Patents
Literature
1064results about "Rotary non-positive displacement pumps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Submersible appartus for generating electricity and associated method
InactiveUS6109863AReduce the impactReduce impactCircumferential flow pumpsWind motor controlElectricityMarine engineering
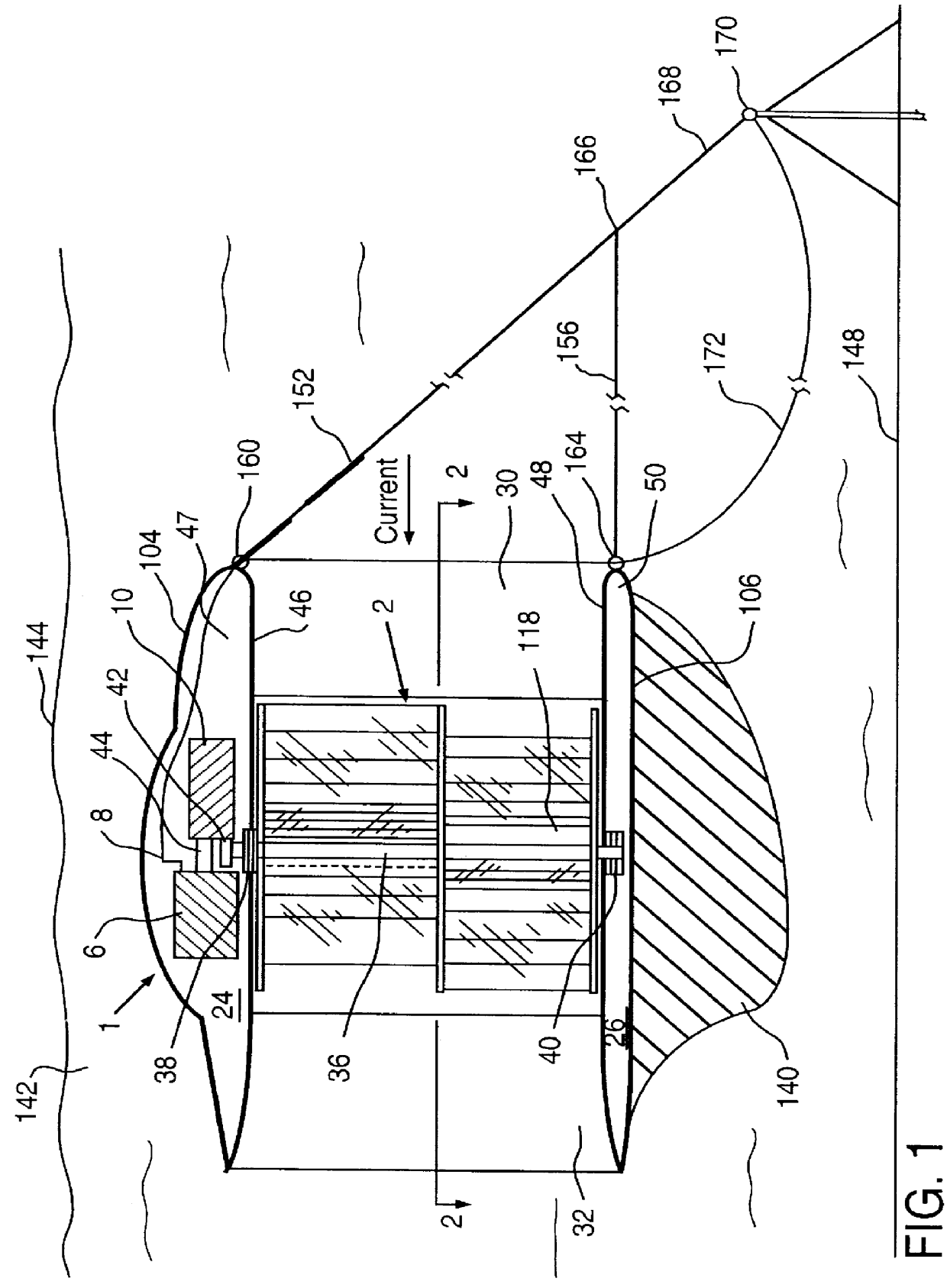
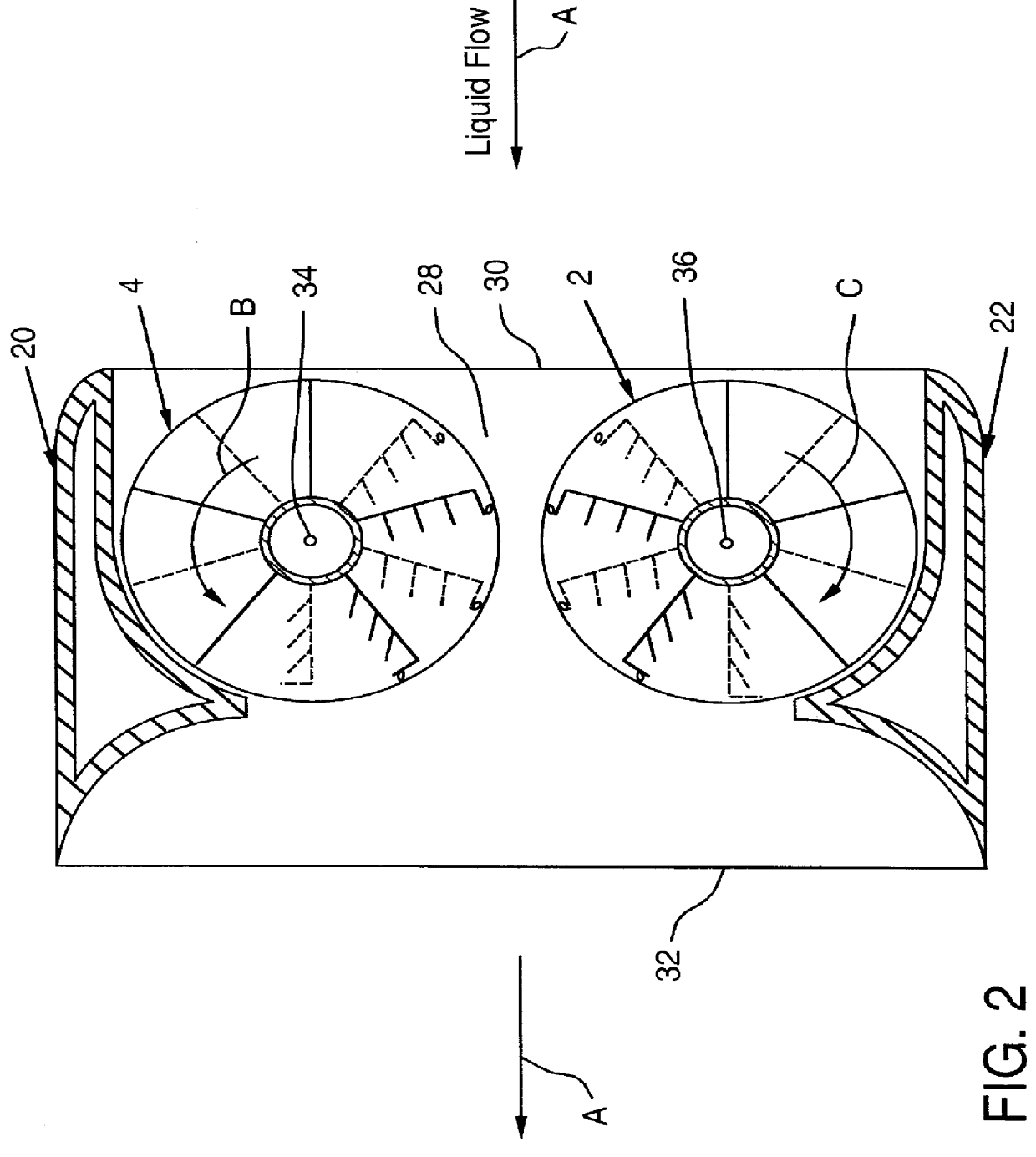
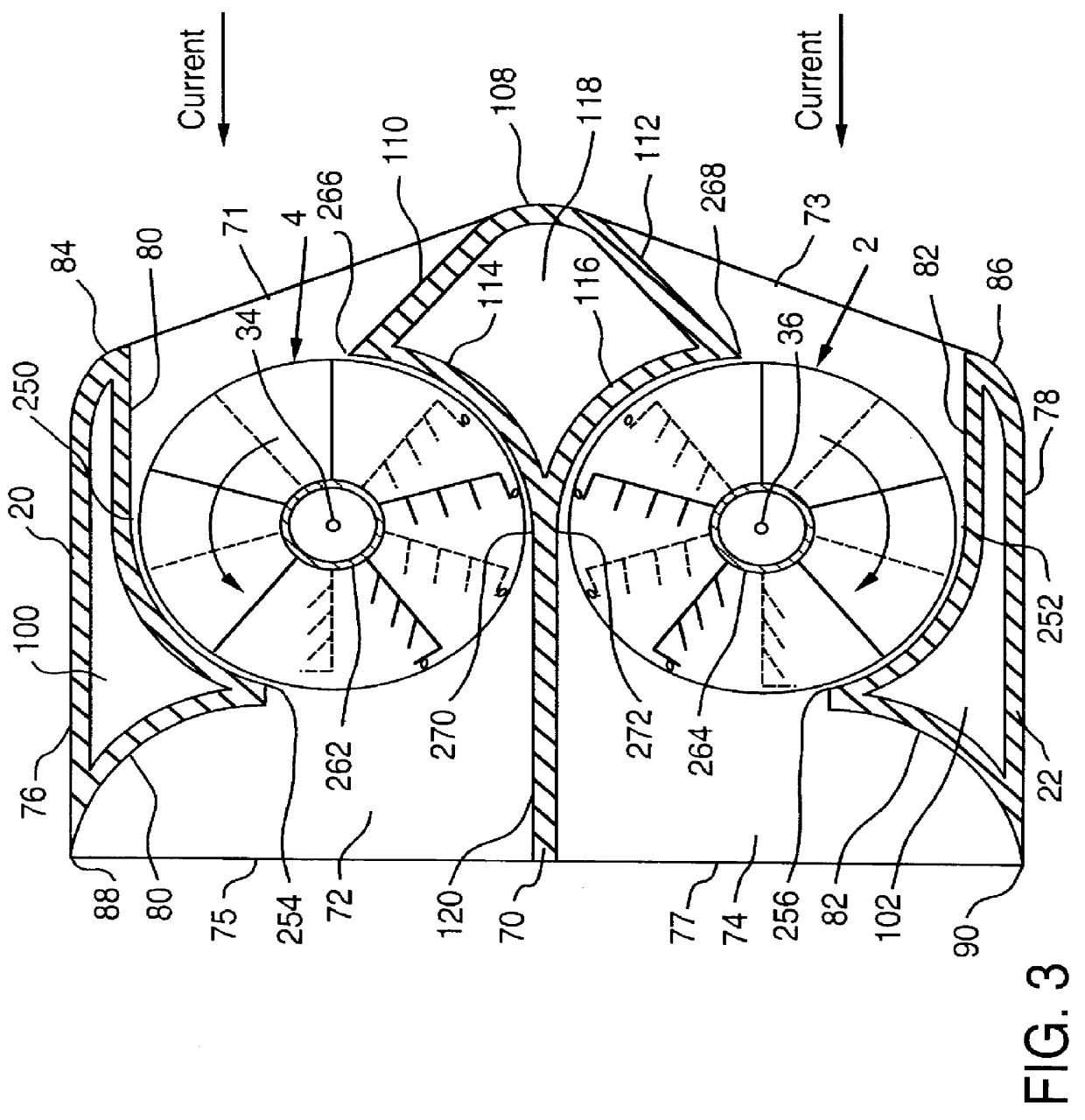
A fully submersible apparatus for generating electricity from liquid flow as in an ocean or river current. A buoyant structure is fully submersible and has at least one pair of counter-rotating side-by-side motors with a plurality of angularly spaced radial vanes each having a plurality of rotatable subvanes such that current impinging upon the motor will impinge on a closed or solid vane to effect rotation of the motor and its shaft during a first phase of the rotational cycle and will impinge on open vanes for free passage therethrough on the return or second phase of rotation of the motor. Motors may also be provided with vanes in overlying and underlying relationship. An associated method is provided.
Owner:MILLIKEN LARRY D
Rotary blood pump and control system therefor
Owner:TC1 LLC +1
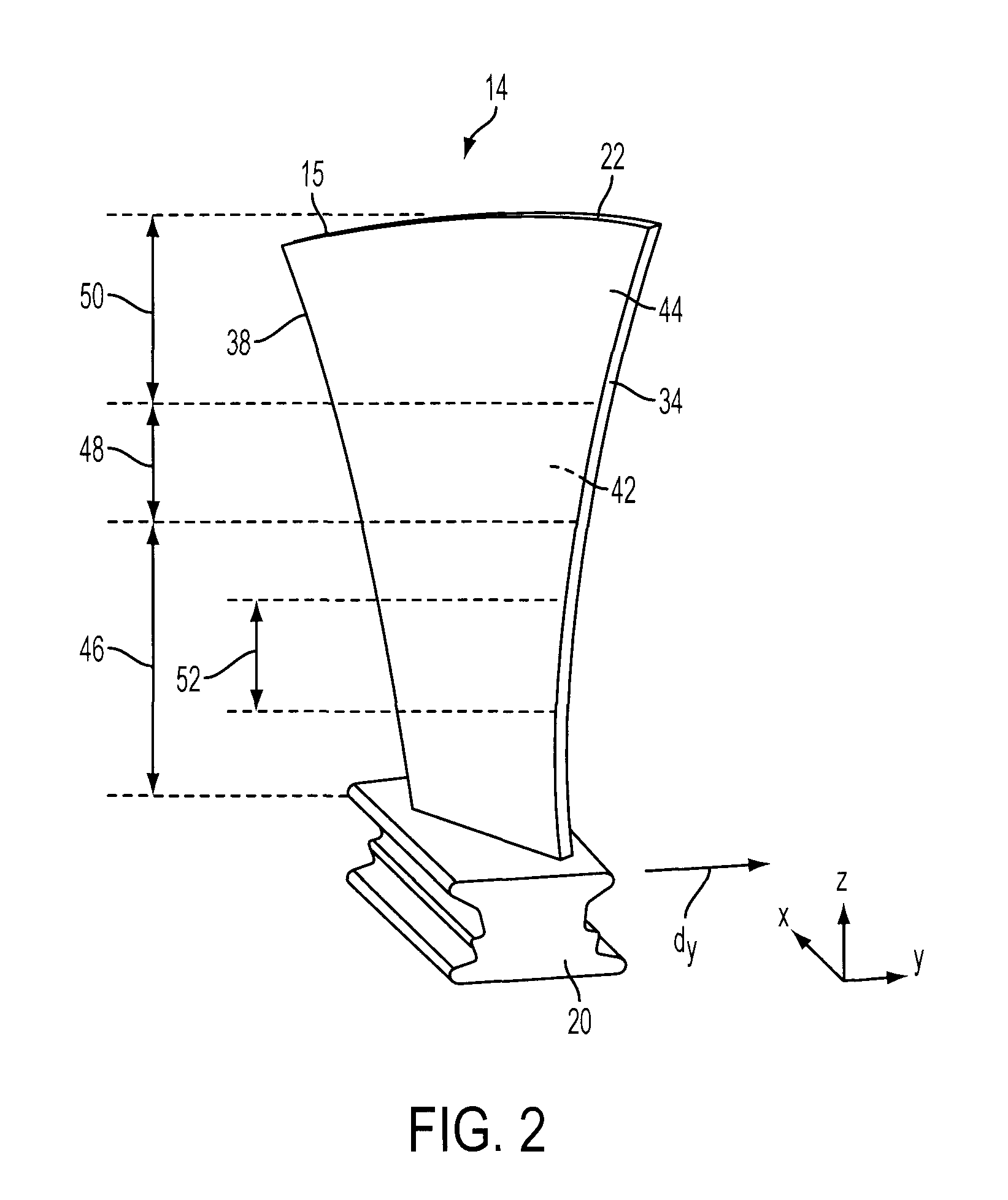
Compressor blade with forward sweep and dihedral
ActiveUS20100054946A1Reduce lossesPropellersRotary non-positive displacement pumpsTip clearanceCompressor blade
An airfoil for use as rotor blades in compressors for turbomachines, such as gas turbine engines. The airfoil includes increased forward sweep and forward dihedral effective to reduce losses generated by interaction of tip clearance flow, secondary flows and passage shocks.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Portable air moving device
ActiveUS20050031448A1Maximize evaporationEfficiently impingePropellersPump componentsAir blowerSupport surface
A stable portable air moving device capable of generating an air stream elevated above a support surface allowing the air stream to be directed as desired by the user is provided. The device includes an air blower assembly located within an elongate housing generating an exhaust air stream that exits the elongate housing at an elevation above the air blower assembly.
Owner:LASKO OPERATION HLDG LLC
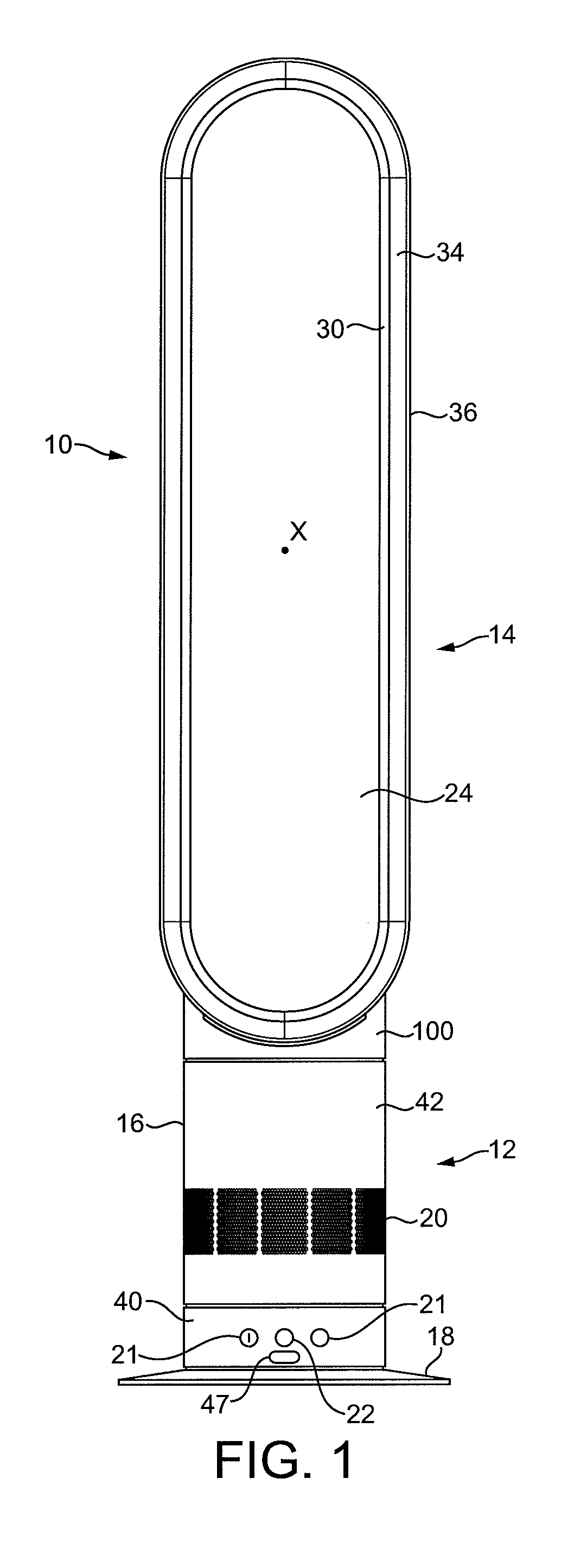
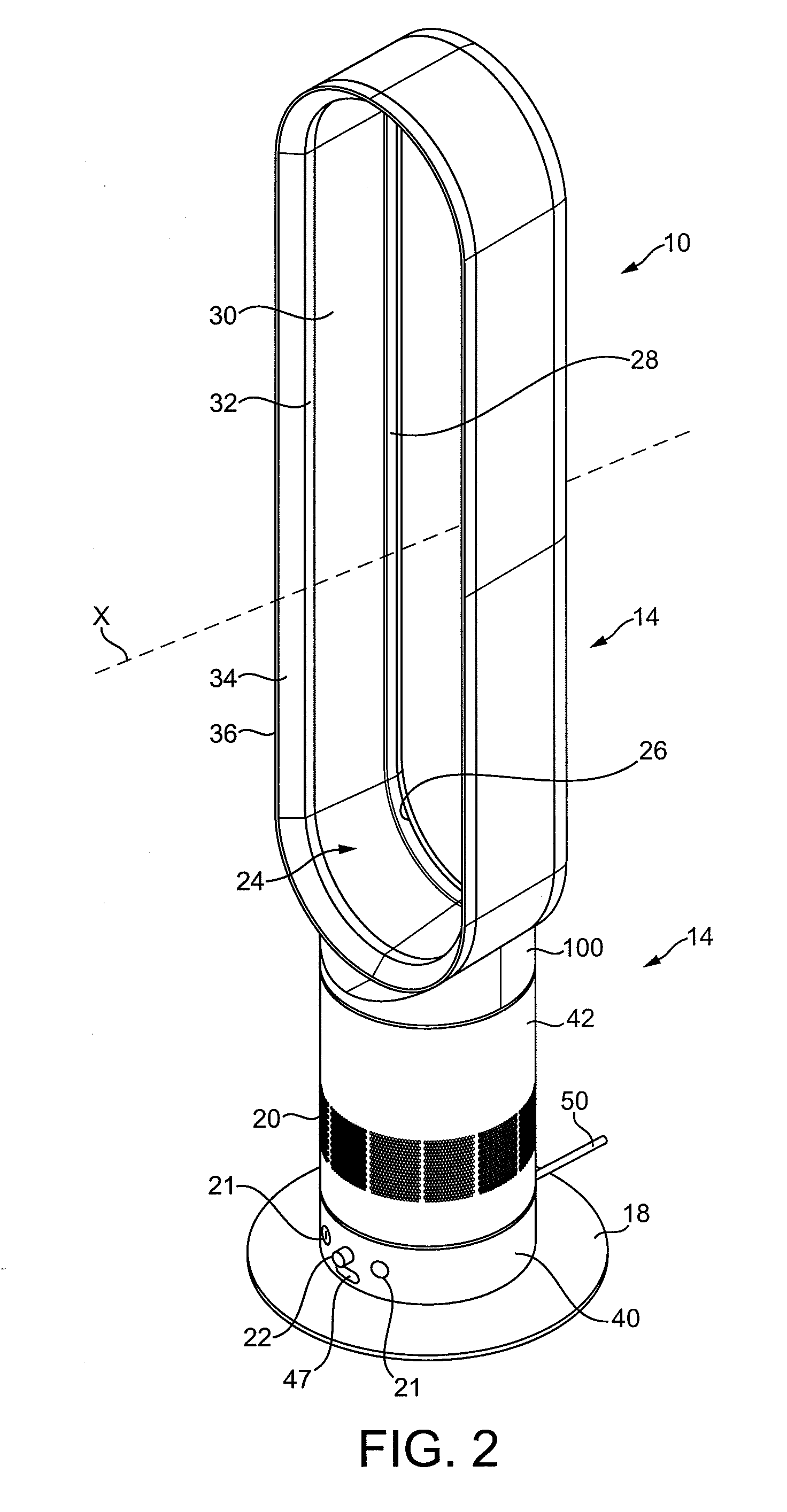
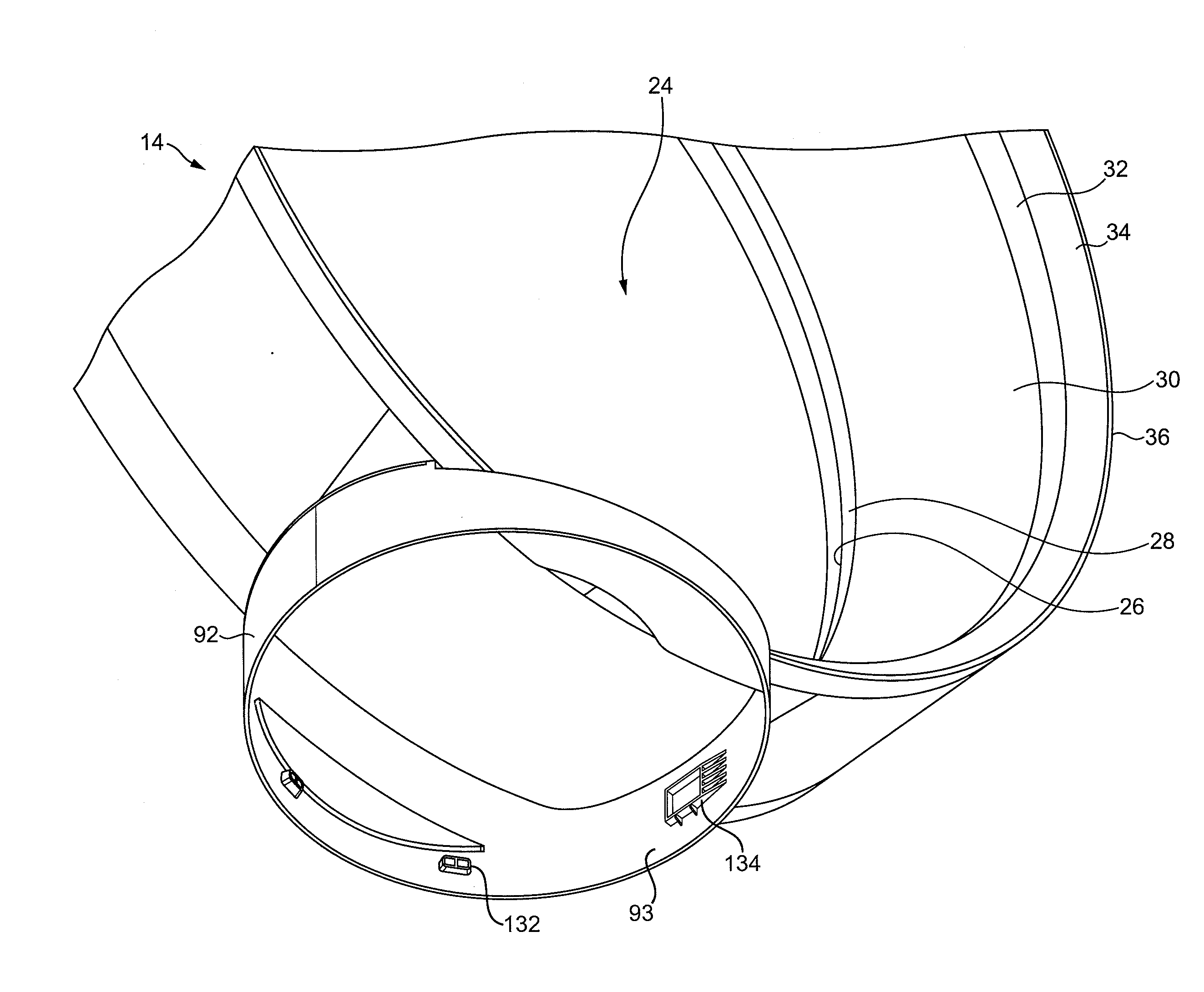
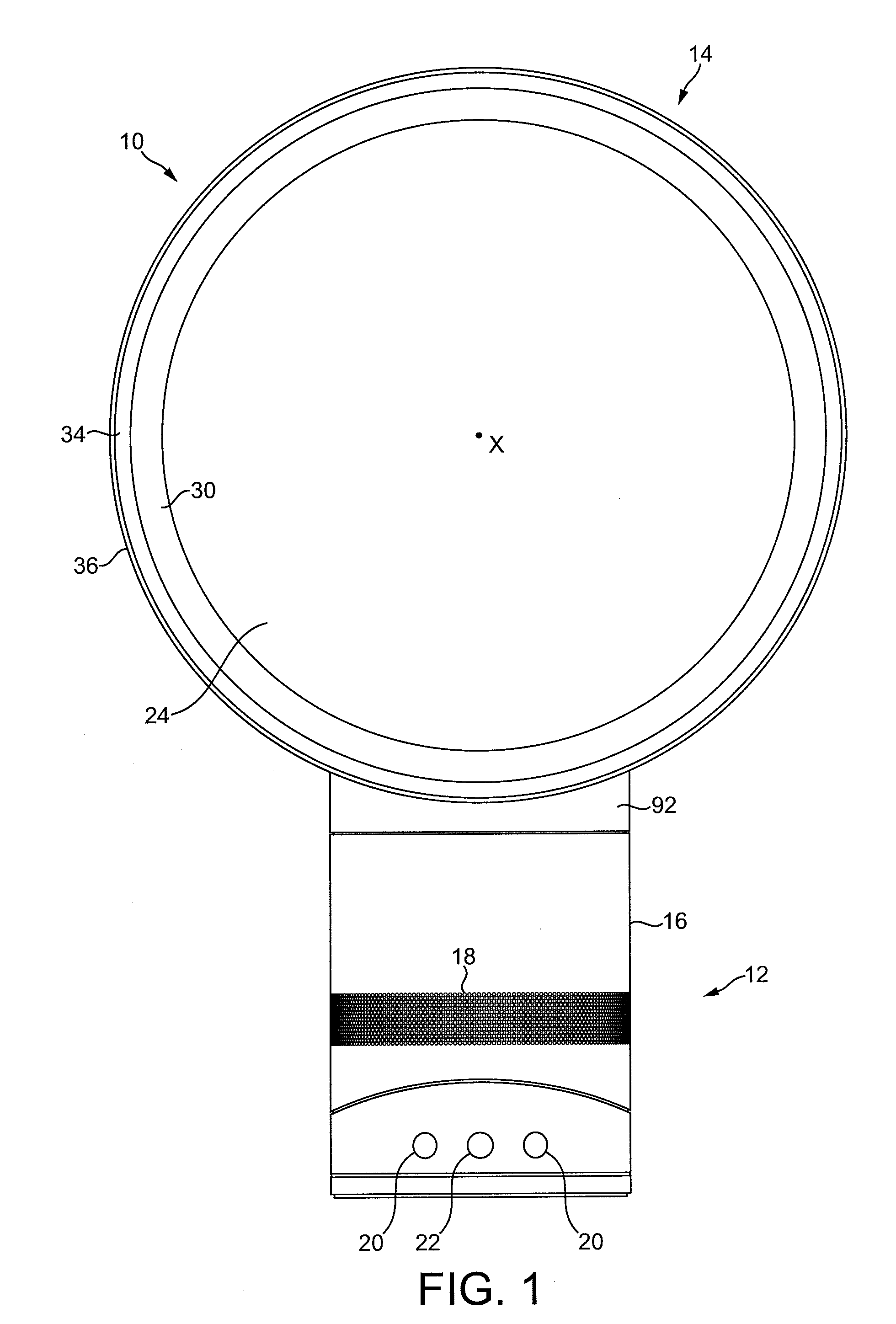
Fan assembly
InactiveUS20100226752A1Improve comfortReduce turbulenceCircumferential flow pumpsPump componentsImpellerEngineering
A fan assembly for creating an air current includes an air inlet, an air outlet, an impeller and a motor for rotating the impeller to create an air flow passing from the air inlet to the air outlet. The air outlet includes an interior passage for receiving the air flow and a mouth for emitting the air flow. The air outlet defines an opening through which air from outside the fan assembly is drawn by the air flow emitted from the mouth. The motor has a rotor which, in use, is capable of rotating at a speed of at least 5,000 rpm.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Fan assembly
ActiveUS20100226763A1Emission reductionWide operating speed rangePump componentsJet pumpsEngineeringAirflow
A bladeless fan assembly for creating an air current includes a nozzle mounted on a base. The nozzle comprises an interior passage and a mouth for receiving the air flow from the interior passage and through which the air flow is emitted from the fan assembly. The nozzle defines an opening through which air from outside the fan assembly is drawn by the air flow emitted from the mouth. The nozzle is detachable from the base, which is preferably sized to be accommodated within the opening of the nozzle for transportation.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Cooling fan and image display apparatus
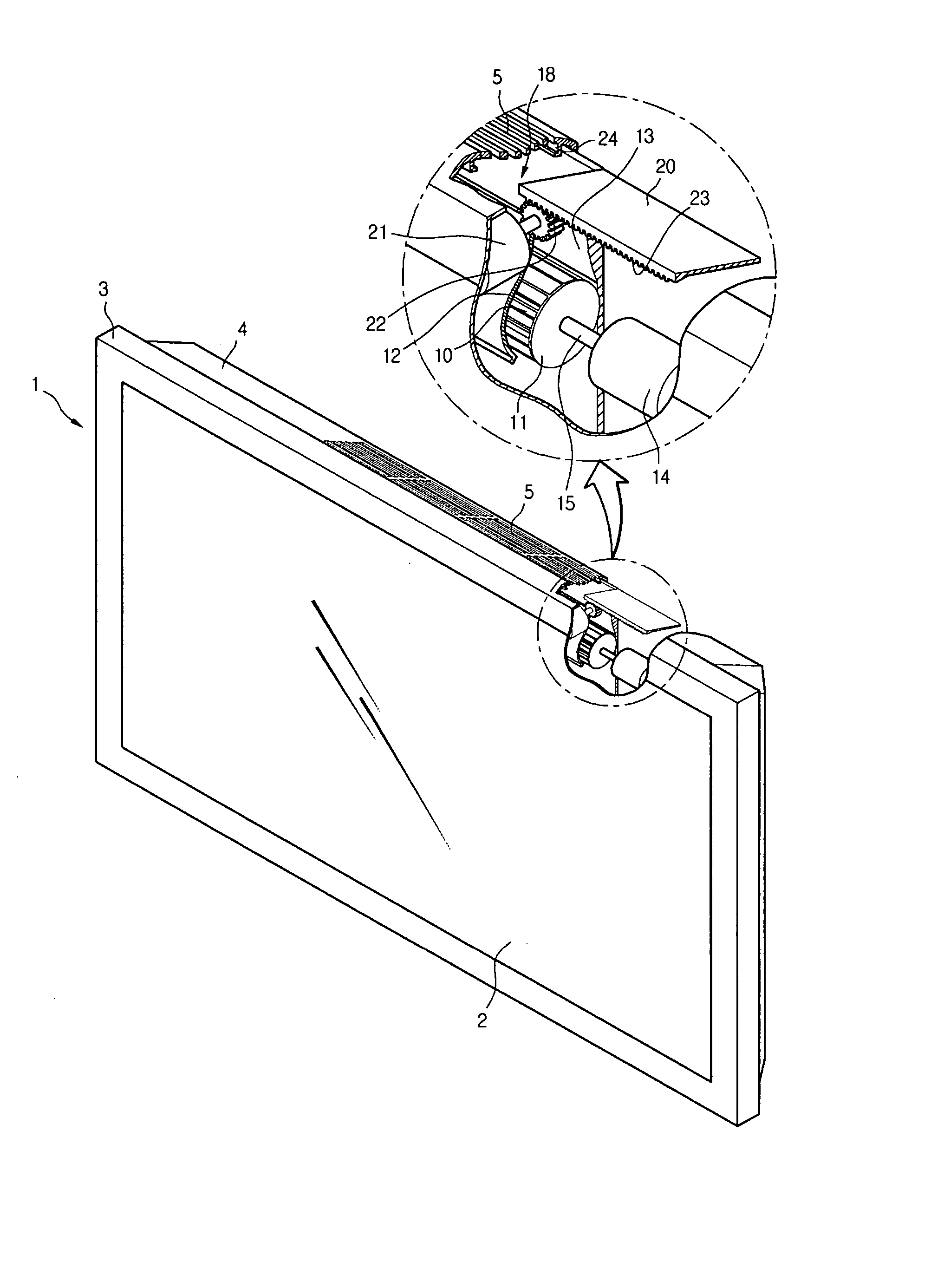
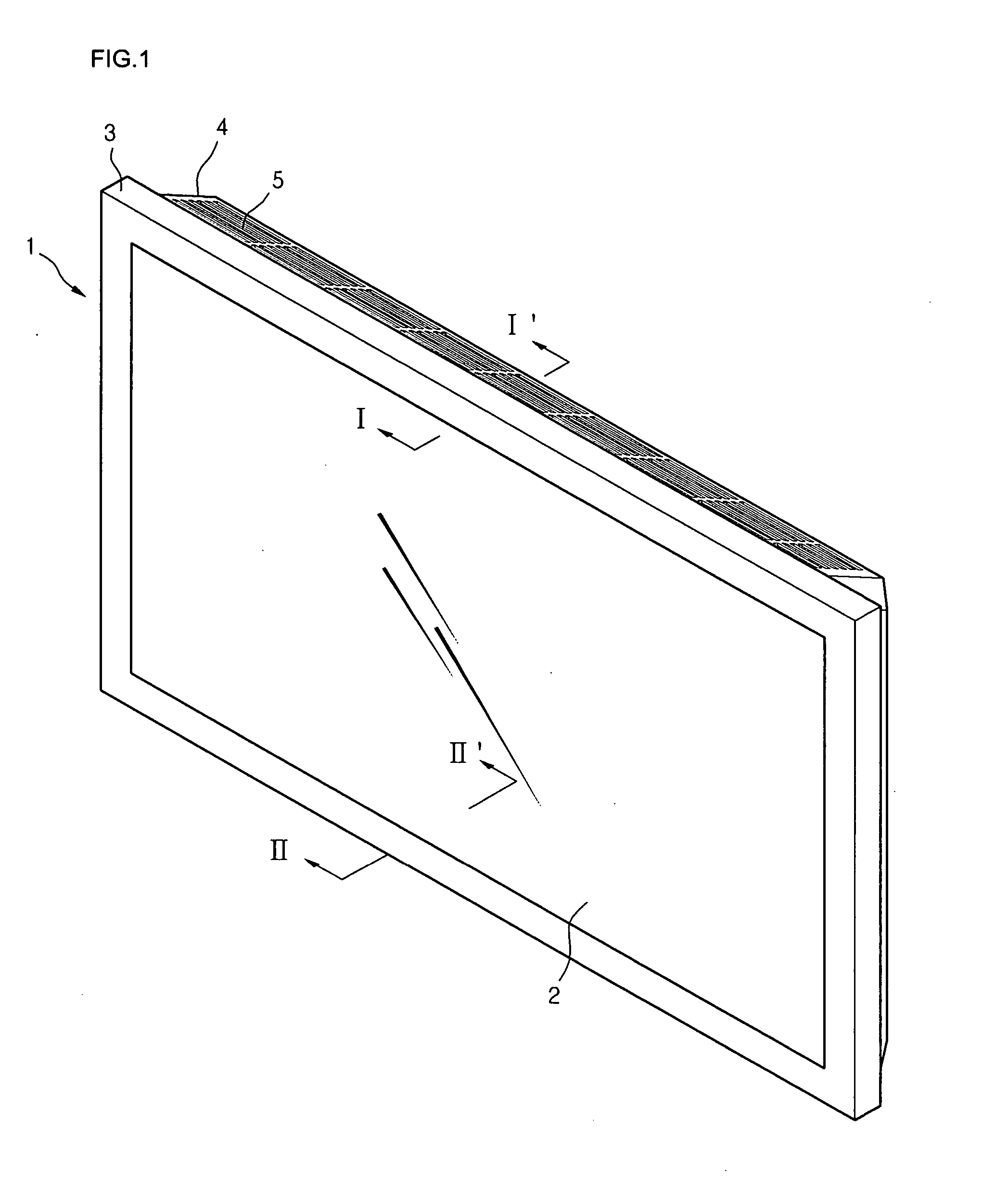
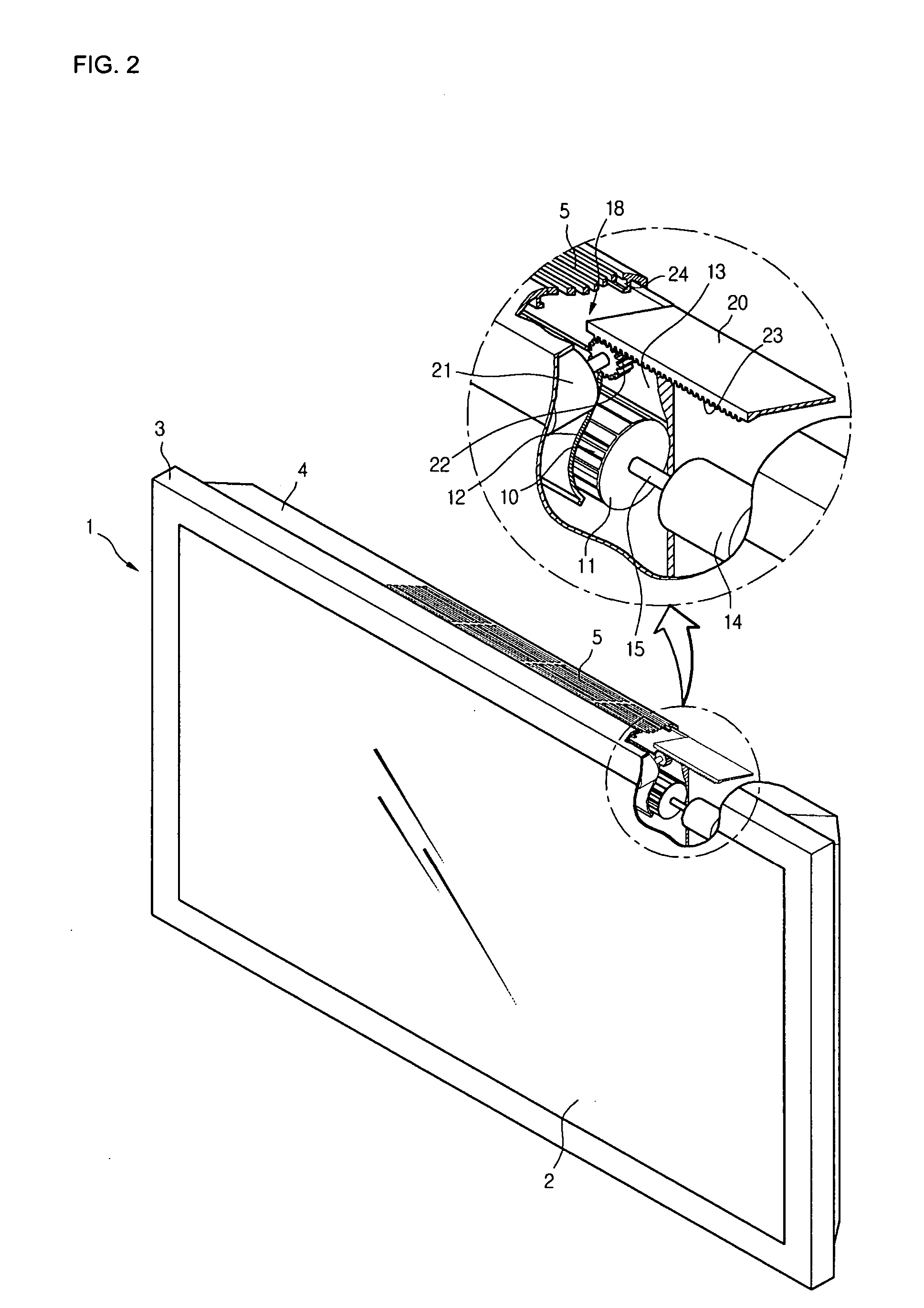
InactiveUS20060199514A1Improve cooling effectQuieter operationTelevision system detailsPropellersRotational axisFree rotation
A cooling fan is provided that does not place limitations on the installation conditions for the fan, is capable of cooling a backlight unit of a display panel with high efficiency, and produces less noise during operation. Also provided is an image display apparatus equipped with the cooling fan. The cooling fan includes a fan rotator composed of a rotational shaft that is rotationally driven by a driving motor and two vanes that have parallel revolution shafts that rotate together with the rotational shaft, are freely rotatable on the shafts, face one another, and revolve around the rotational shafts and a vane angle control unit that implements control so that each vane has a maximum rotation angle when a revolution angle of the vanes is in a vicinity of a first revolution angle and each vane has a rotation angle of 0° when a revolution angle of the vane is in a vicinity of a second revolution angle that is perpendicular to the first revolution angle. By rotating the fan rotator, a wind in a single direction perpendicular to the rotational shaft is generated to cool a back light unit of a flat panel display, for example.
Owner:SONY CORP
Flat display device and cooling apparatus for the same
ActiveUS20070103866A1Improve performanceEliminate dangerTelevision system detailsCircumferential flow pumpsDisplay deviceEngineering
There is provided a cooling apparatus for a flat display device. The cooling apparatus includes a flat display module, a cover for protecting an exterior of the flat display module, an air inlet formed on one side of the cover, for introducing external air, an air outlet formed in the other side of the cover, for discharging high temperature air contained inside the cover, and a shield for selectively closing the air outlet to prevent inflow of foreign substances.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Multi-use personal ventilation/filtration system
A personal ventilation system uses a cross-flow fan and one or more filters, where the filter preferably has a cylindrical or elongated elliptical shape that at least partially surrounds the rotor of the cross-flow fan. The filters preferably remove particles, undesired gases, and micro-organisms.
Owner:PROPULSIVE WING
Gas transfer foot
InactiveUS20090269191A1Specific fluid pumpsRotary non-positive displacement pumpsProduct gasEngineering
The present invention includes a molten metal pump and associated components that enable gas to be released into a stream of molten metal. The gas may be released into the molten metal stream (preferably into the bottom of the stream) flowing through a passage. Such a stream may be within the pump discharge and / or within a metal-transfer conduit extending from the pump discharge. The gas is released by using a gas-transfer foot that is positioned next to and is preferably attachable to the pump base or to the metal-transfer conduit. Preferably, the conduit (and / or discharge) in which the gas is released comprises two sections: a first section having a first cross-sectional area and a second section downstream of the first section and having a second cross-sectional area, wherein the second cross sectional area is larger than the first cross-sectional area. Preferably, the gas is released into or near the second section so that the gas is released into an area of relatively lower pressure.
Owner:MOLTEN METAL EQUIP INNOVIATIONS LLC
Reconfigurable airflow director for modular blade chassis
ActiveUS20050286222A1Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsModularityEmbedded system
A reconfigurable airflow director for modular blade chassis. The airflow director includes multiple duct channels having adjustable inlets and / or outlets. The airflow director may be reconfigured to adjust the amount of airflow across selected blades and selected zones on an individual blade. In one embodiment, snap-in airflow blockers are employed to block all or a portion of selected inlets or outlets to adjust the airflow through corresponding duct channels. In one embodiment, adjustable inlet vanes are employed to increase or decrease the size of adjacent inlets. In one embodiment, the airflow director is formed from multiple airflow director modules, each including an outer shell having multiple ribs extending therefrom to form multiple airflow channels, wherein the airflow director modules are stacked together to form a plurality of duct channels. Modular fan assemblies including multiple hot-swappable fans are employed to push and / or draw airflow through the duct channels of the airflow director.
Owner:RADISYS CORP
Cooling apparatus for flat display device
InactiveUS20070103863A1Efficiently dissipatedThin display deviceCircumferential flow pumpsStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
There is provided a cooling apparatus for a flat display device. The cooling apparatus includes a flat display module, a front cover for protecting a front portion of the flat display module, a back cover for protecting a rear portion of the flat display module, an air inlet formed on a portion of the back cover to allow external air to be introduced into the back cover, an air outlet formed on another portion of the back cover and extending along a longitudinal length of the flat panel display module; a fan disposed inside the back cover and aligned with the air outlet formed on the back cover, and an air outlet channel formed in the back cover and aligned with the air outlet formed on the back cover, the air outlet having an effective exhaust area having a longitudinal length extending in a longitudinal direction of the flat display module.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Compressor blade having a ratio of leading edge sweep to leading edge dihedral in a range of 1:1 to 3:1 along the radially outer portion
ActiveUS8147207B2Reduce lossesPropellersRotary non-positive displacement pumpsLeading edgeTip clearance
An airfoil for use as rotor blades in compressors for turbomachines, such as gas turbine engines. The airfoil includes increased forward sweep and forward dihedral effective to reduce losses generated by interaction of tip clearance flow, secondary flows and passage shocks.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
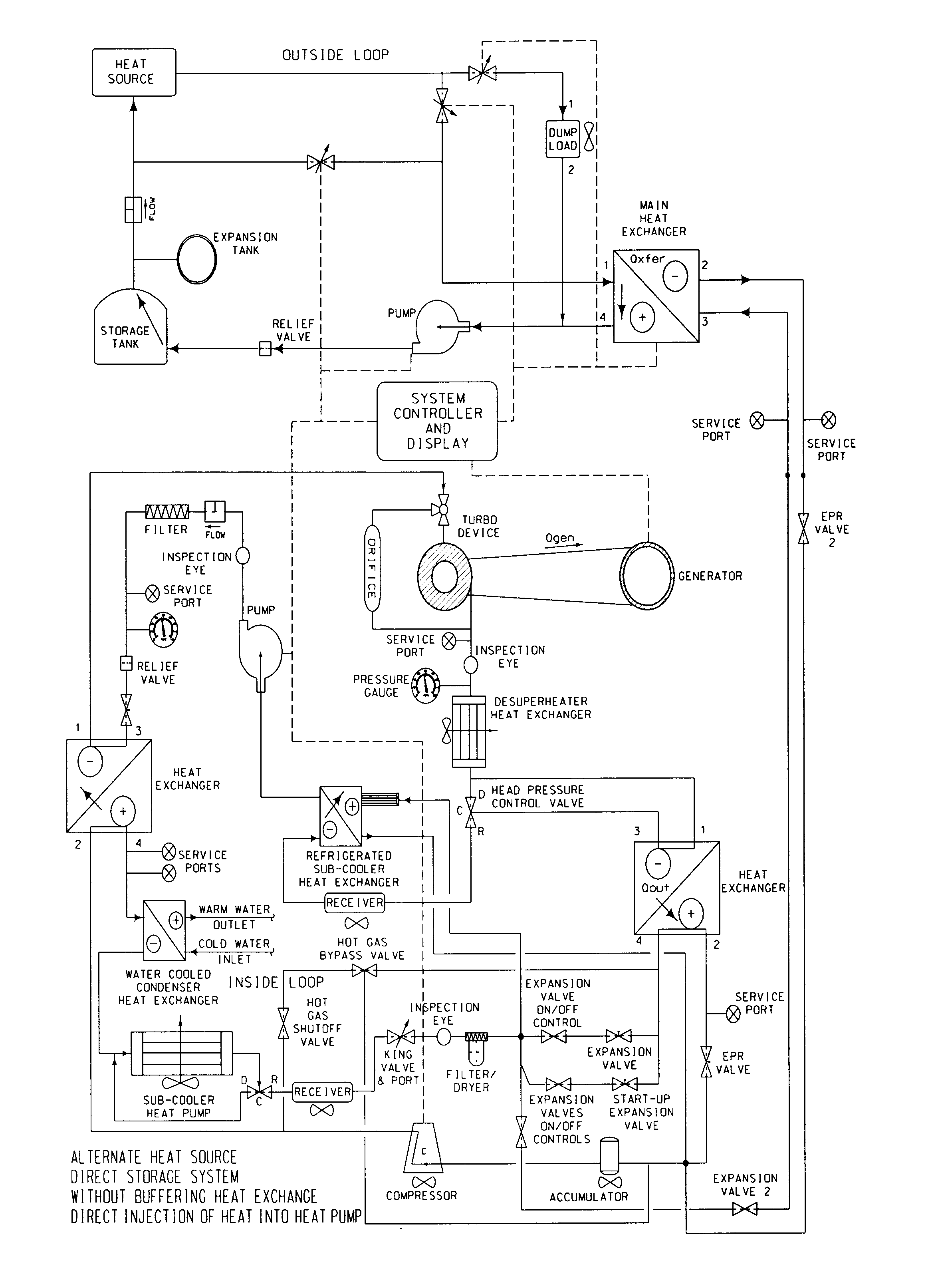
Thermodynamic power generation system
InactiveUS20110036091A1Large volumeEasy to produceAuxillary drivesRotary non-positive displacement pumpsWorking fluidEngineering
A power generation system that includes a heat source loop, a heat engine loop, and a heat reclaiming loop. The heat can be waste heat from a steam turbine, industrial process or refrigeration or air-conditioning system, solar heat collectors or geothermal sources. The heat source loop may also include a heat storage medium to allow continuous operation even when the source of heat is intermittent. Heat from the heat source loop is introduced into the heat reclaiming loop or turbine loop. In the turbine loop a working fluid is boiled, injected into the turbine, recovered condensed and recycled. The power generation system further includes a heat reclaiming loop having a fluid that extracts heat from the turbine loop. The fluid of the heat reclaiming loop is then raised to a higher temperature and then placed in heat exchange relationship with the working fluid of the turbine loop. The power generating system is capable of using low temperature waste heat is approximately of 150 degrees F. or less. The turbine includes one or more blades mounted on a rotating member. The turbine also includes one or more nozzles capable of introducing the gaseous working fluid, at a very shallow angle on to the surface of the blade or blades at a very high velocity. The pressure differential between the upstream and downstream surfaces of the blade as well as the change in direction of the high velocity hot gas flow create a combined force to impart rotation to the rotary member.
Owner:AMERICAN THERMAL POWER
Water Vapor Distillation Apparatus, Method and System
ActiveUS20090025399A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWater vaporEngineering
A fluid vapor distillation apparatus. The apparatus includes a source fluid input, and an evaporator condenser apparatus. The evaporator condenser apparatus includes a substantially cylindrical housing and a plurality of tubes in the housing. The source fluid input is fluidly connected to the evaporator condenser and the evaporator condenser transforms source fluid into steam and transforms compressed steam into product fluid. Also included in the fluid vapor distillation apparatus is a heat exchanger fluidly connected to the source fluid input and a product fluid output. The heat exchanger includes an outer tube and at least one inner tube. Also included in the fluid vapor distillation apparatus is a regenerative blower fluidly connected to the evaporator condenser. The regenerative blower compresses steam, and the compressed steam flows to the evaporative condenser where compressed steam is transformed into product fluid.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
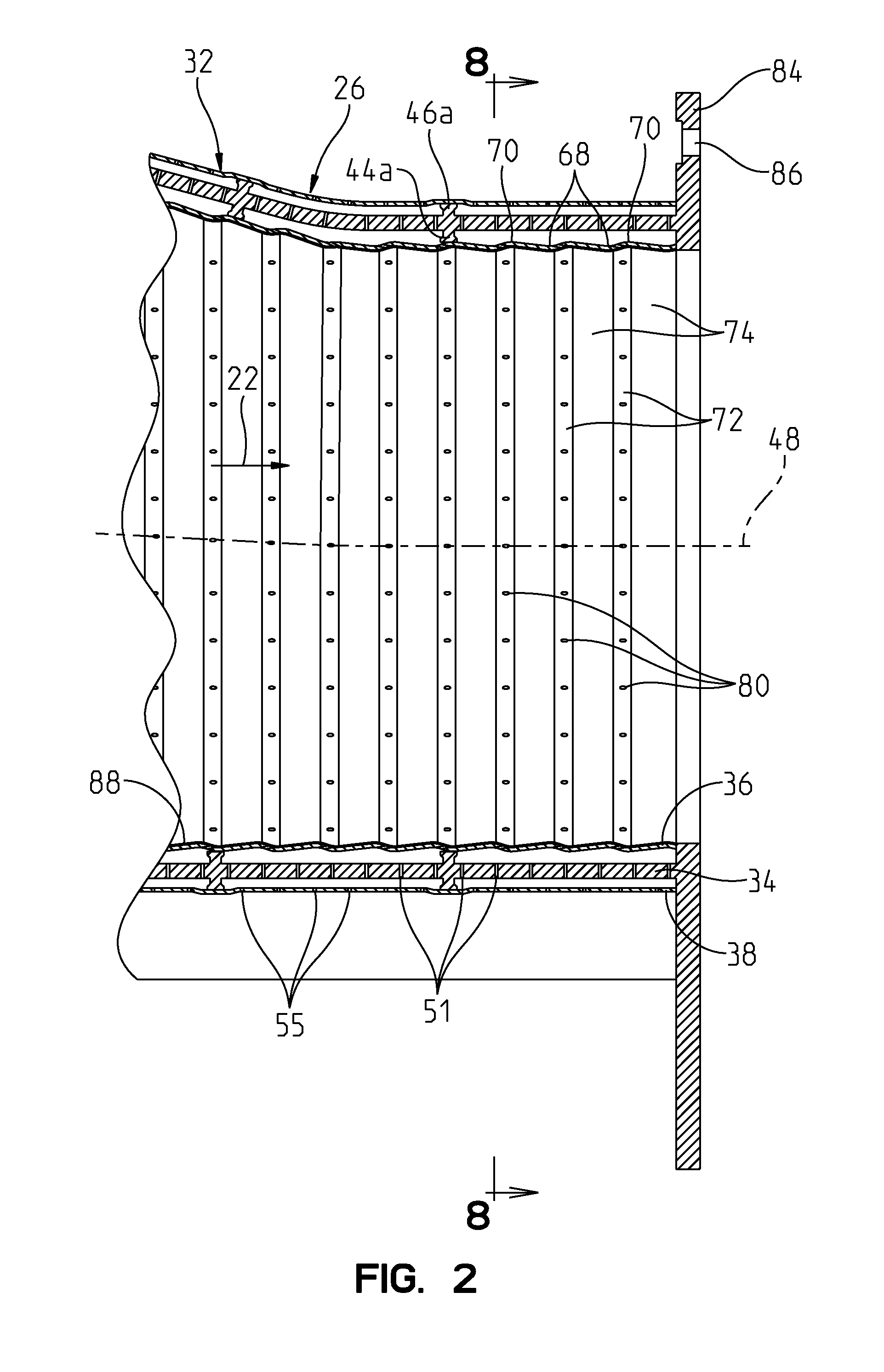
Bulk material pump feeder with reduced disk jamming
A bulk materials pump feeder having a housing and a rotating drive rotor for transferring material from an inlet to an outlet of the housing. The drive rotor has a hub. Drive disks extend away from the hub toward a housing inner wall. Three structural features of the feeder reduce the tendency of material to jam between the drive rotor and the housing or other stationary parts. First, the distance between the circumferential edges of the drive disks and the housing inner wall increases from the inlet to the outlet in the direction of rotation of the drive rotor. Second, a low-friction brush seal disposed on the periphery of the drive disks seals the area between the periphery of the drive disks and the inner wall. Finally, a materials scraper having a flexible tip is mounted in the housing and extends into the drive rotor between the drive disks.
Owner:K TRON TECH INC
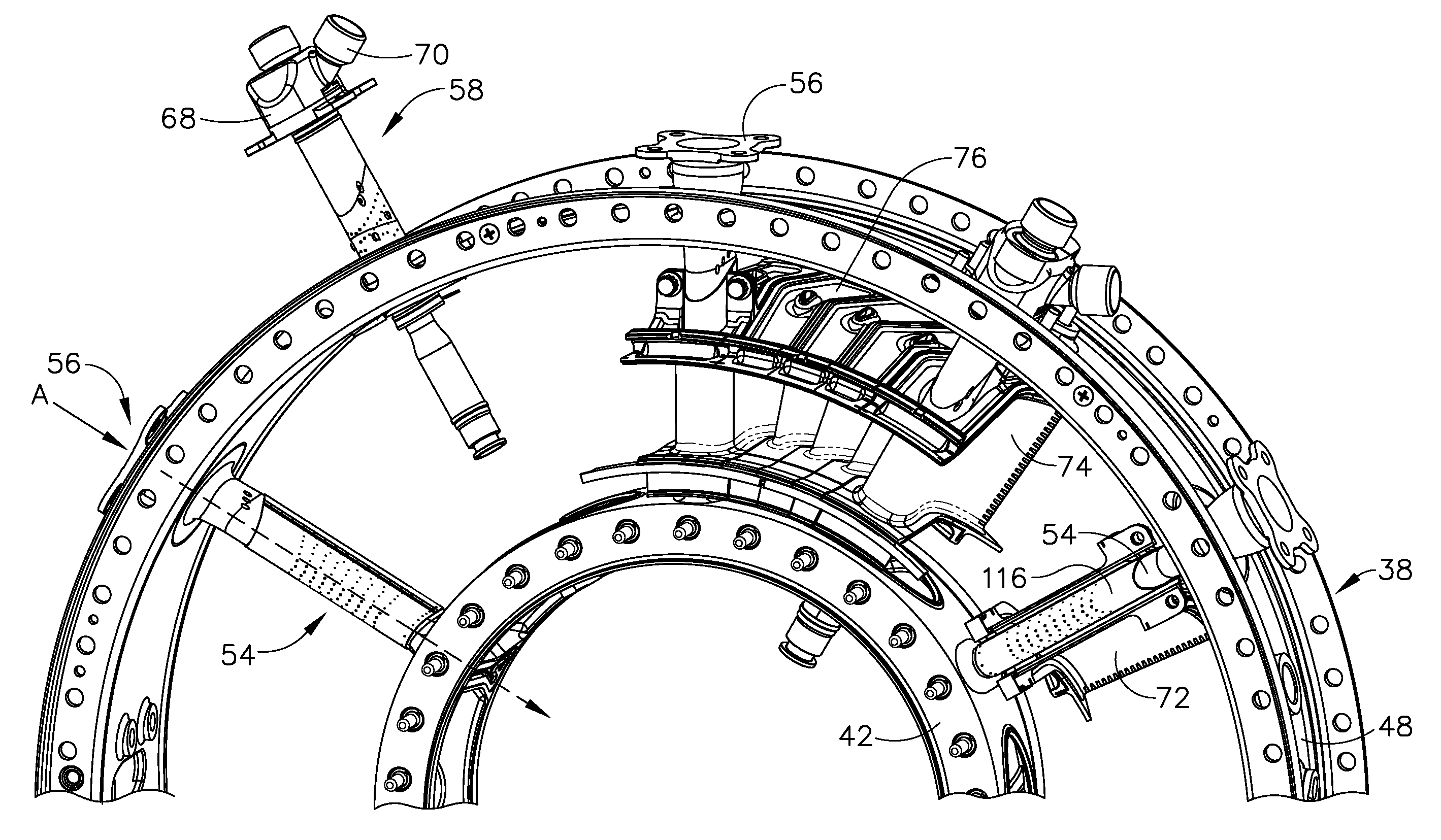
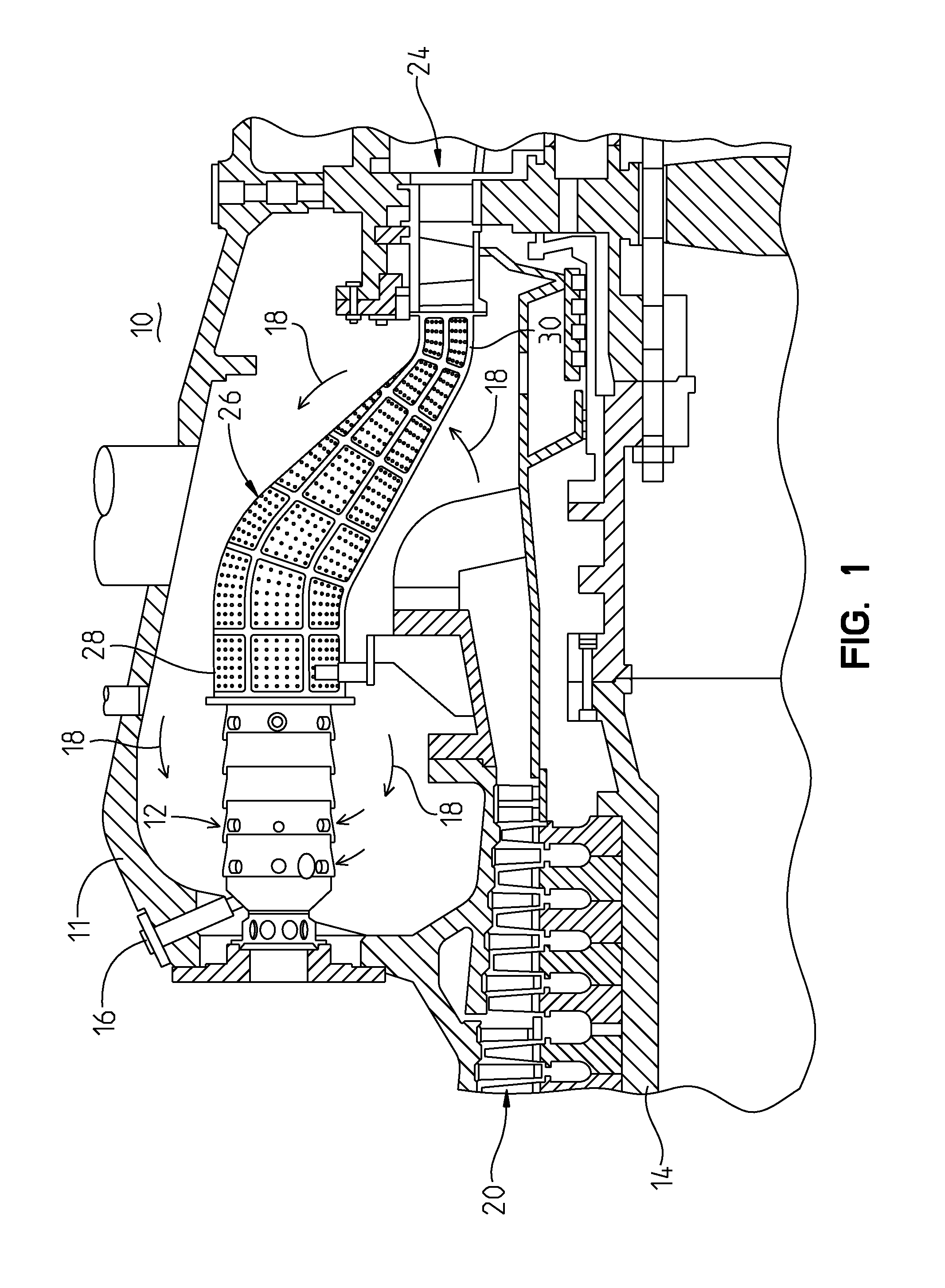
Transition with a linear flow path with exhaust mouths for use in a gas turbine engine
ActiveUS20100037617A1Eliminating damaging stressReduce excitationPump componentsGas turbine plantsCombustorTurbine blade
A transition duct for routing a gas flow from a combustor to the first stage of a turbine section in a combustion turbine engine is disclosed. The transition duct may have an internal passage extending between an inlet to an outlet. An axis of the transition duct body may be generally linear such that gases expelled from the transition duct body flow in a proper direction into the downstream turbine blades. The linear transition duct may include an outlet with exhaust mouths that are configured such that sides of the transition duct are coplanar with adjacent transition ducts, thereby eliminating destructive turbulence between adjacent, linear transition ducts.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Gas turbine transition duct apparatus
A gas turbine transition duct is provided comprising a generally tubular main body having first and second ends, the first end being adapted to be positioned adjacent to a combustor unit and the second end being adapted to be positioned adjacent to a turbine and a collar coupled to the main body second end. The collar may have upper, lower and side portions. At least one of the side portions may be provided with a notched section.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
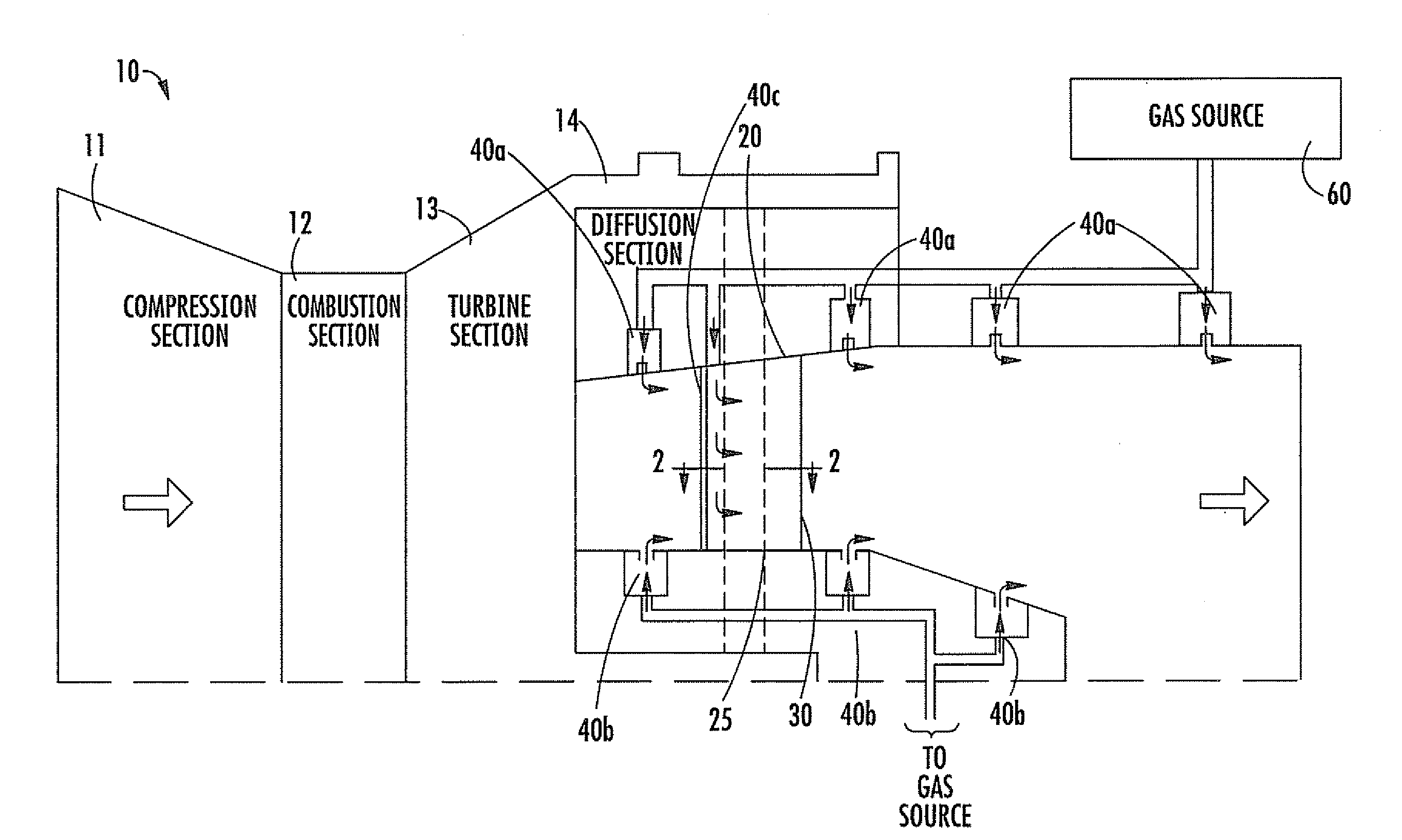
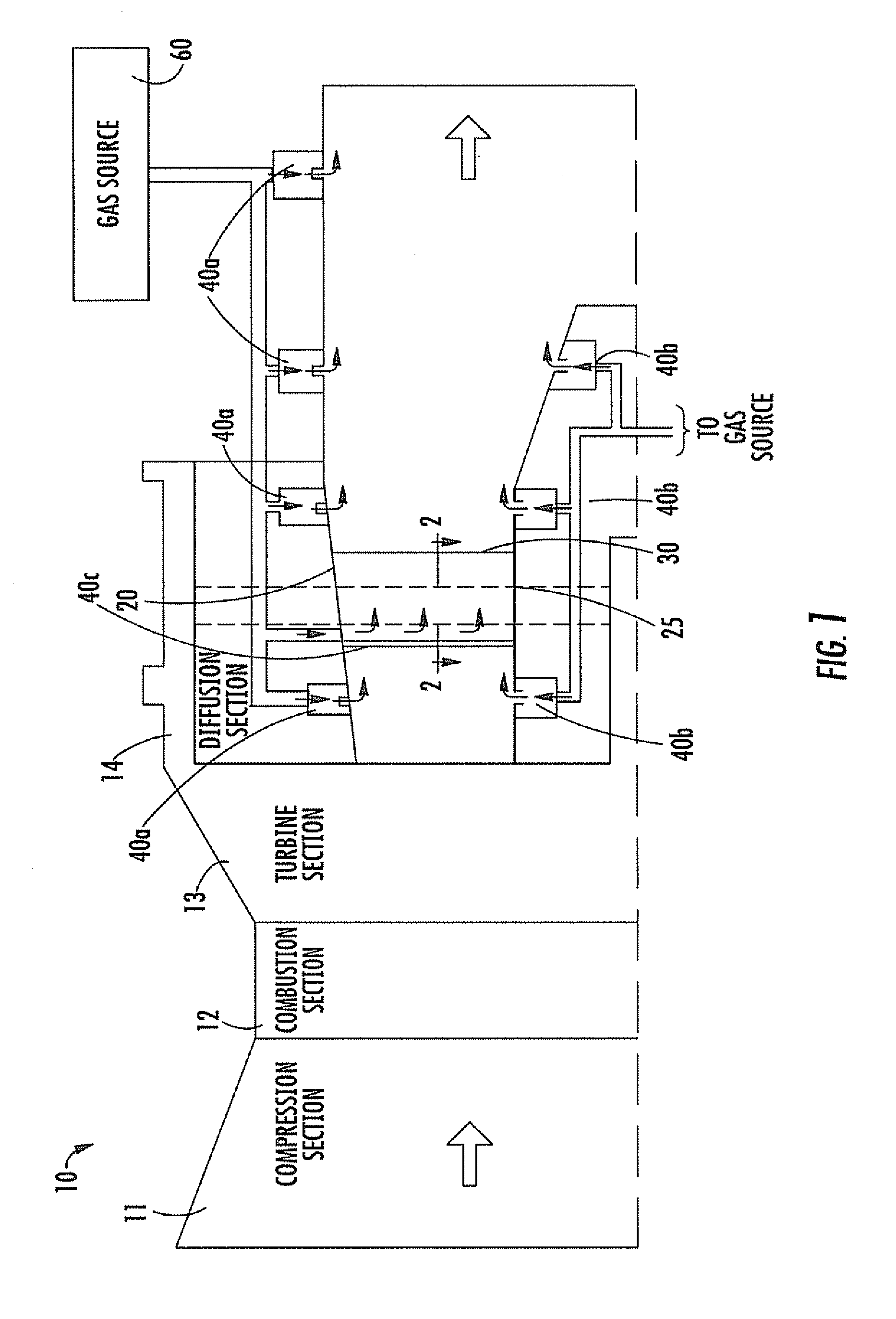
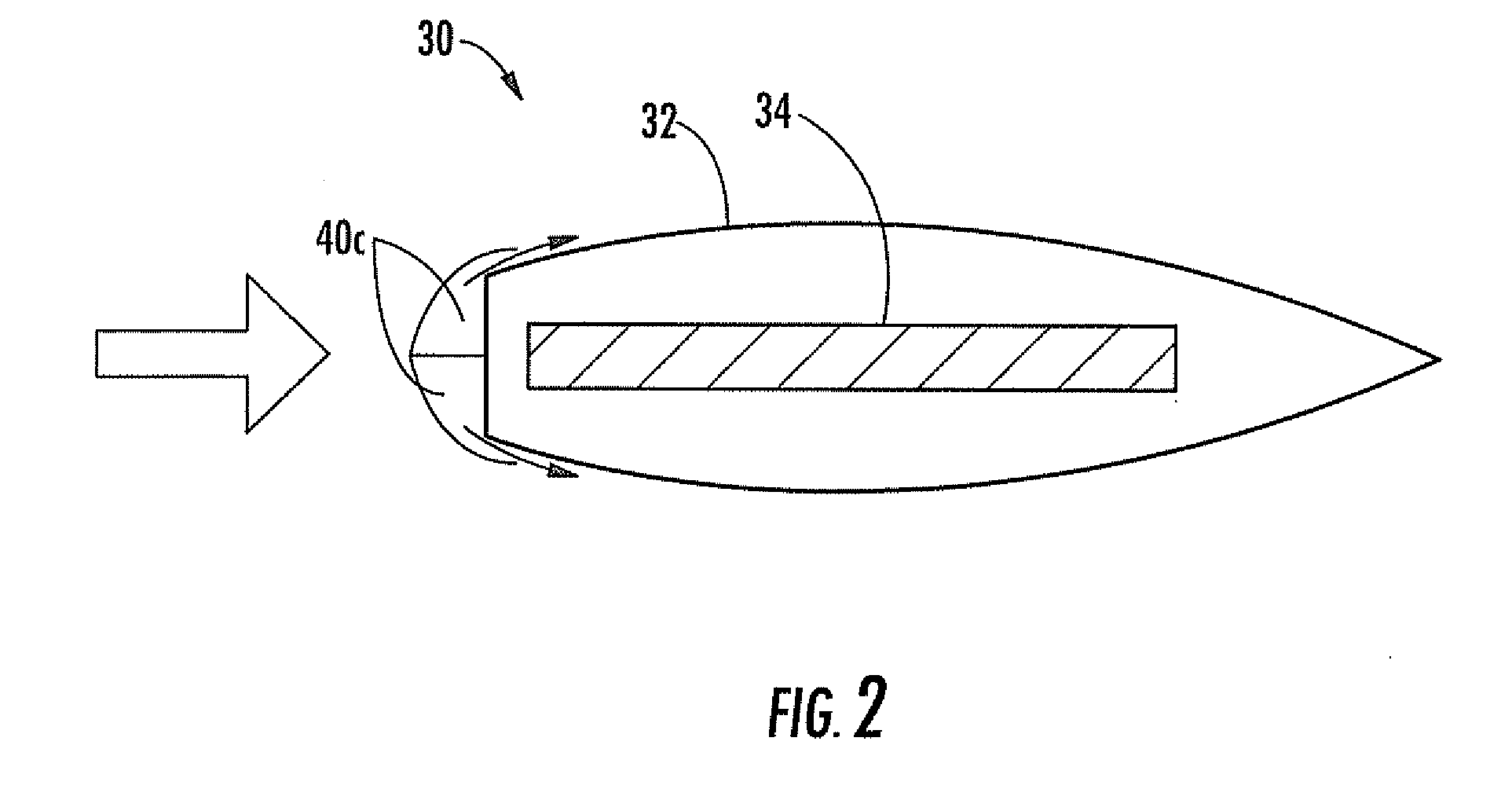
Combustion Turbine Including a Diffuser Section with Cooling Fluid Passageways and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20090263243A1Easy to attachImprove cooling effectPump componentsRotary non-positive displacement pumpsCombustionTurbine
A combustion turbine includes a compressor section, a combustion section downstream from the compressor section, and a turbine section downstream from the combustion section. A diffuser section is downstream from the turbine section and has an outer wall, an inner wall, and at least one strut member extending therebetween. The outer wall has at least one first gas passageway therein, the inner wall has at least one second gas passageway therein, and the at least one strut member has at least one third gas passageway therein. The at least one first, second and third gas passageways deliver gas therethrough to assist attachment of a boundary layer to adjacent surfaces of the outer wall, the inner wall, and the at least one strut, respectively.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Wind-powered pneumatic engine and a motor vehicle equipped with the engine
InactiveUS20070284155A1Improve energy efficiencyIncrease profitAuxillary drivesWind motor controlEngineeringEnergy expenditure
A wind-powered pneumatic engine including one or more impeller chambers and one or more impellers disposed in the impeller chambers is provided. One or more air inlets for receiving external wind resistance airflow are disposed on the impeller chambers, and the external wind resistance airflow entering the air inlets drives the impellers to operate to generate power output. The wind-powered pneumatic engine further includes an air-jet system for jetting HPCA into the impeller chambers, and the internal high-pressure compressed air jetted by the air-jet system in conjunction with the external wind resistance airflow entering the air inlets drives the impellers to operate to generate power output. In the present invention, the external resistance airflow around a motor vehicle moving at a speed is converted into power for use, which greatly reduces energy consumption and improves the moving speed of a motor vehicle. A motor vehicle equipped with wind-powered pneumatic engine is also provided.
Owner:CONG YANG
Wall of turbo machine and turbo machine
ActiveUS20100172749A1Reduce flow turbulenceEngine manufacturePump componentsRadial positionMechanical engineering
The invention relates to wall of a turbo machine having a cascade of blades. The wall includes: a first platform facing a first passage between blades in the cascade of blades; and a second platform facing a second passage between adjacent cascade of blades on an upstream side and cascade of blades on a downstream side, and having a circumferential outline having a distribution of radial positions. According to the invention, loss due to disturbance of flow through the gap of axially adjacent walls can be reduced.
Owner:IHI CORP +1
Bi-directional blowers for cooling computers
A heat dissipating device includes a motor, a rotary unit, and a housing for receiving the motor and the rotary unit. The rotary unit includes a hub mounted to the motor and blades extending from the hub. The housing defines a hot air inlet, a hot air outlet, a cold air inlet, and a cold air outlet. The housing includes a first partition and a second partition located close to outer ends of the blades. The two partitions divide the housing into a first channel coupling the hot air inlet and the hot air outlet, and a second channel coupling the cold air inlet and the cold air outlet. The two partitions have widths greater than a pitch of the blades to prevent air from mixing in the two channels. The two channels create a bi-directional blower that removes hot air from and provides cold air into a computer case.
Owner:ZHENG WEN CHUN
Cooling Structure For Gas Turbine Transition Duct
A transition duct for conveying hot combustion gas from a combustor to a turbine in a gas turbine engine. The transition duct includes a panel including a middle subpanel, an inner subpanel spaced from an inner side of the middle subpanel to form an inner plenum, and an outer subpanel spaced from an outer side of the middle subpanel to form an outer plenum. The outer subpanel includes a plurality of outer diffusion holes to meter cooling air into the outer plenum. The middle subpanel includes a plurality of effusion holes to allow cooling air to flow from the outer plenum to the inner plenum. The inner subpanel includes a plurality of film holes for passing a flow of cooling air from the inner plenum through the film holes into an axial gas flow path adjacent to the inner side of the inner subpanel.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Transition duct assembly
A transition duct assembly with a thermally free aft frame and mounting system for use in a gas turbine engine are disclosed. The aft frame is capable of adjusting to thermal gradients while the mounting system provides for at least transverse movement of the transition duct during engine assembly. The mounting system also provides a means for raising the natural frequency of the transition duct outside of the engine's dynamic excitation ranges.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
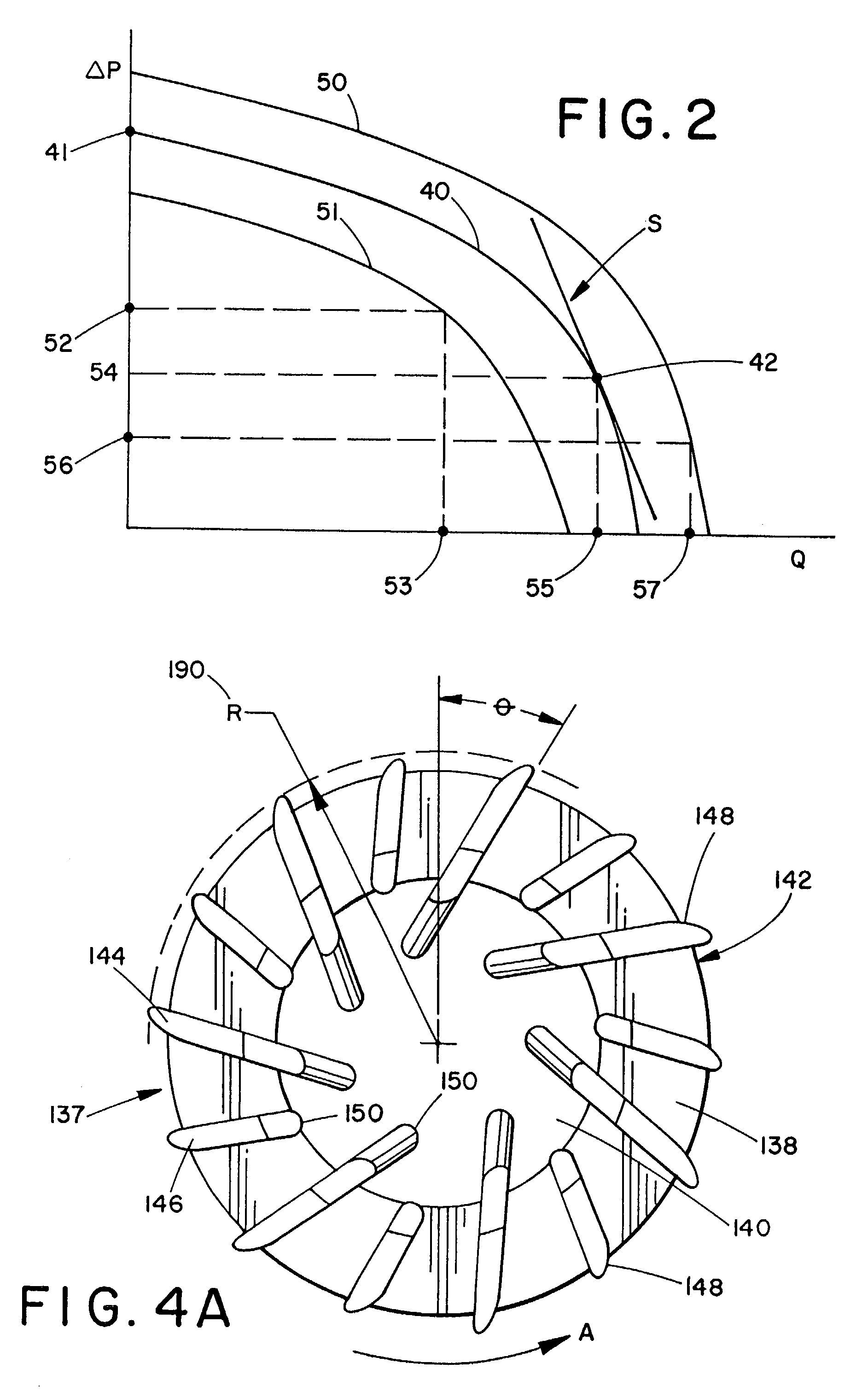
Flow controlled blood pump system
InactiveUS7435059B2Increase rotation speedStrengthen the pressure effectControl devicesBlood pumpsTraffic capacityPower flow
A system for pumping blood to assist or assume the cardiac function of a patient is characterized by a blood pump that exhibits a steep performance curve such that only small changes in pump flow occur for large changes in differential pressure across the pump. The pump therefore exhibits flow-limiting characteristics to protect the physiological system against harmful flow rates or pressures. Pump flow may also be limited by controlling the current provided to a driver from a power supply or by suitable restrictions within or external to the pump housing.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Chordal mounting arrangement for low-ductility turbine shroud
A shroud apparatus for a gas turbine engine includes: a shroud segment comprising low-ductility material and having a cross-sectional shape defined by opposed forward and aft walls, and opposed inner and outer walls, the walls extending between opposed first and second end faces, wherein the inner wall defines an arcuate inner flowpath surface, wherein the shroud segment includes: a radially-inward facing chordal forward mounting surface; and a radially-inward facing chordal aft mounting surface; and an annular case surrounding the shroud segment, the case including: a radially-outward facing chordal forward bearing surface which engages the forward mounting surfaces; and a radially-outward facing chordal aft bearing surface which engages the aft mounting surface of the shroud segment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatuses for low-air-loss (LAL) coverlets and airflow units for coverlets
Owner:HUNTLEIGH TECH LTD
Tidal flow hydroelectric turbine
InactiveUS20090278357A1Increasing the thicknessReduce contactPump componentsFinal product manufactureElectricityWater flow
A hydroelectric turbine for the production of electricity from tidal flow forces, the turbine having a rotor with an open center such that the blades are mounted between an inner rim and outer rim, wherein retaining members and anti-friction members are provided to limit movement of the rotor relative to the housing in either axial direction, such that water flow in either direction operates the turbine, but wherein the retaining members and the anti-friction members allow the rotor to shift in either axial direction in response to water flow. The anti-friction members limiting rotor travel in the axial direction are preferably of increased thickness, such that as the anti-friction members wear down, the rotor is able to shift relative to the housing in the axial direction.
Owner:OPENHYDRO GRP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com