Method for determining separation and distribution of structural-member composite crack front stress intensity factors
A stress intensity factor, crack front technology, applied in the field of structural safety analysis and assessment, can solve problems such as low calculation efficiency, poor mathematical simulation effect, and low accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
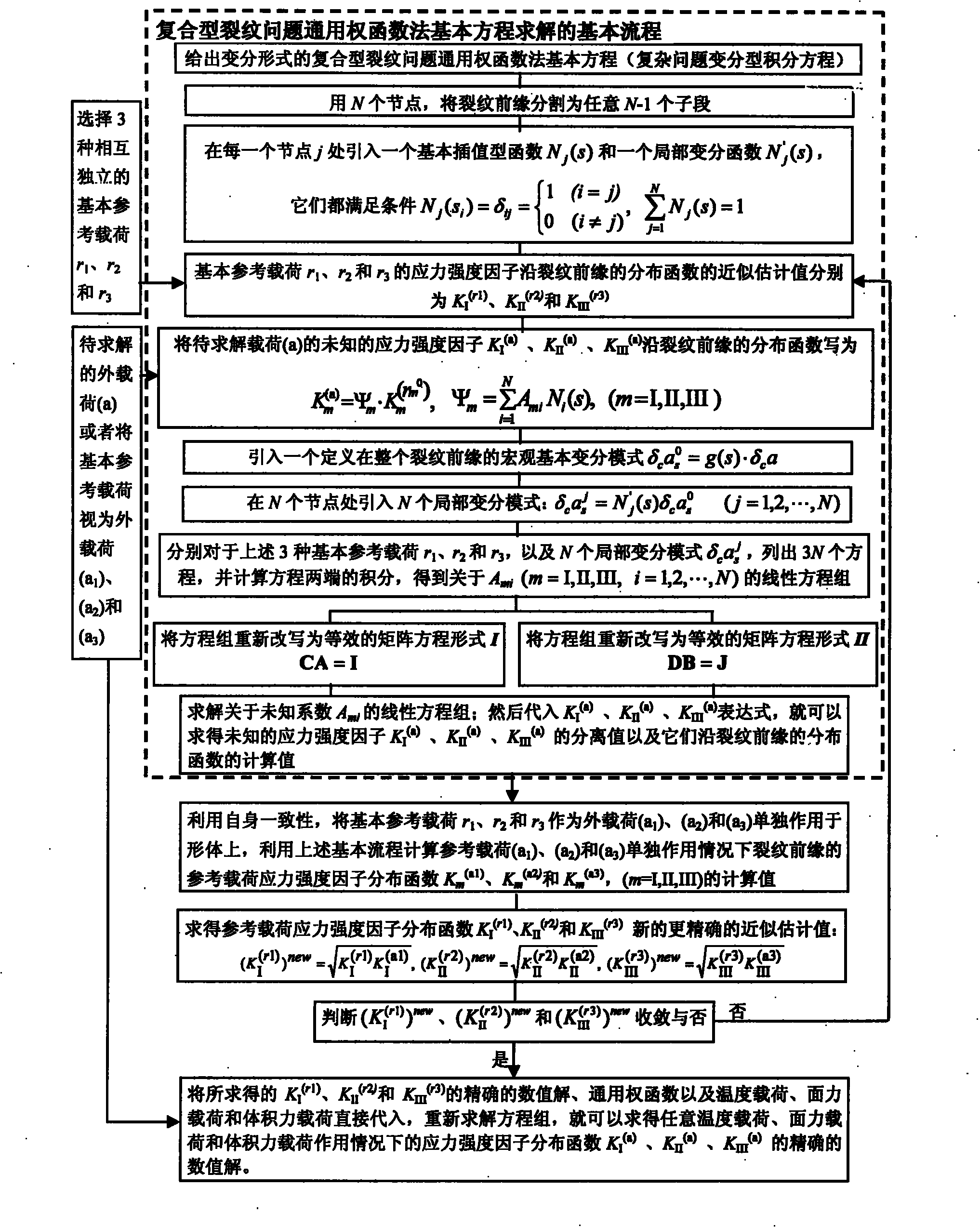
[0105] refer to figure 1 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 , Figure 7 , a method for determining the separation and distribution of stress intensity factors at the front edge of composite cracks in structural parts, the method mainly includes the following steps (see attached figure 1 ):
[0106] 1), give the thermal load, surface force load and body force load borne by the structural member, and the three-dimensional I, II, III expressed in the form of variational integral equation under the action of the three loads alone or together The basic equation of the universal weight function method for the complex crack problem (complex problem variational integral equation), as shown in formula (1);
[0107] 2) Use N nodes to divide the crack front into any N-1 sub-segments, and introduce a basic interpolation function N at each node j j (s) and a local variational function N′ j (s), they all satisfy conditional formula (2);
[0108] 3) Select three independent basic re...
Embodiment 2
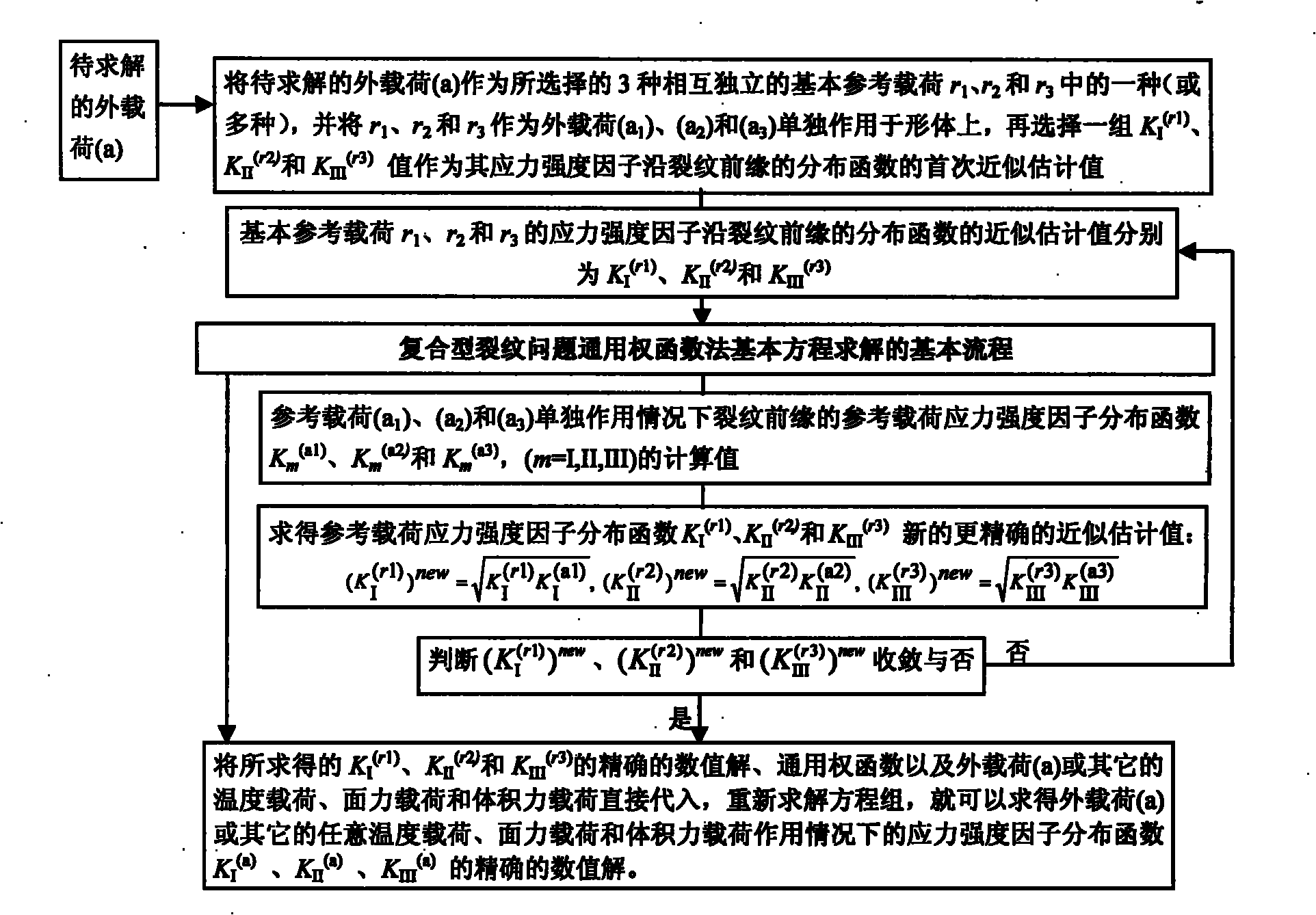
[0120] refer to figure 1 , figure 2 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 , Figure 7 , Figure 8 , according to the method for determining the separation and distribution of the stress intensity factors of the composite crack front of the structural part described in Example 1, the crack front stress intensity of the semi-elliptical surface crack in the Z-direction fixed plate at both ends under the action of three kinds of crack surface forces Factor K I 、K II and K III Separation and its distribution, according to figure 2 The first execution method (high precision execution mode) shown is determined. Figure 8 Represents a semi-elliptical surface crack with a depth ratio of a / T=0.5 and a shape ratio of a / c=0.5, with uniform pressure distribution on the upper and lower crack surfaces, uniform shear force on the crack surface in the X direction, and uniform shear force on the crack surface in the Y direction. Under load, the stress intensity factor K at the crack f...
Embodiment 3
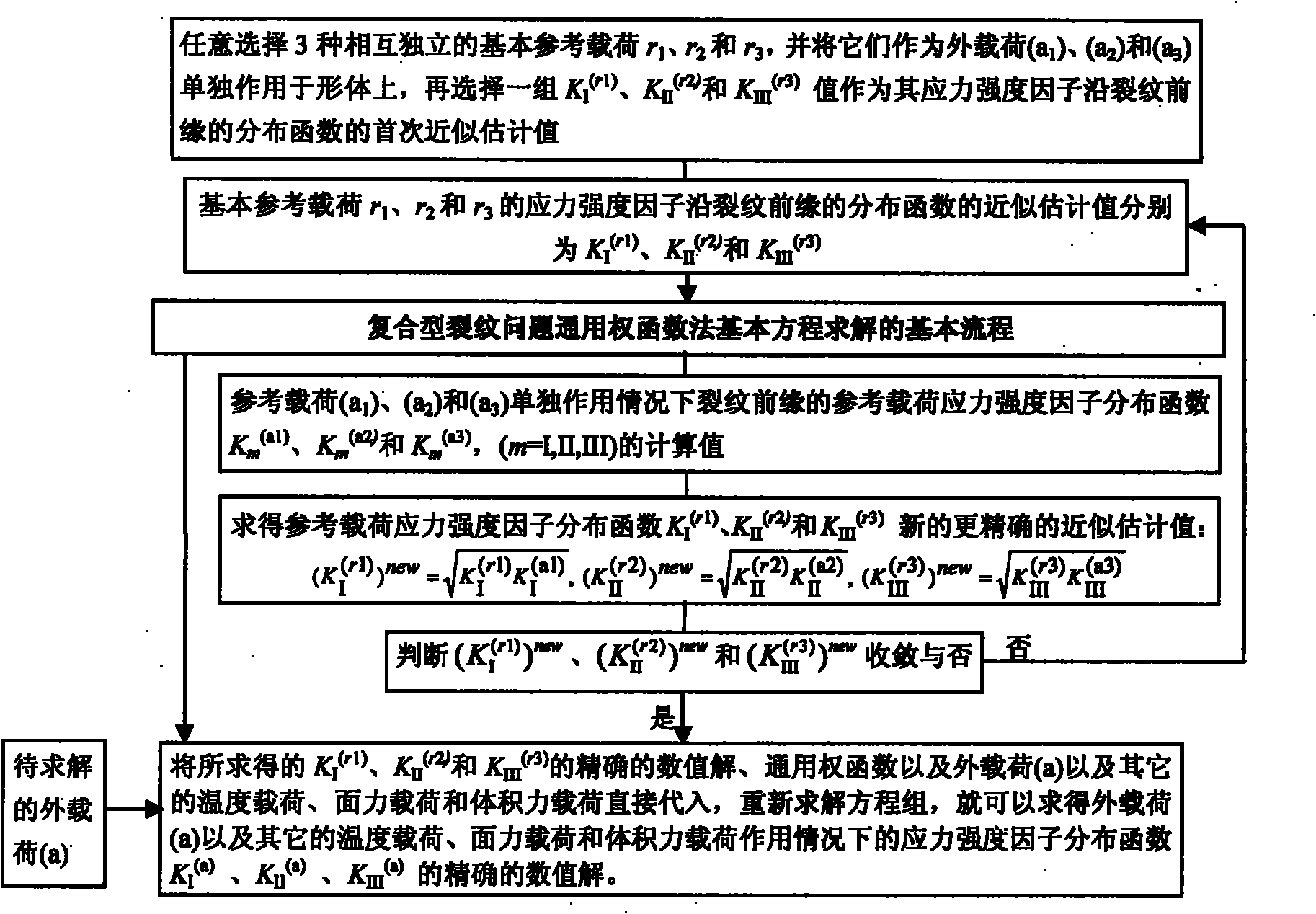
[0122] refer to figure 1 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Figure 6 , Figure 7 , Figure 9 , according to the method for determining the separation and distribution of stress intensity factors at the front edge of composite cracks in structural parts described in Example 1, for cracks on the semi-elliptical surface of a fixed plate in the Z direction at both ends under several plate surface pressures and temperature loads, the crack front edge stress intensity factor K I 、K II and K III Separation and its distribution, according to image 3 The second execution method (high-efficiency execution mode) shown is determined. Figure 9 Indicates the semi-elliptical surface crack with depth ratio a / T=0.5, shape ratio a / c=0.5, uniform pressure on the front surface of the plate, staggered uniform pressure on the front surface of the plate, uniform pressure on the upper half of the plate surface and uniform temperature drop of the whole plate Under the four loading condi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com