Patents
Literature
987 results about "Suction stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
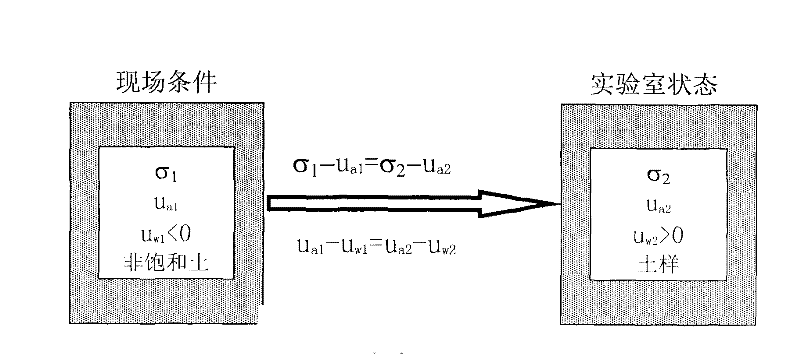
The suction stress refers to the net interparticle force generated within a matrix of unsaturated soil particles due to the combined effects of negative pore water pressure and surface tension. The macroscopic consequence of suction stress is a force that tends to pull the soil grains toward one another.
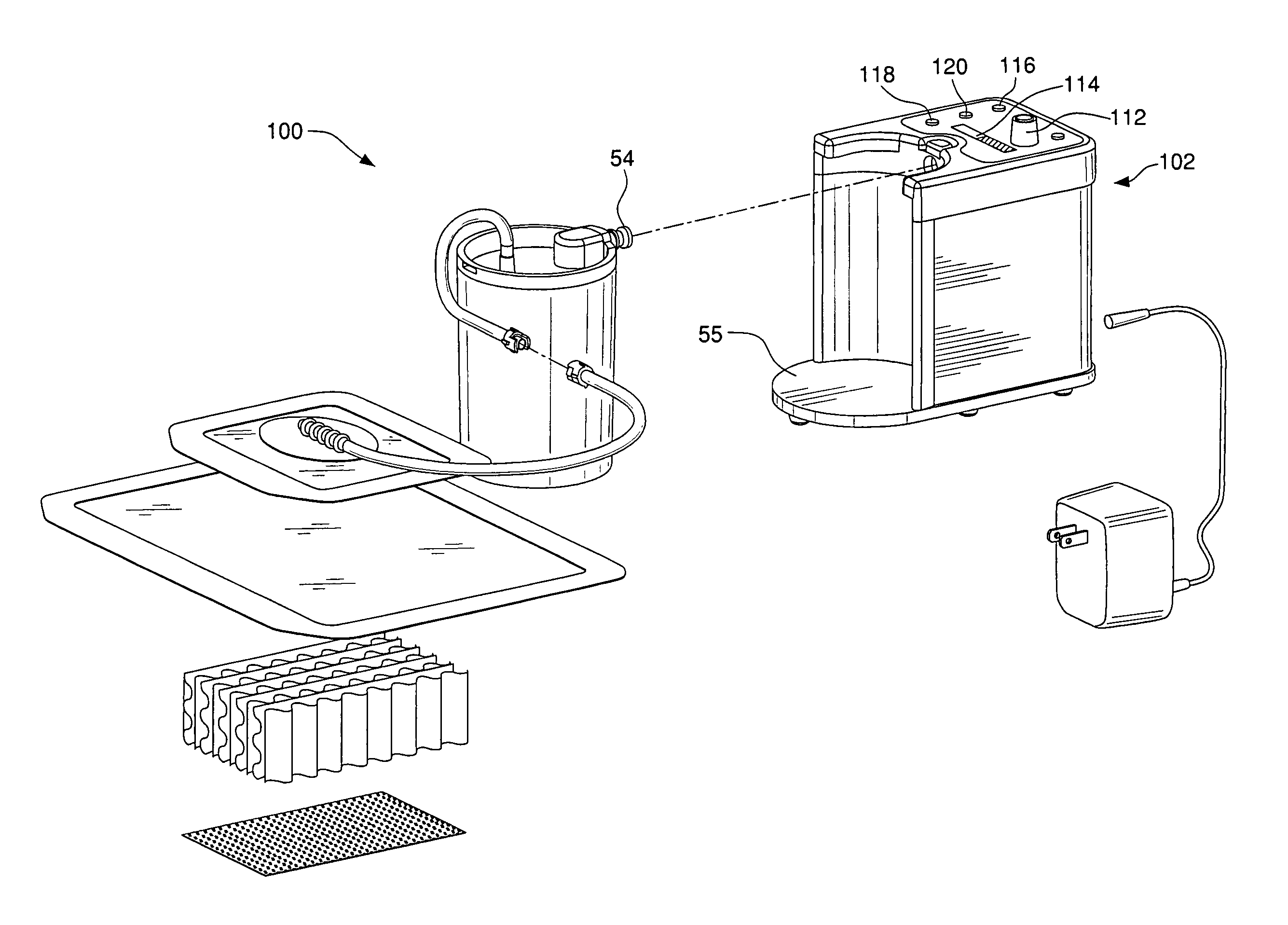
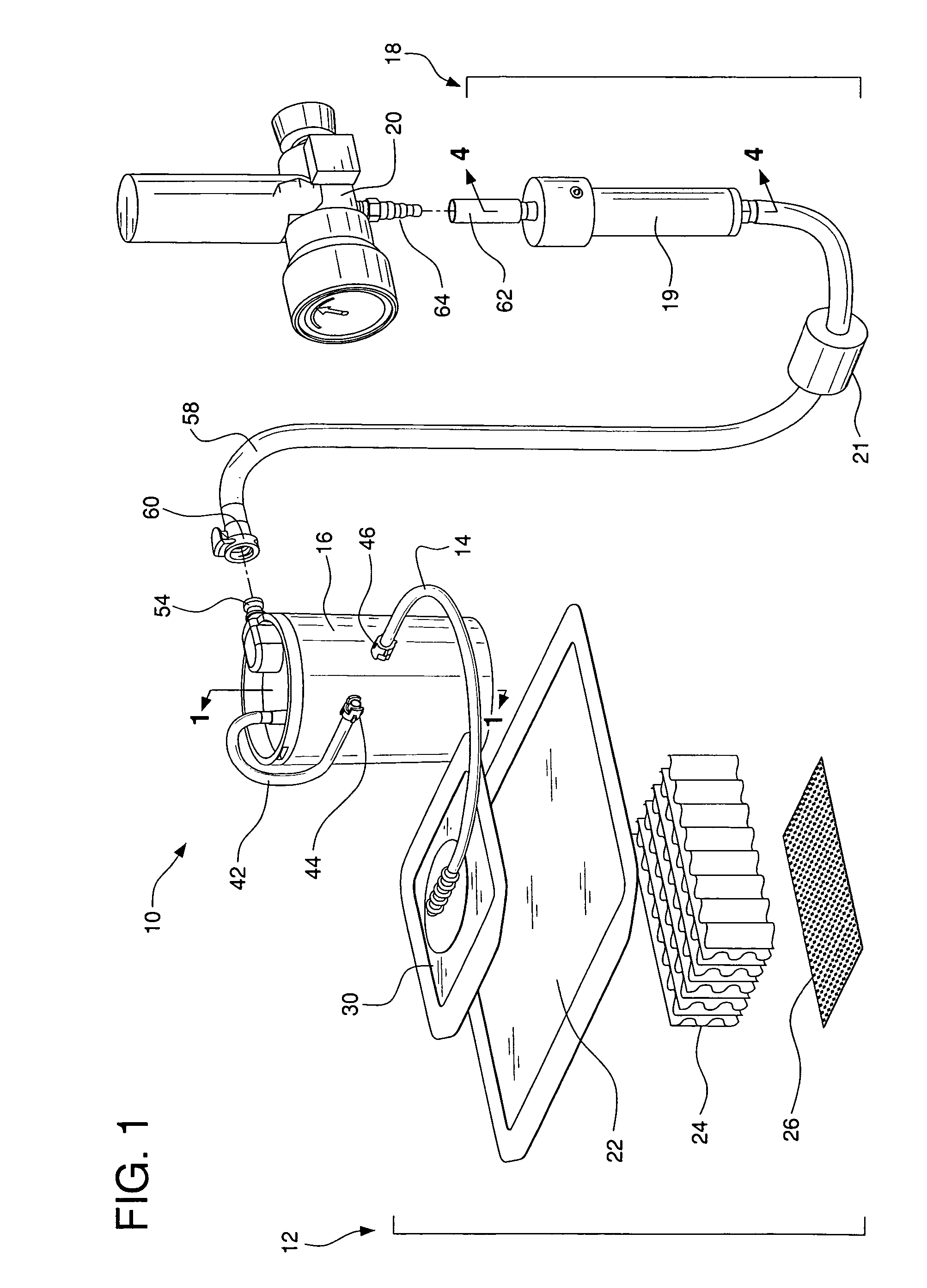
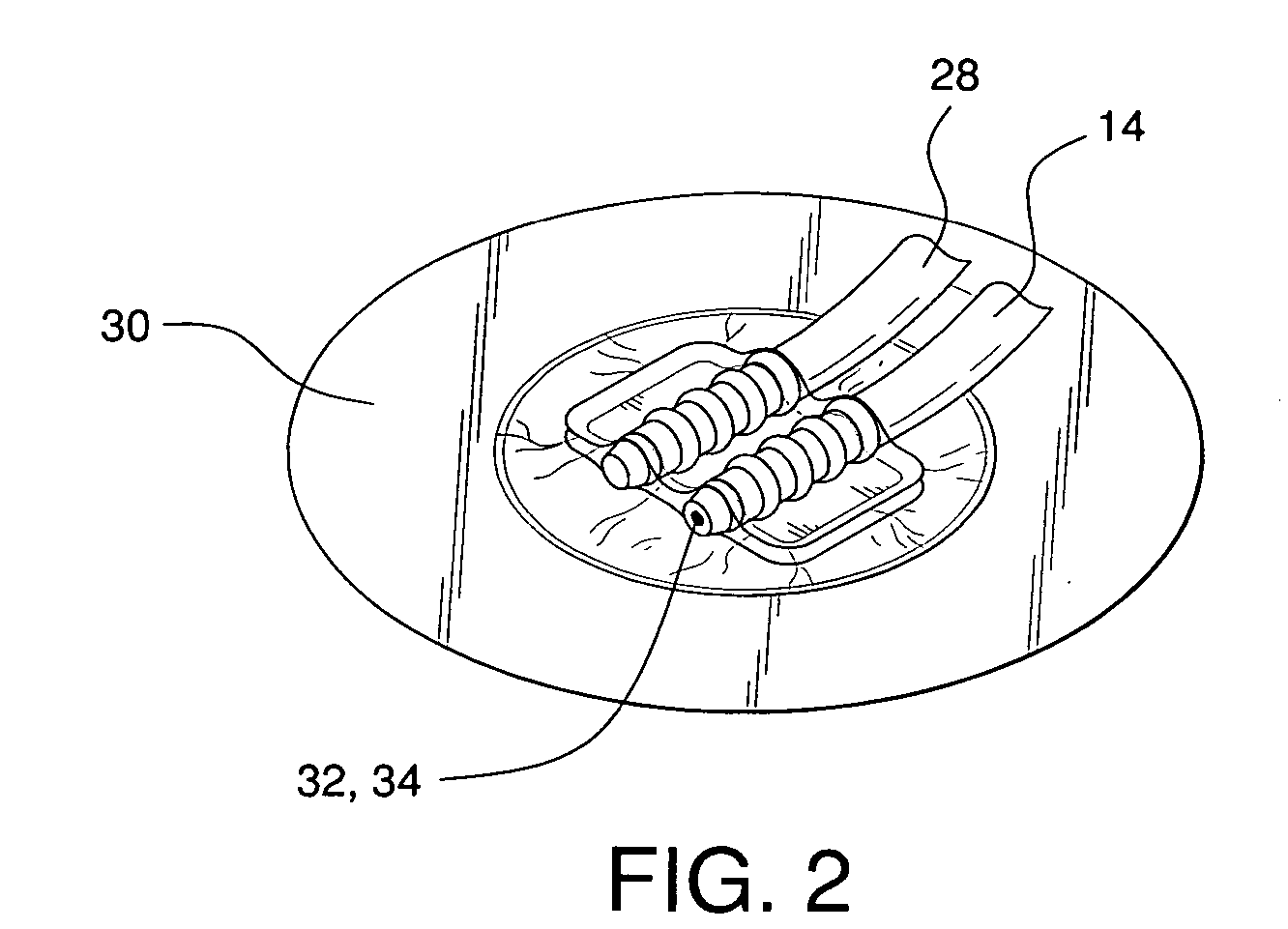
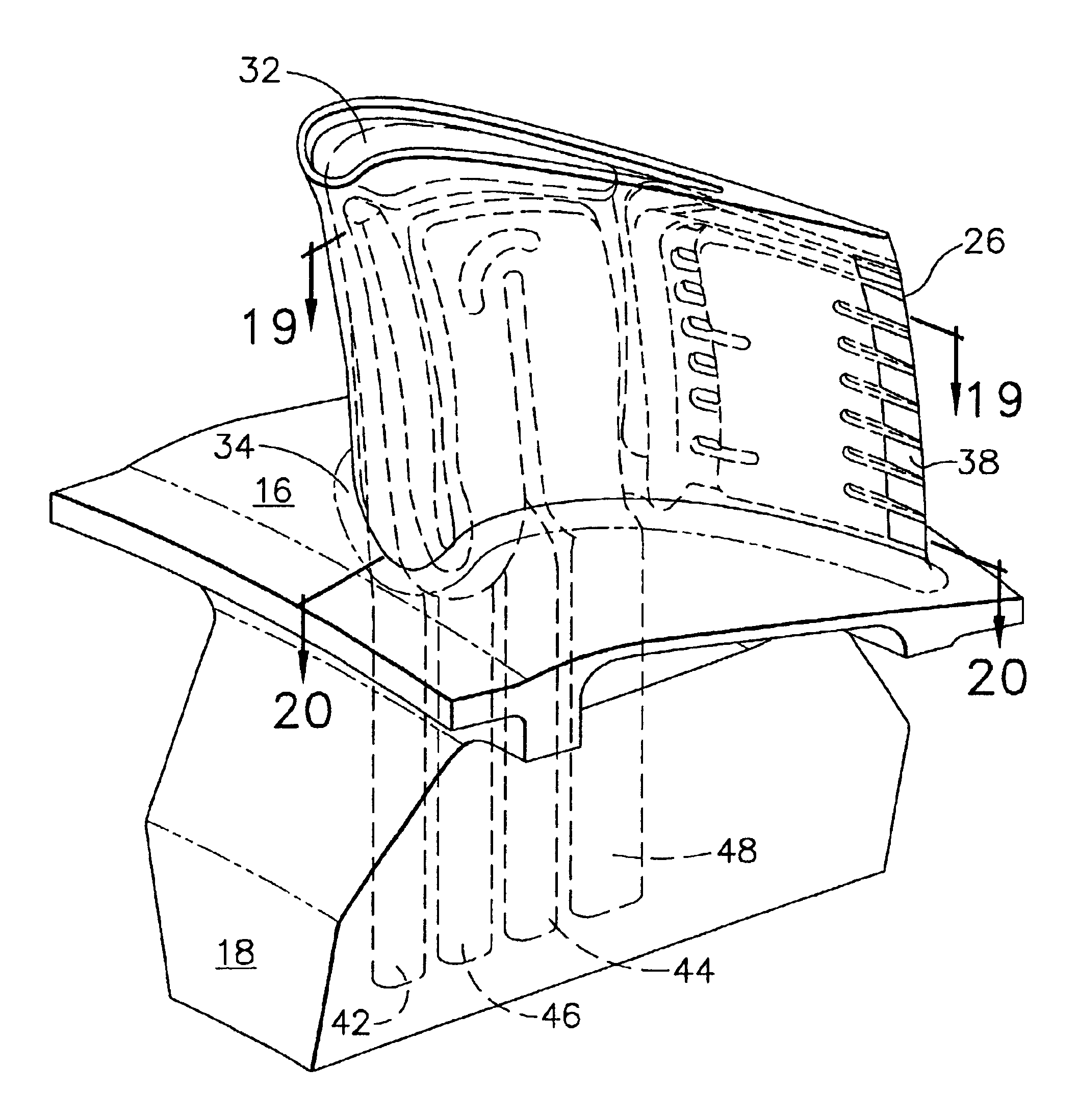
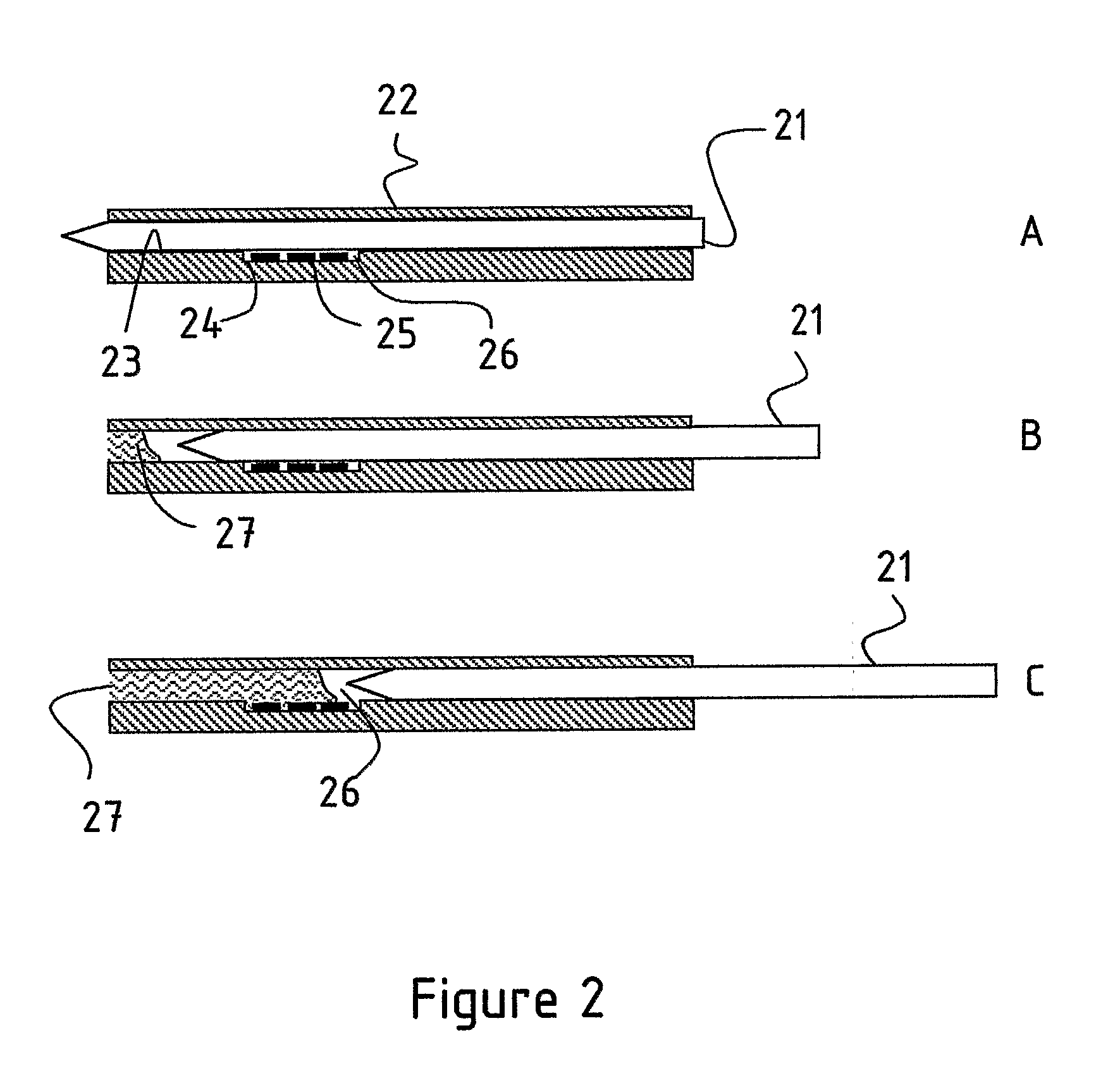
System for treating a wound with suction and method of detecting loss of suction
InactiveUS20070016152A1Minimize the possibilityReduce the possibilityWound drainsMedical devicesSuction stressMonitoring system
A system for applying suction to a wound uses a reference airflow for monitoring system operation. A reference airflow (or “controlled leak”) to the suction source is provided when the system is in operation, such that deviation from the reference airflow can be monitored as an indication of a change in operation, such as a leak in the seal of the wound cover, a blockage of airflow from crimping of the suction conduit or overfill of the waste collector, or an inadvertent turn off or disconnect from the suction source.
Owner:PAUL HARTMANN AG
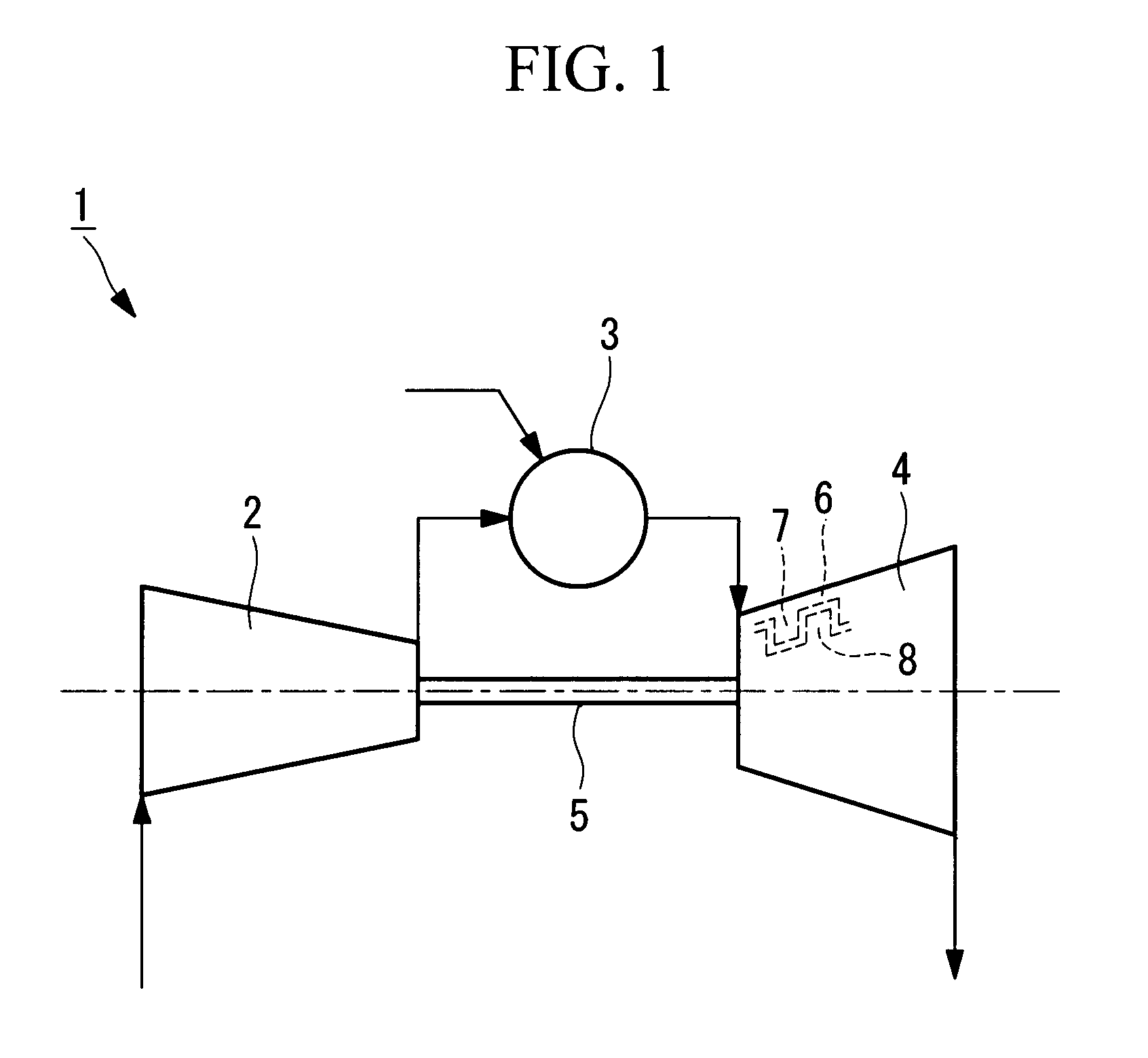
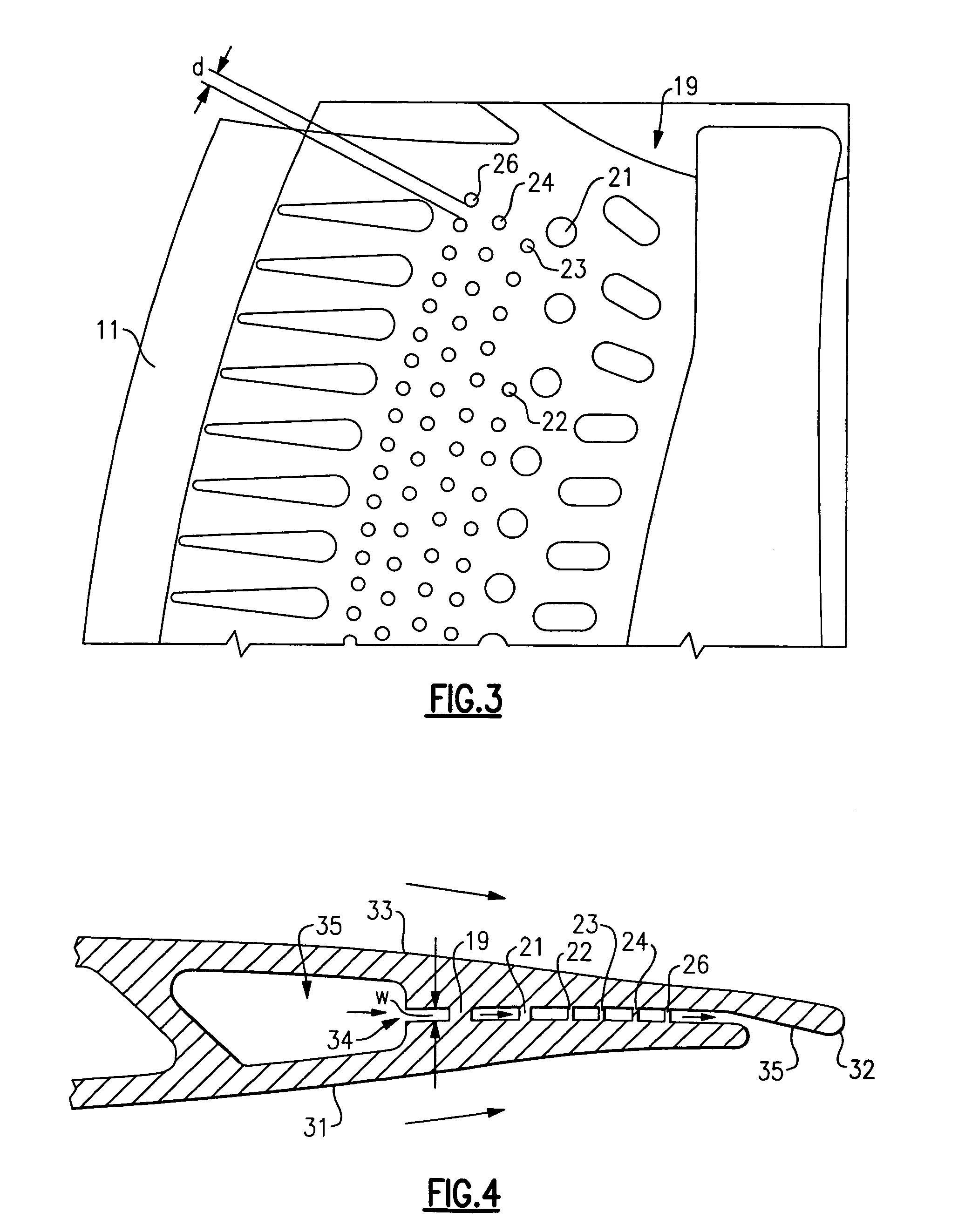
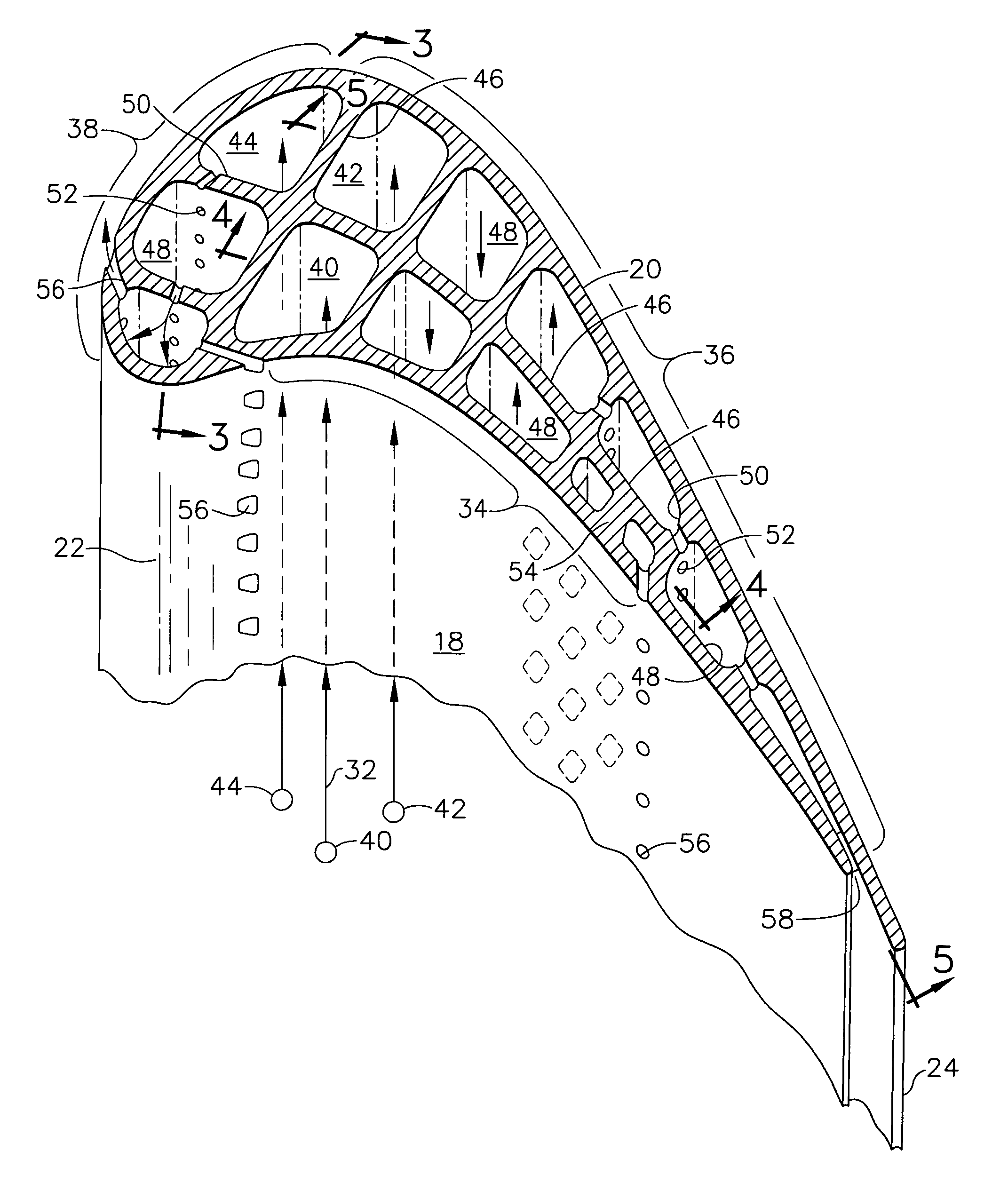
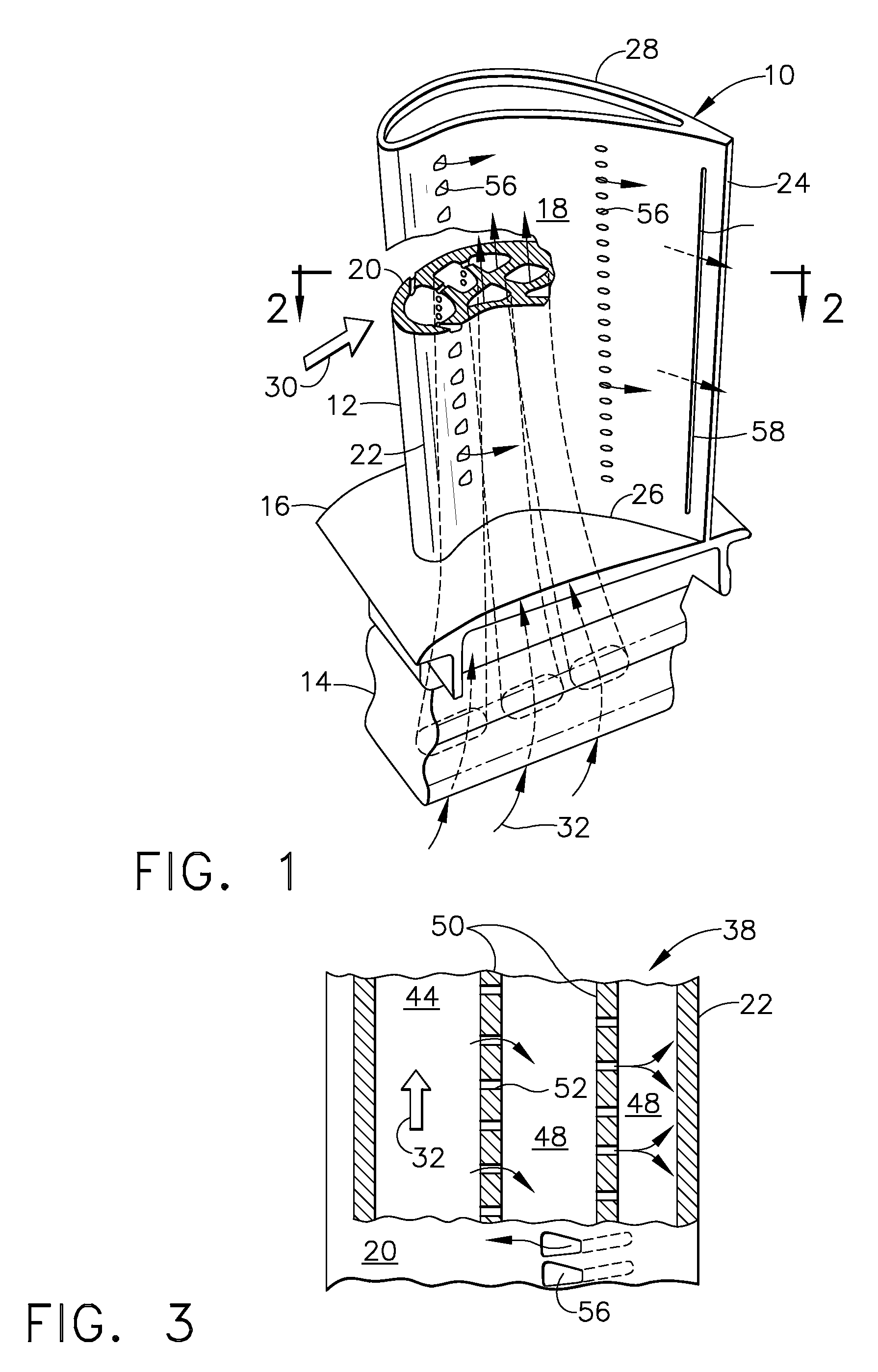
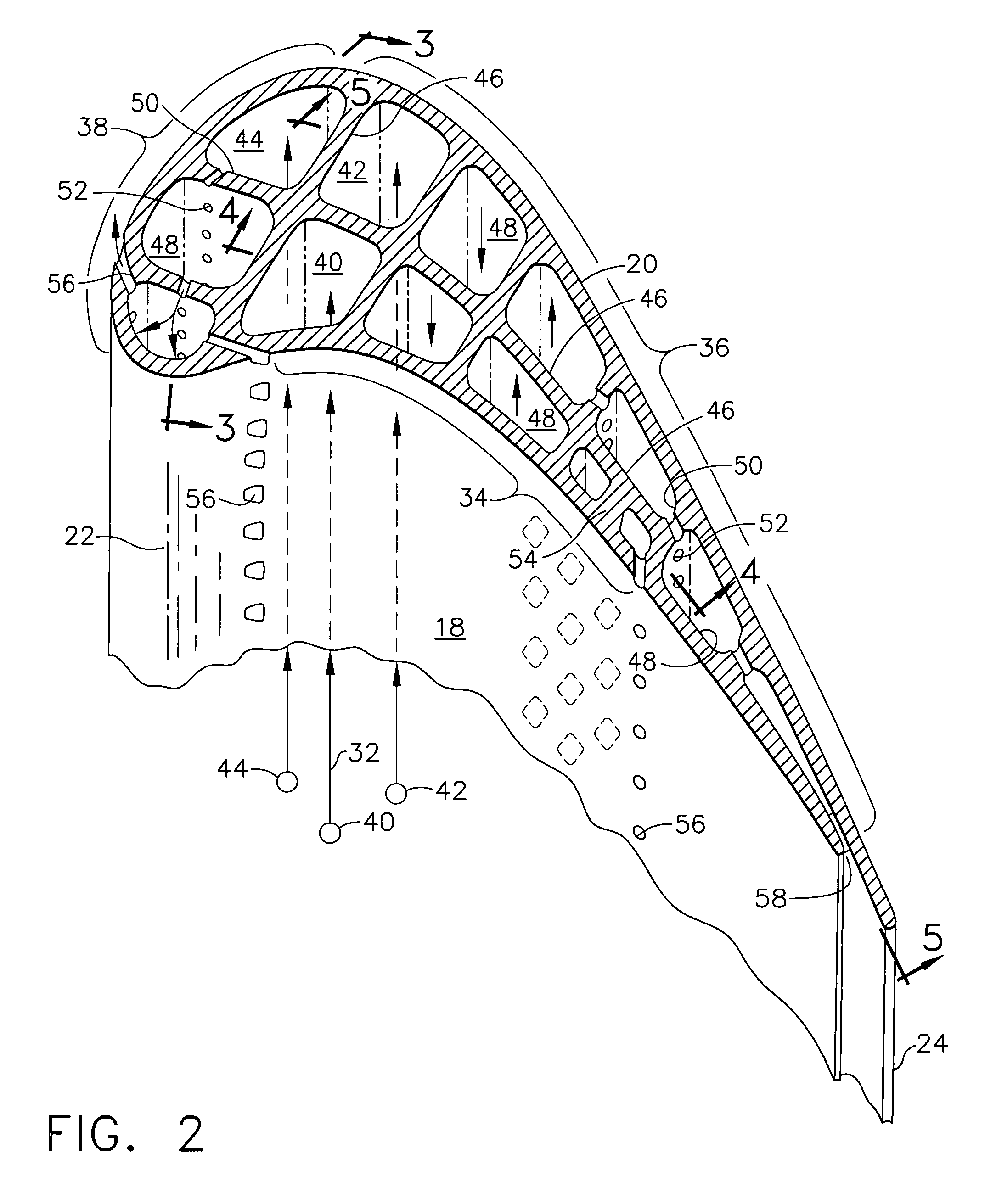
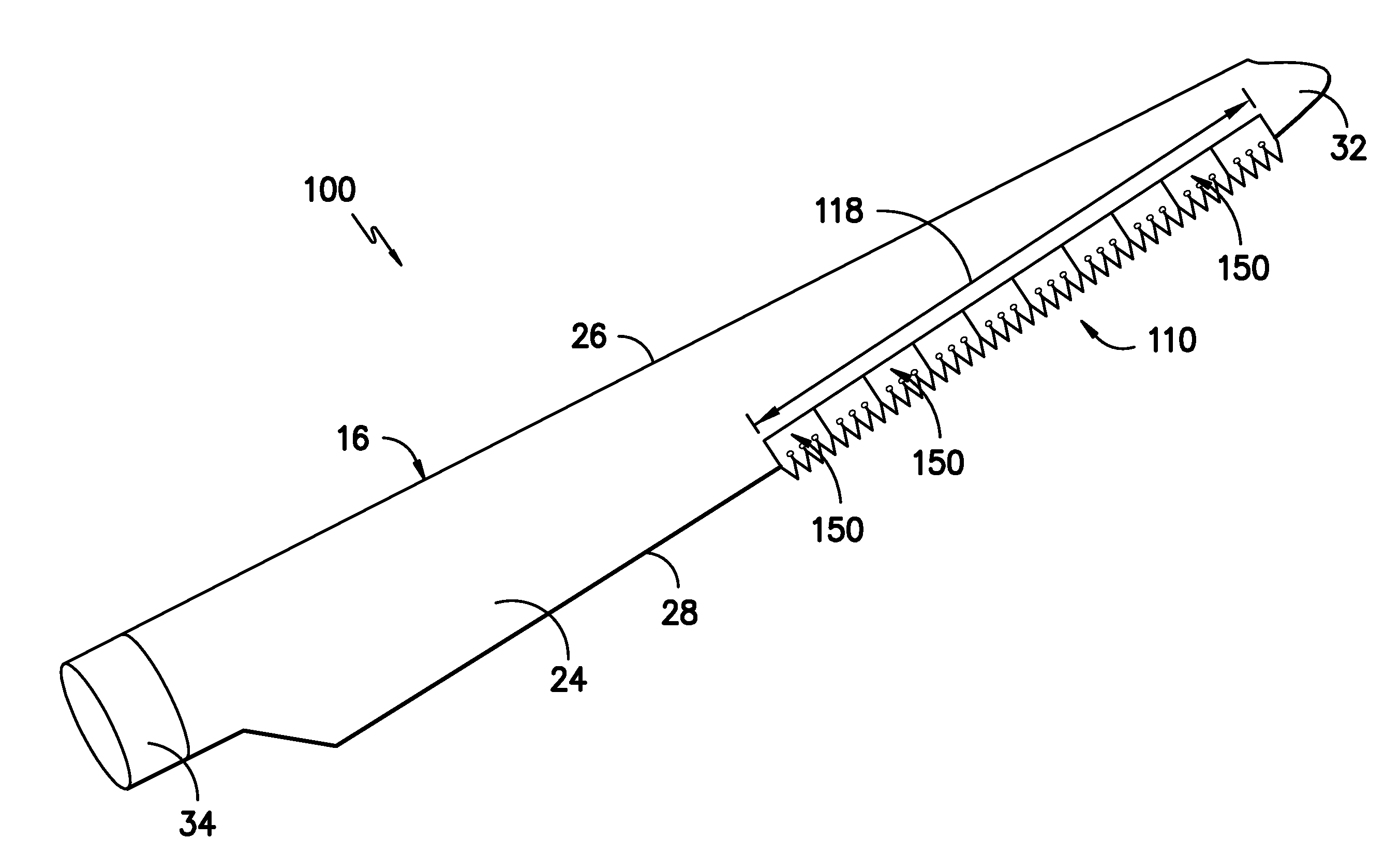
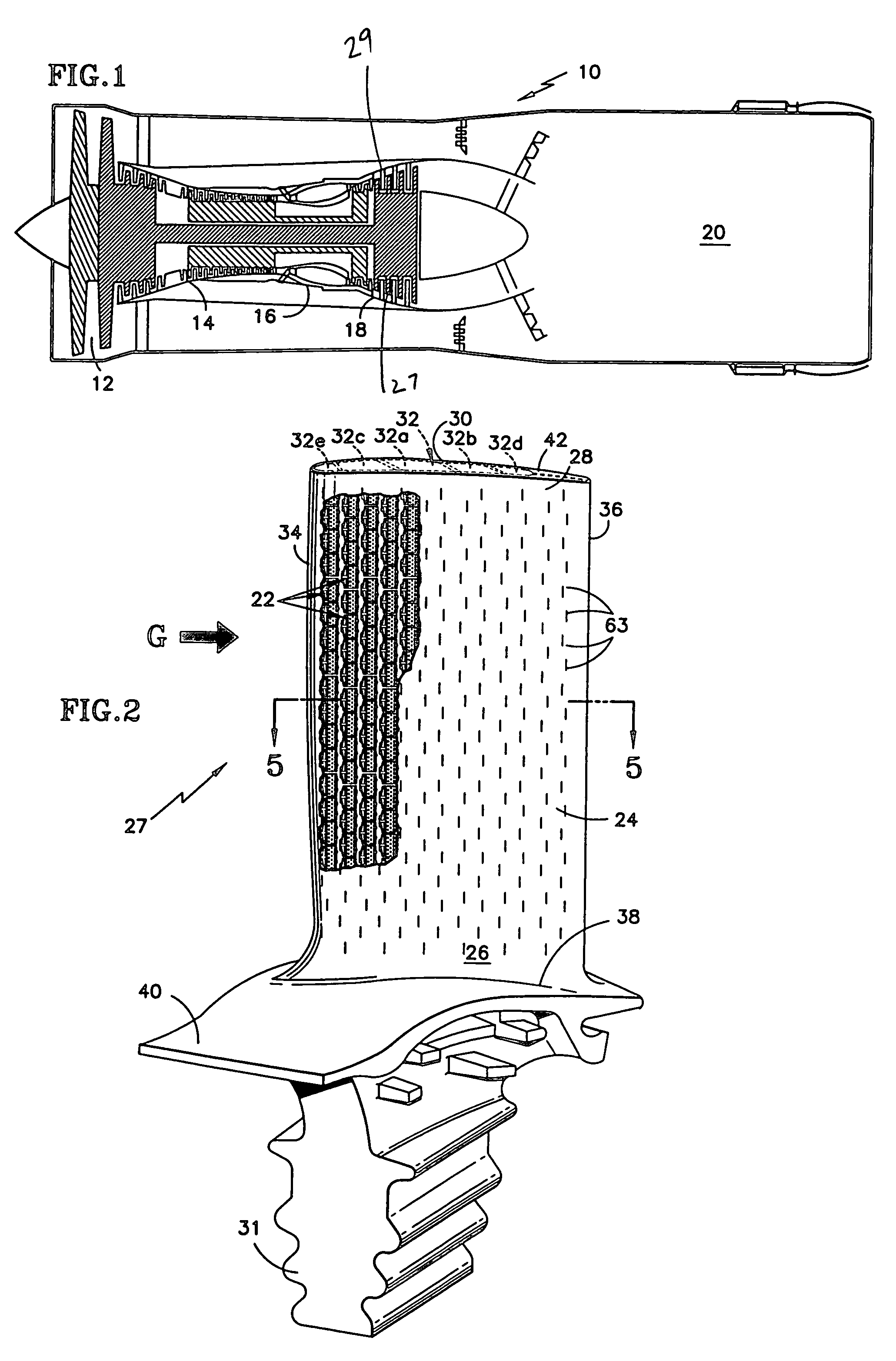
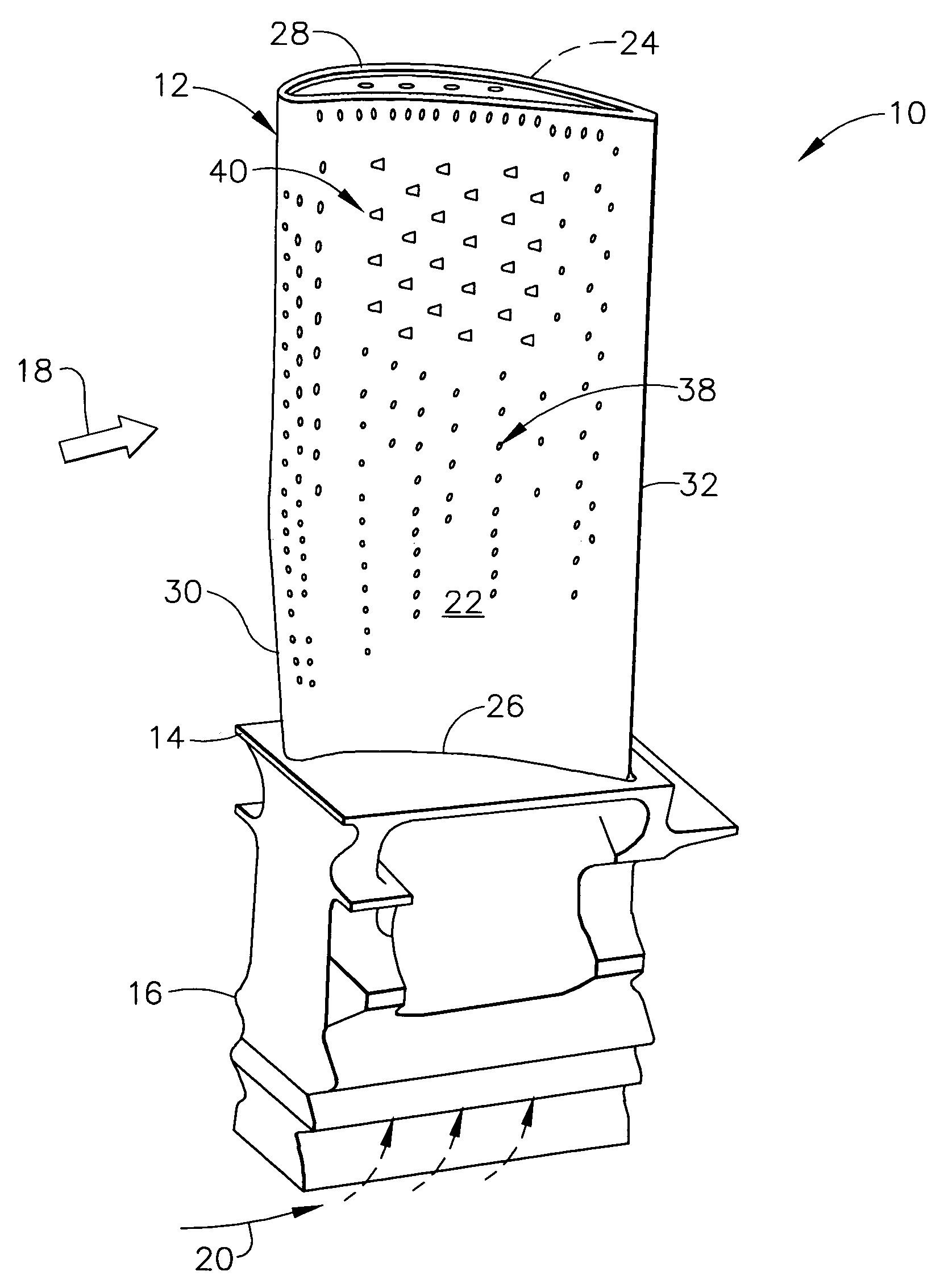
High effectiveness cooled turbine vane or blade
InactiveUS6974308B2Improve cooling efficiencyEasy to manufacturePump componentsEngine fuctionsSuction stressConventional casting
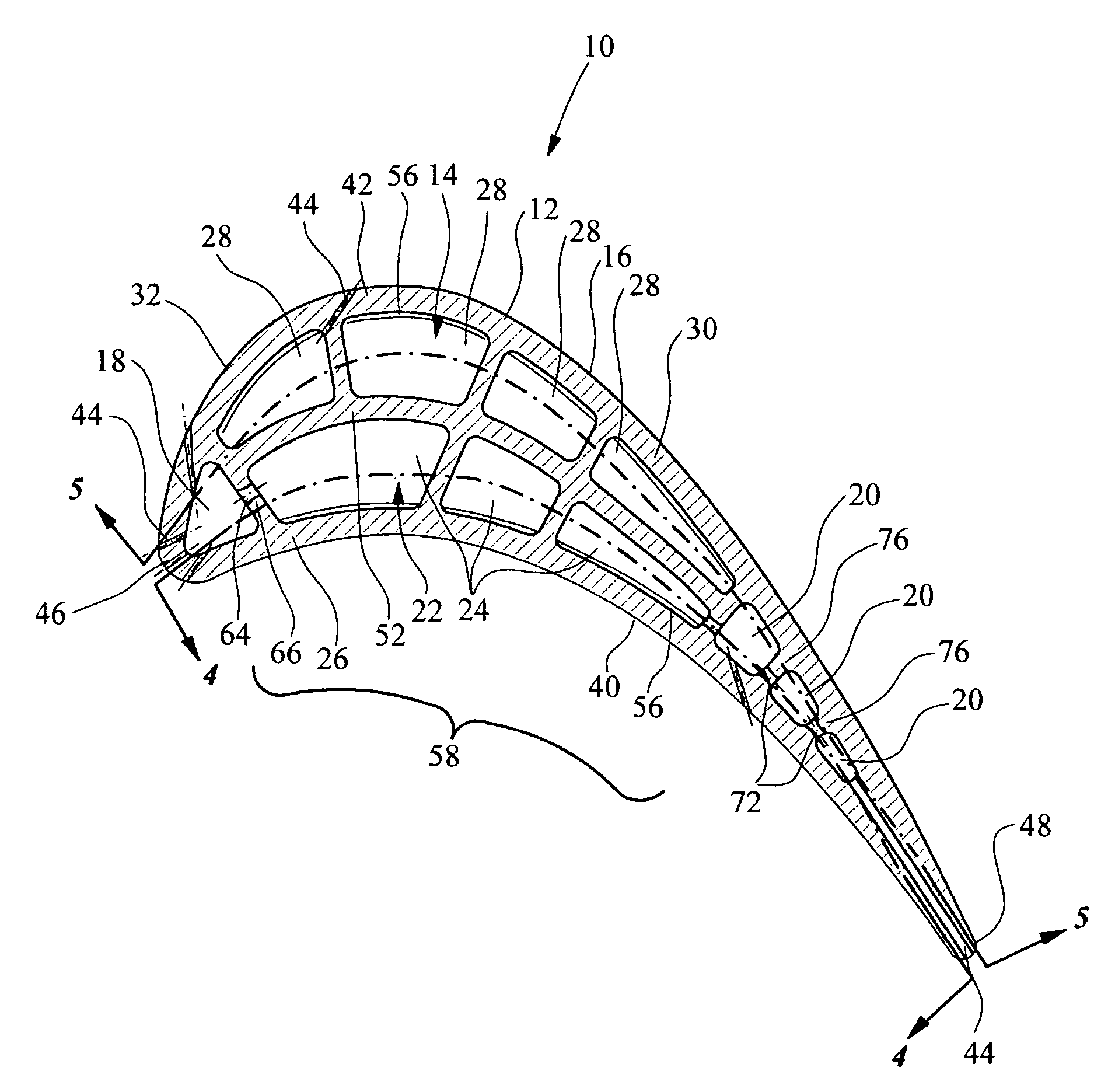
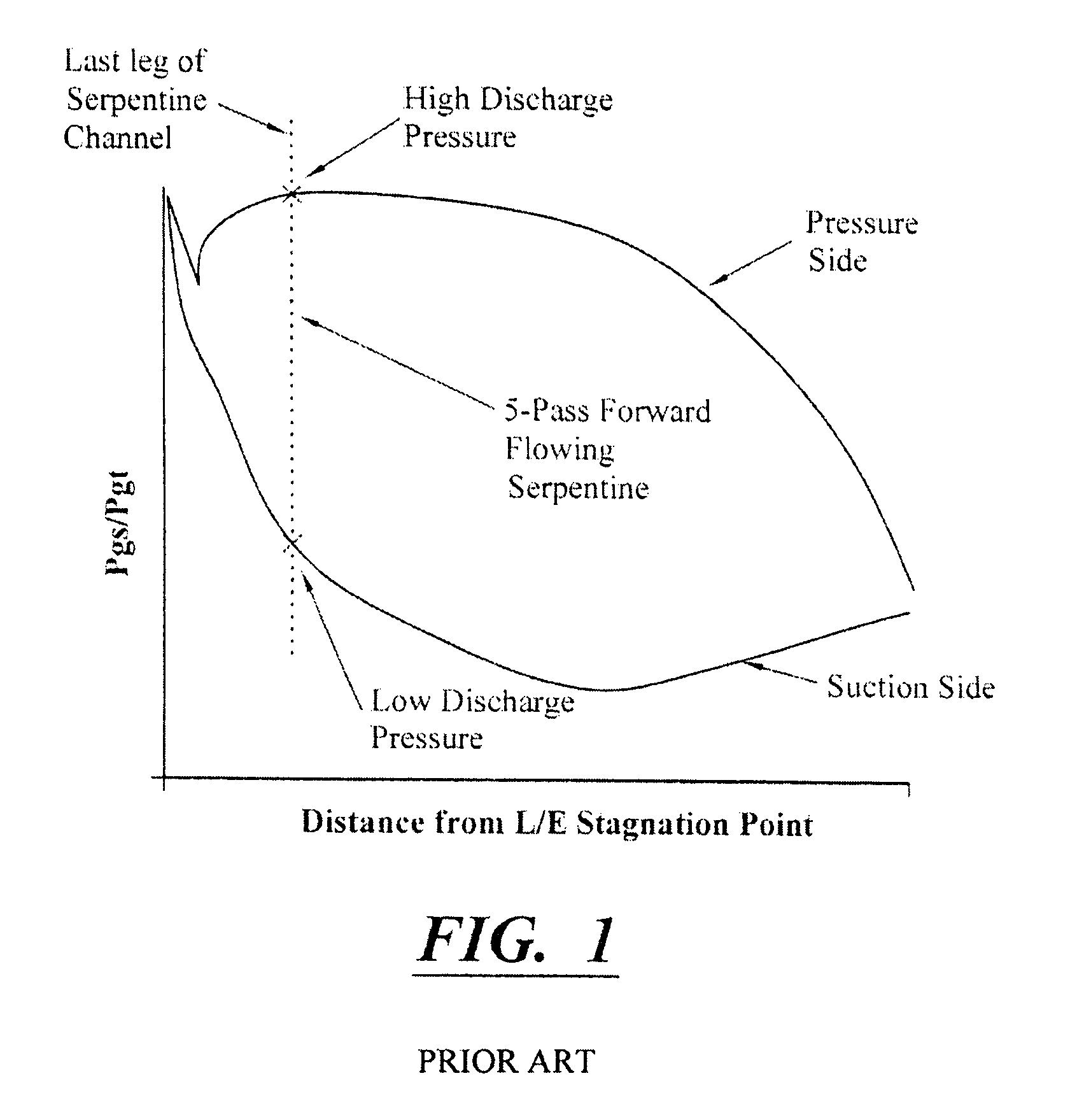
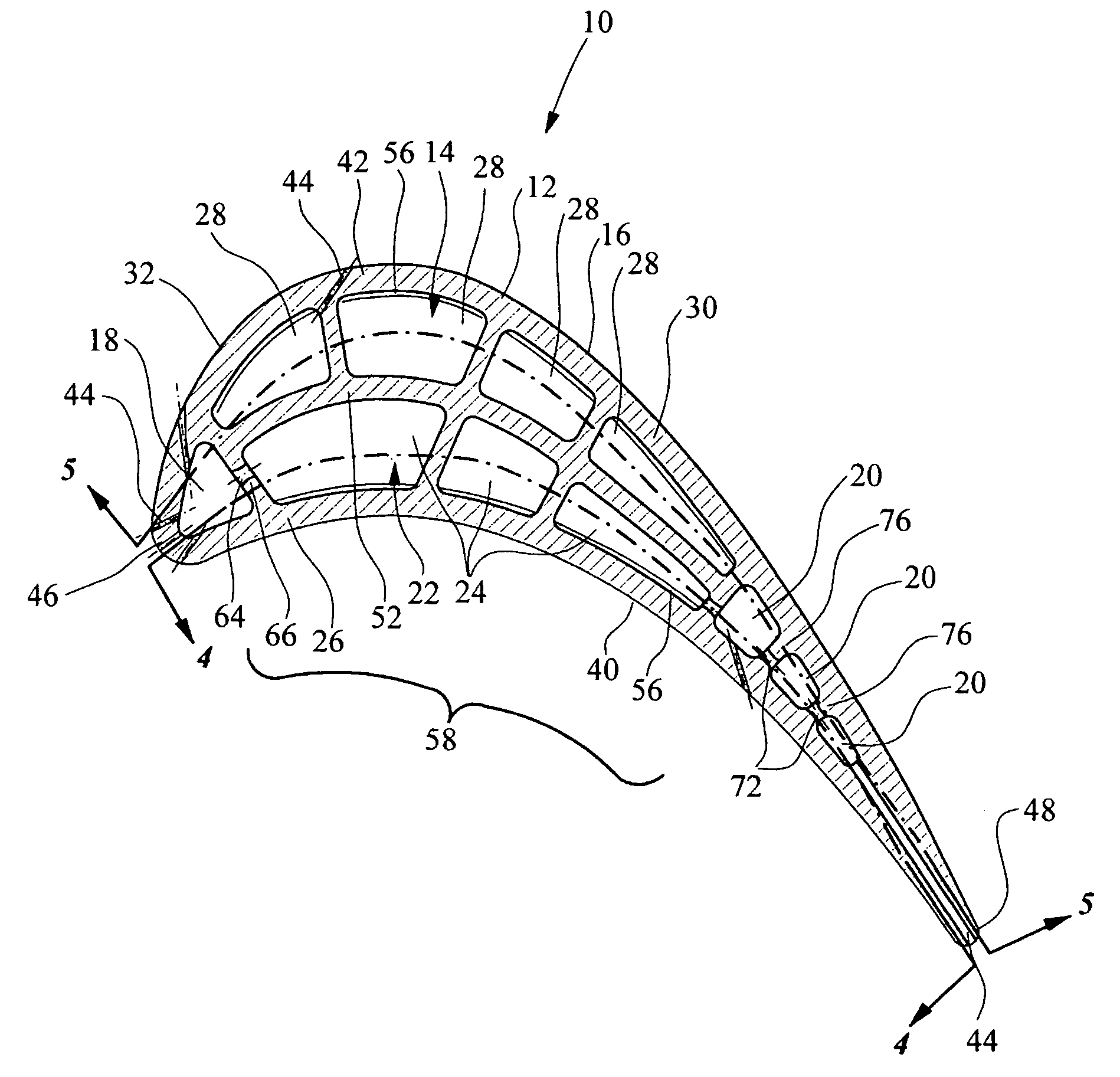
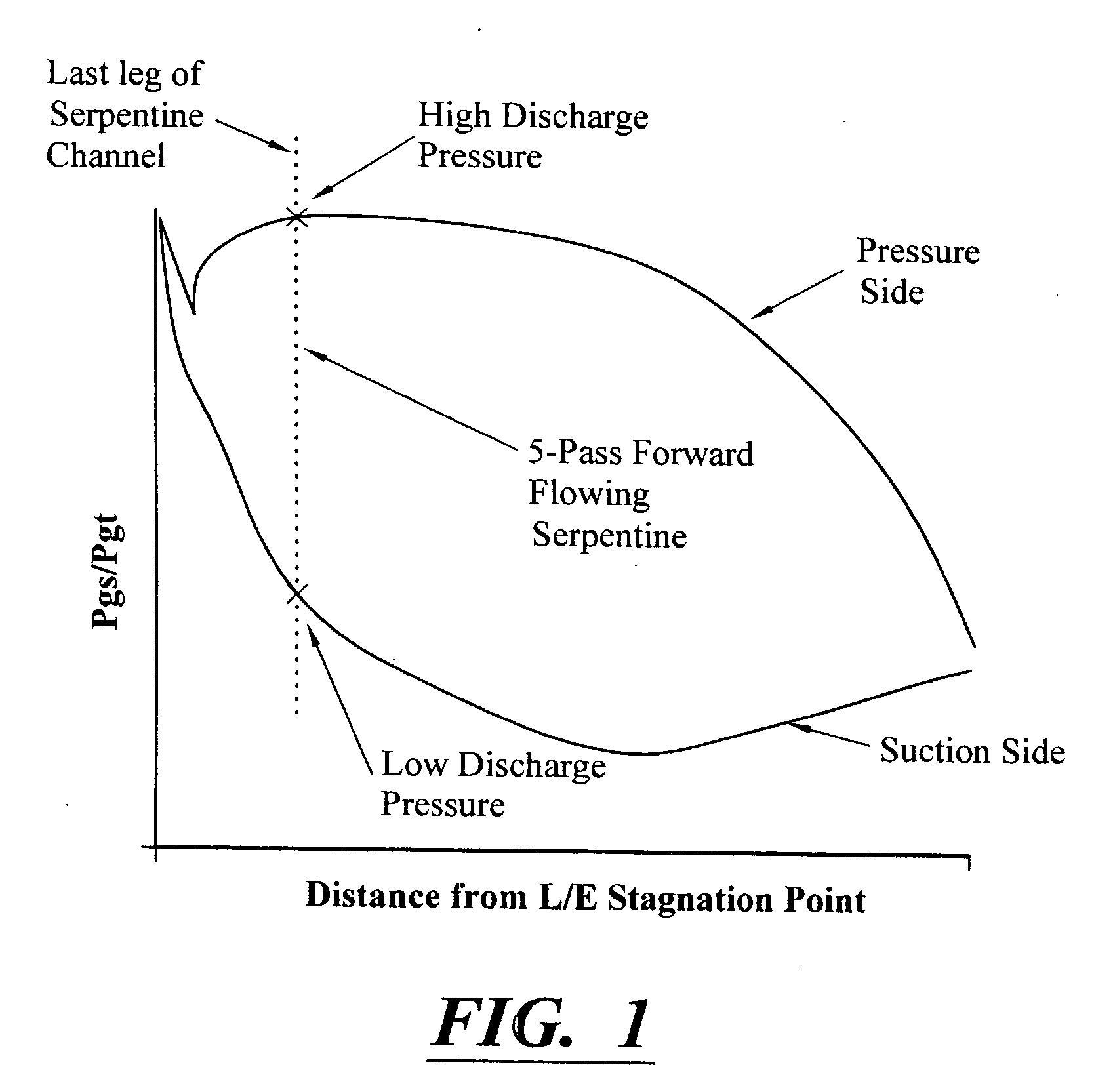
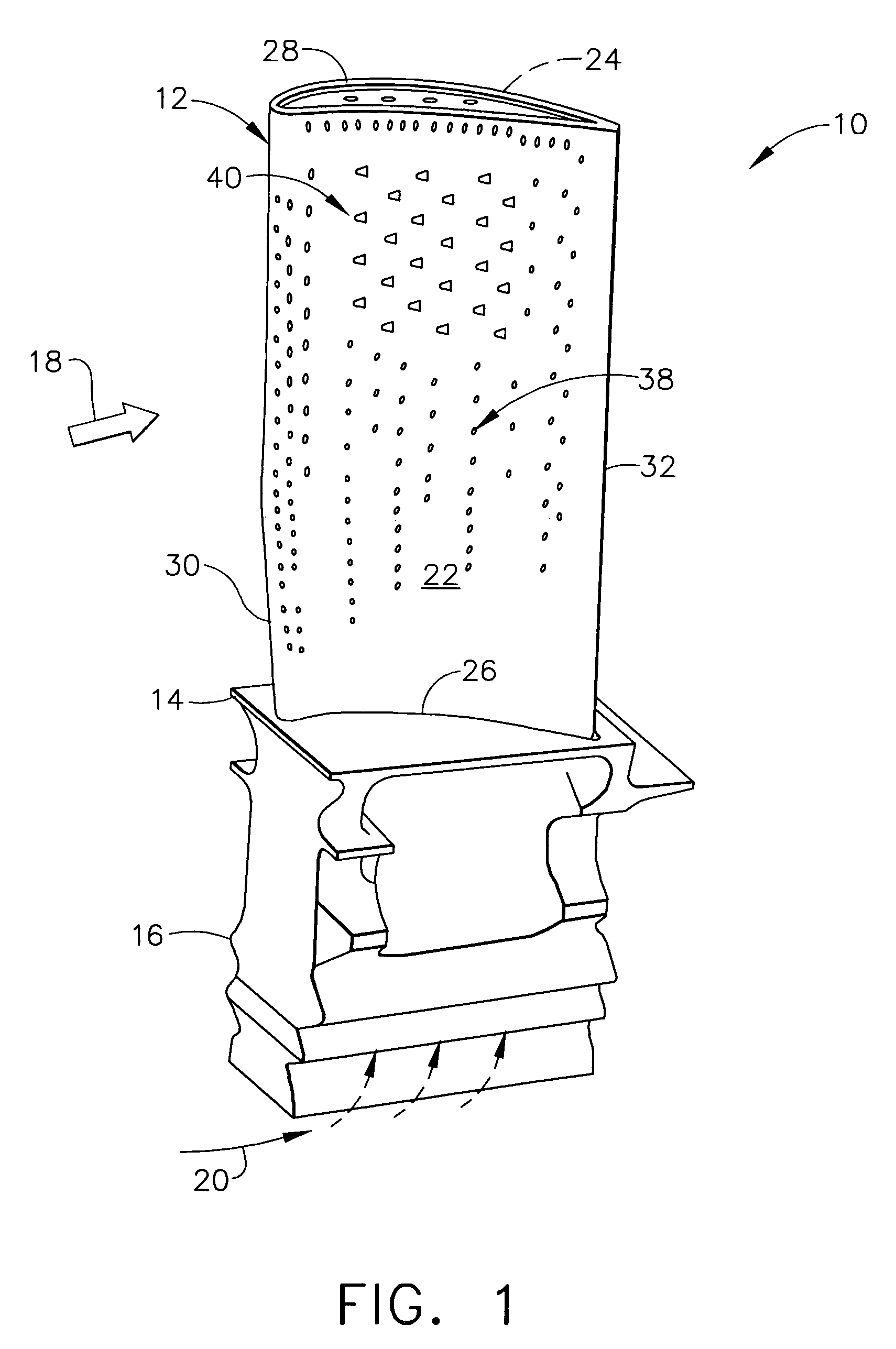
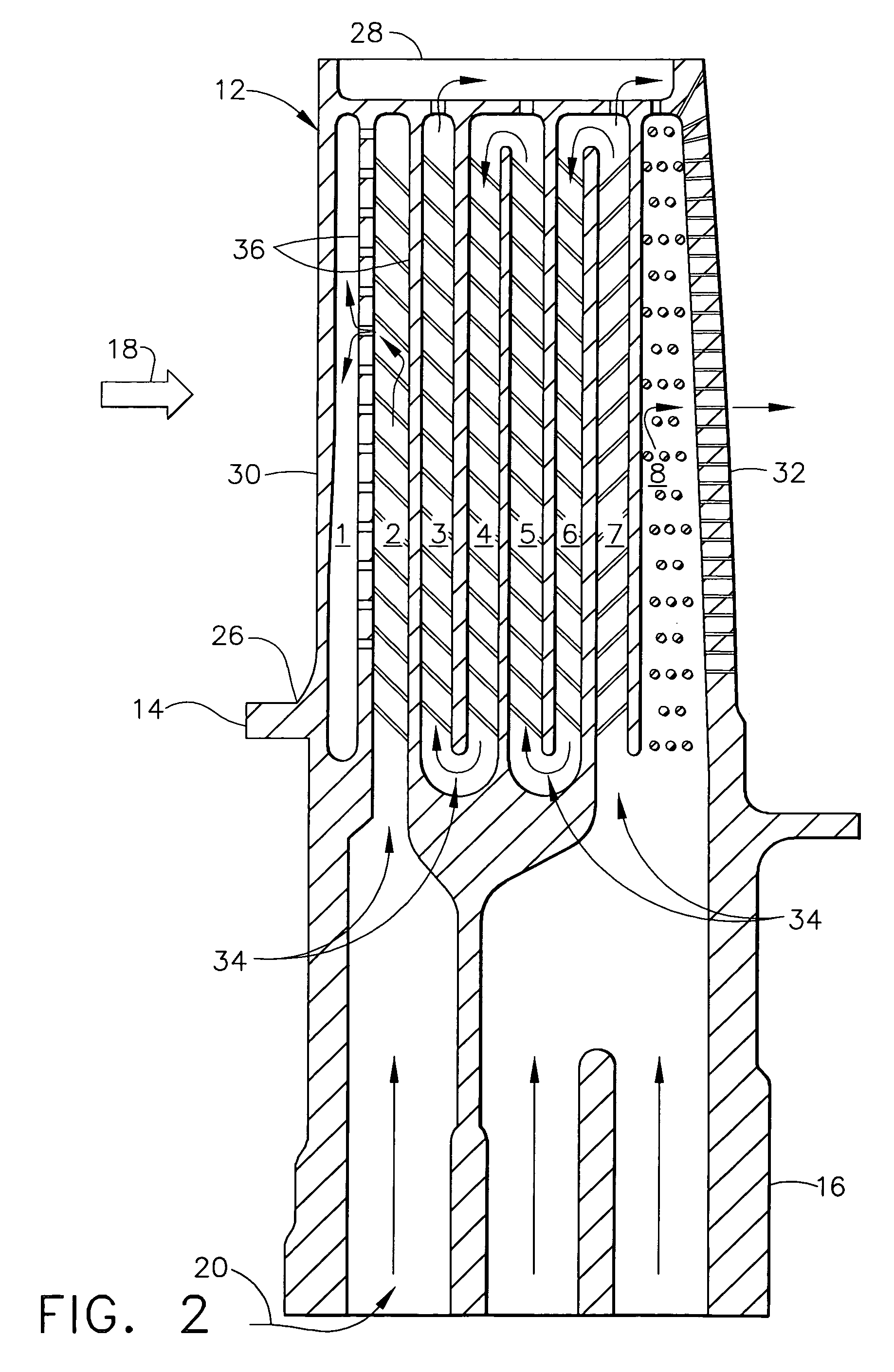
A robust multiple-walled, multi-pass, high cooling effectiveness cooled turbine vane or blade designed for ease of manufacturability, minimizes cooling flows on highly loaded turbine rotors. The vane or blade design allows the turbine inlet temperature to increase over current technology levels while simultaneously reducing turbine cooling to low levels. A multi-wall cooling system is described, which meets the inherent conflict to maximize the flow area of the cooling passages while retaining the required section thickness to meet the structural requirements. Independent cooling circuits for the vane or blade's pressure and suction surfaces allow the cooling of the airfoil surfaces to be tailored to specific heat load distributions (that is, the pressure surface circuit is an independent forward flowing serpentine while the suction surface is an independent rearward flowing serpentine). The cooling air for the independent circuits is supplied through separate passages at the base of the vane or blade. The cooling air follows intricate passages to feed the serpentine thin outer wall passages, which incorporate pin fins, turbulators, etc. These passages, while satisfying the aero / thermal / stress requirements, are of a manufacturing configuration that may be cast with single crystal materials using conventional casting techniques.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and Apparatus for Sampling and Analysis of Fluids
ActiveUS20070232956A1Eliminate needCatheterCharacter and pattern recognitionSuction stressEngineering
A medical device having a housing (2) with a bore (3) and a lancet (1) slidably fitting in the bore. The lancet operates as a positive displacement piston. In a retracted position, in which the lancet is rearwardly displaced along the bore to define a fluid-containing space in the bore forwardly on the lancet tip, the fluid-containing space has a cross-section dimension to allow fluid to be retained therein by surface tension. The device has a seal (6) operable substantially to prevent flow of fluid from the fluid-containing space past the seal means on movement of the lancet. Displacement of the lancet between the puncture and retracted positions provides suction for drawing fluid into and along the fluid-containing space from the forward end of the bore, and / or pressure for expelling fluid from the fluid-containing space via the forward end of the bore. Also disclosed are methods for operating the device.
Owner:MICROSAMPLE
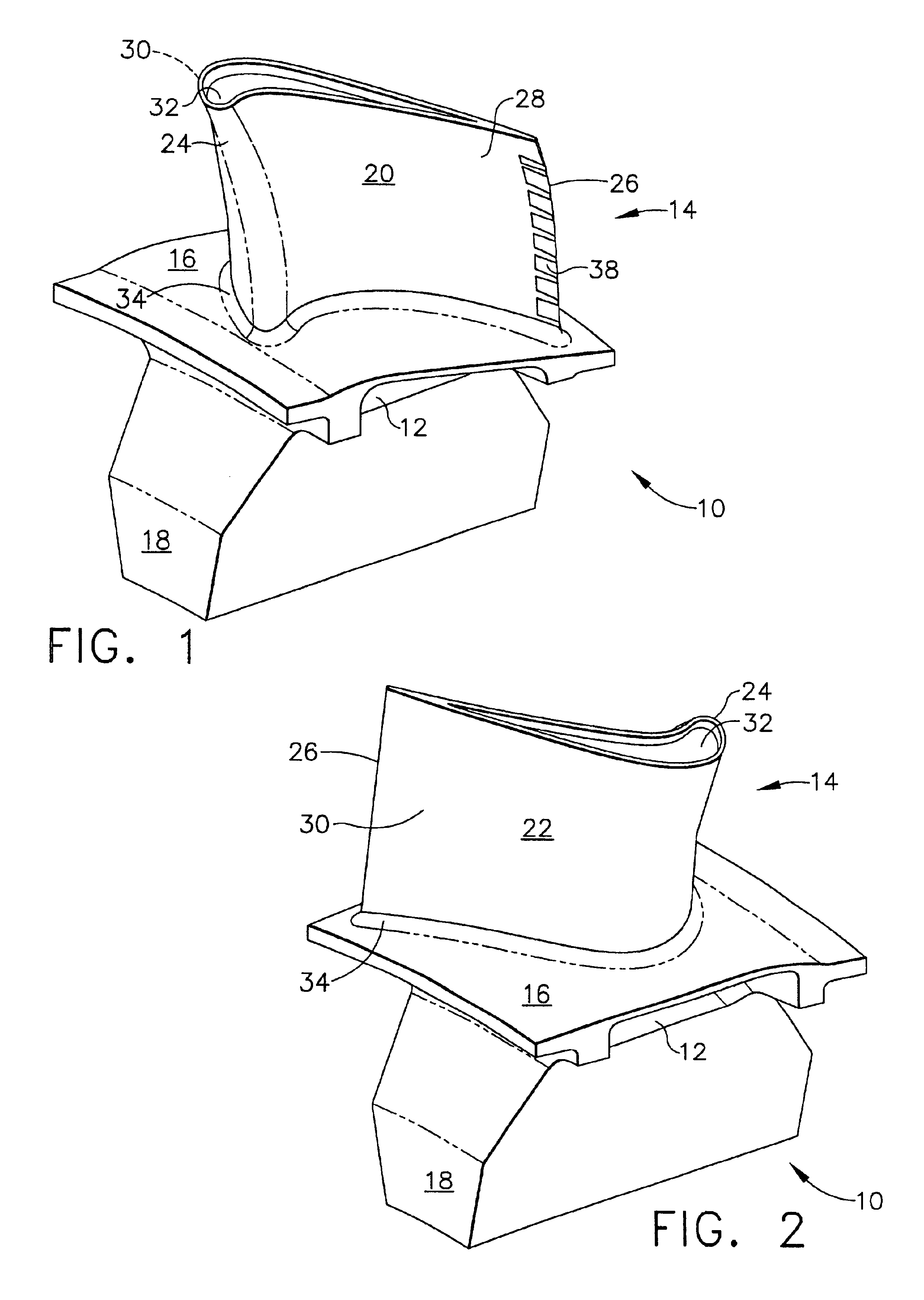
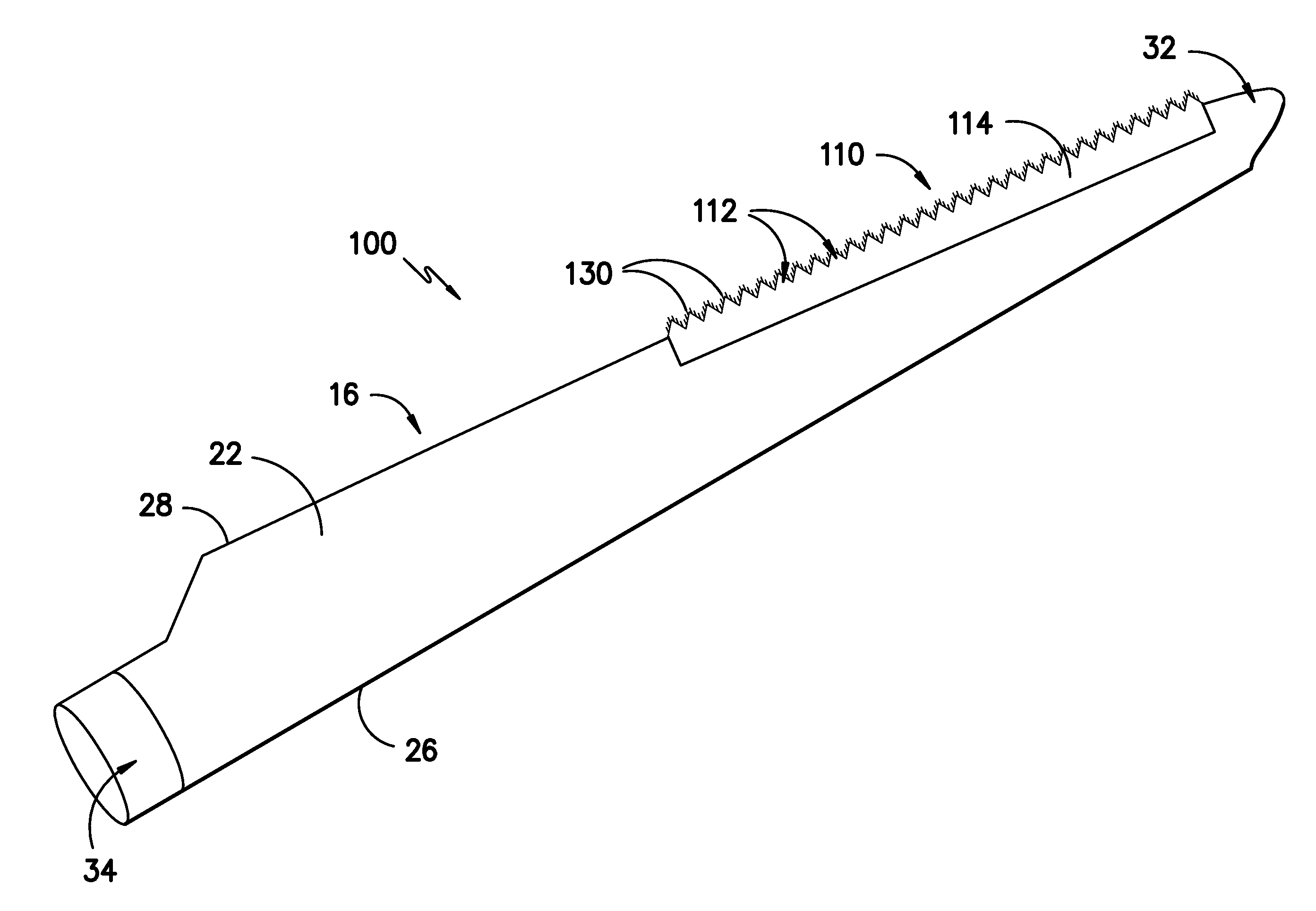
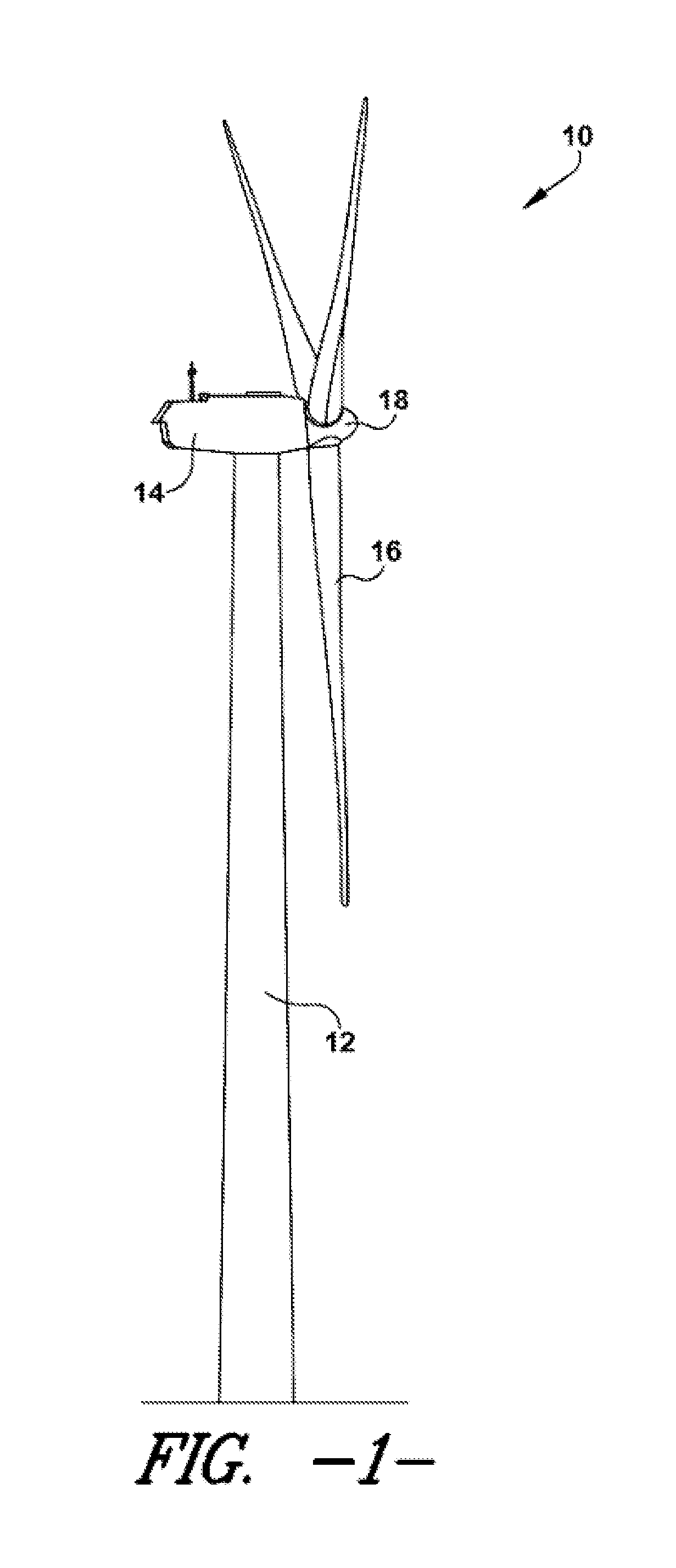
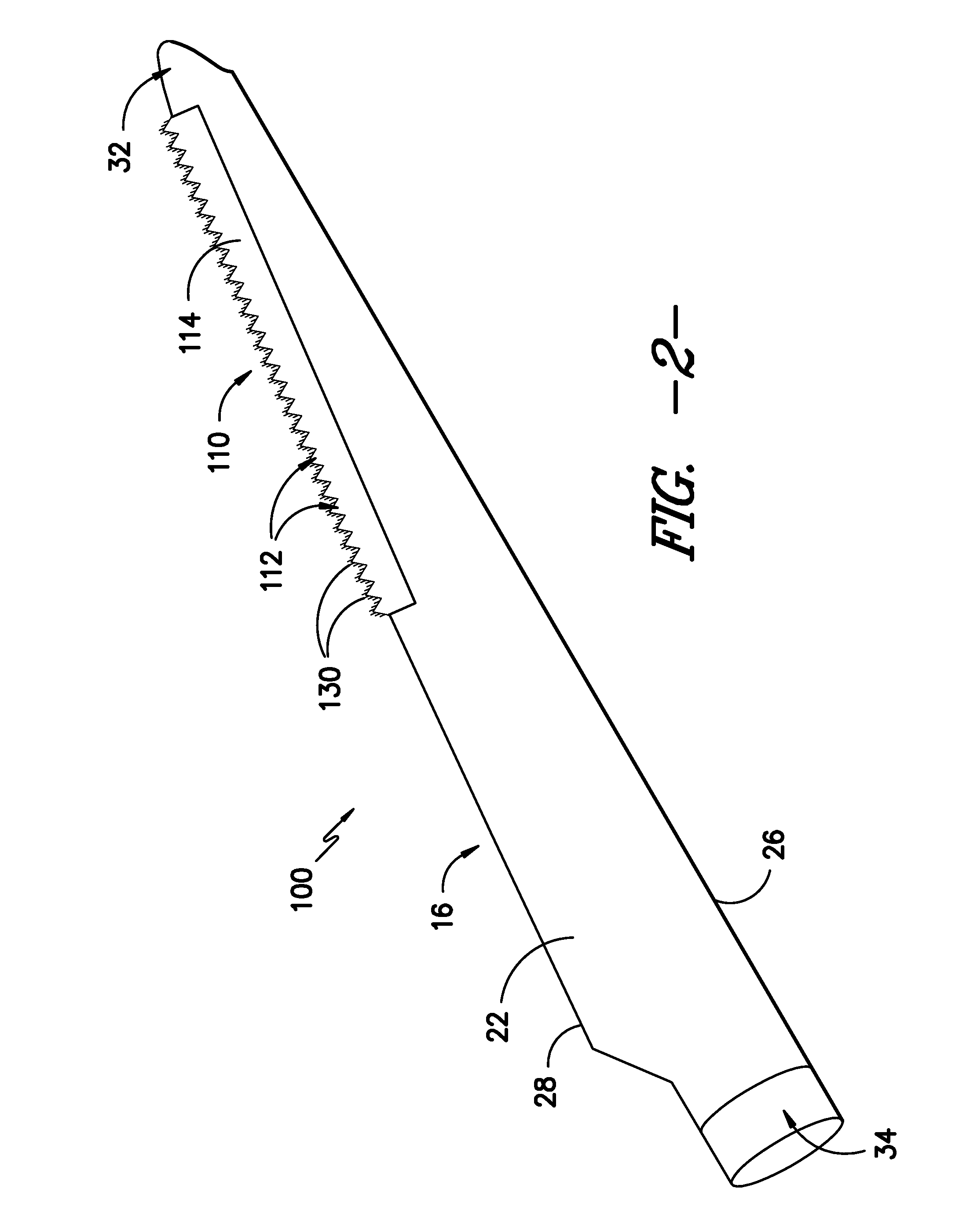
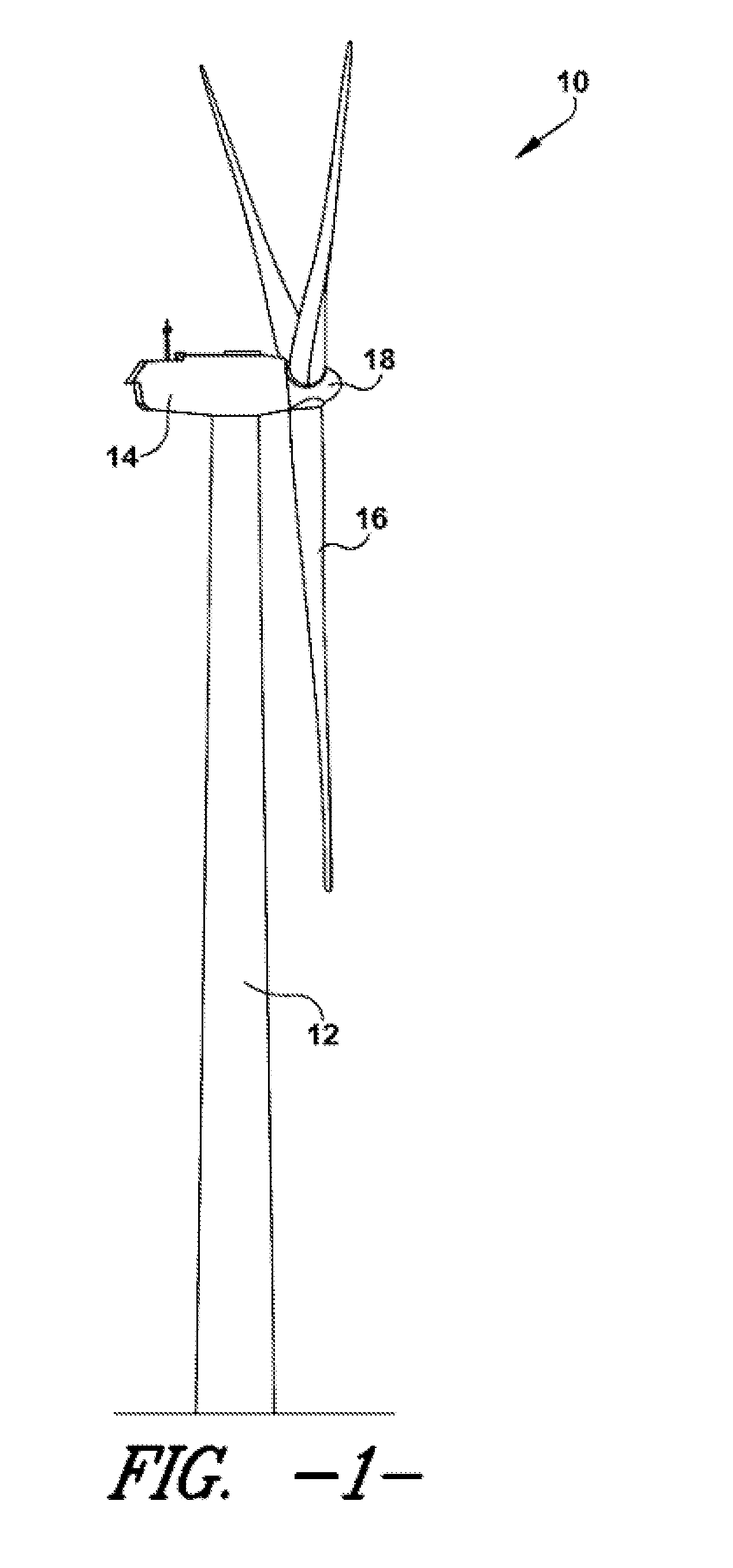
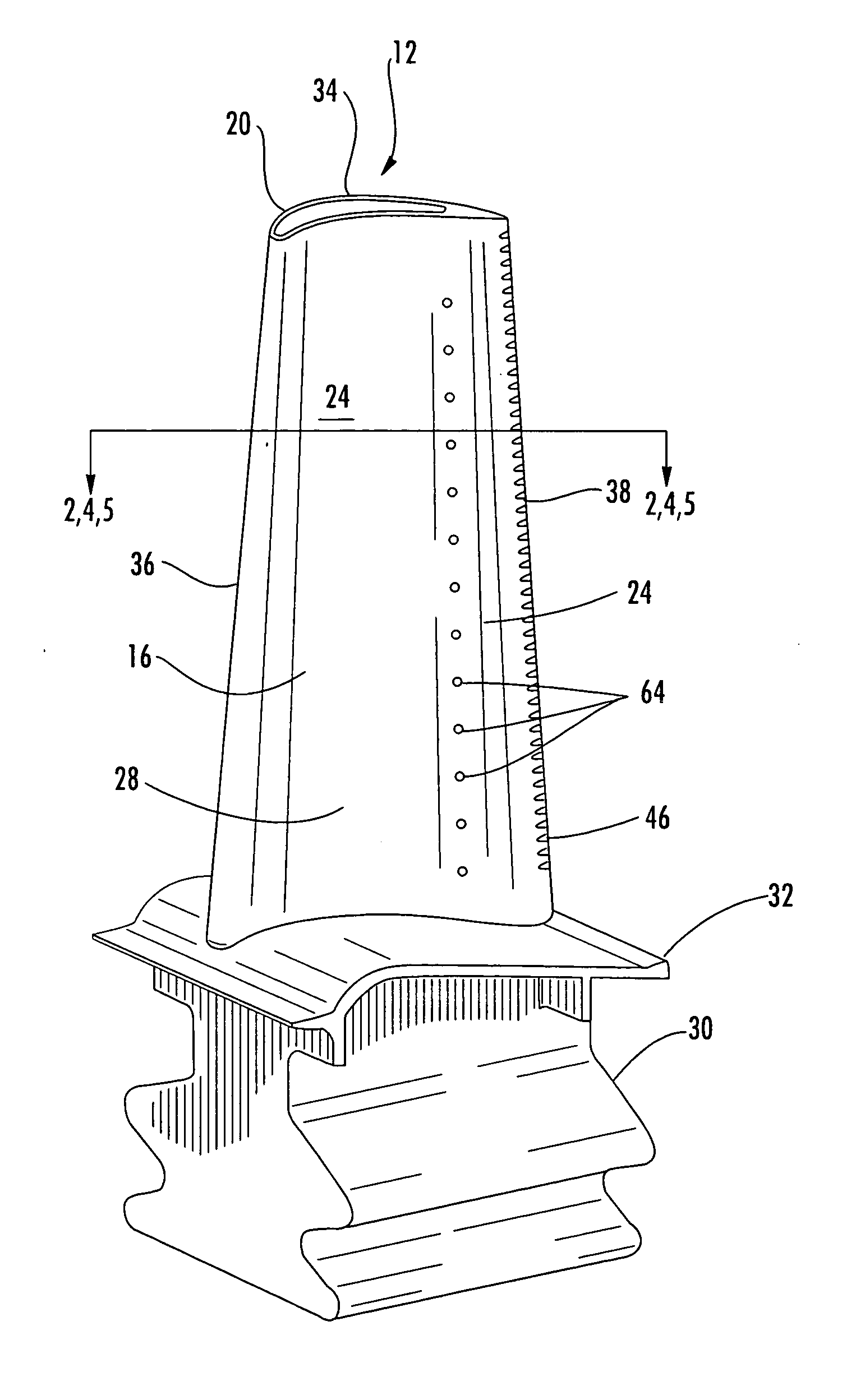
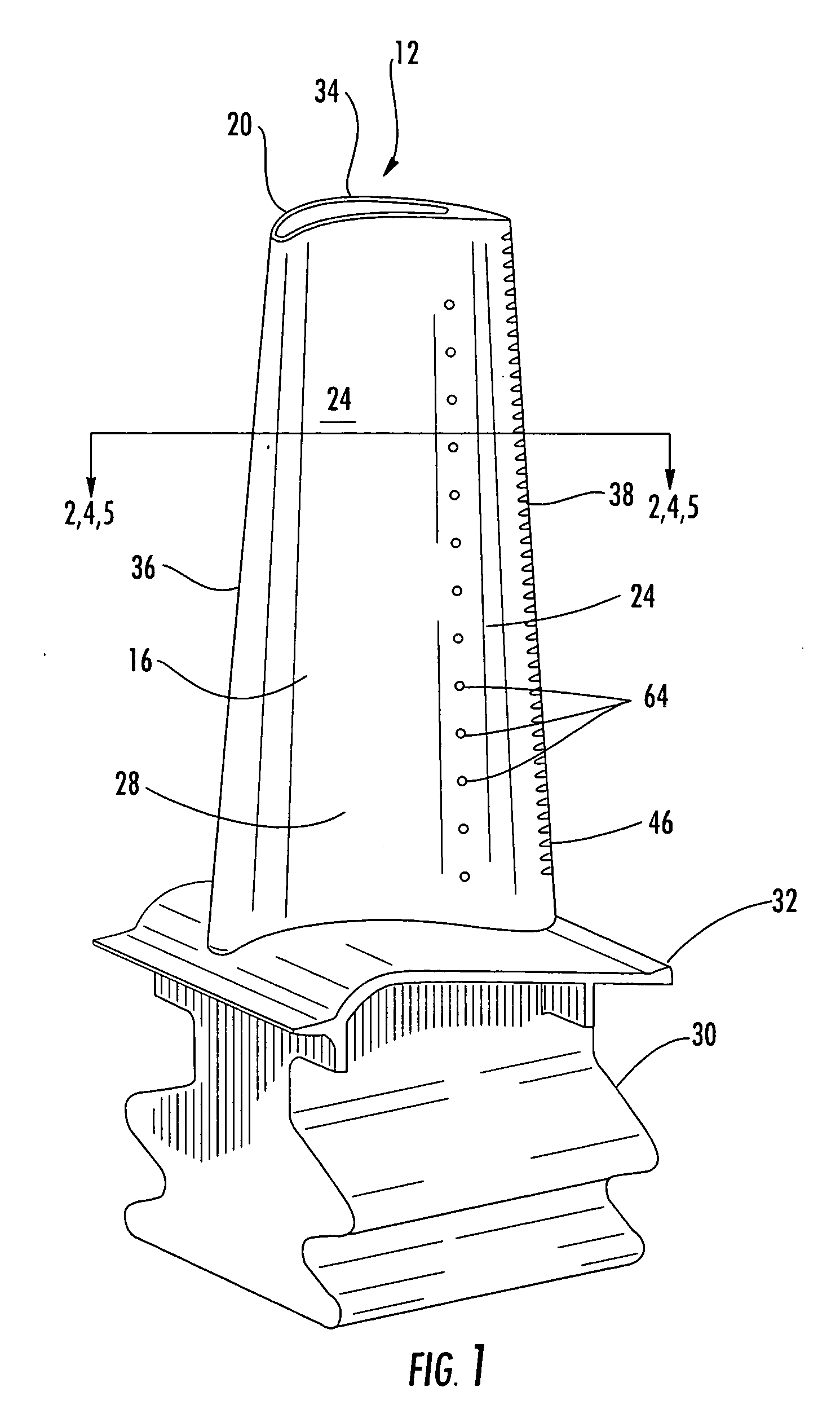
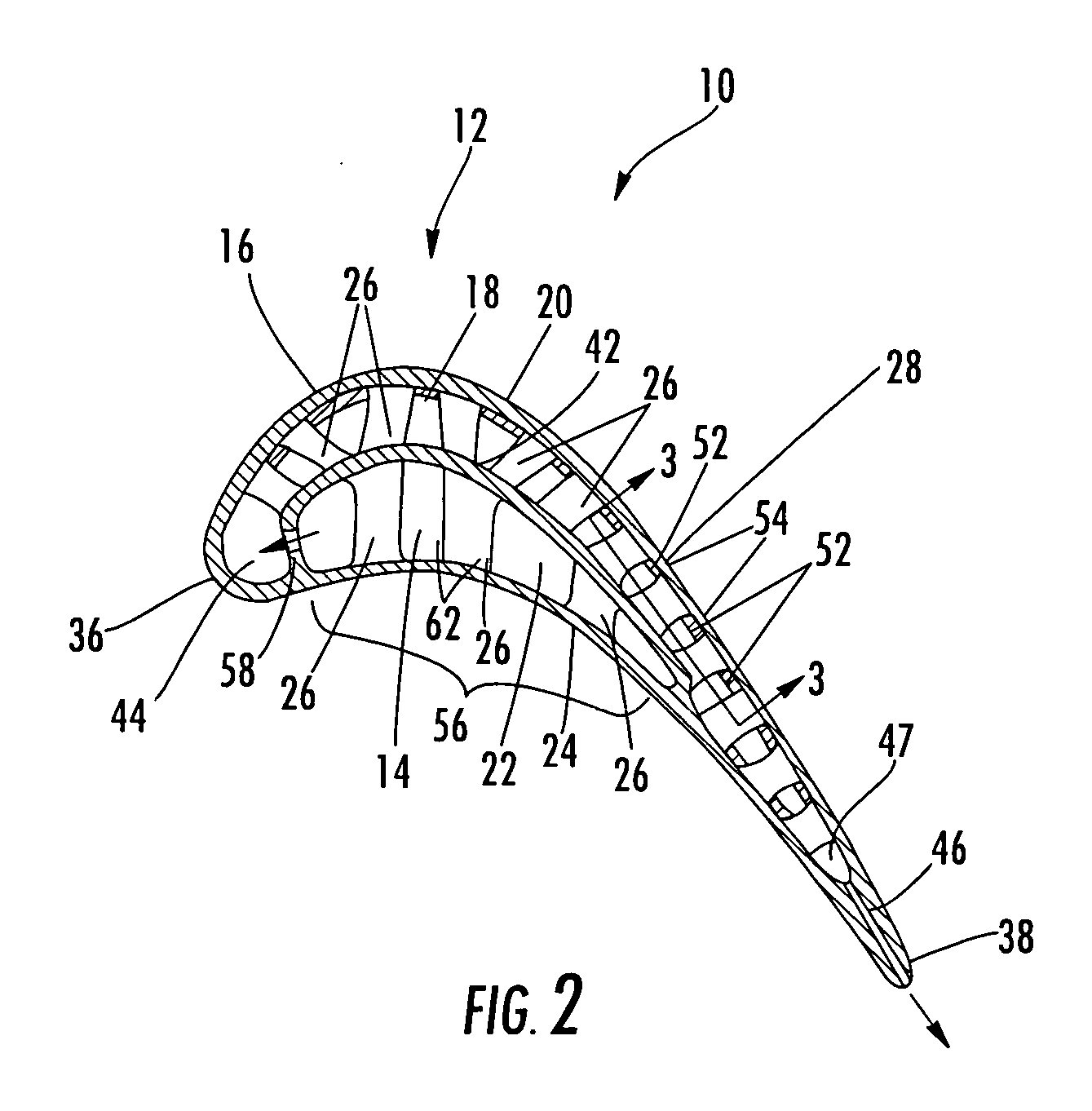
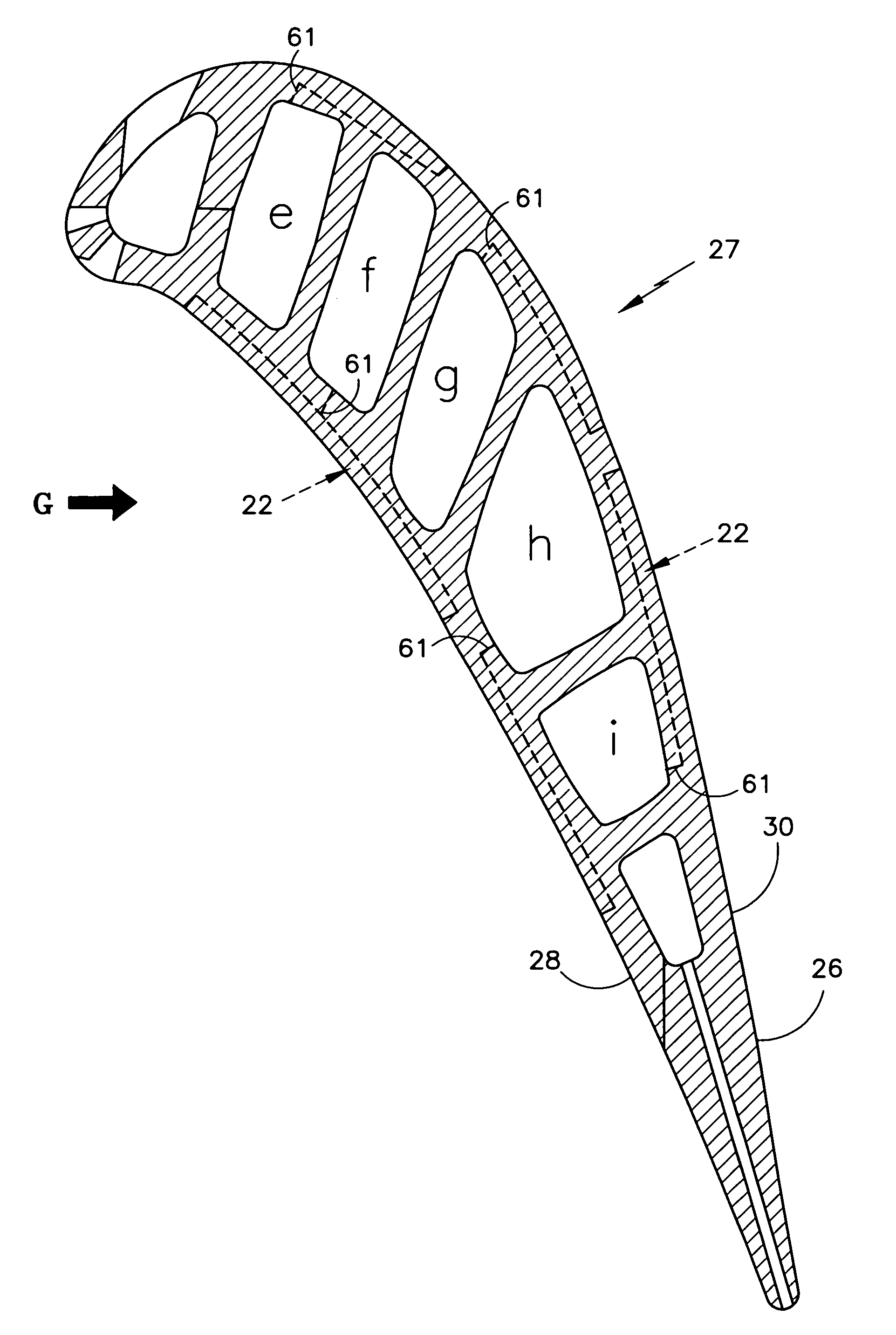
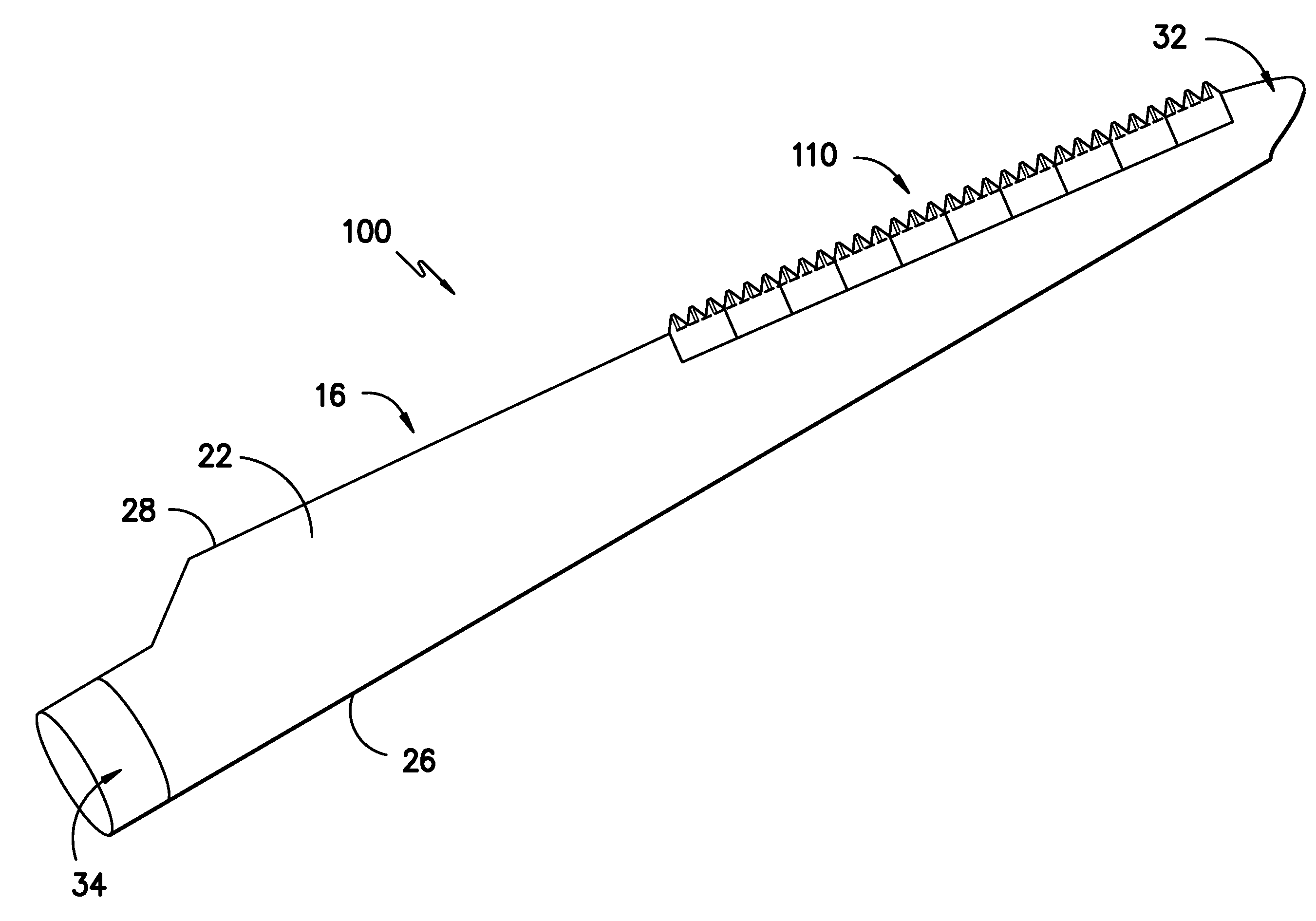
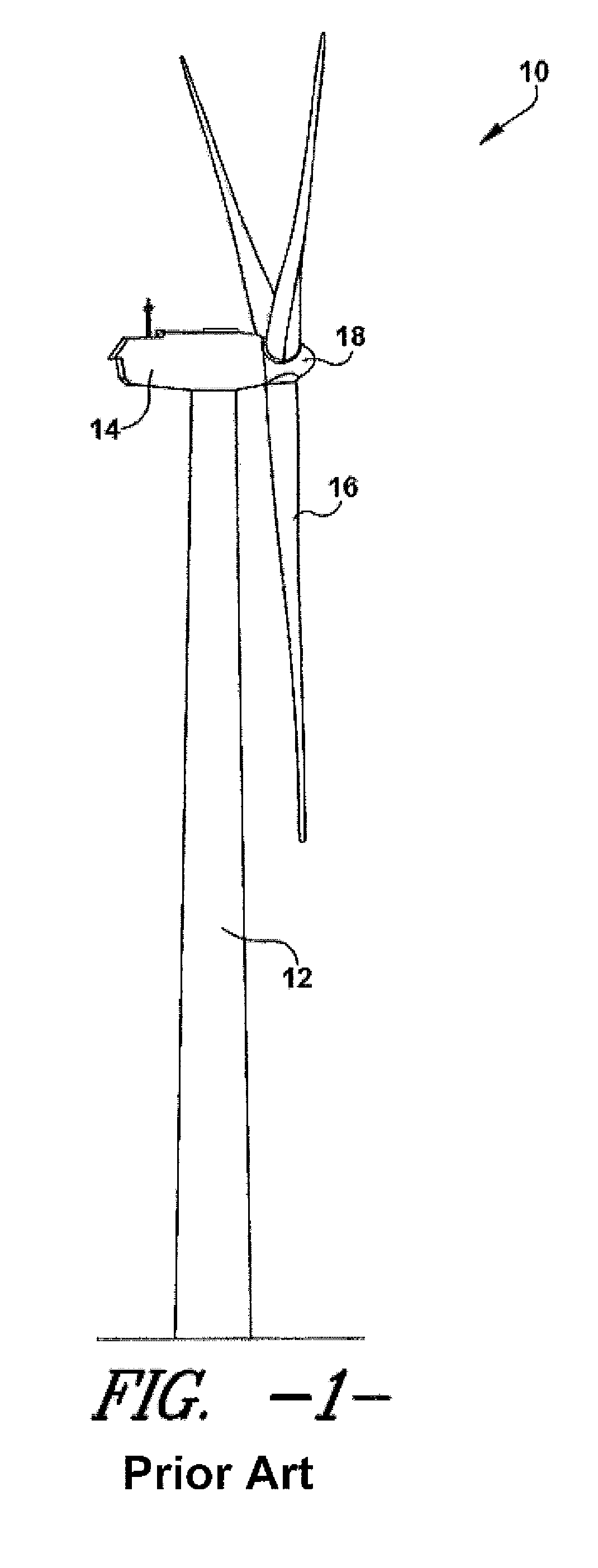
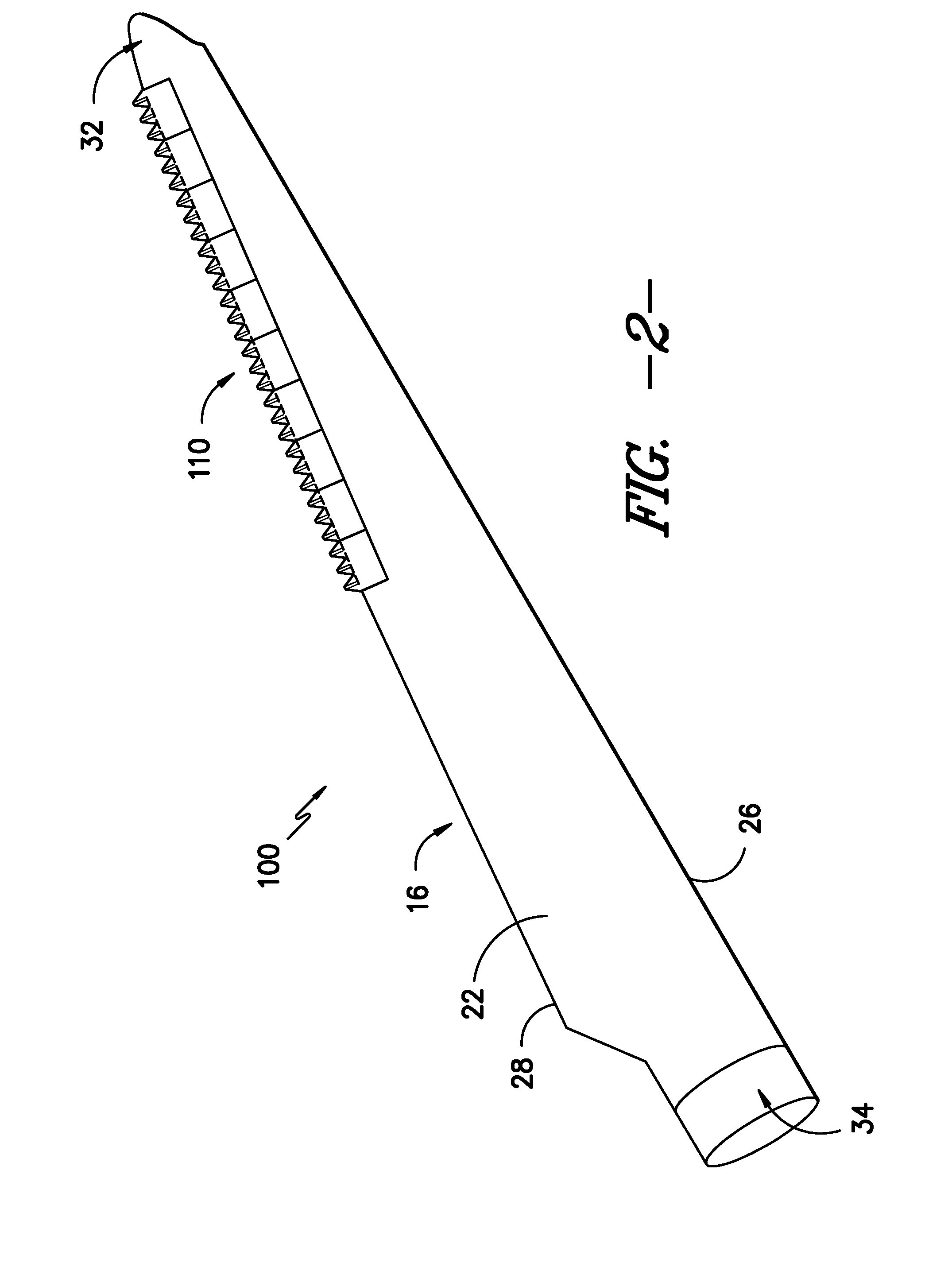
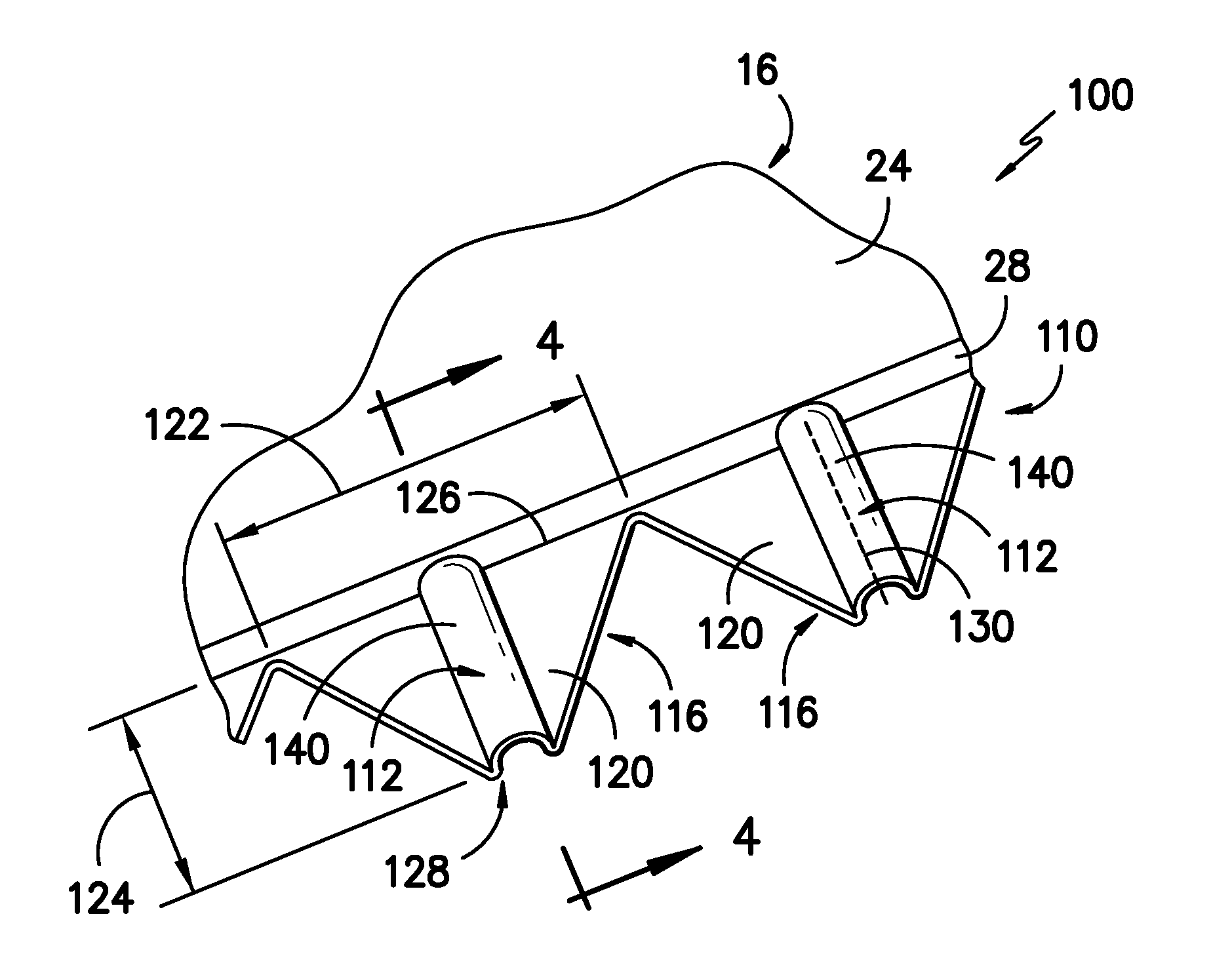
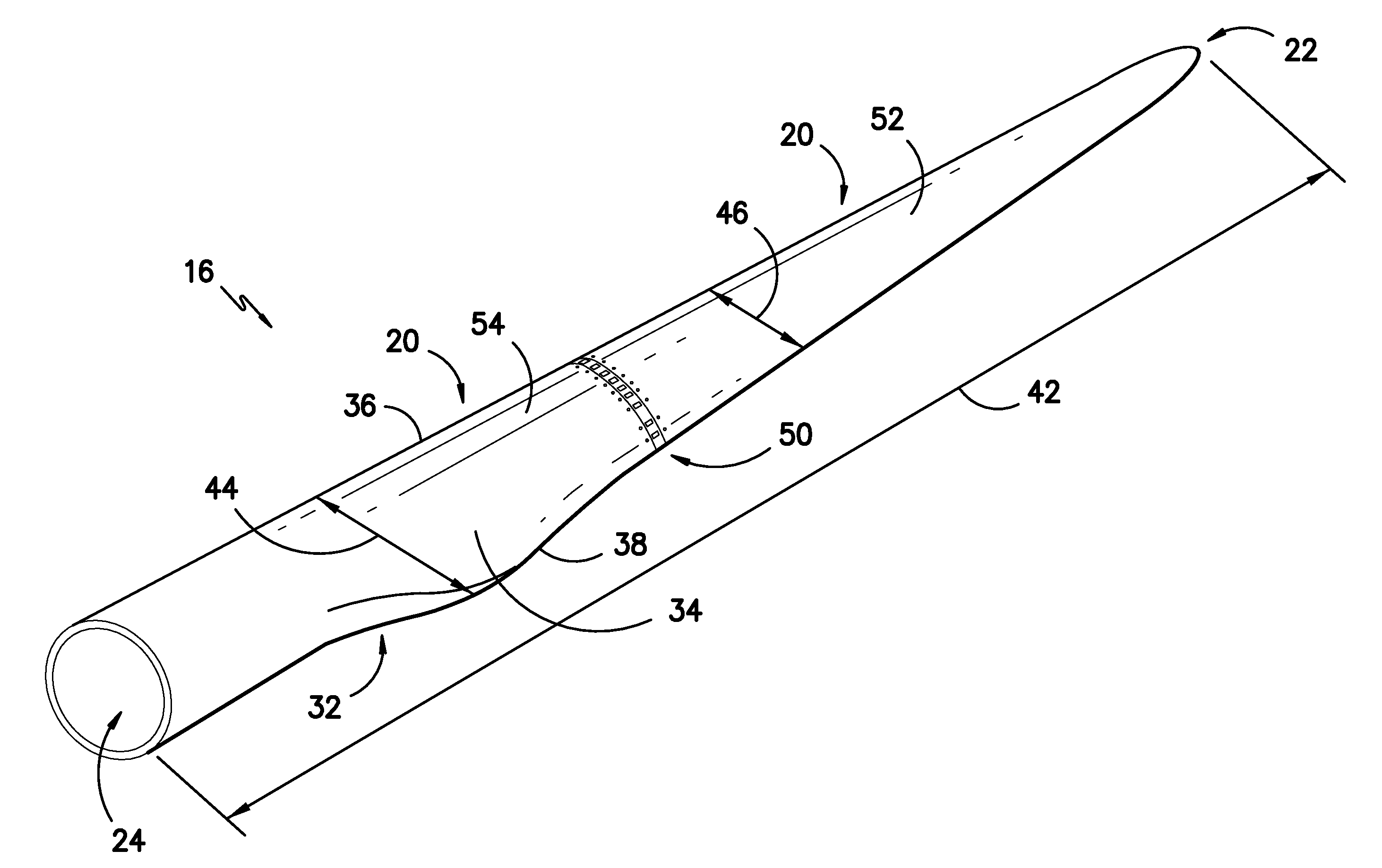
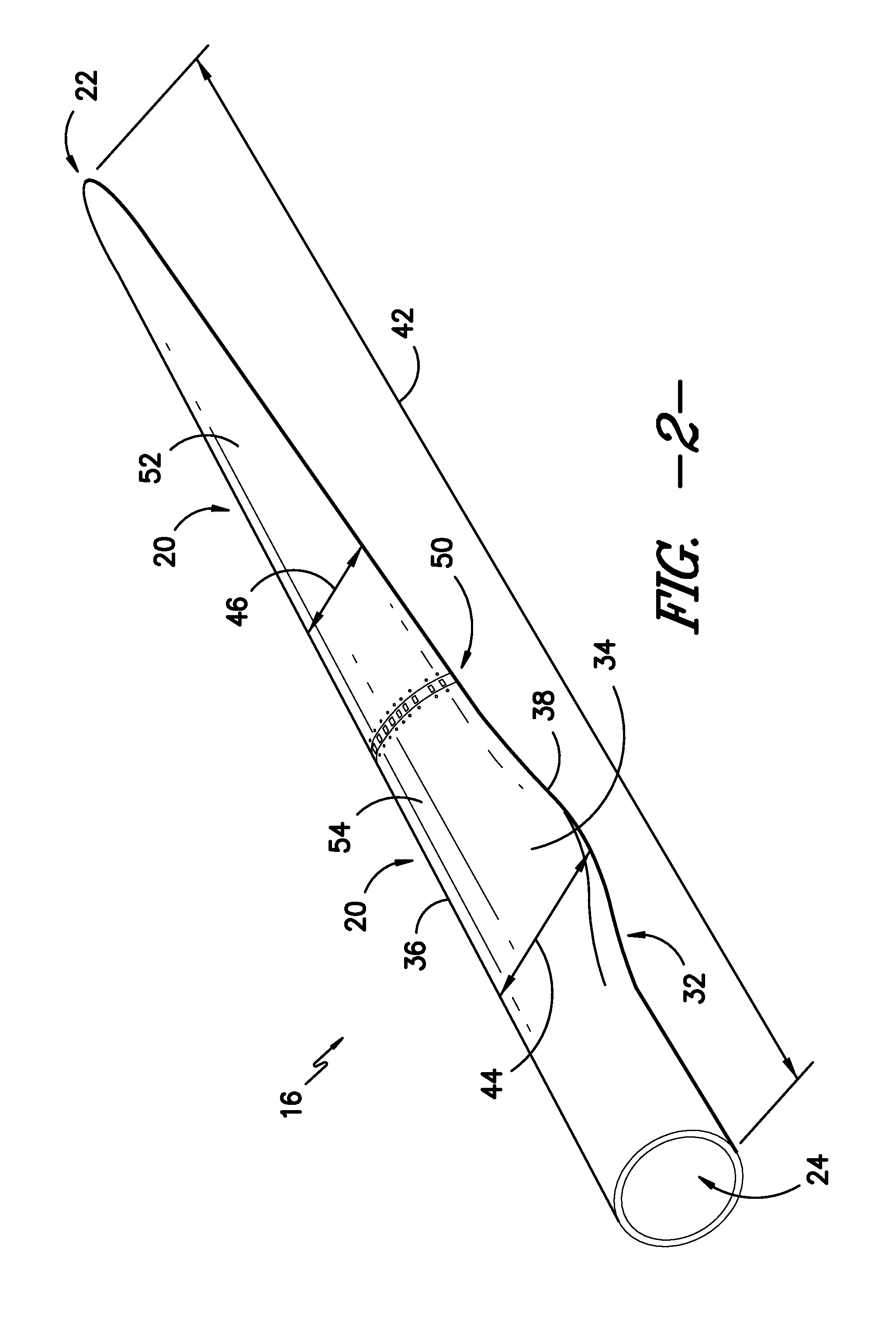
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly and a method for reducing the noise of a rotor blade for a wind turbine are disclosed. The rotor blade has surfaces defining a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer configured on a surface of the rotor blade, the noise reducer including a plurality of noise reduction features. Each of the plurality of noise reduction features includes a first surface and a second surface. The first surface includes a first portion mounted to one of the pressure side or the suction side and a second portion configured to interact with wind flowing past the other of the pressure side or the suction side. The second surface interrupts an aerodynamic contour of the one of the pressure side or the suction side.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
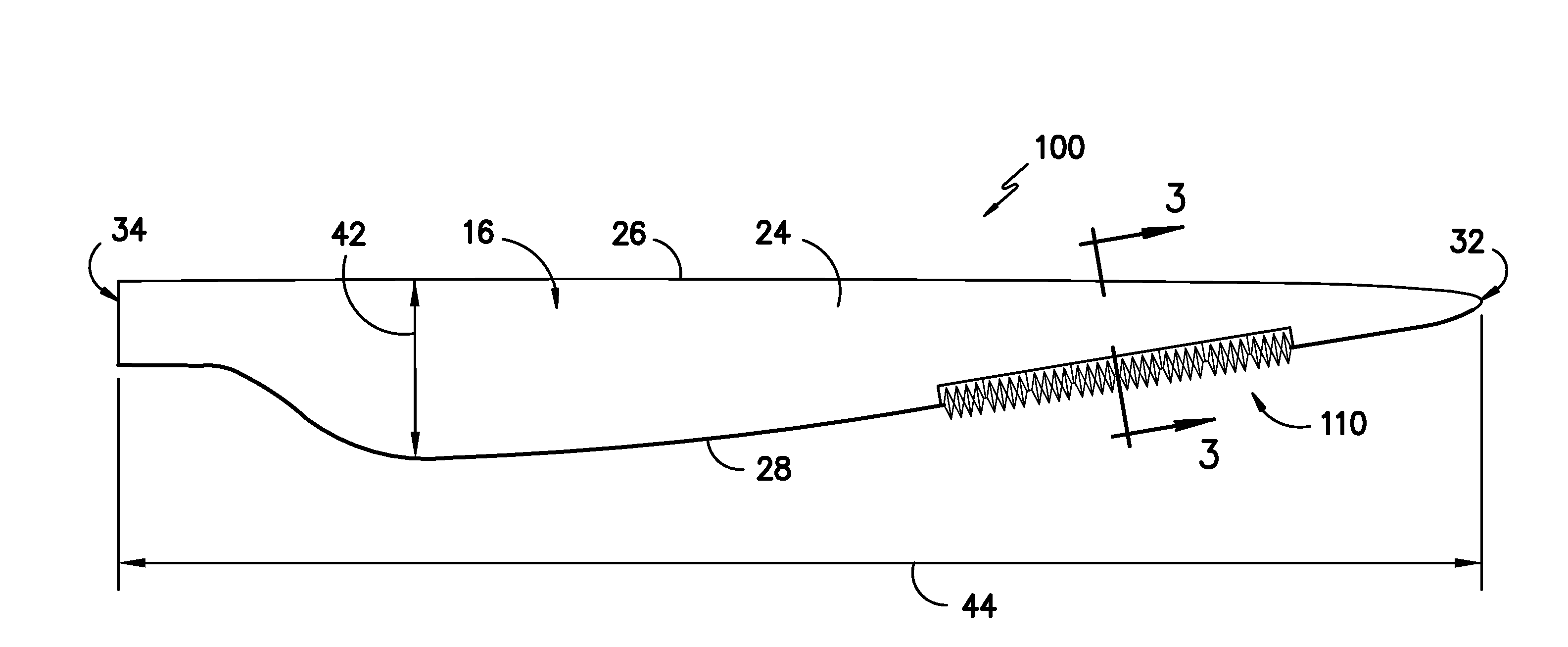
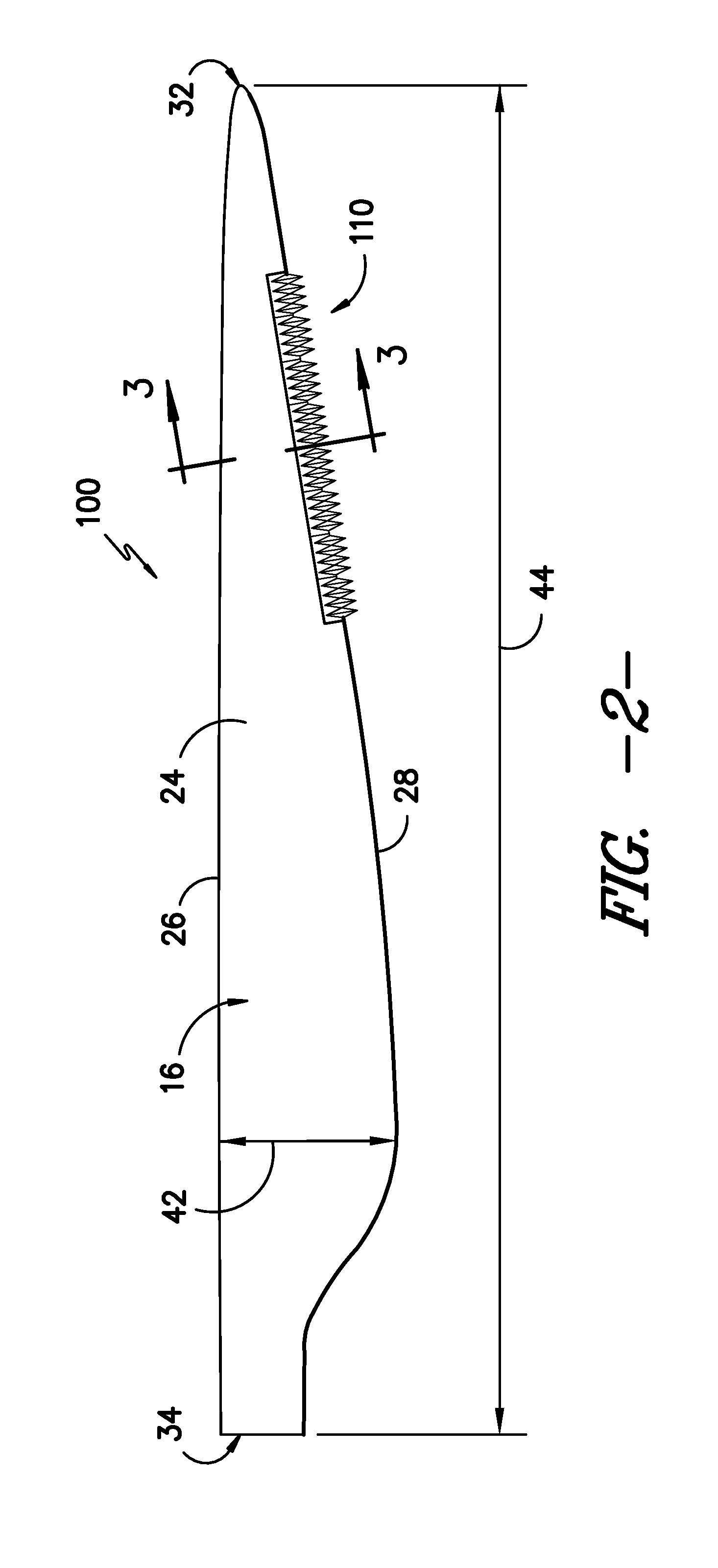
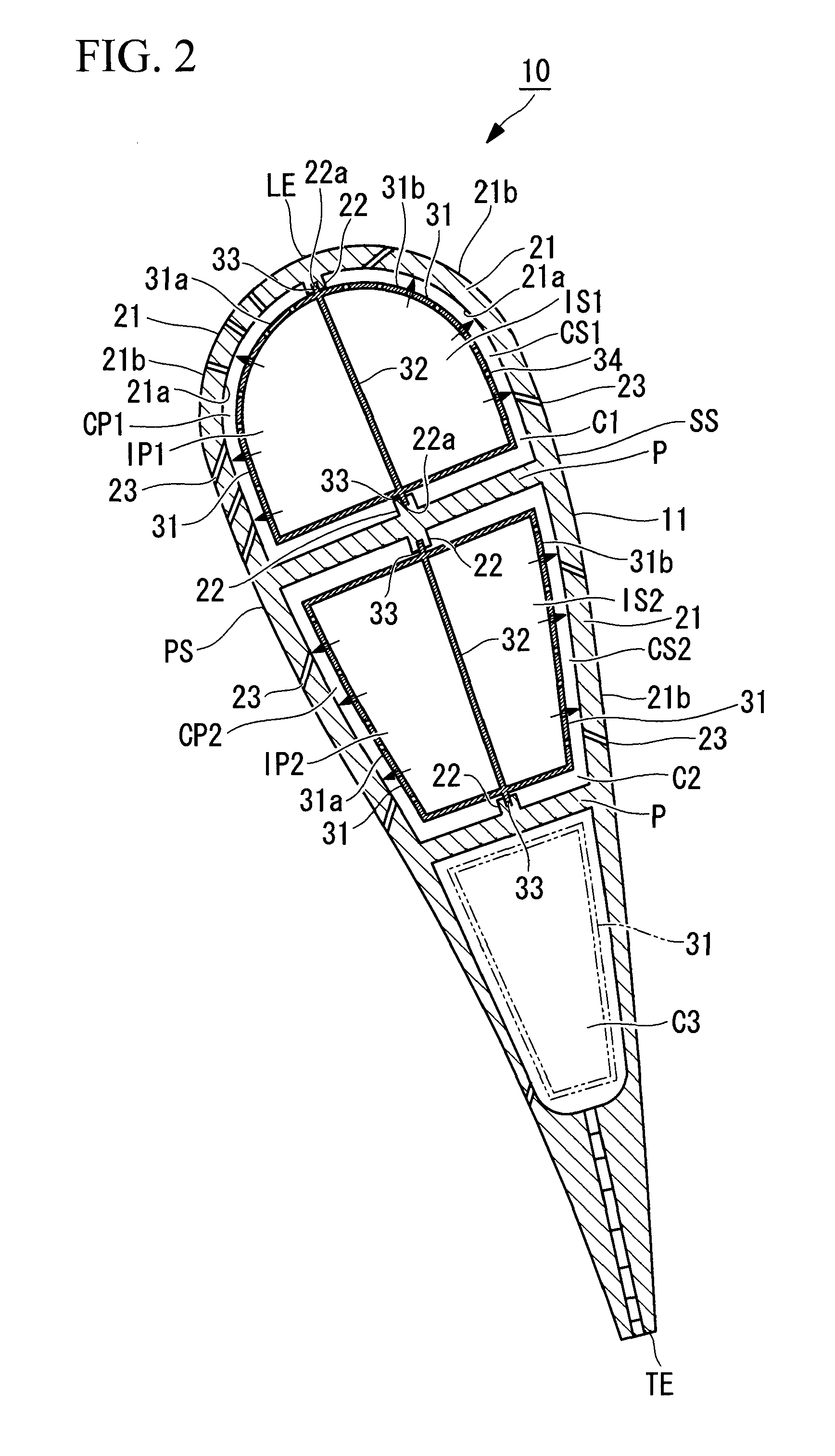
Four-Wall Turbine Airfoil with Thermal Strain Control for Reduced Cycle Fatigue
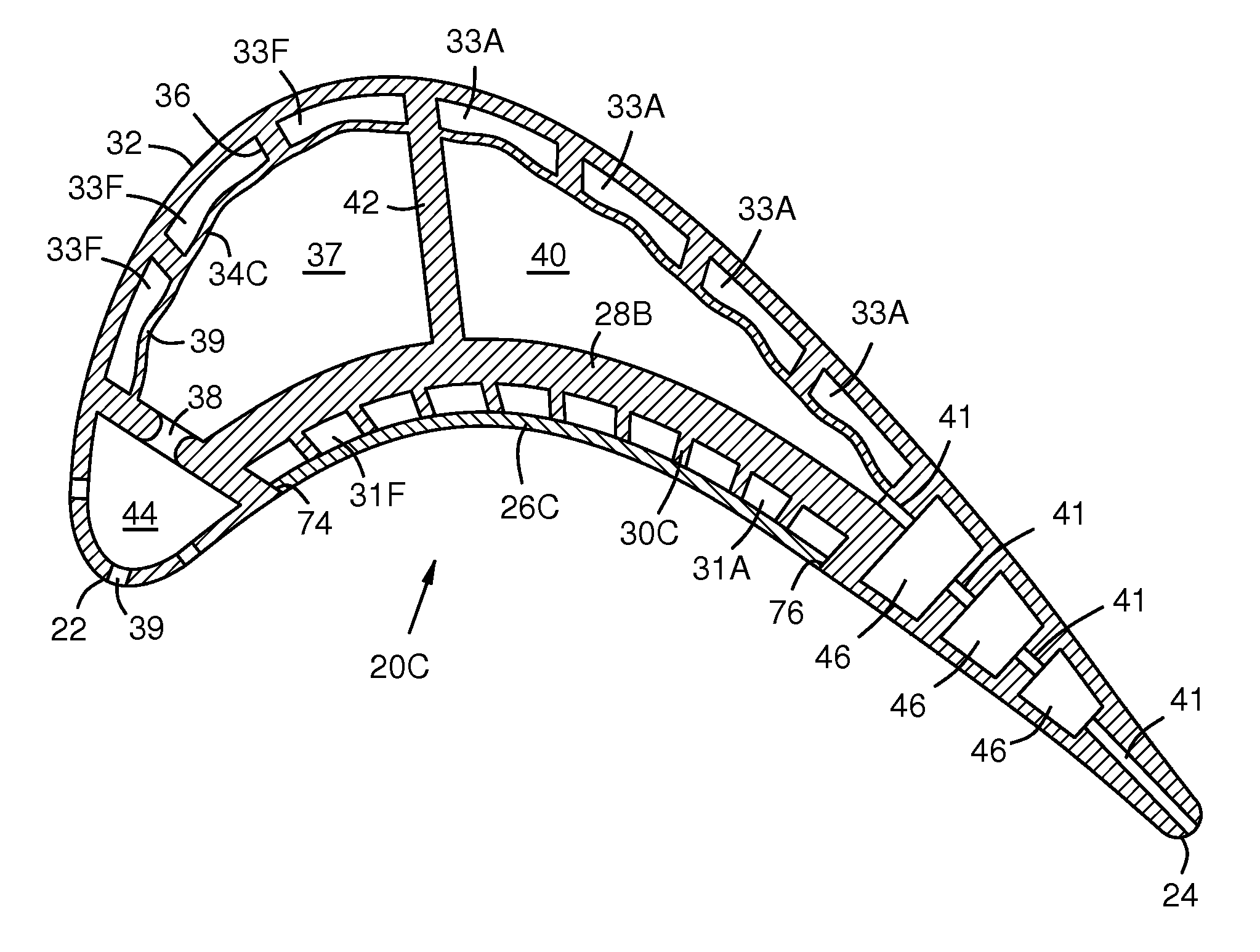
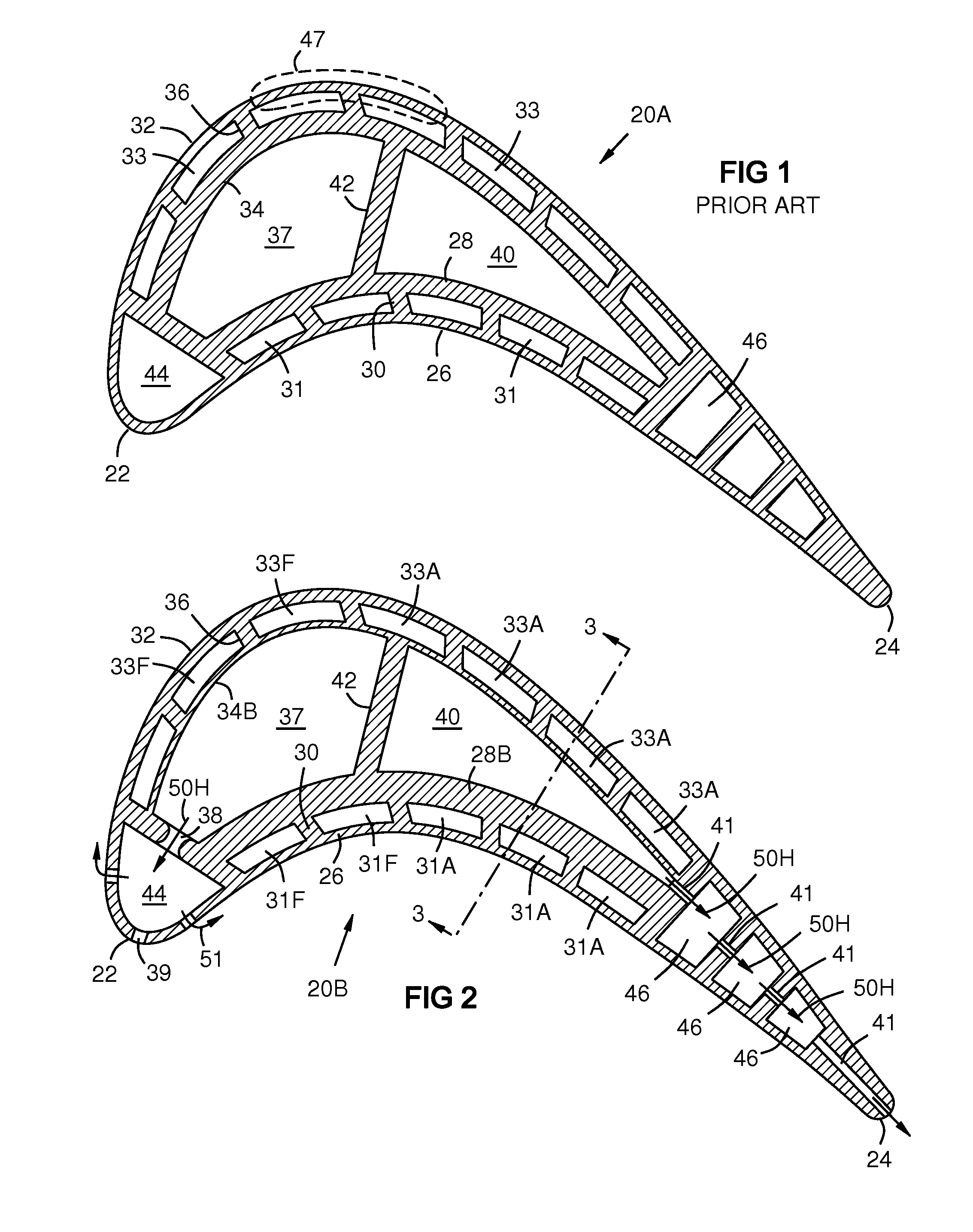
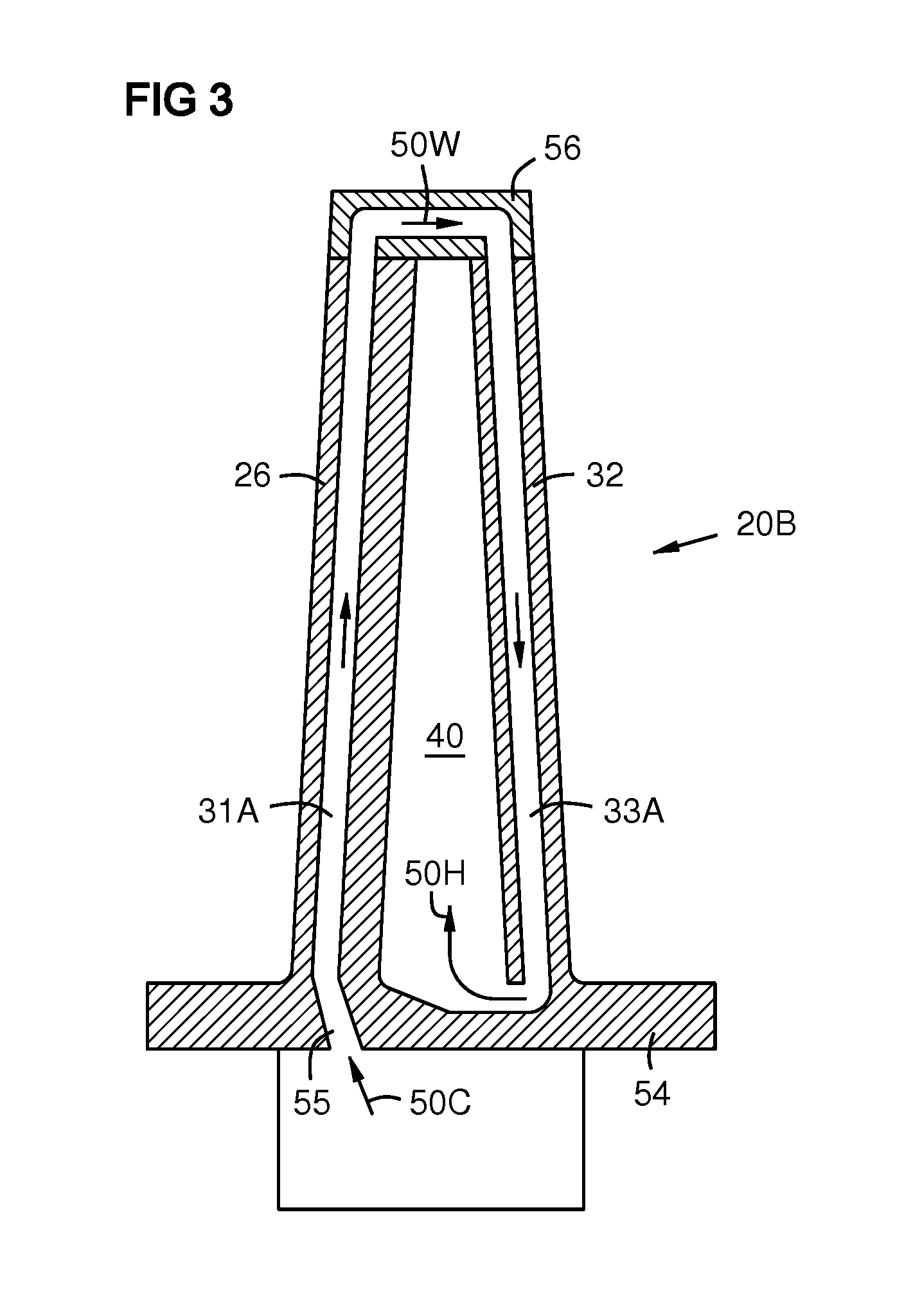
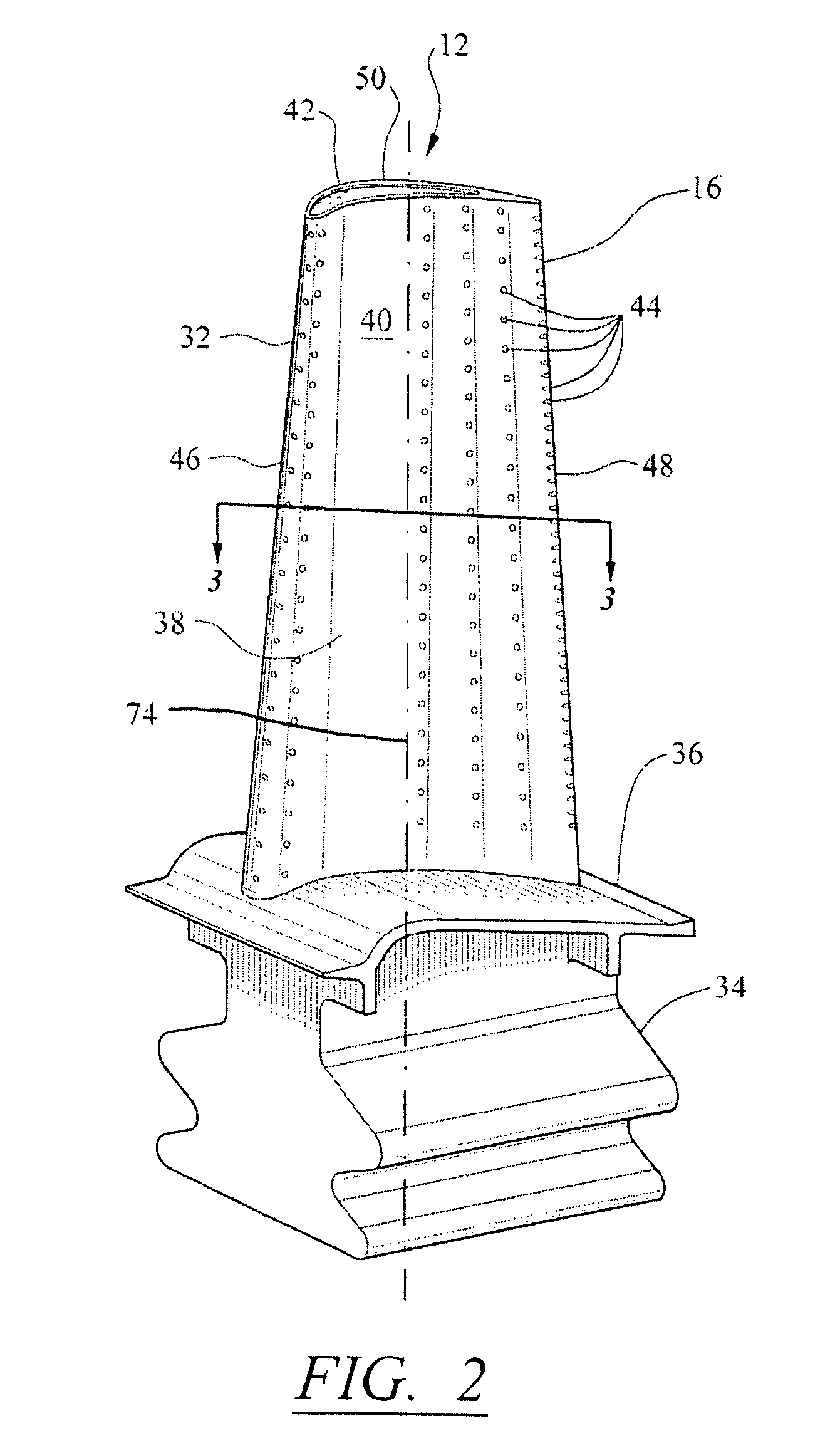
A turbine airfoil (20B) with a thermal expansion control mechanism that increases the airfoil camber (60, 61) under operational heating. The airfoil has four-wall geometry, including pressure side outer and inner walls (26, 28B), and suction side outer and inner walls (32, 34B). It has near-wall cooling channels (31F, 31A, 33F, 33A) between the outer and inner walls. A cooling fluid flow pattern (50C, 50W, 50H) in the airfoil causes the pressure side inner wall (28B) to increase in curvature under operational heating. The pressure side inner wall (28B) is thicker than walls (26, 34B) that oppose it in camber deformation, so it dominates them in collaboration with the suction side outer wall (32), and the airfoil camber increases. This reduces and relocates a maximum stress area (47) from the suction side outer wall (32) to the suction side inner wall (34B, 72) and the pressure side outer wall (26).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Turbine vane and gas turbine
ActiveUS20110123351A1Improve cooling effectAvoid deformationEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesLeading edgeSuction stress
An airfoil part includes a plurality of cooling chambers that are spaces into which the inside of the airfoil part is partitioned, from a leading edge side to a trailing edge side, by a partition wall, that extend in a vane-longitudinal-section direction, and that include division parts on inner walls of a body; insert cylinders that are disposed in the cooling chambers and that have a plurality of impingement holes; and film holes that are provided in the body. The insert cylinders include partitioning parts that extend from the leading edge side to the trailing edge side and that extend in the vane-longitudinal-section direction. The insides of the insert cylinders are partitioned into pressure-surface-side insert spaces close to a pressure surface and suction-surface-side insert spaces close to a suction surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Airfoil trailing edge cooling
A turbine airfoil includes a span wise extending cavity formed from a ceramic mold and a slot extending from the cooling air cavity to a trailing edge being formed by a refractory metal core. The refractory metal core facilitates the reduction in the size of the slot and also in the reduction in the size of pedestals which pass transversely through the slot to interconnect the pressure side to the suction side of the airfoil. The blade has a cutback feature to expose a back surface on the inner side of the suction side wall with dimples being formed on the back surface so as to enhance heat transfer characteristics thereof. Provision is made for fabricating the dimples by way of a photo etching process.
Owner:RTX CORP
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade having surfaces defining a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer configured on a surface of the rotor blade. The noise reducer includes a plurality of noise reduction features and a plurality of auxiliary noise reduction features. Each of the plurality of auxiliary noise reduction features is configured on one of the plurality of noise reduction features.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
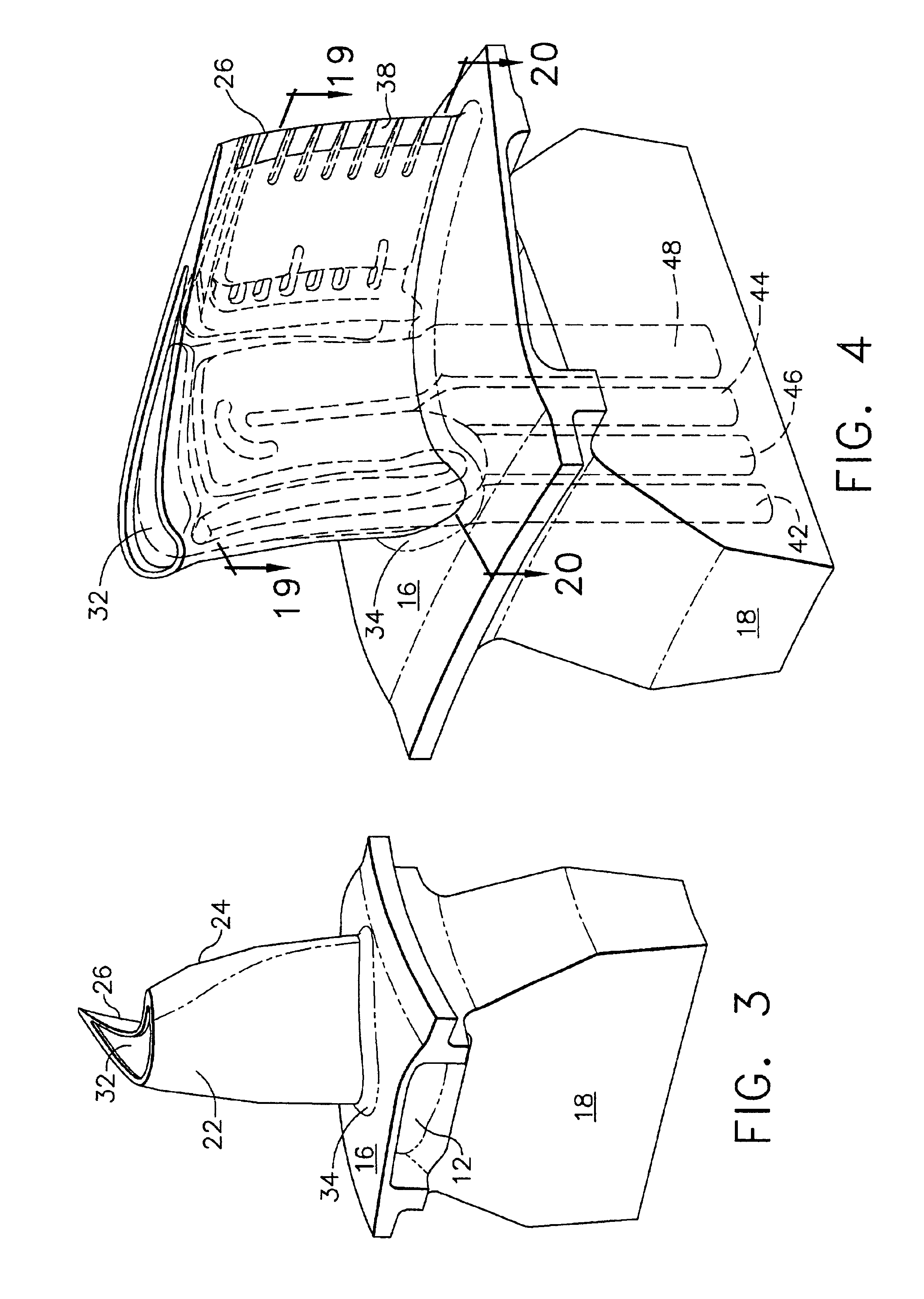
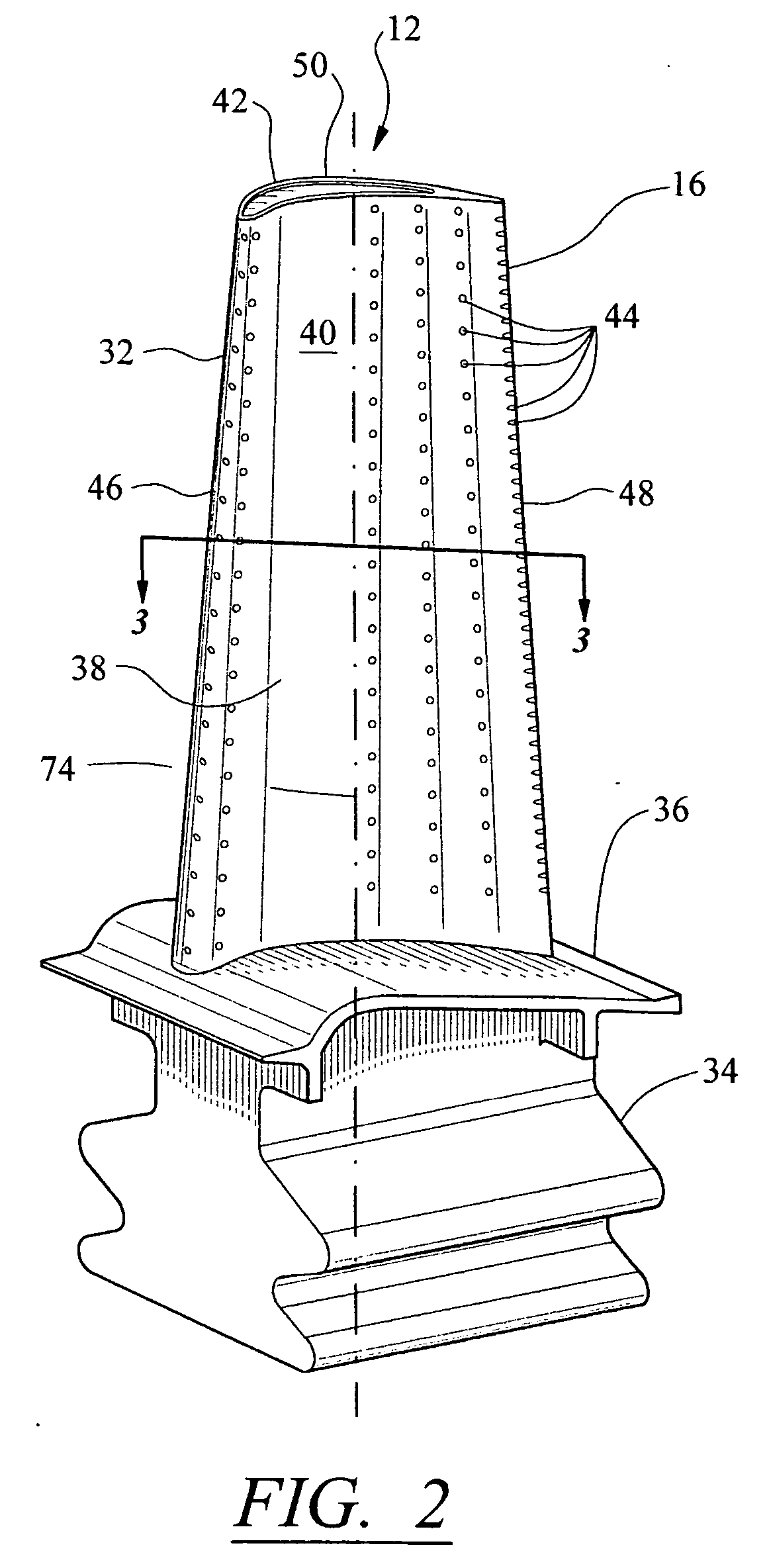
Parallel serpentine cooled blade
A turbine blade includes an airfoil having opposite pressure and suction sidewalls joined together at opposite leading and trailing edges and extending longitudinally from root to tip. A plurality of independent cooling circuits are disposed inside the airfoil correspondingly along the pressure and suction sidewalls thereof. A first serpentine circuit is disposed along the pressure sidewall. A second serpentine circuit is disposed along the suction sidewall in parallel with the first circuit. And a third impingement circuit is disposed at the leading edge forward of the first and second circuits.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade having a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root, the rotor blade further defining a pitch axis. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer mounted to the rotor blade. The noise reducer includes a base plate defining a base line, a plurality of noise reduction features extending from the base line, and a plurality of apertures defined in the base plate. Each aperture is positioned on an opposite side of the base line from the plurality of noise reduction features such that the aperture is fully defined in the base plate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gas delivery system with constant overpressure relative to ambient to system with varying vacuum suction
ActiveUS20080277271A1Minimizes pressure differentialReduce pressureCatalyst activation/preparationDirect contact heat exchangersSuction stressAmbient pressure
A system operating in an environment having an ambient pressure, the system comprising: a reactor configured to combine a plasma stream, powder particles and conditioning fluid to alter the powder particles and form a mixture stream; a supply chamber coupled to the reactor; a suction generator configured to generate a suction force at the outlet of the reactor; a fluid supply module configured to supply the conditioning fluid at an original pressure; and a pressure regulation module configured to: receive the conditioning fluid from the fluid supply module, reduce the pressure of the conditioning fluid from the original pressure to a selected pressure relative to the ambient pressure regardless of any changes in the suction force at the outlet of the reactor, and supply the conditioning fluid at the selected pressure to the supply chamber.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
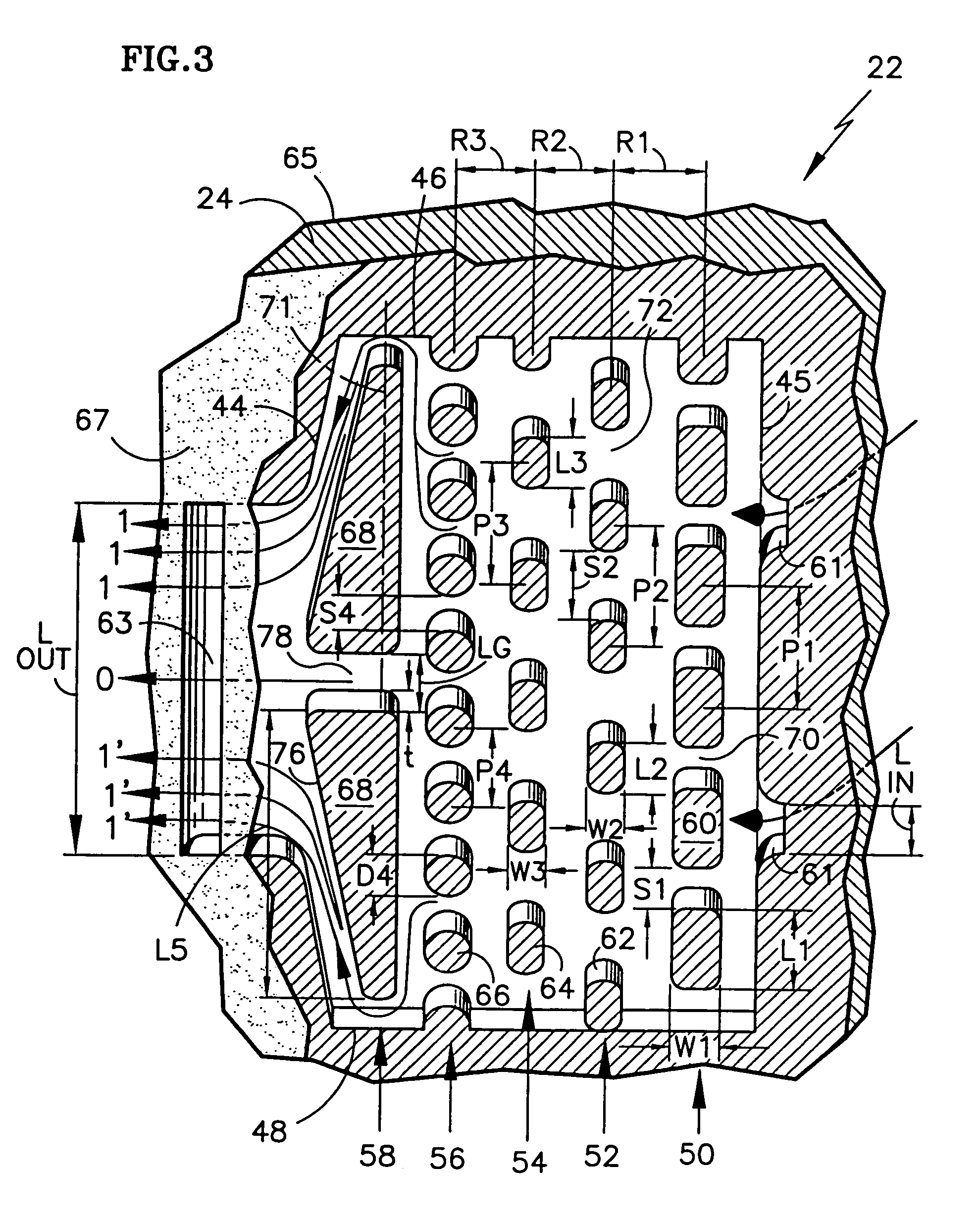
Cooling circuits for a gas turbine blade
ActiveUS20050025623A1Extended service lifeMitigate such drawbackPump componentsEngine fuctionsSuction stressEngineering
A gas turbine blade of a turbomachine includes in its central portion a centrally-located first cooling circuit at least a suction side cavity, at least a pressure side cavity, at least a central cavity extending between the suction side cavity and the pressure side cavity, a first air admission opening at a radially bottom end of the suction side cavity, a second air admission opening at a radially bottom end of the pressure side cavity, at least a first passage putting a radially top end of the suction side cavity into communication with a radially top end of the central cavity, at least a second passage putting a radially top end of the pressure side cavity into communication with the radially top end of the central cavity, and outlet orifices opening out both into the central cavity and into the pressure side face of the blade.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A +2
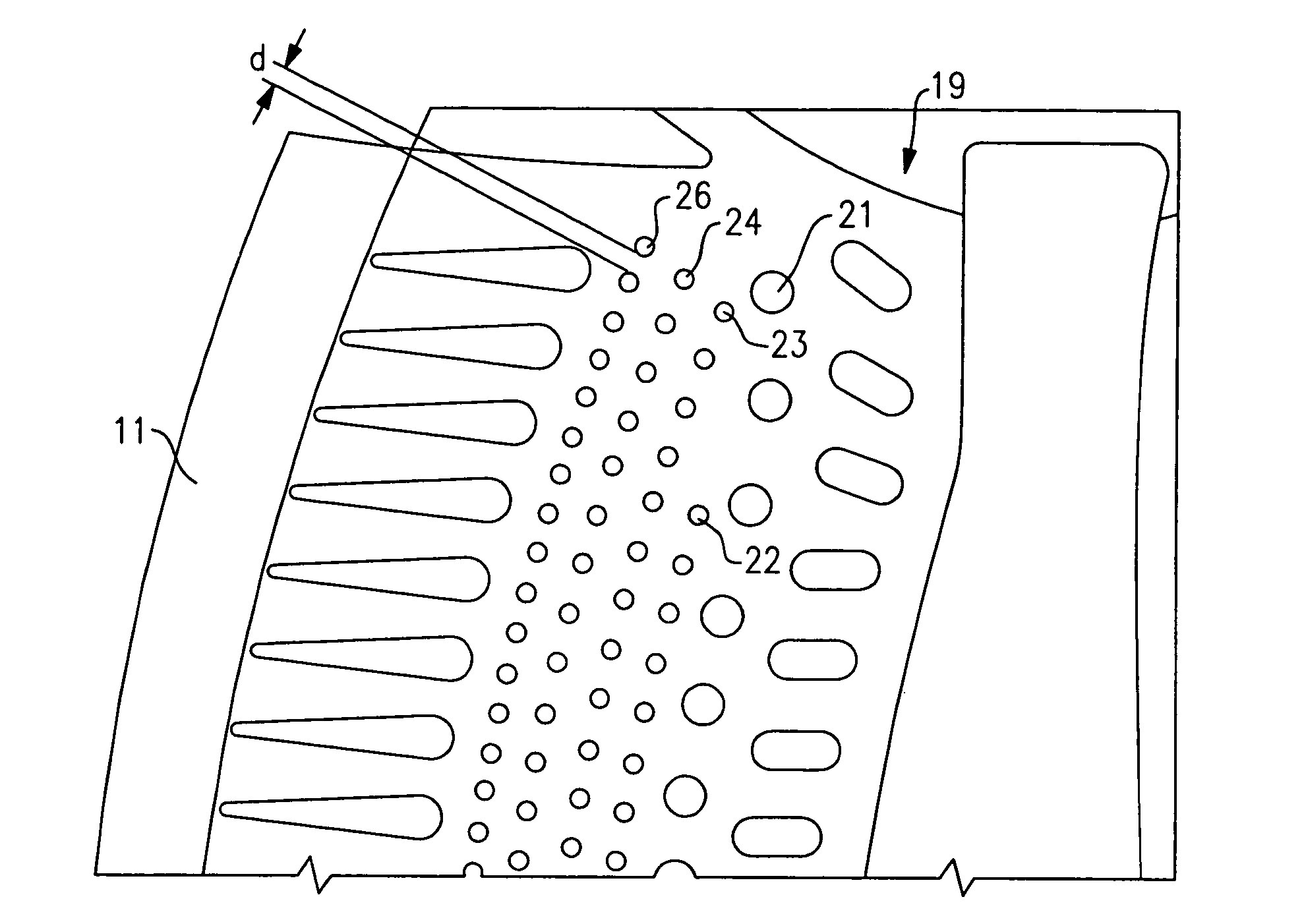
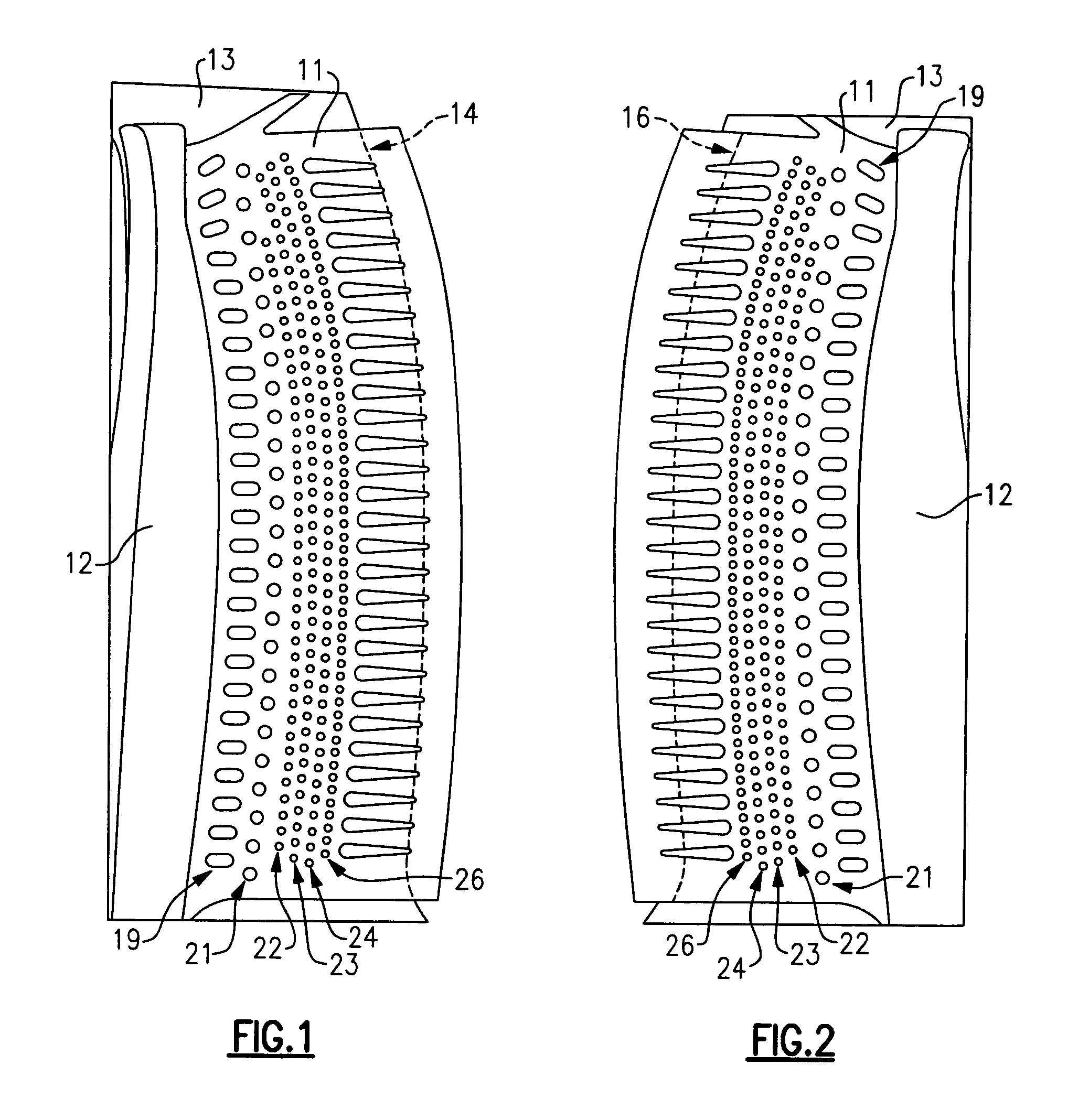
Turbine airfoil cooling system with near wall pin fin cooling chambers
InactiveUS20100221121A1Prolongs effectiveness of coolerImprove effectivenessEngine fuctionsBlade accessoriesLeading edgeSuction stress
A cooling system for a turbine airfoil of a turbine engine having a suction side near wall cooling chamber extending from the leading edge to the trailing edge. The suction side near wall cooling chamber may include a plurality of pin fins for increasing the cooling effectiveness of the suction side near wall cooling chamber. The pin fins may be formed in two or more regions having varying sizes and quantities per unit area to accommodate different cooling requirements across the airfoil. In one embodiment, cooling fluids may flow in a counterflow manner through the suction side near wall cooling chamber relative to a pressure side near wall cooling chamber. In another embodiment, the cooling fluids may flow from the leading edge through the suction side near wall cooling chamber and be exhausted through slots in the trailing edge.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Microcircuit cooling for a turbine airfoil
InactiveUS7097425B2Improve turbine efficiencyMinimize the differenceEngine manufacturePump componentsSuction stressCoolant flow
A turbine airfoil includes a plurality of cooling circuits embedded within the pressure and suction sidewalls and a first and a second flow passage. The first flow passage feeds the coolant fluid to the cooling circuits that are embedded only within the pressure sidewall and the second flow passage feeds the coolant fluid to the cooling circuits that are embedded only within the suction sidewall. A method embodiment of the present comprises placing the inlets of the cooling circuits embedded within the first sidewall in flow communication with only one of the flow passages and placing the inlets of the cooling circuits embedded within the second sidewall in flow communication with at least one of the other flow passages to minimize the difference in sink pressures of the suction and pressure sidewalls to ensure ingestion of the coolant fluid into the inlets of the respective cooling circuits.
Owner:RTX CORP
Microcircuit cooling for vanes
A turbine engine component has an airfoil portion with a suction side. The component includes a cooling microcircuit embedded within a wall structure forming the suction side. The cooling microcircuit has at least one cooling film hole positioned ahead of a gage point for creating a flow of cooling fluid over an exterior surface of the suction side which travels past the gage point. The cooling microcircuit is formed using refractory metal core technology. A method for forming the cooling microcircuit is described.
Owner:RTX CORP
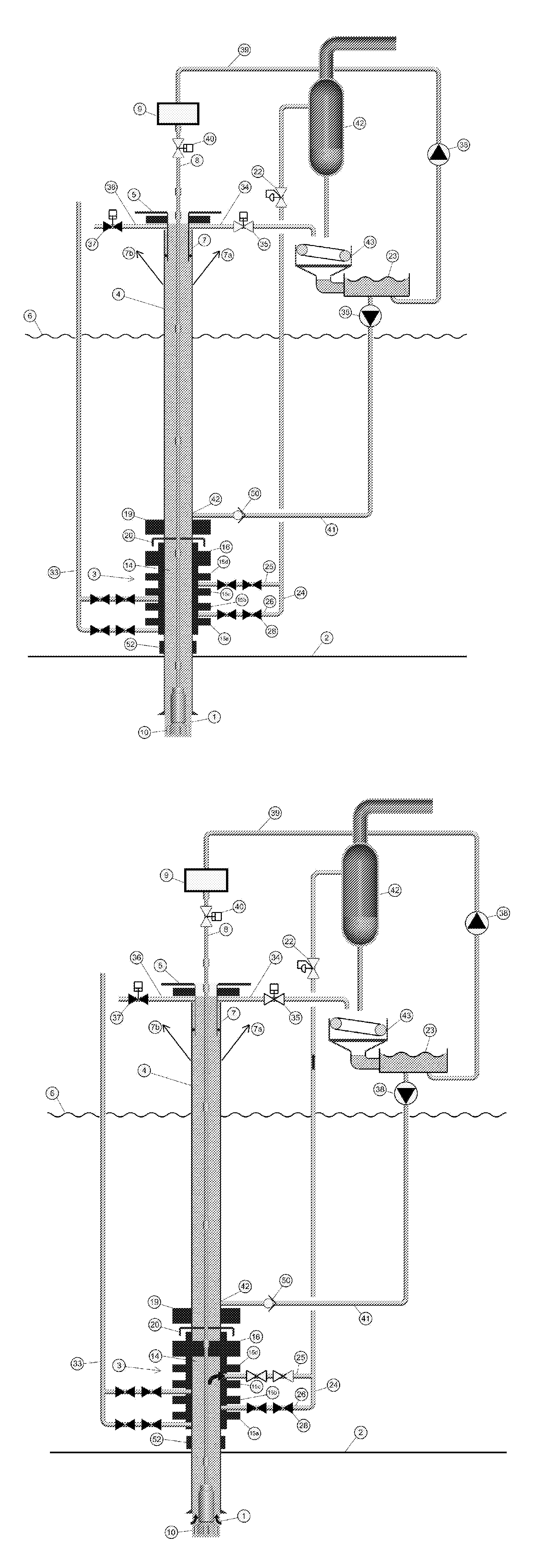
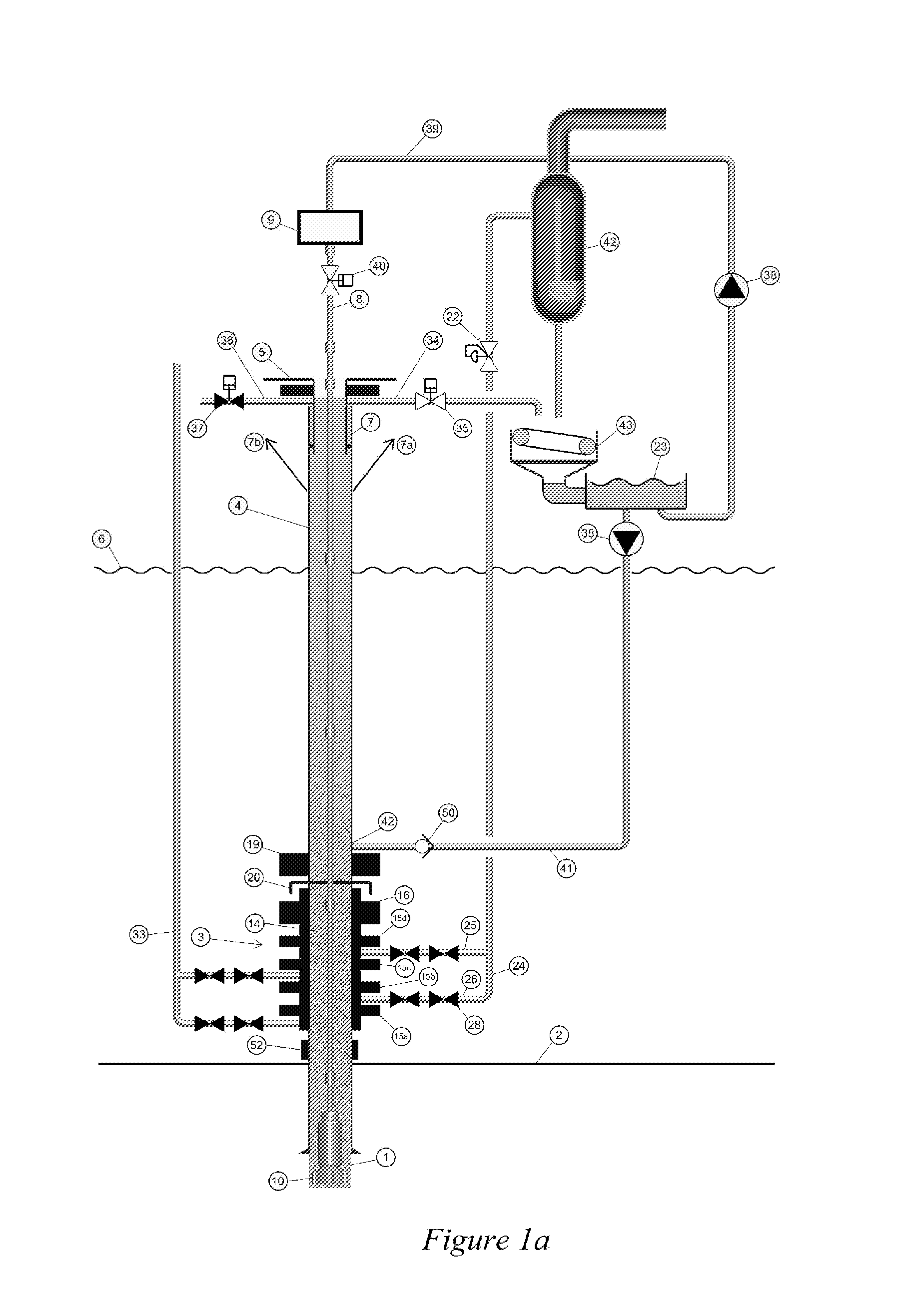
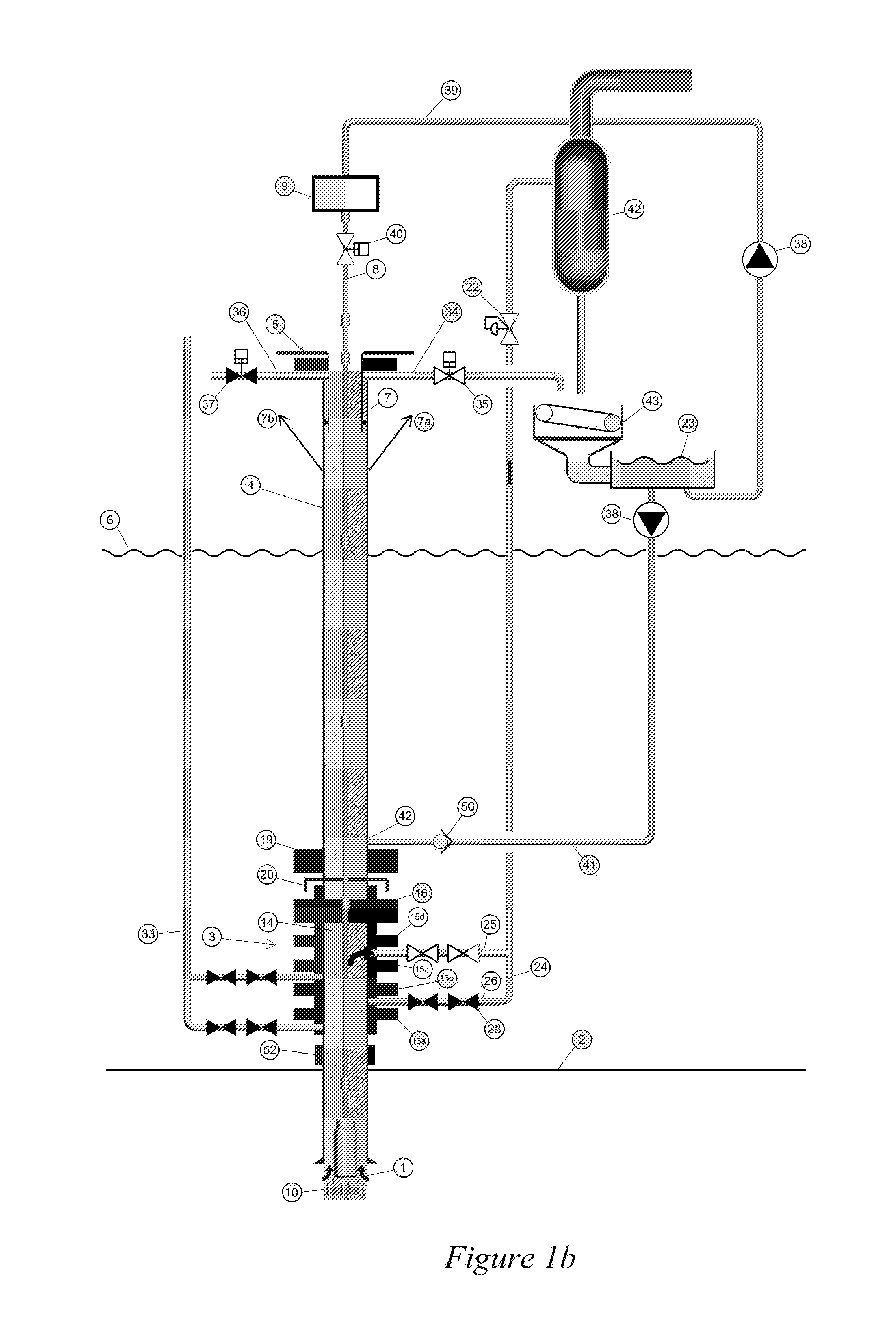
System and method for drilling a subsea well
ActiveUS20120227978A1Increase the differential pressureFluid removalUnderwater drillingBottom hole pressureSuction stress
A subsea mud pump can be used to return heavy drilling fluid to the surface. In order to provide a less stringent requirement for such a pump and to better manage the bottom hole pressure in the case of a gas kick or well control event, the gas should be separated from the drilling fluid before the drilling fluid enters the subsea mud pump and the pressure within the separating chamber. The mud pump suction should be controlled and kept equal or lower than the ambient seawater pressure. This can be achieved within the cavities of the subsea BOP by a system arrangement and methods explained. This function can be used with or without a drilling riser connecting the subsea BOP to a drilling unit above the body of water.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
Turbine blade cooling system with bifurcated mid-chord cooling chamber
InactiveUS7413407B2Uniform temperature distributionImprove efficiencyEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsSuction stressTurbine blade
A cooling system for a turbine blade of a turbine engine having a bifurcated mid-chord cooling chamber for reducing the temperature of the blade. The bifurcated mid-chord cooling chamber may be formed from a pressure side serpentine cooling channel and a suction side serpentine cooling channel. The pressure side and suction side serpentine cooling channels may flow counter to each other, thereby yielding a more uniform temperature distribution than conventional serpentine cooling channels.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Turbine blade cooling system with bifurcated mid-chord cooling chamber
InactiveUS20060222495A1Uniform temperature distributionImprove efficiencyEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsSuction stressTurbine blade
A cooling system for a turbine blade of a turbine engine having a bifurcated mid-chord cooling chamber for reducing the temperature of the blade. The bifurcated mid-chord cooling chamber may be formed from a pressure side serpentine cooling channel and a suction side serpentine cooling channel. The pressure side and suction side serpentine cooling channels may flow counter to each other, thereby yielding a more uniform temperature distribution than conventional serpentine cooling channels.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
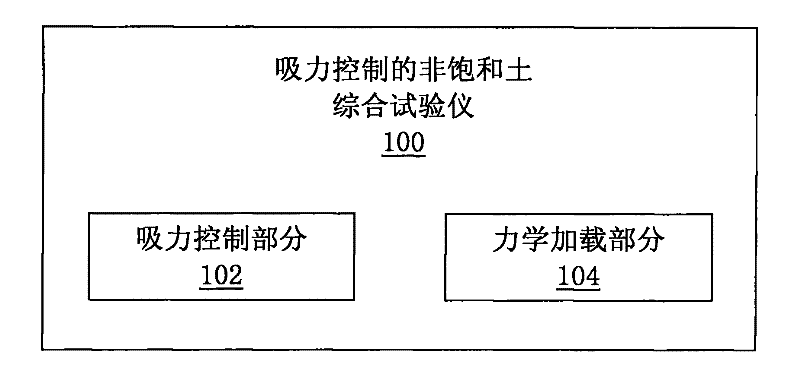
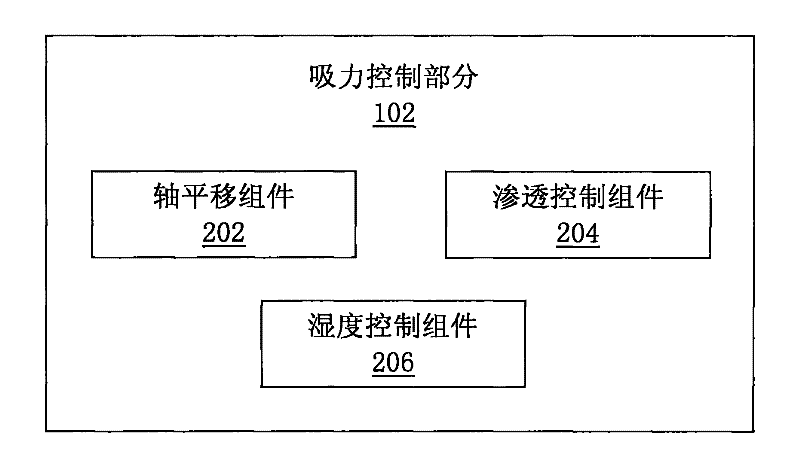
Humidity and osmotic suction-controlled box
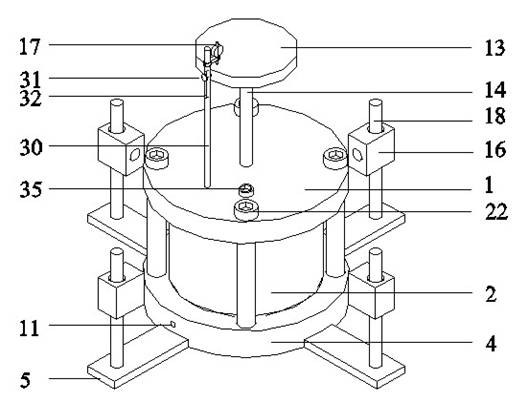
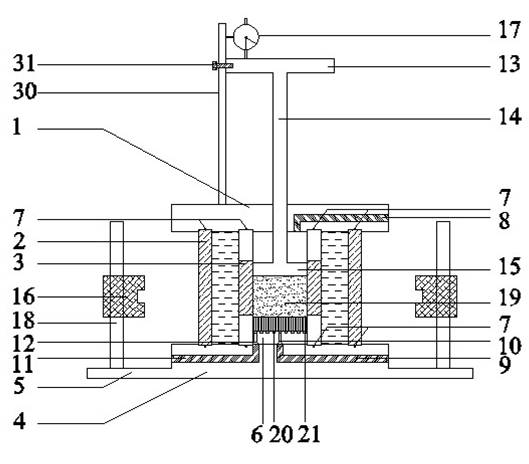
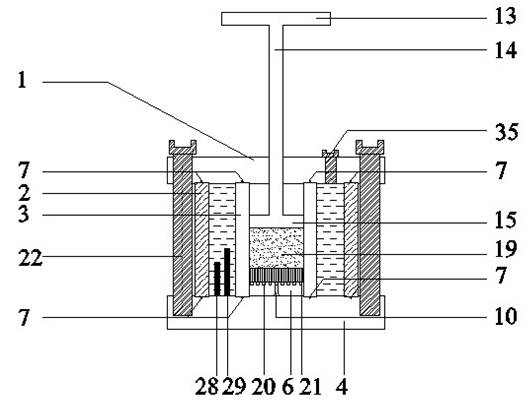
Described herein are systems, apparatuses and methods for the design and use of a suction-controlled box for the measurement of stress-dependent soil and water characteristics, shear strength, volume changes and consolidation characteristics from a single unsaturated soil specimen. The suction-controlled box can include a suction control part and a mechanical loading part, which can apply various suctions and mechanical loadings to test a specimen for a full range of suctions. The suction-controlled box can also include a helical water compartment that can flush diffused air bubbles.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Temperature-controlled type unsaturated soil consolidometer
InactiveCN102221601AReal-time monitoring of lateral deformationImprove sealingEarth material testingMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesTemperature controlSuction stress
The invention discloses a temperature-controlled type unsaturated soil consolidometer, which can be used for geotechnical engineering measuring apparatus manufacture. The temperature-controlled type unsaturated soil consolidometer comprises a combined type pressure chamber with a bidirectional motion loading pressure piston, a diversion system, a displacement meter and laser metering equipment. Heat conducting oil is filled in a sandwich chamber between the outer side of the combined type pressure chamber and an outer-layer transparent sleeve; and moreover, the sandwich chamber is also provided with a thermoelectric couple and a heating rod to control the temperature inside the pressure chamber. When the temperature-controlled type unsaturated soil consolidometer is used, a filter paper method of suction measurement can be employed for measuring the suction of an unsaturated sample under different temperatures; unsaturated soil drying and watering cycle tests controlled under suction and compression tests under constant suction can be implemented to obtain the influence rules of the temperature on the soil-water characteristic and mechanical characteristic of unsaturated soil; andsoaking expansion deformation tests and expansion pressure tests under different temperatures can be implemented, and the expansion deformation of the unsaturated soil and the changing rules of the expansibility are respectively obtained through the displacement meter or a load sensor. The temperature-controlled type unsaturated soil consolidometer has the advantages of complete functions, simplestructure, convenient operation and high test precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
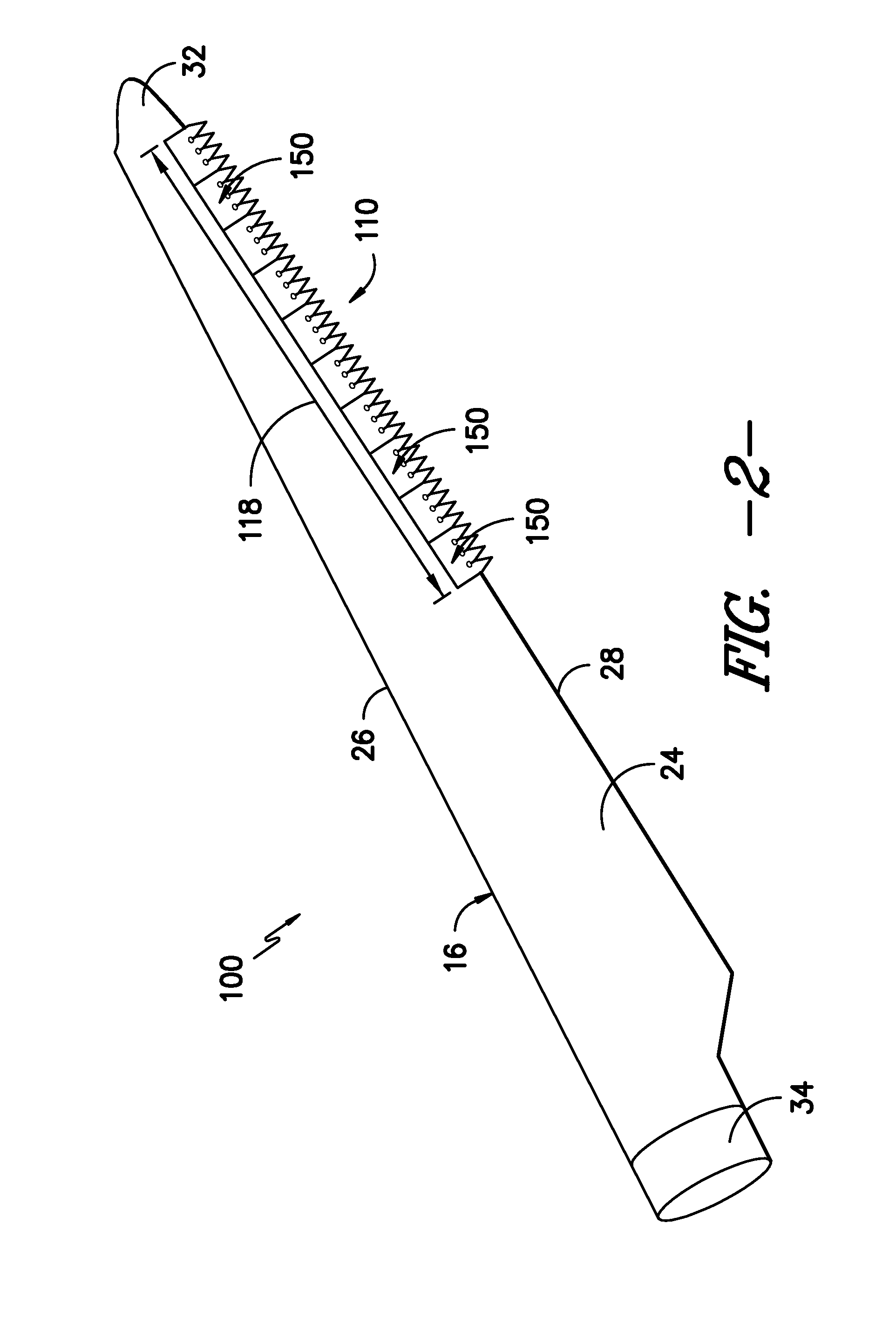
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade having surfaces defining a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer configured on a surface of the rotor blade. The noise reducer includes a plurality of reinforcing members and a plurality of noise reduction features. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members extends outwardly with respect to the rotor blade. Each of the plurality of noise reduction features is connected to one of the plurality of reinforcing members and defines a width. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members causes the connected noise reduction feature to have a variable stiffness throughout at least a portion of the width of the connected noise reduction feature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Modular wind turbine rotor blades and methods of assembling same
The present disclosure is directed to a modular rotor blade for a wind turbine and methods of assembling same. The rotor blade includes a blade root section, a blade tip section, at least one leading edge segment having a forward pressure side surface and a forward suction side surface, and at least one trailing edge segment having an aft pressure side surface and an aft suction side surface. Further, the leading edge segment and the trailing edge segment are arranged between the blade root section and the blade tip section in a generally span-wise direction. In addition, the leading edge segment and the trailing edge segment are joined at a pressure side seam and a suction side seam.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Transonic compressor rotors with non-monotonic meanline angle distributions
InactiveUS20080118362A1Improve efficiencySimple designSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsShock waveLeading edge
Airfoils are provided having non-monotonic meanline angle distributions and local negative camber along a length of the meanline between a point on a leading edge of the airfoil and a point on the trailing edge of the airfoil. The improved airfoil shape decreases the peak of a Mach number of a shock wave that develops in a passage between adjacent airfoils and attenuates or eliminates the shock wave at the suction surface of the airfoil within the passage. A blade constructed by this type of airfoil provides improved fluid flow in the passages between the airfoils, increased efficiency and an improved stall margin, among other benefits.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Liquid ejection apparatus and liquid filling method for liquid ejection apparatus
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Vacuum clamping detection method and vacuum clamping detector
When suction / release-passage-internal pressure Pin is equal to or less than a suction detection pressure Pj, a suction of a workpiece is detected and a transfer operation is started. As long as the suction / release-passage-internal pressure Pin does not rise to pressure having an upper limit value or more of the drop detection range during a transfer, it is recognized that the workpiece is not dropped from the sucker. The drop detection range is computed by adding predetermined allowable deflection width ΔD to the suction / release-passage-internal pressure Pin that is read as reference pressure under the condition that the workpiece is sucked by the sucker.
Owner:KOGANEI
Lifter and separator for stacked flexible flat workpieces
InactiveUS6886827B2Easy constructionEasy to operateDe-stacking articlesArticle feedersSuction stressEngineering
Owner:TRUMPF GMBH & CO
Noise reducer for rotor blade in wind turbine
A rotor blade assembly for a wind turbine is disclosed. The rotor blade assembly includes a rotor blade having surfaces defining a pressure side, a suction side, a leading edge, and a trailing edge extending between a tip and a root. The rotor blade assembly further includes a noise reducer configured on a surface of the rotor blade. The noise reducer includes a plurality of reinforcing members and a plurality of noise reduction features. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members extends outwardly with respect to the rotor blade. Each of the plurality of noise reduction features is connected to one of the plurality of reinforcing members and defines a width. Each of the plurality of reinforcing members causes the connected noise reduction feature to have a variable stiffness throughout at least a portion of the width of the connected noise reduction feature.
Owner:LM WIND POWER US TECH APS
Cleaning device for cleaning a surface comprising a brush and a squeegee element
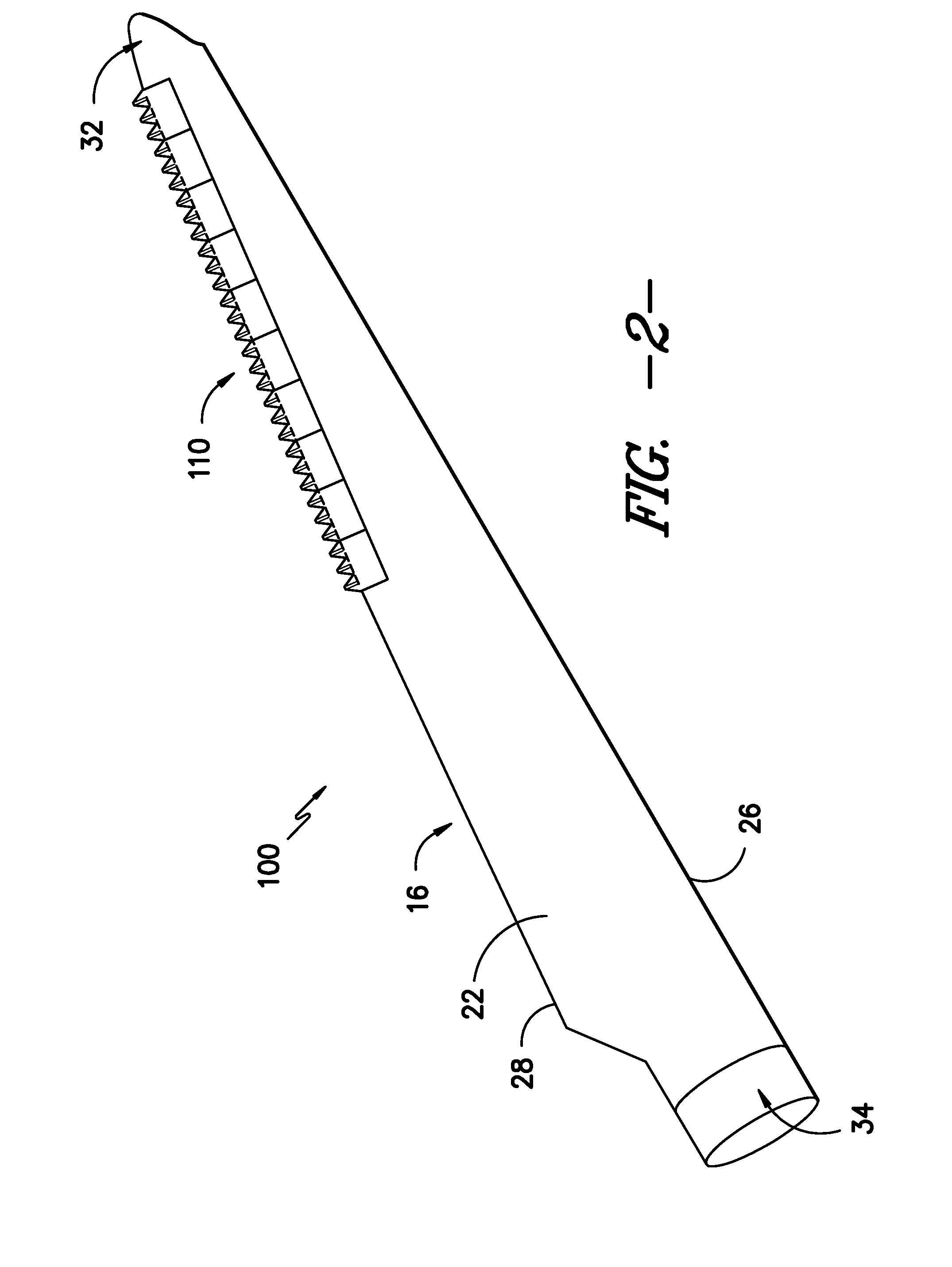
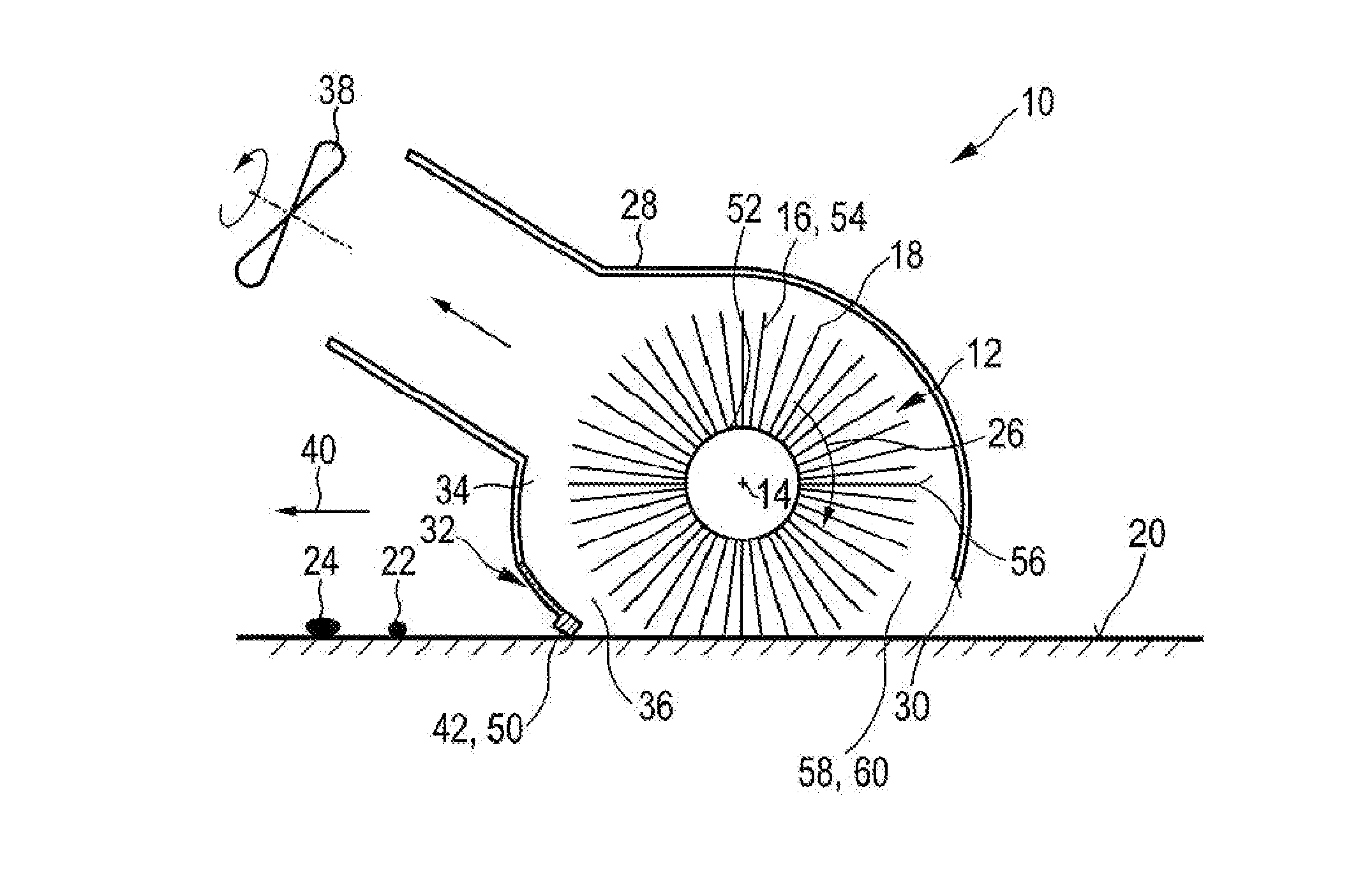
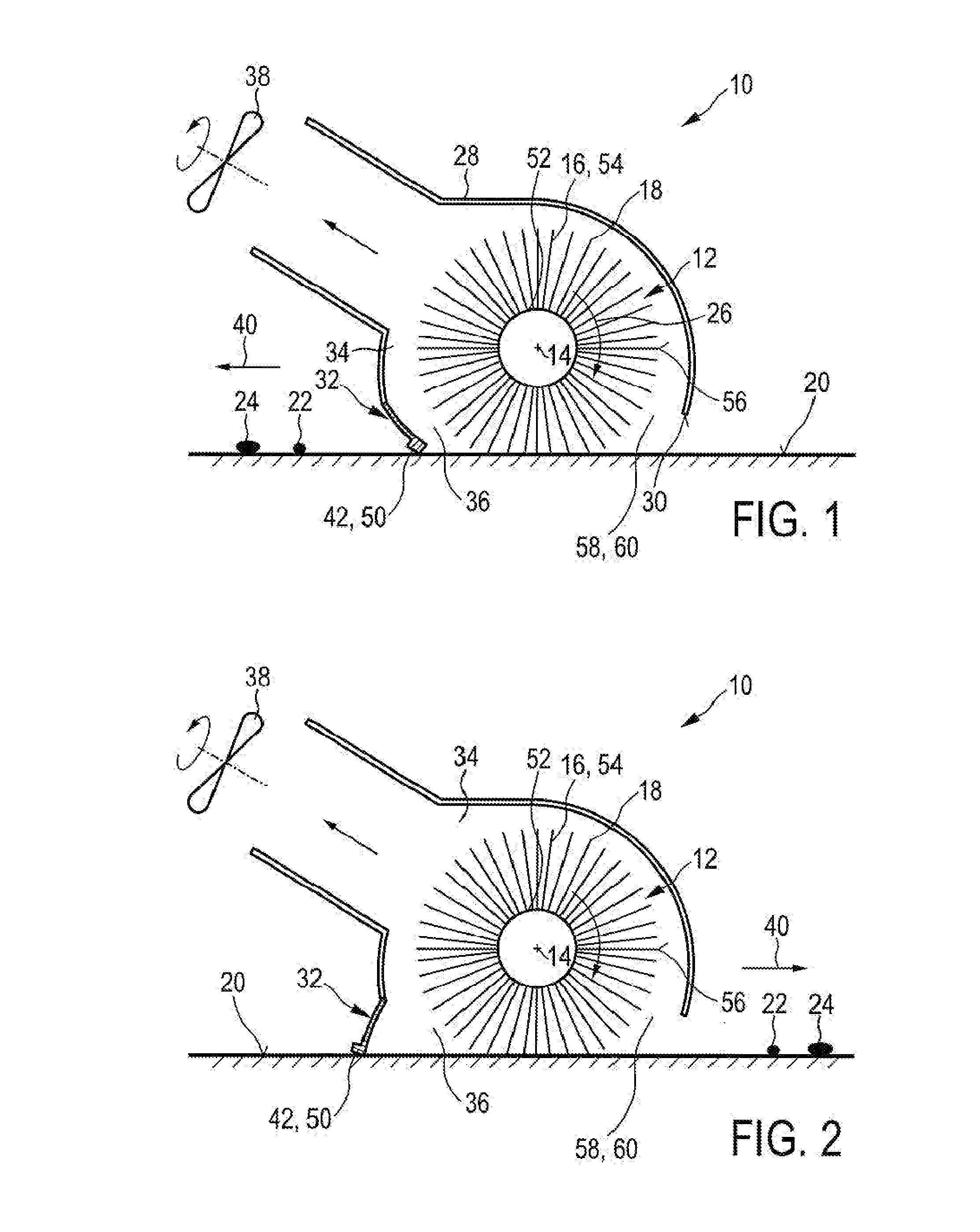
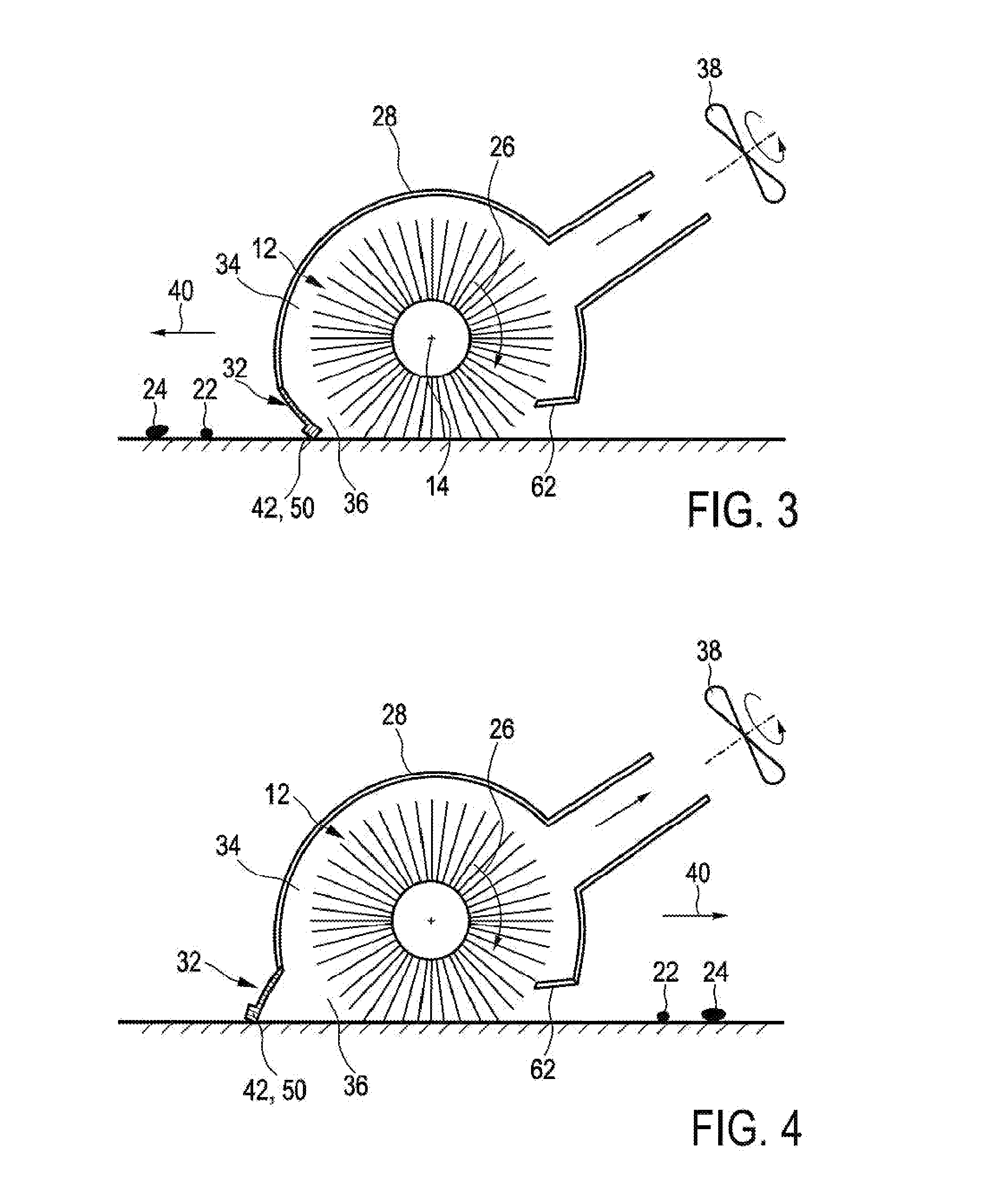
PendingUS20140182079A1Increase heightHigh strengthCarpet cleanersFloor cleanersEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to a cleaning device for cleaning a surface (20), comprising: —a nozzle arrangement (10) that comprises i) a brush (12) rotatable about a brush axis (14), said brush (12) being provided with flexible brush elements (16) having tip portions (18) for contacting the surface to be cleaned (20) and picking up dirt particles (22) and liquid (24) from the surface (20) during a pick-up period when the brush elements (16) contact the surface (20) during the rotation of the brush (12), wherein a linear mass density of a plurality of the brush elements (16) is, at least at the tip portions (18), lower than 150 g per 10 km, and ii) a single squeegee element (32) for pushing or wiping dirt particles (22) and liquid (24) across or off the surface to be cleaned (20) during movement of the cleaning device (100), said squeegee element (32) being spaced apart from the brush (12) and extending substantially along a longitudinal direction (48) being substantially parallel to the brush axis (14), wherein a suction area (34) is defined within the nozzle arrangement (10) between the squeegee element (32) and the brush (12), —a drive means for driving the brush (12) in rotation, wherein the drive means are adapted to realize a centrifugal acceleration at the tip portions (18) which is, in particular during a dirt release period when the brush elements (16) are free from contact to the surface (20) during rotation of the brush (12), at least 3,000 m / s 2, and —a vacuum aggregate (38) for generating an under-pressure in the suction area (34) for ingesting dirt particles (22) and liquid (24).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
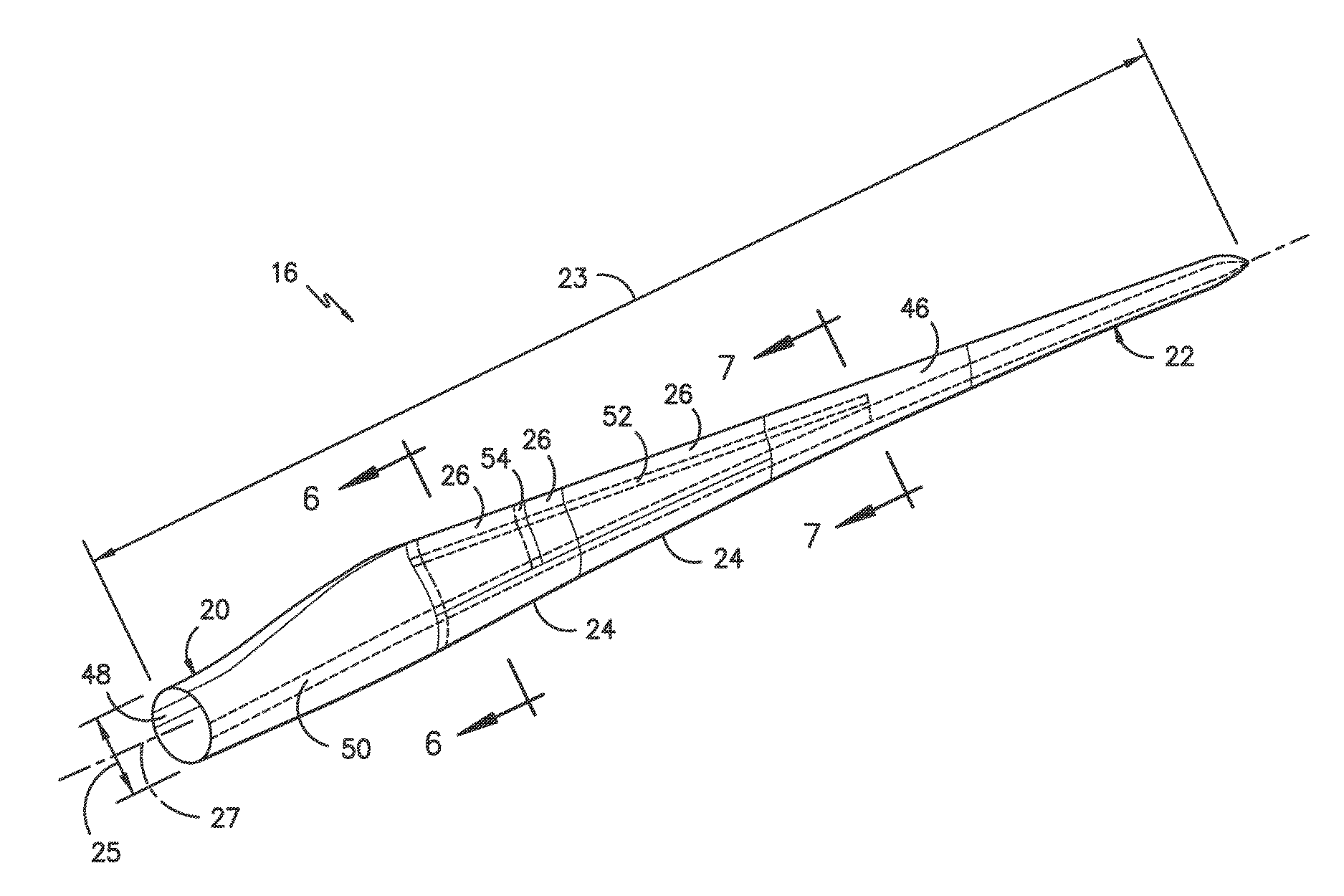
Wind turbine rotor blade joint
A joint for connecting a first blade segment and a second blade segment of a wind turbine rotor blade is disclosed. The joint includes a body, the body including an outer surface and an inner surface. The outer surface has an aerodynamic contour that generally corresponds to an aerodynamic contour of the first blade segment and the second blade segment. The body includes a pressure side and a suction side extending between a leading edge and a trailing edge. In some embodiments, the joint further includes a channel defined in the outer surface of the body. The channel includes a generally continuous base wall extending between opposing sidewalls. The inner surface includes the base wall. In other embodiments, the joint further includes a channel defined in the body, and a shell extending from the body in a generally span-wise direction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pattern cooled turbine airfoil
A hollow turbine airfoil includes pressure and suction sidewalls extending in span between a root and tip and extending in chord between opposite leading and trailing edges. The pressure sidewall includes a first pattern of first holes distributed in span and chord over a majority thereof, and a second pattern of different second holes also distributed in span and chord over a minority of the pressure sidewall between the tip and the midspan of the airfoil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com