Patents
Literature
585 results about "Drag torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
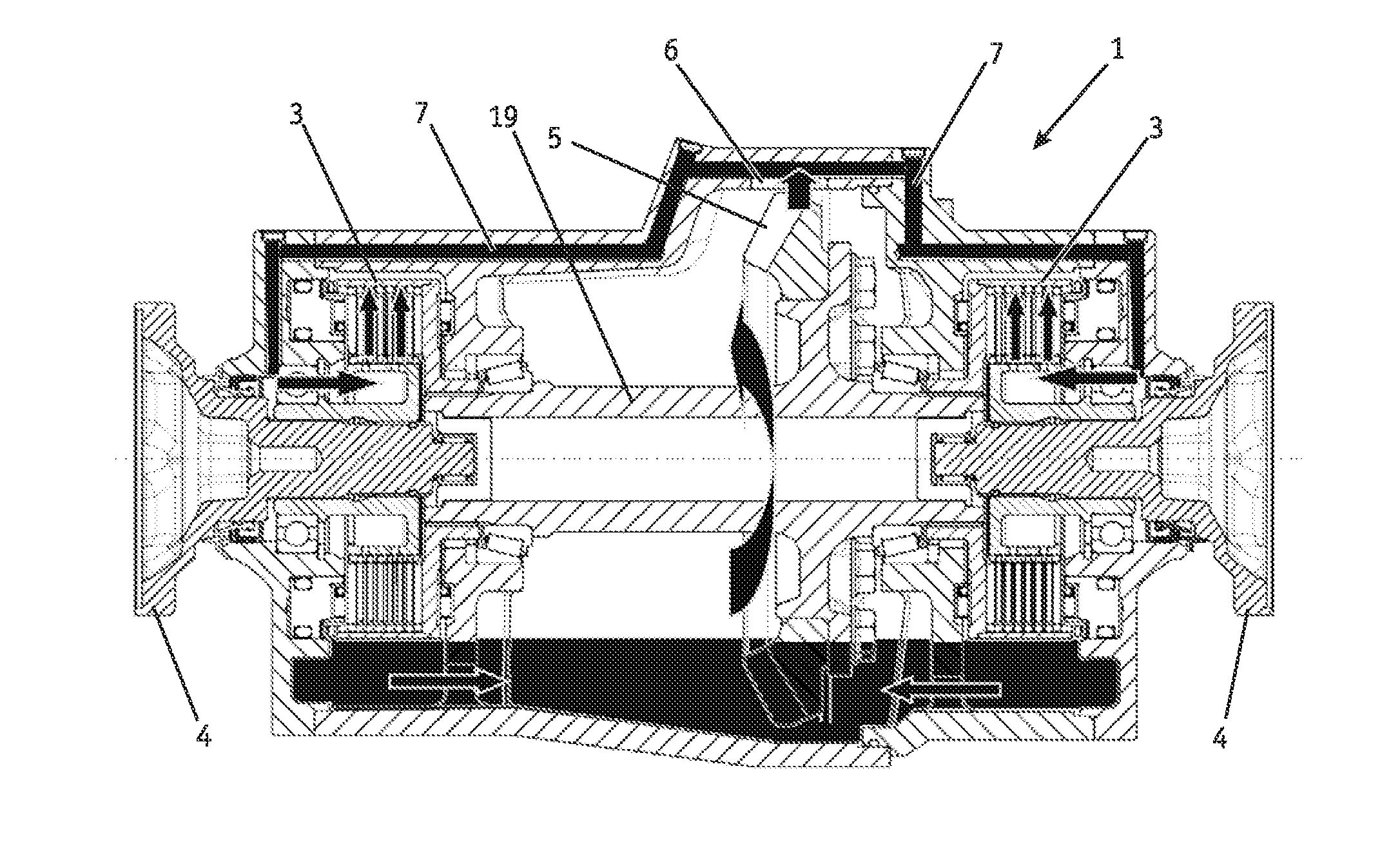
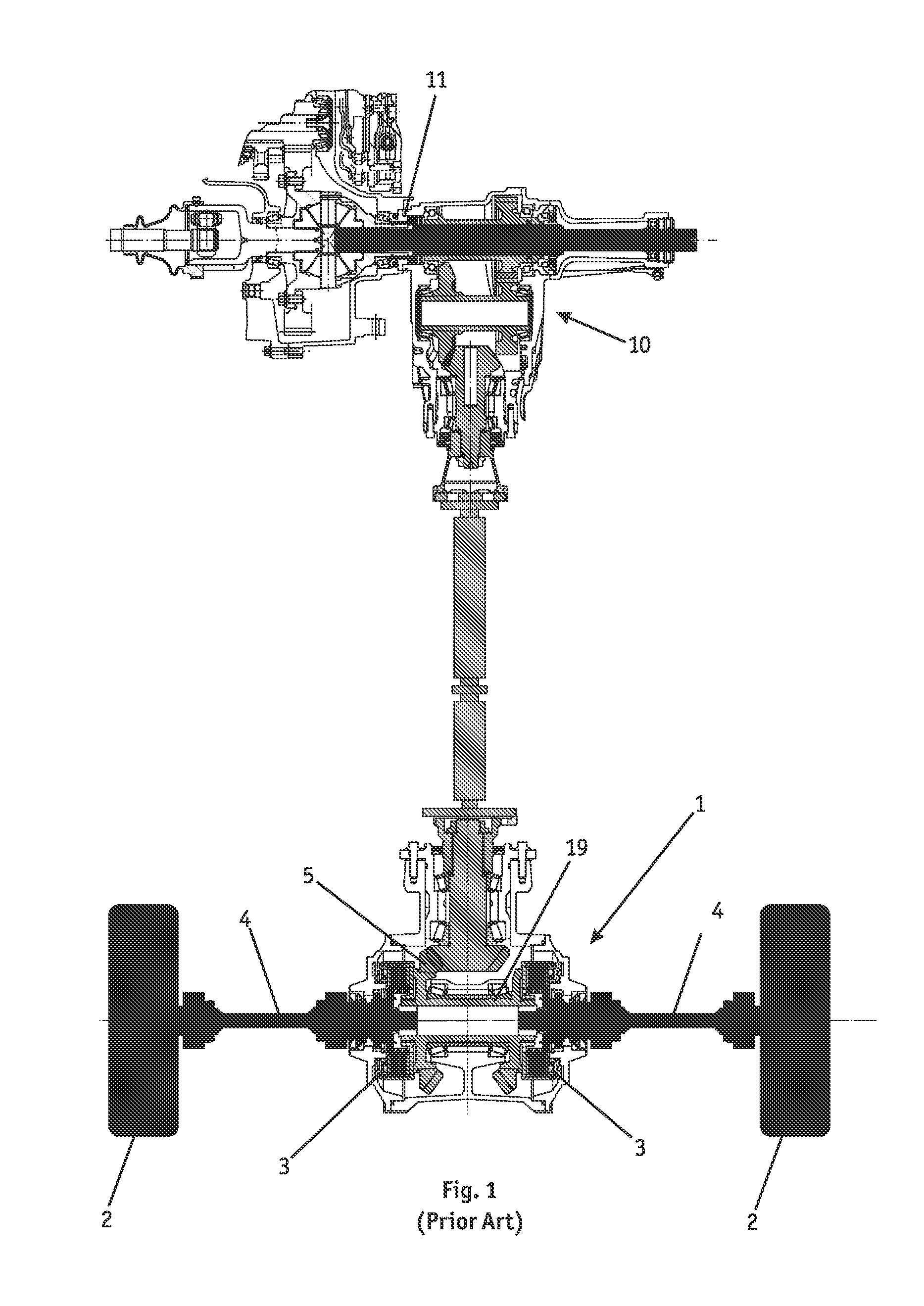
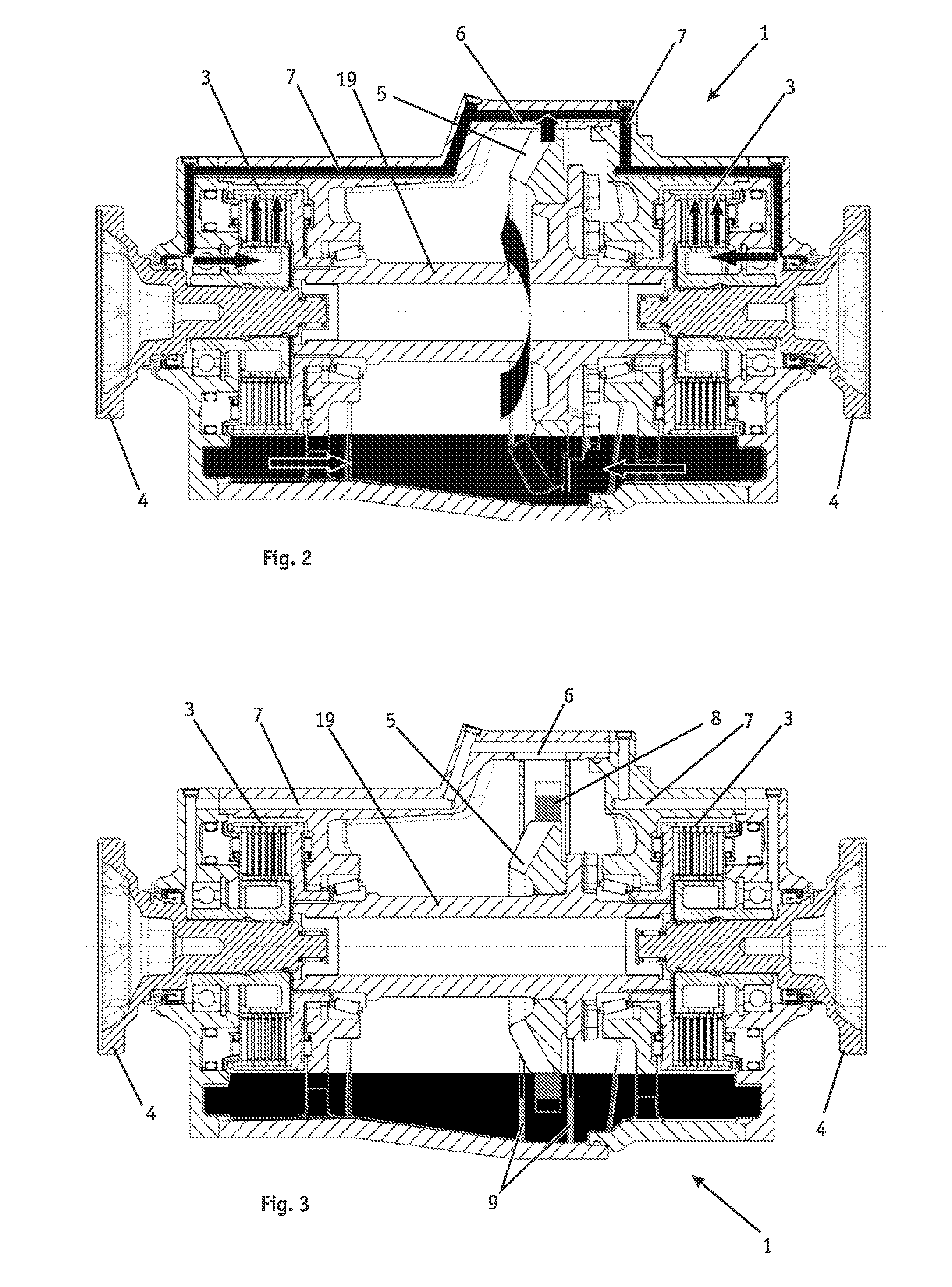
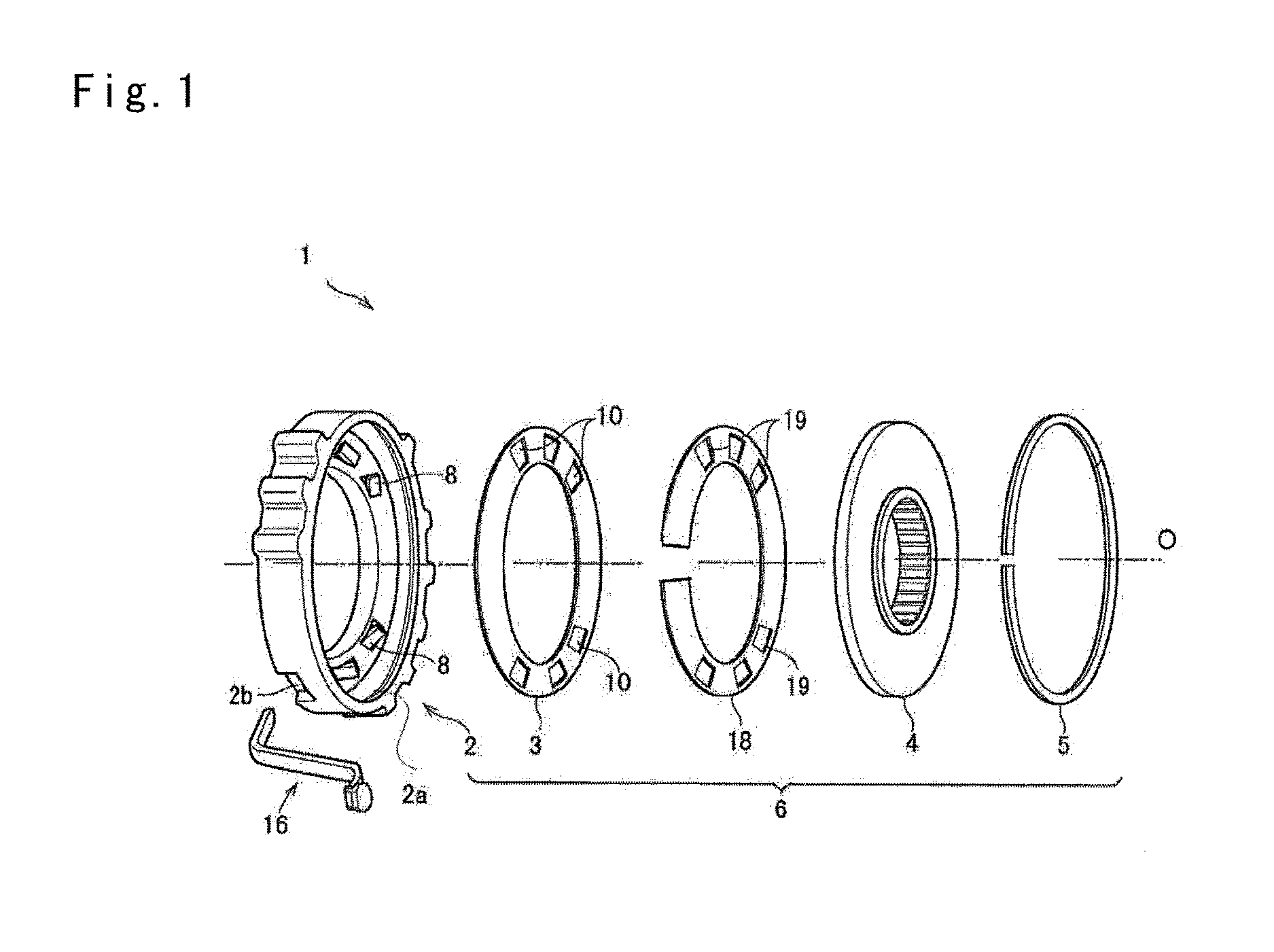
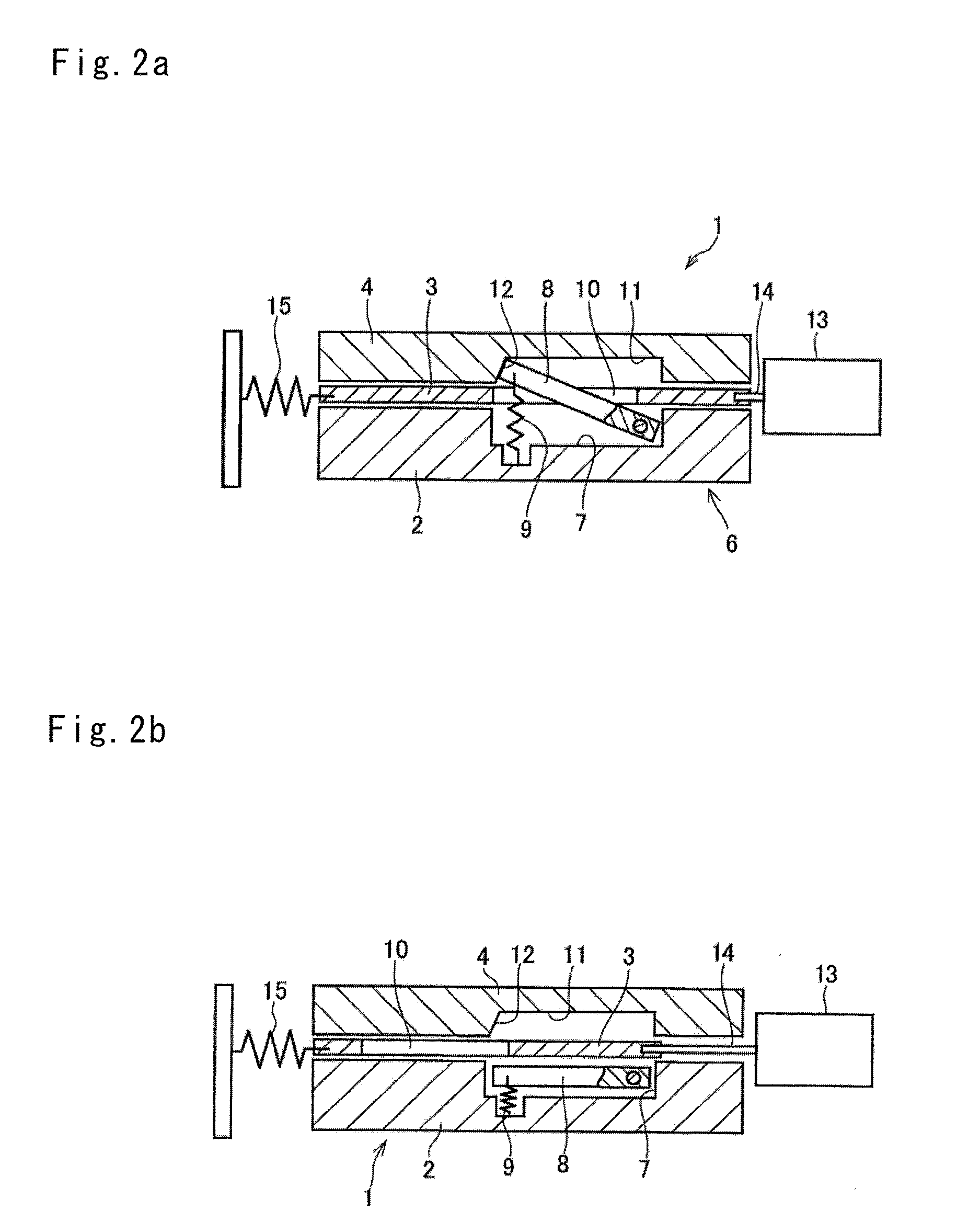
Drag torque is generated in disk brakes as a result of contact (dynamic friction) between brake disk and brake pads when the braking system is not actuated. Among the negative implications of drag torque are, notably, dispensable additional fuel consumption as well as increased pad wear, which can also unfold as uneven along the pads' surfaces.
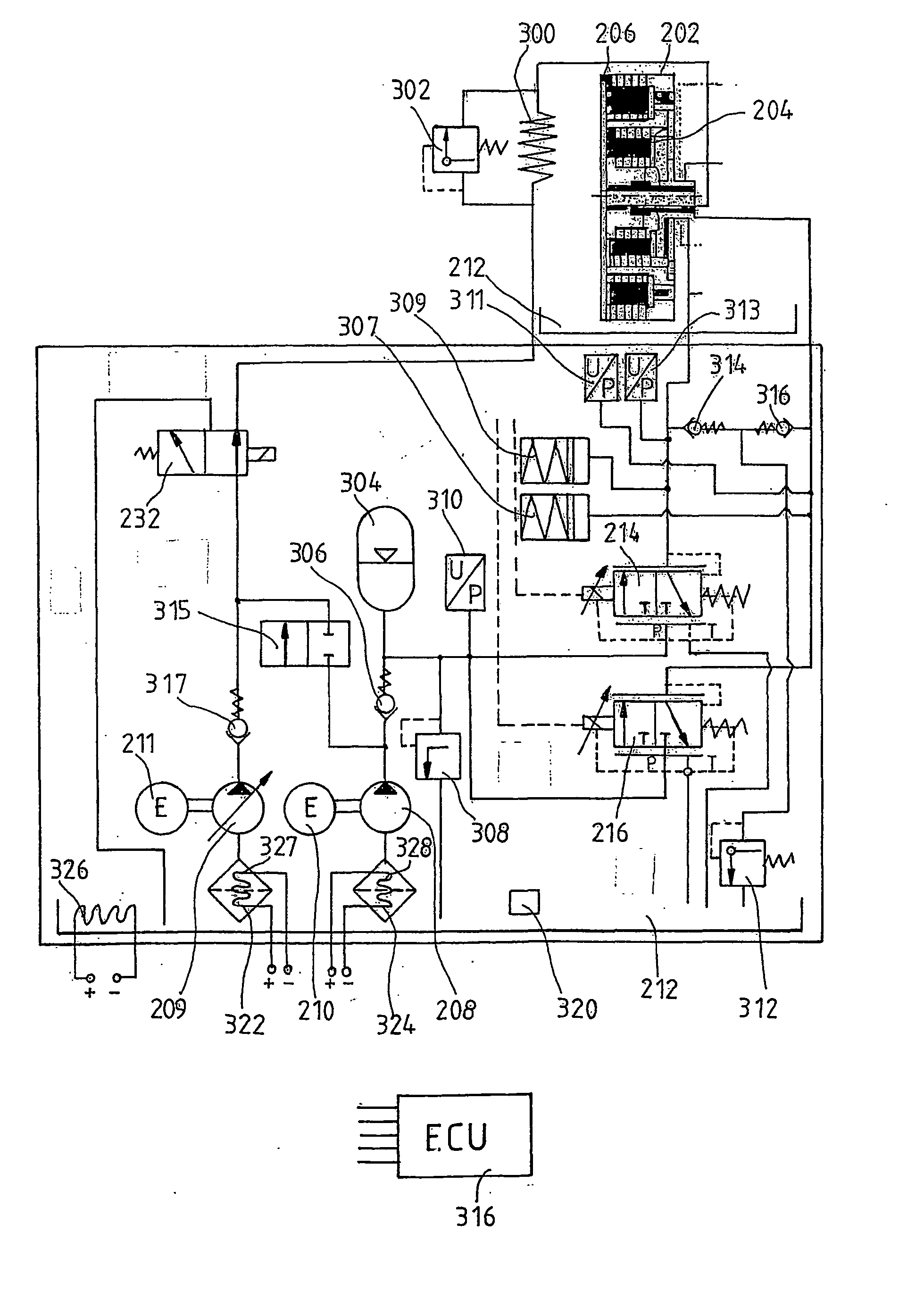
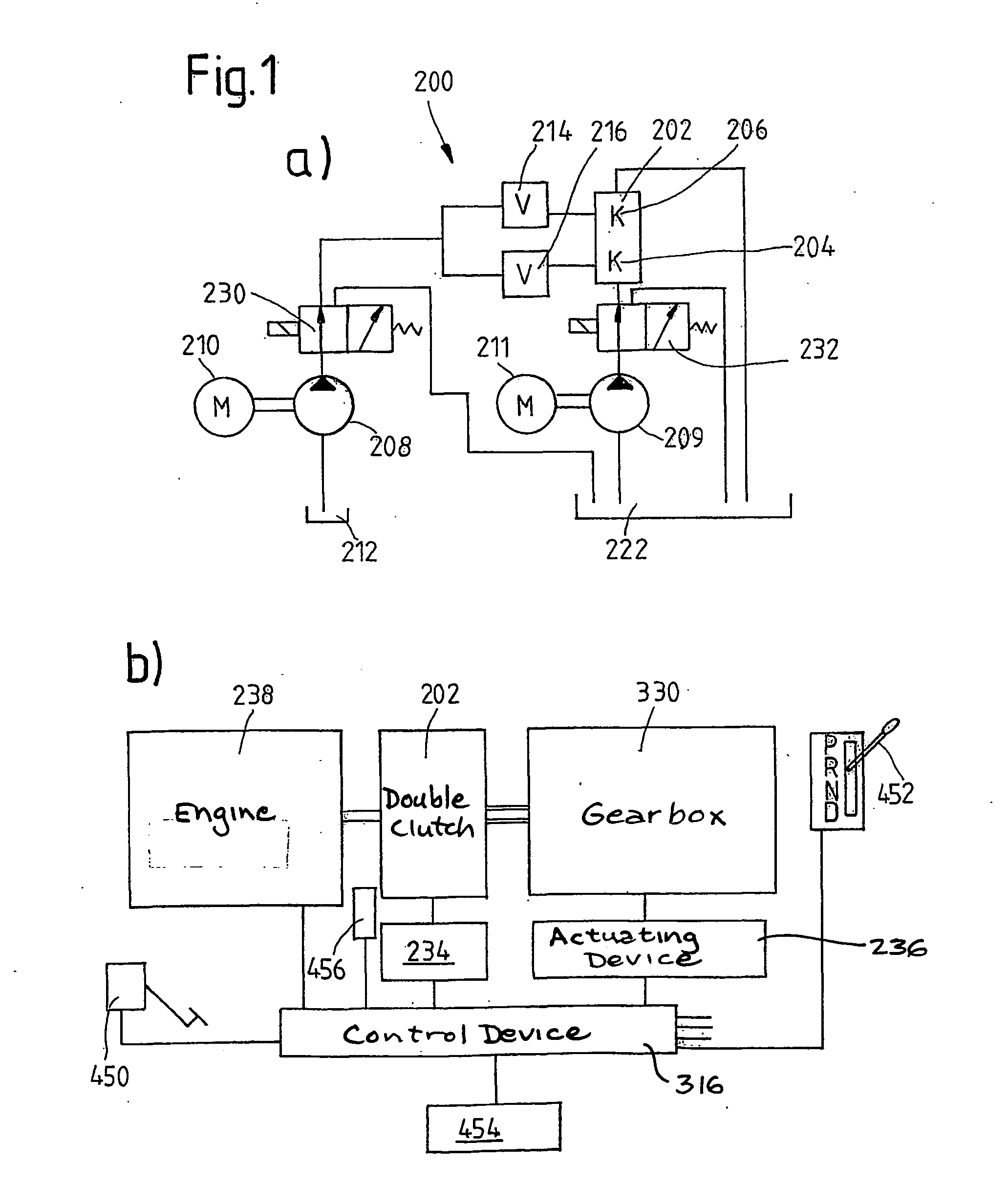
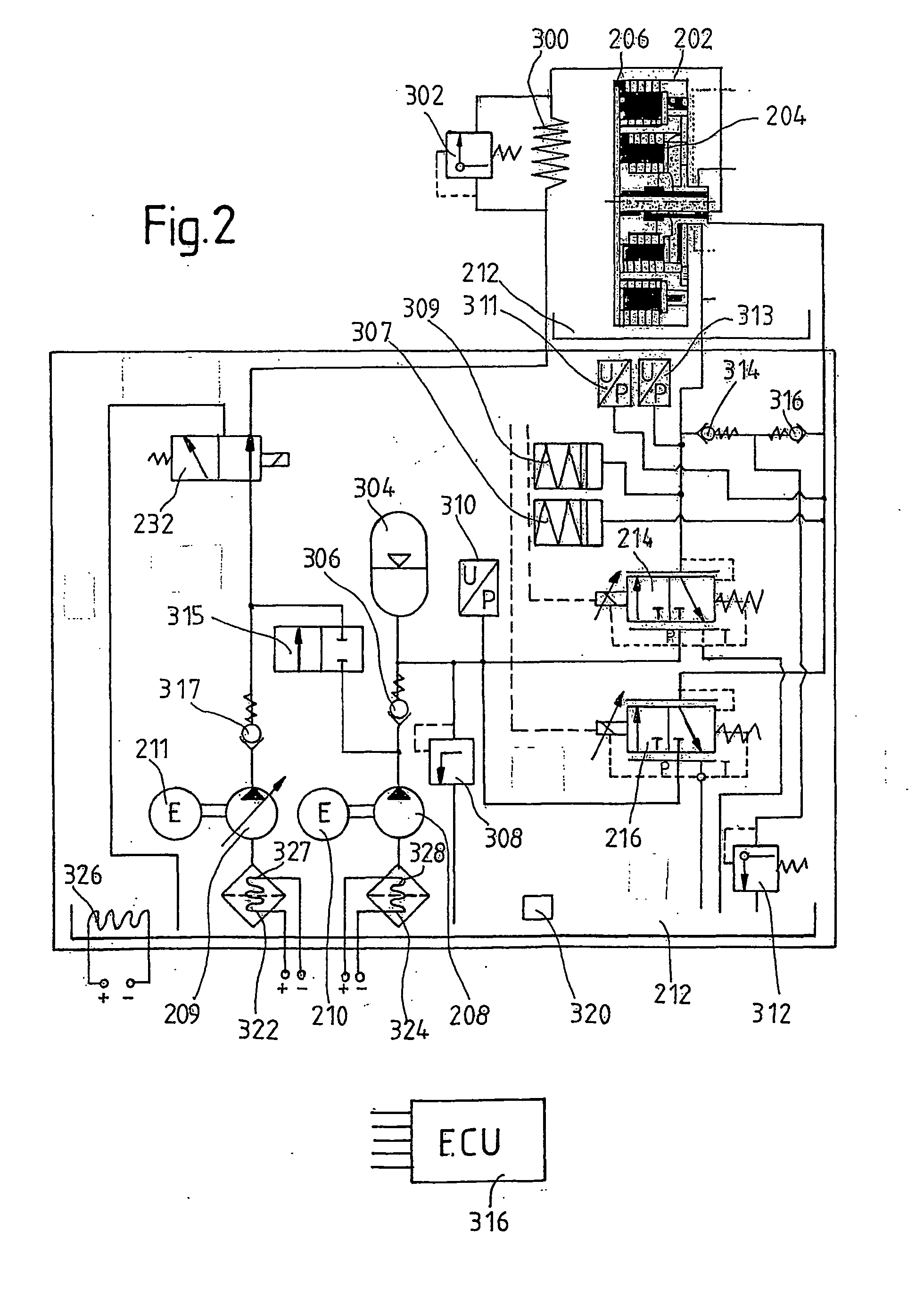
Motor vehicle comprising a drive train having a multiple clutch drive
InactiveUS20040112171A1Easy to participateIncrease engine speedGear lubrication/coolingVehicle sub-unit featuresWorking fluidGear wheel
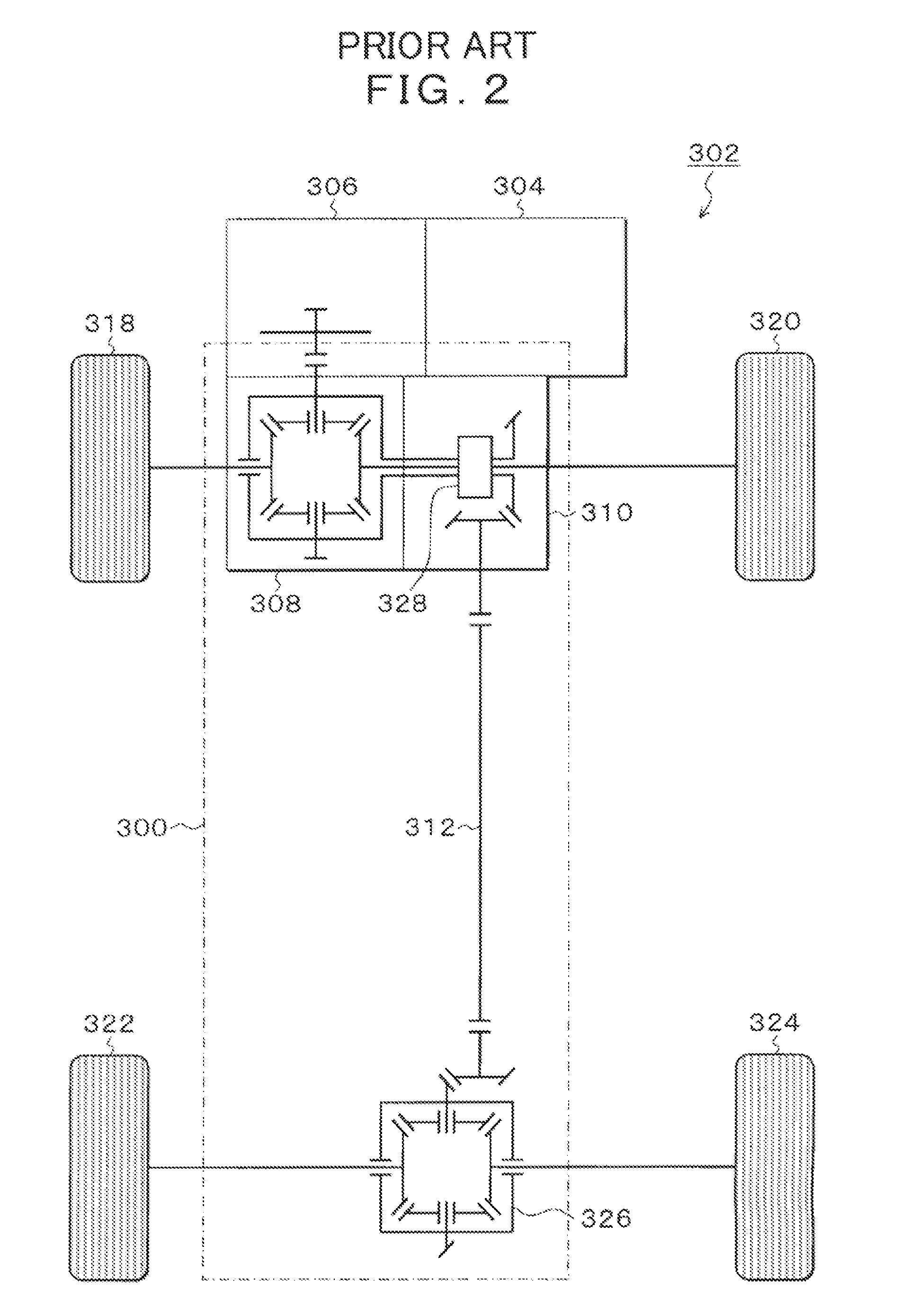
The invention relates to measures for controlling or reducing drag torque occurring in a multi-plate clutch device (202) due to temperature-related increased viscosity of an operating fluid which is supplied to the plates in operation. The aim of the invention is to enable a motor vehicle to be started or operated even at low temperatures. According to one aspect of the invention, a motor vehicle comprising a drive train is especially provided. Said drive train comprises a drive unit (238), gearbox (330) having a first gearbox input shaft and a second gearbox input shaft, and a clutch (202) having a first clutch device which is associated with the first gearbox input shaft, and a second clutch device which is associated with the second gearbox input shaft, for transferring torque between the drive unit and the gearbox. Said clutch devices are embodied in the form of plate clutches to which an operating fluid can be supplied, especially a cooling oil in order to operate the same. Said gearbox (330) is associated with an actuator device and a control device (316) for controlling the actuator device, the arrangement of which enables the gears associated with the first and second gearbox input shafts to be engaged and disengaged. According to the invention, the control device (316) is designed in such a way that at least one gear is automatically engaged by means of the actuator device (236), as a result of the clutch release of the vehicle.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG +1
Variable output rotary power generator
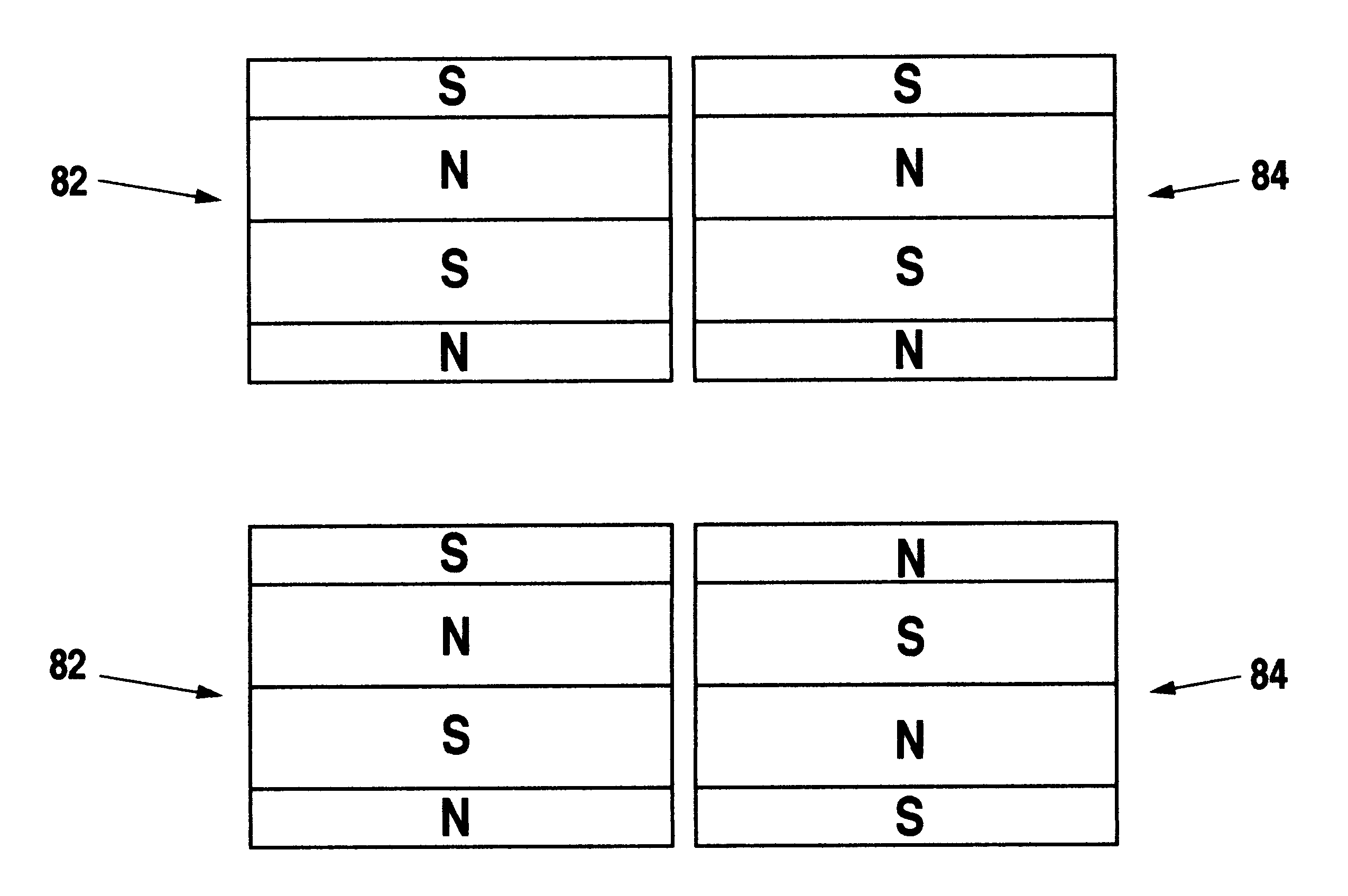
The present invention is directed to a downhole apparatus for quickly generating and regulating variable output electric power by varying the alignment of a pair of axially adjacent permanent magnets rotating within an armature having electrically conductive windings. Each of the permanent magnets comprises a plurality of permanent magnetic segments having circumferentially alternating magnetizations. One of the permanent magnets is fixed to the drive shaft, and the other permanent magnet is movably mounted on the drive shaft to enable the alignment or misalignment, as desired, of the magnetizations of the respective magnetic segments on the pair of permanent magnets. When the magnetizations are completely aligned, the maximum electrical power is generated in the windings of the main armature; conversely, when the magnetizations are completely misaligned, zero electrical power is generated. Thus, the output power is regulated by varying the alignment of the pair of permanent magnets, which is accomplished with a drag torque generator which creates a drag torque that is transmitted to the movable permanent magnet by a torque converter.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
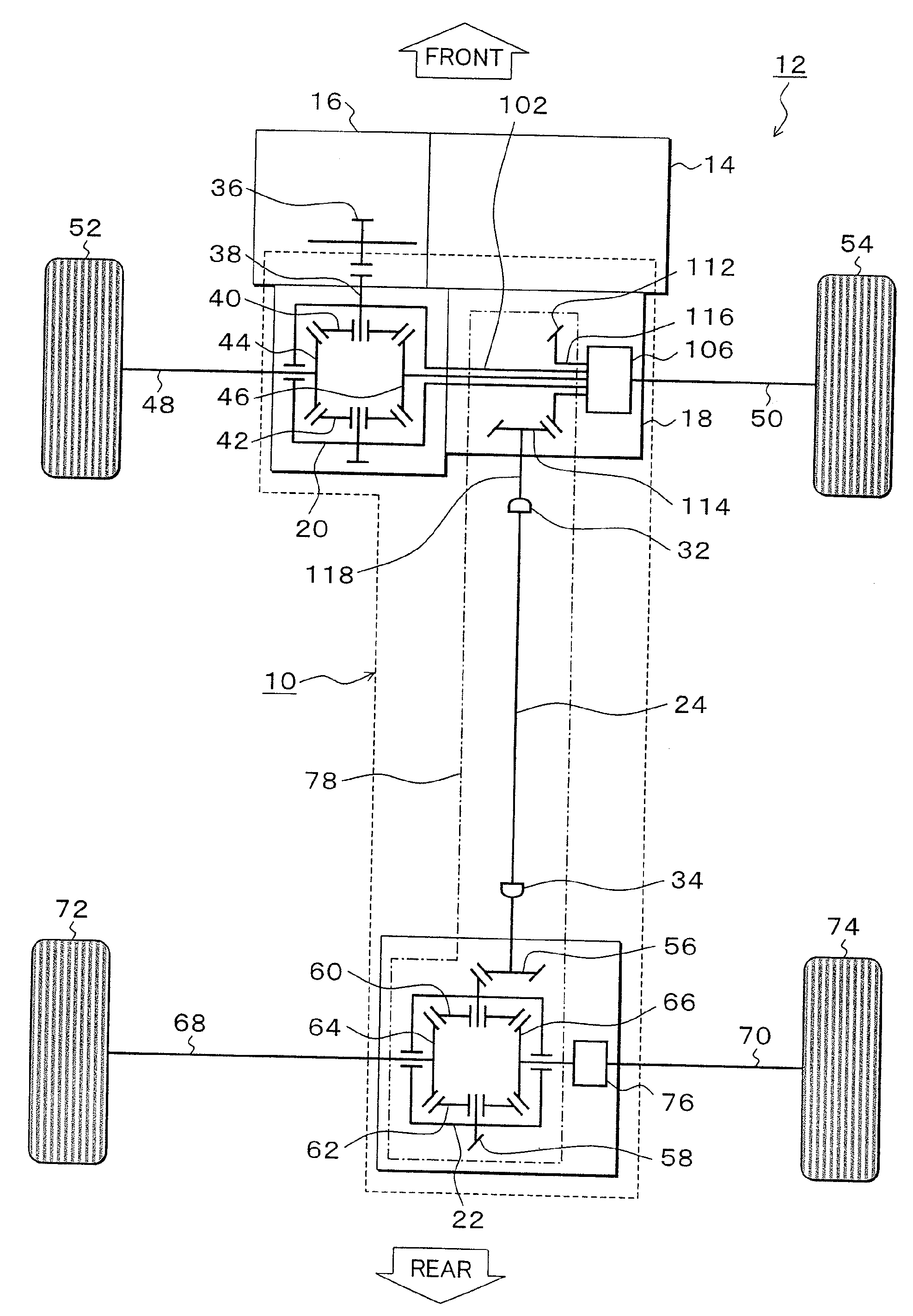
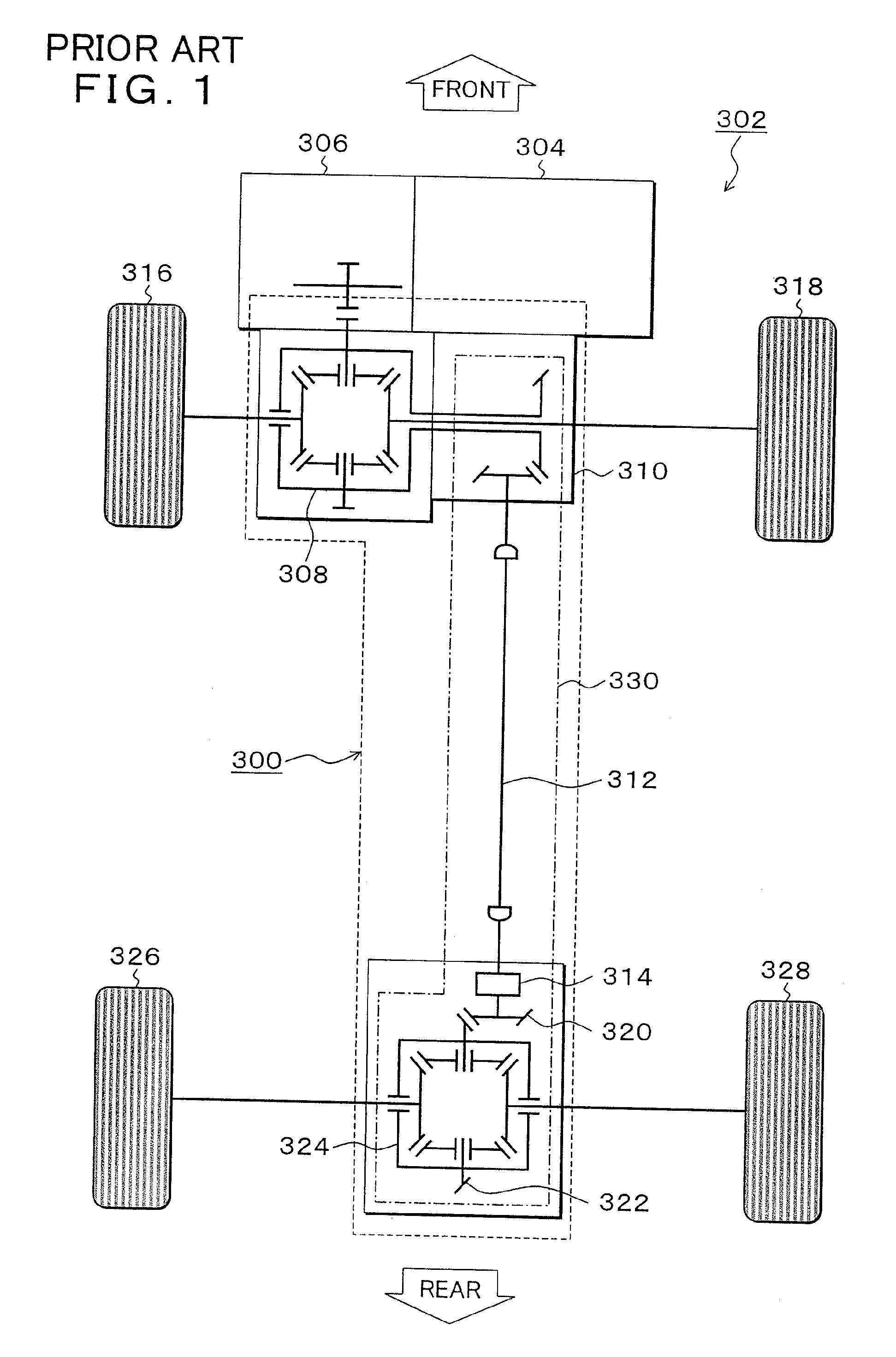
Driving-force transmitting apparatus for four-wheel-drive vehicle
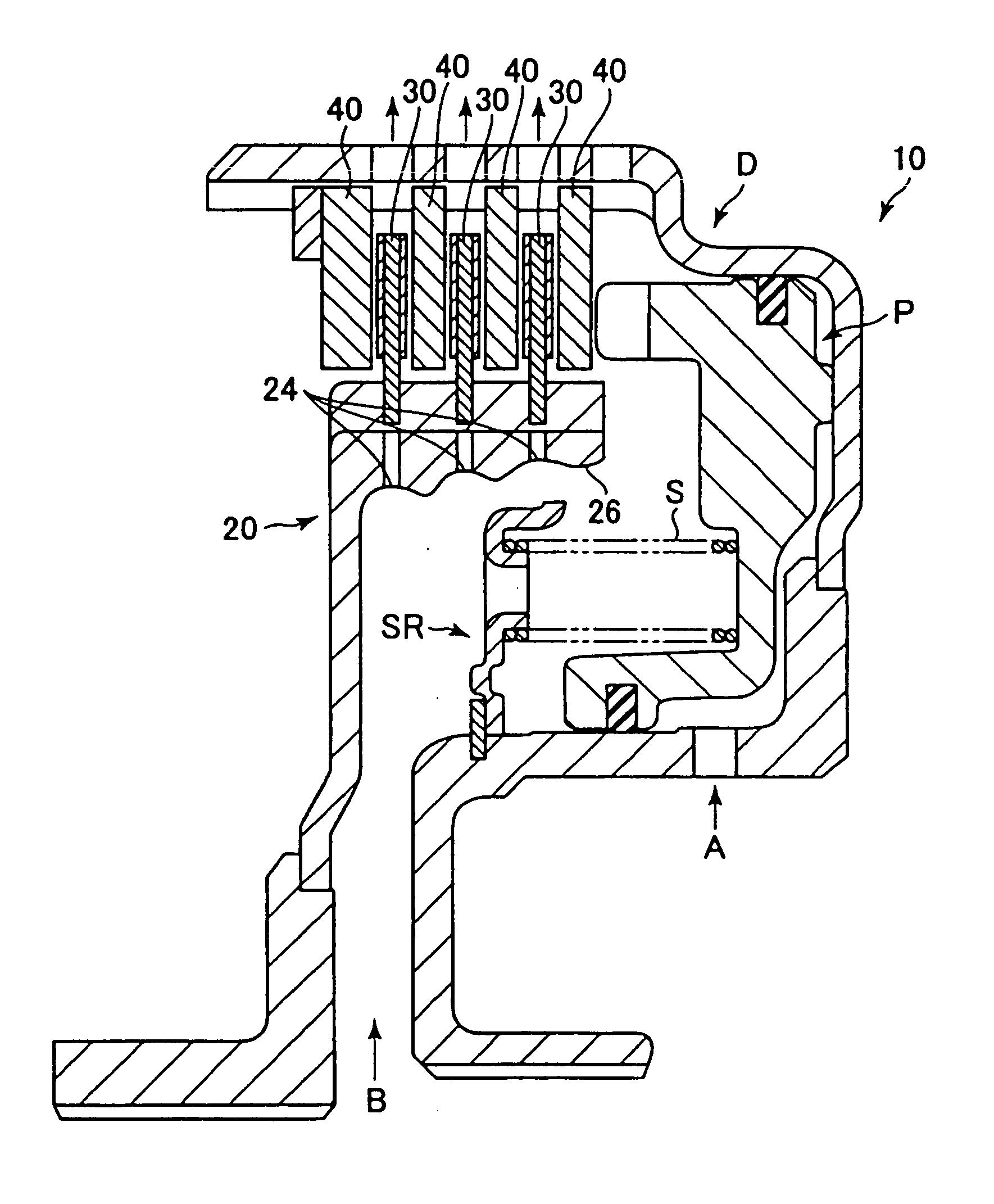
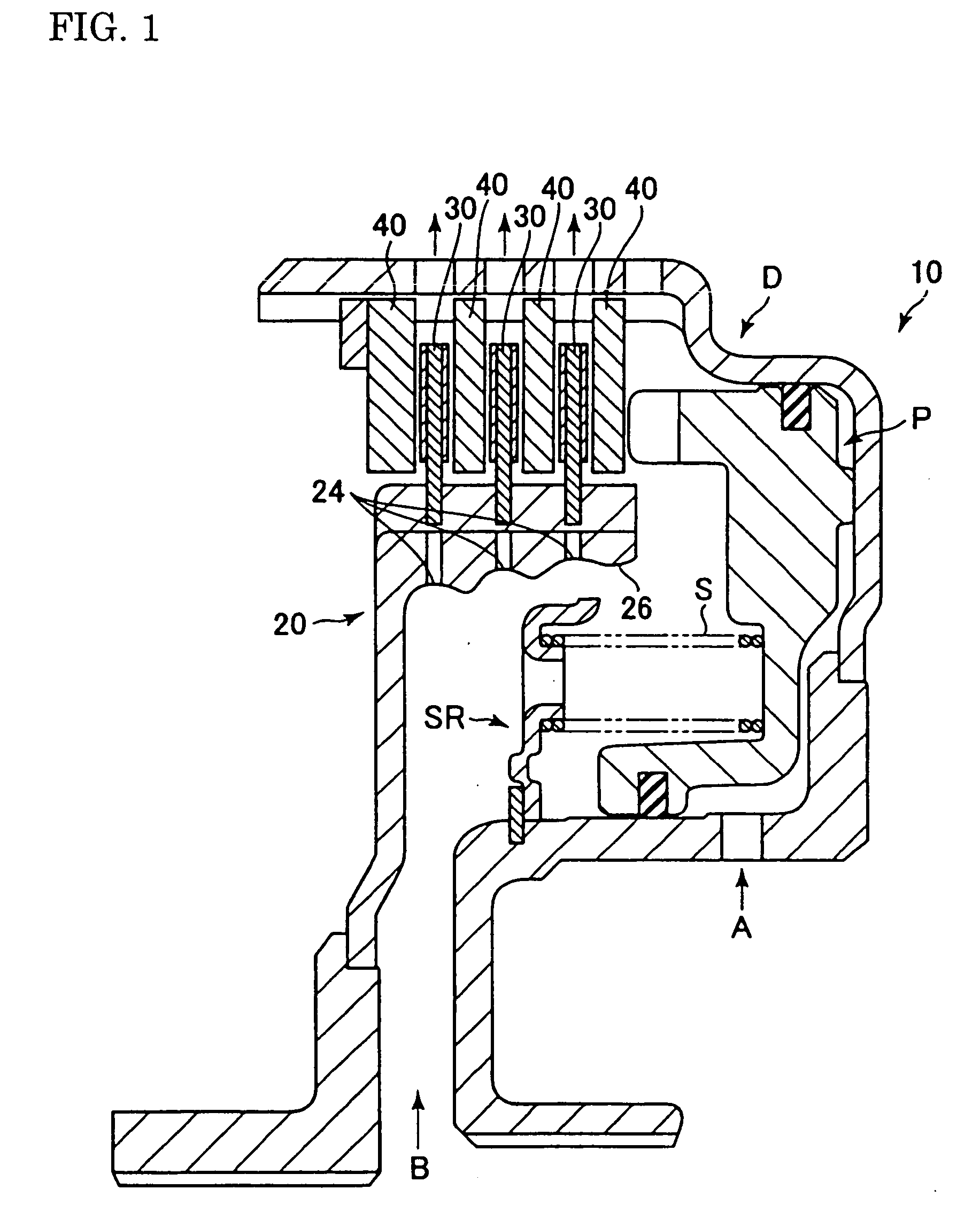
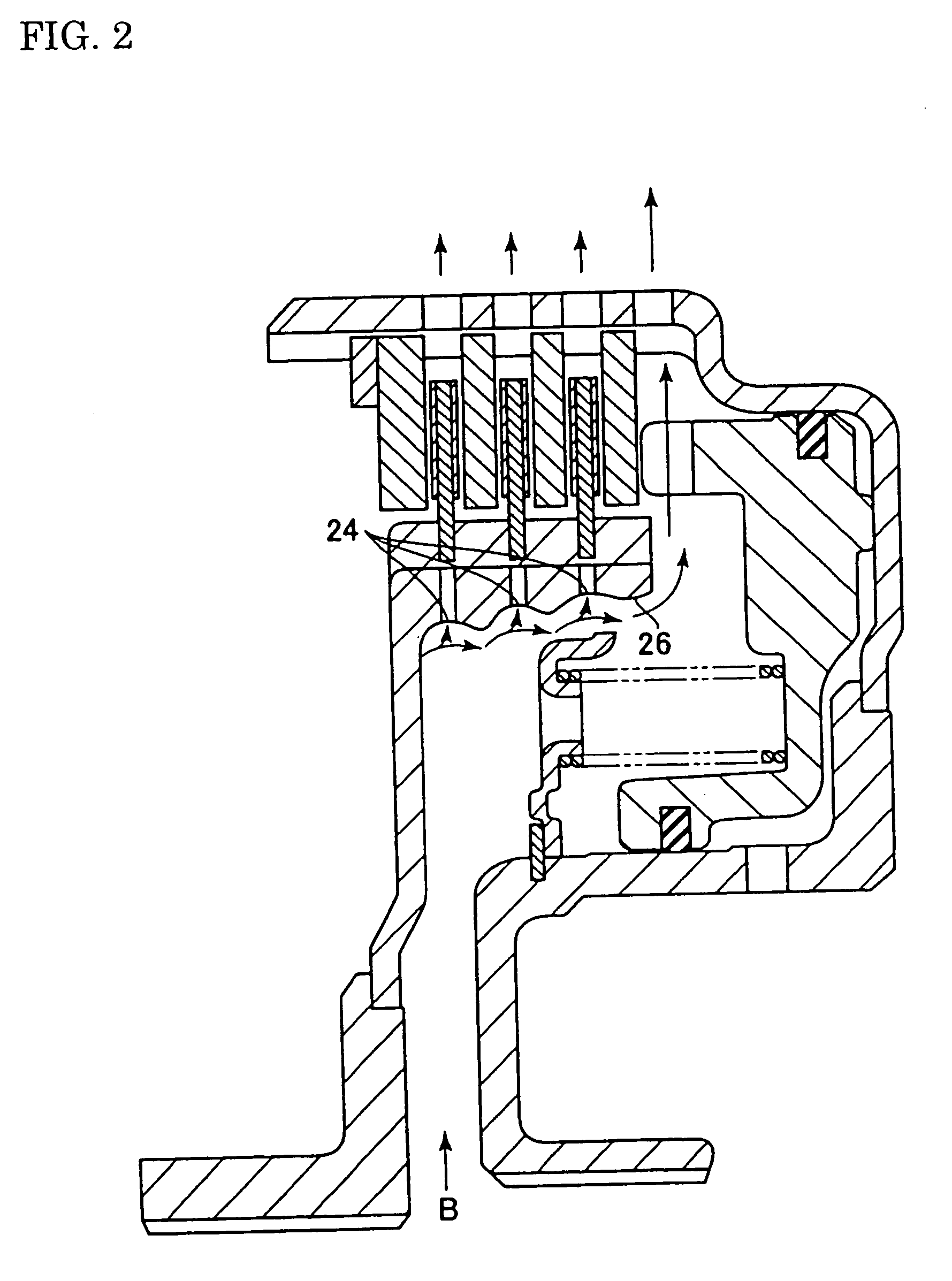
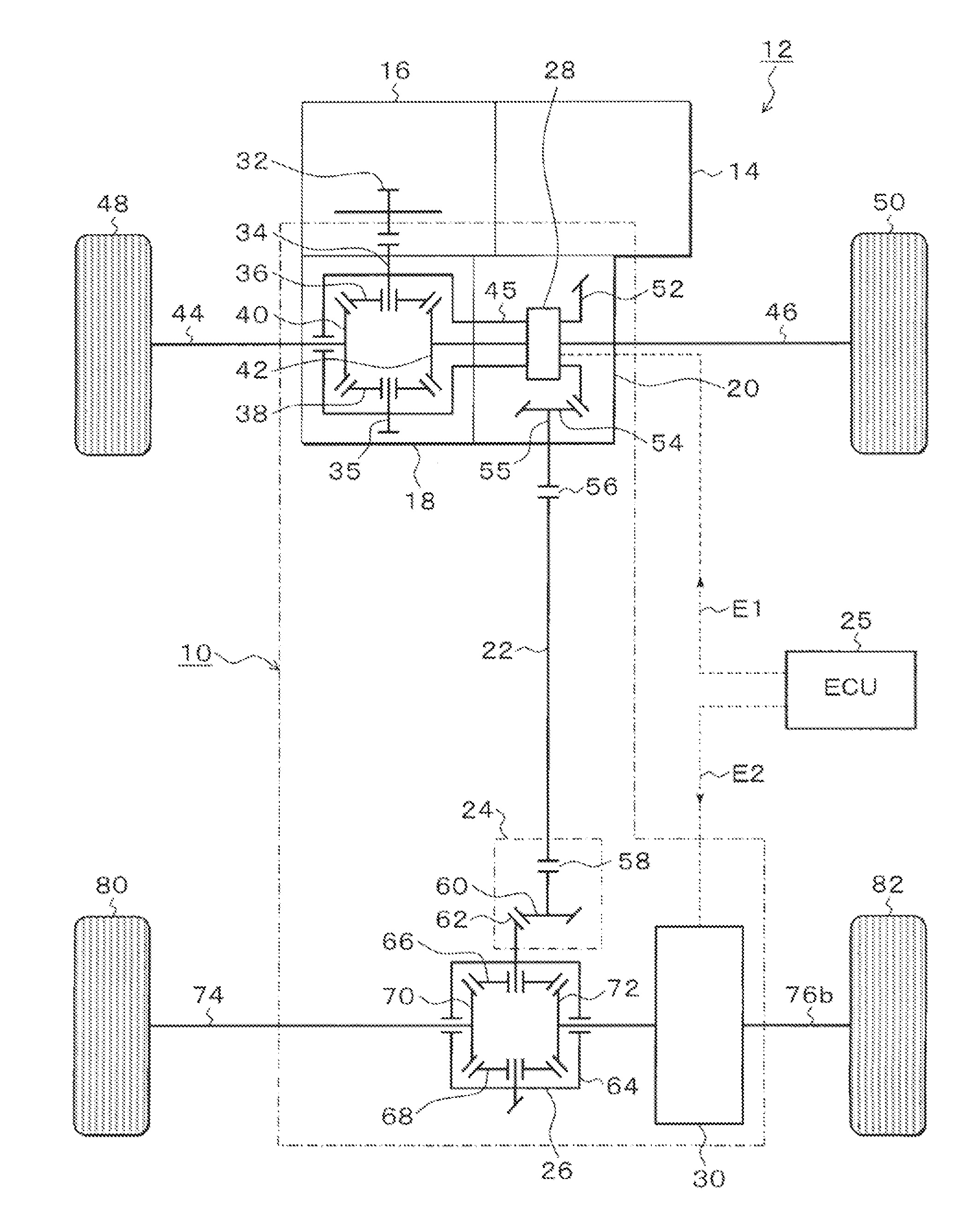
InactiveUS20100274456A1Deterioration in fuel efficiency can be preventedFuel efficiencyManual control with multiple controlled membersDigital data processing detailsFriction torqueDrag torque
A transmitting apparatus includes a disengaging device that disengages a driving force from a front-wheel differential device to a first driving-force transmitting direction converting unit 20 and a multi-plate clutch mechanism provided between an output of a rear-wheel differential device and a right-rear wheel and capable of successively adjusting a fastening force. Drag torque when the fastening of the multi-plate clutch mechanism is released is set smaller than friction torque of a rear-wheel drive system between the first driving-force transmitting direction converting unit and a second driving-force transmitting direction converting unit. A controller unconnects the disengaging device and releases the fastening of multi-plate clutch mechanism when switching to a two-wheel drive mode, thereby stopping the rotation of the rear-wheel drive system.
Owner:UNIVANCE CORP
Methods and systems for assisted direct start control
ActiveUS20100174460A1Reduce exhaust emissionsSave fuelAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlDrag torqueDirect torque control
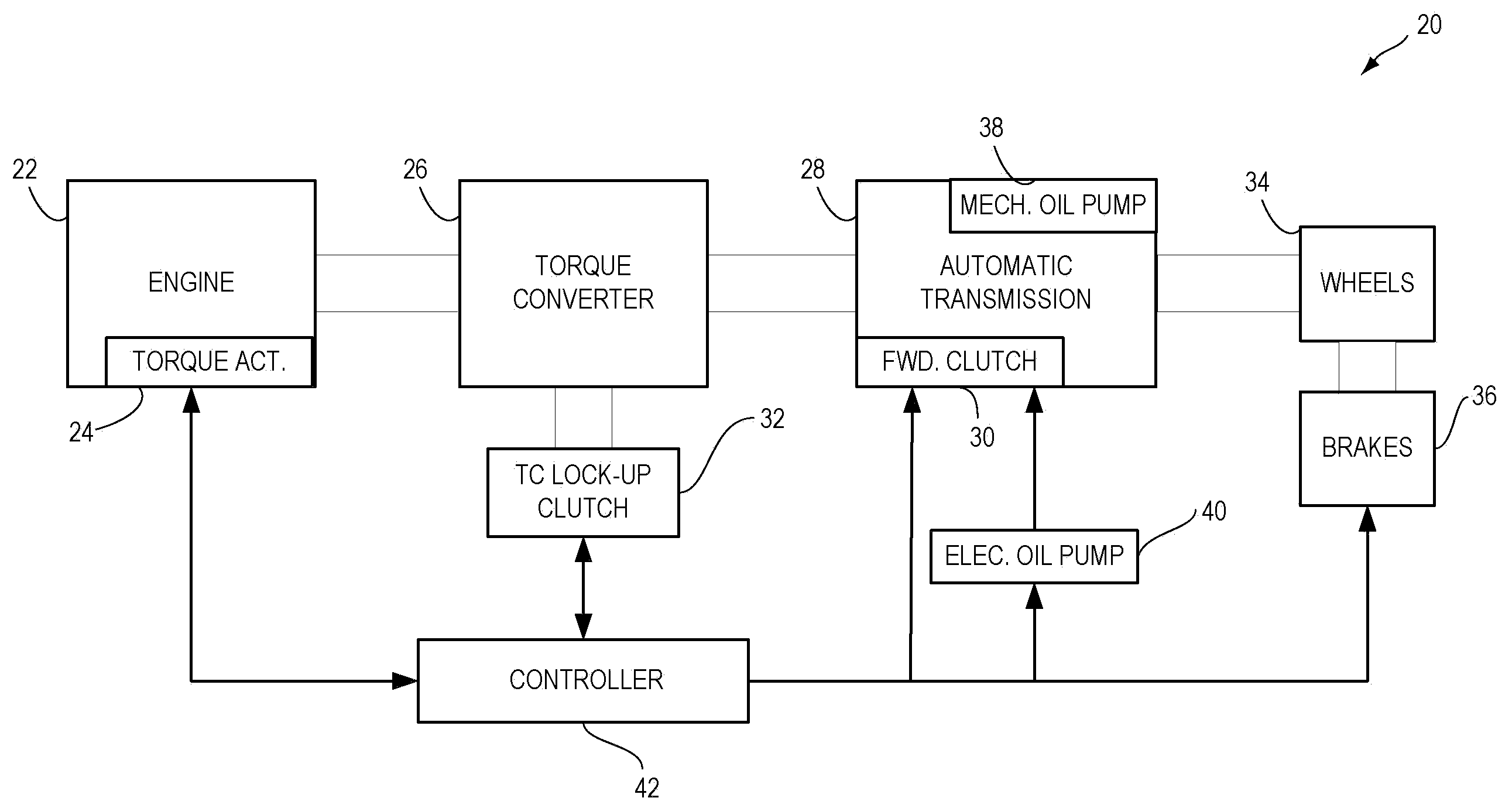
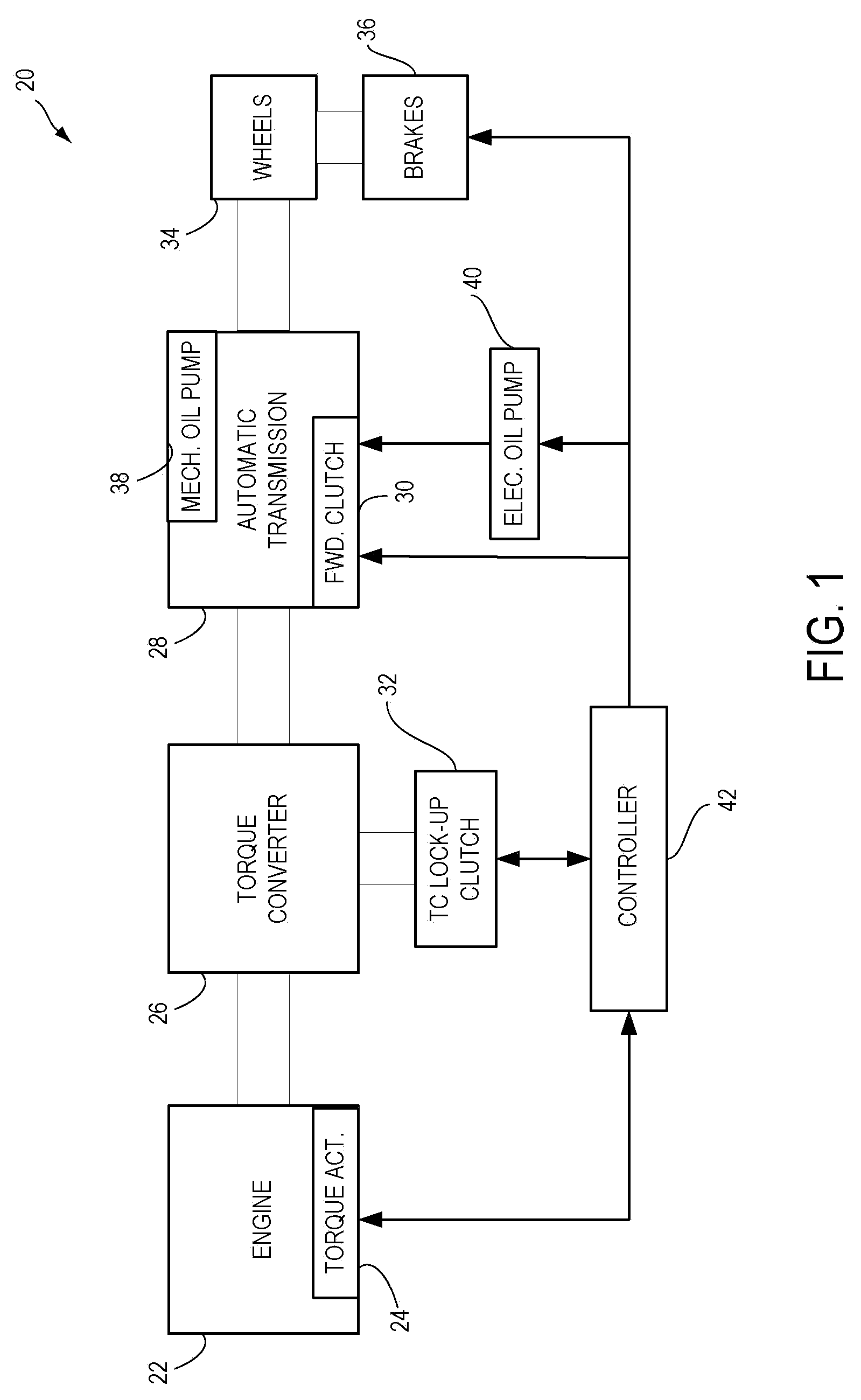
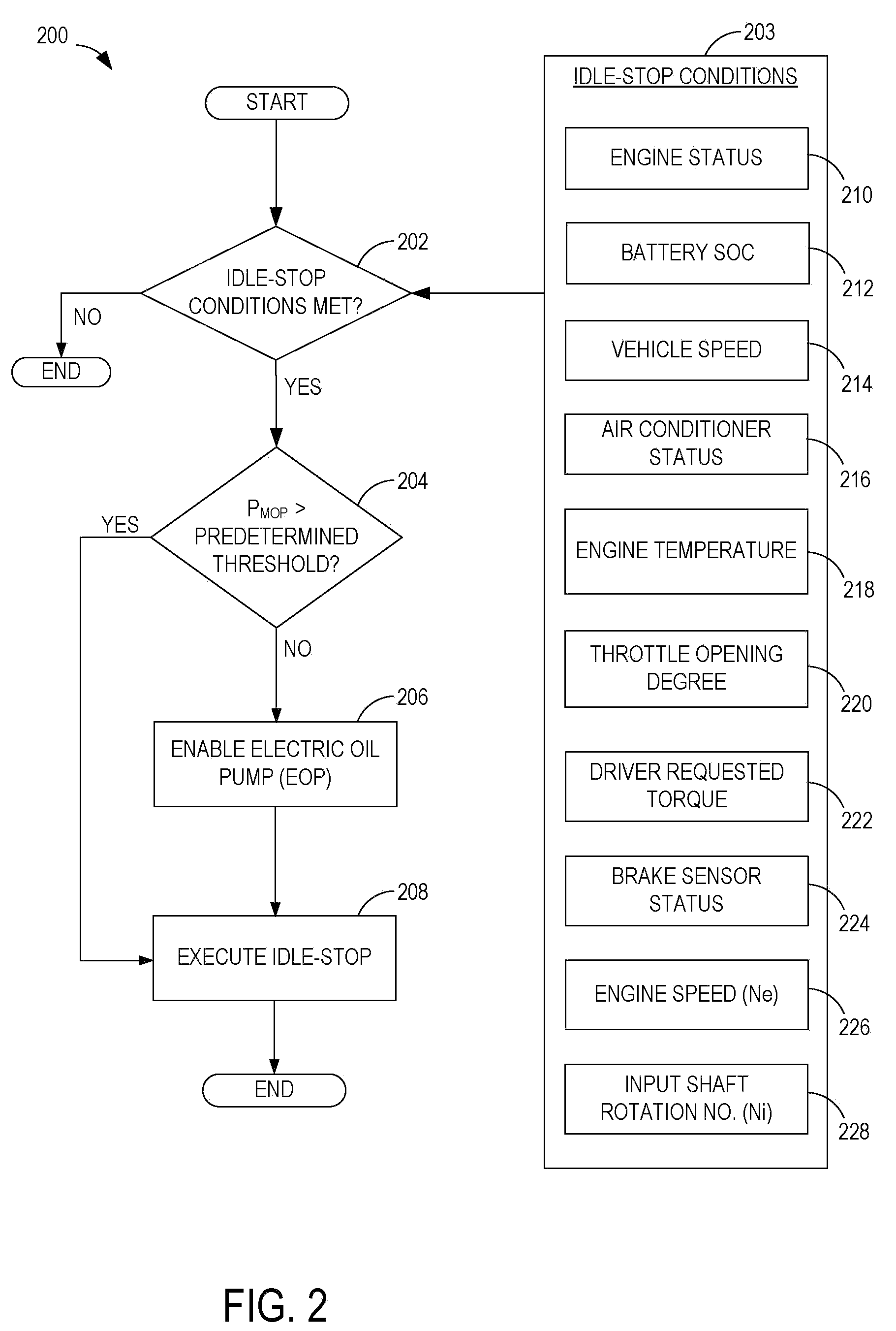
Methods and systems are provided for controlling a vehicle system including an engine that is selectively shut-down during engine idle-stop conditions, the vehicle system further including a hydraulically actuated transmission component. One example method comprises, during an idle-stop engine shut-down, adjusting a hydraulic actuation of the transmission component to adjust drag torque on the engine to stop the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
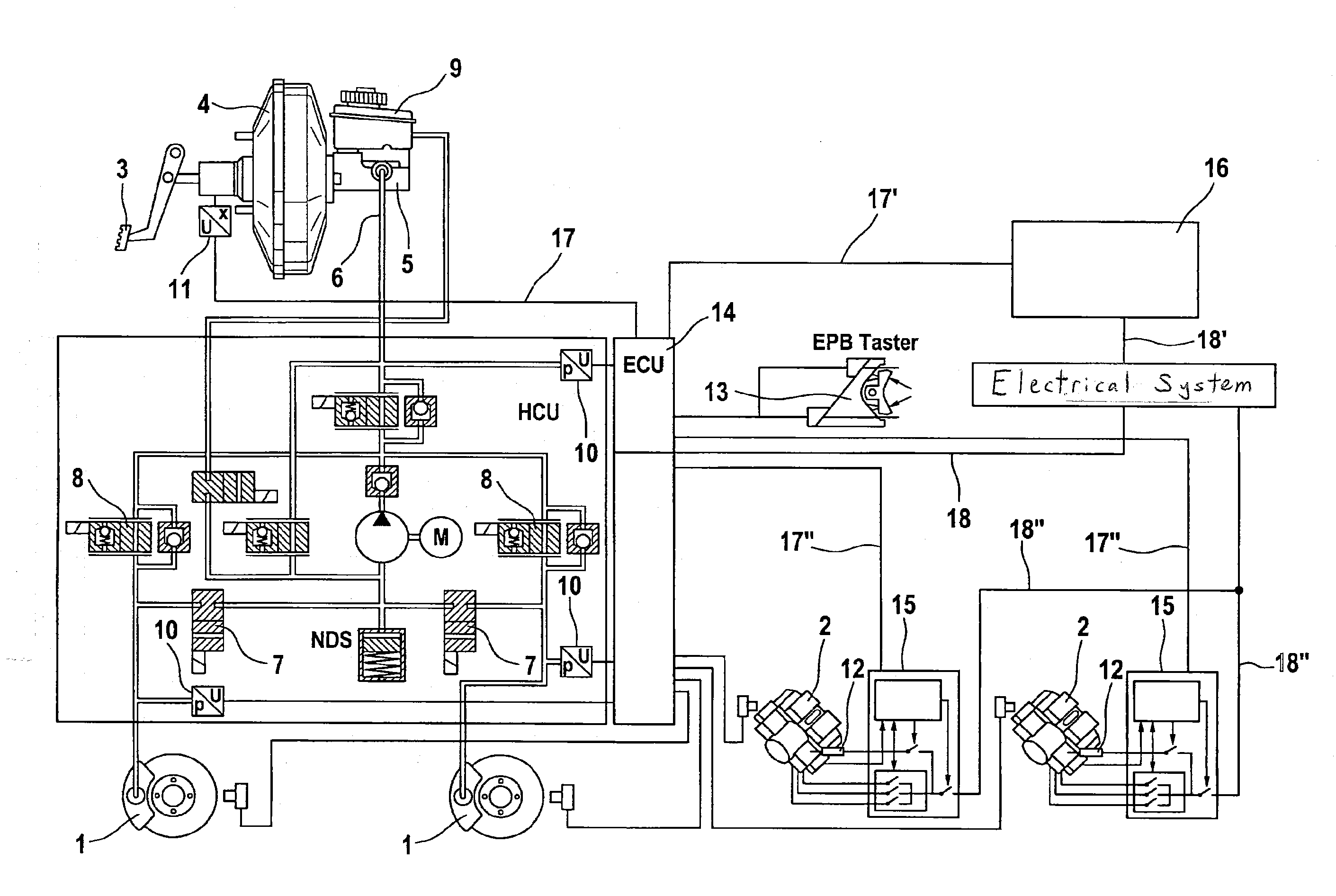
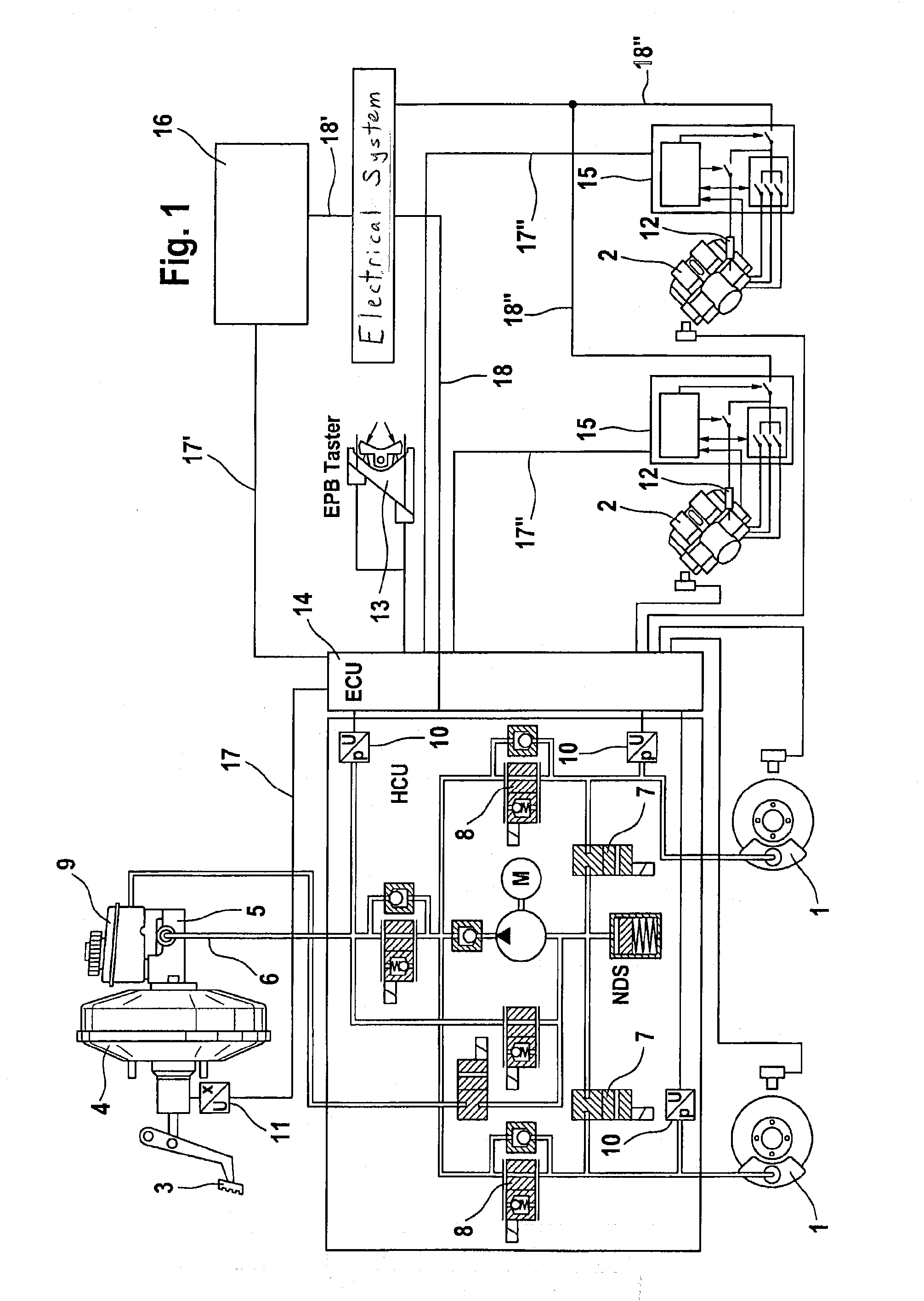
Method for operating a vehicle brake system and vehicle brake system
ActiveUS20100198475A1Prevents overbrakingLoss of driving stabilityHybrid vehiclesBraking element arrangementsDrag torqueEngineering
A method for operating a vehicle braking system for motor vehicles including a hybrid or electric drive and hydraulically actutable wheel brakes on the front axle, wherein the wheels associated with the rear axle are driven at least partially by an electric motor that can be operated as a generator to recover braking energy and, in generator mode, exerts a braking force on the vehicle wheel associated with the respective axle, thereby generating a drag torque including the braking torque and the regeneration torque of the electric drive, the drag torque being separately regulatable on the front and rear axles. To prevent overbraking of the rear axle and a loss of driving stability of the vehicle, a regeneration torque acting on the rear axle is controlled or regulated such that the drag torque acting on the rear axle does not exceed a maximum drag torque value associated with that axle.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Driving force transmitting device for four-wheel drive vehicle
InactiveUS20090229905A1Decreases oil viscosity resistanceDecreases friction lossFluid actuated clutchesRoad transportFriction torqueDrag torque
A driving force transmission device for four-wheel-drive vehicle based on the two-wheel drive of front wheels is provided. In the case of the two-wheel drive of front wheels, a multi-disc clutch mechanism for controlling the driving force distribution to a rear wheel output shaft, and a disconnection / connection mechanism for disconnecting and connecting a rear wheel differential and a right rear wheel drive shaft are provided, and in the two-wheel drive of front wheels, the dragging torque of the multi-disc clutch mechanism is made smaller than the friction torque of a rear wheel driving force transmission section, and the front wheel differential and the right rear wheel drive shaft are disconnected by the disconnection / connection mechanism, thereby the rotation of the rear wheel driving force transmission section is stopped.
Owner:UNIVANCE CORP
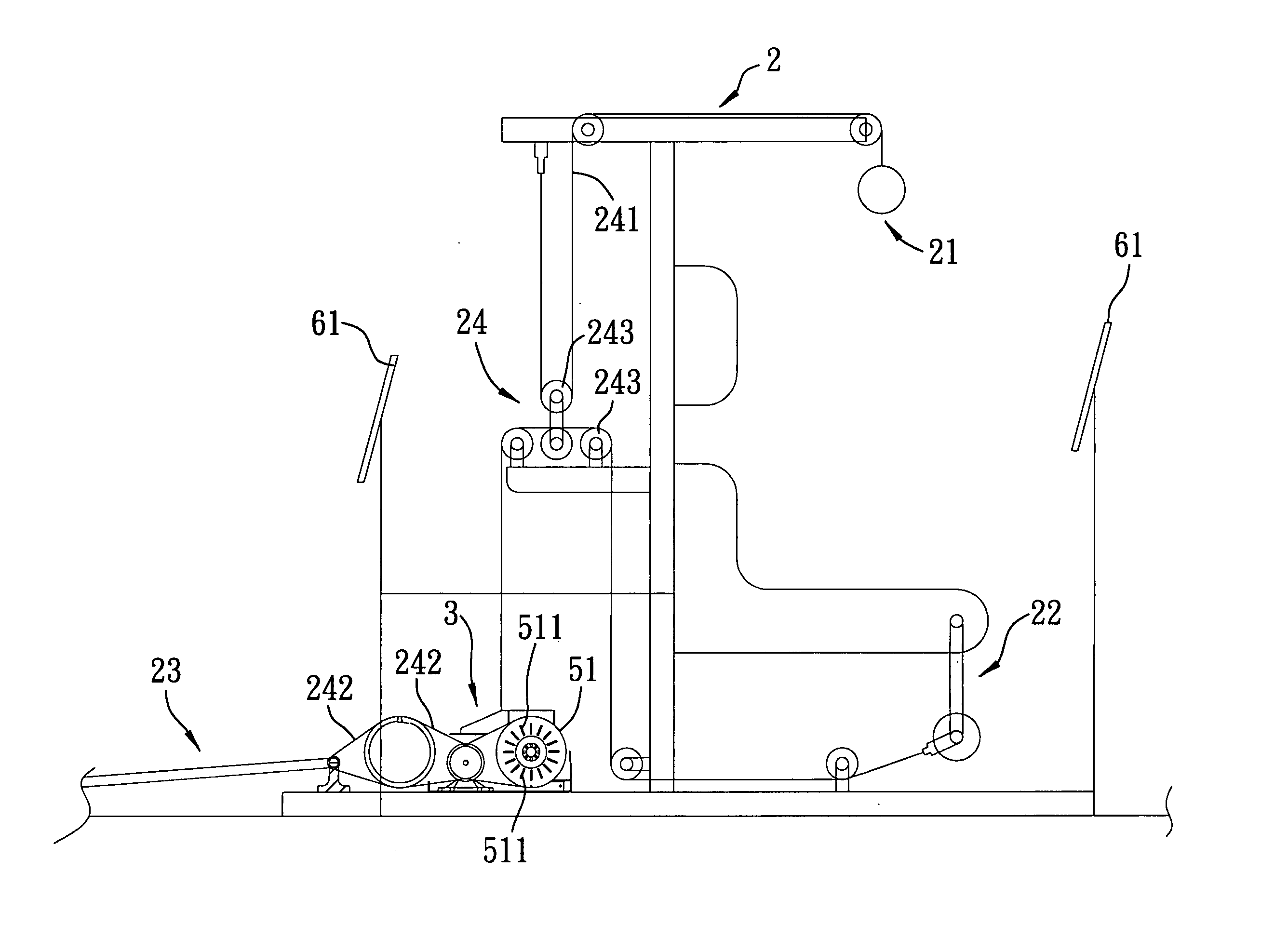
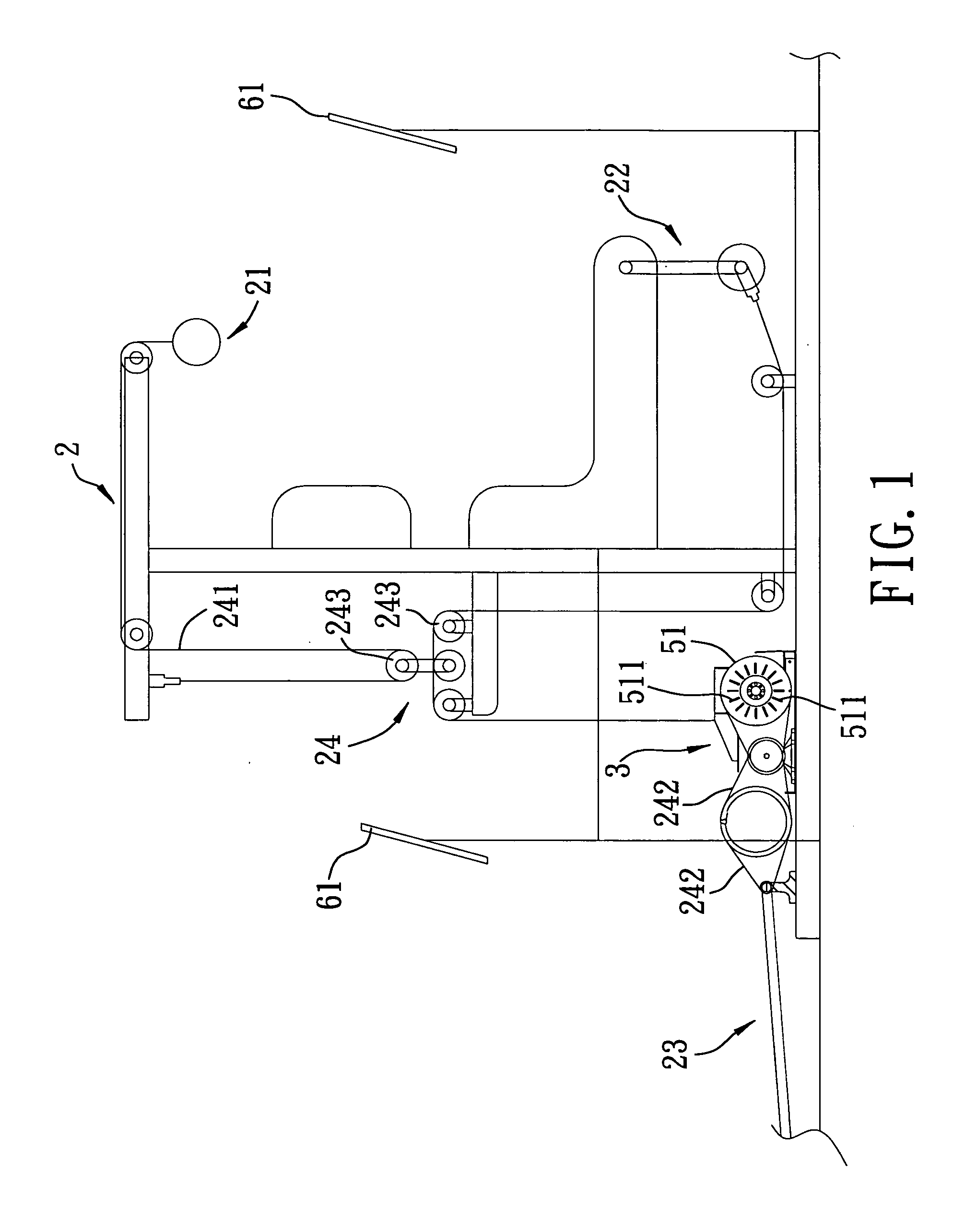
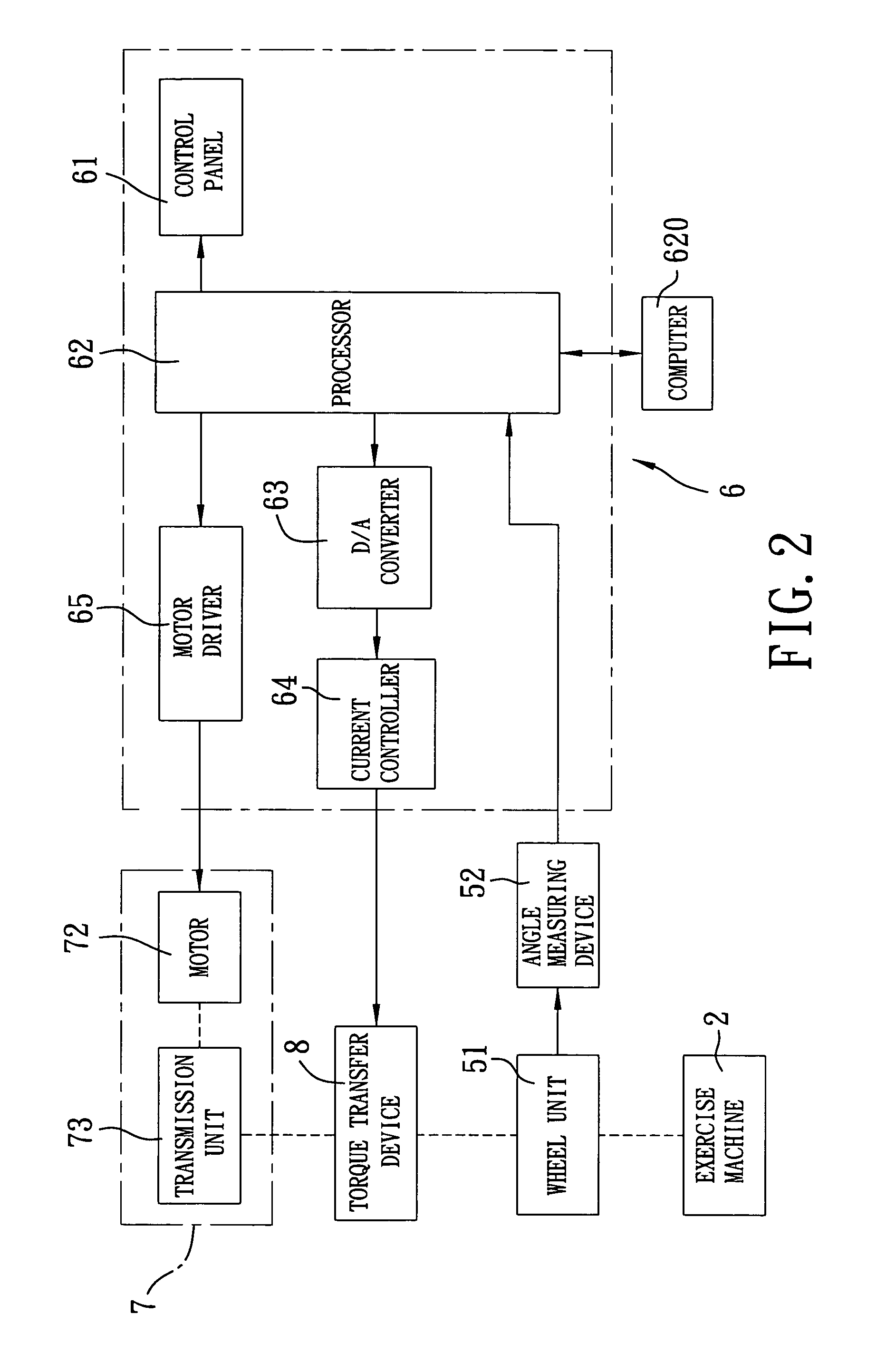
Method and apparatus for providing a dynamically variable resistive load during exercise
InactiveUS20050239600A1Overcomes drawbackClubsMuscle exercising devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceAngular rotation
An apparatus for providing a dynamically variable resistive load during exercise includes a wheel unit, a resistance generator, a torque transfer device, an angle measuring device, and a control unit. The wheel unit rotates in response to exertion of a user-applied force during an exercise stroke. The resistance generator generates a resistive torque for resisting rotation of the wheel unit when the user-applied force is exerted. The torque transfer device transfers a fraction of the resistive torque from the resistance generator to the wheel unit. The angle measuring device detects angular rotation of the wheel unit during each exercise stroke. The control unit, in accordance with the angular rotation of the wheel unit during a current exercise stroke, controls the torque transfer device to adjust the fraction of the resistive torque that is transferred to the wheel unit.
Owner:LIANG HSIU SHUN +1
Equalizing unit of a drive train of a motor vehicle and its construction for loss-minimizing oiling on demand
The invention relates to an oiling concept of an equalizing unit of a drive train of a motor vehicle with a clutch device to be oiled in driving mode. In order to stop drag torques which act on the clutch device from the outside and result in increased dissipation when said clutch device is not required due to the operating state, measures are provided which promote the dry running of the clutch device. The measures include the spatial-functional separation of the oil delivery device from the clutch device and the provision of a braking or decoupling device by means of which the oil delivery device can be deactivated if there is no oil requirement.
Owner:GKN DRIVELINE KOPING
Method and device for verifying a drive torque applied by an electric machine in a hybrid drive of a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20120303196A1Accurate torqueTested rapidly and easilyDigital data processing detailsElectric machinesCombustionElectric machine
A method for verifying a drive torque applied by an electric machine in a hybrid drive of a motor vehicle, the motor vehicle being propelled by the electric machine and / or an internal combustion engine, and it being checked if the drive torque applied by the electric machine is determined accurately. In order to ensure that the operating strategy is correctly implemented and a shift in load level in the power train functions reliably during operation of the motor vehicle, the drive torque applied by the electric machine is evaluated with regard to its accuracy, using a drag torque generated by the combustion engine during an overrun fuel cut off.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Shiftable clutch device, particularly friction wet clutch, drive train for a hybrid system and method for operating the drive train and vehicle including the drive train
ActiveUS20110118079A1BuildMore assembledMechanical actuated clutchesRotary clutchesHybrid systemDrag torque
A shiftable clutch device for disconnecting a first drive machine from a drive train and connecting it thereto, including a control device that can be actuated by a pressure medium, is characterized according to the invention in that the shiftable clutch device includes two partial clutches, a first partial clutch forming a main clutch and a second partial clutch forming a drag clutch, which are disposed and configured such that each is adapted to produce a drag torque in an end position of the control device, a first opening end position characterized by an open state of the main clutch and a second closing end position characterized by a closed state of the main clutch.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Method for optimizing groove structure of friction plate of wet type friction engagement apparatus
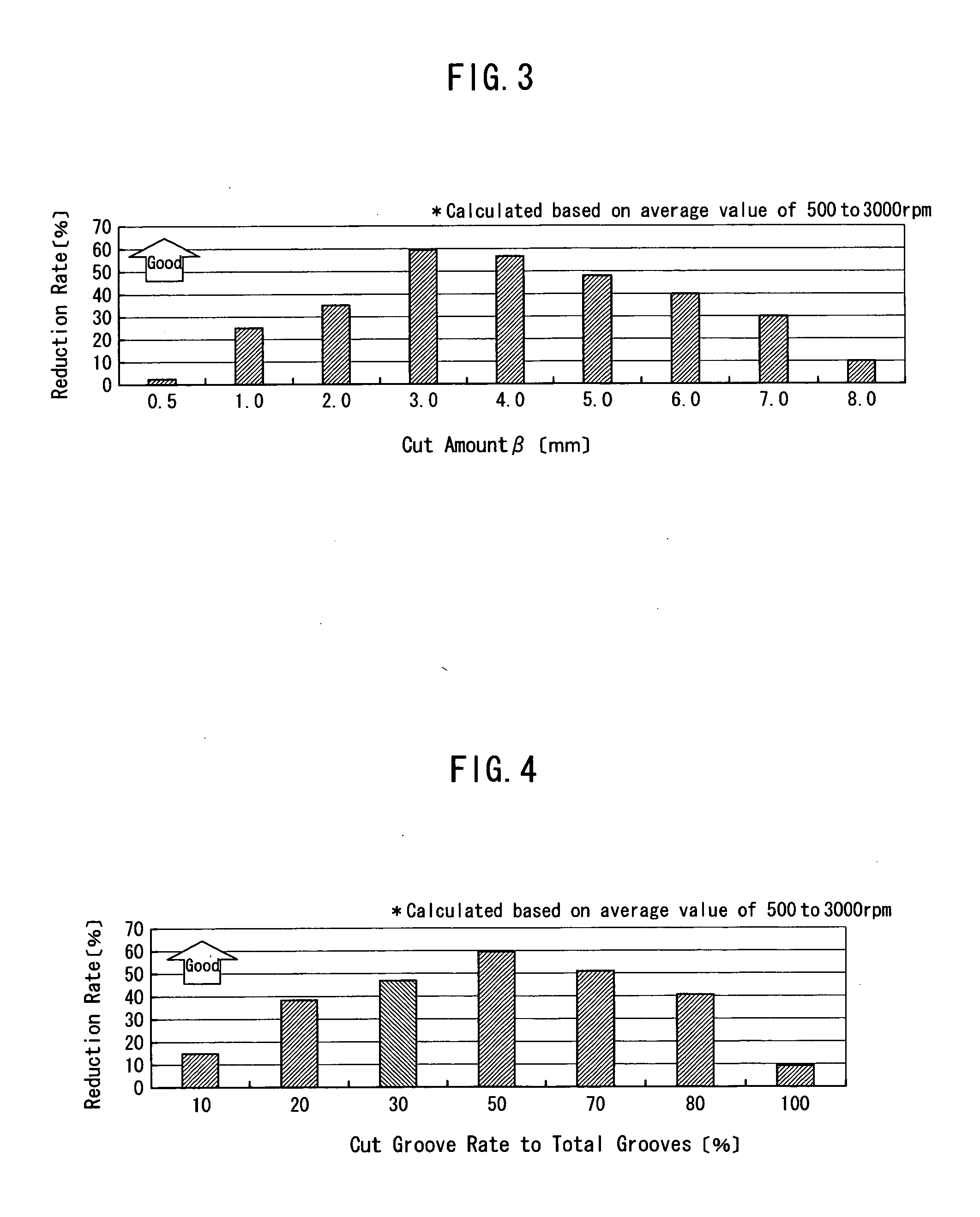
InactiveUS20050224310A1Reduce drag torqueHigh trafficFluid actuated clutchesBraking discsTraffic volumeDrag torque
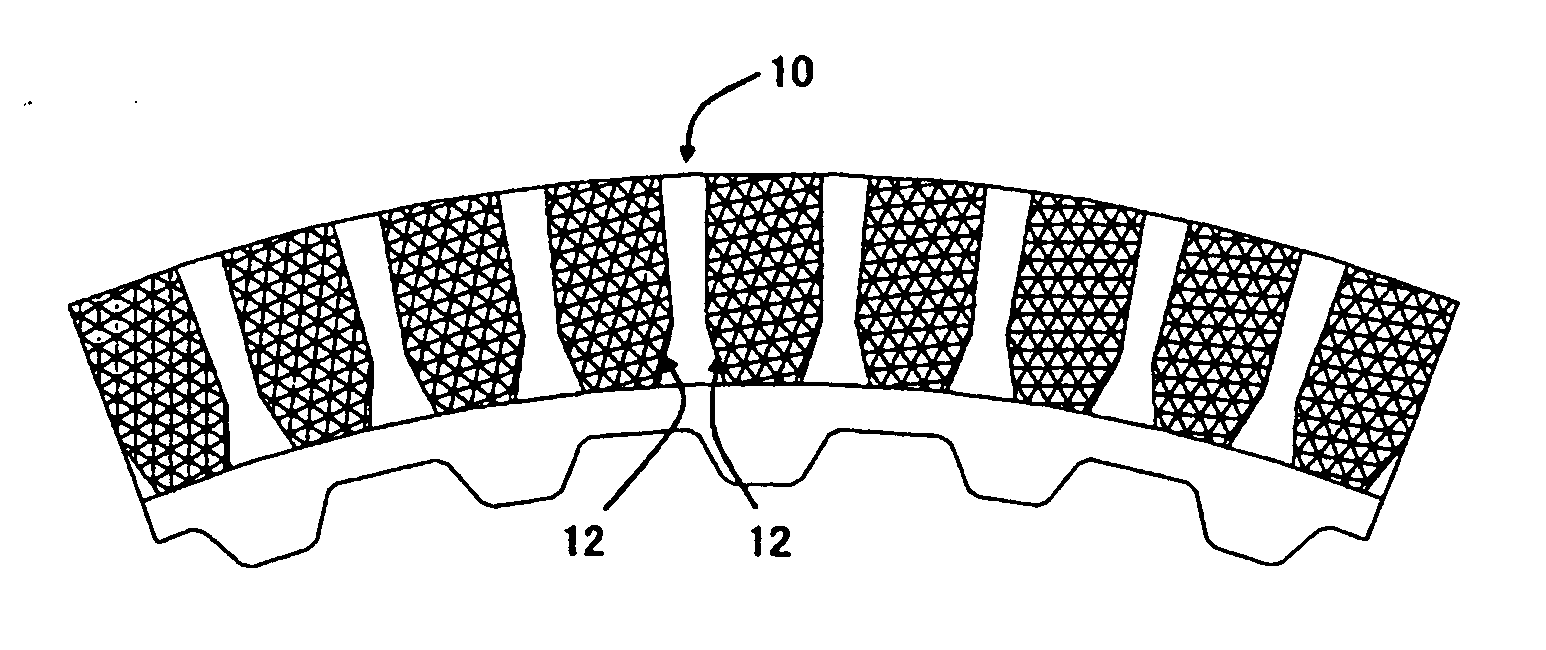
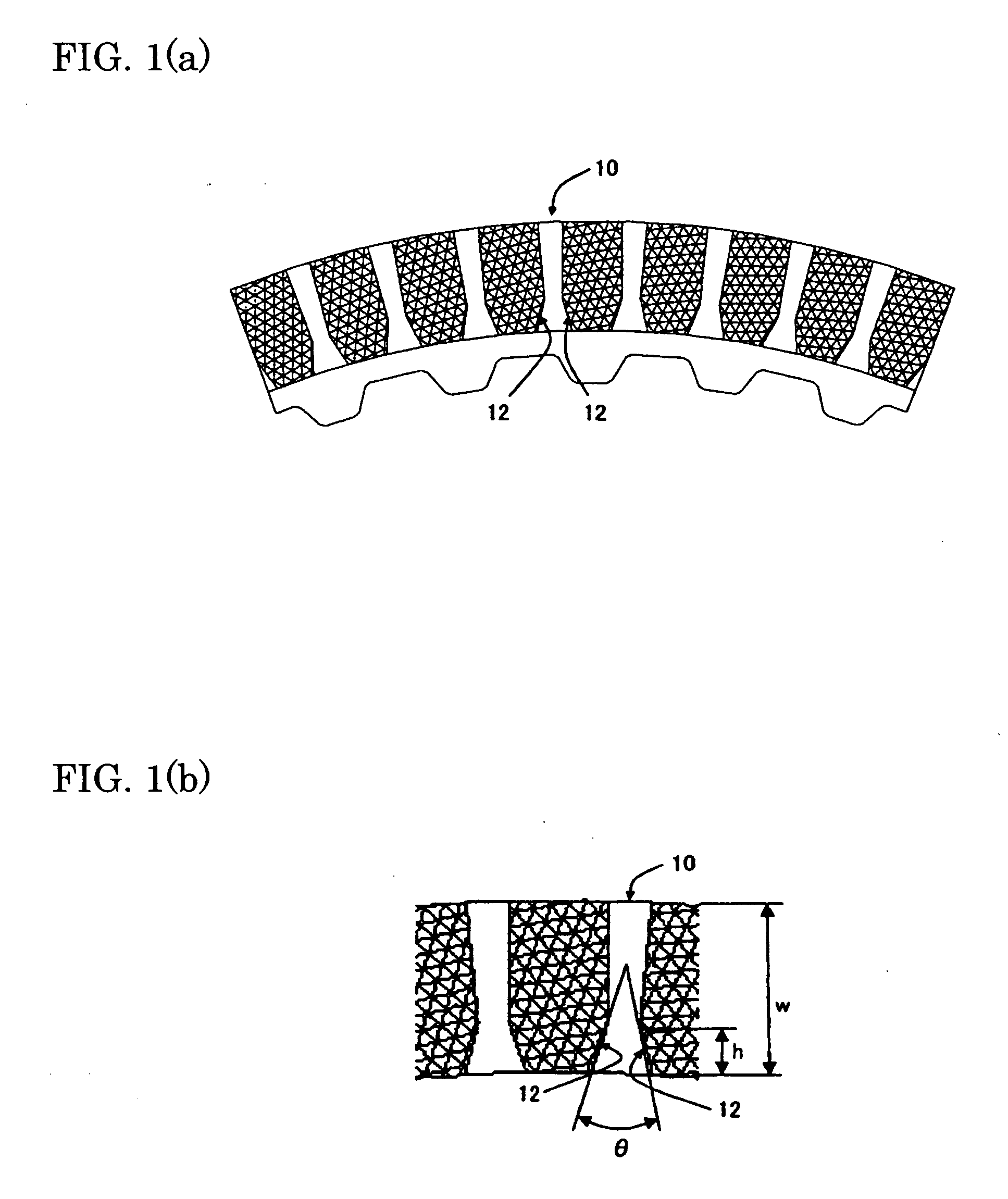
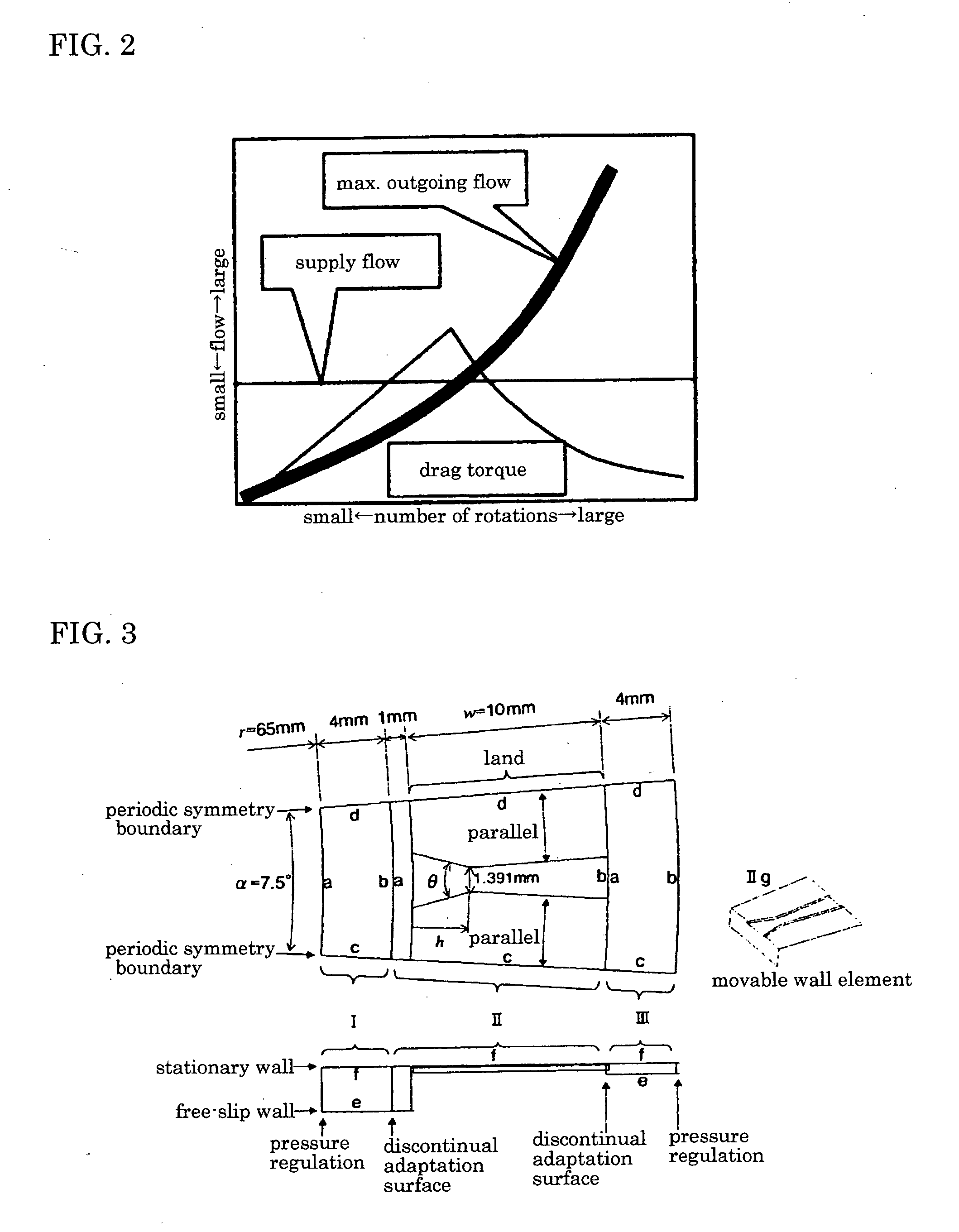
The object of the present invention is to provide an optimizing method for a groove structure of a friction disk of a wet-type friction engaging element, which can reduce drag torque by increasing outgoing flow of lubricating oil on the friction surface and increasing the content of air in the lubricating oil. The optimizing method for a groove structure of a friction disk of a wet-type friction engagement element comprising a sectoral inner section 12 of a groove 10 widening inwardly formed on the surface of a friction member of the wet-type friction engaging element, wherein the outgoing flow per groove area is calculated based on the entrance angle (opening angle) θ of the inner section 12 and the ratio h / w of the full length w of the groove 10 to the length h of the inner section; and then a range of the entrance angle (opening angle) θ of the inner section and the ratio h / w of the full length w of the groove to the length h of the inner section is determined where the outgoing flow per groove area is at least a certain value.
Owner:DAINATSUKUSU
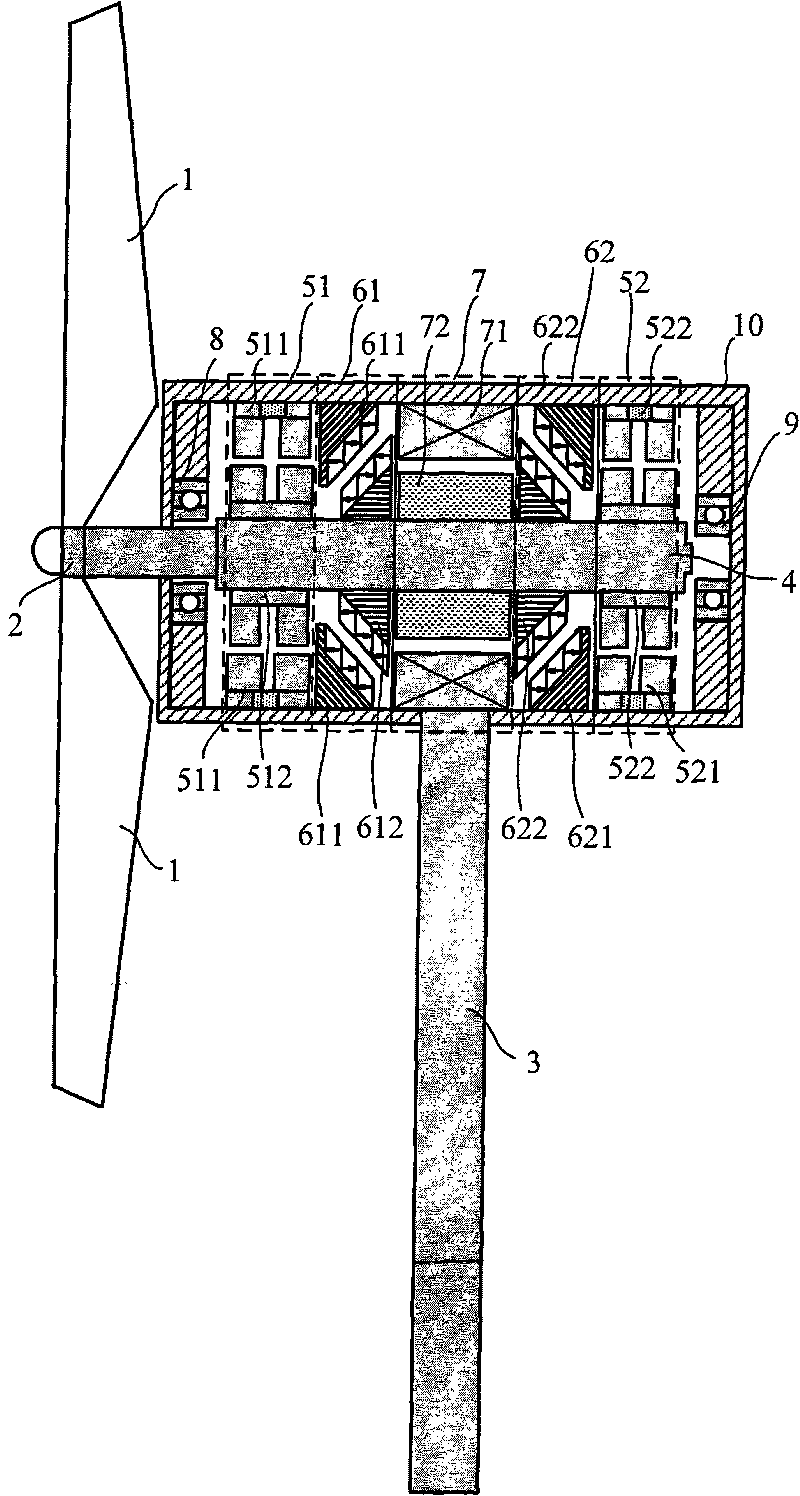
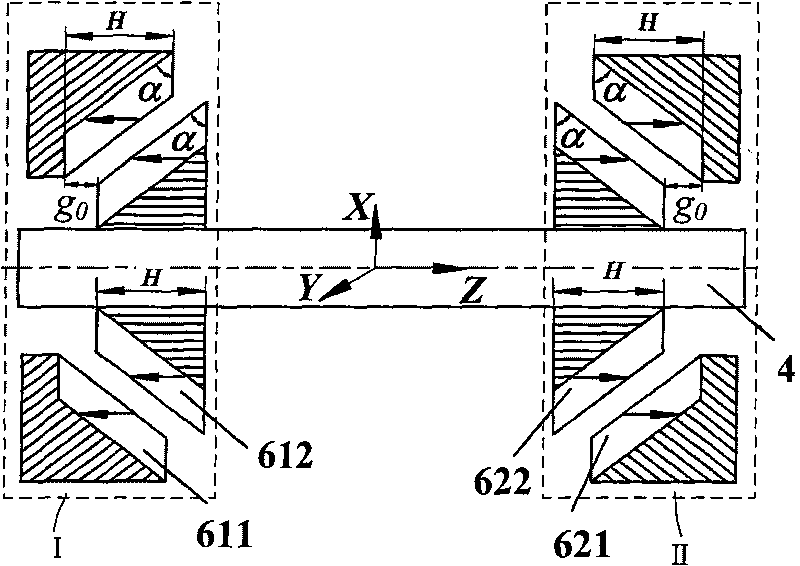
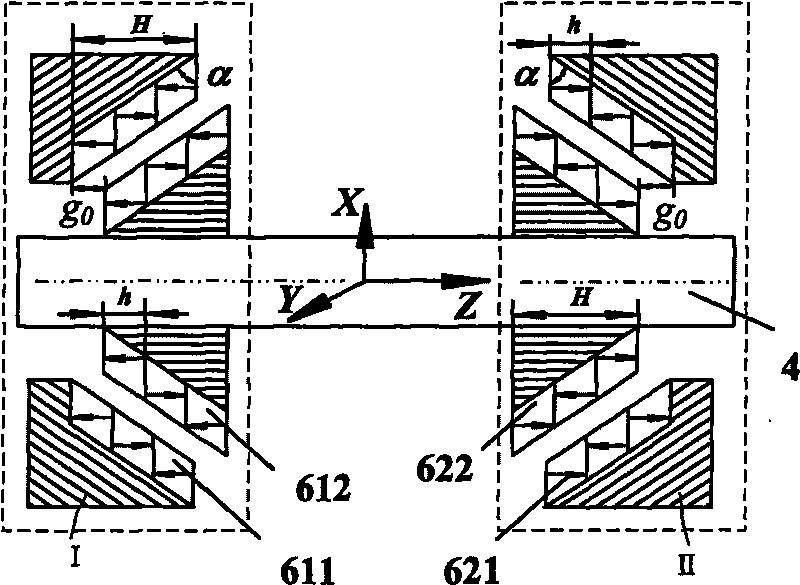
Horizontal shaft magnetic suspension wind driven generator
InactiveCN101701573ARealize full suspension operationReduce maintenanceShaftsWind motor combinationsWind drivenMagnetic bearing
The invention relates to a horizontal shaft magnetic suspension wind driven generator, comprising a stationery part and a rotating part; the stationery part comprises a radial magnetic bearing stator part, an axial magnetic bearing stator part, a generator stator part, a front protective bearing, a rear protective bearing, a stator shell and a blower tower; the rotating part comprises a blade, a hub, a rotating shaft, a radial magnetic bearing rotor part, an axial magnetic bearing rotor part and a generator rotor part; an axial magnetic bearing is composed of a permanent magnet without a control system, a radial magnetic bearing is a permanent magnet bias magnetic bearing, the permanent magnet provides bias flux density, and control force is adjusted by current; the blower rotor realizes five-freedom-degree stable suspension, can completely eliminate the mechanical friction of the rotating part and the stationery part, reduce starting resisting moment and starting wind velocity of the blower and improve the wind energy utilization rate. All components of the invention have rational and compact layout, the maintenance of the blower can be reduced and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
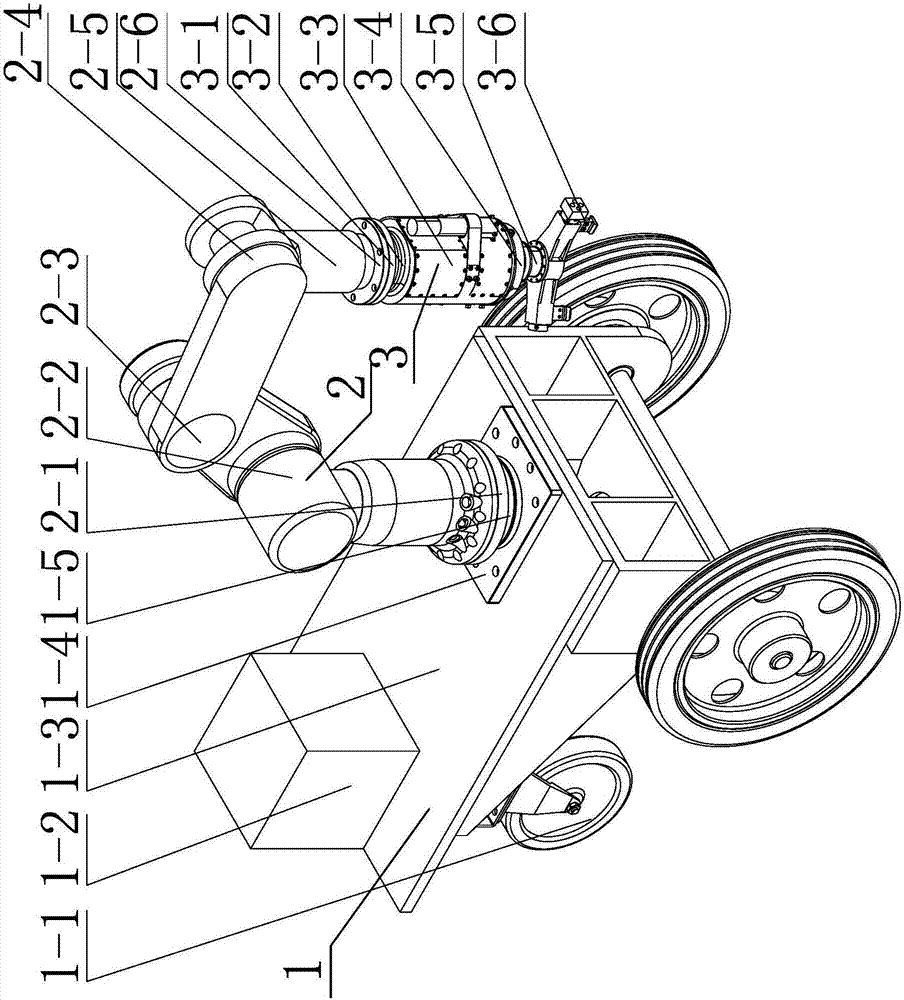
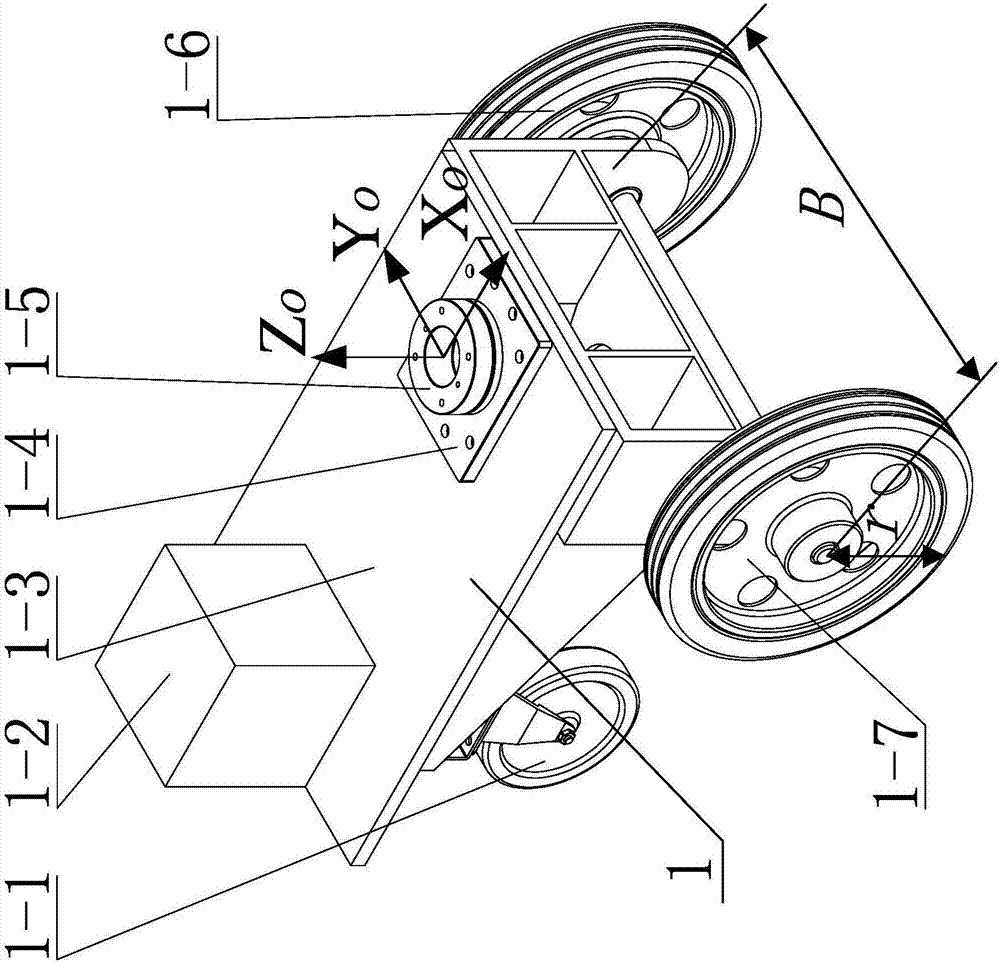
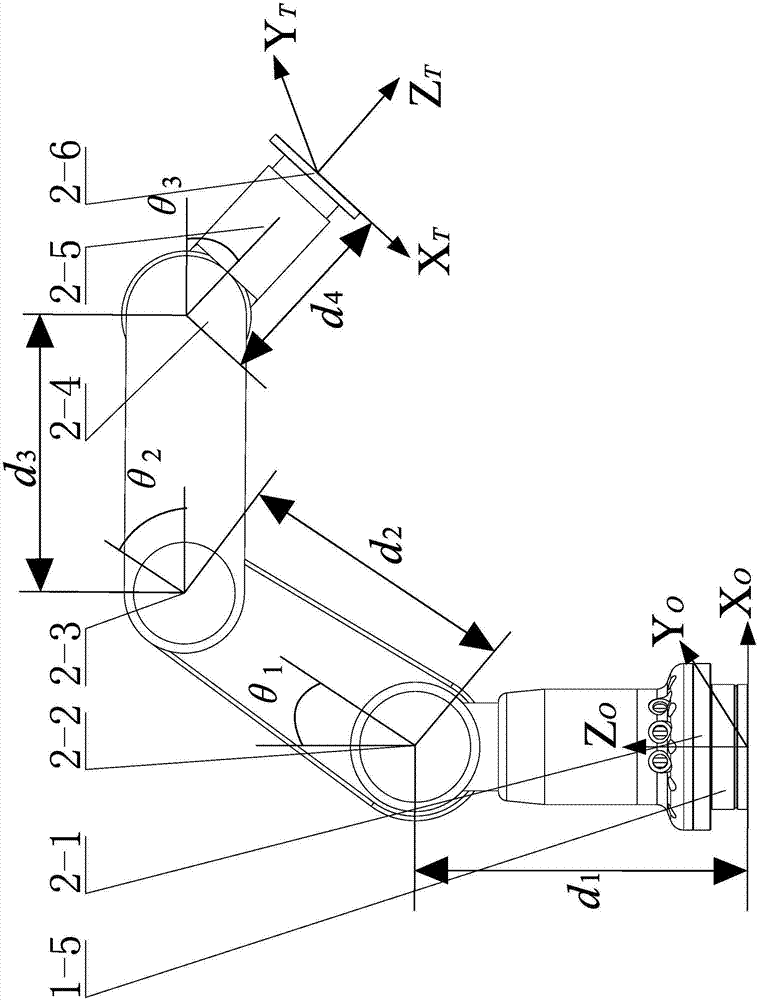
Full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and valve screwing-twisting method utilizing robot
ActiveCN108000477AImprove adaptabilityAvoid Rigid CollisionsGripping headsAxial displacementEngineering
The invention provides a full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and a valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot, and relates to a robot and a valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot. The full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and the valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot aim to solve the problems that an industrial robot cannot conductlarge overall motion, and the operating range is narrow; rigid collision and radial contact force are generated between an end actuator and a valve handwheel; damage of operating devices is possiblycaused due to the fact that screwing-twisting resistance torques of different valves are different; and the valve handwheel can produce axial displacement while rotating, and axial contact force of the tail end is brought. The full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot comprises a wheel type moving platform, a four-degree-of-freedom manipulator and a compliant end actuator, the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator is mounted on the wheel type moving platform, and a six-axis force sensor is mounted between the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator and the wheel type moving platform; the compliant end actuator is mounted at the tail end of the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator, and a six-axis force sensor is mounted between the compliant end actuator and the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator; and through information of the two sensors, impedance control can be conducted on the wheel type moving platform and the four-degree-of-freedom manipulator. The full-pose-and-position active-passive compliant robot and the valve screwing-twisting method utilizing the robot are suitable for robot remote operation, robot compliant control and valve screwing-twisting operation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
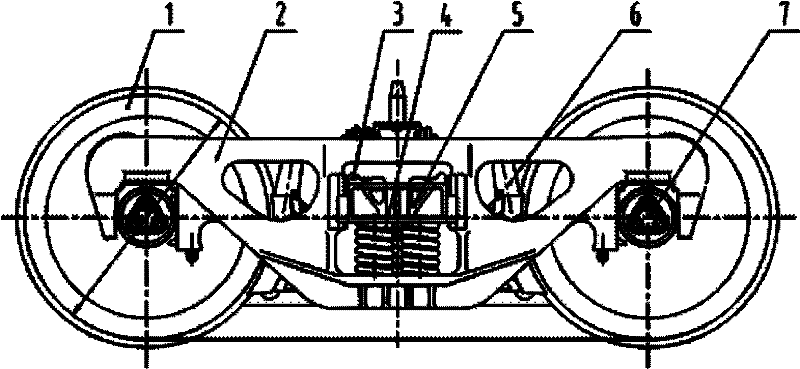
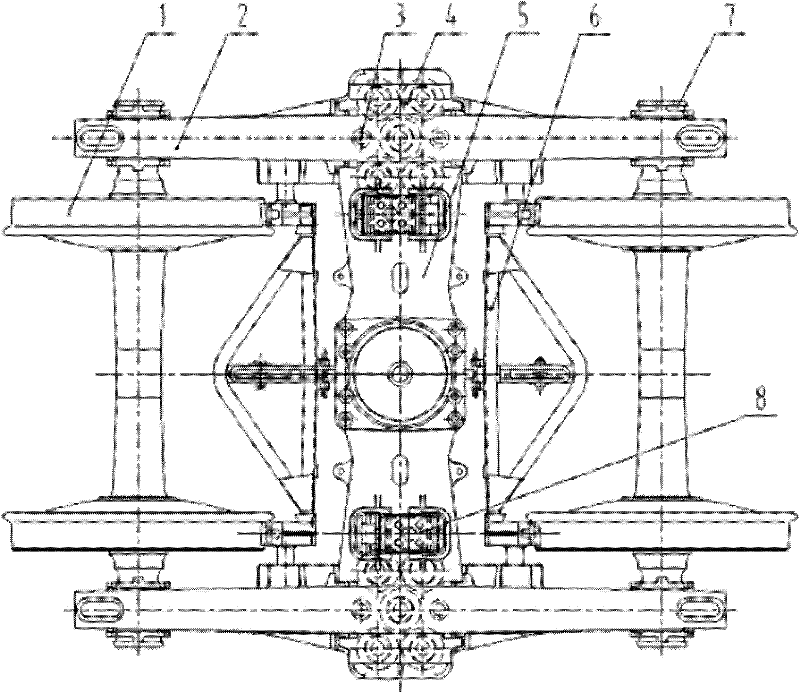
Bogie of narrow gauge railway vehicle
InactiveCN102514584AImprove diamond stiffnessIncrease static deflectionBogiesBogie-underframe connectionsVariable stiffnessBogie
The invention discloses a bogie of narrow gauge railway vehicle, which comprises a wheel pair, a side frame, a vibration absorber, a swing bolster and a braking device. The wheel pair is connected with the side frame in a rolling way through a rolling bearing device; the side frame and the swing bolster form a bogie body structure through central mounting; a dual-acting elastic side bearer is laid in a swing bolster side bearer box; and the swing bolster side bearer box and the swing bolster are cast into a whole body. The invention optimizes structures of the wheel pair, a vehicle axle, the swing bolster and the side frame, and ensures that the wheel pair meets running requirements of narrow gauge (especially 1067mm gauge), and the structural strength of main bearing structures, such as the swing bolster and the side frame, meets bearing requirements of an 18t axle load bogie. The central mounting adopts a dual-stage variable stiffness spring, increases the empty natural bow, and meets different requirements on the central mounting in different operating conditions. By adopting the frictional vibration absorber of the control type bogie, the diamond resistant rigidity of the bogie is improved. By adopting the dual-acting elastic side bearer, stable turning drag torque is provided for the running of a vehicle, and the running speed of the vehicle is increased.
Owner:CRRC MEISHAN
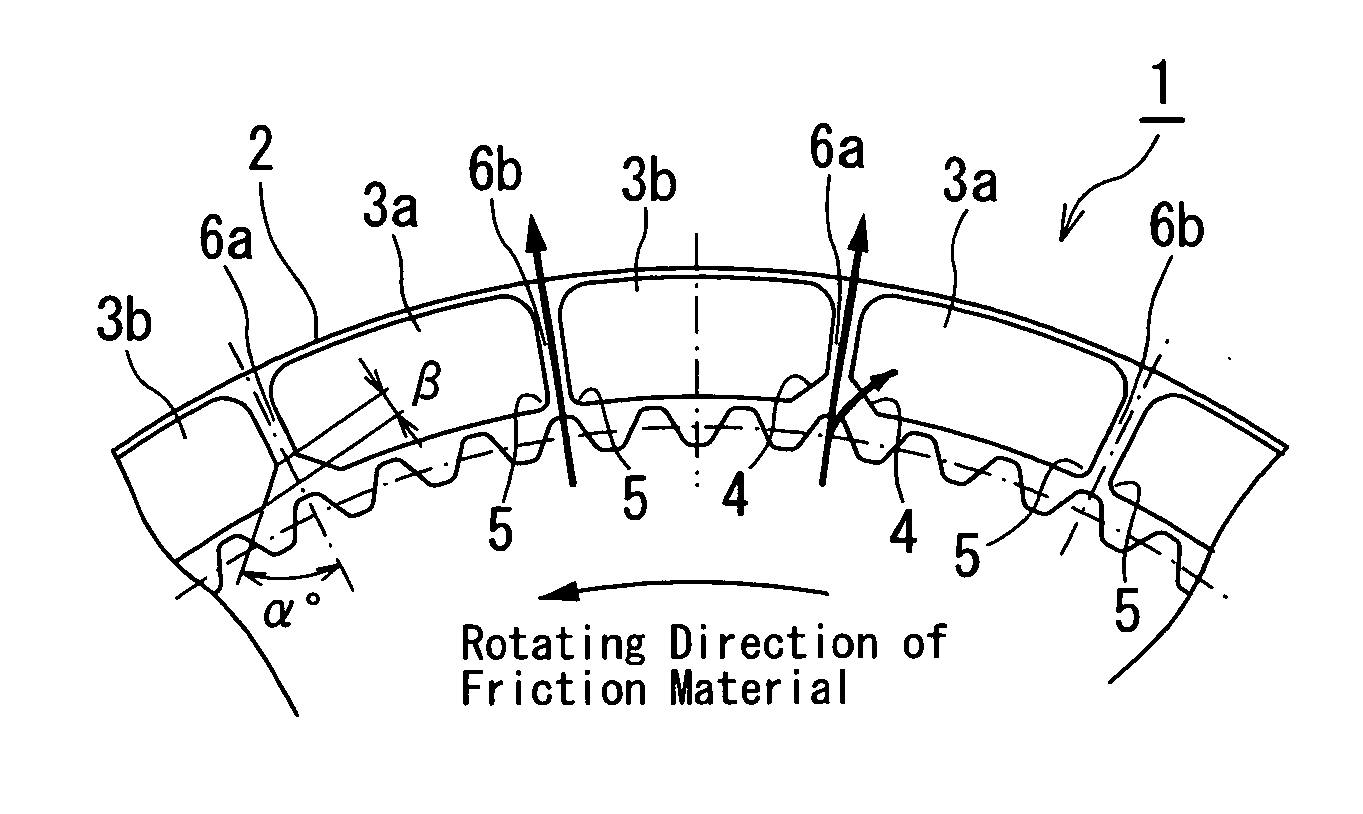
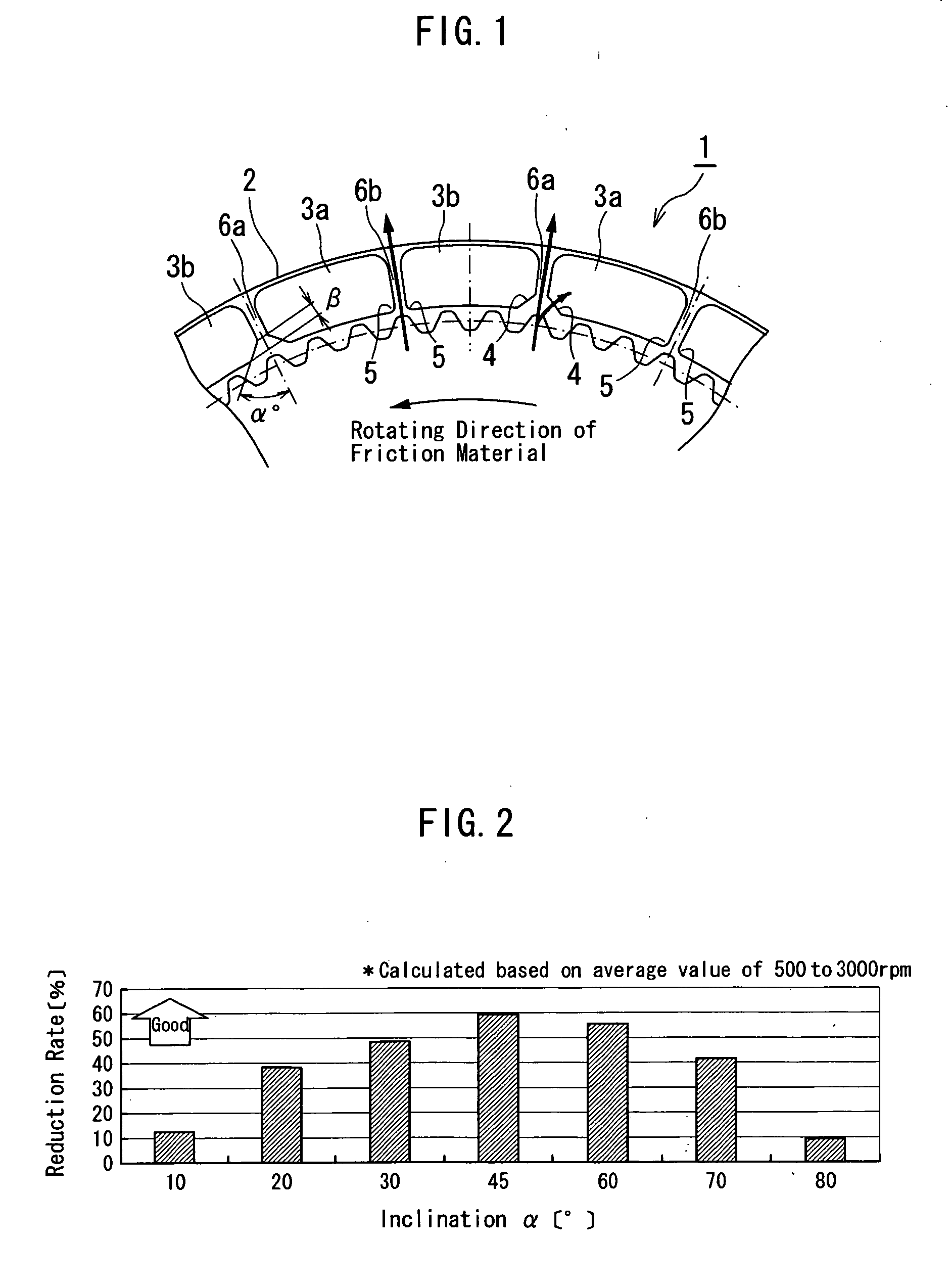
Segment-type friction material
A segment-type friction material comprises segment pieces each having a supply passage formed thereon to supply lubricating oil to a surface of each of the segment pieces. The segment-type friction material further comprises oil grooves each having an outer peripheral opening portion extended in a curved shape or a linear shape. Thereby, lubricating oil is sufficiently supplied to the surface of each of the segment pieces from an outer peripheral side thereof or an inner peripheral side thereof and a clearance between the segment-type friction material and its associated separator plate is assured. Moreover, a space for the lubricating oil to flow through an outer periphery is sufficiently assured and a drag torque is reduced.
Owner:AISIN CHEM CO LTD
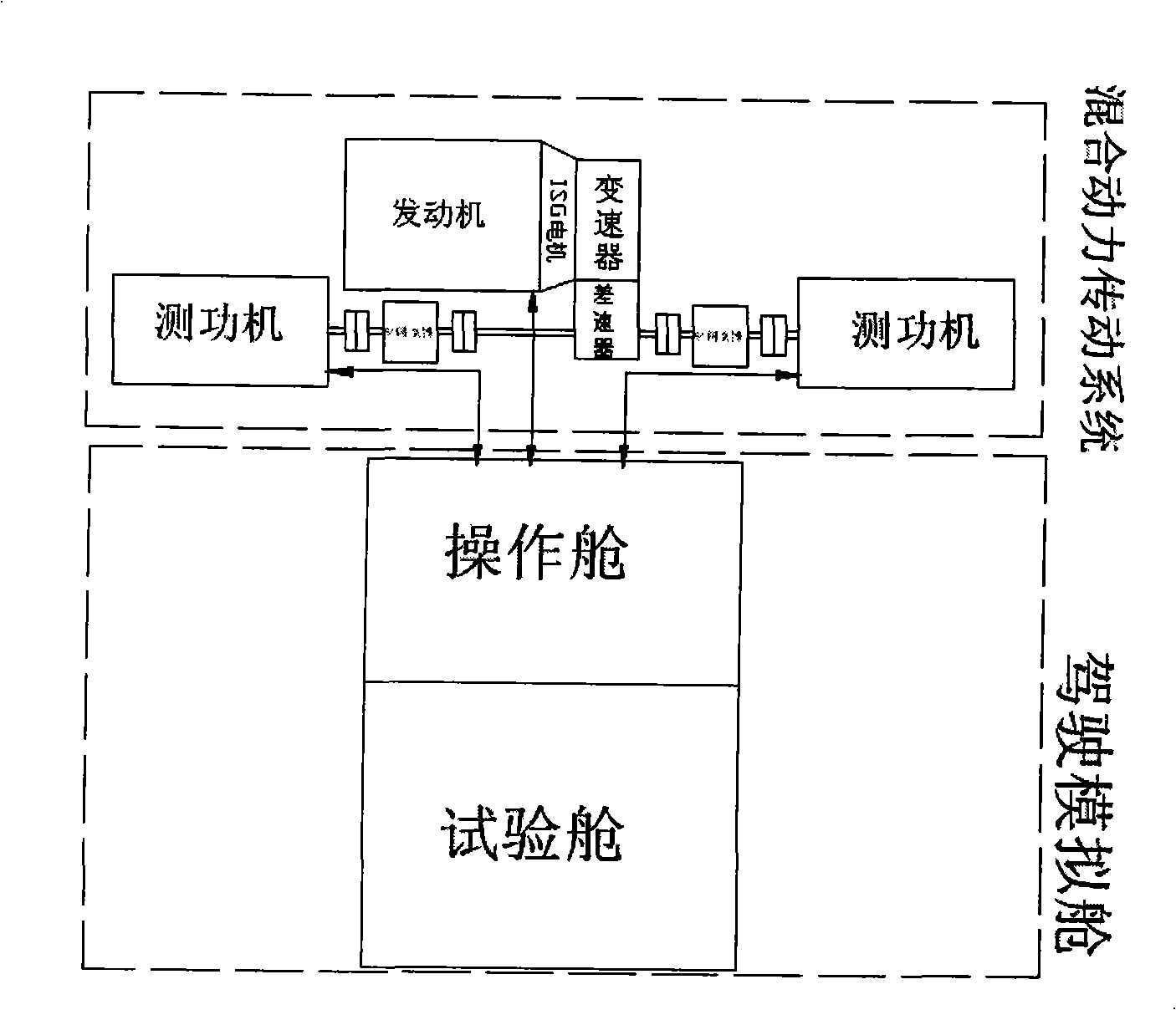
Hybrid power automobile performance test simulation operation apparatus
InactiveCN101303272ASimple structureReliable controlVehicle testingMachine gearing/transmission testingElectric power transmissionDrag torque
The present invention relates to performance test simulation operation equipment for a hybrid car and the equipment comprises a simulated driver cabin and a hybrid power transmission system. The operator controls the power assembly in the front of the simulated equipment by controlling the accelerator pedal, the clutch pedal, the brake pedal and the shift handle. Hybrid power assembly control elements are arranged in the test cabin of the driving simulation cabin as in a real car, and the tester sitting in the simulated driver cabin controls the front hybrid power transmission system according to the operation regulation and loads drag torque on the half shaft through a power measuring machine, therefore, a real rode resistance situation is simulated. In the present invention, all the operations in road test can be performed in a test room, and the performance of the power assembly and critical components of a hybrid car can be simulated factually. The hybrid car performance test simulation operation equipment with a compact arrangement and a simple test method is easy to control and realize.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Wet friction material
ActiveUS20050217965A1Reduces a drag torque sufficientlyShort timeFluid actuated clutchesBraking discsDrag torqueMechanical engineering
In a segment-type wet friction material, an inner peripheral left corner of one segment piece and an inner peripheral right corner of another segment piece are respectively cut off at a fixed angle to a center line of an oil groove. The oil grooves have first oil grooves and second oil grooves. The second oil groove has nearly a uniform width. The first oil groove has an inner peripheral corner portion that is broadened to the center line of the oil groove from a fixed height. In case of being assembled in an automatic transmission, when the segment-type friction material rotates in one direction, an automatic transmission fluid supplied from an inner circumference bumps and touches the portion that is broadened at the fixed angle at a rear side in the rotating direction. Thus, the automatic transmission fluid is positively supplied to a friction surface of the segment piece so as to restrain a contact between a separator plate and the friction surface. Consequently, excess automatic transmission fluid is discharged from the second oil groove, thereby reducing largely a drag torque by the automatic transmission fluid.
Owner:AISIN CHEM CO LTD
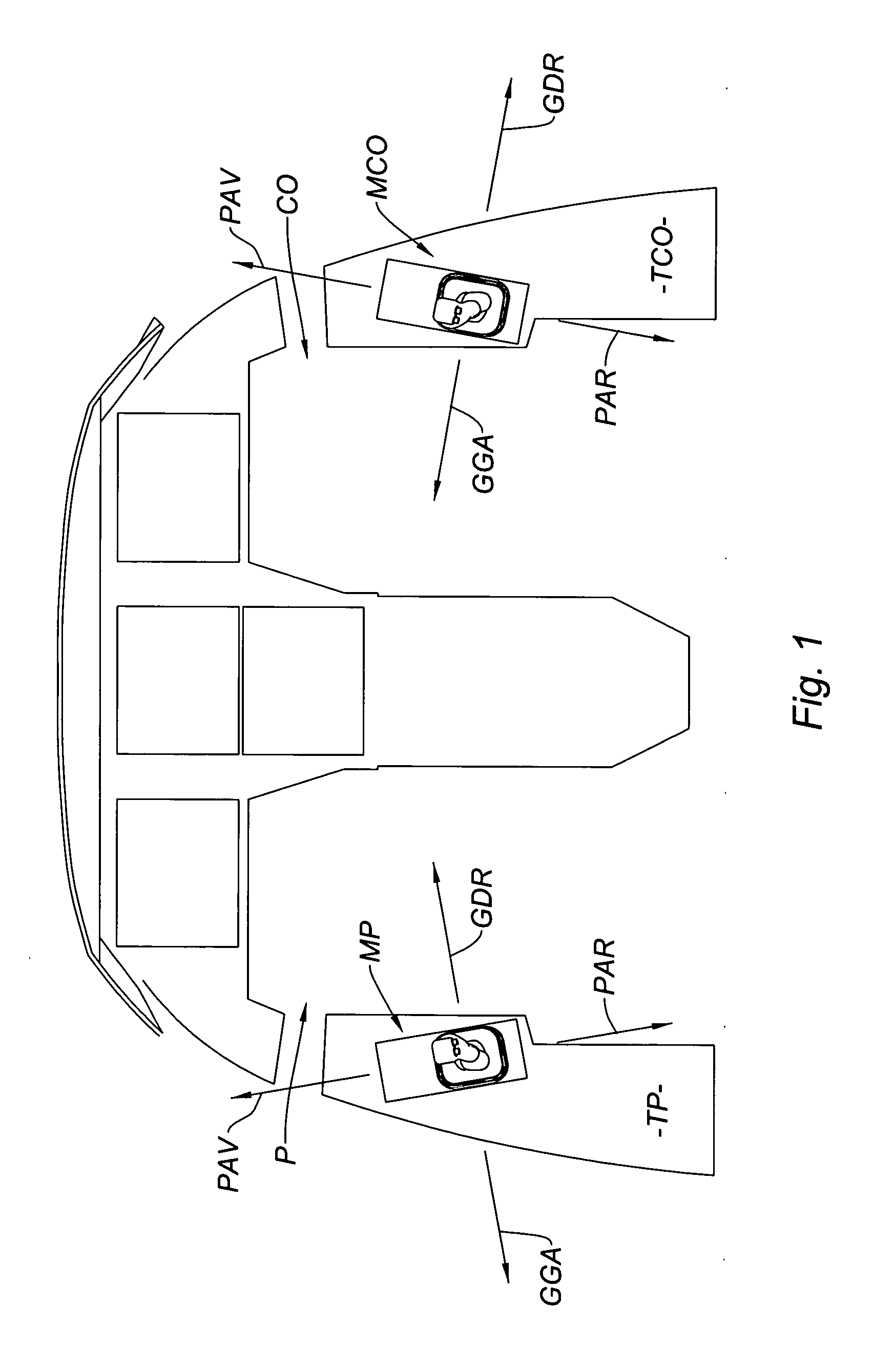
Method and system for promoting a uniform driving style
ActiveUS20150197225A1Improve securityPrevent a critical lateral accelerationHand manipulated computer devicesDigital data processing detailsMobile vehicleEngineering
A method and system for promoting a uniform driving style. A longitudinal speed of a motor vehicle and a route section curvature radius lying ahead of the vehicle are determined when the vehicle approaches the route section. An expected lateral acceleration is determined from the curvature radius and longitudinal speed as the route section is driven through. The lateral acceleration is compared with a permanently predefined lateral acceleration limiting value which can be predefined by the driver. In the event the expected lateral acceleration is greater than at least one of the lateral acceleration limiting values, the longitudinal speed is lowered by an optical, acoustic and / or haptic request to the driver and / or by autonomous braking intervention. If the expected lateral acceleration is smaller than or equal to the lower of the two lateral acceleration limiting values the lowering of the longitudinal speed is reduced by decreasing the engine drag torque.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Lubricating and cooling structure of wet type friction engagement apparatus
InactiveUS6976567B2Reduce frictional contactImprove fuel efficiencyFluid actuated brakesFluid actuated clutchesLow speedDrag torque
Owner:DAINATSUKUSU
Control apparatus for hybrid vehicle
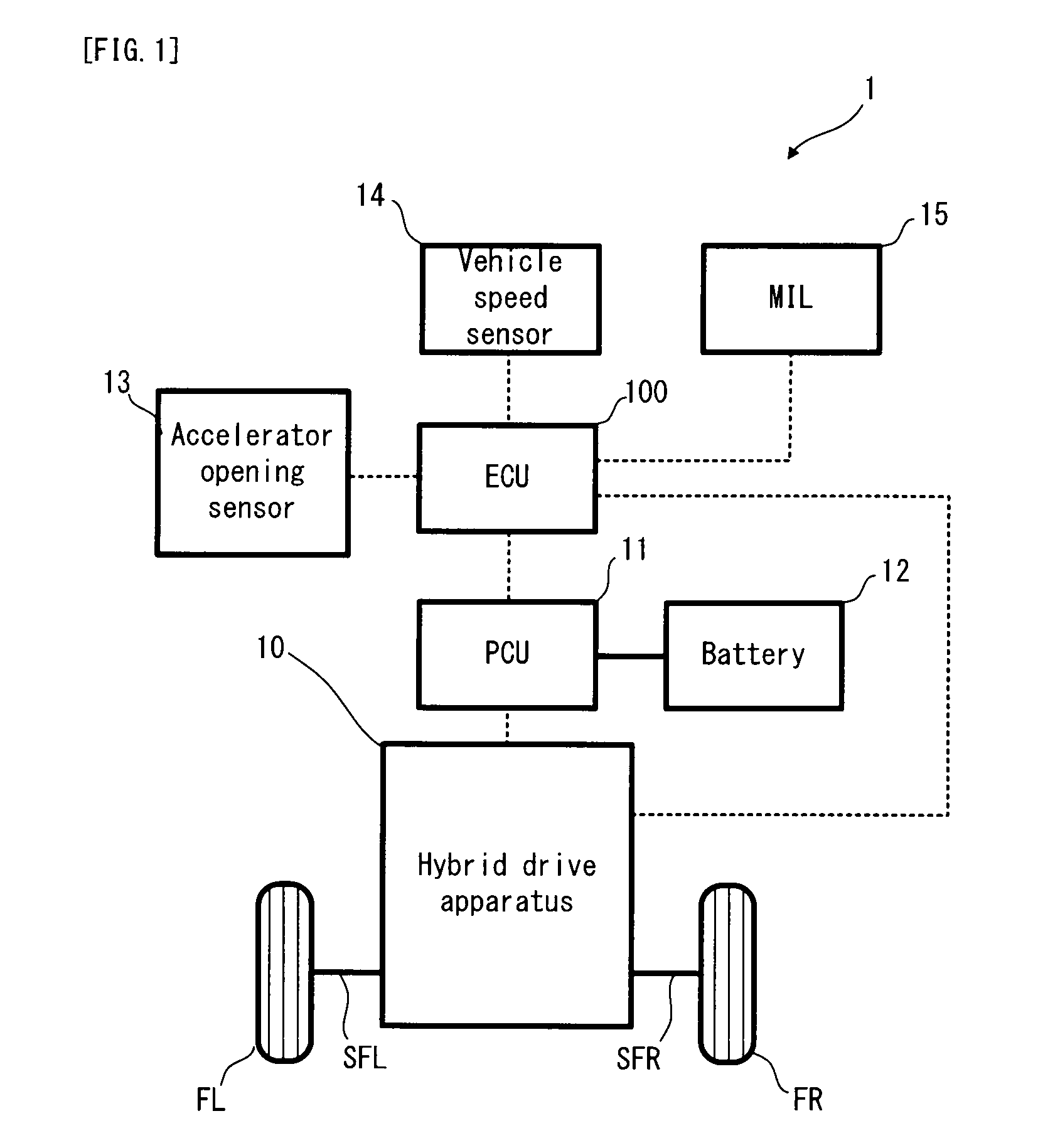
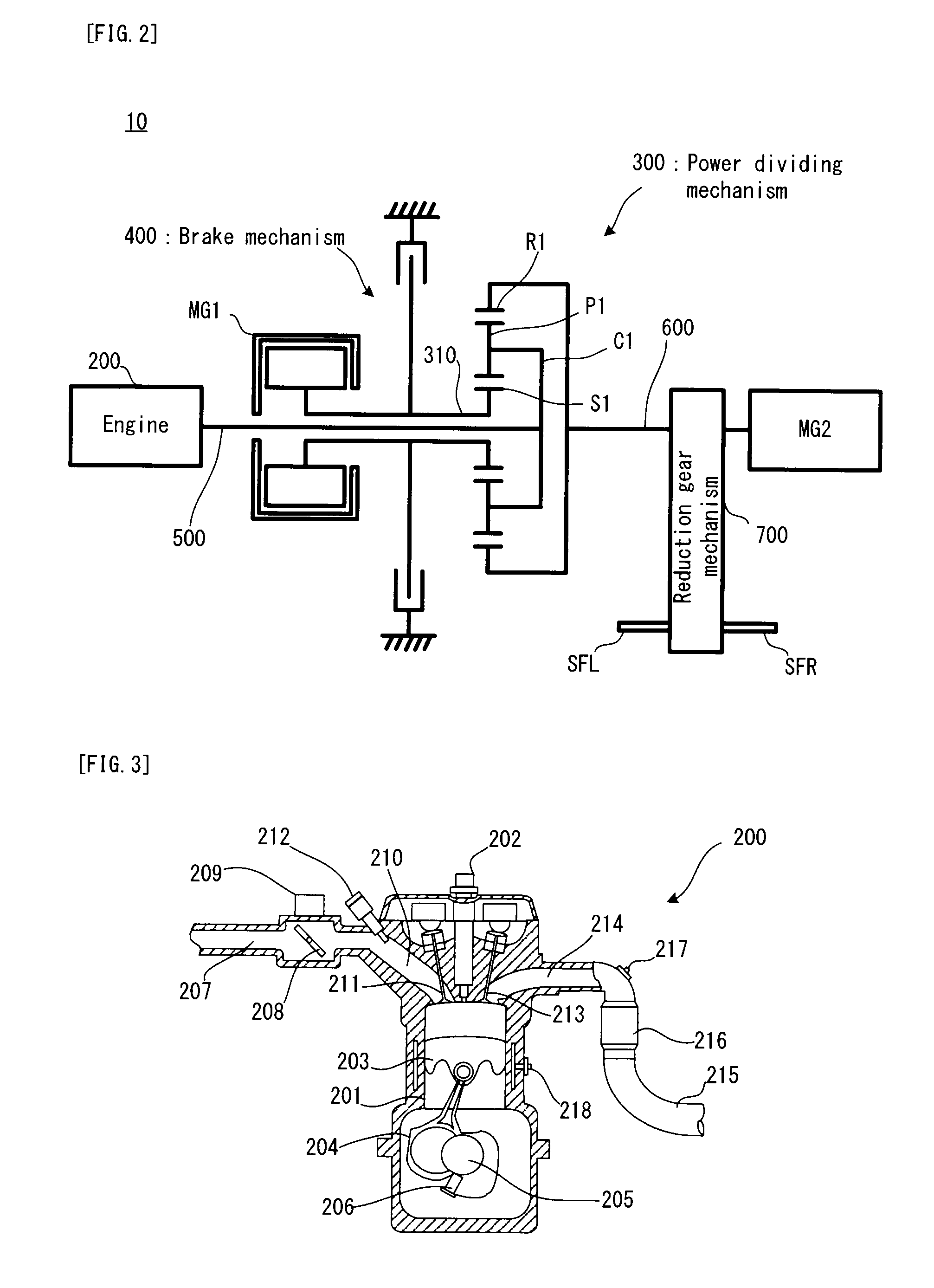
ActiveUS20120095635A1Accurate detectionReduces efficiency of systemDigital data processing detailsPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingLocking mechanismDrag torque
An object of the present invention is to detect the generation of a drag torque in a locking mechanism, in a hybrid vehicle in which a speed change mode can be changed between a fixed speed change mode and a stepless speed change mode by the action of the locking mechanism. In a hybrid vehicle, a brake mechanism is a wet multiplate brake apparatus and can selectively lock a motor generator. On the other hand, in a case where the drag torque is generated in the brake mechanism, if the motor generator is in a positive rotation state, an actual motor generator torque (first torque) is greater than a torque (less as a reaction torque, second torque) calculated from the operating condition of the hybrid vehicle by the amount of the drag torque. If the motor generator is in a negative rotation state, the first torque is less (greater as the reaction torque) than the second torque. The ECU uses this phenomenon to detect the drag torque.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Driving force transmitting device for four-wheel drive vehicle
InactiveUS20090211830A1Decreases oil viscosity resistanceDecreases friction lossRoad transportMagnetically actuated clutchesFriction torqueDrag torque
A driving force transmission device for four-wheel-drive vehicle based on the two-wheel drive of rear wheels or front wheels is provided. In the case of the two-wheel drive of rear wheels, a multi-disc clutch mechanism for controlling the driving force distribution to a front wheel output shaft, and a disconnection / connection mechanism for disconnecting and connecting a front wheel differential and a left front wheel drive shaft are provided, and in the two-wheel drive of rear wheels, the dragging torque of the multi-disc clutch mechanism is made smaller than the friction torque of a front wheel driving force transmission section, and the front wheel differential and the left front wheel drive shaft are disconnected by the disconnection / connection mechanism, thereby the rotation of the front wheel driving force transmission section is stopped.
Owner:UNIVANCE CORP
Device and method for testing disc brake dragging torque
ActiveCN103674391ASimple structureHigh transmission precisionApparatus for force/torque/work measurementRecovery methodDrag torque
The invention relates to the field of automobile part detection devices, and provides a device for testing disc brake dragging torque and a heat energy recovery method. The device for testing the disc brake dragging torque comprises a base plate with a mounting seat and a support, a brake caliper locating seat connected with the base plate, a torque sensor connected with the support, a main shaft in pin joint with the mounting seat, a coupler, a brake test disc and a torque loading device, the brake test disc is connected with the other end of the main shaft, the torque loading device is connected with the other end of the torque sensor, and the two ends of the coupler are connected with one end of the torque sensor and one end of the main shaft respectively. The device for testing the disc brake dragging torque can provide accurate dragging torque testing parameters for improved design. A testing method meets test specifications, high-pressure compressed air is used for replacing hydraulic oil for testing, a brake lining is made to clamp or release the brake test disc fast, and cleanliness is achieved.
Owner:HANGZHOU WOLEI INTELLIGENT TECH
Selectable one-way clutch
ActiveUS20170002877A1Oil temperature can be suppressedSmooth rotationMagnetically actuated clutchesCouplingsDrag torqueEngineering
A selectable one-way clutch that can prevent unintentional rotation of a selector plate by a drag torque is provided. In the selectable one-way clutch, a selector plate having a first aperture for letting through a strut is interposed between a fixed plate and a rotary plate while being allowed to rotate between an engagement position and a disengagement position. The selectable one-way clutch comprises: a protector plate interposed between the rotary plate and the selector plate; and a second aperture formed on the protector plate to let through the strut when the selector plate is rotated to the engagement position.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
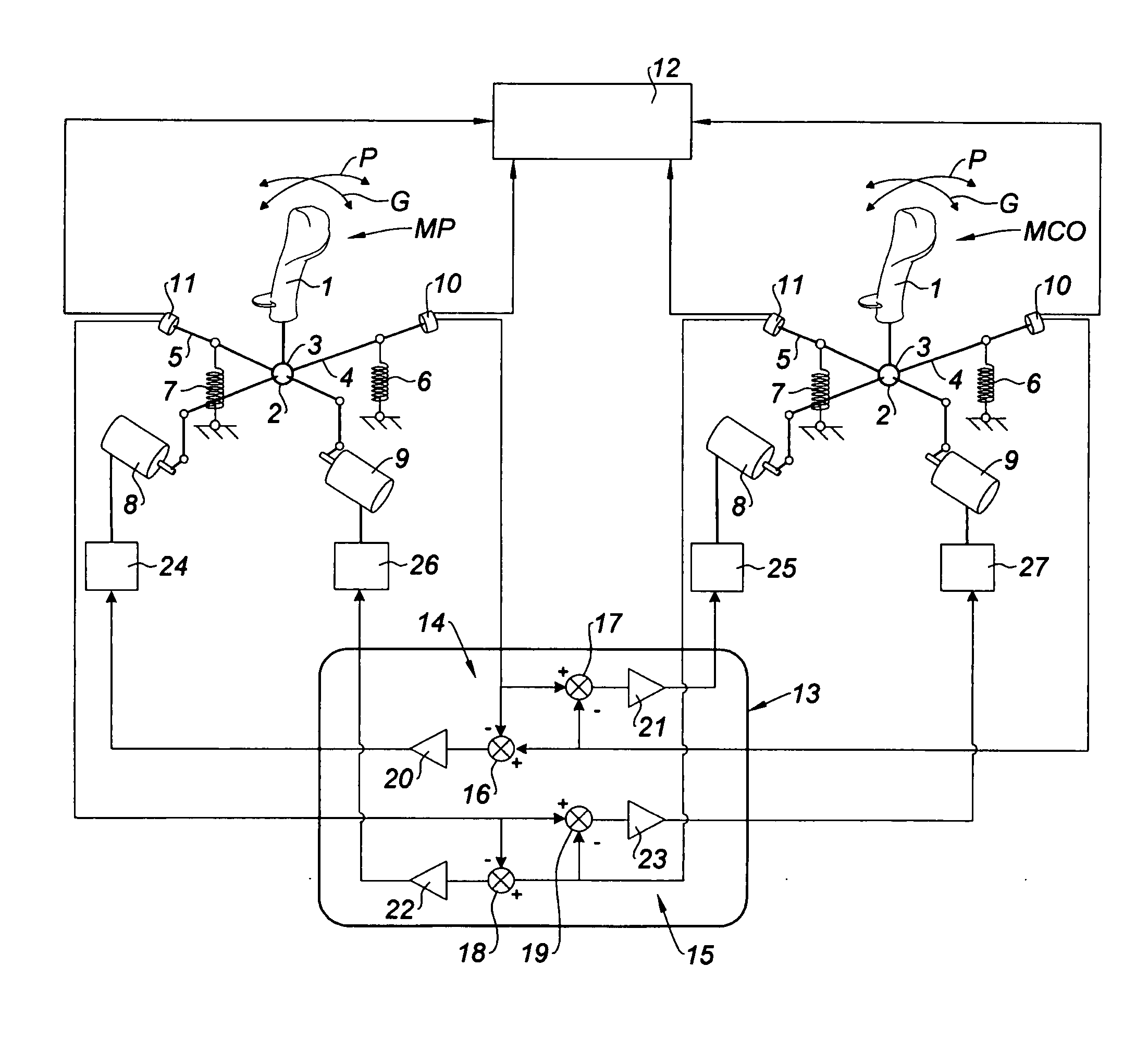
Control system including two control columns that are coupled to enable controlled members to be placed in required positions
ActiveUS20090314901A1Reduce forceWith power amplificationActuated automaticallySpring systemTwo degrees of freedom
A control system for placing controlled members in required positions including two control columns assigned to the controlled members to be moved, each control column having two degrees of freedom. Two actuators controlled by two control circuits apply to their associated control column either a resisting torque or a displacement torque. Each control column is provided with a mechanical spring system spring-loading the associated control column into its neutral position and adapted to provide, in the event of manipulation of the corresponding control column, a resisting torque in support of the resisting torque supplied by the associated actuator.
Owner:DASSAULT AVIATION
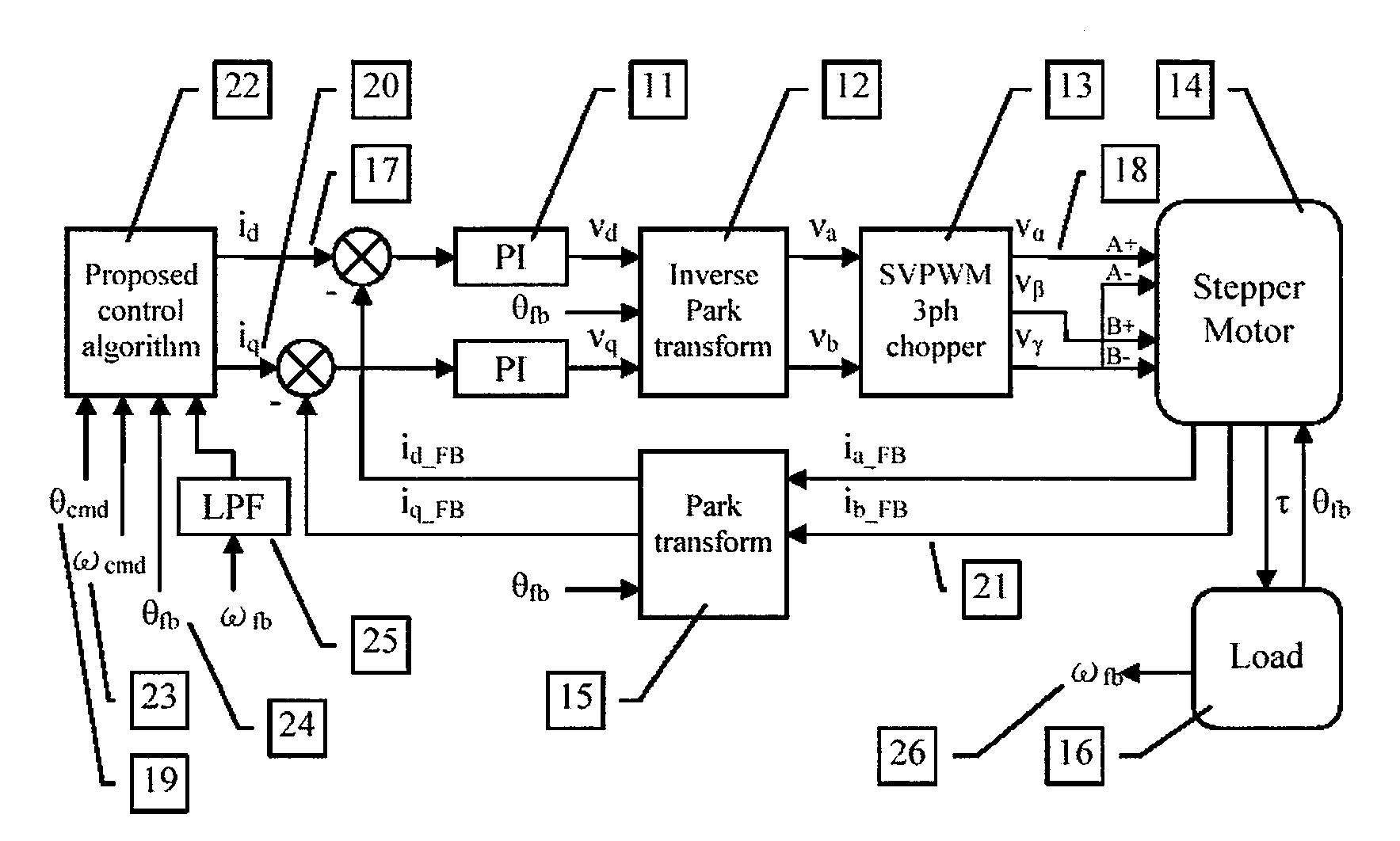
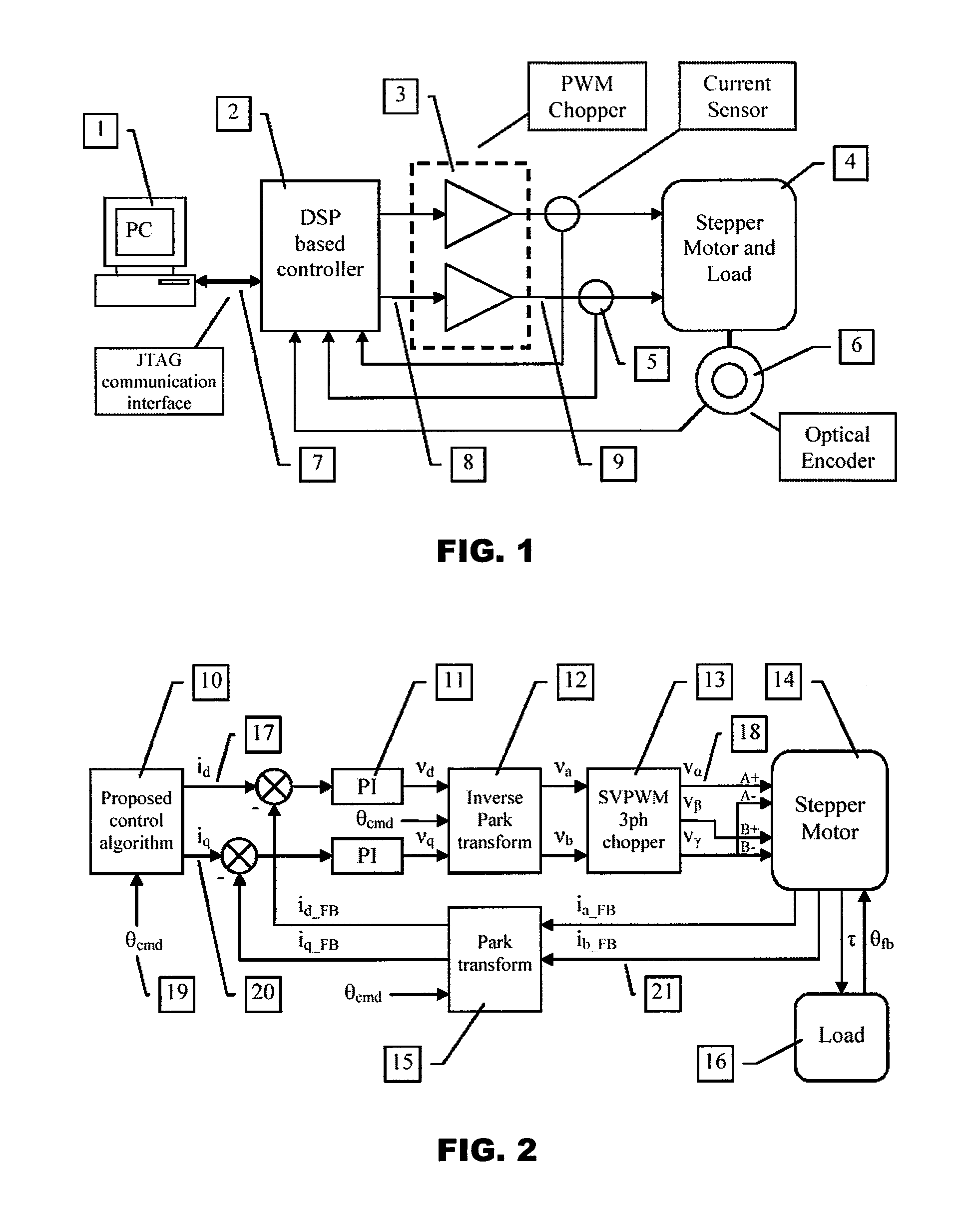
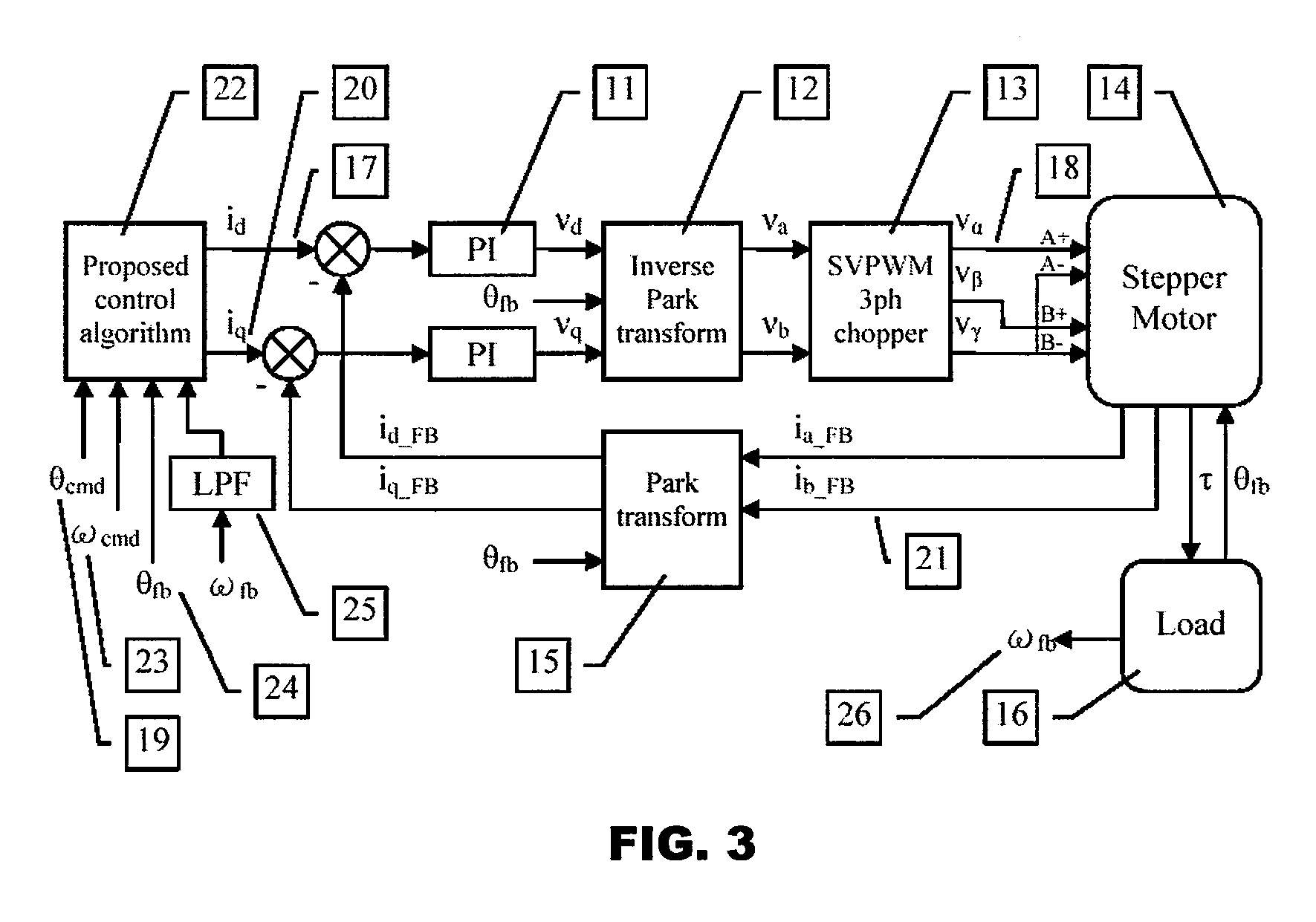
Model-based active electronic damping for stepper motors
ActiveUS20080116835A1Efficient and accurateComputer controlSimulator controlDetentElectric machinery
A method for damping vibrations in a stepper motor with micro-stepping control which comprises the steps of identifying the force amplitudes and phase shifts of multiple harmonic detent torques of the stepper motor, such as the first, second and fourth harmonic detent torques, and tuning the stepper motor with different current commands until minimum friction and resistive torque are obtained. Thereafter, a compensating harmonic current derived from said force amplitudes and phase shifts of the said multiple harmonic detent torques is injected into a current command during operation of the stepper motor to compensate for torque ripples.
Owner:ASM ASSEMBLY AUTOMATION LTD
Lubricating and cooling structure of wet type friction engagement apparatus
InactiveUS20050029072A1Reduce frictional contactImprove fuel efficiencyFluid actuated brakesFluid actuated clutchesLow speedDrag torque
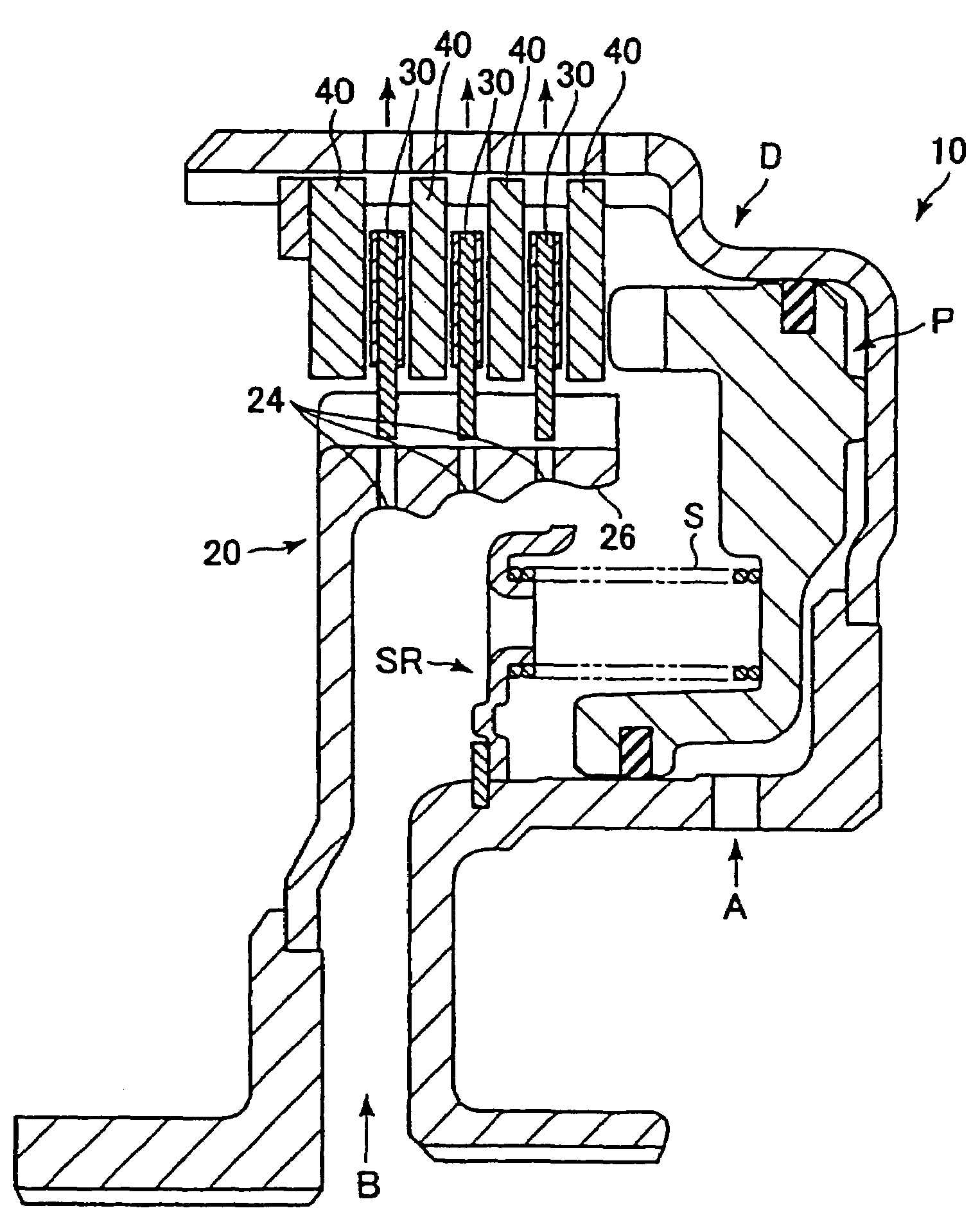
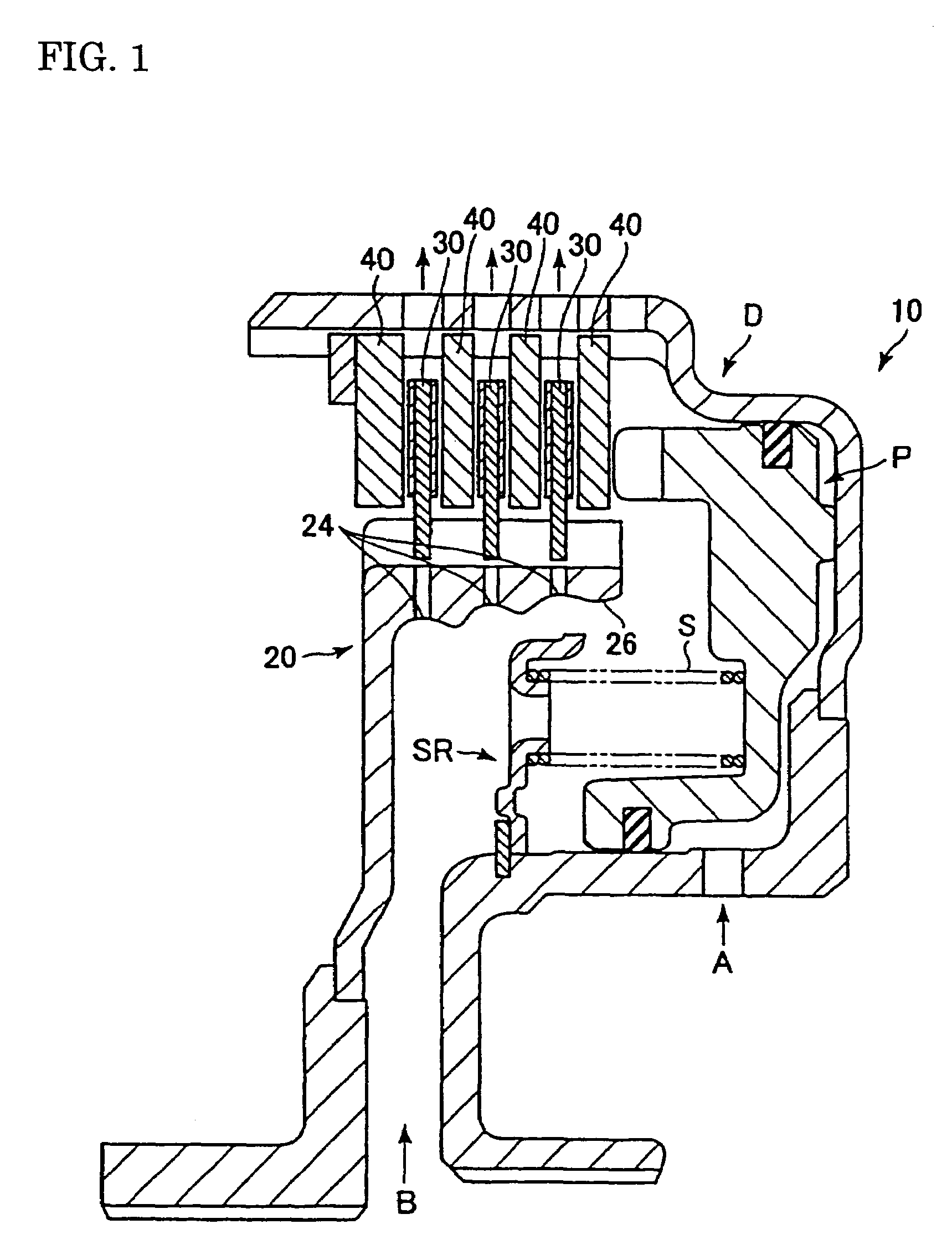
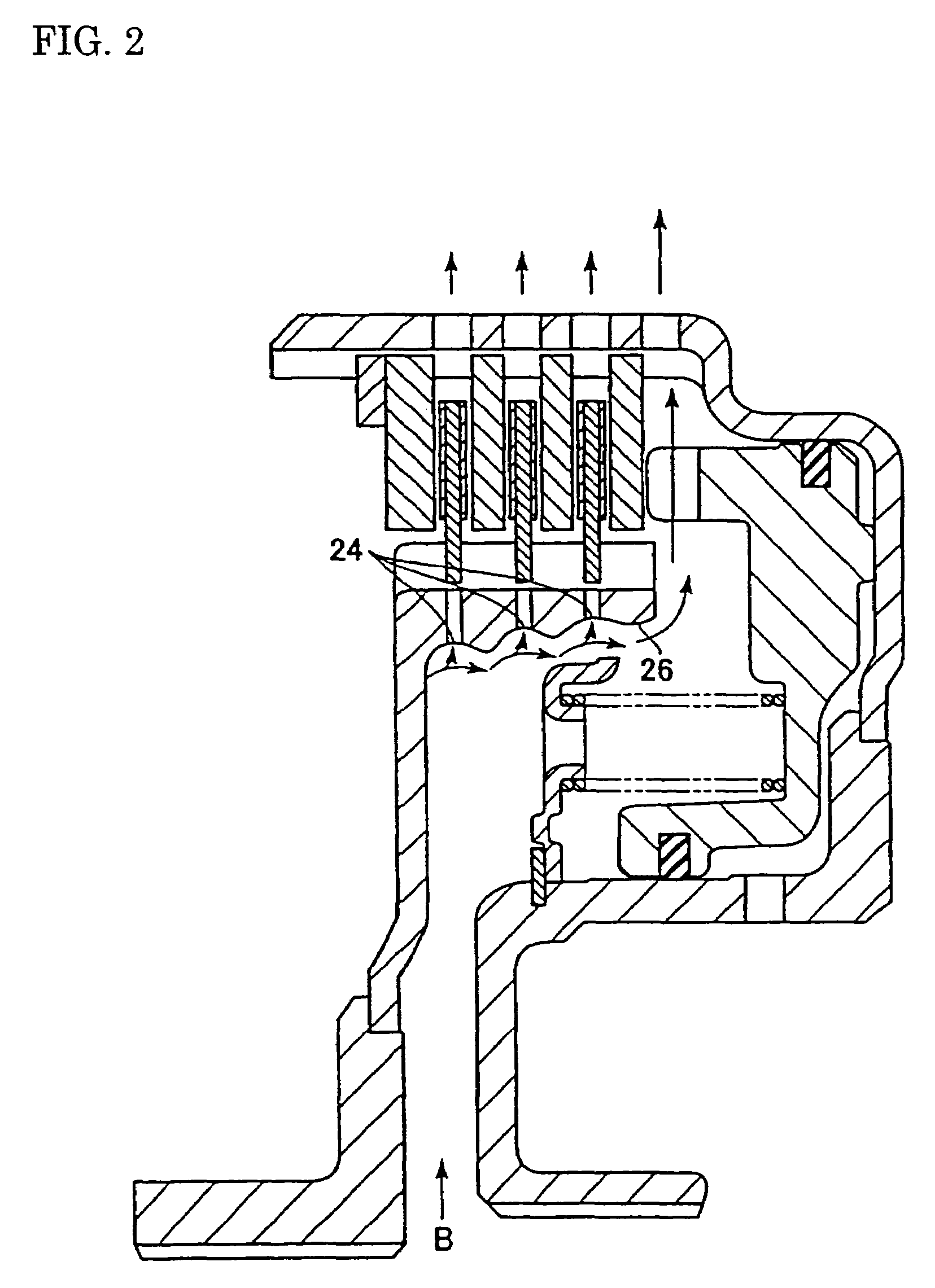
A wet-type friction engaging apparatus 10 comprises a friction disk 30 which is fitted by spline with a hub 20 and a mating plate 40 which is fitted by spline with a drum D. The friction disk 30 and the mating plate 40 are arranged alternately, and torque is transmitted when the friction disk 30 and the mating plate 40 are engaged with each other. The inner surface of the hub 20 is in a stepped taper shape in order to let lubricating oil B leak from an opening end 26 of the hub 20, and an oil bore 24 is provided in each step in a radial direction of the hub 20. A periphery of an inlet of each oil bore 24 is in a concave shape. During low-speed rotation when centrifugal force is relatively small, the lubricating oil B leaks from the opening end 26 of the hub 20 and drag torque is reduced, and during high-speed rotation when centrifugal force is relatively large, lubricating oil which splashes from a shaft is securely concentrated and then be drained through the oil bore 24.
Owner:DAINATSUKUSU
Driving-force transmitting apparatus for four-wheel-drive vehicle
InactiveUS8428838B2Low efficiencyReduce friction lossDigital data processing detailsFriction clutchesFriction torqueDrag torque
A transmitting apparatus includes a disengaging device that disengages a driving force from a front-wheel differential device to a first driving-force transmitting direction converting unit and a multi-plate clutch mechanism provided between an output of a rear-wheel differential device and a right-rear wheel and capable of successively adjusting a fastening force. Drag torque when the fastening of the multi-plate clutch mechanism is released is set smaller than friction torque of a rear-wheel drive system between the first driving-force transmitting direction converting unit and a second driving-force transmitting direction converting unit. A controller unconnects the disengaging device and releases the fastening of multi-plate clutch mechanism when switching to a two-wheel drive mode, thereby stopping the rotation of the rear-wheel drive system.
Owner:UNIVANCE CORP
Control device of hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS20140162839A1Reduce slip timeLess discomfortHybrid vehiclesClutchesDrag torqueControl theory
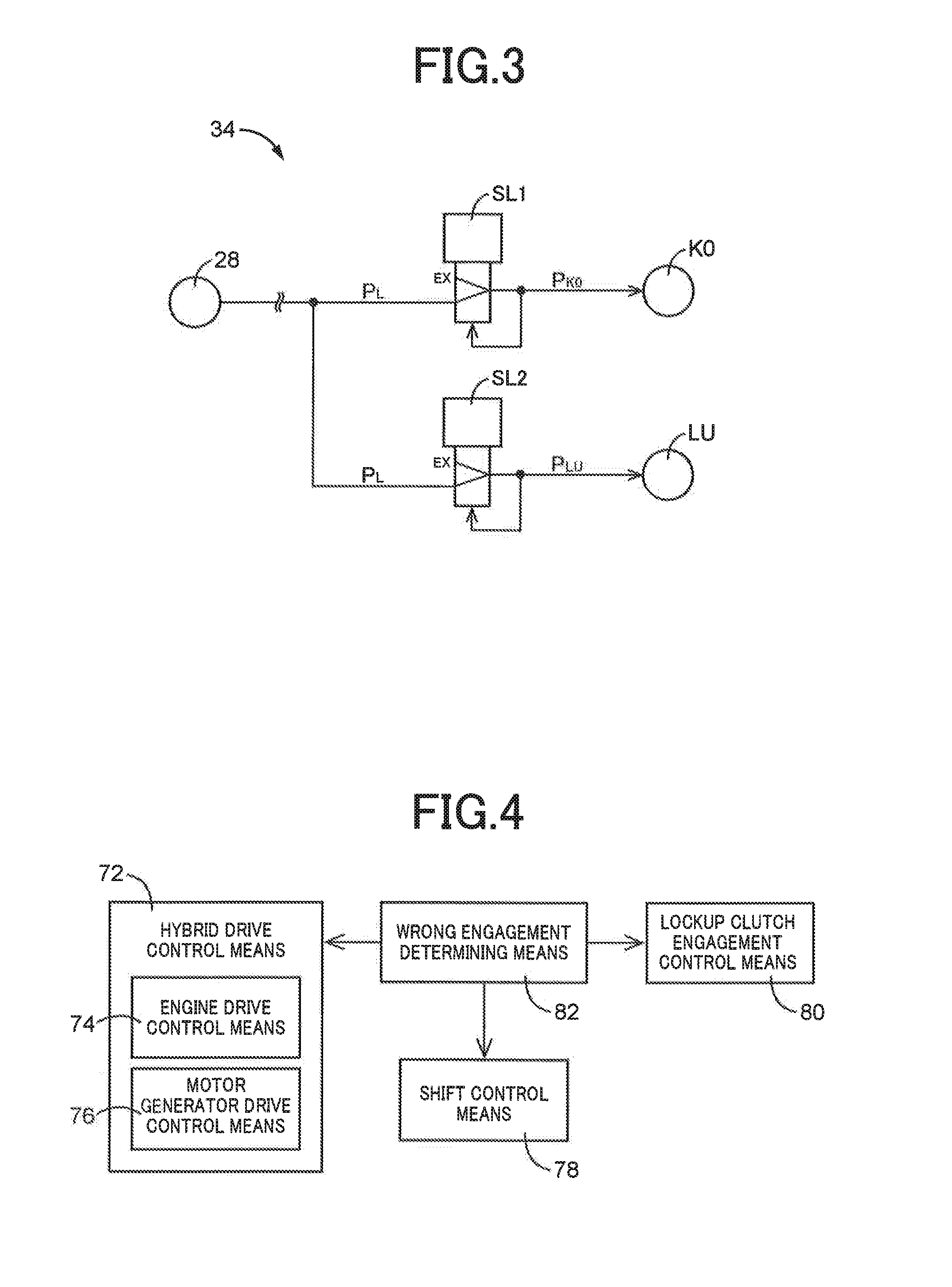
In a case of engagement when a clutch K0 disposed between an engine 12 and a motor generator MG is engaged during EV running while a release instruction for the clutch K0 is output, drive of the engine 12 is changed such that a rotation speed NE of the engine 12 approaches a rotation speed NMG of the motor generator MG and, therefore, a drag torque of the engine 12 can be suppressed regardless of an engagement state of the clutch K0, and generation of longitudinal acceleration can be suppressed by reducing a slip time of the clutch K0. Therefore, a control device of a hybrid vehicle 10 can be provided that reduces a driver's uncomfortable feeling in a simplified manner in a case of wrong engagement of the clutch K0.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and system for promoting a uniform driving style
ActiveUS9399450B2Improve securityPrevent a critical lateral accelerationExternal condition input parametersBraking systemsEngineeringDrag torque
A method and system for promoting a uniform driving style. A longitudinal speed of a motor vehicle and a route section curvature radius lying ahead of the vehicle are determined when the vehicle approaches the route section. An expected lateral acceleration is determined from the curvature radius and longitudinal speed as the route section is driven through. The lateral acceleration is compared with a permanently predefined lateral acceleration limiting value which can be predefined by the driver. In the event the expected lateral acceleration is greater than at least one of the lateral acceleration limiting values, the longitudinal speed is lowered by an optical, acoustic and / or haptic request to the driver and / or by autonomous braking intervention. If the expected lateral acceleration is smaller than or equal to the lower of the two lateral acceleration limiting values the lowering of the longitudinal speed is reduced by decreasing the engine drag torque.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Vascular intervention surgical robot operating handle with handfeel and control method thereof
The invention provides a vascular intervention surgical robot operating handle with handfeel and a control method thereof. The vascular intervention surgical robot operating handle comprises an operating device, a force loading mechanism and a torque loading mechanism, and the operating device, the force loading mechanism and the torque loading mechanism are arranged on a machine frame; the operating device gives out an operating instruction for rotating and / or pushing and pulling a conduit guide wire; the force loading mechanism feeds push-pull resistance exerted by the conduit guide wire when the conduit guide wire is pushed and pulled back to the operating device; the torque loading mechanism feeds resistance torque exerted by the conduit guide wire when the conduit guide wire is rotated back to the operating device; the push-pull resistance is generated by elastic force formed between the force loading mechanism and one end of a handle of the operating device; the resistance torque is generated by friction formed between the torque loading mechanism and the operating device. According to the vascular intervention surgical robot operating handle with the handfeel and the control method thereof, the operating device is utilized to operate the rotation, push-pull and the combination thereof of the conduit guide wire; the resistance or the resistance torque of the conduit guide wire in a patient side in an intervention process can be fed back to the operating device, the handfeel and an operation presence feeling of a doctor are strengthened, and the safety and stability of a surgical operation are improved; coupling of force and torque is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OPERATION ROBOT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com