Patents
Literature
207 results about "Fluid intake" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine determined that an adequate daily fluid intake is: About 15.5 cups (3.7 liters) of fluids for men About 11.5 cups (2.7 liters) of fluids a day for women
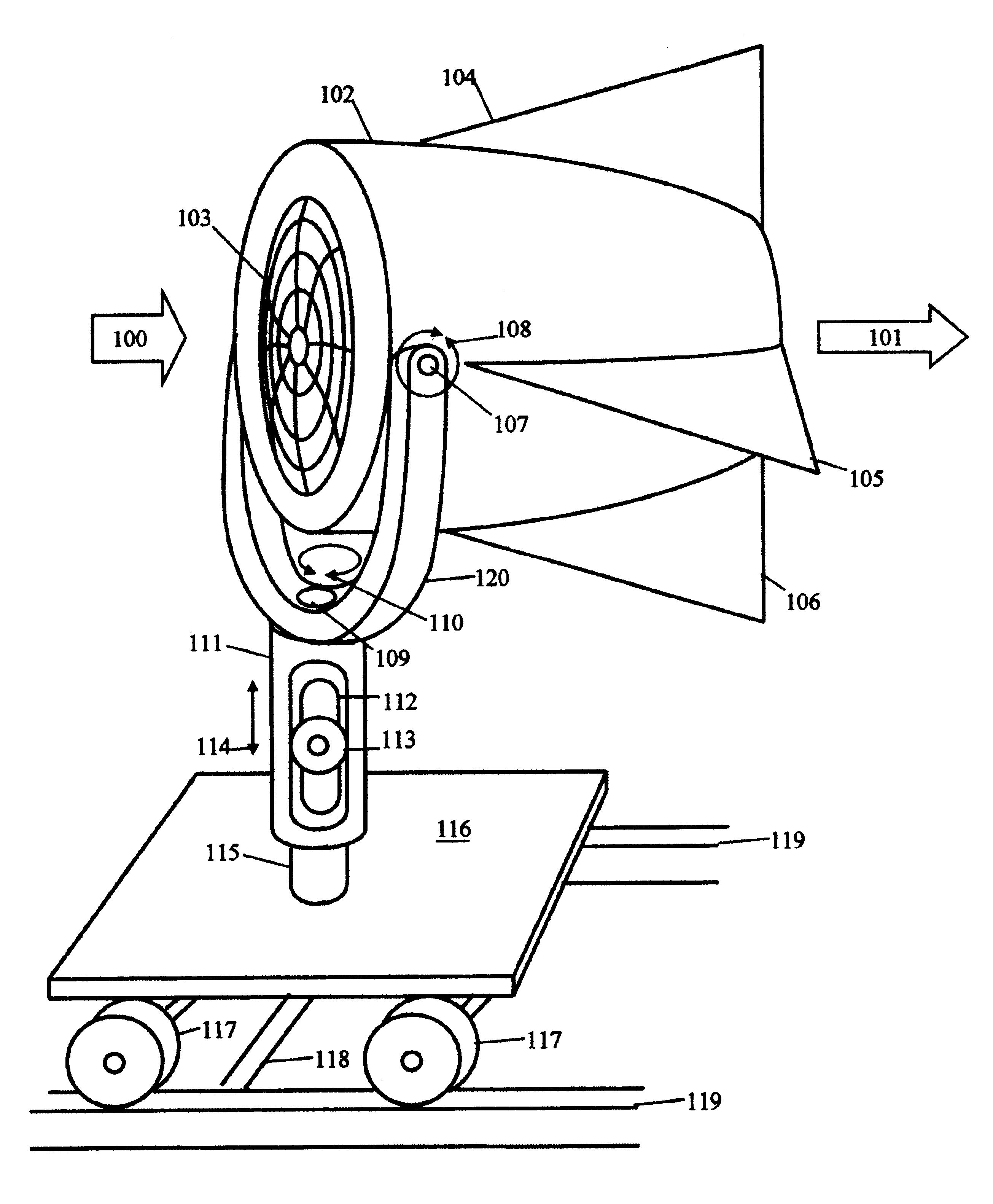
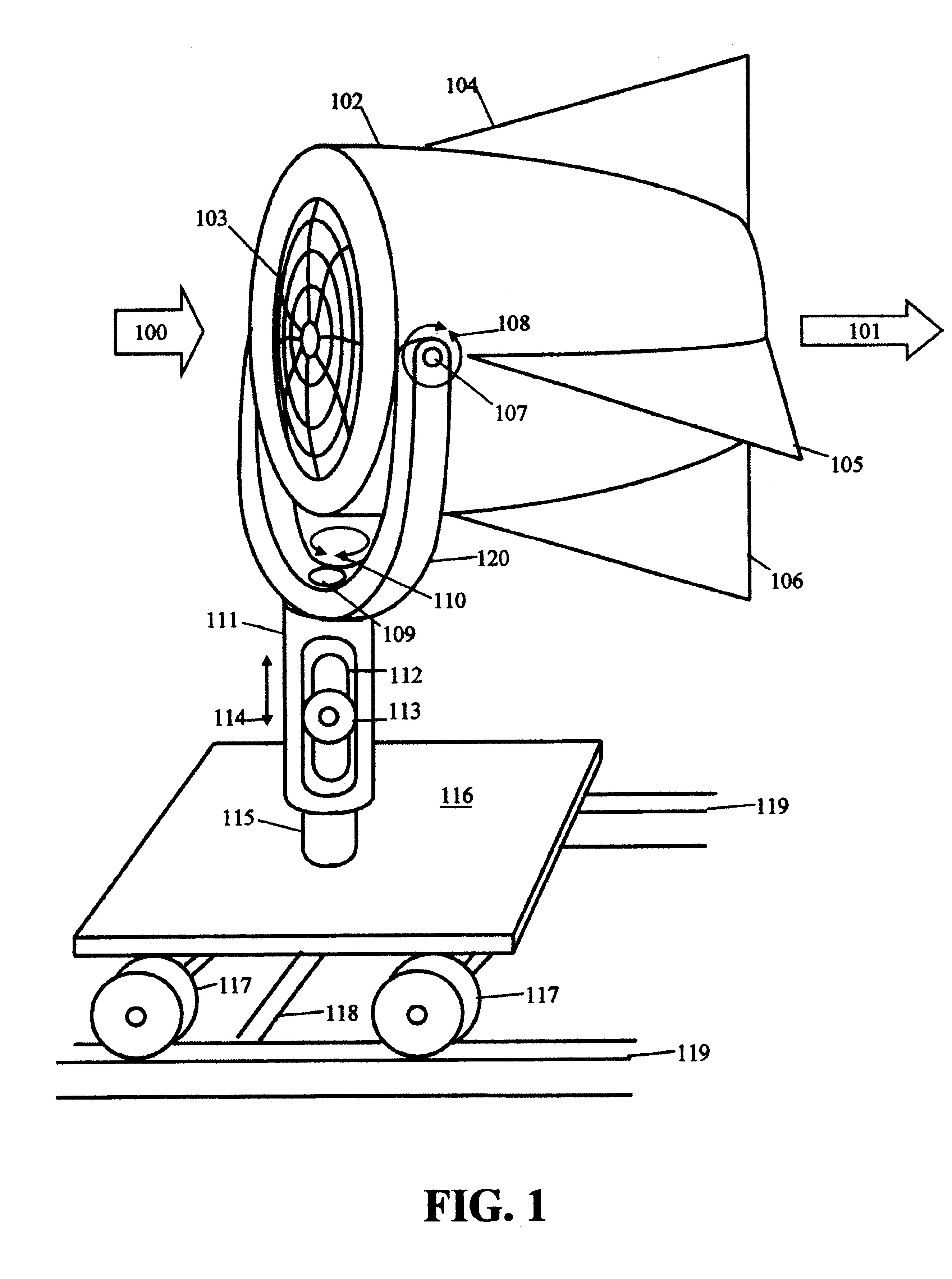
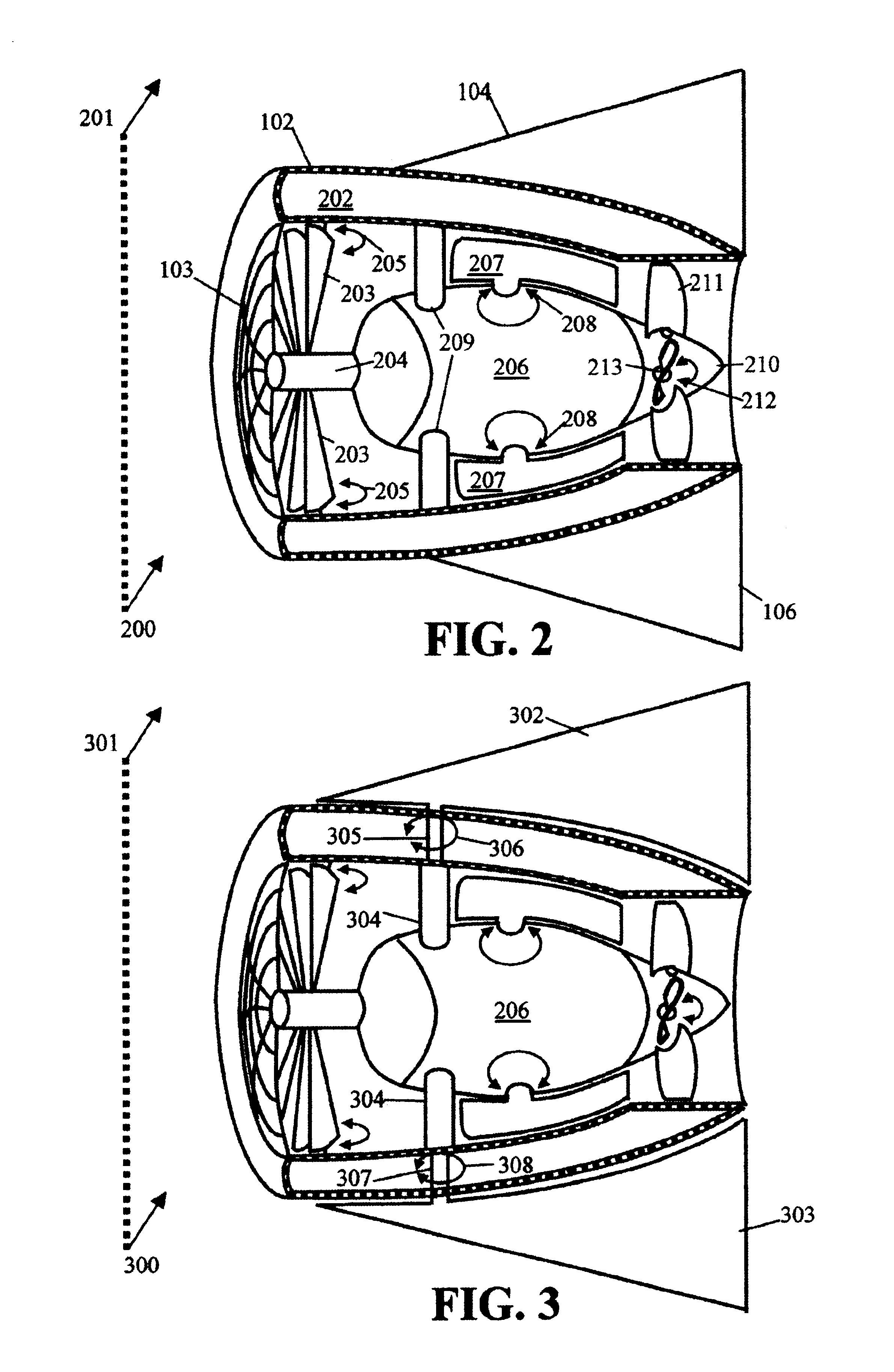
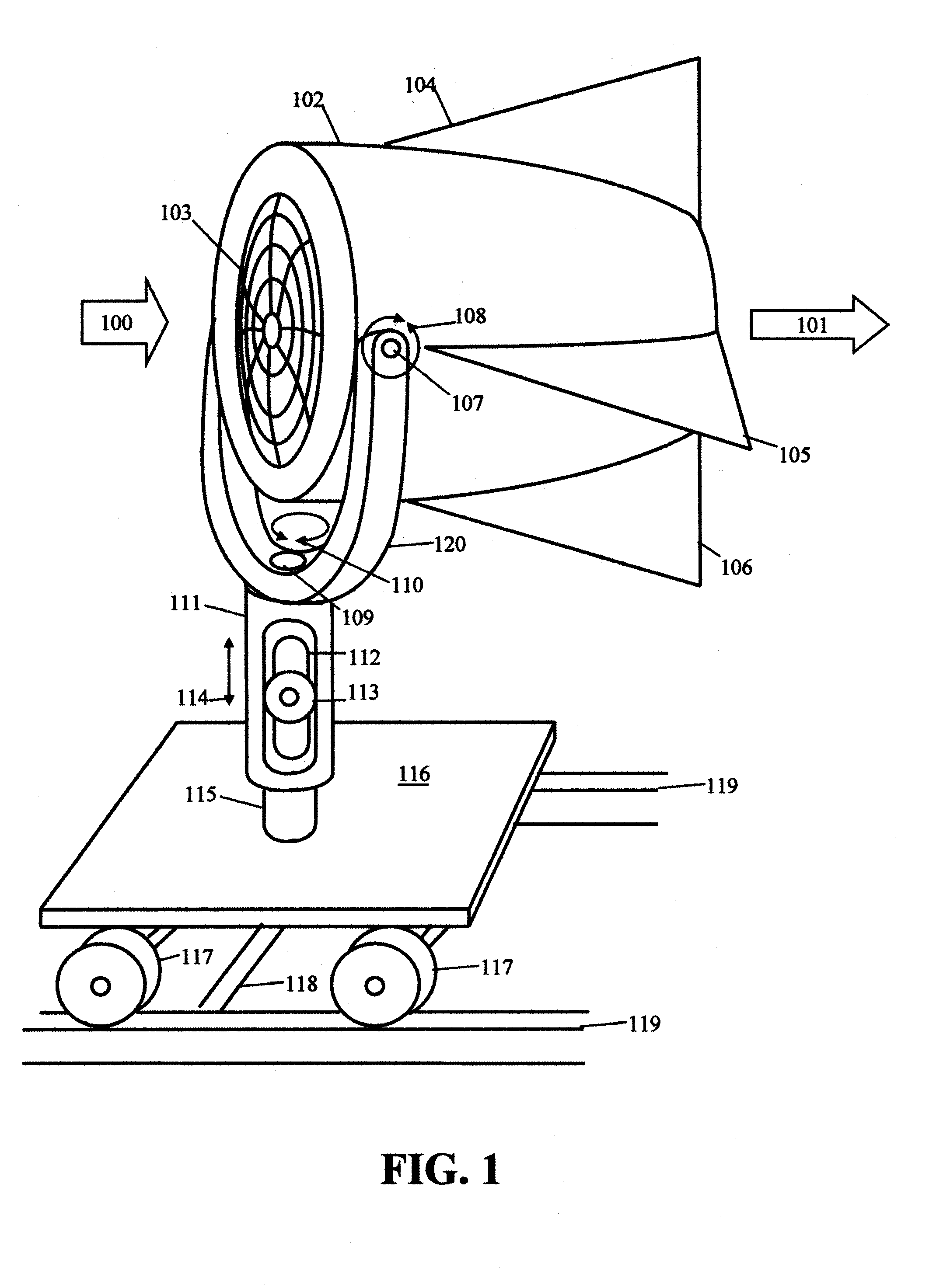
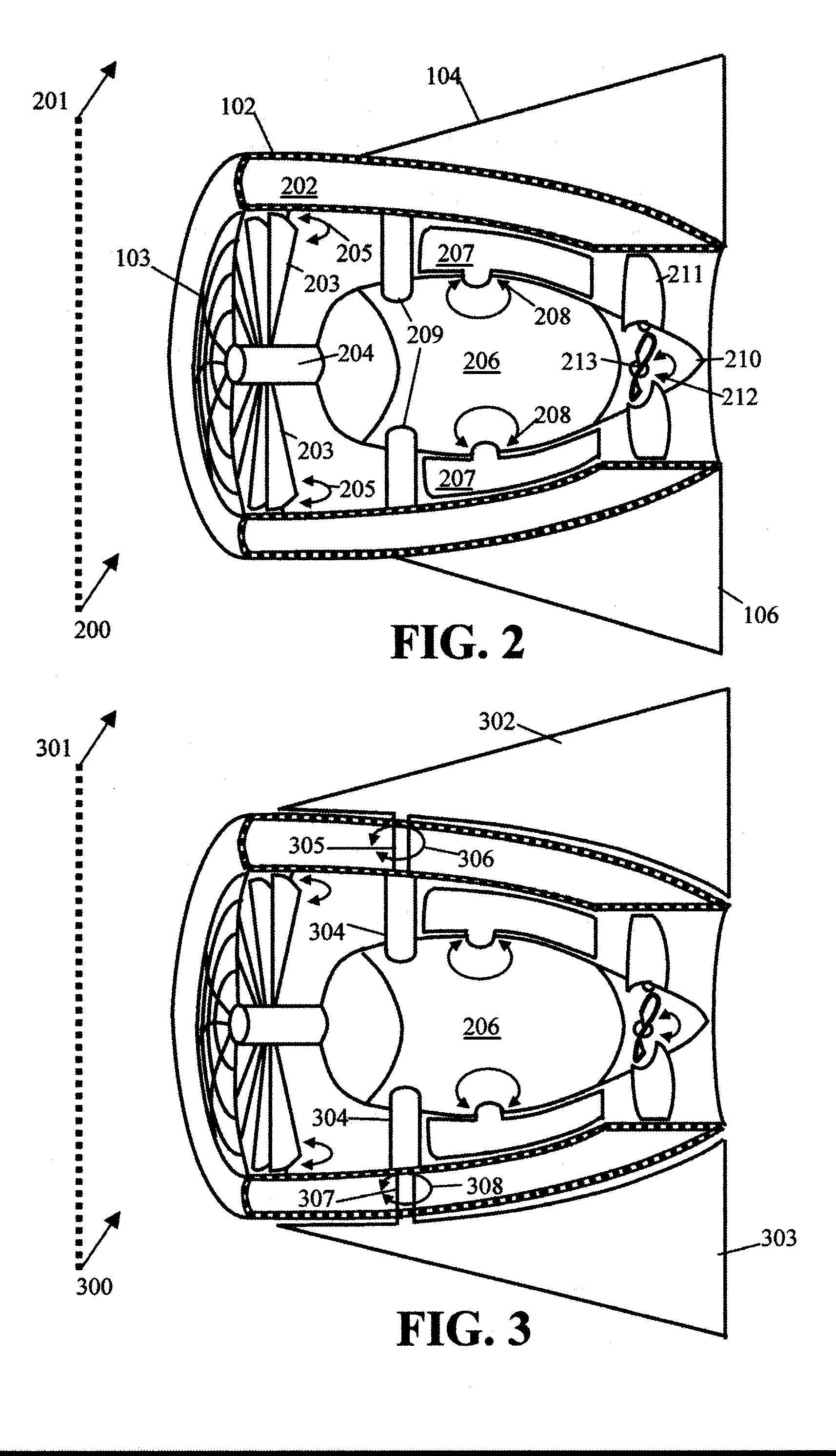
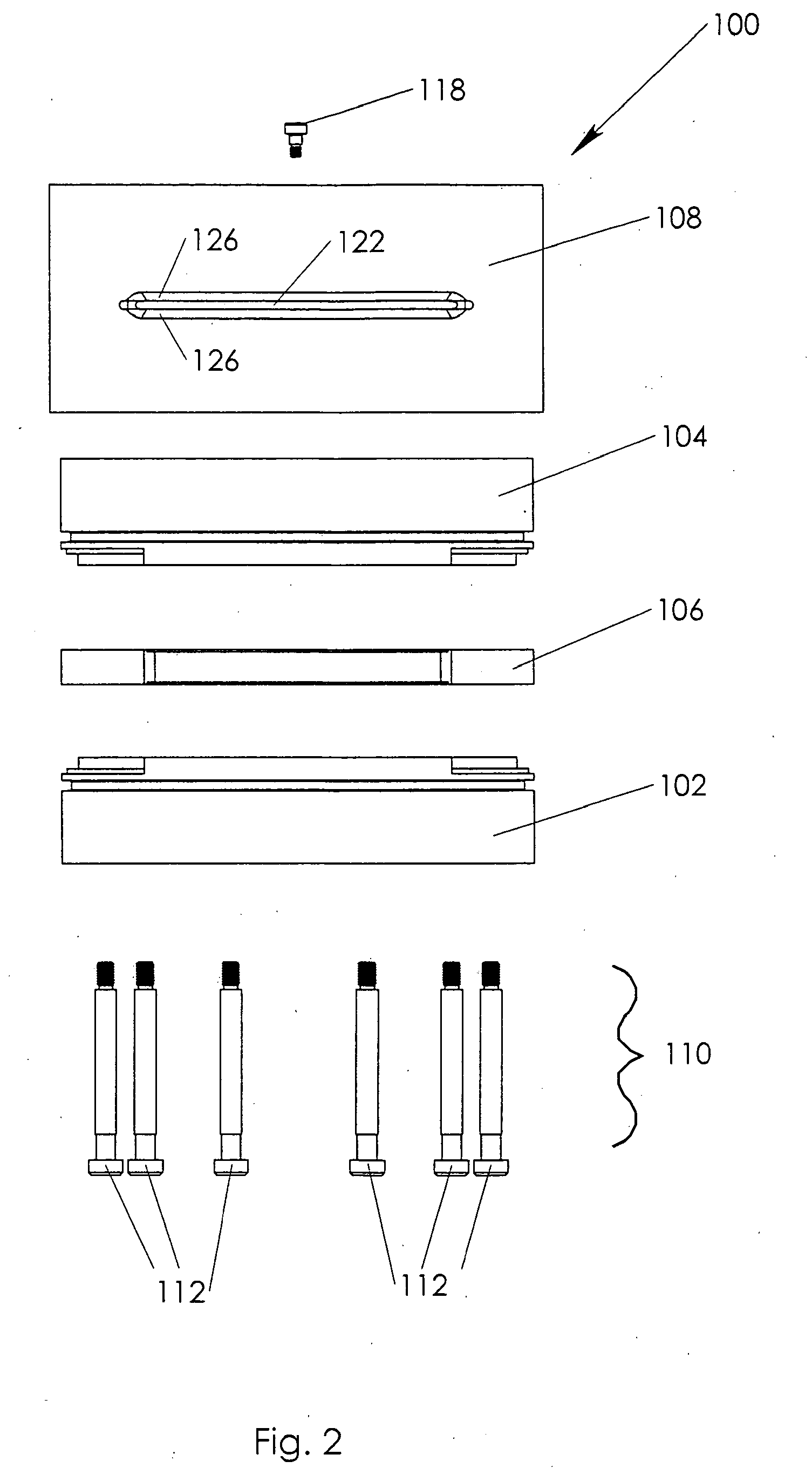
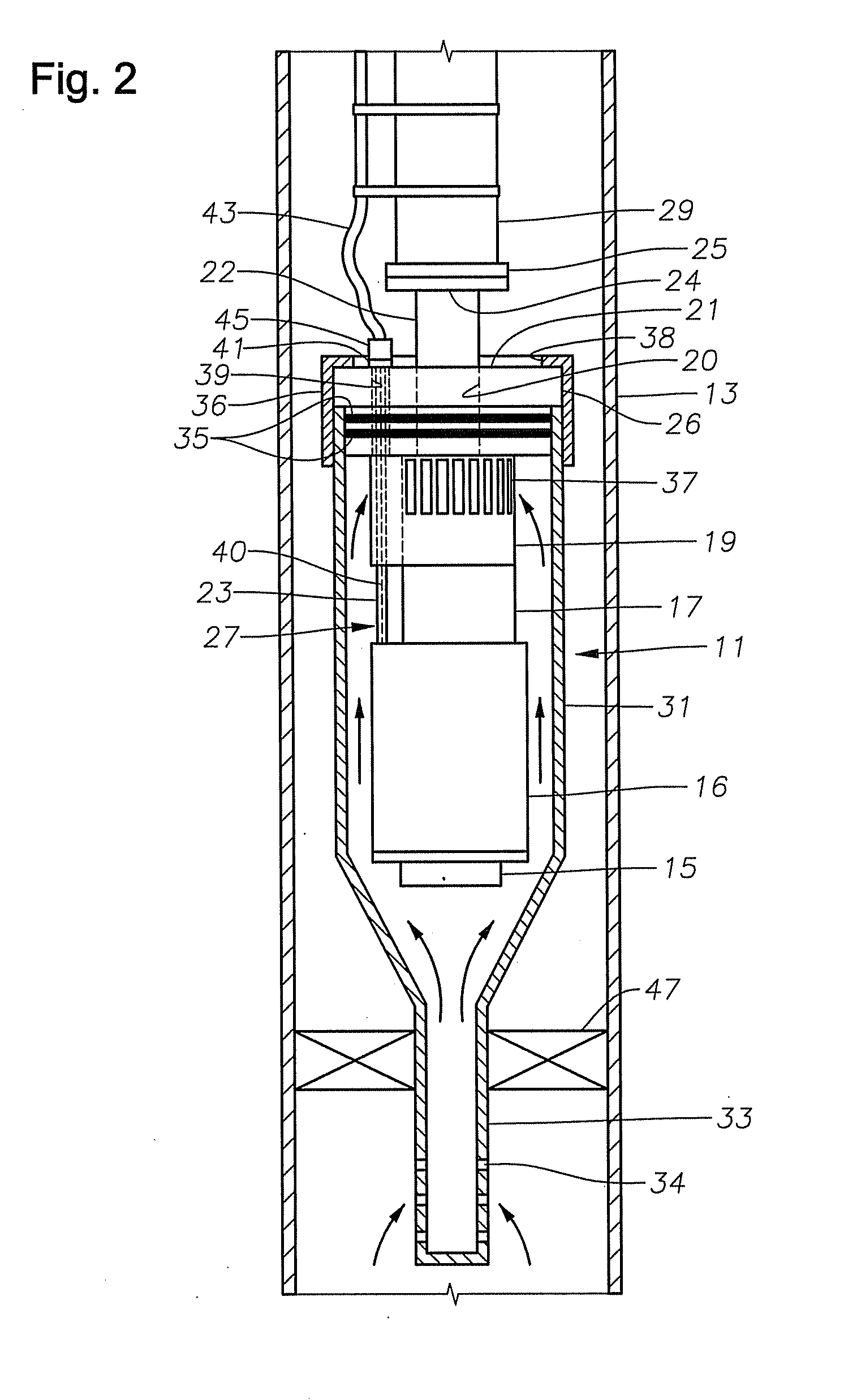
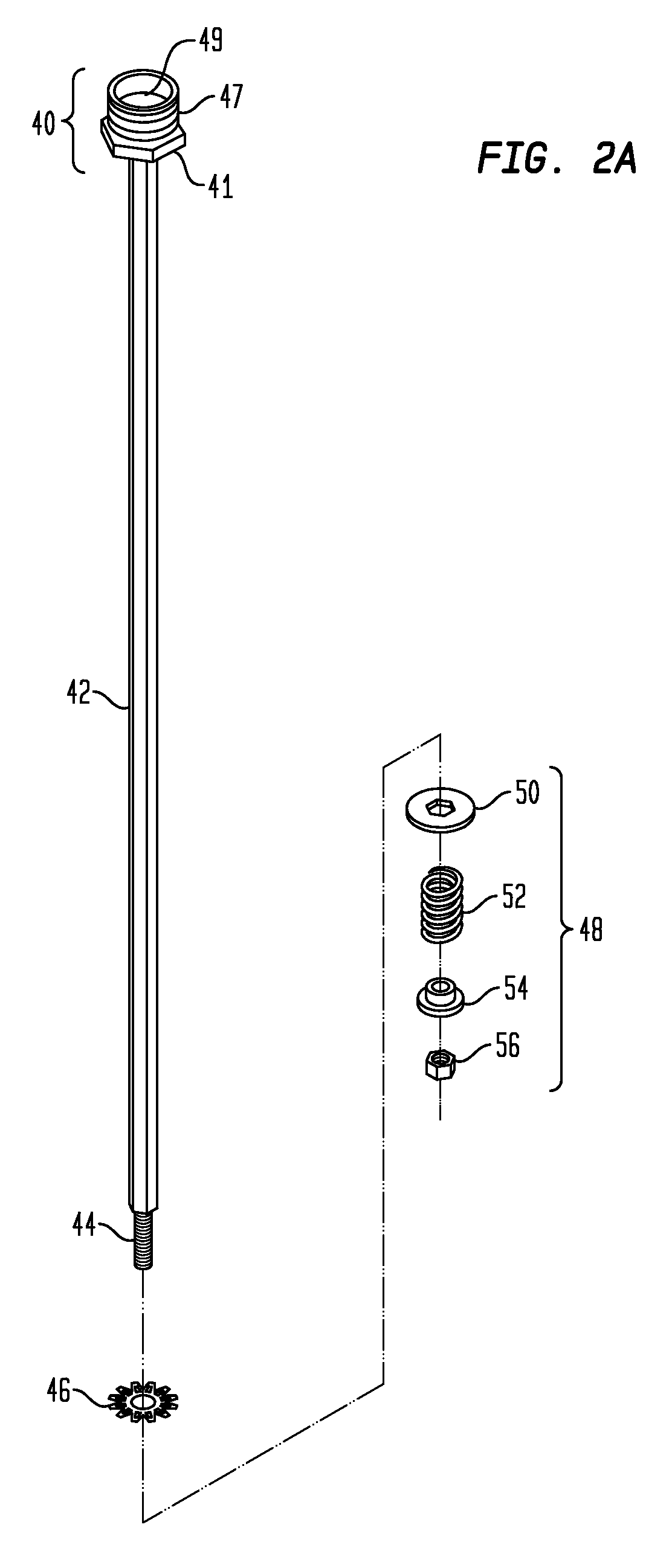
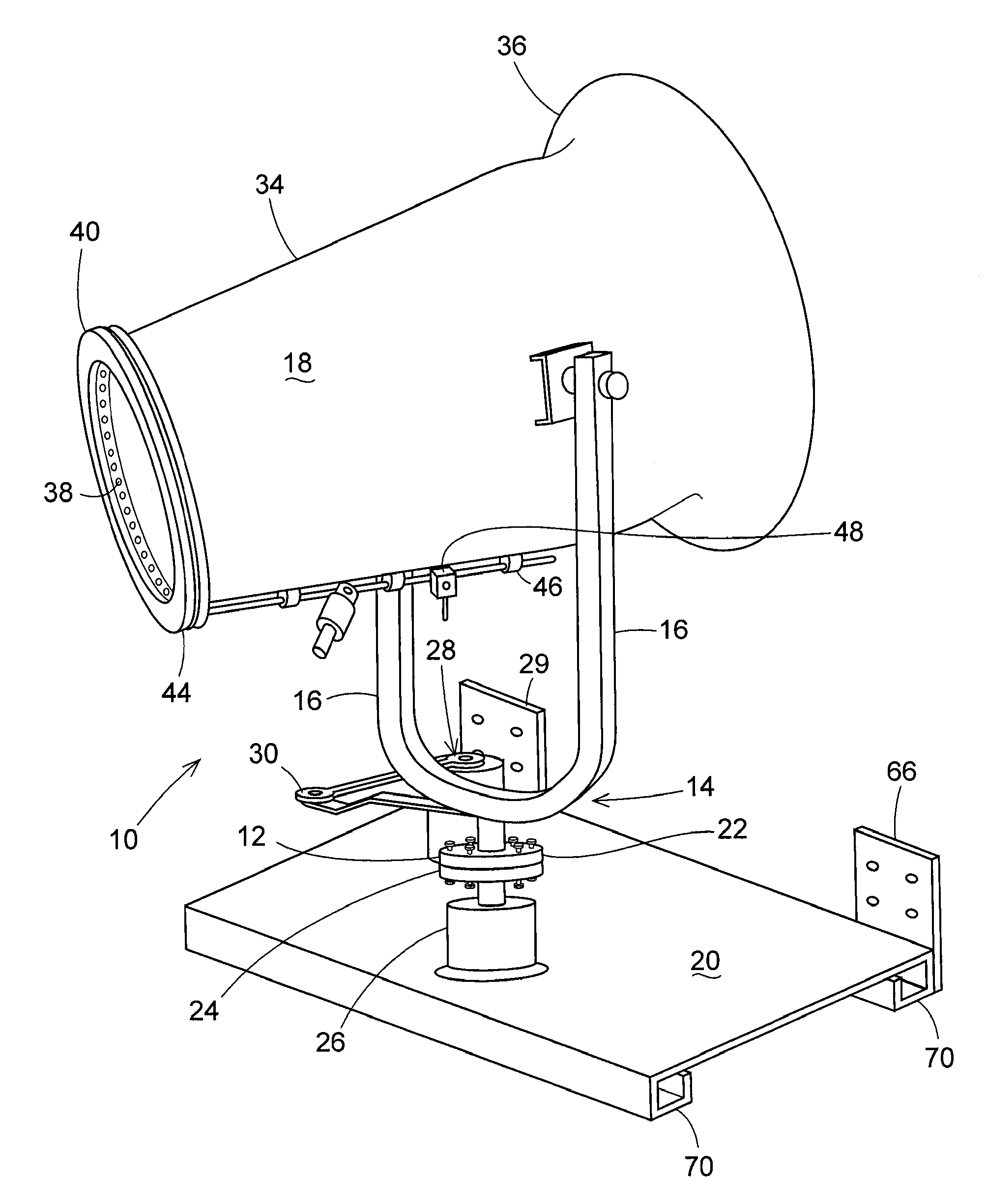
Gimbal-mounted hydroelectric turbine
InactiveUS6956300B2Reduce environmental impactPositive net energyFluid couplingsWind energy with electric storageFluid intakeEngineering
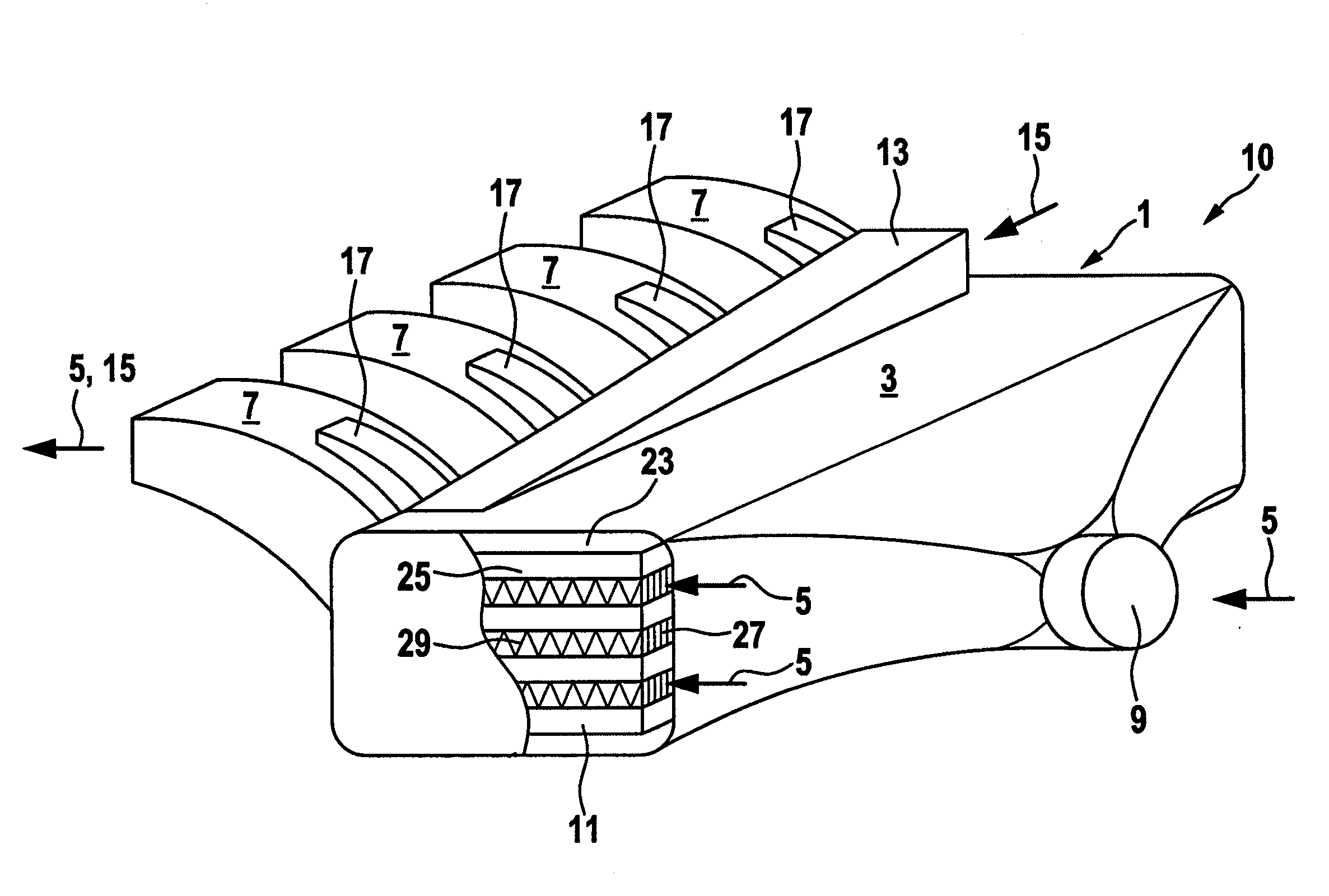
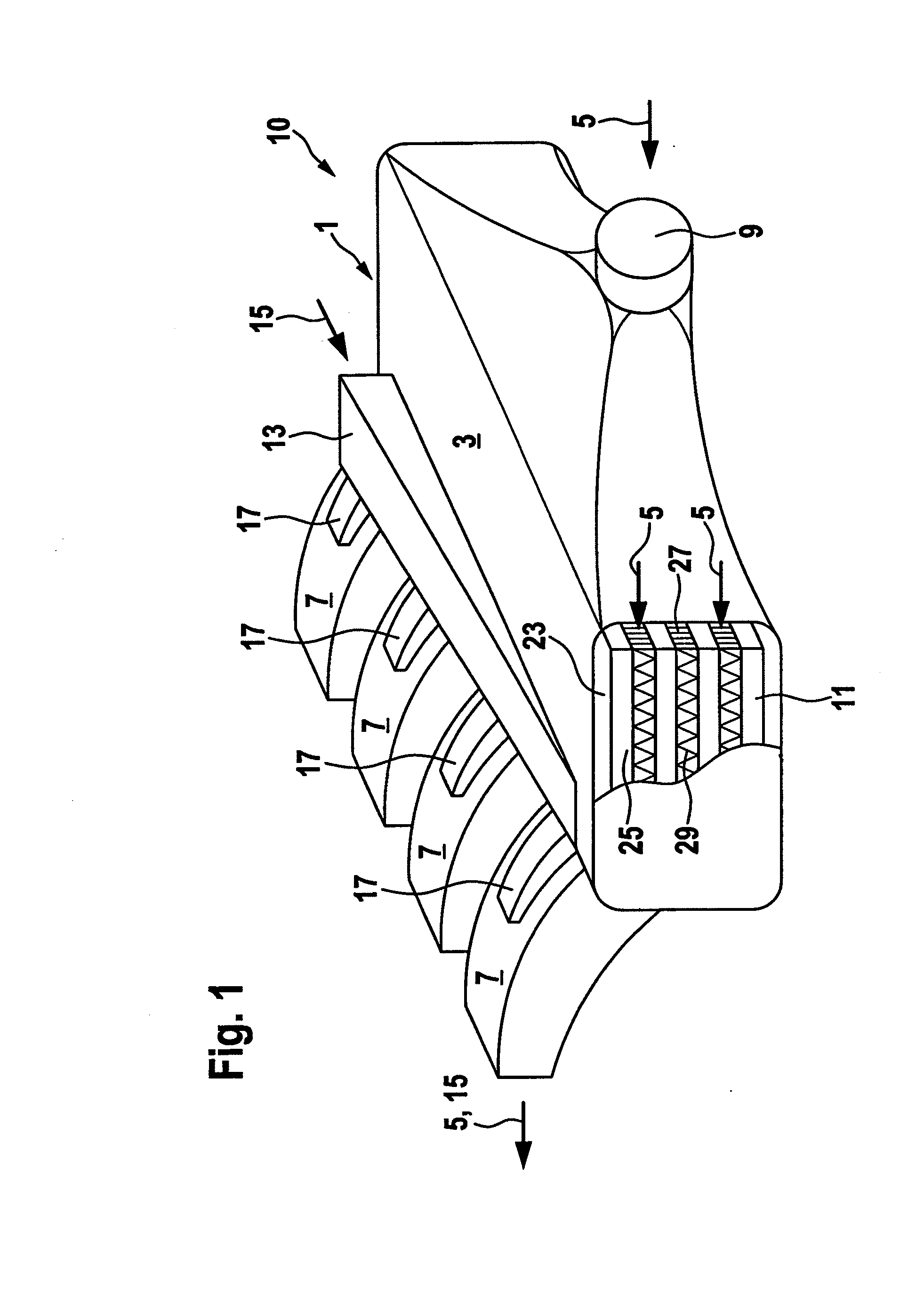
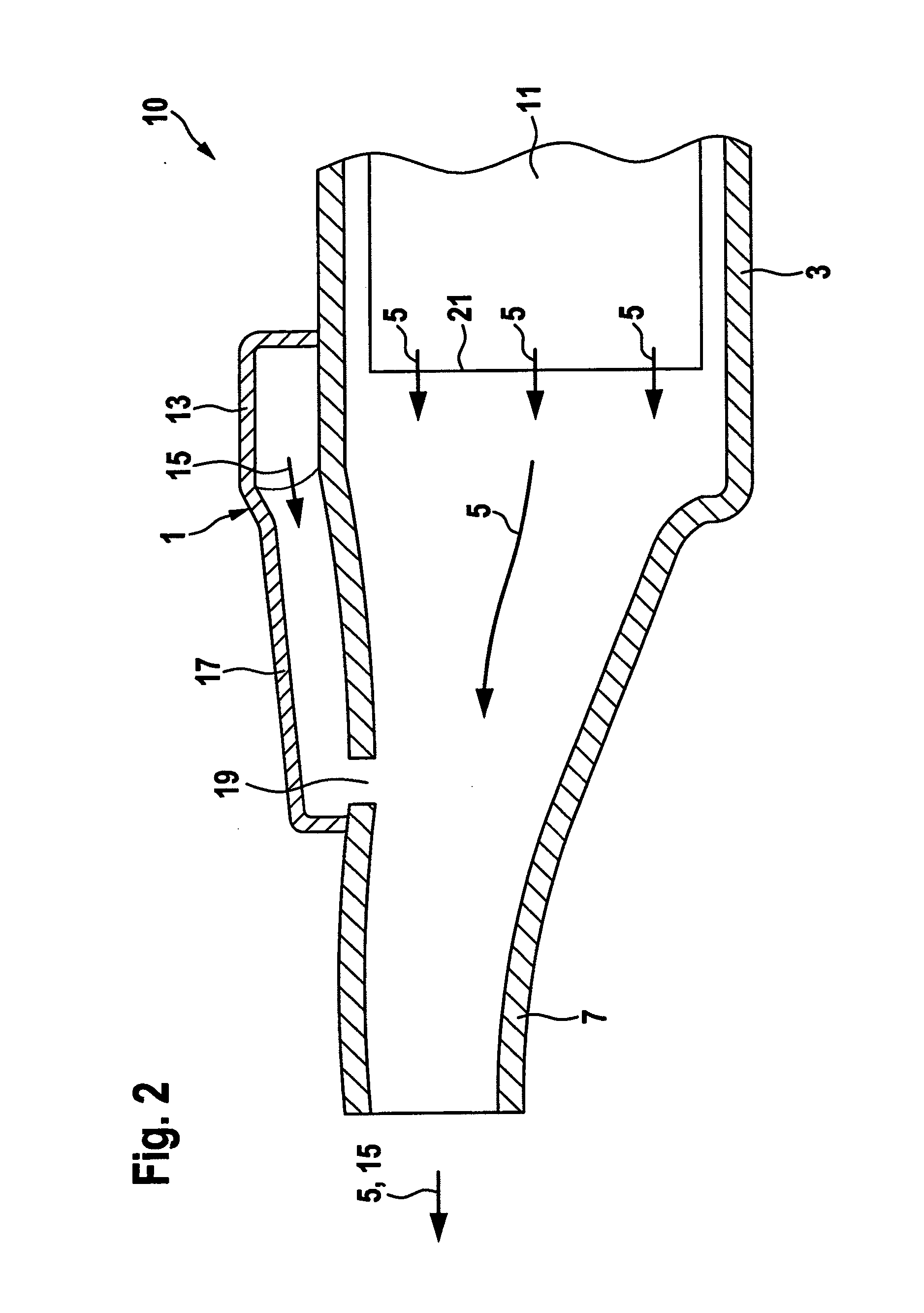
A power plant extracts energy from a free flowing motive fluid by means of a turbine mounted on a gimbal. The shroud element of the fluid intake has external rudders, in conjunction with the gimbal mounting, enabling the enclosed turbine to instantaneously respond to changes in the direction of the free flowing motive fluid thus ensuring the face area of the intake is always physically orthogonal to the direction of the motive fluid streamlines. The shroud element may also be buoyant so as to optimally extract energy from an upper non-turbulent and higher velocity layer of the free flowing motive fluid. To function within an inherently unsteady source of energy, the preferred embodiment of the turbine is coupled to a DC generator which may further be coupled to a voltage and current regulating circuit which either charges a battery, performs electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen fuel, or is further coupled to a DC motor coupled to an AC generator. Alternatively an AC induction generator may be coupled to the turbine. Other mechanical, electrical, electronic, or electromechanical features may optionally be implemented to perform such tasks as adaptively locating the turbine in the maximum velocity flow, adapting internal vane and runner blade pitches for various flow rates and loads, keeping the intake free of obstructions, preventing loss of aquatic life, controlling and communicating the state of charge of the battery, or gauging and controlling the electrolysis process and communicating the fullness of the hydrogen gas output tanks.
Owner:INTEGRATED POWER TECH CORP
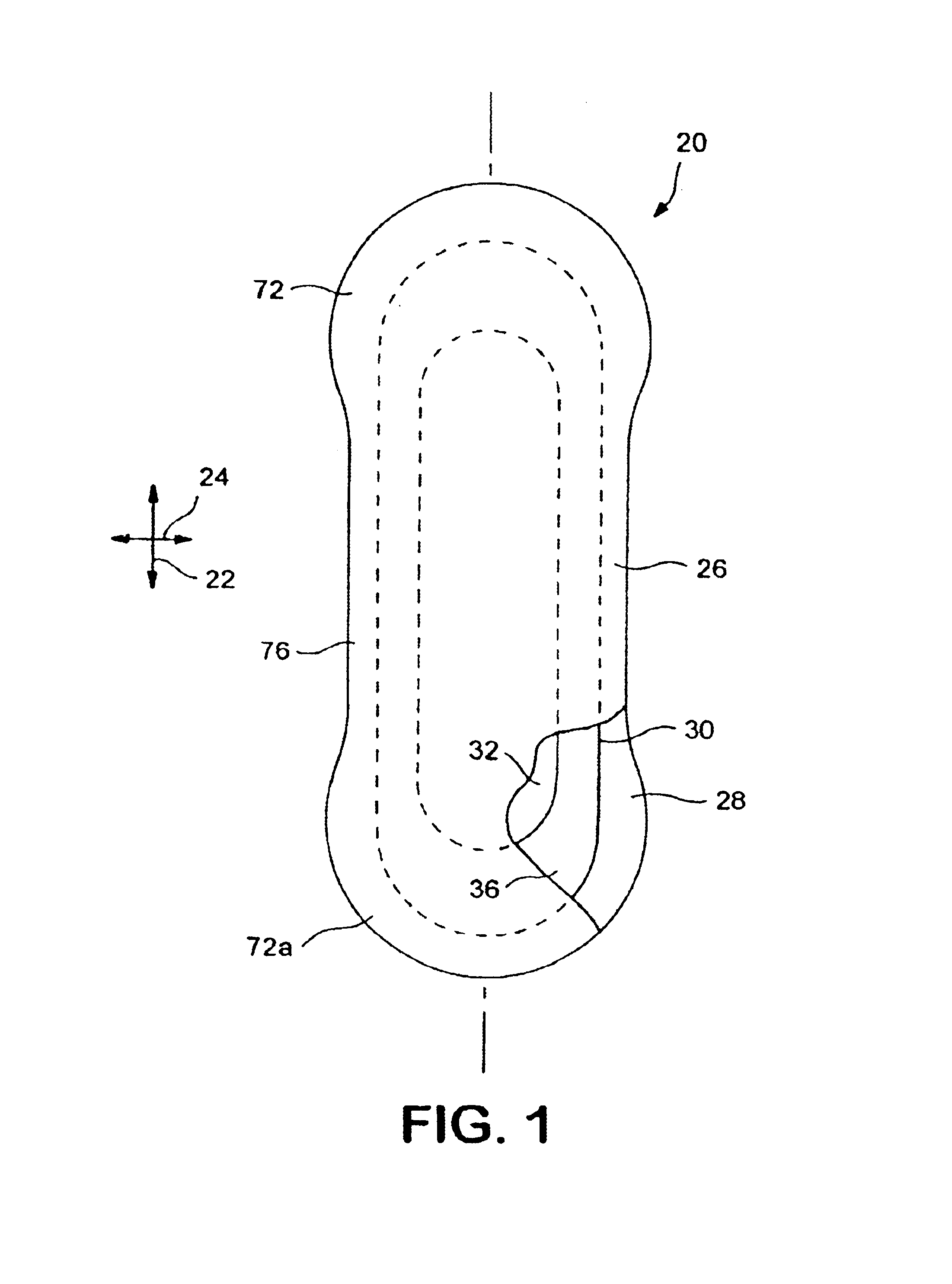
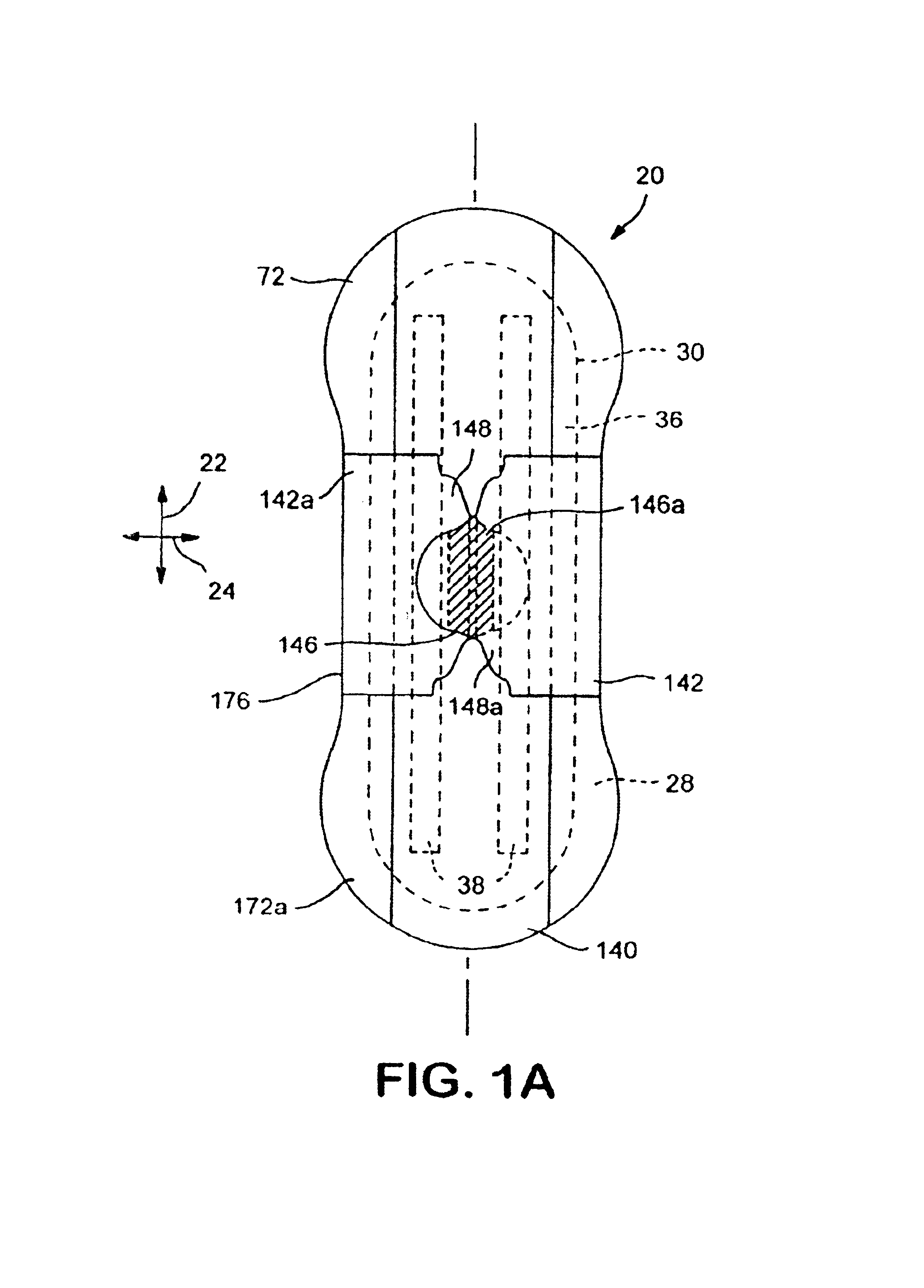
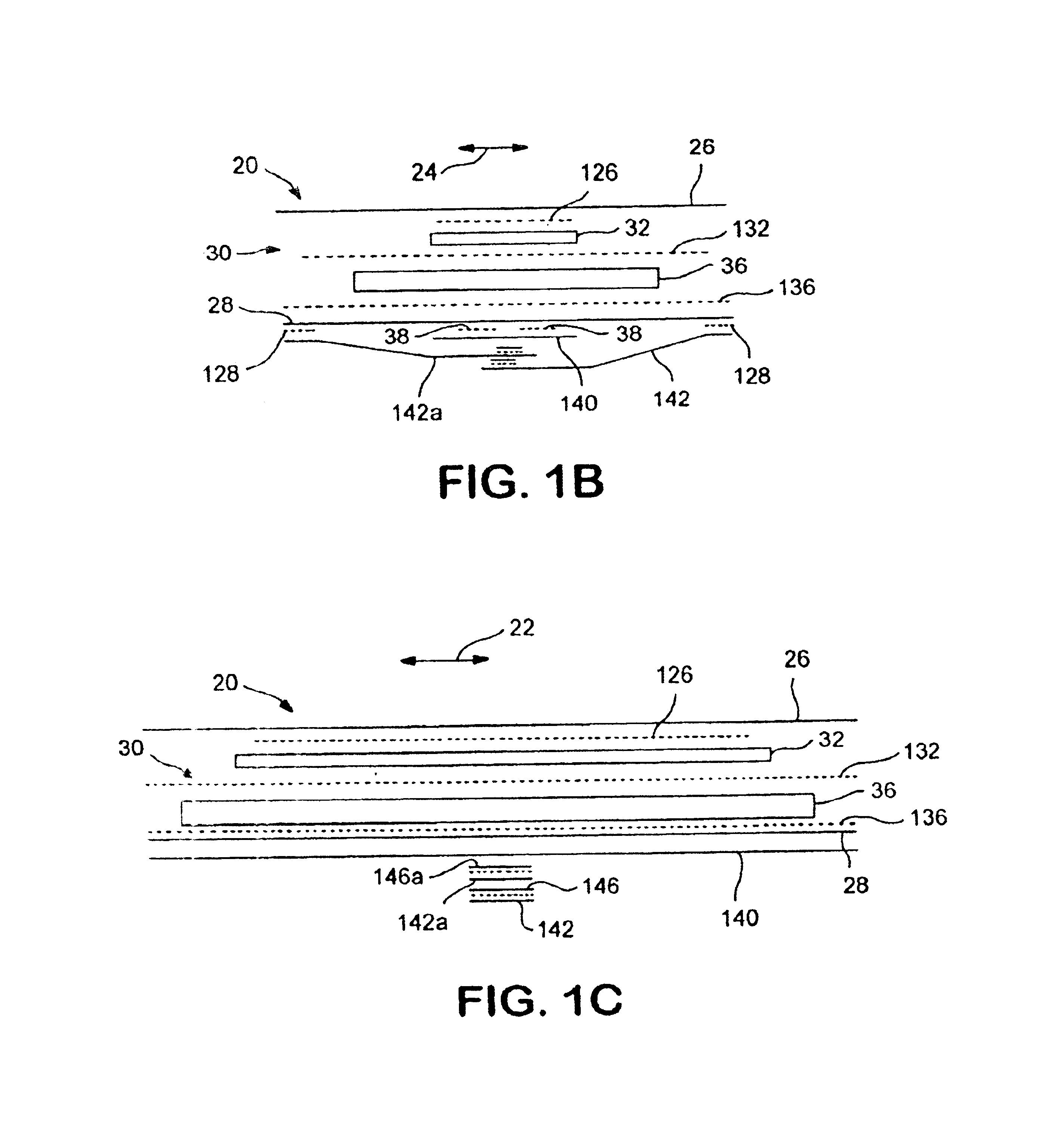
Absorbent articles
The present invention provides an improved disposable article for the absorption and containment of urine or other body exudates, for example a diaper, training pants or an adult incontinence article, that has a high fecal fluid intake rate as measured by the Fecal Fluid Intake Test.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Apparatus and method for heating fluids
InactiveUS7089886B2Risk minimizationEliminate requirementsPump componentsOther heat production devicesFluid intakeRotational axis
An apparatus for heating a liquid comprising a housing having an internal chamber and a rotor disposed in said chamber. A drive shaft rotatably supported in the housing and extending into said chamber for imparting mechanical energy to the rotor. The rotor having a generally hemi-spherically shaped form and provided with a series of openings. A fluid intake passage in said housing preferably arranged to be nearer the rotational axis of the rotor and a fluid exit passage preferably positioned radially outwardly of said rotor.
Owner:THOMA CHRISTIAN HELMUT
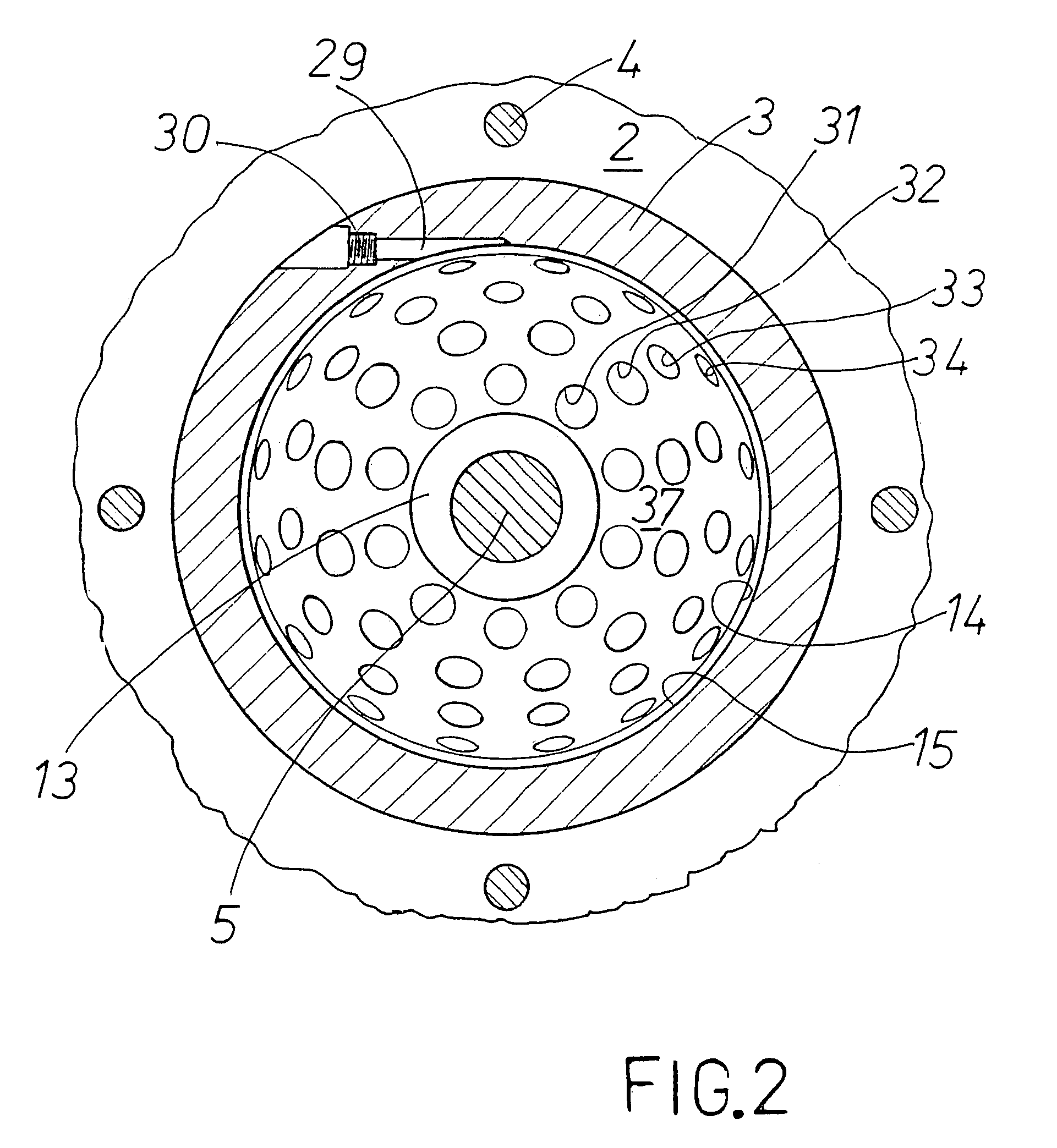
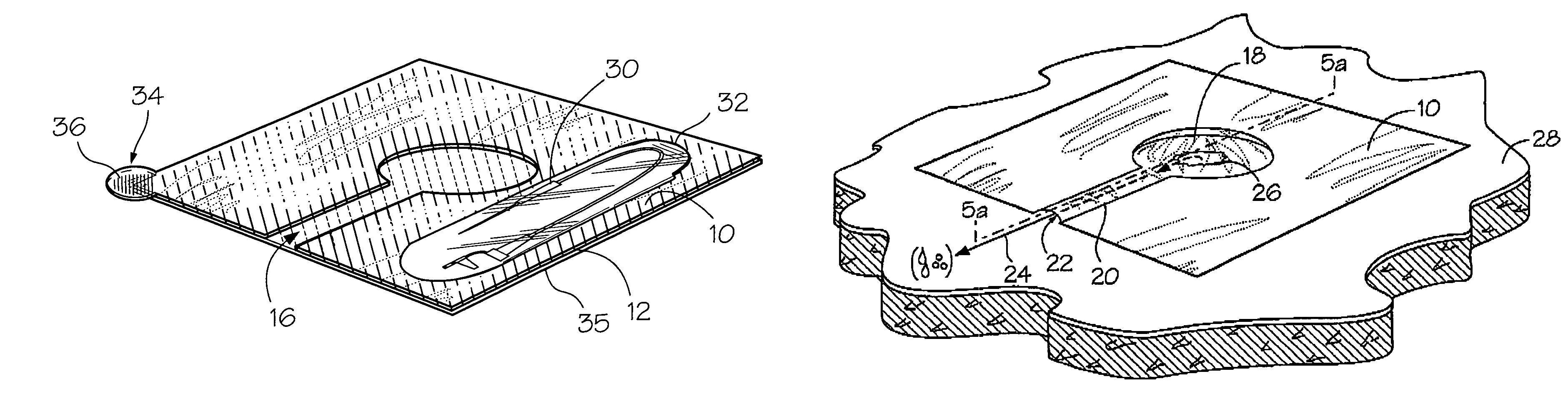
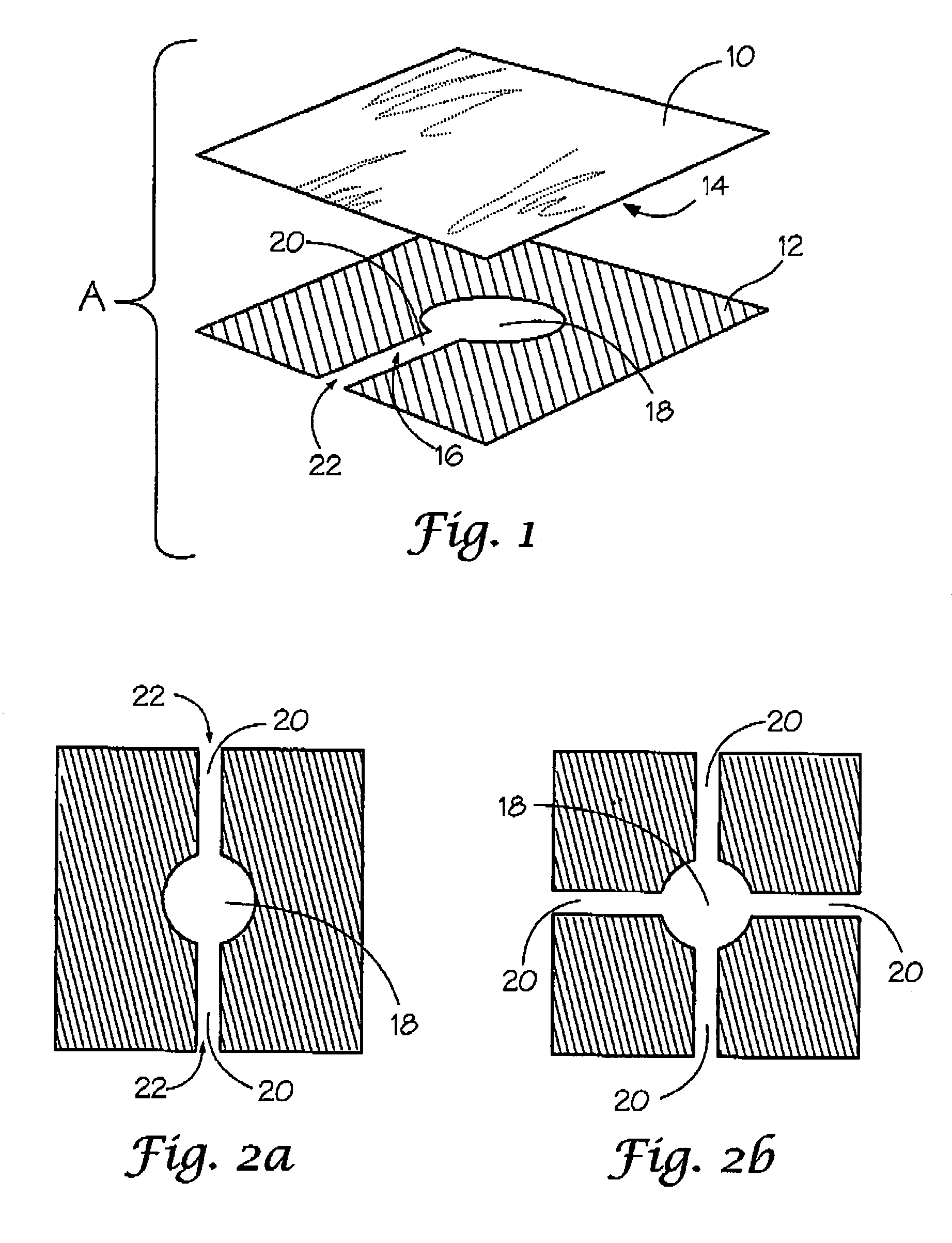
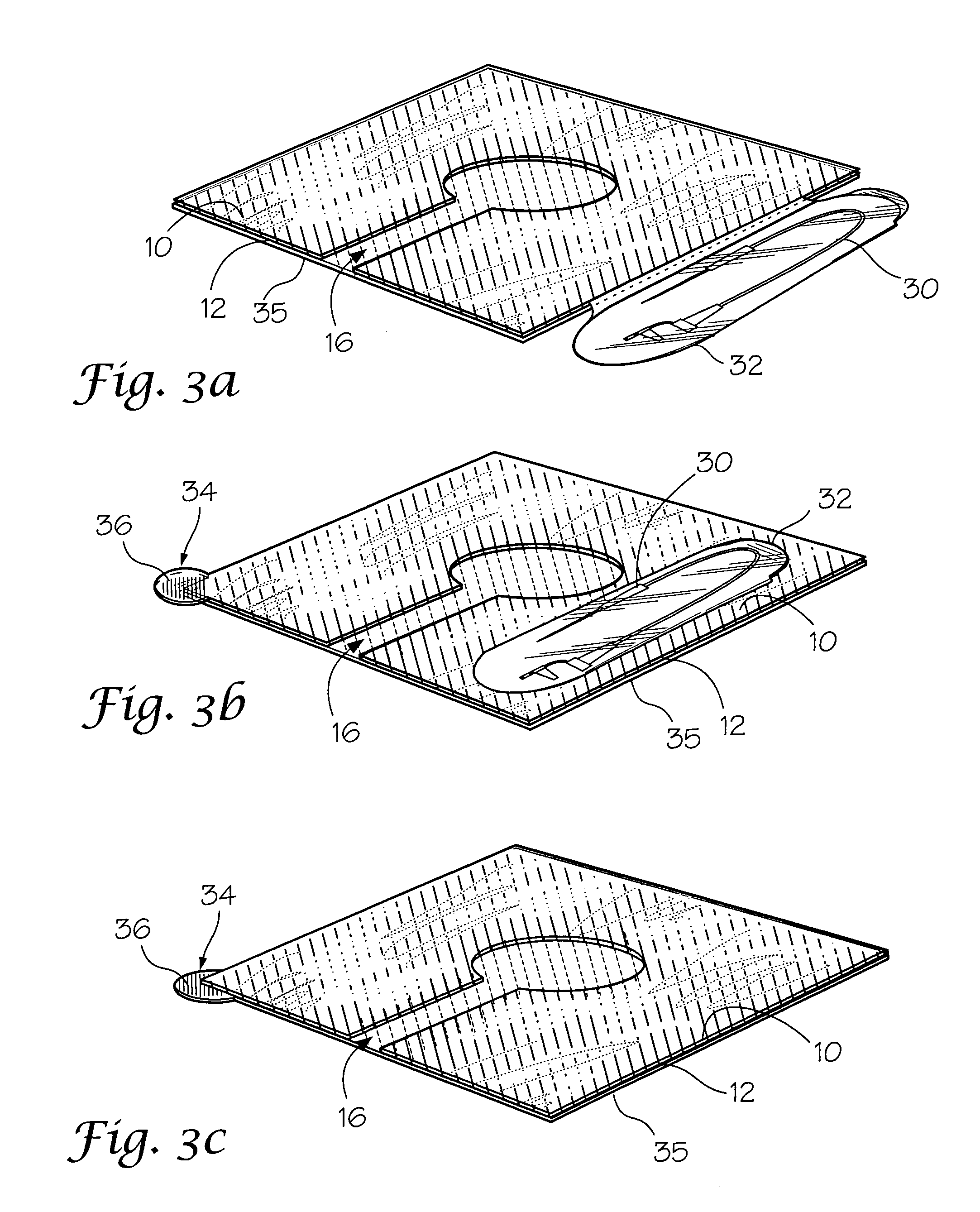
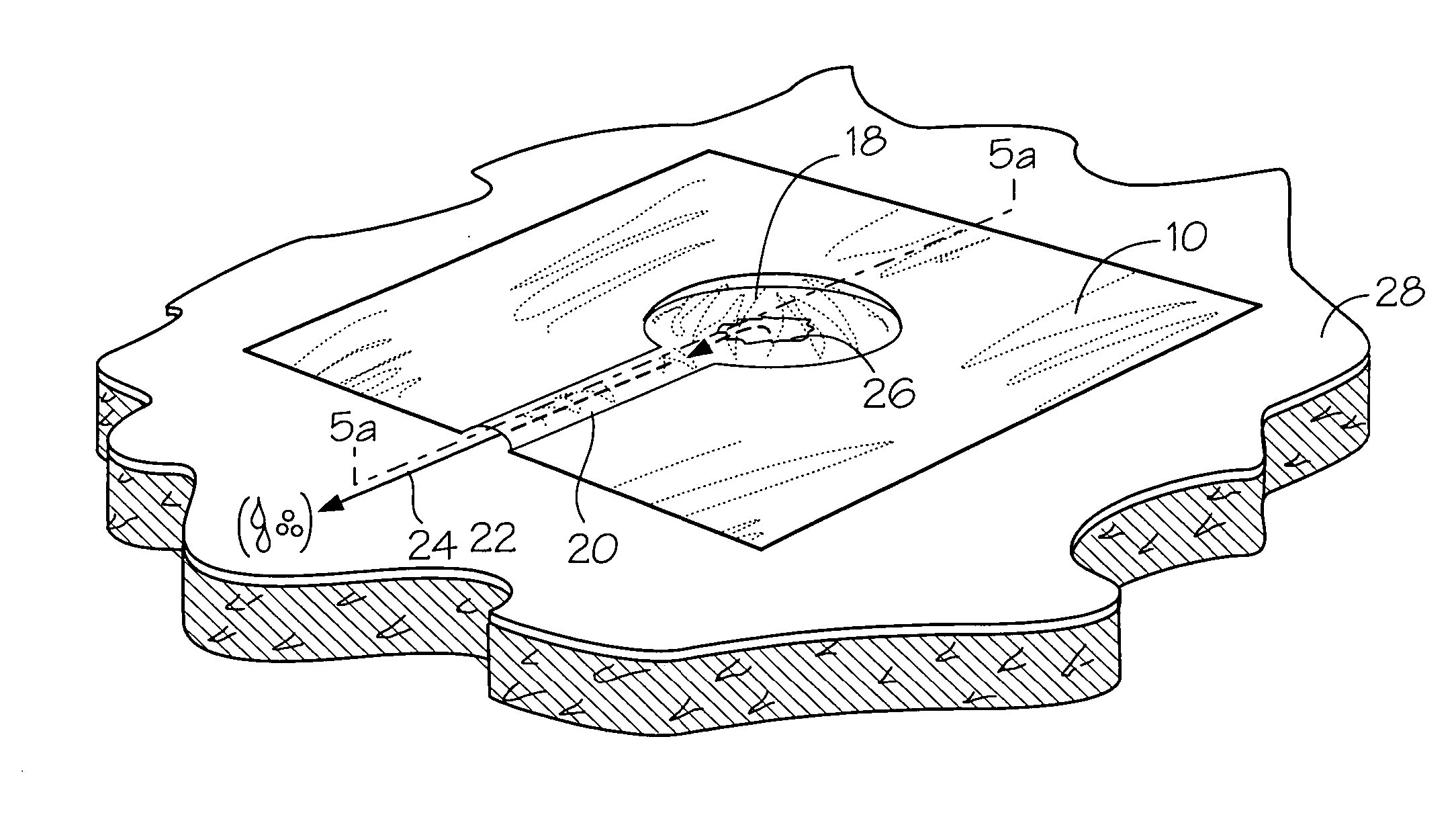
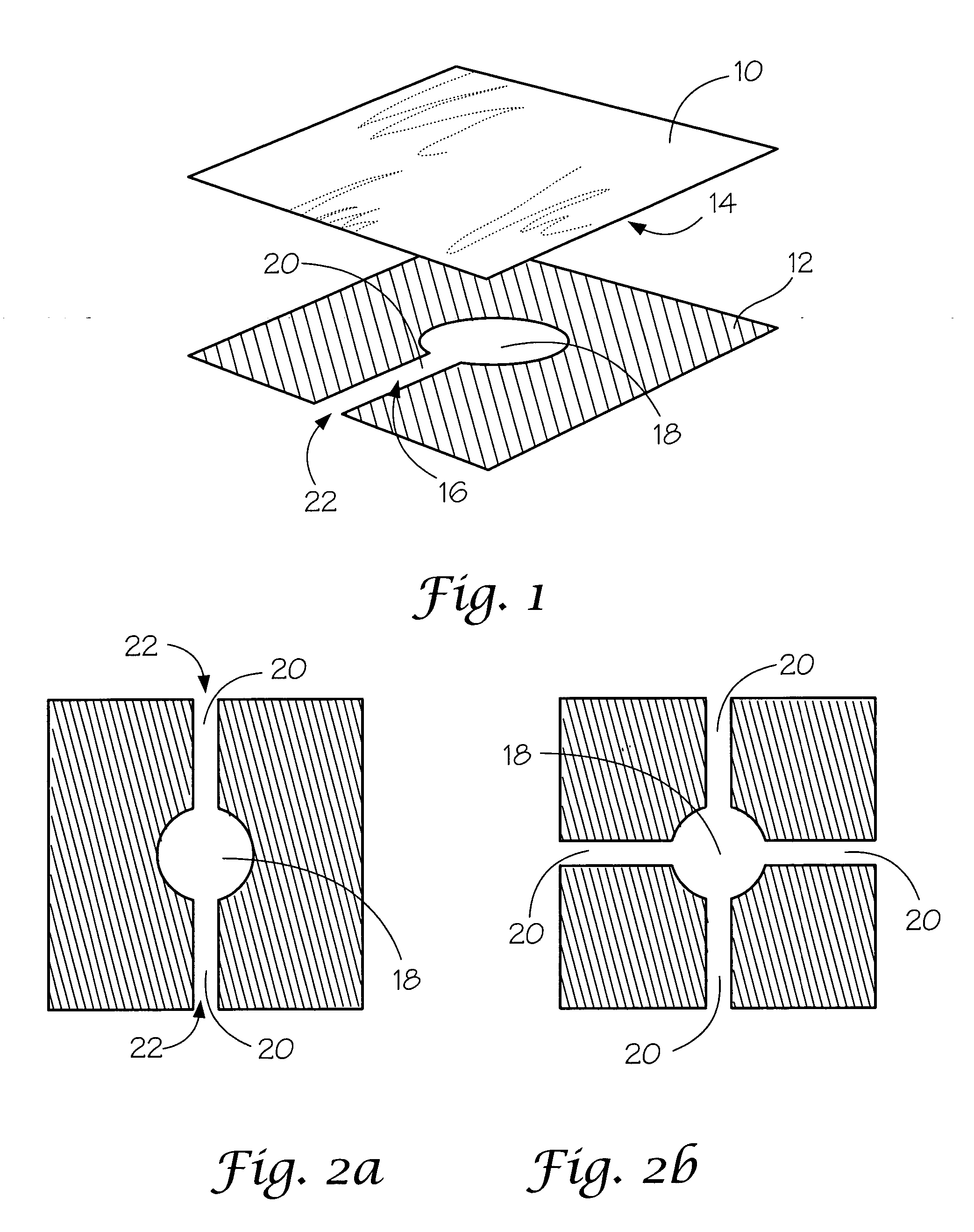
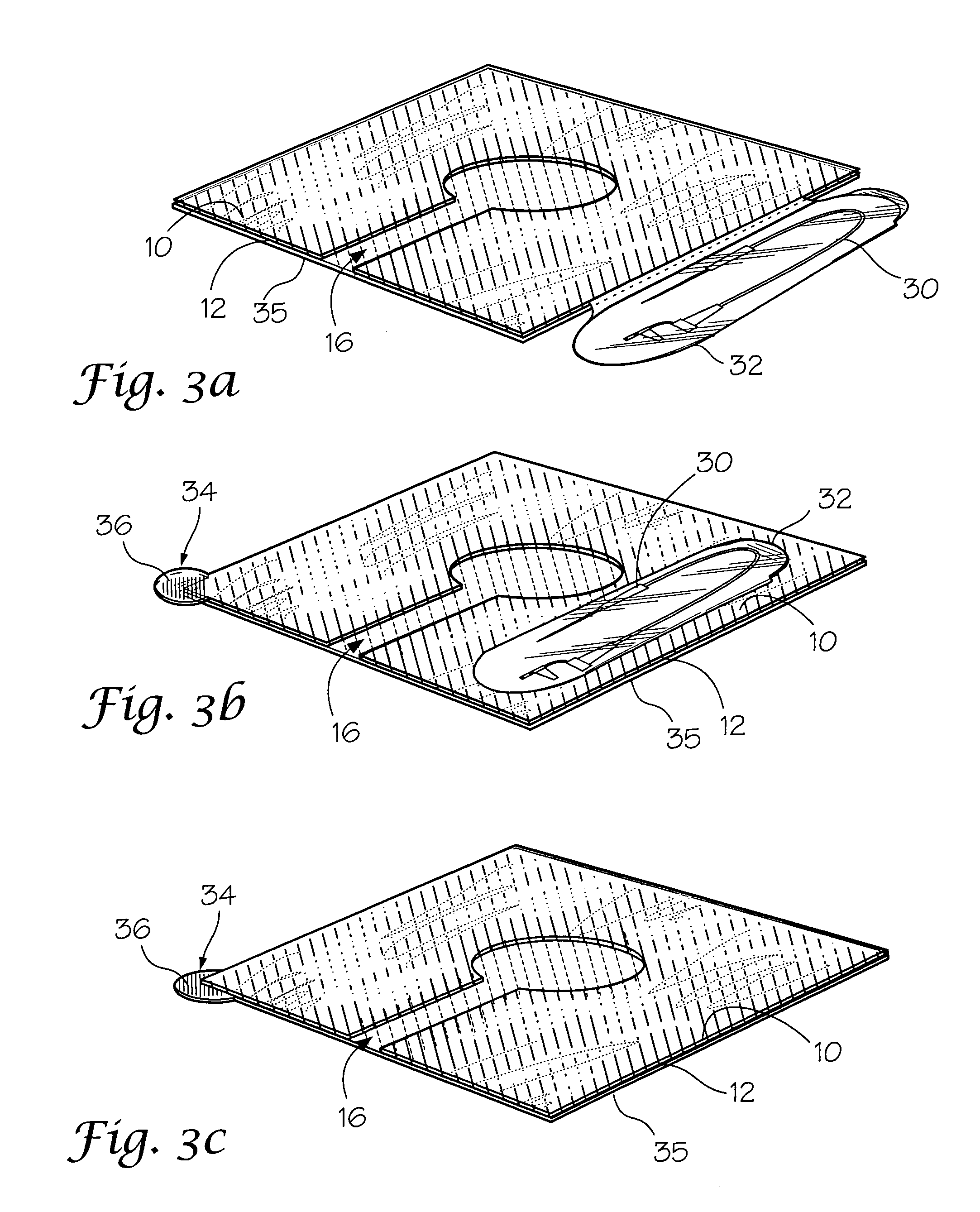
Chest wound seal for preventing pneumothorax and including means for relieving a tension pneumothorax
A flexible sheet having an adhesive layer carried on a bottom side. A collection chamber formed in the adhesive layer by the exclusion of adhesive from a central area of the sheet for receiving fluid from the wound. A drainage channel formed in the adhesive layer by the exclusion of adhesive from a selected area of the sheet extending radially outward from the collection chamber to a drain outlet at a peripheral edge of the sheet to drain fluid from the collection chamber. The collection chamber and drainage channel having an open position allowing fluid to flow outward from the collection chamber through the drain outlet, and a closed position collapsed against the skin to prevent fluid intake through the drain outlet. A storage compartment carried by the flexible sheet including a needle and catheter for immediate access in treating a tension pneumothorax.
Owner:NORTH AMERICAN RESCUE PRODS
Single pump focused sampling
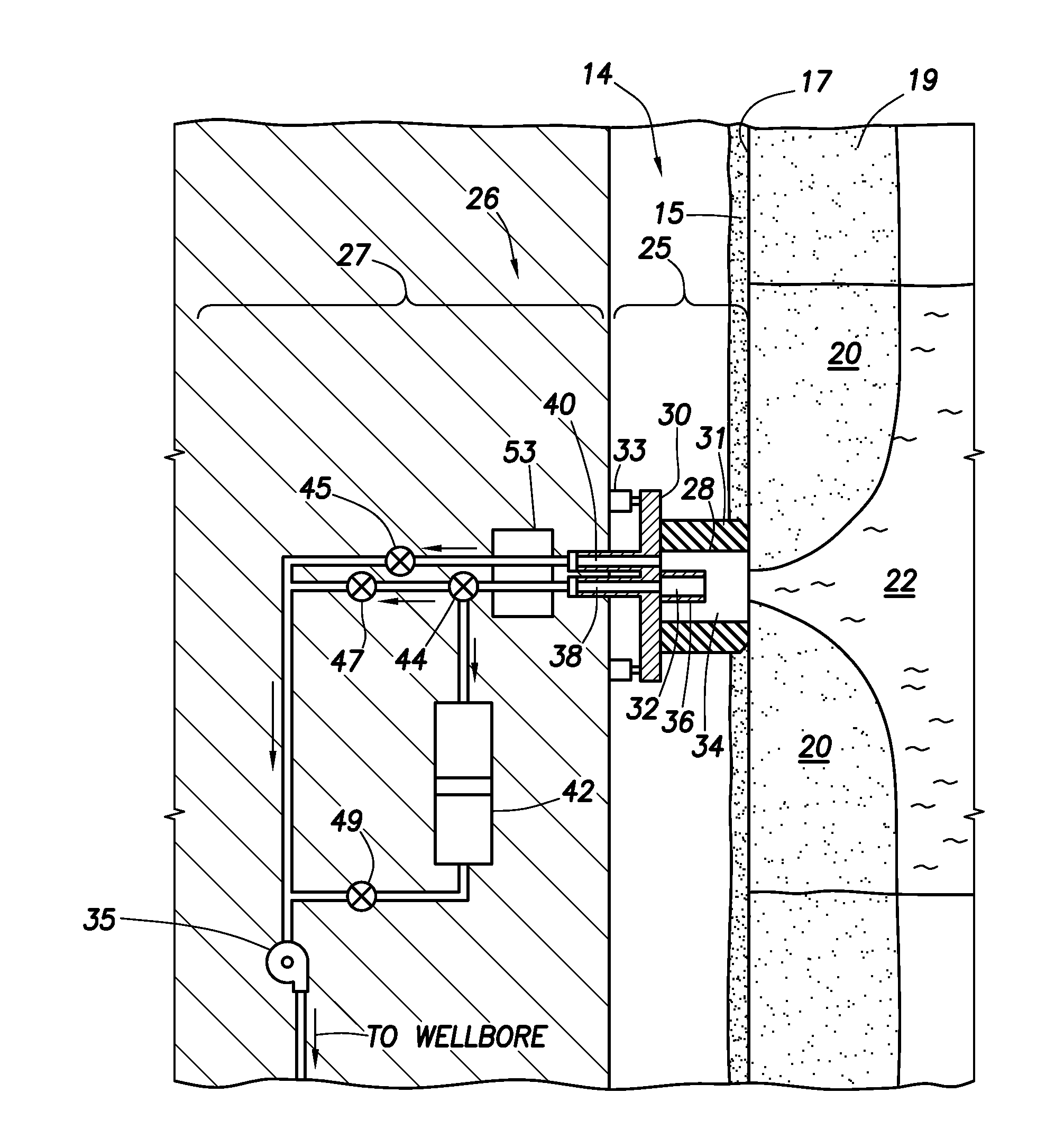
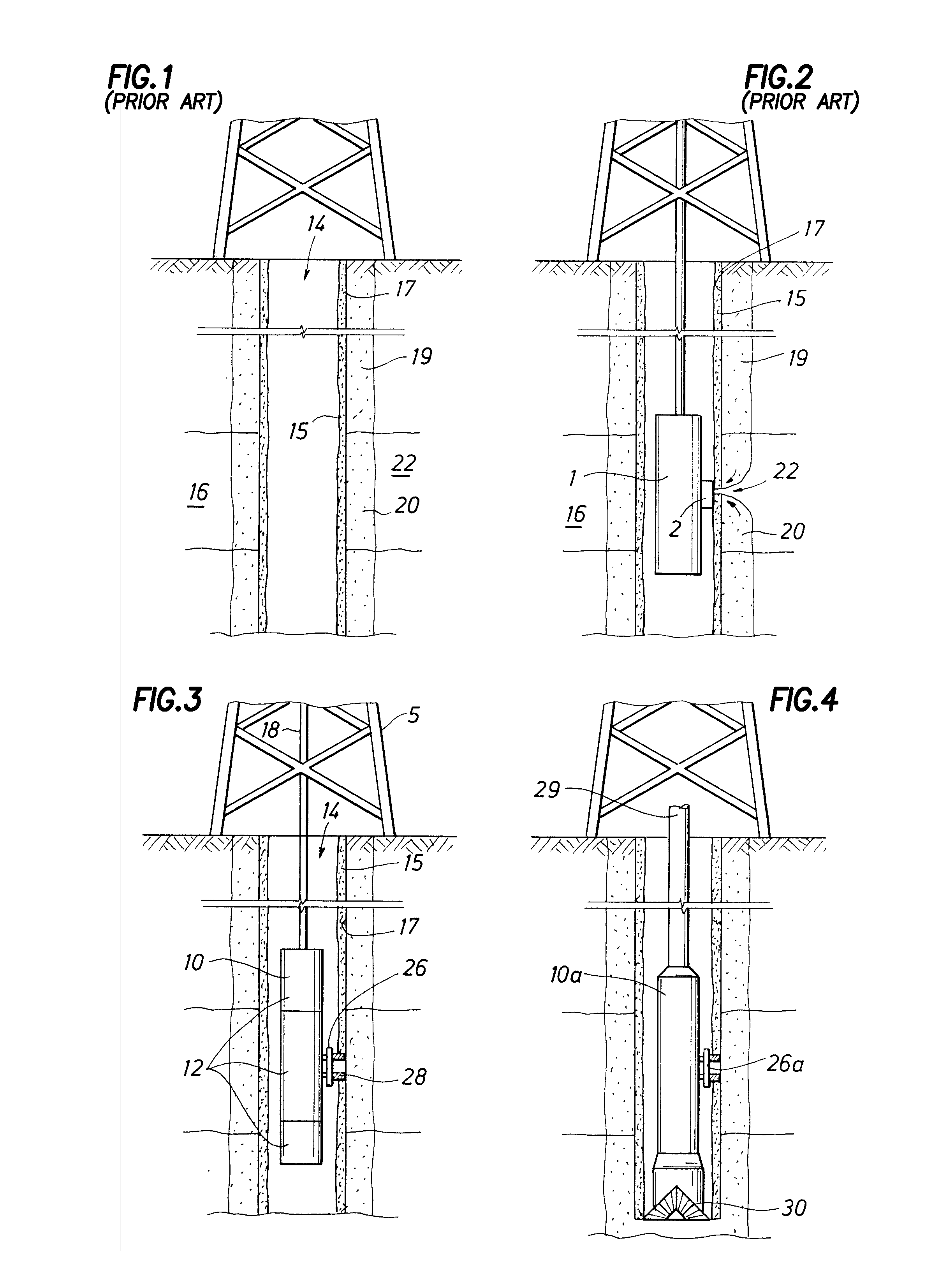
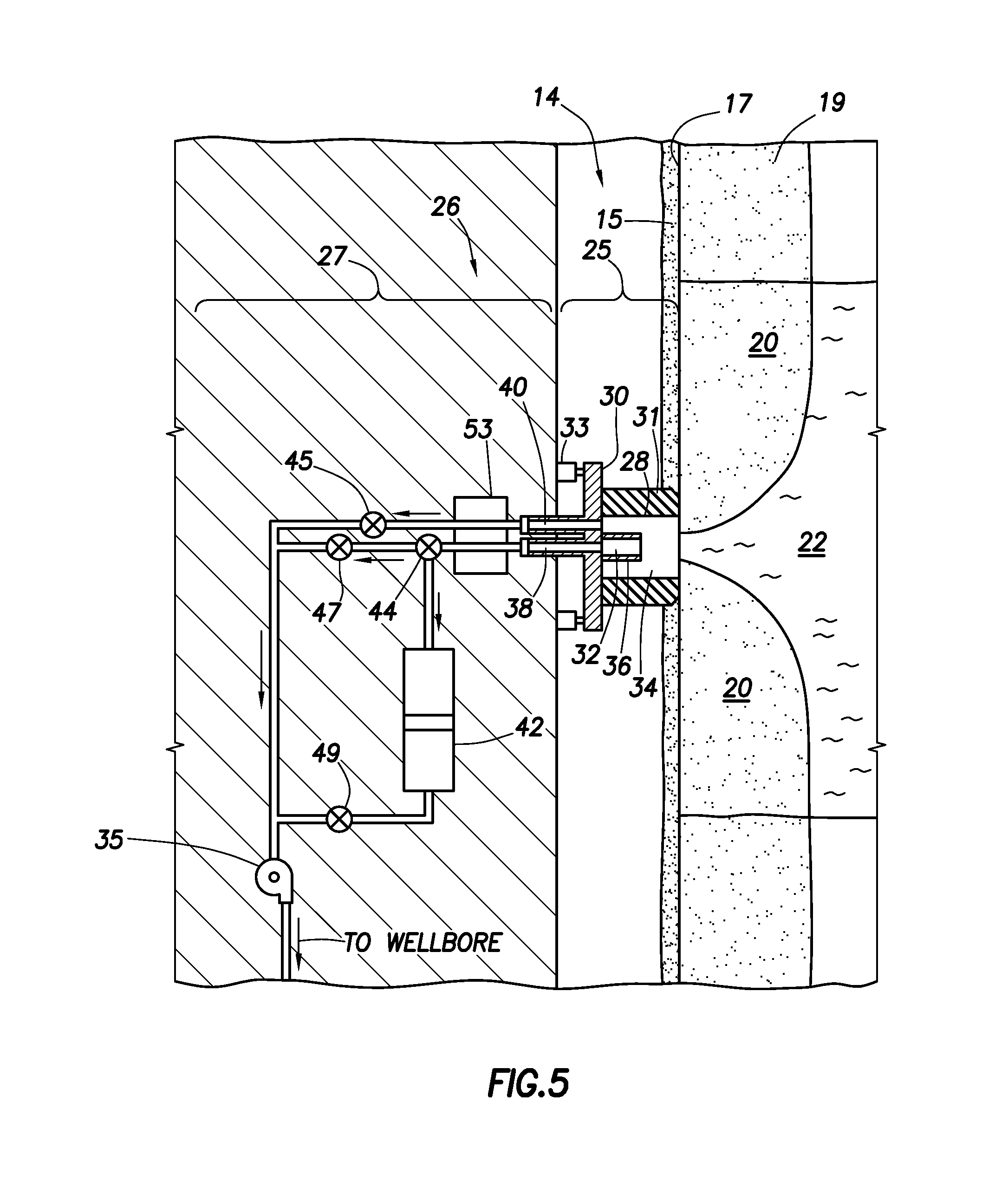
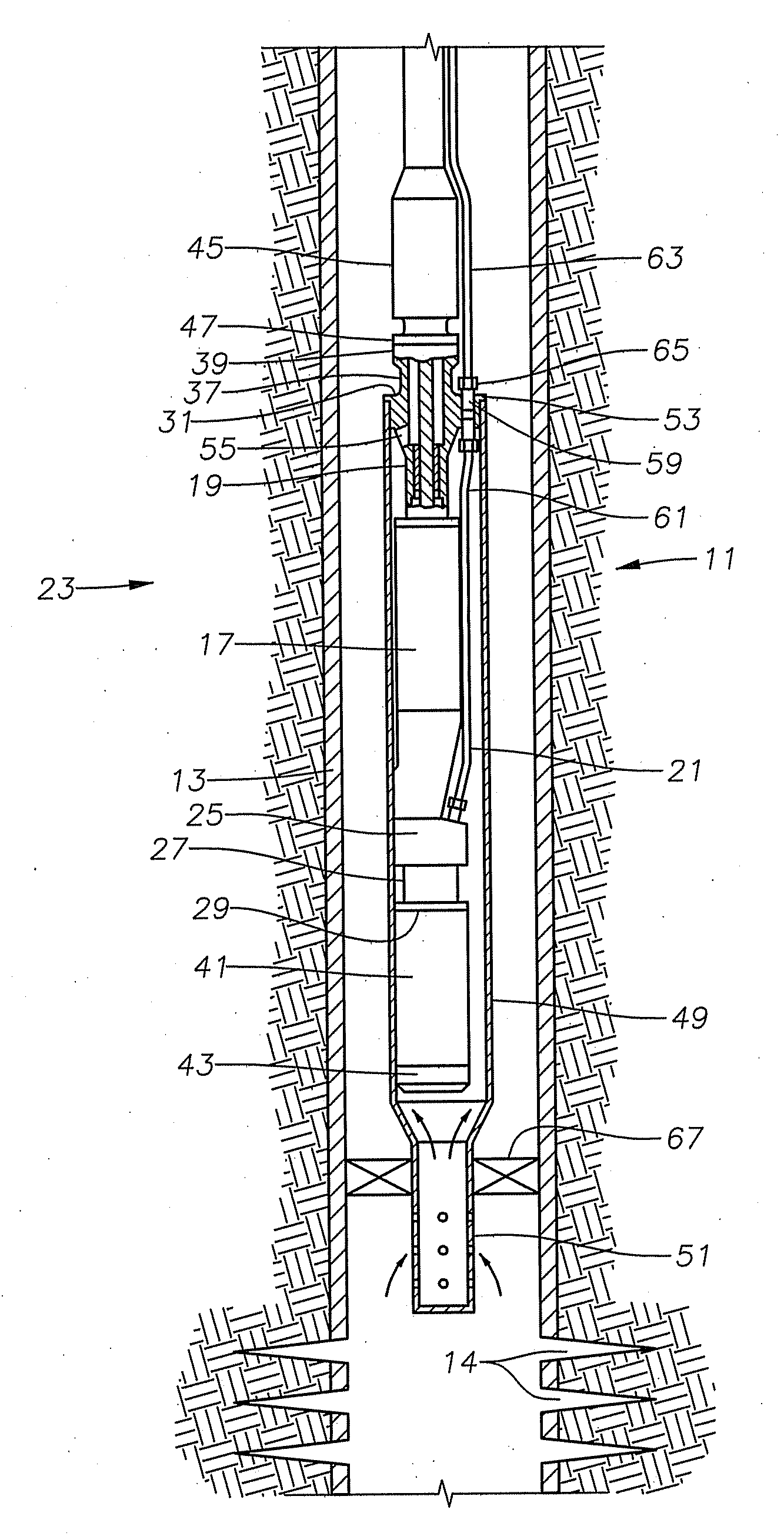
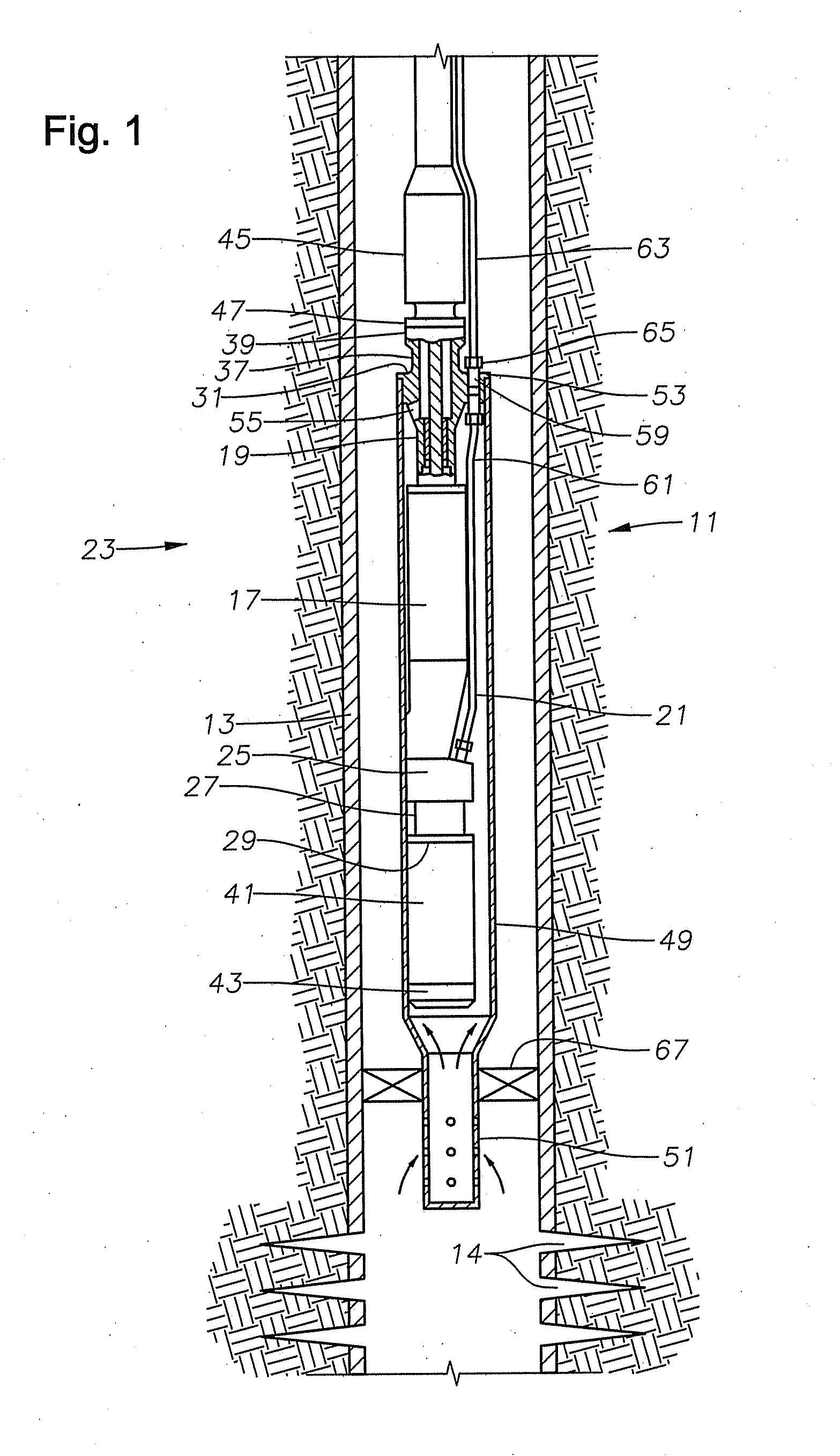
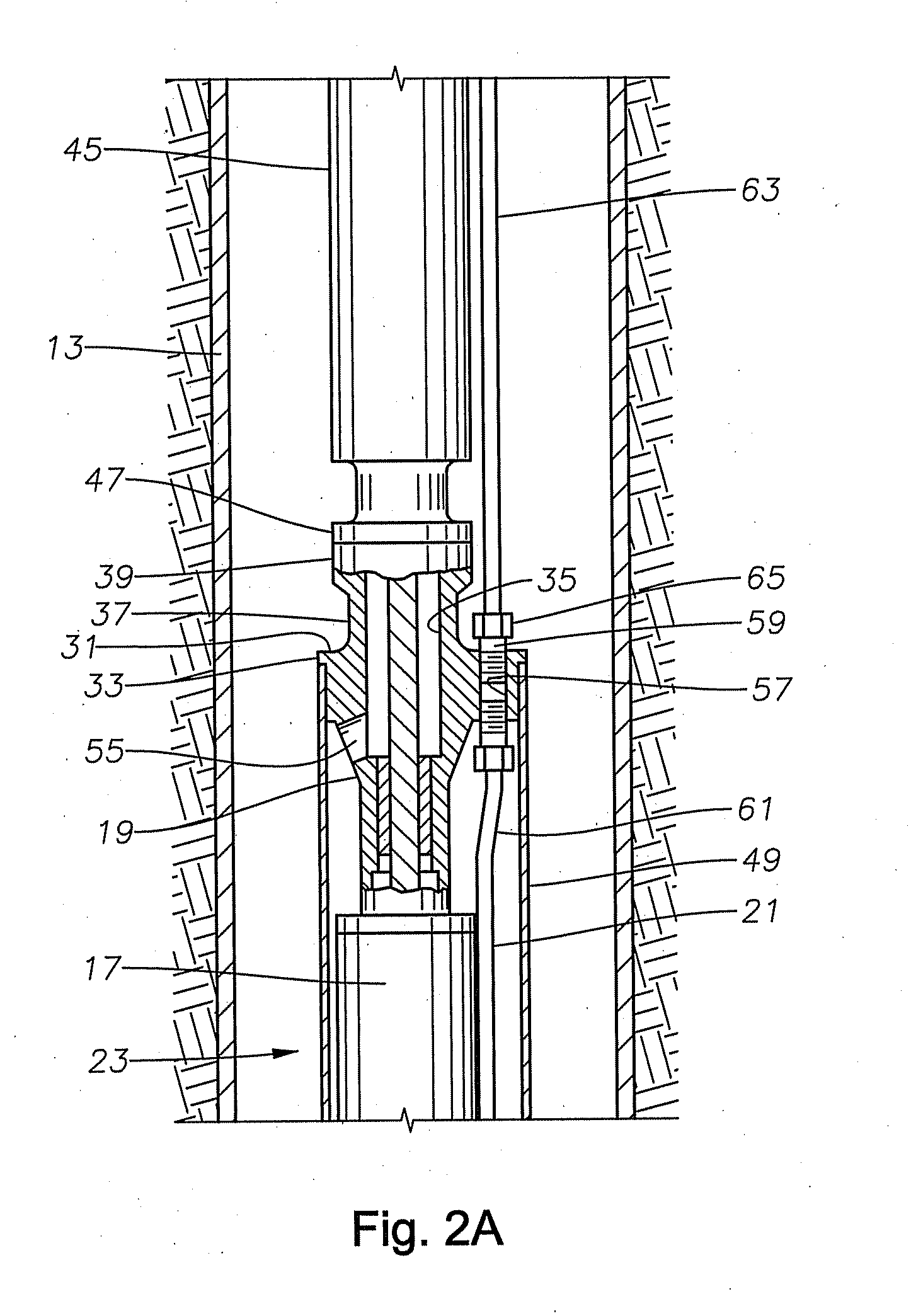
An apparatus comprising first and second fluid intakes, a pump, and a sample chamber, may be positioned in a borehole penetrating a subterranean formation. A method of use thereof may comprise drawing fluid from the subterranean formation and into the first and second fluid intakes using the pump, discharging into the borehole at least a portion of the fluid drawn into the second fluid intake, and selectively diverting at least a portion of the fluid drawn into the first fluid intake to the sample chamber.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
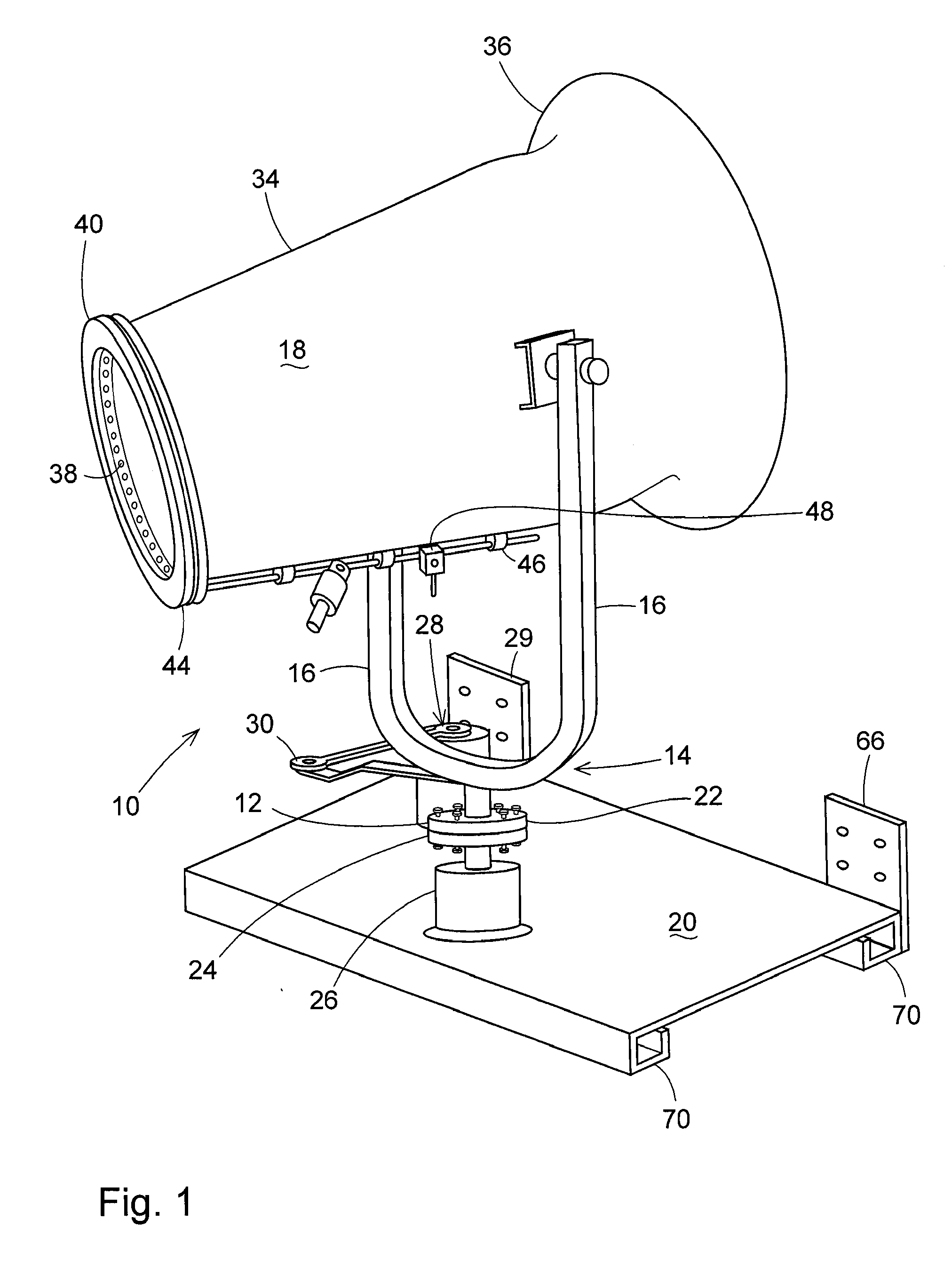
Gimbal-mounted hydroelectric turbine
InactiveUS20050029817A1Reduce environmental impactPositive net energyFluid couplingsWind energy with electric storageFluid intakeEngineering
A power plant extracts energy from a free flowing motive fluid by means of a turbine mounted on a gimbal. The shroud element of the fluid intake has external rudders, in conjunction with the gimbal mounting, enabling the enclosed turbine to instantaneously respond to changes in the direction of the free flowing motive fluid thus ensuring the face area of the intake is always physically orthogonal to the direction of the motive fluid streamlines. The shroud element may also be buoyant so as to optimally extract energy from an upper non-turbulent and higher velocity layer of the free flowing motive fluid. To function within an inherently unsteady source of energy, the preferred embodiment of the turbine is coupled to a DC generator which may further be coupled to a voltage and current regulating circuit which either charges a battery, performs electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen fuel, or is further coupled to a DC motor coupled to an AC generator. Alternatively an AC induction generator may be coupled to the turbine. Other mechanical, electrical, electronic, or electromechanical features may optionally be implemented to perform such tasks as adaptively locating the turbine in the maximum velocity flow, adapting internal vane and runner blade pitches for various flow rates and loads, keeping the intake free of obstructions, preventing loss of aquatic life, controlling and communicating the state of charge of the battery, or gauging and controlling the electrolysis process and communicating the fullness of the hydrogen gas output tanks.
Owner:INTEGRATED POWER TECH CORP
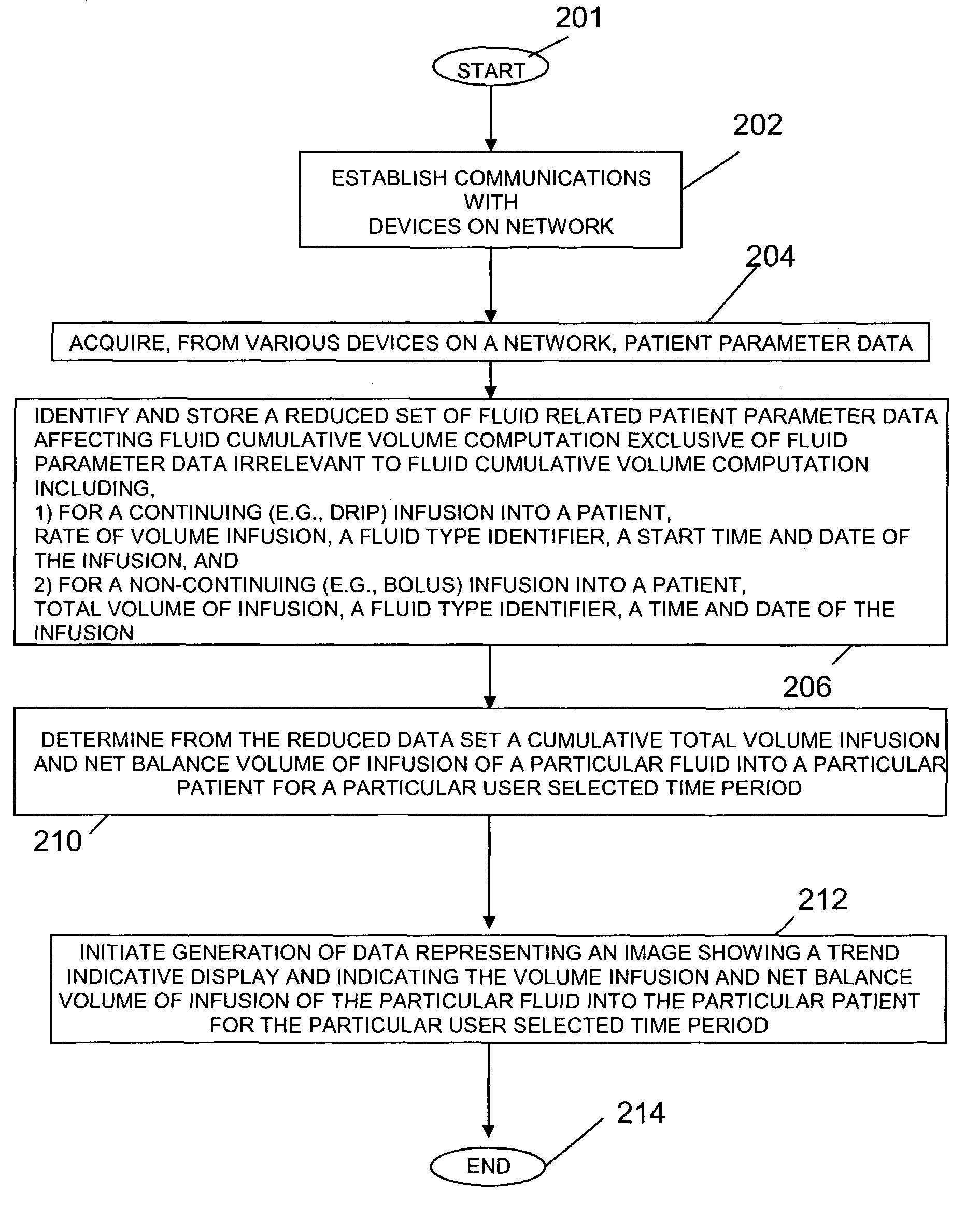
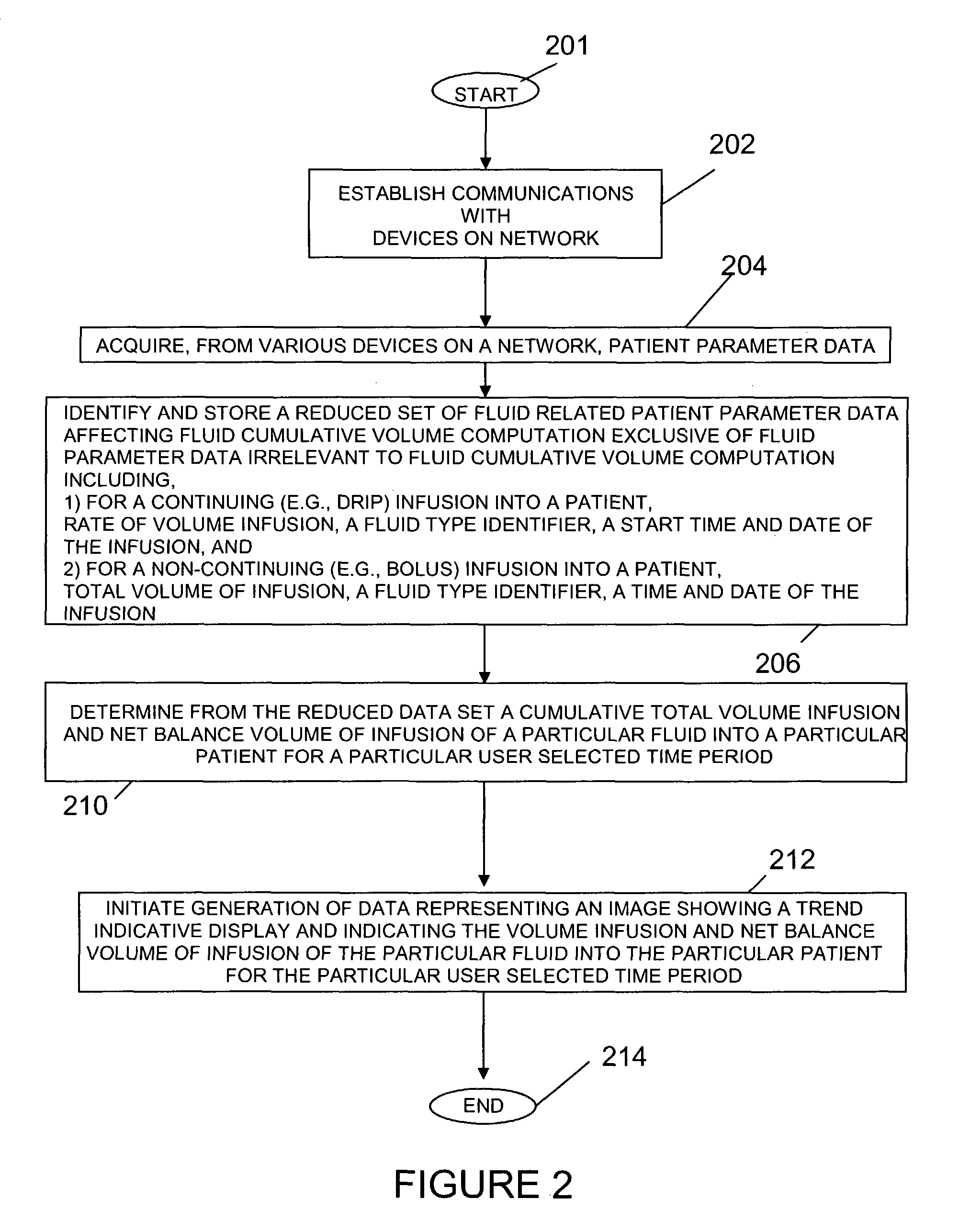
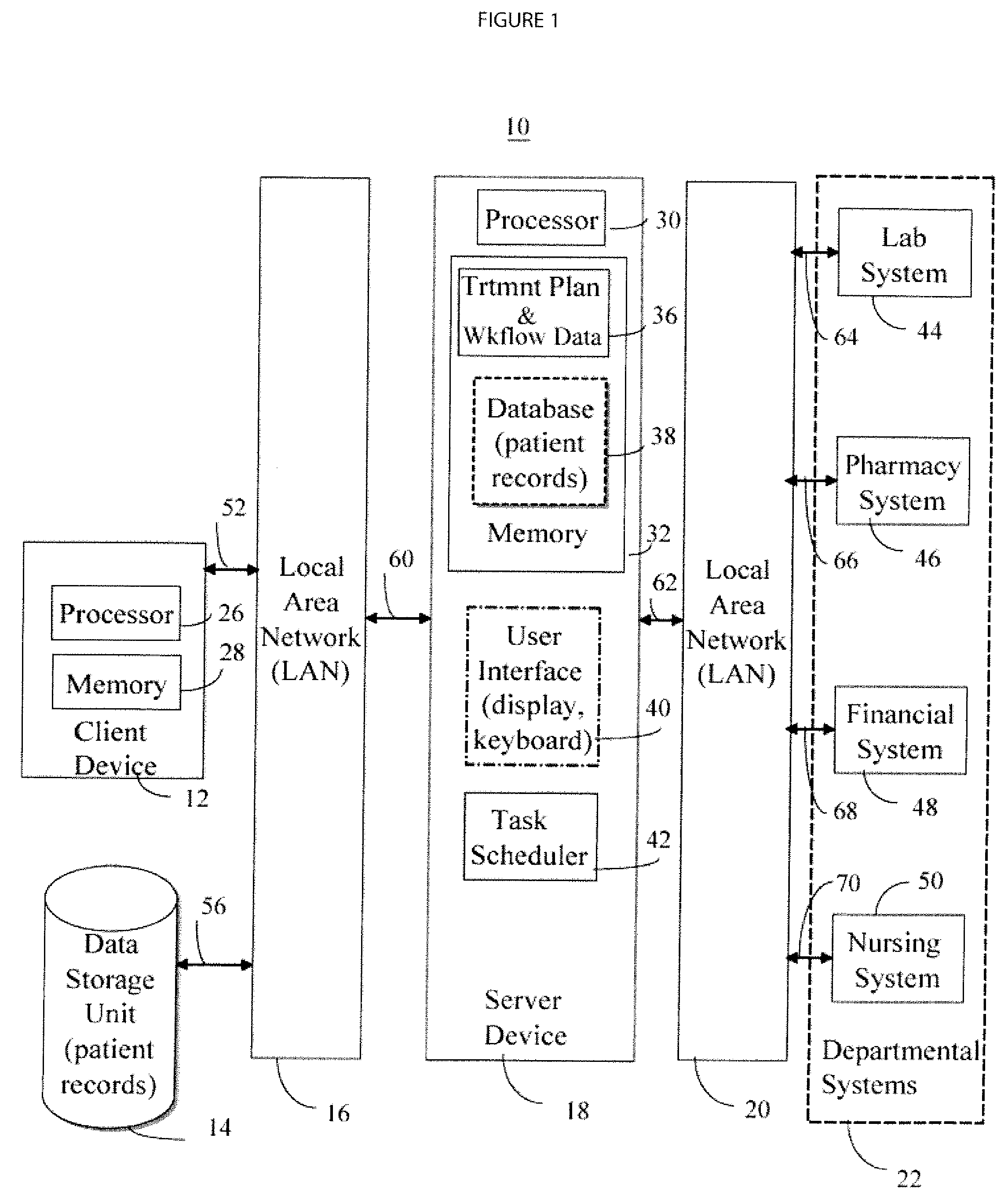
Patient medical fluid parameter data processing system
A system extrapolates and interpolates patient fluid intake or output parameter values and associated cumulative values over variable time intervals from a reduced set of stored fluid parameter values affecting fluid cumulative volume computation or rate of fluid intake or output computation. The extrapolation and interpolation function accomodates drip (continuing) fluid volumes as well as supplemental (non-continuing e.g., bolus) fluid volumes. A patient medical parameter data processing system provides patient medical parameter data for trend indicative display covering a time period comprising user selectable patient parameter acquisition time intervals. The system includes an acquisition processor for receiving data identifying, for a continuing infusion, rate of volume of fluid infusion into a patient, a fluid type identifier and a start time and start date of said continuing infusion. The received data also identifies for a non-continuing infusion, a total volume of fluid infusion, a fluid type identifier and a time and date of the non-continuing infusion. A data processor determines, from the received data, a cumulative total volume infusion of a particular fluid into a particular patient for a particular user selectable patient parameter acquisition time interval.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
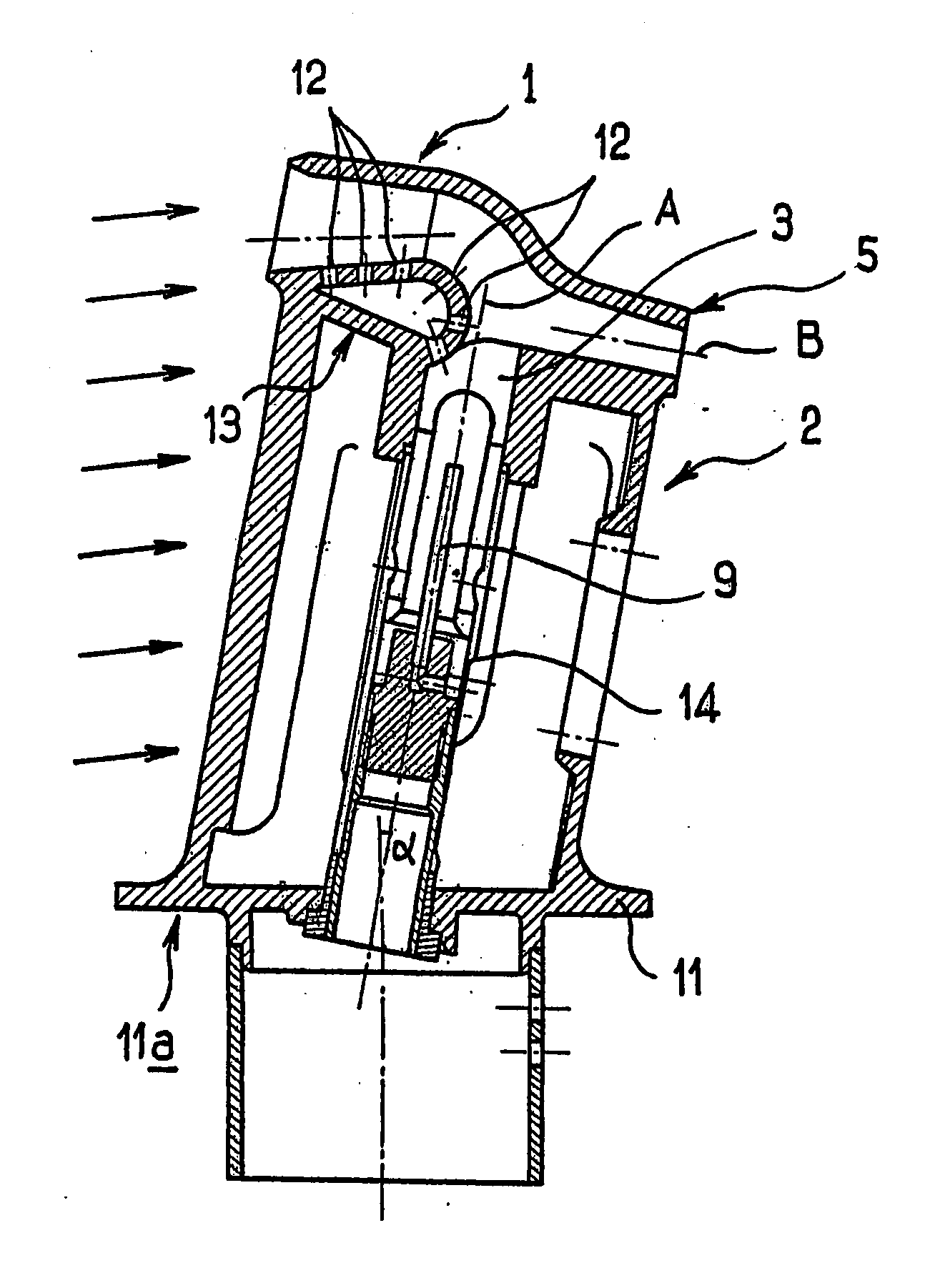
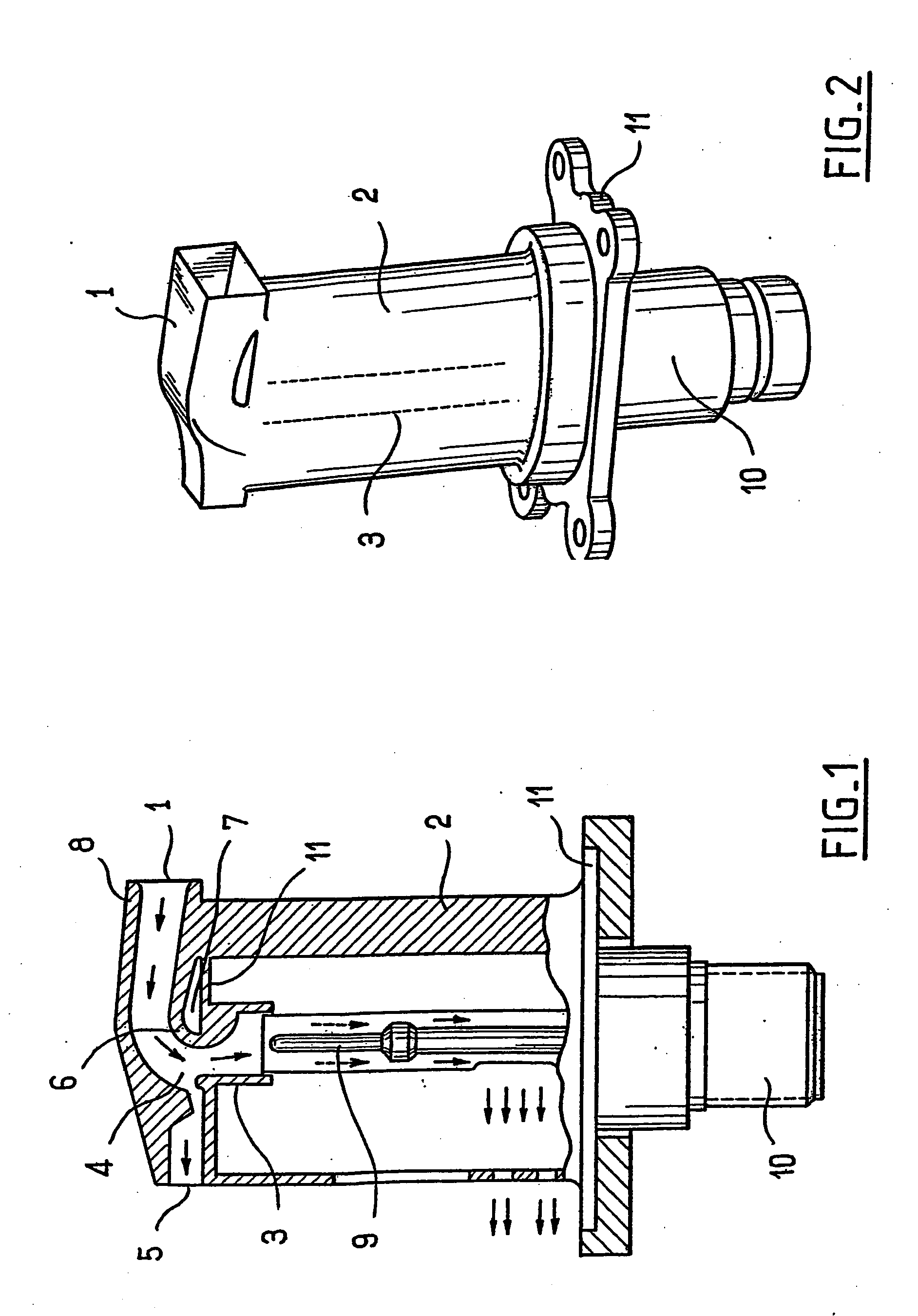
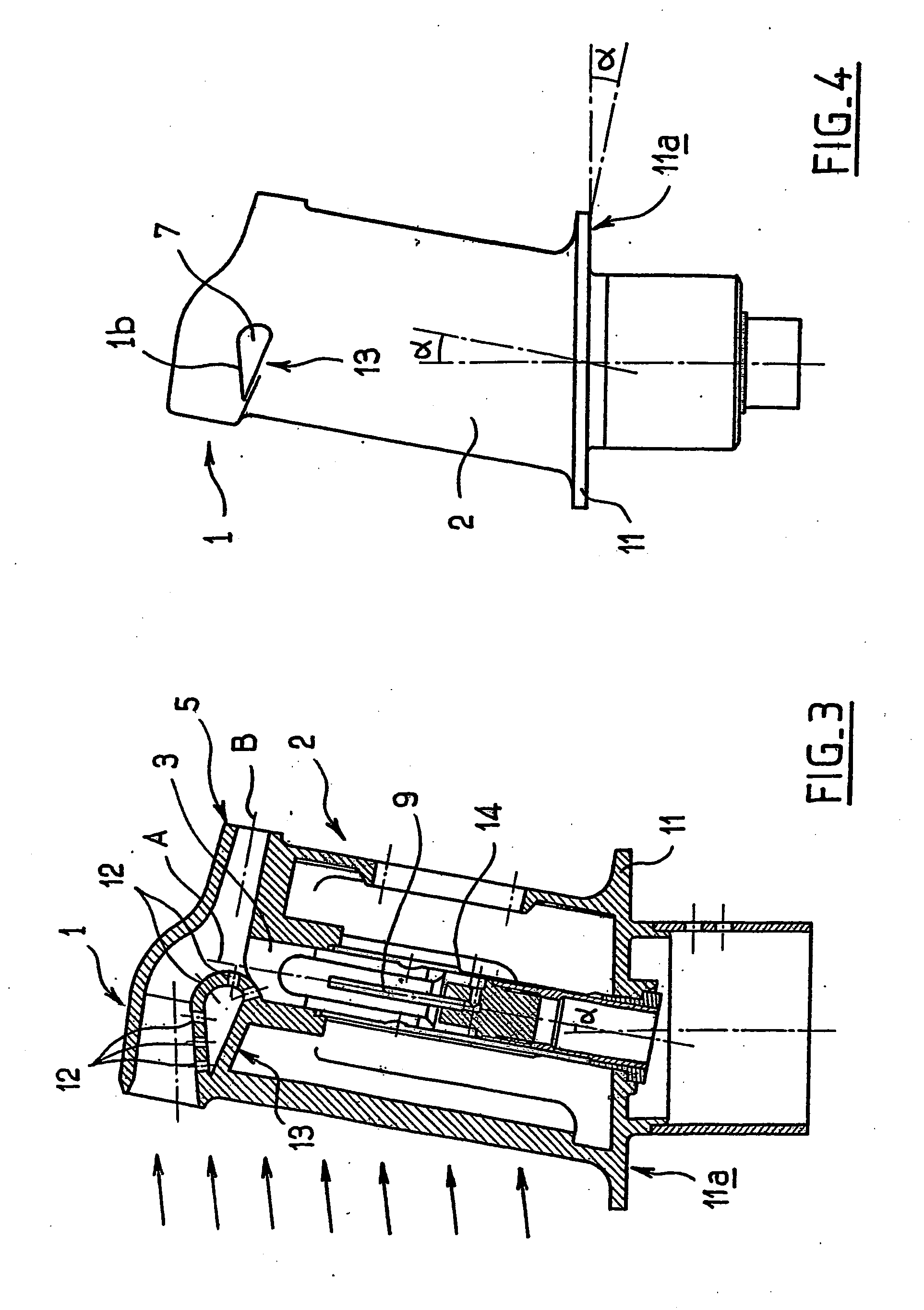
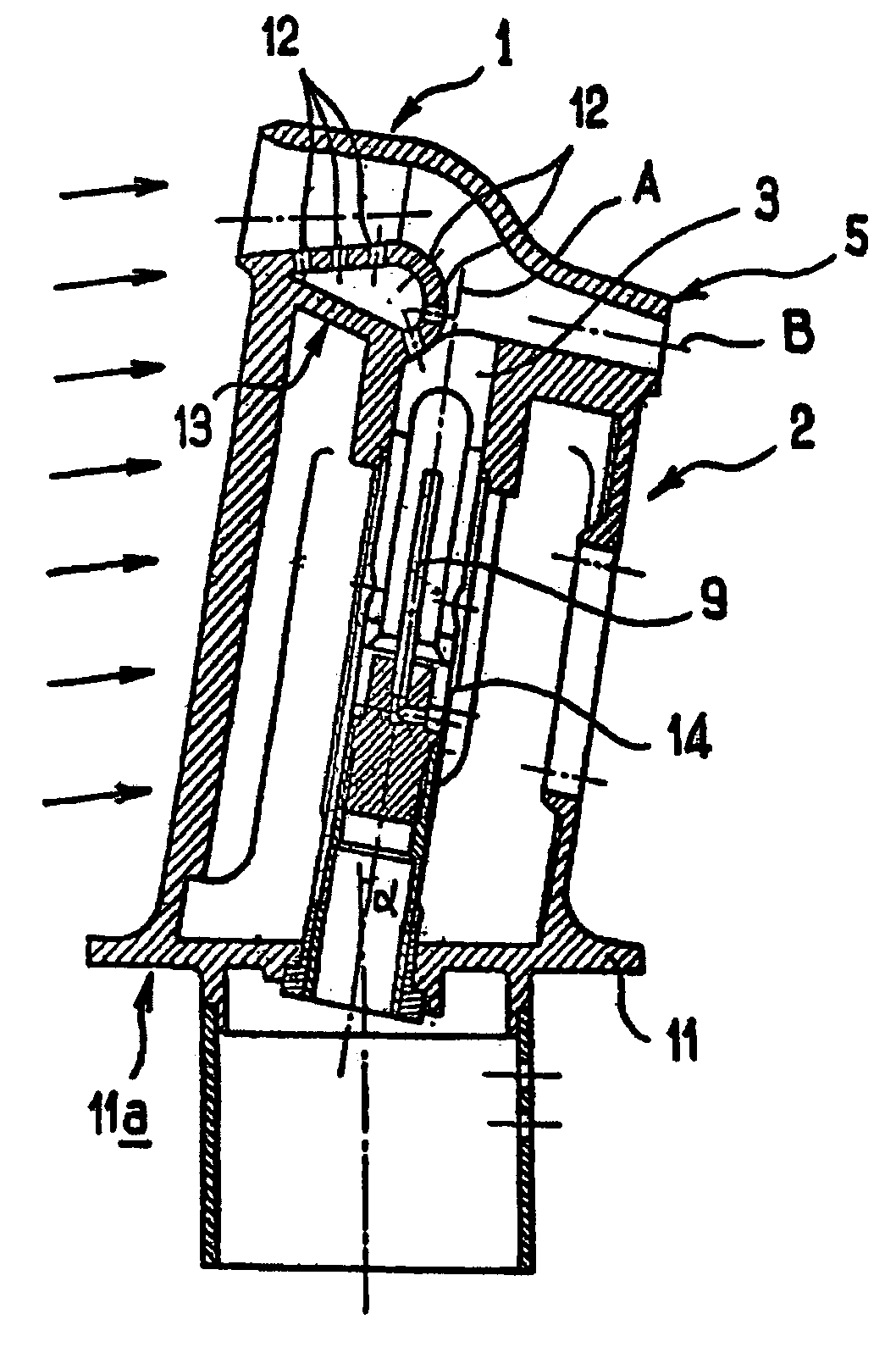
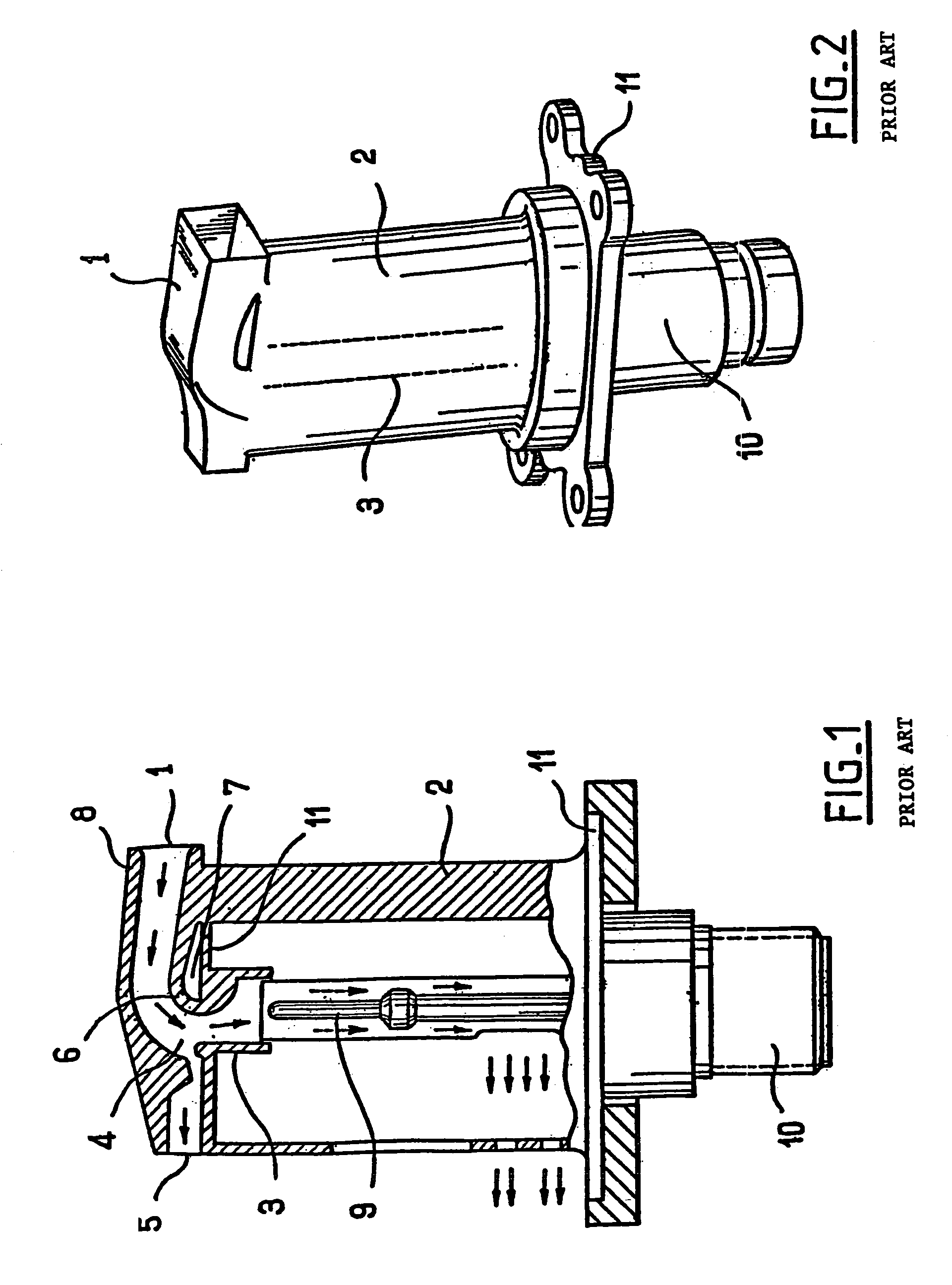
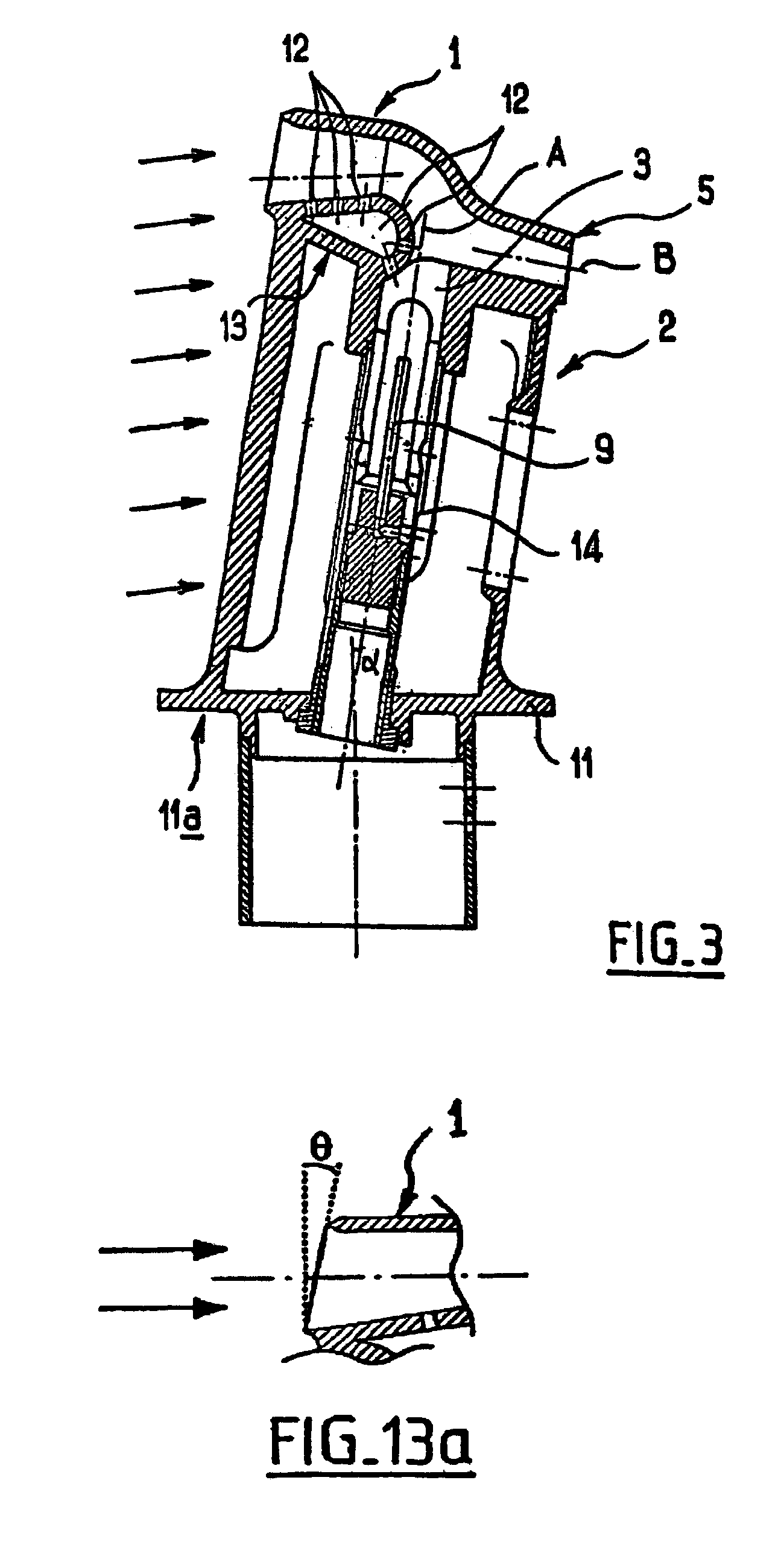
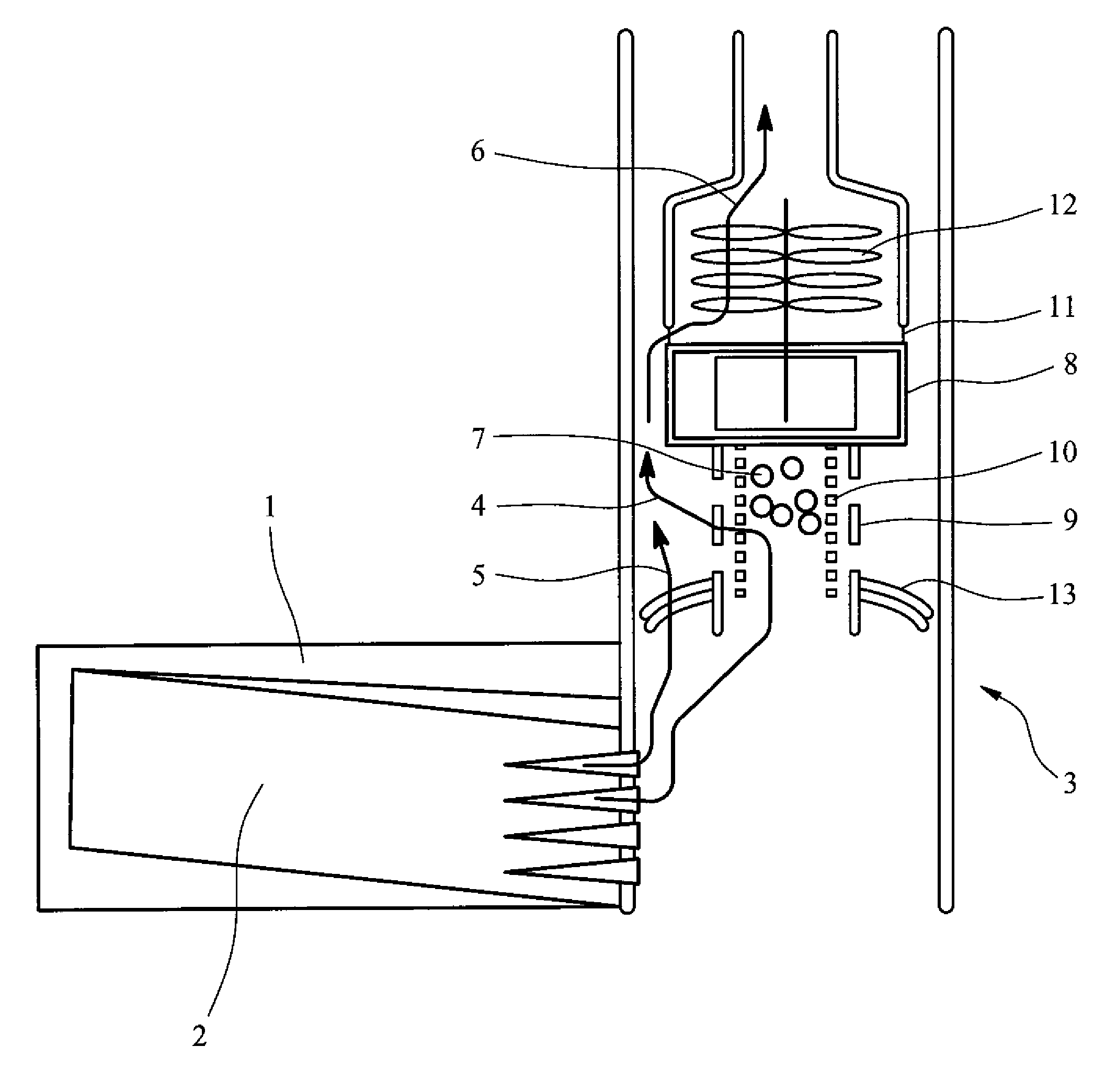
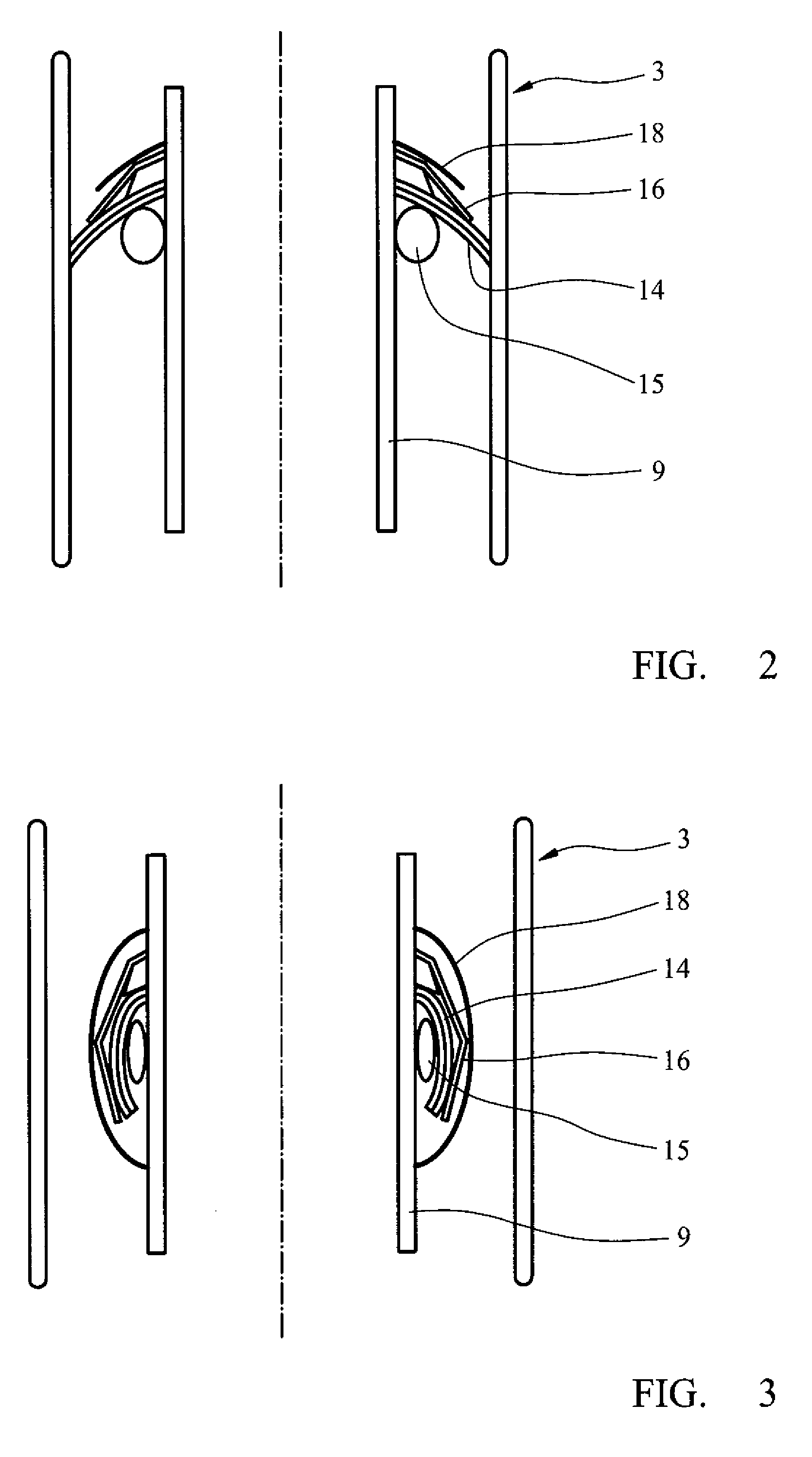
De-iced total air temperature sensor
InactiveUS20060056489A1Degrading measurement performanceIncrease speedAircraft componentsThermometer detailsFluid intakeEngineering
A sensor for measuring a physical parameter of a fluid, in particular for measuring total air temperature, the sensor comprising: a fluid intake (1) fitted to a streamlined body (2); a duct provided in said streamlined body (2) to enable fluid flow, said duct communicating with said fluid intake; and a sensing element disposed inside said duct. The sensor is characterized in that it includes elements that give it improved measurement performance. In particular, the proposed air intake presents an inlet section which extends so as to define a sliding surface suitable for eliminating ice. The invention also provides an improved system for sucking in the boundary layer by using slots, and it also provides a ceramic sensing element that provides better thermal decoupling relative to the de-iced body.
Owner:AUXITROL
Absorbent structures with selectively placed flexible absorbent binder
InactiveUS6964803B2Dispersed particle separationSynthetic resin layered productsFluid intakeElectrical and Electronics engineering
Absorbent structures having controlled liquid intake, distribution and absorption properties include at least one substrate layer and a flexible absorbent binder formed on and bound to the substrate at selected locations. The flexible absorbent binder is selectively formed so as to provide flow channels, regions of higher and lower fluid intake and absorption, dams for preventing fluid leakage, and other desirable features. The absorbent structures are useful in personal care absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins, diapers, training pants, adult incontinence garments and the like.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
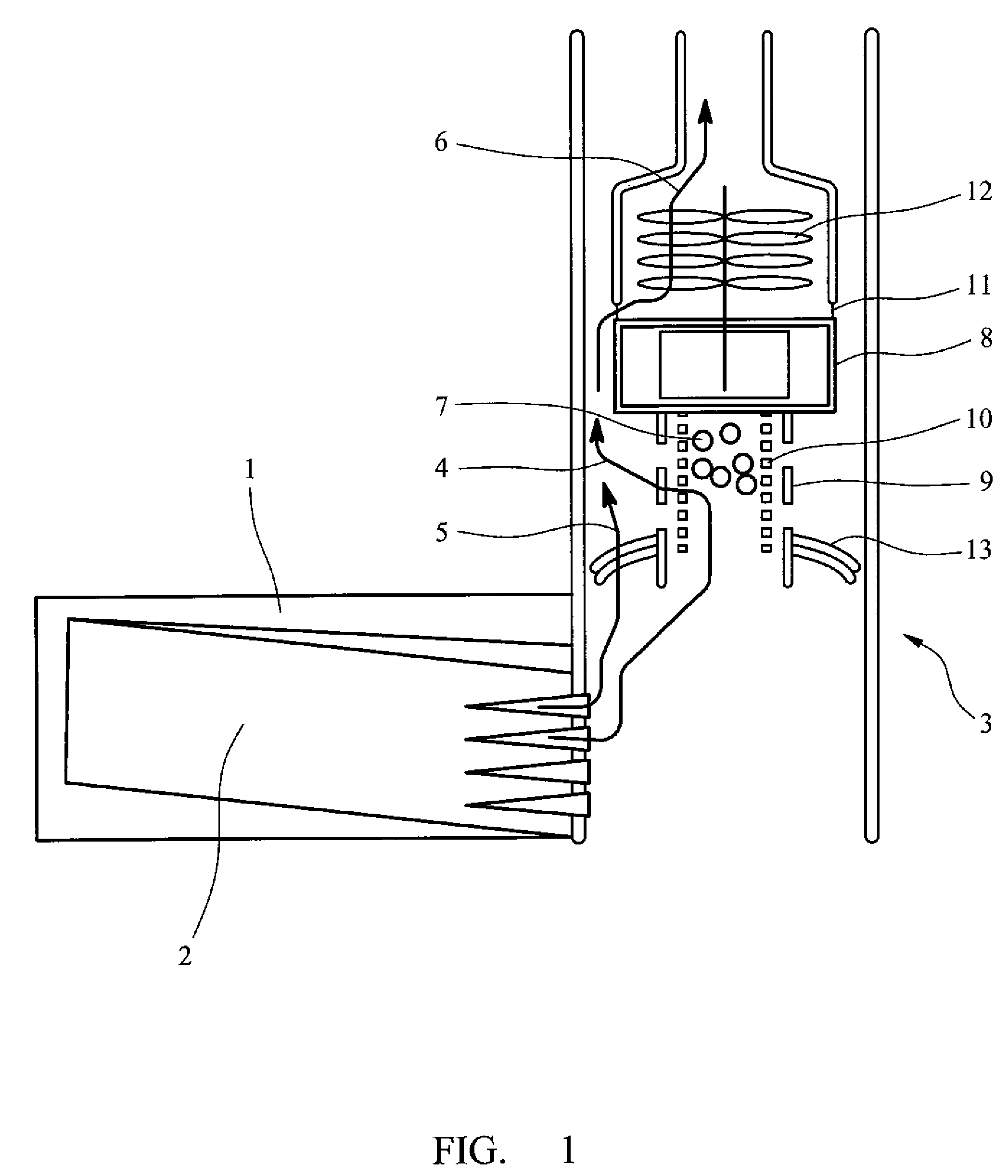
De-iced total air temperature sensor
InactiveUS7441948B2Increase speedMitigate such drawbackAircraft componentsThermometer detailsFluid intakeEngineering
A sensor for measuring a physical parameter of a fluid, in particular for measuring total air temperature, the sensor comprising: a fluid intake (1) fitted to a streamlined body (2); a duct provided in said streamlined body (2) to enable fluid flow, said duct communicating with said fluid intake; and a sensing element disposed inside said duct. The sensor is characterized in that it includes elements that give it improved measurement performance. In particular, the proposed air intake presents an inlet section which extends so as to define a sliding surface suitable for eliminating ice. The invention also provides an improved system for sucking in the boundary layer by using slots, and it also provides a ceramic sensing element that provides better thermal decoupling relative to the de-iced body.
Owner:AUXITROL
Flat jet water nozzles with adjustable droplet size including fixed or variable spray angle
InactiveUS20110168808A1Recreational ice productionLighting and heating apparatusFluid intakeEngineering
A nozzle comprises a lower nozzle plate including a lower impingement surface formed therein, at least one fluid intake port disposed at an inner end of the lower impingement surface, and an upper nozzle plate including an upper impingement surface formed therein and an upper orifice edge disposed along an outer end of the upper impingement surface. The nozzle includes a seal configured for sealing the lower nozzle plate to the upper nozzle plate, such that the lower and upper impingement surfaces are opposed toward one another, thereby forming a fluid channel between the impingement surfaces, directing pressurized fluid from the at least one fluid intake port to a slotted orifice formed between the opposed lower and upper orifice edges. The nozzle includes a droplet size adjustment mechanism configured for attachment to the upper and lower nozzle plates for selectively controlling fluid droplet size ejected from the slotted orifice.
Owner:TMV INVESTMENTS LLC
Water filter spray nozzle cleaning system
Methods and apparatus for generating a small, maneuverable stream of filtered fluid without benefit of a pump or electrical power are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a spray nozzle apparatus for dispensing a maneuverable stream of fluid, that originates from a fluid source at a first pressure includes an adapter assembly, a nozzle subassembly, and a flexible tubing. The adapter assembly is mechanically coupled to the fluid source, and is arranged to allow the fluid to flow from the fluid source through the adapter assembly. The nozzle subassembly dispenses the fluid at a second pressure, and includes a fluid intake end and a fluid dispensing end. The fluid dispensing end allows the fluid to flow therethrough in a small, stream-like configuration at the second pressure, and is in fluid communication with the adapter assembly. The flexible tubing allows the fluid to flow through, and is coupled to the fluid intake end of the nozzle subassembly. In one embodiment, the spray nozzle apparatus includes a filter that is in fluid communication with the flexible tubing and the adapter assembly.
Owner:TRUONG DAVID
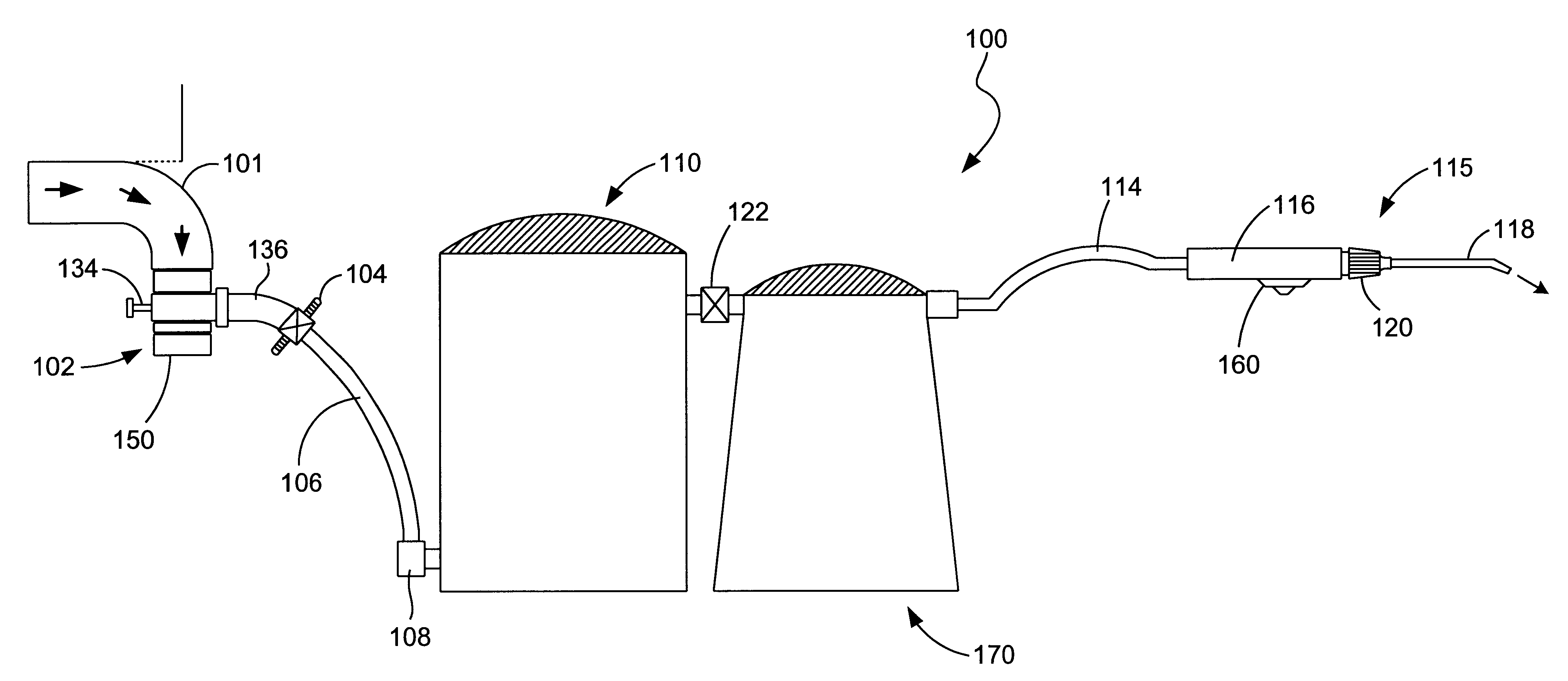
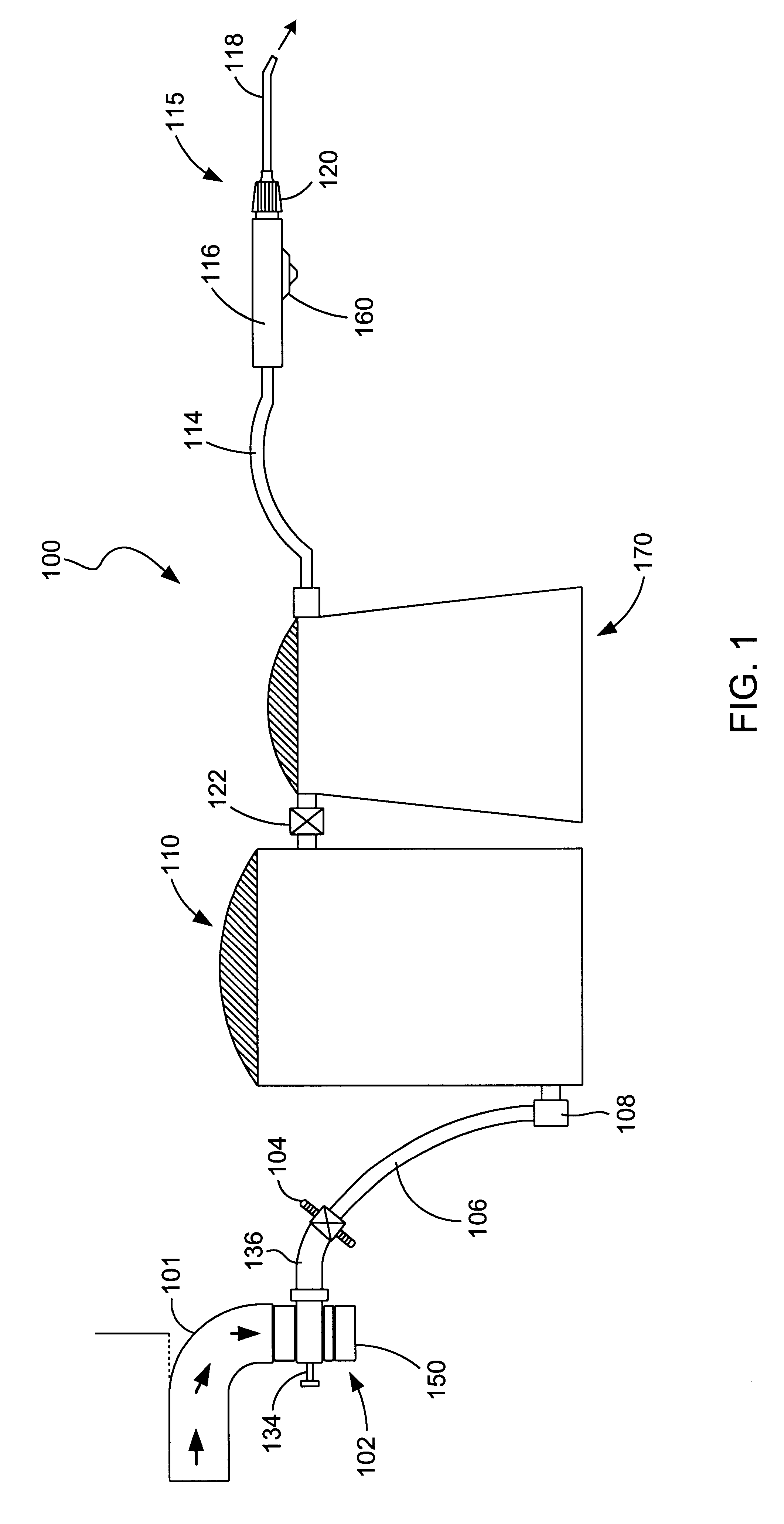
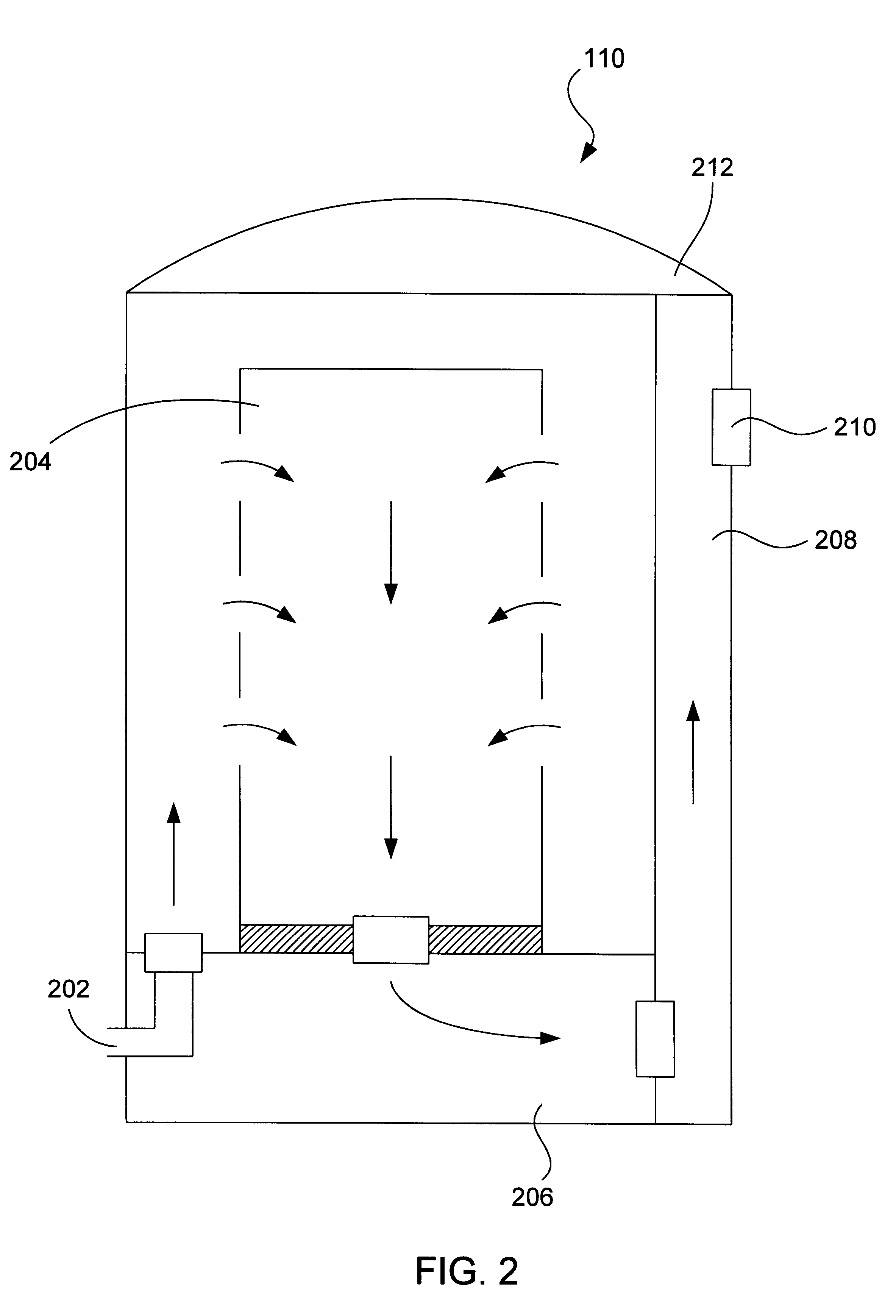
Charging fluid intake module and internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20100077996A1Improve performanceInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFluid intakeInlet channel
A charging fluid suctions module is provided for an internal combustion engine, comprising a housing forming a flow path for a gaseous charging fluid, particularly air, a gas, and / or an air / gas mixture. Whereby, a heat exchanger is disposed in the housing for the gaseous charging fluid. In order to allow for an improved exhaust gas return the housing comprise an inlet channel for an exhaust gas, and the inlet channel flows into the flow path downstream of the heat exchanger for the gaseous charging fluid.
Owner:BEHR GMBH & CO KG
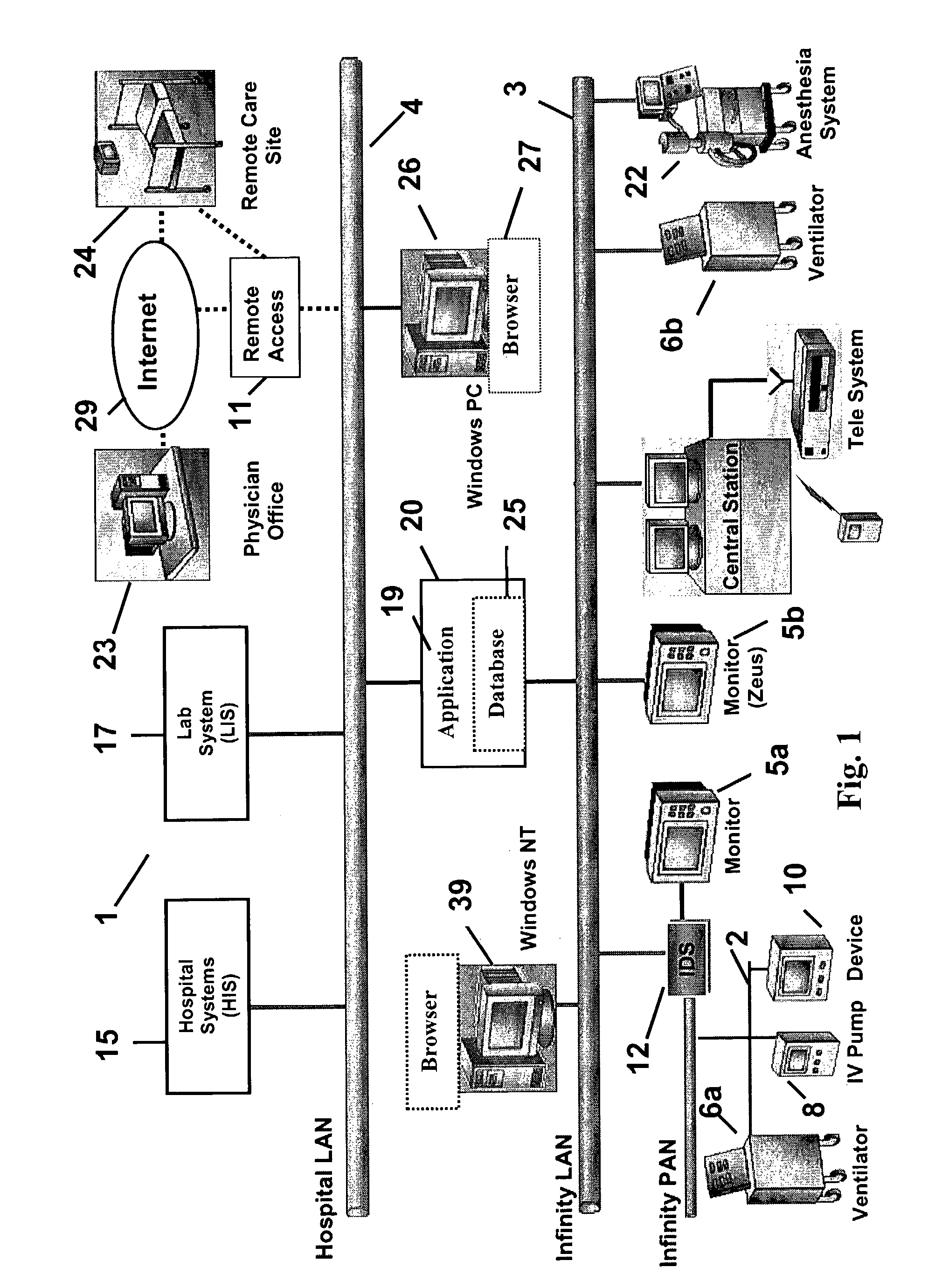
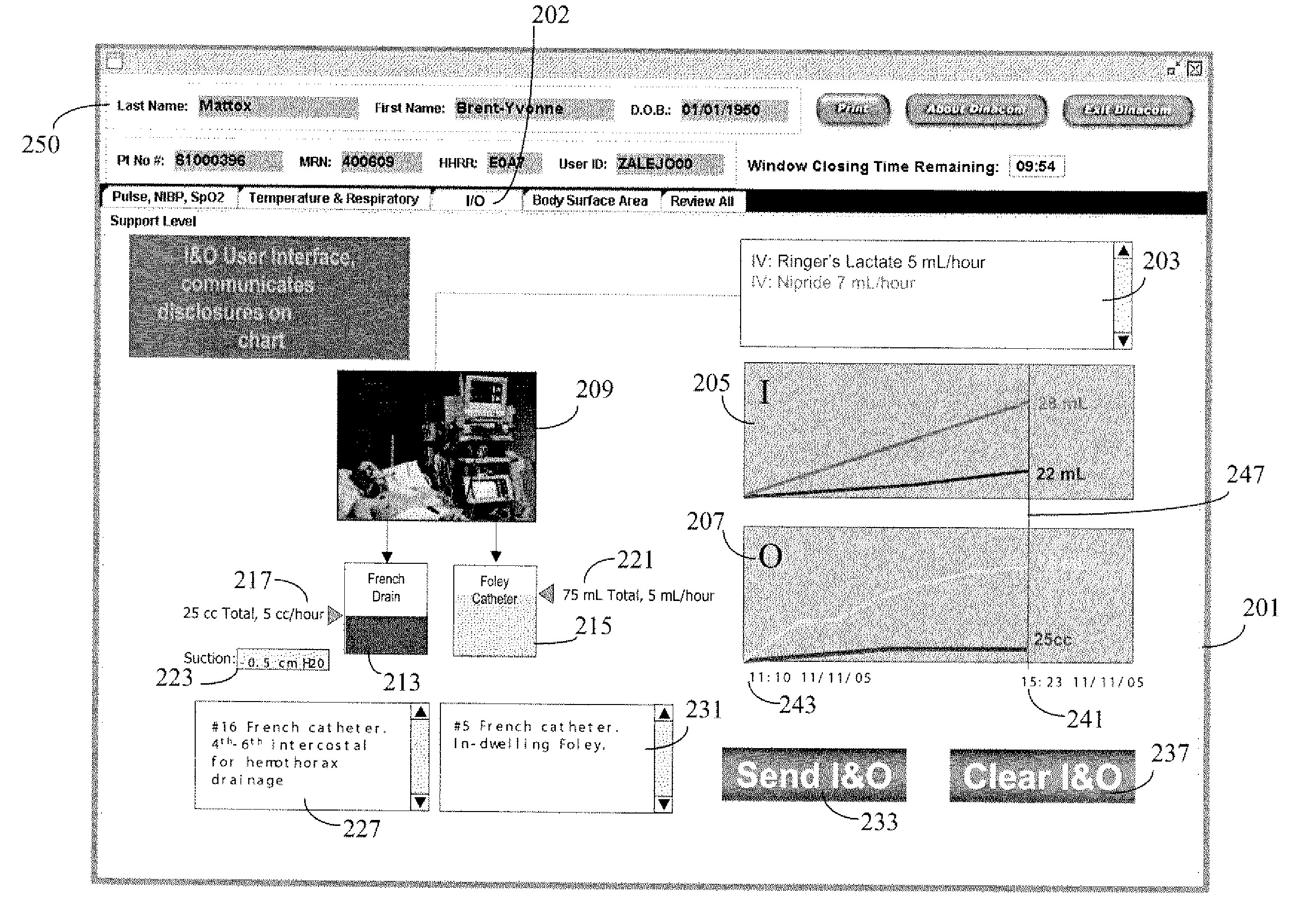
System for Monitoring and Managing Patient Fluid Input and Output
InactiveUS20080004818A1Simplify data presentationInput/output for user-computer interactionDrug and medicationsData displayFluid intake
A fluid intake and output viewer application and user interface automatically records patient fluid intake and output data to support fluid balance calculations and data display. A patient fluid parameter user interface and processing system includes a context processor for receiving patient identification information from an executable application. An acquisition processor automatically acquires fluid parameters of a particular patient identified by the received patient identification information. A display processor automatically initiates generation of a composite display image including fluid data updated using the automatically acquired fluid parameters to present both graphical and text indication of patient fluid input and output values and rates of patient fluid input and output, together with the patient identification information.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Single pump focused sampling
An apparatus comprising first and second fluid intakes, a pump, and a sample chamber, may be positioned in a borehole penetrating a subterranean formation. A method of use thereof may comprise drawing fluid from the subterranean formation and into the first and second fluid intakes using the pump, discharging into the borehole at least a portion of the fluid drawn into the second fluid intake, and selectively diverting at least a portion of the fluid drawn into the first fluid intake to the sample chamber.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
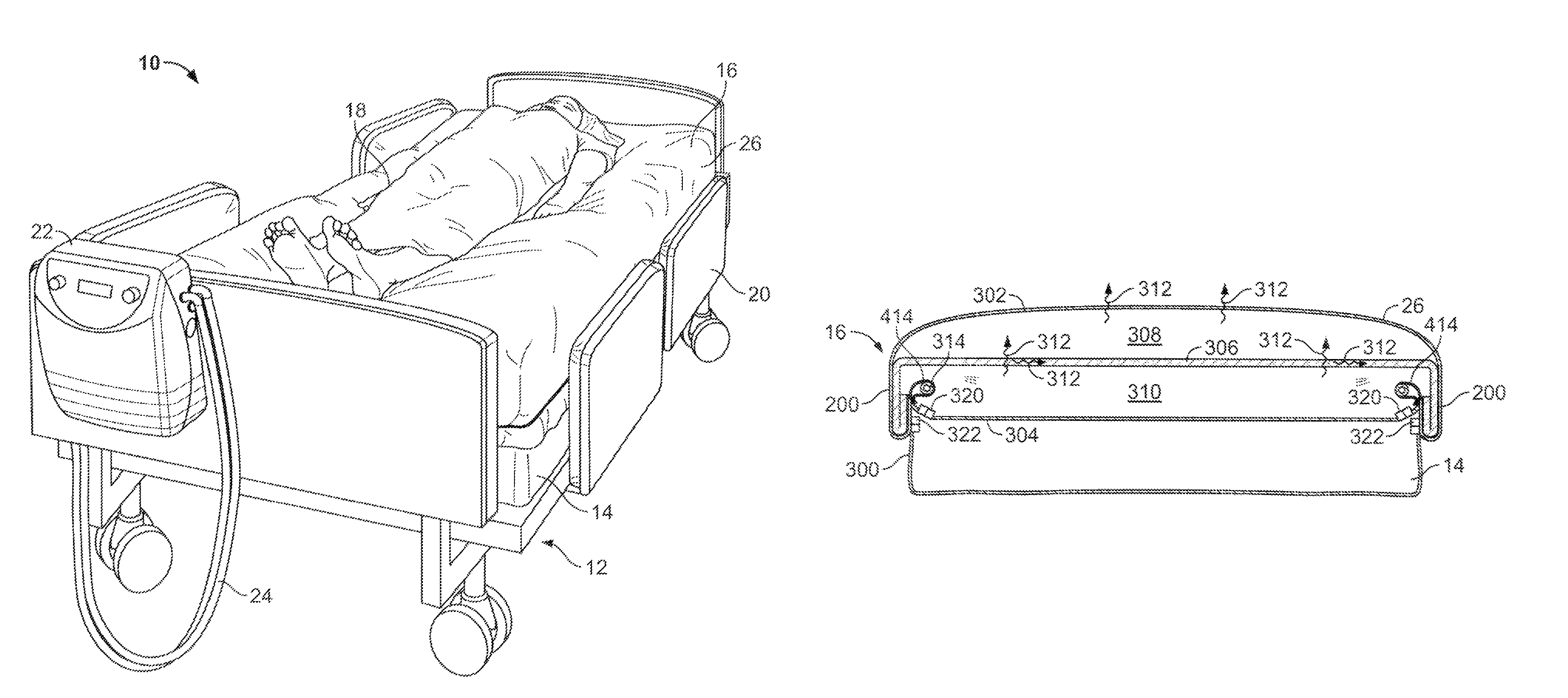
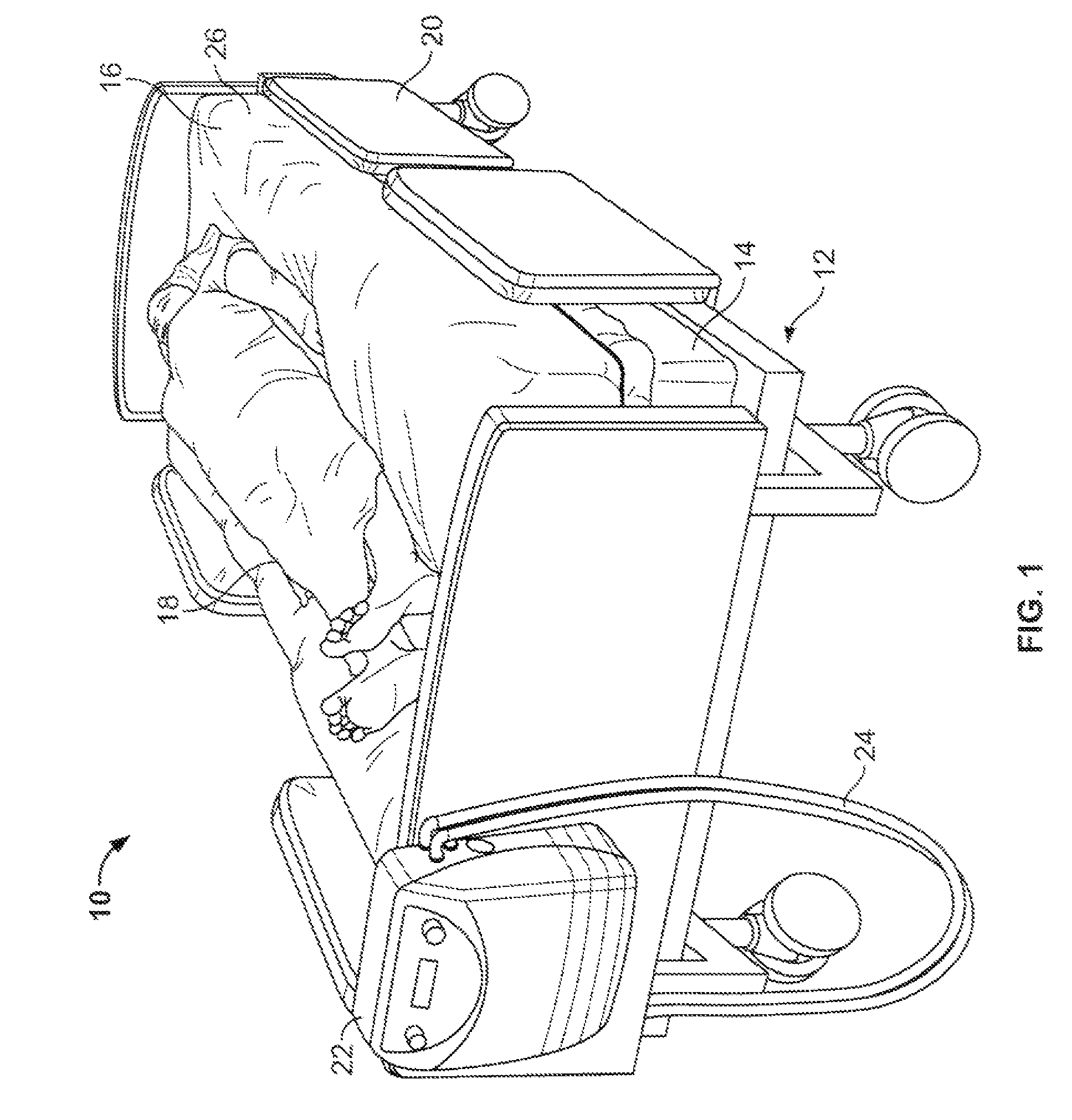
Multi-chamber air distribution support surface product and method
Owner:KAP MEDICAL
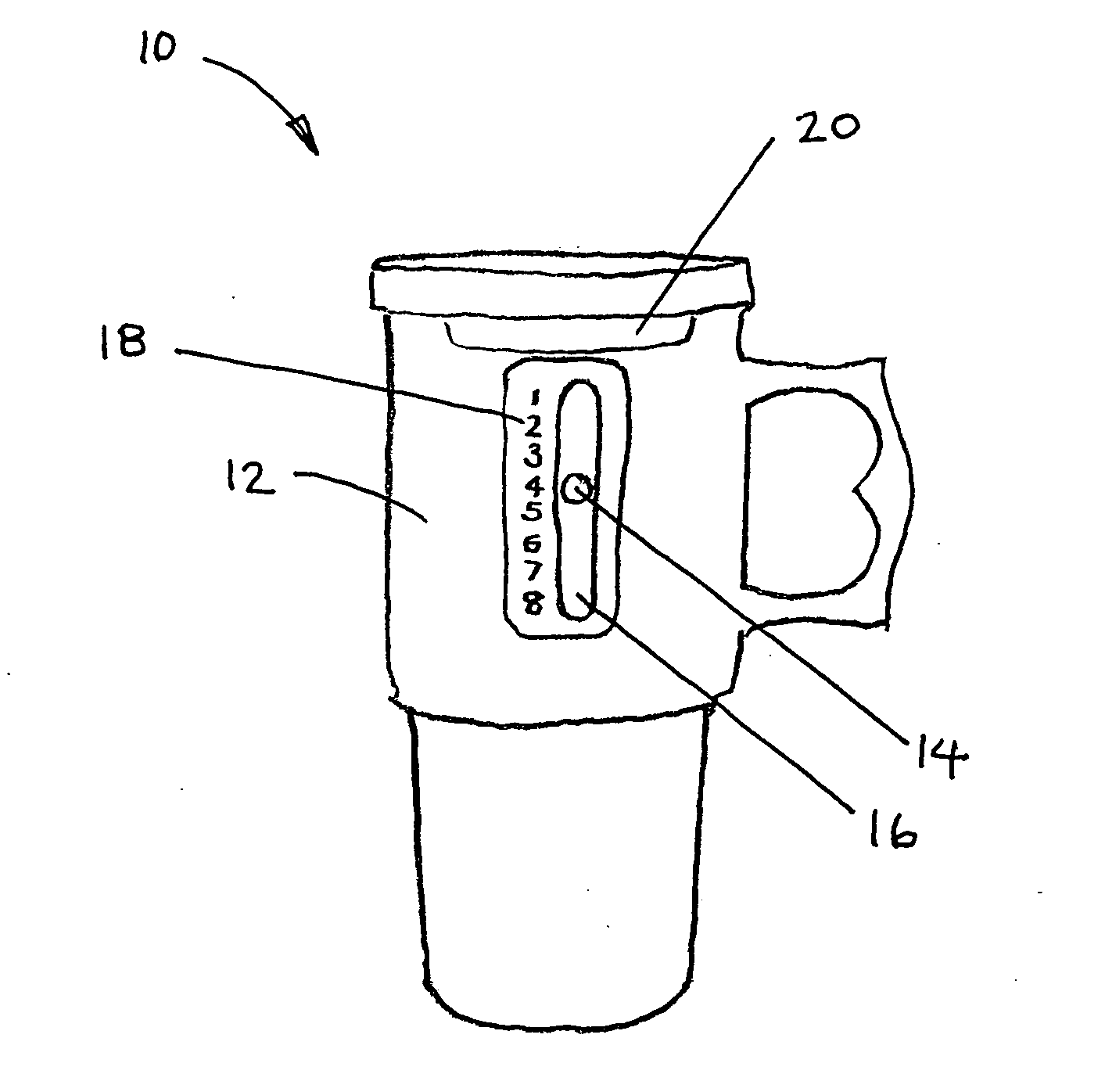
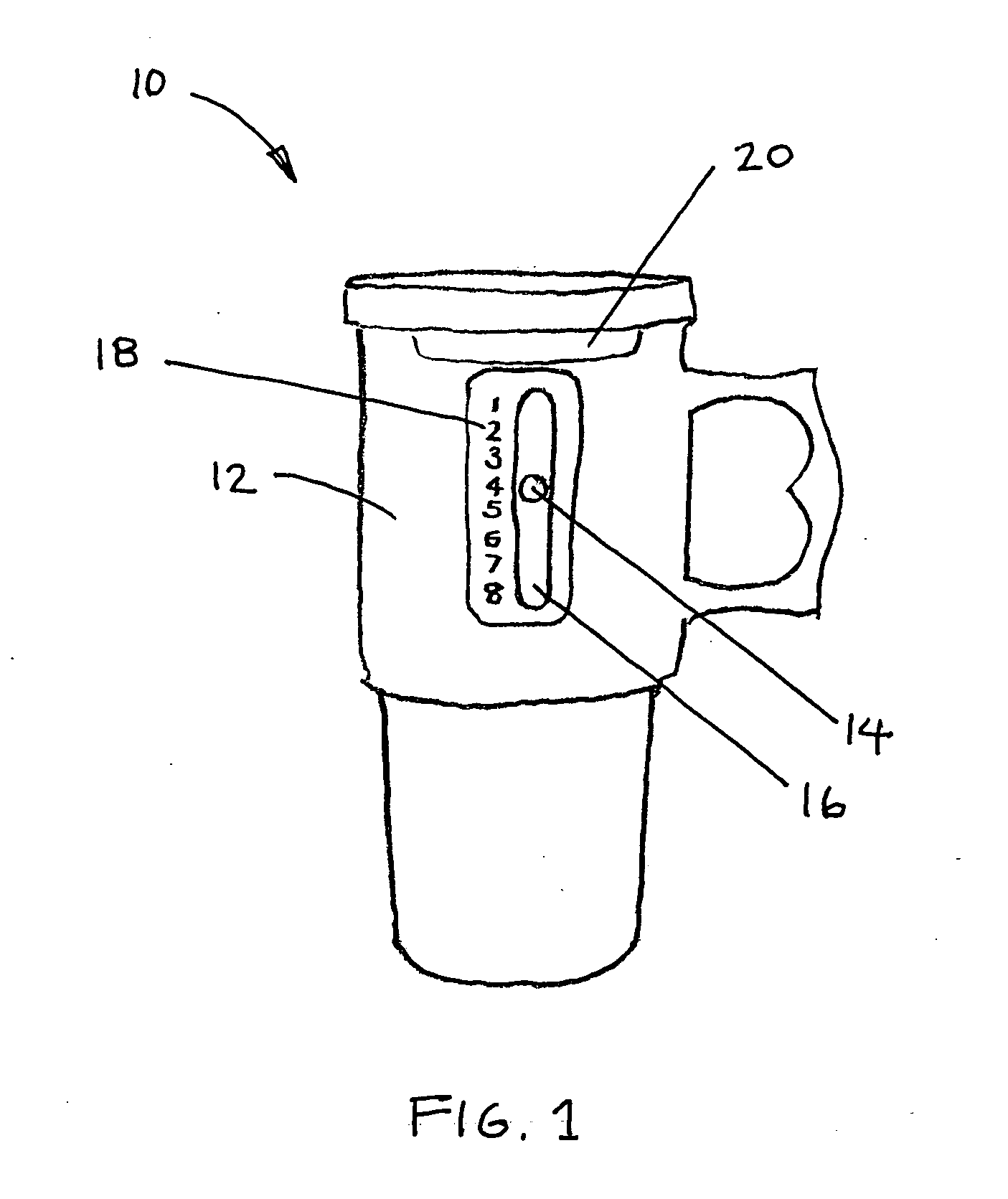
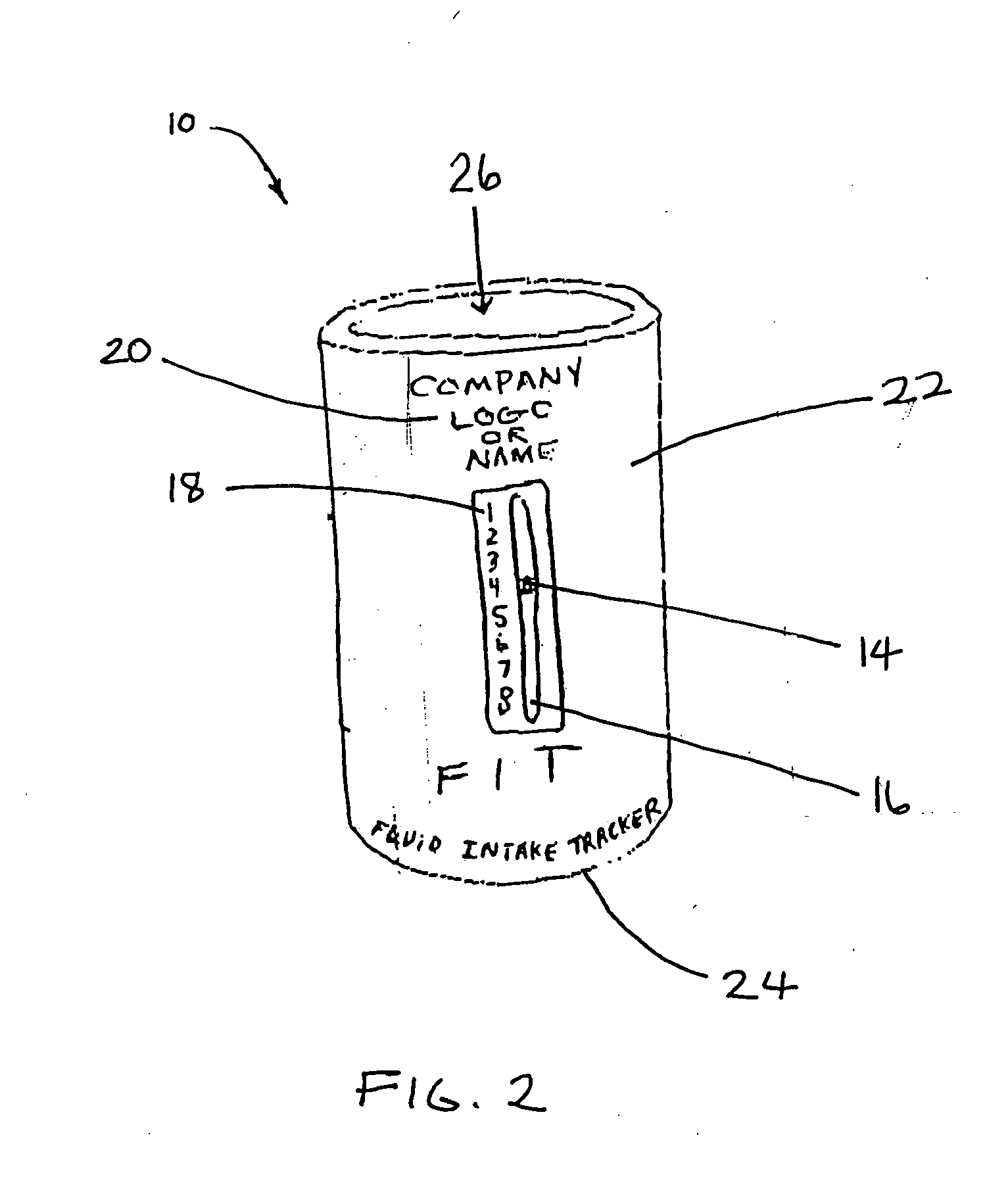
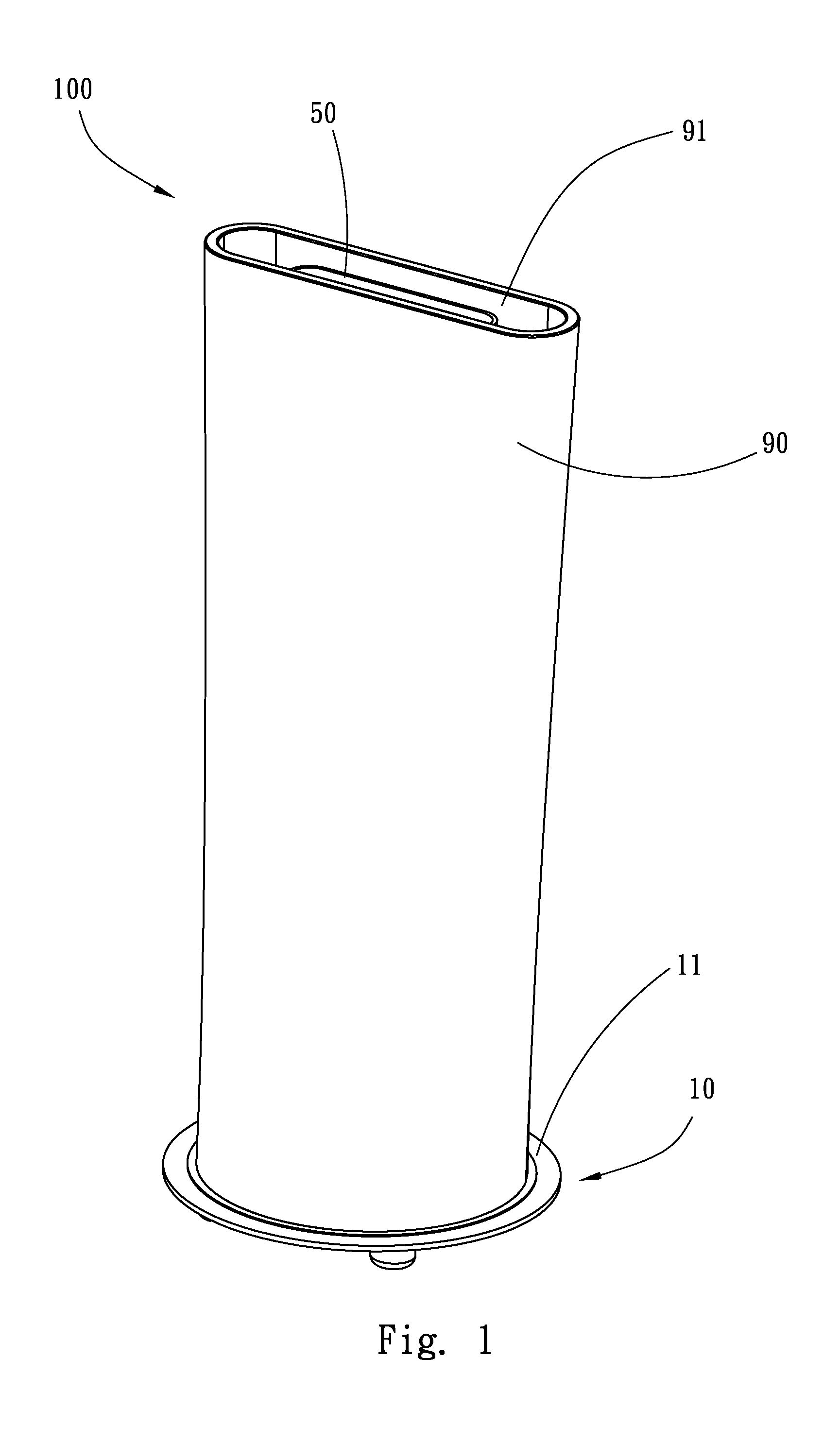
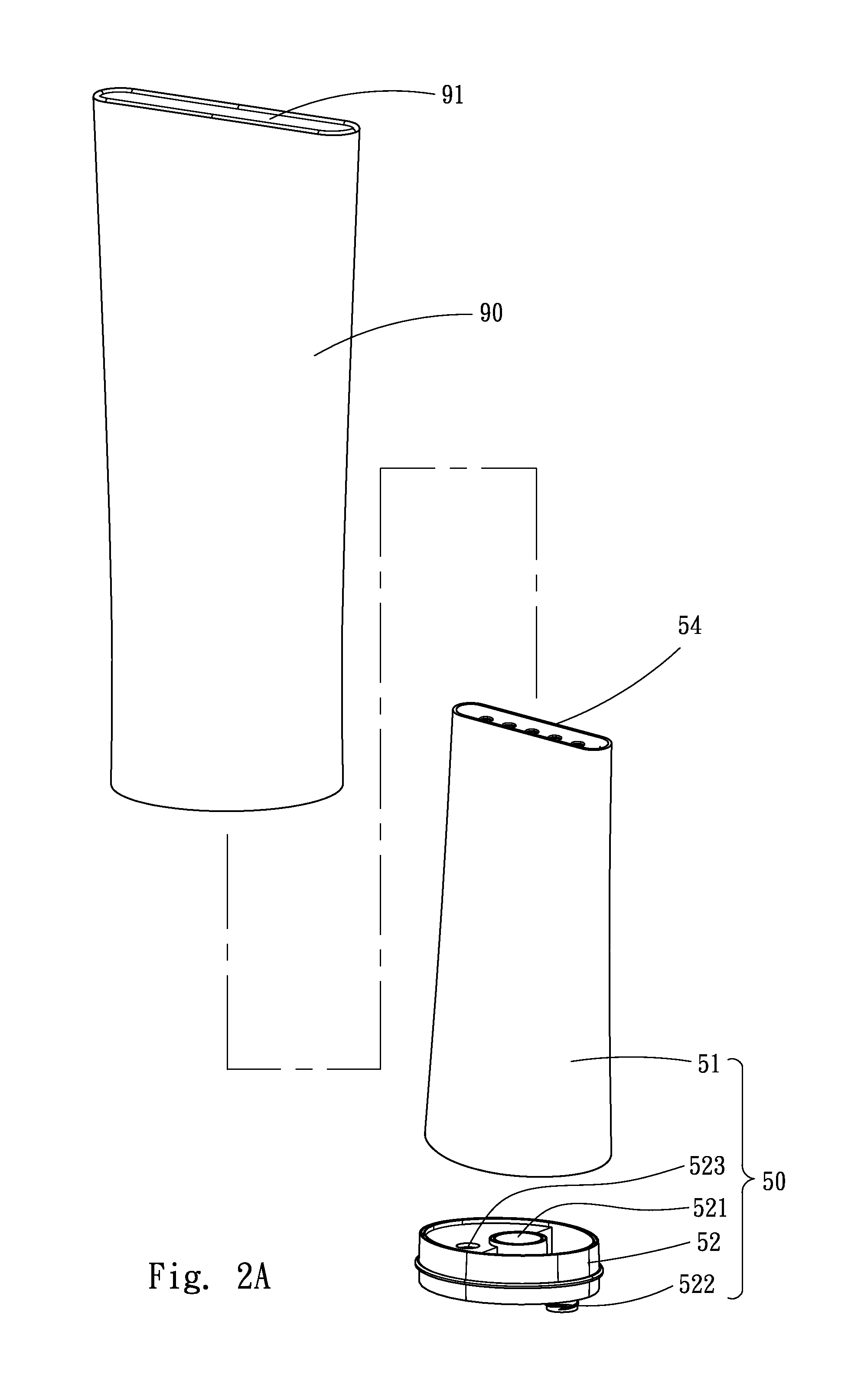
Fluid intake tracker device also know as "FIT"
InactiveUS20060278156A1Effective monitoringEasy transferDwelling equipmentTable equipmentsFluid intakeDisplay device
A fluid intake tracking apparatus that is configured to reversibly couple with a water bottle, mug or other fluid container to keep track of the number of bottles that are consumed by the user during a selected period of time. In one embodiment, the indicator is an electronic device with a display, timer and alarm and powered by a solar cell. In another embodiment, the indicator is permanently mounted to a cup and includes a slidable post within a longitudinal slot and a parallel scale of numbers indicating the intake events.
Owner:MILLER LISA PATRICE
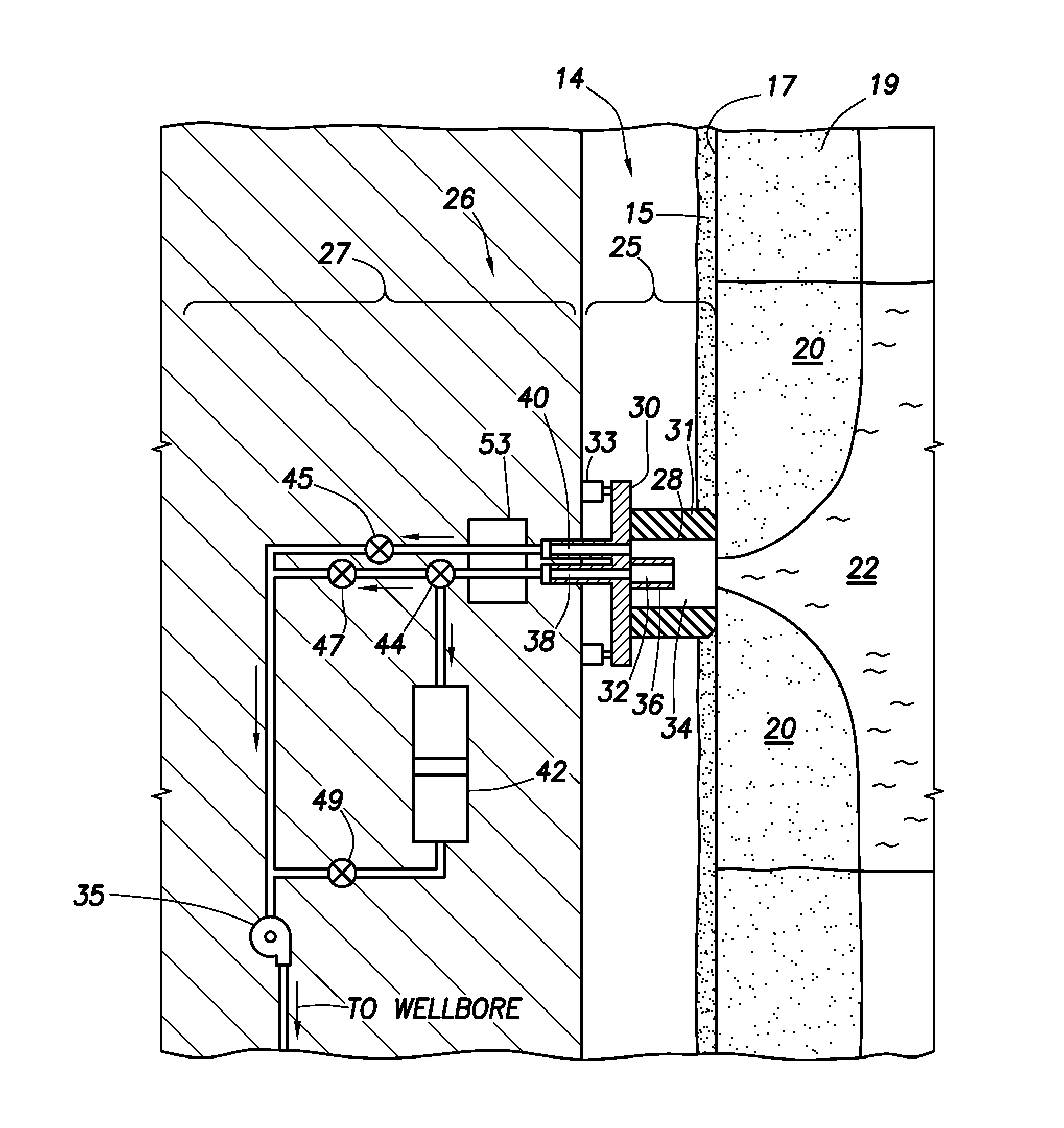
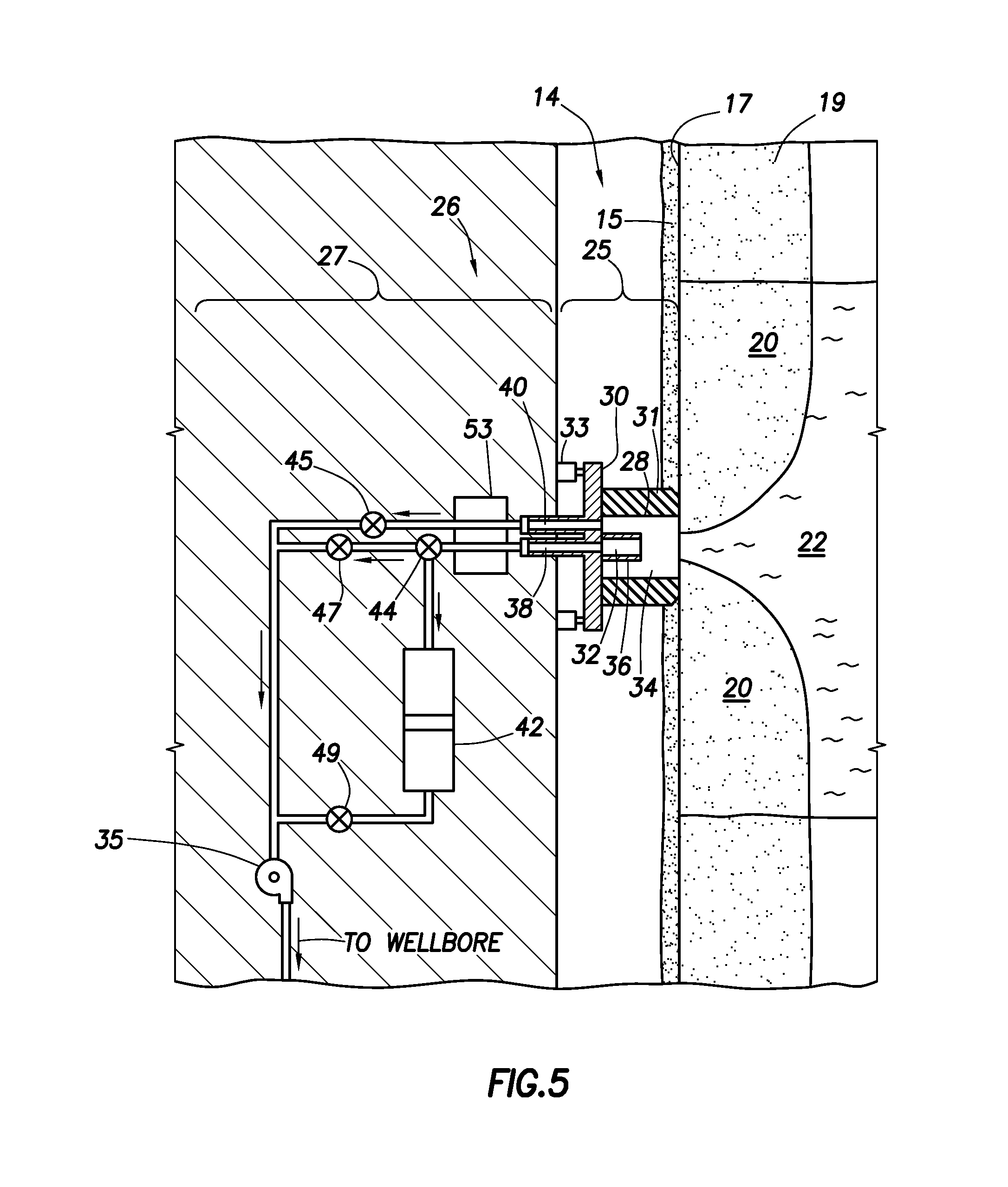
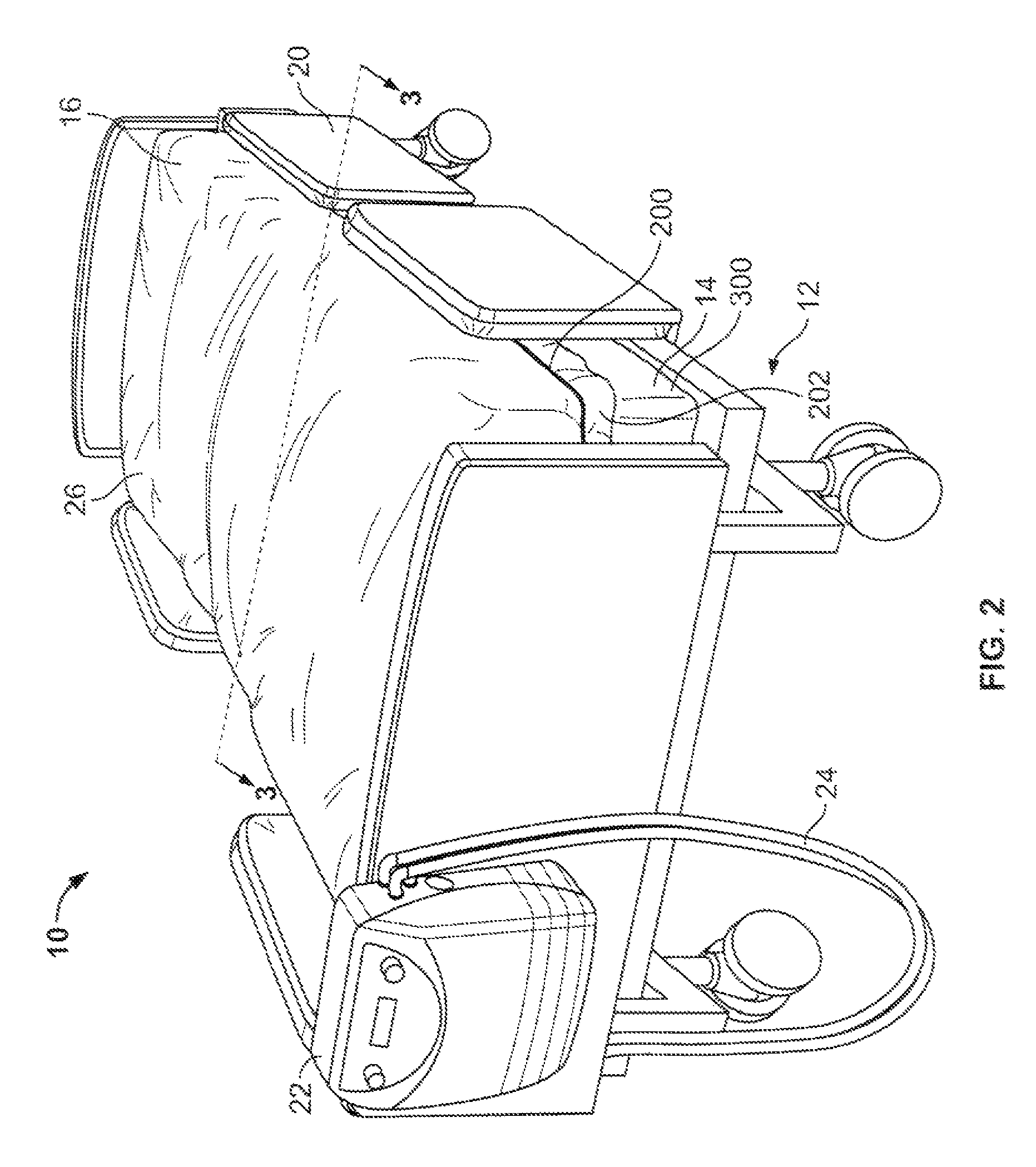
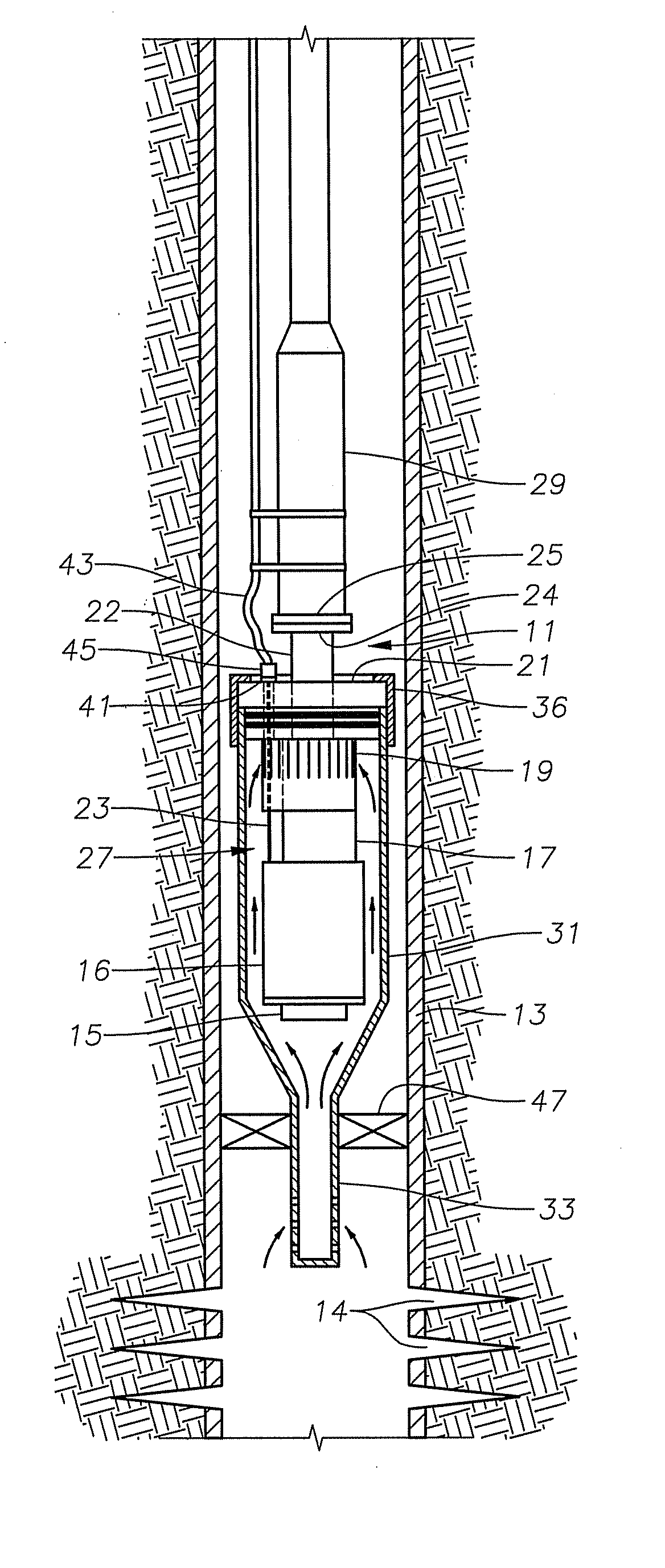
Intake For Shrouded Electric Submersible Pump Assembly
An electric submersible pump (ESP) assembly comprises an integrated sub-assembly encased within a shroud. The integrated sub-assembly comprises a downhole monitoring gauge, a motor, a well fluid intake, a seal section, a mounting member, and an electrical conduit extending between the mounting member and the motor. The intake has a plurality of intake slots positioned a select distance from the mounting member in order to minimize the space for the accumulation of gas within the shroud. The electrical conduit sealingly extends through the mounting member to a receptacle located on an upper portion thereof. Conductors are encased within the conduit and are connected between the receptacle and the motor. The conduit prevents the conductors from being affected by reservoir fluid and pressures.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Surface charge manipulation for improved fluid intake rates of absorbent composites
InactiveUS20050142965A1Improving fluid intake rateIncrease ratingsSynthetic resin layered productsAbsorbent padsFluid intakeFiber
This invention describes a novel means for improving fluid intake rates in disposable absorbent composites by altering the surface charge on the components of such composites through utilization of surface charge treatments (i.e., charge modifiers). The composite components contemplated for the invention may include, but are not limited to, conventional superabsorbent particles (SAP) and fluff fibers (fluff). The surface charge modifiers of the present invention are specifically selected to achieve an ionically (i.e., electrically) generated repulsive force between the individual composite components in the presence of an insulting fluid. This active repulsion between composite components creates a condition in the composite conducive to superabsorbent swelling and generation of void volume and flow channels, thus improving the fluid intake rate.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Airlift type photobioreactor
InactiveCN101550394AEffectively fixedSimple structureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid intakeEngineering
The present invention relates to an airlift type photobioreactor which solves problems of complicated structure, poor gas-liquid mixing efficiency and low microcystis fixing CO2 speed rate in the existing reactor. The reactor includes a glass tank equipped with a culture medium intake, a nutrient fluid intake, a cooling water outlet, an air intake and an air outlet, the glass tank inner side is annual equipped with multi-group recuperator tubes communicated with the cooling water intake and the cooling water outlet, an ascending conduit tube divides the glass tank into an ascending area and a descending area, the glass tank top is equipped with an air separating area, the air inlet communicates with an air distributor located on the ascending area bottom through the air inlet tube, the descending area is equipped with a nutrient fluid outer circulation pipeline, the nutrient fluid outer circulation pipeline communicates with the air inlet pipeline through a water pump. The photobioreactor has simple structure and convenient operation which is particular suitable for photosynthesis fixing CO2 with high efficiency by using microcystis in CO2 emission reduction system. The emission reduction speed rate can reach above 50%, and has low operation cost and is friendly to environment.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP +1
Applicator for applying fluid to a substrate, comprising valve mechanisms, method for cleaning said applicator, and valve mechanisms for said applicator
InactiveUS20100132612A1Easy to removeSensitive to damageLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzlesFluid intakeMedicine
Disclosed is an applicator (1) for applying fluid to a substrate, comprising valve mechanisms (21) which are arranged in a row and are each equipped with an application valve nozzle (31), and a distributing fluid chamber (11) that has a fluid intake duct (110). A cleaning valve mechanism (21) which is incorporated into the row of application valve mechanisms (21) and is fitted with a cleaning valve nozzle (30) is associated with the fluid intake duct (110). A flow path (100) for cleaning the fluid chamber (11) is formed between the fluid intake duct (110) and the cleaning valve mechanism (20) in the distributing fluid chamber (11), said flow path (100) being effective when the cleaning valve nozzle (30) is open. Also disclosed is a method for cleaning said applicator (1). In said method, pressurized cleaning fluid is applied to the distributing fluid chamber (11), the application valve mechanisms (21) are kept closed while the cleaning valve nozzle (30) is opened, and the cleaning valve nozzle (30) is then closed while the application valve mechanisms are opened when the pressurized cleaning fluid is applied to the distributing fluid chamber (11). A valve mechanism (2) of the applicator (1) encompasses a detachably mounted nozzle diaphragm (3, 4) which unblocks a valve piston (51) in the removed state. The valve mechanism (2) further encompasses a straight fluid duct that remains free of flow corners. A setting piston (61) is movably mounted for adjusting and setting the stroke of the valve piston (51).
Owner:J ZIMMER MASCHENBAU GES
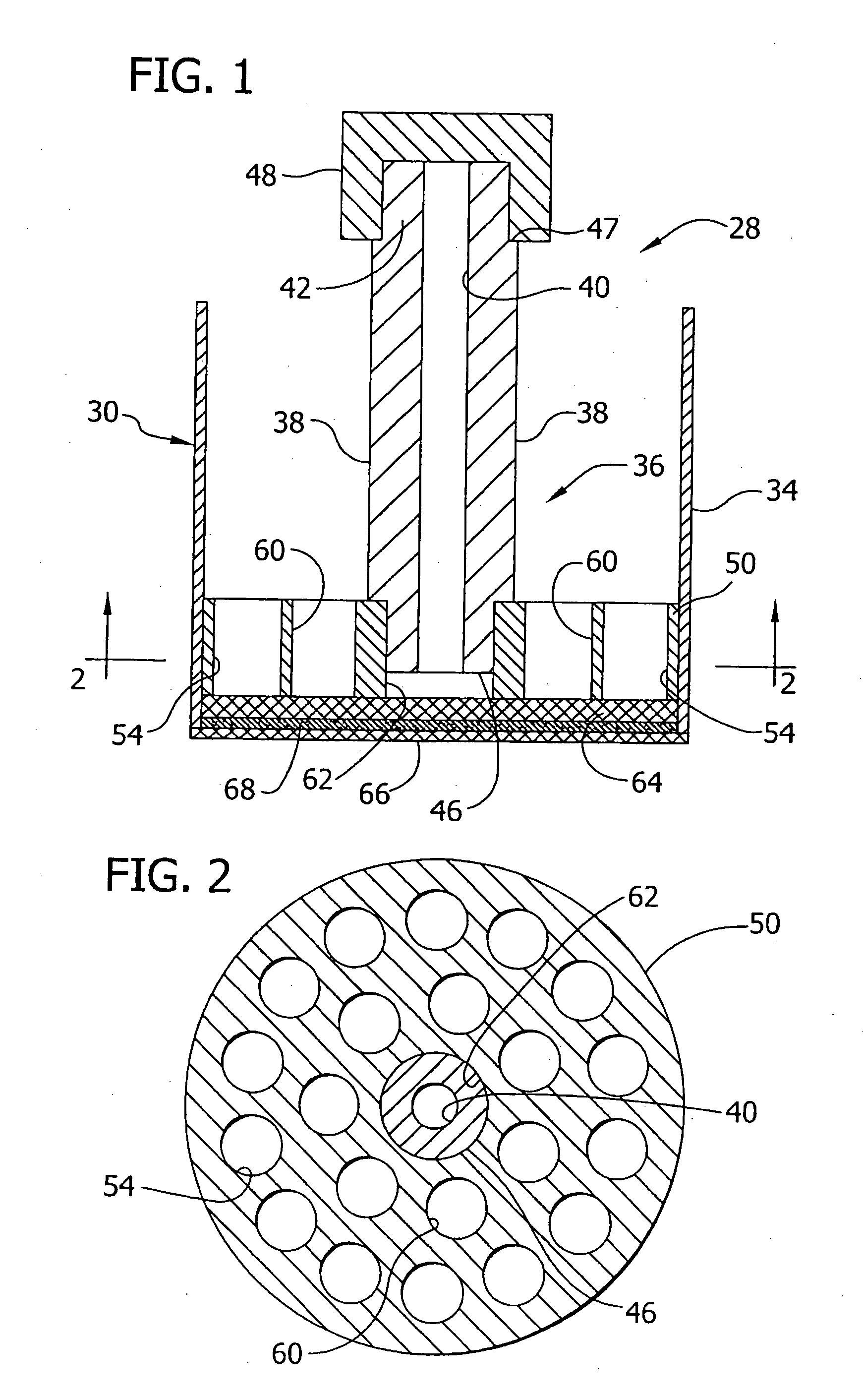
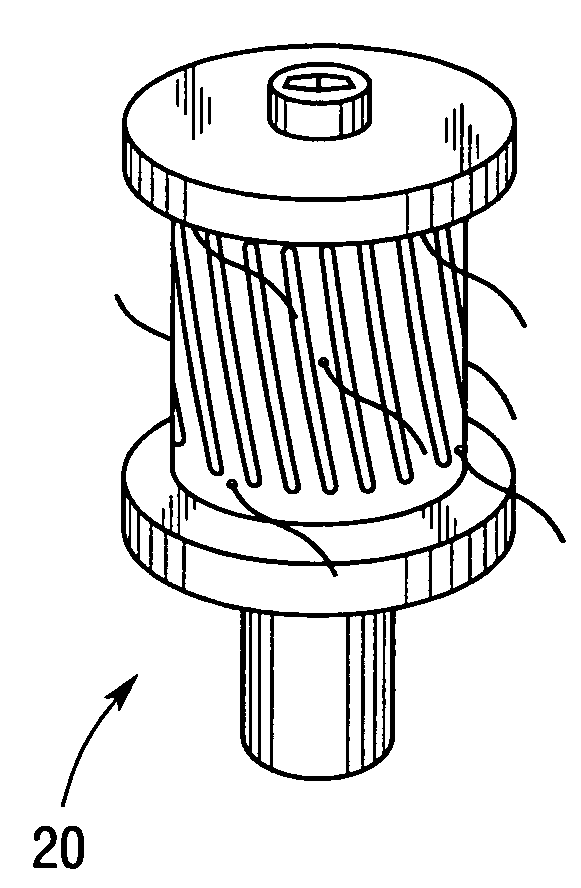
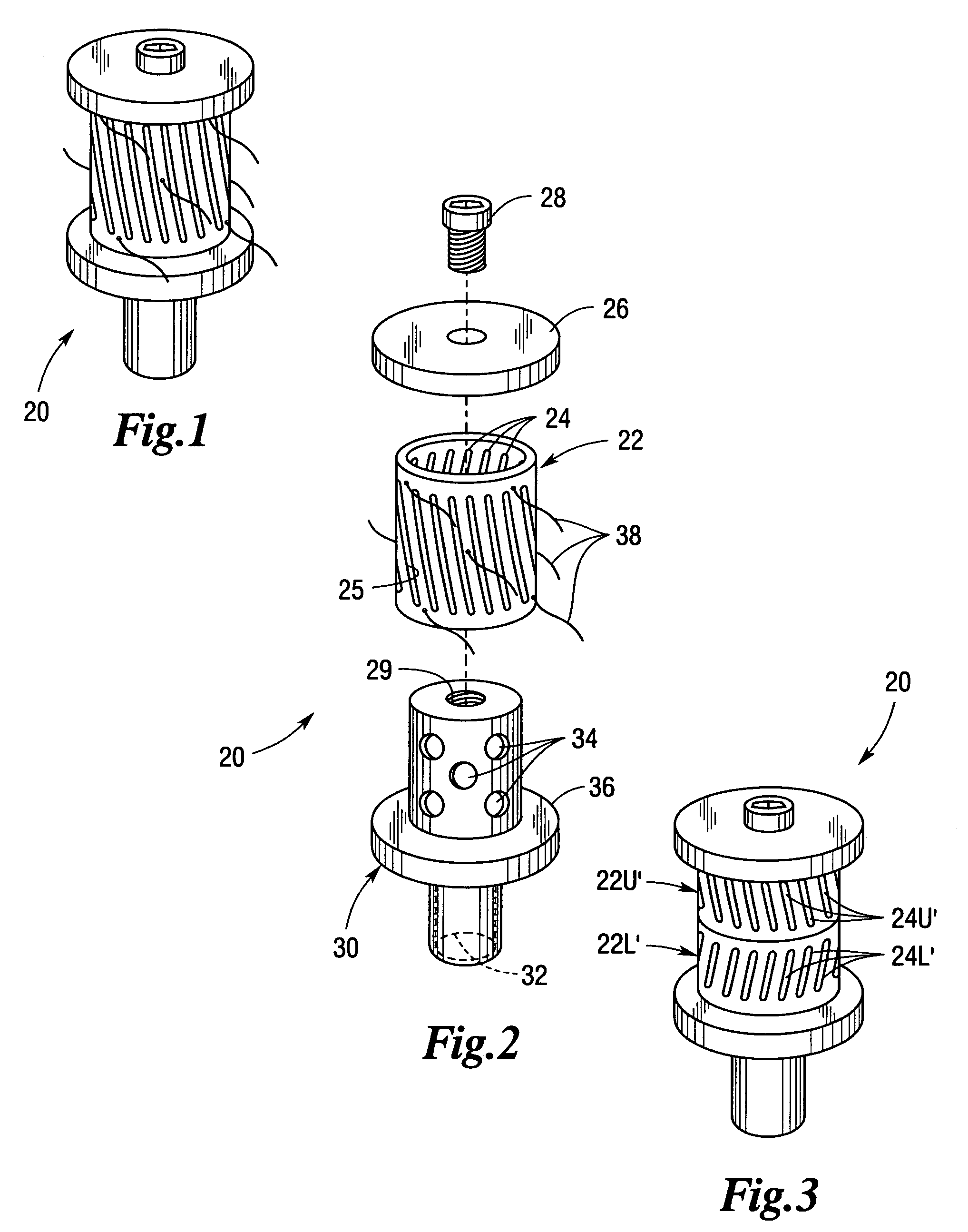
Self-clearing strainer for fluid intake
A cylindrical tumbler has a plurality of angled slots positioned about its periphery, the leading edge face of each slot forming an angled impeller vane. When the tumbler is placed on an intake plug and suction applied through the plug, the tumbler spins throwing off any debris which may otherwise accumulate on the strainer. In alternate embodiments, lengths of flexible strand can be attached to the periphery of the tumbler or two tumblers with oppositely angled slots, and hence, opposite spin directions can be positioned on the same plug to increase turbulence and further reduce debris accumulation.
Owner:LAWRENCE SR JOSEPH W
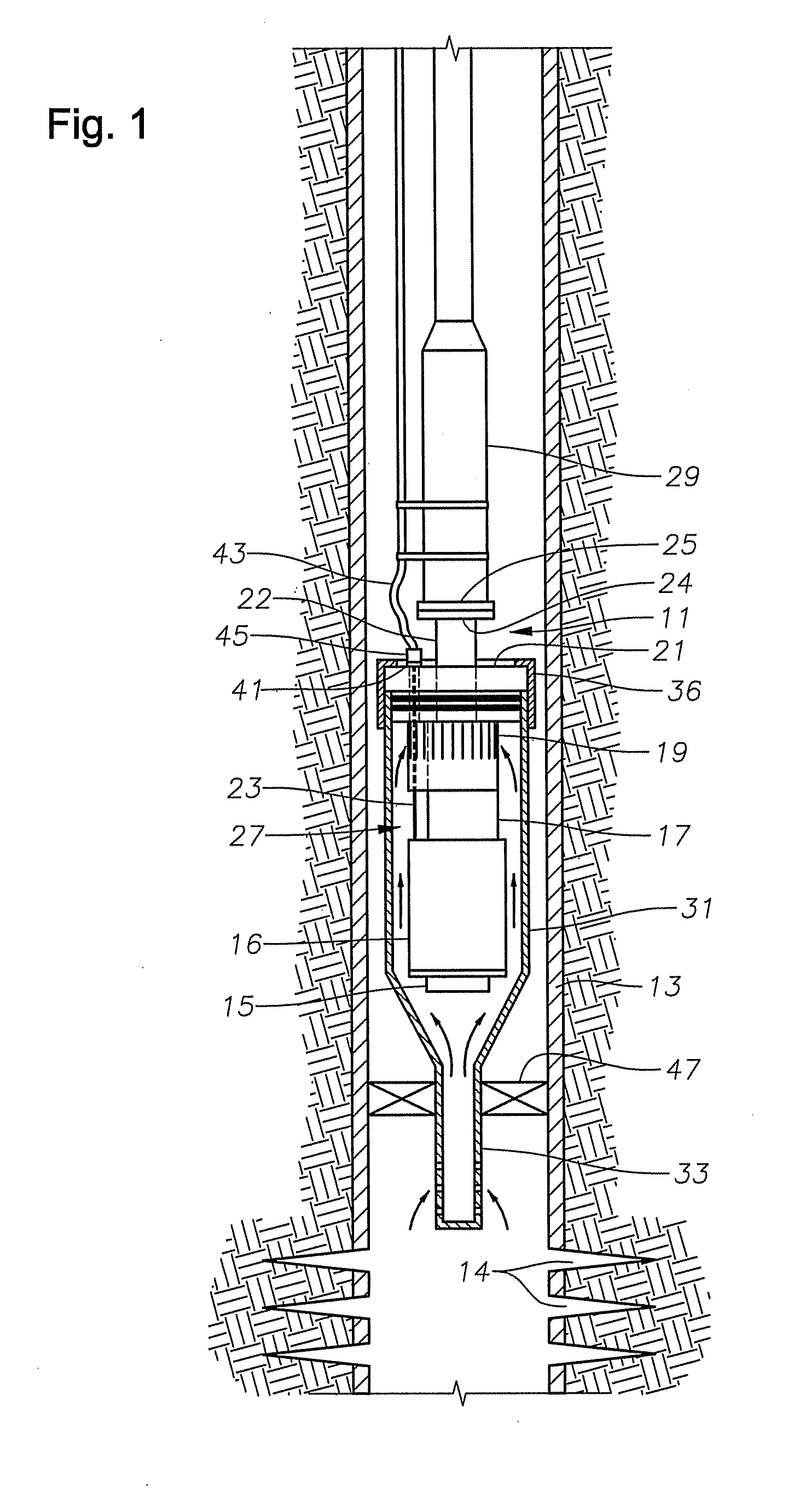
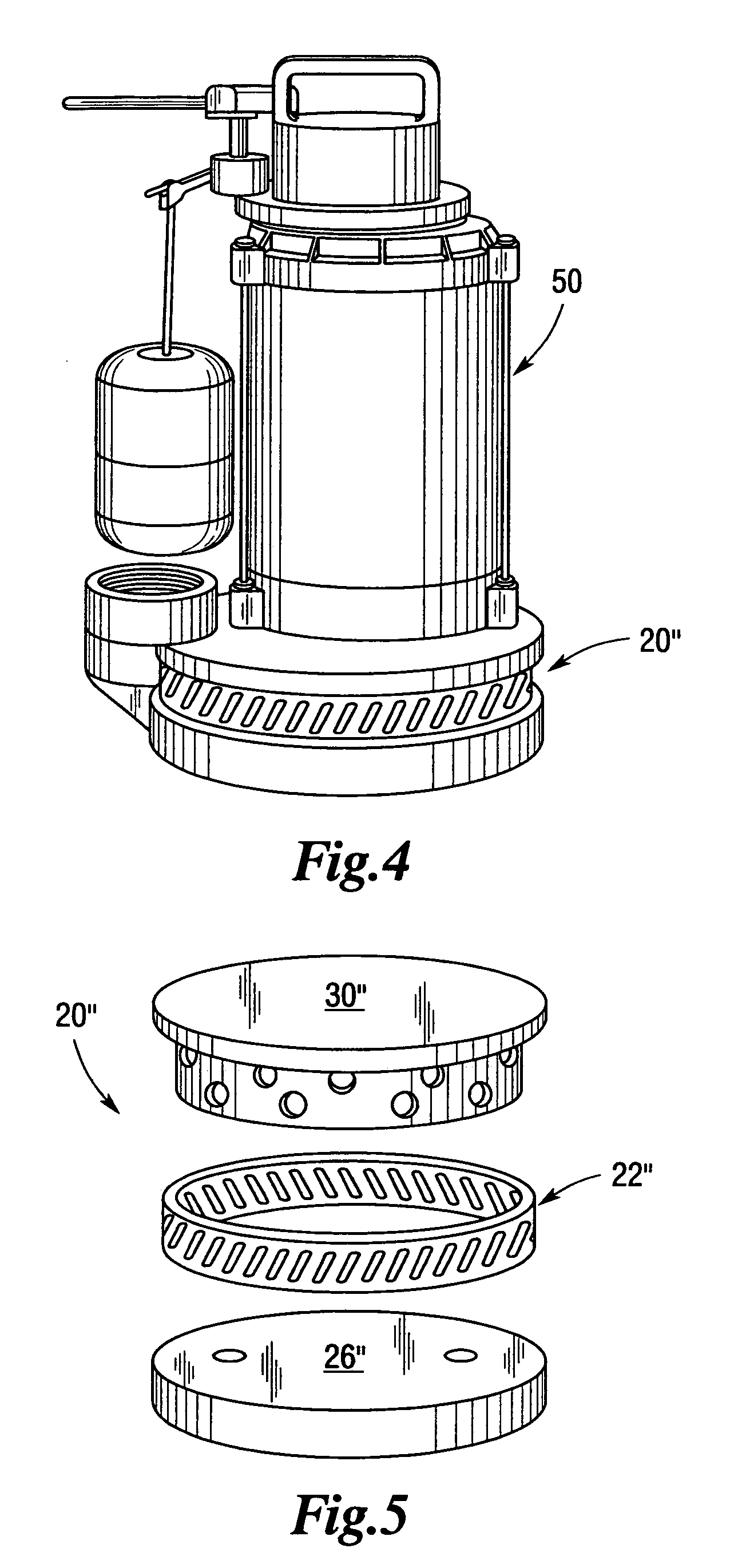
Intake for shrouded electric submersible pump assembly
ActiveUS20120012332A1Space minimizationIncrease productionFluid removalFluid intakeElectrical conductor
An electric submersible pump (ESP) assembly comprises an integrated sub-assembly encased within a shroud. The integrated sub-assembly comprises a well fluid intake having a shroud hanger formed in an upper portion thereof, a seal section having a motor head formed in a lower portion thereof, and an electrical conduit extending between the shroud hanger and the motor head. The intake has a plurality of fluid entry slots positioned a select distance from the shroud hanger in order to minimize the space for the accumulation of gas within the shroud. The electrical conduit sealingly extends through the shroud hanger to a receptacle located on an upper portion thereof. Conductors are encased within the conduit and are connected between the receptacle and the motor head. The conduit prevents the conductors from being affected by reservoir fluid and pressures.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
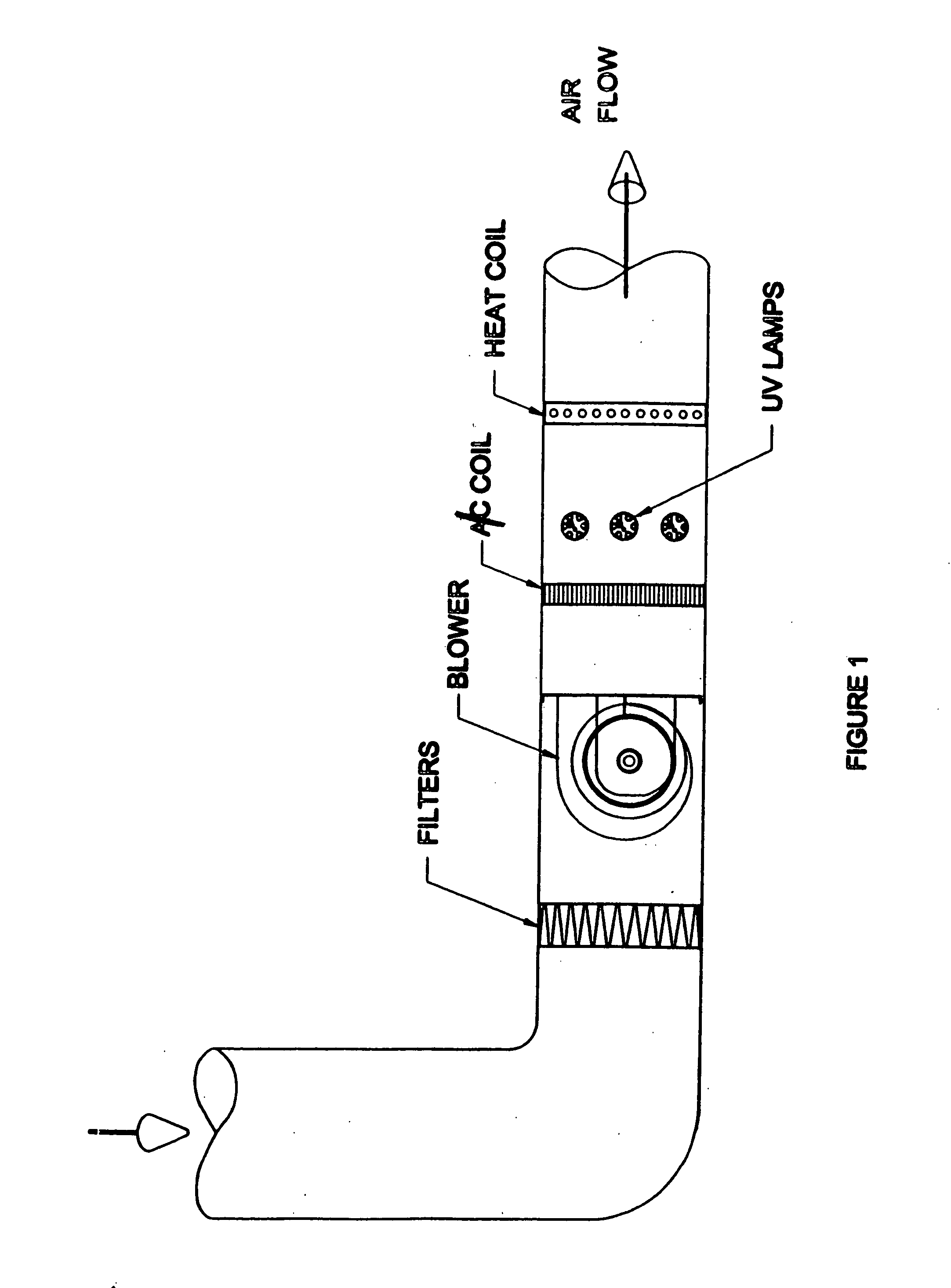
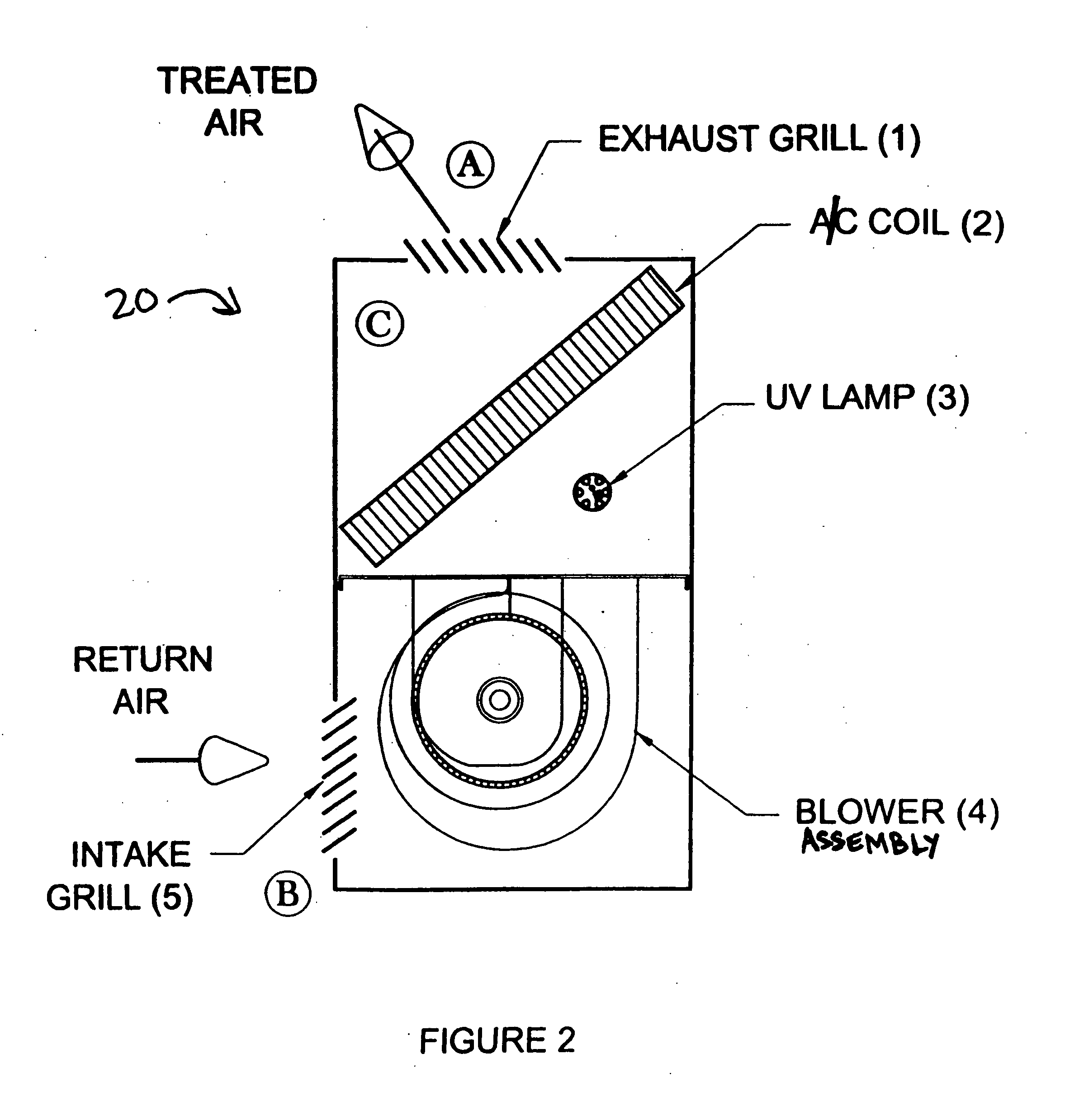
Low level ultraviolet disinfecting system
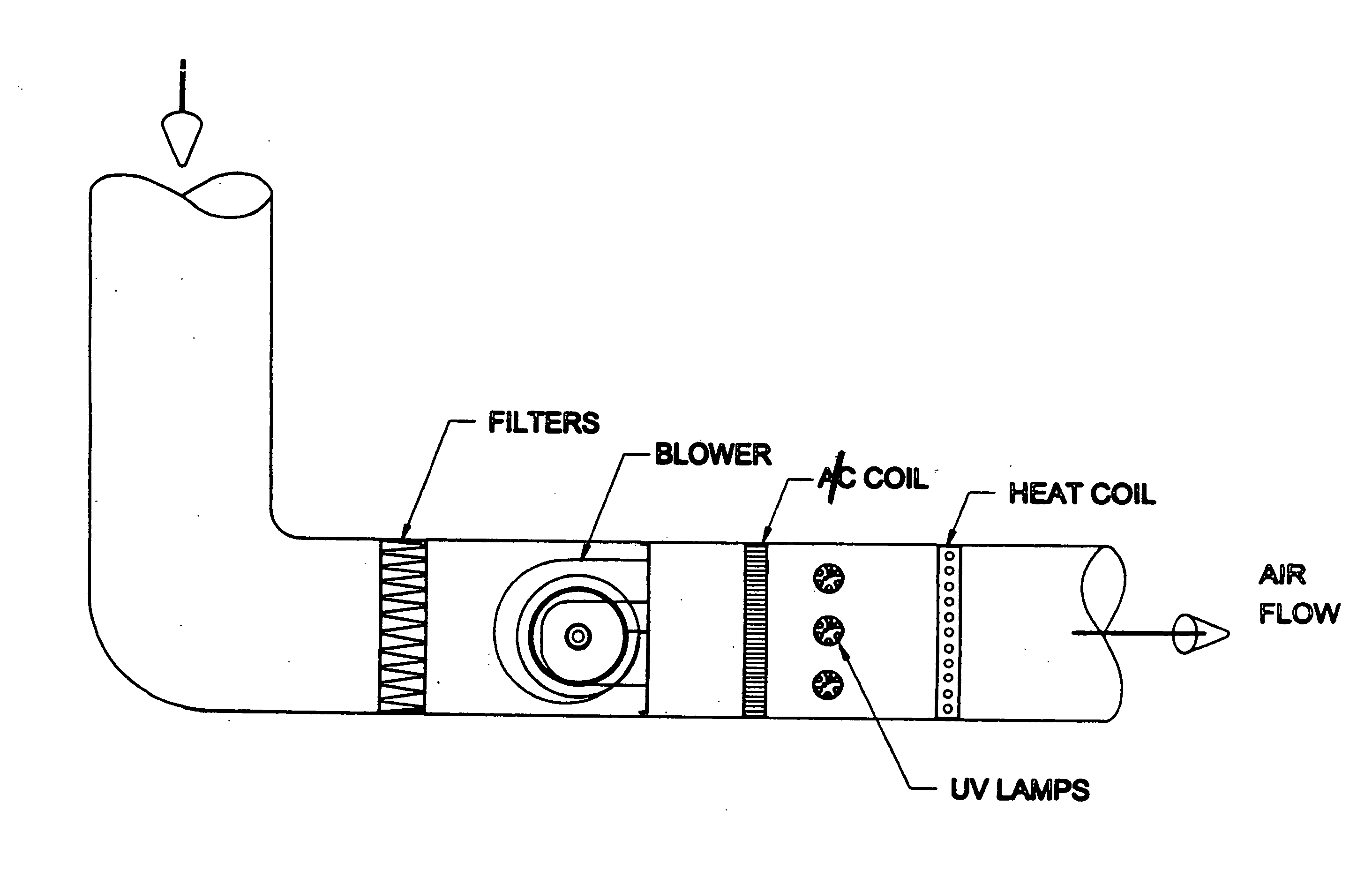
InactiveUS20050163652A1Safe exposure levelAdequate levelMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusFluid intakeHuman exposure
A disinfecting system comprises a light source having output suitable for use as a germicidal agent, and a power supply for the light source that is adapted to limit the output of the light source to levels adequate for microbial growth control. The light source is operatively housed in fluid-conveying equipment for disinfecting fluids and surfaces therein. The limited output is attenuated by fluid-conveying equipment components disposed within the output range of the light source. The attenuated output provides safe human exposure levels in the vicinity of fluid intake and exhaust portions of the fluid-conveying equipment. The limited output inhibits the degradation of fluid-conveying equipment components disposed within the output range of the light source. The light source may be covered with a thin film or sleeve of material being semi-transparent to germicidal UV wavelengths to control the output of the light source.
Owner:ULTRAVIOLET DEVICES
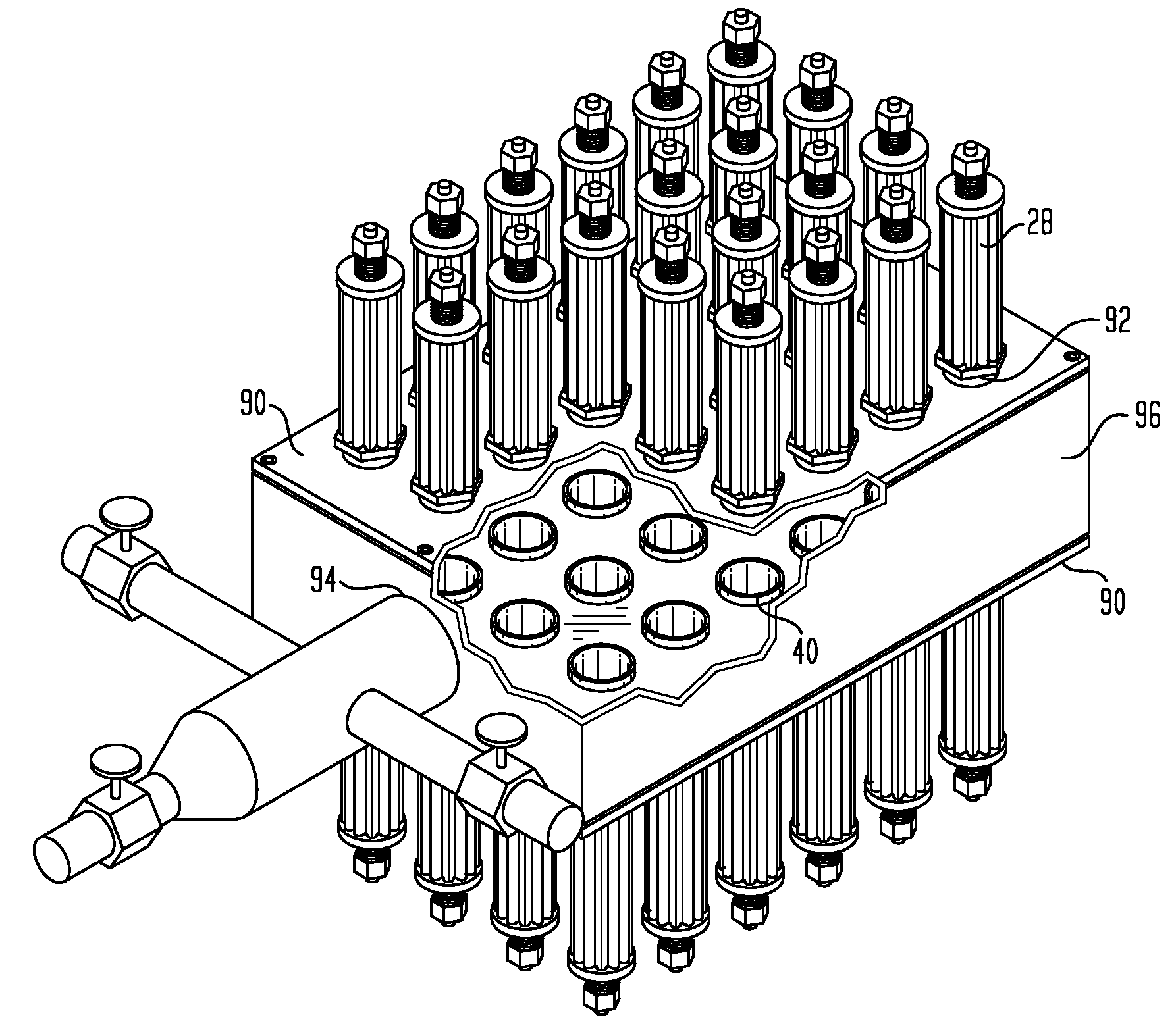
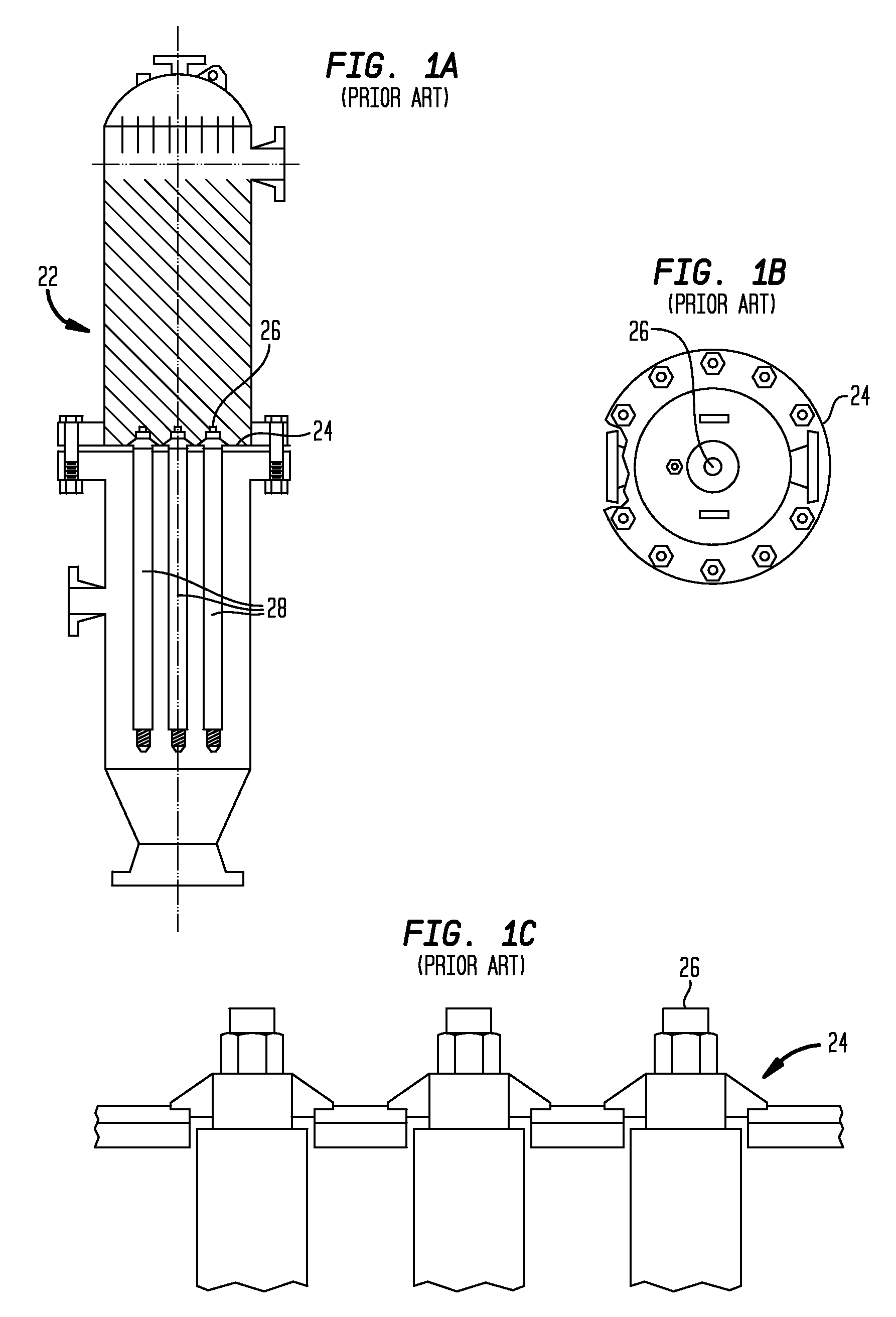
Scalable immersed-filtration method and apparatus
InactiveUS20090184064A1Easy to scaleIncrease capacitySemi-permeable membranesWater cleaningFluid intakeFiltration
A method and apparatus for filtering a large volume fluid intake system using a modular immersed-filtration array that can be easily scaled for use in a wide variety of immersion filtering applications. The immersed-filtration array is composed of a plurality of individual filtration modules. Each filtration module has a mating end that allows the module to be coupled with a base unit or plenum via a common interface port located on the base unit. The array can be scaled in a plurality of ways.
Owner:ZAITER SOHAIL
Wellbore filter for submersible motor-driver pump
This invention related to the geophysics, in particular, to geophysical methods of well survey, and can be applied for removal of wellbore liquid that fill the well, during the well logging process. This invention characterizes a filter for solid particles; which can be mounted at the suction side of submersible motor-driven pumps.A well filter for submersible motor-driven pump comprising an elongated housing in which a cylindrical filtering element is installed. At one end of the filtering element, a fixture for fastening the filter housing to the pump is mounted; at the other end, there is at least one fluid intake port. A shape-deformable sealing element is installed on the housing outer surface.The rigid structure of the sealing element creates problems with lowering the strainer to the well and may cause the damage of the said strainer. This damage creates leakage in the top part of the strainer. The way of resolving the engineering issue is development of a new design of the wellbore filter. The implementation of a new design of a wellbore filter makes the service life of submersible motor-driven pump longer.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
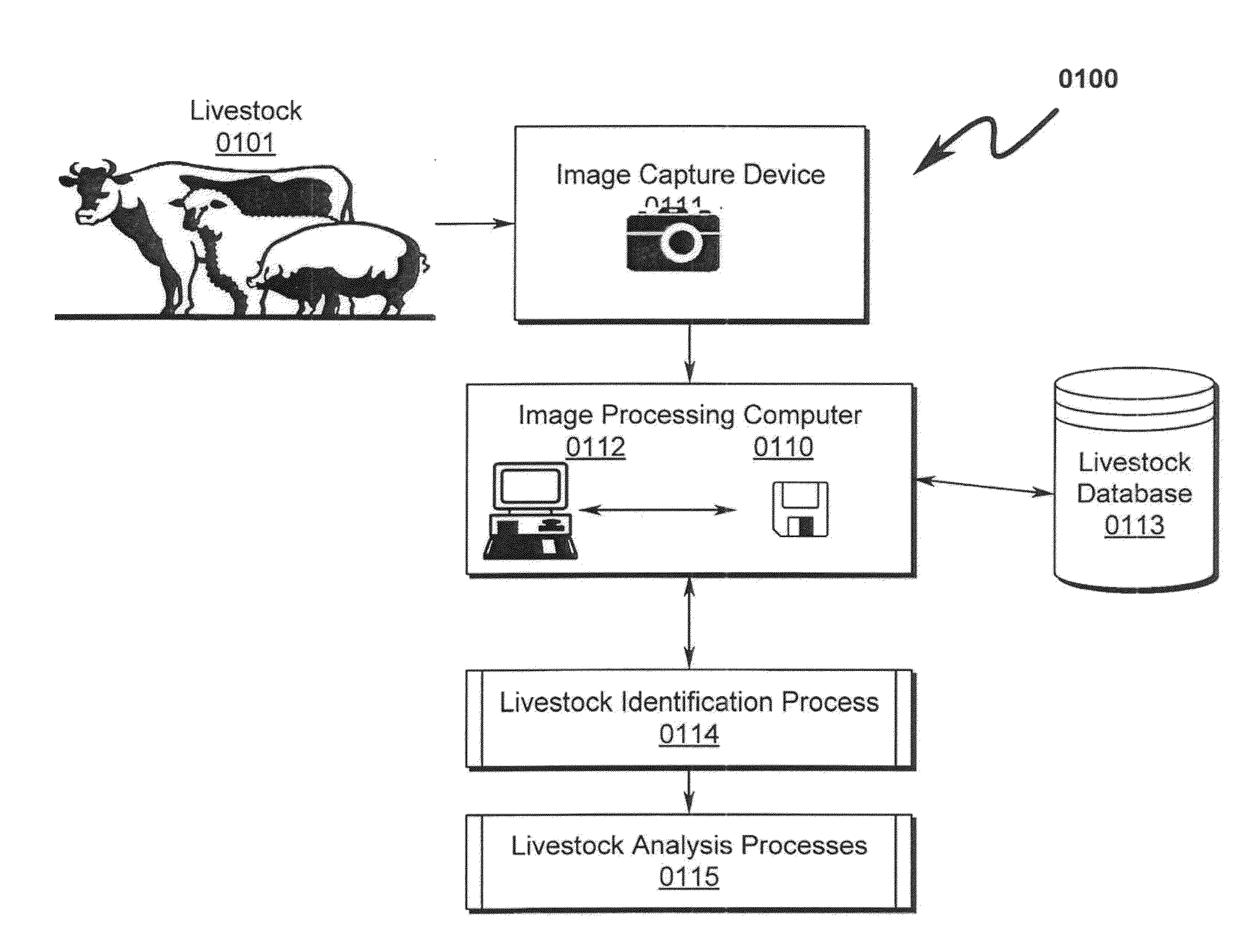
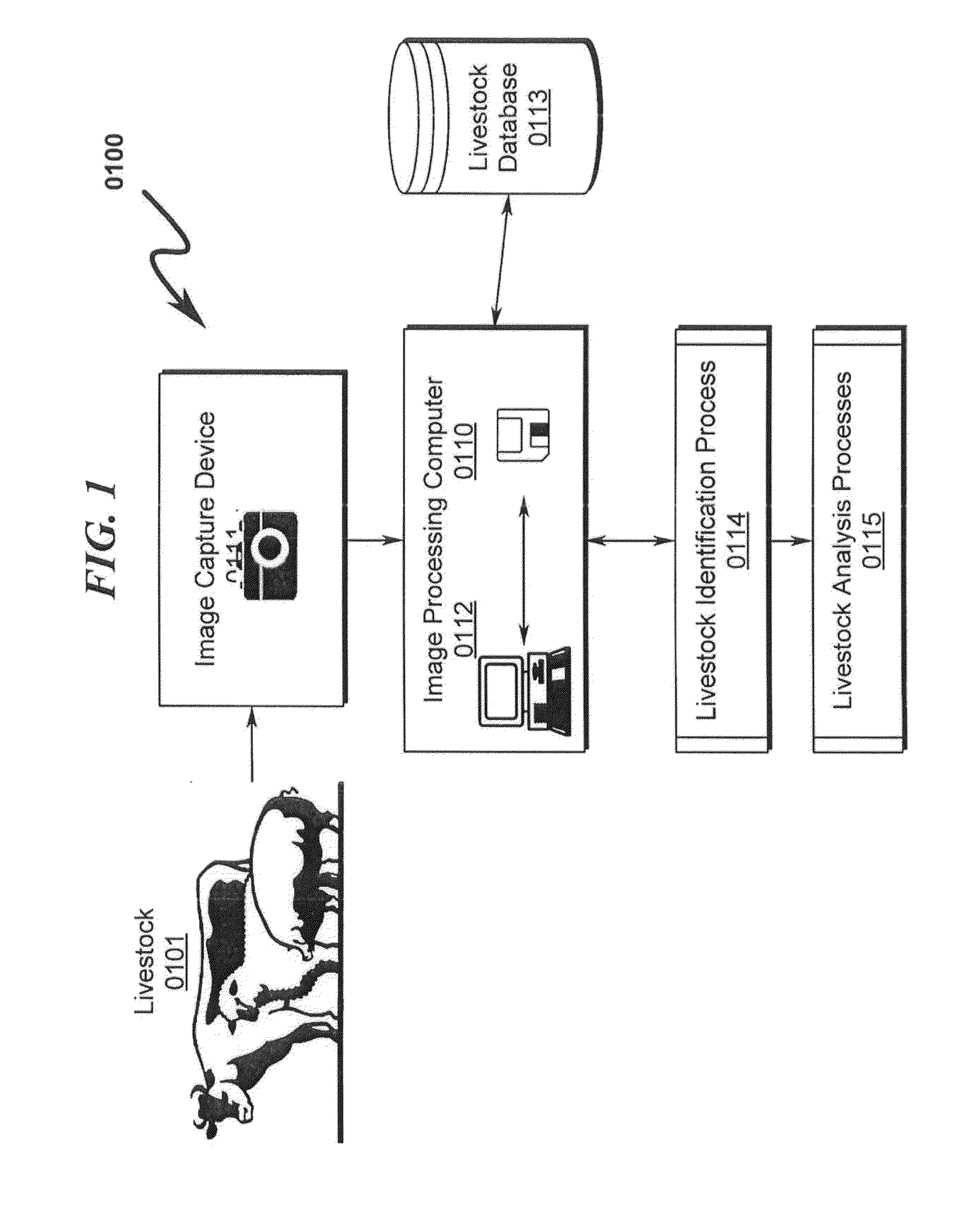
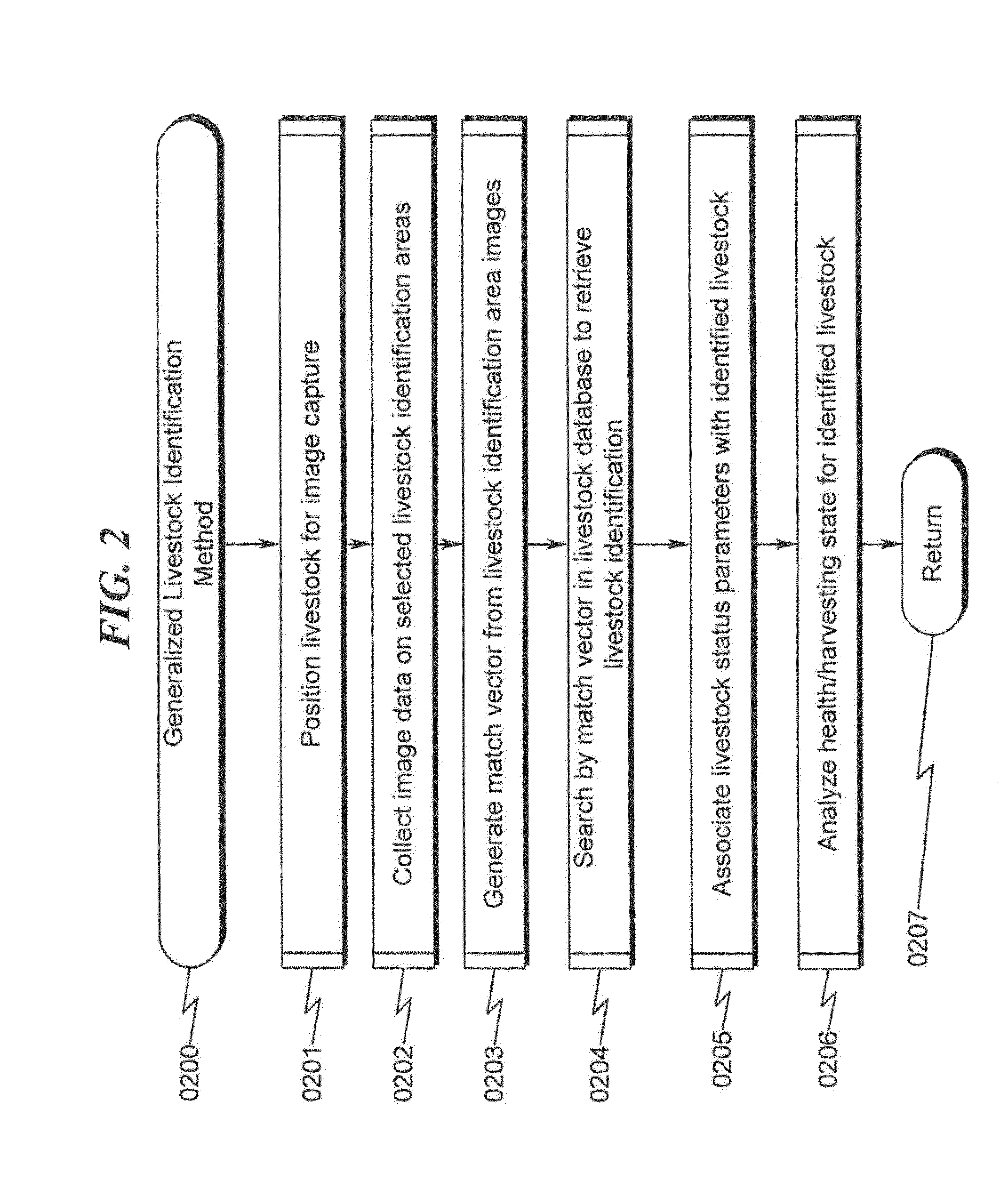
Livestock Identification and Monitoring
ActiveUS20150289478A1Accurate identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionOther apparatusTemporal databaseFluid intake
A livestock identification system / method configured to identify individual animals from a pool of livestock is disclosed. The system / method utilizes images of individual animals and determines the identity of a specific animal based on markers extracted from the image of the animal. These markers may then be used to characterize the state of the animal as to weight, health, and other parameters. The system is configured to log these parameters in a temporal database that may be used to determine historical activity of the animal, including but not limited to activity relating to food and / or fluid intake. This historical record in conjunction with analysis of the animal state parameters is used to determine the animal health status and may also be used to determine whether the animal is ready for harvesting.
Owner:ANIMAL BIOTECH
Aromatic nebulizing diffuser
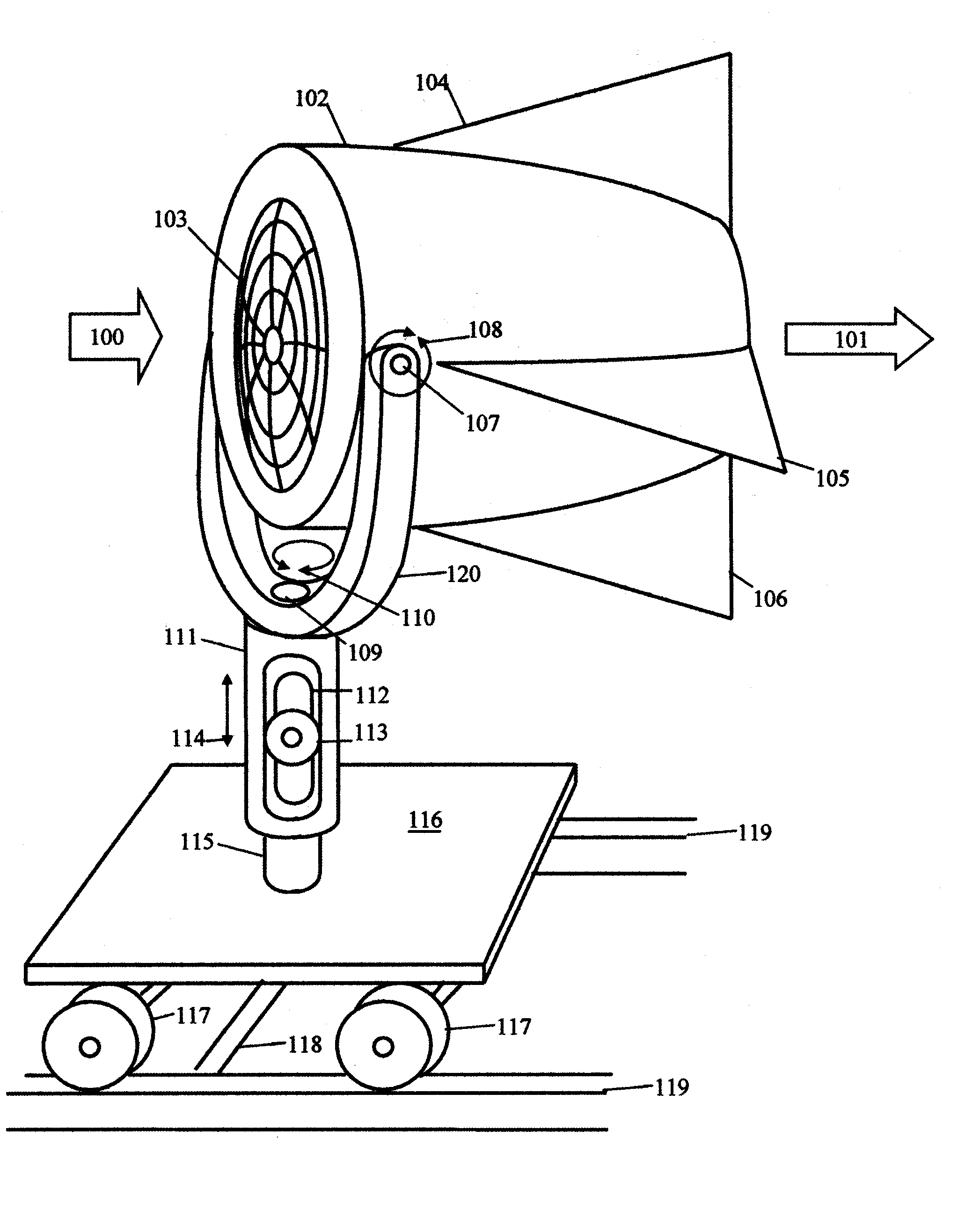
InactiveUS20120251296A1Fine mistGenerate a fine mist of aromatic fluid droplets efficientlyLiquid spraying apparatusPumpsFluid intakeEngineering
An aromatic nebulizing diffuser includes a base panel, a holder defining therein an oscillation chamber, a power switch, an electric fan, a fluid container, an ultrasonic oscillator, a fluid intake control device set in between the oscillation chamber and the fluid container, a dip tube in communication between the oscillation chamber and the fluid container and changeable between an open status and a close status to control the fluid intake control device in closing / opening the passage between the oscillation chamber and the fluid container, an outer housing, an air passage in air communication between the oscillation chamber and the cover for the passing of currents of air caused by the electric fan, an exhaust passage for guiding a generated fine mist of aromatic fluid droplets out of the oscillation chamber into the atmosphere.
Owner:HSIAO MING JEN
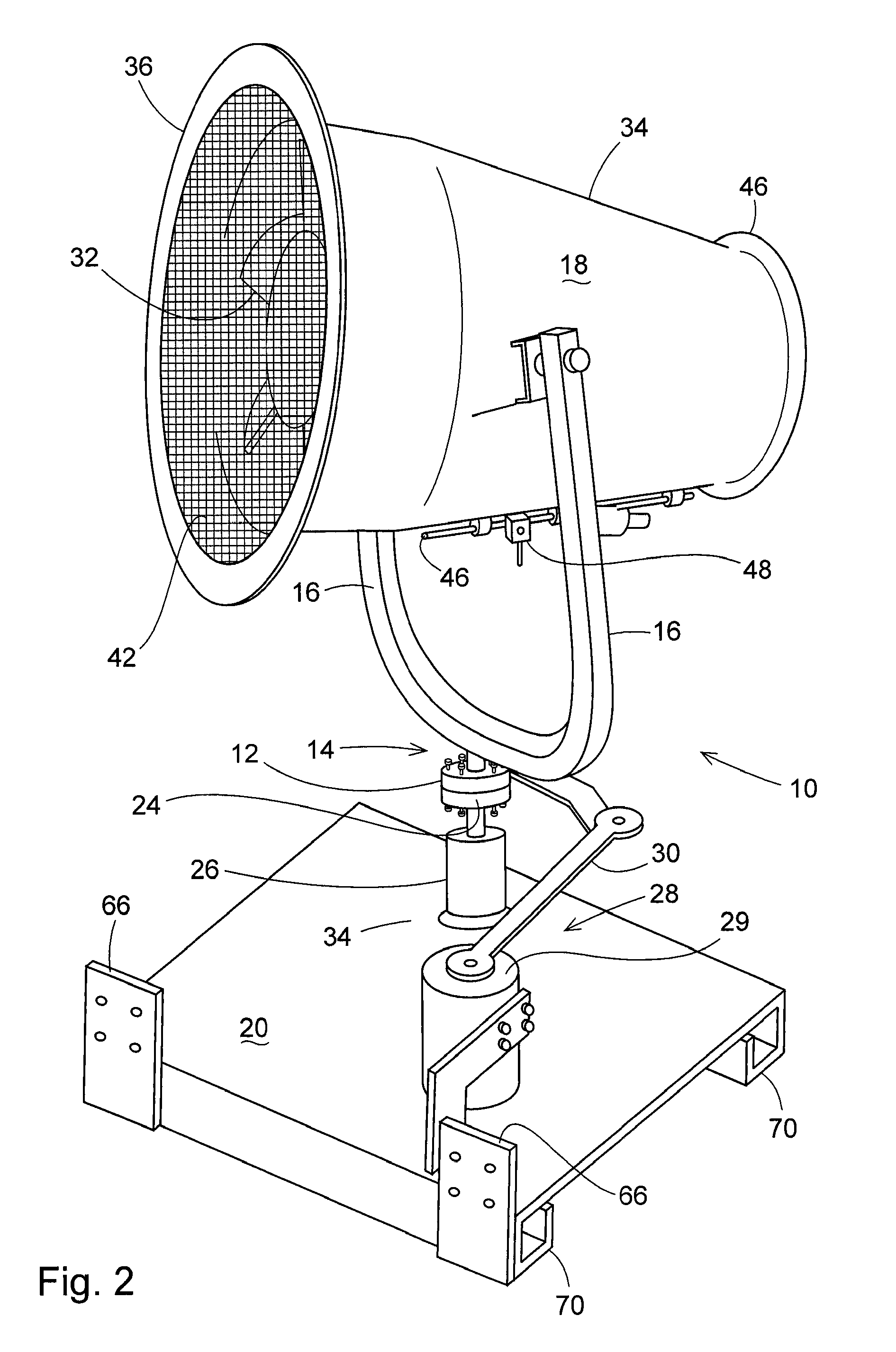
Method for Attaching a Blower Unit to Industrial Equipment and Apparatus Used Therewith and Methods for Using the Same
A blower unit has a base, a frame extending upward from the base and a fan propelled mister attached to the frame. The fan propelled mister comprises a fan, a discharge tube, and a plurality of nozzles operatively connected to a fluid intake for creating a mist. A rigid frame, mobile engine-powered machine having a lift arm with a mount is provided. An attachment is also provided having a first surface with a coupling portion adapted to secure the attachment to the mount on the lift arm and a second surface with a coupling portion adapted to secure the attachment to the base. The attachment is mounted to the lift arm with the first coupling portion of the first surface, and to the base with the second coupling portion of the second mounting surface. The blower unit and attachment and methods of use of the same are described.
Owner:DUST CONTROL TECH
Chest wound seal for preventing pneumothorax and including means for relieving a tension pneumothorax
A flexible sheet having an adhesive layer carried on a bottom side. A collection chamber formed in the adhesive layer by the exclusion of adhesive from a central area of the sheet for receiving fluid from the wound. A drainage channel formed in the adhesive layer by the exclusion of adhesive from a selected area of the sheet extending radially outward from the collection chamber to a drain outlet at a peripheral edge of the sheet to drain fluid from the collection chamber. The collection chamber and drainage channel having an open position allowing fluid to flow outward from the collection chamber through the drain outlet, and a closed position collapsed against the skin to prevent fluid intake through the drain outlet. A storage compartment carried by the flexible sheet including a needle and catheter for immediate access in treating a tension pneumothorax.
Owner:NORTH AMERICAN RESCUE PRODS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com