Patents
Literature
107 results about "Temporal database" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A temporal database stores data relating to time instances. It offers temporal data types and stores information relating to past, present and future time. Temporal databases could be uni-temporal, bi-temporal or tri-temporal.
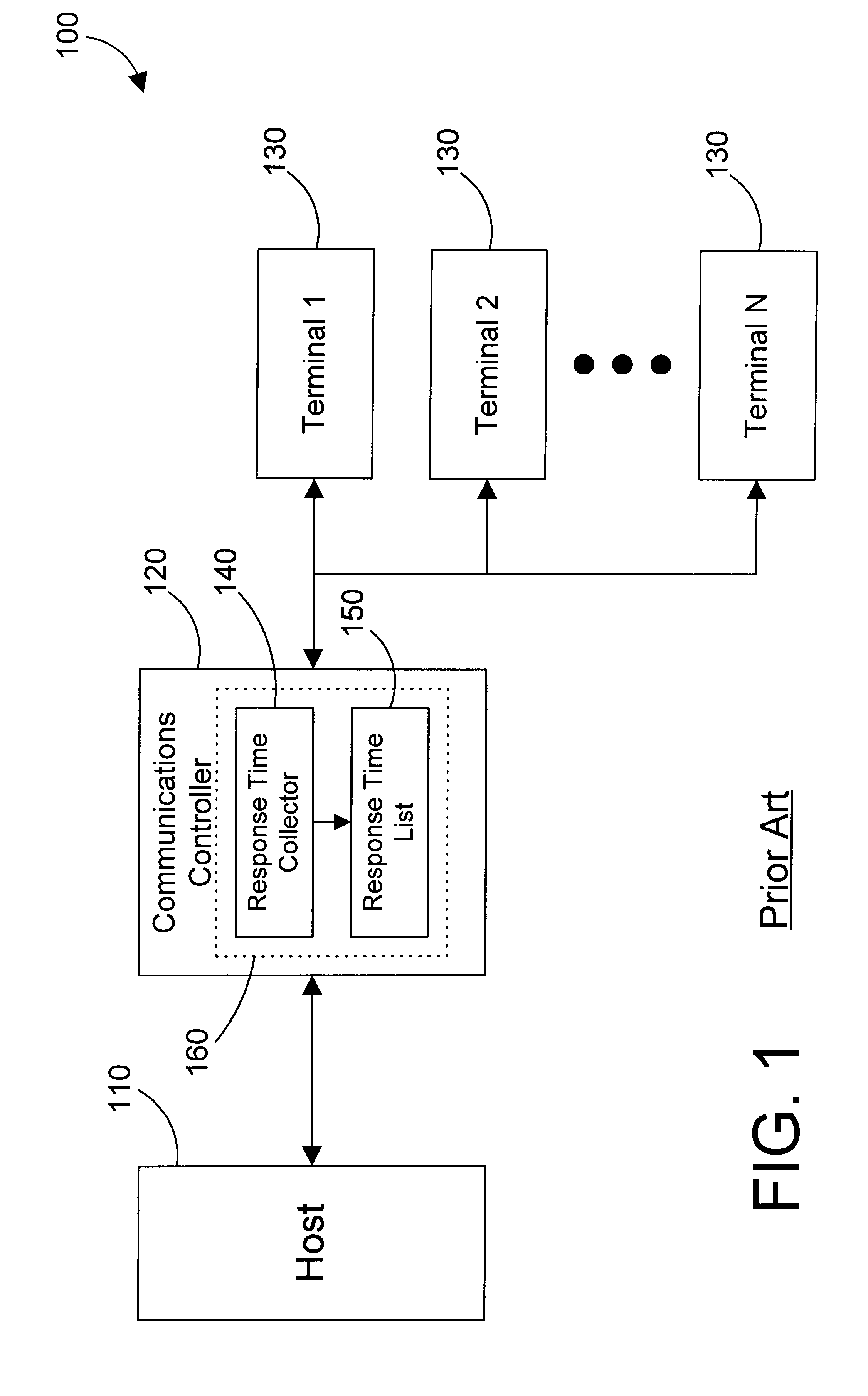
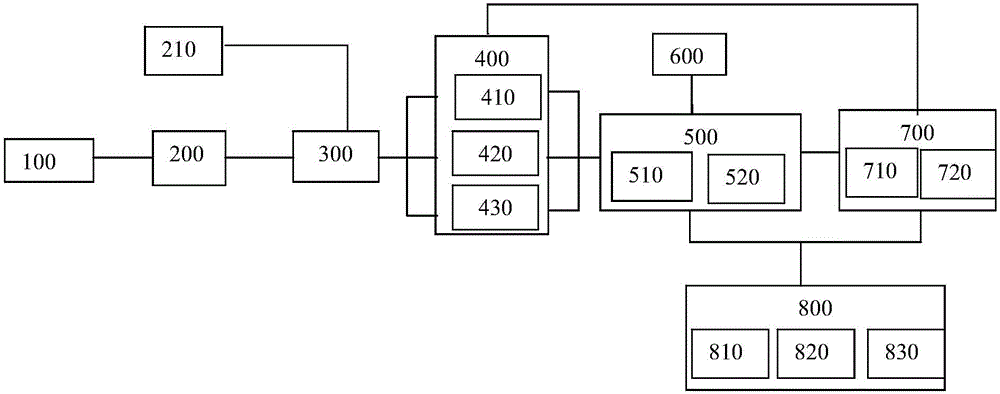
System and method for maintaining temporal data in data storage
ActiveUS20050071379A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTemporal informationTemporal database
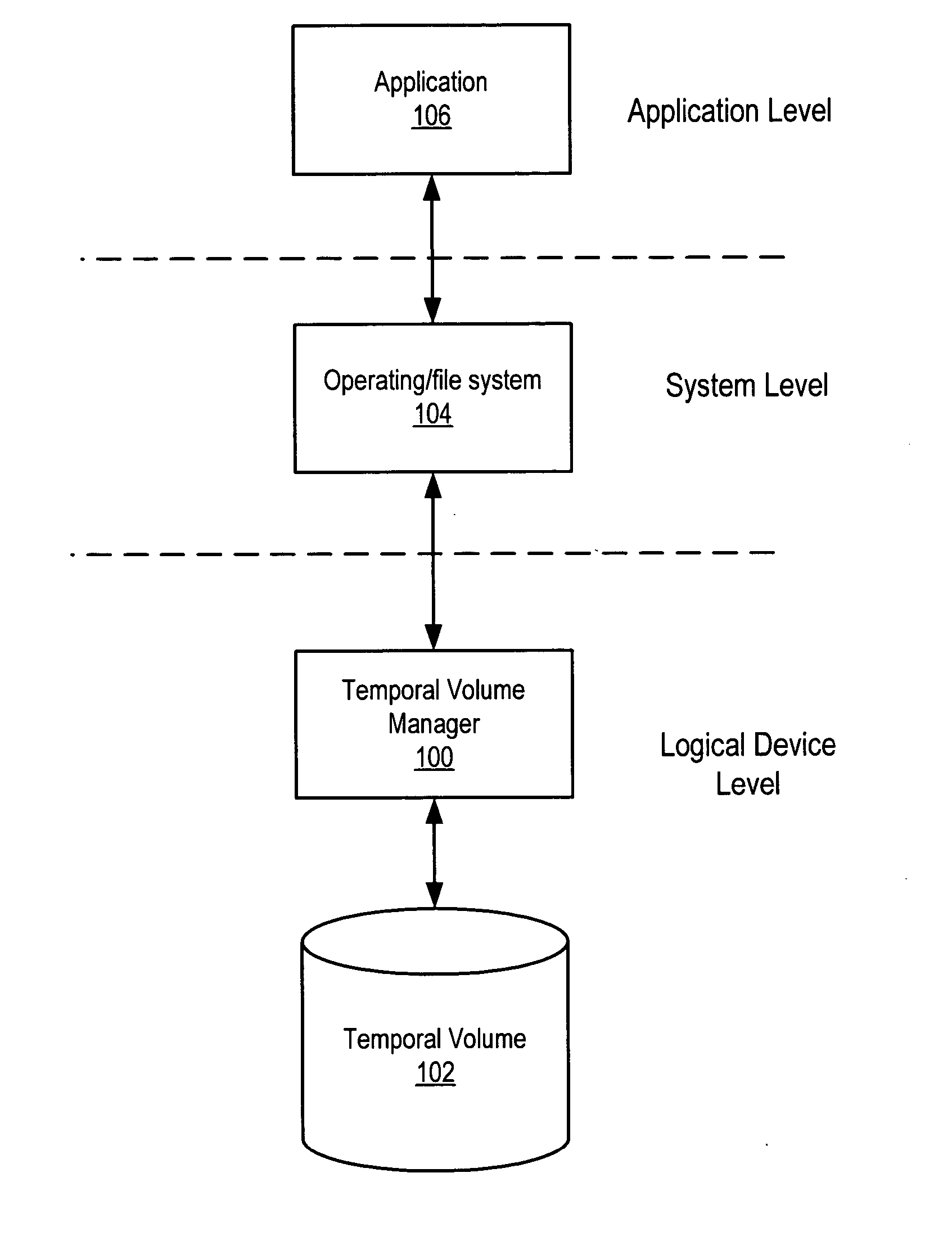
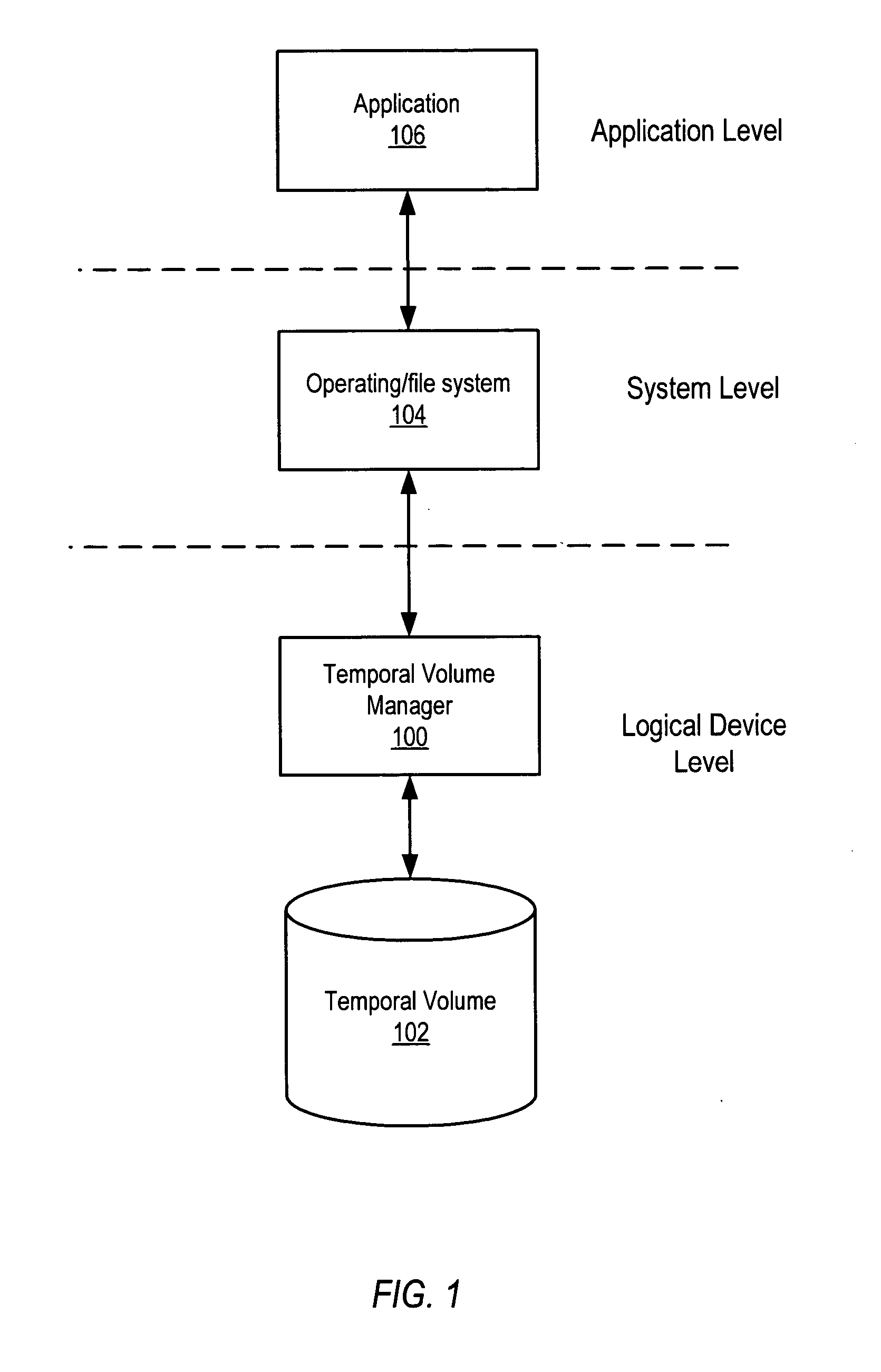
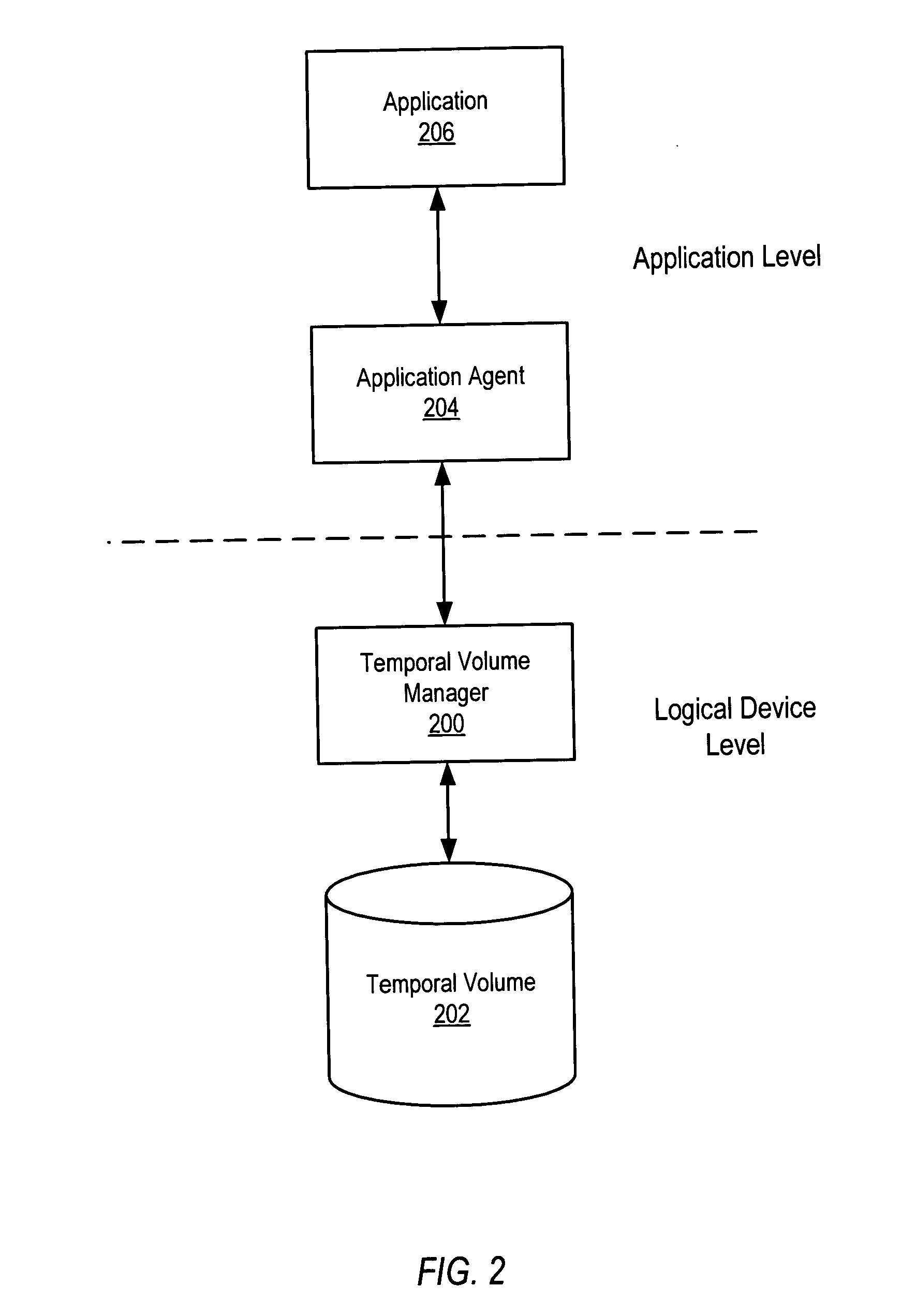
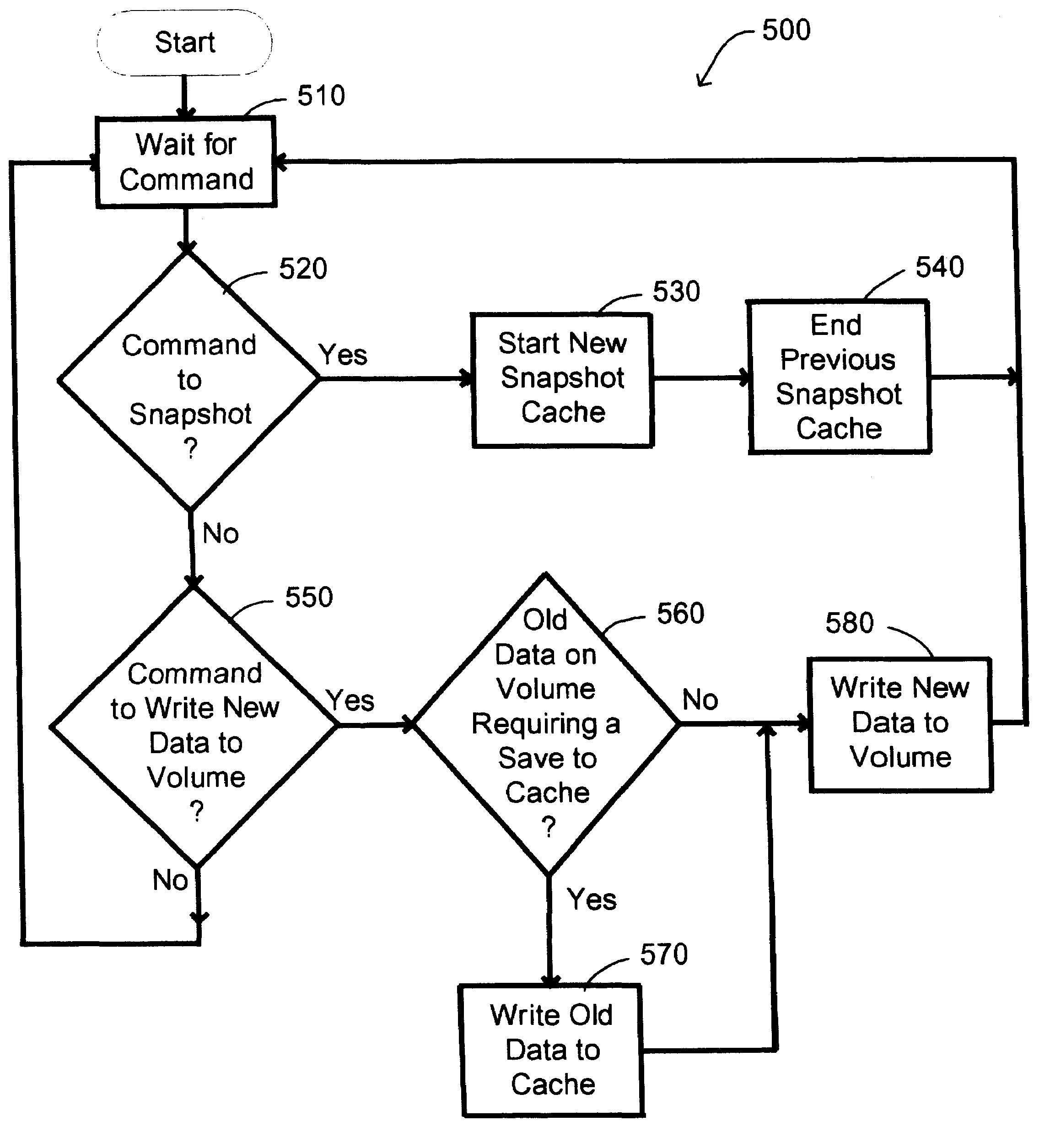
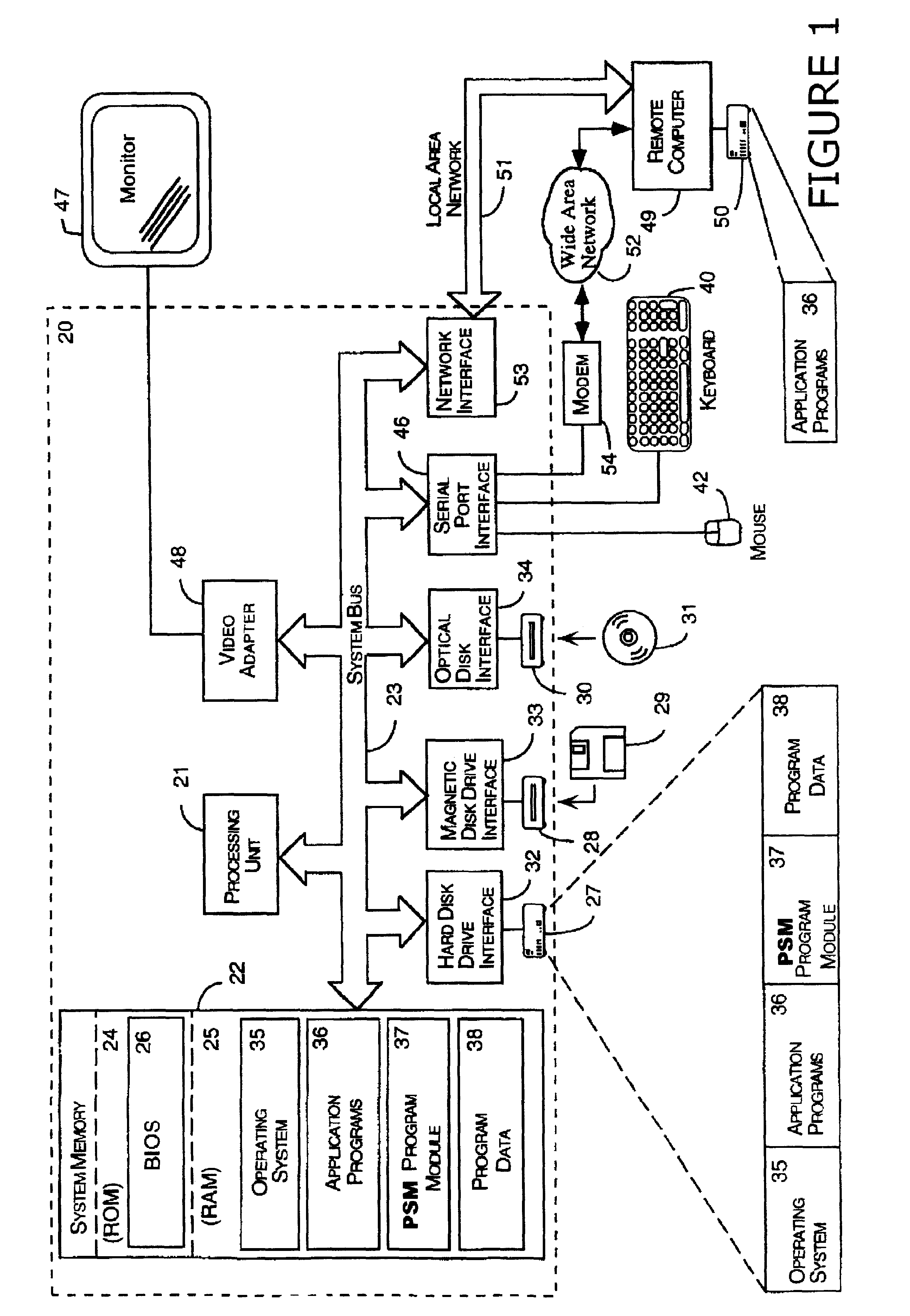
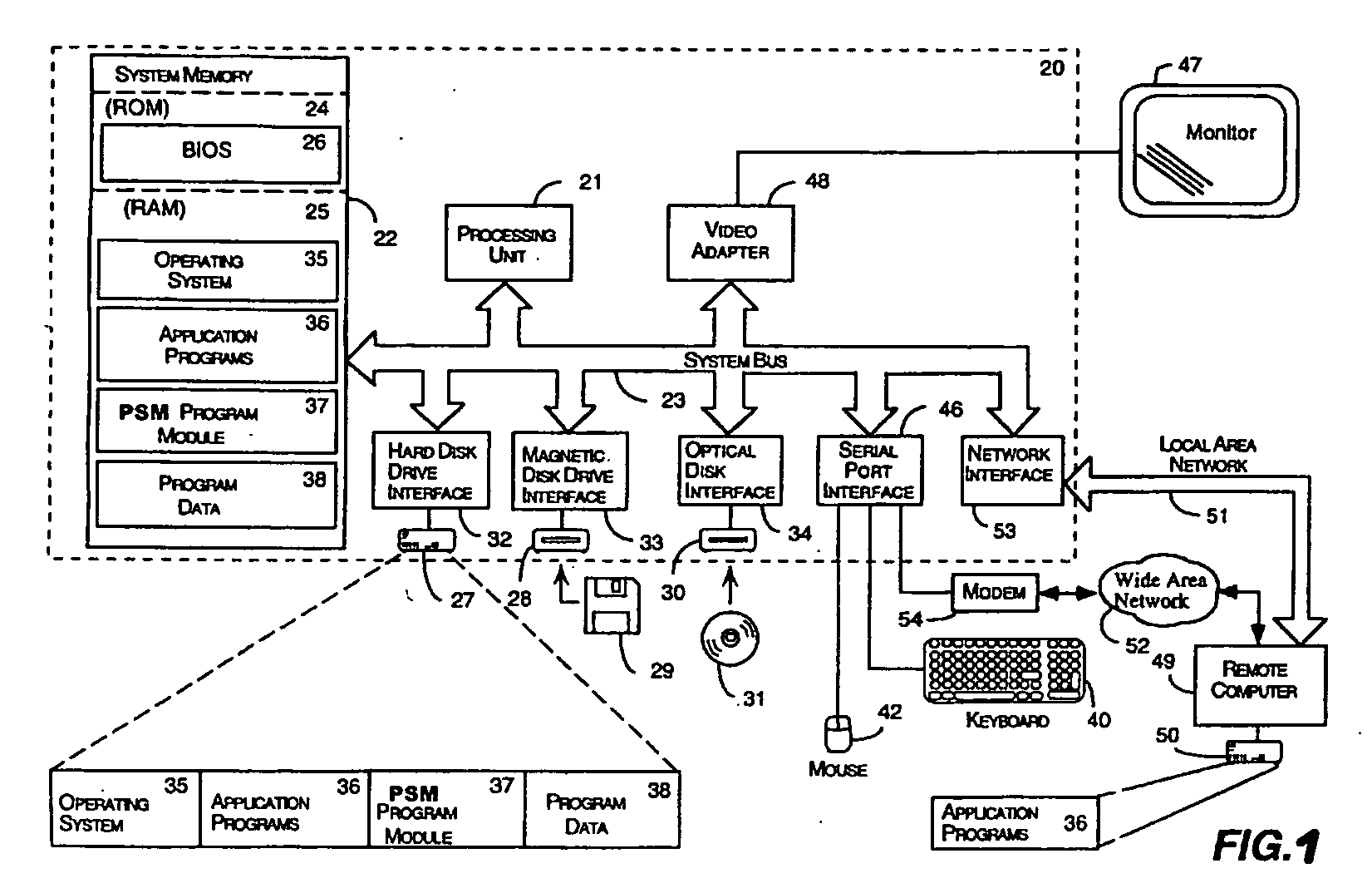
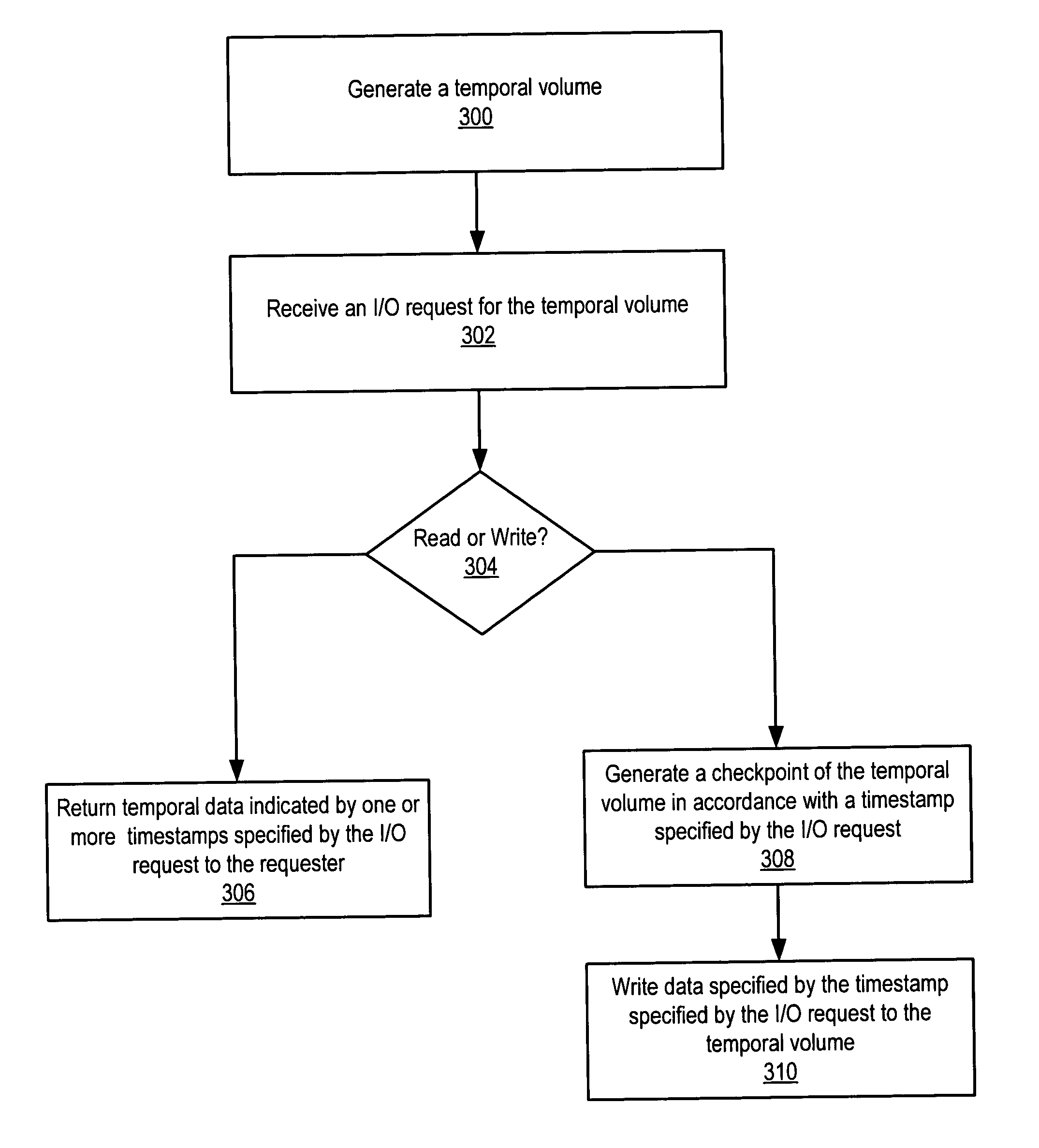
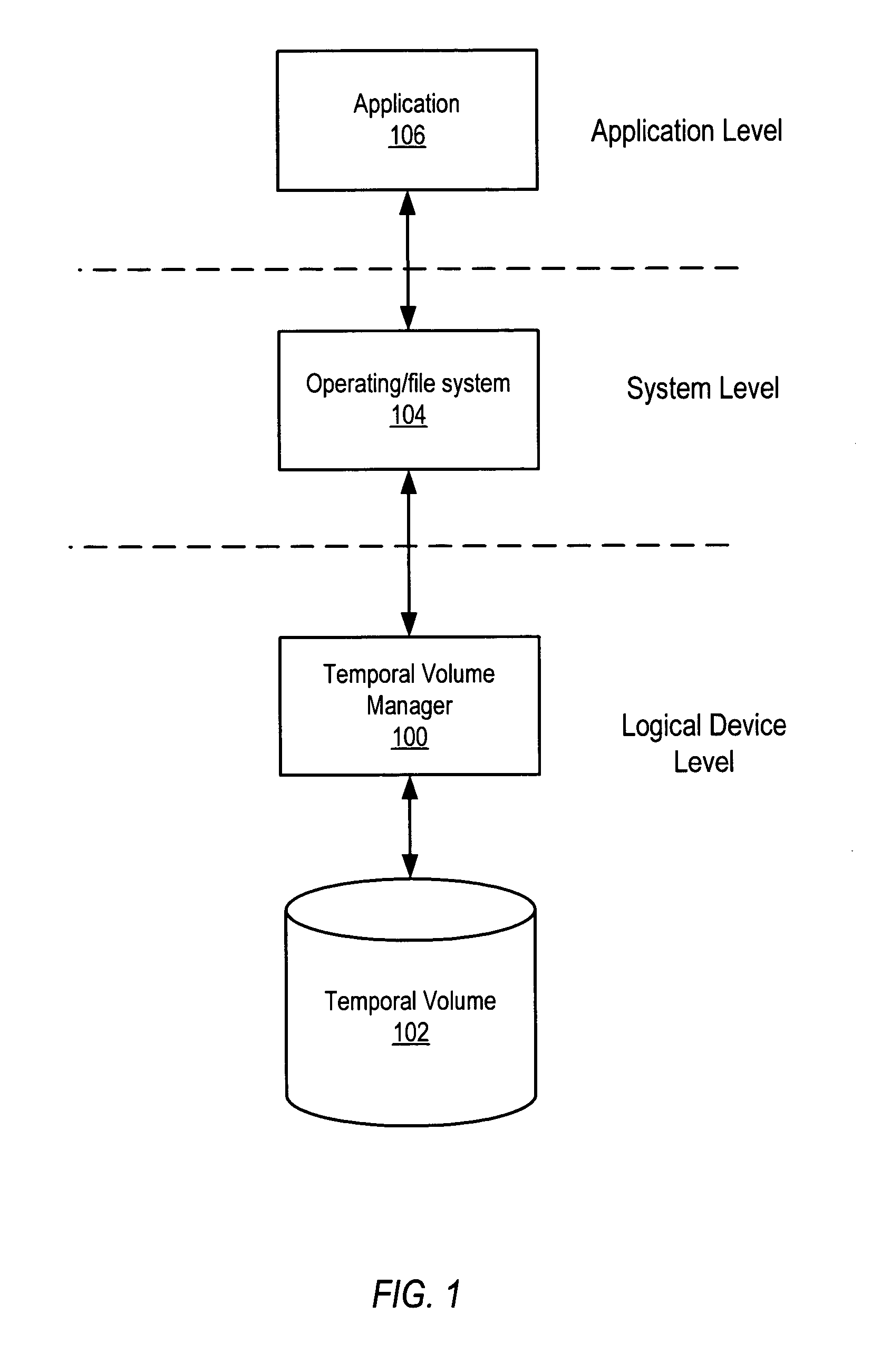
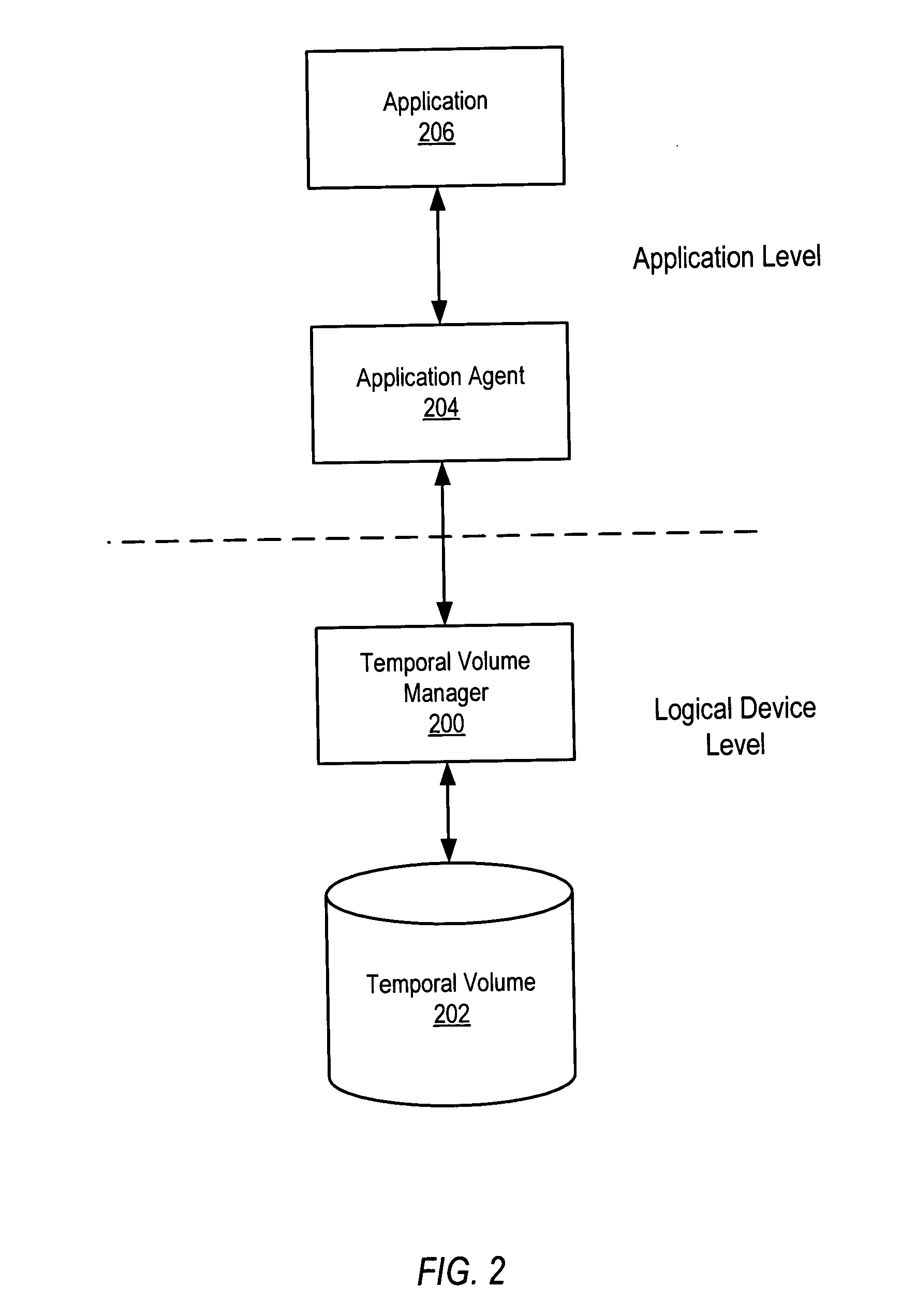
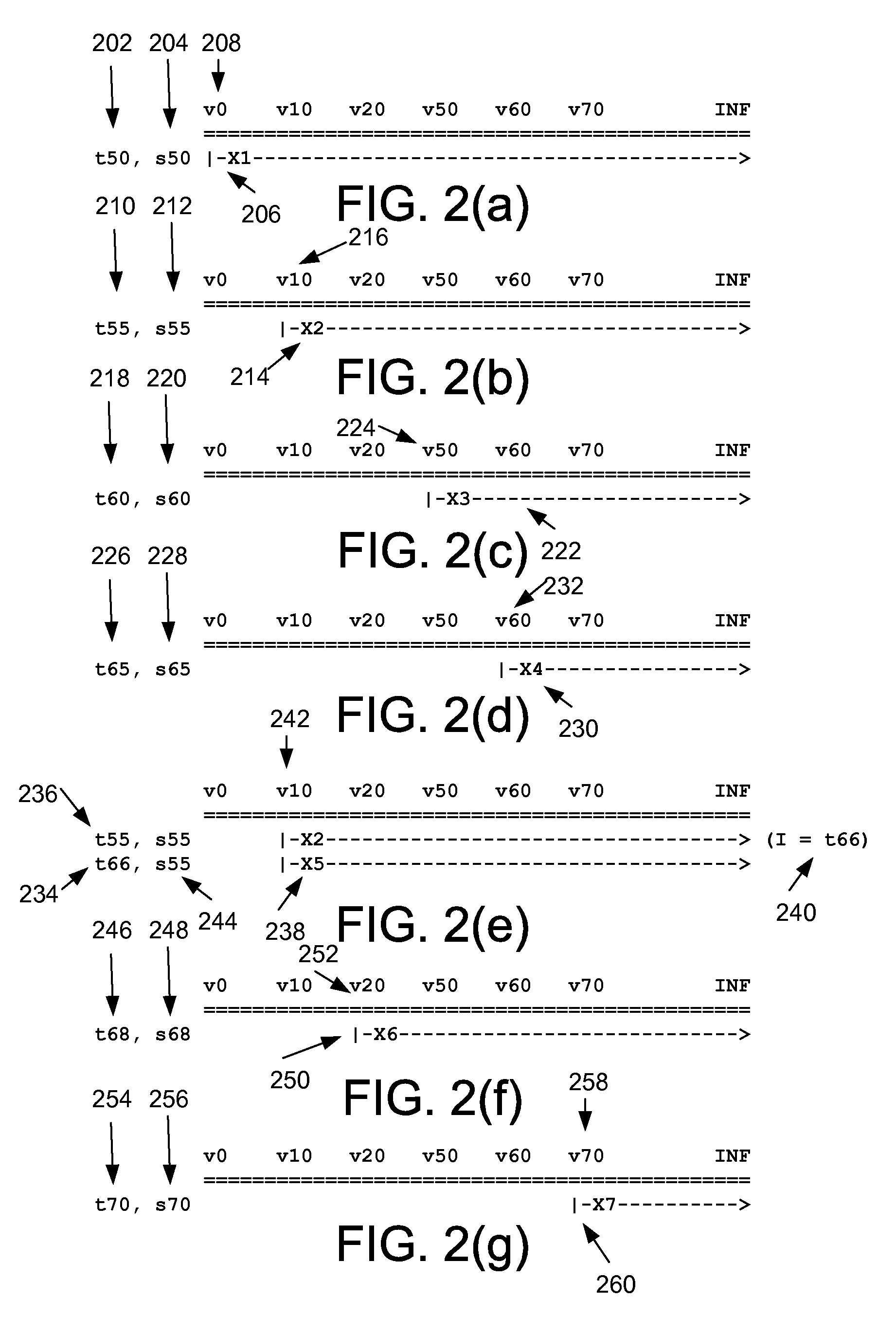
System and method for maintaining temporal data in data storage at the logical device level. Embodiments of the temporal volume manager may provide an interface that allows applications and / or application agents to communicate with the temporal volume manager to manage and keep track of the temporal information on one or more temporal volumes. Embodiments may provide an infrastructure for applications that work on the history of data such as temporal databases, versioning file-systems / repositories, data archives, and streaming media to manage temporal data. In one embodiment, if an application does not want to use the temporal volume directly, application agents may be used to access the temporal volume. Embodiments may provide I / O controlled, application-controlled, and / or periodic checkpointing of temporal data on the temporal volume. One embodiment may provide a mechanism for generating temporal images (e.g. point-in-time and slice-in-time images) of a temporal volume that may have their own independent history.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Persistent snapshot methods
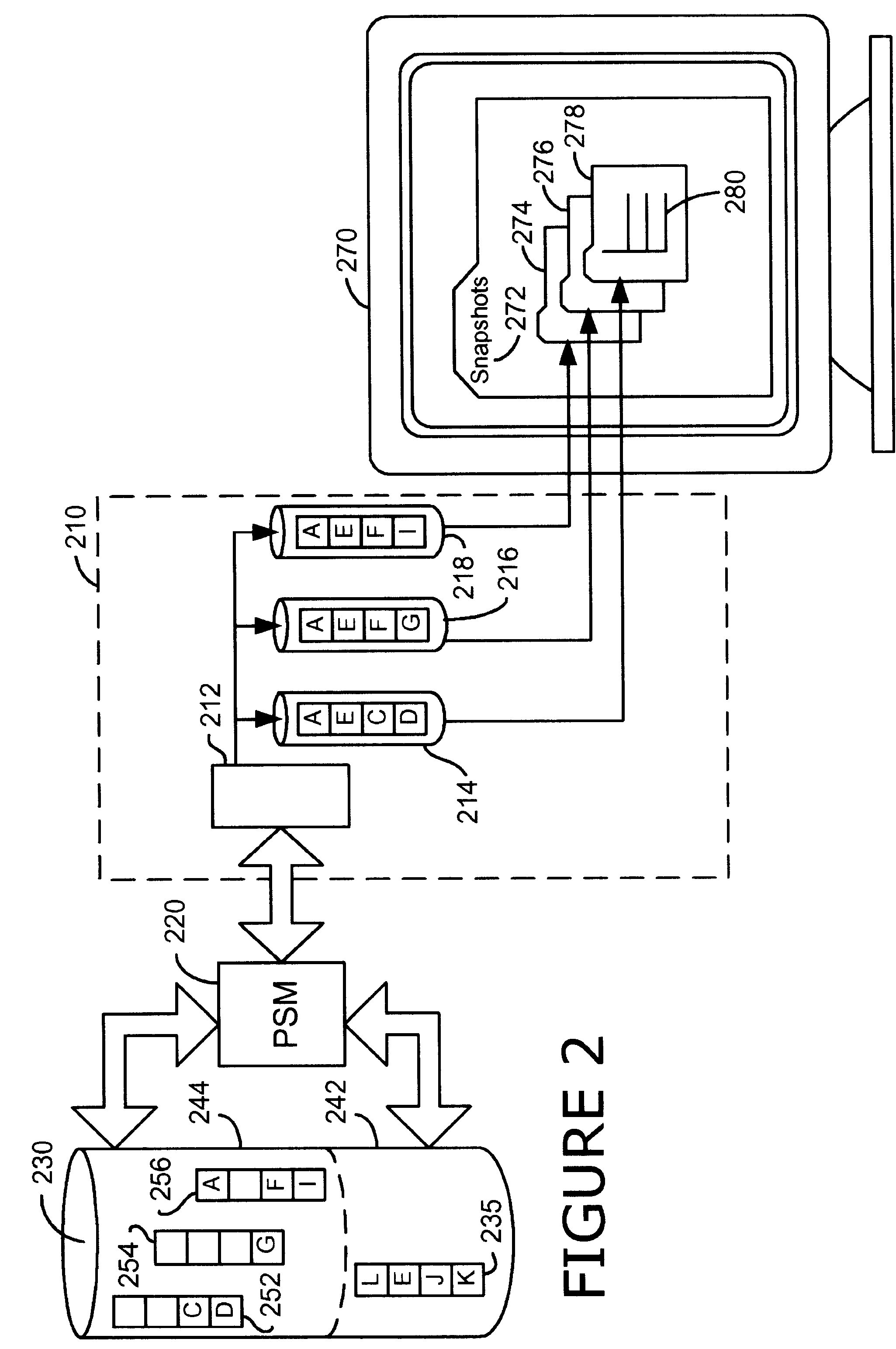
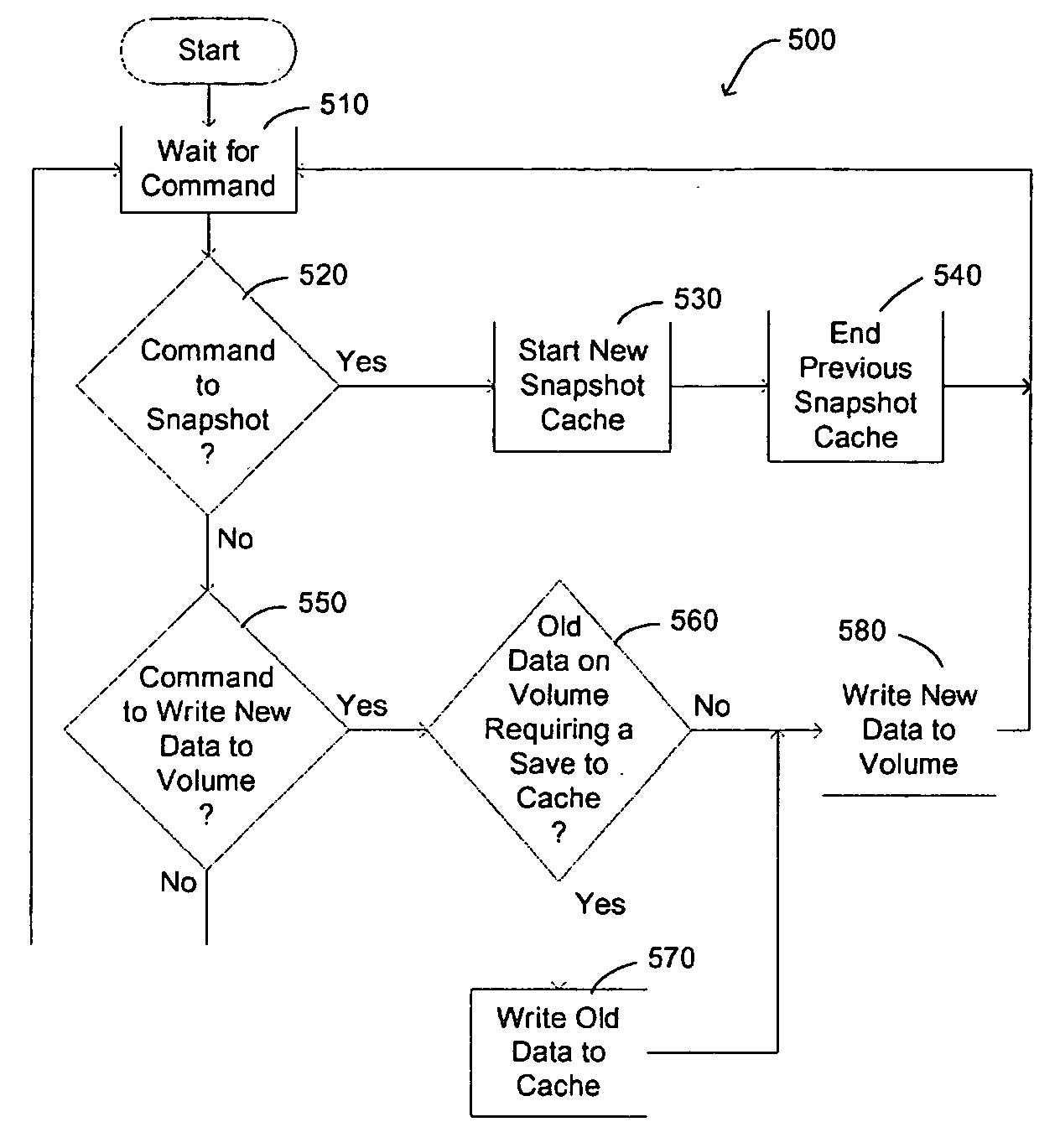
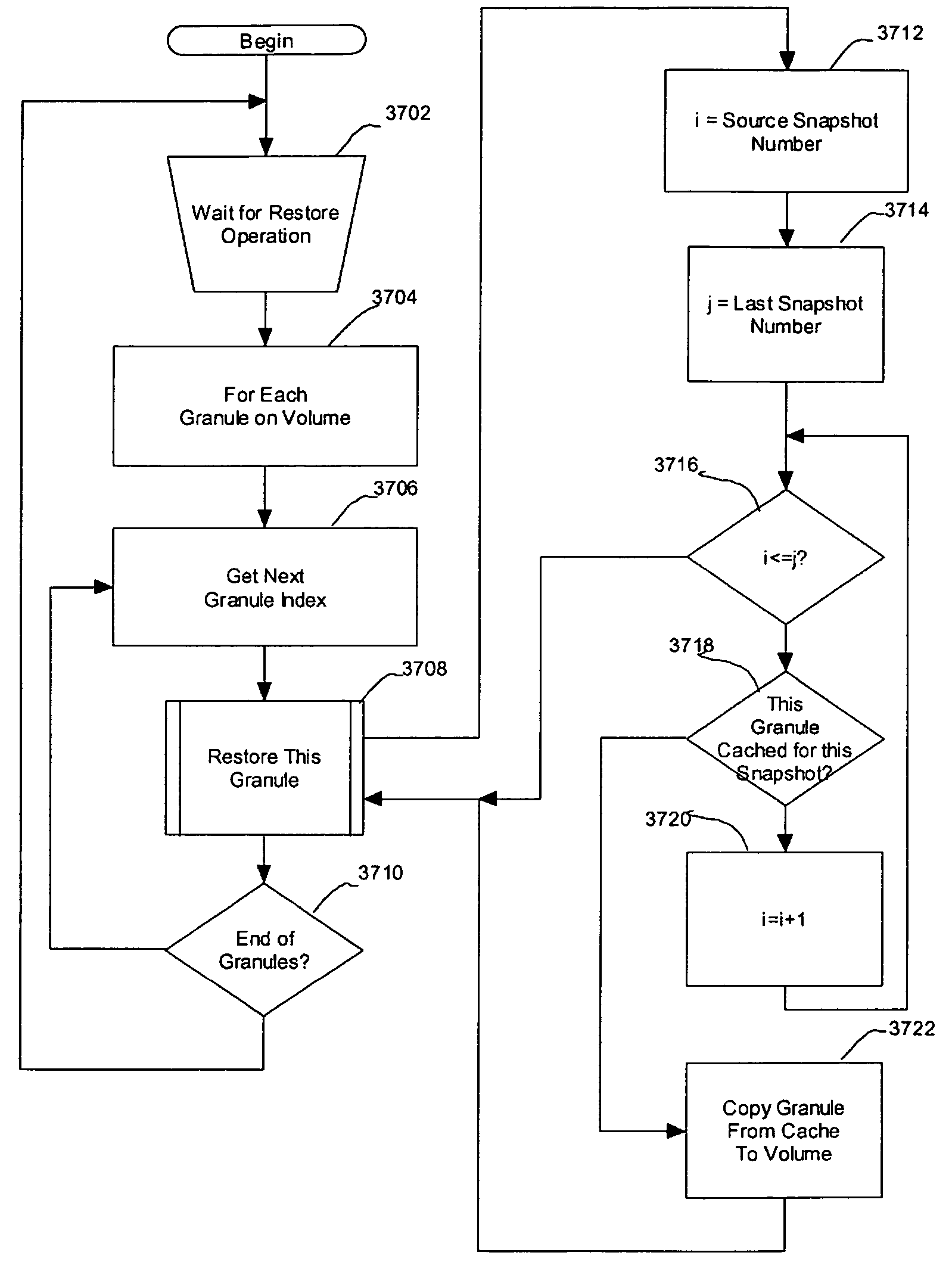
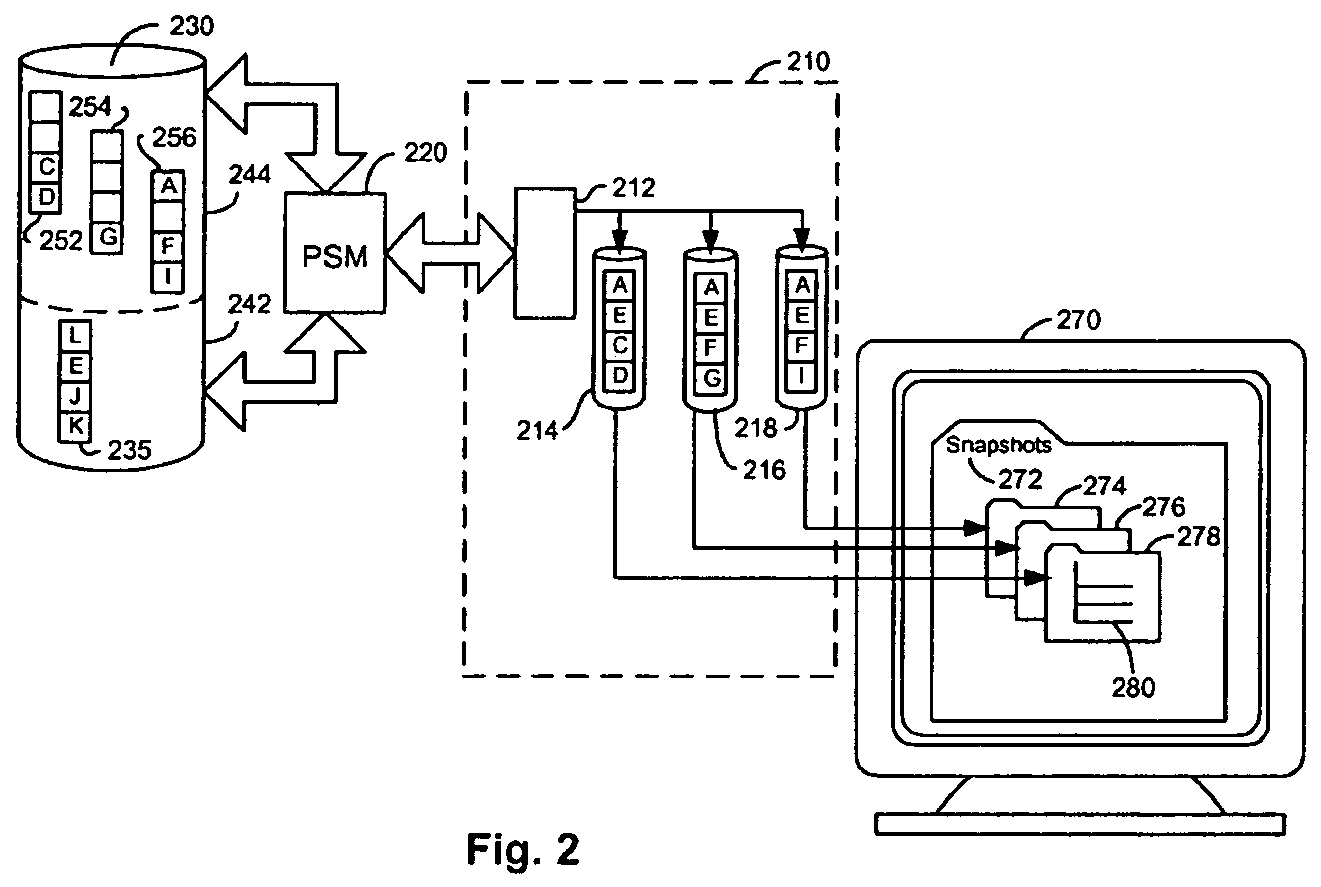
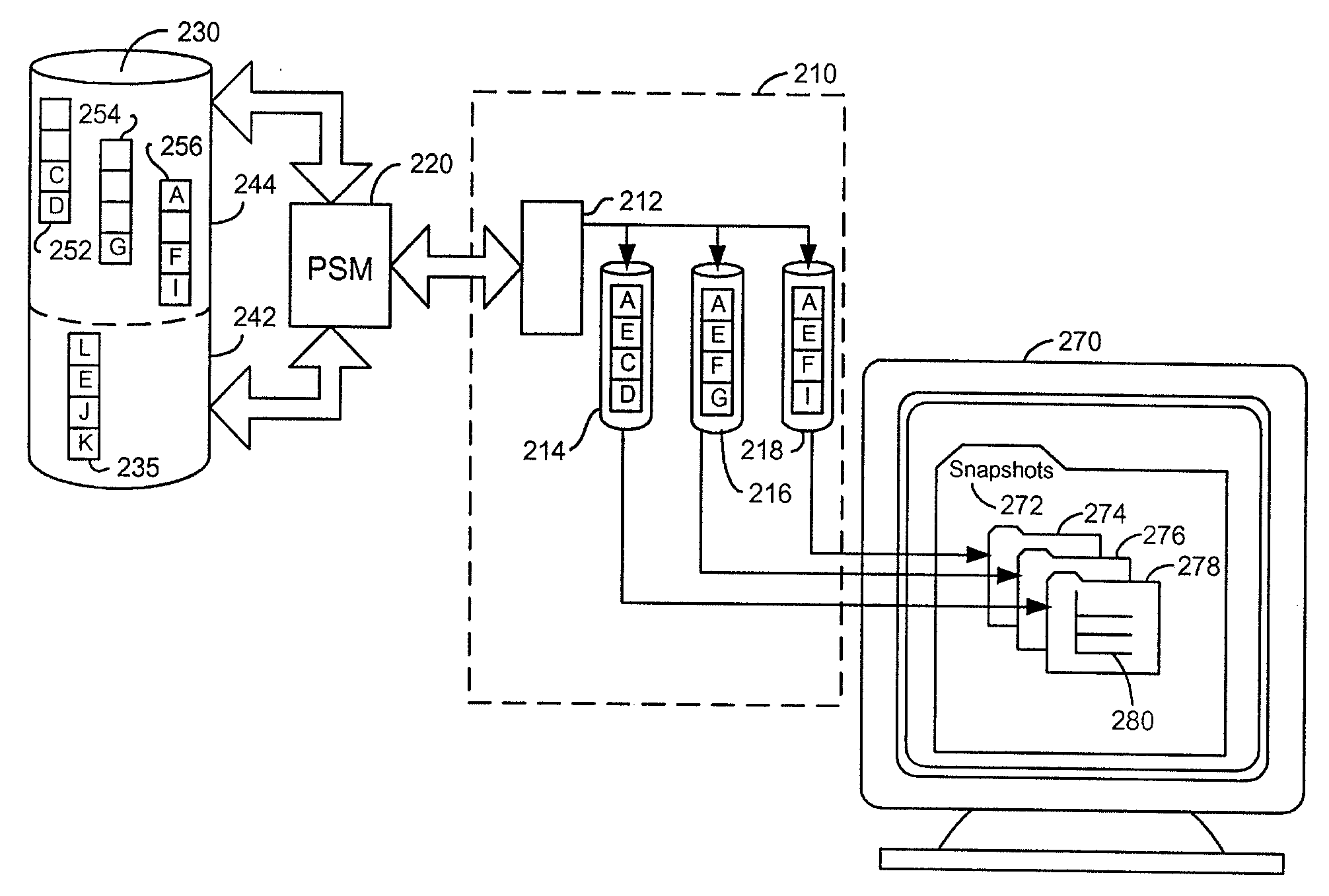
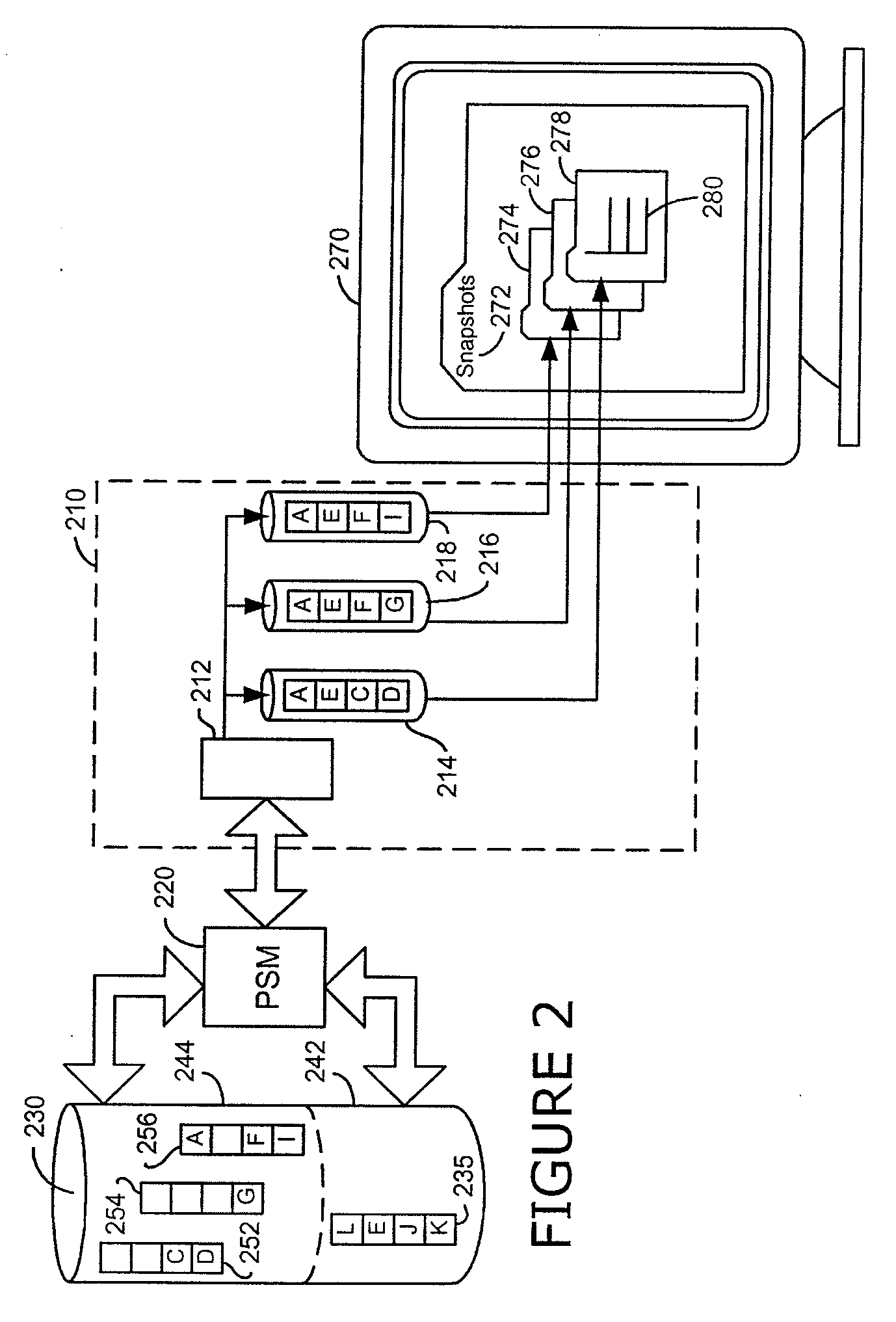
A persistent snapshot is taken and maintained in accordance with a novel method and system for extended periods of time using only a portion of a computer readable medium of which the snapshot is taken. Multiple snapshots can be taken in succession at periodic intervals and maintained practically indefinitely. The snapshots are maintained even after powering down and rebooting of the computer system. The state of the object of the snapshot for each snapshot preferably is accessible via a folder on volume of the snapshot. A restore of a file or folder may be accomplished by merely copying that file or folder from the snapshot folder to a current directory of the volume. Alternatively, the entire computer system may be restored to a previous snapshot state thereof. Snapshots that occurred after the state to which the computer is restored are not lost in the restore operation. Different rule sets and scenarios can be applied to each snapshot. Furthermore, each snapshot can be written to within the context of the snapshot and later restored to its pristine condition. Software for implementing the systems and methods of snapshots in accordance with the present invention may comprise firmware of a hard disk drive controller or a disk controller board or within the HDD casing itself. The present invention further comprises novel systems and methods in which the systems and methods of taking and maintaining snapshots are utilized in creating and managing temporal data stores, including temporal database management systems. The implications for data mining and exploration, data analysis, intelligence gathering, and artificial intelligence (just to name a few areas) are profound.
Owner:COLUMBIA DATA PRODUCTS
Persistent snapshot management system
InactiveUS20060107006A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsHard disc drivePrimitive state
A persistent snapshot is taken and maintained in accordance with a novel method and system for extended periods of time using only a portion of a computer readable medium of which the snapshot is taken. Multiple snapshots can be taken in succession at periodic intervals and maintained practically indefinitely. The snapshots are maintained even after powering down and rebooting of the computer system. The state of the object of the snapshot for each snapshot preferably is accessible via a folder on volume of the snapshot. A restore of a file or folder may be accomplished by merely copy that file or folder from the snapshot folder to a current directory of the volume. Alternatively, the entire computer system may be restored to a previous snapshot state thereof. Snapshots that occurred after the state to which the computer is restored are not lost in the restore operation. Different rule sets and scenarios can be applied to each snapshot. Furthermore, each snapshot can be written to within the context of the snapshot and later restored to its pristine condition. Software for implementing the systems and methods of snapshots in accordance with the present invention may comprise firmware of a hard disk drive controller or a disk controller board or within the HDD casing itself. The present invention further comprises novel systems and methods in which the systems and methods of taking and maintaining snapshots are utilized in creating and managing temporal data stores, including temporal database management systems. The implications for data mining and exploration, data analysis, intelligence gathering, and artificial intelligence (just to name a few areas) are profound.
Owner:COLUMBIA DATA PRODUCTS
Lazy timestamping in transaction time database
InactiveUS20060167960A1Minimize accessEfficient record timestamping processData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTemporal databaseTimestamp
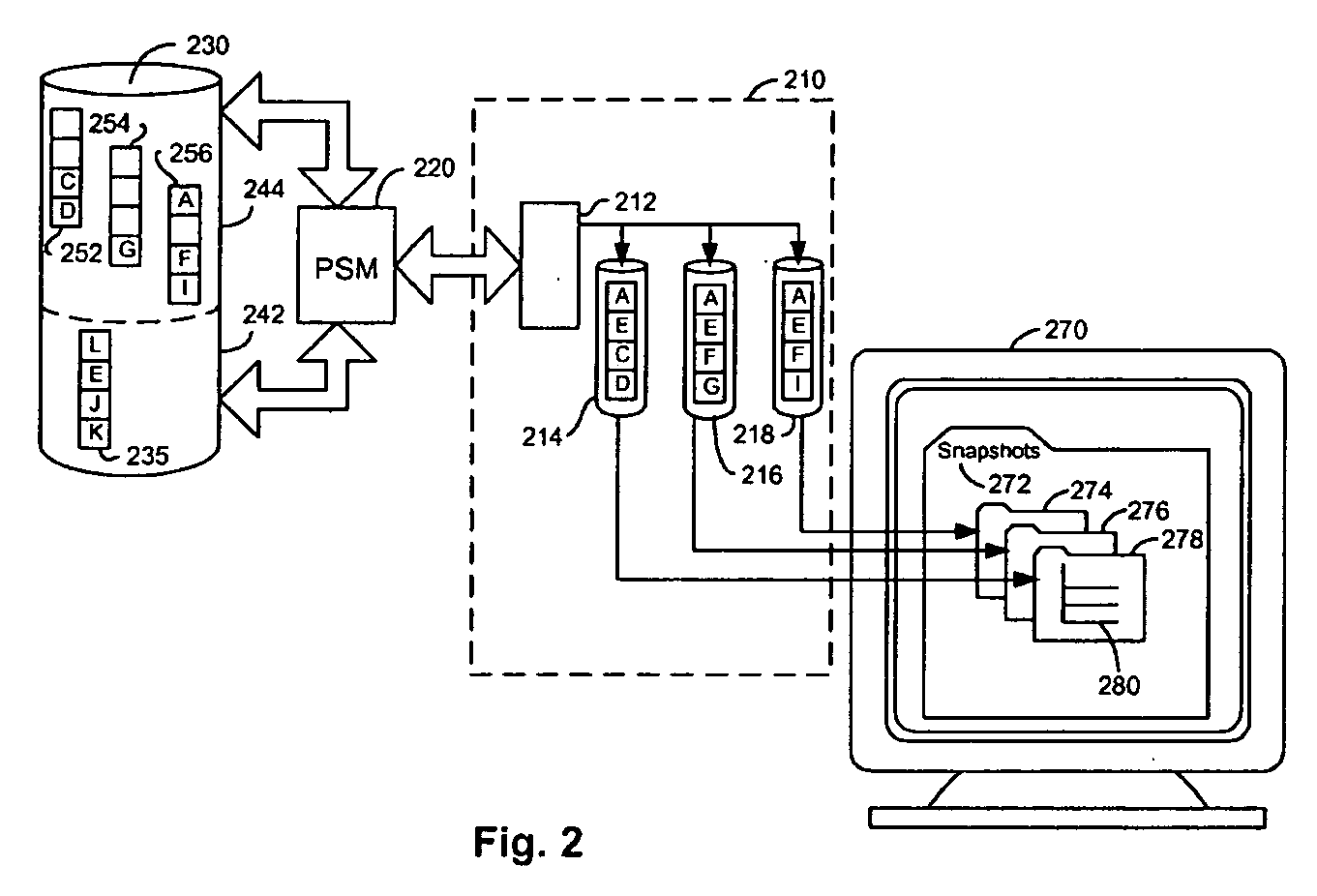
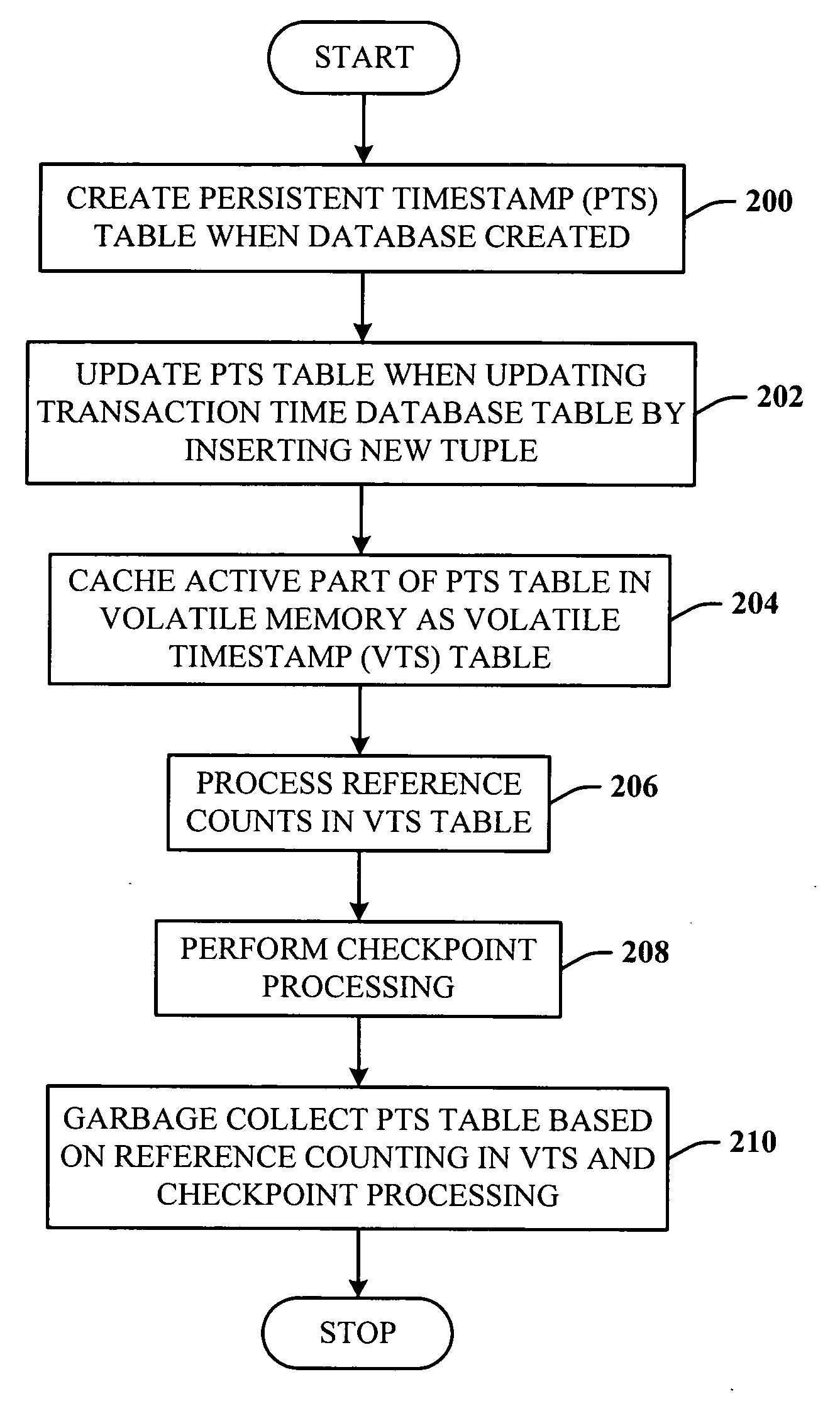
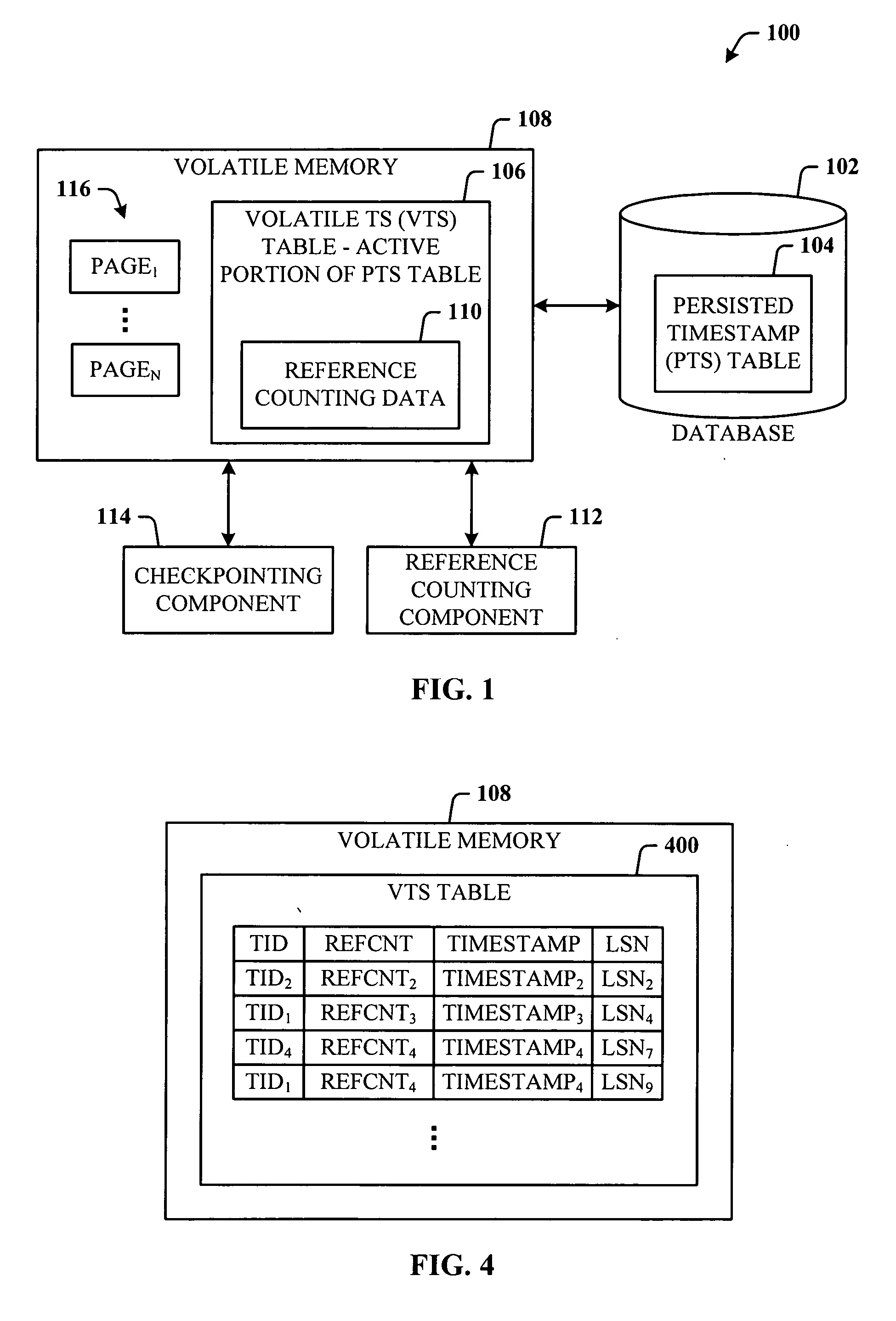
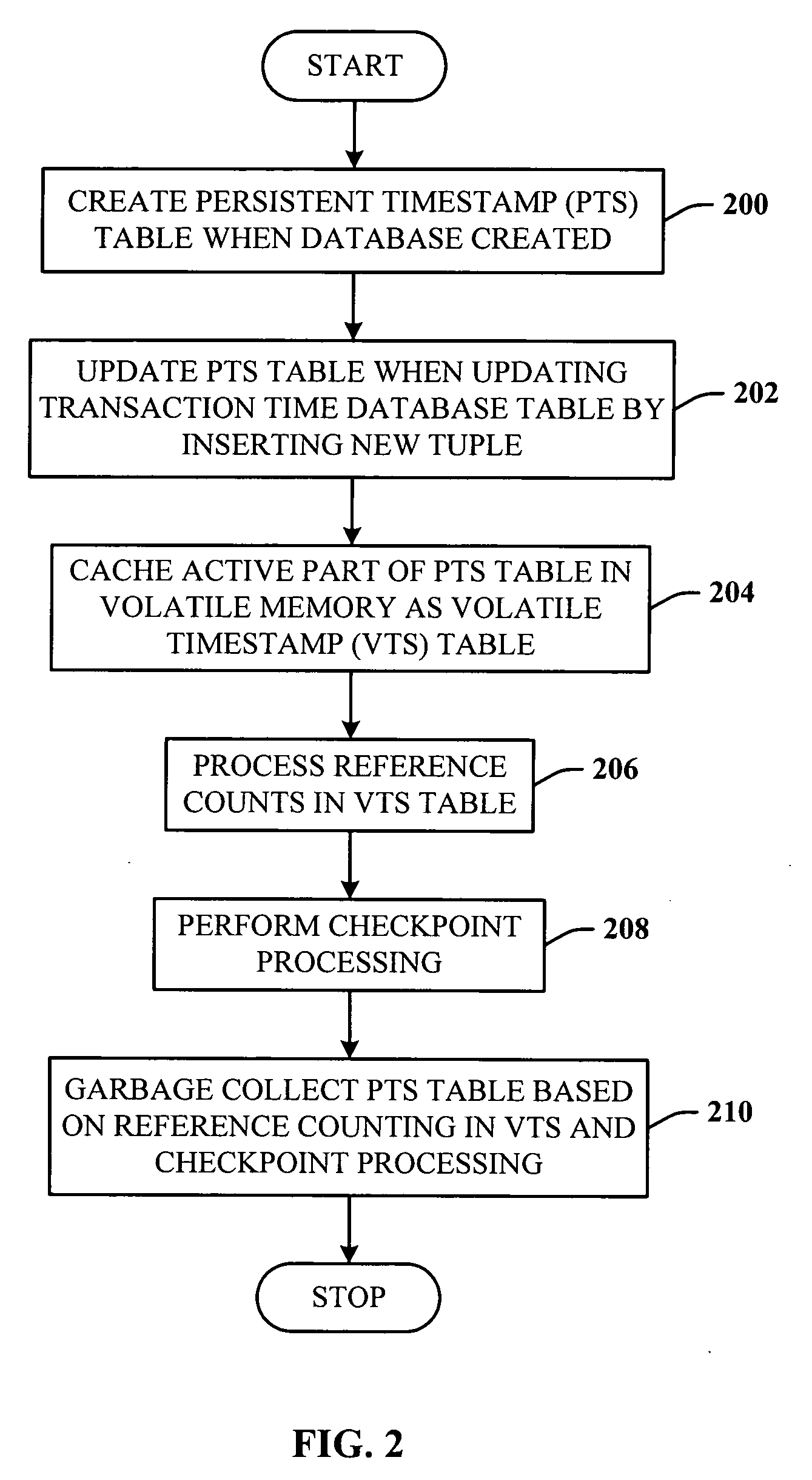
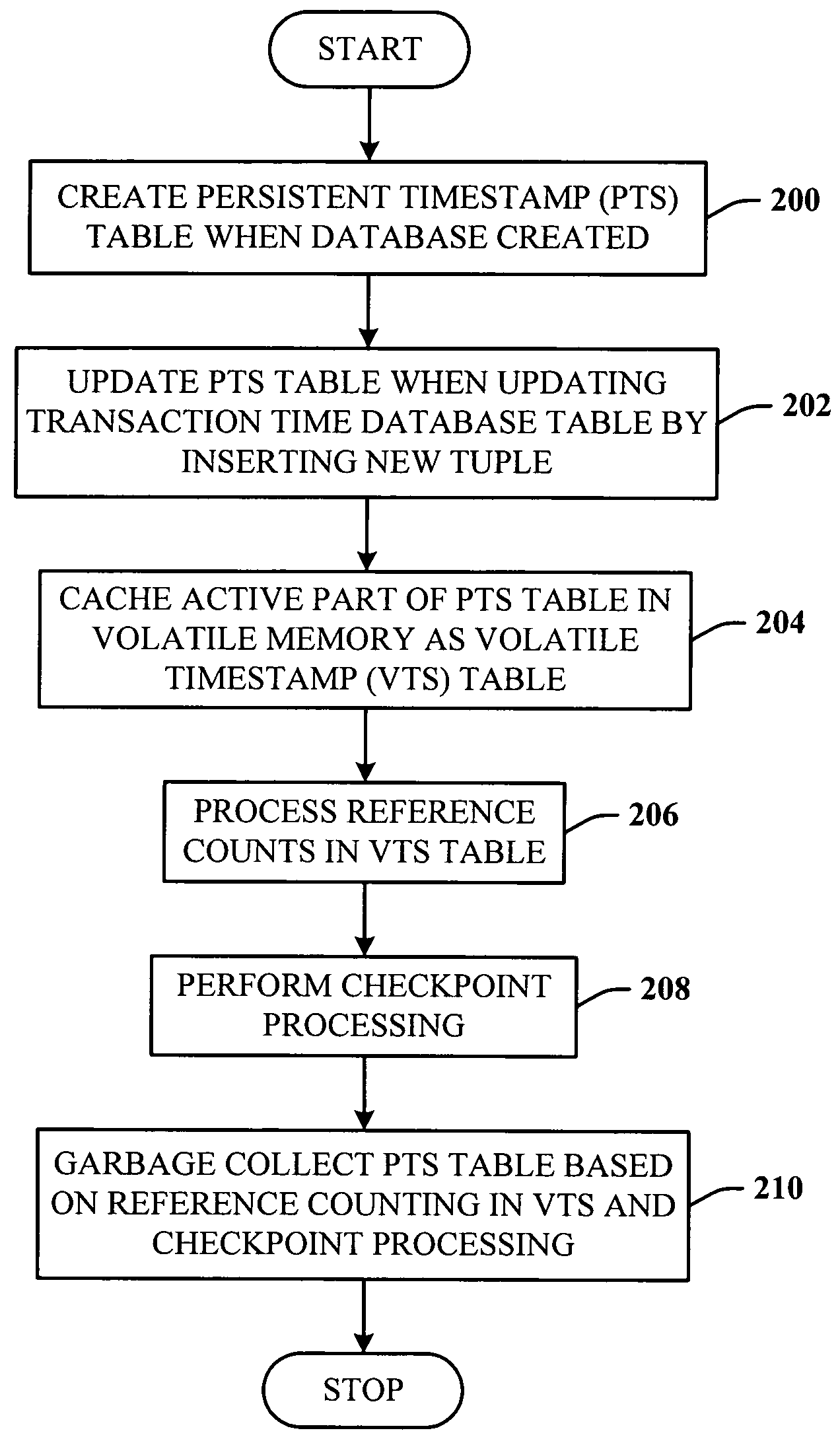
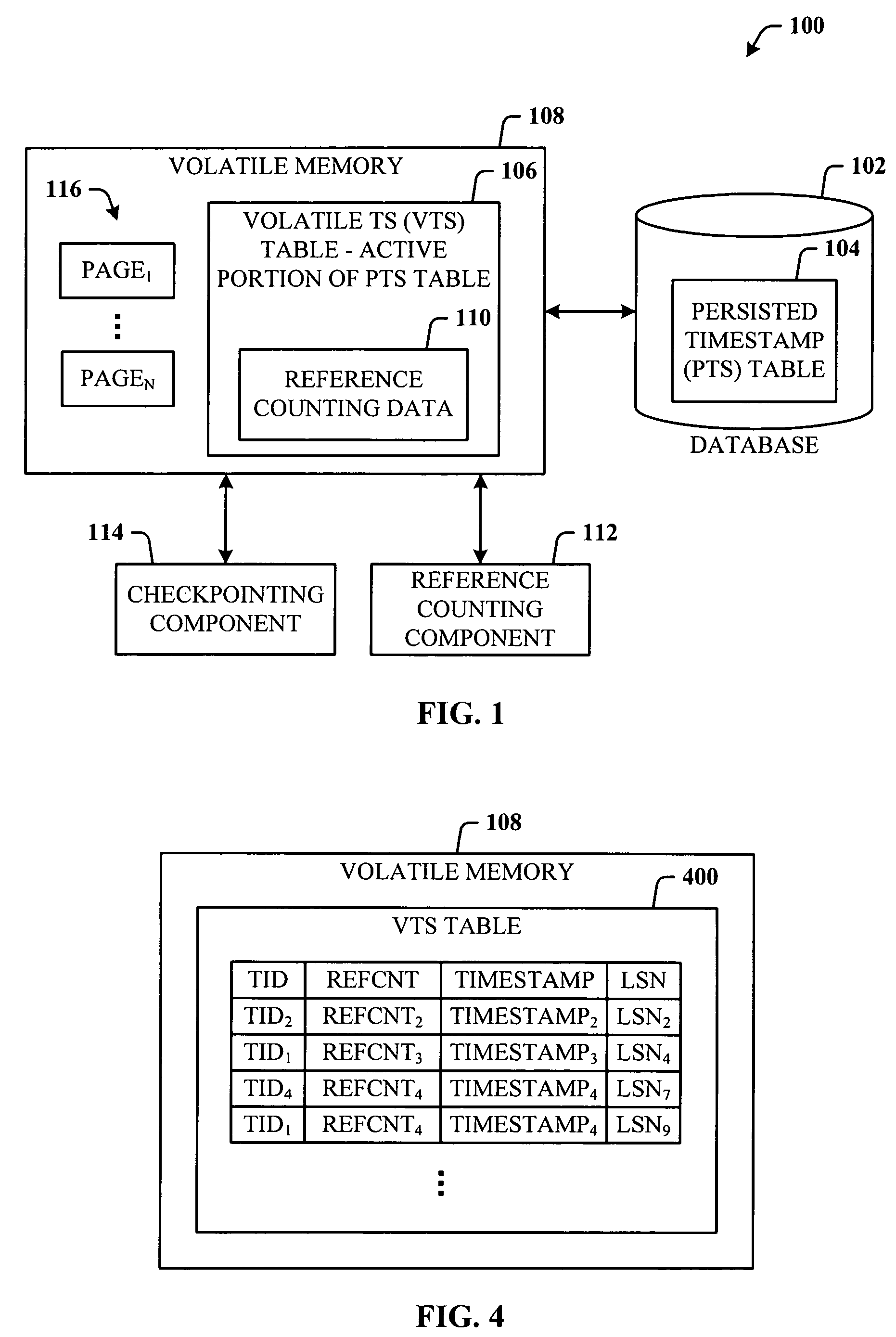
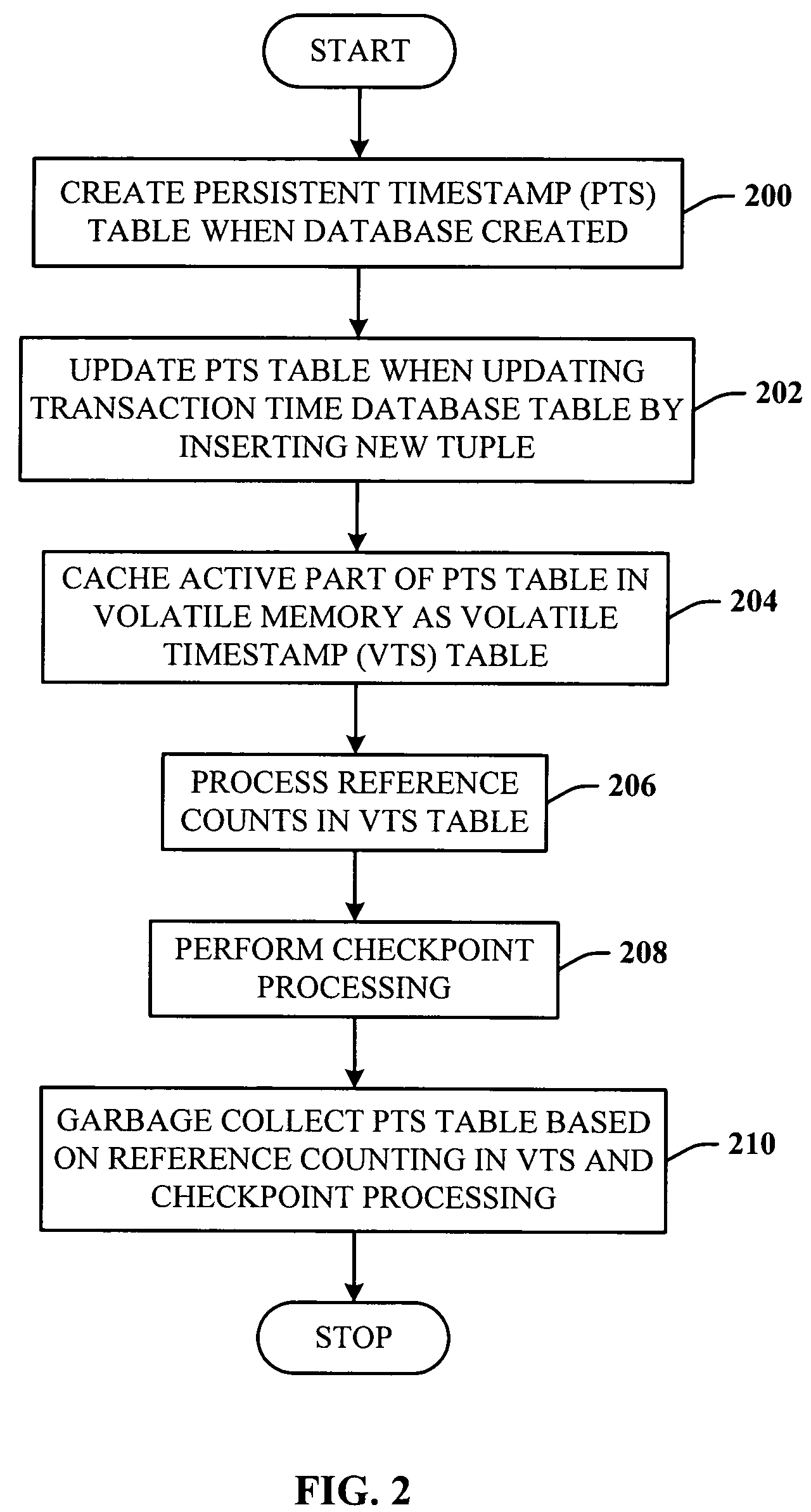
Lazy timestamping in a transaction time database is performed using volatile reference counting and checkpointing. Volatile reference counting is employed to provide a low cost way of garbage collecting persistent timestamp information about a transaction by identifying exactly when all record versions of a transaction are timestamped and the versions are persistent. A volatile timestamp (VTS) table is created in a volatile memory, and stores timestamp, reference count, transaction ID, and LSN information. Active portions of a persisted timestamp (PTS) table are stored in the VTS table to provide faster and more efficient timestamp processing via accesses to the VTS table information. The reference count information is stored only in the VTS table for faster access. When the reference count information decrements to zero, it is known that all record versions that were updates for a transaction were timestamped. A checkpointing component facilitates checkpoint processing for verifying that timestamped records have been written to the persistent database and that garbage collection of the PTS table can be performed for transaction entries with zero reference counts.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
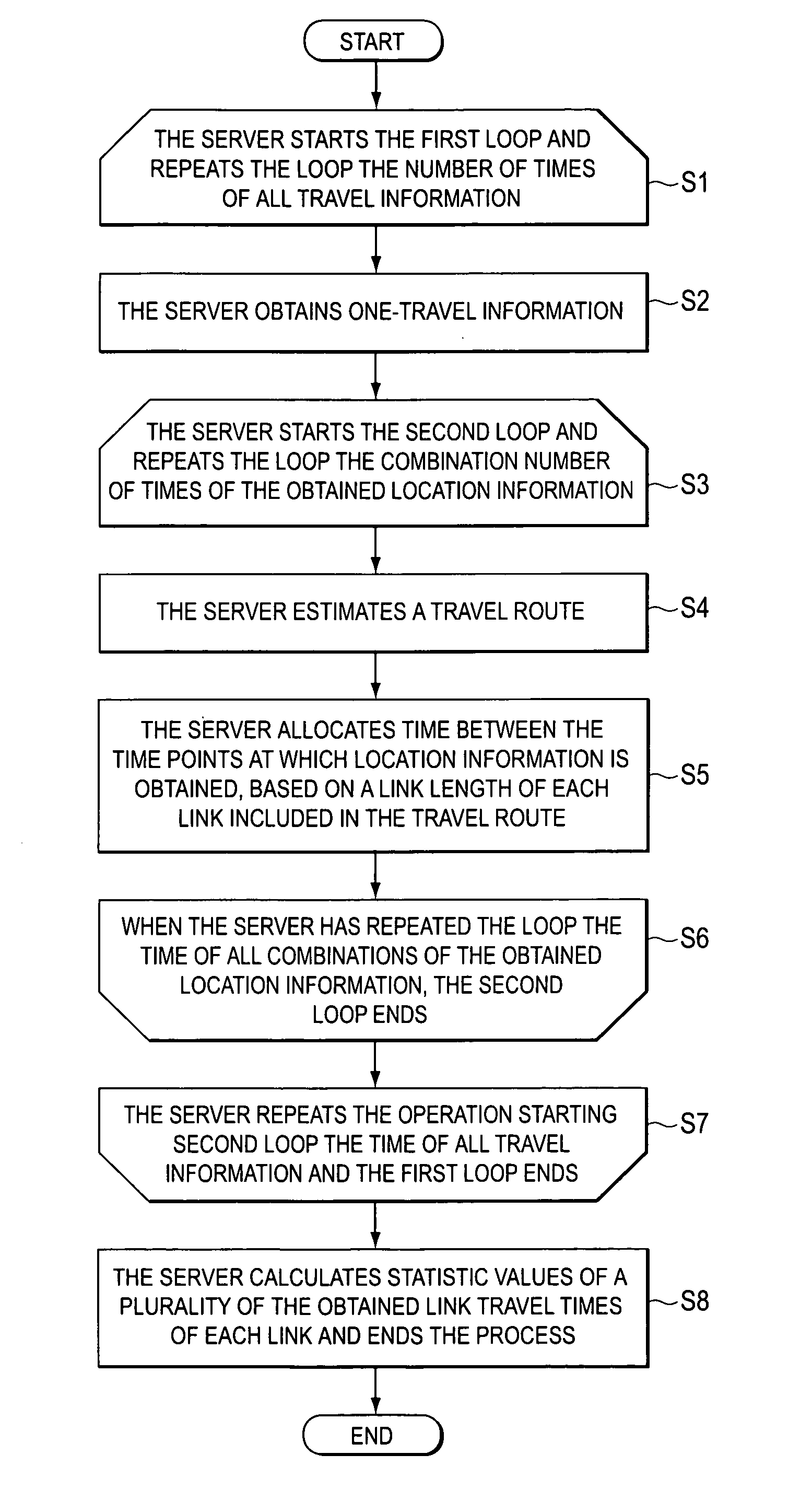
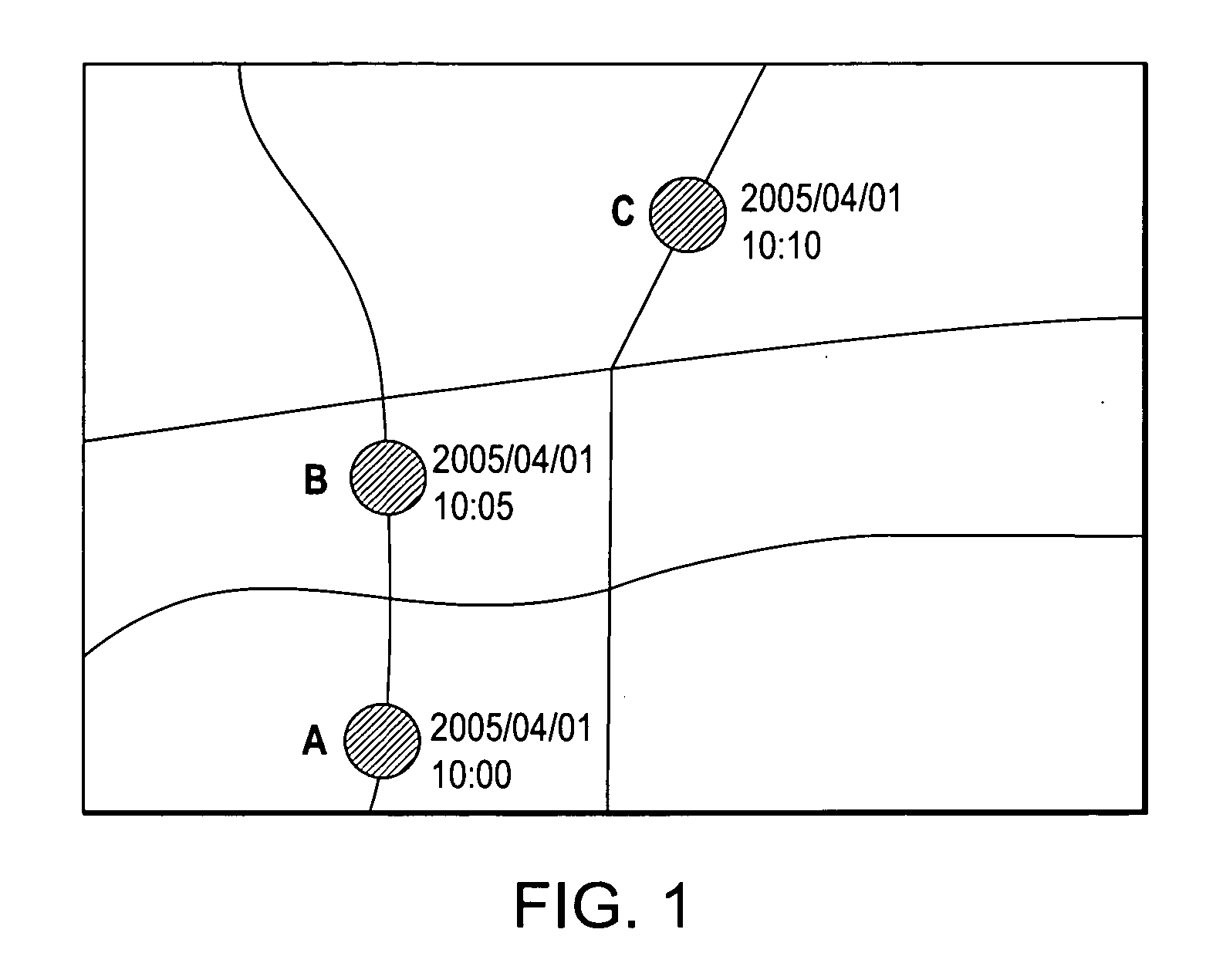
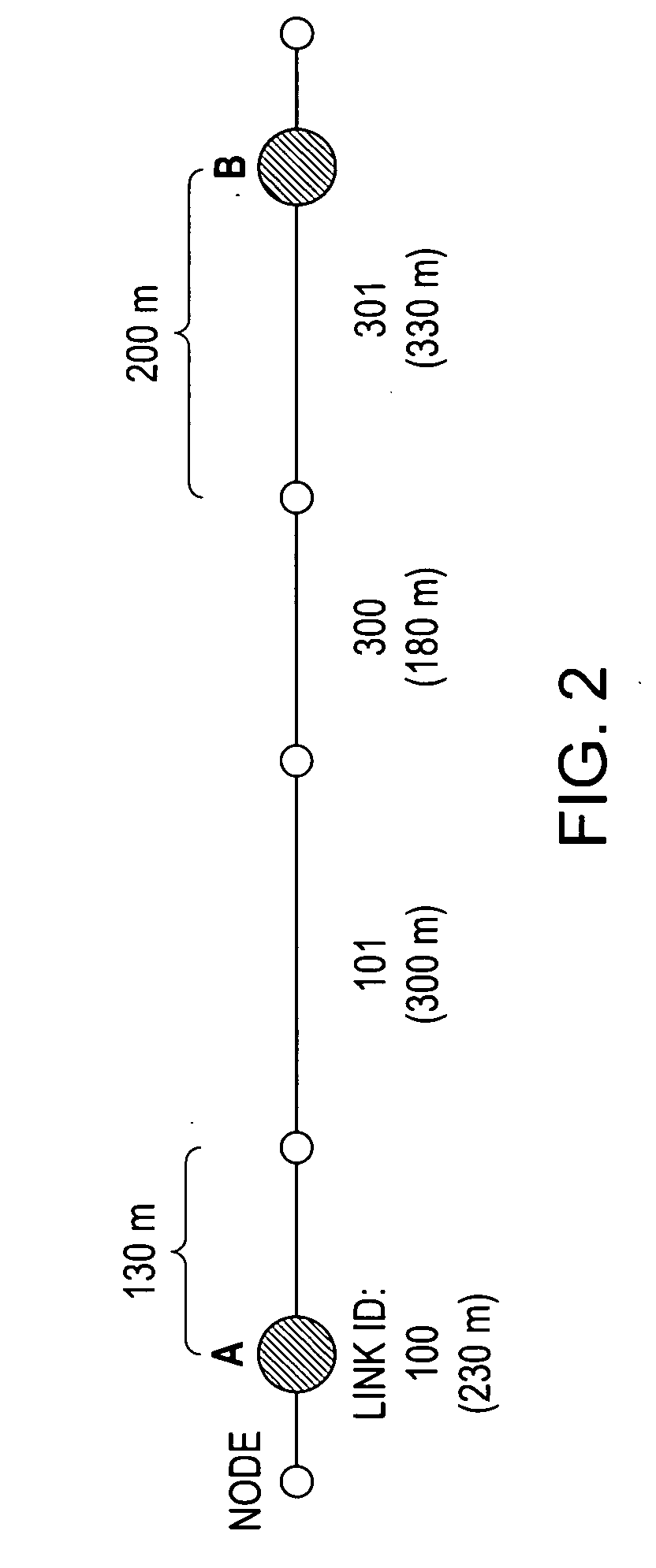
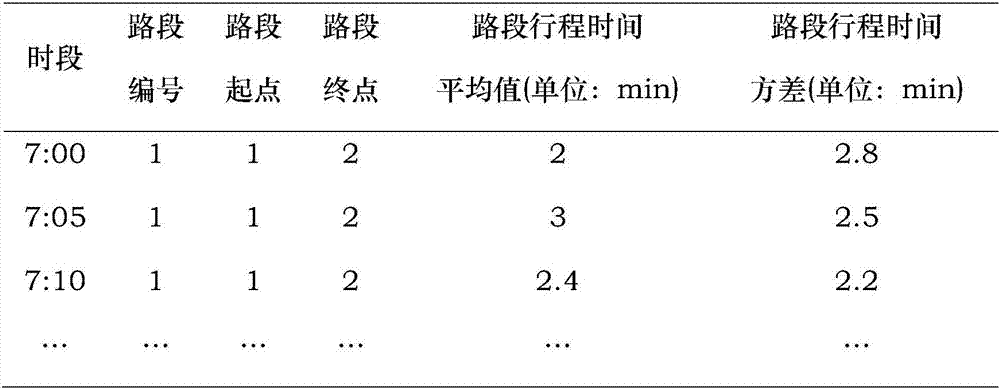
Travel time database generating device, method and program
InactiveUS20070001873A1Reduce in quantityHigh transmission costInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTemporal databaseSystems approaches
Travel time database generating systems, methods, and programs receive a vehicle's present location information and calculate a link travel time for each link included in the present location information. The systems, methods, and programs generate a travel time database including link travel times by estimating a travel route between the vehicle's present locations detected every predetermined time period and calculating a link travel time of links included in the estimated travel route.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
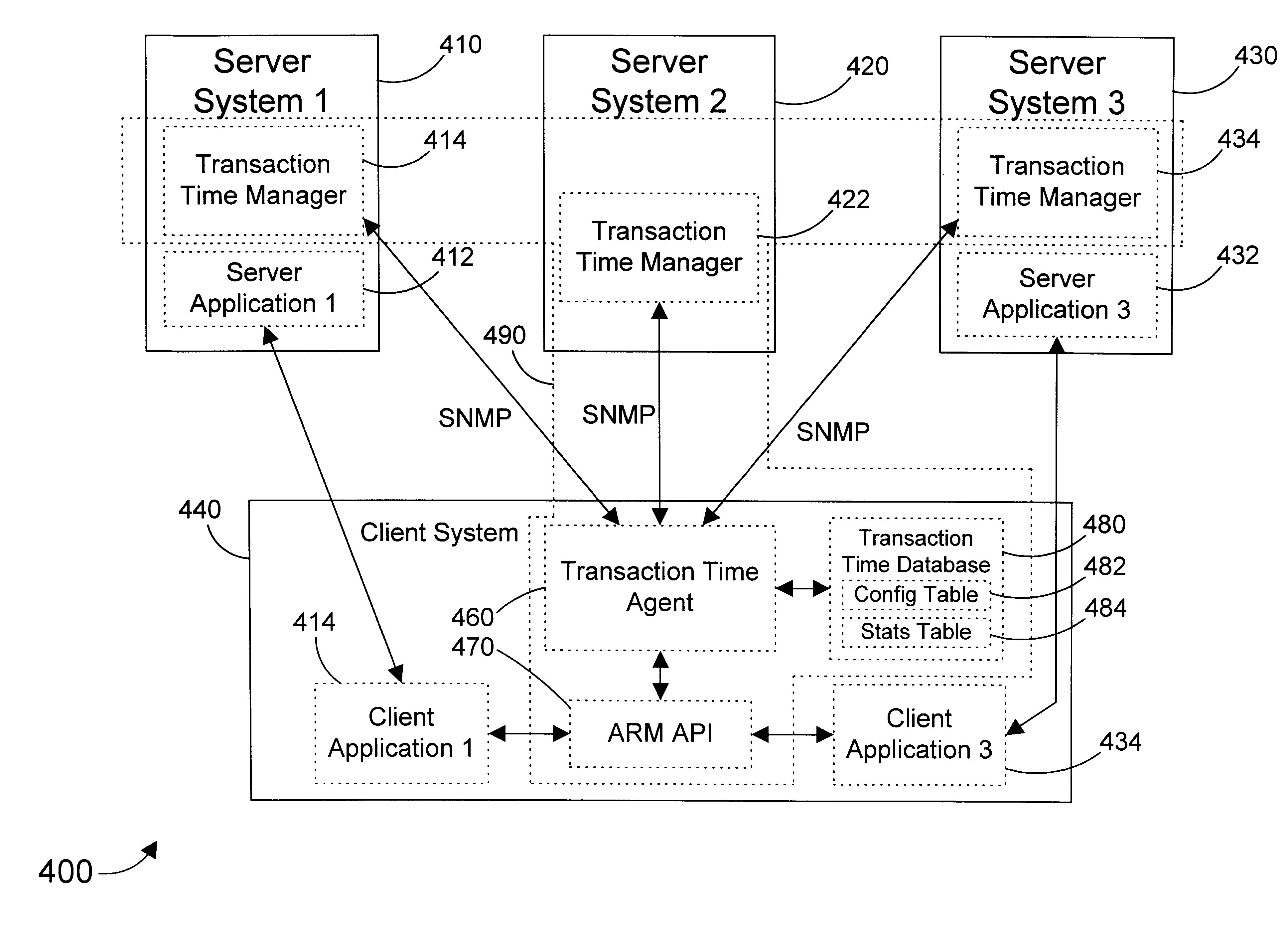
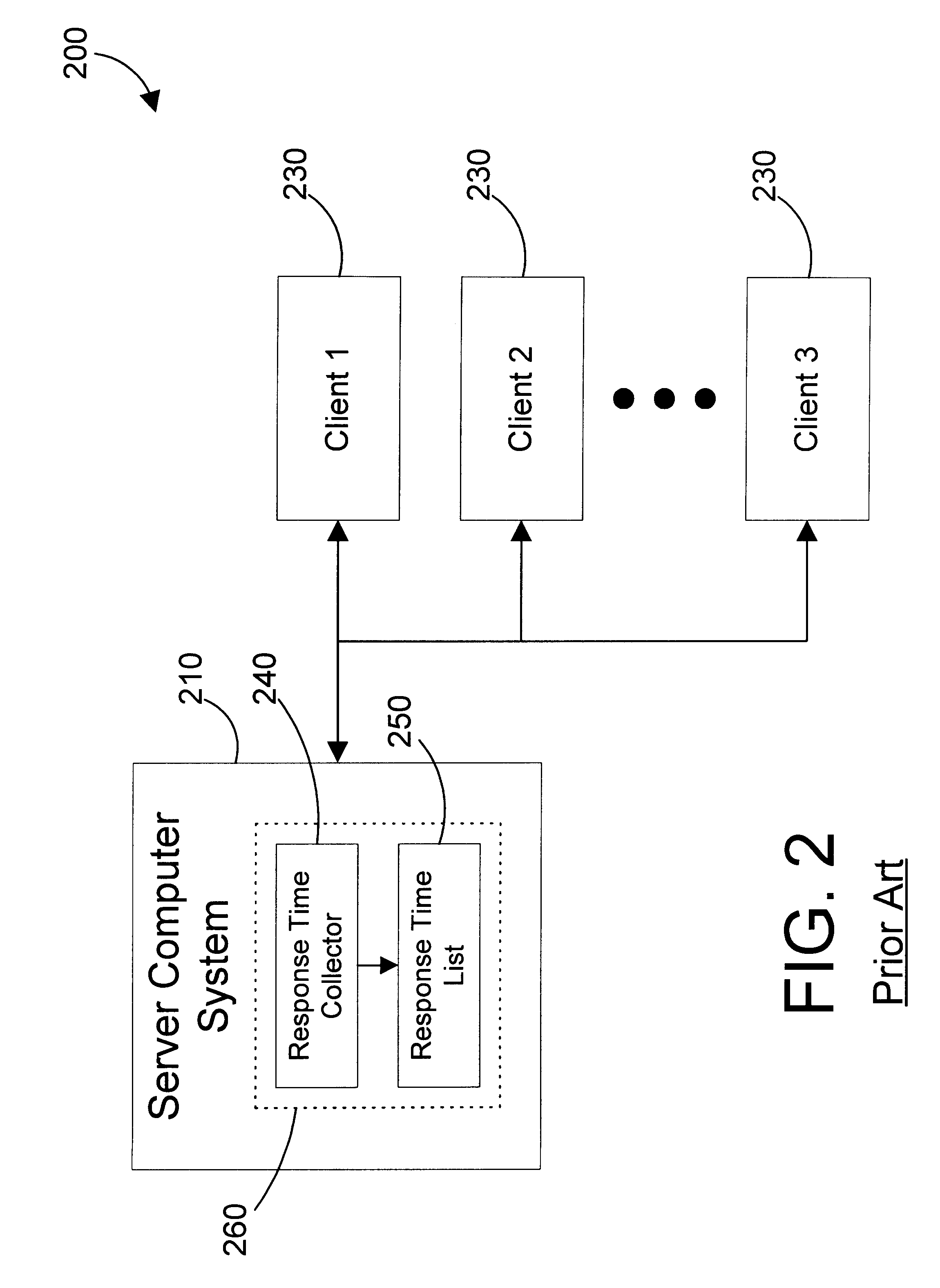
Apparatus and method for measuring transaction time in a computer system
InactiveUS6178449B1Simple protocolEfficient communicationHardware monitoringMultiple digital computer combinationsTime dataClient machine
A transaction time measurement mechanism has a transaction time manager running on a server computer system, a transaction time agent running on a client computer system that is coupled to the server computer system via a network, and a simple protocol for allowing them to directly and efficiently communicate. The transaction time agent is configured according to configuration data stored in a configuration table in a transaction time database, and stores transaction time data in a statistics table according to this configuration. The data in the statistics table is indexed to allow retrieving only the transaction time data of interest. The simple communication protocol supports multiple transaction time managers in a network computing environment that may all communicate with a single client.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for maintaining temporal data in data storage
ActiveUS7158991B2Input/output to record carriersData processing applicationsTemporal informationTemporal database
System and method for maintaining temporal data in data storage at the logical device level. Embodiments of the temporal volume manager may provide an interface that allows applications and / or application agents to communicate with the temporal volume manager to manage and keep track of the temporal information on one or more temporal volumes. Embodiments may provide an infrastructure for applications that work on the history of data such as temporal databases, versioning file-systems / repositories, data archives, and streaming media to manage temporal data. In one embodiment, if an application does not want to use the temporal volume directly, application agents may be used to access the temporal volume. Embodiments may provide I / O controlled, application-controlled, and / or periodic checkpointing of temporal data on the temporal volume. One embodiment may provide a mechanism for generating temporal images (e.g. point-in-time and slice-in-time images) of a temporal volume that may have their own independent history.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
Persistent snapshot management system
InactiveUS7237080B2Digital data processing detailsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHard disc drivePrimitive state
Owner:COLUMBIA DATA PRODUCTS
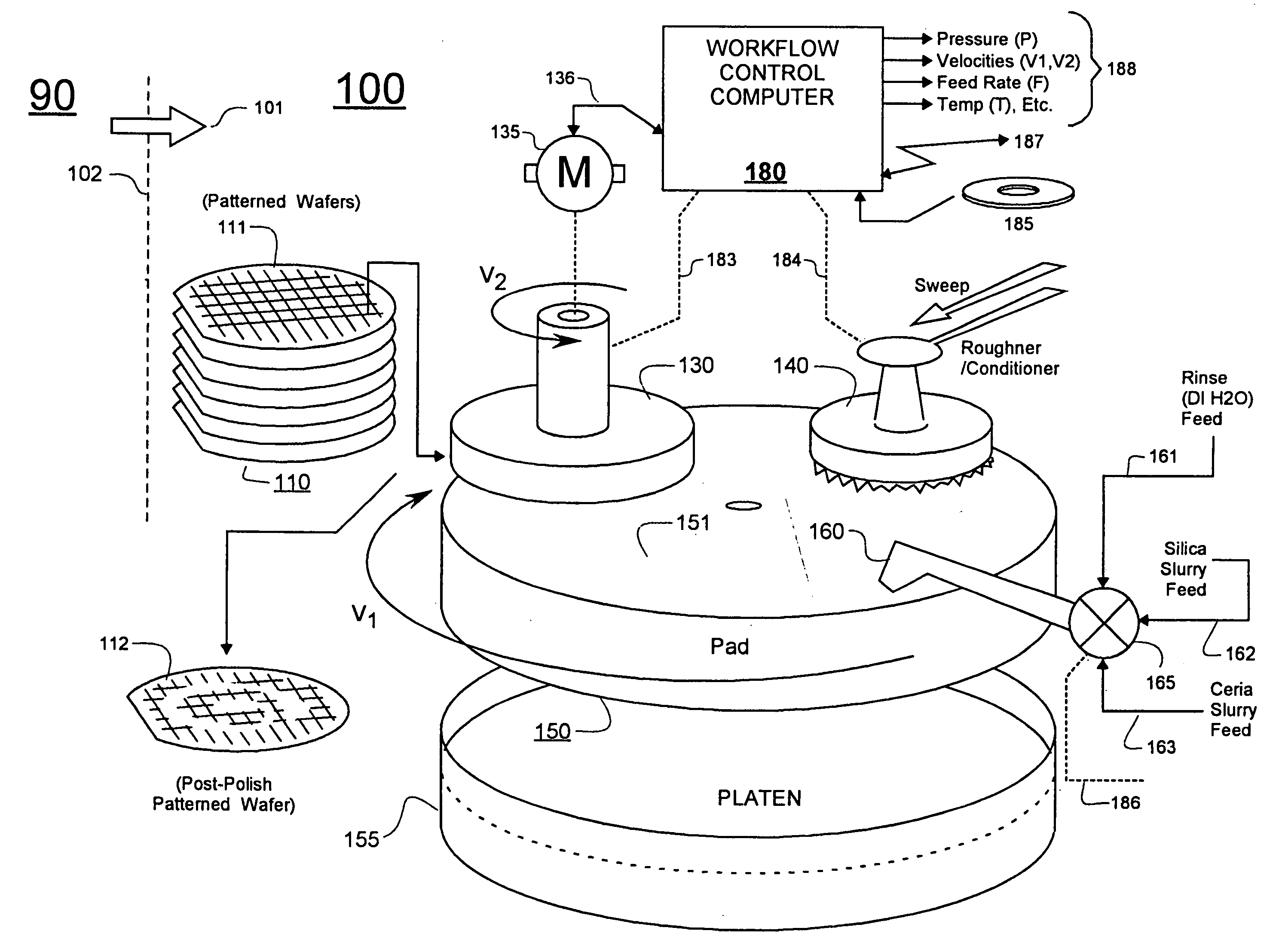
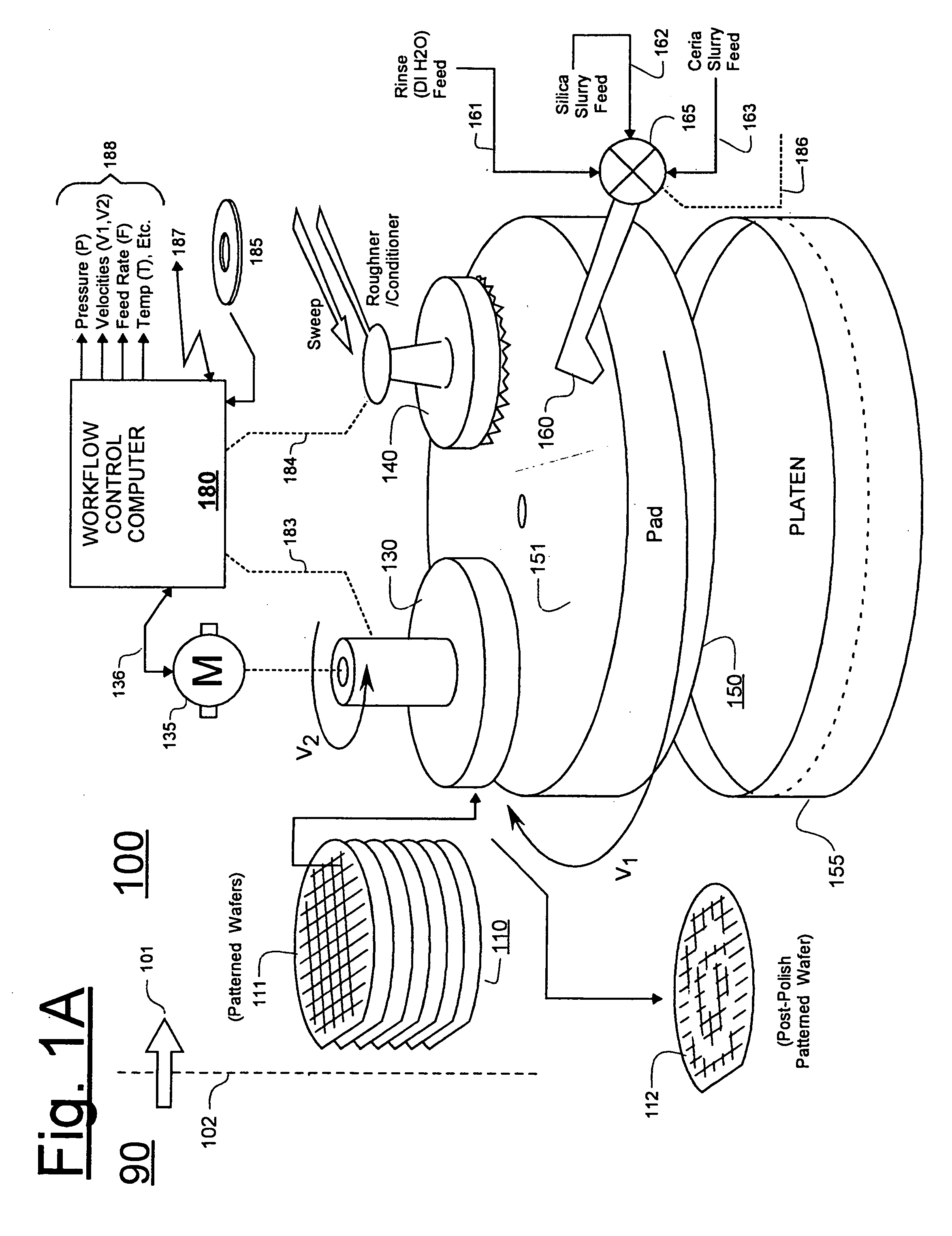
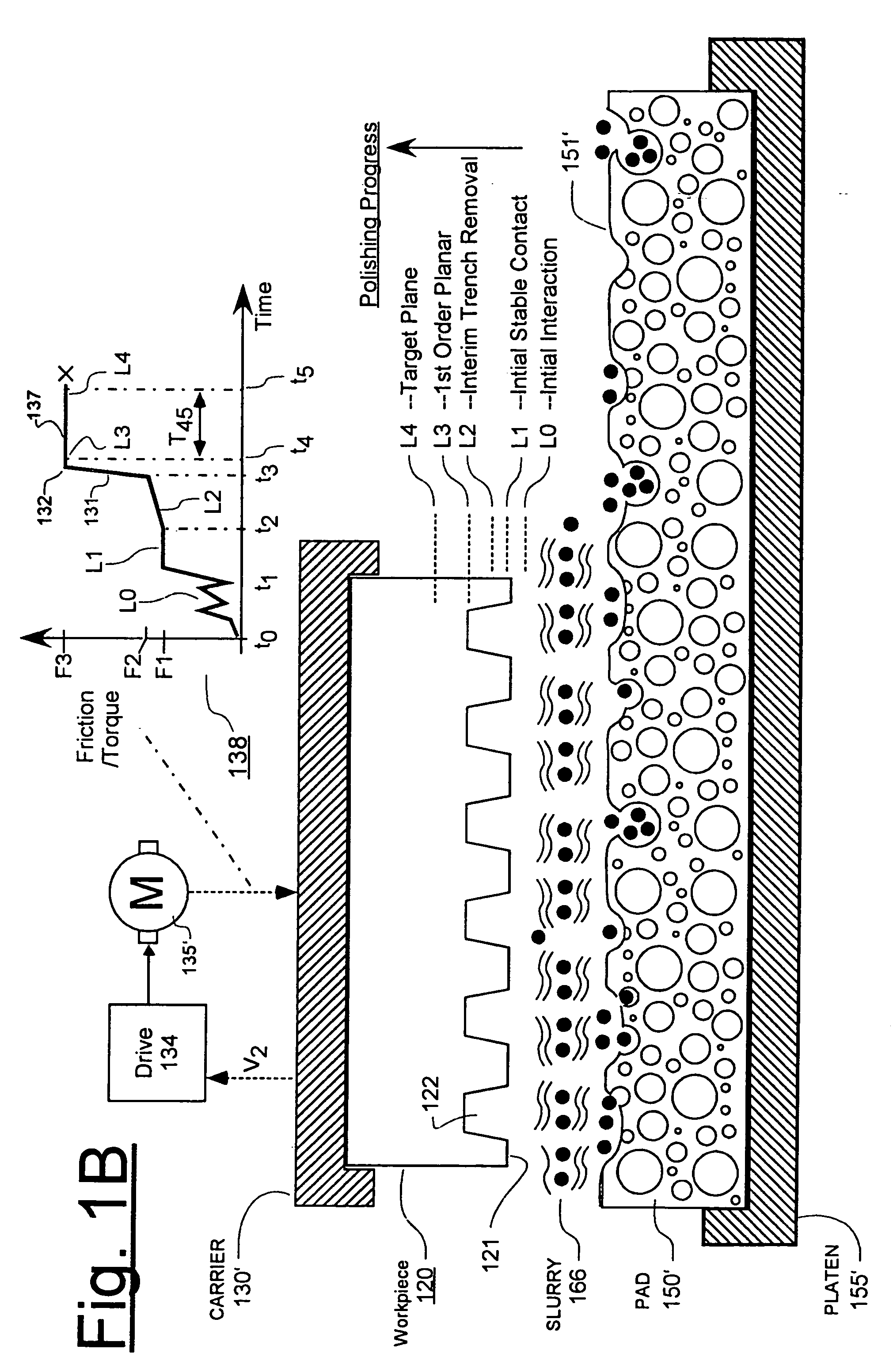
Torque-based end point detection methods for chemical mechanical polishing tool which uses ceria-based CMP slurry to polish to protective pad layer
A chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) method is disclosed in which a torque-based end-point algorithm is used to determine when polishing should be stopped. The end-point algorithm is applicable to situations where a ceria (CeO2) based CMP slurry is used for further polishing, pre-patterned and pre-polished workpieces (e.g., semiconductor wafers) which have a high friction over-layer (e.g., HDP-oxide) and a comparatively, lower friction and underlying layer of sacrificial pads (e.g., silicon nitride pads). A mass production wise, reliable and consistent signature point in the friction versus time waveform of a torque-representing signal is found and used to trigger an empirically specified duration of overpolish. A database may be used to define the overpolish time as a function of one or more relevant parameters.
Owner:PROMOS TECH INC
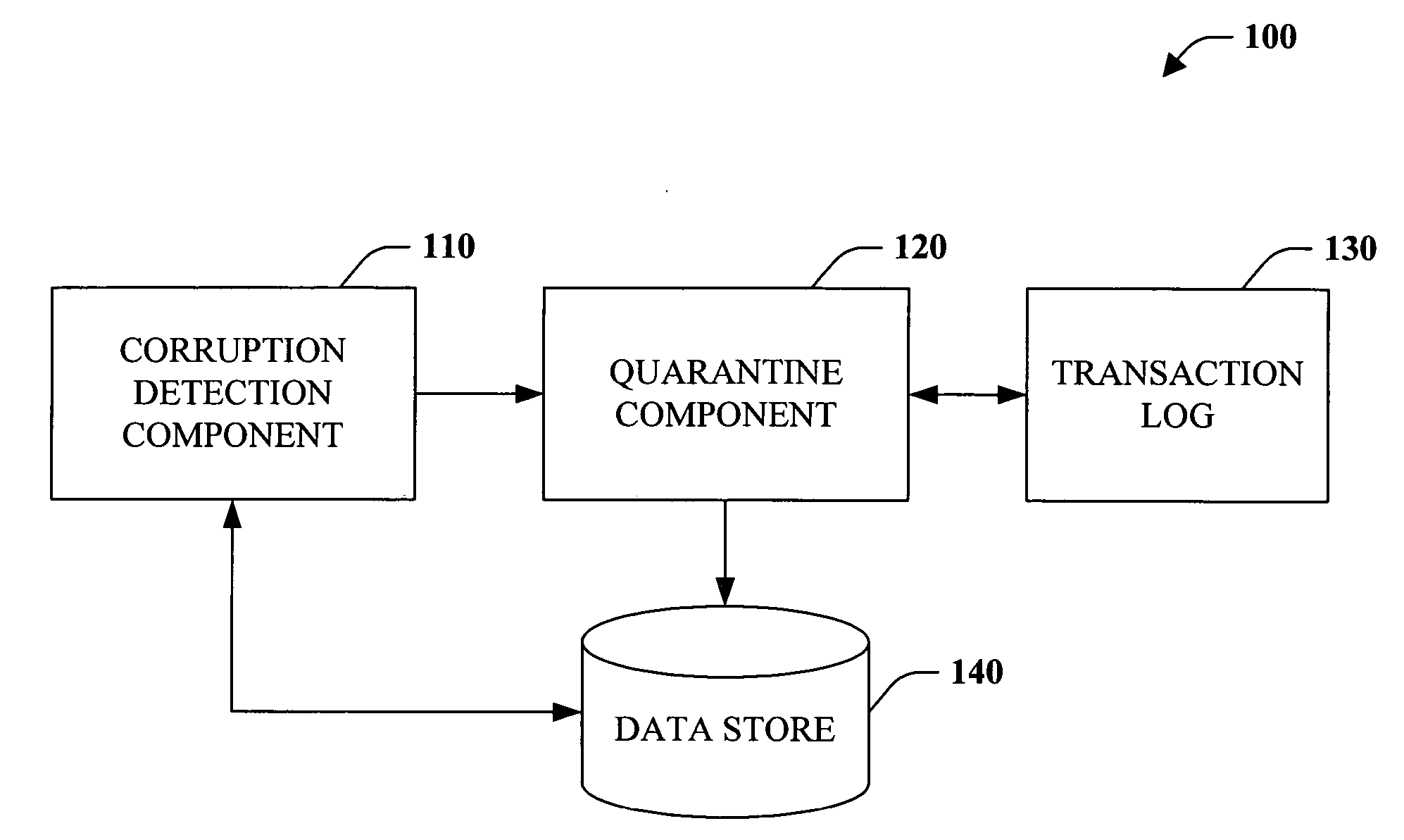
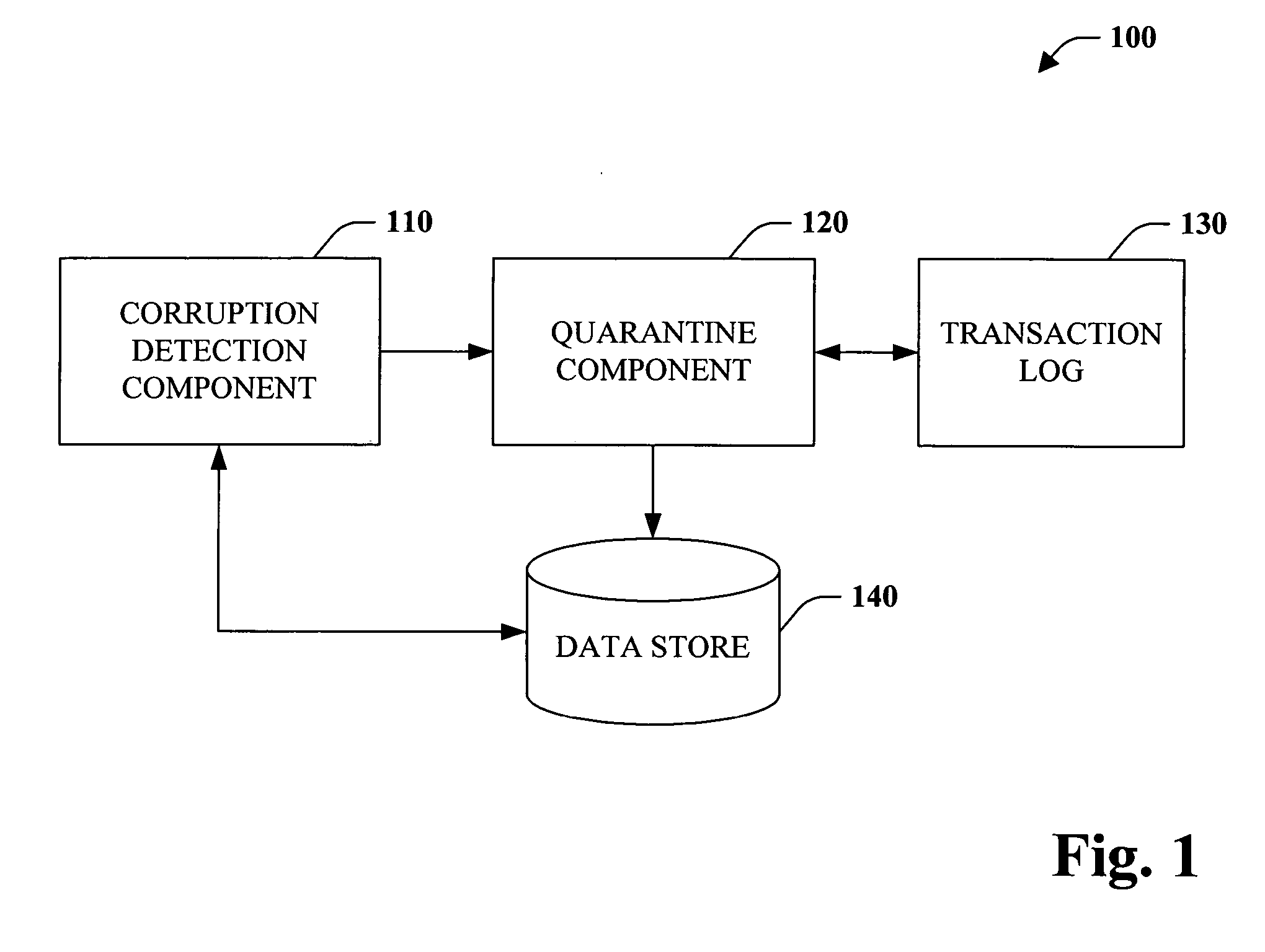
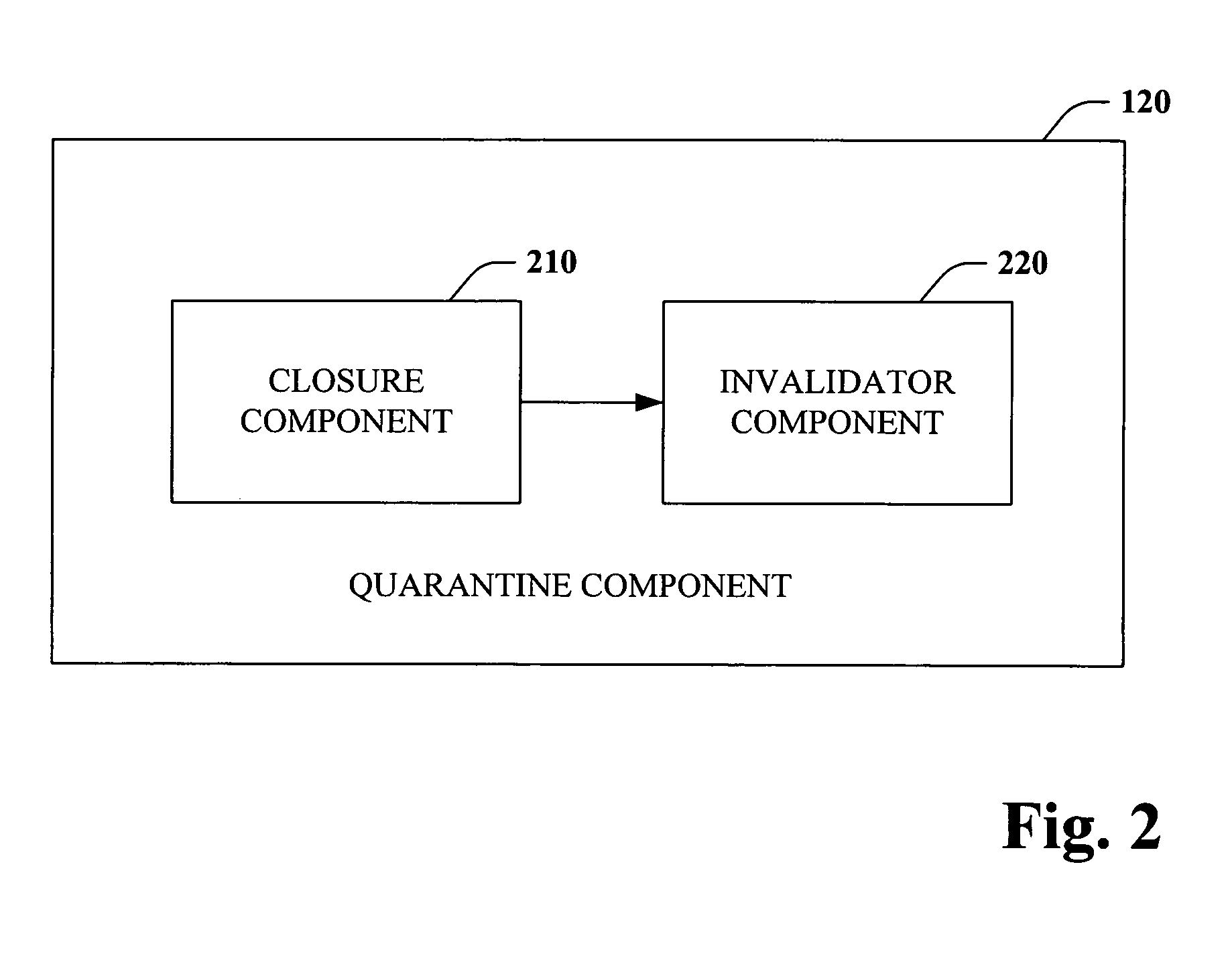
Database corruption recovery systems and methods
ActiveUS20060259518A1Improve abilitiesEliminate needDigital data processing detailsData acquisition and loggingTemporal databaseData needs
The subject invention pertains to data store corruption recovery. More specifically, the invention concerns systems and methods for identifying corrupt data in a manner that prevents de-committing or removal of valid or consistent transactions from a database. This can be accomplished at least in part by logging the identities of data items that a transaction reads. Furthermore, the subject invention provides for employment of a multi-version (or transaction-time) database to reduce significantly reduce any down time or database unavailability caused by a corrupt transaction and associated corrupt data items. Accordingly, no backups need to be installed and only updates by the original corrupt transaction and transactions that read corrupt data need to be de-committed or removed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
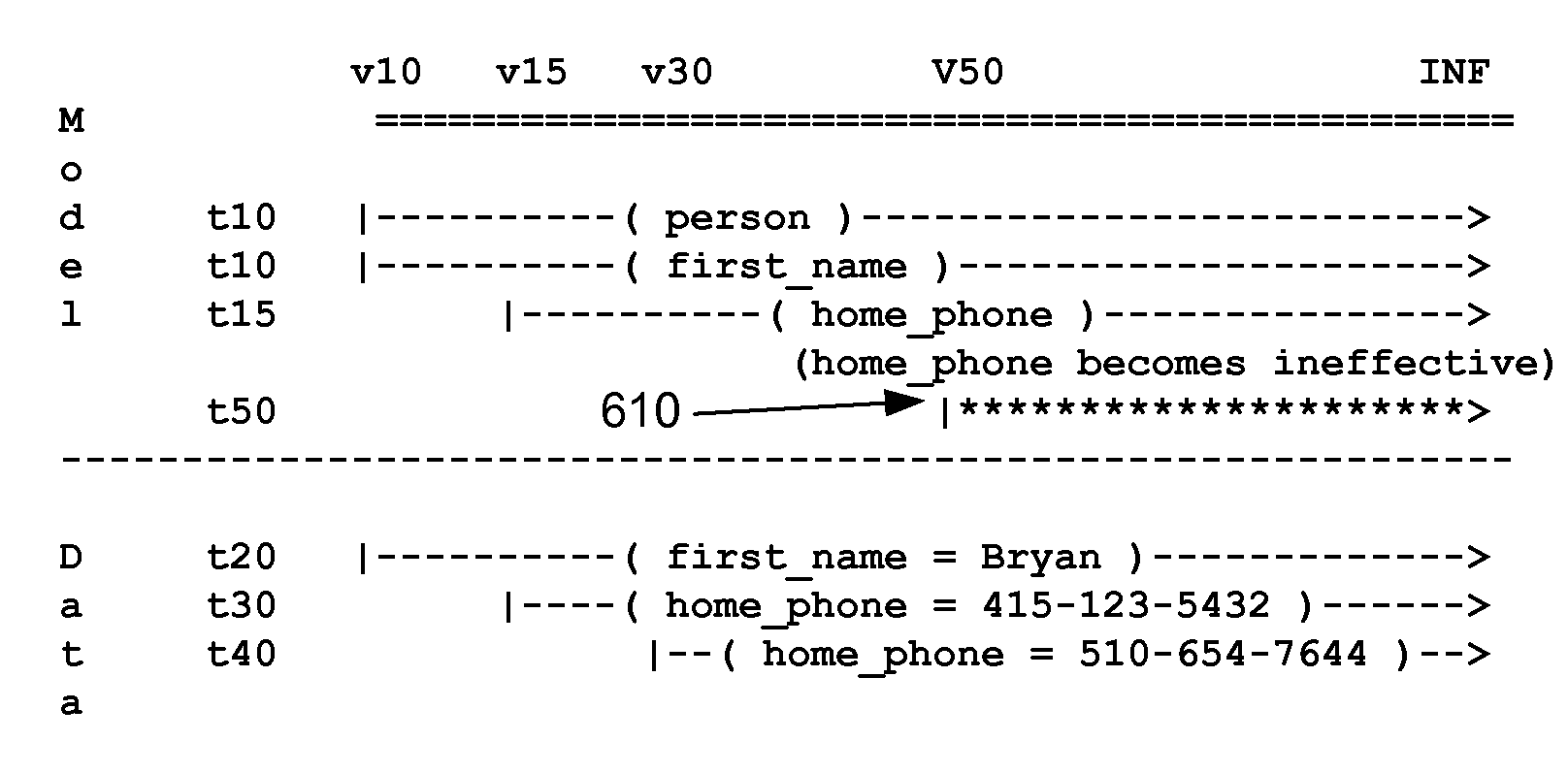
Temporal relational database management system
ActiveUS20090248727A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTemporal databaseRelational database management system
A temporal relational database includes a relational database framework that allows for all the capabilities of a standard relational database with the addition of the concept of time. Transactions, which can be modifications of attribute values or changes to the database schema, can be stored with temporal histories. Through the use of these temporal histories, the temporal database is able to seamlessly respond to queries for times that are in the past, present, or future. Furthermore, transactions can be entered into the temporal relational database that are not effective until some point in the future, thus allowing for seamless migration of the data and schema of a database. Applications that access data in a temporal database may retrieve a time appropriate schema from the temporal database. An exemplary use of a temporal database to manage roles and responsibilities within an organization is described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Persistent Snapshot Methods
InactiveUS20070250663A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionHard disc drivePrimitive state
A persistent snapshot is taken and maintained in accordance with a novel method and system for extended periods of time using only a portion of a computer readable medium of which the snapshot is taken. Multiple snapshots can be taken in succession at periodic intervals and maintained practically indefinitely. The snapshots are maintained even after powering down and rebooting of the computer system. The state of the object of the snapshot for each snapshot preferably is accessible via a folder on volume of the snapshot. A restore of a file or folder may be accomplished by merely copying that file or folder from the snapshot folder to a current directory of the volume. Alternatively, the entire computer system may be restored to a previous snapshot state thereof. Snapshots that occurred after the state to which the computer is restored are not lost in the restore operation. Different rule sets and scenarios can be applied to each snapshot. Furthermore, each snapshot can be written to within the context of the snapshot and later restored to its pristine condition. Software for implementing the systems and methods of snapshots in accordance with the present invention may comprise firmware of a hard disk drive controller or a disk controller board or within the HDD casing itself. The present invention further comprises novel systems and methods in which the systems and methods of taking and maintaining snapshots are utilized in creating and managing temporal data stores, including temporal database management systems. The implications for data mining and exploration, data analysis, intelligence gathering, and artificial intelligence (just to name a few areas) are profound.
Owner:COLUMBIA DATA PRODUCTS
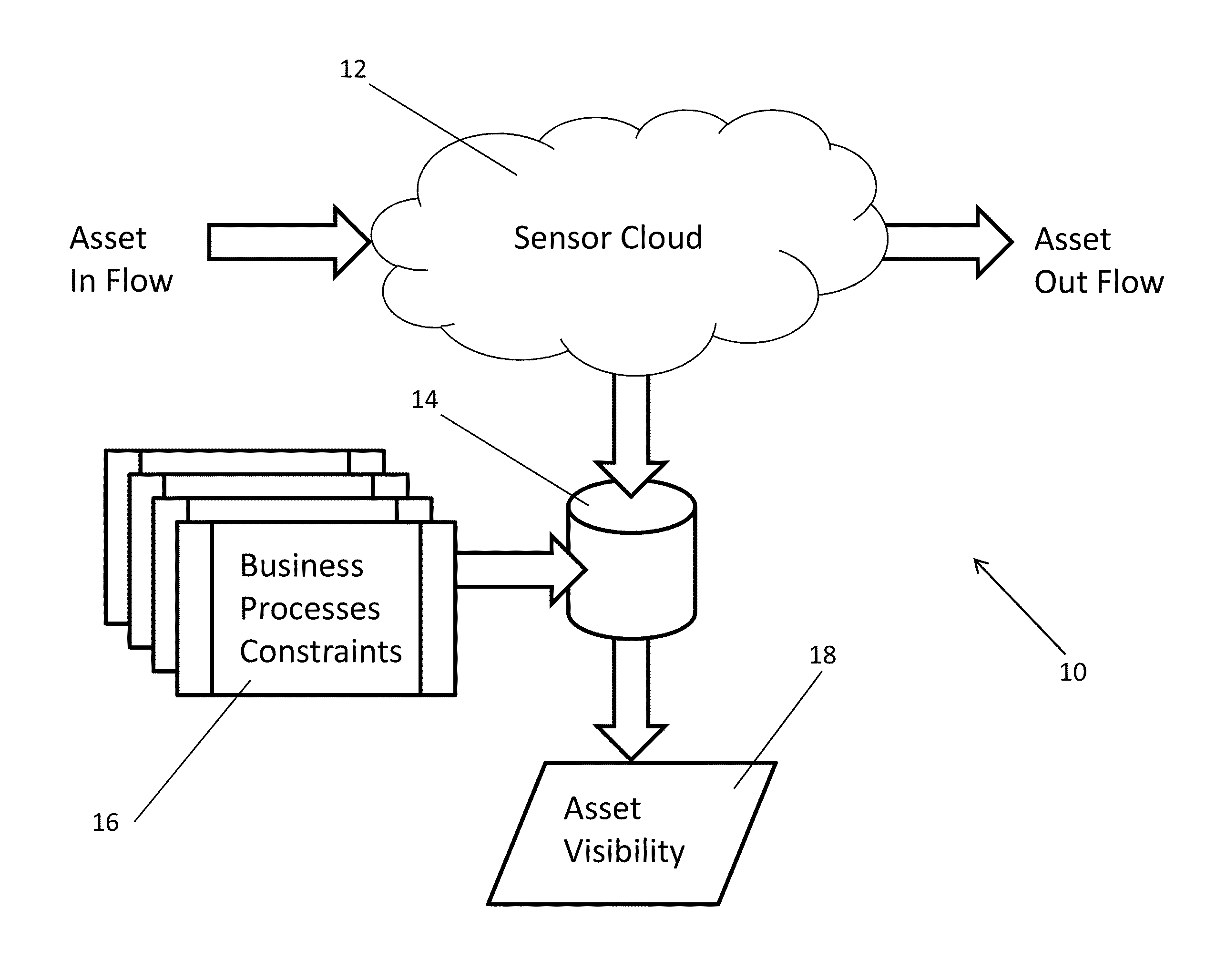
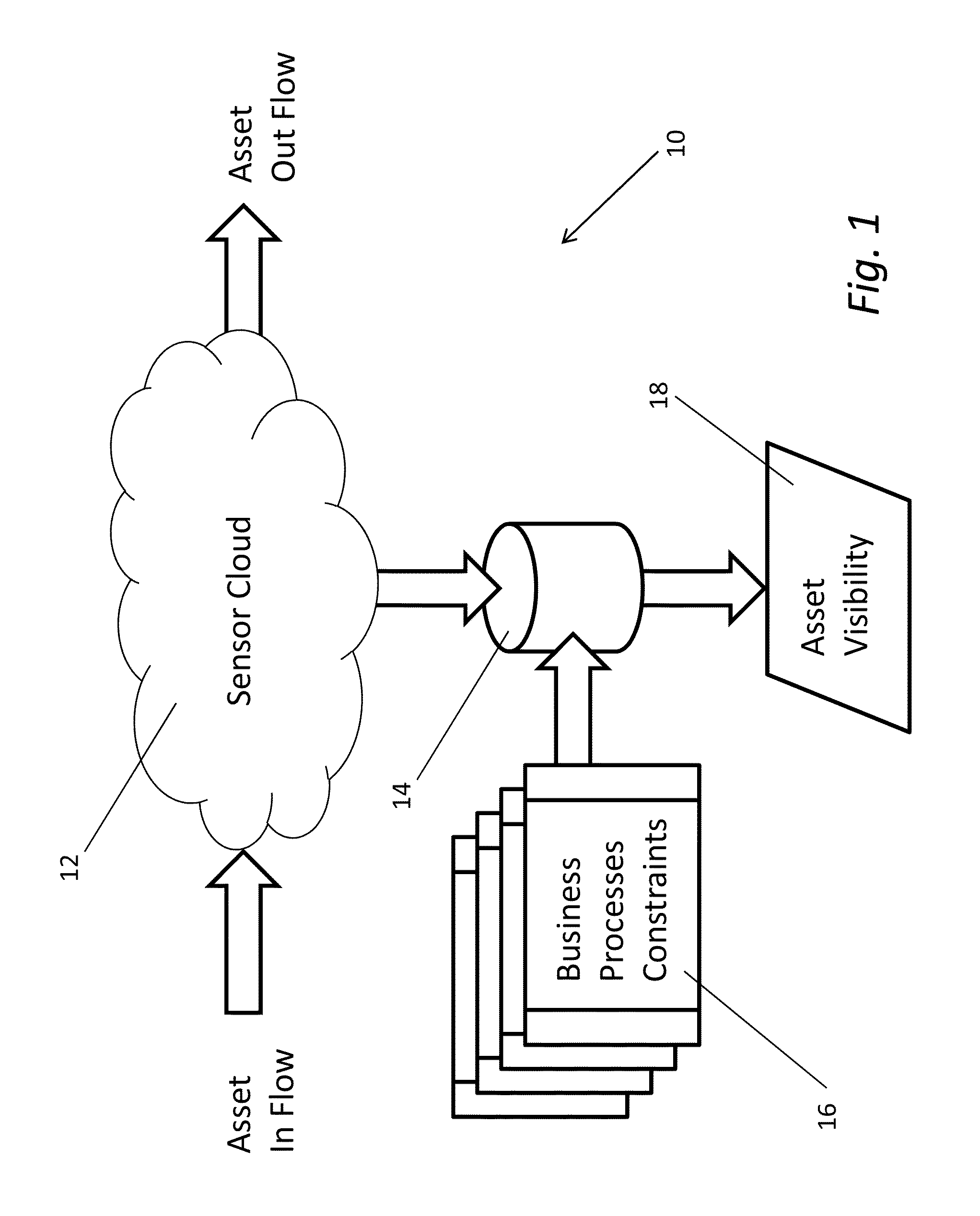
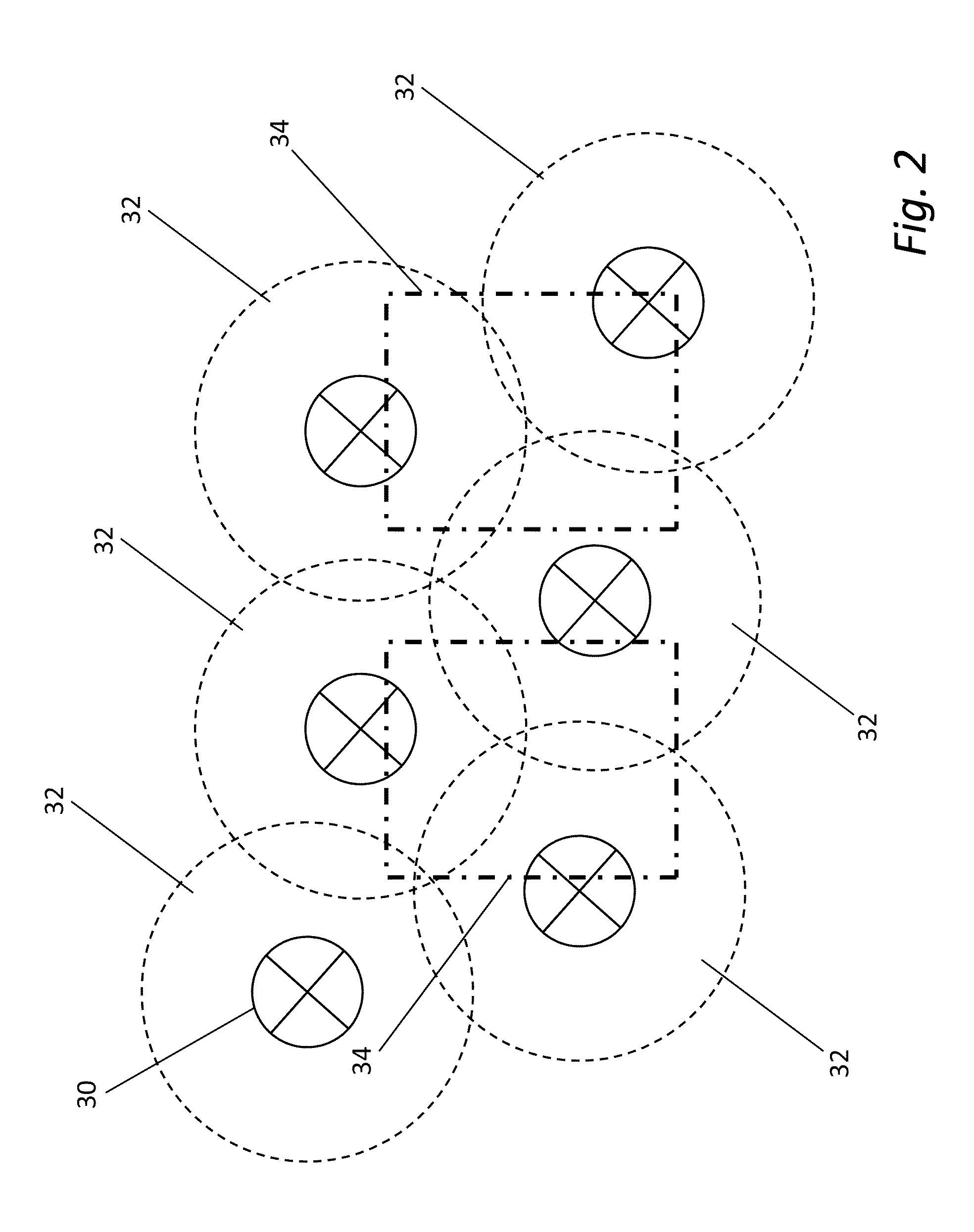
Systems and methods for detecting patterns in spatio-temporal data collected using an RFID system
InactiveUS20110254664A1Optimize business processesWireless architecture usageSubscribers indirect connectionTemporal databaseApplication server
Systems and methods are described that collect spatio-temporal data using an RFID system that is capable of locating the spatial position of a sensor, which is typically unaware of its location. Such systems and methods can be contrasted with conventional RFID systems in that they are able to determine the location of sensors in space as opposed to with respect to read zones related to the underlying RFID reader infrastructure. One embodiment includes an RFID system having a plurality of read zones and configured to obtain the spatio-temporal state of sensors within a sensor cloud, where the spatio-temporal state of each sensor includes sensor information, a time stamp, and a spatial location specified independently of the read zones of the RFID system, a spatio-temporal database configured to store spatio-temporal state of a plurality of sensors over time, and an application server configured to trigger events based upon the detection of at least one condition by applying at least one filter to the data within the spatio-temporal database.
Owner:MOJIX
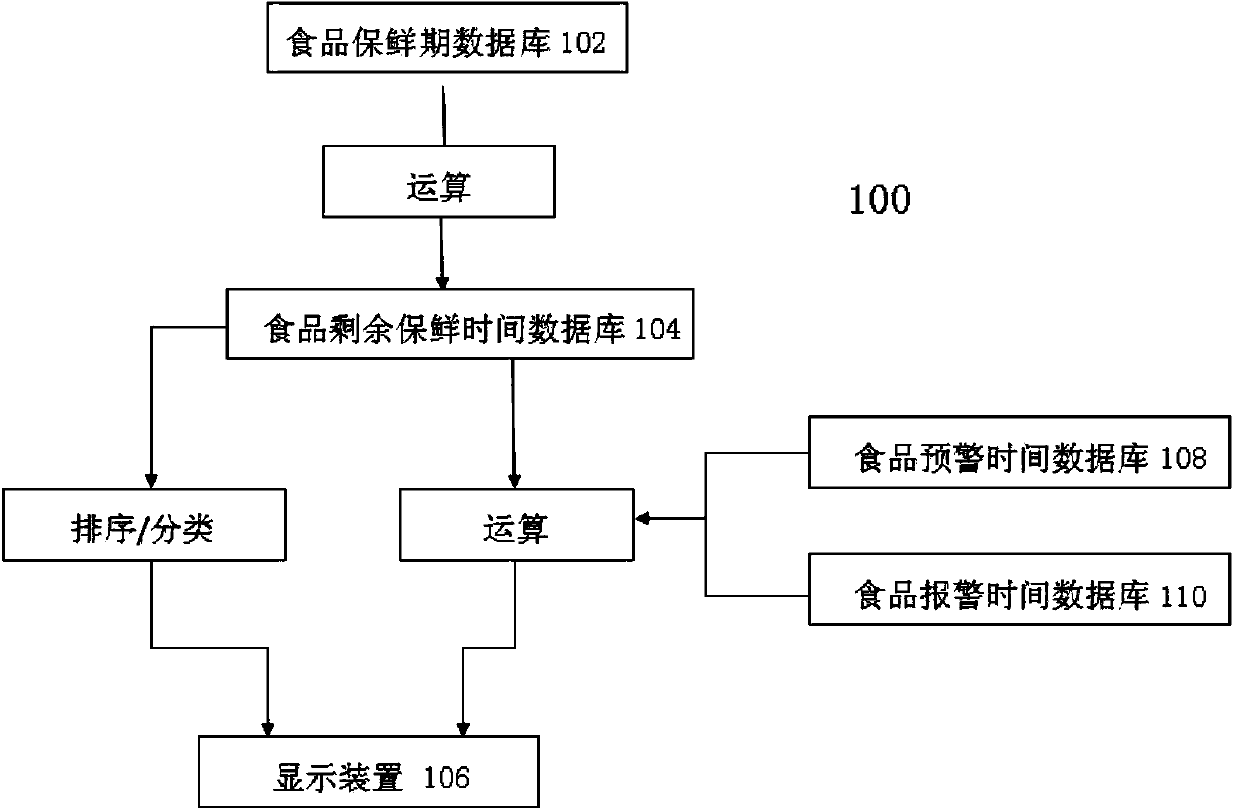
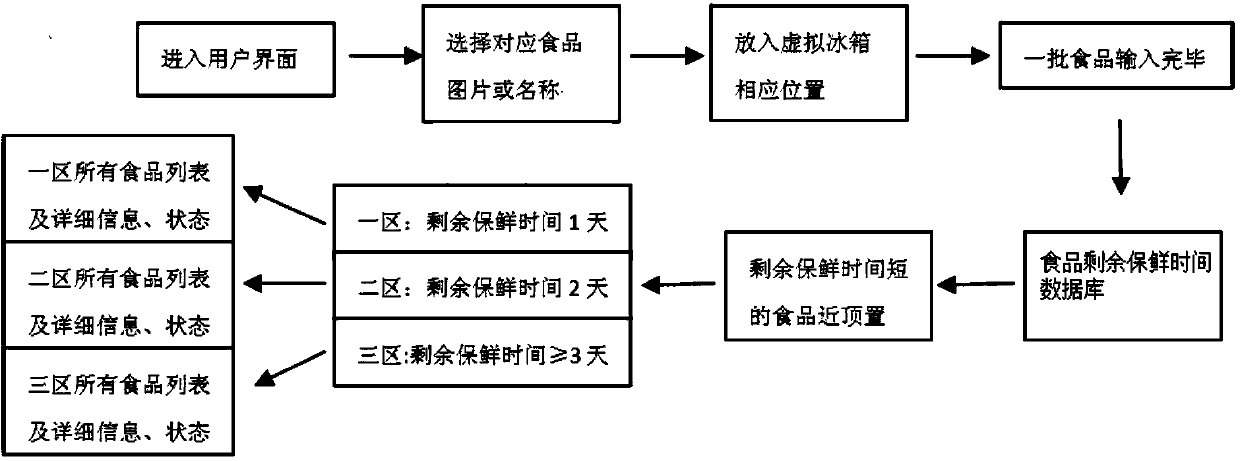
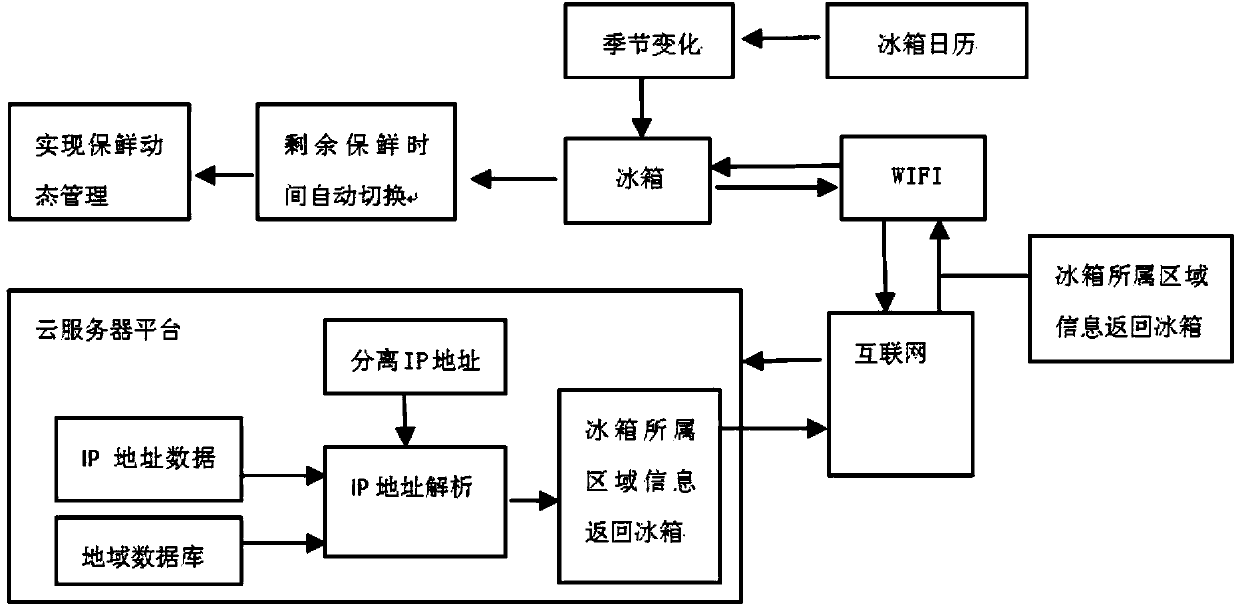
Food preservation management refrigerator and food preservation management method
ActiveCN104197633AEasy to findAvoid wasting power consumptionDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusTemporal databaseDisplay device
A food preservation management refrigerator comprises a food preservation period database, a food remaining preservation time database and a display device. The food preservation period database stores original food preservation periods; according to the food remaining preservation time database, when food is stored into a refrigerator body, the refrigerator body starts timing and reads the original food preservation period of the food from the food preservation period database, the food remaining preservation time of the food can be acquired through calculation according to the original food preservation period and the actual storage time and can be stored in the food remaining preservation time database, all foods in the refrigerator body are sequenced according to the food remaining preservation time through the food remaining preservation time database, foods with the food remaining preservation time smaller than a first preset value are classified into a first class, foods with the food remaining preservation time which is larger than or equal to the first preset value but smaller than a second preset value larger than the first preset value are classified into a second class, and foods with the food remaining preservation time larger than or equal to the second preset value as a third class; the display device displays the foods of the first, second and third classes respectively.
Owner:HEFEI MIDEA INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
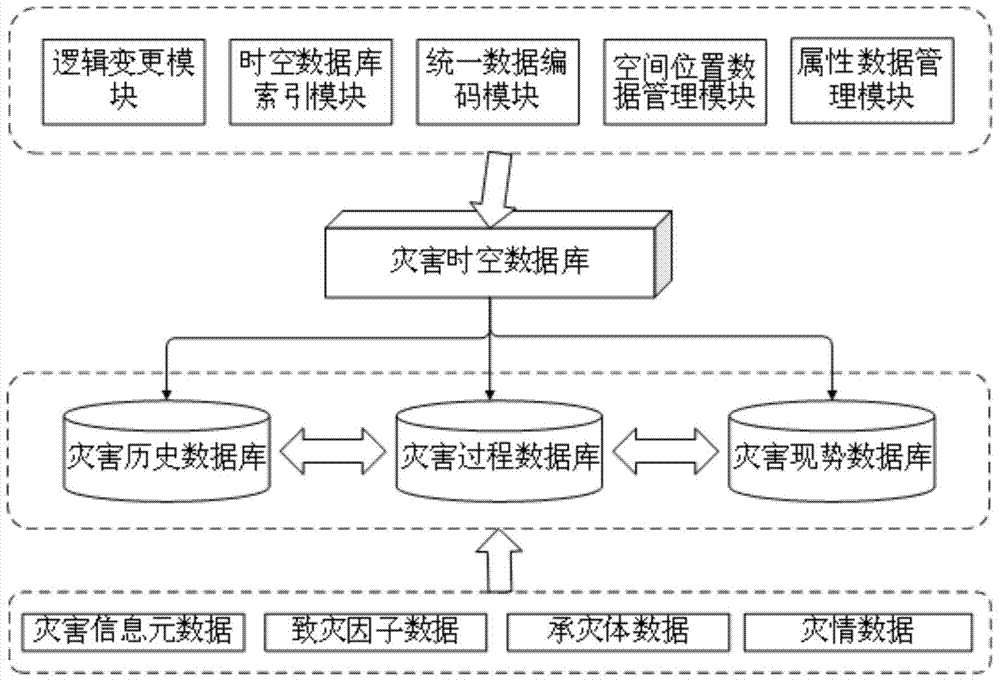
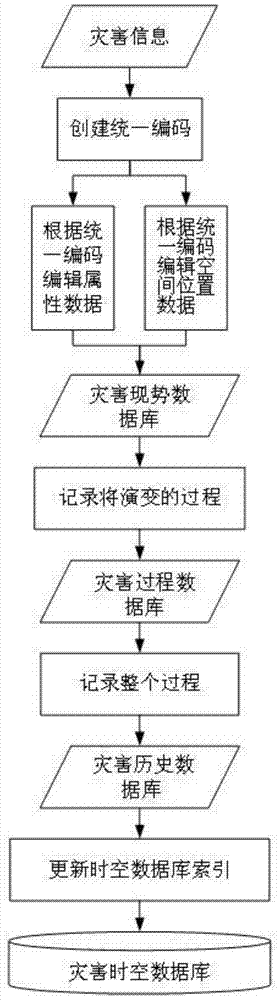
Disaster information spatial-temporal database
InactiveCN103678712AEnhanced backtracking query capabilitiesImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsDatabase design/maintainanceCode moduleTemporal database
The invention provides a disaster information spatial-temporal database, which comprises three disaster information databases including a disaster current simulation database, a disaster process database and a disaster historical database, wherein a unified coding module carries out layered coding on the received disaster information data, an attribute data management module and a space position management module guide in disaster information attribute data and space position data to the corresponding disaster information database, the disaster information data is transmitted among all disaster information databases through a logic conversion module, a spatial-temporal database index module builds updating index for the disaster information spatial-temporal database according to the time sequence, the logic conversion module and the spatial-temporal database index module form the basis of the disaster information spatial-temporal database, and the preparation is made for the disaster attribute management and maintenance, spatial-temporal logic index conversion and maintenance, statistics data entry, index and spatial-temporal inquiry. The disaster information spatial-temporal database solves the problems of lower work efficiency and high data redundancy during the realization of spatial-temporal data storage, management and historical review.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for temporal database
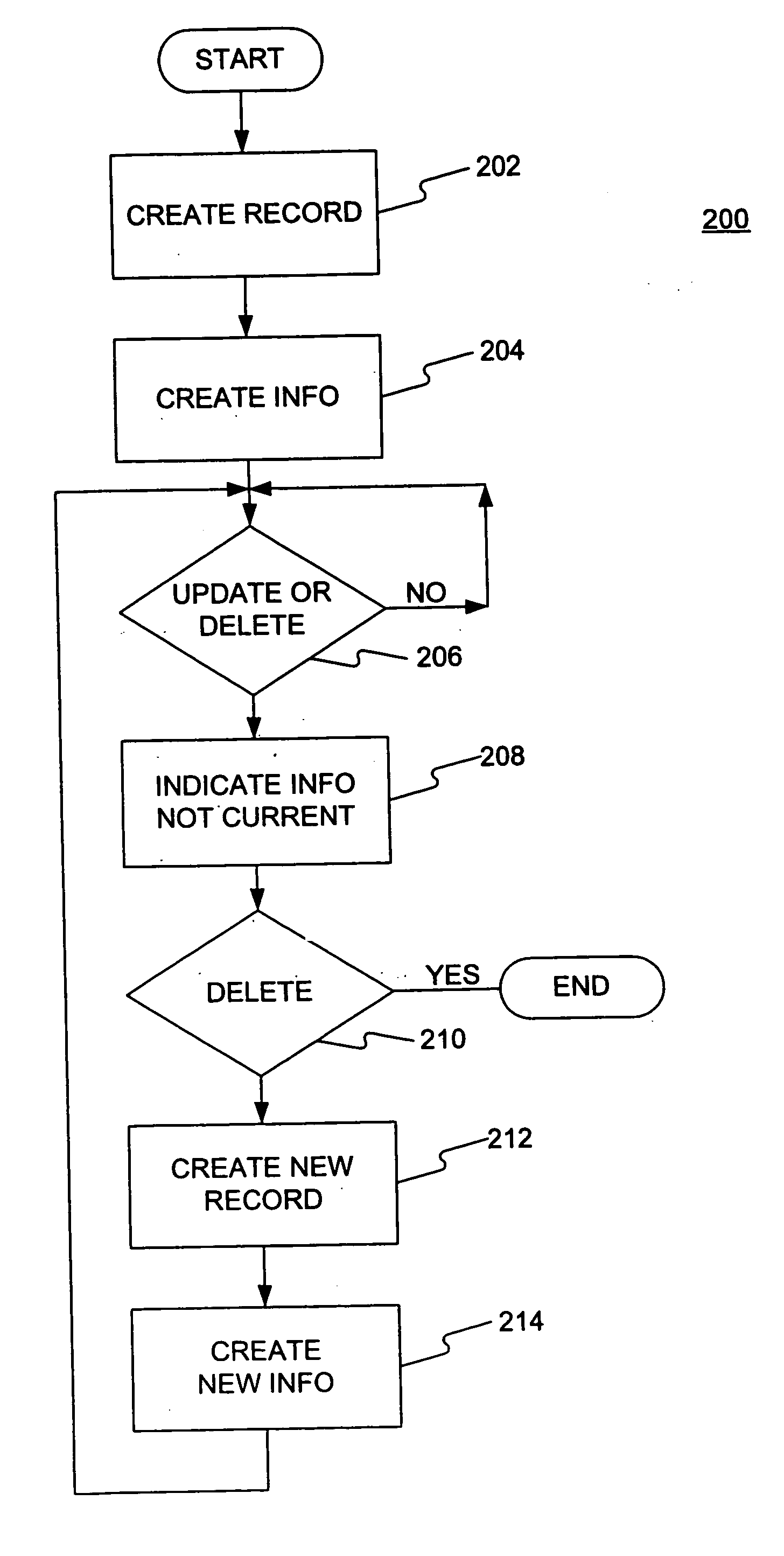
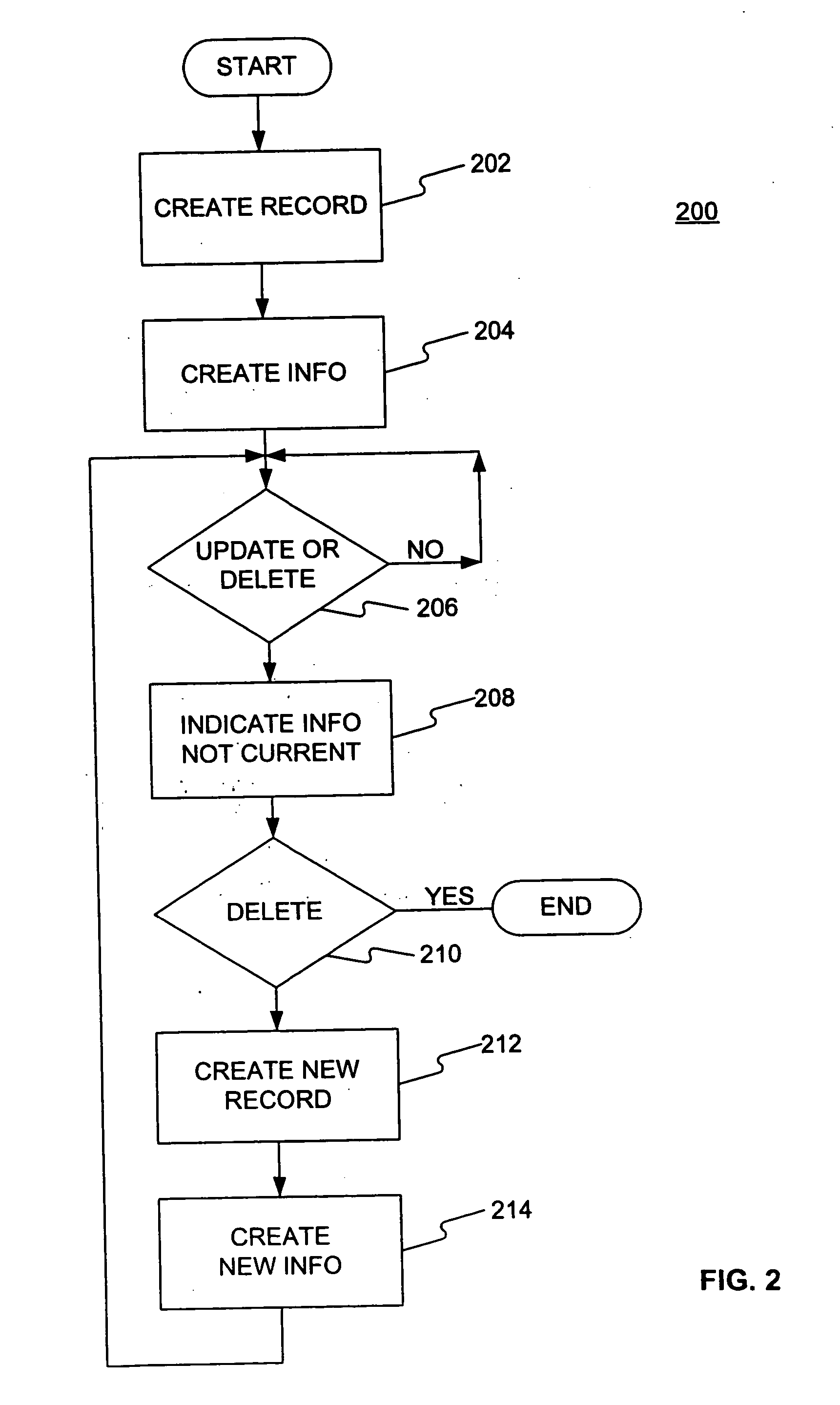
InactiveUS20060184563A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTemporal databaseStart time
Methods and systems consistent with the invention store data in a database. A method or system consistent with the invention create a first record for a first time period, the first record comprising an identifier and an attribute, create a second record for a second time period, the second record comprising the identifier and the attribute, and create first information indicative of a start time and an end time of the first time period, wherein data in the attribute in the first record is valid for the first time period, and second information indicative of a start time and an end time of the second time period, wherein data in the attribute in the second record is valid for the second time period. The identifier may indicate a lineage. A method or system consistent with the invention may update the first record for the first time period by indicating in the first information that the first time period is not current, indicating in the second information that the second time period is current, and updating the attribute data in the second record for the second time period. A method or system consistent with the invention may delete a record in the second time period by indicating in the second information that the second time period is not current.
Owner:CIBERNET CORP
Lazy timestamping in transaction time database
InactiveUS7424499B2Low cost of executionPerformance is minimally impactedData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTemporal databaseTimestamp
Lazy timestamping in a transaction time database is performed using volatile reference counting and checkpointing. Volatile reference counting is employed to provide a low cost way of garbage collecting persistent timestamp information about a transaction by identifying exactly when all record versions of a transaction are timestamped and the versions are persistent. A volatile timestamp (VTS) table is created in a volatile memory, and stores timestamp, reference count, transaction ID, and LSN information. Active portions of a persisted timestamp (PTS) table are stored in the VTS table to provide faster and more efficient timestamp processing via accesses to the VTS table information. The reference count information is stored only in the VTS table for faster access. When the reference count information decrements to zero, it is known that all record versions that were updates for a transaction were timestamped. A checkpointing component facilitates checkpoint processing for verifying that timestamped records have been written to the persistent database and that garbage collection of the PTS table can be performed for transaction entries with zero reference counts.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
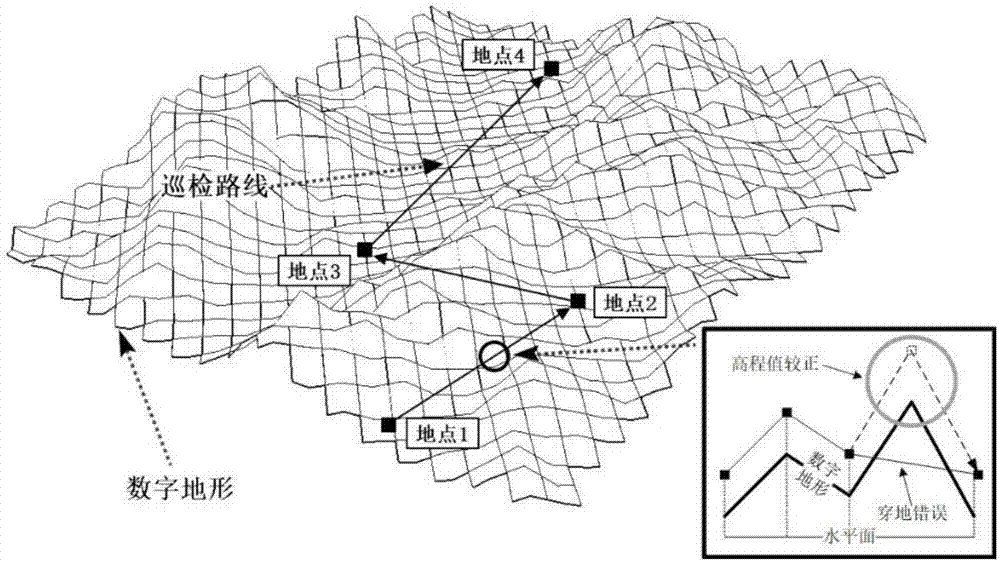
Method for monitoring reservoir patrolling in real time based on three-dimensional GIS
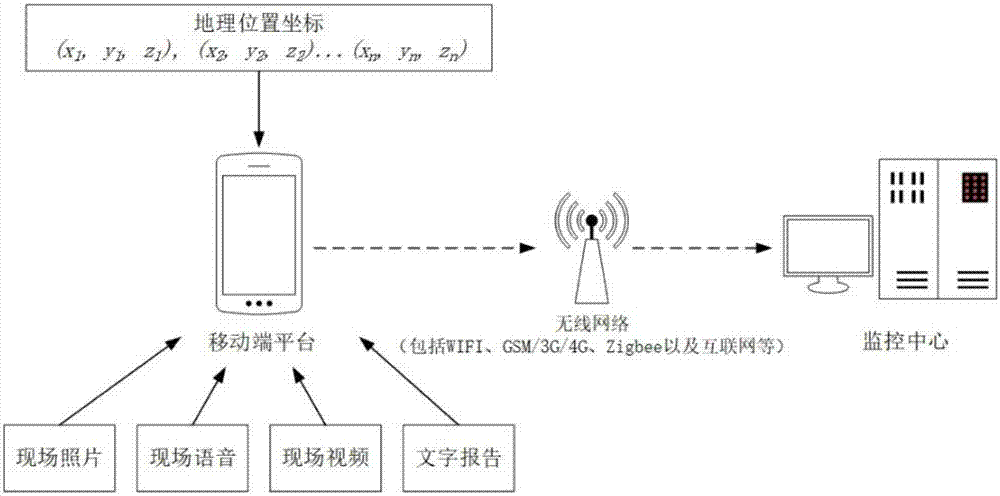
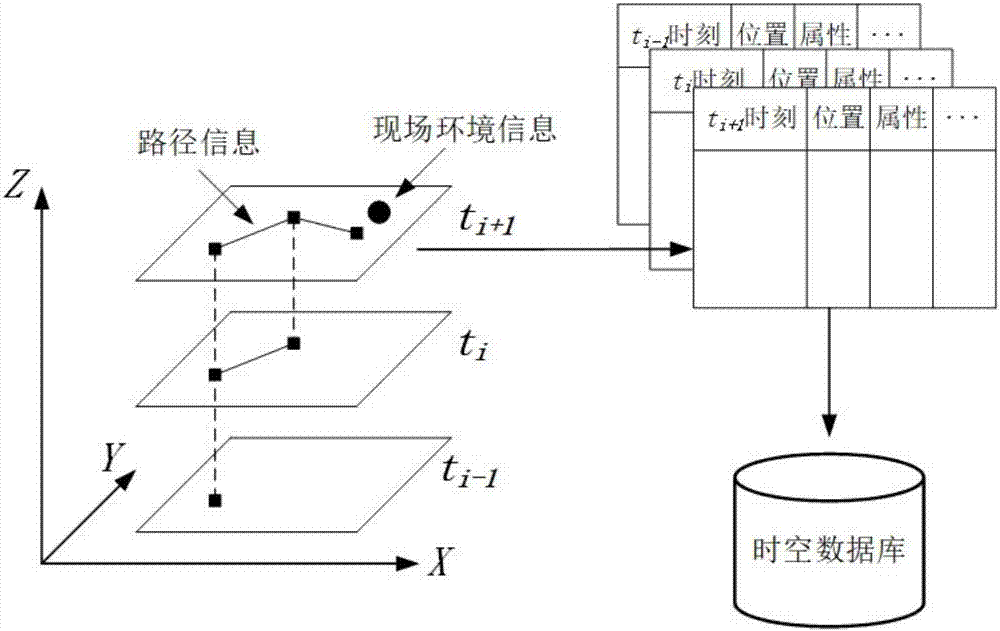
ActiveCN107576311AAchieve informatizationRealizePhotogrammetry/videogrammetryOpen water surveyGeographic siteTemporal database
The invention discloses a method for monitoring reservoir patrolling in real time based on three-dimensional GIS. The method comprises the following steps: communicating a mobile terminal platform with a monitoring center to transmit geographic location coordinates and site environment information; constructing a reservoir patrolling spatio-temporal database for recording patrolling task information by the monitoring center; constructing a three-dimensional digital scene model of a reservoir region by utilizing a three-dimensional GIS and unmanned aerial vehicle oblique photography to displaypatrolling track information of the patrolling task and site environment attribute information; updating patrolling task progress in real time, displaying a complete patrolling route change in a three-dimensional digital geographic scene of the reservoir region, and providing real-time browsing of patrolling information; and after finishing the reservoir patrolling task, storing space data acquired in the patrolling task and historical data information, providing task backtracking at any angle of view in the three-dimensional digital geographic scene, and submitting a reservoir patrolling digital report. The method provided by the invention can simulate site conditions and progress of the patrolling task more accurately, and achieve purposes of informationization, contextualization and effectuation of the monitoring of the reservoir patrolling task.
Owner:CHANGJIANG RIVER SCI RES INST CHANGJIANG WATER RESOURCES COMMISSION
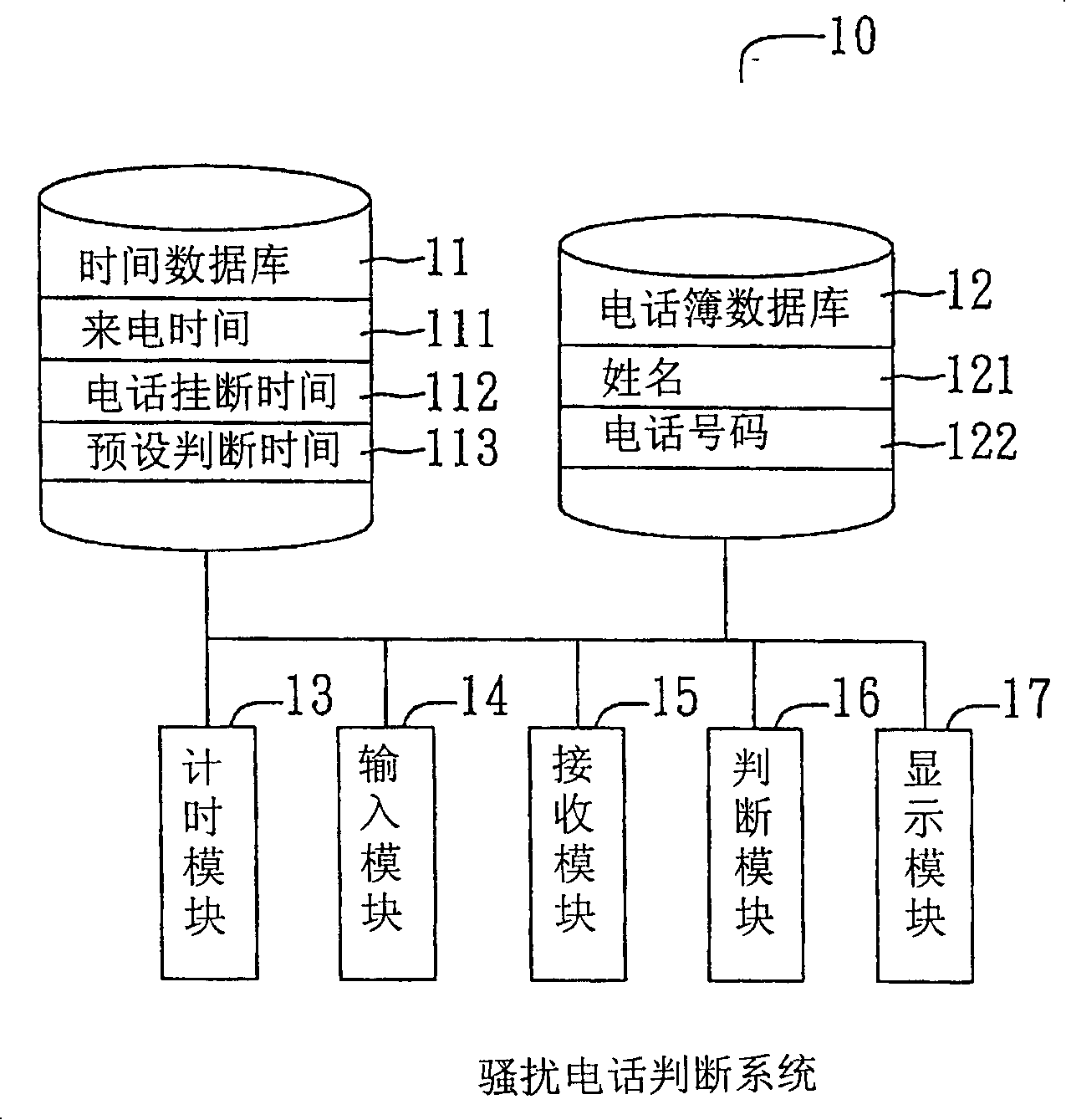
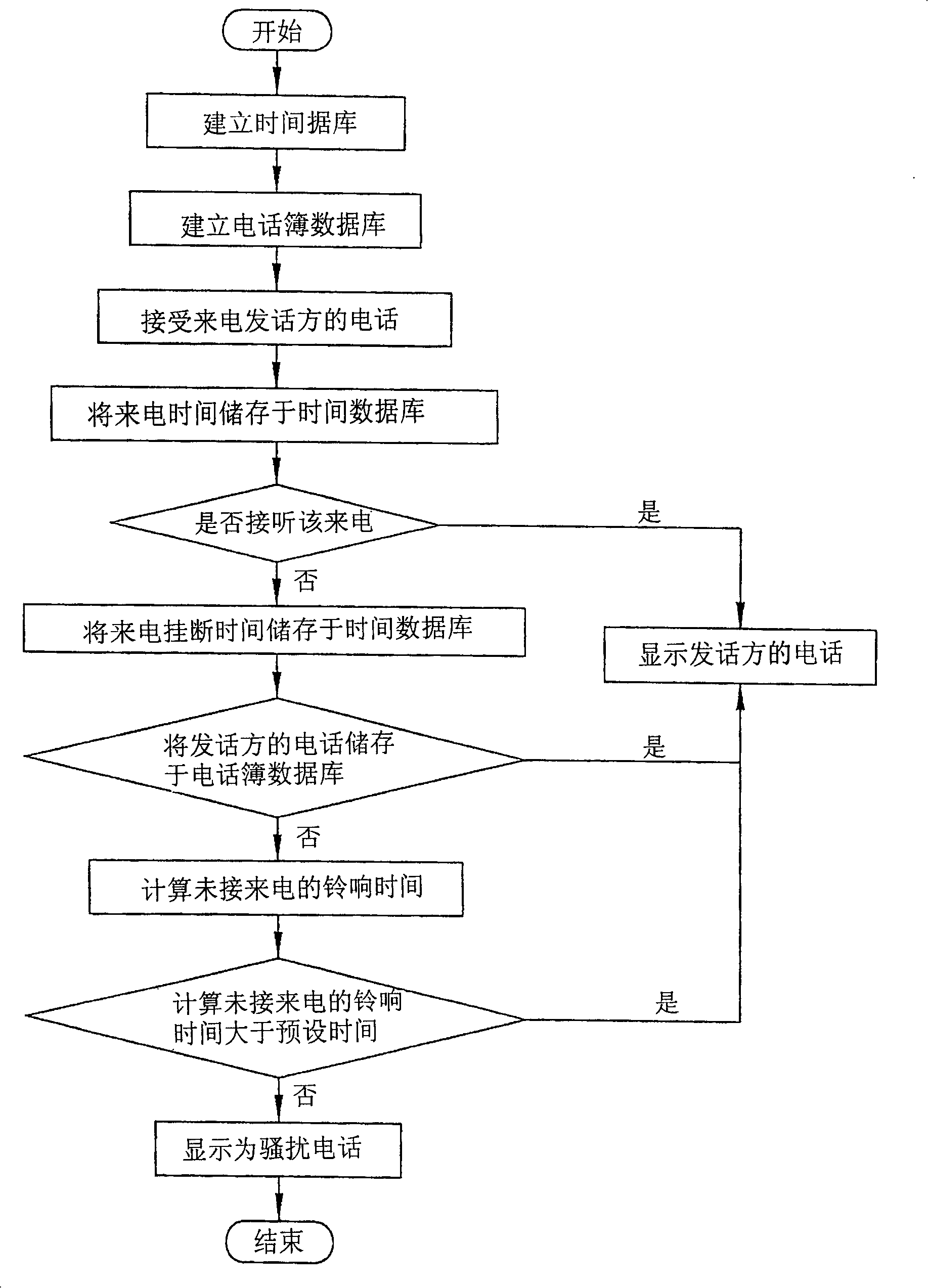
Method and system for judgment of annoy telephone
InactiveCN101202791AAvoid wastingSpecial service for subscribersCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationTemporal databaseData bank
The invention relates to a disturbing call judging system and method for a user to automatically judge whether a missed call is a disturbing call or not and offering a corresponding indication so as to avoid the user from time and money waste caused by calling back according to the caller ID. The disturbing call judging system includes a time database used for storing a calling time, a calling hanging up time and a preset judging time; a telephone list database used for storing frequently used names and telephone numbers; a timing module used for calculating and displaying the current time; an input module used for the user to input the telephone list data and the preset judging time; a receiving module used for receiving the telephone numbers of each calling party; a judging module used for judging whether the call is a disturbing call or not according to the ringing length of the call; and a display module used for displaying the calling telephone numbers and the judging result of the judging module to lead the user to be prevented from mistakenly taking a disturbing call or a fraud call as an important call and calling back.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
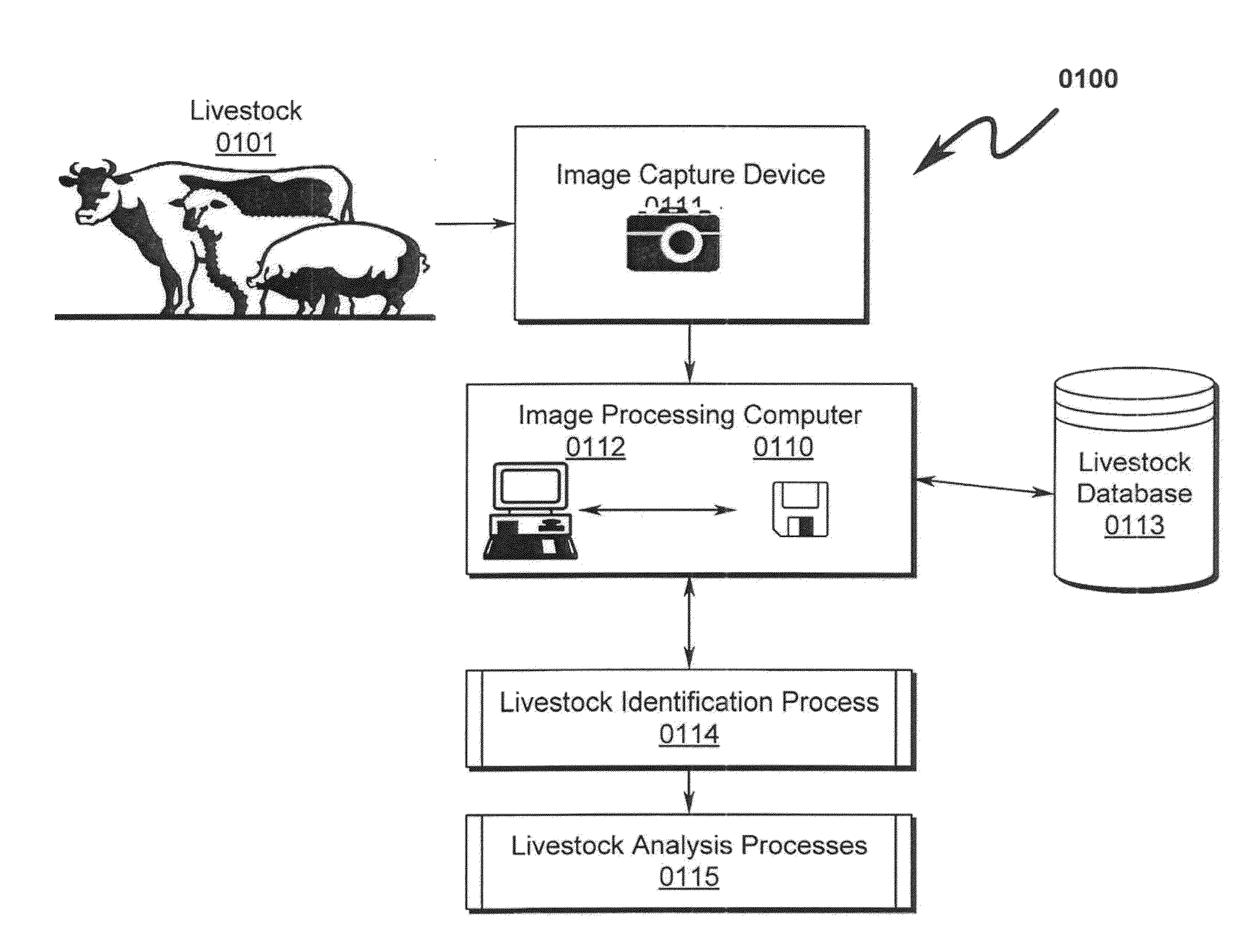
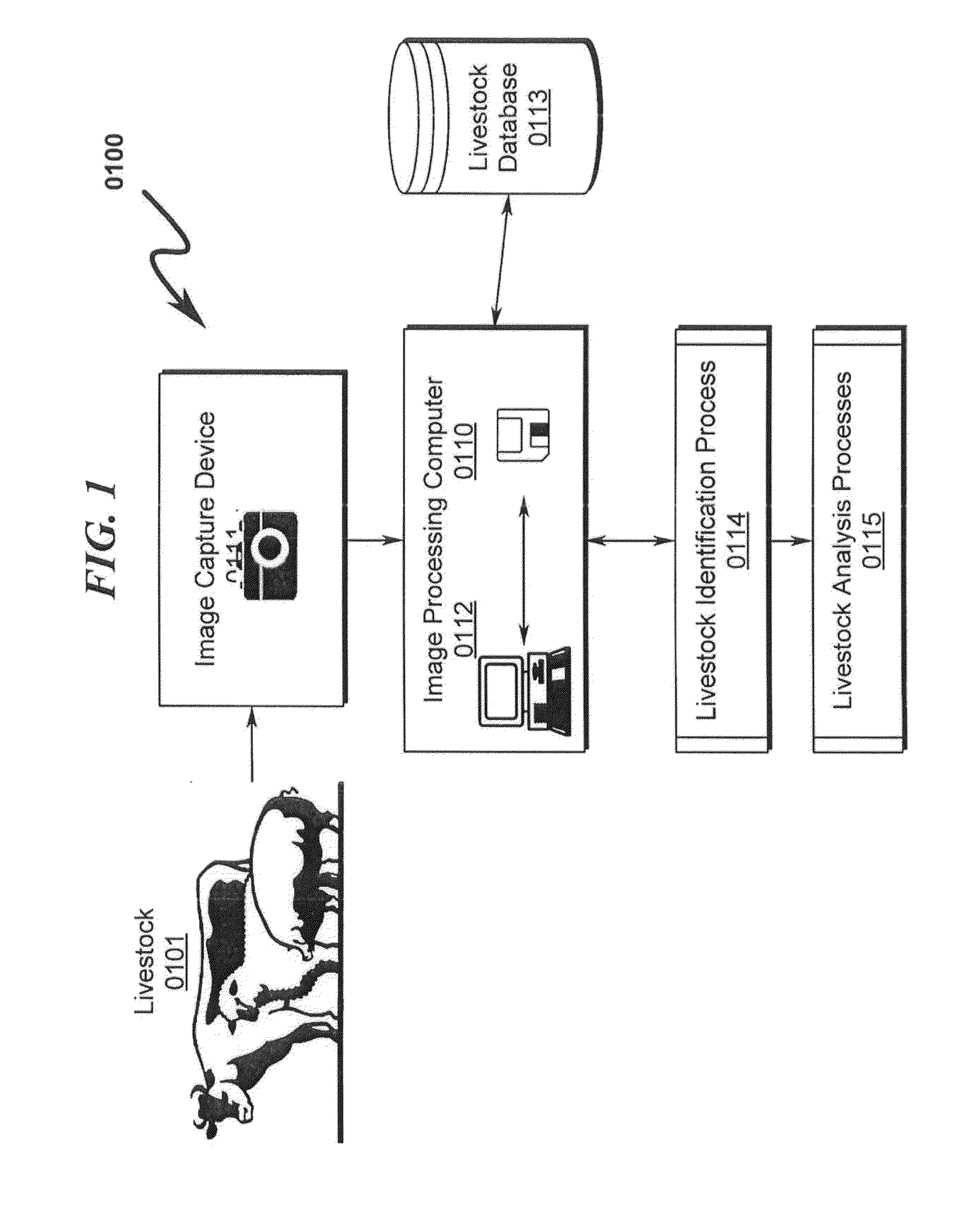
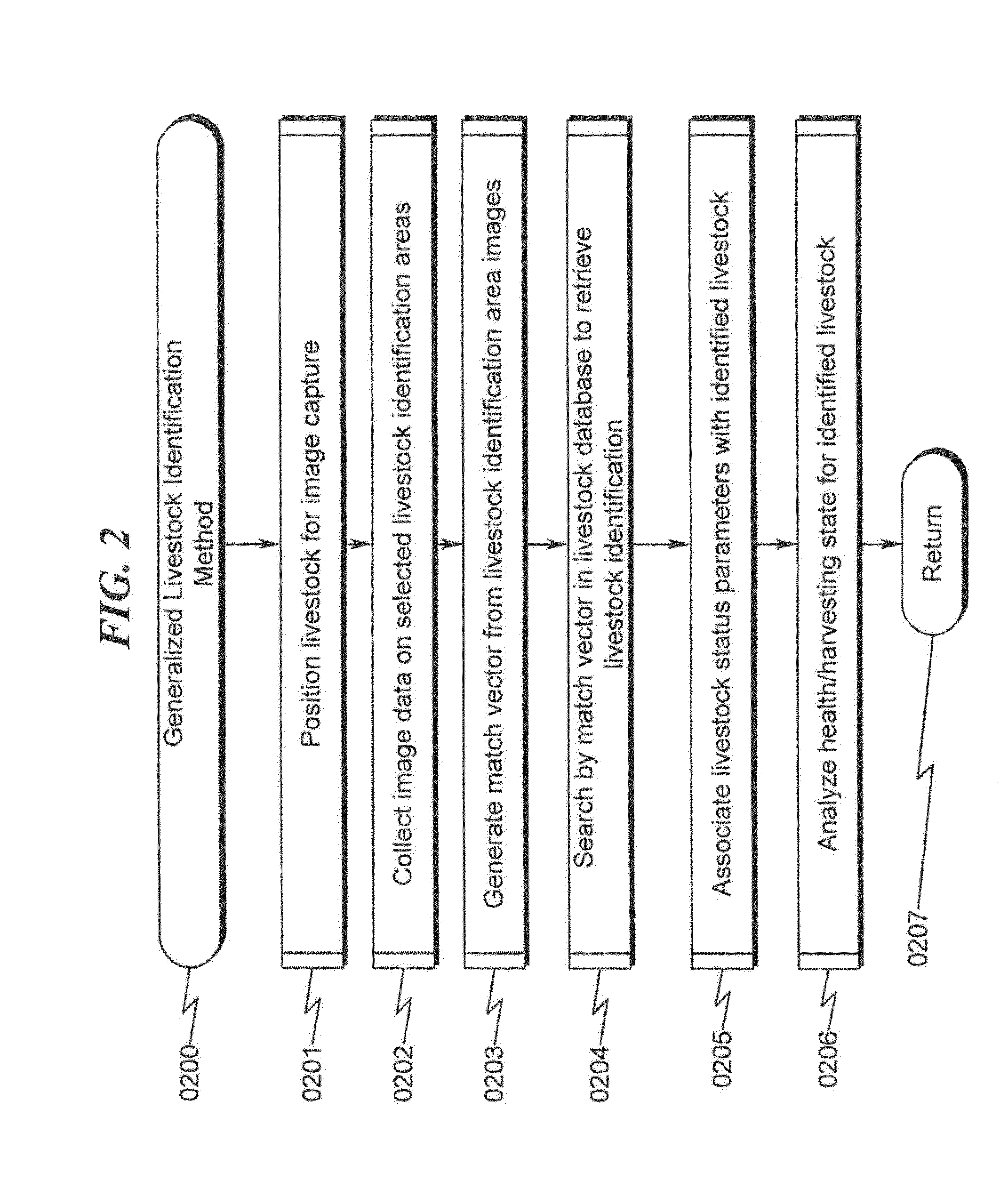
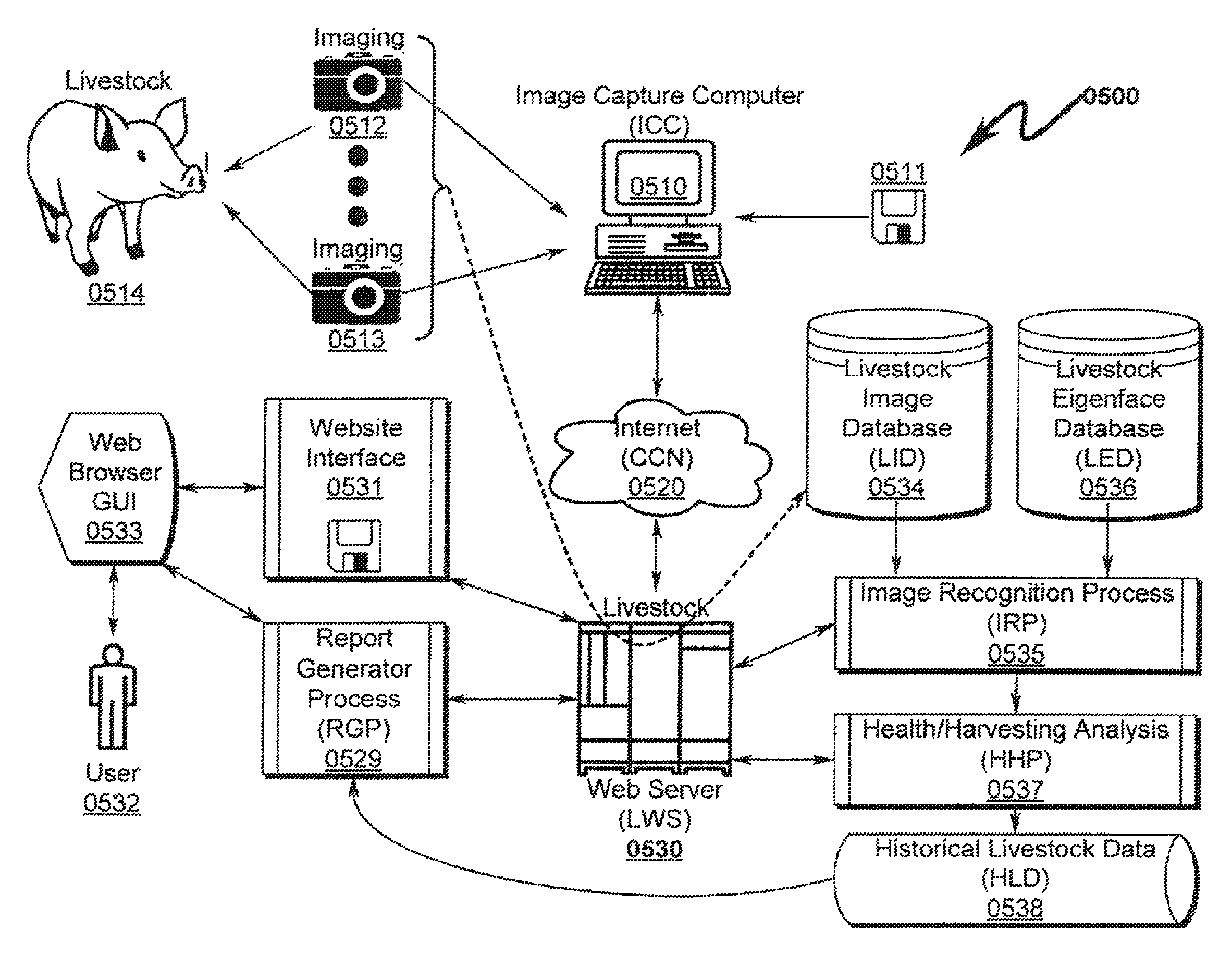
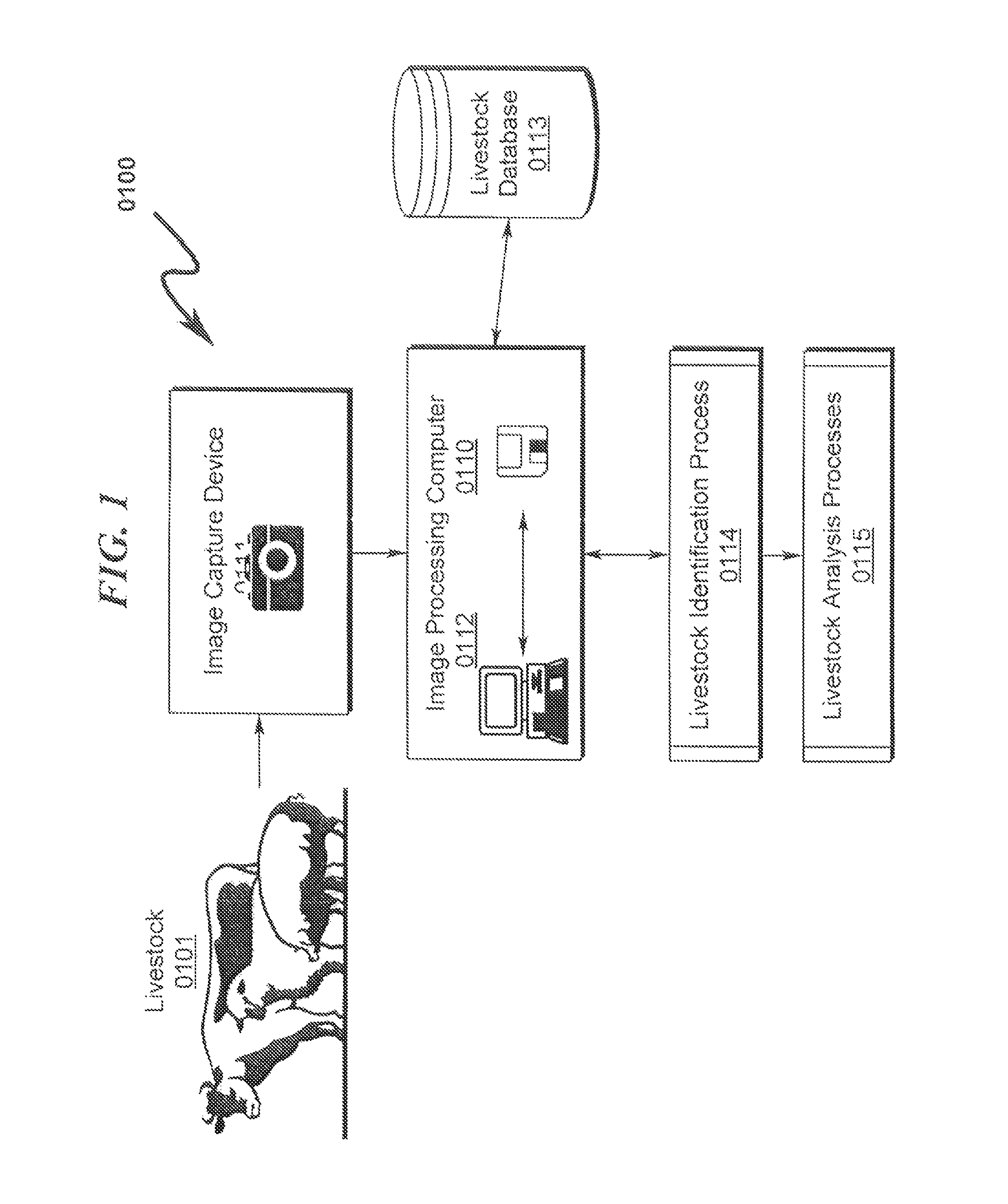
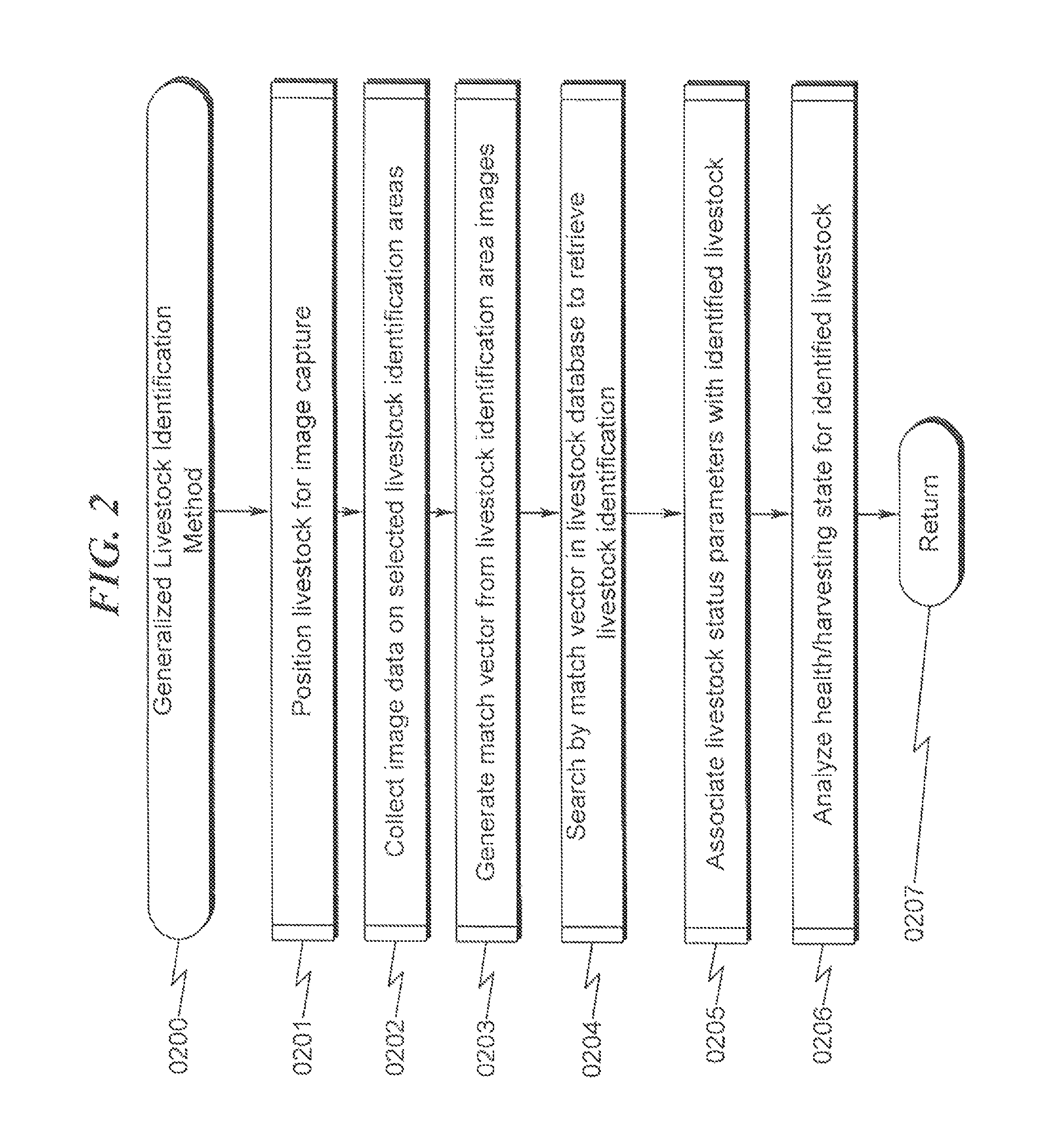
Livestock Identification and Monitoring
ActiveUS20150289478A1Accurate identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionOther apparatusTemporal databaseFluid intake
A livestock identification system / method configured to identify individual animals from a pool of livestock is disclosed. The system / method utilizes images of individual animals and determines the identity of a specific animal based on markers extracted from the image of the animal. These markers may then be used to characterize the state of the animal as to weight, health, and other parameters. The system is configured to log these parameters in a temporal database that may be used to determine historical activity of the animal, including but not limited to activity relating to food and / or fluid intake. This historical record in conjunction with analysis of the animal state parameters is used to determine the animal health status and may also be used to determine whether the animal is ready for harvesting.
Owner:ANIMAL BIOTECH
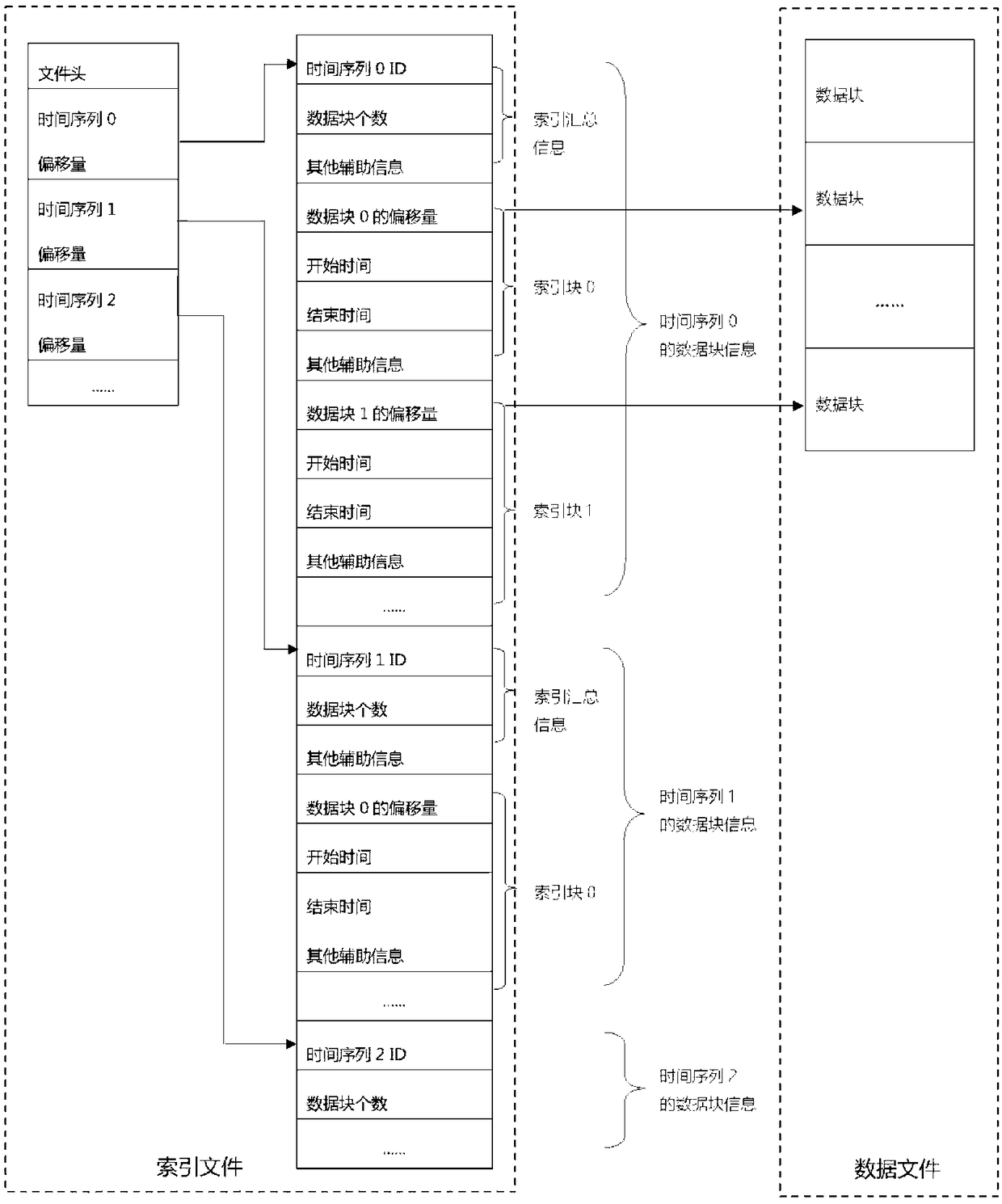
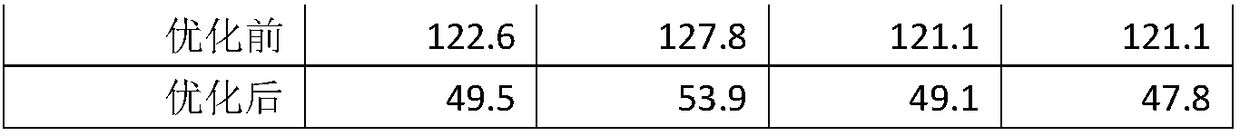
A method for aggregation optimization of time series data
PendingCN109164980AReduce the number of IOsImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersTemporal databaseTime series
A method for aggregation optimization of temporal data includes dividing a temporal database file into a data block file and a block index file; scanning the block index file according to the calculated start and end time period, extracting the data blocks that meet the time period condition and other filtering conditions, and sorting according to the offset of each data block in the data block file; scanning the data files inexpensively by sorted data blocks, after the calculation of each data block, gathering the calculation results. The method can be completed by opening a data file for scanning whether it is for reading a single time series data or for aggregating multiple time series data, which greatly improves the overall performance.
Owner:TAOS DATA
Simply querying across time
ActiveUS20090248638A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTemporal databaseRelational database
A temporal relational database includes a relational database framework that allows for all the capabilities of a standard relational database with the addition of the concept of time. Transactions, which can be modifications of attribute values or changes to the database schema, can be stored with temporal histories. Through the use of these temporal histories, the temporal database is able to seamlessly respond to queries for times that are in the past, present, or future. Furthermore, transactions can be entered into the temporal relational database that are not effective until some point in the future, thus allowing for seamless migration of the data and schema of a database. Applications that access data in a temporal database may retrieve a time appropriate schema from the temporal database. An exemplary use of a temporal database to manage roles and responsibilities within an organization is described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
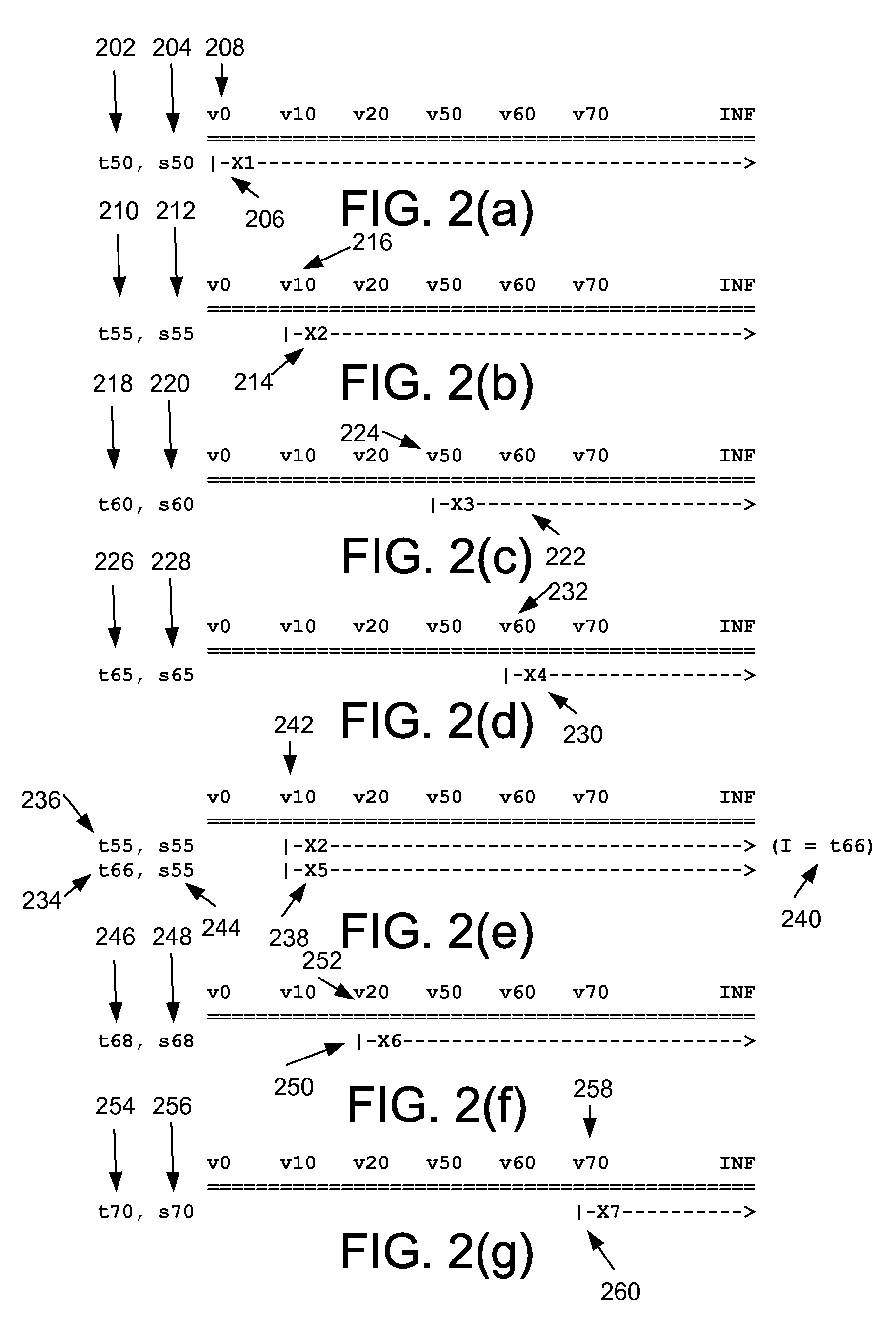
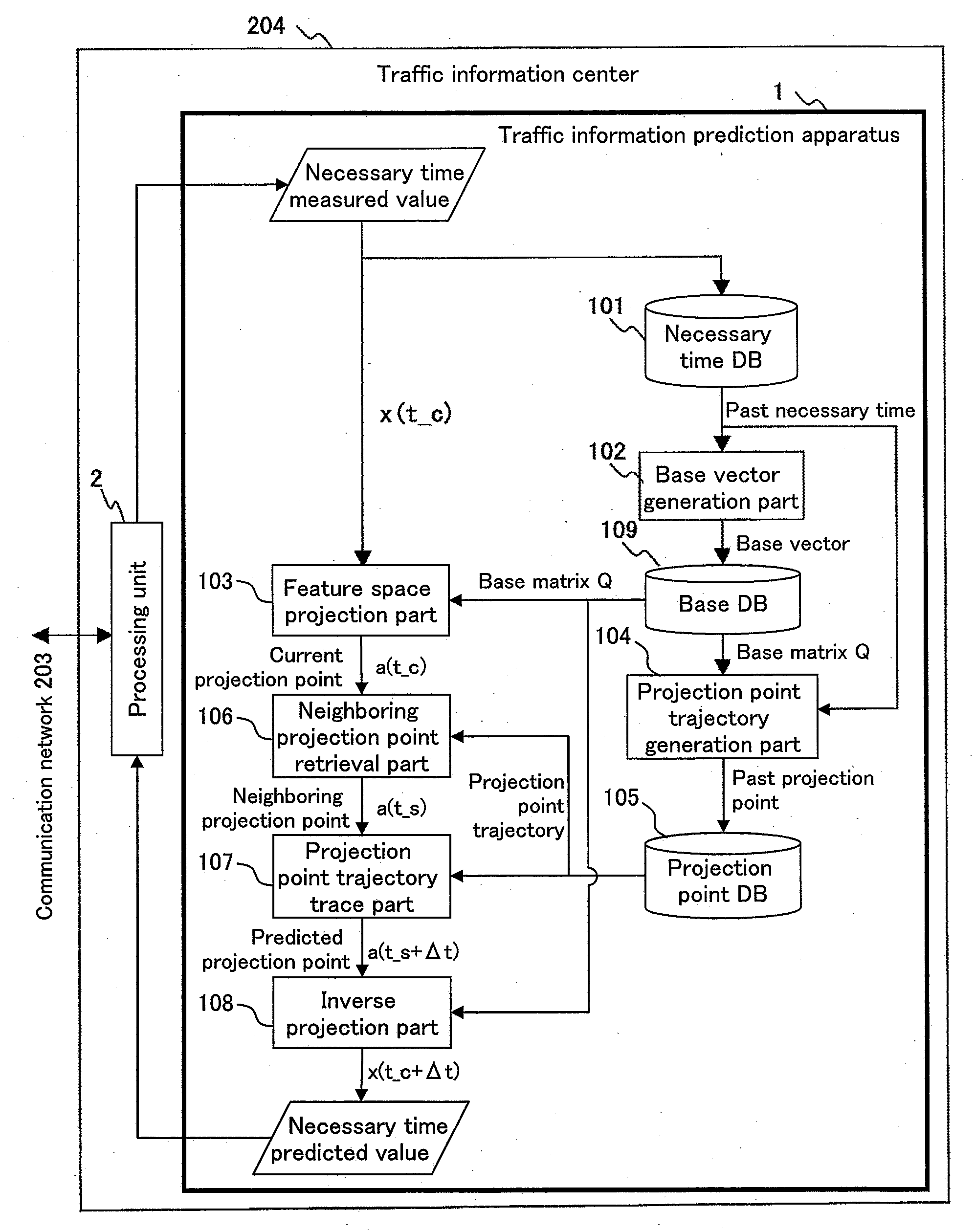
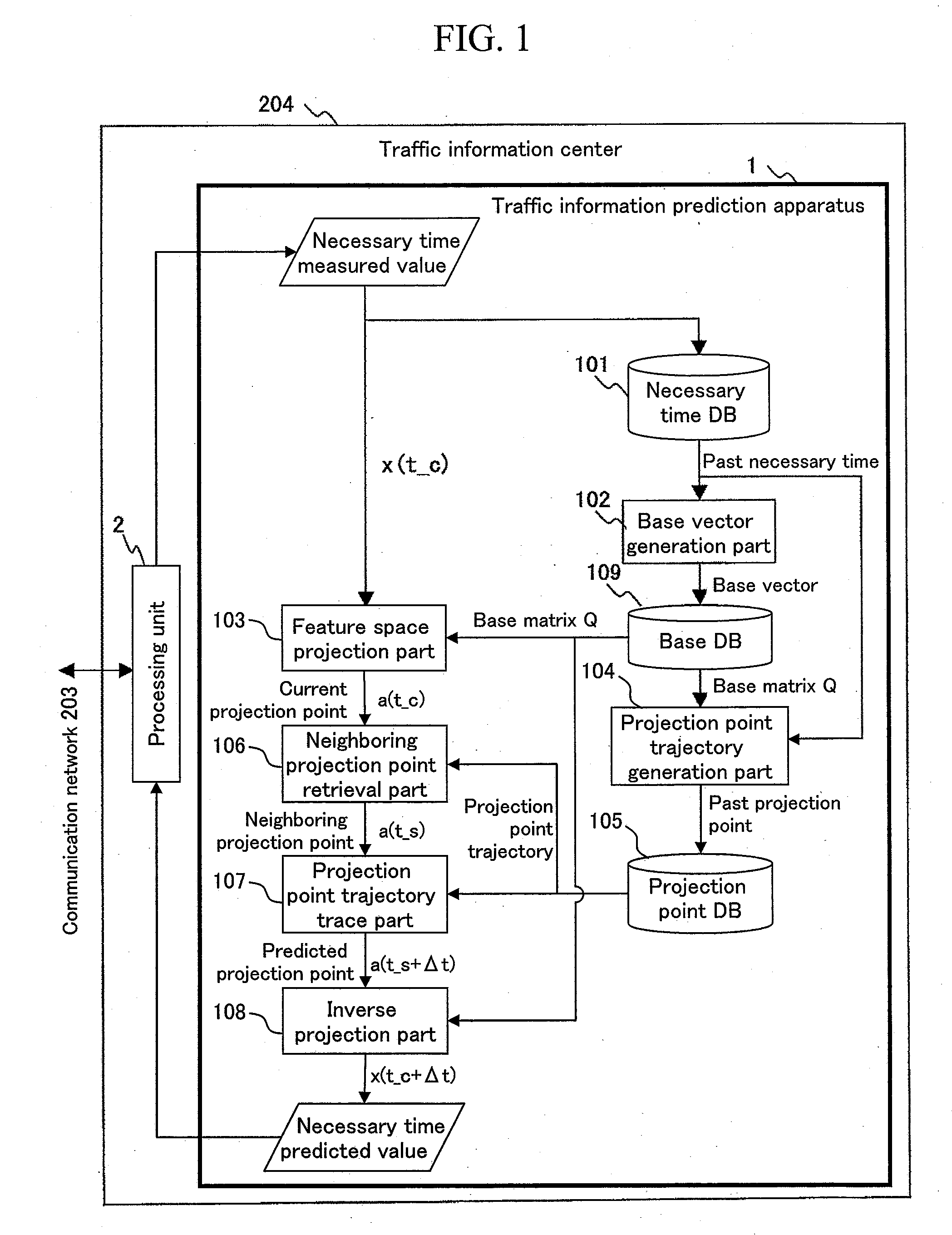
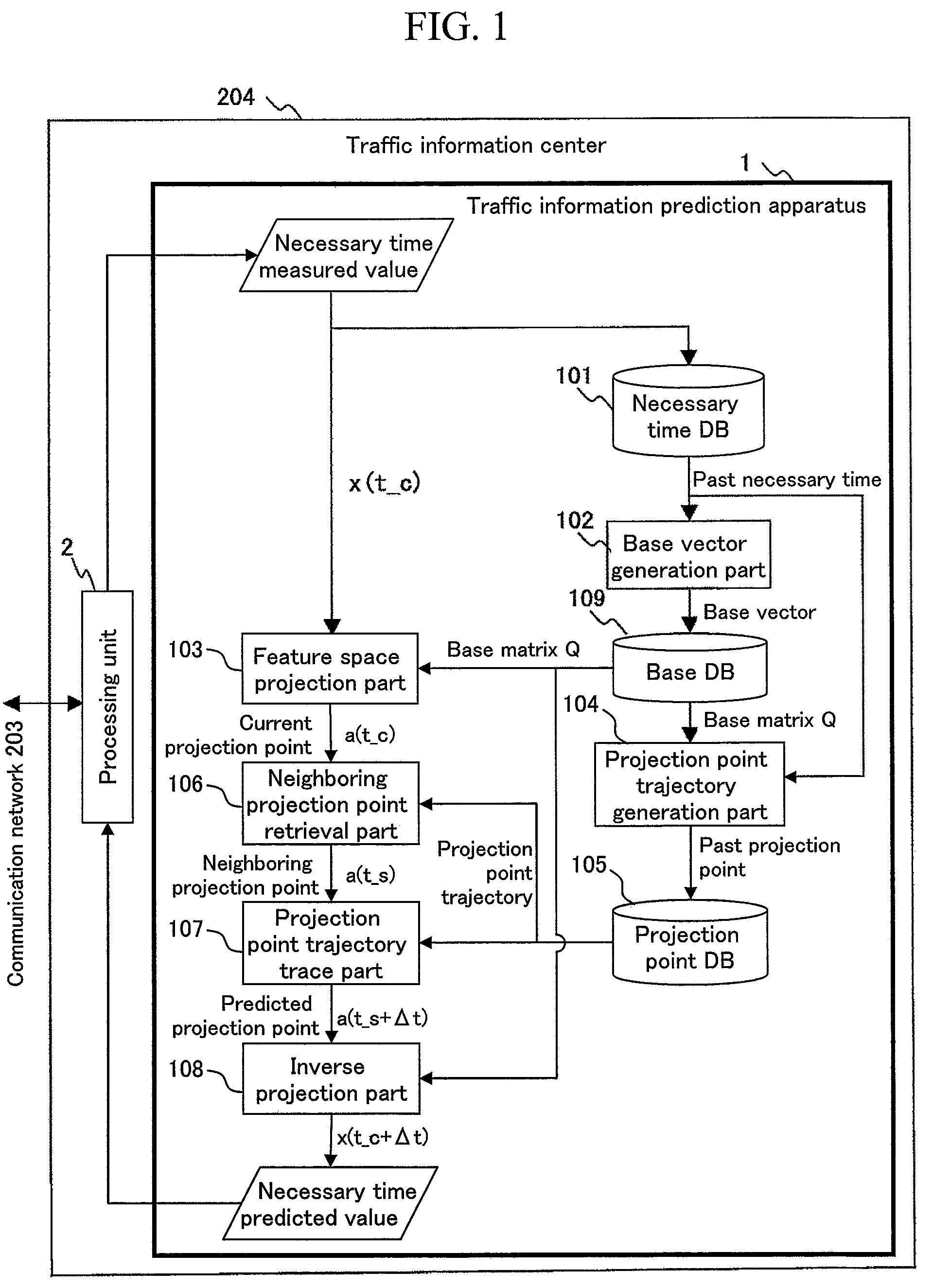
Dynamic Prediction of Traffic Congestion by Tracing Feature-Space Trajectory of Sparse Floating-Car Data
InactiveUS20090070025A1Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficTemporal databasePrincipal component analysis
A traffic situation is predicted based on the correlation in the traffic situation between road sections. A base vector generation unit generates the base vectors constituting a feature space representing the correlation between a plurality of links by making a principal component analysis for the necessary time in the past recorded in a necessary time database. A projection point trajectory generation unit records a projection point trajectory of projecting the necessary time in the past recorded in the necessary time database to the feature space in a projection point database. A feature space projection unit projects the necessary time at present to the feature space, and a neighboring projection point retrieval unit retrieves a past projection point in the neighborhood of the concerned projection point from the projection point database, and a projection point trajectory trace unit traces the trajectory of past projection points starting from the retrieved neighboring projection point for a prediction target time width, and an inverse projection unit inversely projects the end point of the concerned trajectory to calculate the predicted value of the necessary time.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Livestock identification system and method
ActiveUS9084411B1Great degree of confidenceIncrease probabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionOther apparatusTemporal databaseFluid intake
A livestock identification system / method configured to identify individual animals from a pool of livestock is disclosed. The system / method utilizes images of individual animals and determines the identity of a specific animal based on markers extracted from the image of the animal. These markers may then be used to characterize the state of the animal as to weight, health, and other parameters. The system is configured to log these parameters in a temporal database that may be used to determine historical activity of the animal, including but not limited to activity relating to food and / or fluid intake. This historical record in conjunction with analysis of the animal state parameters is used to determine the animal health status and may also be used to determine whether the animal is ready for harvesting.
Owner:ANIMAL BIOTECH
Temporal class loader
ActiveUS20090248717A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTemporal databaseRelational database
A temporal relational database includes a relational database framework that allows for all the capabilities of a standard relational database with the addition of the concept of time. Transactions, which can be modifications of attribute values or changes to the database schema, can be stored with temporal histories. Through the use of these temporal histories, the temporal database is able to seamlessly respond to queries for times that are in the past, present, or future. Furthermore, transactions can be entered into the temporal relational database that are not effective until some point in the future, thus allowing for seamless migration of the data and schema of a database. Applications that access data in a temporal database may retrieve a time appropriate schema from the temporal database. An exemplary use of a temporal database to manage roles and responsibilities within an organization is described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method for searching data target on basis of spatial-temporal database
ActiveCN106446278AThe search method is simple and convenientEasy for production managementDatabase distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsTemporal databaseManagement object
The invention relates to a method for searching a data target on basis of a spatial-temporal database. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: according to the temporal state and the spatial state of a target to be managed, performing modularization on the managed target; according to a management model of the target to be managed, setting a specific attribute which is described by using a natural language, of the target to be managed; on the basis of the type of the management model of the managed target, and a temporal attribute and / or spatial attribute which is defined by modularization and is described by using the natural language, performing retrieval, so as to confirm the operation state of the managed target. According to the spatial-temporal database, data information of production monitoring management is described by using three sections of times of history, real time and planning, a user does not need to master a computer language, but only with a spatial-temporal meta language, spatial-temporal data of the managed target can be retrieved and understood, and the spatial-temporal operation state of the managed target can be understood, namely both computer content can be saved and management is facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING WELLINTECH CO LTD
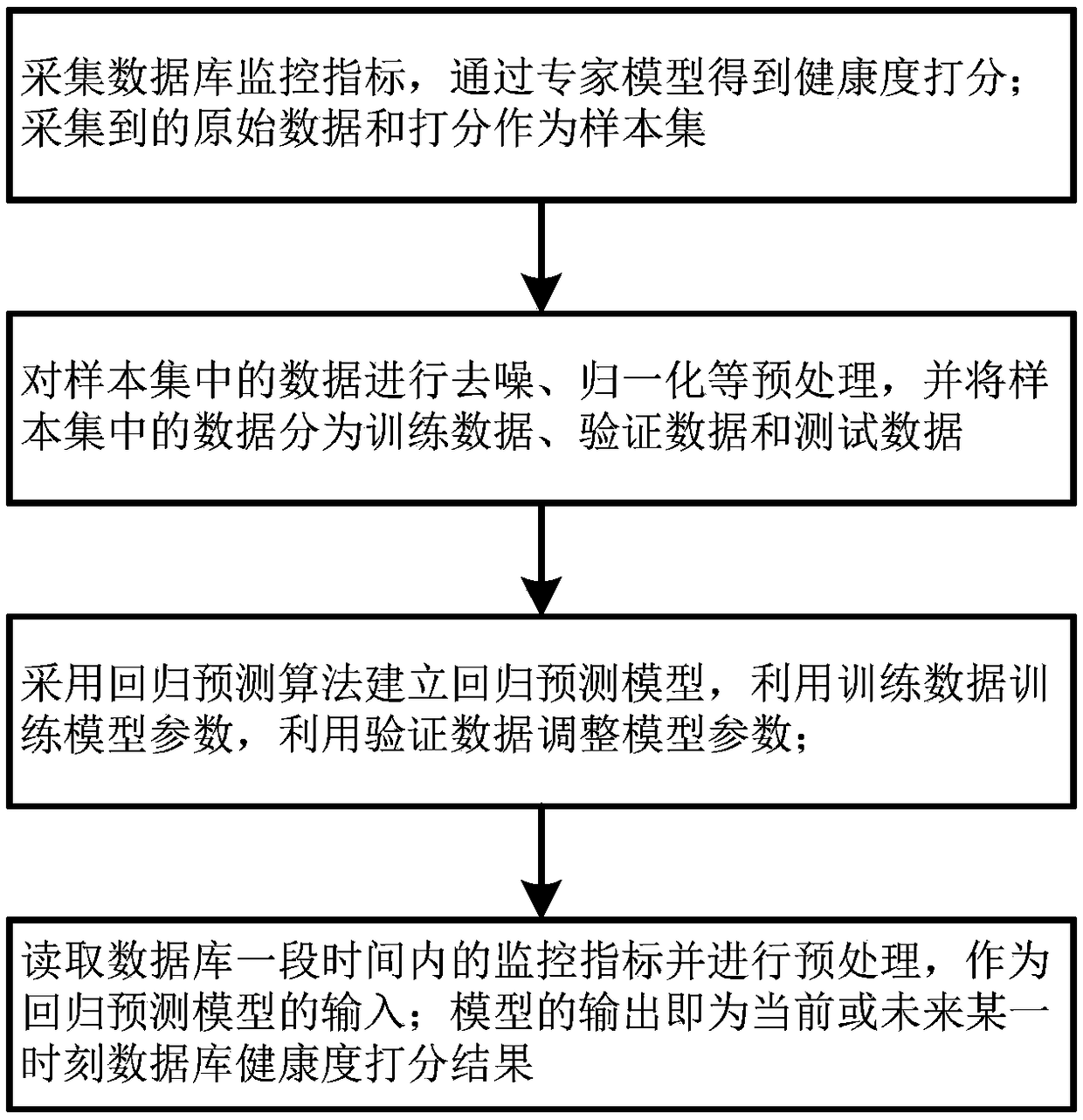
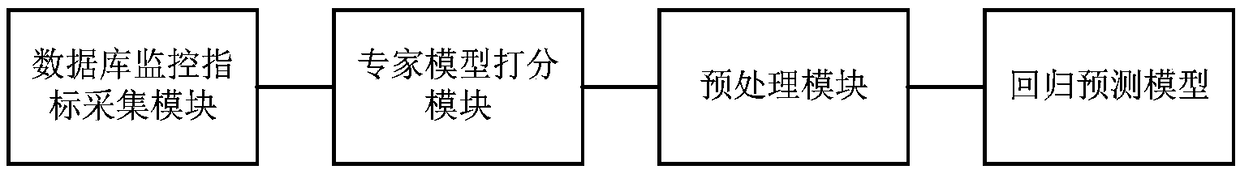
A database health scoring method and scoring system based on machine learning
ActiveCN109271374AHealth Scoring and PredictionComputing modelsSoftware testing/debuggingTemporal databasePrediction algorithms
The invention discloses a database health scoring method and scoring system based on machine learning, wherein, the scoring method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting database monitoring indexes and obtaining health scoring through an expert model; using collected raw data and scores as sample sets; 2, preprocessing the data in the sample set, such as denoising and normalization, and dividing the data into training data, verification data and test data; 3, establishing a regression prediction model by adopting a regression prediction algorithm, train model parameters by using trainingdata, adjusting model parameter by using verification data, and testing that effect of the model by using test data; 4. reading the monitoring indexes of the database for a period of time and preprocess them. As the input of the regression prediction model, the output of the model is the health score result of the database for the current or future period of time. This method can analyze a largenumber of database monitoring indicators, and get the current or future database health scoring results through the establishment of the regression prediction model.
Owner:INFORMATION & COMM BRANCH OF STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER +2
Dynamic prediction of traffic congestion by tracing feature-space trajectory of sparse floating-car data
InactiveUS7542844B2Analogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficTemporal databasePrincipal component analysis
A traffic situation is predicted based on the correlation in the traffic situation between road sections. A base vector generation unit generates the base vectors constituting a feature space representing the correlation between a plurality of links by making a principal component analysis for the necessary time in the past recorded in a necessary time database. A projection point trajectory generation unit records a projection point trajectory of projecting the necessary time in the past recorded in the necessary time database to the feature space in a projection point database. A feature space projection unit projects the necessary time at present to the feature space, and a neighboring projection point retrieval unit retrieves a past projection point in the neighborhood of the concerned projection point from the projection point database, and a projection point trajectory trace unit traces the trajectory of past projection points starting from the retrieved neighboring projection point for a prediction target time width, and an inverse projection unit inversely projects the end point of the concerned trajectory to calculate the predicted value of the necessary time.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Road segment correlation considering time-varying random network dynamic path search method
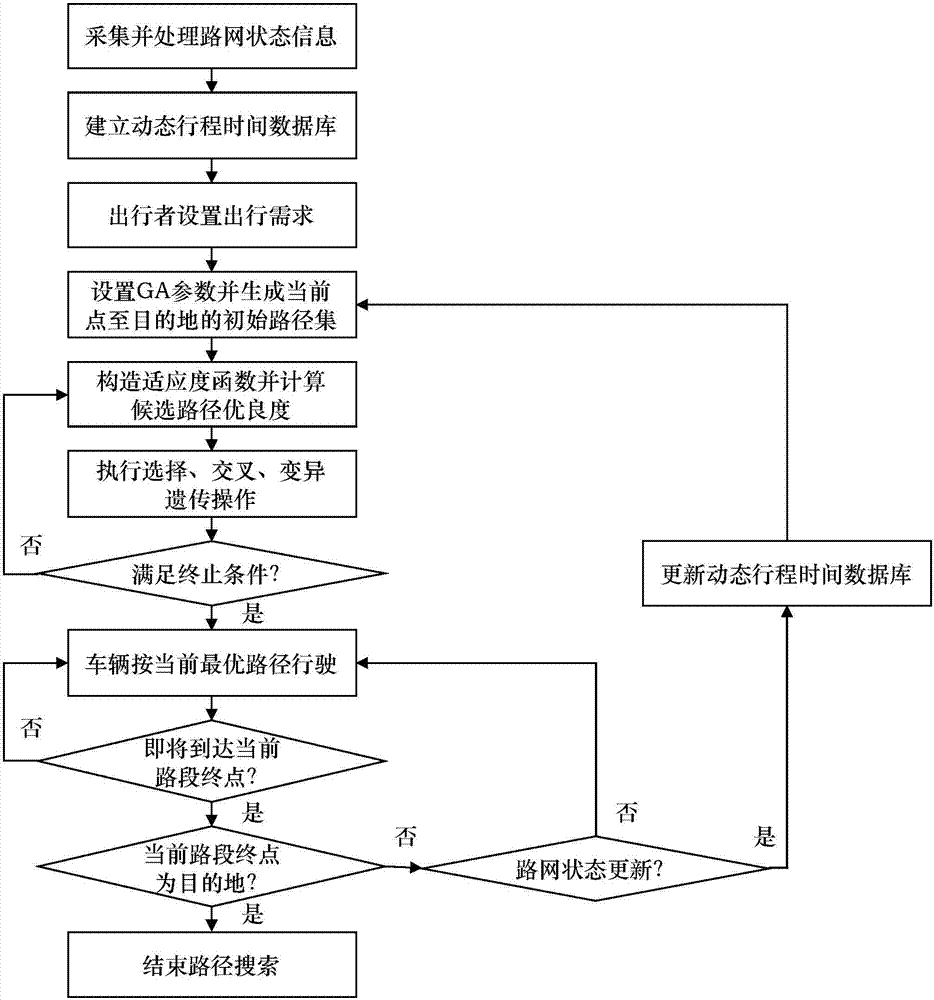
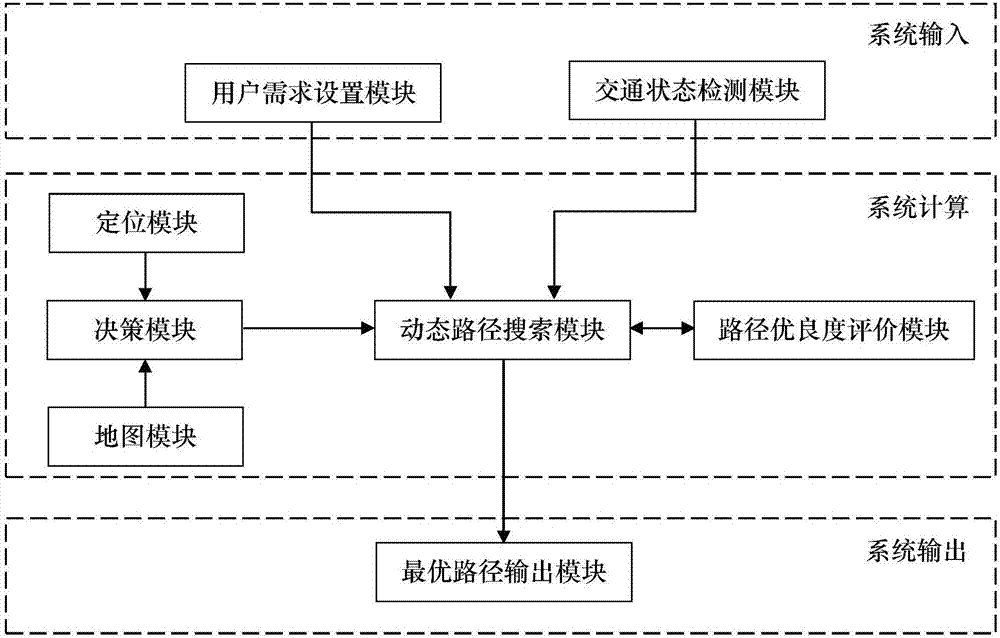
ActiveCN107145991AGuaranteed accuracySmall amount of calculationForecastingGenetic algorithmsTemporal databaseRoad networks
The invention discloses a road segment correlation considering time-varying random network dynamic path search method, and belongs to the field of intelligent transportation. The method comprises the steps of 1, acquiring road network state information, and building a dynamic travel time database based on preprocessed data; 2, setting a current travel demand by a traveler; 3, setting parameter of a genetic algorithm, generating an initial path set, and building a fitness function to calculate the fitness of each candidate path; 4, iteratively searching an optimal path based on the genetic algorithm, wherein a vehicle drives according to the optimal path acquired by iteration; and 5, realizing real-time update of the optimal path through judging the state of the vehicle and the state of the road network so as to ensure the vehicle to continuously drive within the optimal path until arriving at the destination. The algorithm provided by the invention not only sufficiently considers a series of complex factors such as the road network time varying, travel time random distribution and road segment correlation, but also well ensures the solving speed and the solving accuracy of the genetic algorithm at the same time, thereby being more conducive to realizing the dynamic path search method.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Future modeling
ActiveUS20090248719A1Overcome deficienciesDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsTemporal databaseRelational database
A temporal relational database includes a relational database framework that allows for all the capabilities of a standard relational database with the addition of the concept of time. Transactions, which can be modifications of attribute values or changes to the database schema, can be stored with temporal histories. Through the use of these temporal histories, the temporal database is able to seamlessly respond to queries for times that are in the past, present, or future. Furthermore, transactions can be entered into the temporal relational database that are not effective until some point in the future, thus allowing for seamless migration of the data and schema of a database. Applications that access data in a temporal database may retrieve a time appropriate schema from the temporal database. An exemplary use of a temporal database to manage roles and responsibilities within an organization is described.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com