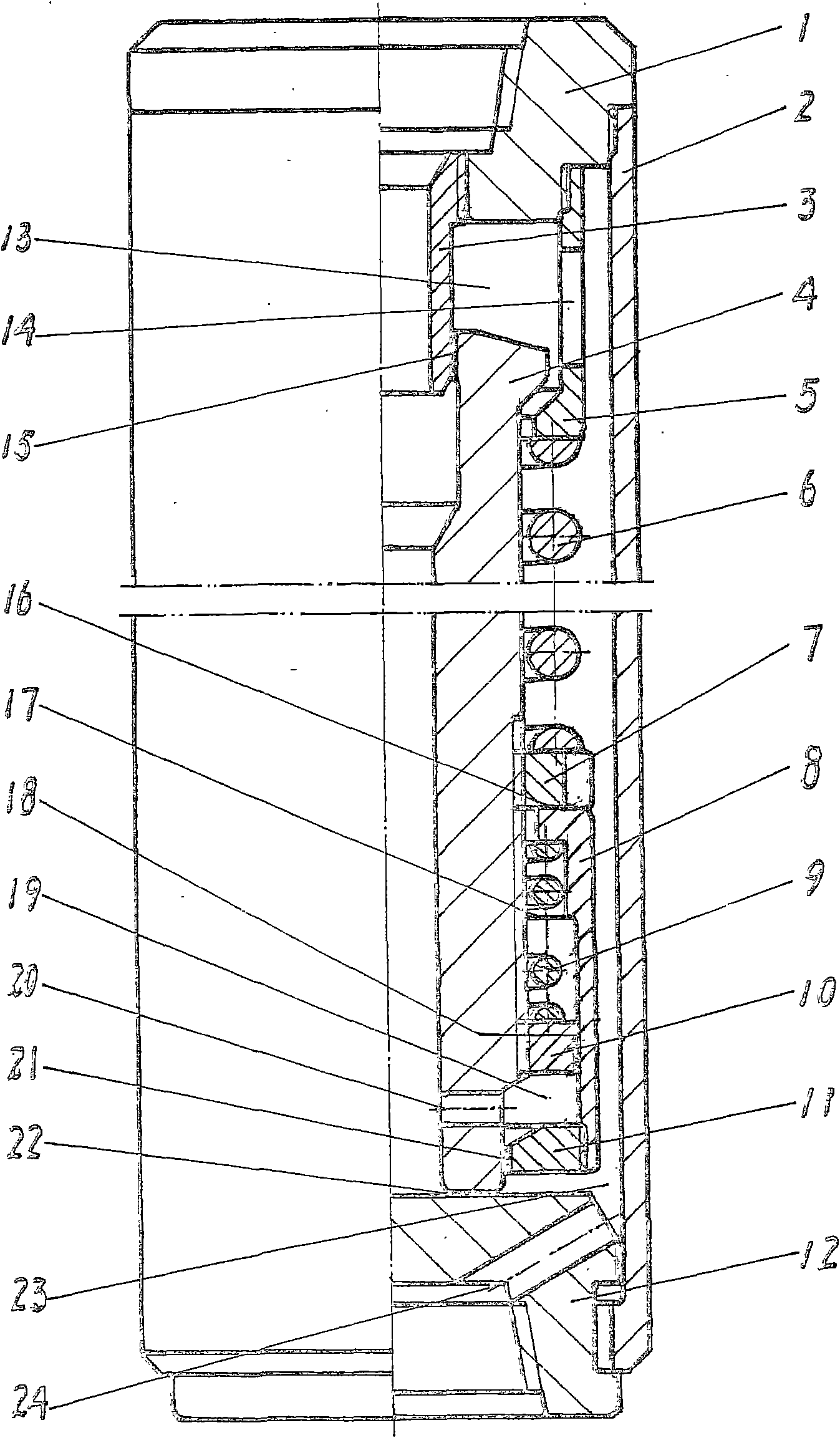
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Surface force" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface force denoted fₛ is the force that acts across an internal or external surface element in a material body. Surface force can be decomposed into two perpendicular components: normal forces and shear forces. A normal force acts normally over an area and a shear force acts tangentially over an area.
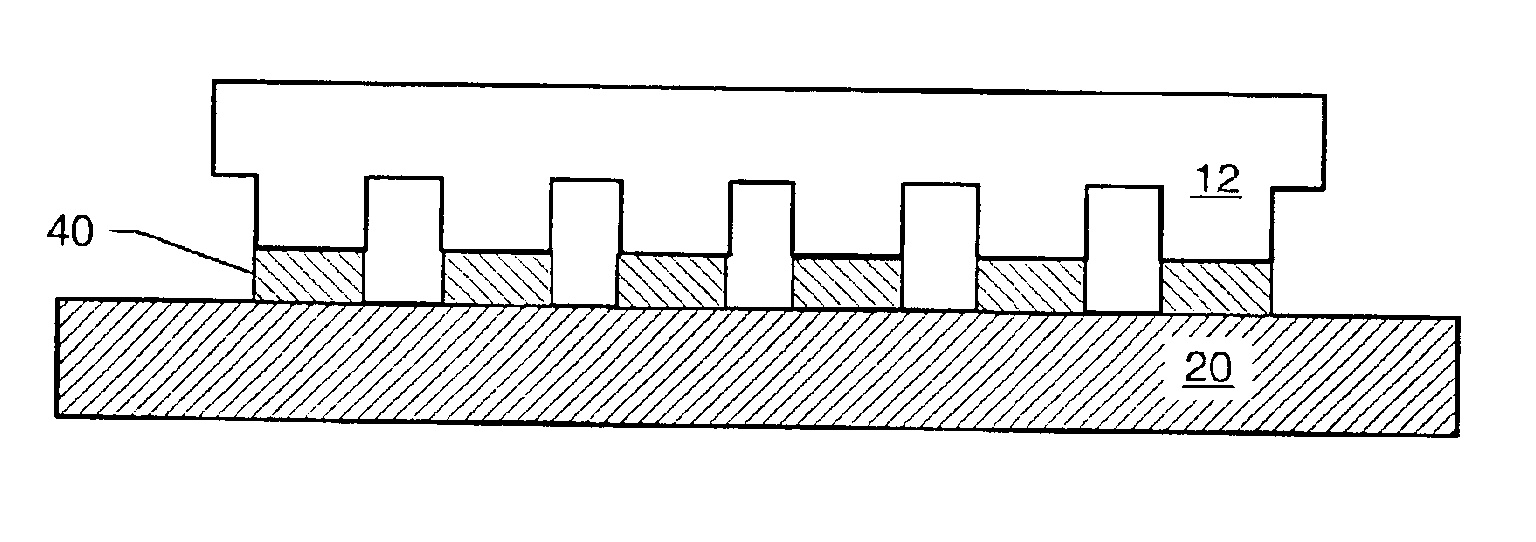
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
ActiveUS6932934B2Low viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithography processLithographic artist
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. An imprint lithography method includes placing a curable liquid on a substrate. A template may be contacted with the curable liquid. Surface forces at the interface of the curable liquid and the template cause the curable liquid to gather in an area defined by a lower surface of the template. Alternately, the curable liquid may fill one or more relatively shallow recesses in the template and the area under the template lower surface. Activating light is applied to the curable liquid to form a patterned layer on the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
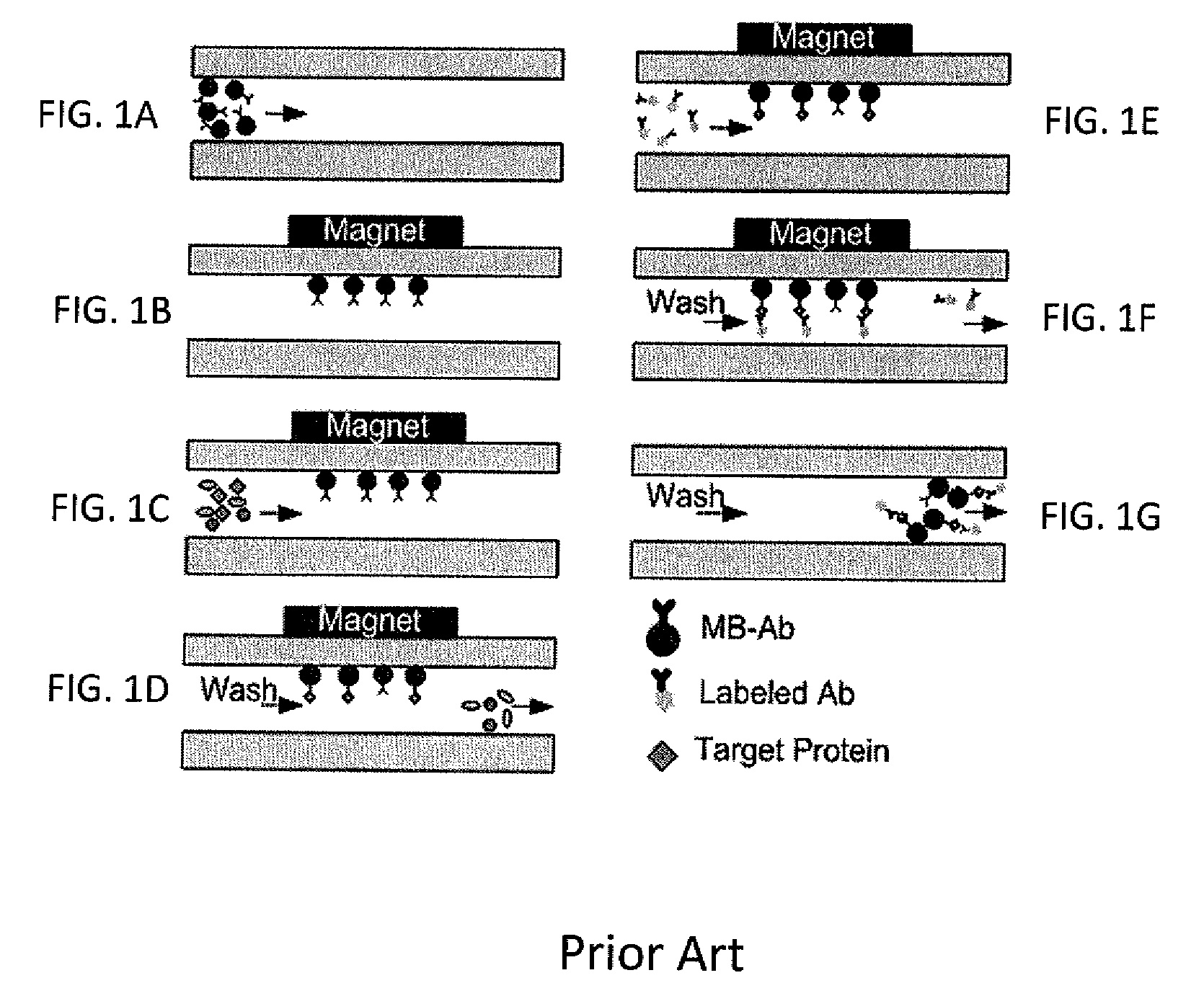
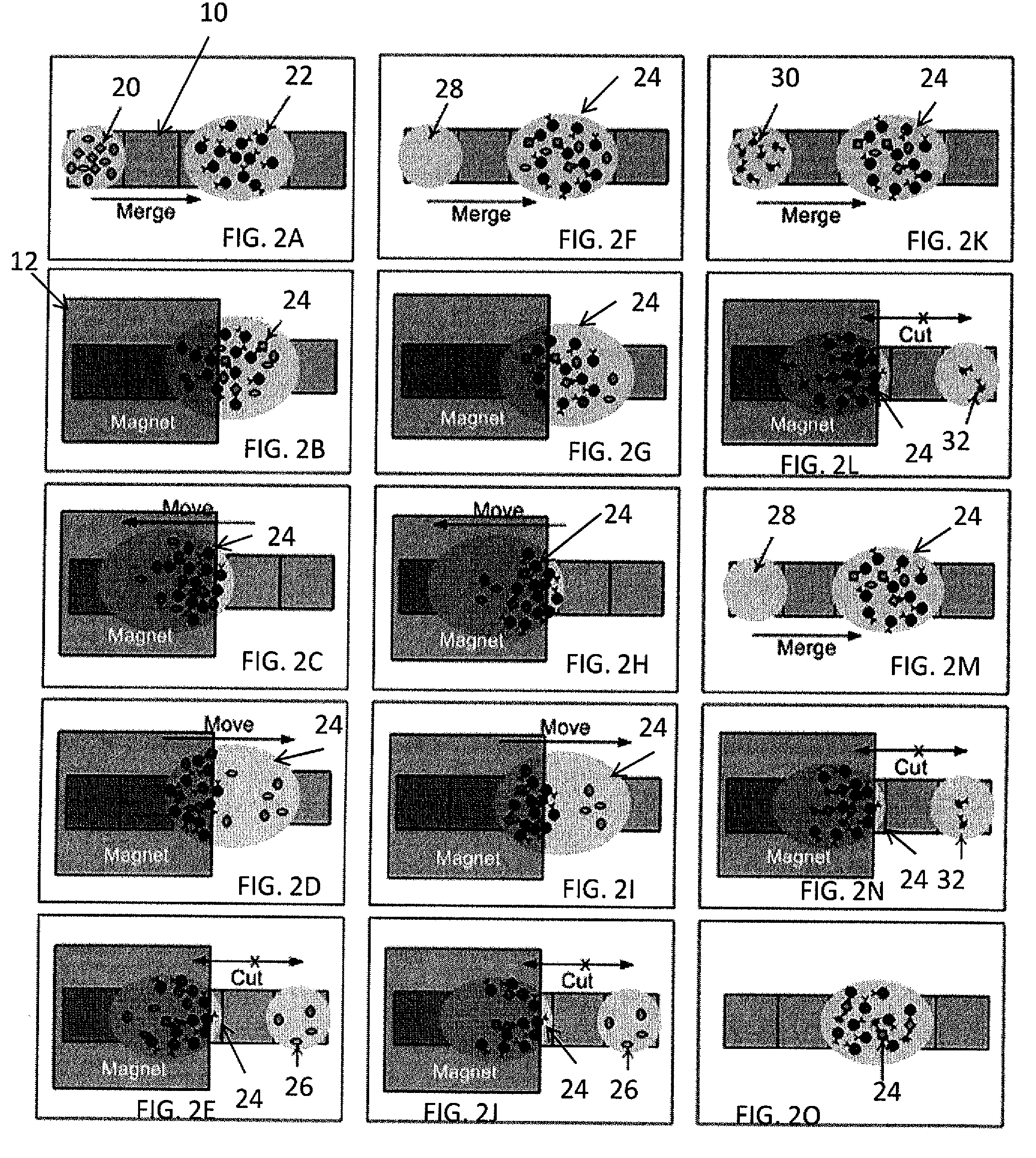
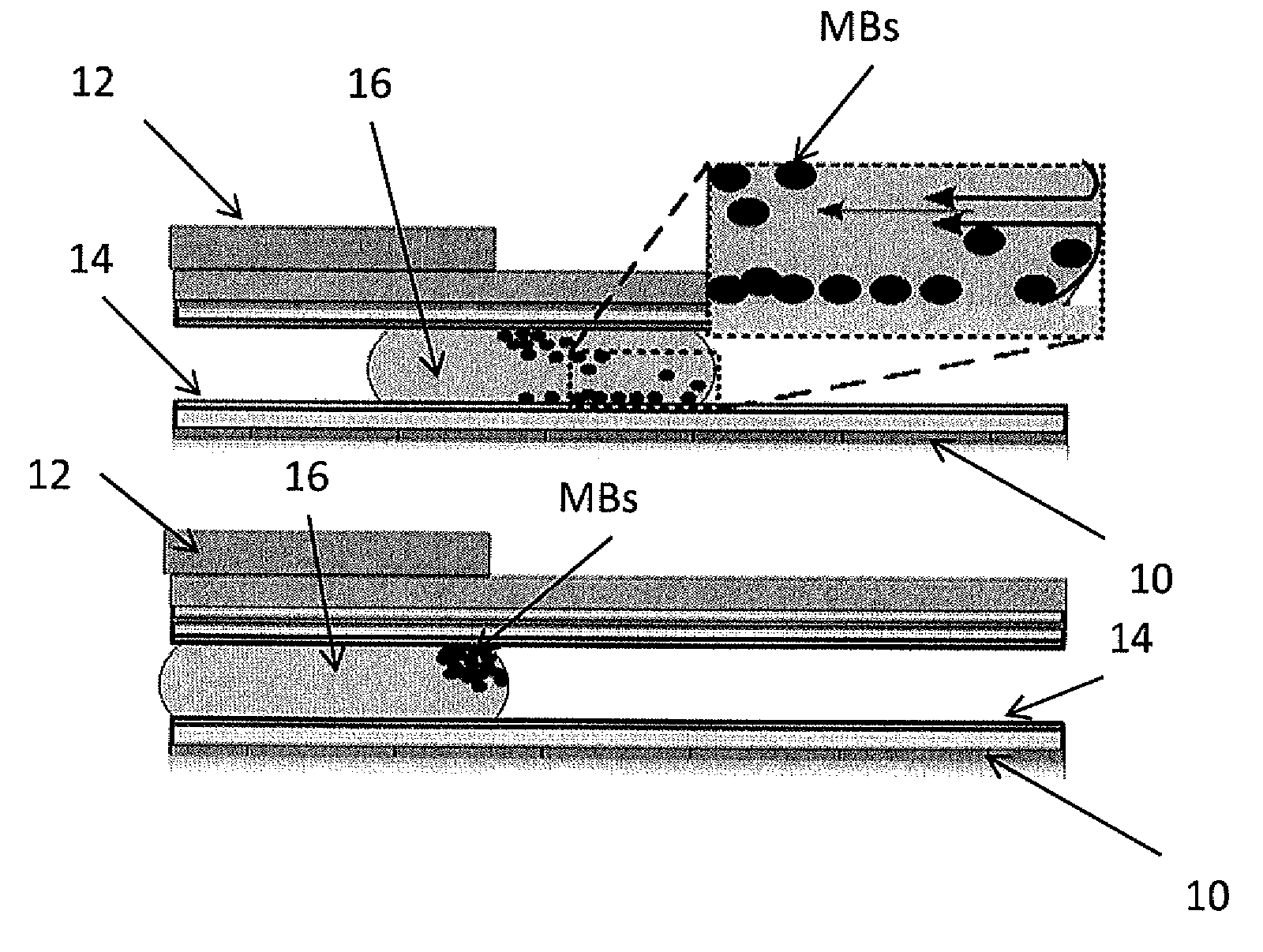
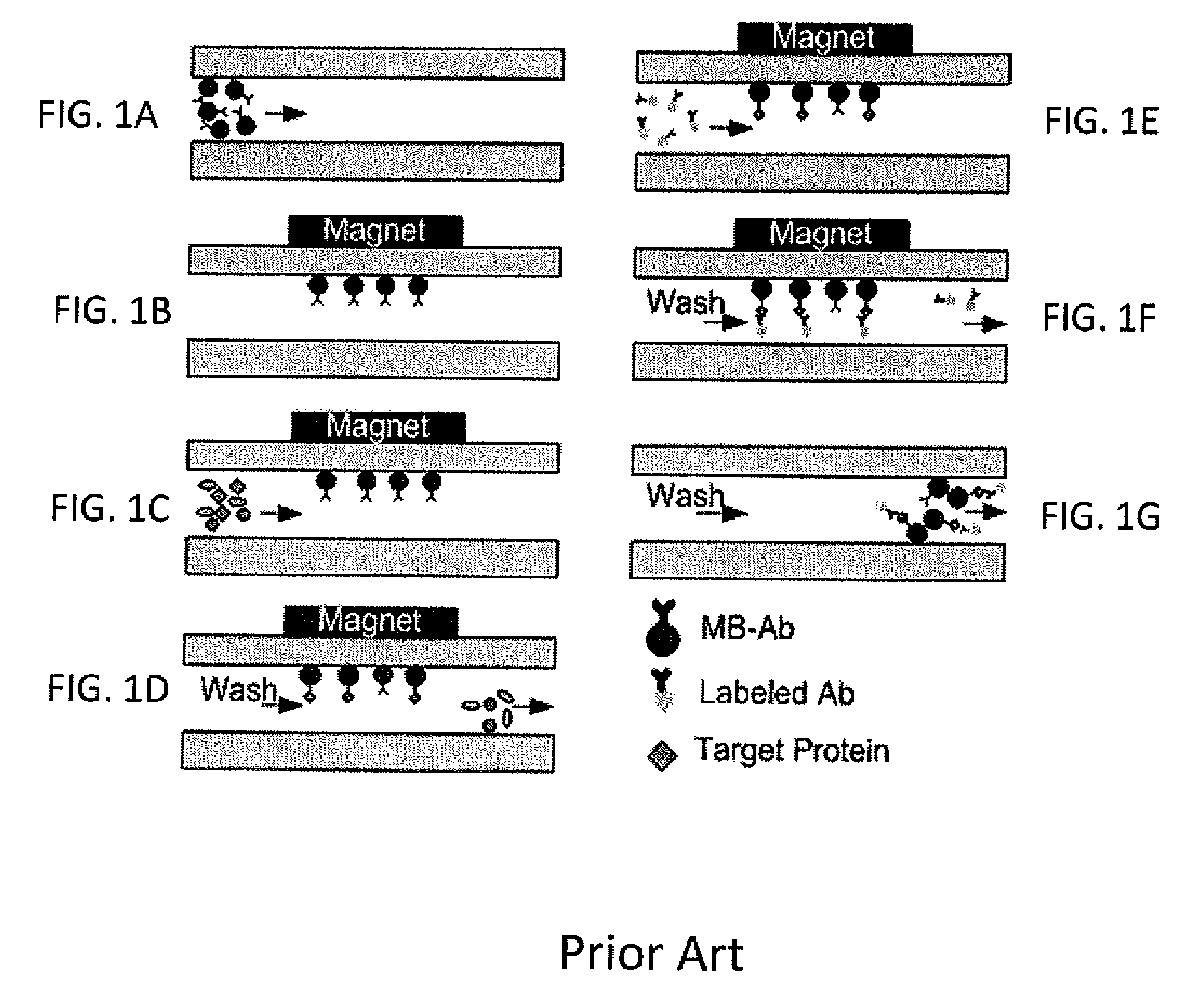
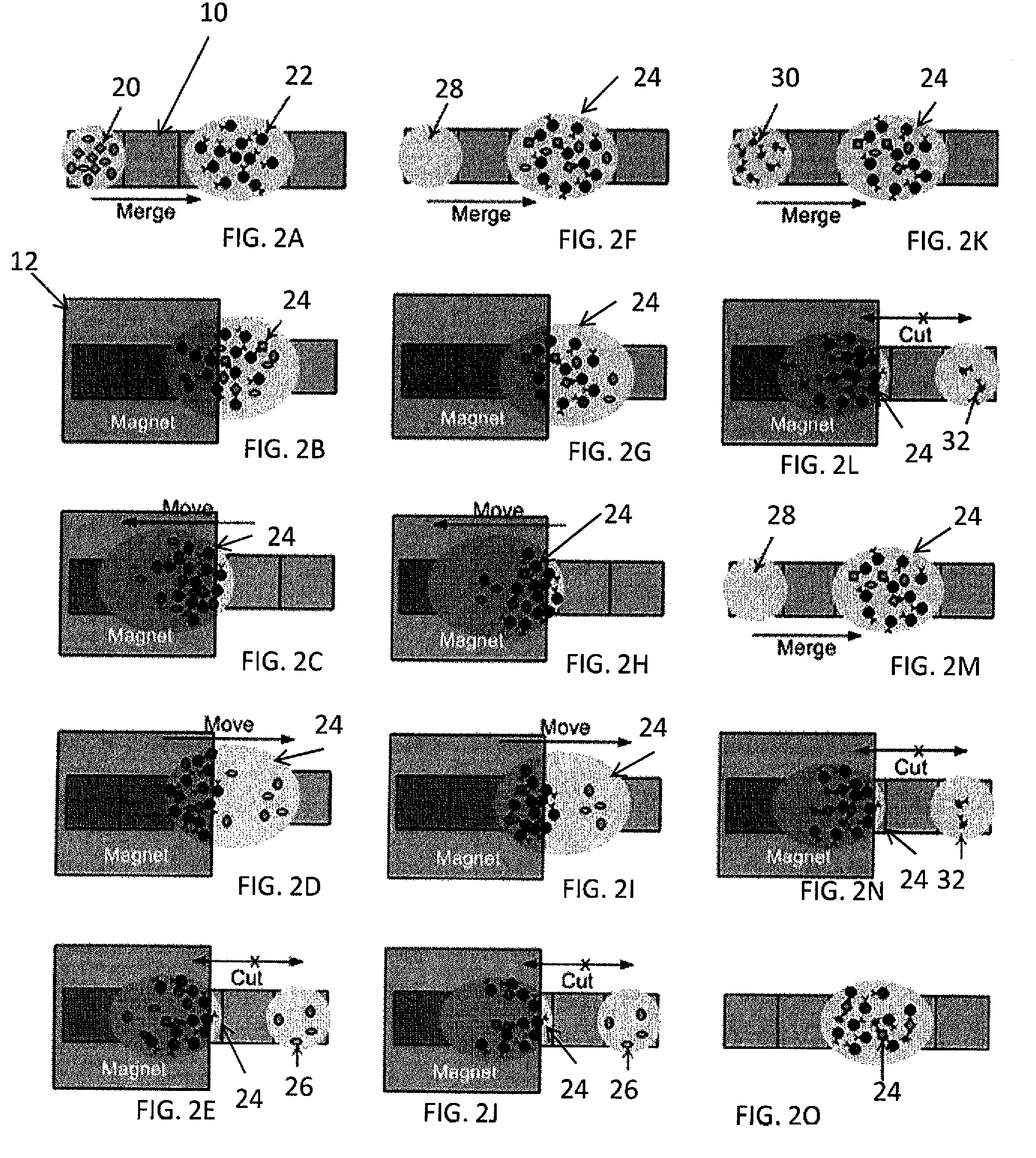
Method for using magnetic particles in droplet microfluidics
ActiveUS20090283407A1Increasing concentration of targetReduce concentrationElectrostatic separatorsLiquid separation by electricityEngineeringDroplet microfluidics
Methods of utilizing magnetic particles or beads (MBs) in droplet-based (or digital) microfluidics are disclosed. The methods may be used in enrichment or separation processes. A first method employs the droplet meniscus to assist in the magnetic collection and positioning of MBs during droplet microfluidic operations. The sweeping movement of the meniscus lifts the MBs off the solid surface and frees them from various surface forces acting on the MBs. A second method uses chemical additives to reduce the adhesion of MBs to surfaces. Both methods allow the MBs on a solid surface to be effectively moved by magnetic force. Droplets may be driven by various methods or techniques including, for example, electrowetting, electrostatic, electromechanical, electrophoretic, dielectrophoretic, electroosmotic, thermocapillary, surface acoustic, and pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for using magnetic particles in droplet microfluidics
Methods of utilizing magnetic particles or beads (MBs) in droplet-based (or digital) microfluidics are disclosed. The methods may be used in enrichment or separation processes. A first method employs the droplet meniscus to assist in the magnetic collection and positioning of MBs during droplet microfluidic operations. The sweeping movement of the meniscus lifts the MBs off the solid surface and frees them from various surface forces acting on the MBs. A second method uses chemical additives to reduce the adhesion of MBs to surfaces. Both methods allow the MBs on a solid surface to be effectively moved by magnetic force. Droplets may be driven by various methods or techniques including, for example, electrowetting, electrostatic, electromechanical, electrophoretic, dielectrophoretic, electroosmotic, thermocapillary, surface acoustic, and pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
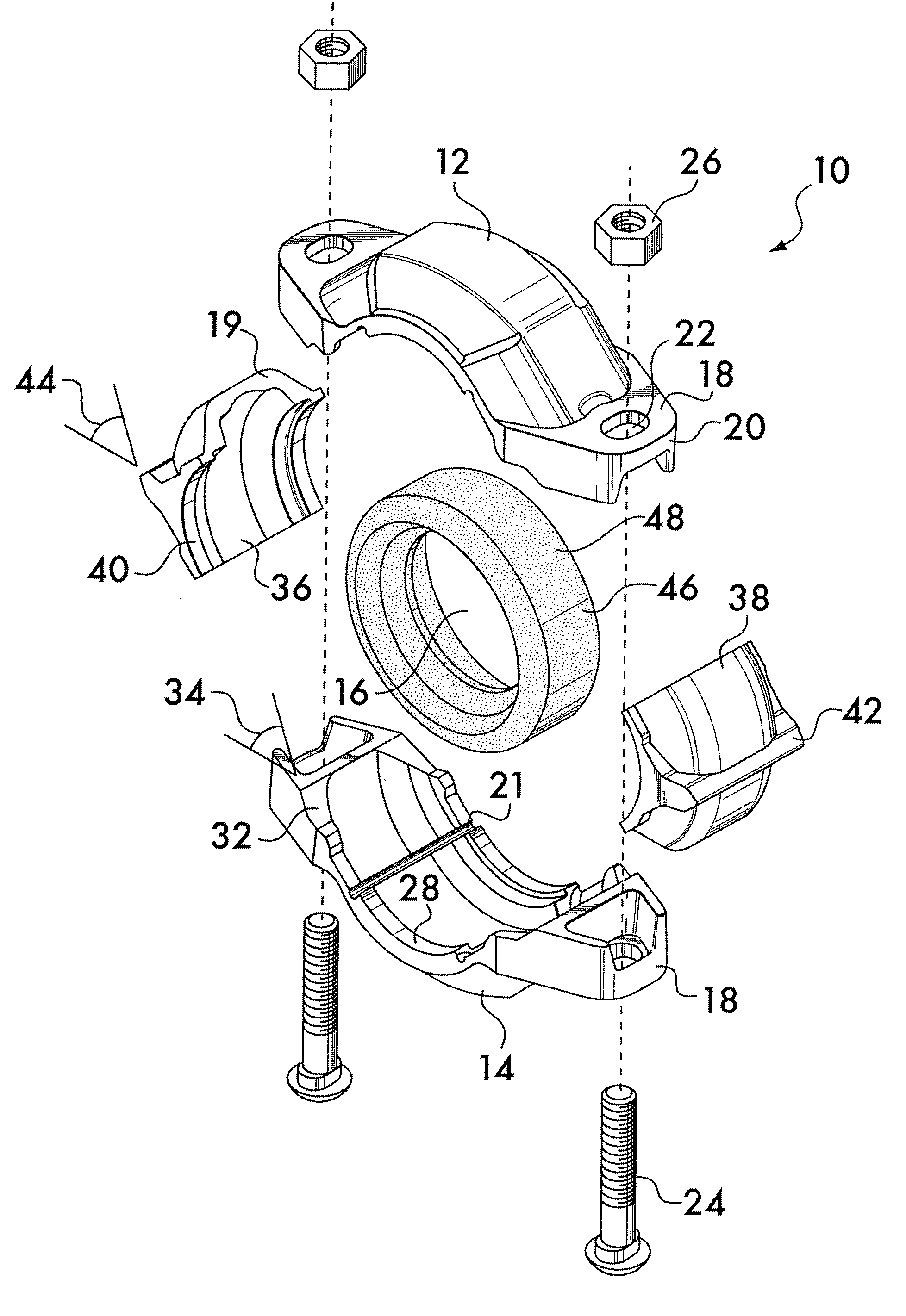
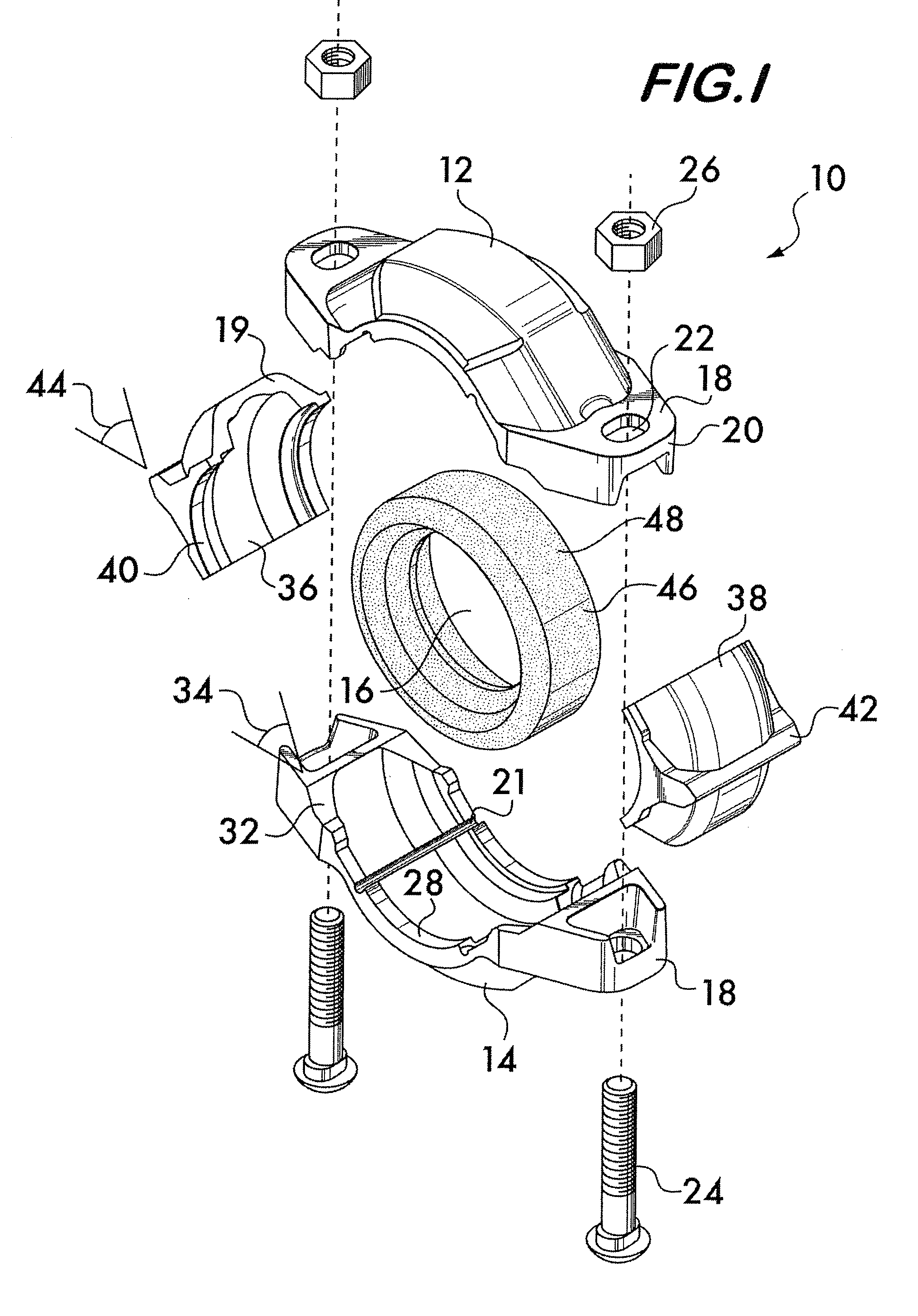
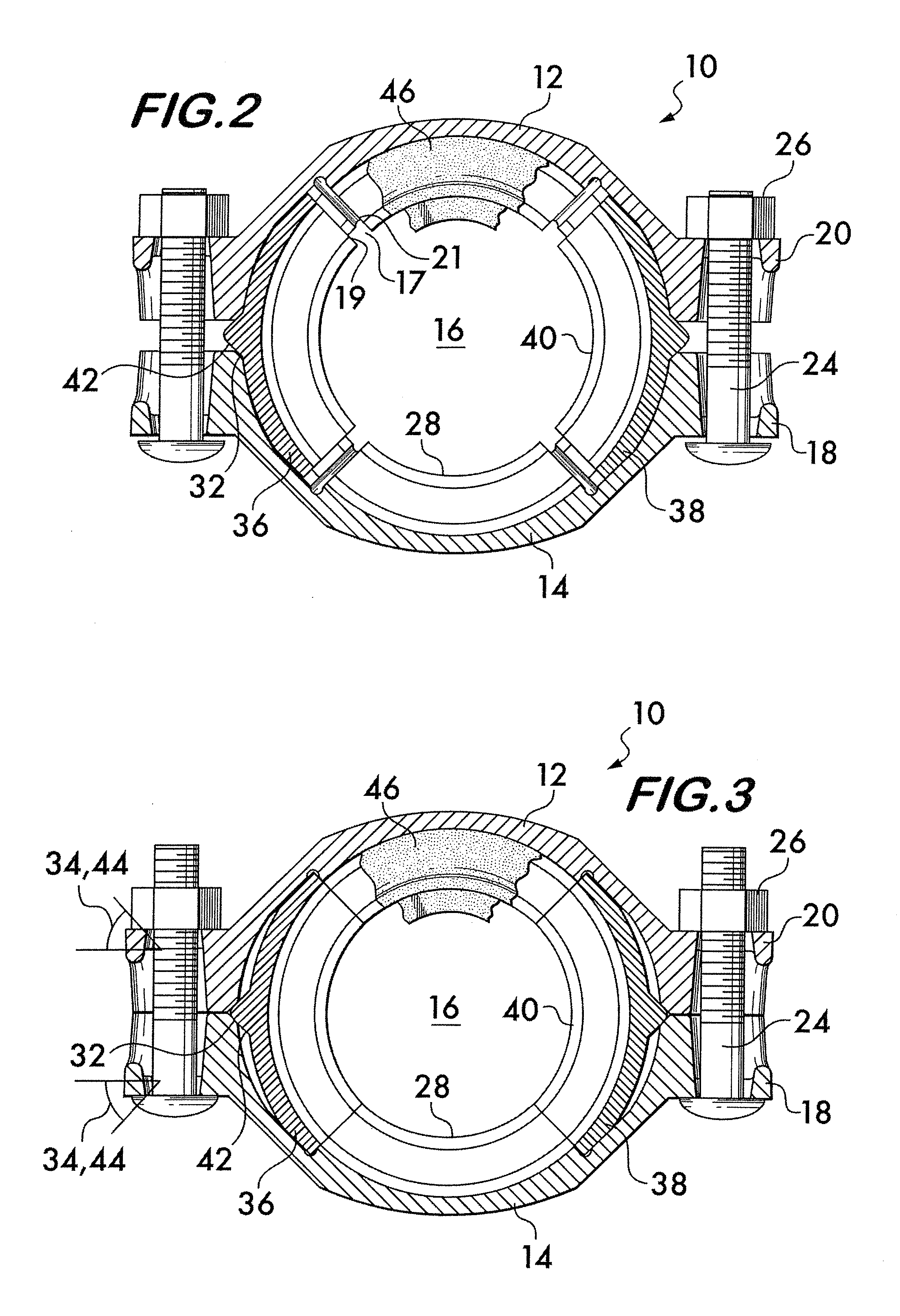
Pipe coupling having movable gripping bodies
A coupling for securing pipe elements together in end-to-end relation is disclosed. The coupling has segments joined end-to-end by adjustable connection members. The segments surround a central space which receives the pipe elements. One or more gripping bodies are captured between the segments. The gripping bodies are arranged opposite to each other. The segments have angularly oriented reaction surfaces on the connection members. The gripping bodies have angularly oriented contact surfaces which interface with the reaction surfaces. When the segments are drawn toward each other by the connection members, interaction between the reaction surfaces and the contact surfaces forces the gripping bodies radially inwardly. Inwardly facing arcuate surfaces on the segments and the gripping bodies engage and retain the pipe elements.
Owner:VICTAULIC
Self-cleaning connector
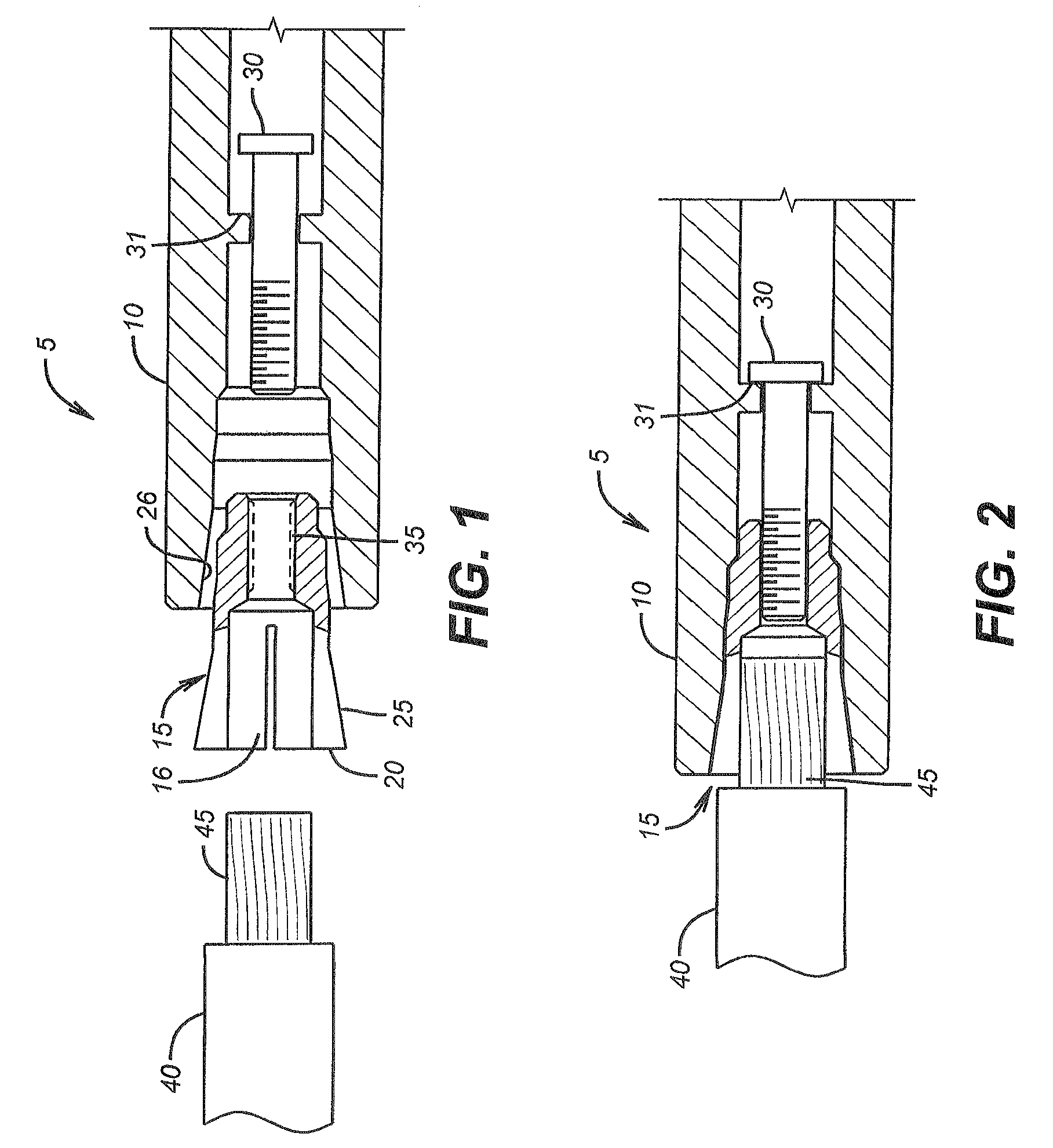
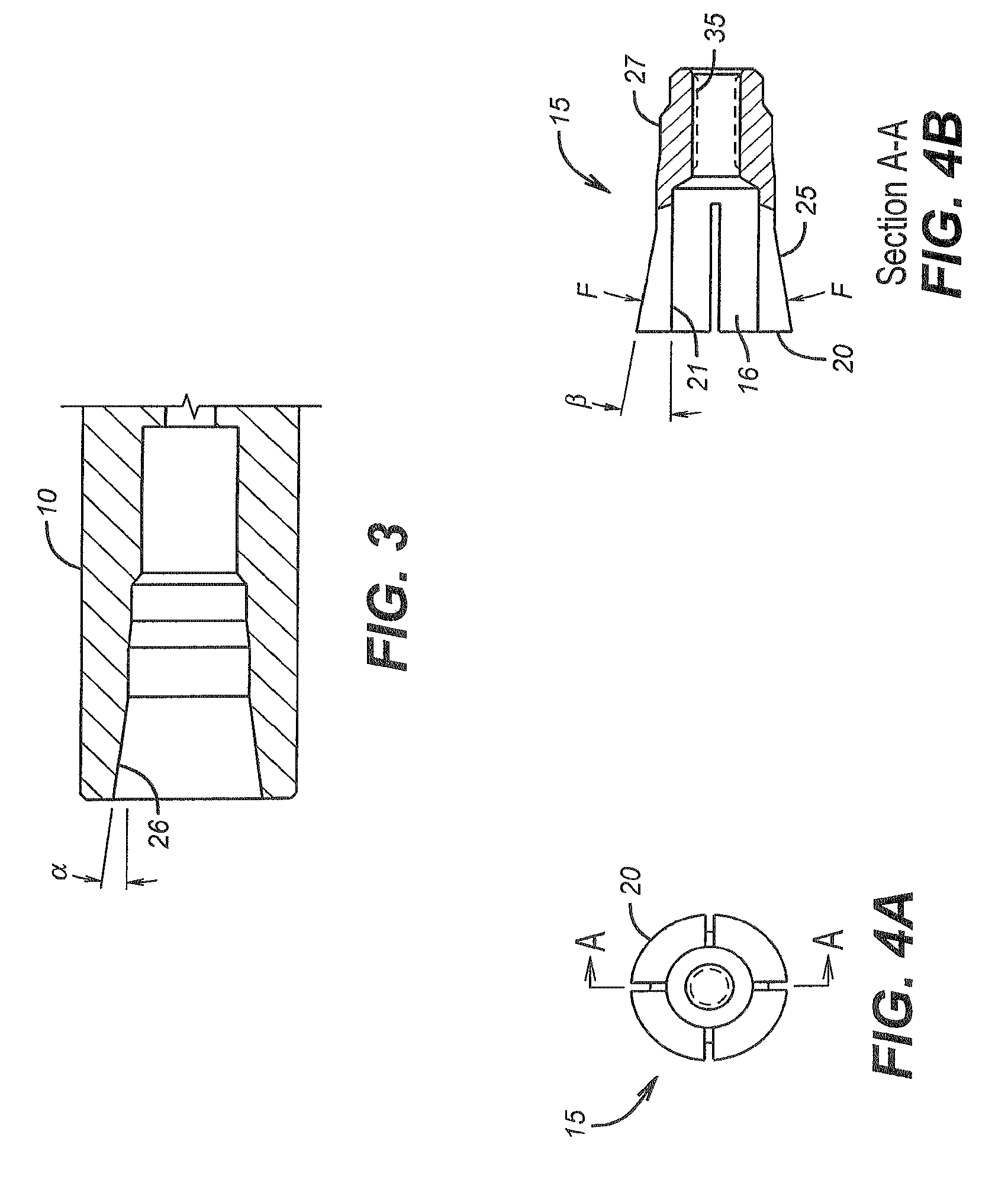
InactiveUS20050064765A1Coupling device engaging/disengagingCoupling contact membersSurface forceBiomedical engineering
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Apparatus and method for manufacturing positive or negative microlenses
A variety of structures and methods used to adjust the shape, radius and / or height of a microlens for a pixel array. The structures affect volume and surface force parameters during microlens formation. Exemplary microlens structures include a microlens frame, base, material, protrusions or a combination thereof to affect the shape, height and / or radius of the microlens. The frame, base and / or protrusions alter the microlens flow resulting from the heating of the microlens during fabrication such that a height or radius of the microlens can be controlled. The radius can be adjusted by the height differences between the microlens and frame. The bigger the difference, the smaller the radius will be.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Suspension type monorail vehicle coupling dynamic simulation system and method
ActiveCN108256278ASolve decouplingReduce simulation errorSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationVehicle dynamicsDynamic models
The invention discloses a suspension type monorail vehicle dynamic model and a vehicle-bridge coupling power simulation method, belongs to the technical field of rail traffic and aims to solve the technical problem that an existing suspension type monorail dynamics simulation device is large in simulation result errors during rail beam local vibration research. By providing the suspension type monorail vehicle system dynamic model, a rubber wheel-rail surface contact mechanical model, a rail beam bottom plate and web equivalent surface force application method and a vehicle and rail beam coupling dynamic model building method, a suspension type monorail vehicle-rail beam coupling dynamic simulation system is built. By the model, the system and the method, suspension type monorail vehicle system suspension mechanism decoupling and equivalent treatment are achieved, and the technical problems that the existing suspension type monorail dynamics simulation device is large in simulation result errors during the rail beam local vibration research, rail beam dynamic stress and strain results are hard to extract, rail beam local strength destroying cannot be evaluated accurately and the like are solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
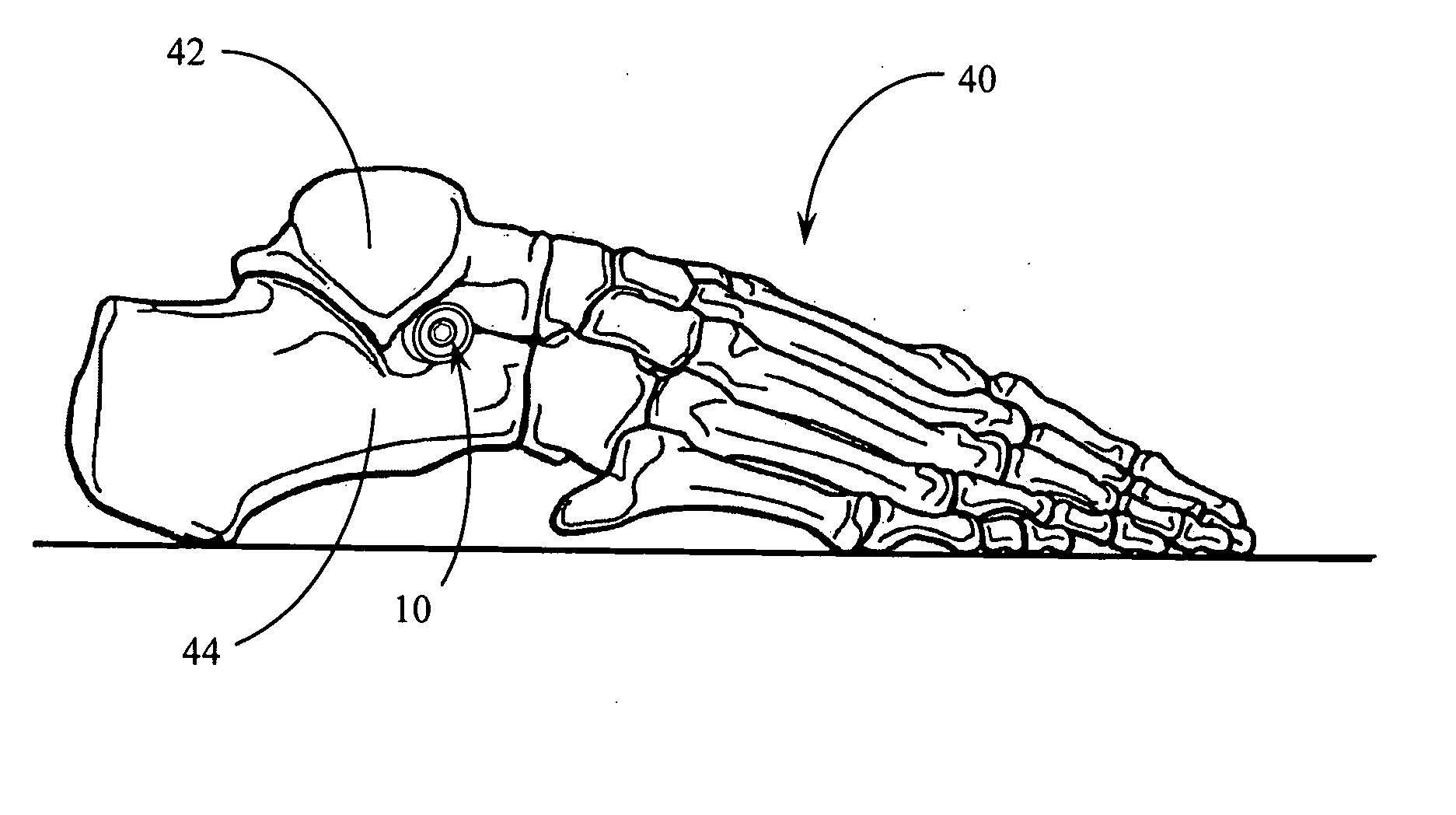
Expandable subtabar implant
InactiveUS20080208349A1Block excessive motionIncrease the diameterInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsMedicineImplanted device
An expandable subtalar implant device suitable for addressing a flatfoot condition. The device is a sinus tarsi implant that blocks excessive motion between the talus and calcaneus bones in the foot while permitting normal motion and alignment. The device comprises a generally cylindrical metal structure having a first proximal expandable end and a second distal adjustment end. A first component of the implant forms each of the cylindrical end sections and a second component comprises a movable internal rod that serves to progressively expand the outer cylinder of the implant. The internal rod is externally threaded and mates with internal threading on the cylindrical outer component. Progressive turning of the internal rod engages a number of radially arranged inclined surfaces that form the interior walls of the cylindrical shell component. Progressive engagement of the rod with these inclined surfaces forces the end of the cylindrical shell component outward; expanding the overall diameter of the implant once it has been positioned within the sinus tarsi.
Owner:LOWE JOHN PATRICK TRUSTEE CHAPTER 7 CASE NO 09 51026 C IN THE UNITED STATES BANKRUPTCY COURT FOR THE WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS SAN ANTONIO DIV
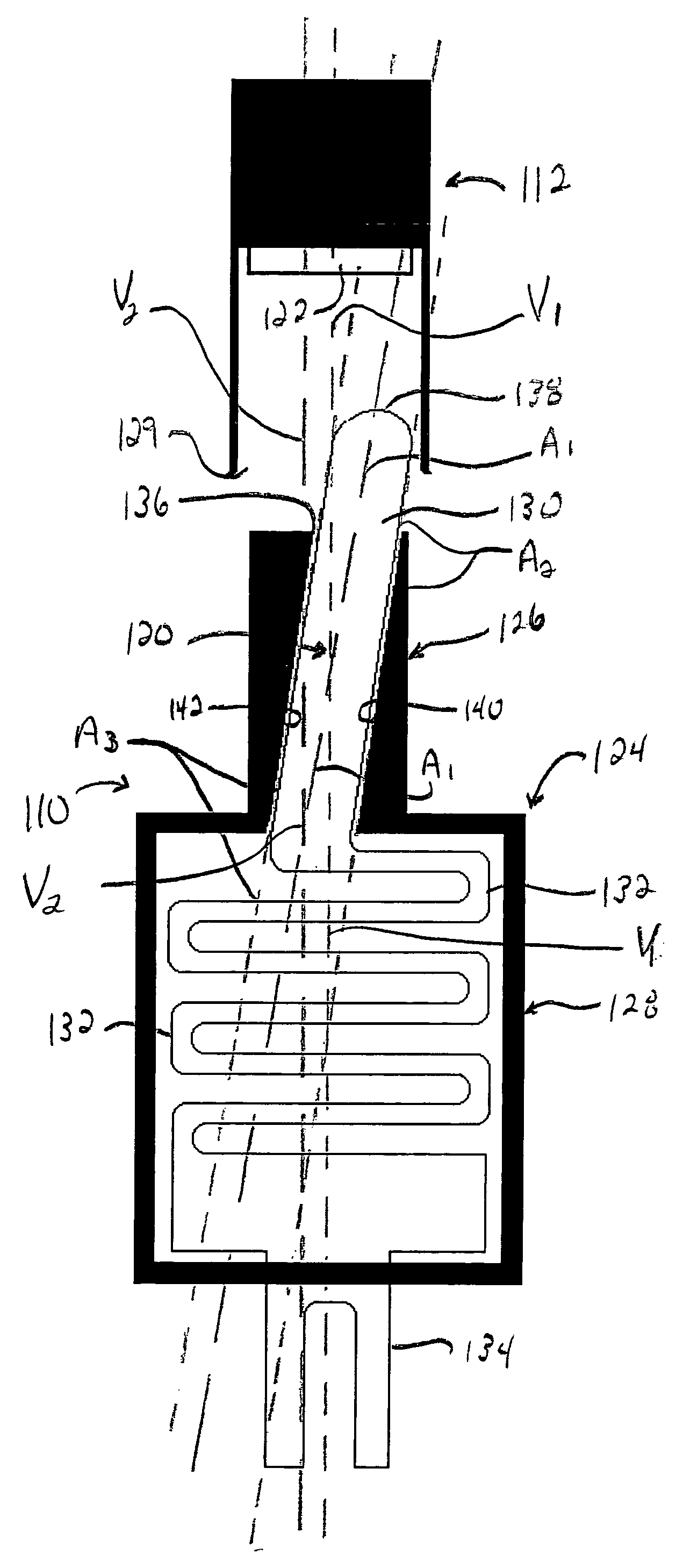
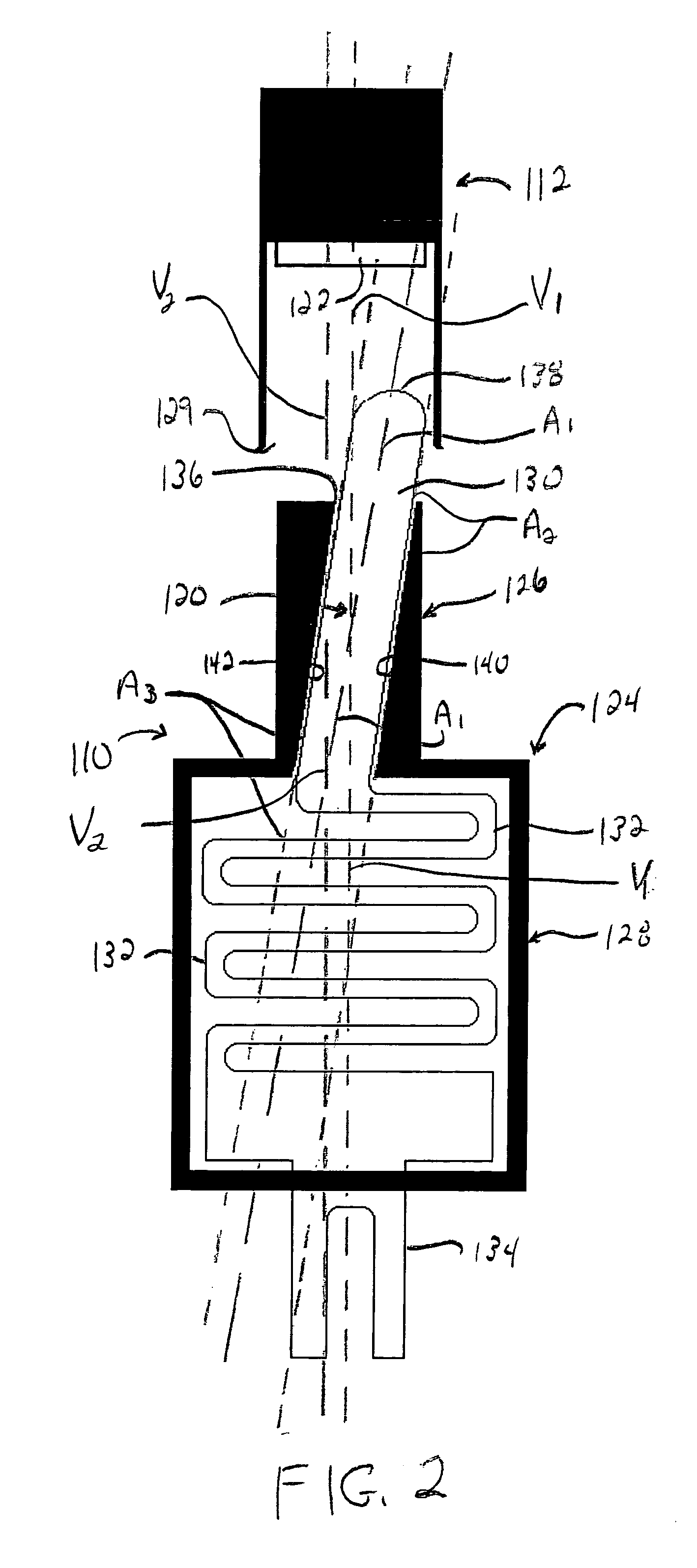
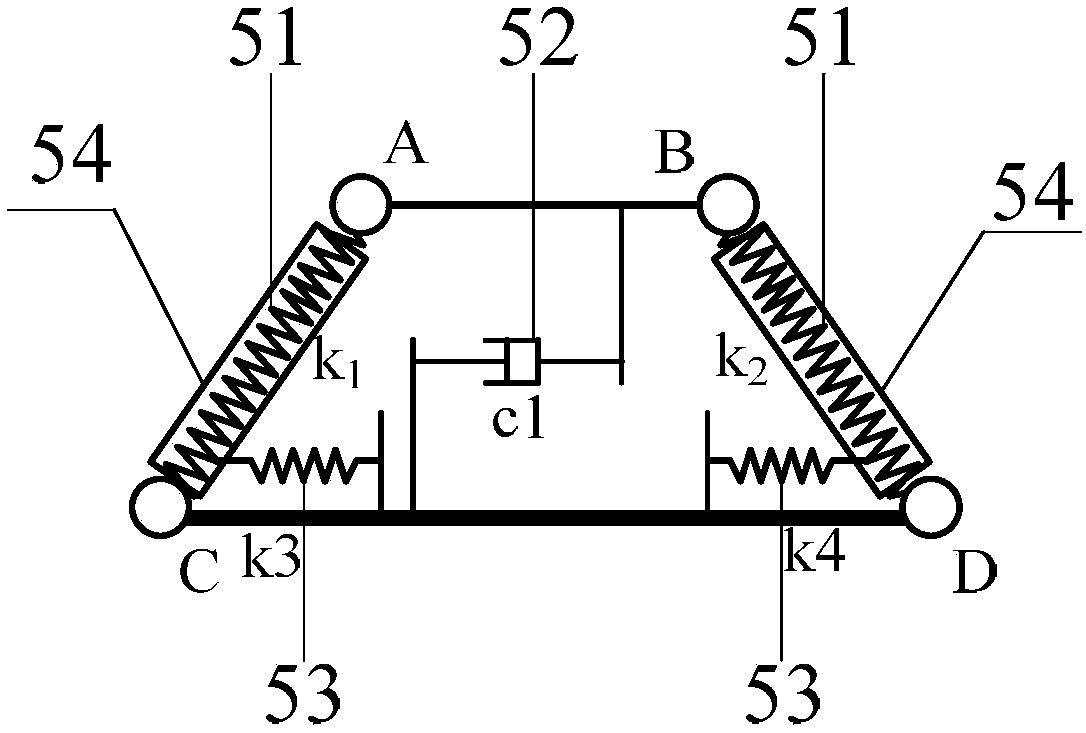
Apparatus and method for detecting surface shear force on a display device
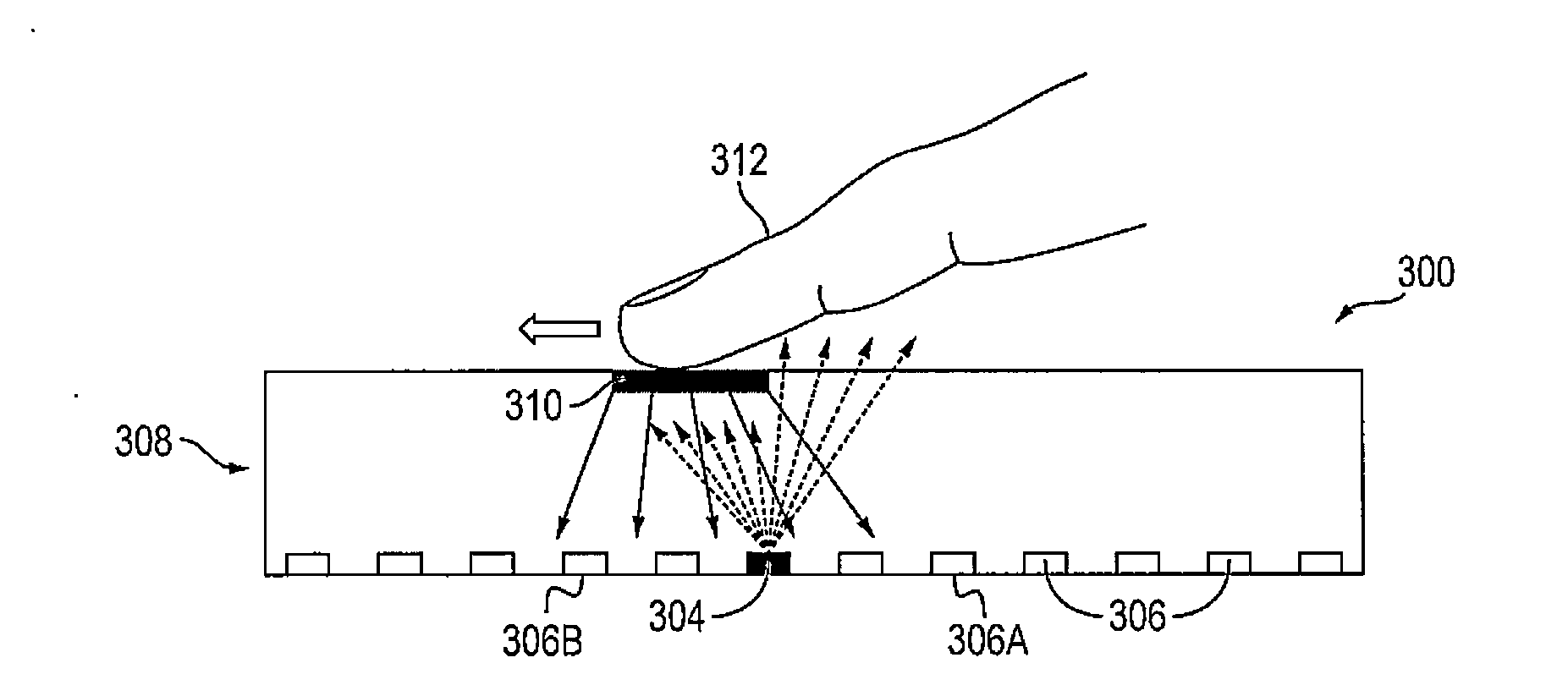
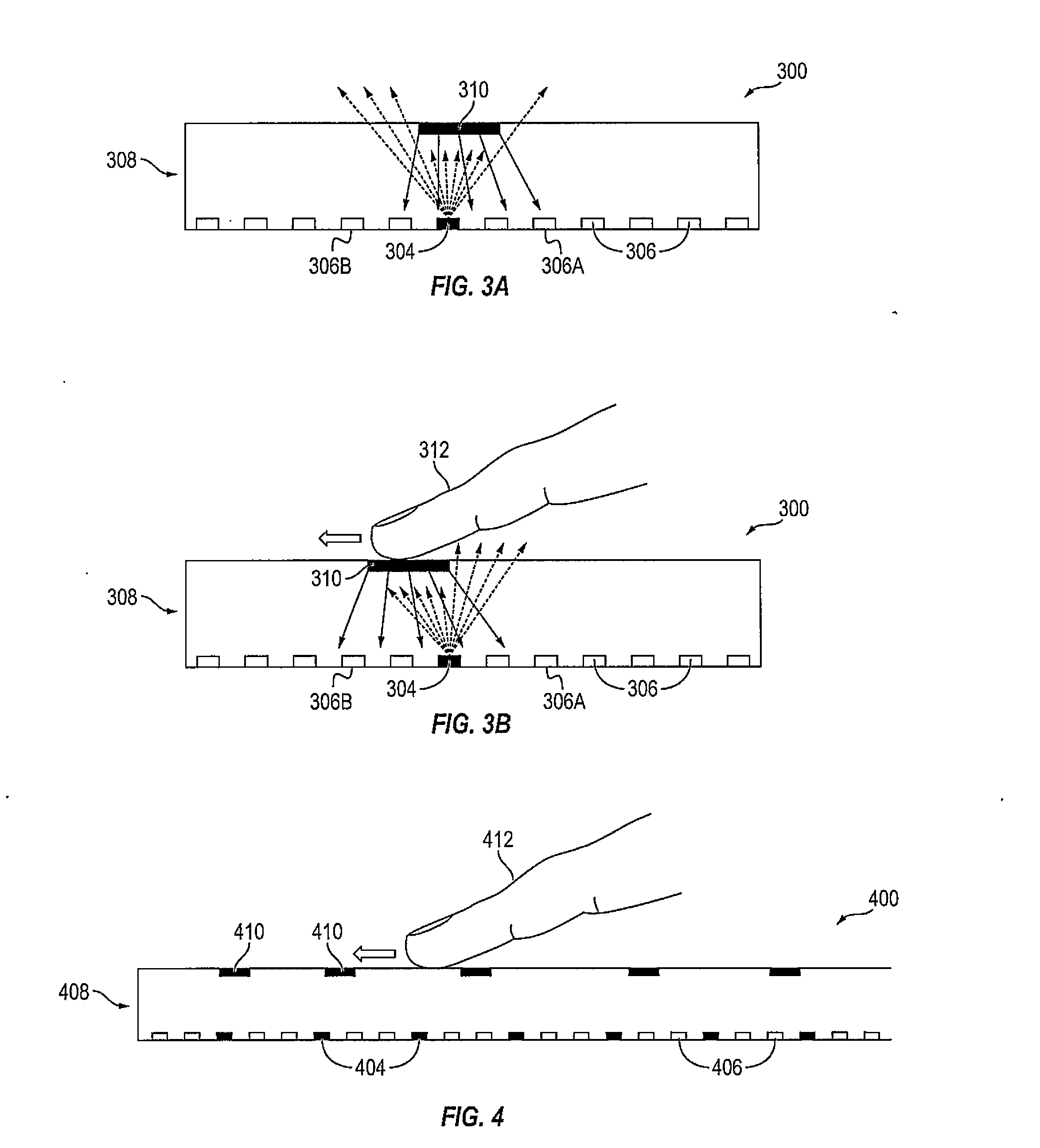
ActiveUS20150242056A1Practical and inexpensive to manufactureImprove Sensing PerformanceInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceSurface force
A display device includes: a pixel array including a plurality of pixels; a plurality of infrared (IR) emitters to emit IR light towards a surface of the display device; a plurality of IR detectors to detect IR light; a deformable layer on the pixels, on the IR emitters, on the IR detectors, and at the surface of the display device; and a plurality of tracers at the deformable layer to reflect the IR light emitted by the IR emitters towards the IR detectors and to, while a shear force is being applied at a point of contact at the surface of the display device, shift ones of the tracers around the point of contact in a direction of the shear force such that IR reflectance at the surface of the display device is changed.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Apparatus and method for manufacturing tilted microlenses
ActiveUS7012754B2Easy to manufactureTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSurface forceMaterials science
Asymmetrical structures and methods are used to adjust the orientation of a microlens for a pixel array. The asymmetrical structures affect volume and surface force parameters during microlens formation. Exemplary microlens structures include an asymmetrical microlens frame, base, material or a combination thereof to affect the focal characteristics of the microlens. The asymmetrical frame alters the microlens flow resulting from the heating of the microlens during fabrication such that orientation of the microlens relative to an axis of the imager can be controlled.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Apparatus and method for electrical and mechanical connection
ActiveUS20070287323A1Promote disseminationCoupling device detailsContact members penetrating/cutting insulation/cable strandsElectrical conductorConical forms
An apparatus for engaging an electrical conductor comprises a gripping contact having a plurality of fingers, where the plurality of fingers has a substantially conical outer surface. A contact receptacle has a substantially conical inner surface. A tension member urges the gripping contact toward the contact receptacle such that interaction between the substantially conical outer surface and the substantially conical inner surface forces the plurality of fingers to engagingly compress the electrical conductor placed between the fingers. A method of engaging an electrical conductor comprises inserting an electrical conductor between a plurality of fingers of a gripping contact, lo where the plurality of fingers has a substantially conical outer surface. The substantially conical outer surface of the gripping contact is urged to interact with a substantially conical inner surface of a contact receptacle such that the interaction forces the plurality of fingers to engage the electrical conductor.
Owner:POWER FEED THRU SYST & CONNECTORS
Self-cleaning connector
InactiveUS6935901B2Coupling device engaging/disengagingCoupling contact membersSurface forceBiomedical engineering
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Energy accumulation type hydraulic hole drilling hammer
The invention relates to an energy accumulation type hydraulic hole drilling hammer which has large impact power and high energy utilization rate, is suitable for drilling deep wells with slurry, is mainly applied to engineering, such as petroleum drilling, water well drilling, core drilling, foundation pile hole drilling and other projects, and is a rock breaking tool enhancing the drilling efficiency and quality greatly and lowering the drilling cost. The energy accumulation type hydraulic hole drilling hammer comprises an upper joint, a casing, a beakiron and a valve control hammer strike mechanism which is arranged in the casing and has the functions of valve control, hammer raise, energy accumulation and hammer strike. Hydraulic surface force pushes a piston to apply work so as to utilize liquid energy with high efficiency, and a hammer spring can obtain the design energy of hammer strike just by smaller pressure intensity and flow rate; the line of liquid flow is simple, the section of a passage is large, and drilling liquid discharged into a lower cavity at the time of hammer strike can quickly flow to an upper cavity in a negative-pressure state by little energy consumption; and the processes of hammer raise, energy accumulation and liquid discharge to the bottom of a well are all completed in the return stroke, and the instantaneous flow rate discharged to the bottom of the well at the time of stroke is nearly zero, therefore, the drilling liquid only applies work at the time of hammer raise after entering the hole drilling hammer, and the instantaneous energy consumption of hammer strike is very little.
Owner:昆明国经液压锤制造有限公司
High-reliability method for rapidly forecasting rolling dynamic derivative of aircraft
ActiveCN103400035AQuick forecastIncrease credibilitySpecial data processing applicationsRotation velocityComputer science
The invention discloses a high-reliability method for rapidly forecasting a rolling dynamic derivative of an aircraft. The high-reliability method includes the steps of generation of model surface grids and division of spatial grids, calculation of aerodynamic parameters under a rotating coordination system, and difference calculation of the rolling dynamic derivative. A calculation method for the aerodynamic parameters under the rotating coordination system includes (1), transforming a Navier-Stokes equation under an inertial system to the rotating coordinate system; (2), performing numerical solution on the transformed equation to acquire a flow field of each state; (3), acquiring aerodynamic force through surface integration of object-plane pressure and viscous stress, taking moment from the center of mass through surface force and integrating to acquire aerodynamic moment acting on the center of mass. The difference calculation includes calculating the aerodynamic force and the aerodynamic moment of a model at two different revolving speeds, and acquiring the rolling dynamic derivative of the model by a difference method. The method is high in reliability of calculation results, has a much smaller calculated amount as compared with a non-steady forced vibration method which is time-consuming for accurate solution, and can quickly forecast the rolling dynamic derivative of the aircraft in a highly reliable manner.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Energy theory-based prediction method for stress of TMB (tunnel boring machine) disk hob
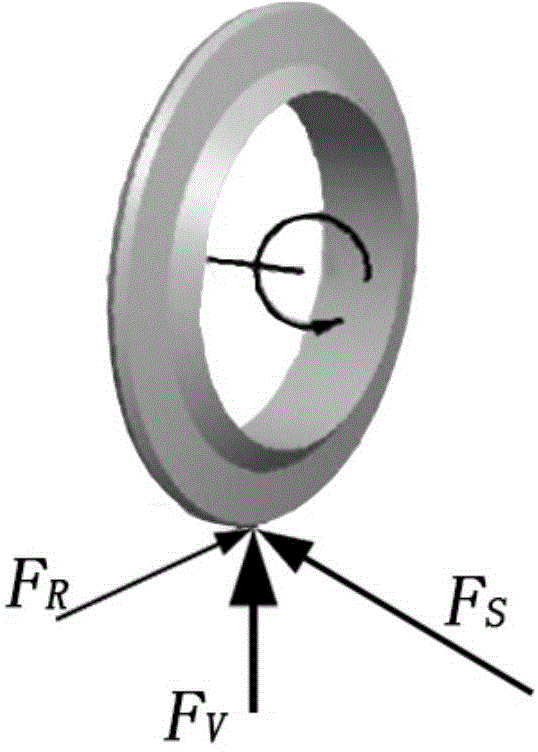
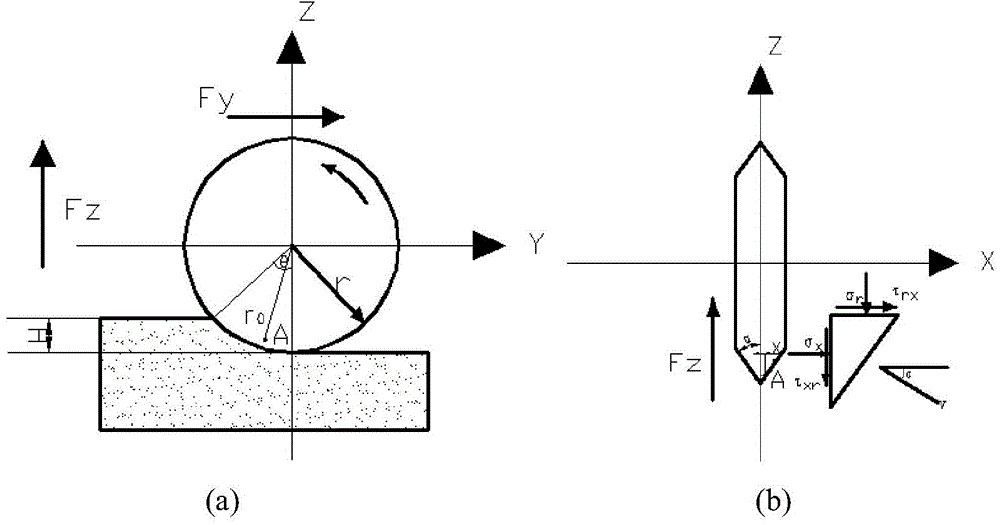
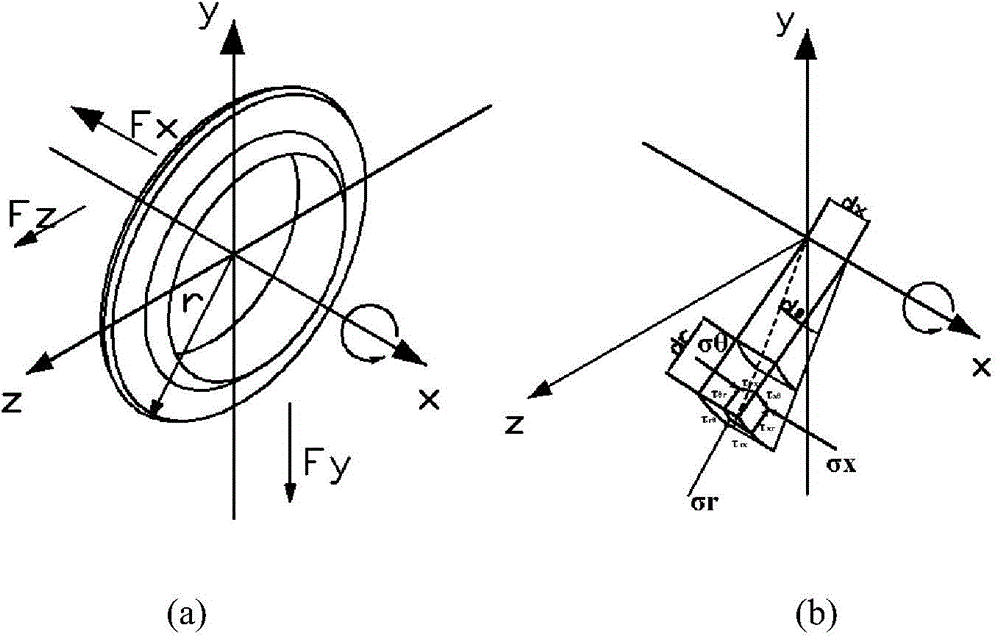
The invention discloses an energy theory-based prediction method for stress of a TMB (tunnel boring machine) disk hob. The prediction method comprises the following steps: (1) determining the normal pushing vertical force FV, the tangential rolling force FR and the lateral force FS of the hob in a rock breaking process; (2) establishing a hob stress model in the rock breaking process; (3) establishing a rock strain model during the rock breaking process of the hob; (4) establishing an energy-balance equation for the hob and rock; (5) according to the established rock strain model, by setting the principal stress direction of the rock and the principal stress direction of the hob under a cylindrical coordinate to be corresponding, obtaining surface forces on a wedge-shaped surface when the hob breaks the rock, and predicting the stress of the TMB disk hob. Aiming at analysis and research status of all influence factors in the mechanical property of the existing TMB disk hob, the invention discloses the microcosmic energy theory-based novel prediction method for the stress of the hob; through the influence of the added rotation speed of the hob on the stress characteristics of the hob to in previous studies, a basis is provided for the design theory of a cutter with TBM boreability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Outer surface force control type flexible polishing equipment of bearing outer ring
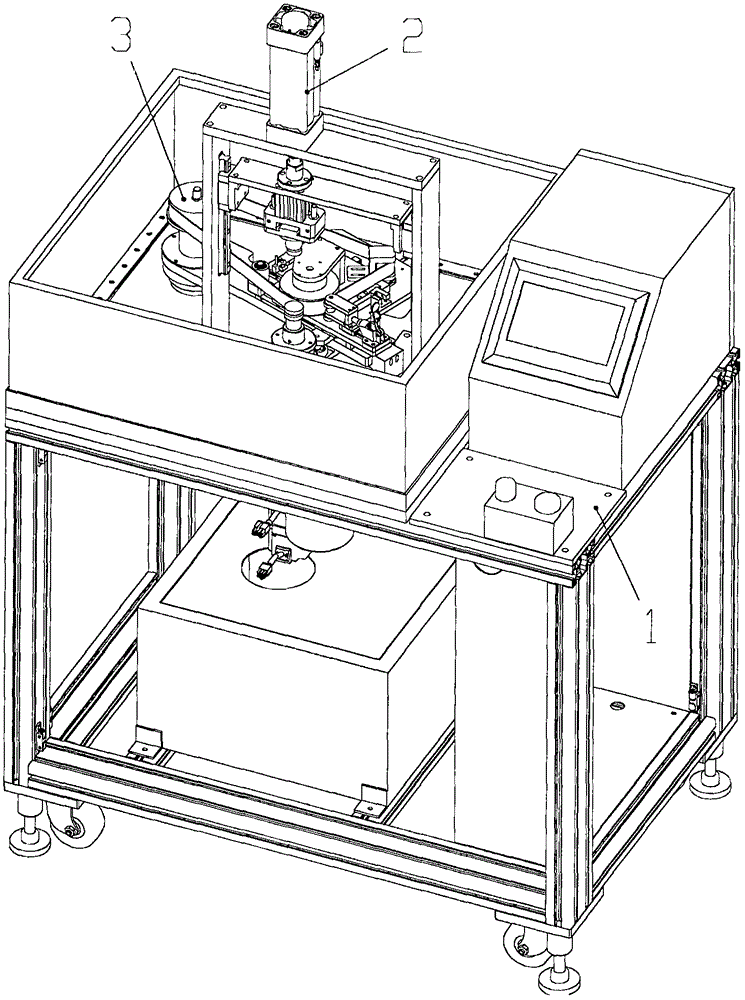
ActiveCN105773359AHigh strengthImprove stabilityBelt grinding machinesGrinding work supportsSurface finishConstant force
The invention relates to automatic polishing equipment, in particular to automatic polishing equipment of bearing fittings. The equipment comprises a worktable, a clamping mechanism for realizing clamping and positioning of the bearing outer ring, a polishing mechanism for realizing polishing of the outer surface of the bearing outer ring, and a fixture for mounting the bearing outer ring; the clamping mechanism, the polishing mechanism and the fixture are fixedly connected to the worktable; the fixture is positioned at the lower part of the clamping mechanism; and an abrasive belt of the polishing mechanism is contacted with the outer surface of the bearing outer ring. The outer surface force control type flexible polishing equipment of the bearing outer ring is used for polishing the outer surface of the bearing outer ring to improve the surface smoothness in a mode of not removing materials, realizes flexible contact between the abrasive belt and the outer surface of the bearing outer ring, realizes polishing by dint of constant force, monitors tangential force suffered by the bearing outer ring in real time, keeps constant tangential force and pressure of the bearing outer ring, and guarantees the polishing quality consistency; and after the bearing outer ring coats the fixture, the automatic mounting and polishing operation can be realized, and the automation degree is high.
Owner:滁州辉煌无纺科技有限公司
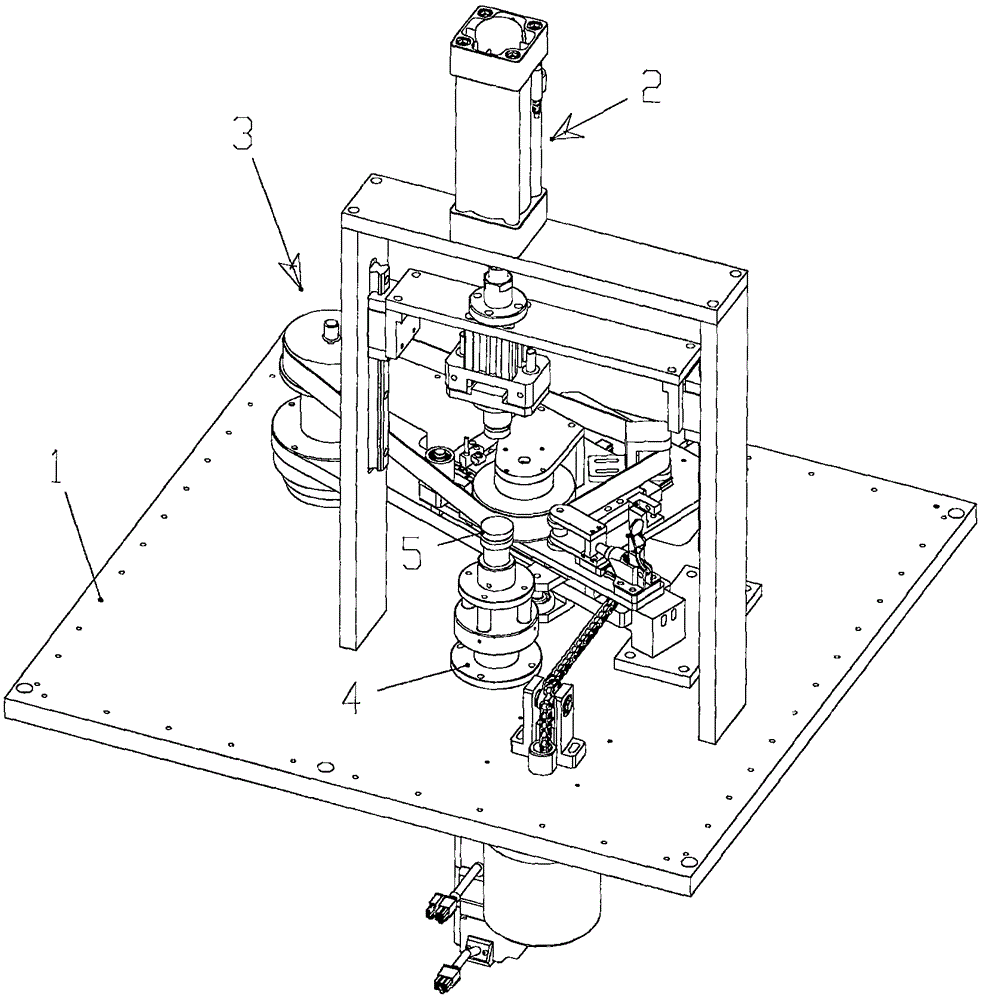
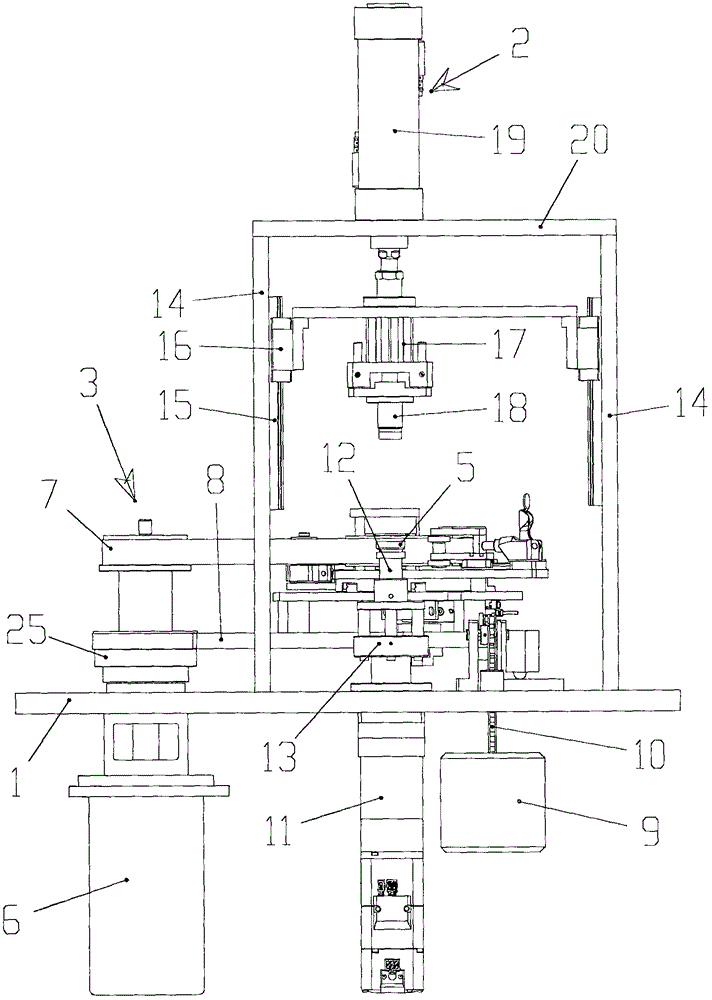
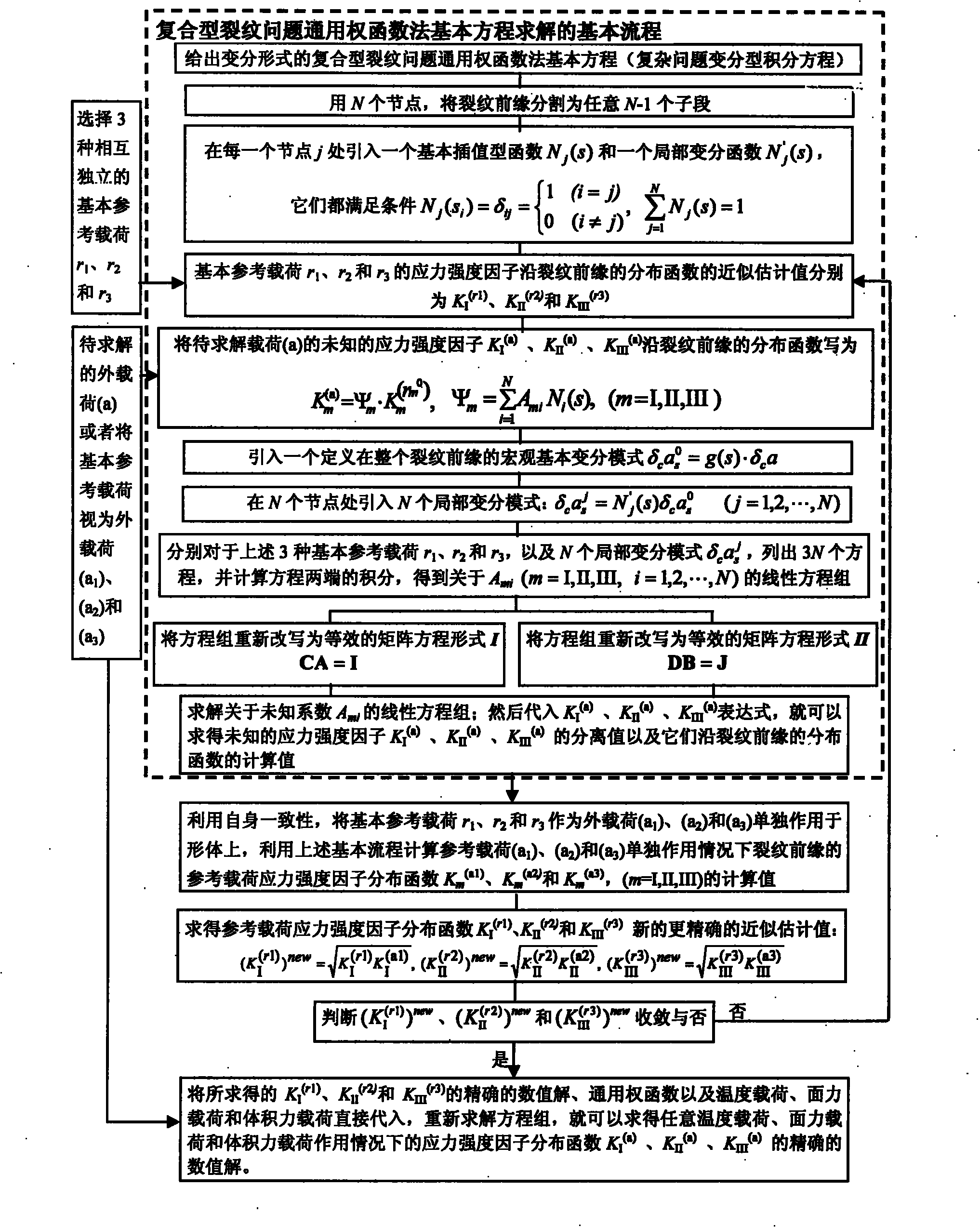
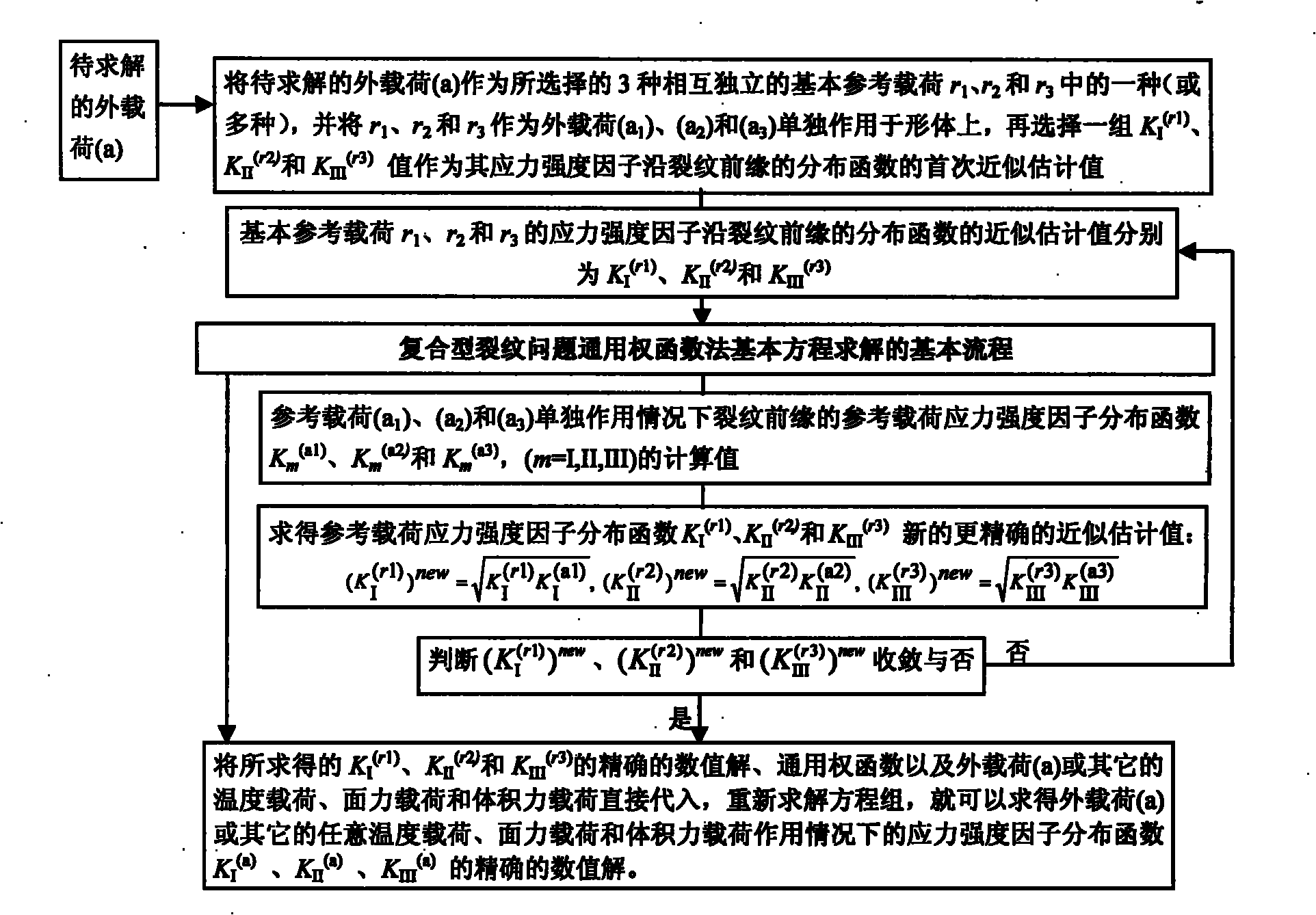
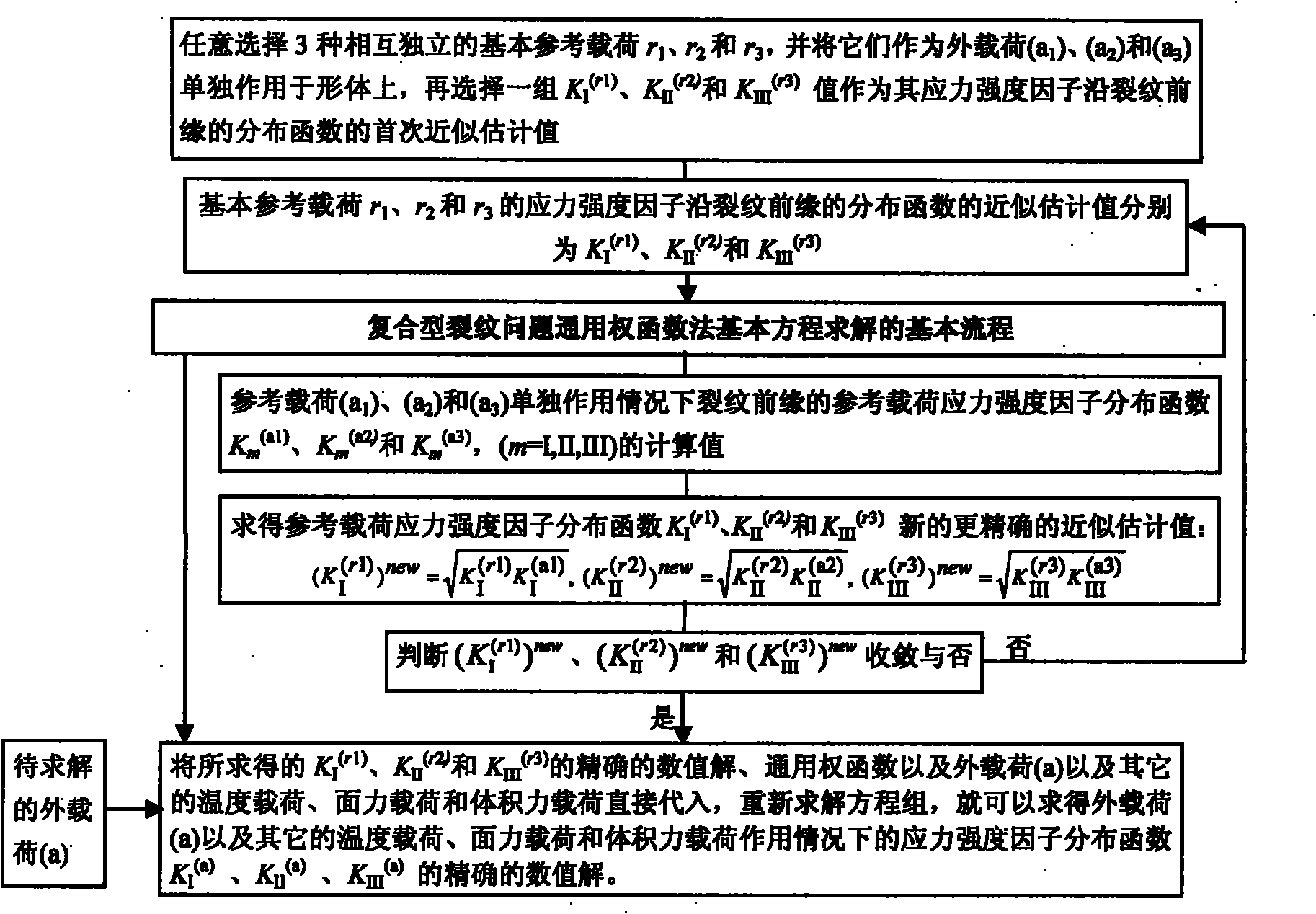
Method for determining separation and distribution of structural-member composite crack front stress intensity factors
InactiveCN101788425AHigh precisionImprove calculation accuracyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSpecial data processing applicationsStress intensity factorEngineering
The invention relates to a method determining separation and distribution of structural-member composite crack front stress intensity factors. The method comprises the following steps: giving thermal load, surface force load and volume force load borne by a structural member, and a universal weighting function method basic equation for three-dimensional I, II, III composite crack problems under the independent or combined actions of the thermal load, the surface force load and the volume force load; dividing the crack front into random N-1 numbered subsections through N numbered nodes, and introducing a basic interpolation function Nj(s) and a partial variation function N'j(s) at each node j, thereby constructing a finite number of partial variation modes and interpolation modes; and then introducing 3 basic reference loads to solve the basic equation, thereby determining the numerical solution of the separation and distribution of composite stress intensity factors KI, KII and KIII. By utilizing the self consistency, the method can obtain the high-precision exact solution of the distribution of the three-dimensional crack front composite stress intensity factors KI, KII and KIII by constructing an iterative process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Flotation aids and processes for using the same
InactiveUS8915374B2Increase profitPoorly solubleTransportation and packagingMixingOrganic chemistrySurface force
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
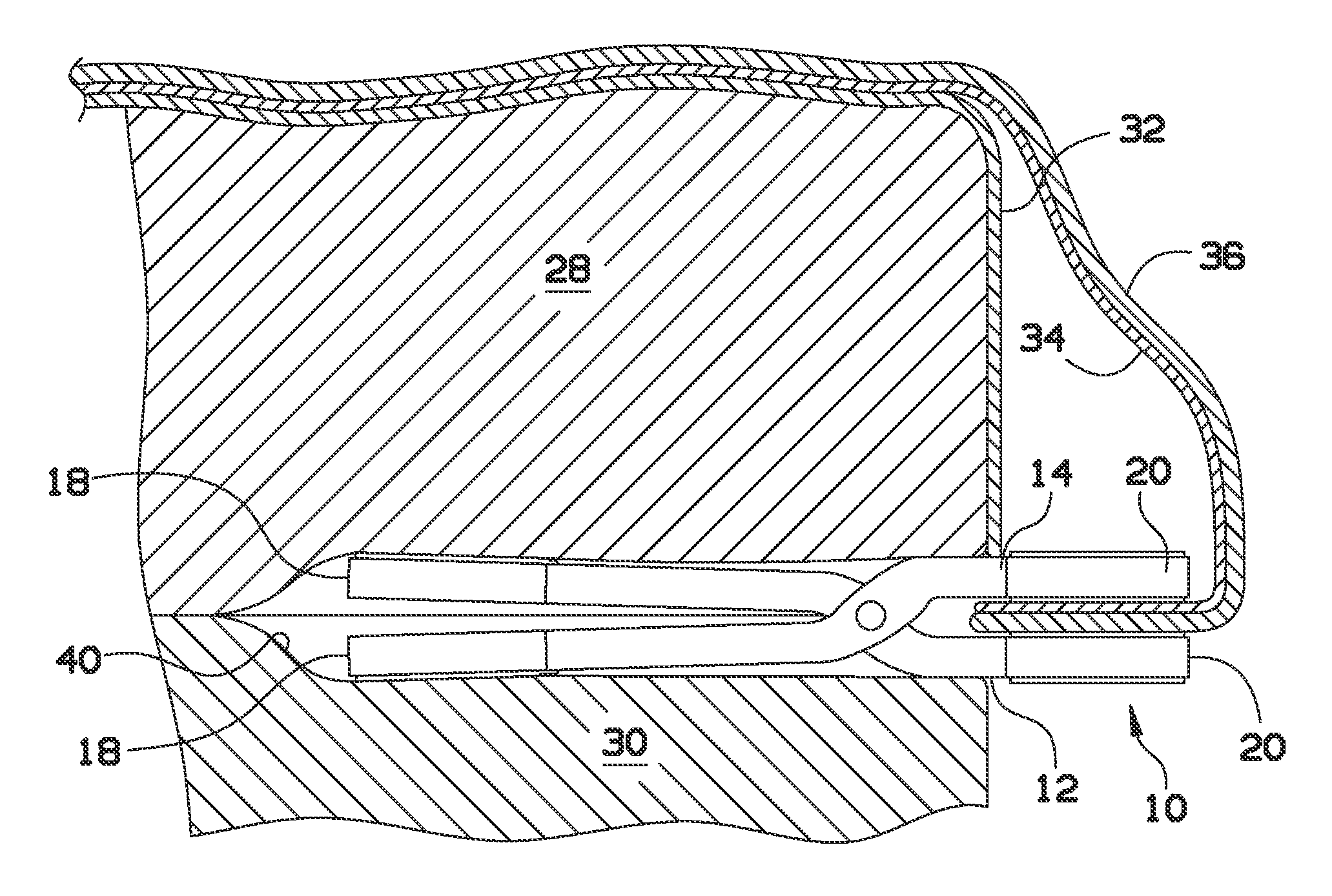
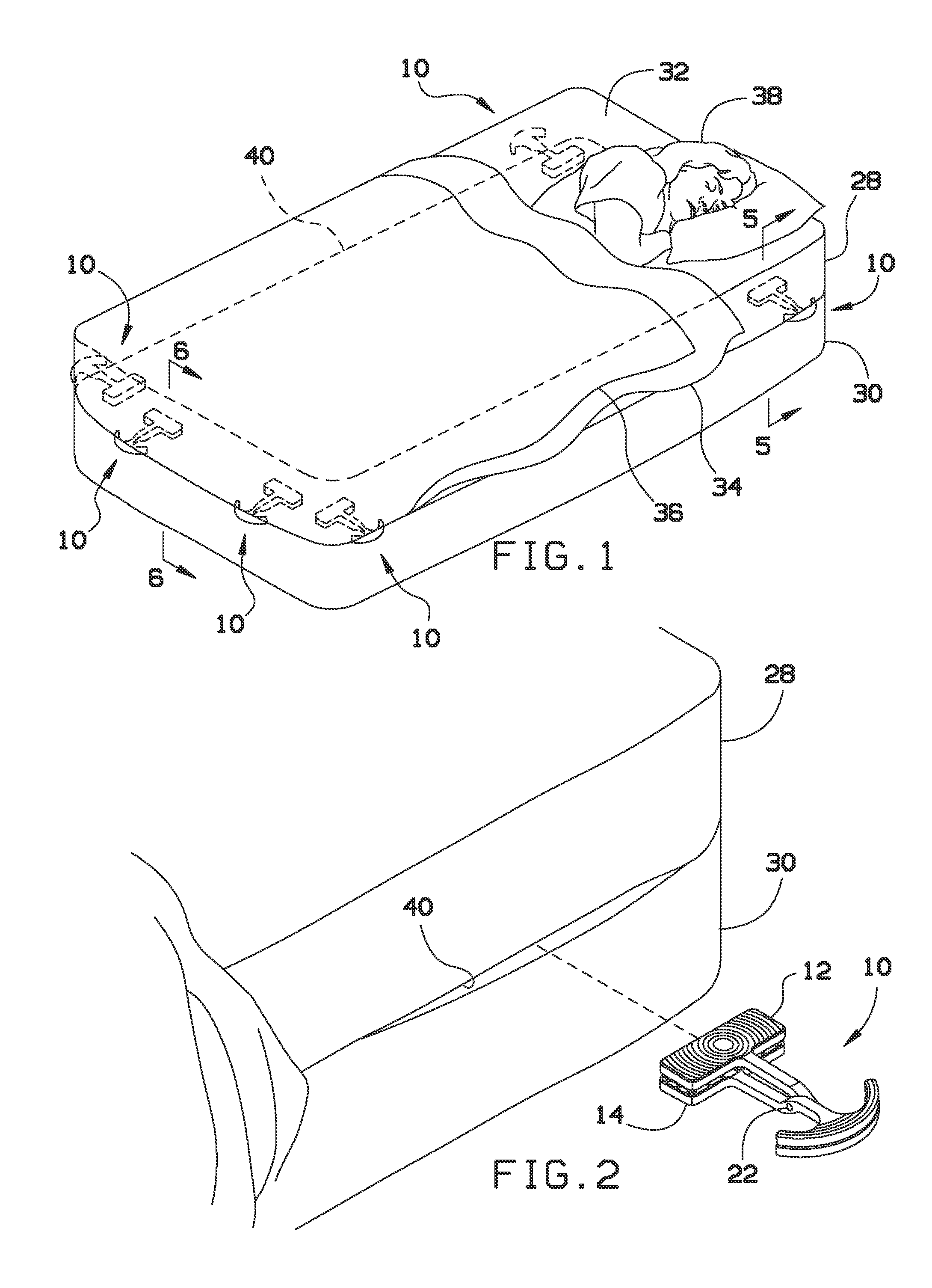
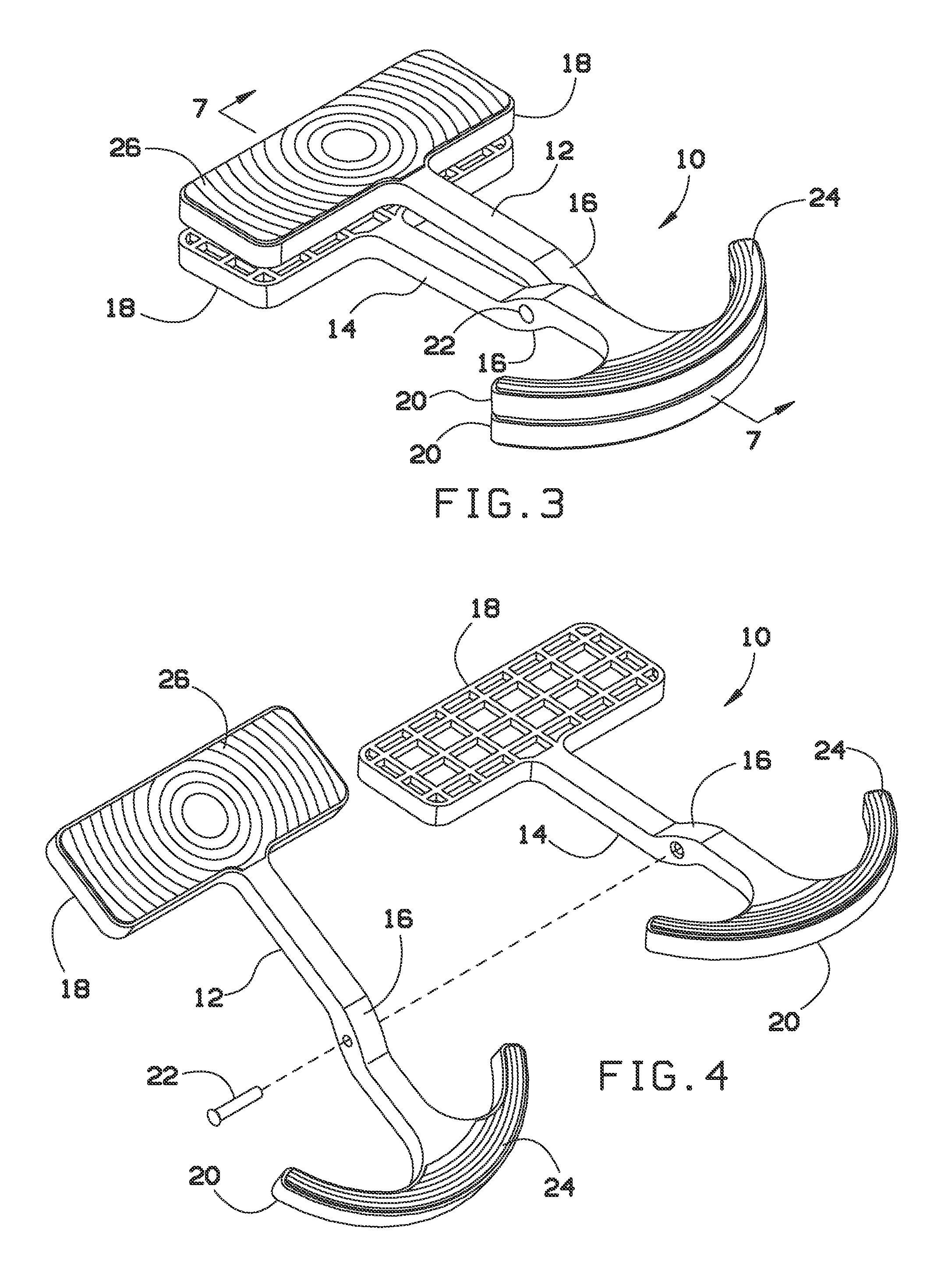
Bed sheet anchoring system
A sheet anchoring system is provided to restrain the periphery of a fitted sheet on a bed, where the sheet anchoring system includes a plurality of pivotable clips each having a first end and a second end with engaging friction surfaces to grasp between the surfaces a portion of the periphery of the sheet without the need for a spring or other force-biasing mechanism. The second end also has engaging surfaces forced into engagement by the weight of the mattress on top of the second end when the second end is placed between the mattress and a box spring below the mattress.
Owner:HEIMLICH NATHAN RICHARD
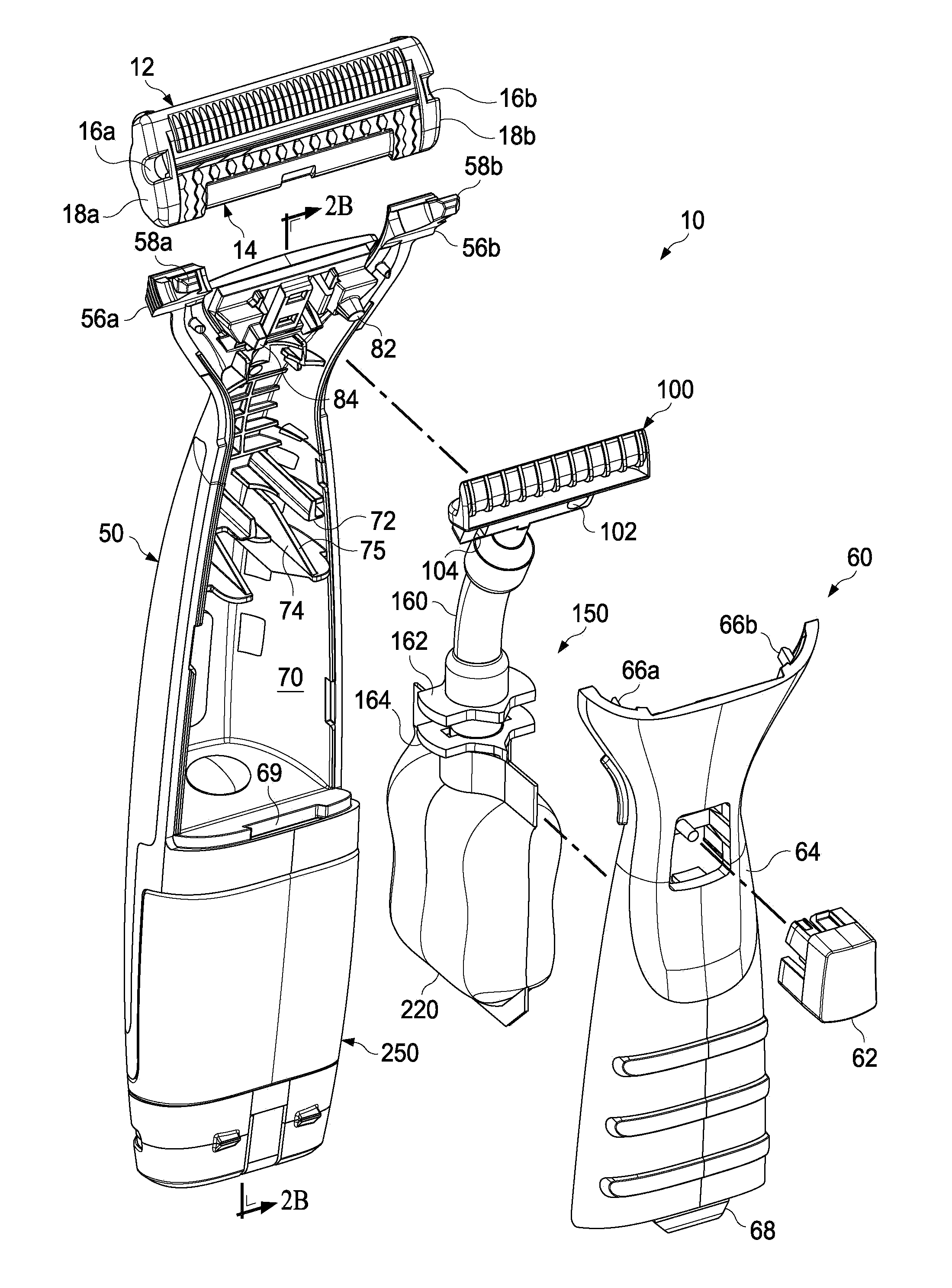
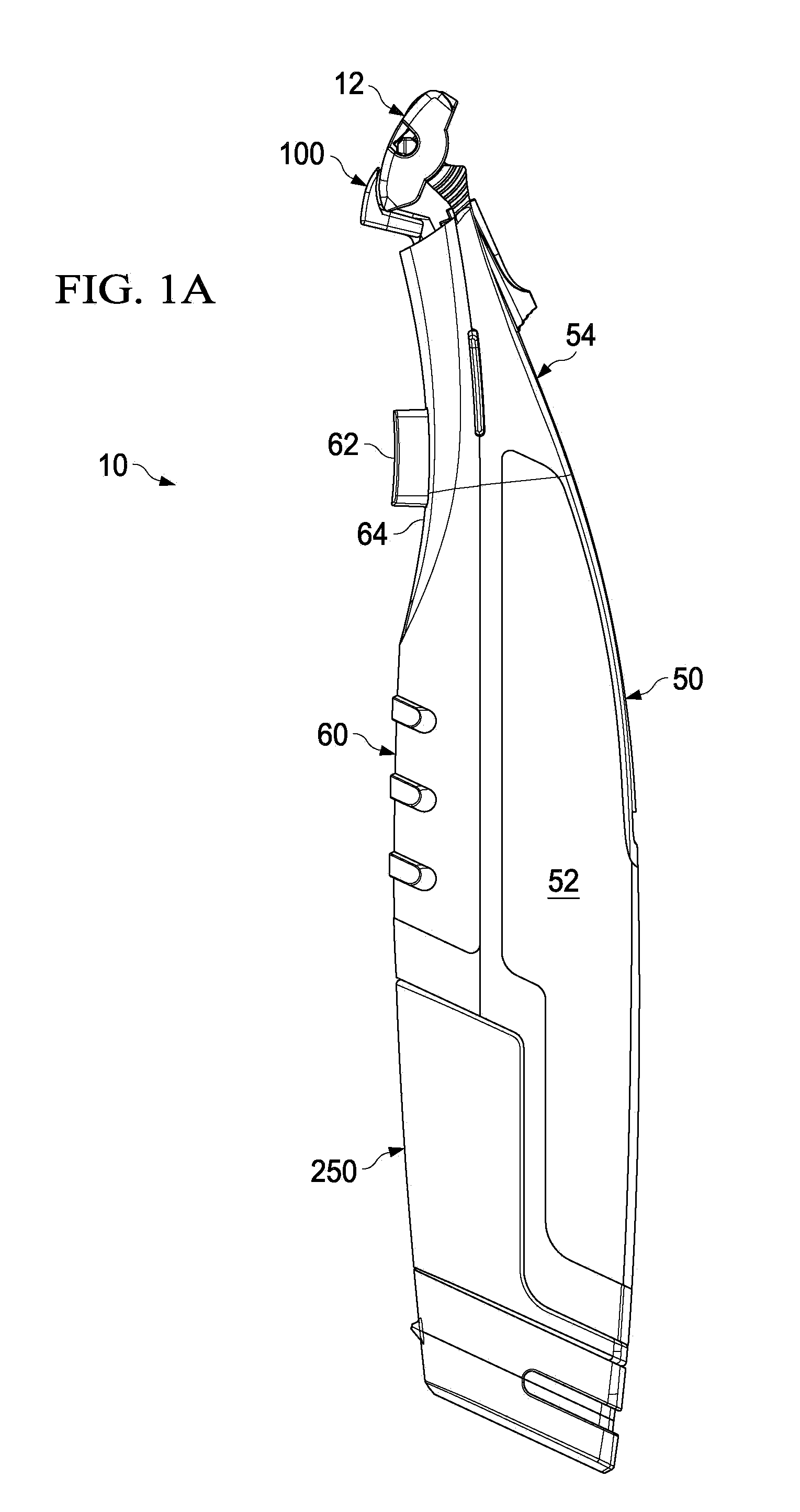
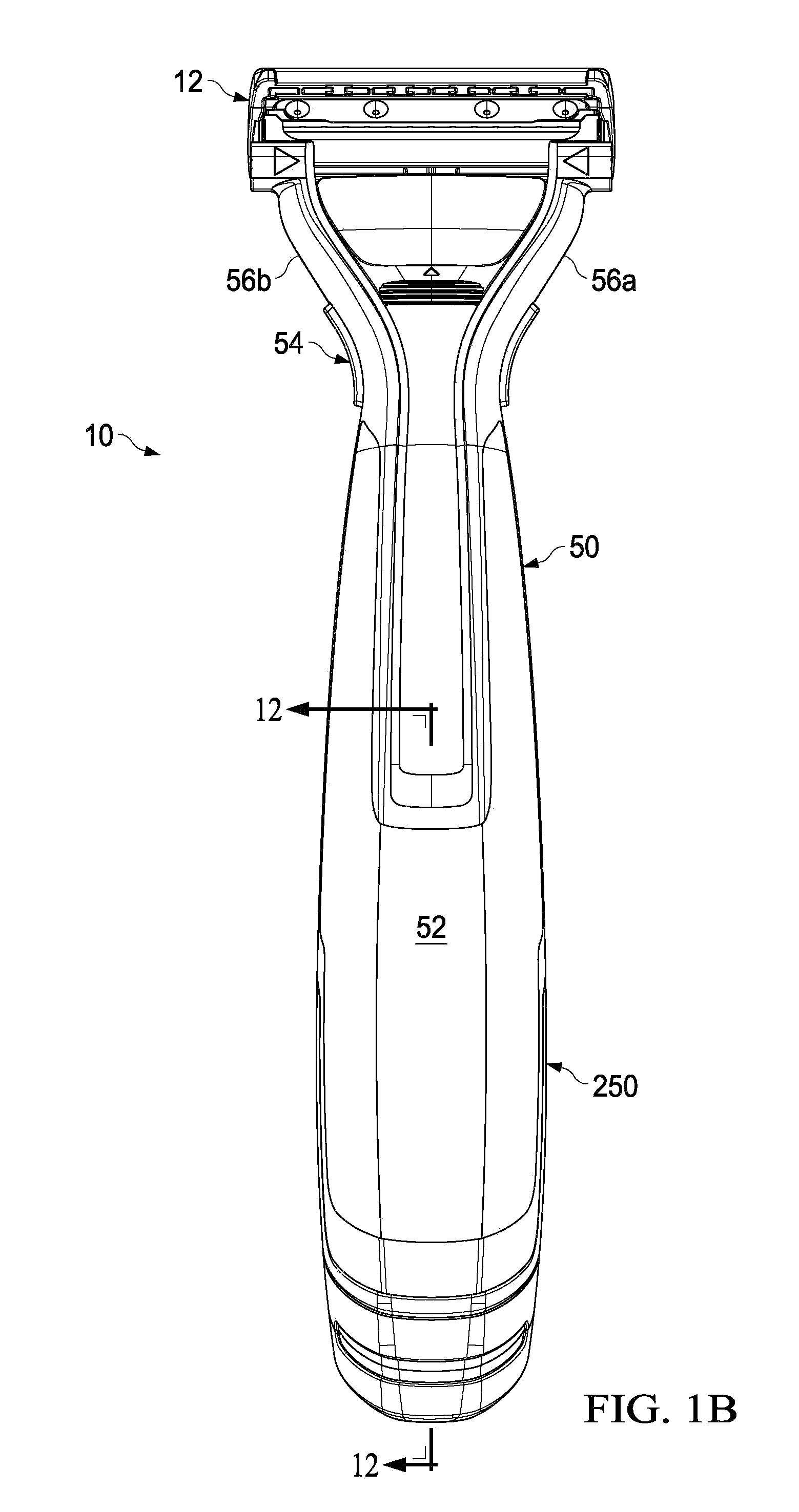
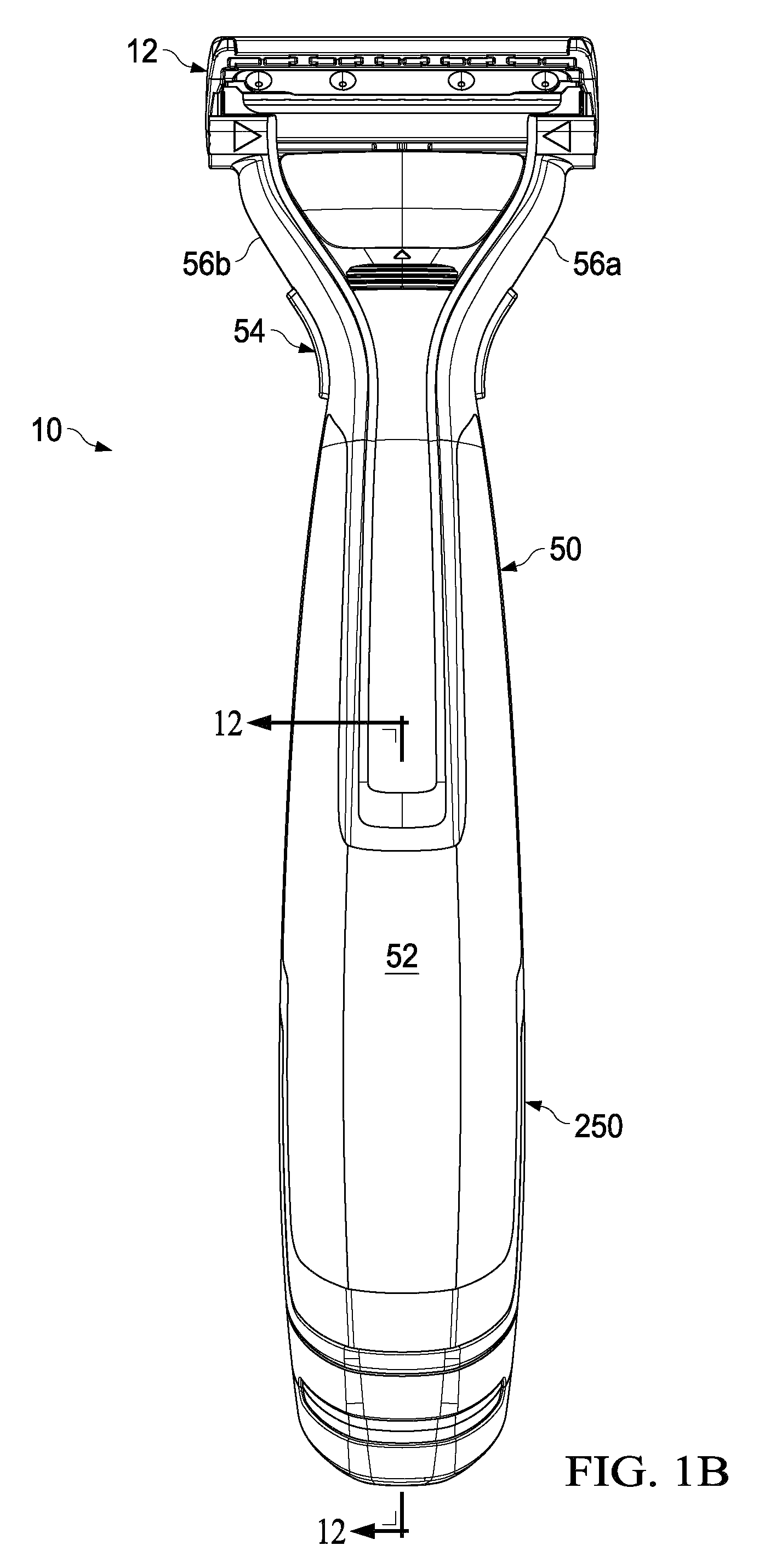
Handle for a liquid dispensing hair removal device
A hair removal device having a handle with a first interior wall and a second opposing interior wall that has a tapered surface. A cover is mounted to the handle. A dispensing unit having a first and second position is within the handle. The dispensing unit has a reservoir containing a liquid, a pump in liquid communication with the reservoir in the second position, and first and second connectors that are spaced apart. The mounting of the cover to the handle urges at least one of the connectors to slide along the tapered surface forcing the first and second connectors toward each other.
Owner:THE GILLETTE CO
Non-impact transfer printing method and device therefor
InactiveCN1883957AAchieve varietyImprove resolutionTransfer printingPattern printingAnti solventImage resolution
The invention discloses a non-plate transfer printing method and an apparatus therefor. The apparatus comprises: a non-plate transfer paper with a PVC plastic paper on its base layer, a pattern layer above the PVC plastic paper and sequentially provided with a resin type releasing agent, an anti-solvent transparent ink, a full-color image, a white ink, and a print hot transfer glue; a press transfer machine to provide vacuum, pressurizing and a thermostatic environment with a temperature of 75~120 centigrade, wherein the press transfer machine has a special plastic material mould turning jig to hold and fix a transferred object, the non-plate transfer paper is disposed above the transferred object and coated with a silica gel layer evenly to fix the surface force bearing, so that the non-plate transfer paper can evenly reach to the vertical corners to perform transfer printing. The invention can obtain a pattern with high solution without damnifying a notebook computer casing, and can perform transfer printing at low temperature.
Owner:何名升
Material performance testing system under suspension type multi-field coupling action in supergravity environment
PendingCN110261216AIn line with the concept of high strength and light weightShort experiment preparation periodStrength propertiesMulti fieldEngineering
The invention discloses a material performance testing system under the suspension type multi-field coupling action in a supergravity environment. The material performance testing system comprises a hoisting sealed cabin, a bearing frame, a high-temperature furnace, a mechanical testing device and a buffer device; the bearing frame and the high-temperature furnace are fixedly installed inside the hoisting sealed cabin, the bearing frame covers the high-temperature furnace, the buffer device is installed at the bottom inside the high-temperature furnace, the upper end and the lower end of the mechanical testing device are connected to the top of the bearing frame and the bottom of the high-temperature furnace, and the sample is connected and installed at the tail end of the mechanical testing device. The material performance testing system solves the problem of material dynamic performance testing under the coupling action of volume force-surface force-temperature under the high-speed rotation state, and is simple in structure, convenient to operate, safe and reliable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Apparatus and method for electrical and mechanical connection
ActiveUS7467979B2Promote disseminationCoupling device detailsContact members penetrating/cutting insulation/cable strandsElectrical conductorConical forms
An apparatus for engaging an electrical conductor comprises a gripping contact having a plurality of fingers, where the plurality of fingers has a substantially conical outer surface. A contact receptacle has a substantially conical inner surface. A tension member urges the gripping contact toward the contact receptacle such that interaction between the substantially conical outer surface and the substantially conical inner surface forces the plurality of fingers to engagingly compress the electrical conductor placed between the fingers. A method of engaging an electrical conductor comprises inserting an electrical conductor between a plurality of fingers of a gripping contact, where the plurality of fingers has a substantially conical outer surface. The substantially conical outer surface of the gripping contact is urged to interact with a substantially conical inner surface of a contact receptacle such that the interaction forces the plurality of fingers to engage the electrical conductor.
Owner:POWER FEED THRU SYST & CONNECTORS
Apparatus and method for manufacturing tilted microlenses
ActiveUS20050270653A1Easy to manufactureTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSurface forceMaterials science
Asymmetrical structures and methods are used to adjust the orientation of a microlens for a pixel array. The asymmetrical structures affect volume and surface force parameters during microlens formation. Exemplary microlens structures include an asymmetrical microlens frame, base, material or a combination thereof to affect the focal characteristics of the microlens. The asymmetrical frame alters the microlens flow resulting from the heating of the microlens during fabrication such that orientation of the microlens relative to an axis of the imager can be controlled.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
System and method of interactive evaluation of a geometric model
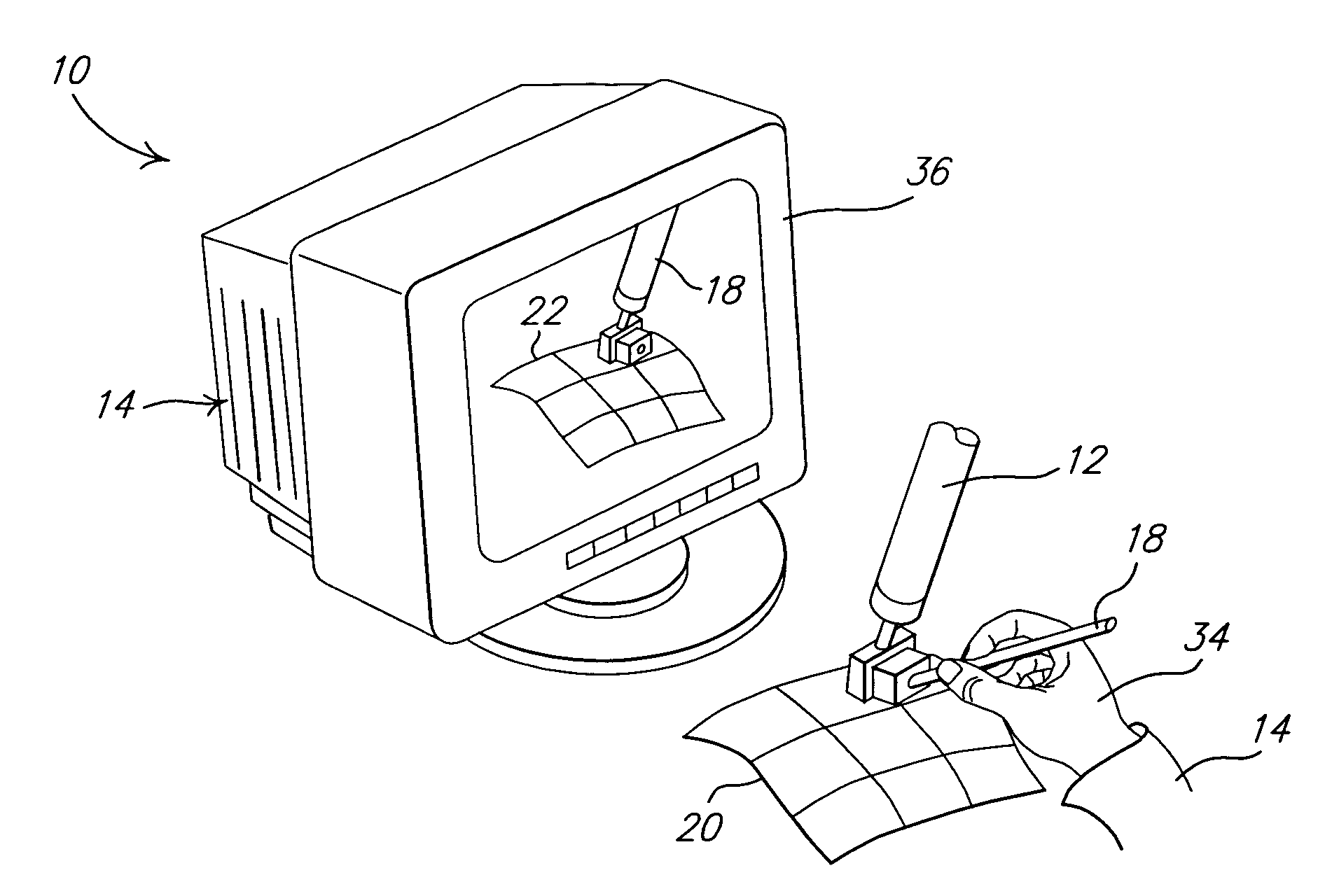
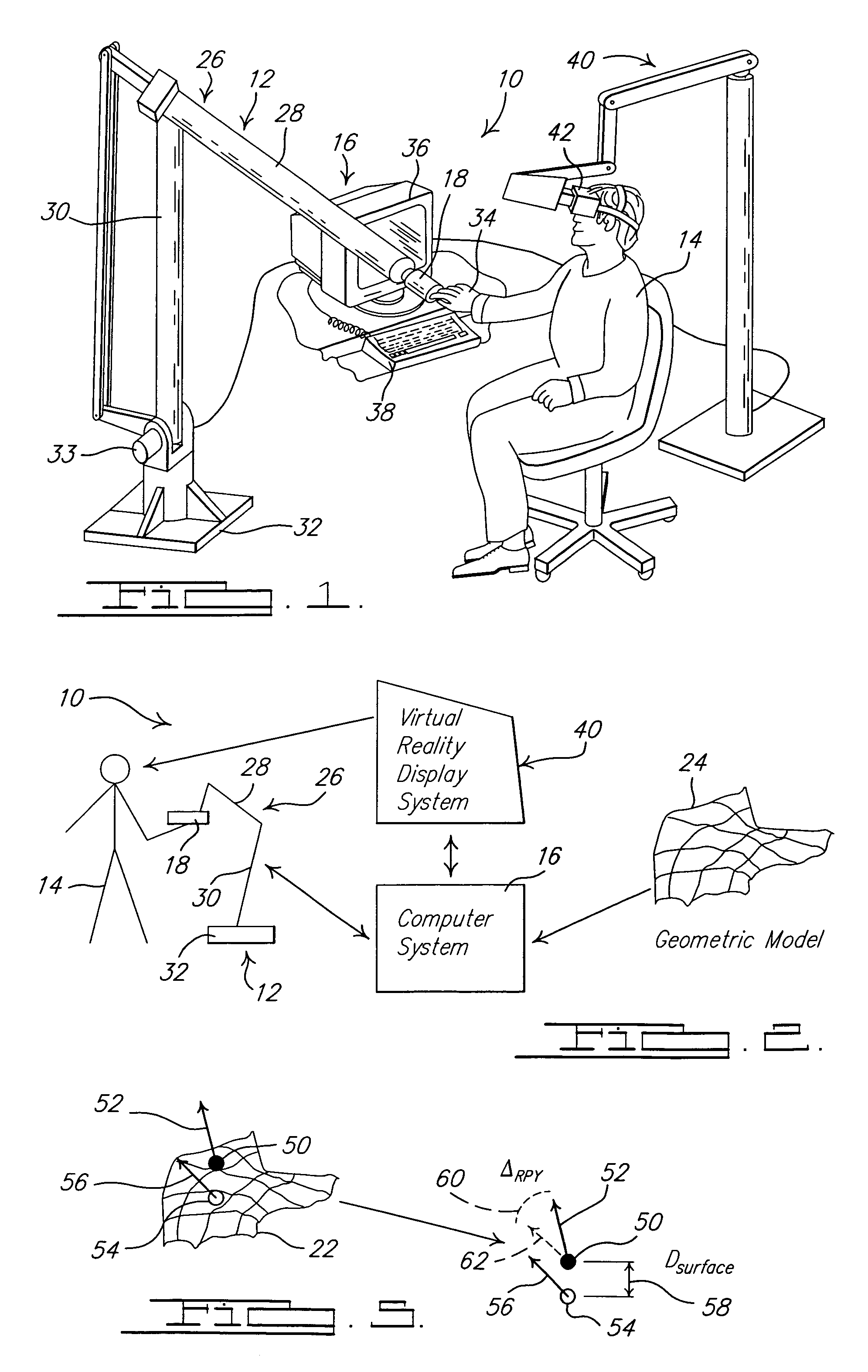
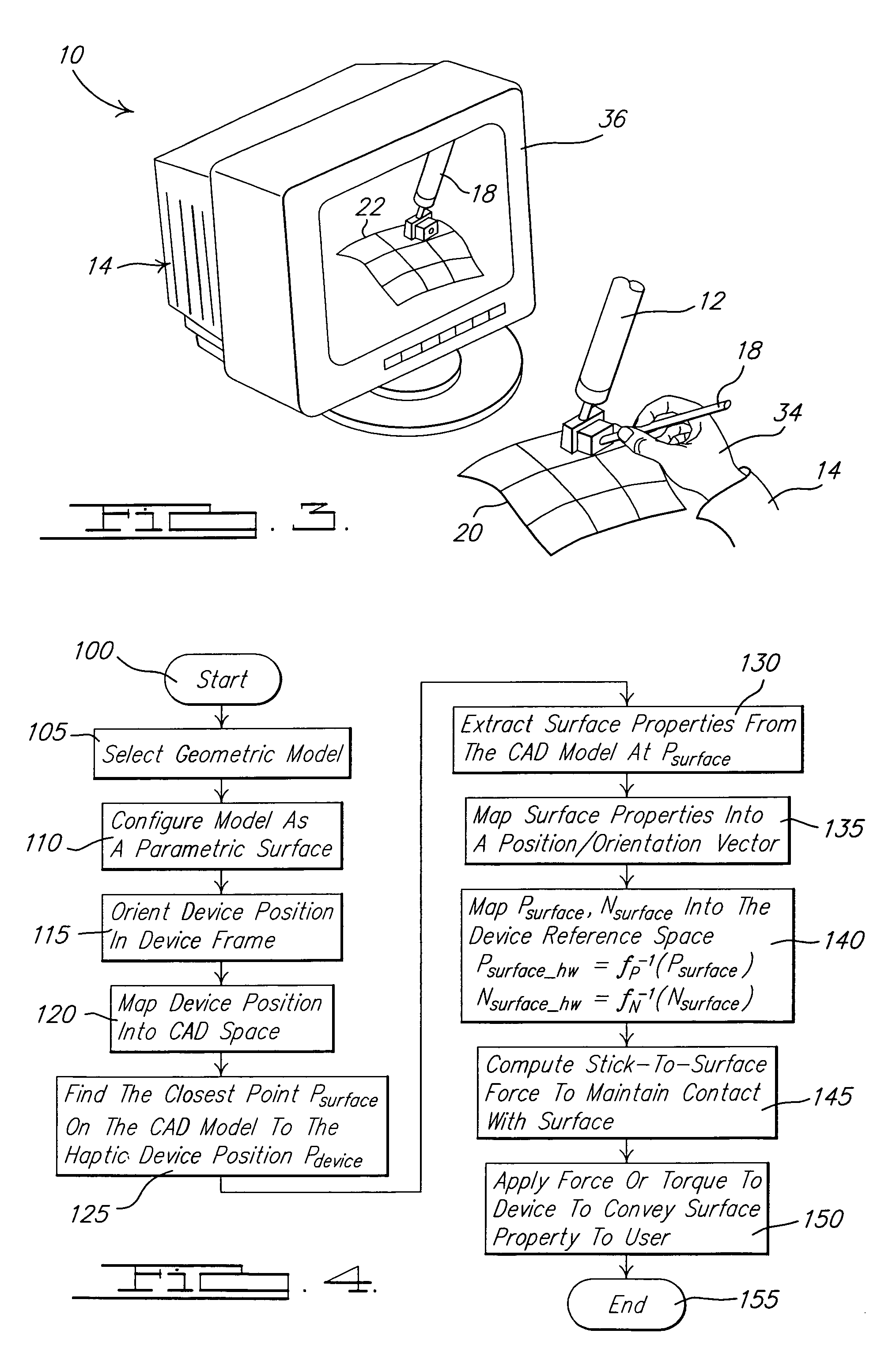
InactiveUS7155673B2Improve understandingInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsClosest pointGeometric modeling
A system and method of interactive evaluation of a geometric model is provided. The method includes the steps of acquiring a haptic device position and orientation with respect to a surface of the geometric model and mapping the haptic device position and orientation into a geometric model coordinate reference system. The method also includes the steps of determining a closest point position and orientation on the surface of the geometric model to the haptic device position and extracting a surface property at the closest point position and orientation. The method further includes the steps of determining a stick-to-surface force and a property feedback force using the surface property at the closet point position and orientation and applying the stick-to-surface force and property feedback force to control a location and force output of the haptic device.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Material performance testing system under fixed multi-field coupling action in supergravity environment
PendingCN110261238APerformanceCapable of performanceMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFurnace typesMulti fieldEngineering
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Liquid mechanical seal device applicable to variable pressure environment
The invention discloses a liquid mechanical seal device applicable to a variable pressure environment. The device comprises a rotational seal ring, a stationary seal ring, an elastic component, liquid drain tubes, direct-action overflow valves, multiple stages of pressure-regulating slide valves and multiple stages of glands. Each pressure-regulating slide valve comprises a piston, an elastic body seal ring, a metal corrugated pipe and a pressure-regulating overflow ring. The pistons slide axially on the pressure-regulating overflow rings. Each elastic body seal ring comprises an inner ring body and an outer ring body which are mounted on the inner side and the outer side of a piston ring in the radial direction of the piston ring correspondingly. Multiple stages of pressure-regulating overflow holes are machined in the pressure-regulating overflow rings and communicate with two adjacent medium cavities. Opening of the multiple stages of pressure-regulating overflow holes is controlled by the algebra and amplitude of the piston end surface force, the metal corrugated pipe elastic force and the friction force between the inner elastic body seal ring bodies and the outer elastic body seal ring bodies; and the multiple stages of pressure-regulating slide valves and the corresponding glands are mounted from left to right in sequence, and bolts are connected with a machine shell to achieve press sealing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Handle for a liquid dispensing hair removal device
A hair removal device having a handle with a first interior wall and a second opposing interior wall that has a tapered surface. A cover is mounted to the handle. A dispensing unit having a first and second position is within the handle. The dispensing unit has a reservoir containing a liquid, a pump in liquid communication with the reservoir in the second position, and first and second connectors that are spaced apart. The mounting of the cover to the handle urges at least one of the connectors to slide along the tapered surface forcing the first and second connectors toward each other.
Owner:THE GILLETTE CO
Non-Newtonian fluid lining support structure and construction method
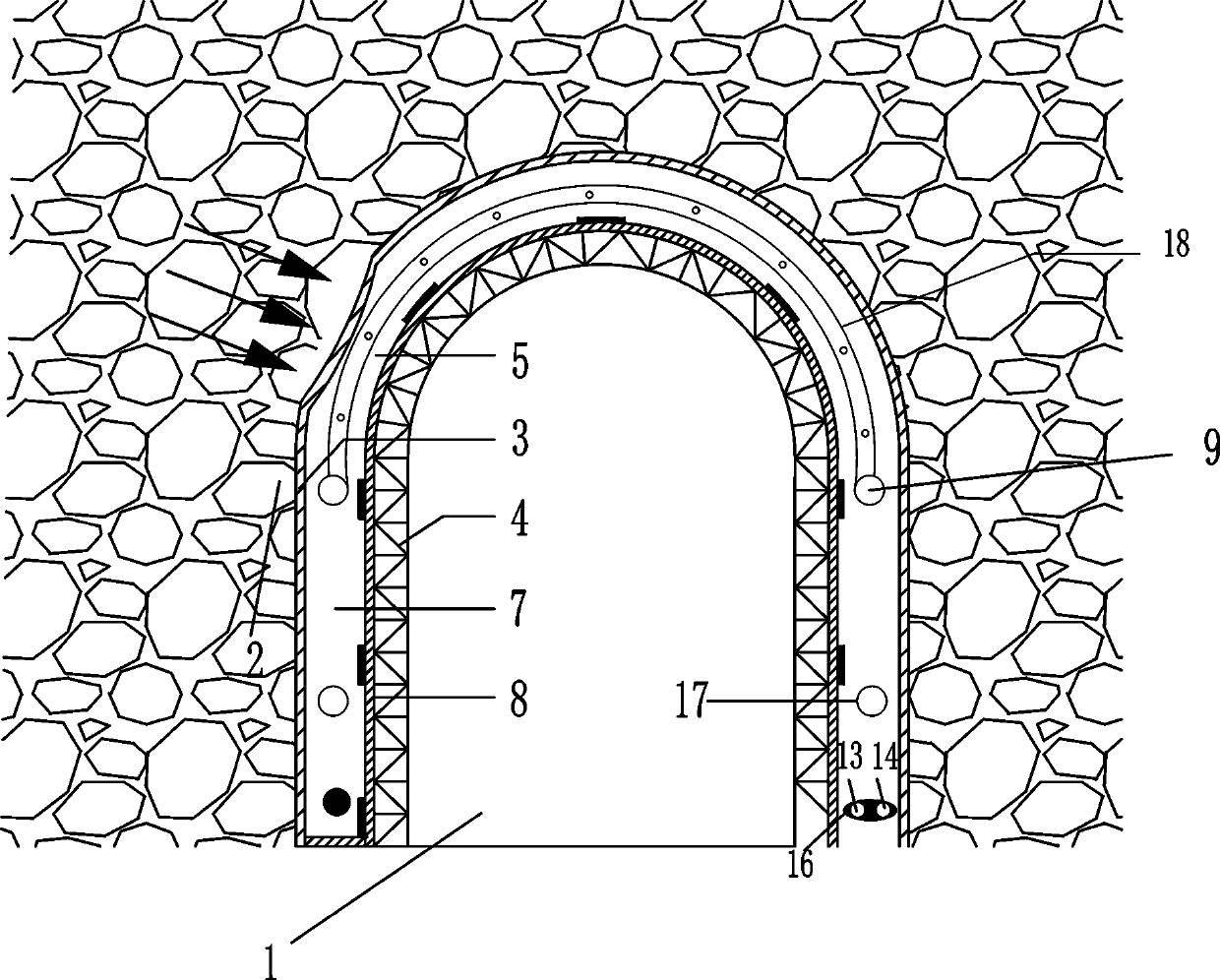
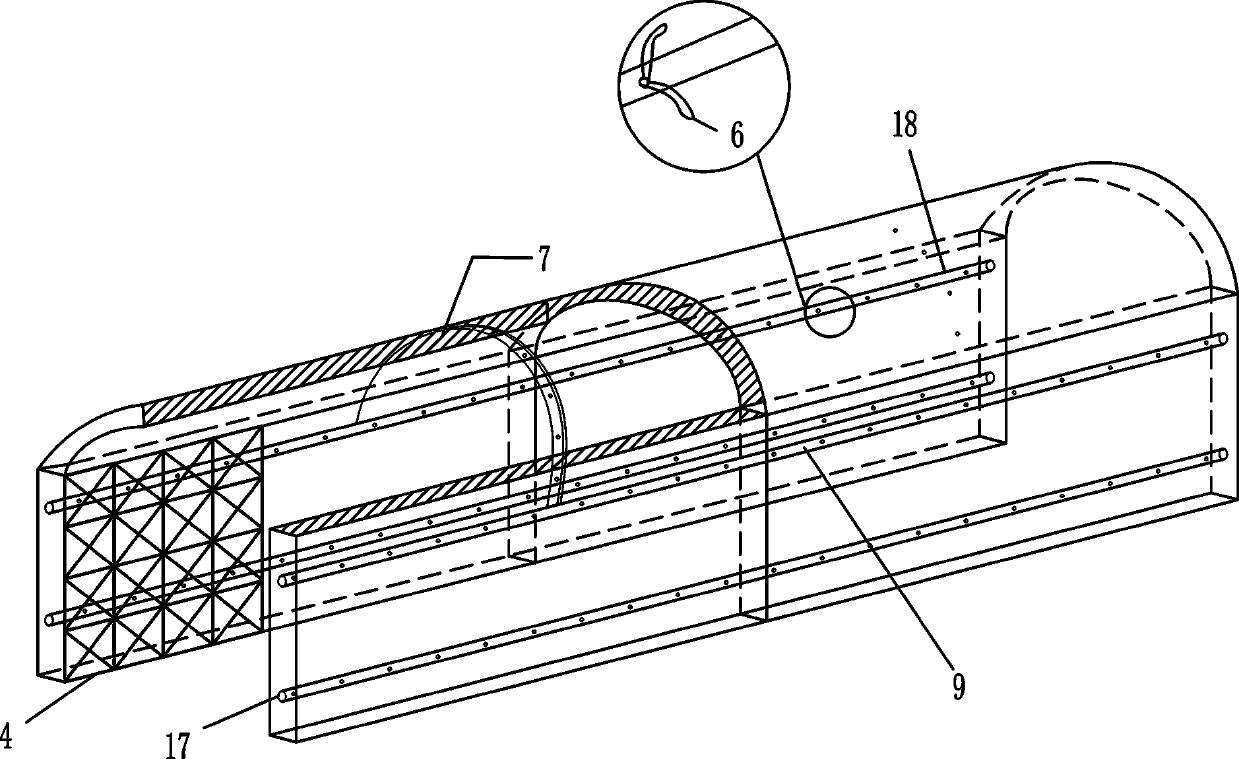
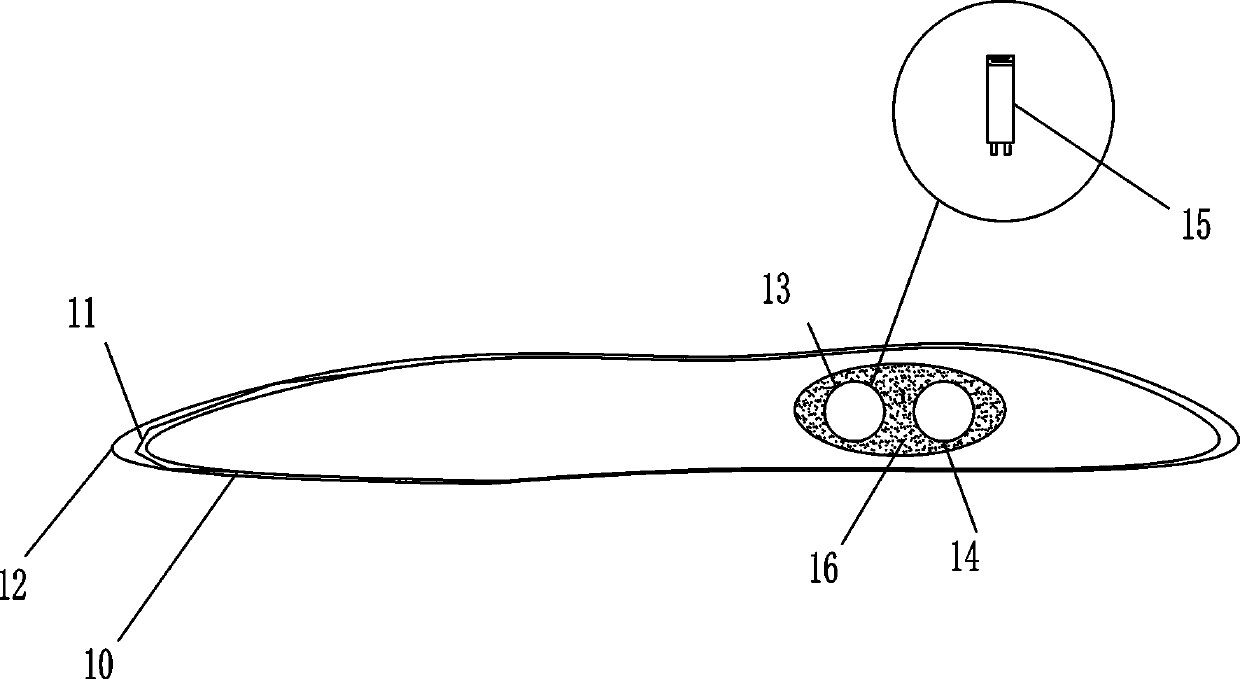
ActiveCN110094215AMake full use of supportAvoid wastingUnderground chambersTunnel liningEngineeringSurface force
The invention relates to a non-Newtonian fluid lining support structure. The non-Newtonian fluid lining support structure comprises a tunnel primary lining body, a reserved deformation layer formed bya certain space is arranged between the tunnel primary lining body and a tunnel secondary lining body, and a non-Newtonian fluid filling material is placed in the reserved deformation layer; the non-Newtonian fluid filling material comprises a fully-enclosed bag body filled with non-Newtonian fluid inside; a rubber valve is provided with a water injection hole and a pressure relief / grouting hole,a second water injection hole is further formed in the outer side surface, corresponding to the wall rock, of the enclosed bag body, the second water injection hole communicates with a second main water injection pipe embedded in the non-Newtonian fluid of the non-Newtonian fluid filling material, and the second main water injection pipe is connected with arc-shaped sub water injection pipes at intervals. According to the Non-Newtonian fluid lining support structure and a construction method, the problems that stress of a secondary lining steel arc frame is not uniform, and the supporting ability is poor are solved, point force or line force of the wall rock on the secondary lining structure is transformed to surface force, and the using ratio of the secondary structure is improved.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
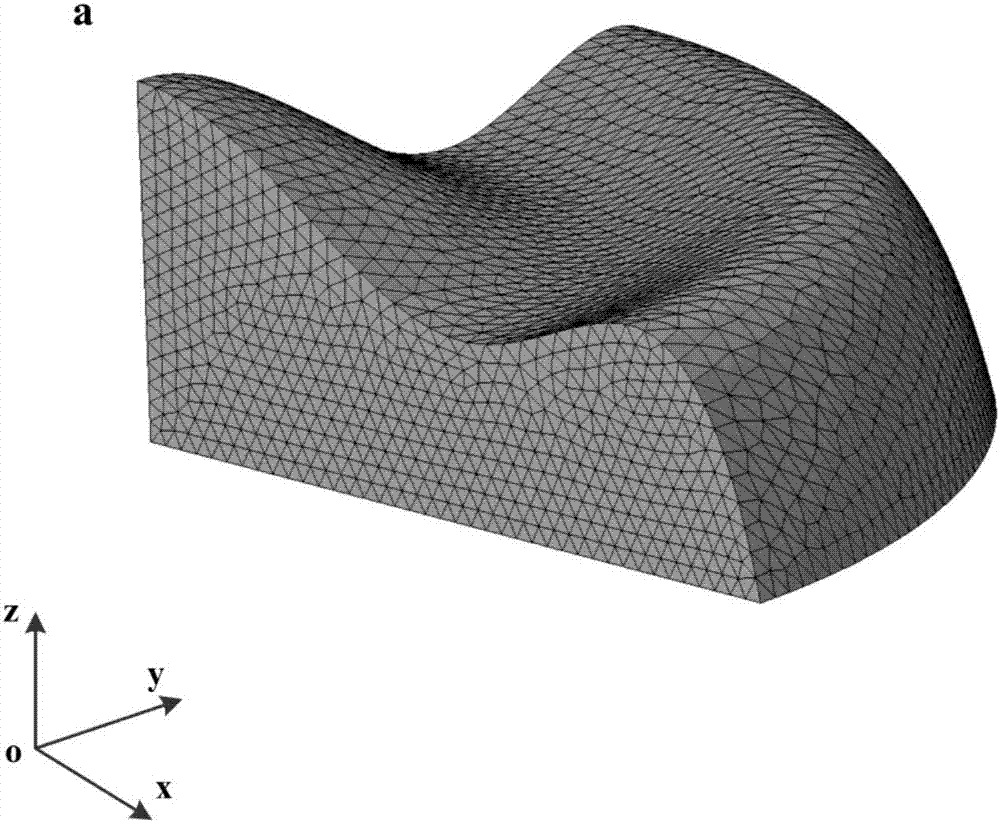
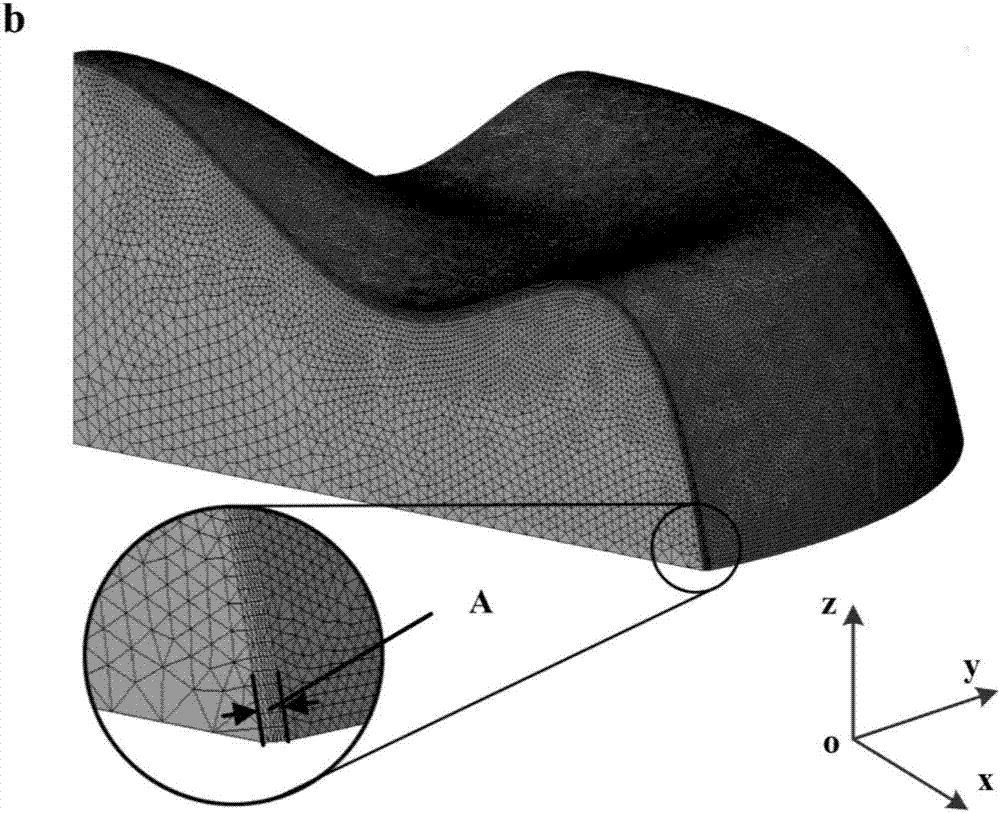
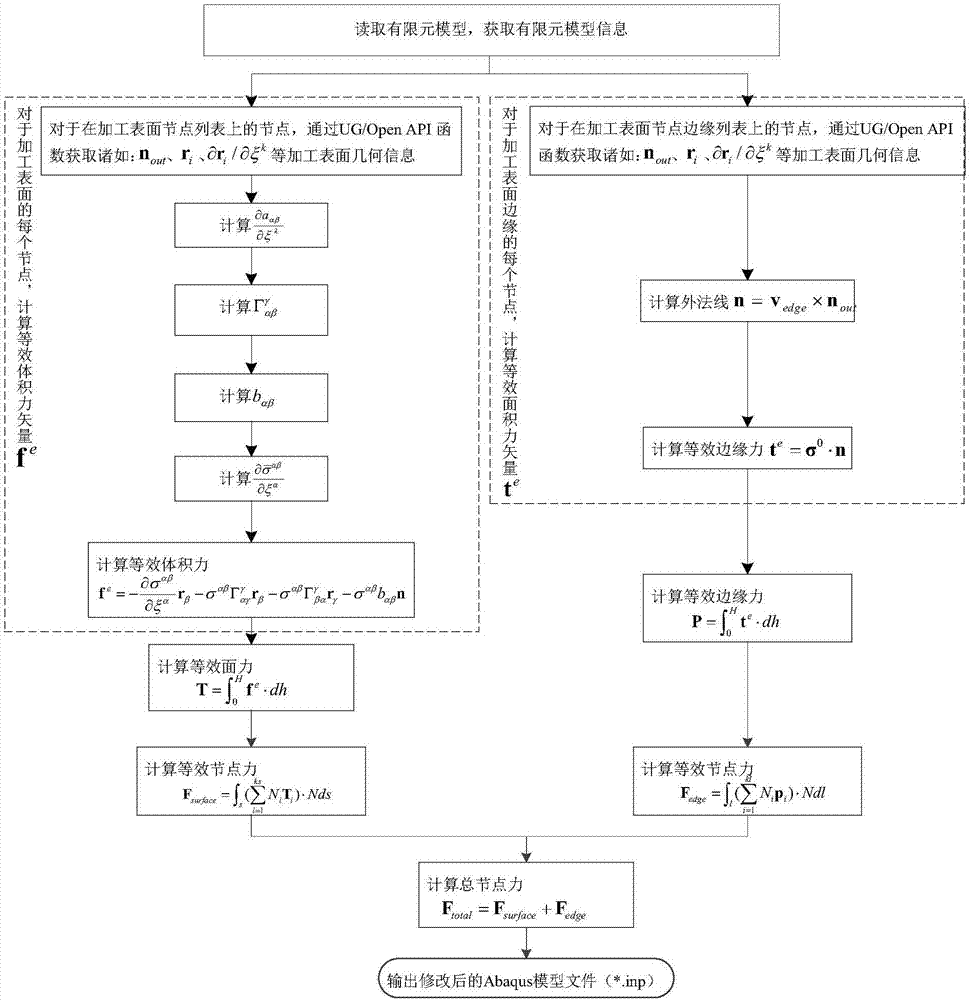
Calculation method for machining deformation caused by surface machining residual stress field
ActiveCN107038270ALow skill level requiredOvercome applicabilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelMachining deformation
The invention discloses a calculation method for machining deformation caused by a surface machining residual stress field. In the method, through the modeling and the analysis of a part surface machining residual stress field, the action of the surface residual stress field for deformation is equivalent to one group of surface force and edge force. Corresponding surface force and edge force is applied in a finite element model to finish deformation calculation caused by the surface machining residual stress field. Compared with a traditional method, the method disclosed by the invention needs a small unit number, does not have special requirements on mesh generation, a large-scale problem can be processed, and the application of the calculation method on the large blades of a steam turbine and an aircraft engine as well as a marine large-scale propeller becomes possible.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com