Patents
Literature
911results about "Conjoint control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
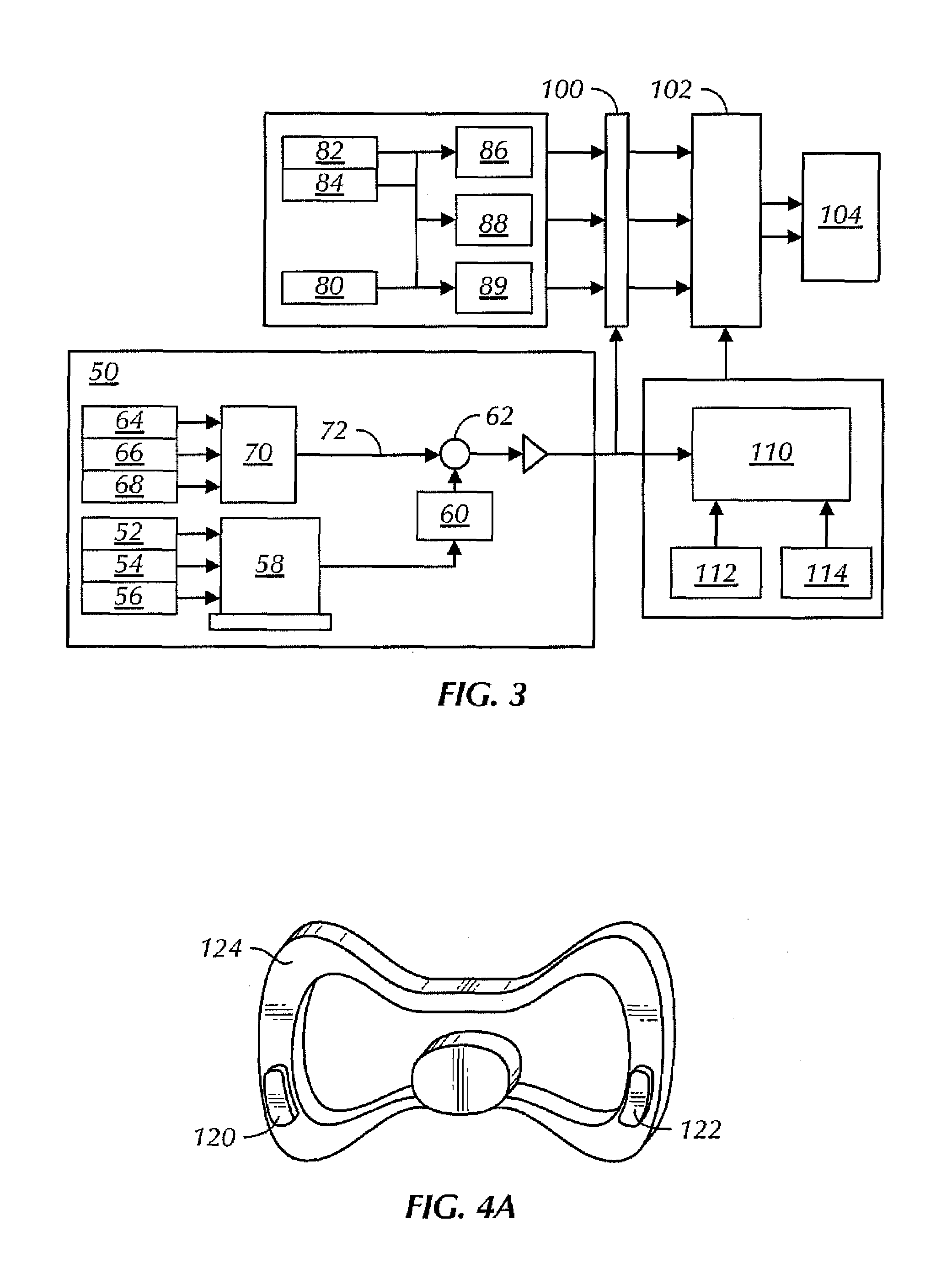
Vehicle control
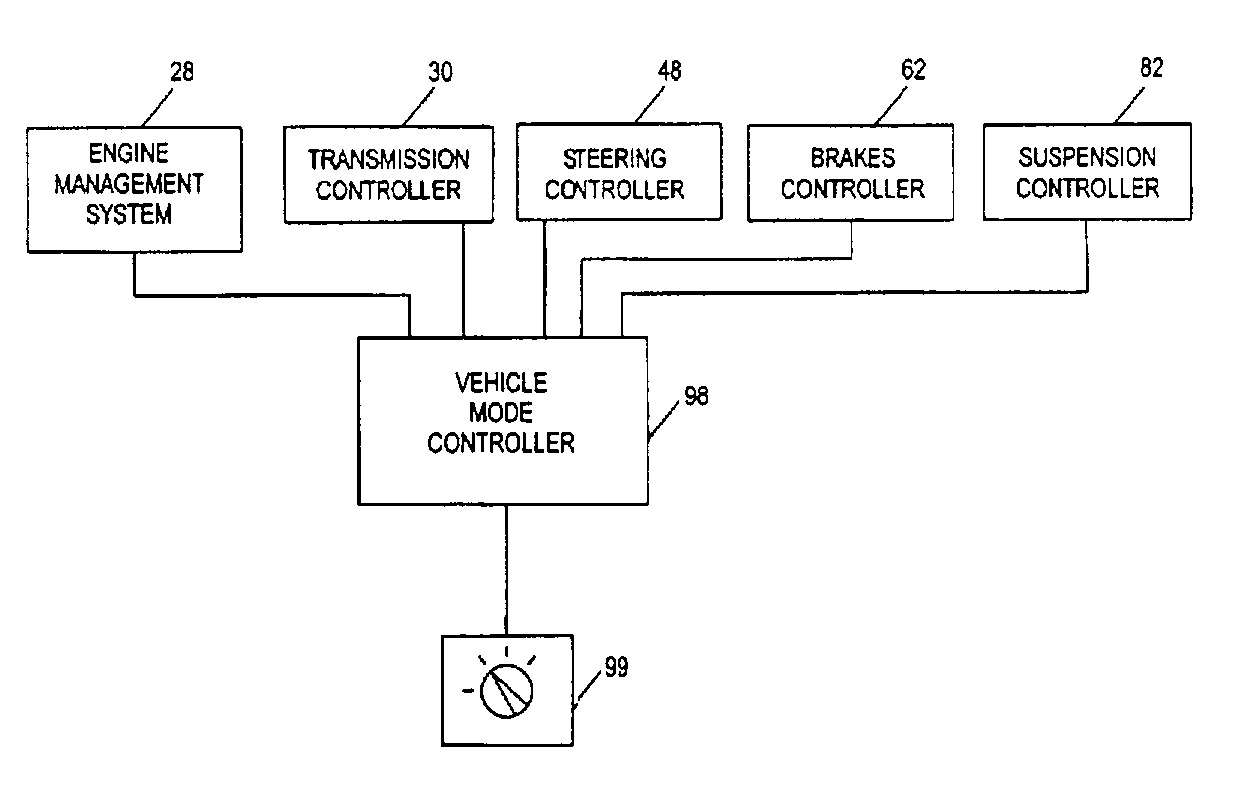
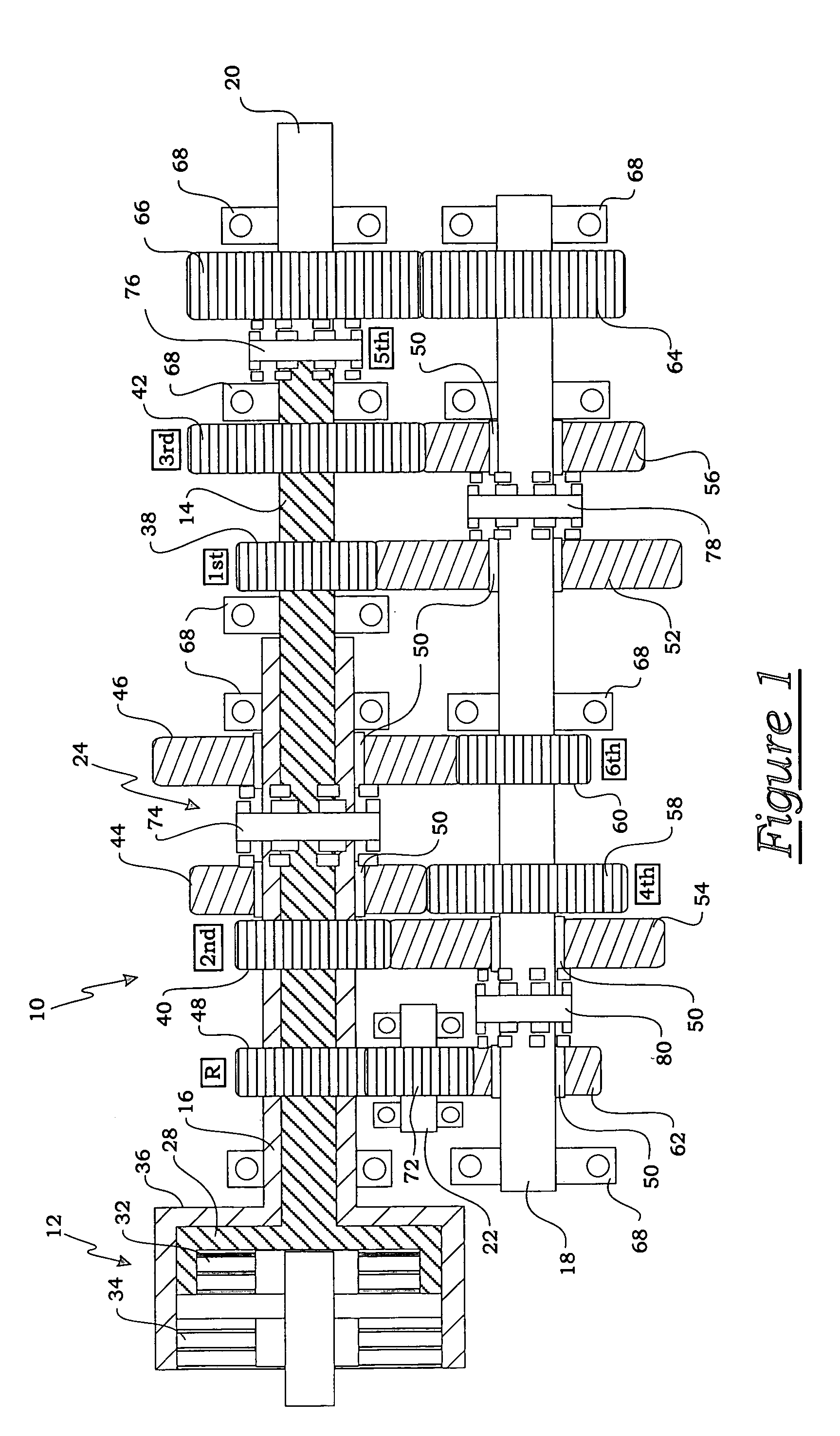
ActiveUS7349776B2Improved vehicle controlEasy to controlBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsControl systemMode control
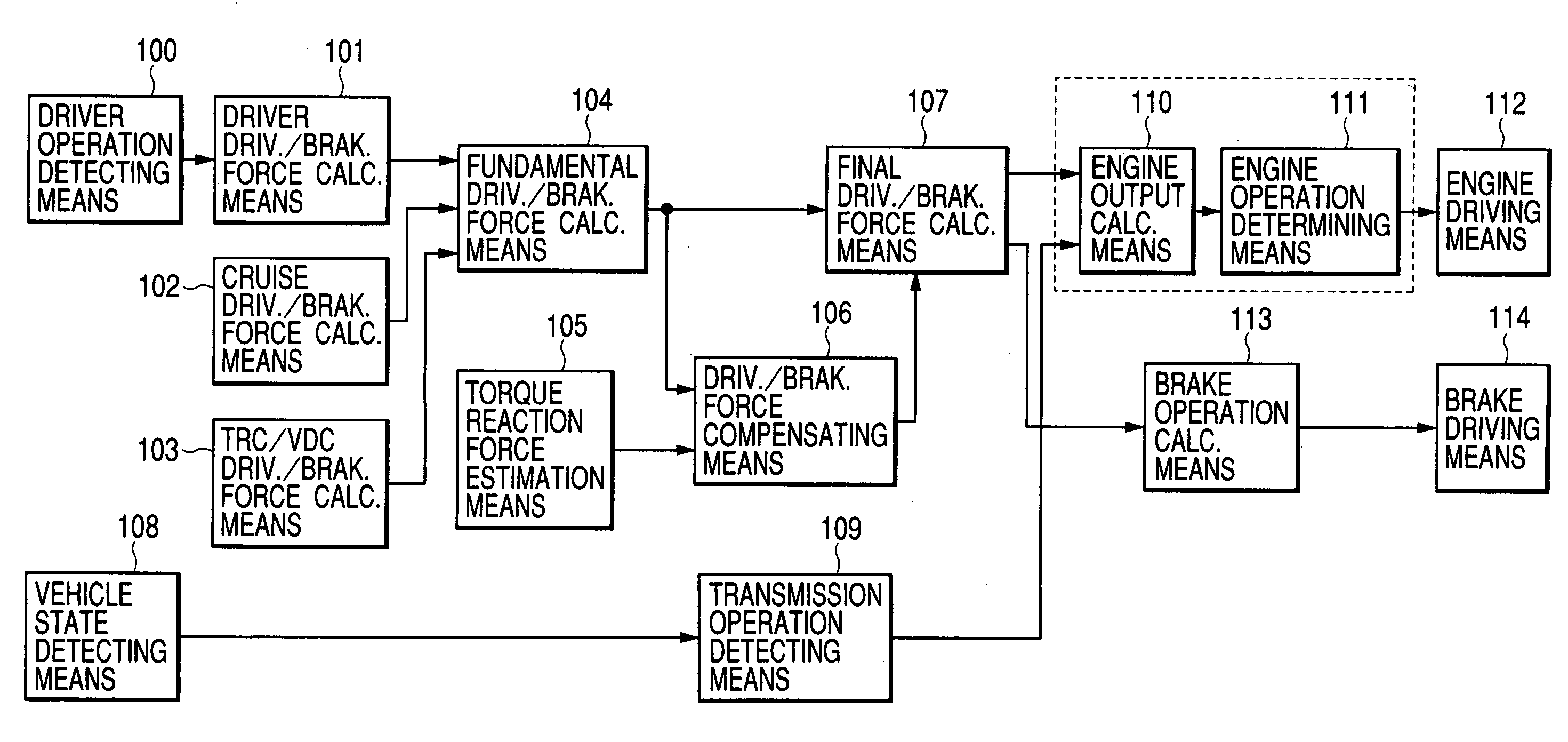
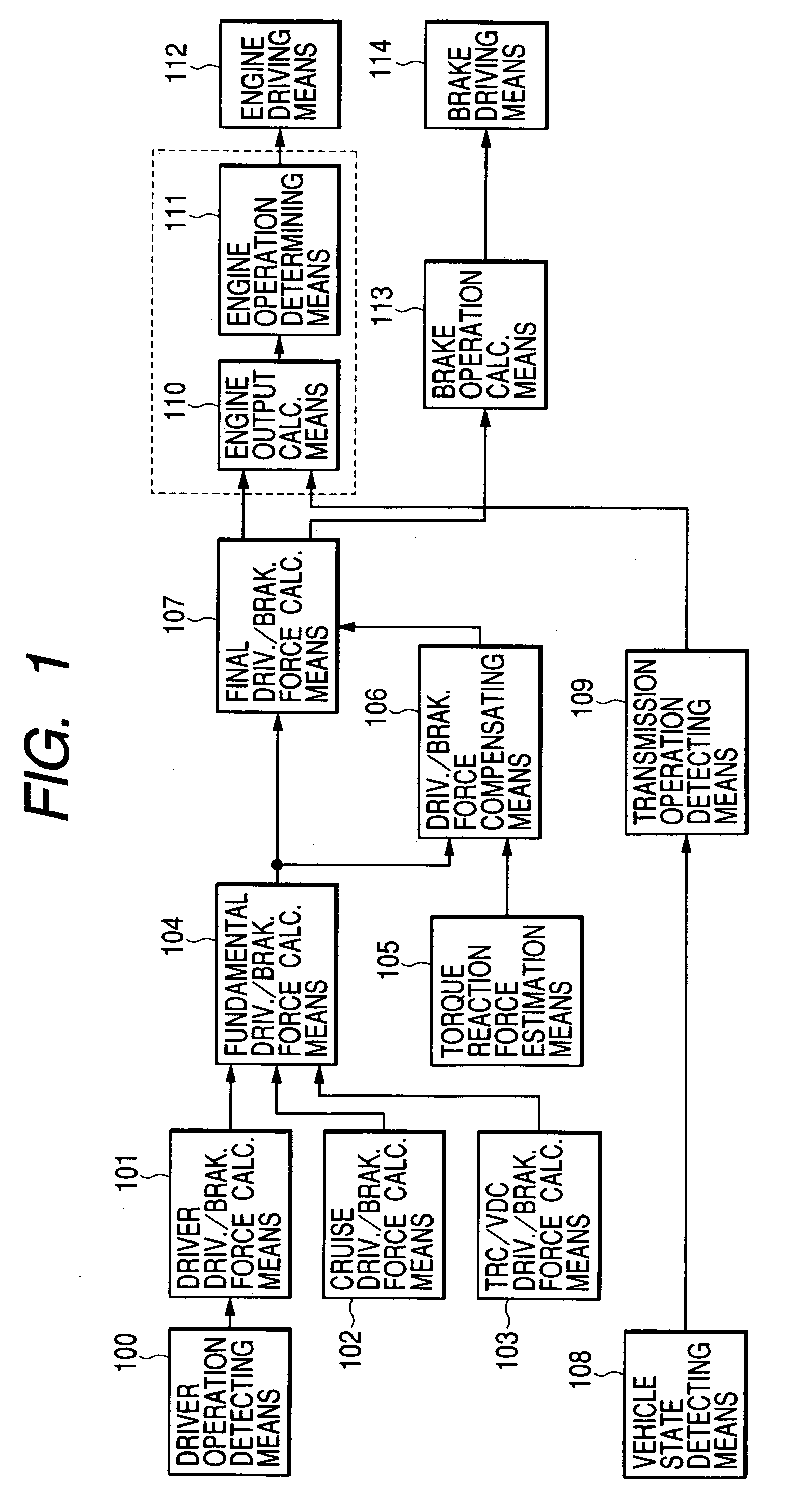
A vehicle control system has a plurality of subsystem controllers including an engine management system 28, a transmission controller 30, a steering controller 48, a brakes controller 62 and a suspension controller 82. These subsystem controllers are each operable in a plurality of subsystem modes, and are all connected to a vehicle mode controller 98 which controls the modes of operation of each of the subsystem controllers so as to provide a number of driving modes for the vehicle. Each of the modes corresponds to a particular driving condition or set of driving conditions, and in each mode each of the functions is set to the function in mode most appropriate to those conditions.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
Methods for regulating the gear ratio of an automatic power-branched transmission, and automatic power-branched transmission
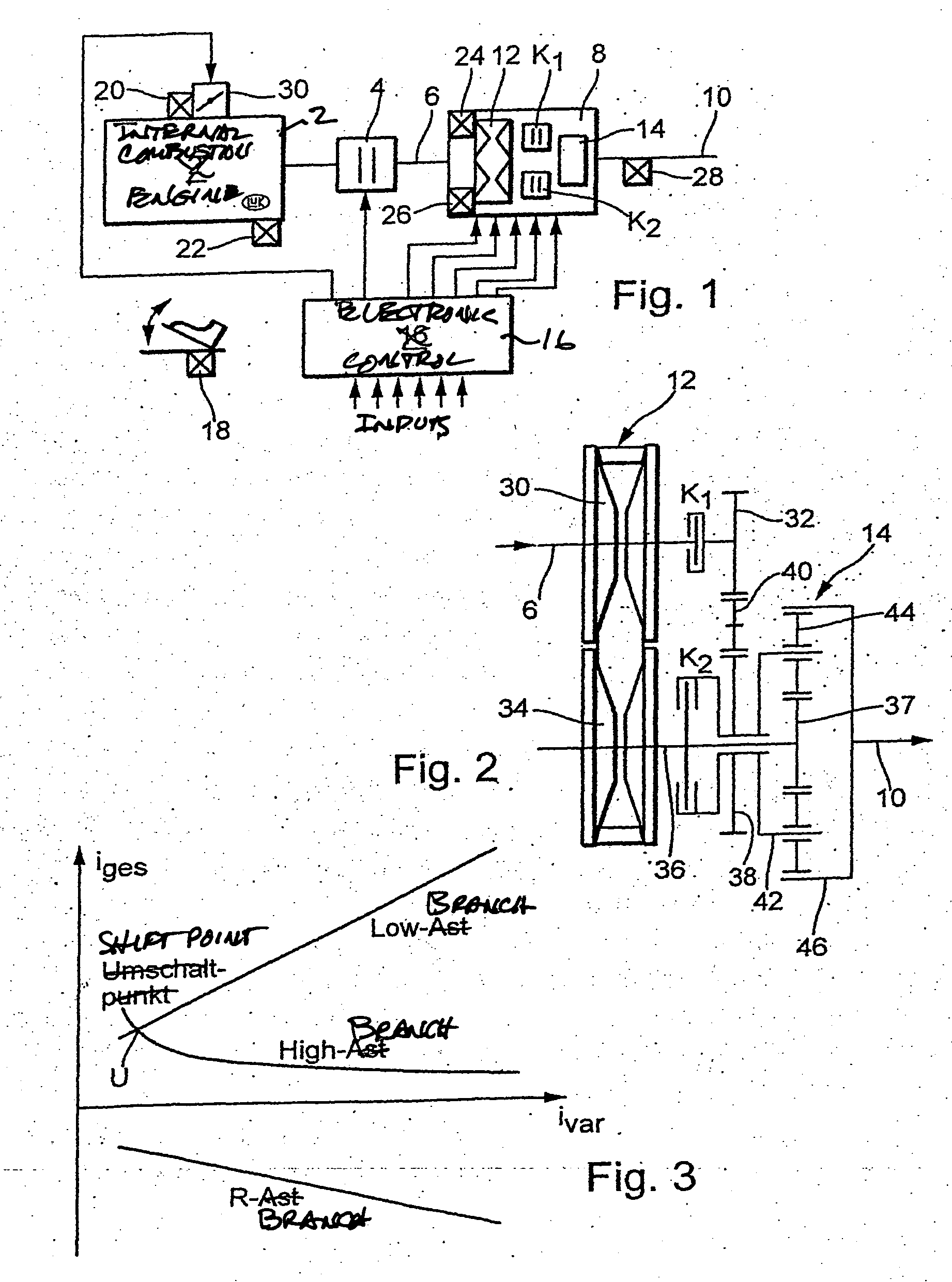
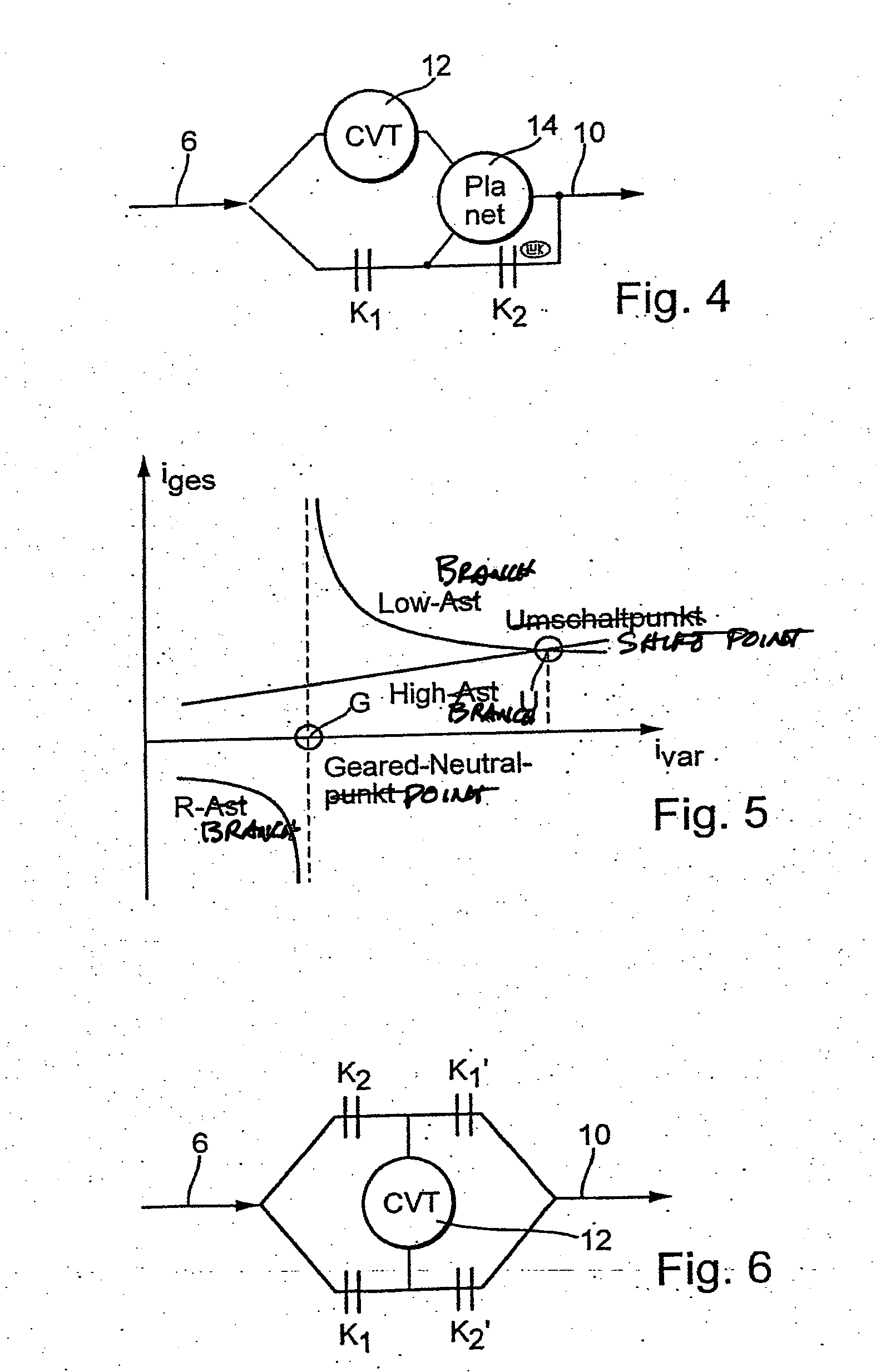
A method for regulating or controlling the transmission ratio of an automatic power-branched transmission. Power is transmitted through a shaft driven by an engine, a variable speed drive, a gear transmission, a driven shaft, and at least two control clutches. The variable speed drive and the gear transmission are connected to each other in such a way that the regulating range of the variable speed drive is traversed in one direction within a first range of transmission ratios, and is traversed in the opposite direction within a second range of transmission ratios during traversing of the entire range of transmission ratios. The shifting strategies result in reduced wear of the endless belt device and allow for comfortable changing between the transmission ratio ranges.
Owner:LUK LAMELLEN & KUPPLUNGSBAU BETEILIGUNGS KG
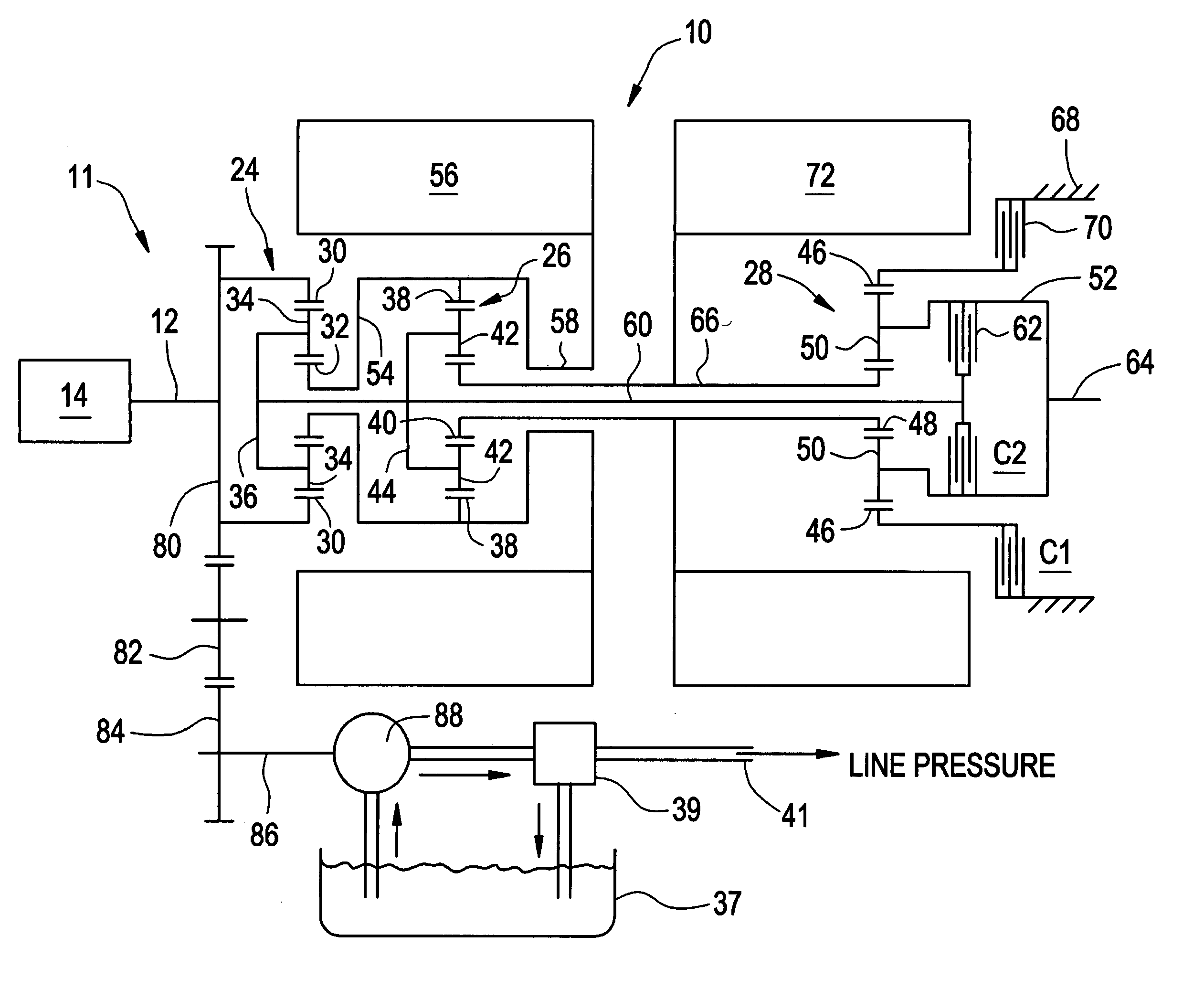
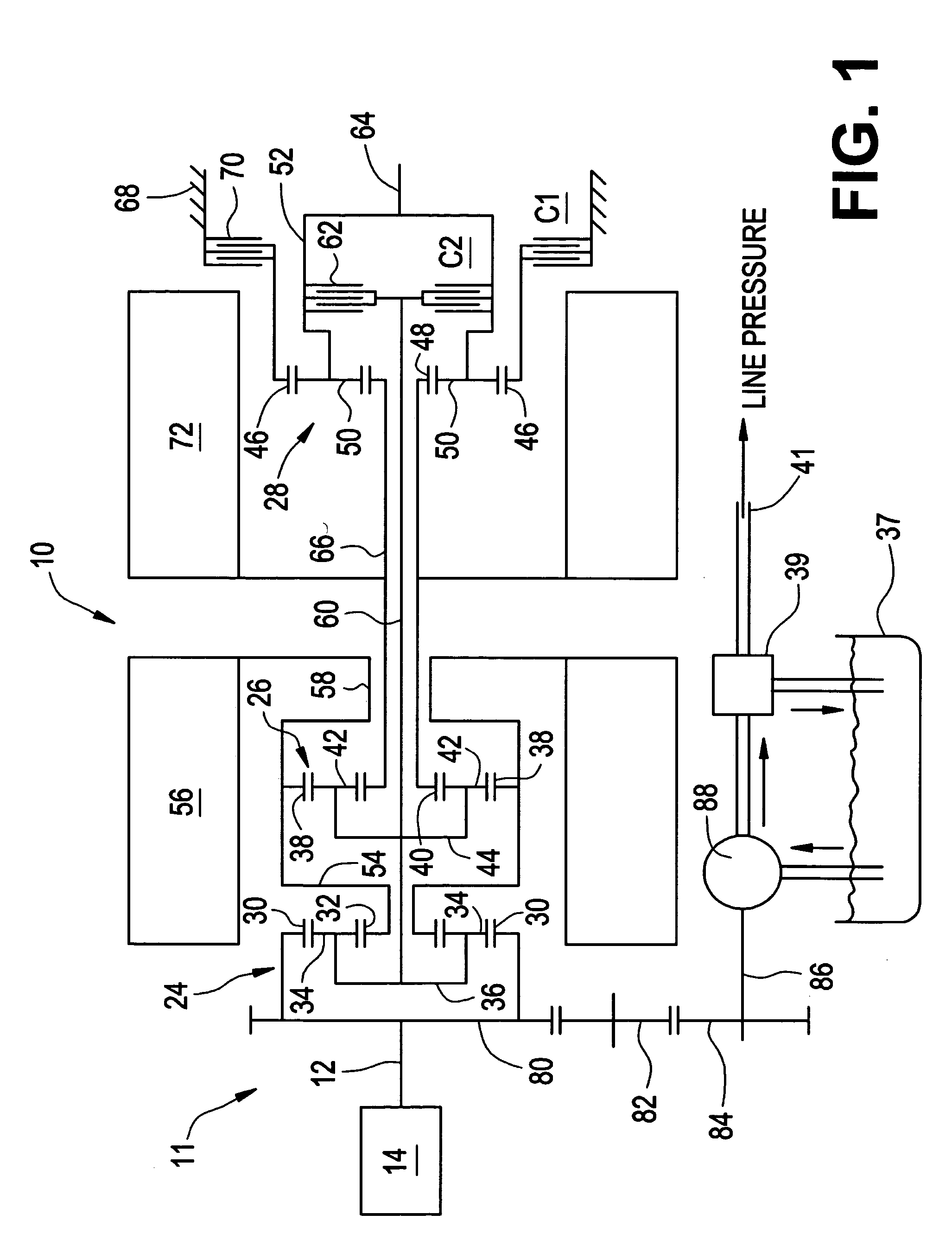
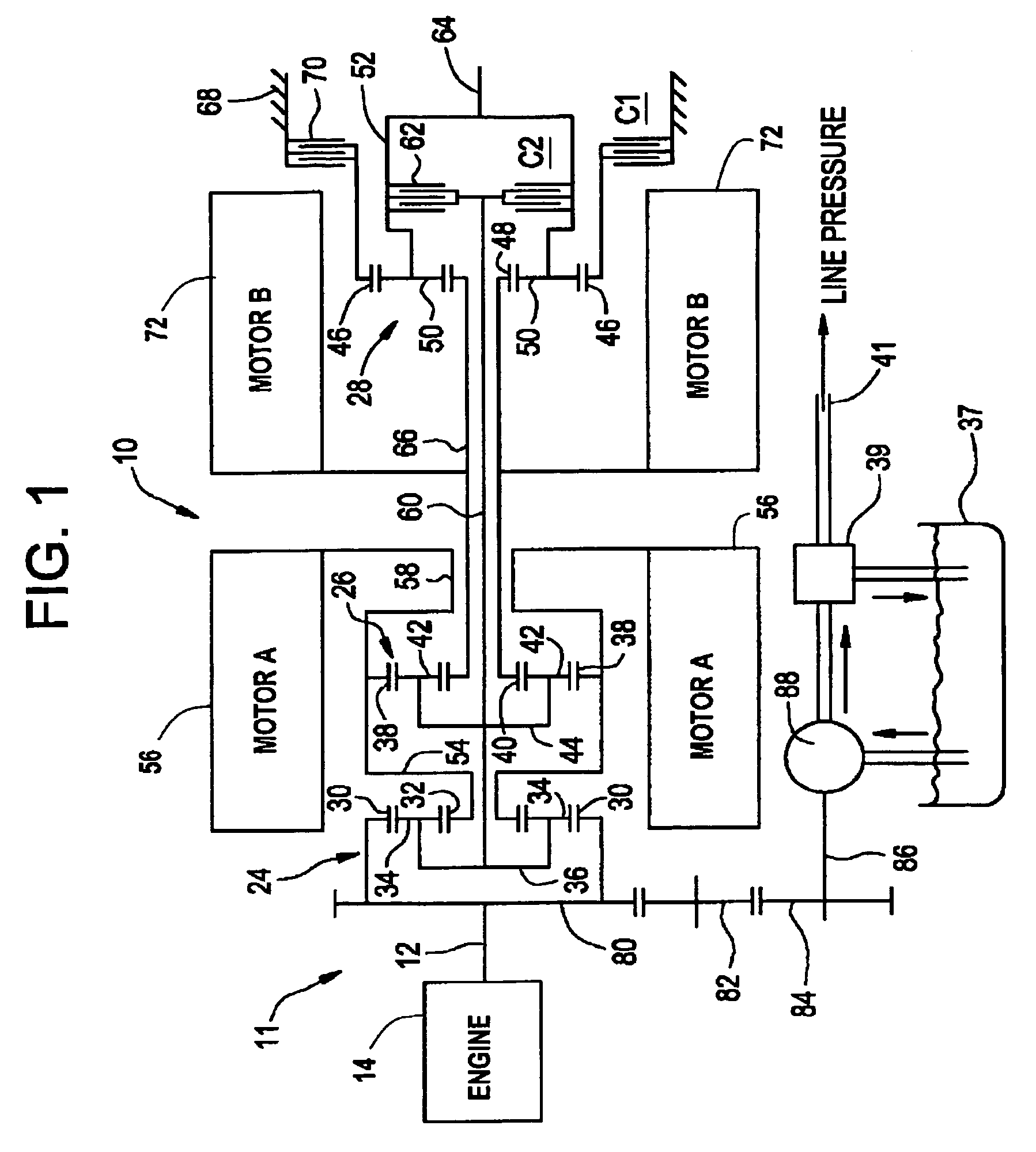
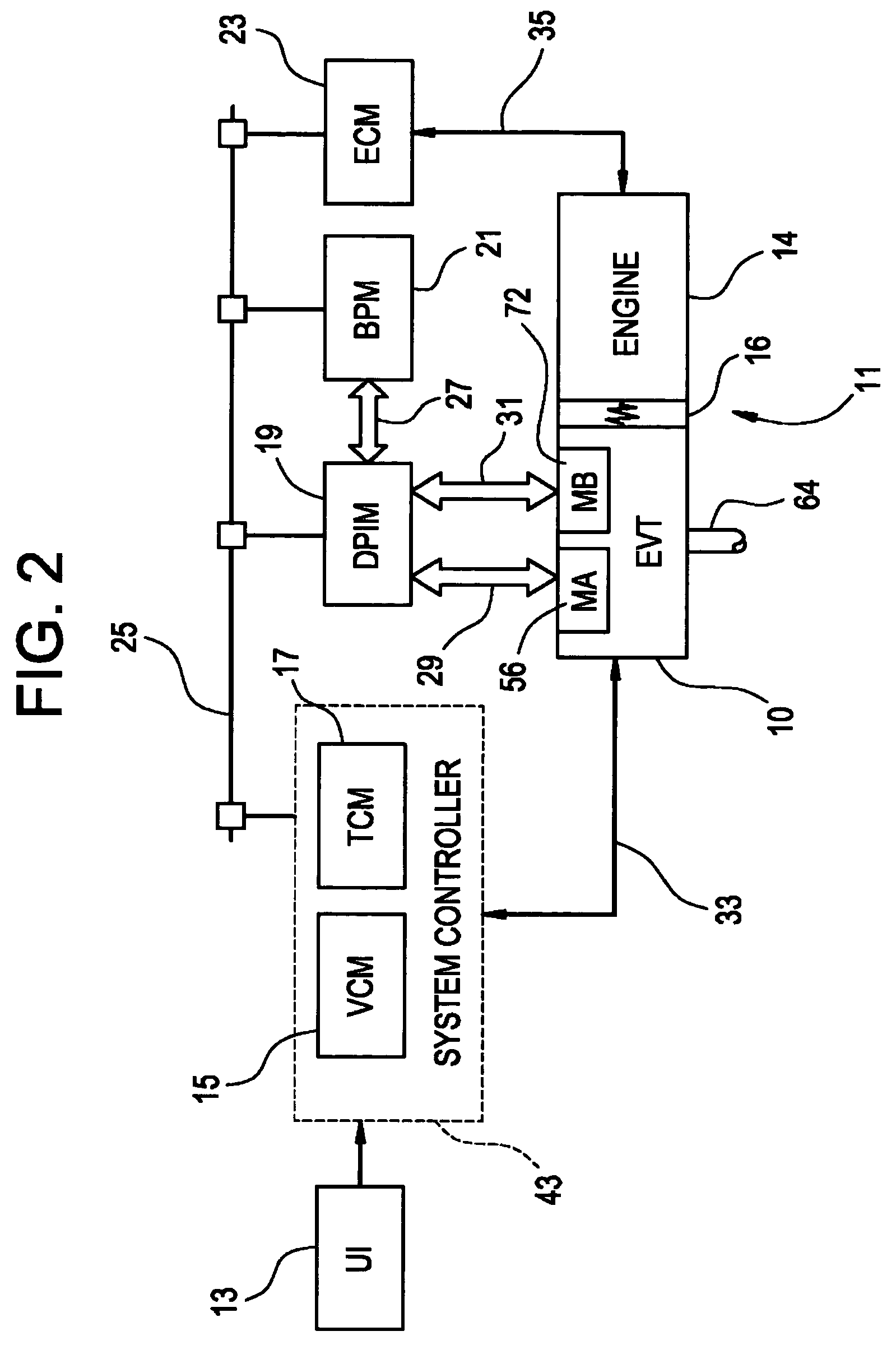
Method for dynamically determining peak output torque in an electrically variable transmission
A method for determining output torque limits of a powertrain including an electrically variable transmission relies upon a model of the electrically variable transmission. Transmission operating space is defined by combined electric machine torque constraints and engine torque constraints. Output torque limits are determined at the limits of the transmission operating space.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Coordinated regenerative and engine retard braking for a hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20050255965A1Increases the engine retard braking contributionReduce contributionHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsPower flowGear wheel
A hybrid vehicle includes a powertrain having a retarded diesel engine, an electric machine and energy storage system. The engine and motor are operatively coupled through one or more planetary gearsets and selective coupling paths in accordance with application and release of various torque transfer devices to a drivetrain via an output. Regenerative and retarded engine braking are coordinated to provide priority to energy return to an energy storage system in accordance with predetermined power flow limits. Power flow in excess of the limits are handled by increased engine retard braking contributions via engine speed increases.
Owner:ALLISON TRANSMISSION INC
Diagnostic method for a torque control of an electrically variable transmission
ActiveUS20050252283A1Impaired speed controlImpaired torque controlVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLoop controlLow speed
A condition of impaired speed and torque control of a parallel electrically variable transmission due to factors beyond nominal modeling and estimation errors is diagnosed under low speed operation. The transmission includes at least one electric machine and a motor torque controller for regulating the transmission input speed and output torque. The motor torque controller includes an open-loop control path based on predetermined torques and accelerations and a closed loop control path based on input speed error. The presence of a larger than expected closed-loop correction magnitude, combined with low output speed and one or more other conditions is used to diagnose a condition of potential torque error, in which case the transmission control is altered to prevent unwanted operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Continuously variable transmission apparatus
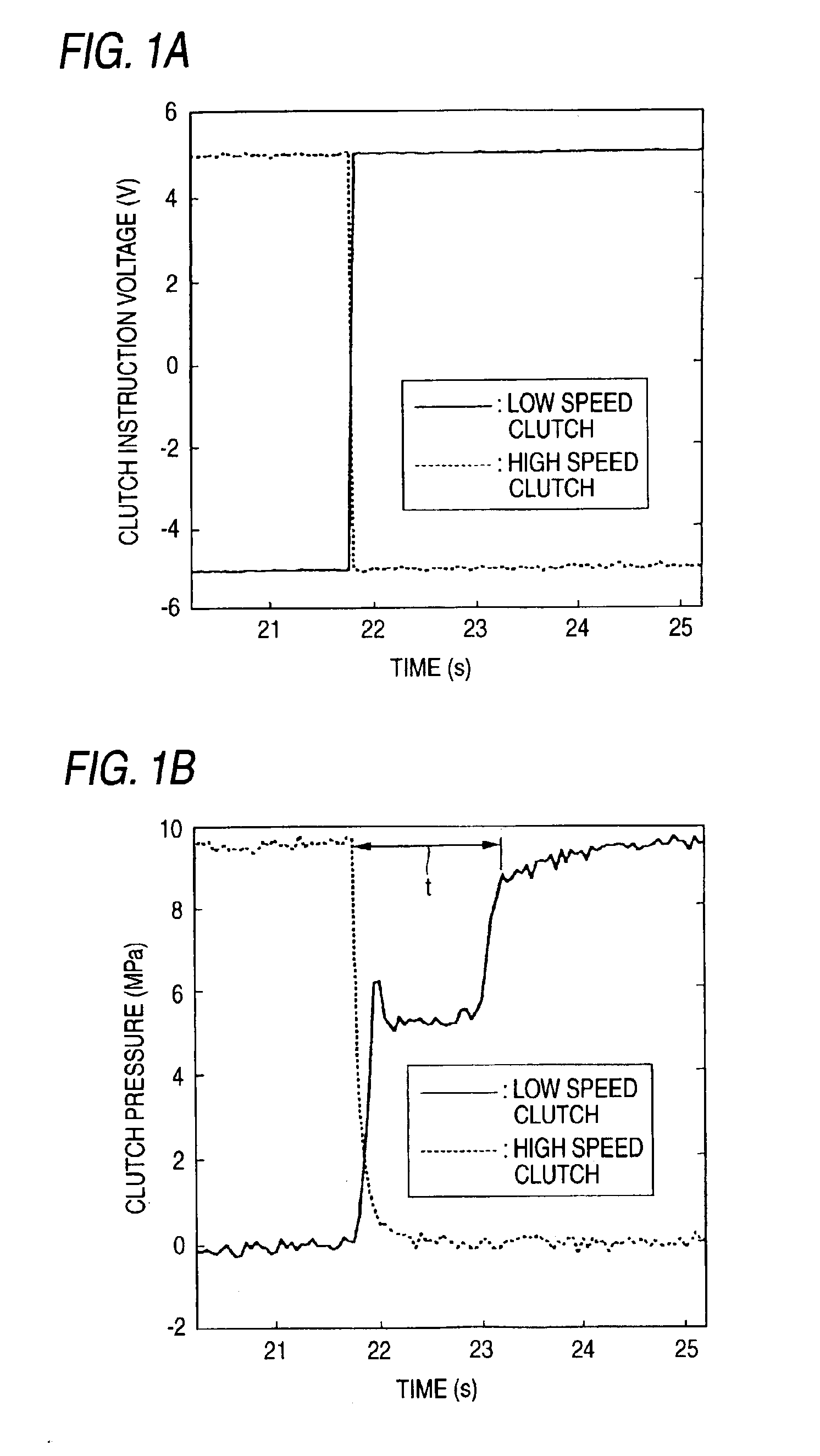
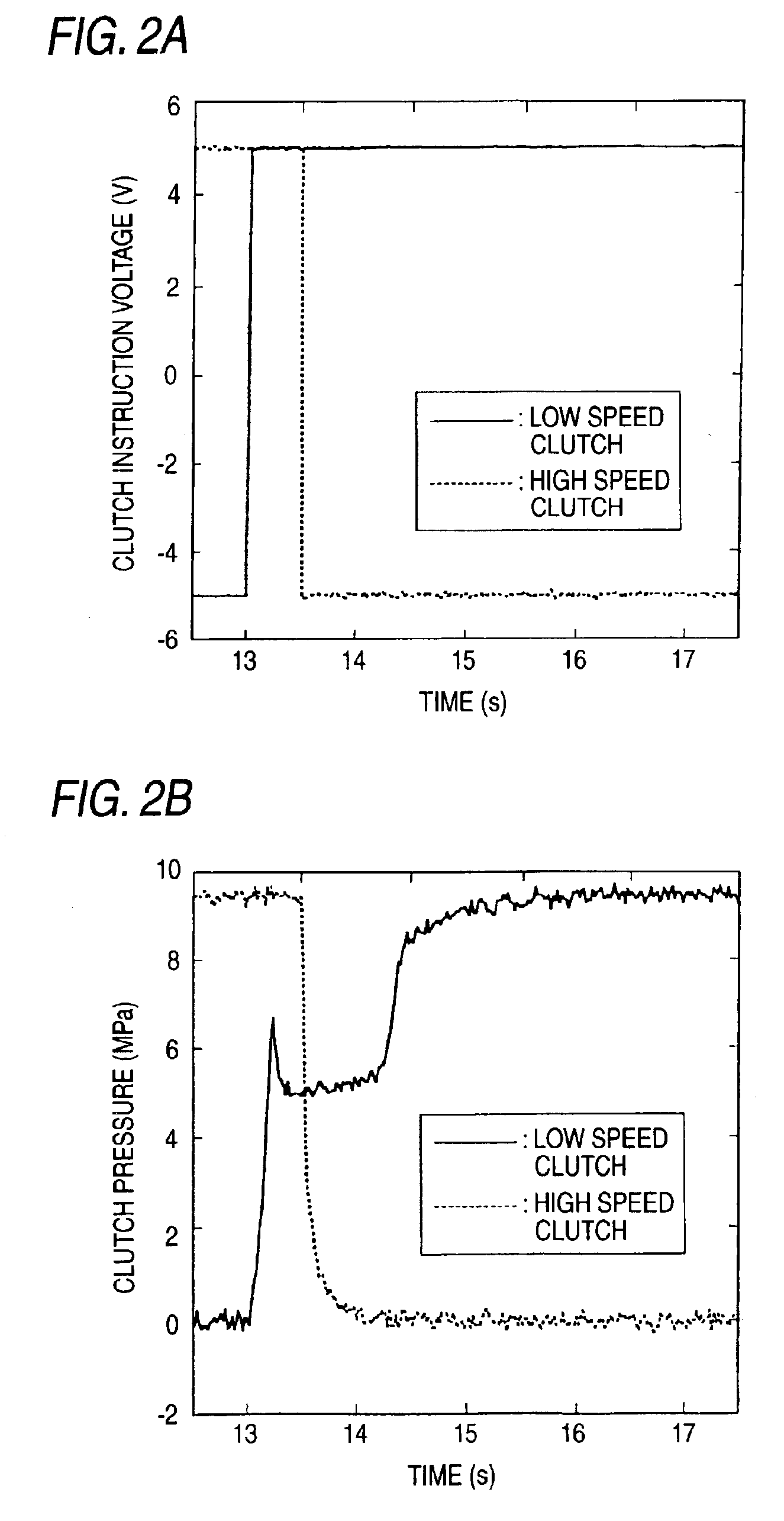
A continuously variable transmission apparatus has clutch device having a low speed clutch; a high speed clutch; and, a controller switching the transmission state into any one of a low speed mode and a high speed mode by connecting any one of the clutches, wherein timings for signaling by the controller for switching the connected and disconnected states of the clutches vary according to the switching directions of the low speed and high speed modes; and, a timing for signaling for connecting the low speed clutch with respect to the moment for signaling for cutting off the connection of the high speed clutch in order to switch the high speed mode over to the low speed mode is set earlier than a timing for signaling for connecting the high speed clutch with respect to the moment for signaling for cutting off the connection of the low speed clutch.
Owner:NSK LTD
Vibration control apparatus for automotive vehicle
InactiveUS20050049761A1Accurate compensationRapid responseInternal combustion piston enginesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMobile vehicleResidual vibration
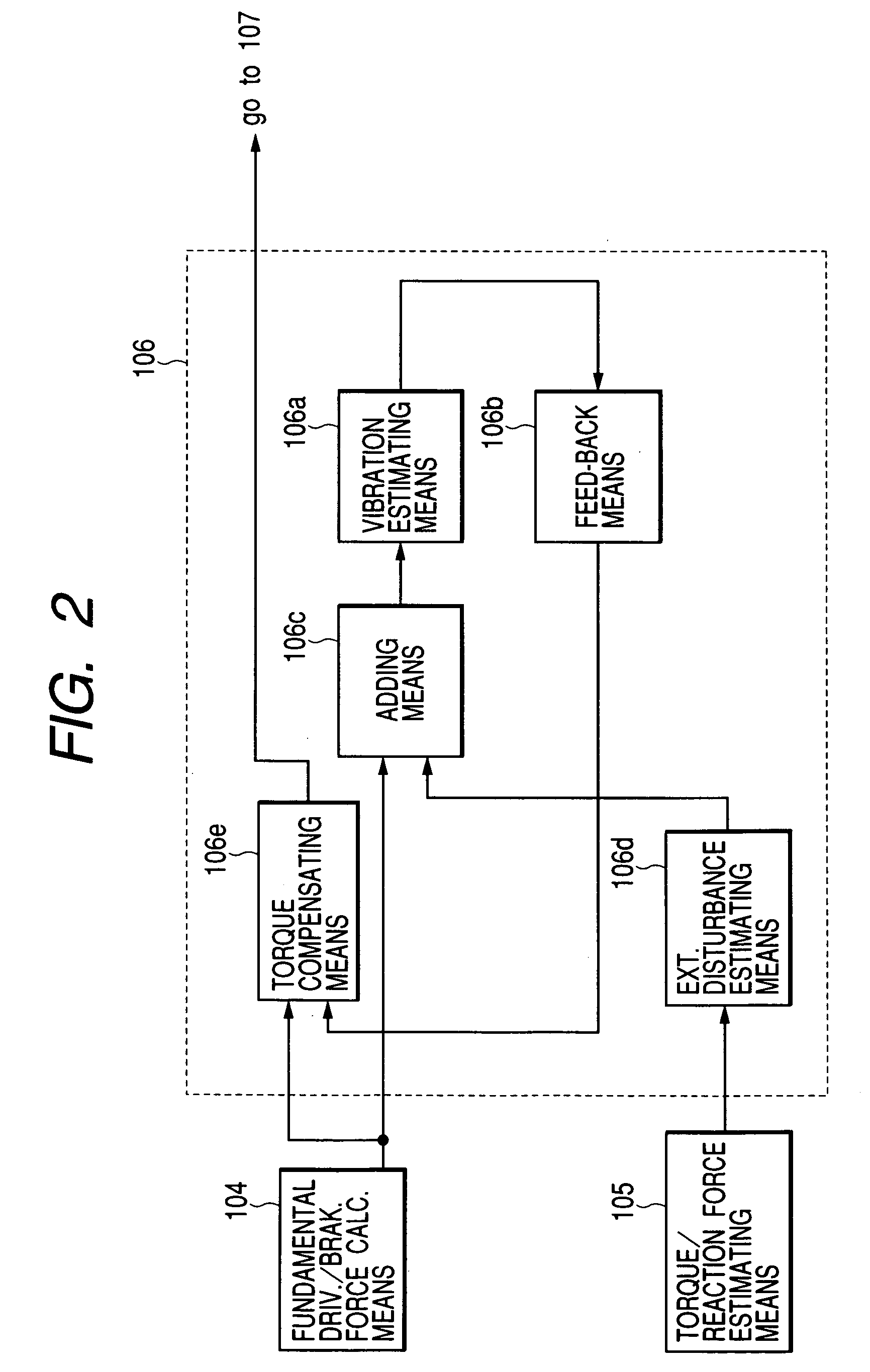
An object of the present invention is to execute an optimum control of vibrations due to a driver's operation of an accelerator pedal, steering wheel and brake pedal. The operation instructions are inputted into a vibration calculating means (kinetic model) comprising a vehicle body model, suspension model and tire model. Conventional kinetic model controlled the suspension in order to suppress the vehicle body vibration. However, in the kinetic model of the present invention, the tire vibration due to a change in the engine output is first absorbed by the suspension, whereby a residual vibration which was not be absorbed yet by the suspension is transferred to the vehicle body. The operation inputs are compensated by the three feed-back loops between the outputs of the above-mentioned three portions and input of the tire portion, giving the highest priority on the vehicle body model.
Owner:DENSO CORP
System and method for real-time recognition of driving patterns
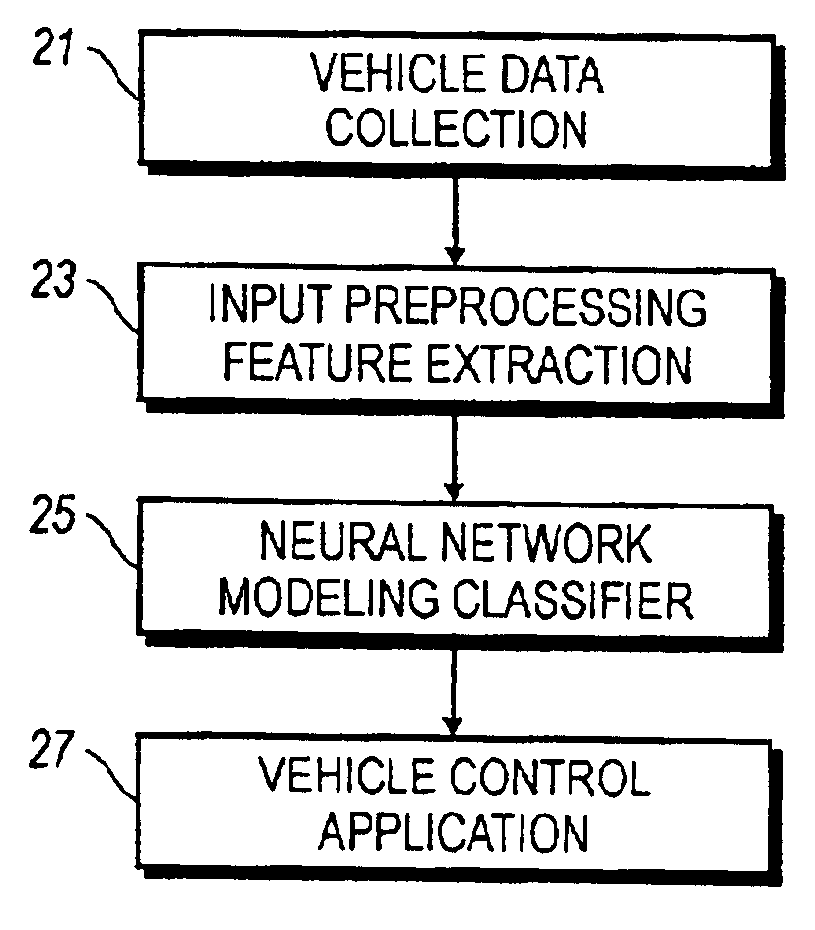
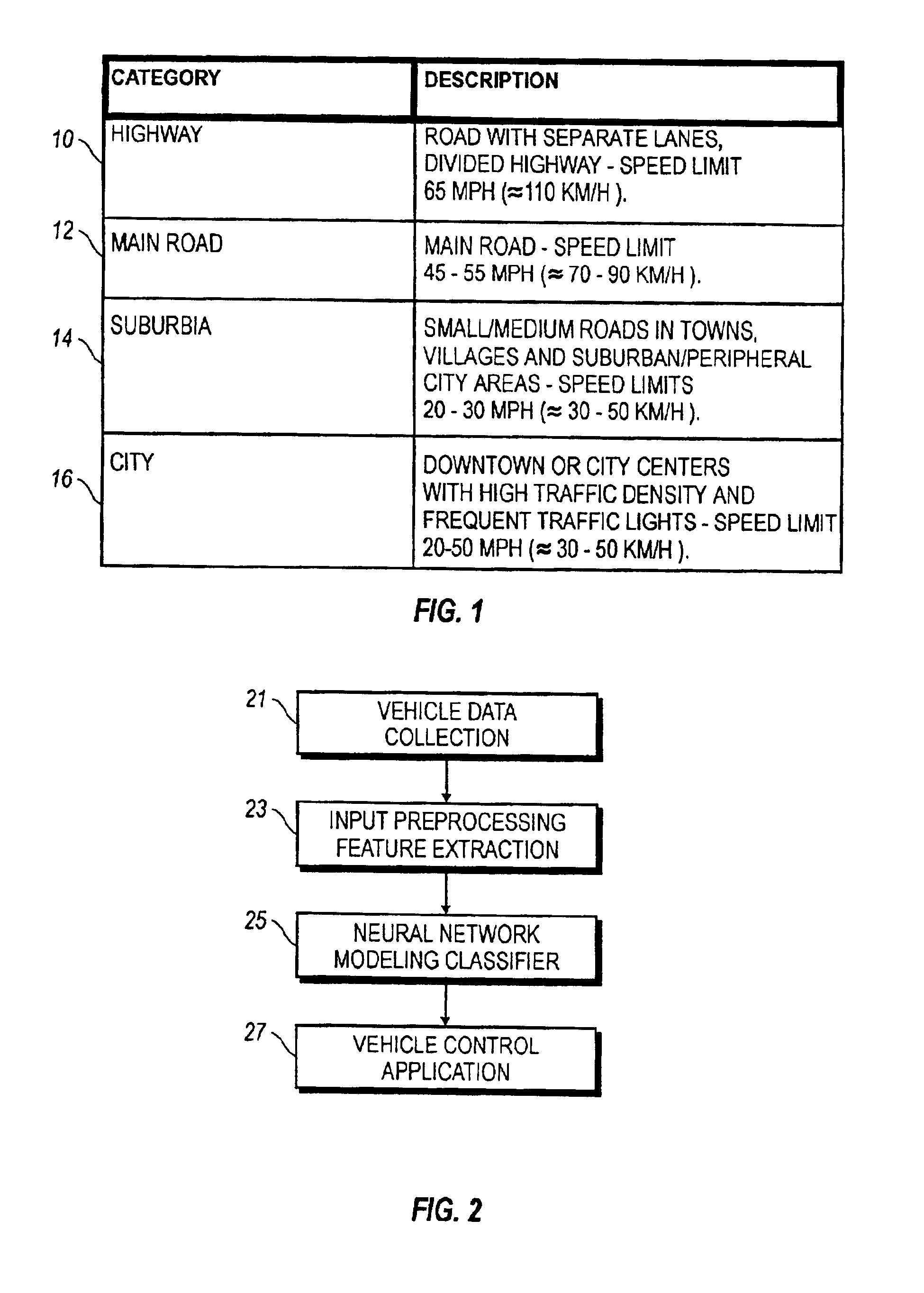
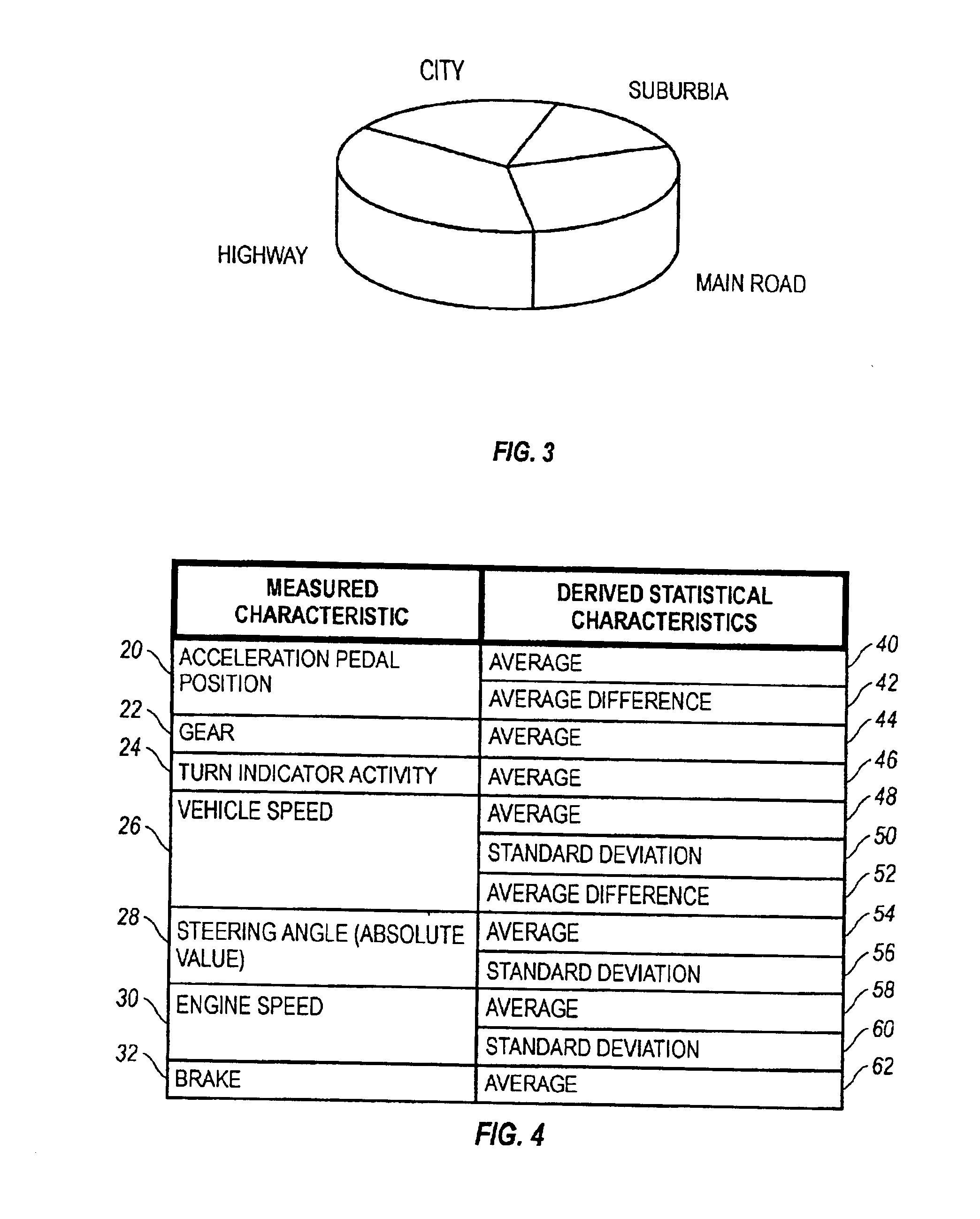
System and method for real-time, automatic, recognition of large time-scale driving patterns employs a statistical pattern recognition framework, implemented by means of feed-forward neural network utilizing models developed for recognizing, for example, four classes of driving environments, namely highway, main road, suburban traffic and city traffic, from vehicle performance data. A vehicle control application effects changes in vehicle performance aspects based on the recognized driving environment.
Owner:VOLVO TECH
Device for controlling vehicle turn behavior with discrimination of drive direction
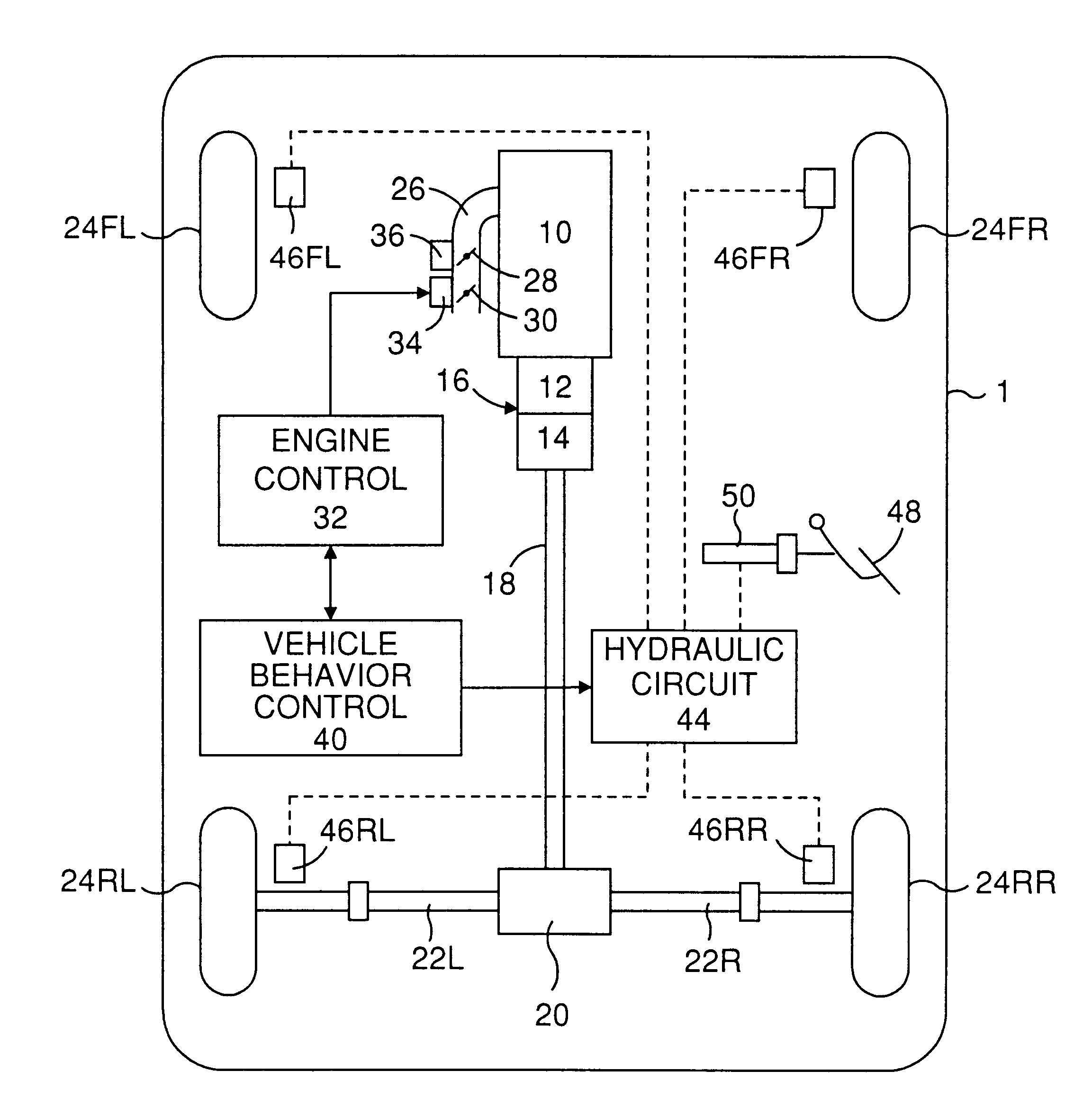
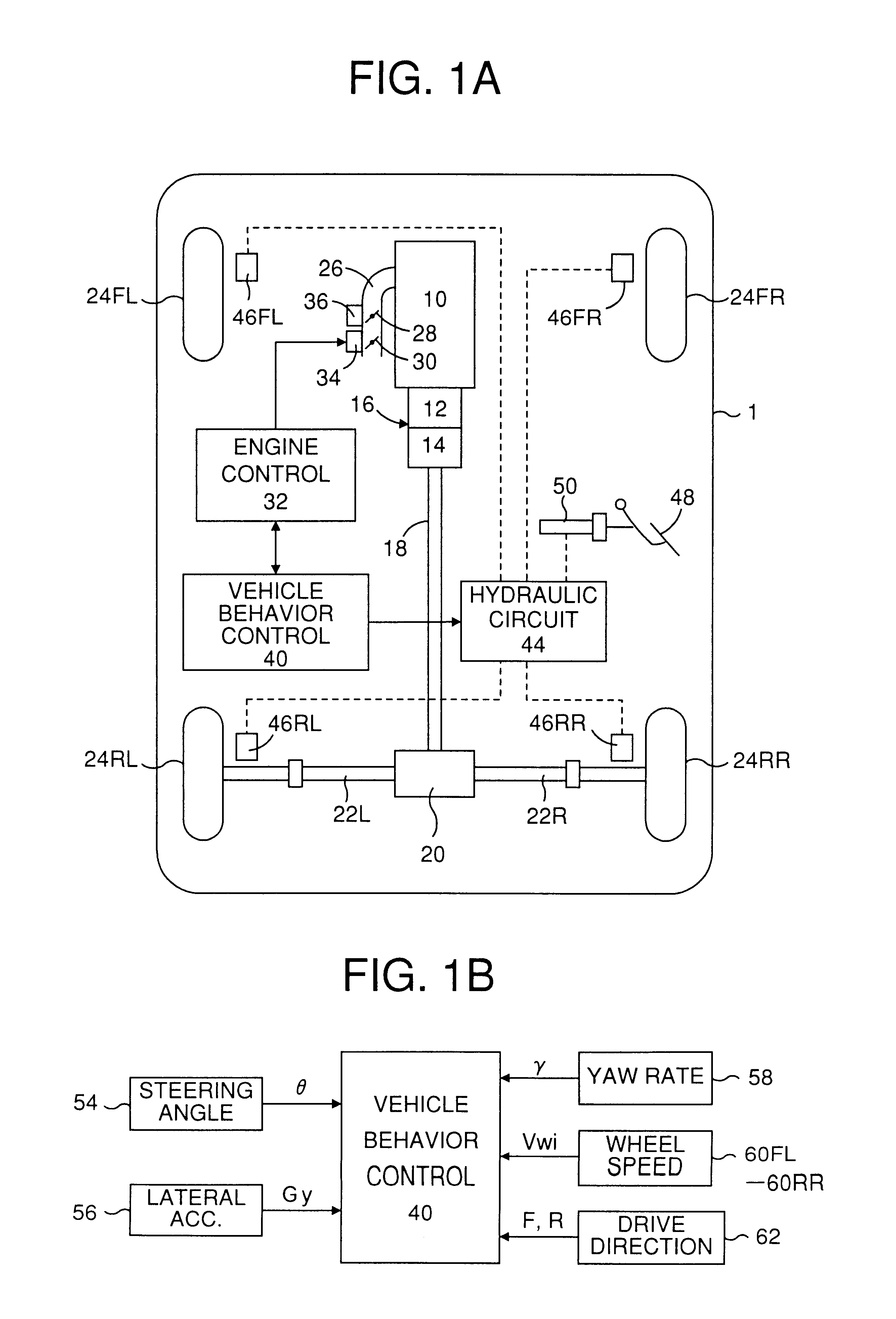
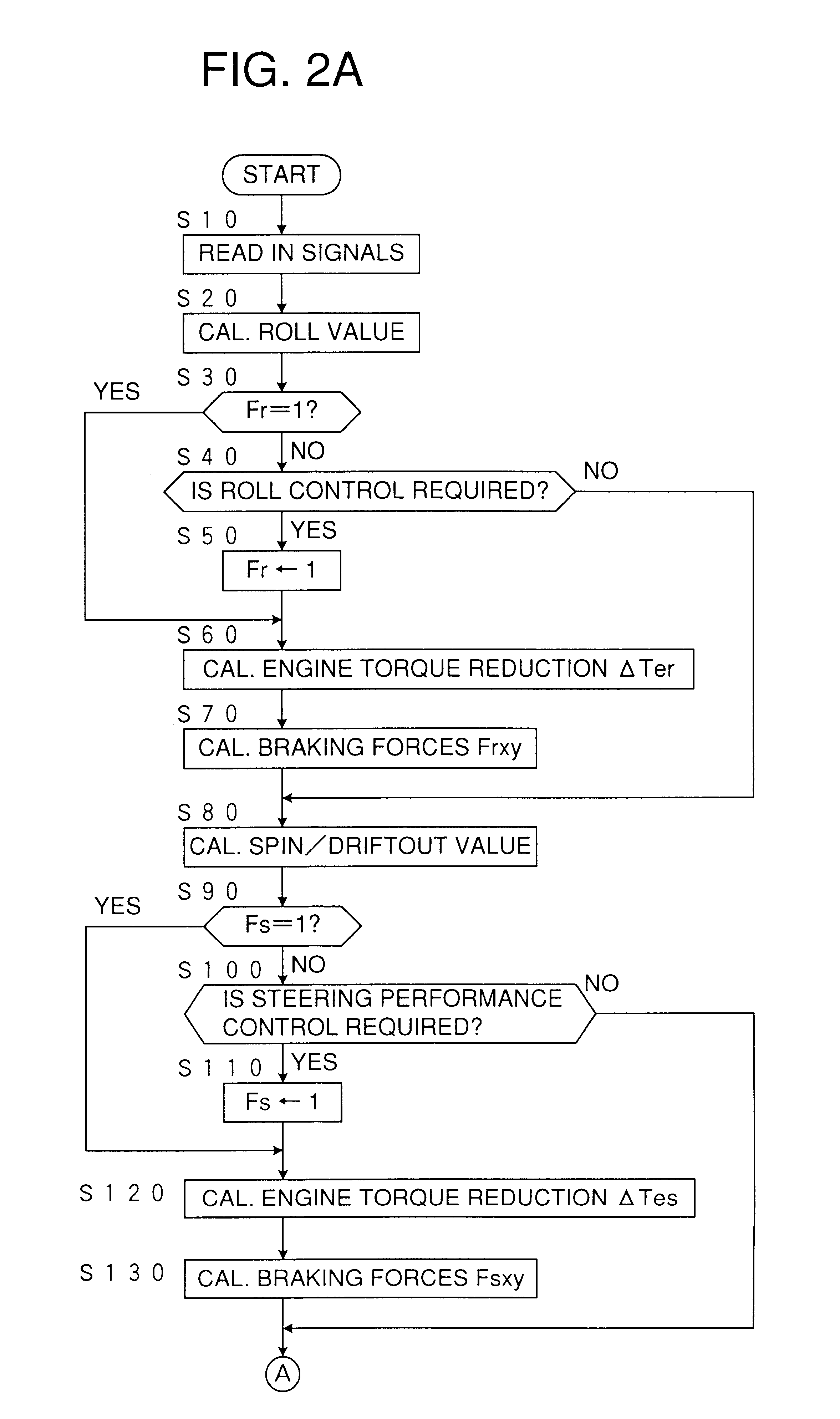
InactiveUS6324458B1Vehicle body stabilisationDigital data processing detailsControl theoryBraking system
A device for controlling a turn running behavior of a vehicle detects at least one parameter (V, gamma, Gy, Gyh, gammat, gammat-gamma) with respect to the turn running behavior in addition to a drive direction of the vehicle, the one parameter being indicative of a higher desirability of the turn running behavior control according to changes of a magnitude thereof, calculates an amount (DELTATer, Froq, Friq, DELTATes, Fsop, Fsiq, Fsoq) for the turn running behavior control based upon the detected turn running behavior parameters, determines a start of the turn running behavior control according to the one turn running behavior parameter traversing a threshold value (Vrp, Vrq, gammarp, gammarq, Gyp, Gyq, Gyhp, Gyhq, Vsp, Vsq, gammasp, gammasq, gammatsp, gammatsq, DELTAgammap, DELTAgammaq) determined therefor, and executes the turn running behavior control by operating at least one of the engine and the brake system according to the turn running behavior control amount, wherein threshold value is changed in a rearward drive of the vehicle as compared in a forward drive thereof such that the turn running behavior control is started at a lower degree of the desirability thereof in the rearward drive than in the forward drive.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
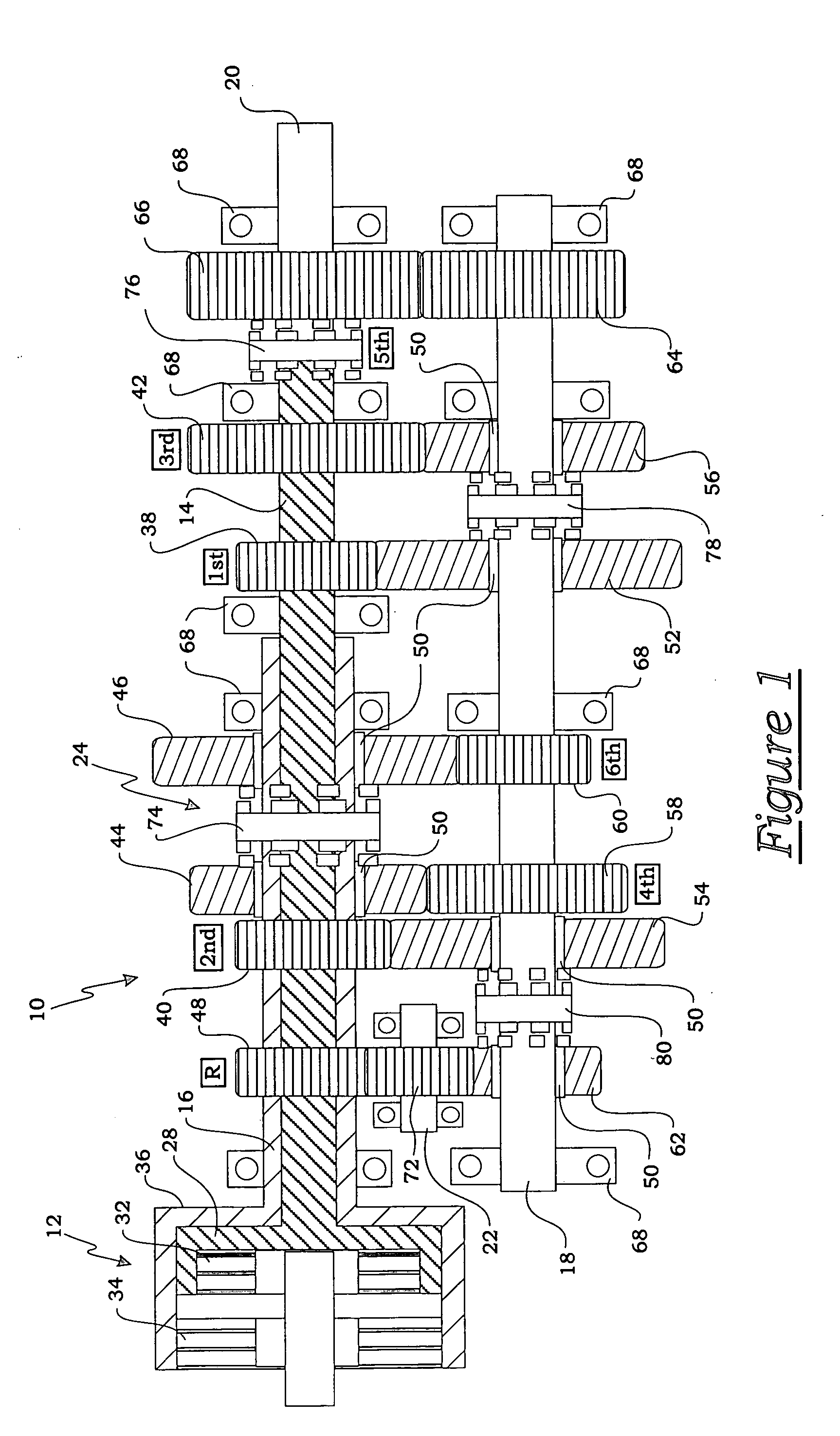
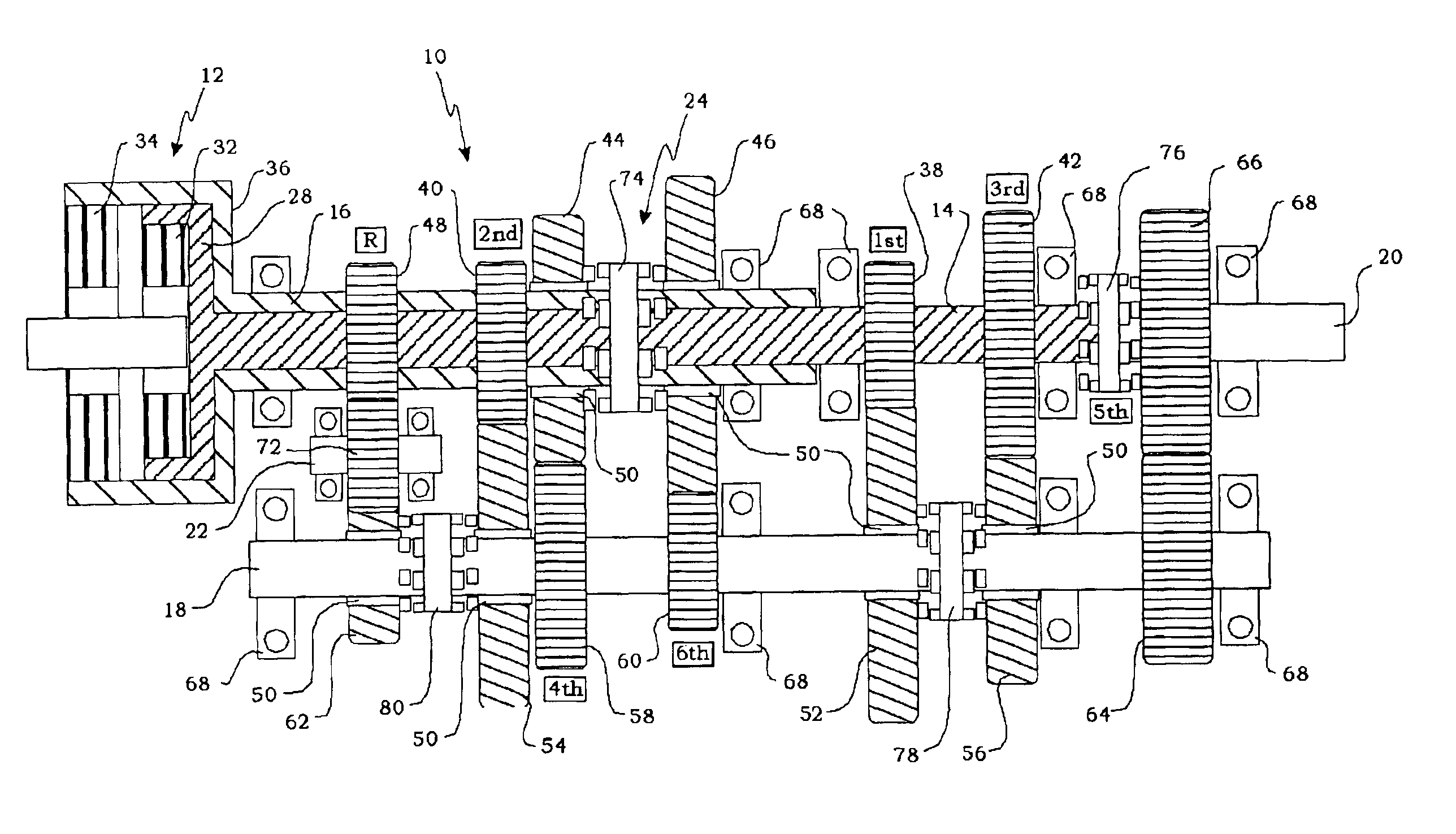
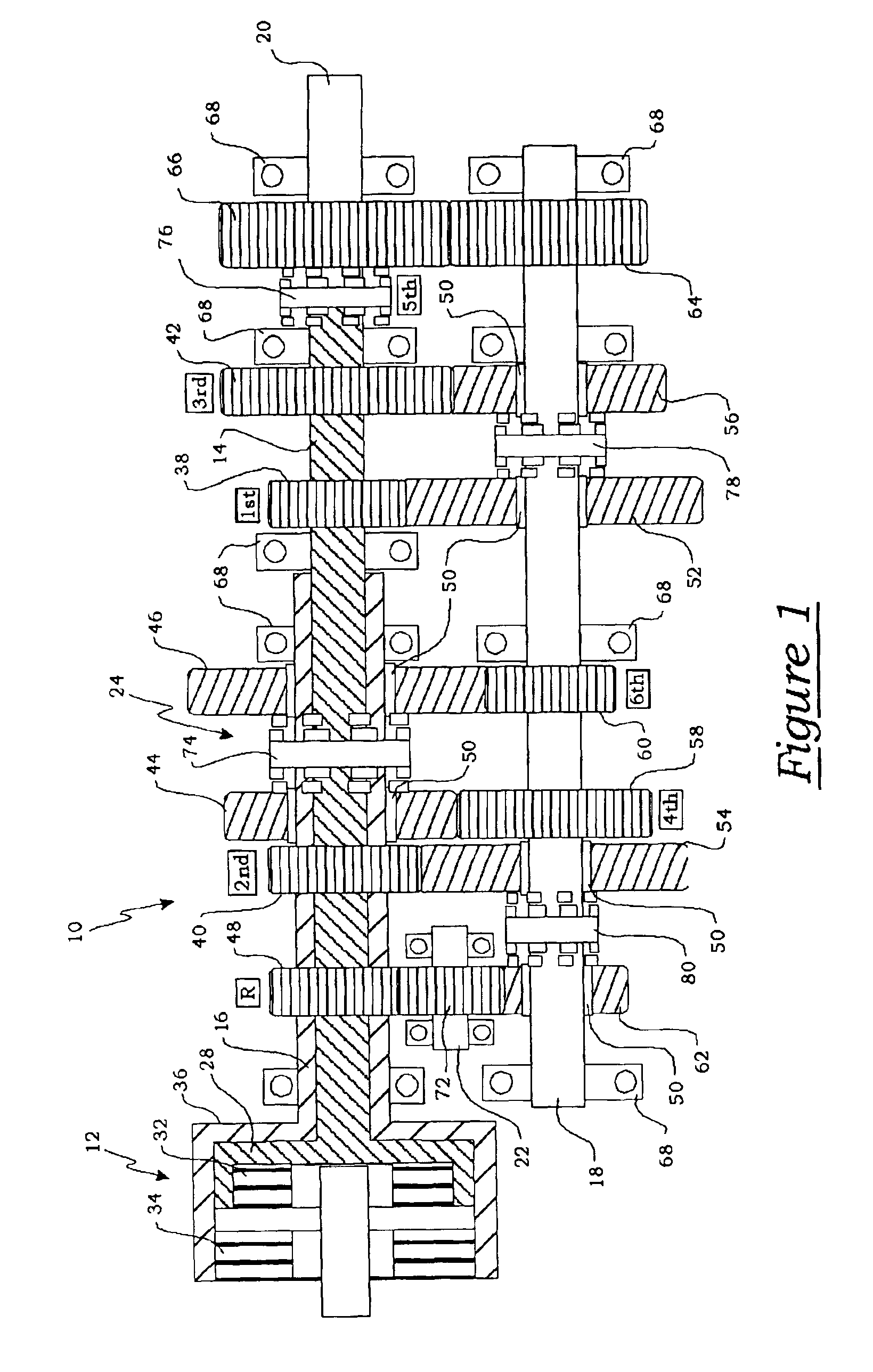
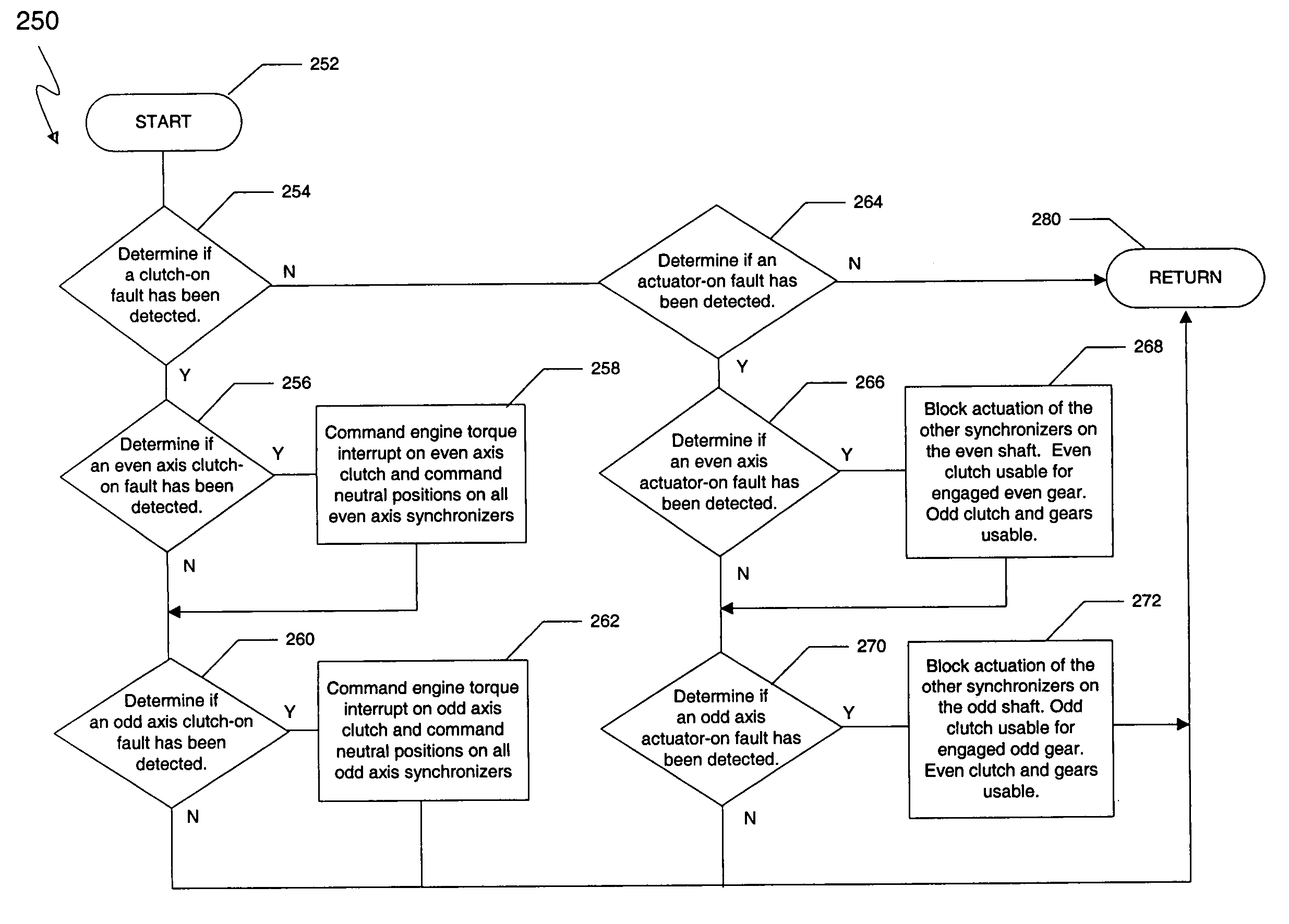
Method for controlling a dual clutch transmission
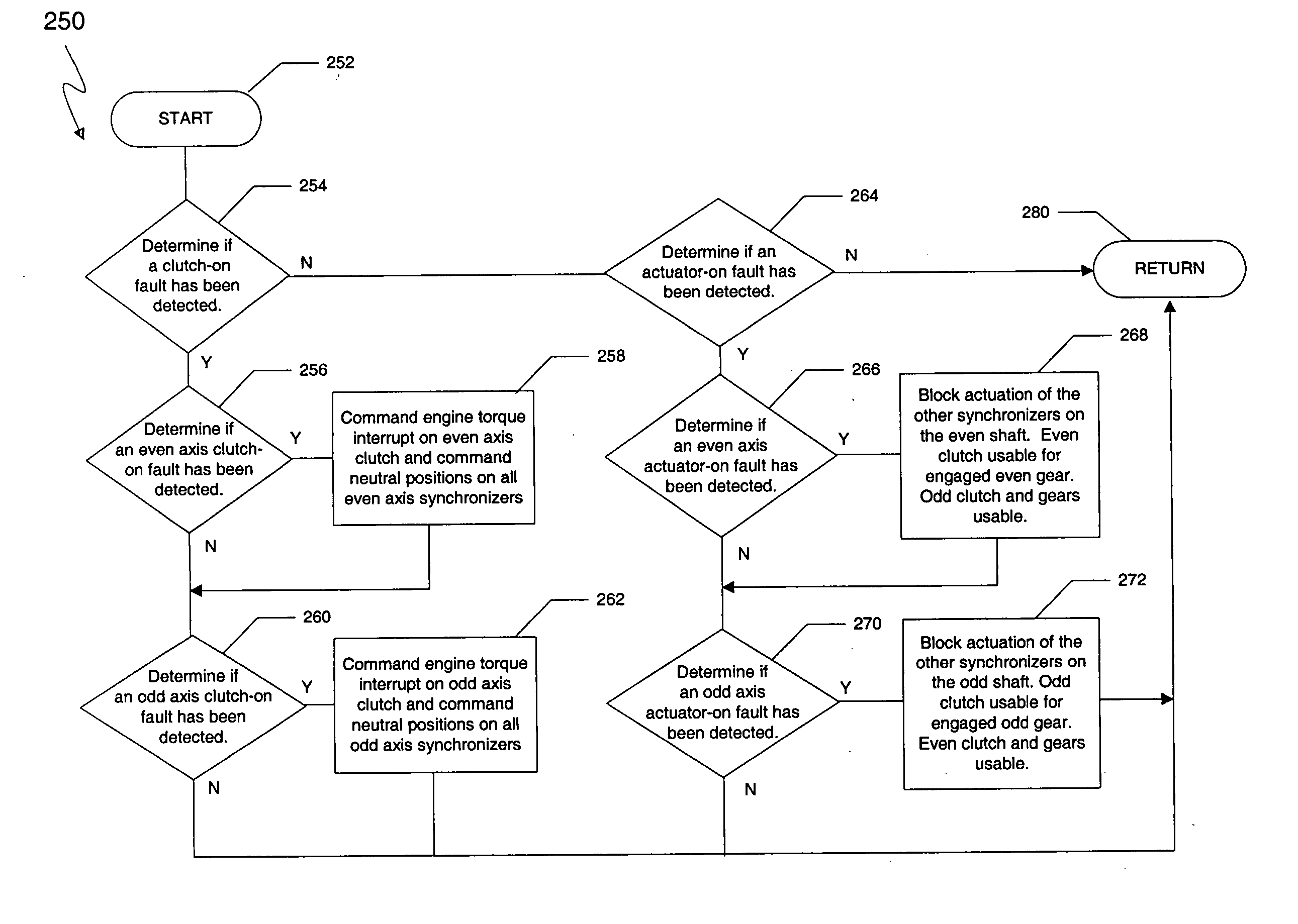
ActiveUS20050107214A1Reduce complexityReduce in quantityFluid actuated clutchesToothed gearingsEngineeringActuator
A method of controlling the hydraulic actuation of the clutches and the synchronizers in a dual clutch transmission in the event of a clutch or synchronizer fault. The method includes the steps of determining which clutch is faulted when a clutch-on fault is detected, then commanding an interruption of engine torque to the faulted clutch and a neutralization of all synchronizers of the same axis shaft as the faulted clutch. The method further senses if a synchronizer actuator-on fault has occurred, then determines which synchronizer is faulted if an actuator-on fault has is detected. The method steps further include preventing the further actuation of the other synchronizers on the same axis shaft as the faulted actuator.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Method of controlling a dual clutch transmission
InactiveUS6887184B2Improving overall drivability and comfortClutchesDigital data processing detailsGear driveTorque transmission
A method of controlling the clutches of a dual clutch transmission during a two-gear positive downshift, wherein the first clutch drives an initial gear and the final gear and the second clutch drives an intermediate gear. The torque transfer across each clutch is controlled so that the torque output of the transmission will be linearly changed over from the first clutch to the second clutch to cause the engine to track a target engine speed profile. The method changes over the gears driven by the first clutch from the initial gear to the final gear as the engine continues to tracks the target speed. The torque transfer across each clutch is controlled so that the torque output will be linearly changed back from the second clutch to the first clutch in an inversely proportional rate to continue to cause the engine to track the target engine speed profile.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
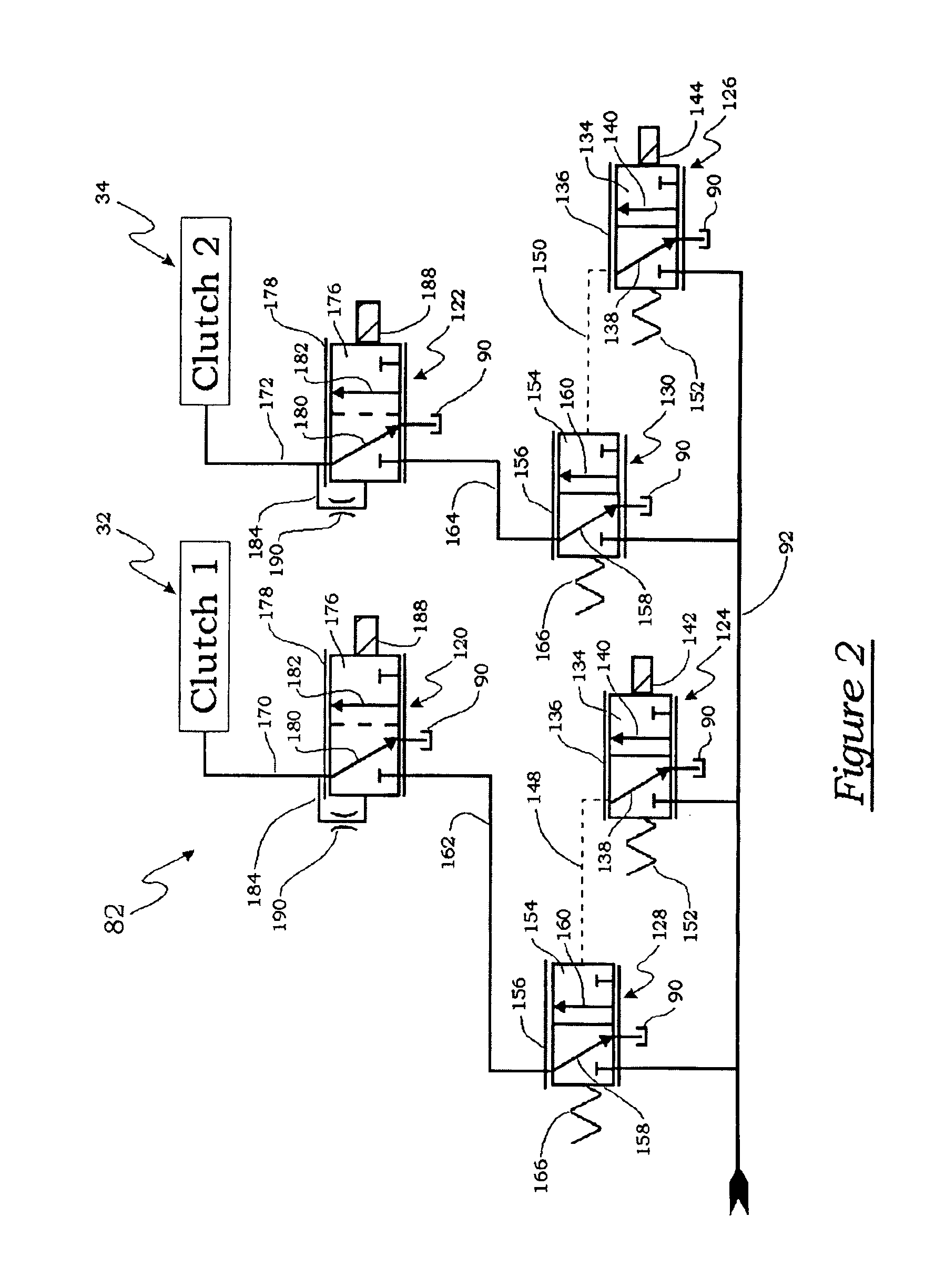
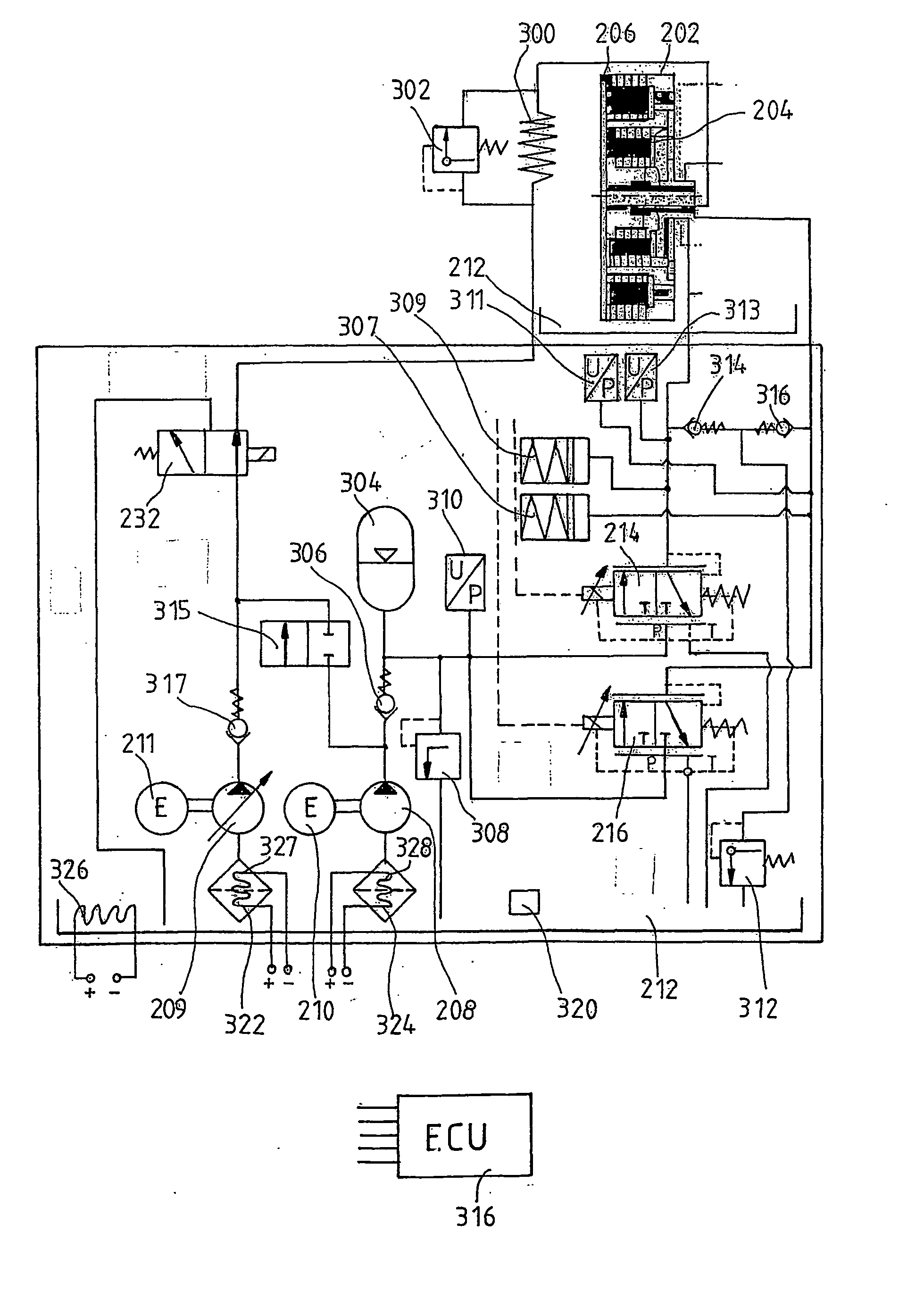
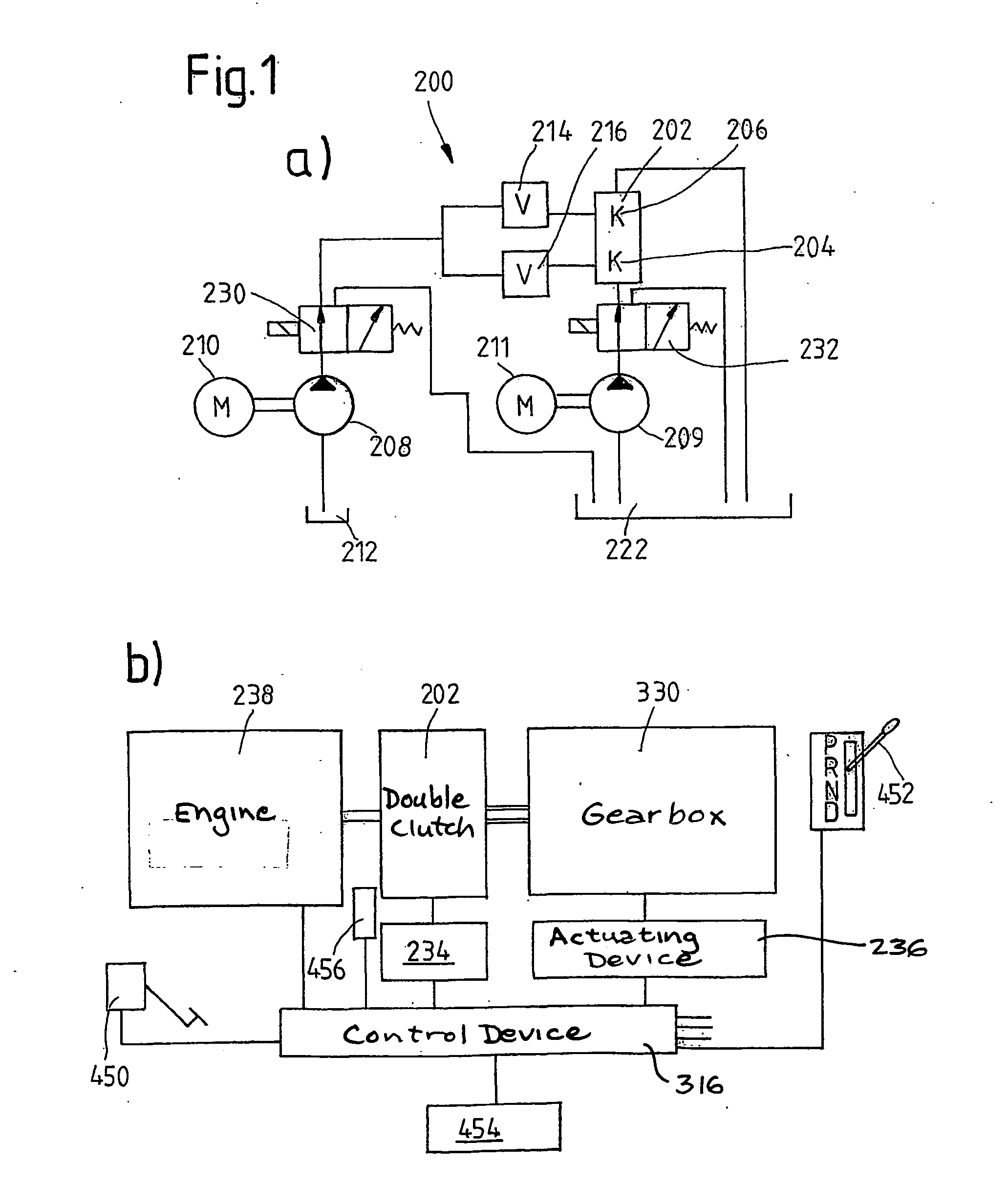
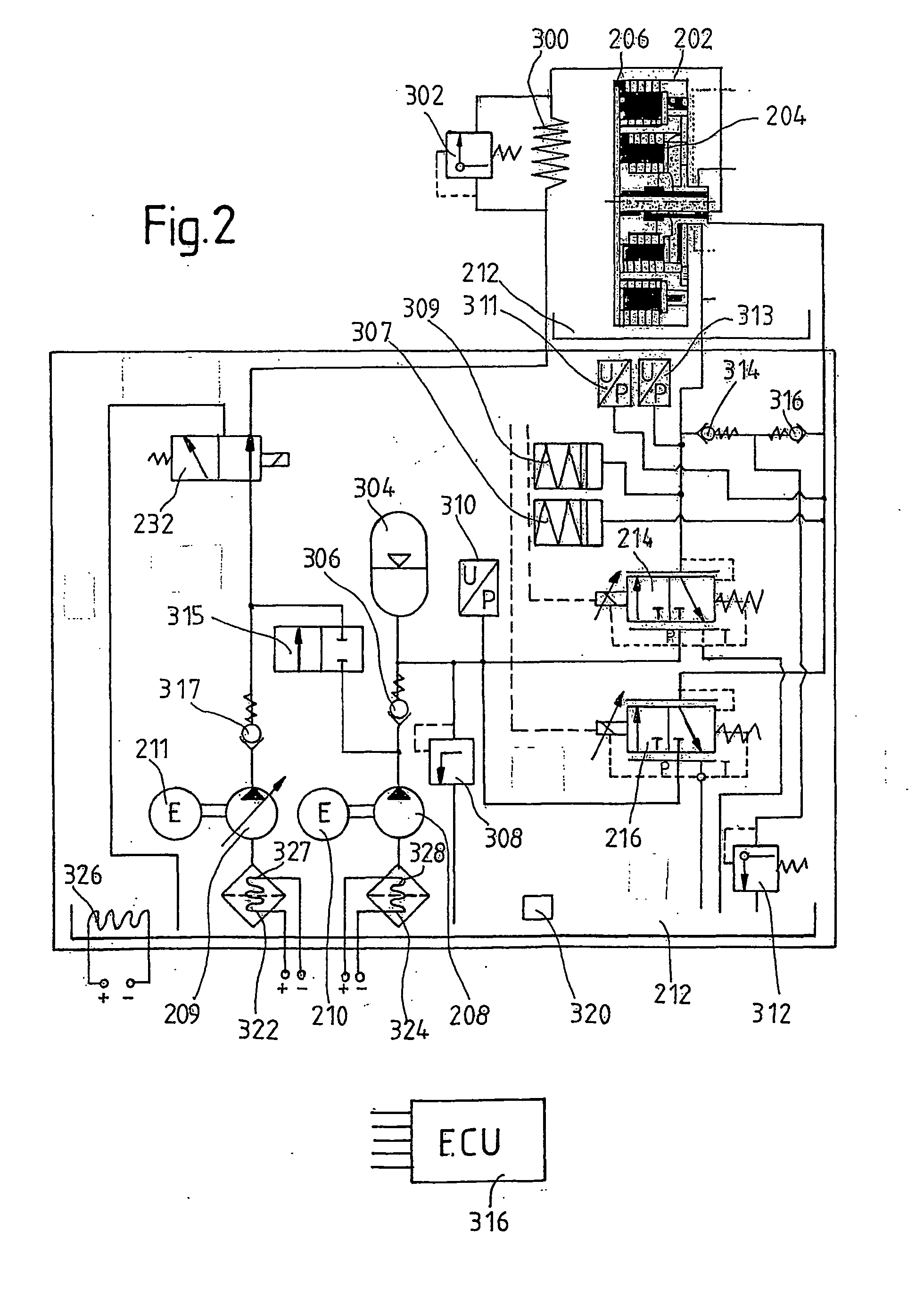
Motor vehicle comprising a drive train having a multiple clutch drive
InactiveUS20040112171A1Easy to participateIncrease engine speedGear lubrication/coolingVehicle sub-unit featuresWorking fluidGear wheel
The invention relates to measures for controlling or reducing drag torque occurring in a multi-plate clutch device (202) due to temperature-related increased viscosity of an operating fluid which is supplied to the plates in operation. The aim of the invention is to enable a motor vehicle to be started or operated even at low temperatures. According to one aspect of the invention, a motor vehicle comprising a drive train is especially provided. Said drive train comprises a drive unit (238), gearbox (330) having a first gearbox input shaft and a second gearbox input shaft, and a clutch (202) having a first clutch device which is associated with the first gearbox input shaft, and a second clutch device which is associated with the second gearbox input shaft, for transferring torque between the drive unit and the gearbox. Said clutch devices are embodied in the form of plate clutches to which an operating fluid can be supplied, especially a cooling oil in order to operate the same. Said gearbox (330) is associated with an actuator device and a control device (316) for controlling the actuator device, the arrangement of which enables the gears associated with the first and second gearbox input shafts to be engaged and disengaged. According to the invention, the control device (316) is designed in such a way that at least one gear is automatically engaged by means of the actuator device (236), as a result of the clutch release of the vehicle.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG +1
Downhill speed controller
InactiveUS20050096183A1Reduced controllabilityImprove controllabilityVehicle fittingsAutomatic initiationsControl systemSpeed control system
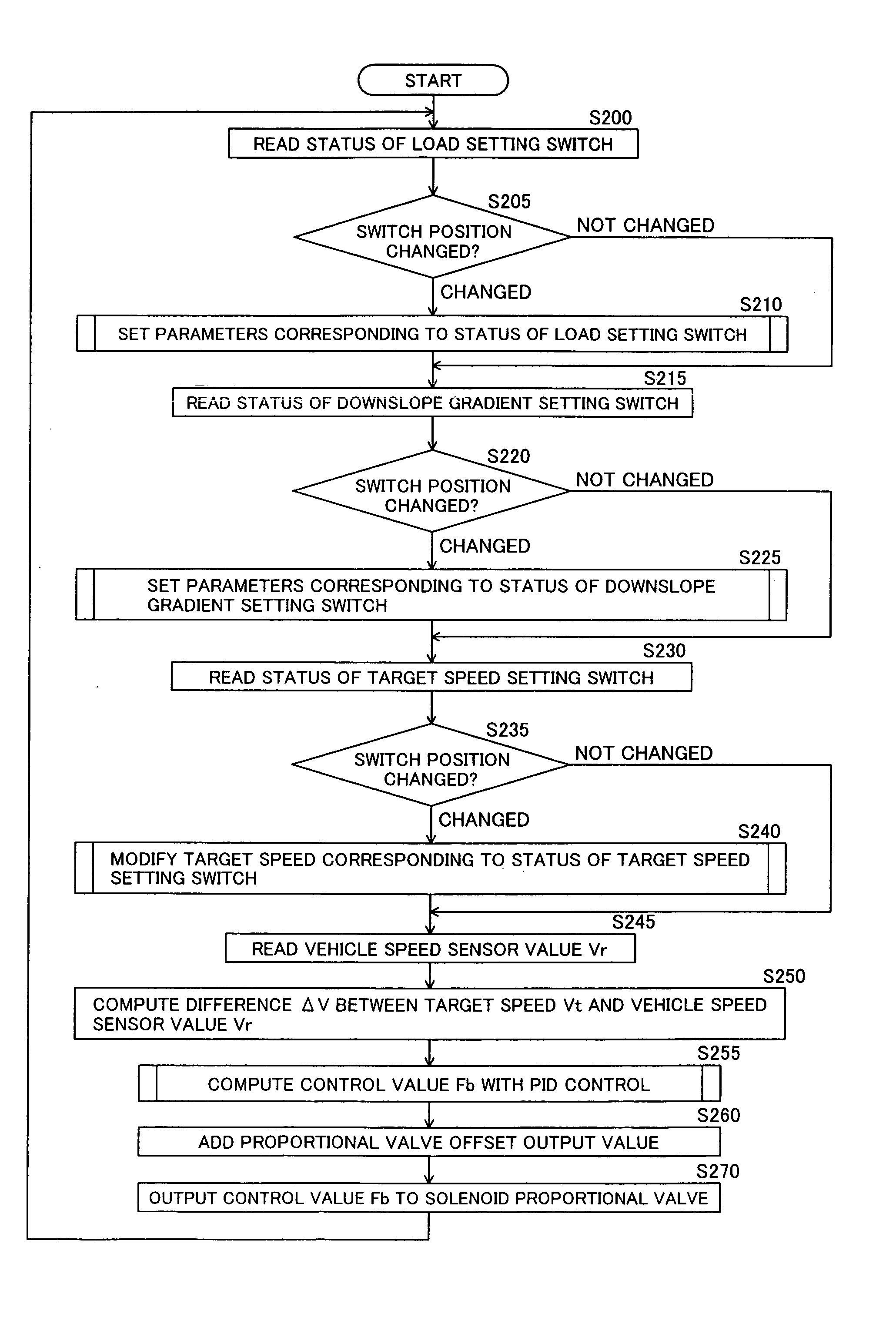
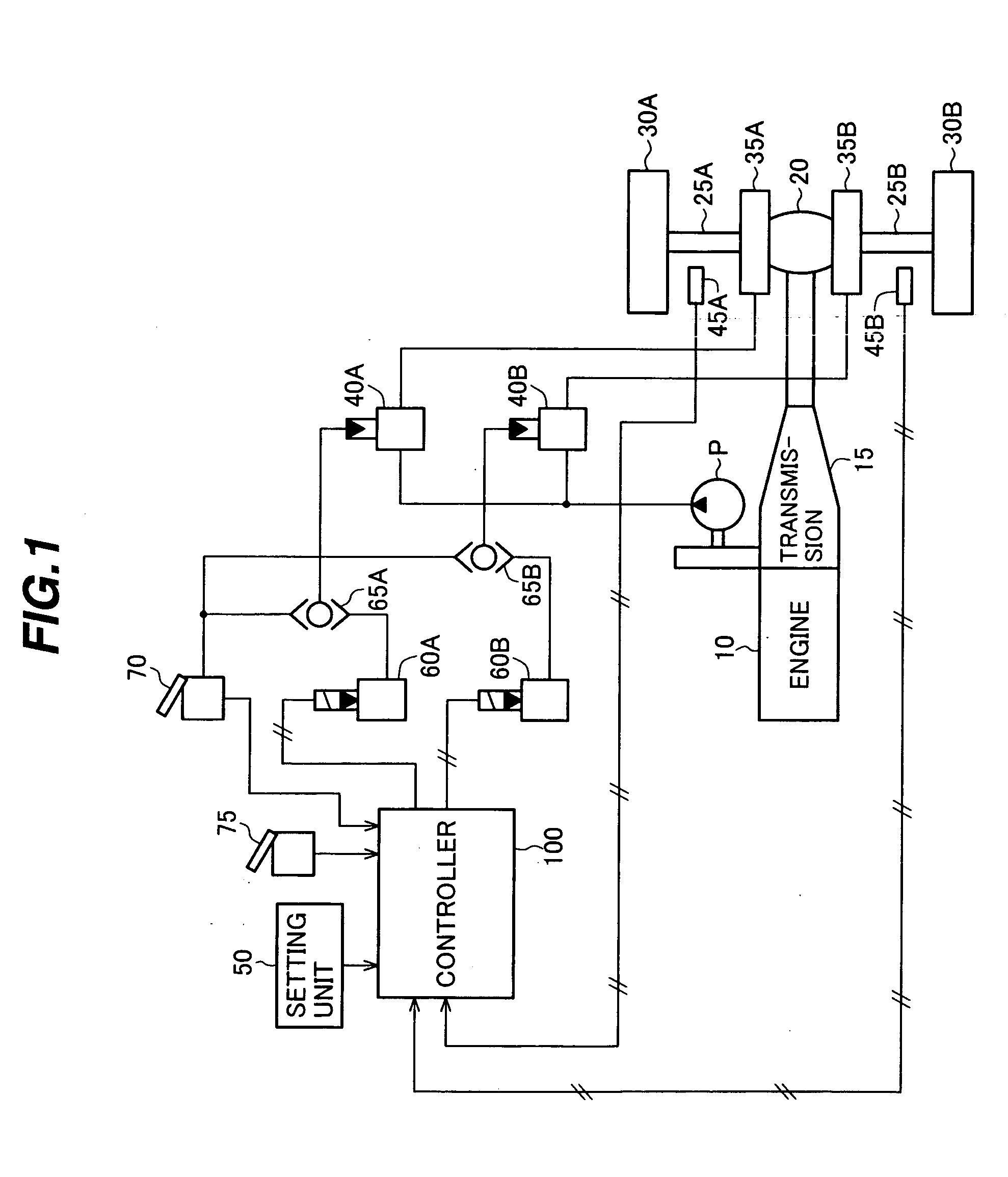
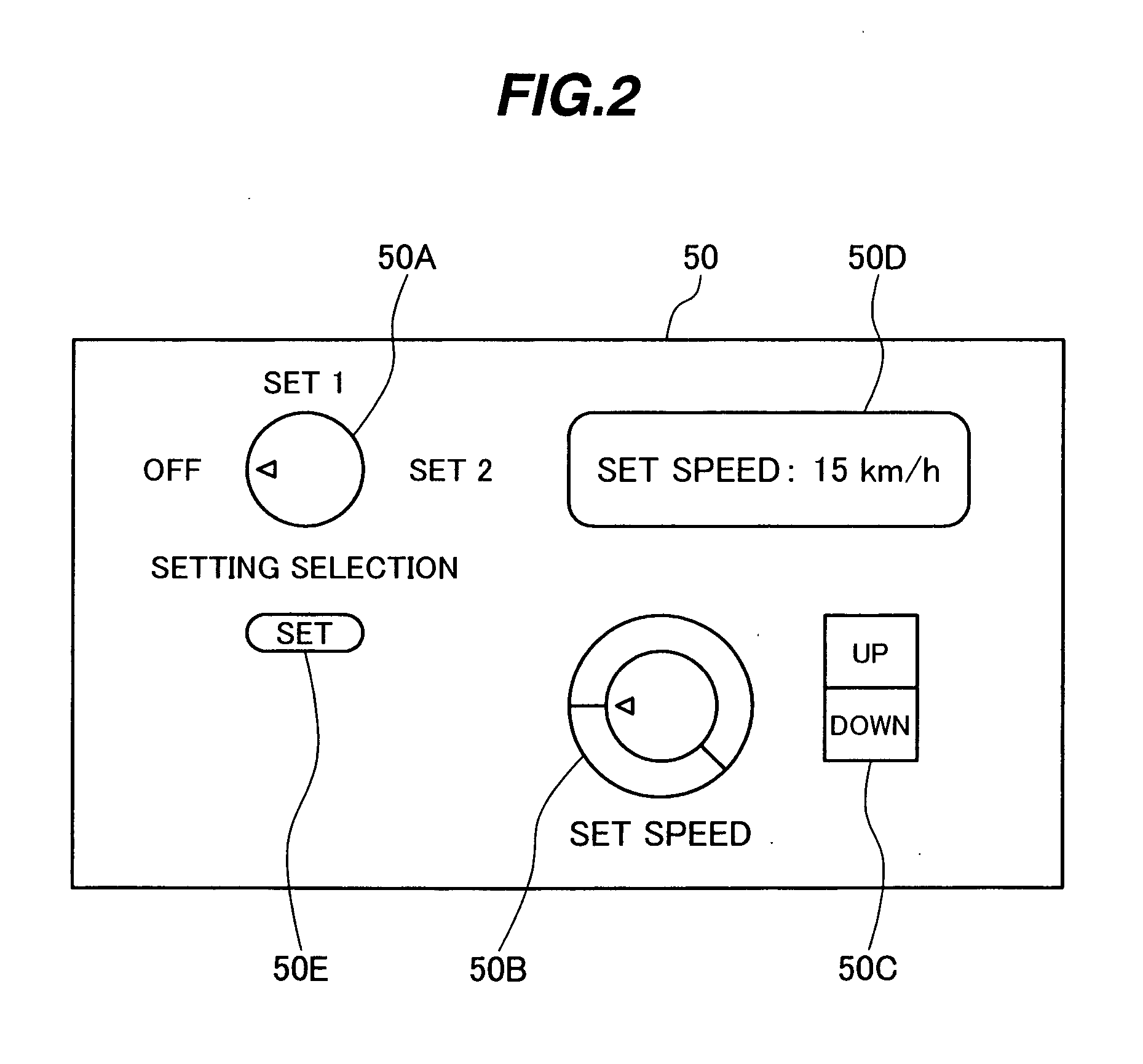
The invention is intended to provide a downhill speed control system which employs a method of setting a target vehicle speed in advance, thereby improving controllability when a vehicle runs down a slope, and giving an operator improved operability in setting of the target vehicle speed. Brakes are controlled so that, when the vehicle runs down the slope, an actual vehicle speed is matched with a target speed set by a switch which can set the target speed by selectively or continuously changing plural preset speeds. Also, control constants for PID control are modified depending on settings of a downslope gradient setting switch and a load setting switch. When an acceleration computed from the actual vehicle speed is larger than a target acceleration, the strength of applied brake is increased.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
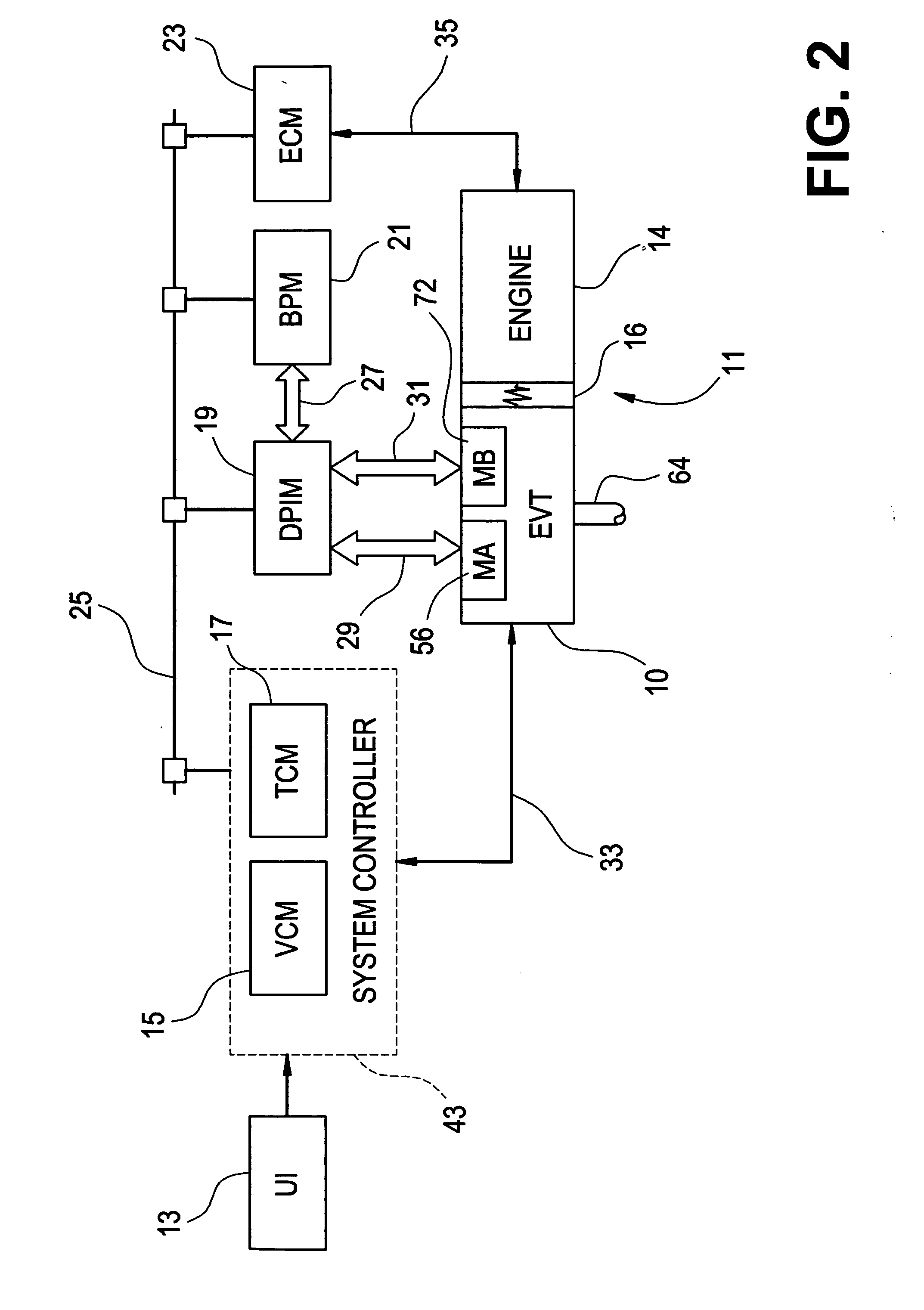
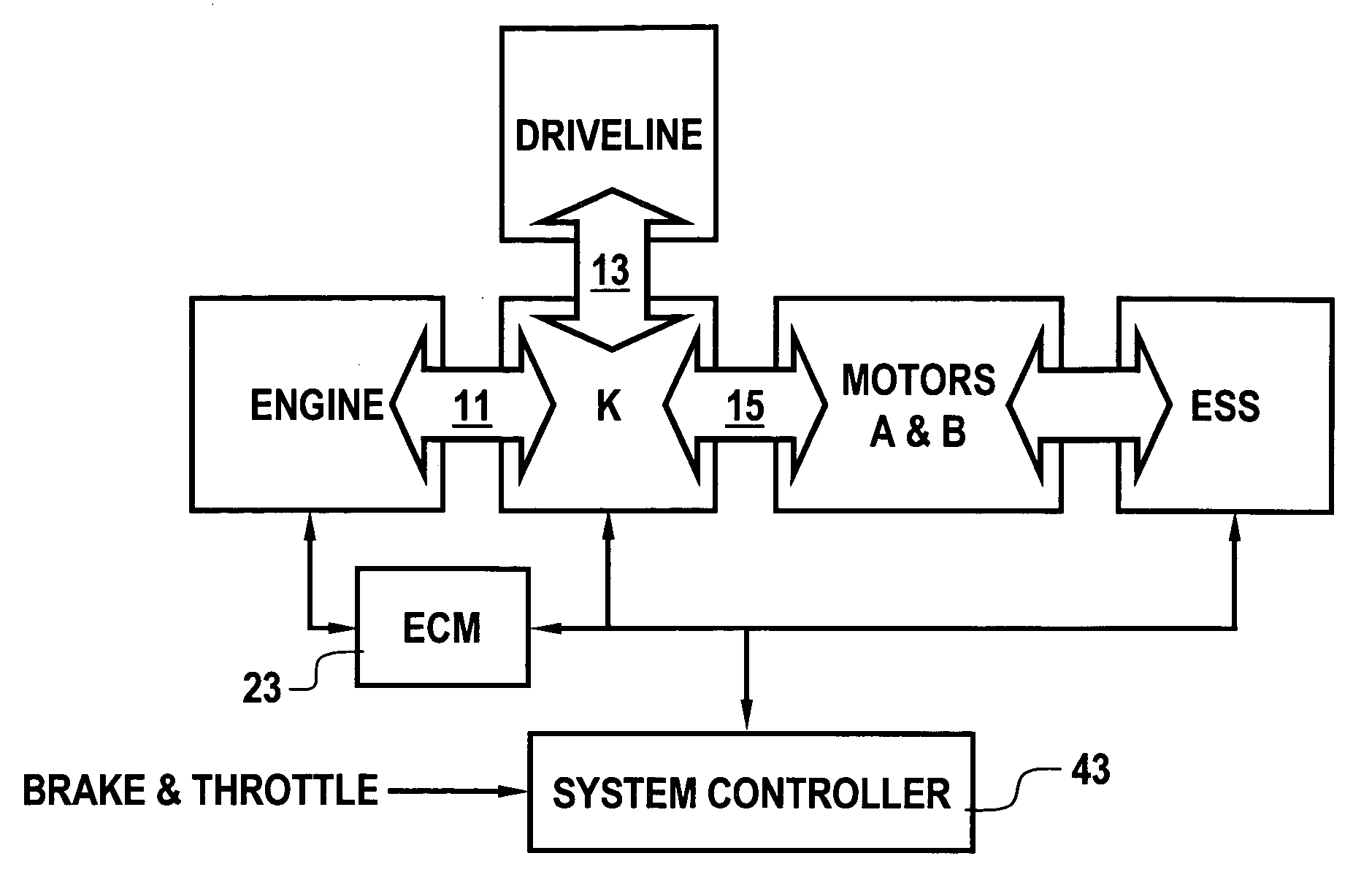
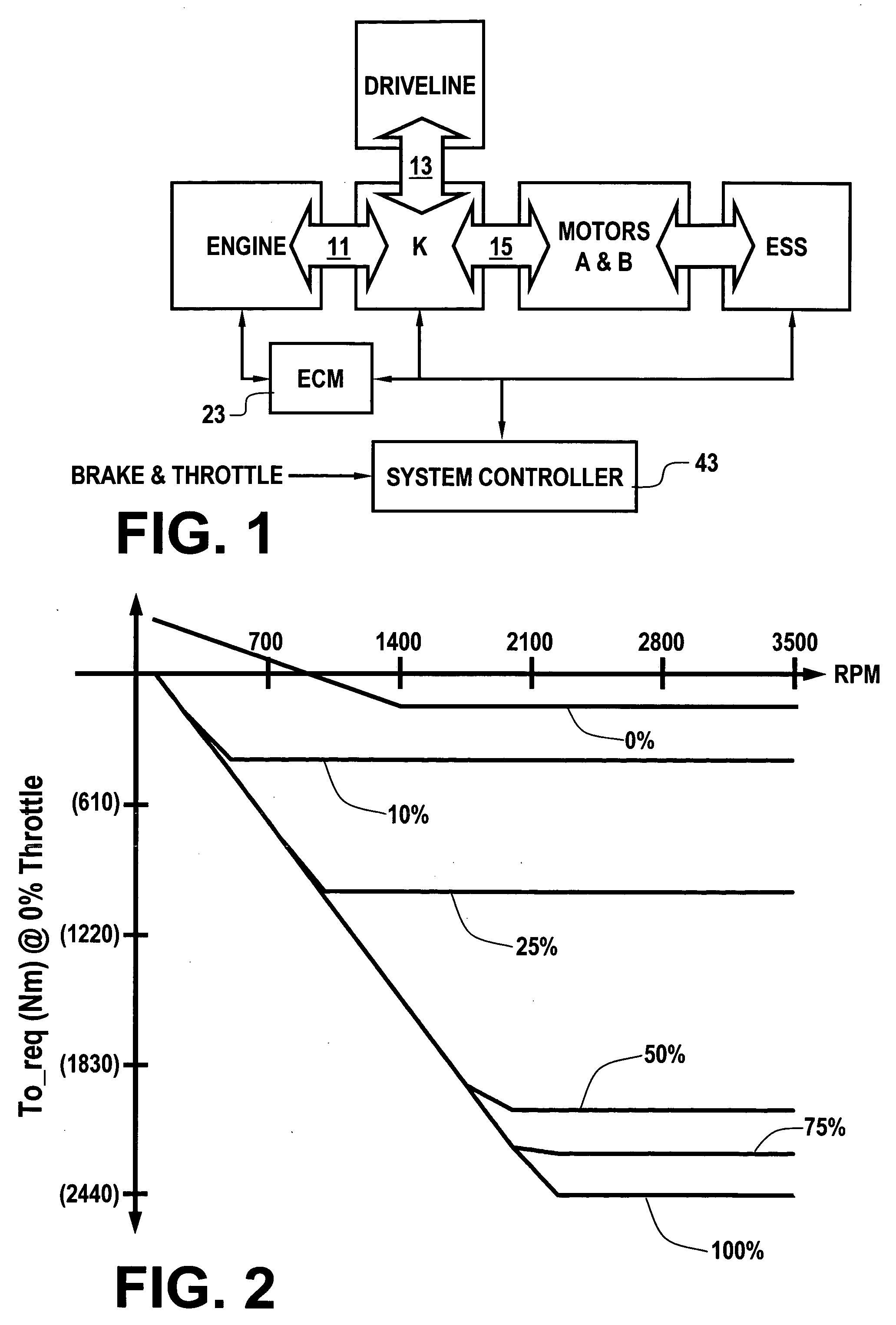
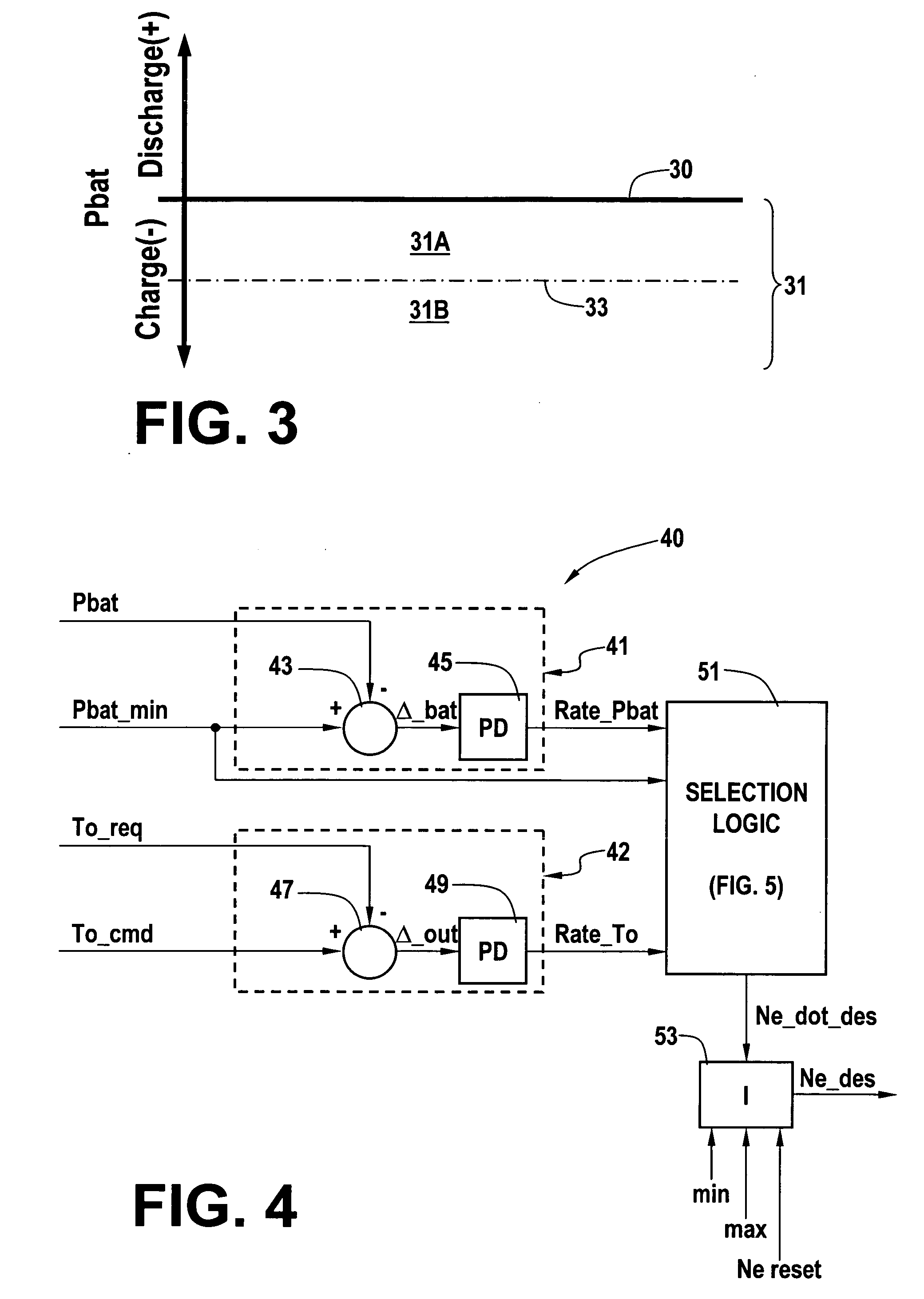
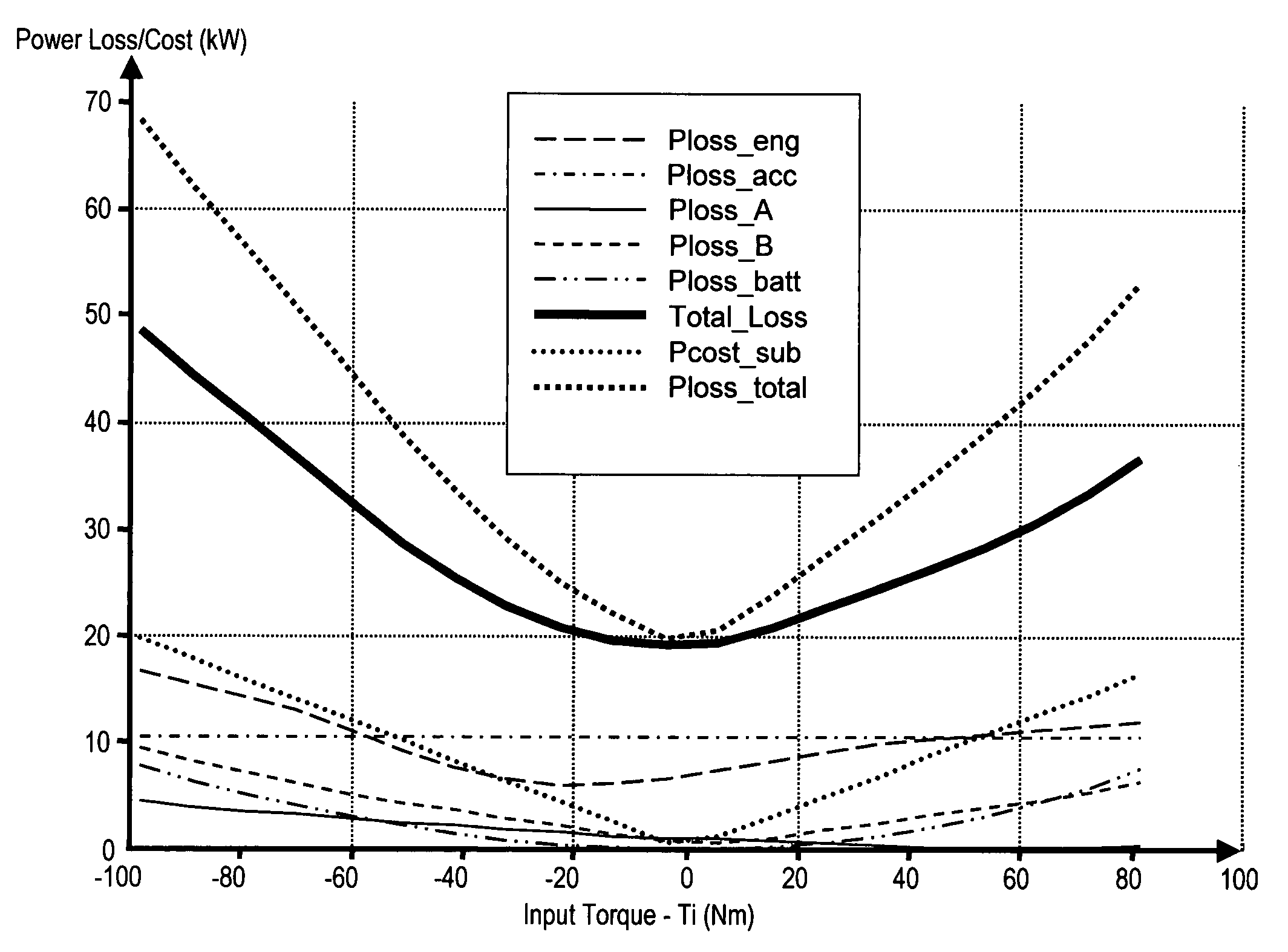
Optimal selection of input torque with stability of power flow for a hybrid electric vehicle
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Manager level device/service arbitrator and methods
A method for managing access to service entities (e.g., such as a devices, resources, and services, which are limited resources) is provided. The method includes requesting a priority level. In response, a priority object with an assigned priority level is returned. A service is then requested from a service manager, and the request includes data for carrying out the requested service and the priority object. The service manager is configured to identify at least one service entity that is required to carry out the requested service. Access is then requested to at least one service entity. A determination is made as to whether the at least one service entity is in-use. If at least one service entity is in-use, a further determination is made as to whether at least one service entity that is in-use has an assigned priority level that is higher than the assigned priority level, which is associated with a current request. The requester, such as a carlet, which has the higher assigned priority will gain control of the requested entity.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Control system for the drive of a pto for an agricultural vehicle
InactiveUS6942595B2High power uptakeIncrease powerAuxillary drivesAgricultural machinesControl systemActuator
A control system for the drive of a power take-off mechanism on an agricultural tractor that records machine-specific values of the implement attached to the tractor. The drive train between the tractor engine and the power take-off includes a CVT transmission. The control device is connected with a processor via a signal lead for receiving its output signals. The control device is connected for the formation of output signals via input leads with switches, controls, sensors, and actuators for the tractor to read the machine specific parameters of the attached implement.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC +1
Integrated control apparatus for vehicle
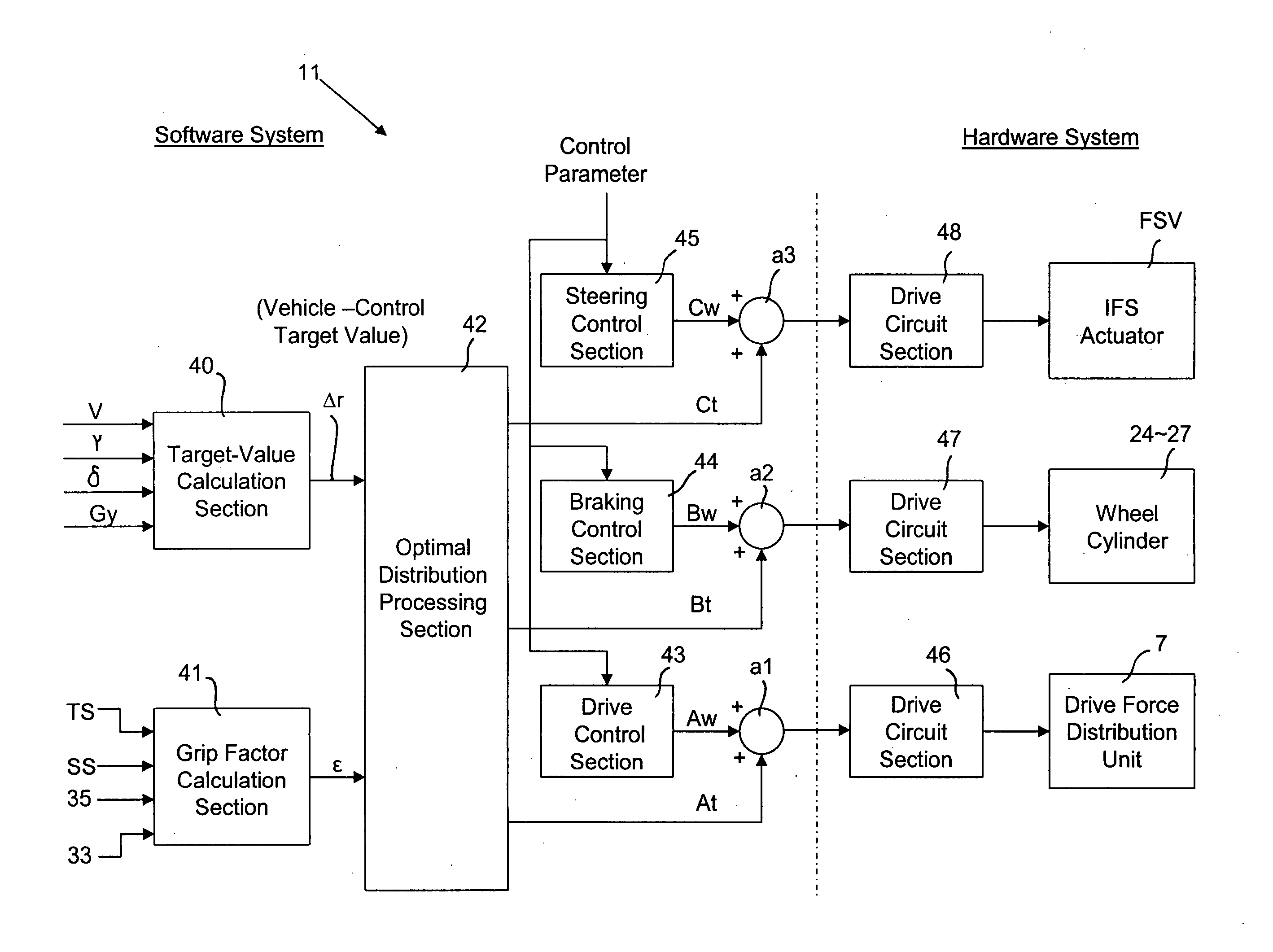
InactiveUS20050125131A1Improve vehicle stabilityVehicle body stabilisationDigital data processing detailsSteering angleRoad surface
An electronic control unit calculates a target yaw rate in accordance with a vehicle speed and a steering angle and calculates the yaw rate difference on the basis of the target yaw rate and an actual yaw rate. The electronic control unit estimates the grip factor of a front wheel to road surface and sets a distribution ratio for distribution of a vehicle-control target value among actuators of a steering system, a brake system, and a drive system in accordance with the estimated grip factor. The electronic control unit controls the actuators of the three systems in accordance with control instruction values distributed on the basis of the vehicle-control target value and the distribution ratio.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
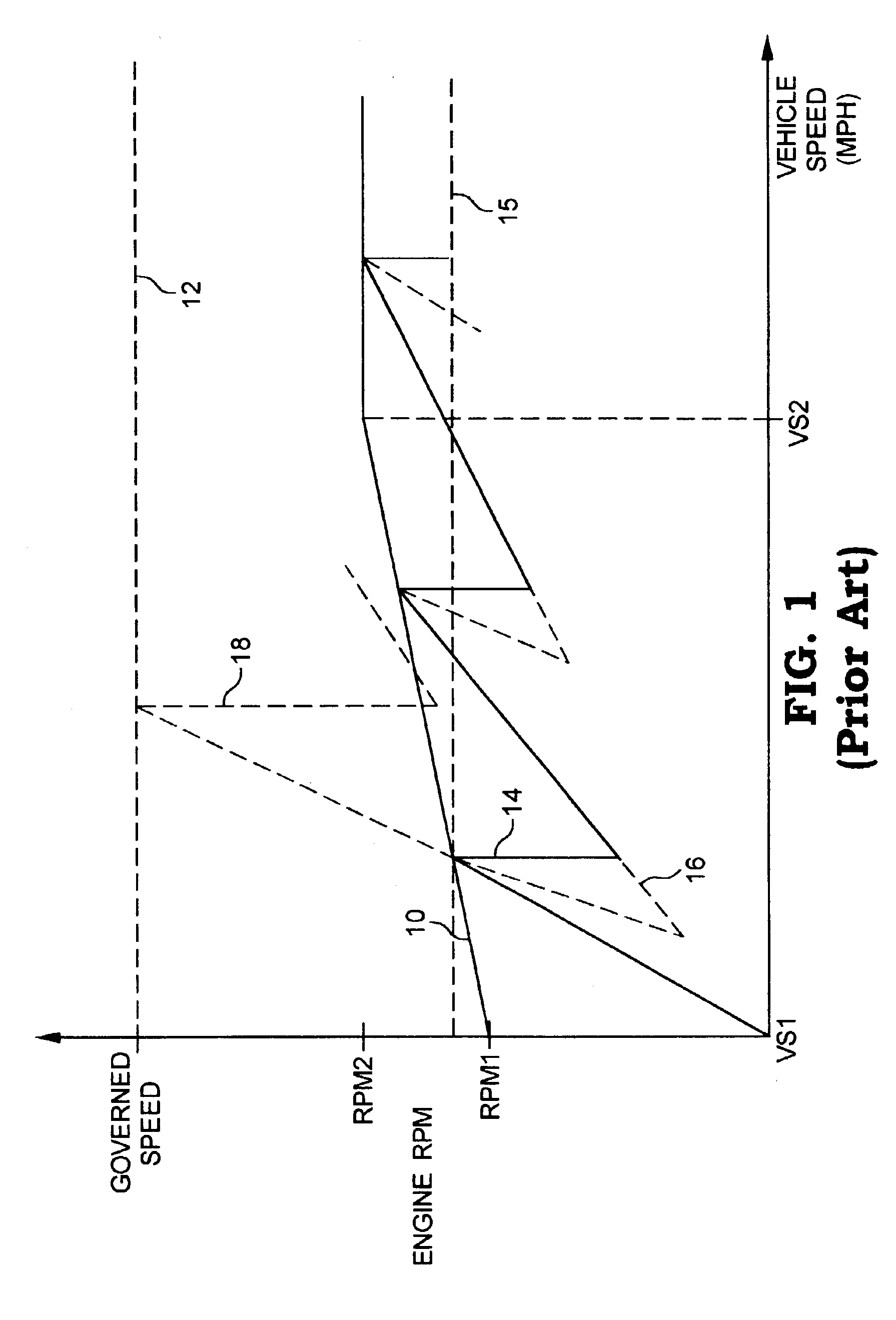
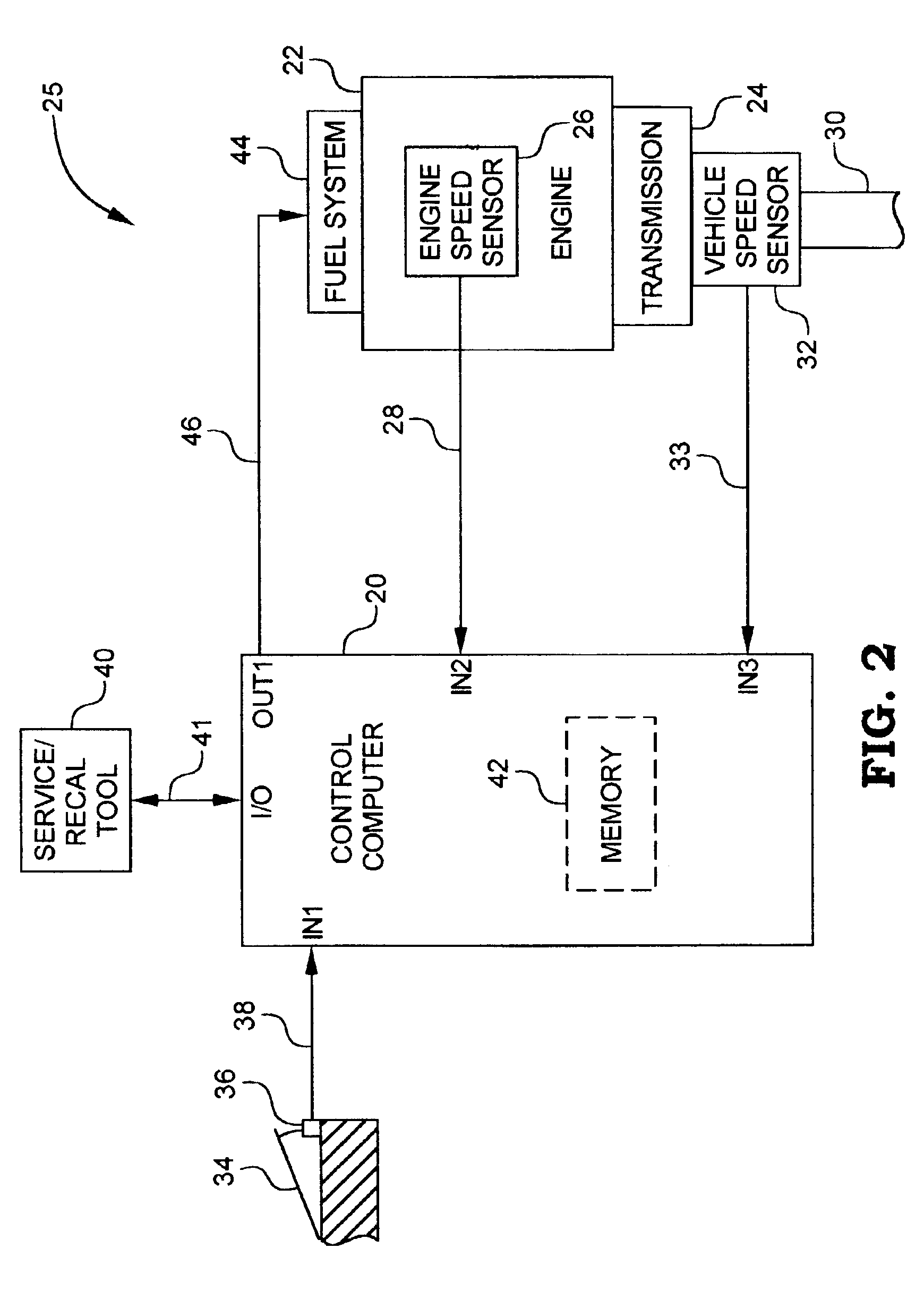
System for controlling an internal combustion engine in a fuel efficient manner
InactiveUS6944532B2Internal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsExternal combustion engineFuel efficiency
A system for controlling an engine in a fuel efficient manner includes a memory having stored therein an engine output characteristics map bounded by a maximum engine output curve. The map defines a region of undesirable operation having a first border defined as a function of engine speed and intersecting the maximum engine output curve. A control computer is configured to control engine operation in a fuel efficient manner by limiting engine operation within the map to the first border while also allowing the engine to operate anywhere on the maximum engine output curve. The control computer may be configured to so limit engine operation to the first border only if an engine or vehicle acceleration value is outside of an acceleration range, and further only if an engine work value is greater than an engine work threshold, and otherwise to allow engine operation anywhere on or within the map.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
Shifter with park lock and neutral lock device
InactiveUS6325196B1Prevent movementManual control with multiple controlled membersGearing controlCenter shiftEngineering
A shifter is provided for shifting a vehicle transmission between an automatic shifting mode that includes the automatically shifting gear positions of park, reverse, neutral, drive, and low drive, and a manual-shifting mode including upshift and downshift gear positions. The shifter includes a base, a lever carrier pivoted to the base for movement along a center shift path and side shift paths, and a shift lever pivoted to the lever carrier for movement between the different shift paths. The lever carrier has notches corresponding to the gear positions, and the shift lever has a pawl operably engaging the notches to control movement of the shift lever between the automatically shifting gear positions on the center shift path. The pawl is disengaged when the shift lever is moved into the side-located shift paths.
Owner:GRAND HAVEN STAMPED PRODS DIV OF JSJ
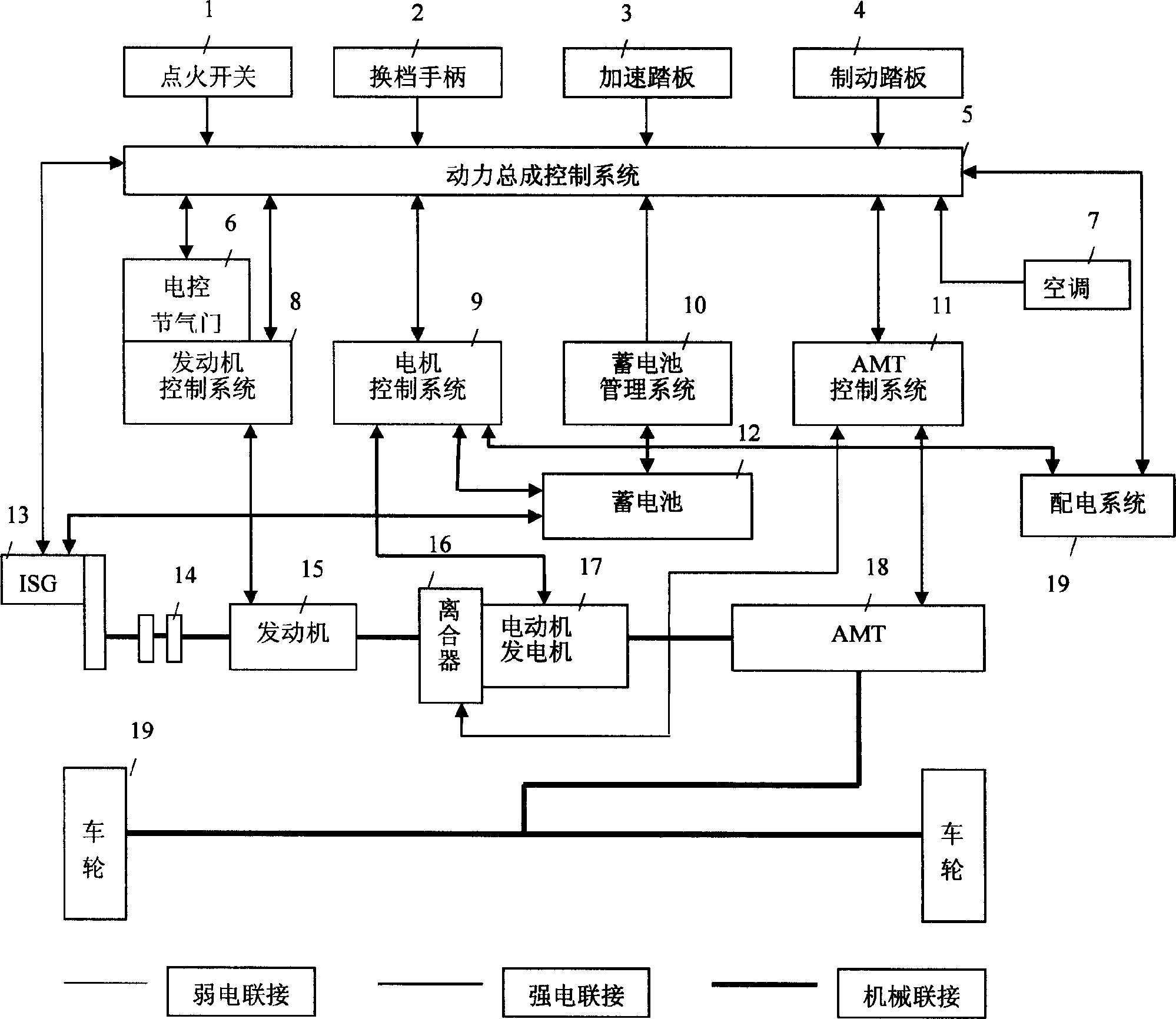
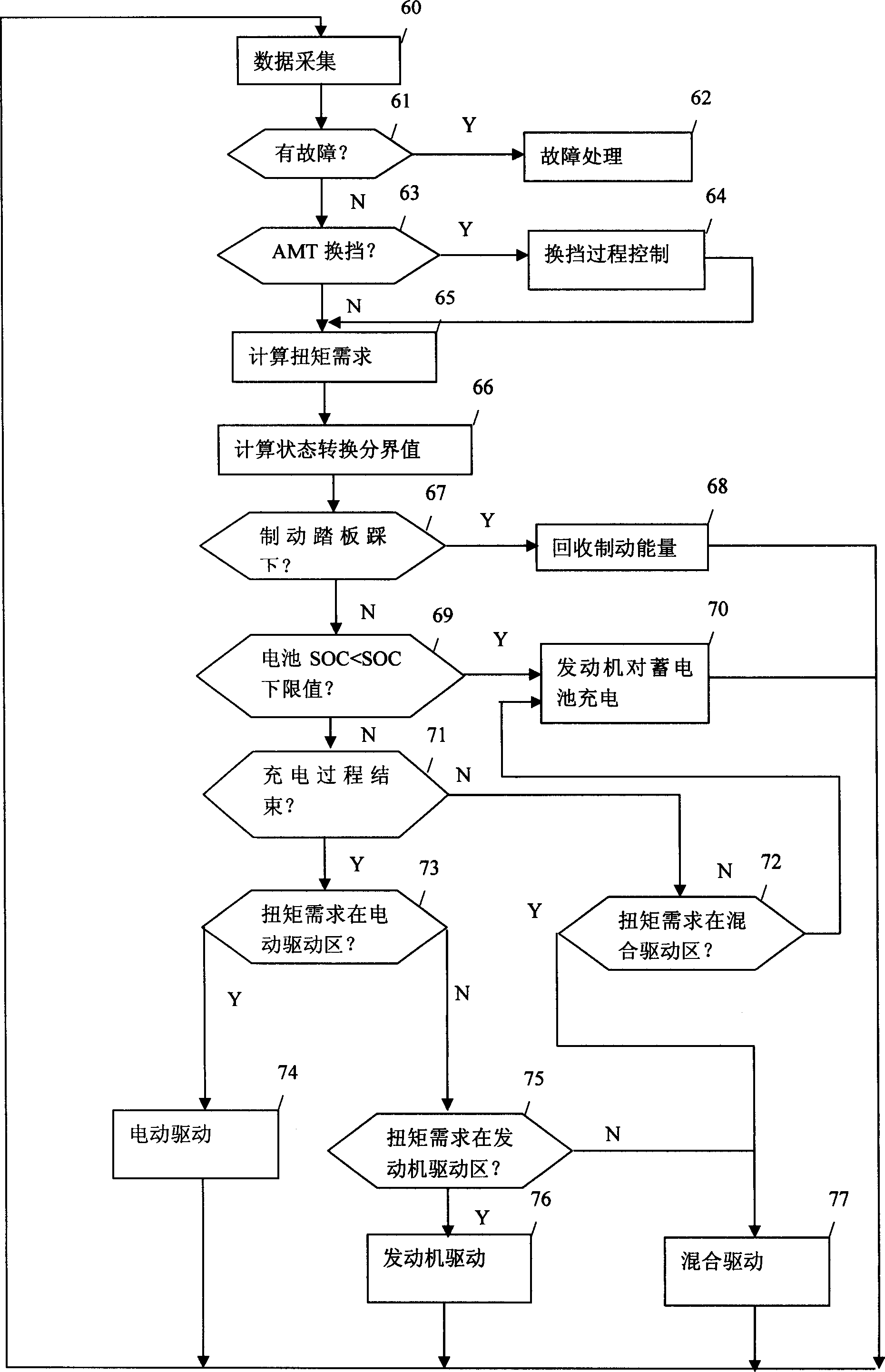
Power output changing-over method and control system for power assembly of mixed powder car
ActiveCN1528612AEmission reductionReduce fuel consumptionHybrid vehiclesGas pressure propulsion mountingBoundary valuesData acquisition
The invention is a power output switching method and control system of power assembly of mixed power saloon car. It can switch the power output and manage system energy, and according to state switching boundary value and result judgment of data collection, makes the power assembly switch to the states such as reclaiming plugging energy; charging accumulator by engine; electric driving; mixed driving; engine driving; etc to make coordination treatment. Its control system includes main chip, as well as switch quantity conditioning circuit, analogue quantity conditioning circuit, pulse signal conditioning circuit, CAN bus interface, D / A converting circuit, drive isolating circuit, etc, where they are all connected with the main chip. It can make the output torque realize fast smooth switch in a large range, and heightens the energy using efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
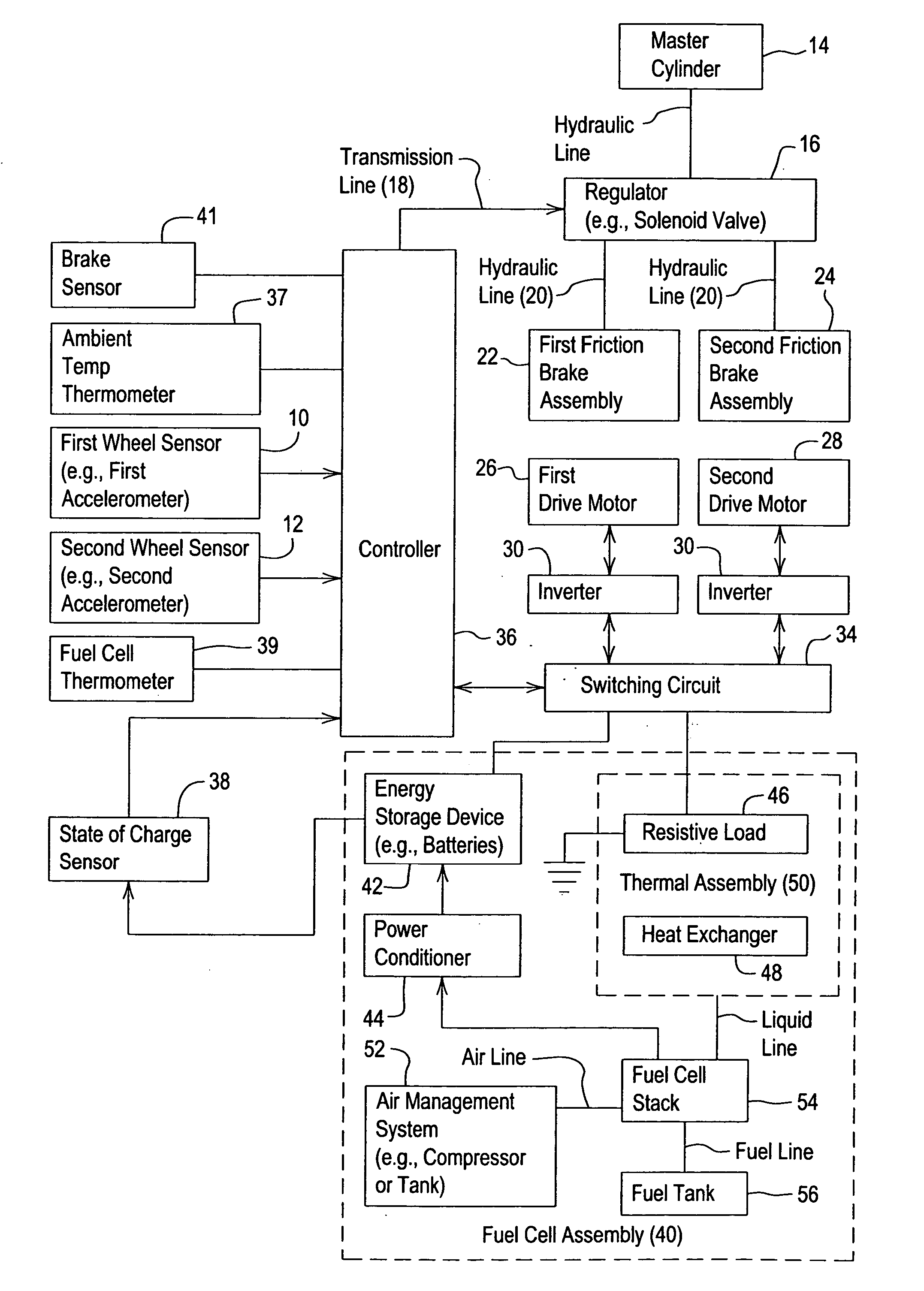
Vehicular control system for regenerative braking
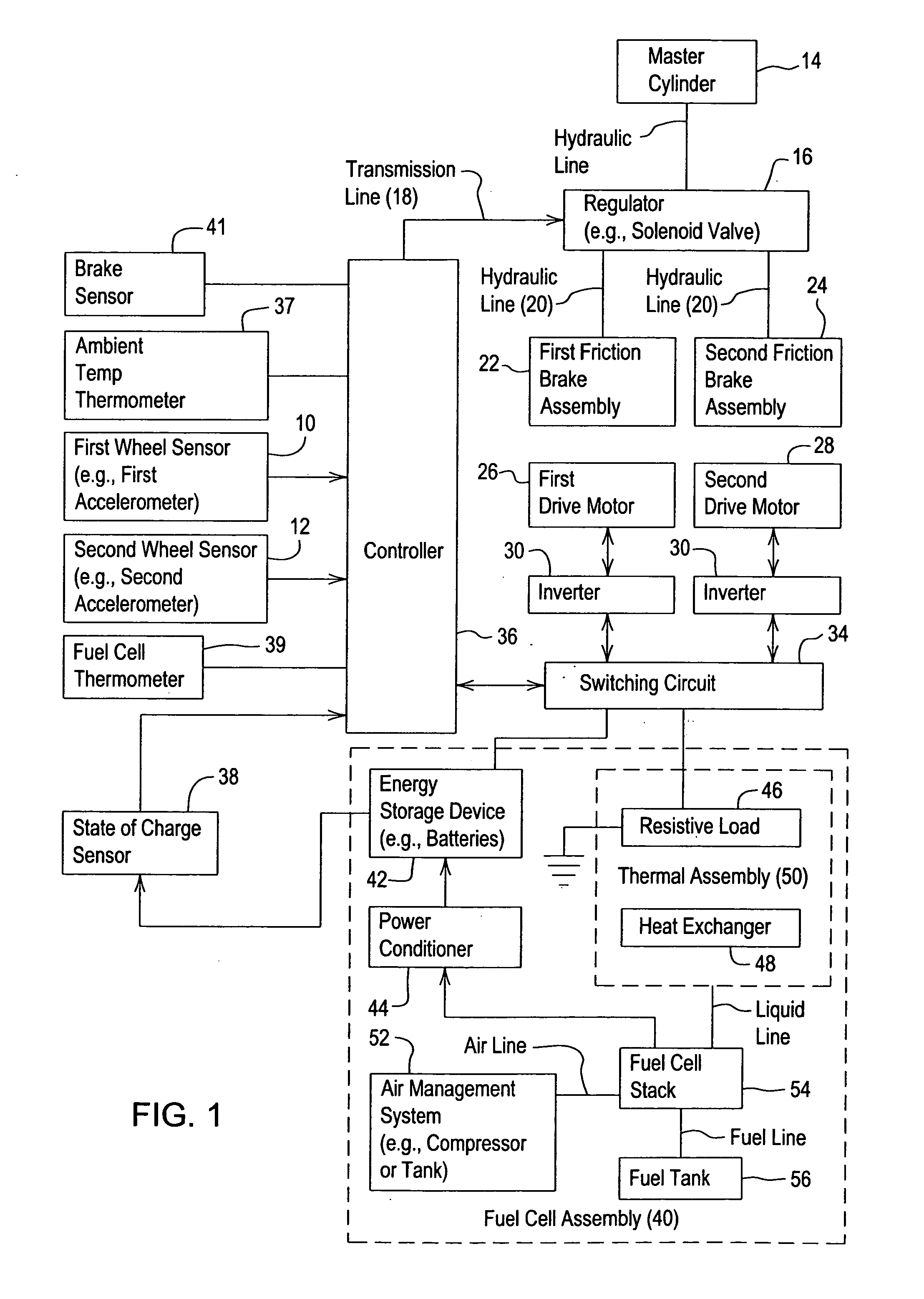
InactiveUS20060046895A1Shorten warm-up timeFuel cell heat exchangeRailway vehiclesFuel cellsRegenerative brake
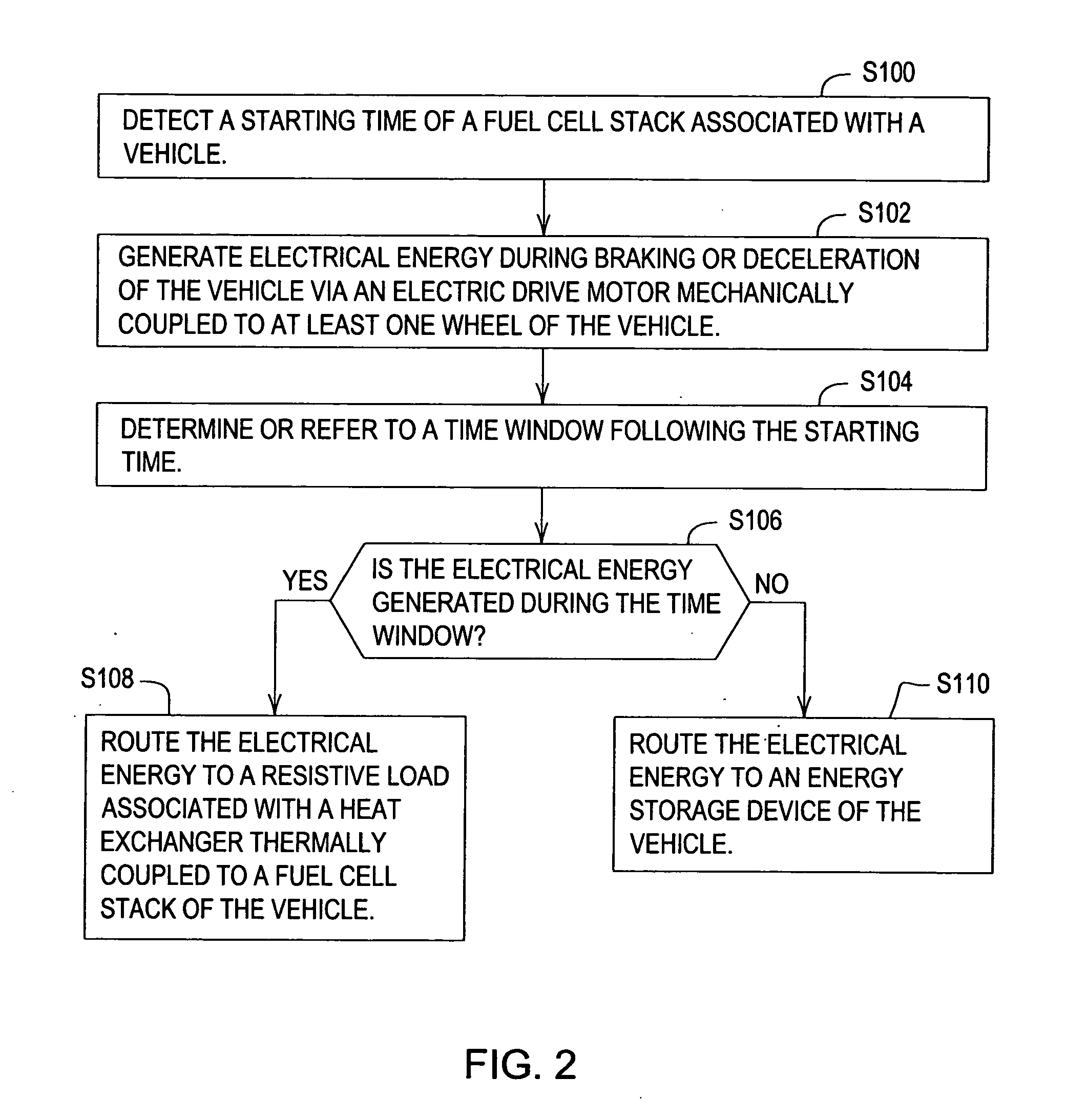
A system and method for controlling a vehicle for regenerative braking facilitates decreasing the warm-up time of the fuel cell stack from start-up to full electrical power generation capacity. A controller detects a starting time of a fuel cell stack associated with a vehicle. A drive motor generates electrical energy during braking or deceleration of the vehicle, where the drive motor is mechanically coupled to at least one wheel of the vehicle. A controller refers to or determines a time window following the starting time. The switching unit routes the electrical energy to a resistive load associated with a heat exchanger thermally coupled to a fuel cell stack of the vehicle if the electrical energy is generated during the time window.
Owner:DEERE & CO
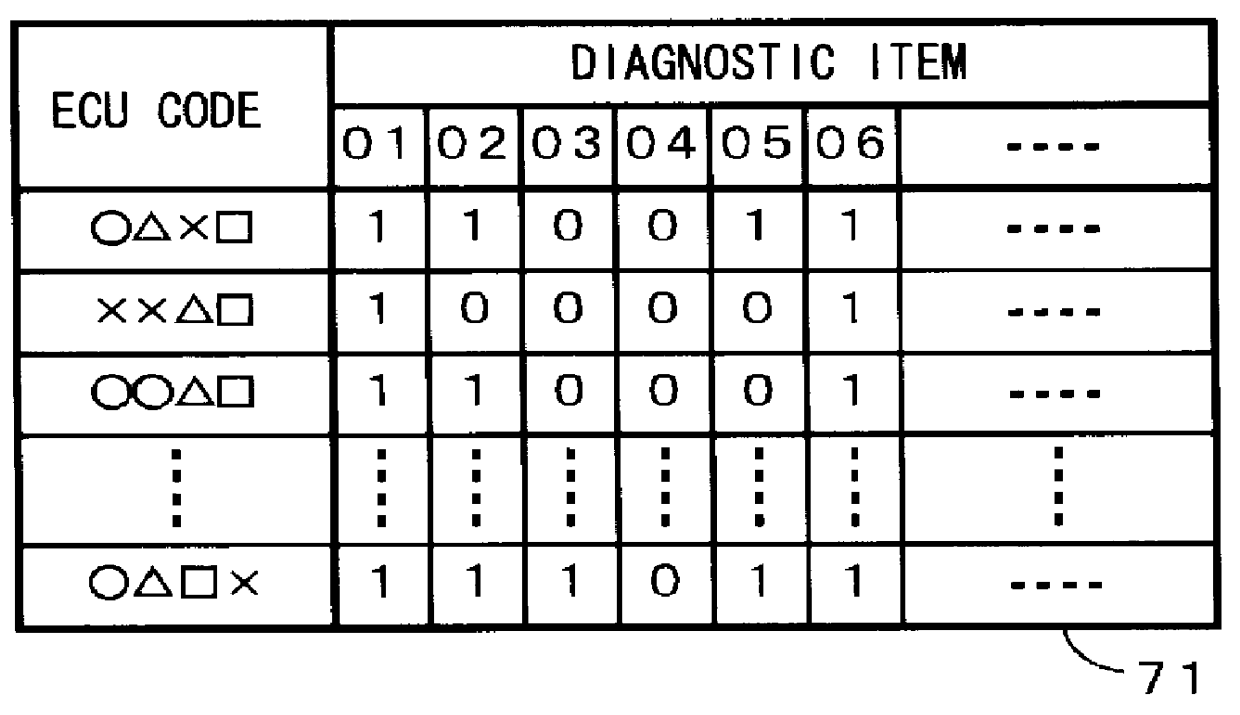
Method and device for diagnosis for vehicle
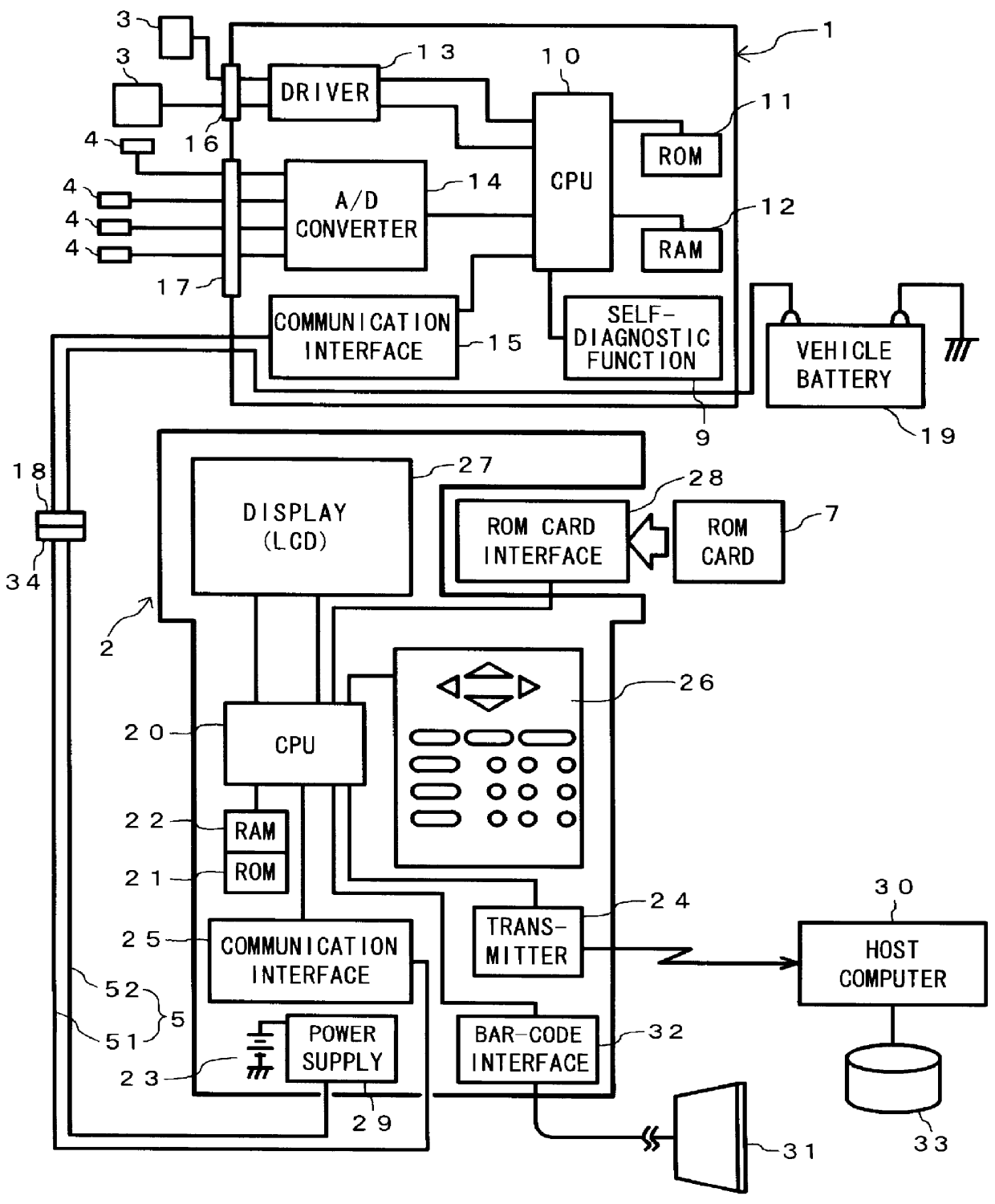
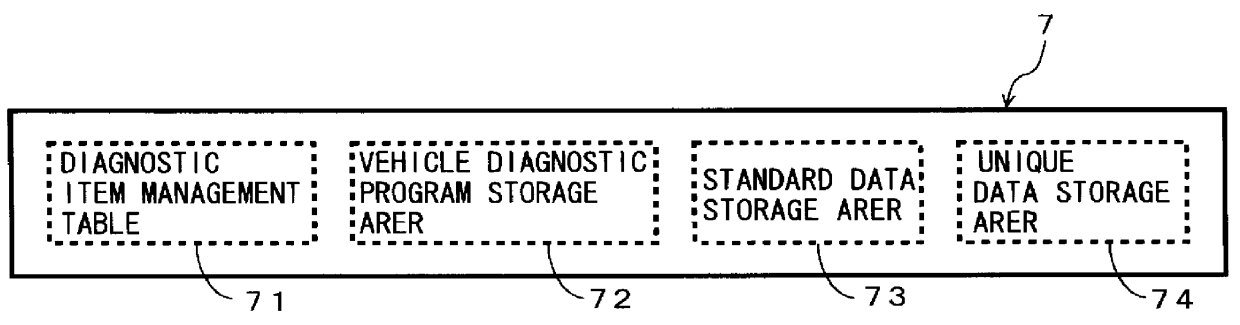
InactiveUS6134488AThe solution result is accurateVehicle testingElectrical controlDiagnosis methodsEngineering
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 00975 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 16, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 16, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 10, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 40715 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 17, 1998Forced activation signal supplier 550 supplies a forced activation signal Sx to a diagnostic target part 101 related to a diagnostic item requiring a forced activation signal. Vehicle-state detector 552 detects a current state of the diagnostic target part 101 through an ECU 1. Diagnostic element 553 compares the currently detected state of the diagnostic target part 101 with a state predicted when the forced activation signal Sx is given to diagnose the diagnostic target part 101. When the forced activation signal Sx is supplied to the part of the vehicle, self-diagnosis stopping element 554 gives an instruction to stop a self diagnosis for at least an item the diagnostic result of which may vary under the influence of the forced activation signal Sx, or to invalidate the diagnostic result.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
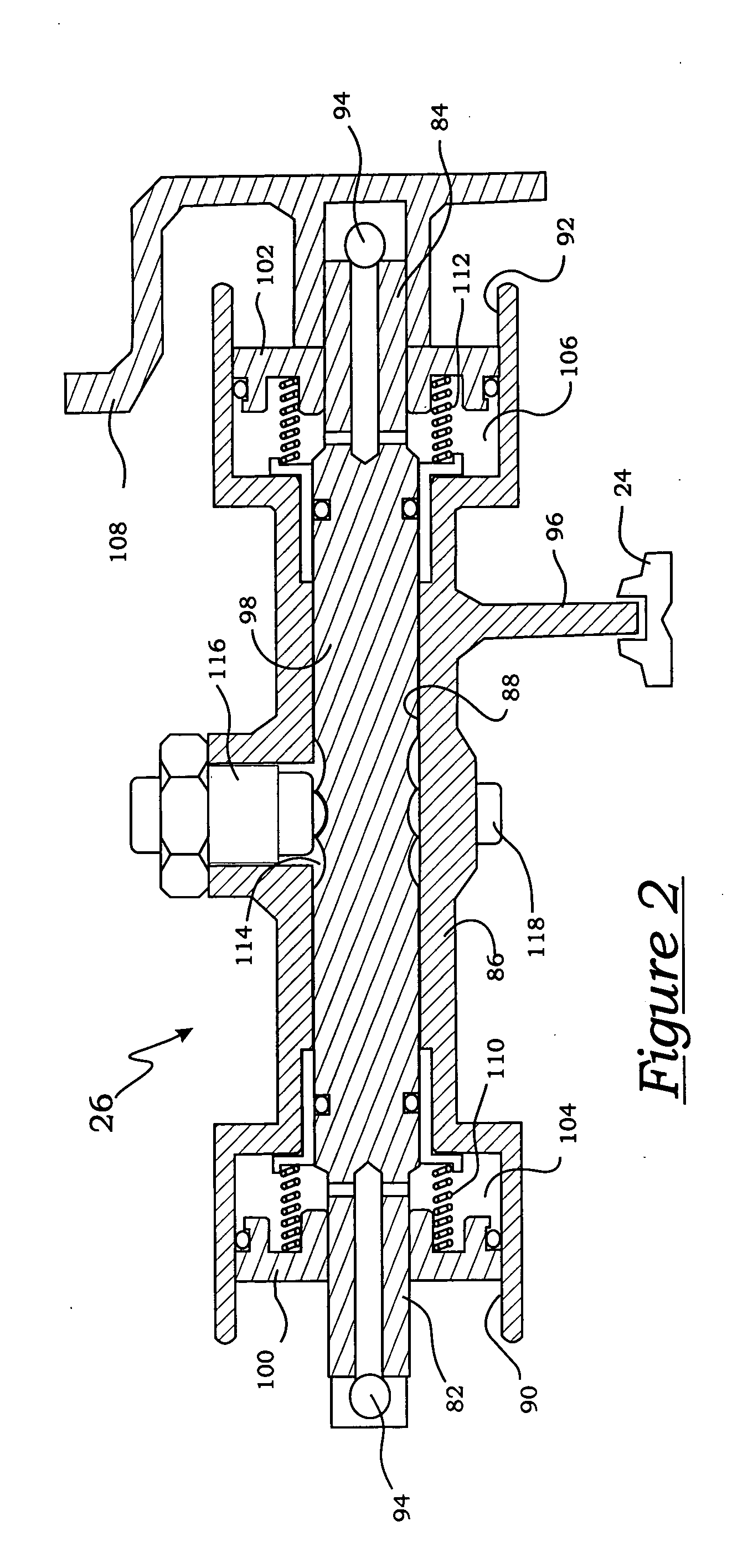
Electromagnetic brake for a multiple-ratio power transmission in a vehicle powertrain
InactiveUS20050217966A1Reduce the cross-sectional areaLimited amountBraking element arrangementsToothed gearingsActuatorControl theory
An electromagnetic brake, including an electromagnetic brake actuator coil surrounding a power input shaft for a multiple-ratio transmission in a vehicle powertrain, is disclosed. An electromagnetic flux flow path for the actuator coil is electromagnetically isolated from the power input shaft and other elements of the powertrain thereby avoiding residual magnetization.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
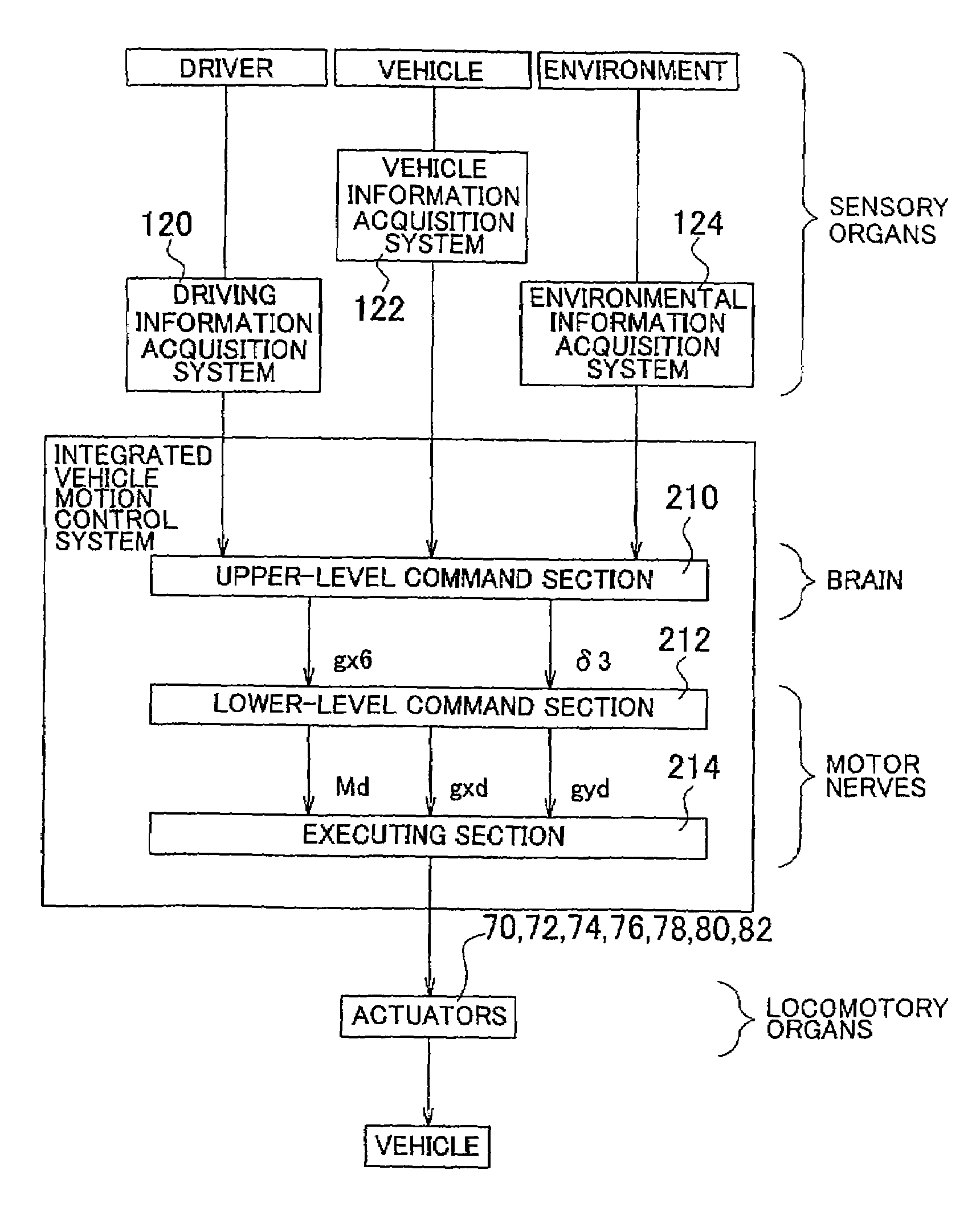
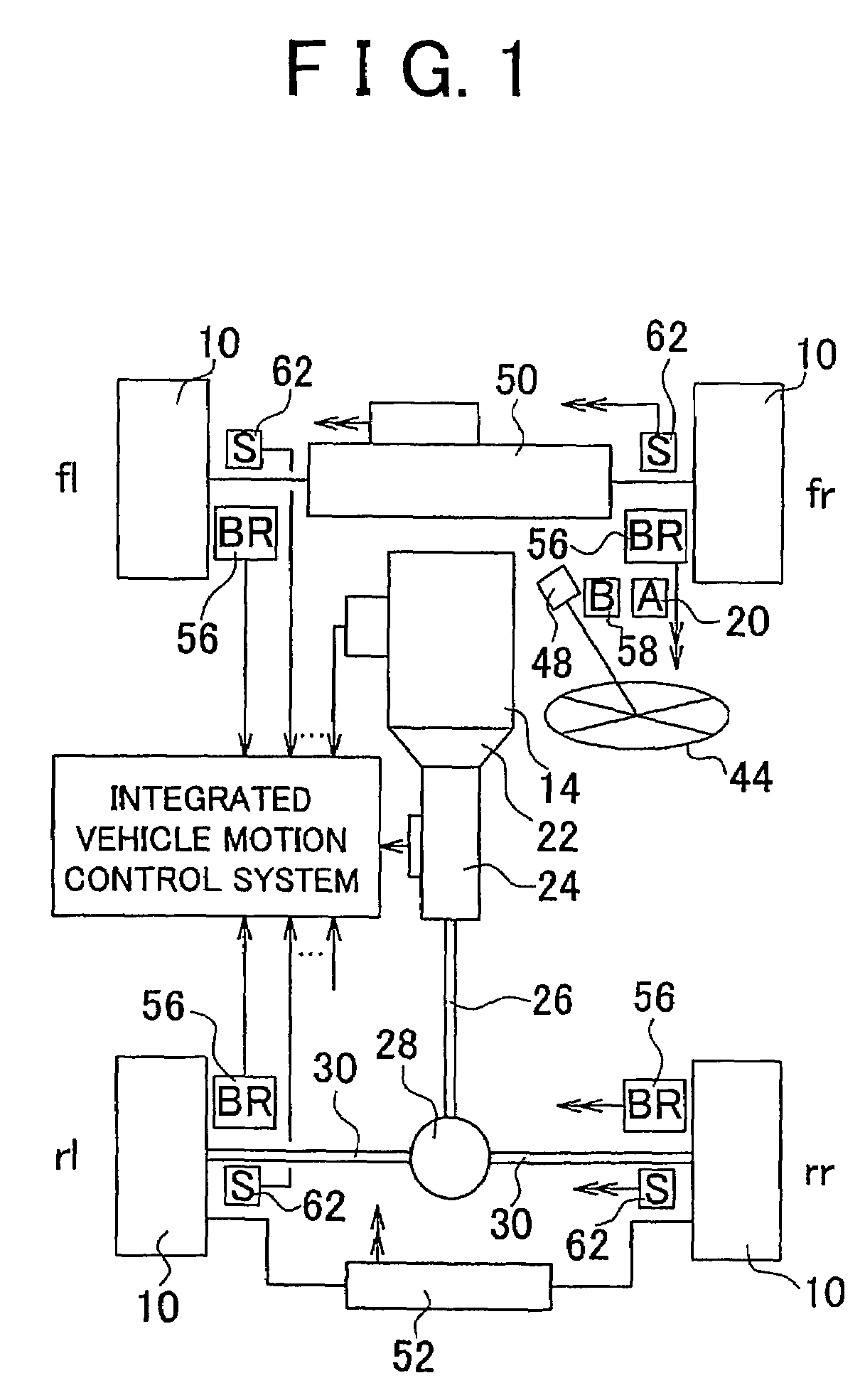
Integrated vehicle motion control system
InactiveUS7162333B2Shorten the timeImprove accuracyVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRelevant informationControl system
An integrated vehicle motion control system is provided in which the software configuration is formed in a hierarchical structure, and includes (a) a command section adapted to determine target vehicle state quantities based on driving related information, and (b) an executing section adapted to receive the target vehicle state quantities as commands from the command section, and execute the commands by means of a plurality of actuators. The command section includes an upper-level command section adapted to determine first target vehicle state quantities based on the driving related information, without taking account of the dynamic behavior of the vehicle, and a lower-level command section adapted to determine second target vehicle state quantities inview of the dynamic behavior of the vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
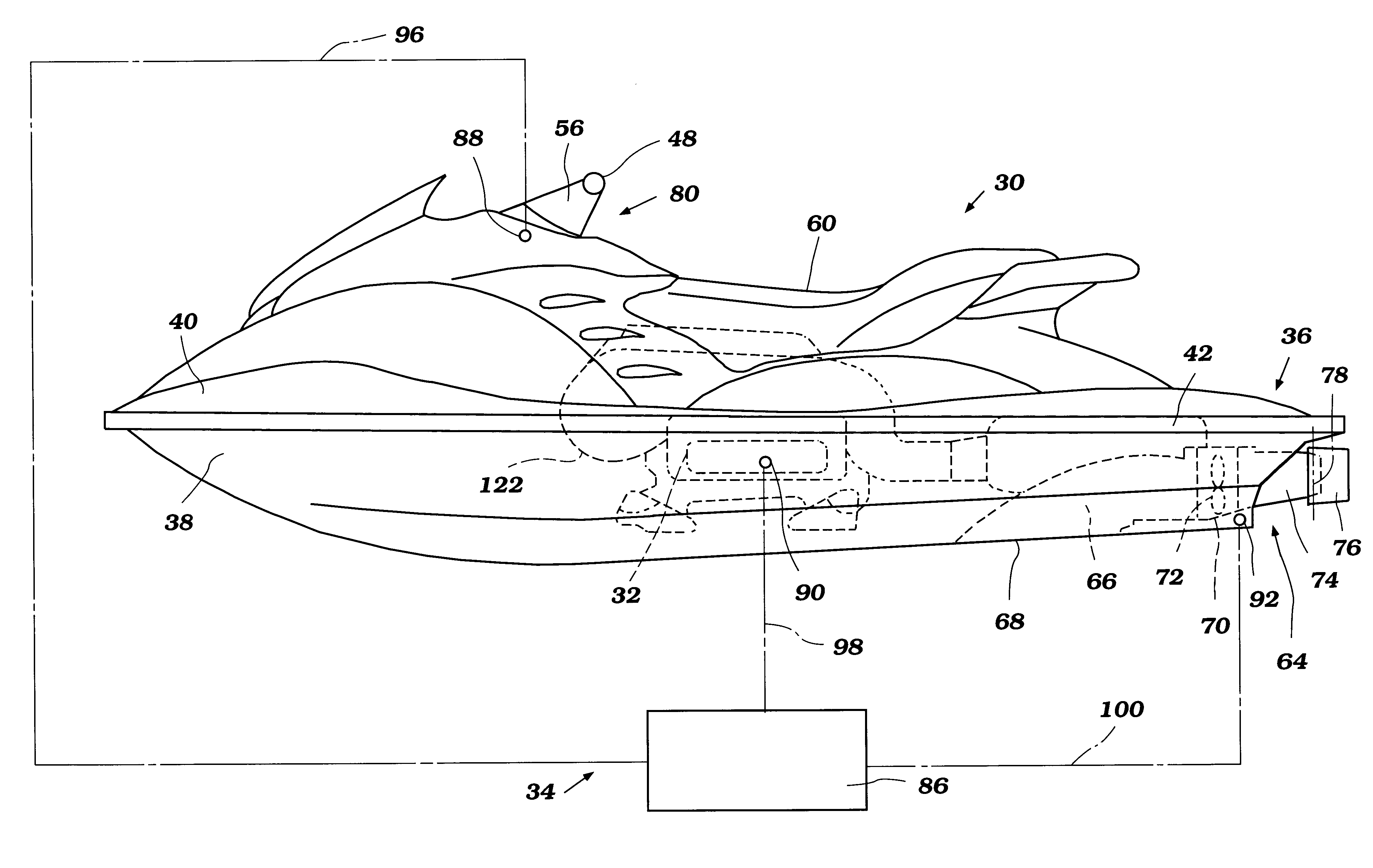
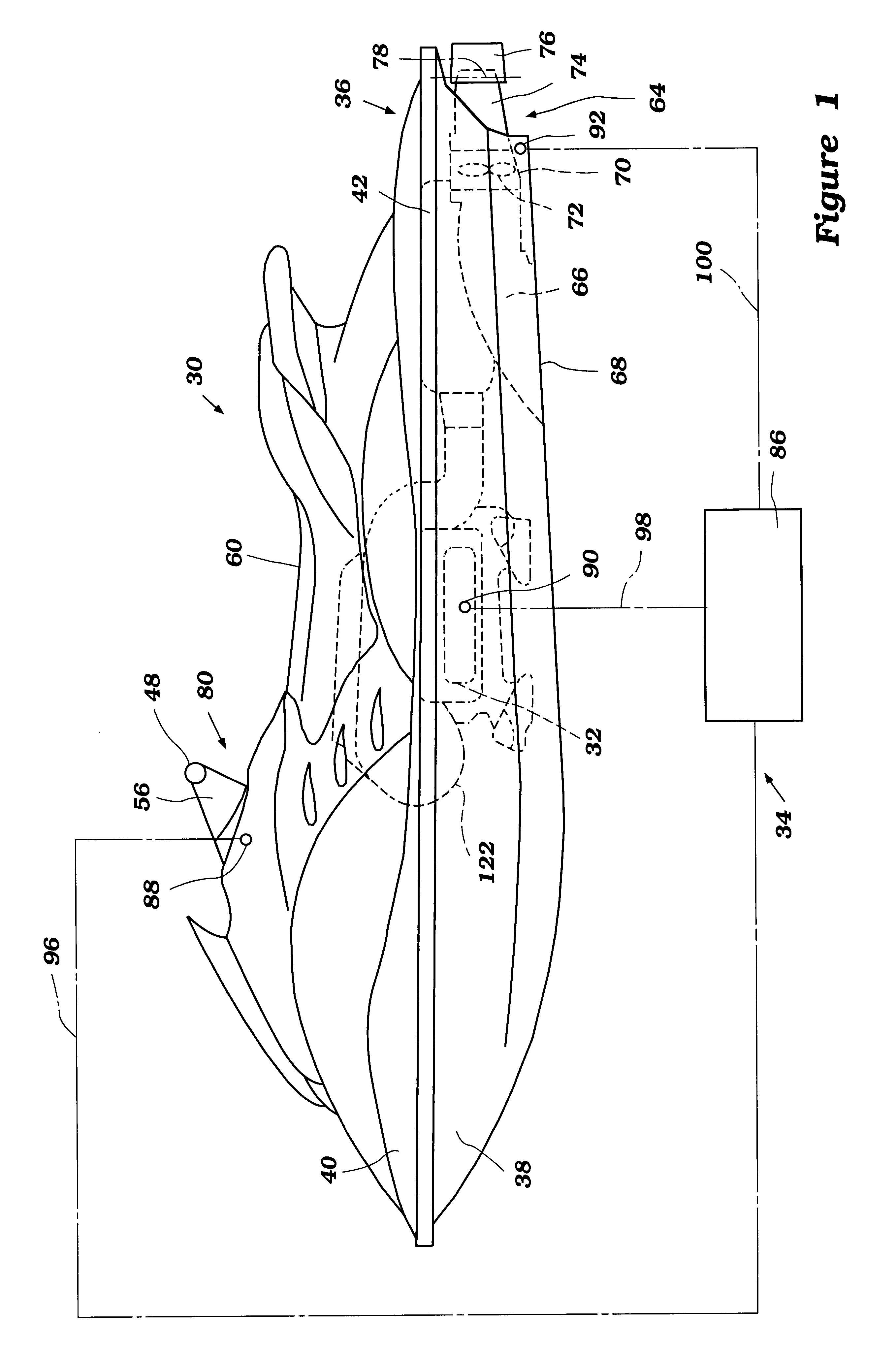
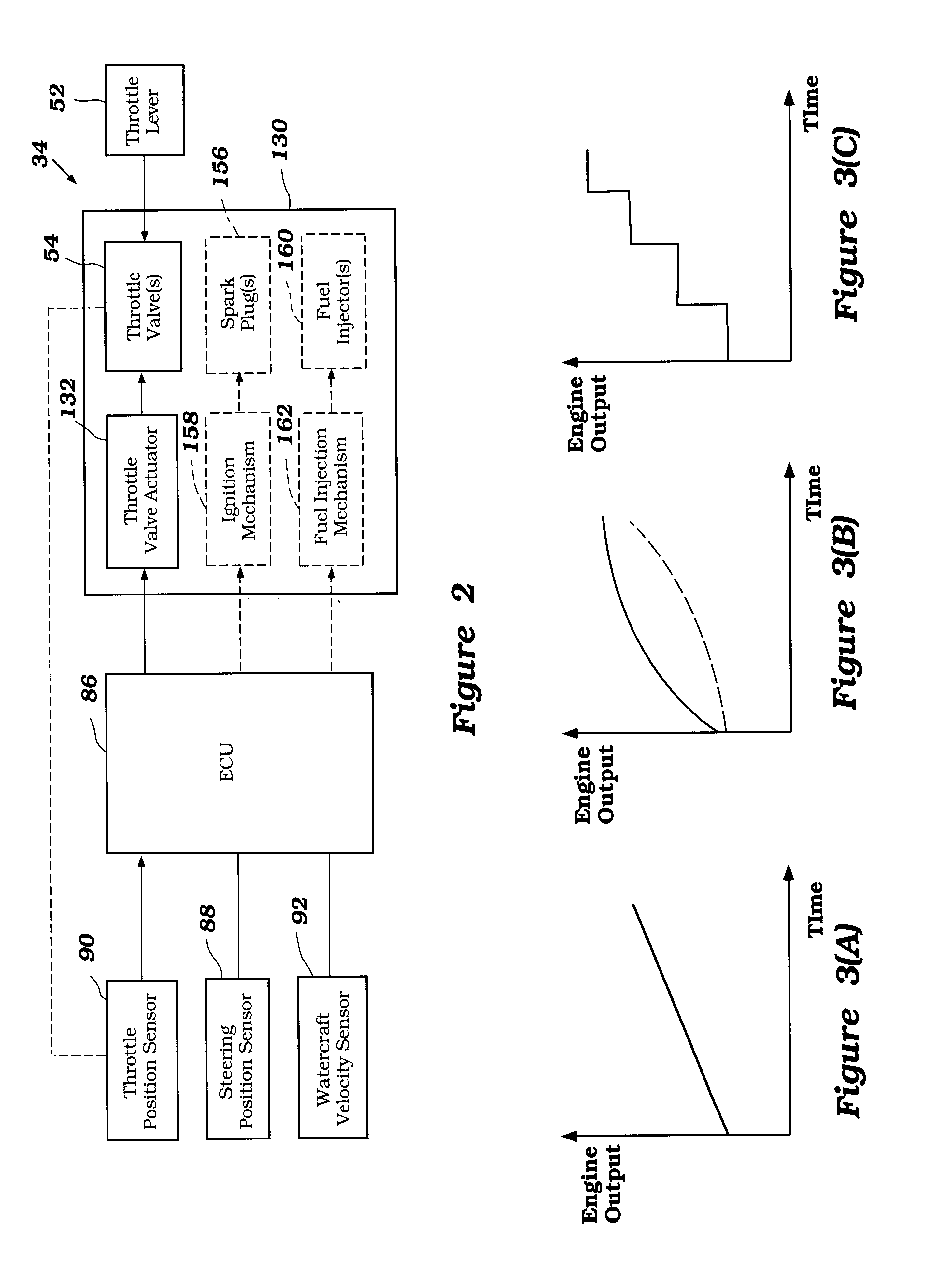
Engine output control for watercraft
A watercraft includes an improved engine control system that enhances the responsiveness of the watercraft and eases watercraft operation. The watercraft includes a propulsion device, such as a jet propulsion unit, and an engine that powers the propulsion device. The engine control system is configured to maintain or increase engine speed under certain operating conditions.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
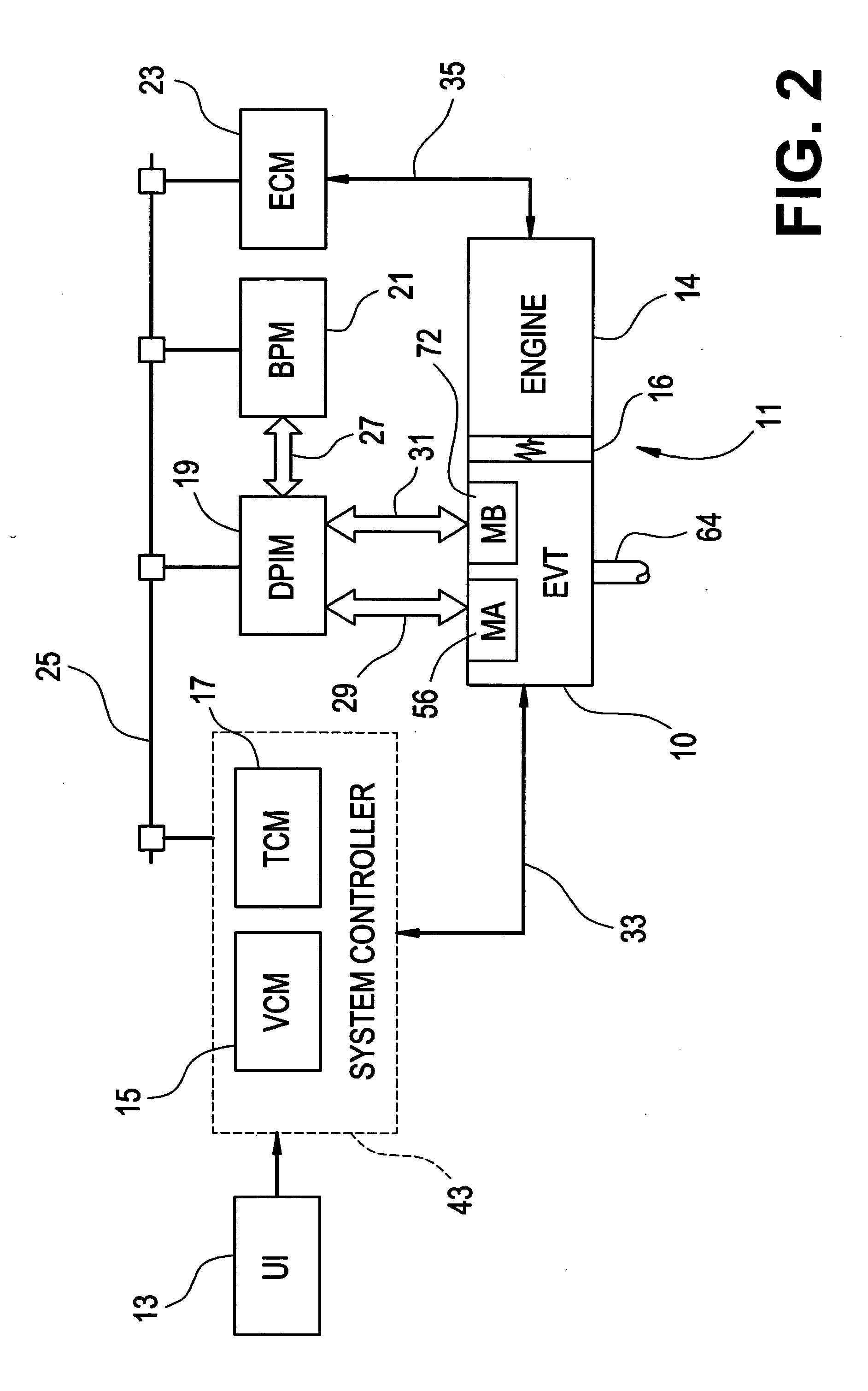
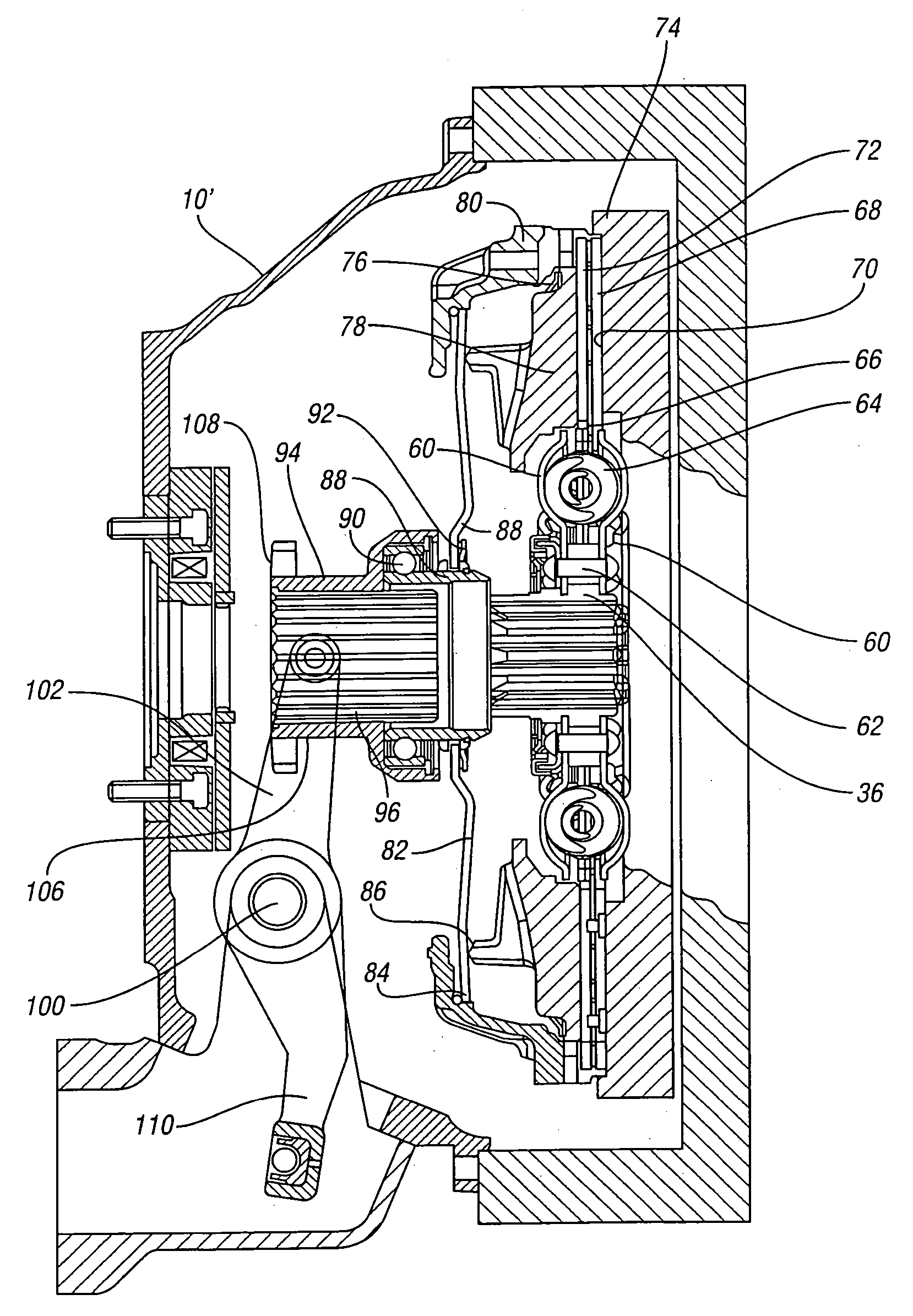
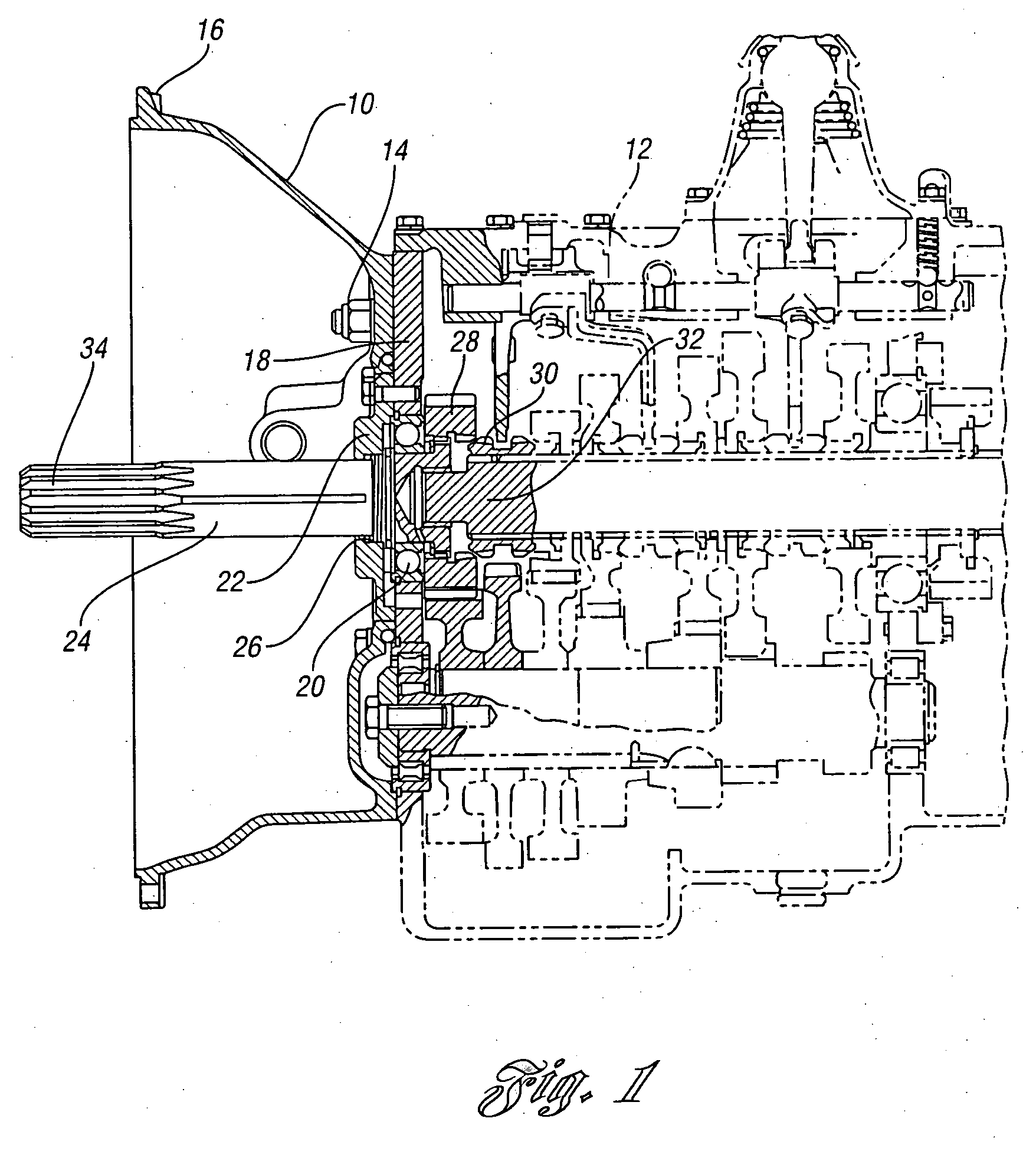
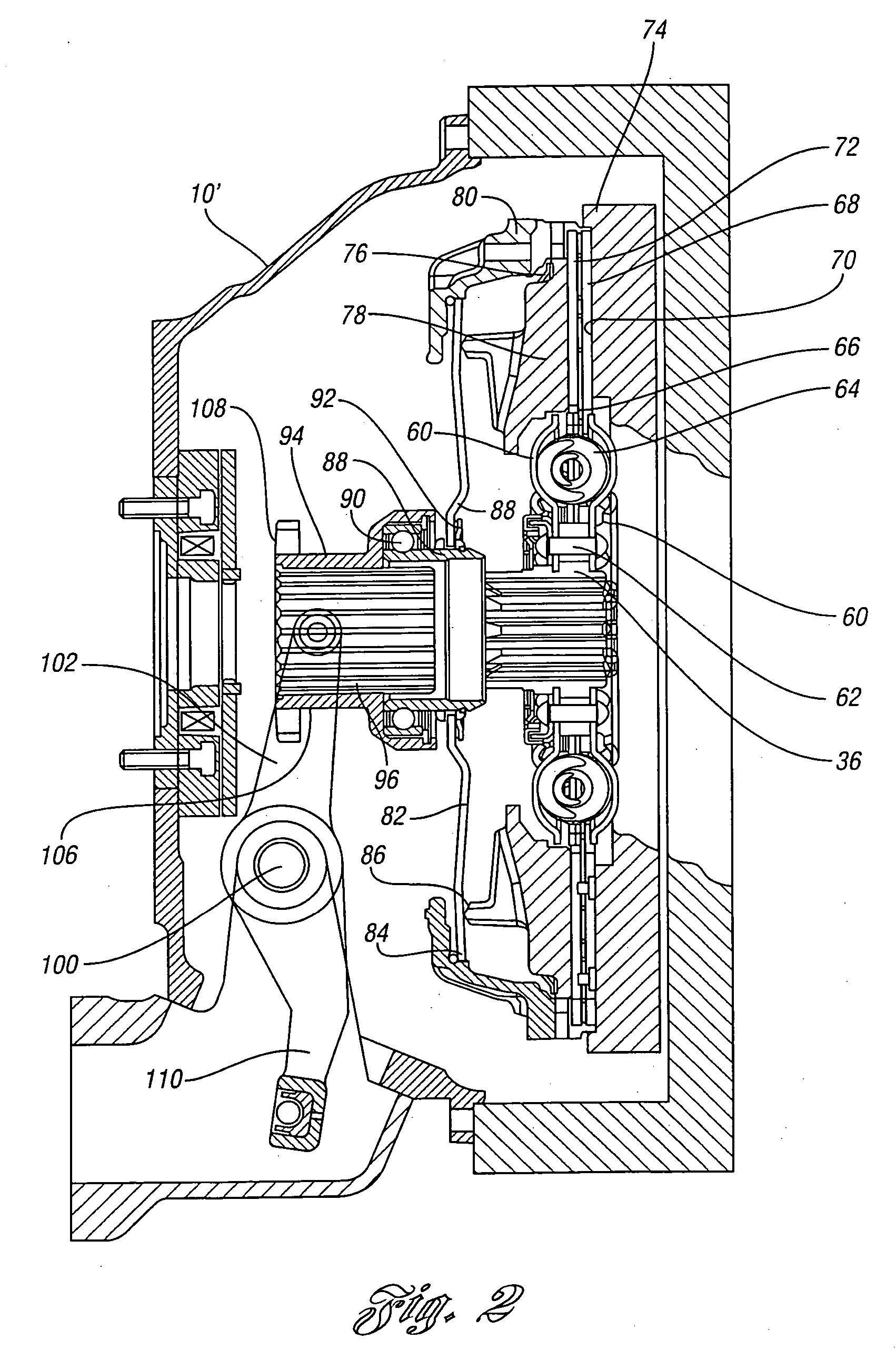
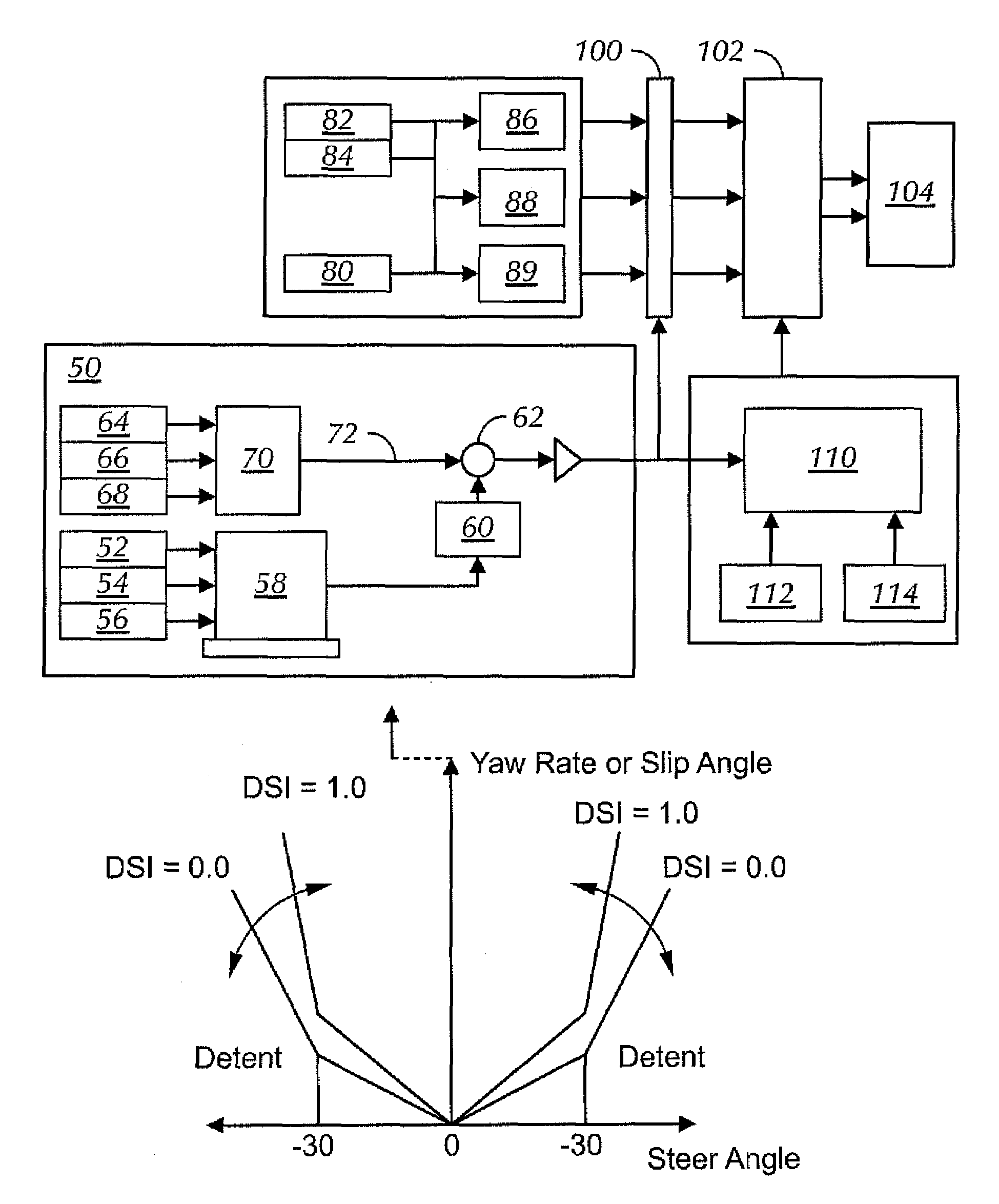
Vehicle control
InactiveUS7263419B2System is enhancedProvide feedbackDigital data processing detailsGearing controlDriver/operatorControl system
A vehicle control system includes at least one driver input, a supervisor and at least one sub-system controlled by the supervisor. The supervisor assesses the driver input to establish actual driver demand and controls the sub-systems accordingly. As a result intuitive driver demand is identified and met.
Owner:RICARDO UK LTD
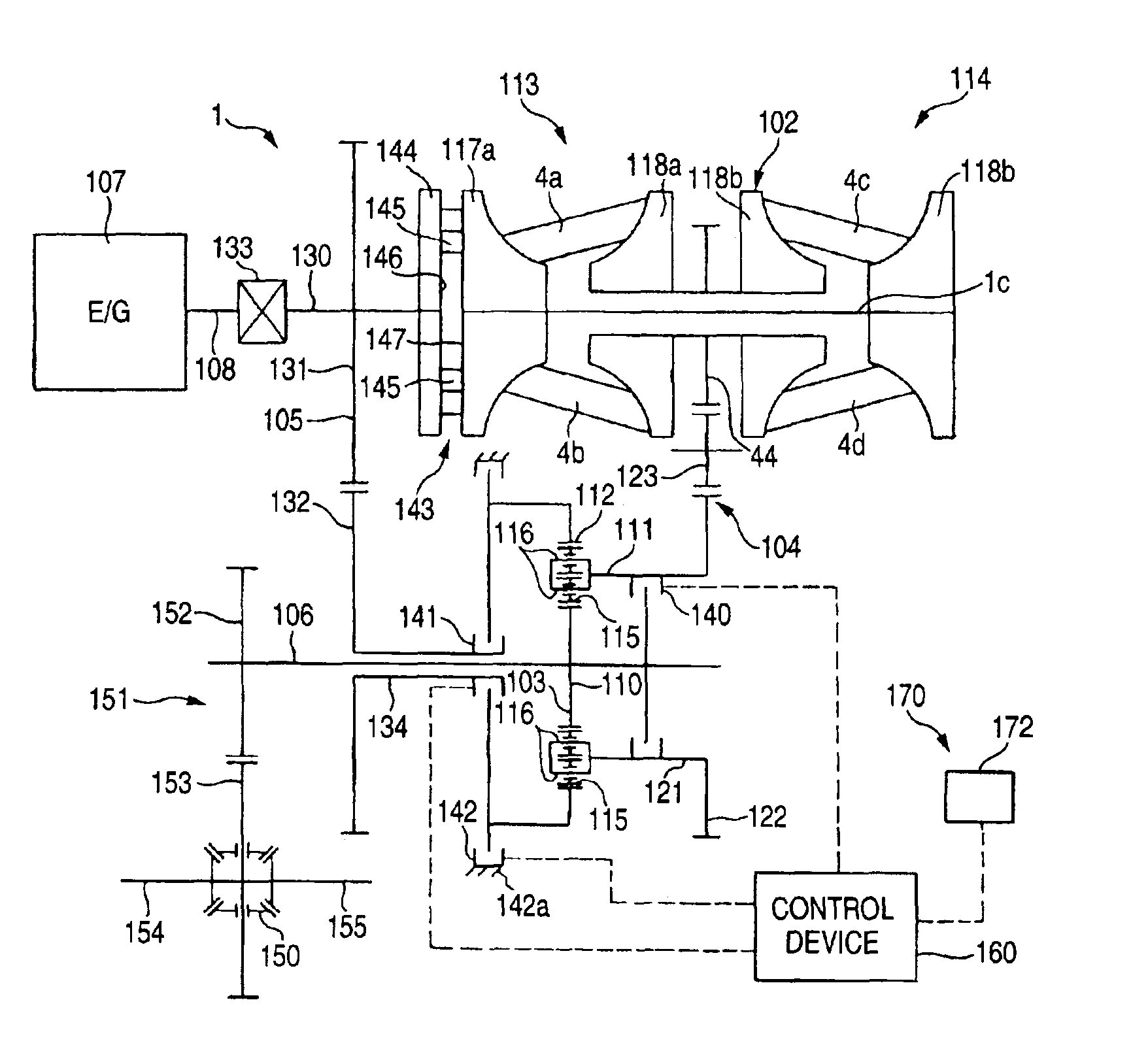
Method of and apparatus for actuating the torque transmitting system and the transmission in the power train of a motor vehicle
PCT No. PCT / DE96 / 01755 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 23, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 23, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 12, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 10456 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 20, 1997The friction clutch between the engine and an automated transmission in the power train of a motor vehicle are operated and controlled by an actuator which effects changes in the extent of engagement of the clutch as well as the selection of and shifting into particular gears. The actuator forms part of a unit which receives a pressurized hydraulic fluid from a source including an accumulator and a proportional valve which latter selects the fluid pressure necessary to shift the transmission into a selected gear.
Owner:LUK GETRIEBE SYST +3
Vehicle with automatic engine stop/restart function and automatic engine stop/restart system and method for vehicle
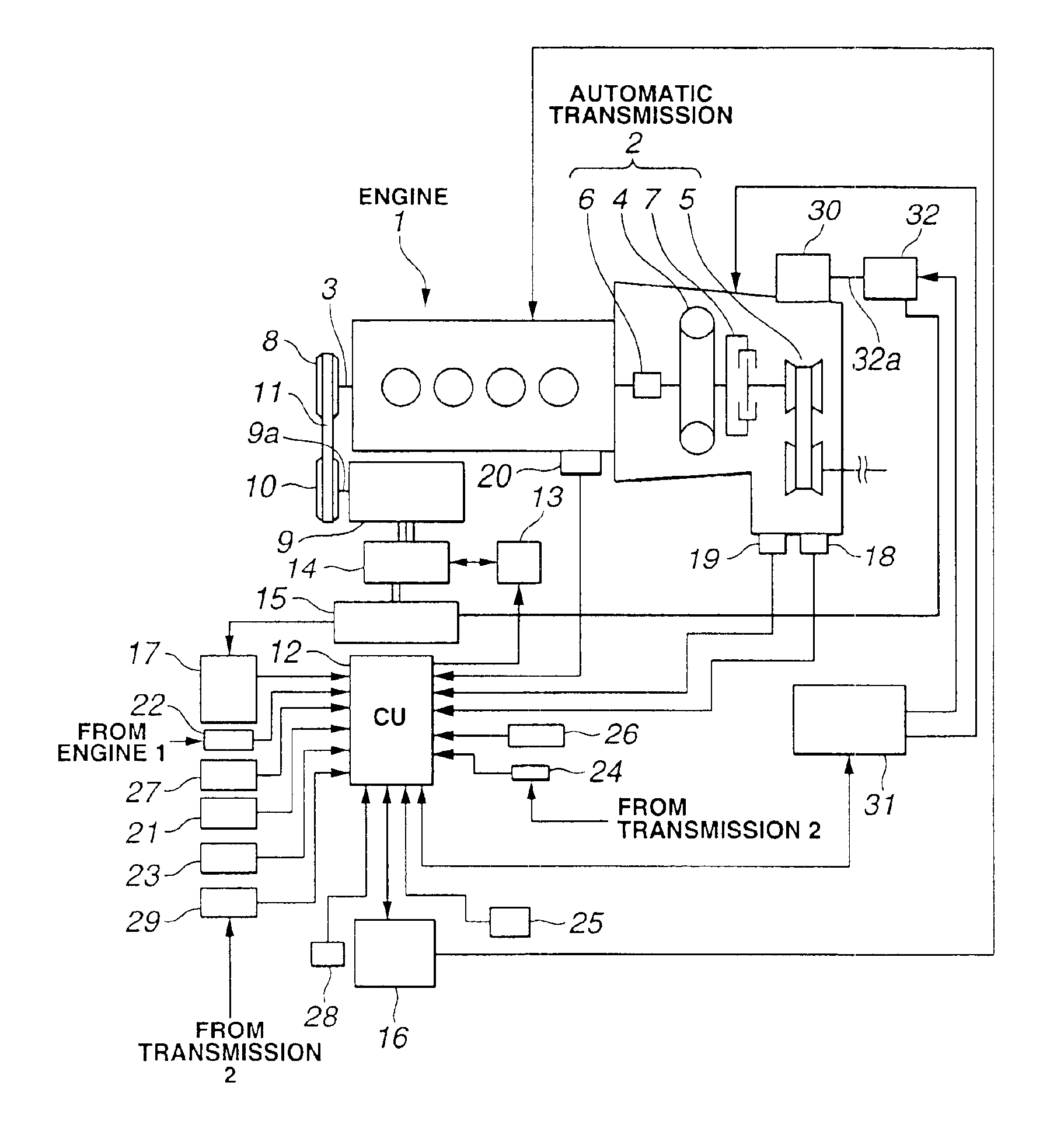
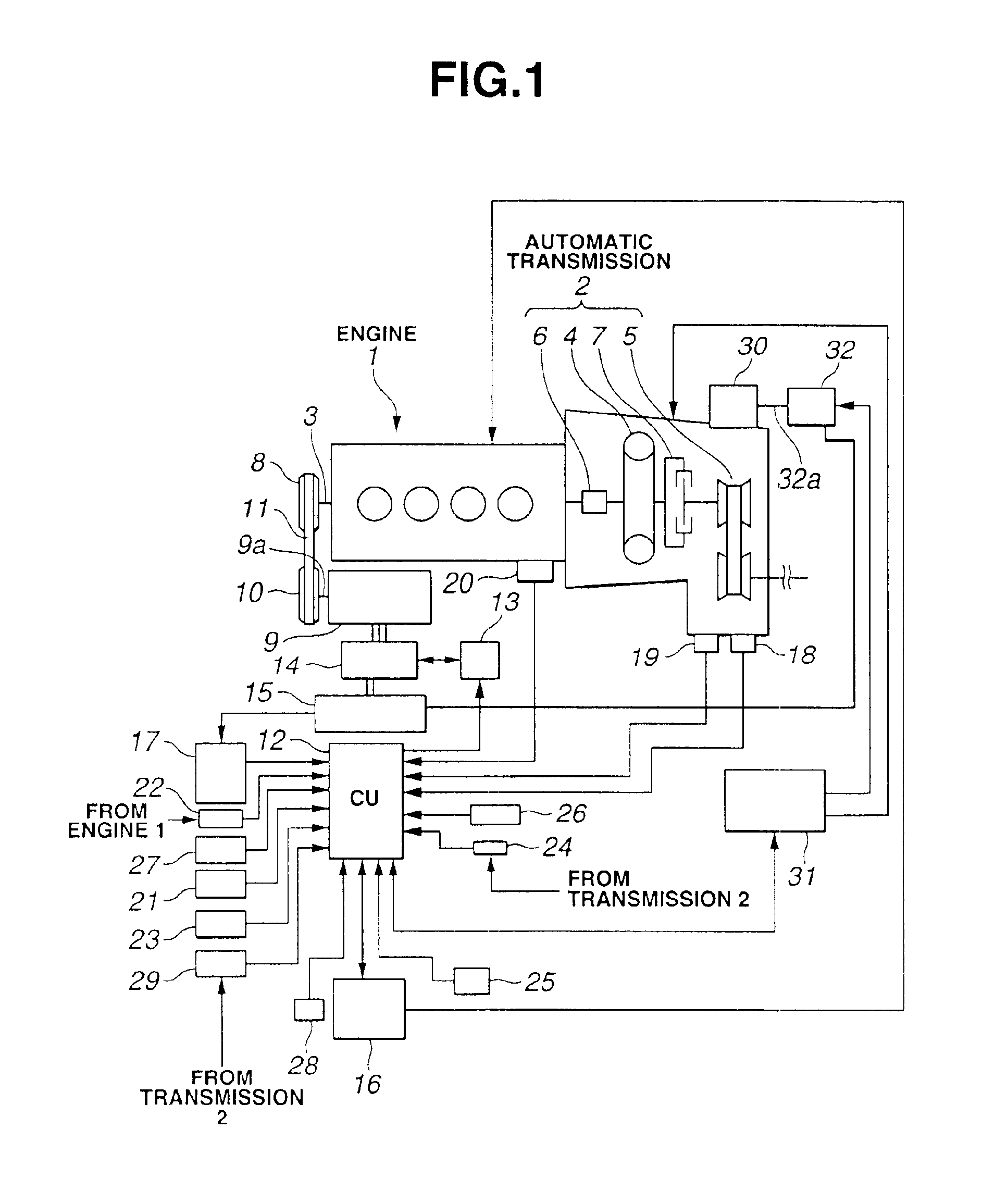
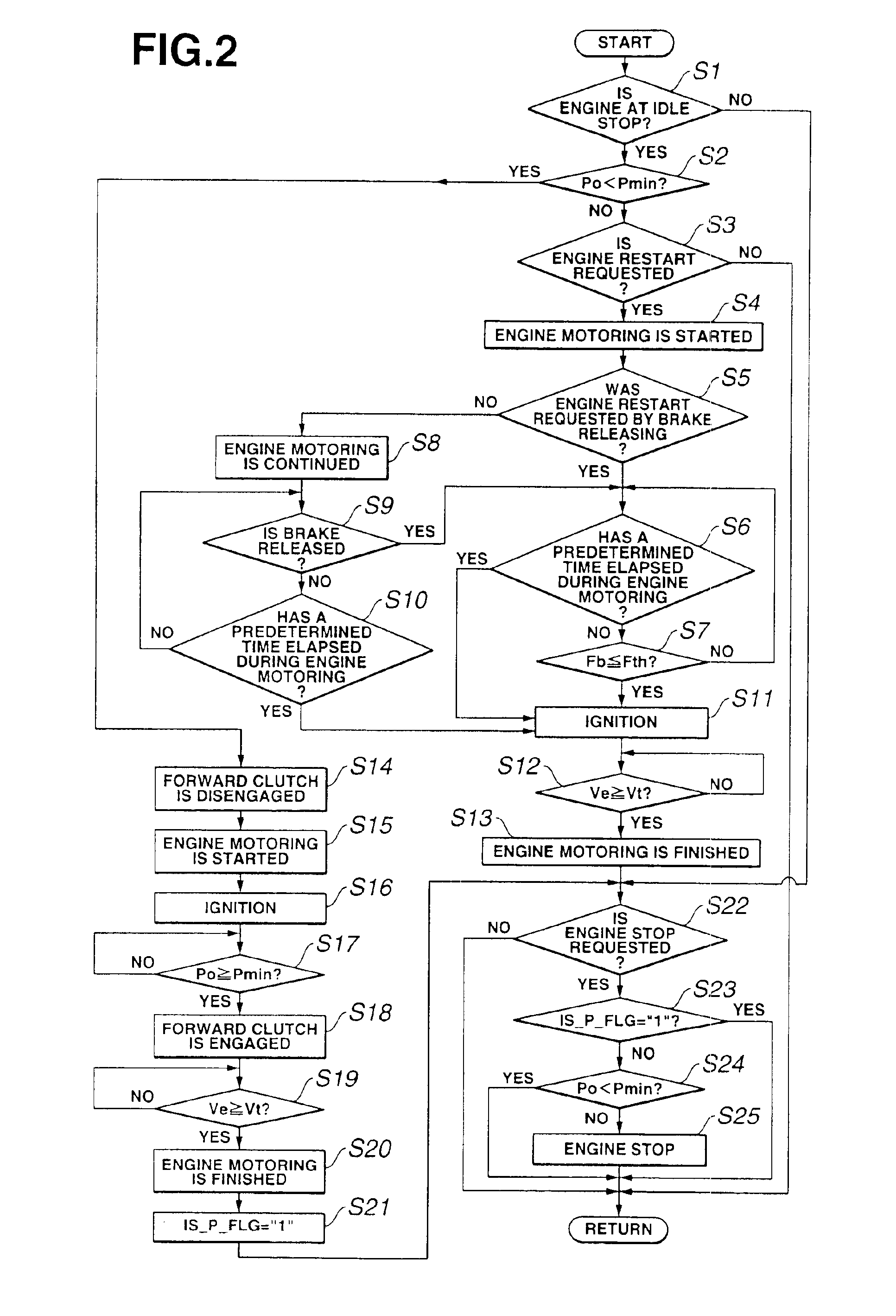
InactiveUS6881170B2Deteriorating durabilityElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAutomatic transmissionControl system
A vehicle with an automatic engine stop / restart function comprises an engine, an automatic transmission having an oil pump driven in synchronism with the engine to supply an oil pressure to the automatic transmission, an oil pressure controller to hold the oil pressure in the automatic transmission during an automatic stop of the engine, and a control system. The control system is configured to: determine whether the oil pressure in the automatic transmission becomes lower than a predetermined value during the engine automatic stop; shift the automatic transmission into a neutral state when the oil pressure in the automatic transmission becomes lower than a predetermined value during the engine automatic stop; restarts the engine; and then, shift the automatic transmission into a drive state after the oil pressure in the automatic transmission is increased to the predetermined value by the oil pump driven in synchronism with the engine.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method for controlling a dual clutch transmission
ActiveUS6953417B2Reduce complexityReduce in quantityFluid actuated clutchesToothed gearingsActuatorControl theory
A method of controlling the hydraulic actuation of the clutches and the synchronizers in a dual clutch transmission in the event of a clutch or synchronizer fault. The method includes the steps of determining which clutch is faulted when a clutch-on fault is detected, then commanding an interruption of engine torque to the faulted clutch and a neutralization of all synchronizers of the same axis shaft as the faulted clutch. The method further senses if a synchronizer actuator-on fault has occurred, then determines which synchronizer is faulted if an actuator-on fault has is detected. The method steps further include preventing the further actuation of the other synchronizers on the same axis shaft as the faulted actuator.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
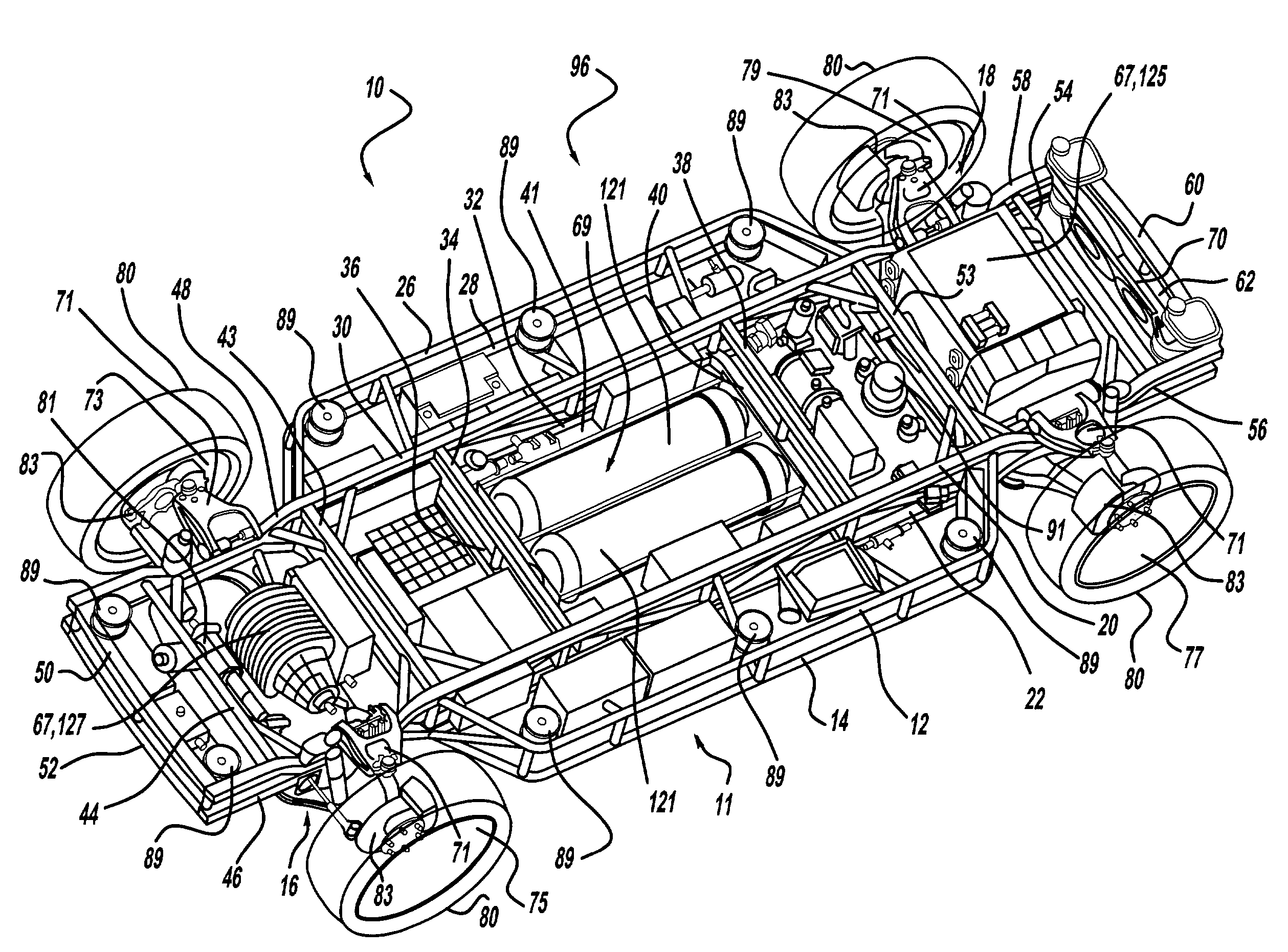
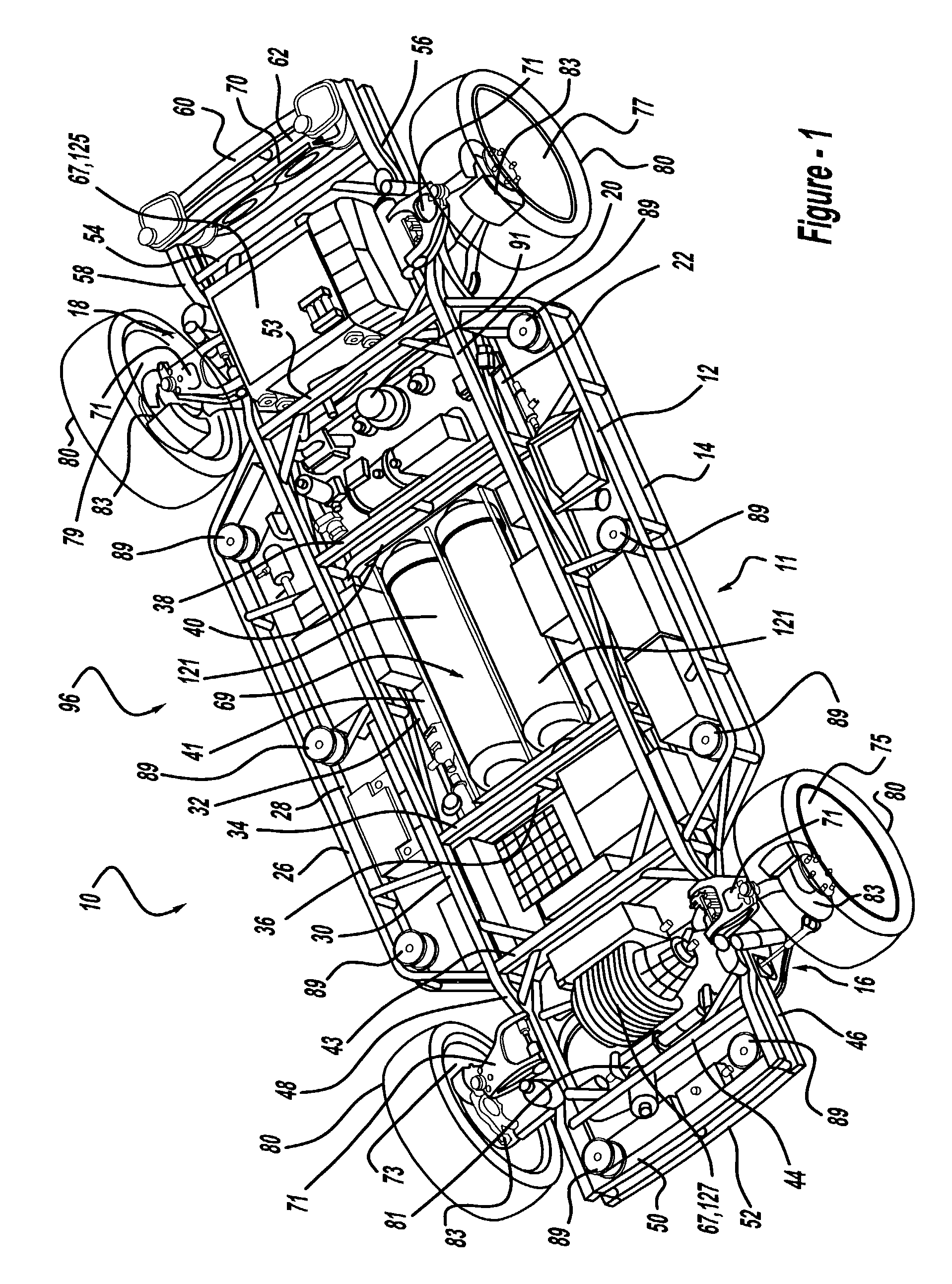
Modular chassis with simplified body-attachment interface
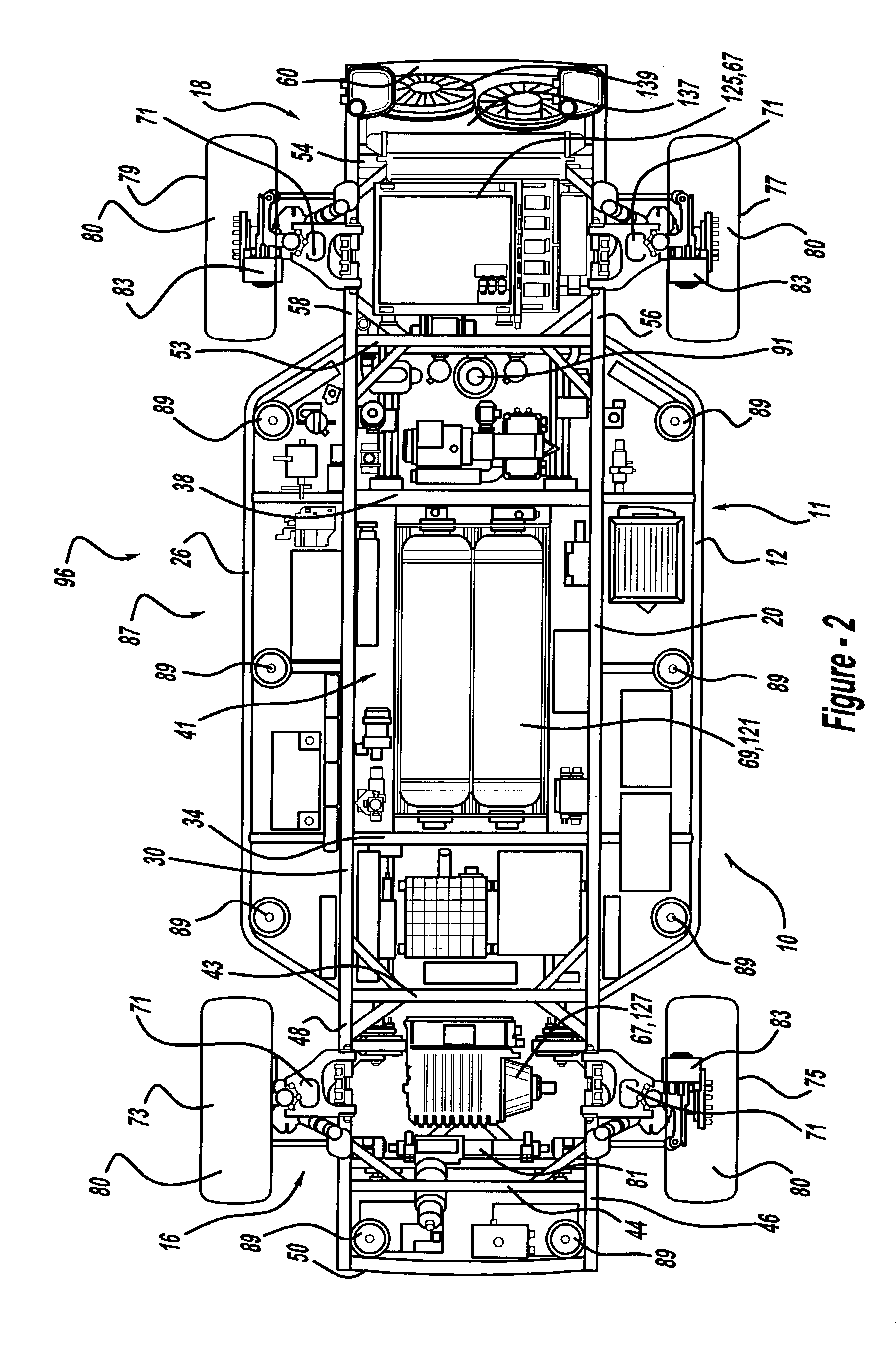
InactiveUS7441615B2Simple interfaceEliminateAuxillary drivesVehicle seatsControl signalComputer module
A chassis having systems responsive to a nonmechanical control signals and a simplified body-attachment interface includes preassembled modules to enhance ease and simplicity of chassis assembly. The chassis is preferably configured to minimize the possibility of a preassembled module being incorrectly positioned within the chassis. Methods for advantageously employing preassembled modules to assemble vehicle chassis are also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com