Patents
Literature
22793 results about "Variator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A variator is a device that can change its parameters, or can change parameters of other devices. Often a variator is a mechanical power transmission device that can change its gear ratio continuously (rather than in steps).
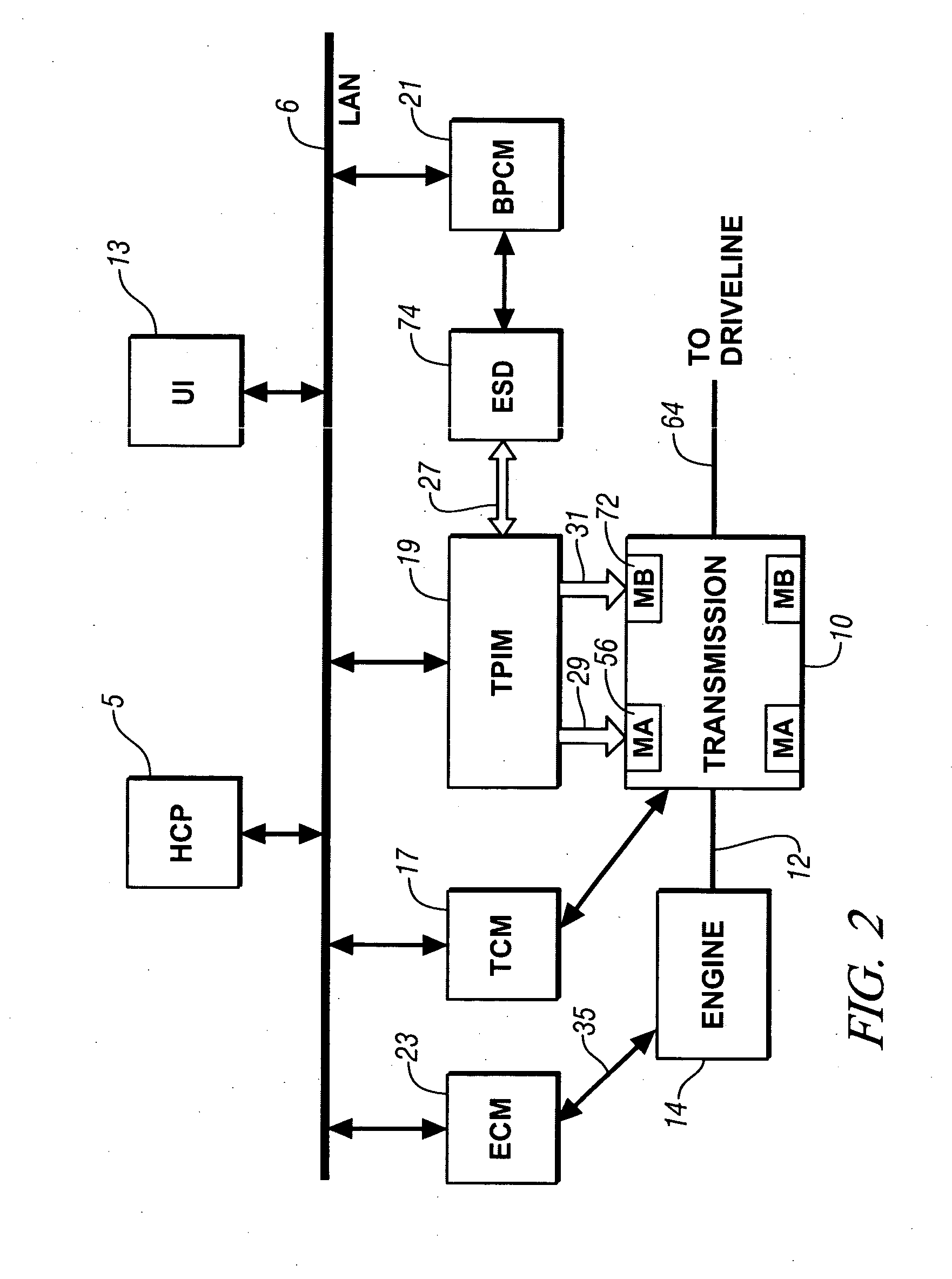
Marine transmission with a cone clutch used for direct transfer of torque
A transmission for a marine propulsion system uses a cone clutch in such a way that, when in a forward gear position, torque is transmitted from an input shaft, or driving shaft, to an output shaft, or driven shaft, solely through the cone clutch. When in forward gear position, driving torque between the driving and driven shafts is not transmitted through any gear teeth. When in reverse gear position, torque is transmitted through an assembly of the bevel gears.
Owner:BRUNSWICK CORPORATION
Automatic transmission for a power tool
Owner:TECHTRONIC POWER TOOLS TECHNOLOGY LTD
Transmission
InactiveUS7028570B2Easy to participateSmooth connectionTilling equipmentsToothed gearingsDrive wheelTransmitted power
A transmission for a working machine including a drive transmission mechanism and a working transmission mechanism operated by swinging a shift lever is provided. The drive transmission mechanism has a key-sliding transmission mechanism axially mounted on a drive shaft. The key-sliding transmission mechanism causes a selected one of a plurality of gears rotatably mounted on the drive shaft and the drive shaft to rotate together to transmit power to drive wheels.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
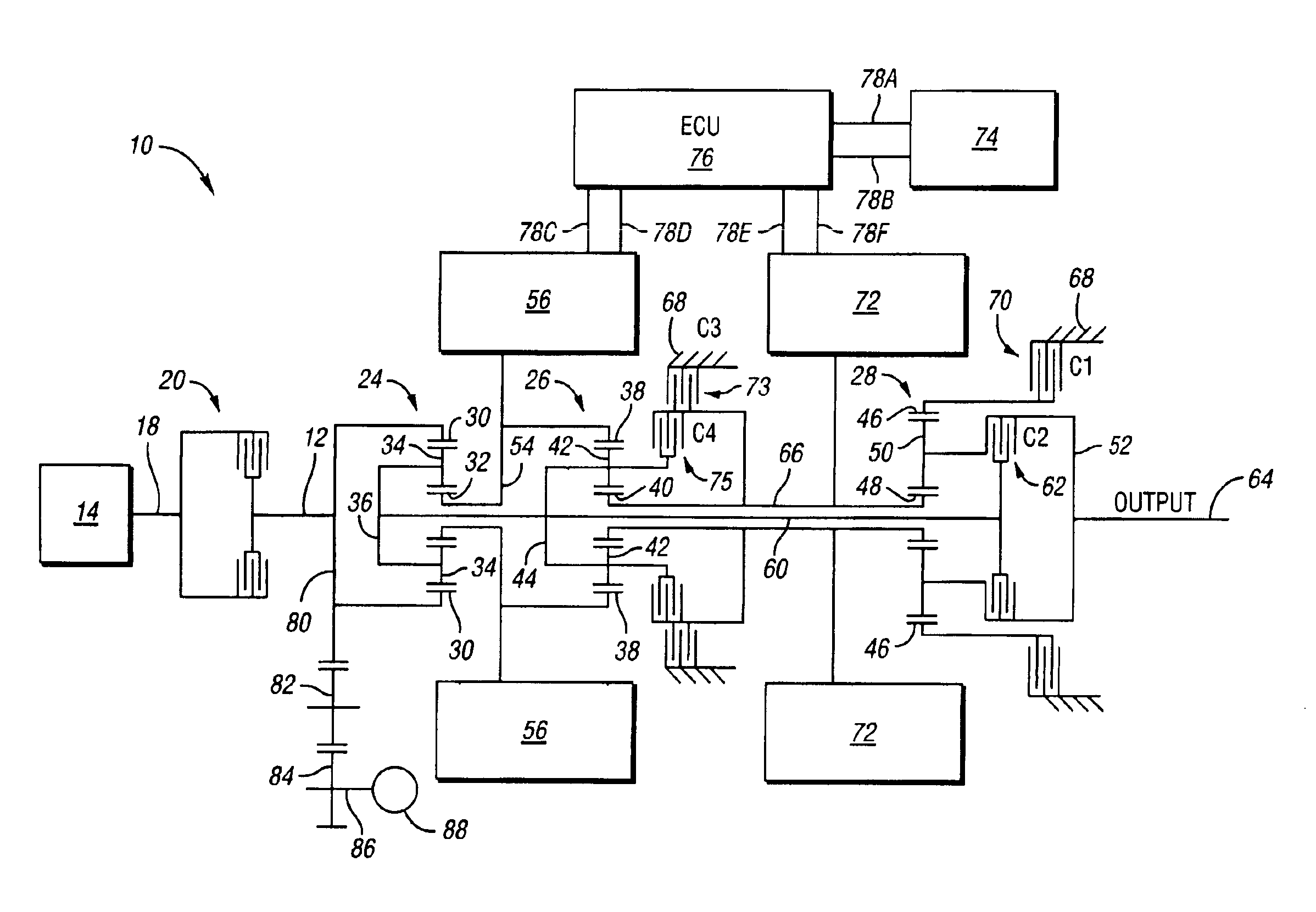
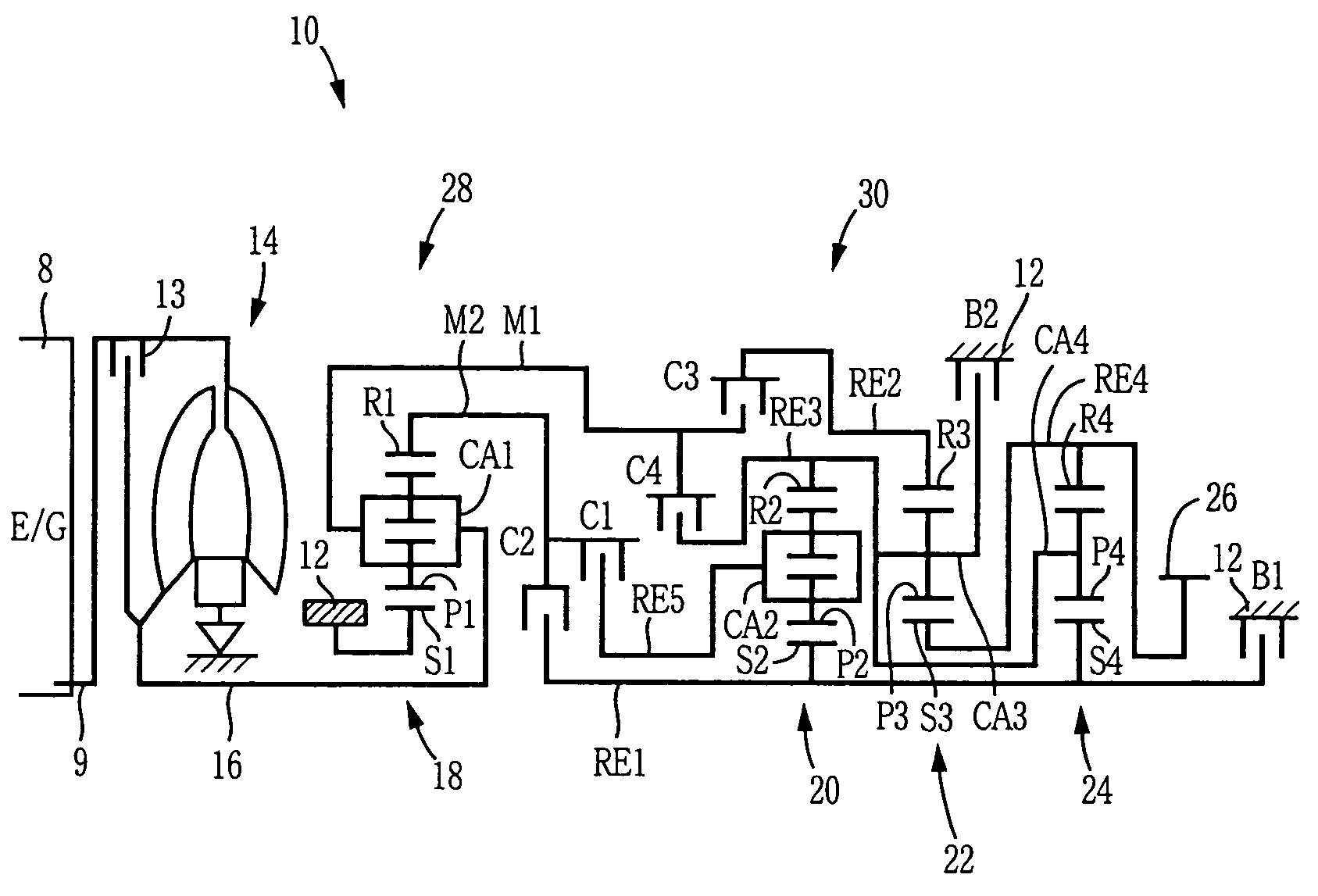
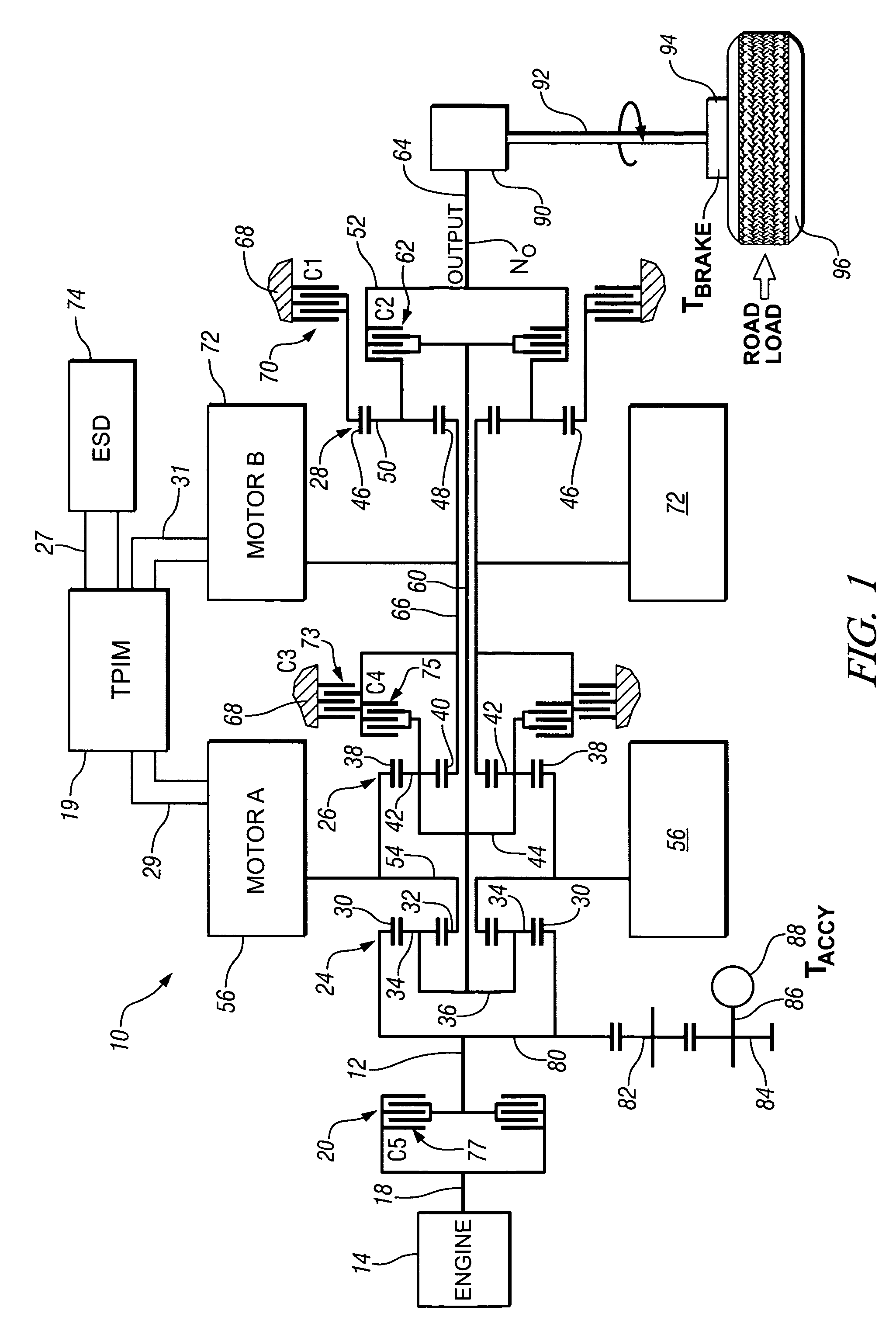
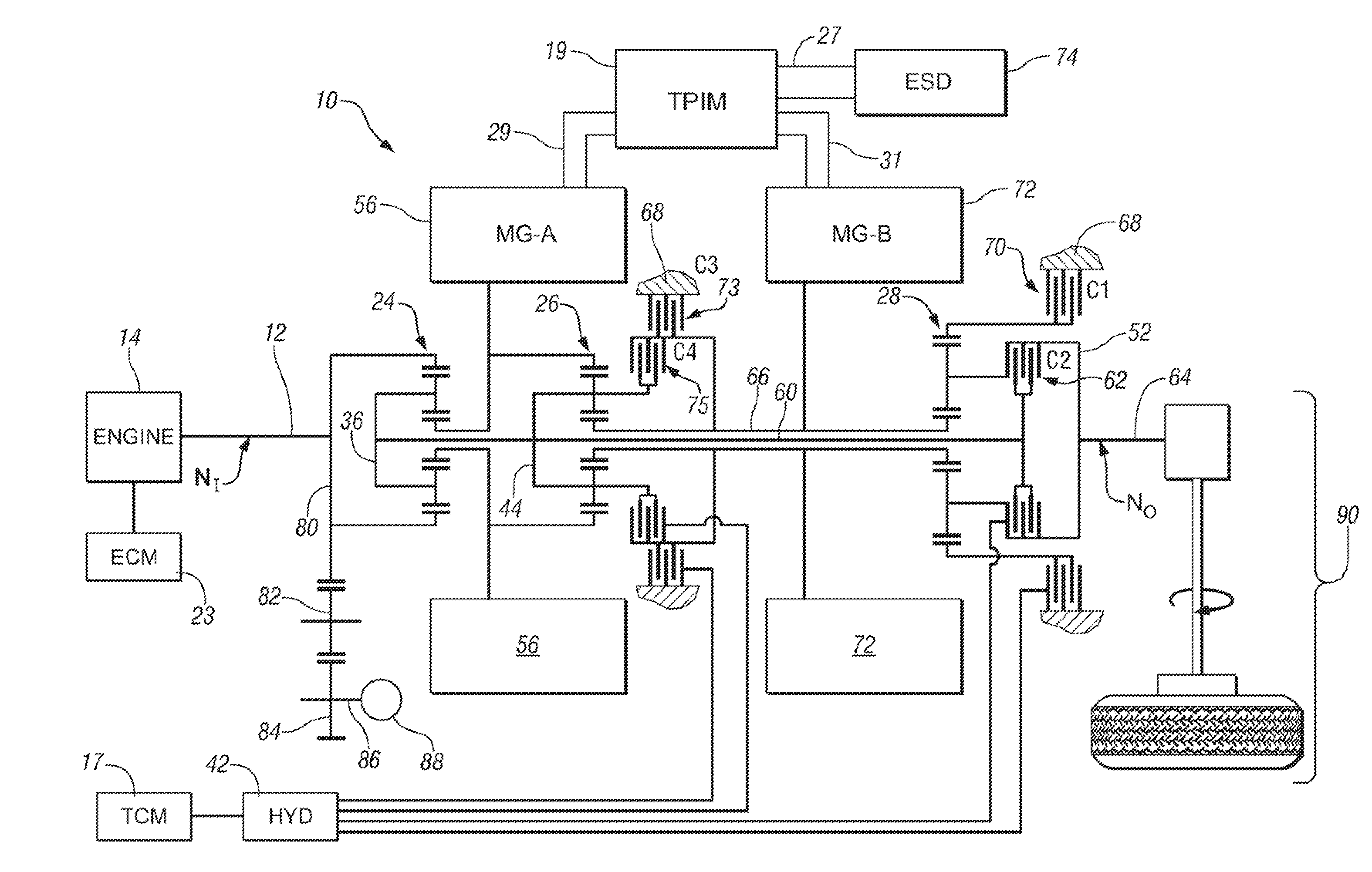
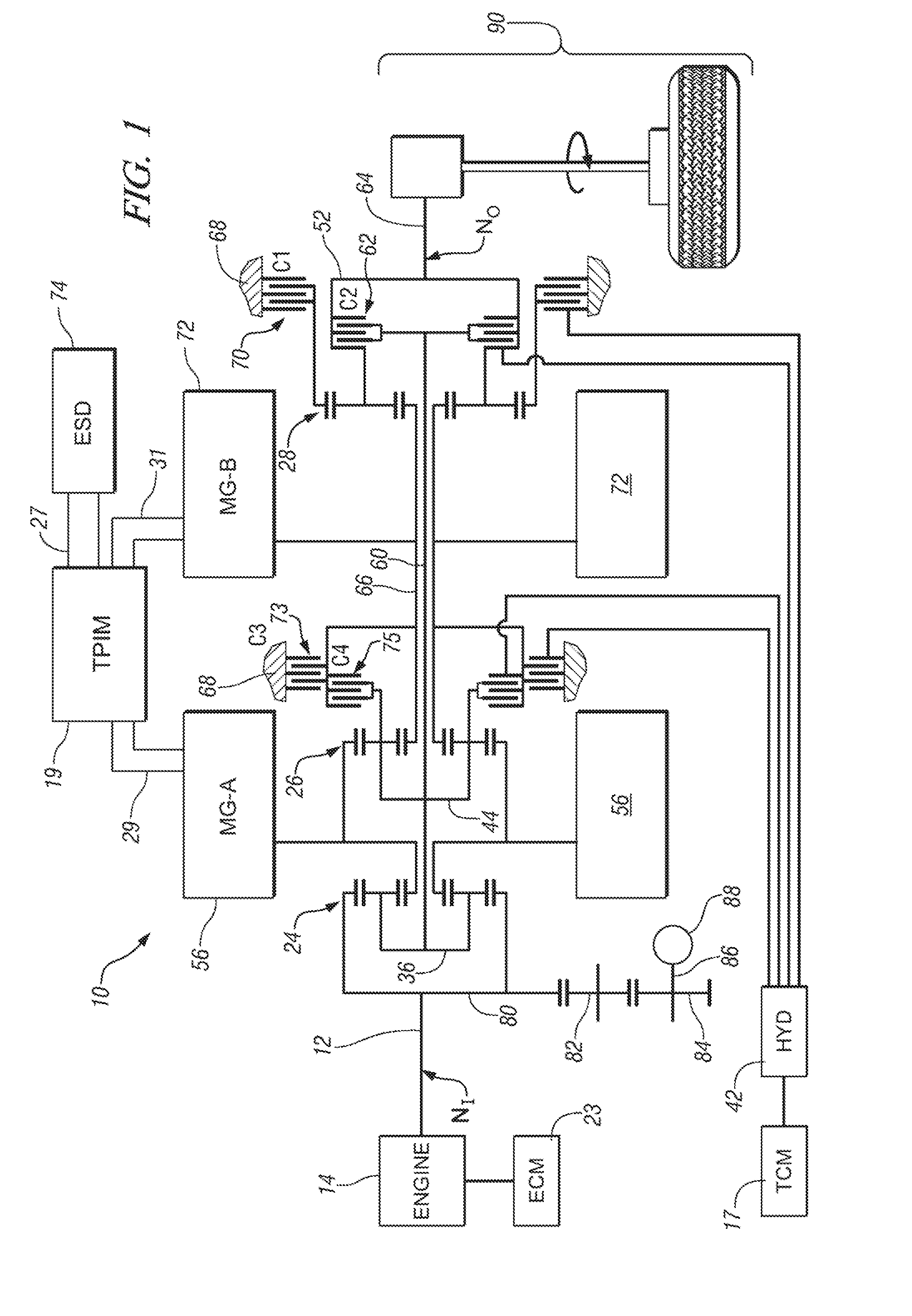
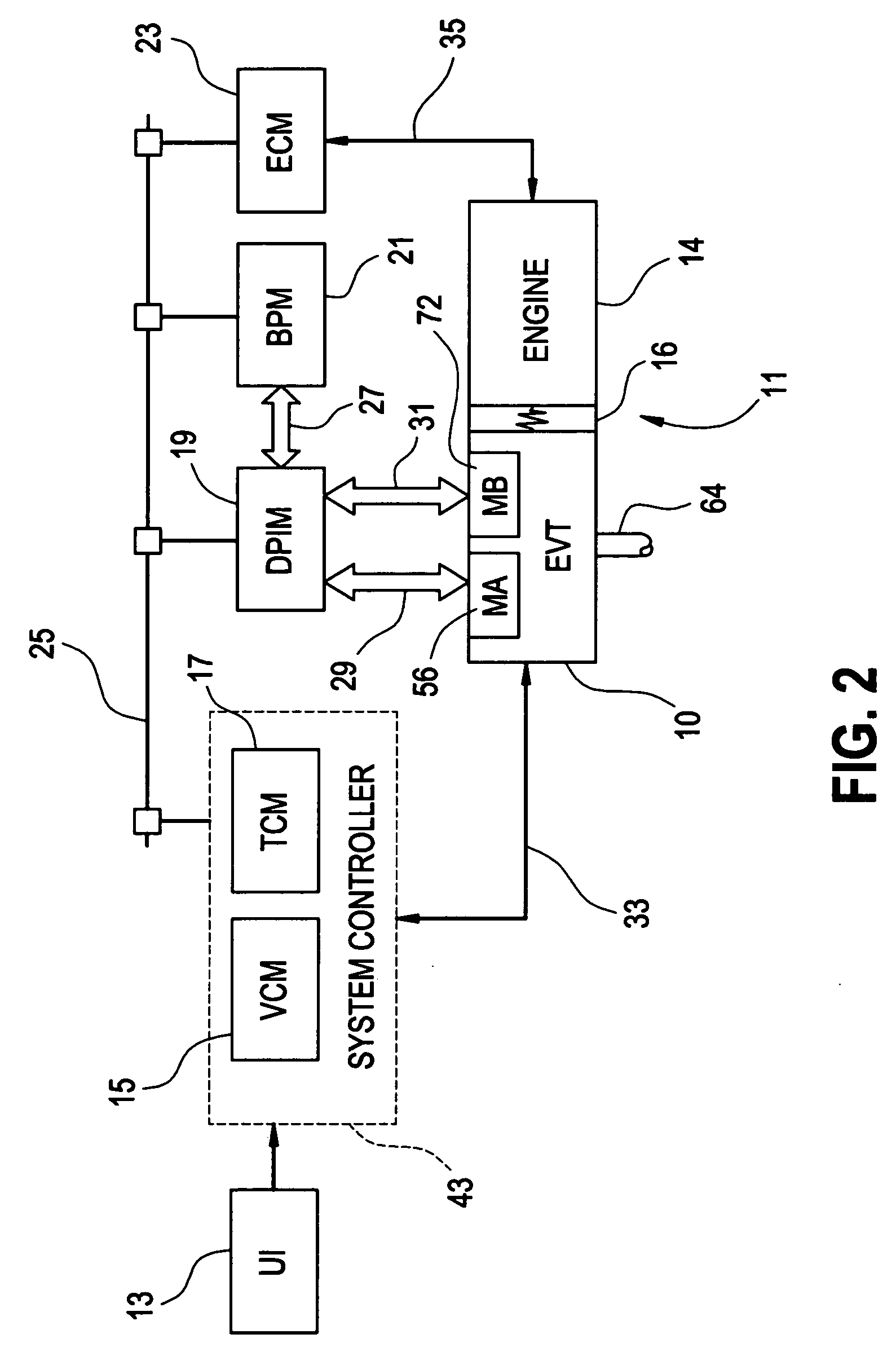
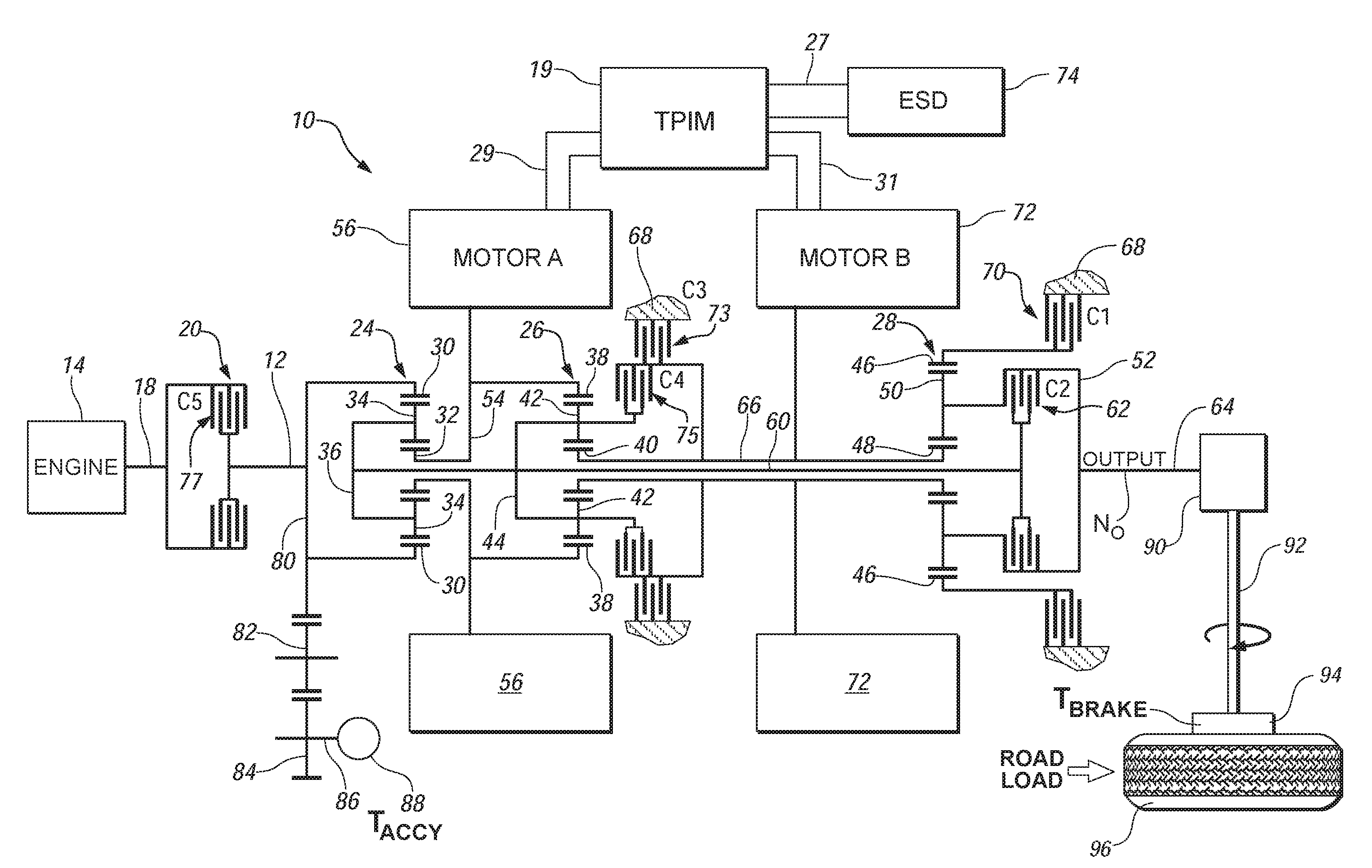
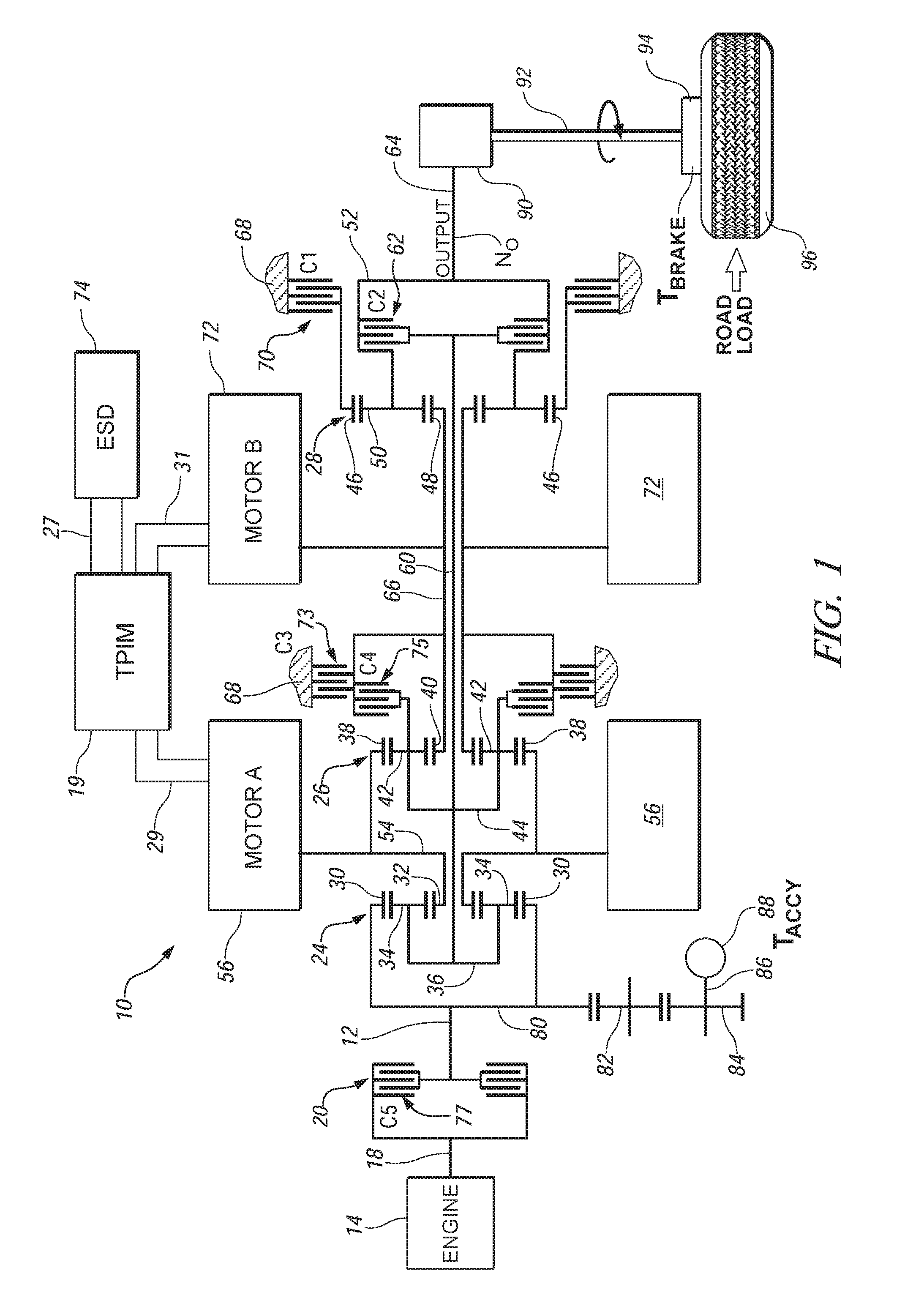
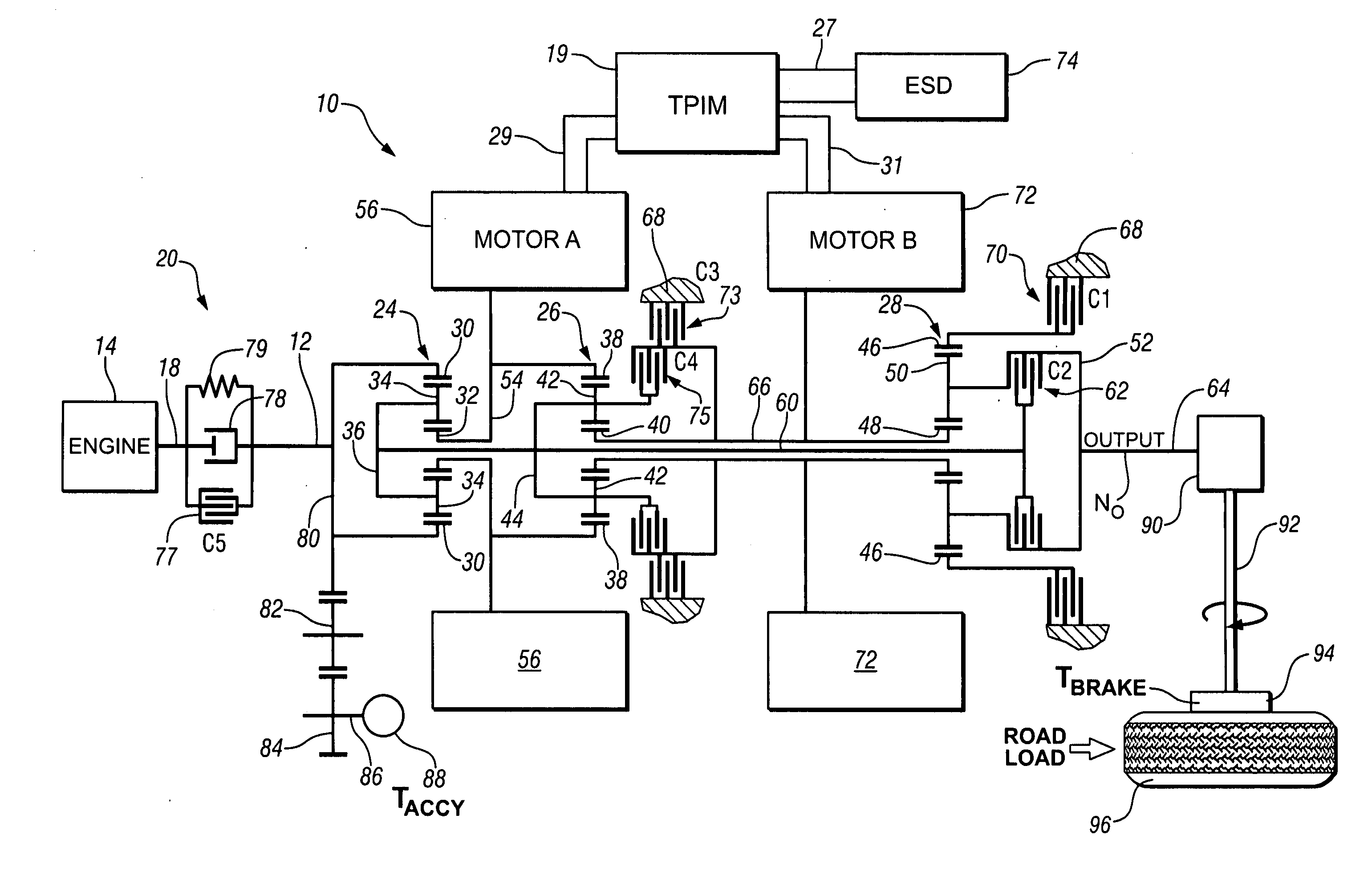
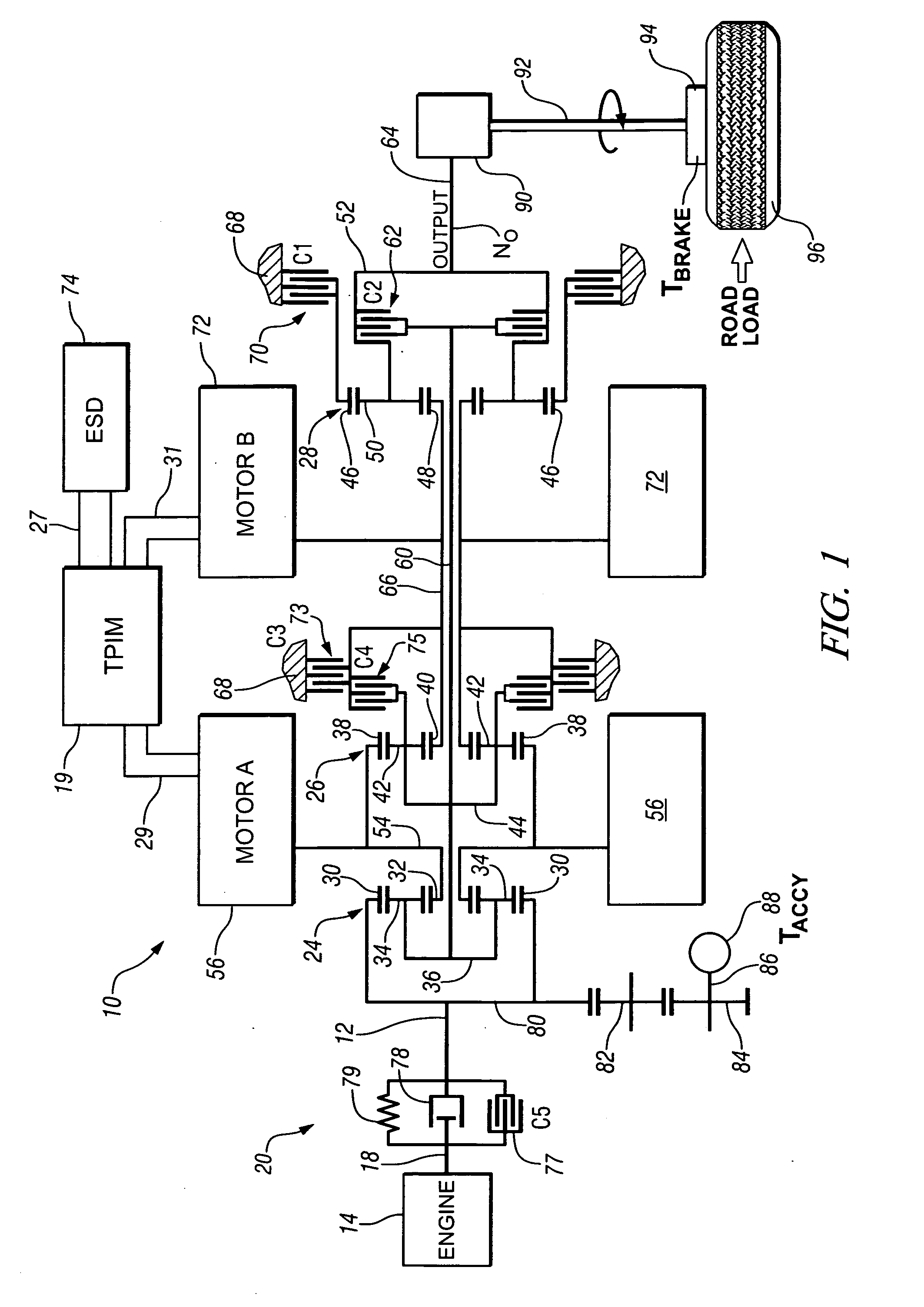
Two-mode, compound-split, hybrid electro-mechanical transmission having four fixed ratios
ActiveUS6953409B2Increase powerCost-effectivelyElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingFixed ratioEngineering
A two-mode, compound-split, electra-mechanical transmission utilizes an input member for receiving power from an engine, and an output member for delivering power from the transmission. First and second motor / generators are operatively connected to an energy storage device through a control for interchanging electrical power among the storage device, the first motor / generator and the second motor / generator. The transmission employs three planetary gear sets. Each planetary gear arrangement utilizes first, second and third gear members. Moreover, one gear member of the first or second planetary gear set is operatively connected to the input member, and one gear member of the third planetary gear set is selectively connected to ground. A lock-up clutch selectively locks two of the planetary gear sets in a 1:1 ratio.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Hybrid propulsion system for road vehicles
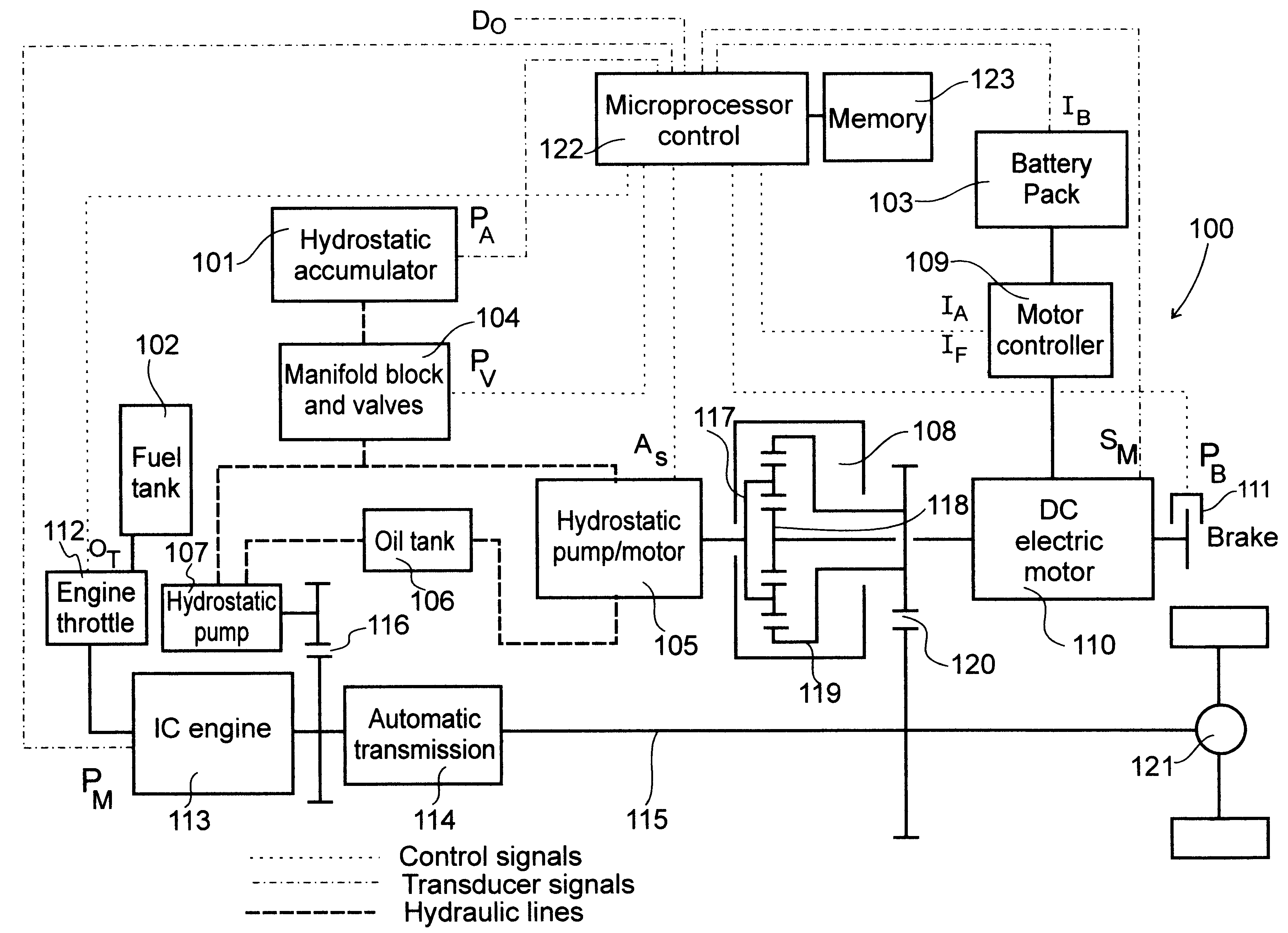
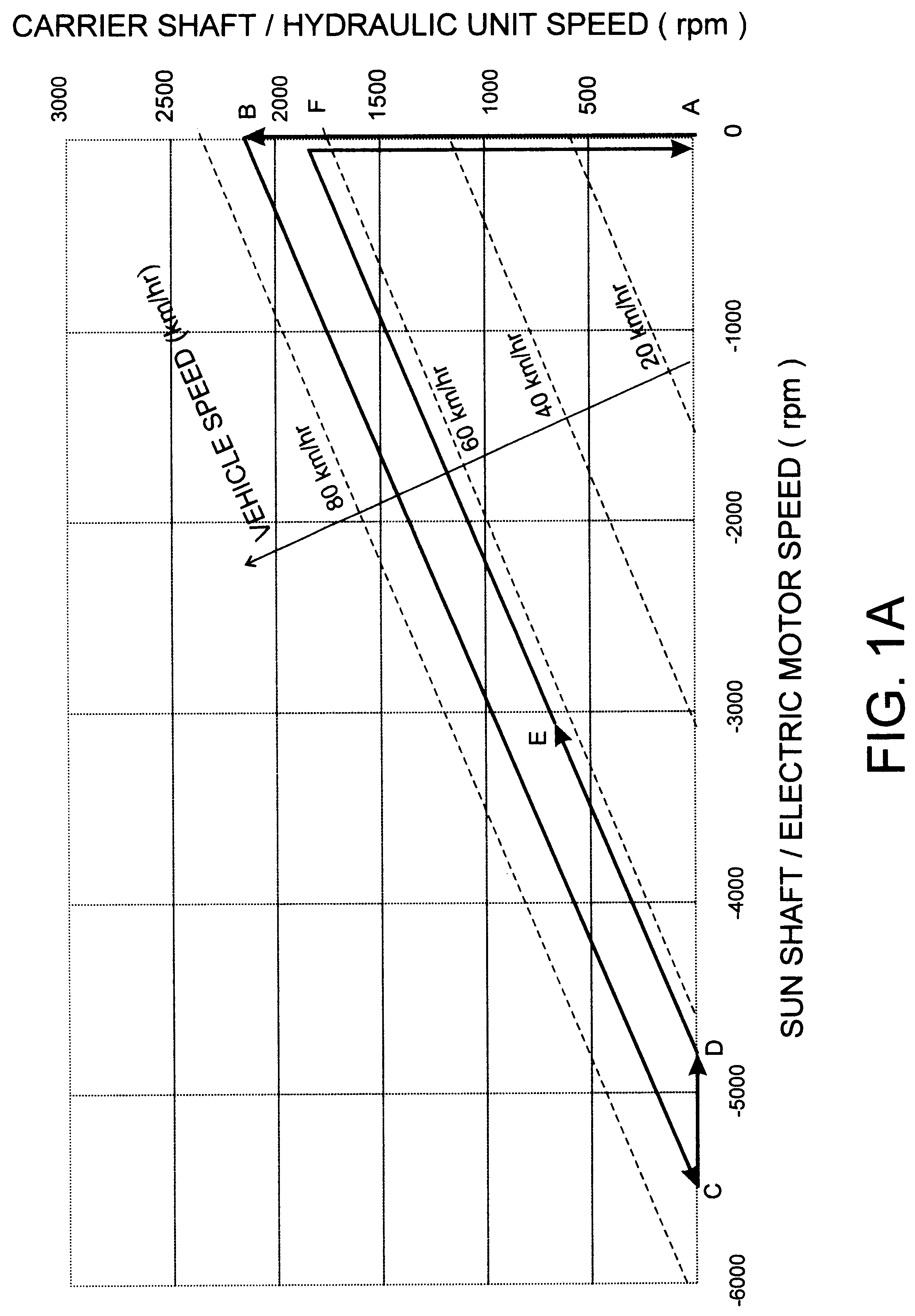
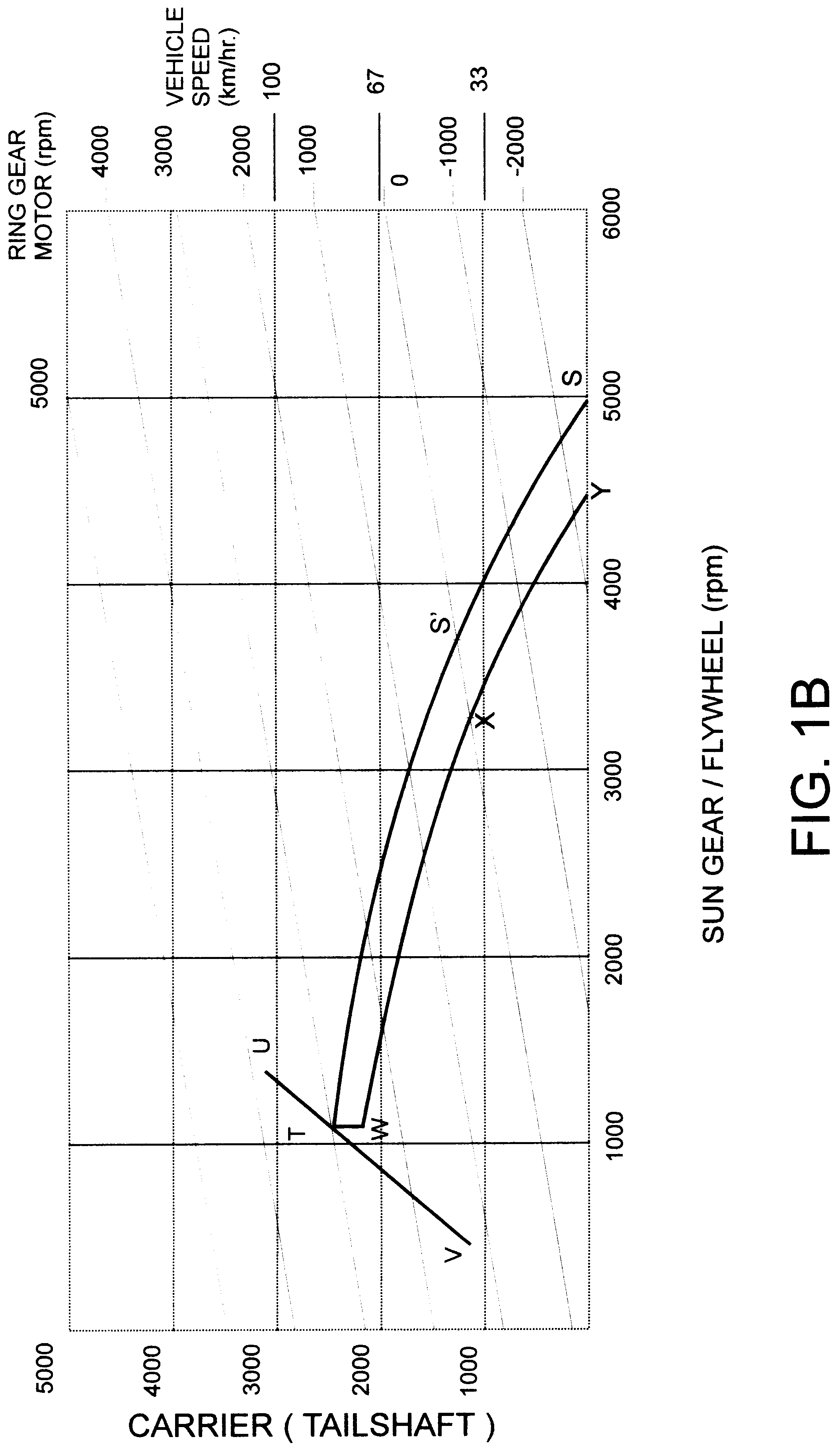
A hybrid propulsion system (100) for use in road vehicle operations, which propulsion system includes a power splitting mechanical transmission (108), suitably a three shaft epicyclic gearbox (117, 118, 119), for coupling to a tailshaft (115) of the vehicle; a first drive unit (105) arranged for regenerative operation and coupled to the power splitting mechanical transmission (108); a second drive unit (110) arranged for regenerative operation and coupled, independently of said first drive unit, to the power splitting mechanical transmission (108); a non-regenerative third drive unit (113) for coupling, in parallel to said power splitting mechanical transmission, to the tailshaft; and a propulsion control system (122) for coordinating operation of the drive units in accordance with a plurality of predetermined modes corresponding to a drive cycle of the vehicle. Two forms of the invention are disclosed, being suited to non-transit and transit operations, respectively. Methods for the optimal control of the hybrid propulsion system of each form of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:TRANSPORT ENERGY SYST
Planetary-gear-type multiple-step transmission for vehicle
InactiveUS7101305B2Small axial lengthShorten the axial lengthToothed gearingsTransmission elementsGear wheelEngineering
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
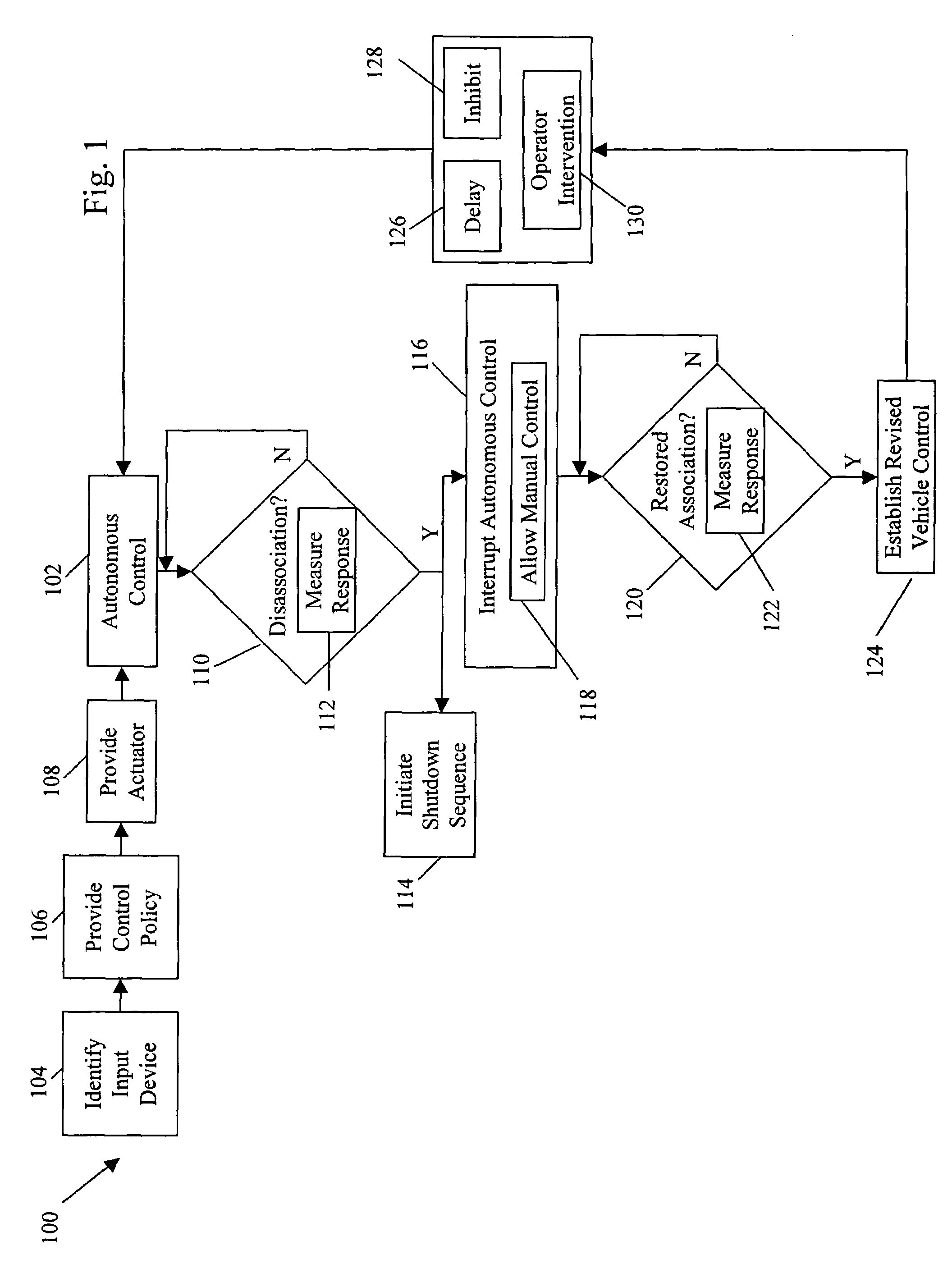
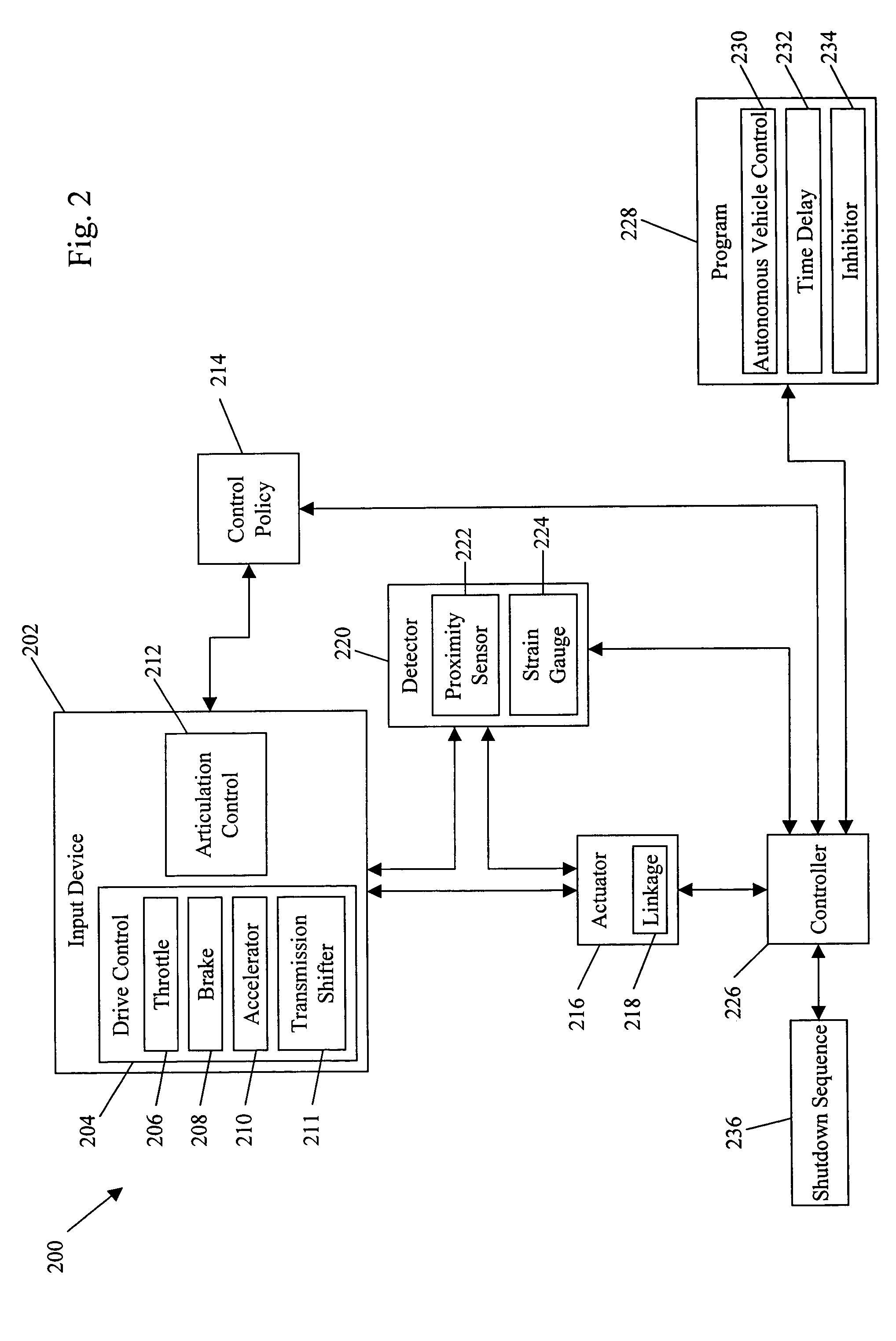
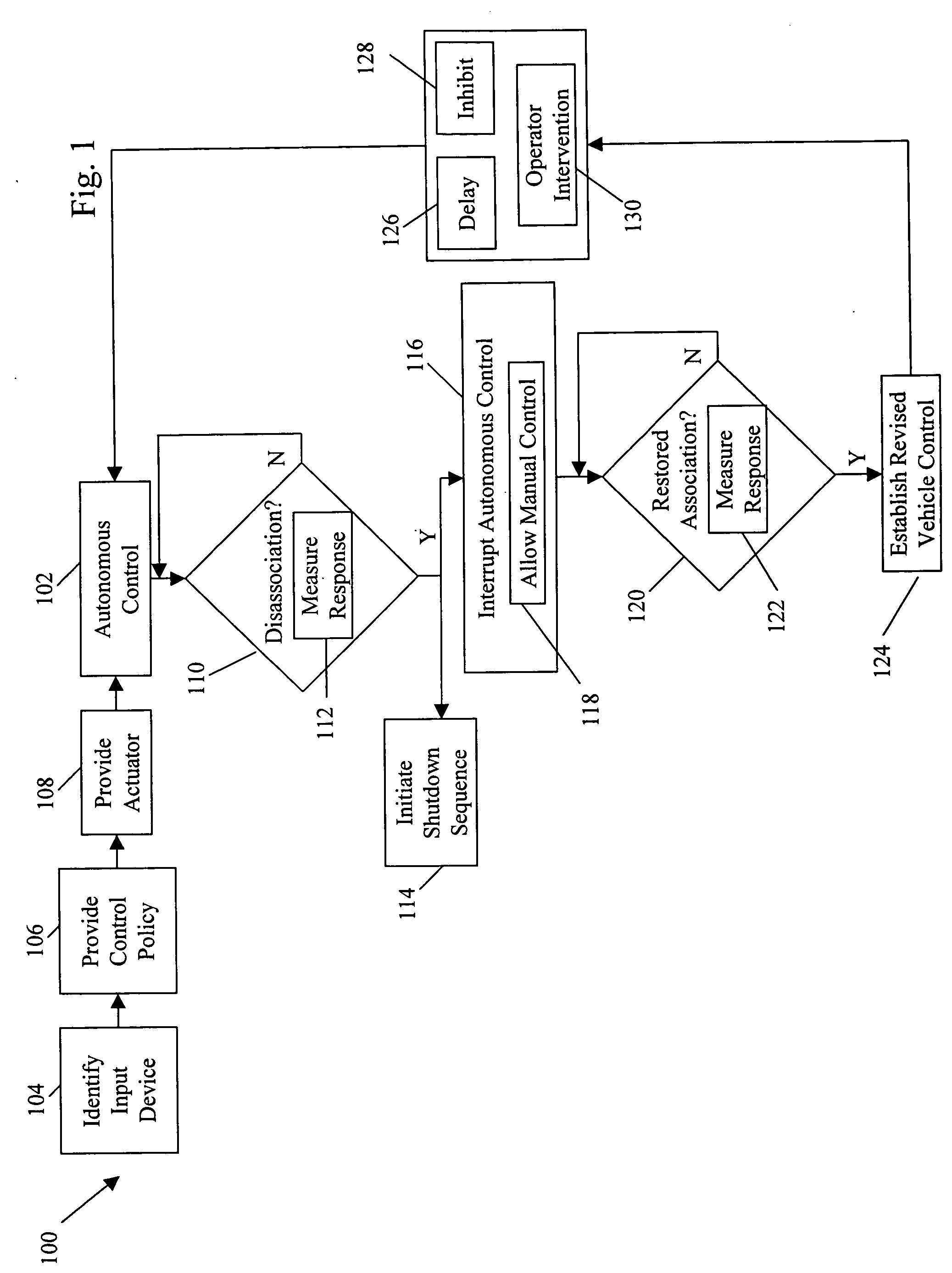
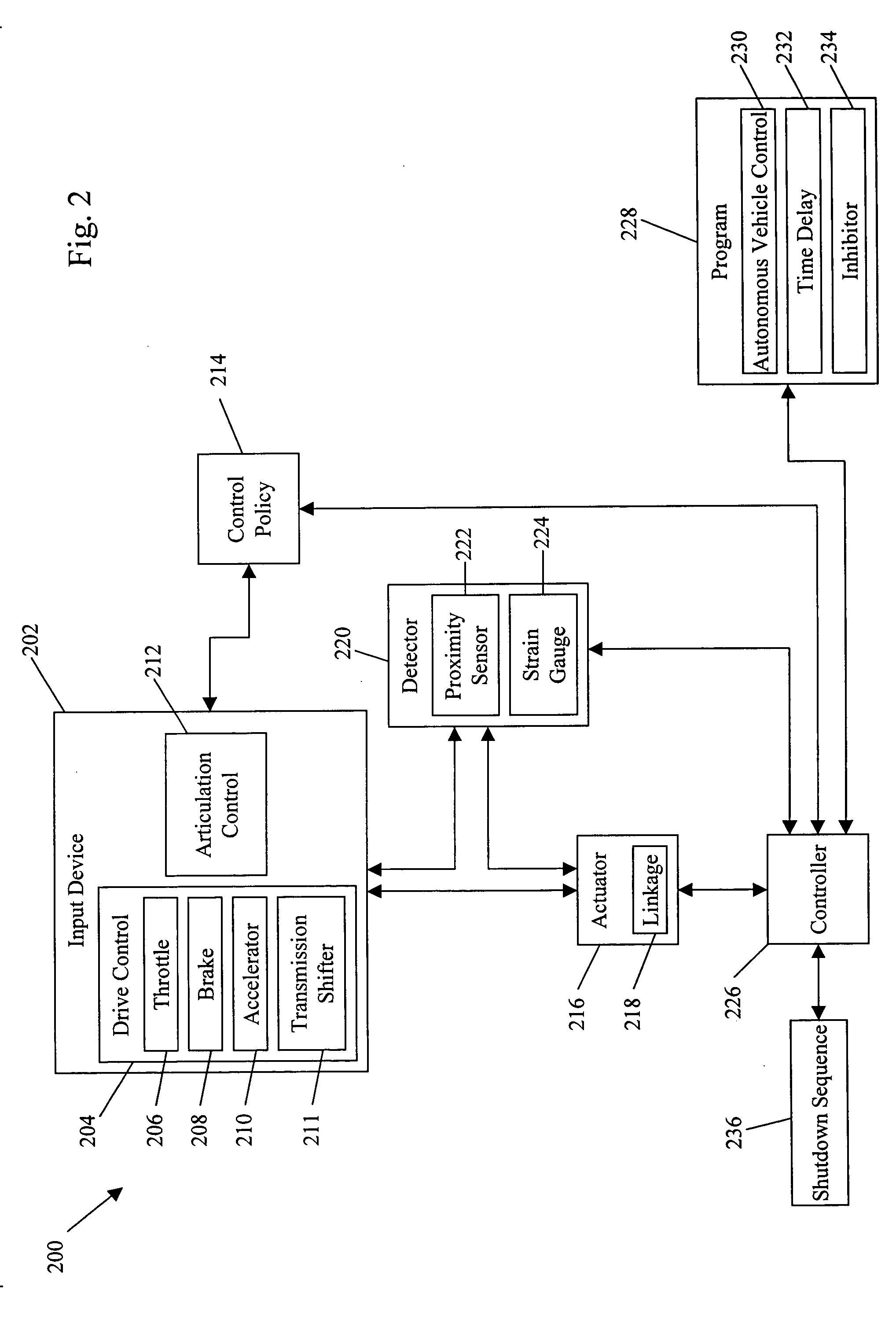
System and method for behavior based control of an autonomous vehicle
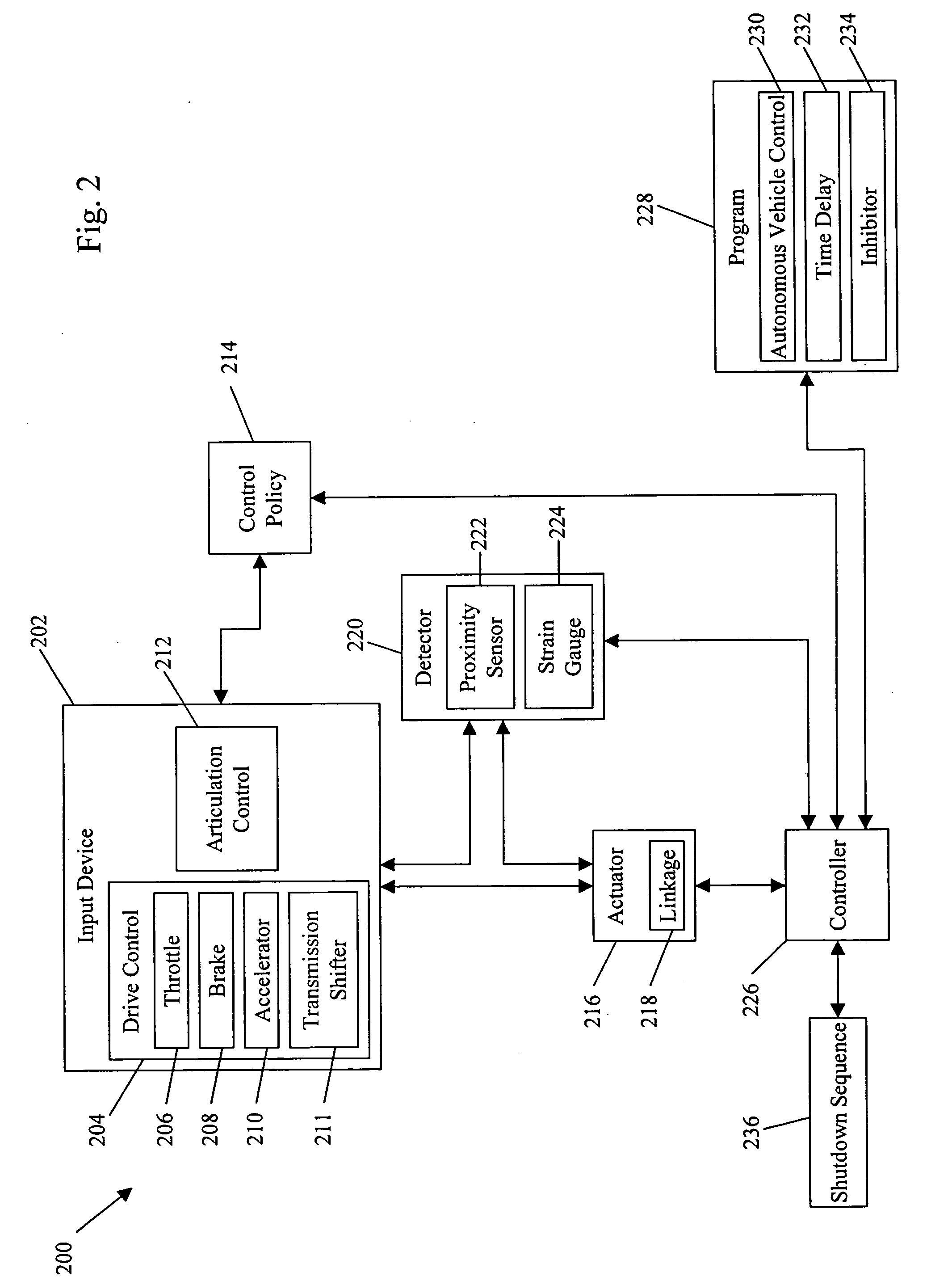
ActiveUS20060089765A1Facilitate mission executionMore focusedAutonomous decision making processActuated automaticallyOperation modeActuator
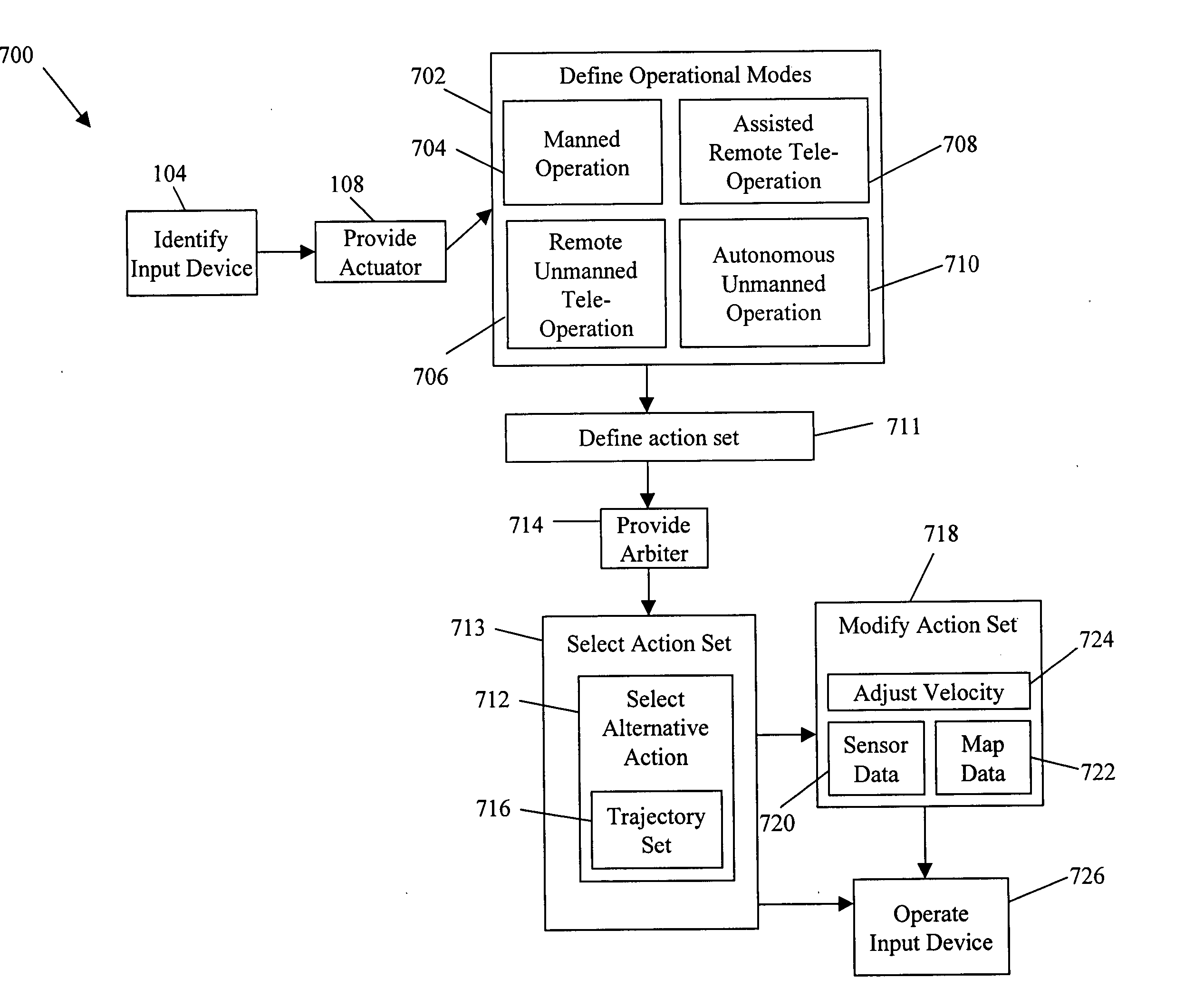
System and method for behavior based control of an autonomous vehicle. Actuators (e.g., linkages) manipulate input devices (e.g., articulation controls and drive controls, such as a throttle lever, steering gear, tie rods, throttle, brake, accelerator, or transmission shifter) to direct the operation of the vehicle. Behaviors that characterize the operational mode of the vehicle are associated with the actuators. The behaviors include action sets ranked by priority, and the action sets include alternative actions that the vehicle can take to accomplish its task. The alternative actions are ranked by preference, and an arbiter selects the action to be performed and, optionally, modified.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
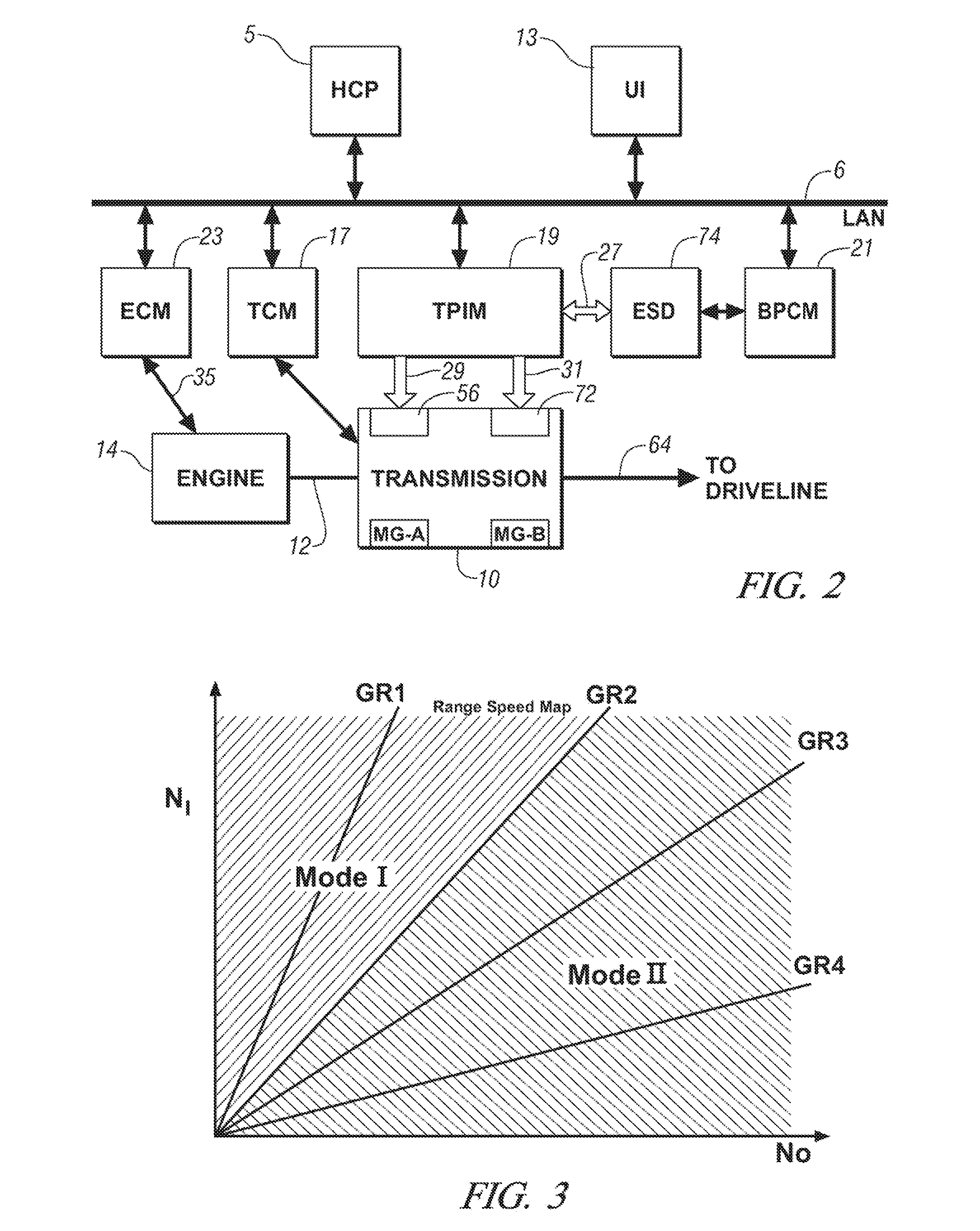
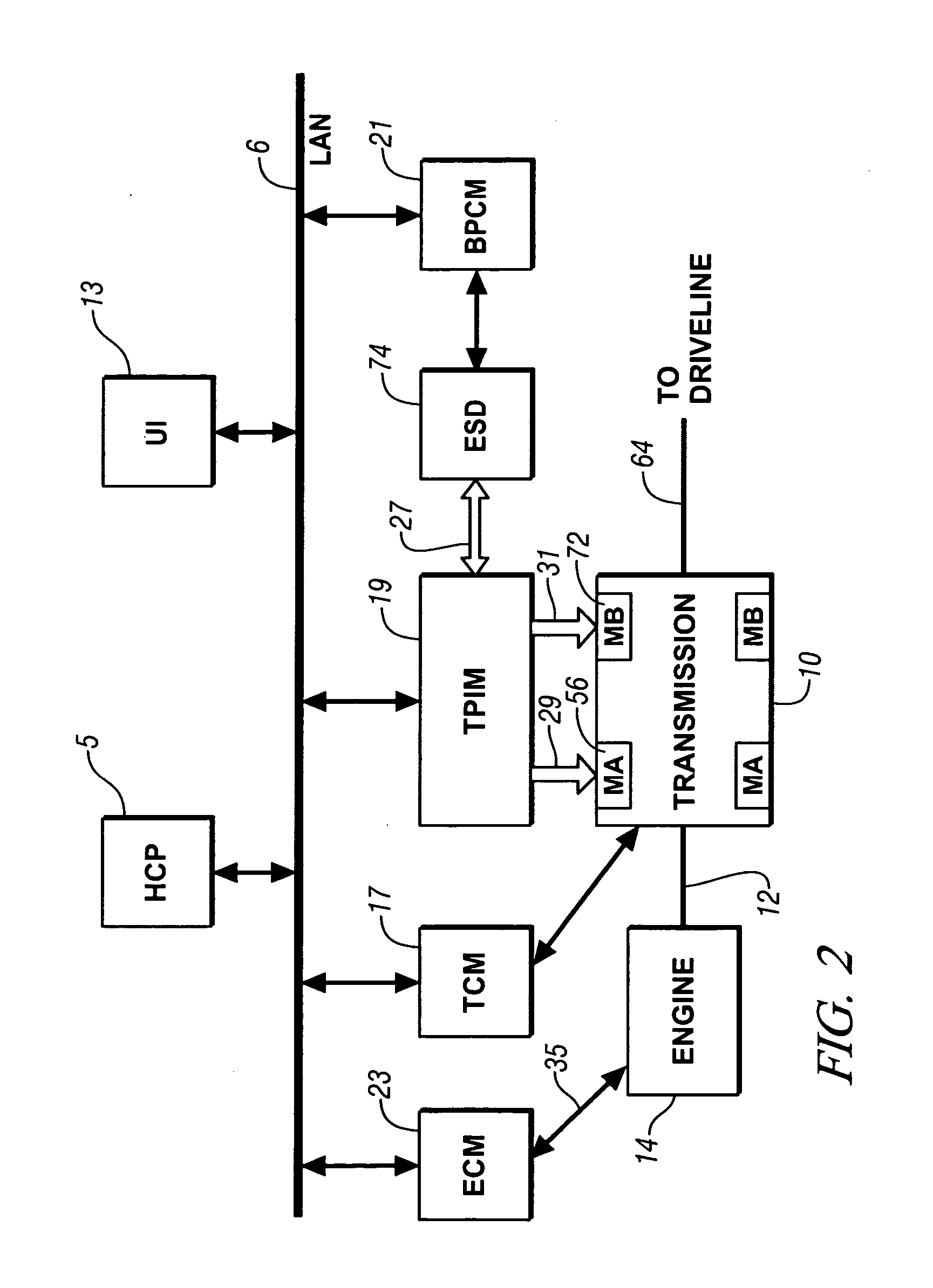
Real-time operating parameter selection in a vehicular transmission
Preferred operating points for a vehicle powertrain including an engine and a transmission are determined in accordance with a comprehensive operational mapping of input and output conditions and corresponding aggregate system losses corresponding to engine and transmission losses. In a hybrid transmission application, additional losses from motors and batteries are aggregated into the system losses and battery constraints are considered in determining preferred operating points. Preferred operating points are provided in one or more sets of minimized data for on-vehicle implementation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Toroidal type continuously variable transmission
A toroidal type continuously variable transmission having first and second discs supported around a rotating shaft and receiving power rollers therebetween includes a ball spline having a first spline groove formed in an outer circumferential surface of the rotating shaft, a second spline groove formed in an inner circumferential surface of the first disc, and balls provided between the first spline groove and the second spline groove rollably. An axial position of an end portion of an effective groove portion of the first spline groove is located to correspond to an axial position of an inner end portion of the second spline groove or more closely to the second disc than the axial position thereof when a pressing unit, a preload spring and the first disc are installed around the rotating shaft, pressure oil is not fed to the pressing unit, and the preload spring is not elastically deformed.
Owner:NSK LTD
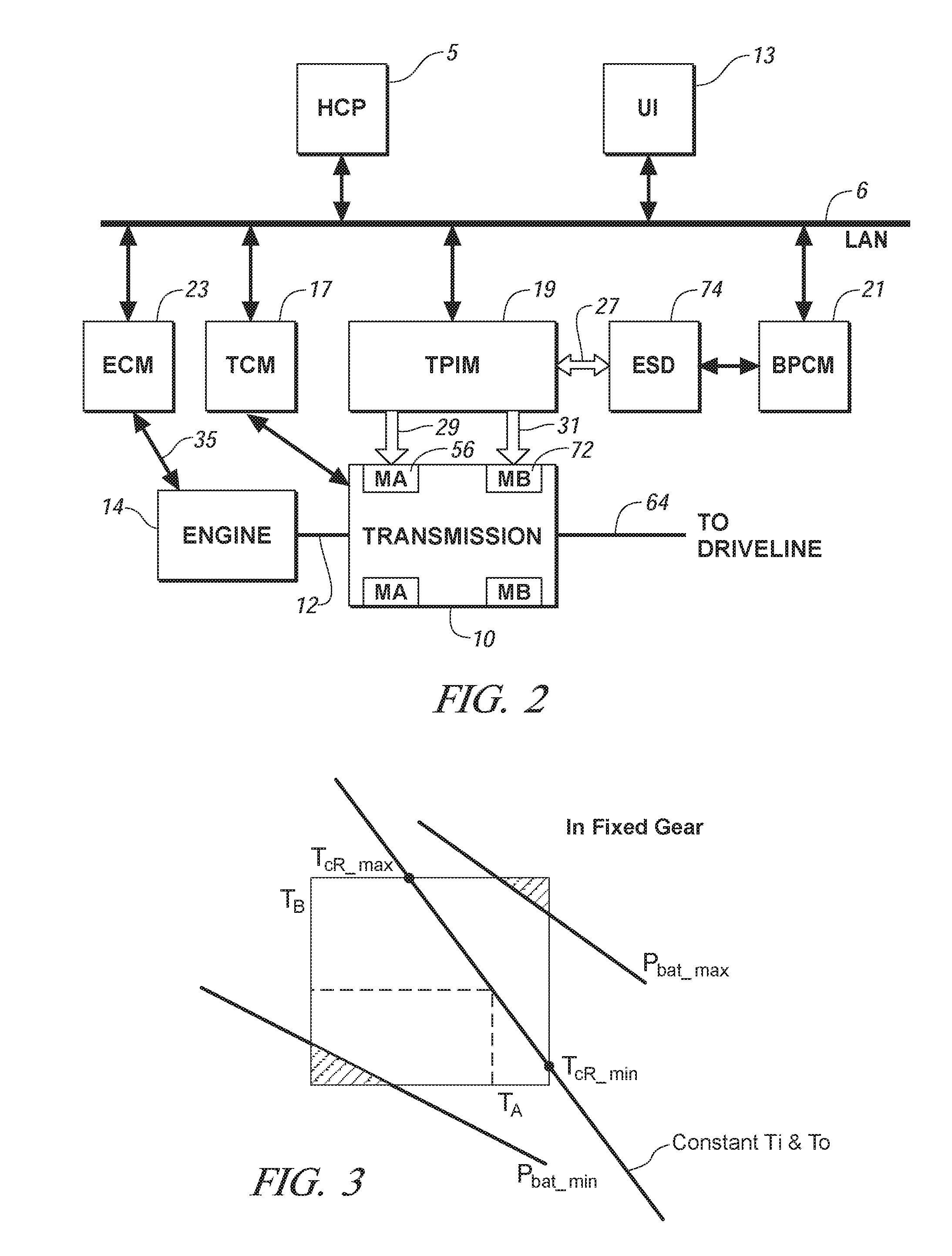
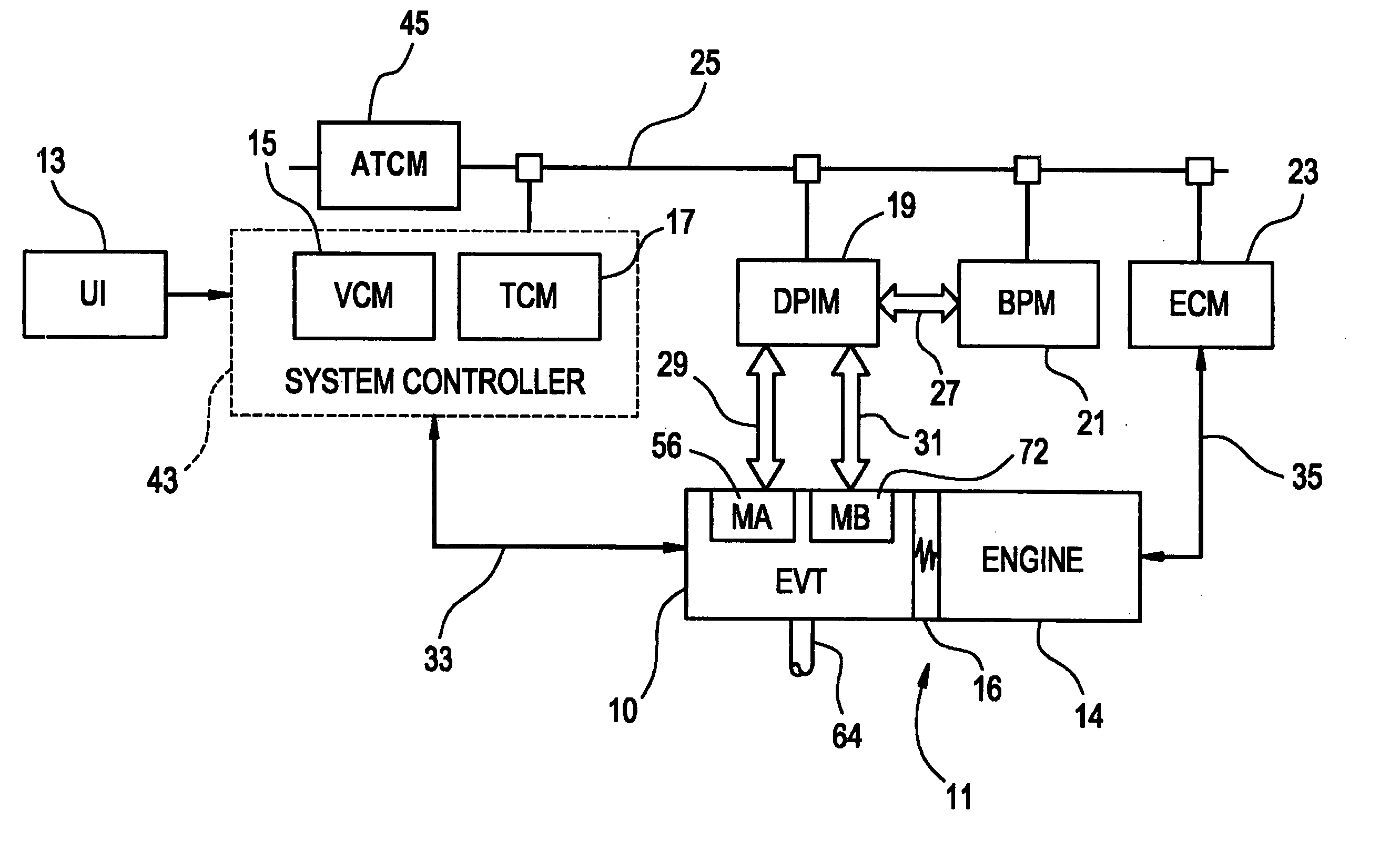
Control system for hybrid powertrain
InactiveUS7154236B1Optimizes power flowEfficiently usHybrid vehiclesFluid couplingsElectrical energy storageVariator
A method and apparatus for determining a preferred operating range for a plurality of torque-generative devices is provided. Each device is operable to provide motive torque to a transmission. The invention includes defining a first and a second operating range in a first operating space. The first operating range and the second operating range are mathematically transformed to a second operating space. The preferred operating range is defined in the second operating space based upon the transformed first operating range and the transformed second operating range. The first operating range is defined based upon torque output for each of the torque-generative devices. The second operating range is defined based upon output of an electrical energy storage device operable to provide electrical energy to each of the torque-generative devices.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
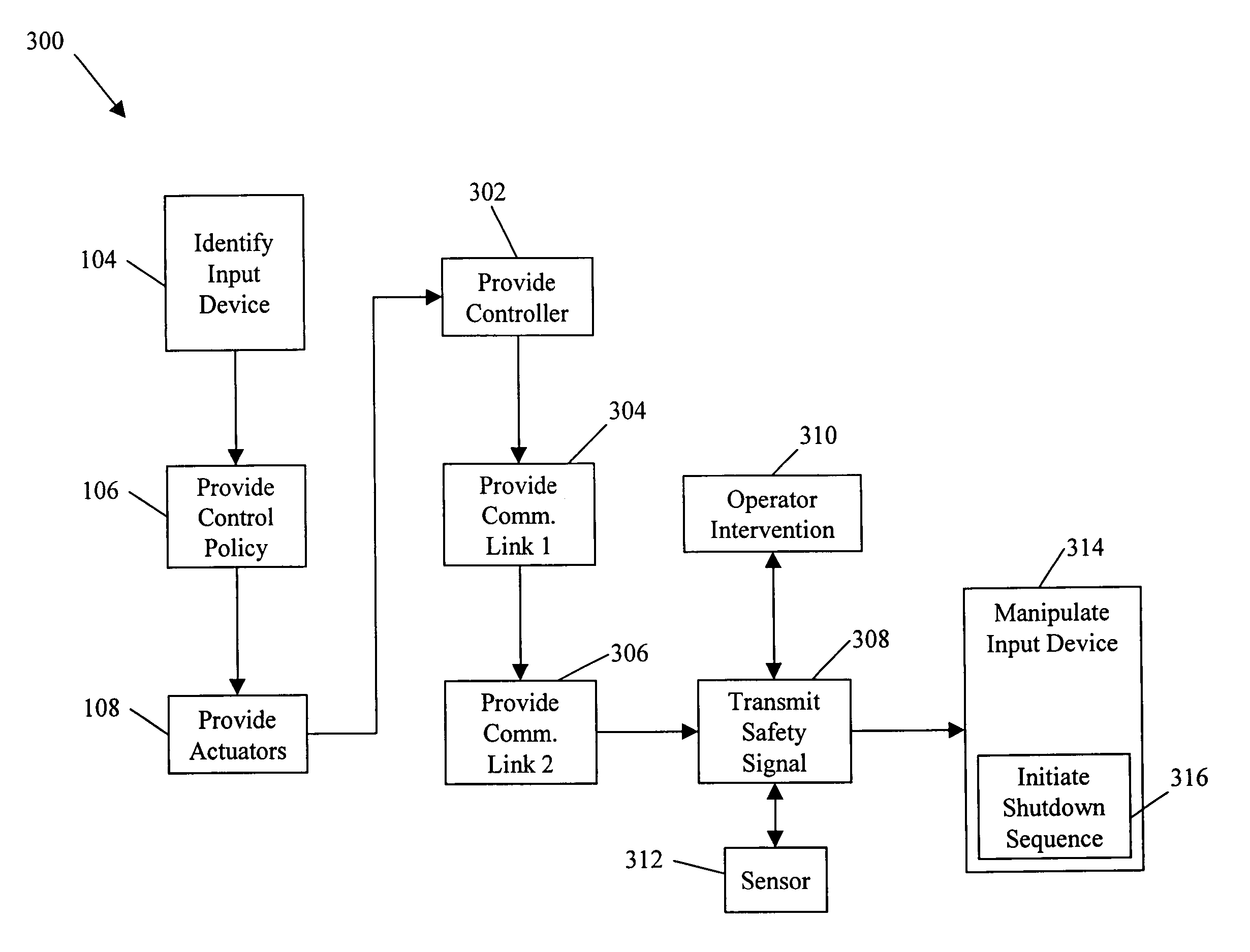
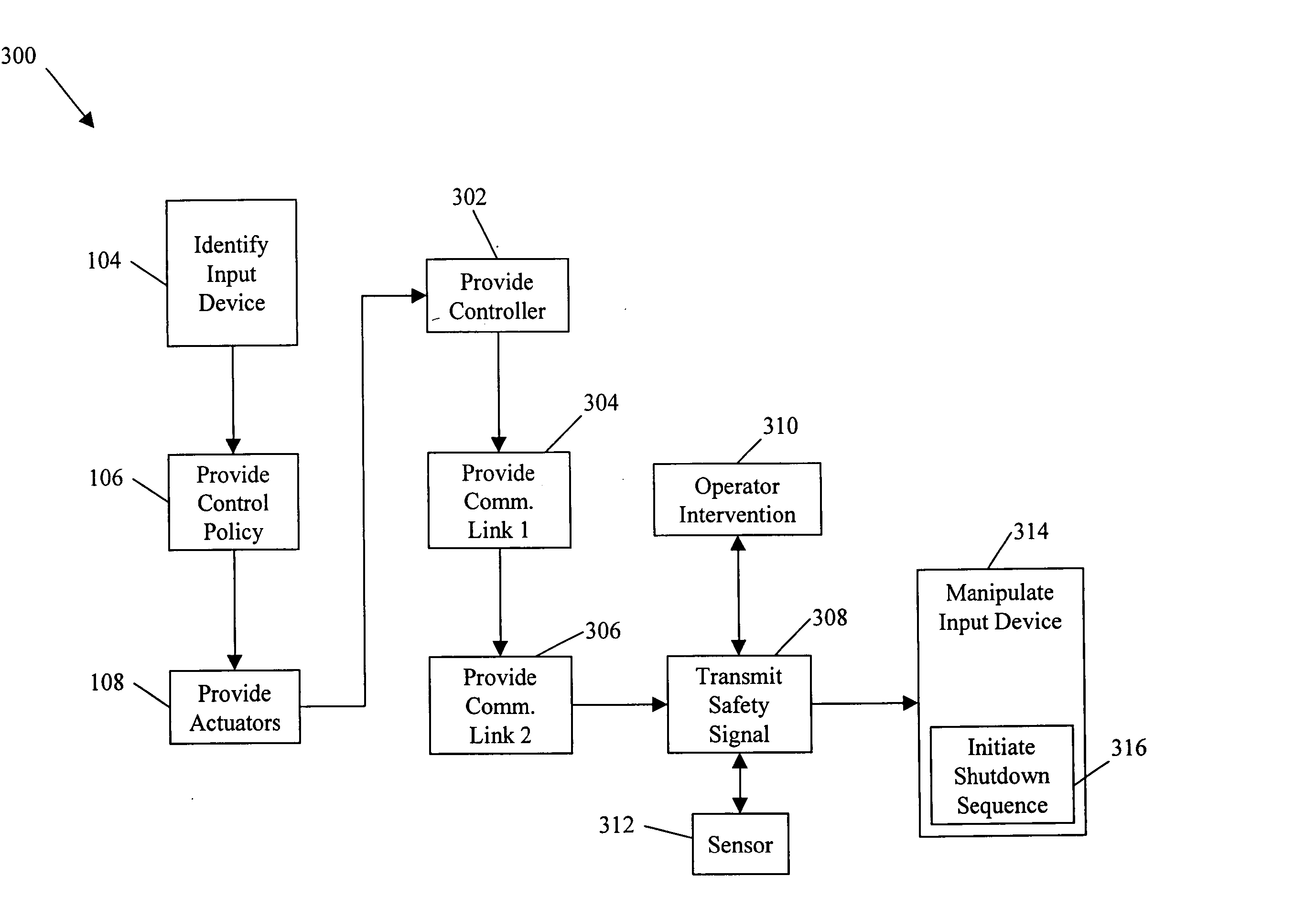
System and method for processing safety signals in an autonomous vehicle
InactiveUS7499774B2Decrease and eliminates need for manual interventionImprove securityDigital data processing detailsAnti-theft devicesUnsafe conditionProcess safety
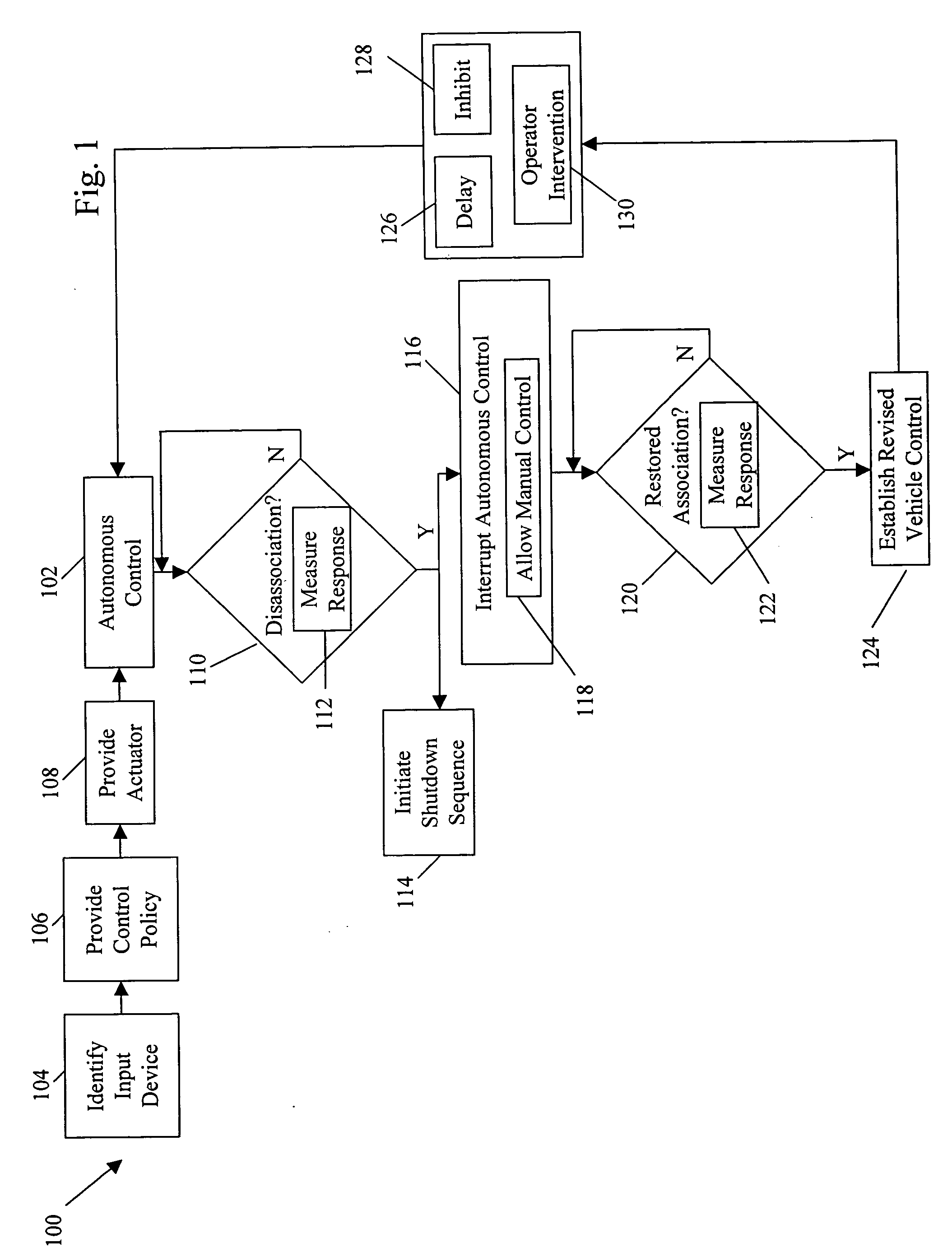
System and method for processing a safety signal in an autonomous vehicle. Safety signals are typically generated in response to the detection of unsafe conditions or are sent by the vehicle operator. In either case, the safety signals are conveyed using redundant communication paths. The paths include a computer network and a current loop. The safety signals are processed, thereby causing actuators (e.g., linkages) to manipulate input devices (e.g., articulation controls and drive controls, such as a throttle, brake, tie rods, steering gear, throttle lever, accelerator, or transmission shifter). The manipulation ensures the vehicle responds appropriately to the safety signals, for example, by shutting down the vehicle.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling an electro-mechanical transmission during a shift execution
InactiveUS20080119320A1Limit output torqueLimit in magnitude of outputElectric propulsion mountingGearing controlElectric machineClutch
A method and apparatus to control an electro-mechanical transmission during a shift event, including identifying a fault in an off-going clutch, is provided. The method includes deactivating an off-going torque-transfer clutch, monitoring slippage of the off-going torque-transfer clutch, and limiting a change in operation of an electrical machine operatively connected to the transmission until the slippage of the off-going torque-transfer clutch exceeds a threshold. Limiting a change in operation of the electrical machine comprises limiting an output torque of the electrical machine, comprising limiting a time-rate change in the output torque and limiting a magnitude of the output torque. The limit of the change Is discontinued when the slippage of the off-going torque-transfer clutch exceeds the threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
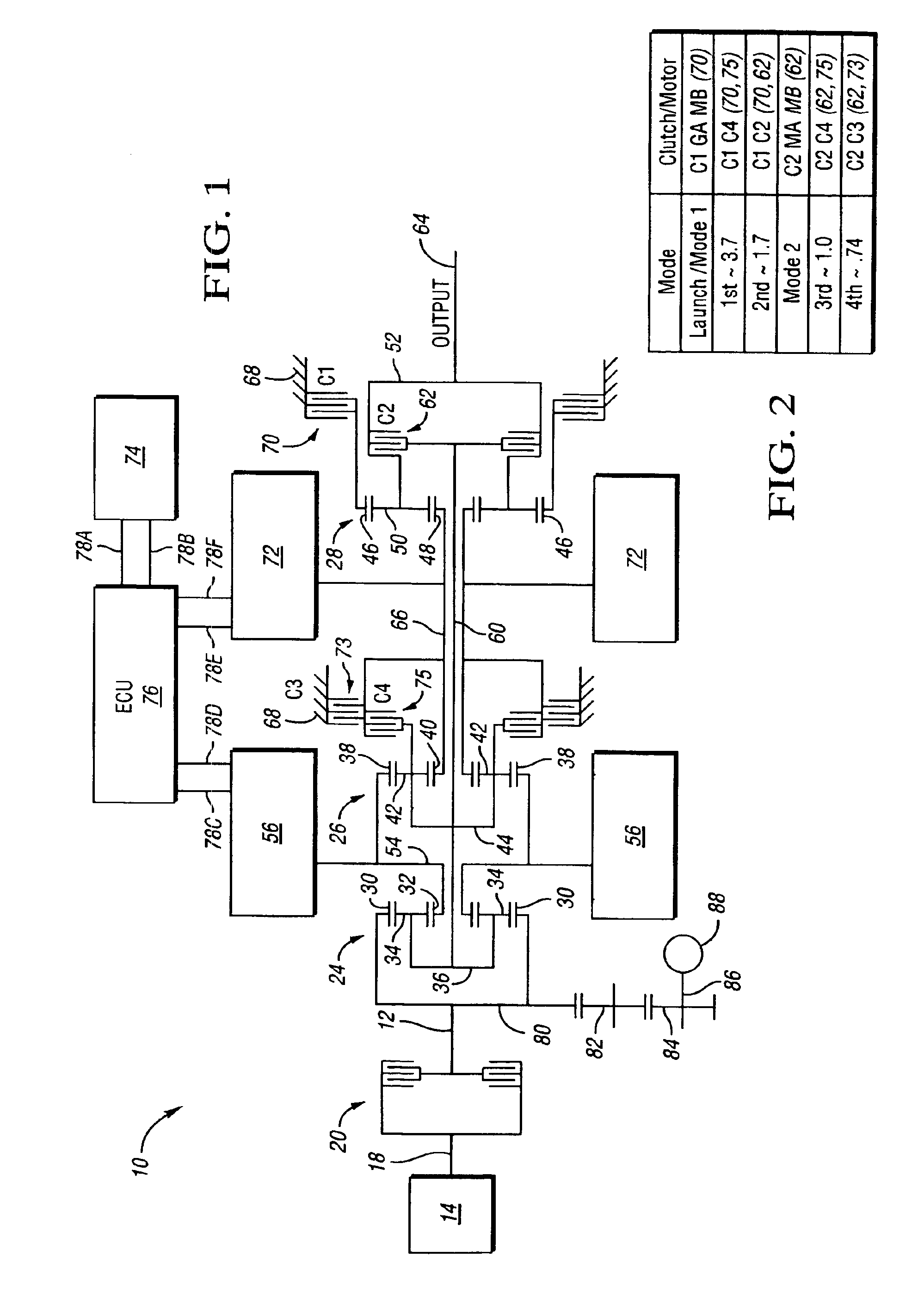
Two clutch fixed-ratio exit control for multi-mode hybrid drive
ActiveUS20050080541A1Hybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsControl engineeringConfidence factor
An electrically variable transmission has a pair of clutches and a first mode when the first clutch is applied and the second clutch released, a second mode when the second clutch is applied and the first clutch released, and a fixed-ratio mode when both clutches are applied. Upshifts and downshifts out of fixed-ratio are accomplished in accordance with a control based upon shift confidence factors determined in accordance with proportional and derivative input speed error quantities. Additional authority limits are placed upon the shift confidence factors in accordance with output speed derivative quantities. Additional override downshift control is provided in accordance with additional input speed condition determinations.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
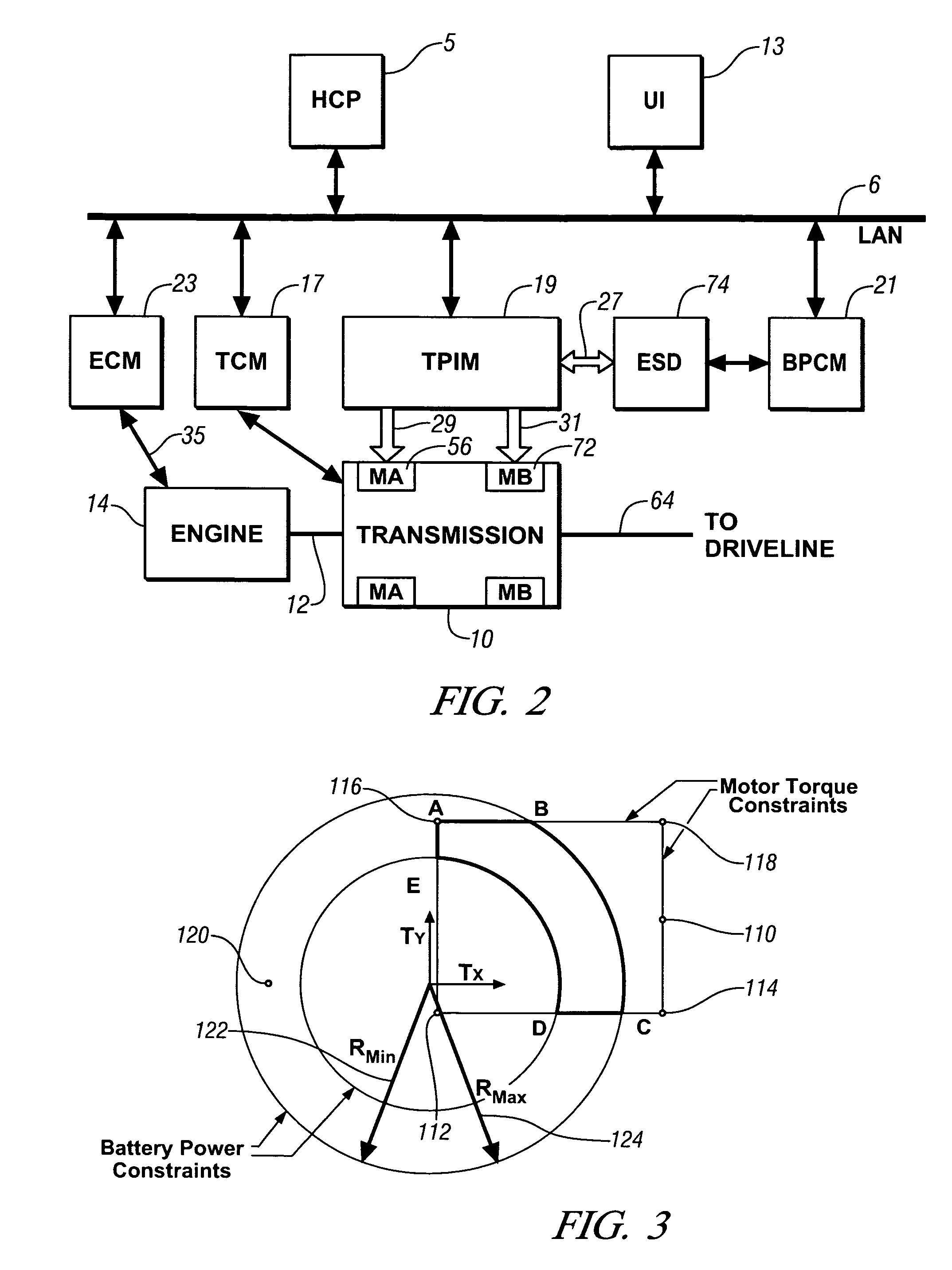
Method for dynamically determining peak output torque within battery constraints in a hybrid transmission including a parallel hybrid split
InactiveUS20050256623A1Digital data processing detailsEngine controllersElectric machineControl theory
A method for determining output torque limits of a powertrain including an electrically variable transmission relies upon a model of the electrically variable transmission. Transmission operating space is defined by electric machine torque constraints, engine torque constraints and battery power constraints. Output torque limits are determined at the limits of the transmission operating space.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus to monitor operation of an auxiliary hydraulic pump in a transmission
The invention comprises a method and apparatus to monitor operation of an electrically-actuated hydraulic pump selectively operative to supply pressurized fluid to a hydraulic circuit for a transmission device operably connected to an internal combustion engine of a vehicle. It includes monitoring vehicle operation and passively and intrusively monitoring hydraulic circuit pressure. The hydraulic pump is functioning properly when the monitored pressure in the hydraulic circuit exceeds a threshold. A fault related to the hydraulic circuit is identified when the monitored pressure in the hydraulic circuit does not exceed the threshold.
Owner:ELECTRONICS DATA SYST CORP +1
Multi speed transmission
ActiveUS20060270516A1Reduce internal loadSlow internal speedToothed gearingsTransmission elementsGear wheelEngineering
A transmission is provided having four planetary gearsets, each having respective first, second, and third members, and a plurality of selectively engageable torque transmitting devices configured to selectively interconnect selected members of the four planetary gearsets for unitary rotation thereby to provide a plurality of forward speed ratios and at least one reverse speed ratio between an input member and an output member.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
Apparatus and method to control transmission torque output during a gear-to-gear shift
A control system is provided to effect a method to control torque output from a two-mode, compound-split, electro-mechanical transmission during gear-to-gear shifting event when an off-going torque-transfer device is disengaged. It includes a computer program which controls transmission operation. A predetermined preferred torque output from the transmission device is determined. Torque output from torque-generative devices device is controlled. Torque transmitted across a selectively actuated torque transfer device is controlled, and limited based upon available battery power. Actuation of the oncoming torque-transfer device is preferably based upon a temperature of the device during the shifting event. The temperature during the shifting event is determined based upon a rotational speed of an input shaft to the transmission and an elapsed time to shift.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Driveline lash estimation and clunk management using multivariable active driveline damping
ActiveUS20070225888A1Minimize impactHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDrivetrainEngineering
Driveline lash and clunk are controlled in a powertrain system having multiple torque-generative and torque control devices using a multivariable feedback control approach to provide active driveline damping. Control parameters used by a state estimator are different, depending on whether the driveline lash is taken up or is currently slack. When the estimated driveline axle torque is not substantially zero, the nominal parameters for transmission mode or gear are used in the state estimator. When the estimated axle torque is substantially zero, the parameters are switched to neutral parameters, the lash estimator indicates neutral lash state, and angle of lash is tracked until it accumulates an expected amount of lash in the driveline. During a lash transition time, active damping controls the driveline component speeds so that the effect of lash take-up is minimized. After lash take-up occurs, desired axle torque is used by the system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method of providing electric motor torque reserve in a hybrid electric vehicle
ActiveUS20050255964A1Improve control robustnessImproved shift qualityHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsDrivetrainBattery electric vehicle
A method of operating a vehicle powertrain system comprising an electric motor and transmission where the electric motor is operably and selectively coupled to the transmission and adapted to provide an output torque contribution thereto, and the electric motor has a predetermined maximum motor output torque and a predetermined minimum motor output torque which are used to determine a range of permissible control points for at least one transmission control parameter. The method includes establishing a motor torque reserve by performing at least one of decreasing the predetermined maximum motor output torque to a maximum reserved motor output torque and increasing the minimum motor output torque to a minimum reserved motor output torque, wherein the maximum reserved motor output torque and the minimum reserved motor output torque are used in place of the predetermined maximum motor output torque and the predetermined minimum motor output torque, respectively, to determine the range of permissible control points for the at least one transmission control parameter. The motor torque reserve may include a static motor torque reserve, a dynamic motor torque reserve, or a combination of both static and dynamic torque reserves. The dynamic torque reserve may include a predictive dynamic reserve, a reactive dynamic reserve, or a combination of a predictive reserve and a reactive reserve or reserves.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
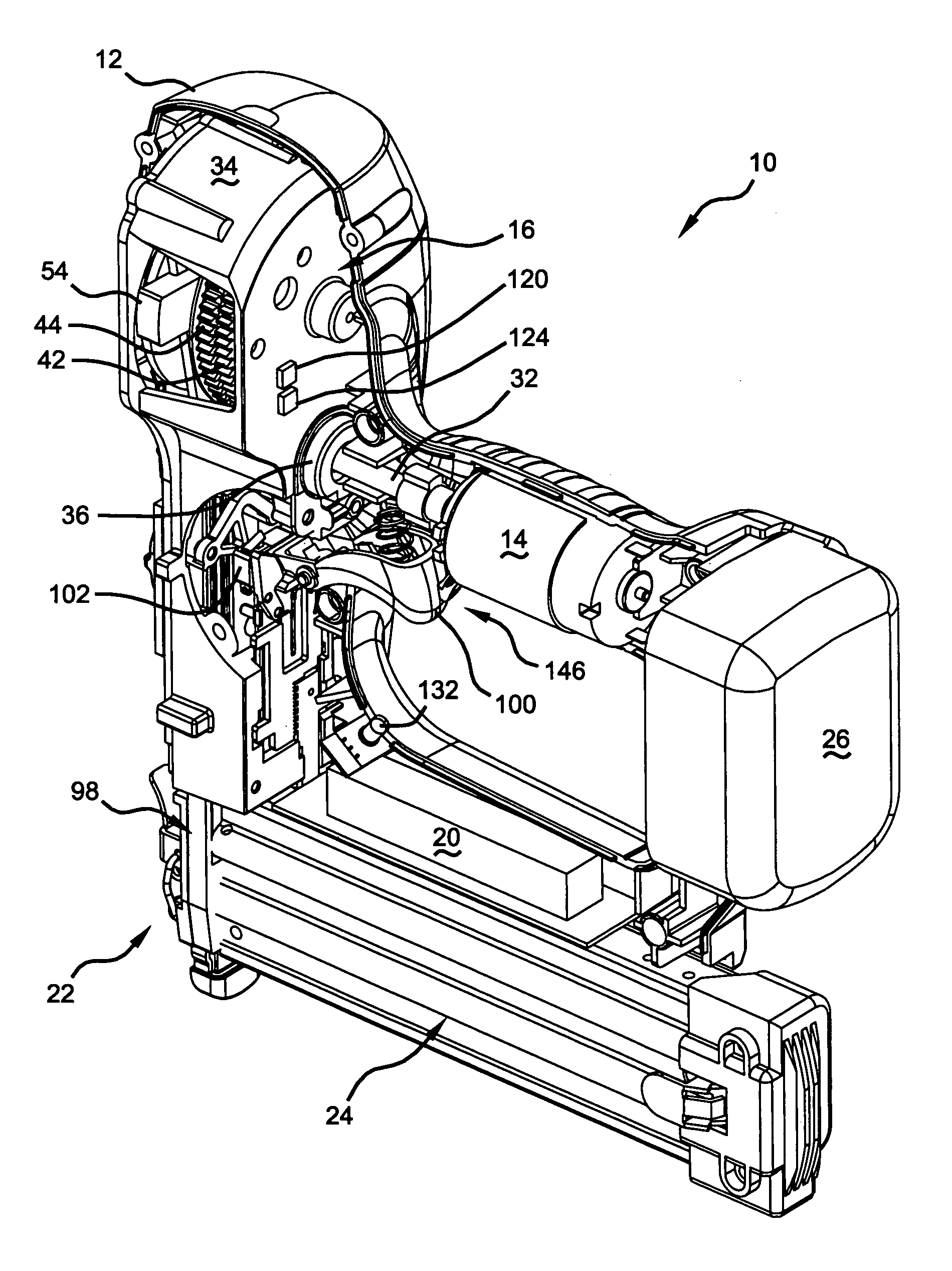
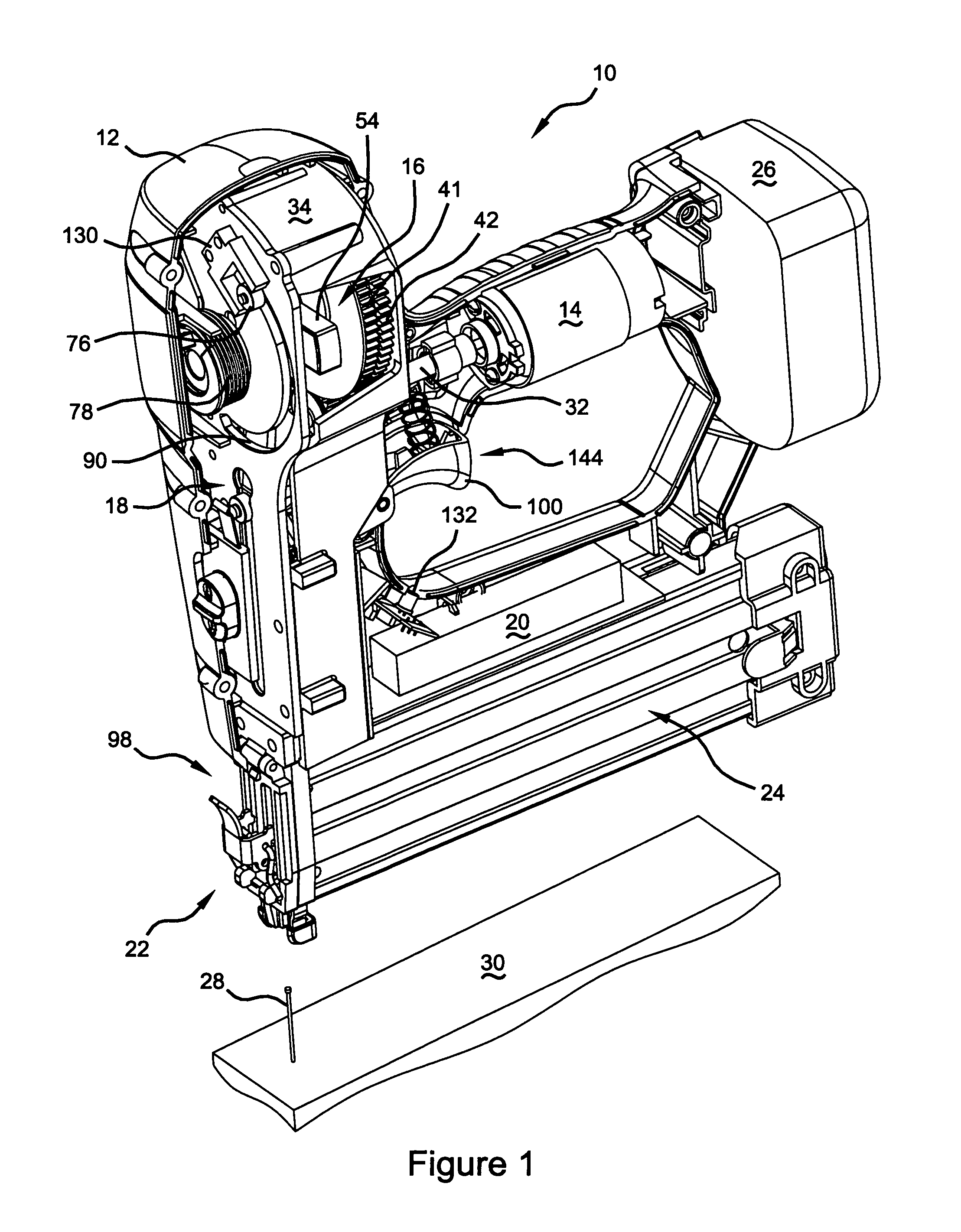
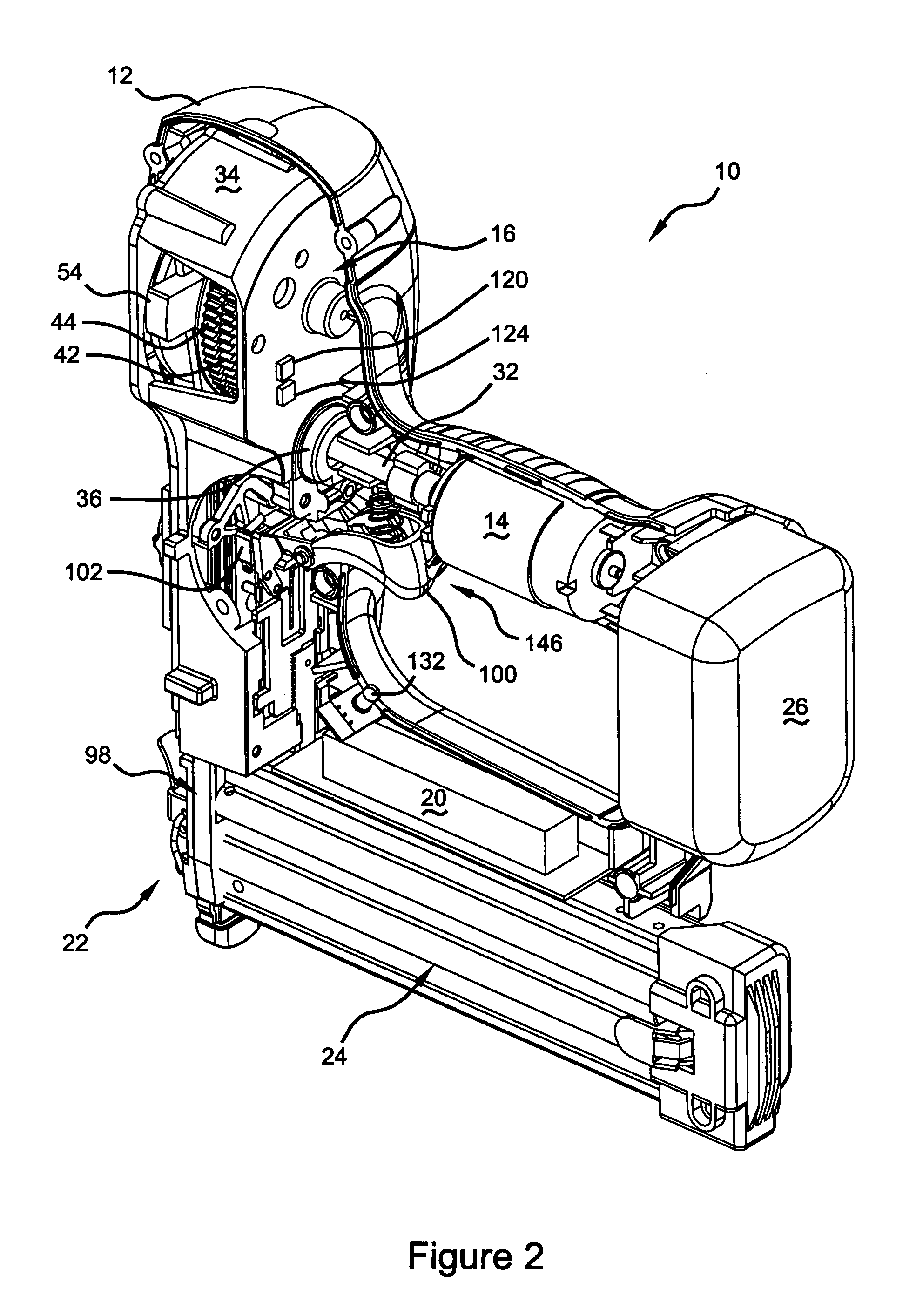
Electronic control of a cordless fastening tool
A fastening tool that drives a fastener into a work-piece. The tool includes a motor that is connected to a transmission. The transmission includes a flywheel. The tool also includes a driver mechanism that is adapted to drive the fastener into the work-piece. The flywheel is connected to the driver mechanism when the flywheel is in a flywheel firing position. The tool includes a control module that detects a flywheel position and compares the flywheel position to the flywheel firing position. The control module also adjusts the flywheel position based on the comparison. The control module ensures that the transmission has enough rotations to ensure that enough momentum can be generated to drive the fastener into the work-piece.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Clutch control for hybrid transmission
A method and system to off-load motive torque from a clutch to execute a transmission shift is provided. The powertrain includes torque-generative devices operably connected to a two-mode, compound-split, hybrid electro-mechanical transmission. The method includes determining a commanded output torque, and a shift command. A first torque is transmitted by electrical motors, and is limited by their torque capacities. A supplemental motive torque is transmitted from an oncoming clutch. The supplemental motive torque is limited by a torque capacity of the oncoming clutch. Output torque of an internal combustion engine to the transmission is adjusted by an amount substantially equal to a difference between the commanded output torque and the first and the supplemental motive torques.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for multivariate active driveline damping
A multivariate control method and system to control torque output from a powertrain system to a driveline is provided, to reduce driveline oscillations. The powertrain preferably comprises hybrid powertrain having a plurality of torque-generative devices connected to a transmission. Desired powertrain and driveline operating states are determined, as are a plurality of operating state errors. Each torque-generative device is controlled, based upon the operating state errors, and operating mode of the transmission. A damping torque command, additive to a commanded torque, is determined for one or more of the torque-generative devices based upon the determined transmission operating mode. Determined operating states include operator input, and powertrain / driveline including driveline torque; transmission input torque, rotational speed of the torque-generative devices; road load; and, accessory load.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
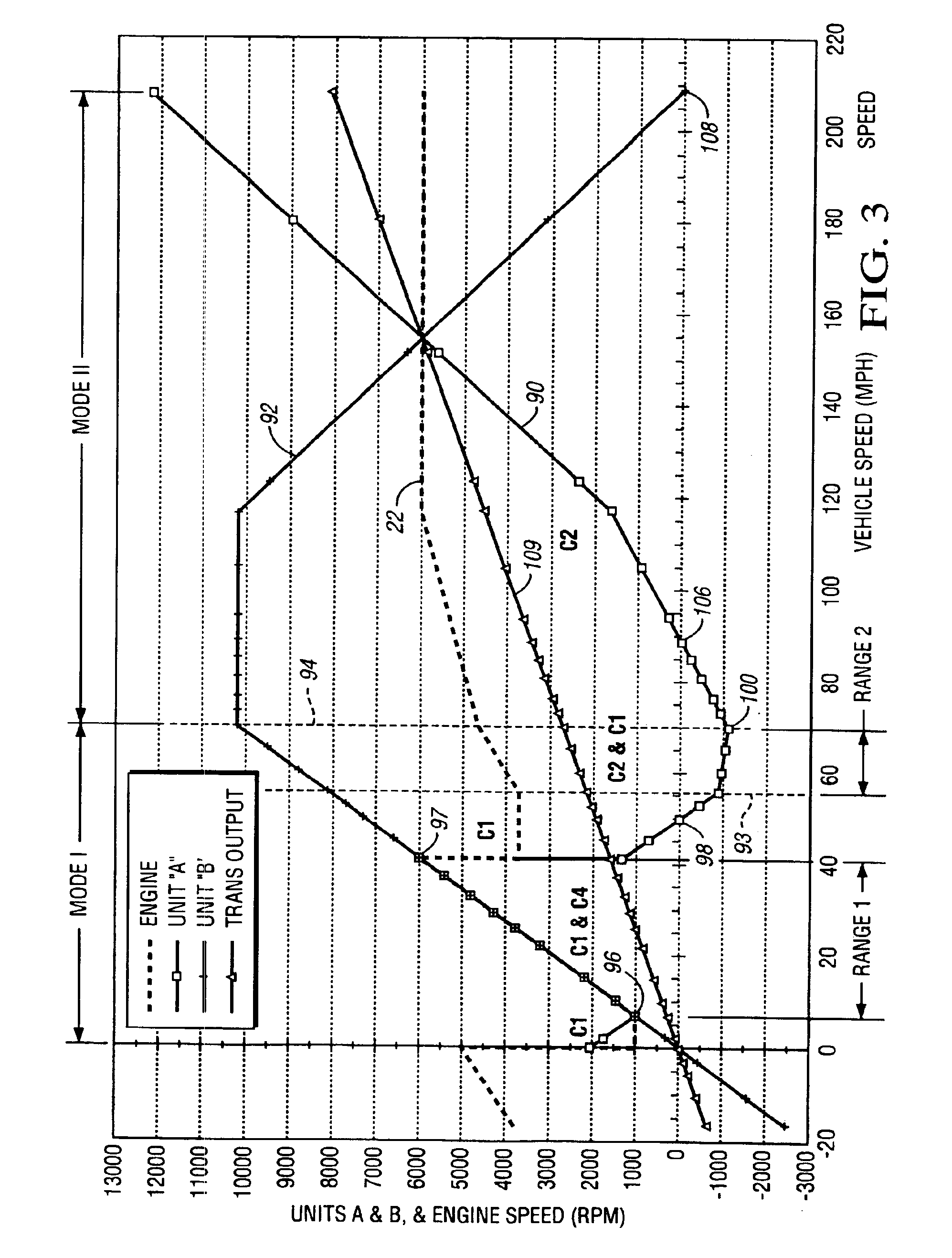
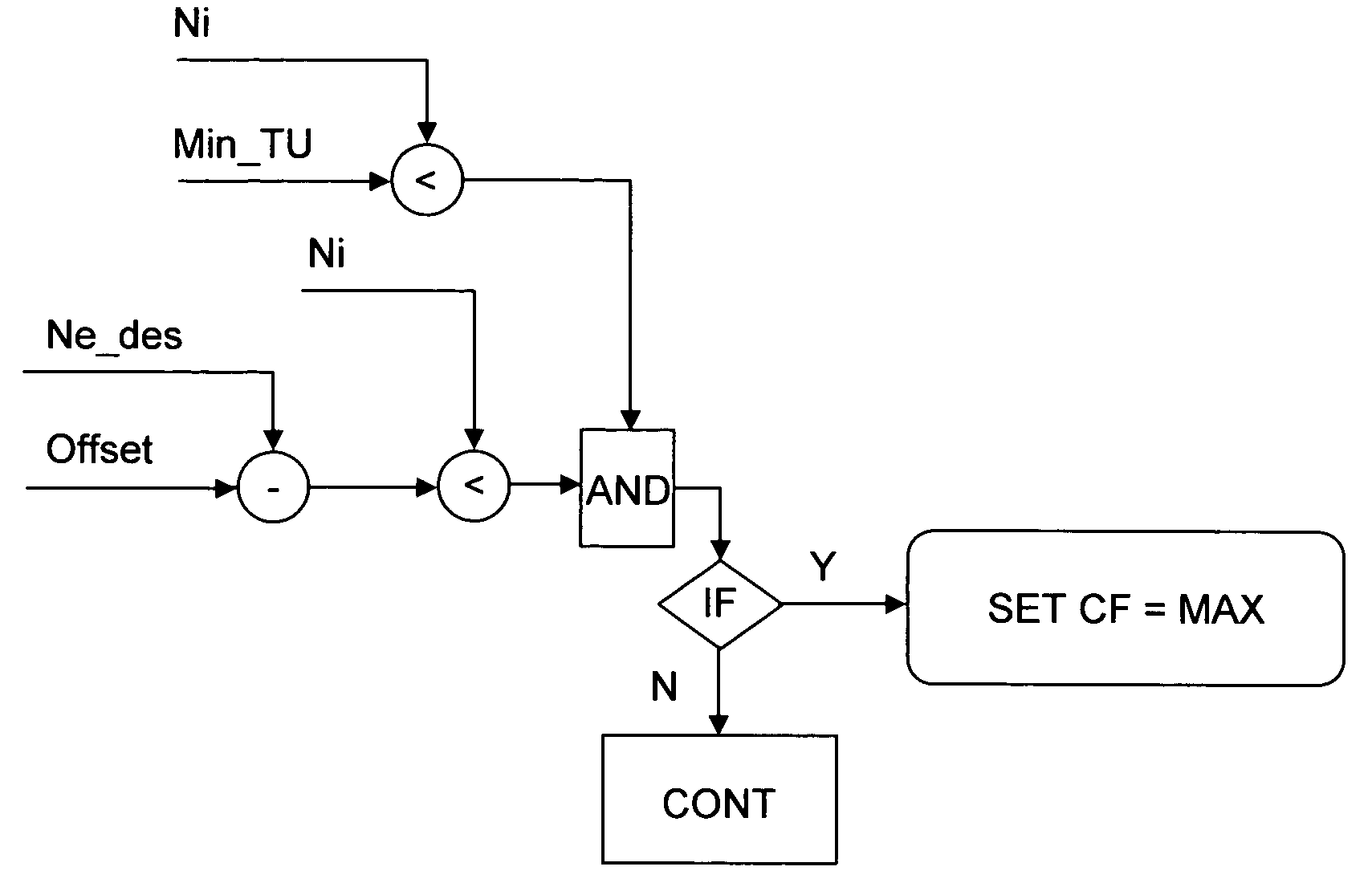
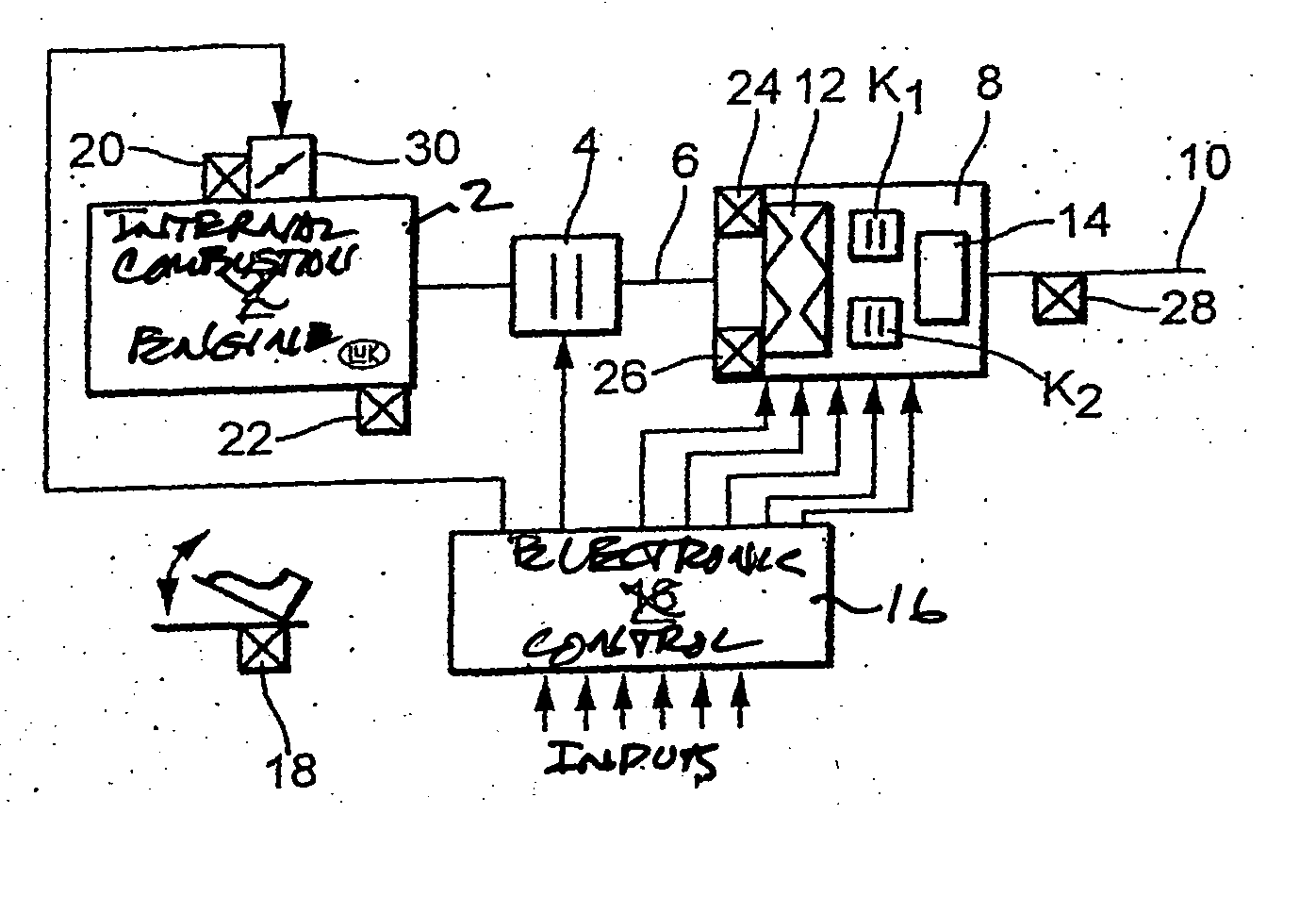
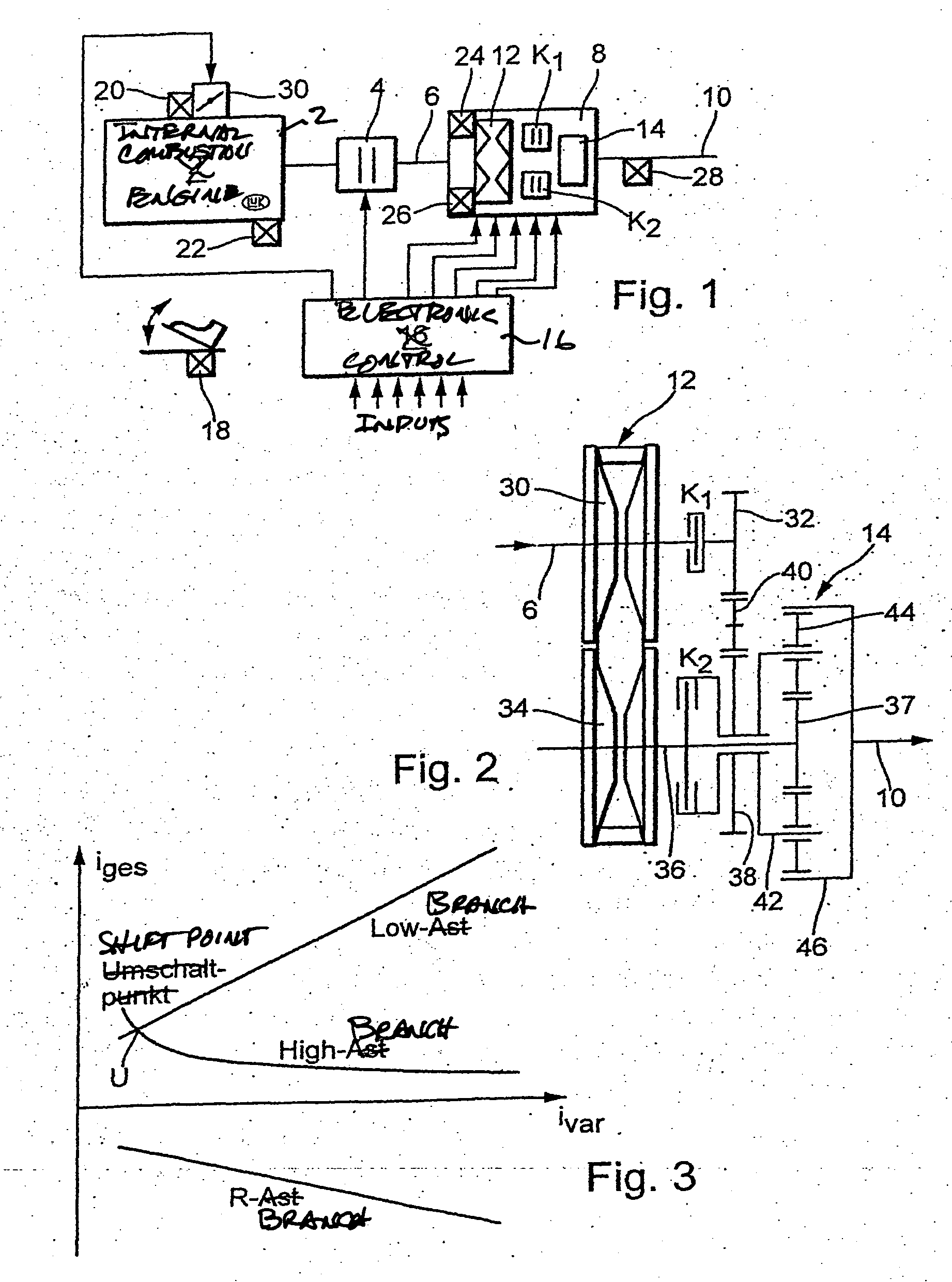
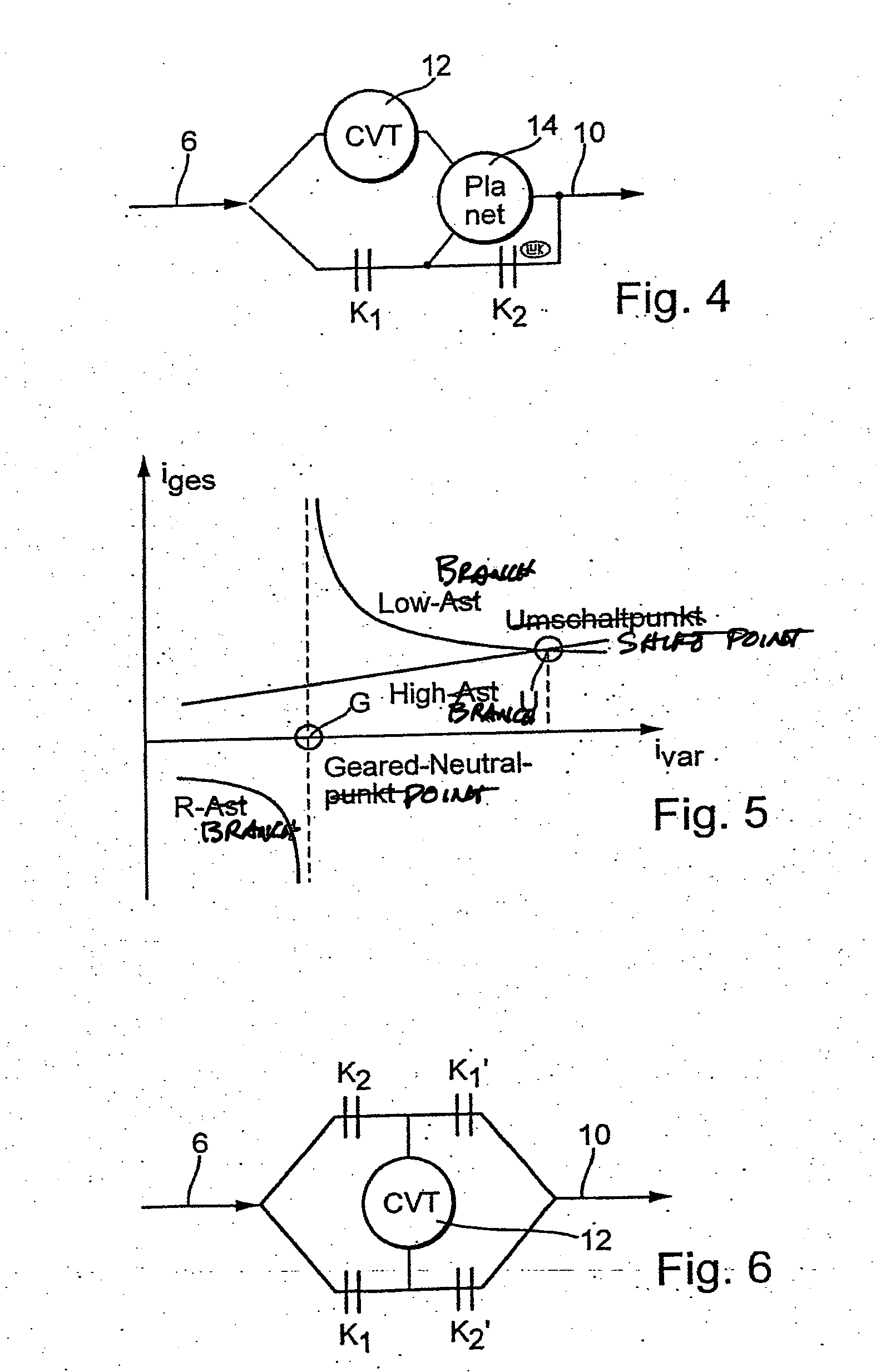
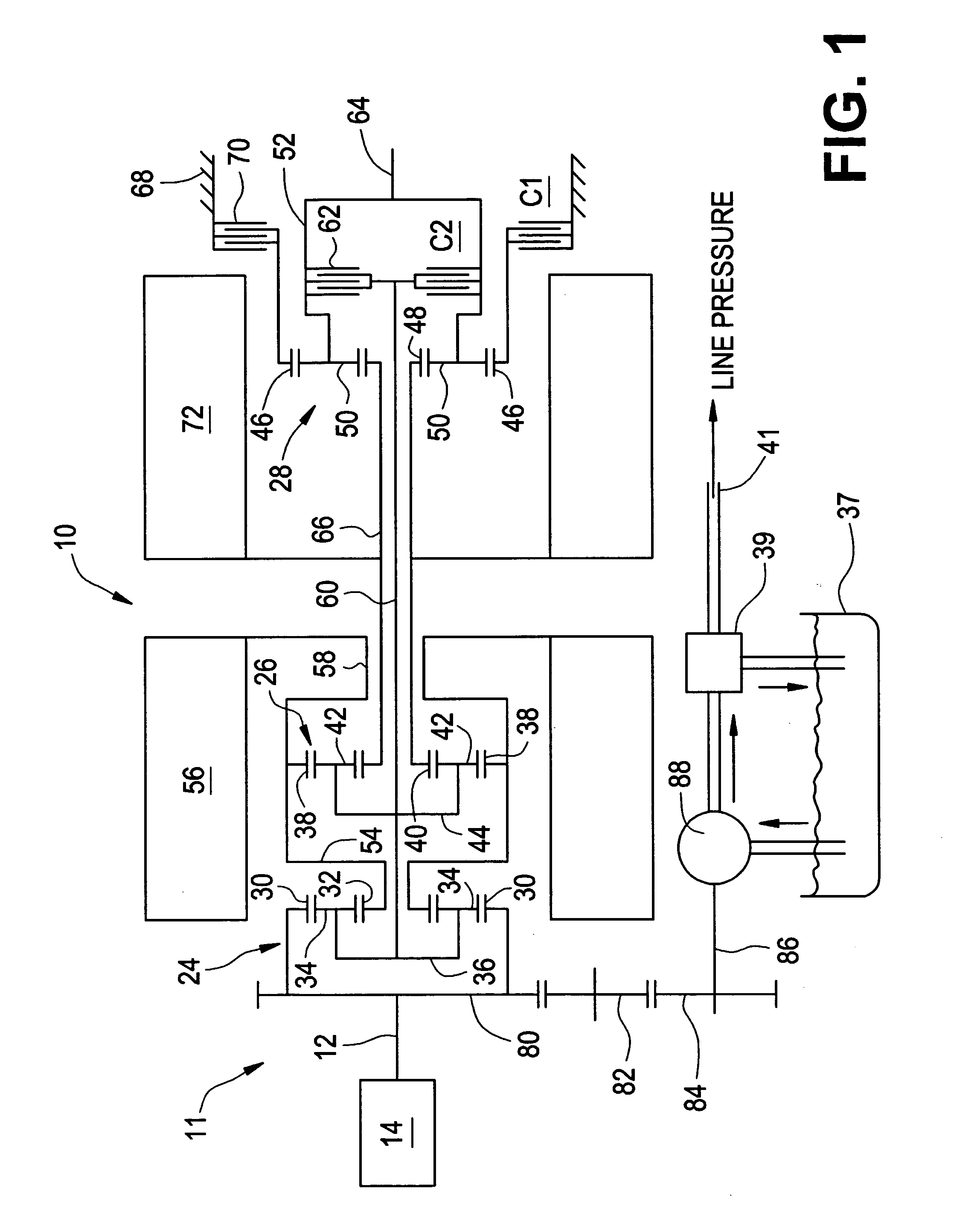
Methods for regulating the gear ratio of an automatic power-branched transmission, and automatic power-branched transmission
A method for regulating or controlling the transmission ratio of an automatic power-branched transmission. Power is transmitted through a shaft driven by an engine, a variable speed drive, a gear transmission, a driven shaft, and at least two control clutches. The variable speed drive and the gear transmission are connected to each other in such a way that the regulating range of the variable speed drive is traversed in one direction within a first range of transmission ratios, and is traversed in the opposite direction within a second range of transmission ratios during traversing of the entire range of transmission ratios. The shifting strategies result in reduced wear of the endless belt device and allow for comfortable changing between the transmission ratio ranges.
Owner:LUK LAMELLEN & KUPPLUNGSBAU BETEILIGUNGS KG
Planetary-gear-type multiple-step transmission for vehicle
InactiveUS20050090362A1Easy constructionSmall sizeToothed gearingsTransmission elementsGear wheelEngineering
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for dynamically determining peak output torque in an electrically variable transmission
A method for determining output torque limits of a powertrain including an electrically variable transmission relies upon a model of the electrically variable transmission. Transmission operating space is defined by combined electric machine torque constraints and engine torque constraints. Output torque limits are determined at the limits of the transmission operating space.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
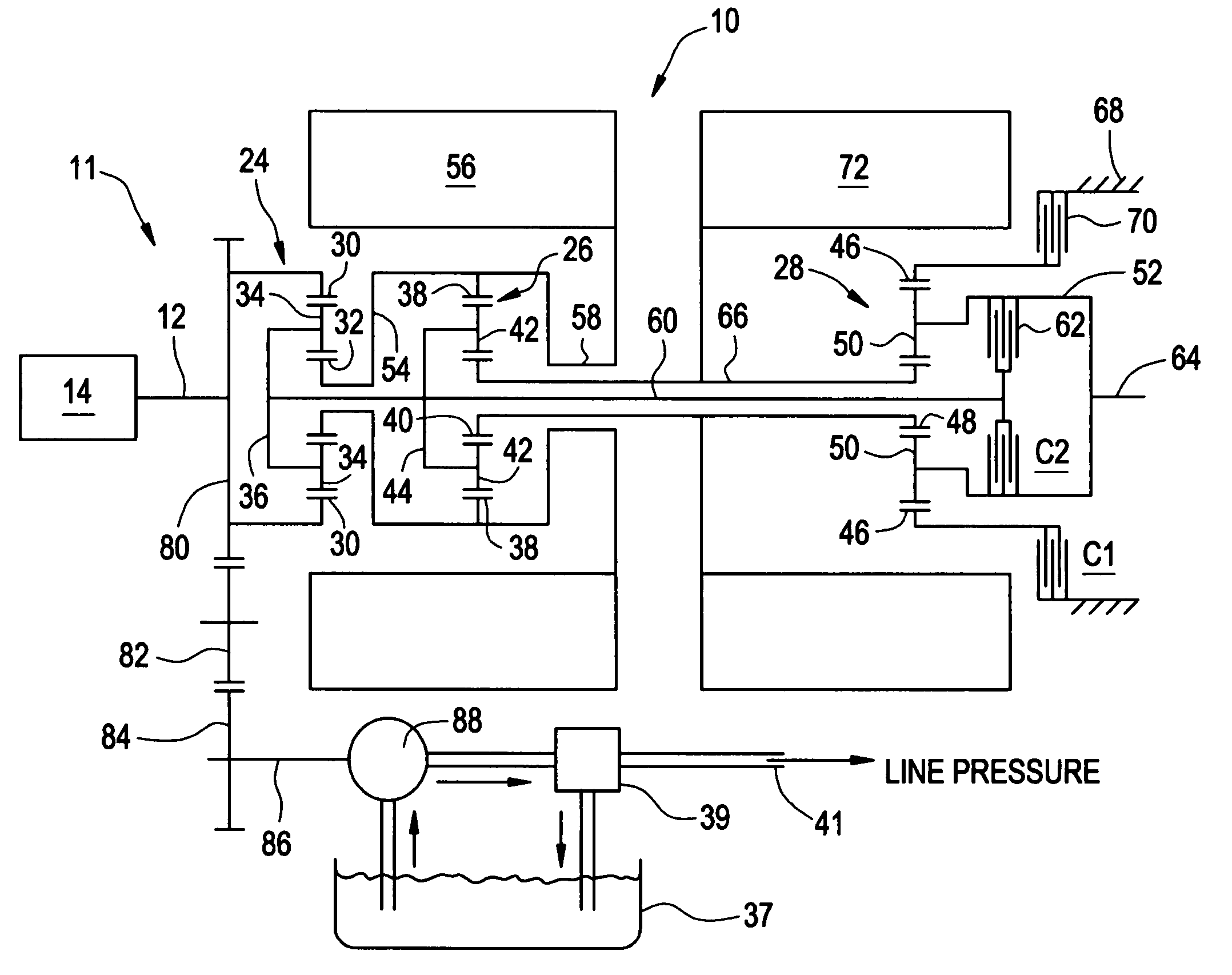
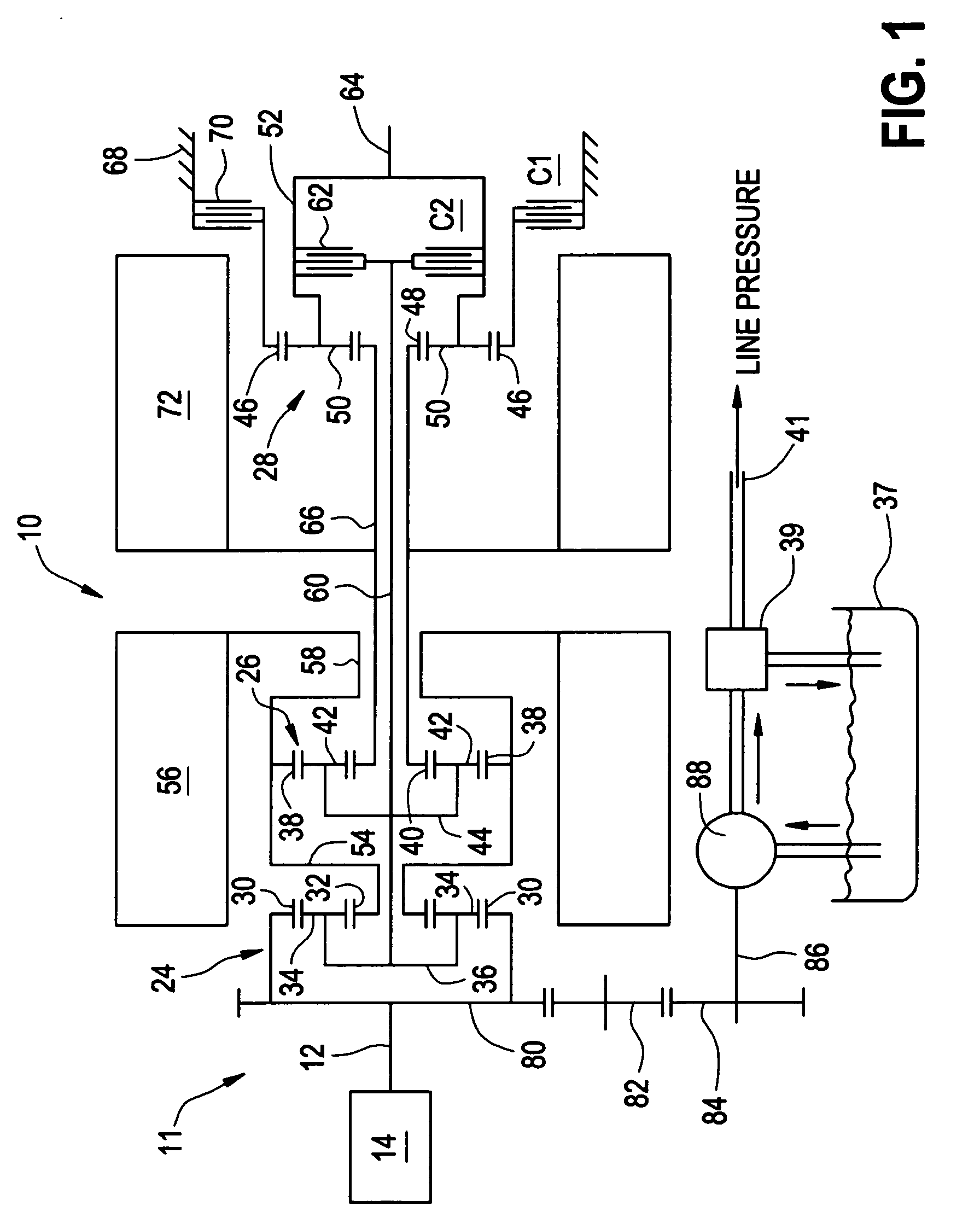
Continuously variable transmissions and methods therefor
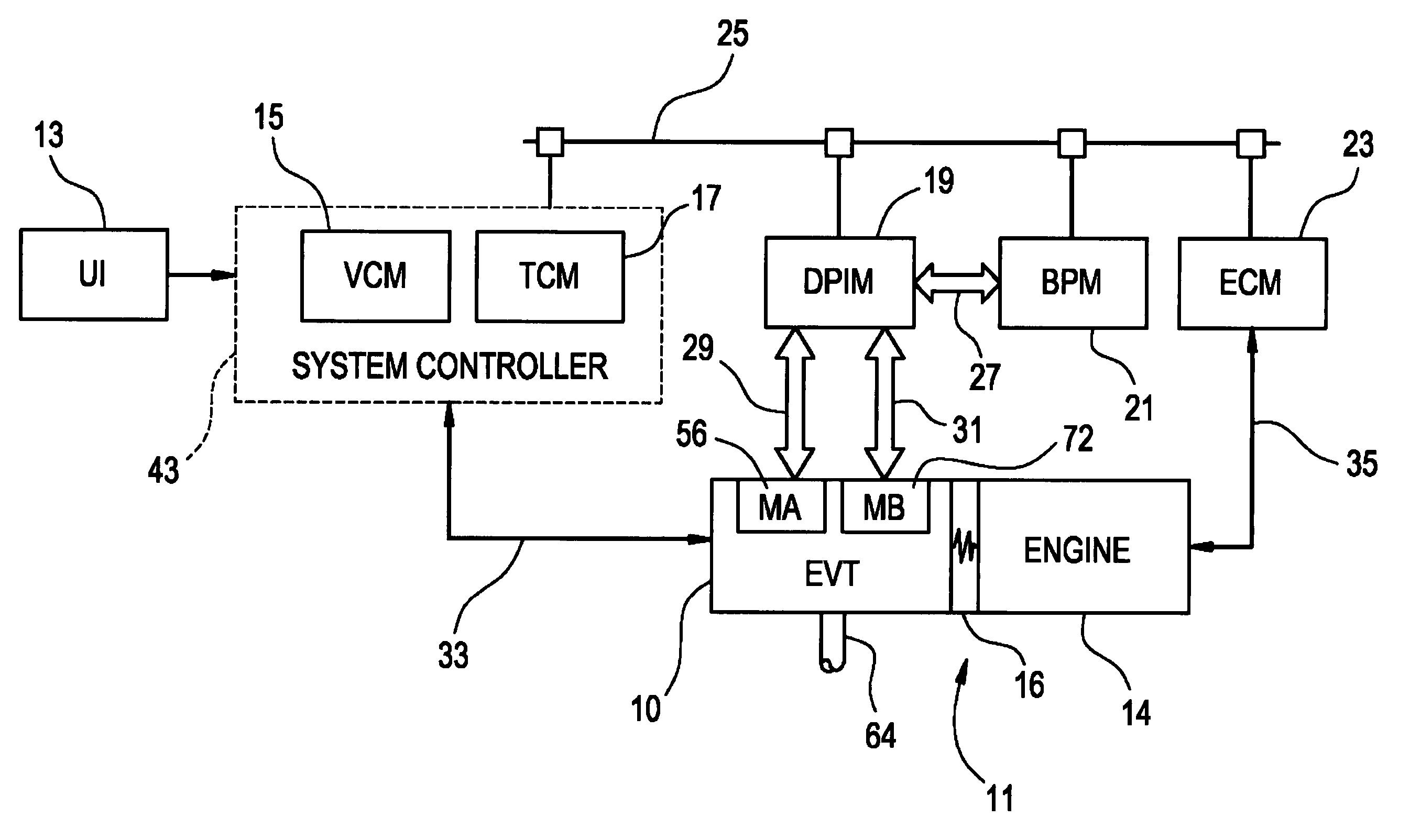
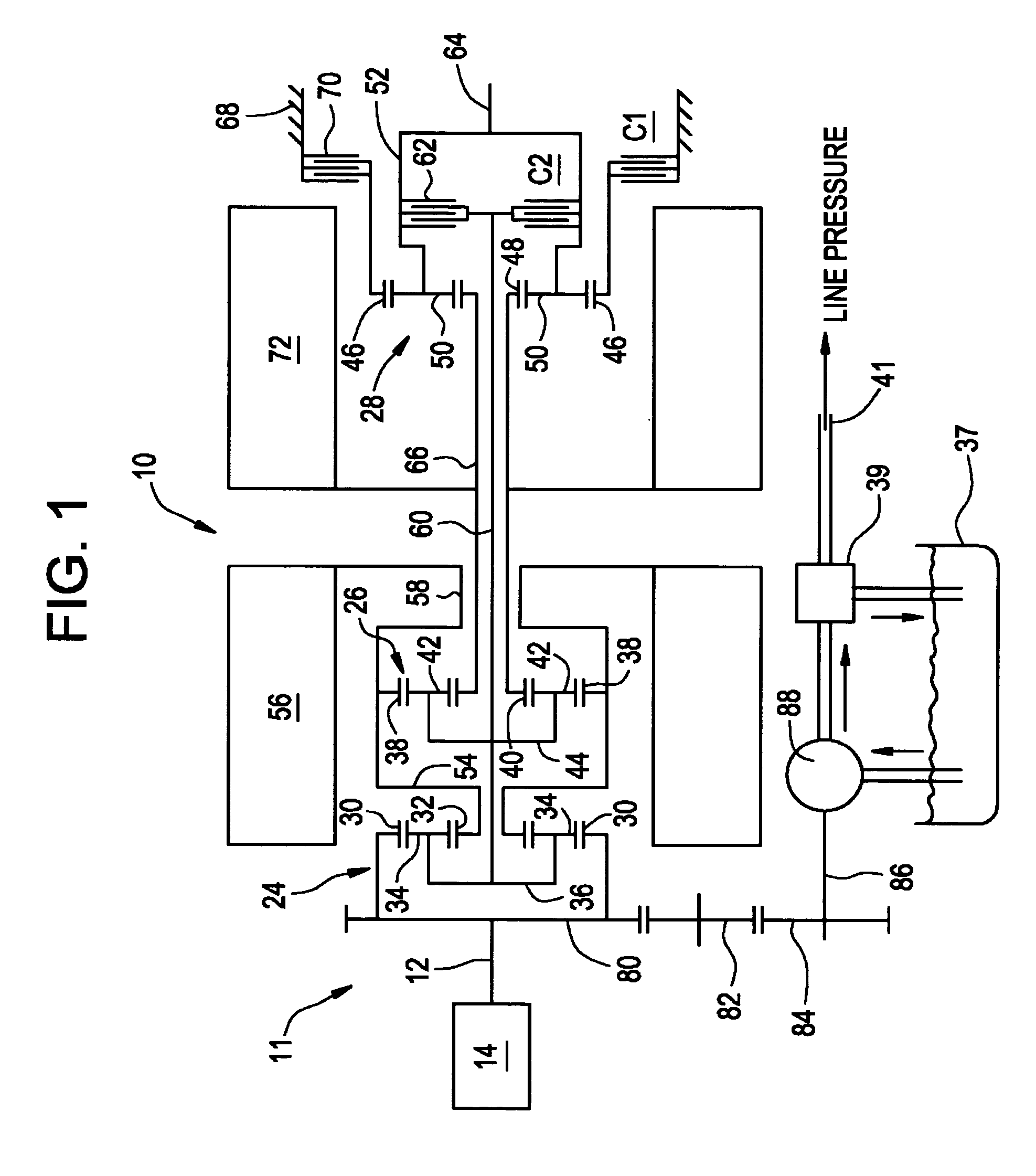
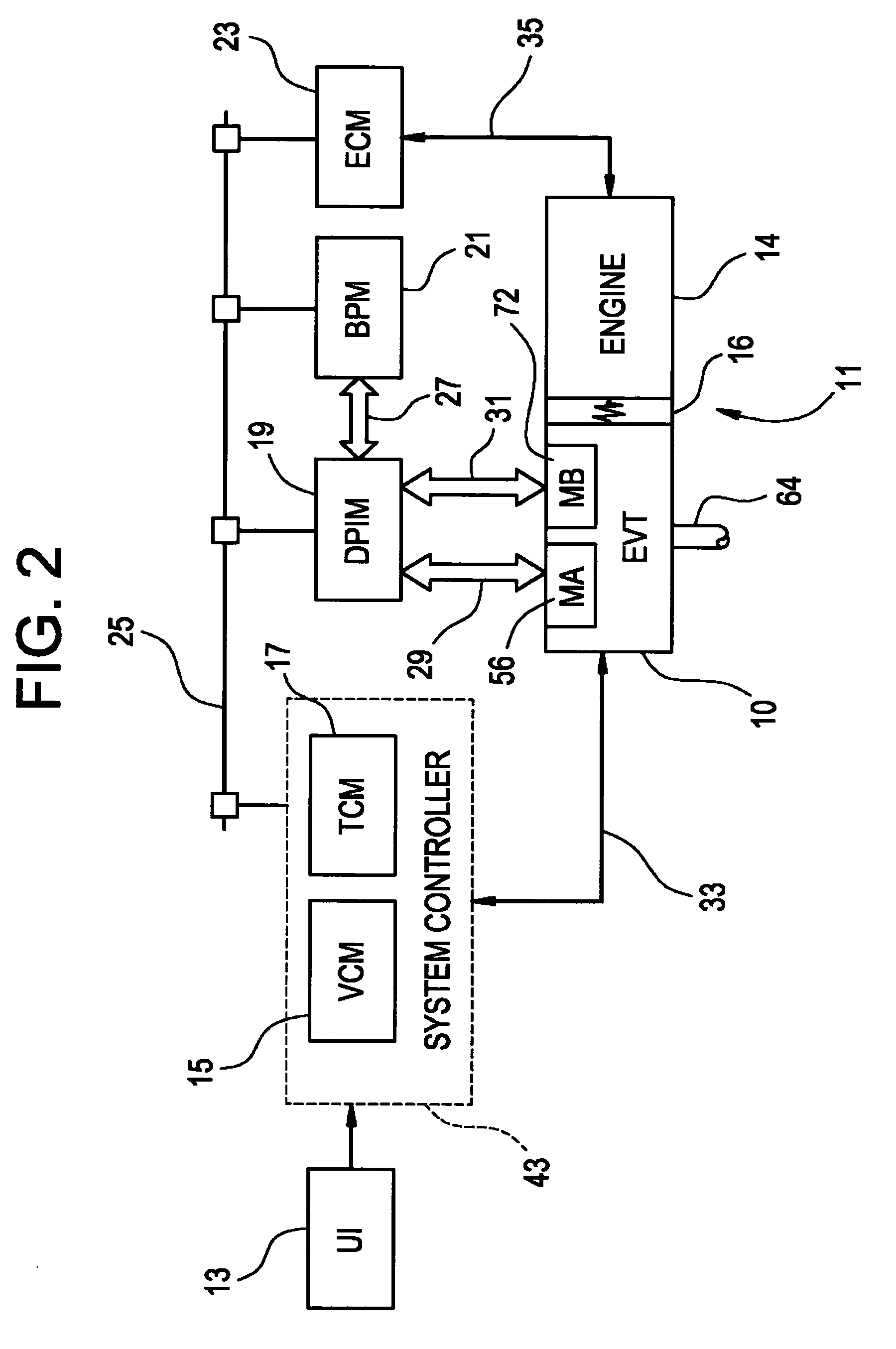
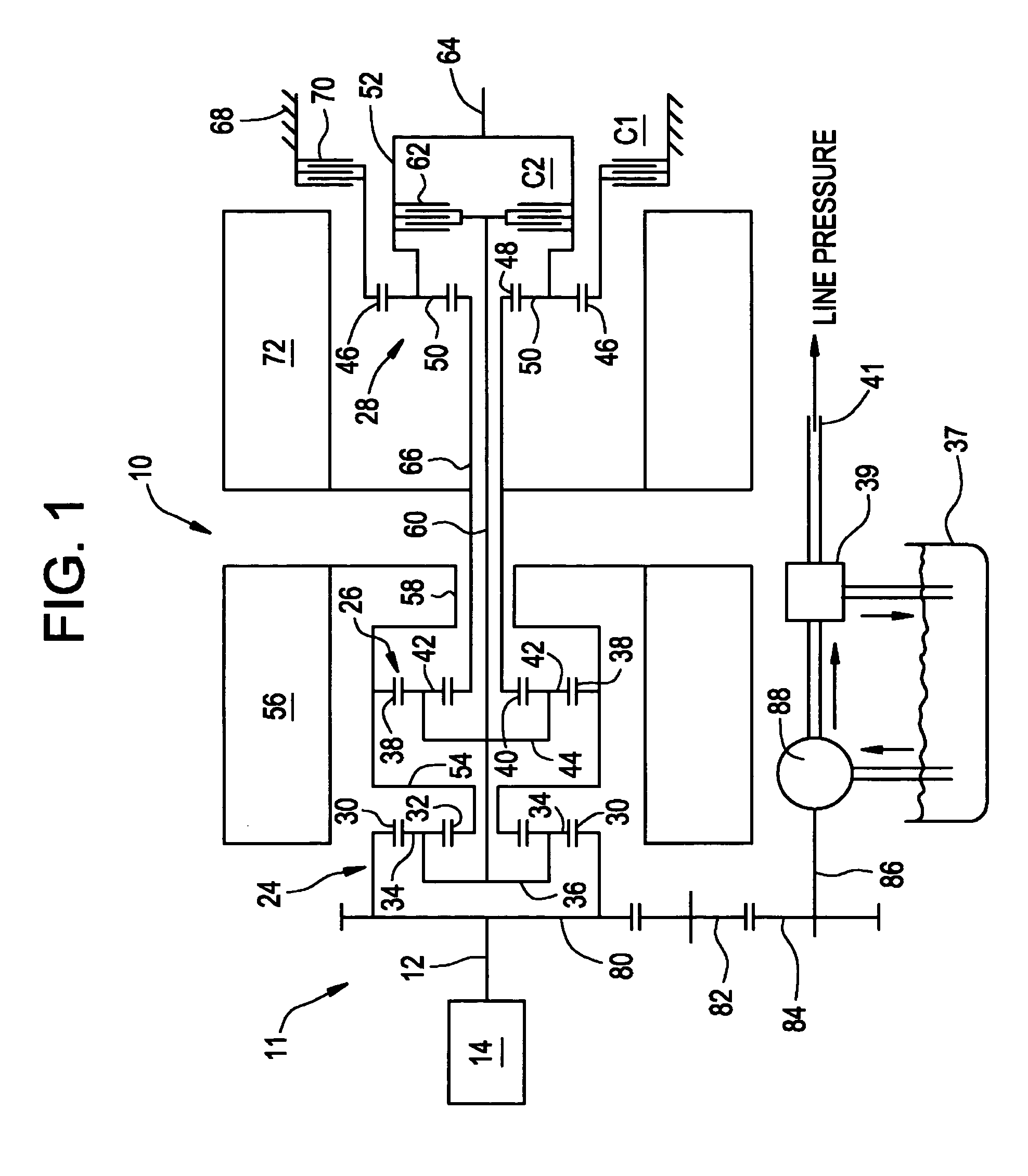
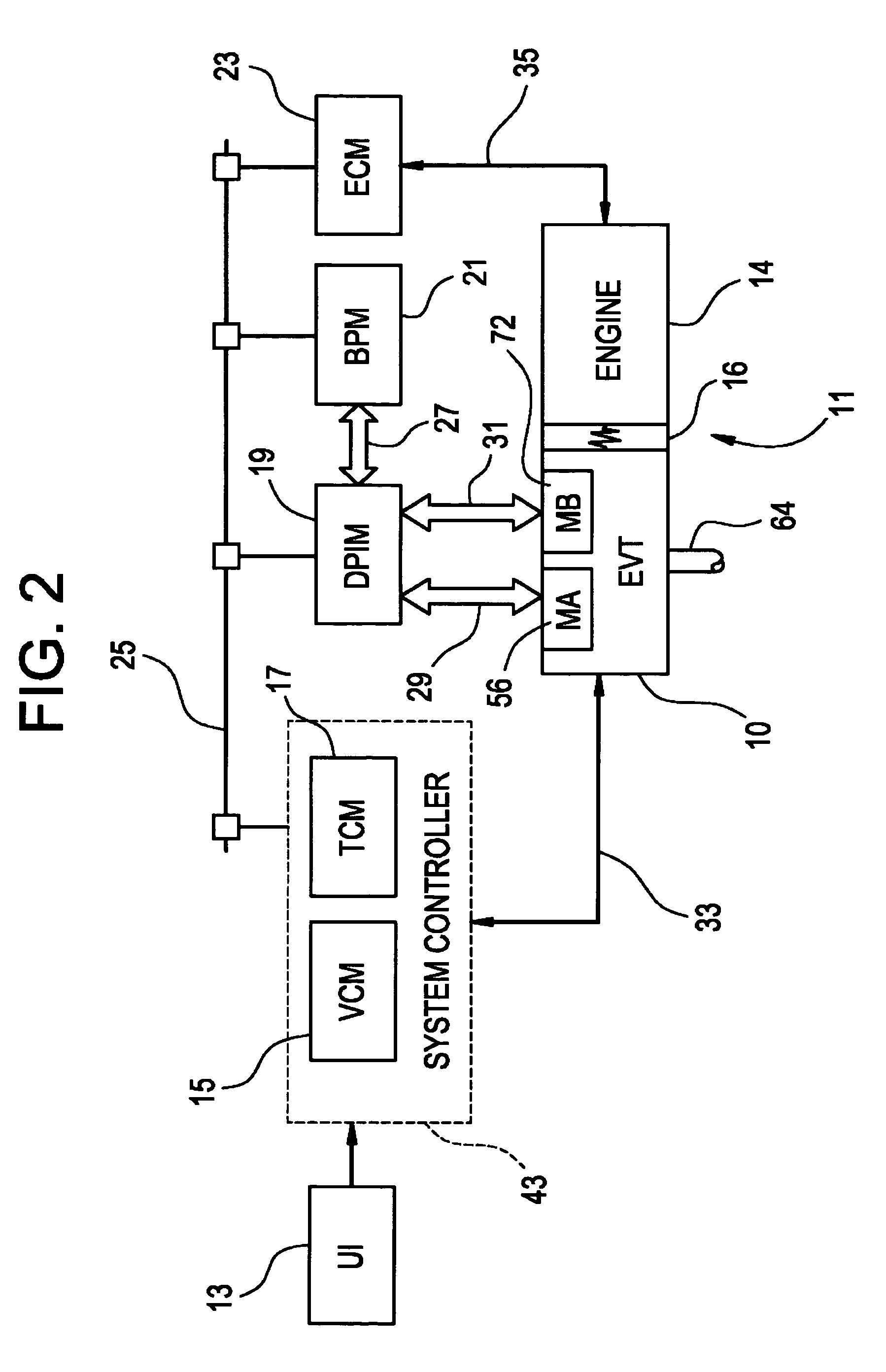
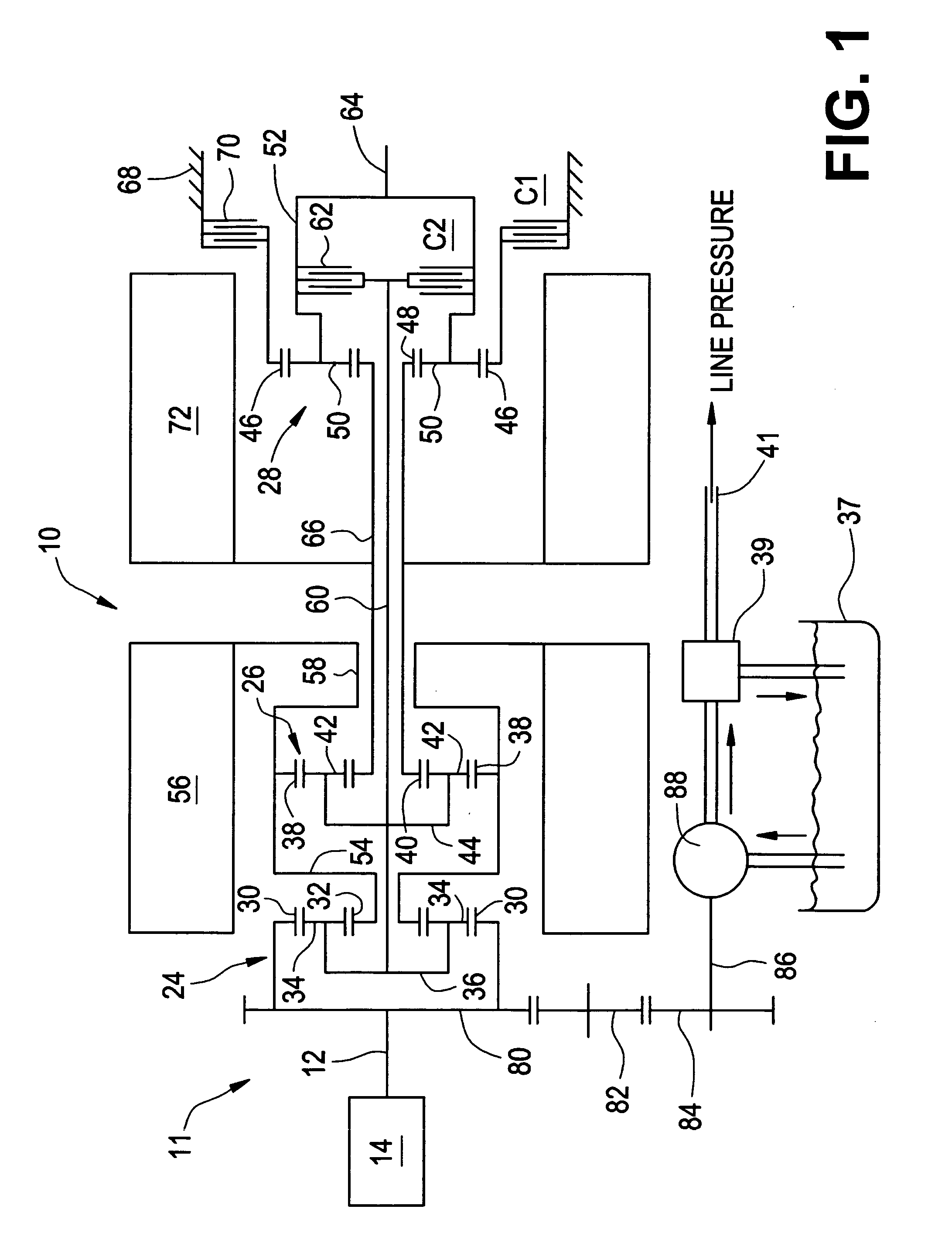
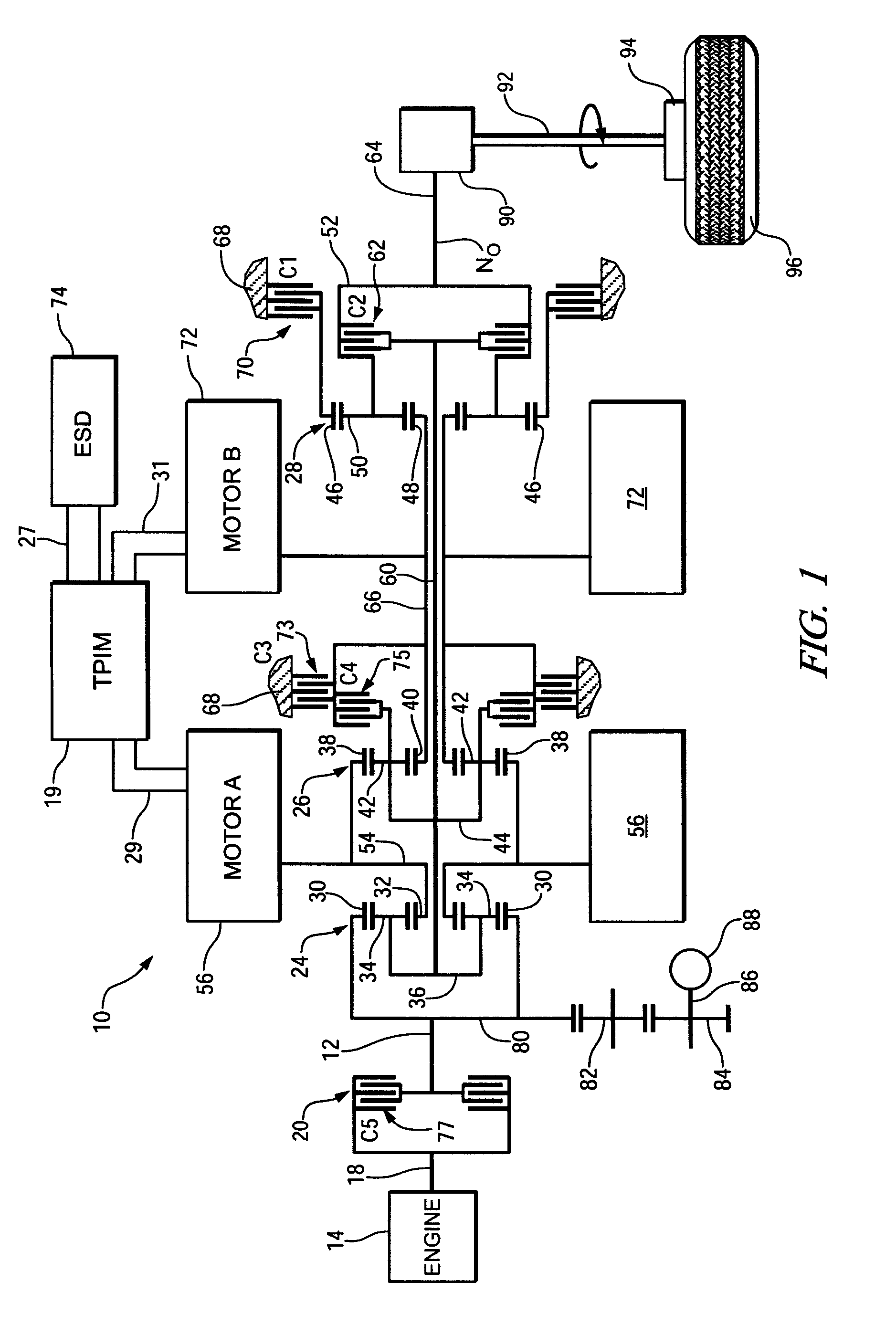
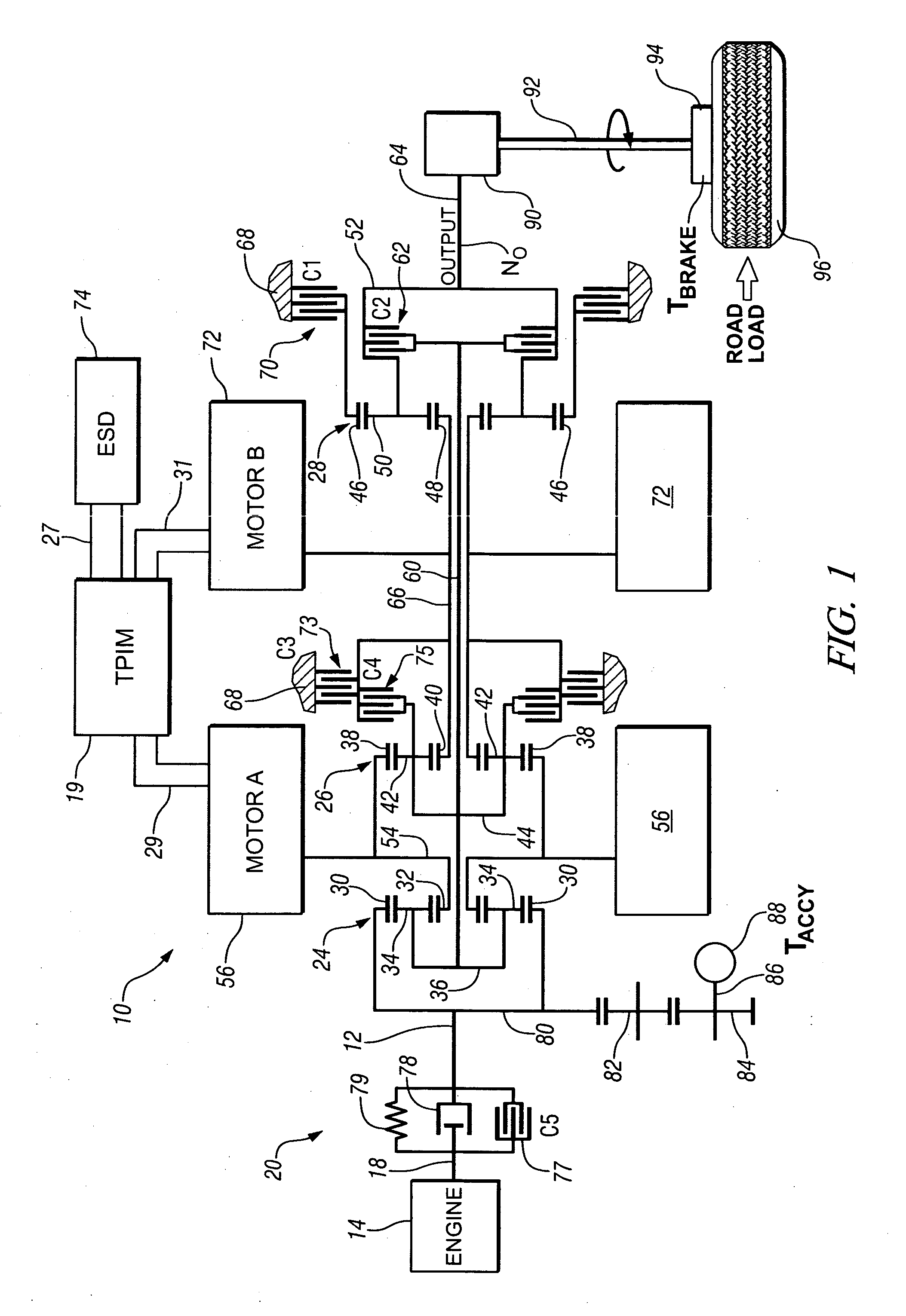
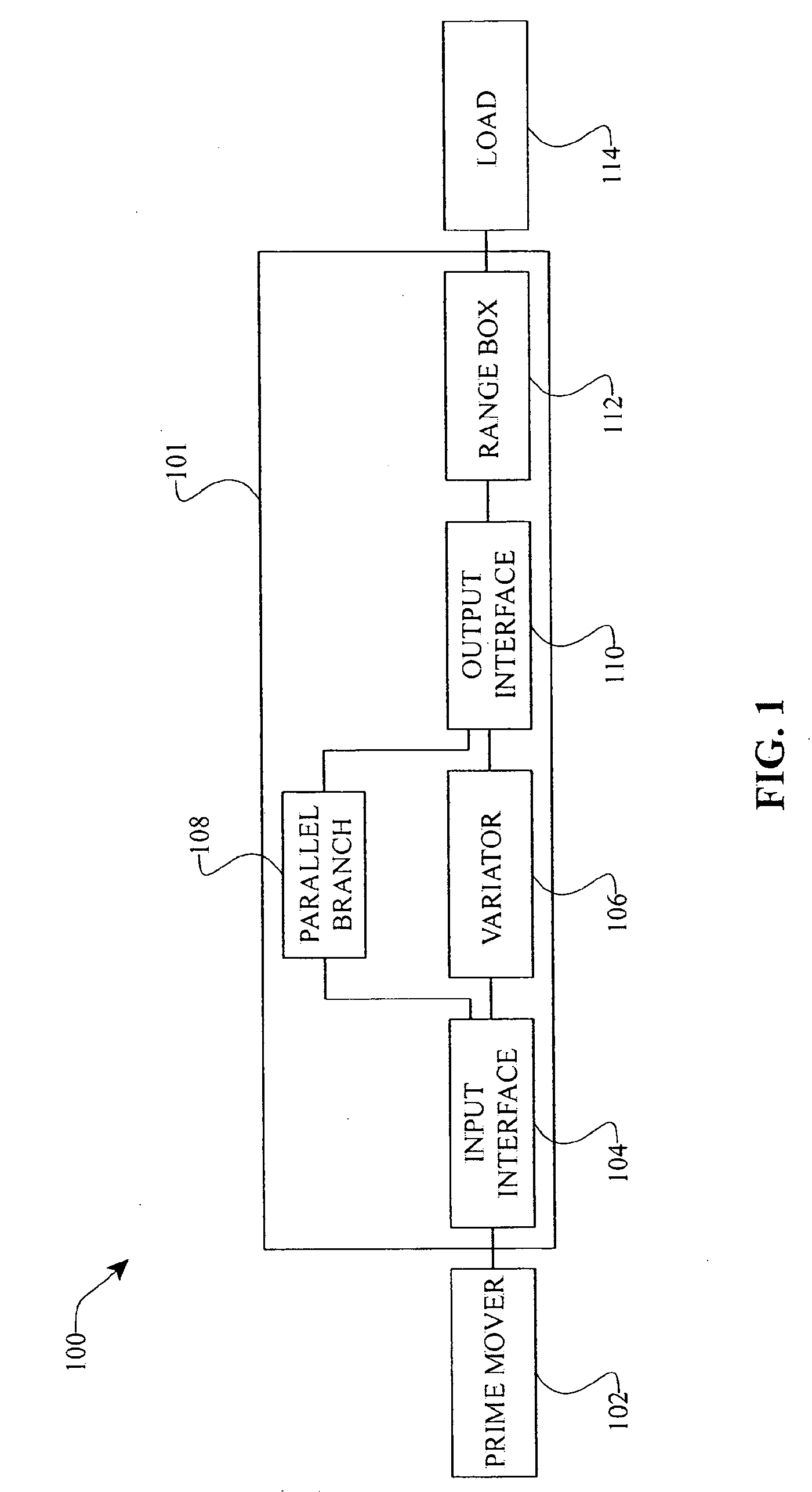
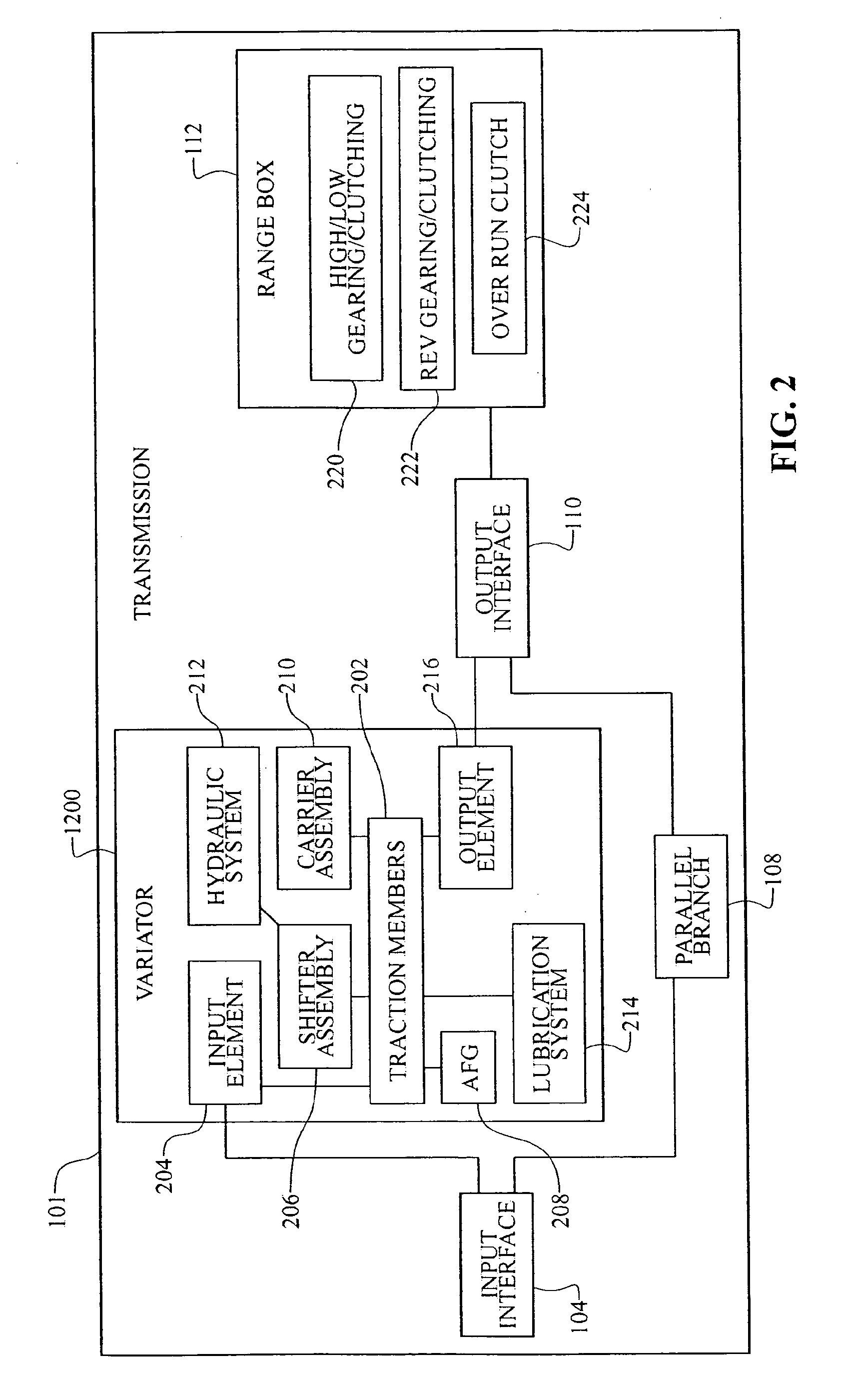
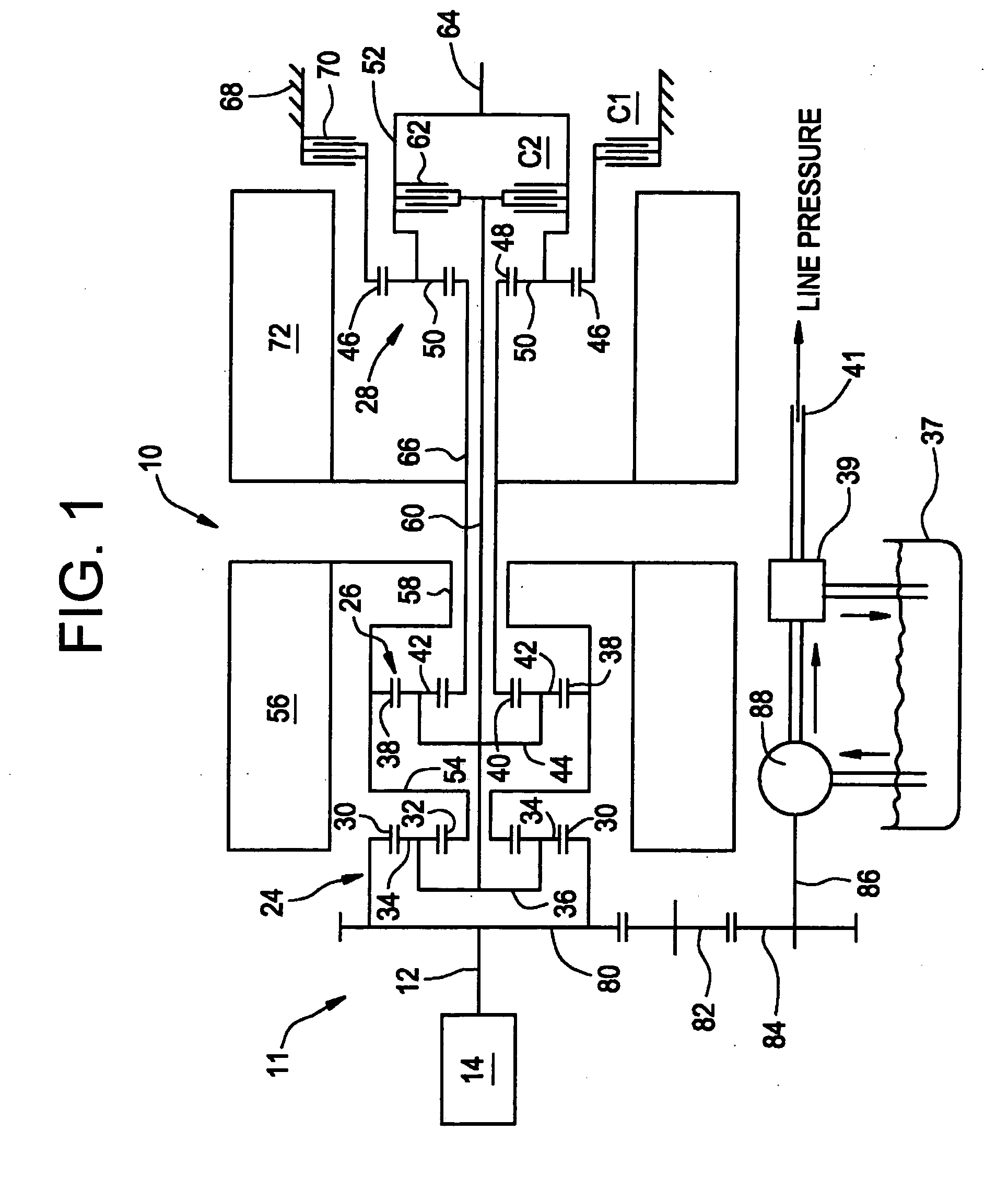
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for continuously variable transmissions (CVT) having a variator provided with a plurality of tilting, traction planets and traction rings. In one embodiment, a variator is coupled to a rangebox to provide multiple operating modes. In another embodiment, a hydraulic system is configured to control the transmission ratio of the variator and the rangebox. Various inventive shift-cam-and-sun subassemblies can be used to facilitate shifting of the transmission ratio of a CVT. Embodiments of a transmission housing and bell housing are adapted to house components of a CVT and, in some embodiments, to cooperate with other components of the CVT to support operation and / or functionality of the CVT. Various related devices include embodiments of, for example, a pivot arm, a control feedback mechanism, axial force generation and management mechanisms, a control valve integral with an input shaft, a pivot pin hub, and a rotatable carrier configured to support planet-pivot arm assemblies. FIG. 72 shows a torque-split ball-type rolling traction CVT with a ball-type rolling traction variator (1200) and planetary gearset (1400) which is followed by a rangebox (1600).
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
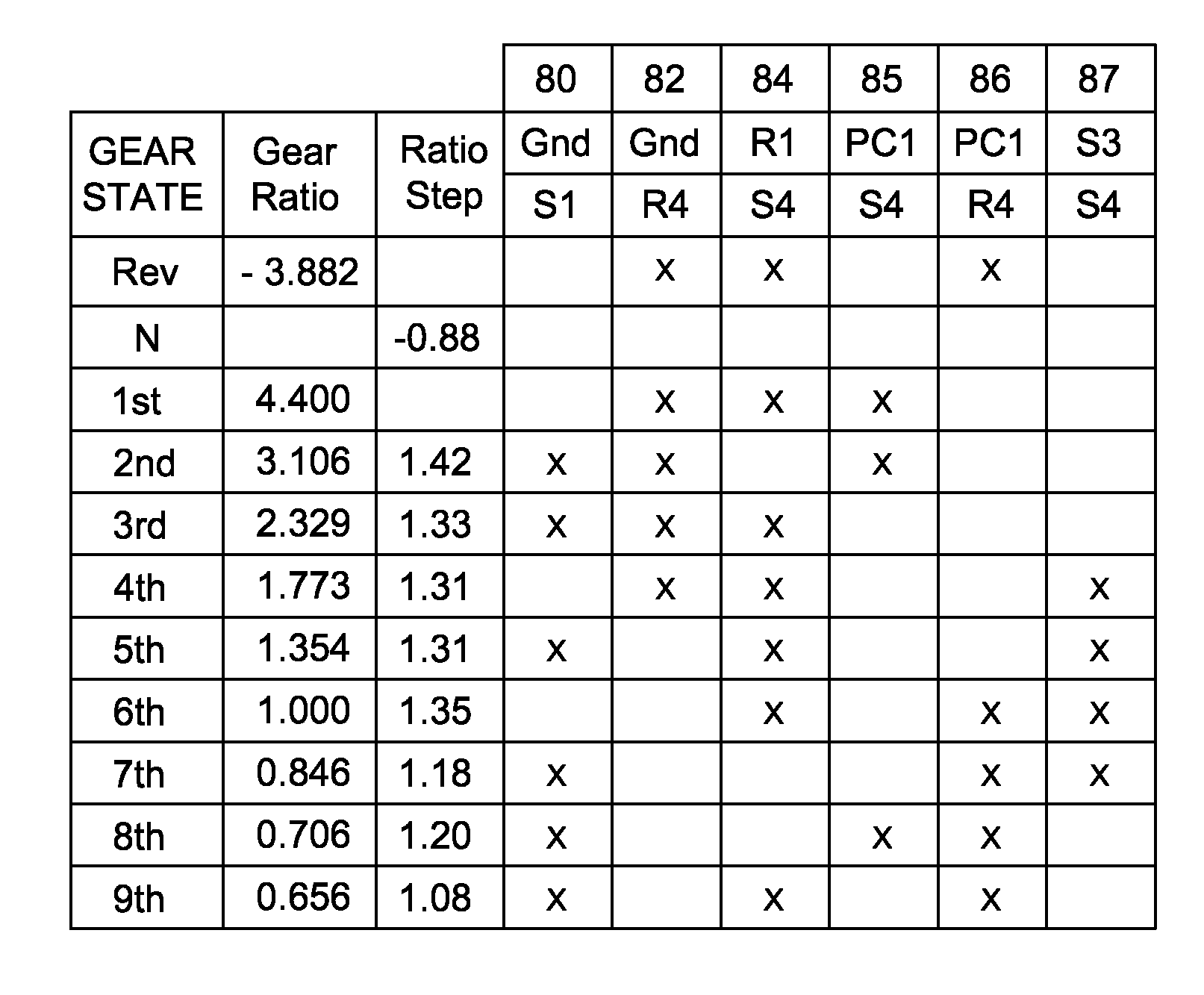
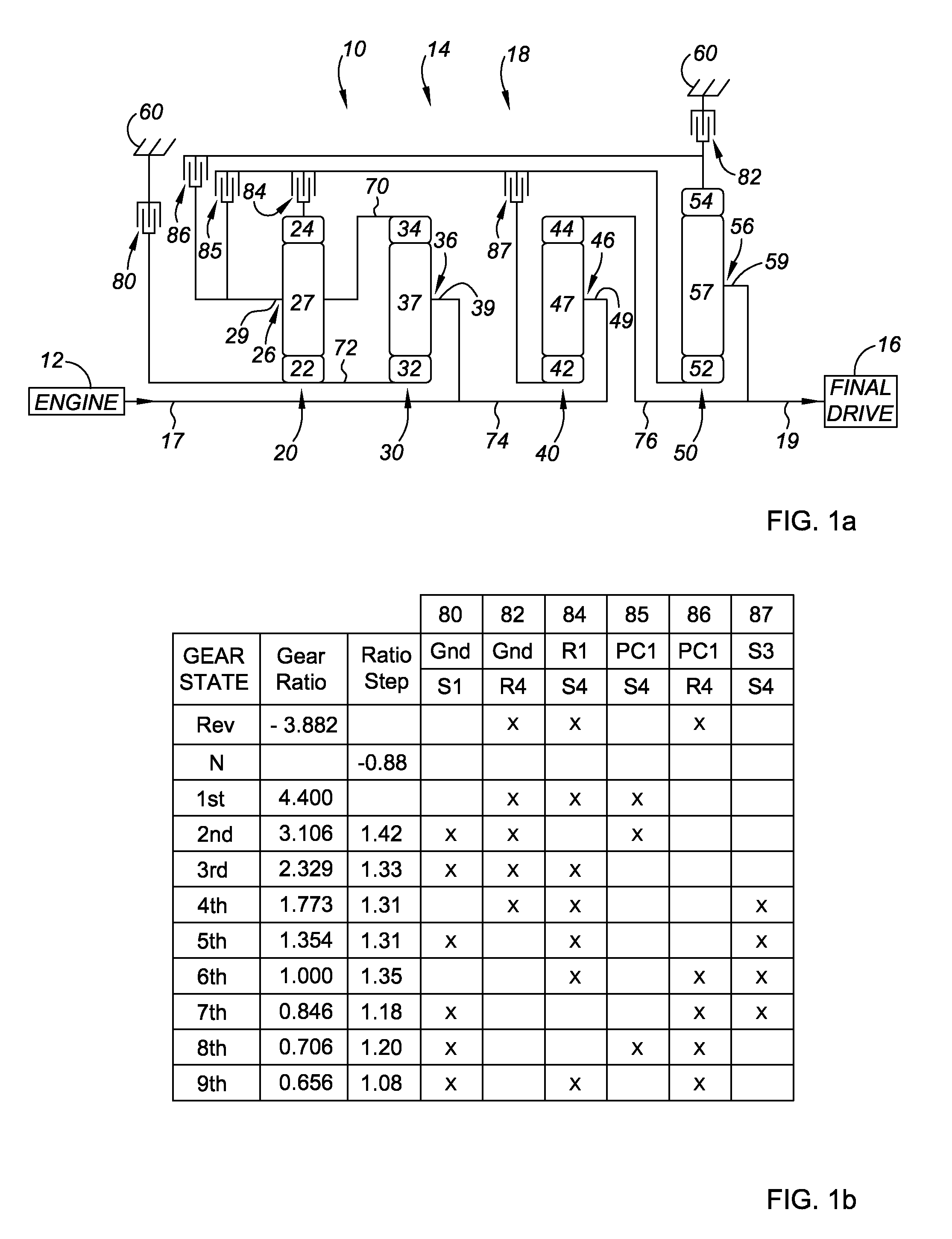
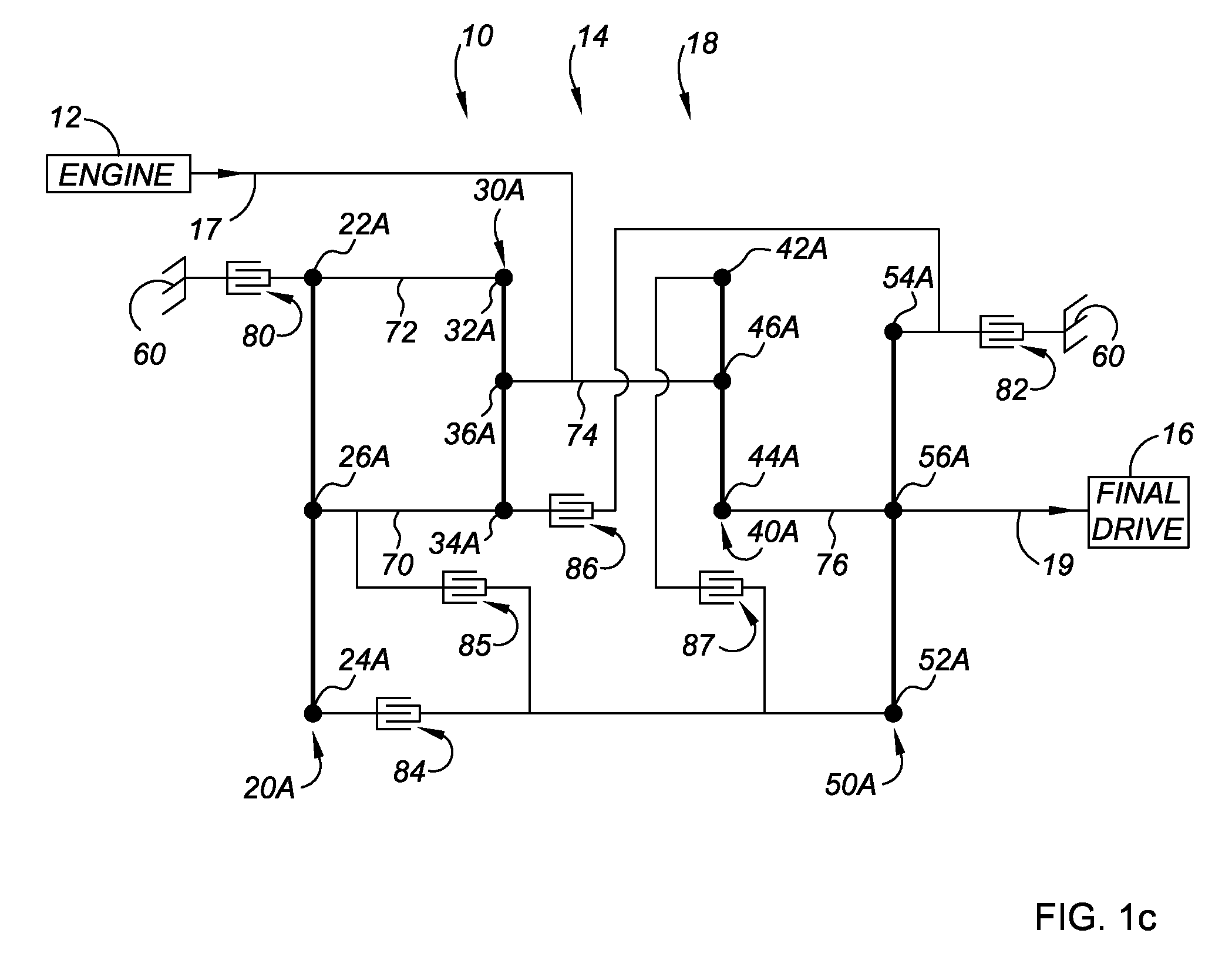
9-Speed Transmission
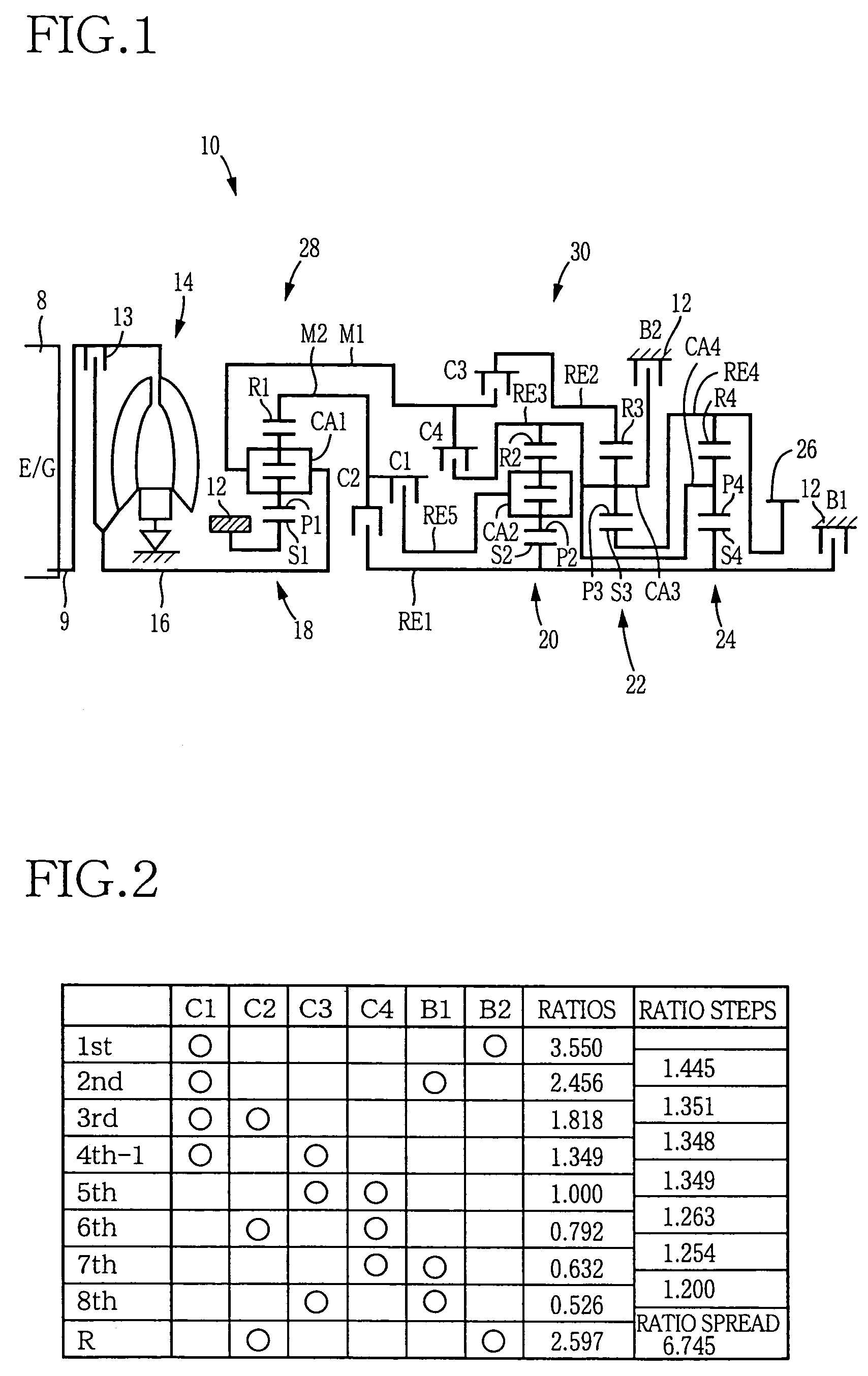
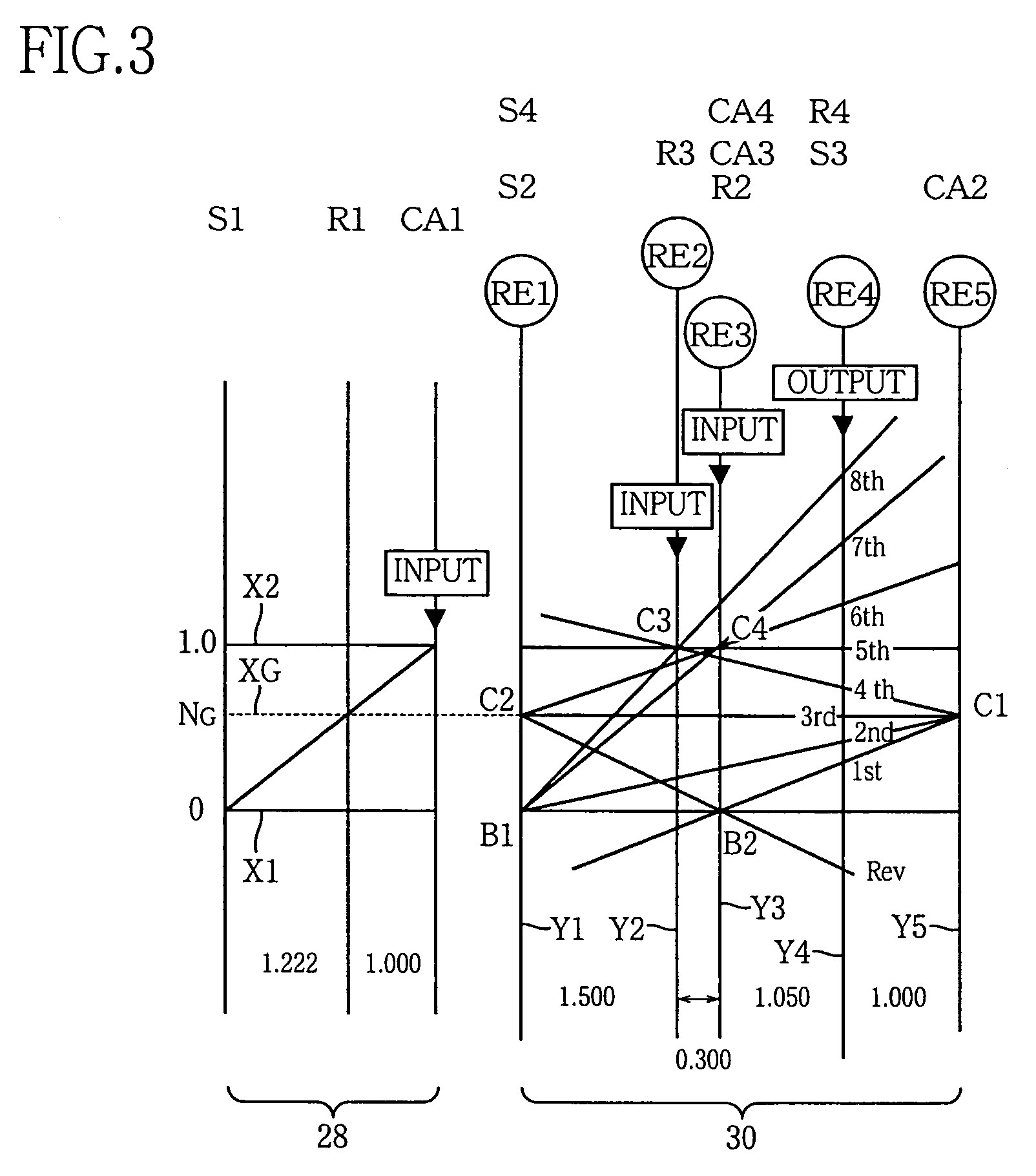
The transmission has a plurality of members that can be utilized in powertrains to provide nine forward speed ratios and one reverse speed ratio. The transmission includes four planetary gear sets, six torque-transmitting devices and four fixed interconnections. The powertrain includes an engine and torque converter that is continuously connected to one of the planetary gear members and an output member that is continuously connected with another one of the planetary gear members. The six torque-transmitting devices provide interconnections between various gear members, and the transmission housing, and are operated in combinations of three to establish nine forward speed ratios and one reverse speed ratio.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for processing safety signals in an autonomous vehicle
InactiveUS20060089763A1Improve securityDecrease and eliminates need for manual interventionDigital data processing detailsAnti-theft devicesUnsafe conditionActuator
System and method for processing a safety signal in an autonomous vehicle. Safety signals are typically generated in response to the detection of unsafe conditions or are sent by the vehicle operator. In either case, the safety signals are conveyed using redundant communication paths. The paths include a computer network and a current loop. The safety signals are processed, thereby causing actuators (e.g., linkages) to manipulate input devices (e.g., articulation controls and drive controls, such as a throttle, brake, tie rods, steering gear, throttle lever, accelerator, or transmission shifter). The manipulation ensures the vehicle responds appropriately to the safety signals, for example, by shutting down the vehicle.
Owner:IROBOT CORP
Method for automatic traction control in a hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS20050256629A1Improve system performanceHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsElectric machineIn vehicle
A method for providing traction control in vehicle powertrain systems is particularly adapted for traction control in a powertrain system of a hybrid electric vehicle comprising an internal combustion engine, an electric machine and a transmission that is operatively coupled to the electric machine and the engine and adapted to provide a transmission torque output in response to a transmission torque input received as a torque output from either or both of the engine and the electric machine. The method is adapted to utilize conventional traction control and engine control hardware, software and communication standards to implement traction control. In one embodiment of the invention, a conventional traction controller is used to detect a wheel spin condition and provide a plurality of first output torque command messages in response thereto. The plurality of first output torque command messages are used to obtain a torque reduction which is applied to a reference output torque to obtain a corresponding plurality of traction control output torque commands for the powertrain system during the wheel spin condition. A rate limit may also be applied to control the rate of change between successive ones of the traction control output torque commands in order to reduce the possibility of extension of the wheel spin condition, or recurrence of another wheel spin condition. Each traction control output torque command may be used to determine an associated traction control engine torque output command and traction control electric machine torque output command.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Toroidal type continuoulsy variable transmission
InactiveUS7029418B2Deterioration of hardnessAvoid unnecessary wasteGear lubrication/coolingDynamo-electric brake controlCentre of rotationVariator
A toroidai type continuously variable transmission wherein a rolling member is clamped between rotary members; and wherein a rolling face of rotary members being opposed to each other has a curved face, in which its sectional face along the plane including a center axis of rotation is shaped into an arc, in order to allow said rolling face of said rolling member inclining against the center axis of the rotation of said rotary member, characterized by: an oiling hole formed on the portion on the center side of the rotation in said rolling face of the rotary members being opposed to each other, or on the portion on the center side of the rotation leading to said rolling face; and the oil passage for feeding the lubricating oil to the oiling hole, formed on the center side of the rotation in said rotary member, with being communicated with the oiling hole.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com