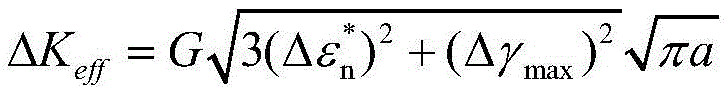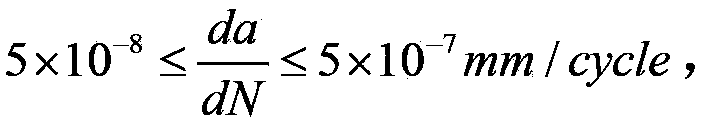Patents
Literature
276 results about "Stress intensity factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The stress intensity factor, K, is used in fracture mechanics to predict the stress state ("stress intensity") near the tip of a crack or notch caused by a remote load or residual stresses. It is a theoretical construct usually applied to a homogeneous, linear elastic material and is useful for providing a failure criterion for brittle materials, and is a critical technique in the discipline of damage tolerance.
Method for evaluating fatigue life of aged reinforced concrete bridge
ActiveCN105825030AThe prediction method is reasonableGeometric CADForecastingStress concentrationCrazing
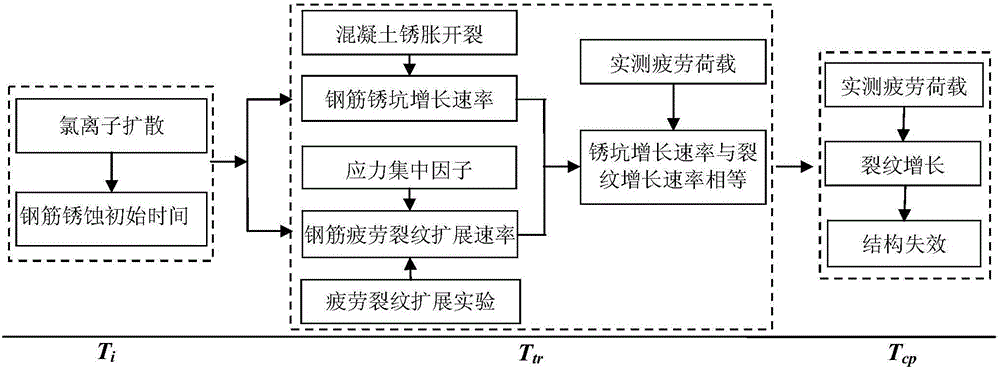
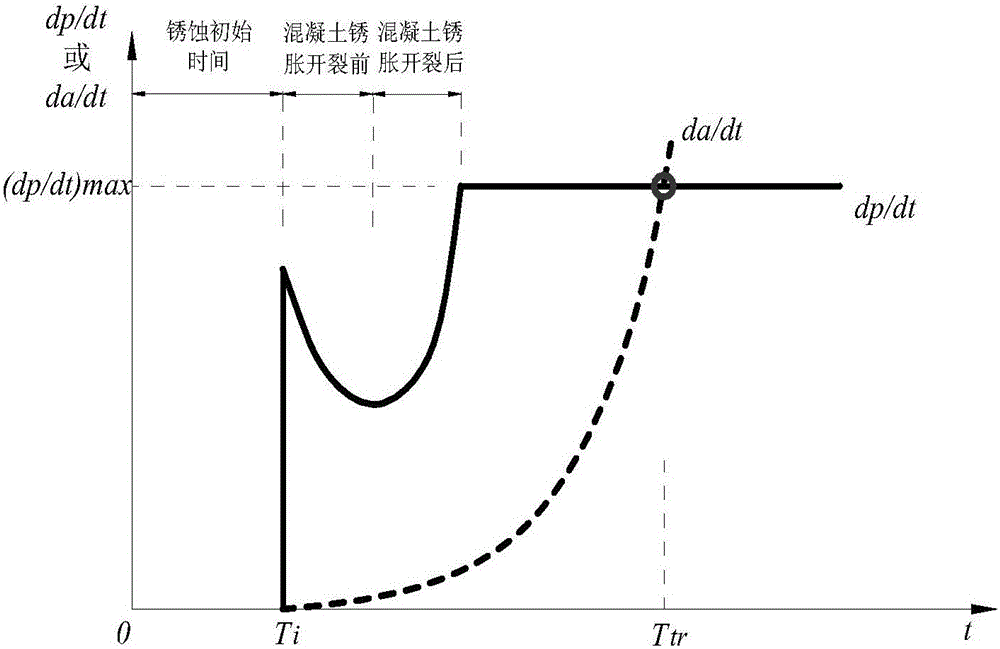
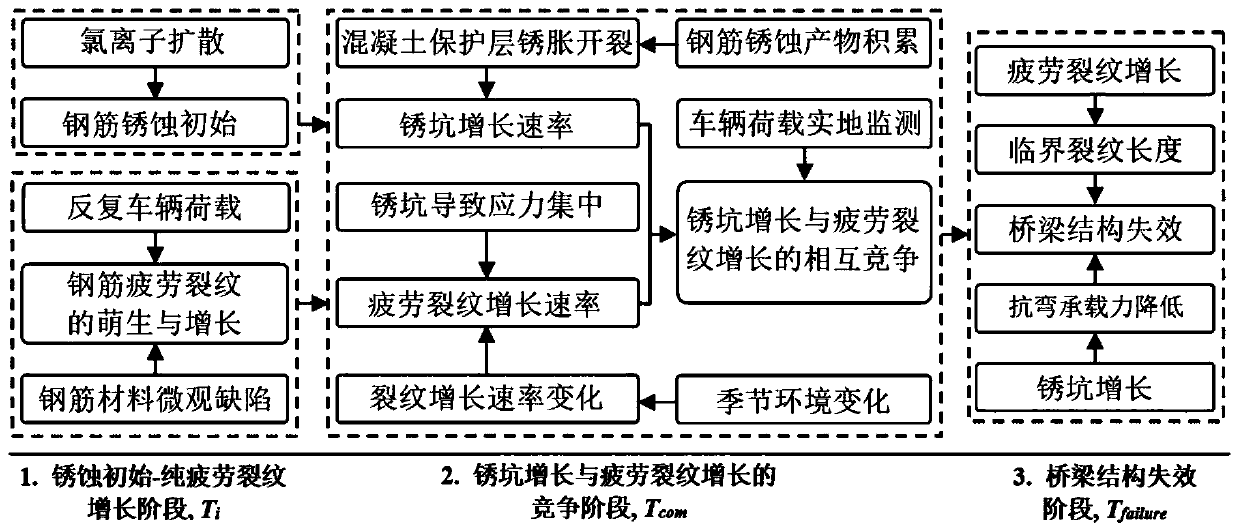
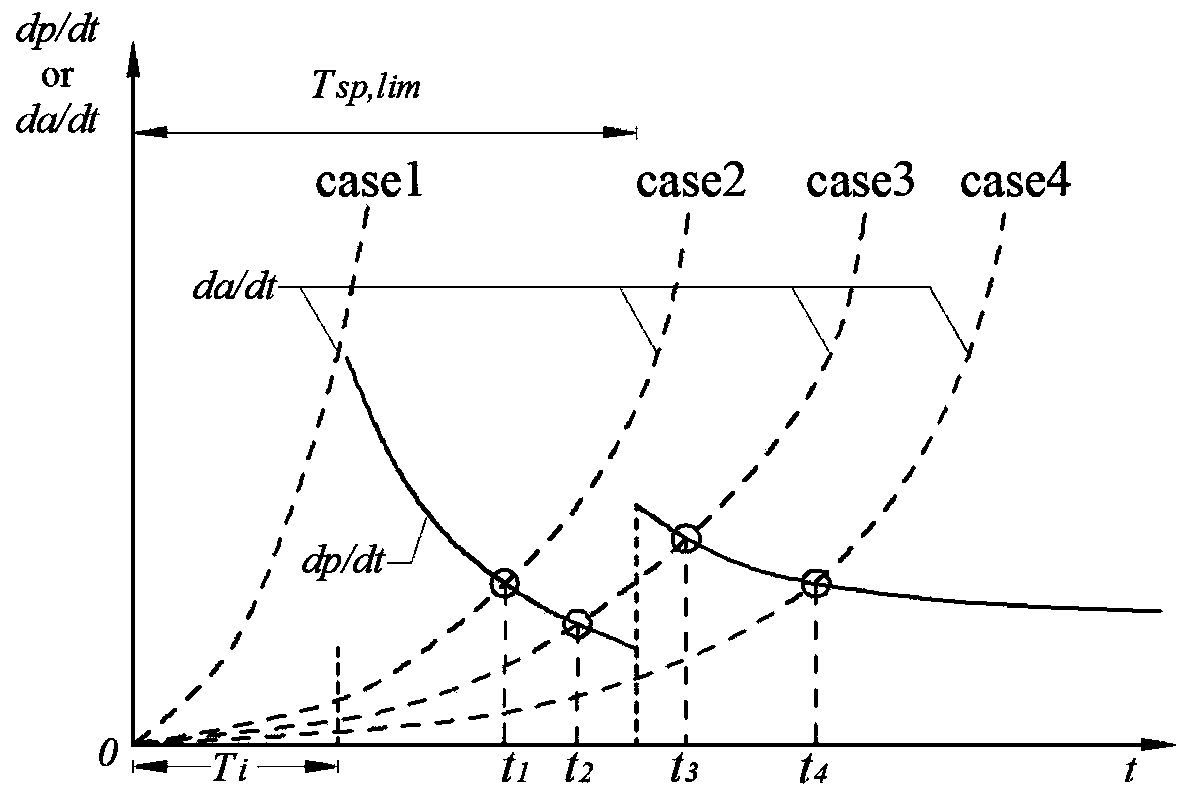
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the fatigue life of an aged reinforced concrete bridge. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining initial corrosion time of reinforcement in concrete based on the second diffusion law of Fick, and considering the influence of concrete cracking due to corrosion expansion in a corrosion rate model; adopting a small crack growth and near threshold growth analysis and determining relevant parameters of fatigue crack propagation rate of materials by developing a fatigue crack propagation test of reinforced concrete materials; performing a corrosion fatigue test or finite element analysis on corroded reinforcement to obtain stress concentration factors at different corrosion levels, and integrating into a stress intensity factor model to obtain the fatigue crack propagation rate of the reinforcement under the influence of corrosion; comparing the magnitude of a corrosion pit growth rate and the fatigue crack propagation rate and gradually converting into a single growth analysis on fatigue cracks of the reinforcement; meanwhile, combining with vehicle load observing information to realize life evaluation of a bridge at different service stages. The prediction method disclosed by the invention is reasonable and high in popularization, and can provide technical support for evaluating the life of the concrete bridges.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for measuring fracture toughness of pipeline steel by using unilateral notched tensile test
ActiveCN103604694AAvoid wastingReasonable fracture toughness valueMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCrack resistanceStress intensity factor
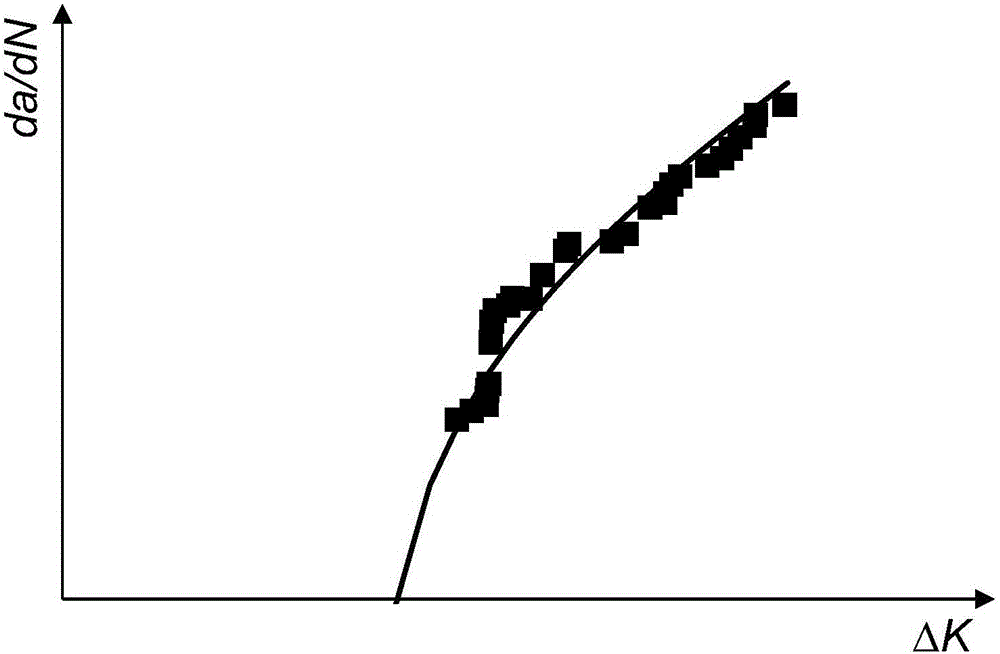
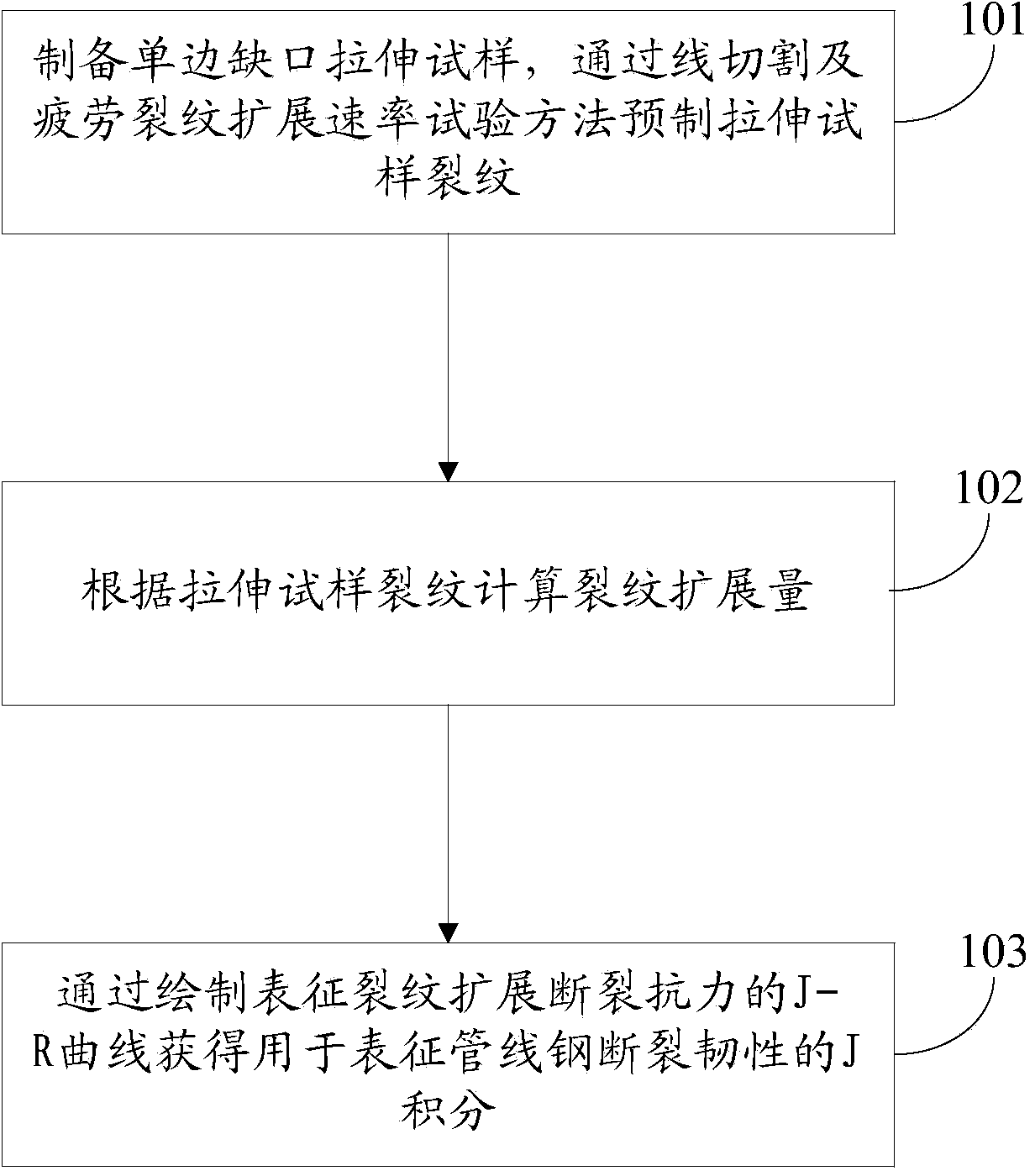
The invention discloses a method for measuring fracture toughness of pipeline steel by using a unilateral notched tensile test. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of preparing a unilateral notched tensile test sample; prefabricating a tensile sample crack by wire-electrode cutting and fatigue crack growth rate test method; calculating crack growth amount according to the tensile sample cracks; and acquiring J integration and stress intensity factor K for characterizing the fracture toughness of the pipeline steel by drawing a J-R curve for characterizing crack resistance of the crack growth. The method measures the fracture toughness of the pipeline steel by using tensile samples (SENT samples), overcomes the defects that the scope of measurement results of tensile samples (SENT samples) by a conventional technology is so small that the fracture toughness of the pipeline steel can not be evaluated; the crack toughness value of the tensile samples (SENT samples) can be more reasonable; waste of test for pipeline steel materials can be prevented; and the method has the advantages of high measurement accuracy.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
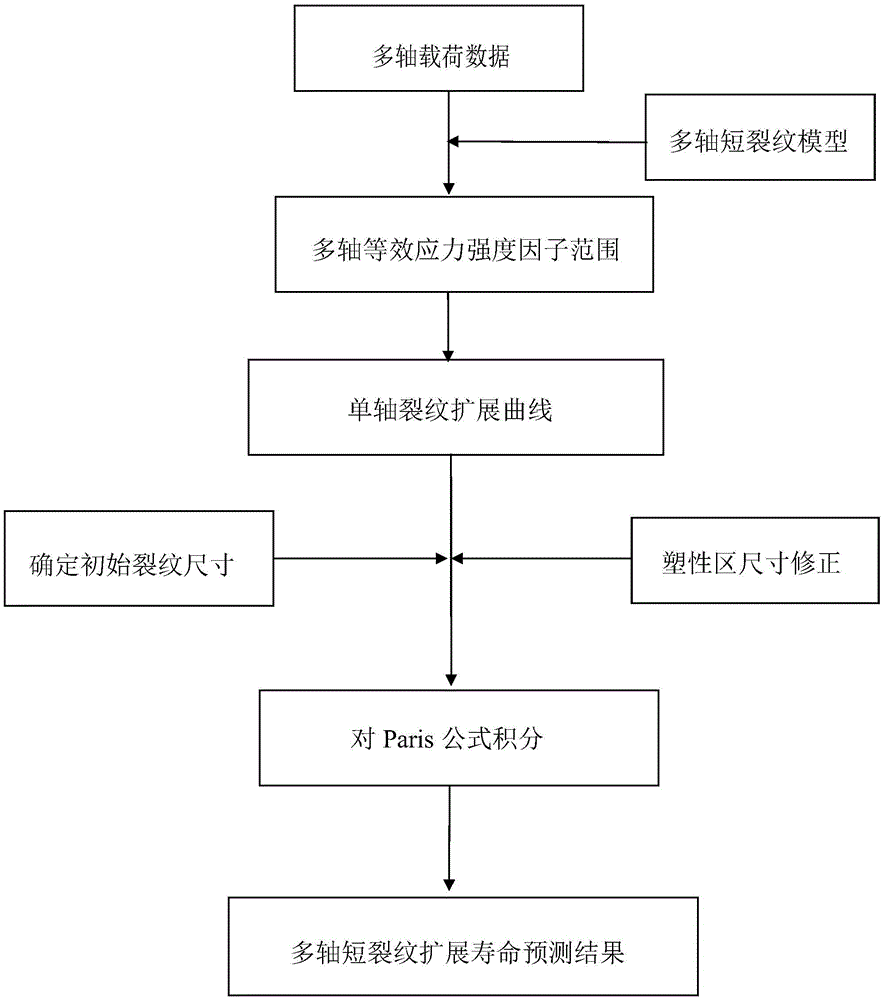
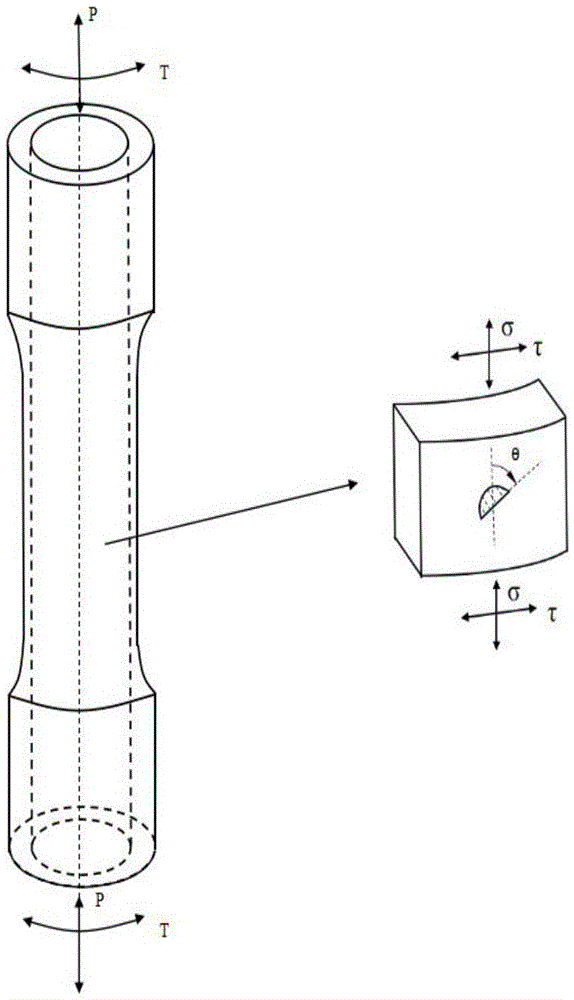
Multiaxial short crack propagation life prediction method based on critical surface method
ActiveCN105466772APromote engineering applicationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady torsional forcesFatigue damageEngineering
The present invention provides a multiaxial short crack propagation life prediction method based on a critical surface method, and relates to the field of multiaxial fatigue strength theory. The algorithm comprises the steps of: (1) selecting a plane, which contains the maximum shearing strain range, as a critical surface, and using the damage parameters on the critical surface to characterize a short crack propagation driving force; (2) based on the shear-type multiaxial fatigue damage parameters, establishing an equivalent crack stress intensity factor applicable to the multiaxial stress state; (3) fitting the short crack propagation rate data under uniaxial loading to obtain an uniaxial short crack propagation curve; and (4) carrying out plastic zone size correction on the crack tip, and calculating the short crack propagation life by a fracture mechanics method. The method can well descript the influence of non-proportional loading on crack propagation. The results show that the method can well predict the short crack propagation life under multiaxial proportional and non-proportional loading.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Turbine disc-based low-cycle fatigue crack propagation life prediction method
InactiveCN106644783AExtended Life SatisfactionMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesElasticity measurementStress intensity factorScanning electron microscope
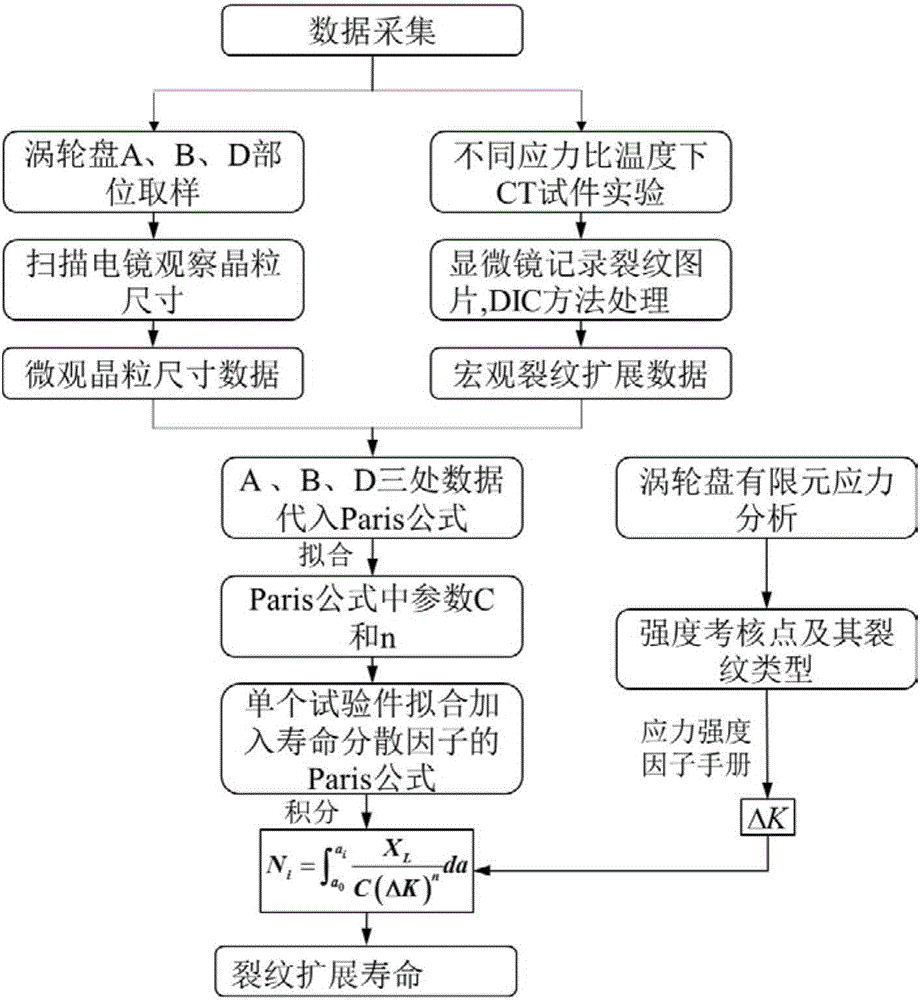
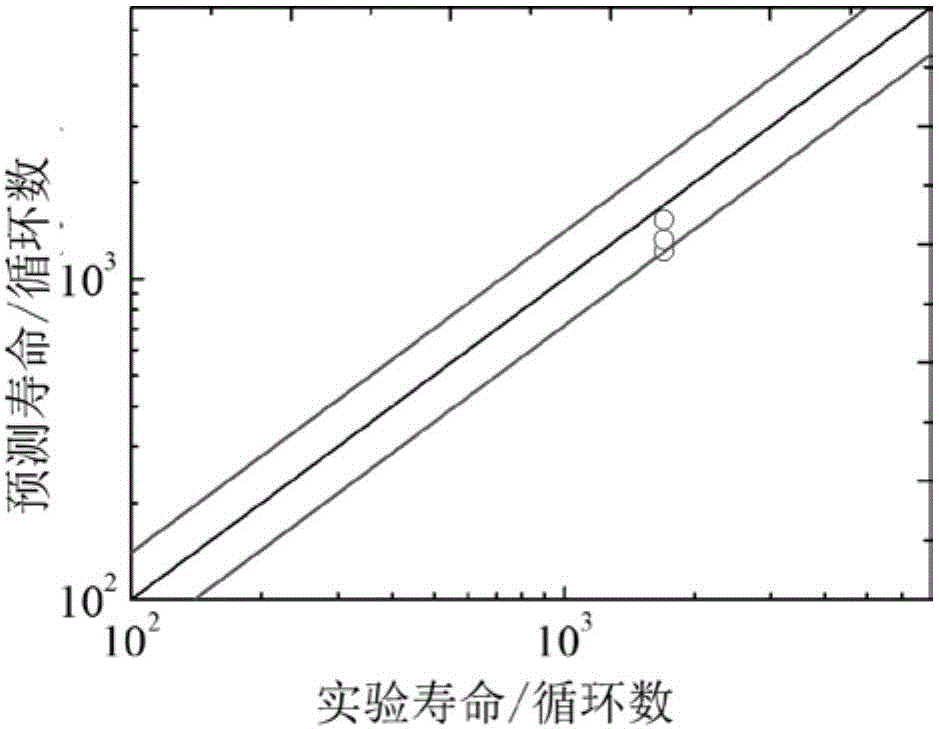
The invention relates to a turbine disc-based low-cycle fatigue crack propagation life prediction method, comprising the following steps: (1) collecting micro-data of different sampling positions of a turbine disc by using a scanning electron microscope, and obtaining a distribution rule; (2) designing a low-cycle fatigue test for the different positions, and collecting macro-data; (3) according to the data collected in steps (1) and (2), obtaining the distribution of a life scattering factor and a Paris formula considering the life dispersibility of the different sampling positions of the turbine disc; (4) performing static strength analysis to obtain a dangerous point position stress intensity factor deltaK, integrating by using the life scattering factor and the Paris formula considering the life dispersibility, which are obtained in step (3), then acquiring the relationship between crack propagation life and crack length, and giving the crack propagation life according to the crack length.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
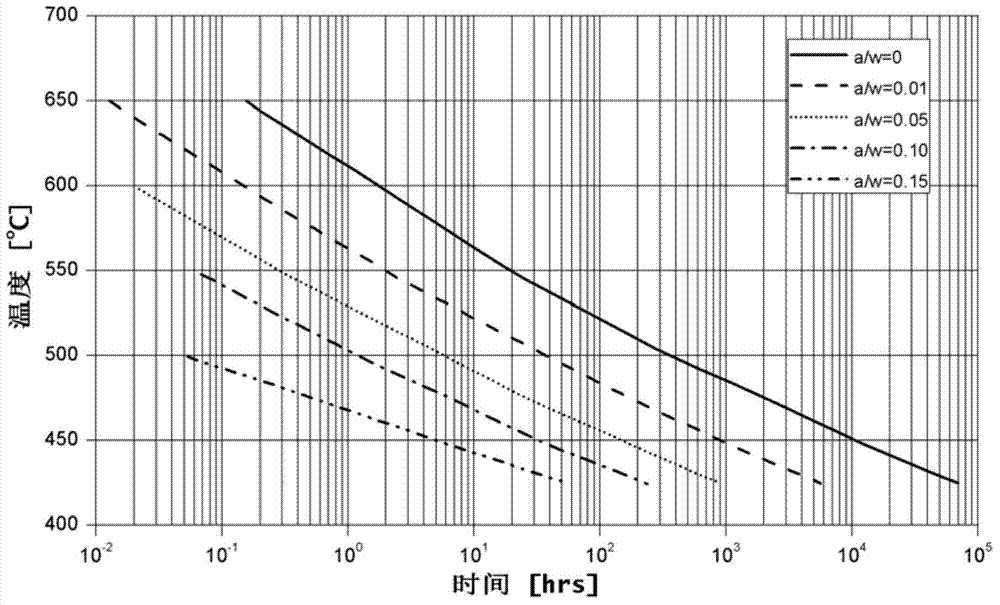
Method for measuring high-temperature creep crack growth threshold value of material
ActiveCN103217346AImprove scalabilityIncrease costInvestigating material ductilityStress intensity factorTest requirements
The invention discloses a method for measuring high-temperature creep crack growth threshold value of material. The method comprises the following steps of: for a specific material, according to the creep crack growth test requirement, processing at least 6 standard compact tension specimens, performing crack prefabrication for the well processed at least 6 specimens on a fatigue performance tester, wherein the prefabricated crack length is 0.5 times of the width of each specimen; wedging a wedge-shaped block into an initial notch of each specimen, placing the headmost end of the straight part of the wedge-shaped block at the position of a loading line, providing displacement for the loading line, forming a stress-strain field characterized by a stress strength factor at the tip of the specimen crack, and providing a driving force for the creep crack growth, wherein the specimens with different initial stress strength factors grow after certain time under creep effect in high-temperature environment, and in the same time interval, the crack growth lengths are different; drawing for the different stress strength factors and the corresponding crack growth rates, and solving the creep crack growth threshold value of the material through an extrapolation method. According to the method provided by the invention, multiple specimens can be tested for one time, and thus, the test cost is greatly reduced and the test time is greatly shortened.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
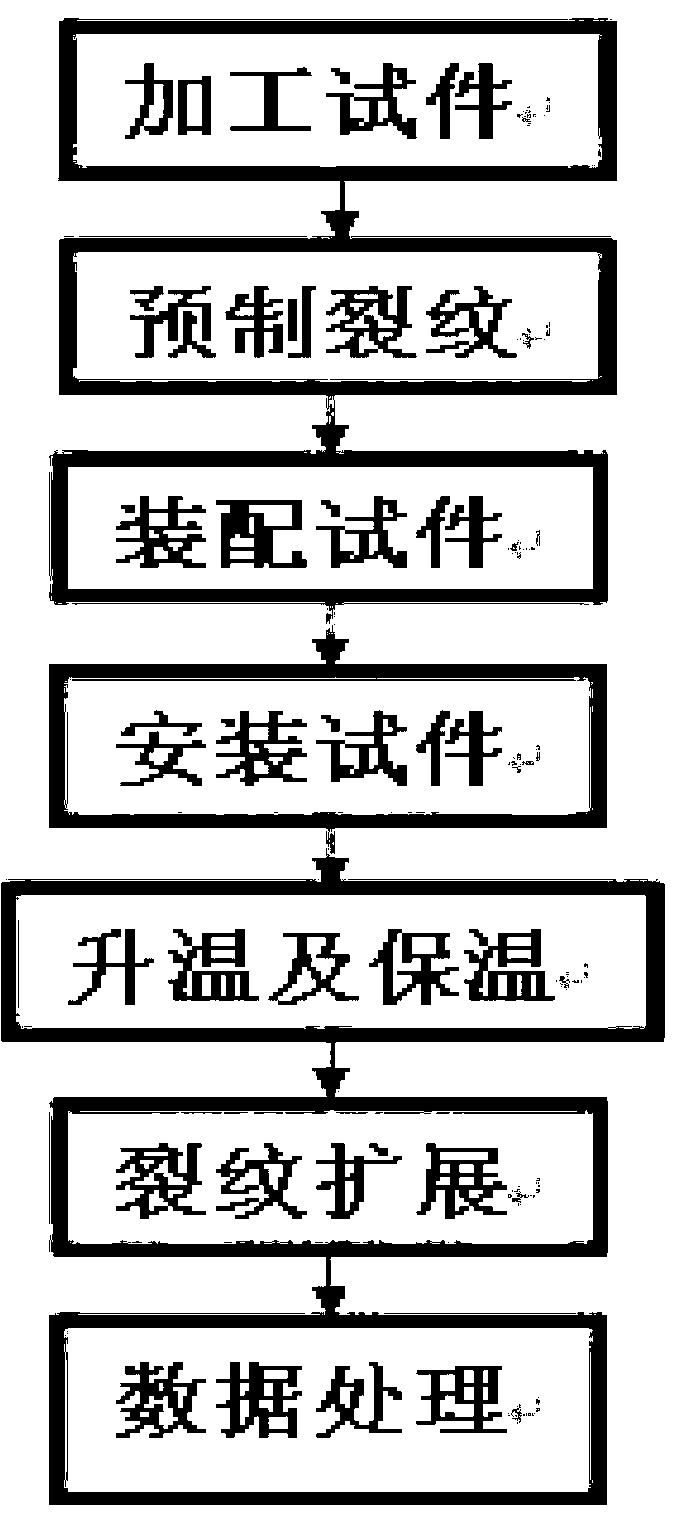
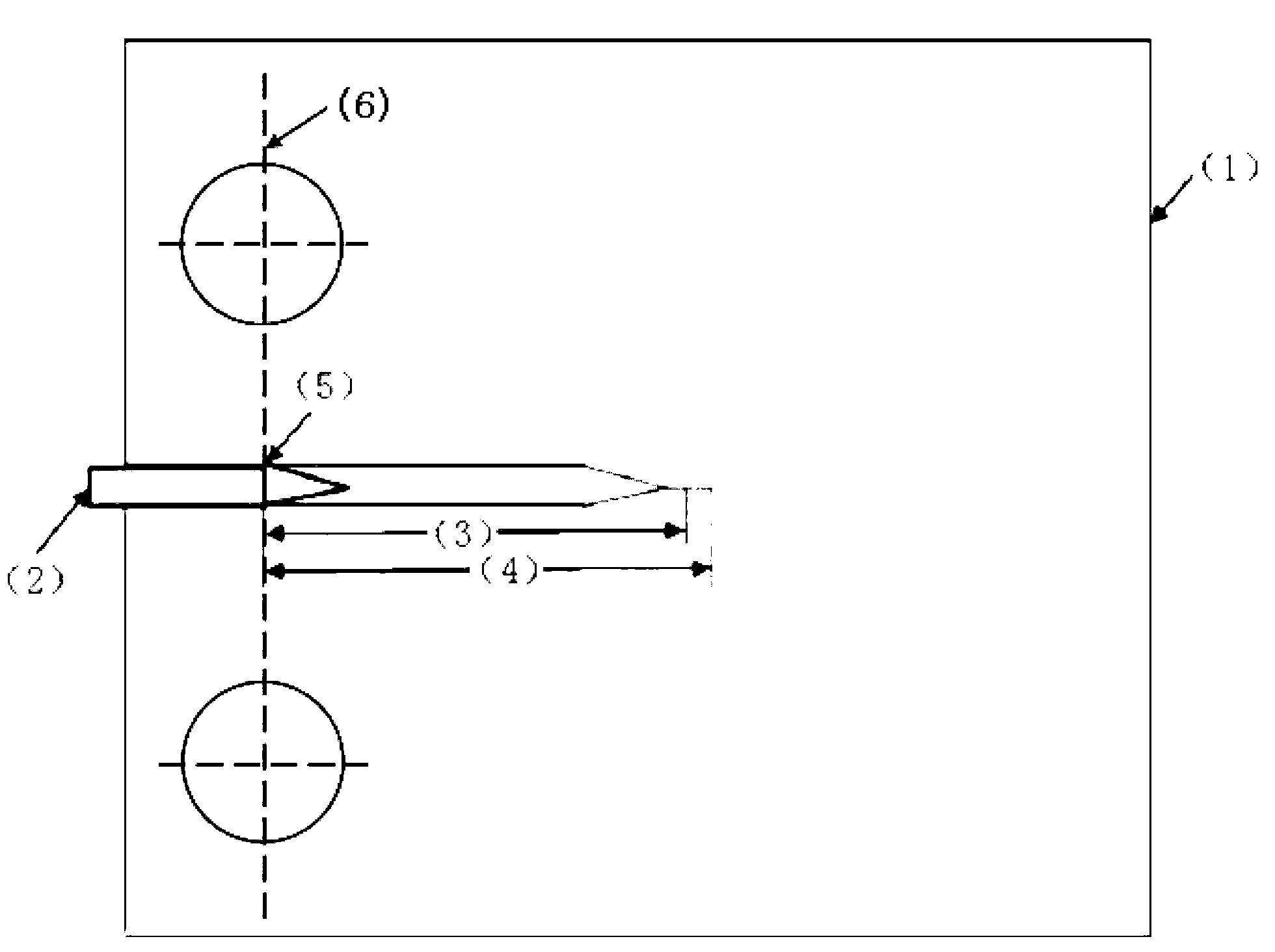
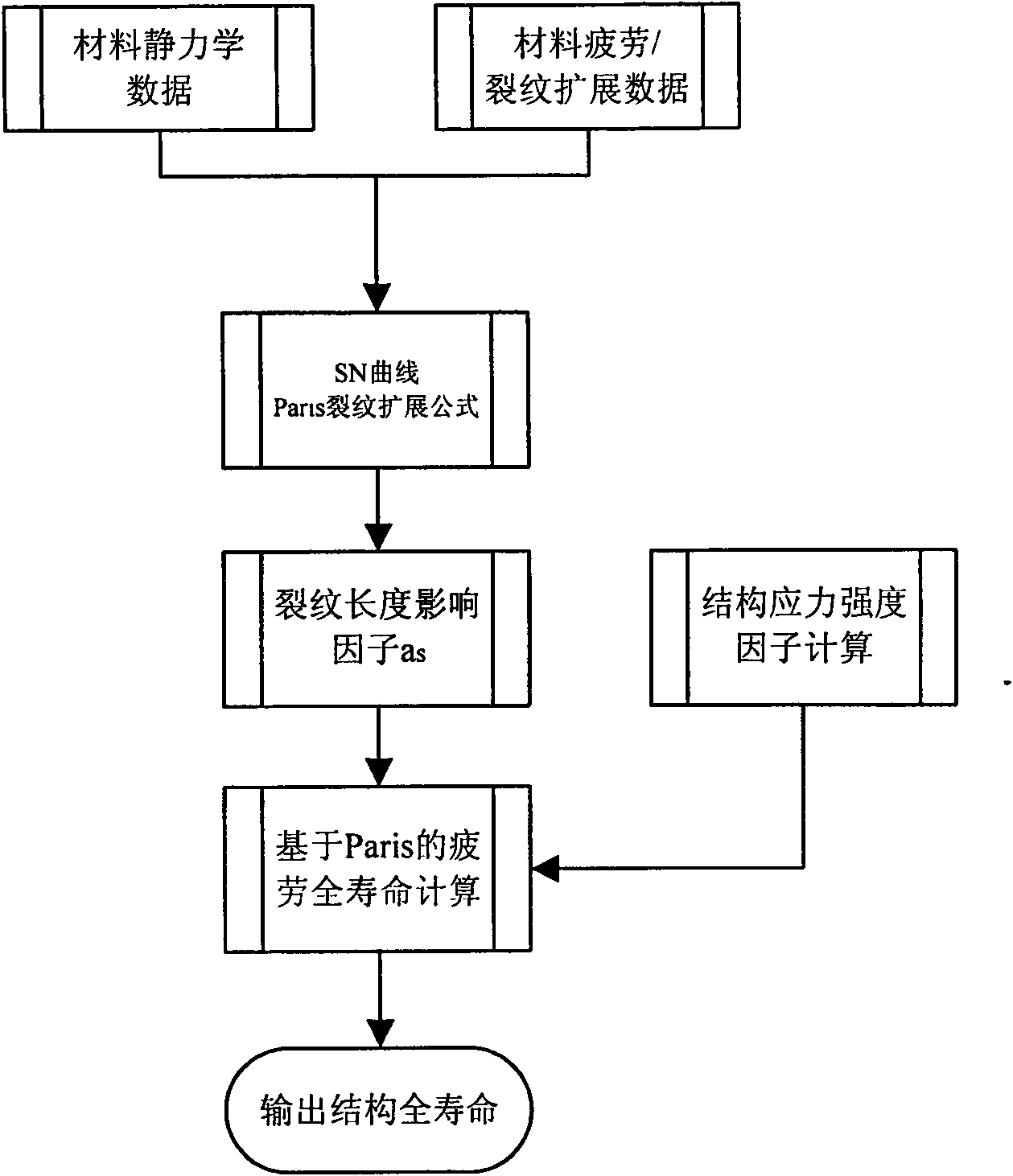
Fatigue life analyzing method based on Paris formula
InactiveCN102129512AAvoid Experimental MeasurementsRealize fatigue life calculationSpecial data processing applicationsStress intensity factorStress ratio
The invention discloses a fatigue life analyzing method based on a Paris formula, comprising the following steps of: acquiring the mechanical property data and a fatigue SN (Serial Number) curve of materials as well as the Paris material constants of the materials when stress ratio R=0 and a stress intensity factor curve of a suture, and then calculating the influence factors of a crack length; and carrying out crack propagation life integral calculation from an initial crack length to a critical crack length by adopting a fatigue life-cycle calculation formula based on the Paris so as to obtain and output a final structure fatigue life-cycle. In the invention, only the basic common material constants are needed, therefore, the test measurement of a large quantity of material constants is prevented; and the prevention of the test measurement of the large quantity of material constants is very important for the structure life-cycle analysis of engineering application.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
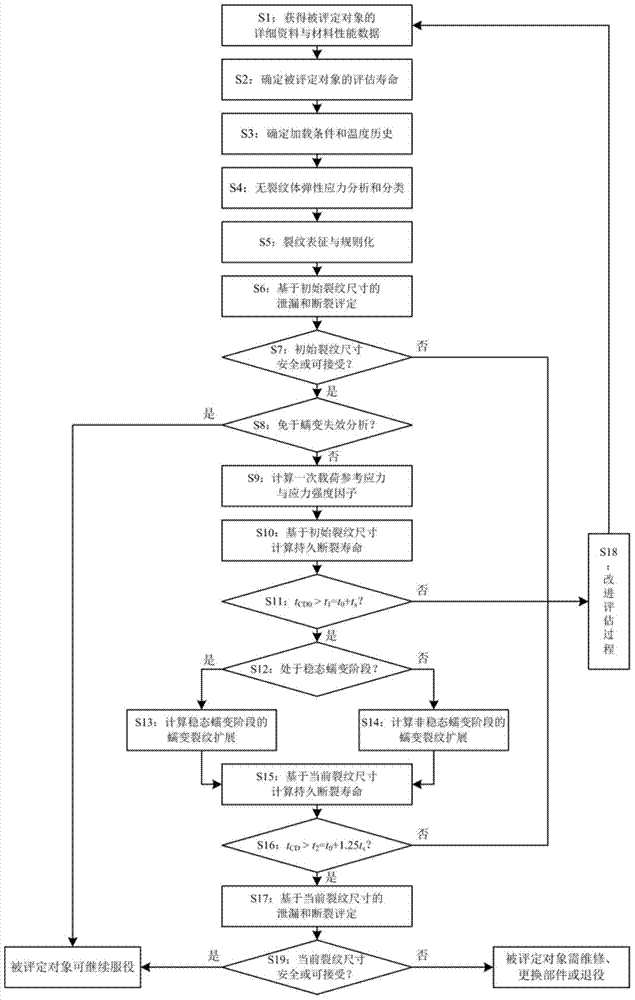
Safety assessment method for high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects
The invention discloses a safety assessment method for a high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects. The safety assessment method for the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects includes steps that 1, gathering data; 2, definitely evaluating the life span; 3, determining load and temperature; 4, analyzing elastic stress; 5, characterizing crack; 6, assessing initial crack leakage and rupture; 7, judging whether the initial crack is safe; 8, judging whether the initial crack is free of creep analysis; 9, calculating reference stress and stress intensity factors; 10, calculating creep rupture life based on the initial crack size; 11, judging whether the creep rupture life is long enough; 12, judging whether the creep is steady creep; 13, calculating steady state creep crack growth; 14, calculating unsteady state creep crack growth; 15, calculating the creep rupture life based on the current crack size; 16, judging whether the current creep rupture life is long enough; 17, assessing the current crack leakage and rupture; 18, refining and evaluating; 19, judging whether the assessed object is safe. The safety assessment method for the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects can be used for assessing the safety of the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects under creep load effect.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST
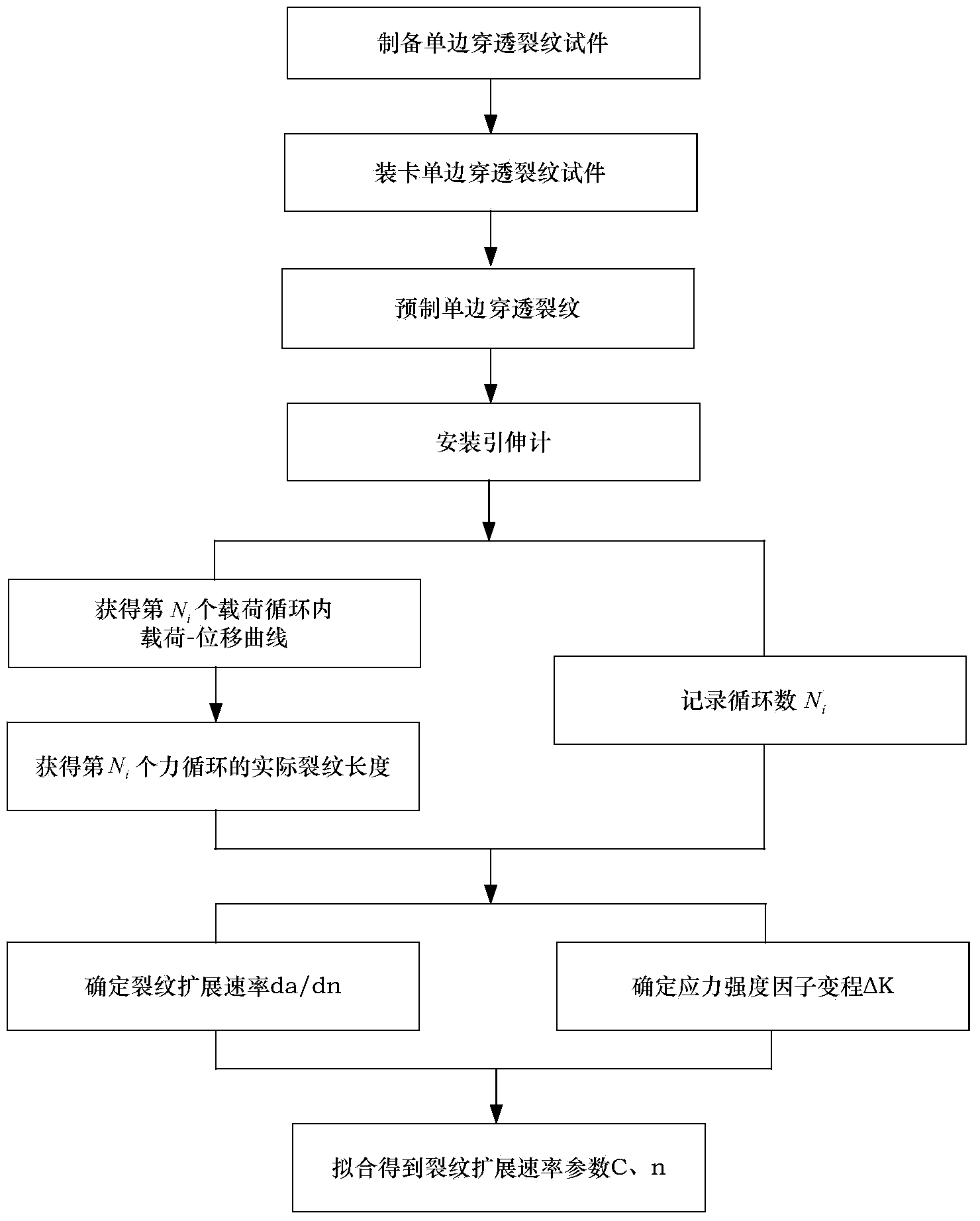
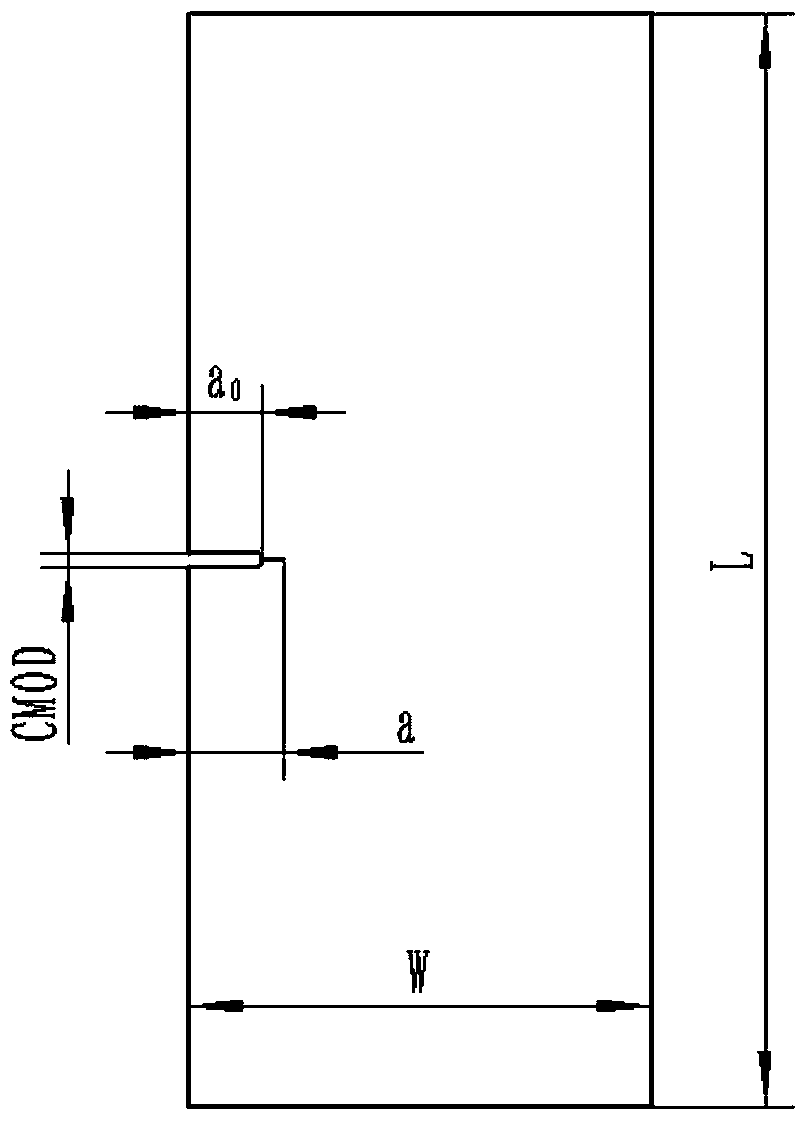
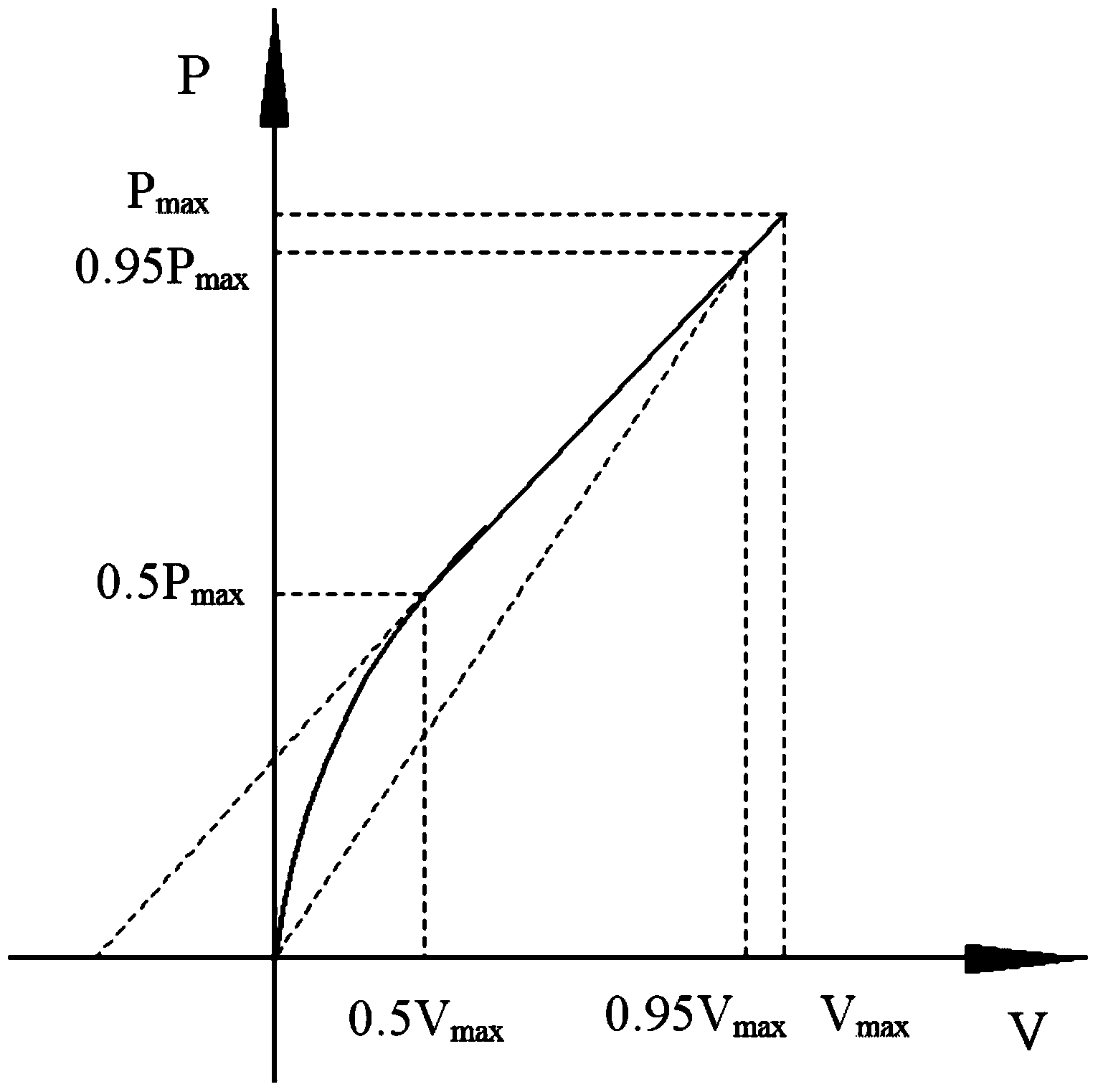
Crack propagation rate measurement method
InactiveCN103674741AAvoid invalid situationsSave materialMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesStress intensity factorStress ratio
The invention discloses a crack propagation rate measurement method. The method comprises the steps of applying alternating load to a test piece with a single-side penetrated crack by a testing machine; measuring load-displacement curves at an interval of certain loading cycles and fitting a linear segment to obtain the non-dimensional flexibility value of the test piece; acquiring the length of the crack according to the relation of the non-dimensional flexibility value of the single-side penetrated crack and the length of the crack under a clamped boundary condition; recording the number of the current loading cycles to obtain a crack length-load cycle number curve, and determining the crack propagation rate; and calculating the corresponding stress intensity factor, acquiring discrete data and fitting to obtain the parameters of the crack propagation rate. The method has the advantages that the method is suitable for measuring the crack propagation rate under positive and negative stress ratios and can be used for measuring the crack length automatically; and the measurement system has wide application range and is particularly suitable for measuring the crack propagation rate of novel materials such as a metal laminated board, a metal / composite material laminated board, a ceramic matrix composite material, a welding material.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Testing method of steel fiber reinforced concrete fracture test crack initiation load
ActiveCN103760036AReduce test costsLower requirementMaterial strength using steady bending forcesStress intensity factorClassical mechanics
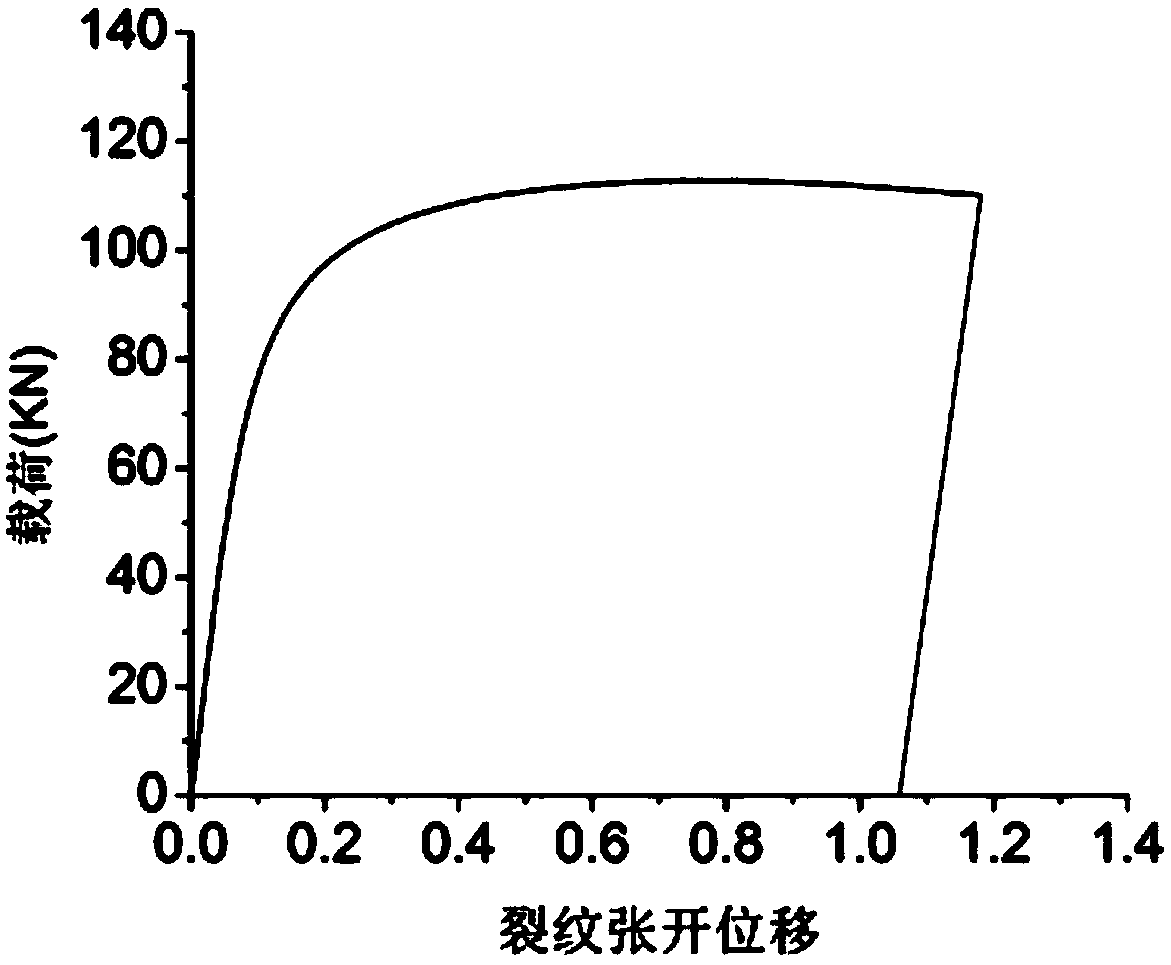
The invention relates to a testing method of steel fiber reinforced concrete fracture test crack initiation load, and belongs to the technical field of concrete cracking parameter testing. The testing method provided by the invention is characterized in that when a steel fiber reinforced concrete coped beam specimen cracks, a stress intensity factor of a prefabrication crack front edge achieves concrete fracture toughness, and the steel fibre blocking action is not exerted; the stress intensity factor generated by external load and concrete cracking toughness(i)K( / i) IC are equal, the external load value which is corresponding to a numerical value (i)K( / i)IC of the stress intensity factor generated by the external load can be used for determining the crack initiation load according to the curve relation graph of the external load and the stress intensity factor (i)K generated by the external load (img file='2014100081259100004dest_path_image002.TIF'wi='8'he='21' / )( / i)-(i)P( / i) curve relational graph. The testing method provided by the invenytion has the advantages that the required equipment, analyzing and processing method are simple, the cost is low, and the precision is high.
Owner:YELLOW RIVER INST OF HYDRAULIC RES YELLOW RIVER CONSERVANCY COMMISSION
Method for assessing detail fatigue crack propagation of steel bridge
ActiveCN106055784AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsStress intensity factorElement analysis
The invention discloses a method for assessing the detail fatigue crack propagation of a steel bridge. Aiming at a steel bridge which is widely used in a road bridge system and is severe in fatigue crack dangers, the method comprises the steps: firstly building a bridge model and a local zone crack submodel through finite elements, obtaining an existing bridge load according to the definition and sampling of a vehicle and other random variables, and obtaining the boundary conditions of the submodel based on the whole bridge finite element analysis and the submodel technology; secondly updating the submodel through employing local remeshing, and carrying out the crack propagation finite element analysis; thirdly extracting a stress intensity factor amplitude, calculating a mean crack propagation rate, a mean crack propagation angle, the circulating number of times of each crack propagation step, the mean number of the stress intensity factor amplitude caused by a single vehicle, and the fatigue life; finally achieving the simulation of the fatigue crack of the steel bridge and the assessment of the fatigue life, so as to guide the subsequent maintenance and reinforcing operation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
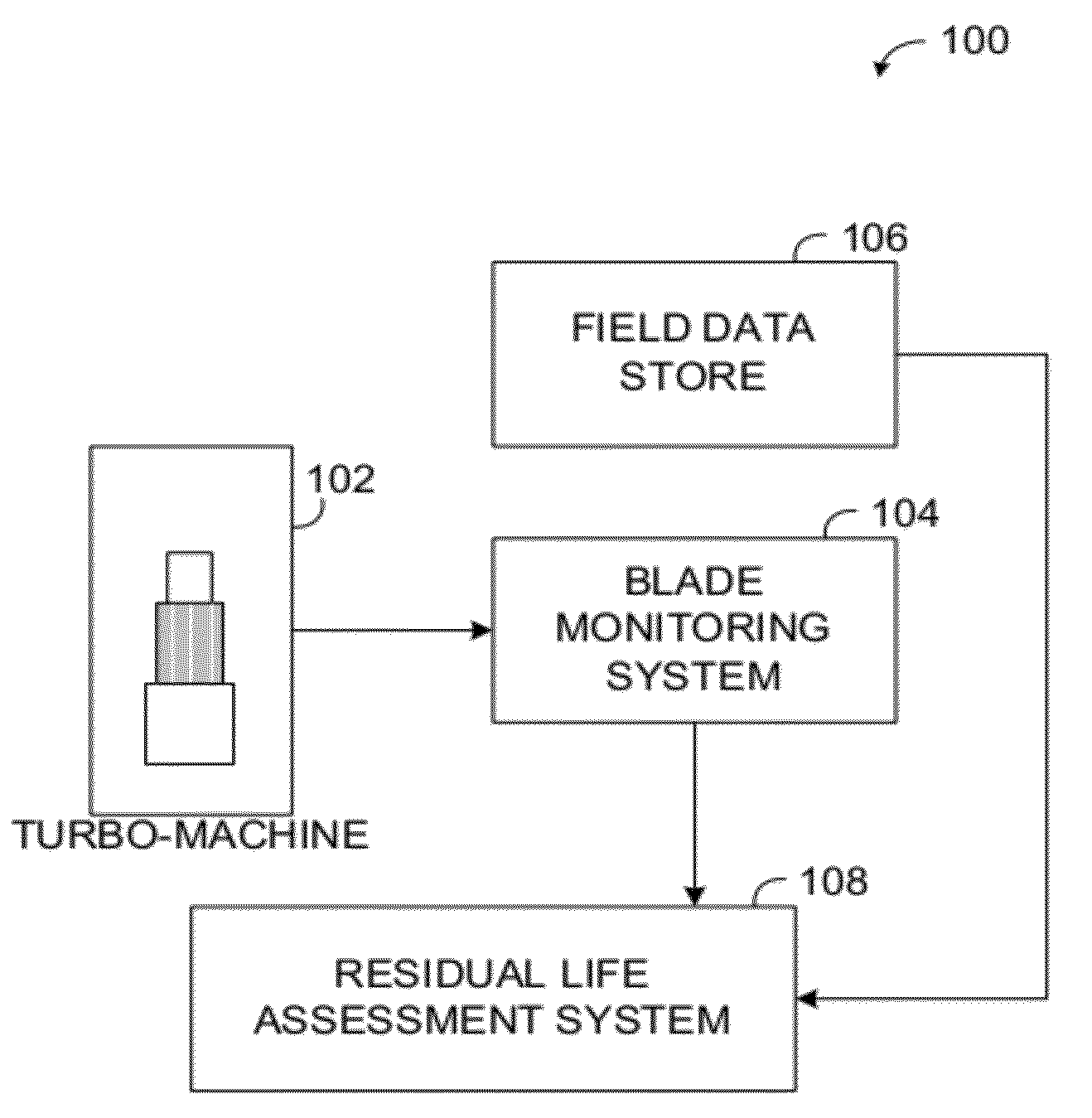
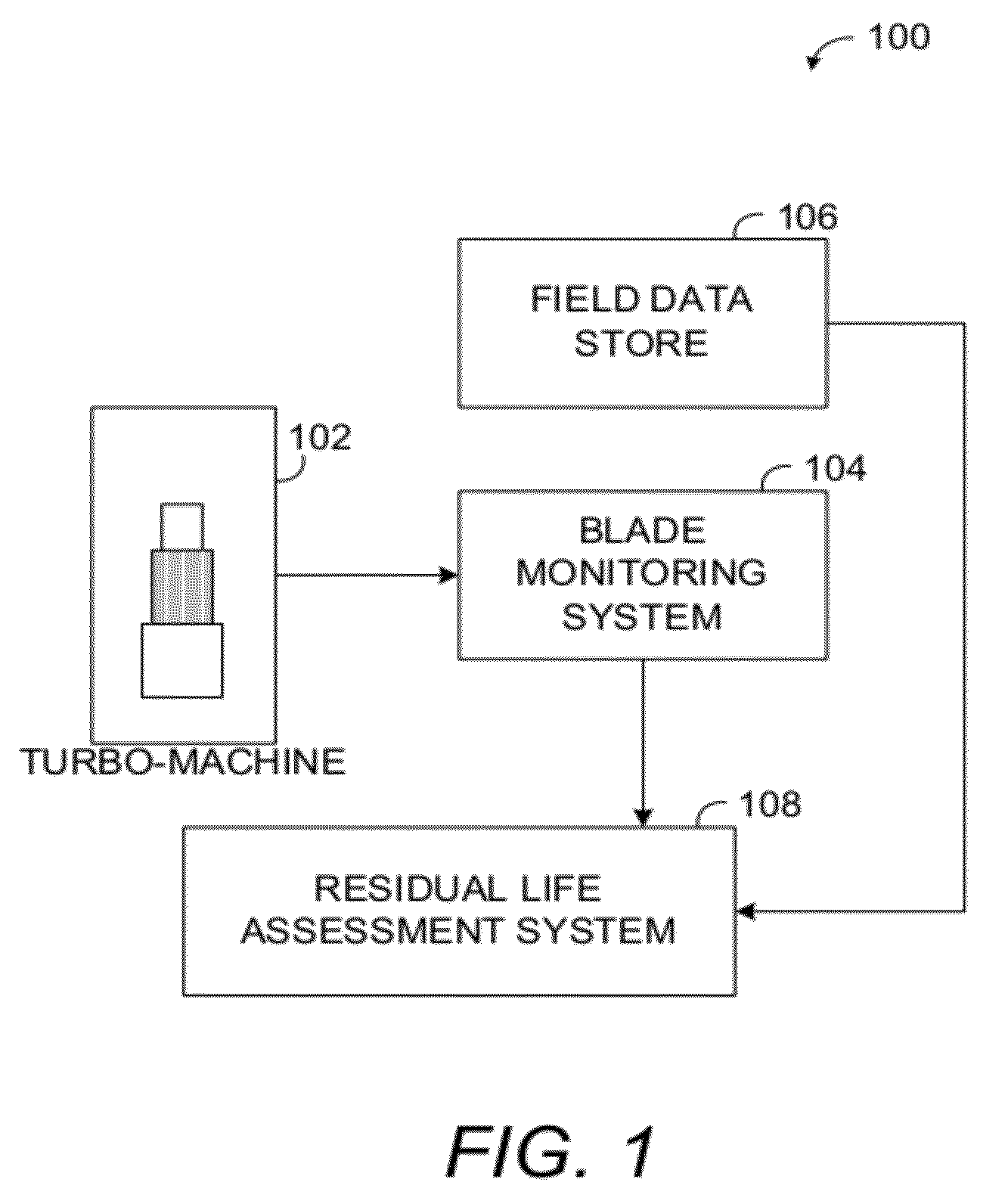
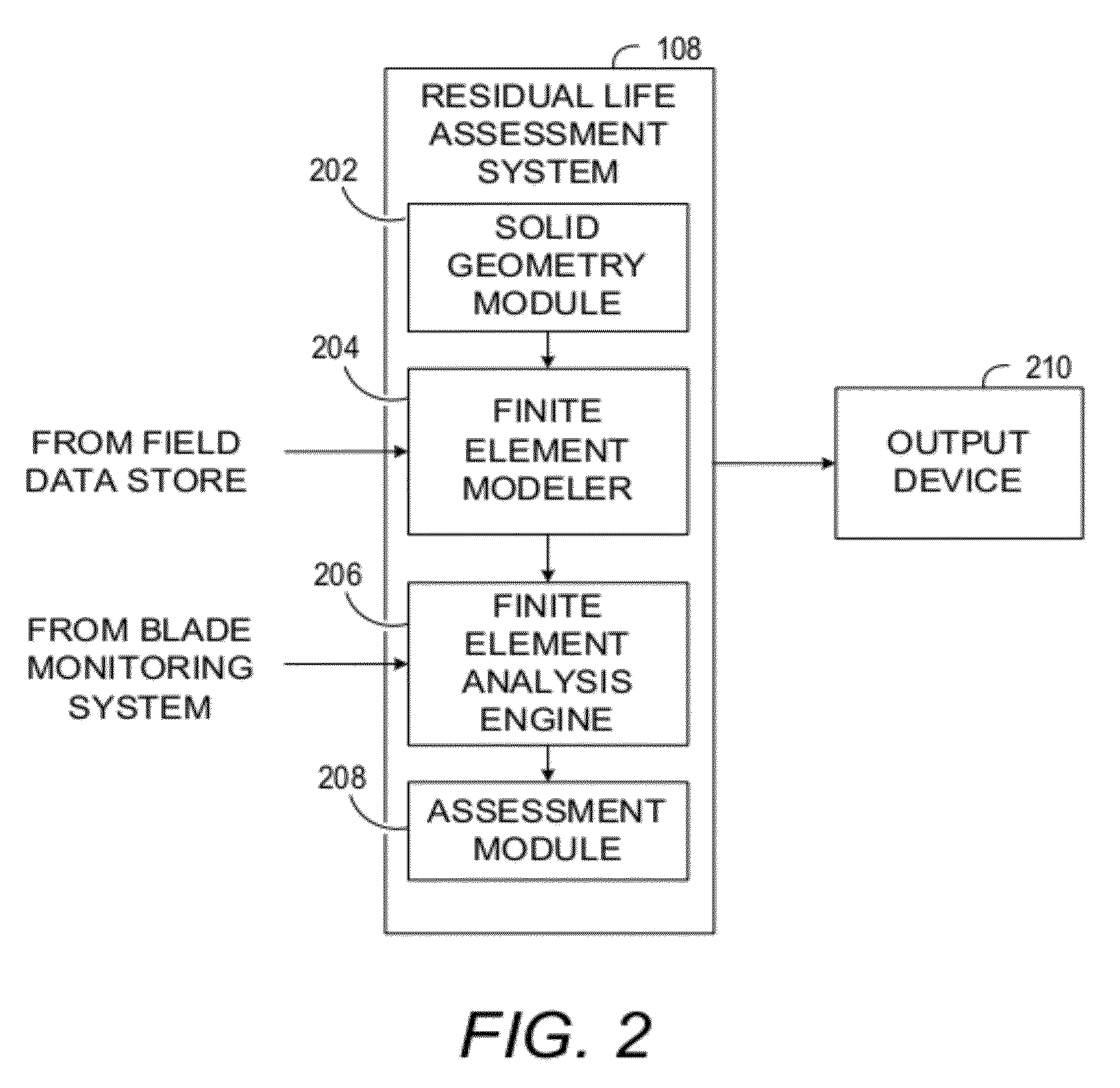
Methods and systems for assessing residual life of turbomachine airfoils
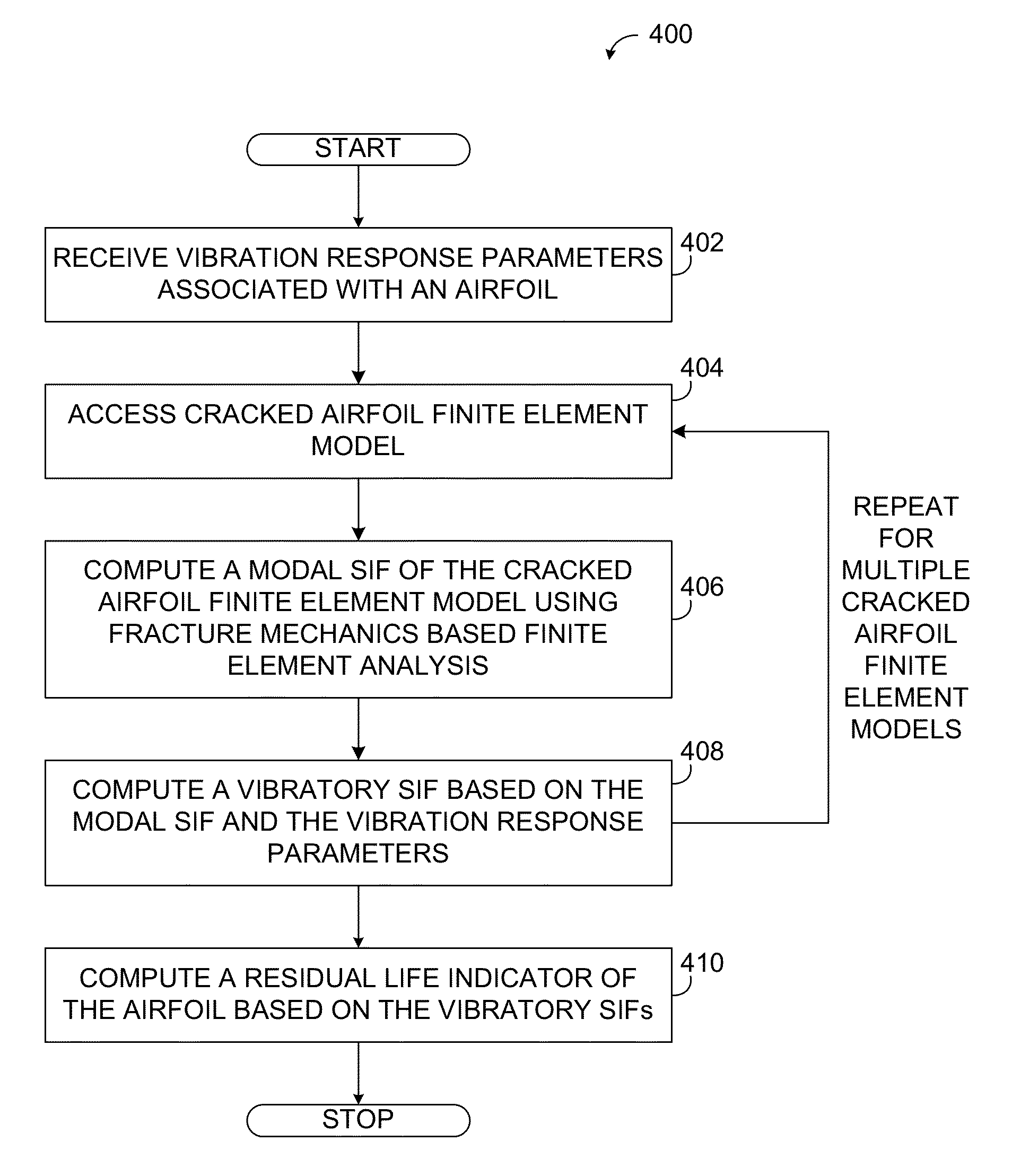
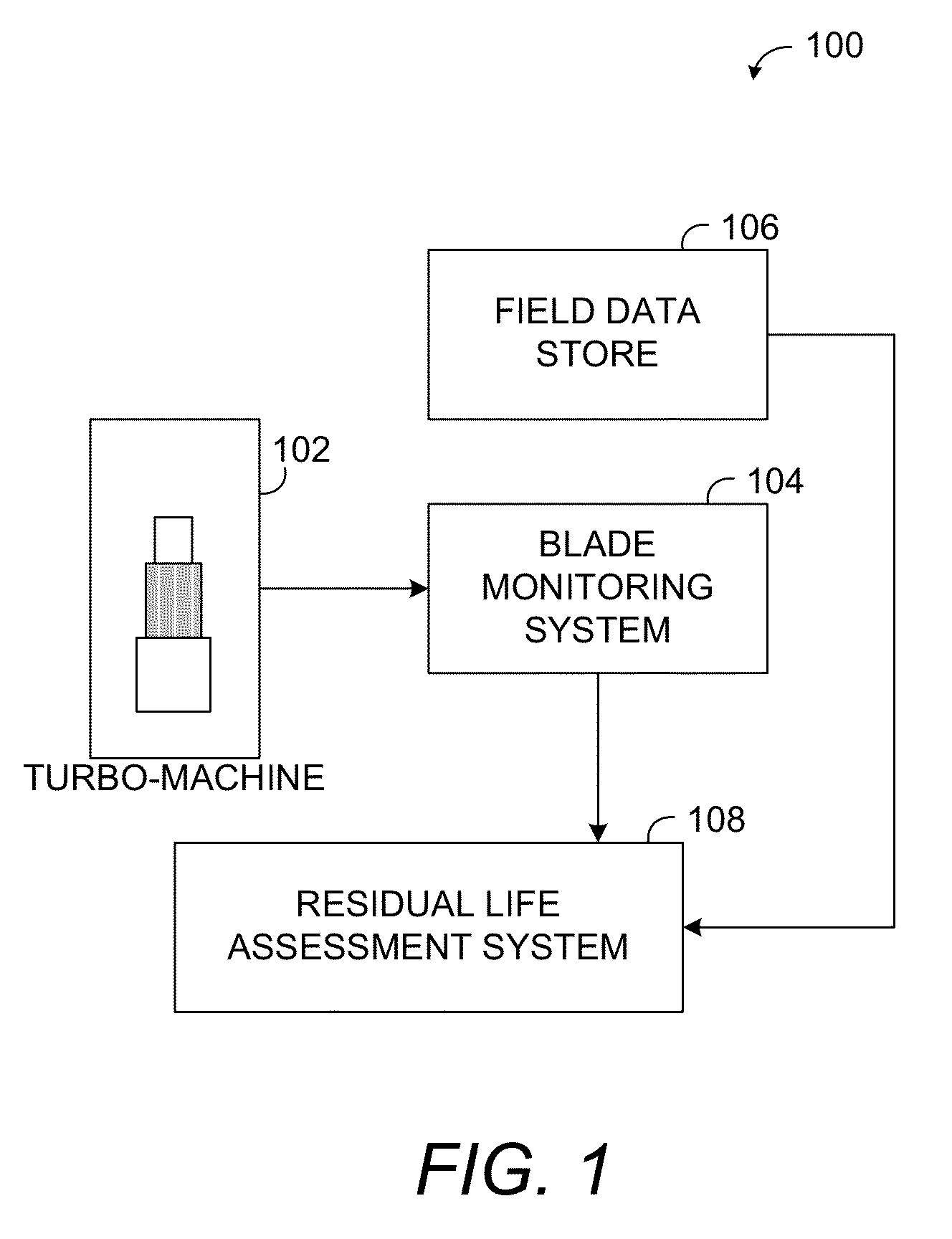
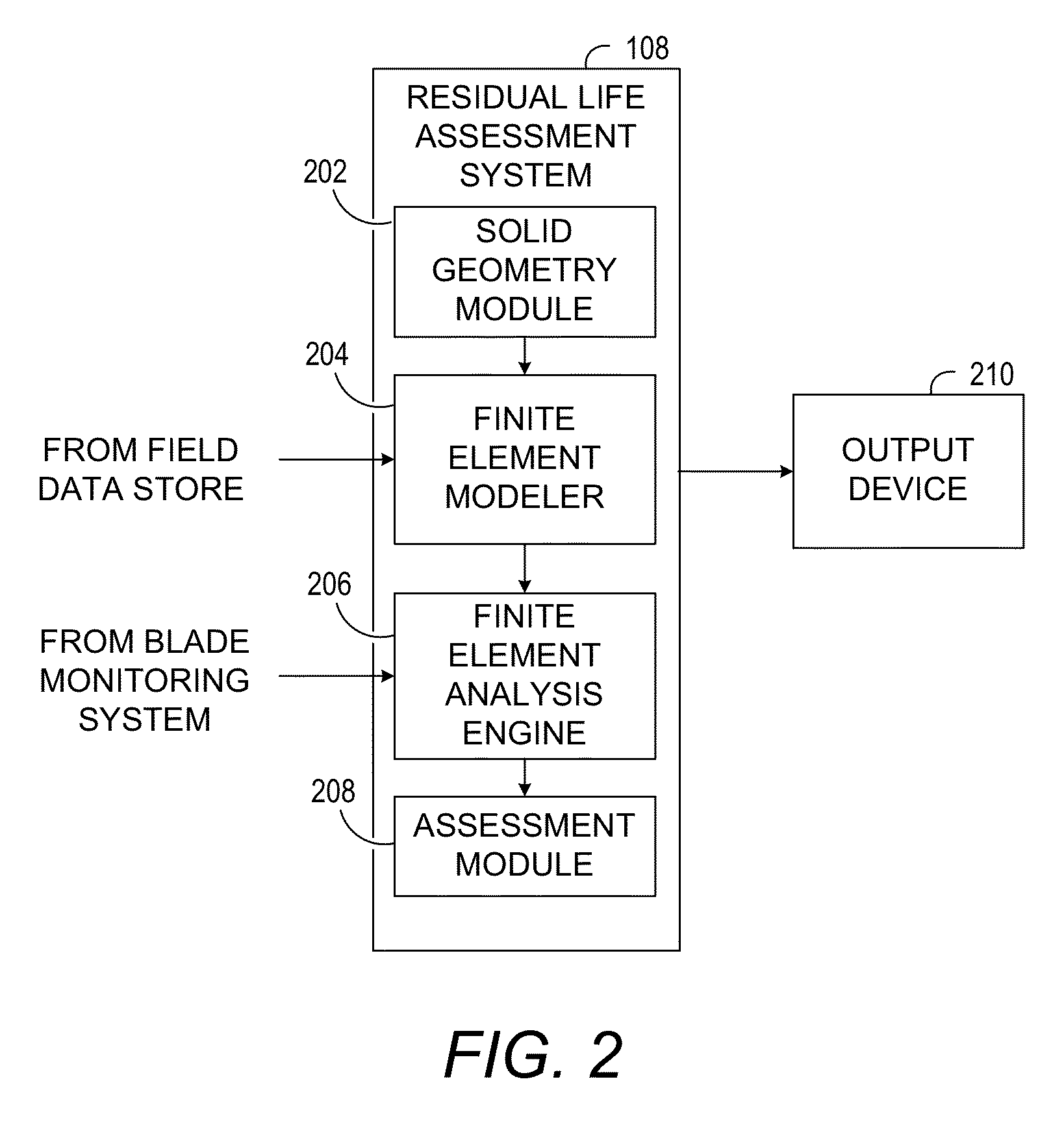
Methods, systems and computer program products for assessing residual life of an airfoil, which would experience high cycle fatigue failure under at- or near-resonance vibration condition, are provided. The method includes receiving, at a processing system, at least one vibration response parameter associated with the airfoil. The method processes at least one cracked airfoil finite element model. Processing the cracked airfoil finite element model includes accessing the cracked airfoil finite element model, computing a modal stress intensity factor (SIF) of the cracked airfoil finite element model using fracture mechanics based finite element analysis, and computing a vibratory SIF based, at least in part, on the modal SIF and the at least one vibration response parameter. The method then computes a residual life indicator of the airfoil based, at least in part, on the vibratory SIF.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Test analysis method for bolt connecting piece fatigue crack expanding
InactiveCN102023116AClear principleWide applicabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress intensity factorStress ratio
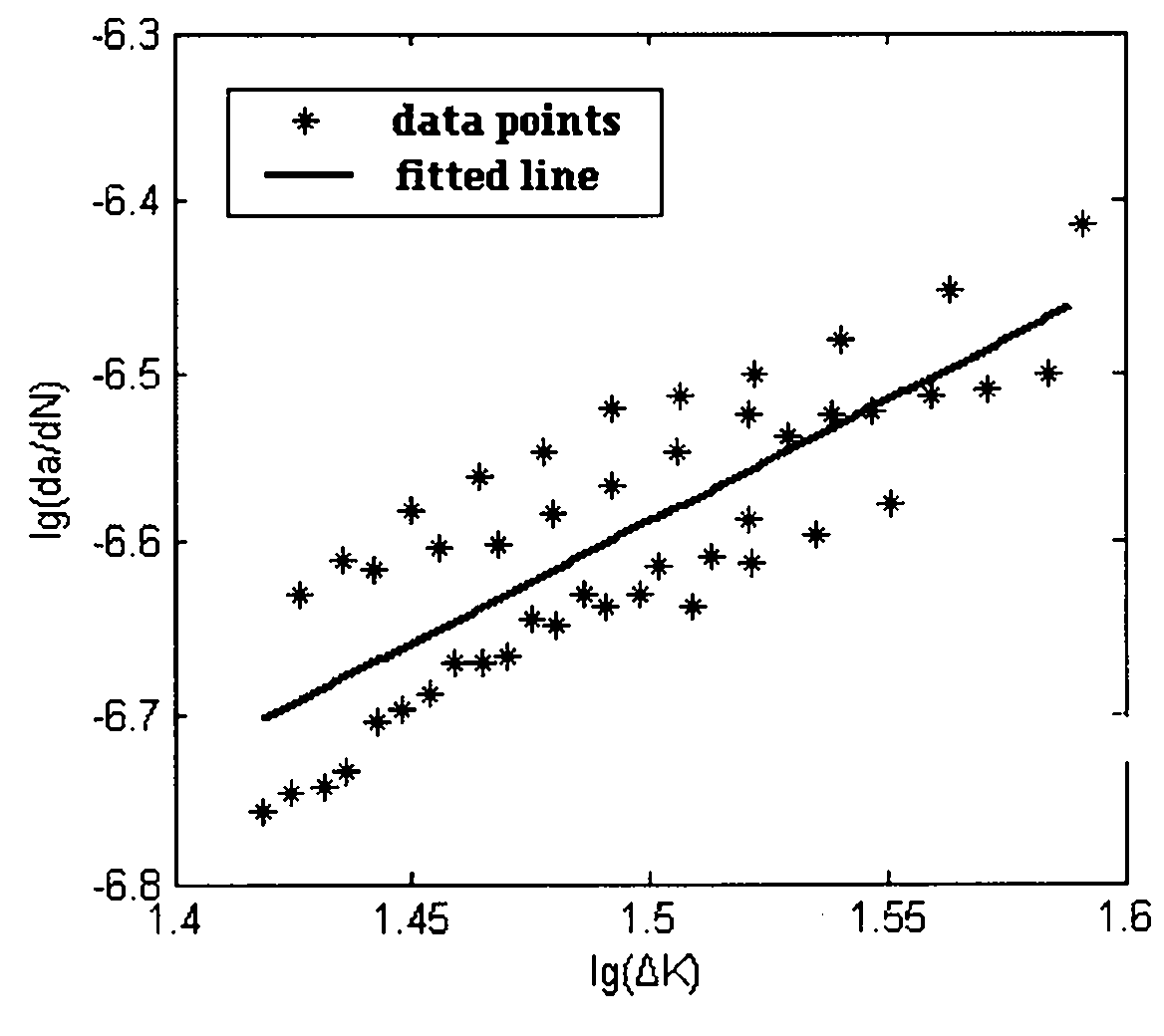
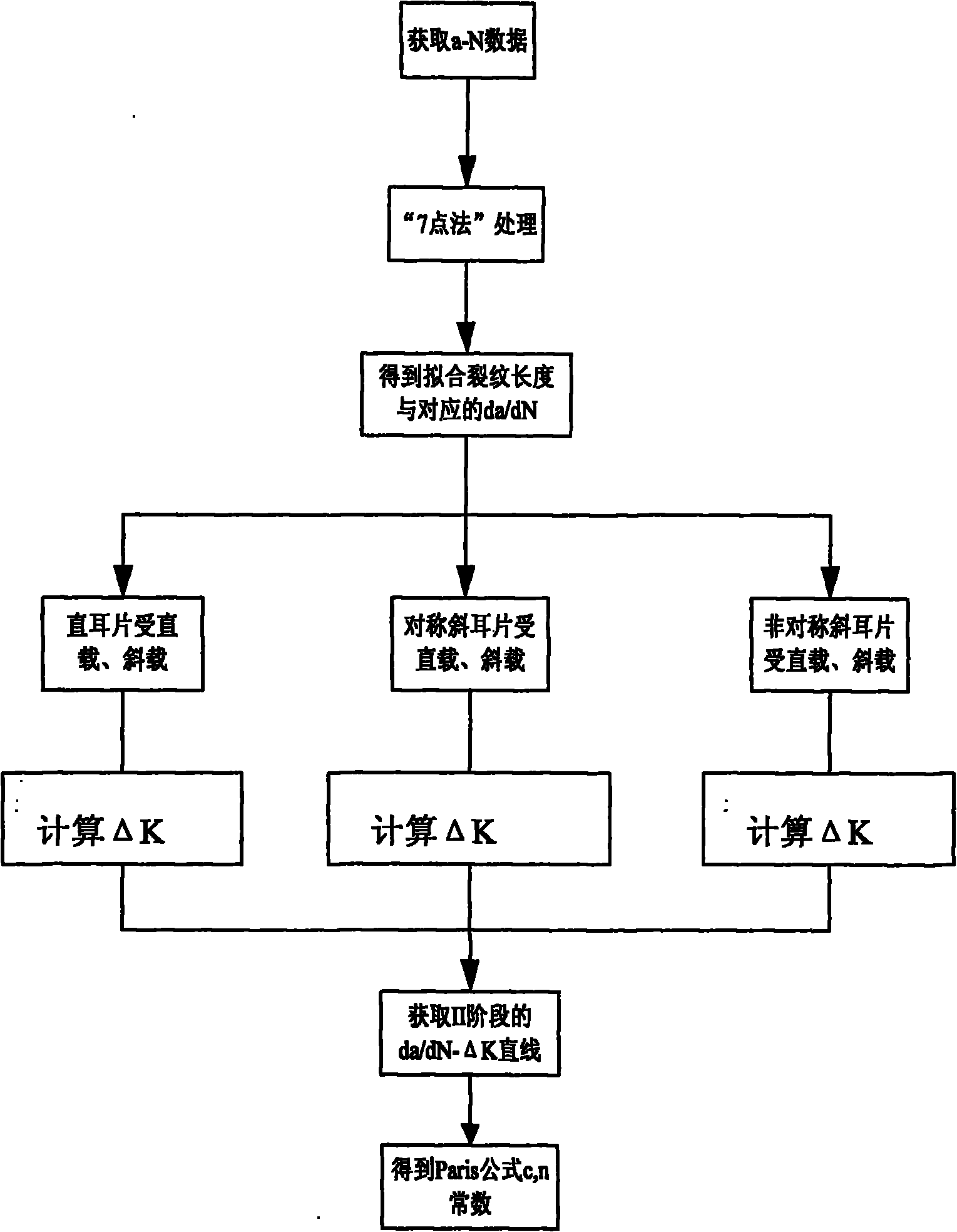
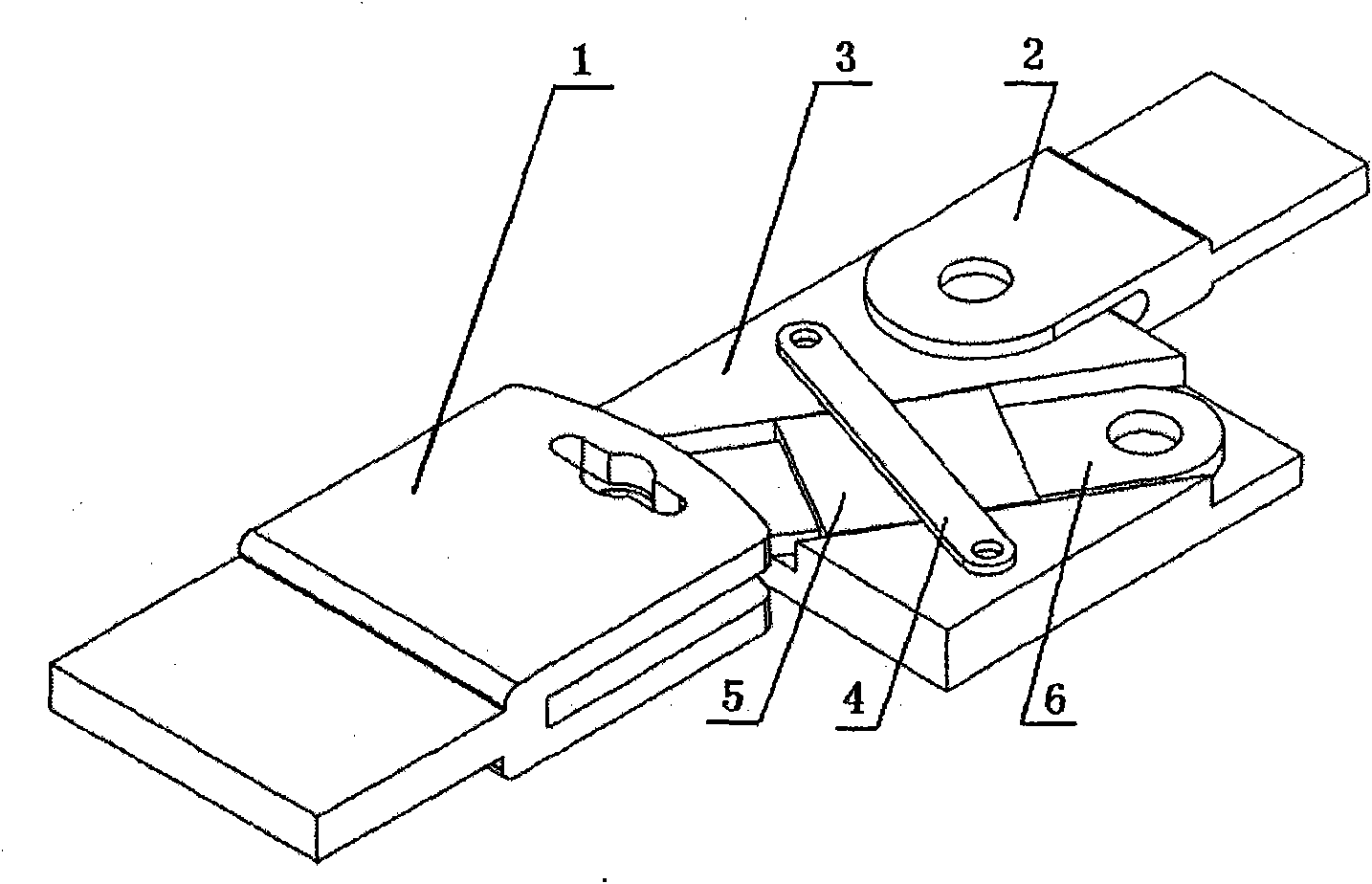
The invention relates to a test analysis method for lug connecting piece fatigue crack expanding, which is technically characterized by installing a test lug on a testing machine; then loading and producing fatigue crack on the lug; adopting a stress intensity factor comprising a straight lug pulled and loaded lengthwise, the straight lug loaded obliquely smaller than 45 degrees, a symmetrical oblique lug pulled and loaded lengthwise, the symmetrical oblique lug loaded obliquely smaller than 45 degrees, an asymmetrical oblique lug pulled and loaded lengthwise and the asymmetrical oblique lug loaded obliquely smaller than 45 degrees to the corresponding delta K; taking a slope factor of 1g(da / dN)-1g(delta K) line as a constant n in the Paris formula, an intercept of a straight line and axis y as a constant C in the Paris formula, and obtaining the Paris formula when the stress ratio is R; and the lug fatigue crack expanding life NC is estimated according to the obtained Paris formula. The invention has the advantages that the applicability is wide, and the test analytical method plays a directive role in researching the lug hole edge fatigue crack expanding properties under various pulling and loading conditions.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Method for predicting service life of reinforced concrete bridge under conditions of seasonal corrosion and fatigue coupling
ActiveCN109827855AEnables corrosion fatigue life assessmentNovel forecasting methodWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMaterial testing goodsStress concentrationRebar
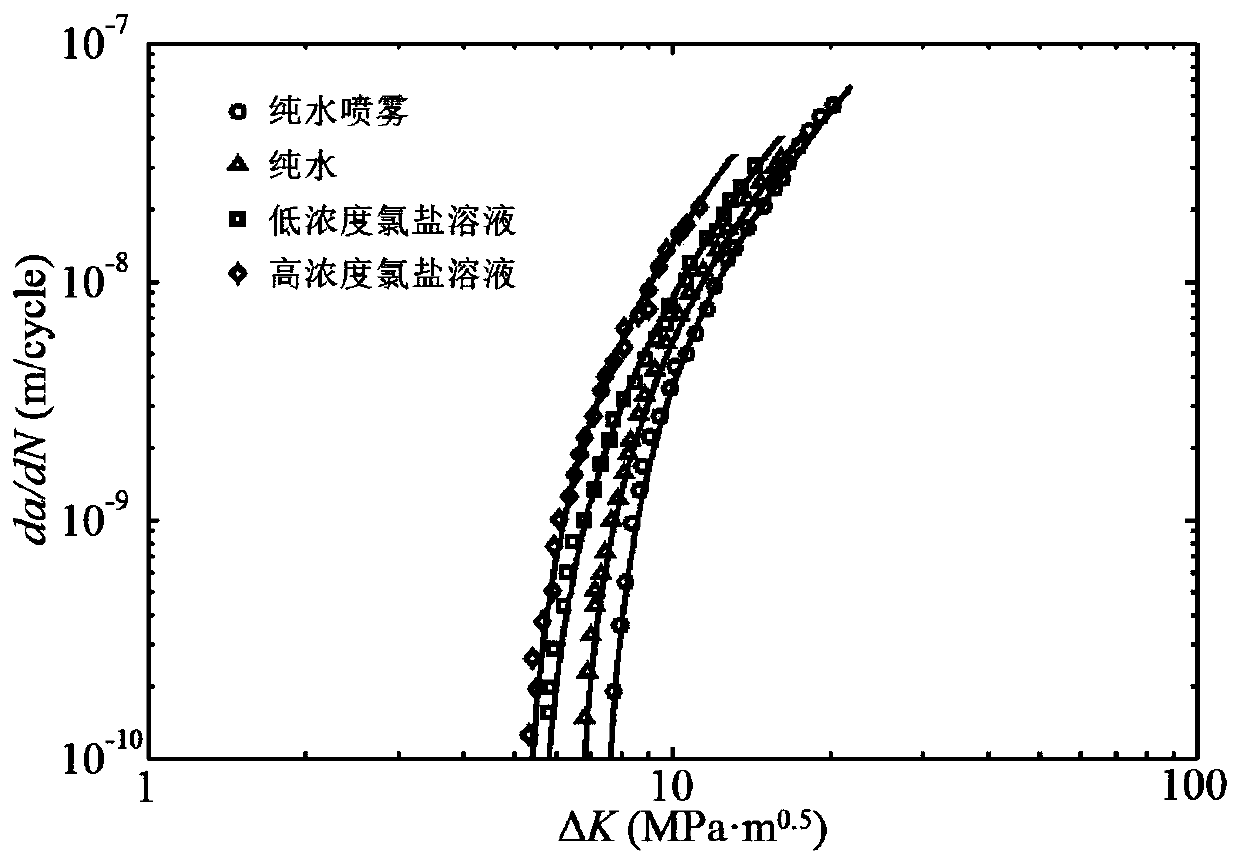
The invention discloses a method for predicting the service life of a reinforced concrete bridge under the conditions of seasonal corrosion and fatigue coupling. The method comprises the steps: dividing the service life of the reinforced concrete bridge into three stages: corrosion initiation-pure fatigue crack development stage, a rust pit and fatigue crack competing development stage and a structure failure stage; establishing an initial reinforcing steel bar corrosion model and a rust pit growth model based on the Fick second diffusion law and the consideration of the influence of concreterust expansion cracking damage; testing and simulating a reinforcing steel bar crack propagation rule under the influence of a four-season environment, and determining fatigue crack growth characterization parameters; constructing a stress intensity factor model considering the influence of stress concentration, and proposing a steel bar corrosion fatigue crack growth analysis method correspondingto a four-season environment; enabling the structural failure criterion to be clear, combining with the vehicle load observation information, performing the systematic consideration of the competitive coupling relation between rust pit growth and fatigue crack growth, judging a failure mode in real time, and achieving the prediction of the service life of the bridge. The method is novel and reasonable, and can provide technical support for safety assessment of the concrete bridge.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
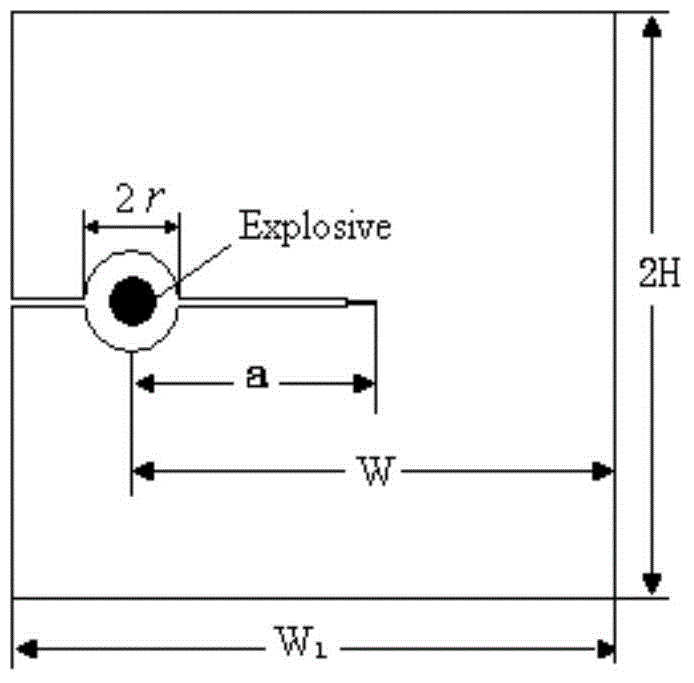
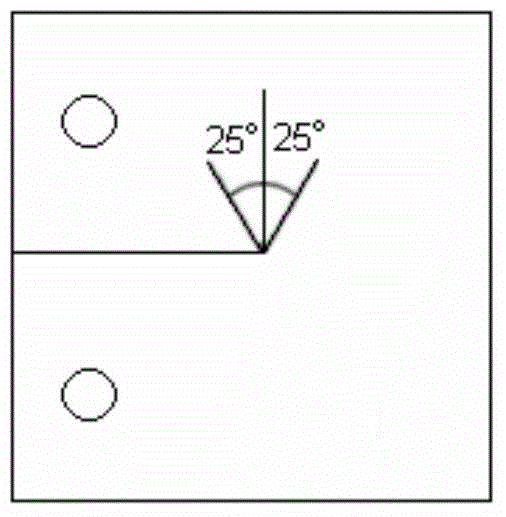
Testing method of I-type crack dynamic fracture toughness under explosive load
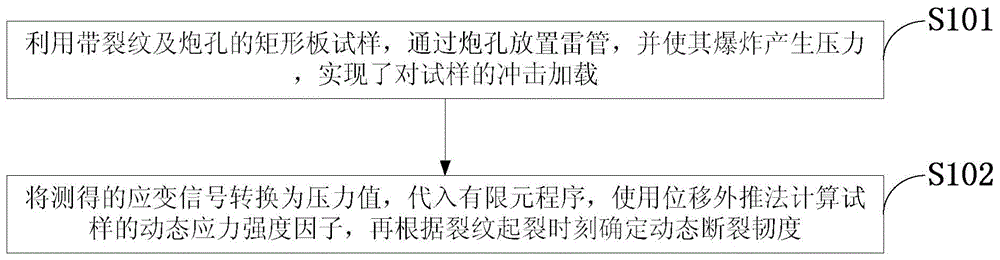
The invention discloses a testing method of I-type crack dynamic fracture toughness under explosive load. Detonators and a cement mortar sample with a crack are utilized to perform bursting testing research, the dynamic fracture toughness of the sample is determined by an experiment-numerical method, the sample bearing load and the crack initiation time are determined by a strain signal obtained through testing, the obtained time travel curve is input into a finite element program Ansys, the near field displacement of a crack tip is calculated by a 1 / 4 node unit, then the time travel curve of the I-type dynamic fracture stress intensity factor of the sample is obtained by a displacement extrapolation method, and the dynamic fracture toughness of the material is the stress intensity factor at the crack initiation moment, therefore, the new testing method of the I-type crack dynamic fracture toughness under explosive load is given. The method is simple, the operation is convenient, and the testing method has the practical application significance to the research of the dynamic fracture character of the rock under explosive load.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for testing microzone fracture toughness of material
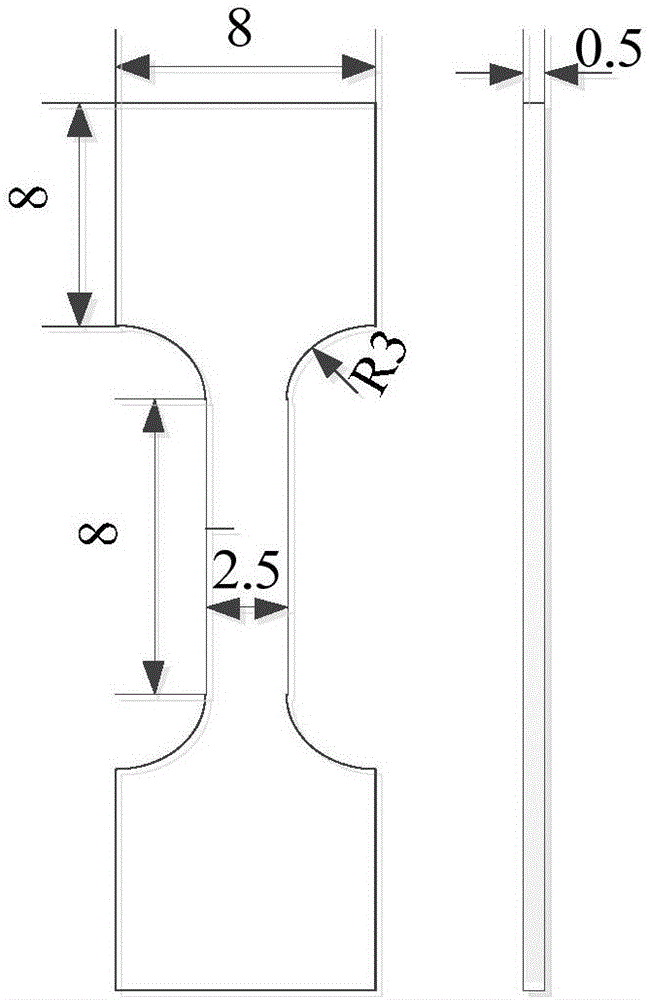
ActiveCN106289975APrecise positioningAccurate tip positioningPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesLarge specimenStress intensity factor
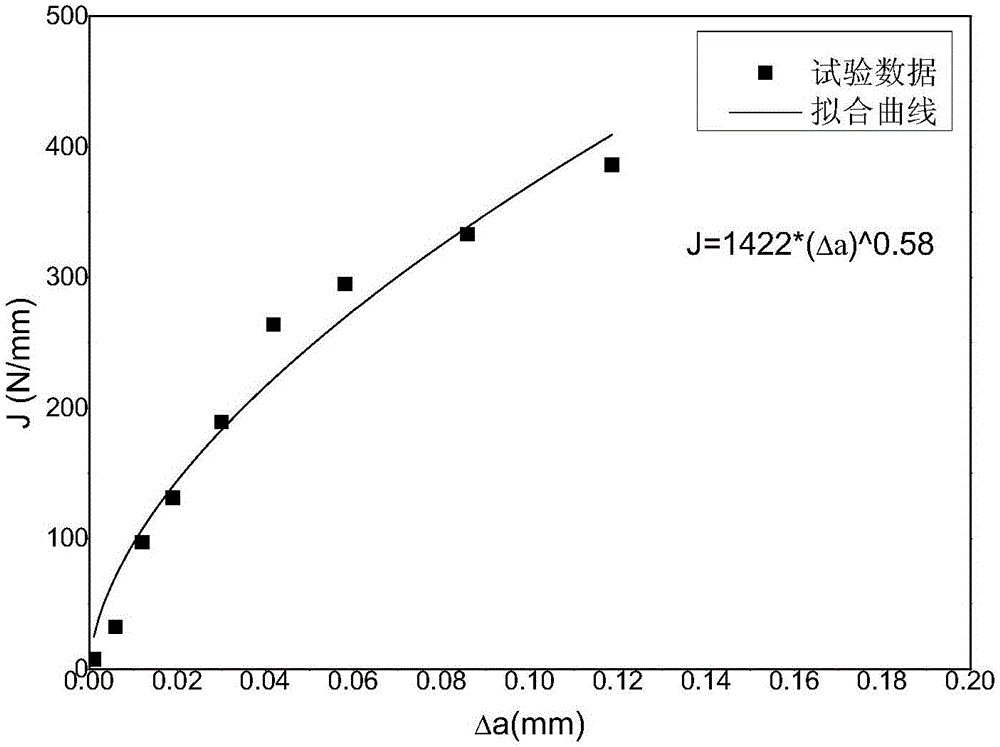
The invention provides a method for testing the microzone fracture toughness of a material. The method comprises the following steps: preparing an ultrathin single-edge notched tensile (SENT) specimen; performing repeated loading and unloading operations on an in-situ tensile test machine; recording test load Fi, crack length ai and notch opening displacement Vi by virtue of a scanning electron microscope in-situ test machine; calculating a Ki value for a brittle material and calculating a Ji value for a ductile material; and drawing a K-a curve or J-R curve capable of characterizing crack propagation fracture resistance, thereby obtaining a stress intensity factor K or J integral capable of characterizing the fracture toughness of a miniature specimen. The ultrathin SENT specimen is adopted to measure the microzone fracture toughness of a metallic material, so that the problem that measurement on fracture toughness of ultrathin members and accurate microzones of a large specimen based on traditional standards cannot be realized is solved, and the method has the characteristics of accurate crack tip positioning and high dimension measurement accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC POWER GENERATION EQUIPMENT CO LTD
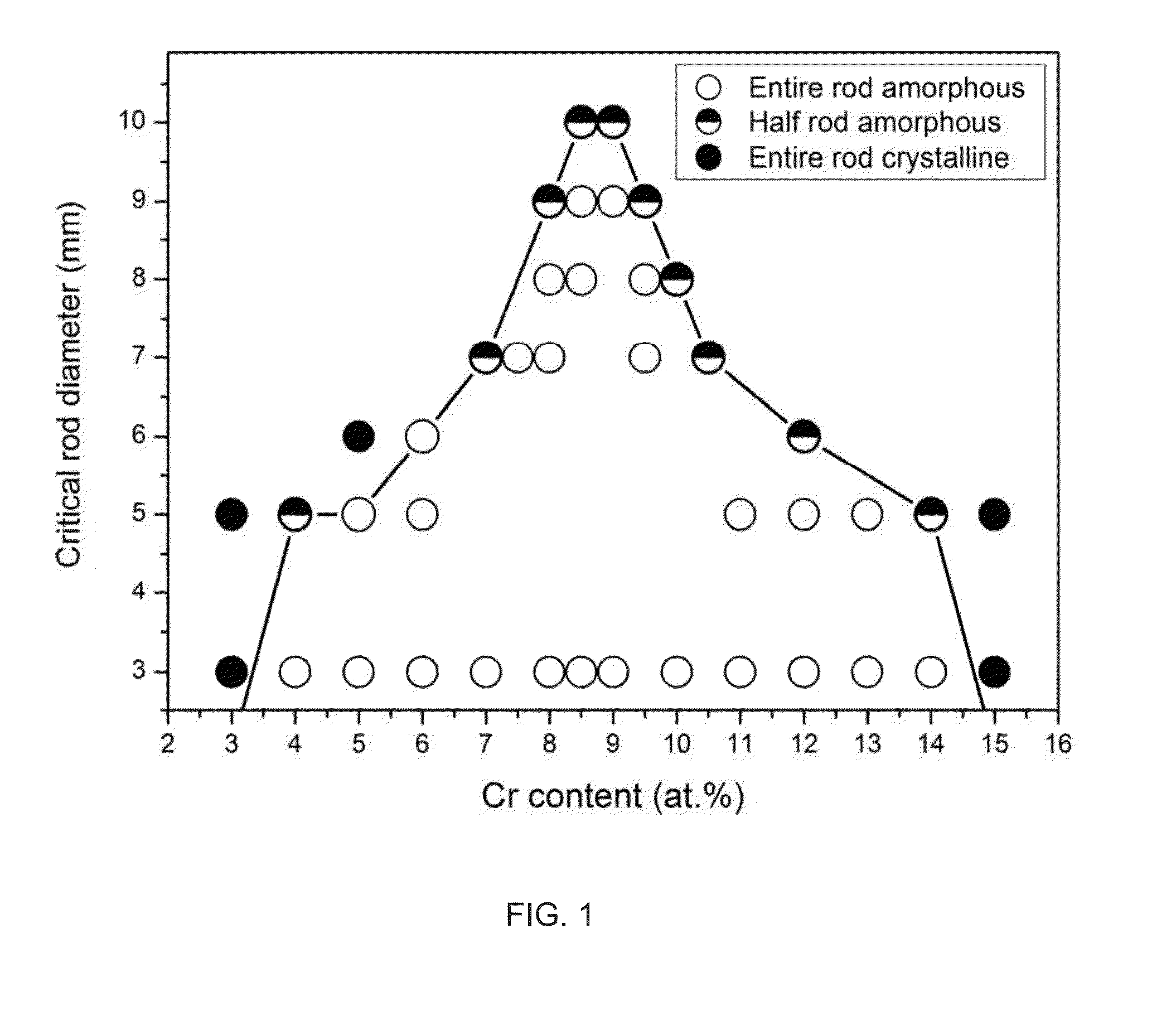
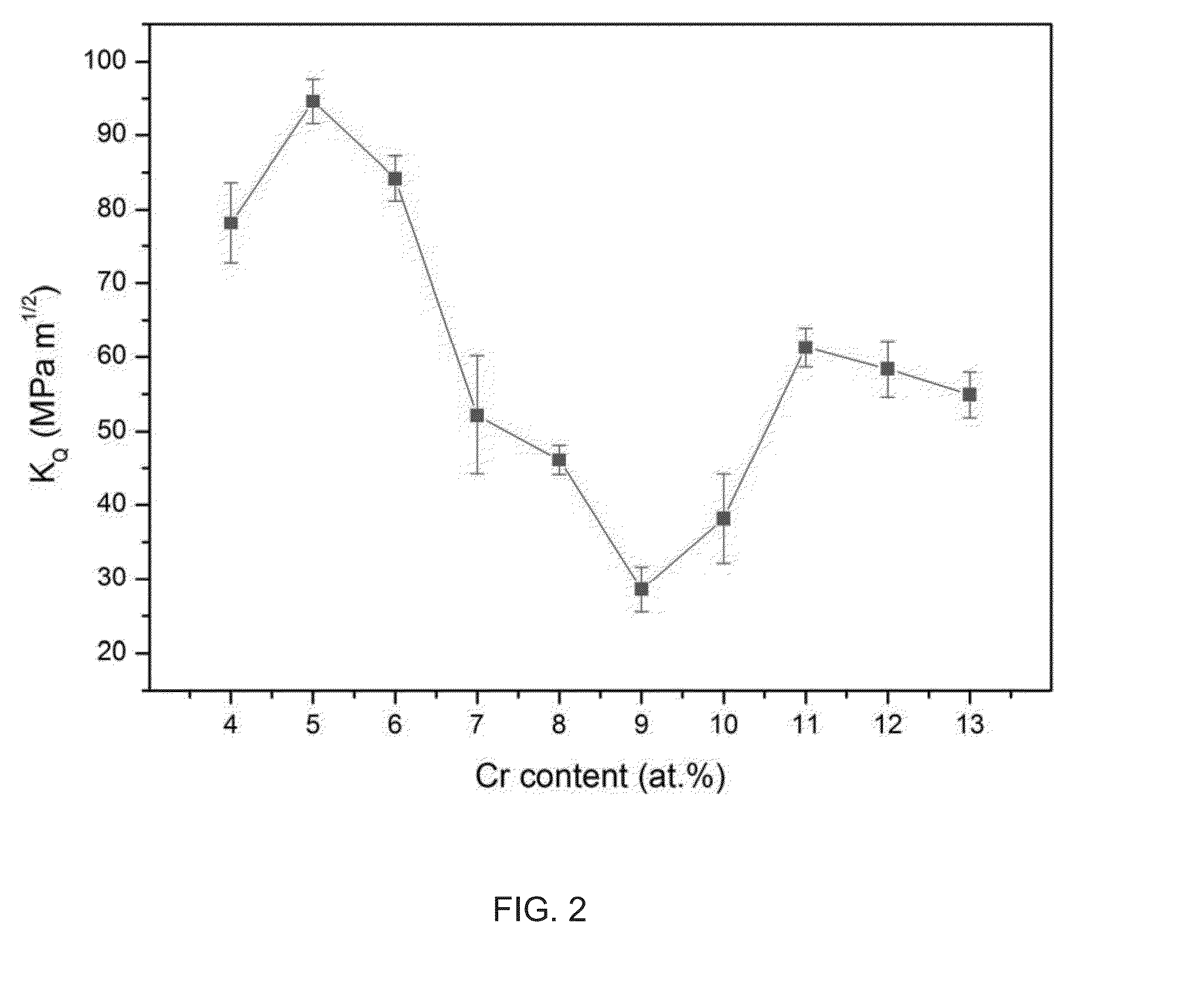
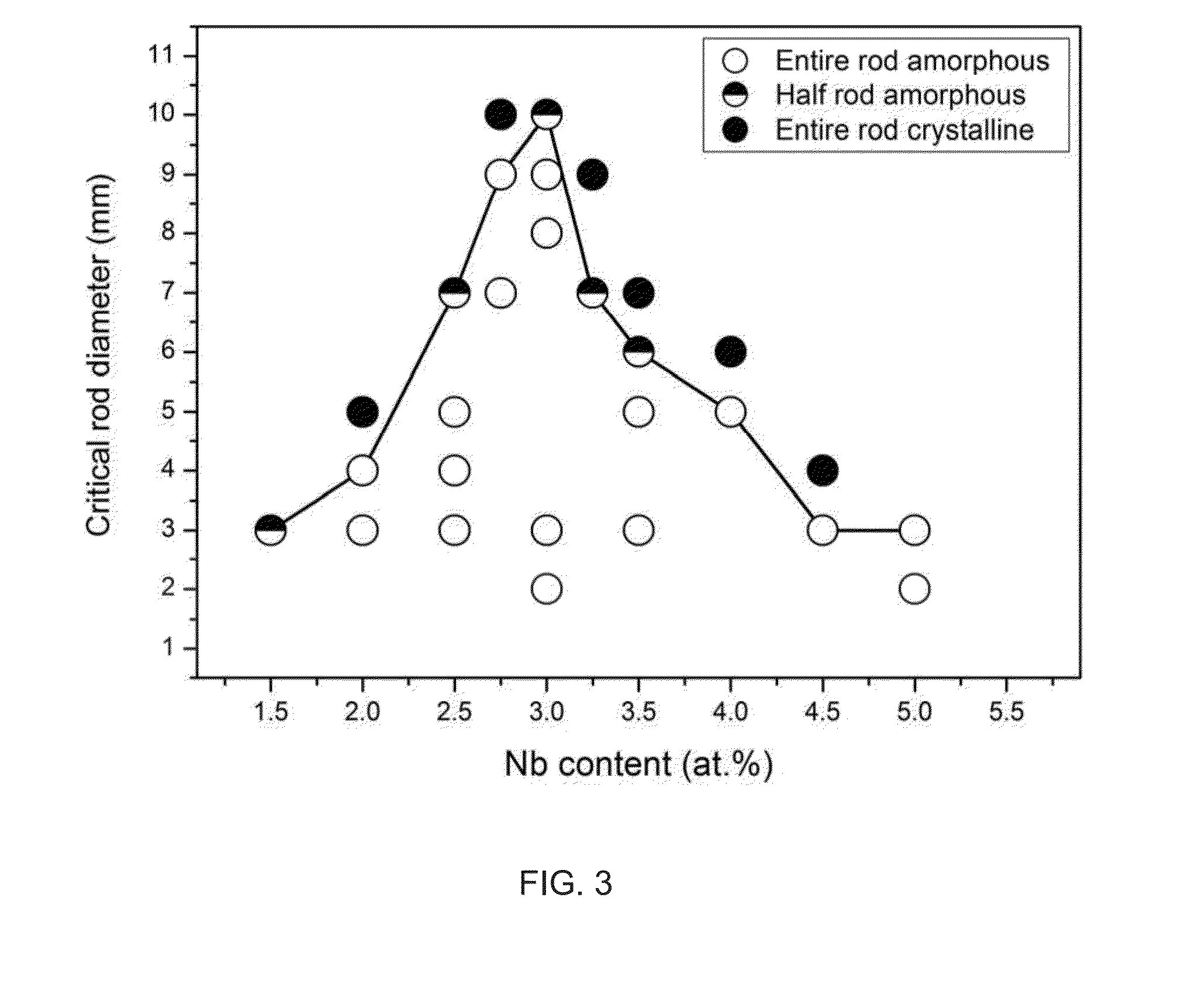
Bulk nickel-based chromium and phosphorus bearing metallic glasses with high toughness
A Ni-based bulk metallic glass forming alloy is provided. The alloy includes Ni(100-a-b-c-d)CraNbbPcBd, where an atomic percent of chromium (Cr) a ranges from 3 to 13, an atomic percent of niobium (Nb) b is determined by x−y*a, where x ranges from 3.8 to 4.2 and y ranges from 0.11 to 0.14, an atomic percent of phosphorus (P) c ranges from 16.25 to 17, an atomic percent of boron (B) d ranges from 2.75 to 3.5, and the balance is nickel (Ni), and where the alloy is capable of forming a metallic glass object having a lateral dimension of at least 6 mm, where the metallic glass has a stress intensity factor at crack initiation when measured on a 3 mm diameter rod containing a notch with length between 1 and 2 mm and root radius between 0.1 and 0.15 mm, the stress intensity factor being at least 70 MPa m1 / 2.
Owner:APPLE INC
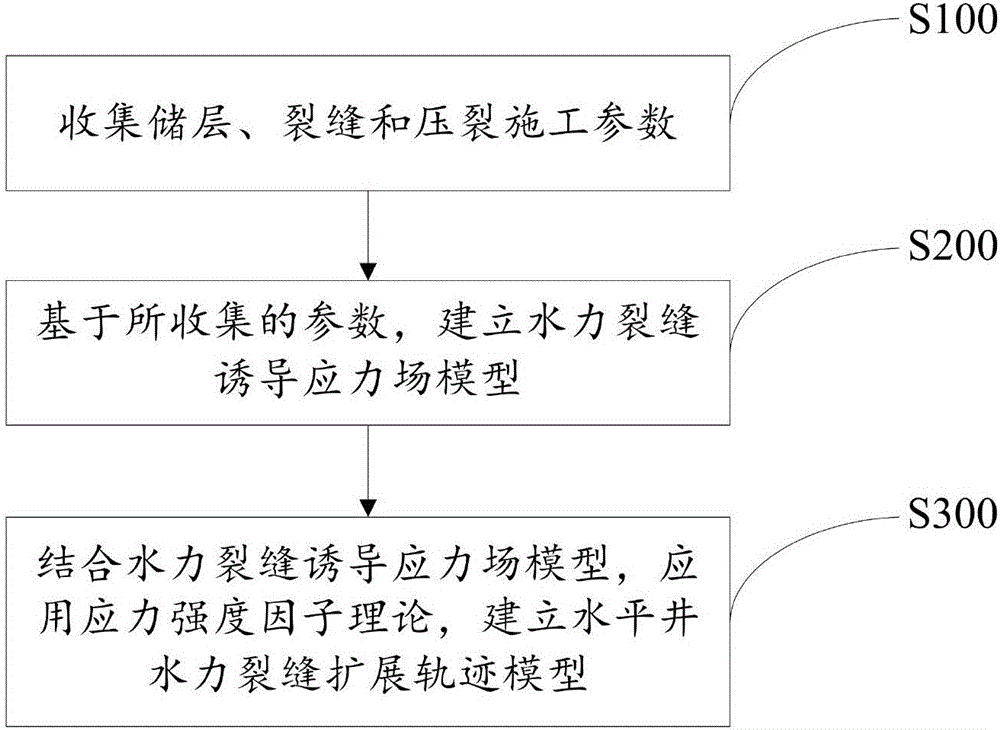
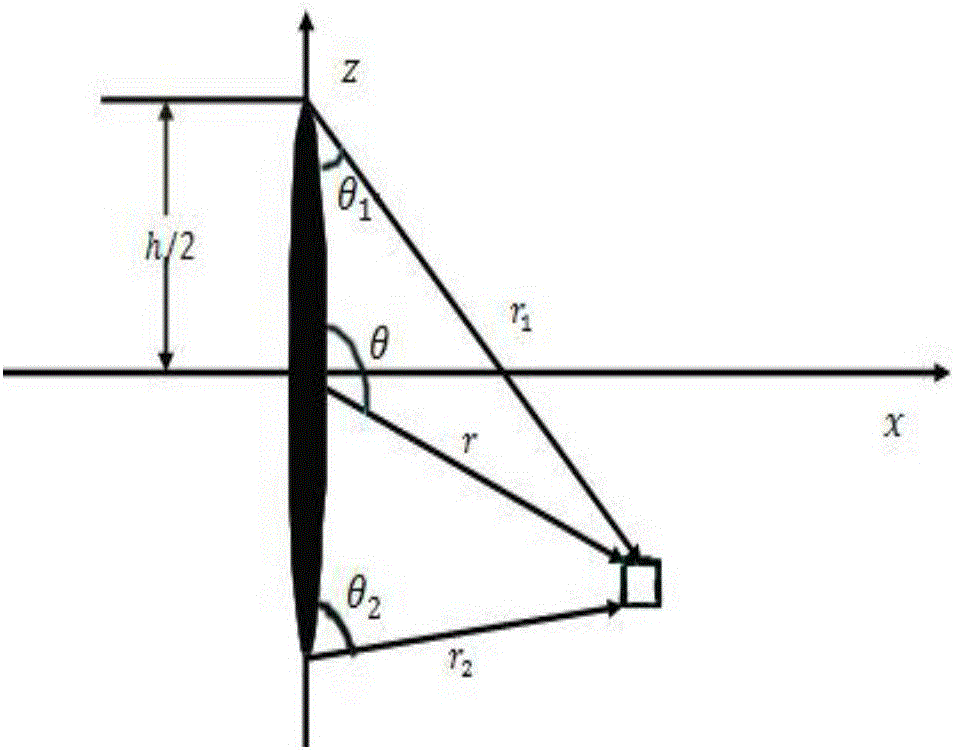
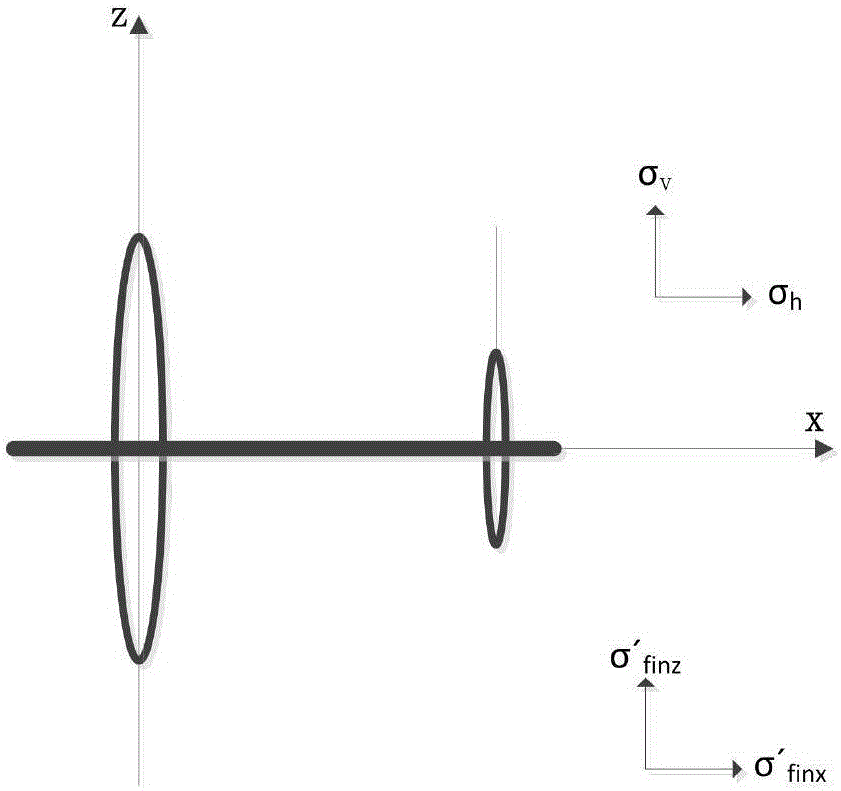
Method for simulating horizontal well staged fracturing fracture expanding track
ActiveCN106593390AAccurate descriptionRealize simulationFluid removalInternal pressureStress intensity factor
The invention discloses a method for simulating a horizontal well staged fracturing fracture expanding track and belongs to the field of oil and gas reservoir exploitation. The method comprises the following steps that the reservoir stratum, fracture and fracturing construction parameters are collected; a hydraulic fracture induced stress field model is established based on the collected parameters; and a horizontal well hydraulic fracture expanding track model is established through application of the stress intensity factor theory according to the hydraulic fracture induced stress field model. According to the method for simulating the horizontal well staged fracturing fracture expanding track, influence of induced stress generated by the well shaft inner pressure, a prior fracturing fracture and fracturing fluid loss on the subsequent hydraulic fracture expanding track is fully considered, and the horizontal well staged fracturing fracture expanding track can be simulated quantitatively and veritably.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Simple method for measuring fatigue crack propagation threshold value of metal material
InactiveCN103454140ASimple test methodAvoid Overload HysteresisStrength propertiesSingle stageStress intensity factor
The invention relates to the technical field of fatigue crack propagation, in particular to a simple method for measuring fatigue crack propagation threshold value of a metal material. The simple method comprises the steps of estimating the initial stress intensity factor range delta K1 and the fatigue crack propagation threshold value delta Kth by referring to related documents or experimental data firstly; selecting whether to use a single-stage experiment or a multi-stage experiment according to the suggestion of the invention; substituting the delta K1 into the formula provided by the invention and calculating the c value and the delta a value; finally calculating the fatigue crack propagation threshold value delta Kt according to the experimental data. The method is suitable for the metal material, and the measured fatigue crack propagation threshold value is in accordance with the national standard GB / T 6398-2000; furthermore, the measurement method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to use, and can quickly obtain the fatigue crack propagation threshold value of the metal material.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-level assessment method for defects of welding joint area at piping safety end of pressure vessel of AP1000 nuclear reactor
ActiveCN102157211ASimplify Advanced AssessmentNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringFailure assessmentUltimate load
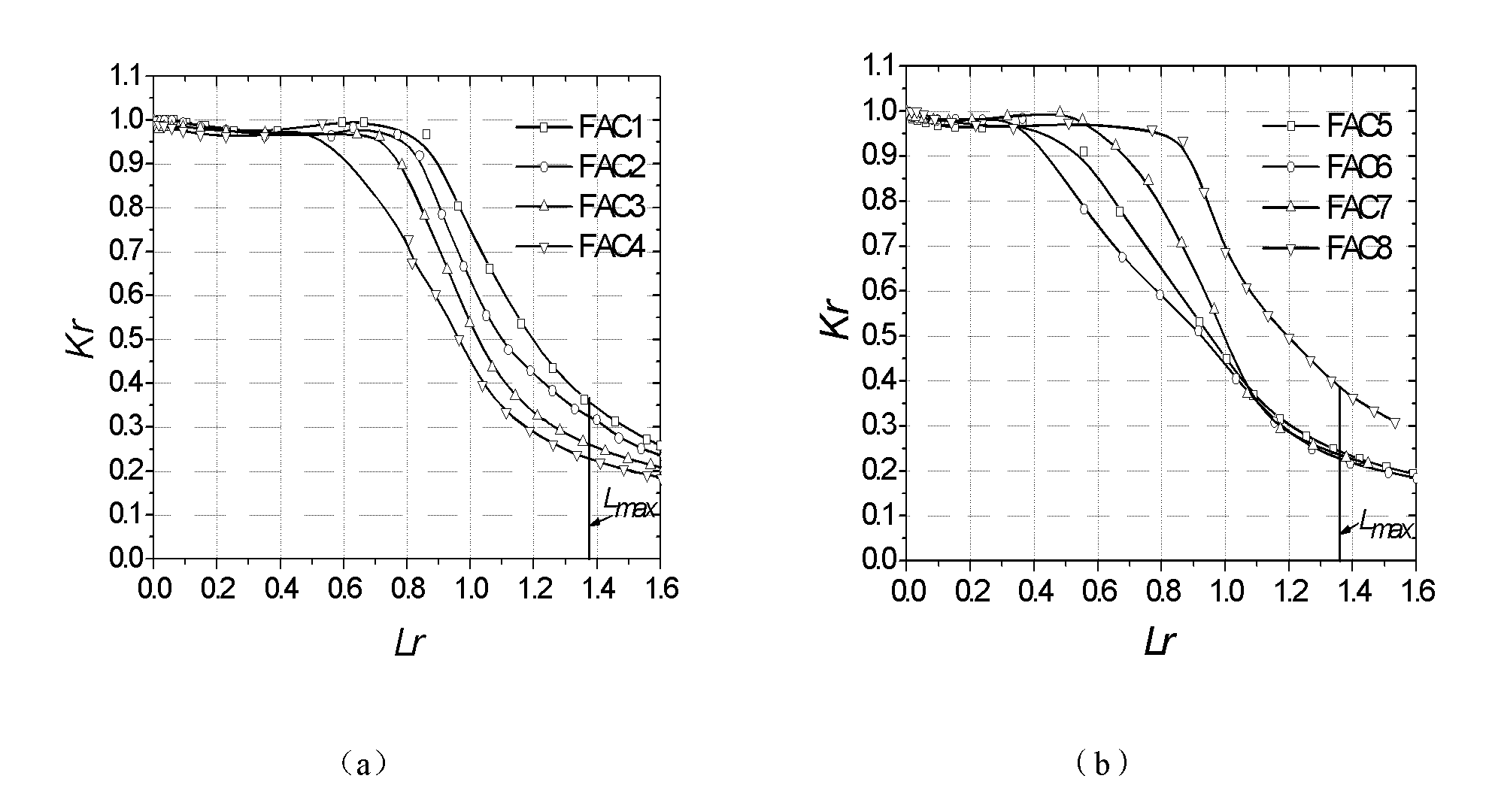
The invention relates to a high-level assessment method for defects of a welding joint area at a piping safety end of a pressure vessel of an AP1000 nuclear reactor. The method comprises the following steps of: characterizing the detected dimensions of unpenetrated circumferential inner surface defects; establishing a failure assessment graph, wherein the failure assessment graph comprises the family of the failure assessment curves of the unpenetrated circumferential inner surface defects in the different dimensions, which are acquired on the basis of three-dimensional finite element calculation; selecting the failure assessment curves according to the dimensions of the defects; based on the three-dimensional finite element calculation, calculating the family of the curves that stress intensity factors change along an extra resultant bending moment at the deepest points of the unpenetrated circumferential inner surface defects in the different dimensions; determining the stress intensity factors according to the resultant bending moment and the dimensions of the defects; calculating a specific breaking strength parameter Kr; based on the three-dimensional finite element calculation, acquiring the family of the ultimate load bending moment curves of the unpenetrated circumferential inner surface defects in the different dimensions; determining ultimate load bending moments according to the dimensions of the defects; calculating a load ratio parameter Lr; and marking a calculated coordinate (Lr, Kr) on the failure assessment graph, and judging whether falling into an area which is encircled by the selected failure assessment curves, a vertical end line and coordinate axes or not.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for predicting residual fatigue life of composite material adhesive bonding repair structure
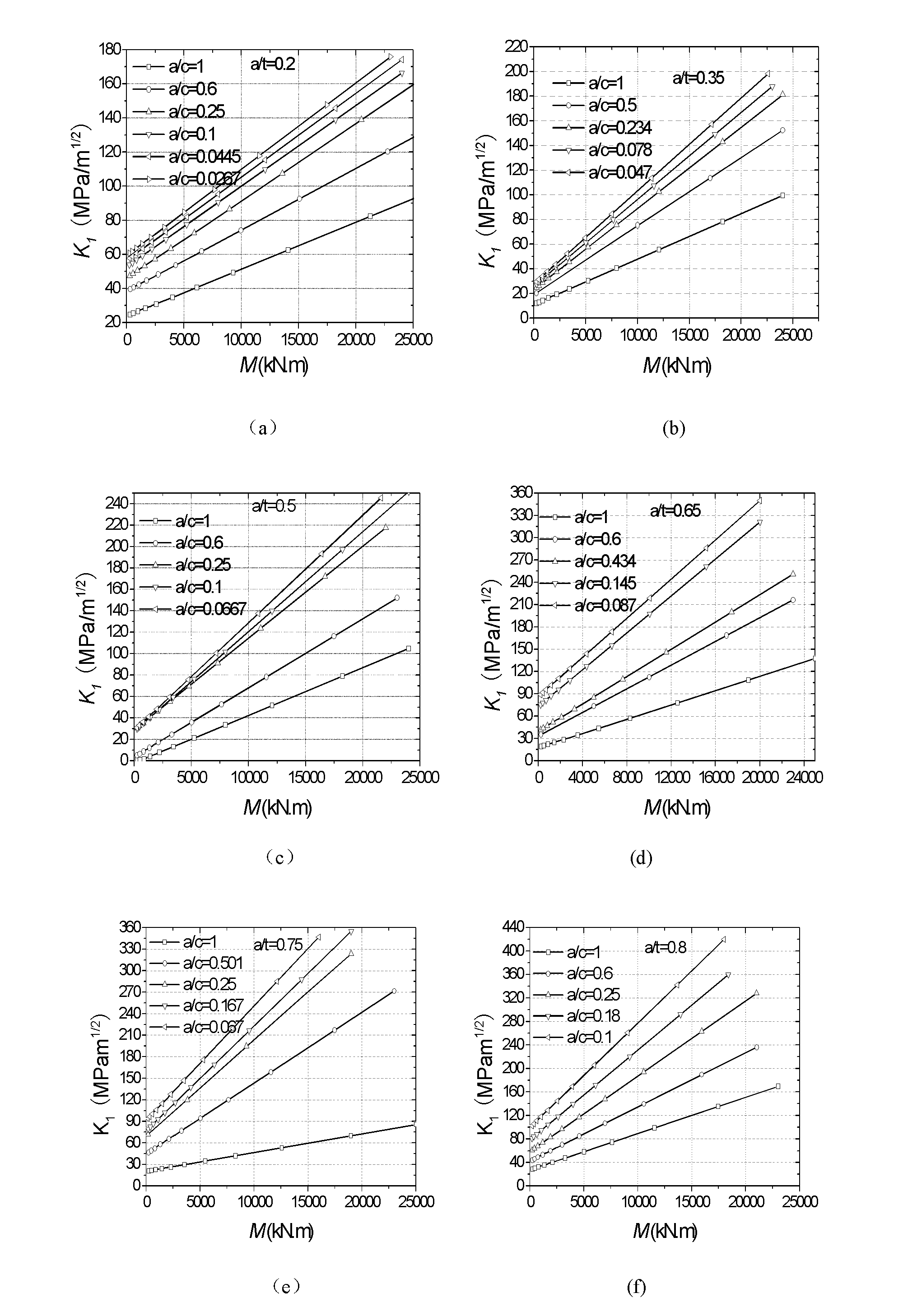
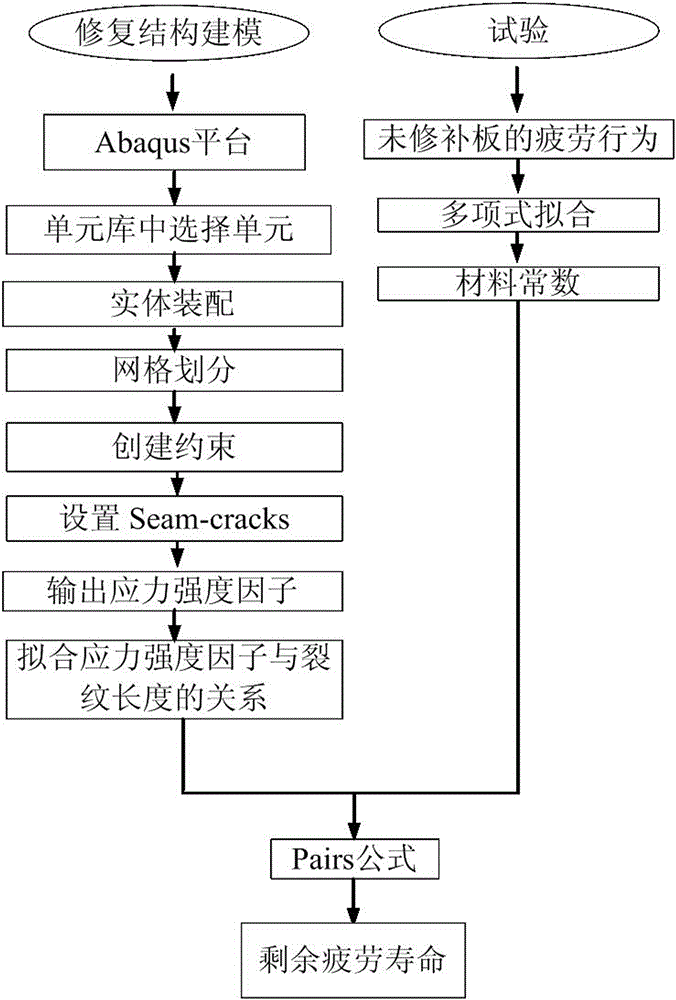
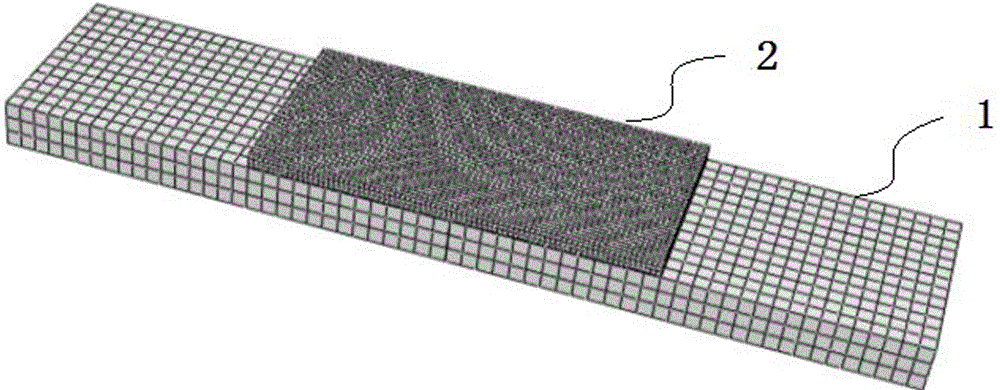
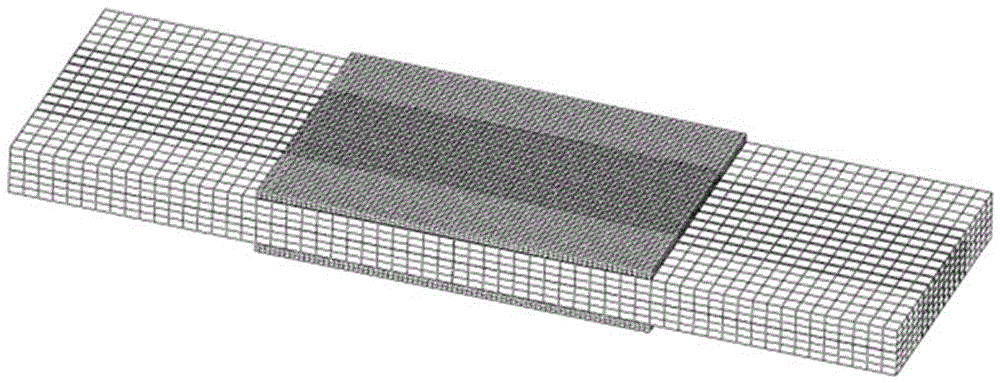
ActiveCN106568660AImproving the Prediction Accuracy of Remaining Fatigue LifeImprove forecast accuracyMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesStress intensity factorPredictive methods
The invention provides a method for predicting the residual fatigue life of a composite material adhesive bonding repair structure. The method comprises the following steps: (1) determining the material constants of an unrepaired structure; (2) establishing a model of a repaired structure, after the establishment, assembling entities, dividing grids, and creating constraints; (3) solving the relational expression between the stress intensity factor amplitude and the crack length; (4) according to the breaking tenacity of a metal material, based on the stress intensity factor output by software, determining the final failure crack length of the repaired structure; and (5) substituting the material constants, the final failure crack length, and the relational expression between the stress intensity factor change amplitude and the crack length into Paris formula, and calculating the residual fatigue life of the repaired structure through integration. The calculation steps are simplified, the prediction efficiency on the residual fatigue life of a composite material adhesive bonding repair structure is obviously improved, the calculation cost is reduced, and the development of the composite material adhesive bonding repair technology is promoted.
Owner:QINGDAO CAMPUS AVIATION ENG COLLEGE OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY NAVY
Methods and systems for assessing residual life of turbomachine airfoils
ActiveUS9103741B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelStress intensity factor
Methods, systems and computer program products for assessing residual life of an airfoil, which would experience high cycle fatigue failure under at- or near-resonance vibration condition, are provided. The method includes receiving, at a processing system, at least one vibration response parameter associated with the airfoil. The method processes at least one cracked airfoil finite element model. Processing the cracked airfoil finite element model includes accessing the cracked airfoil finite element model, computing a modal stress intensity factor (SIF) of the cracked airfoil finite element model using fracture mechanics based finite element analysis, and computing a vibratory SIF based, at least in part, on the modal SIF and the at least one vibration response parameter. The method then computes a residual life indicator of the airfoil based, at least in part, on the vibratory SIF.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
New enginering structure and material deformation measuring technology
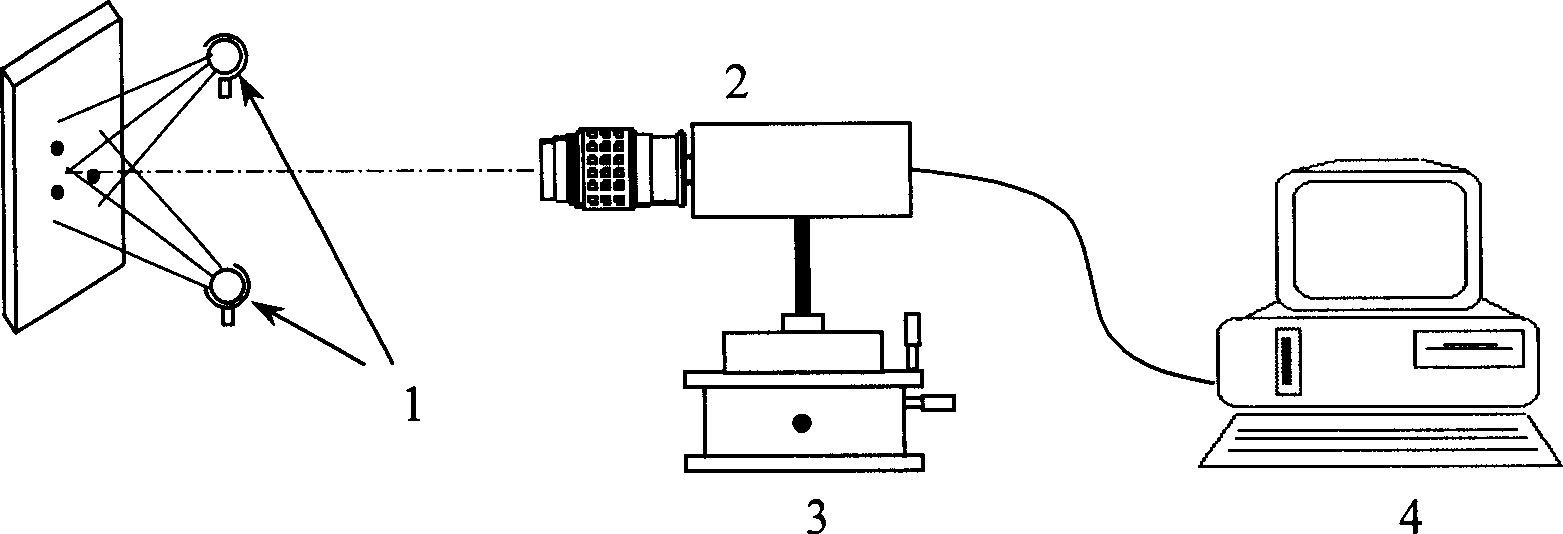
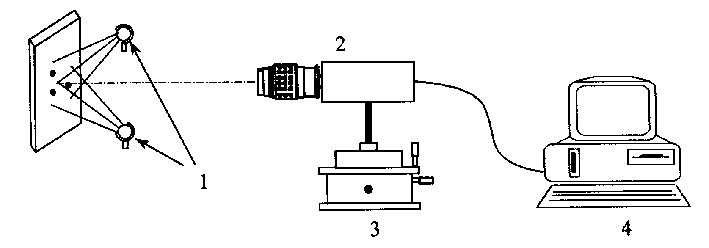
InactiveCN1458528ARealize measurementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationStructural deformationData file
The present invention provides the characteristic point analyzing and distinguishing technology for accurate measurement of deformation in engineering structure and material. The new measurement technology adopts light source, CCD camera, 3D shift stage, control computer and analysis and distinguishing system. On the surface of the tested object, several "characteristic points" for describing the structural deformation are made or selected, their images before and after deformation or in different deformation stages are taken via the CCD camera and the obtained video signals are transmittedinto the control computer and formed into data files. The "characteristic points" relevant coefficient judgment criterions are used in the measurement of object deformation. The present invention may be used in engineering site measurement, has no special limitation in measured object and deformation causes, and may be used in the measurement of various mechanical performance of different materials.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Process to fracture connecting rods and the like with resonance-fatigue
A process to fracture connecting rods and the like, that are made of high strength materials, comprises of the following mechanisms:(a) Fatigue: fluctuation of stresses in a pre-notched connecting rod due to the use of harmonic excitation will extend the notch tip in the connecting rod and will weaken the predetermined fracture plane by creating micro-cracks,(b) Resonance: resonance occurs when the frequency of the used harmonic excitation matches a natural frequency of the connecting rod, idealized as a structural system,(c) Pre-stressing forces: by applying pre-stressing forces acting in the same loading mode, the stresses in the connecting rod due to several force components can be superimposed,(d) Dynamic force: applying a dynamic force will raise the stress intensity factor, exceeding the fracture toughness of the material.
Owner:FATIGUE FRACTURE TECH
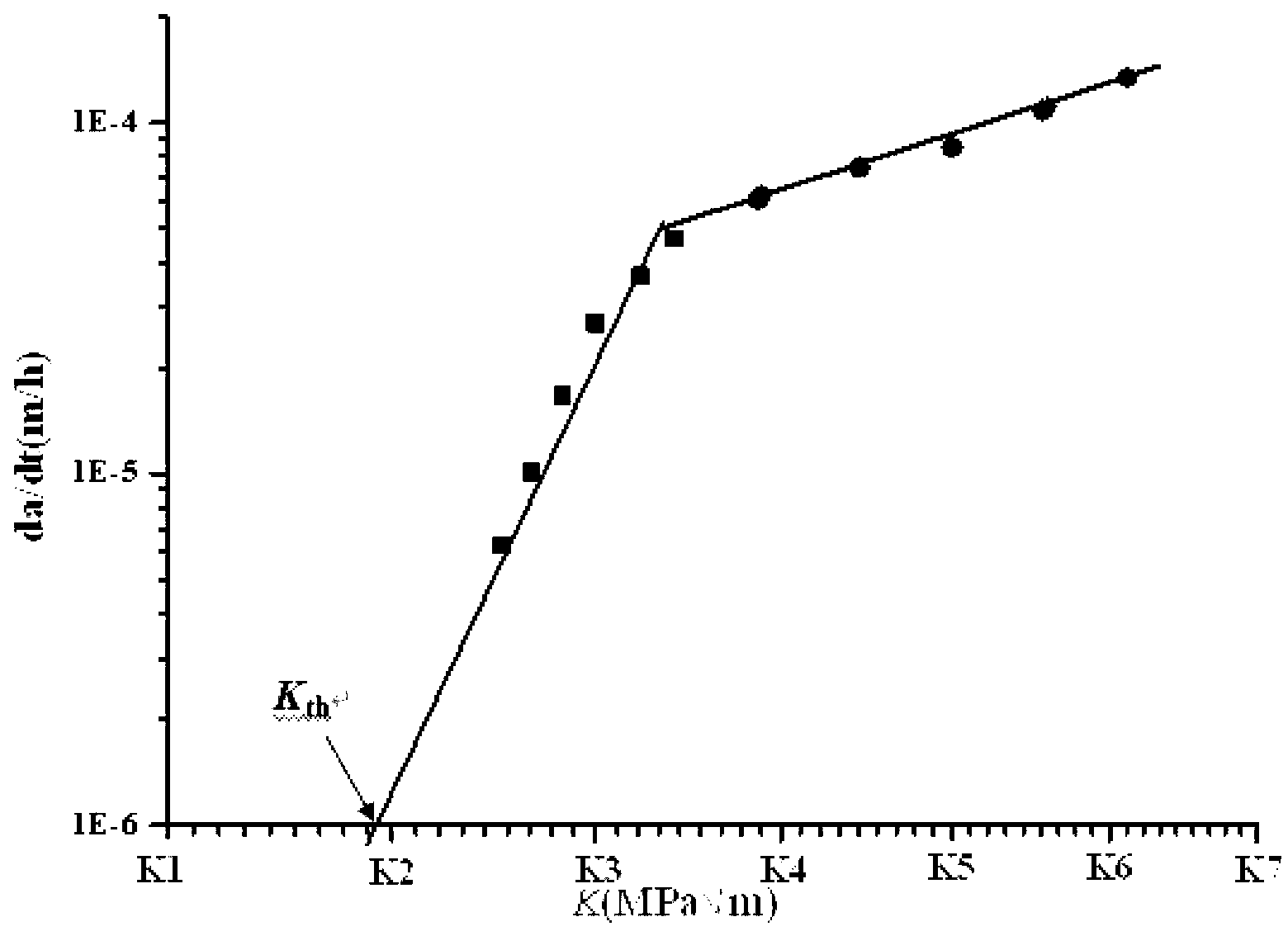
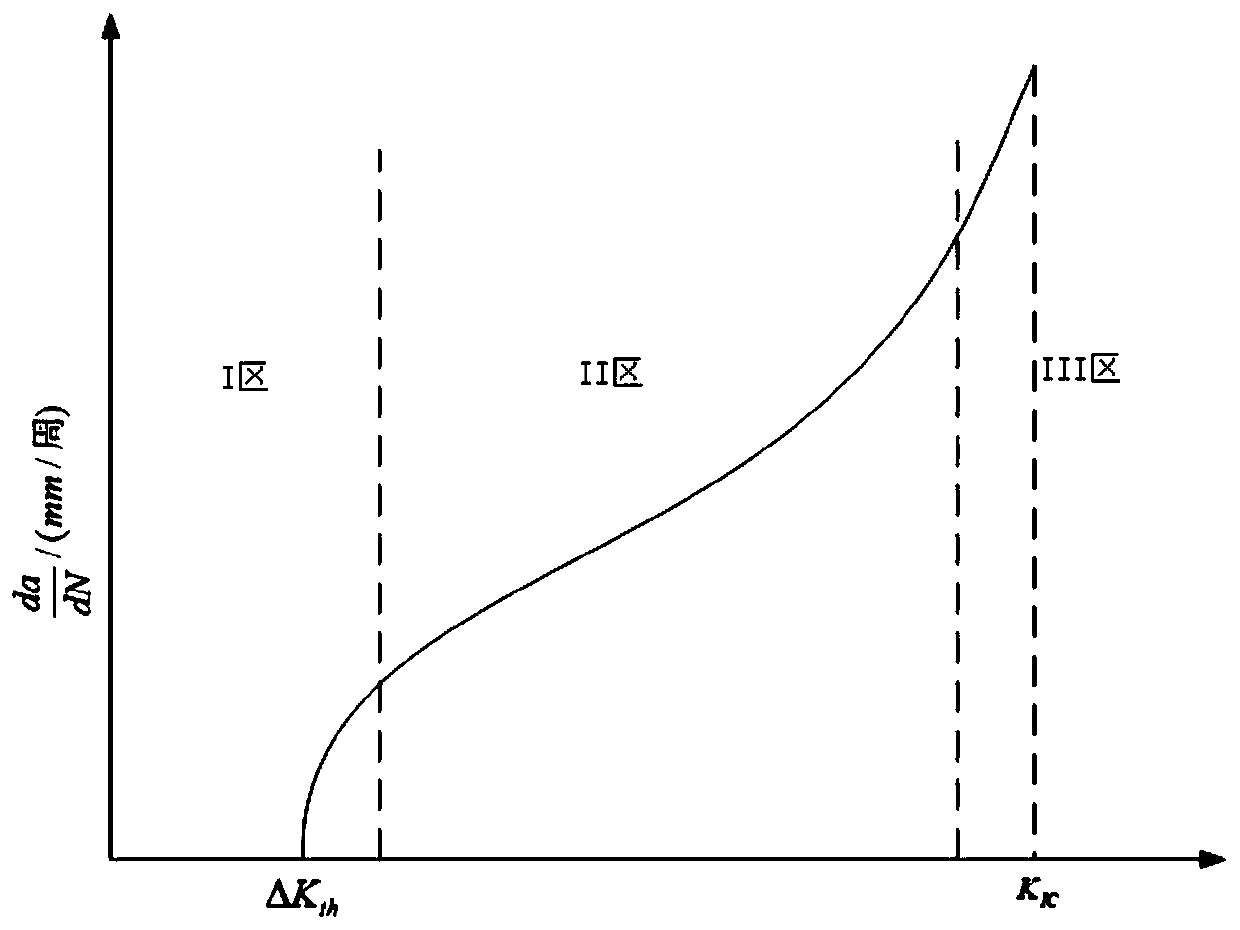
Method for determining region turning point of titanium alloy fatigue crack growth rate curve Paris
InactiveCN106066287AFit closelyScientific basis is sufficientMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesStress intensity factorDamage tolerance
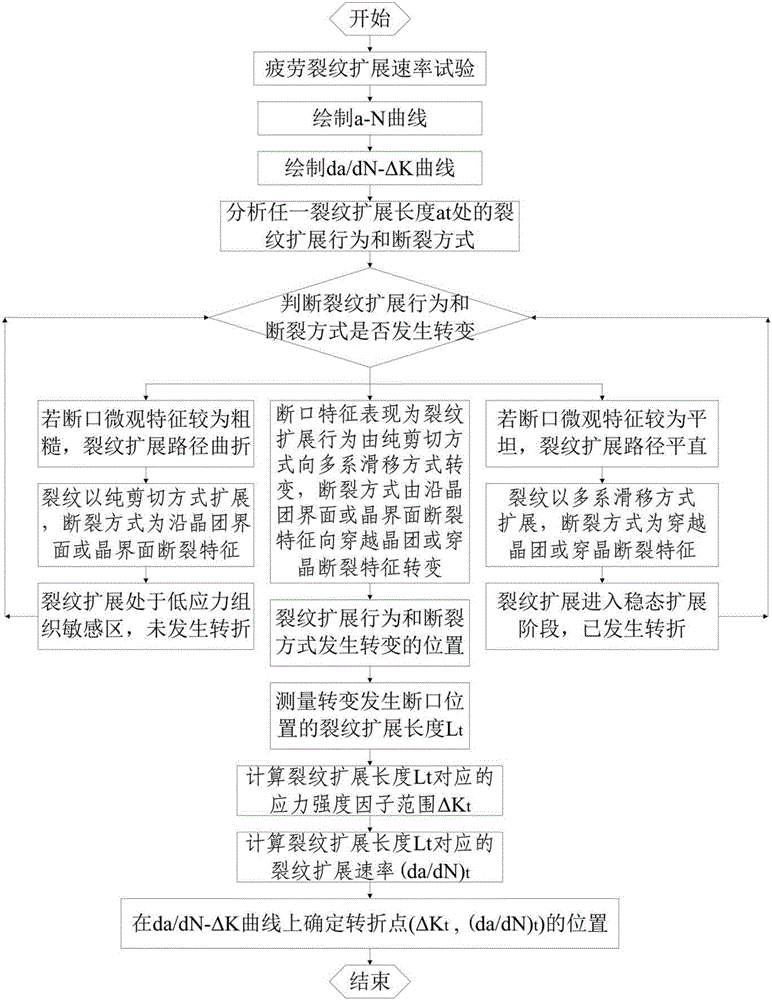
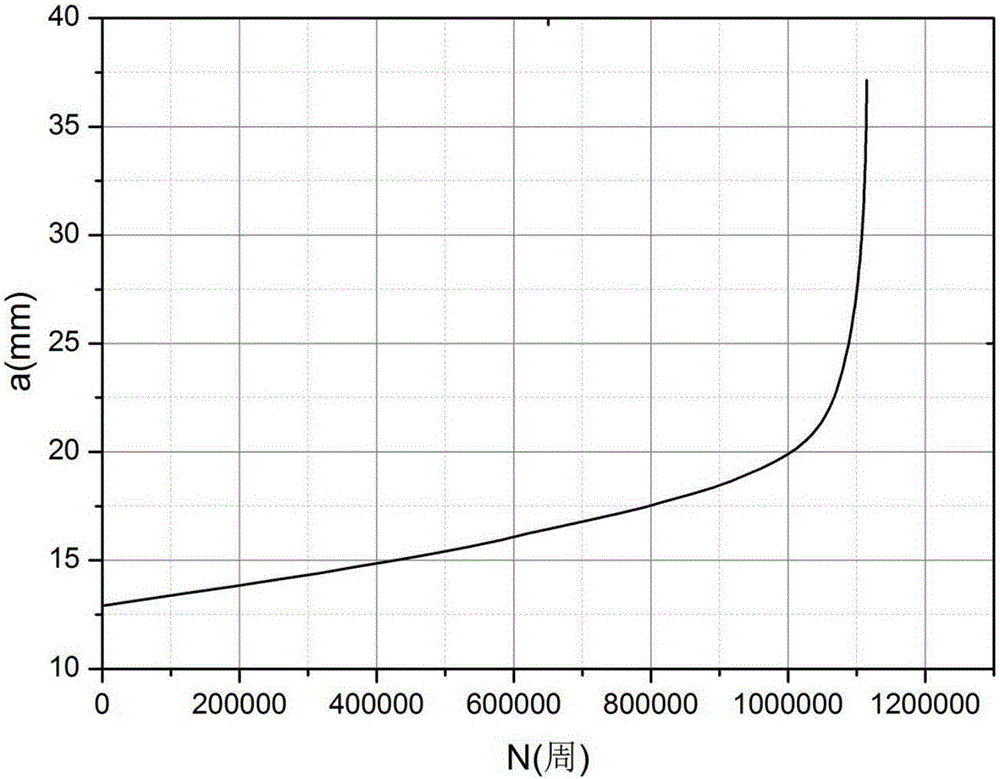
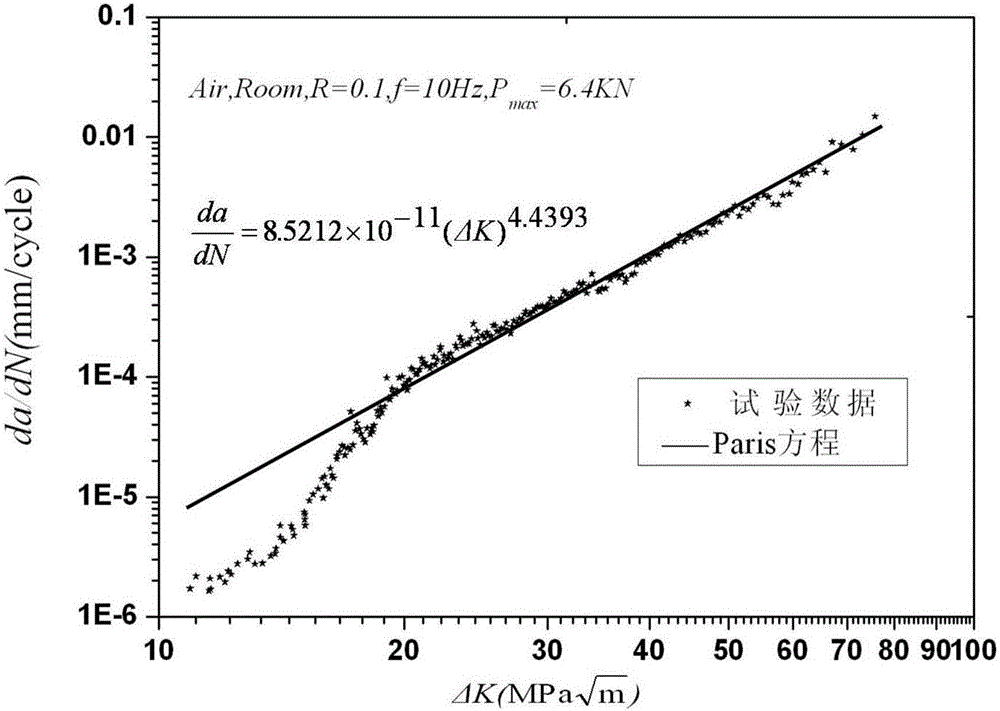
The invention belongs to the technical field of material fatigue crack growth behavior analysis, and provides a method for determining a region turning point of a titanium alloy fatigue crack growth rate curve Paris. The method determines the crack growth length during change of a fatigue crack growth mechanism according to the changes of crack growth behavior and fracture mode shown by micro characteristics of the fracture; and solving the stress intensity factors and the fatigue crack growth rate corresponding to the crack propagation length, so as to determine the turning point position of the fatigue crack growth rate curve Paris. The invention has full scientific basis and high accuracy, can satisfy material performance evaluation and damage tolerance design by designers and users, and is beneficial to the application of modern engineering.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
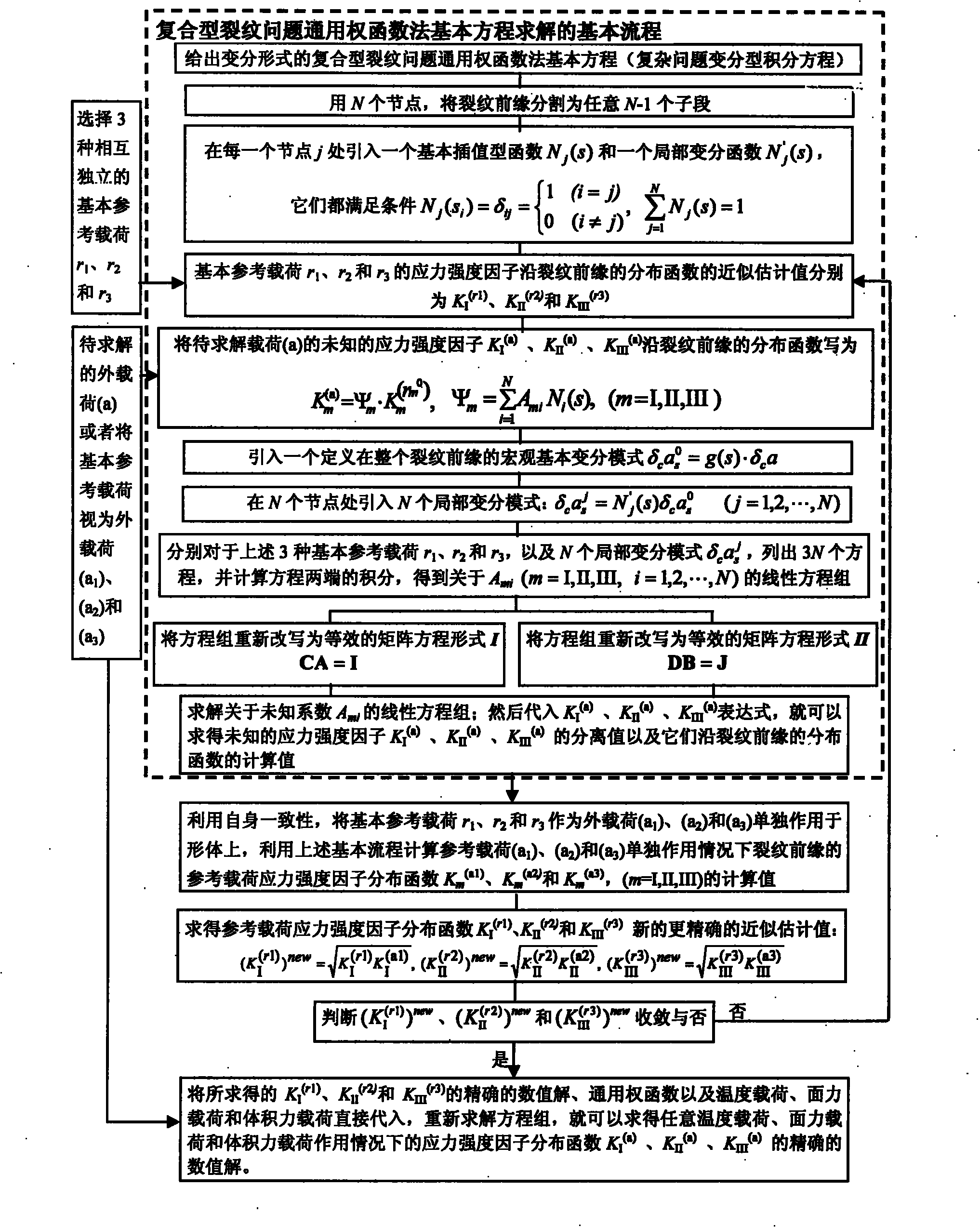
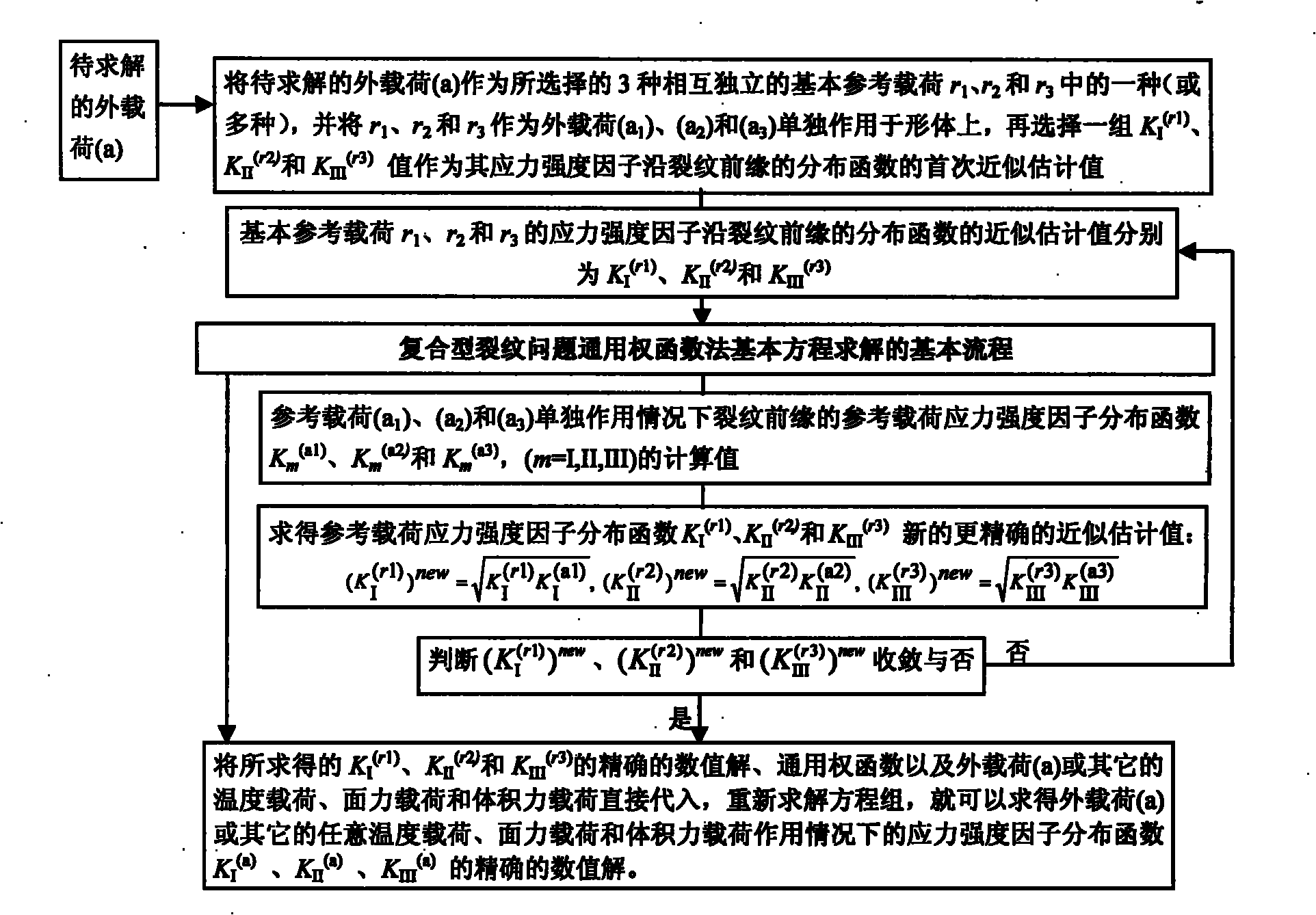
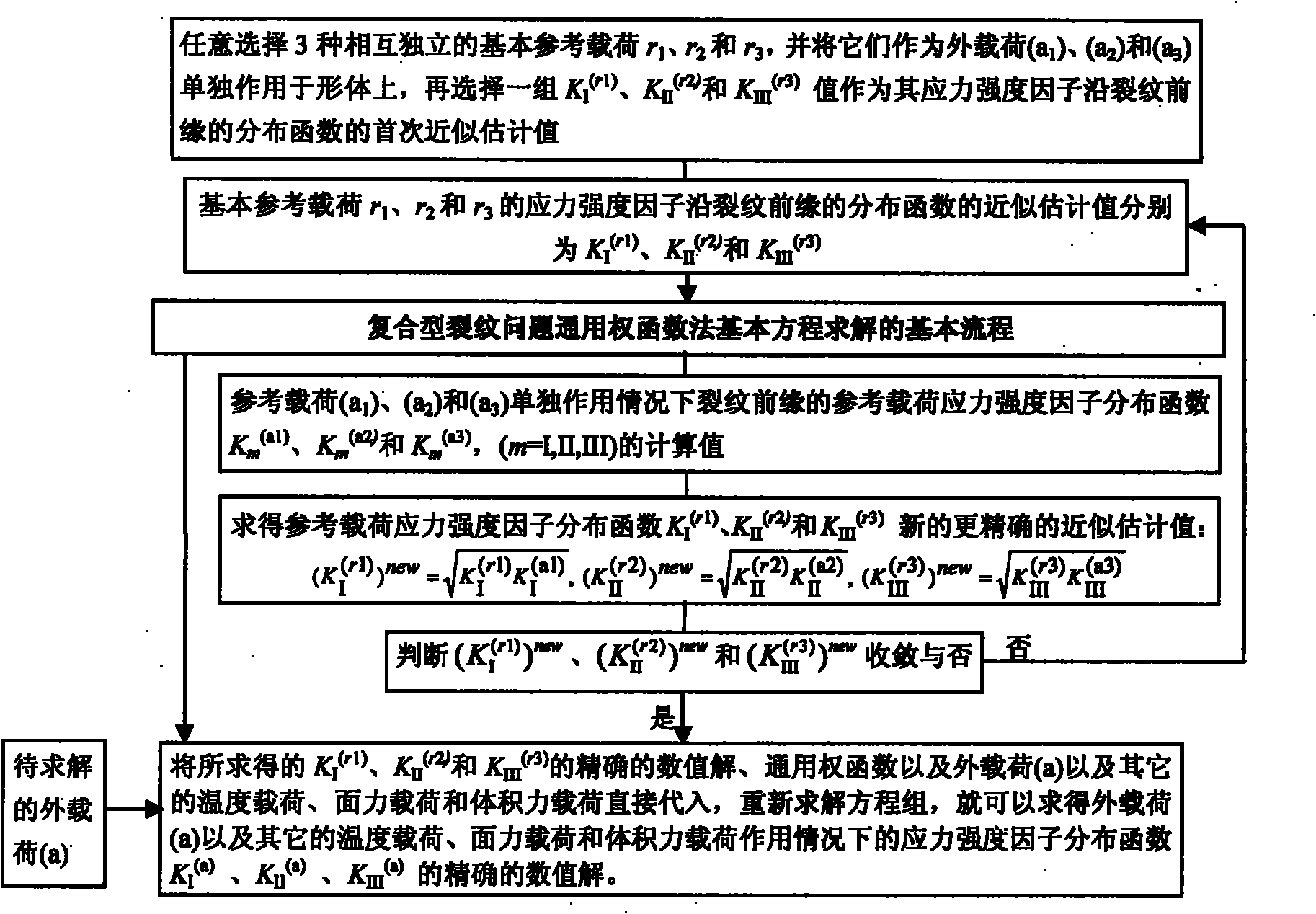
Method for determining separation and distribution of structural-member composite crack front stress intensity factors
InactiveCN101788425AHigh precisionImprove calculation accuracyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsStress intensity factorEngineering
The invention relates to a method determining separation and distribution of structural-member composite crack front stress intensity factors. The method comprises the following steps: giving thermal load, surface force load and volume force load borne by a structural member, and a universal weighting function method basic equation for three-dimensional I, II, III composite crack problems under the independent or combined actions of the thermal load, the surface force load and the volume force load; dividing the crack front into random N-1 numbered subsections through N numbered nodes, and introducing a basic interpolation function Nj(s) and a partial variation function N'j(s) at each node j, thereby constructing a finite number of partial variation modes and interpolation modes; and then introducing 3 basic reference loads to solve the basic equation, thereby determining the numerical solution of the separation and distribution of composite stress intensity factors KI, KII and KIII. By utilizing the self consistency, the method can obtain the high-precision exact solution of the distribution of the three-dimensional crack front composite stress intensity factors KI, KII and KIII by constructing an iterative process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
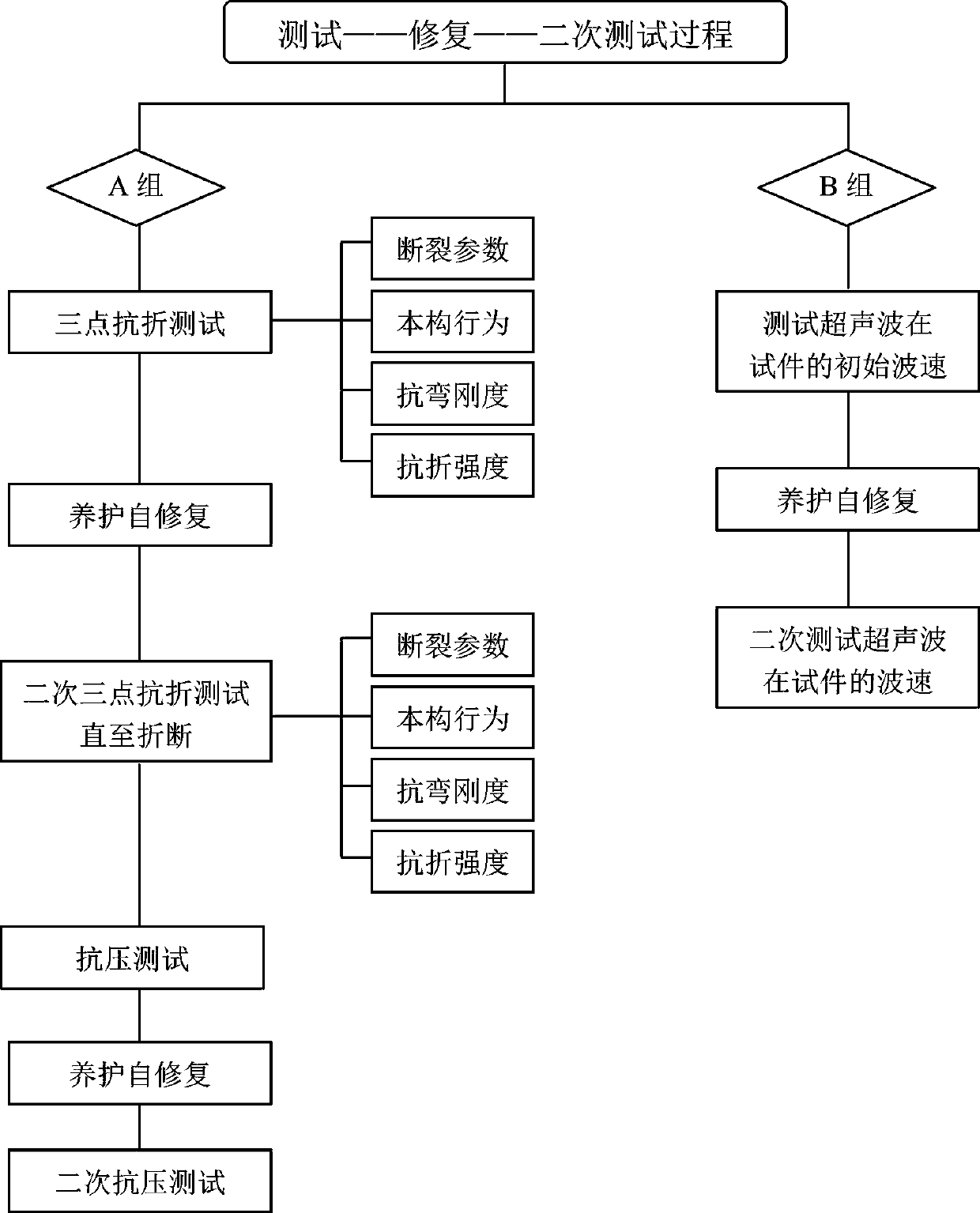
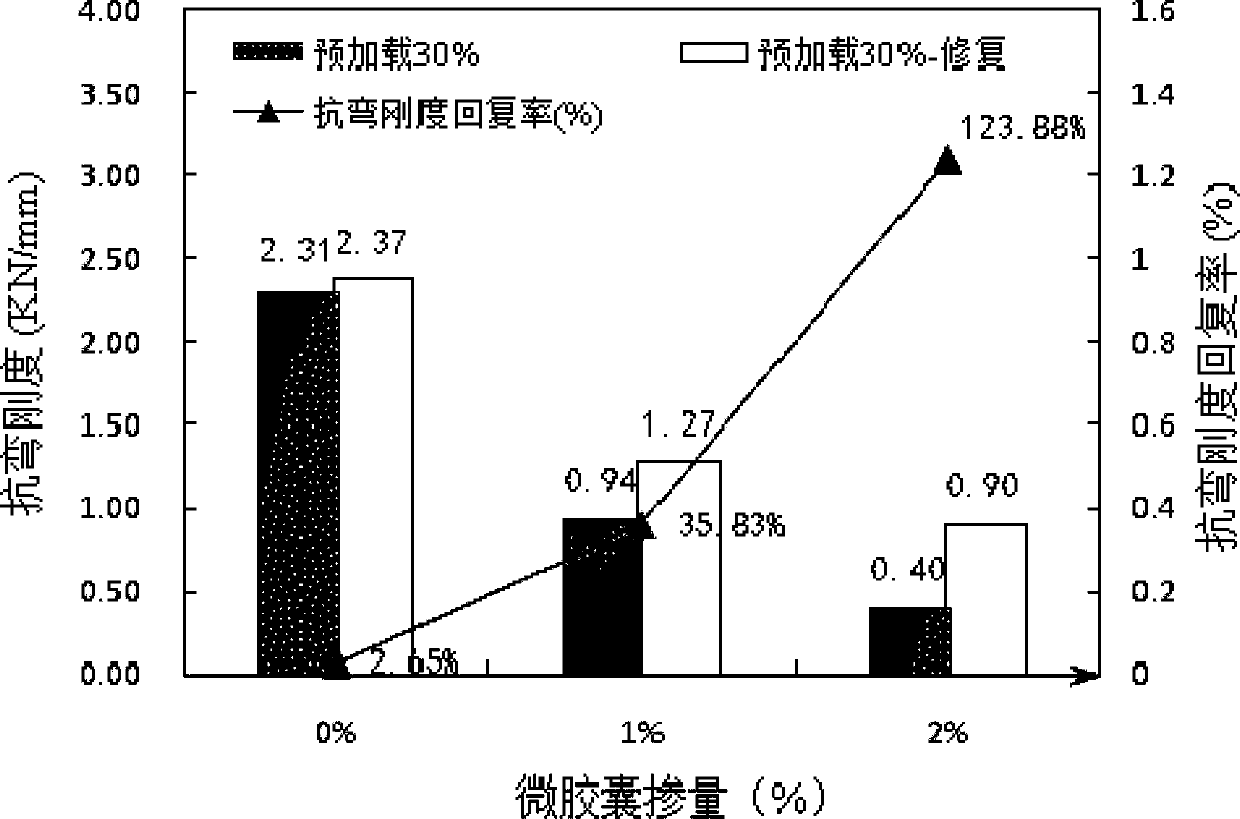
Evaluation method of self-repairing effect of self-repairing cement-based material
InactiveCN105300801AControl diversificationComprehensive performance response evaluationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress intensity factorPhysical property
The invention relates to the field of methods for testing or analyzing concrete by virtue of the chemical or physical properties of a measuring material, particular to an evaluation method of the self-repairing effect of a self-repairing cement-based material. The evaluation method of the self-repairing effect of the self-repairing cement-based material is characterized in that the evaluation indexes comprise relative dynamic elasticity modulus, fracture behaviors (stress intensity factor recover rate and fracture toughness recover rate), constitutive behavior comparison, flexural rigidity recover rate and strength recover rate. The evaluation method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing a test piece; step 2, prefabricating local cracks and dispersed cracks; step 3, testing all the parameters; step 4, completing self repairing; step 5, testing all the parameters; step 6, calculating, processing, and evaluating the repairing effect. The method is comprehensive in evaluation.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
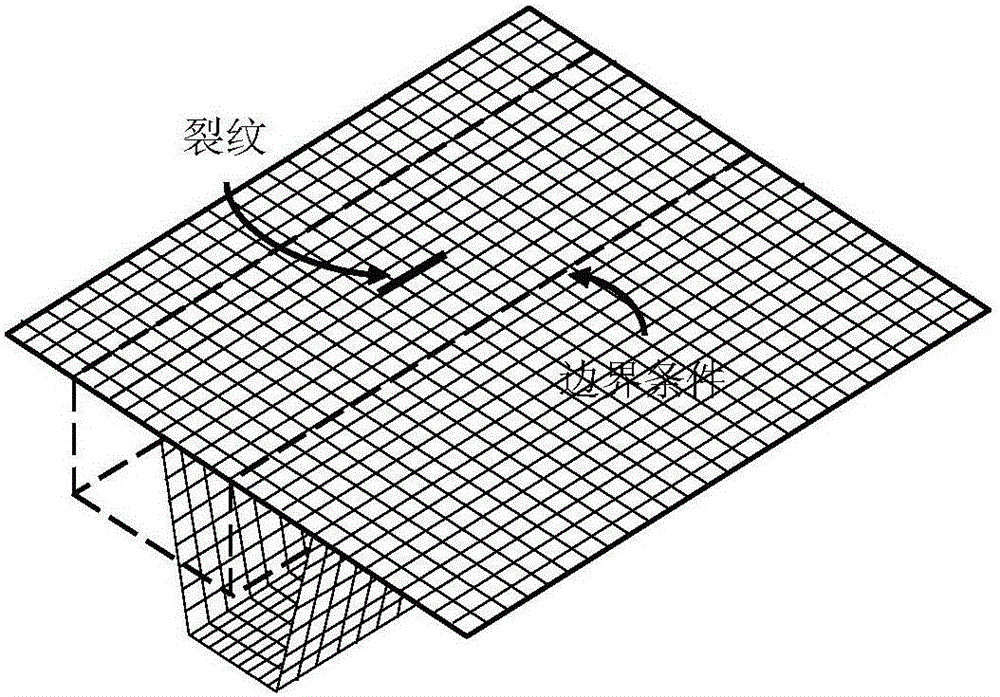
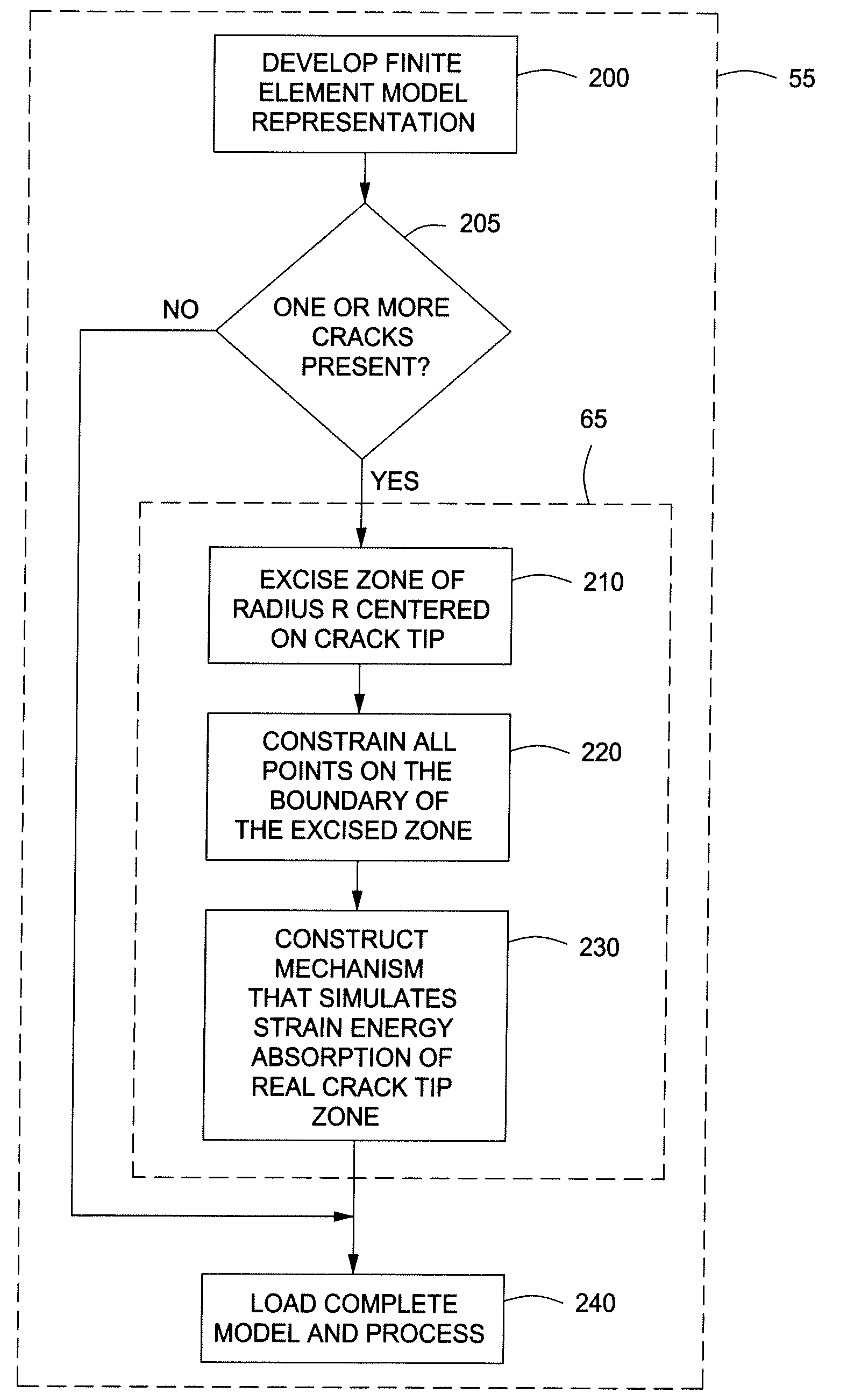
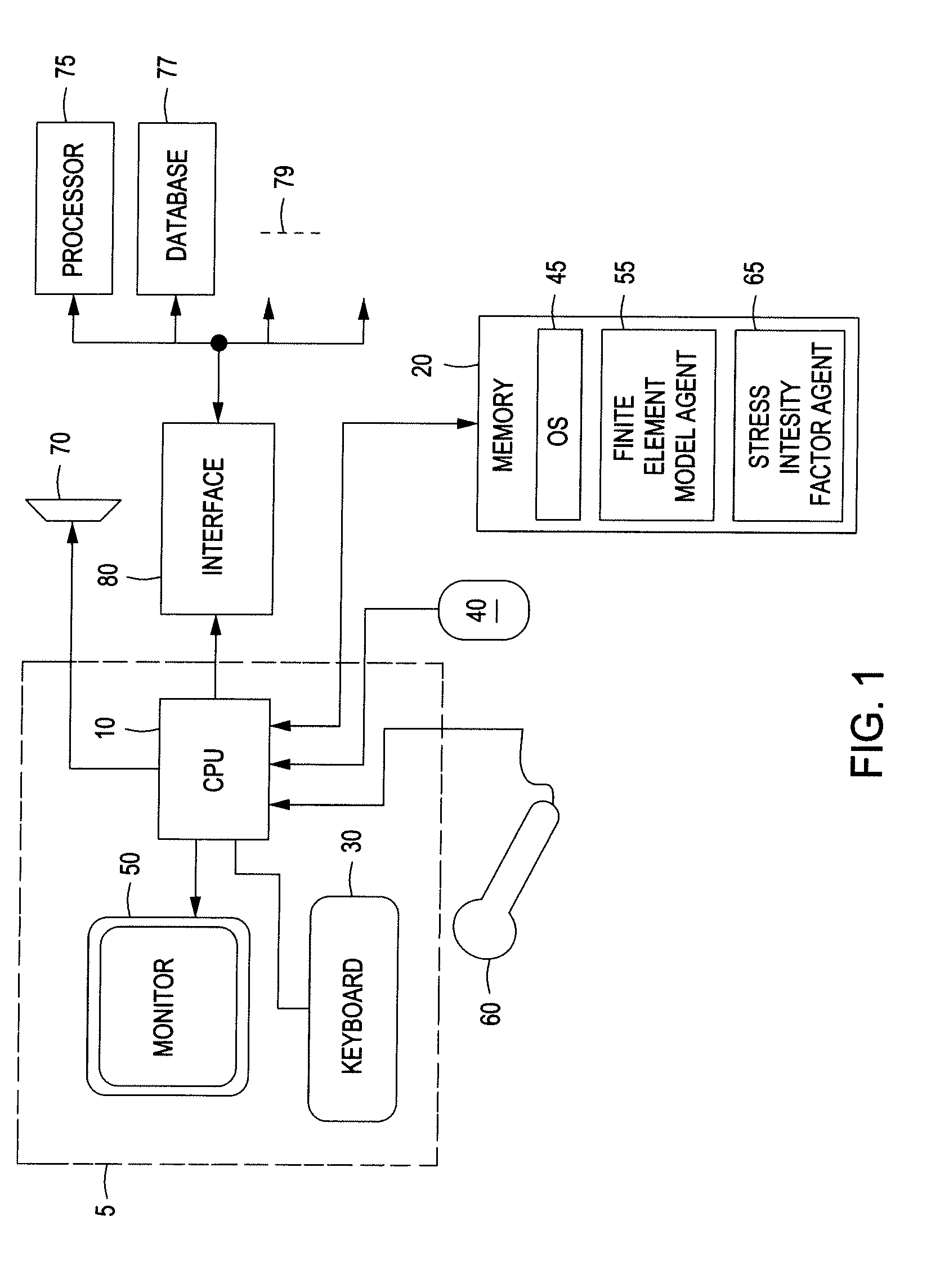
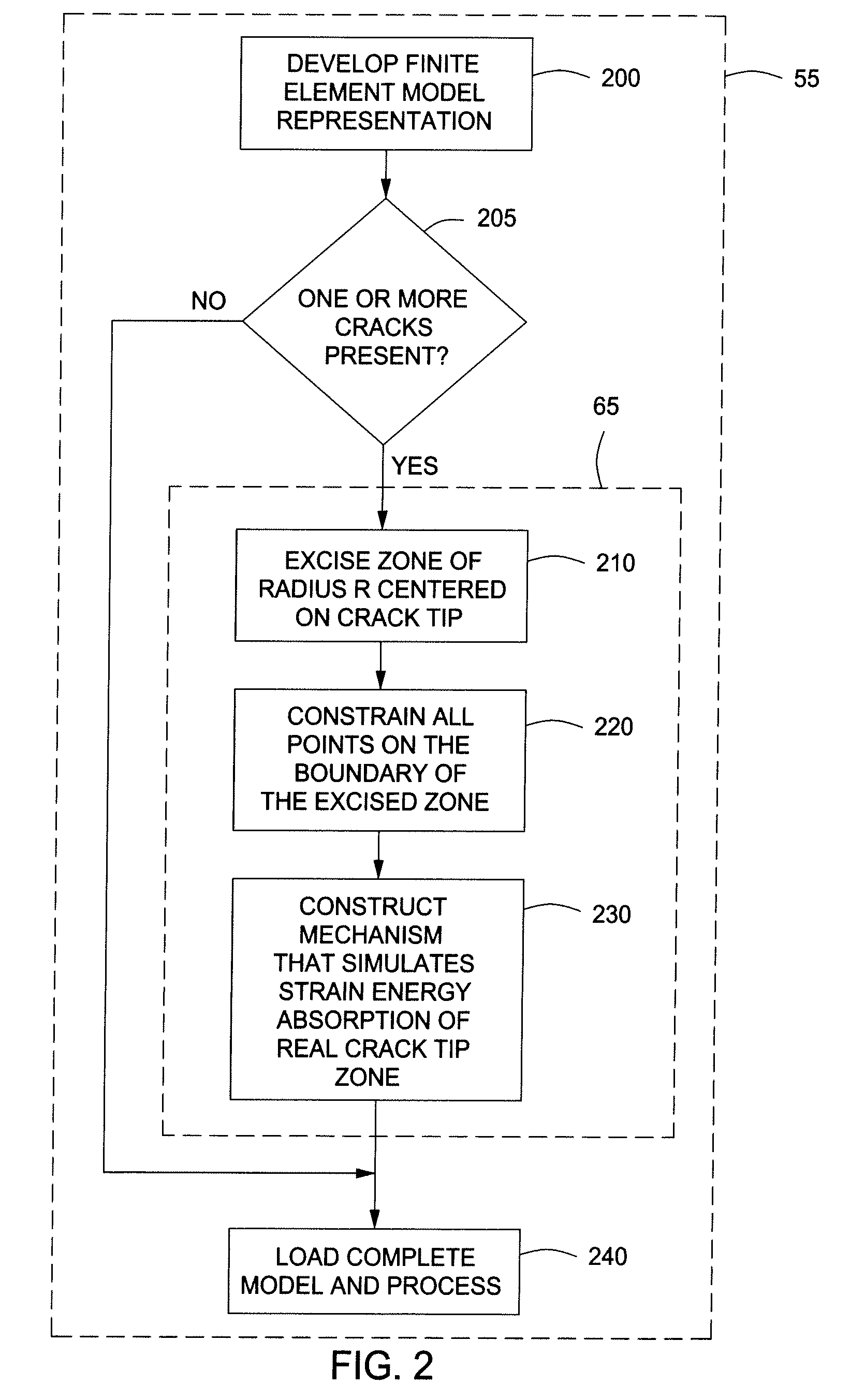
Systems and Methods for Performing Stress Intensity Factor Calculations Using Non-Singluar Finite Elements
ActiveUS20110191074A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelStress intensity factor
Systems and methods are disclosed for determining stress intensity factors. In one or more embodiments, the method can include the steps of defining a crack tip zone about one or more crack tips of one or more arbitrarily shaped cracks in an arbitrarily shaped solid. The one or more crack tip zones can be constrained within a finite element model representation mesh of the arbitrarily shaped solid to provide one or more constrained crack tip zones. The combination of the finite element model representation mesh and the one or more constrained crack tip zones can be processed to determine the stress intensity factor for each of the one or more arbitrarily shaped cracks.
Owner:KELLOGG BROWN & ROOT LLC
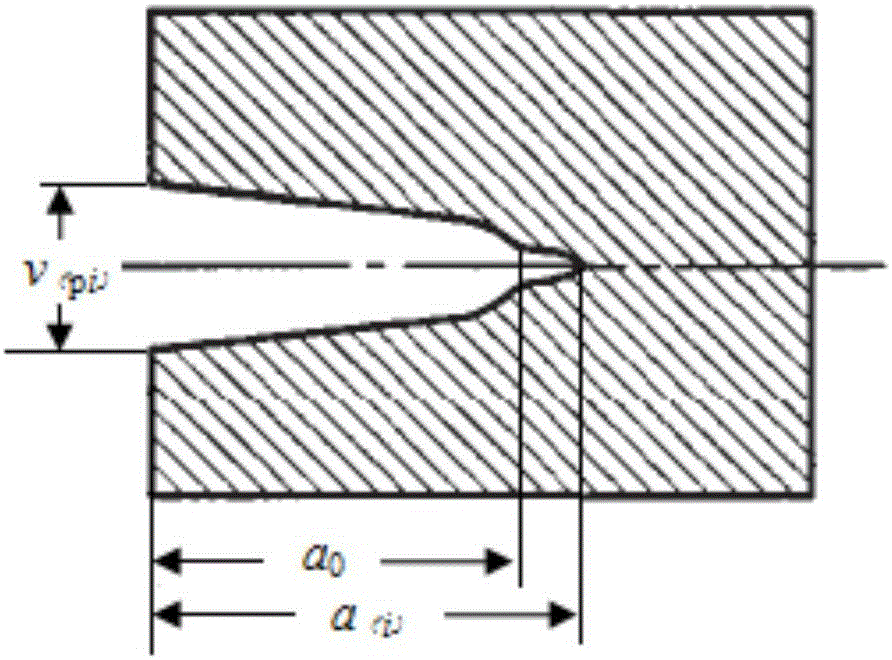
Testing method for dynamic crack arrest toughness of I-type crack under impact load
InactiveCN106290012ASimple methodEasy to operateMaterial strength using single impulsive forceConfiguration designStress intensity factor
The invention discloses a testing method for the dynamic crack arrest toughness of an I-type crack under the impact load, and belongs to the technical field of geotechnical engineering. The method includes the steps of conducting impact test research through a large-diameter separated type Hopkinson pressing rod and a test configuration designed by an inventor, determining the dynamic crack toughness of a sample through an experiment-numerical value method, calculating the load borne by the sample and the moment of crack arrest through strain signals obtained through a test, inputting an obtained time travel curve to a finite element program Ansys, calculating the near-field displacement of a crack tip through a 1 / 4 node unit, obtaining the time travel curve of the I-type dynamic rupture stress strength factor of the sample through a displacement extrapolation method, obtaining the strain strength factor value corresponding to the crack arrest moment as the dynamic crack arrest toughness of the material, and then obtaining the pure I-type crack dynamic crack arrest toughness under the effect of the impact load. The method is simple and convenient to operate and should have more practical application meaning in research of the dynamic crack arrest characteristic of rock under the impact dynamic load.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
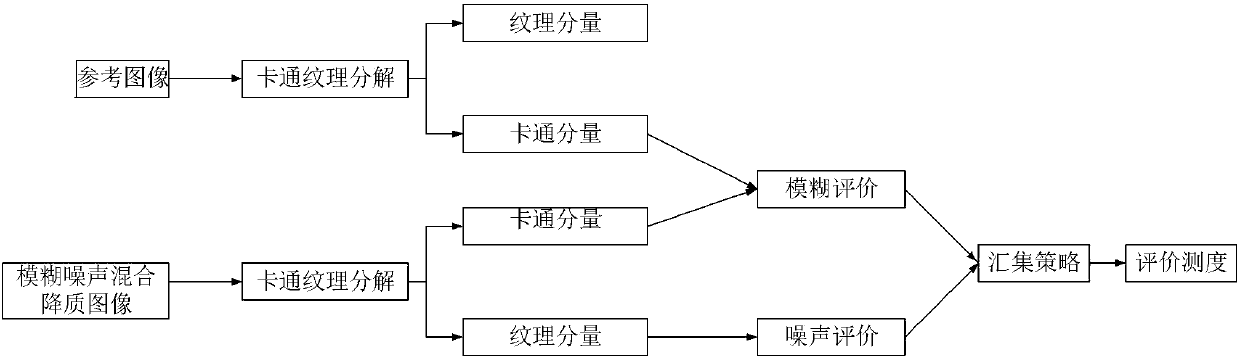
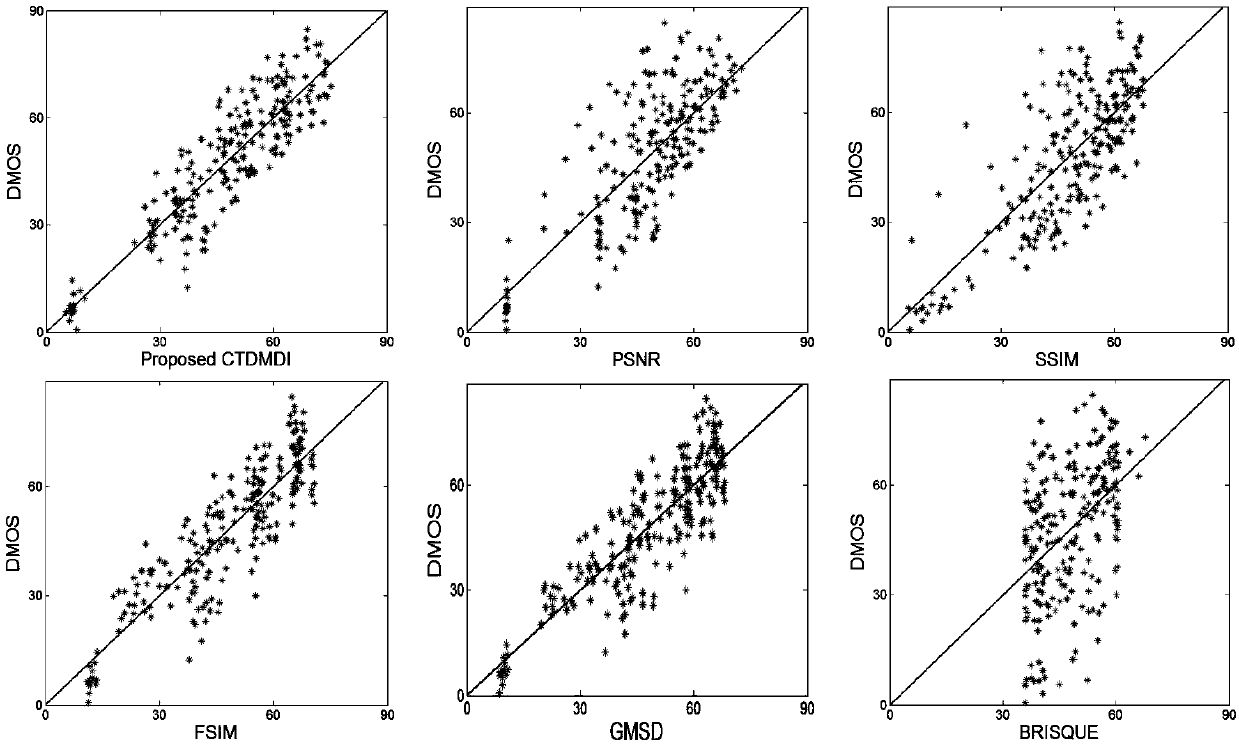
Composite degraded image quality assessment method and system based on cartoon texture decomposition
InactiveCN108230325AAccurate evaluationHigh subjective and objective consistencyImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionStress intensity factor
The invention belongs to the technical field of image assessment and discloses a composite degraded image quality assessment method and system based on cartoon texture decomposition. Firstly, significant edge structure information and texture detail information of an image are effectively distinguished with a cartoon texture decomposition algorithm; secondly, a cartoon component of the image is subjected to fuzzy assessment with a feature similarity algorithm, and fuzzy assessment factors are obtained; a noise intensity factor is obtained by use of the texture component; the factors are subjected to consistency correction, a weight parameter is given in combination with human eye vision characters, and a quality assessment model of a fuzzy noise composite degraded image is obtained finally. As for fuzzy and noise composite degraded image in an LIVEMD image library, the assessment result of the algorithm has higher subjective and objective consistency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
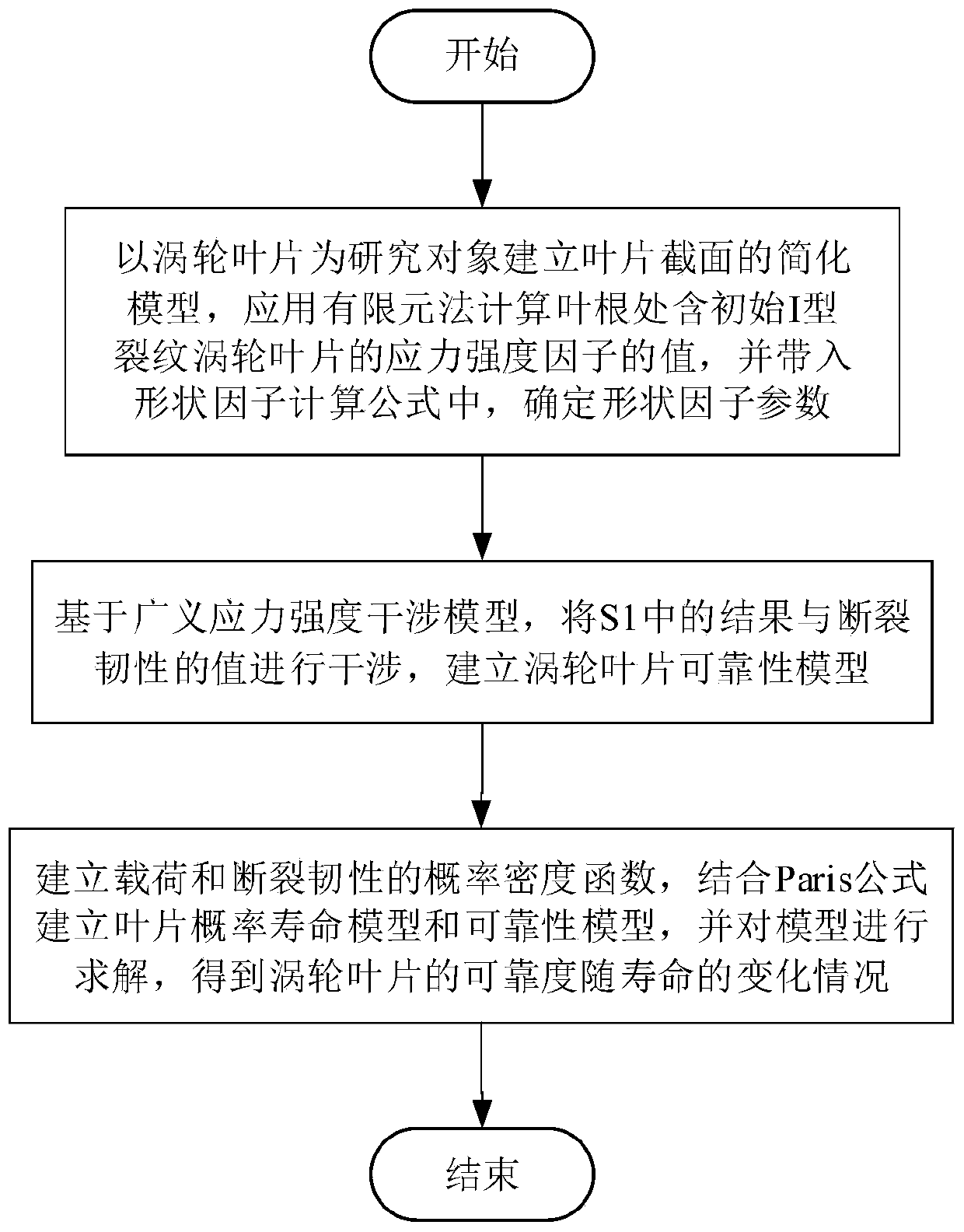
Aero-engine turbine blade reliability evaluation method based on fracture mechanics
InactiveCN110147618AAccurate lifeAccurate and reliableGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationReduced modelAviation
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com