Patents
Literature
1084results about "Gear vibration/noise damping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parameter state estimation
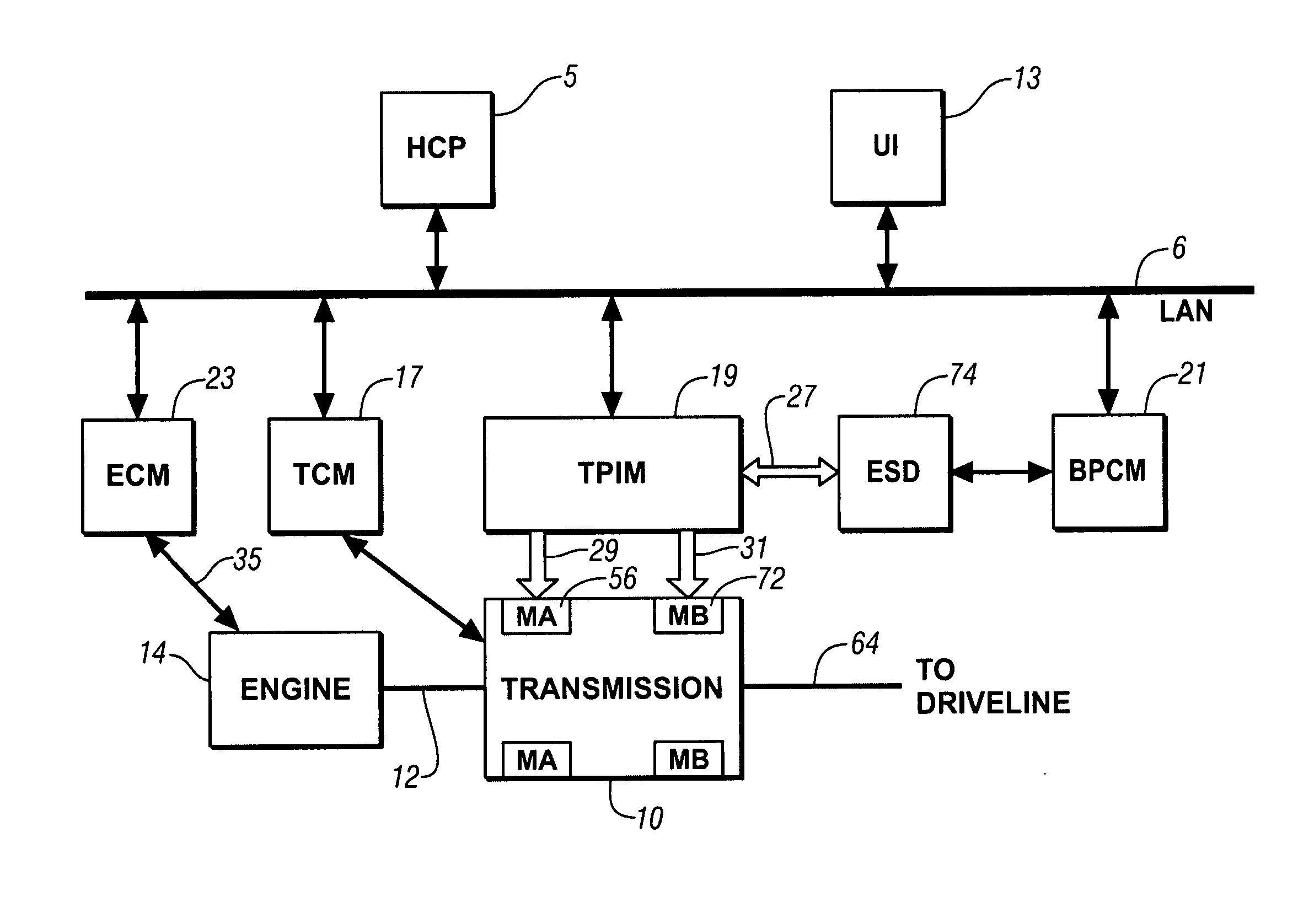
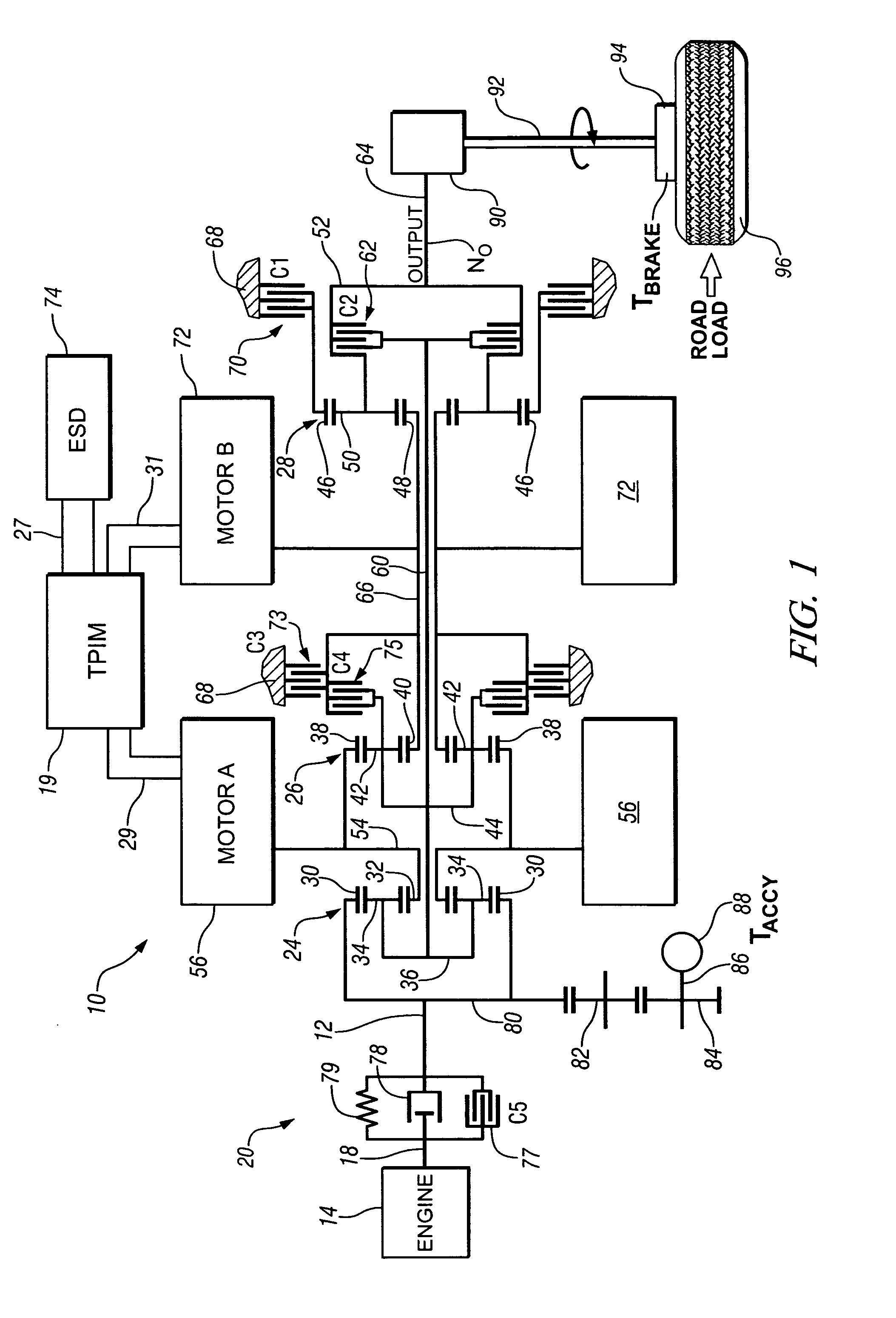
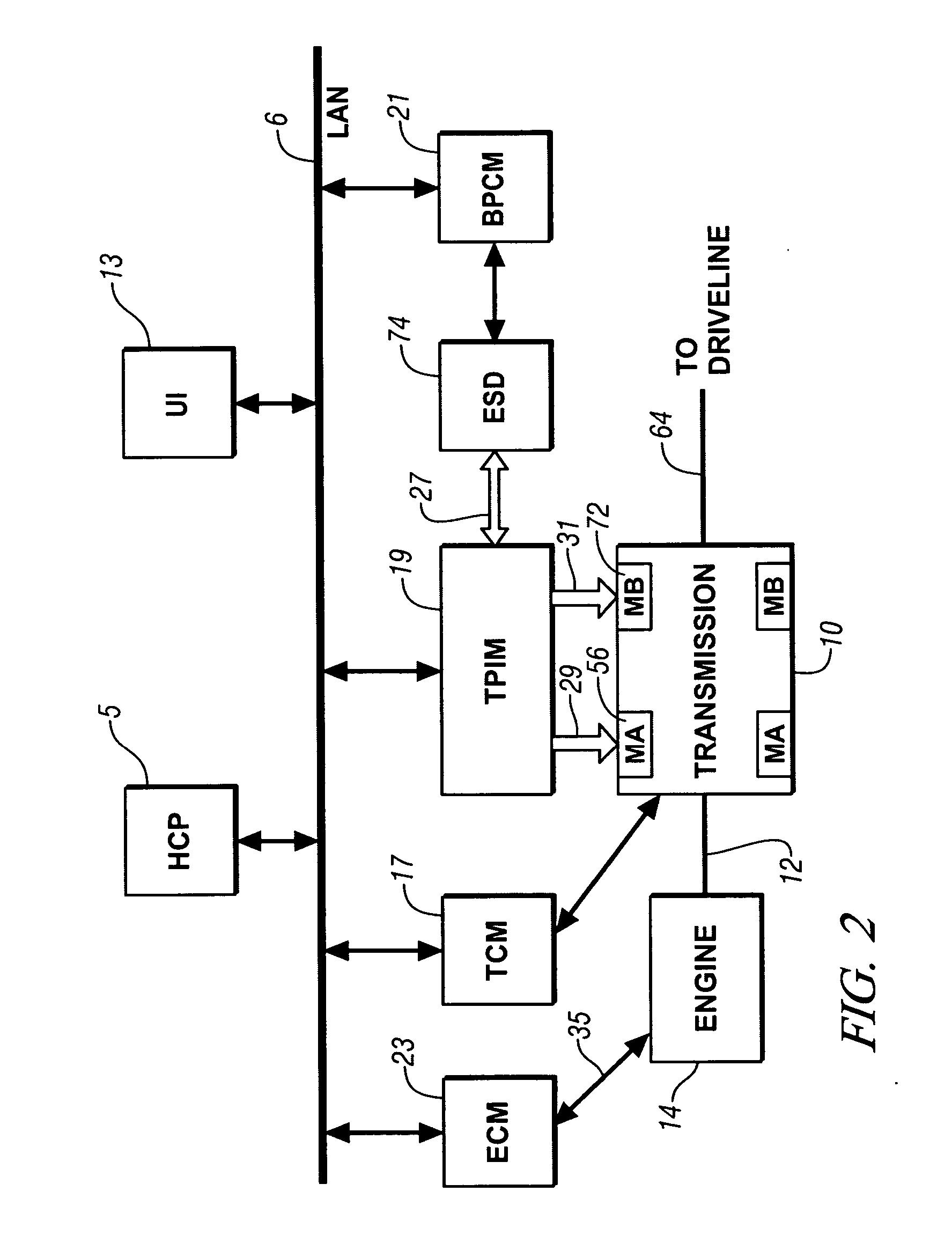
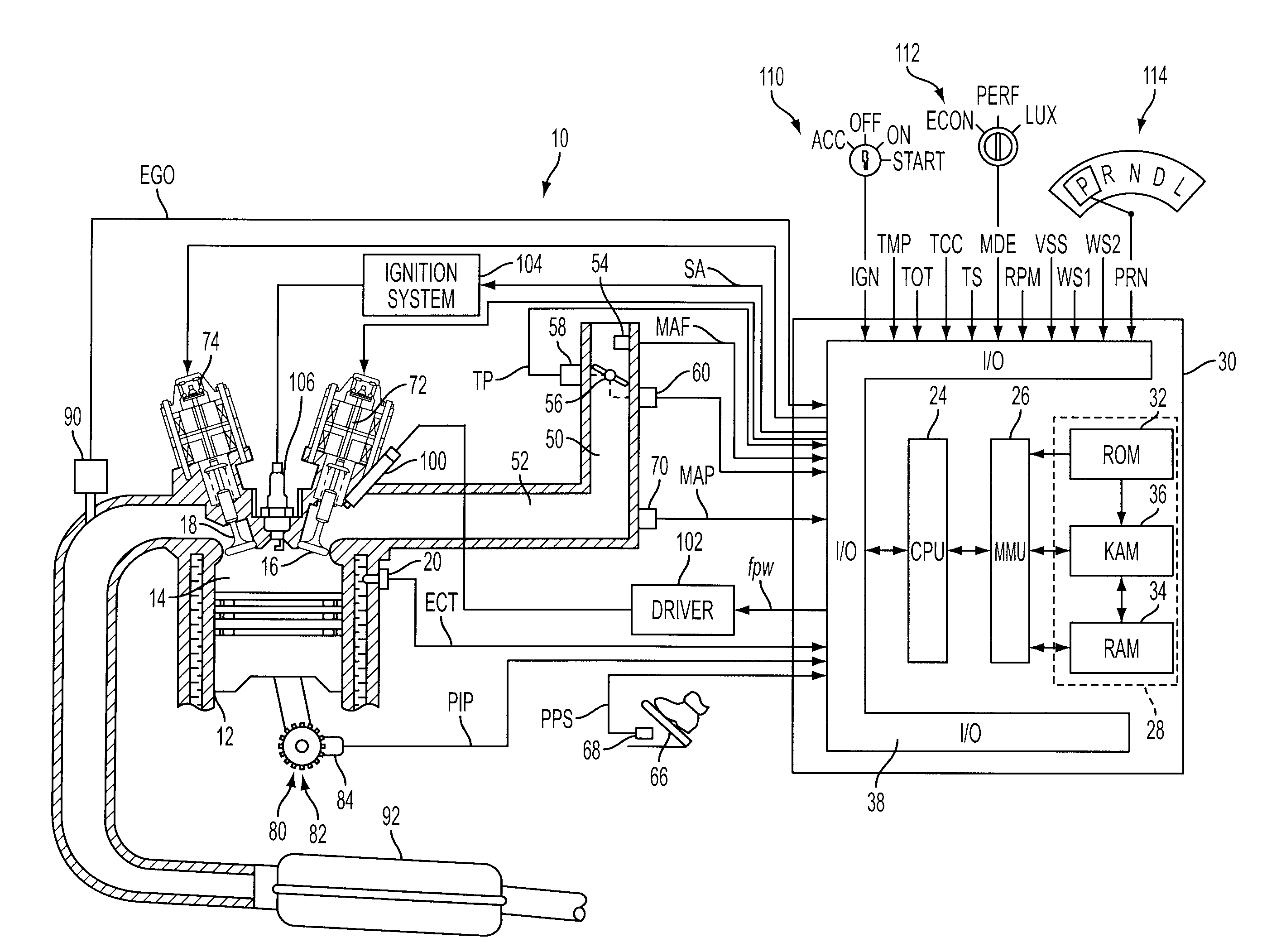
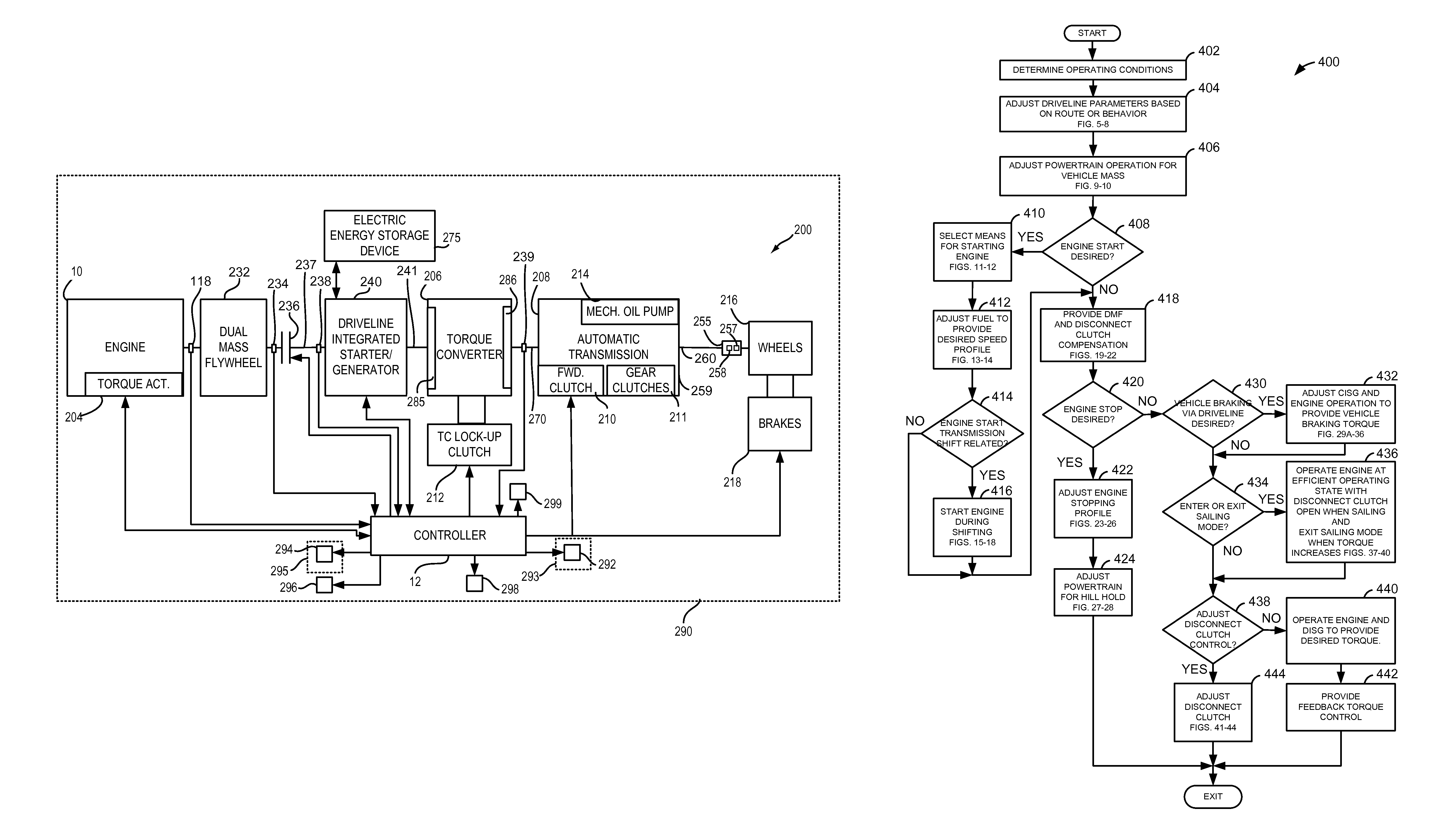
InactiveUS20070225886A1Easy to implementIncrease signal levelHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsPowertrainOperating speed
The state estimator provides parametric estimates for operating states not readily measurable with production powertrain and driveline hardware, such as real-time torque values of axles and dampers. This facilitates implementation of torque oscillation damping control schemes which use multivariable feedback. A control parameter is estimated for a powertrain system having multiple torque-generative devices operably connected to a transmission device having a torque output to a driveline. This includes establishing a plurality of equations operable to estimate the control parameter and other operating parameters based upon torque inputs. The operating parameters comprise operating speeds of the powertrain system and driveline. The operating parameters that comprise operating speeds of the powertrain system and driveline are determined. Coefficients of the plurality of equations are adjusted based upon the operating speeds of the powertrain system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
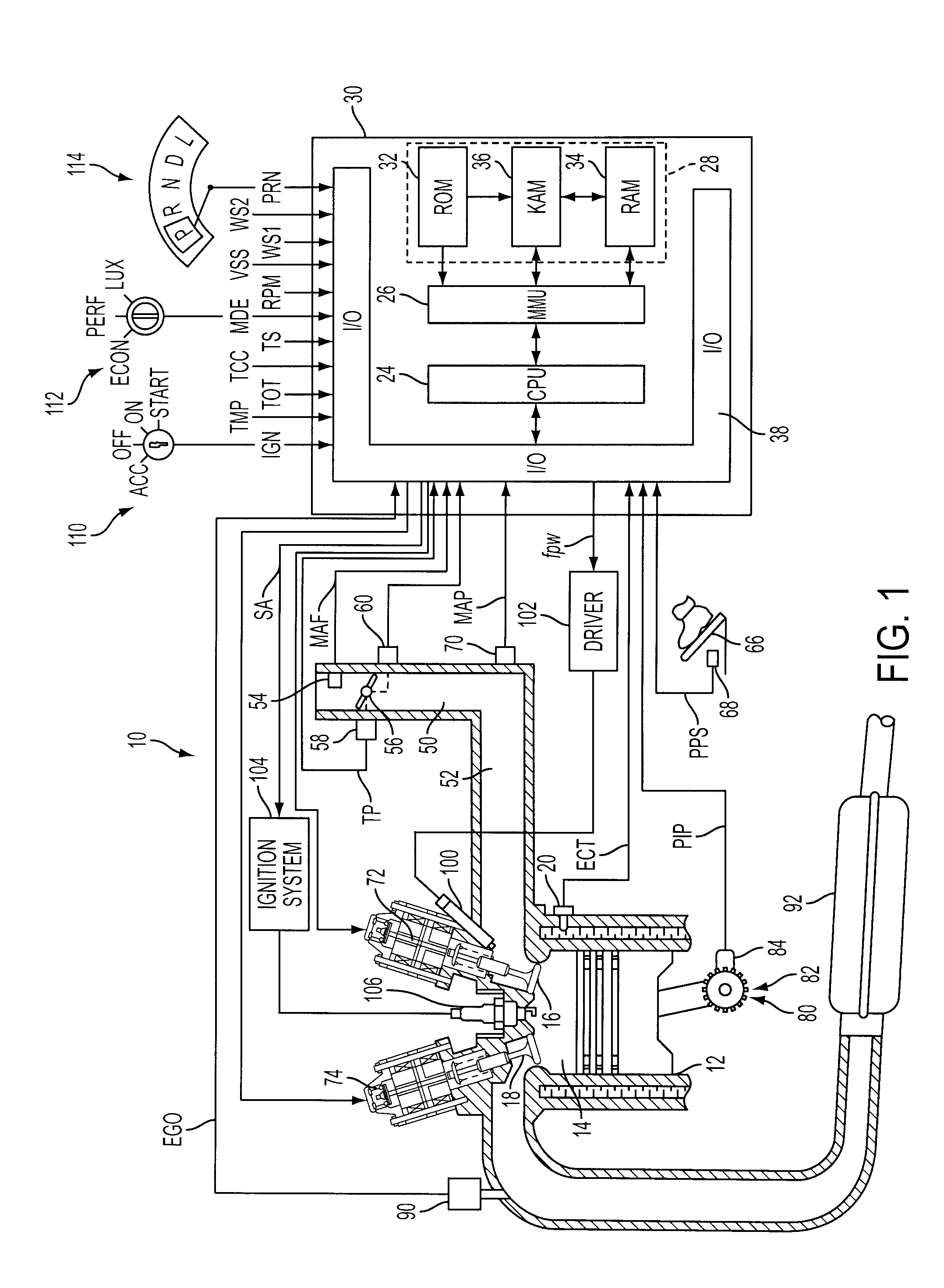
Variable Displacement Engine Operation With NVH Management
InactiveUS20080154468A1Reduce and eliminate torque reactionNo backlashAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsClose couplingDrivetrain
A system and method for controlling an internal combustion engine operable with a first cylinder firing frequency and a second cylinder firing frequency to reduce or eliminate transmission of torsional vibrations associated with the second cylinder firing frequency to reduce or eliminate constraints on reduced displacement mode operation using a closely coupled drive train component rotating in an opposite direction relative to rotating components of the engine. A close coupling device allows the inertia of the counter-rotating elements to reduce or eliminate the torque reaction of the drivetrain associated with acceleration and deceleration of the engine crankshaft in response to the second cylinder firing frequency in the reduced displacement mode.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
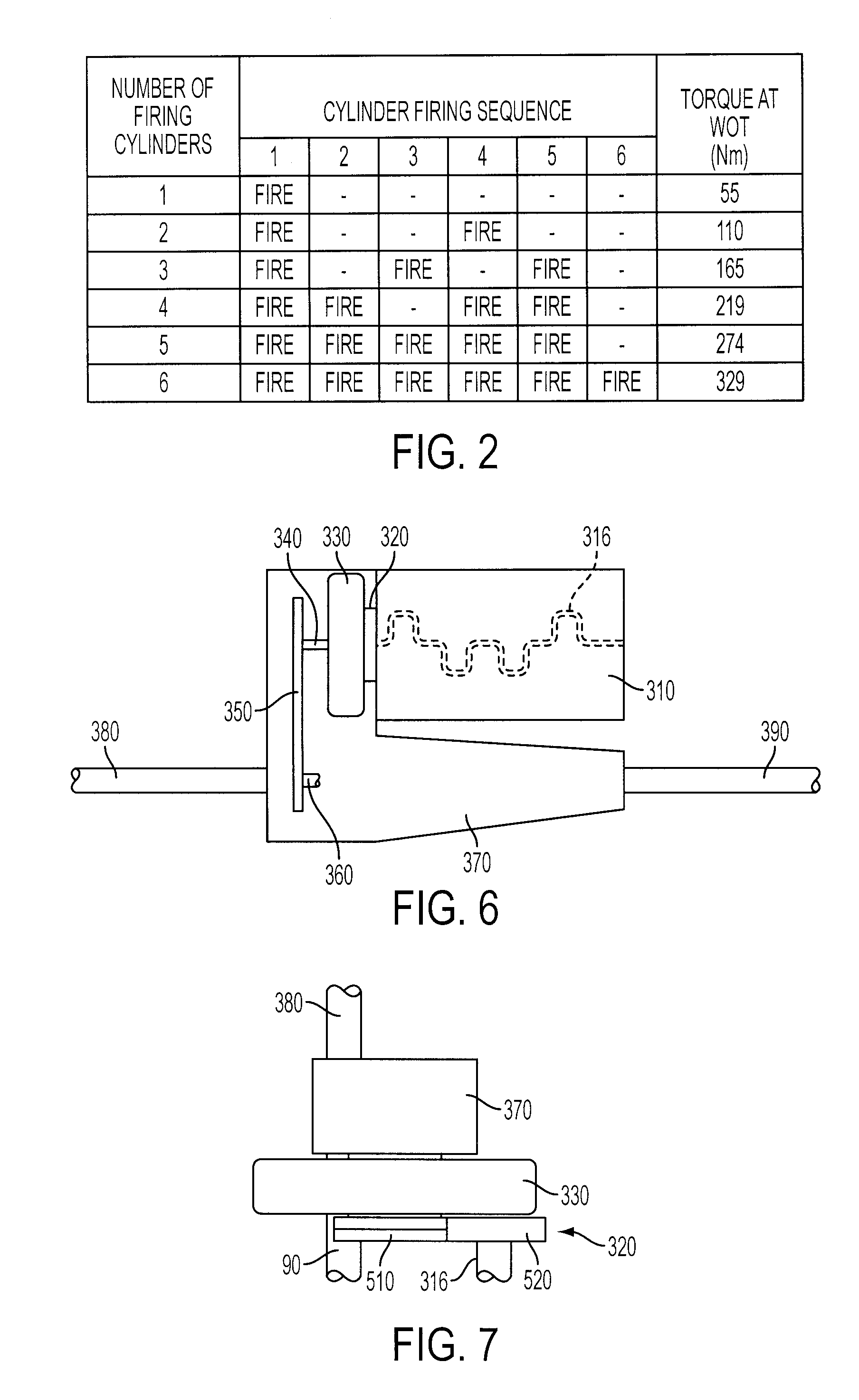
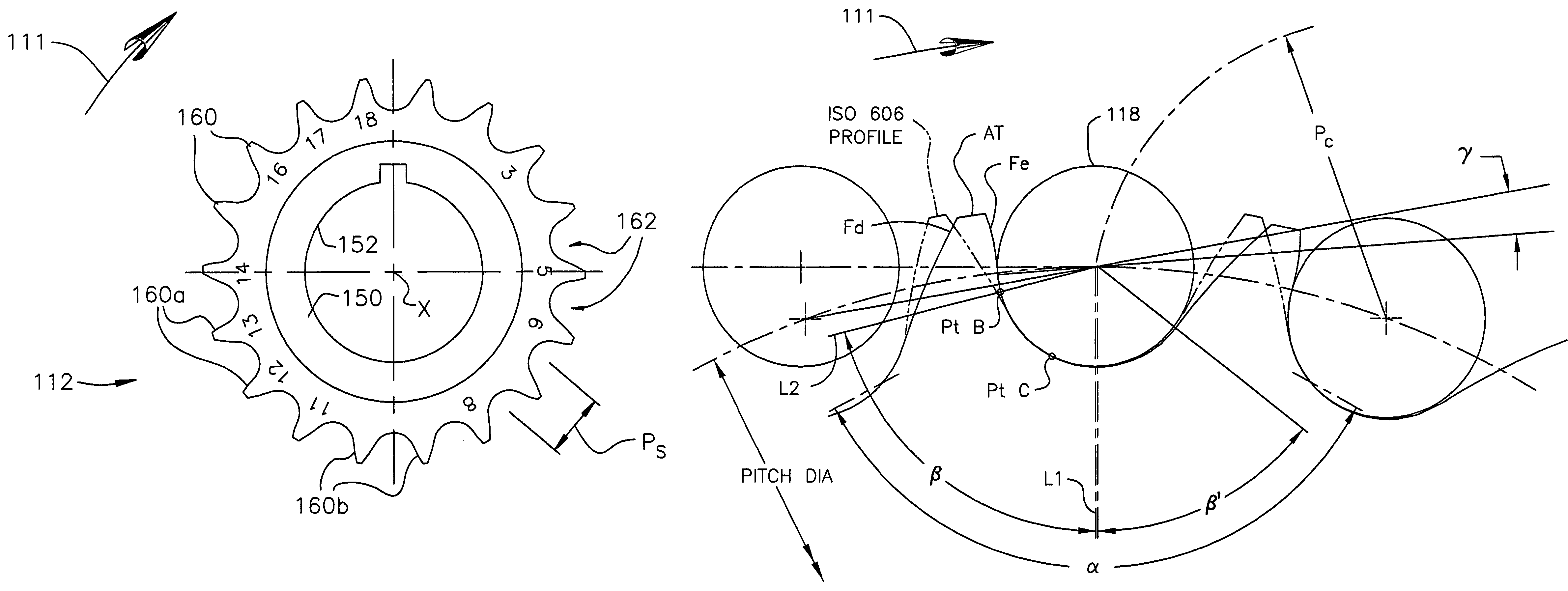
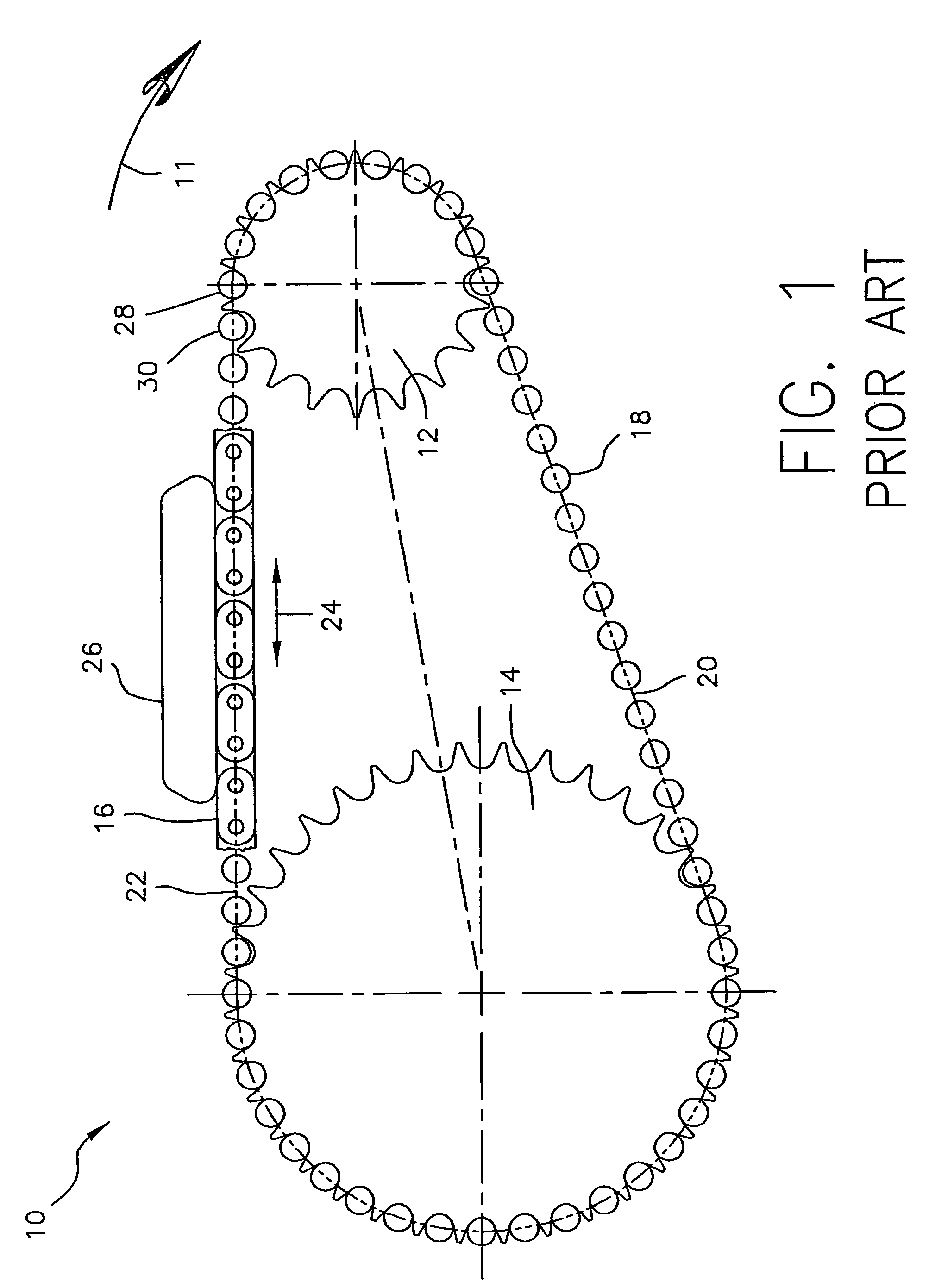
Random engagement roller chain sprocket and timing chain system including same
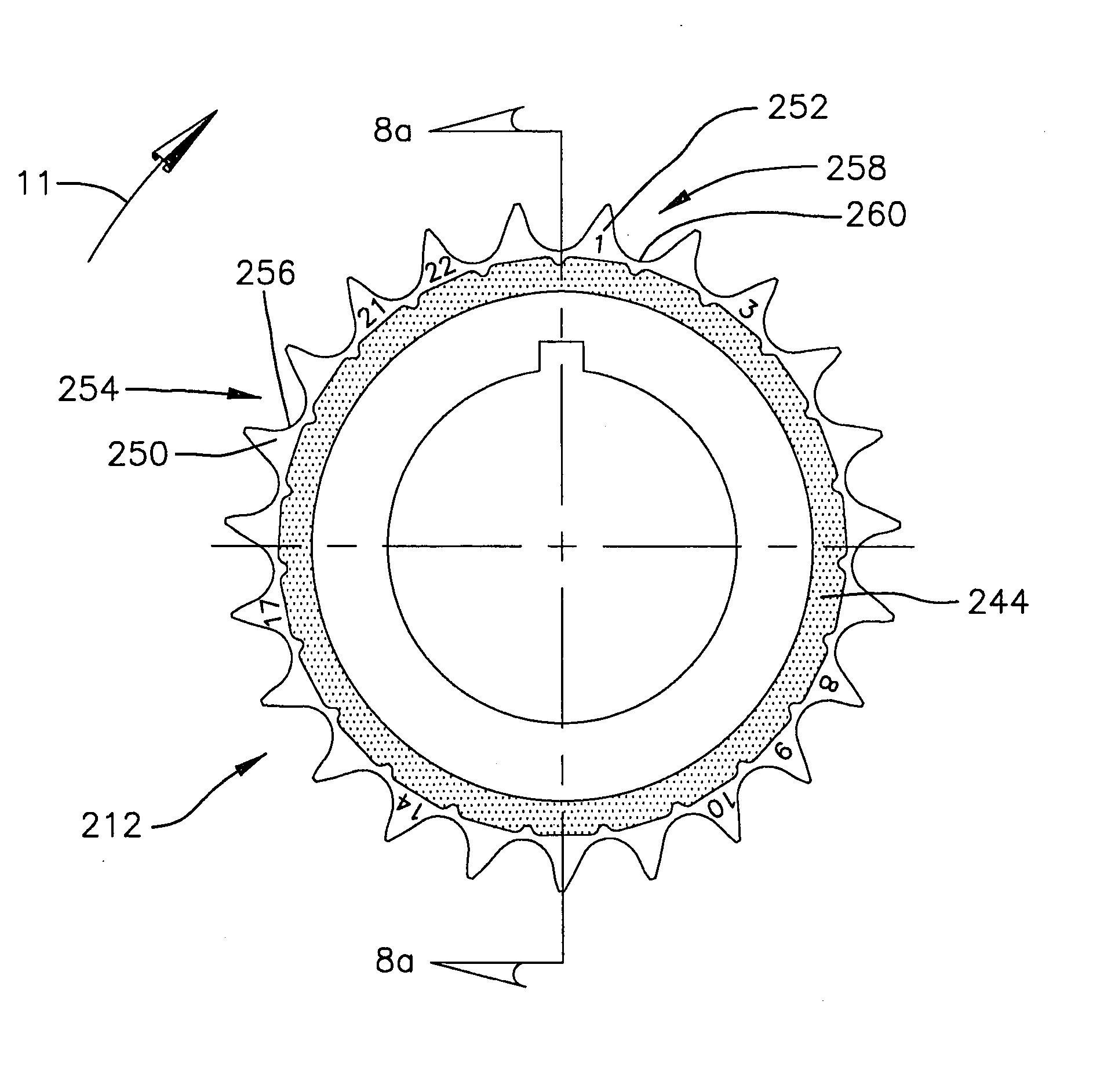
A sprocket and a roller chain drive system including same are disclosed. The sprocket is a random engagement sprocket comprising a first plurality of A-profile teeth formed with a first asymmetric profile and a second plurality of B-profile teeth formed with a second asymmetric profile. The A-profile teeth each define a first pressure angle and the B-profile teeth each define a second pressure angle that is at least 5 degrees greater than said first pressure angle so that a minimum separation Δ is defined. The sprocket is defined with added chordal pitch reduction of 0.2% up to 1% relative to the link pitch of the associated roller chain. The sprocket can be defined with root relief and / or can comprise resilient cushion rings. Initial roller contacts made with the A-profile and B-profile teeth are modulated owing to the pressure angle separation and added chordal pitch reduction.
Owner:HH CLOYES INC
Parameter state estimation
InactiveUS7739016B2Easy to implementIncrease signal levelHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsPowertrainOperating speed
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Methods and systems for reducing gear lash noise
InactiveUS20130297123A1Reducing gear tooth to gear tooth impactReduce gear tooth to gear tooth impactHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsElectric machineEngineering
Systems and methods for improving operation of a hybrid vehicle are presented. In one example, driveline gear lash gear tooth to gear tooth impact may be reduce via adjusting operation of an electric machine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Sprung gear set and method
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
Gear backlash elimination and adjustable gear backlash mechanism
The gear mechanism for minimizing backlash may include a convoluted spring positioned between an external spline of a gear or shaft and an internal spline of a gear. The gear mechanism may include a cam and cam follower arrangement upon two adjacent gears positioned on the same shaft. Two stacked gears may include a U-shaped backlash eliminating element passing through both gears. The gear mechanism may include rollers which may be conically shaped.
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
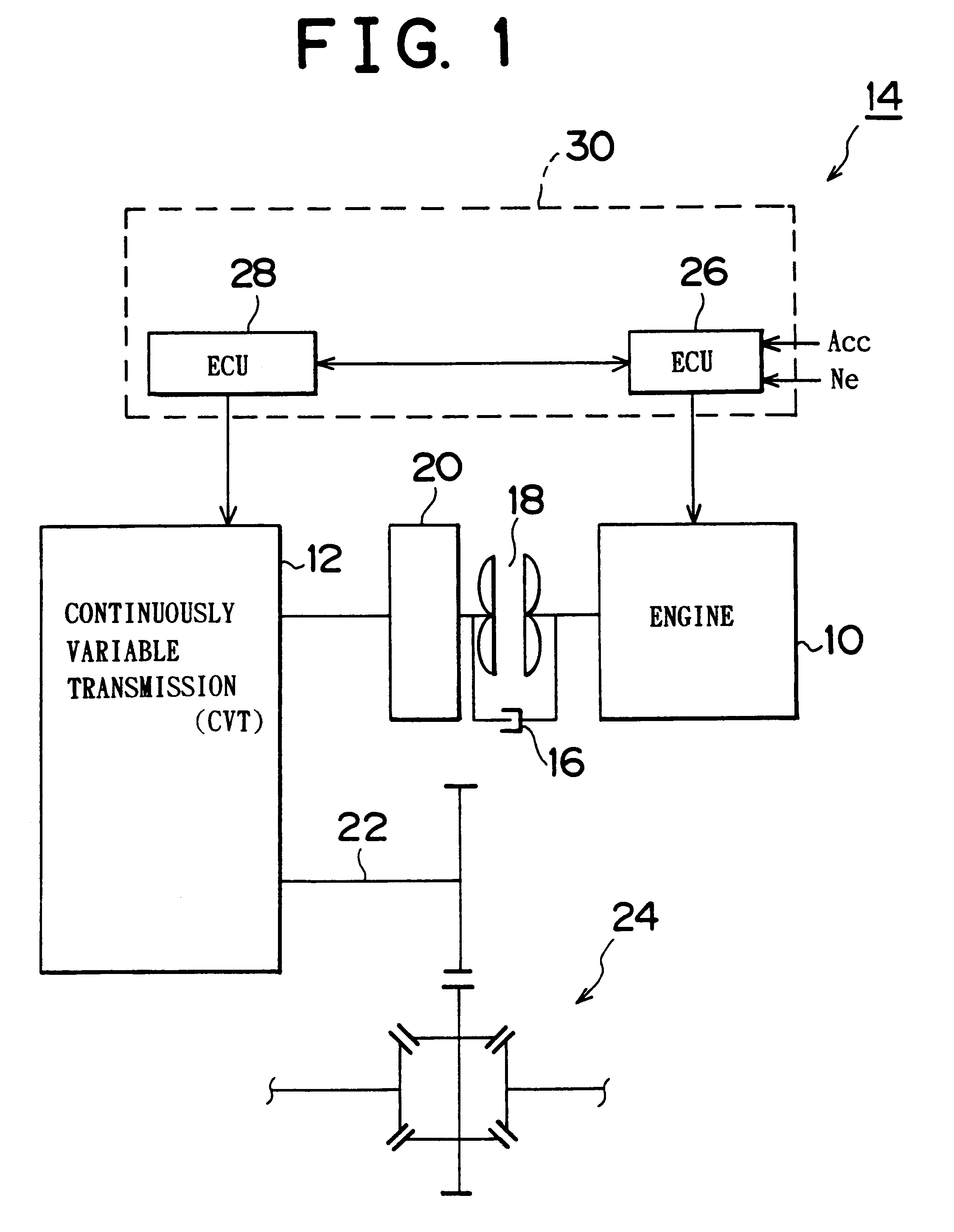
Vehicle control apparatus having power source and continuously variable transmission, and control method of the apparatus
InactiveUS6377882B1Reduce vibrationEliminate backlashHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlControl theoryControl torque
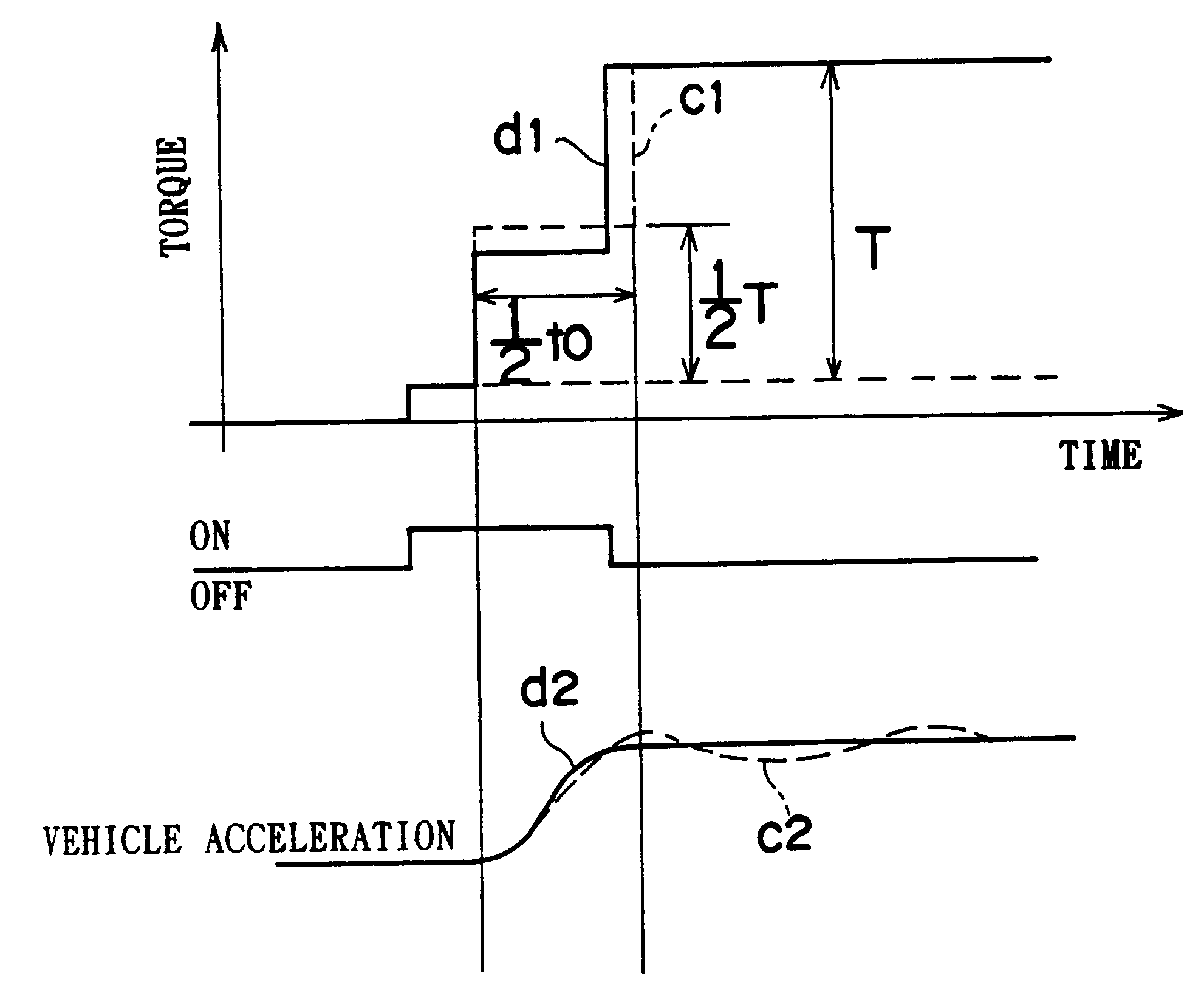
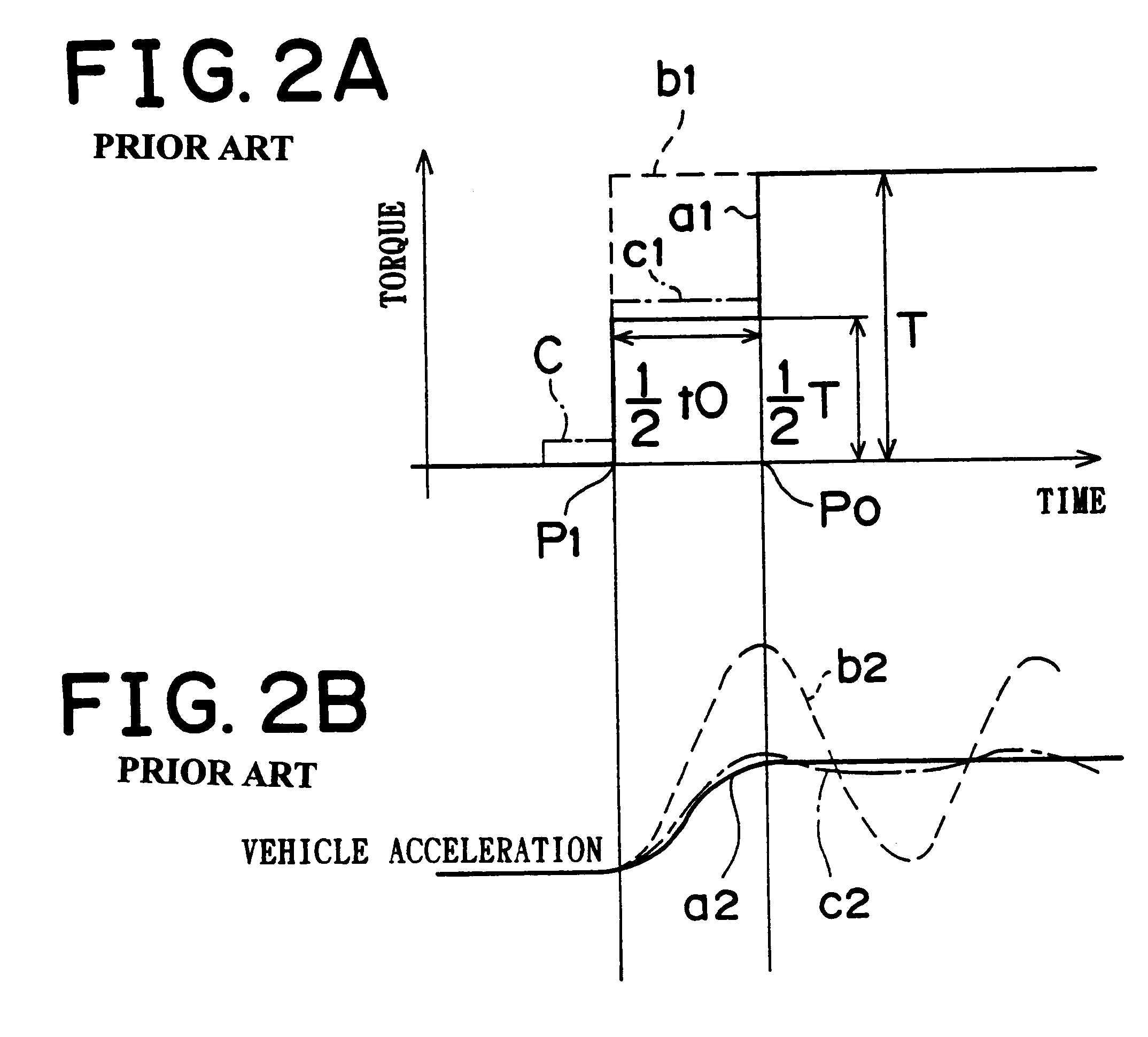
A control apparatus for a vehicle that has a power source and a continuously variable transmission. If a backlash-reducing control execution flag is on, a central control section utilizes an inertia torque produced during a backlash-reducing control as a part of a transient surge-reducing control that follows the backlash-reducing control, by setting at least one of a control duration and a control torque of the transient surge-reducing control to a value that is less than the control duration or torque set for an ordinary transient surge-reducing control. Therefore, the vehicle control apparatus is able to effectively perform the transient surge-reducing control and therefore further reduce vibrations of the vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Noise reduction in epicyclic gear systems
InactiveUS20070275816A1Quiet and cost-effective arrangementEngine fuctionsGear vibration/noise dampingGear wheelGear system
An epicyclic gear system having a sun gear, a ring gear and P planet gears. The planet gears include a load equalisation system such as a flexible spindle. The gears are structured according to a K factor which depends on the number of planet gears and the number of teeth on the sun gear. A gear system of this kind can be relatively quiet and cost effective, and suitable for use in a wind turbine.
Owner:WINDFLOW TECHNOLOGY
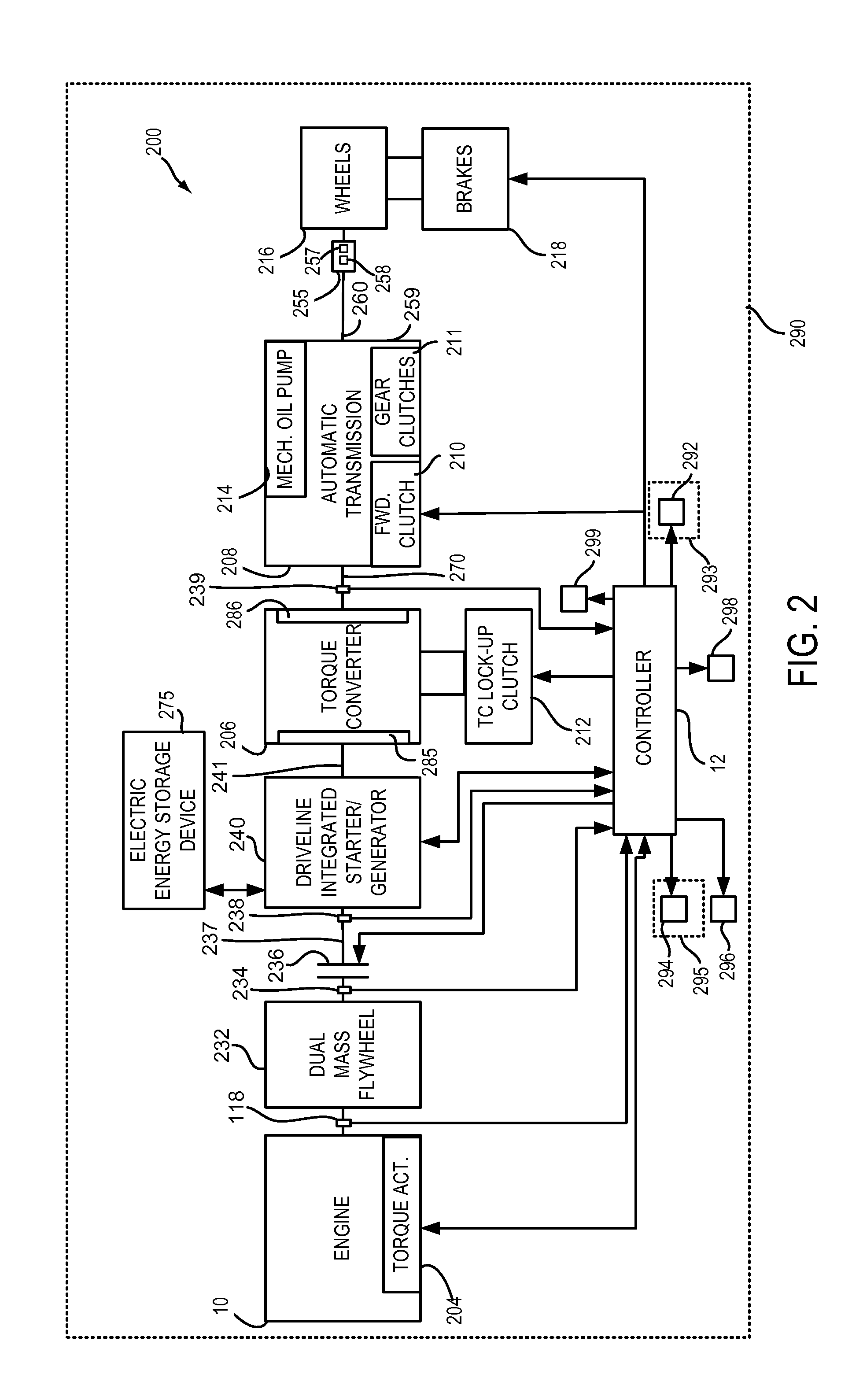
Control device for hybrid vehicle drive apparatus
ActiveUS20100004089A1Increase rotation speedReduce bias loadHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingEngineeringHybrid vehicle
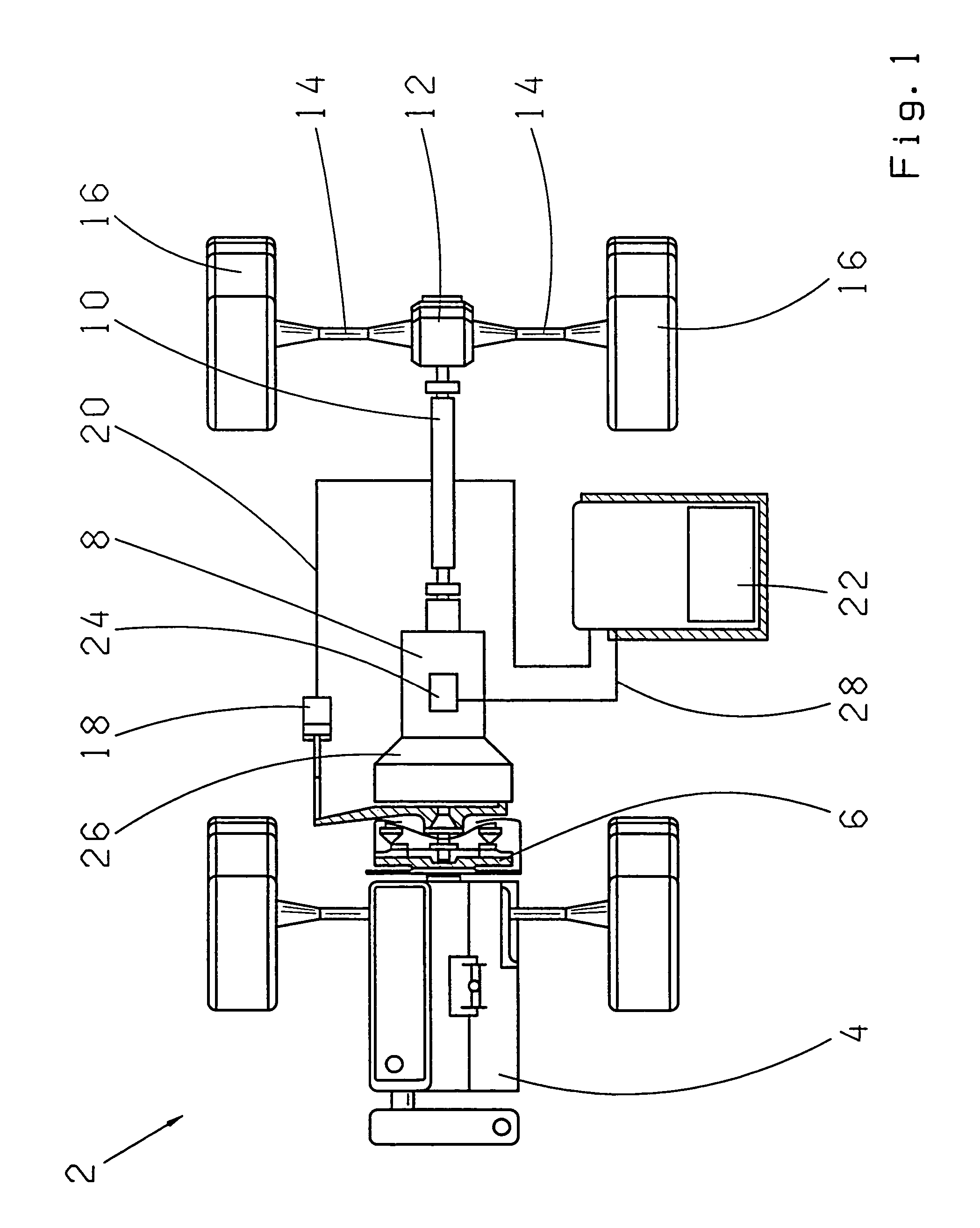
A control device for hybrid vehicle drive apparatus is disclosed. Upon receipt of a start-up request on an engine (8), if a determination is made that a rattling gear noise in a power distributing mechanism (16) exceeds a given value, first and second clutches (C1 and C2) are disengaged to cause a power transmitting path to be placed in a power interrupting state, and the first and second clutches (C1 and C2) are engaged to cause the power transmitting path to be placed in a non-differential state. Thus, engine start-up is initiated. This allows the engine (8) to be started up with a limited occurrence of rattling between gears incorporated in the power distributing mechanism (16) with a reduction in rattling gear noise.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Driving Device With Rotating Electric Machine
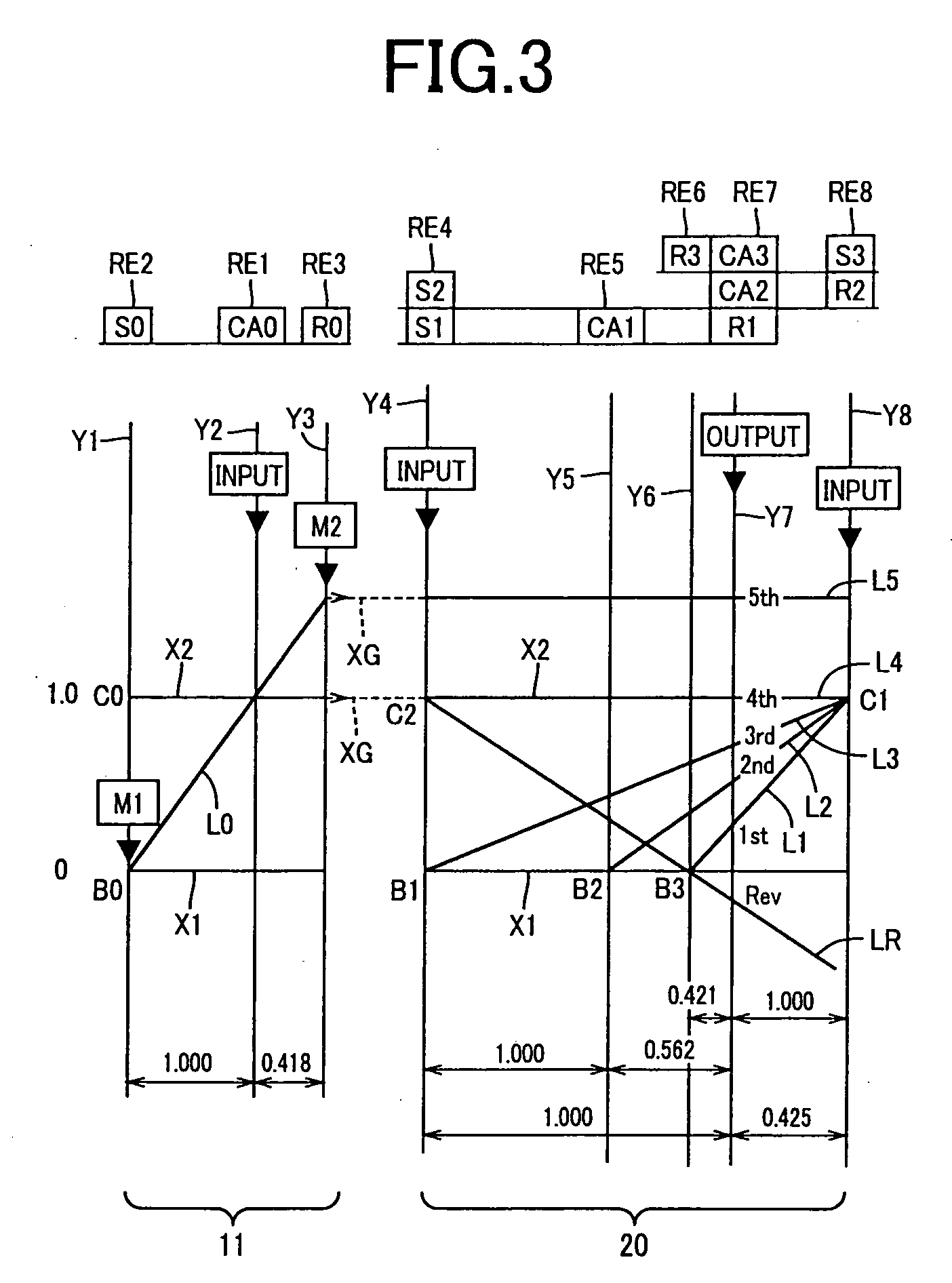
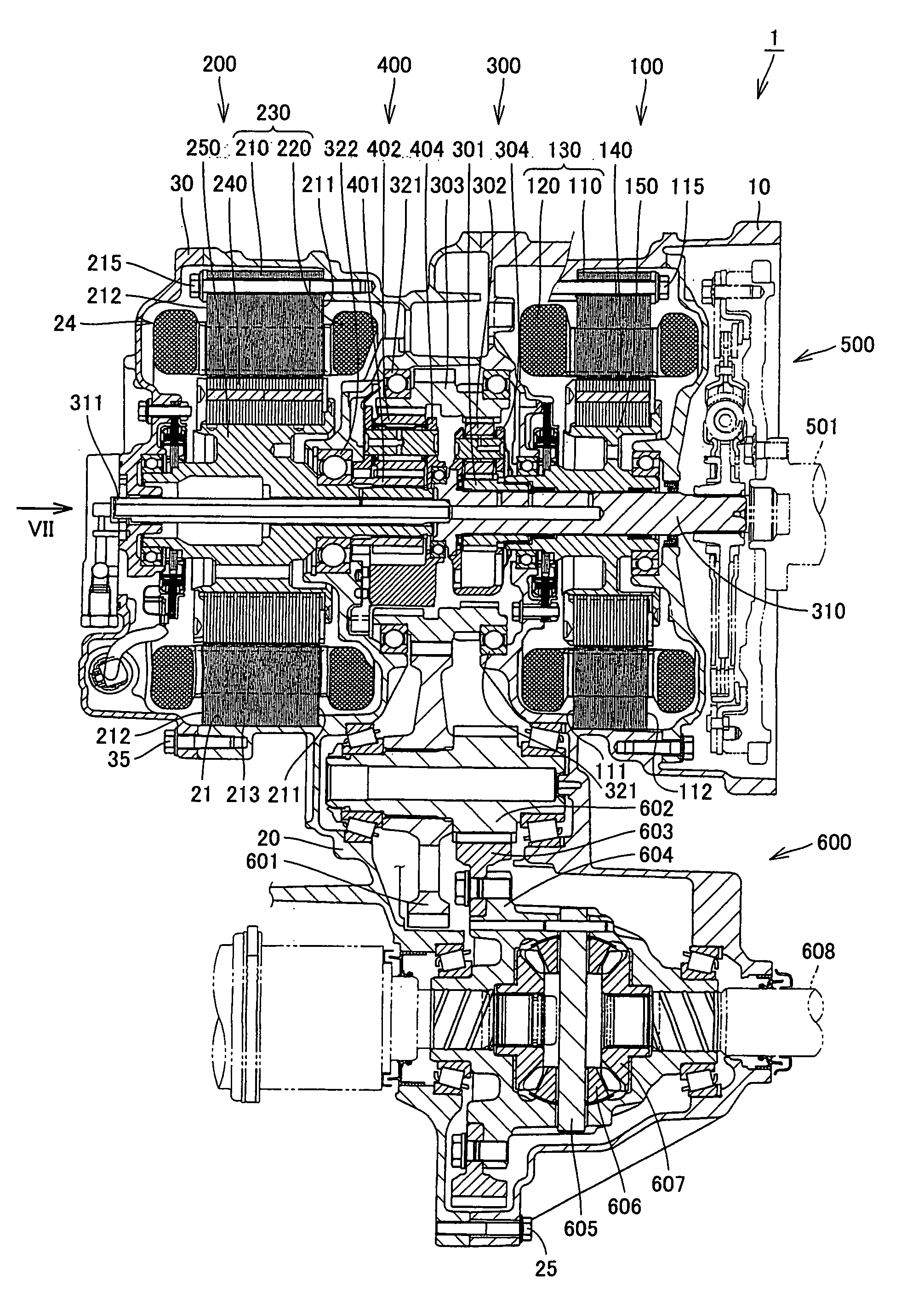
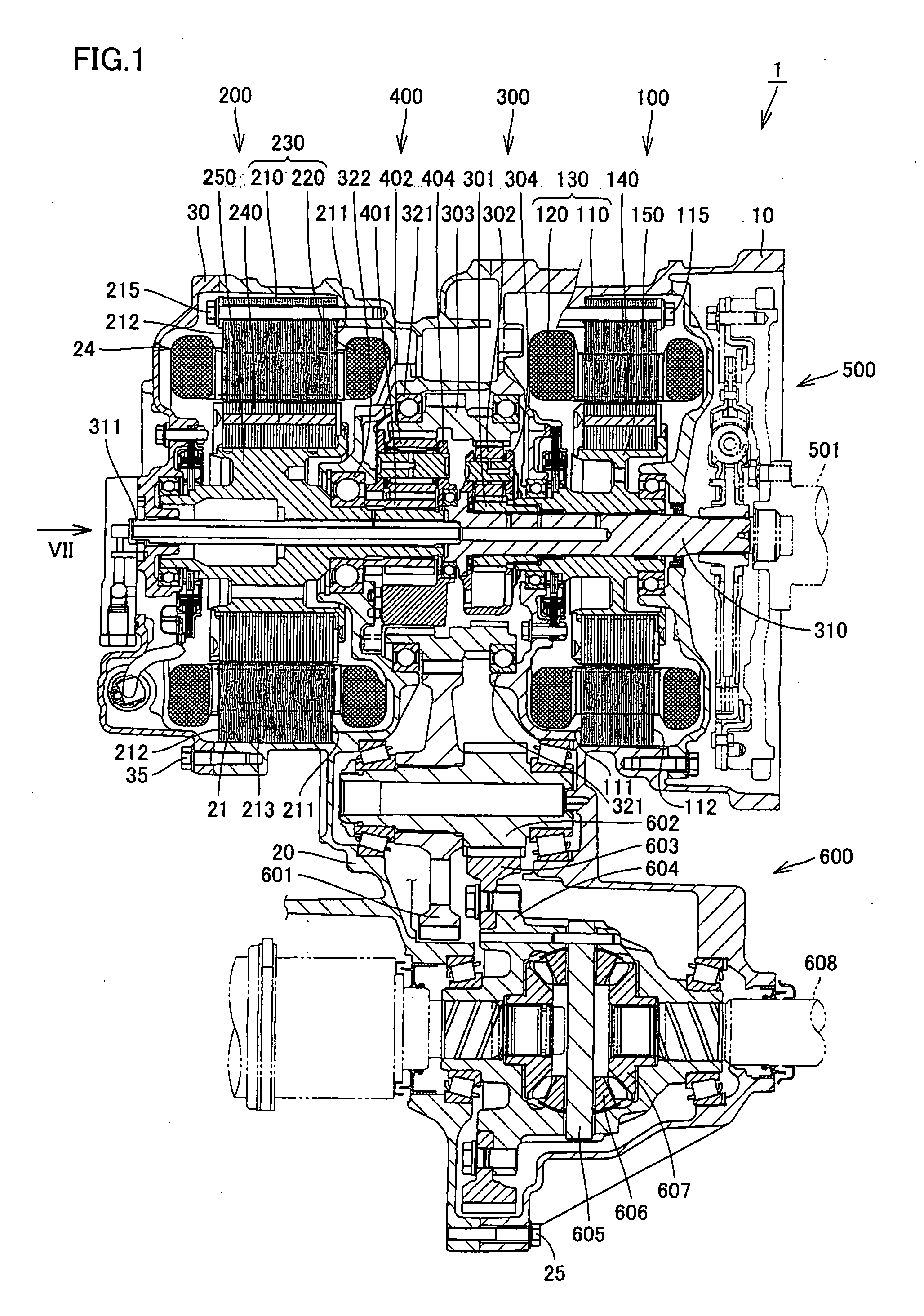
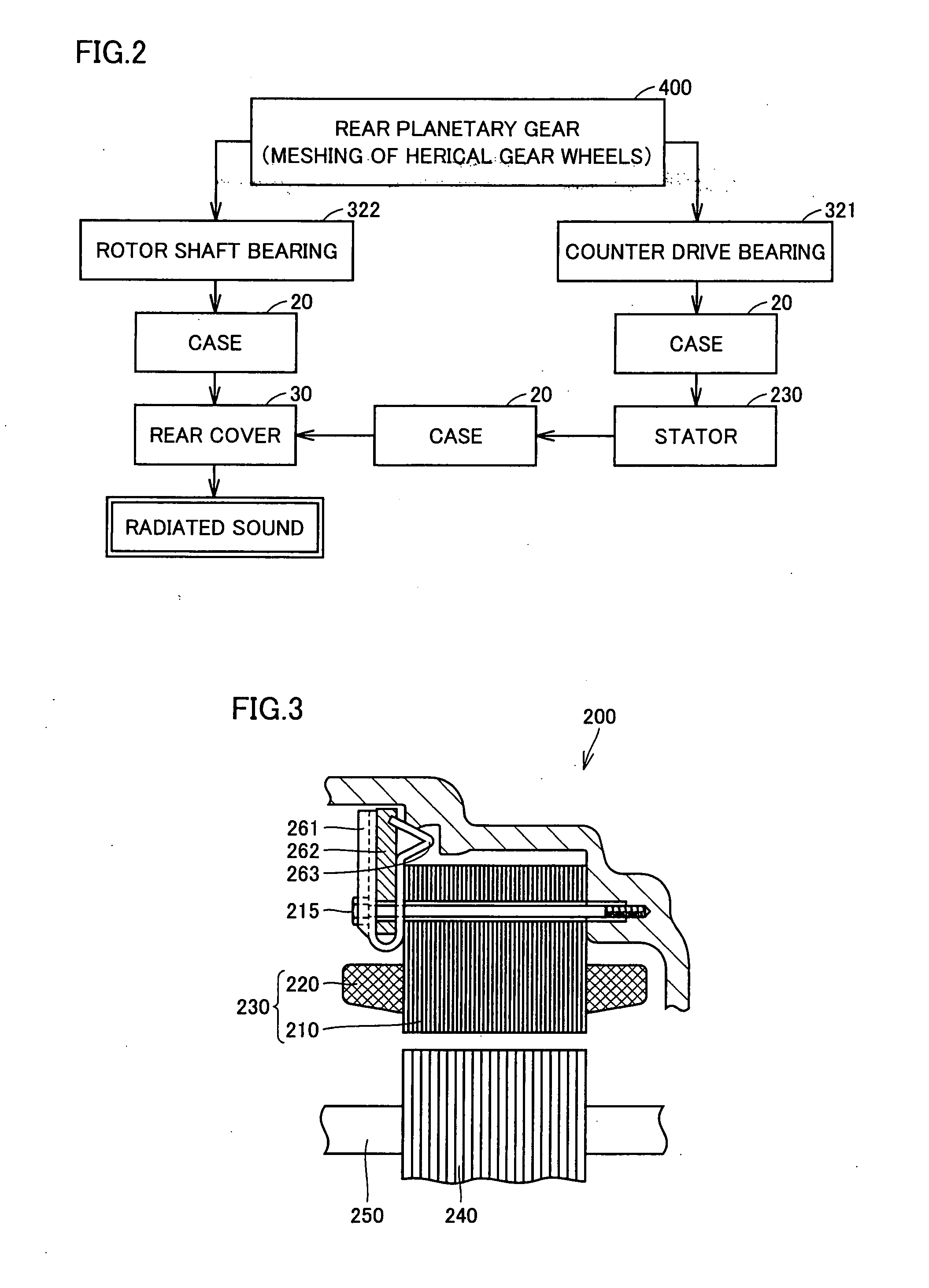
InactiveUS20080106163A1Improve appearance qualityAvoid vibrationHybrid vehiclesGear vibration/noise dampingElectric machineGear wheel
A transaxle includes a case having an opening, a second rotating electric machine stored in the opening of the case and having a stators, a rear planetary gear stored in the transaxle case and connected to the second rotating electric machine, a transaxle rear cover sealing the opening and a bolt fixing the second rotating electric machine to the transaxle case. The stator has first and second thrust end faces defining an axial length thereof. The first thrust end face is pressed against an inner surface of the case.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Automatic transmission case
InactiveUS20020017159A1Effective fasteningGearboxesGear vibration/noise dampingAutomatic transmissionMechanical engineering
The level of quietness for an automatic transmission case is ensured by preventing vibration by improving the rigidity while suppressing the increase in the mass of a transmission case. In an automatic transmission case in which a valve body is attached to a case wall that covers the transmission mechanism, the rigidity of the automatic transmission case is increased by providing, in the case, an enclosing wall that projects out from the case wall and encloses the periphery of the valve body.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Gearbox Noise Reduction By Electrical Drive Control
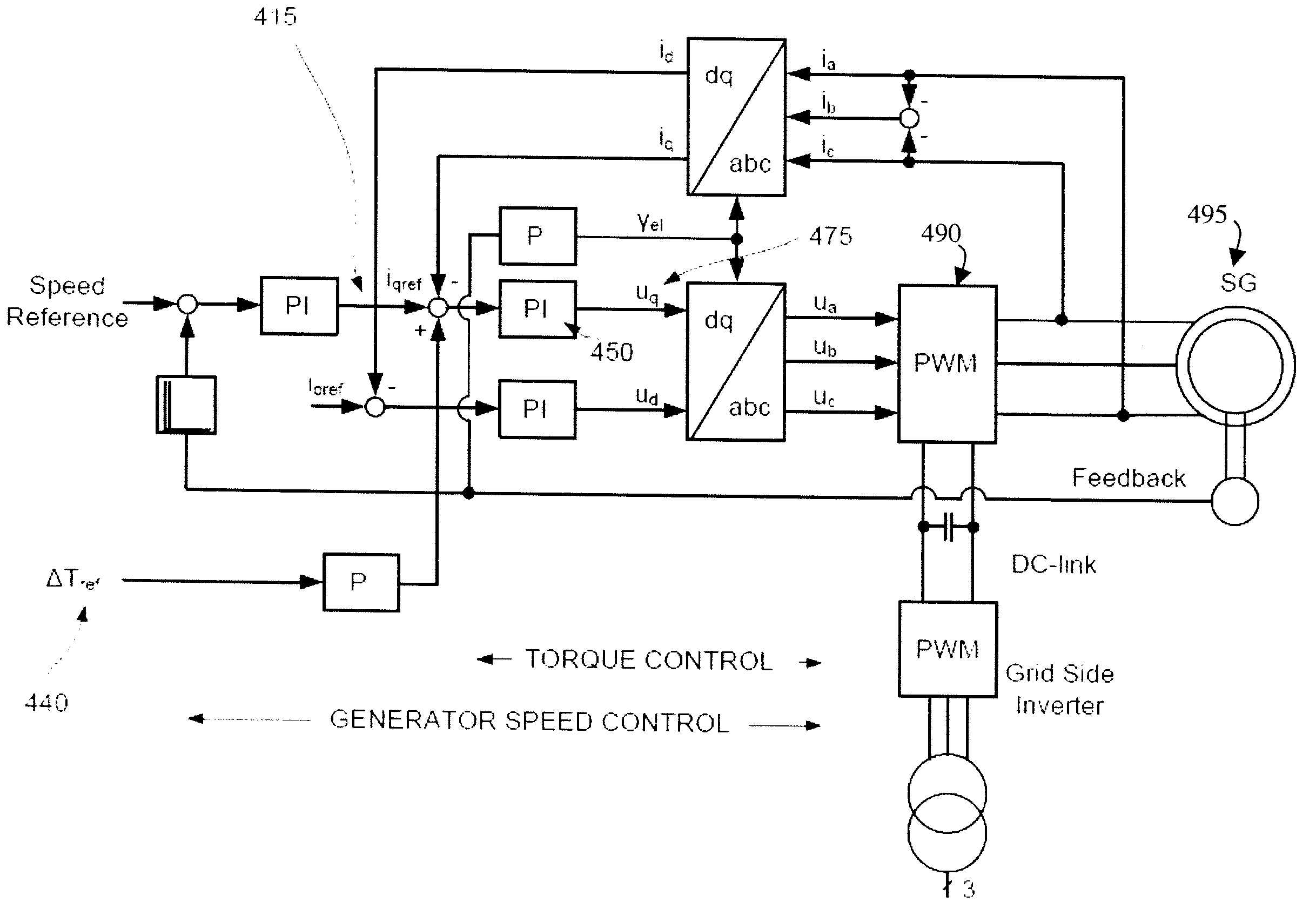
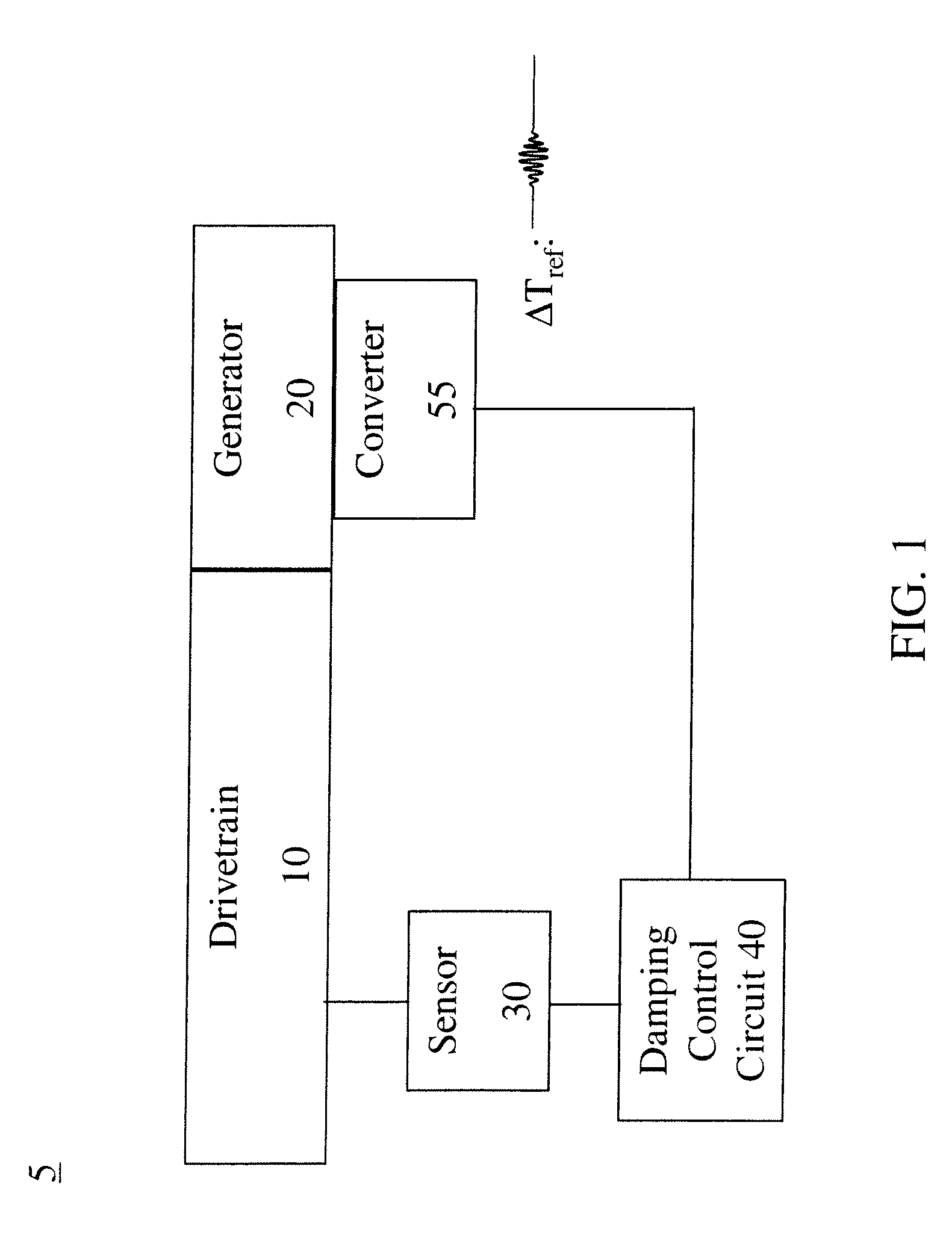
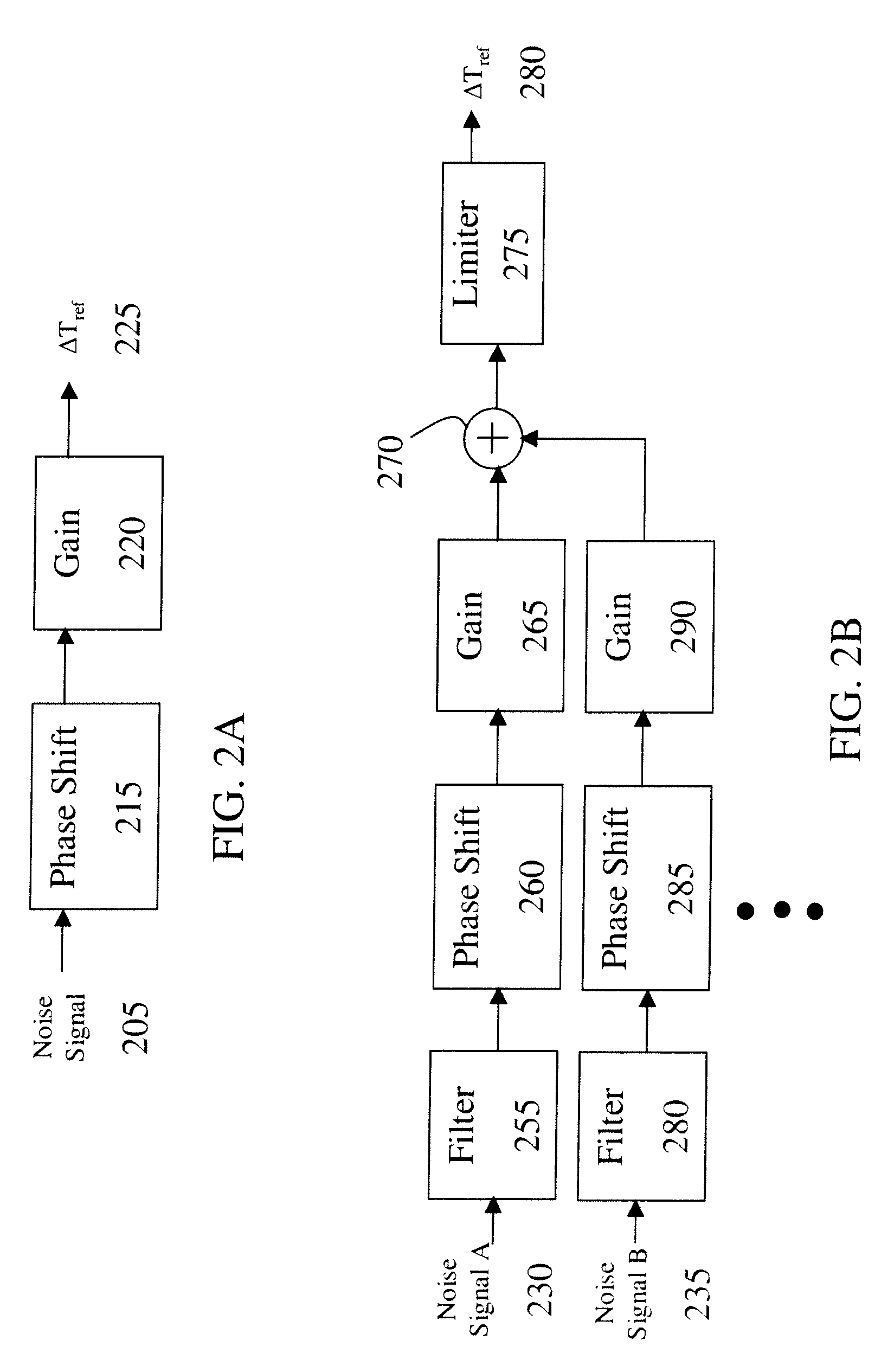
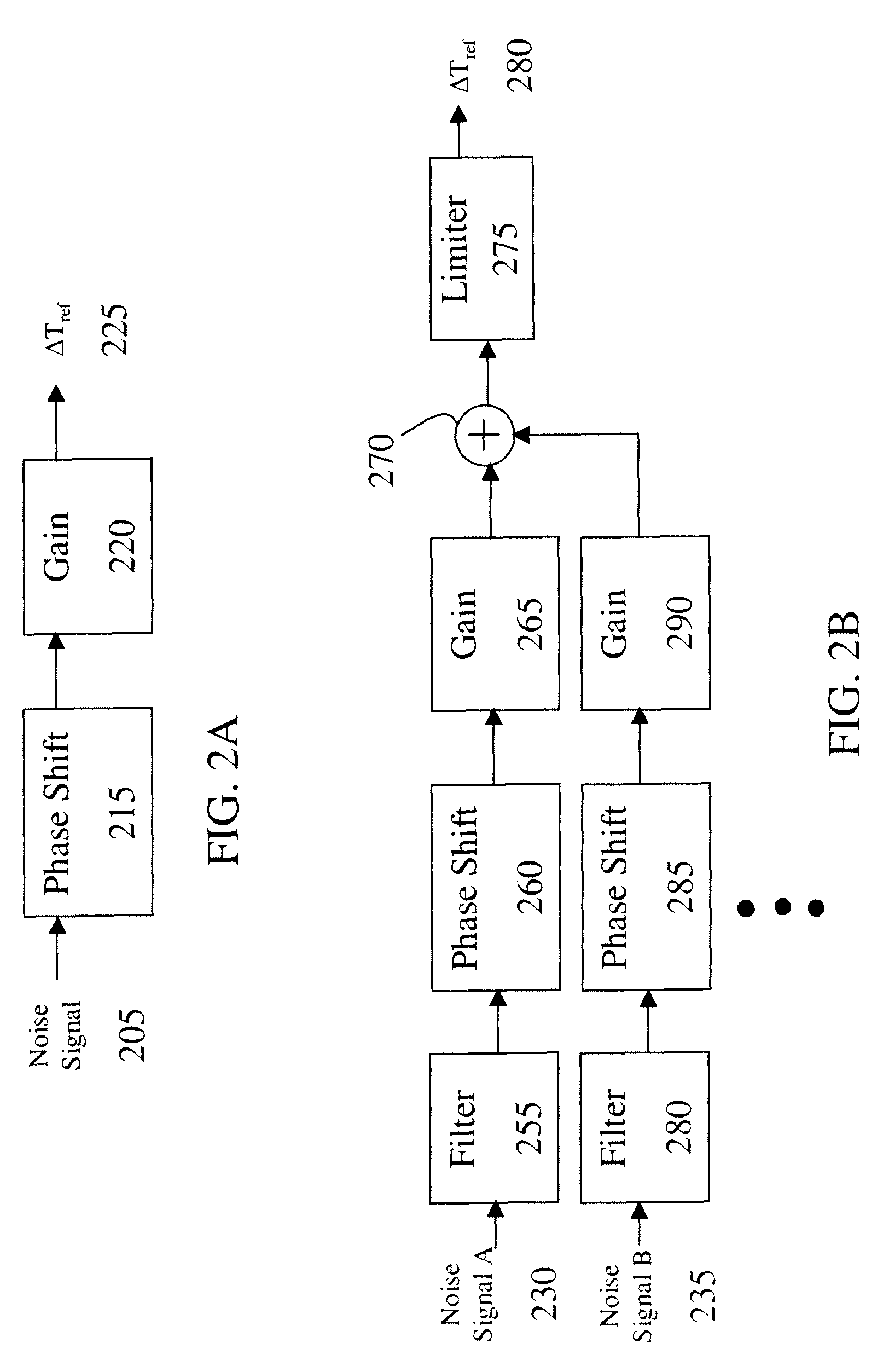
ActiveUS20090149999A1Reduce audible noiseReducing audibleNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTemperatue controlPhase shiftedDamping torque
A system for damping audible noise from a drive train. One embodiment is a system with an audible noise signal from a drive train wherein a damping circuit produces a damping torque that is a phase shifted and amplified version of the noise signal that is applied to the air-gap torque of a generator or motor coupled to the drive train and effectively reduces the audible noise.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for inertial torque reaction management
InactiveUS20060234829A1Reduce and eliminate backlashReduce and eliminate and associated noiseGear vibration/noise dampingGearing controlEngineeringMoment of inertia
A system and method for managing inertial torque reactions on stationary powertrain structure rotate at least one selected engine component and at least one selected drive train component in opposite directions so the rotational inertia of the selected drive train component acts in a direction opposite to that of the rotational inertia of the selected engine component to reduce or eliminate the inertial torque reactions on stationary powertrain structure caused by rotational acceleration and deceleration of powertrain components and improves performance with respect to noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Superfinishing large planetary gear systems
ActiveUS20050014597A1Reduces and eliminates lubricant debrisAvoid damageEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesGear wheelEngineering
Disclosed herein is a new improved large planetary gear system used on the input stage of wind turbine power generators. This improved planetary gear system reduces or eliminates lubricant debris traditionally generated from the gear teeth, thereby eliminating an initiating source for bearing failure. To achieve these results, some and preferably all of the gear teeth within the planetary gear system are superfinished using chemically accelerated vibratory finishing to a surface roughness of approximately 0.25 micron or less. Several objects and advantages of the invention are to provide a gearbox with reduced metal debris, improved bearing life, reduced wear, reduced vibro-frictional noise, improved contact fatigue, improved fretting resistance, improved lubrication, to simplify the run-in process, and to enhance the durability and efficiency of the gearbox.
Owner:OSRO GMBH +1
Methods and systems for reducing gear lash noise
InactiveUS8965616B2Reduce impactReduce gear toothHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsElectric machineGear tooth
Systems and methods for improving operation of a hybrid vehicle are presented. In one example, driveline gear lash gear tooth to gear tooth impact may be reduced via adjusting operation of an electric machine. For example, gear tooth to gear tooth impact may be reduced by operating the electric machine in a speed control mode to manage torque during driveline torque transition from a negative torque to a positive torque.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
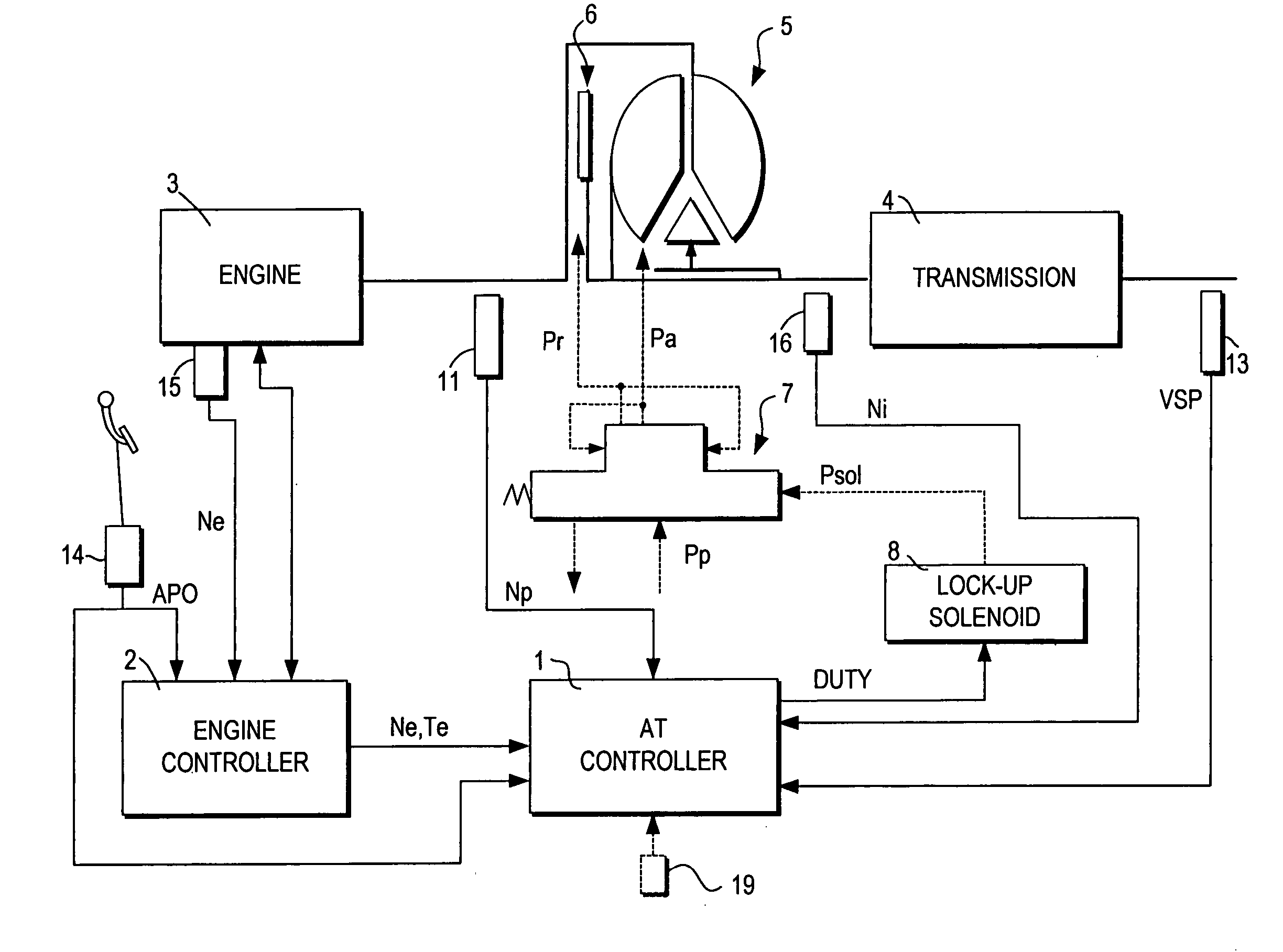
Lock-up control for torque converter
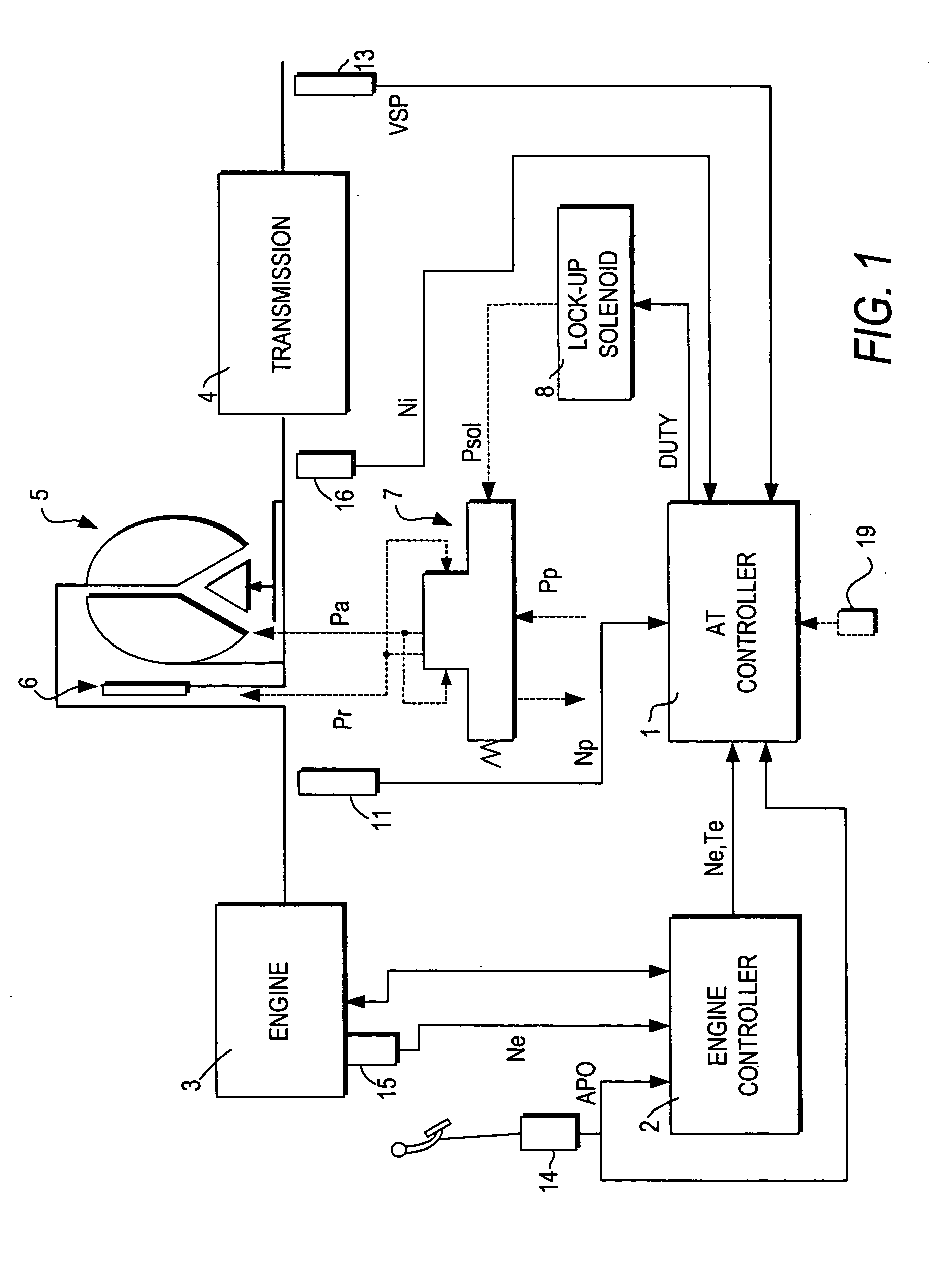
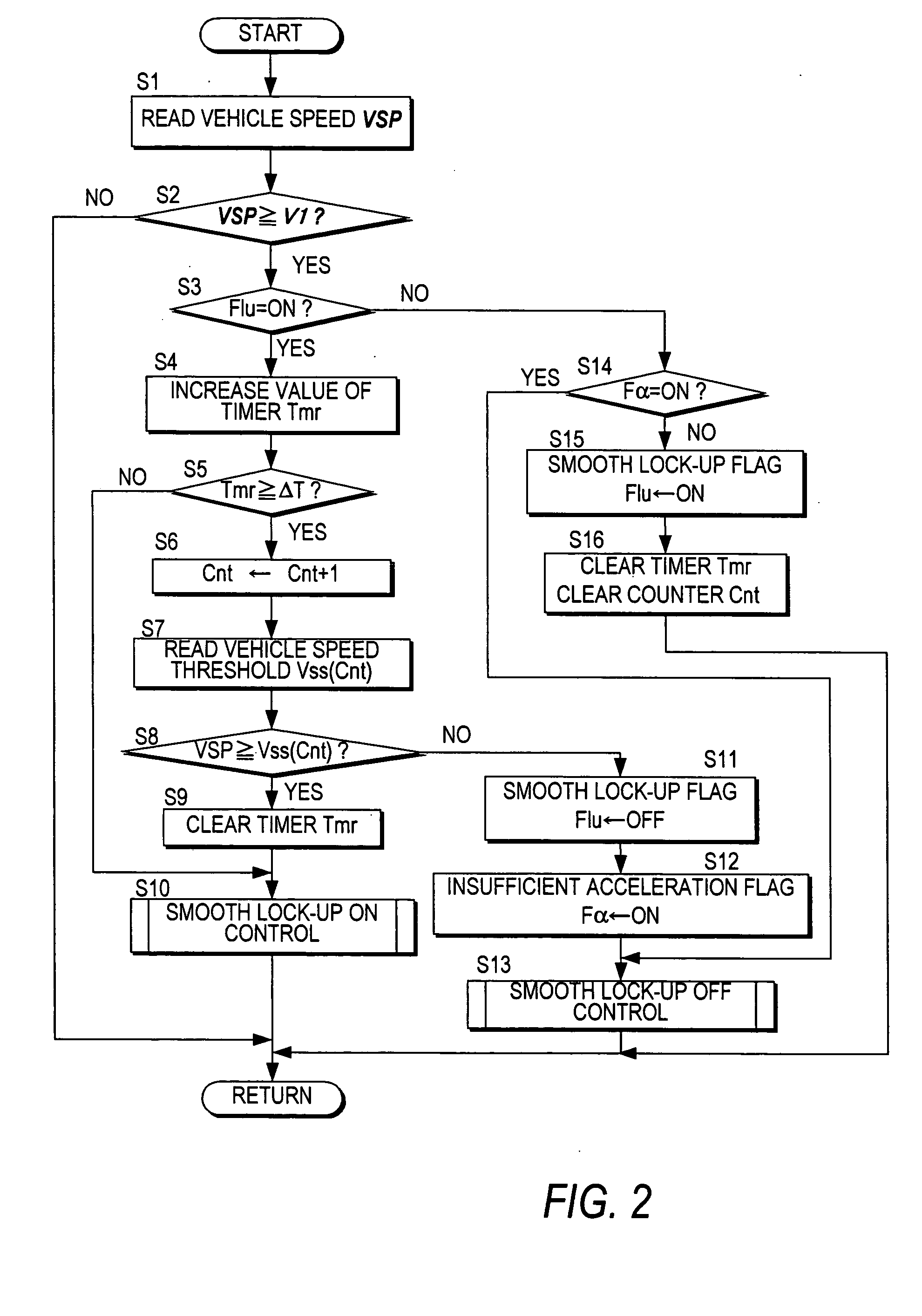
ActiveUS20050222737A1Increase speedAvoid noiseDigital data processing detailsGear vibration/noise dampingClutch controlDifferential pressure
A lock-up clutch control device controls a lock-up clutch (6) provided in a torque converter (5) which is mounted between the engine (3) and transmission (4) provided in a vehicle. The lock-up clutch control device switches the state of the torque converter (5) between a converter state and a lock-up state by controlling a differential pressure supplied to the lock-up clutch. The lock-up clutch control device includes a sensor (13, 19) for detecting a rise of a vehicle speed; a differential pressure generator (7, 8) which generates the differential pressure supplied to the lock-up clutch; and a controller (1). The controller is programmed to command the differential pressure generator (7, 8) to lock the lock-up clutch (6) when the vehicle speed exceeds a predetermined low vehicle speed (V1), after the vehicle is started; subsequently monitor the rise of the vehicle speed; and command the differential pressure generator (7, 8) to unlock the lock-up clutch when the monitored rise of the vehicle speed is lower than a preset value (Vss / αs).
Owner:JATCO LTD
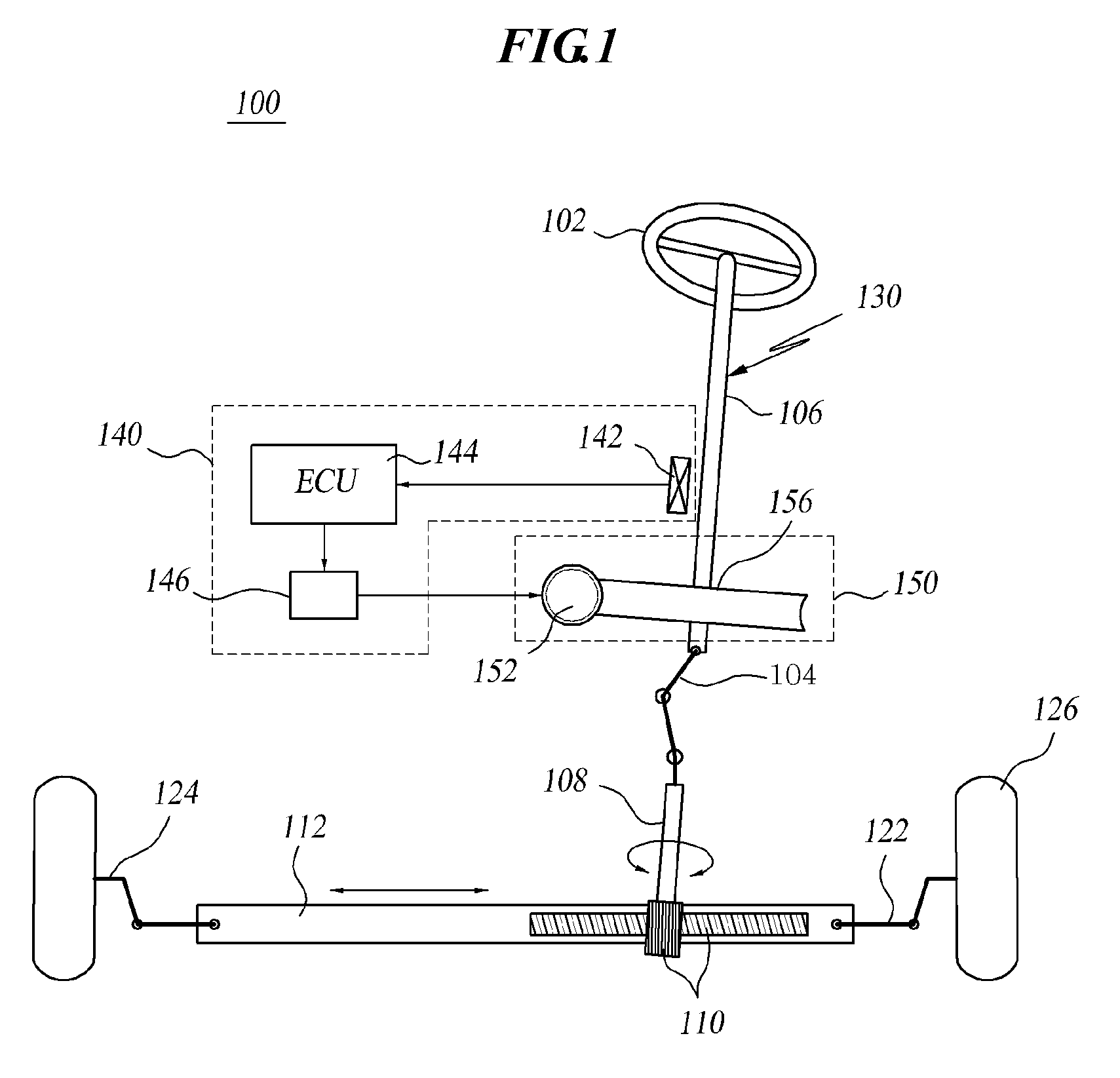
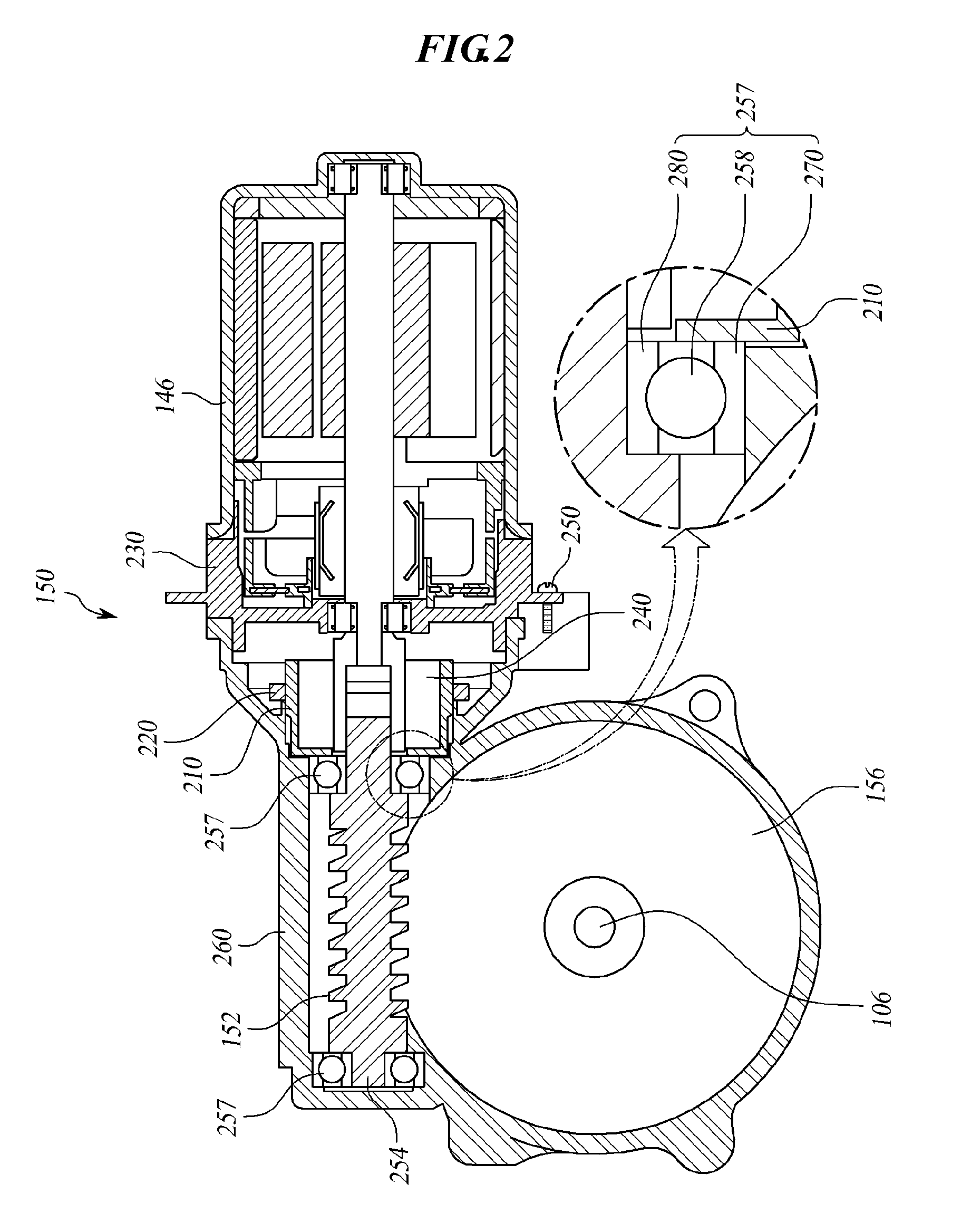
Electric power steering apparatus
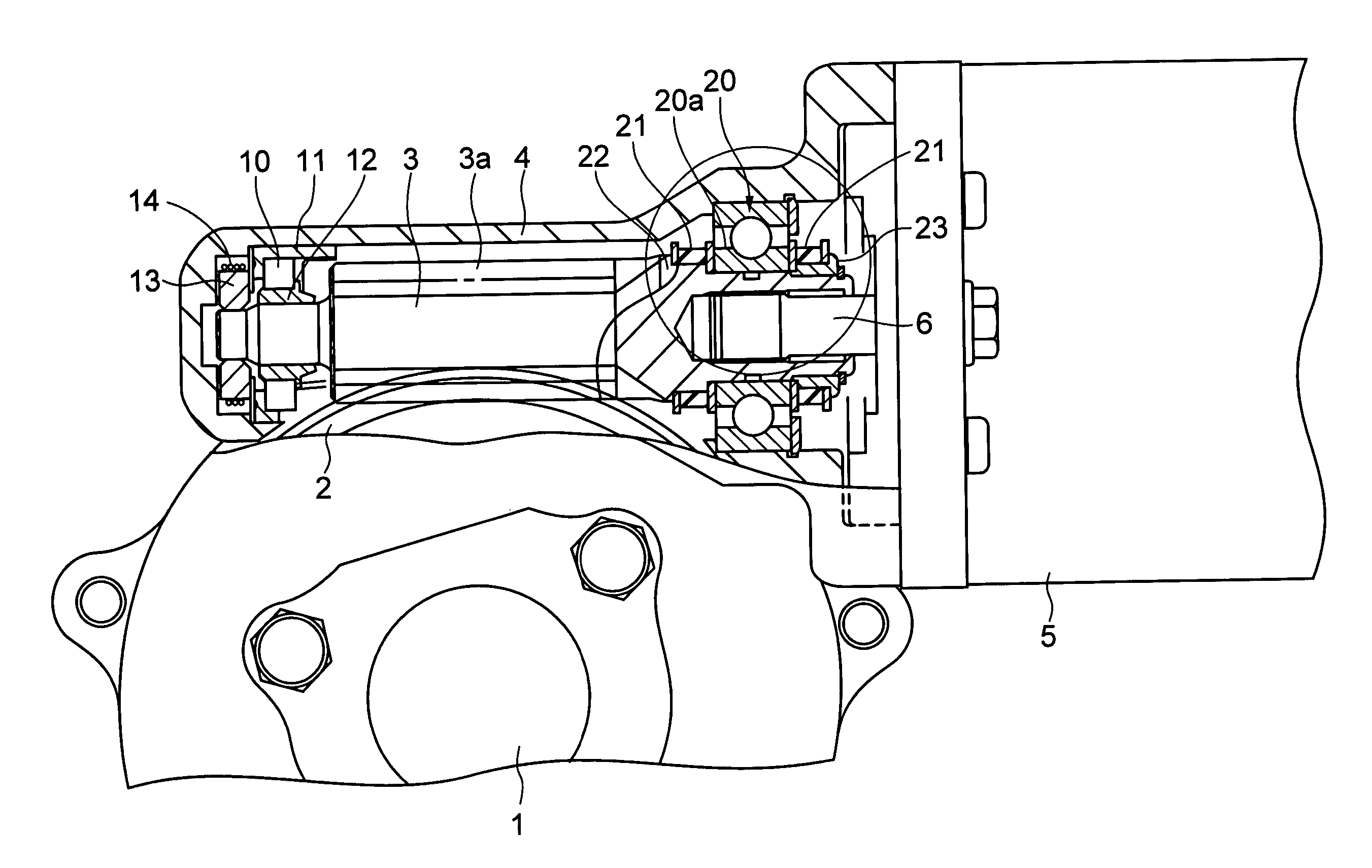
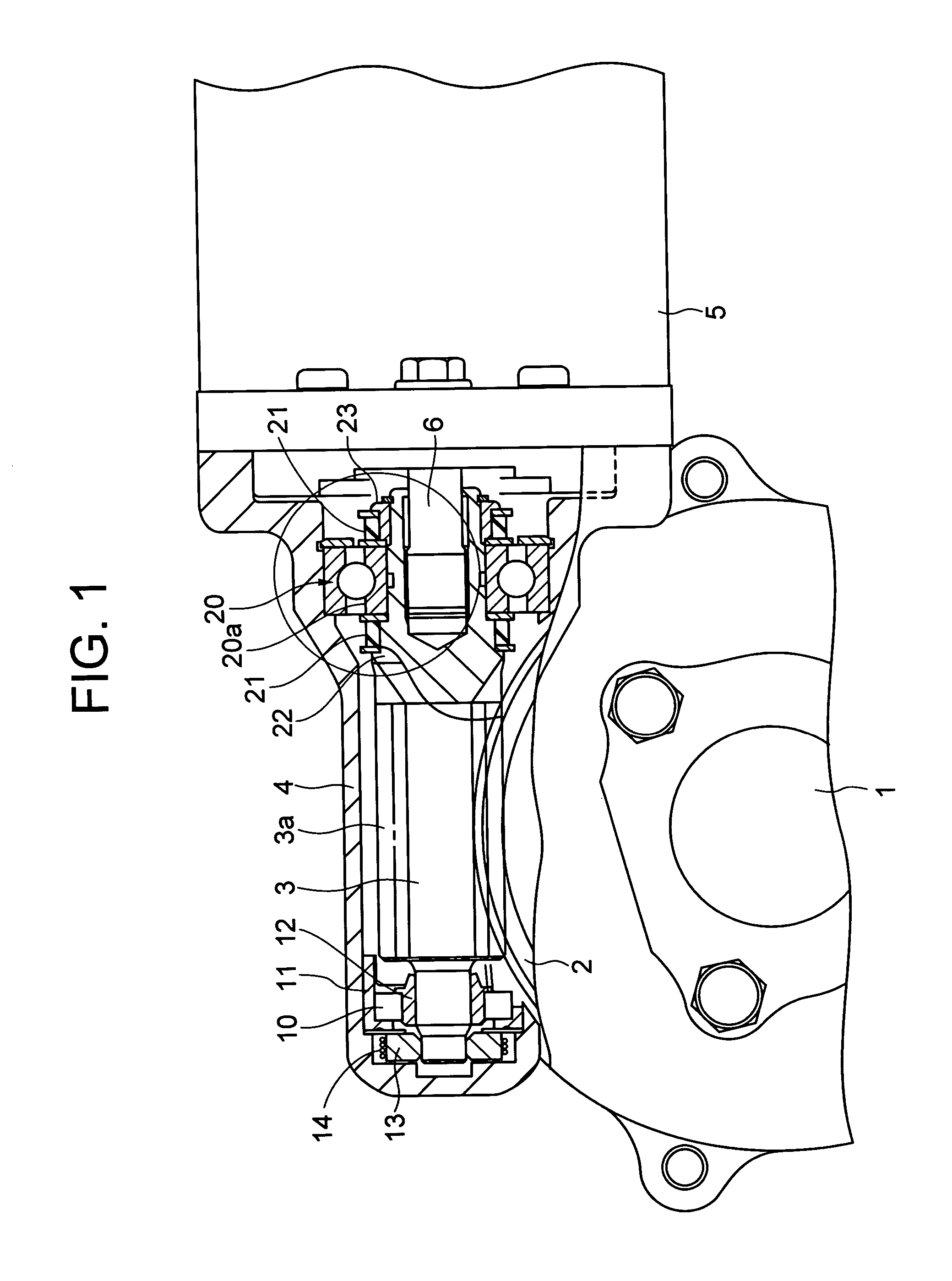
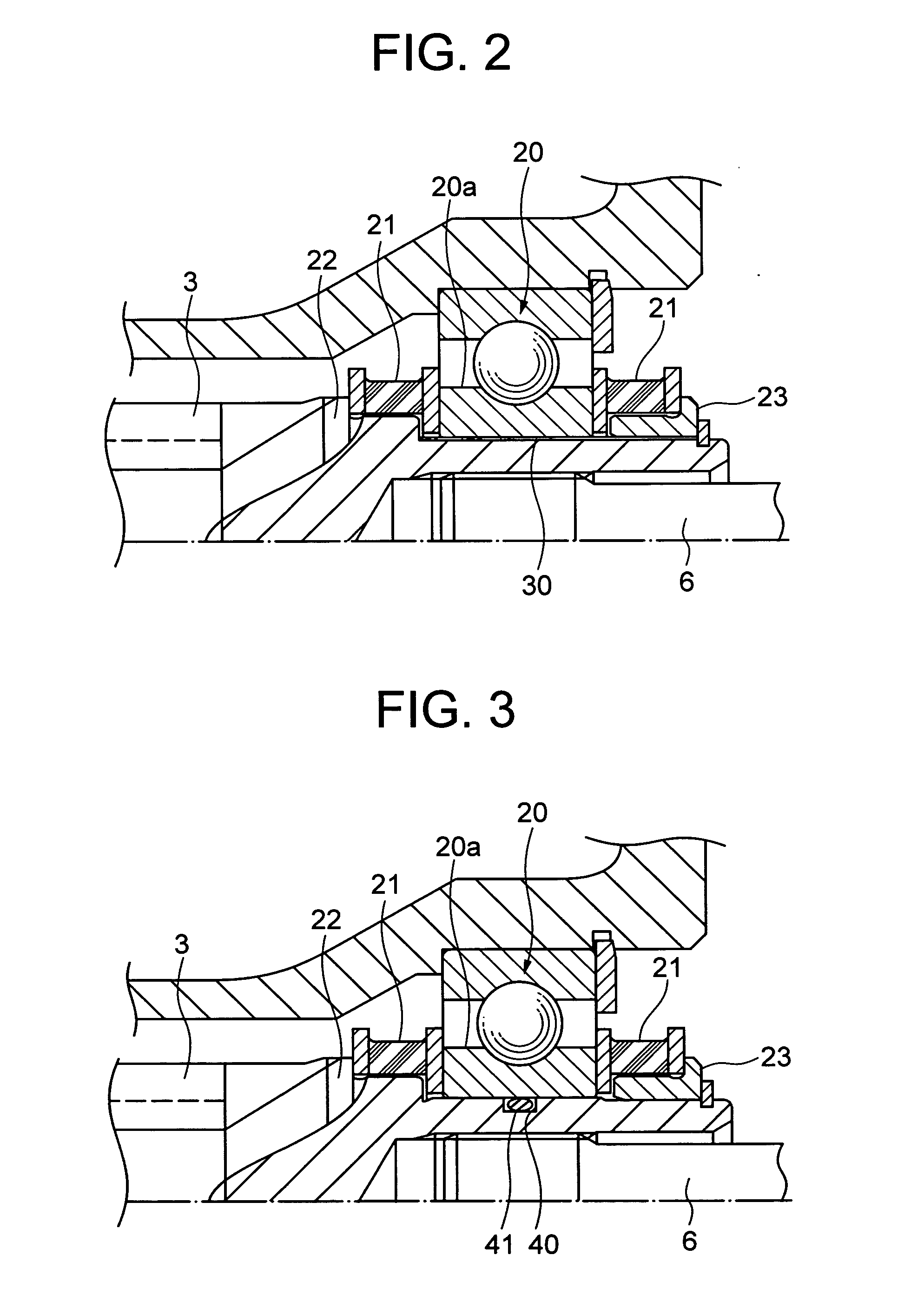
ActiveUS20050224278A1High precision in machiningIncrease manufacturing costRolling contact bearingsGear vibration/noise dampingElectric power steeringTorsion spring
A small gap is formed between a worm shaft 3 and a second bearing 20, so that the worm shaft can be tilted relative to the inner ring 20a of the second bearing 20 without fail when preloaded by a torsion spring 14. An elastic member 41 is provided in at least portion of a circumferential groove 40 in the small gap. The worm shaft 3 and the inner ring 20a of the second bearing 20 are not in contact with each other, and their metallic clank in the small gap can be prevented. By providing a projecting portion(s) 3b on one side or both sides, with respect to the axial direction, of the circumferential groove 40, the small gap between the worm shaft 3 and the inner ring 20a of the second bearing 20 can be made large, and it is possible to enlarge the range over which the worm shaft 3 can swing.
Owner:NSK LTD
Torque converter slip control for multi-displacement engine
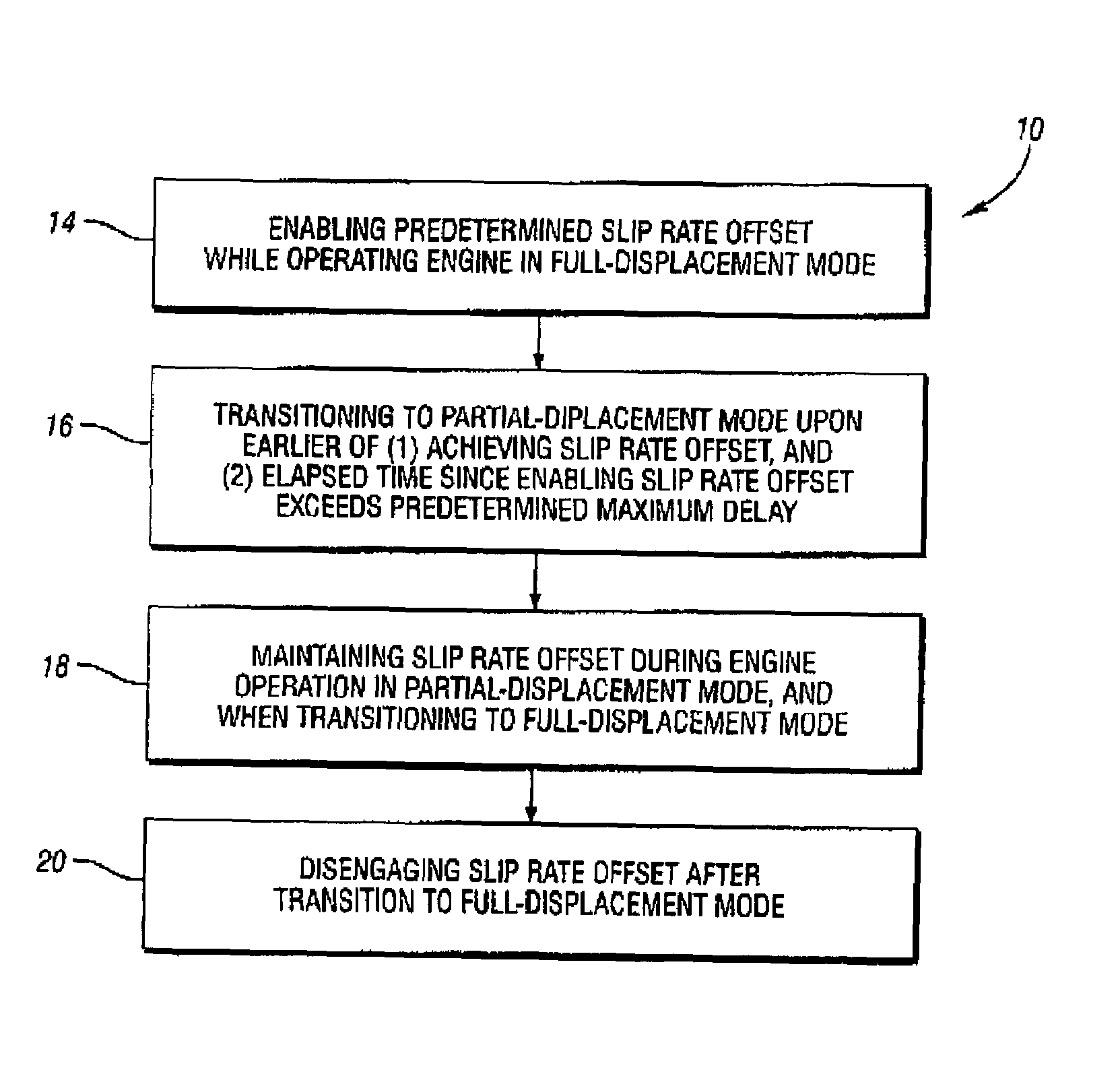
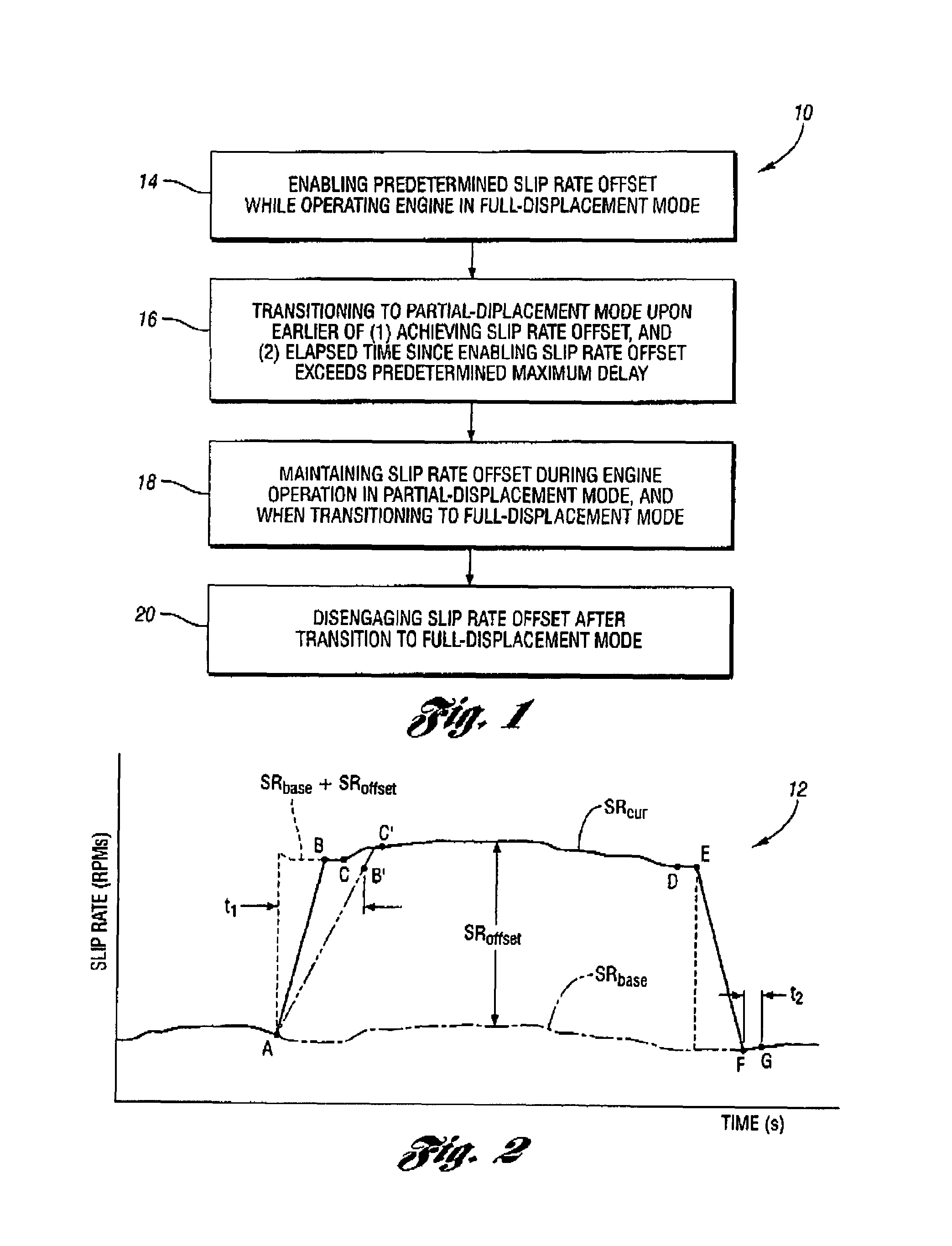
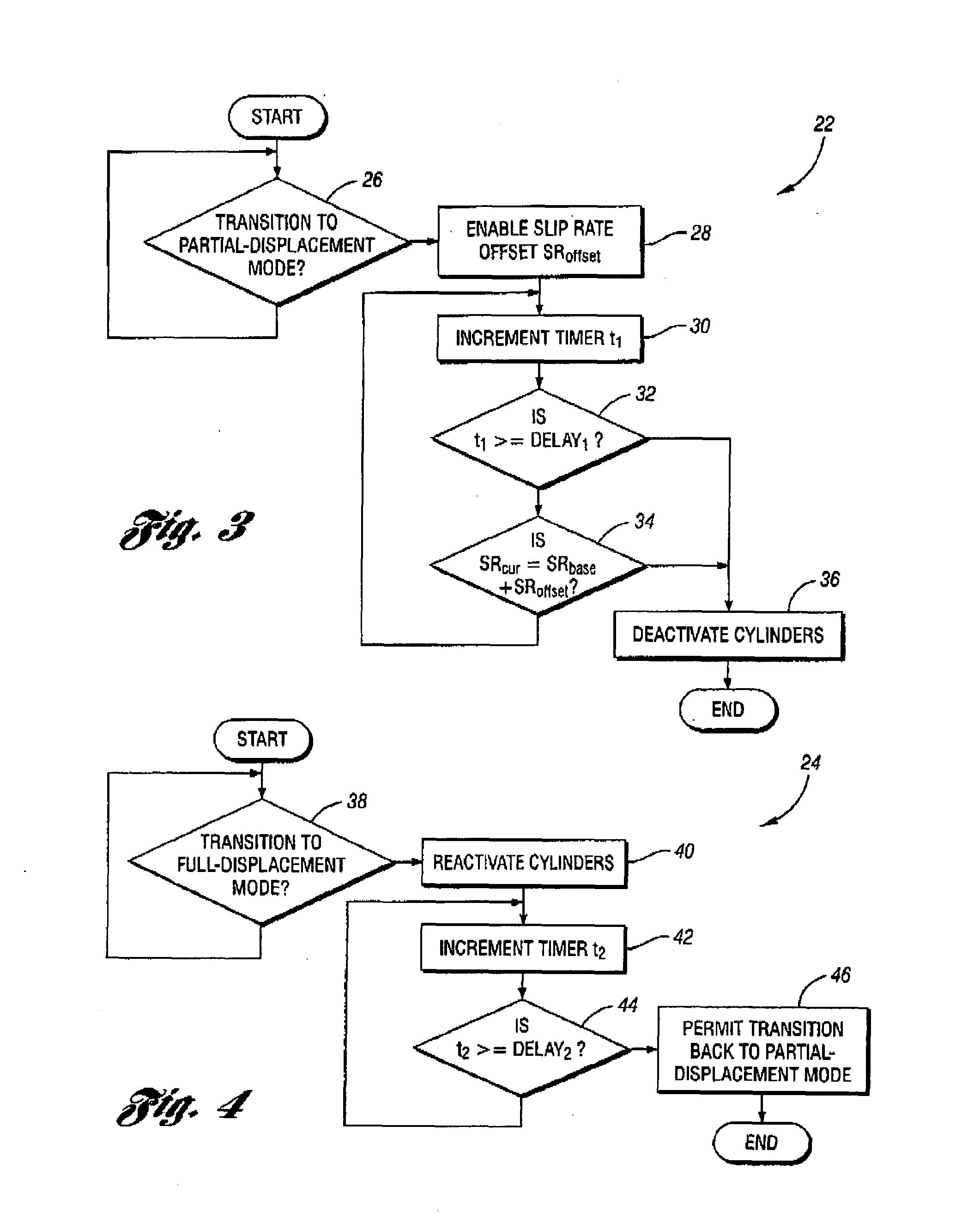
Prior to transitioning a multiple-displacement engine from a full-displacement engine operating mode to a partial-displacement engine operating mode, a base slip rate of a torque converter coupled to the engine engine is increased by a predetermined slip rate offset. The engine is then transitioned to partial-displacement mode upon the earlier of either achieving the desired offset slip rate, or once a maximum time delay has occurred since the slip rate offset was enabled. An offset slip rate is maintained throughout partial-displacement engine operation, and through a transition back to a full-displacement mode. The slip rate offset is removed or disenabled once the engine is again operating in the full-displacement mode. The slip rate offset is either a calibratable constant or is determined as a function of one or more suitable engine or vehicle operating parameters affecting vehicle NVH levels, such as engine speed and vehicle speed.
Owner:FCA US
Automatic transmission case
InactiveUS6729206B2Improve rigidityGearboxesGear vibration/noise dampingAutomatic transmissionEngineering
The level of quietness for an automatic transmission case is ensured by preventing vibration by improving the rigidity while suppressing the increase in the mass of a transmission case. In an automatic transmission case in which a valve body is attached to a case wall that covers the transmission mechanism, the rigidity of the automatic transmission case is increased by providing, in the case, an enclosing wall that projects out from the case wall and encloses the periphery of the valve body.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Gearbox
InactiveUS20060156861A1Improve rigidityReduce noiseRotating vibration suppressionGearboxesEngineeringMechanical engineering
In a gearbox including three or more shaft holes, a vibration suppressor is formed with the gearbox and extends from at least one of shaft hole in a radial direction of the shaft hole. The vibration suppressor ensures a width which is greater than or equal to one fourth of the shaft hole diameter of the shaft hole, and a height that is greater than or equal to one sixth of the shaft hole diameter at a highest portion of the bivration suppressor.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Gearbox noise reduction by electrical drive control
ActiveUS8532828B2Reduce audible noiseReducing audibleNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementDigital data processing detailsDamping torqueEngineering
A system for damping audible noise from a drive train. One embodiment is a system with an audible noise signal from a drive train wherein a damping circuit produces a damping torque that is a phase shifted and amplified version of the noise signal that is applied to the air-gap torque of a generator or motor coupled to the drive train and effectively reduces the audible noise.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Roller chain sprocket with resilient cushion rings and root relief
InactiveUS20060252592A1Improve fatigue lifeReduce noise levelGearingGear vibration/noise dampingTransverse grooveEngineering
A sprocket includes a hub and a plurality of teeth projecting radially outwardly from the hub. At least one cushion ring is located adjacent the teeth, and the cushion ring defines a plurality of compression pads separated from each other by transverse grooves. Each of the compression pads is defined symmetrically about a circumferential mid-point. When part of a sprocket with symmetric tooth spaces, the cushion ring is being operable identically in first and second opposite rotational directions. In one arrangement, the compression pads each include a planar outer surface having a leading and a trailing end, wherein the leading end and trailing end are located a common radial distance from a center of the hub about which the sprocket rotates. The tooth spaces of the sprocket can be symmetric, asymmetric and the root surface can be relieved. The sprocket can include multiple tooth profiles distributed randomly about the hub.
Owner:HH CLOYES INC
Sprung gear set and method
Owner:STEERING SOLUTIONS IP HLDG +1
Gearbox comprising an electromechanical actuator
InactiveUS7350432B2Shrink the necessary spaceSupply is assuredGear vibration/noise dampingToothed gearingsControl signalEngineering
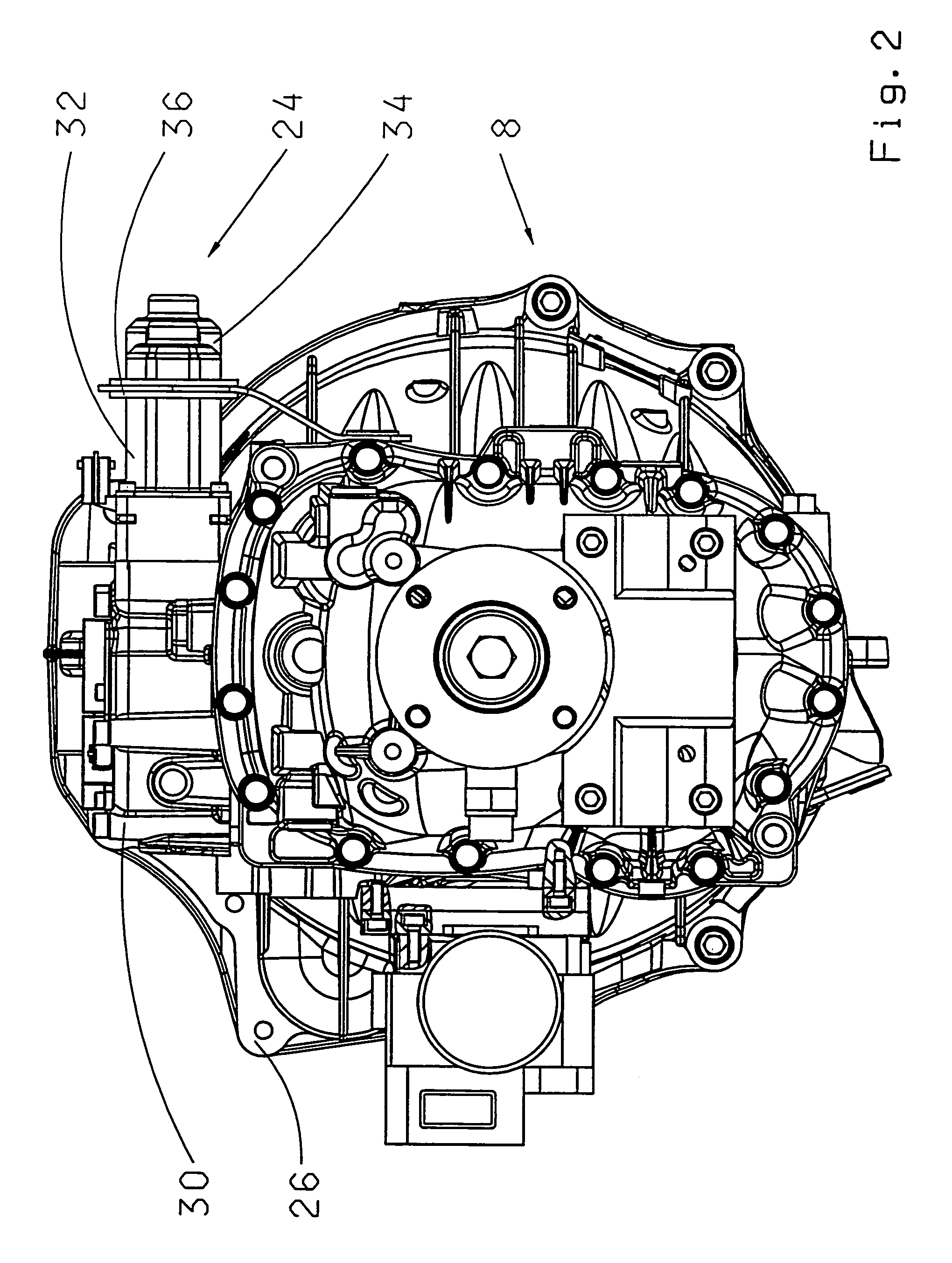
A transmission (8) for a motor vehicle (2) with a housing (26) and a shifting apparatus arranged therein and with an electromechanical transmission actuator (24) with a first electric motor (32) for exercising a selection motion of the shifting device with a second electric motor (34) for exercising a shifting motion of the shifting apparatus and with a control unit (22) for receiving sensor signals, for processing the sensor signals and for emitting control signals to the electric motors (32, 34) the axis of rotation of the first electric motor (32) and the axis of rotation of the second electric motor (34) lie parallel to each other.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Vehicle output control limiter
InactiveUS20020129788A1Minimize impactImprove driving comfort performanceElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsControl theoryPowertrain
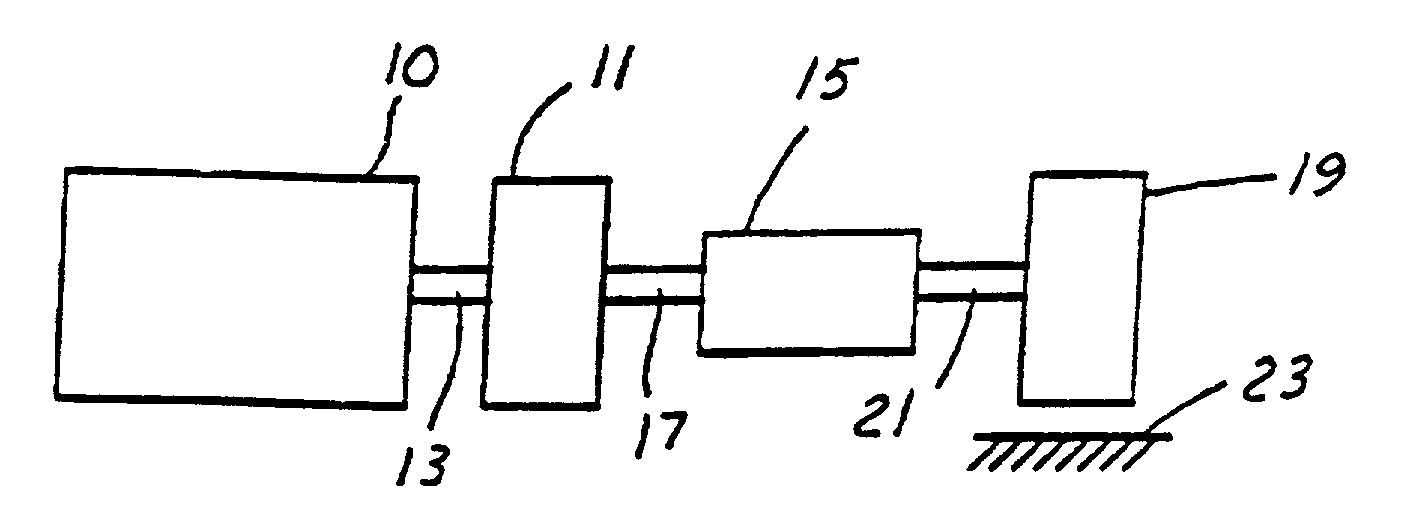
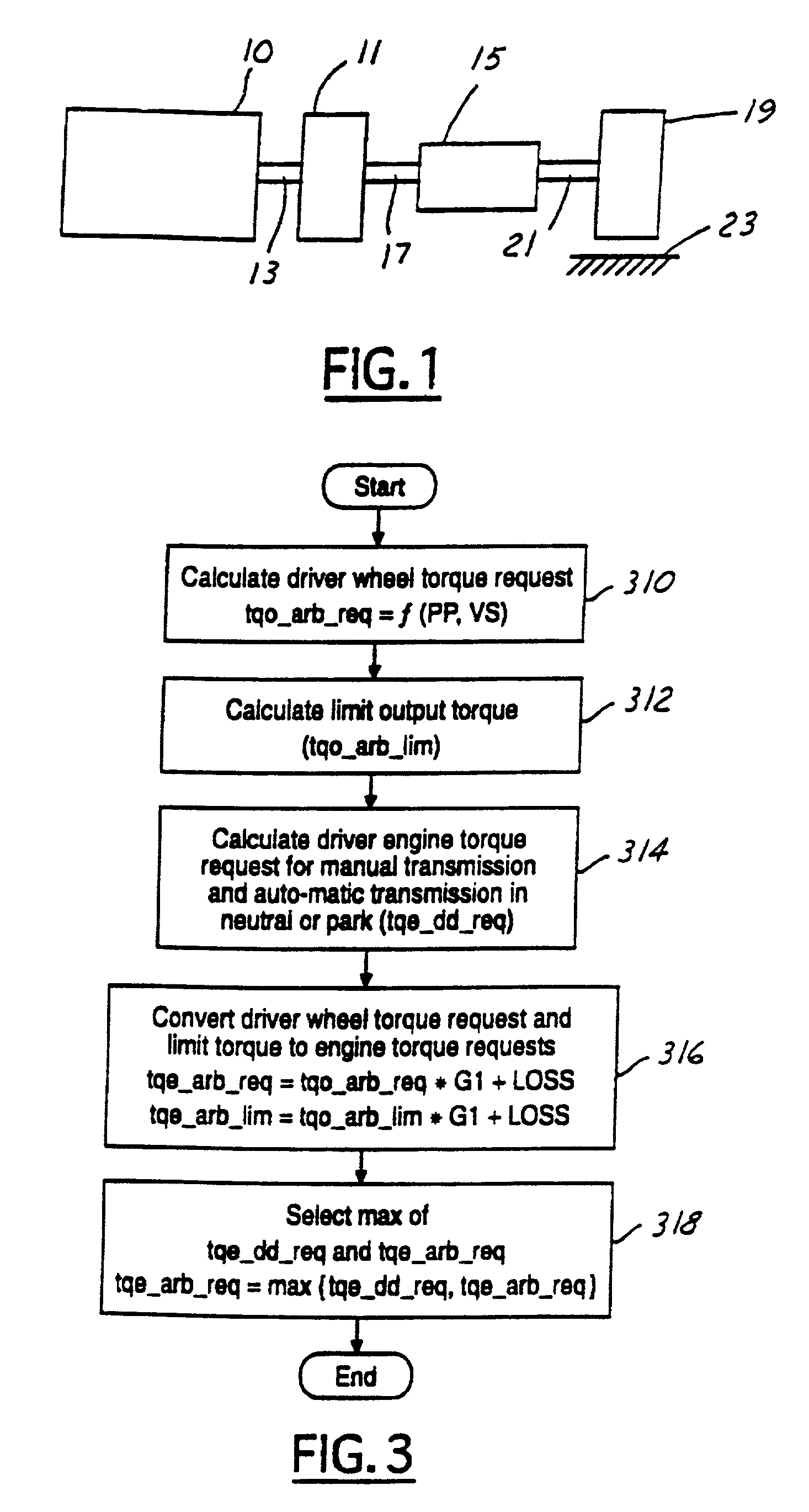
A method is described for limiting a change in torque transmitted through a vehicle powertrain when in a predetermined range. Such a method minimizes transmission gear separation, or "clunk". In one approach, the rate of change of powertrain output is limited when powertrain output is near zero transmitted torque. The limitation is not used under other circumstances so as not to hinder driver performance.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus of controlling acceleration/deceleration of a vehicle
ActiveUS20050234624A1Simple methodDiscomfort given to an operator/passenger may also be reducedAnalogue computers for trafficGear vibration/noise dampingControl theoryAcceleration Unit
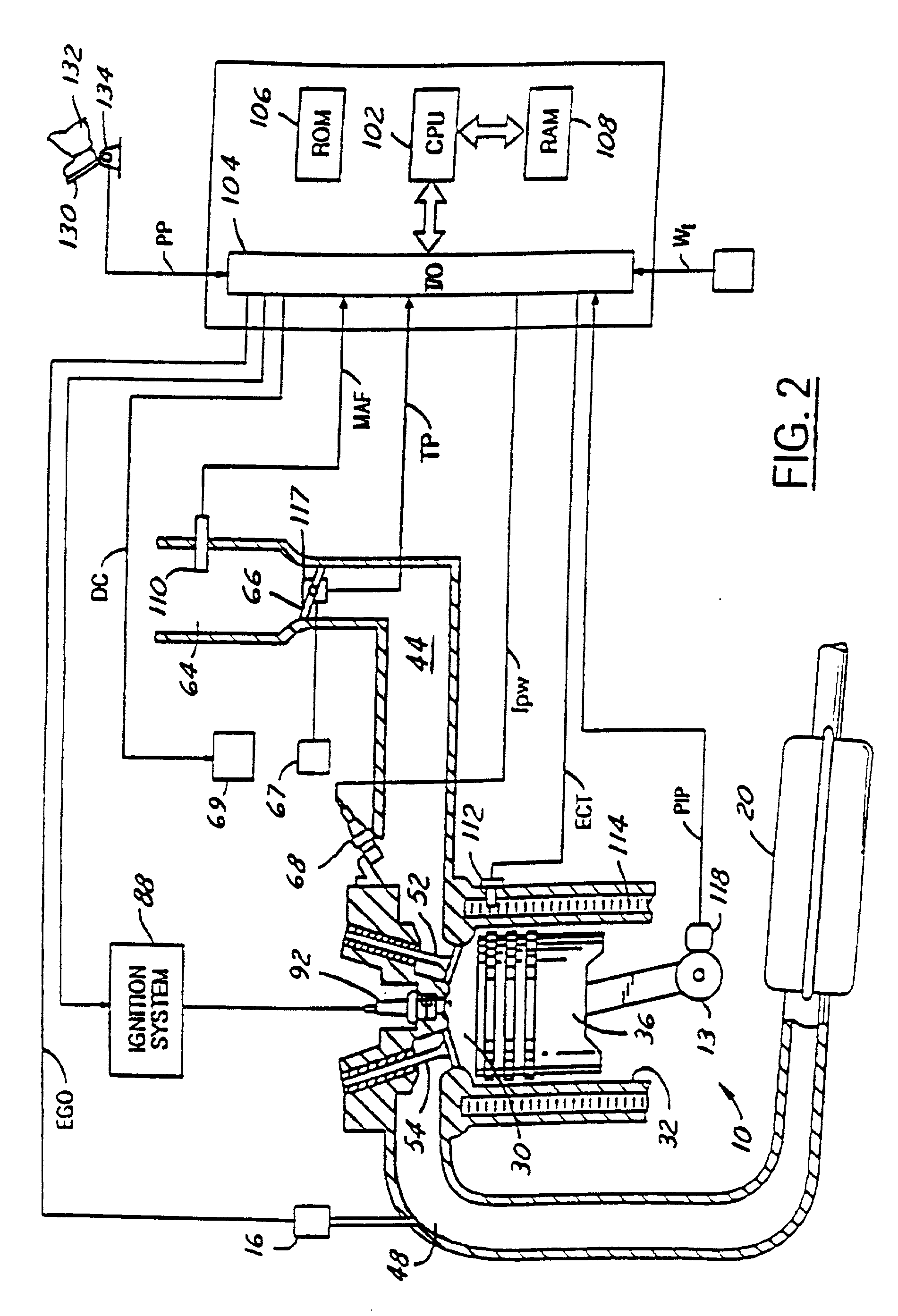
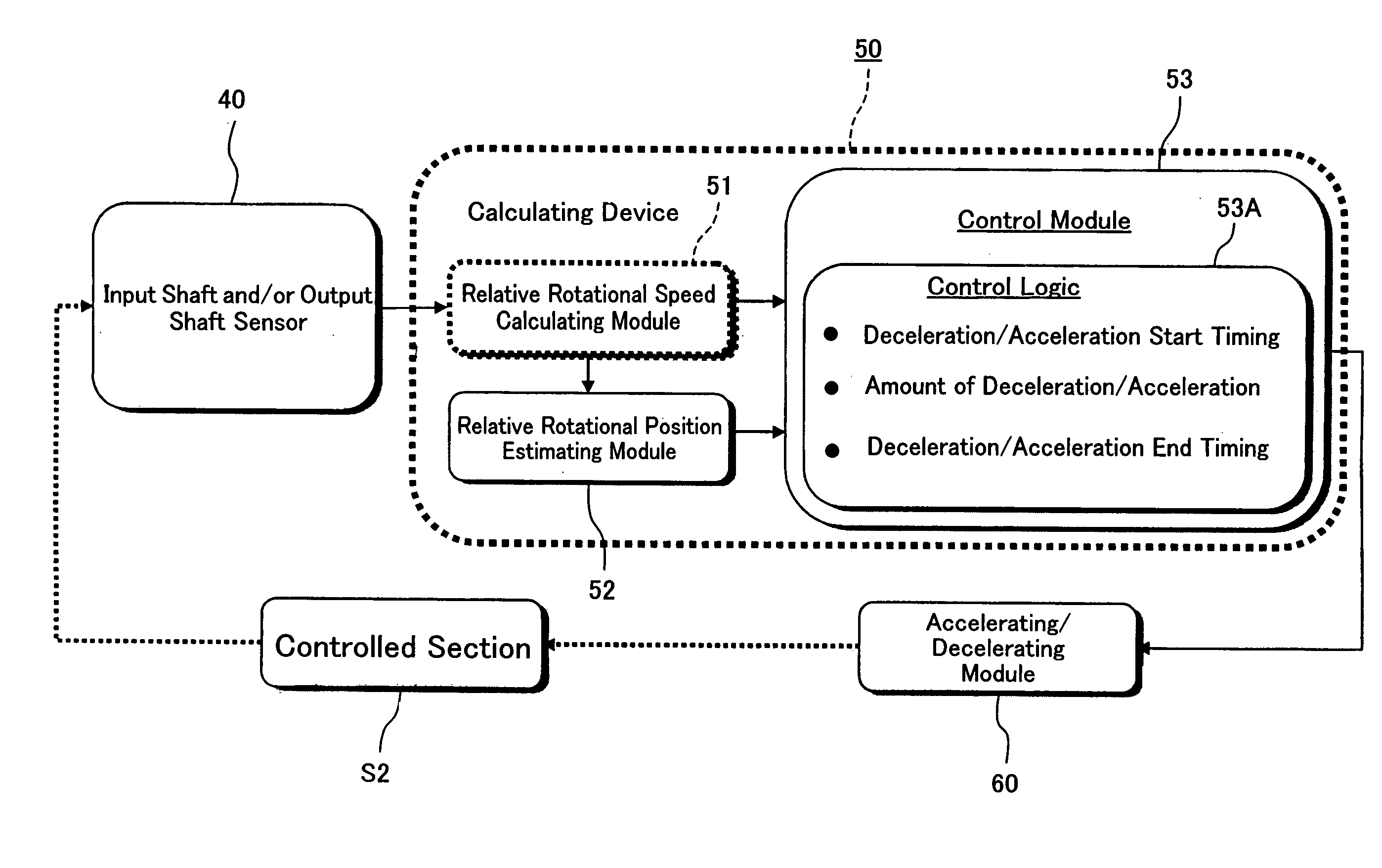
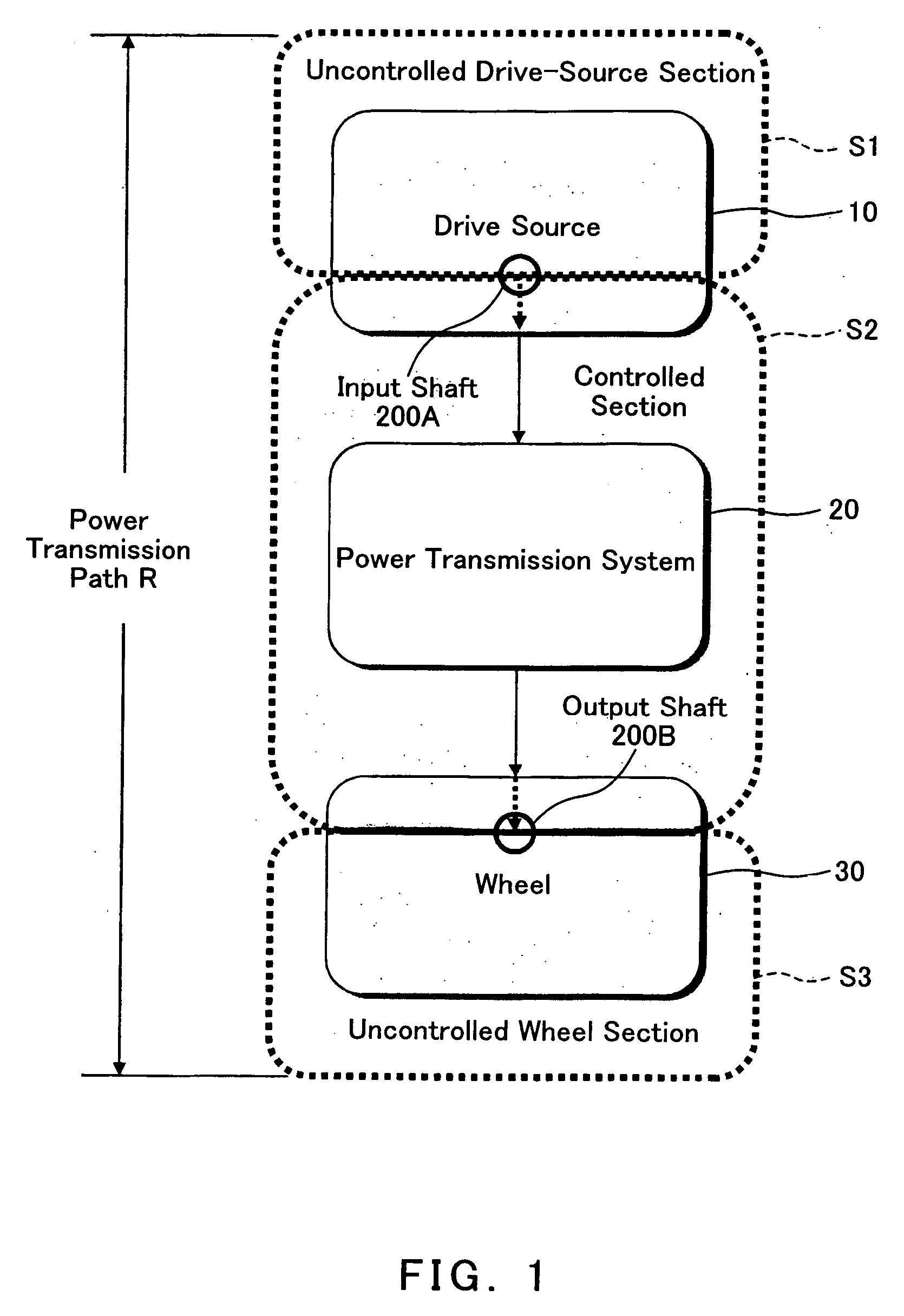
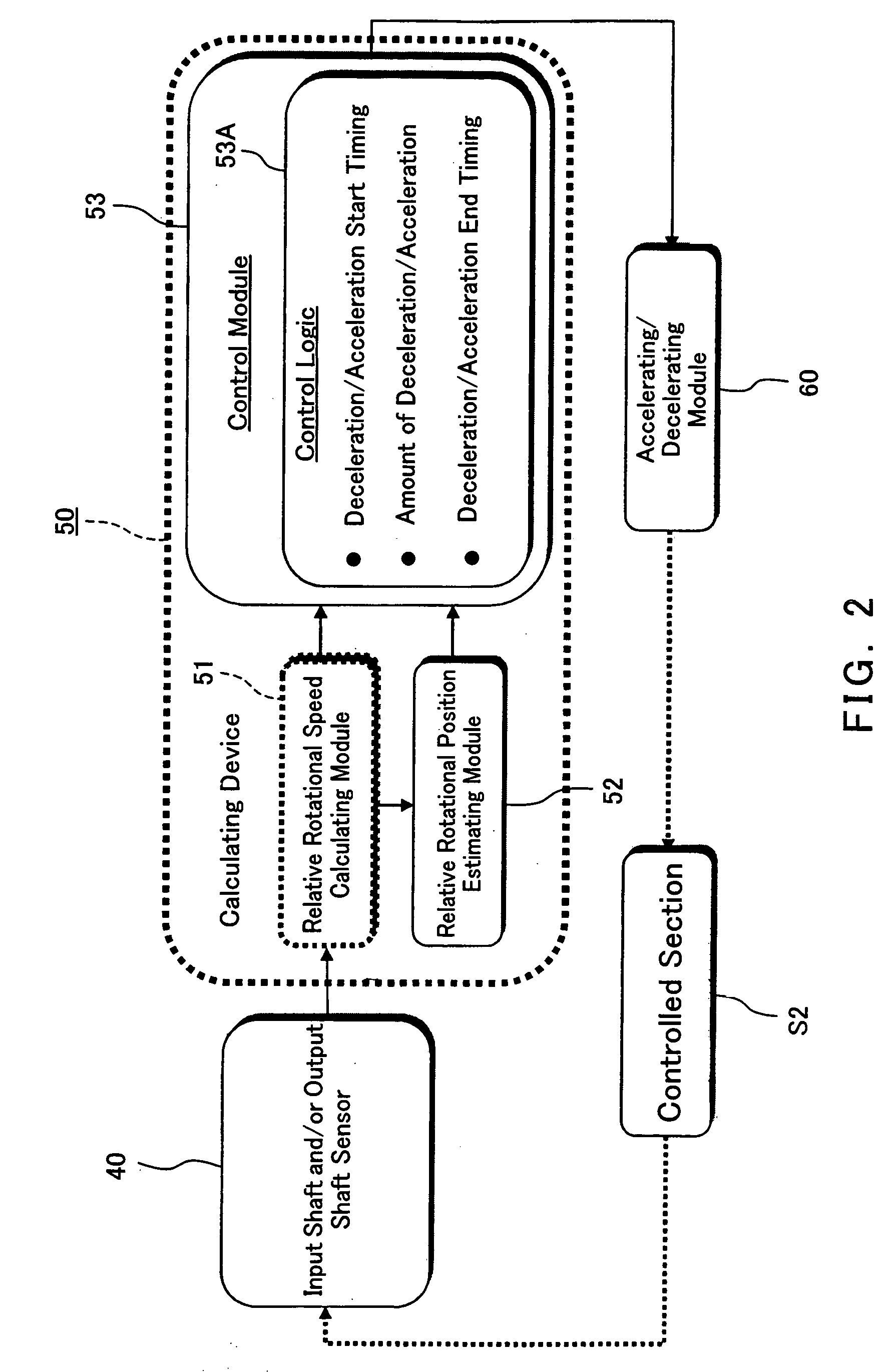
A method of reducing at least one of a contact speed and a transmitting torque between power transmission members, when a slack between the power transmission members in a power transmission path from a drive source to a wheel is apparently gone upon an acceleration or deceleration of the drive source or the wheel. The method includes the steps of detecting an information relating to a rotational speed of an input shaft of a controlled section in the power transmission path, the controlled section being defined as to be reduced in the at least one of the contact speed and the transmitting torque, calculating a relative rotational position between the input shaft and an output shaft of the controlled section based on the detected information relating to the rotational speed of the input shaft, and accelerating or decelerating at least one of the input shaft and the output shaft so as to reduce the at least one of the contact speed and the transmitting torque between the power transmission members based on the calculated relative rotational position.
Owner:KAWASAKI MOTORS LTD
Vehicle control apparatus and vehicle control method
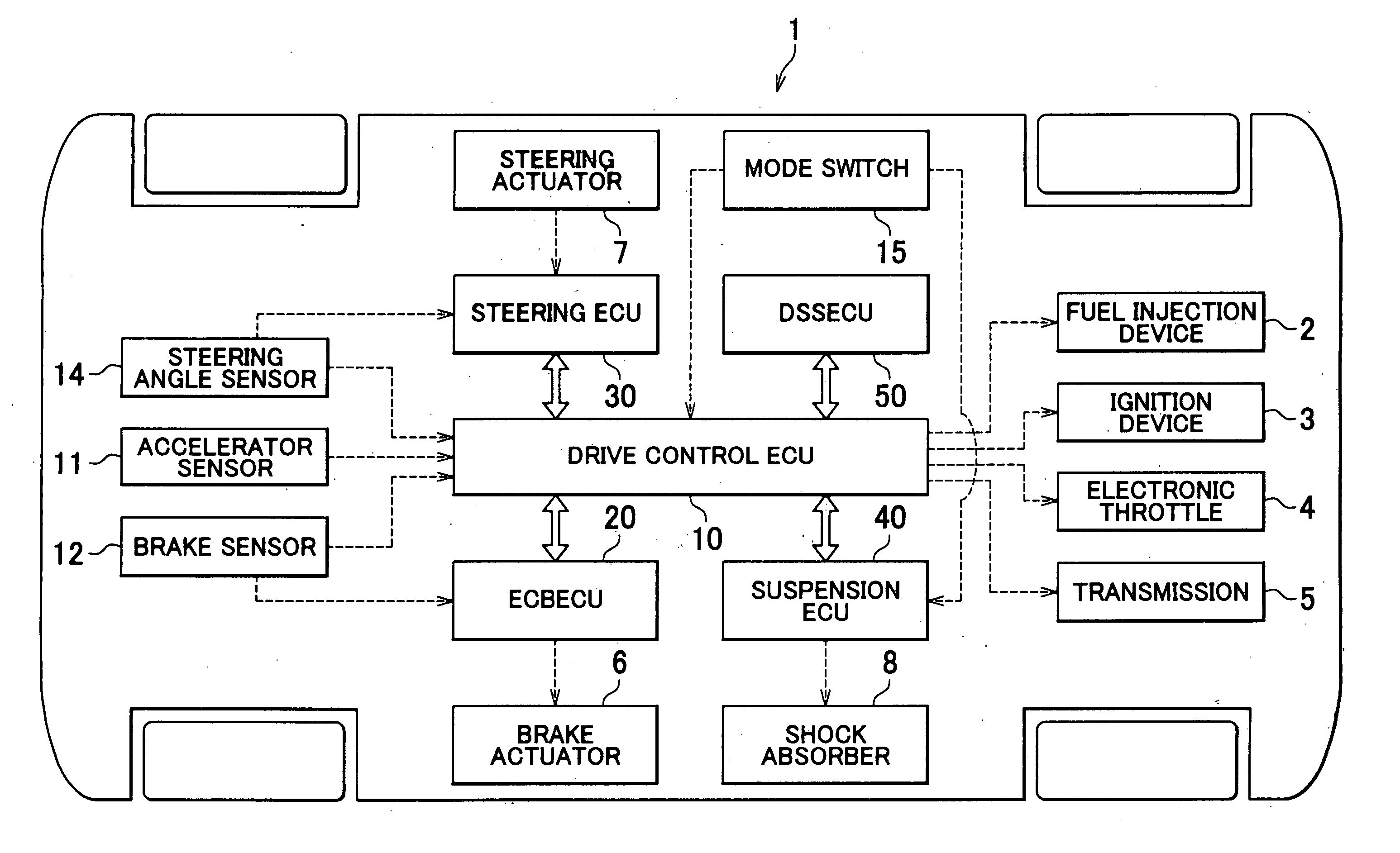
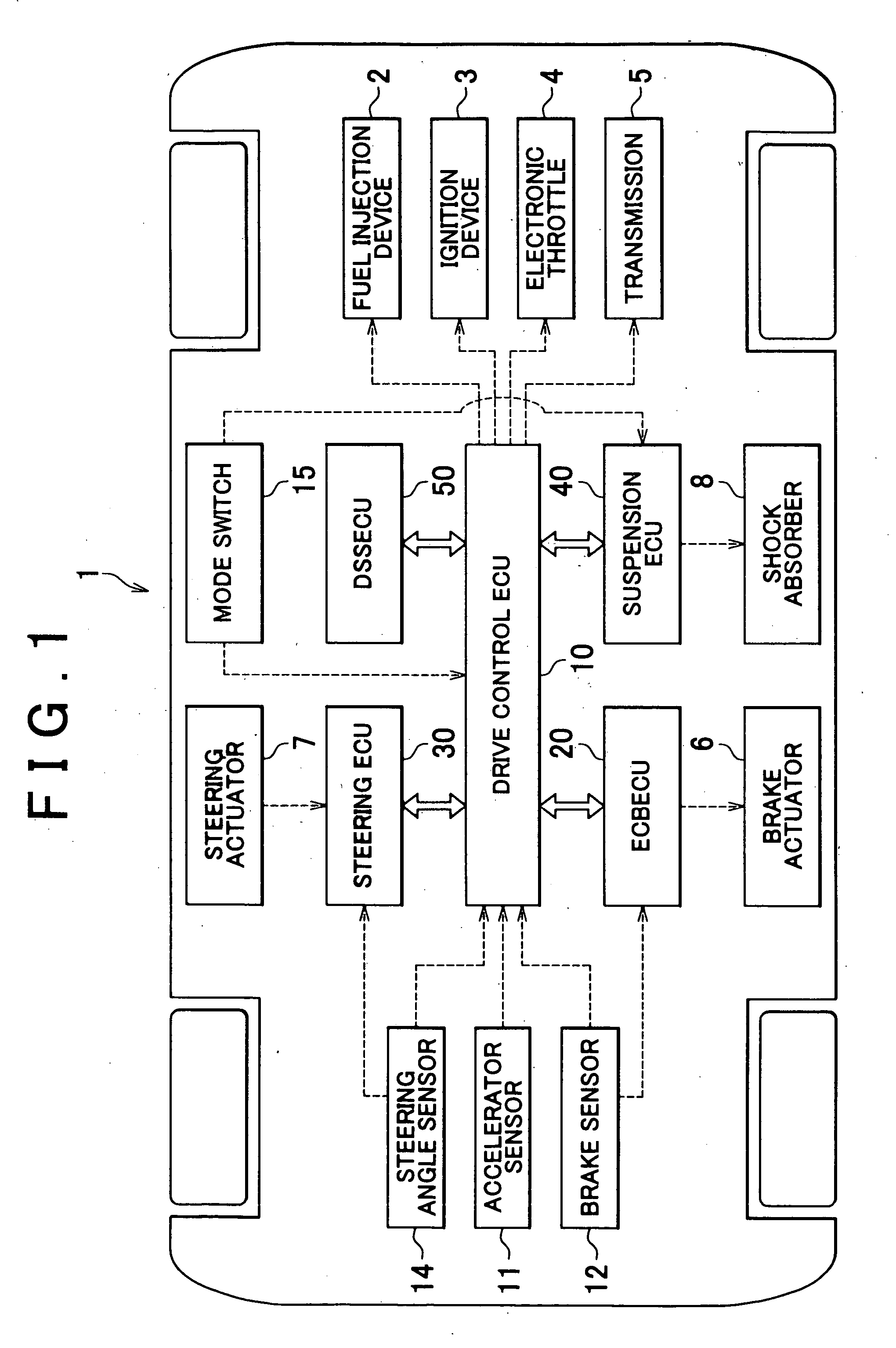
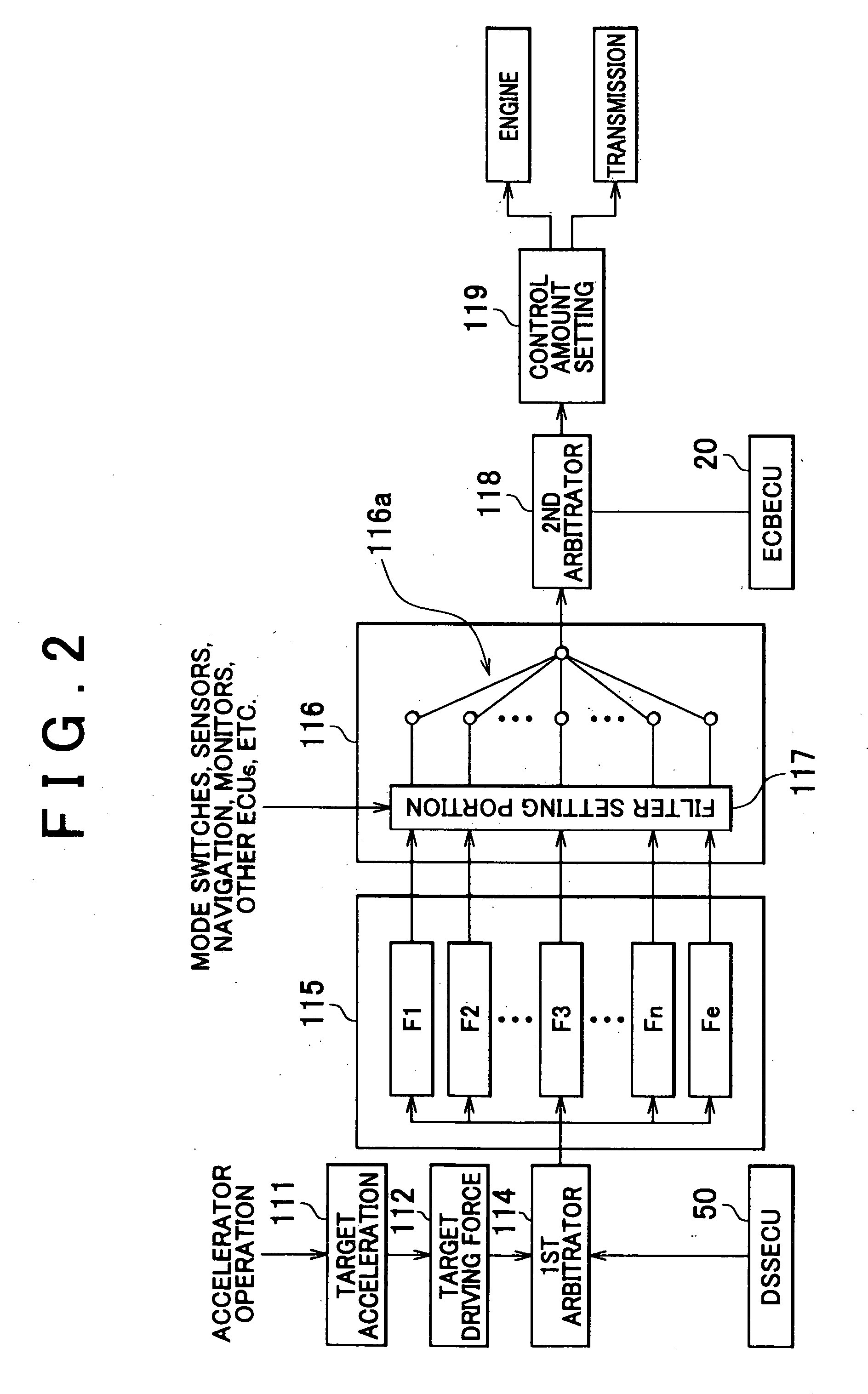
ActiveUS20070004553A1Good vibration controlDigital data processing detailsGear vibration/noise dampingVariatorInternal combustion engine
A vehicle has a drive control ECU that controls an internal combustion engine or a transmission on the basis of a target drive force. The drive control ECU has a first arbitrator that sets the target drive force on the basis of a driver's request and the like, and filters that have individually different damping characteristics and that correct the target drive force from the first arbitrator so that the vibration of a sprung weight of the vehicle is controlled, as well as a switch that includes a switching portion and a filter setting portion. The filter setting portion determines whether a pitching resonance frequency has changed. If having determined that the pitching resonance frequency has changed, the filter setting portion switches the filter having been used for correcting the target drive force to a filter corresponding to a post-change pitching resonance frequency.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
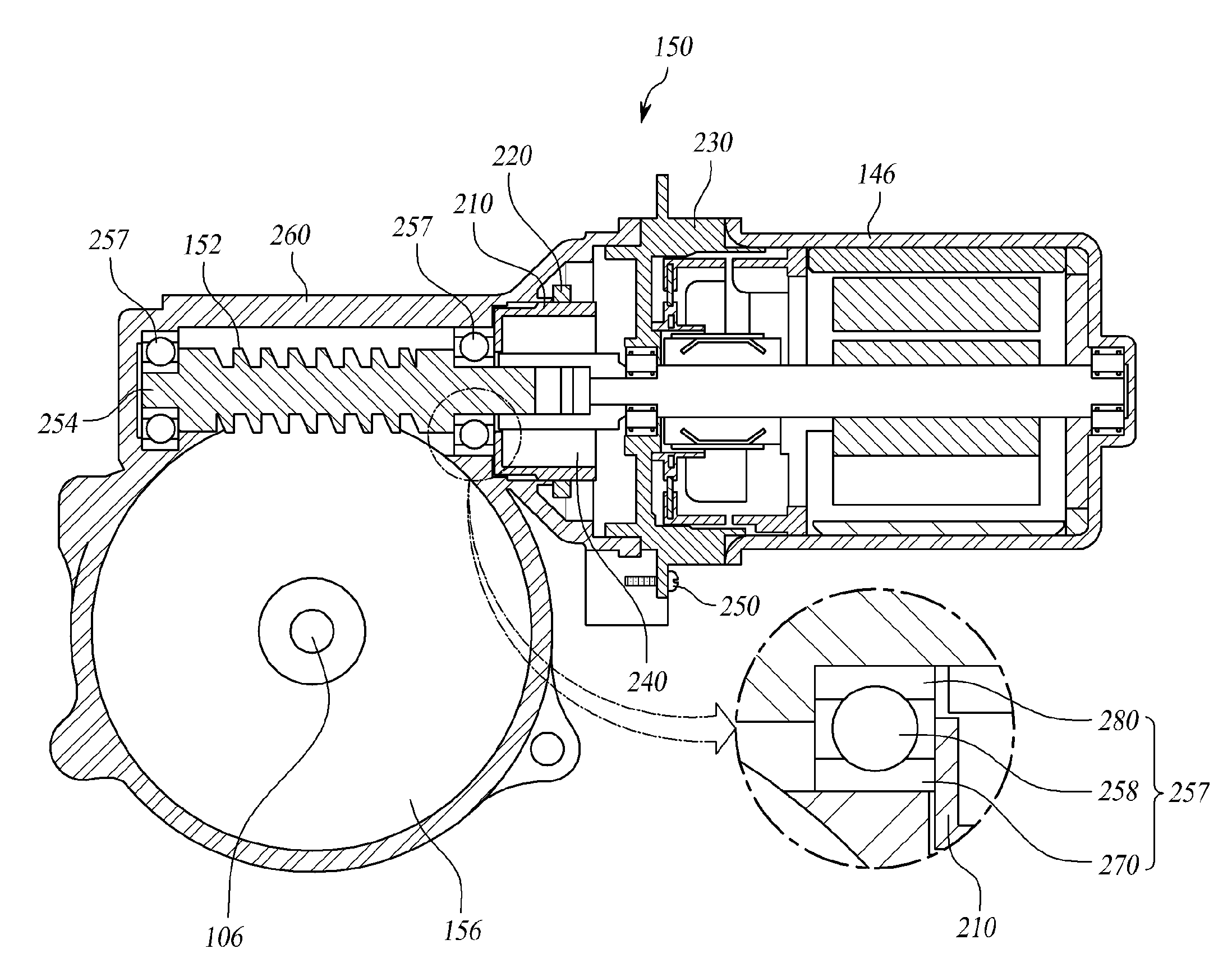
Reducer of electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20110017542A1Reduce rattling noisePleasant driving conditionBall bearingsGear vibration/noise dampingElectric power steeringReduction drive
Disclosed is a reducer of an electric power steering apparatus. The disclosed reducer includes: a worm shaft bearing coupled with an end of the worm shaft's motor shaft coupling portion in such a manner that a ball coupled between an inner wheel and an outer wheel supports rotation of the worm shaft; and a first damper and a second damper which are tightly fitted in one side and the other side of the worm shaft bearing, respectively, while being insertedly-coupled with the worm shaft, so as to support the worm shaft and absorb a rattle noise transferred via the worm shaft, wherein each of the first damper and the second damper is provided with supporting plates at both sides thereof, and between the supporting plates, a damper made of an elastic material is coupled and formed. The reducer of the electric power steering apparatus reduces a rattle noise which occurs by an increase in backlash caused by abrasion of the worm and the worm wheel, or occurs by an impact transferred from a road via a wheel and the steering shaft, thereby providing a pleasant driving condition to the driver.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com