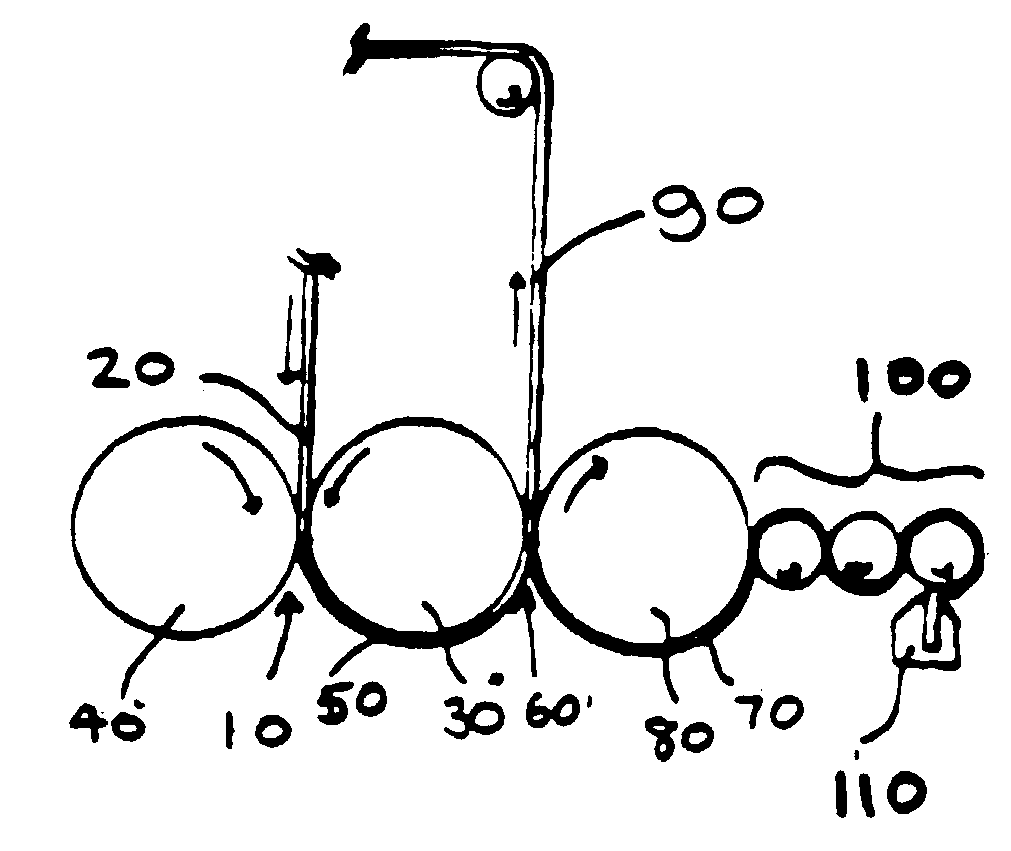
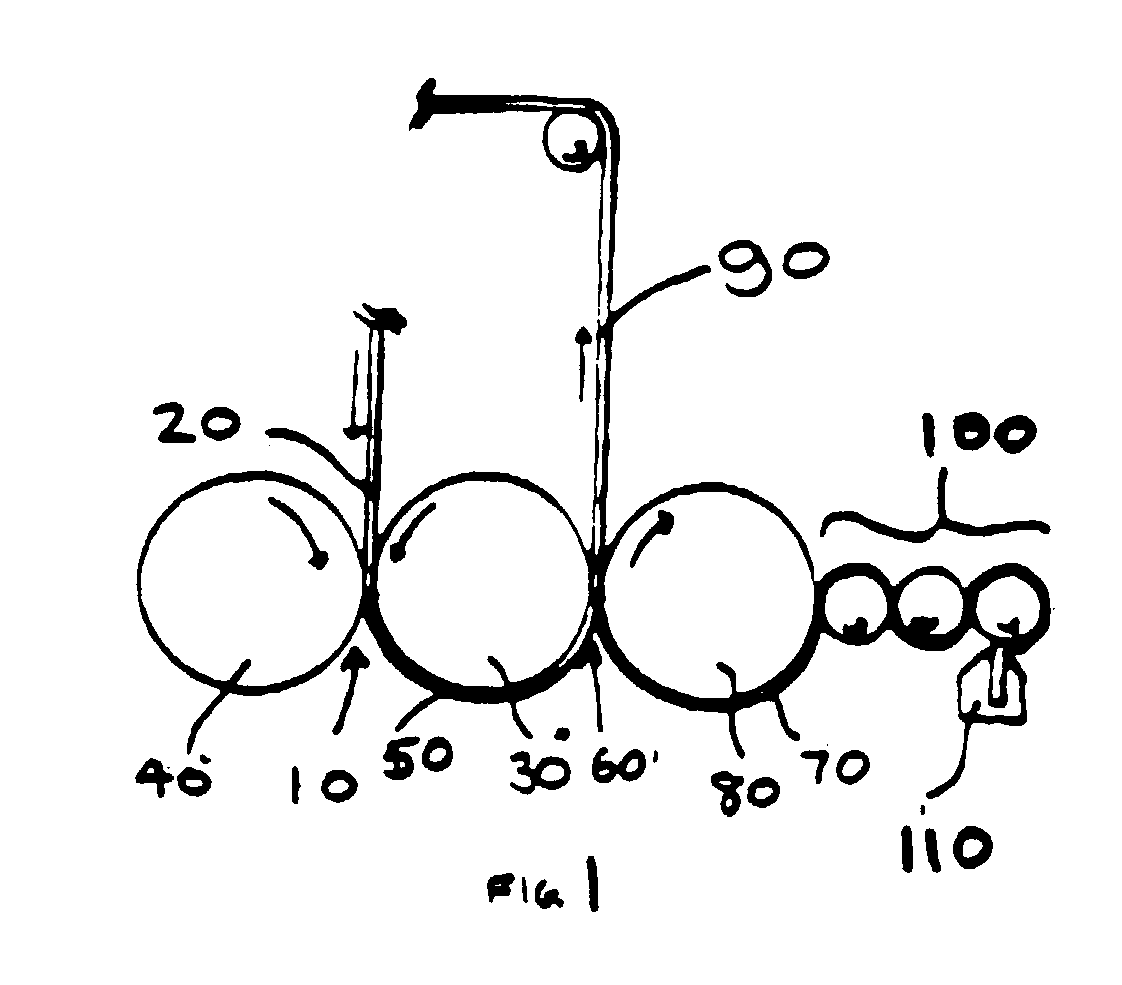
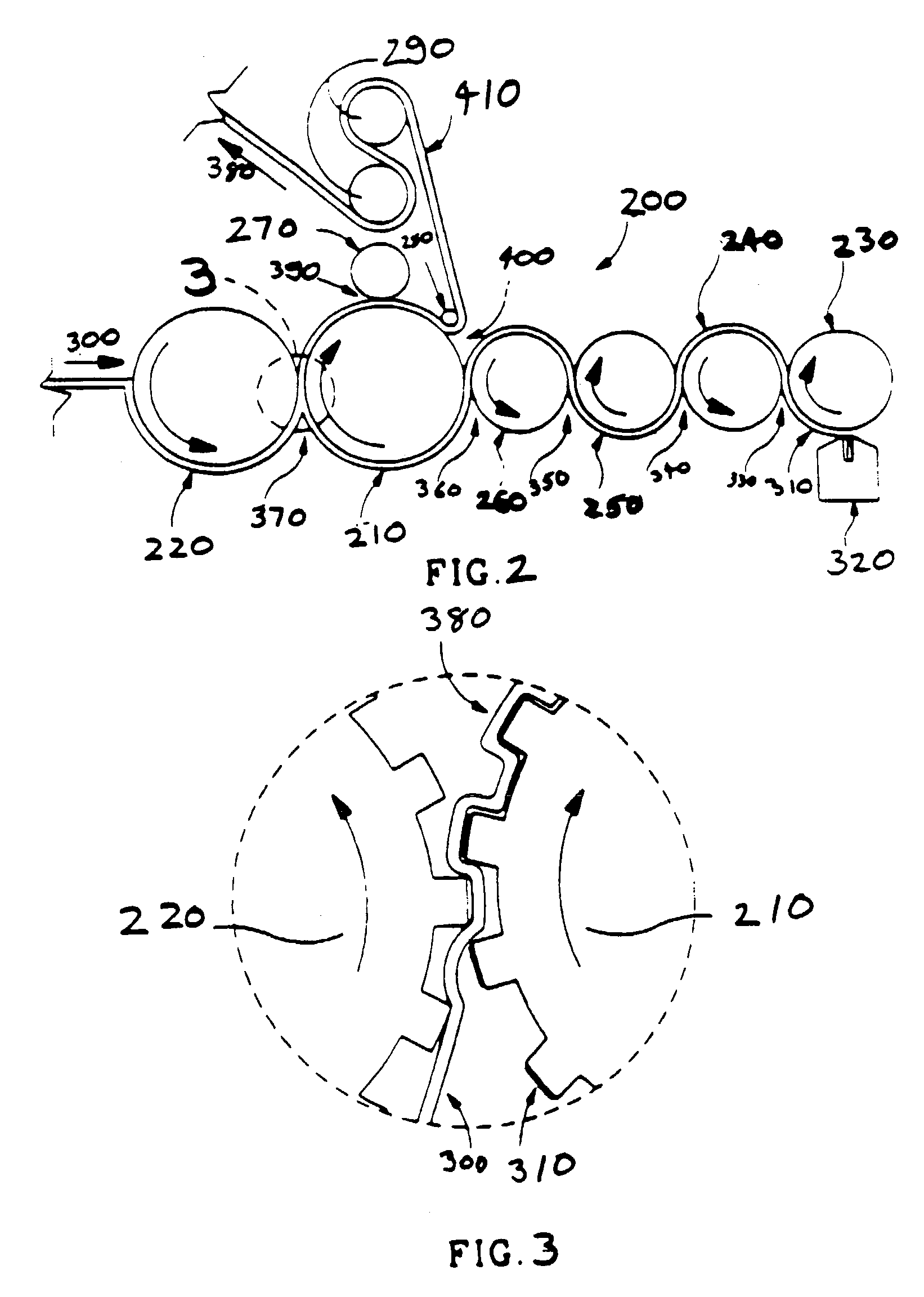
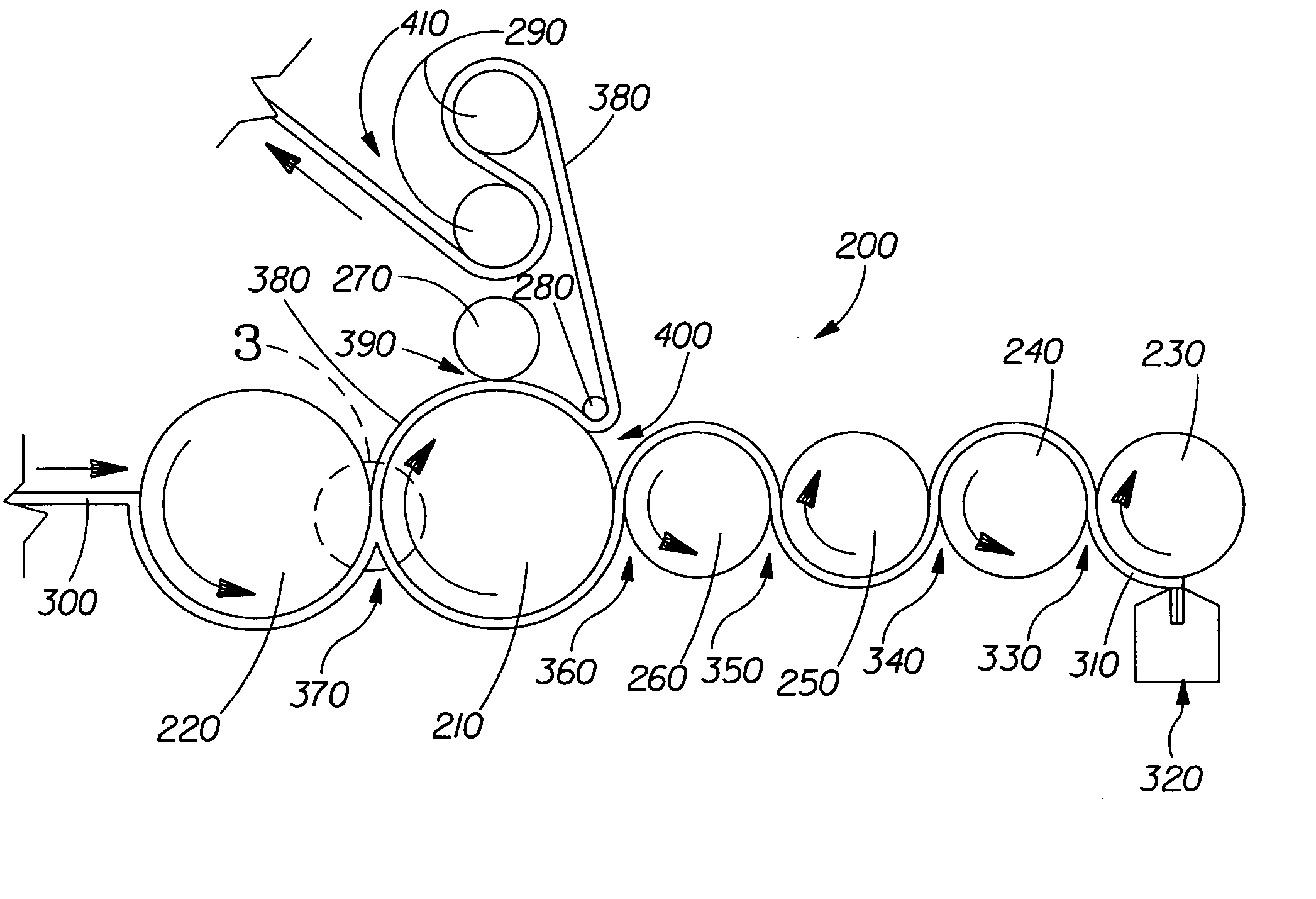
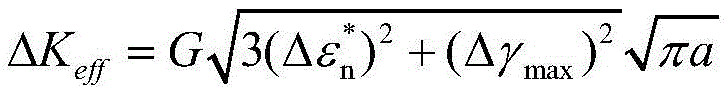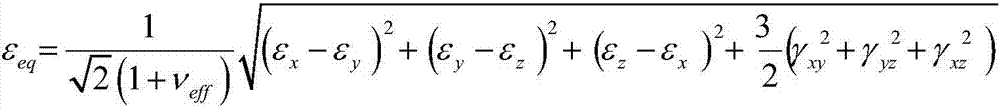Patents
Literature
181 results about "Critical surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
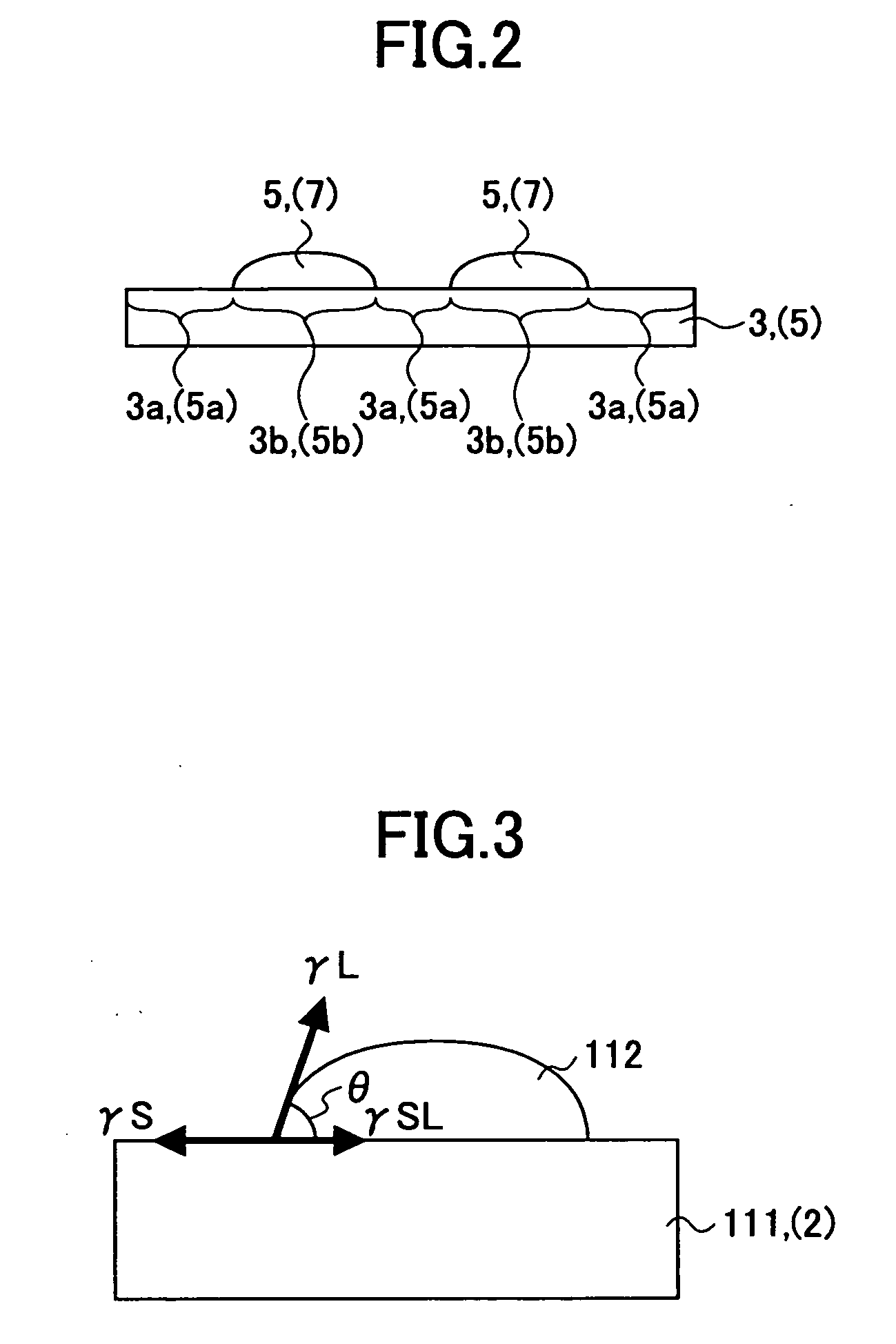
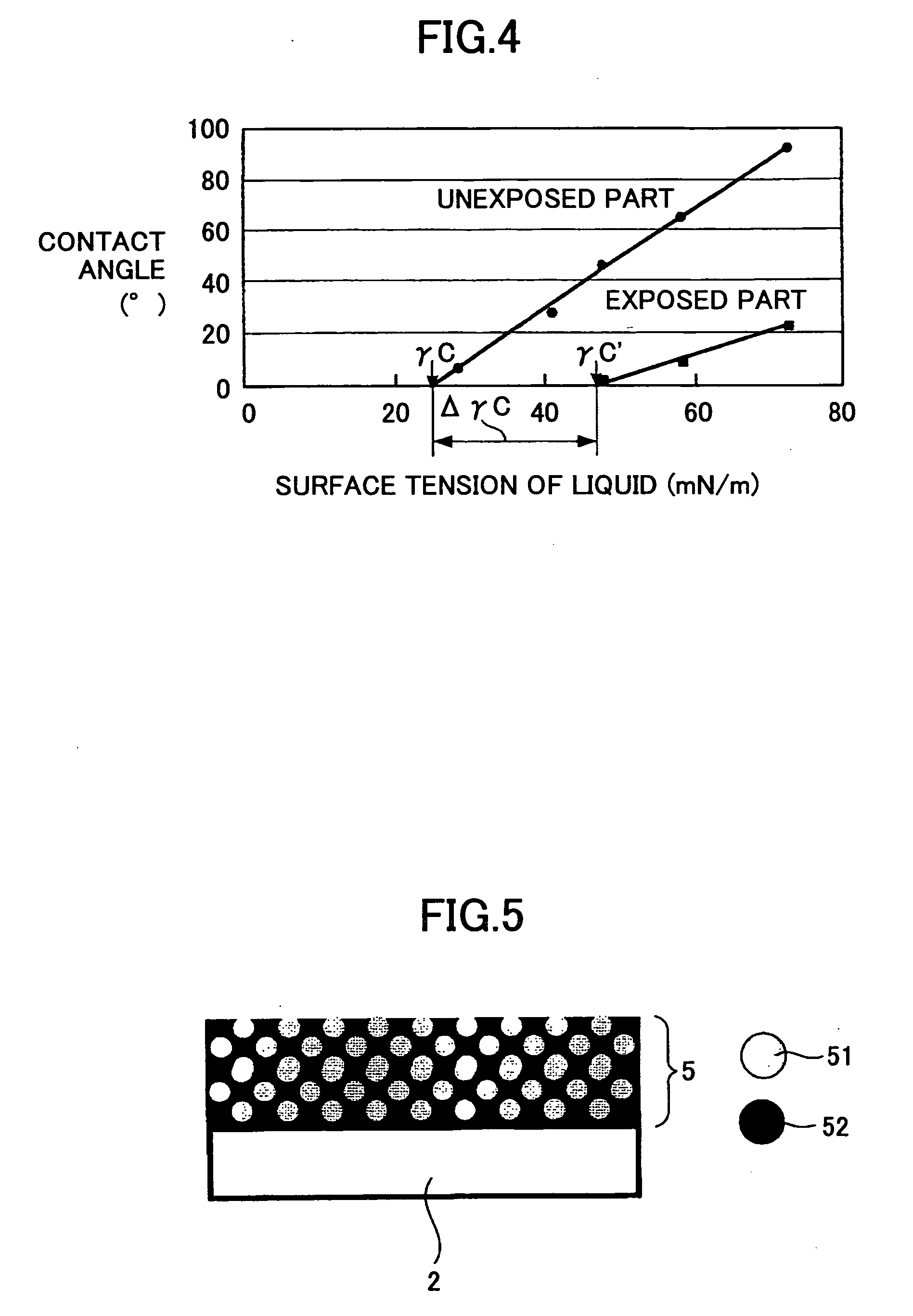
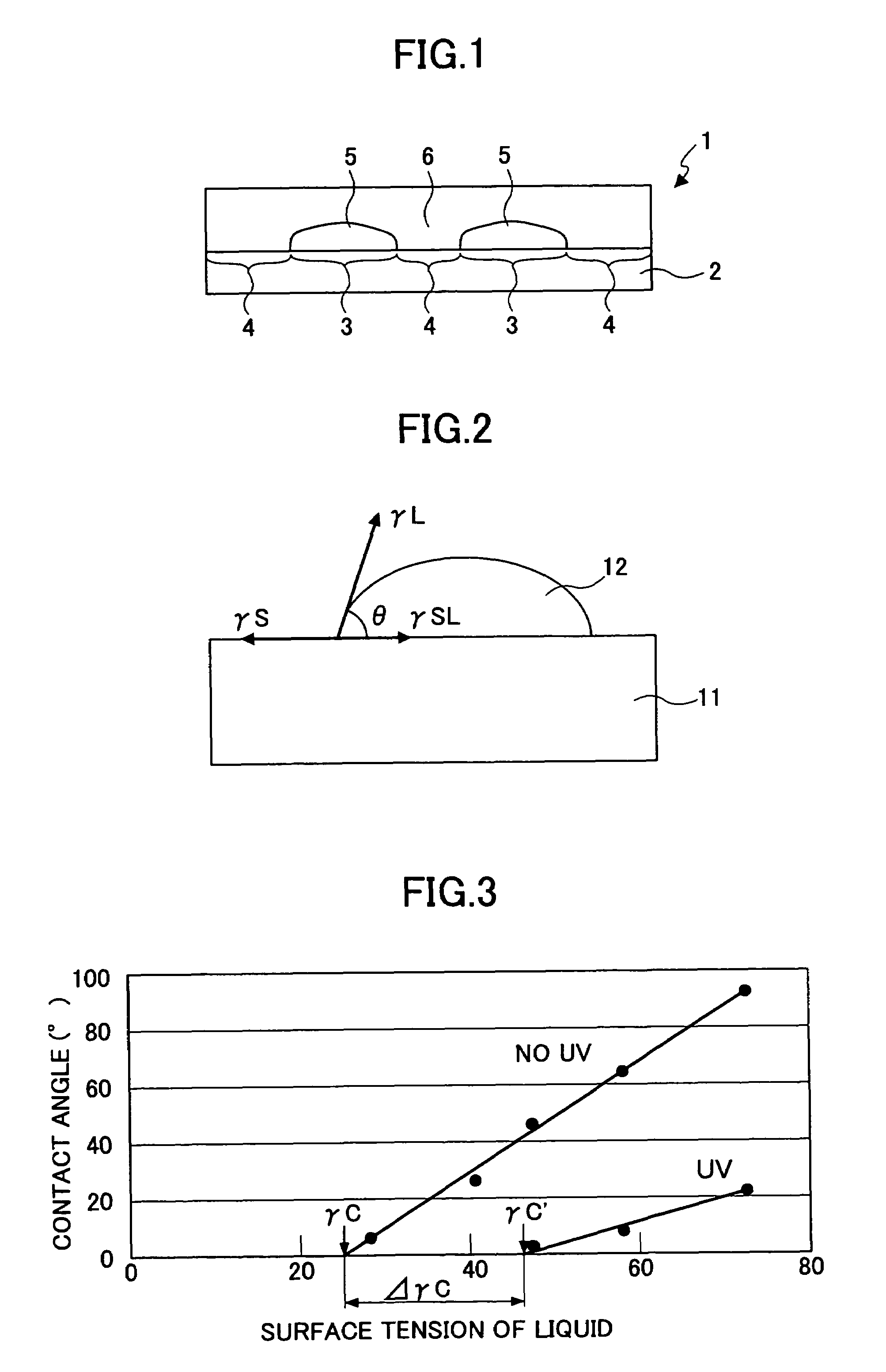
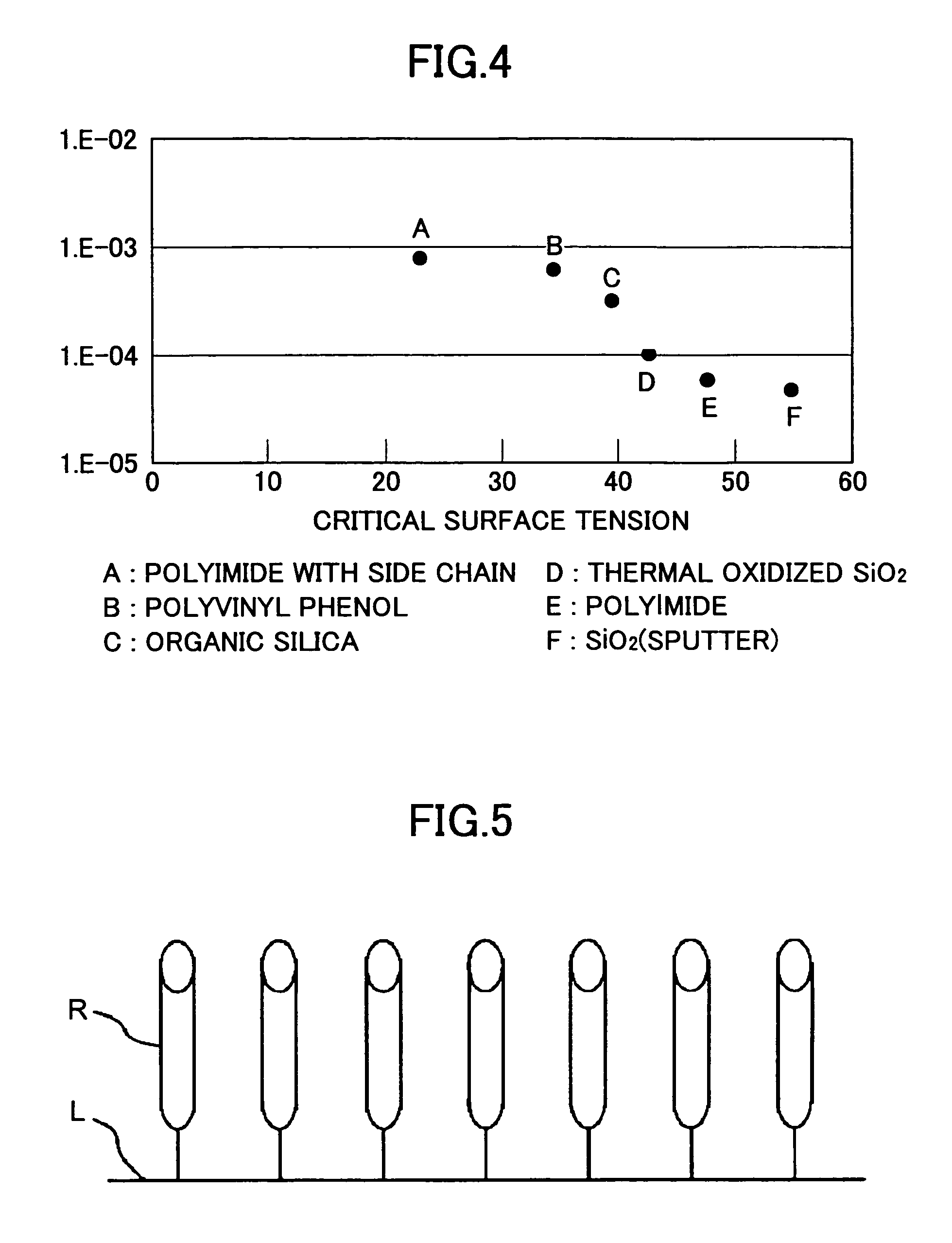
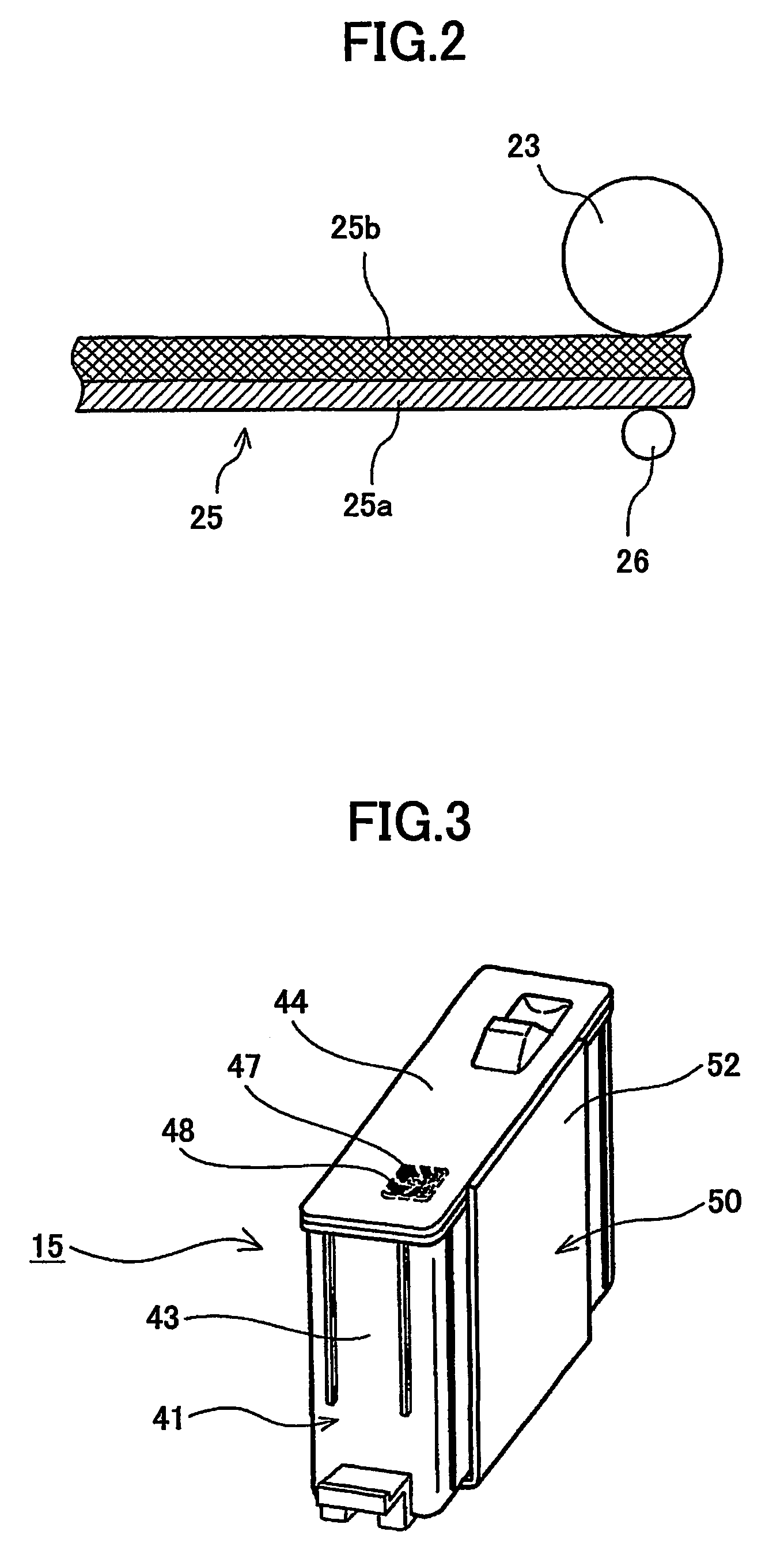
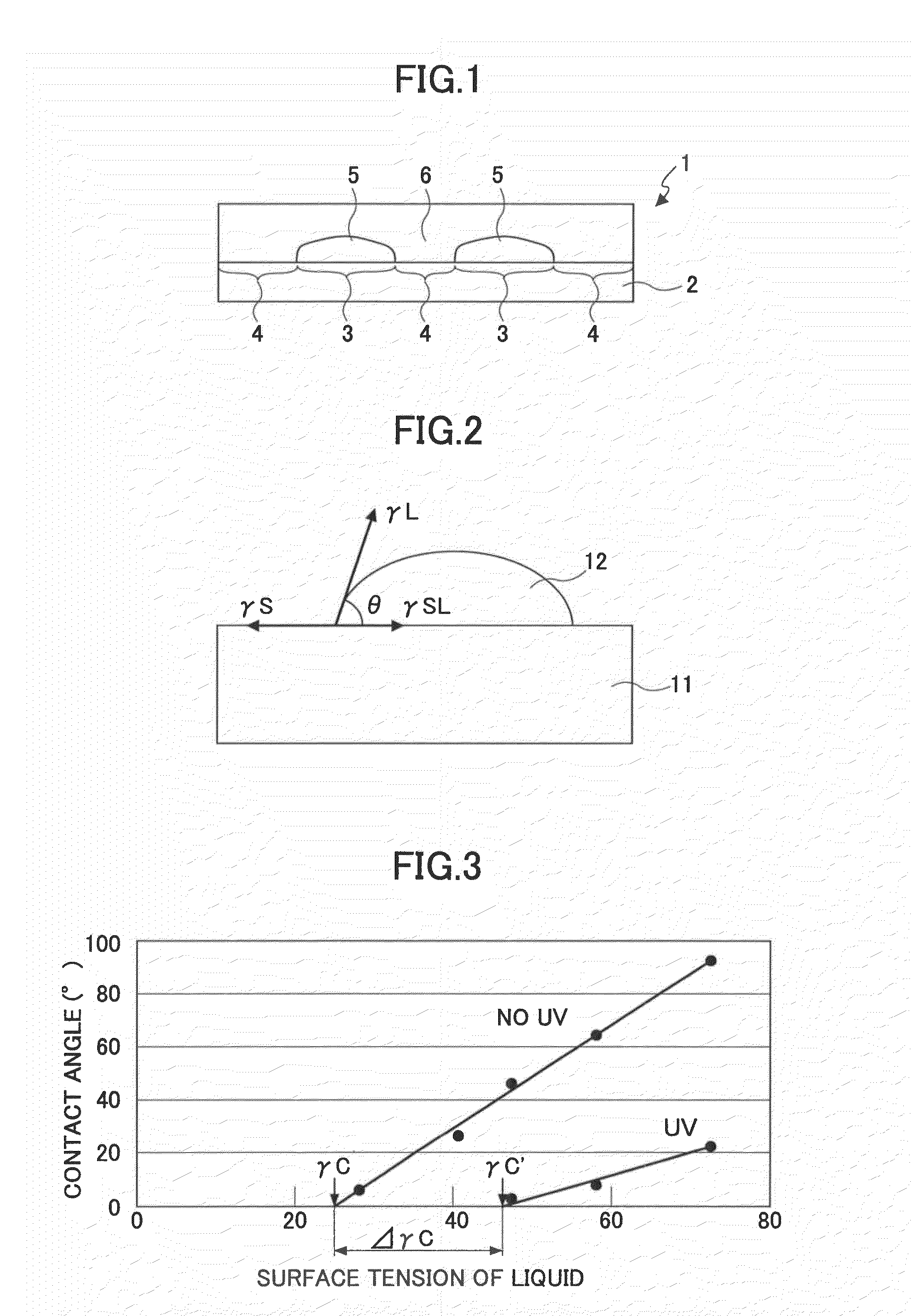
Critical surface tension. According to the Zisman method, the critical surface tension is the surface tension at which a liquid just completely wets a solid. The surface tension of different liquids is plotted against the cosine of the contact angle θ in order to determine the critical surface tension.
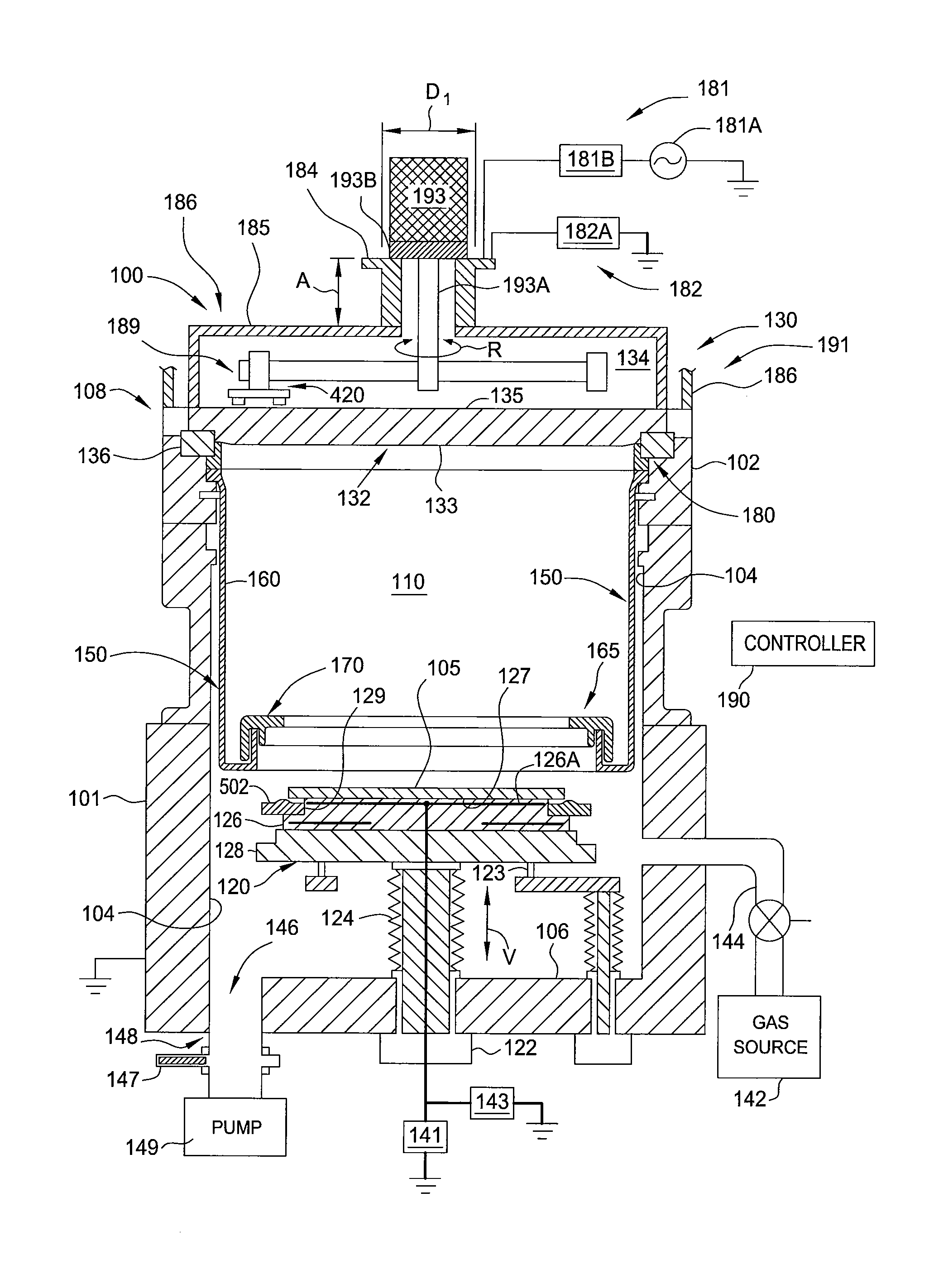
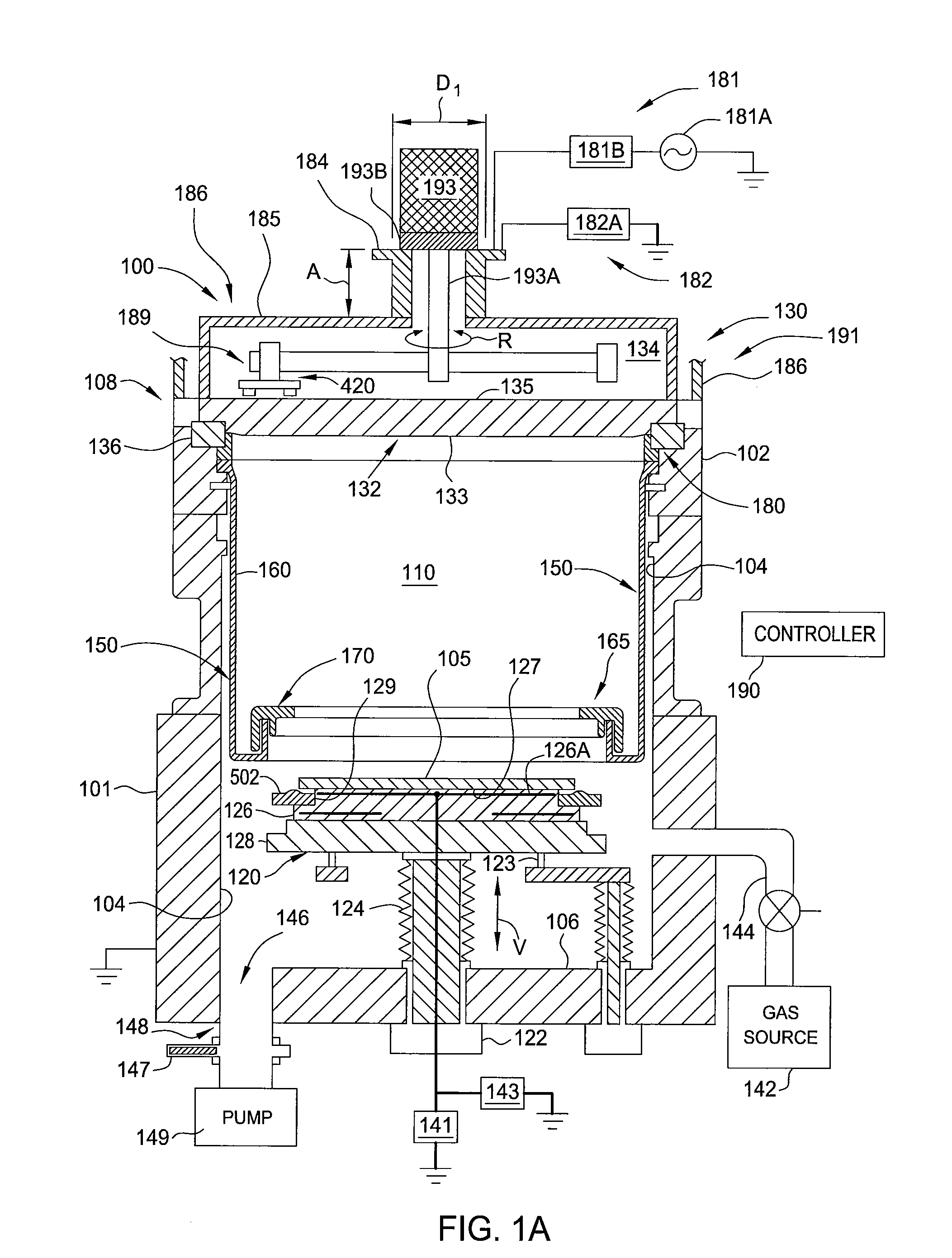
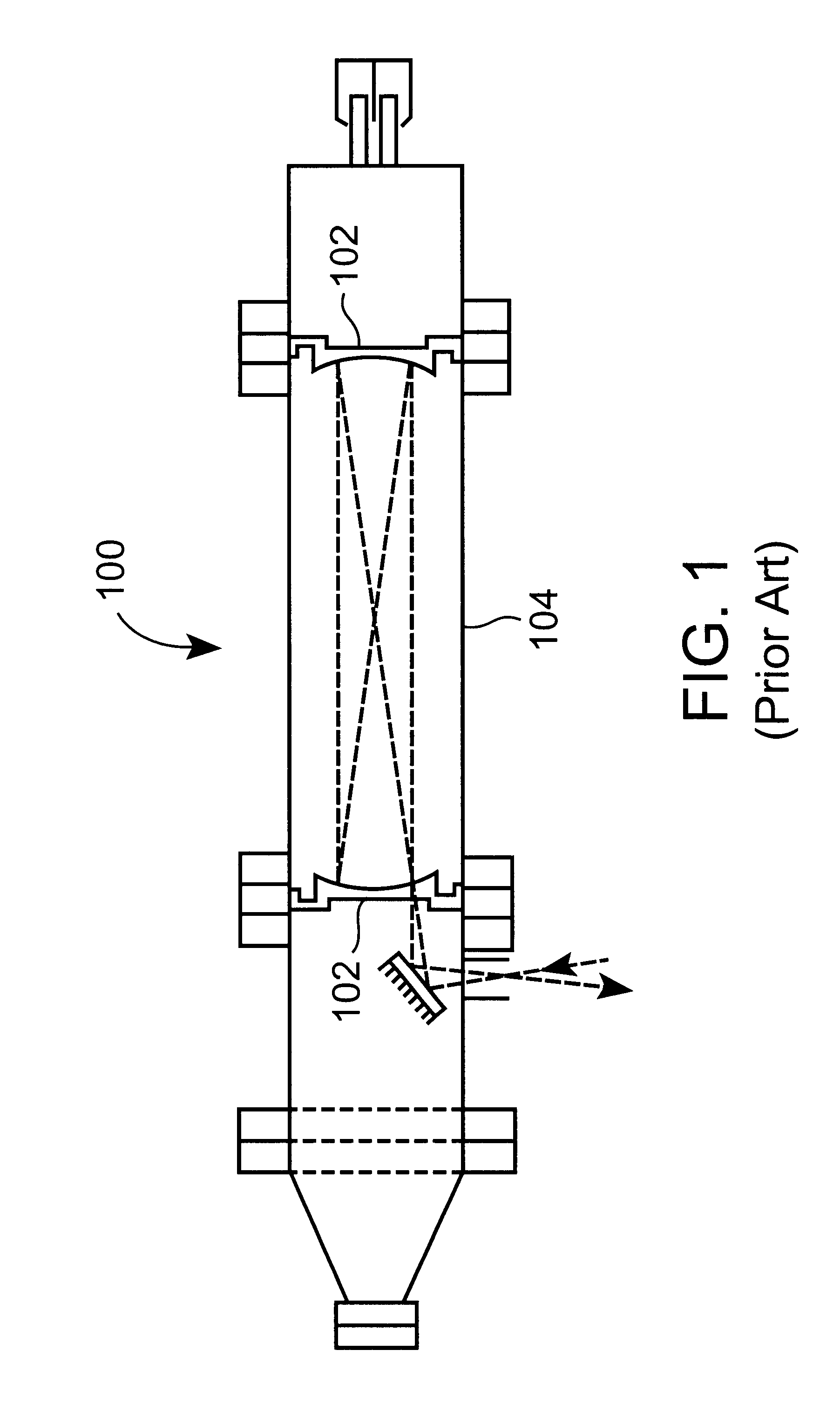
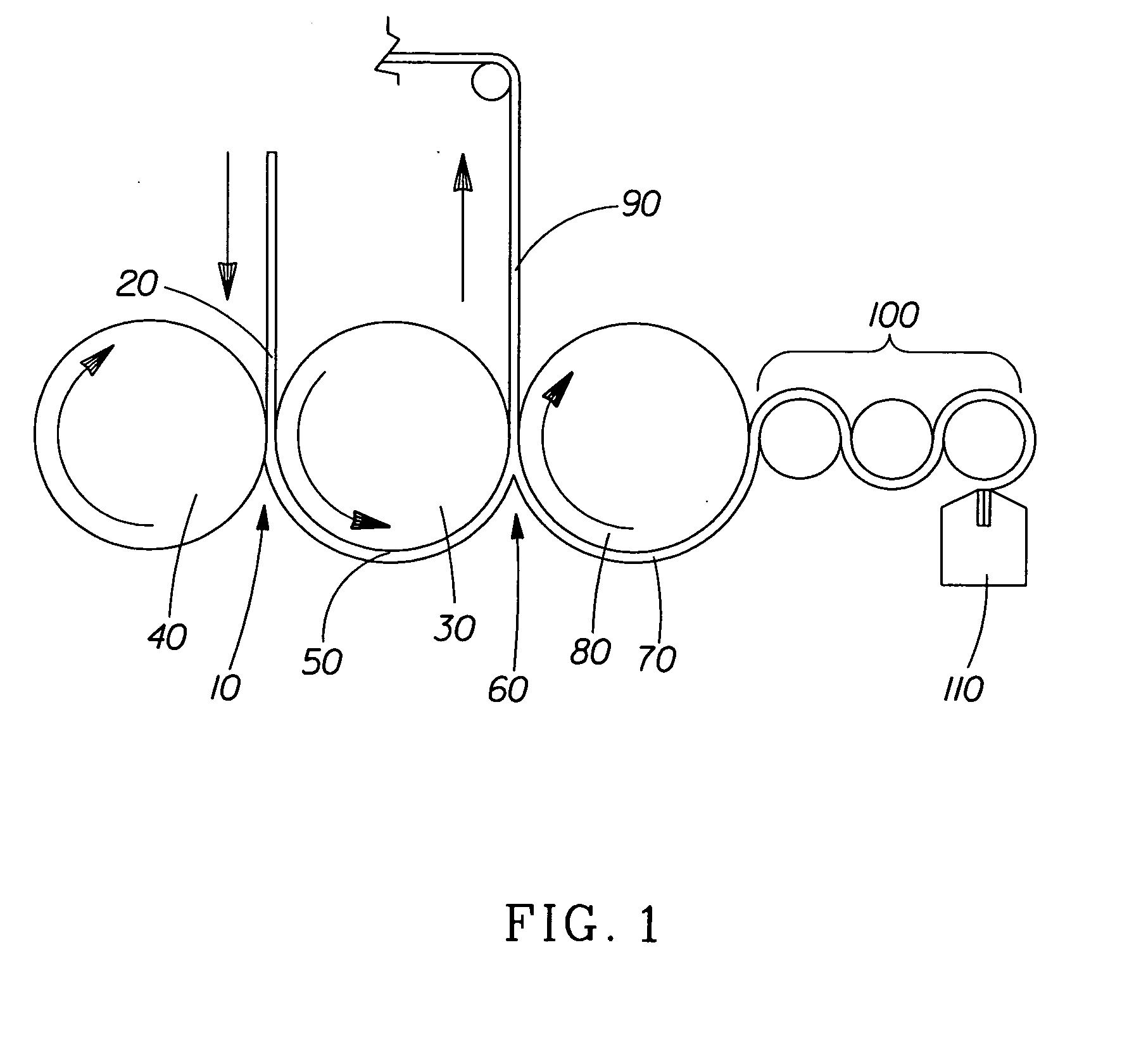
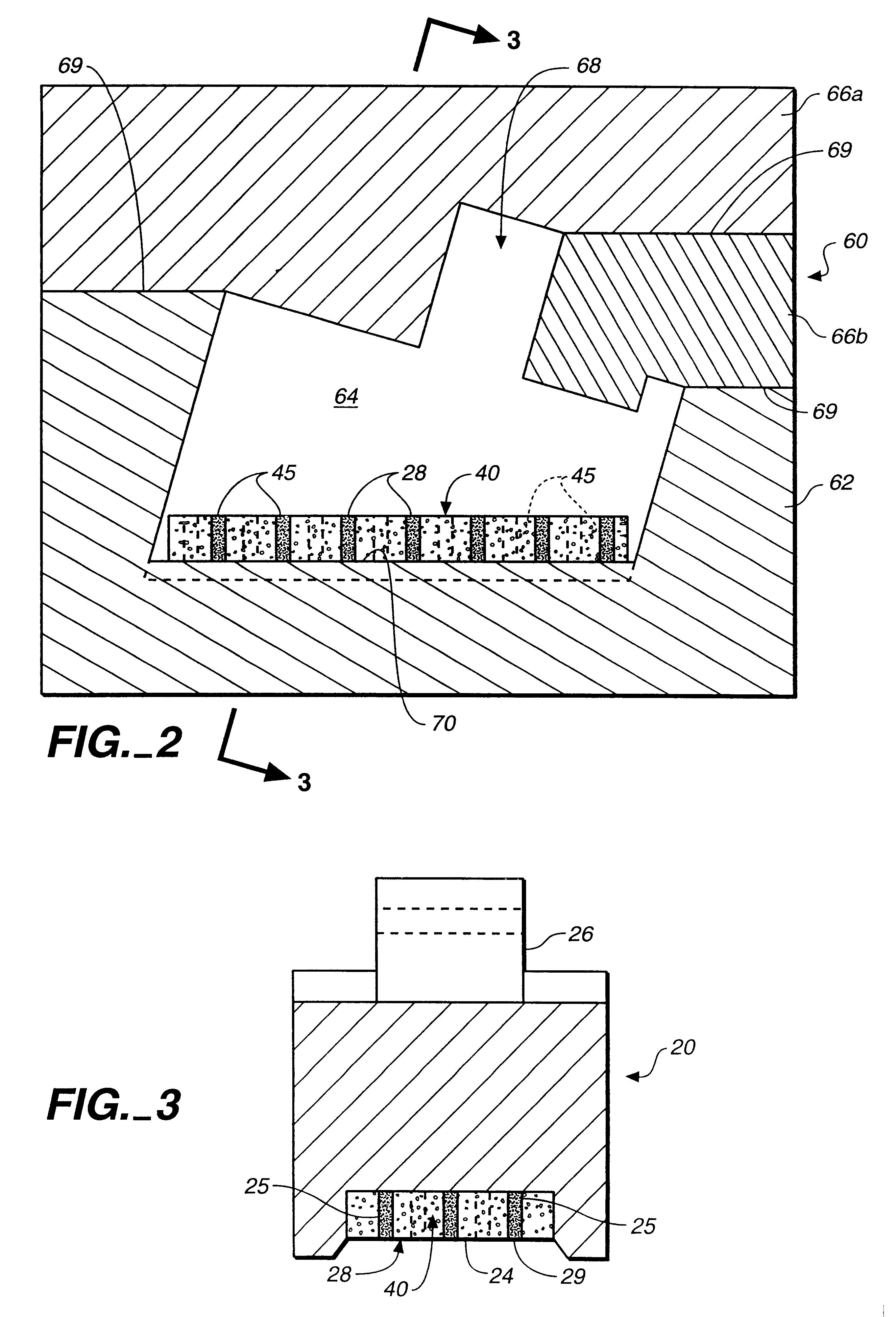
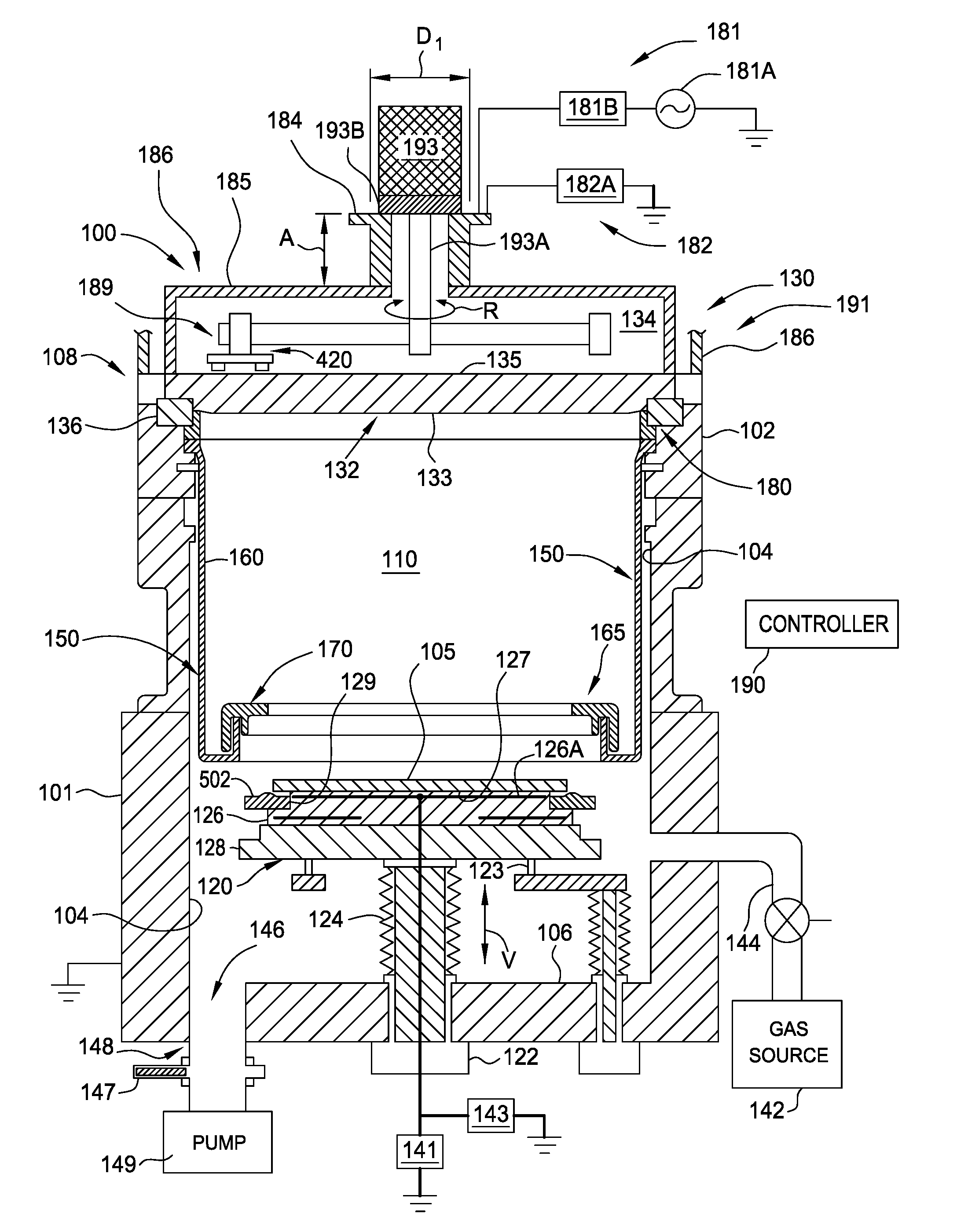
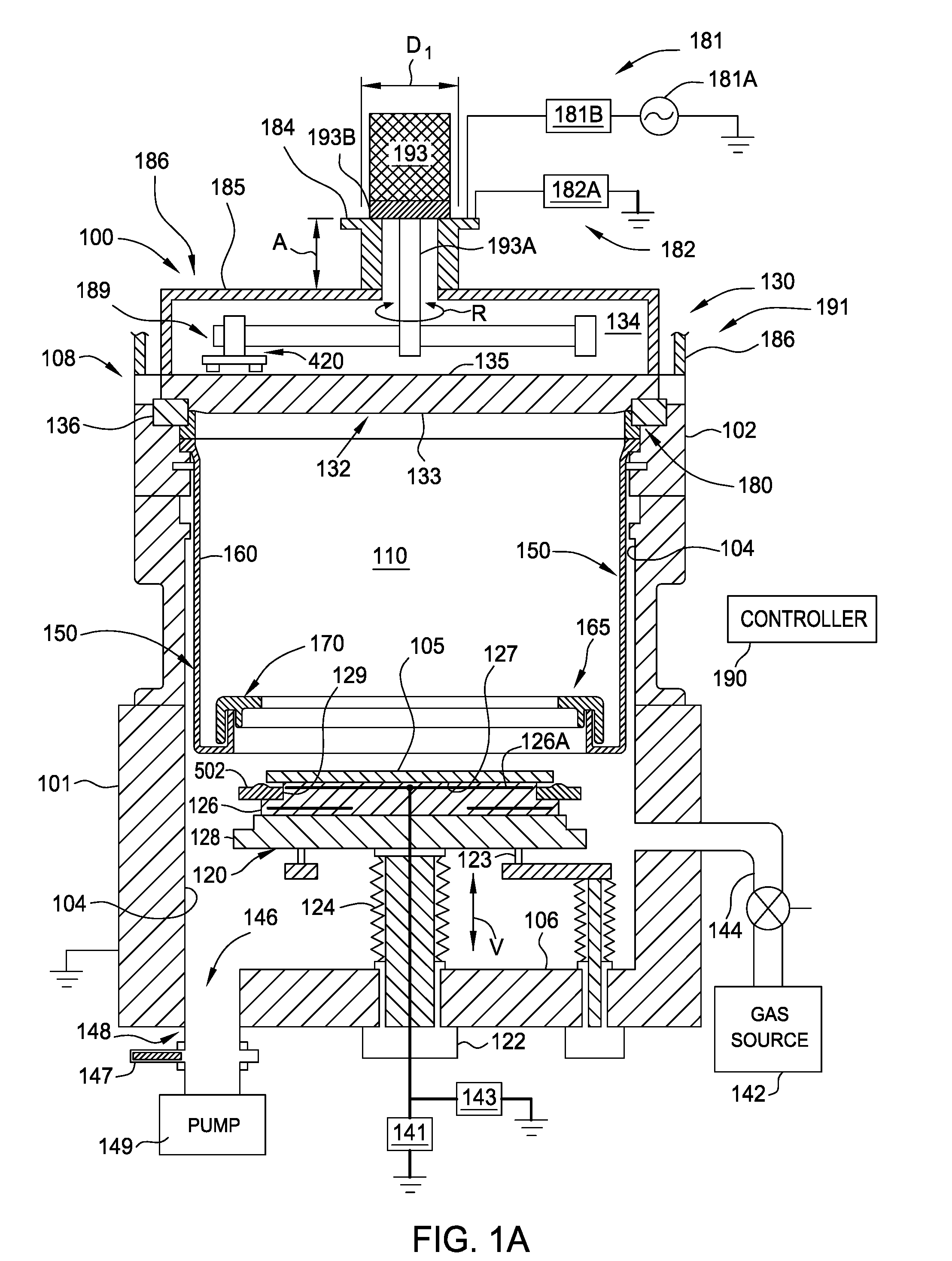
High pressure rf-dc sputtering and methods to improve film uniformity and step-coverage of this process
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a processing chamber used to perform a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process and methods of depositing multi-compositional films. The processing chamber may include: an improved RF feed configuration to reduce any standing wave effects; an improved magnetron design to enhance RF plasma uniformity, deposited film composition and thickness uniformity; an improved substrate biasing configuration to improve process control; and an improved process kit design to improve RF field uniformity near the critical surfaces of the substrate. The method includes forming a plasma in a processing region of a chamber using an RF supply coupled to a multi-compositional target, translating a magnetron relative to the multi-compositional target, wherein the magnetron is positioned in a first position relative to a center point of the multi-compositional target while the magnetron is translating and the plasma is formed, and depositing a multi-compositional film on a substrate in the chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
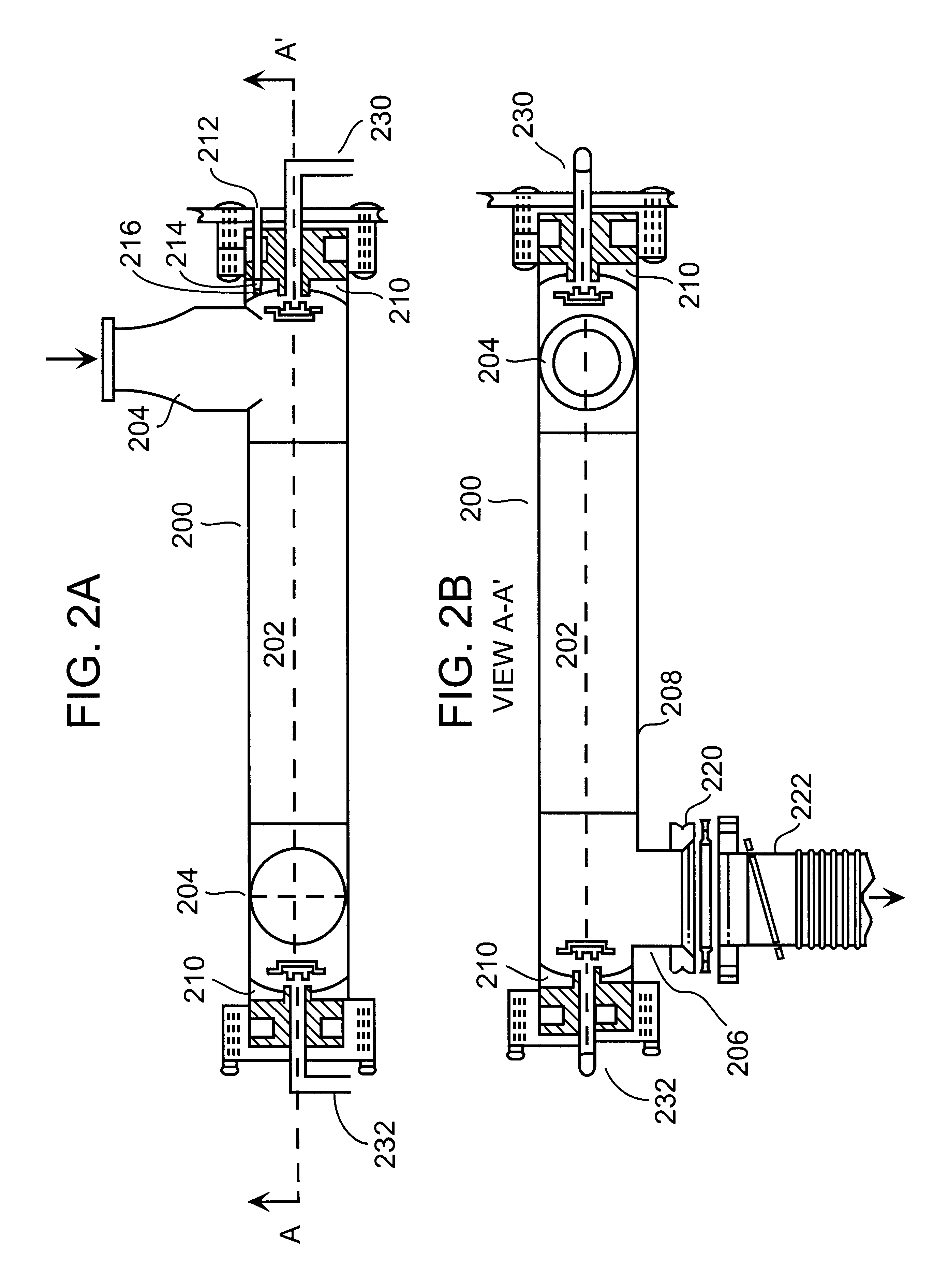
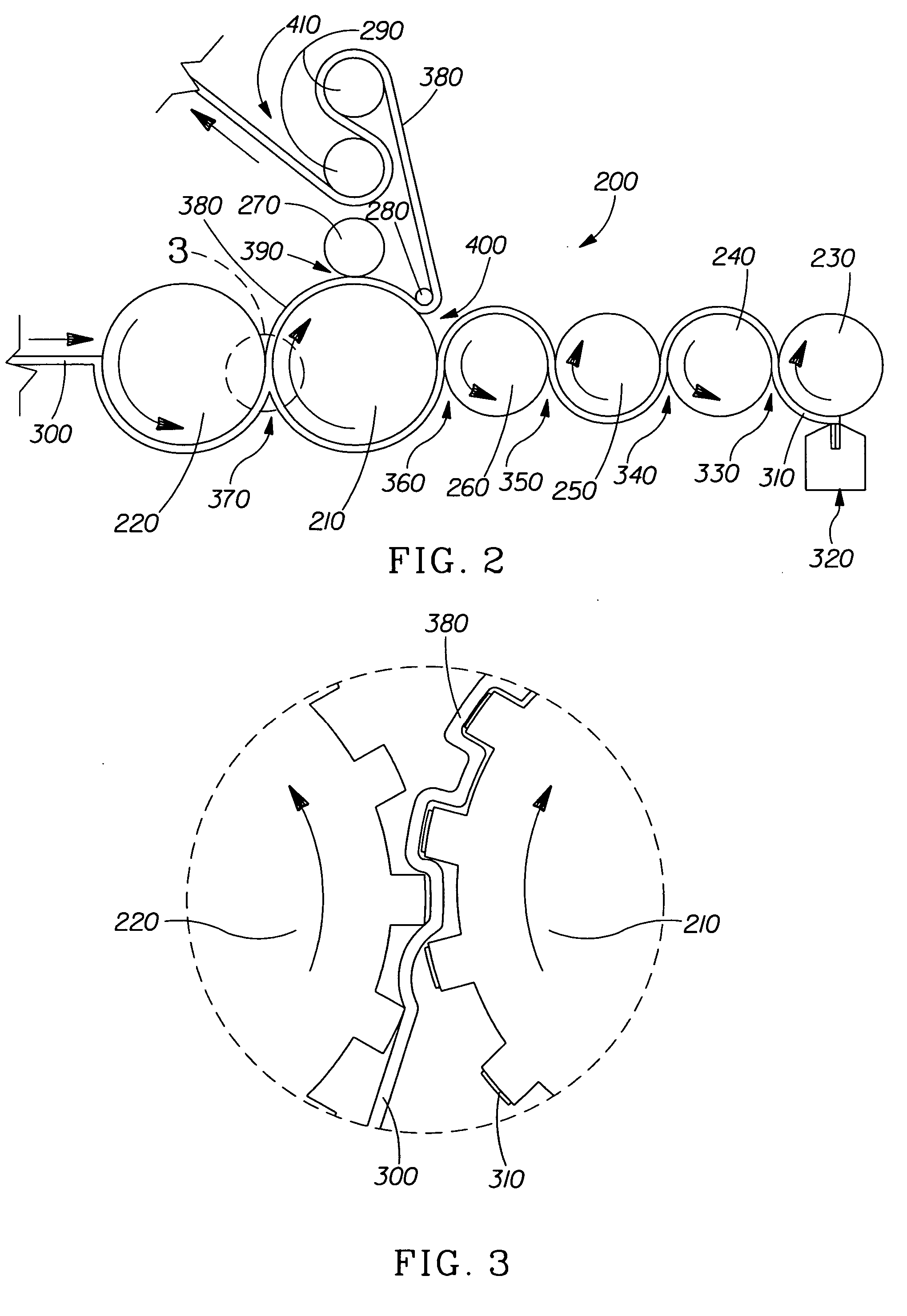
Method and system for preventing deposition on an optical component in a spectroscopic sensor
Provided are novel methods of preventing deposition on an optical component in an absorption spectroscopy measurement cell. The methods involve performing an absorption spectroscopy measurement of a sample gas introduced into the cell, and introducing a flow of purge gas from a purge gas inlet pipe across a critical surface of the optical element at a velocity effective to prevent deposition on the critical surface. The gas inlet is disposed adjacent said critical surface. Also provided are devices for practicing the inventive method, measurement cells useful in absorption spectroscopy measurements, apparatuses for performing an absorption spectroscopy measurement and semiconductor processing apparatuses. The invention allows for the performance of accurate spectroscopic measurements. Because deposits are prevented from forming on the surface of an optical element, interference therefrom can effectively be avoided.
Owner:LAIR LIOUIDE POUR LETUD ET LEXPL DES PROCEDES GEORCLAUDE +1
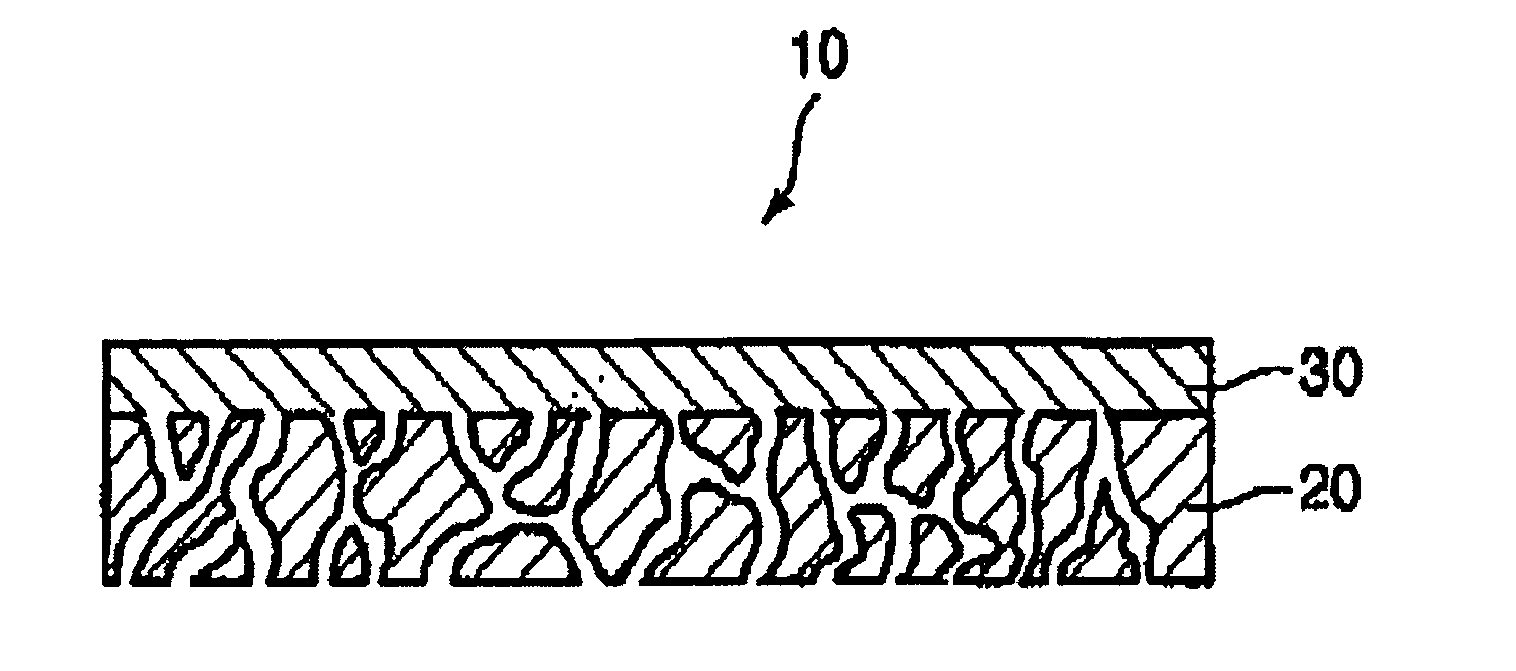
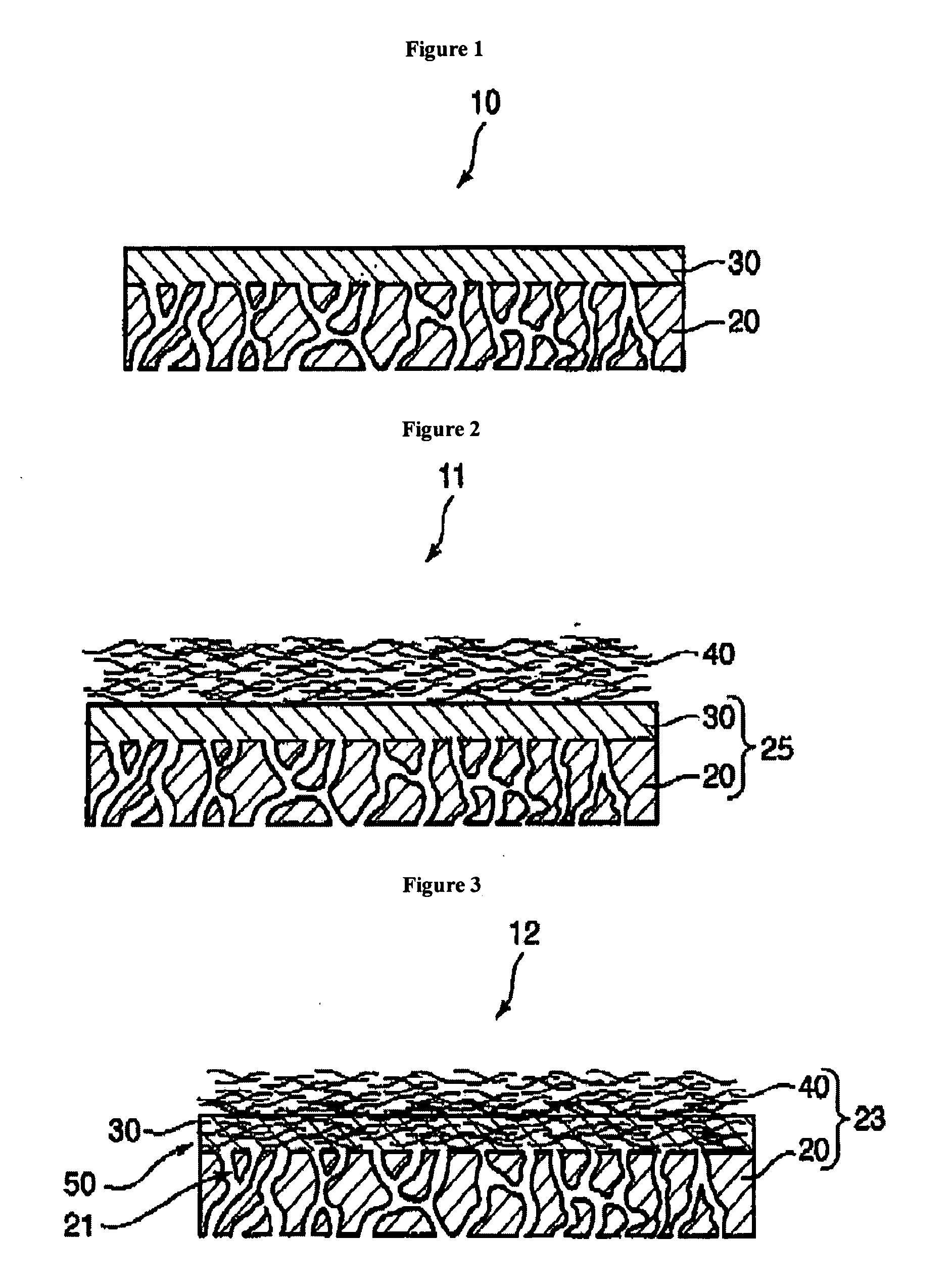
Membrane, method of making same and heat exchanger furnished with said membrane
ActiveUS20060090650A1Solid sorbent liquid separationPretreated surfacesPolyvinyl alcoholWater soluble
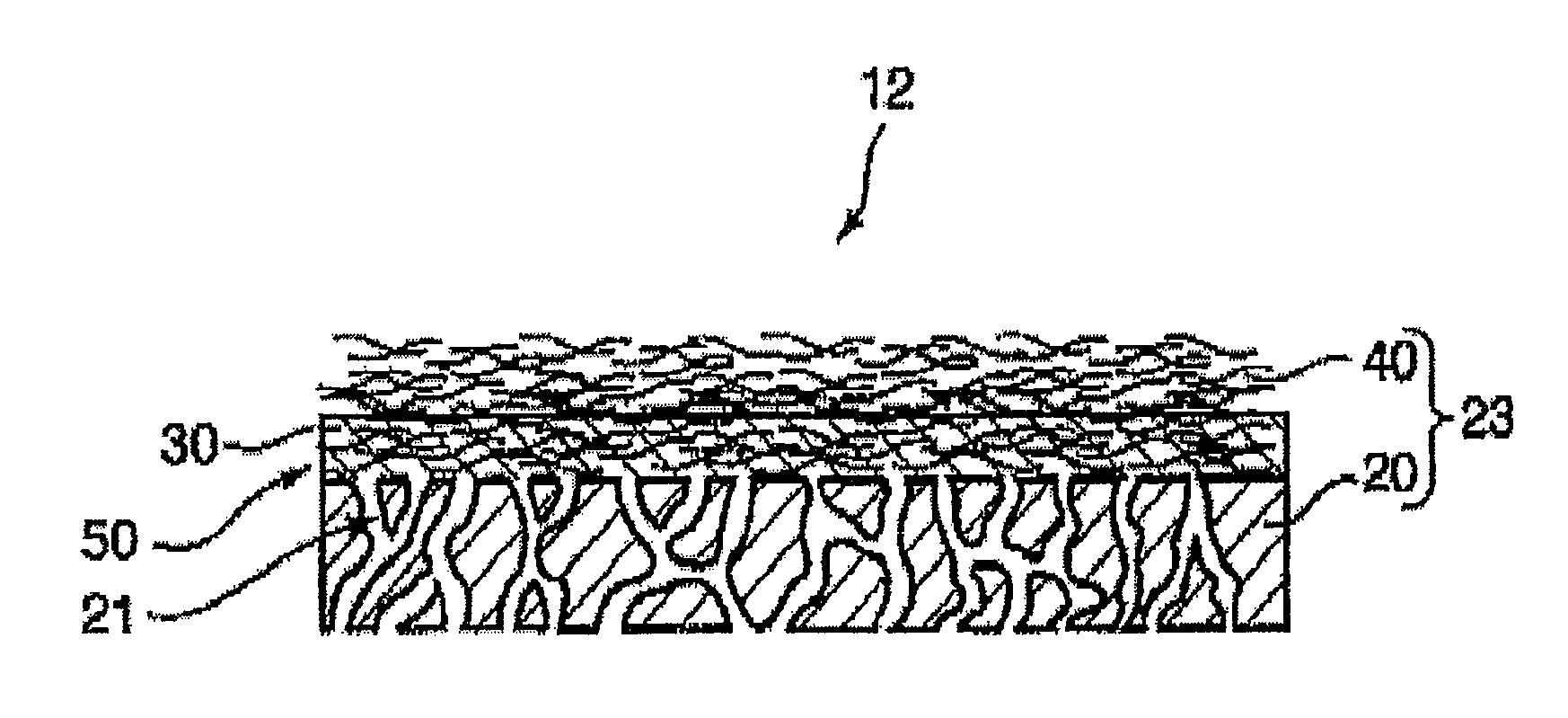
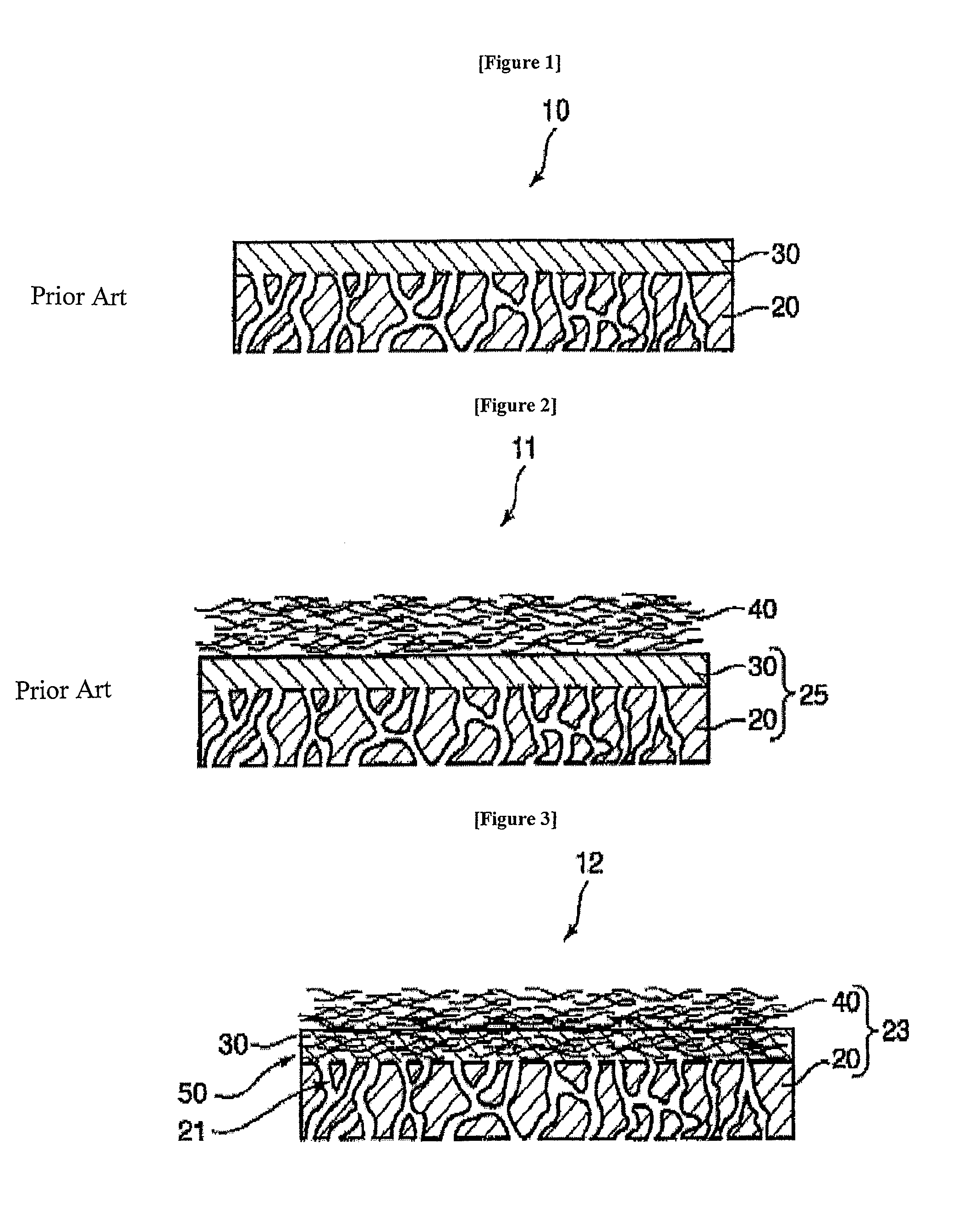
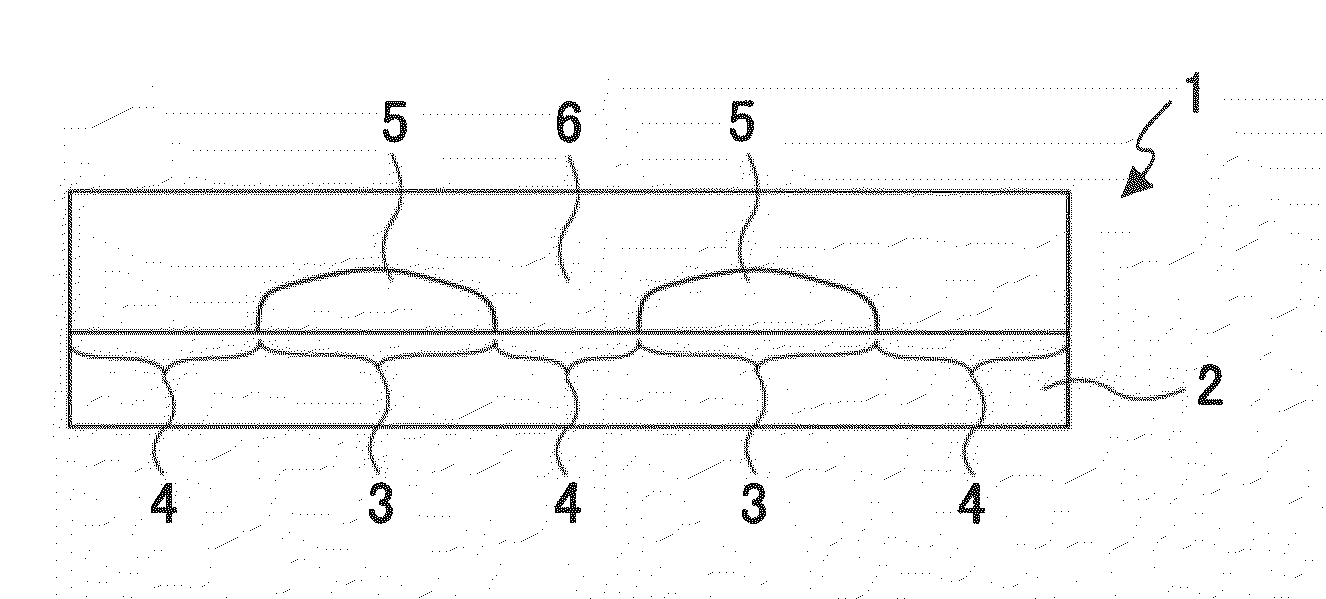
A membrane 12 that exhibits superior condensation resistance regardless of the type of moisture-permeable resin, that has satisfactory adhesion between a porous film and a reinforcing member, and that can be manufactured in a simple manner. The membrane 12 is a laminated article 23 containing a porous film 20 and a reinforcing member 40, and the reinforcing member 40 has a moisture-permeable resin layer 30 on the side of an interface 50 with the porous film 20. To reliably form the moisture-permeable resin layer (moisture-permeable resin film) 30, the average pore diameter of the porous film 20 is preferably 0.01 to 10 μm, and the porosity of the reinforcing member 40 is preferably 30 to 95%. According to the membrane 12 of the present invention, even if the moisture-permeable resin is water-soluble (for example, polyvinyl alcohol), condensation resistance is still satisfactory. If the difference between the critical surface tension γc2 of the reinforcing member 40 and the critical surface tension γc1 of the porous film 20 (γc2−γc1) is set in advance to −5 mN / m or greater, the moisture-permeable resin layer 30 can be disposed internally at a specific location.
Owner:JAPAN GORE TEX INC
Self-cleaning submerged instrumentation
ActiveUS20100042389A1Reduce eliminateExtends optimum high-performance lifeFouling preventionResistance/reactance/impedenceBiofoulingAcoustics
Techniques and apparatus inhibit, limit, or remove biofouling and certain inorganic accumulations, to increase the longevity of accurate in-situ oceanographic and other underwater measurements and transducing processes. The invention deters formation of an initial bacterial layer and other precipitation, without harming the environment. The invention integrates an ultrasonic source into a sensor or other device, or its supporting structures. The ultrasonic source vibrates one or more critical surfaces of the device at a frequency and amplitude that dislodge early accumulations, thus preventing the rest of the fouling sequence. The ultrasonic driver is activated for short periods and low duty cycles, and in some cases preferably while the device is not operating.
Owner:ARETE ASSOCIATES INC
Filter for the separation of leukocytes from whole blood or blood preparations, method for production of said filter, corresponding device and use thereof
ActiveUS7775376B2Simple and inexpensive to produceLong durabilitySemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesHydrophilic monomerWhite blood cell
Owner:FRESENIUS HEMOCARE ITAL
Elements for embossing and adhesive application
A patterned element for use in an embossing and adhesive application process. The patterened element comprises a material having an pattern disposed thereon, wherein the material comprises a polymer and has a Shore A hardness of greater than about 70, and has a critical surface energy of less than about 30 dynes / cm.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Elements for embossing and adhesive application
A patterned element for use in an embossing and adhesive application process. The patterened element comprises a material having an pattern disposed thereon, wherein the material comprises a polymer and has a Shore A hardness of greater than about 70, and has a critical surface energy of less than about 30 dynes / cm.
Owner:BOUTILIER GLENN DAVID +9
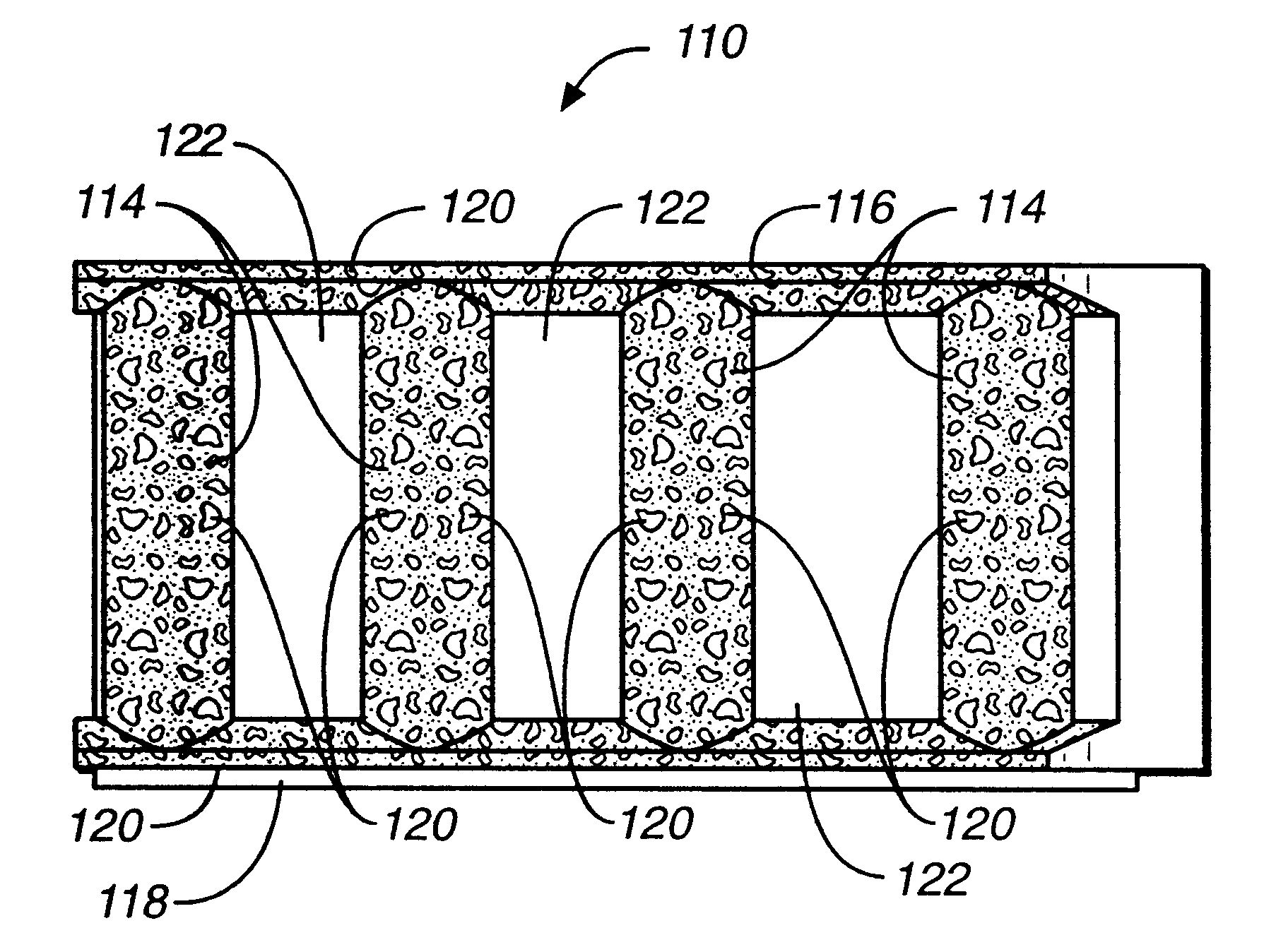
Iron alloy member and method
An impeller shoe (110) having a front side (112) with a series of half column members (114) and raised upper and lower rims (116, 118) that form the impact surface of the impeller shoe. Half columns (114) and raised rims (116, 118) are formed with carbide material (120) formed therein in order to improve wear resistance at these critical surfaces.
Owner:DALLESPORT FOUNDRY
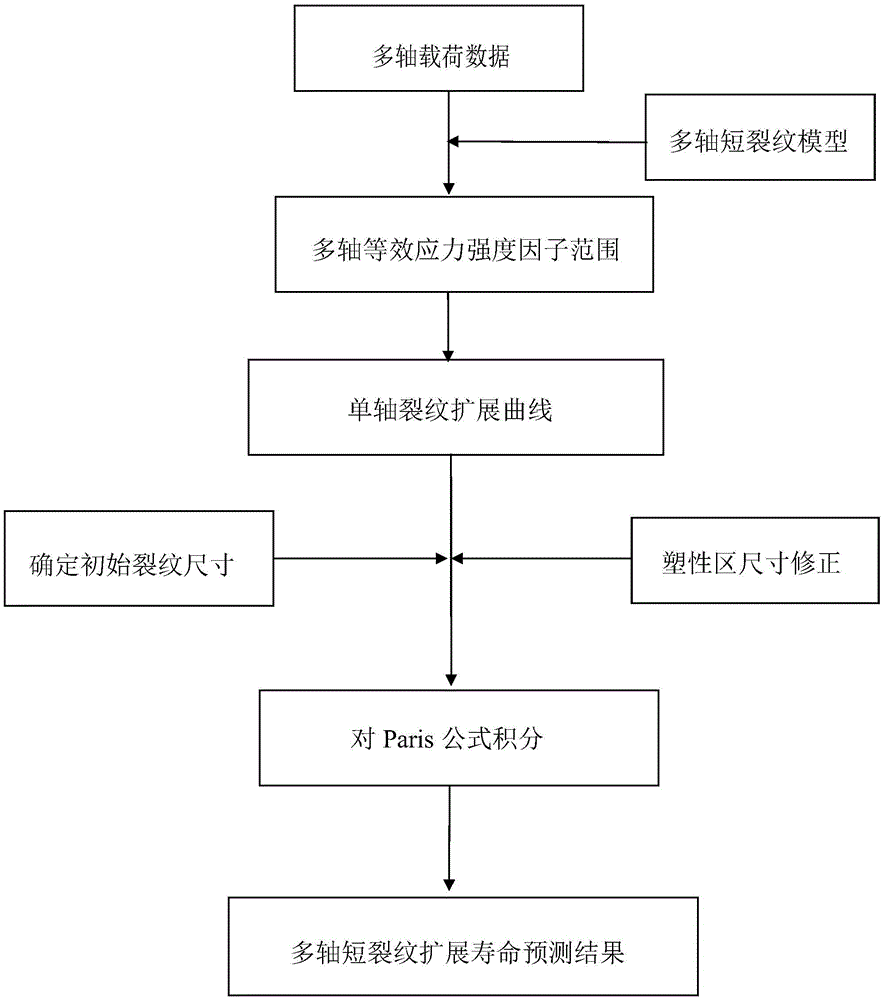
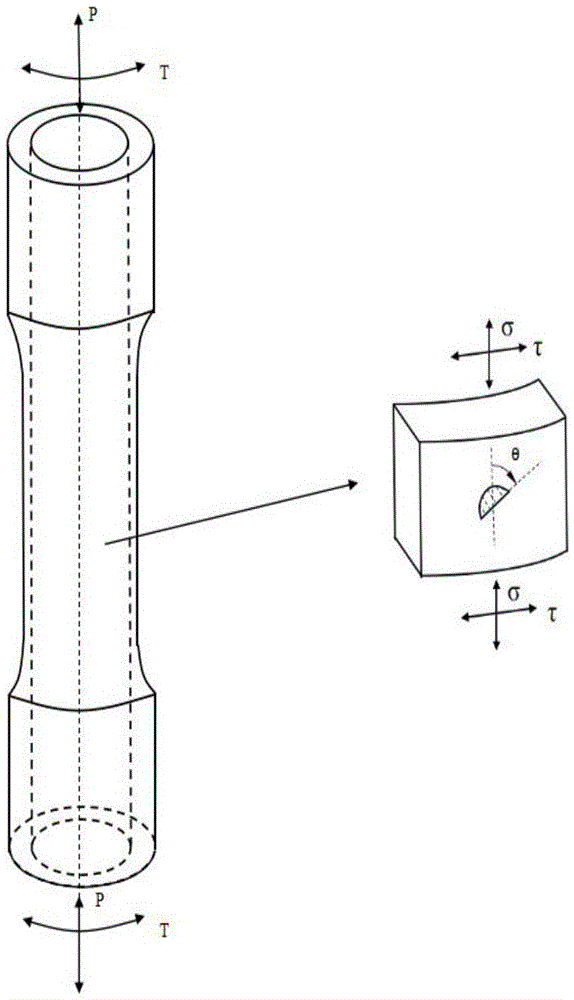
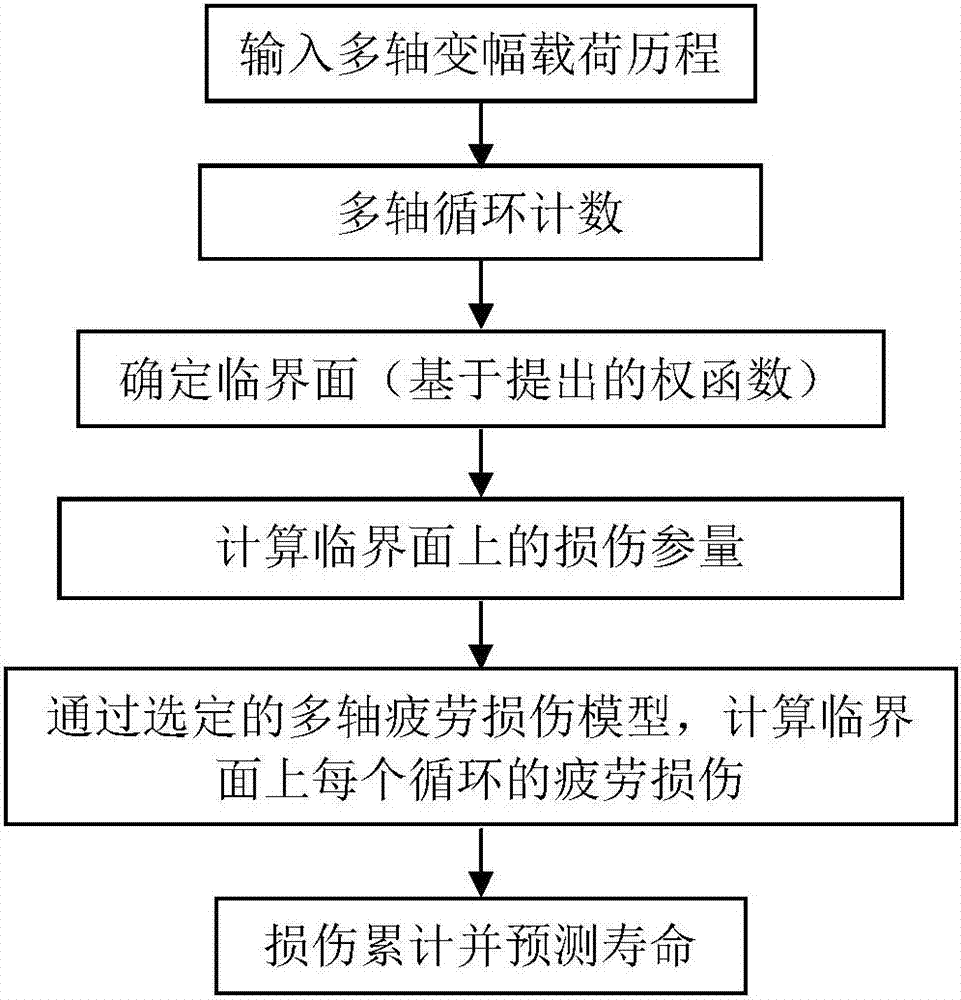
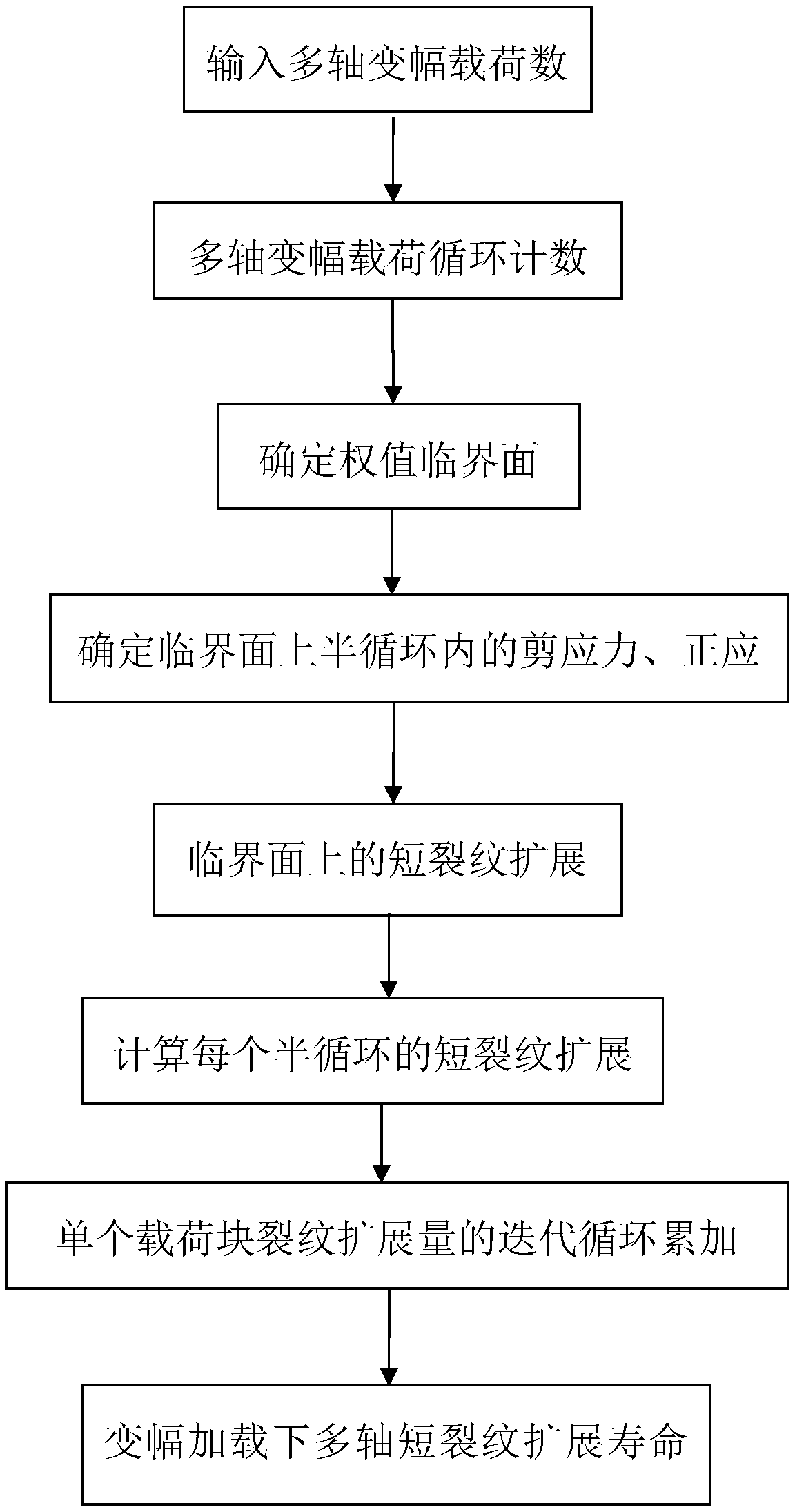
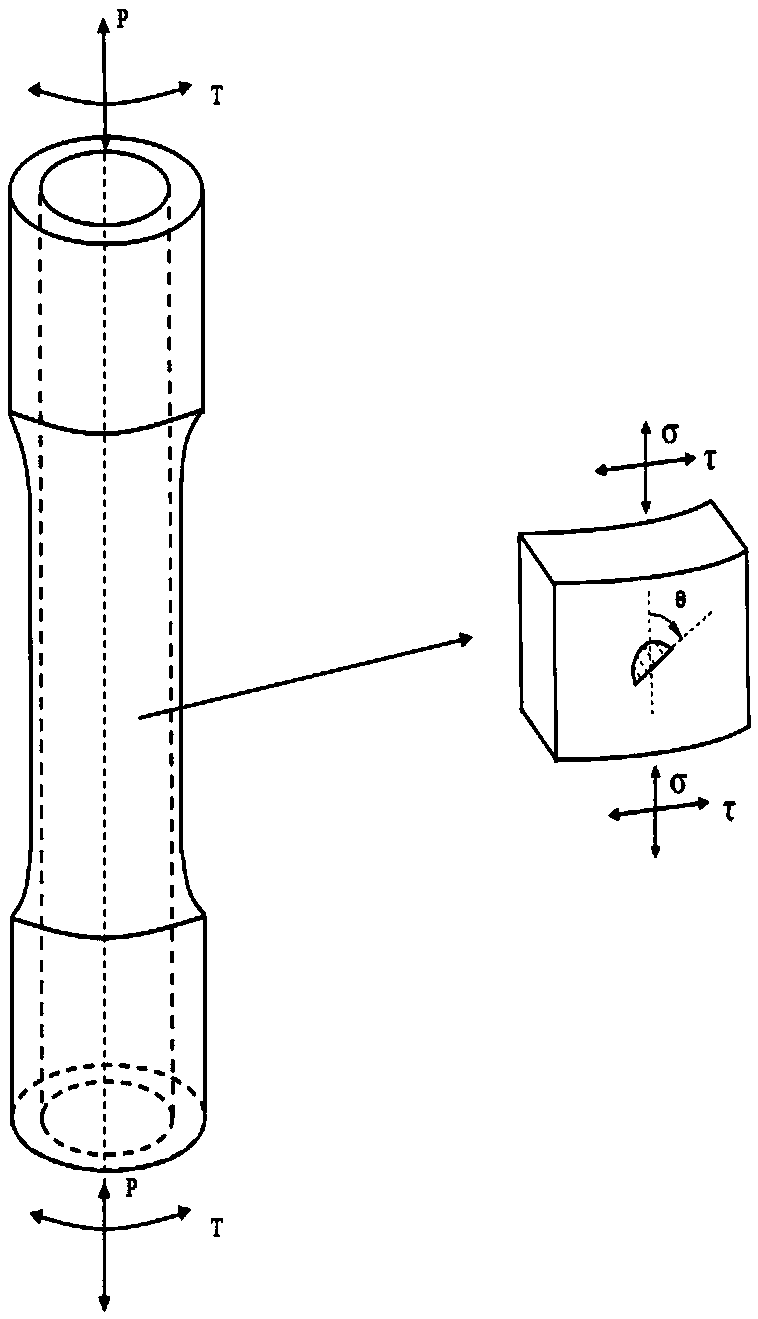
Multiaxial short crack propagation life prediction method based on critical surface method
ActiveCN105466772APromote engineering applicationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady torsional forcesFatigue damageEngineering
The present invention provides a multiaxial short crack propagation life prediction method based on a critical surface method, and relates to the field of multiaxial fatigue strength theory. The algorithm comprises the steps of: (1) selecting a plane, which contains the maximum shearing strain range, as a critical surface, and using the damage parameters on the critical surface to characterize a short crack propagation driving force; (2) based on the shear-type multiaxial fatigue damage parameters, establishing an equivalent crack stress intensity factor applicable to the multiaxial stress state; (3) fitting the short crack propagation rate data under uniaxial loading to obtain an uniaxial short crack propagation curve; and (4) carrying out plastic zone size correction on the crack tip, and calculating the short crack propagation life by a fracture mechanics method. The method can well descript the influence of non-proportional loading on crack propagation. The results show that the method can well predict the short crack propagation life under multiaxial proportional and non-proportional loading.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Large high density foam glass tile
InactiveUS6964809B2High densityHigh strengthCovering/liningsGlass shaping apparatusShock waveHigh density
A large, high density foam glass tile which can be used as a facade on both exterior and interior building walls. The foam glass tile can also be used with other materials to form a panel or a composite. The present invention may be used on the critical surfaces of buildings at high risk for terrorist attacks, in combination with cement, steel or other high strength building materials. The present invention may also be used in surfaces of typical buildings. The present invention has the advantage of absorbing a substantial portion of a shock wave caused by an explosion. The present invention also has the advantage of being more resistant to earthquakes.
Owner:BUARQUE DE MACEDO PEDRO M
Electronic device, method for manufacturing electronic device, contact hole of electronic device, method for forming contact hole of electronic device
InactiveUS20060170836A1Eliminate the problemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerEngineering
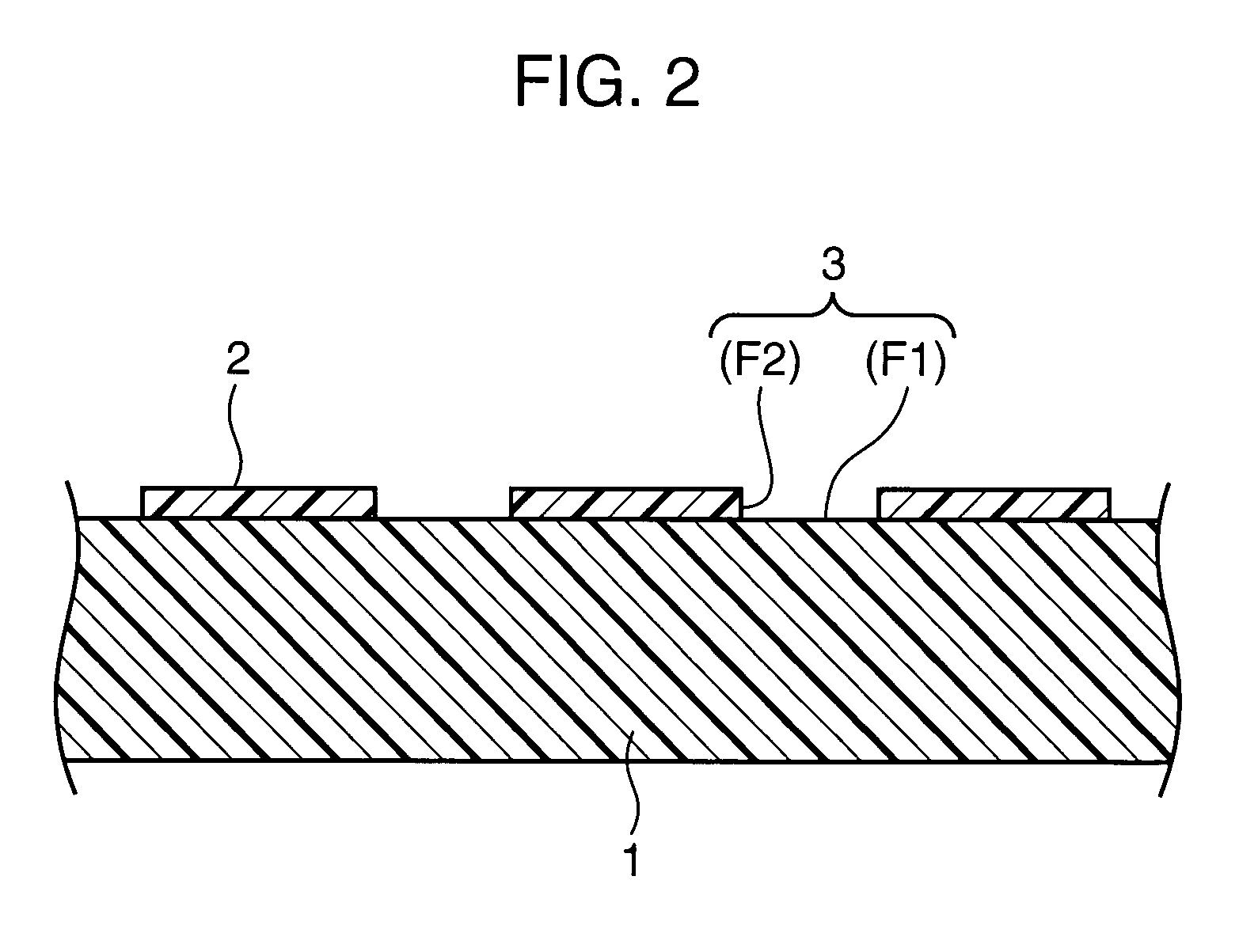
An electronic device includes a substrate, a first conductive material layer formed on the substrate, a patterning layer formed on the first conductive material layer, the patterning layer including first and second patterning layer parts having different critical surface tension, an insulation layer formed on the second patterning layer part of the patterning layer, the insulation layer including first and second insulation layer parts having different critical surface tension, and a second conductive material layer formed on the first patterning layer part and the first insulation layer part.
Owner:RICOH KK
Multi-axial fatigue life prediction method based on weighted average maximum shear strain amplitude plane
InactiveCN107423540AOptimization determination methodFatigue Life PredictionInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageLife time
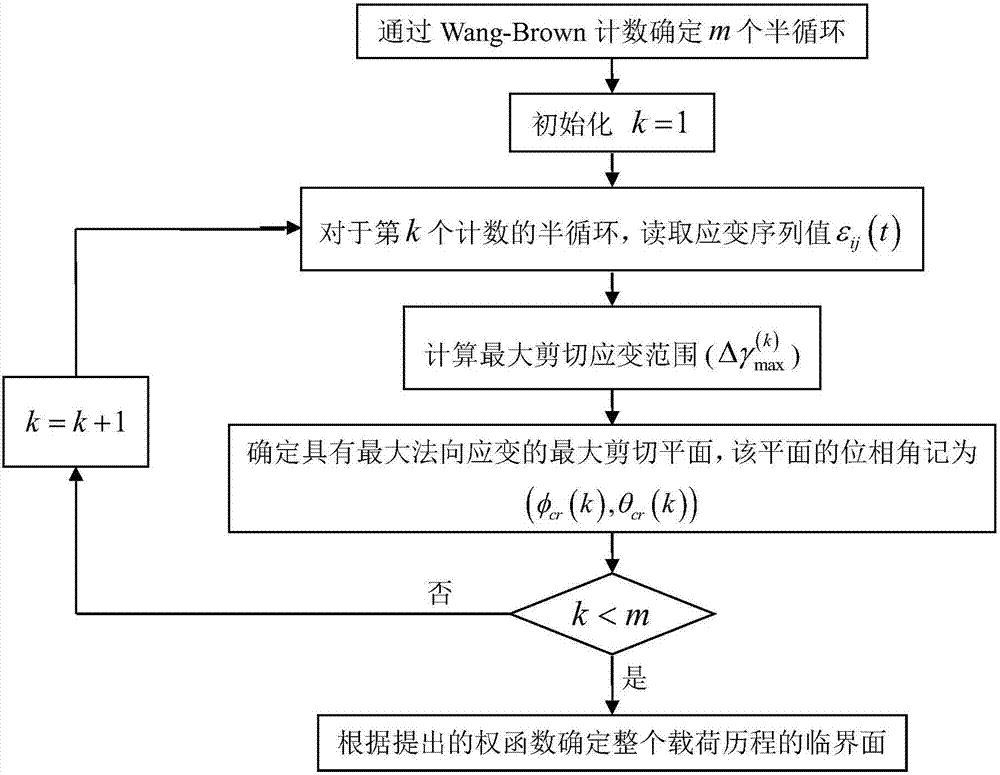
The present invention discloses a multi-axial fatigue life prediction method based on the weighted average maximum shear strain amplitude plane, and relates to the field of the multi-axial fatigue strength theory. The method comprises: synthesizing the multi-axis amplitude-varying load history into a von Mises equivalent strain history by using the equivalent von Mises strain formula, and carrying out Wang- Brown cycle counting on the von Mises equivalent strain history; determining the critical plane under the multi-axial amplitude-varying load by using the proposed weight average maximum shear strain amplitude plane; calculating fatigue damage parameters on the critical surface in each half-cycle obtained by counting; carrying out damage calculation by using the Wang and Brown damage models or the Fatemi and Socie damage models; and accumulating the calculated damage in each half-cycle by using the Miner's linear cumulative law, and calculating the fatigue life. The proposed life prediction method is validated by four kinds of materials, and the results show that the proposed method can predict the failure plane and fatigue life under the multi-axial amplitude-varying load.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Micro Lens, Micro Lens Array, and Method of Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20080186585A1Excellent resistance to separationShorten the optical path lengthSolid-state devicesCoatingsOptoelectronicsMicro lens array
A micro lens includes a base material and a lens formed on the base material, wherein the lens is disposed at an opening on the base material, and the opening is formed by covering a surface of the base material with a first monolayer; and the first monolayer has critical surface energy of 22 mN / m or lower and shows non-affinity for a lens material in comparison with a region within the opening, and is fixed to the surface of the base material via a covalent bind.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Layered structure for electron device including regions of different wettability, electron device and electron device array that uses such a layered structure
InactiveUS7612455B2Low costReduce usageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh surfaceElectron
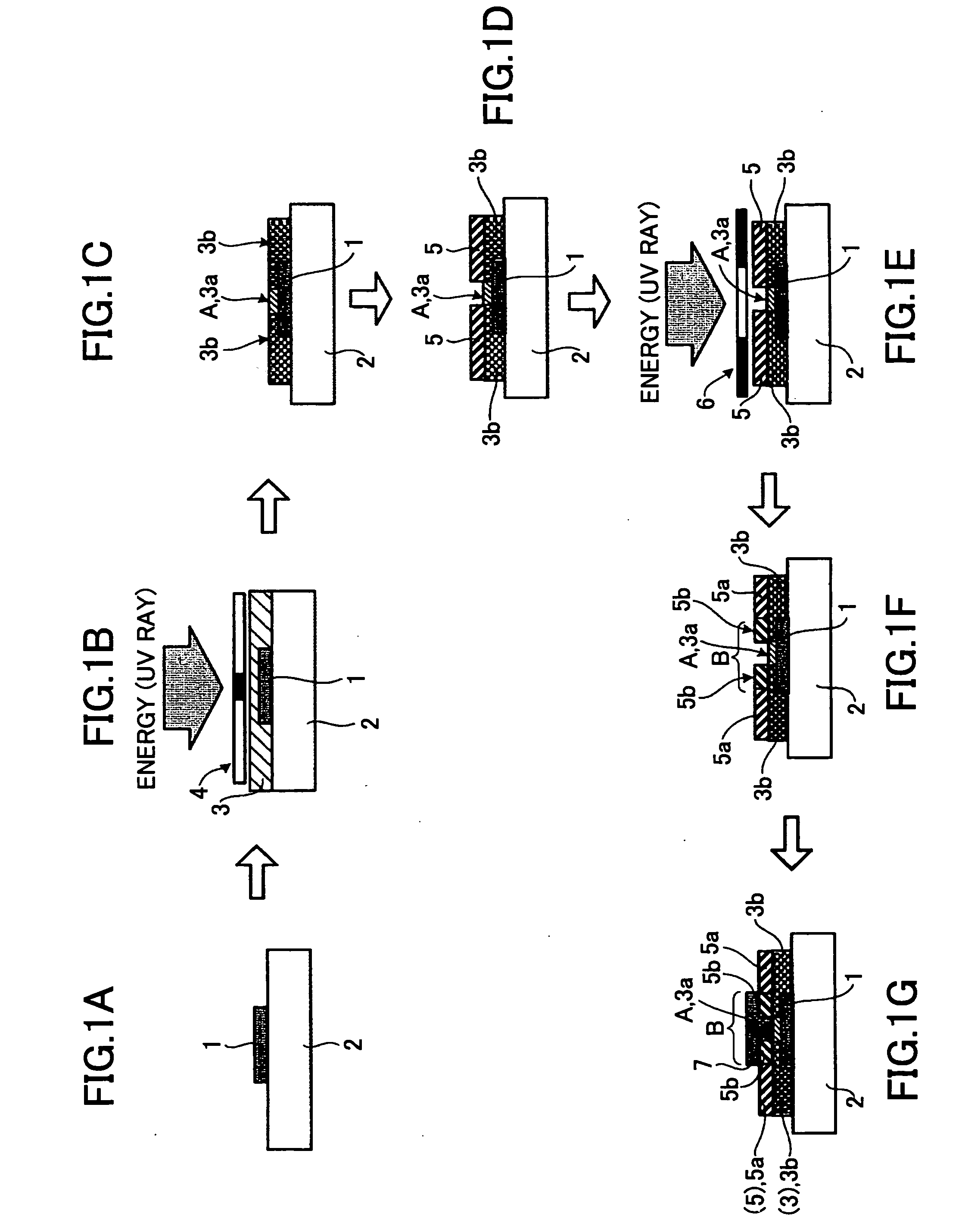
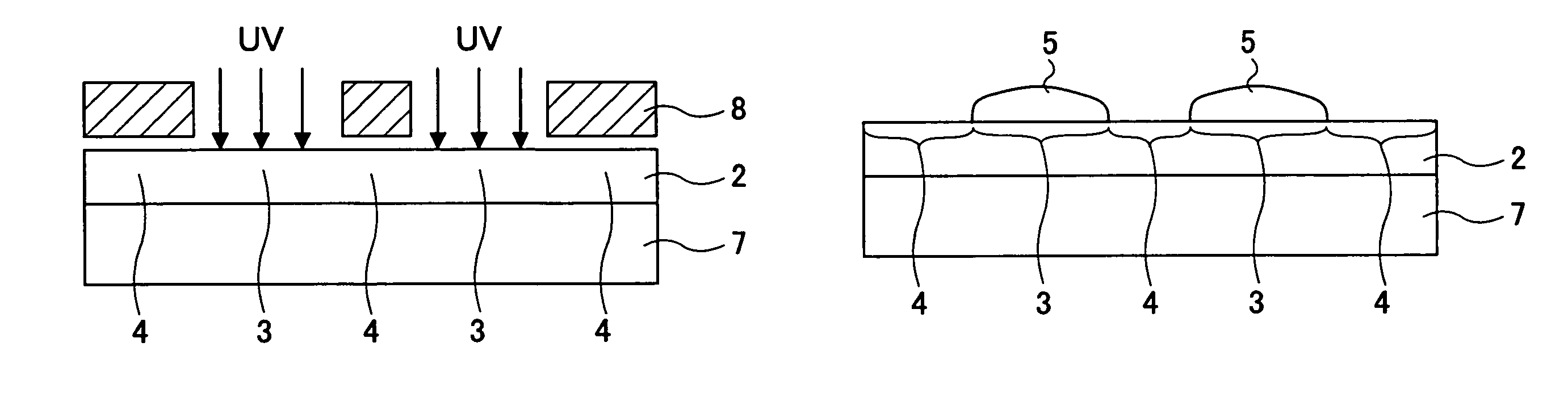
A layered structure comprises a variable wettability layer including a material that changes a critical surface tension in response to energy provided thereto, the wettability changing layer including at least a high surface energy part of large critical surface tension and a low surface energy part of low critical surface tension, a conductive layer formed on the variable wettability layer at the high surface energy tension part, and a semiconductor layer formed on the variable wettability layer at the low surface energy part.
Owner:RICOH KK
Membrane, method of making same and heat exchanger furnished with said membrane
A membrane 12 that exhibits superior condensation resistance regardless of the type of moisture-permeable resin, that has satisfactory adhesion between a porous film and a reinforcing member, and that can be manufactured in a simple manner.The membrane 12 is a laminated article 23 containing a porous film 20 and a reinforcing member 40, and the reinforcing member 40 has a moisture-permeable resin layer 30 on the side of an interface 50 with the porous film 20. To reliably form the moisture-permeable resin layer (moisture-permeable resin film) 30, the average pore diameter of the porous film 20 is preferably 0.01 to 10 μm, and the porosity of the reinforcing member 40 is preferably 30 to 95%. According to the membrane 12 of the present invention, even if the moisture-permeable resin is water-soluble (for example, polyvinyl alcohol), condensation resistance is still satisfactory. If the difference between the critical surface tension γc2 of the reinforcing member 40 and the critical surface tension γc1 of the porous film 20 (γc2−γc1) is set in advance to −5 mN / m or greater, the moisture-permeable resin layer 30 can be disposed internally at a specific location.
Owner:JAPAN GORE TEX INC
Filter for the separation of leukocytes from whole blood or blood preparations, method for production of said filter, corresponding device and use thereof
ActiveUS20060207937A1Long durabilityReduce washoutSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesHydrophilic monomerWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a filter for the separation of leukocytes from whole blood, comprising a hydrophobic support material and a polymeric coating material, whereby the surface of the filter has a critical surface wetting tension in the range 50 to 80 dyn / cm and the polymeric coating material may be obtained by polymerisation reaction of mixtures comprising hydrophobic and hydrophilic monomers. The invention further relates to a method for production of said filter and devices for the separation of leukocytes from whole blood and the use of the filter.
Owner:FRESENIUS HEMOCARE ITAL
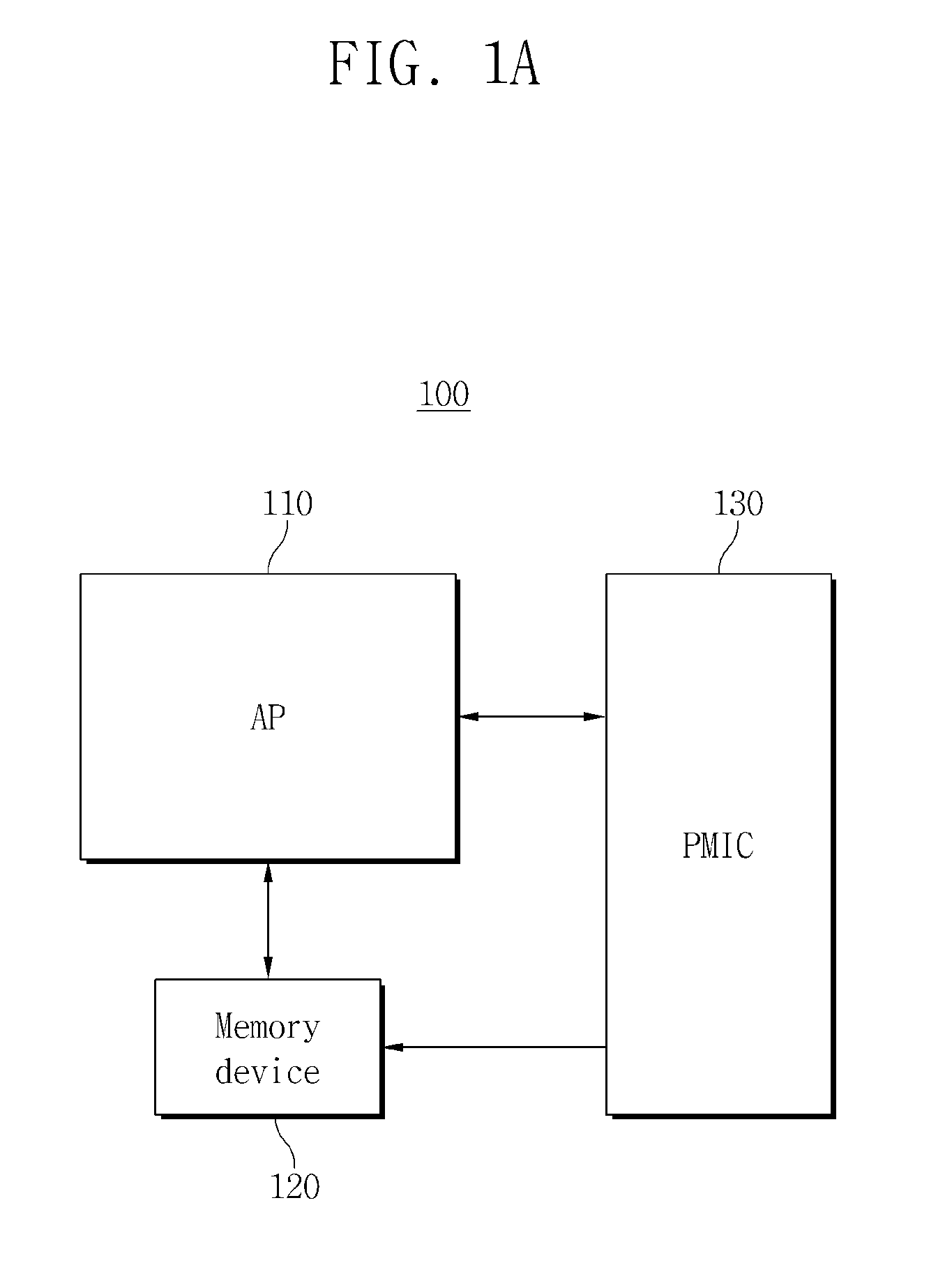
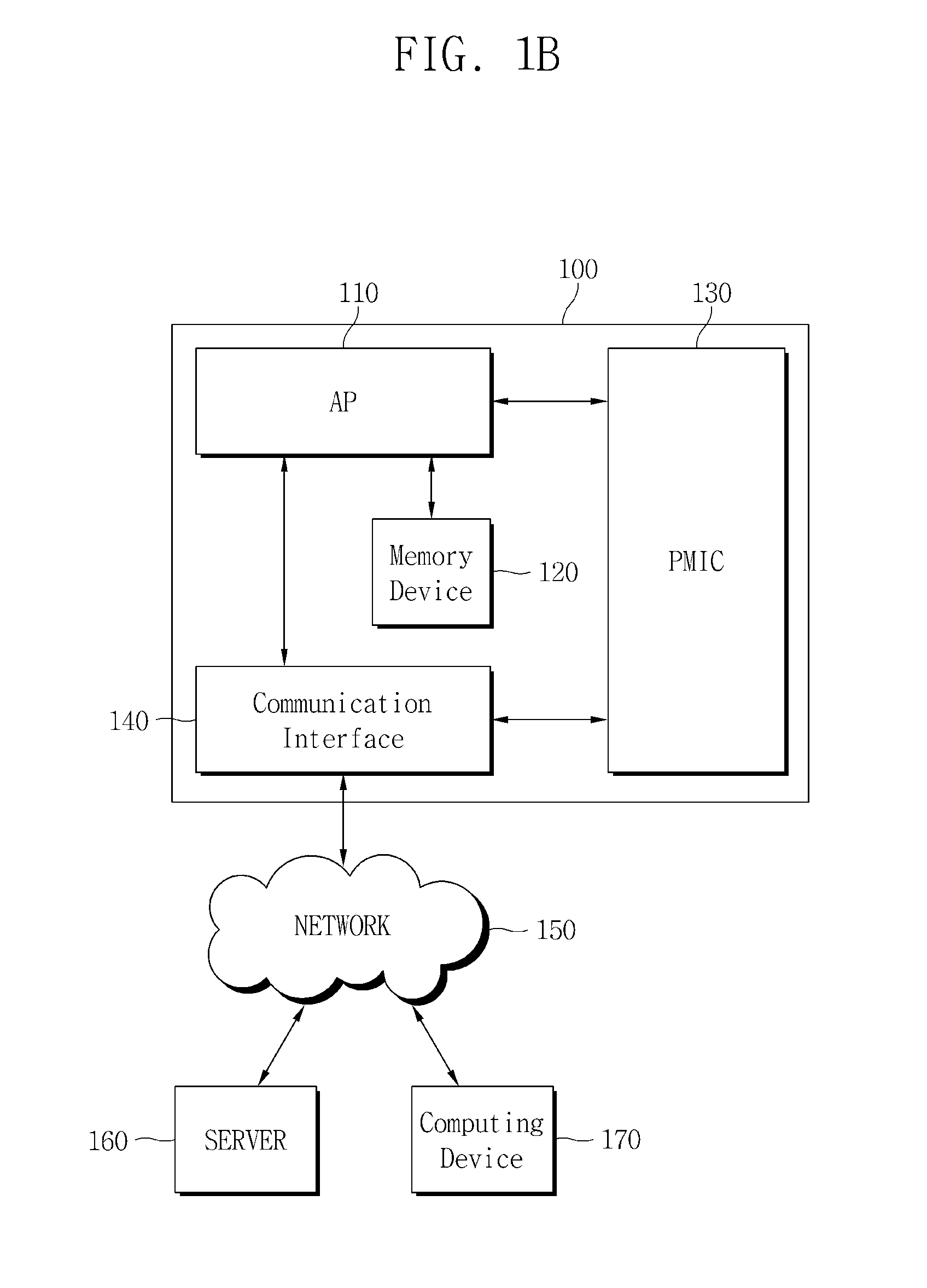
Application processor and dynamic thermal management method thereof
InactiveUS20140324245A1Performance maximizationLower performance requirementsProgram control using stored programsDigital data processing detailsMobile deviceComputer science
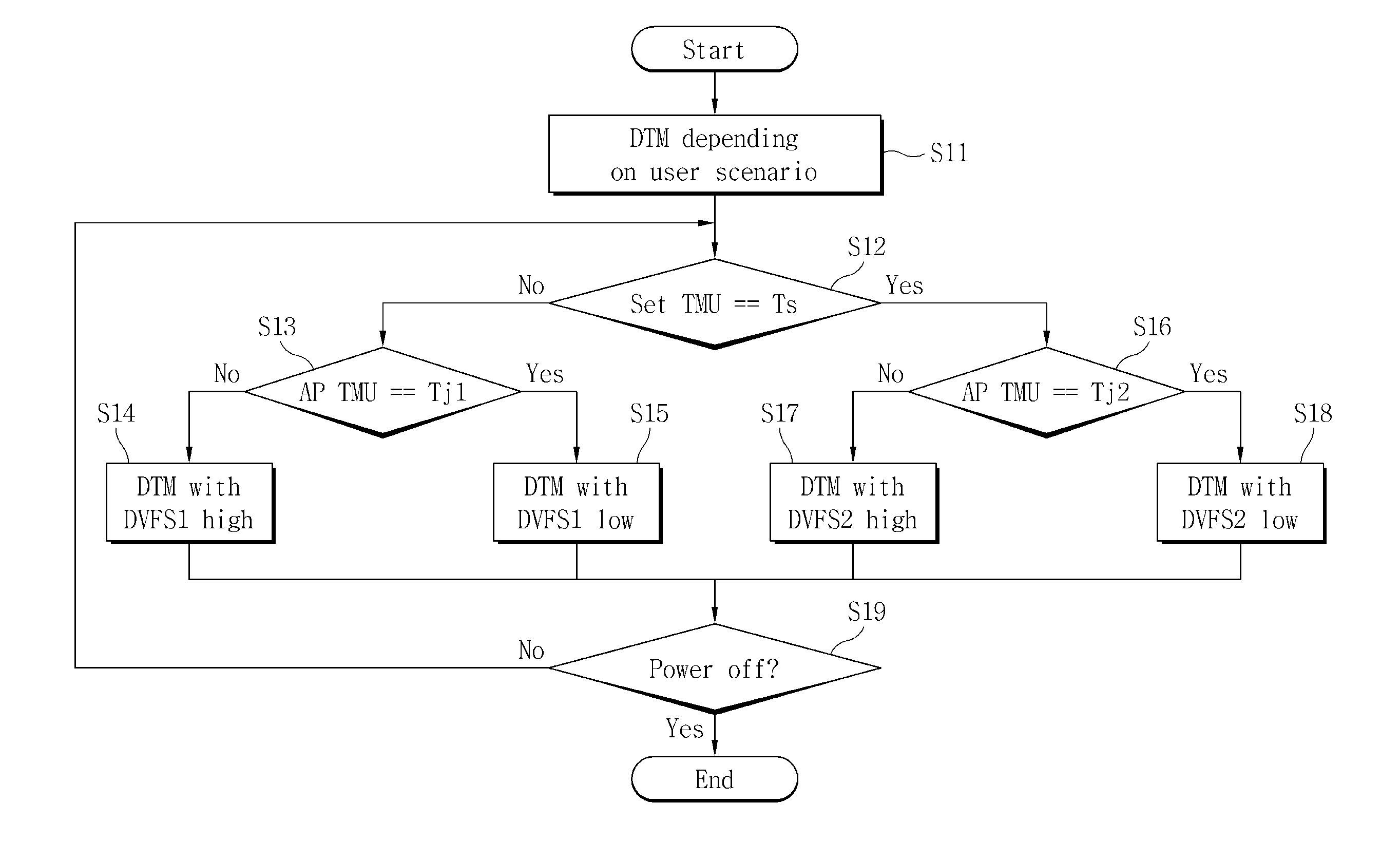
Provided is a dynamic thermal management method performed by an application processor which stores a first dynamic voltage and frequency scaling (DVFS) table and a second DVFS table, the method including comparing a surface temperature of a mobile apparatus with a critical surface temperature, controlling performance of the application processor according to the first DVFS table when the surface temperature is less than the critical surface temperature, and controlling performance of the application processor according to the second DVFS table when the surface temperature is not less than the critical surface temperature.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
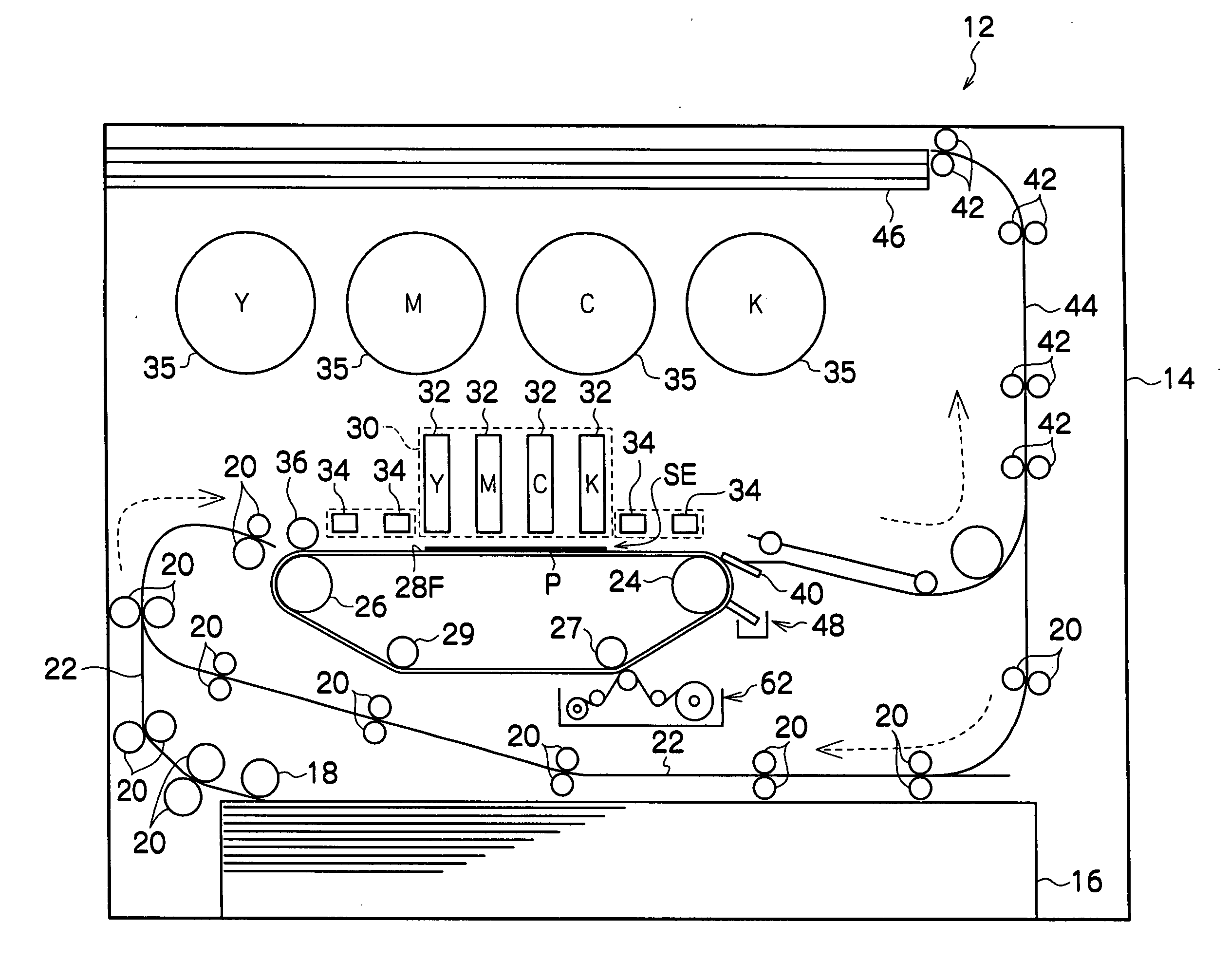
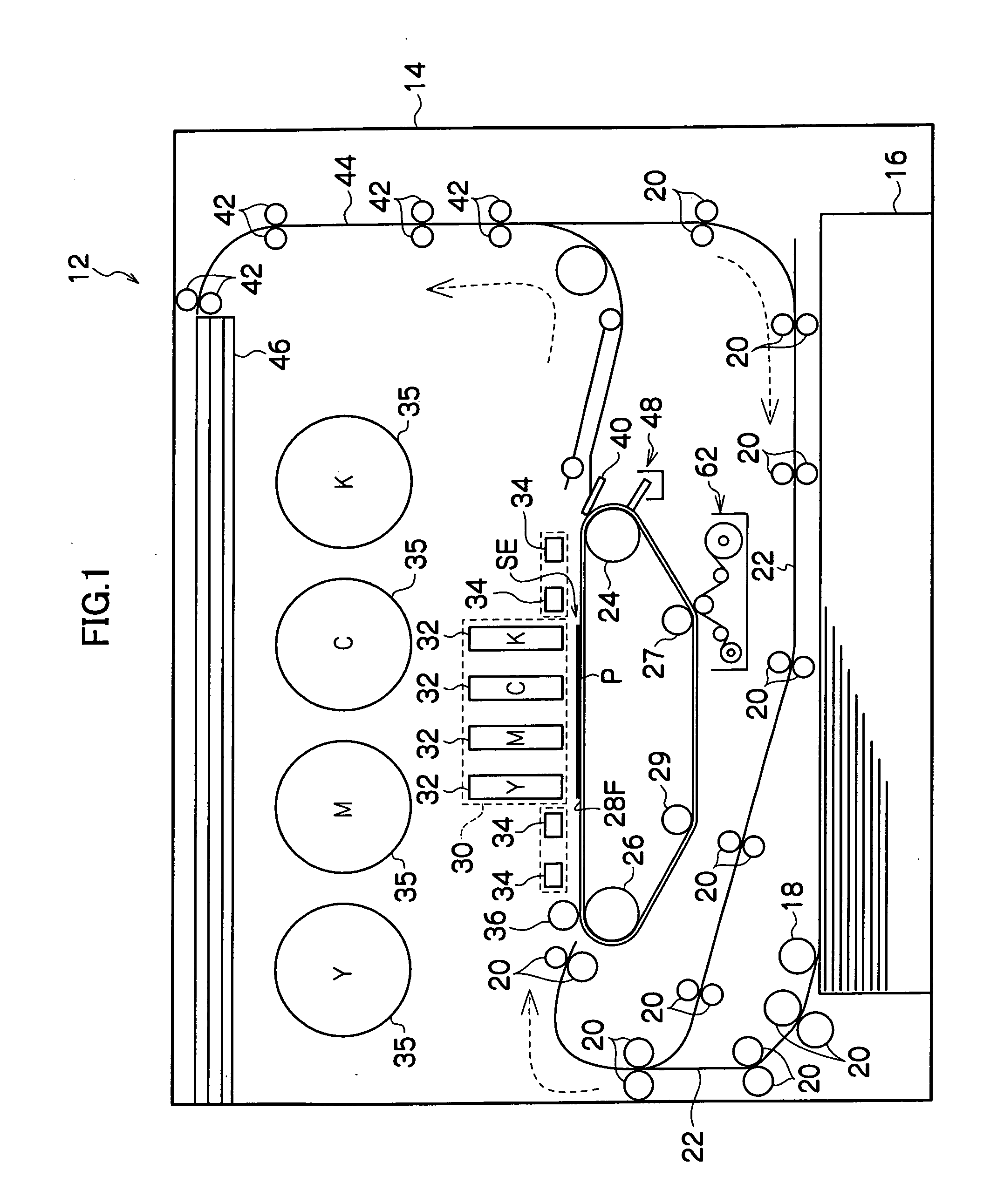
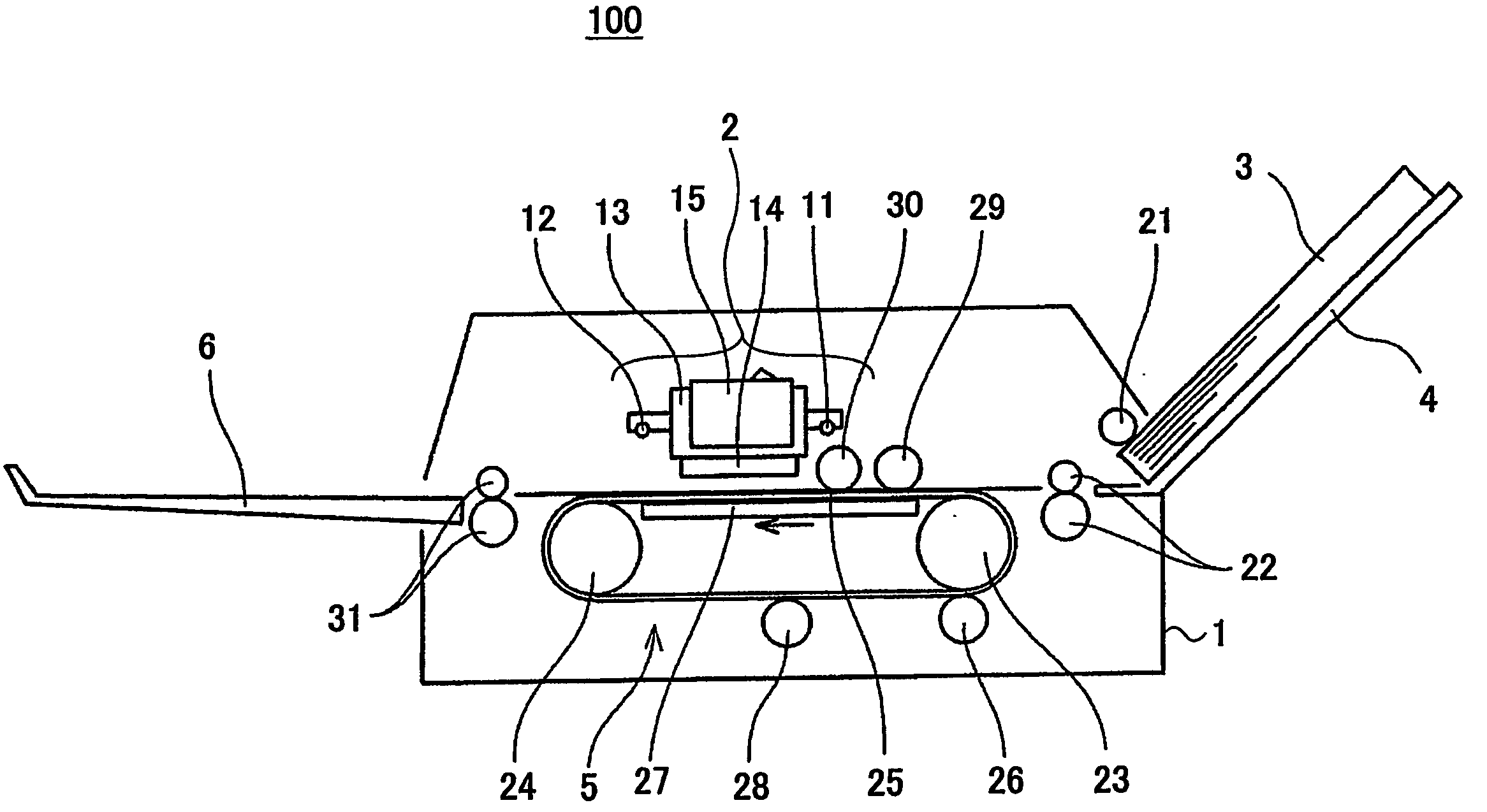
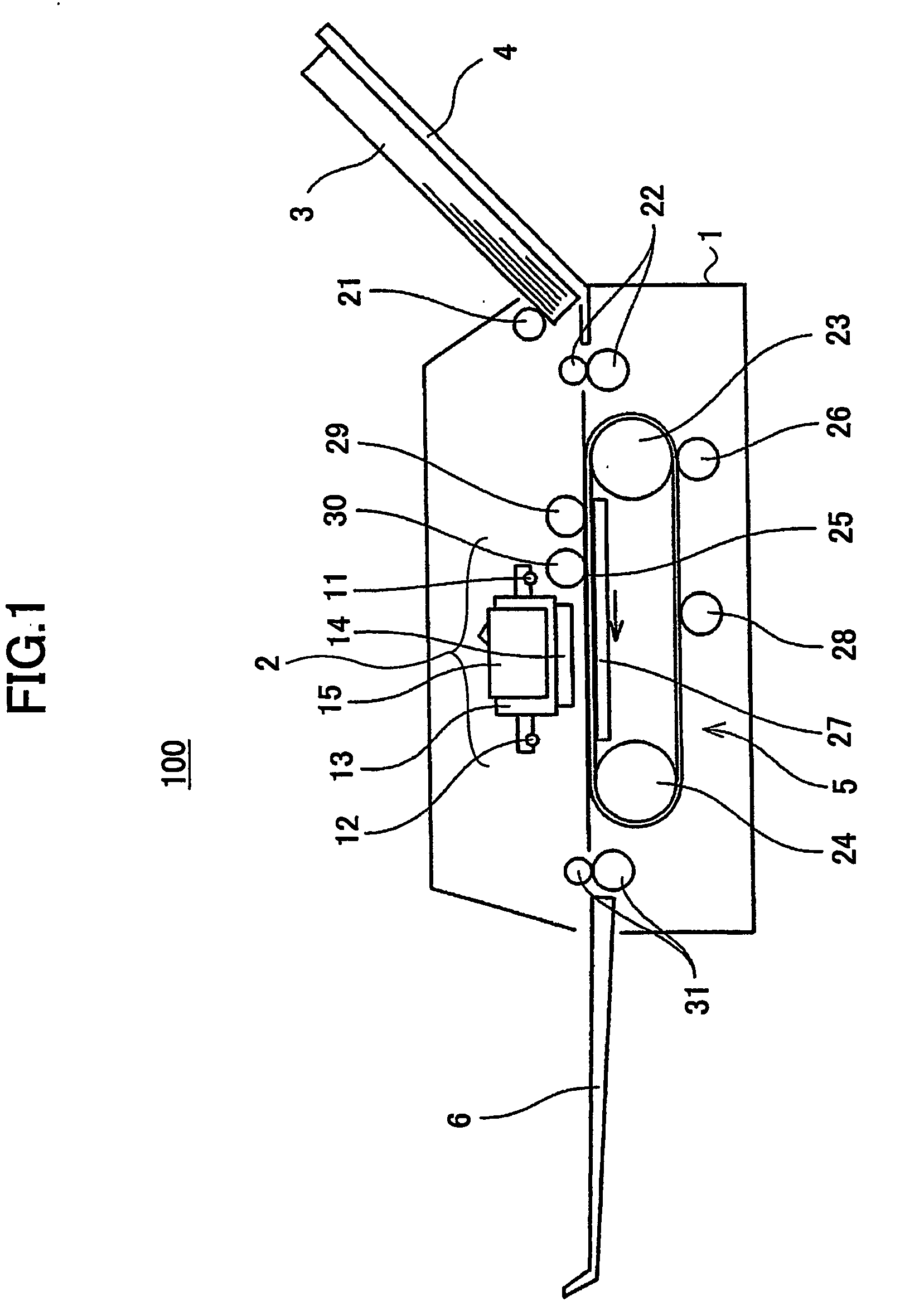
Droplet ejection device
InactiveUS20070171251A1Measurement apparatus componentsOther printing apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A droplet ejection device includes a droplet ejection head, a conveyance member, a cleaning unit and a coating unit. The droplet ejection head ejects droplets. The conveyance member retains a recording medium and conveys the recording medium to oppose the droplet ejection head. The cleaning unit cleans the conveyance member. The coating unit applies a coating liquid, with a characteristic of repelling the liquid that is ejected from the droplet ejection head, onto the conveyance member. A surface tension γo of the coating liquid, a critical surface tension γb of the conveyance member, and a surface tension γi of the liquid that is ejected from the droplet ejection head satisfy the following equations (1) and (2).γo<γb (1)γo<γi (2)
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Laminated body, separator, and nonaqueous secondary battery
ActiveUS20170033347A1Easy injectionHigh dielectric strengthLayered productsFinal product manufacturePolyolefinPorous layer
A laminated body of the present invention includes: a porous film containing a polyolefin as a main component; and a porous layer on at least one surface of the porous film, the porous layer containing a resin, the laminated body satisfying 0≦(A)−(B)≦20 mN / m, where (A) represents the critical surface tension over the outermost surface of the porous layer, and (B) represents the critical surface tension that, in a case where the porous layer has been peeled from the laminated body at an interface with the porous film, the porous film has on the side of the interface.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Polishing pad, polyurethane layer therefor, and method of polishing a silicon wafer
InactiveCN102448669ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesMicrometerHydrophobic polymer
A polyurethane layer for forming a polishing pad for a semiconductor wafer is described, wherein the polyurethane layer comprises: a foamed polyurethane, wherein the polyurethane foam has a density of about 640 to about 960 kg / m3, and a plurality of cells having an average diameter of about 20 to about 200 micrometers; and particles of a hydrophobic polymer having a critical surface energy of less than 35 mN / m and having a median particle size of 3 to 100 micrometers. Polishing pads as well as methods for polishing are also described.
Owner:ROGERS CORP
Mold shell for precision casting or directional solidification of TiAl-based alloy and method for manufacturing mold shell
InactiveCN105642831AImprove heat resistanceAccelerated corrosionFoundry mouldsFoundry coresSlurryChemical stability
The invention belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of precision investment casting mold shells, and relates to a mold shell for precision casting or directional solidification of a TiAl-based alloy and a method for manufacturing the mold shell. In slurry of a surface layer and a critical surface layer of the mold shell involved in the method, alumina sol serves as a binder, and high-purity electric smelting yttrium oxide powder and electric smelting white corundum powder serve as fireproof filler; and at least one of Y2O3 and three kinds of yttrium-aluminum oxide, namely, Y3Al5O12, Y4Al2O9 and YAlO3, serves as ingredients of the surface layer of the mold shell obtained after roasting. The mold shell is manufactured through the precision investment casting technology, and the procedures of mold waxing, slurry hanging, sand spreading, dewaxing, roasting and the like are included. The slurry of the mold shell is stable in performance, good in smearing, hanging and flowing performance and easy to store; the mold shell has the beneficial effects of being high in chemical stability, excellent in high-temperature strength, thermal shock resistance and high-temperature creep resistance and the like; and the TiAl-based alloy obtained through precision casting or directional solidification is smooth in surface, and a pollution layer is thin.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Fatigue short crack propagation life prediction method under multi-axis variable amplitude loading
ActiveCN108897900APromote engineering applicationNuclear energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationFatigue IntensityFracture mechanics
The invention discloses a fatigue short crack propagation life prediction method under multi-axis variable amplitude loading, and relates to the multi-axis fatigue strength theory field. The algorithmincludes the following steps: (1) using the Wang-Brown multi-axis cycle counting under stress loading to obtain a plurality of half cycles, and realizing multi-axis constant amplitude loading of eachhalf cycle; (2) using the weighted average maximum shear stress method to determine a weight critical surface for the characteristic that the critical surface is not fixed; (3) obtaining the crack propagation amount of a single variable amplitude load block by using a multi-axis fatigue short crack propagation model on the weight critical surface; and (4), performing plastic zone size correctionon crack tips, and calculating the short crack propagation life by the fracture mechanics method. The method can well describe the influence of multi-axis variable amplitude loading on crack propagation. The results show that the method can predict the short crack propagation life under multi-axis variable amplitude loading.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
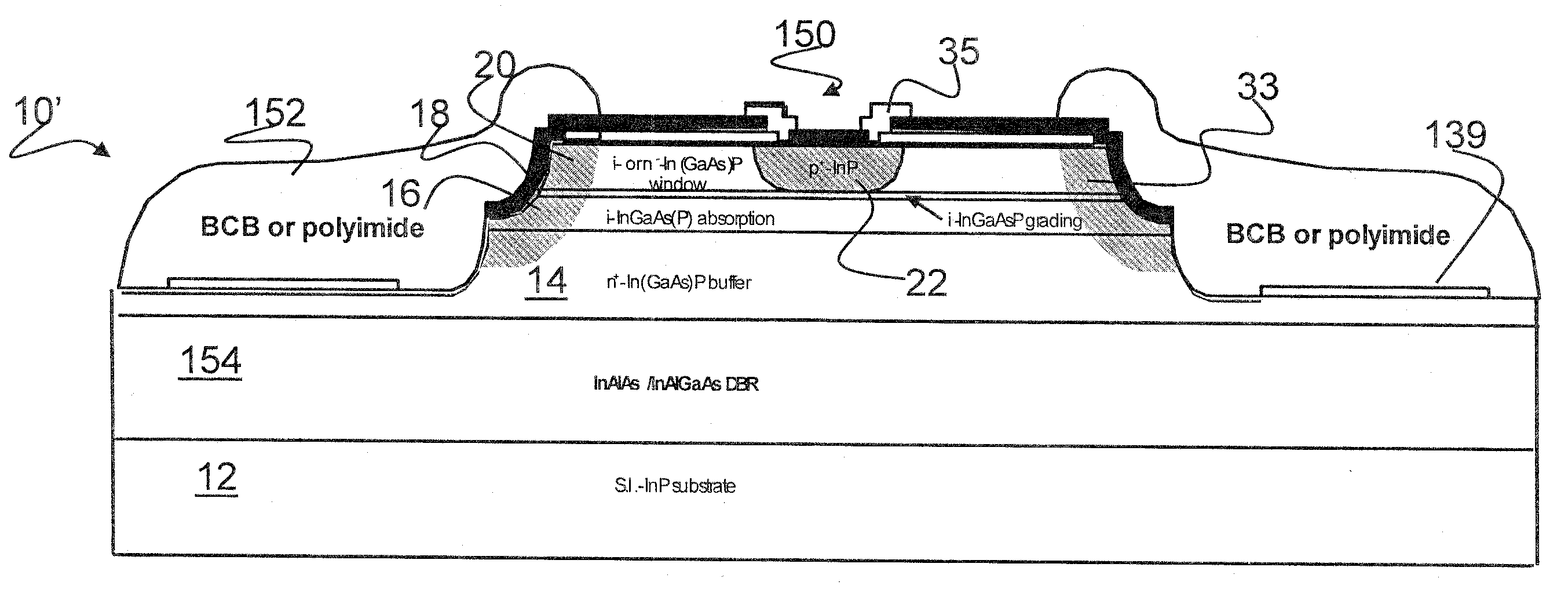
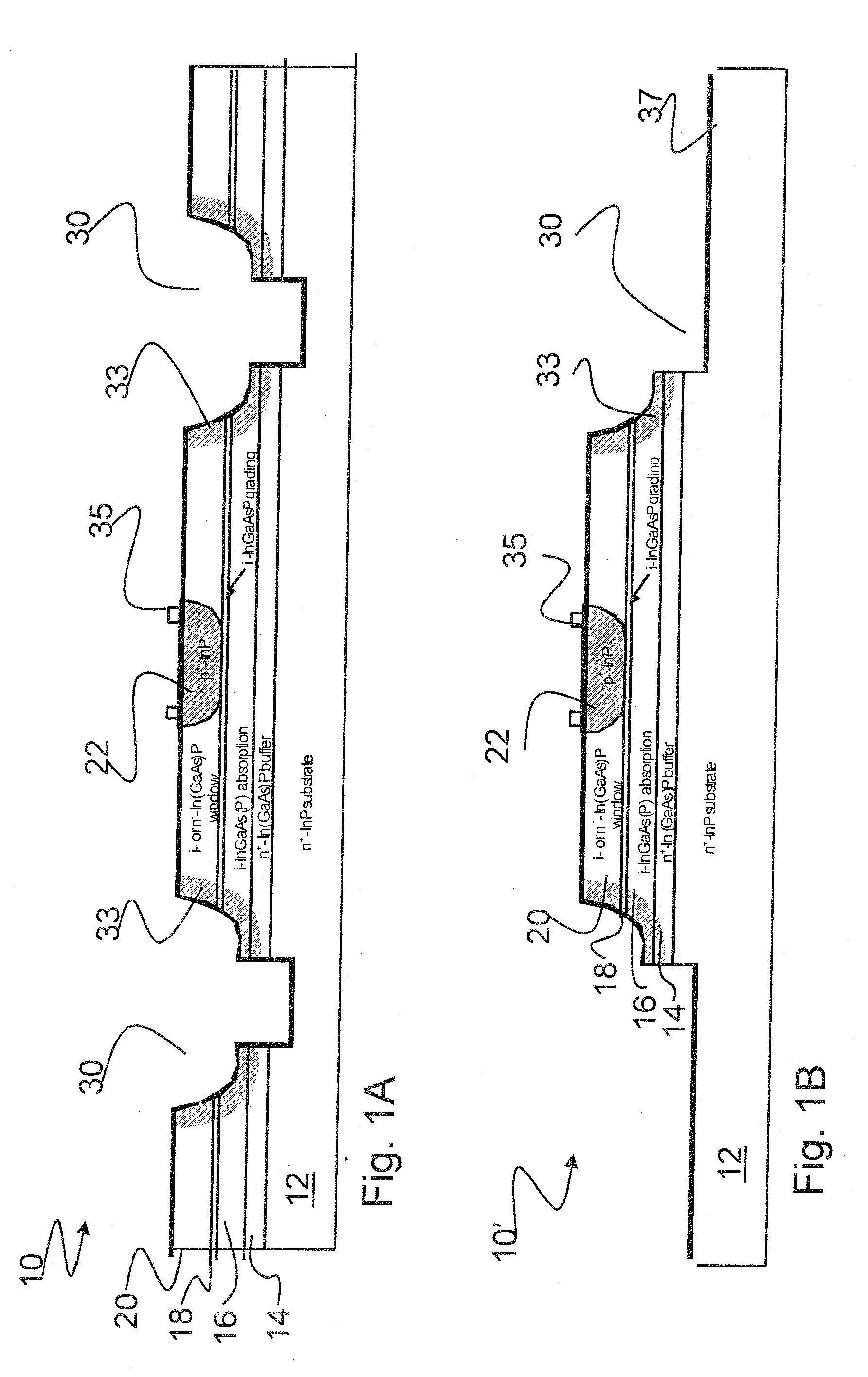
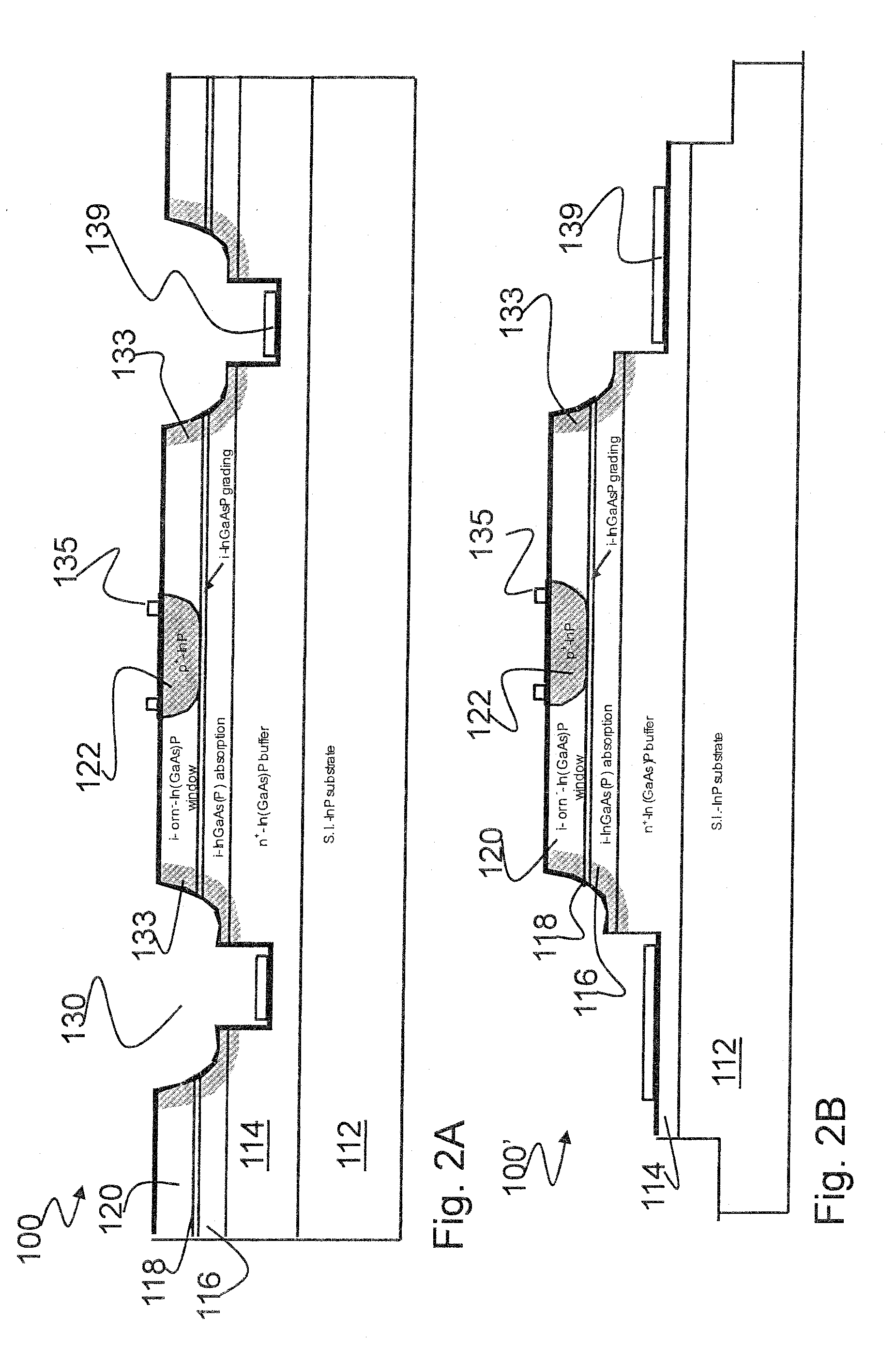
Mesa-Type Photodetectors With Lateral Diffusion Junctions
ActiveUS20090020841A1Improve reliabilityQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationDopantImpurity diffusion
The present invention relates to a stable mesa-type photodetector with lateral diffusion junctions. The invention has found that without resorting to the complicated regrowth approach, a simple Zn diffusion process can be used to create high-quality semiconductor junction interfaces at the exposed critical surface or to terminate the narrow-bandgap photon absorption layers. The invention converts the epi material layers near or at the vicinity of the etched mesa trench or etched mesa steps into a different dopant type through impurity diffusion process. Preferably the diffused surfaces are treated with a subsequent surface passivation. This invention can be applied to both top-illuminating and bottom-illuminating configurations.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Gemini surfactant containing triazine ring
InactiveCN101343254AImprove stabilityHigh activityOrganic chemistryTransportation and packagingCritical micelle concentrationOrder of magnitude
Disclosed is a Gemini surface active agent as indicated in a general formula (I), the surface active agent has a molecular structure taking a triazine ring as a linking group and possesses rather high stability, and the critical surface tension thereof is far weaker than that of the common surface active agent, the critical micelle concentration is lower than that of the common surface active agent by 2 to 3 orders of magnitude, and the surface activity is excellent.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
High pressure rf-dc sputtering and methods to improve film uniformity and step-coverage of this process
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a processing chamber used to perform a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process and methods of depositing multi-compositional films. The processing chamber may include: an improved RF feed configuration to reduce any standing wave effects; an improved magnetron design to enhance RF plasma uniformity, deposited film composition and thickness uniformity; an improved substrate biasing configuration to improve process control; and an improved process kit design to improve RF field uniformity near the critical surfaces of the substrate. The method includes forming a plasma in a processing region of a chamber using an RF supply coupled to a multi-compositional target, translating a magnetron relative to the multi-compositional target, wherein the magnetron is positioned in a first position relative to a center point of the multi-compositional target while the magnetron is translating and the plasma is formed, and depositing a multi-compositional film on a substrate in the chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Image forming apparatus, recording liquid, conveyor belt, recording liquid cartridge
InactiveUS20060050124A1Eliminate the problemMeasurement apparatus componentsInksImage formationEngineering
An image forming apparatus for forming an image on a recording medium by ejecting a recording liquid to the recording medium at a recording part is disclosed. The image forming apparatus includes a conveyor belt for conveying the recording medium to the recording part, the conveyor belt satisfying a relation of γ>γc, wherein γ (mN / m) is a static surface tension of the recording liquid at 25° C., and γc (mN / m) is a critical surface tension of the conveyor belt, wherein the recording liquid contains a color material in a disperse state.
Owner:RICOH KK
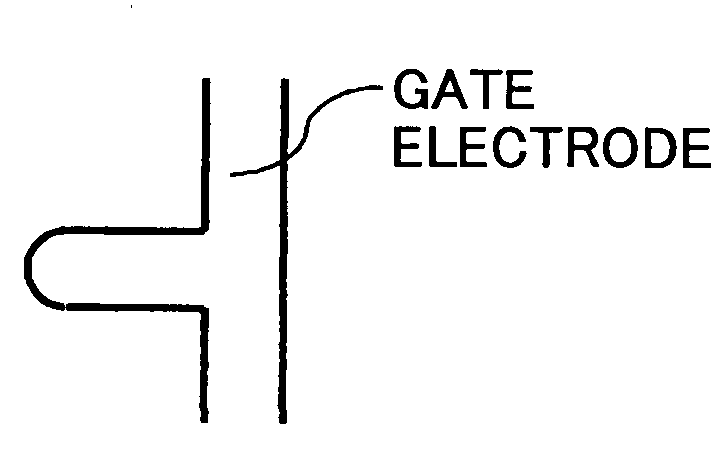
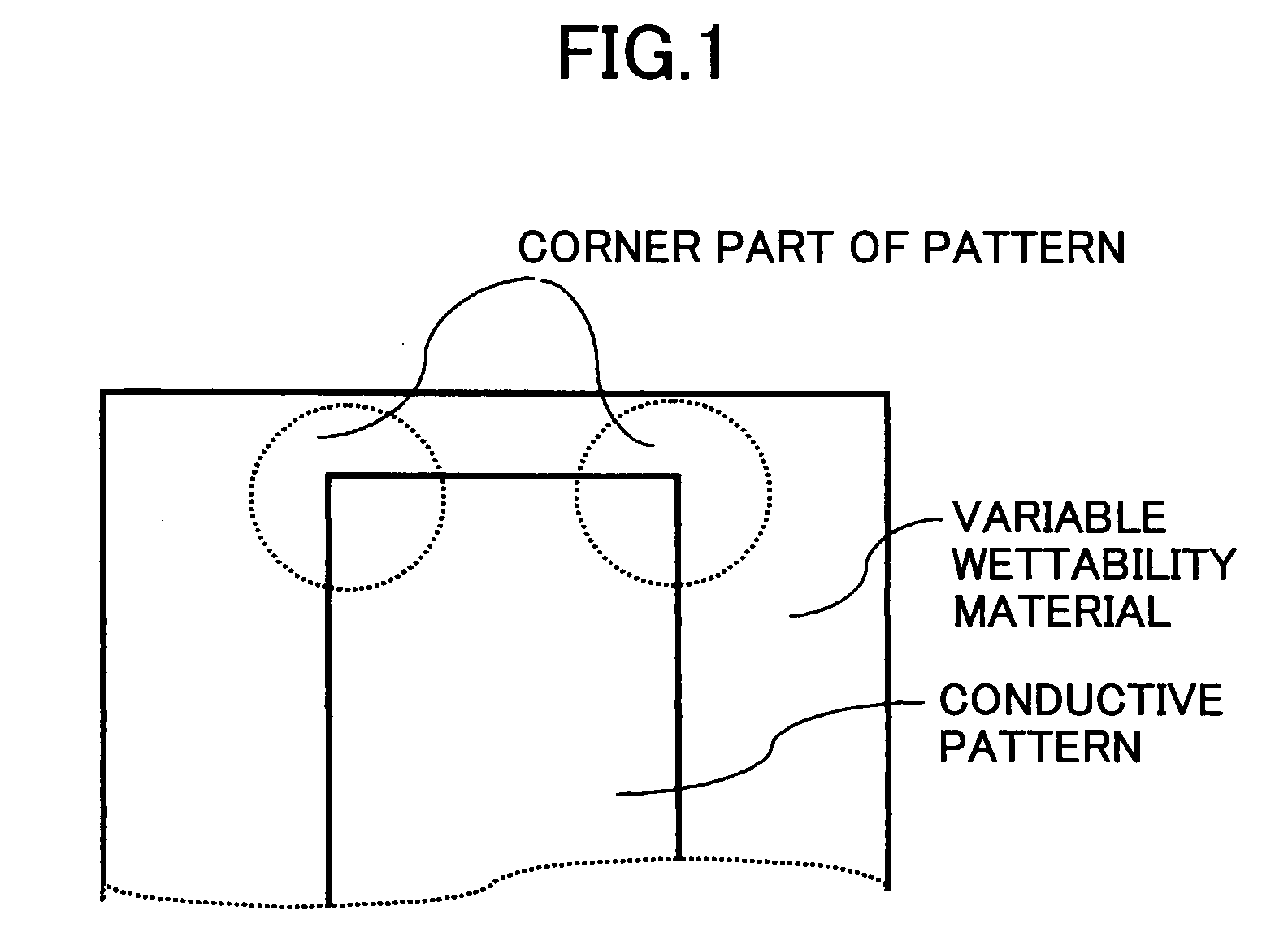
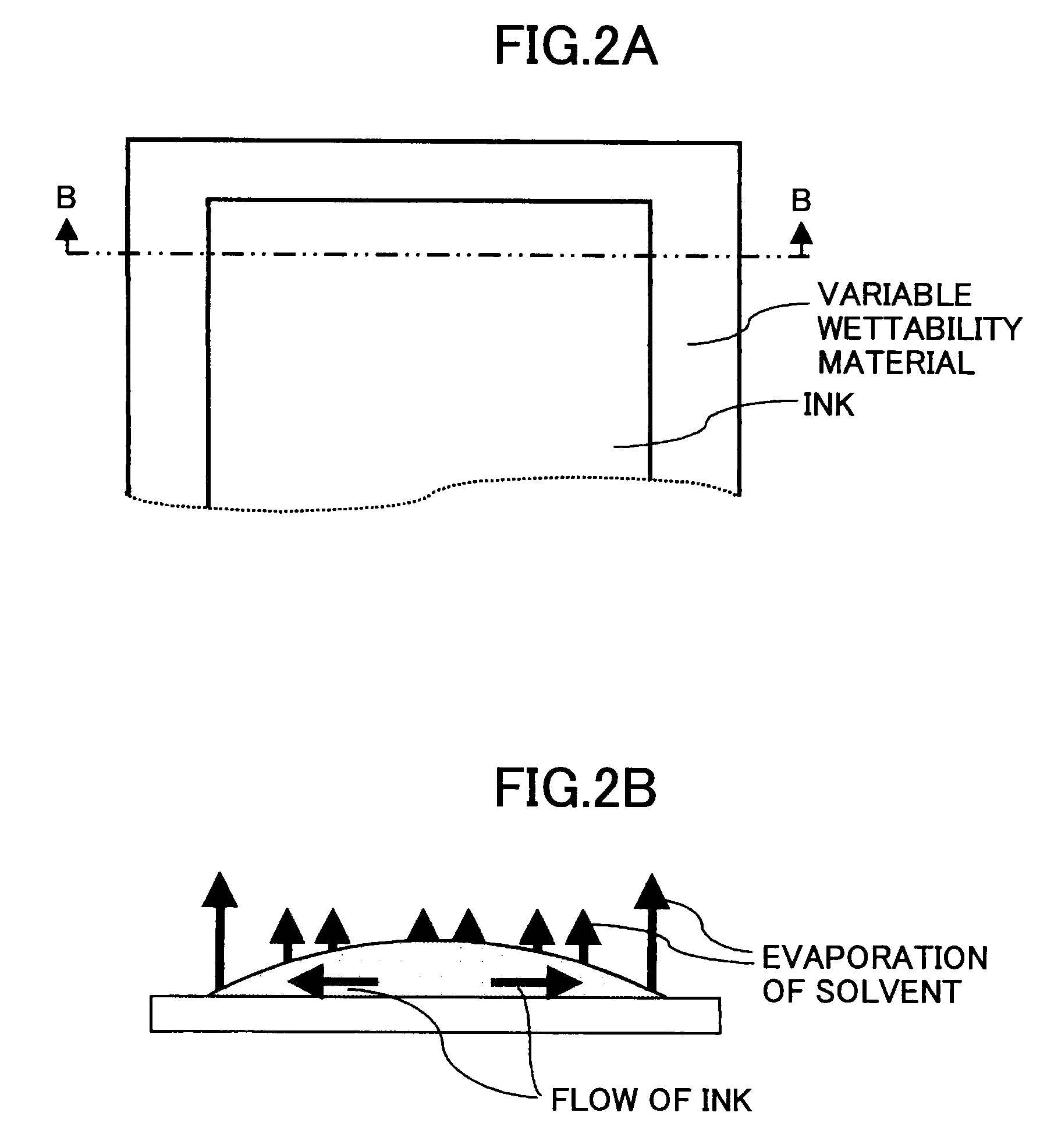
Wiring pattern, electronic device, organic semiconductor device, layered wiring pattern, and layered wiring substrate using the wiring pattern
InactiveUS20080061288A1Eliminate the problemPrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesHigh surfaceOrganic semiconductor
A wiring pattern is disclosed including: a variable wettability layer including a material whose critical surface tension changes in response to energy provided thereto, the wettability changing layer including a high surface energy part exhibiting a high critical surface tension and a low surface energy part exhibiting low critical surface tension; and a conductive pattern layer formed on the variable wettability layer at the high surface energy part. The conductive pattern layer has an elongated shape with a chamfered corner part in a plan view.
Owner:RICOH KK
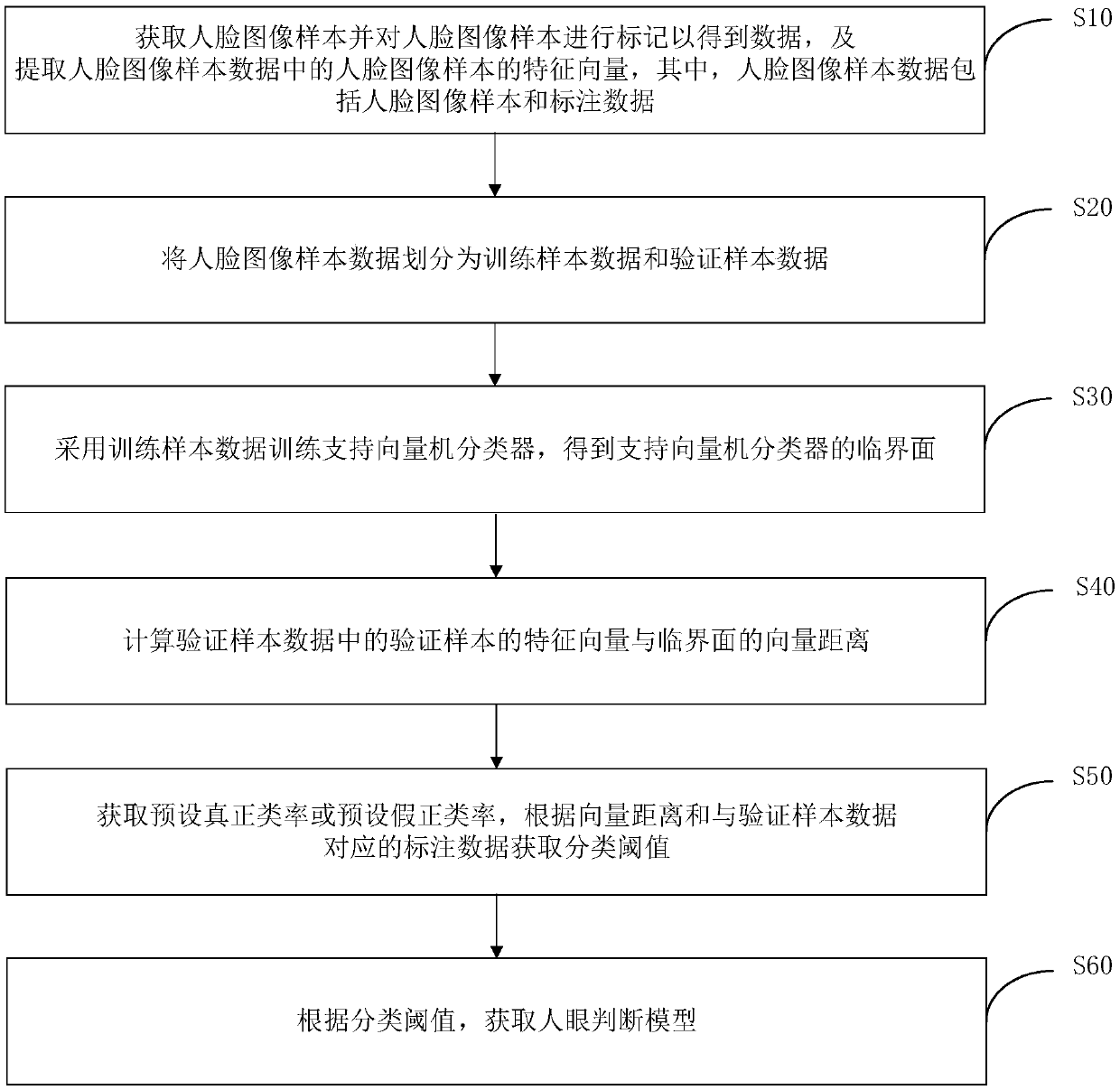
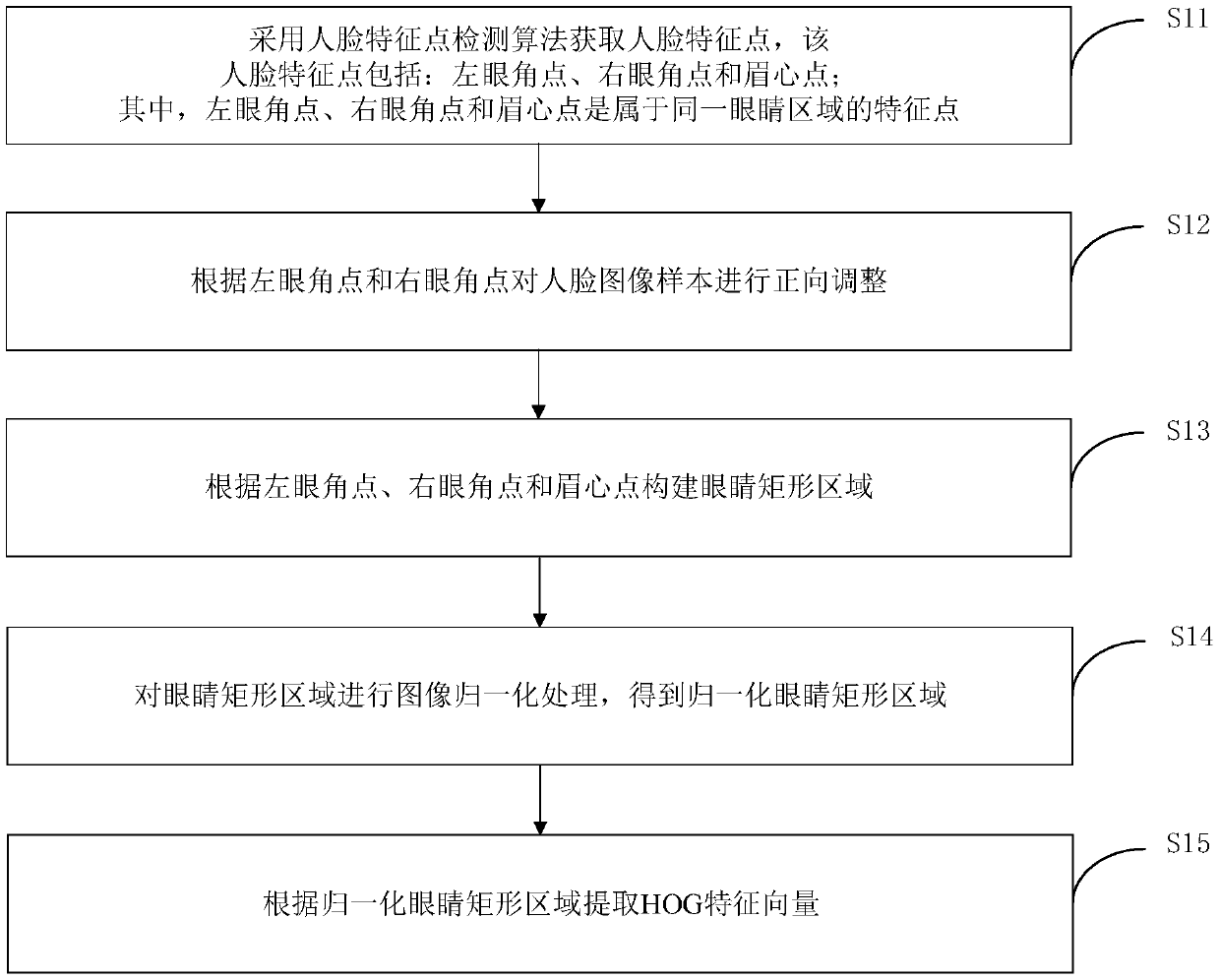
Human eye model training method, human eye identification method, apparatus and device, and medium
InactiveCN108985159AImprove training efficiencySimplify the classification processCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorSupport vector machine classifier
Disclosed are a human eye model training method, a human eye identification method, apparatus and device, and a medium. The method comprises: acquiring a face image sample and marking the face image sample to obtain face image sample data, extracting a feature vector of the face image sample, and dividing the face image sample data into training sample data and verification sample data; training asupport vector machine classifier through the training sample data, and obtaining the critical surface of the support vector machine classifier; calculating the distance between the eigenvector of the verification sample and the vector of the critical surface in the verification sample data; obtaining a preset real class rate or a preset pseudo-positive class rate, obtaining a classification threshold according to the vector distance and the labeling data corresponding to the verification sample, and obtaining a human eye judgment model according to the classification threshold. Through the training method of the human eye model, a human eye judgment model with high accuracy of judging whether the human eye is occluded or not can be obtained.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
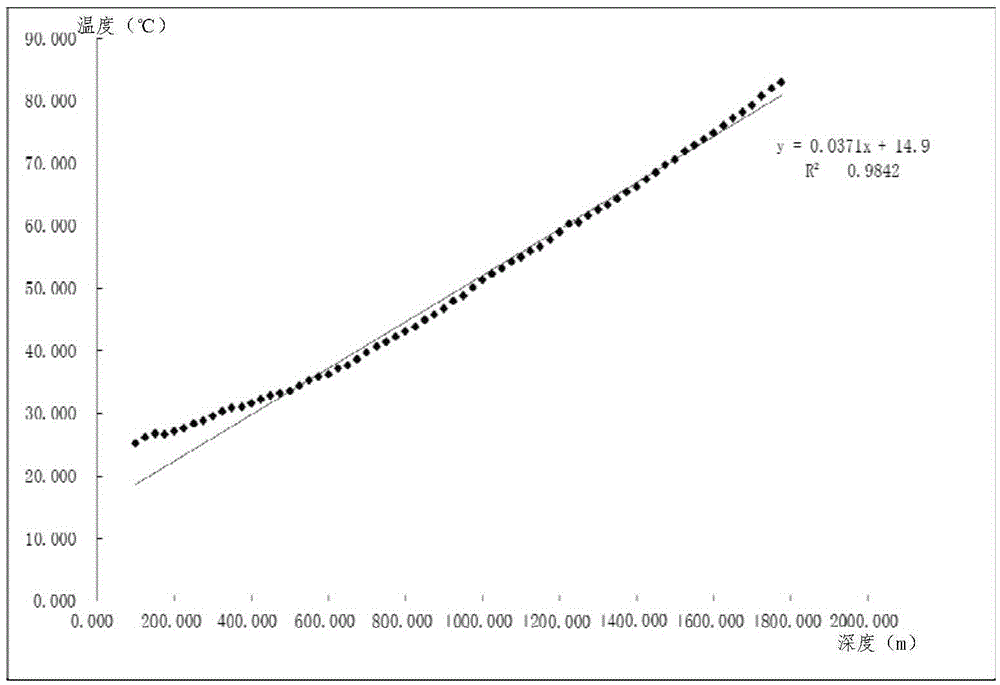
Sectional type ground temperature gradient fitting method based on stratigraphic unconformity surface
InactiveCN105652342AAccurate responseOvercoming the problem of insufficient ability to identify ground temperature anomaliesDetection/prospecting using thermal methodsComplex mathematical operationsGround temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a sectional type ground temperature gradient fitting method based on a stratigraphic unconformity surface. The method comprises the steps of: 1) determining the distribution and burial depth of the stratigraphic unconformity surface, obtaining temperature measurement data, and drawing a ground temperature curve with the temperature and the burial depth respectively serving as a transverse coordinate and a longitudinal coordinate; 2) in the range of 0-100 m downward from the stratigraphic unconformity surface, selecting the most bending part of the ground temperature curve as a ground temperature gradient critical surface, and dividing the ground temperature curve into an upper cure and a lower curve; 3) carrying out linear fitting respectively on temperature measurement data corresponding to the upper curve and the lower curve, and obtaining an upper straight line and a lower straight line, wherein the gradients thereof are respectively the ground temperature gradients of a shallow stratum and a deep stratum and reflect the practical ground temperature field of a temperature measurement well area. The method is characterized in that according to the development characteristics of stratums in different areas, the ground temperature gradients above and below the ground temperature gradient critical surface are independently fitted, so that the ground temperature gradients of upper and lower stratums are obtained, the ground temperature field characteristics of new and old stratums are really reflected, and a reliable basis is provided for oil and gas and geothermal resources exploration, development and utilization.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Layered structure and electron device that uses such a layered structure, fabrication process thereof, electron device array and display apparatus
ActiveUS20100078642A1Improve efficiencyWell formedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHigh surface
A layered structure comprises a variable wettability layer including a material that changes a critical surface tension in response to energy provided thereto, the wettability changing layer including at least a high surface energy part of large critical surface tension and a low surface energy part of low critical surface tension, a conductive layer formed on the variable wettability layer at the high surface energy tension part, and a semiconductor layer formed on the variable wettability layer at the low surface energy part.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com