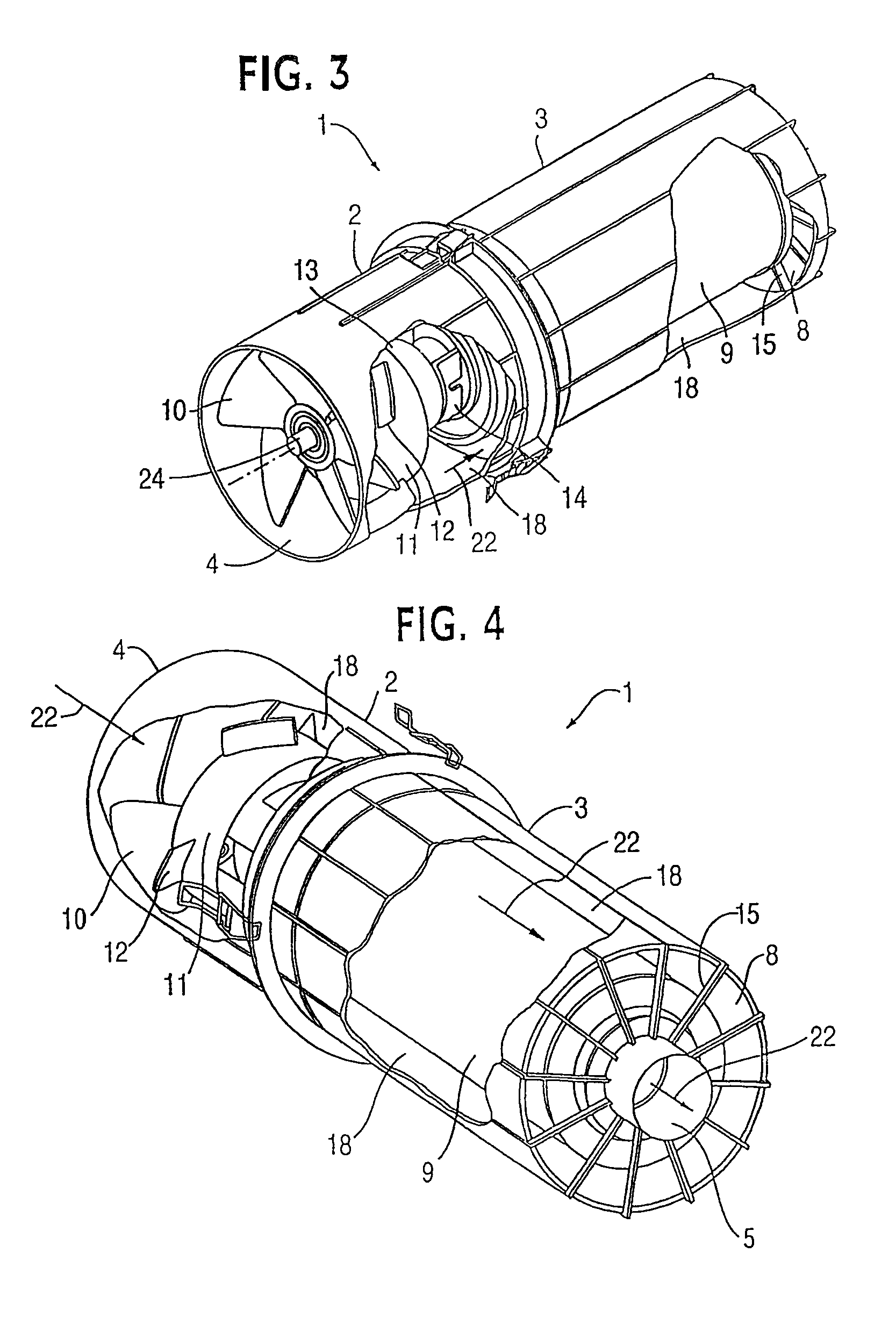
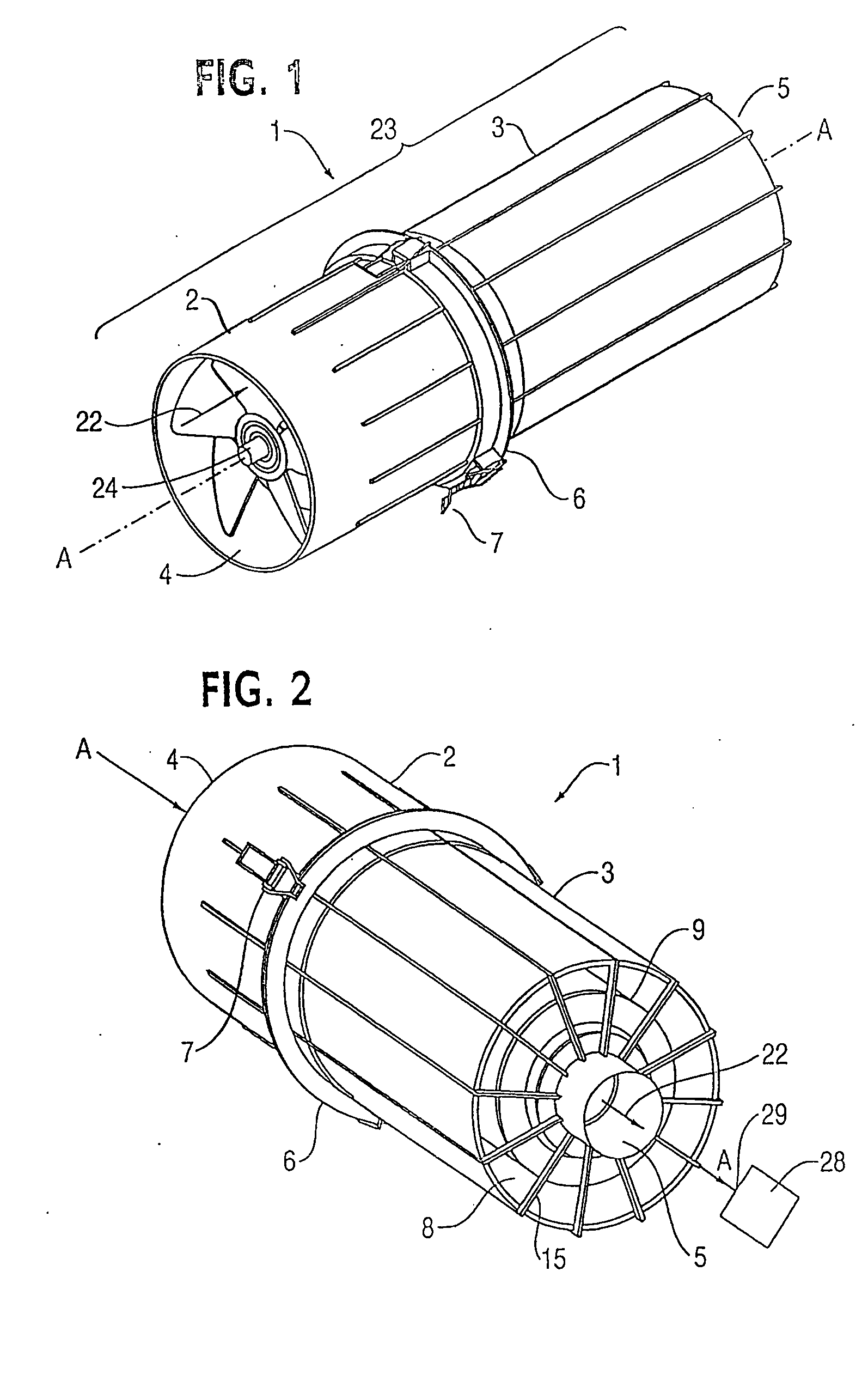
ActiveUS20070173188A1Efficient removalAvoids and reduces problemAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesParticulate debrisHeavy particle
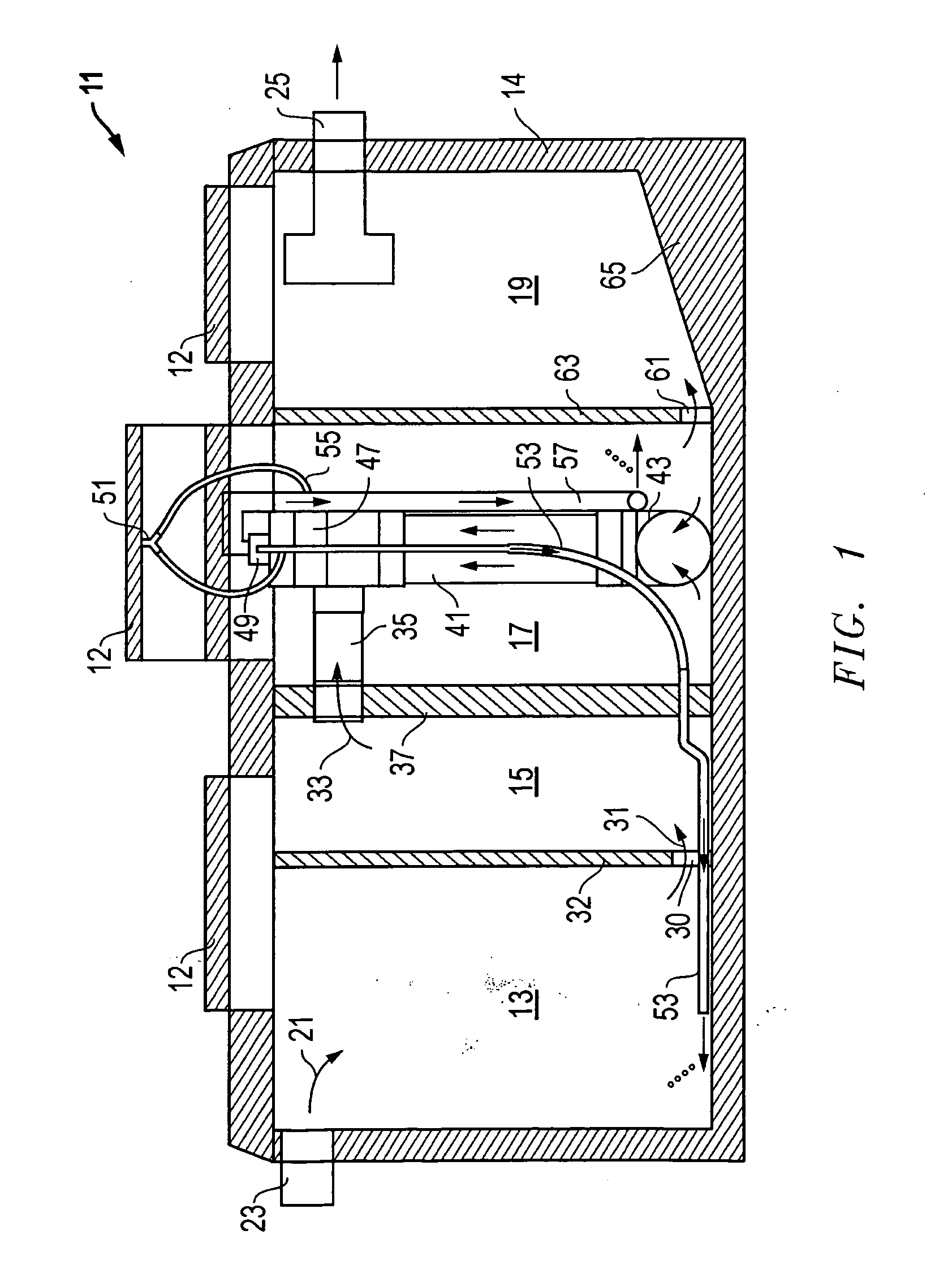
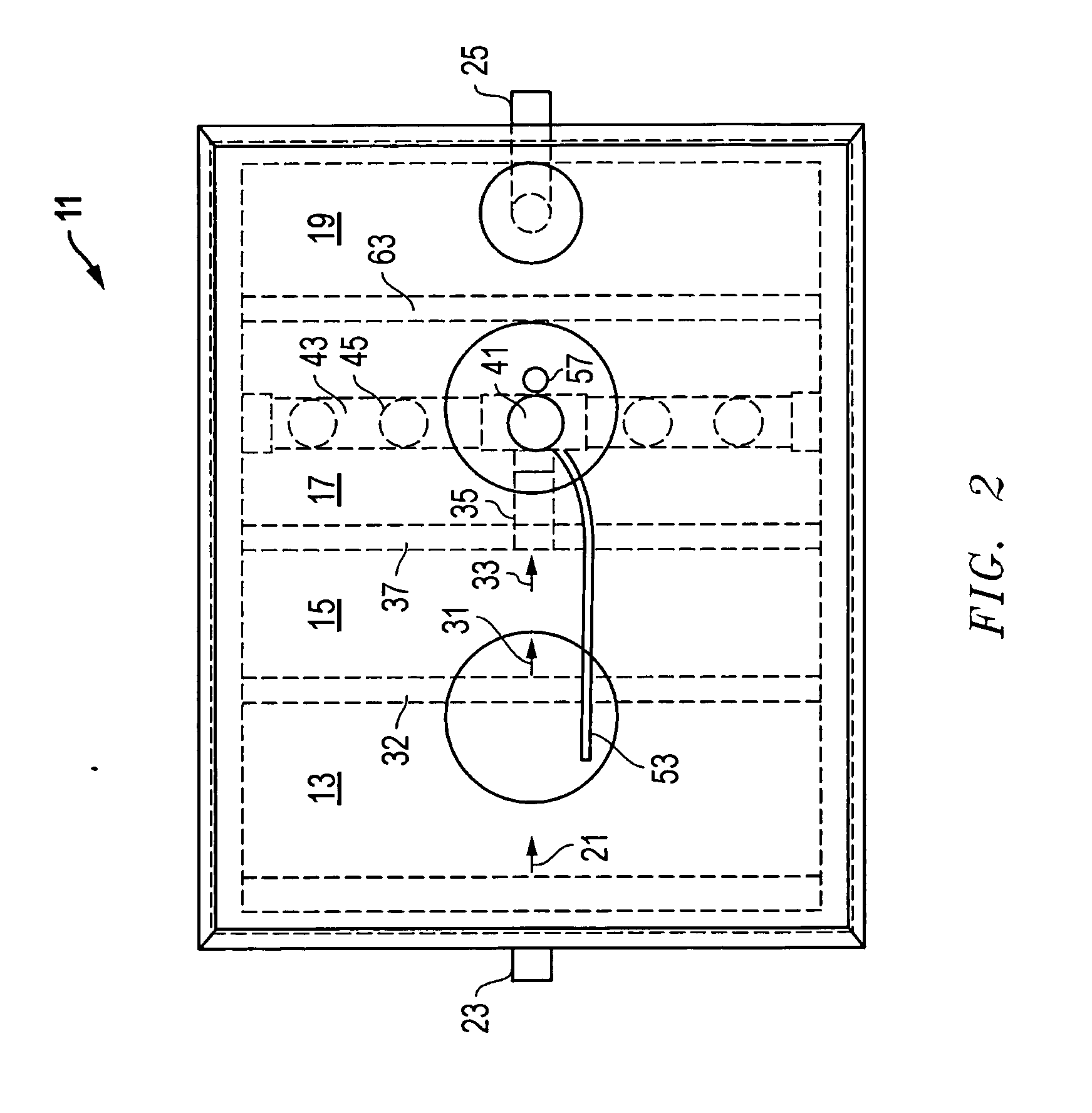
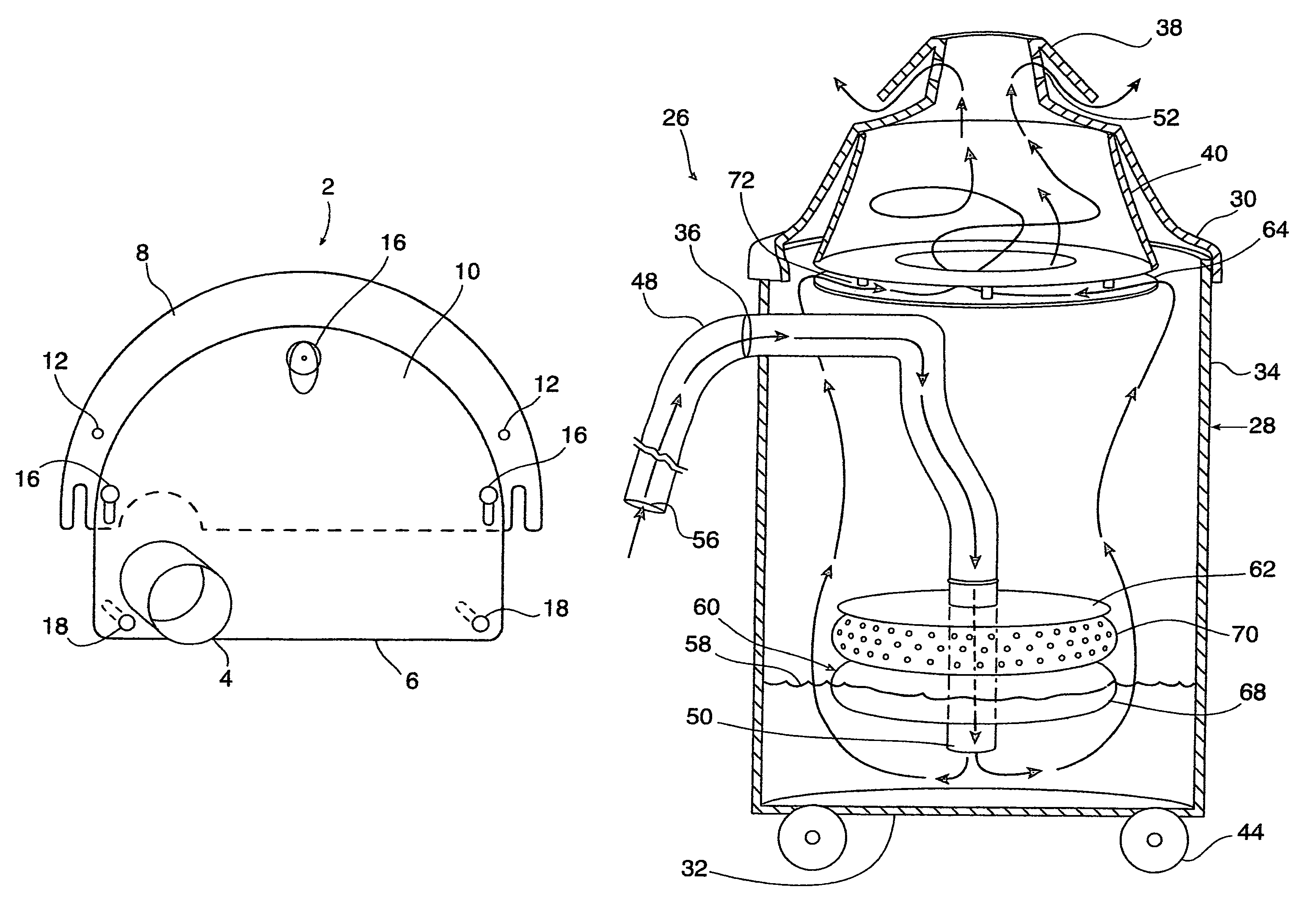
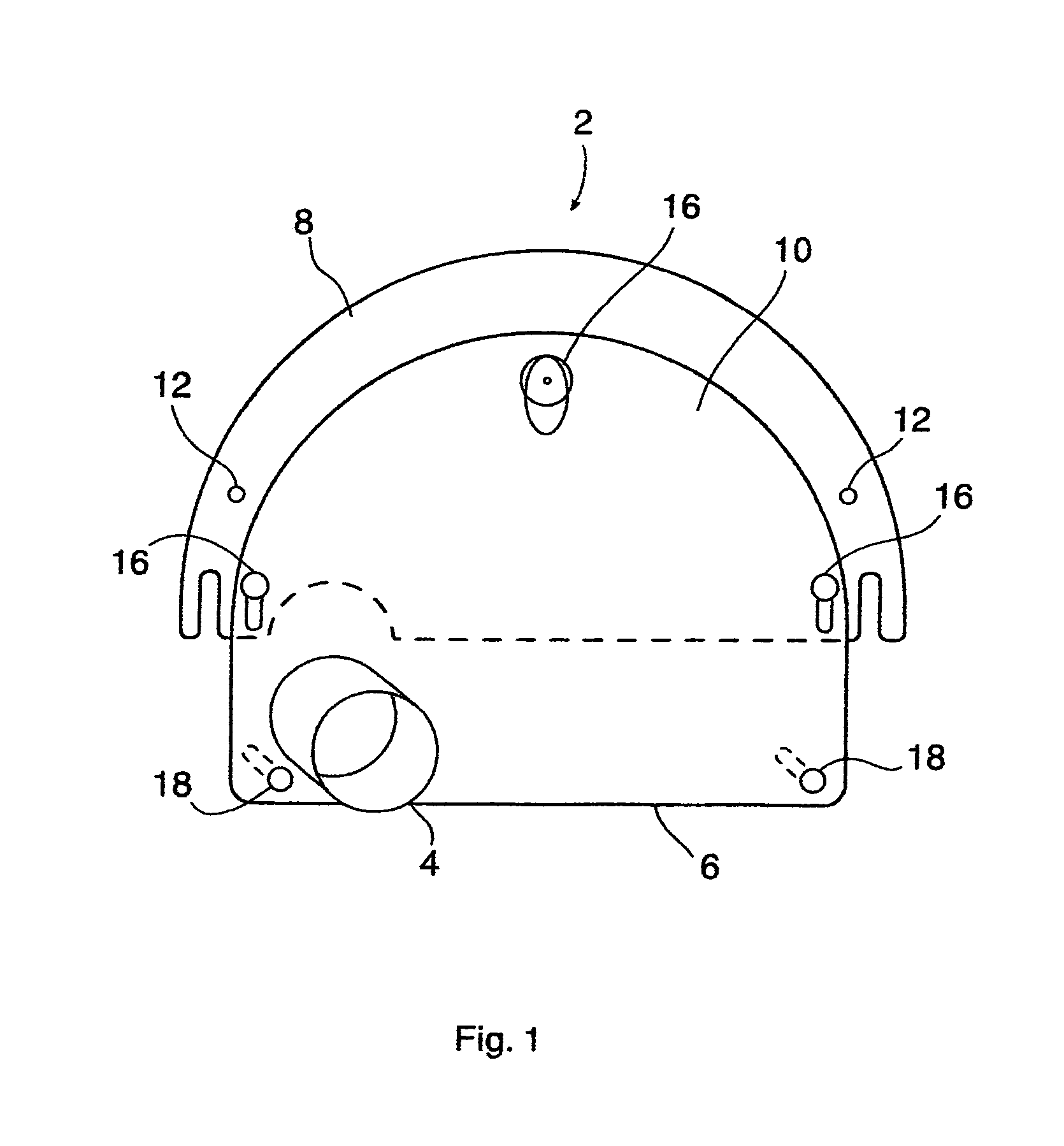
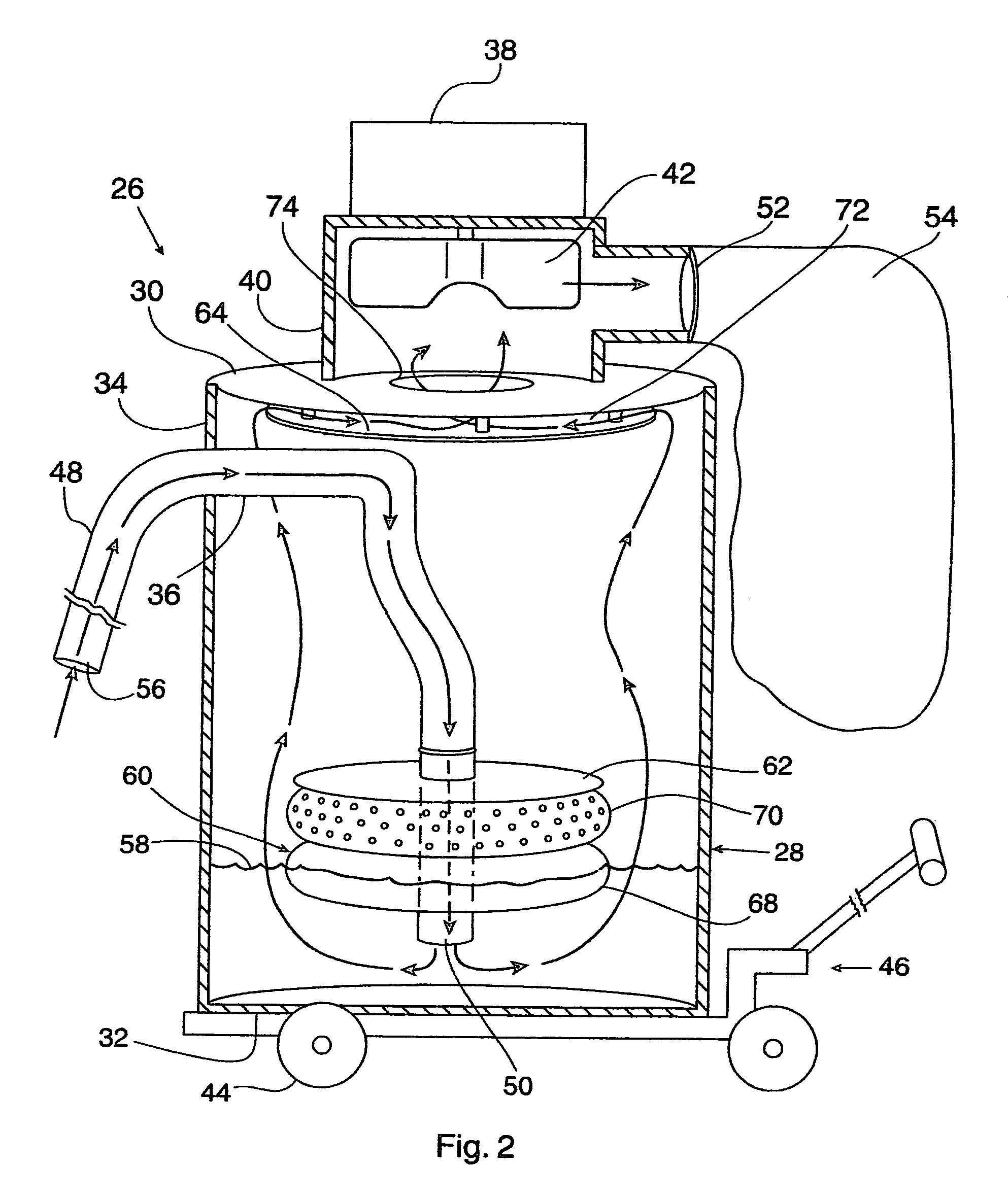
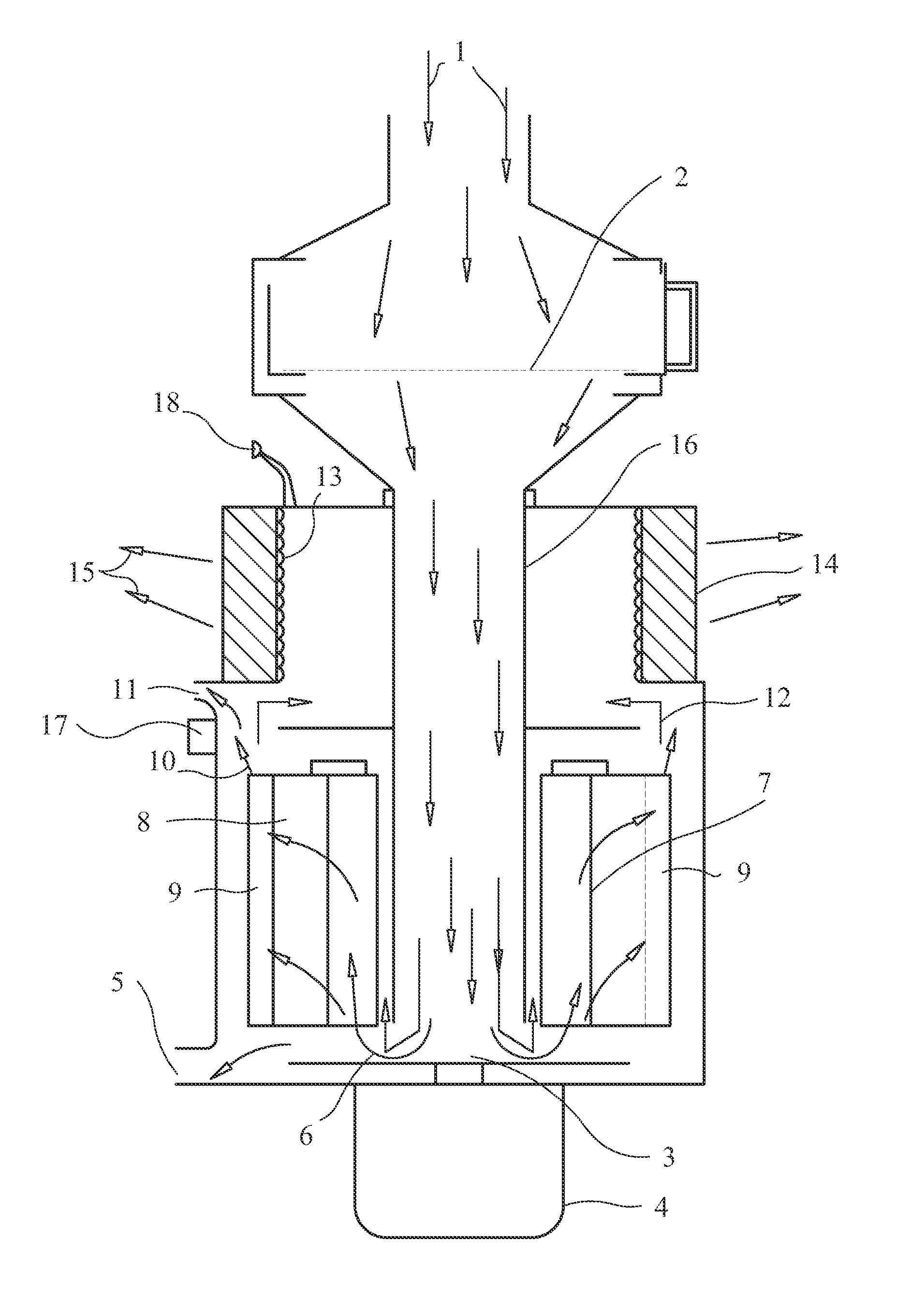
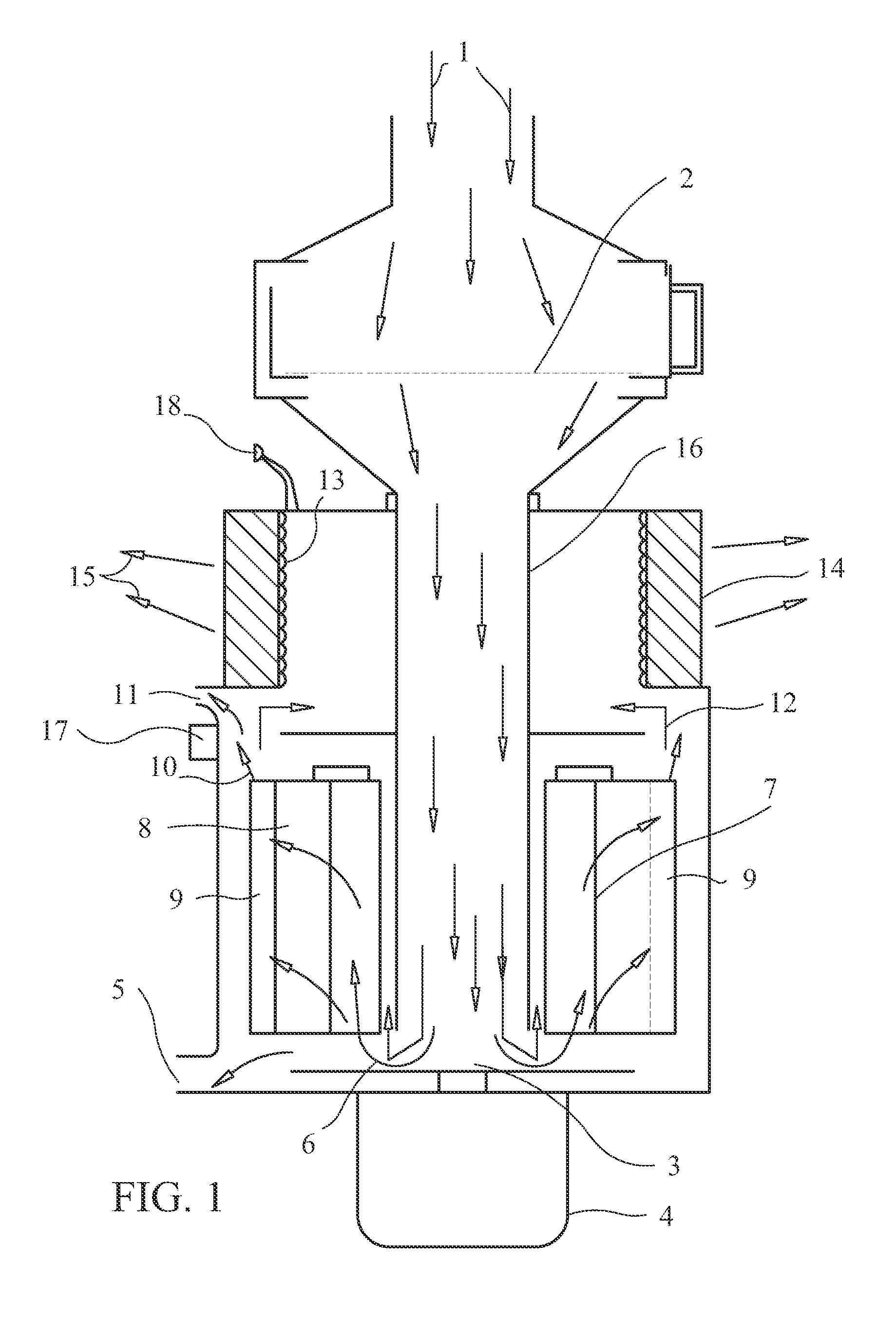
A powered air cleaning system (31) and a method of making the system are disclosed. The system comprises a flow path (22) extending through the system from an air inlet (4) to a clean air outlet (5). A motor-driven fan (24) located along the flow path draws particulate debris laden air into the inlet and rotates it about an axis (A-A) to form a rotating flow that stratifies the debris laden air with the heaviest particles in the outermost orbits of the rotating flow. An ejector port (8) is provided for ejecting particulate debris laden air from the stratified rotating flow in the system to the environment. An air filter (9) located within the rotating flow and across the flow path upstream of the outlet filters air from the innermost orbits of the stratified rotating flow. The system is formed of a plurality of components (2, 3) separately mountable in remote locations (32, 33) in a device to be supplied with clean air. The components are interconnected with an intermediate pipe assembly (34).
Owner:SY KLONE
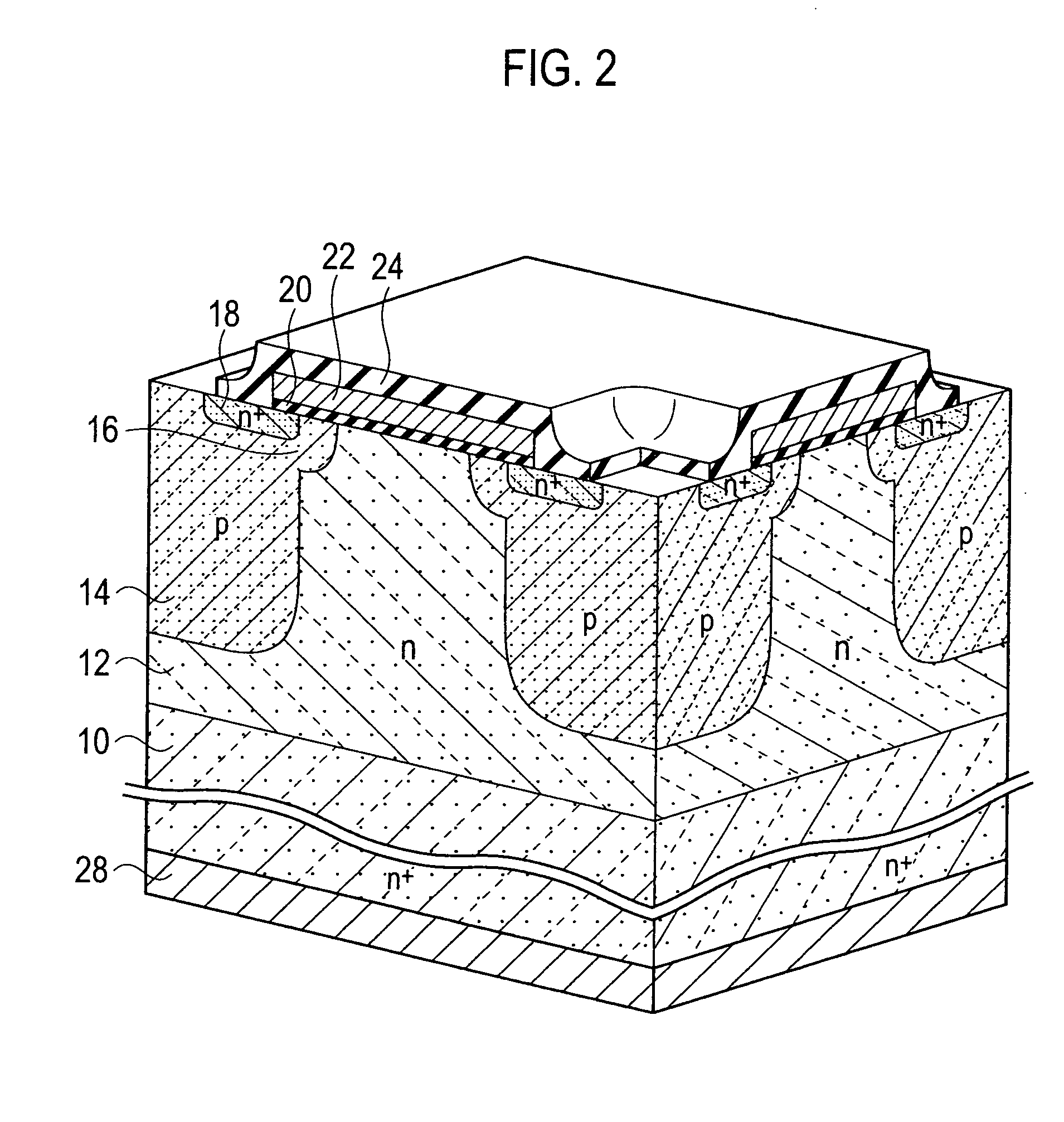
Semiconductor device and fabrication method for the same
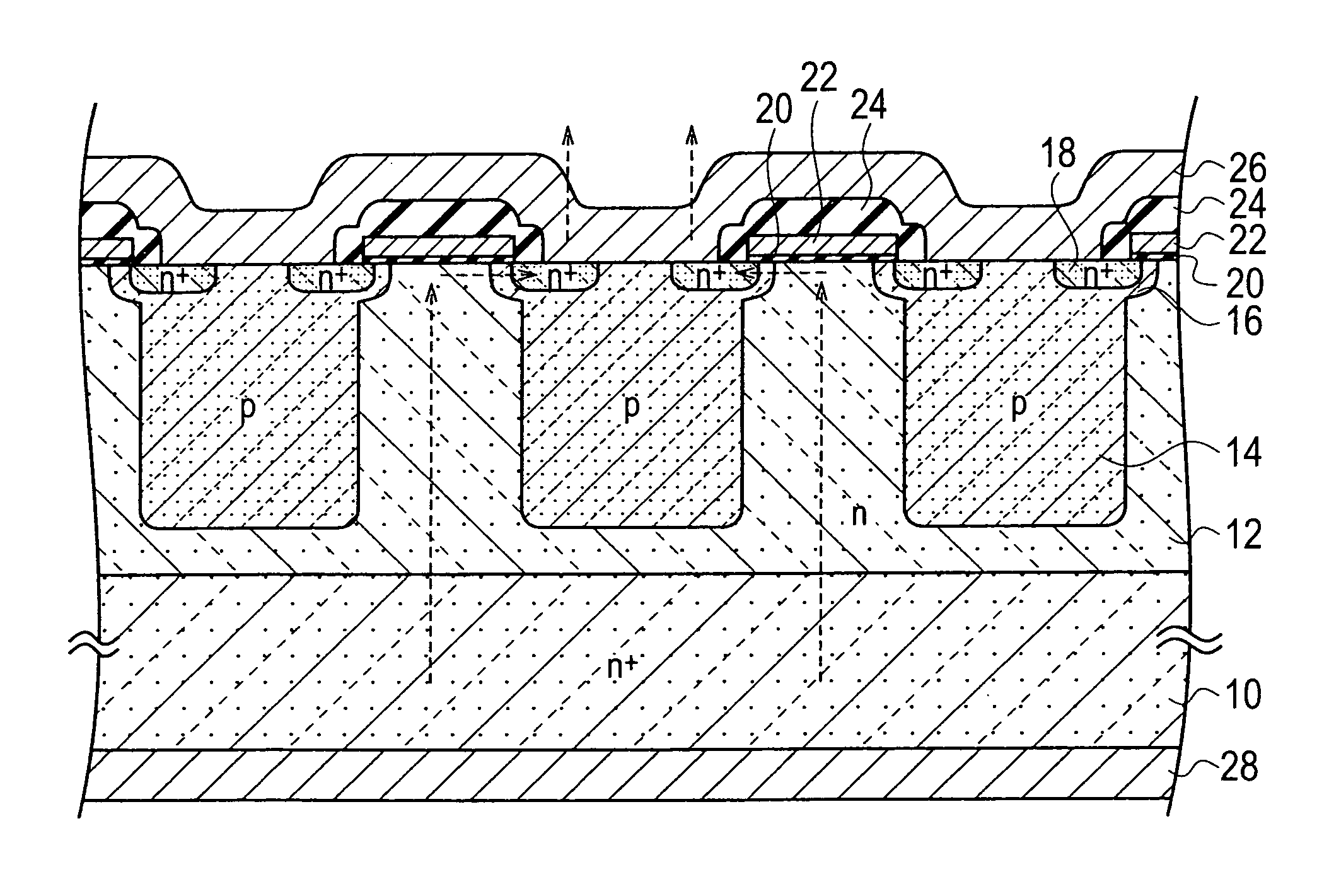
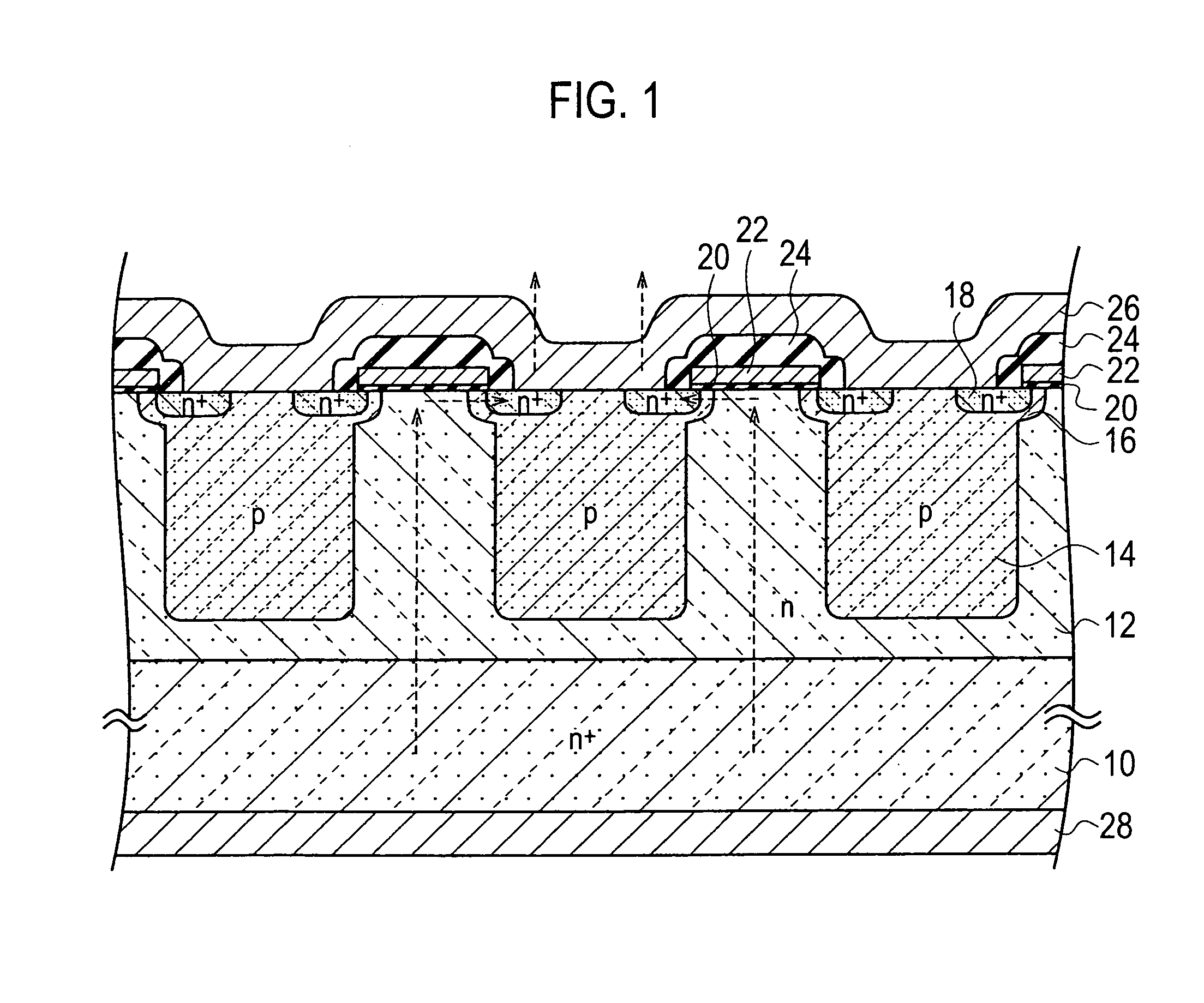
ActiveUS20110147829A1Shorten recovery timeTransistorSolid-state devicesHeavy particleReverse recovery
Provided are a semiconductor device which can shorten reverse recovery time without increasing leakage current between the drain and the source, and a fabrication method for such semiconductor device.The semiconductor device includes: a first base layer (12); a drain layer (10) disposed on the back side surface of the first base layer (12); a second base layer (16) formed on the surface of the first base layer (12); a source layer (18) formed on the surface of the second base layer (16); a gate insulating film (20) disposed on the surface of both the source layer (18) and the second base layer (16); a gate electrode (22) disposed on the gate insulating film (20); a column layer (14) formed in the first base layer (12) of the lower part of both the second base layer (16) and the source layer (18) by opposing the drain layer (10); a drain electrode (28) disposed in the drain layer (10); and a source electrode (26) disposed on both the source layer and the second base layer, wherein heavy particle irradiation is performed to the column layer (14) to form a trap level locally.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
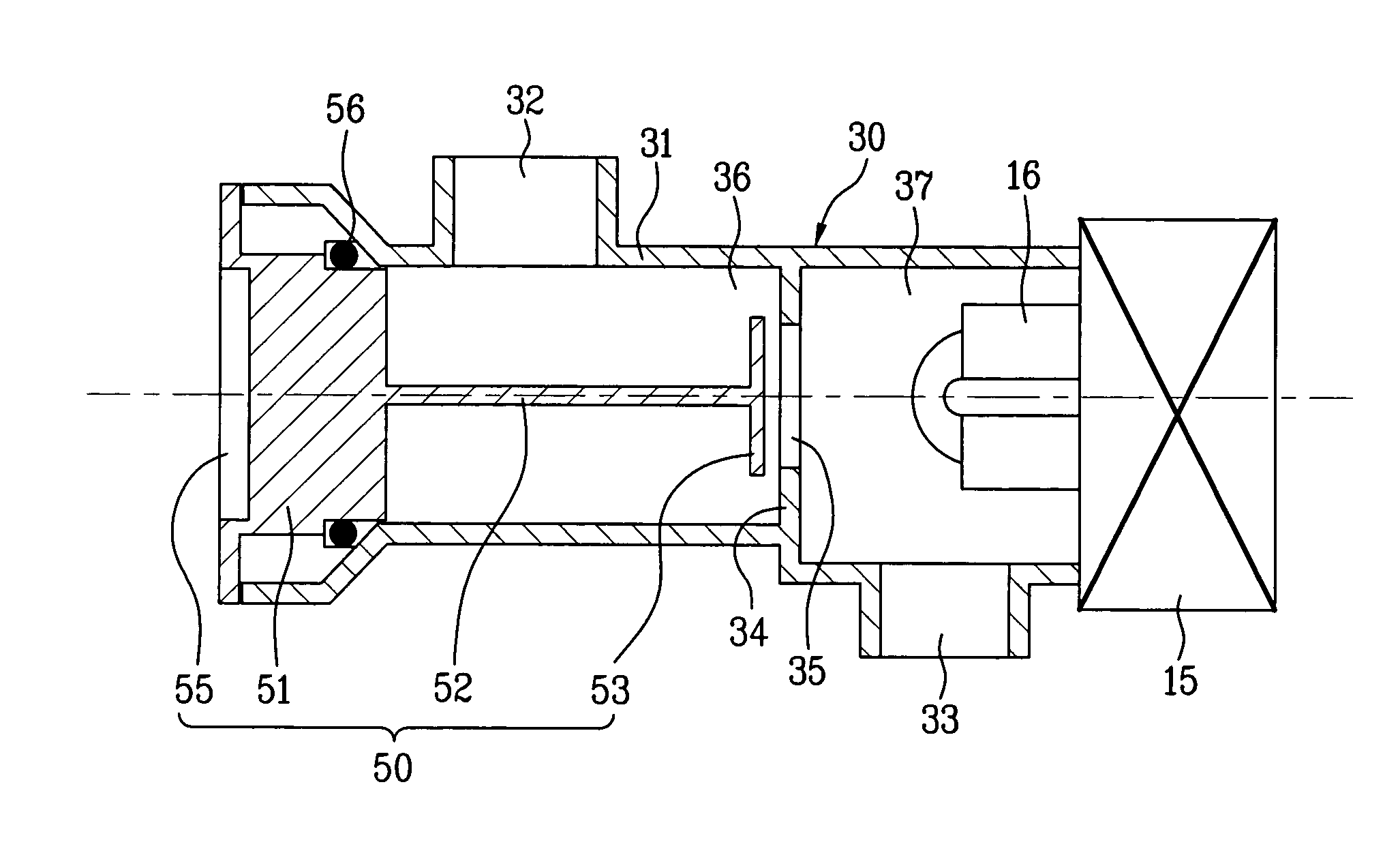
Powered air cleaning system and air cleaning method
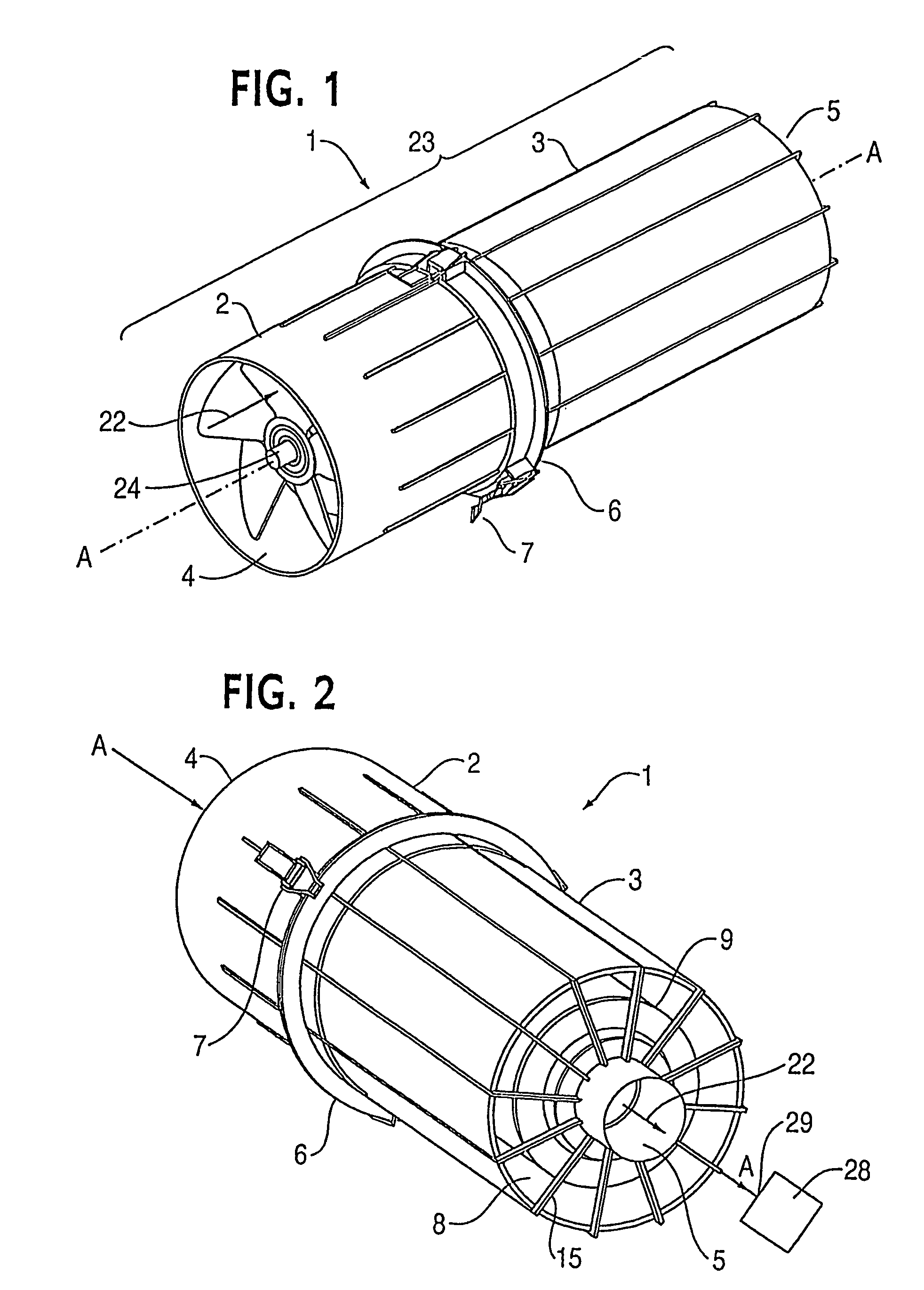
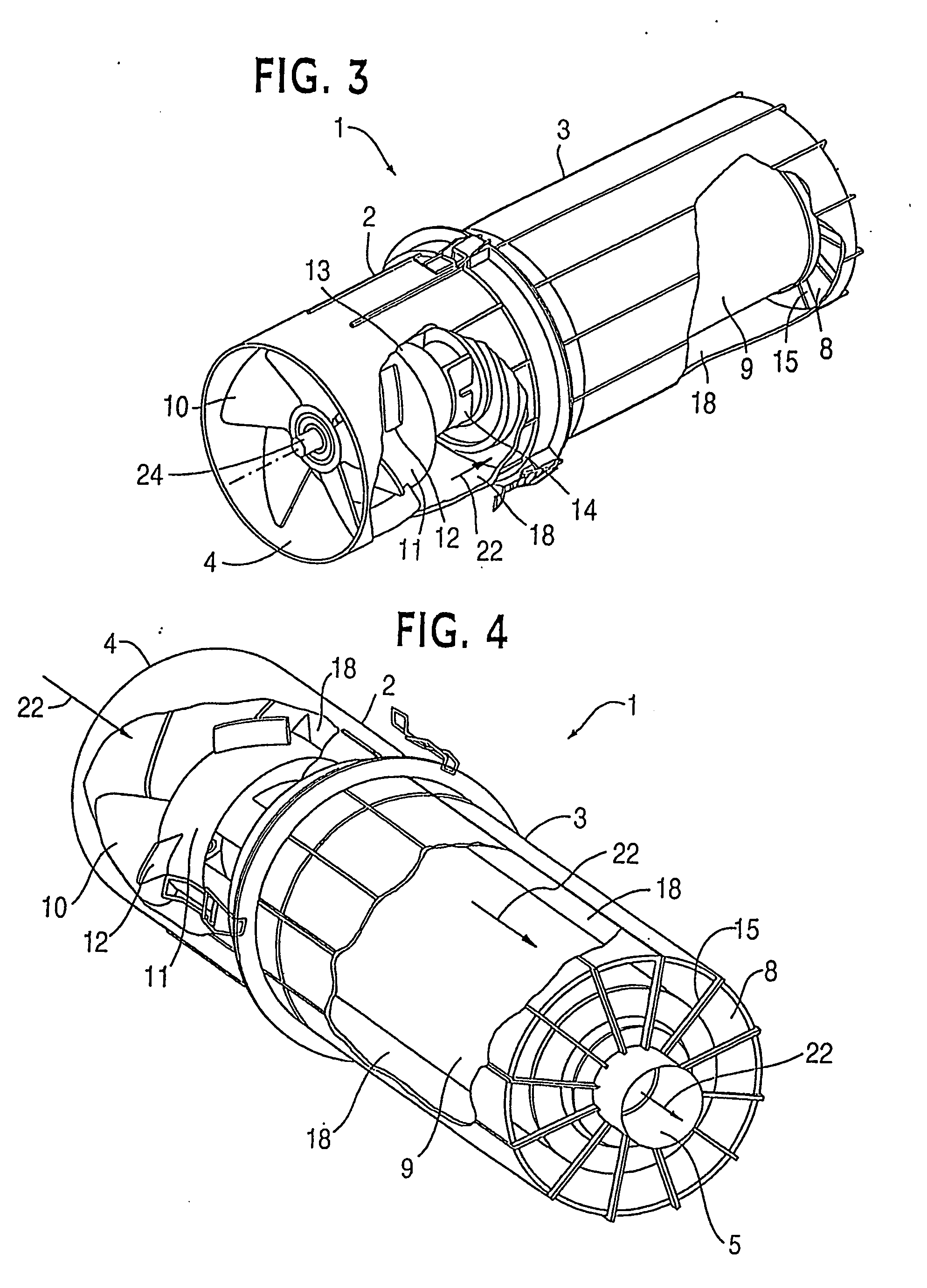
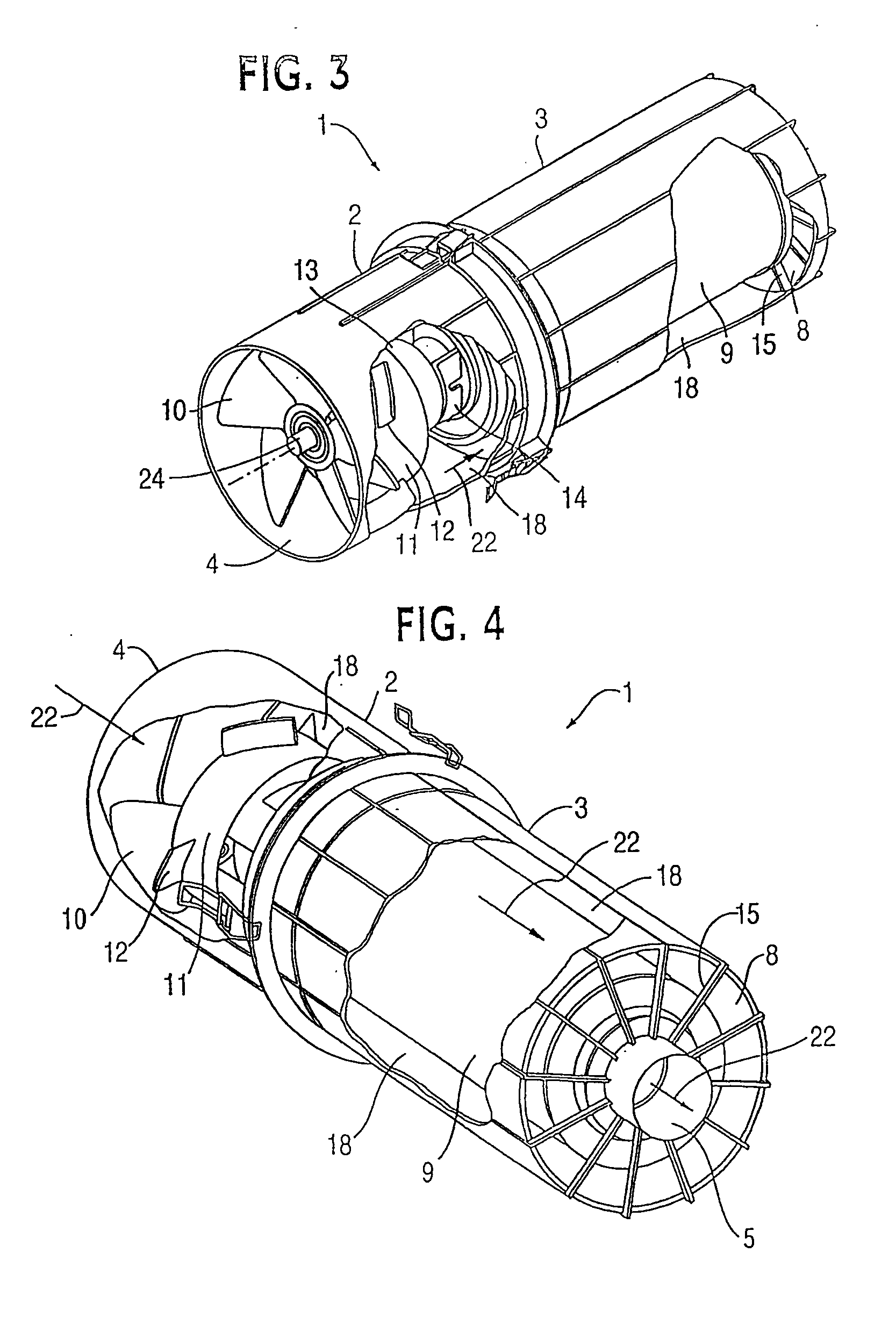
ActiveUS7452409B2Efficient removalLower performance requirementsCombination devicesLiquid degasificationParticulate debrisHeavy particle
A powered air cleaning system (31) and air cleaning method are disclosed. The system comprises a flow path (22) extending through the system from an air inlet (4) to a clean air outlet (5). A motor-driven fan (24) located along the flow path draws particulate debris laden air into the inlet and rotates it about an axis (A-A) to form a rotating flow that stratifies the debris laden air with the heaviest particles in the outermost orbits of the rotating flow. An ejector port (33) is provided for ejecting particulate debris laden air from the stratified rotating flow in the system to the environment. An air filter (9) located within the rotating flow and across the flow path upstream of the outlet filters air from the innermost orbits of the stratified rotating flow. The motor-driven fan is operated to maintain a positive air pressure in the system on the filter even with cyclic air flow demands so that the rotating air flow continually sweeps the outside surface of the air filter to minimize buildup of debris on the filter.
Owner:SY KLONE
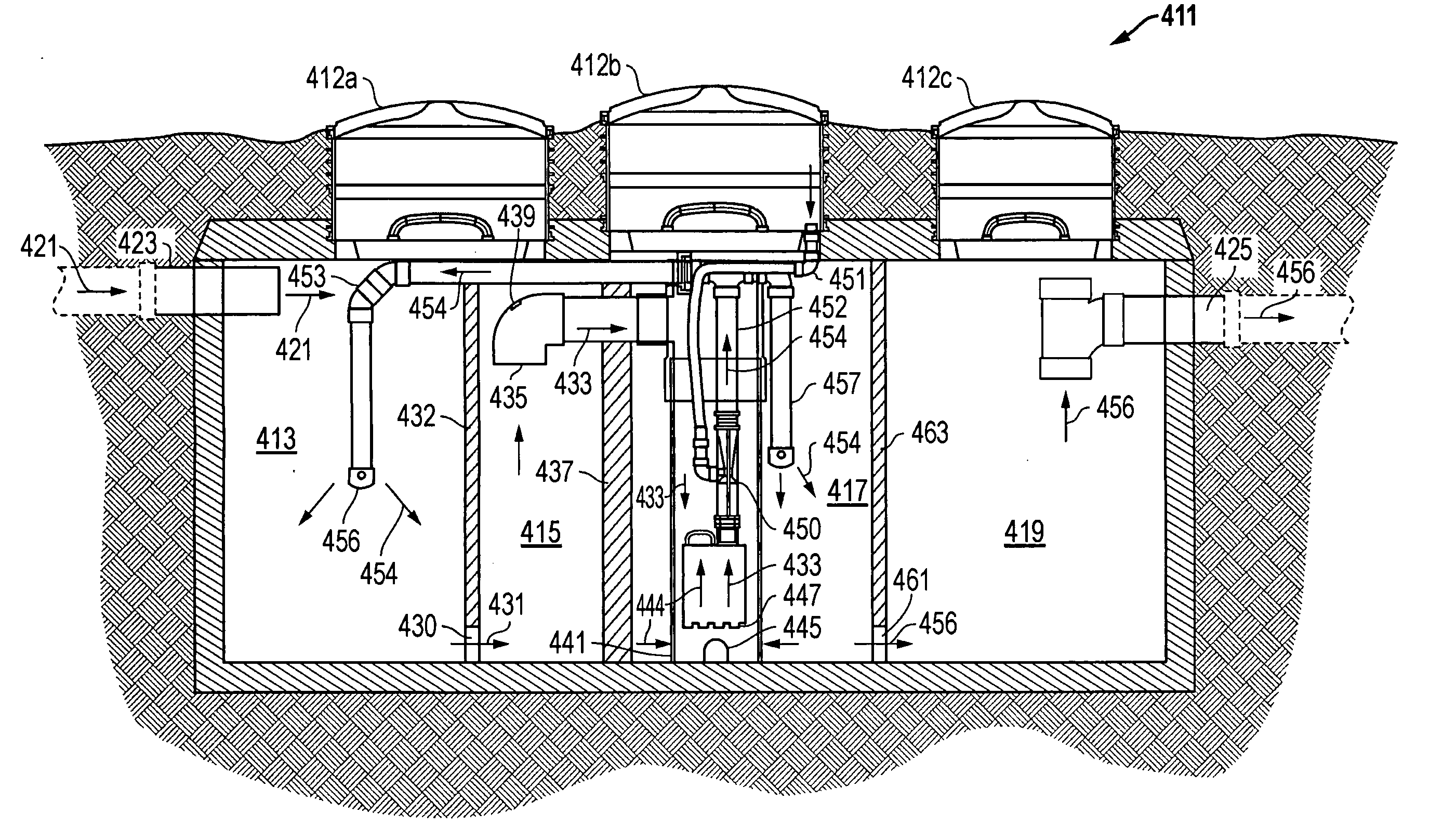
Aerobic wastewater management system, apparatus, and method
InactiveUS20050126995A1Improve performance and efficiencyBreak down and digest wasteTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsHeavy particleSludge
A wastewater processing and treatment system utilizes aerobic bacteria in two separate compartments to break down and digest waste. The first settling compartment between the trash tank and the mix liquor compartment is non-existent in conventional aerobic units. The first settling compartment allows for settling of heavy particles and keeps floating debris out of the circulating pump that is located in the mix liquor compartment. In the mix liquor compartment, 100% of the liquid is blended with air several times per hour to increase the efficiency and performance of the unit. The pump intakes on the bottom of the mix liquor compartment allow the pump to remove sludge build-up.
Owner:PROLINE WASTEWATER EQUIP
Powered air cleaning system and air cleaning method
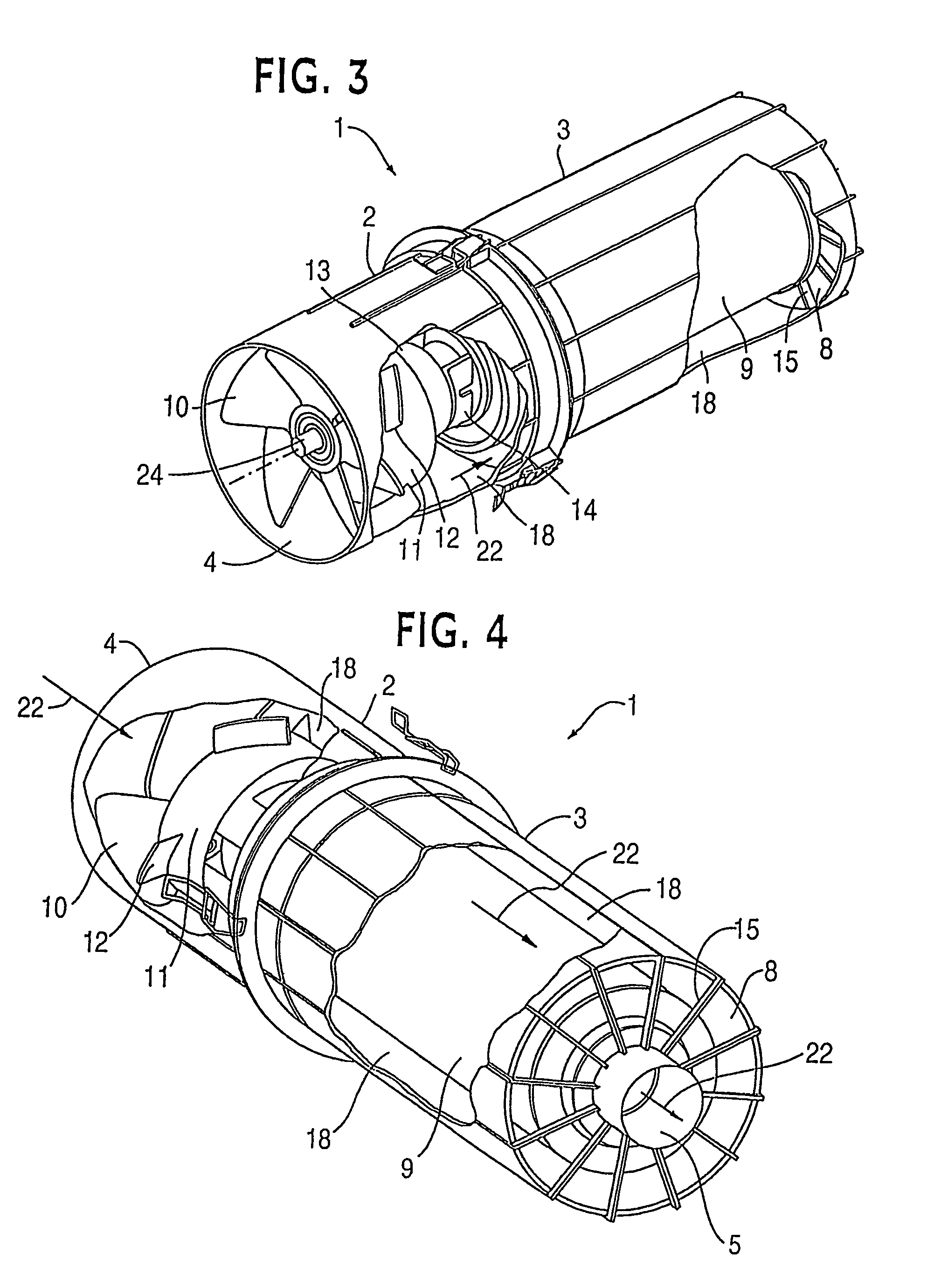
ActiveUS20050172587A1Efficient removalAvoids and reduces problemCombination devicesLiquid degasificationParticulate debrisHeavy particle
A powered air cleaning system (31) and air cleaning method are disclosed. The system comprises a flow path (22) extending through the system from an air inlet (4) to a clean air outlet (5). A motor-driven fan (24) located along the flow path draws particulate debris laden air into the inlet and rotates it about an axis (A-A) to form a rotating flow that stratifies the debris laden air with the heaviest particles in the outermost orbits of the rotating flow. An ejector port (33) is provided for ejecting particulate debris laden air from the stratified rotating flow in the system to the environment. An air filter (9) located within the rotating flow and across the flow path upstream of the outlet filters air from the innermost orbits of the stratified rotating flow. The motor-driven fan is operated to maintain a positive air pressure in the system on the filter even with cyclic air flow demands so that the rotating air flow continually sweeps the outside surface of the air filter to minimize buildup of debris on the filter.
Owner:SY KLONE
Density screening outer wall transport method for fluid separation devices
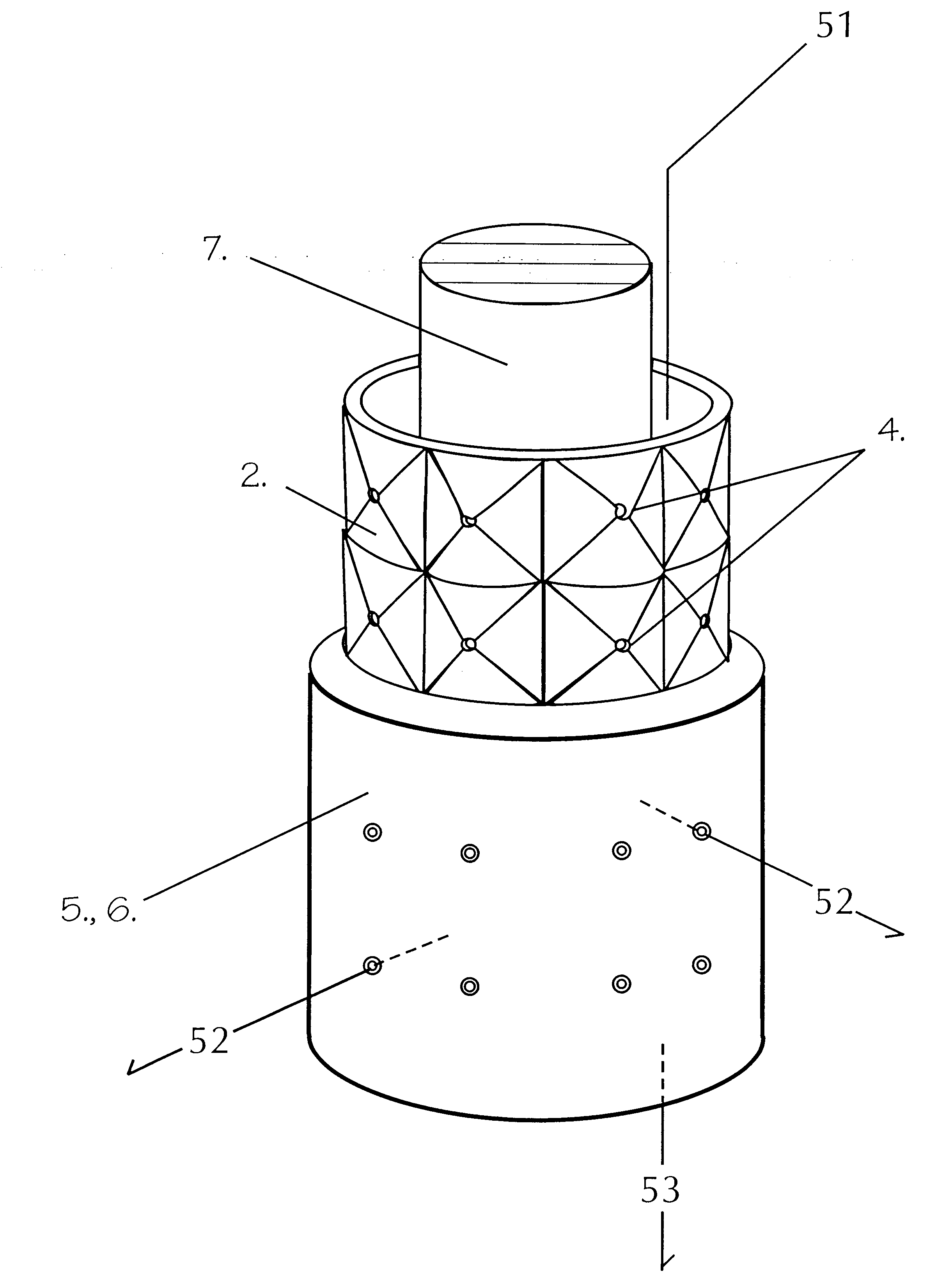
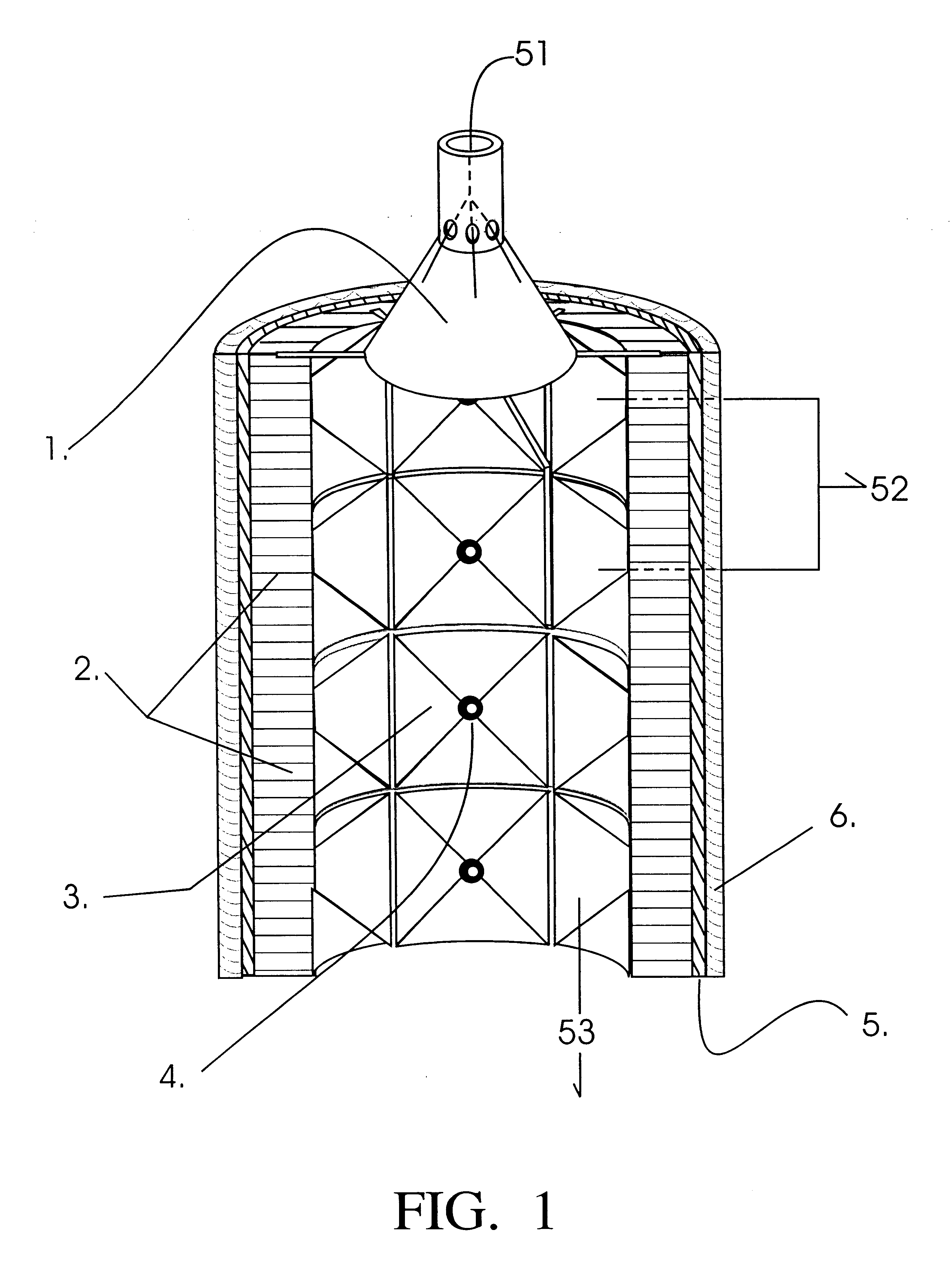
InactiveUS6312610B1Water/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationDispersed particle separationHeavy particleVolumetric Mass Density
A method for segregating and transporting heavy particles thrown by centrifugal force from a flowing, spinning column of liquid or gas, whereby an outer cylinder whose inner walls present or face the center core with horizontal, circular bands of pyramidal or conical shaped voids, which bands can be vertically stacked to surround a device of any length, and the voids of which present to the heavy particles being thrown from the fluid a receiving surface consisting entirely of outward sloping surfaces, all of which sloped-surface voids accept, accumulate and gravitationally guide said heavy particles towards exit orifices or nozzles, which nozzles penetrate the outer cylinder and together with the sloped voids, permit the continuous, non-mechanically assisted accumulation and ejection of said heavy particles along the entirety of a centrifugal device of any length and thus for any desired duration (or residence time) of fluid flow.
Owner:PHASE
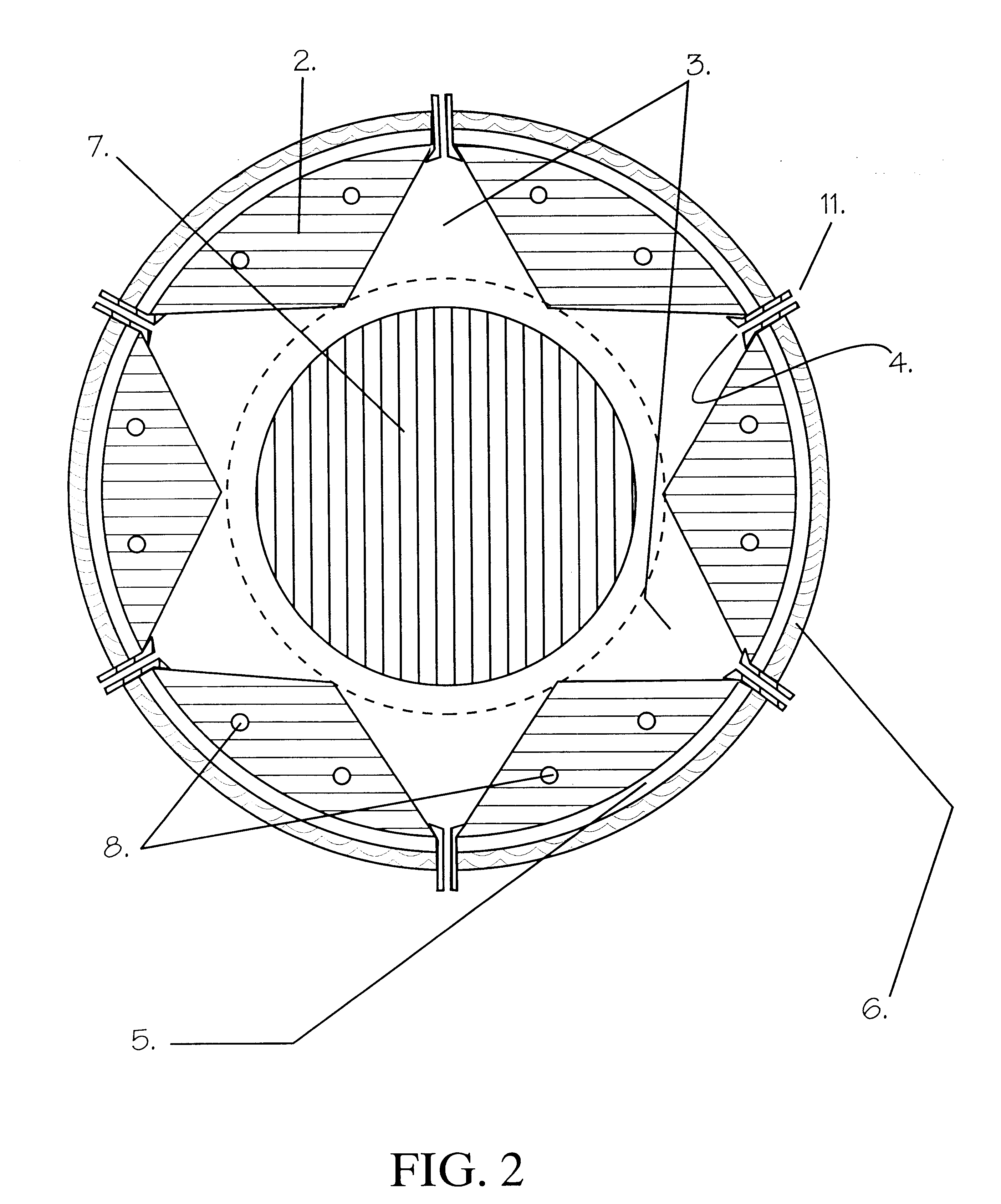
Filter assembly of washing machine
InactiveUS7243512B2Avoid passingLow costCentrifugal force sediment separationOther washing machinesHeavy particleWater flow
A filter assembly for a washing machine is provided which uses a simple structure to separate dirt and / or particles from washing water using. The filter assembly includes a filter case with an inlet and an outlet each positioned along its circumference, and an opening within the filler case which allows for communication between the inlet and outlet. A filter is provided in the filter case, the filter having a plate disposed in front of the opening to prevent particles from passing through the opening. Rather, the heavy particles are gathered in a central area of the filter by a centrifugal force generated by the water flowing in the filter case.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Thin Gap Chamber Neutron Detectors
ActiveUS20160018538A1Improve detection efficiencyAdjustable spacingMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHeavy particleGamma ray
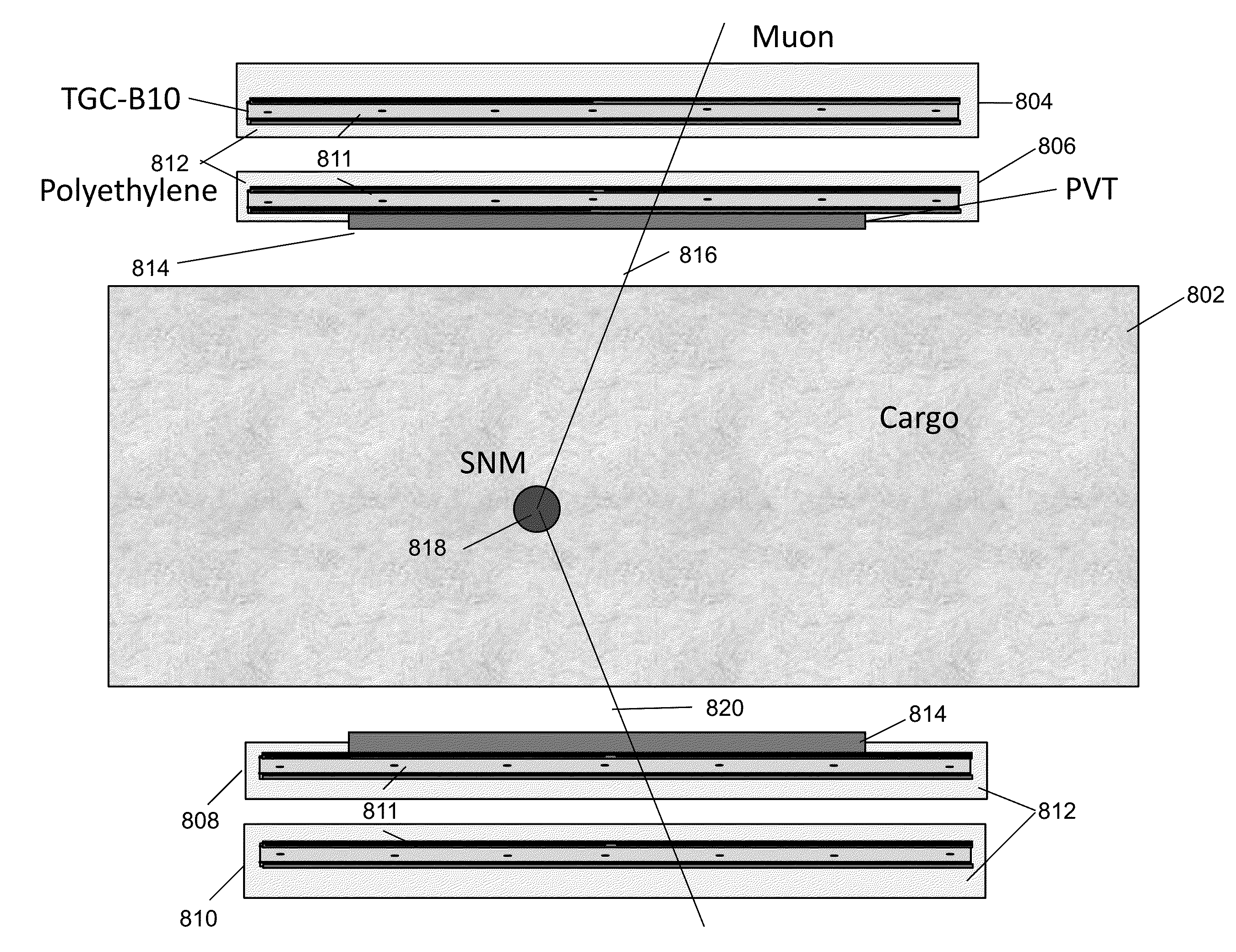
The present specification describes systems and methods for the simultaneous detection of radioactive materials such as neutrons, muons and gamma rays based on thin gap chamber technology. A thin-gap chamber (TGC) is disclosed having a thermal neutron absorber material, such as 10B4C or 10B8C, which interacts with neutrons to emit heavy particles. The heavy particles, in turn, interact with the gas present in chamber to produce ionization that is converted into a measurable signal. The TGC is embedded in a neutron moderating medium. The detector systems are fabricated from commercially available construction materials and are easy to manufacture at a reasonable cost when compared to conventional He-3 neutron detector systems.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
Method and system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy doses
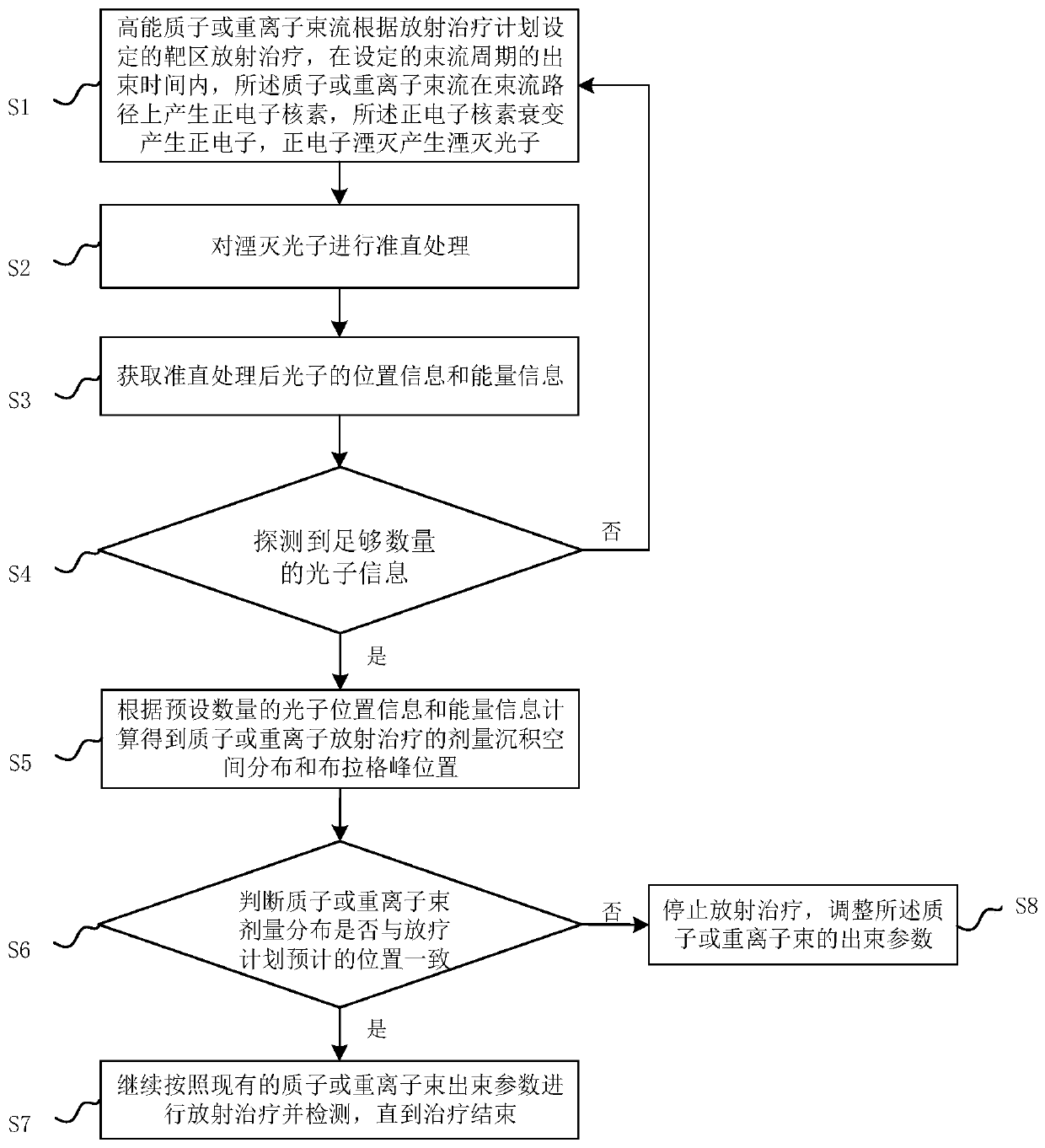
InactiveCN110270014AHigh precisionImprove detection efficiencyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyHeavy particleHeavy Ion Radiotherapy
The invention relates to a method and a system for real-time monitoring proton or heavy ion radiotherapy heavy particle radiotherapy doses. The monitoring method utilizes distribution information of positron radionuclide produced during the high-energy proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, and measures position and energy information of annihilation photons in the intermittent time of beams according to beam cycles of protons or heavy ions to obtain dose deposition spatial distributions in the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy, thereby realizing the monitoring of dose distributions of proton or heavy ion beams. Compared with the traditional instantaneous gamma measurement method, the method has a higher detection efficiency, and the method effectively reduces statistical noise, and improves accuracy of the dose deposition of the proton or heavy ion radiotherapy; compared with the traditional positron emission tomography method, the method can realize a faster one-dimensional distribution of dose along the beam direction by carrying out a collimation treatment on the annihilation photons along the beam direction and then detecting the position and energy information of the photons, thus the method is conducive to improving monitoring efficiency.
Owner:彭浩
Sluice assembly for separating heavy particles from slurry
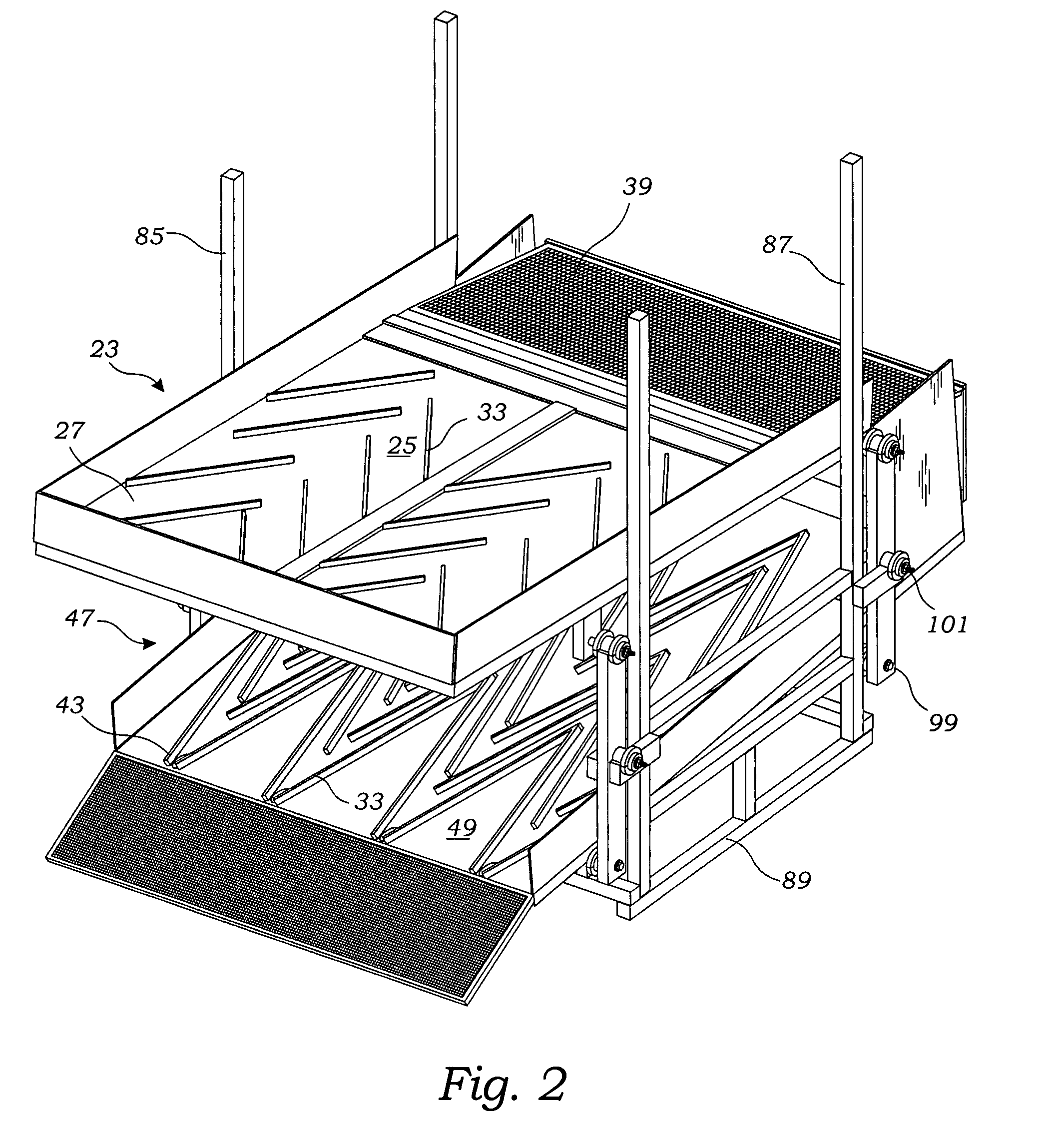
InactiveUS20090078615A1Efficient collectionReduce manufacturing costGas current separationSortingStatic friction coefficientHeavy particle
A sluice assembly for separating heavy particles from slurry is provided. The sluice assembly includes one or more sluice boxes having decks made of plastic having a Shore D hardness between 50-75, a static coefficient of friction less than 0.3 and a kinetic coefficient of friction less than 0.2. In a preferred embodiment, the sluice assembly includes a pair of sluice boxes in which a top sluice box is positioned above the bottom sluice box so that slurry flowing from the downstream end of the first sluice box is received by the upstream end of the bottom sluice box. The bottom deck includes tapered riffles which are arranged to provide “V” shaped diverters for diverting heavier particles for collection. The sluice box upper deck may include laterally extending riffles for collection of heavier particles.
Owner:RAINWATER CHUCK +1
Dust collection system
Owner:YARBROUGH GLEN ALLEN +1
Method and Apparatus for the Separation of Solid Particles Having Different Densities
A method and apparatus for separating solid particles of different densities, using a magnetic process fluid. The solid particles are thoroughly mixed in a small partial flow of the process fluid. The small turbulent partial flow is added to a large laminar partial flow of the process fluid, after which the obtained mixture of the respective partial process fluids is conducted over, under, or through the middle of two magnet configurations, wherein the particles are separated into lighter particles at the top of the laminar process fluid and heavier particles at the bottom of the laminar process fluid, each of which are subsequently removed with the aid of a splitter. After that furthermore the particles of low density and the particles of high density are separated from the respective process streams, dried and stored. Finally, the process fluid from which the particles have been removed is returned to the original starting process stream. The method according to the invention is especially suitable, for example, for separating a mixture of polypropylene particles and polyethylene particles.
Owner:URBAN MINING CORP BV
Canal type thickener
InactiveCN103100242AShorten the lengthSave materialSedimentation settling tanksHeavy particleMedicine
The invention relates to a canal type thickener, which is a canal overall. Along an ore pulp flow path, the thickener includes a canal head, a canal body and a canal tail in order. Ore pulp enters a thickening pond through a feeding port, heavy particles in the ore pulp undergo preliminary settlement in the thickening pond. The low concentration ore pulp overflowing the canal head enters the canal body to undergo further settlement. When the low concentration ore pulp flows to the canal tail, it is already in a clear water state basically and enters a clear water pond, and is discharged through a drain hole. In the invention, the thickener is changed from the traditional ''round pond'' type to the ''canal type'', thus effectively solving the problem of large floor area of the thickener. The canal structure is in linear arrangement, can be subjected to buried installation, and does not take up the volume of a concentrating mill basically. With a long canal and a large actual settlement area, the structure of the thickener can be simpler, thereby effectively reducing the production cost.
Owner:蔡宏武
Vertical Filtering and Separating Suction Machine of Chips, Steam and Smoke by Change of Air Direction, for Machining Center, Lathe Machine or Other Machines Generating Steam from Oil or Coolant
InactiveUS20120111168A1Reduce the required powerGreat energy expenditureCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentSuction stressHeavy particle
The invention hereby disclosed is a vertical filtering and separating suction machine of chips, steam and smoke for machining center, lathe machine or other machines, which operates by sudden changes of sucked air, thus generating hits which separate heavy particles, whose suction pipe extends almost up to the bottom of the rotor, which only uses filters at the end of the process of air purification, whose rotor has outer paddles modified in order to improve suction power and to cause more hits of air flow, and which includes an air pressure alarm showing the filter is saturated.
Owner:OTA TOMIO
Aerobic wastewater management system, apparatus, and method
InactiveUS7018536B2Improve performance and efficiencyBreak down and digest wasteTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsHeavy particleSludge
A wastewater processing and treatment system utilizes aerobic bacteria in two separate compartments to break down and digest waste. The first settling compartment between the trash tank and the mix liquor compartment is non-existent in conventional aerobic units. The first settling compartment allows for settling of heavy particles and keeps floating debris out of the circulating pump that is located in the mix liquor compartment. In the mix liquor compartment, 100% of the liquid is blended with air several times per hour to increase the efficiency and performance of the unit. The pump intakes on the bottom of the mix liquor compartment allow the pump to remove sludge build-up.
Owner:PROLINE WASTEWATER EQUIP
Apparatus for separating fibers from reject material
InactiveUS7461744B2Easy to operate and controlSimple and inexpensive to manufactureSievingScreeningFiberHeavy particle
An apparatus for separating fibers from reject material produced in the manufacture of recycled pulp. The apparatus comprises a rotating reject cylinder provided with openings, to one end of which the reject material is fed and from the other end of which it is discharged, water nozzles for feeding water to the reject material in the cylinder to separate fibers from it, a collecting basin for recovering water and the fibers separated with it, and discharge channels connected with the collecting basin, and means for discharging fibrous water and light and heavy particles from the collecting basin. The collecting basin is formed of two basin structures at least partly within each other and connected with each other.
Owner:VALMET TECH INC
Aerobic wastewater management system, apparatus, and method
InactiveUS7022237B2Improve performance and efficiencyBreak down and digest wasteTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsHeavy particleWater management system
A septic tank (11) having two separate compartments, a trash tank (13) and a mix liquor compartment, using aerobic bacteria to process waste, and methods of its use. A settling compartment allows heavy particles to settle while keeping lighter debris out of a pump (47).
Owner:PROLINE WASTEWATER EQUIP
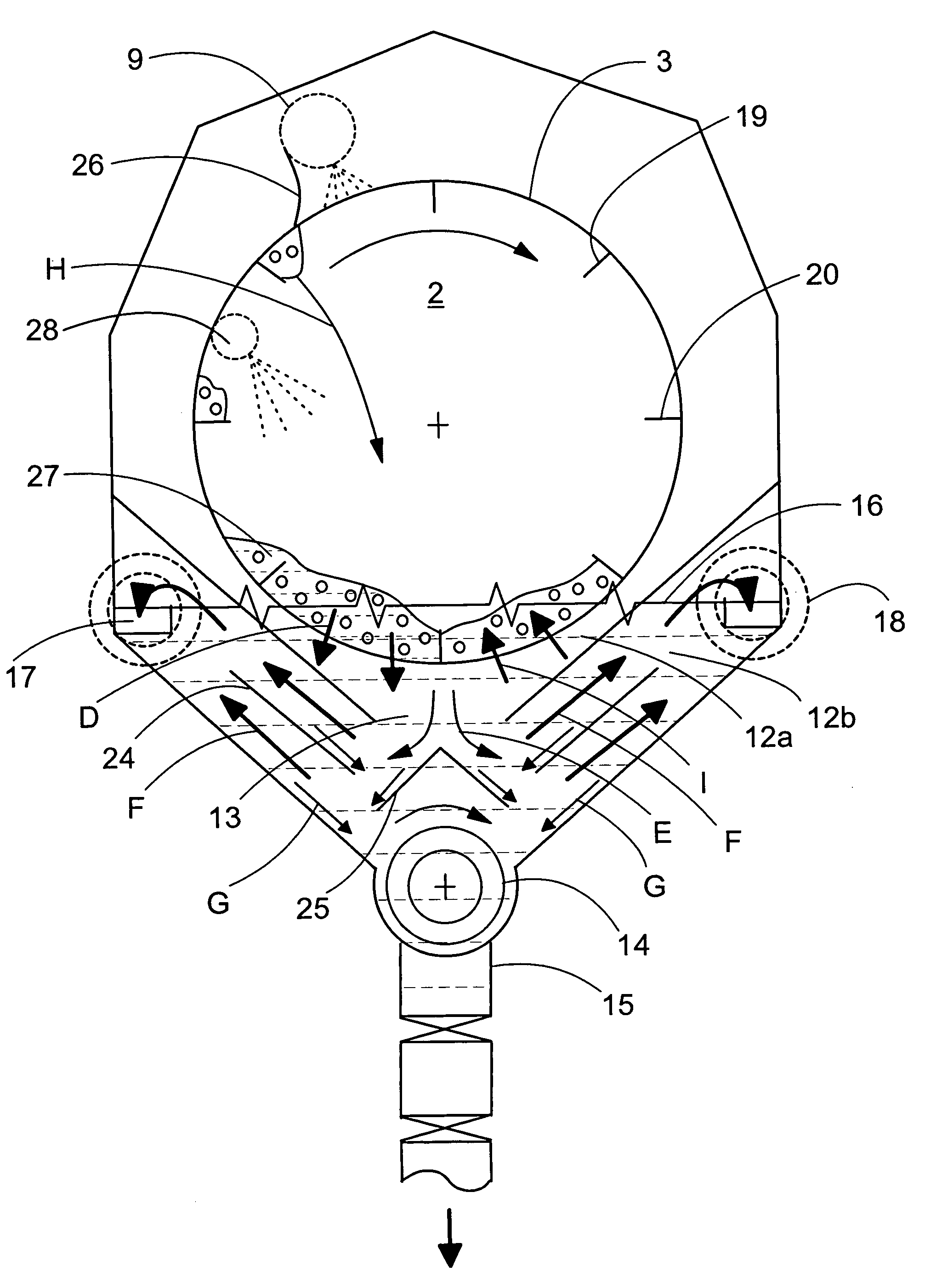
Flow deflecting member for hydrocyclone
ActiveUS20140124437A1Reduce disadvantagesReversed direction vortexCentrifugal force sediment separationHeavy particleEngineering
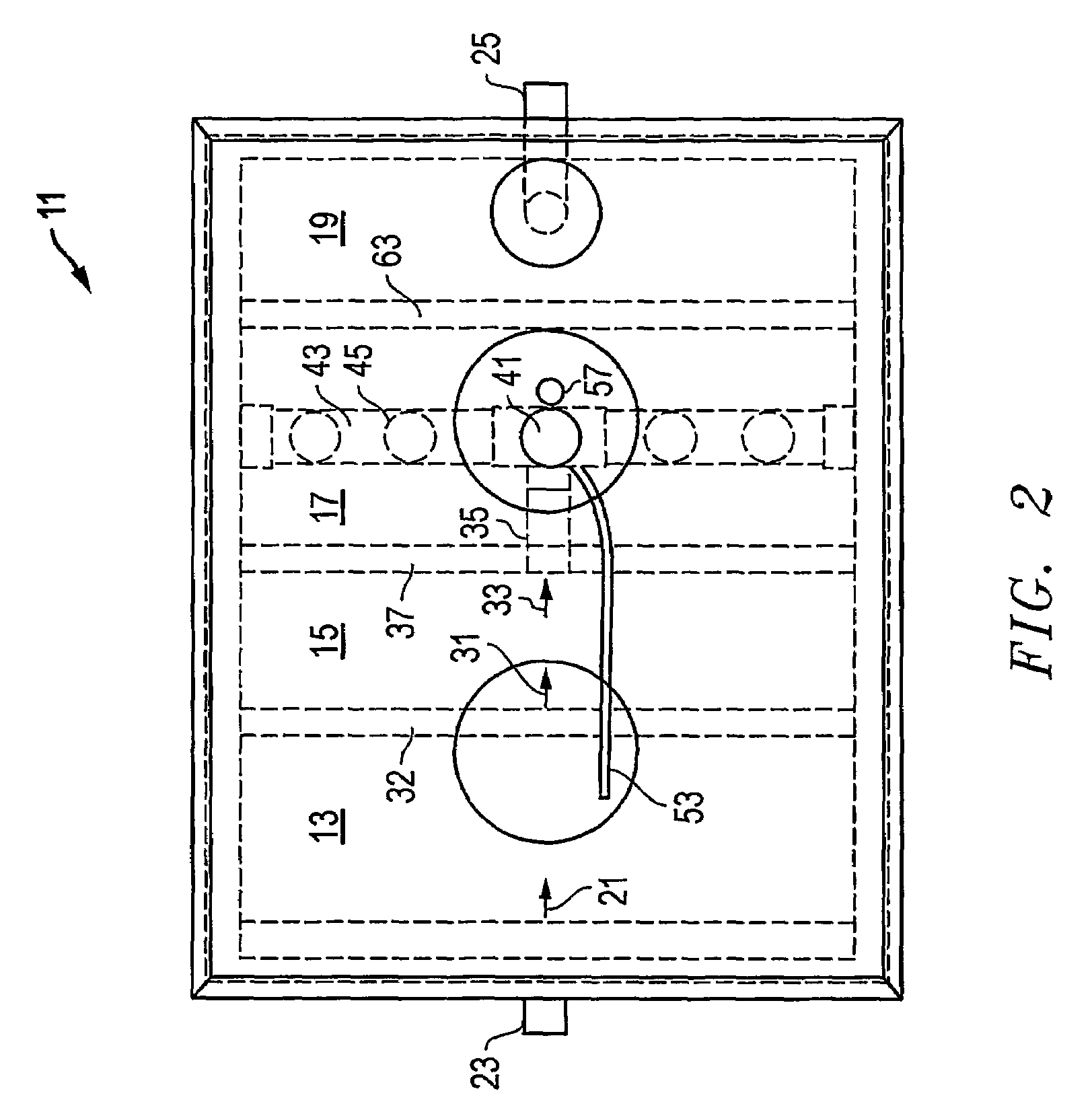
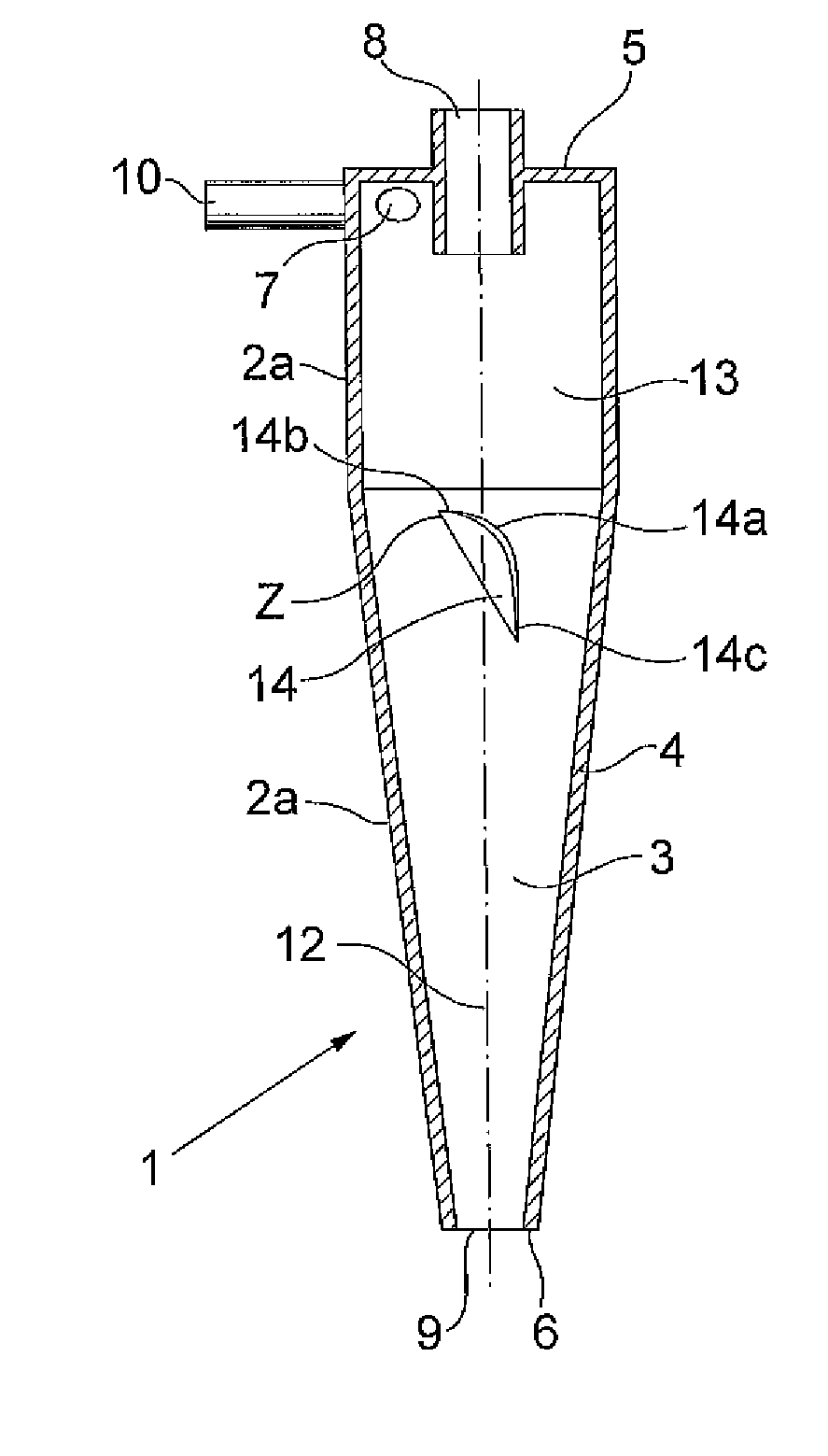
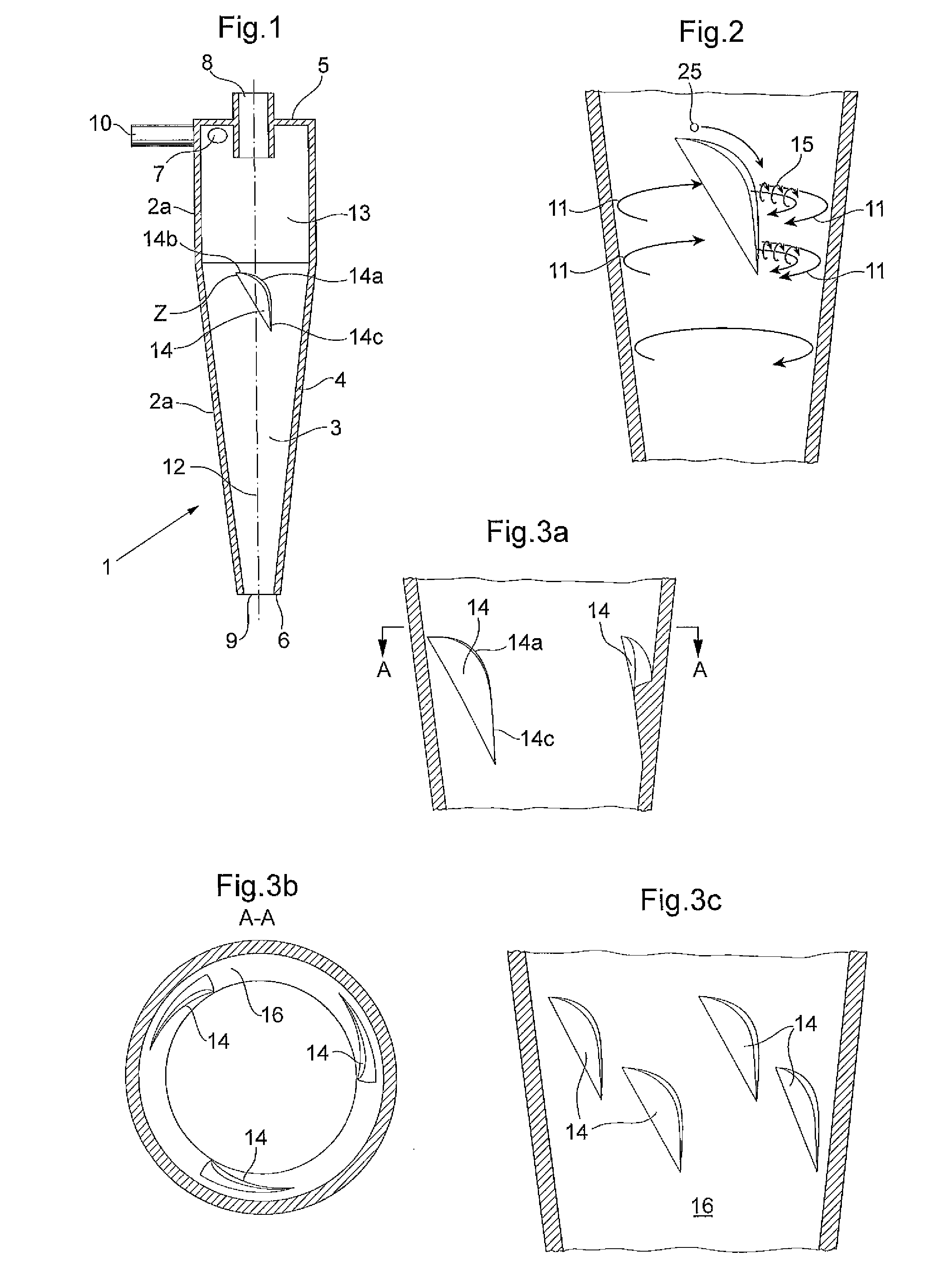
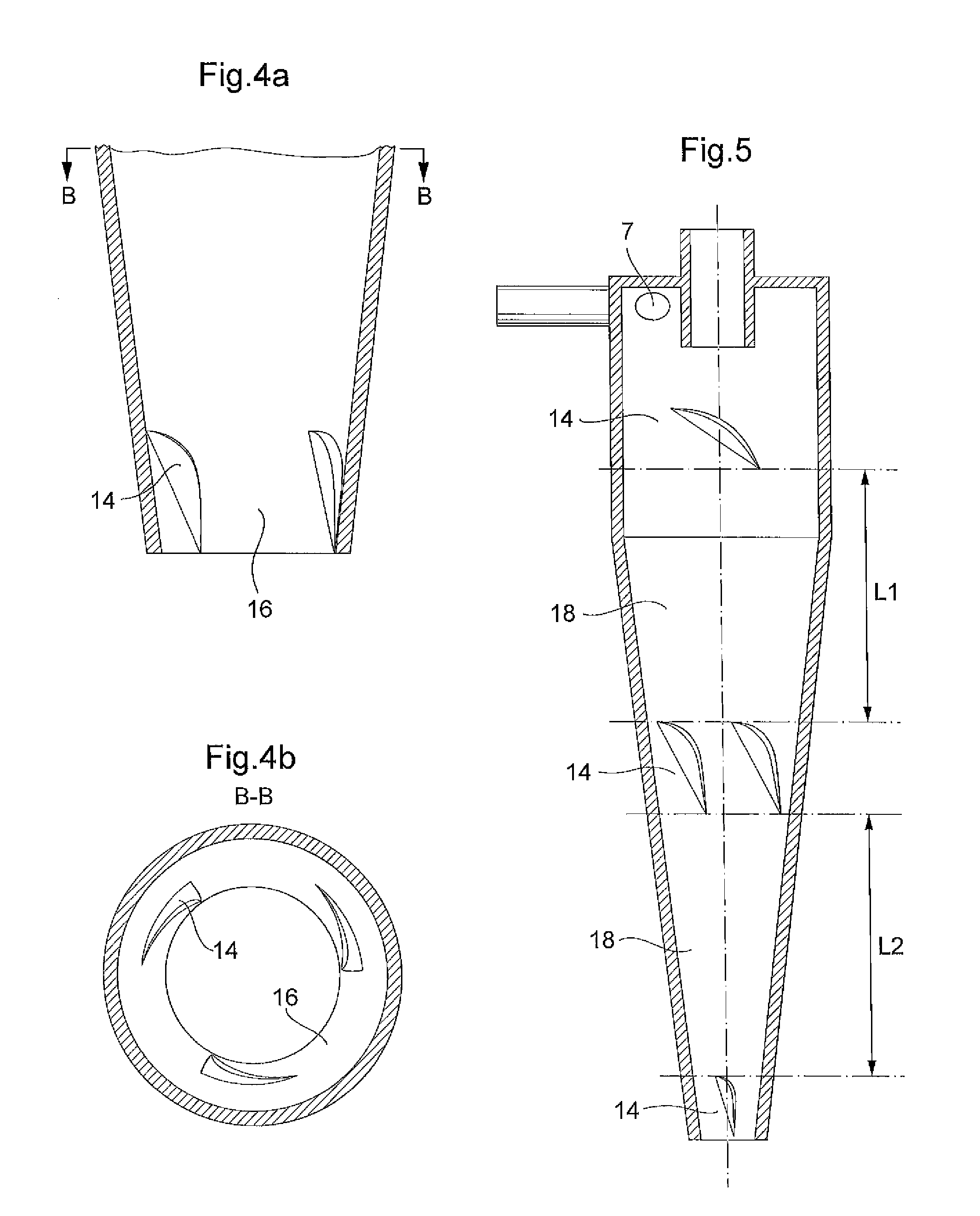
A hydrocyclone (1) for separating a liquid mixture into a heavy fraction including heavy particles and alight fraction, comprising a housing (2) forming an elongated separation chamber (3) having a circumferential wall (4), abase end (5),an apex end (6), at least one inlet member (7) for supplying a liquid mixture into the separation chamber (3), at least one of the inlet member / s(7) positioned at the base end (5), a first outlet member (8) for discharging separated light fraction from the separation chamber (3) at the base end (5), a second outlet member (9) for discharging separated heavy fraction from the separation chamber (3) at the apex end (6), means (10) for supplying the liquid mixture to the separation chamber (3) via the at least one inlet member (7), so that during operation a liquid stream is generated as a helical vortex (11) about a centre axis (12) in the separation chamber (3), said helical vortex (11) extending from the base end (5) to the apex end (6), a first flow deflection means arranged in the circumferential wall (4) which comprises at least one member (14) in the path 13 of the liquid stream showing a decrease of the radius of the separation chamber, followed by an increase of the radius of the separation chamber,where in the at least one member comprises a rounded curve portion 14a for transporting the heavy 14c particles.
Owner:OVIVO LUXEMBOURG R L
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com