Patents
Literature
467 results about "Tip clearance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
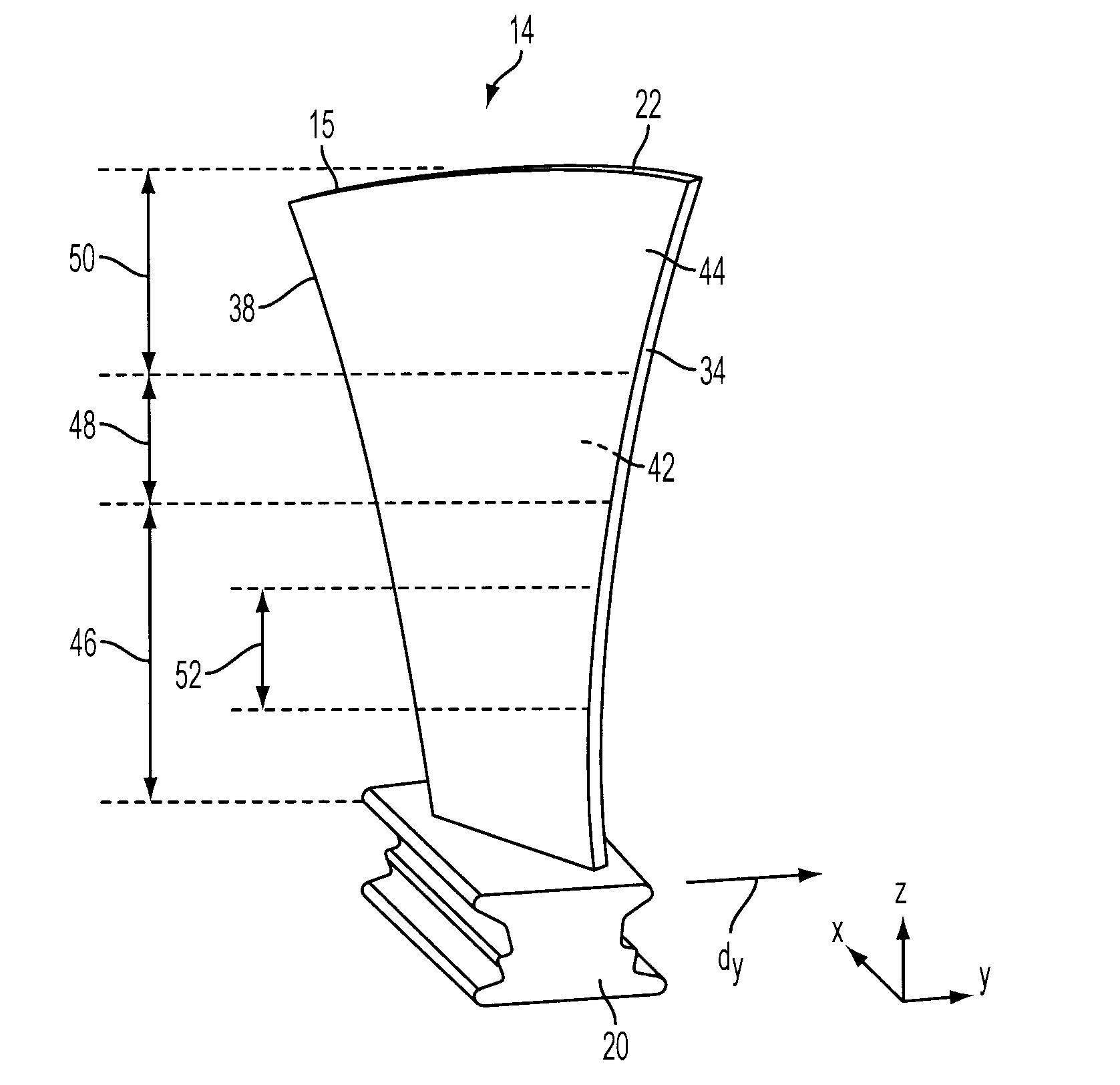
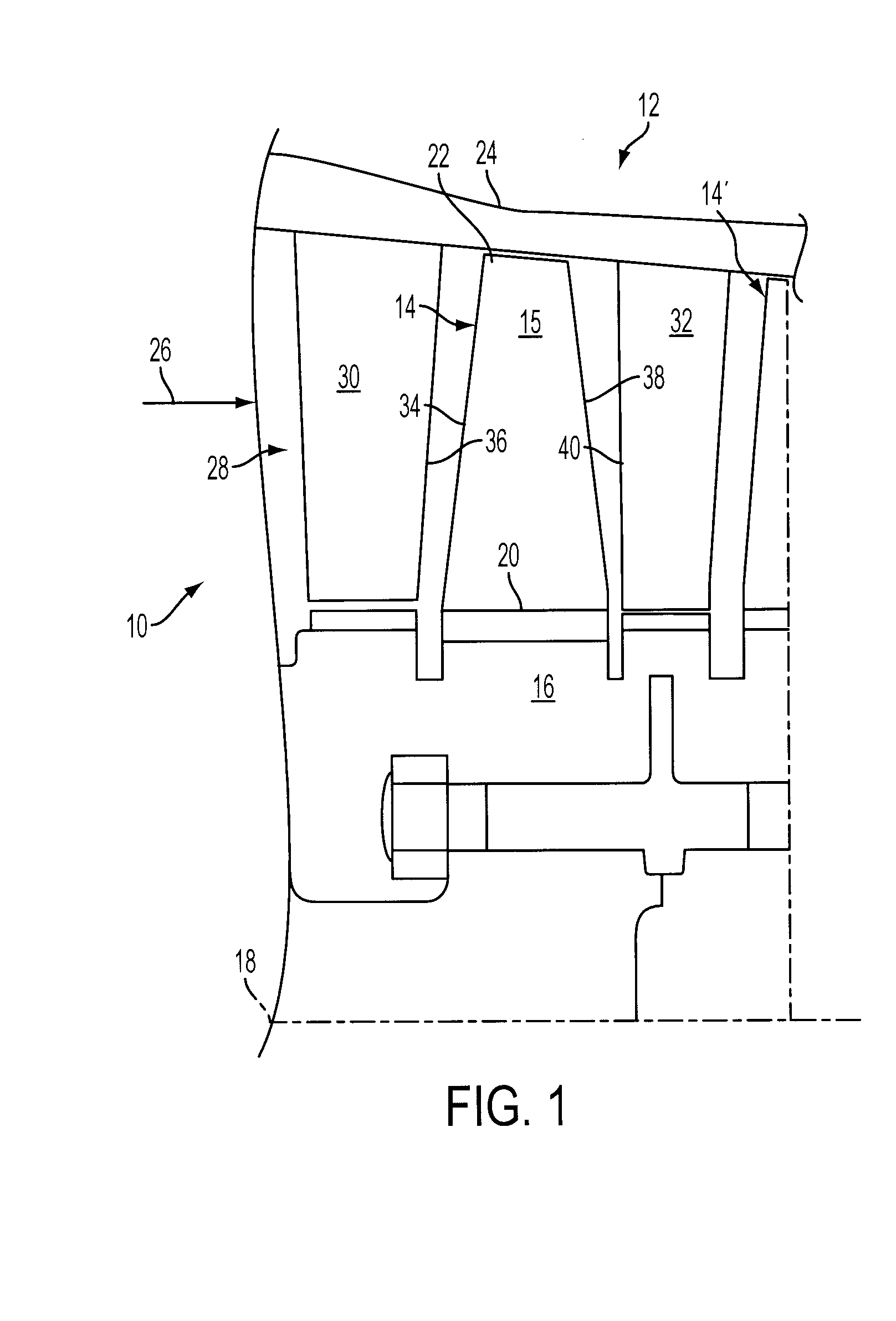
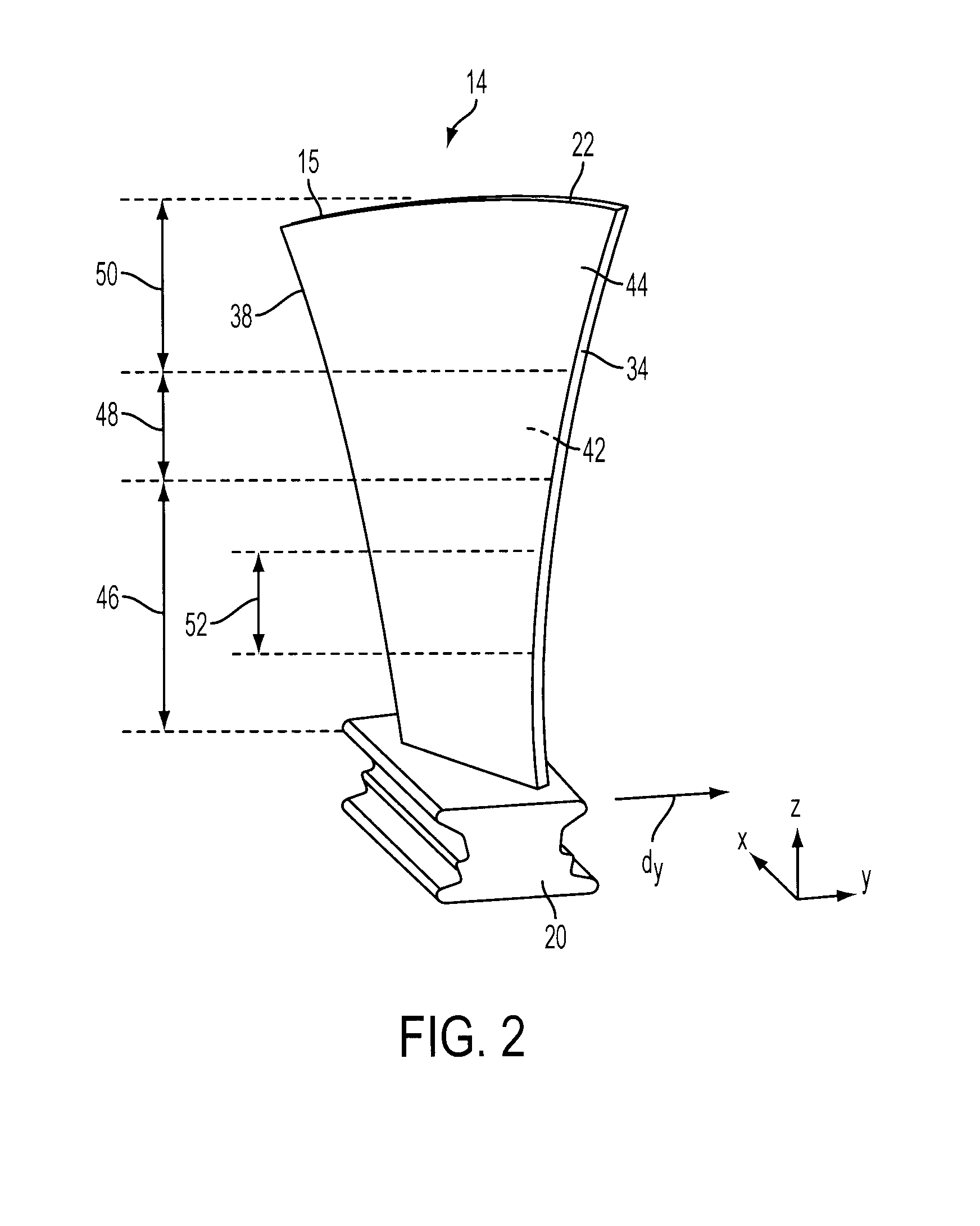
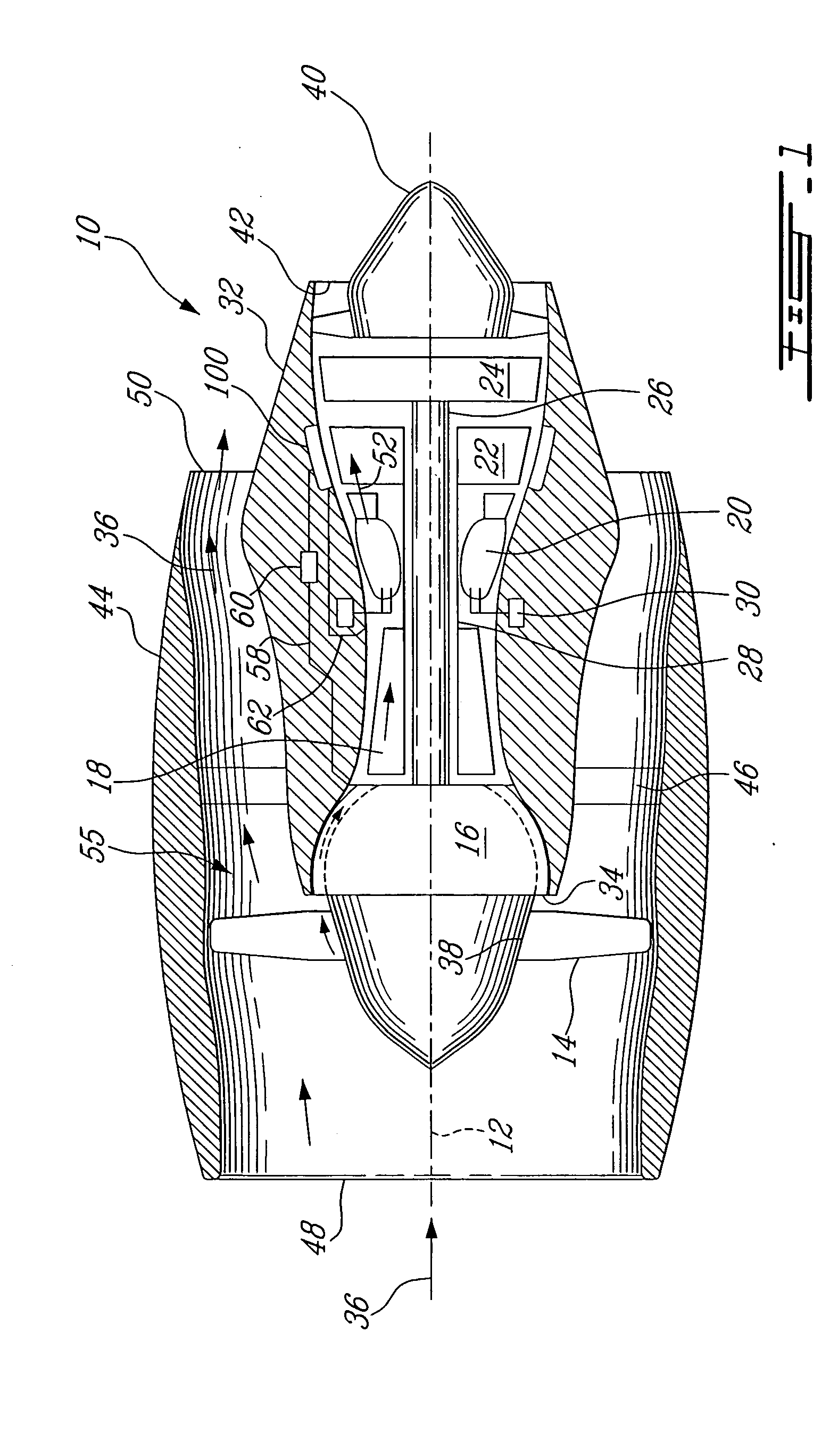
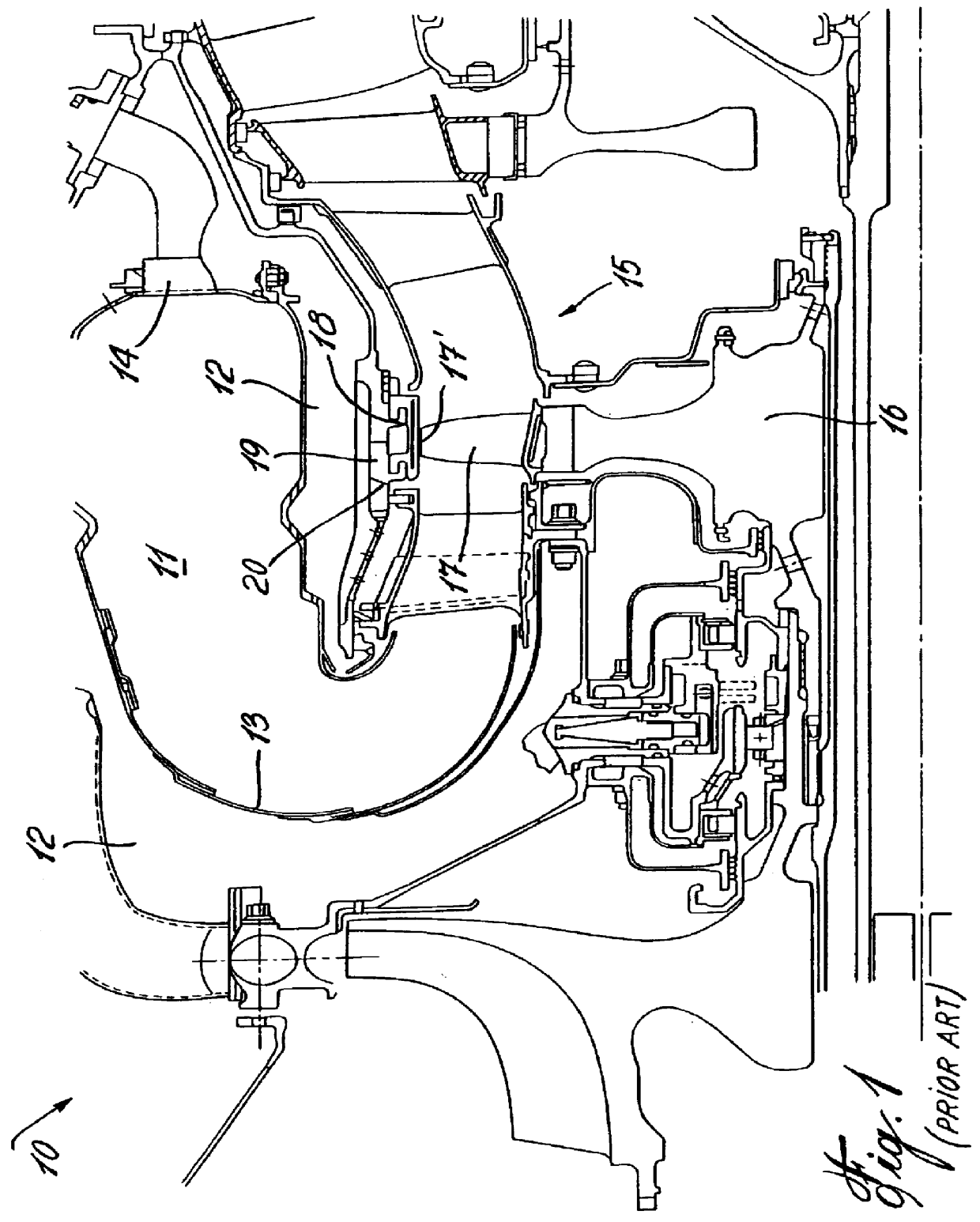
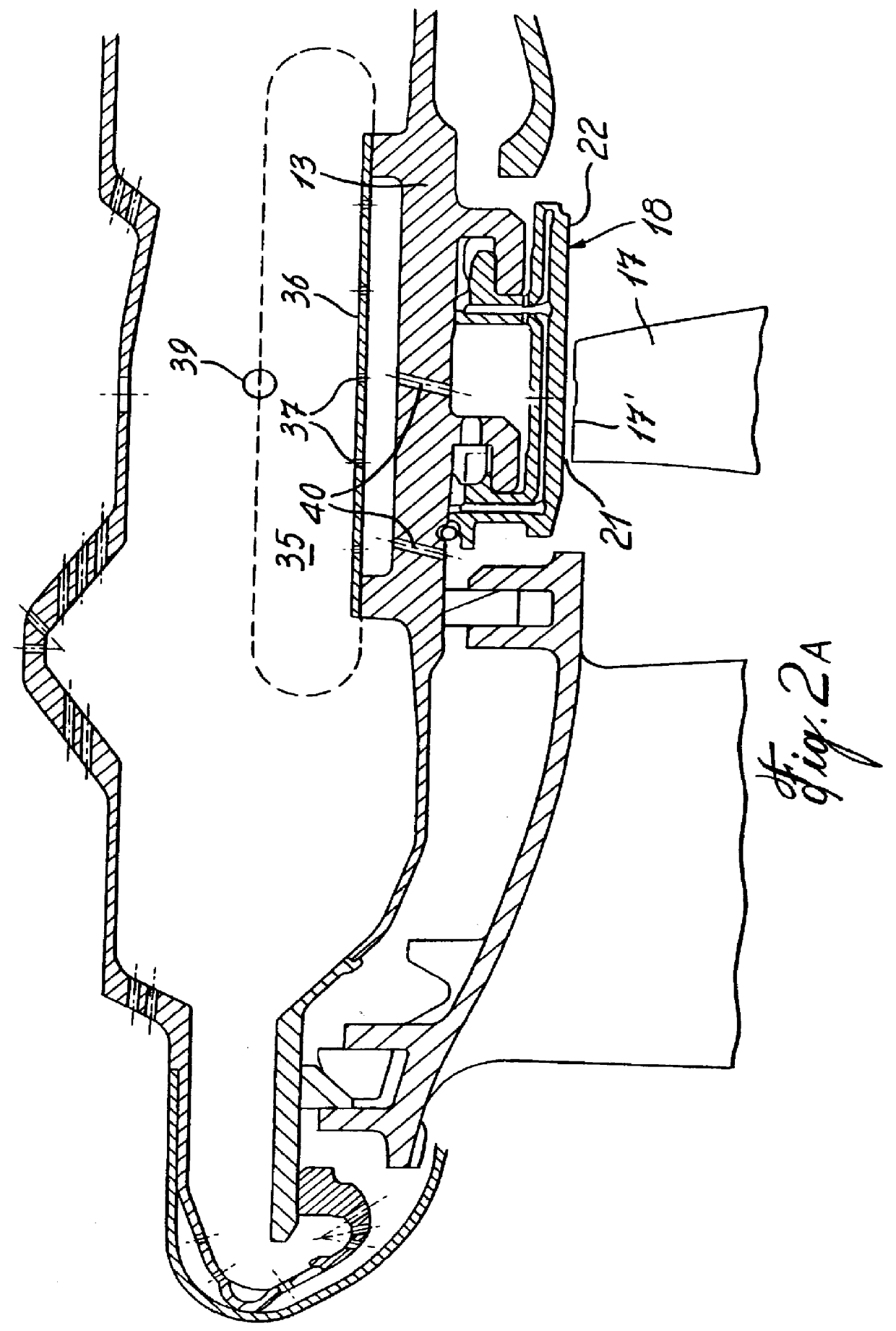
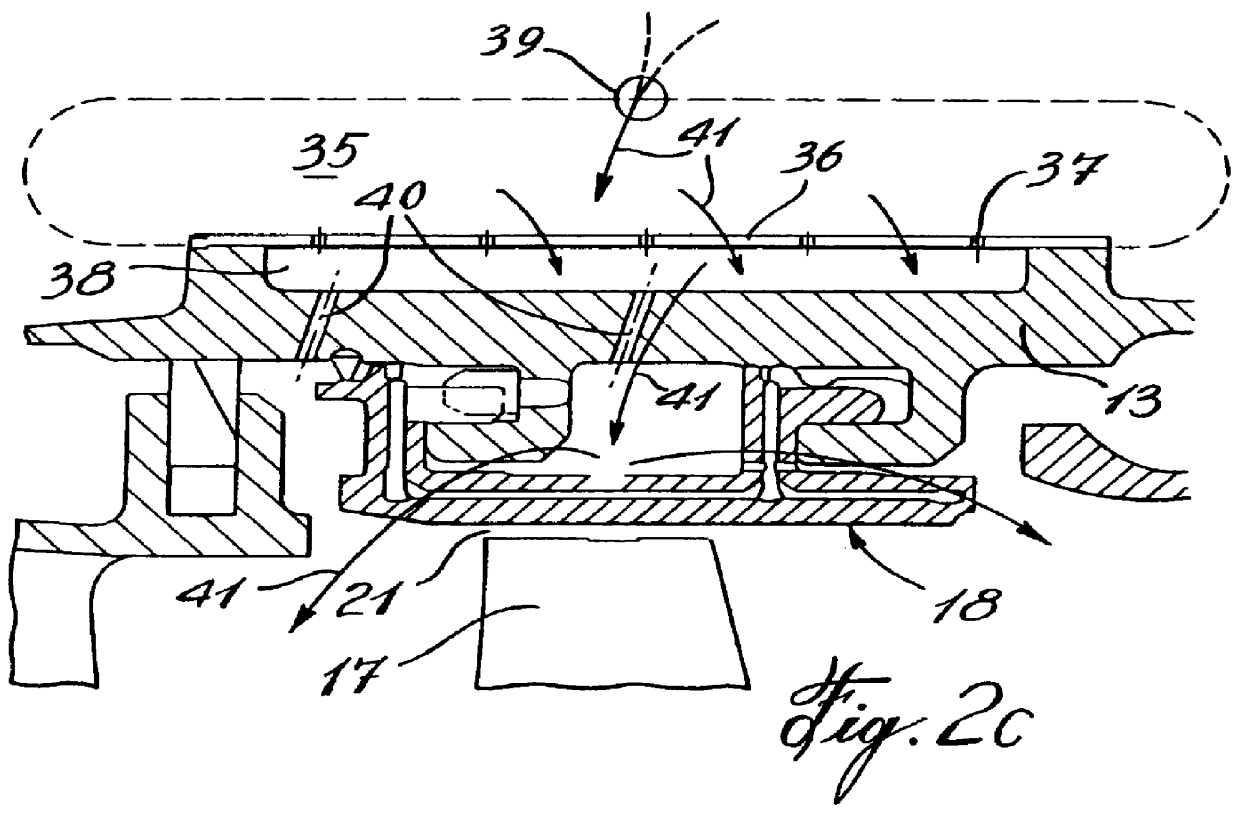
Tip clearance is the distance between the tip of a rotating airfoil and a stationary part.
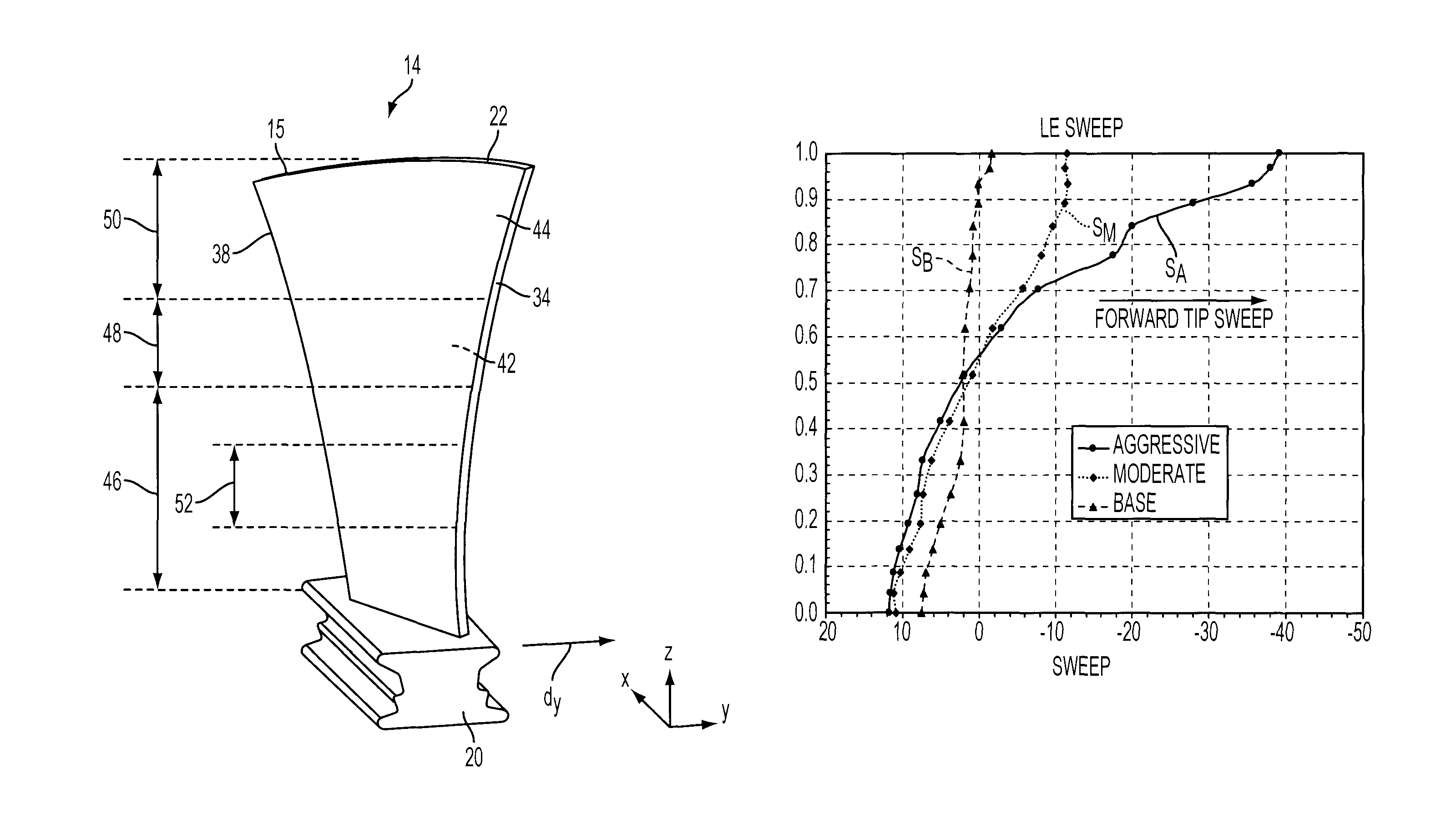
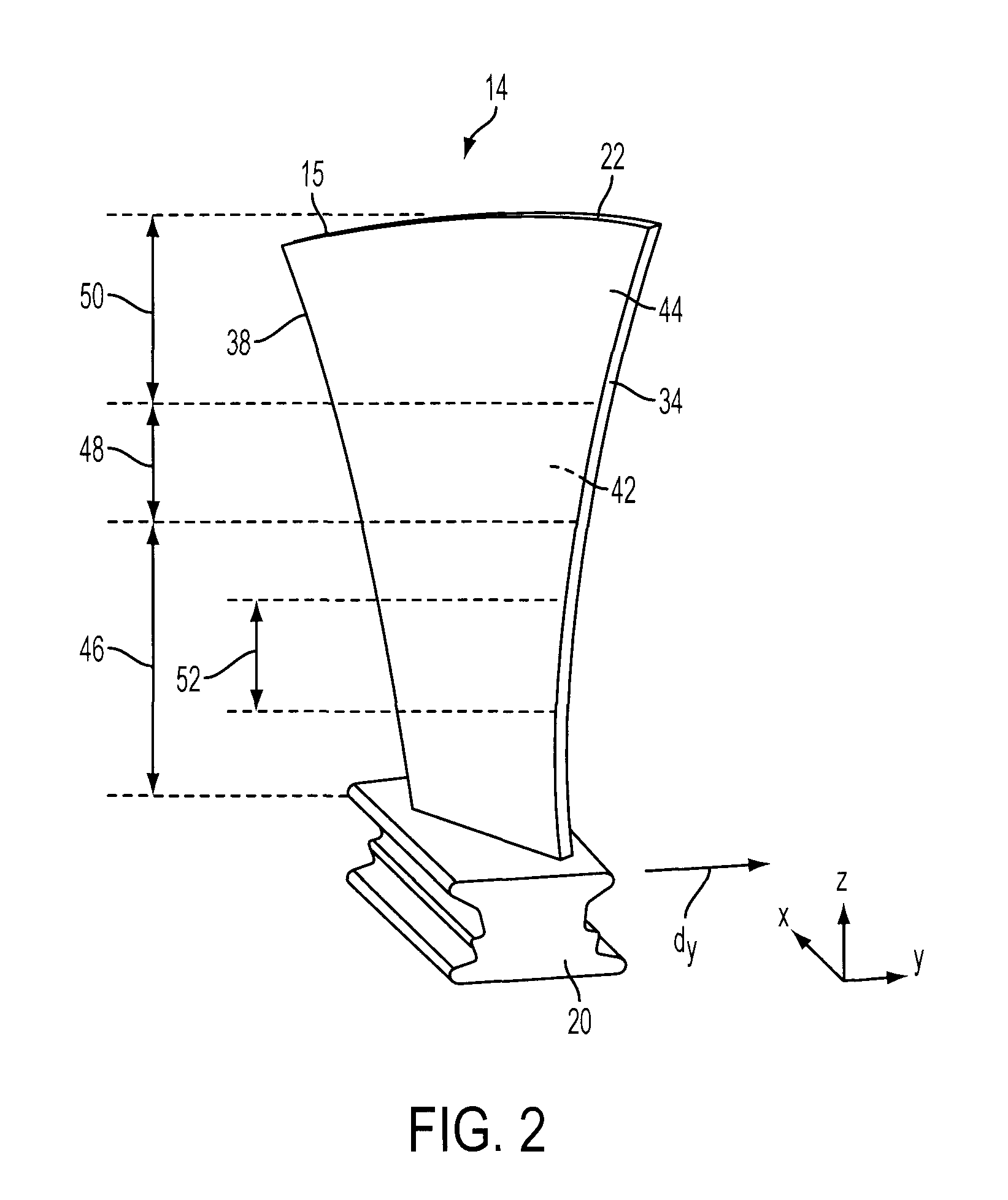
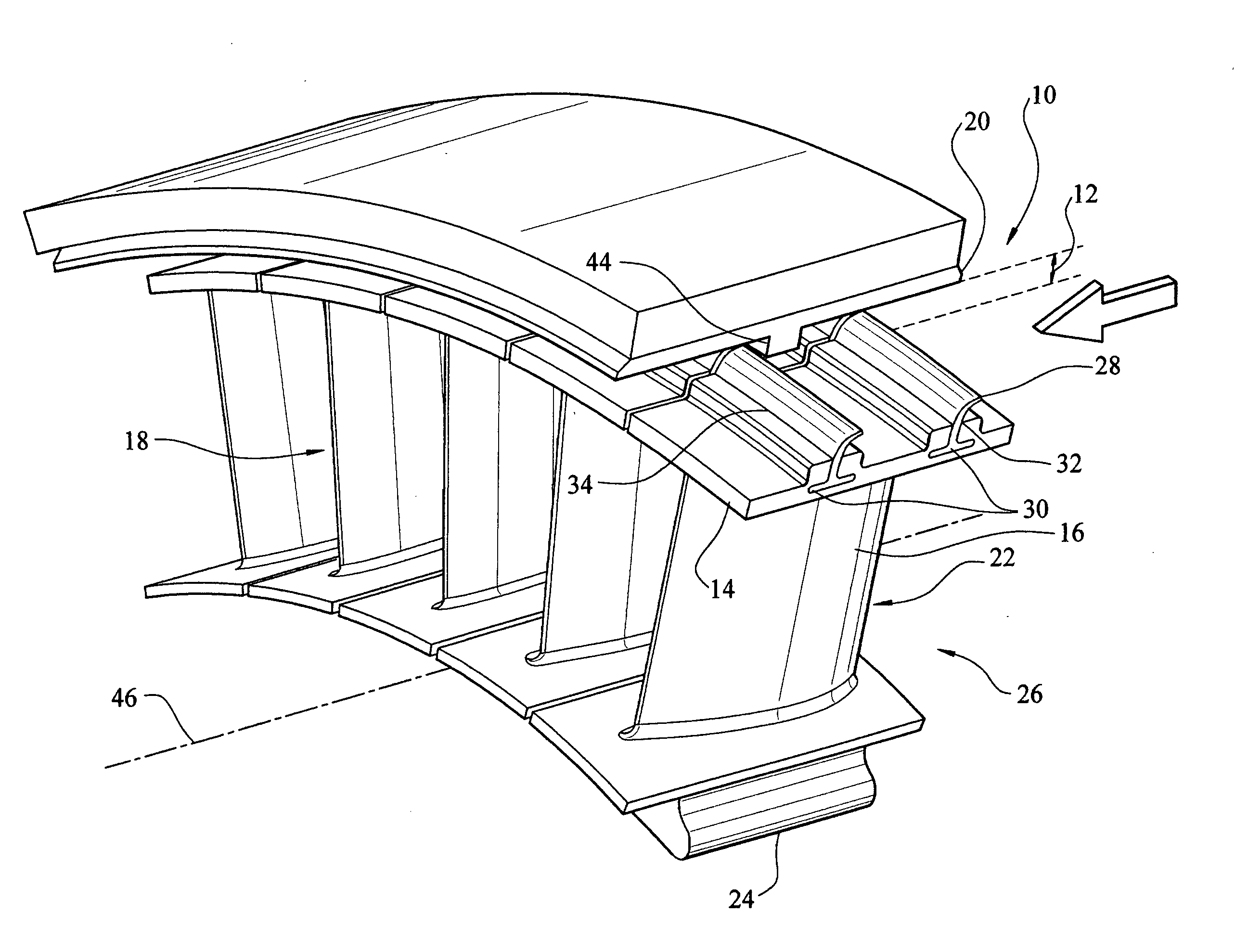
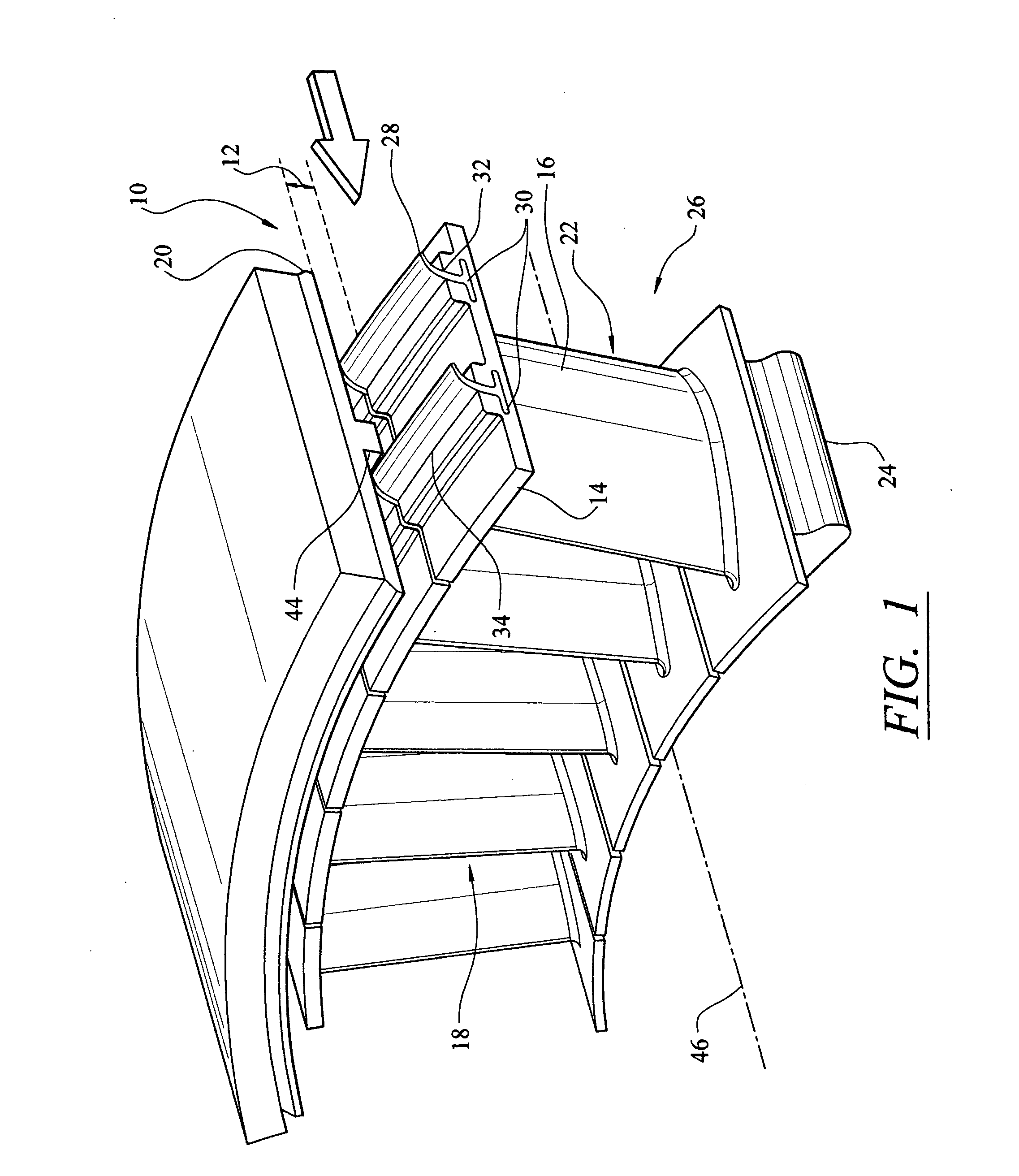
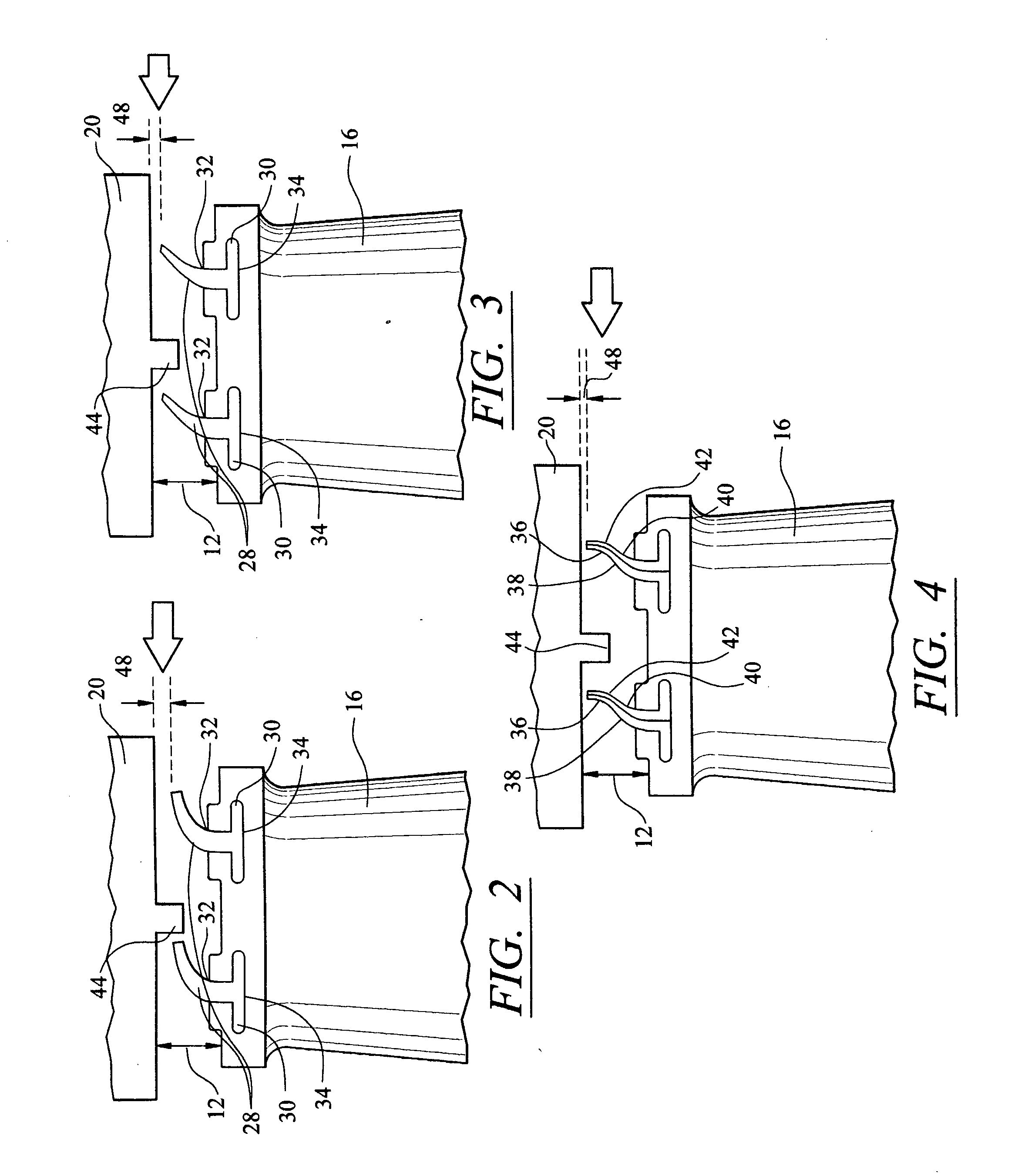
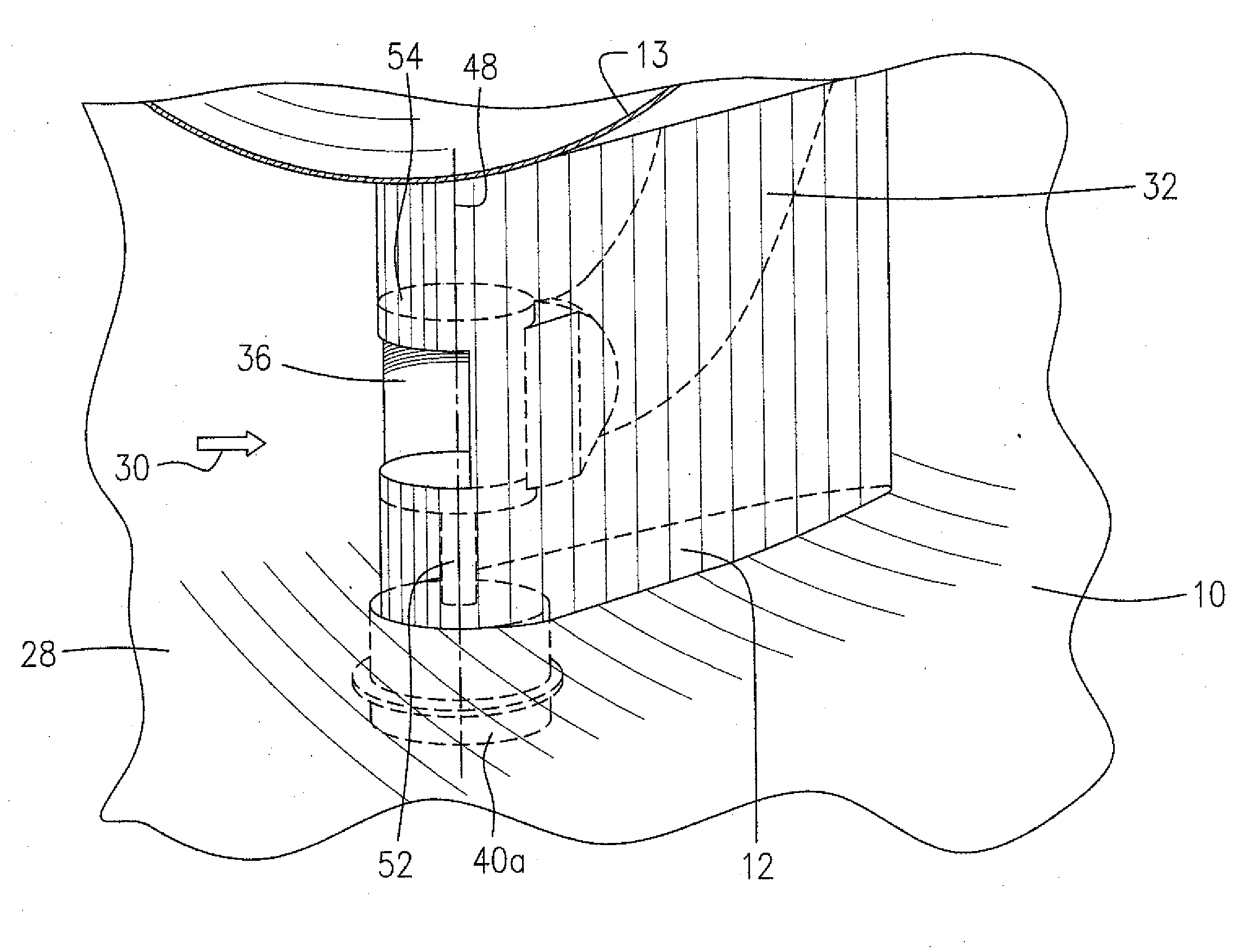
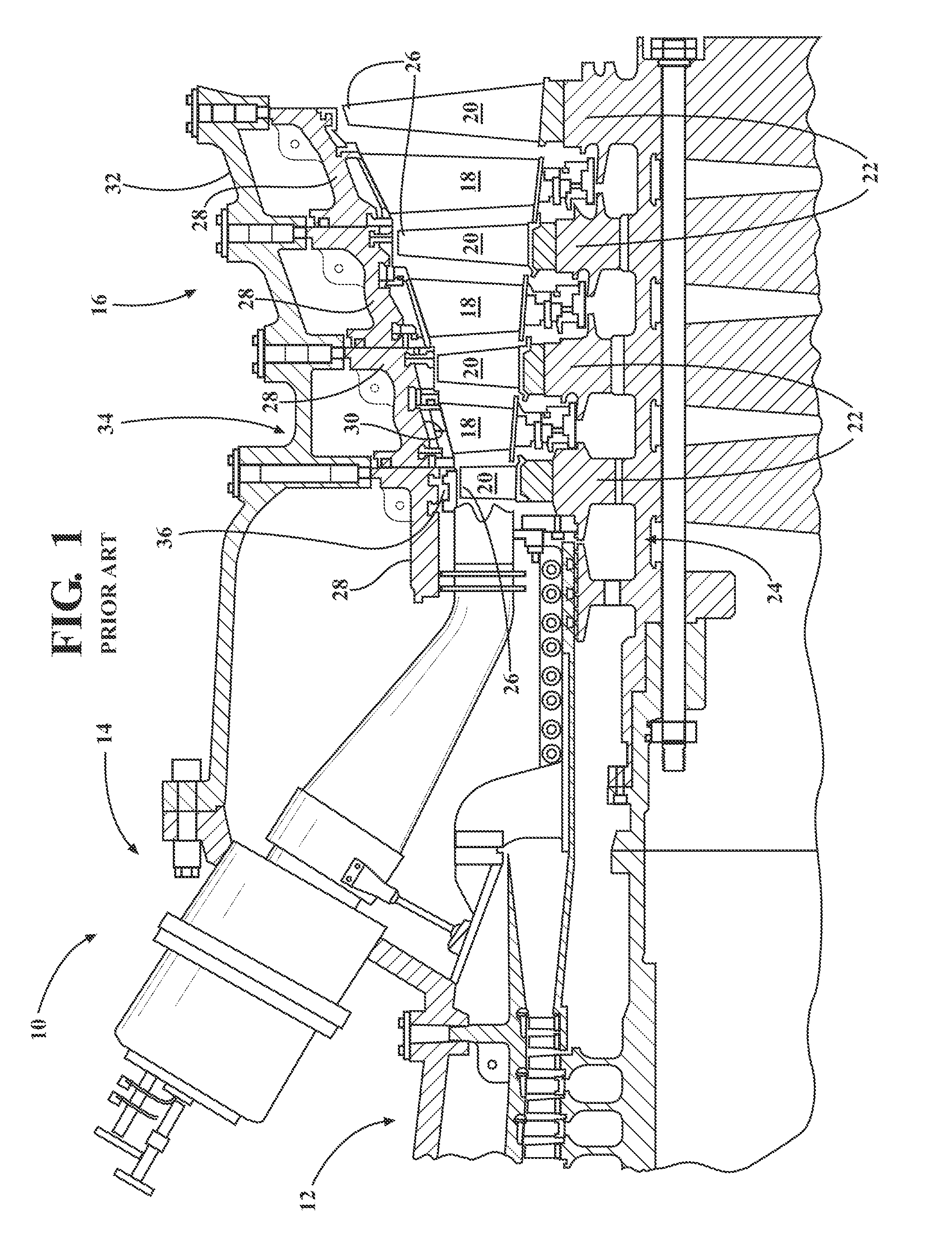
Compressor blade with forward sweep and dihedral
ActiveUS20100054946A1Reduce lossesPropellersRotary non-positive displacement pumpsTip clearanceCompressor blade
An airfoil for use as rotor blades in compressors for turbomachines, such as gas turbine engines. The airfoil includes increased forward sweep and forward dihedral effective to reduce losses generated by interaction of tip clearance flow, secondary flows and passage shocks.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Gas turbine high temperature turbine blade outer air seal assembly
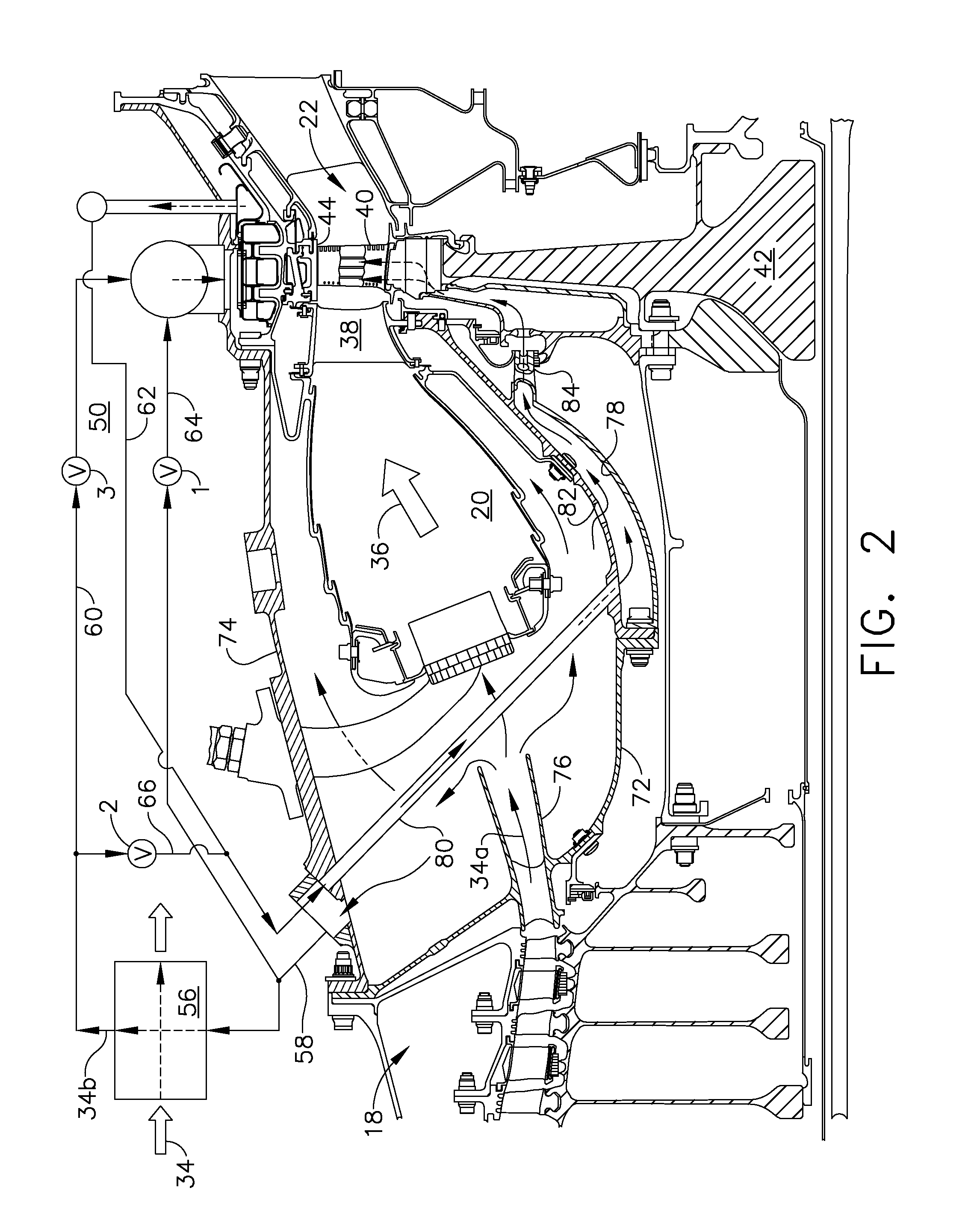
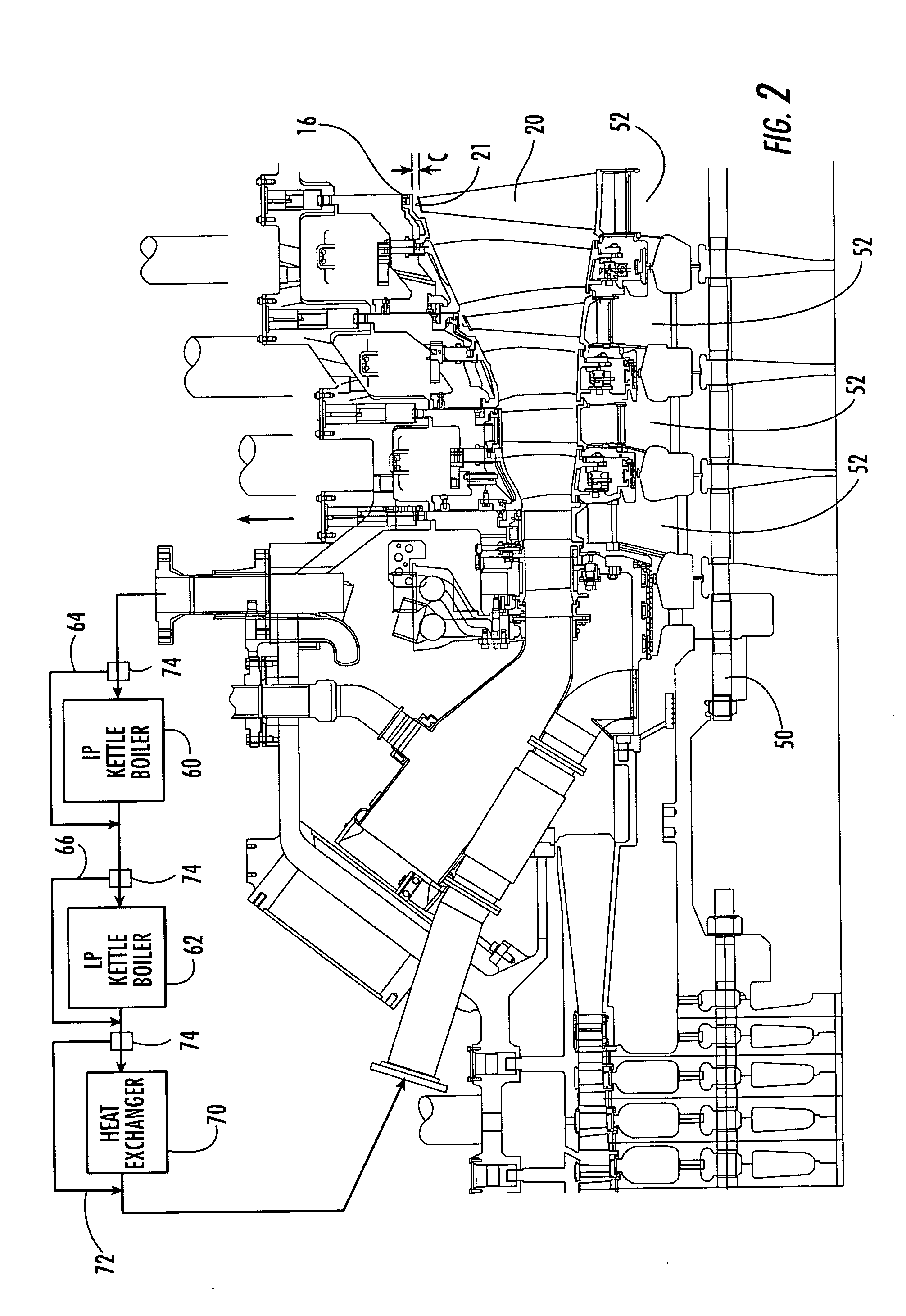
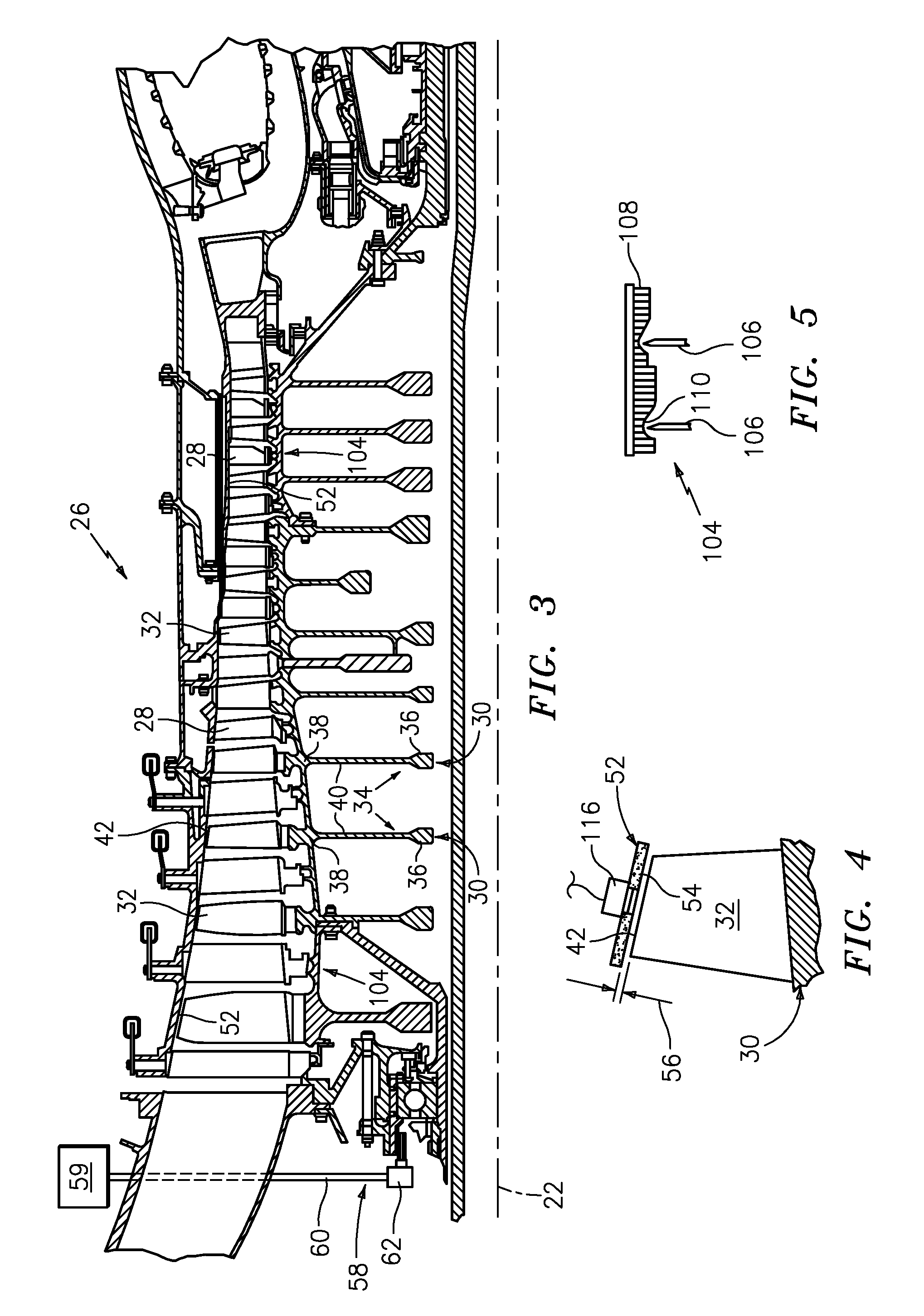
A turbine shroud assembly includes forward and aft hangers, an axisymmetric plenum assembly, ceramic shroud segments, ceramic spacers, and forward and aft rope seals. The plenum assembly supplies impingement cooling to the shroud and the hangers. The impingement cooling to the forward and aft hangers is controlled independently to improve blade tip clearance. The rope seals are radially inward from the hangers and reduce cooling flow leakage. The turbine shroud assembly can operate in a higher temperature environment using less cooling flow than the prior art.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Compound clearance control engine
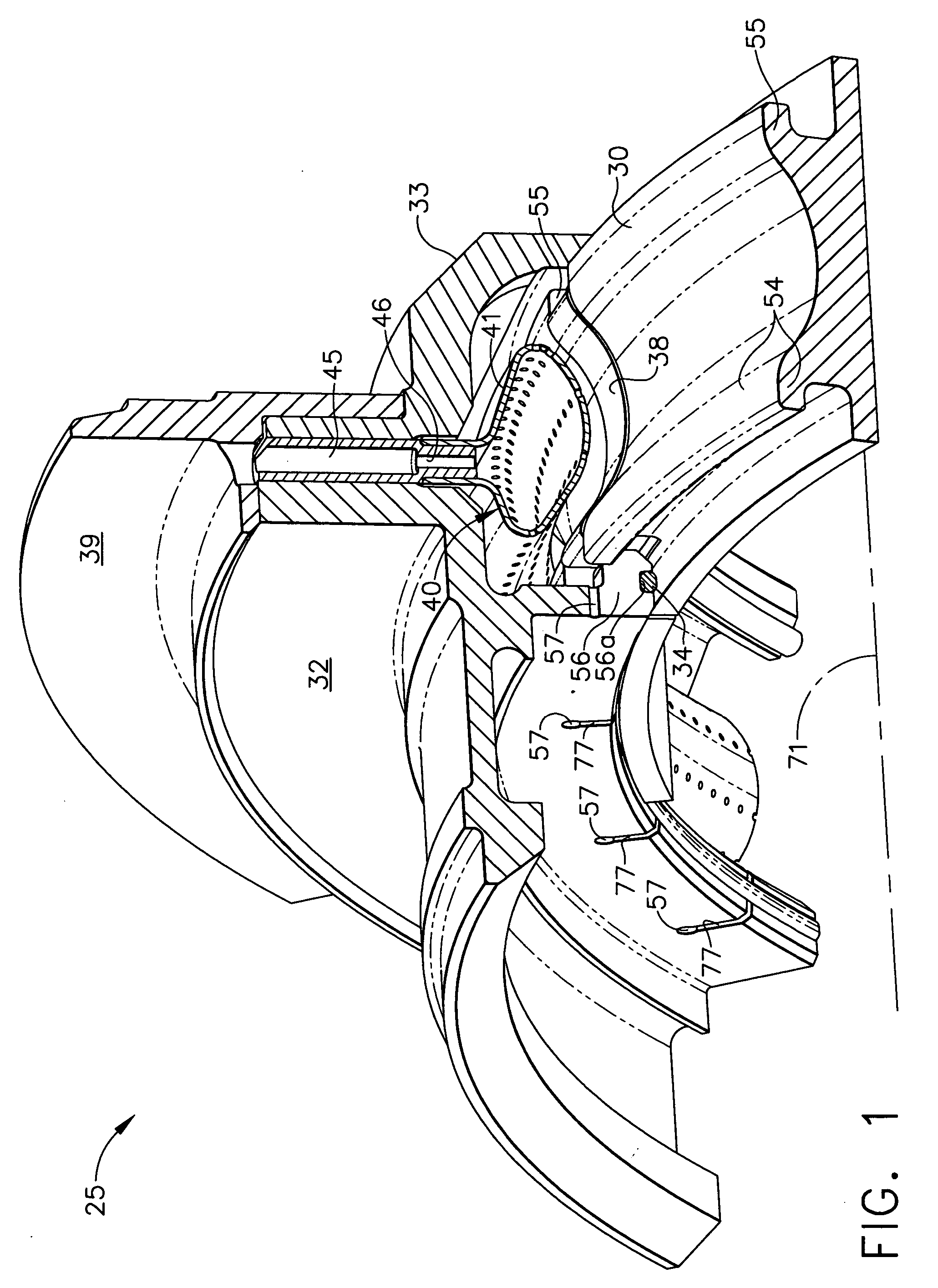
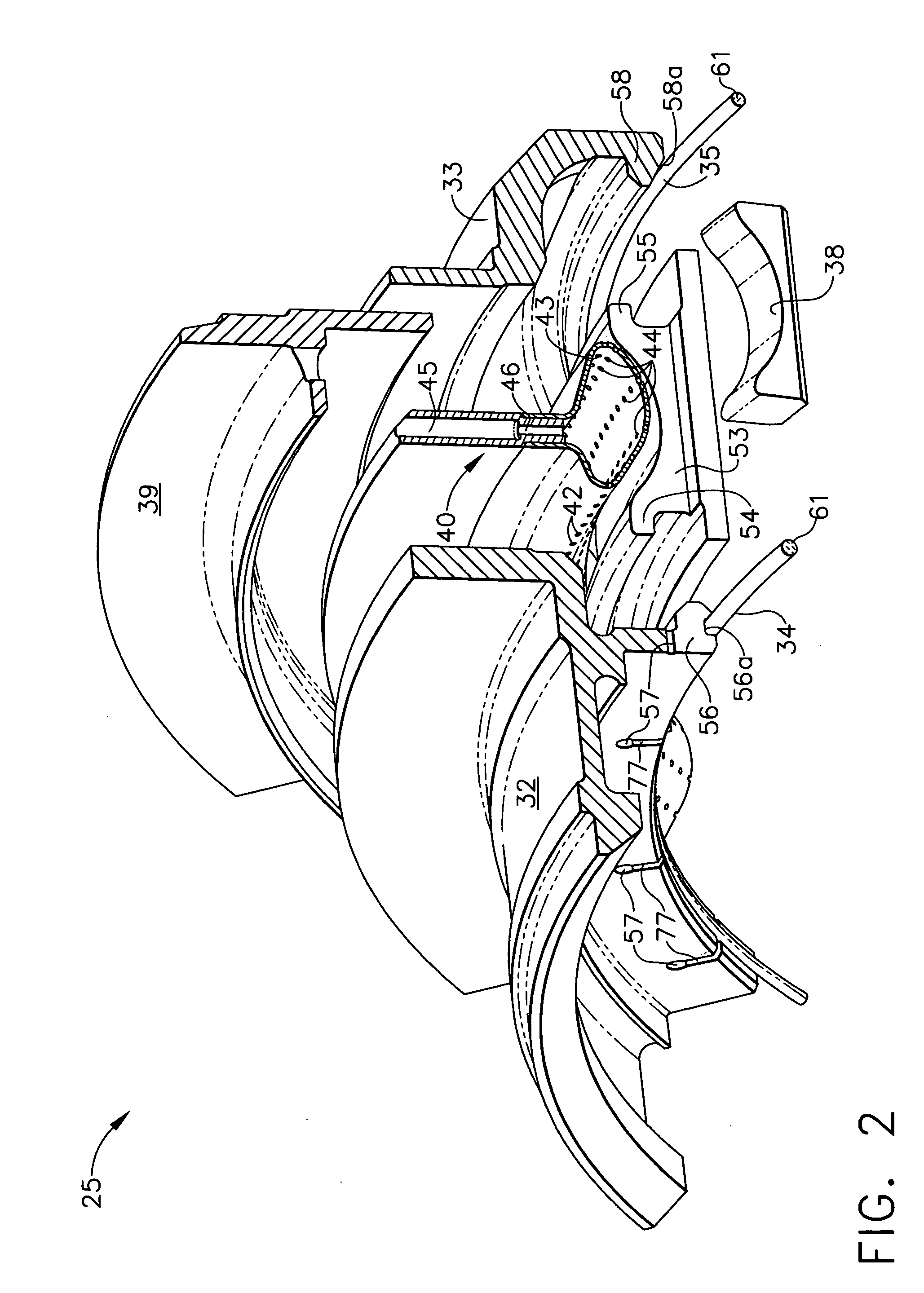
A gas turbine engine includes a compressor, combustor, and turbine having a row of blades mounted inside a surrounding turbine shroud. A heat exchanger is used for cooling pressurized air bled from the compressor. A distribution network joins the heat exchanger to the turbine for selectively channeling air from the heat exchanger below the blades and above the shroud for controlling blade tip clearance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Turbomachine with reduced leakage penalties in pressure change and efficiency
InactiveUS20080044273A1Reduce adverse effectsReduce trafficPump componentsReaction enginesEngineeringTip clearance
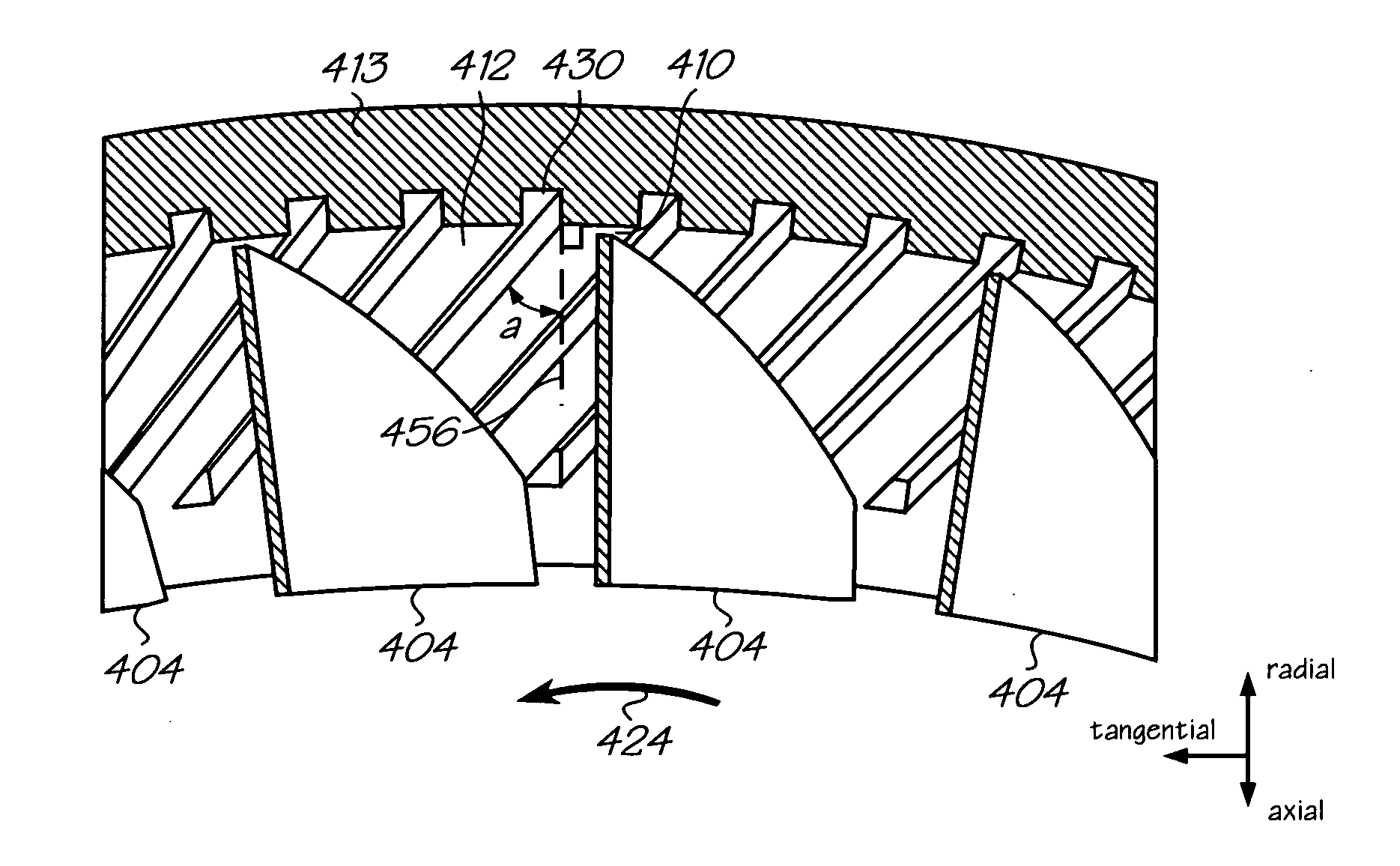
A turbomachine is provided having at least one row of blades oriented at a predetermined stagger. Casing grooves are provided proximate to at least a portion of the tip of the blades. The grooves are oriented substantially normal to the stagger of the blades. The normal of the blade is determined from a chord of the blade. The chord may be taken across a pair of corresponding points one the upstream and downstream end of the blade, hence across the extent of the cross-sectional shape of the blade. Alternatively, a blade chord may be determined over only a portion of the blade, for instance, from a point along the centerline of the upstream end of the blade to a second point on the centerline midway down the blade from the upstream end. Optimally, the grooves are positioned adjacent to the upstream half of the blades, but may continue across the axial extent of the blades. The spacing between grooves can be optimized for blade stagger in order to find an optimal number of grooves that concurrently cross the blade. Additionally, obtaining an optimal groove depth for a particular turbomachine requires knowing only the tip clearance gap as groove depth is directly related to the tip clearance. Furthermore, since the groove may be substantially smaller than prior art casing treatments, fluid recirculation is reduced. The blade-normal groove may take a variety of cross-sectional shapes. Optimally, the aft surface of the groove will have less than a 45° incline to the radial at that point.
Owner:KHALID SYED ARIF
Gas turbine high temperature turbine blade outer air seal assembly
A turbine shroud assembly includes forward and aft hangers, an axisymmetric plenum assembly, ceramic shroud segments, ceramic spacers, and forward and aft rope seals. The plenum assembly supplies impingement cooling to the shroud and the hangers. The impingement cooling to the forward and aft hangers is controlled independently to improve blade tip clearance. The rope seals are radially inward from the hangers and reduce cooling flow leakage. The turbine shroud assembly can operate in a higher temperature environment using less cooling flow than the prior art.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
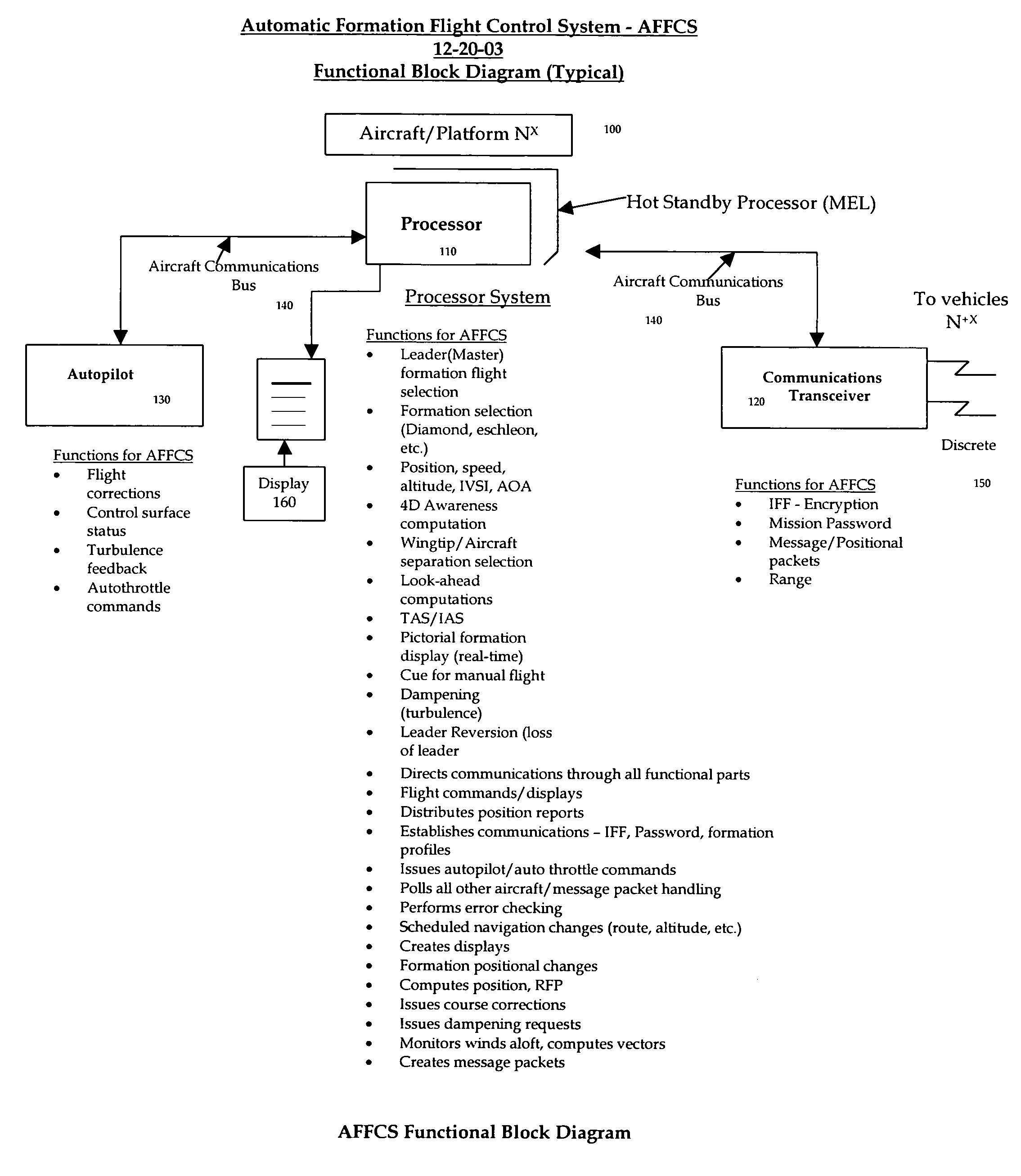
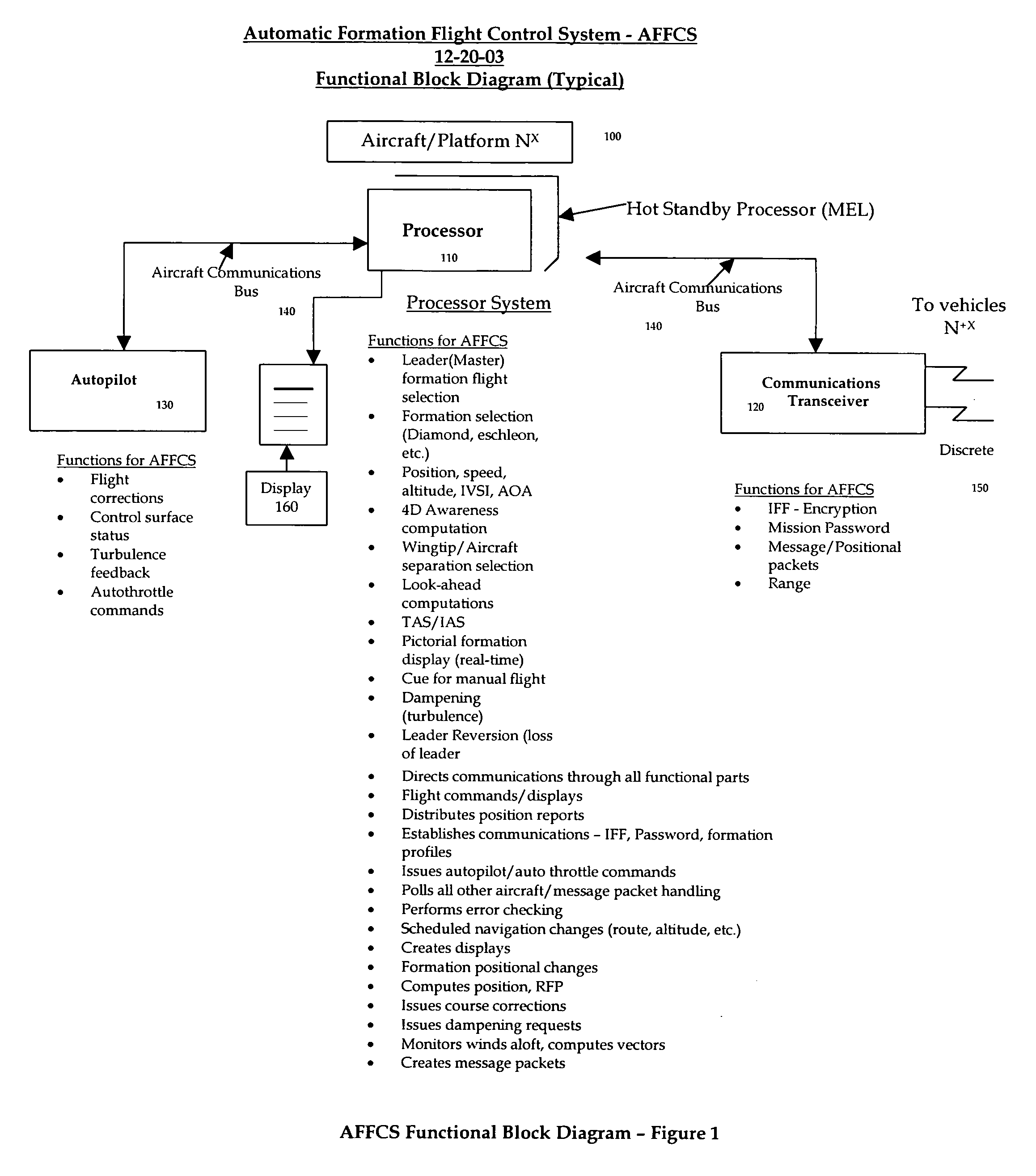
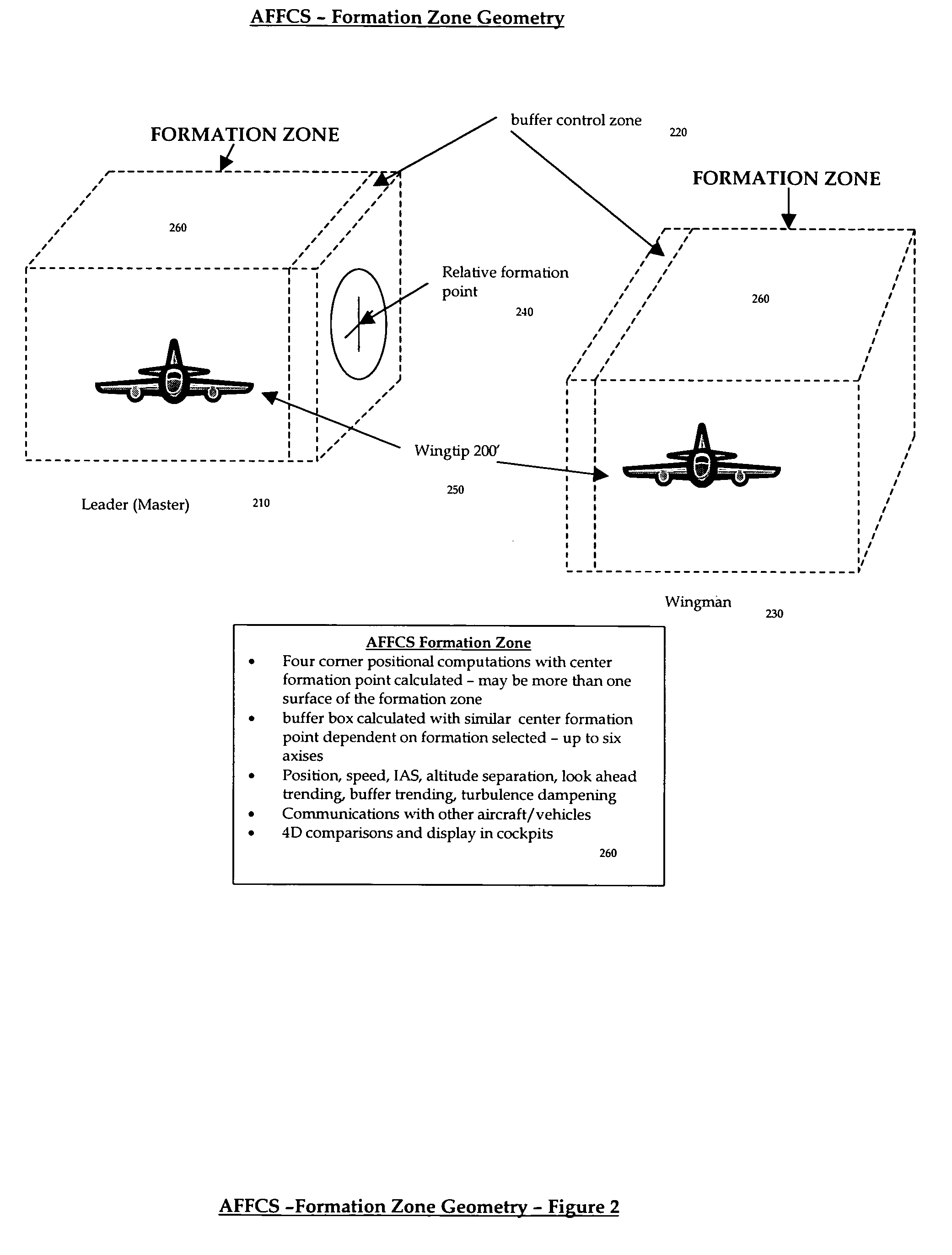
Automatic formation flight control system (AFFCS)-a system for automatic formation flight control of vehicles not limited to aircraft, helicopters, or space platforms
ActiveUS6926233B1Discrete and precise and positive controlProvide controlAircraft stabilisationActuated automaticallyTransceiverTelecommunications link
A totally integrated system for automatic formation flight control of multiple vehicles not limited to aircraft, helicopters, or space platforms. For instance, the system may be used to control any number of aircraft in a pre-determined flight formation and provide “positive” identification, control and discrete communications between any number of vehicles. Thus the invention prevents mid-air collisions between vehicles in formation flight. The system generally includes a processor located on the vehicles to enable communications, unique position computations and control messaging between any number of aircraft in formation flight, a communications transceiver located on the vehicle that provides discrete communication links to any number of aircraft in formation flight an autopilot and a display. The processor may take into consideration velocity, direction, winds aloft, wing tip clearance of any number of vehicles. On aircraft, the system will display the current formation and vehicles relative position under control by this invention. The system may be overridden in flight.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Compound clearance control engine
A gas turbine engine includes a compressor, combustor, and turbine having a row of blades mounted inside a surrounding turbine shroud. A heat exchanger is used for cooling pressurized air bled from the compressor. A distribution network joins the heat exchanger to the turbine for selectively channeling air from the heat exchanger below the blades and above the shroud for controlling blade tip clearance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
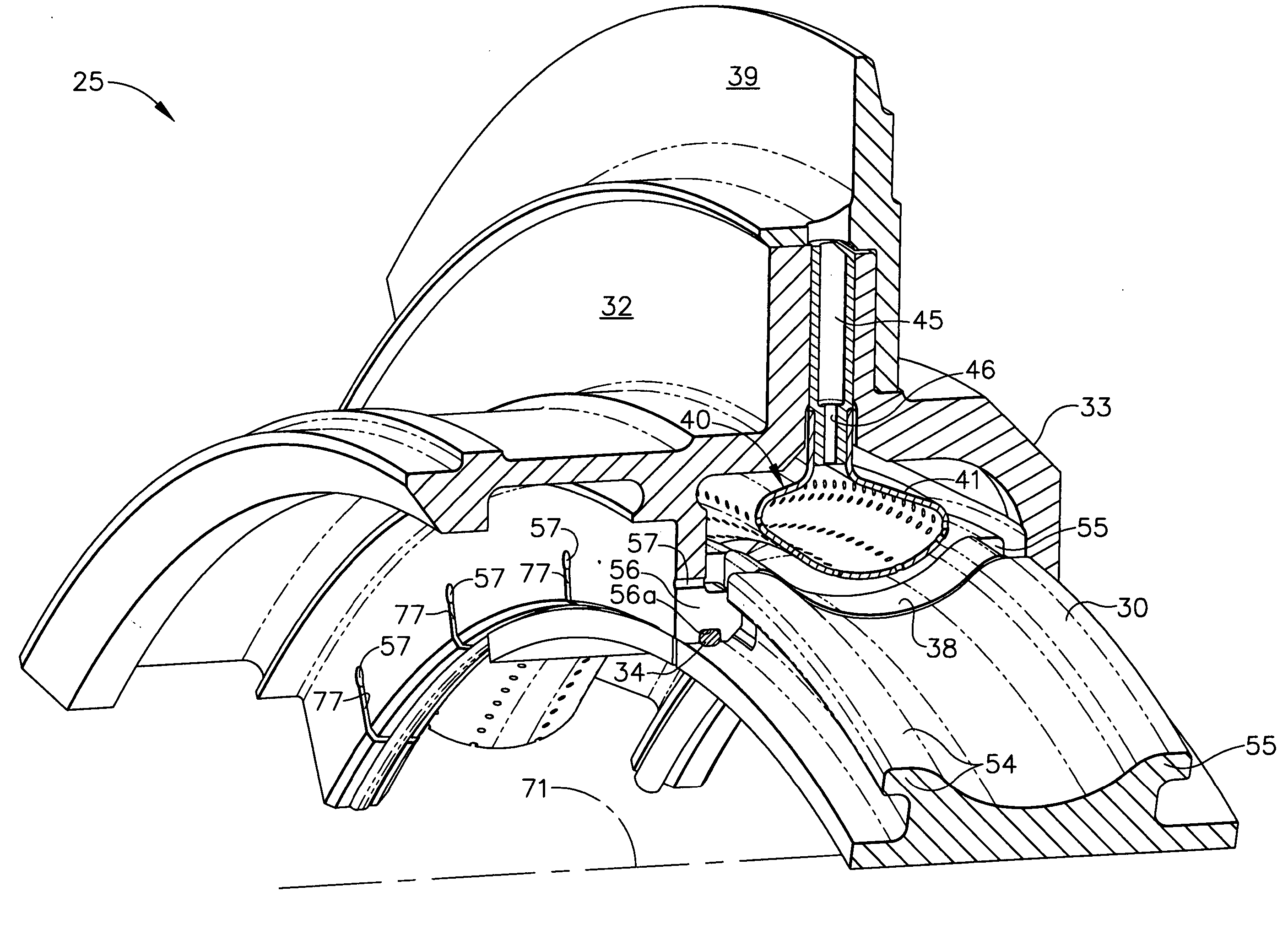
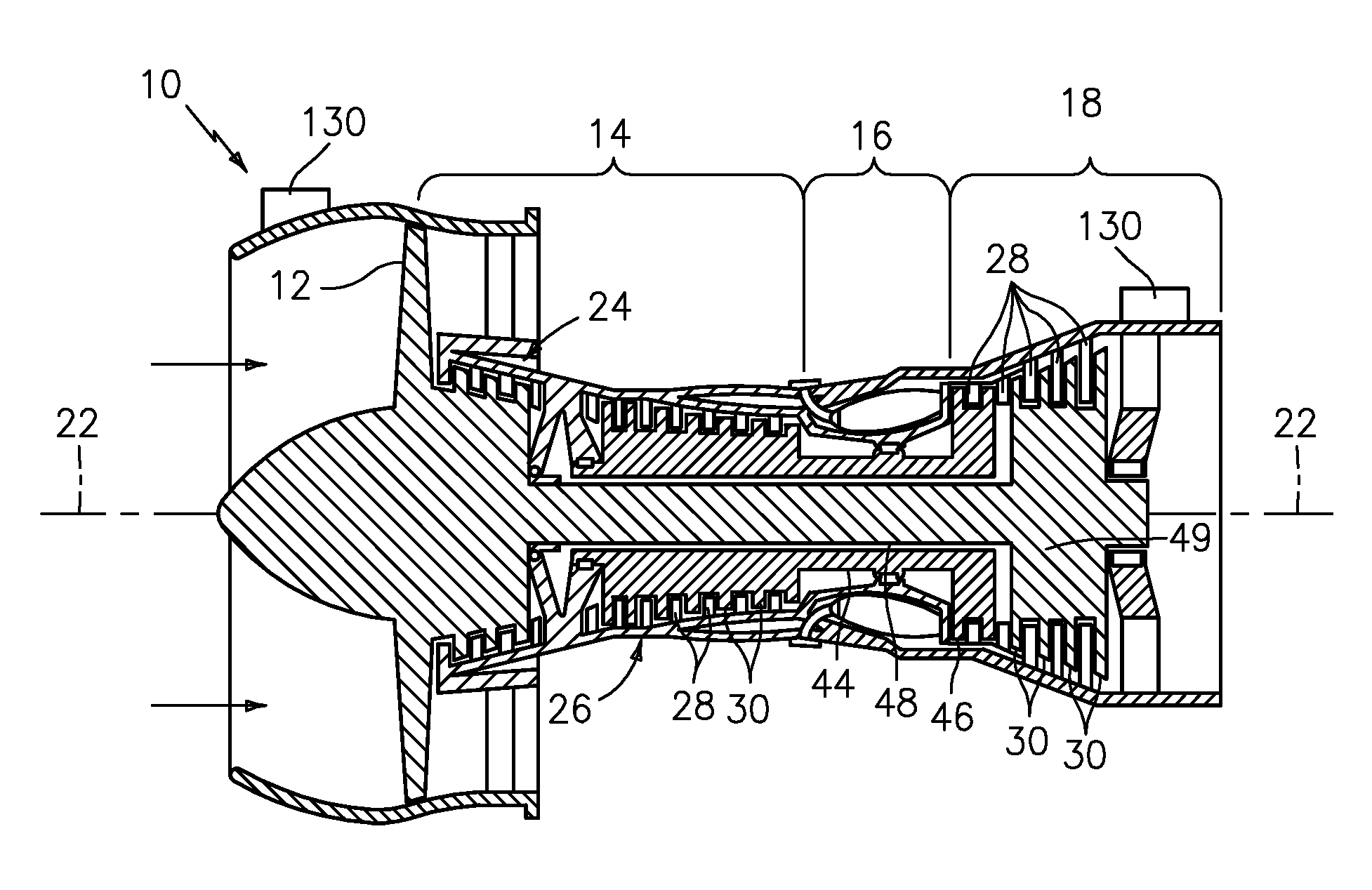
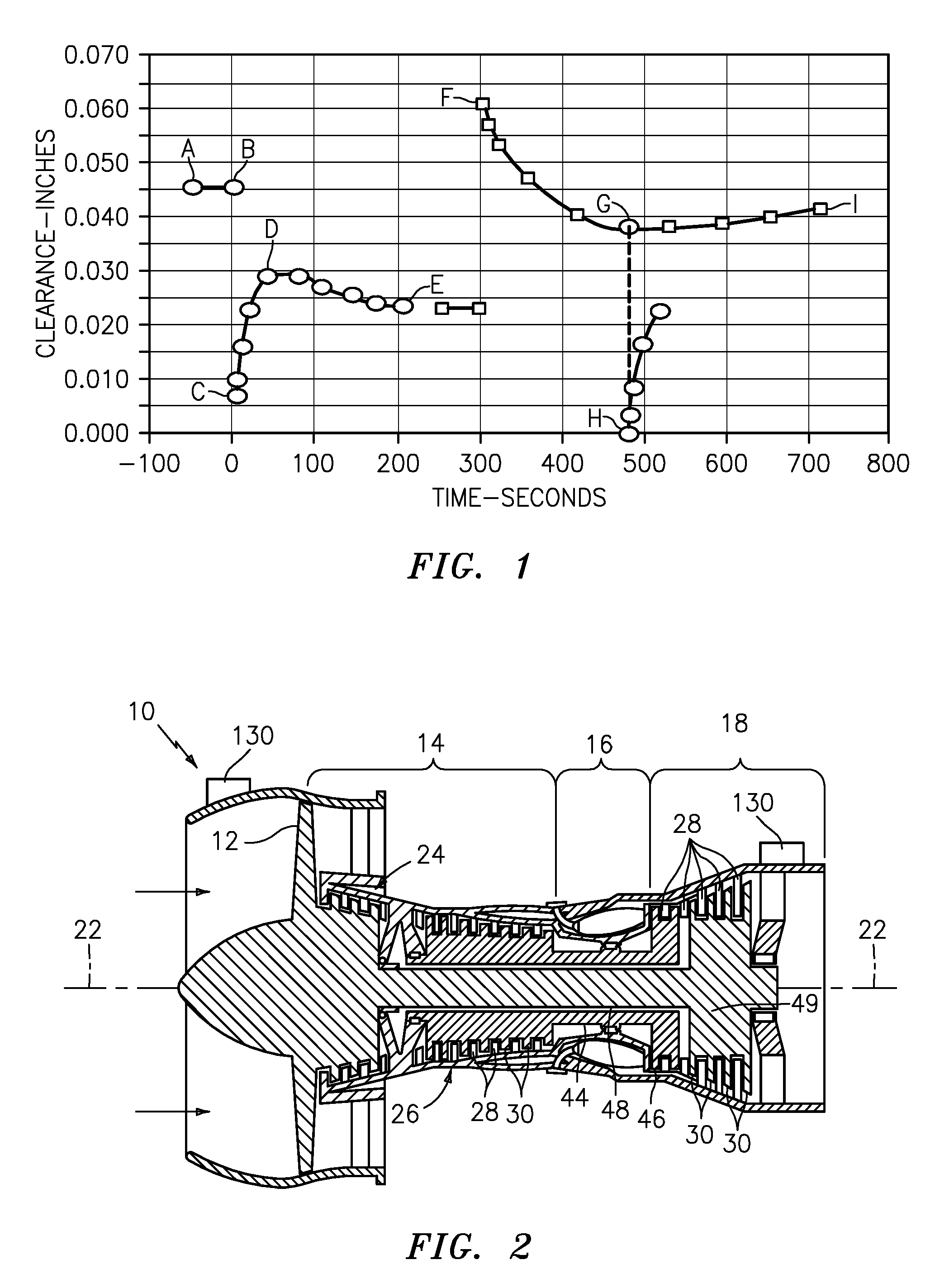
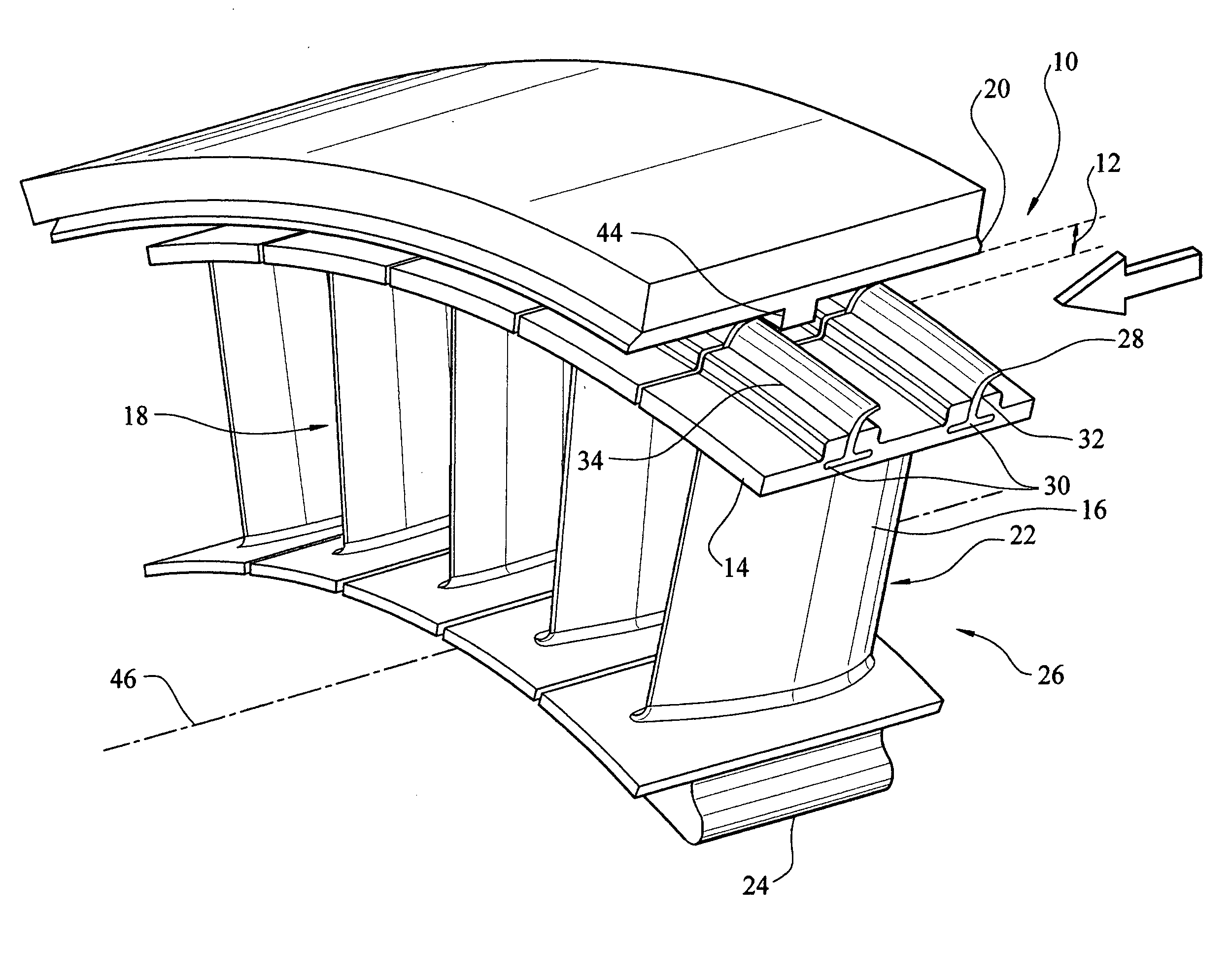
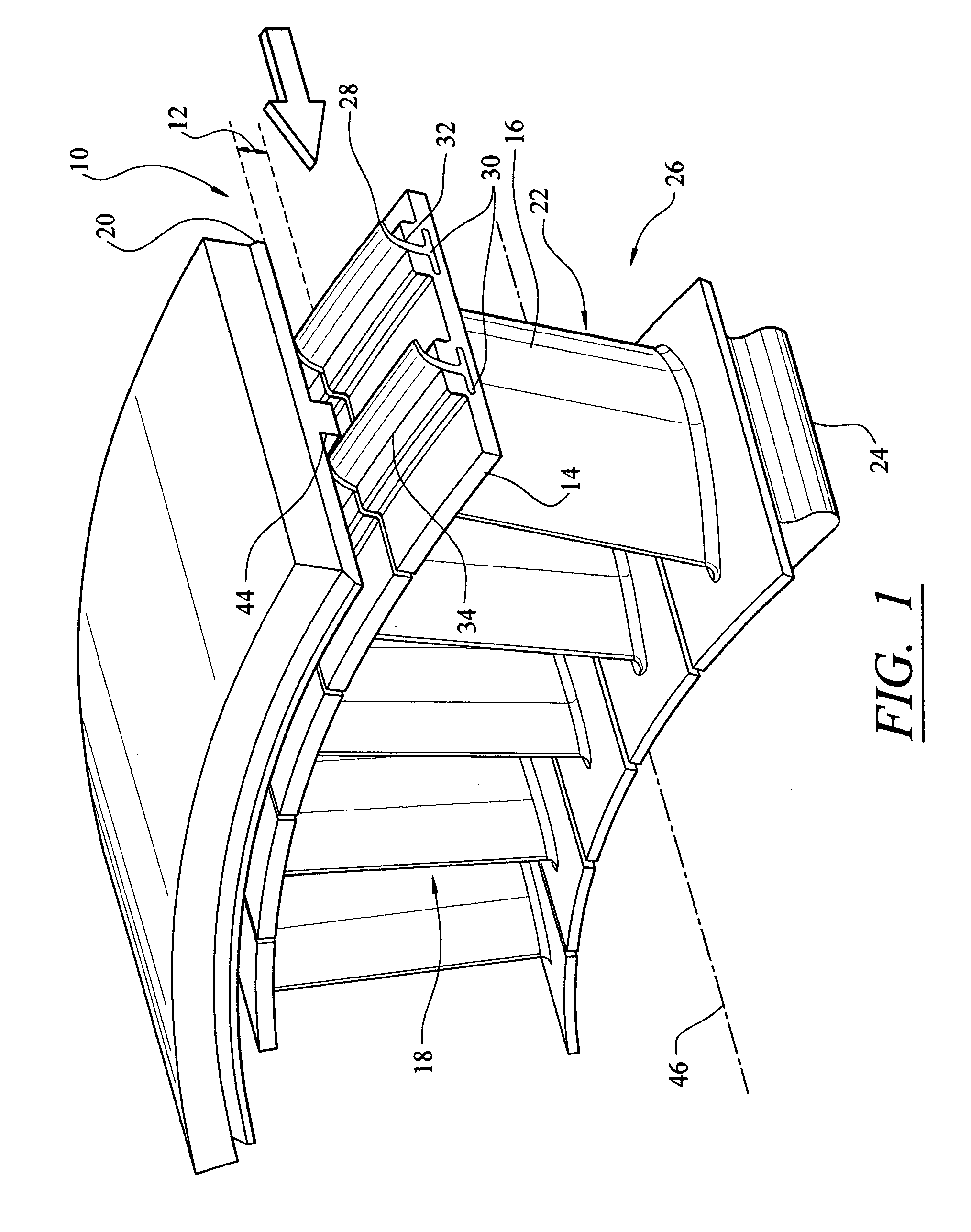
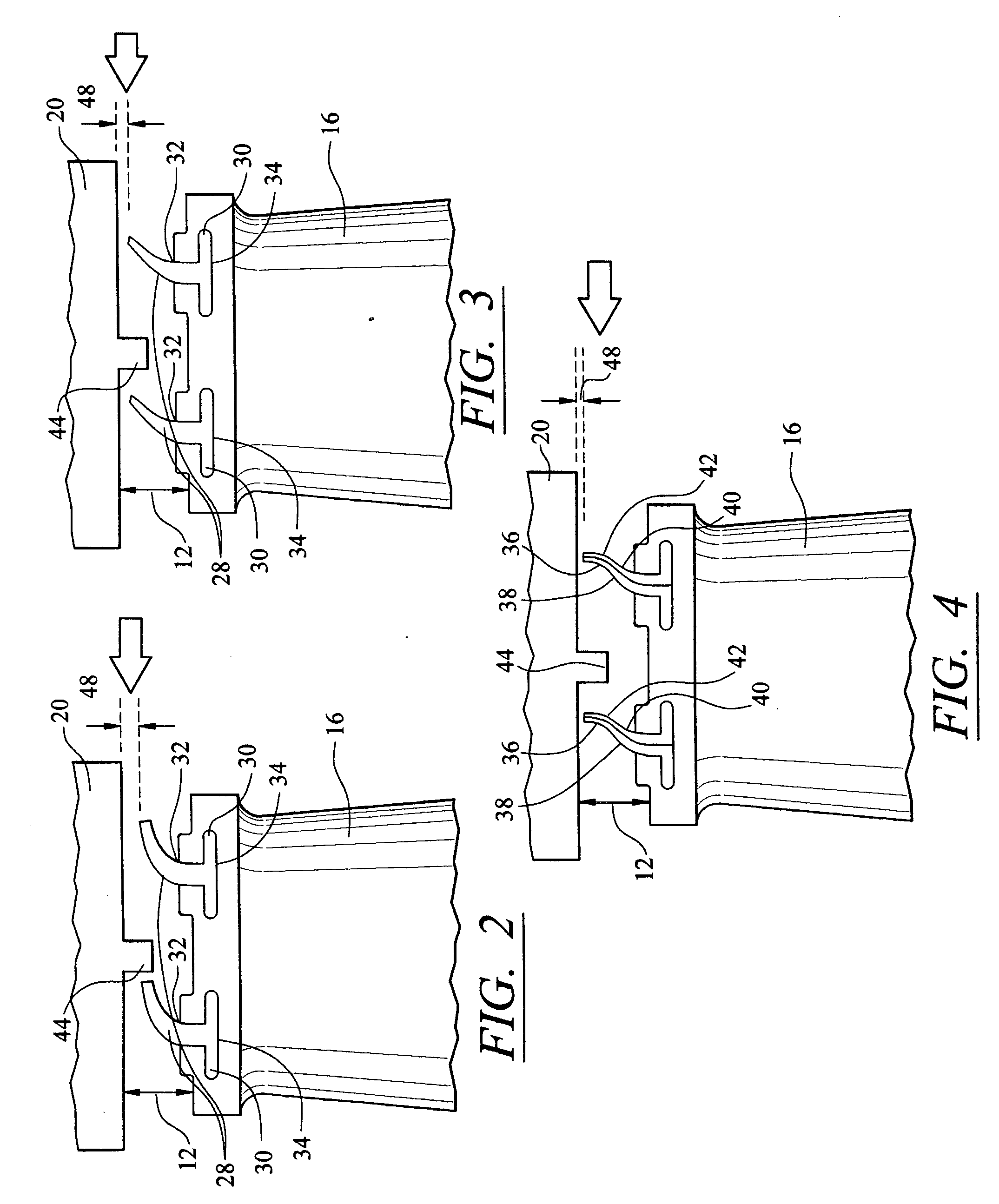
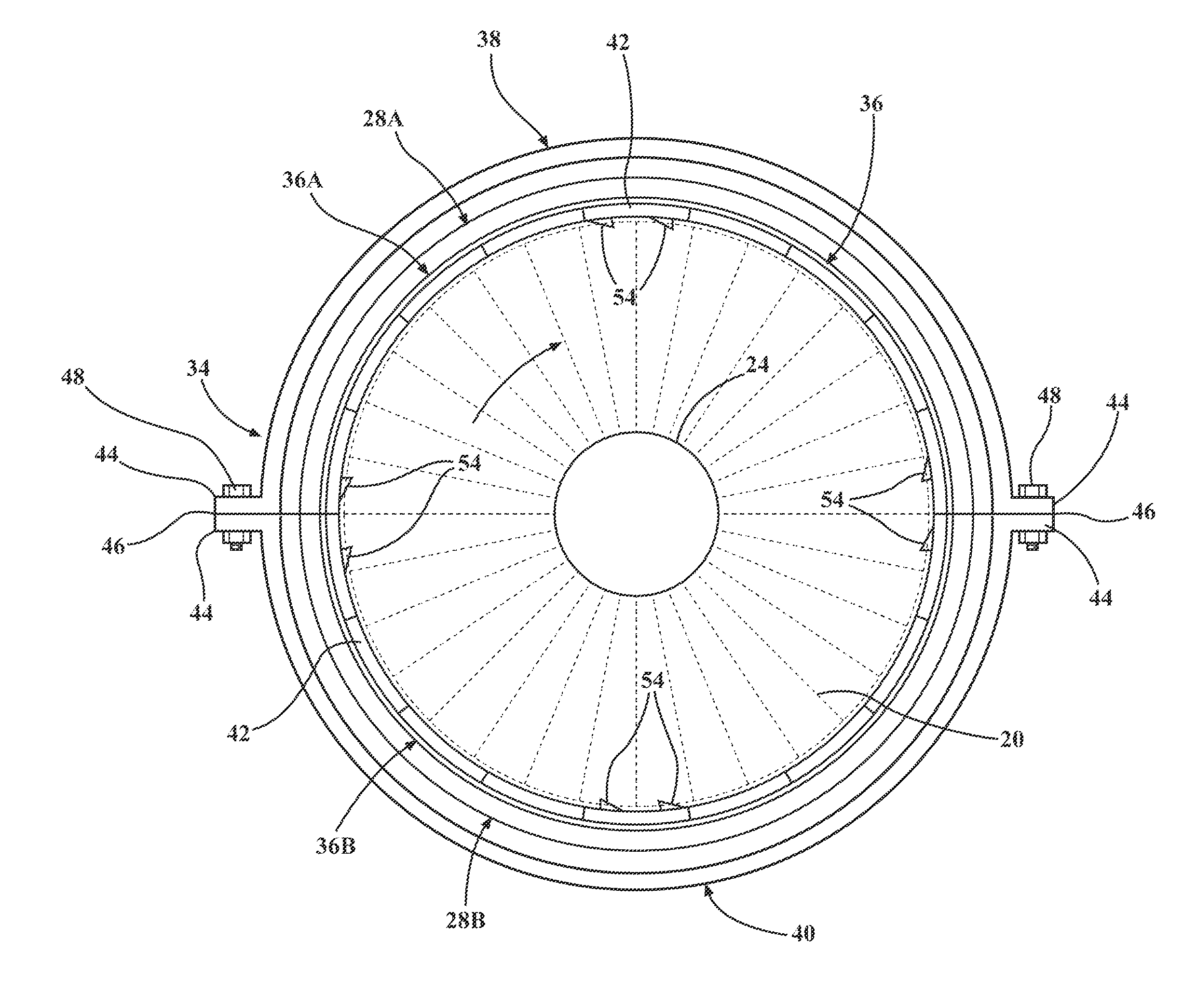
Compressor casing with passive tip clearance control and endwall ovalization control
A passive clearance control system for a gas turbine engine component. The system provides a blade shroud that is isolated from the component case and can move radially to maintain blade clearance. A plurality of vane sectors define a stator ring including a blade shroud. The stator ring and the control ring are coupled together and mounted within the component by a plurality of radial extending mounting members.
Owner:ALLISON ADVANCED DEVMENT
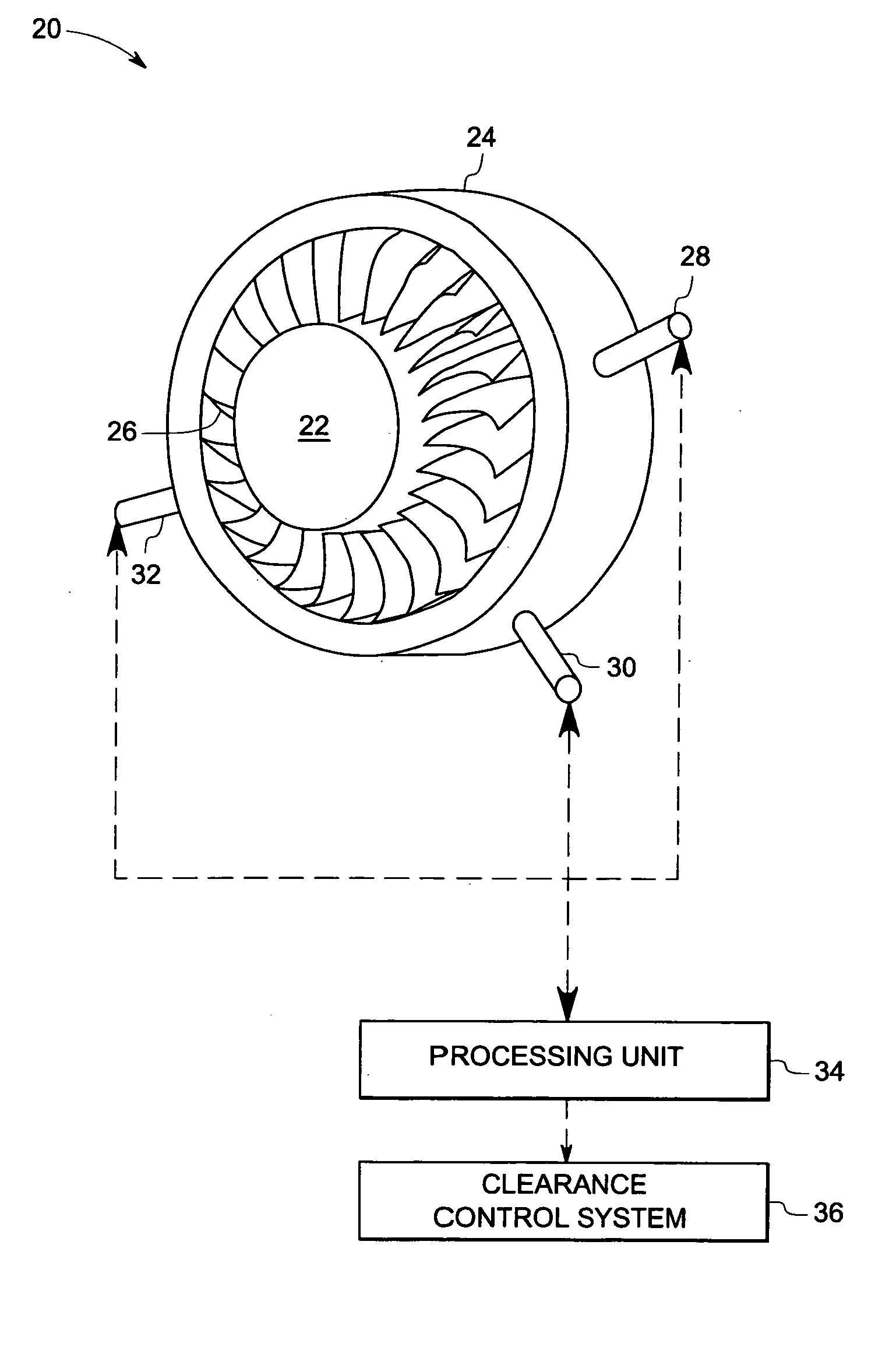
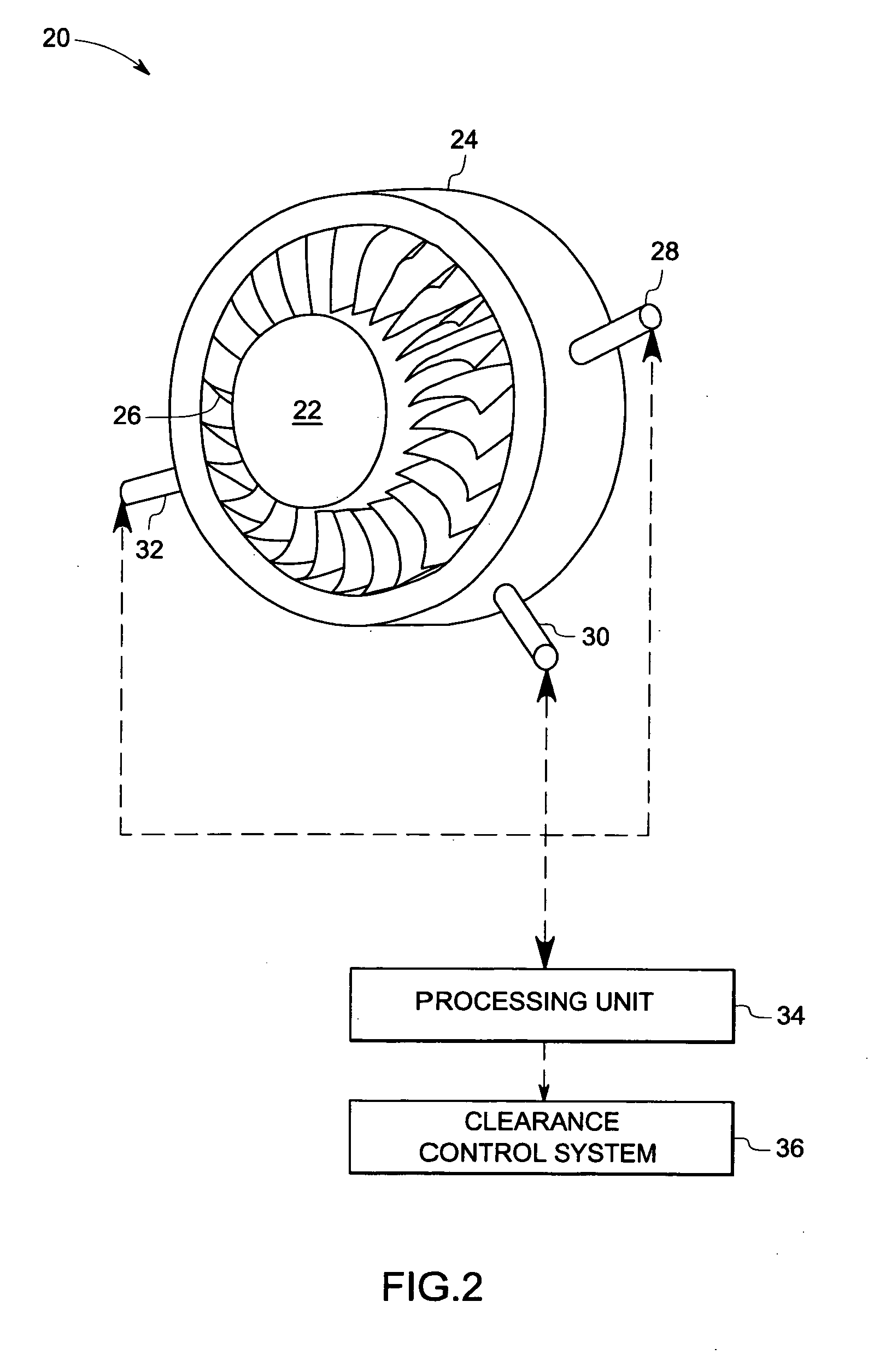
Multi tip clearance measurement system and method of operation
A multi tip clearance measurement system is provided. The clearance measurement system includes a sensor disposed on a first object, wherein the sensor comprises a plurality of probe tips configured to generate signals representative of a sensed parameter corresponding to a second object and a processing unit configured to evaluate the signals from subsets of the sensed parameters from the probe tips to detect an outlier probe tip and to adjust a gain, or an offset of the respective outlier probe tip for estimating the clearance between the first and second objects based upon the signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Turbine tip clearance control system
An apparatus and method for selectively cooling a gas turbine engine component for the purpose of controlling blade tip clearance during transient conditions, wherein cooling air is admitted intermittently according to a desired a duty cycle based on a present or anticipated transient condition.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Part load blade tip clearance control
InactiveUS20050050901A1Reduce the temperatureLow cooling temperatureTurbine/propulsion engine coolingBlade accessoriesCircular discTurbine blade
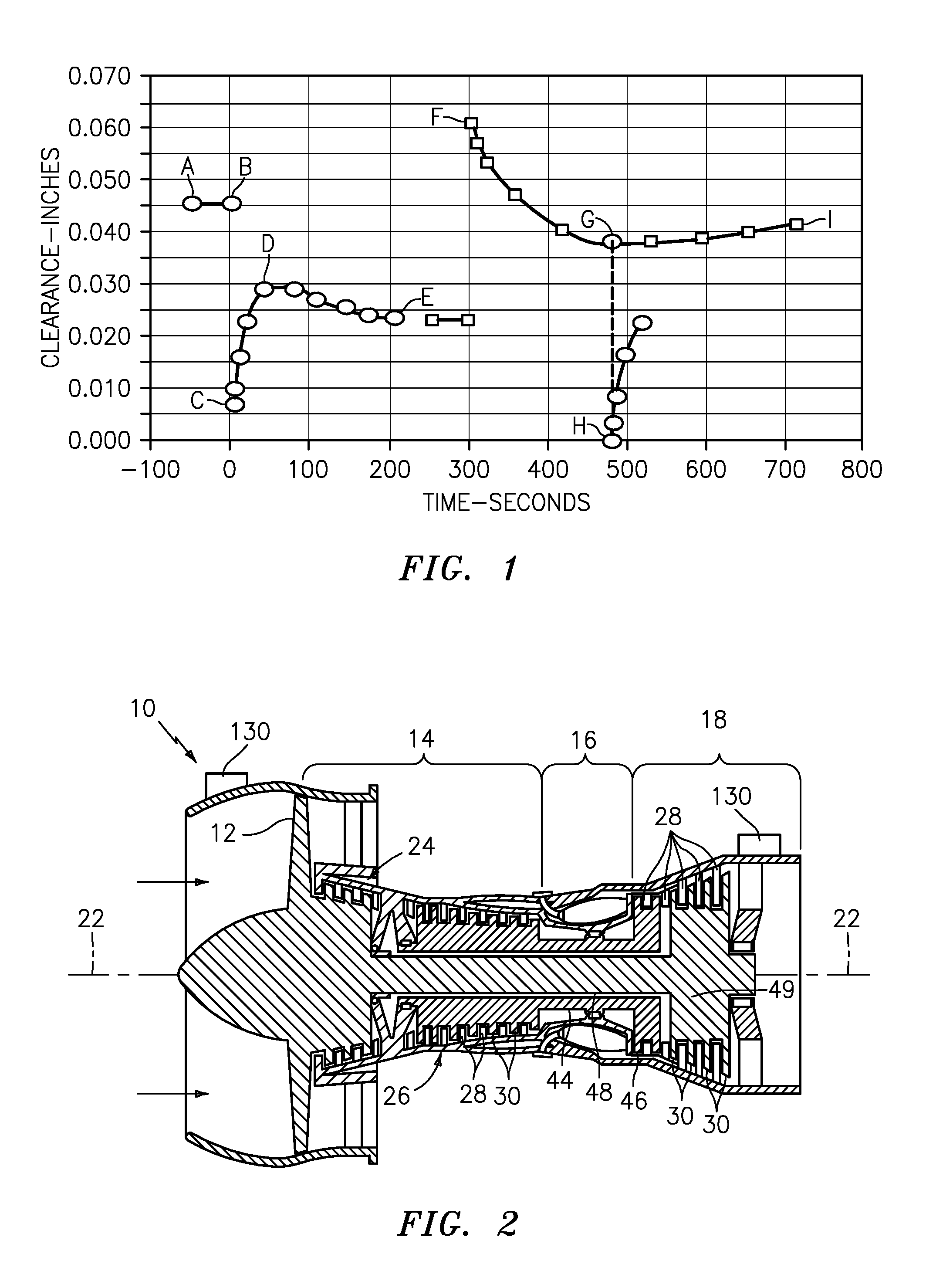
Aspects of the invention relate to a turbine engine configuration and method for overcoming a turbine blade tip clearance problem that can arise when the turbine inlet temperature is maintained at a high level during part load operation of the turbine. Aspects of the invention relate to reducing rotor cooling air to a temperature below the design temperature level by using, for example, additional heat extraction devices or by reconfiguring or resizing existing heat exchanger devices. Upon exposure to the cooled air, the discs and blades of the turbine will shrink so as to provide a clearance between the blade tips and surrounding stationary support structure. The design rotor cooling air temperature can be from about 350 degrees Fahrenheit to about 480 degrees Fahrenheit. Aspects of the present invention can be used to decrease the rotor cooling air to about 150 degrees Fahrenheit at about 70 percent load.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Turbine passive thermal valve for improved tip clearance control
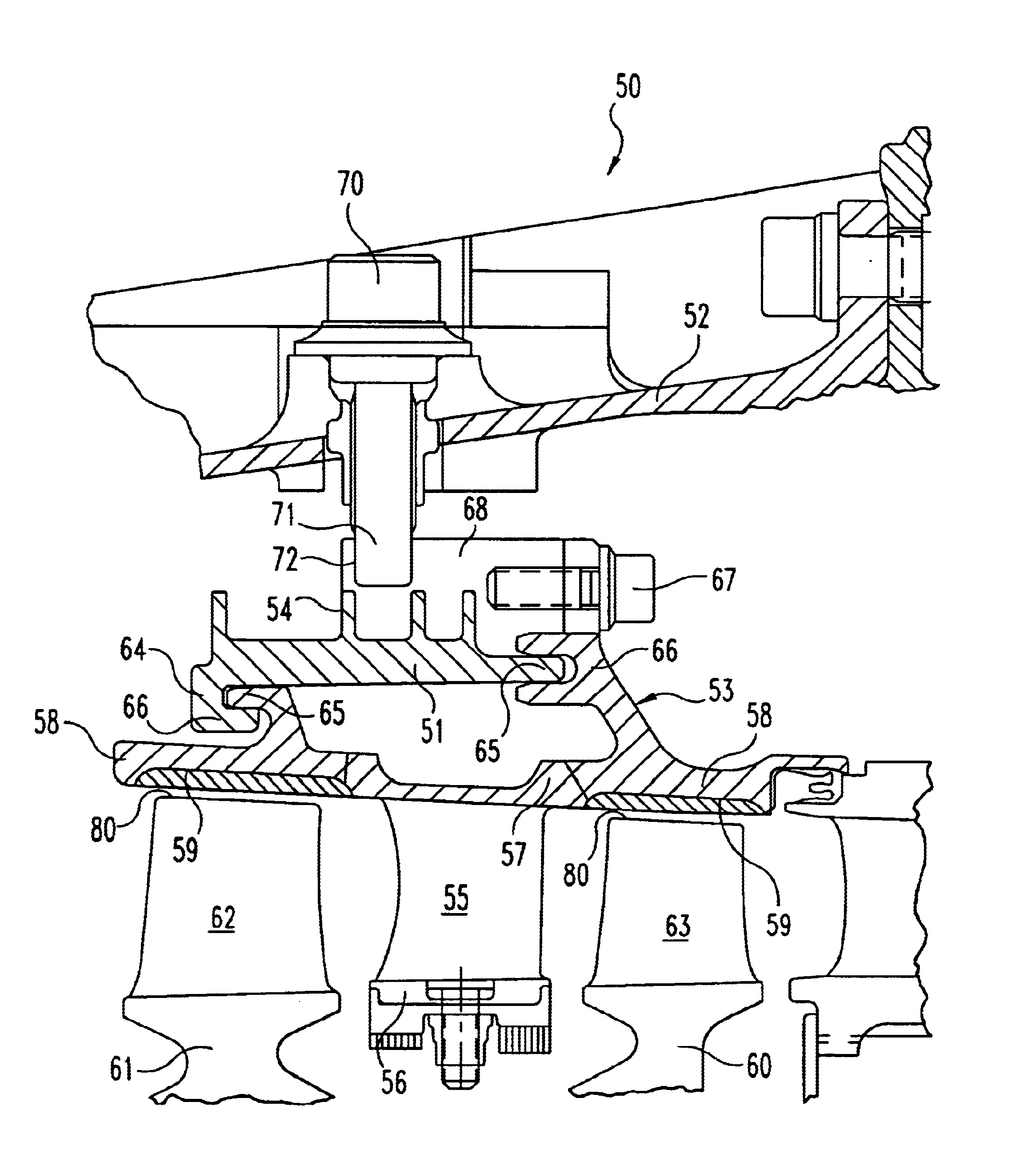
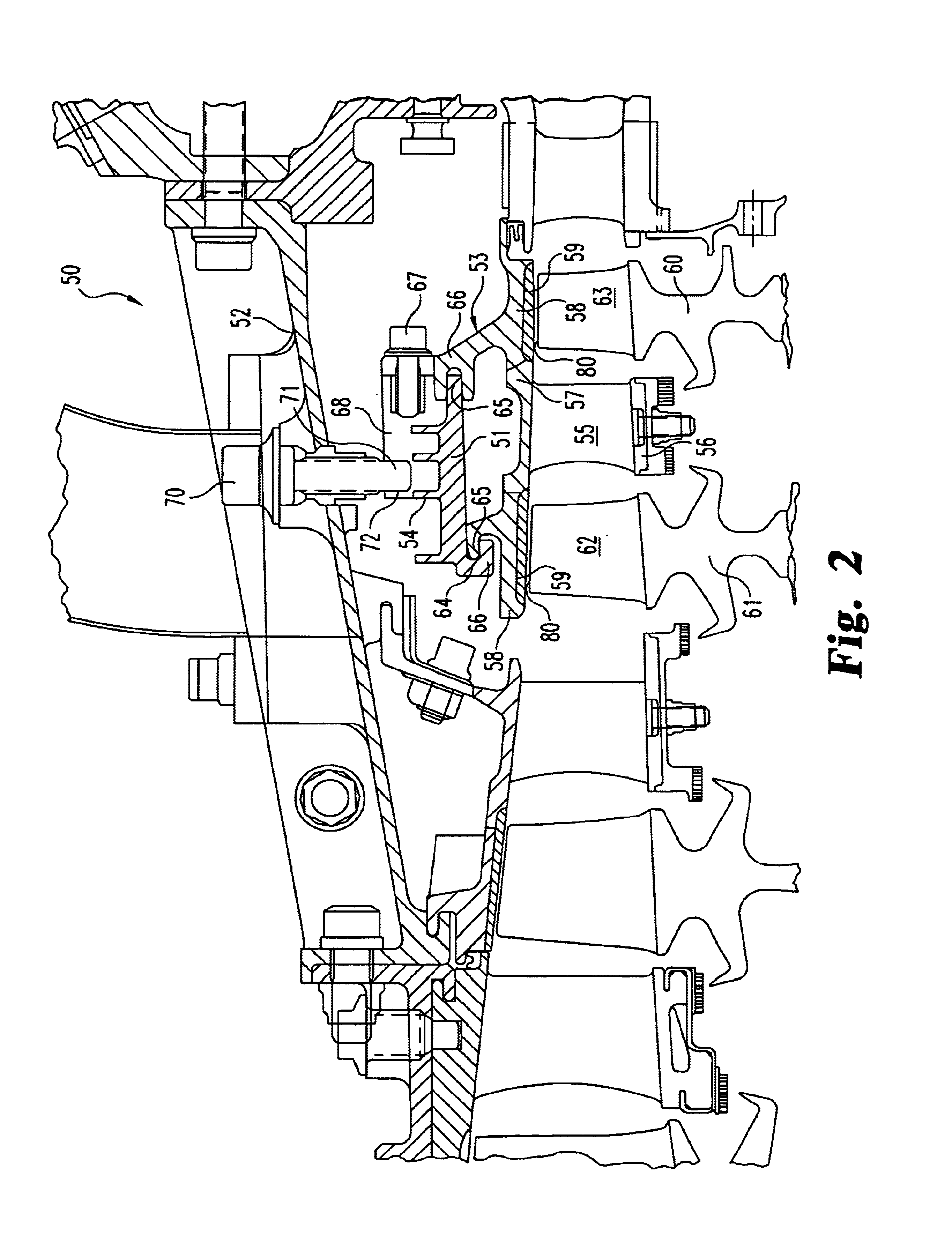
A gas turbine engine blade tip clearance control system and method is described. An annular housing is formed about an engine casing to which an annular shroud segment assembly is secured and closely spaced about blade tips of a stage of blades. The annular housing forms an air passage means communicating with the casing for directing a cooling air stream to the casing. A thermally operable passive ring valve is formed by two overlapped metal ring segments having a dissimilar coefficient of thermal expansion selected whereby to produce a radial gap between the ring segments when the valve temperature reaches a predetermined value. The radial gap admits a cooling air flow into the housing for cooling the casing and its associated shroud segment assembly to control radial growth and thereby prevent blade tip pinching.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
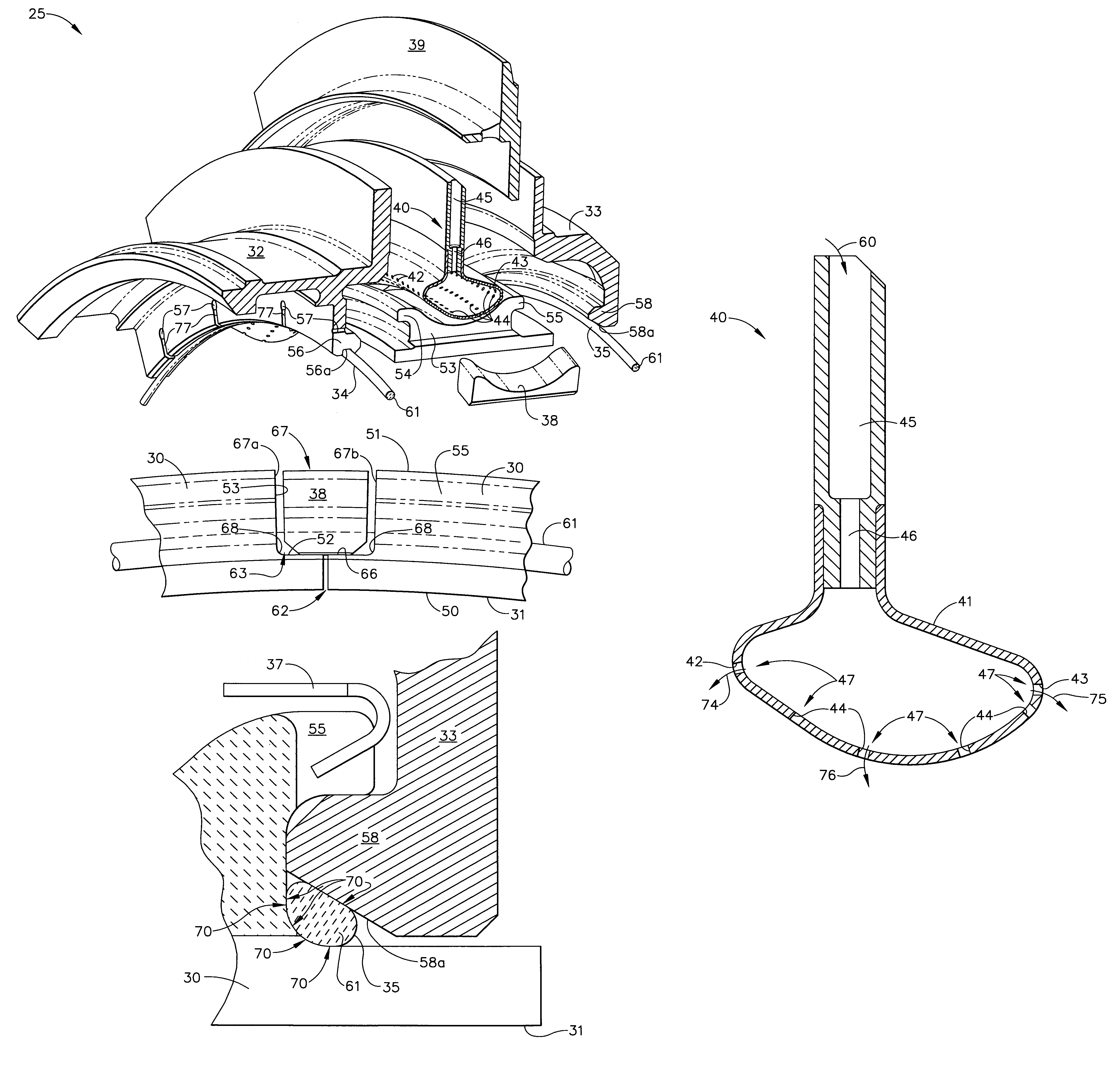
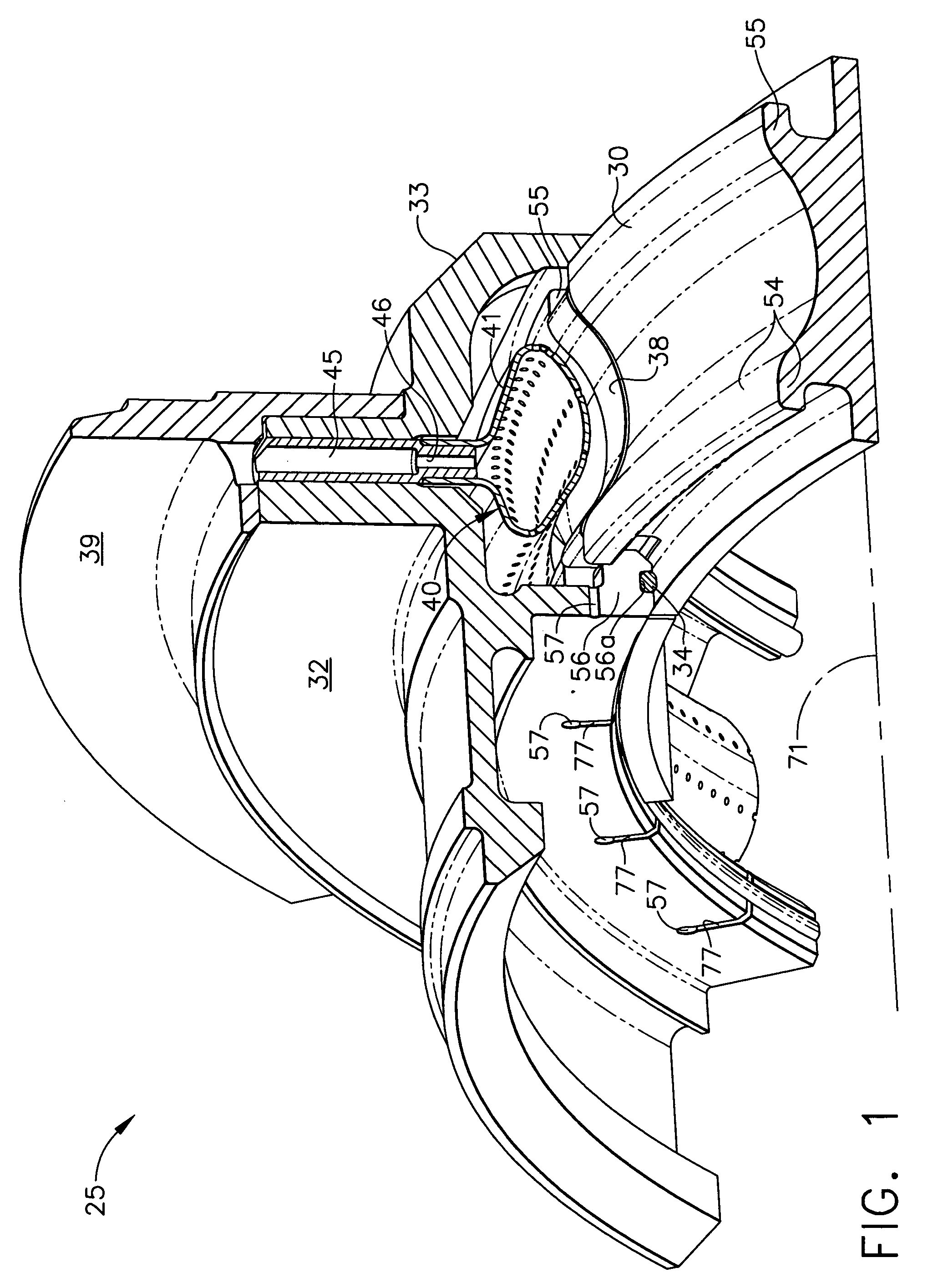
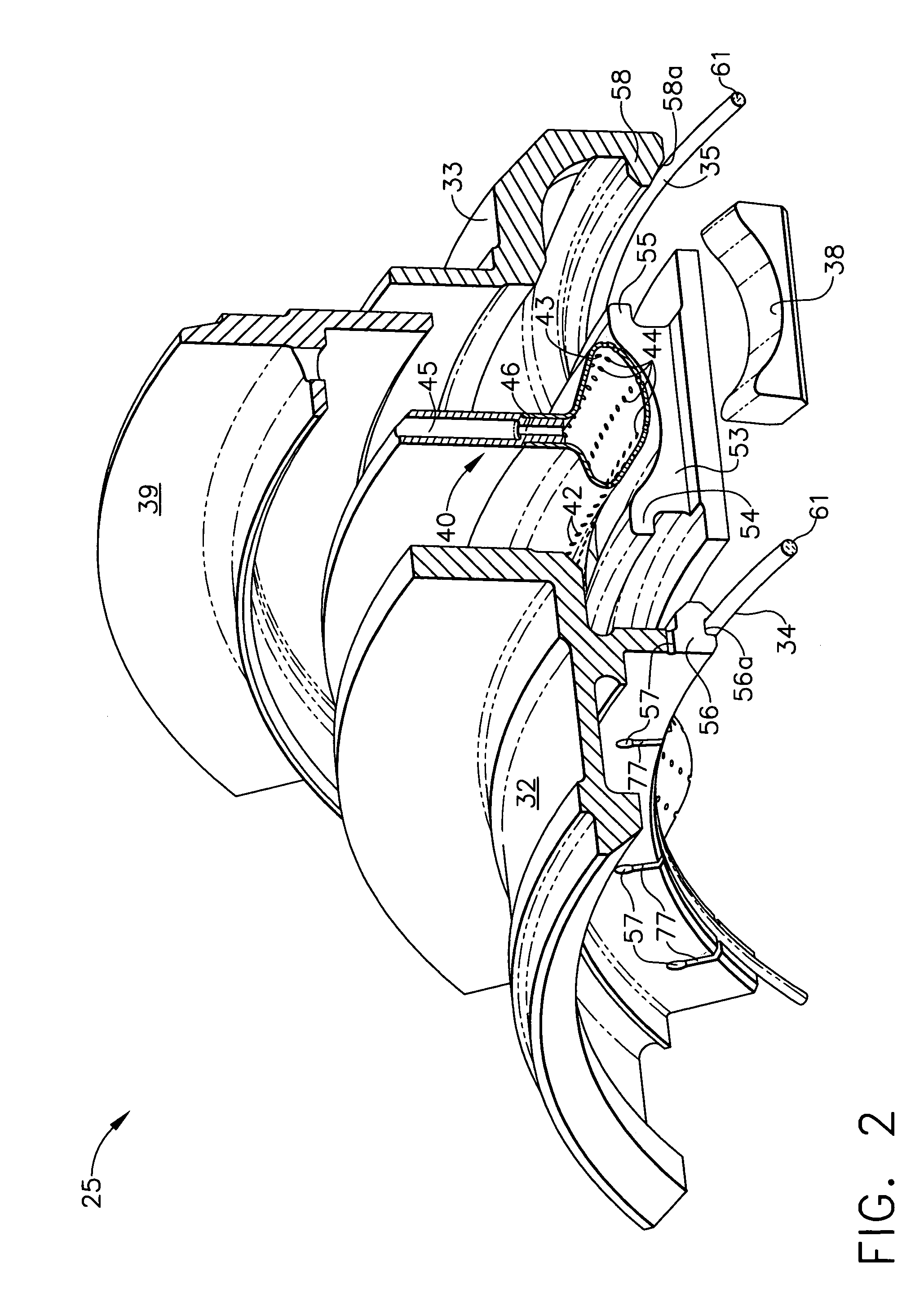
Compressor blade having a ratio of leading edge sweep to leading edge dihedral in a range of 1:1 to 3:1 along the radially outer portion
ActiveUS8147207B2Reduce lossesPropellersRotary non-positive displacement pumpsLeading edgeTip clearance
An airfoil for use as rotor blades in compressors for turbomachines, such as gas turbine engines. The airfoil includes increased forward sweep and forward dihedral effective to reduce losses generated by interaction of tip clearance flow, secondary flows and passage shocks.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
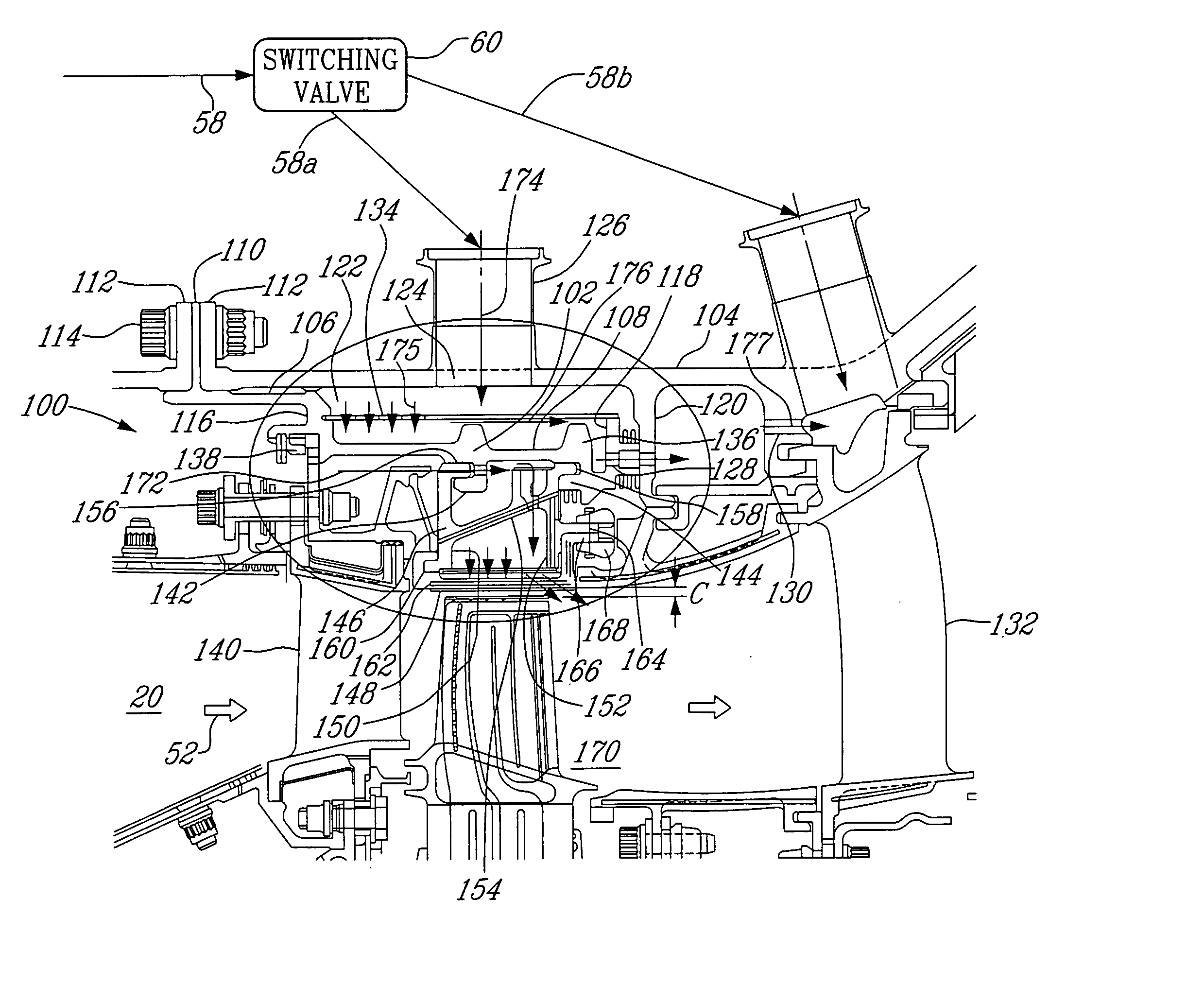
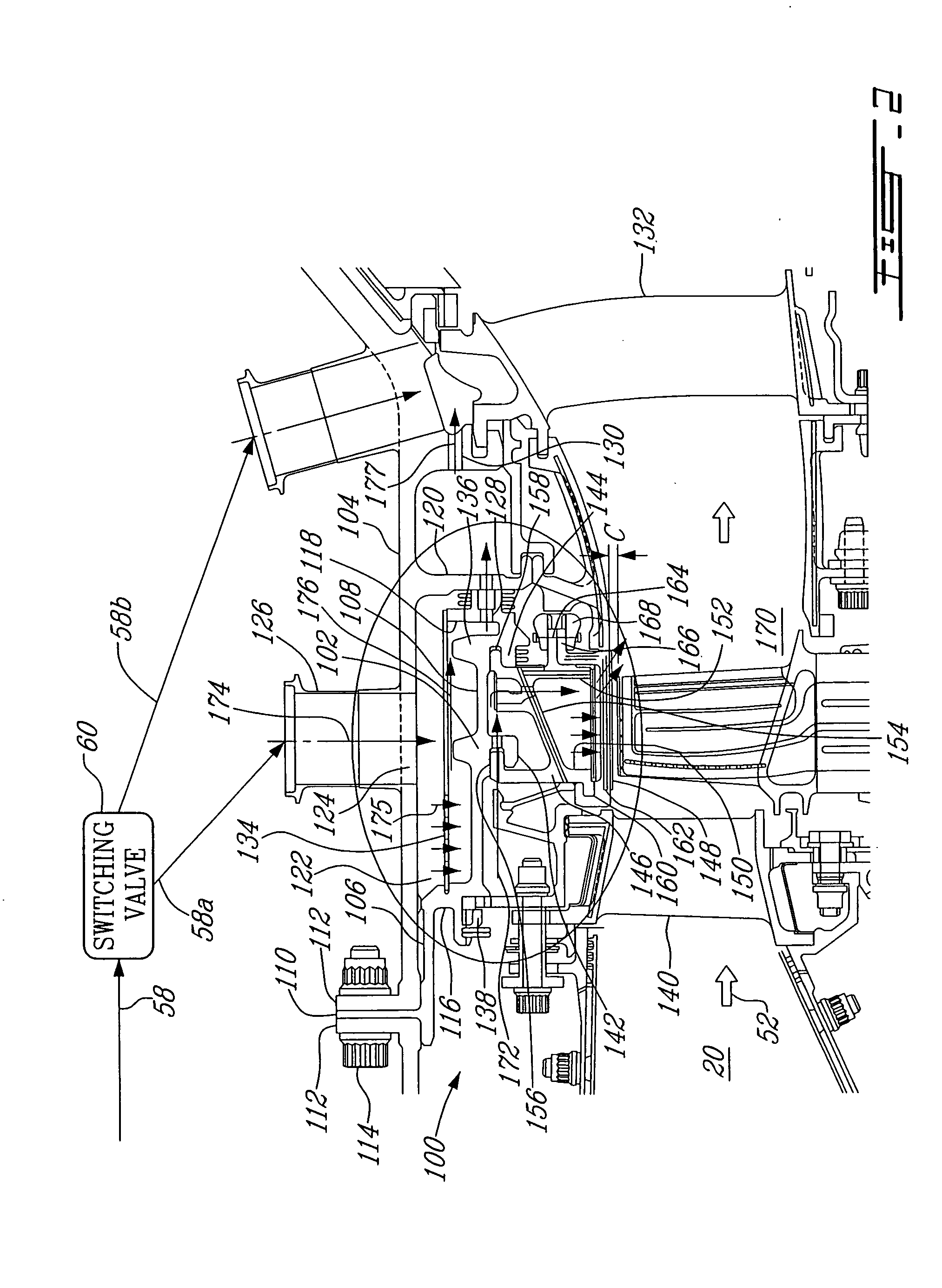
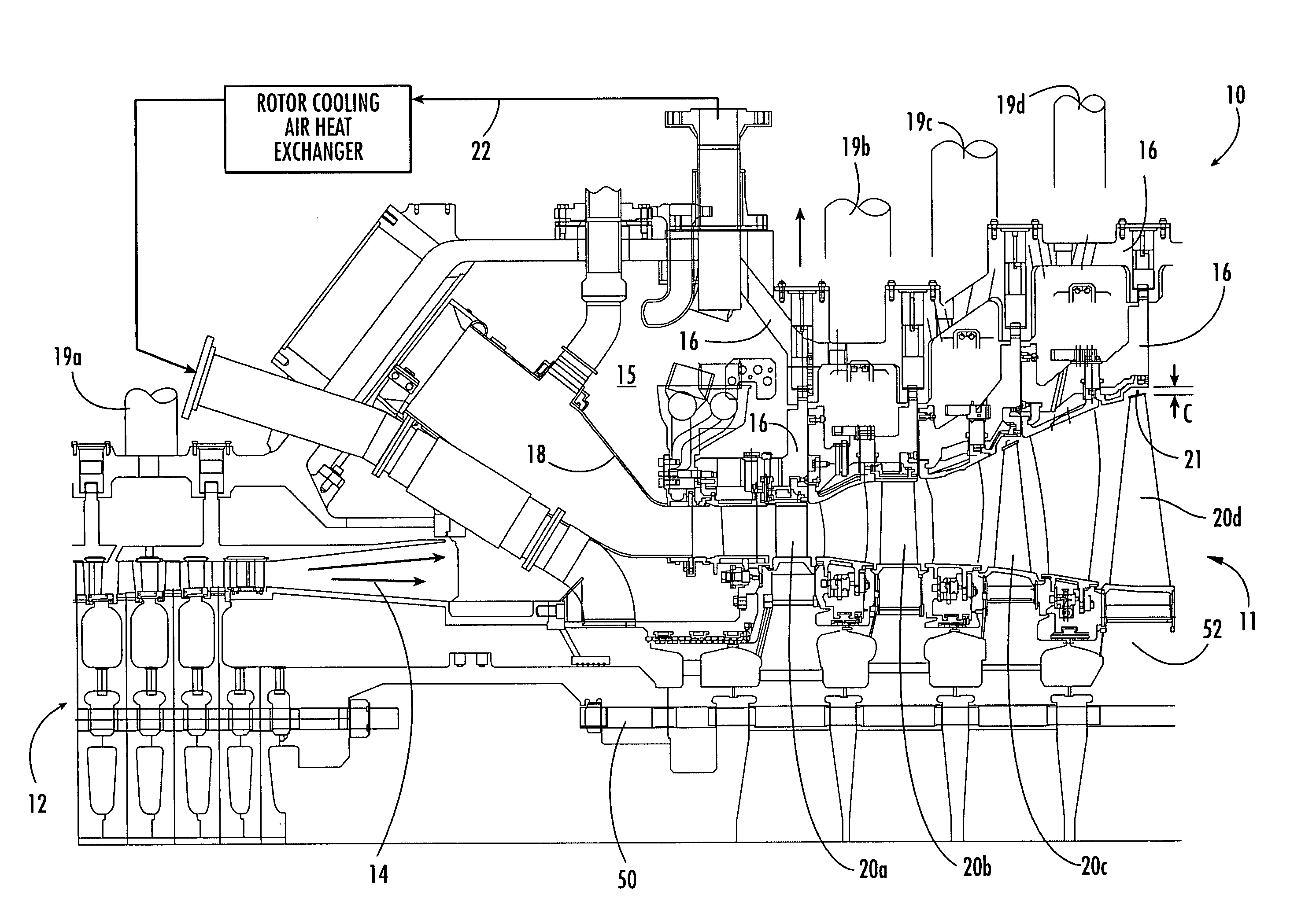
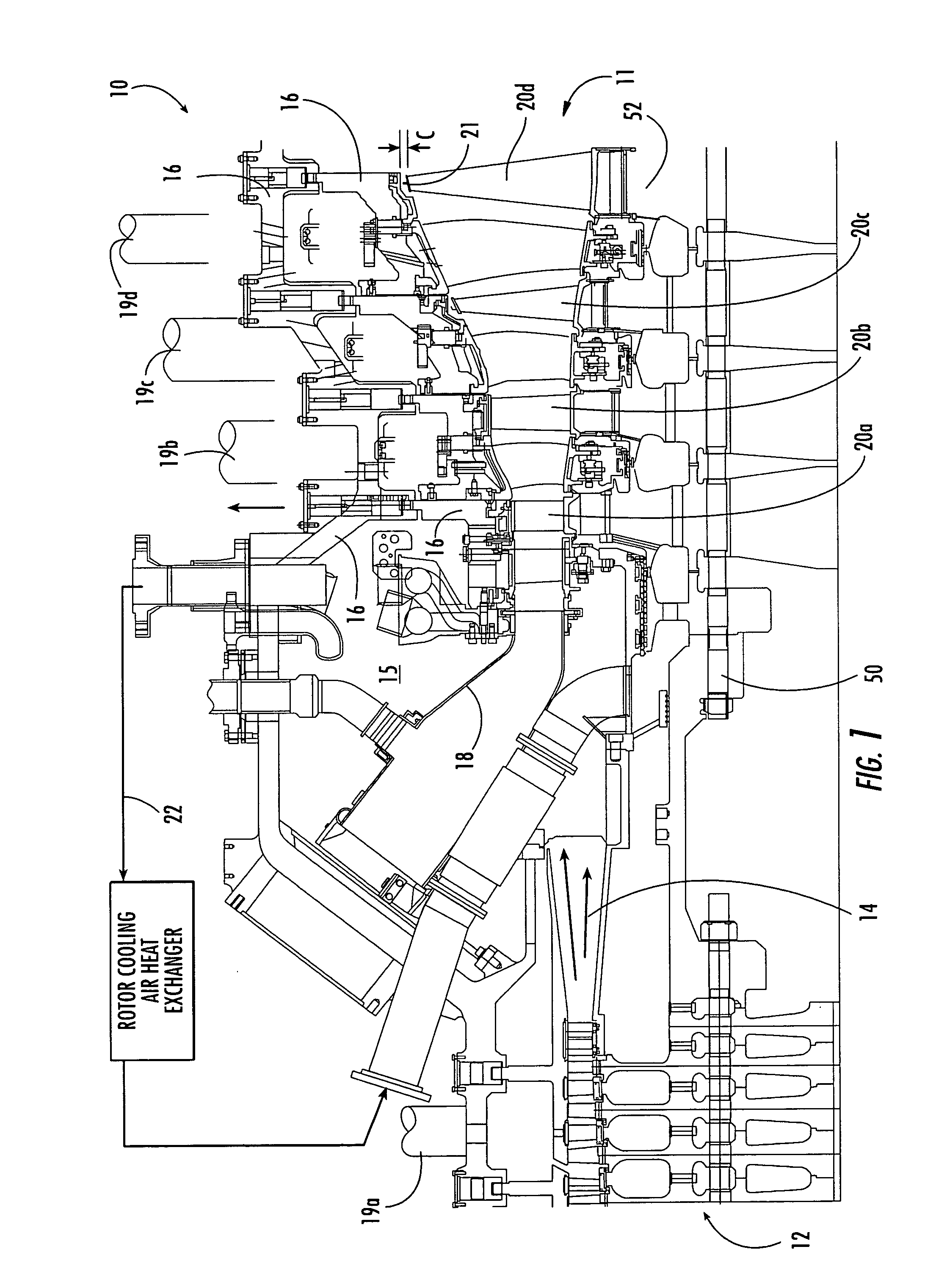
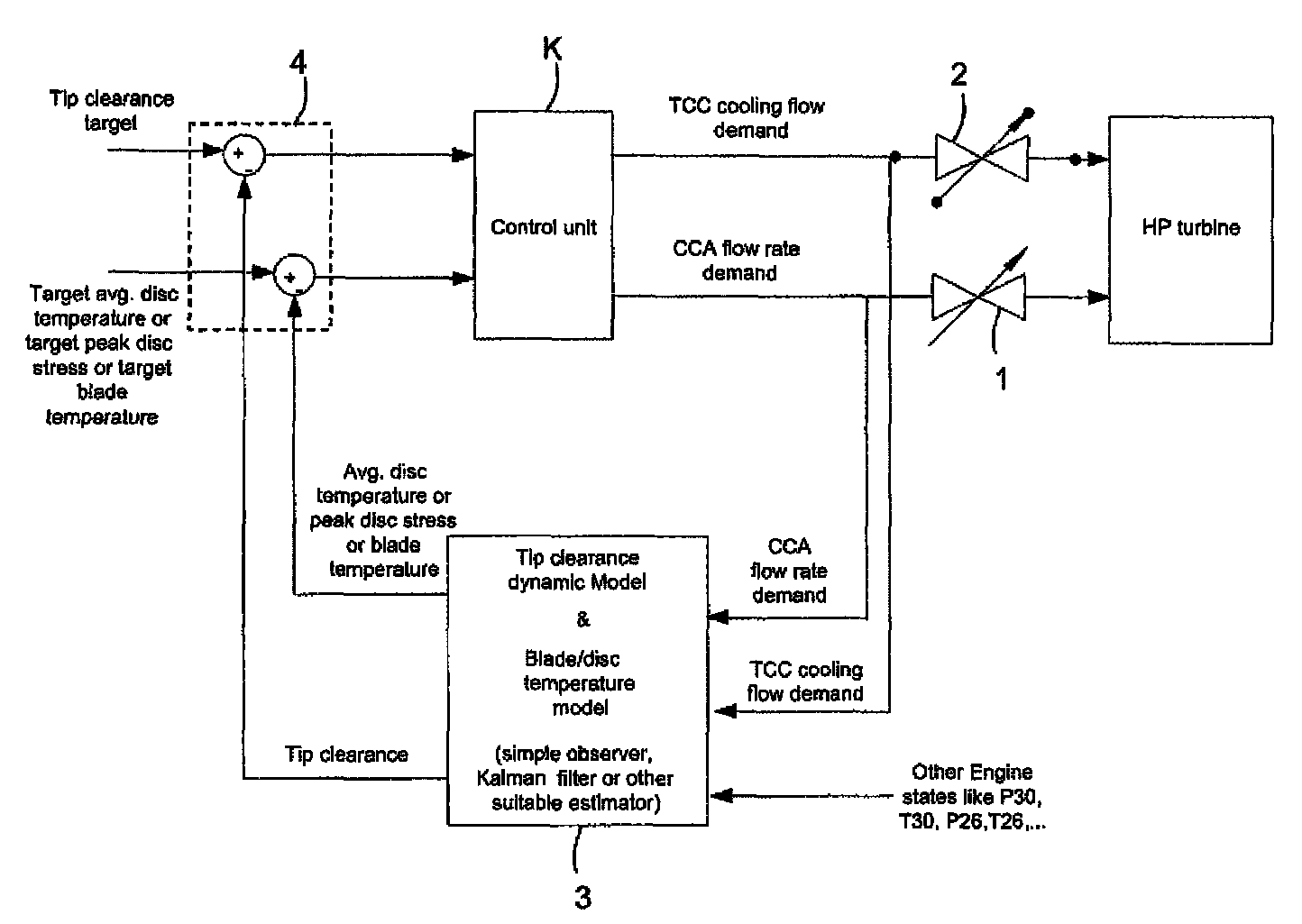
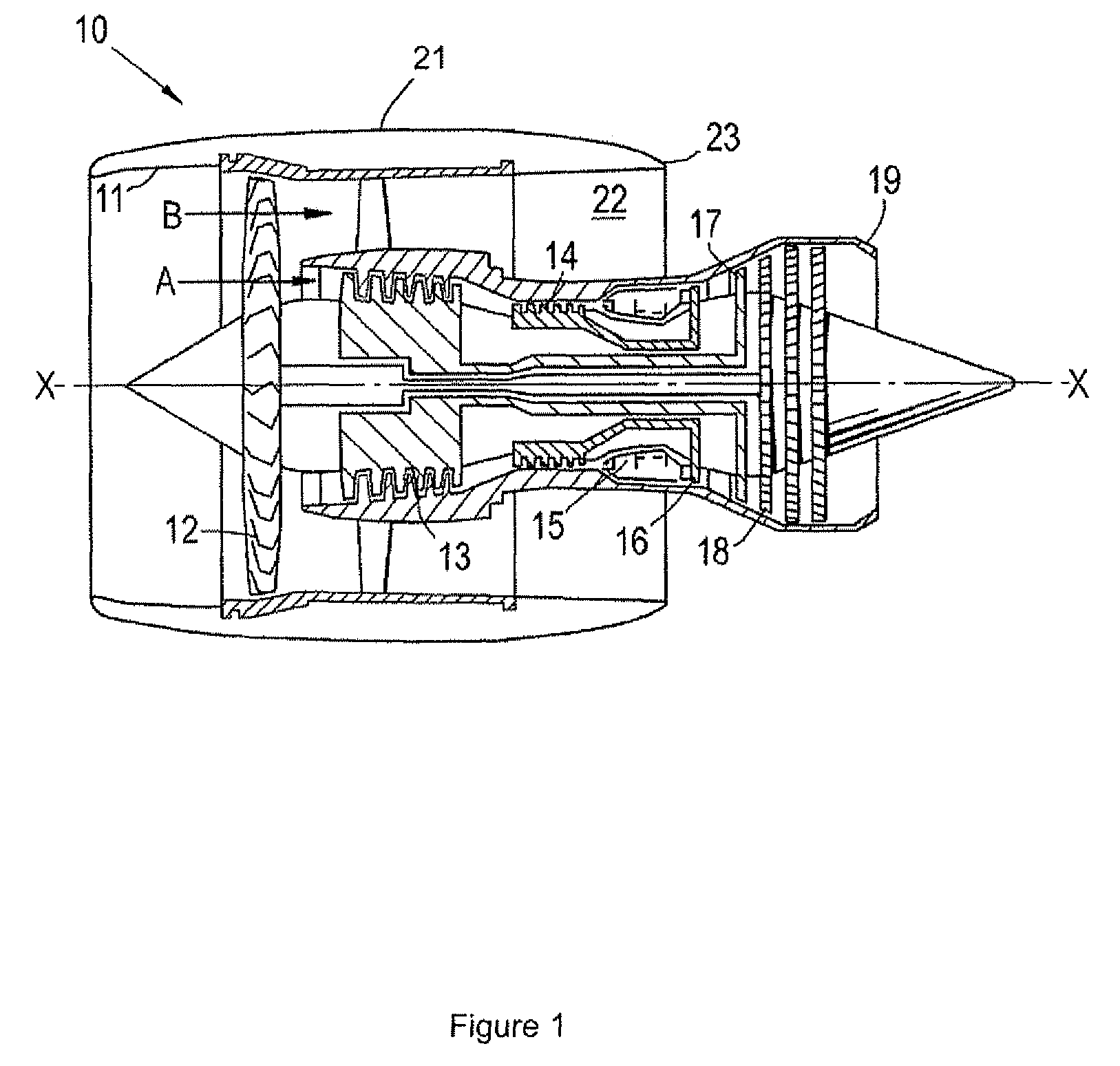
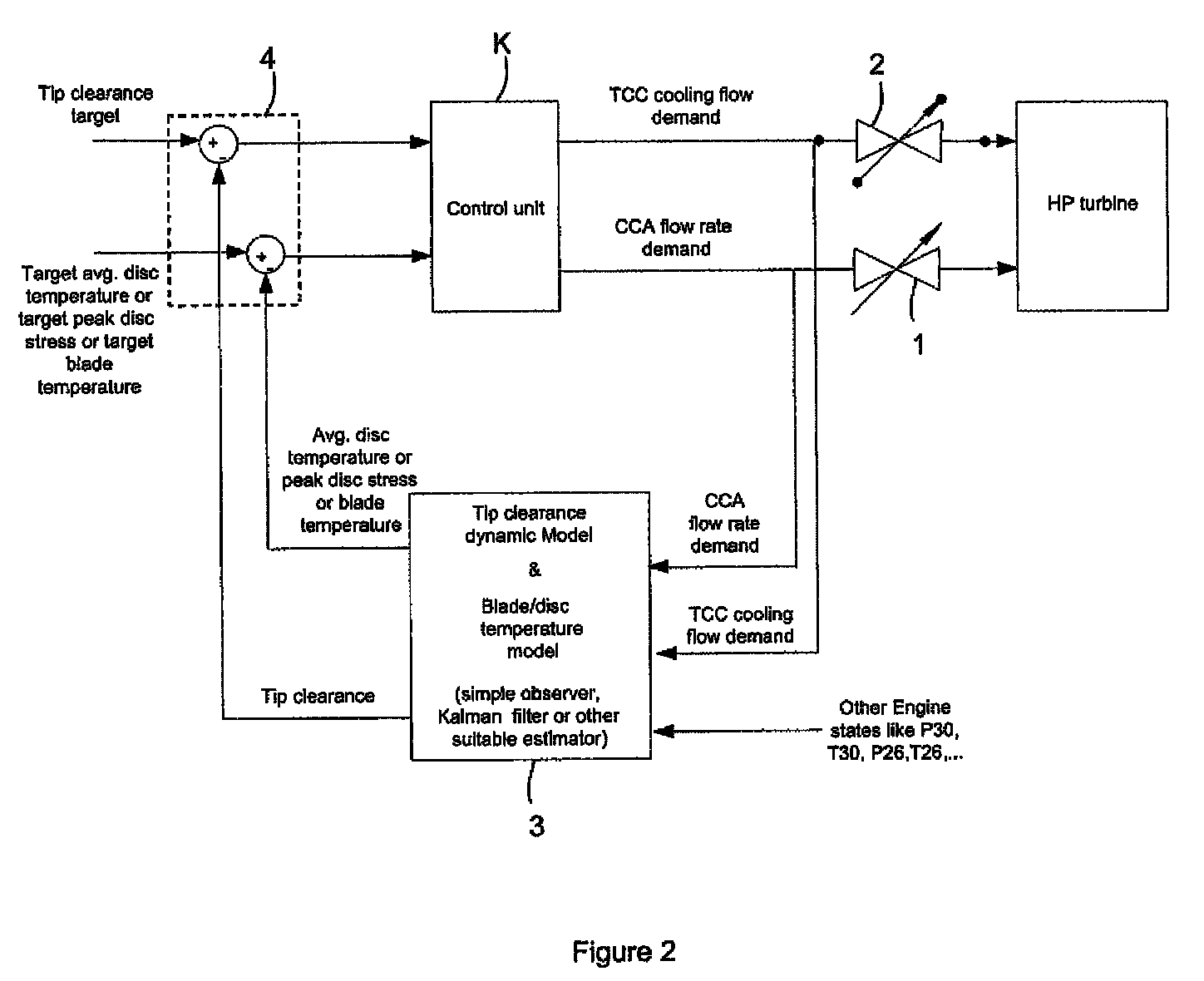
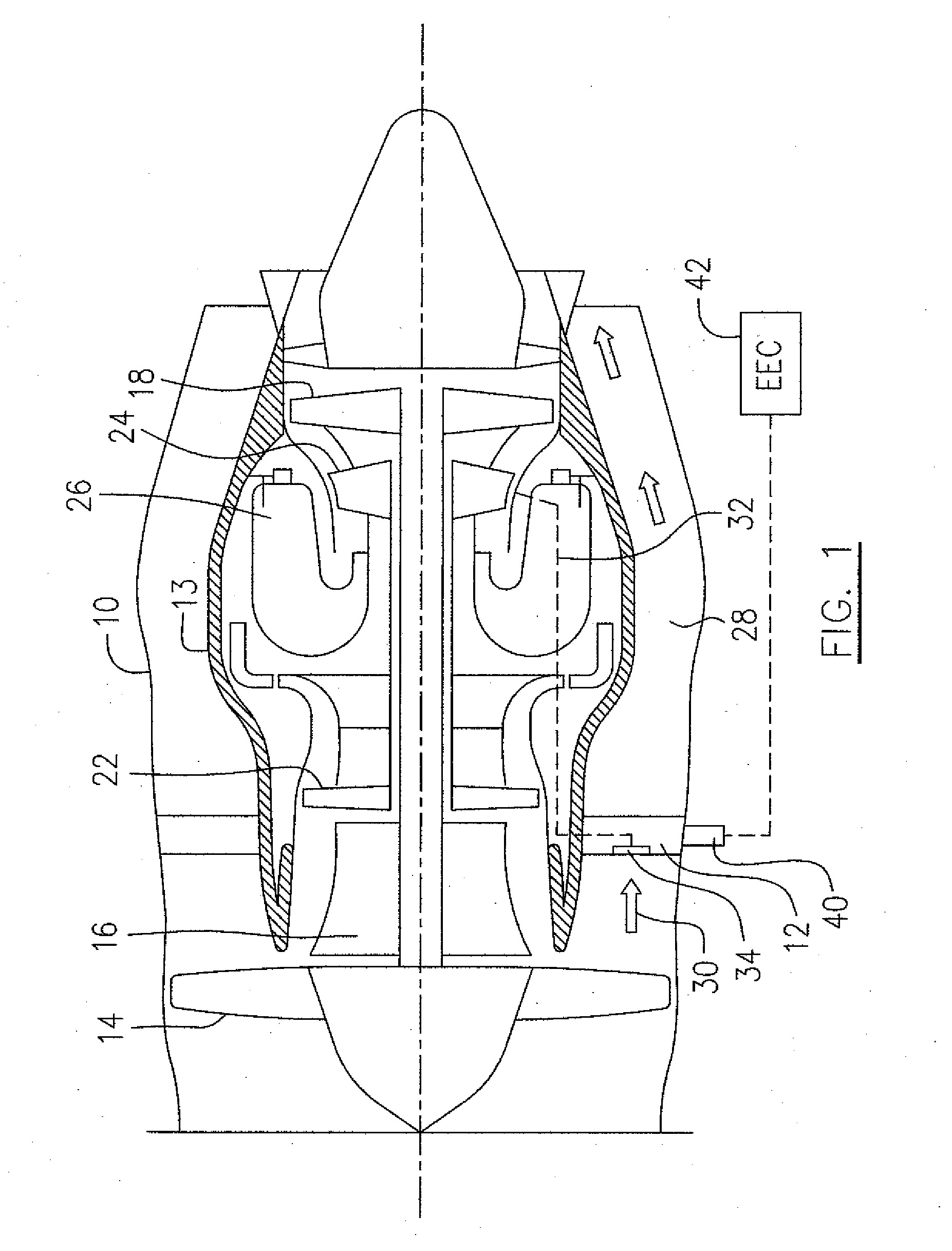
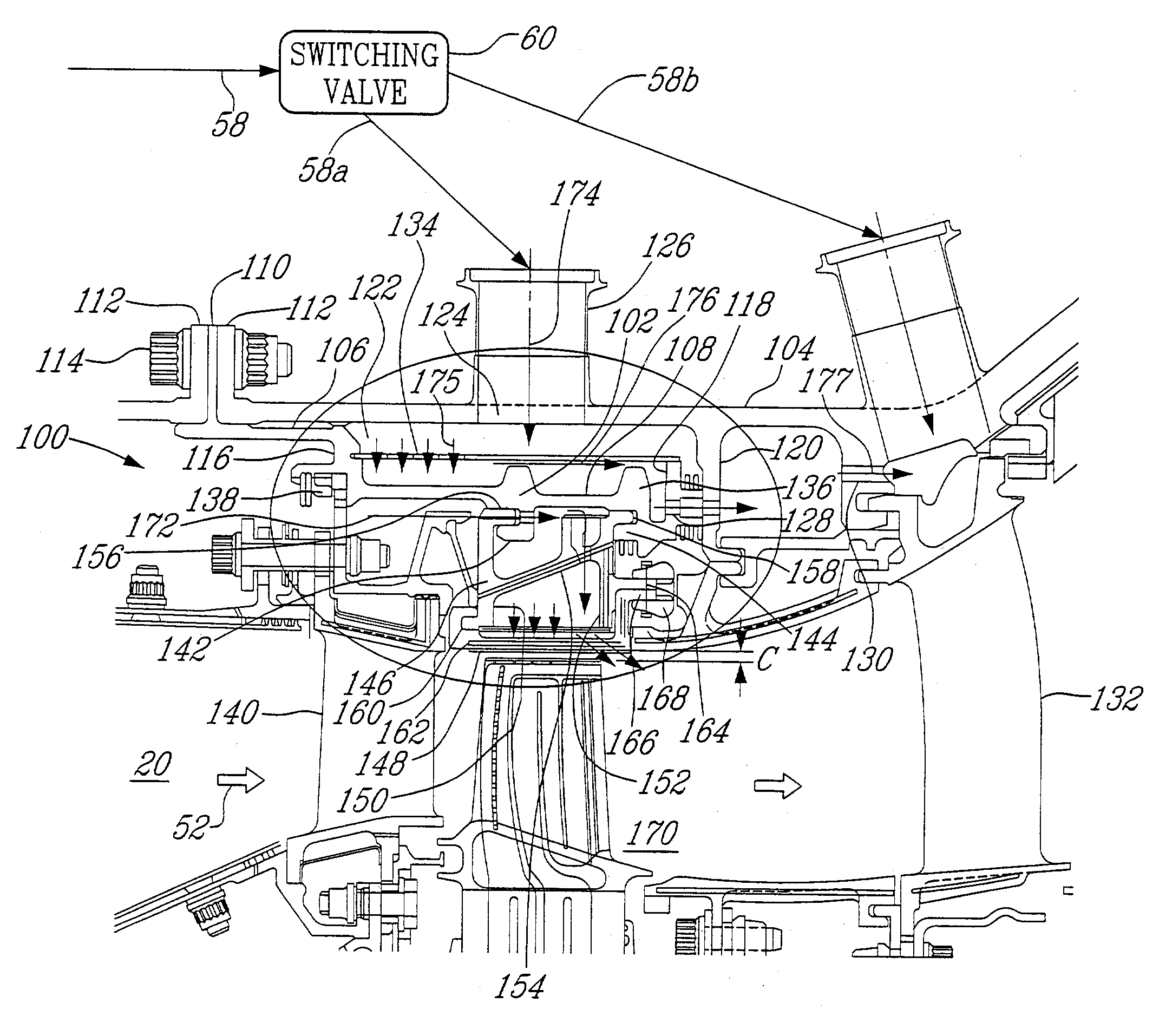
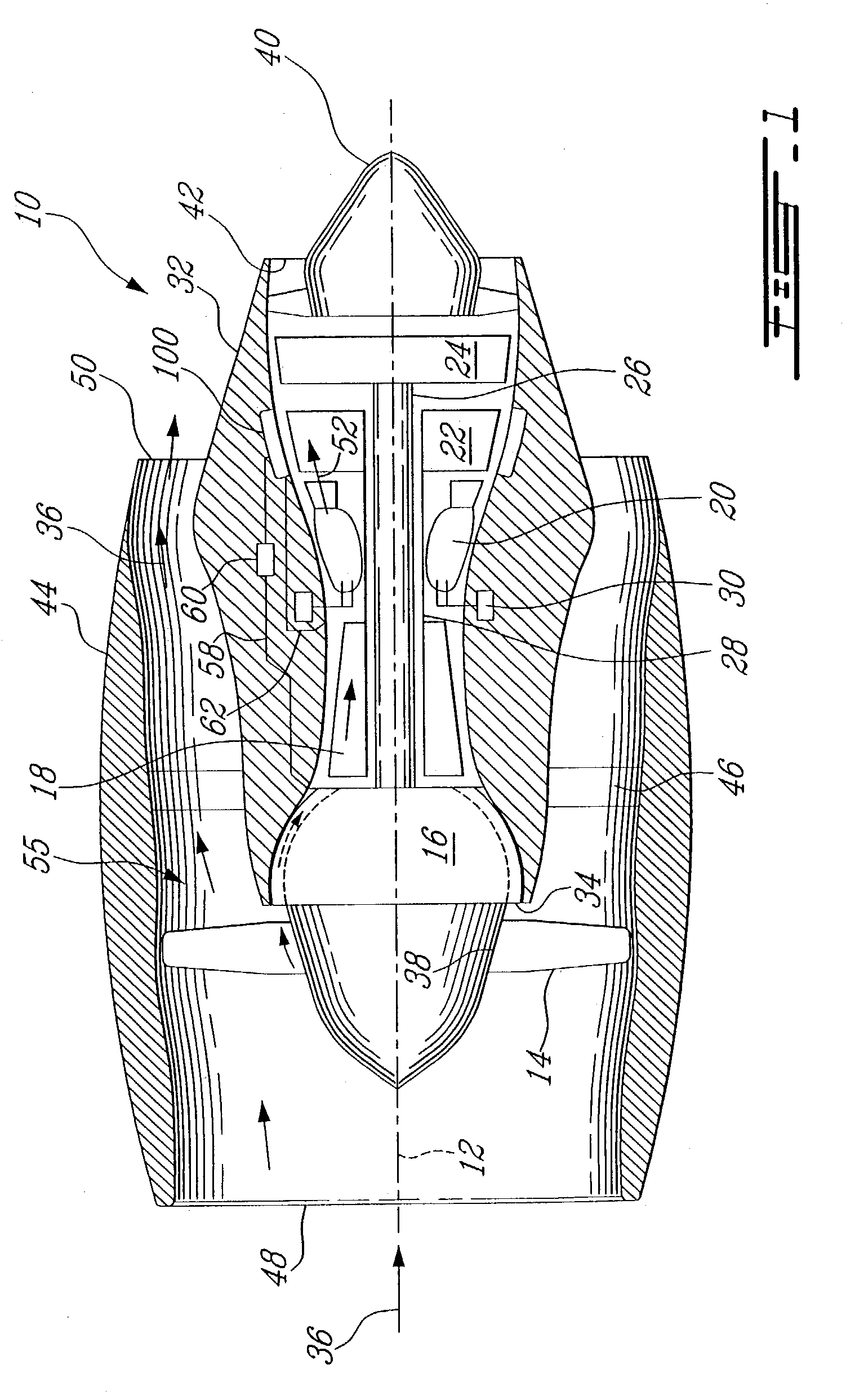
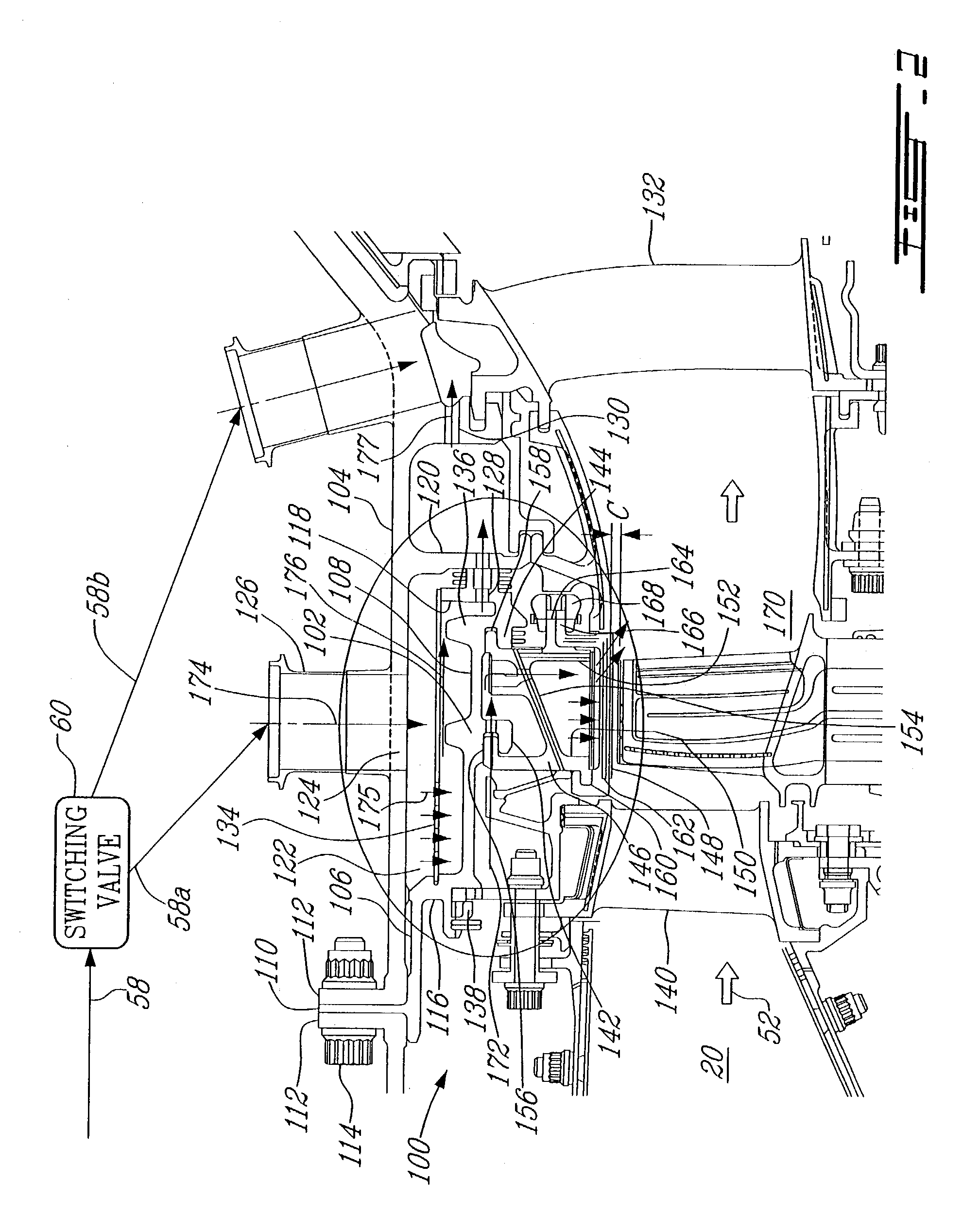
Gas turbine engine having a multi-variable closed loop controller for regulating tip clearance
ActiveUS9255492B2Improve engine efficiencyImprove efficiencyEngine fuctionsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingCombustorTurbine blade
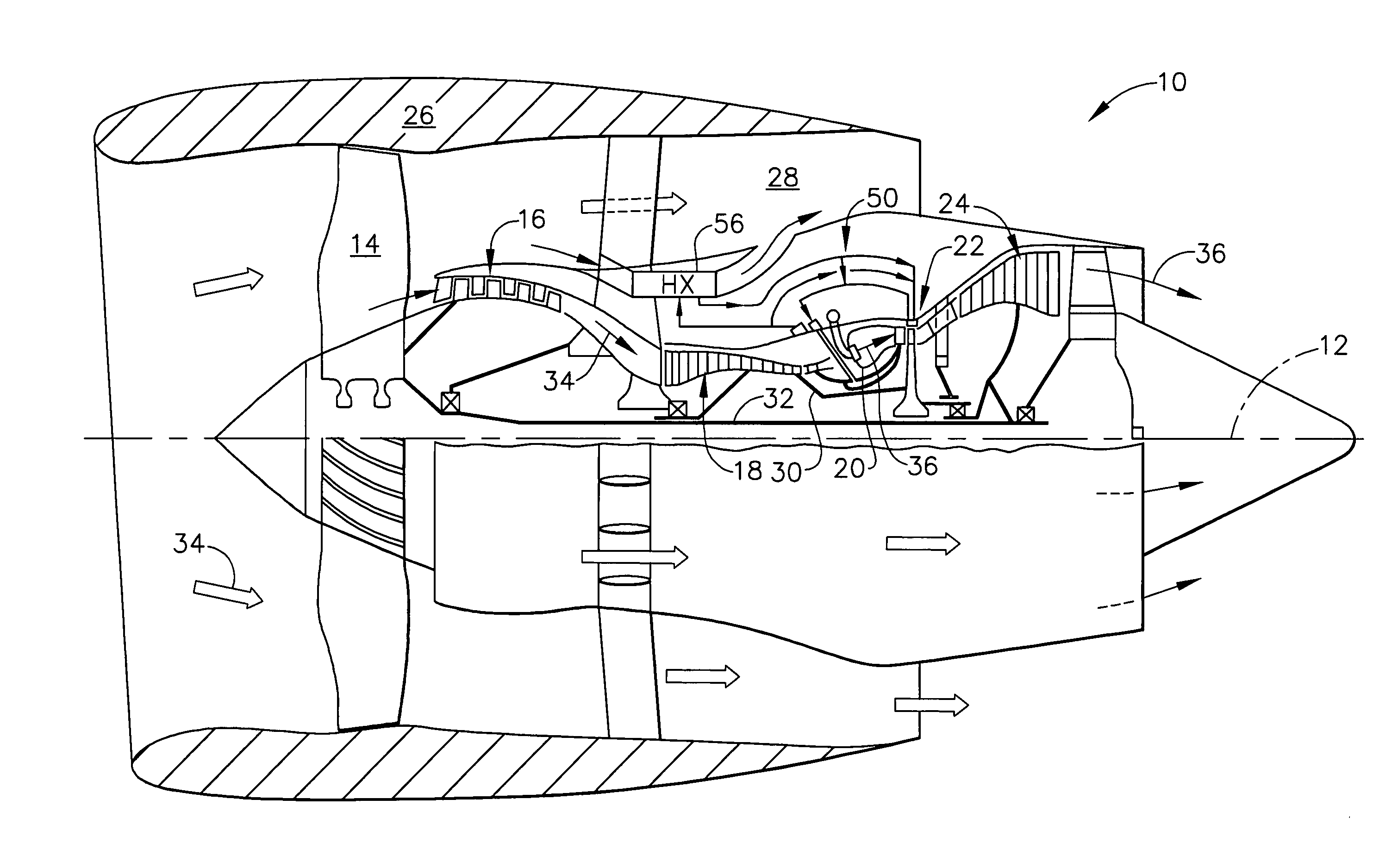
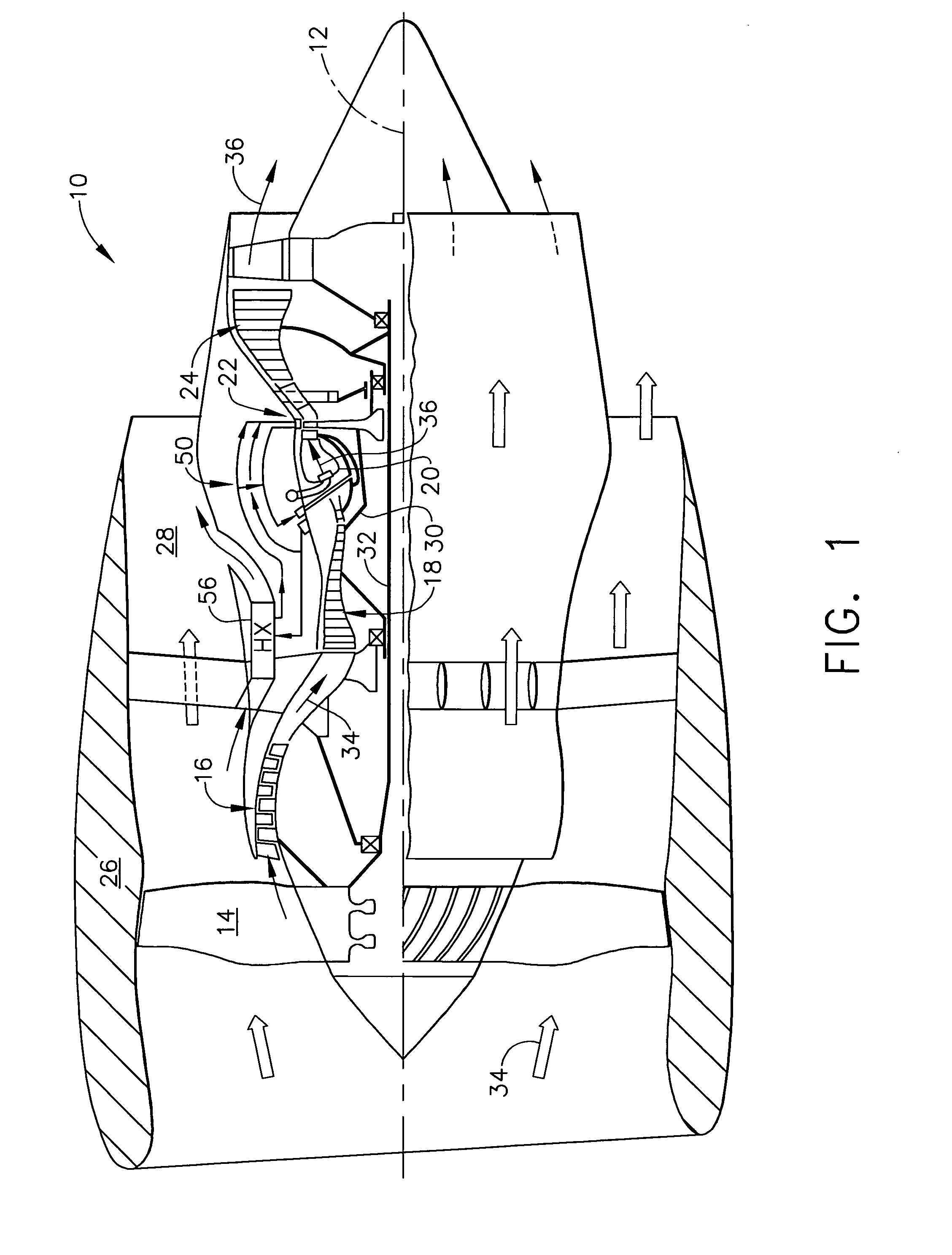
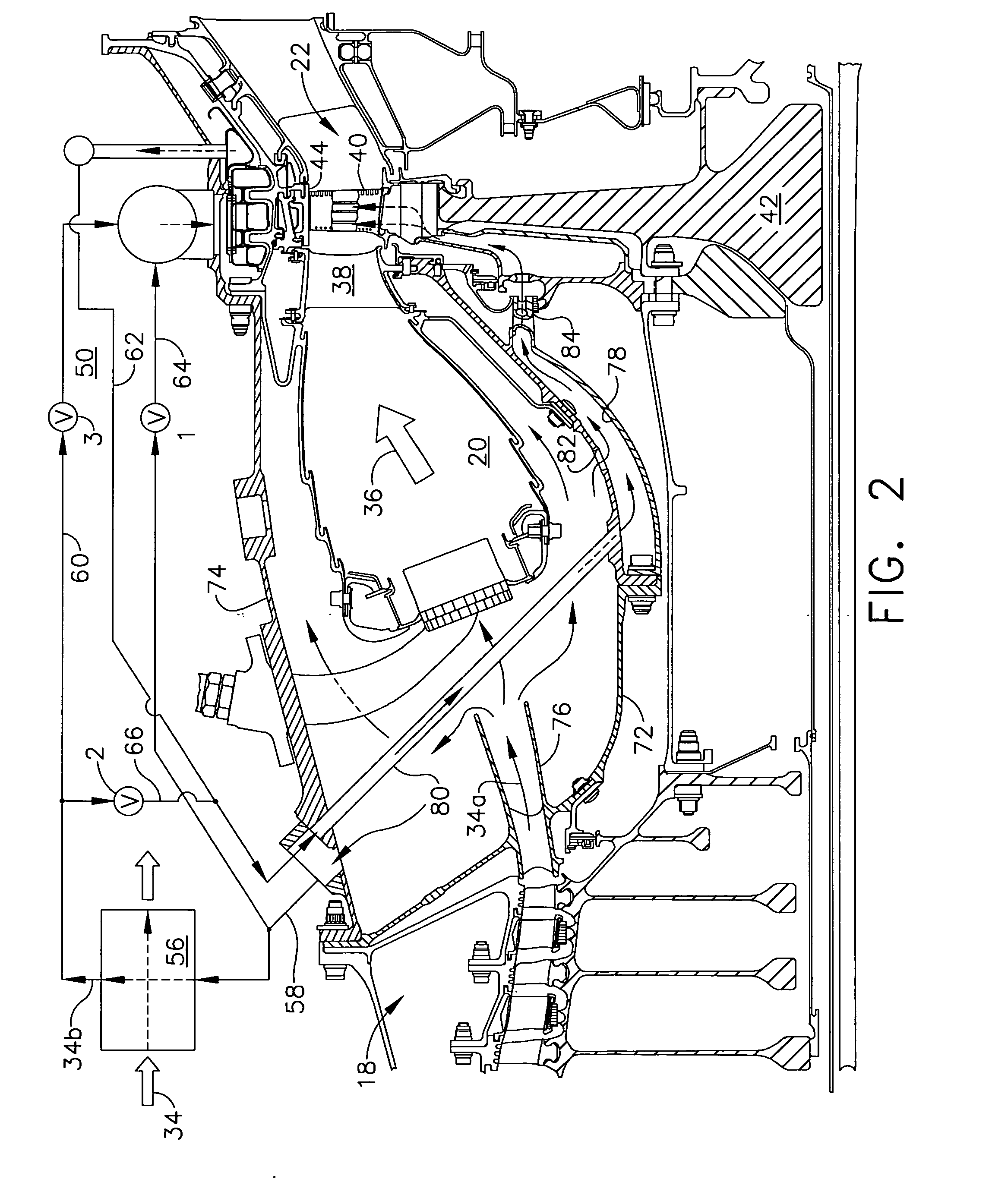
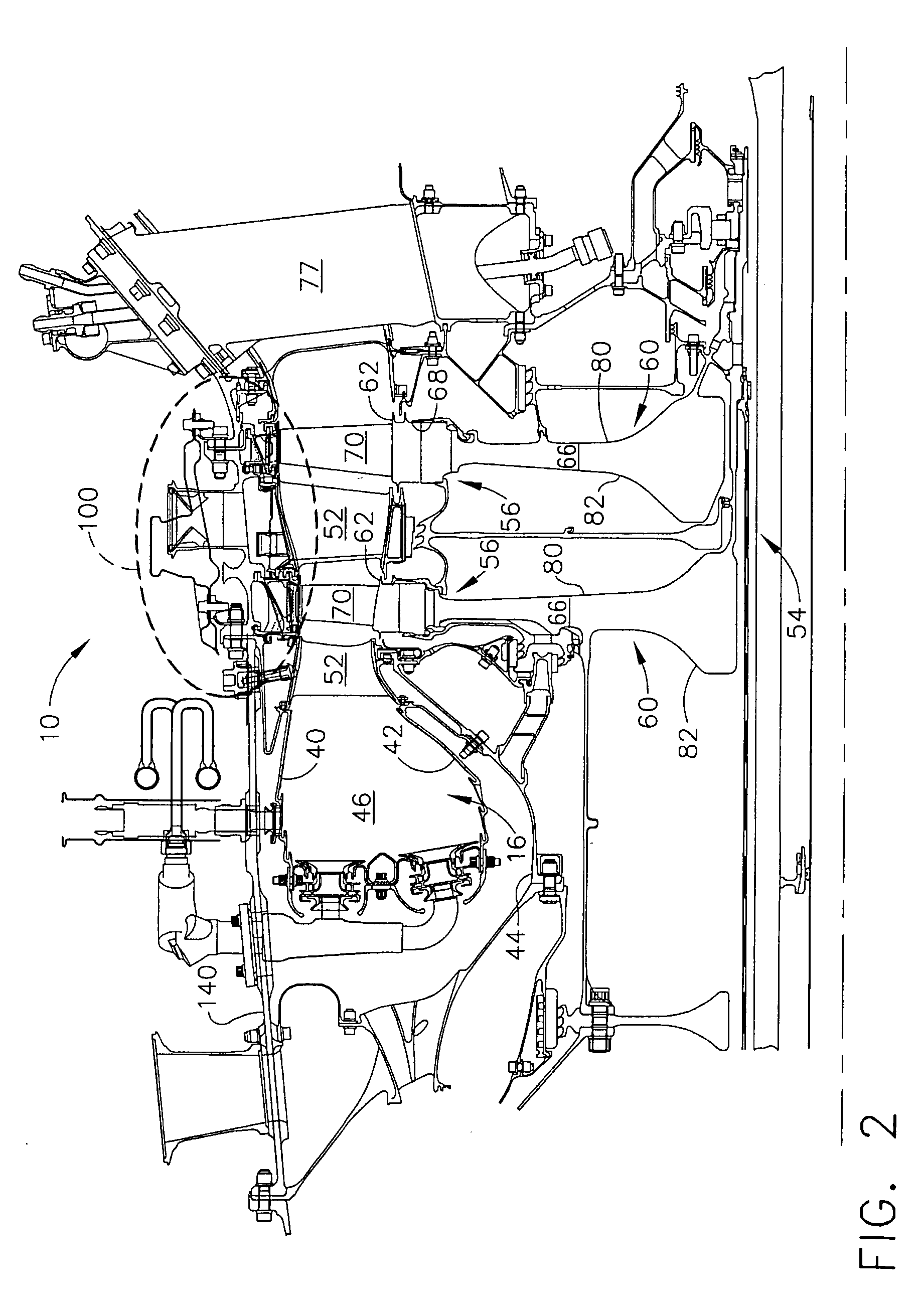
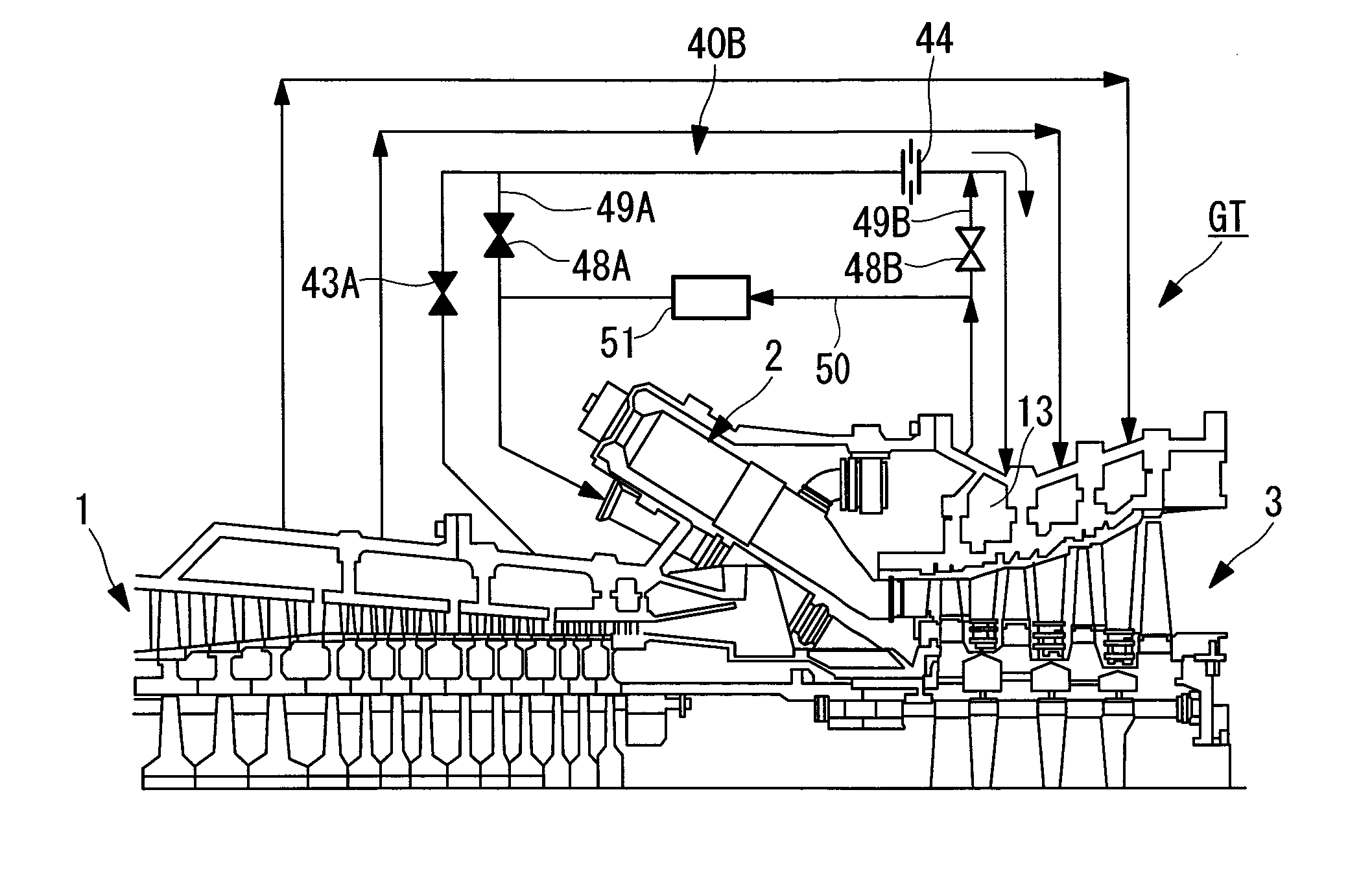
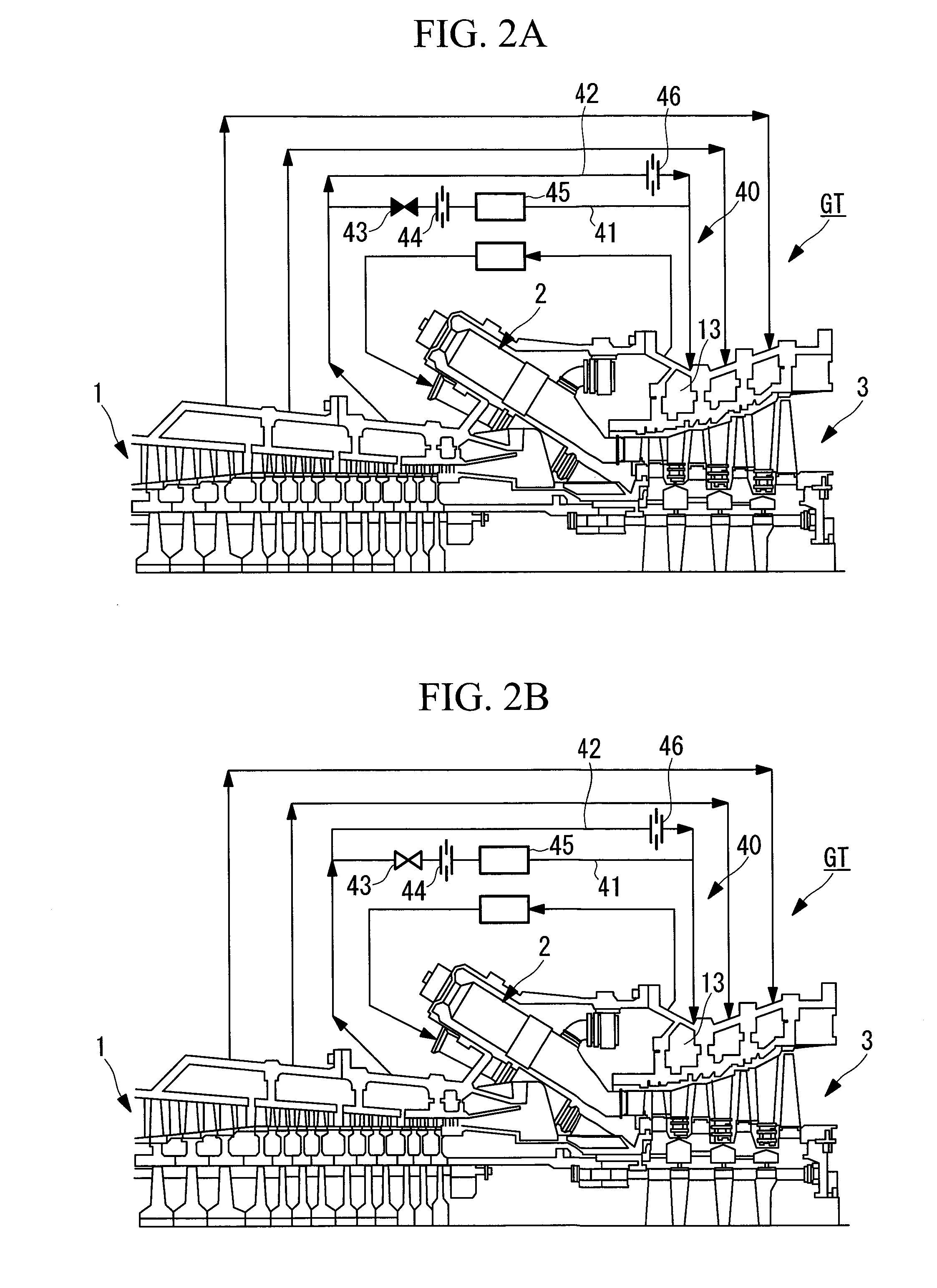
A gas turbine engine has, in flow series, a compressor section, a combustor, and a turbine section. The gas turbine engine further has a system (i) for cooling the turbine section and (ii) for providing tip clearance control between turbine blades of the turbine section and a plurality of circumferentially distributed segments which form an annular shroud surrounding the outer tips of the turbine blades. The system includes a turbine section cooling sub-system which diverts a first cooling air flow received from the compressor section to a heat exchanger and then to the turbine section to cool components thereof. The first cooling air flow by-passes the combustor and is cooled in the heat exchanger. The turbine section cooling subsystem has a first valve arrangement which regulates the first cooling air flow. The system further includes a tip clearance control sub-system which supplies a second cooling air flow to an engine case to which the segments are mounted. The second cooling air flow regulates thermal expansion of the case and thereby controls the clearance between the segments and the outer tips. The tip clearance control sub-system has a second valve arrangement which regulates the second cooling air flow. The system further includes a closed-loop controller which issues first and second demand signals to respectively the first and the second valve arrangements. Each of the first and second demand signals are determined on the basis of: (i) a value of the first demand signal at a previous time step, and a measurement or estimate of turbine section component temperature, and (ii) a value of the second demand signal at a previous time step, and a measurement or estimate of tip clearance.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
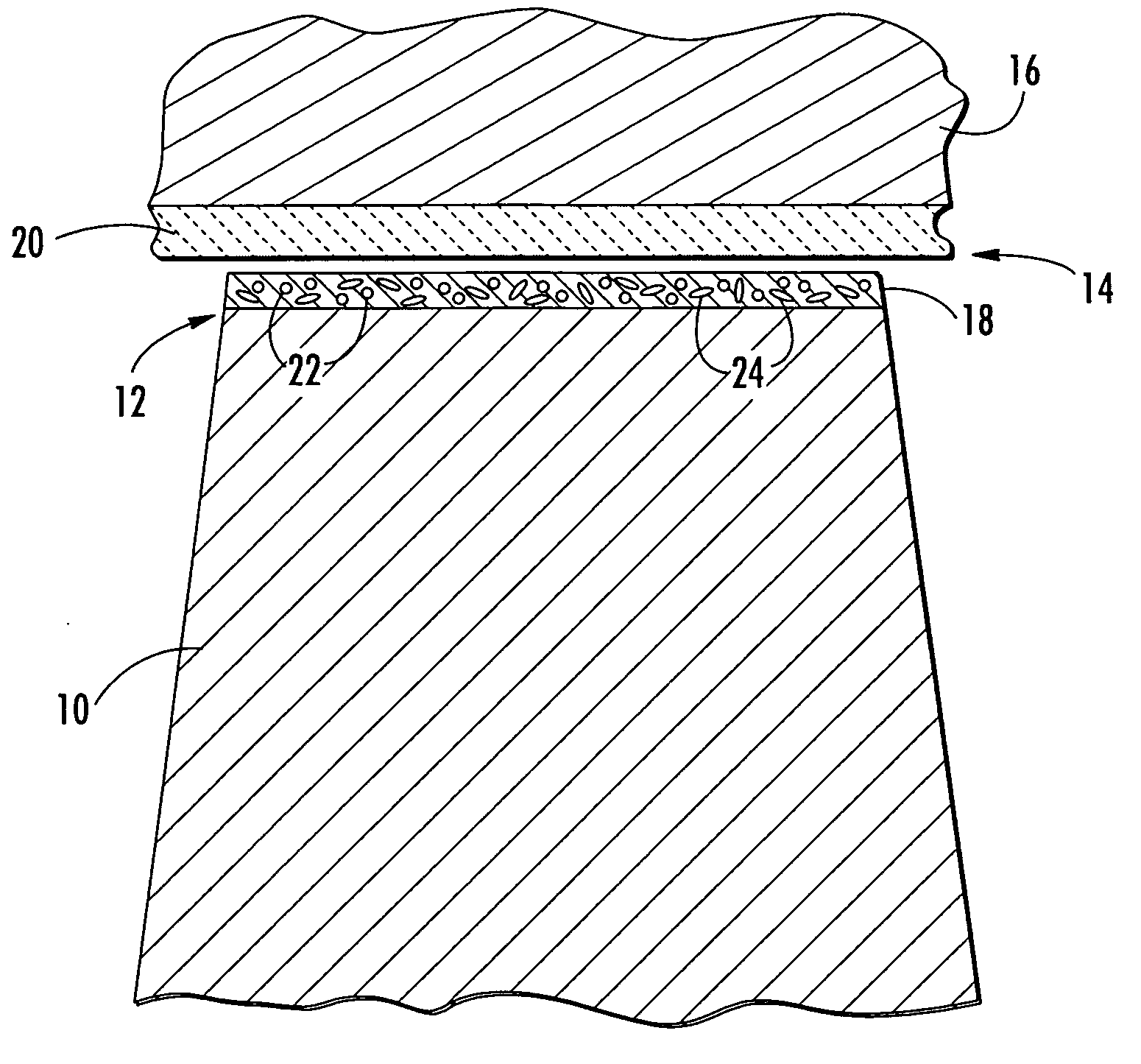
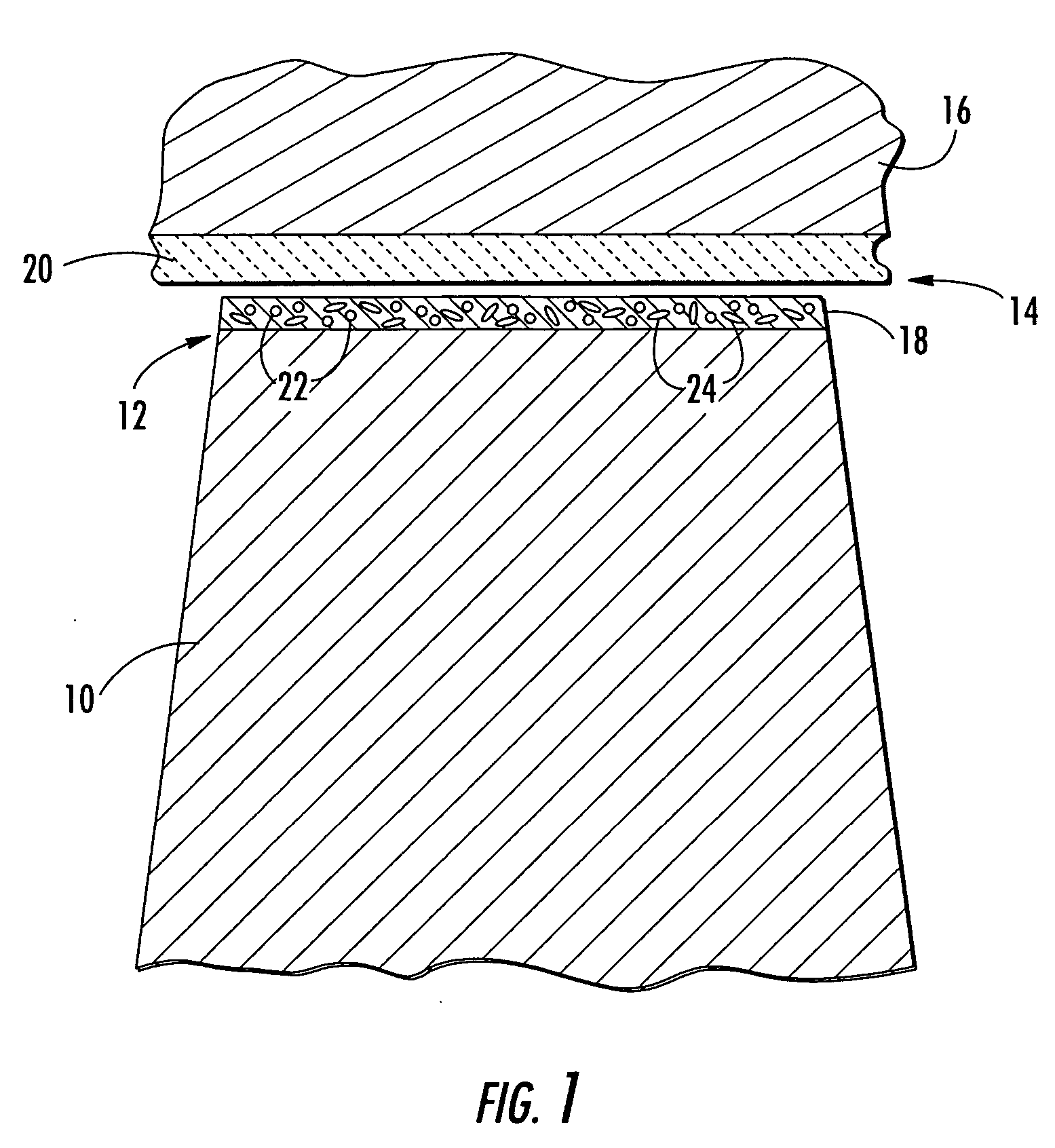
Turbine blade tip with optimized abrasive
InactiveUS20050129511A1Improved blade tip clearance controlImprove engine efficiencyElectrolytic coatingsPump componentsIndustrial gasTurbine blade
A new abrasive blade tip treatment is disclosed with the potential to provide improved blade tip clearance control in the turbine section of modern industrial gas turbines (IGT's). This blade tip treatment is composed of a unique combination of abrasive compounds that result in improved resistance to thermal degradation while retaining desirable initial cutting capacity.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Turbine blade tip clearance control device
InactiveUS20050058539A1Improve efficiencyReduce gap sizeWind motor controlPump componentsTurbine bladeTip clearance
A sealing system for reducing a gap between a tip of a shrouded turbine blade and a stationary shroud of a turbine engine. The sealing system includes one or more seal lands extending from a shrouded turbine blade toward a stationary shroud of a turbine engine. During operation of the turbine engine, the seal lands straighten and extend towards the stationary shroud of the turbine engine, thereby reducing the leakage of air past the shrouded turbine blades and increasing the efficiency of the turbine engine. The sealing system may also include one or more protrusions extending from the stationary shroud towards the tips of the shrouded turbine blades.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
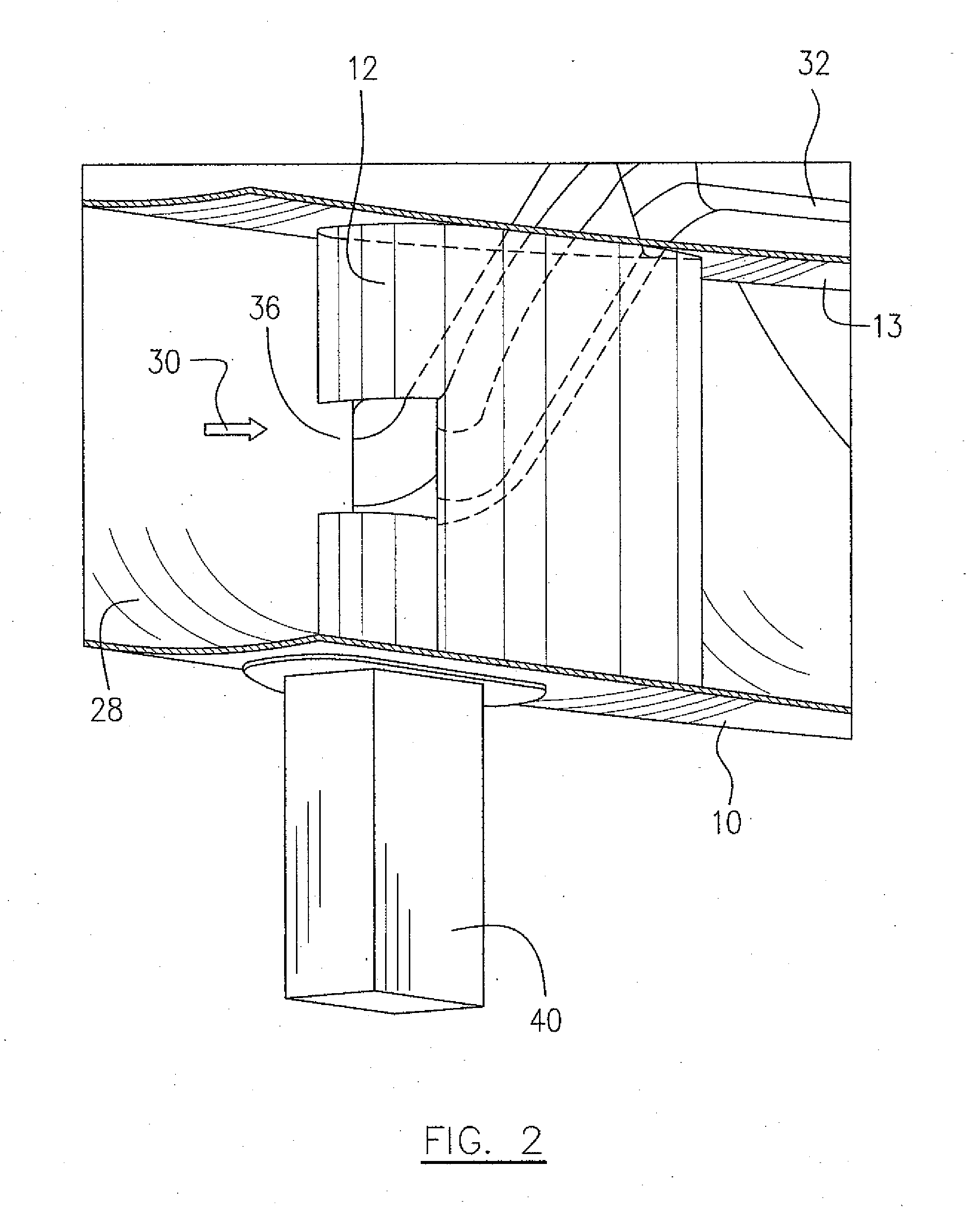
Bypass air scoop for gas turbine engine
A gas turbine engine has a plurality of radial struts in a bypass duct. At least one strut has a scoop incorporated with the fairing of the strut and in communication with an air passage of an engine secondary air system. The scoop faces a bypass air flow to scoop a portion of the bypass air flow using available dynamic pressure in the bypass duct. Scooped air may be provided, for example, to an active tip clearance control apparatus in a long duct turbofan engine.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
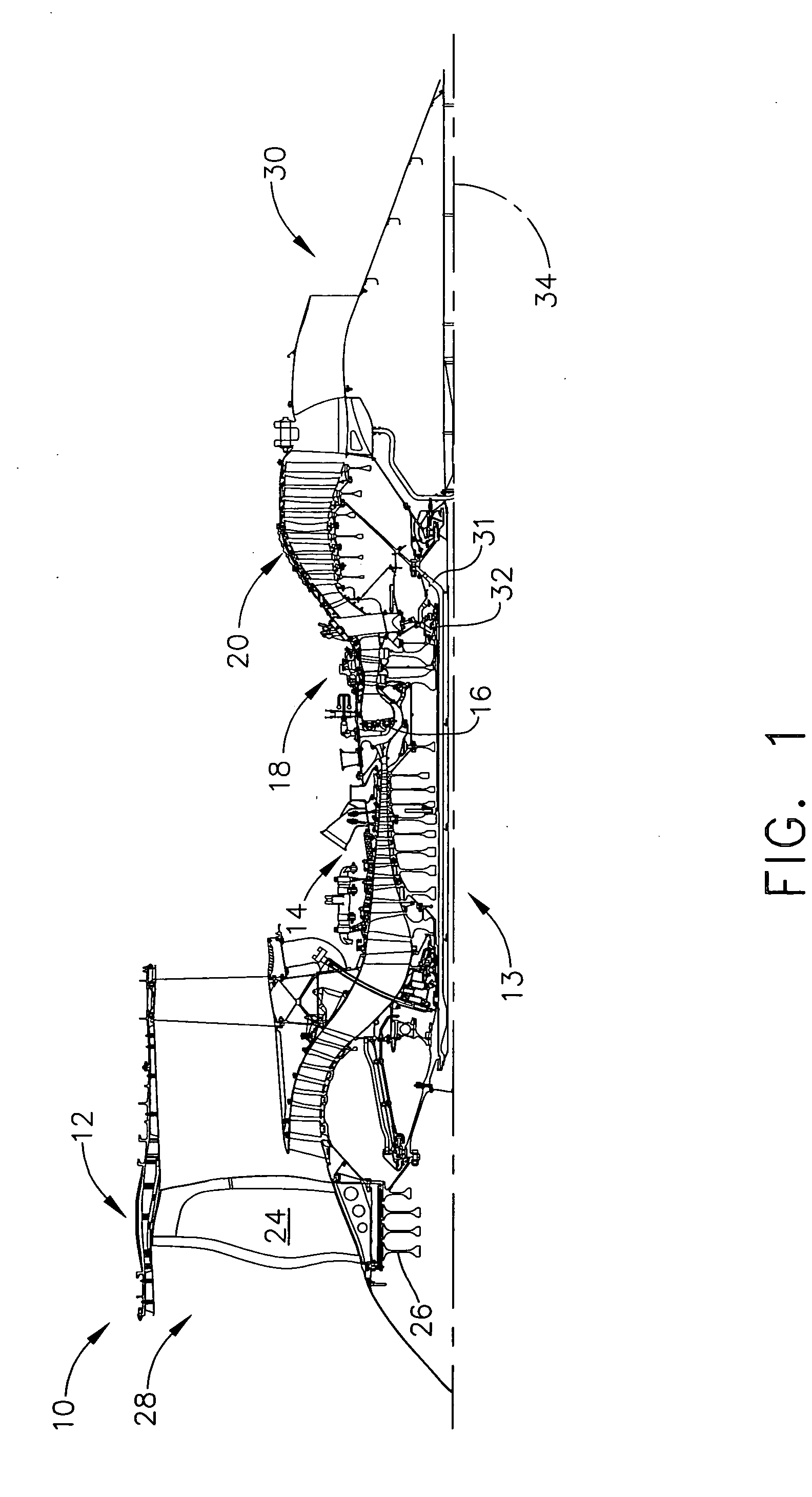
Methods and apparatus for maintaining rotor assembly tip clearances
ActiveUS7165937B2Easy to removeEasy maintenanceEngine manufacturePump componentsControl systemEngineering
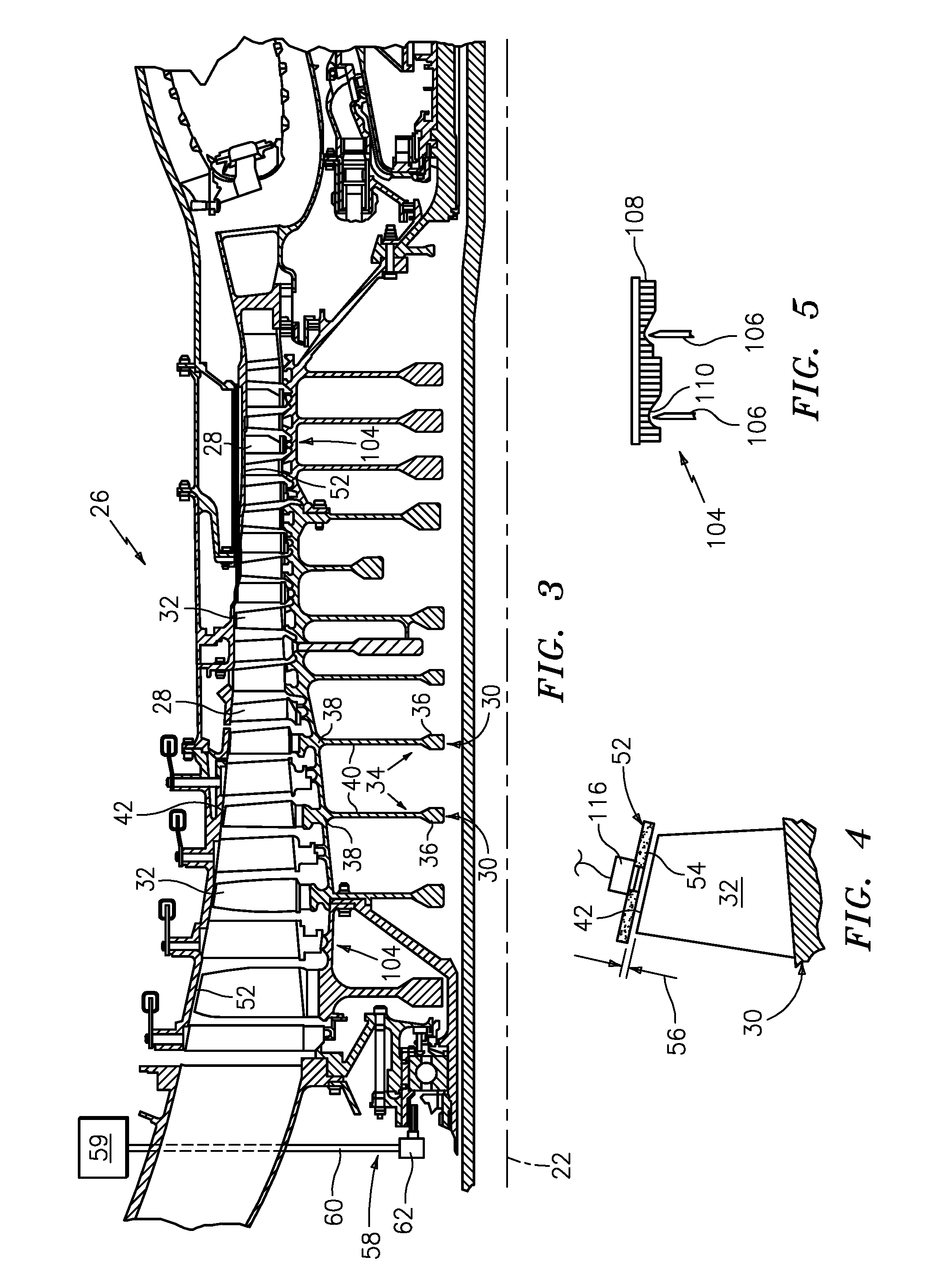
A method enables a gas turbine engine to be assembled. The method comprises coupling a rotor assembly including a plurality of circumferentially-spaced rotor blades downstream from, and in flow communication with, a compressor, coupling a casing assembly circumferentially around the rotor assembly such that a clearance is defined between an inner shroud surface of the casing assembly and the rotor blade tips, and coupling a clearance control system to the casing assembly to facilitate maintaining the clearance between the casing assembly and the rotor blade tips, wherein at least a portion of an external surface of the clearance control system is formed with a textured pattern that facilitates increasing the clearance control closure capability during engine operation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
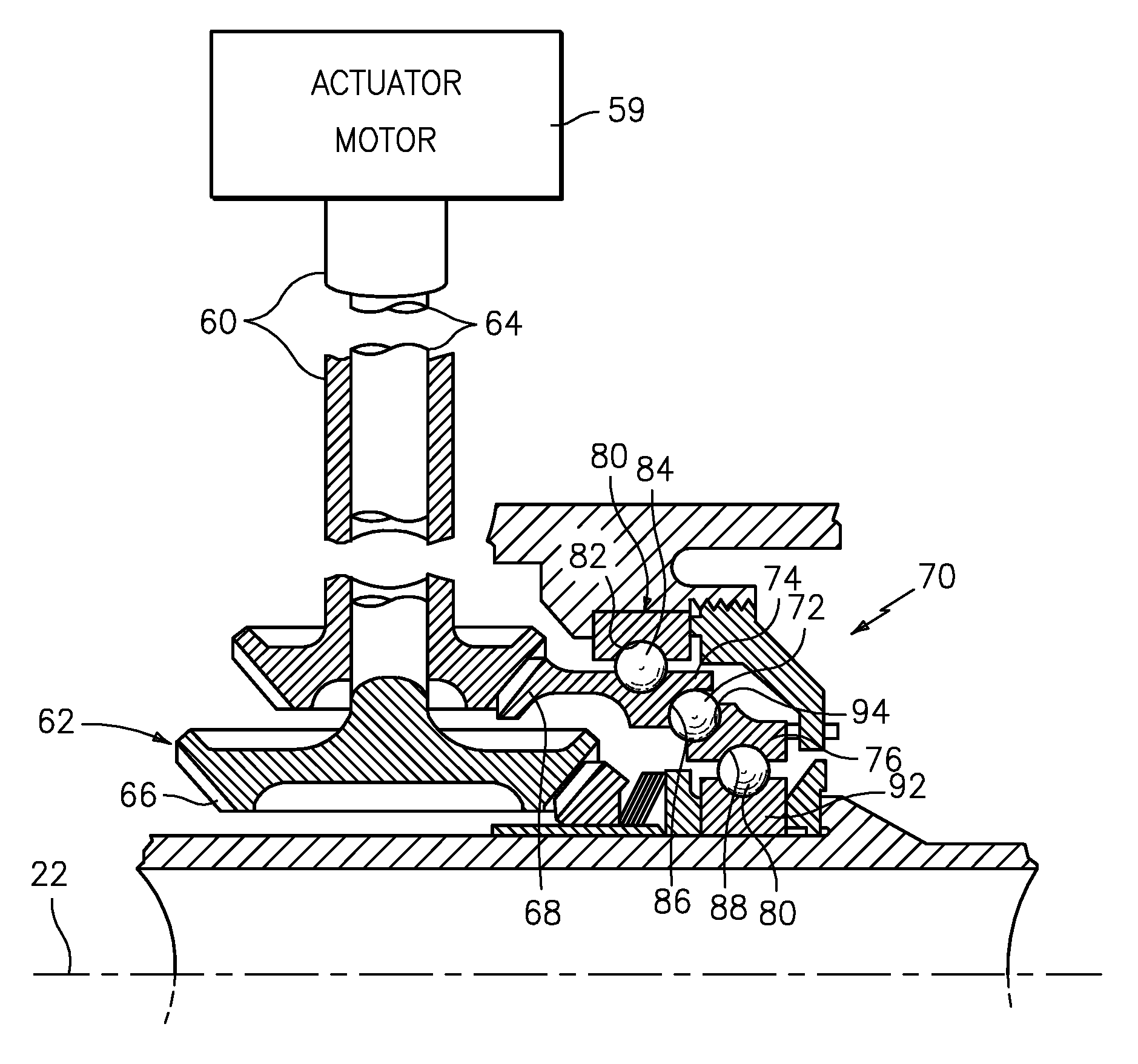
Gas turbine engine blade tip clearance apparatus and method
A method for controlling blade tip clearance within a gas turbine engine includes the steps of providing a compressor having at least one first rotor assembly, each first rotor assembly having a plurality of blades with each blade having a blade tip, at least one first stator assembly disposed adjacent at least one first rotor assembly, and a shroud having at least one blade seal surface disposed radially outside of at least one first rotor assembly, wherein the blade tips in each of at least one first rotor assembly has a mating geometry with at least one of at least one blade seal surfaces, and a clearance distance extending between the blade tips and the blade seal surfaces; providing a turbine having at least one second rotor assembly, each second rotor assembly having a plurality of blades with each blade having a blade tip, at least one second stator assembly disposed adjacent at least one second rotor assembly, and the shroud having at least one blade seal surface disposed radially outside of at least one second rotor assembly, wherein the blade tips in each of at least one second rotor assembly has a mating geometry with at least one of at least one blade seal surfaces, and a clearance distance extending between the blade tips and the blade seal surfaces; providing an actuator selectively operable to move at least one rotor assembly relative to the shroud; providing an electronic engine controller having a control logic for operating the actuator; and moving at least one first rotor assemblies and at least one second rotor assembly relative to the shroud using the actuator at a response rate according to the control logic to alter the clearance distance.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
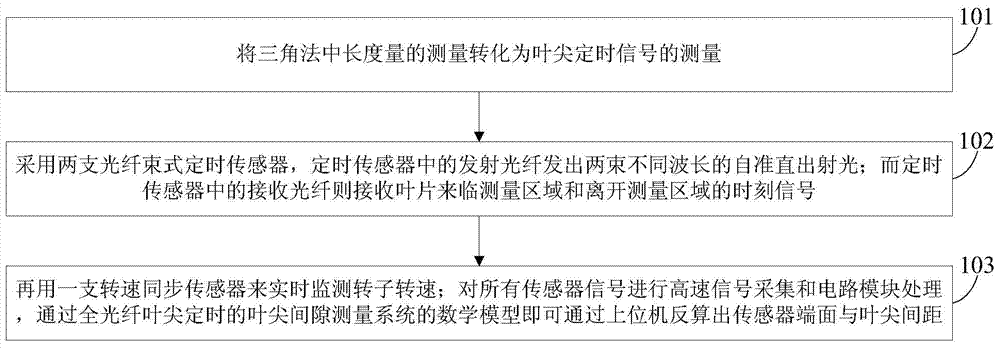
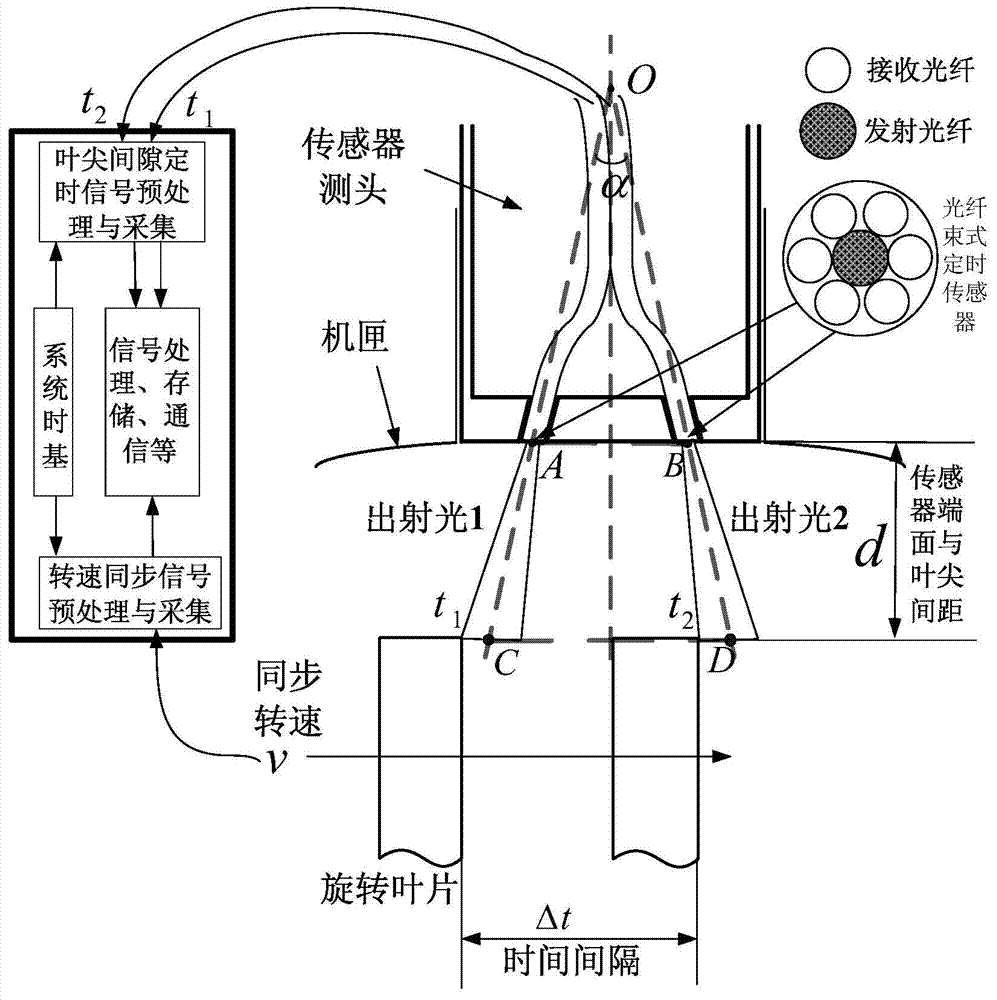
Tip clearance measurement method based on all-fiber tip timing
InactiveCN104501728AImprove anti-electromagnetic interference performanceFast dynamic responseUsing optical meansMathematical modelLength measurement
The invention discloses a tip clearance measurement method based on all-fiber tip timing. The method comprises the following steps: converting measurement on length measurement in a triangle method into measurement on a tip timing signal; adopting two fiber bundle type timing sensors, and enabling emission fibers in the timing sensors to emit two beams of auto-collimation emergent light with different wavelengths; enabling receiving fibers in the timing sensors to receive moment signals when leaves approach and leave a measurement region; monitoring the rotating speed of a rotor in real time by a rotating speed synchronization sensor; performing high-speed signal acquisition and circuit module processing on all the sensor signals, and reversely calculating a distance between the end face of each sensor and each leaf tip by an upper computer through a math model. According to the tip clearance measurement method, a clearance value is ingeniously converted into a tip timing signal relevant to the clearance value, so that a measurement system is irrelative to most environmental factors such as the leaf and electromagnetic interference, and the interference resistance and the clearance measurement precision of the system are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
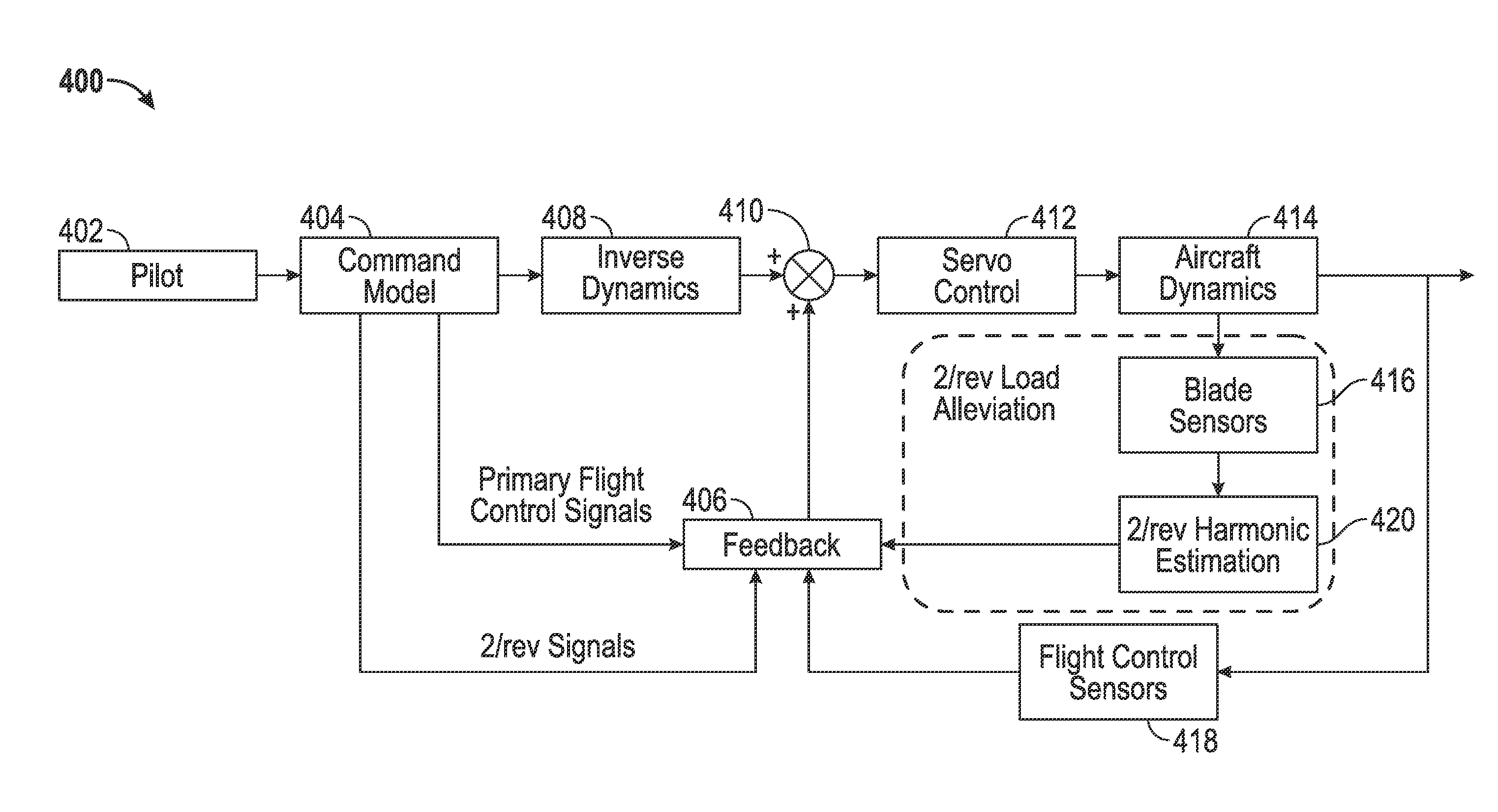
Helicopter rotor load reduction and tip clearance control
A method of controlling a helicopter having a rotor with blades is provided. The method includes receiving, by a computing device comprising a processor, at least one input associated with the helicopter; generating, by the computing device, control signals configured to counteract blade bending associated with the rotors based on the received at least one input; measuring, by the computing device, blade signals using sensors for the blades; extracting, by the computing device, harmonic loads from the measured blade signals; adapting, by the computing device, the control signals based on the harmonic loads; and controlling, by the computing device, servos connected to the blades to adjust the blades according to the adapted control signals to reduce vibratory loads on the blades.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
Gas turbine engine blade tip clearance apparatus and method
A method for controlling blade tip clearance within a gas turbine engine includes a compressor having at least one first rotor assembly, wherein the blade tips in each of at least one first rotor assembly has a mating geometry with at least one of at least one blade seal surfaces, and a clearance distance extending between the blade tips and the blade seal surfaces; a turbine having at least one second rotor assembly, wherein the blade tips in each of at least one second rotor assembly has a mating geometry with at least one of at least one blade seal surfaces, and a clearance distance extending between the blade tips and the blade seal surfaces; providing an actuator selectively operable to move at least one rotor assembly relative to the shroud; providing an electronic engine controller having a control logic for operating the actuator; and moving at least one first rotor assemblies and at least one second rotor assembly relative to the shroud using the actuator at a response rate according to the control logic to alter the clearance distance.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Gas turbine plant
ActiveUS20110135456A1Reducing tip clearanceReduce metal temperaturePump componentsWind motor controlThermal expansionGas turbines
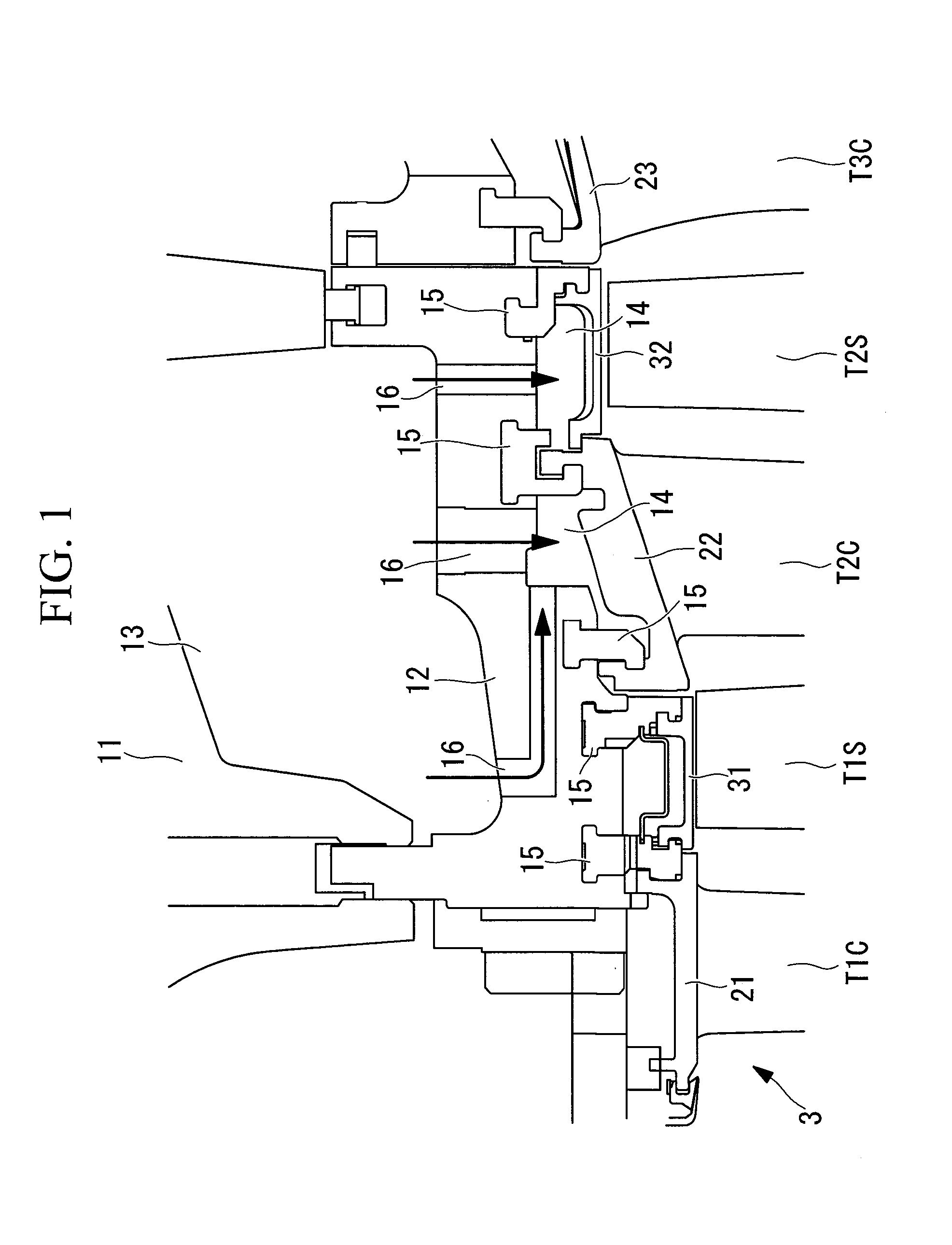
Provided is a gas turbine plant that enables active clearance control for ensuring tip clearance of first-stage turbine rotor blades required during start-up and for achieving the minimum tip clearance during load operation. In a gas turbine plant including a cooler in an air system used for cooling second-stage turbine stator blades, a first-stage segmented ring and a second-stage segmented ring that oppose tips of first-stage turbine rotor blades and second-stage turbine rotor blades are supported by the same blade ring member, and a cooling-air for the second-stage turbine stator blades forms a cooling air flow cooling the blade ring, to control thermal expansion of the blade ring and to control the clearance with respect to the tips.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Compliant mounting system for turbine shrouds
The mounting of low expansion full ring shrouds in a turbine engine requires radial compliance to limit the stresses experienced by the shroud due to thermal growth differences between the shroud and its support. A method provides radial compliance with no looseness in a mounting system. The mounting system also allows for axial motion of the shroud, should such motion be needed or desired. The lack of looseness in the mounting system results in an ability to achieve smaller tip clearances and thus better engine performance.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Distal bearing support
In various embodiments, a catheter pump is disclosed herein. The catheter pump can include an elongated catheter body having a distal portion including an expandable cannula having an inlet and an outlet. The expandable cannula can have a delivery profile and an operational profile larger than the delivery profile. An impeller assembly can include an impeller shaft, and an impeller body can include one or more blades. The impeller blades can draw blood into the cannula when rotated. Further, an expandable support can have a mounting portion disposed on the impeller shaft distal of the impeller body and a cannula contact portion for reducing a change in tip gap due to bending of the cannula. The cannula contact portion can be disposed distal of the mounting portion.
Owner:TC1 LLC
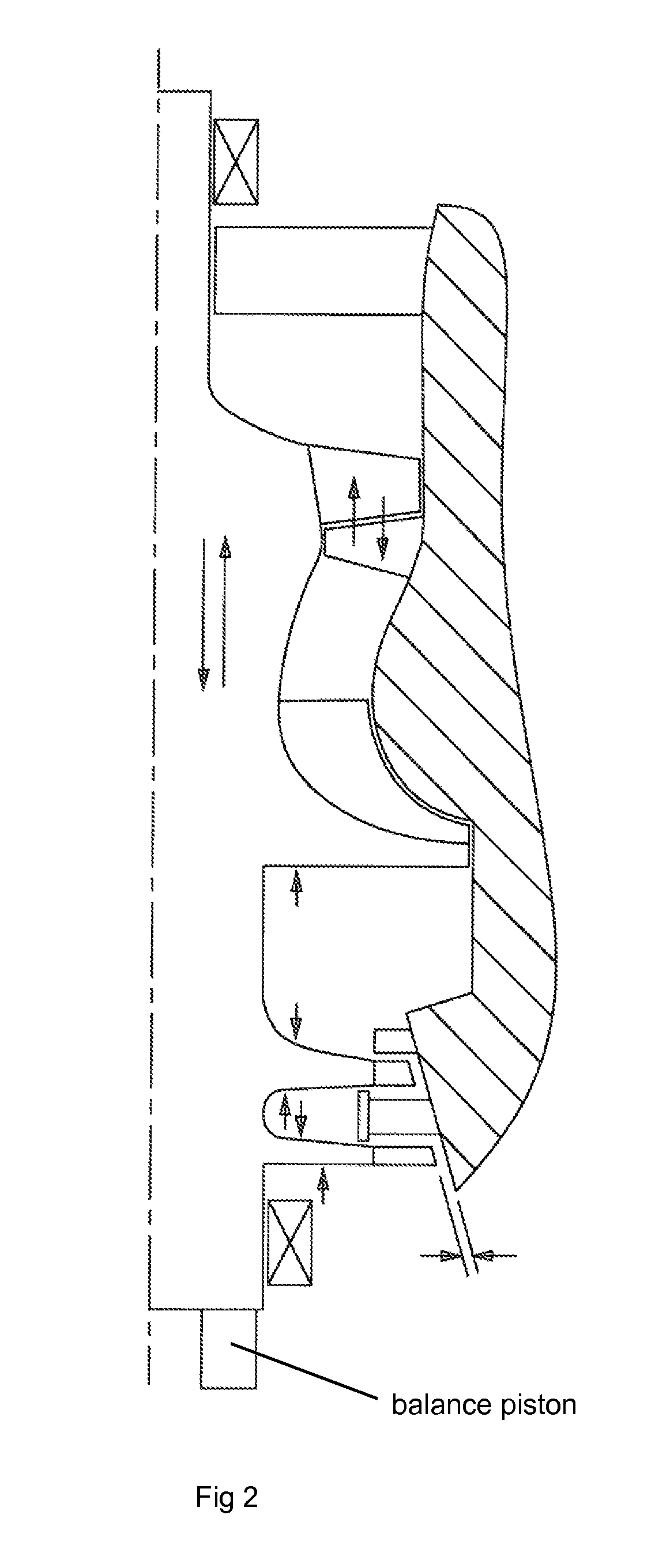
Rotor thrust balance activated tip clearance control system
InactiveUS7909566B1Increase in gap spacingReduce gap spacingPump componentsWind motor controlControl systemGas turbines
A gas turbine engine with a rotor shaft that is moveable in an axial direction so change a blade tip clearance, where the rotor is displaced by a spring to increase the blade tip clearance and is displaced by a pressure created by the compressor and turbine during engine operation that will close the blade tip clearance. This is especially useful during engine shutdown to prevent blade tip rubbing against the stationary shrouds.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
Hybrid turbine tip clearance control system
InactiveUS6925814B2Avoid less flexibilityMinimizes parasitic secondary air system lossesPump componentsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingControl systemGas turbines
A turbine shroud cooling system used in a gas turbine engine for controlling tip clearance between a turbine shroud assembly and turbine rotor blades comprises a cooling air passage for selectively directing a cooling air flow between components to be cooled and a turbine shroud support assembly for controlling the tip clearance and then later re-directing the cooling air flow to cool a downstream turbine component.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Turbine blade tip clearance control device
InactiveUS6926495B2Reduce air leakageImprove efficiencyWind motor controlPump componentsTurbine bladeTip clearance
A sealing system for reducing a gap between a tip of a shrouded turbine blade and a stationary shroud of a turbine engine. The sealing system includes one or more seal lands extending from a shrouded turbine blade toward a stationary shroud of a turbine engine. During operation of the turbine engine, the seal lands straighten and extend towards the stationary shroud of the turbine engine, thereby reducing the leakage of air past the shrouded turbine blades and increasing the efficiency of the turbine engine. The sealing system may also include one or more protrusions extending from the stationary shroud towards the tips of the shrouded turbine blades.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Turbine tip clearance measurement
A measuring assembly for use in a gas turbine engine includes an indicia portion that extends radially inwardly from an inner surface of a ring seal structure to a location radially inwardly from tips of blades mounted on a rotor. The indicia portion of the measuring assembly comprises a section that is abraded by the blades during rotational movement of the rotor to provide a visual indication of a distance between the tips of the blades and the inner surface.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
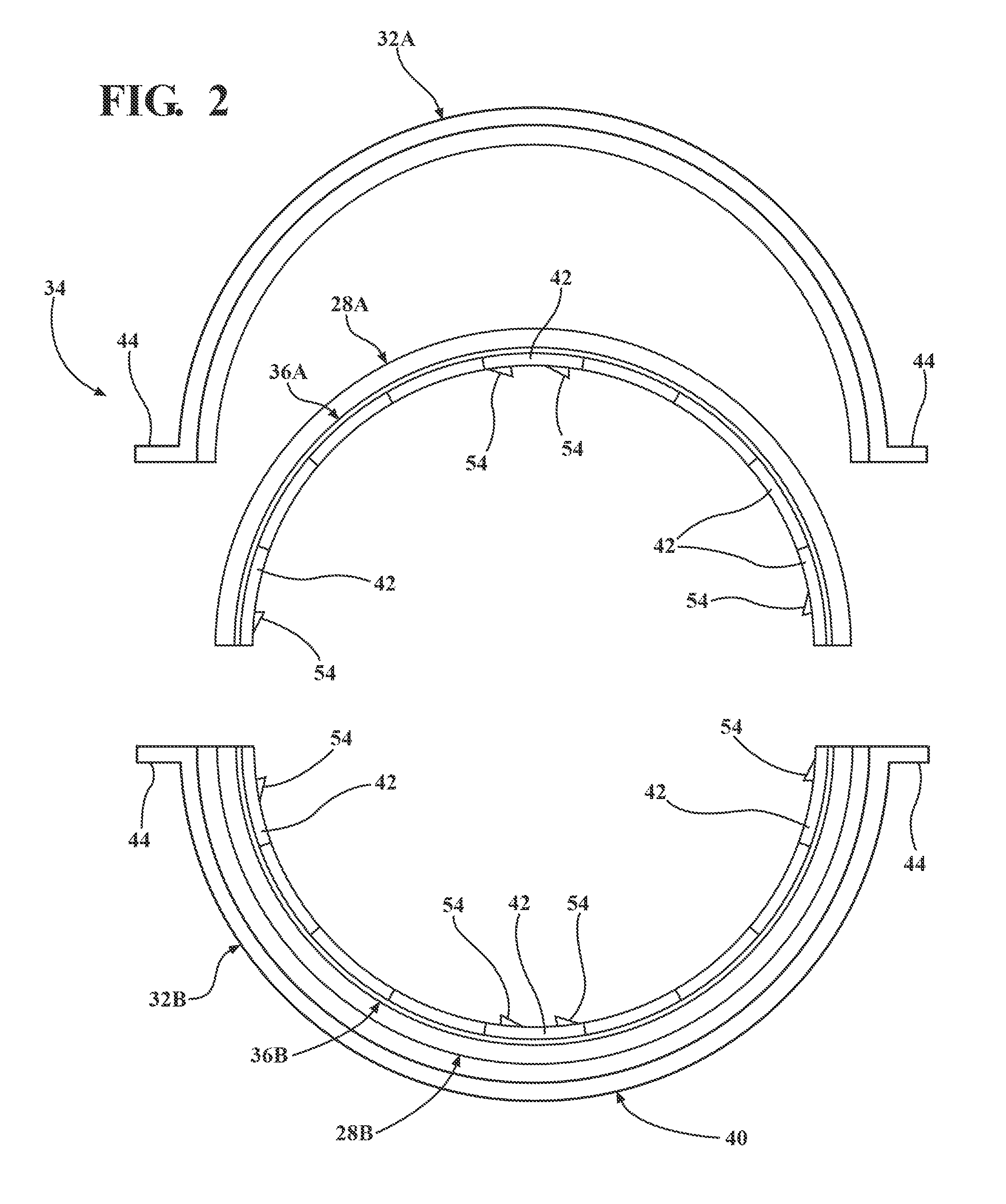
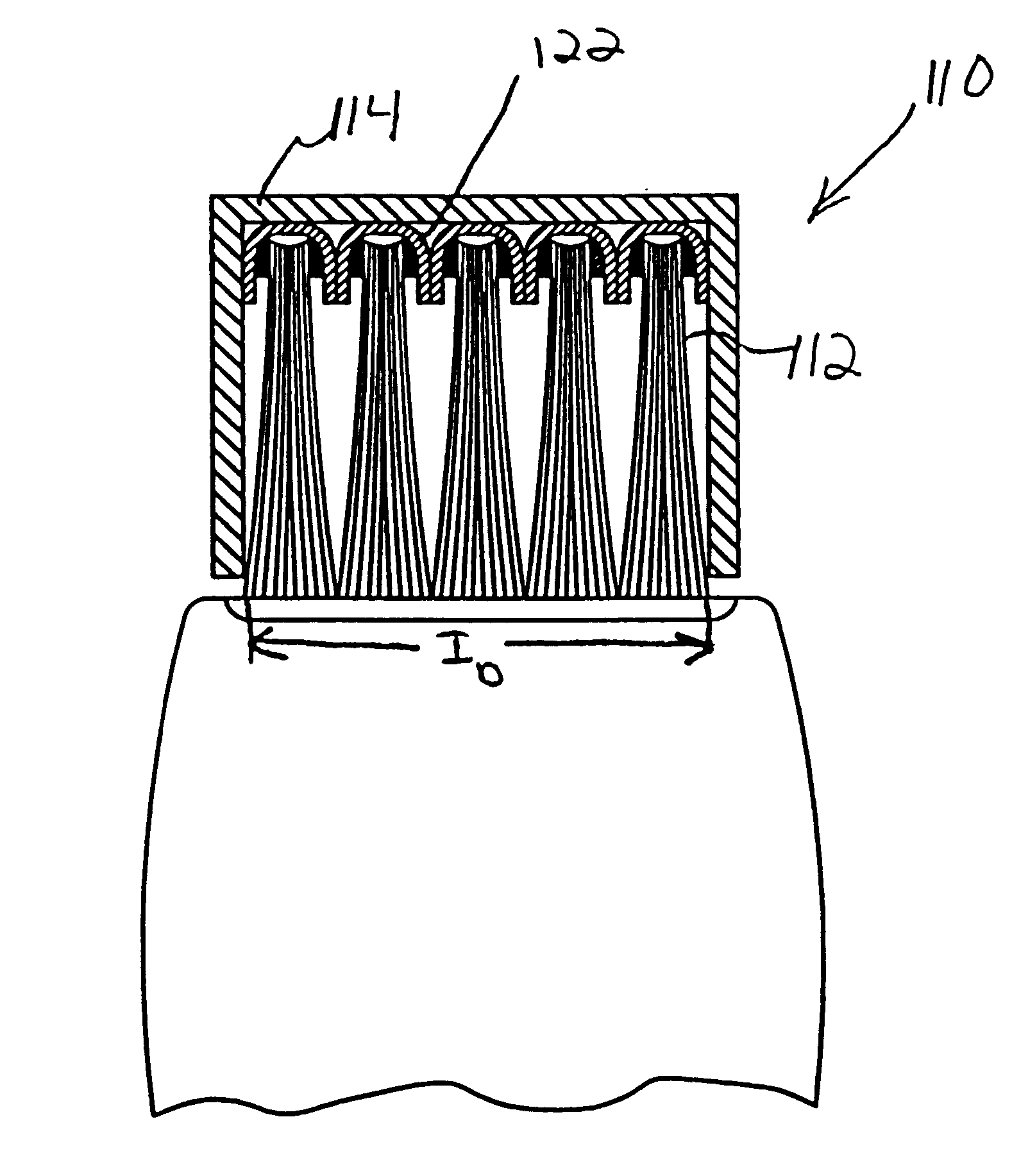
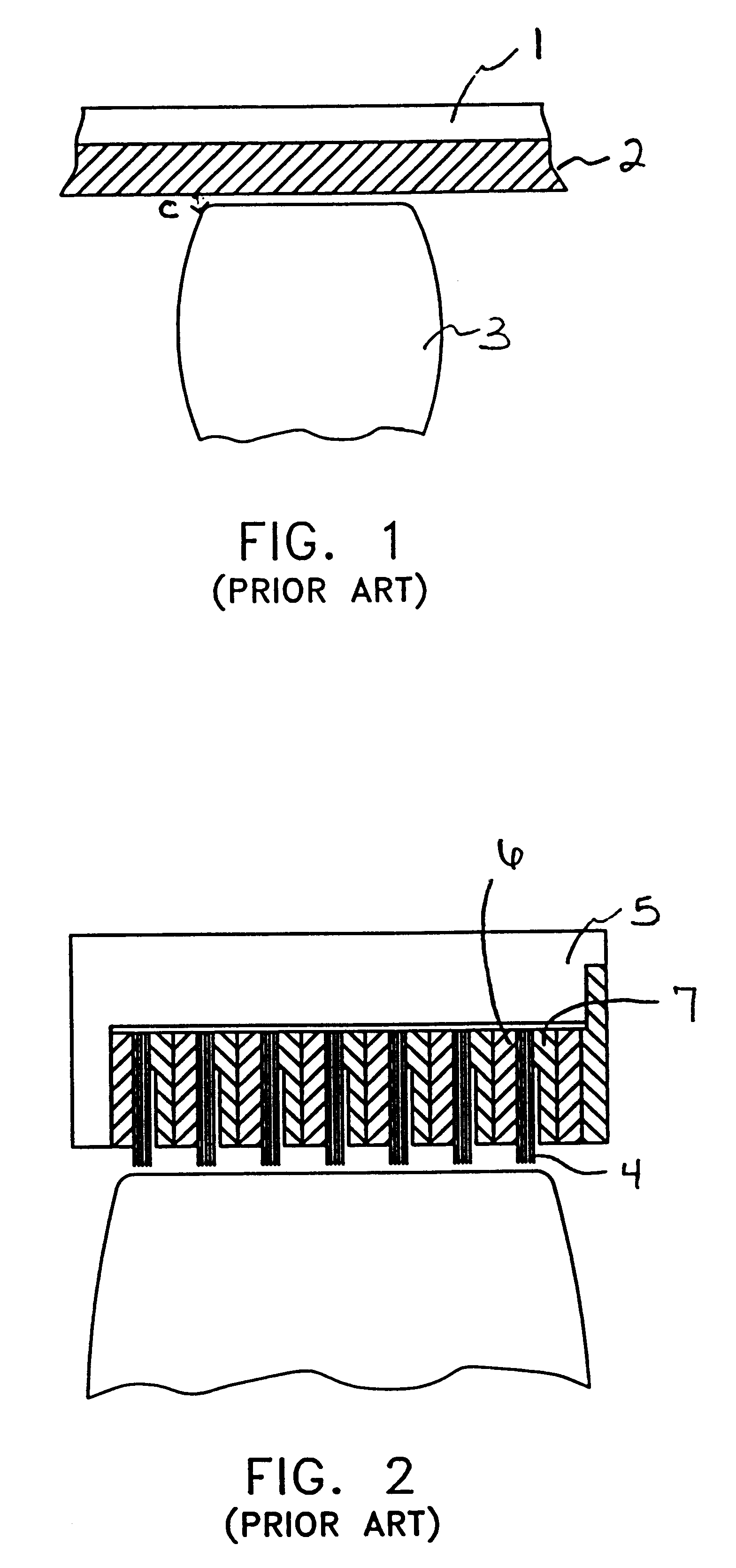
Compliant brush shroud assembly for gas turbine engine compressors
A brush shroud assembly for reducing the tip clearance between a rotating blade and an engine casing is disclosed. The assembly includes a plurality of bristle packs supported within a housing such that the bristle distribution at the inner diameter of the bristle packs is substantially continuous. The continuous surface is created by mounting the bristles packs within a housing such that the packs are flared, i.e. width at the outer diameter of the bristle pack is smaller than that at the inner diameter. Various embodiments are disclosed for mounting the flared bristle packs to form a substantially continuous inner diameter. The bristle strips may be mounted in one or more annular rings, may be secured within one or more channels in the housing, the bristle packs may be formed into a tufted ring, or any of these may be utilized in combination with a backplate supporting an abradable seal, i.e. a hybrid design.
Owner:ADVANCED COMPONENTS & MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com