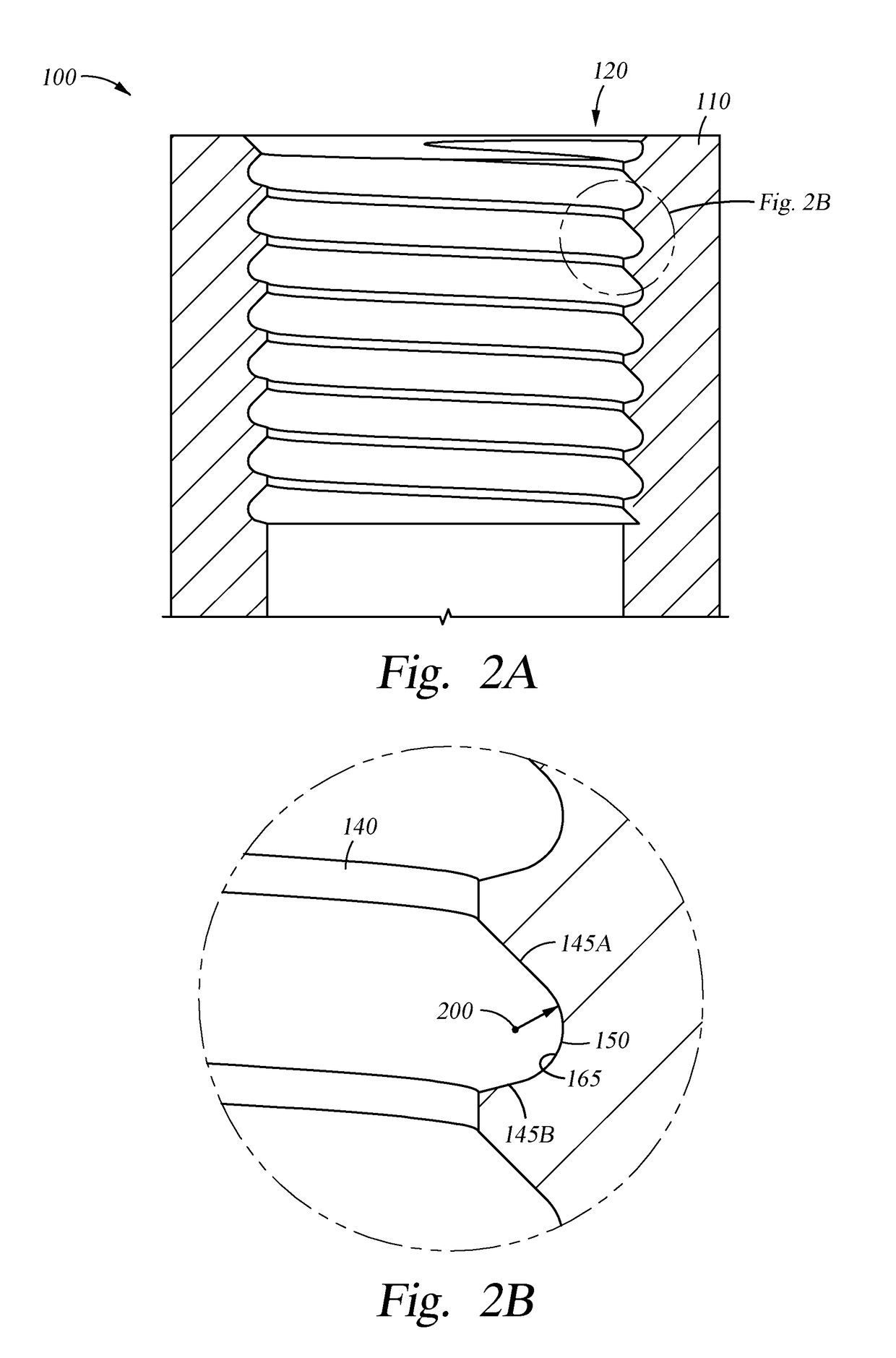
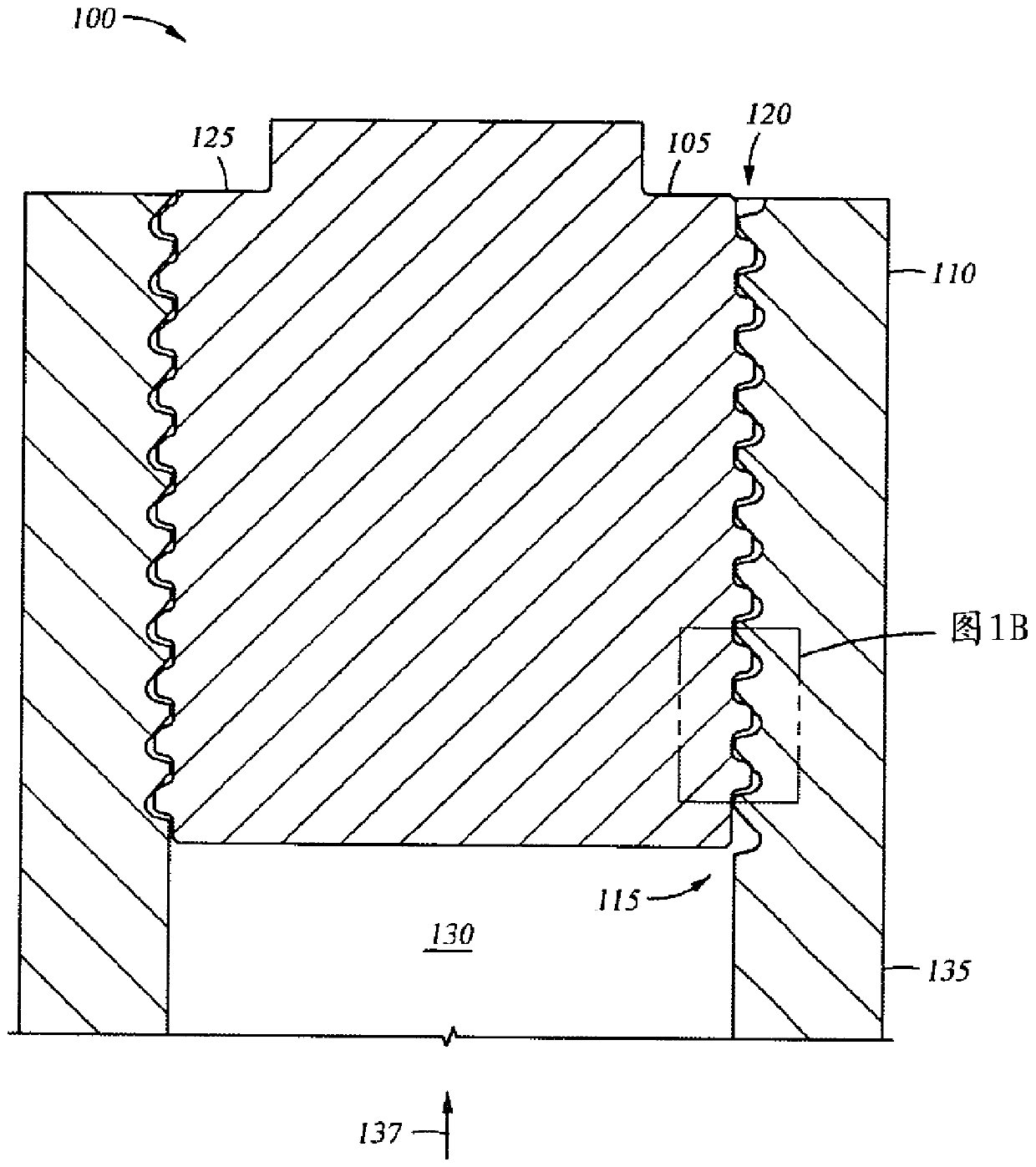
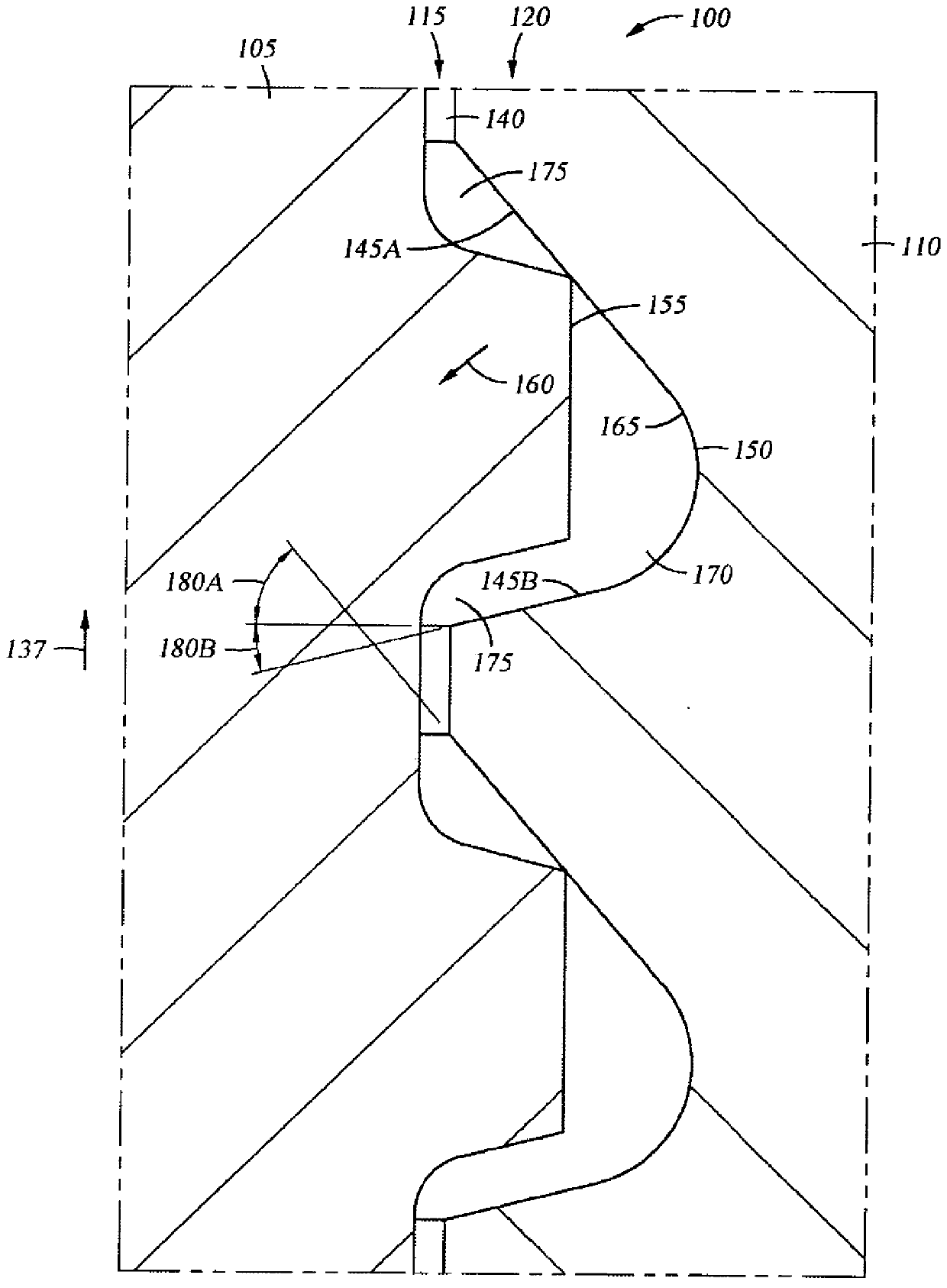
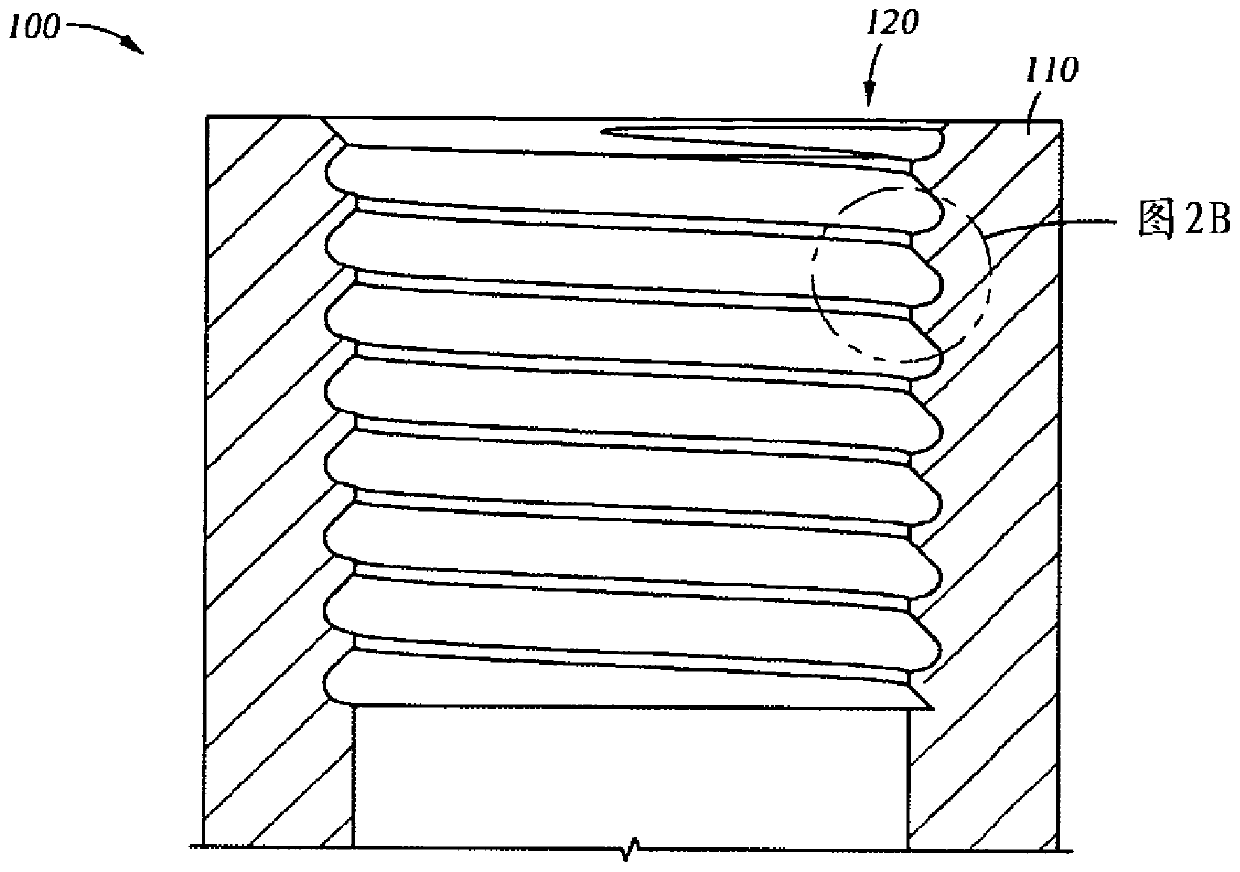
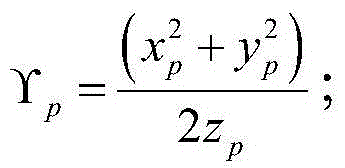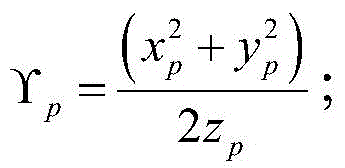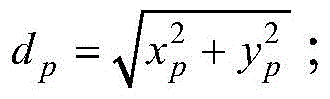Patents
Literature
35 results about "Root radius" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
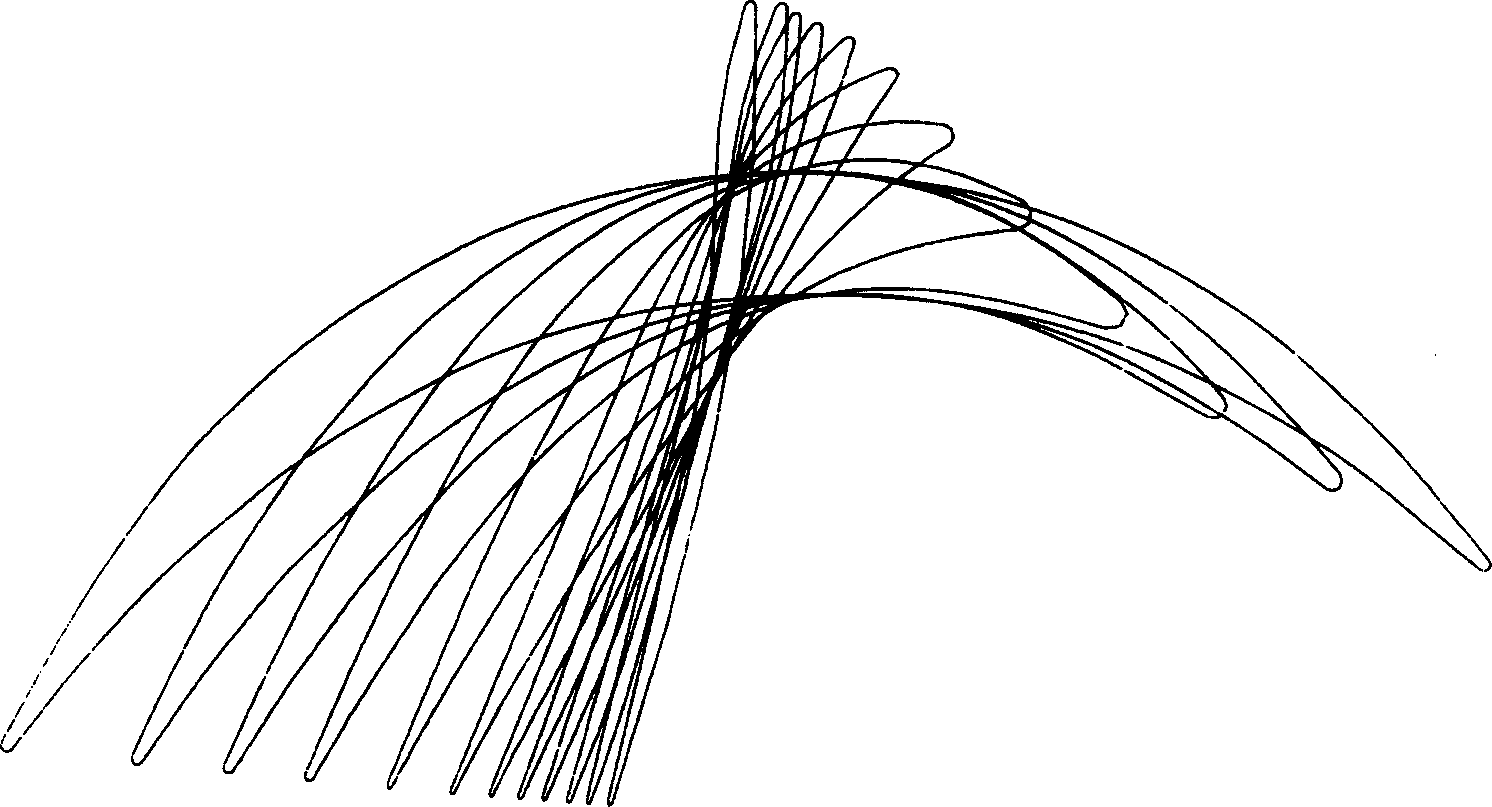
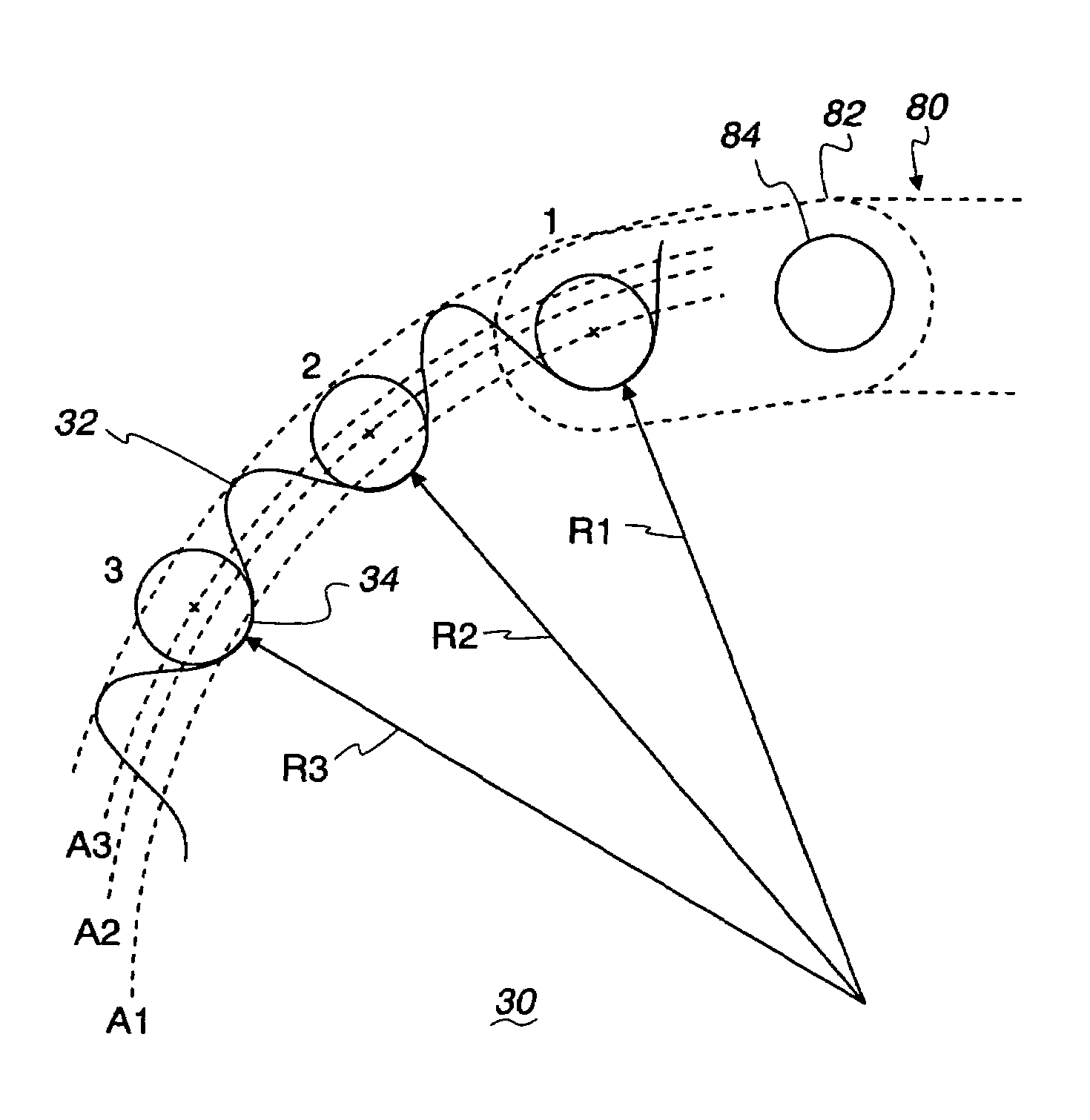
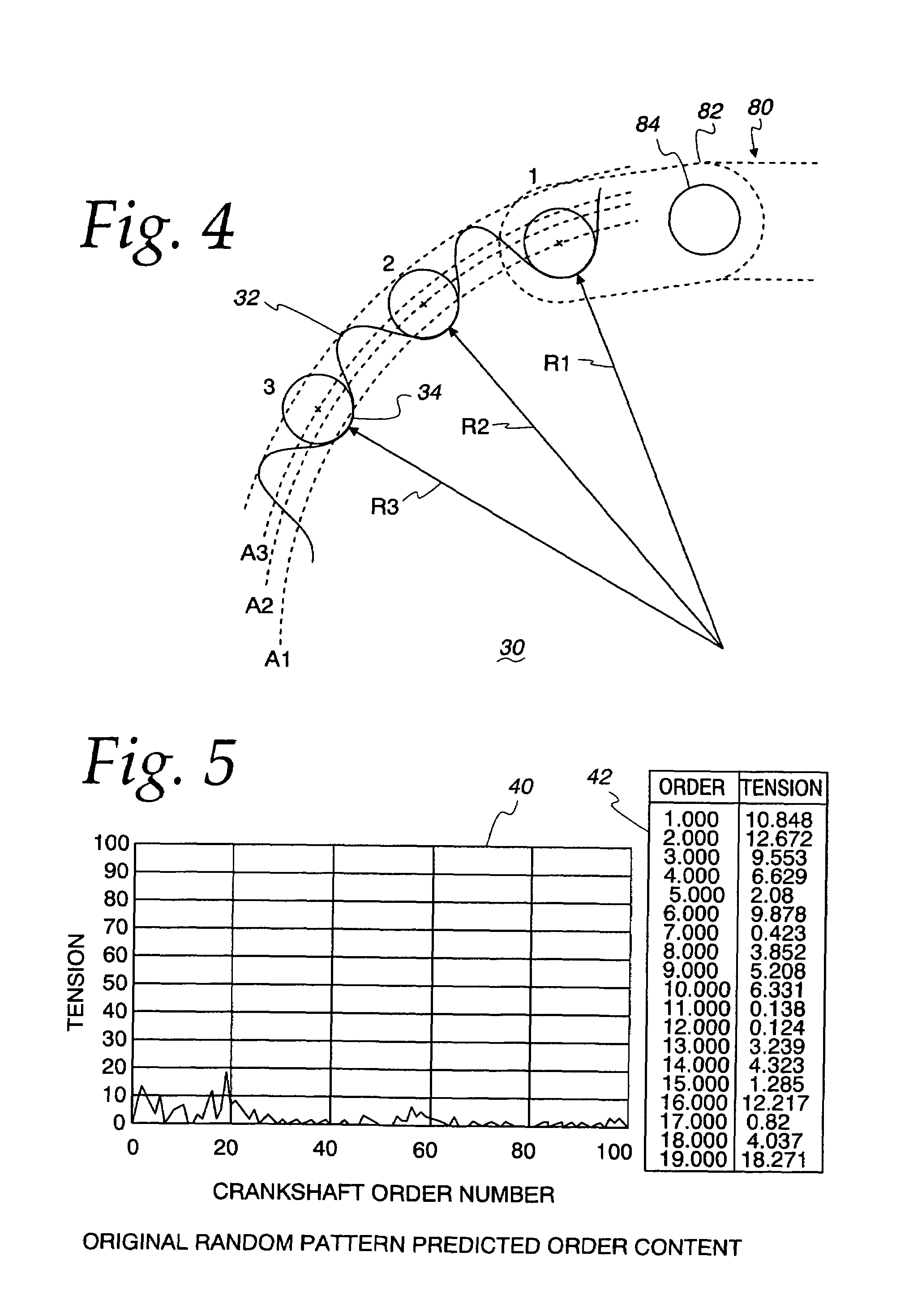
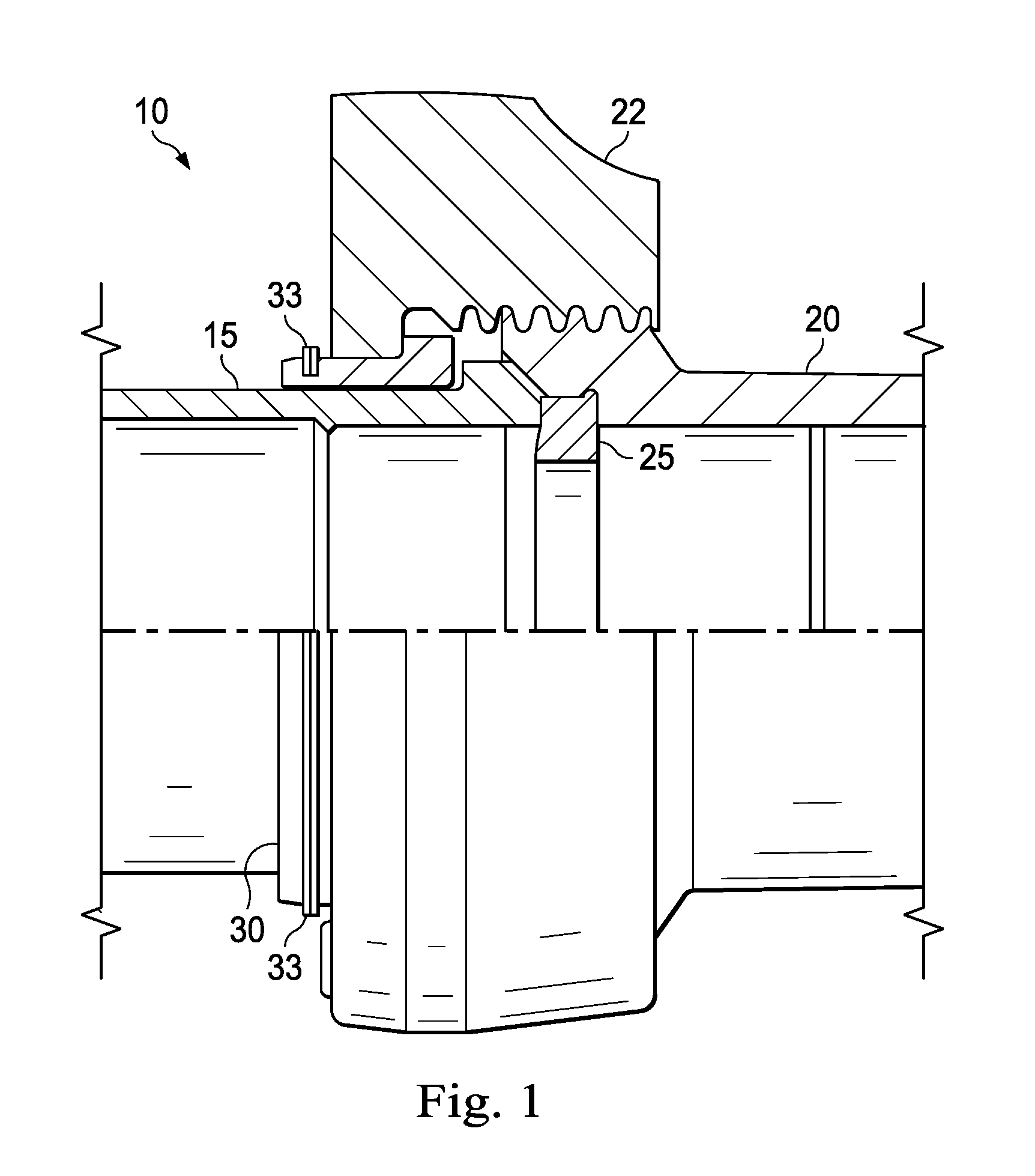
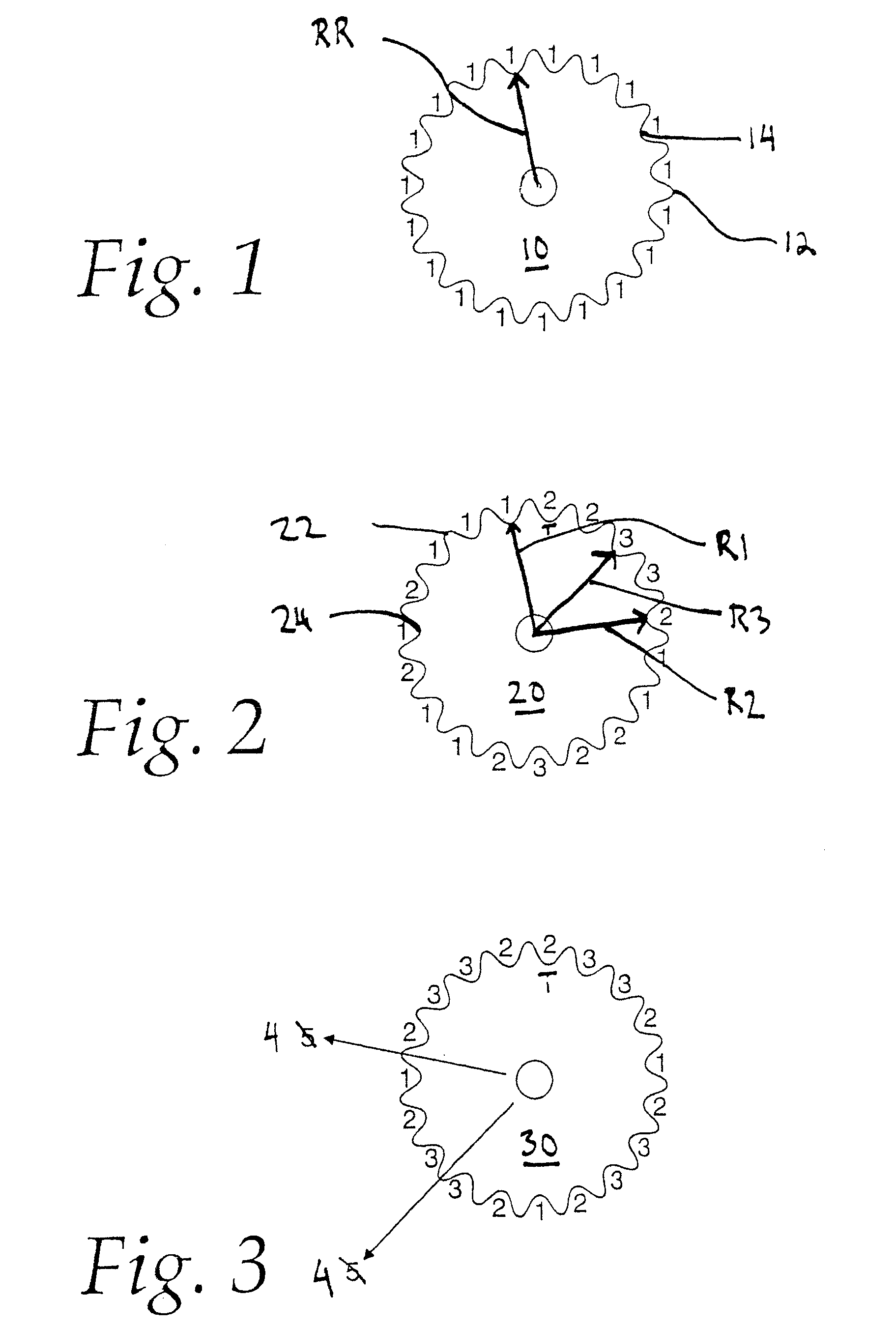
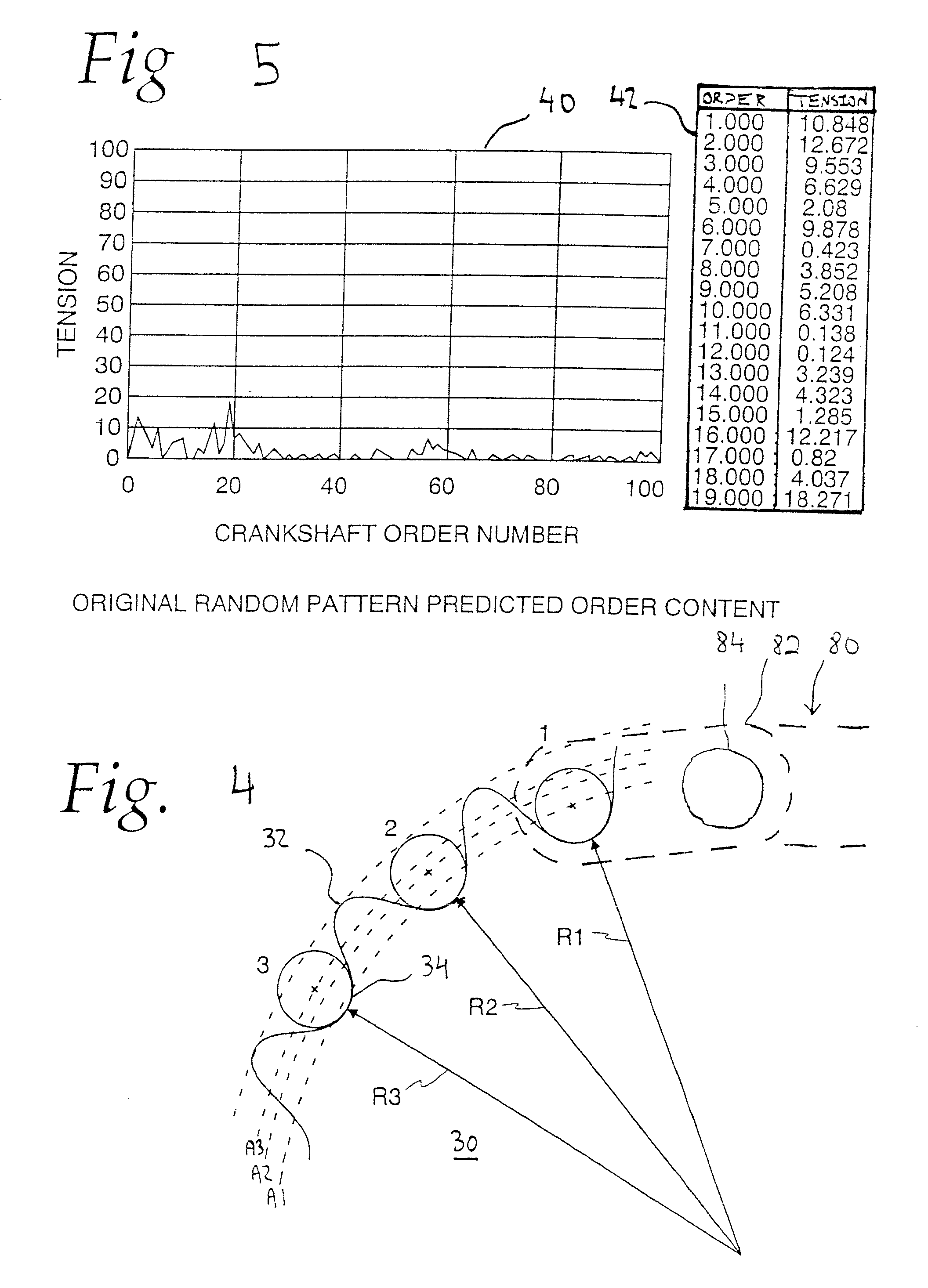
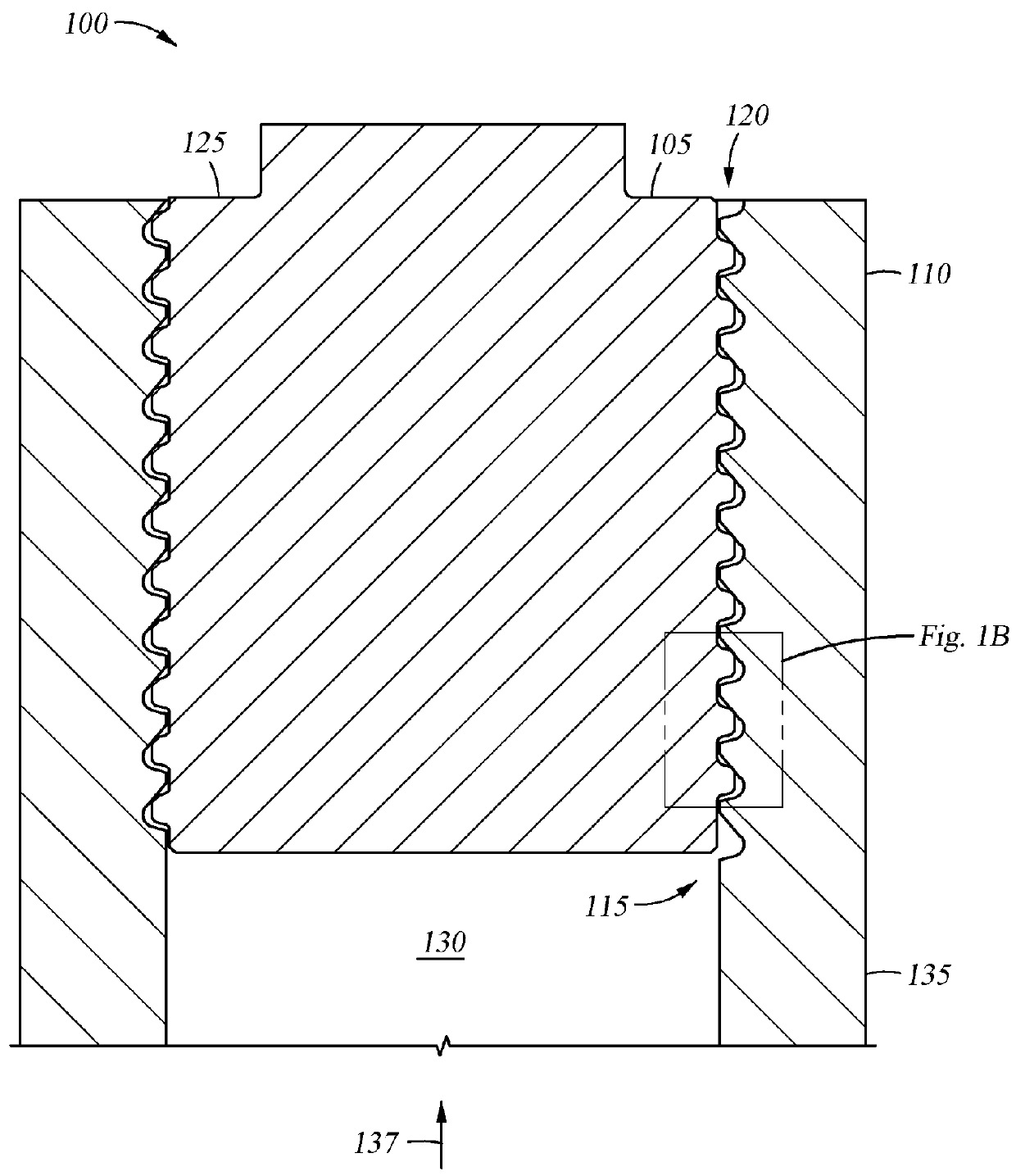
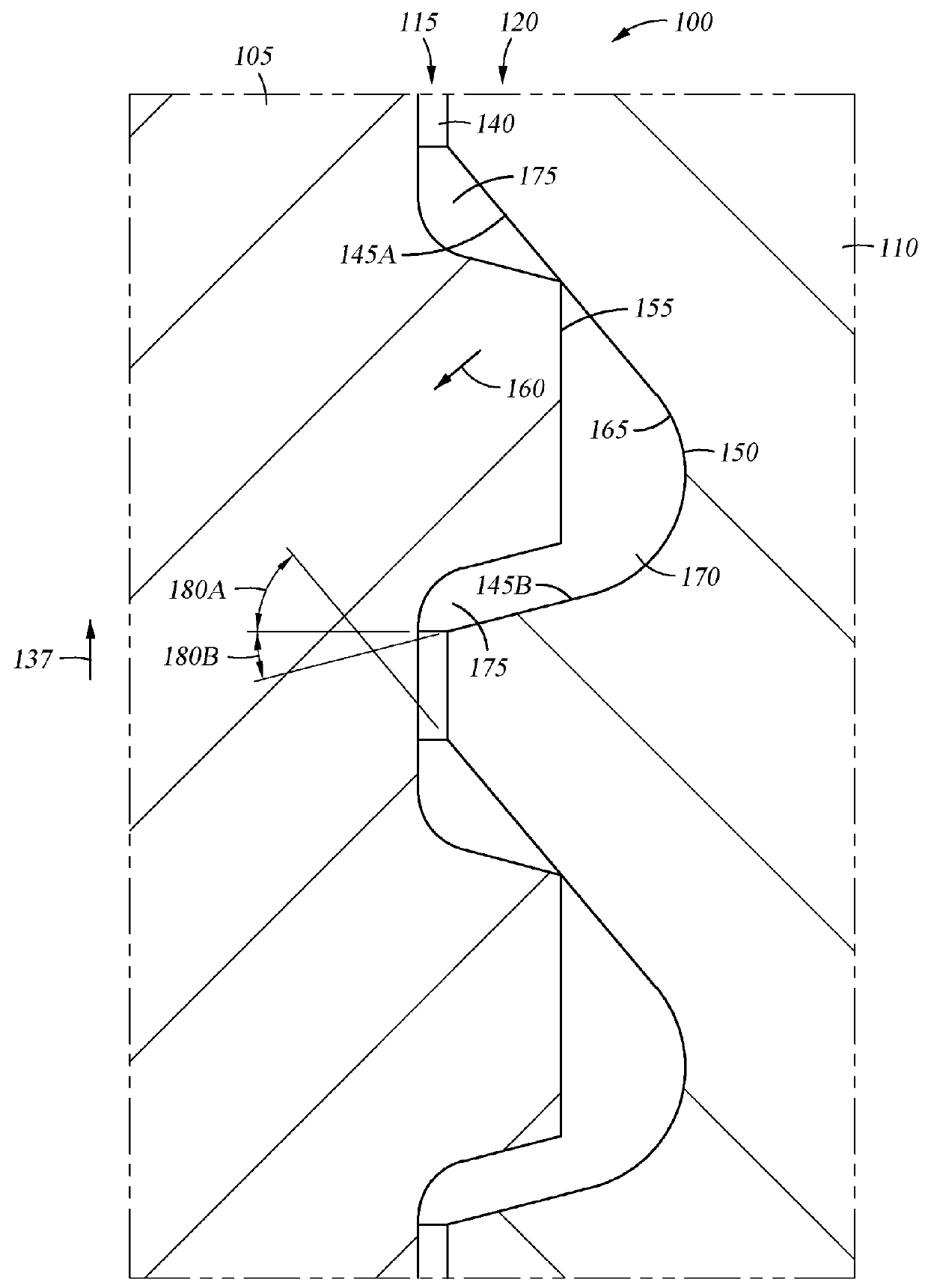
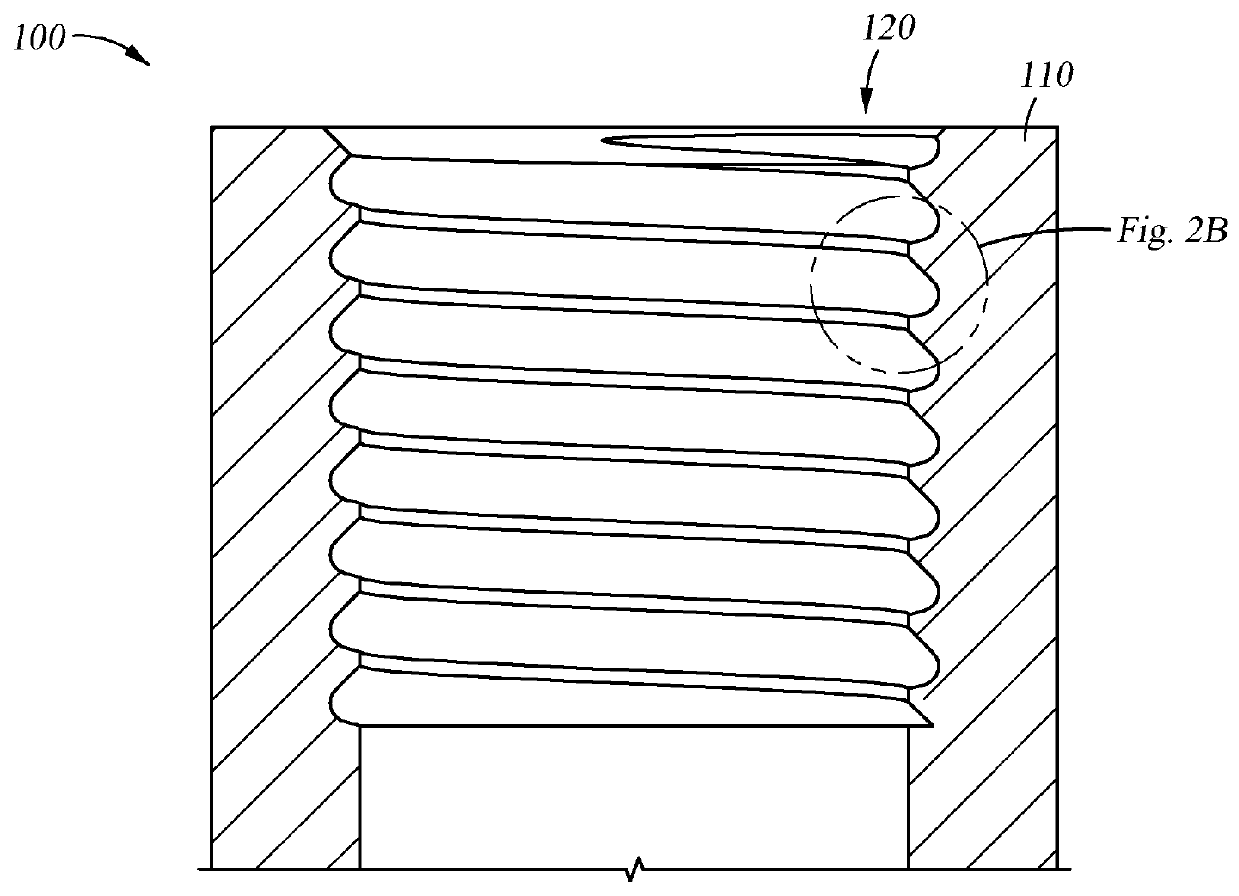
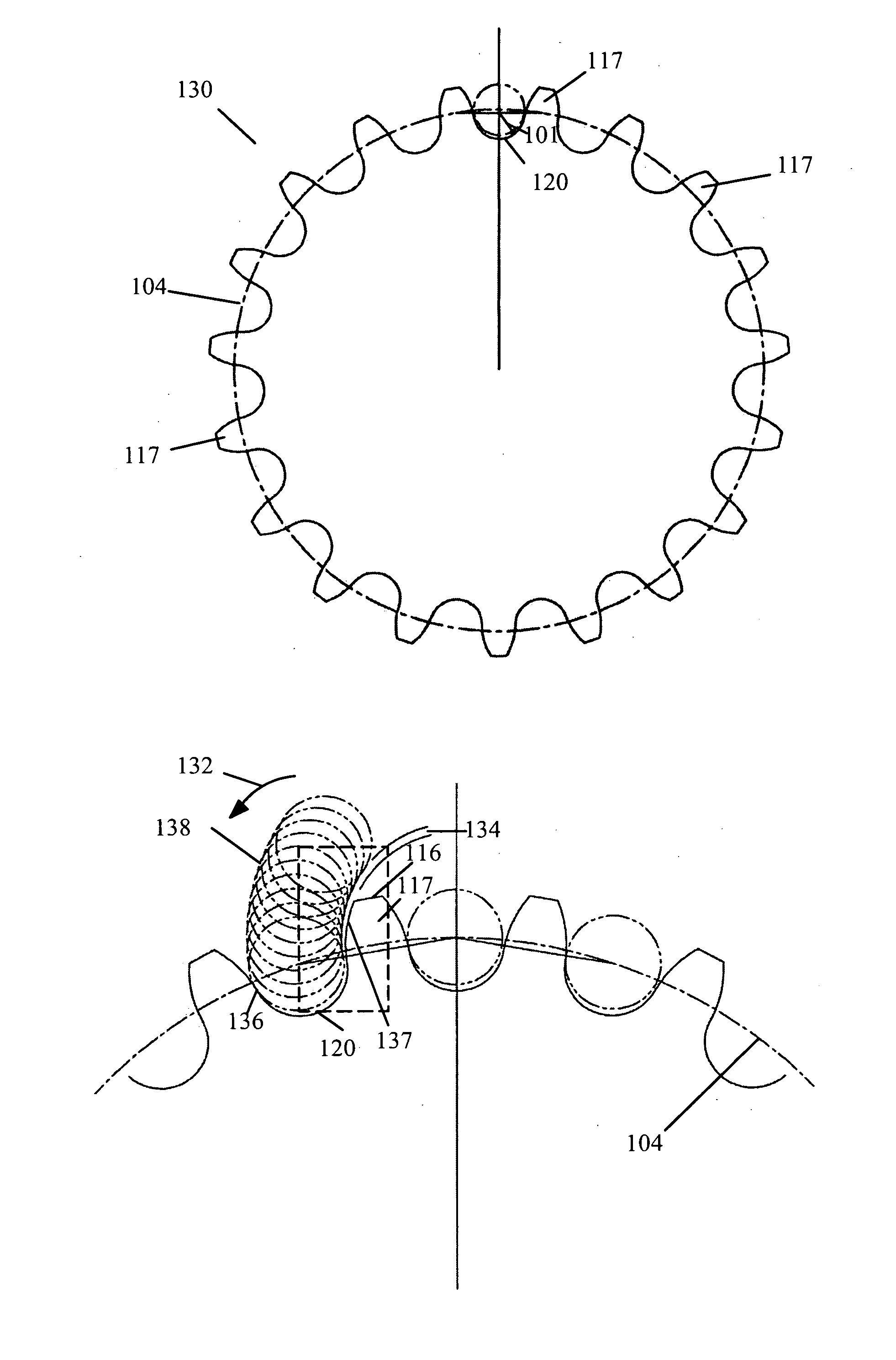
Tension-reducing random sprocket
InactiveUS7125356B2Promotes reduced and controlled chain tensionReduce noiseV-beltsGearingEngineeringSprocket
A sprocket is provided having a plurality of teeth around its circumference. Adjacent teeth are separated by roots each having a root radius defined as the distance between the center of the sprocket and a point along the root closest to the sprocket center in a radial direction. In one aspect of the invention, the sprocket comprises at least two different root radii arranged in a pattern effective to redistribute tensions imparted to a chain by the sprocket at one or more predetermined sprocket orders.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
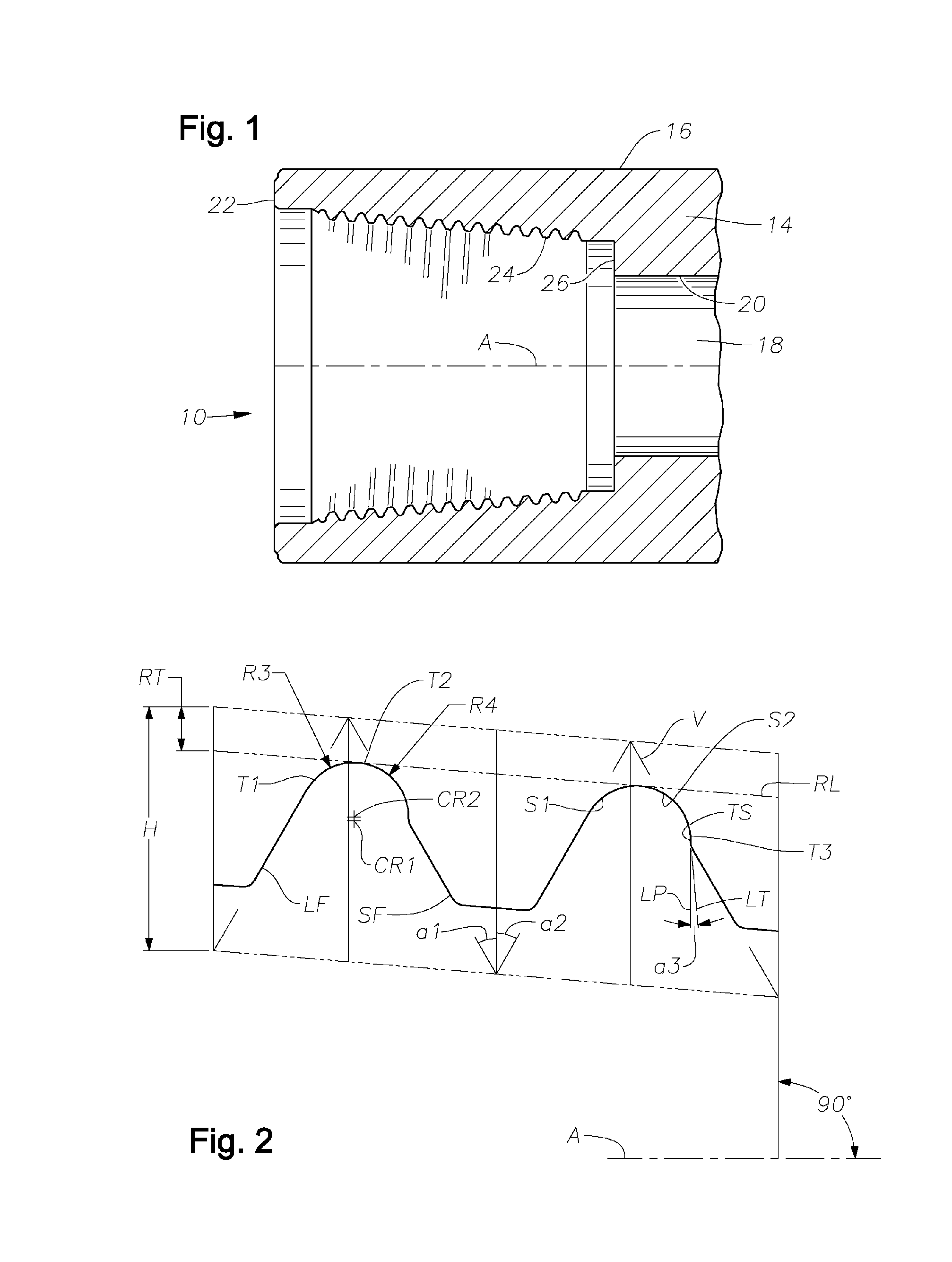
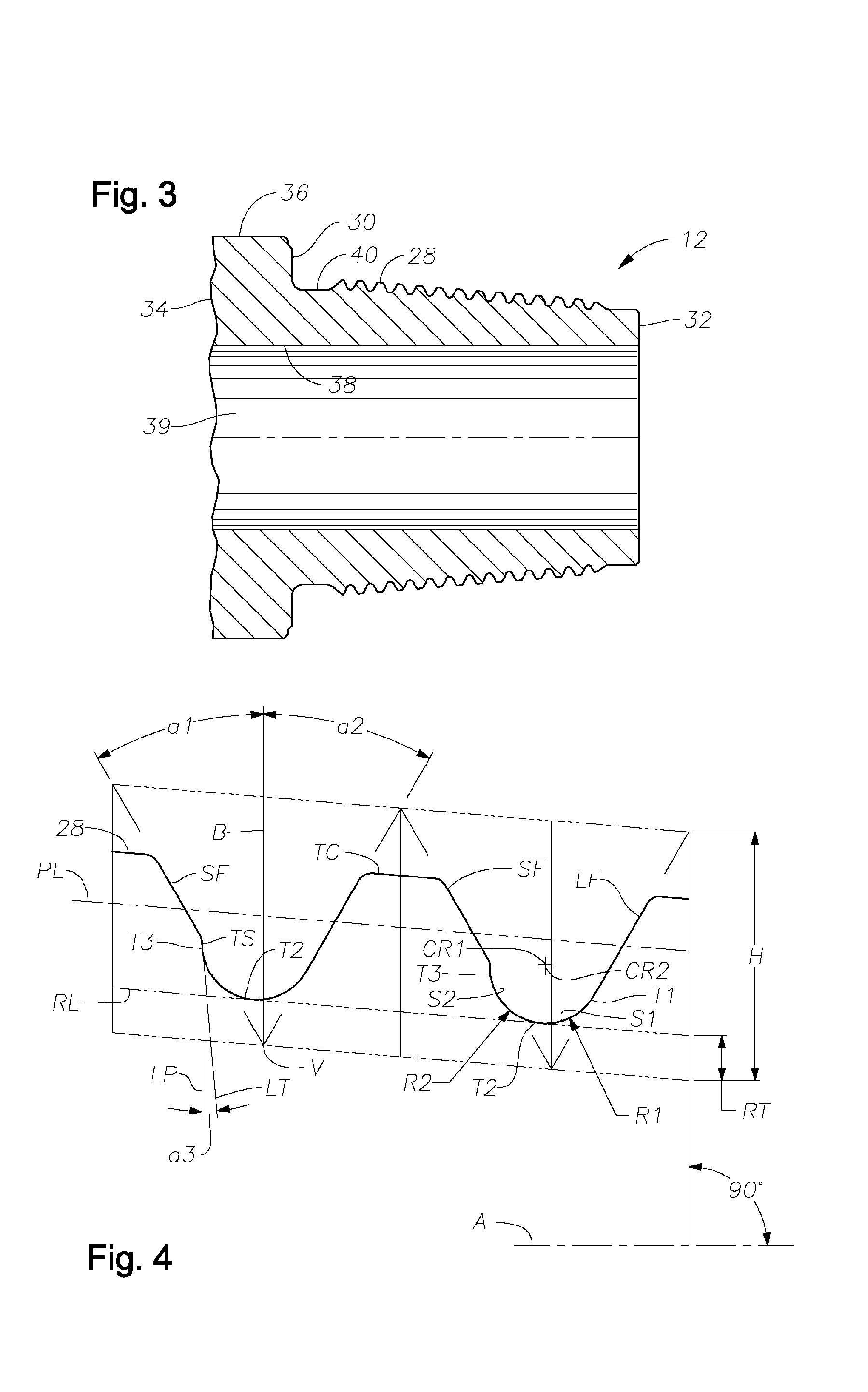
Fatigue Resistant Rotary Shouldered Connection and Method
InactiveUS20060214421A1Space maximizationImprove operational capabilitiesDrilling rodsHose connectionsHigh resistanceFatigue damage
Threaded connections are provided with a thread form that permits the construction of enlarged root radii between adjacent threads. Relatively coarse thread leads formed along conical surfaces with relatively extended tapers cooperate with relatively tall thread heights and an enlarged root radius (or radii) to produce a fatigue resistant, rotary-shouldered connection that can be assembled with reasonably attainable high torque forces. The ratios between the thread lead, measured in threads per inch, as the numerator, and denominators comprising the untruncated thread height of the thread, and / or the root truncation and / or the root radius (or radii) are maintained at low values compared to those existing in conventional prior art connections. The ratio of the untruncated thread height to the root radius (or radii) is also retained at a relatively low value as compared to that existing in many prior art configurations. The connection design produces an unexpectedly high resistance to fatigue damage or failure. The connection may be employed in any rotary-shouldered connection and is particularly effective in preventing fatigue damage in the stiffer components of drill stem assemblies including single shoulder and double shoulder drill collar connections.
Owner:GRANT PRIDECO LP
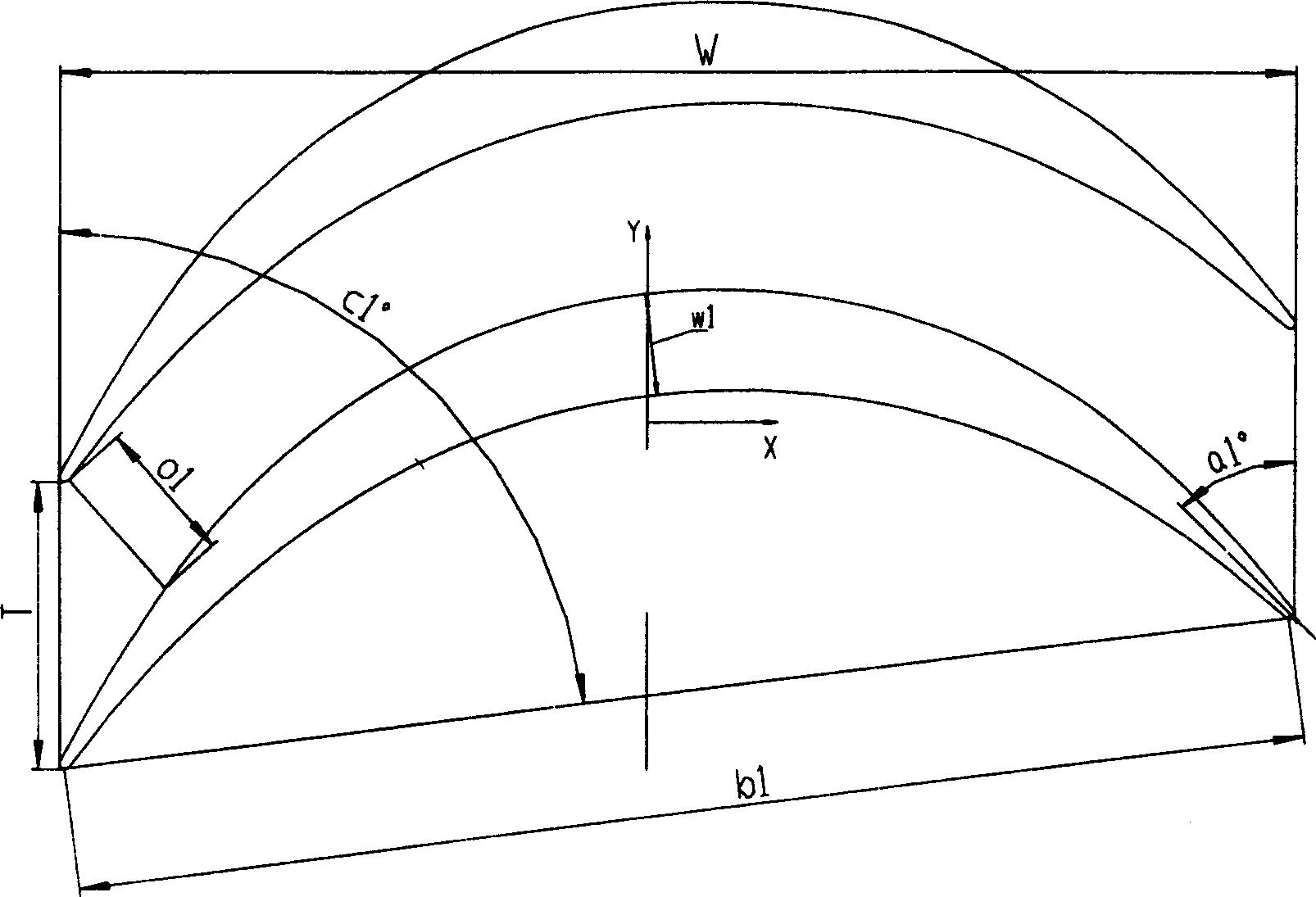
Last stage rotor blade of steam turbine
ActiveCN1730912AMeet flowReduce flow lossBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesRelative maximumRoot radius
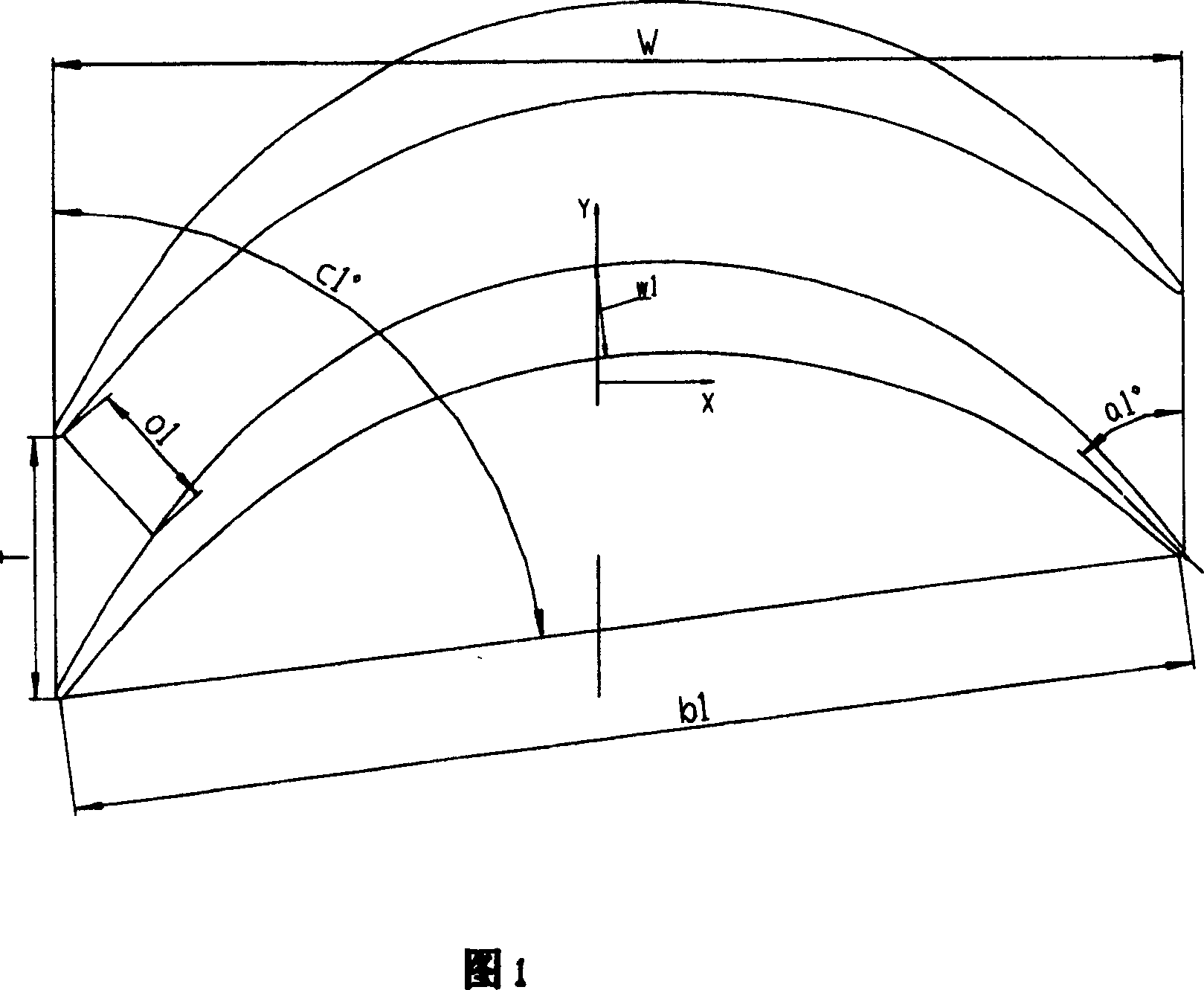
The last stage movable blade of steam turbine features the relative blade height H monotonously increased from 0.0 to 1.0, blade body profile with assembling angle c1 monotonously decreased from 82.81 deg to 10.1 deg, inlet geometric angle a1 monotonously increased from 36.65 deg to 168.0 deg, outlet geometric angle a2 monotonously decreased from 31.4 deg to 10.6 deg, relative maximum thickness w1 monotonously decreased from 3.47 to 1.0, relative chord length b1 monotonously decreased from 1.84 to 1.0, relative cross section area S monotonously decreased from 7.98 to 1.0, and the ratio between blade height H to root radius of 0.5-0.7. The present invention is especially suitable for sub-critical and supercritical steam turbine with effective blade height not smaller than 1200 mm, power of 600-1200 MW and rotation speed of 3000 rpm.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
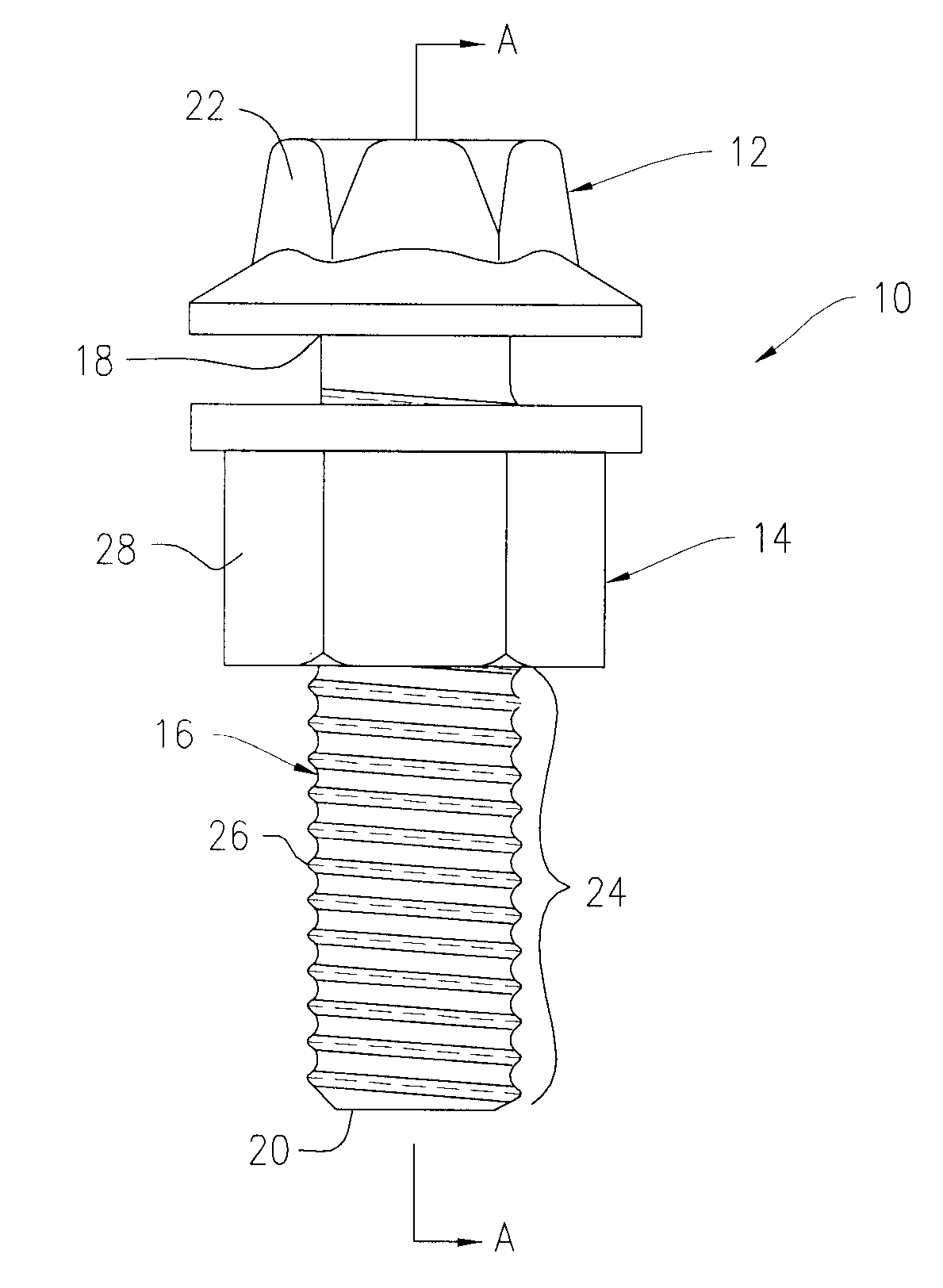
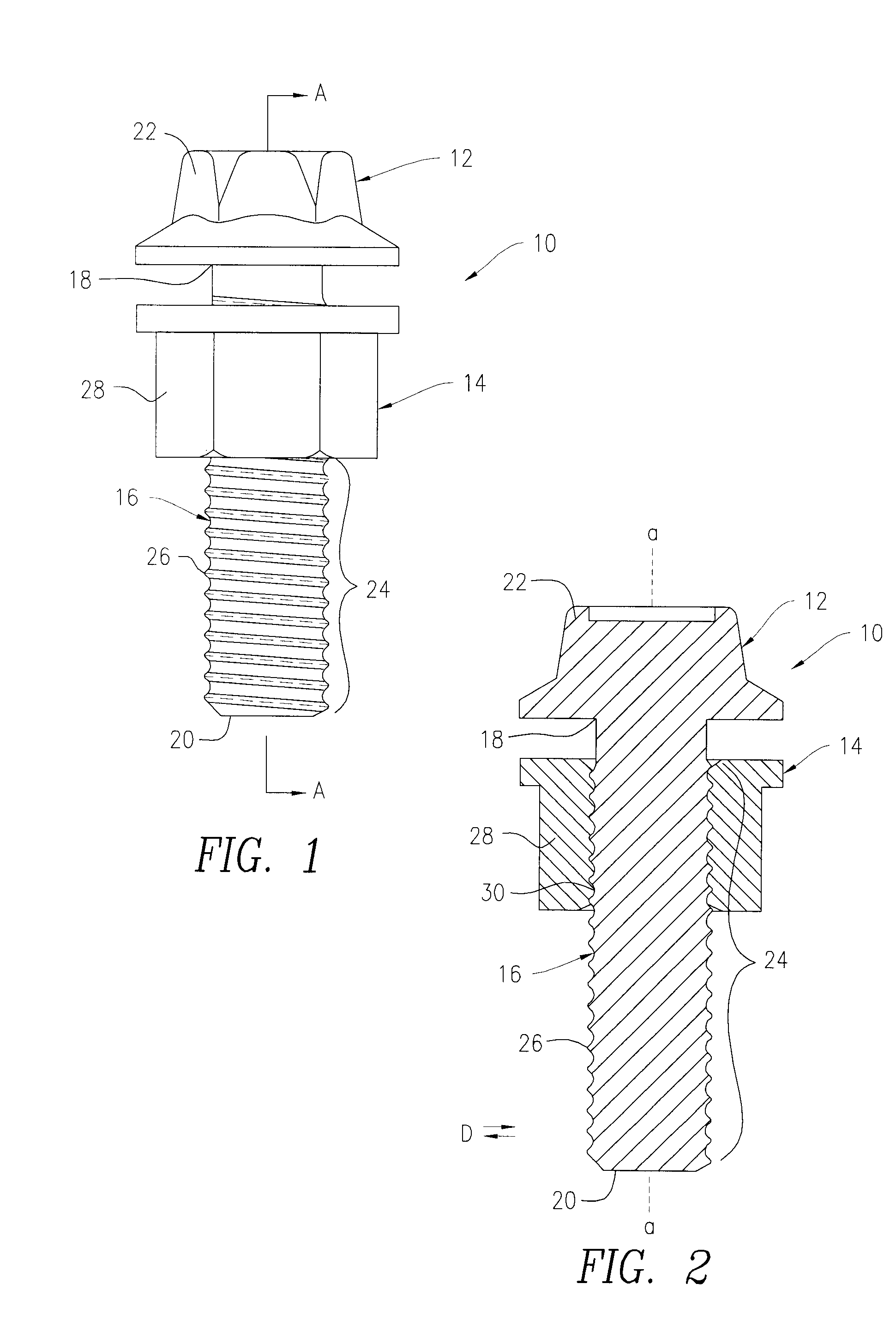
Advanced nut and bolt
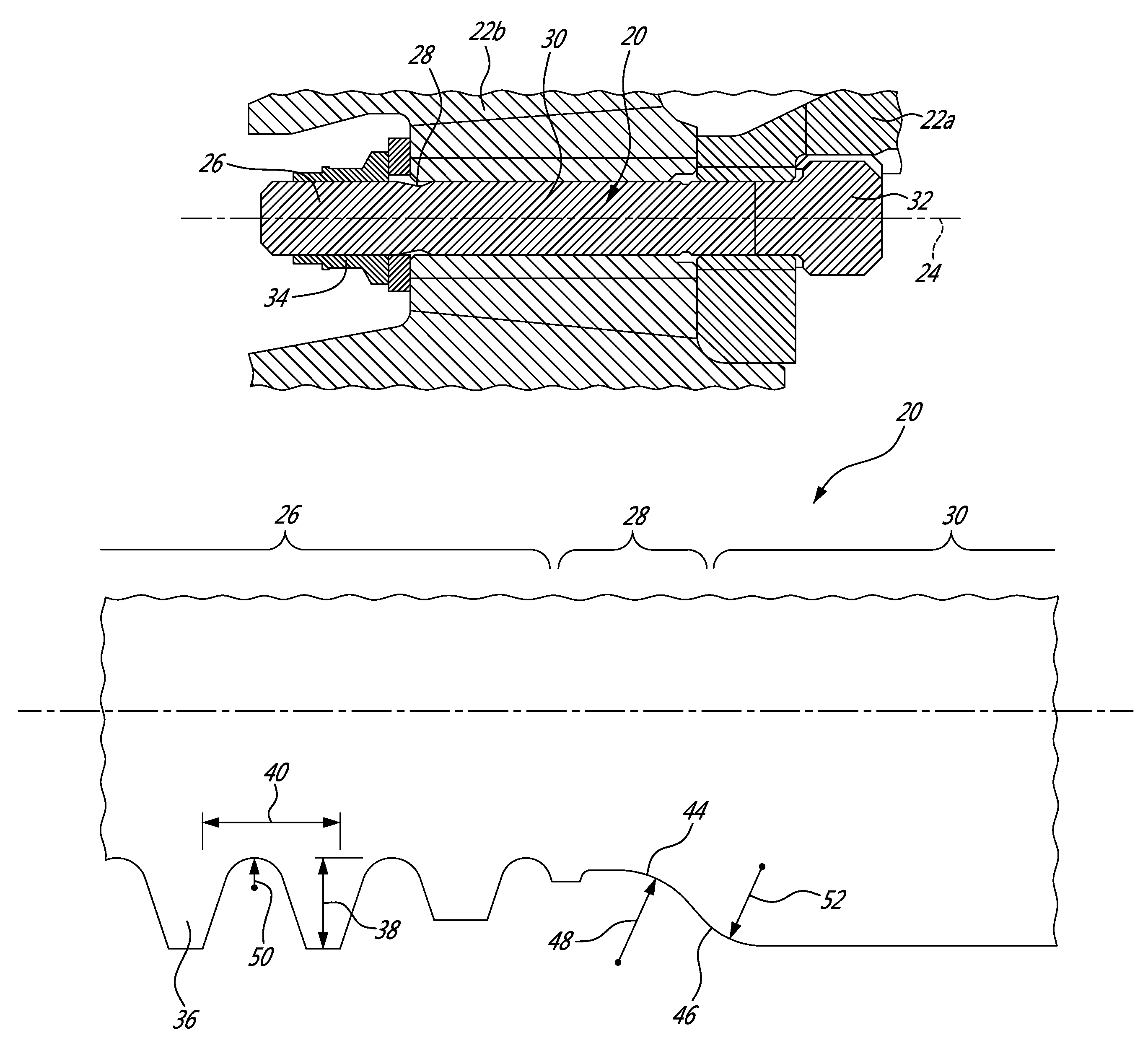
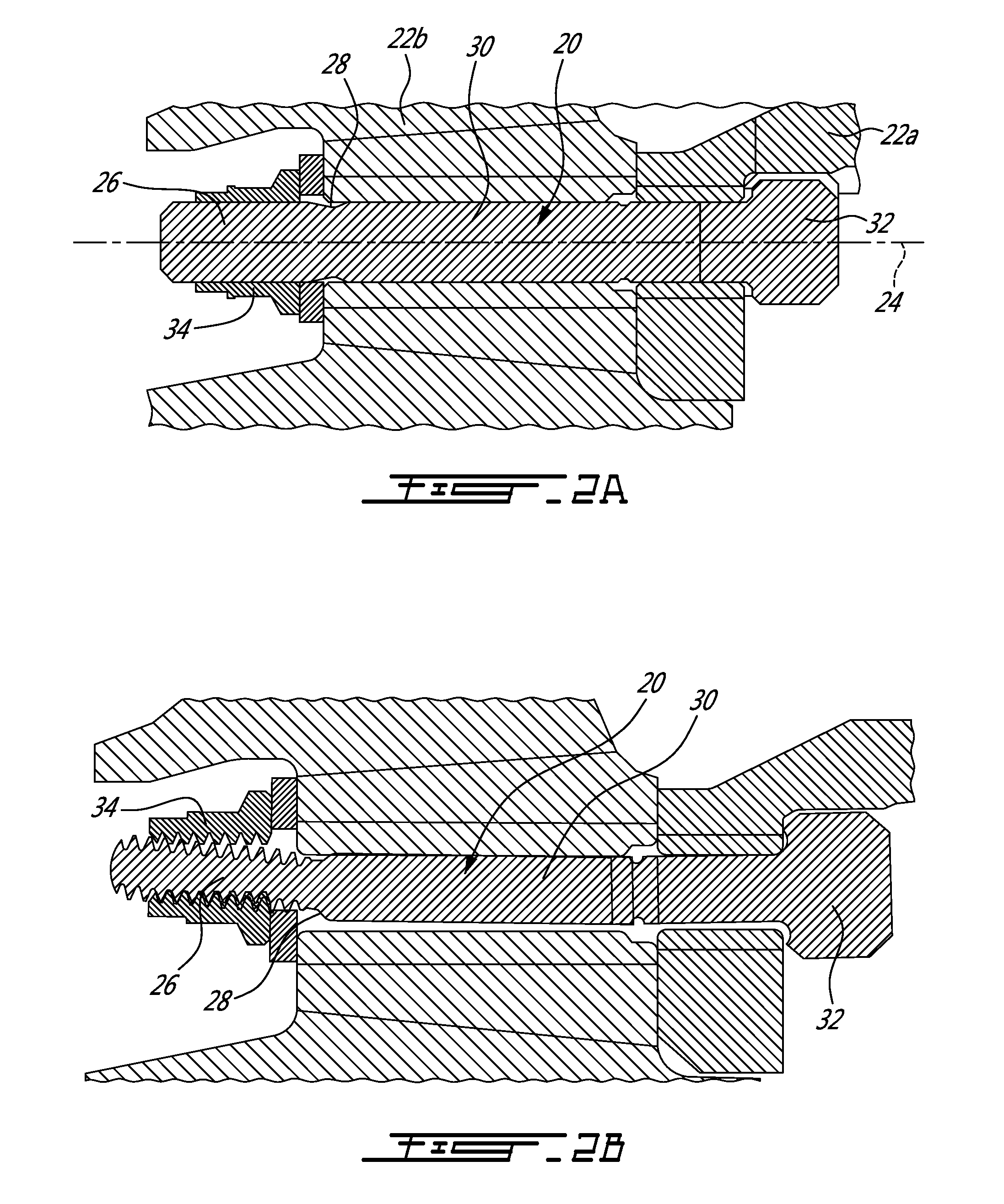
A vibration resistant fastening system including a high fatigue strength bolt made from a first material and a nut made from a second material that is softer than the first material of the bolt. The bolt includes bolt threads and the nut includes pre-tapped nut threads that match with the bolt threads. The fastening system utilizes a combination of unique geometry of the nut and bolt threads and a hardness differential between the nut and bolt to provide vibration resistance. When tightened, crests of the bolt threads embed into the soft bearing flanks of the nut threads. Simultaneously with the bolt crest embedment, the softer nut thread crests flow radially inward into the root radius of the bolt threads. This complete contact between the nut and the bolt restricts the nut from moving in a transverse direction relative to a longitudinal axis of the bolt.
Owner:HOWMET AEROSPACE INC
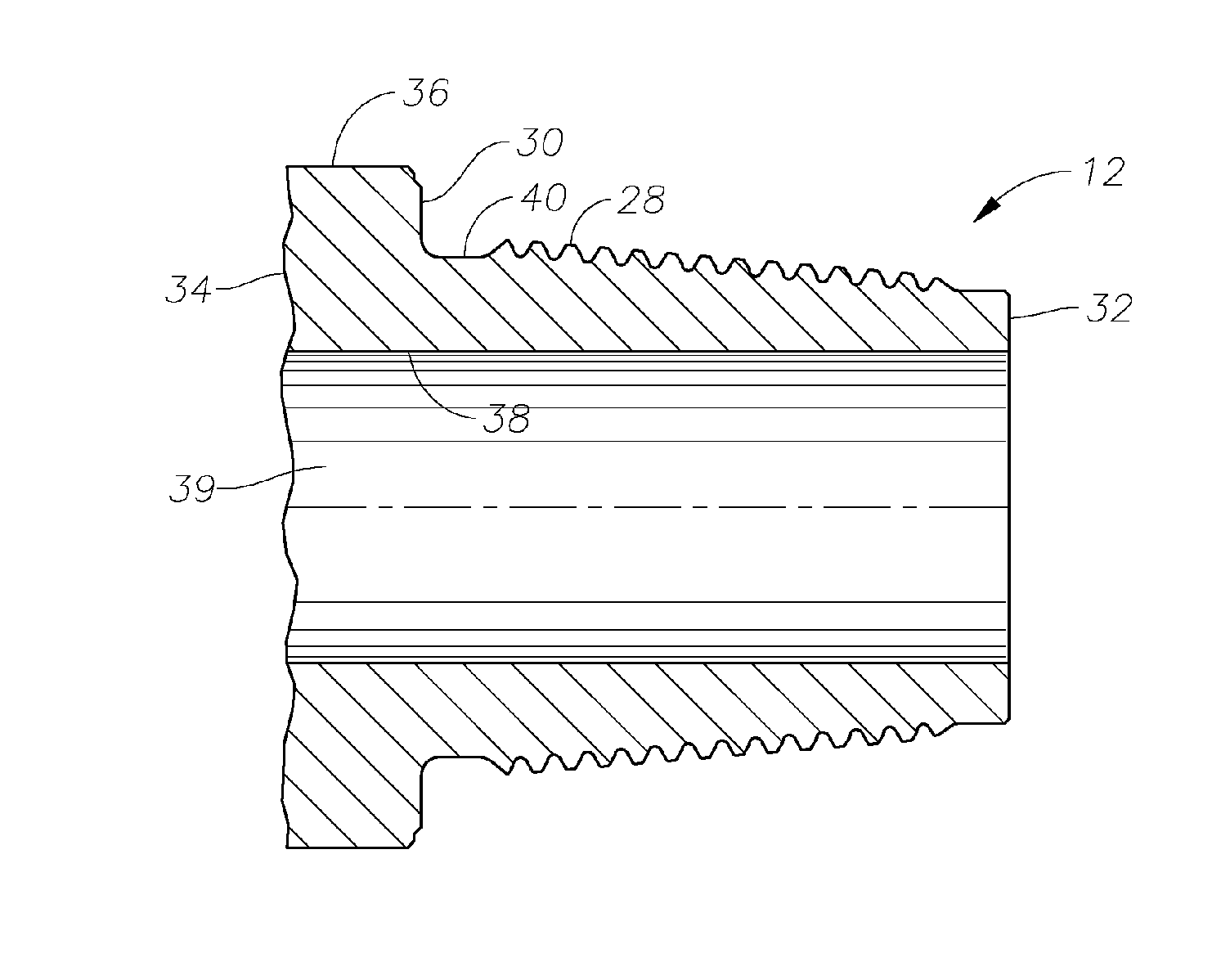
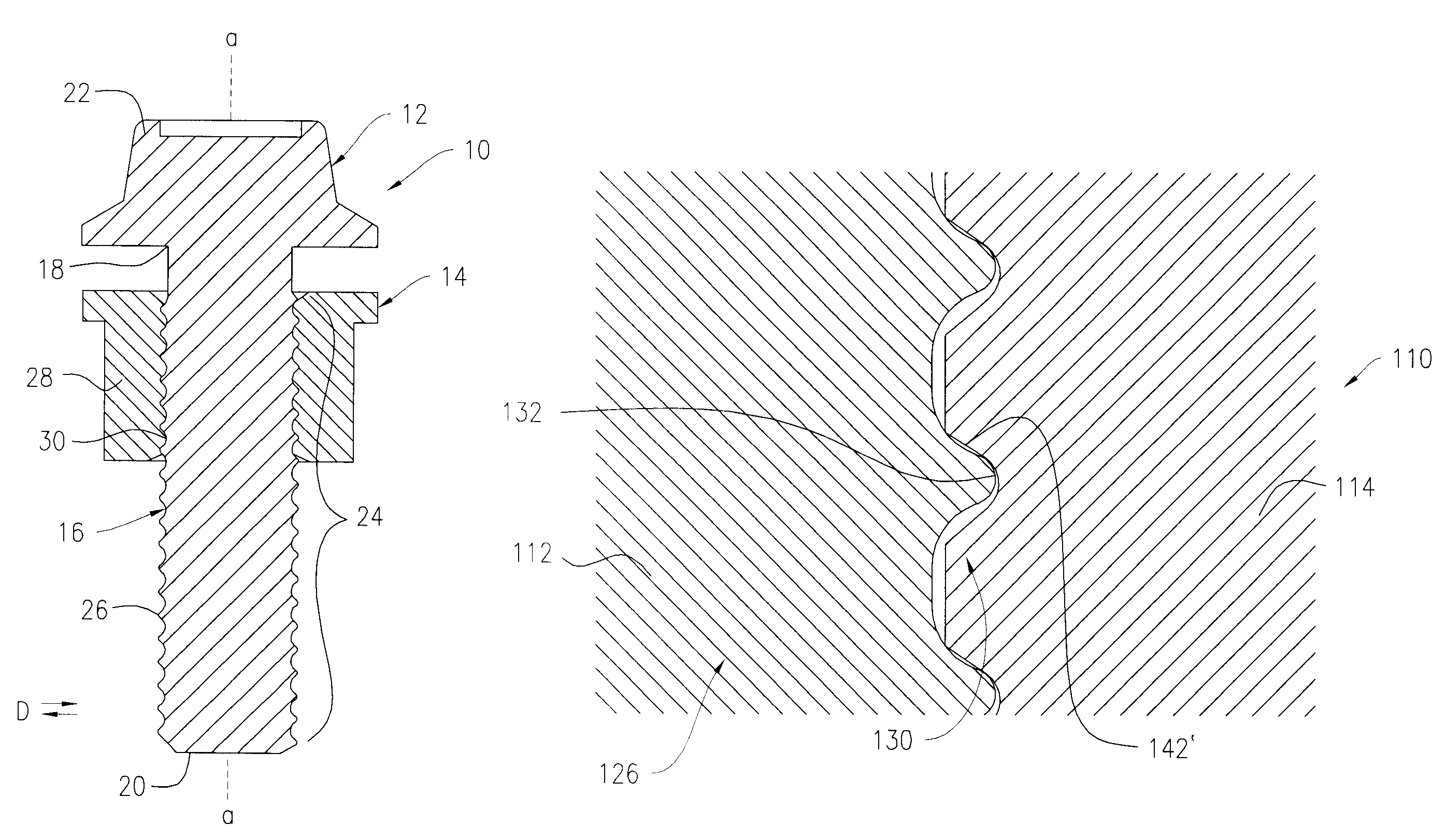
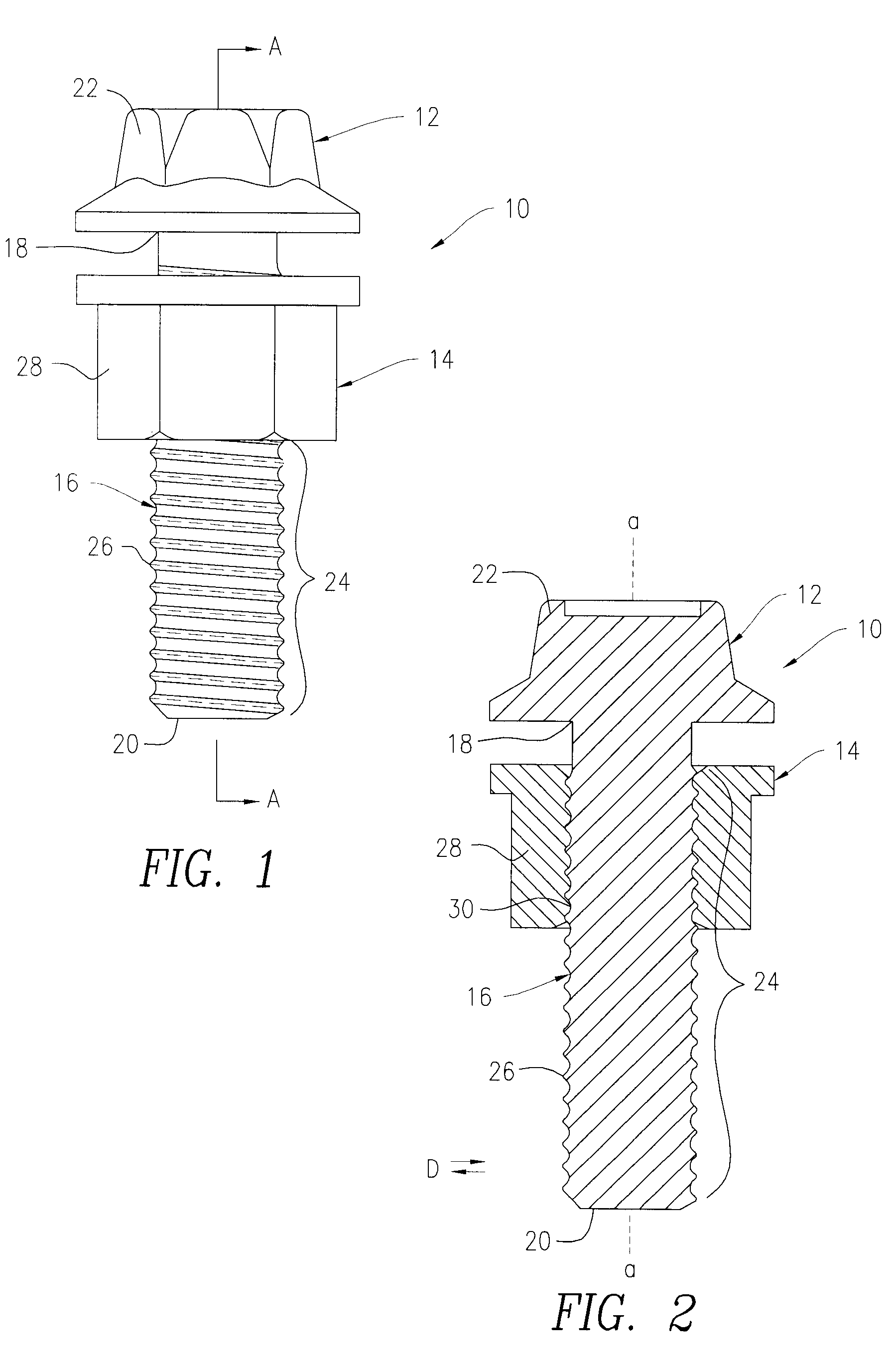
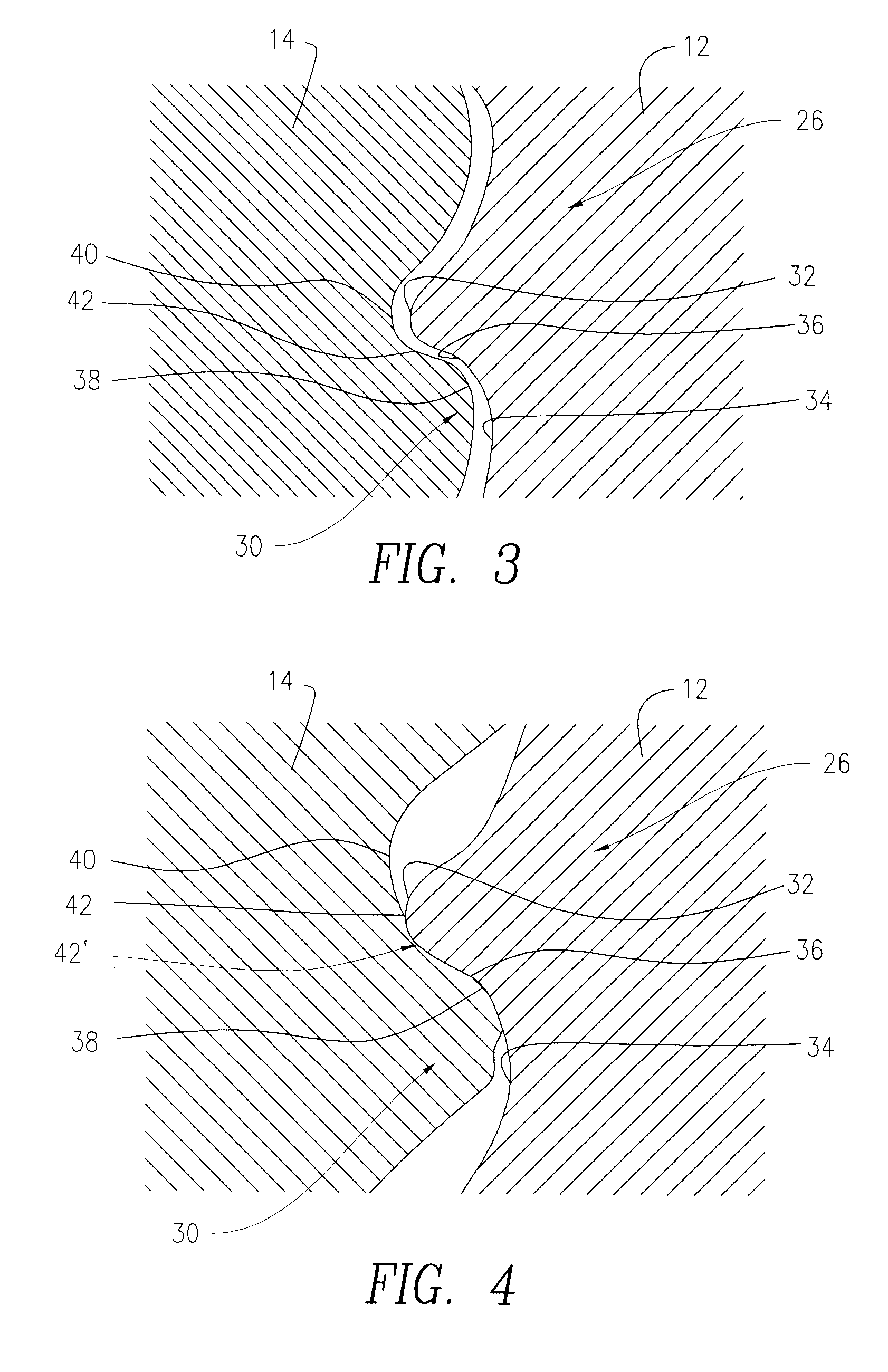
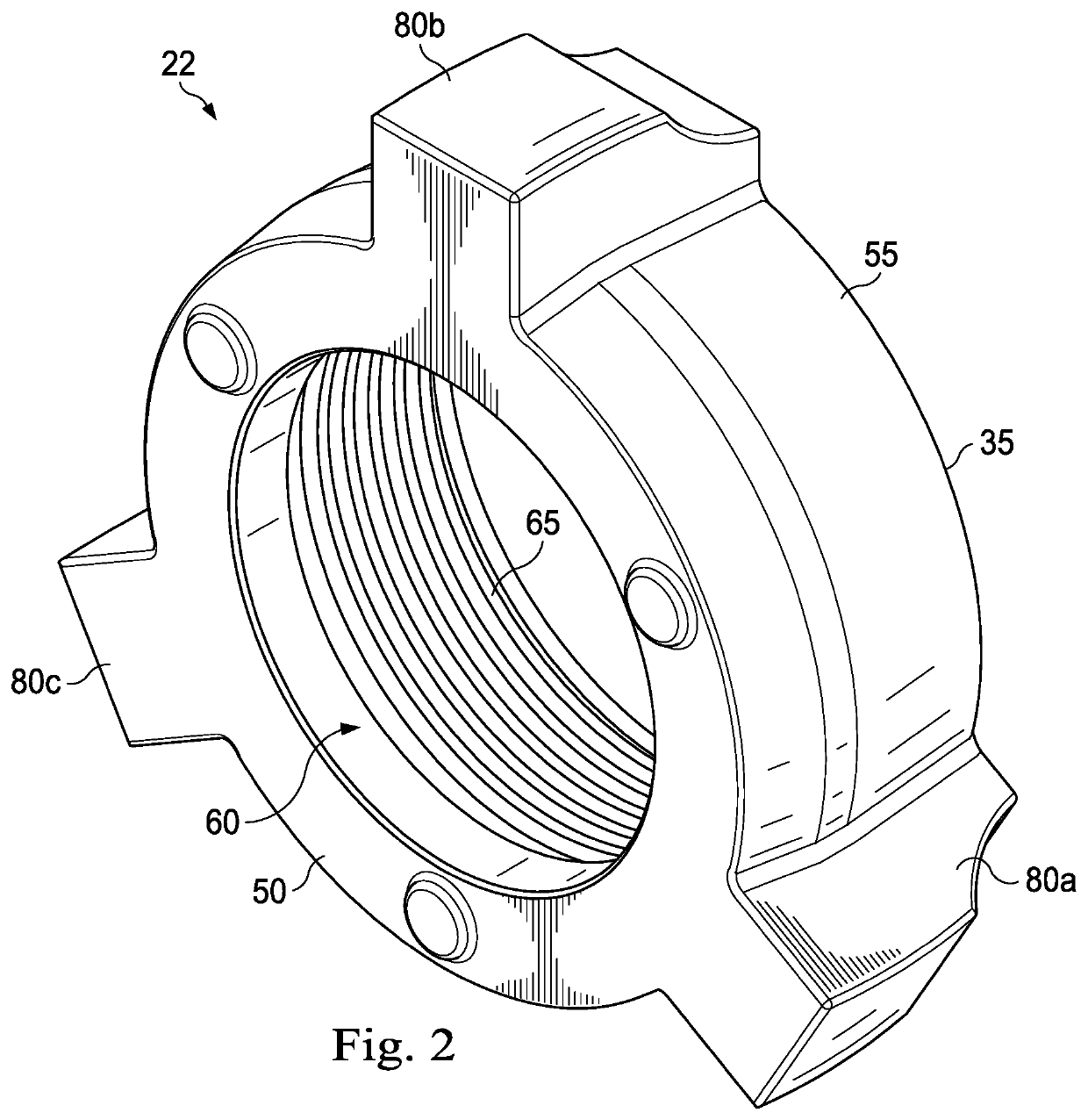
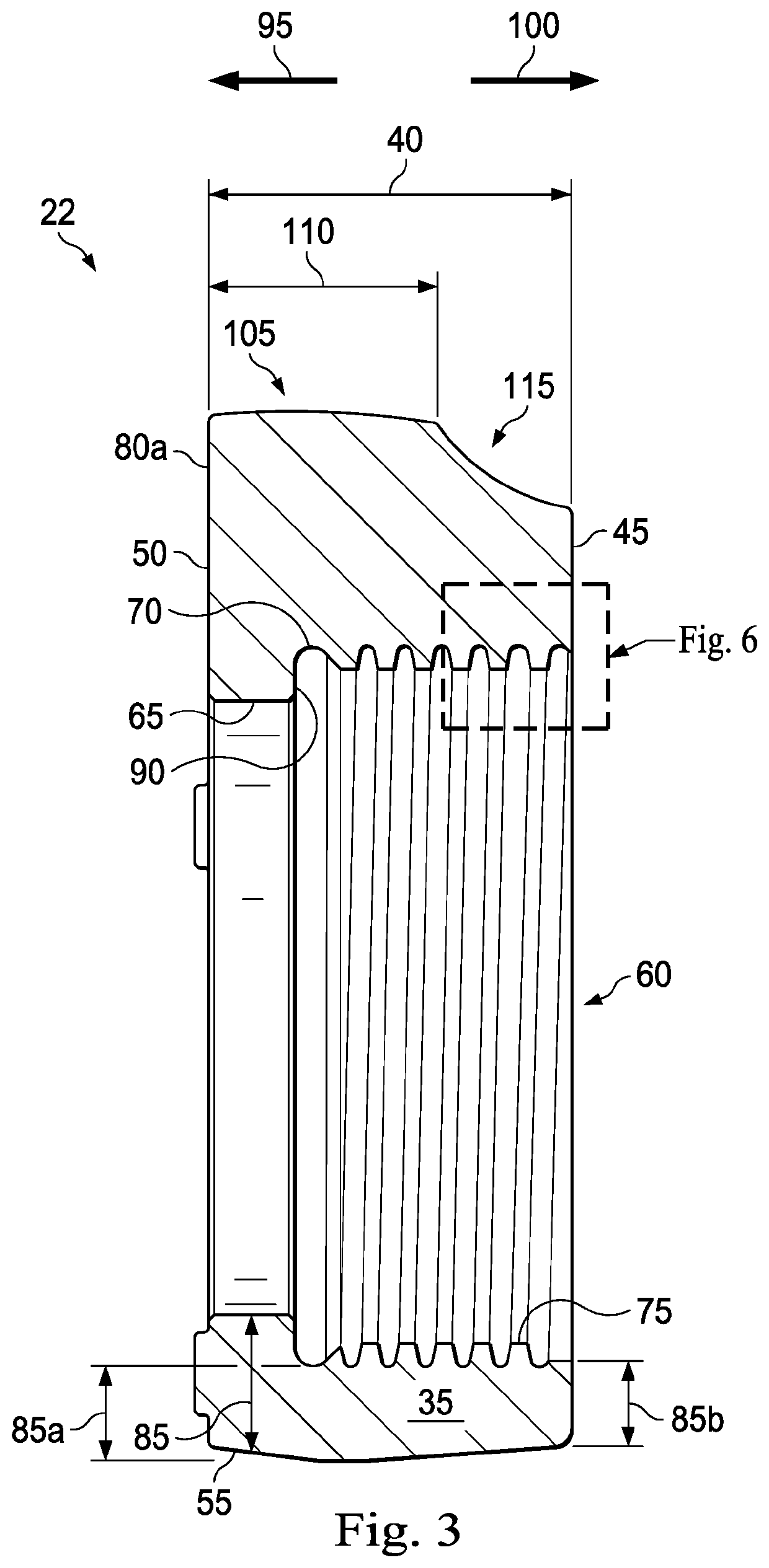
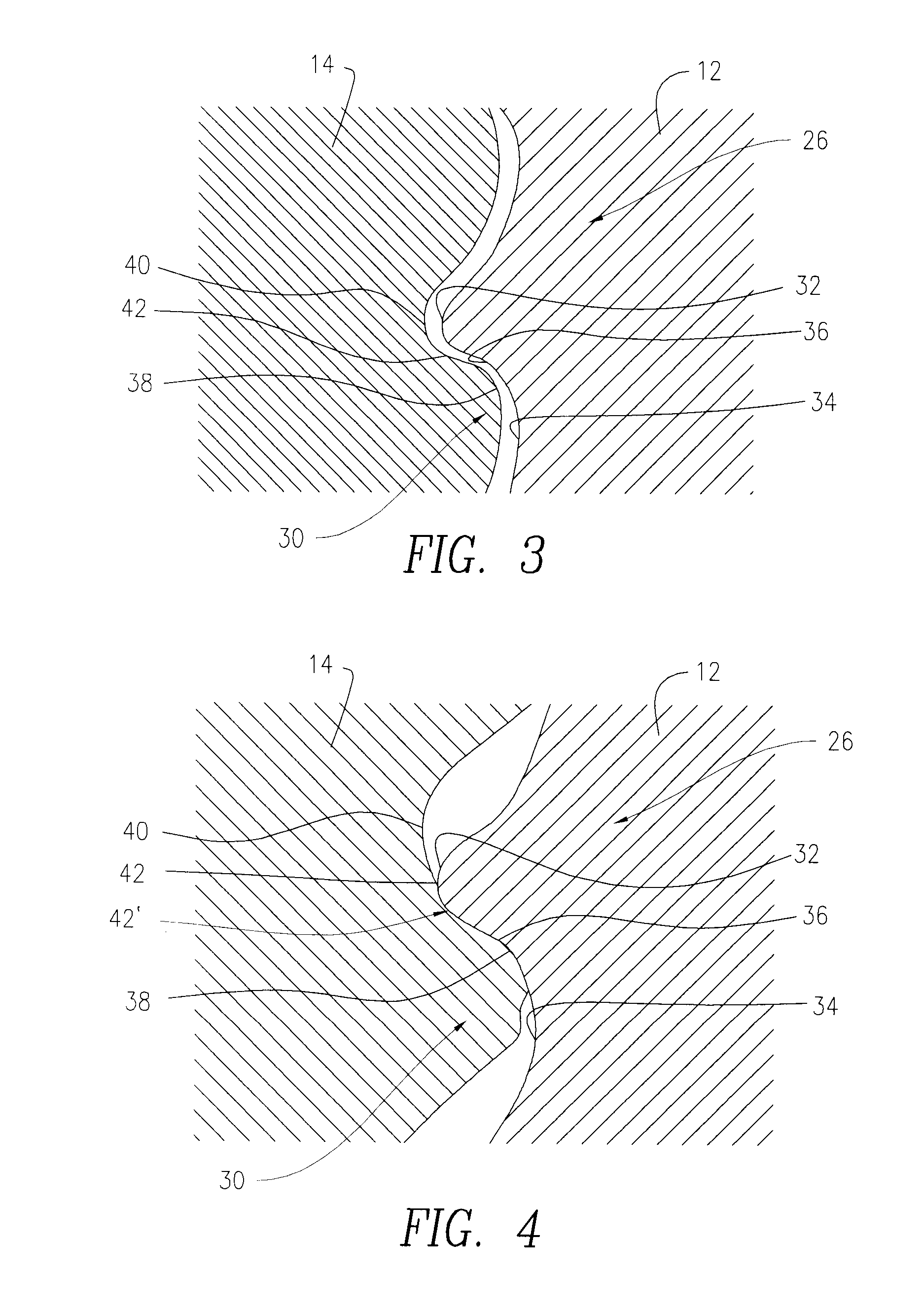
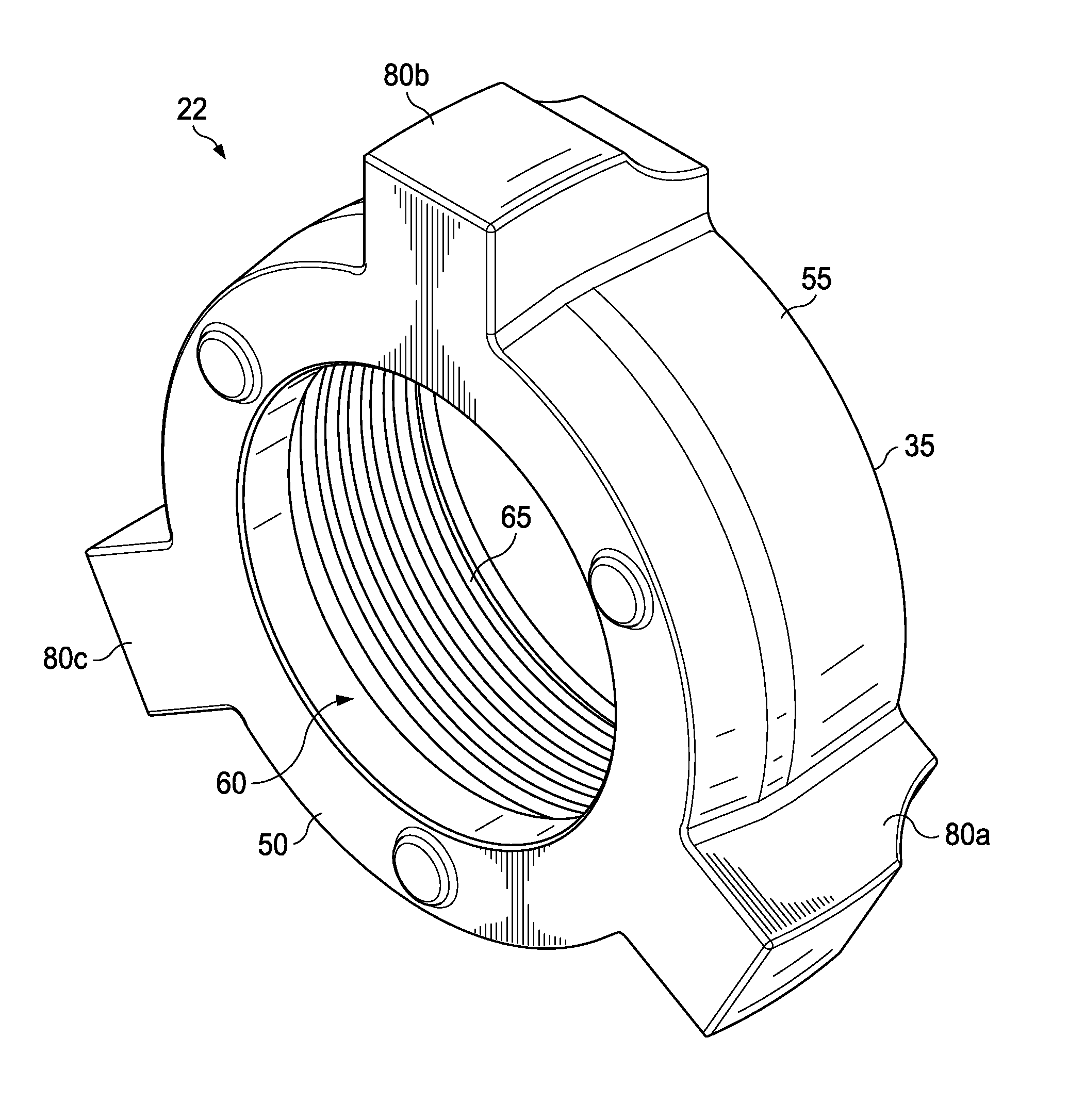
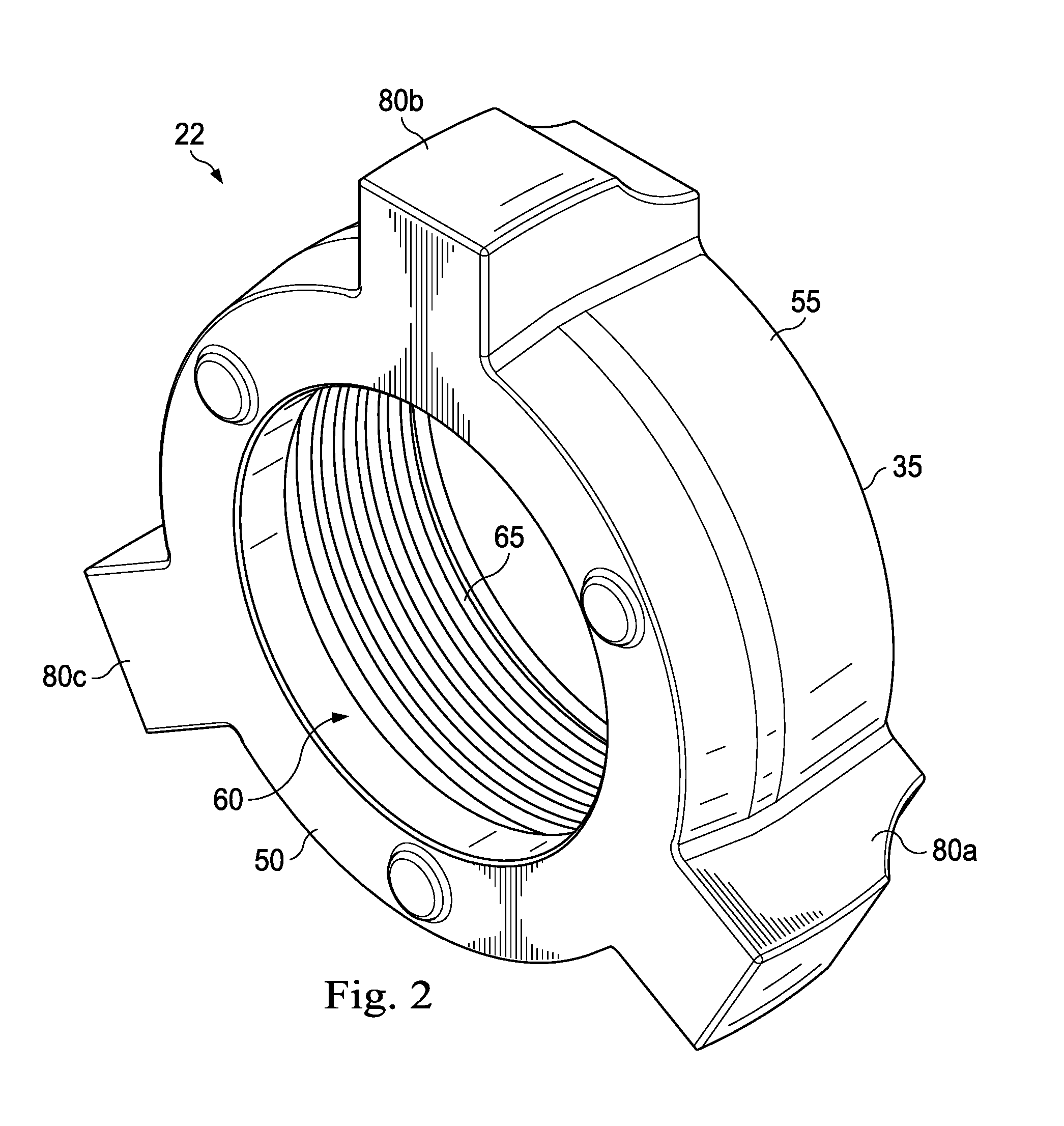
Full-root-radius-threaded wing nut having increased wall thickness
ActiveUS10557576B2Improve body rigidityReduce the amount requiredDrilling rodsJoints with sealing surfacesScrew threadRoot radius
A hammer union includes a female sub; a male sub; and a wing nut that is concentrically disposed about the female and male subs. The wing nut includes a body having first and second end surfaces, and an exterior surface extending therebetween; a passage extending through the body from the first to second end surface that defines an interior surface of the body; an internal shoulder formed by the interior surface; an internal threaded connection that extends from the first end surface and towards the internal shoulder; and lugs extending radially from the exterior surface. The body has a wall thickness defined between the interior and exterior surfaces, with a greater wall thickness at the internal shoulder than at the first end surface; the internal threaded connection has a full-root radius; and a lug that extends along the axial length of the body.
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
Advanced nut and bolt
A vibration resistant fastening system including a high fatigue strength bolt made from a first material and a nut made from a second material that is softer than the first material of the bolt. The bolt includes bolt threads and the nut includes pre-tapped nut threads that match with the bolt threads. The fastening system utilizes a combination of unique geometry of the nut and bolt threads and a hardness differential between the nut and bolt to provide vibration resistance. When tightened, crests of the bolt threads embed into the soft bearing flanks of the nut threads. Simultaneously with the bolt crest embedment, the softer nut thread crests flow radially inward into the root radius of the bolt threads. This complete contact between the nut and the bolt restricts the nut from moving in a transverse direction relative to a longitudinal axis of the bolt.
Owner:HOWMET AEROSPACE INC
Full-root-radius-threaded wing nut having increased wall thickness
ActiveUS20160377207A1Improve body rigidityReduce the amount requiredDrilling rodsJoints with sealing surfacesEngineeringMechanical engineering
According to one aspect, a hammer union includes a female sub; a male sub; and a wing nut that is concentrically disposed about the female and male subs. The wing nut includes a body having first and second end surfaces, and an exterior surface extending therebetween; a passage extending through the body from the first to second end surface that defines an interior surface of the body; an internal shoulder formed by the interior surface; an internal threaded connection that extends from the first end surface and towards the internal shoulder; and lugs extending radially from the exterior surface. In one aspect, the body has a wall thickness defined between the interior and exterior surfaces, with a greater wall thickness at the internal shoulder than at the first end surface; the internal threaded connection has a full-root radius; and a lug that extends along the axial length of the body.
Owner:SPM OIL & GAS INC
Gas turbine engine fan blade
ActiveUS20180231021A1Reduce sensitivityIncreasing the thicknessPump componentsBlade accessoriesLeading edgeFan blade
A fan blade is provided with an aerofoil portion for which, for cross-sections through the aerofoil portion at radii between 15% and 25% of the blade span from the root radius, the average leading edge thickness is greater than the leading edge thickness at the tip. The geometry of the fan blade may result in a lower susceptibility to flutter.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Tension-Reducing Random Sprocket
InactiveUS20060240925A1Promotes reduced and controlled chain tensionReduce noiseGearingPortable liftingEngineeringSprocket
A sprocket is provided having a plurality of teeth around its circumference. Adjacent teeth are separated by roots each having a root radius defined as the distance between the center of the sprocket and a point along the root closest to the sprocket center in a radial direction. In one aspect of the invention, the sprocket comprises at least two different root radii arranged in a pattern effective to redistribute tensions imparted to a chain by the sprocket at one or more predetermined sprocket orders.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
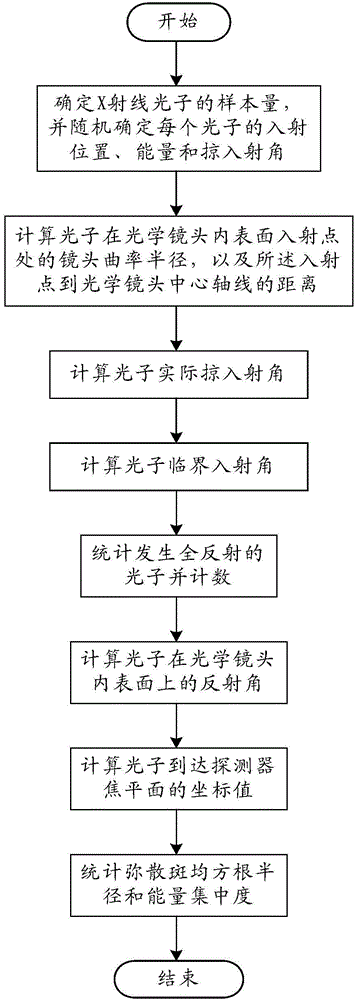
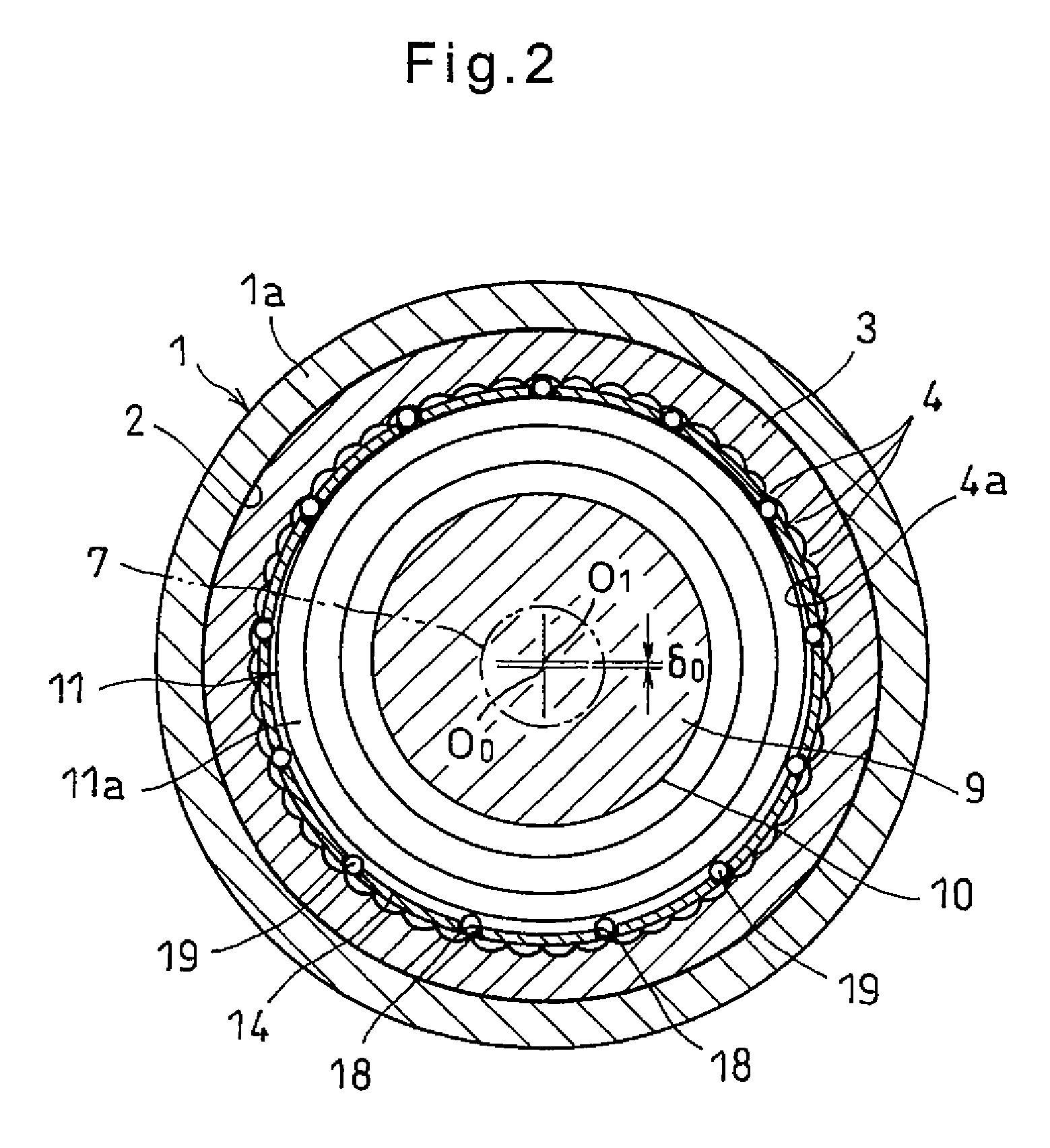
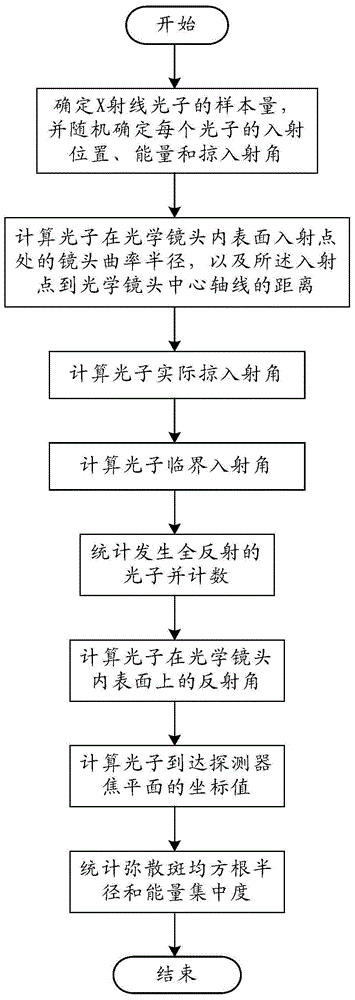
Focusing performance analysis method for grazing incidence optical system based on X-ray optical simulation
ActiveCN104865050AImprove the efficiency of optical simulationRealize TrackingTesting optical propertiesStructural deformationConcentration ratio
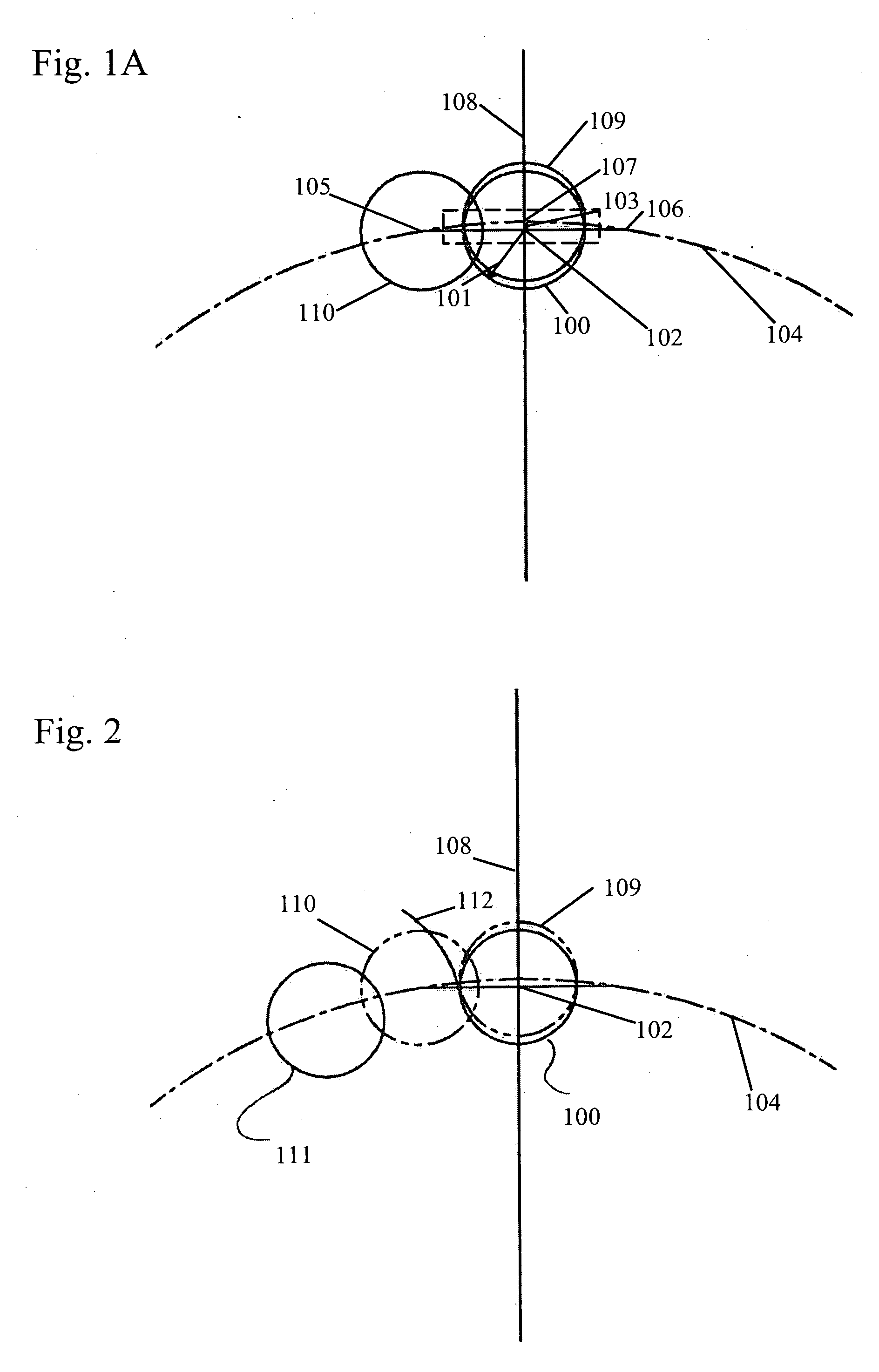
The invention provides a focusing performance analysis method for a grazing incidence optical system based on X-ray optical simulation. The method fully considers characteristic information of X-ray photon energy and reflectivity, irons out a defect in the prior art that only single-energy X-ray photons are considered and the reflectivity is not considered, can achieve engineering actual condition closer to X-ray pulsar navigation apparatus, and improves the efficiency of X-ray optical simulation and analysis. The method can achieve the analysis of the focusing performance of an optical system under the conditions of thermal deformation, structural deformation or thermal-structural coupling deformation, and obtains the mean square root radiuses of a disc of confusion of the optical system, 100% energy concentration ratio and 50% energy concentration ratio under different conditions, thereby achieving the quantification of impact degree on the focusing performance of the optical system from different deformations, and providing support for the reliability design and optimization of a product.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
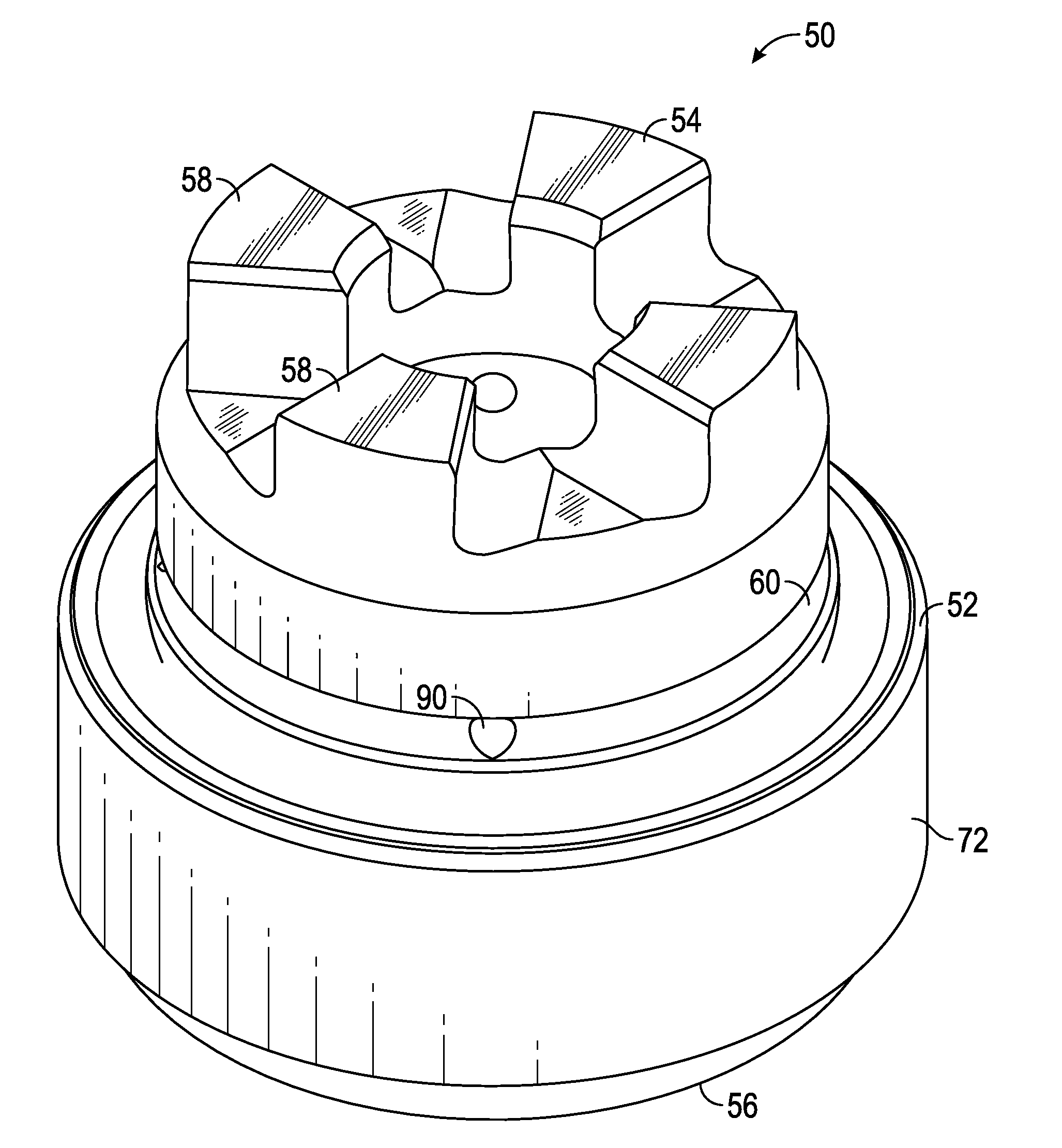
Sprocket tooth profile for a roller or bush chain
An improved sprocket profile for engaging a roller or bush chain smoothly and preventing radial impact with the root of the tooth during engagement. Contact between the sprocket teeth and the roller chain is altered by providing teeth with a root radius equivalent to that of the chain engaging component, with the center point of the root radius located one chordal distance inside the sprocket's pitch circle. This profile allows chain rollers or bushings to impact sprocket teeth tangentially on their flanks rather than radially on their tooth root.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
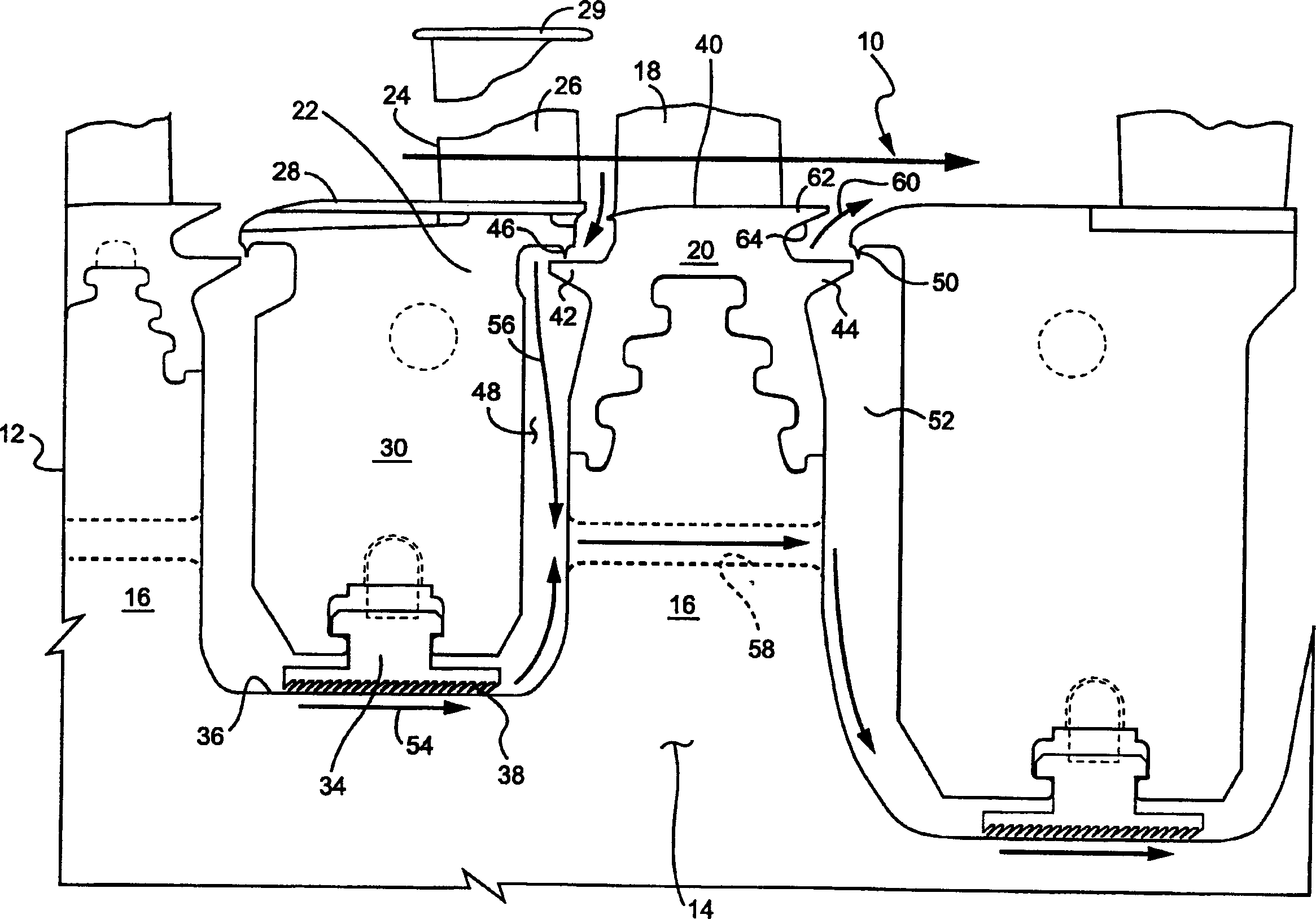
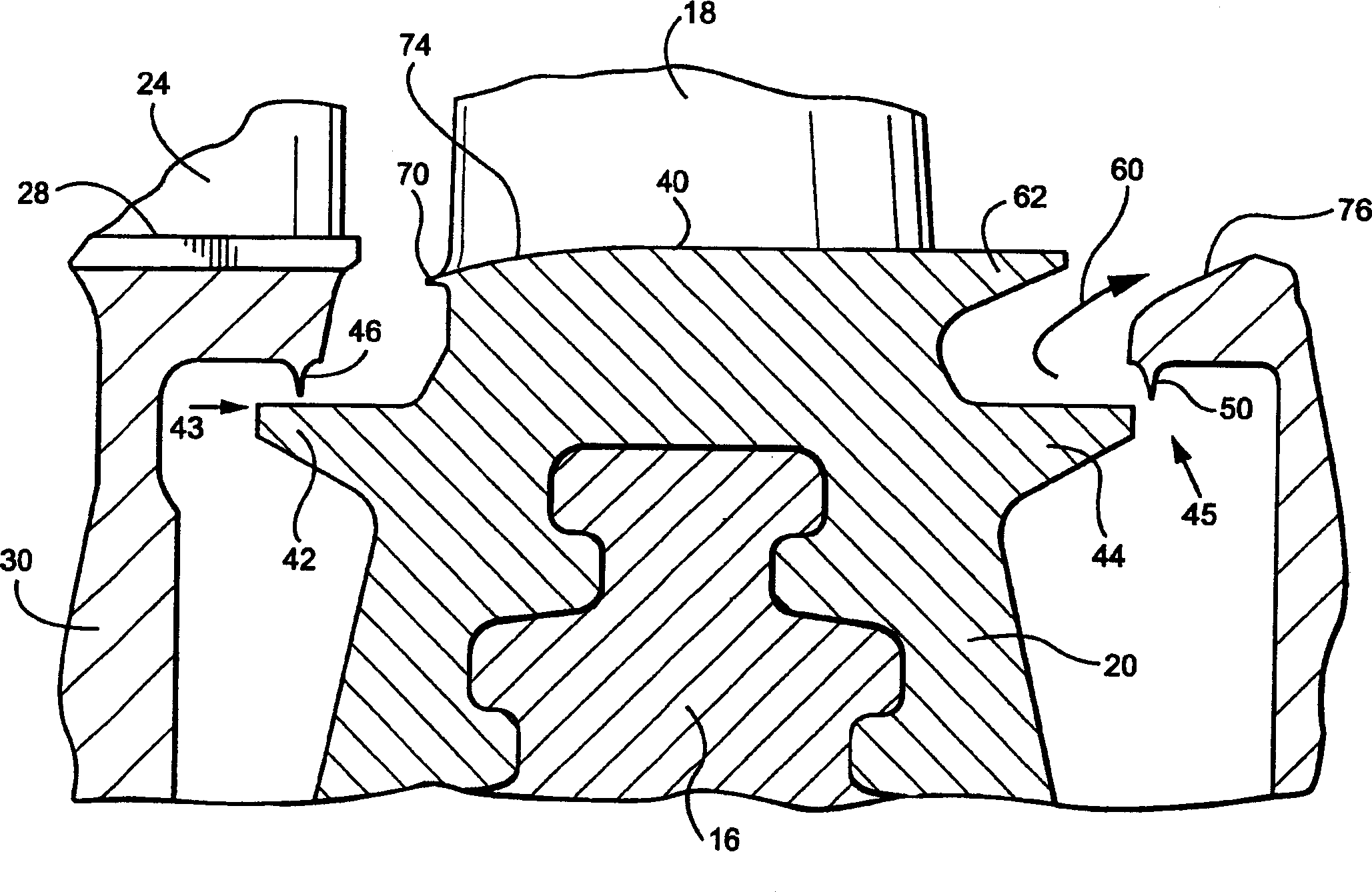
Flow passage sealing of turbine and streamline structure thereof
InactiveCN1499044ADisturbance minimizationShorten the axial distanceEngine sealsBlade accessoriesEngineeringTurbine
The root region of a flowpath through a turbine includes a sealing configuration for minimizing leakage flow and secondary aerodynamic losses. Entrance and exit root radial seals are provided between upstream and downstream nozzles at locations radially inwardly of the root region of the flowpath to minimize radial leakage flow. To minimize intrusion flow into the flowpath from rotor pumping action and consequent aerodynamic losses, an exit flow guide on each bucket turns the exiting radial flow in a predominantly axial direction. Additionally, the upstream bucket root radius and nozzle root radius are faired or tapered to minimize the possibility of a protuberance projecting into the flowpath at steady state operation. An additional entrance root axial fin is provided on the buckets to reduce the flow coefficient and afford further reduction in leakage flow.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
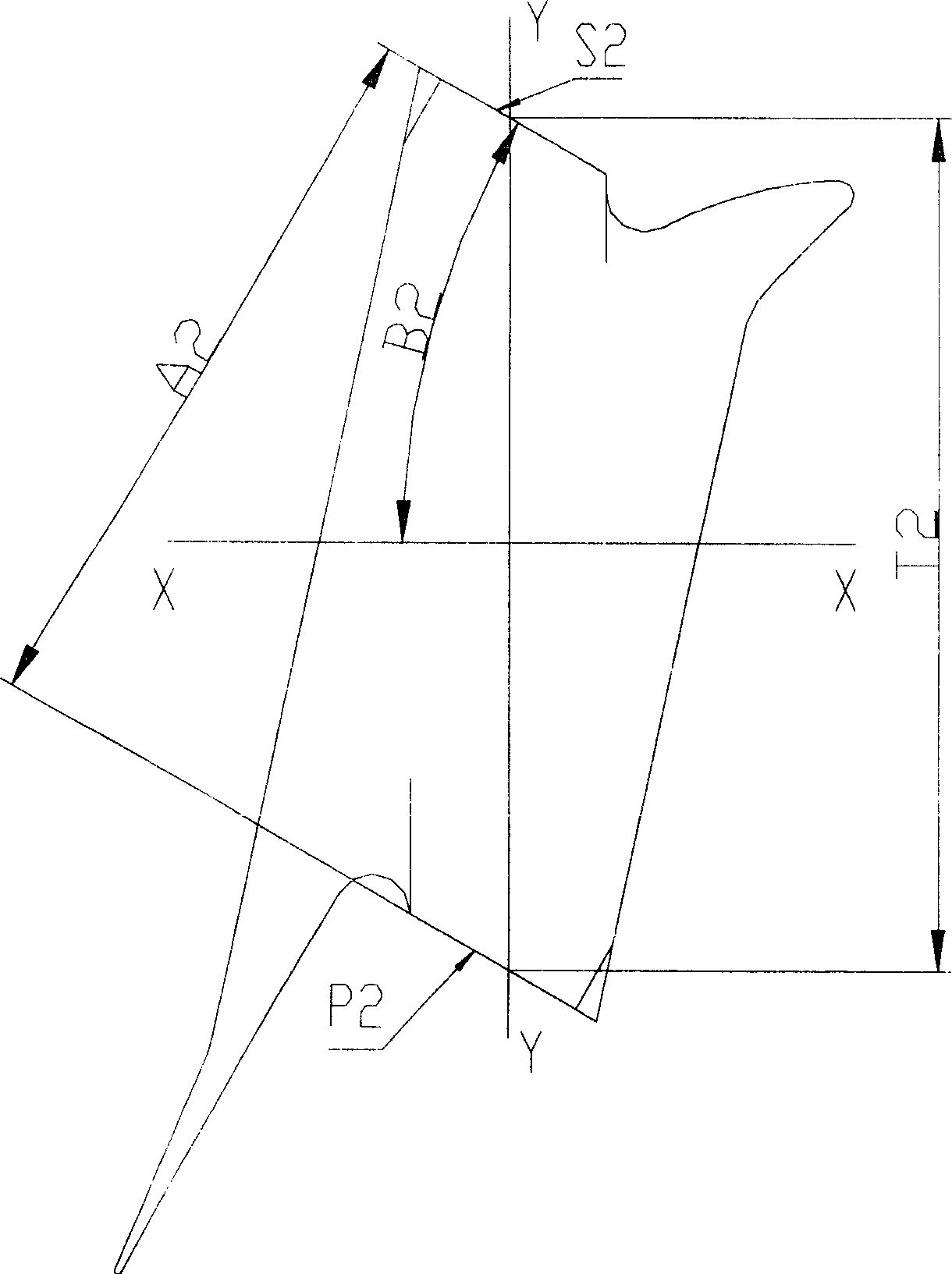
Unsymmetrical profile threads for use in a positive displacement motor housing
InactiveUS20050161259A1Low experience requirementIncrease the root radiusDrilling rodsNutsScrew threadRoot radius
The present invention provides an unsymmetrical thread profile used to connect stator housings of a positive displacement motor. The unsymmetrical thread profile comprises one or more non-load bearing flanks angled with respect to the longitudinal axis of the thread profile such that the root radius is greater than the root radius of a symmetrical thread profile having substantially the same pitch and first angle.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Modular thread connection with high fatigue resistance
ActiveUS7150479B2High resistance against cyclical bending fatigueSufficient performanceDrilling rodsNutsHigh resistanceTransmitted power
A connector for oilfield applications has high resistance against cyclical bending stress and fatigue failure. In a preferred embodiment, the threaded connector has a pin-box arrangement for joining two components. The pin and box have threads with a pre-determined profile different from that specified by conventional (e.g., API) specification and provide improved strength characteristics. Certain embodiments of the present invention include a pitch-to-root radius ratio that is less than that specified by the API, a thread height-to-root radius ratio that is less than that specified by the API, a flank angle that is less than that specified by the API, and a taper that is less than that specified by the API for said pre-determined outside diameter. Certain other embodiments have less than all of these ratios and dimensions. Optionally, the connector has (a) wiring for transmitting power and / or data through the connector; and (b) at least one seal disposed adjacent the wiring for protecting the wiring from contact with wellbore fluids.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
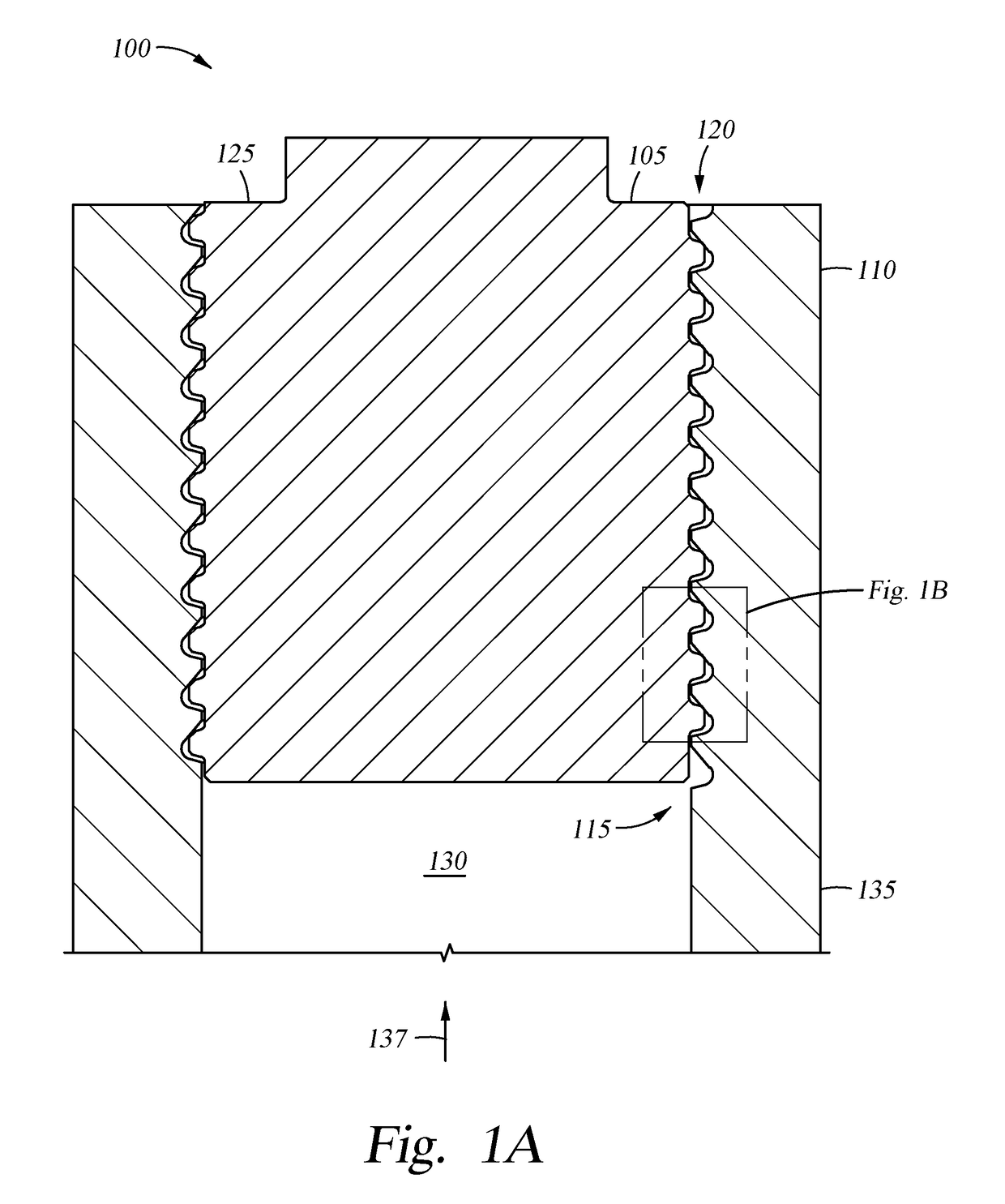
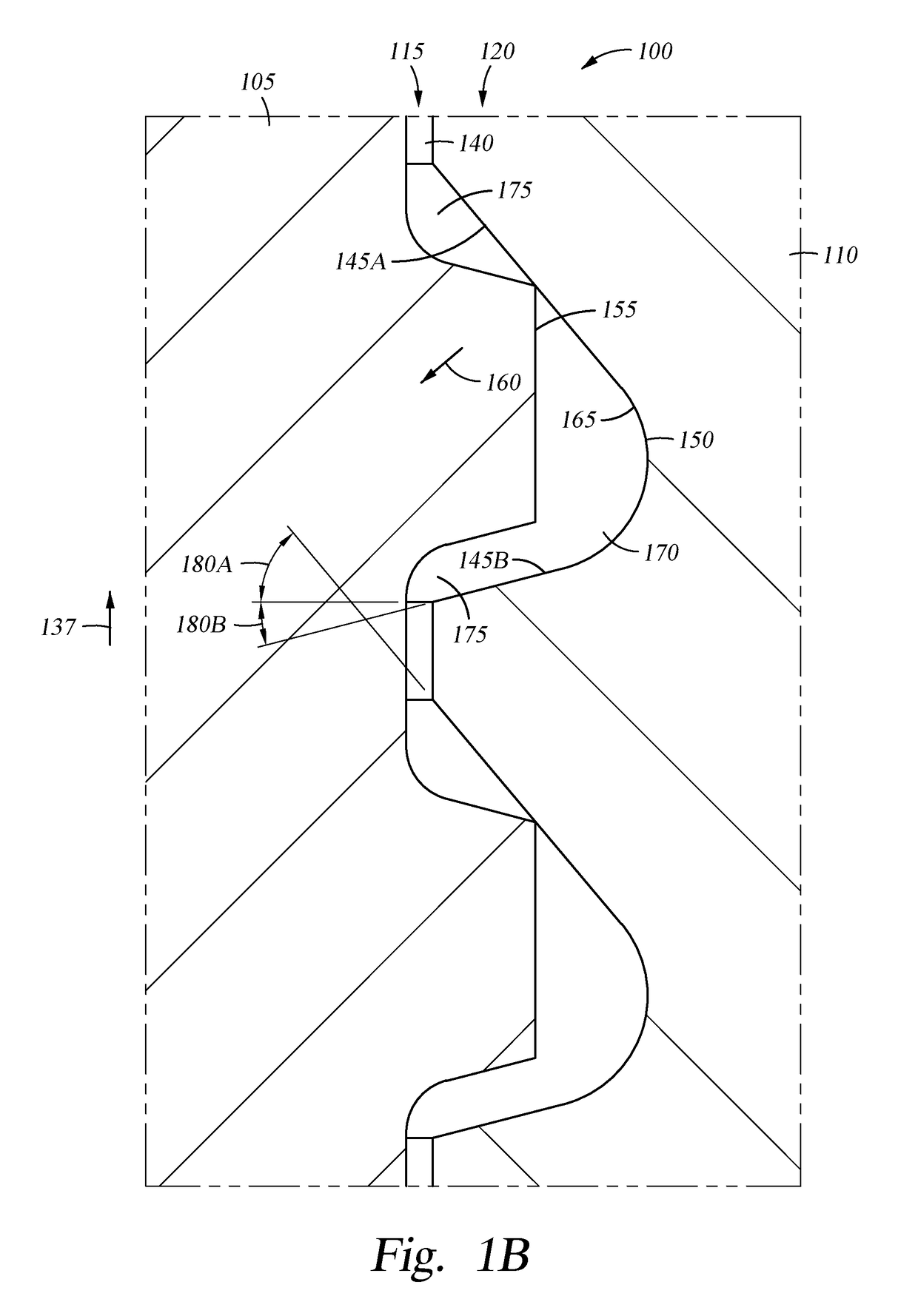
Stress reducing thread form
A thread form for a threaded connection comprising a plurality of threads, wherein at least a portion of each of the threads comprise a root having a root radius that extends from a point central to the root and having planar flanks extending from both sides thereof.
Owner:FORUM US
Sprocket tooth profile for a roller or bush chain
An improved sprocket profile for engaging a roller or bush chain smoothly and preventing radial impact with the root of the tooth during engagement. Contact between the sprocket teeth and the roller chain is altered by providing teeth with a root radius equivalent to that of the chain engaging component, with the center point of the root radius located one chordal distance inside the sprocket's pitch circle. This profile allows chain rollers or bushings to impact sprocket teeth tangentially on their flanks rather than radially on their tooth root.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Screw compressor rotor
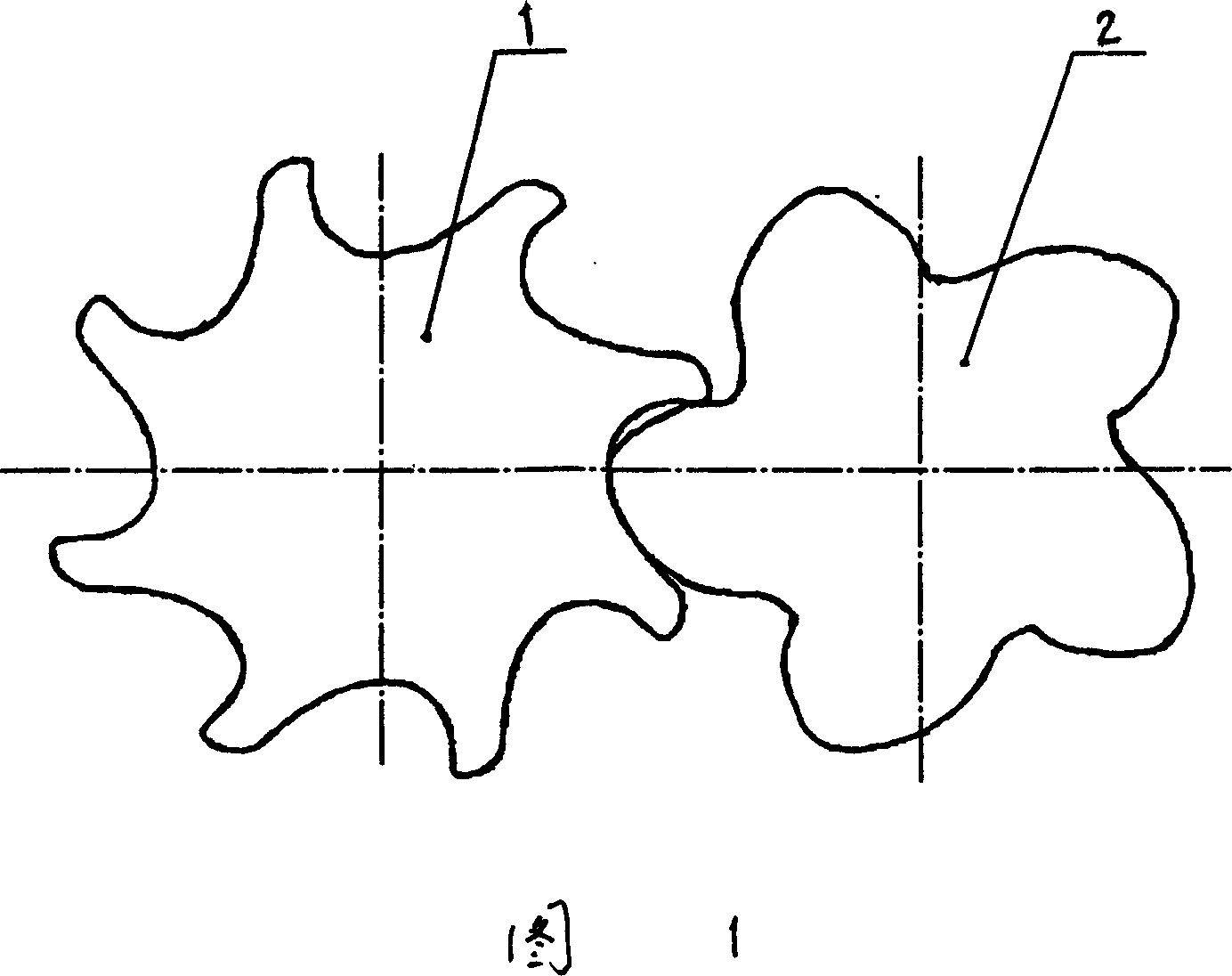
InactiveCN101012829AReduce wearImprove efficiencyRotary piston pumpsRotary piston liquid enginesLow noiseEngineering
The invention relates to a rotor of screw compressor, wherein, two edges of cathode rotor (1) and anode rotor (2) are asymmetry, and the tooth curvatures are arc and relative envelope, the teeth ratio between cathode and anode rotors is 8:5; the space between two rotors is 0.05mm; the diameters of tip radius of two rotors is rated at 1.0880; the diameters of root radius of two rotors is rated at 1.1375; the diameters of pitches of two rotors is rated at 1.600; the torsion angles of two rotors is rated at 0.625; the strikes of two rotors is rated at 1.6. The invention has stable mesh, reduced abrasion, better sealing, low noise and improved efficiency.
Owner:YANTAI MOON
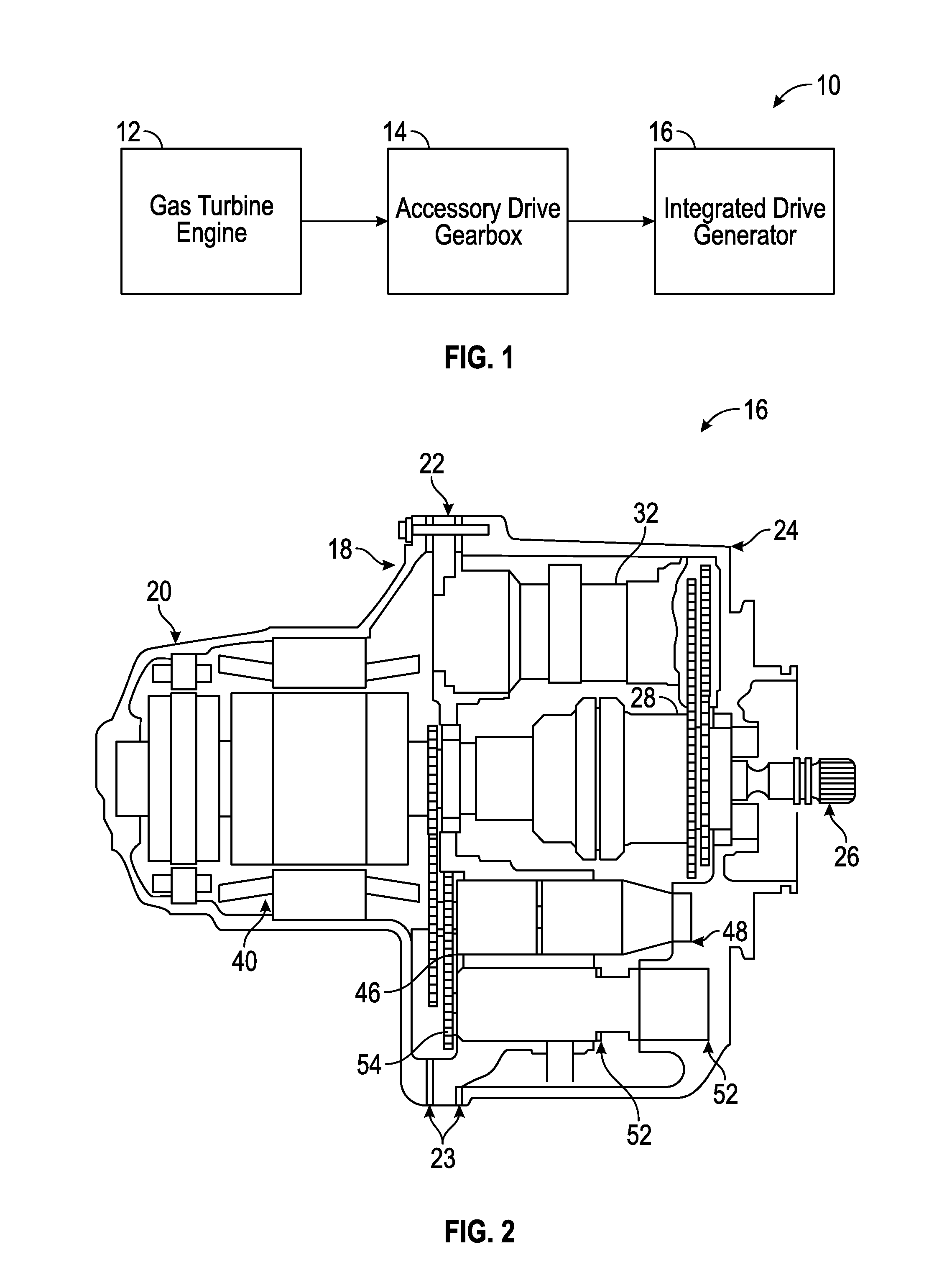
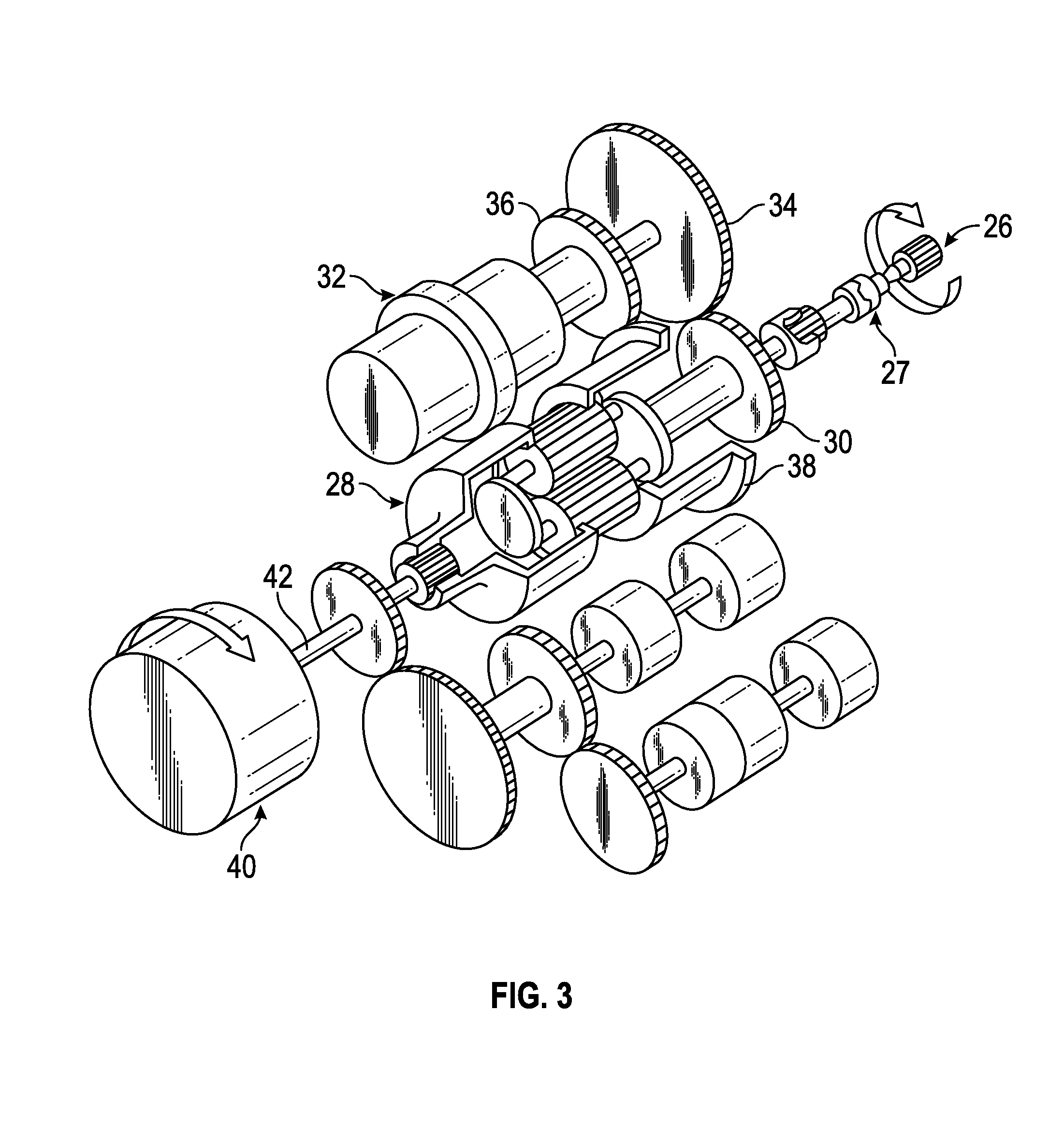
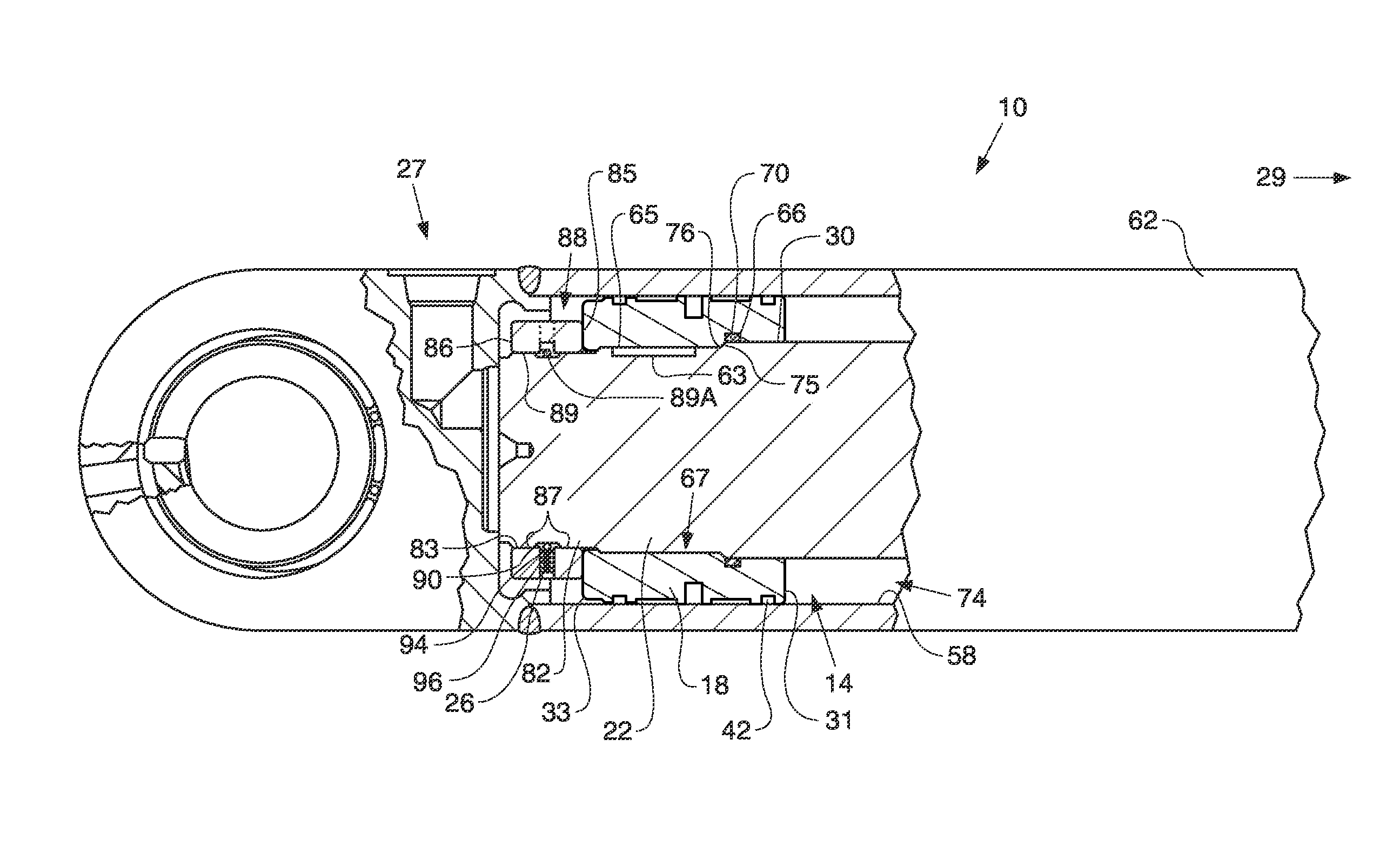
Disconnect shaft for an integrated drive generator (IDG)
A disconnect shaft of an integrated drive generator is provided including a body configured to rotate about an axis of rotation. The body has a first end, a second opposite end, and a plurality of teeth formed adjacent the first end and configured to engage a complementary portion of an adjacent component. A relief is formed in the body such that a first portion is defined between the relief and the plurality of teeth. The first portion includes a plurality of threads having at least one of a major diameter between about 1.3044 and about 1.3125 inches (3.313-3.334 centimeters), a minor diameter between about 1.2482 and about 1.2547 inches (3.170-3.187 centimeters), a pitch diameter between about 1.2765 and about 1.2800 inches (3.242-3.251 centimeters), and a root radius between about 0.0075 and 0.0090 inches (0.0190-0.0029 centimeters).
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Stress reducing thread form
A thread form for a threaded connection comprising a plurality of threads, wherein at least a portion of each of the threads comprise a root having a root radius that extends from a point central to the root and having planar flanks extending from both sides thereof.
Owner:FORUM US
Stress reducing thread form
A thread form for a threaded connection comprising a plurality of threads, wherein at least a portion of each of the threads comprise a root having a root radius that extends from a point central to the root and having planar flanks extending from both sides thereof.
Owner:FORUM US
Bulk nickel-based chromium and phosphorus bearing metallic glasses with high toughness
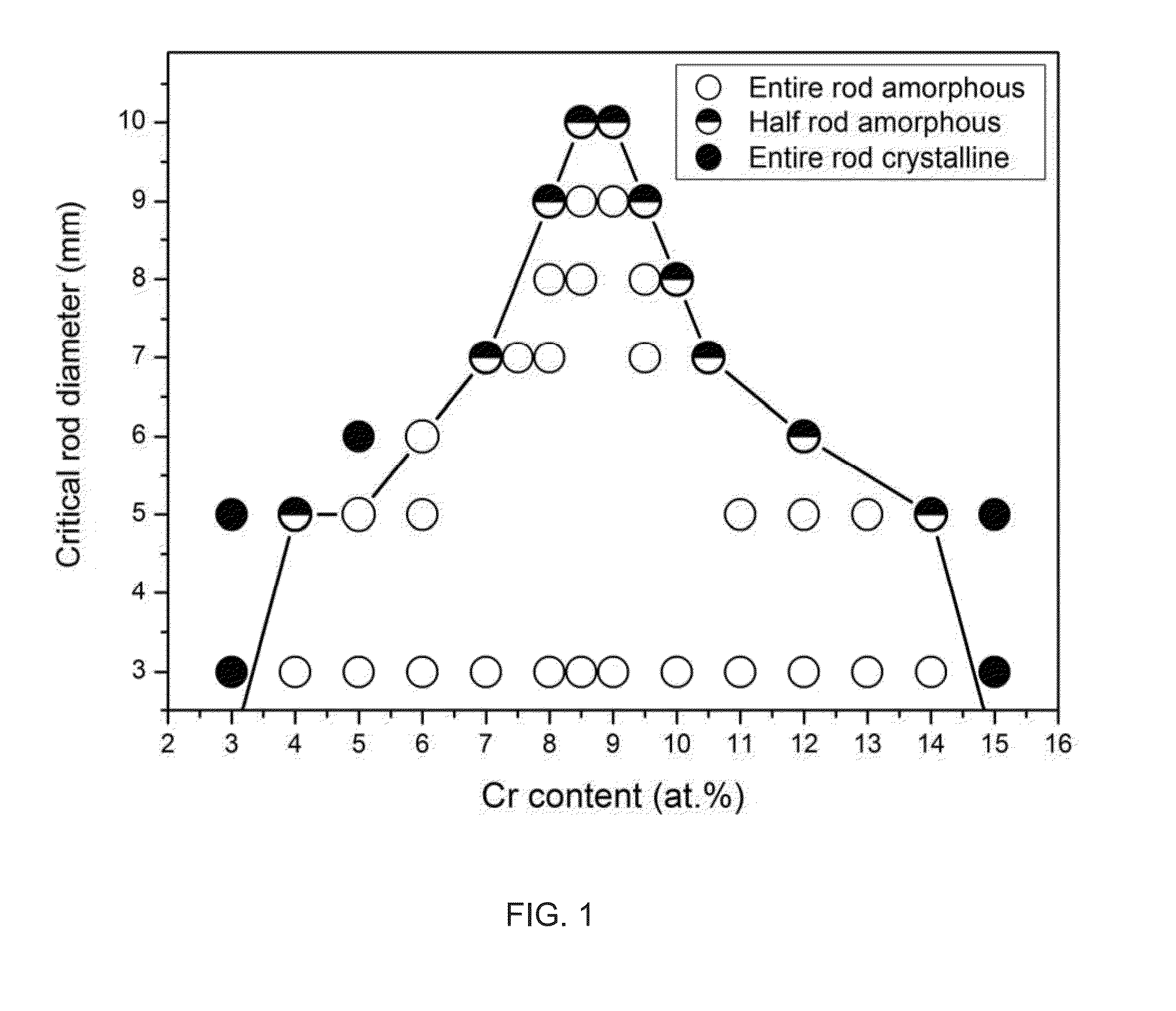
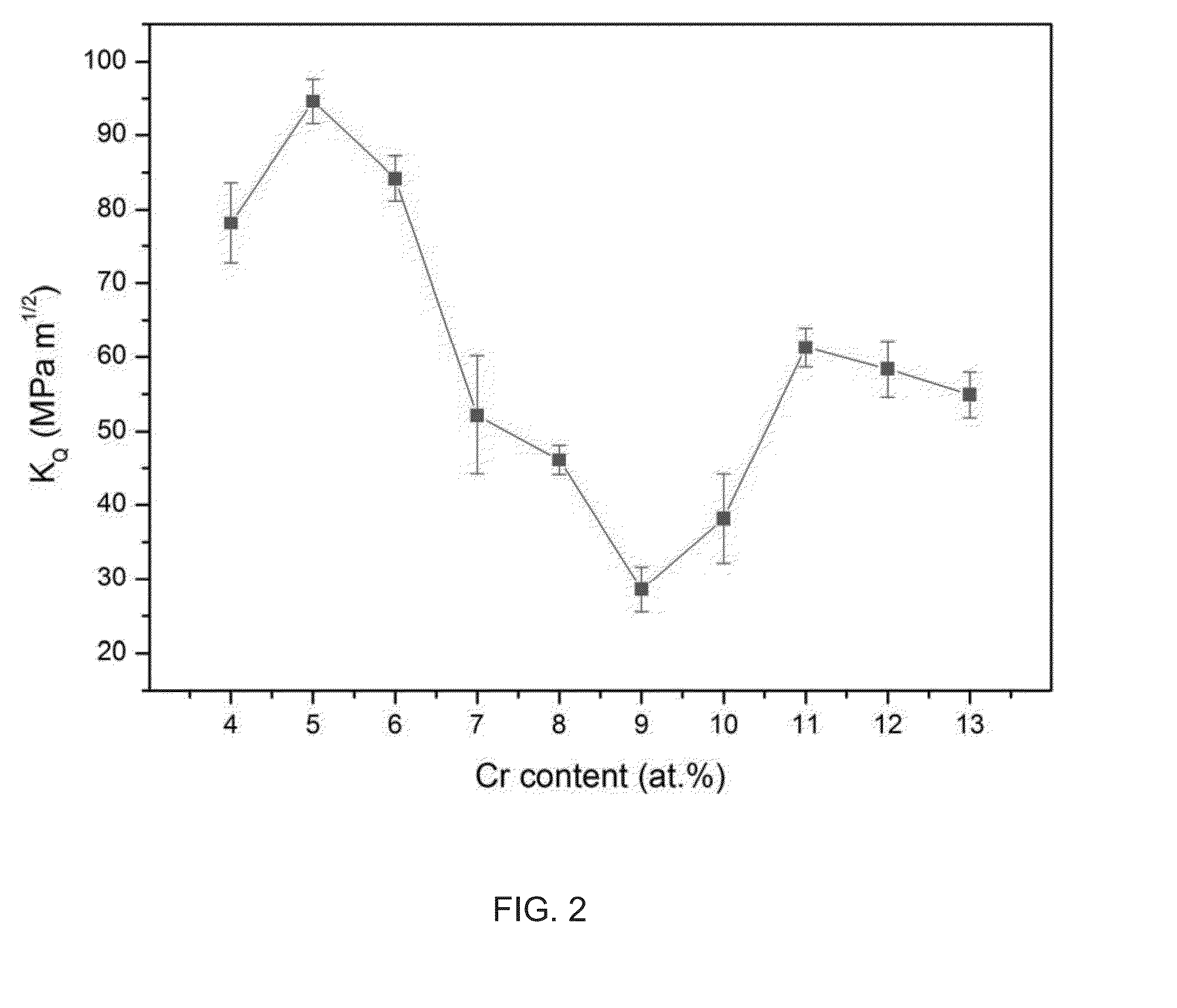
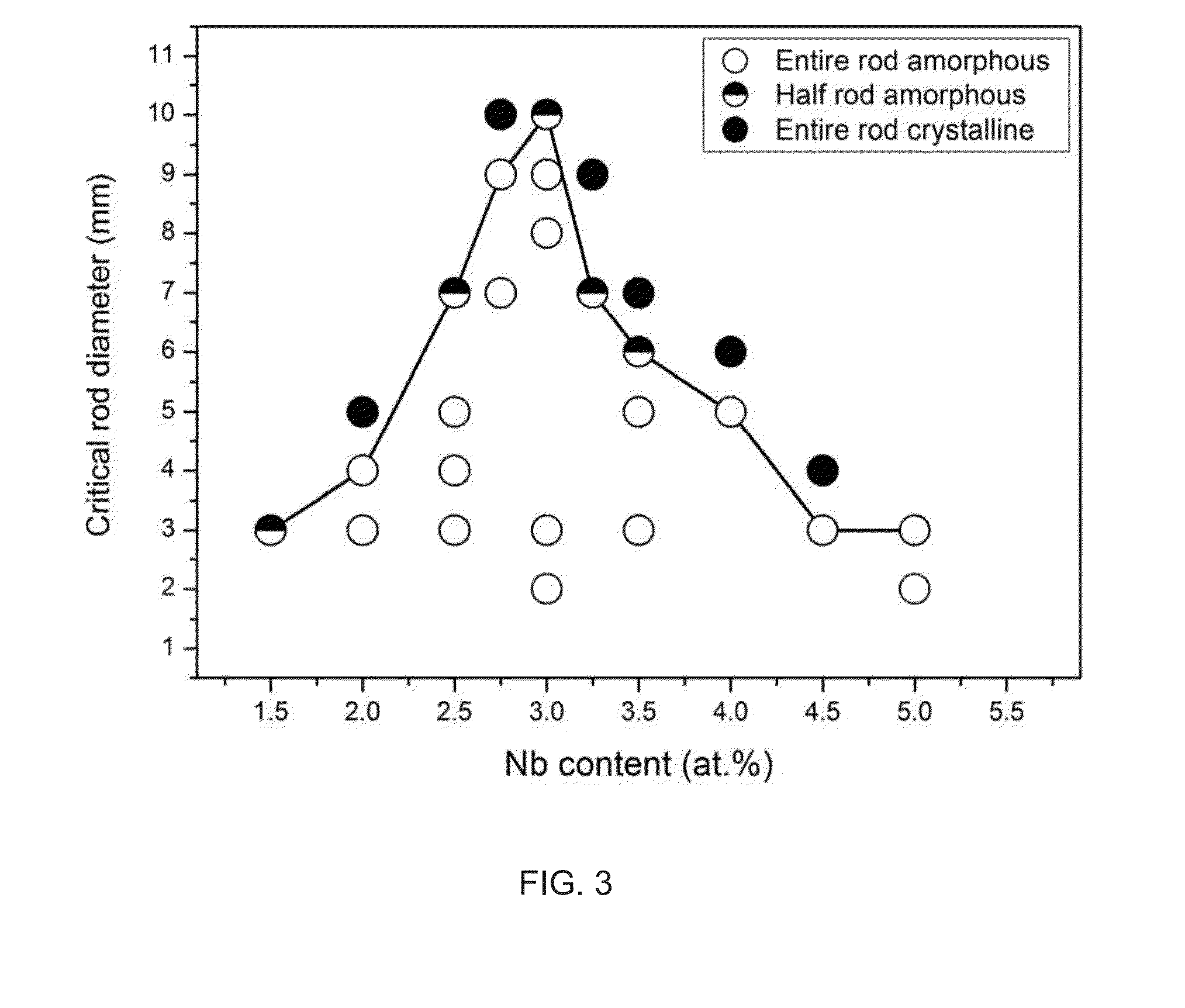
A Ni-based bulk metallic glass forming alloy is provided. The alloy includes Ni(100-a-b-c-d)CraNbbPcBd, where an atomic percent of chromium (Cr) a ranges from 3 to 13, an atomic percent of niobium (Nb) b is determined by x−y*a, where x ranges from 3.8 to 4.2 and y ranges from 0.11 to 0.14, an atomic percent of phosphorus (P) c ranges from 16.25 to 17, an atomic percent of boron (B) d ranges from 2.75 to 3.5, and the balance is nickel (Ni), and where the alloy is capable of forming a metallic glass object having a lateral dimension of at least 6 mm, where the metallic glass has a stress intensity factor at crack initiation when measured on a 3 mm diameter rod containing a notch with length between 1 and 2 mm and root radius between 0.1 and 0.15 mm, the stress intensity factor being at least 70 MPa m1 / 2.
Owner:APPLE INC
Axial flow pump
InactiveCN109654034ANo cloggingEasy to operatePump componentsPump installationsAxial-flow pumpImpeller
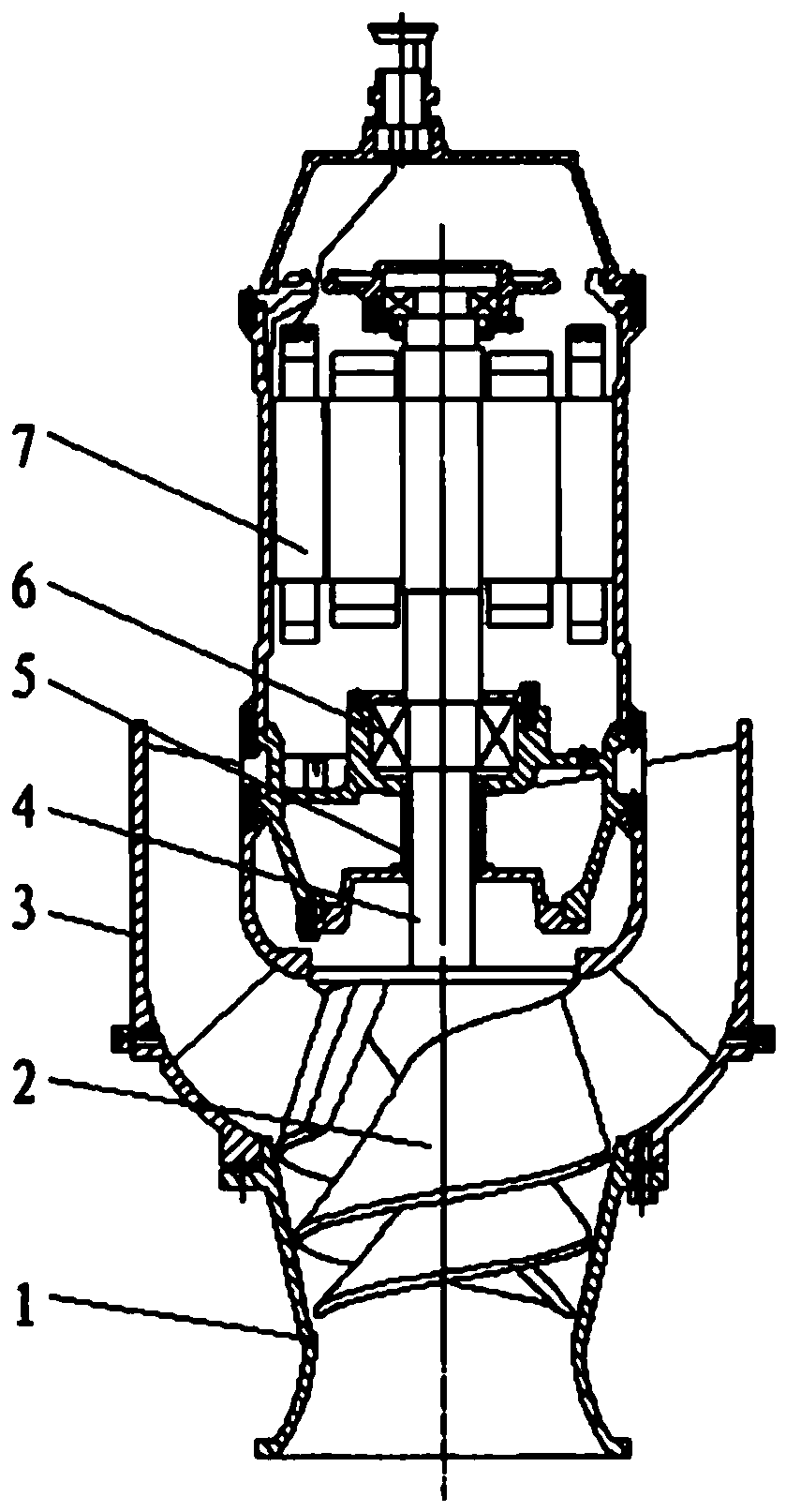
The invention discloses an axial flow pump which comprises a shell part and a pump body part, and is mainly composed of a submersible motor, a bearing, a shaft, a guide vane, a shaft, an impeller andthe like. The pump body part of the axial flow pump is composed of the bearing, the motor, the guide vane, the impeller and the shaft. The blade tip clearance dimension of blades is reduced by 20-30%compared with the conventional size. The impeller is fixed to the rotating shaft and located below an inner cylinder of the guide vane, the appearance of the lower end of the shell is in a horn mouthshape, the blades are vertically arranged on the surface of a wheel center cone at a certain inclination and spacing, the structure is similar to a screw propeller having a small end radius and a large root radius, and the outlet portion is in an axial flow type. The novel axial flow pump is large in flow, free of clogging, high in efficiency and capable of saving energy, and has the advantages ofbeing easy to operate, convenient to maintain and low in price.
Owner:曲世友
Bolt for gas turbine engine rotor
The bolt has, in sequence along a bolt axis: a threaded portion, a thread run-out portion, a shank, and a head, the threaded portion having a thread with a given root radius and a given depth, the thread run-out portion connected to the shank via a thread run-out fillet having a thread run-out fillet radius, the thread run-out fillet radius being between two and six times the thread root radius.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
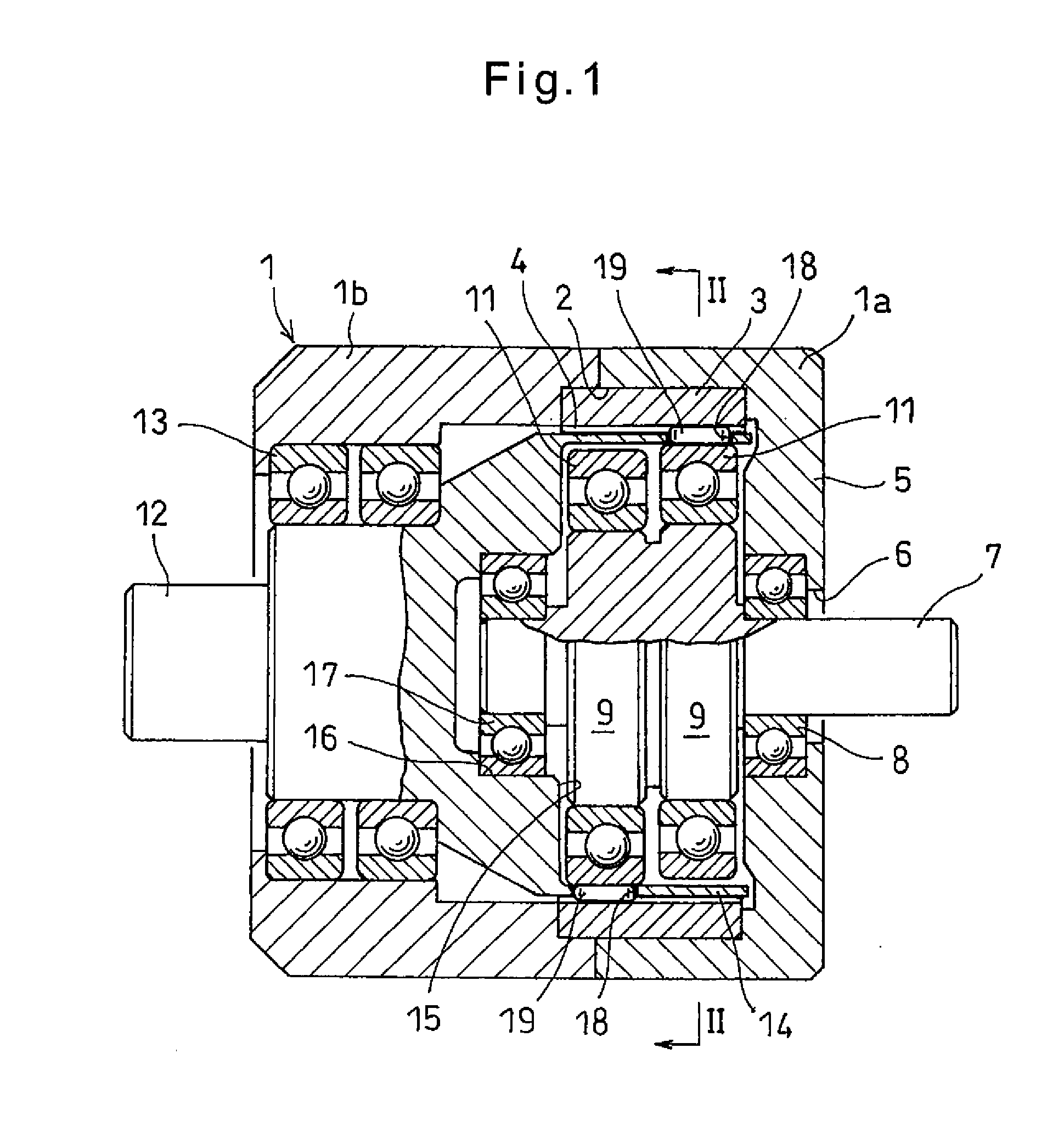
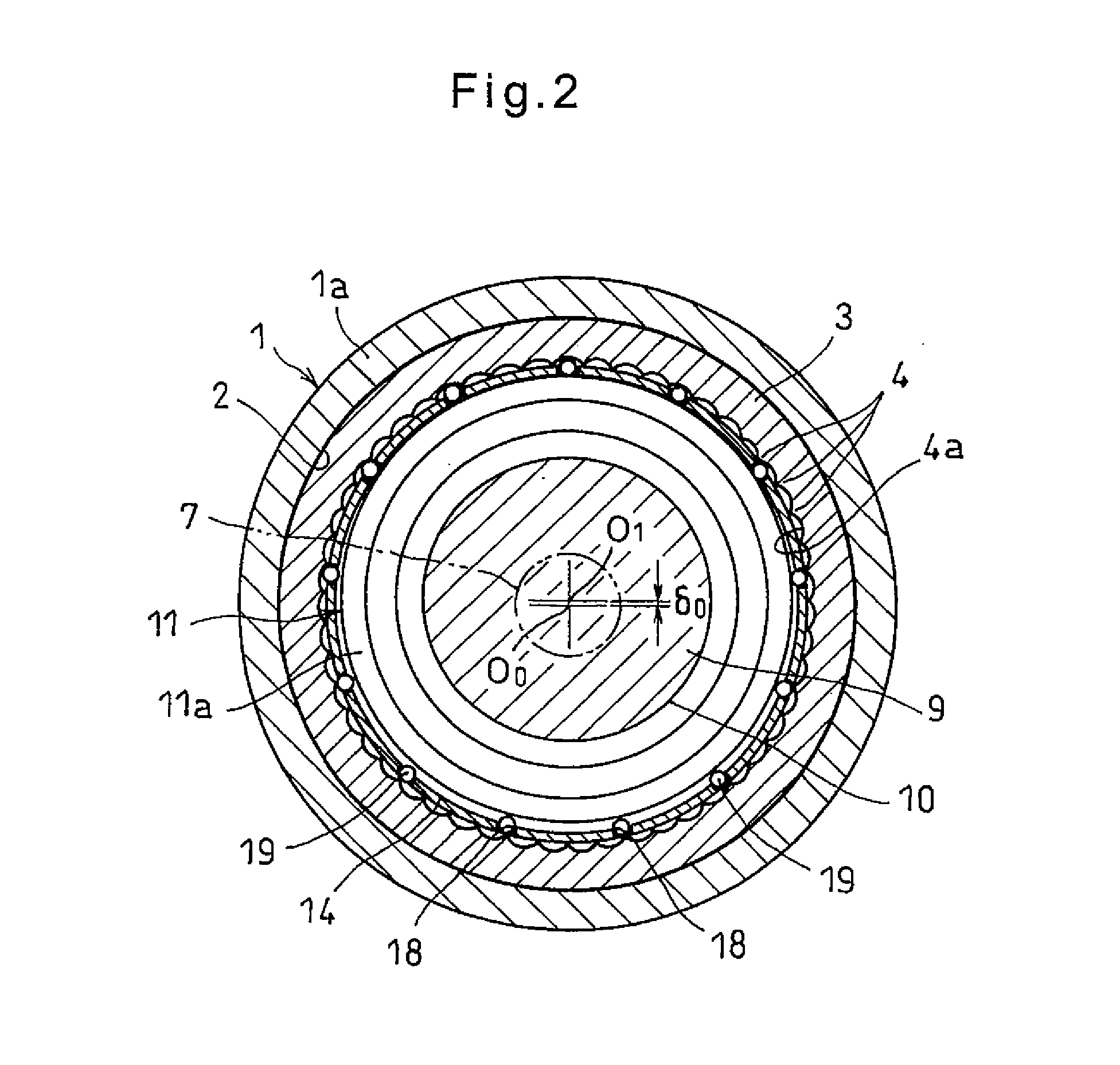
Speed reducer
ActiveUS20140228161A1Quality improvementShorten speedGear vibration/noise dampingToothed gearingsReduction driveRolling-element bearing
A speed reducer includes an internal gear, an input shaft coaxial with the internal gear, and an eccentric disk on the input shaft and rotatable inside the internal gear, and an eccentric disk on the input shaft and rotatable inside the internal gear. A cage at an end of an output shaft, coaxial with the input shaft, and rotatable between the internal gear and the eccentric disk has pockets fewer in number than the internal gear's internal teeth. Rollers are received in the respective pockets such that when the input shaft rotates once, the rollers circumferentially move by a distance equal to one internal tooth width, causing the output shaft to be rotated at a reduced speed. The root radius of the internal gear, the radius of the circumcircle of the rolling bearing, and the outer diameter of the rollers are determined such that roller gaps defined between the rollers and the tooth bottoms of the internal gear are controlled by reduce vibration.
Owner:NTN CORP
Piston retention apparatus and method
An apparatus and method for coupling a piston to a rod to form a cylinder assembly are provided. The piston has a tapped bore extending therethrough for coupling to a first threaded region of the rod. The rod end extends beyond the piston member and includes a second threaded region for coupling to a tapped bore of a retaining member. The piston member is coupled to the rod member at a low torque, e.g., up to about 1000 Nm. An external thread of each of the threaded segment of the piston bore and the first threaded region of the first portion of the rod member may be formed with a root radius of greater than 0.125 pitch or with MJ class thread. The retaining member may include setscrews offset from one another for frictional engagement with the rod end. The thread pitch between the rod and the piston may be coarser than between the rod and the retaining member. An interface and a seal region between the rod and the piston may be disposed closer to the rod end side of the piston member than the threaded coupling.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Flow passage sealing of turbine and streamline structure thereof
InactiveCN100383364CDisturbance minimizationShorten the axial distanceEngine sealsBlade accessoriesTurbineLeakage flow
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Bolt for gas turbine engine rotor
The bolt has, in sequence along a bolt axis: a threaded portion, a thread run-out portion, a shank, and a head, the threaded portion having a thread with a given root radius and a given depth, the thread run-out portion connected to the shank via a thread run-out fillet having a thread run-out fillet radius, the thread run-out fillet radius being between two and six times the thread root radius.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Speed reducer
ActiveUS9127753B2Reduce vibrationQuality improvementGear vibration/noise dampingToothed gearingsReduction driveReducer
Owner:NTN CORP
Analysis method of focusing performance of grazing incidence optical system based on x-ray optical simulation
ActiveCN104865050BImprove the efficiency of optical simulationRealize TrackingTesting optical propertiesStructural deformationConcentration ratio
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Last stage rotor blade of steam turbine
ActiveCN100339559CMeet flowReduce flow lossBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesRelative maximumRoot radius
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com