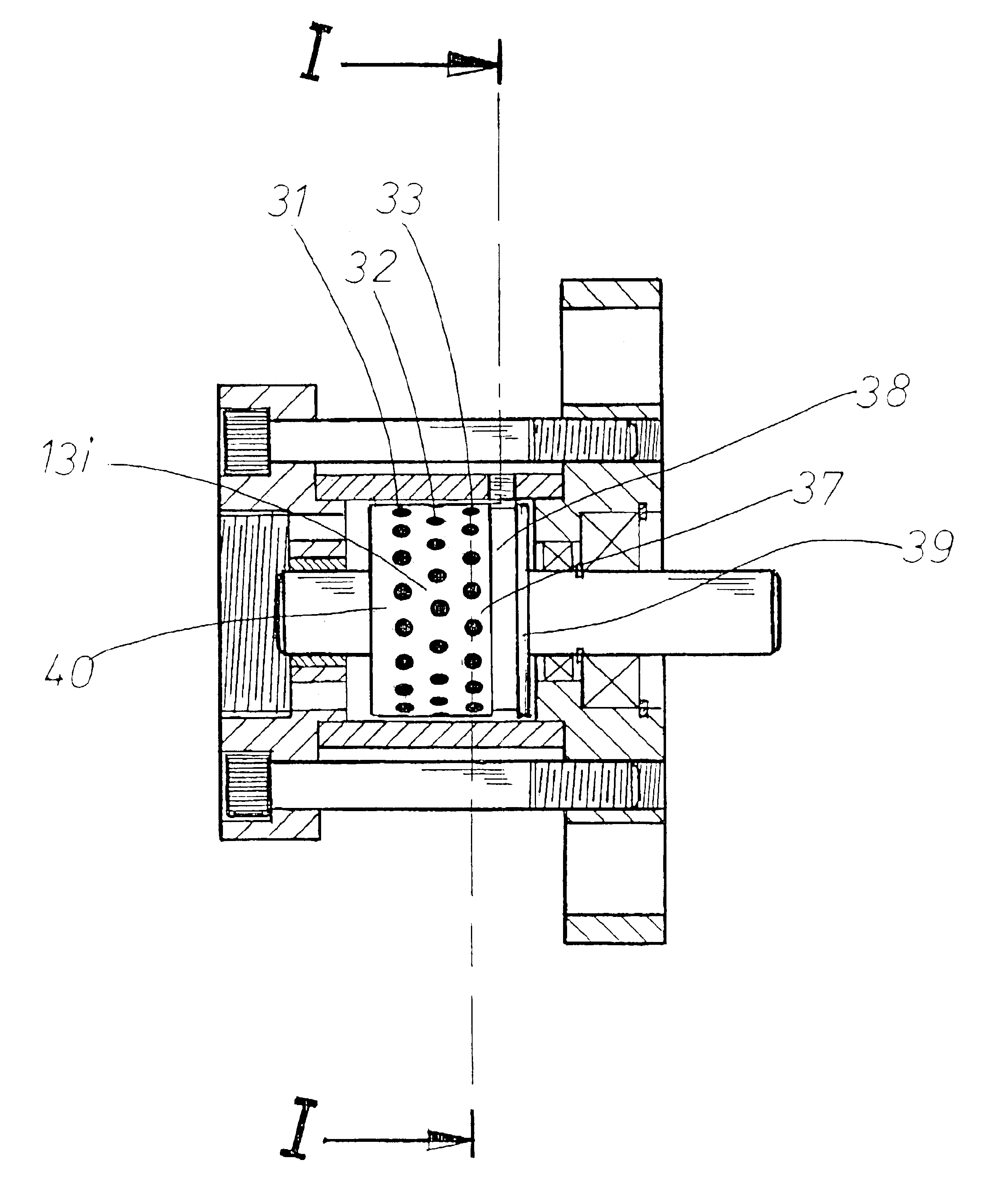
Patents
Literature
1694results about "Direct contact heat exchangers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tetrafluoropropene compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100122545A1Lower global warming potentialCompressorHeat pumpsAir conditioningHeat transfer fluid
The present invention relates to compositions for use in refrigeration, air-conditioning, and heat pump systems wherein the composition comprises a tetrafluoropropene and at least one other component. The compositions of the present invention are useful in processes for producing cooling or heat, as heat transfer fluids, foam blowing agents, aerosol propellants, and fire suppression and fire extinguishing agents.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
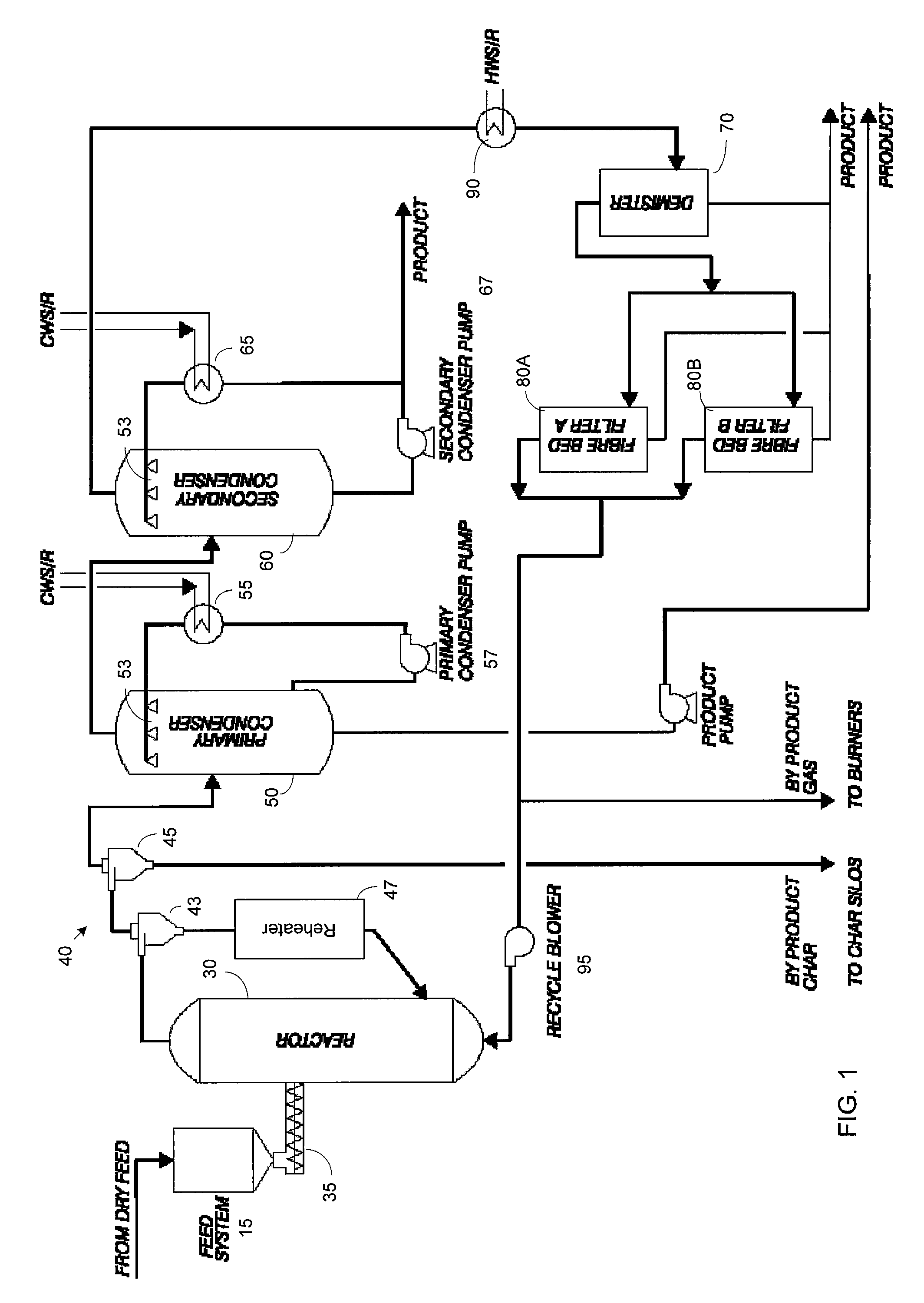
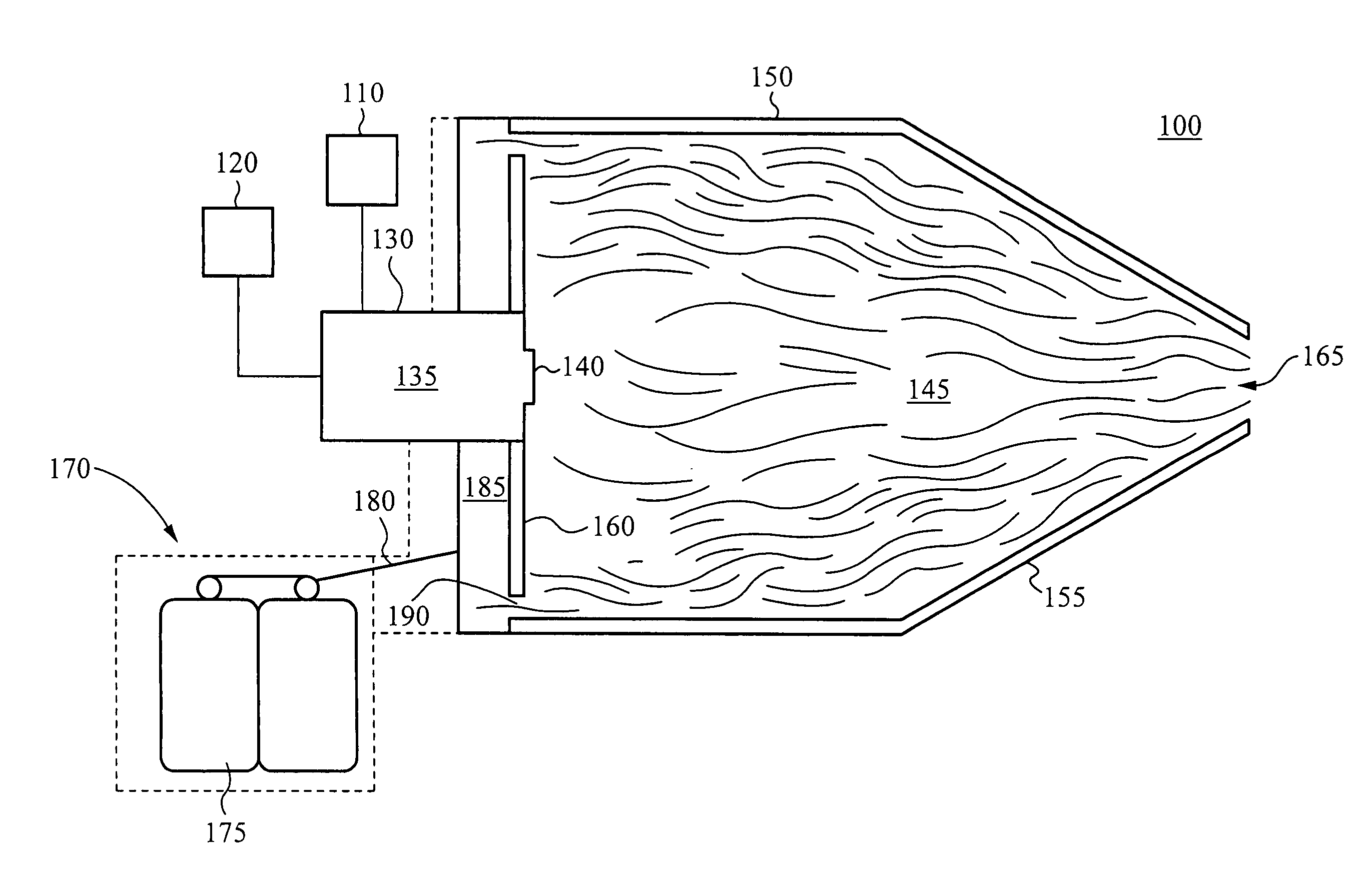
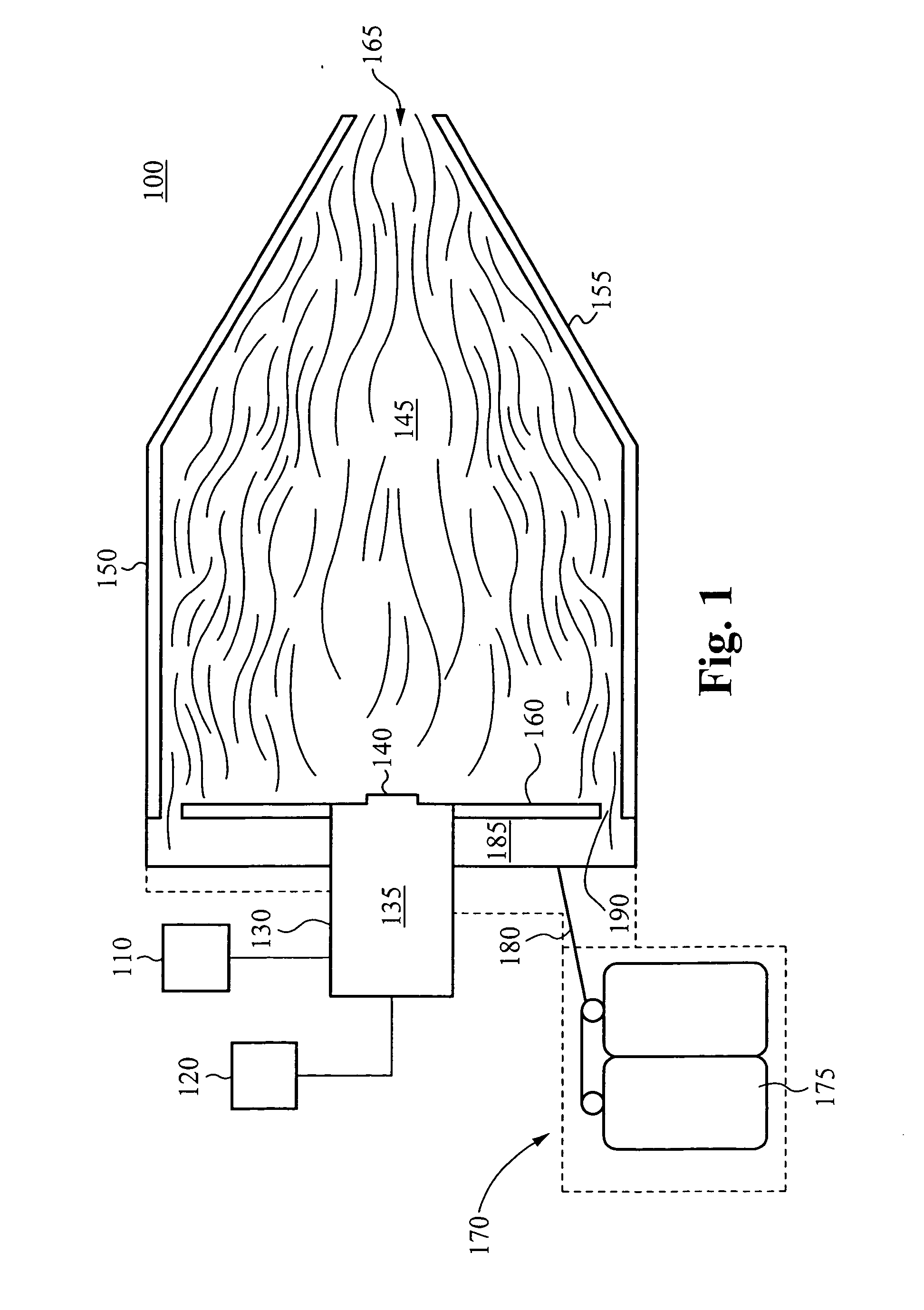
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
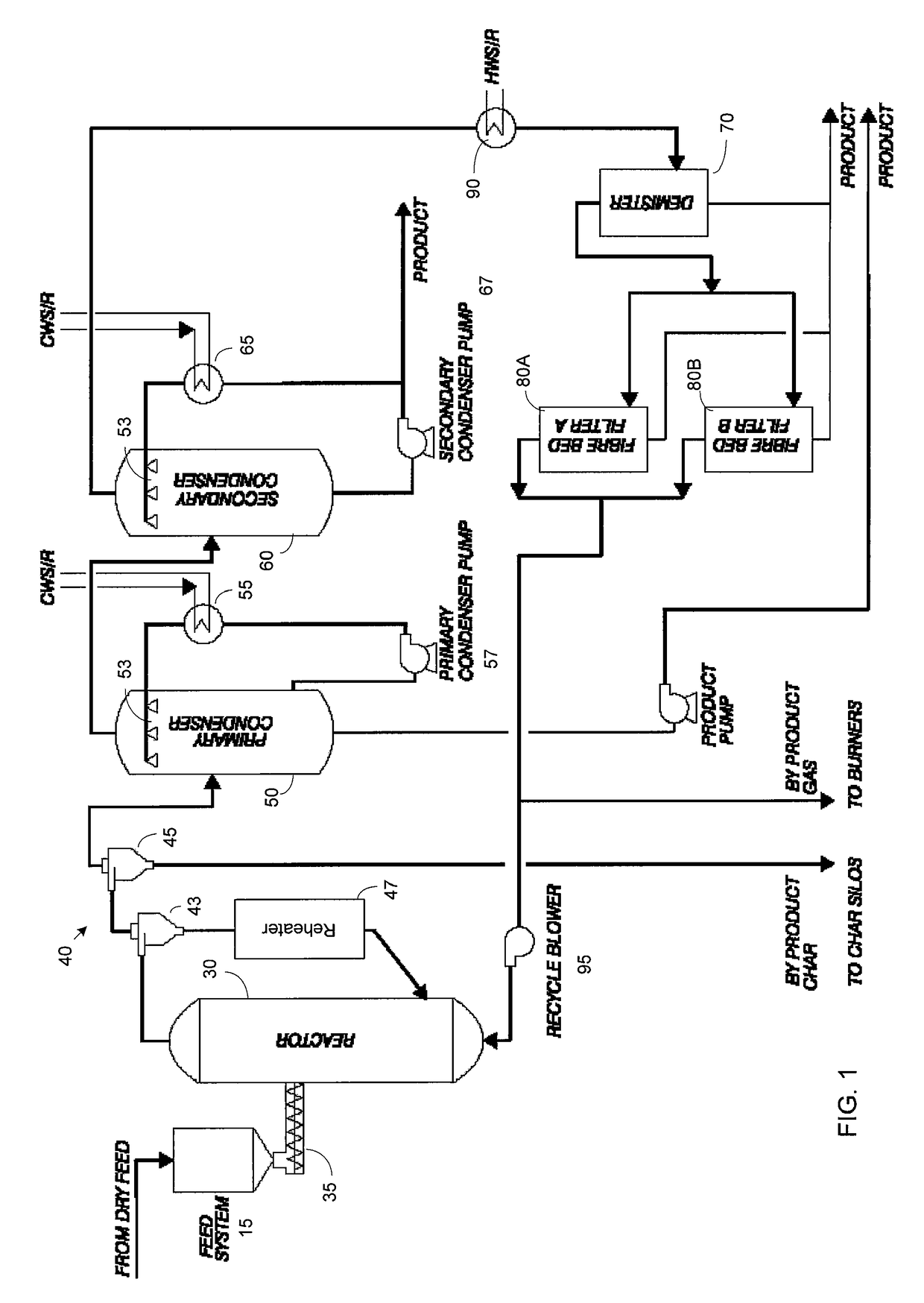
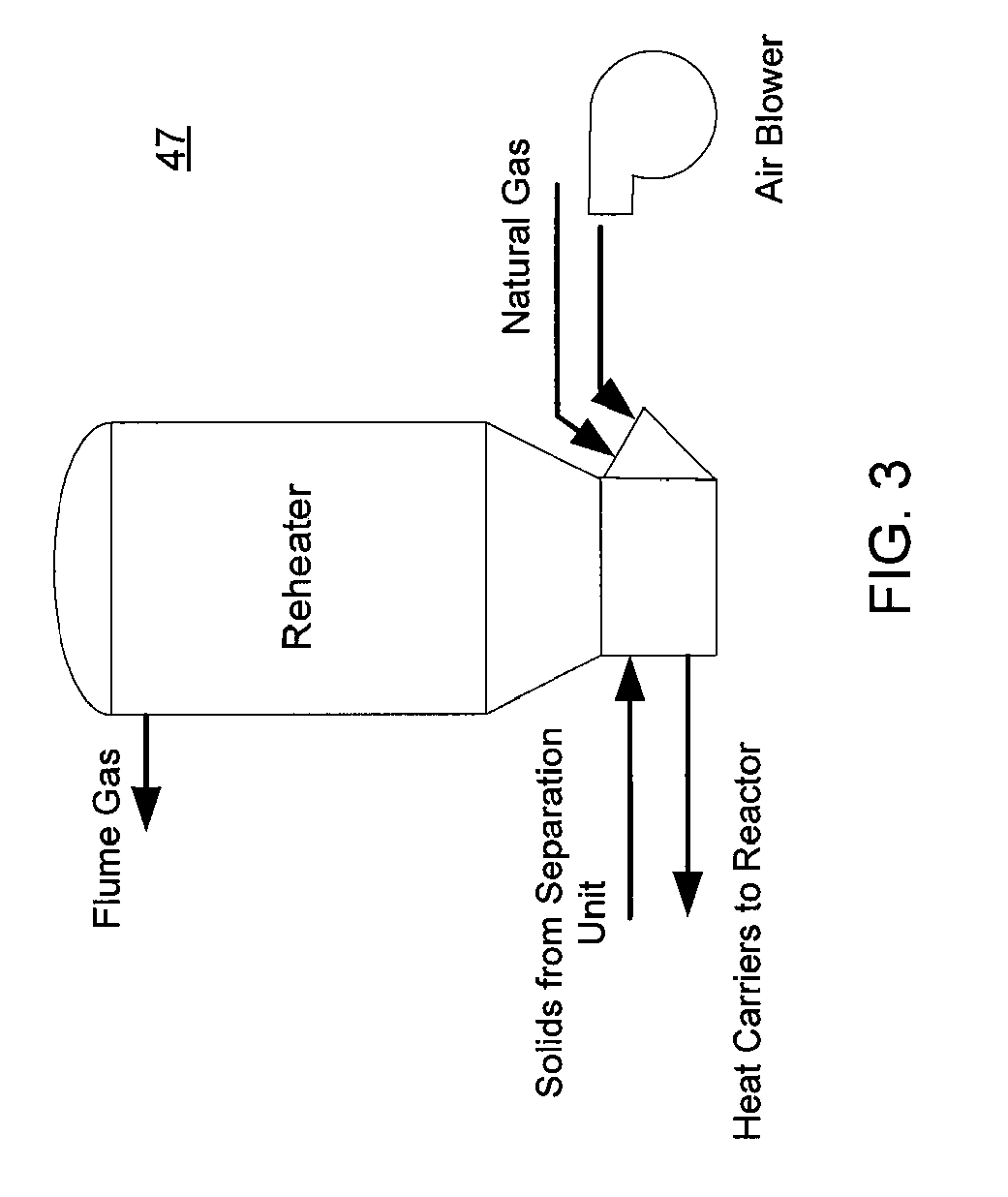
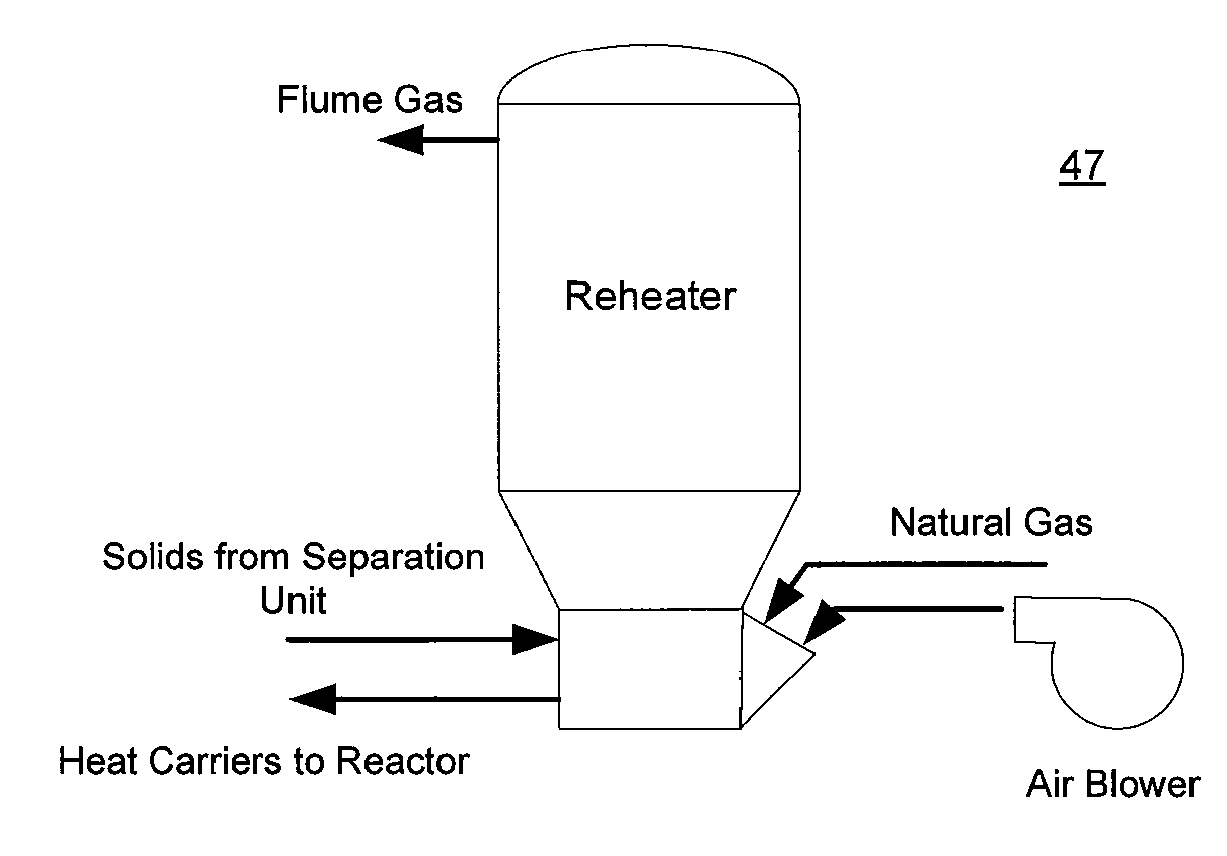
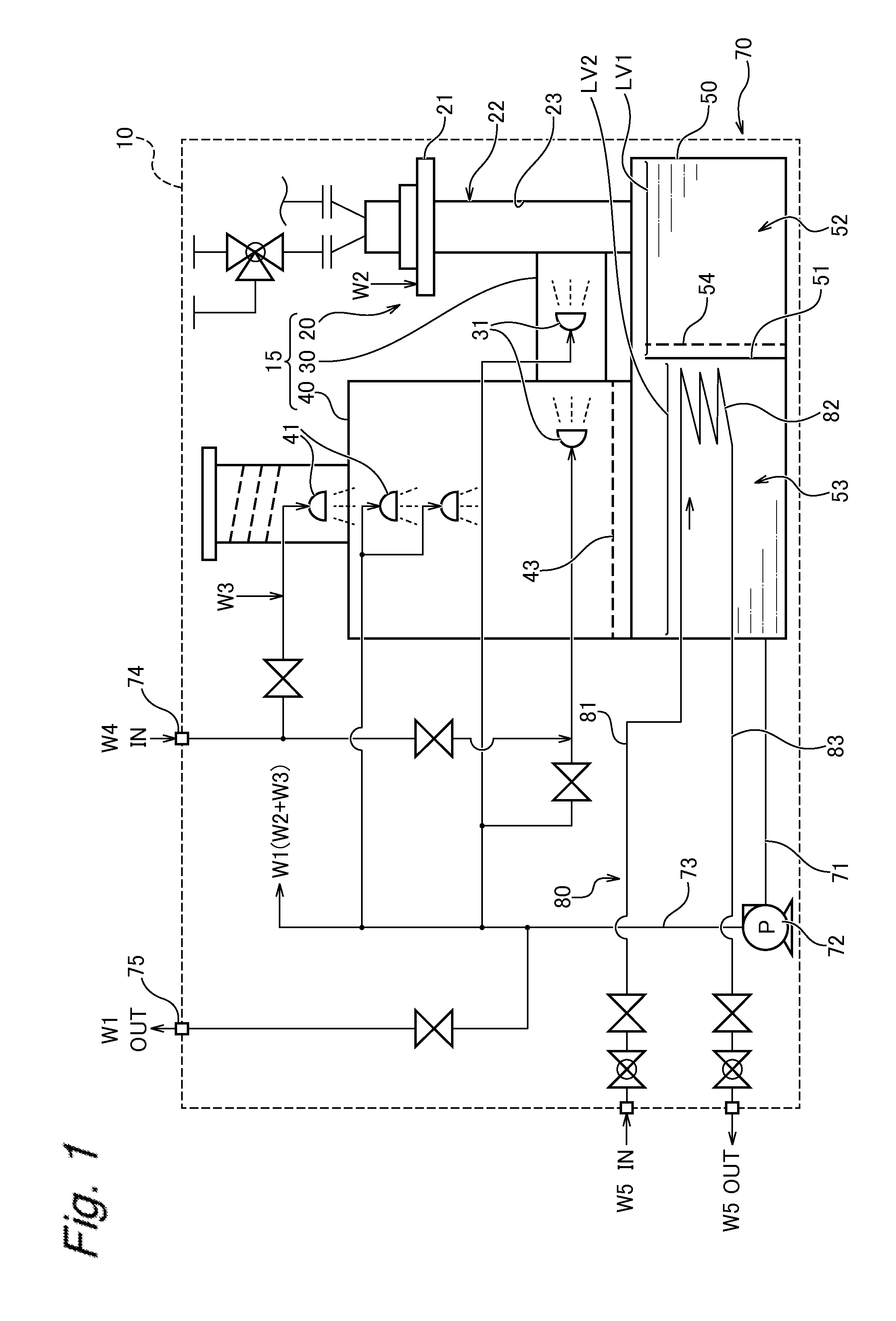
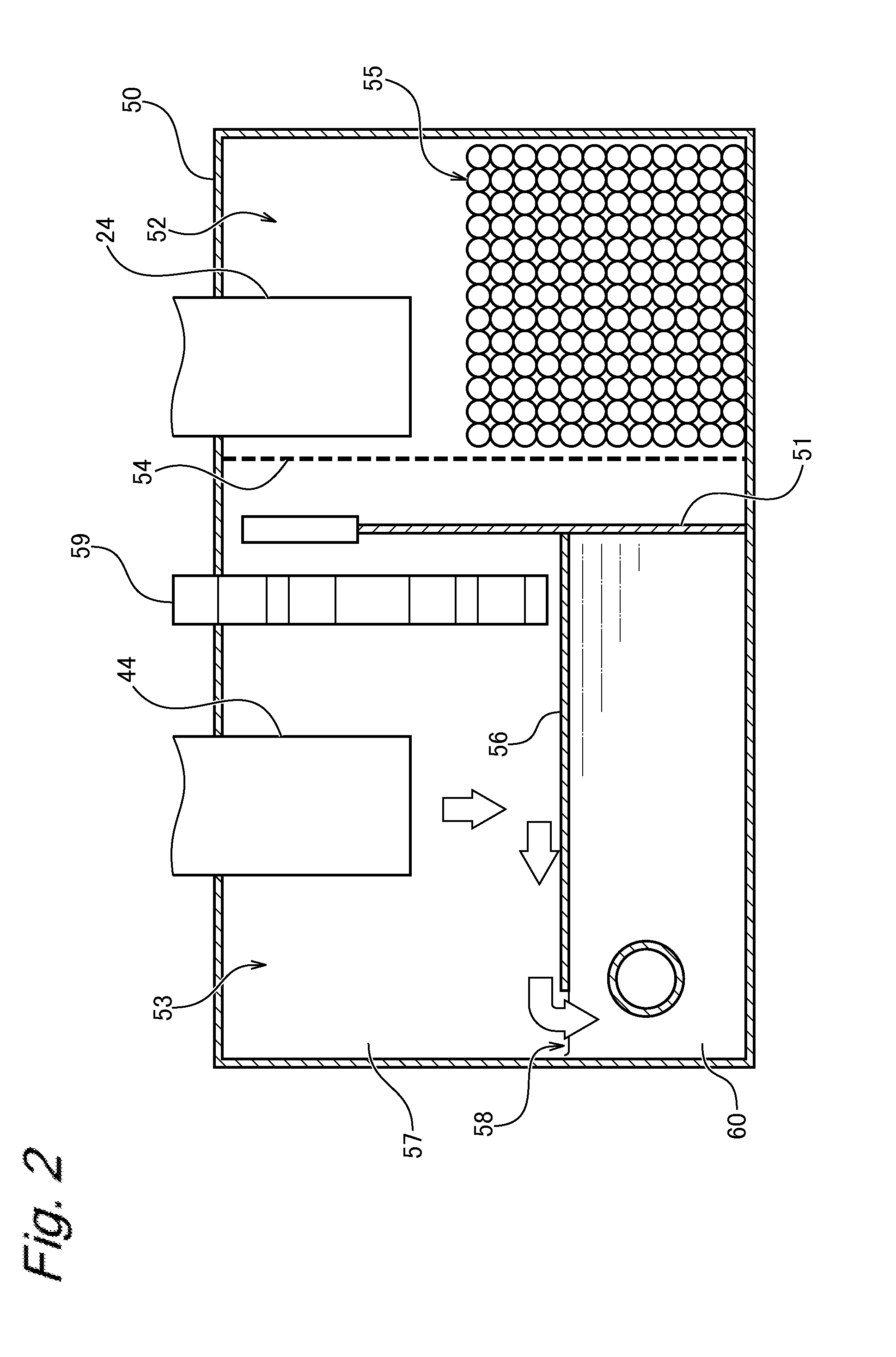
ActiveUS7905990B2Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingSolid waste disposalLiquid productHeat carrier
A rapid thermal conversion process for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. Biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. The liquid product may itself be used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
Rapid thermal conversion of biomass
ActiveUS20090139851A1Improved rapid thermal conversion processEffective recoveryThermal non-catalytic crackingCoke quenchingLiquid productHeat carrier
The present invent provides improved rapid thermal conversion processes for efficiently converting wood, other biomass materials, and other carbonaceous feedstock (including hydrocarbons) into high yields of valuable liquid product, e.g., bio-oil, on a large scale production. In an embodiment, biomass material, e.g., wood, is feed to a conversion system where the biomass material is mixed with an upward stream of hot heat carriers, e.g., sand, that thermally convert the biomass into a hot vapor stream. The hot vapor stream is rapidly quenched with quench media in one or more condensing chambers located downstream of the conversion system. The rapid quenching condenses the vapor stream into liquid product, which is collected from the condensing chambers as a valuable liquid product. In one embodiment, the liquid product itself is used as the quench media.
Owner:ENSYN RENEWABLES
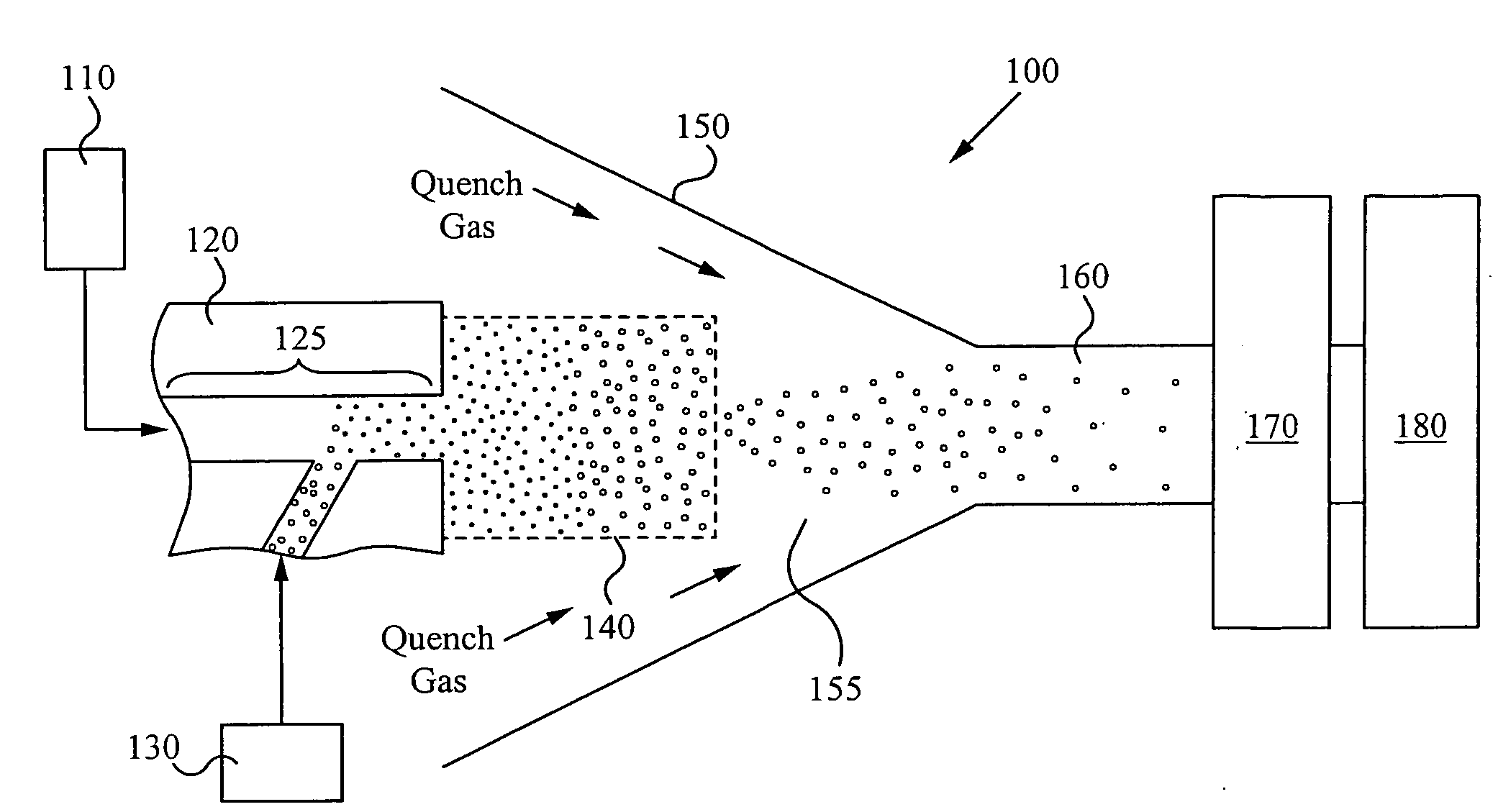
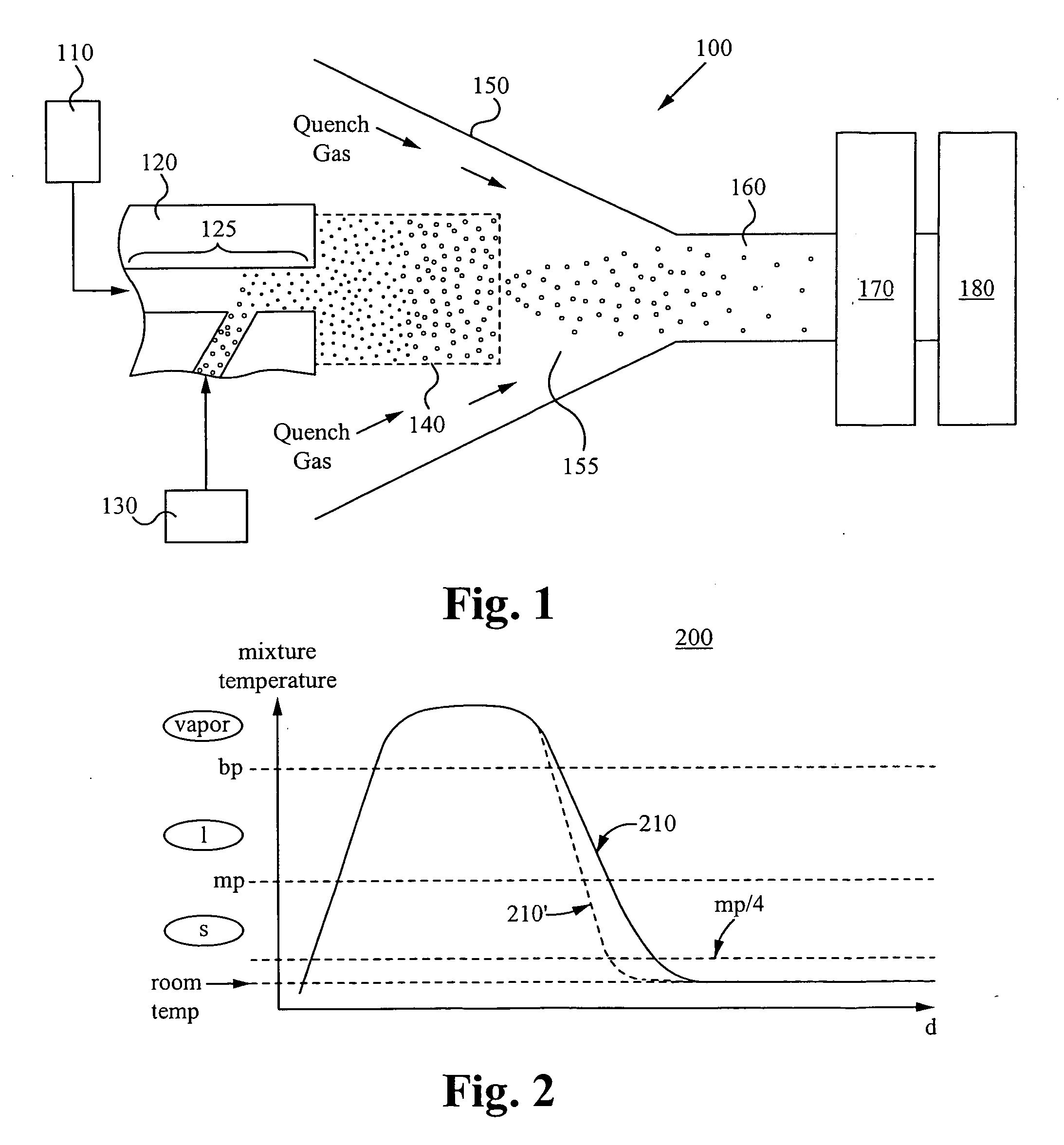
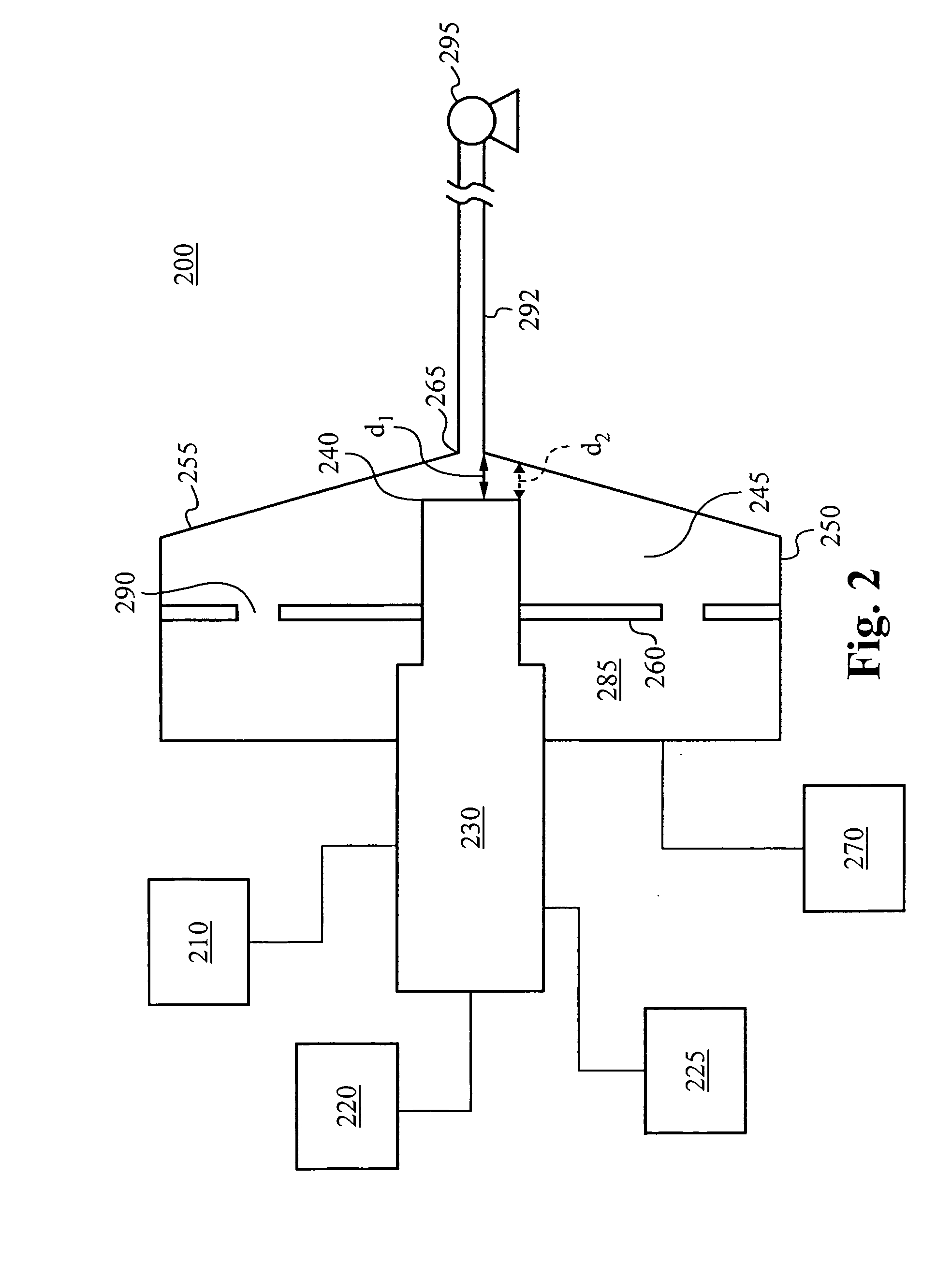
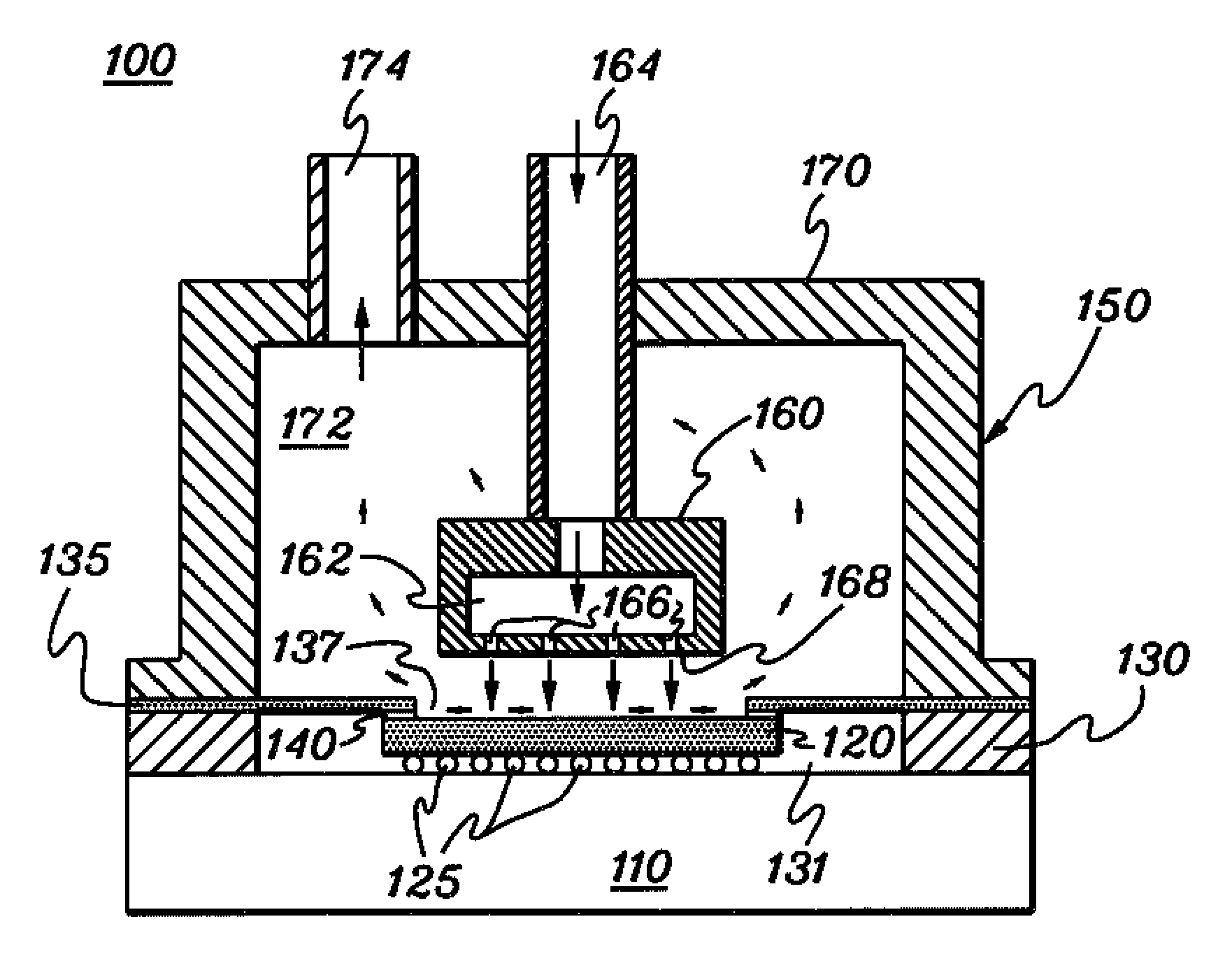
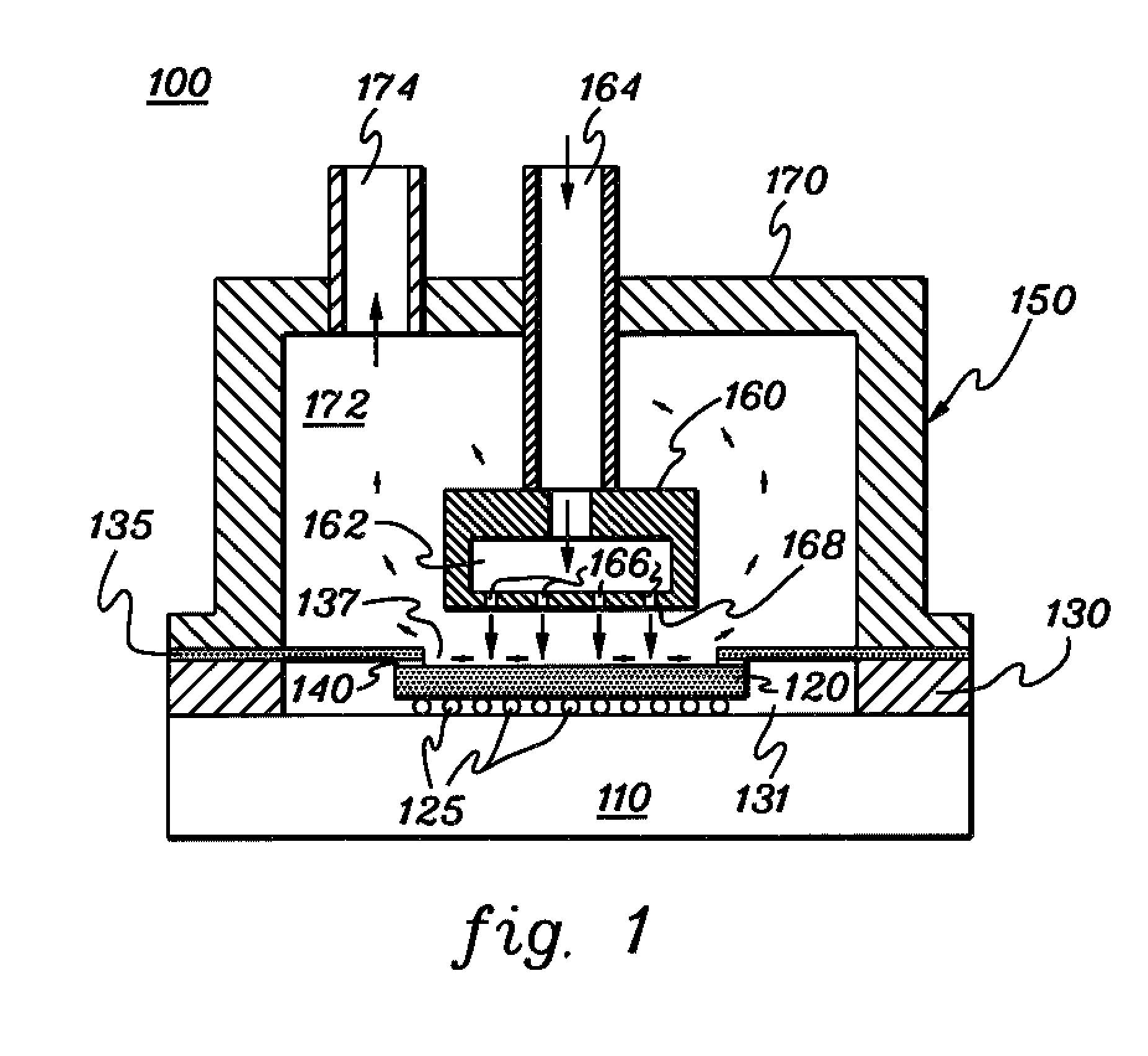
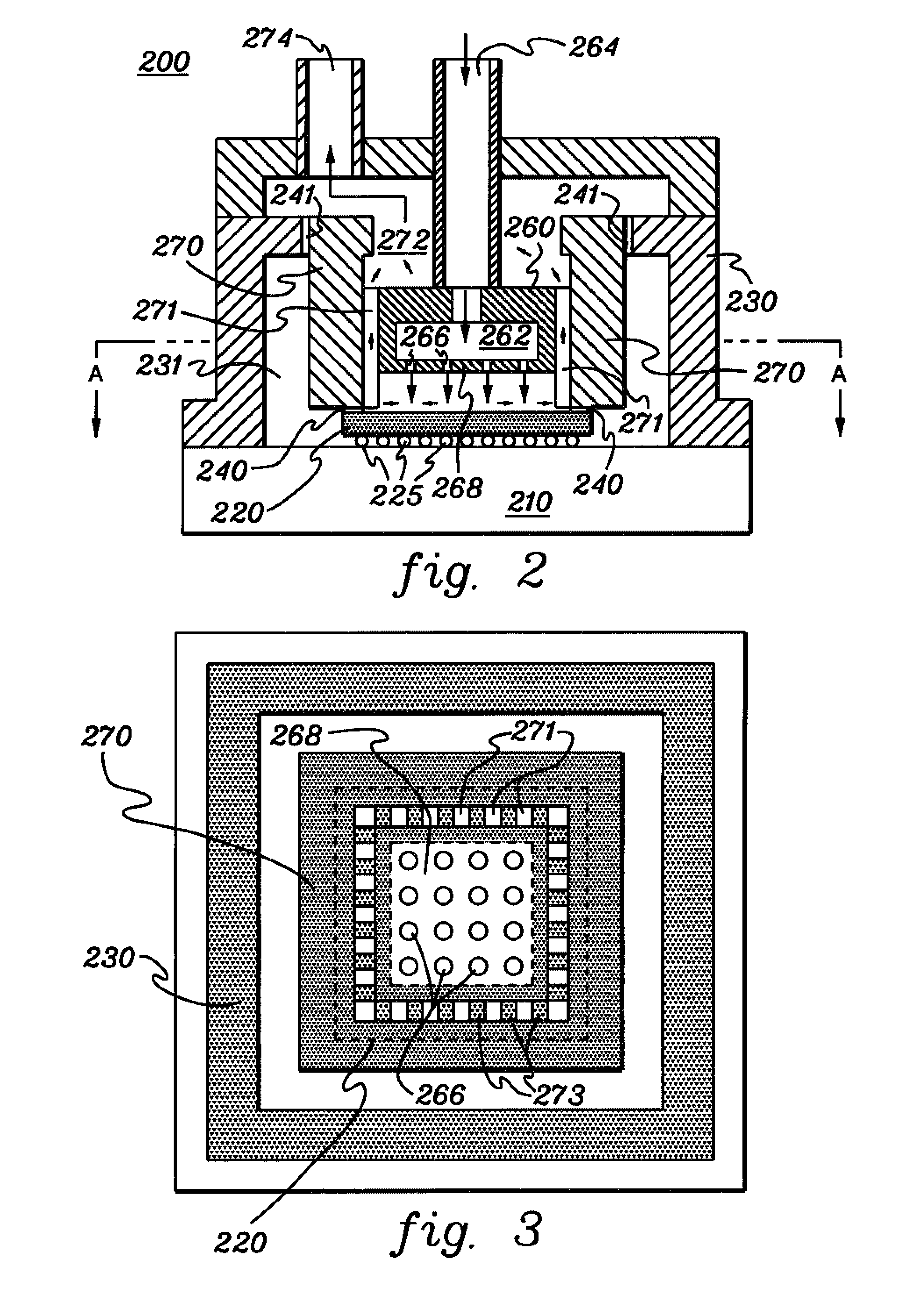
Method and apparatus for making uniform and ultrasmall nanoparticles
ActiveUS20080277270A1Catalyst activation/preparationDirect contact heat exchangersNanoparticleEngineering
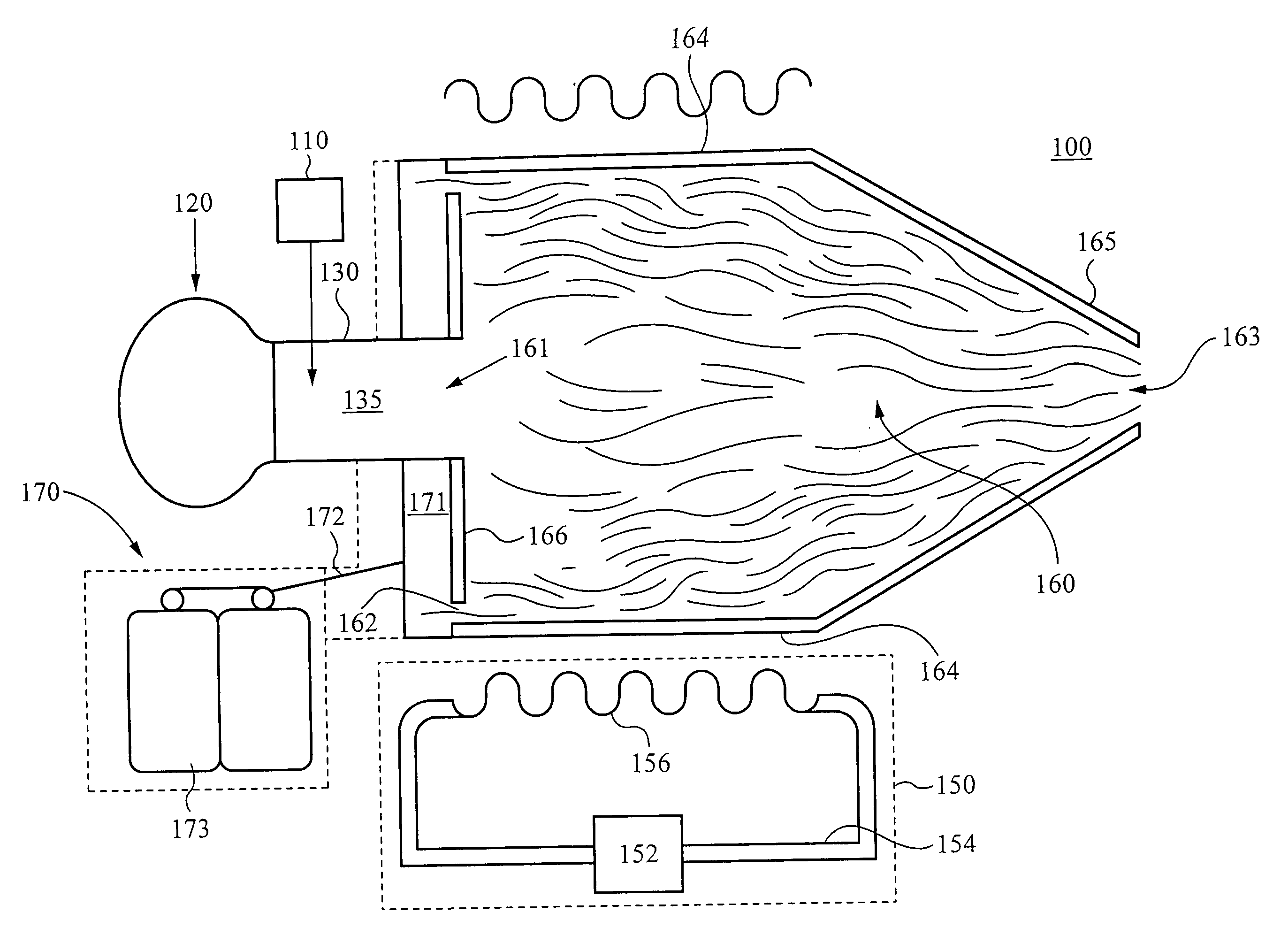
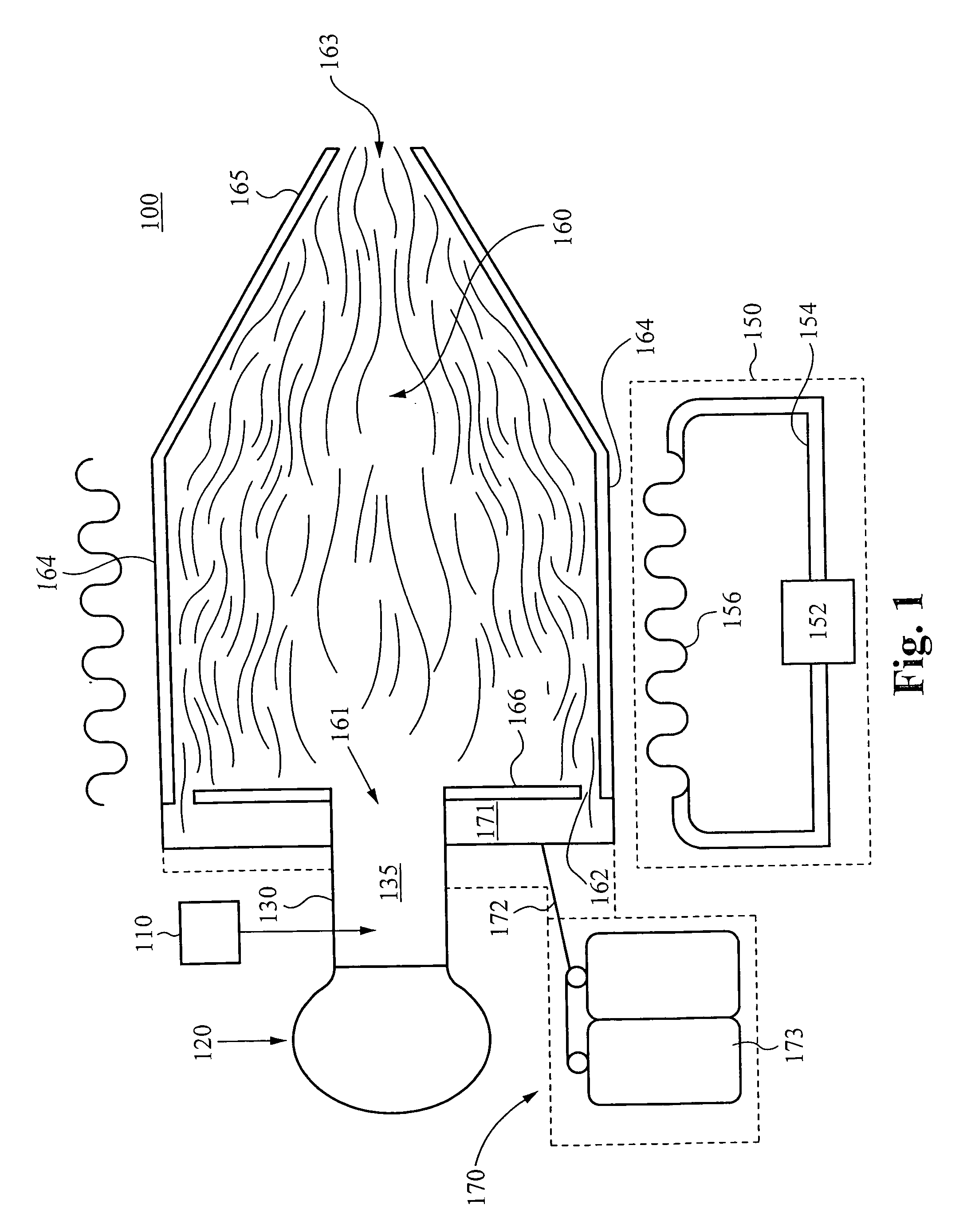
A system comprising: a plasma production chamber configured to produce a plasma; a reaction chamber vaporize a precursor material with the plasma to form a reactive mixture; a quench chamber having a frusto-conical surface and a quench region formed within the quench chamber between an ejection port of the reaction chamber and a cooled mixture outlet, wherein the quench region configured to receive the reactive mixture from the ejection port, to cool the reactive mixture to form a cooled mixture, and to supply the cooled mixture to the cooled mixture outlet; and a conditioning fluid injection ring disposed at the ejection port and configured to flow a conditioning fluid directly into the reactive mixture as the reactive mixture flows through the ejection port, thereby disturbing the flow of the reactive mixture, creating turbulence within the quench region and cooling the reactive mixture to form a cooled mixture comprising condensed nanoparticles.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS +1
Highly turbulent quench chamber
ActiveUS20080277267A1Temperature controlDirect contact heat exchangersStationary tubular conduit assembliesEngineeringQuenching
An apparatus for cooling a reactive mixture, comprising: a reactor configured to form the reactive mixture; a quench chamber comprising a frusto-conical body having a wide end, a narrow end, and a quench region formed between the wide and narrow end, wherein the quench chamber is configured to receive the reactive mixture from the plasma reactor through a reactive mixture inlet into the quench region, to receive a conditioning fluid through at least one fluid inlet, and to flow the conditioning fluid into the quench region, wherein the frusto-conical body is configured to produce a turbulent flow within the quench region with the flow of the conditioning fluid into the quench region, thereby promoting the quenching of the reactive mixture to form a cooled gas-particle mixture; and a suction generator configured to force the cooled gas-particle mixture out of the quench chamber.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Gas delivery system with constant overpressure relative to ambient to system with varying vacuum suction
ActiveUS20110006463A1Reduce pressureMinimizes pressure differentialCatalyst activation/preparationDirect contact heat exchangersSuction forceComputer module
A system operating in an environment having an ambient pressure, the system comprising: a reactor configured to combine a plasma stream, powder particles and conditioning fluid to alter the powder particles and form a mixture stream; a supply chamber coupled to the reactor; a suction generator configured to generate a suction force at the outlet of the reactor; a fluid supply module configured to supply the conditioning fluid at an original pressure; and a pressure regulation module configured to: receive the conditioning fluid from the fluid supply module, reduce the pressure of the conditioning fluid from the original pressure to a selected pressure relative to the ambient pressure regardless of any changes in the suction force at the outlet of the reactor, and supply the conditioning fluid at the selected pressure to the supply chamber.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
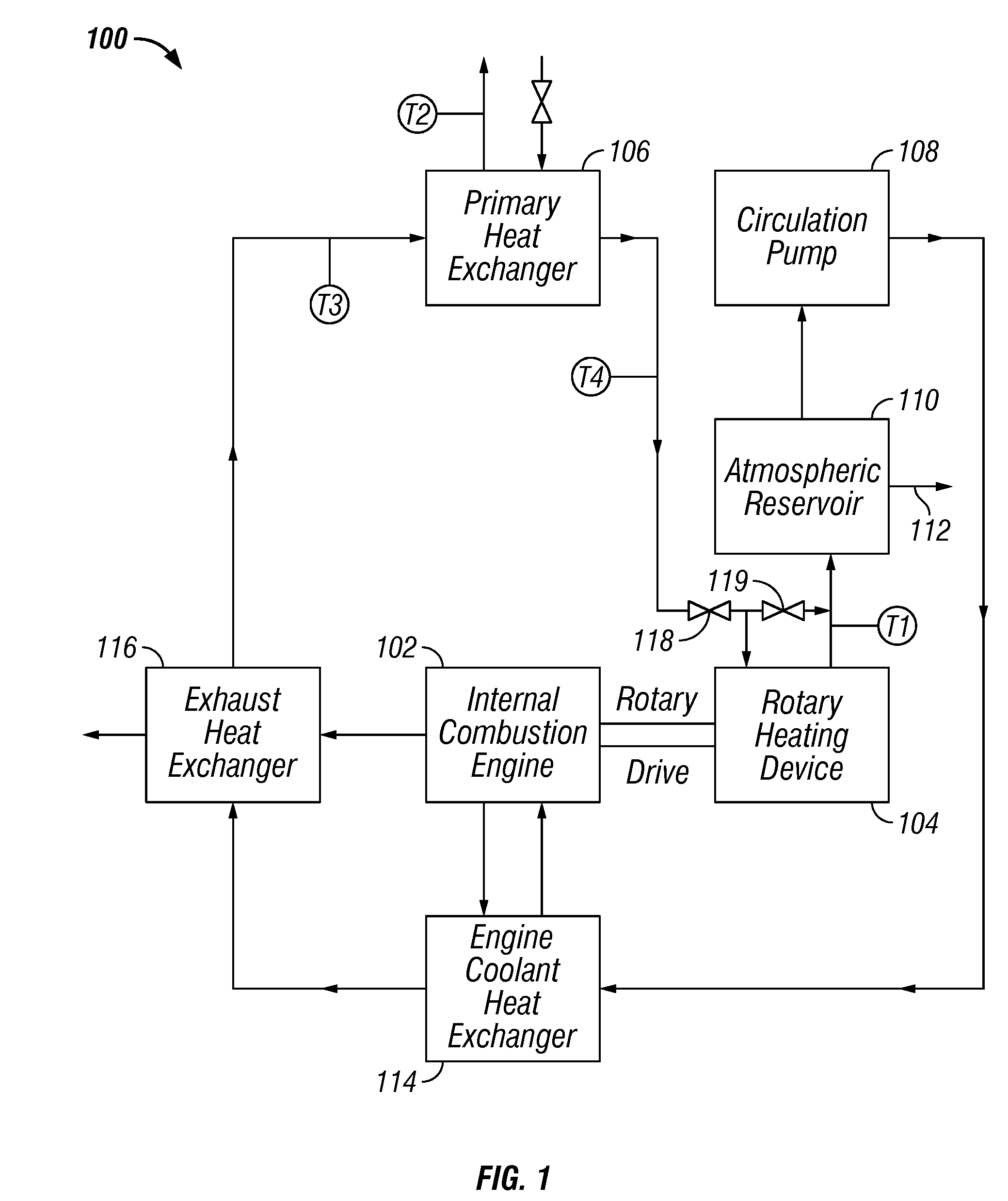
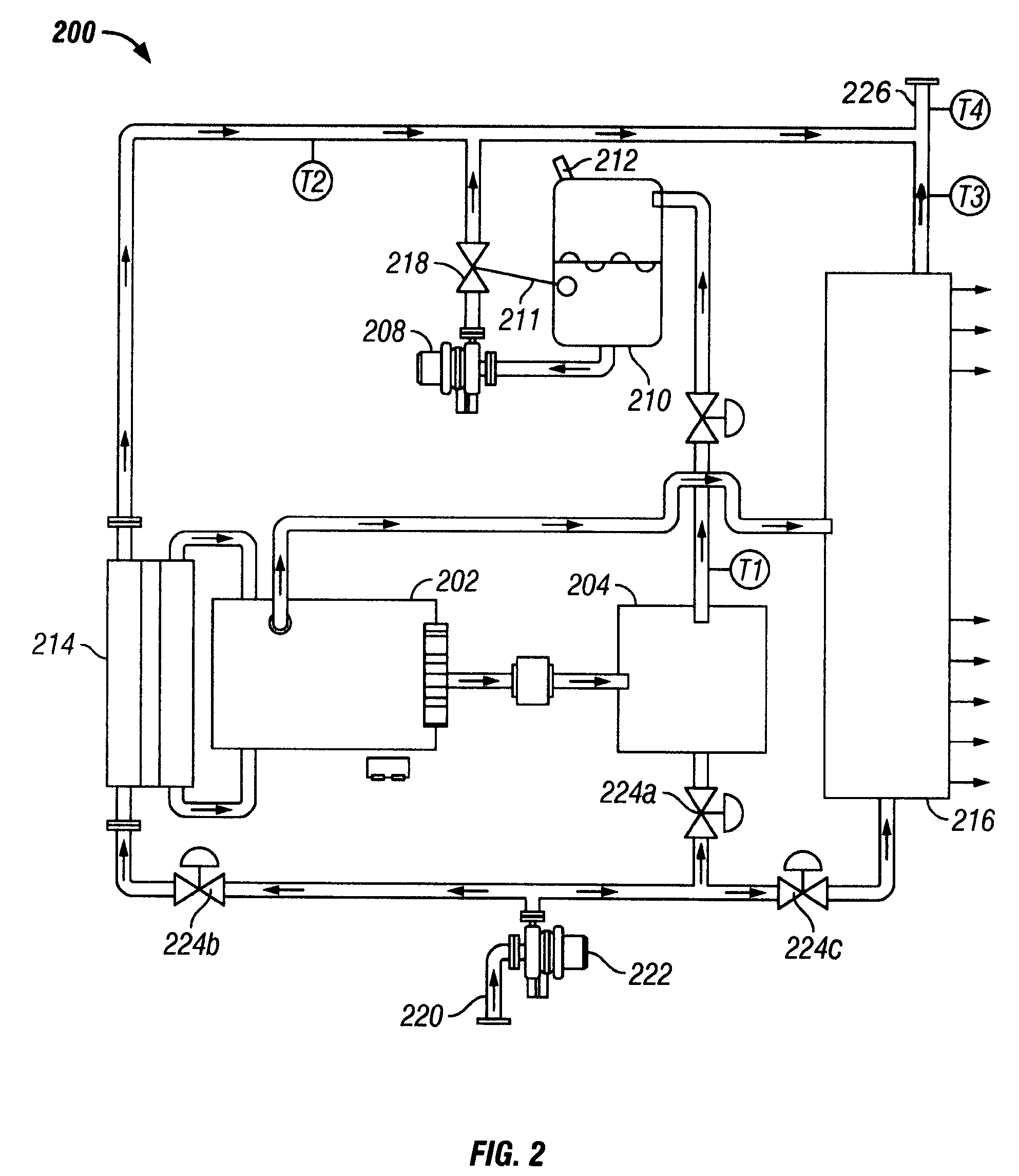
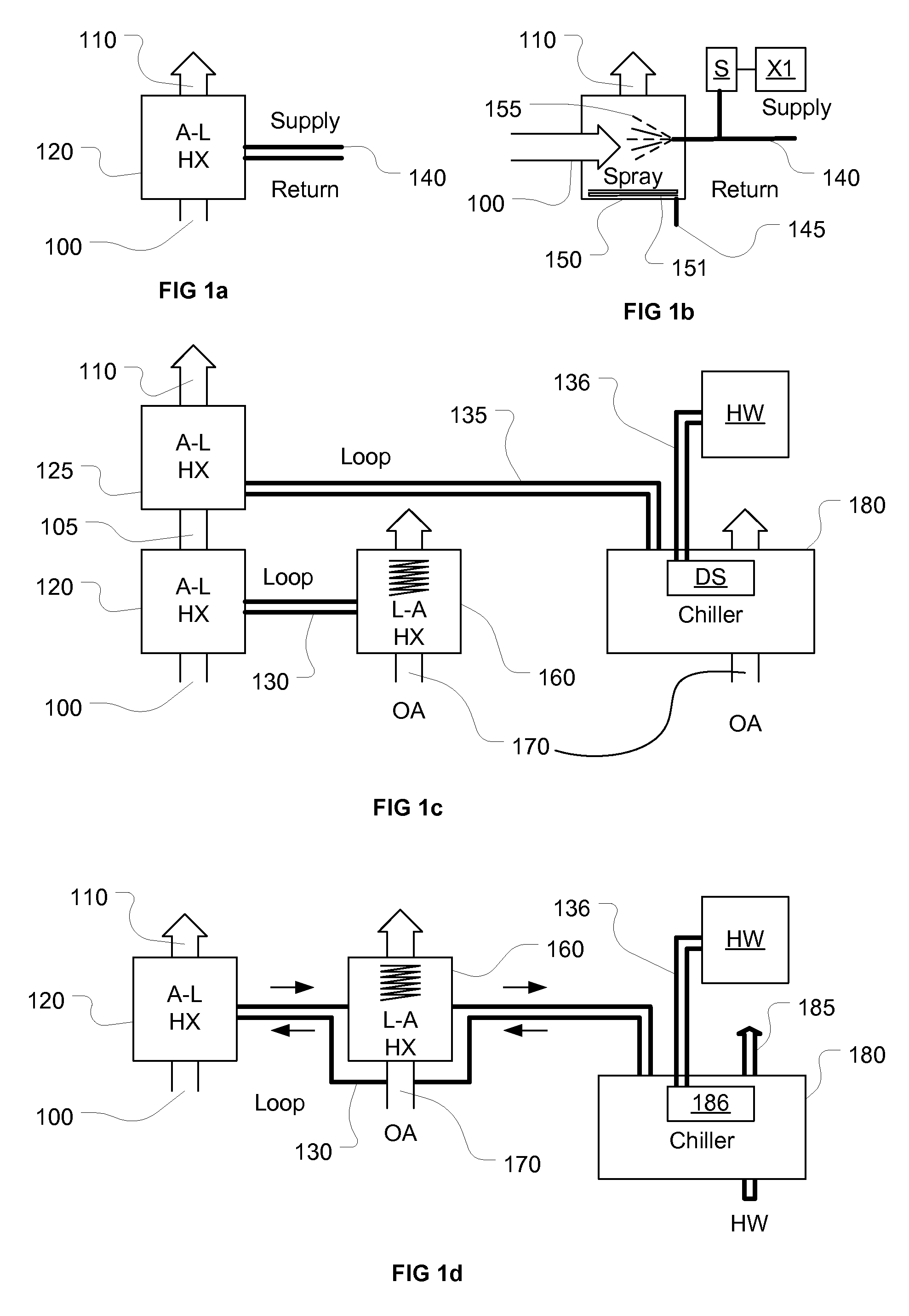
Method and apparatus for heating, concentrating and evaporating fluid
InactiveUS7614367B1Steam generation using mechanical energyAir-treating devicesWater brakeEvaporation
A system and method are provided for heating, concentrating and / or evaporating a fluid by heating the fluid in a heating subsystem comprising a rotary heating device, such as a water brake dynamometer, and then evaporating all or a portion of the fluid in an evaporation subsystem and / or concentrating the fluid in a concentration subsystem.
Owner:PHOENIX CALIENTE INC
Fluid recirculation system for use in vapor phase particle production system
ActiveUS20080277268A1Reduce pressureDispersed particle filtrationDirect contact heat exchangersTemperature controlProduct gas
A method of and system for recirculating a fluid in a particle production system. A reactor produces a reactive particle-gas mixture. A quench chamber mixes a conditioning fluid with the reactive particle-gas mixture, producing a cooled particle-gas mixture that comprises a plurality of precursor material particles and an output fluid. A filter element filters the output fluid, producing a filtered output. A temperature control module controls the temperature of the filtered output, producing a temperature-controlled, filtered output. A content ratio control module modulates the content of the temperature-controlled, filtered output, thereby producing a content-controlled, temperature-controlled, filtered output. A channeling element supplies the content-controlled, temperature-controlled, filtered output to the quench chamber, wherein the content-controlled, filtered output is provided to the quench chamber as the conditioning fluid to be used in cooling the reactive particle-gas mixture.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS +1
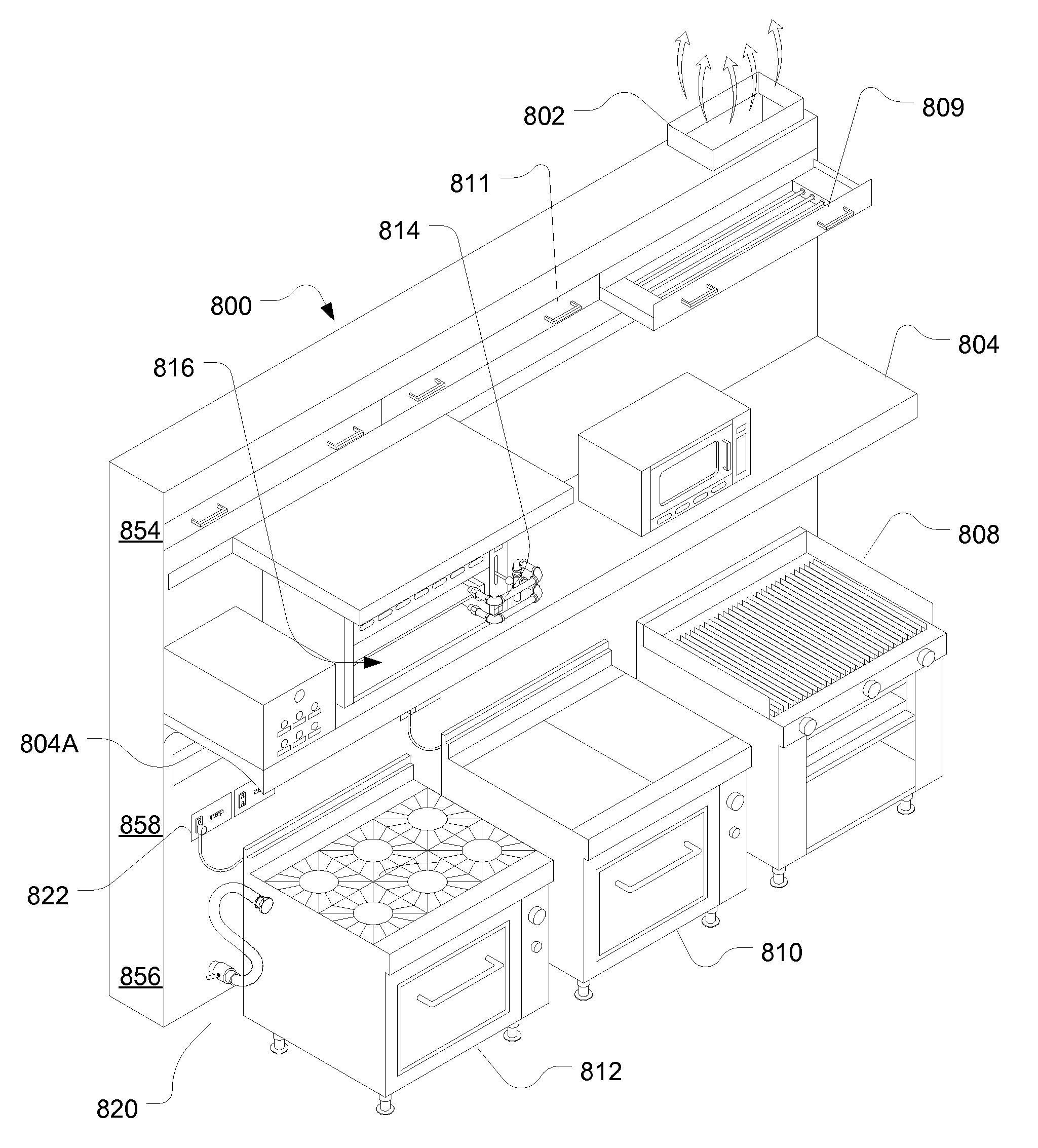
Recirculating exhaust system
ActiveUS20090264060A1Reduce net energy lossDomestic stoves or rangesRecuperative heat exchangersModularityEngineering
Systems, devices and methods provide energy recover, modular systems to build and revise commercial kitchen services, closed circuit exhaust, and high efficiency capture and containment of fumes from cooking processes.
Owner:HALTON GROUP LTD
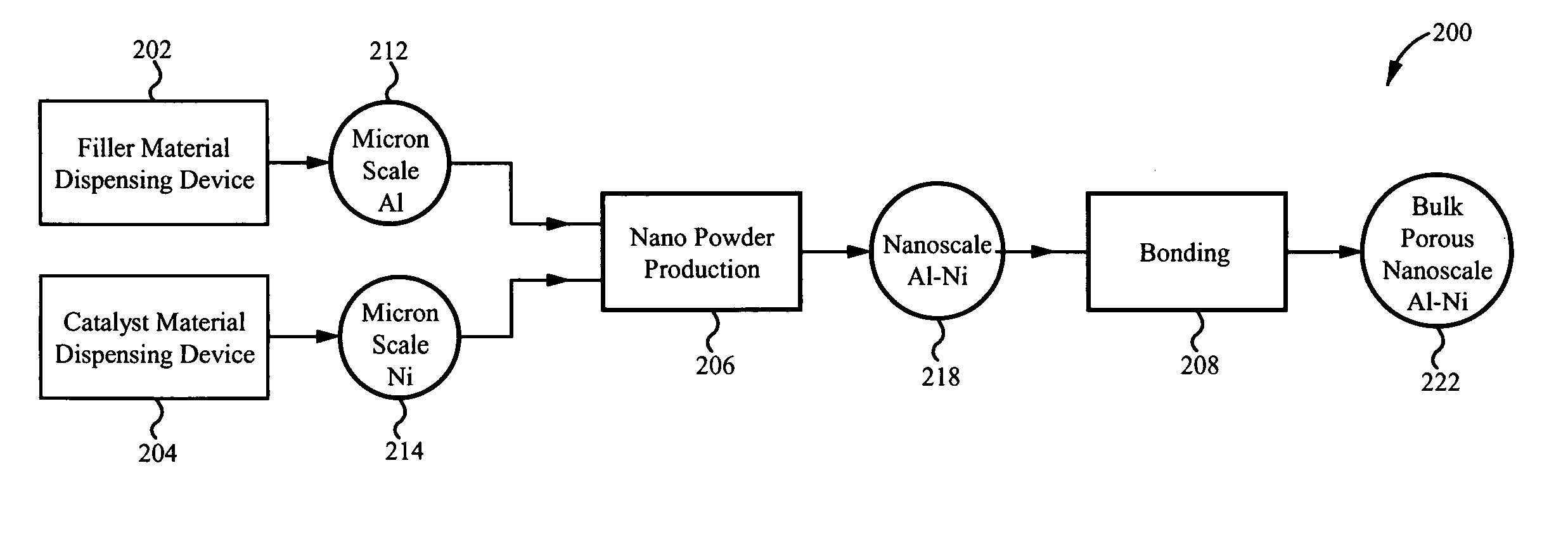
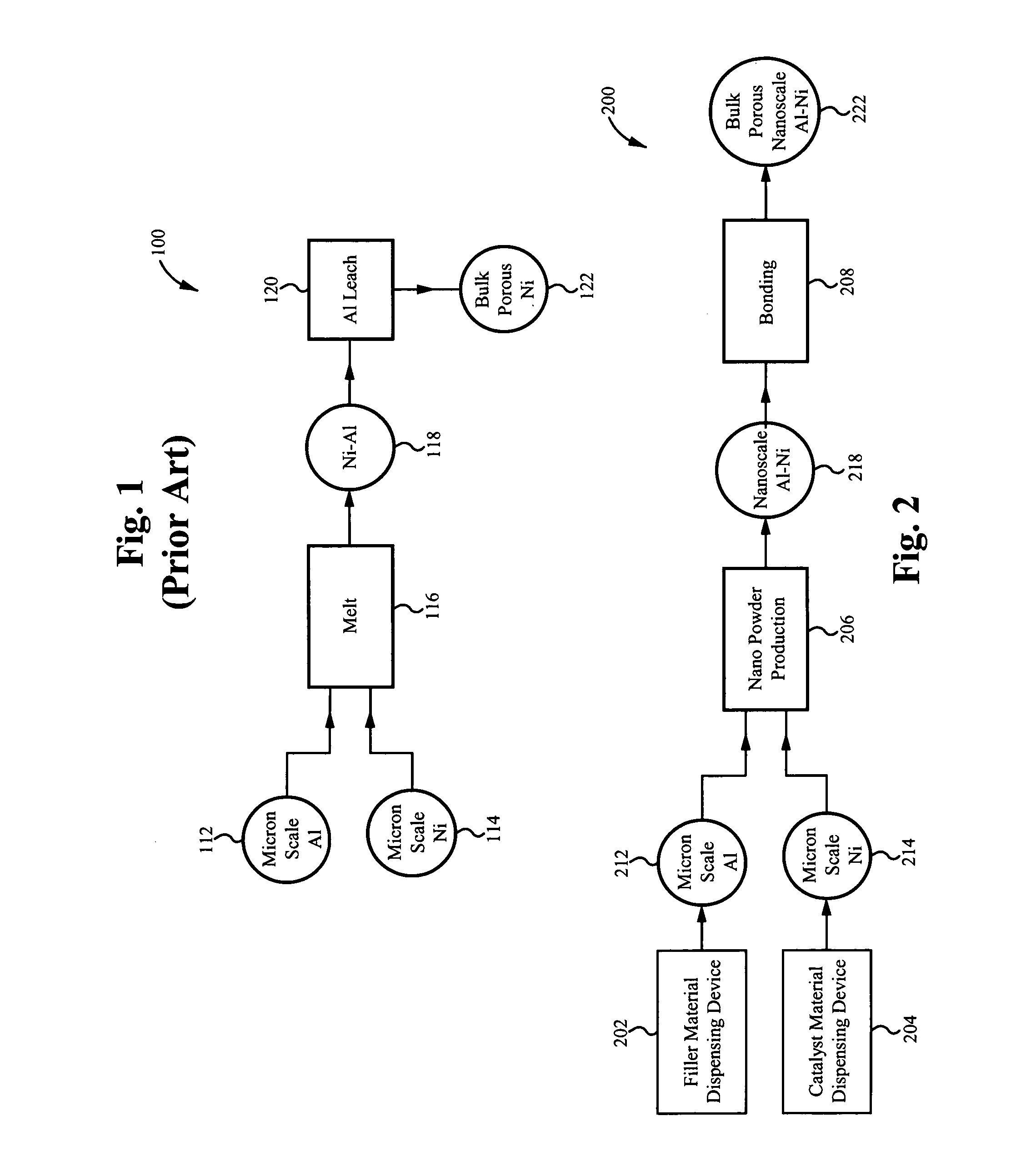
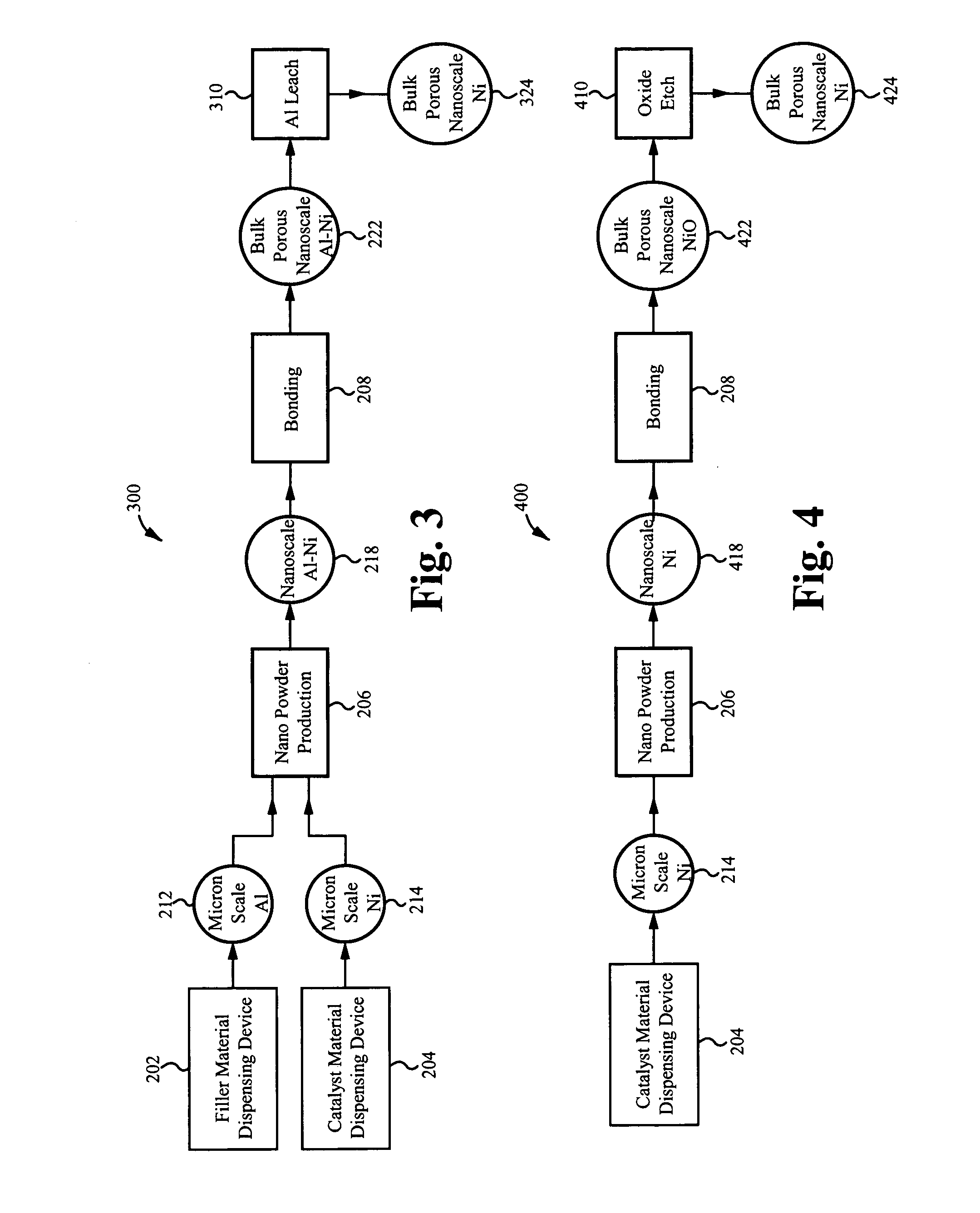
Nano-skeletal catalyst
ActiveUS20080280756A1Increase surface areaMassive costMechanical working/deformationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer scienceScale structure
A method of producing a catalyst material with nano-scale structure, the method comprising: introducing a starting powder into a nano-powder production reactor, the starting powder comprising a catalyst material; the nano-powder production reactor nano-sizing the starting powder, thereby producing a nano-powder from the starting powder, the nano-powder comprising a plurality of nano-particles, each nano-particle comprising the catalyst material; and forming a catalyst precursor material from the nano-powder, wherein the catalyst precursor material is a densified bulk porous structure comprising the catalyst material, the catalyst material having a nano-scale structure.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS +1
Oxygen transport membrane system and method for transferring heat to catalytic/process reactors
A method and apparatus for producing heat used in a synthesis gas production process is provided. The disclosed method and apparatus include a plurality of tubular oxygen transport membrane elements adapted to separate oxygen from an oxygen containing stream contacting the retentate side of the membrane elements. The permeated oxygen is combusted with a hydrogen containing synthesis gas stream contacting the permeate side of the tubular oxygen transport membrane elements thereby generating a reaction product stream and radiant heat. The present method and apparatus also includes at least one catalytic reactor containing a catalyst to promote the steam reforming reaction wherein the catalytic reactor is surrounded by the plurality of tubular oxygen transport membrane elements. The view factor between the catalytic reactor and the plurality of tubular oxygen transport membrane elements radiating heat to the catalytic reactor is greater than or equal to 0.5.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
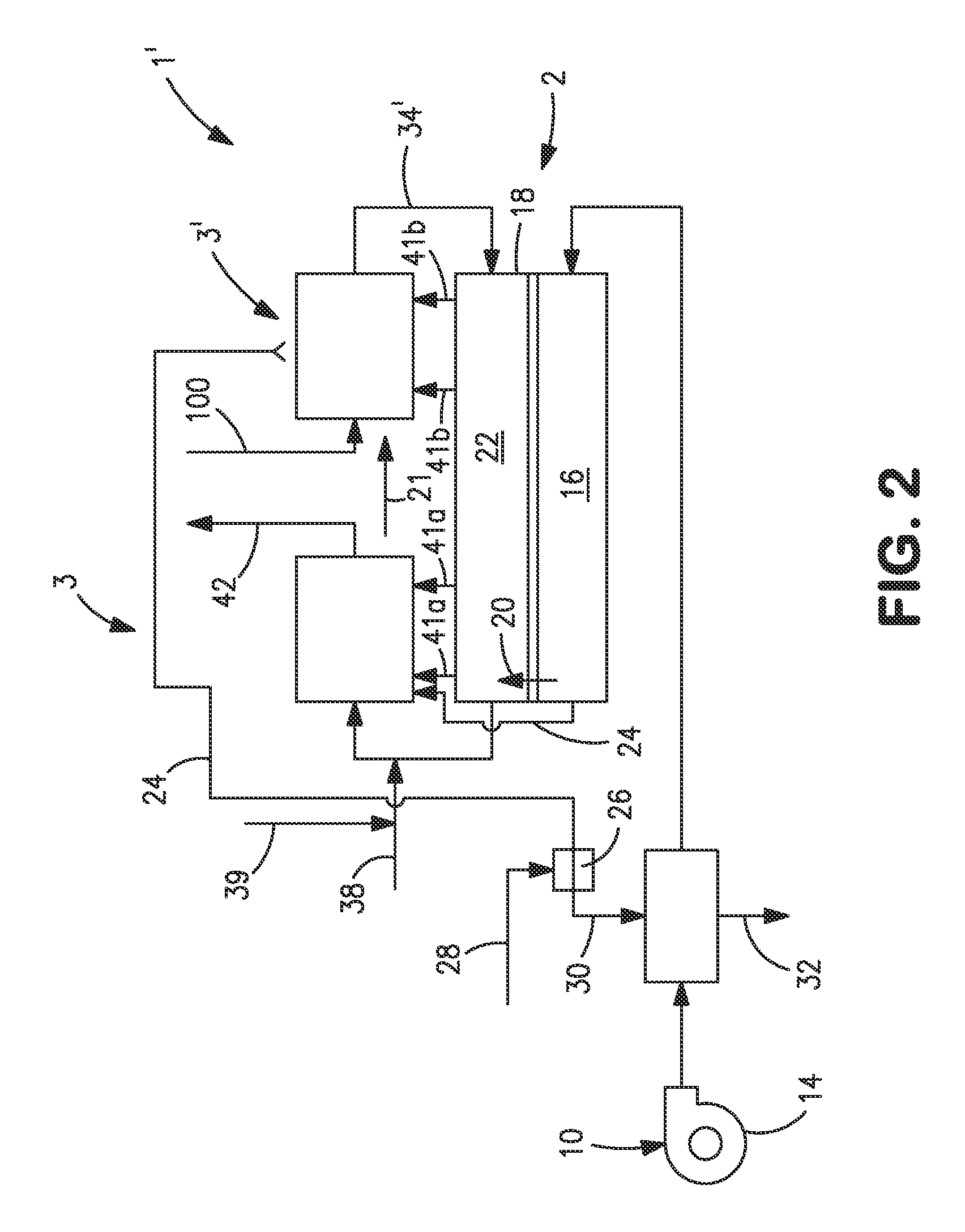
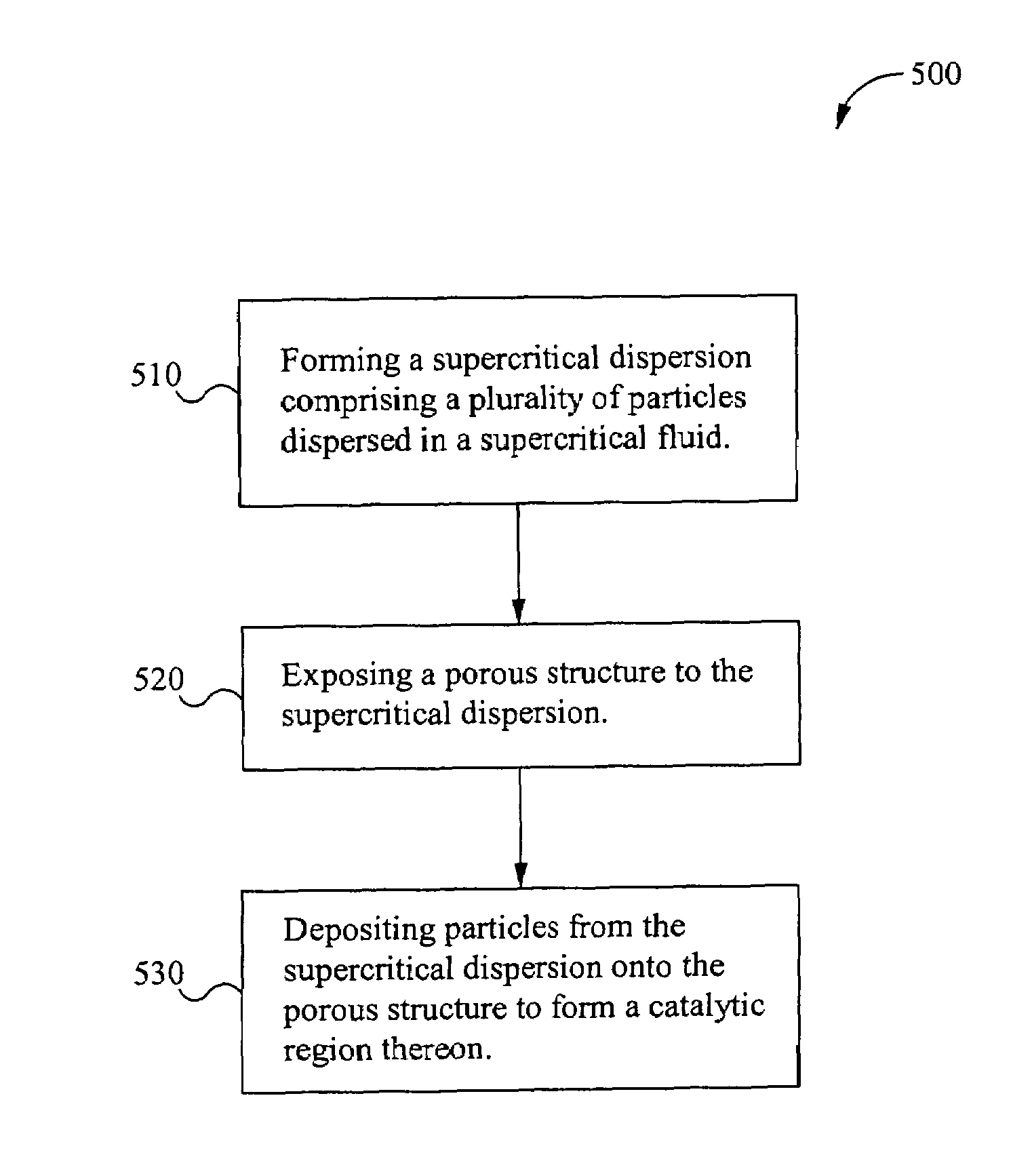
Formation of catalytic regions within porous structures using supercritical phase processing
InactiveUS7678419B2Pretreated surfacesDirect contact heat exchangersMaterials scienceSupercritical fluid
A method of forming a catalytic region on a porous structure having an exterior surface and a plurality of pores, the method comprising: forming a supercritical dispersion, wherein the supercritical dispersion comprises a plurality of particles dispersed in a supercritical fluid; exposing the porous structure to the supercritical dispersion; and depositing the plurality of particles from the supercritical dispersion onto the porous structure, wherein each one of the deposited plurality of particles is catalytic, thereby forming one or more catalytic regions on the porous structure. The method is particularly well suited for creating catalytic regions within pre-formed microporous structures.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
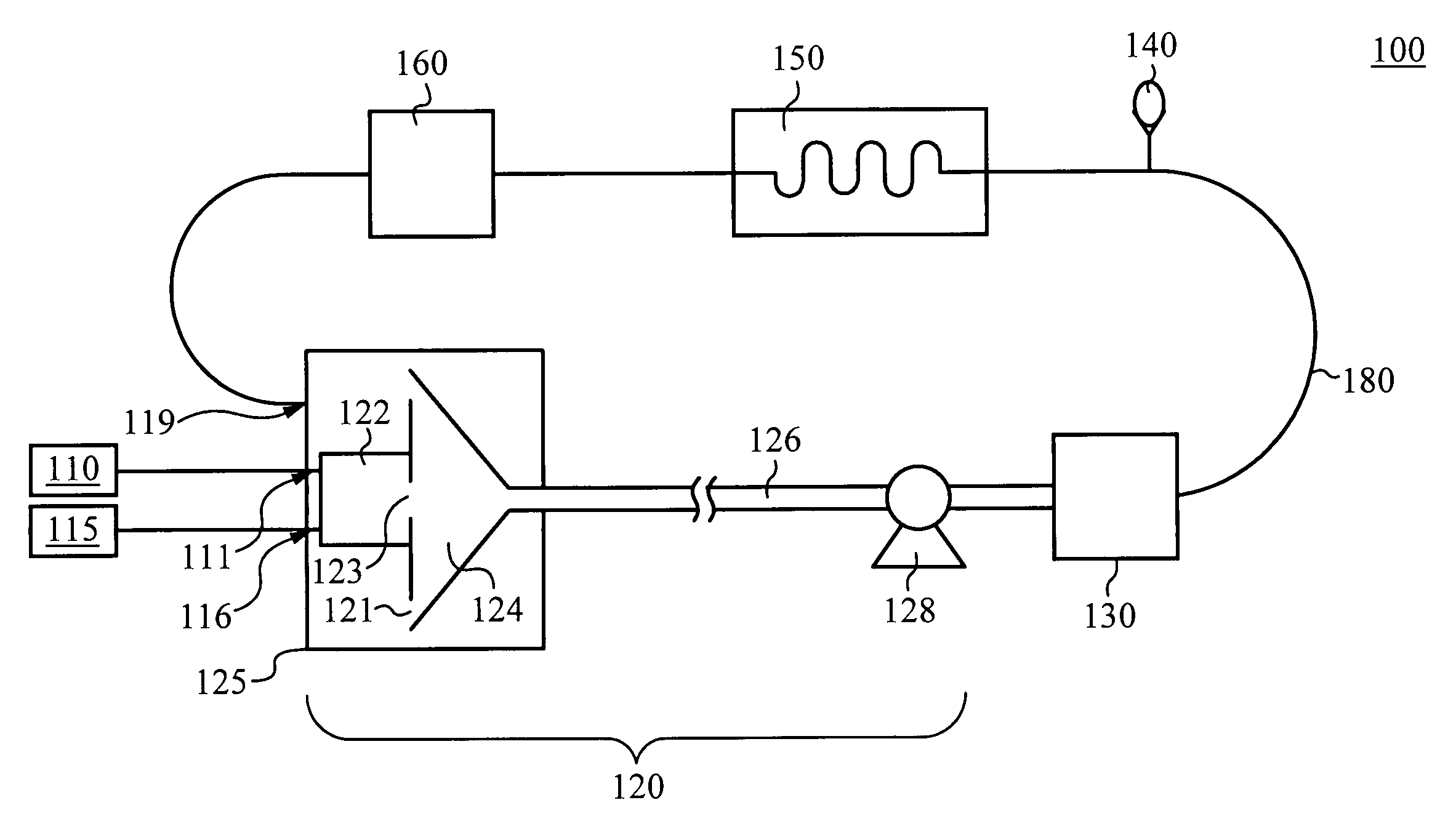
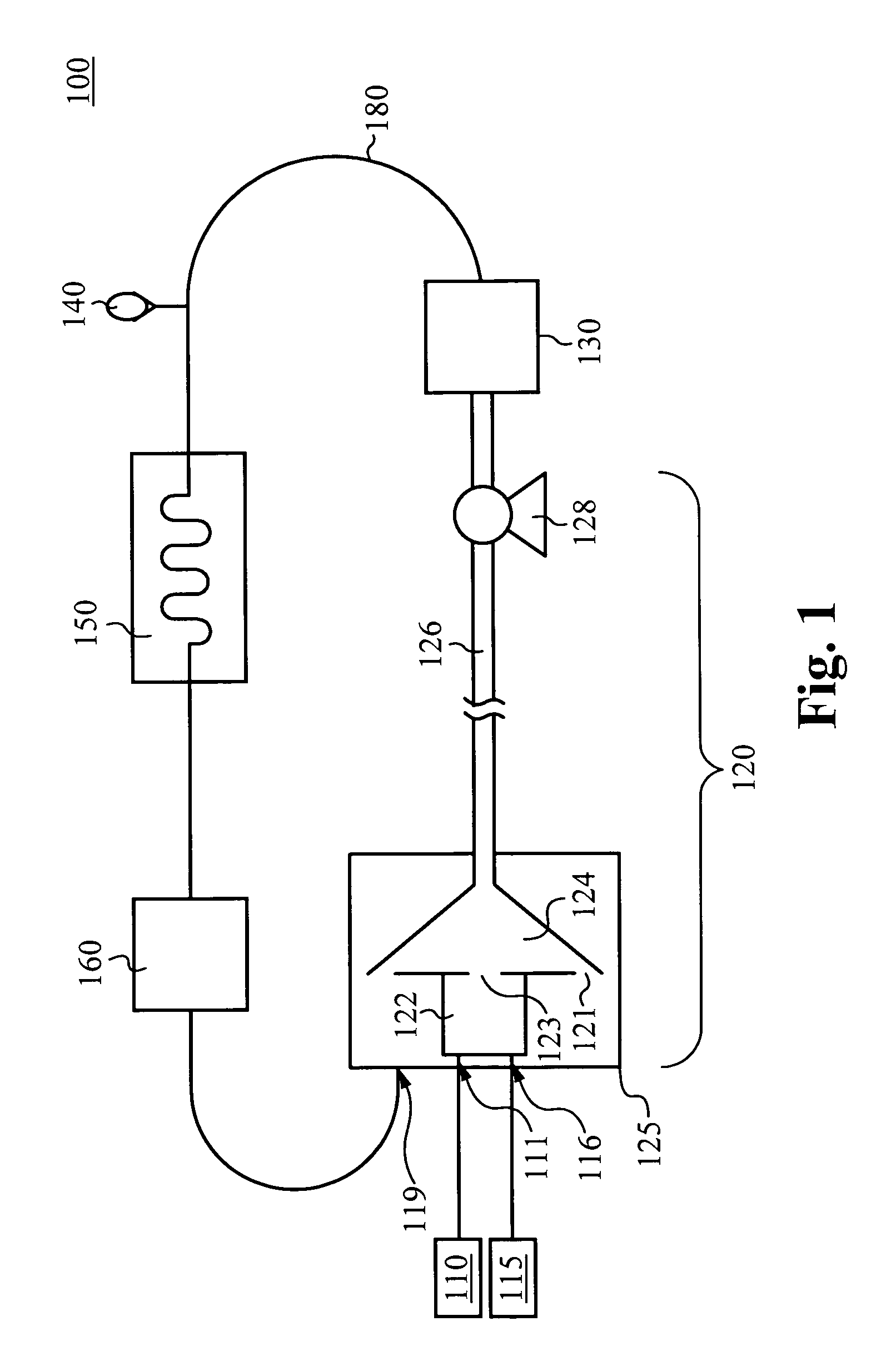
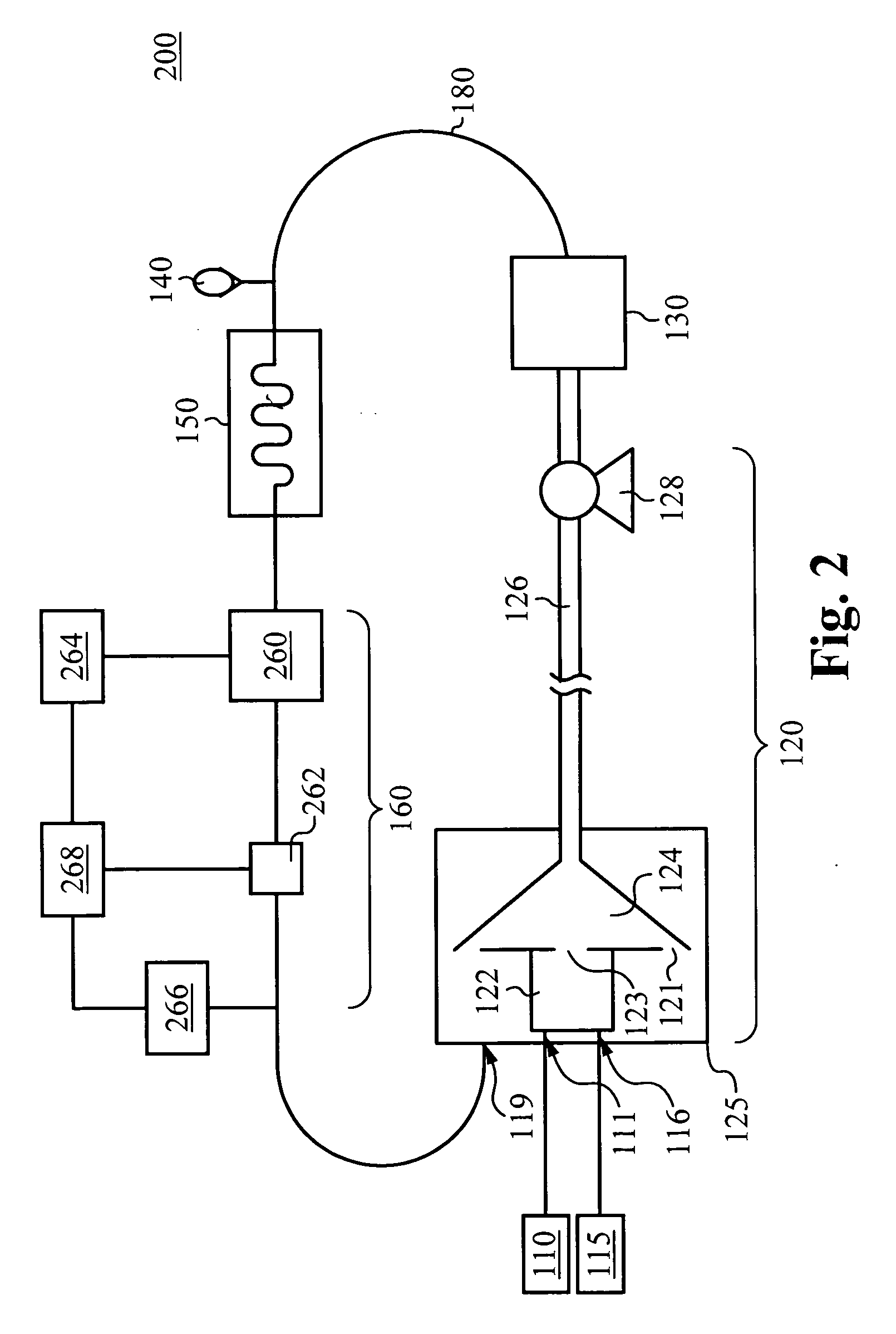
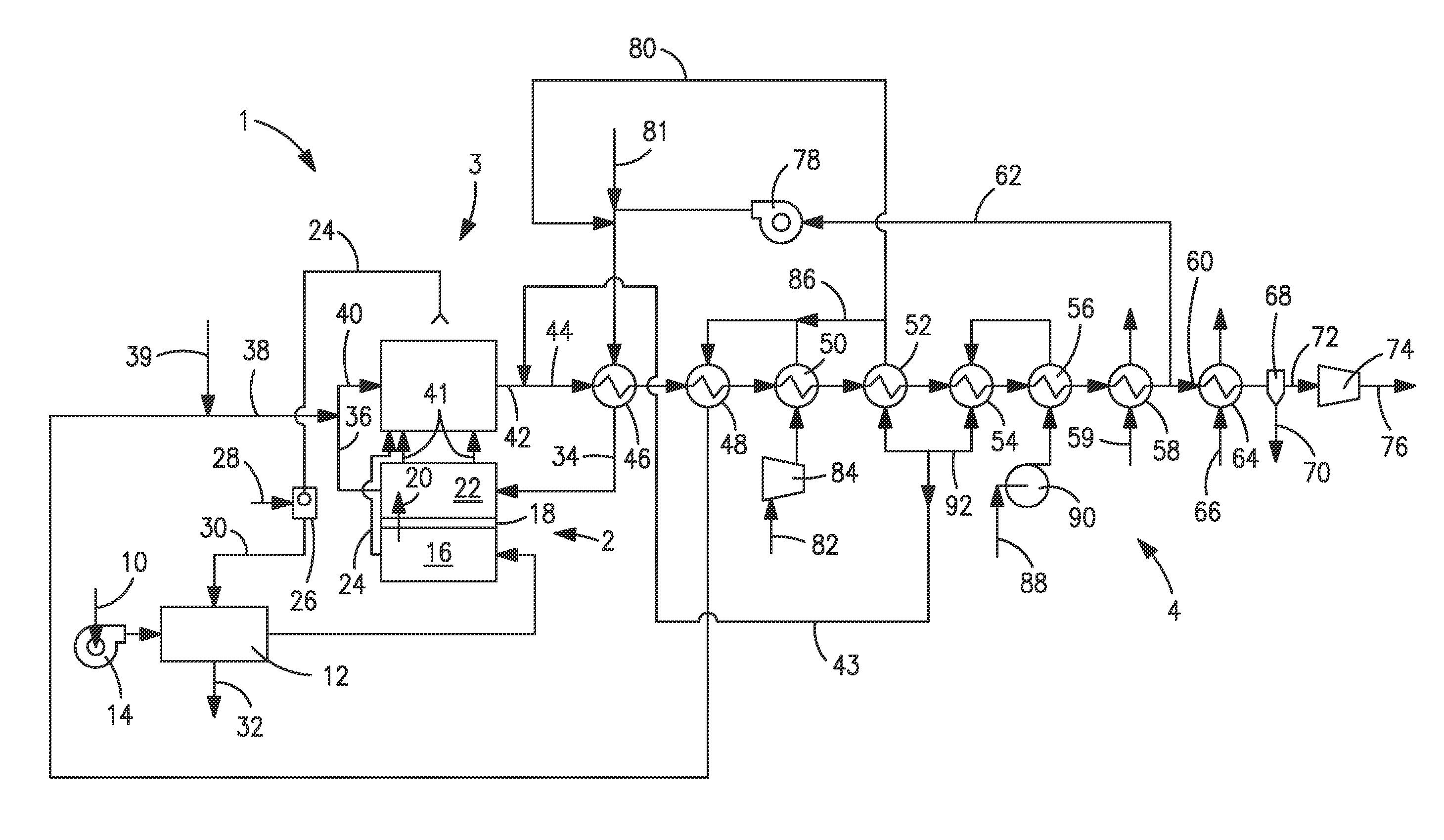
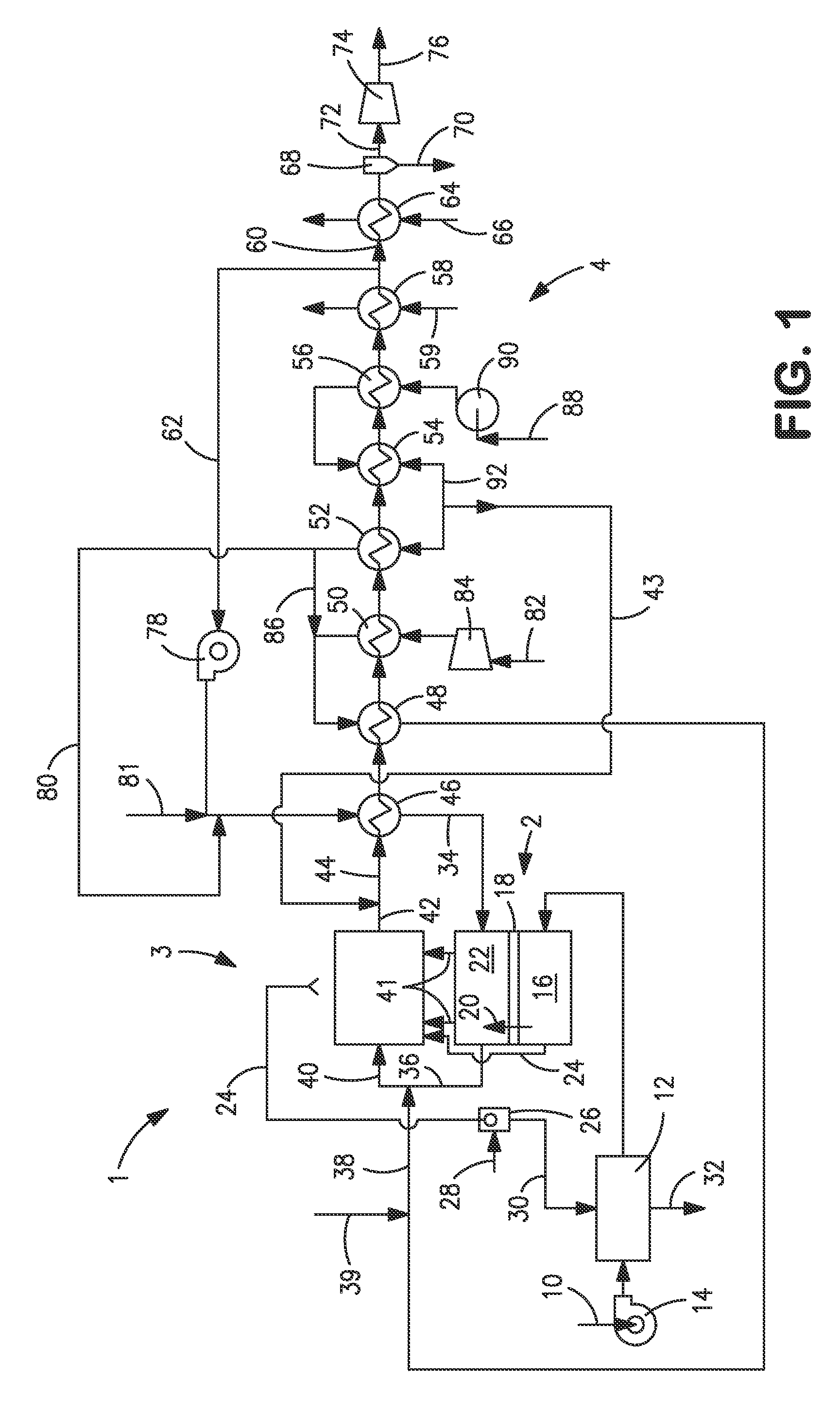
Methods and Apparatus for Power Generation
InactiveUS20080289335A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalWorking fluid for enginesDual stageWorking fluid
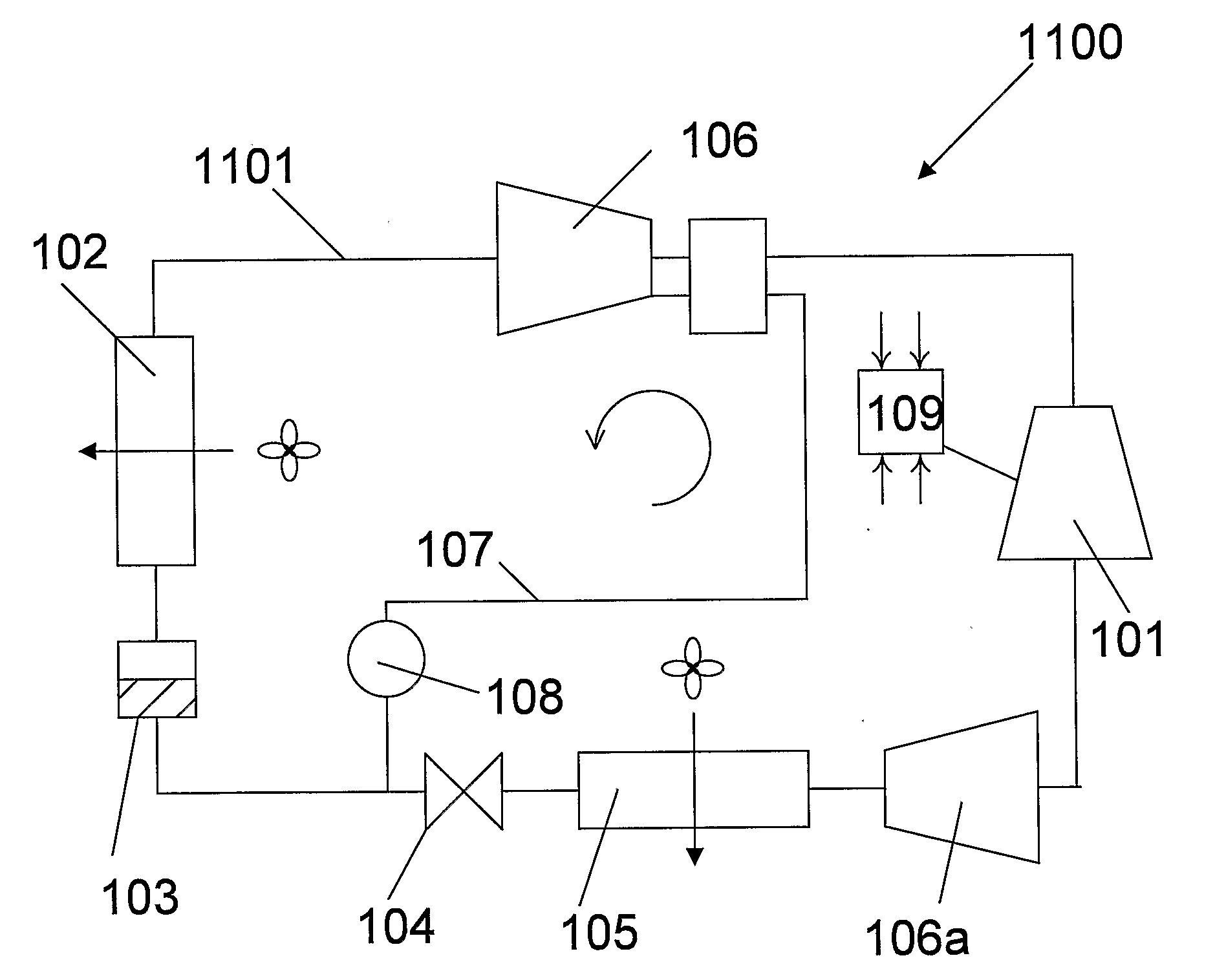
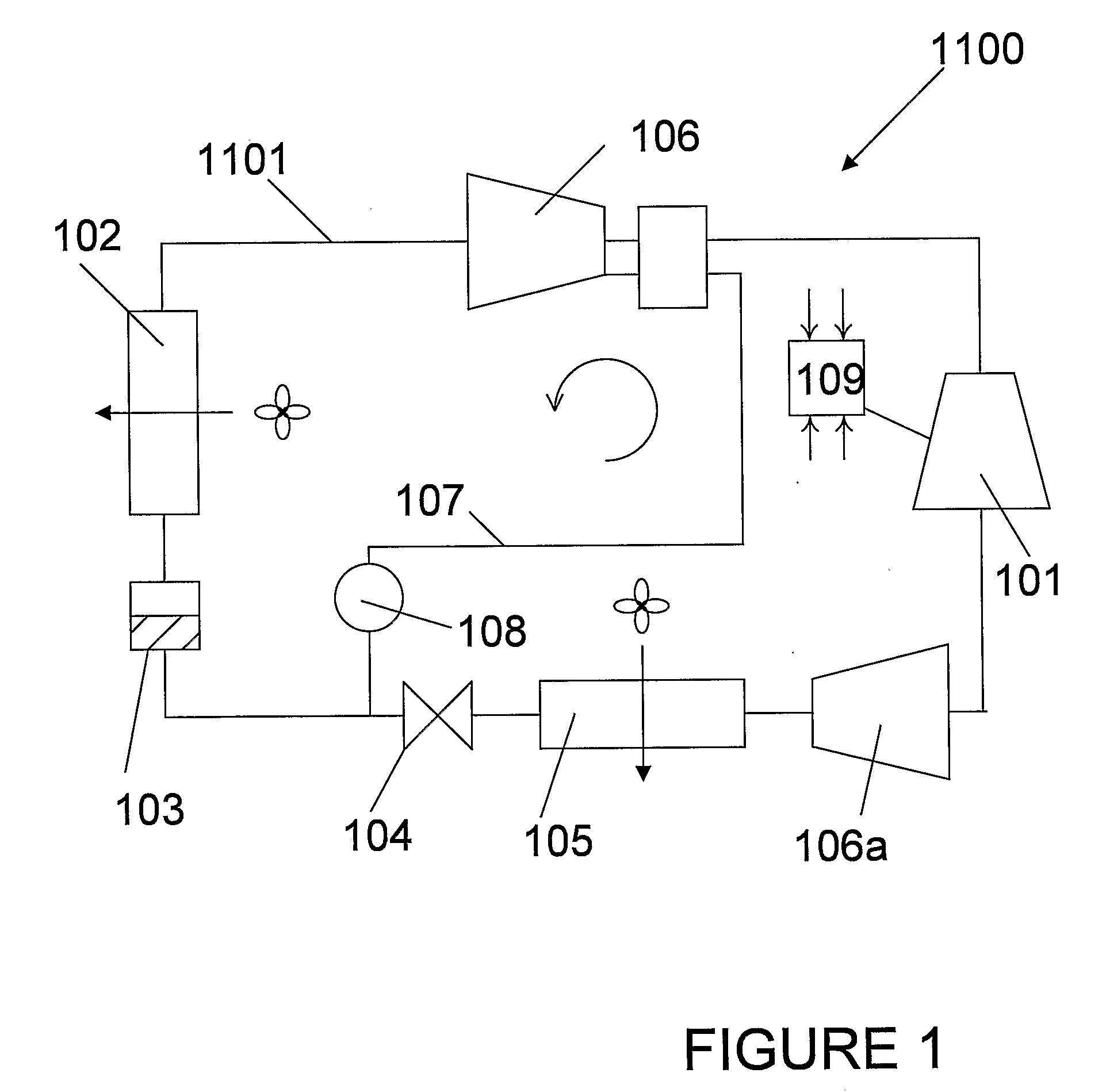
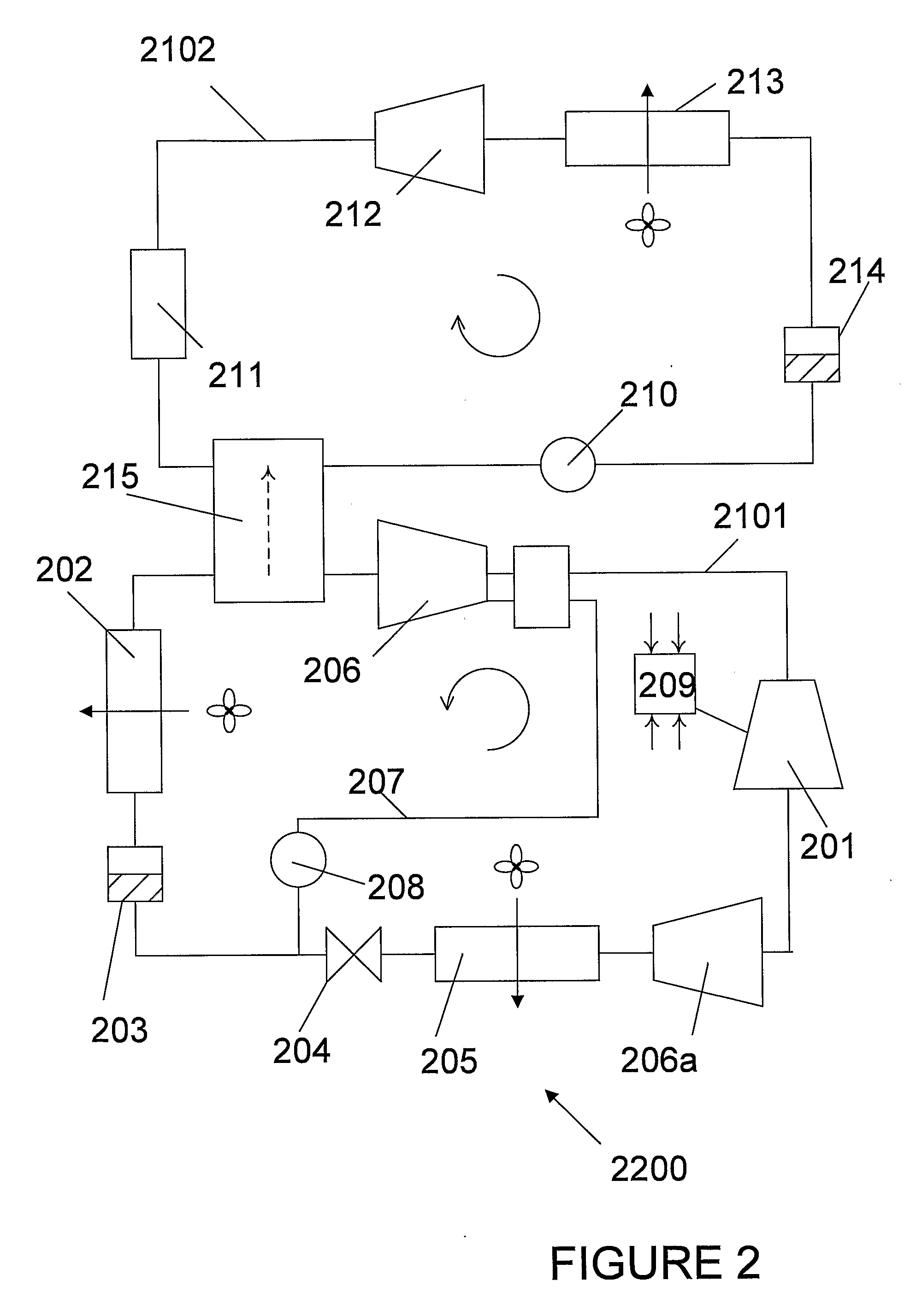
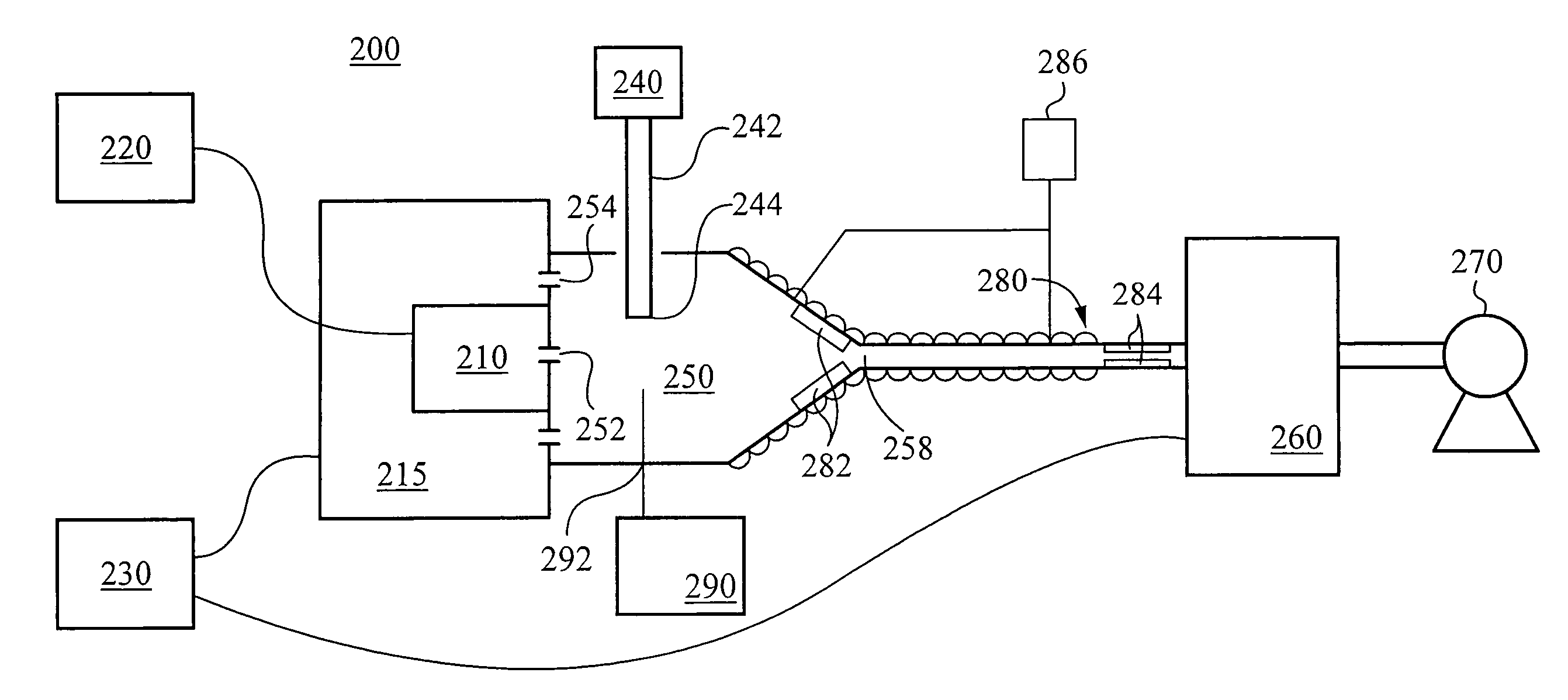
A refrigeration apparatus (7200) includes a heat pump circuit (7201) and a power generation circuit (7100). The power generation circuit (7100) includes an evaporator (701) including a first and a second heat exchanger (710a, 710b), a turbine (702), a condenser (703) and a pump (704). The first heat exchanger (710a) absorbs heat rejected from the heat pump circuit (7201) into a power generation circuit (7100) while the second heat exchanger (710b) further heats the fluid. The power generation circuit (7100) includes a bypass (707) which allows a portion of working liquid to enter the turbine (702) without passing through the evaporator (701). A heat pump (704) with similar bypass is also disclosed. Also disclosed are dual stage turbine design and a nozzle (10300) for a turbine which includes two fluid paths (1011, 1014) that adapted to receive and mix the liquid and vapour streams of working fluid, so that the liquid working fluid is vaporized by the heat from the vapour working fluid.
Owner:RENEWABLE ENERGY SYST LTD
Cooling Apparatus, Cooled Electronic Module and Methods of Fabrication Thereof Employing A Thermally Conductive Return Manifold Structure Sealed To The Periphery Of A Surface To Be Cooled
InactiveUS20070274045A1Overcomes shortcomingEnhanced advantageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesComputer moduleConductive materials
Owner:IBM CORP
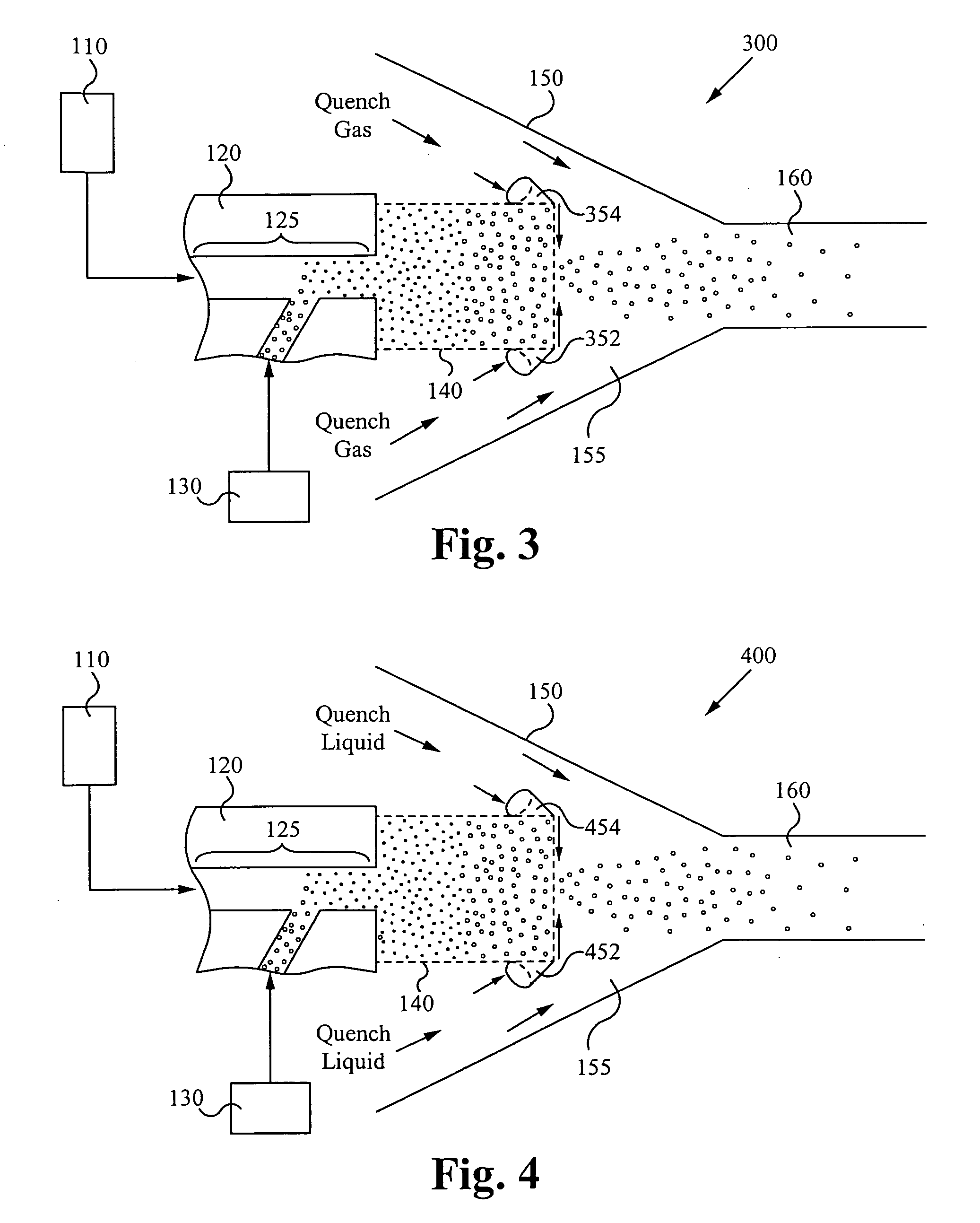
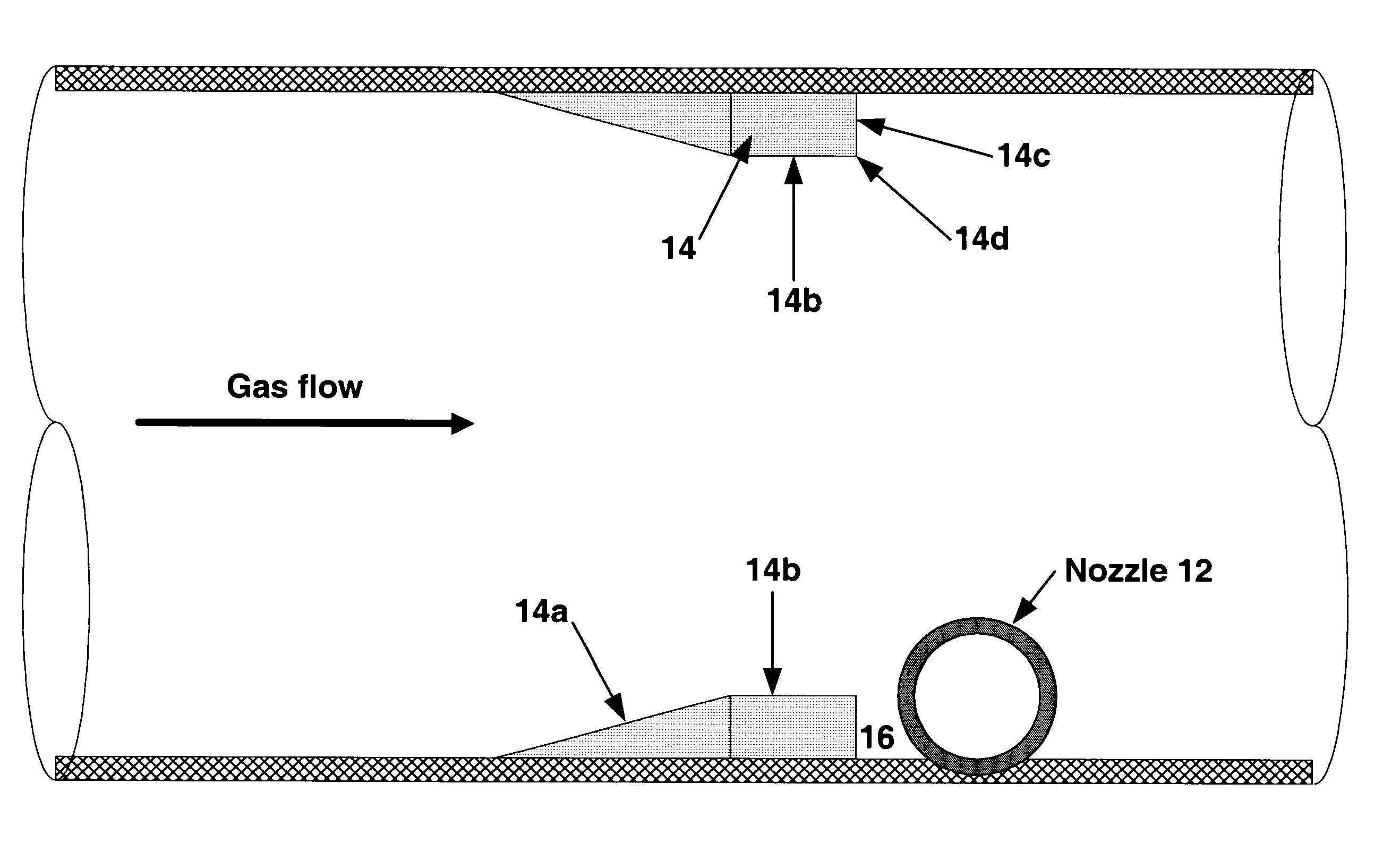
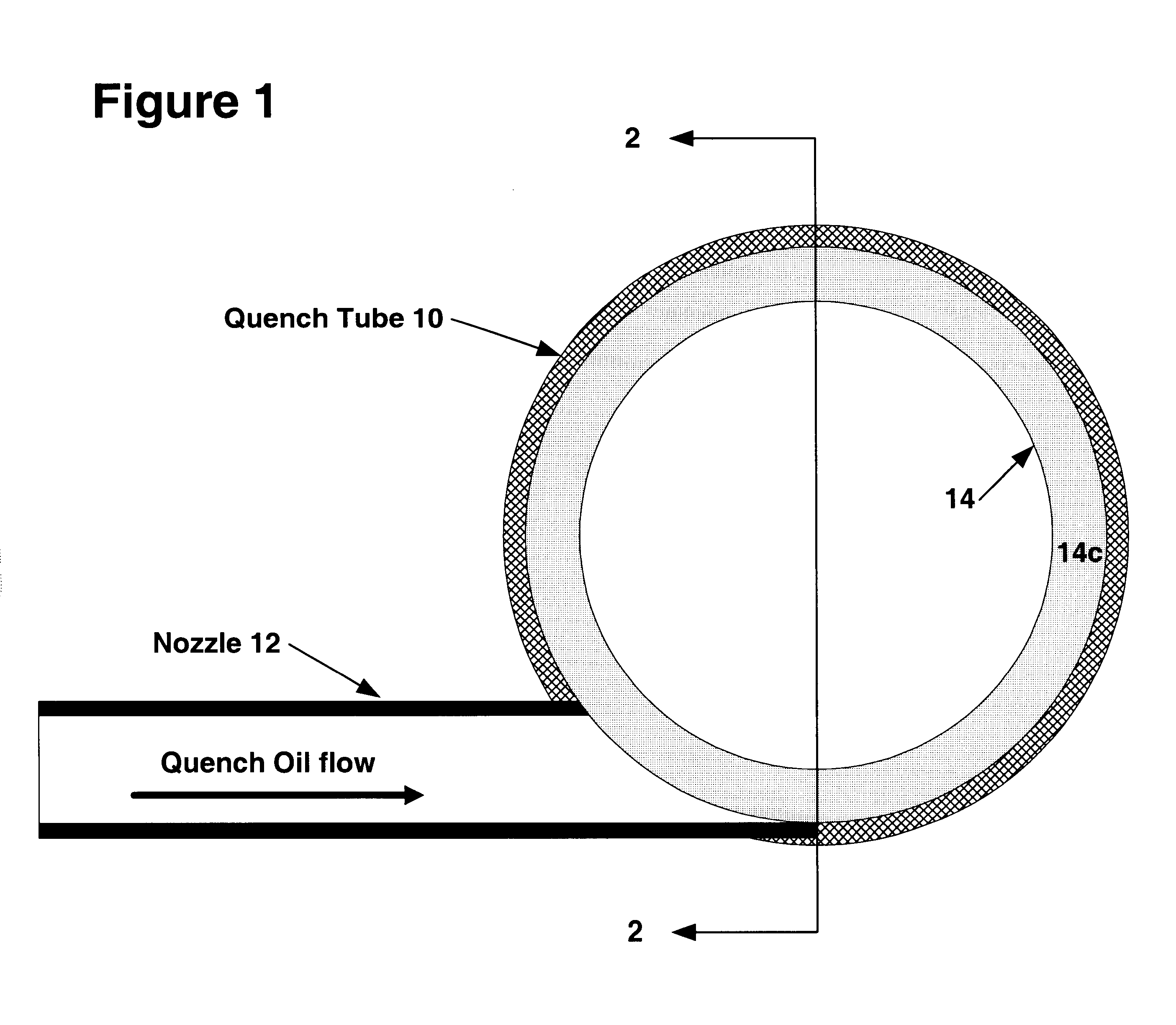
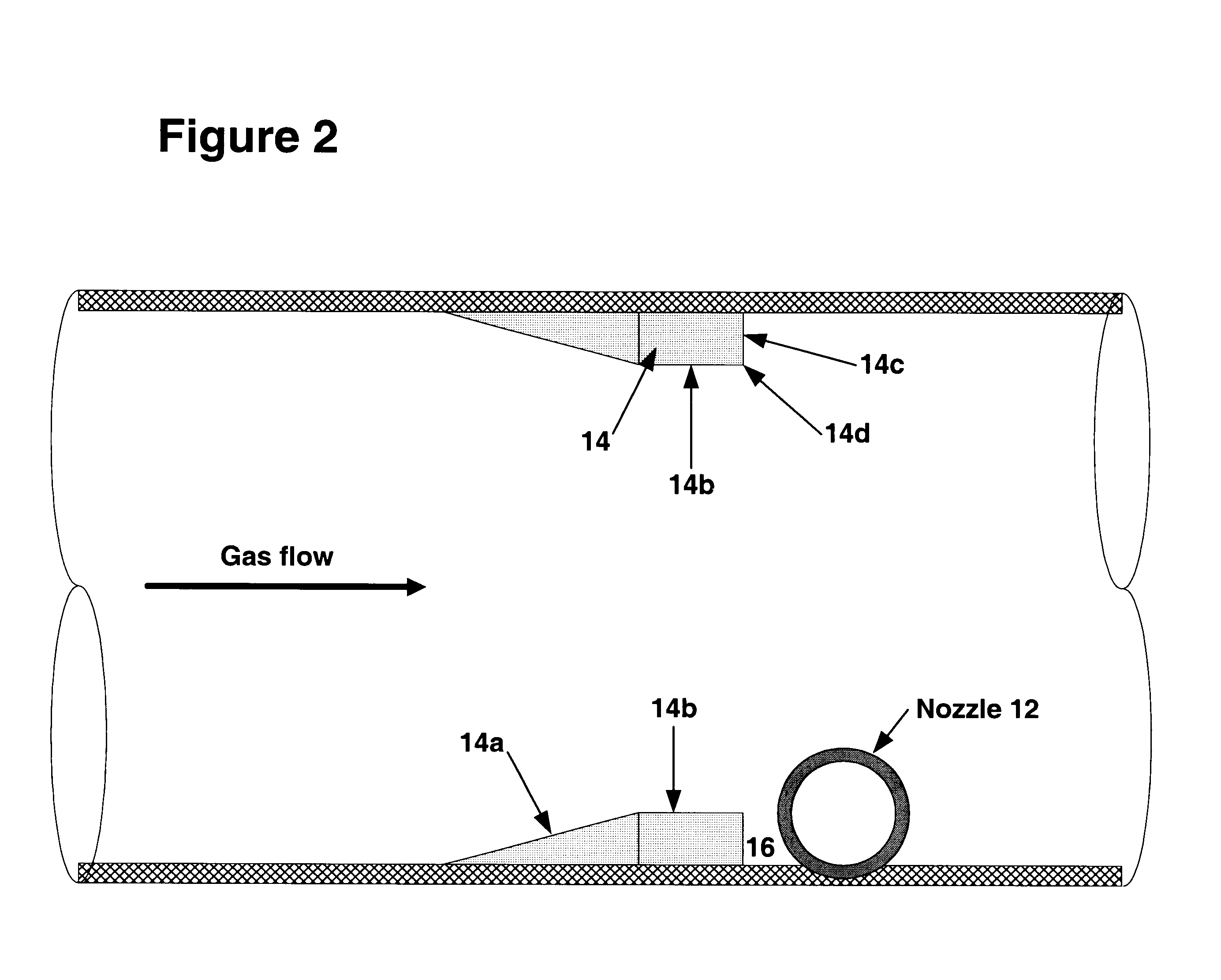
Quench nozzle
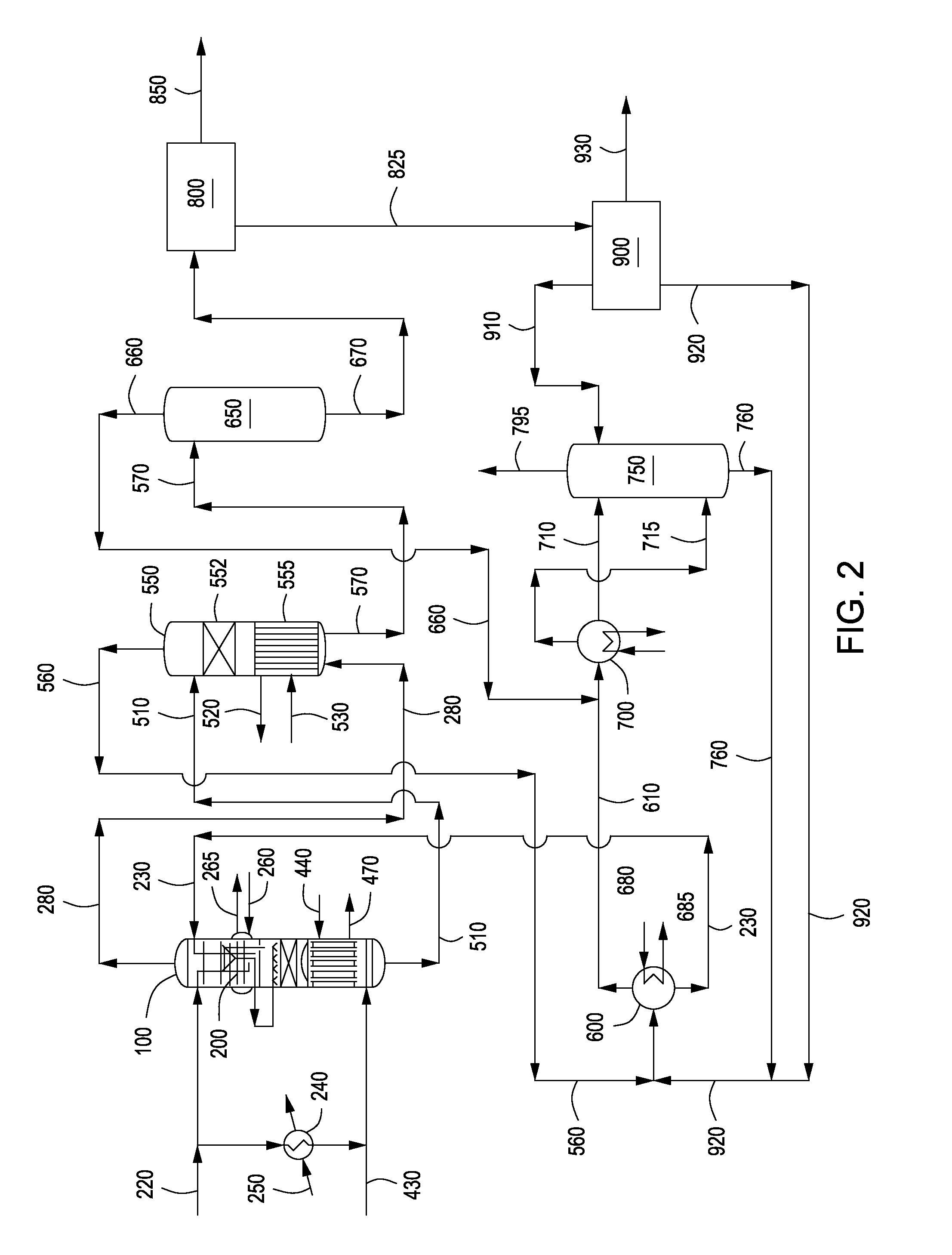
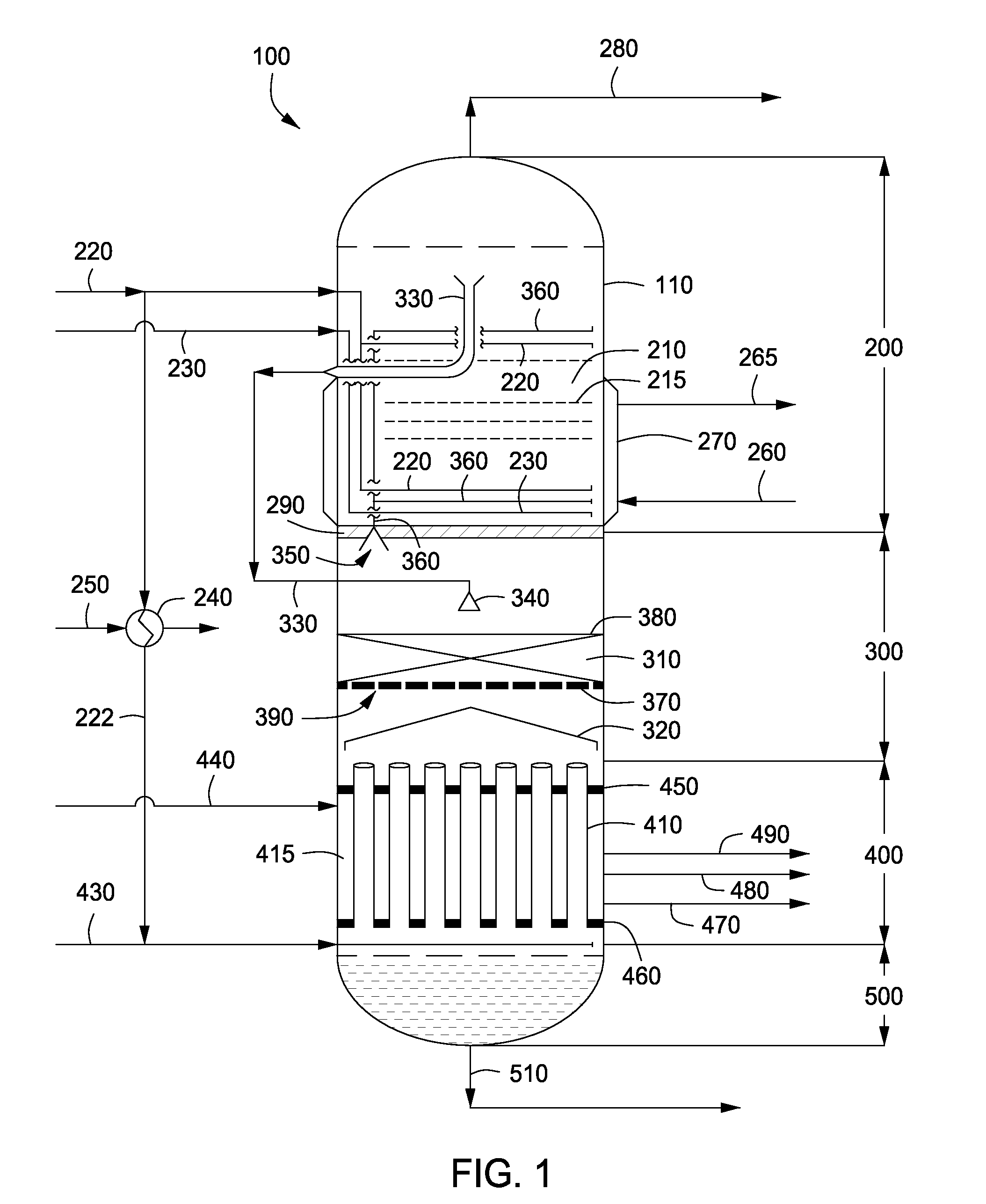
A quench nozzle design introduces quench oil tangentially into the quench tube which cools the hot gaseous pyrolysis products coming out of the hot radiant tubes in a pyrolysis furnace (in ethylene manufacture). Besides cooling the hot gases, the quench oil introduced into the quench tube by this nozzle design keeps the wall of the quench tube wetted, which is necessary to prevent coke deposition on the quench tube. The nozzle has one quench oil entry, which eliminates the need for any restriction orifice required to evenly distribute quench oil flows that would otherwise be required with several nozzle entries. Also, the one-nozzle oil introduction has a larger diameter than that required where more than one nozzle is employed in this service. The replacement of multiple nozzles with a single larger diameter nozzle eliminates plugging problems caused by coke solids or, coke solid precursors, present in the quench oil.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
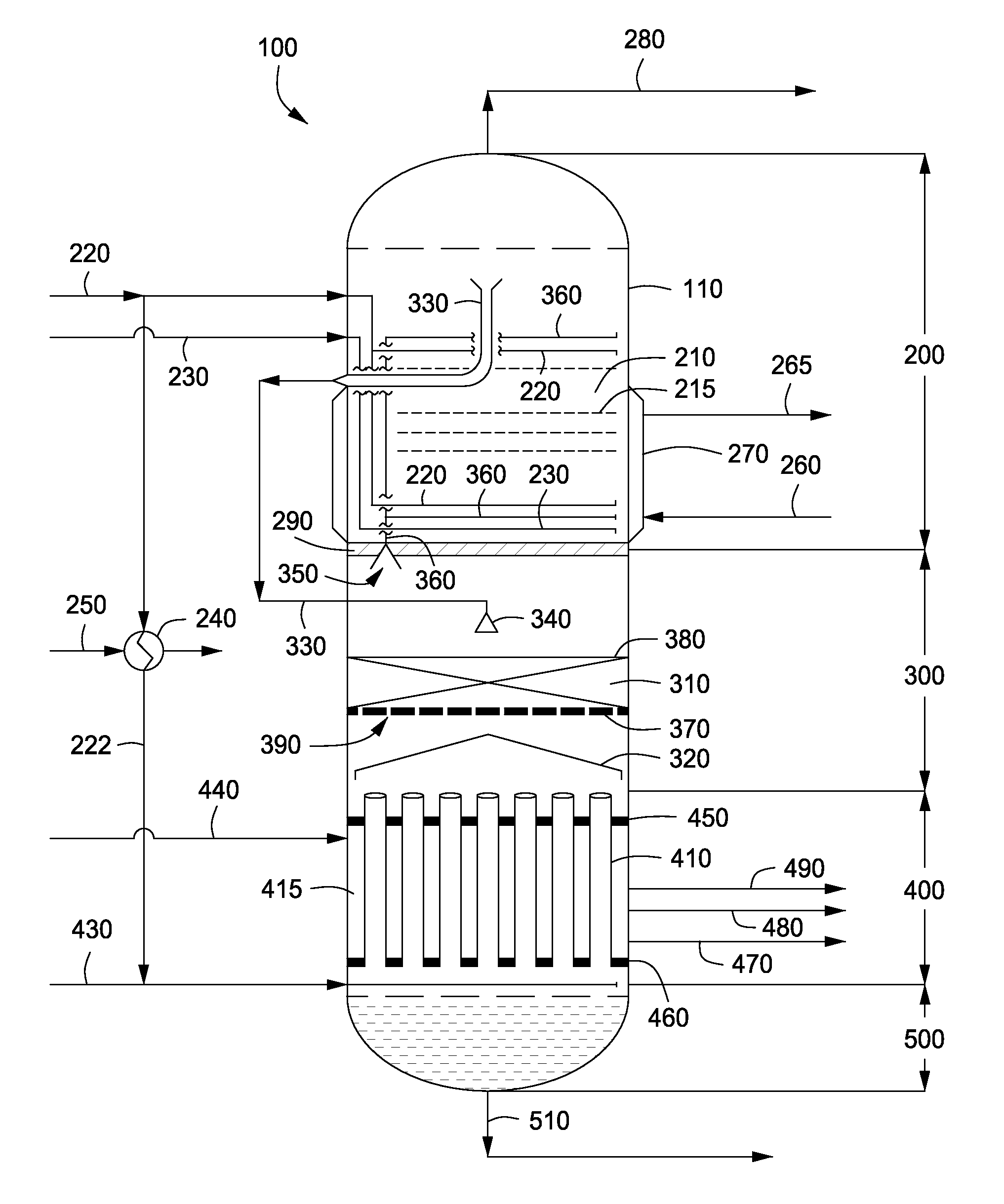
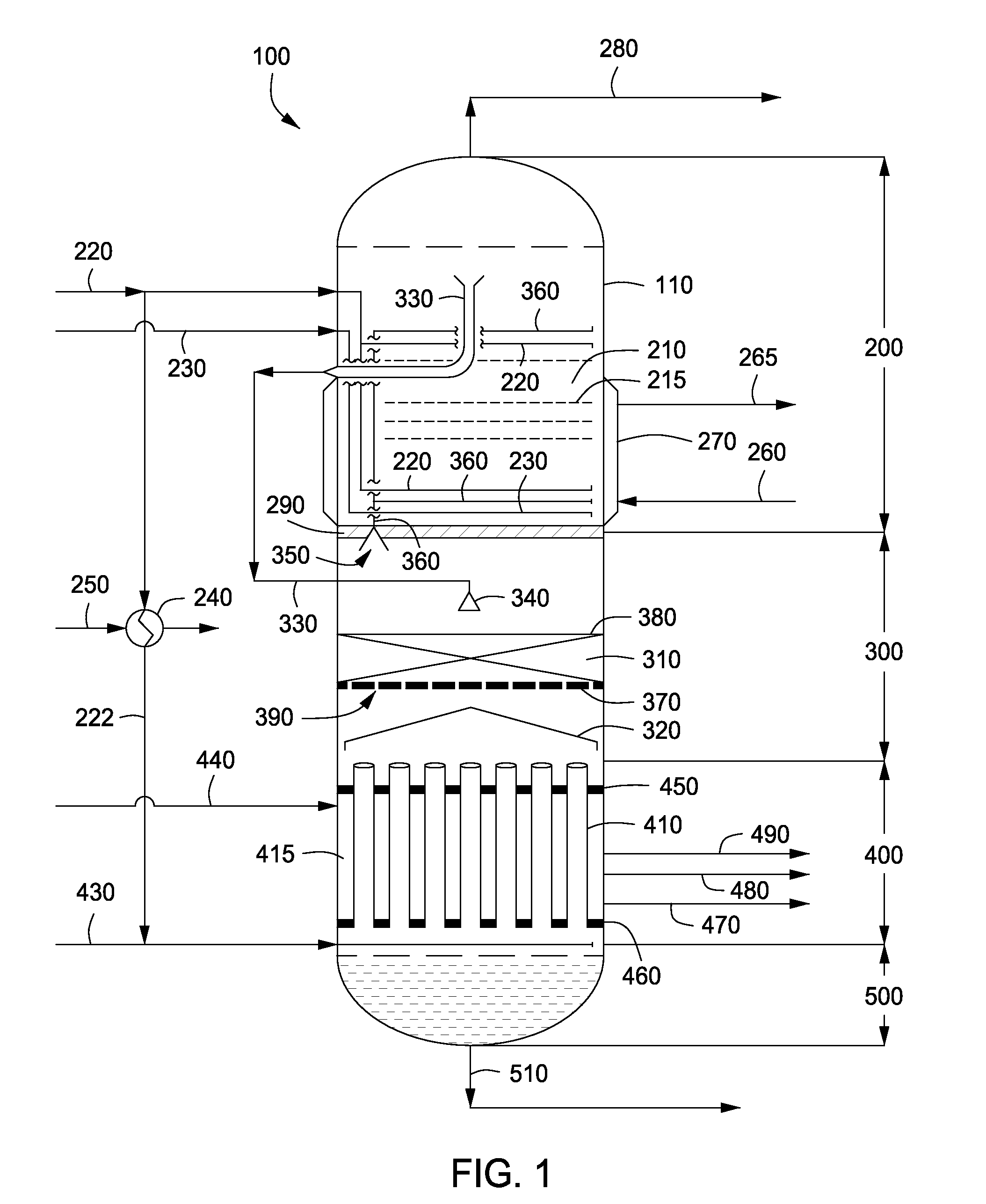
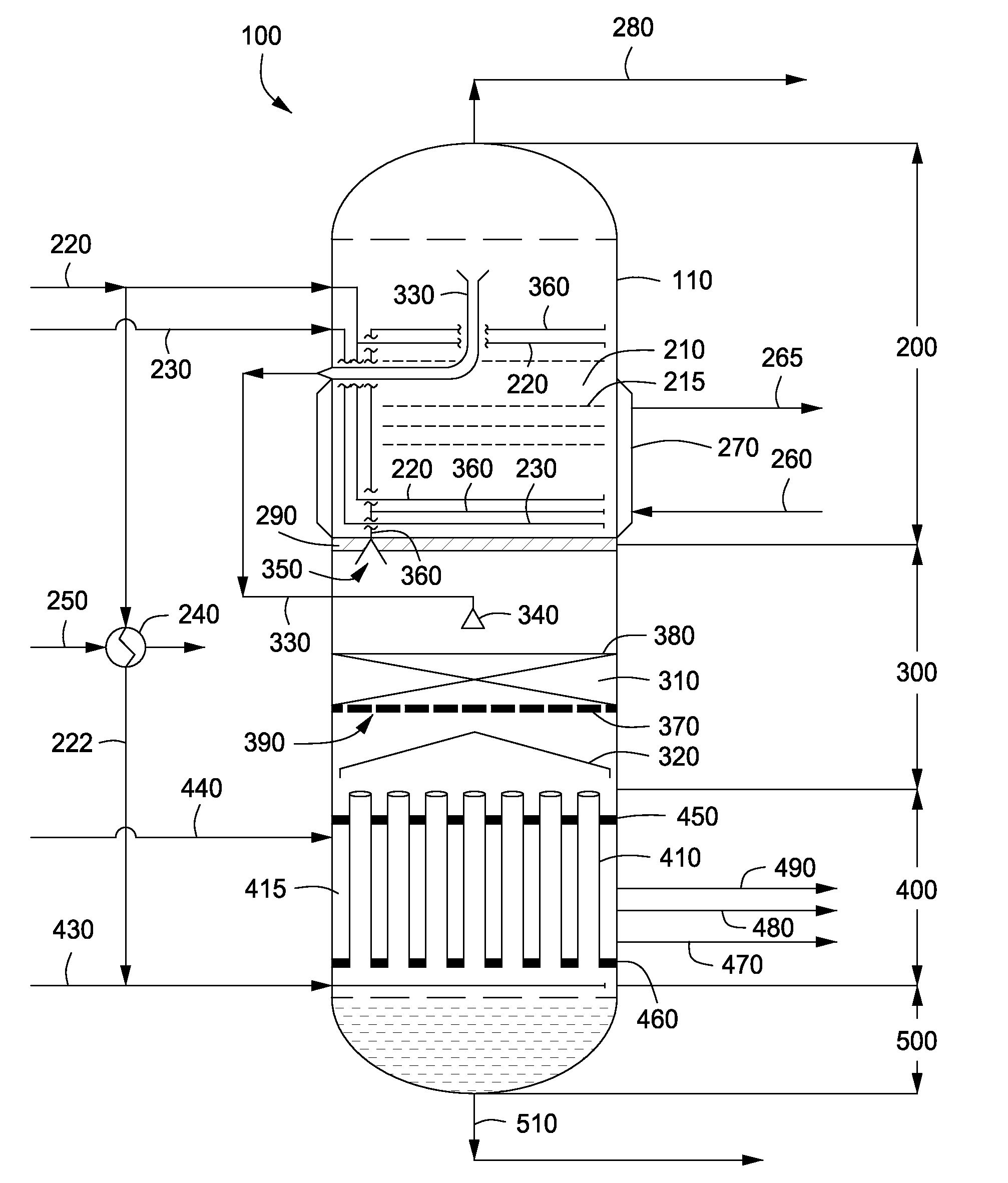
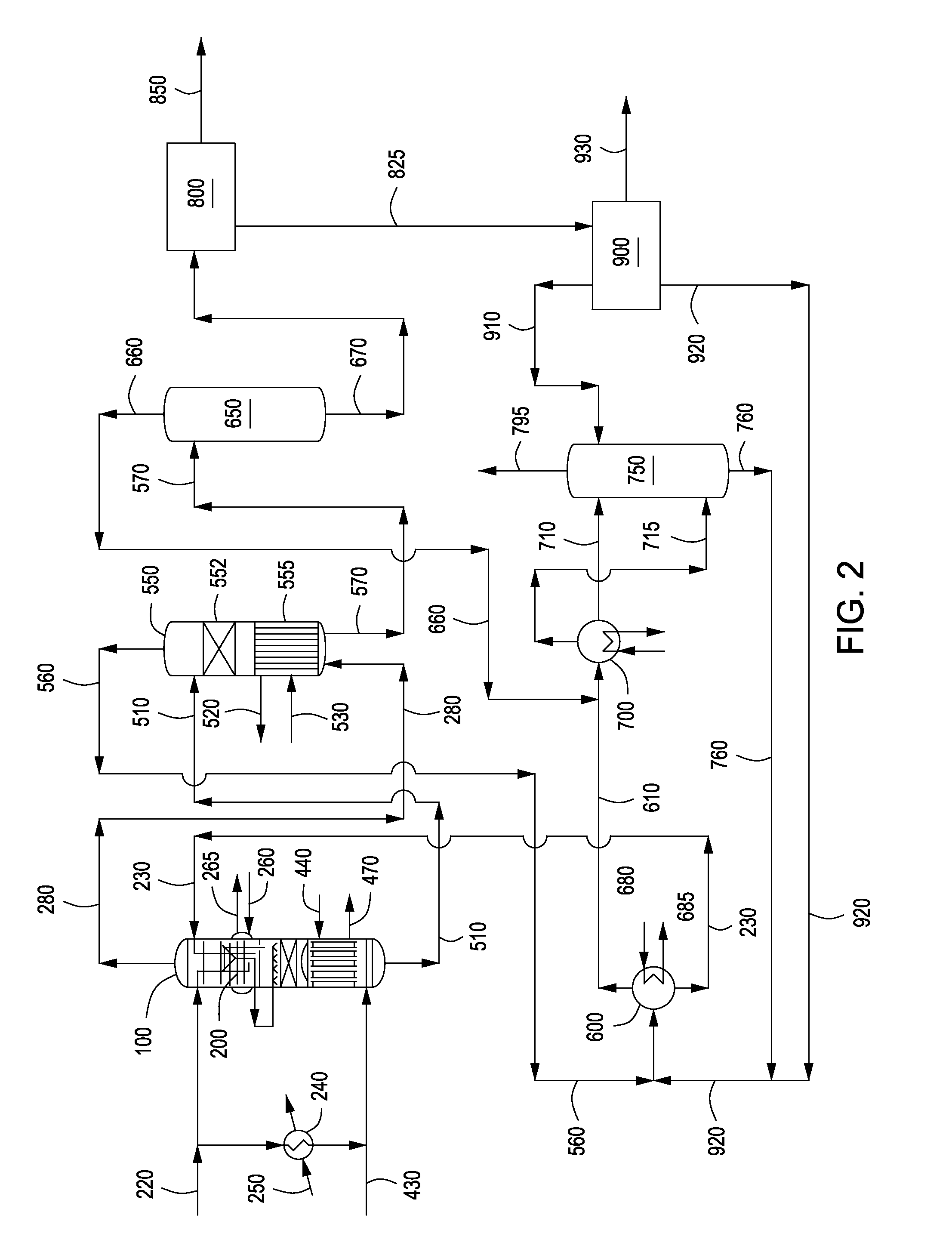
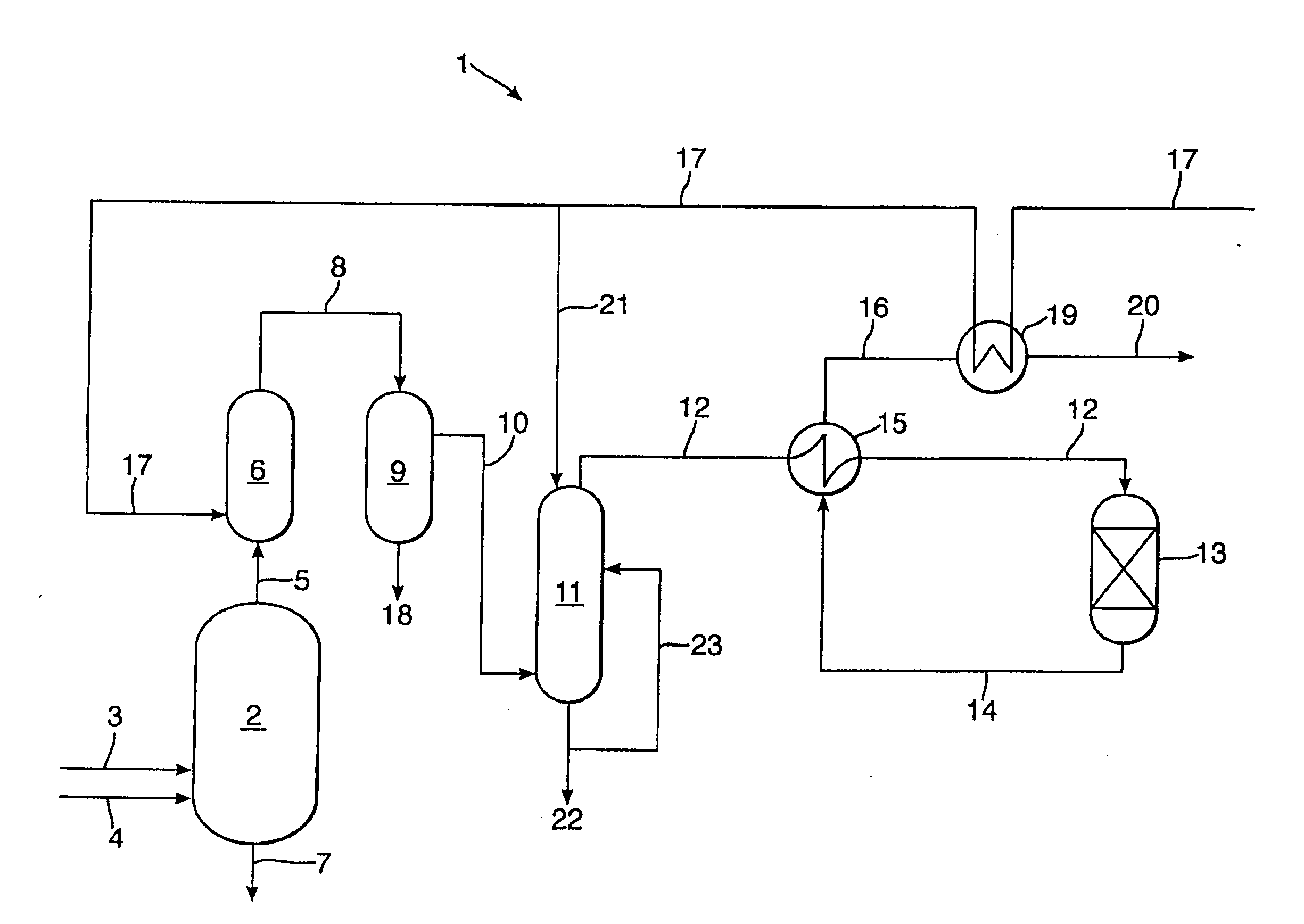
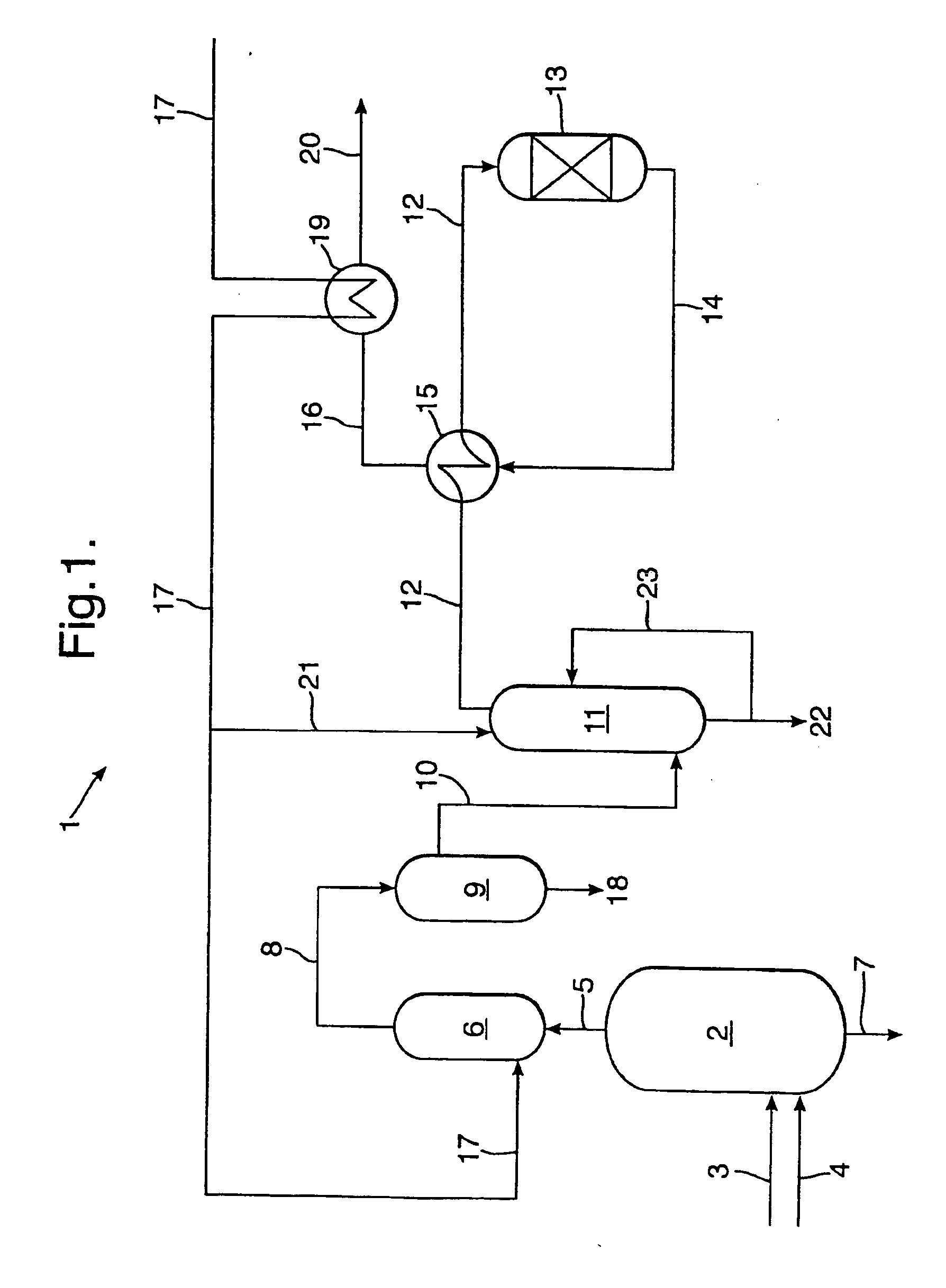
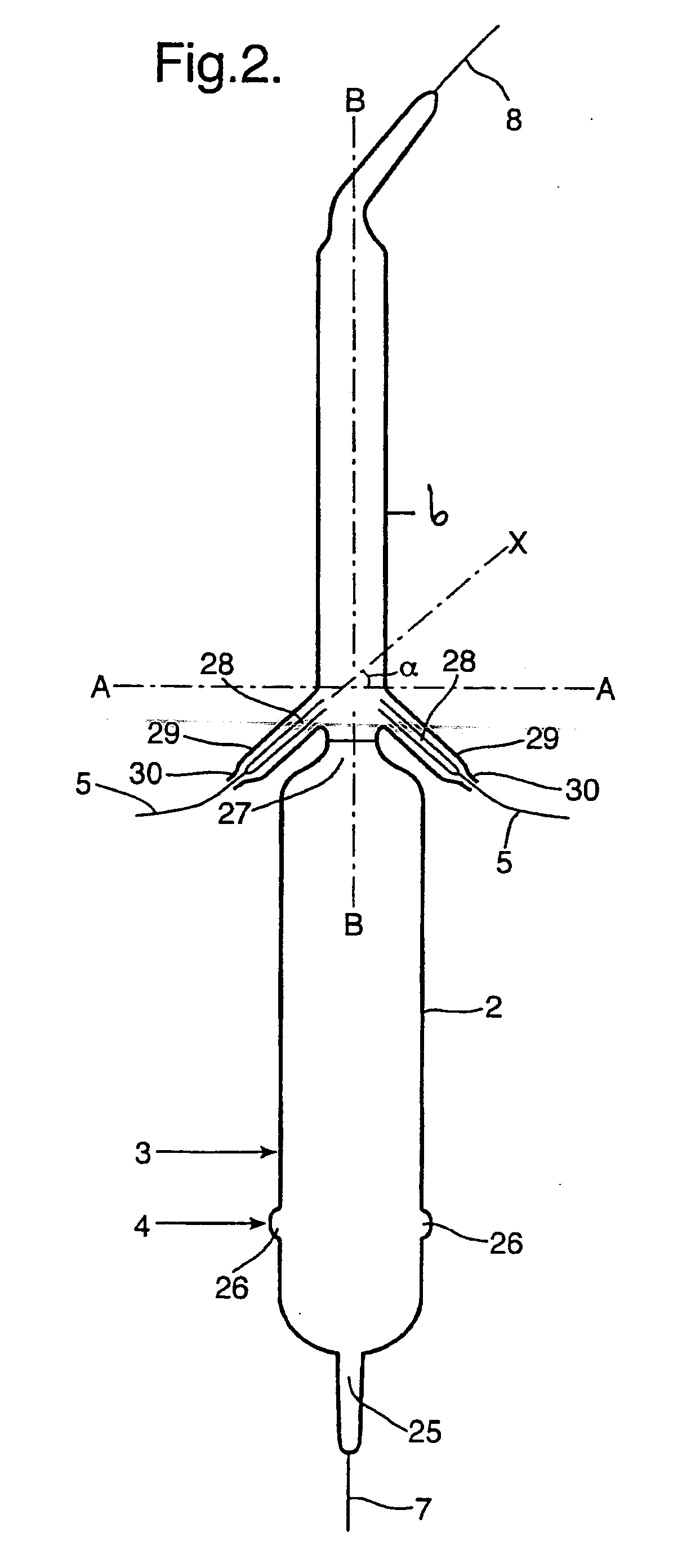
Apparatus and methods for urea production
Apparatus and methods for producing urea are provided. In one or more embodiments, an apparatus for producing urea can include a first zone, which can include a first flow channel in fluid communication with a first tube disposed about a first end of a plurality of trays, a second flow channel in fluid communication with a second tube disposed about the first end of the trays and a second end of the trays, and a third flow channel in fluid communication with a third tube disposed about the first and second ends of the trays. The apparatus can include a second zone, which can include a fixed bed comprising one or more inert packing materials disposed therein to provide additional surface area. The apparatus can include a third zone, which can include a plurality of tubes disposed therein. The second zone can be disposed between the first and third zones.
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
Apparatus and methods for urea production
ActiveUS20090216045A1Urea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationFilling materialsFixed bed
Apparatus and methods for producing urea are provided. In one or more embodiments, an apparatus for producing urea can include a first zone, which can include a first flow channel in fluid communication with a first tube disposed about a first end of a plurality of trays, a second flow channel in fluid communication with a second tube disposed about the first end of the trays and a second end of the trays, and a third flow channel in fluid communication with a third tube disposed about the first and second ends of the trays. The apparatus can include a second zone, which can include a fixed bed comprising one or more inert packing materials disposed therein to provide additional surface area. The apparatus can include a third zone, which can include a plurality of tubes disposed therein. The second zone can be disposed between the first and third zones.
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
Shape of cone and air input annulus
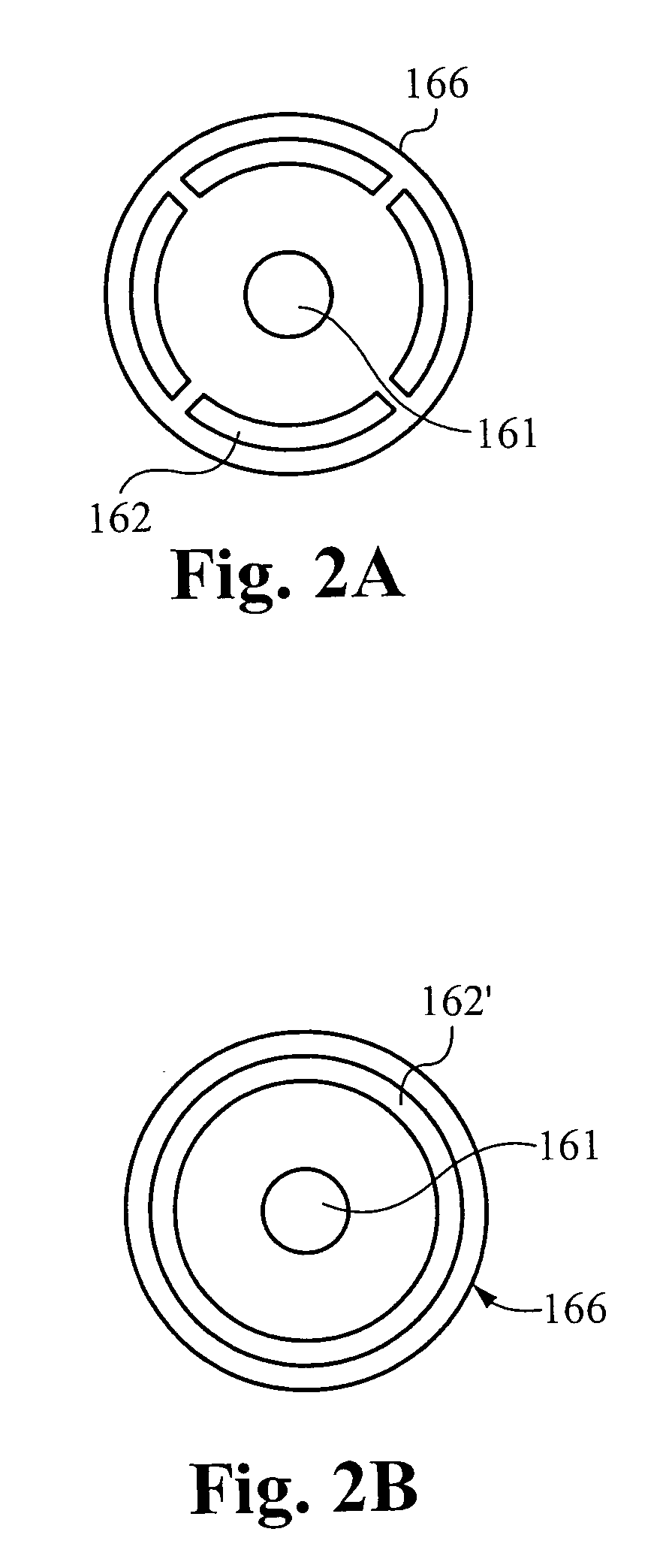
InactiveUS20080277266A1Minimize occurrenceHigh molecular weightDirect contact heat exchangersStationary tubular conduit assembliesInterior spaceInjection port
A constricting chamber having first and second ends, the chamber comprising: an interior surface formed between the first and second ends, disposed circumferentially around and defining an interior space and a longitudinal axis of the chamber; a frusto-conical surface disposed between the first and second ends and narrowing as it extends away from the first end and into the second end; an ejection port disposed at the second end and substantially aligned with the longitudinal axis; a cover disposed at the first end, substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis, and comprising a center substantially aligned with the longitudinal axis; an injection port disposed on the cover proximate the center, and configured to receive a reactive mixture into the chamber; and an annular supply portion disposed circumferentially around the longitudinal axis and comprising supply port(s) configured to supply conditioning fluid into the chamber in an annular formation along the interior surface.
Owner:SDC MATERIALS +1
Gas delivery system with constant overpressure relative to ambient to system with varying vacuum suction
ActiveUS20080277271A1Minimizes pressure differentialReduce pressureCatalyst activation/preparationDirect contact heat exchangersSuction stressAmbient pressure
A system operating in an environment having an ambient pressure, the system comprising: a reactor configured to combine a plasma stream, powder particles and conditioning fluid to alter the powder particles and form a mixture stream; a supply chamber coupled to the reactor; a suction generator configured to generate a suction force at the outlet of the reactor; a fluid supply module configured to supply the conditioning fluid at an original pressure; and a pressure regulation module configured to: receive the conditioning fluid from the fluid supply module, reduce the pressure of the conditioning fluid from the original pressure to a selected pressure relative to the ambient pressure regardless of any changes in the suction force at the outlet of the reactor, and supply the conditioning fluid at the selected pressure to the supply chamber.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Formation of catalytic regions within porous structures using supercritical phase processing
InactiveUS20080280049A1Enable formationPretreated surfacesDirect contact heat exchangersMaterials scienceSupercritical fluid
A method of forming a catalytic region on a porous structure having an exterior surface and a plurality of pores, the method comprising: forming a supercritical dispersion, wherein the supercritical dispersion comprises a plurality of particles dispersed in a supercritical fluid; exposing the porous structure to the supercritical dispersion; and depositing the plurality of particles from the supercritical dispersion onto the porous structure, wherein each one of the deposited plurality of particles is catalytic, thereby forming one or more catalytic regions on the porous structure. The method is particularly well suited for creating catalytic regions within pre-formed microporous structures.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG +1
Solar thermal aerosol flow reaction process
InactiveUS6872378B2Short stayCost-effectiveSolar heating energyHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesForming gasChemical reaction
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Apparatus and method for heating fluids
InactiveUS6910448B2Solve the power is smallSteam generation using mechanical energyDomestic stoves or rangesCavitationDrive shaft
A fluid heating apparatus has a housing with a main chamber in which a rotor is situated. A drive shaft drives the rotor about a longitudinal axis of rotation. The housing has a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet, the fluid outlet communicating with an inlet region and the fluid outlet communicating with an exit region. The outer surface of the rotor forms one boundary for the fluid heat generating region and is confronted by the inner surface of the main chamber which is the other boundary. The fluid inlet is positioned closer to the longitudinal axis of the machine as compared to the fluid exit. The rotor is provided with at least one array of cavitation-inducing holes. Preferably, several rows of holes are configured on the rotor surface, some of which may have a depth dimension extending the radial width of the rotor.
Owner:THOMA CHRISTIAN
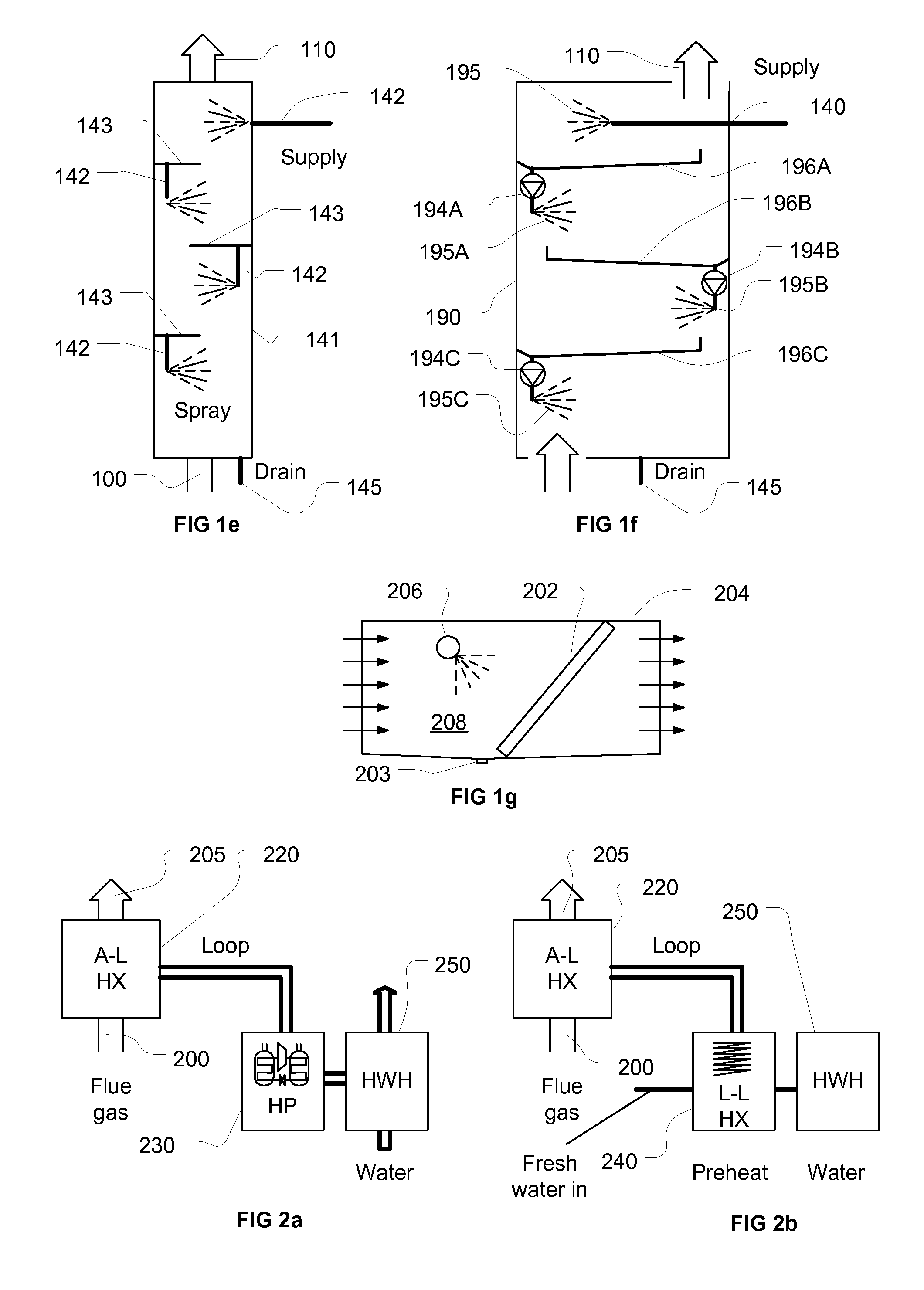
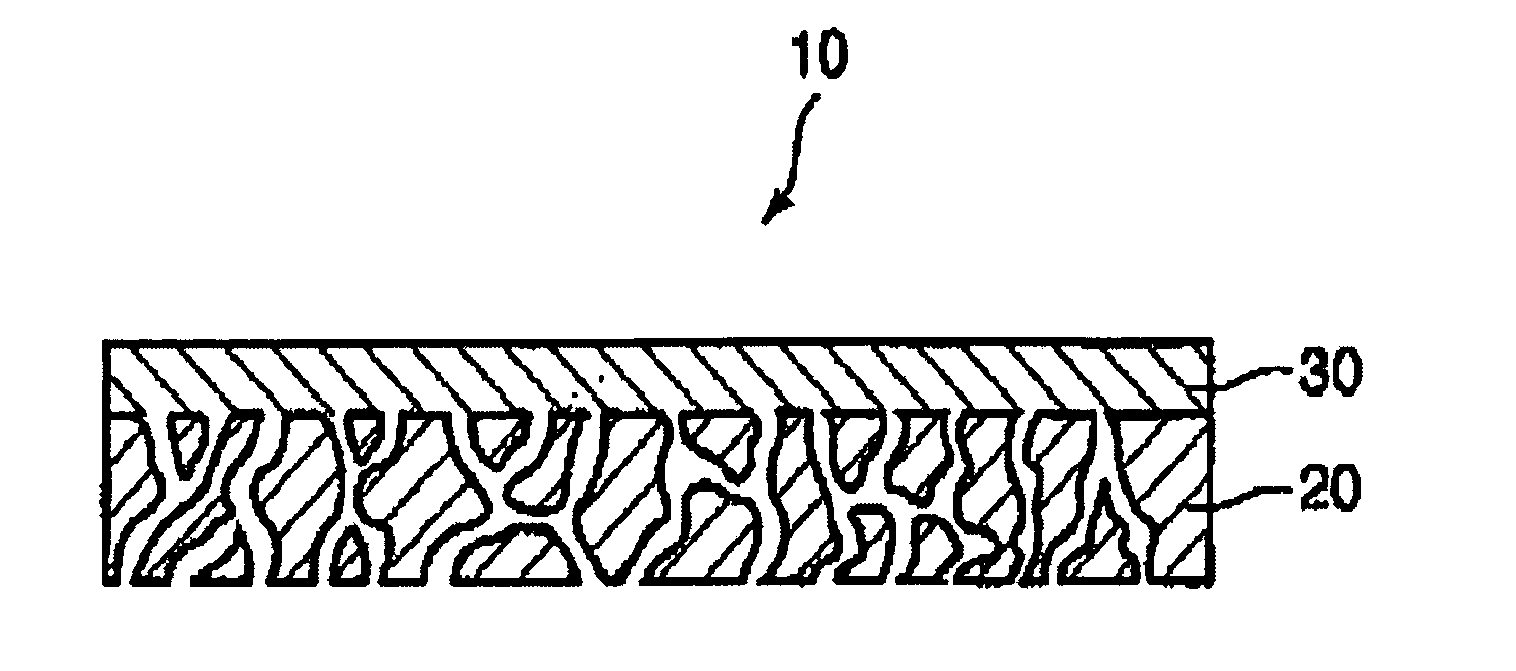
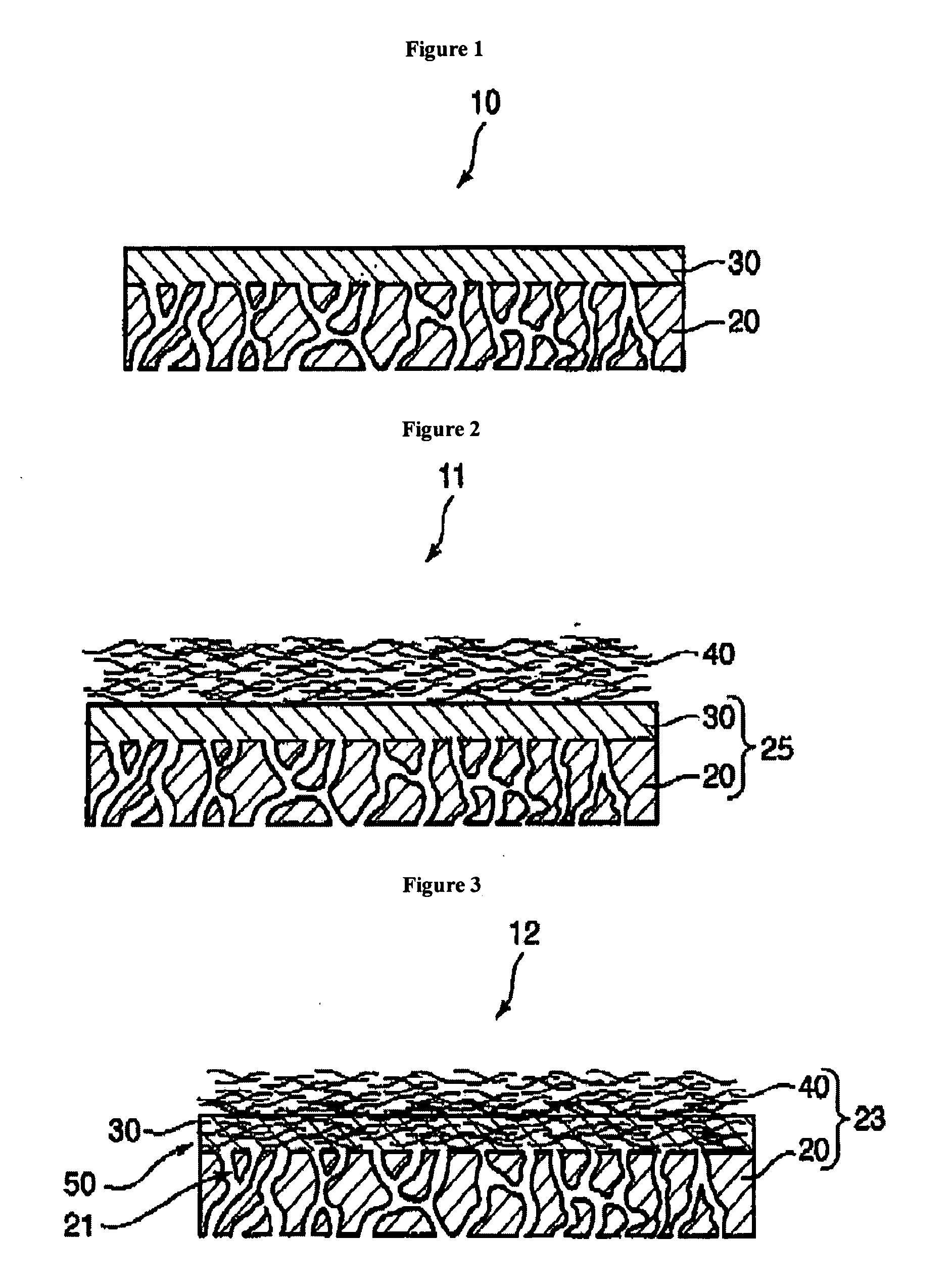
Membrane, method of making same and heat exchanger furnished with said membrane
ActiveUS20060090650A1Solid sorbent liquid separationPretreated surfacesPolyvinyl alcoholWater soluble
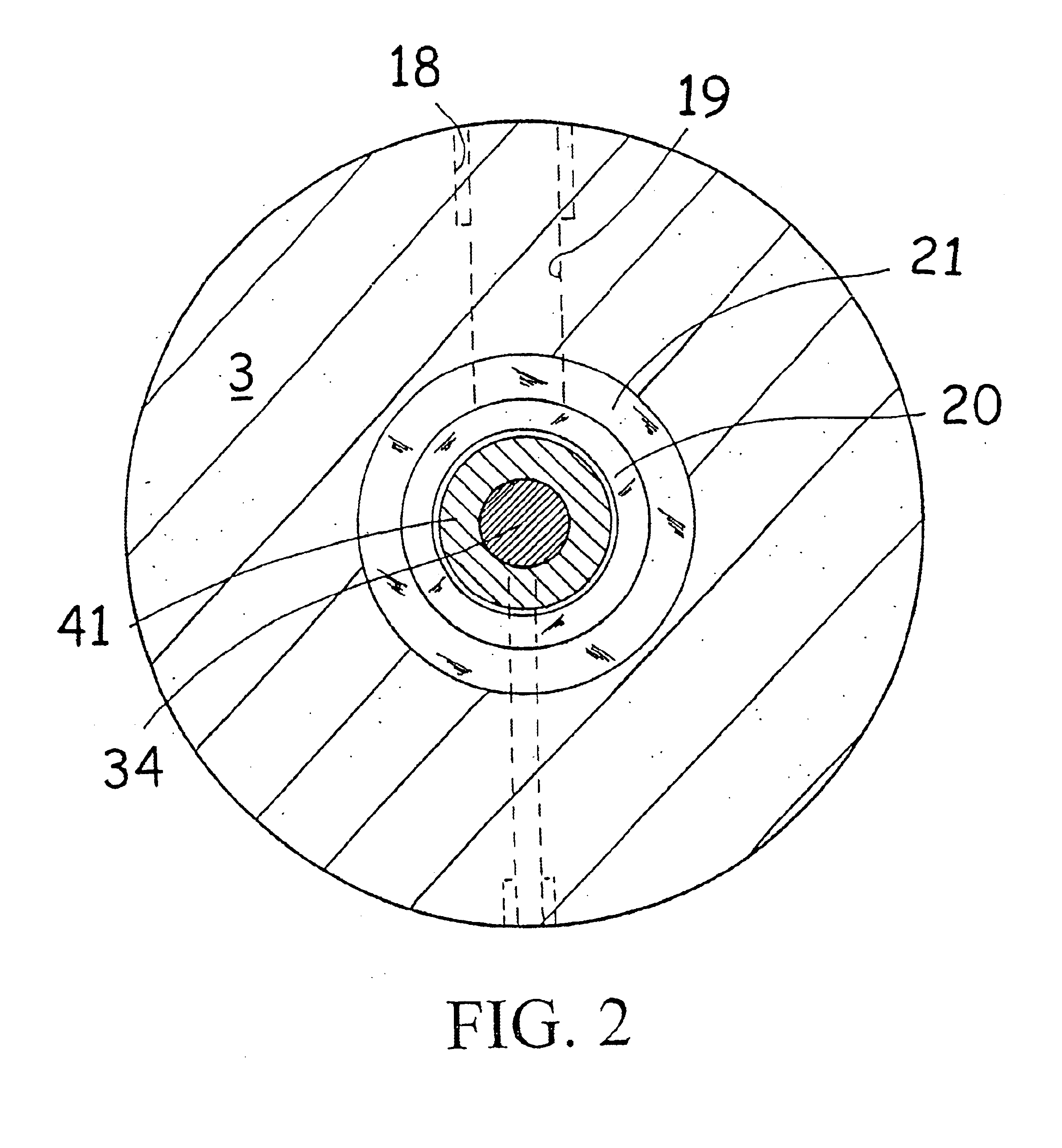
A membrane 12 that exhibits superior condensation resistance regardless of the type of moisture-permeable resin, that has satisfactory adhesion between a porous film and a reinforcing member, and that can be manufactured in a simple manner. The membrane 12 is a laminated article 23 containing a porous film 20 and a reinforcing member 40, and the reinforcing member 40 has a moisture-permeable resin layer 30 on the side of an interface 50 with the porous film 20. To reliably form the moisture-permeable resin layer (moisture-permeable resin film) 30, the average pore diameter of the porous film 20 is preferably 0.01 to 10 μm, and the porosity of the reinforcing member 40 is preferably 30 to 95%. According to the membrane 12 of the present invention, even if the moisture-permeable resin is water-soluble (for example, polyvinyl alcohol), condensation resistance is still satisfactory. If the difference between the critical surface tension γc2 of the reinforcing member 40 and the critical surface tension γc1 of the porous film 20 (γc2−γc1) is set in advance to −5 mN / m or greater, the moisture-permeable resin layer 30 can be disposed internally at a specific location.
Owner:JAPAN GORE TEX INC
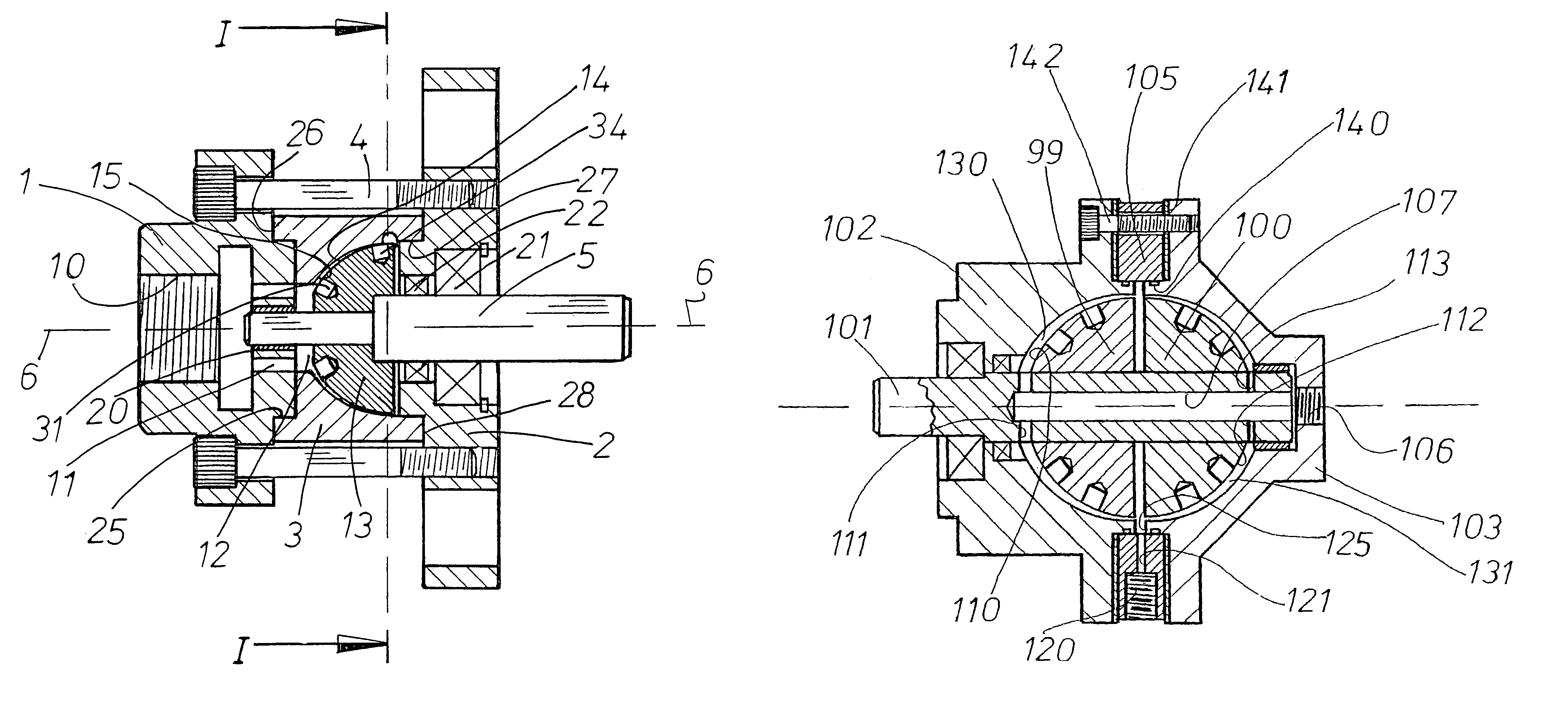
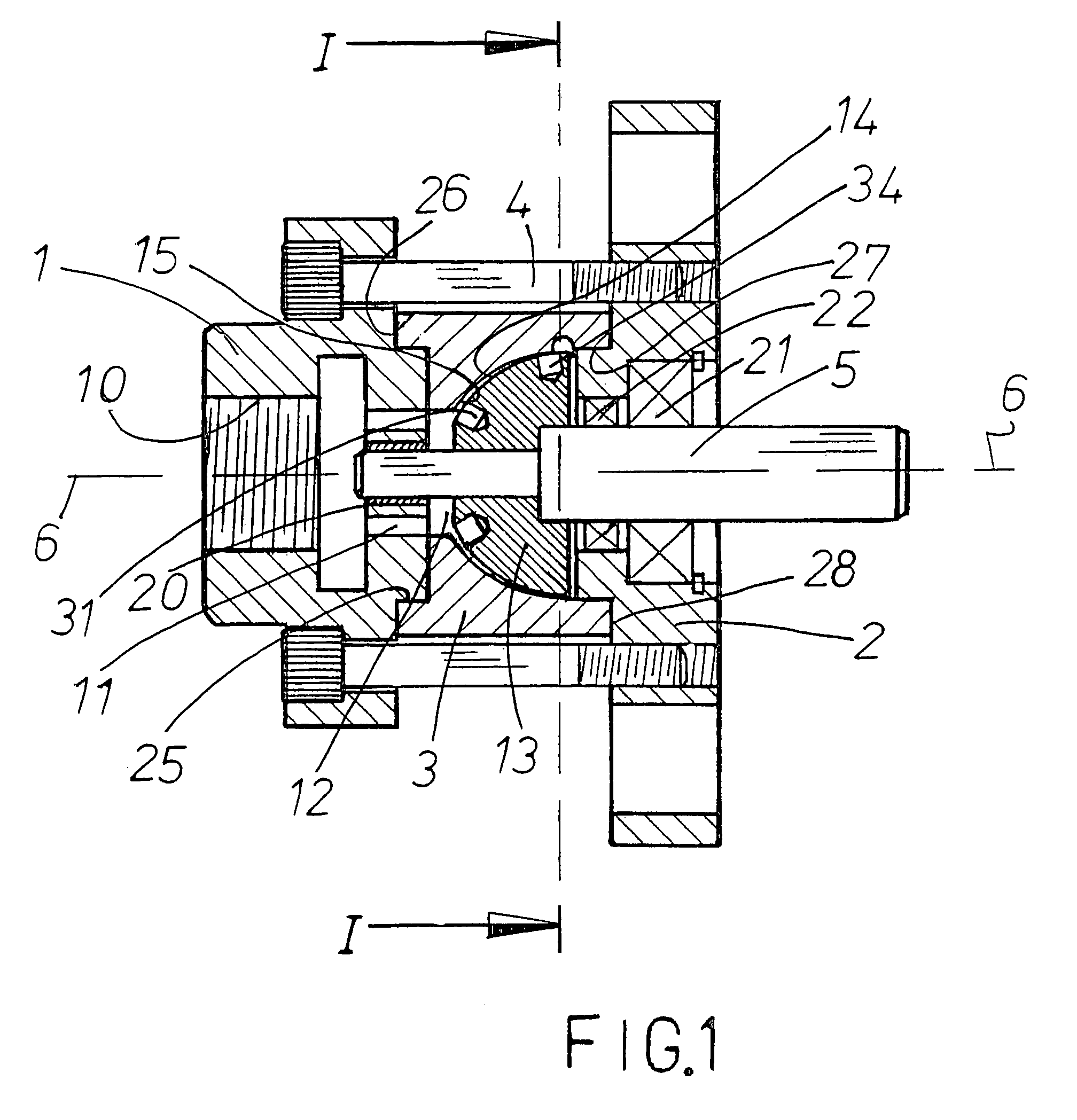
Apparatus and method for heating fluids
InactiveUS7089886B2Risk minimizationEliminate requirementsPump componentsOther heat production devicesFluid intakeRotational axis
An apparatus for heating a liquid comprising a housing having an internal chamber and a rotor disposed in said chamber. A drive shaft rotatably supported in the housing and extending into said chamber for imparting mechanical energy to the rotor. The rotor having a generally hemi-spherically shaped form and provided with a series of openings. A fluid intake passage in said housing preferably arranged to be nearer the rotational axis of the rotor and a fluid exit passage preferably positioned radially outwardly of said rotor.
Owner:THOMA CHRISTIAN HELMUT
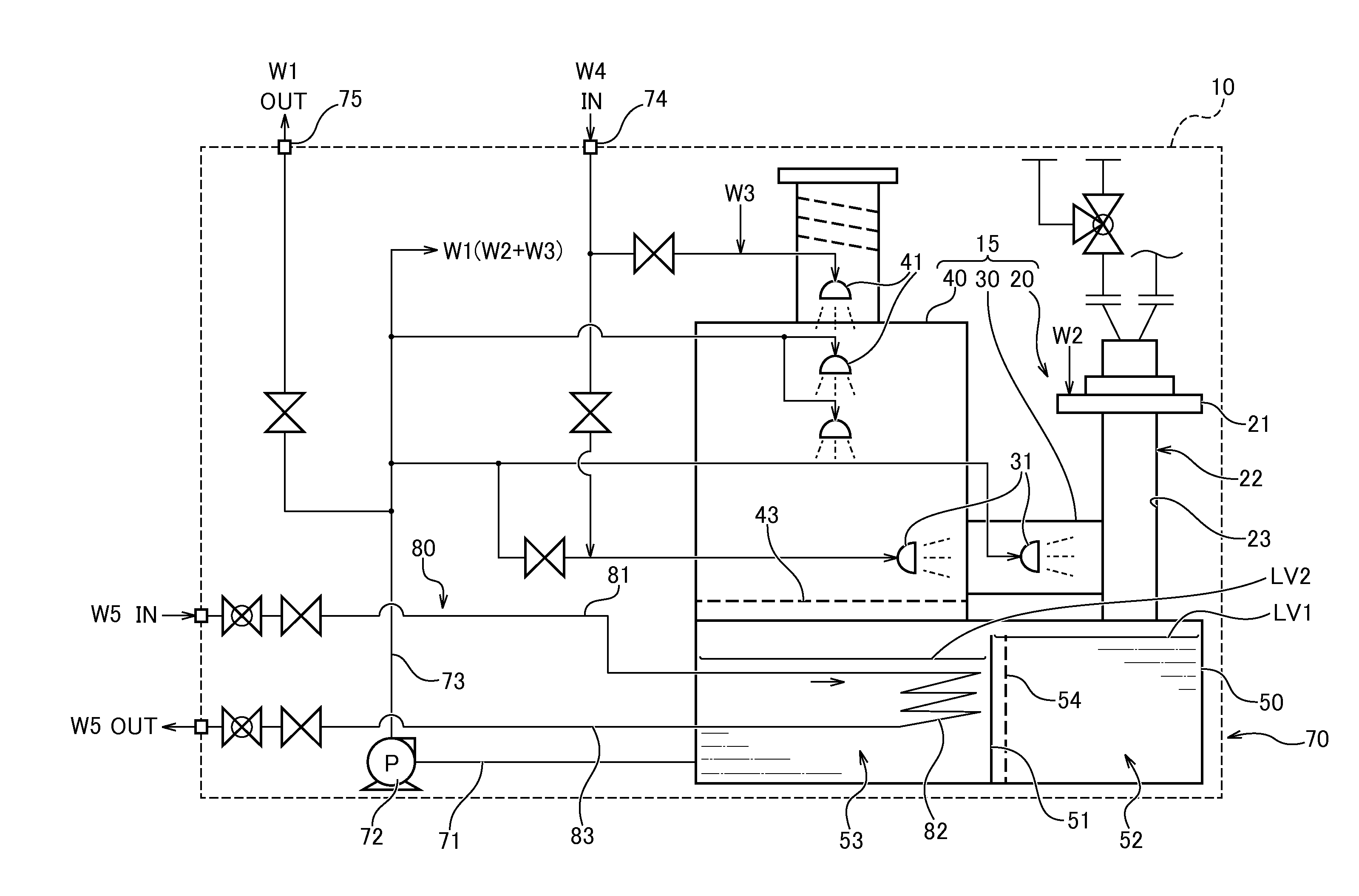
Cooling module for modular data center and system comprising the cooling module and at least one server module
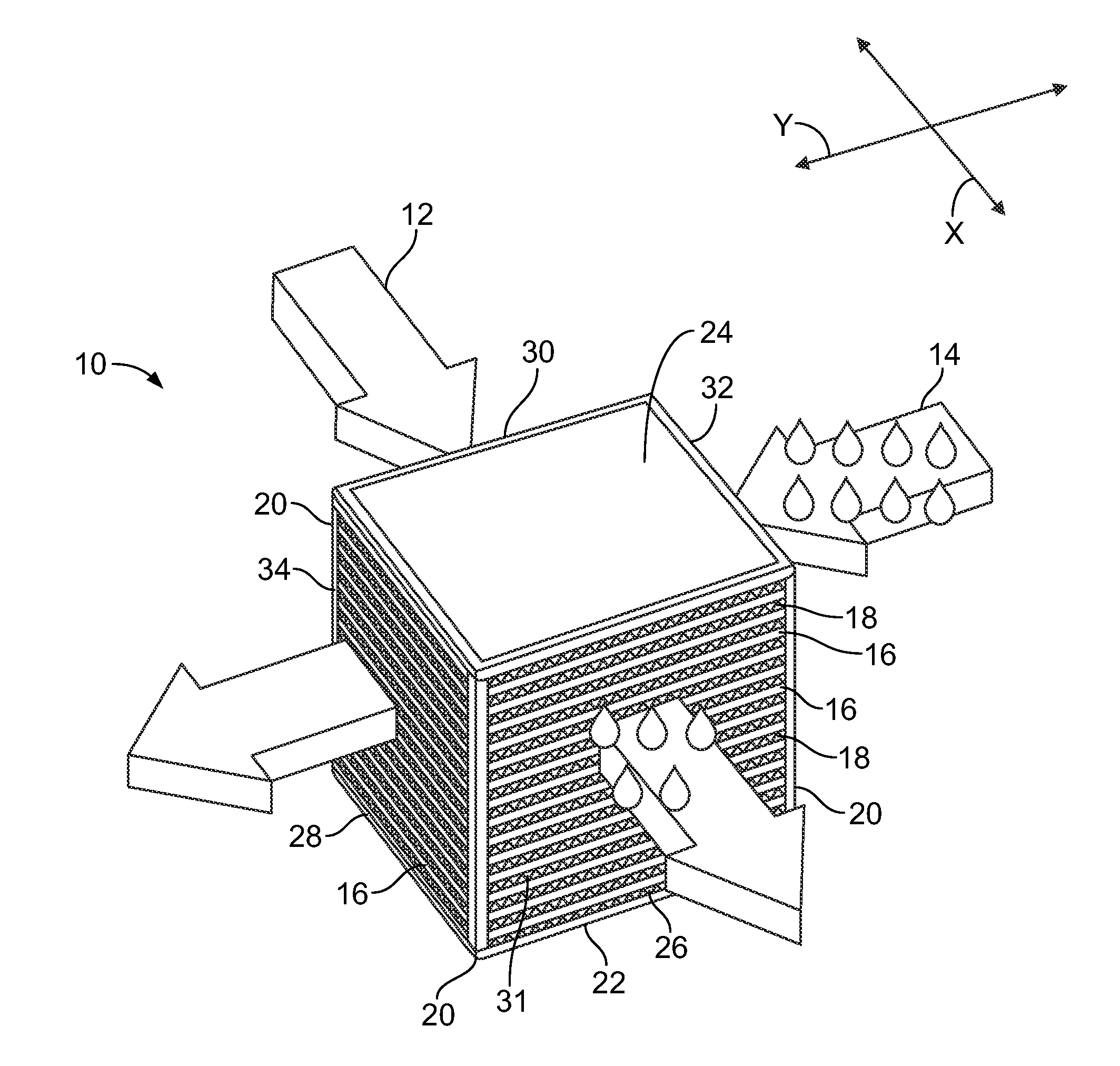
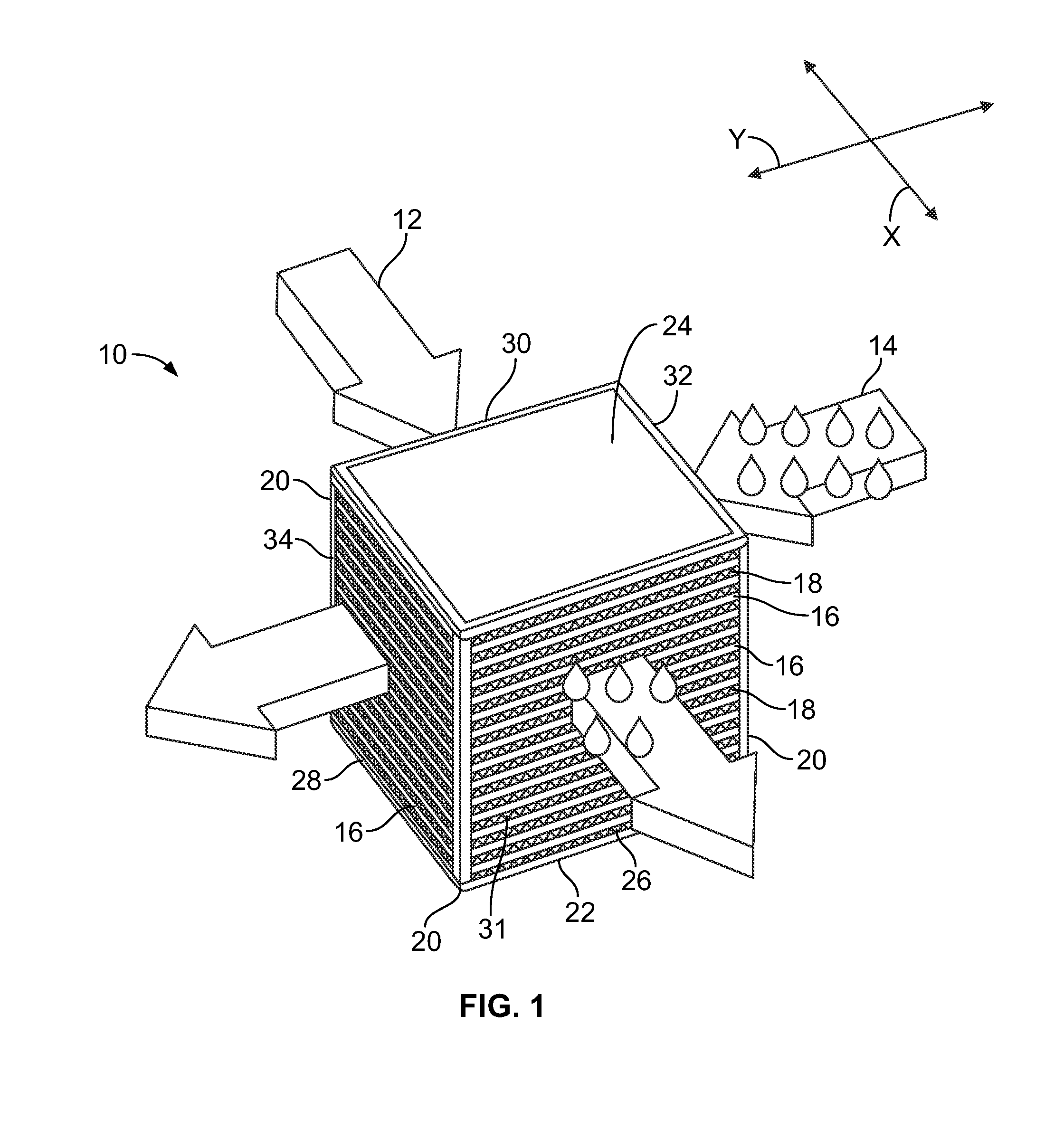
A cooling module for cooling at least two server modules that are configured to house a plurality of servers, the cooling module including a housing having an interior containing air, an intake into the housing, an outlet from the housing, at least one fan configured to move the air from the intake to the outlet and at least one sprayer configured to spray a mist into the air in the interior for evaporative cooling of the interior. Also a system formed of the cooling module, first and second server modules and a plenum connecting the outlet of the cooling module and intakes of the first and second server modules.
Owner:COMMSCOPE INC
Method and system for producing synthesis gas, gasification reactor, and gasification system
ActiveUS20060260191A1Increase pressureLower cost of capitalHydrogenGasification processes detailsSyngasPartial oxidation
A method and system for producing synthesis gas comprising CO, CO2, and H2 from a carbonaceous stream using an oxygen containing stream. A stream containing a carbonaceous material, and a stream containing oxygen are injected into a gasification reactor, where the carbonaceous stream is partially oxidised to obtain a raw synthesis gas. The raw synthesis gas is removed from the gasification reactor and directed into a quenching section wherein a liquid, preferably water, is injected in the form of a mist.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Exhaust gas abatement system
An exhaust gas abatement system includes an exhaust gas abatement section configured to abate exhaust gases by utilizing thermal energy and to cool the abated gases by using a liquid, a circulating section configured to circulate the liquid within a circulation path as a circulating liquid, a heat exchange tube configured to cool the circulating liquid and to executes a heat exchange between a cooling liquid which flows in an interior of the heat exchange tube and the circulating liquid which flows outside the heat exchange tube, and a circulating liquid storage portion configured to store the circulating liquid. The heat exchange tube is disposed in a heat exchange tube installation space which is in at least part of an interior of the circulating liquid storage portion.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Apparatus for heating fluids
InactiveUS6959669B2High yieldEasy to controlSteam generation using mechanical energyAir-treating devicesDrive shaftEngineering
The apparatus has a housing with a main chamber in which a rotor is situated. A drive shaft drives the rotor about a longitudinal axis of rotation. The housing has a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet, the fluid inlet communicating with an inlet region and a fluid outlet communicating with an exit region. The outer surface of the rotor forms one boundary for the fluid heat generating region and is confronted by the inner surface of the main chamber which is the other boundary. At least one of these surfaces is angularly inclined relative to the axis of rotation of the drive shaft and rotor. By bodily shifting the rotor in a direction along the longitudinal axis, an increase or decrease in the distance between the outer and inner surfaces is possible in order to adjust for wear or to change the degree of shear experienced by the passing fluid.
Owner:THOMA CHRISTIAN HELMUT
Heat treatment apparatus and method of obtaining toner
InactiveUS20140137428A1Sharp particle size distributionDrying solid materials with heatDevelopersCold airEngineering
A heat treatment apparatus for heat-treating powder particles each containing a binder resin and a colorant includes: a powder particle supply unit (3); a hot air supply unit (2); a cold air supply unit (4); a regulating unit (6); and a collection unit (5). The apparatus is characterized in that: a protrusion with a height of 2 mm or more and 50 mm or less is provided in a region on a downstream side of the powder particle supply unit and on an upstream side of the cold air supply unit in an inner wall surface of the treatment chamber; and the heat treatment apparatus has a cross-section plane, which is perpendicular to a center axis of the treatment chamber and situated at the region where the protrusion is provided, and Dmin and Dmax satisfy the following relation 0.50≦Dmin / Dmax<1.0 where, Dmin represents a minimum value of the distance of a gap between the treatment chamber and the columnar member measured in the cross-section plane, and Dmax represents a maximum value of the distance of a gap between the treatment chamber and the columnar member measured in the cross-section plane.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for forming an energy exchange assembly
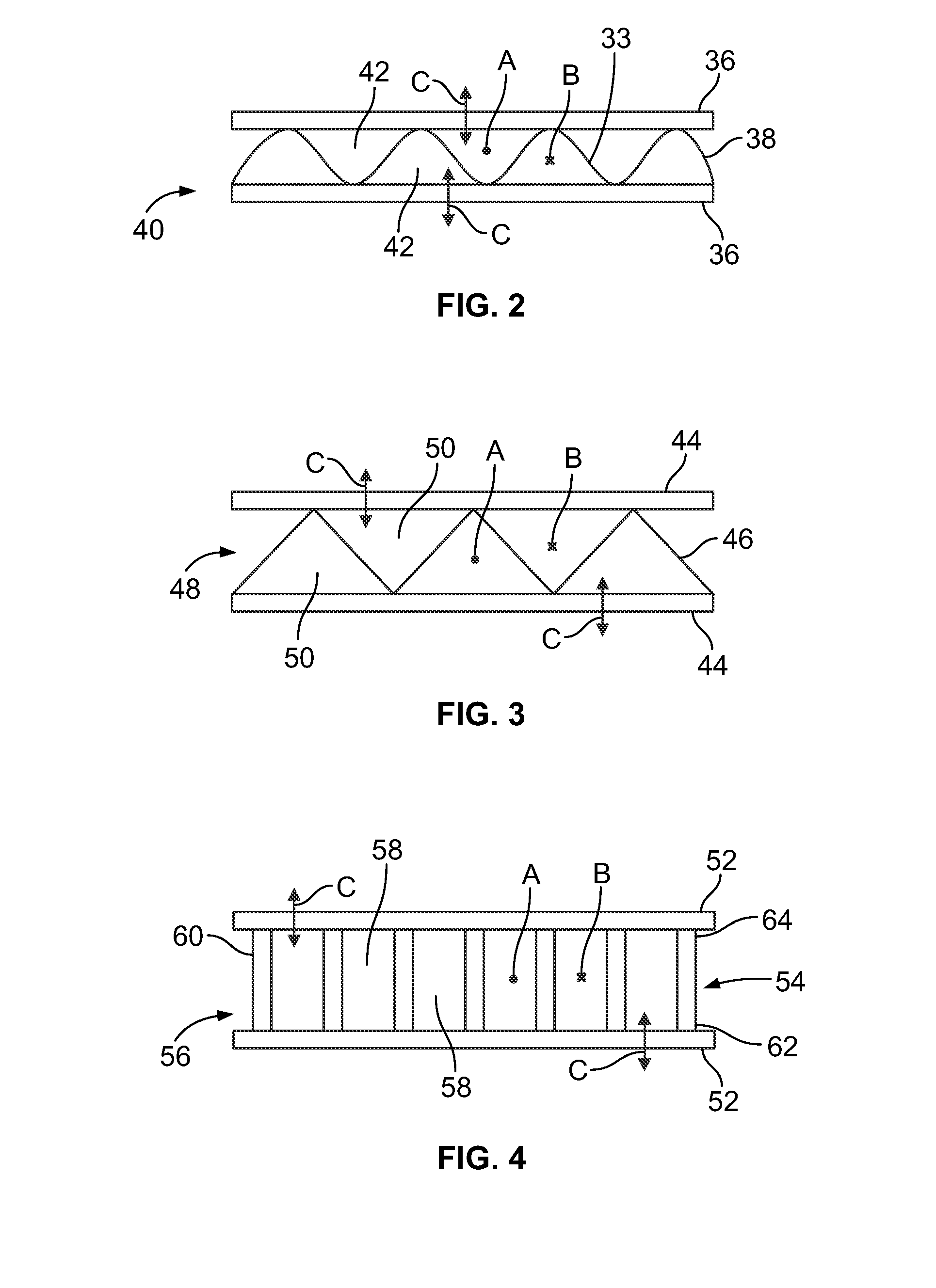
ActiveUS20140264968A1Energy recovery in ventilation and heatingHeat recovery systemsEngineeringEnergy exchange
A method of forming an energy exchange assembly may include forming a plurality of creases and a plurality of slits in a membrane sheet according to a predefined pattern, positioning a first spacer on top of a first forming area of the membrane sheet, folding the membrane sheet over a top of the first spacer so that a second forming area is positioned over the top of the first spacer, sealing a first portion of the first forming area to a first outer lateral wall of the first spacer, and positioning a second spacer on top of the second forming area, thereby stacking the second spacer over the first spacer.
Owner:NORTEK AIR SOLUTIONS CANADA INC
Popular searches
Other chemical processes Heat storage plants Compression machines with non-reversible cycle Heat-exchange elements Compression machines with reversible cycle Base-materials Direct heating destructive distillation Biofuels Indirect and direct heating destructive distillation Liquid hydrocarbon mixture production
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com