Patents
Literature
682results about "Brake system interactions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
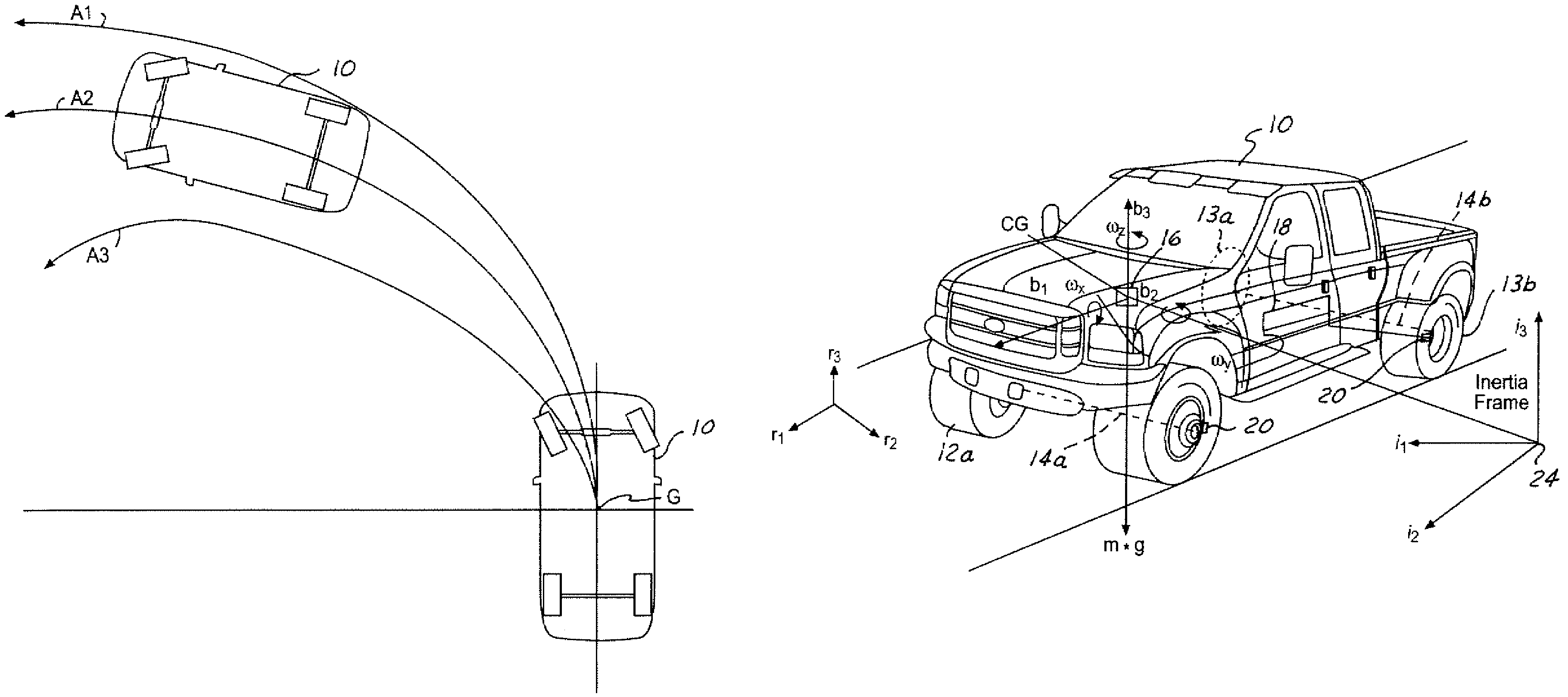
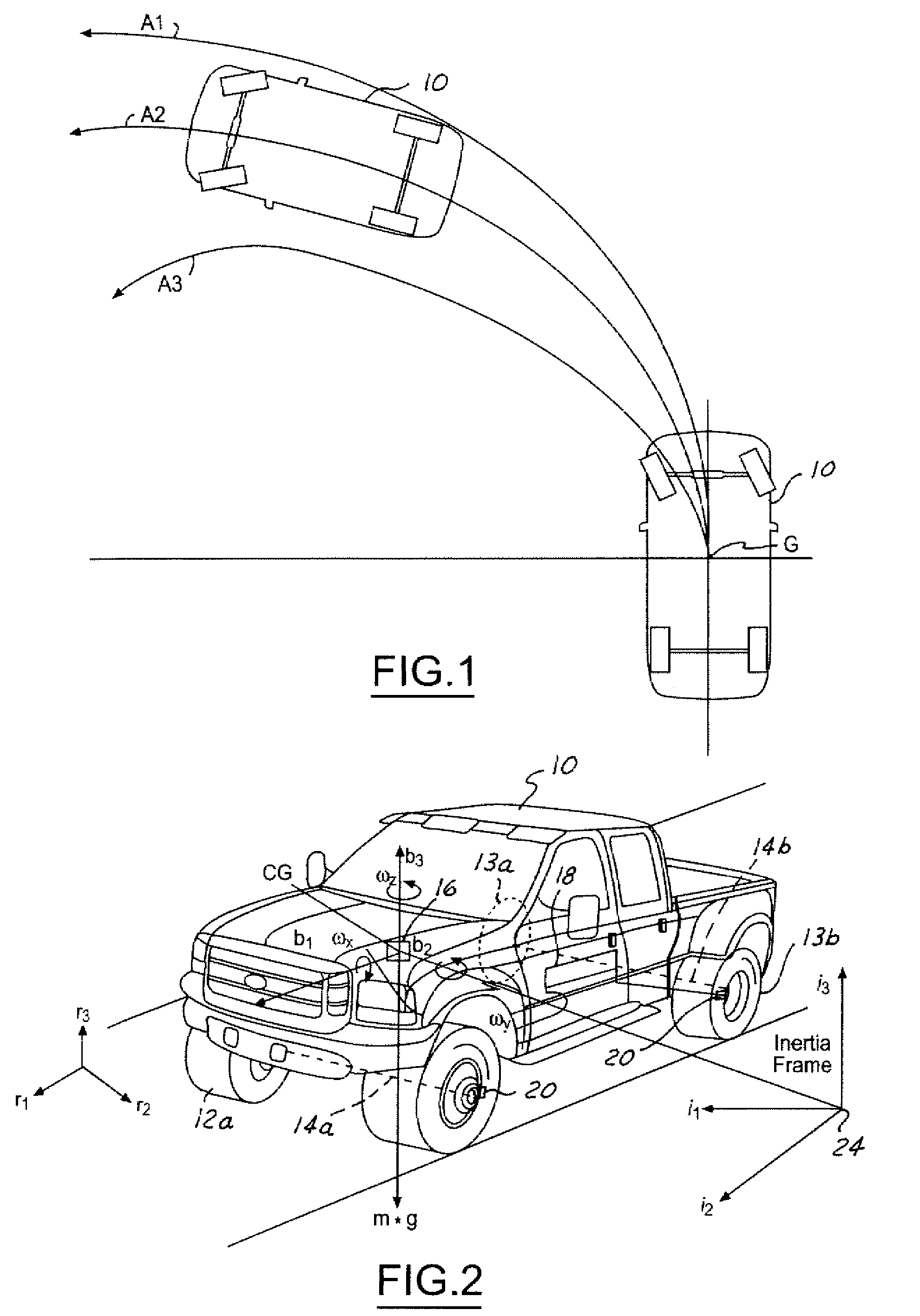
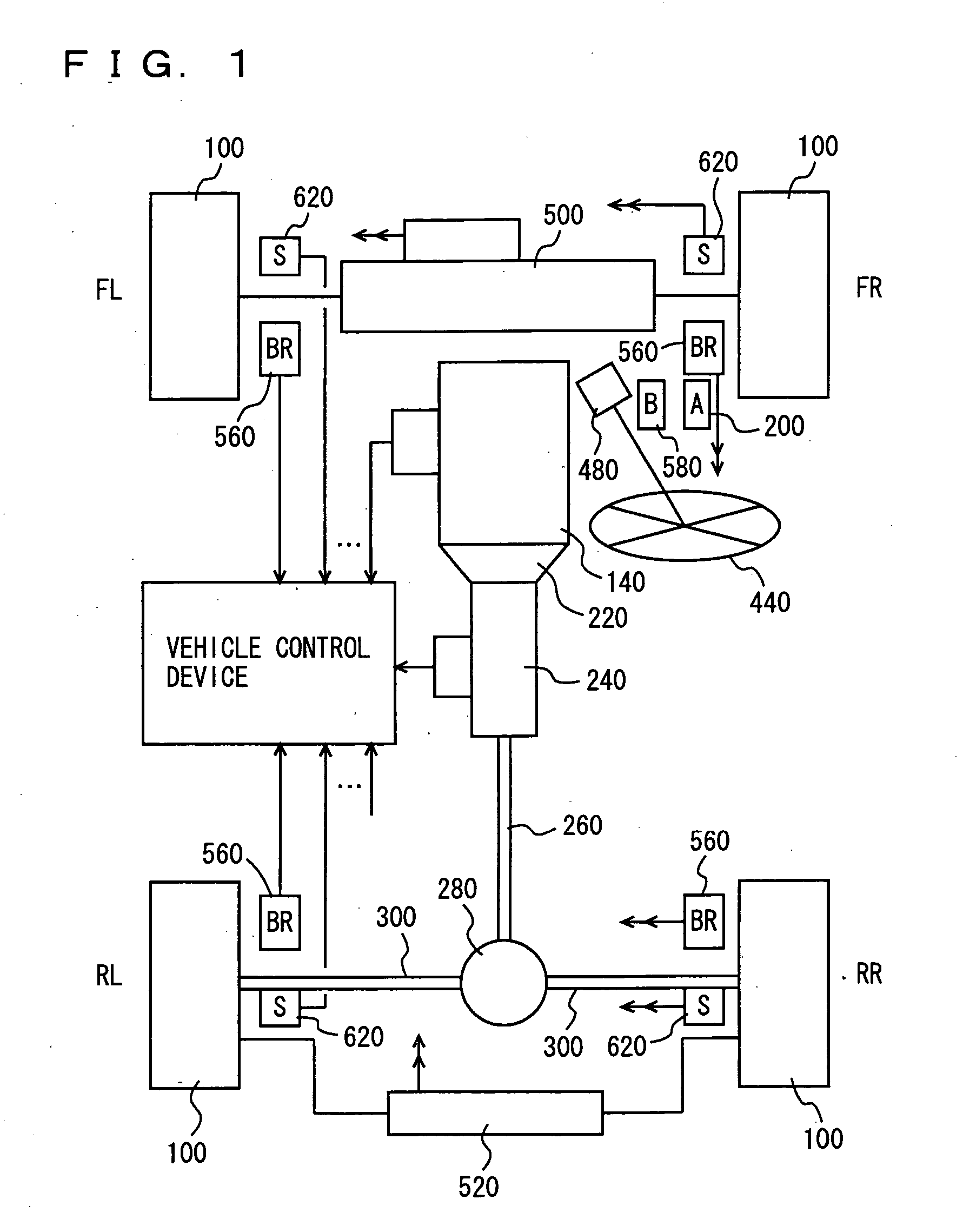
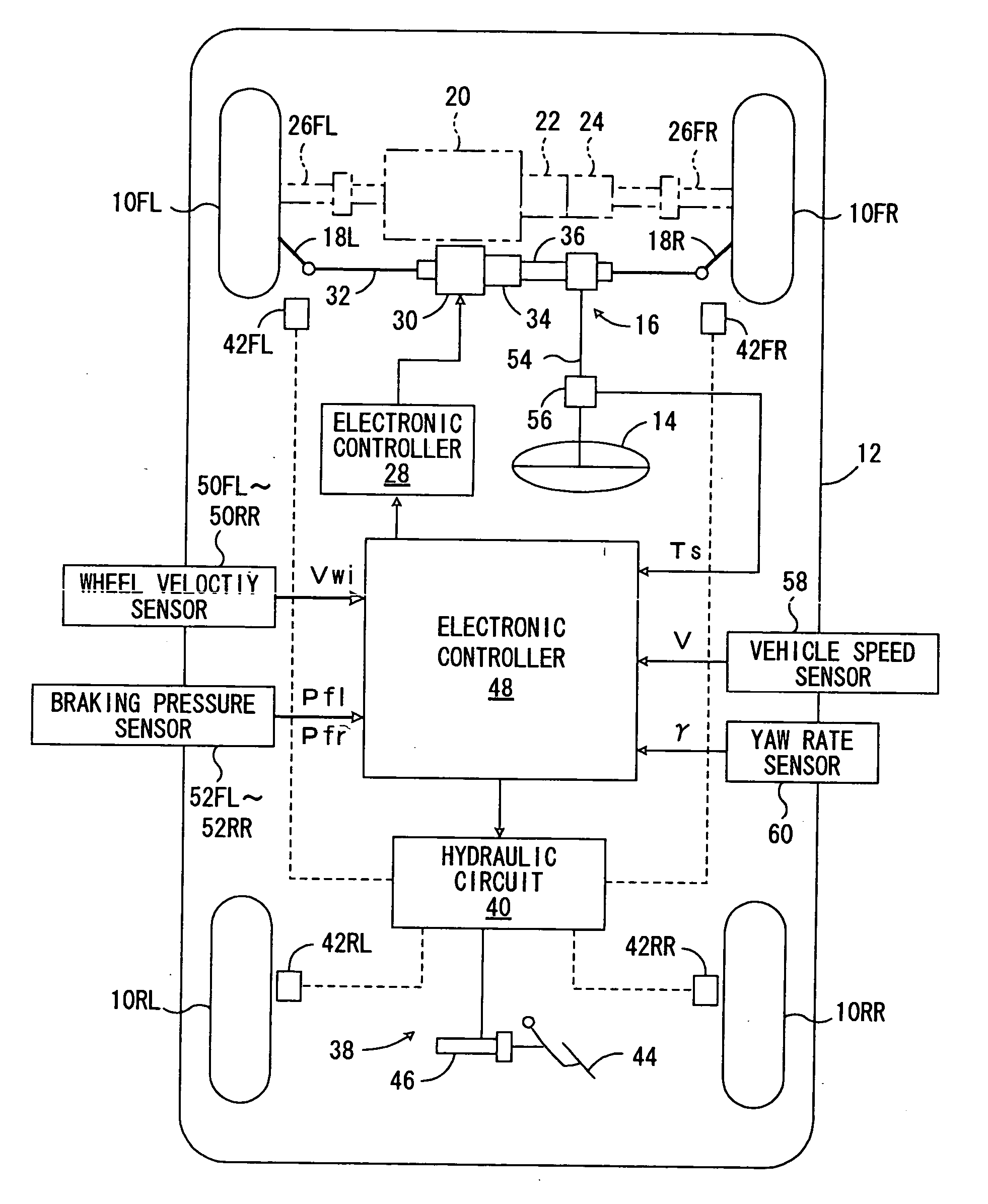
Vehicle control
ActiveUS7349776B2Improved vehicle controlEasy to controlBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsControl systemMode control
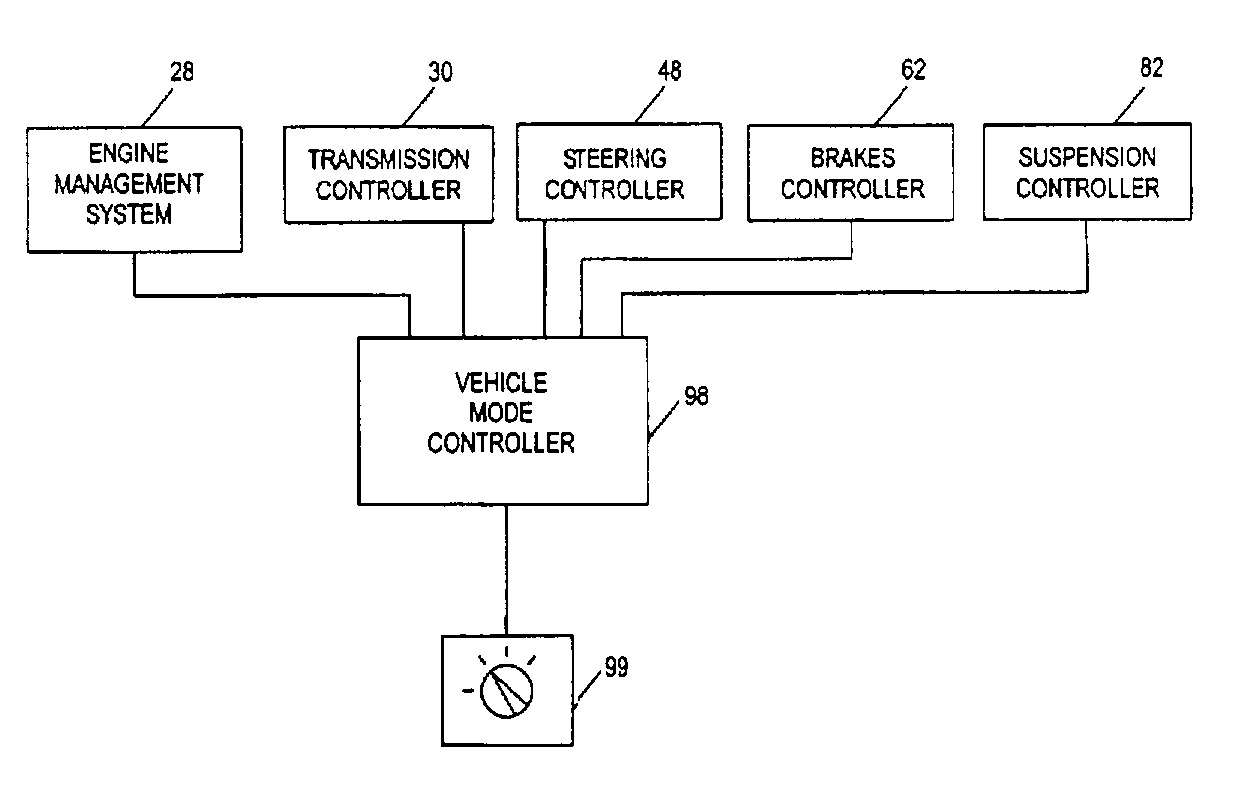
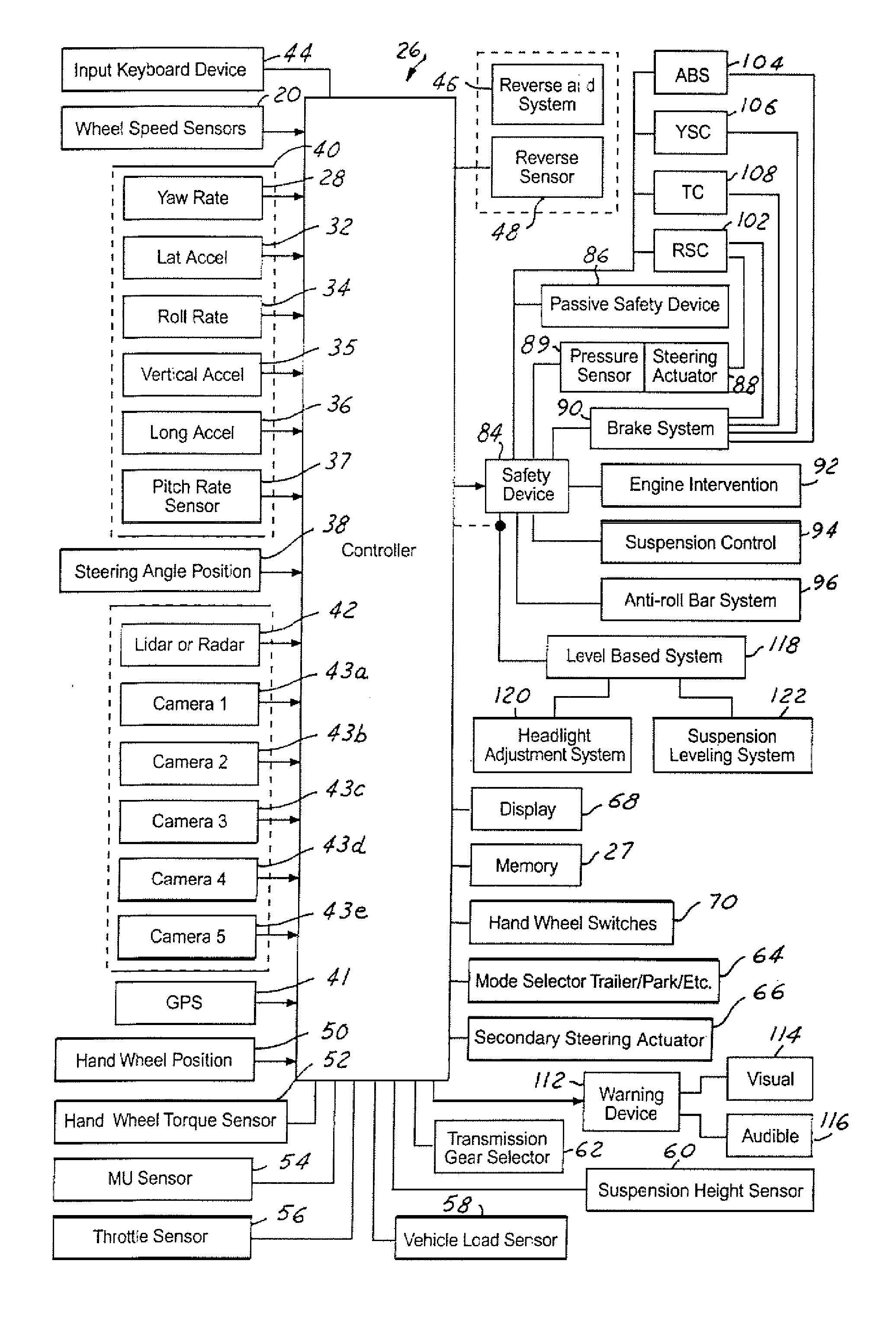
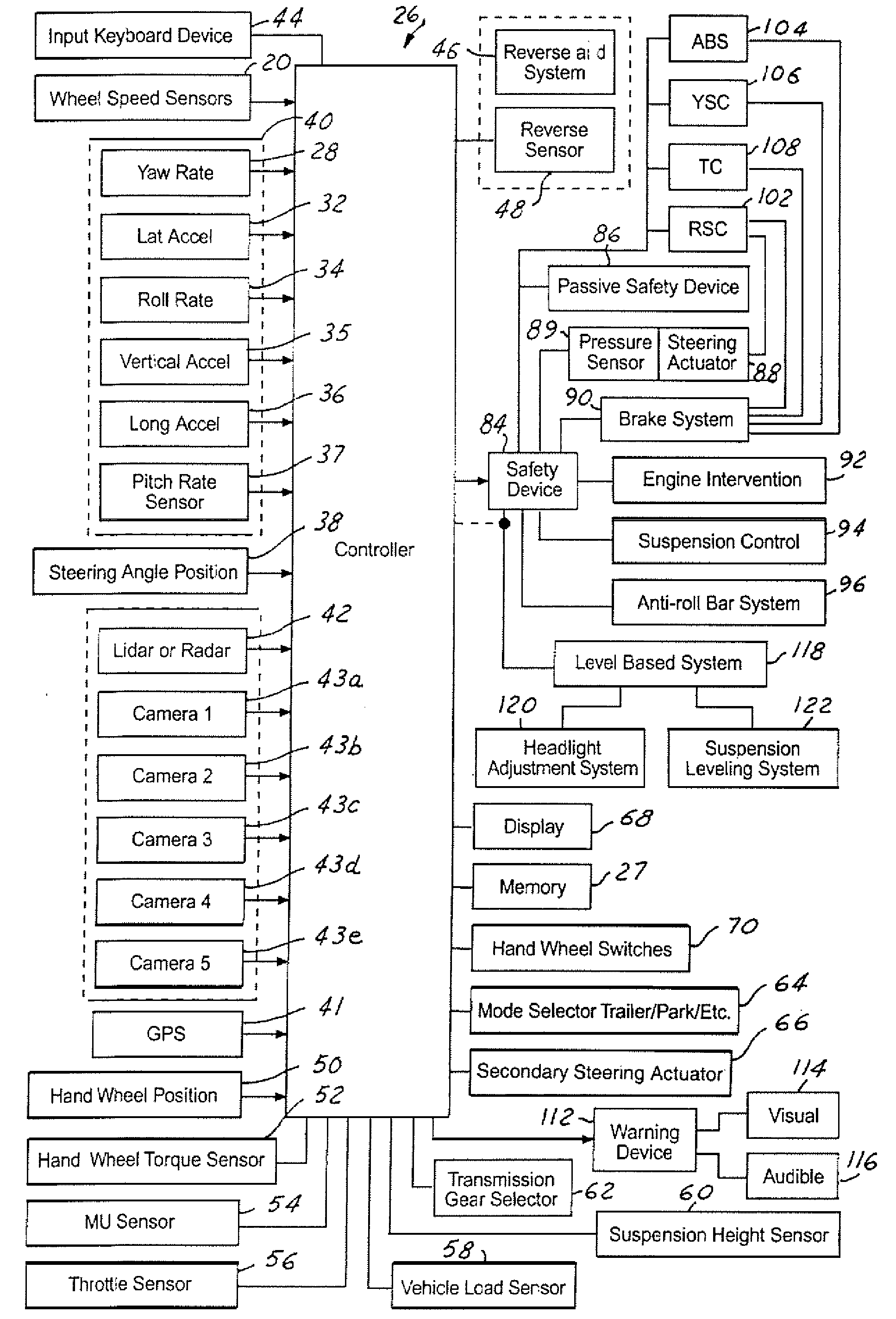
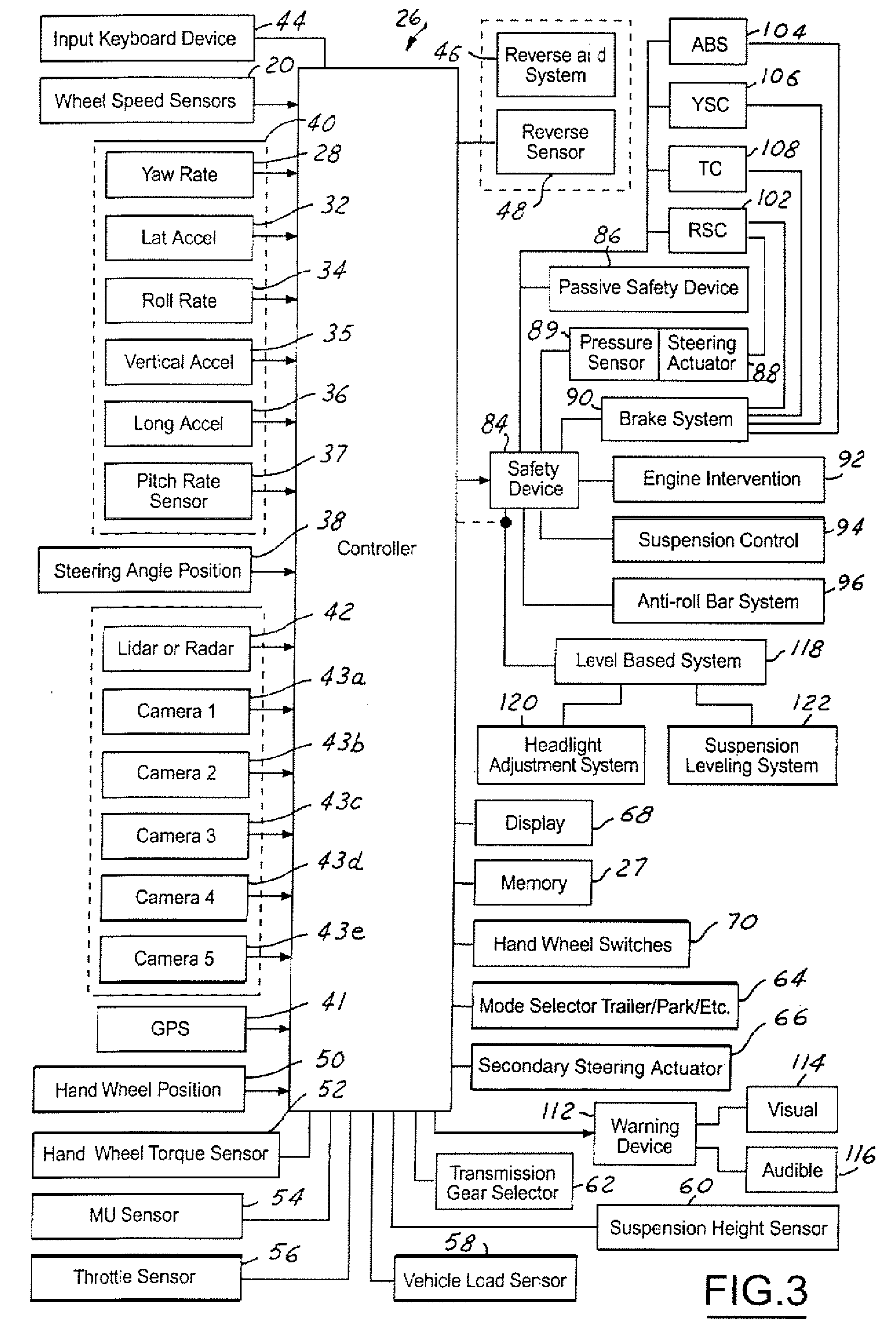
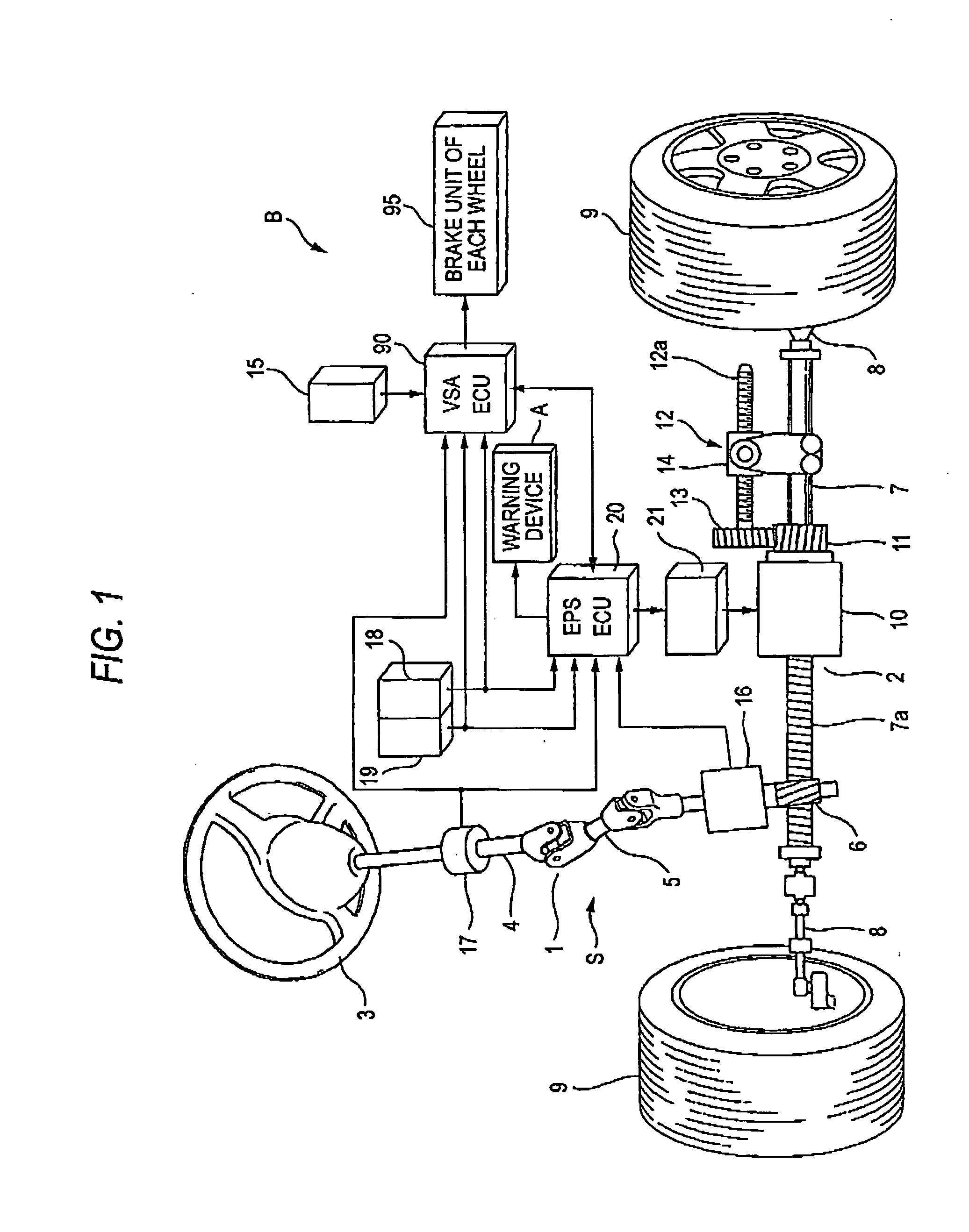
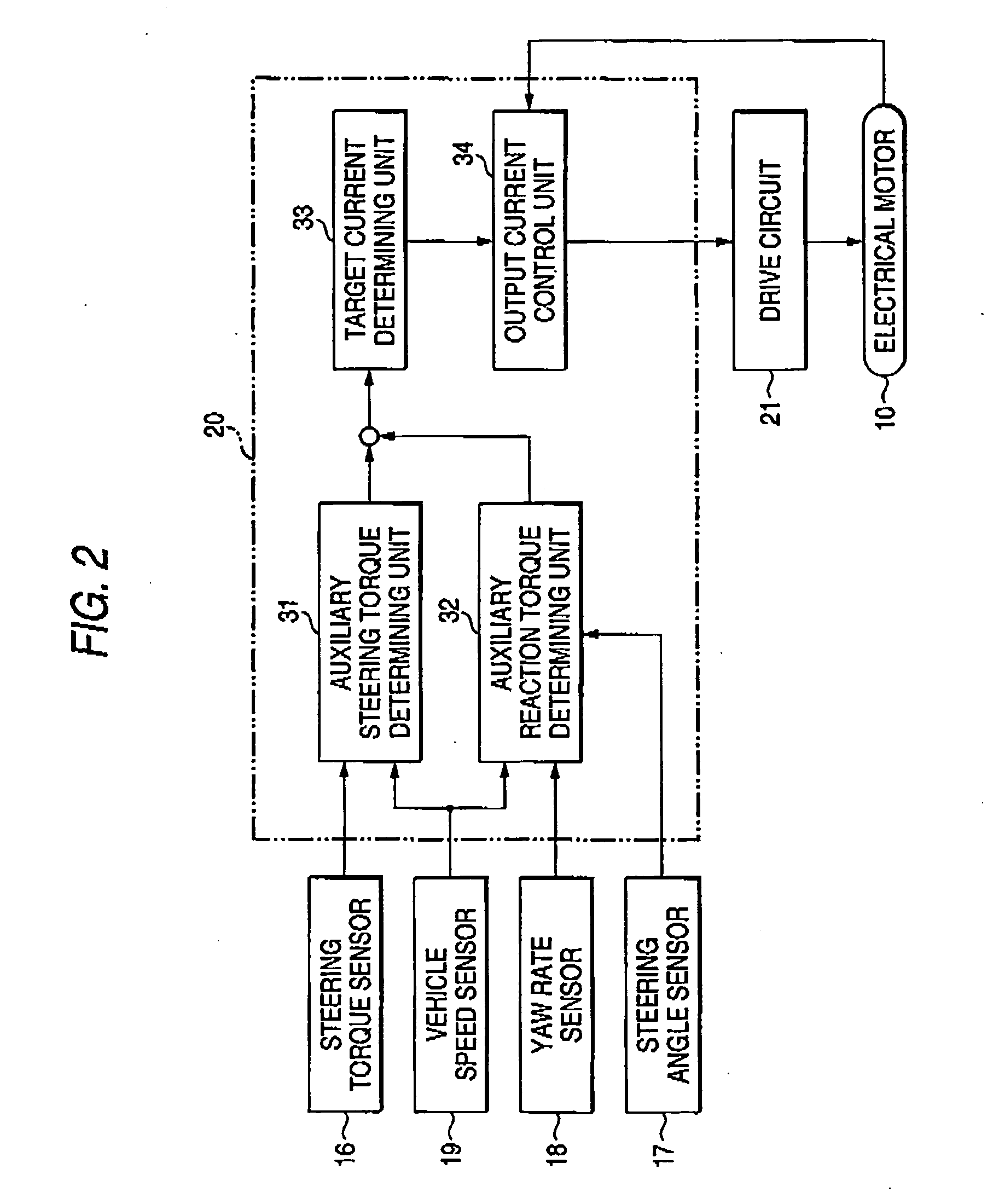
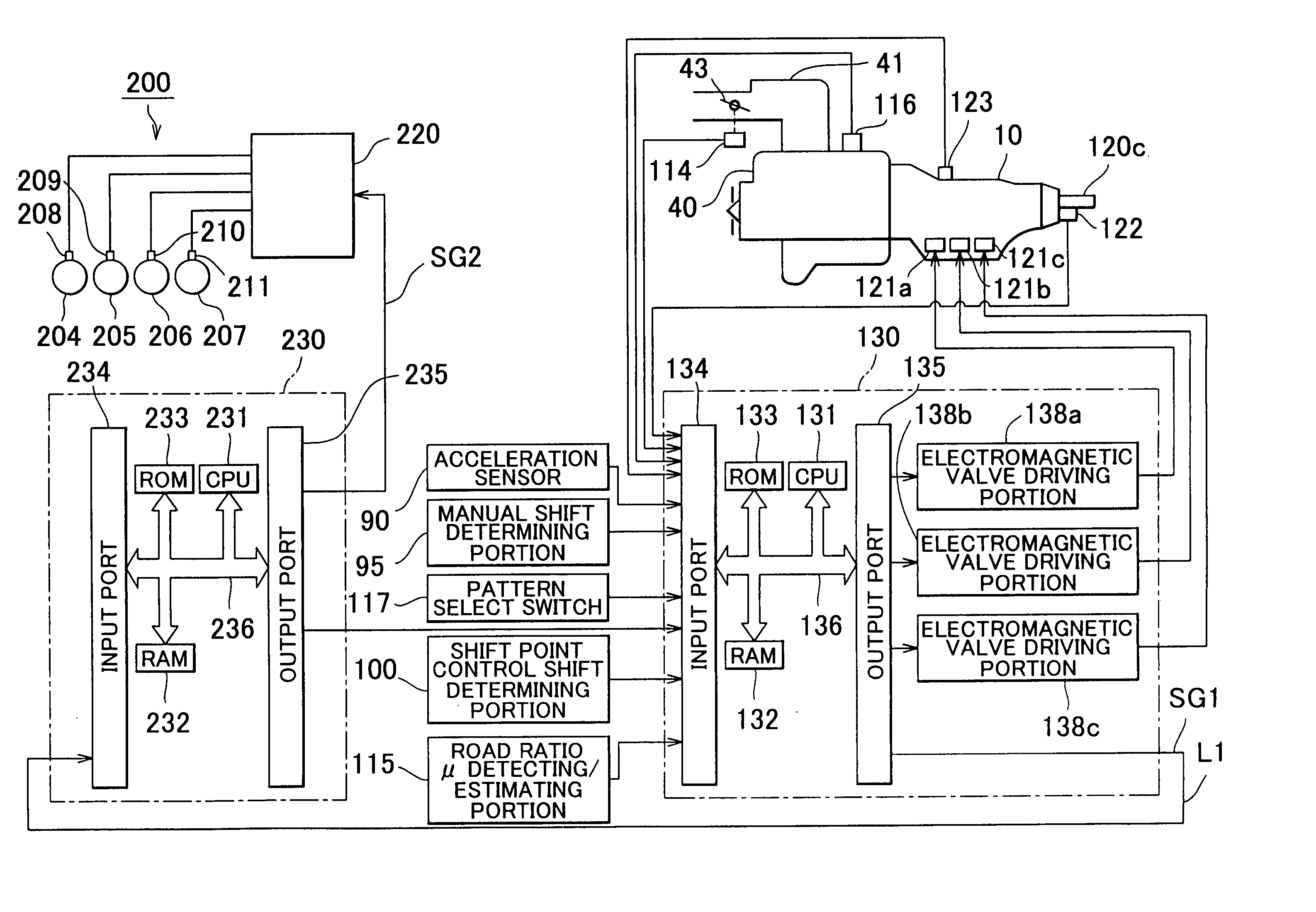
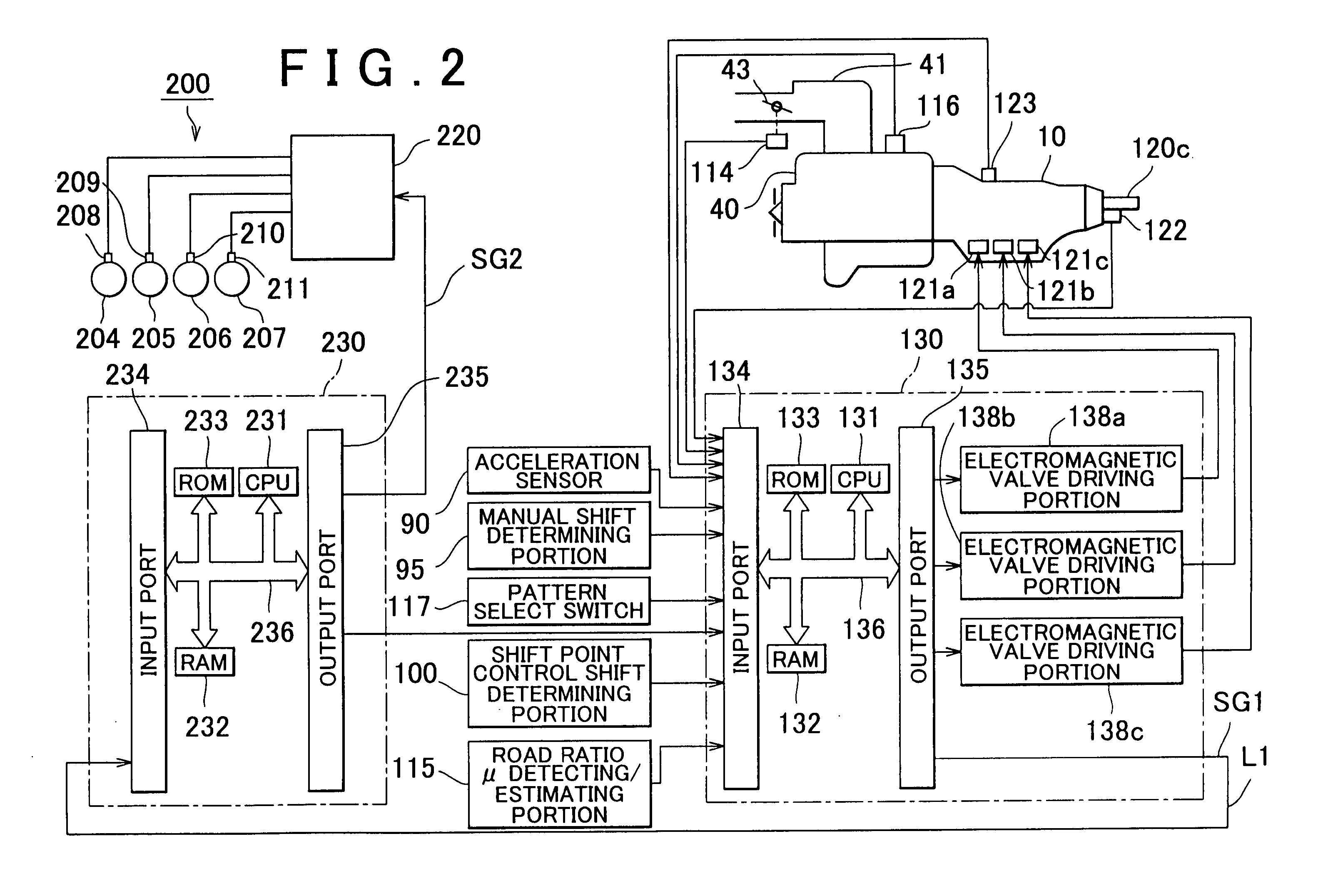
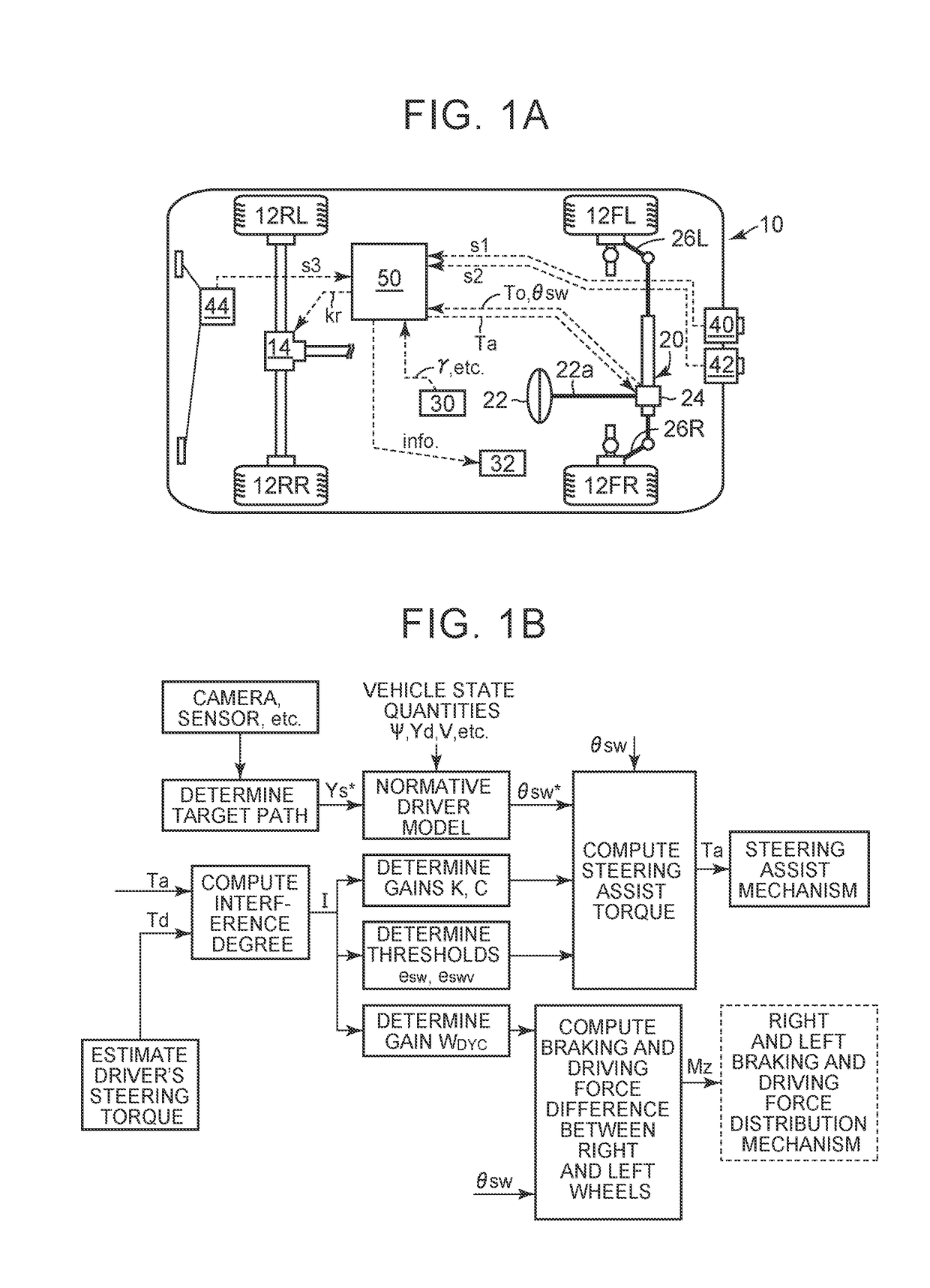
A vehicle control system has a plurality of subsystem controllers including an engine management system 28, a transmission controller 30, a steering controller 48, a brakes controller 62 and a suspension controller 82. These subsystem controllers are each operable in a plurality of subsystem modes, and are all connected to a vehicle mode controller 98 which controls the modes of operation of each of the subsystem controllers so as to provide a number of driving modes for the vehicle. Each of the modes corresponds to a particular driving condition or set of driving conditions, and in each mode each of the functions is set to the function in mode most appropriate to those conditions.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
Absolute acceleration sensor for use within moving vehicles
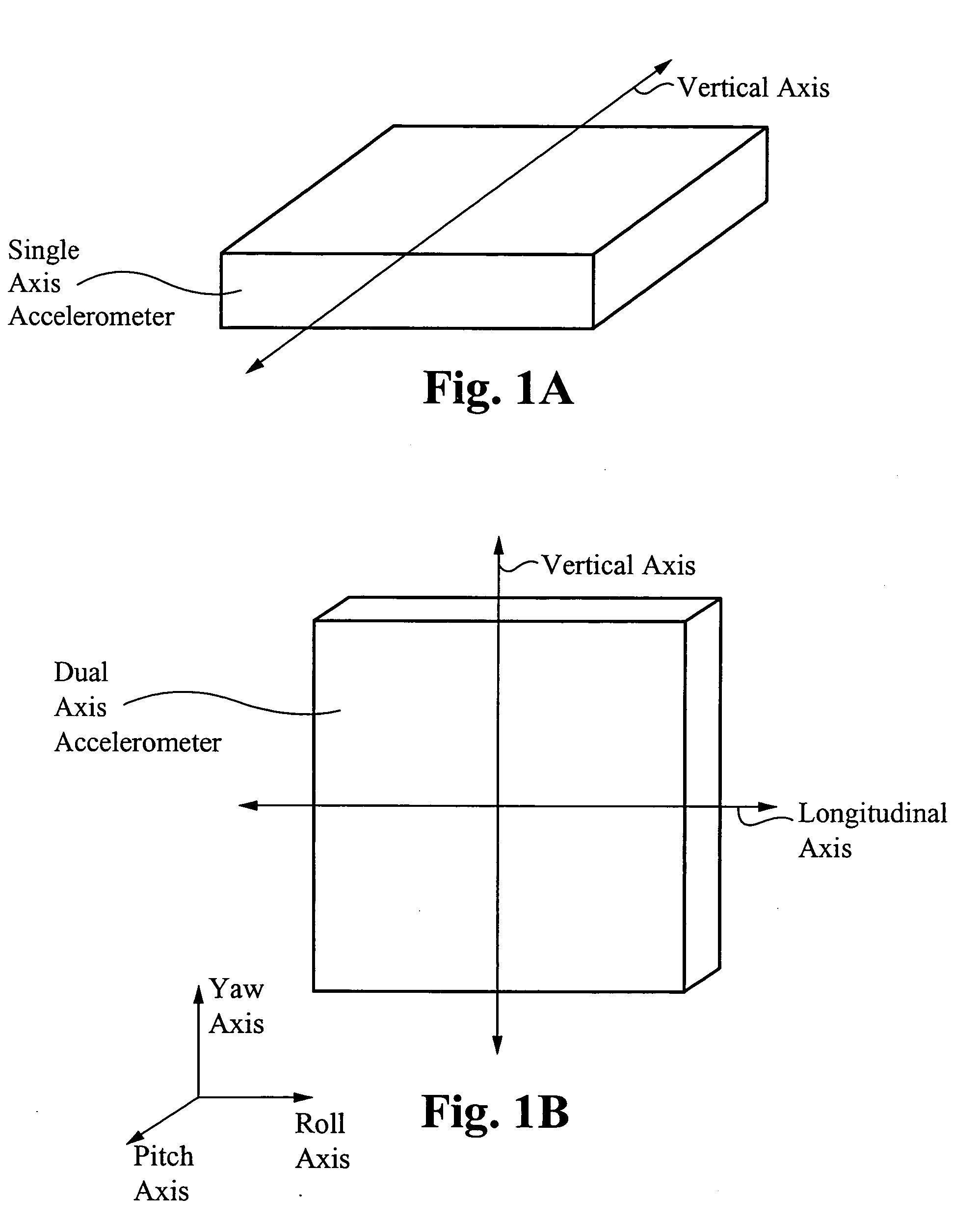
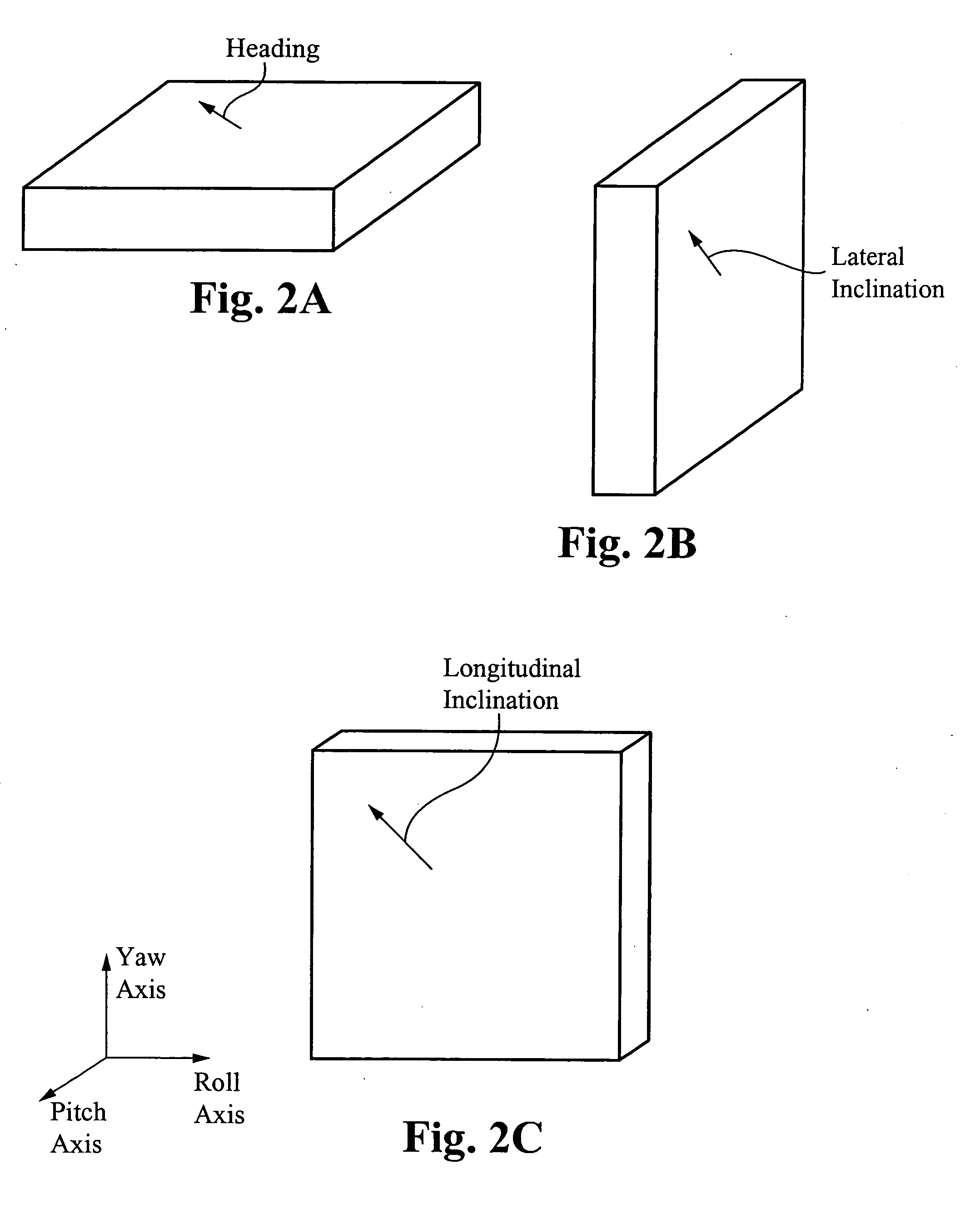
InactiveUS20060074540A1Digital data processing detailsAcceleration measurementMobile vehicleEngineering
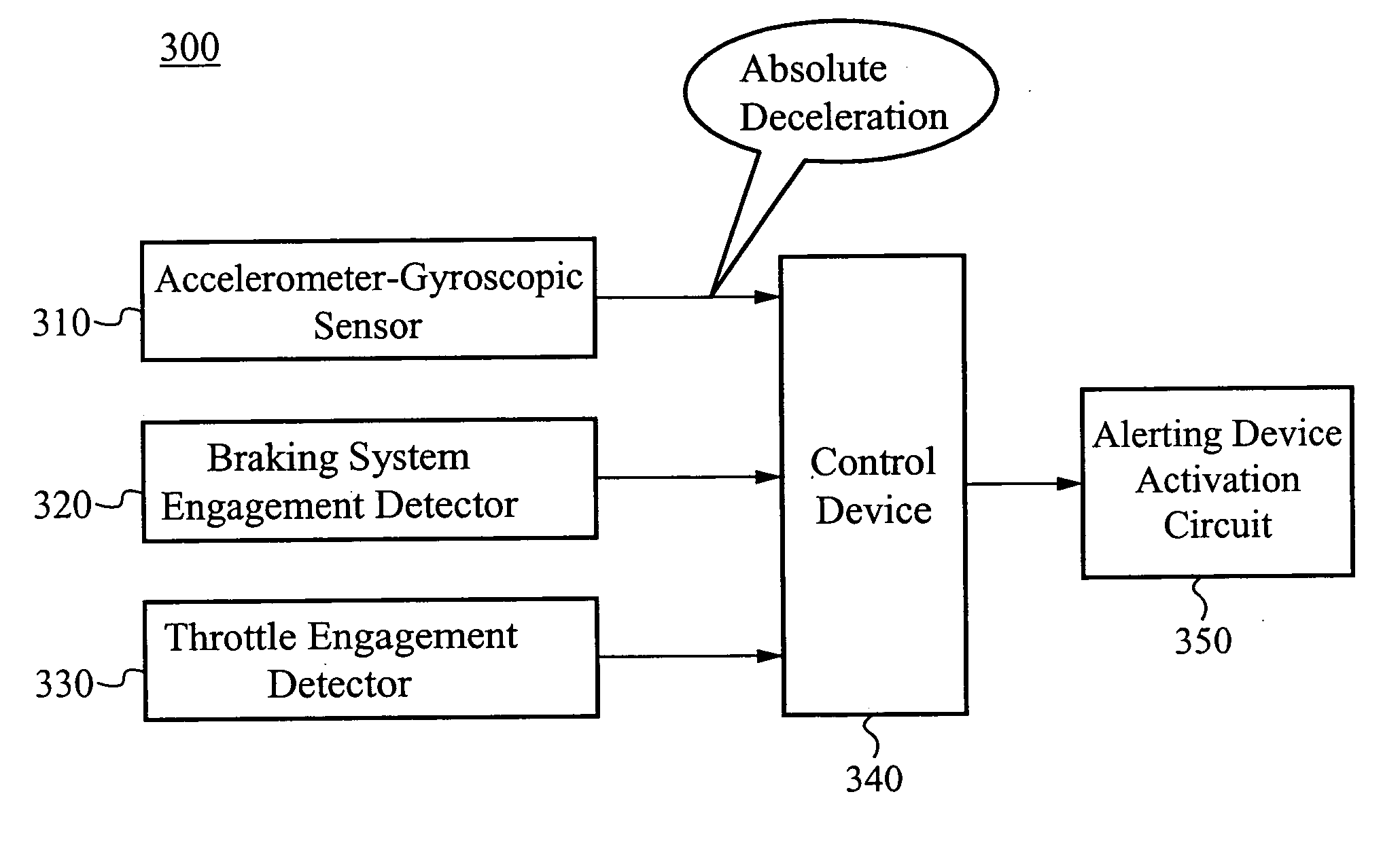
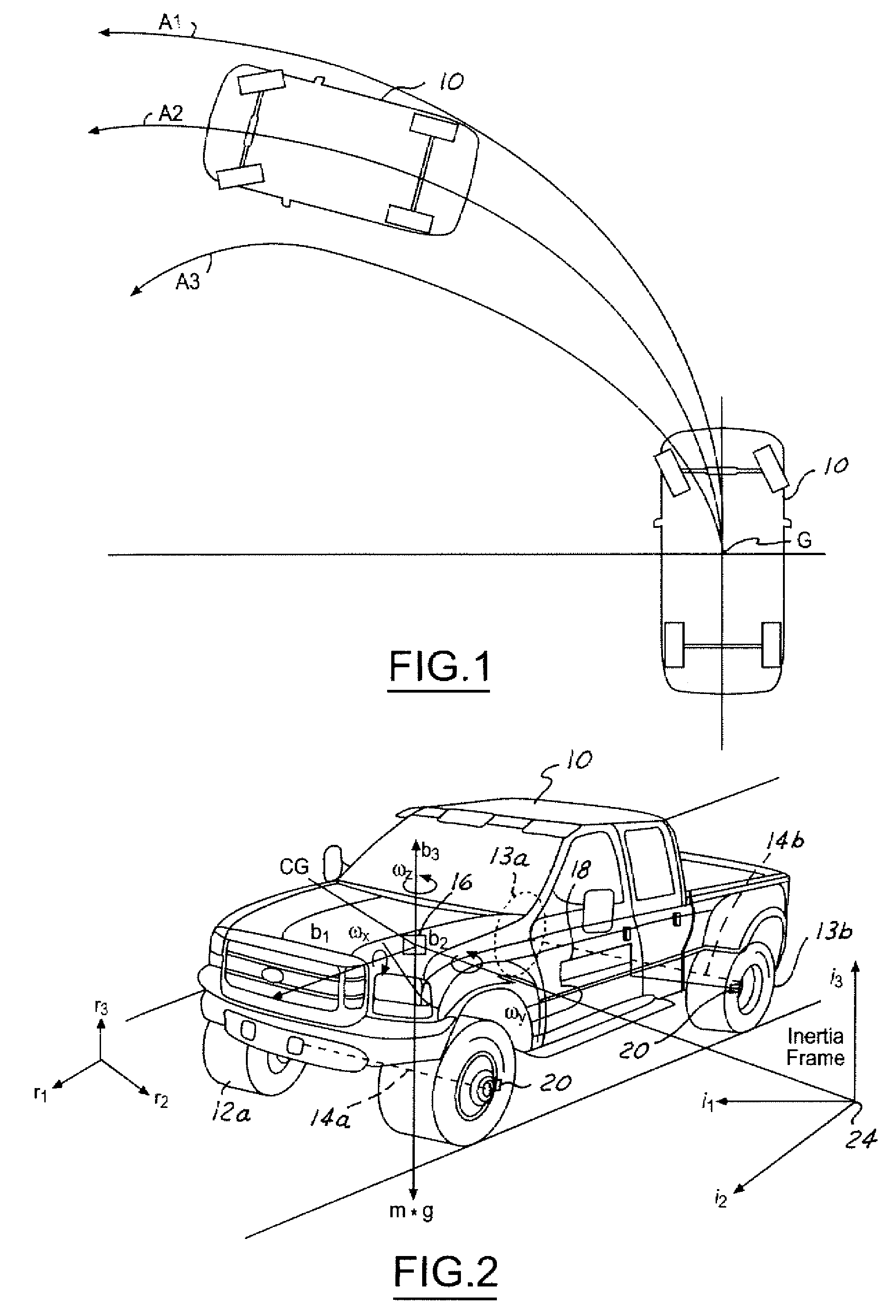
A method of and system for detecting absolute acceleration along various axes relative to a desired movement vector while moving relative to a gravity source includes steps of determining a vertical acceleration, perpendicular to the desired movement vector and substantially anti-parallel to a gravitational acceleration due to the gravity source; determining a longitudinal acceleration, parallel to the desired movement vector and to output at vertical acceleration signal and a longitudinal acceleration signal; determining an inclination of the desired movement vector relative to the gravitational acceleration; and processing the vertical acceleration signal, the longitudinal acceleration signal, and the inclination signal to produce an absolute vertical acceleration signal and an absolute longitudinal acceleration signal.
Owner:VISION WORKS IP CORP
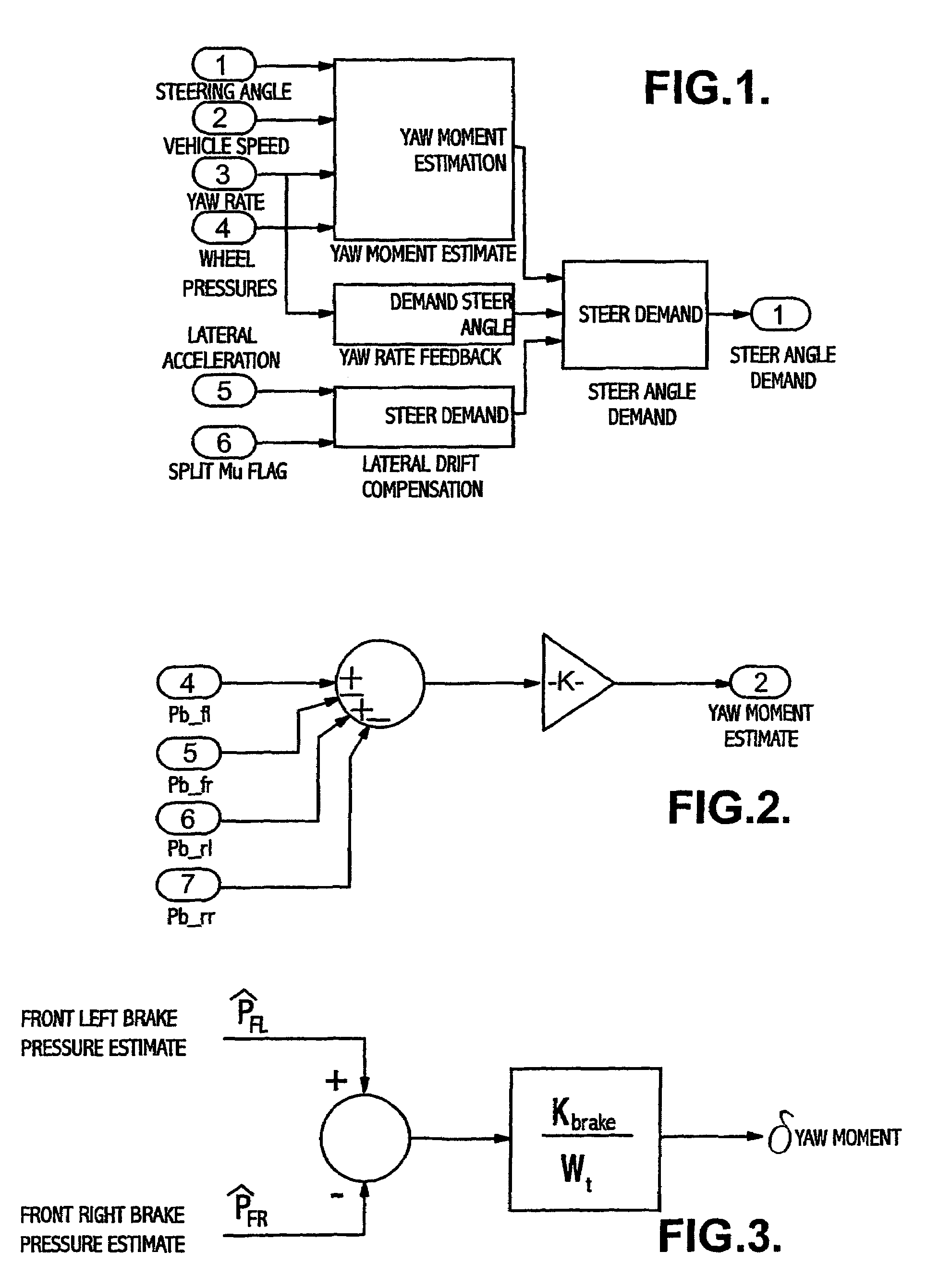
Control system for brake-steer assisted parking and method therefor
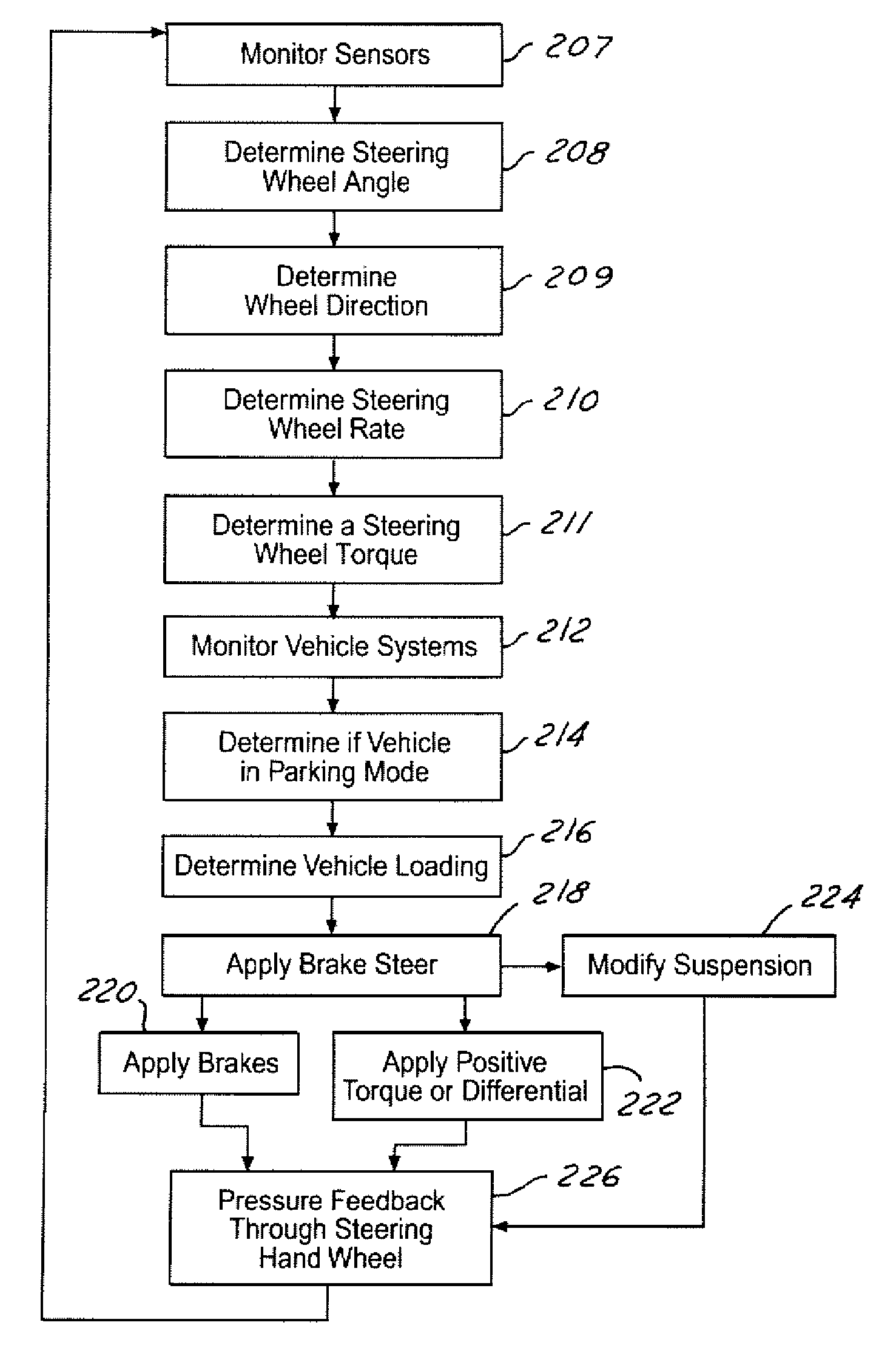
InactiveUS20050236894A1Improving parkabilityBrake system interactionsVehicle body stabilisationSteering wheelControl system
A system and method of controlling an automotive vehicle includes determining a steering wheel angle, determining a steering wheel direction, determining a steering wheel angular rate and applying brake-steer as a function of steering wheel angle, steering wheel angular rate and steering wheel direction.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Vehicle torque coordination
InactiveUS20050060079A1More robustLess prone to failureBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsControl theory
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Control system for brake-steer assisted parking and method therefor
InactiveUS7229139B2Improving parkabilityBrake system interactionsVehicle body stabilisationMobile vehicleSteering wheel
A system and method of controlling an automotive vehicle includes determining a steering wheel angle, determining a steering wheel direction, determining a steering wheel angular rate and applying brake-steer as a function of steering wheel angle, steering wheel angular rate and steering wheel direction.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
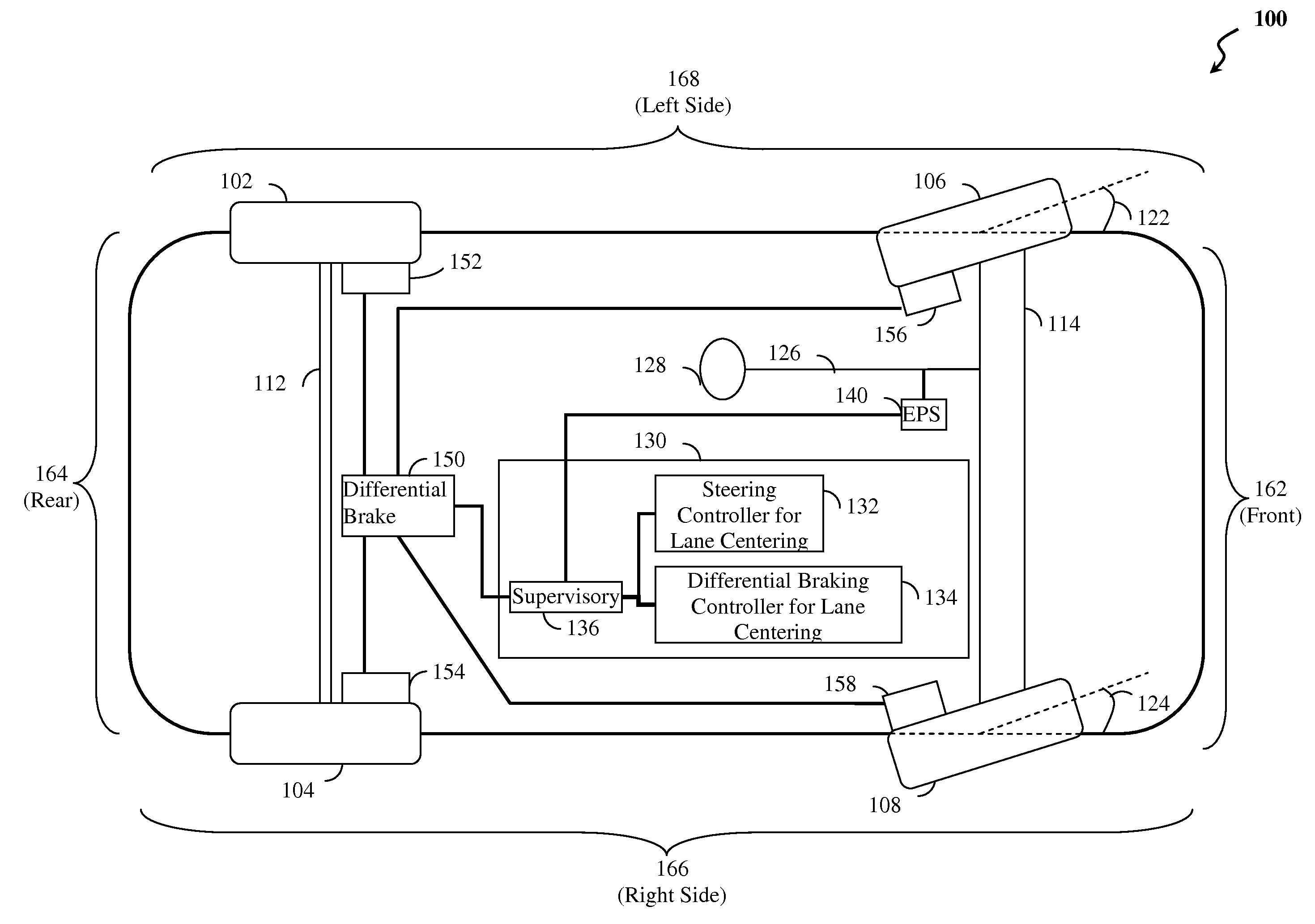
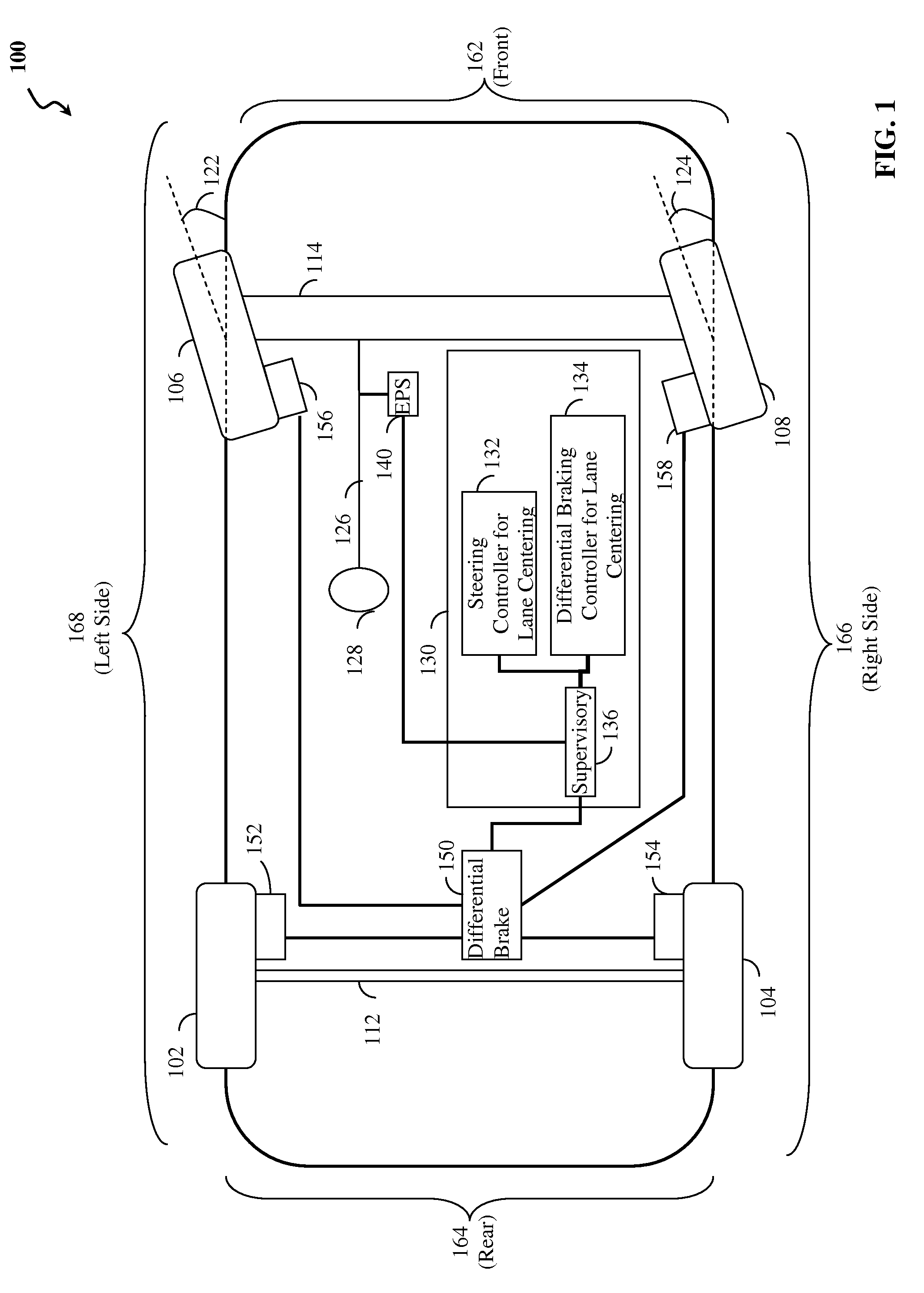
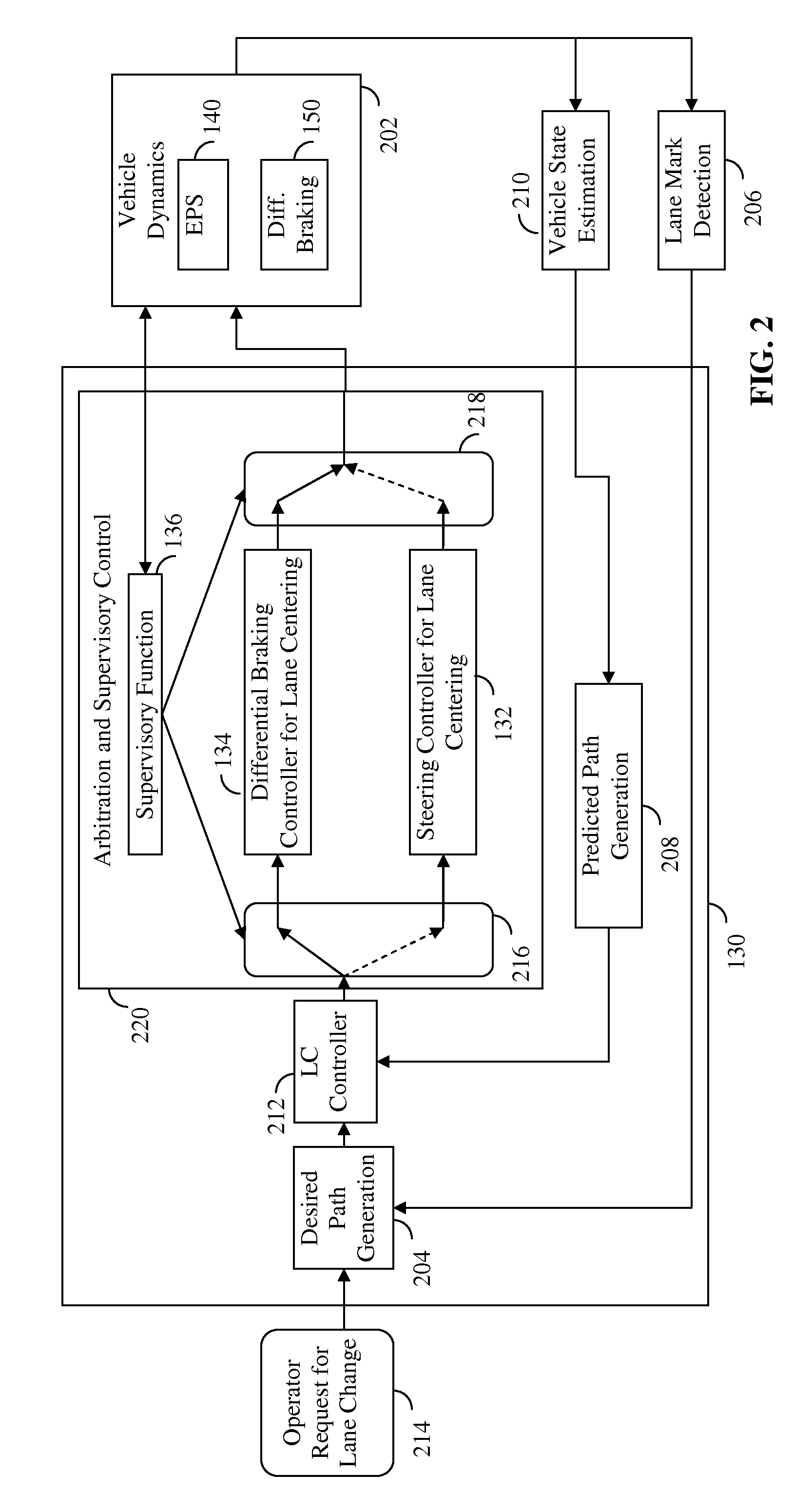
Lane centering fail-safe control using differential braking
ActiveUS20120283907A1Minimize the differenceOffset errorVehicle testingBrake system interactionsElectric power steeringEngineering
Method, system and non-transitory computer-readable medium for fail-safe performance of a lane centering system. An electrical power steering (EPS) system of a vehicle is monitored for a failure and operation of the lane centering system is switched to a differential braking controller to output differential braking commands to a differential breaking system upon determining that a failure of the EPS system has occurred, where the output braking commands direct the differential braking system to apply force a brake for a wheel of vehicle, such by the applied braking force the vehicle follows a desired path determined for a lane centering operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
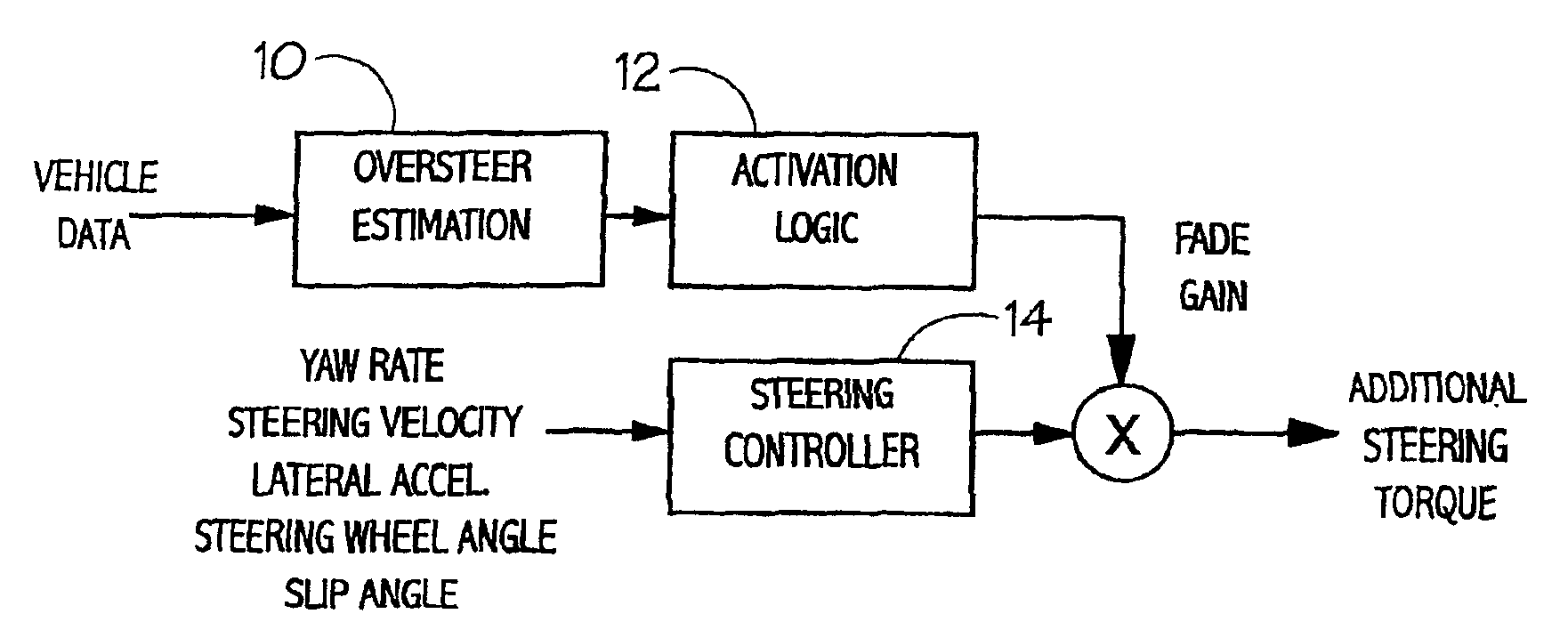
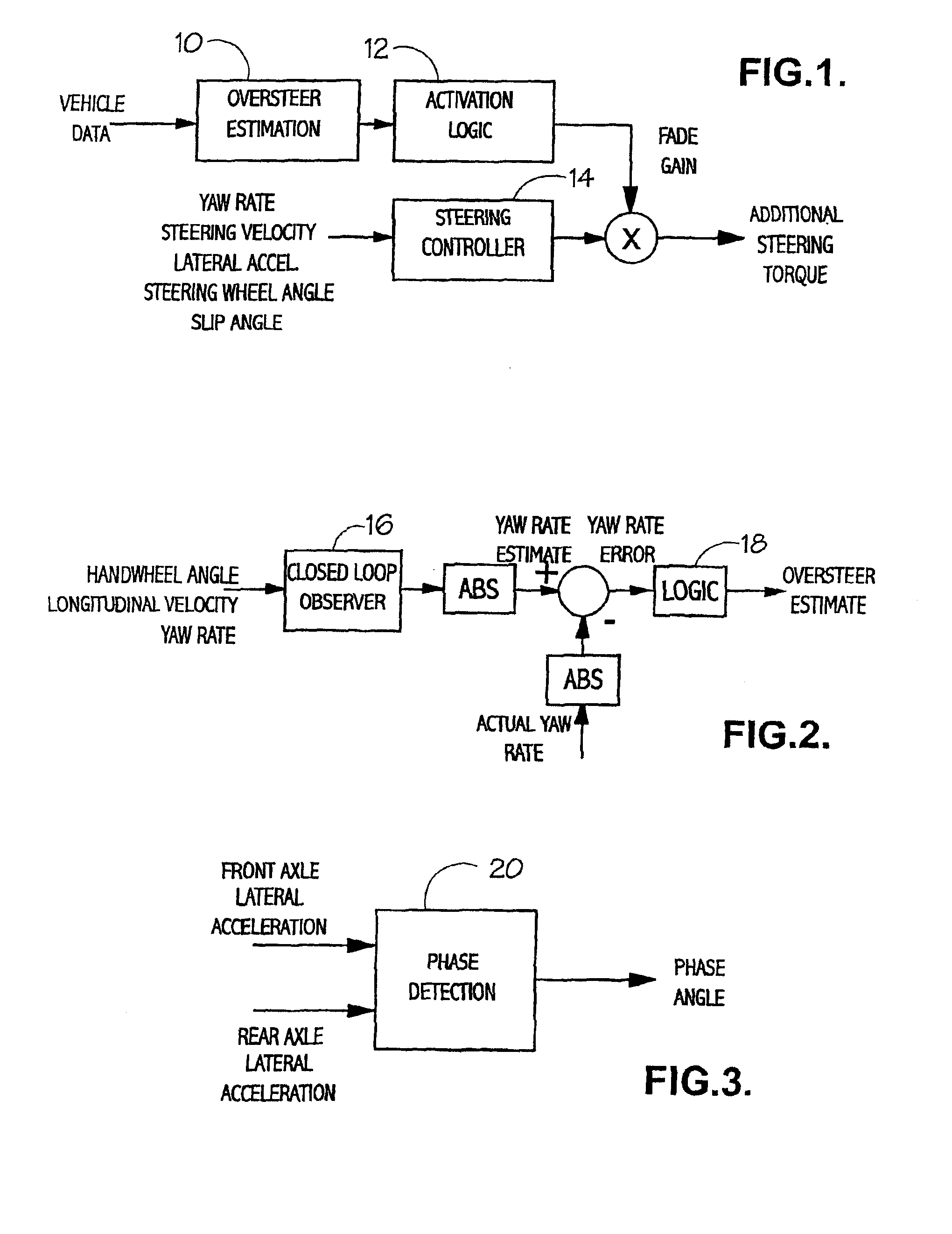
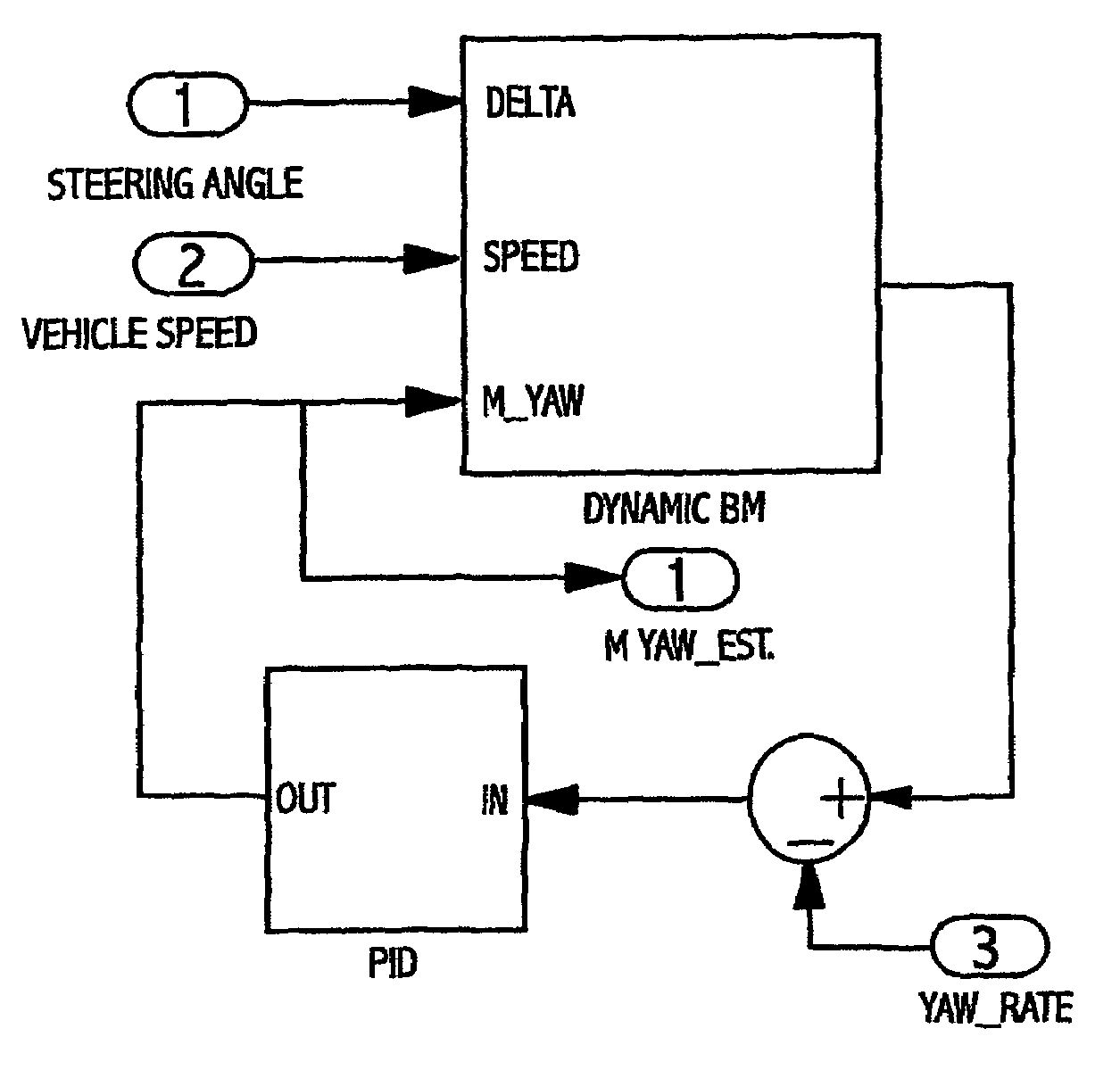
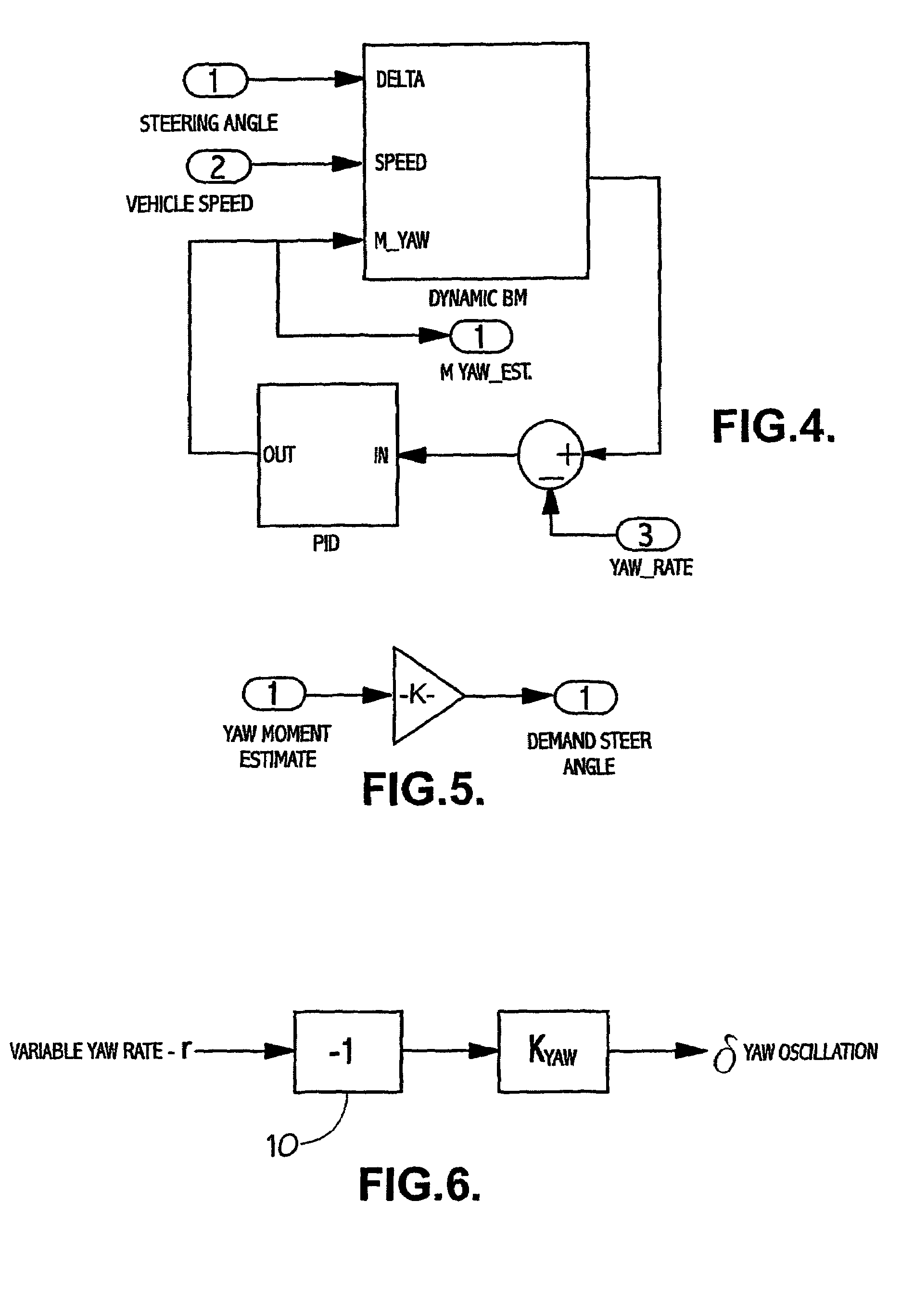
Oversteer steering assistance controller
InactiveUS6895318B1Improve vehicle stabilityImprove stabilityBrake system interactionsSteering initiationsDriver/operatorEngineering
Owner:TRW LIMITED
Vehicle torque coordination
InactiveUS6862511B1Less prone to failureImprove driveabilityBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsControl theory
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling brake-steer in an automotive vehicle in reverse
ActiveUS20050209763A1Low costImprove directionBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling brake-steer in an automotive vehicle in reverse
ActiveUS8380416B2Low costImprove directionBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsMotorized vehicle
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for Controlling Vehicle Dynamics
InactiveUS20100114431A1Improve accuracy and reliabilityBrake system interactionsSteering initiationsVehicle dynamicsRoad surface
A method for controlling vehicle dynamics includes acquiring steering torque data indicative of forces acting on at least one tire of a vehicle and acquiring image data by capturing images of an area outside the vehicle. The friction coefficient between a tire of the vehicle and a road surface is determined as a function of vehicle data including at least the steering torque data. The lateral velocity of the vehicle is determined as a function of vehicle data including the steering torque data and / or the image data. A vehicle dynamics control is performed as a function of the lateral velocity and the friction coefficient.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN GROUP OF AMERICA
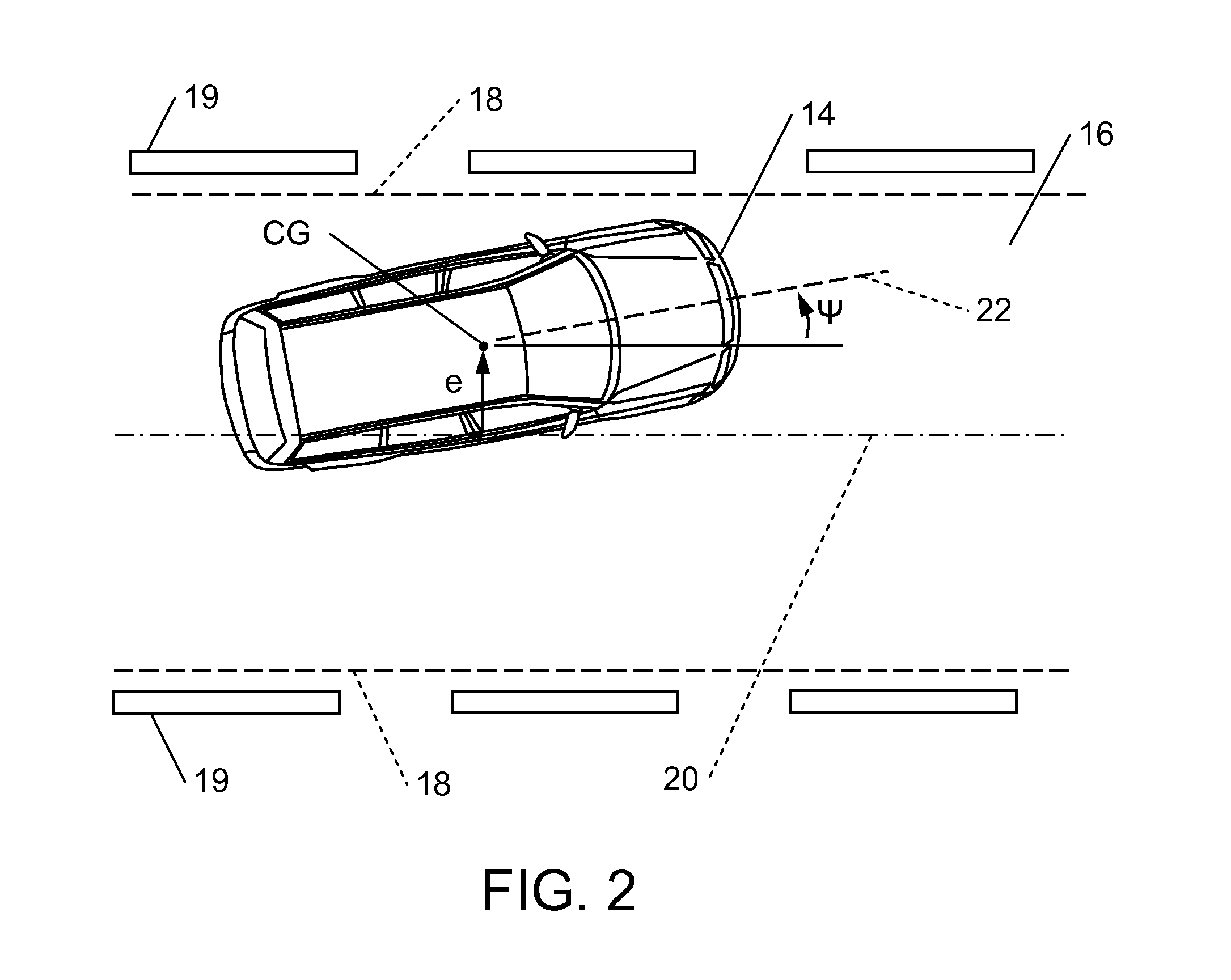
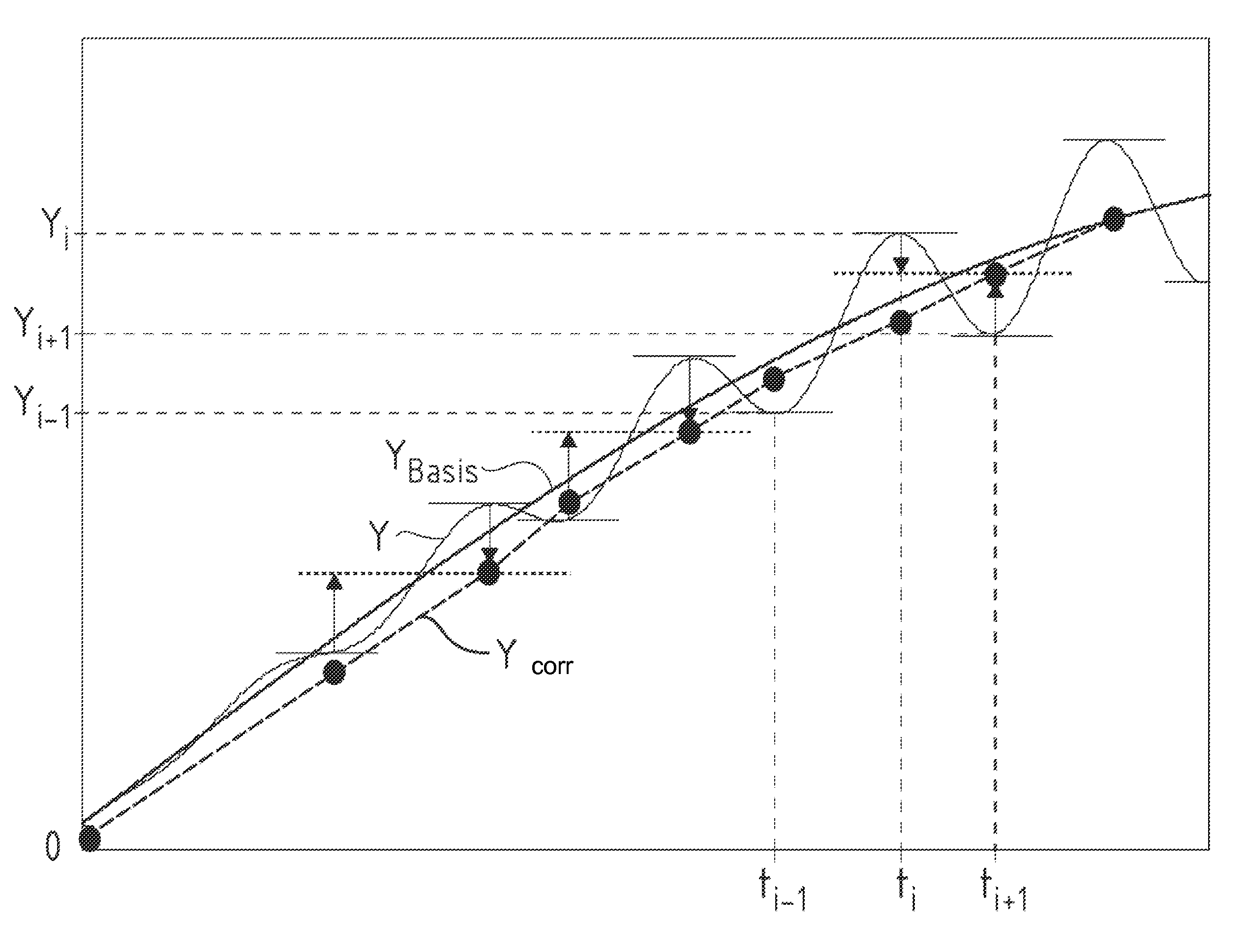
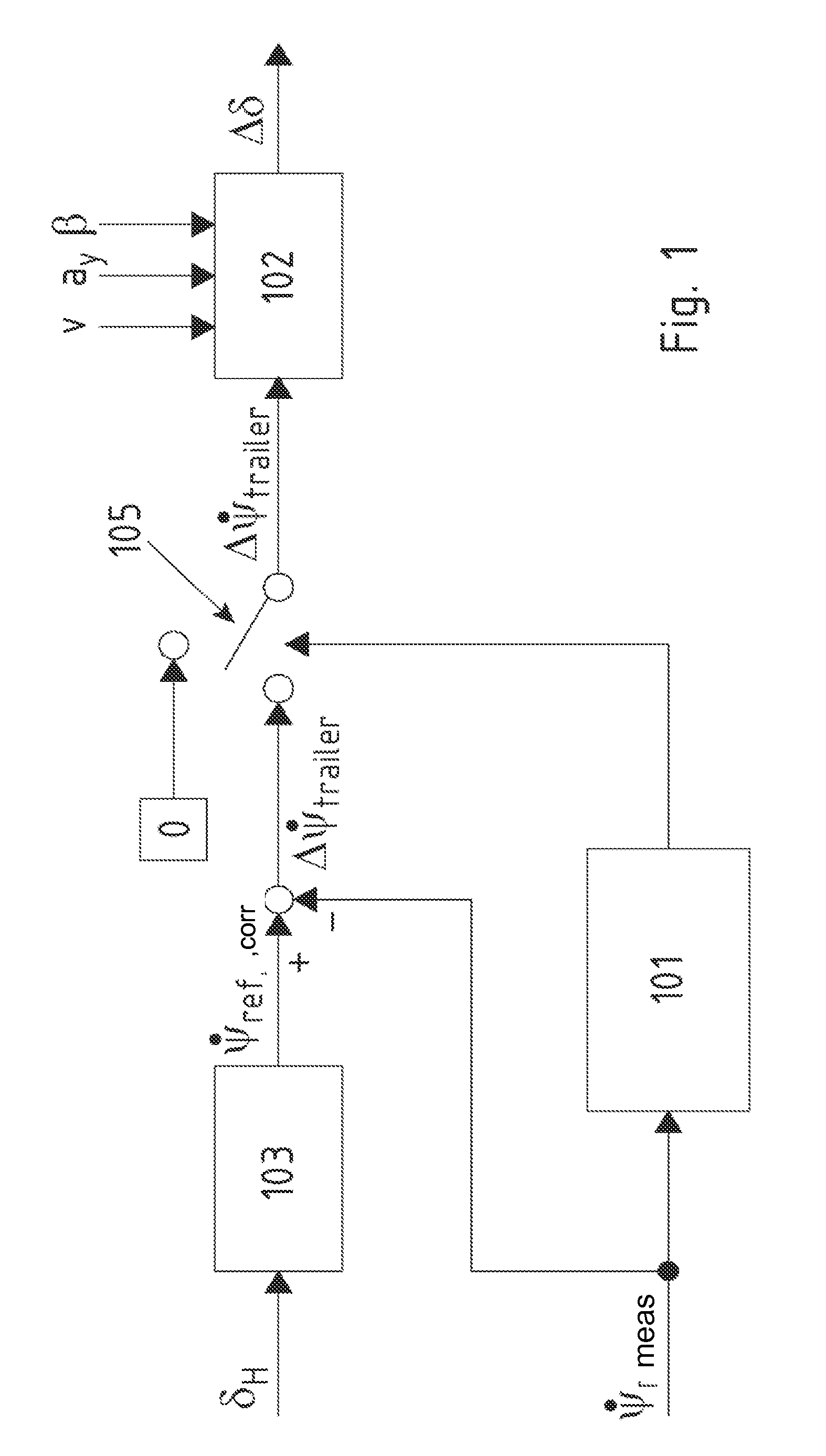
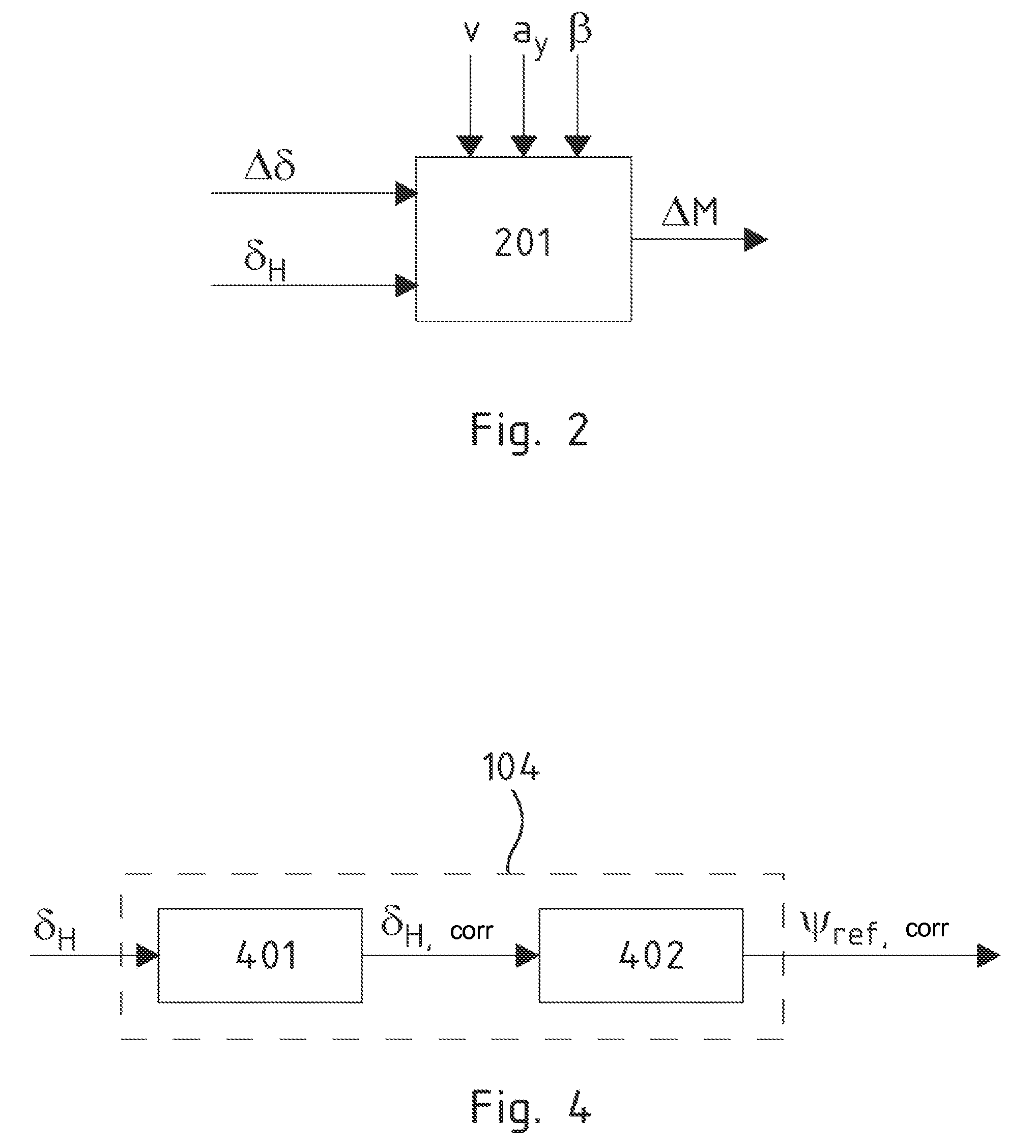
Method and Driving Dynamics Control System for Stabilizing a Car-Trailer Combination
ActiveUS20090228182A1Reliably carry-outHand manipulated computer devicesBrake system interactionsControl systemSemi-trailer
When swaying motions of a trailer or semi-trailer of a car-trailer combination are encountered, input signals which are taken into consideration to calculate a reference signal frequently include also oscillation components, due to which driving dynamics control for stabilization of the car-trailer combination can become very unreliable. To enhance the reliability of driving dynamics control of this type, a method is disclosed in which an input signal (Y) is sensed that includes signal oscillations which are due to a swaying motion of the trailer or semi-trailer and are superimposed on a base component (YBasis) of the input signal (Y). A reference signal is calculated from the input signal (Y), in which case the calculation is executed in such a way that the reference signal by approximation corresponds to a reference signal which is determined from the base component (YBasis) of the input signal (Y). A correcting variable for influencing the driving behavior of the towing vehicle of the car-trailer combination is then determined depending on a deviation between the reference signal and a detected actual signal. Furthermore, the invention discloses a driving dynamics control system which is appropriate to implement the method.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Vehicle speed control system
ActiveUS20150203117A1Control speedFocusBrake system interactionsVehicle fittingsUser inputSpeed control system
A vehicle speed control system for a vehicle having a plurality of wheels, the vehicle speed control system comprising one or more electronic control units configured to carry out a method that includes applying torque to at least one of the plurality of wheels, detecting a slip event between any one or more of the wheels and the ground over which the vehicle is travelling when the vehicle is in motion and providing a slip detection output signal in the event thereof. The method carried out by the one or more electronic control units further includes receiving a user input of a target speed at which the vehicle is intended to travel and maintaining the vehicle at the target speed independently of the slip detection output signal by adjusting the amount of torque applied to the at least one of the plurality of wheels.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
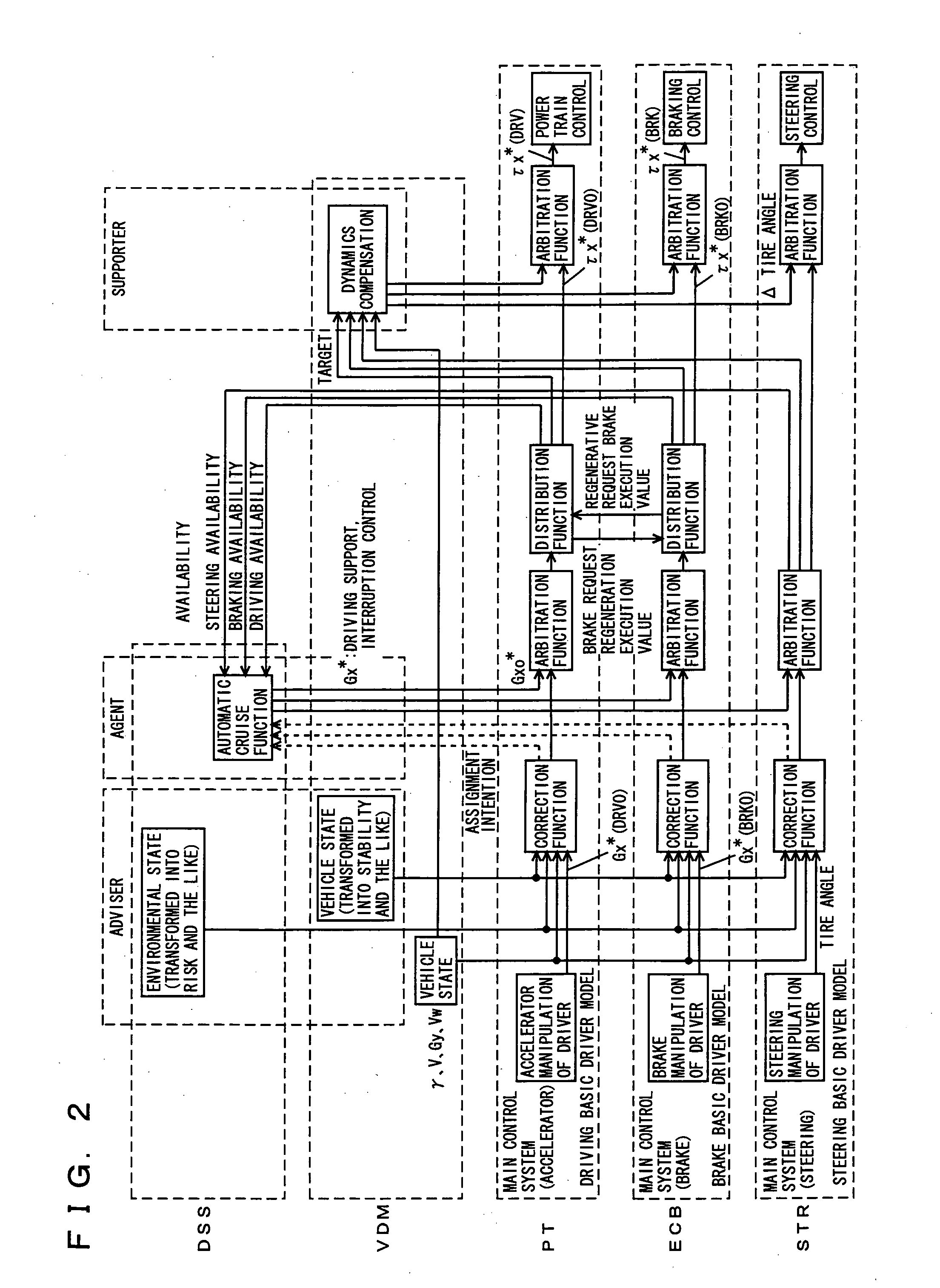
Vehicle integrated control system
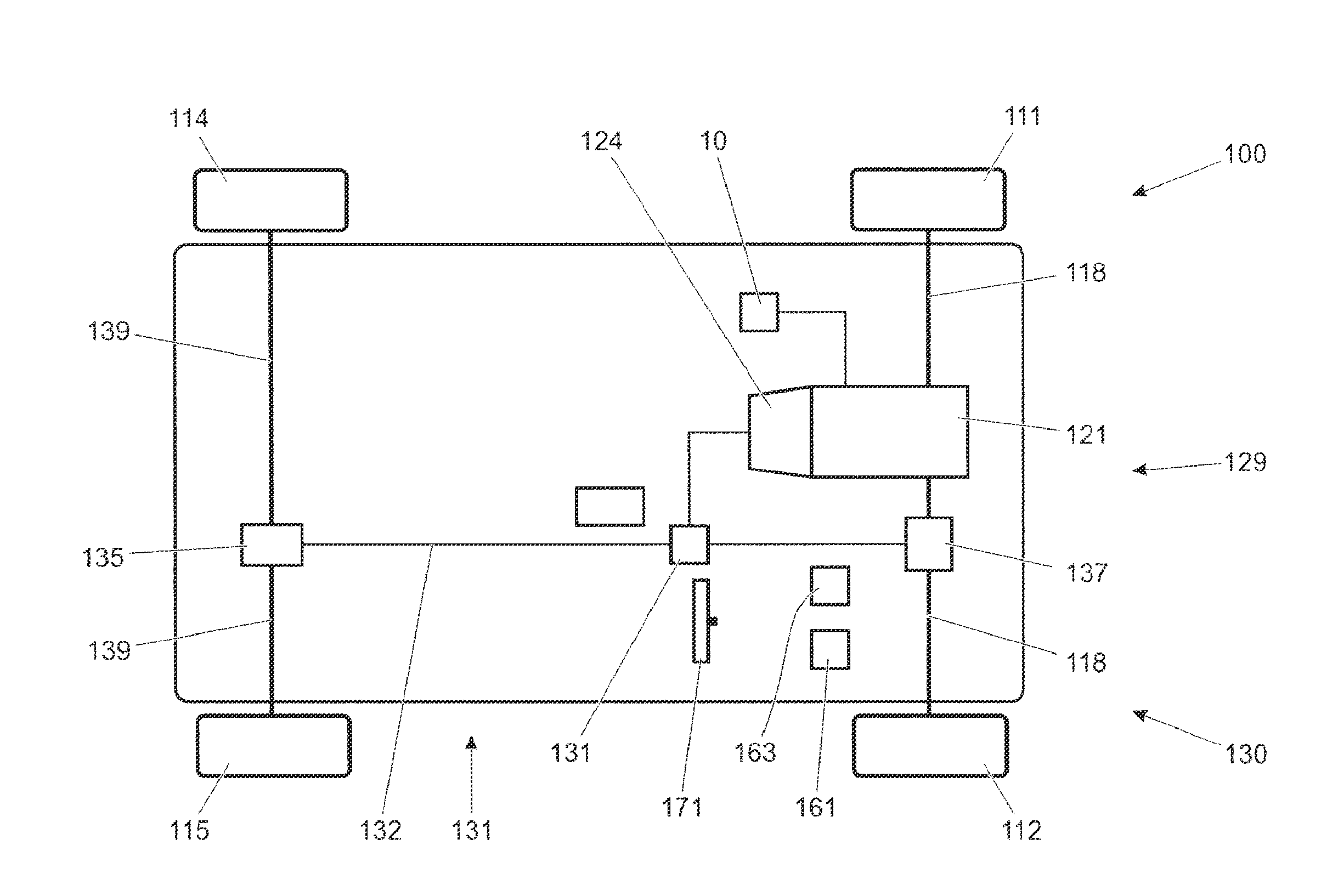
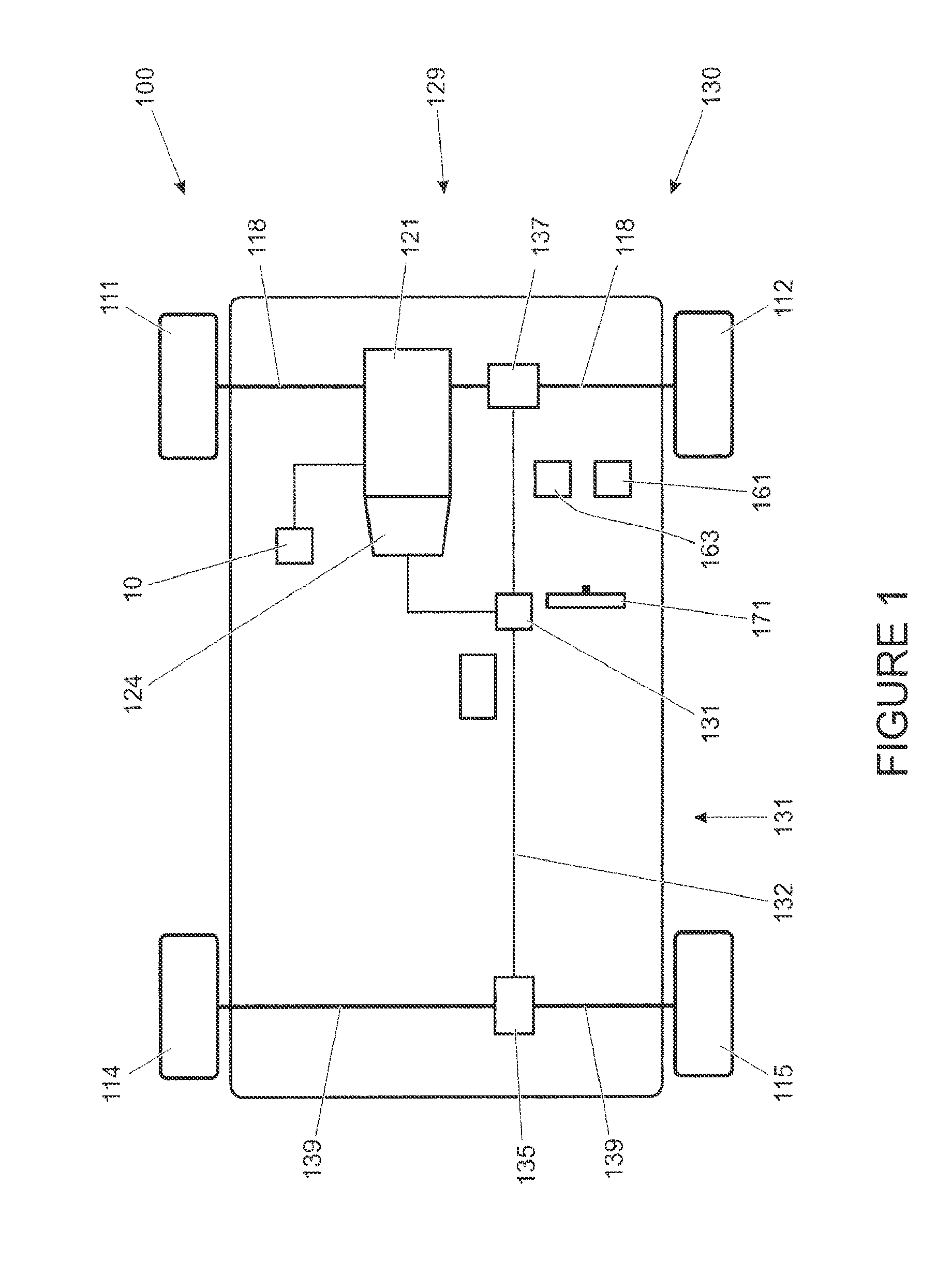
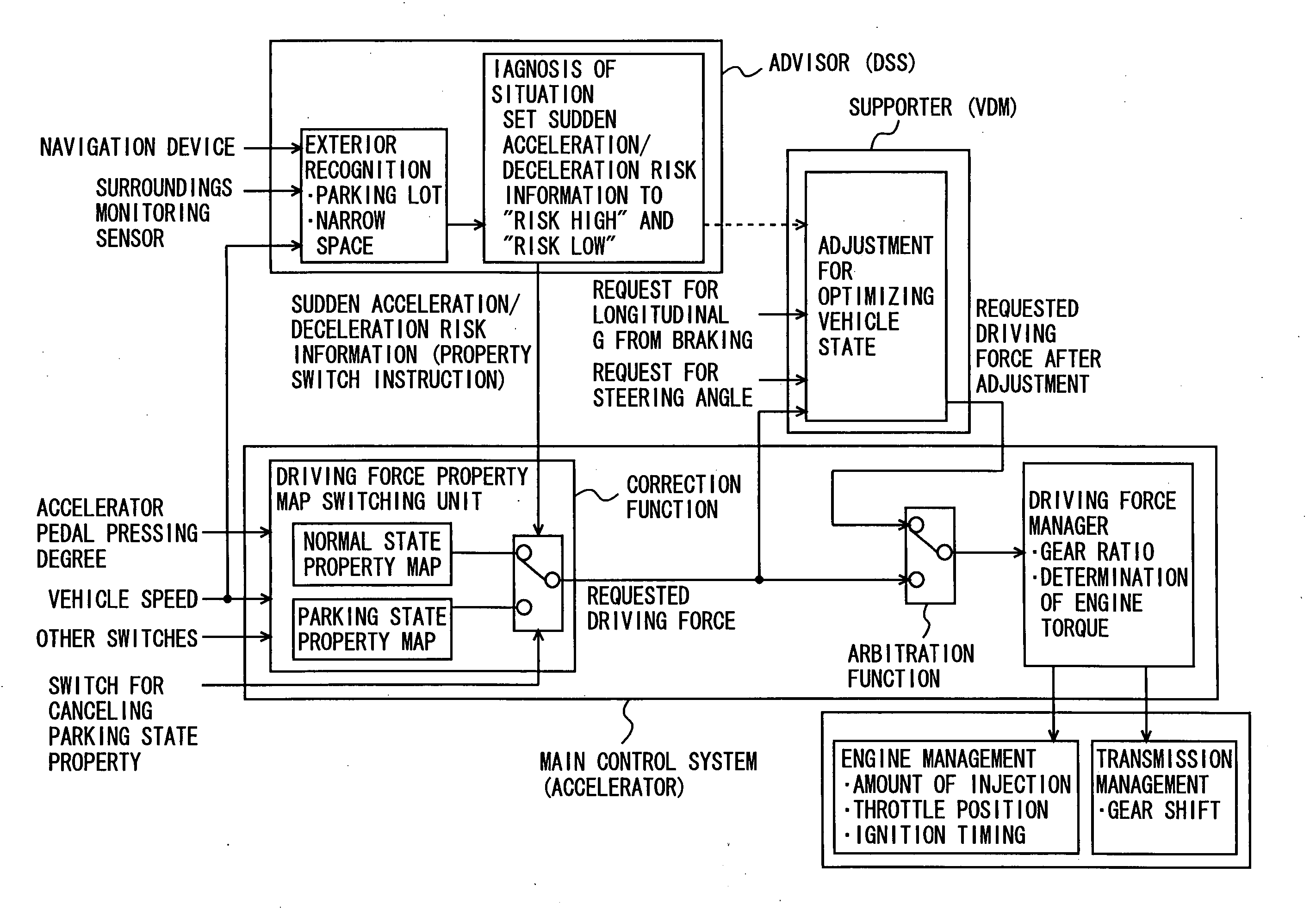
InactiveUS20050137766A1Avoiding inadvertent sudden acceleration/decelerationIncreased fail-safetyBrake system interactionsVehicle fittingsControl systemEngineering
An integrated control system includes a main control system (accelerator) controlling a driving system, a main control system (brake) controlling a brake system, and a main control system (steering) controlling a steering system, based on manipulation by a driver, as well as an adviser unit generating and providing information to be used at each main control system based on environmental information around the vehicle or information on a driver. The advisor unit outputs to the main control system (accelerator) sudden acceleration / deceleration risk information having the risk set to “high” when the vehicle is parked in a parking lot, based on information from a navigation device or a surroundings monitoring sensor. The main control system (accelerator) selects a parking state property map based on the sudden acceleration / deceleration risk information having the risk set to “high”, and calculates a target driving force smaller than that corresponding to accelerator pressing by the driver.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
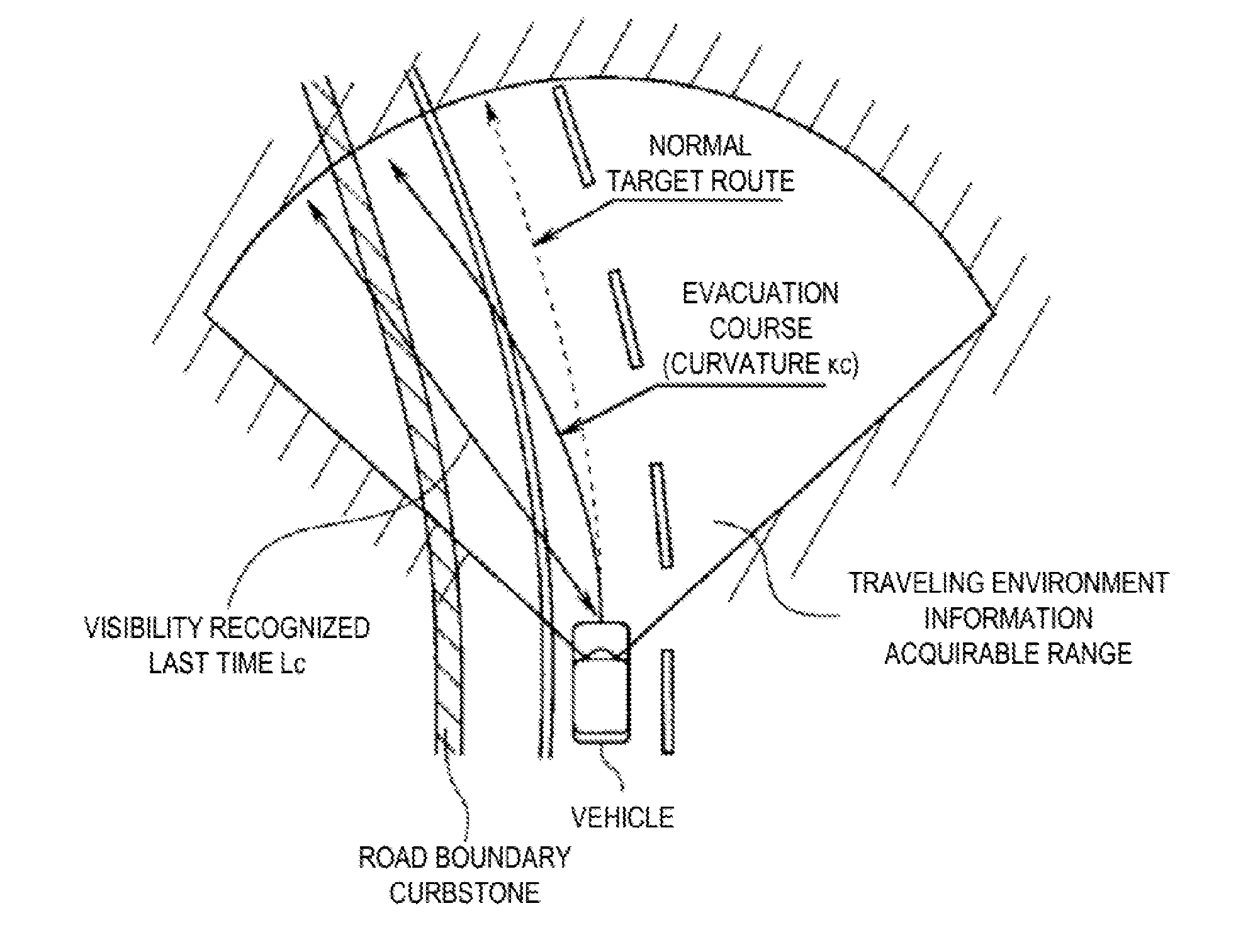
Driving control apparatus for vehicle
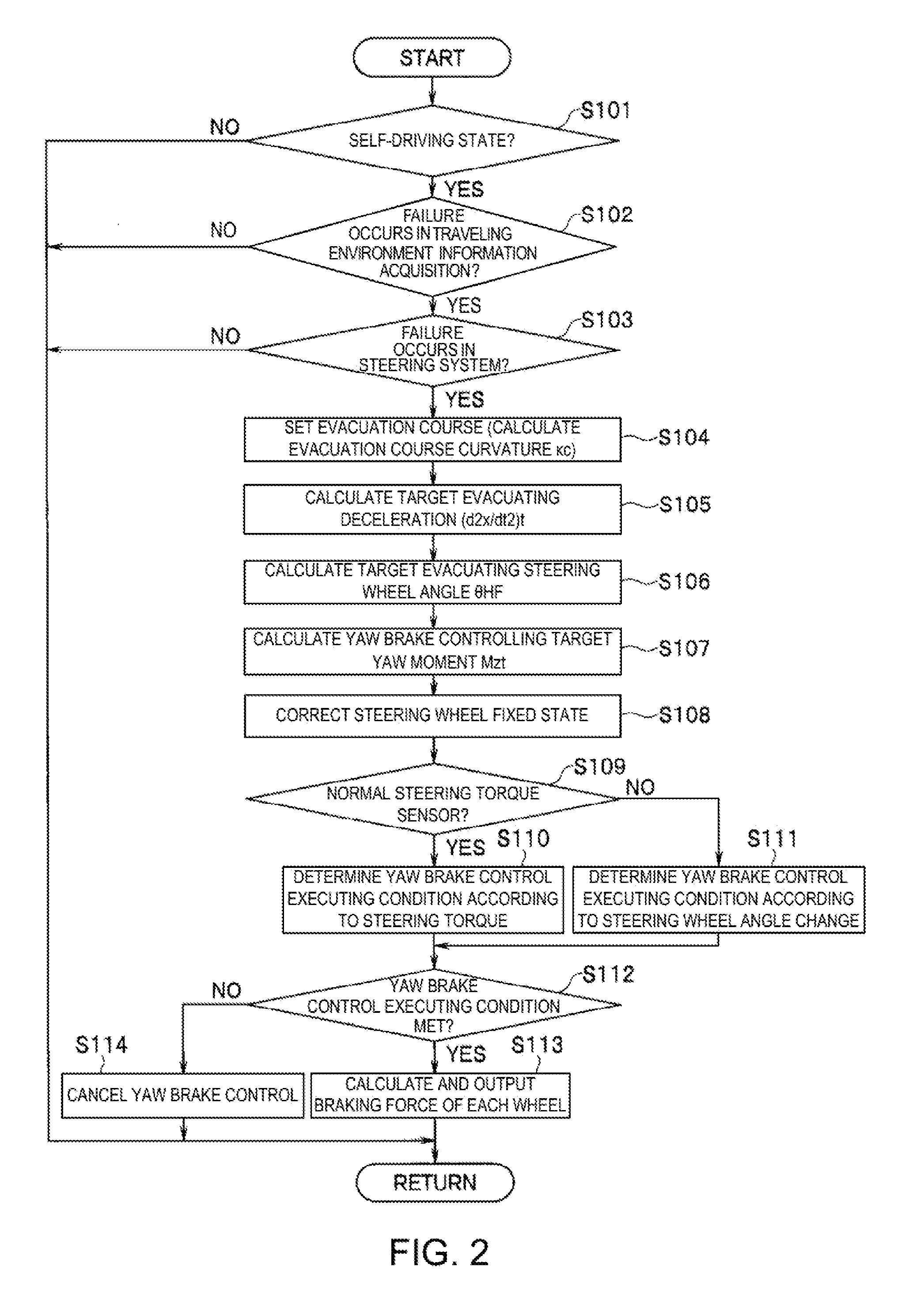
ActiveUS20160090100A1Ensure safetyBrake system interactionsAutomatic initiationsVehicle drivingSelf driven
During a self-driving control, when an acquisition failure occurs in traveling environment information acquisition required for performing self-driving, and a failure of a steering system of a vehicle equipped with the vehicle driving control apparatus is detected, a brake controller sets an evacuation course along which the vehicle is to travel safely within traveling environment, based on traveling environment information detected last time before the acquisition failure of the traveling environment information, and executes a deceleration of the vehicle and a yaw brake control that applies a yaw moment to the vehicle based on the evacuation course.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Absolute acceleration sensor for use within moving vehicles
Owner:VISION WORKS IP CORP
Re-positionable vehicle control-by-wire assembly, method, and system
ActiveUS20050283288A1Digital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsControl theoryVehicle control
A vehicle control assembly and a method and system for controlling a vehicle. The assembly includes a controller. A steer-by-wire component, a brake-by-wire component, and an accelerator-by-wire component are each operably attached to the controller. A track is operably attached to the vehicle. The controller is laterally re-positionable with respect to the track. The method includes the steps of providing a controller, and steering, braking, and accelerating the vehicle by-wire with the controller. The method further includes the step of re-positioning the controller between a first vehicle side to a second vehicle side. The system includes controller means, and means for steering, braking, and accelerating the vehicle by-wire with the controller means. The system further includes means for reversibly positioning the controller means from a first vehicle side to a second vehicle side.
Owner:FCA US
Understeer suppressing apparatus for vehicle
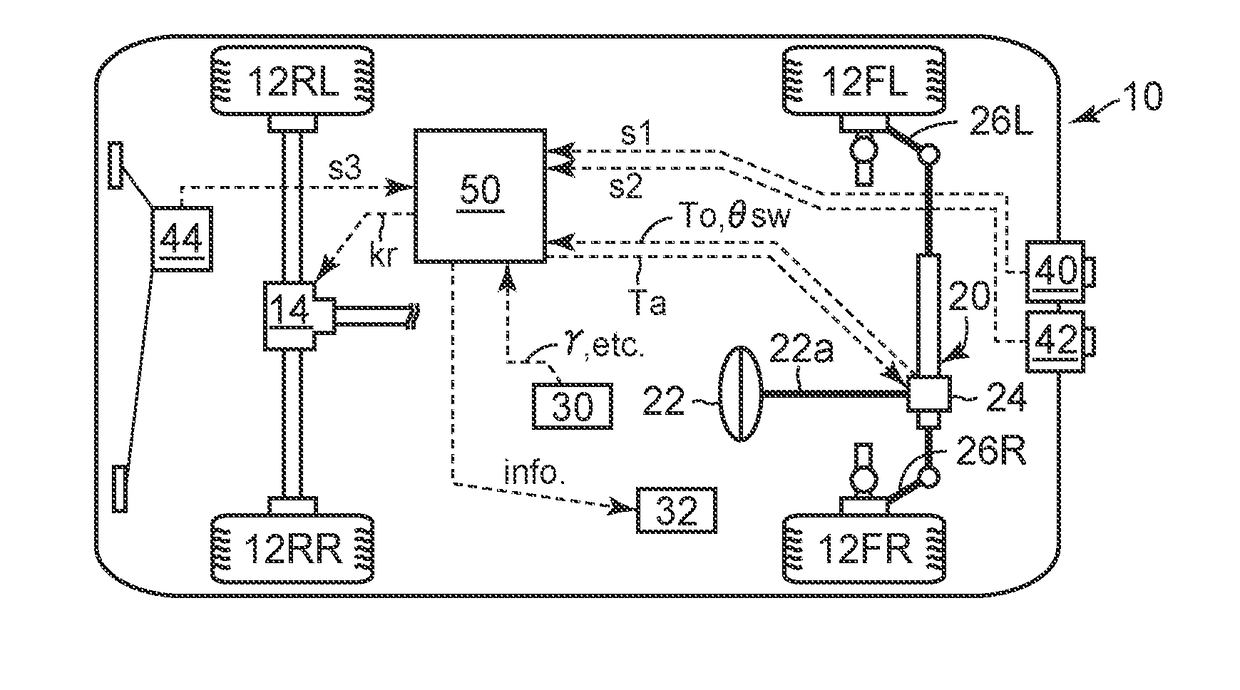
InactiveUS20060208564A1Improve understeer stateDegree of understeer is rather increasedBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringLow speed
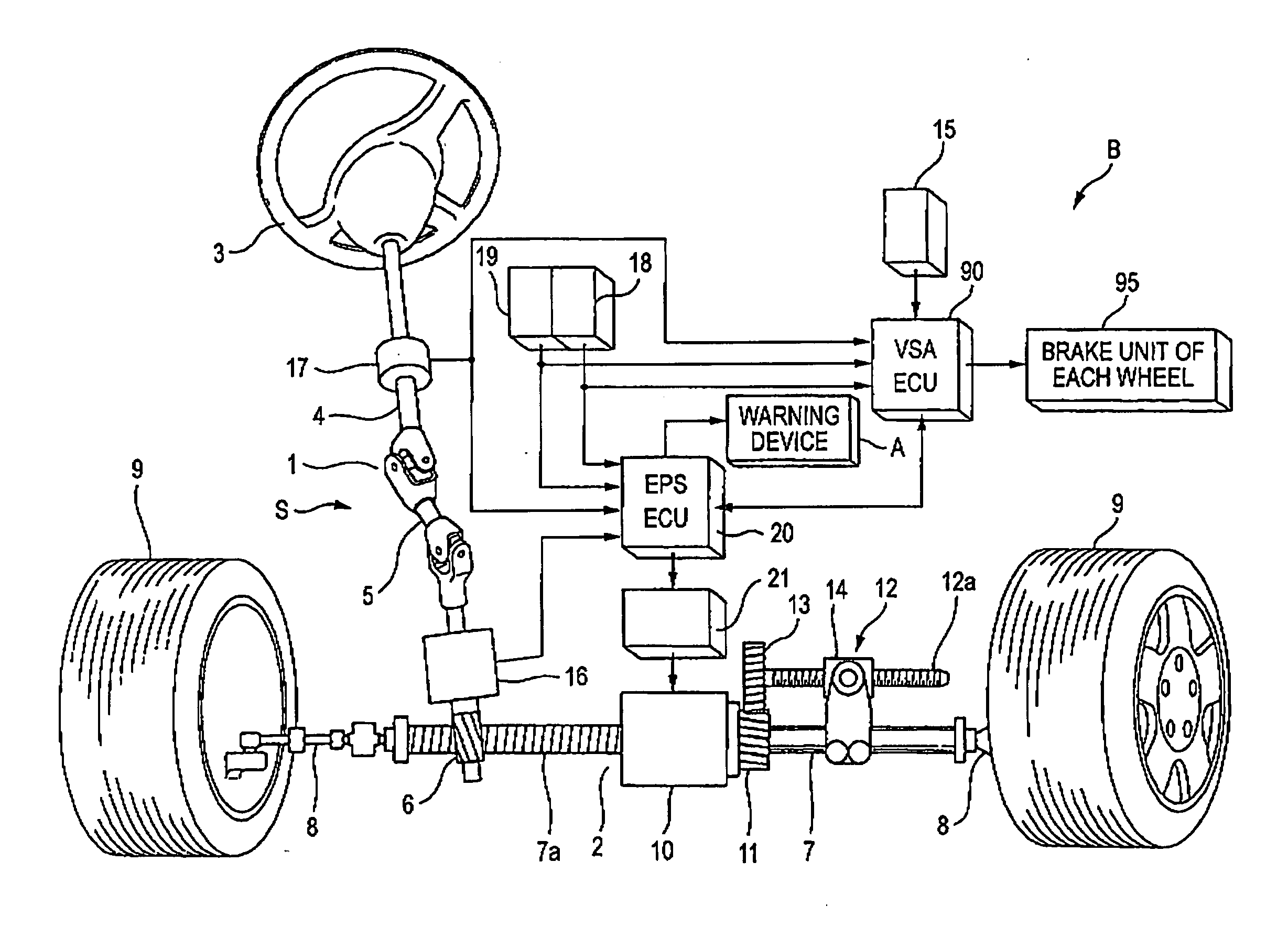
An understeer suppressing apparatus for a vehicle includes an electric power steering device S for suppressing steering when the vehicle is in the understeer state, an alarm device A for informing a driver that the vehicle is in the understeer state, and a braking force distribution device B for generating moment of the vehicle by applying braking forces different from each other to the left and right wheels. As the degree of understeer is increased, the electric power steering device S, the alarm device A, and the braking force distribution device B are operated in this order.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
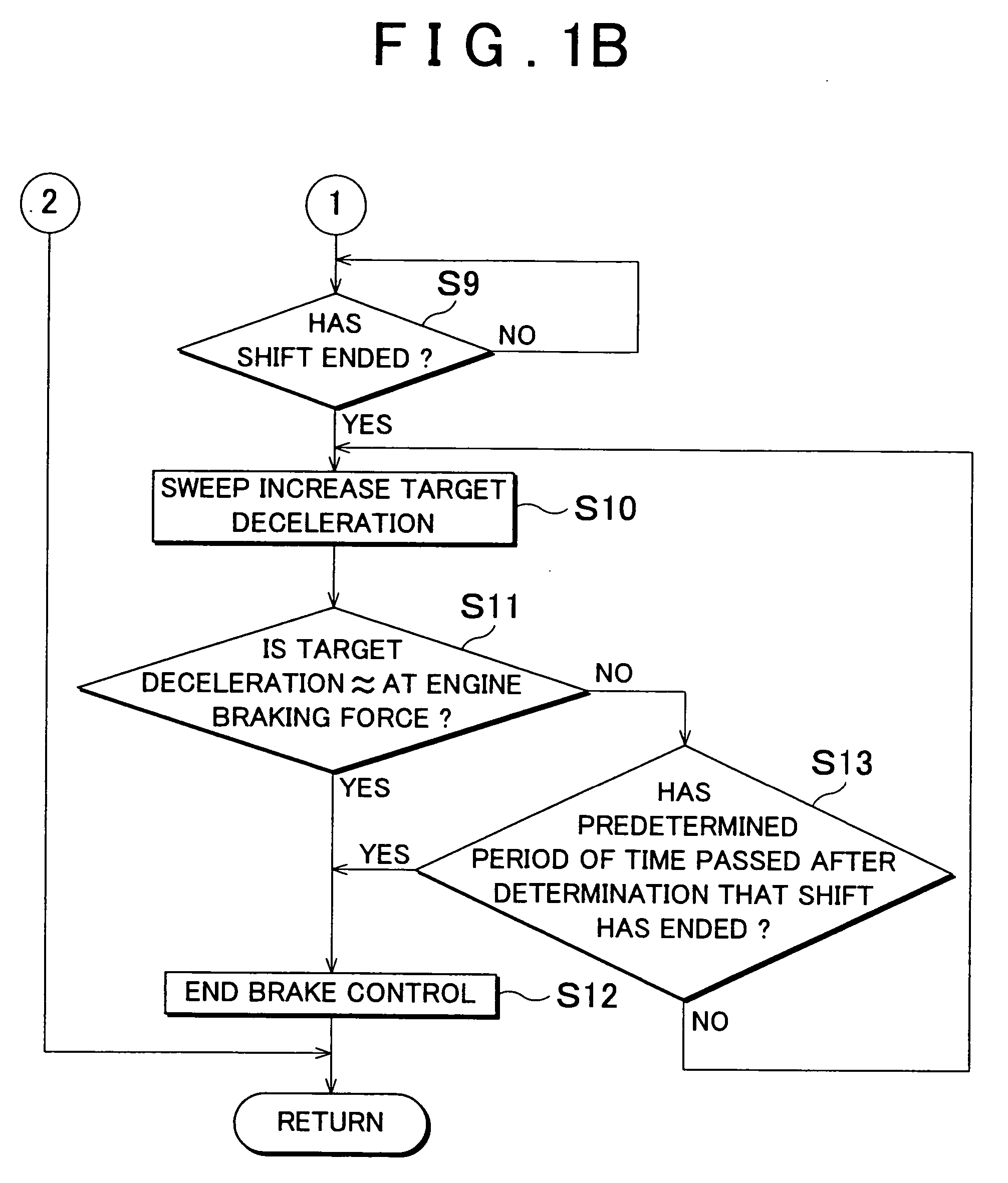
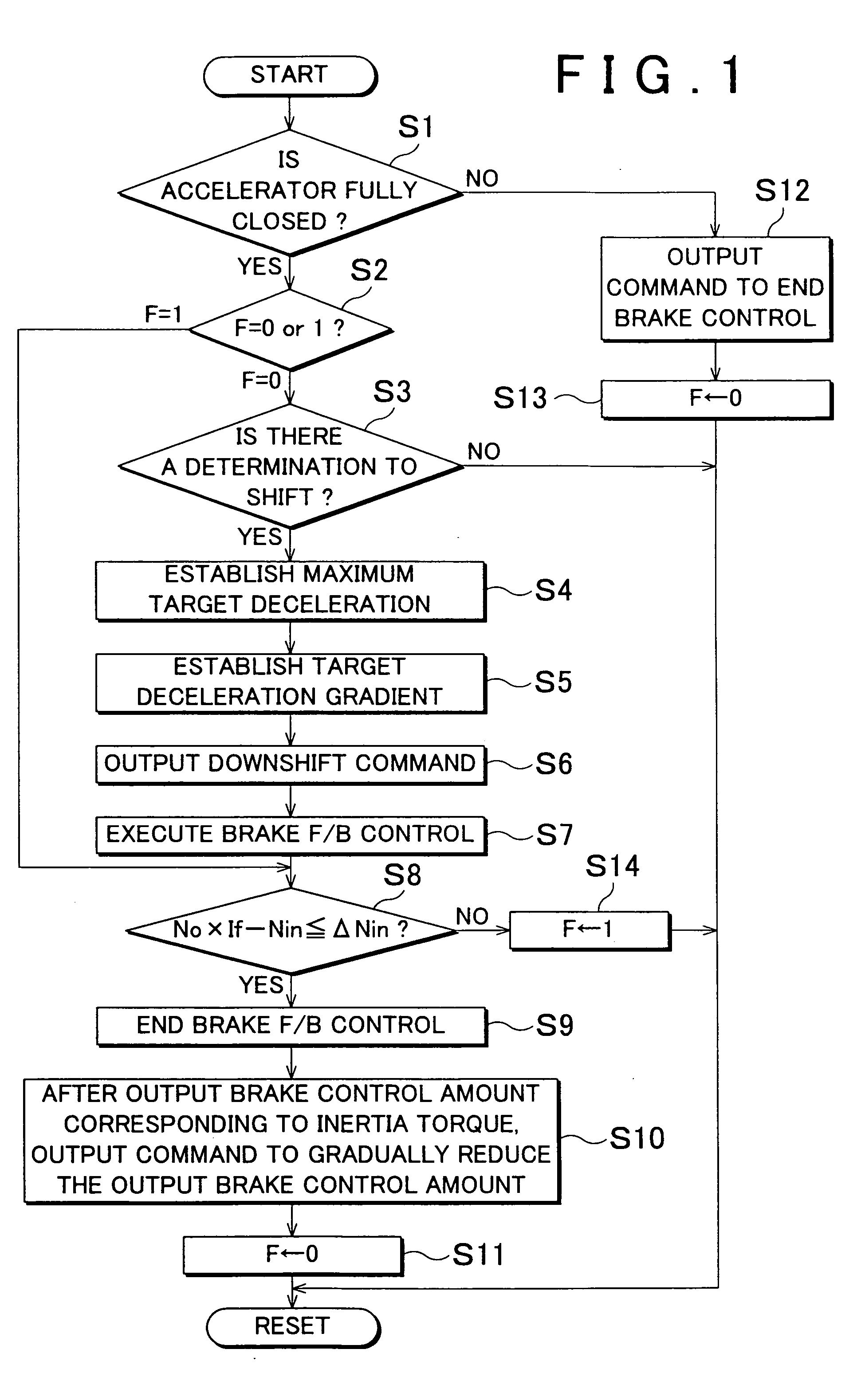
Deceleration control apparatus and method for a vehicle
InactiveUS20050187694A1Easy to set upSuitable characteristicBrake system interactionsAnalogue computers for trafficLow speedClassical mechanics
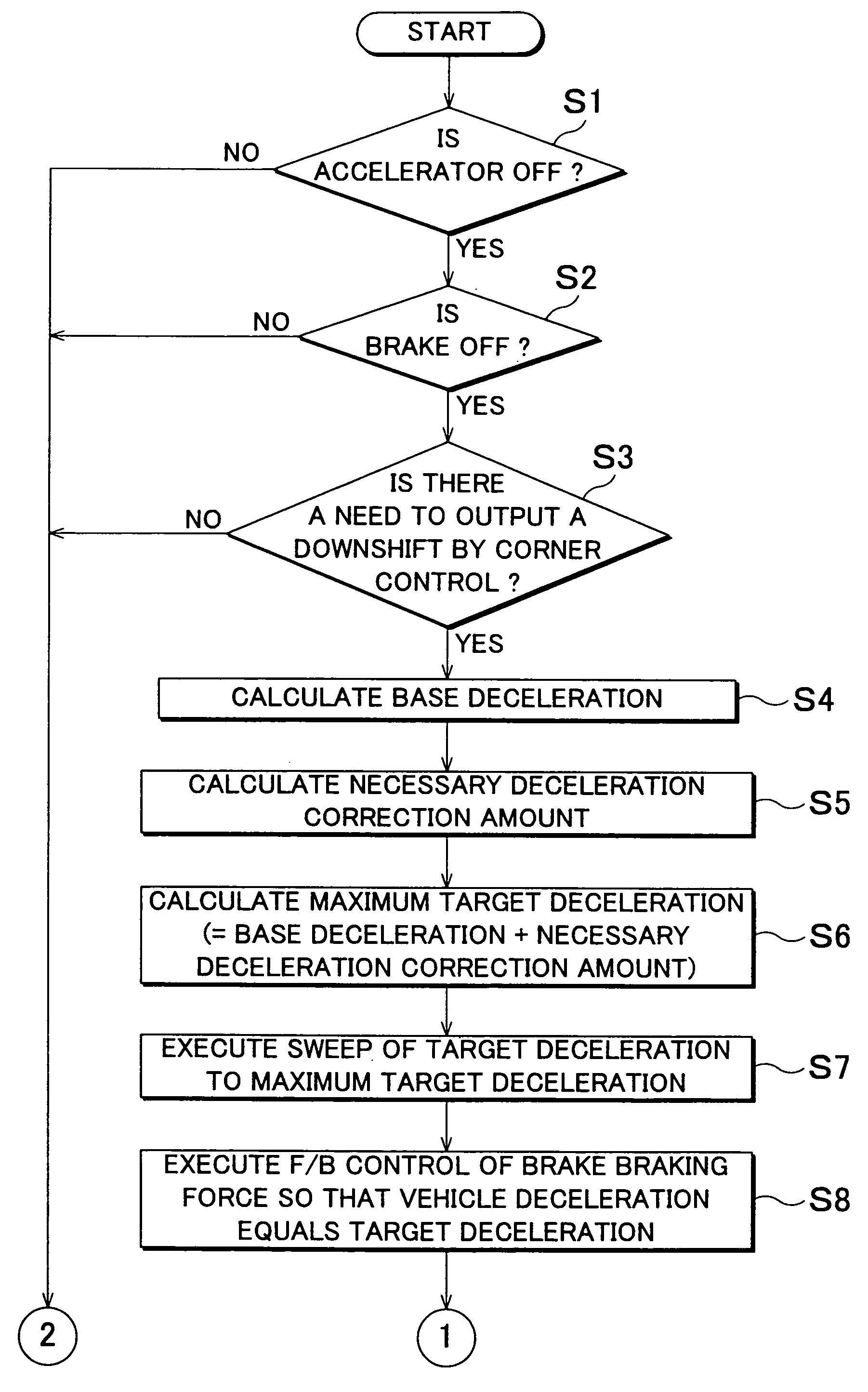
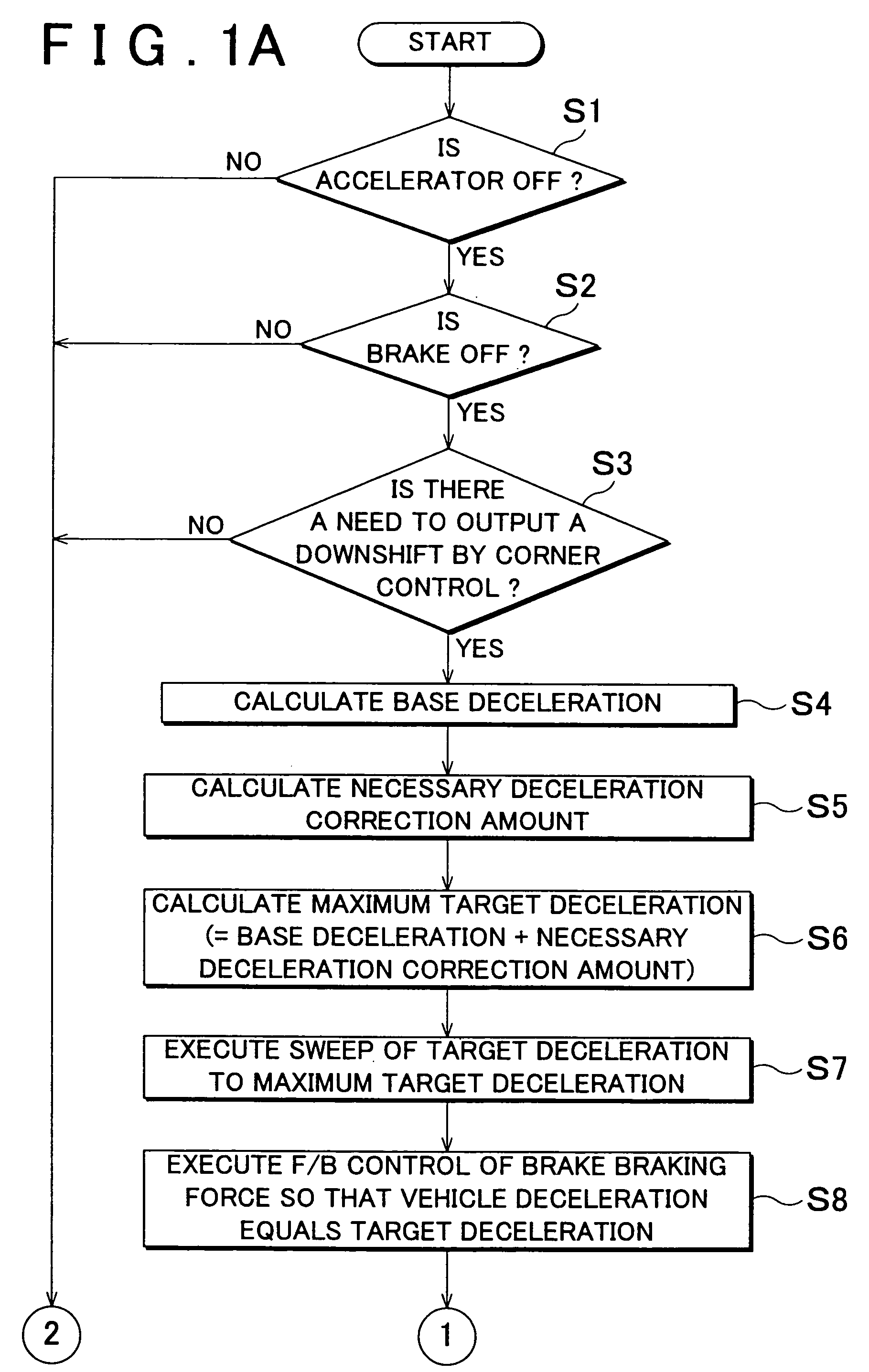
A deceleration control apparatus and method for a vehicle, which performs deceleration control on the vehicle by an operation of a brake system which applies a braking force to the vehicle and a shift operation which shifts a transmission of the vehicle into a relatively low speed or speed ratio, performs the shift operation and the operation of the brake system such that a target deceleration set based on a curvature or curvature radius of a curve in a road ahead of the vehicle, a distance to the curve, and a vehicle speed, acts on the vehicle. As a result, a desired deceleration according to the distance to the curve is able to be applied to the vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
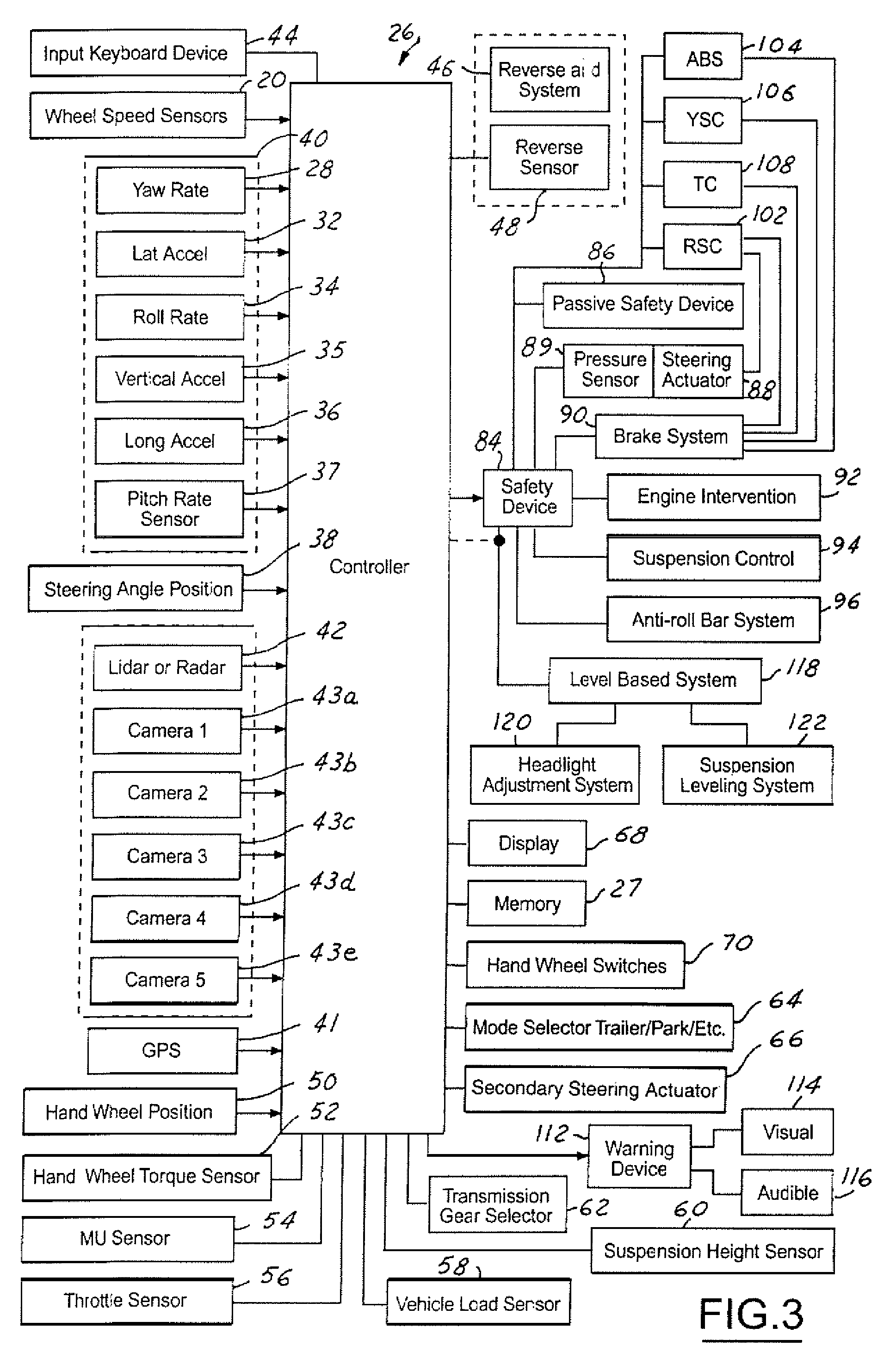
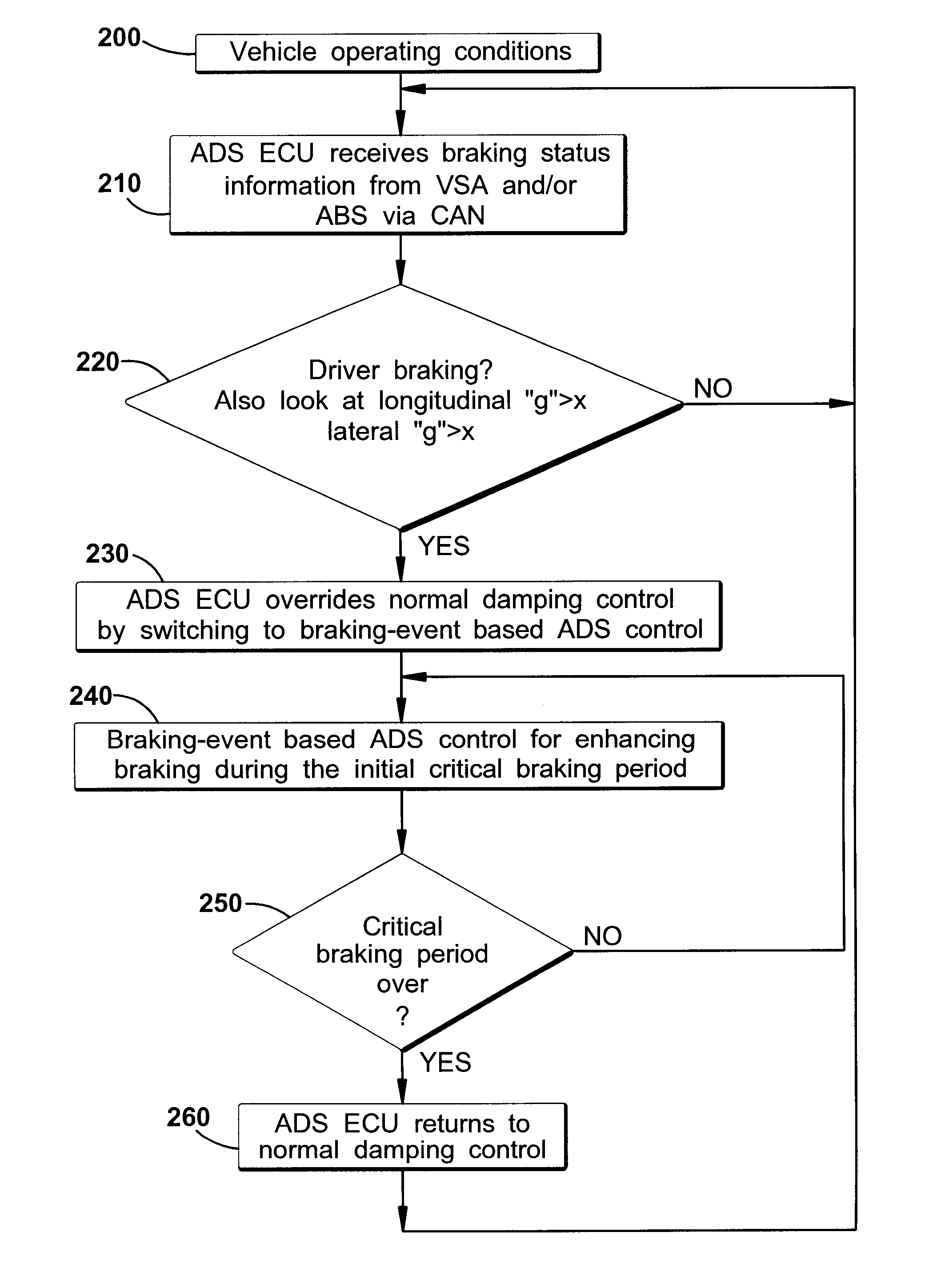
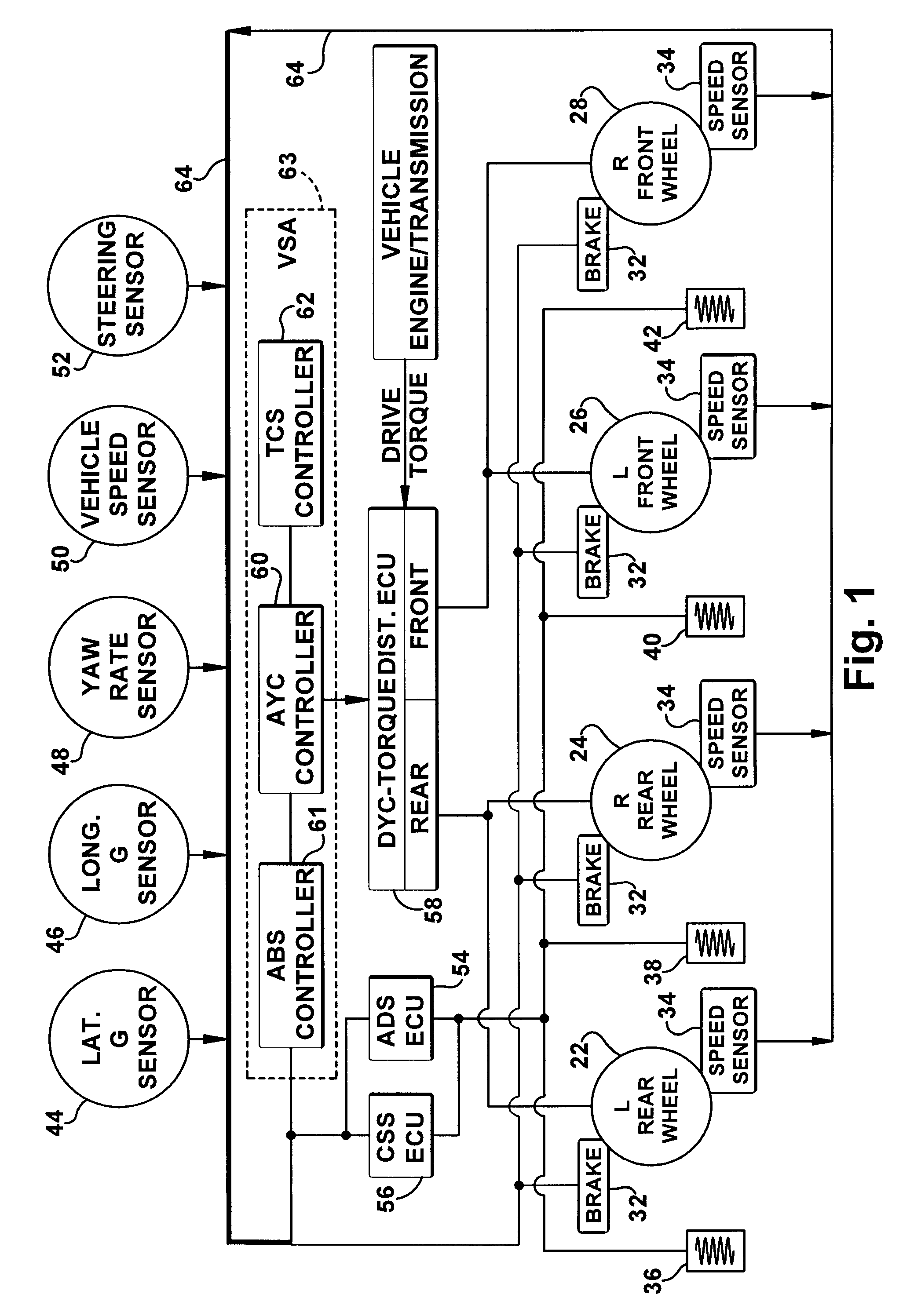
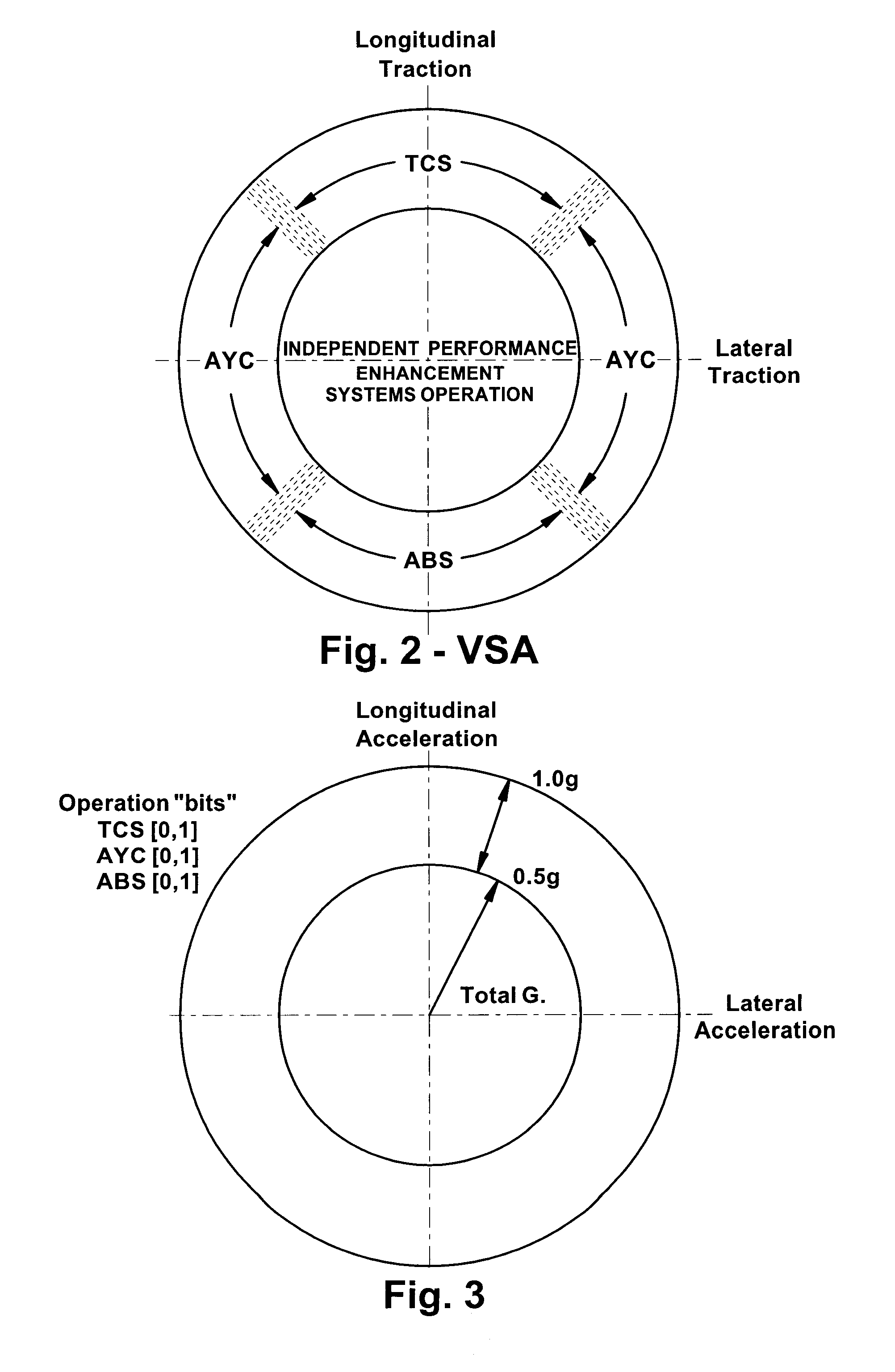
Vehicle systems control for improving stability
InactiveUS8229642B2Improve vehicle stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesTraction control systemControl system
Improved methods of controlling the stability of a vehicle are provided via the cooperative operation of vehicle stability control systems such as an Active Yaw Control system, Antilock Braking System, and Traction Control System. These methods use recognition of road surface information including the road friction coefficient (mu), wheel slippage, and yaw deviations. The methods then modify the settings of the active damping system and / or the distribution of drive torque, as necessary, to increase / reduce damping in the suspension and shift torque application at the wheels, thus preventing a significant shift of load in the vehicle and / or improving vehicle drivability and comfort. The adjustments of the active damping system or torque distribution temporarily override any characteristics that were pre-selected by the driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Deceleration control apparatus and method for a vehicle
InactiveUS20050125134A1Good deceleration transitional characteristicVehicle fittingsBrake system interactionsLow speedEngineering
A deceleration control apparatus for a vehicle provided with a brake system for generating braking force in the vehicle, and a transmission, controls the brake system and the transmission such that a deceleration acting on the vehicle matches a target deceleration set as a deceleration to be applied to the vehicle by a brake operation of the brake system and a shift operation which shifts the transmission into a relatively low speed or speed ratio.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
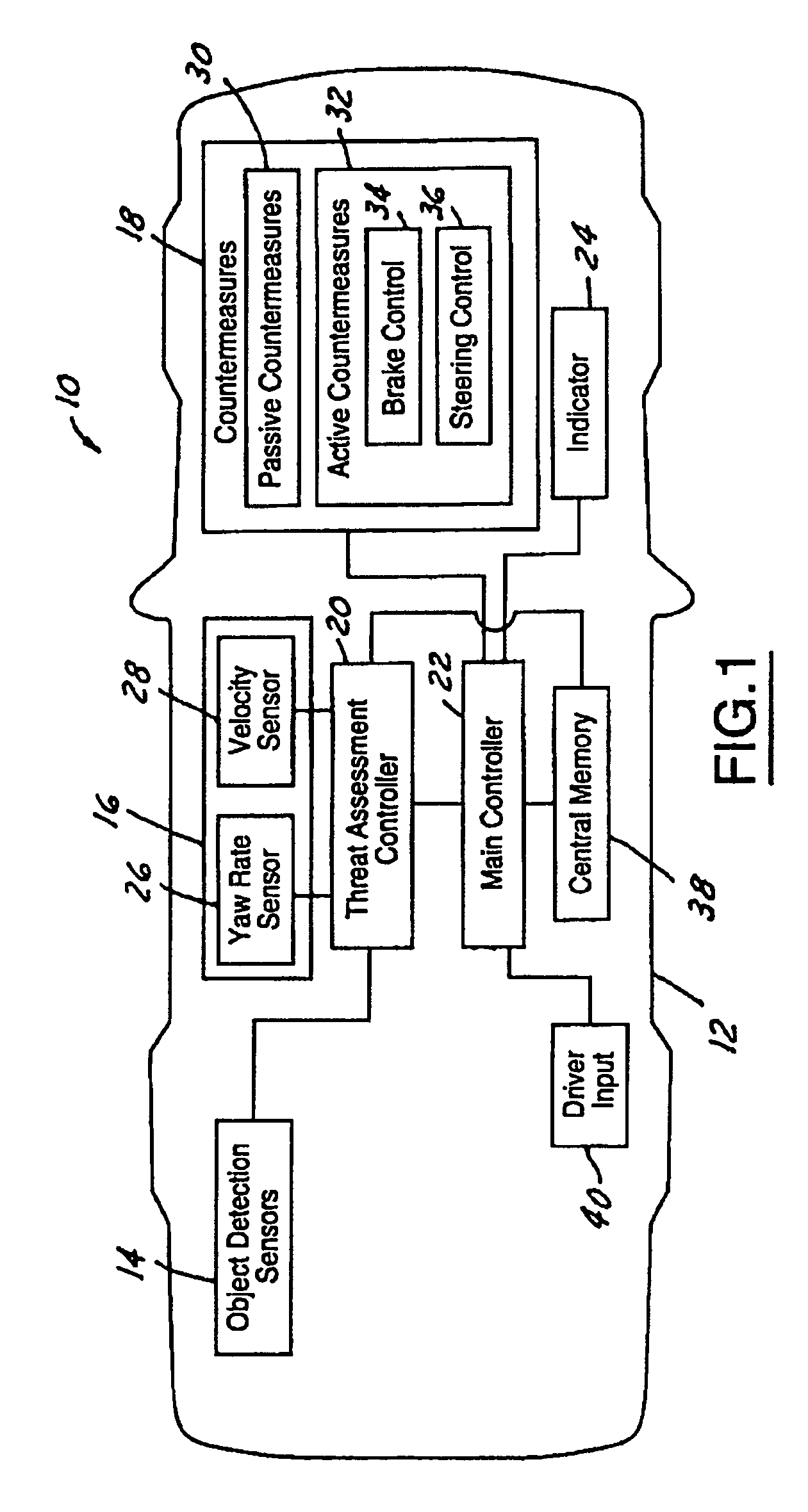
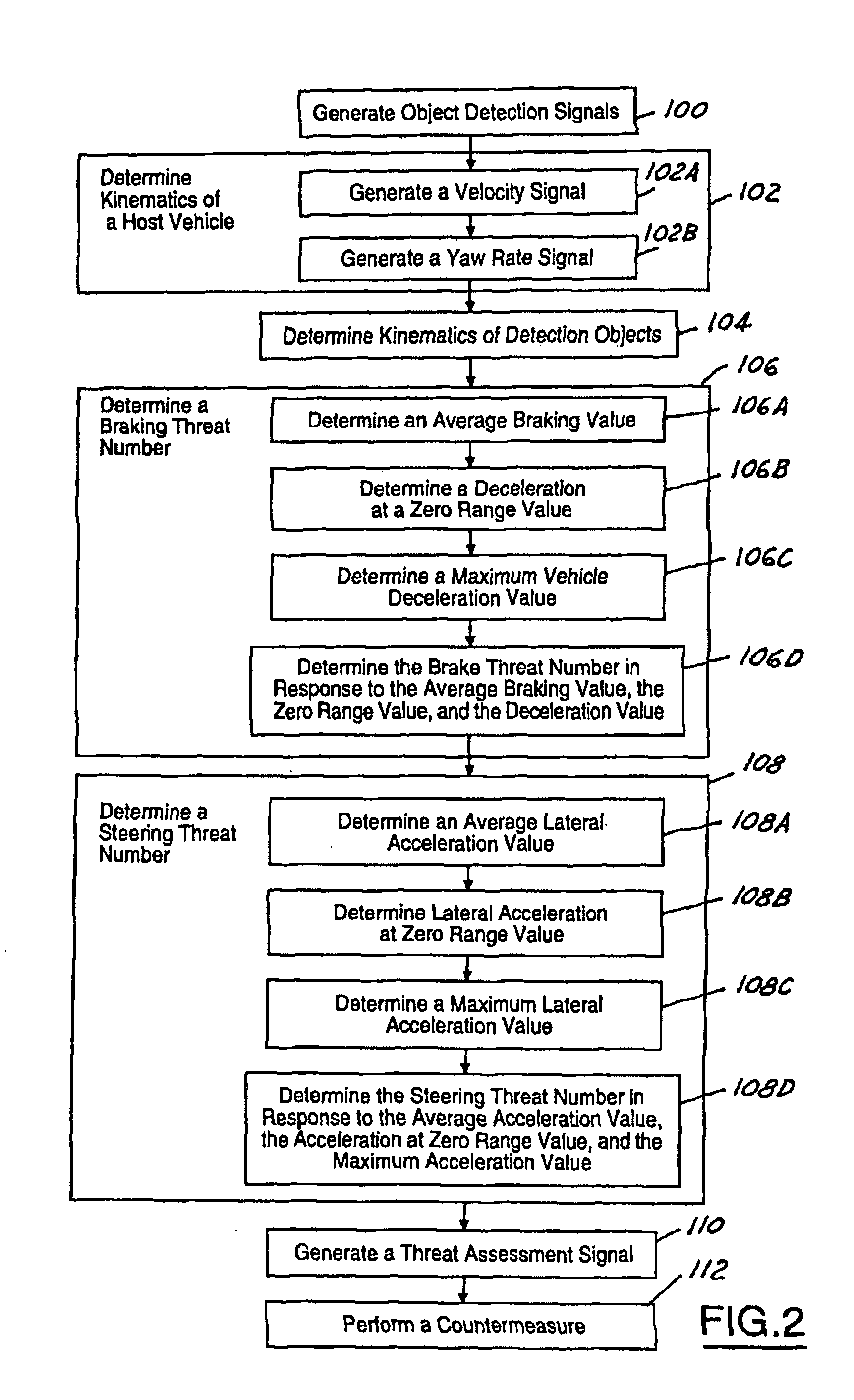
Threat level identification and quantifying system
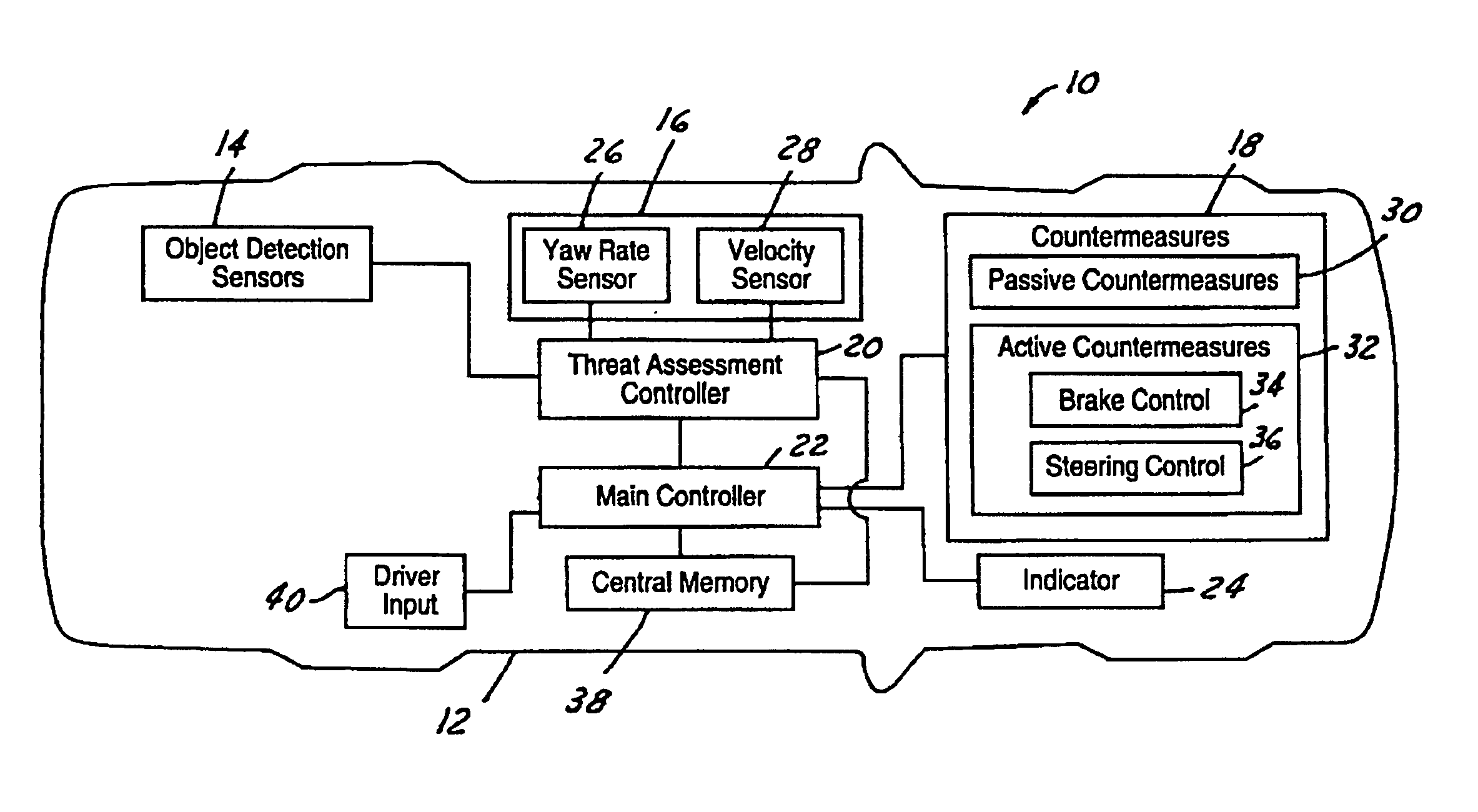
ActiveUS7034668B2Technique is effectiveSimplifies threat assessmentBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsKinematicsEngineering
Methods of performing threat assessment of objects for a vehicle include detecting an object. Kinematics of the vehicle and of the object are determined. A brake threat number and a steering threat number are determined in response to the kinematics of the vehicle and the object. The threat posed by the object is determined in response to the brake threat number and the steering threat number.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Reference signal generator for an integrated sensing system
InactiveUS7010409B2Improve accuracyBrake system interactionsAnalogue computers for trafficEngineeringBiological activation
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
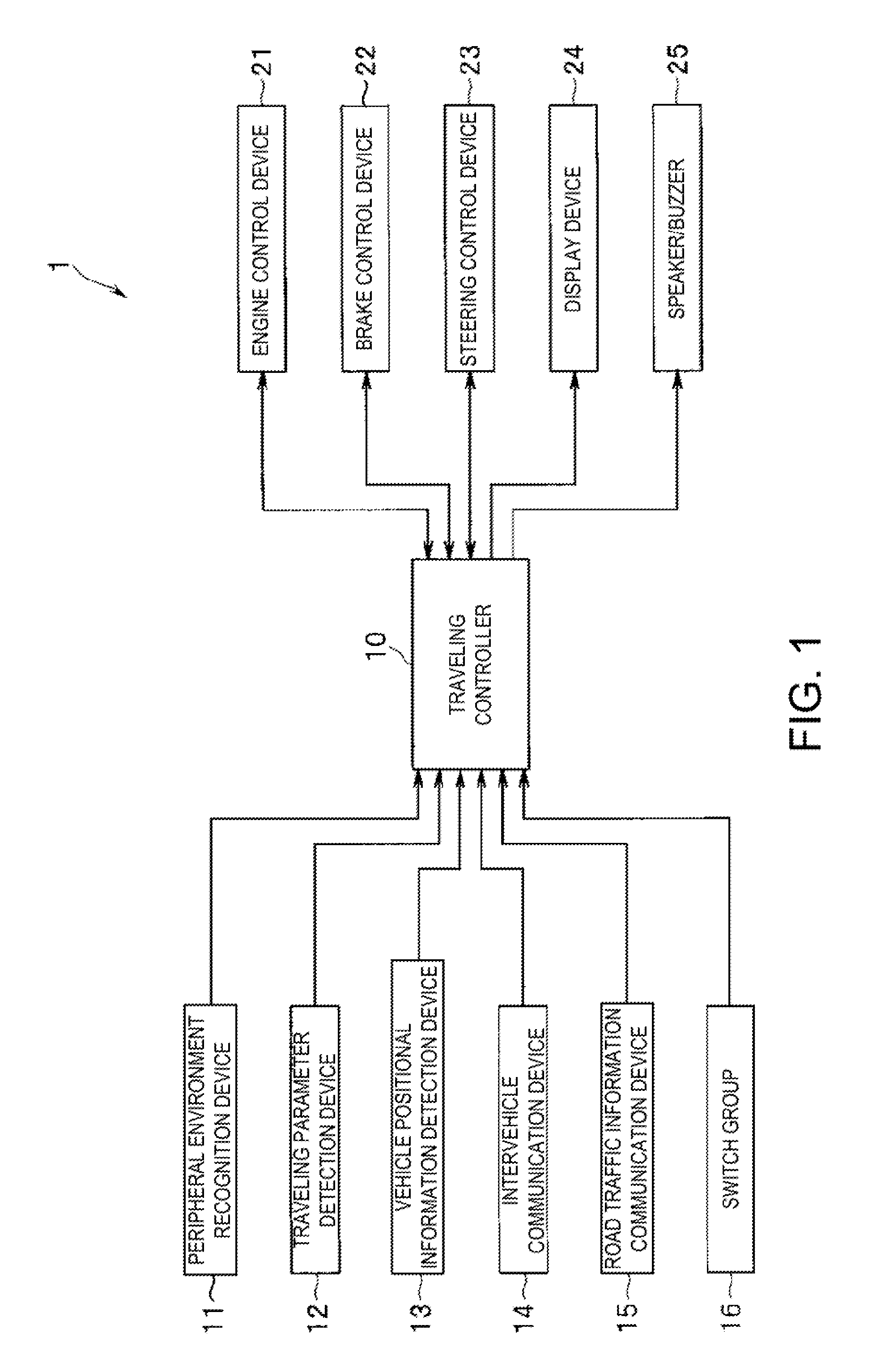
Automotive lane deviation prevention apparatus
ActiveUS20050113999A1Avoids tendencyDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlSteering controlControl variable
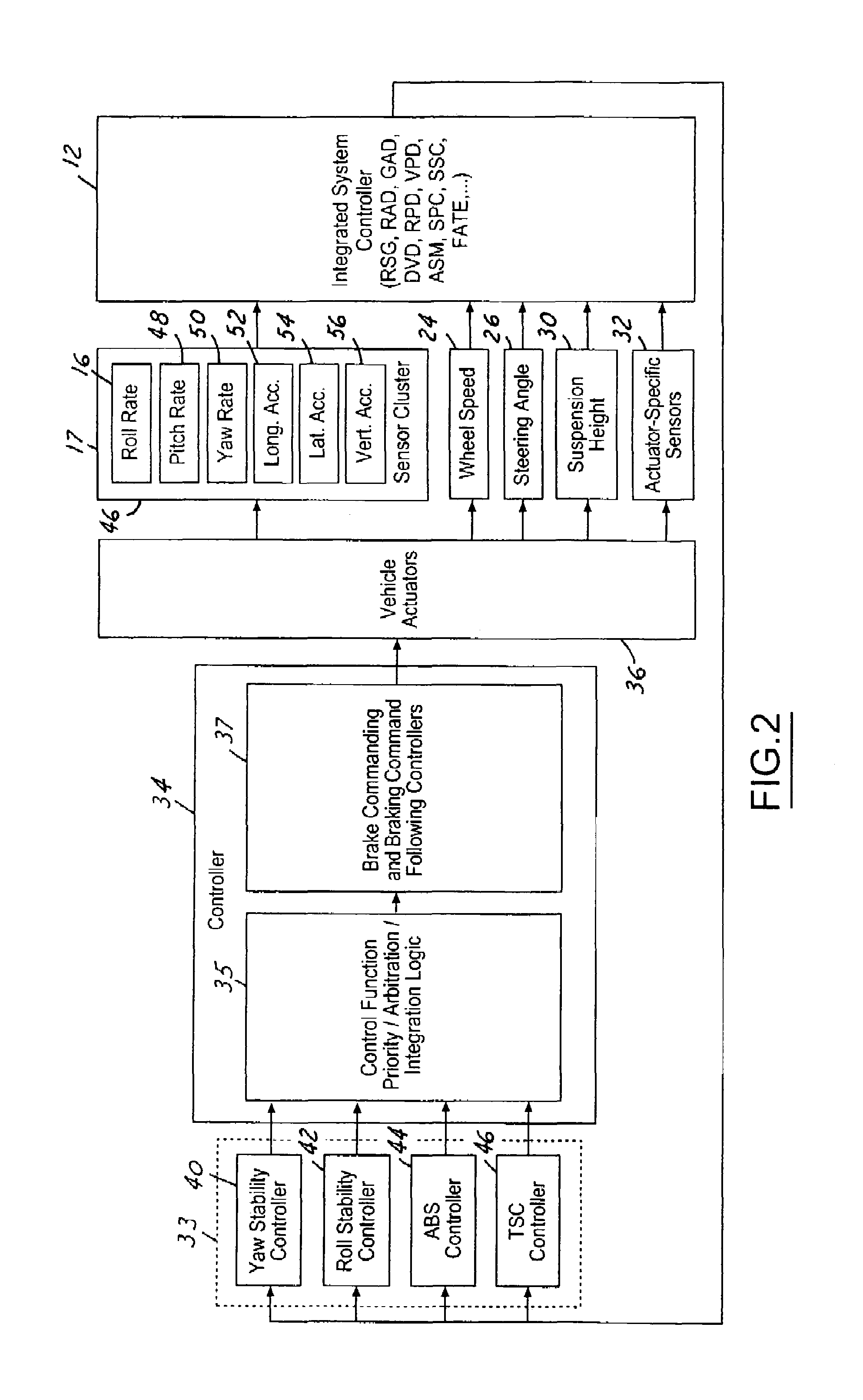
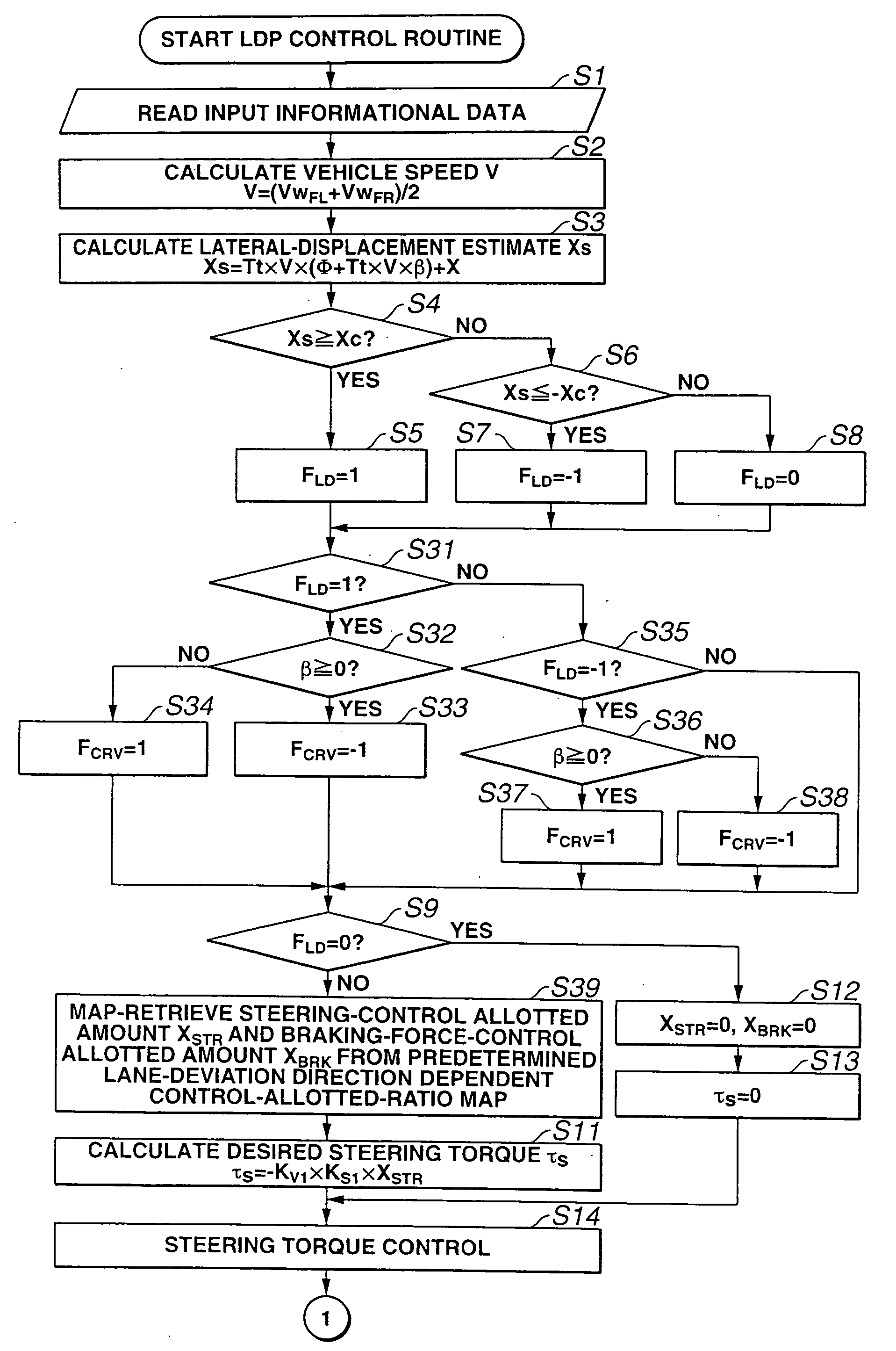
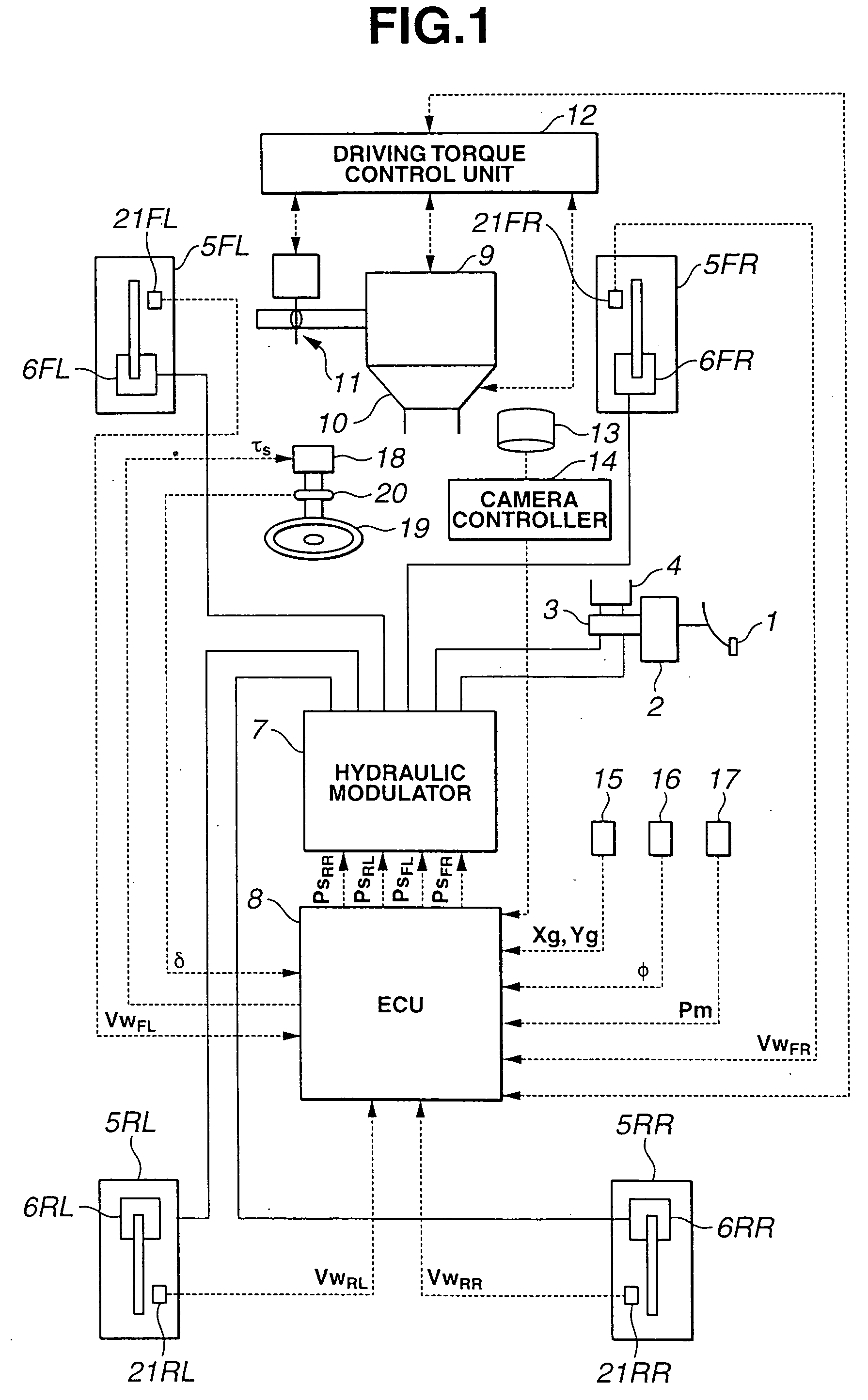
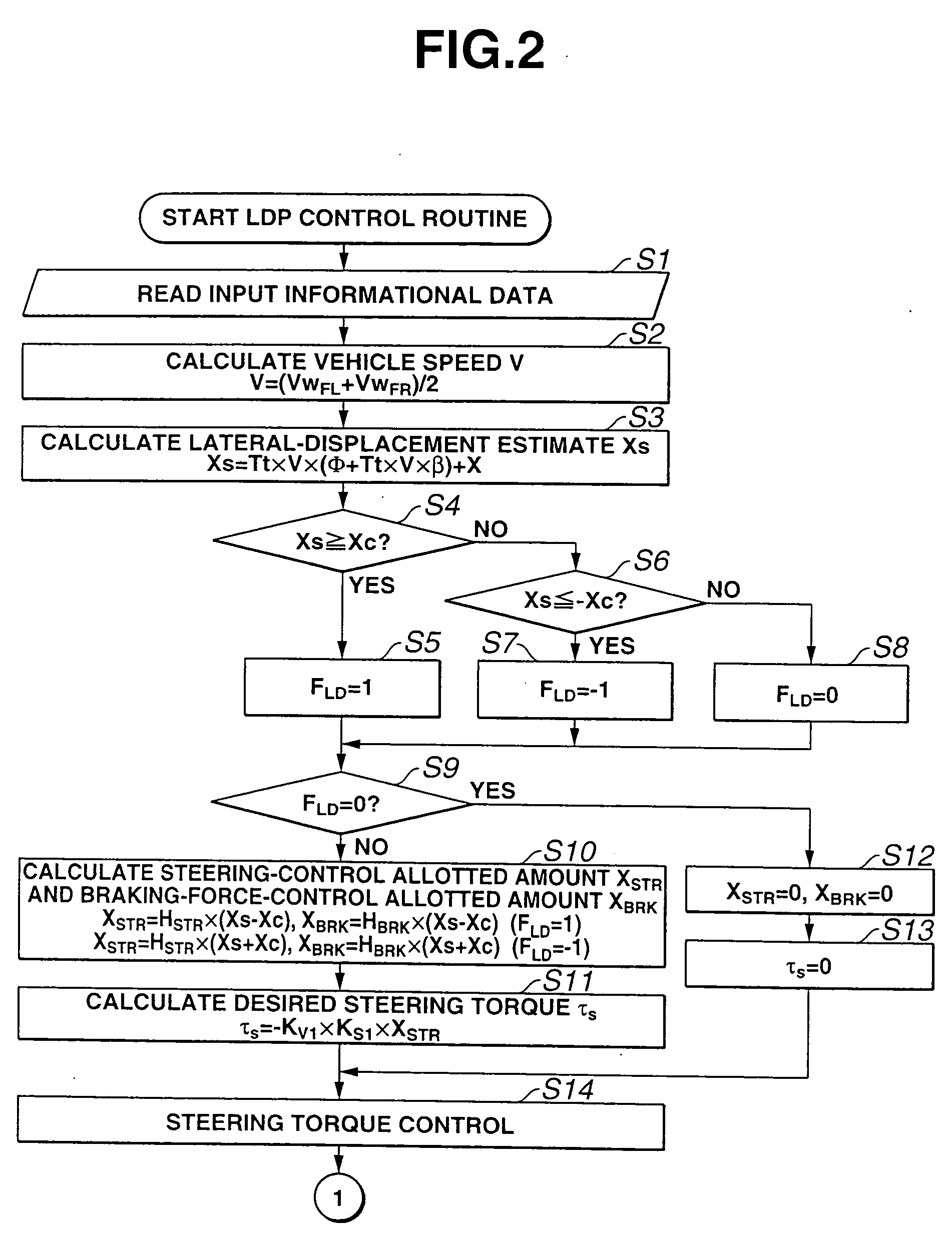
In an automotive lane deviation prevention (LDP) apparatus capable of executing LDP control by which a host vehicle is avoided from deviating from a driving lane, a control unit includes an LDP control allotted amount calculation section that calculates, responsively to a host vehicle's turning state, a steering-control allotted amount for LDP control and a braking-force-control allotted amount for LDP control, in presence of the host vehicle's lane-deviation tendency from the driving lane. In order to avoid the host vehicle's lane-deviation tendency, steering torque is controlled responsively to a steering-torque-control controlled variable determined based on the steering-control allotted amount, whereas braking forces applied to respective road wheels are controlled responsively to braking-force-control controlled variables determined based on the braking-force-control allotted amount.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for vehicle integrated chassis control system
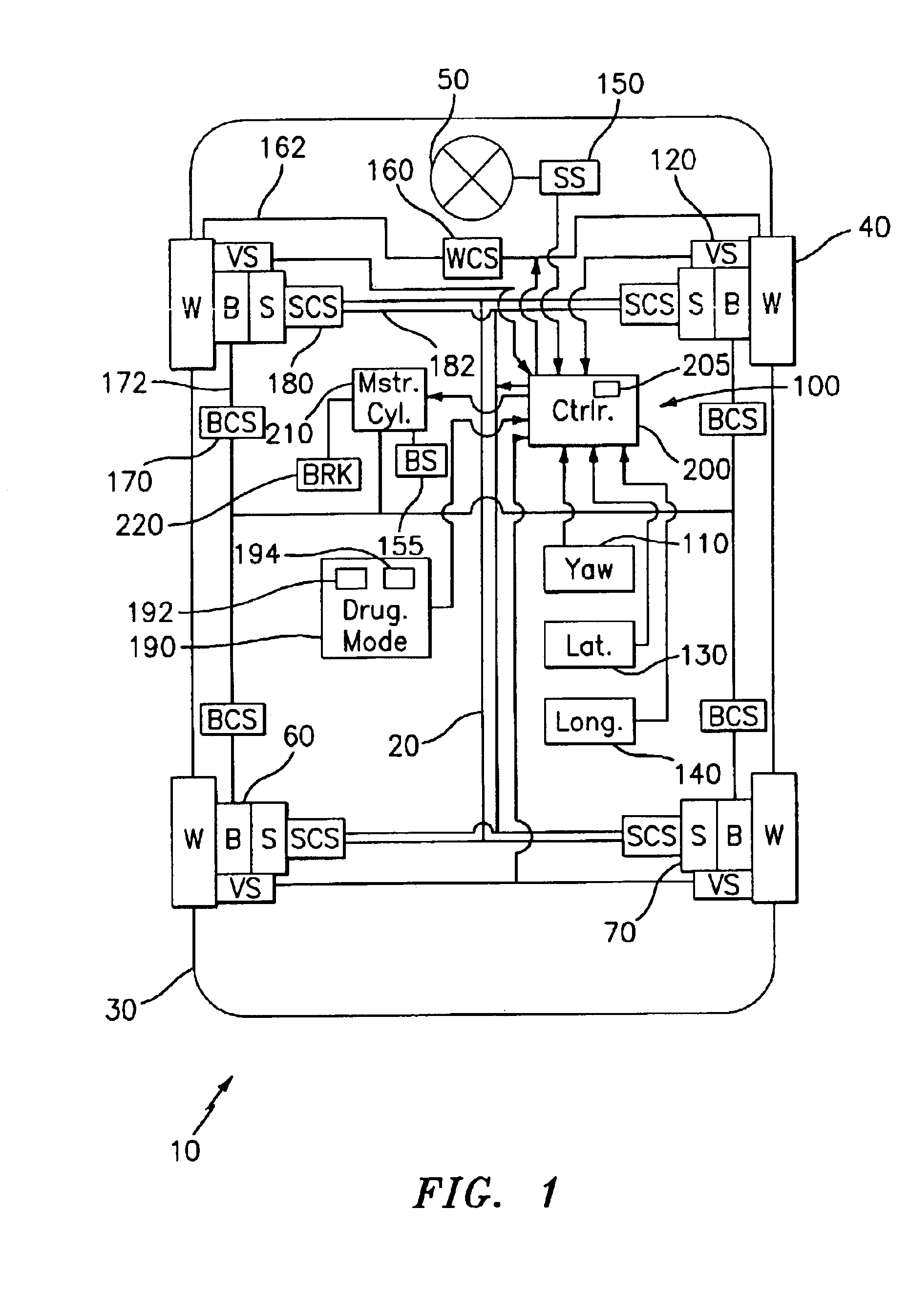
InactiveUS6879898B2Brake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsControl systemEngineering
An integrated chassis control system for a vehicle having at least one vehicle subsystem is provided, which includes; at least one sensor for sensing at least one vehicle parameter, at least one vehicle control system for adjusting the at least one vehicle subsystem, a driving mode switch for selecting at least one driving mode, and a controller responsive to the at least one sensor and the driving mode switch. The controller is adapted for controlling the at least one vehicle control system in accordance with the at least one driving mode.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Driving assistance control apparatus for vehicle
ActiveUS20170088174A1Reduce steering angle deviationSolve the large energy consumptionBrake system interactionsSteering linkagesSteering angleEngineering
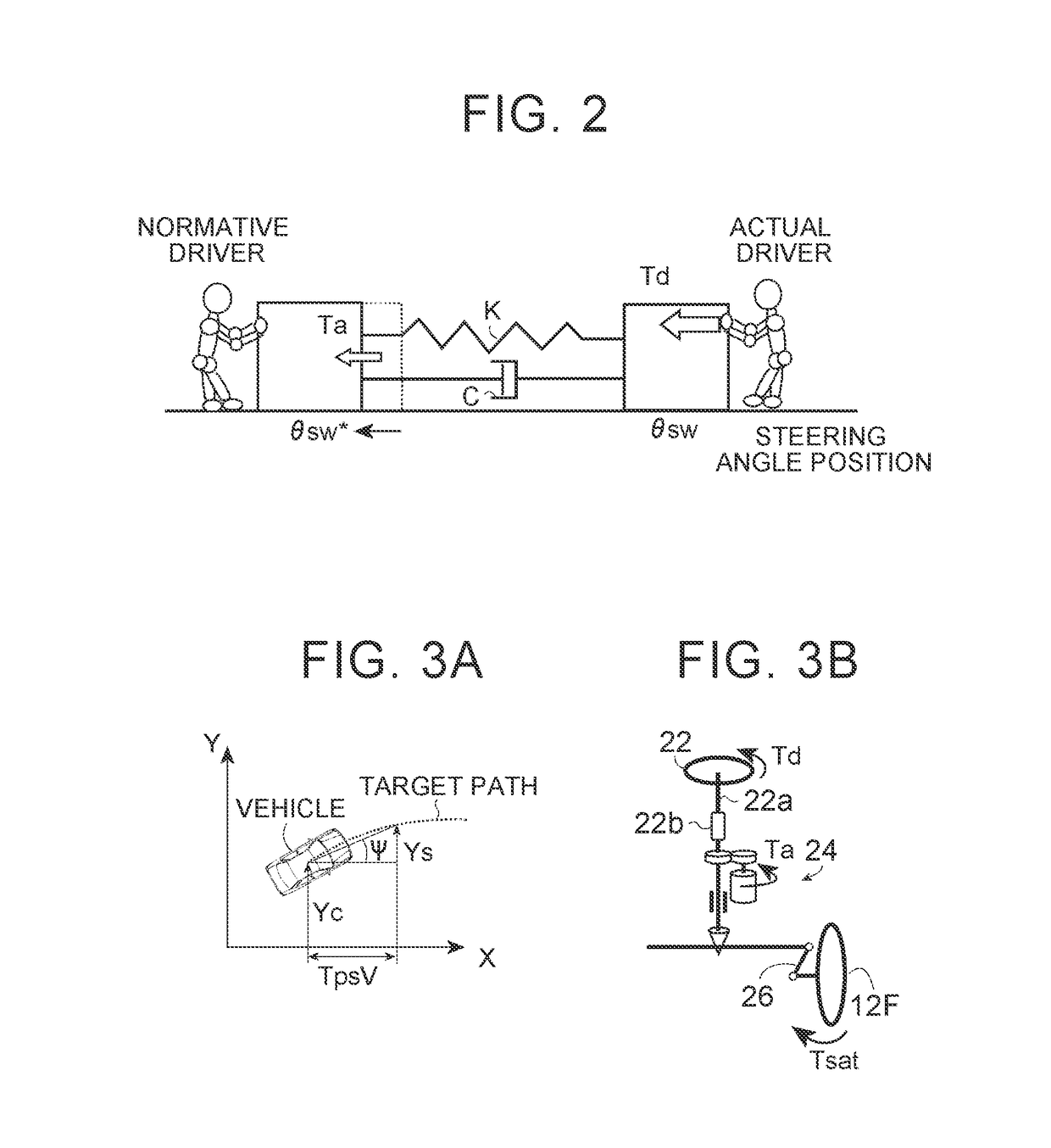
An apparatus includes a steering assist torque determination unit and a steering assist torque control unit. The steering assist torque determination unit determines a steering assist torque including a first component that is determined on the basis of a deviation between an actual steering angle and a target steering angle for achieving a target path determined irrespective of driver's steering. The steering assist torque control unit controls a steering assist mechanism such that the steering assist torque is applied. The ratio of the magnitude of the first component of the steering assist torque to the deviation between the target steering angle and the actual steering angle is determined on the basis of the magnitude of the deviation between the steering assist torque and the driver's steering torque in a past predetermined period.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control device for vehicle power steering
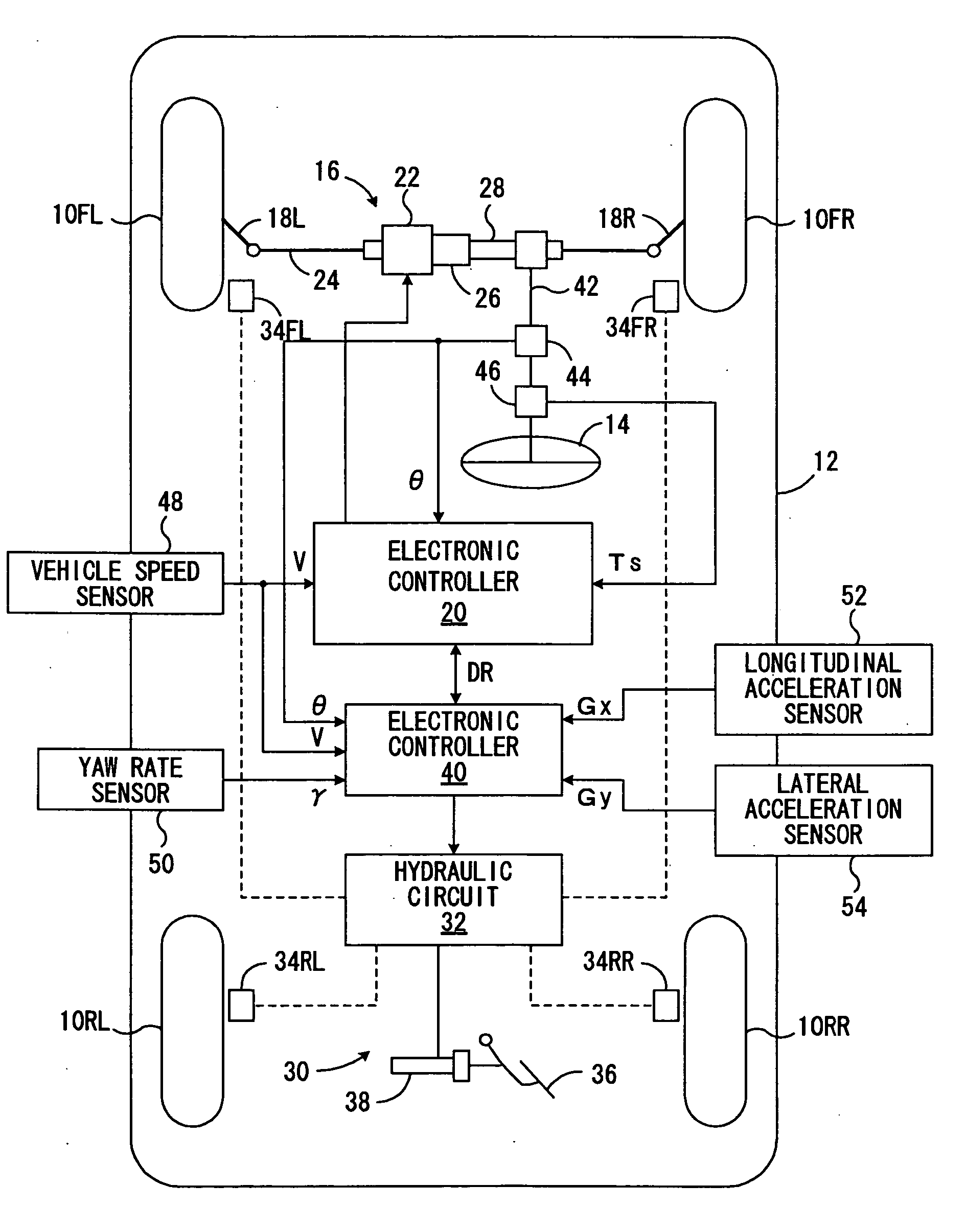
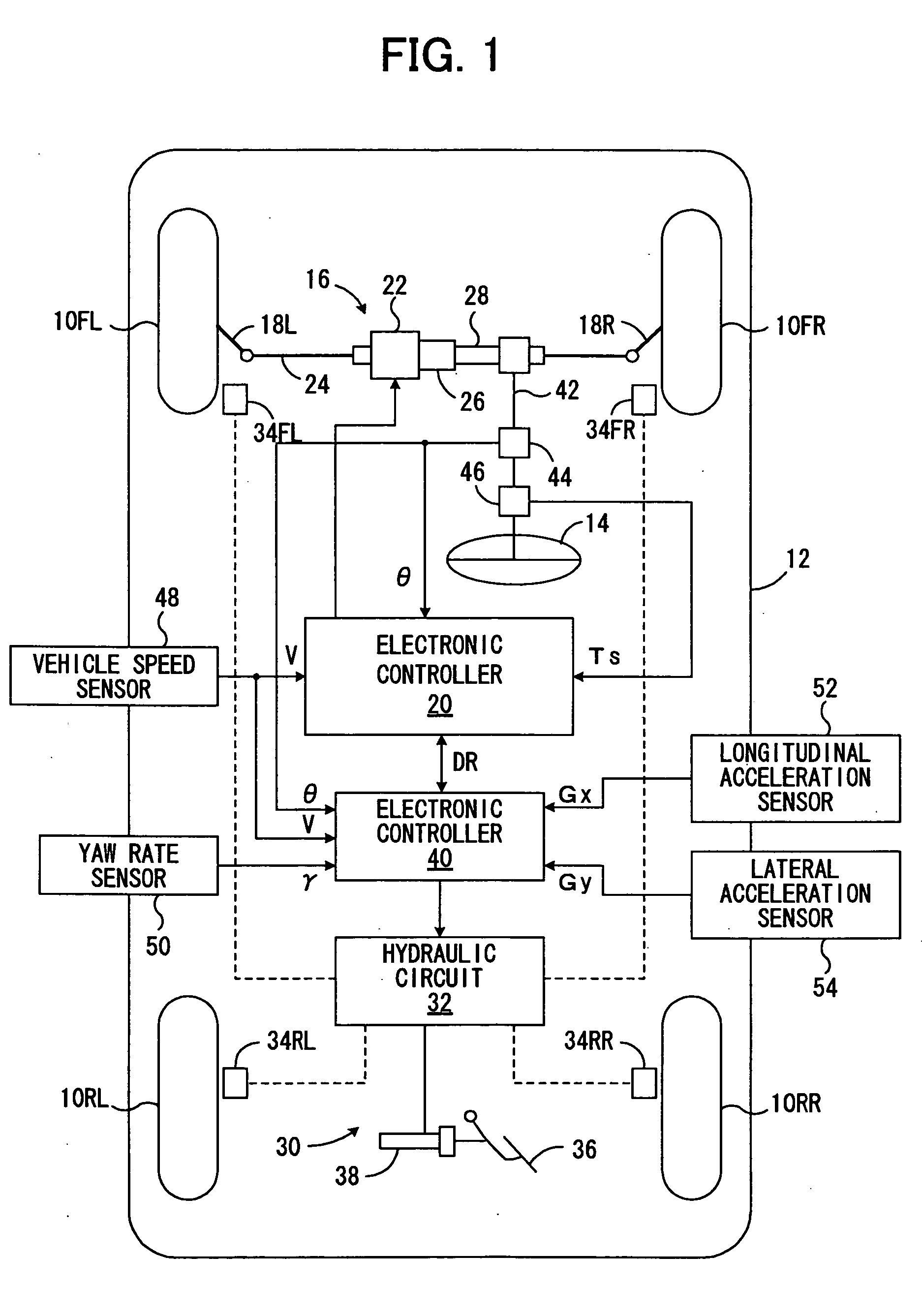
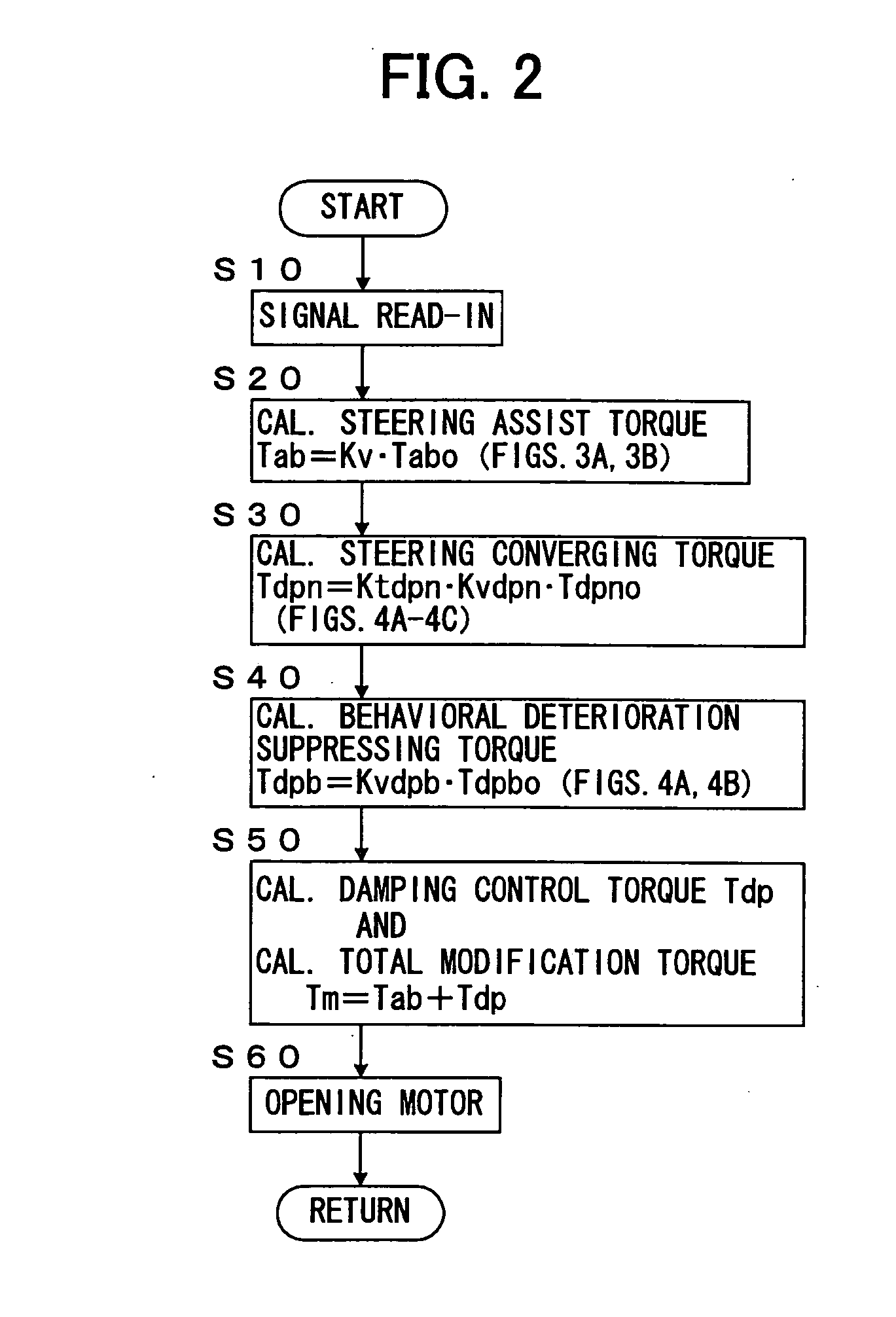
ActiveUS20050049769A1Steering smoothnessSuppress fluctuationsBrake system interactionsSteering initiationsVehicle behaviorPower steering
A novel control device for a vehicle power steering apparatus or system is improved for providing preferable steering convergnecy even under the execution of VSC, while ensuring the steering smoothness under normal running conditions. In the control device, the target value of total modification torque to be added to steering torque through an power steering apparatus, is calculated based upon steering assist torque, calculated based upon at least steering torque; steering converging torque, based upon a steering velocity; and behavioral deterioration-suppressing torque for suppressing unwanted steering motions which would cause further deterioration of a vehicle behavior under oversteered or understeered conditions. In this calculation, when a predetermined condition is satisfied, the degree of contribution of the target value of the behavioral deterioration-suppressing torque to the target value of the total modification torque is rendered higher than the degree of contribution of the target value of the steering converging torque to the target value of the total modification torque.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Steering control during split-mu ABS braking
InactiveUS6968920B2Maintain stableMaintain controllableBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorElectricity
A vehicle stability compensation system, which is arranged to adjust dynamically the self-centering position and the steering feel of the vehicle steering system during split mu braking operation. The adjustment being based on at least one operational variable representing a corrective steer angle for the vehicle and hence representing a target self-centering position. A target self-centering error is derived from the difference between the target self-centering position and an actual vehicle steering angle. A torque demand that is proportional to the target self-centering error is then added to an assistance torque generated by the electrically assisted steering system to shift the self-centering position so as to encourage the vehicle driver to move the steering wheel such as to reduce the target self-centering error to zero for maintaining the vehicle stable and controllable.
Owner:TRW LIMITED
Vehicle steering control device
InactiveUS20040099469A1Restricting undesirableRestricting unexpected modificationHand manipulated computer devicesBrake system interactionsSteering angleFrictional coefficient
A new and novel device for controlling a steering characteristic of a vehicle such as automobile so as to enhance an effect of suppressing a change in a behavior of the vehicle body due to a difference between driving and braking forces on the left and right wheels is characterized in that the device makes an amount of controlling the steering characteristic smaller as an index indicating an amount of a shift of vertical loads between the left and right wheels is increased. The steering characteristic is modified through controlling steering assist torque or a steering angle of the steered wheels. The steering assist by the steering control device is fully effective when the vehicle is running on a straight road having surfaces of different frictional coefficients while less effective on a curved road having a uniform frictional surface, preventing undesirable and unexpected modification of the steering characteristic during turning of the vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
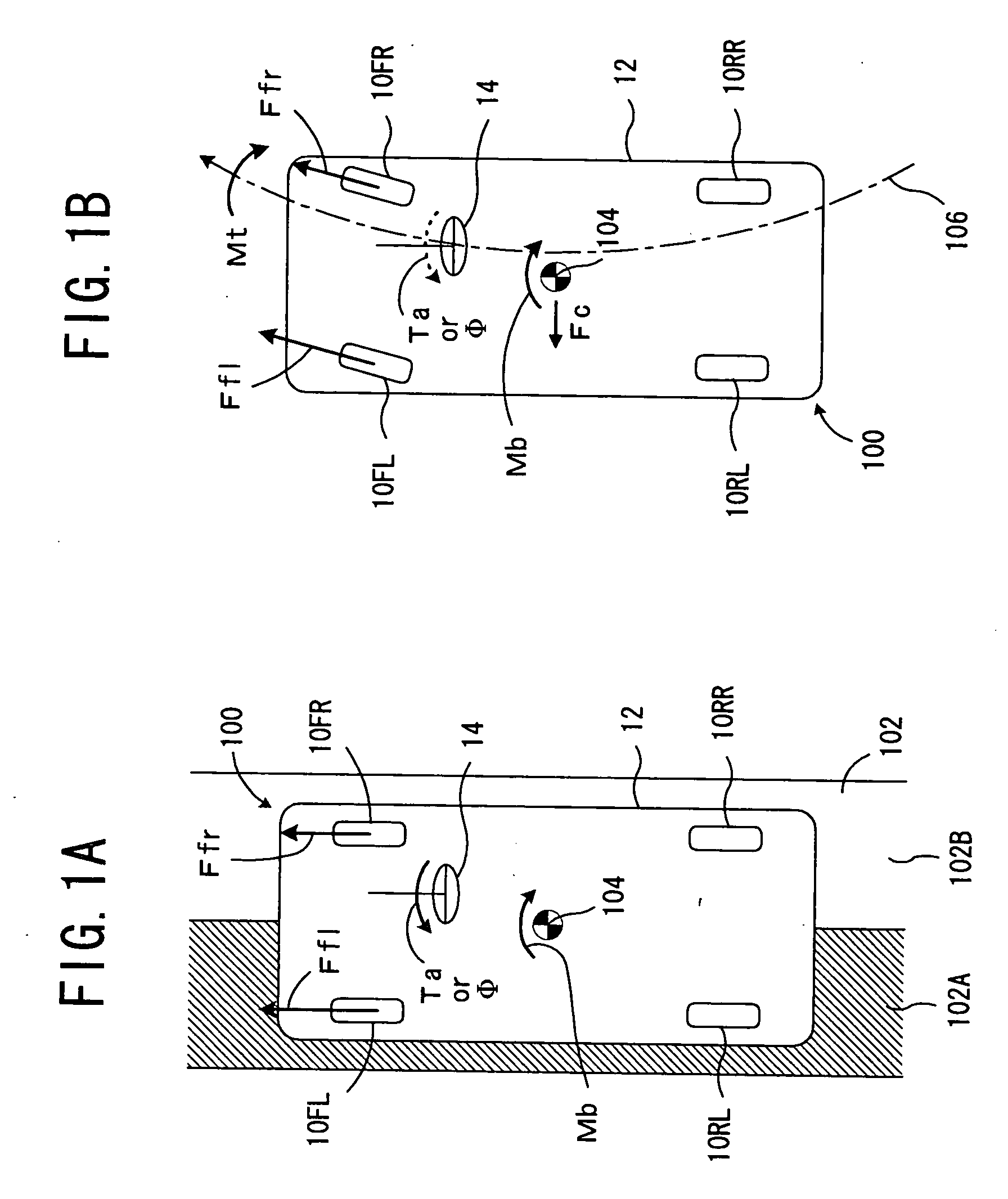
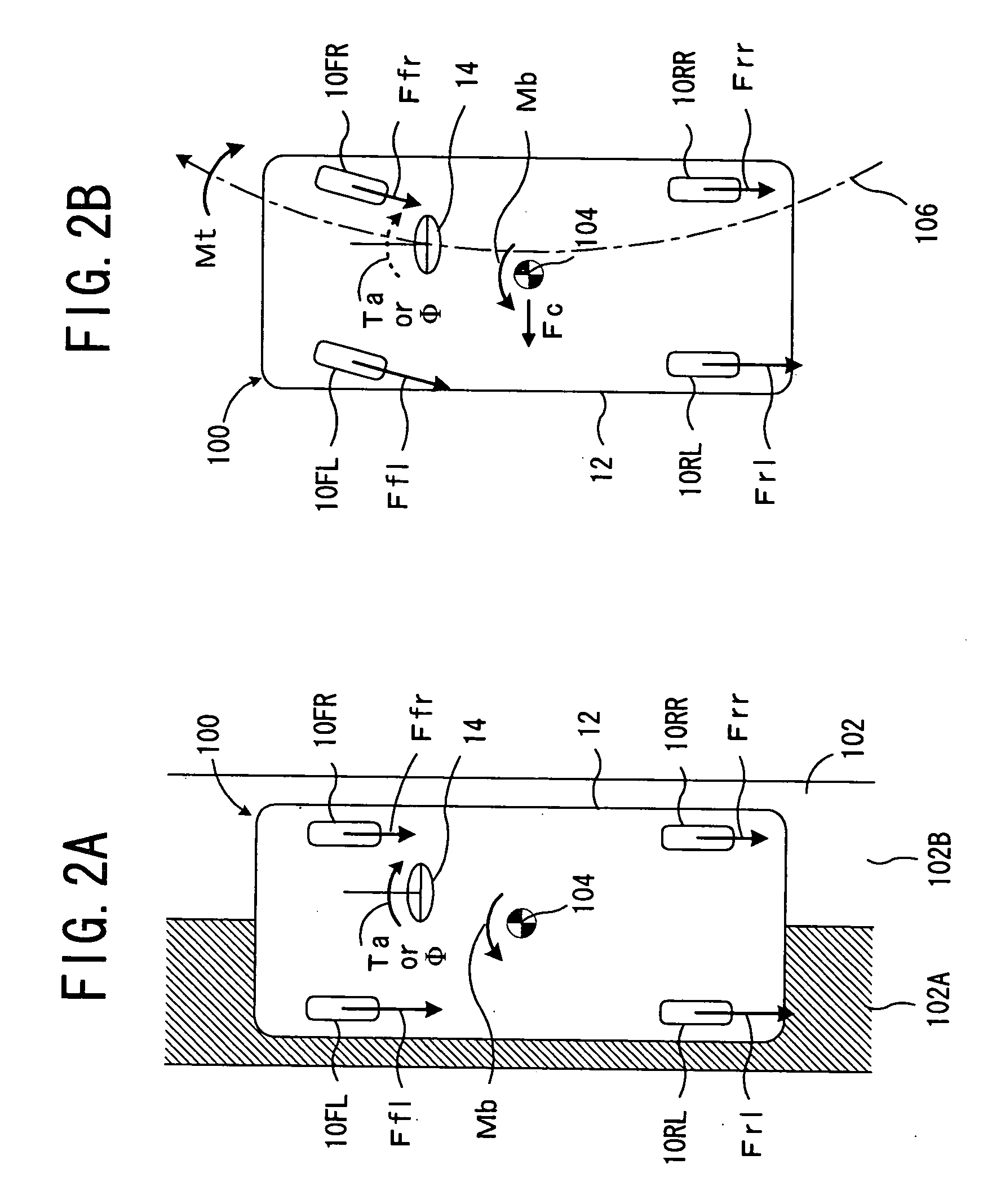
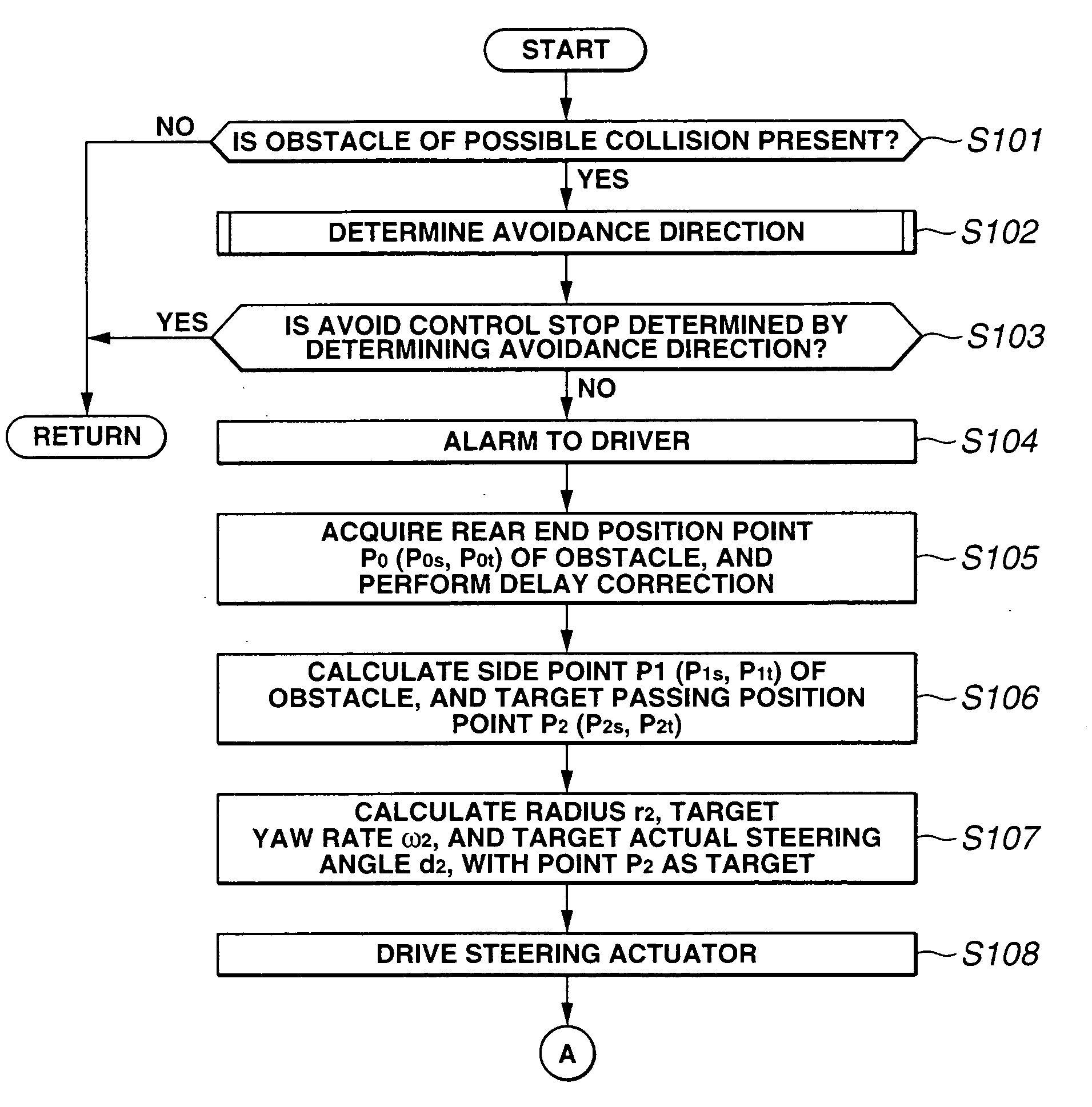
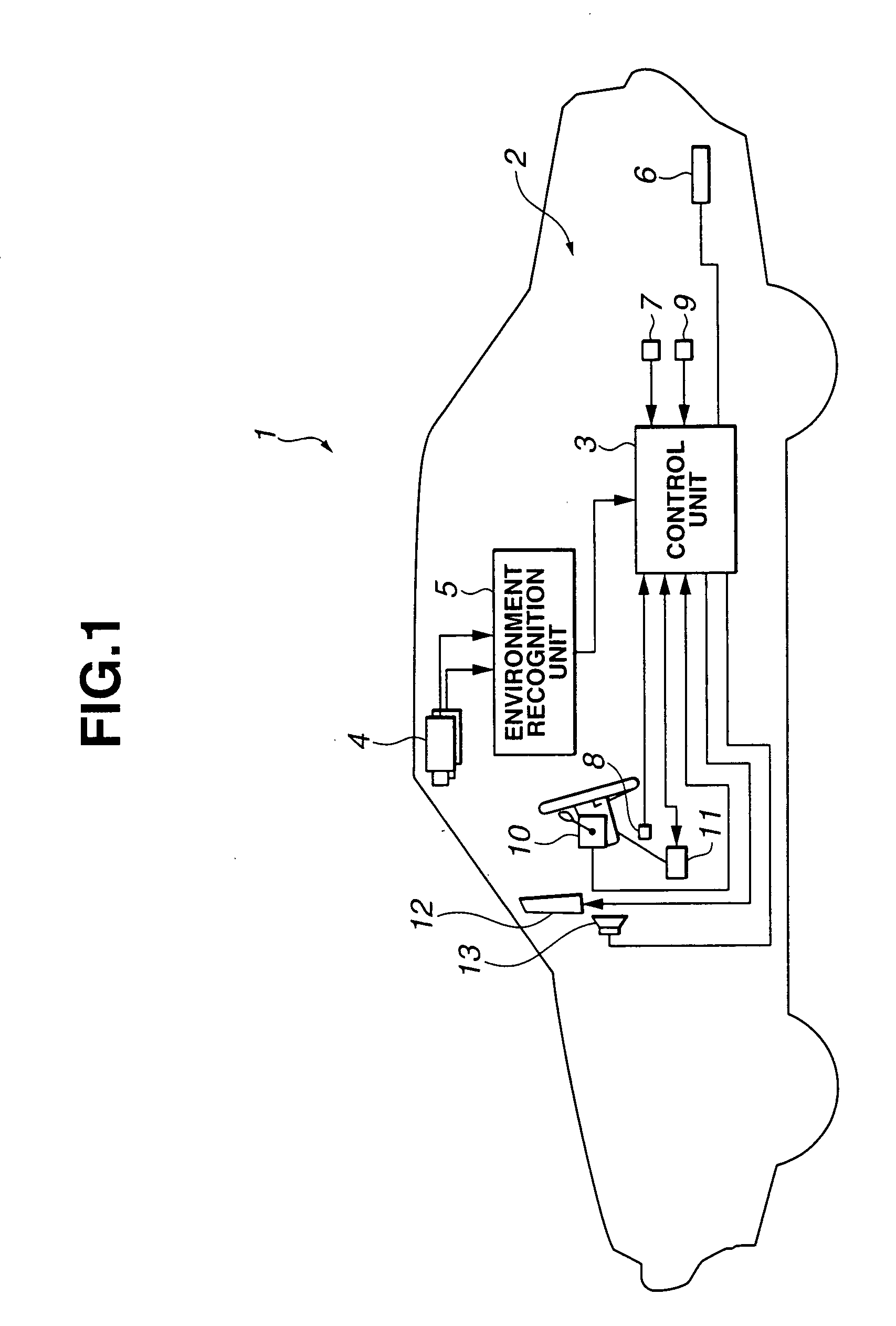
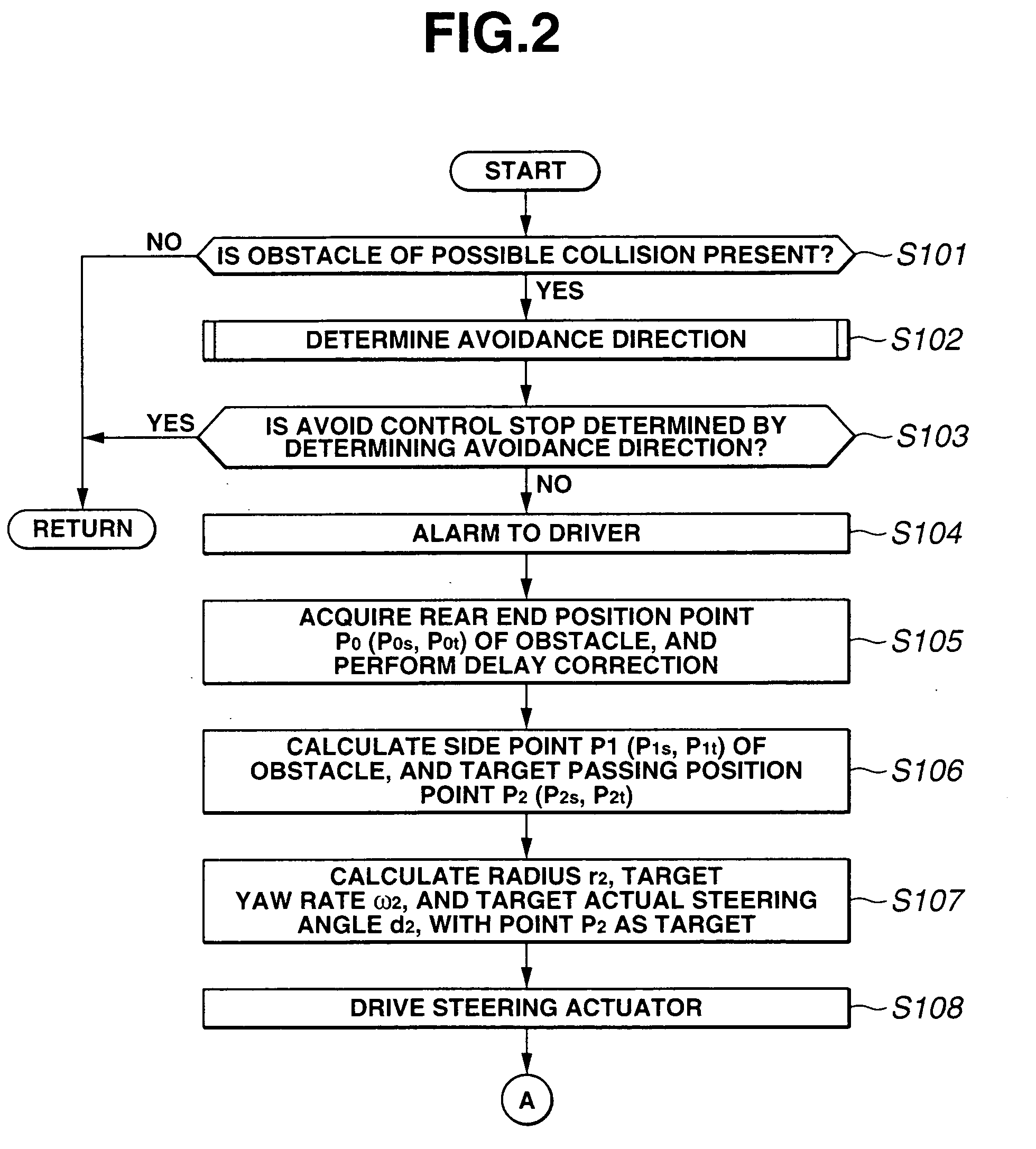
Vehicle traveling control device
InactiveUS20050125155A1Increase the number ofSmoothly and efficiently and stably avoidingBrake system interactionsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringStereo camera
A control device sets avoidance traveling reaching points, avoidance traveling target points, and a final avoidance target point of an obstacle to be avoided based on the position of the obstacle to be avoided and the position of the vehicle for the target passing position based on obstacle information recognized by a stereo camera, and an environment recognition unit, inputs the target actual steering angle as a vehicle motion parameter obtained according to a vehicle motion model to an electric power steering control device with these target passing positions as a target, and guides the avoidance traveling. The increase of the number of operations is controlled thereby to a minimum, and the obstacle is smoothly, efficiently and stably avoided based on actual behavior of the vehicle.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com