Patents
Literature
136results about How to "Offset error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
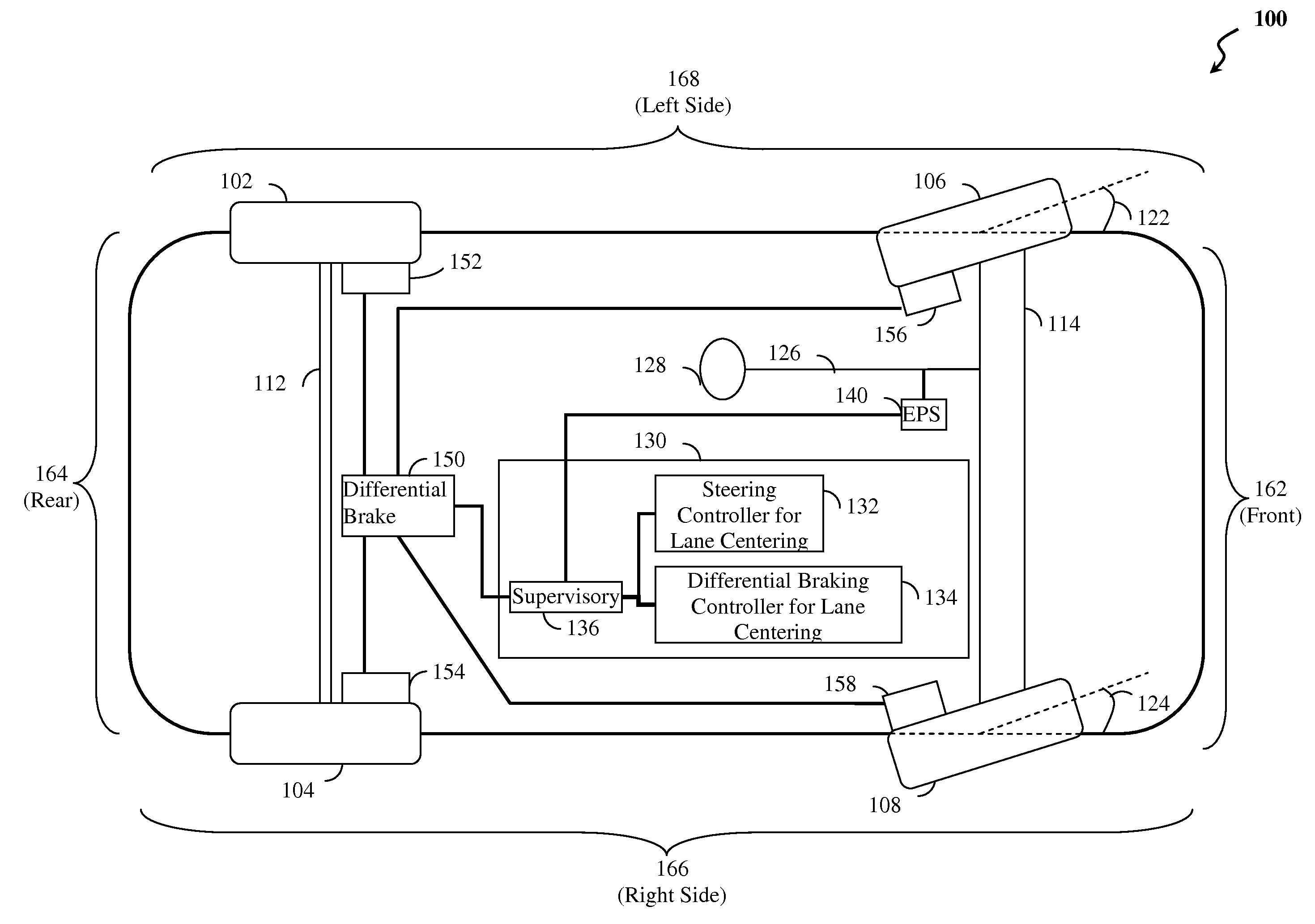
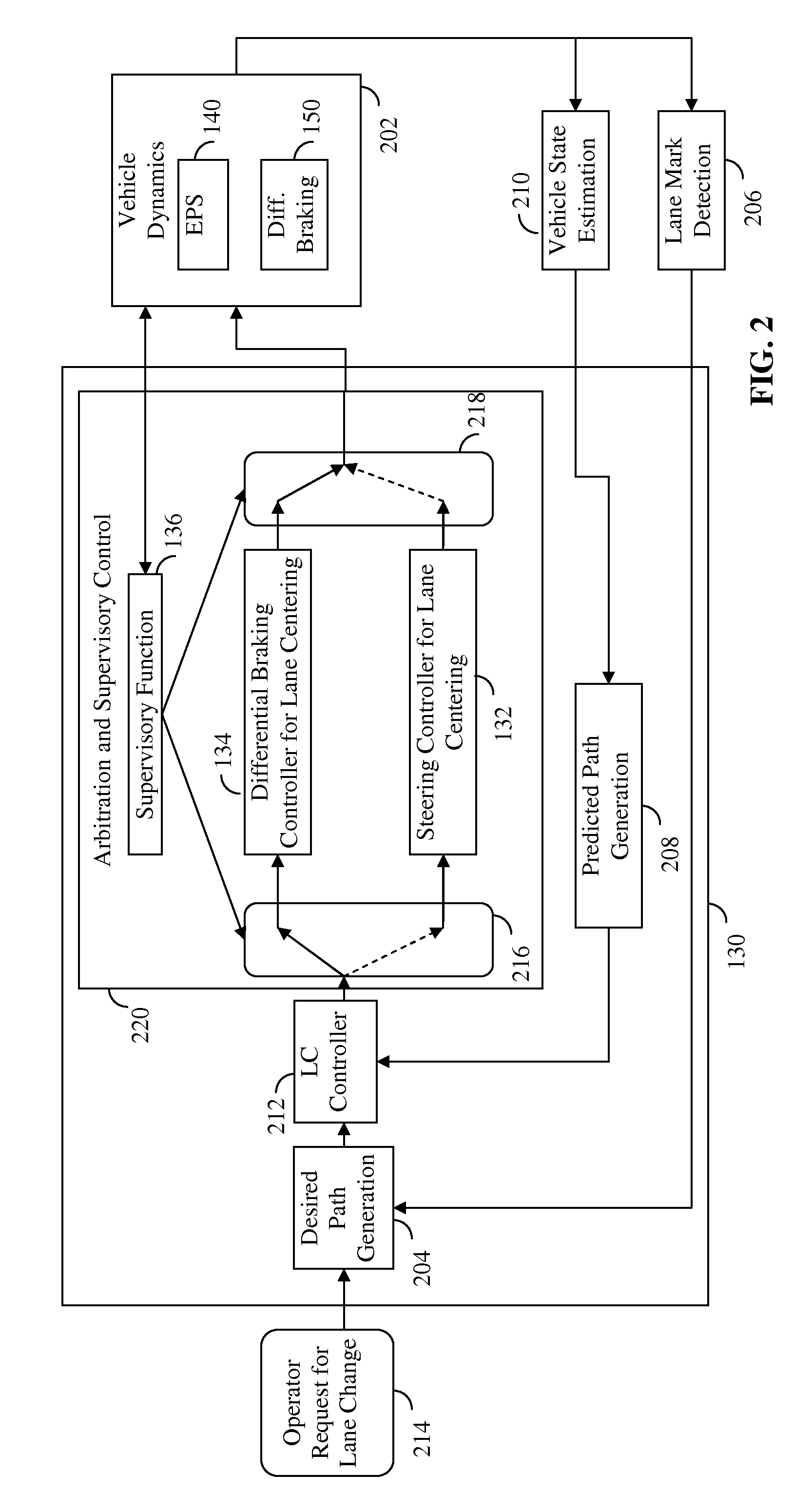
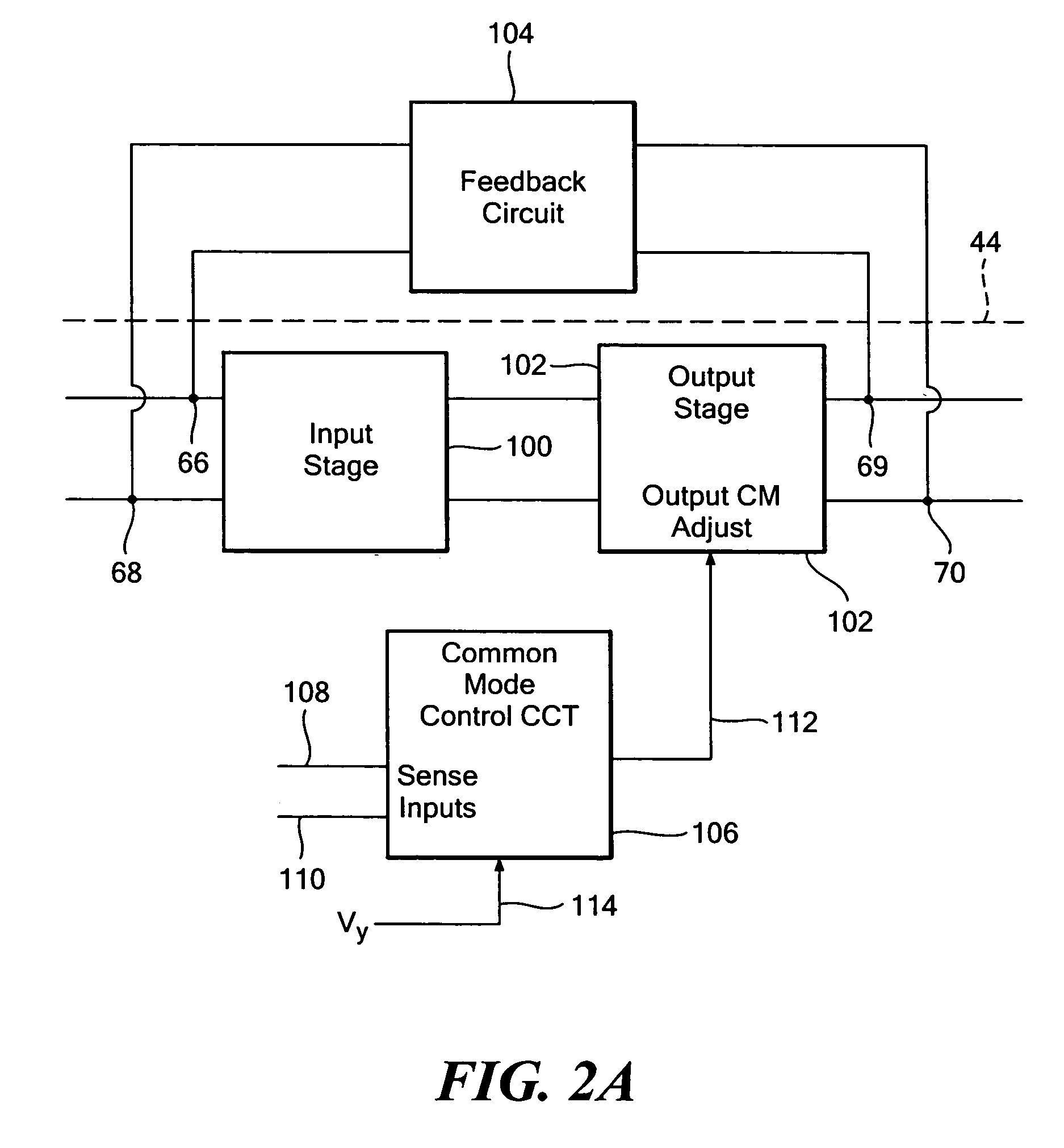
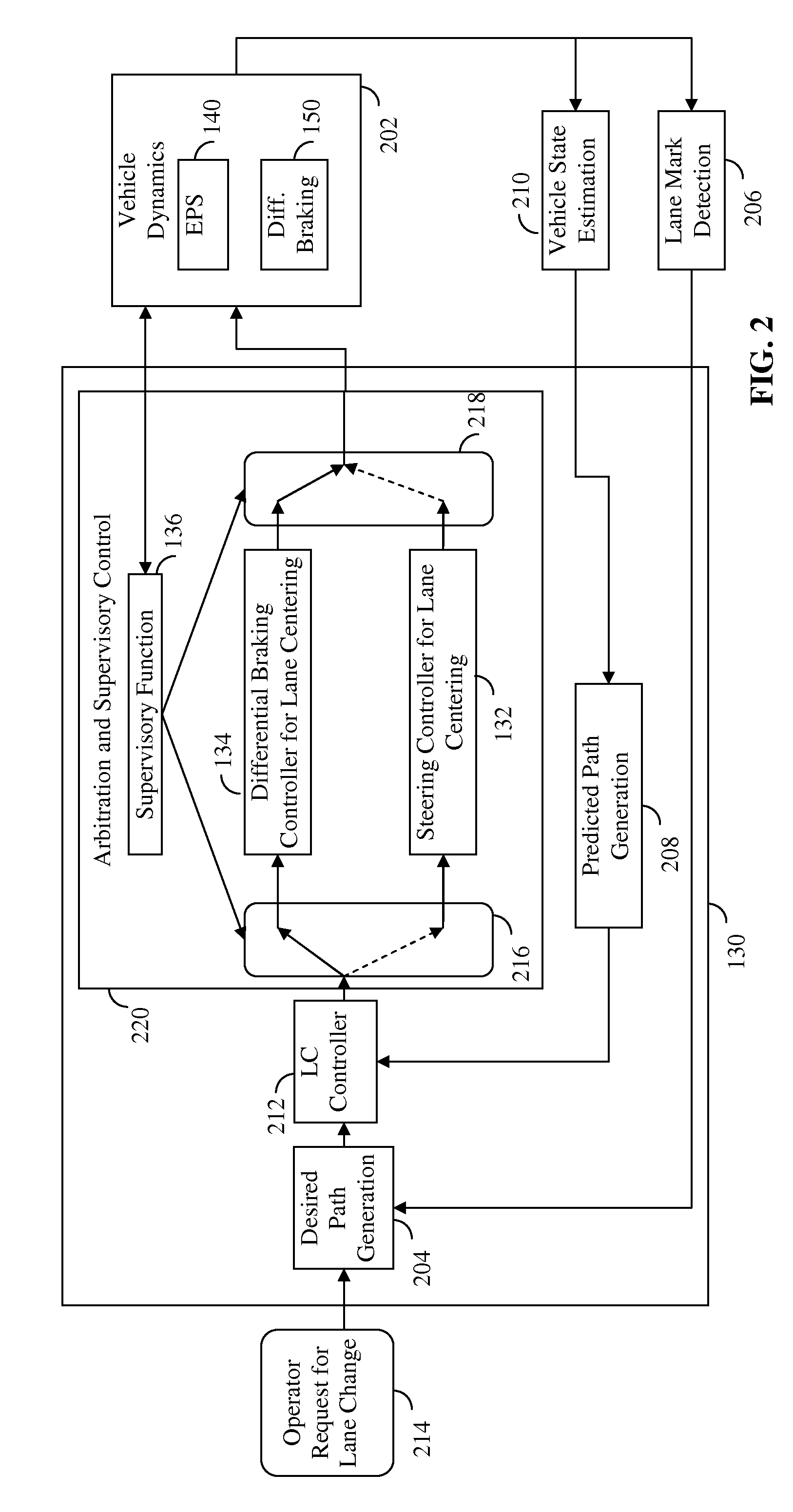
Lane centering fail-safe control using differential braking
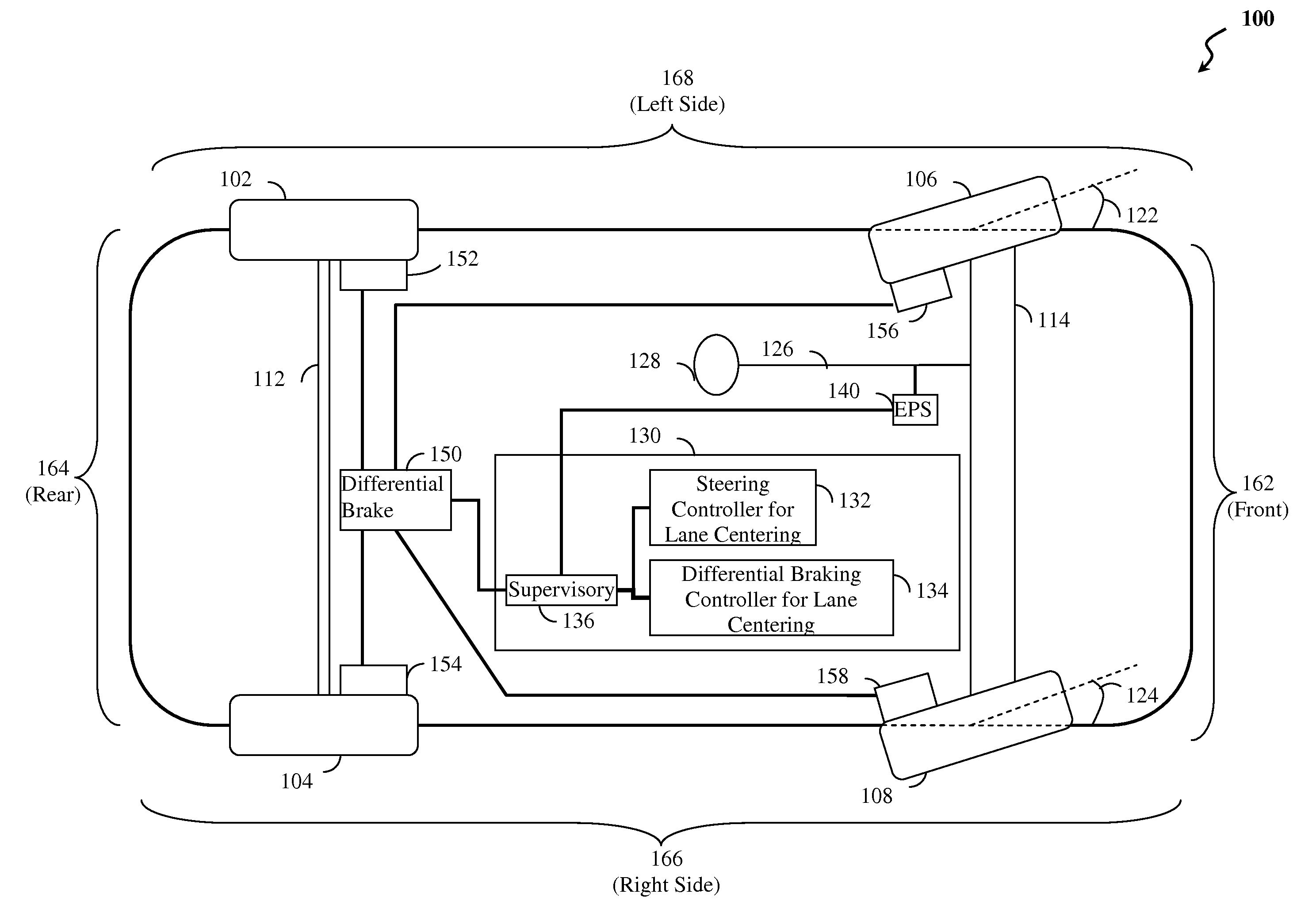
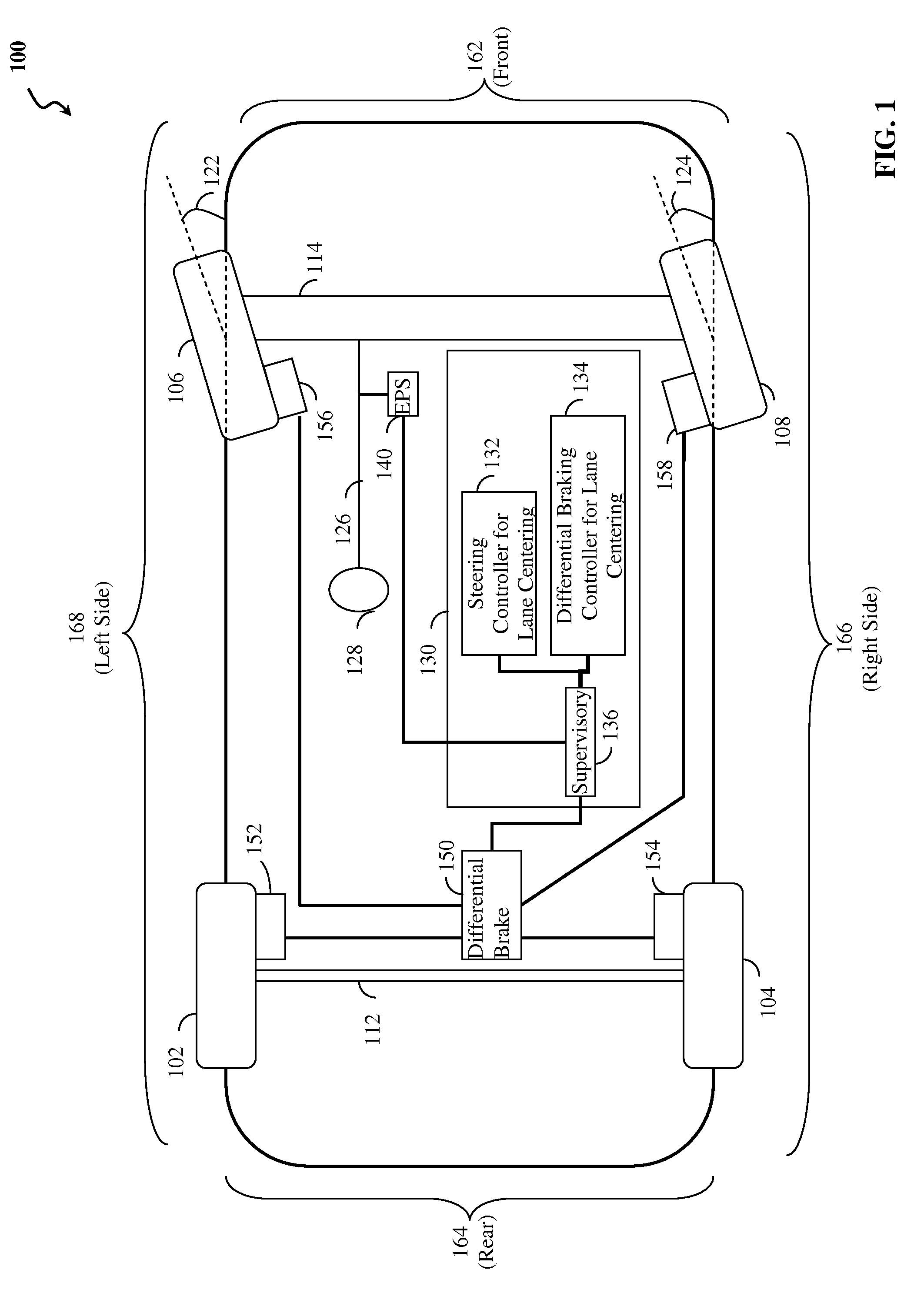
ActiveUS20120283907A1Minimize the differenceOffset errorVehicle testingBrake system interactionsElectric power steeringEngineering
Method, system and non-transitory computer-readable medium for fail-safe performance of a lane centering system. An electrical power steering (EPS) system of a vehicle is monitored for a failure and operation of the lane centering system is switched to a differential braking controller to output differential braking commands to a differential breaking system upon determining that a failure of the EPS system has occurred, where the output braking commands direct the differential braking system to apply force a brake for a wheel of vehicle, such by the applied braking force the vehicle follows a desired path determined for a lane centering operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
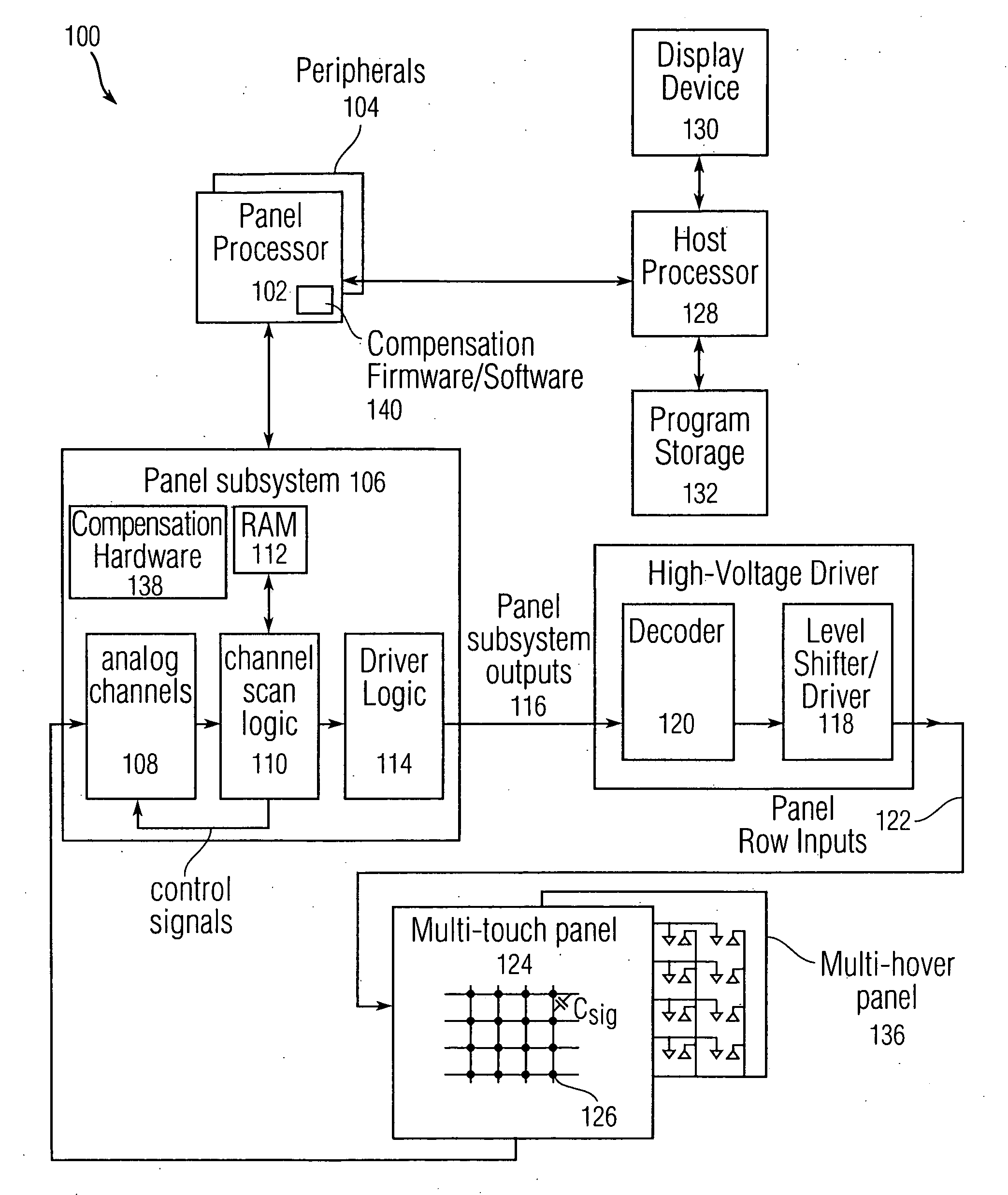
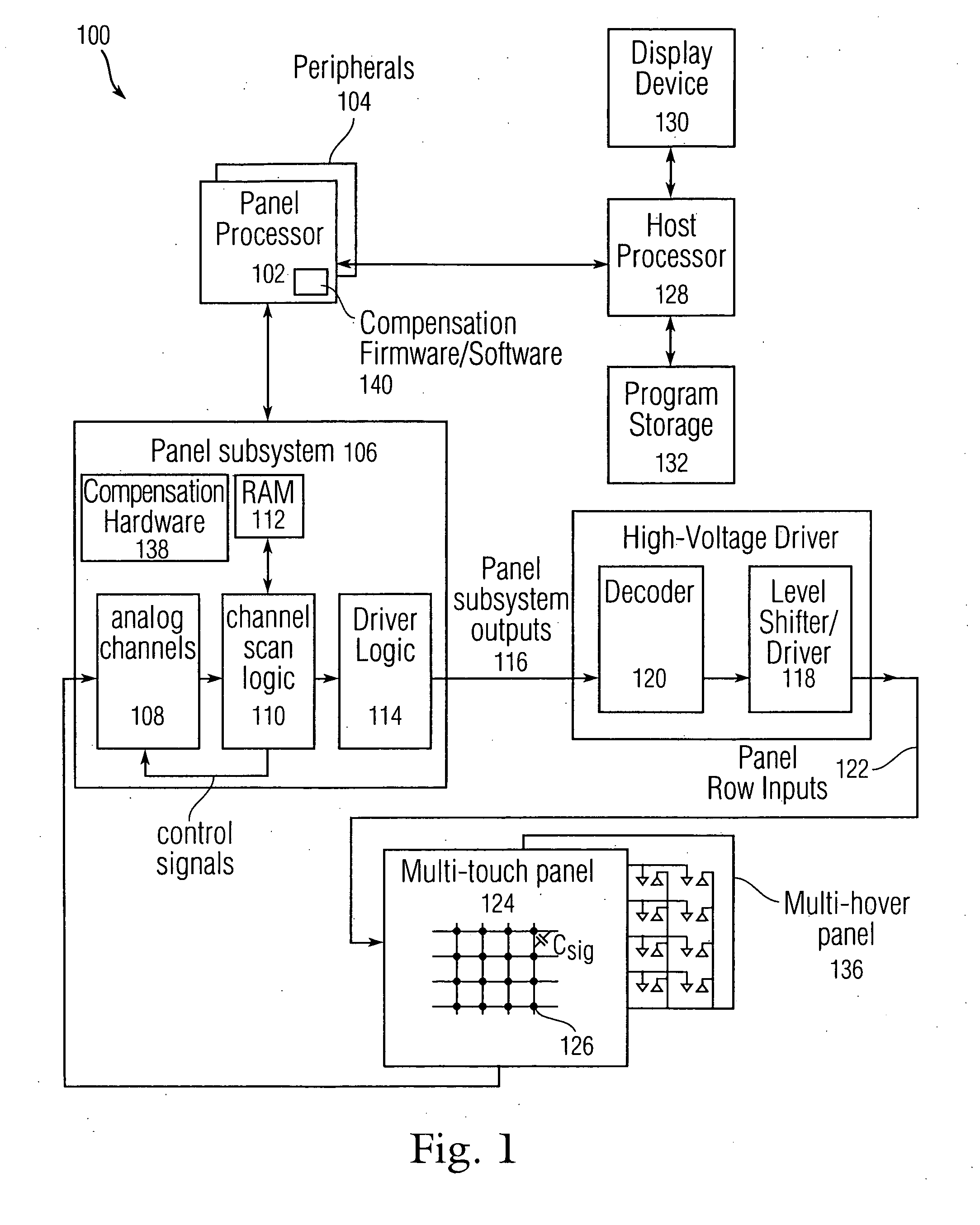
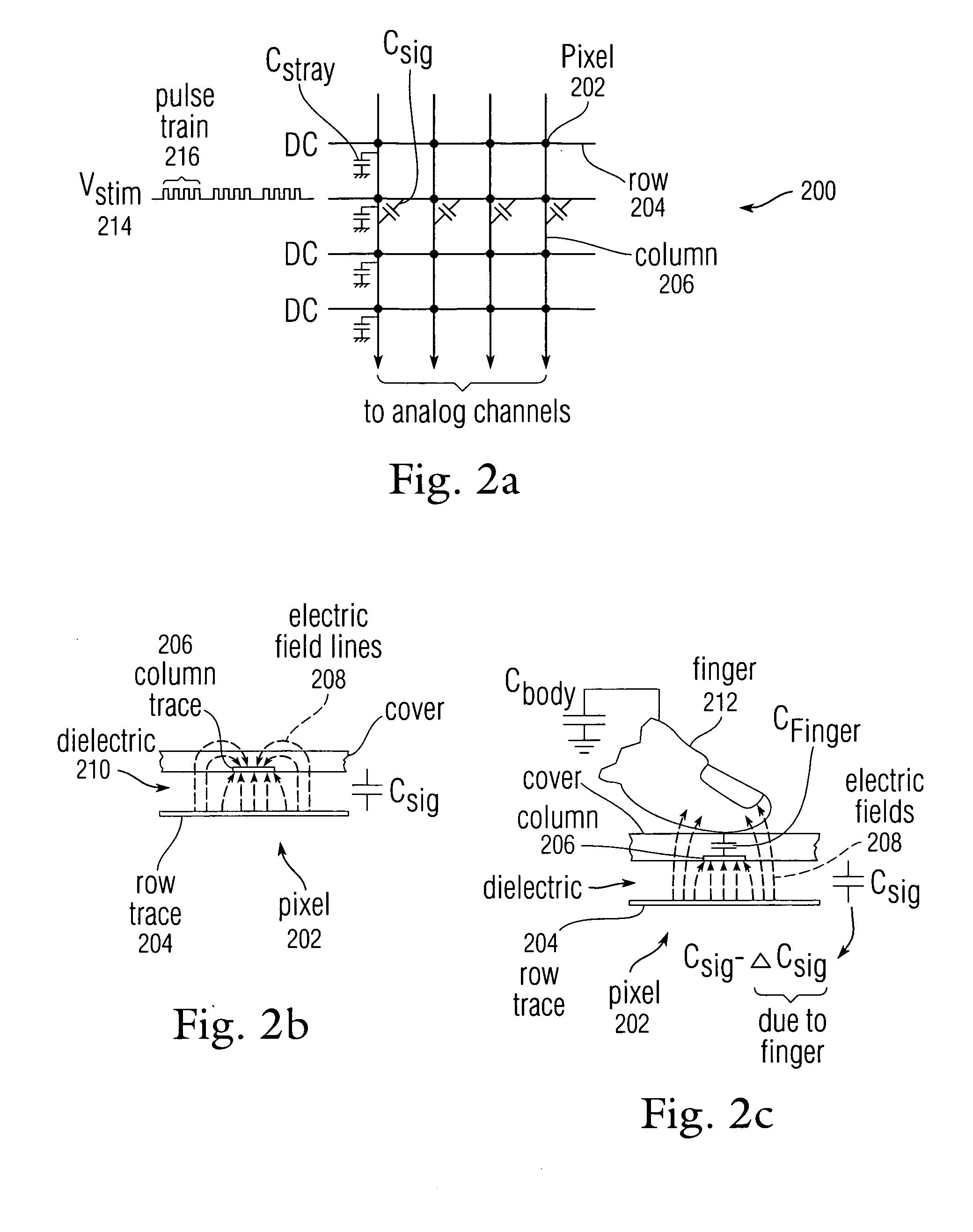
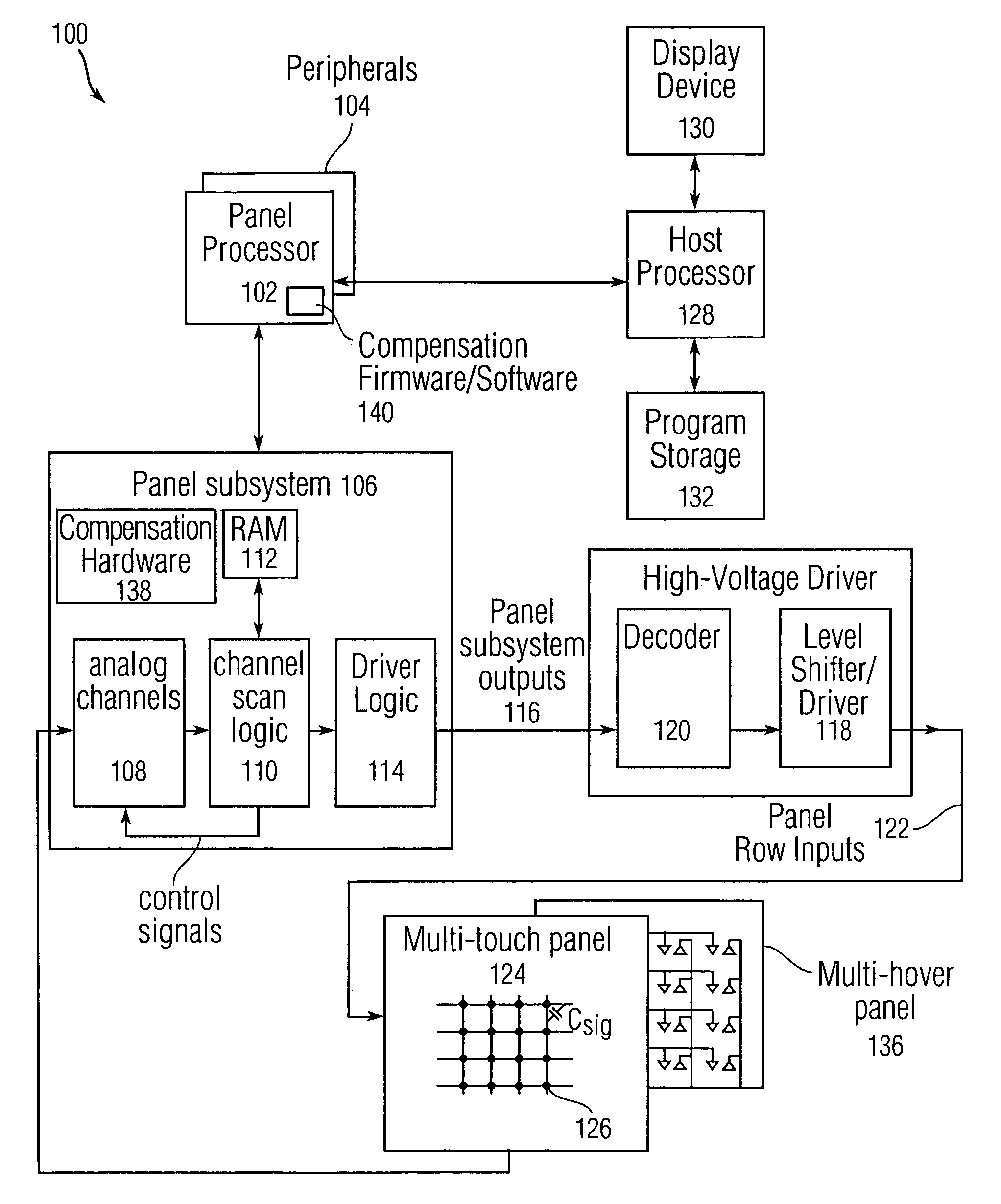
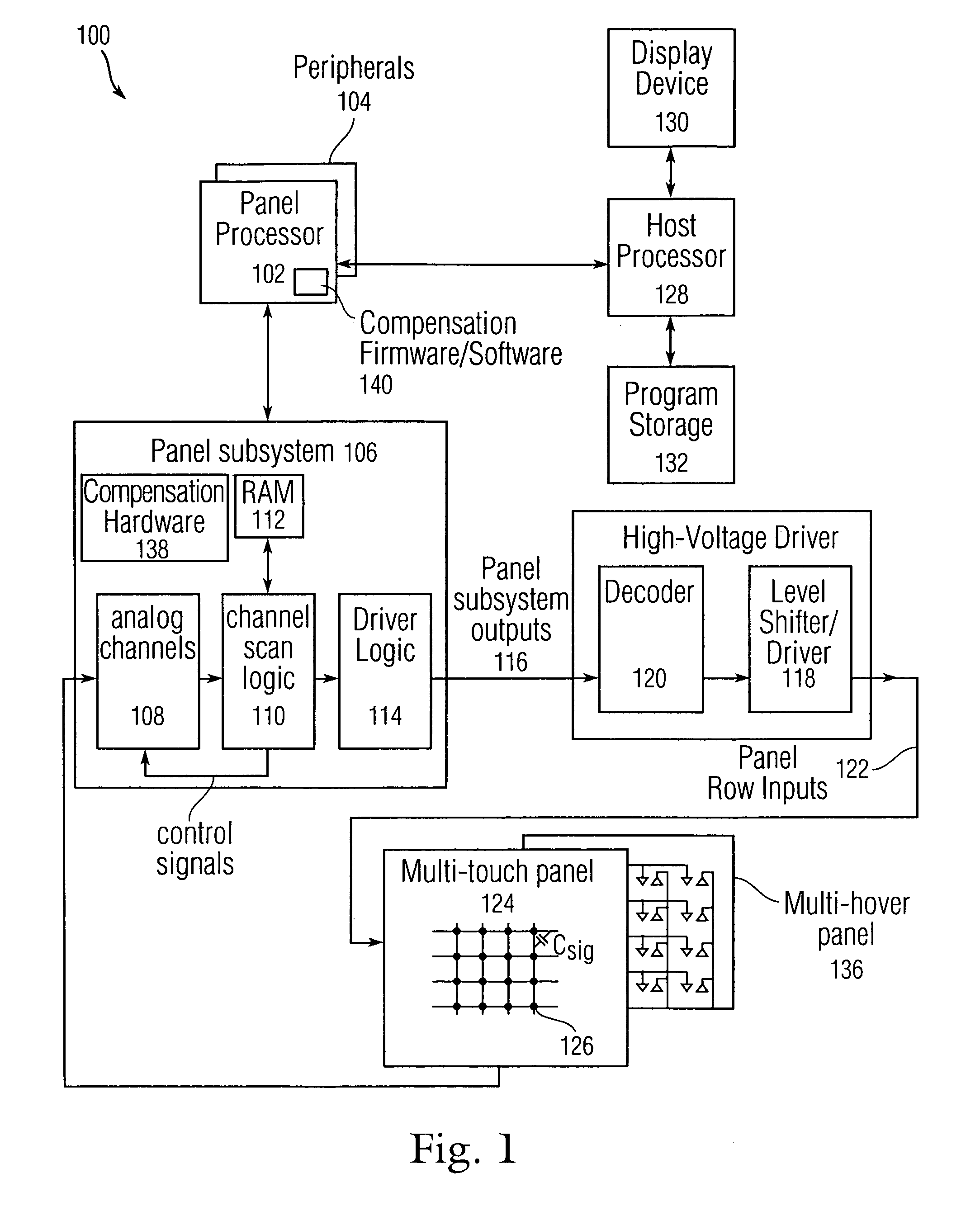
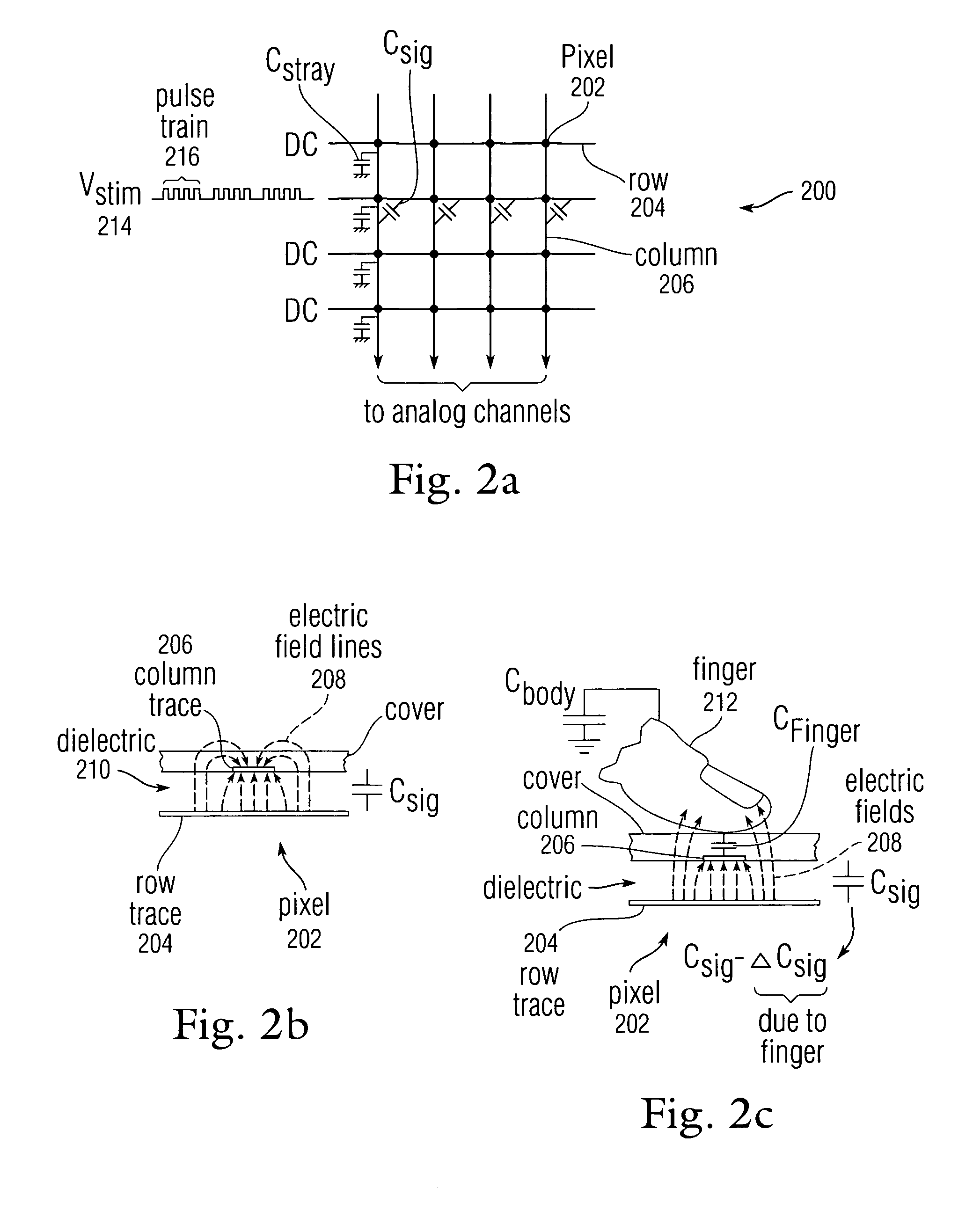
Error compensation for multi-touch surfaces
ActiveUS20080158184A1Minimize effectReduce and eliminate image distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingDistortionTemperature coefficient
Normalization of the built-in DC offset error in each analog channel is disclosed to reduce image distortion in multi-event (multi-touch or multi-hover) sensor panels. By eliminating the component-dependent offset error from each analog channel, each analog channel will generate approximately the same output value for a given dynamic input signal. Normalization can include “phantom row” compensation, which involves measuring the static output value of each analog channel when no stimulus is applied to any row of a multi-event sensor panel, and subtracting this value out of any subsequent output value generated by the analog channel. Normalization can also include DAC offset compensation, which involves setting the offset compensation voltage of each analog channel to some fraction of its normal value, measuring the output of the analog channel over temperature, determining a temperature coefficient, and adjusting any subsequent output value generated by the analog channel to account for this drift.
Owner:APPLE INC
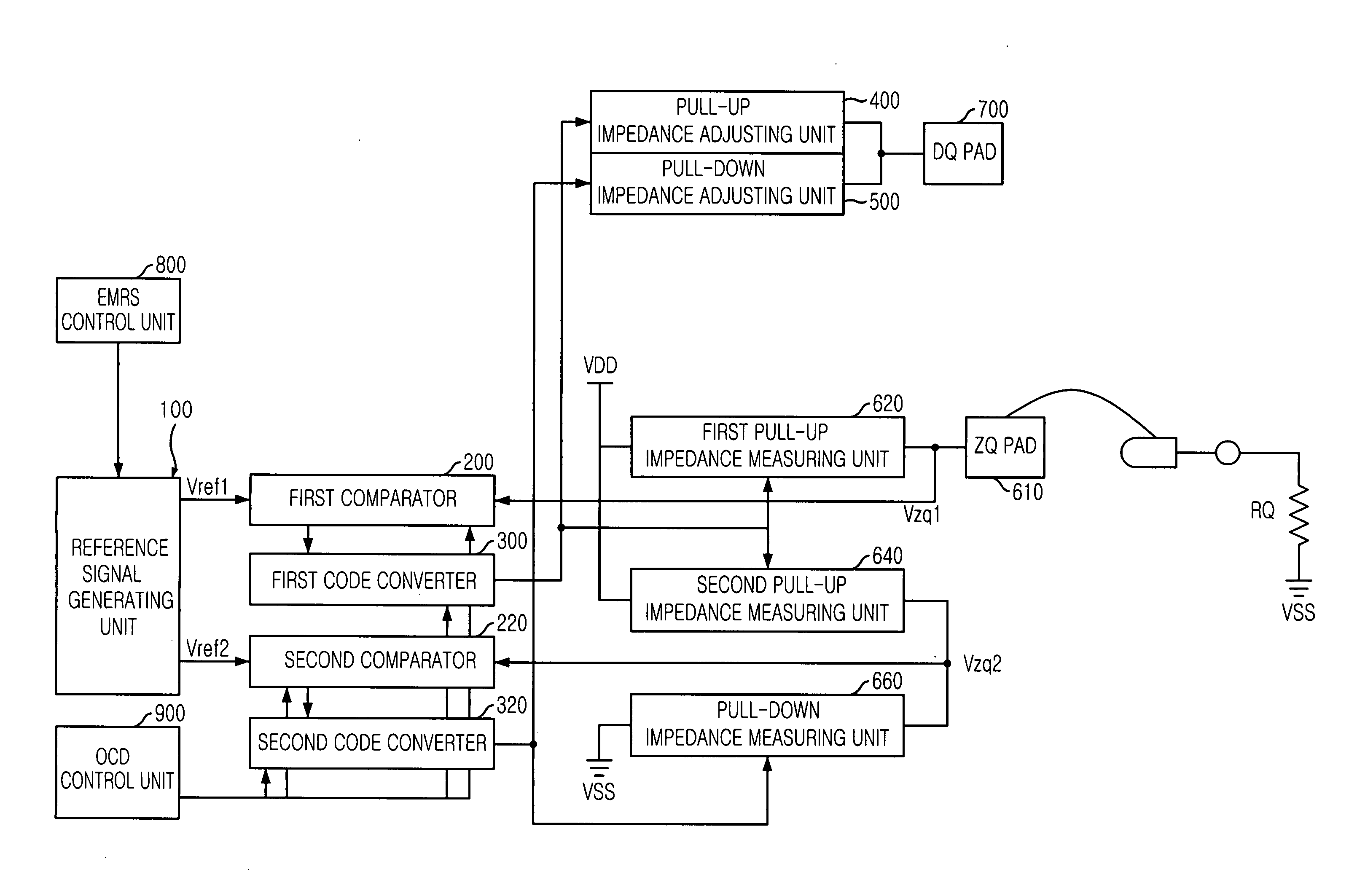
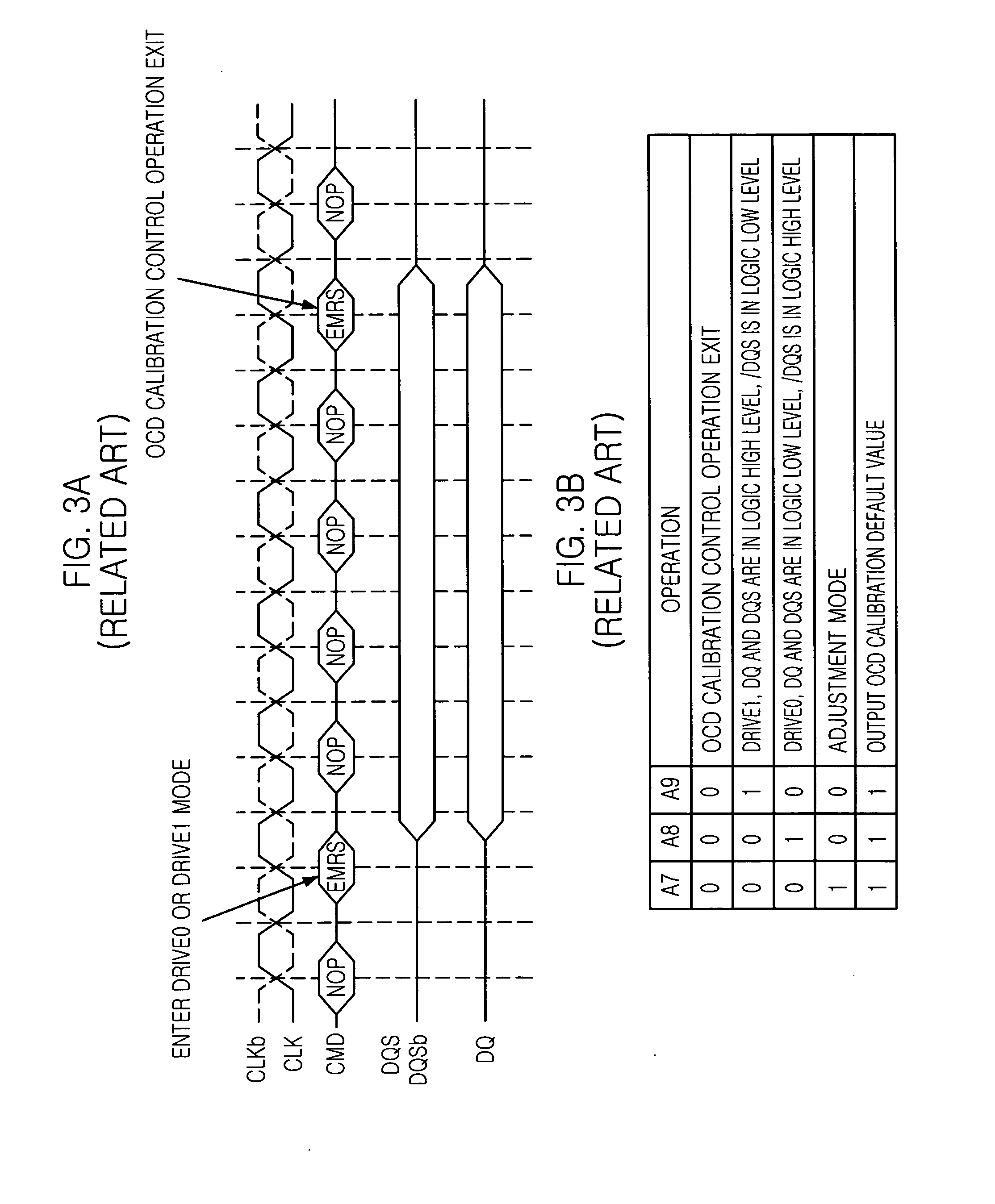
Semiconductor memory device for adjusting impedance of data output driver
An apparatus for comparing inputted signals by removing an offset voltage during adjusting an output impedance of a semiconductor memory device, includes a voltage comparator for comparing a first input signal applied to its positive input node with a second input signal applied to its negative input node to output a first output signal to its positive output node and its second output signal to a negative output node; a switched capacitive unit for removing an offset voltage occurred in the positive input node, the negative input node, the positive output node and the negative output node of the voltage comparator; and a latch unit for latching the first output signal and the second output signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
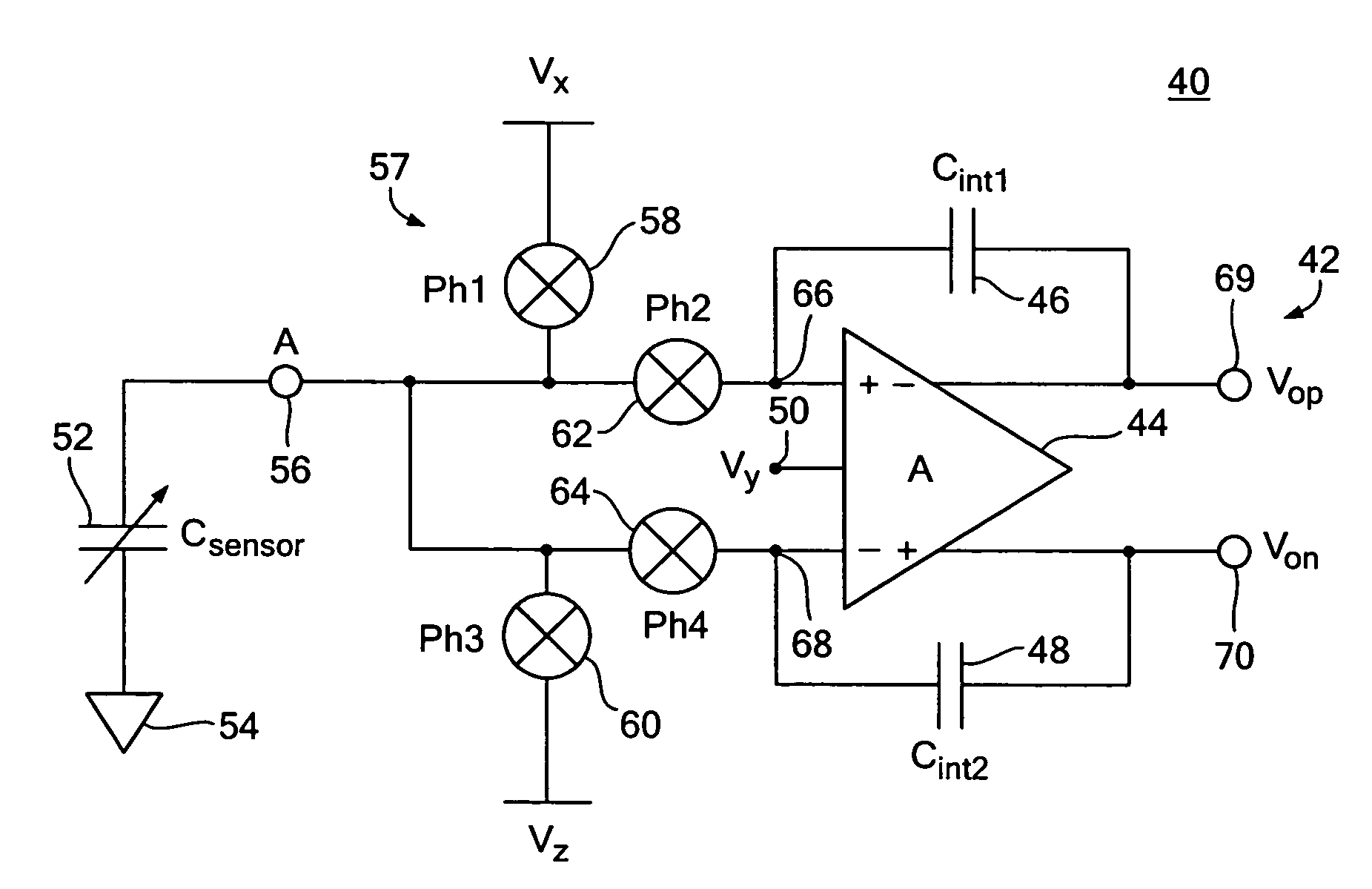
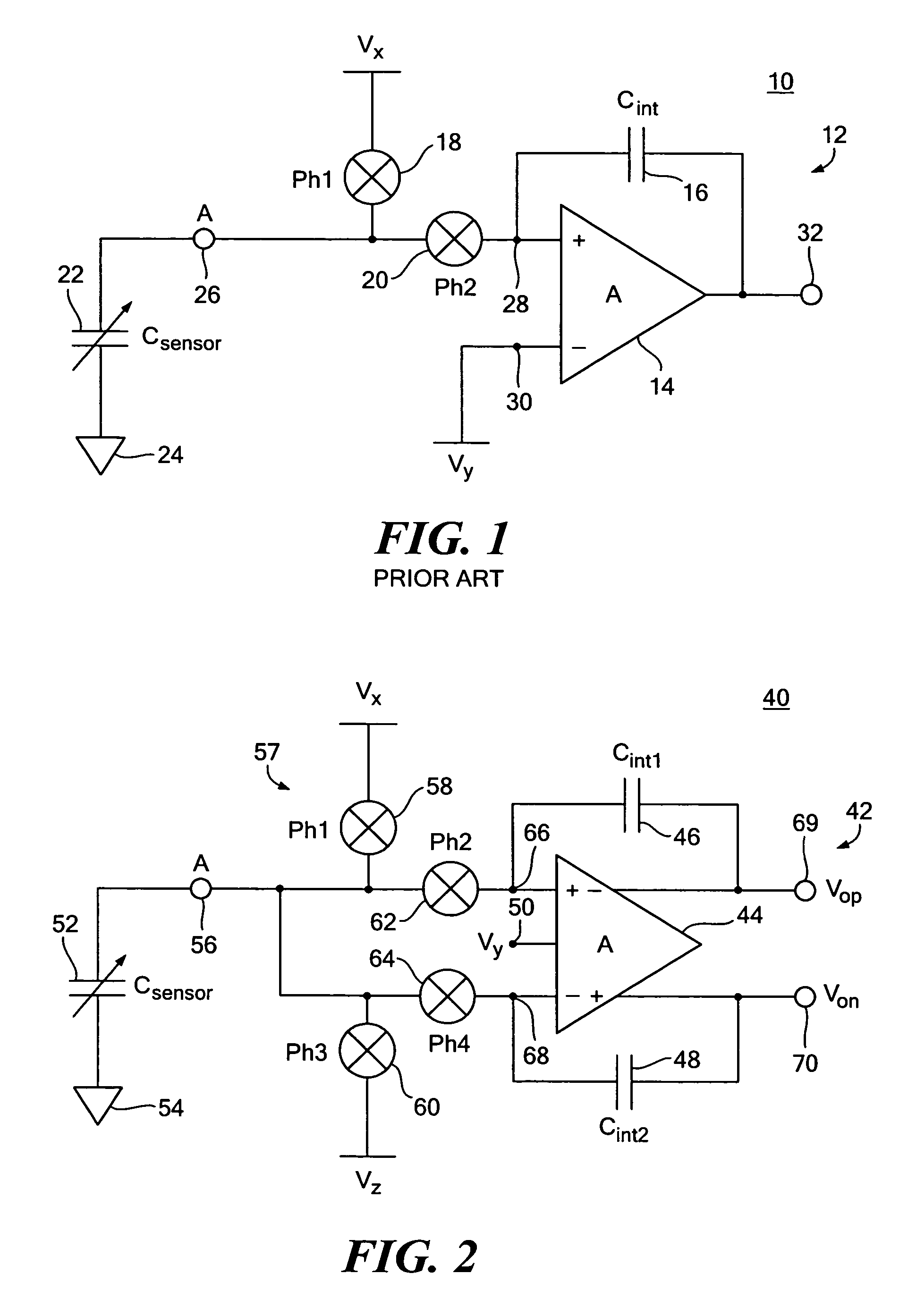
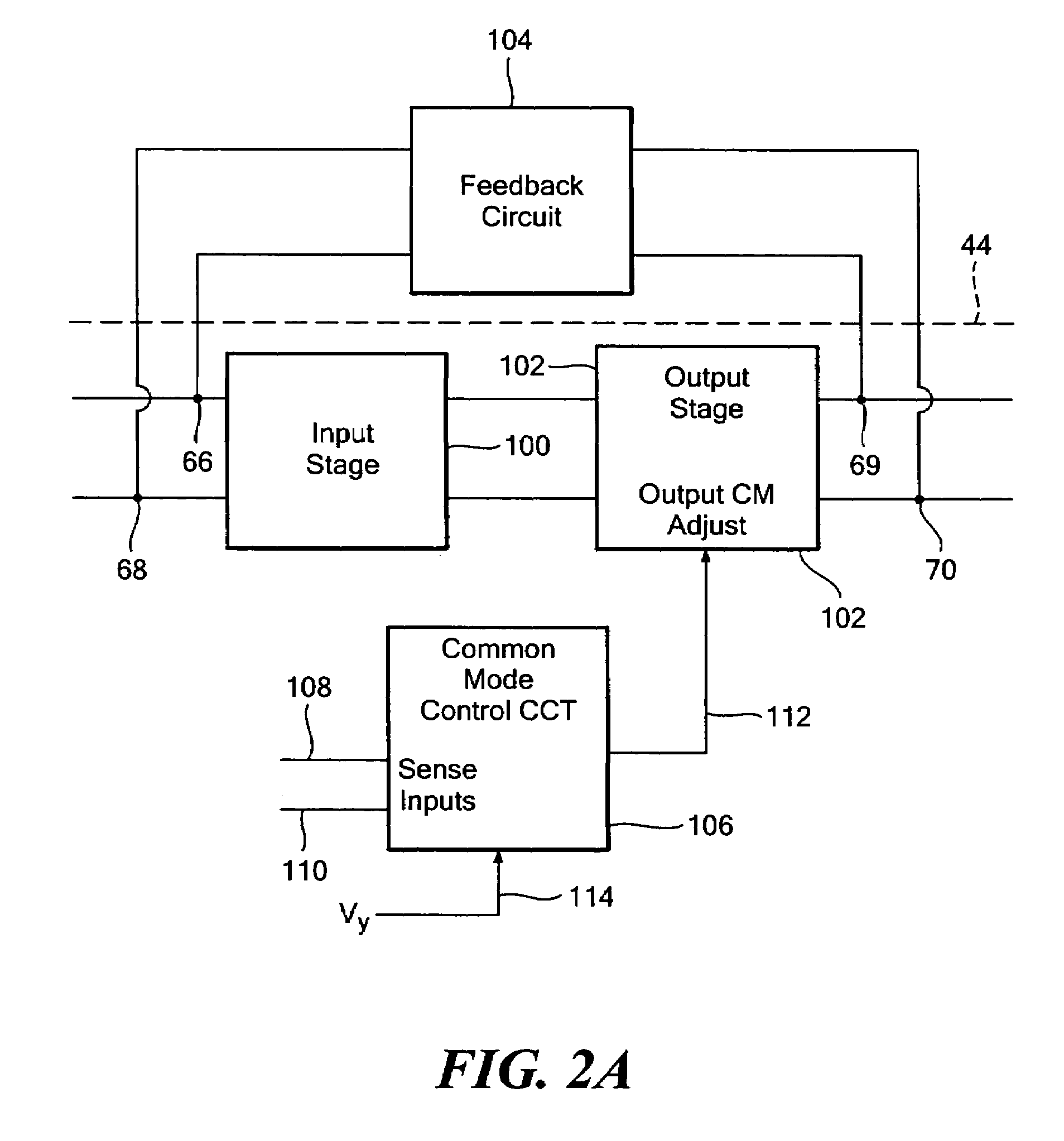
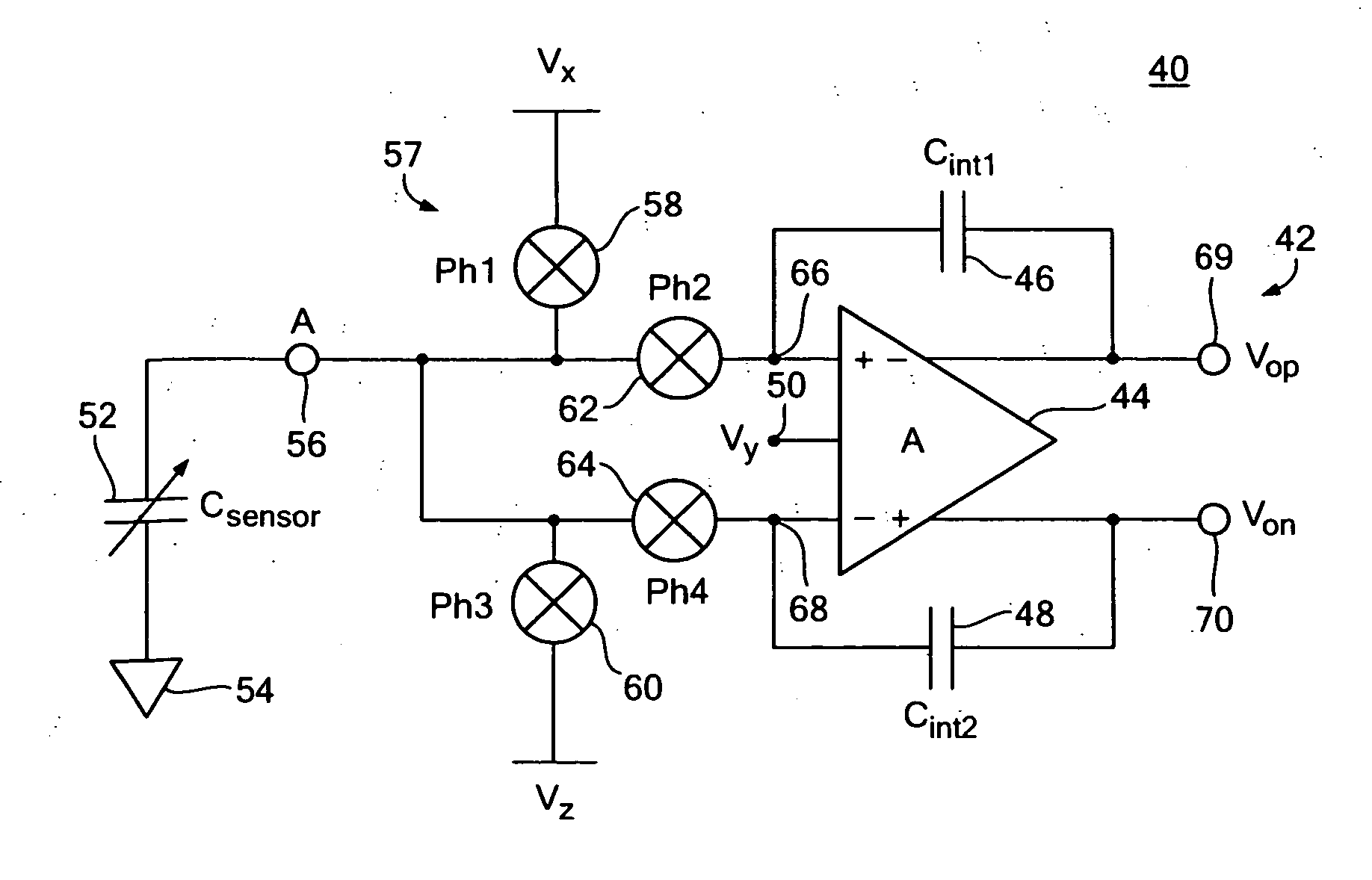
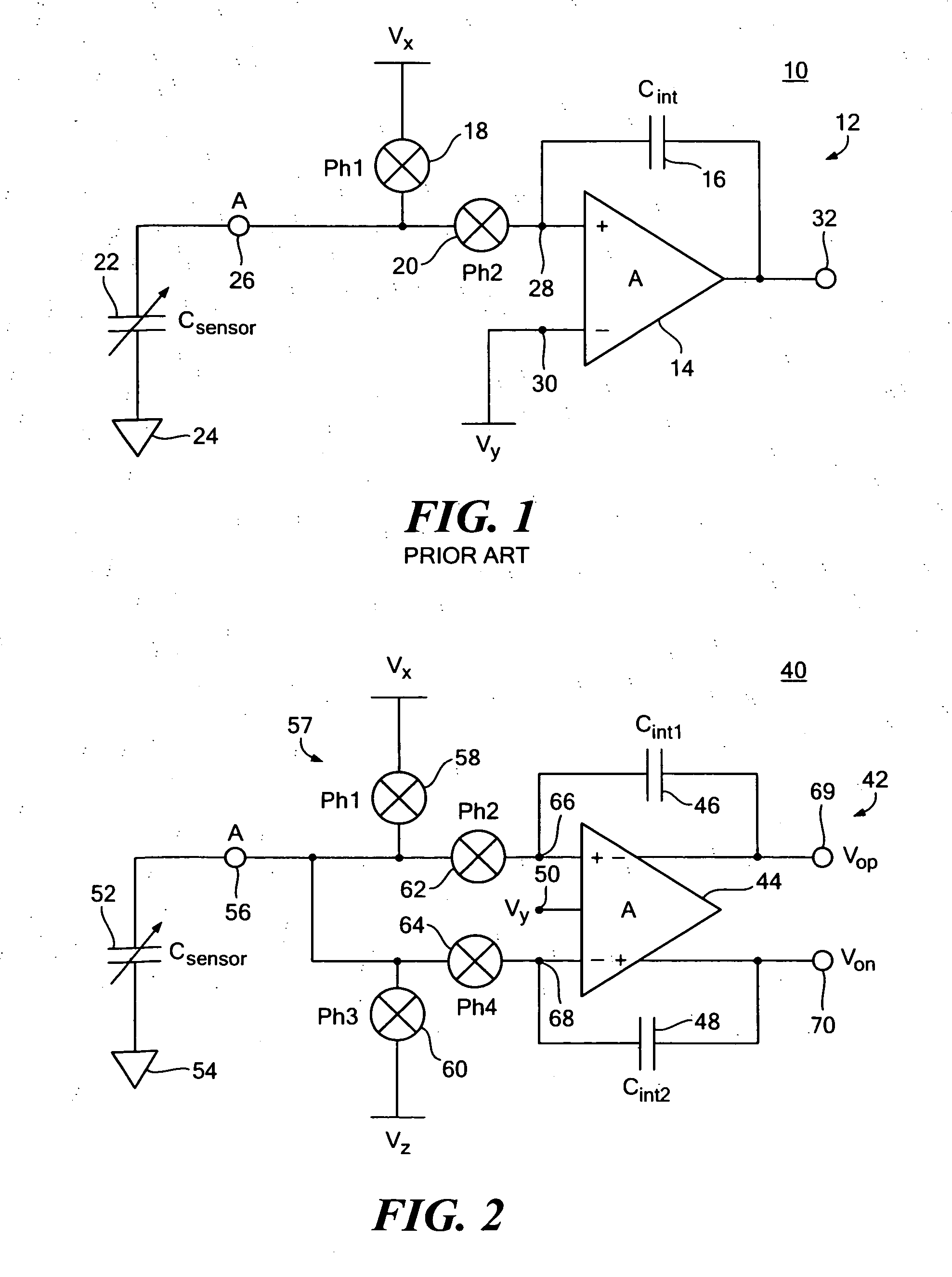
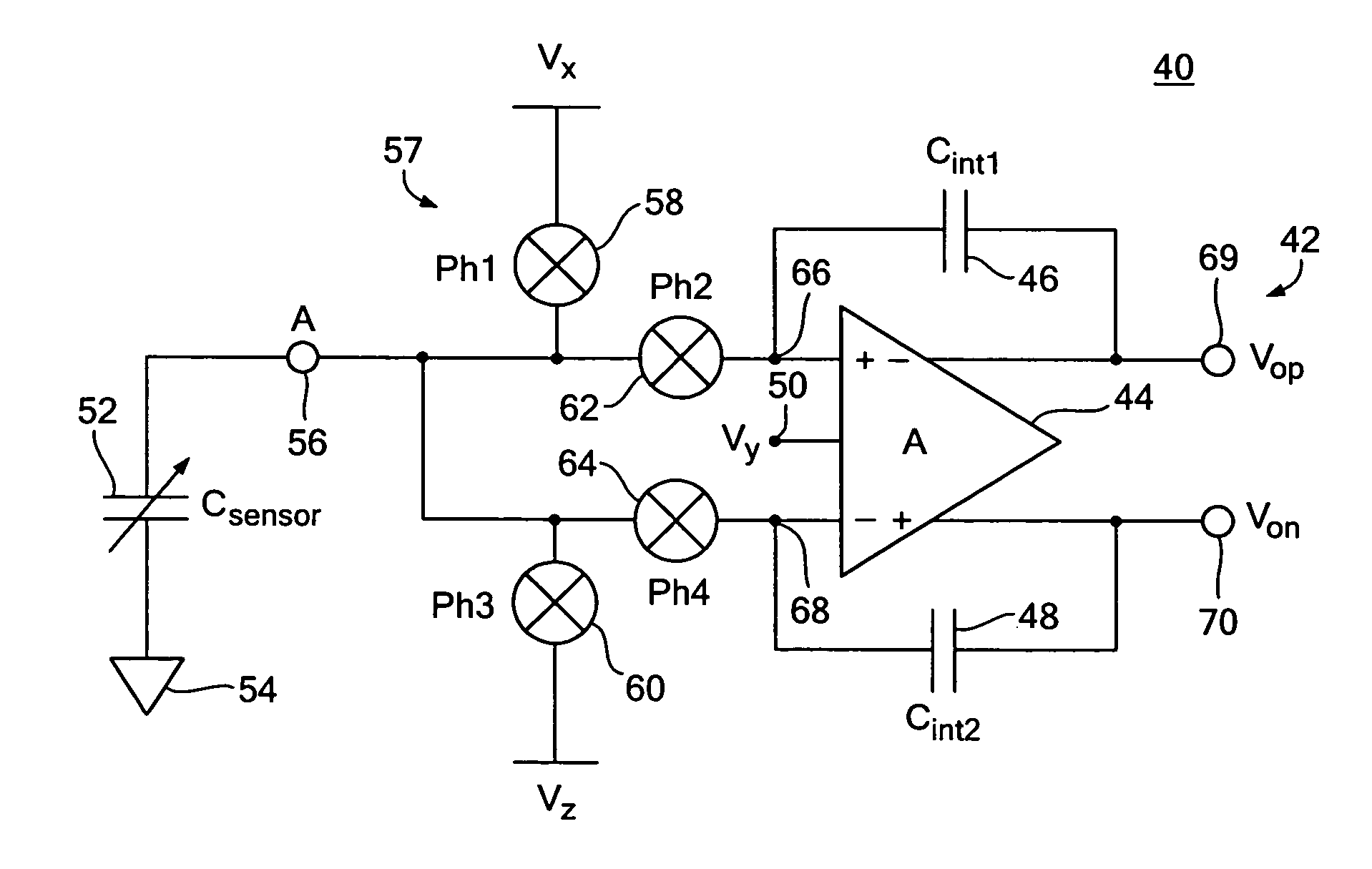
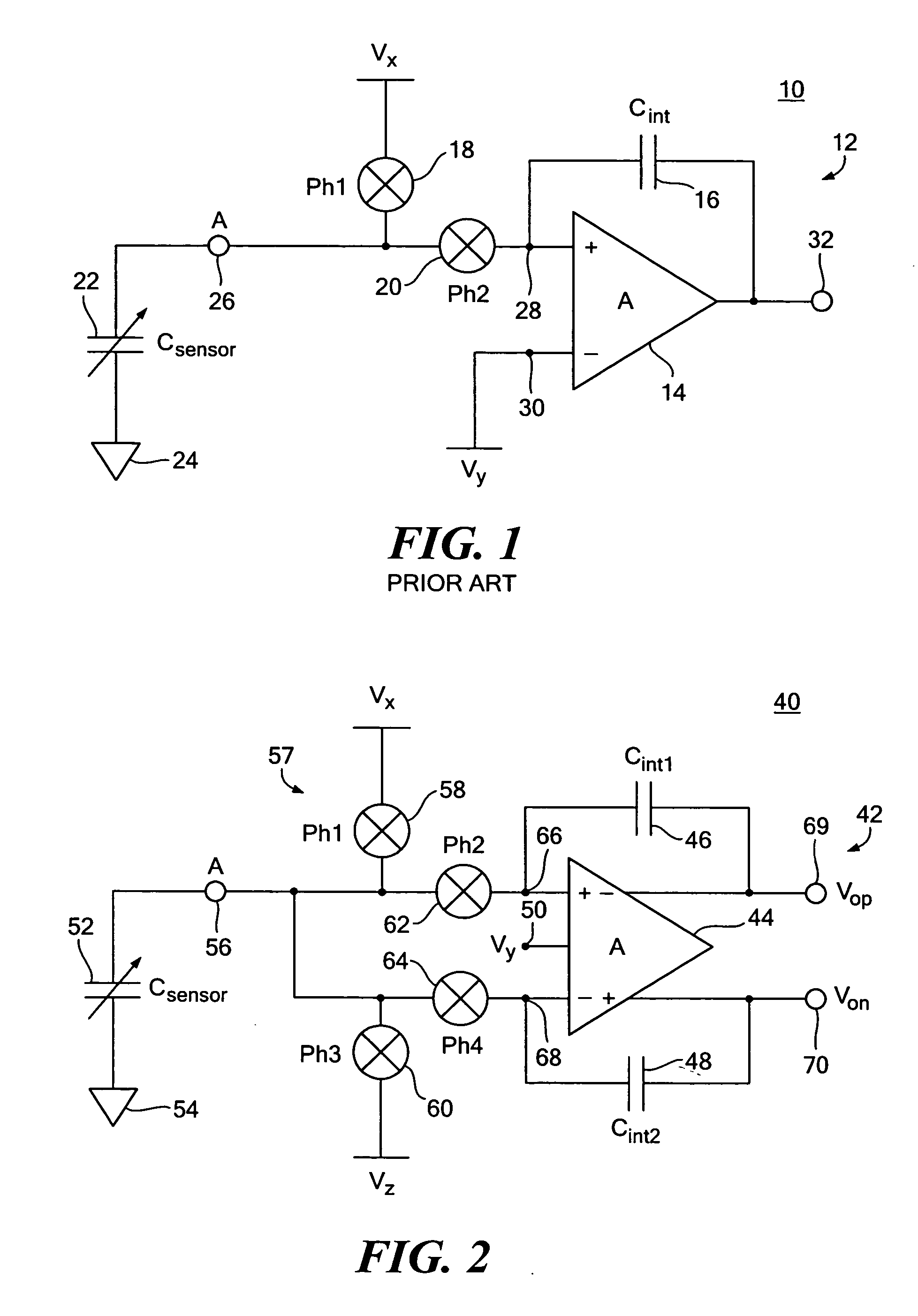
One terminal capacitor interface circuit
ActiveUS7235983B2Offset errorLow frequency noiseResistance/reactance/impedenceAnalogue conversionCapacitanceSecondary stage
A one terminal capacitor interface circuit for sensing the capacitance of a capacitor includes a differential integrating amplifier having an input common mode voltage and two summing nodes whose voltage is substantially equal to the input common mode voltage, a switching circuit for charging the capacitor to a first voltage level in a first phase, connecting, in a second phase, the capacitor to one of the summing nodes of the differential amplifier to provide a first output change substantially representative of the difference between the first voltage level and the input common mode voltage, and also representative of the capacitor; charging the capacitor to a second voltage level in a third phase, and connecting, in a fourth phase, the capacitor to the other summing node of the differential amplifier to provide a second output change substantially representative of the difference between the second voltage level and the input common mode voltage, and also representative of the capacitor; the combined first and second output changes representing the capacitance of the capacitor substantially independent of the input common mode voltage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Error compensation for multi-touch surfaces
ActiveUS7692638B2Reduce and eliminate image distortionMinimize distortionElectric signal transmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsEngineeringMulti event
Owner:APPLE INC
One terminal capacitor interface circuit
ActiveUS20070247171A1Offset errorLow frequency noiseResistance/reactance/impedenceAnalogue conversionCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A differential capacitor one terminal capacitor interface circuit for sensing the capacitance of first and second capacitors includes a differential integrating amplifier having first and second summing nodes and an input common mode voltage; and a switching circuit for charging a first capacitor of said differential one terminal capacitor to a first voltage level and a second capacitor of said differential one terminal capacitor to a second voltage level in a first phase, in a second phase connecting said first capacitor to said first summing node and said second capacitor to said second summing node of said amplifier to provide first and second output changes substantially representative of the difference between said first and second voltage levels and said input common mode voltage, in a third phase charging said first capacitor to said second voltage level and said second capacitor to said first voltage level, and in a fourth phase connecting said first capacitor to said second summing node and said second capacitor to said first summing node of said amplifier to provide third and fourth output changes substantially representative of the difference between said first and second voltage levels and said input common mode voltage, the combined first, second, third and fourth changes representing the capacitance of said first and second capacitors substantially independent of said input common mode voltage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
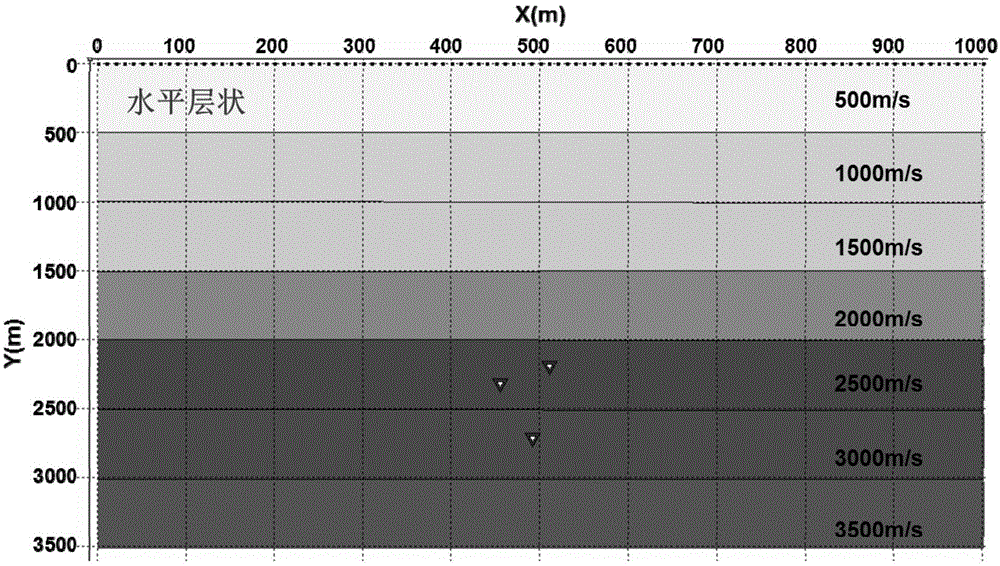
Microseism focus positioning method based on double-difference method
The invention provides a microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method, and belongs to the field of geophysical prospecting of petroleum. The microseism focus positioning method selects a perforation event as the main event, and picks the observation travel time for a microseism event, and can determine the relative distance between the perforation and the microseism event by calculating the residual error (double difference) between the observation travel time of the perforation and the microseism event and the theoretically calculated travel time difference. The microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method is high in operation speed and efficiency, and is easy for local convergence. As the microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method has the relative main event, the relative positioning accuracy is higher and the microseism focus positioning method is not limited by the spacial scale. The microseism focus positioning method based on a double-difference method offsets the error caused by changes of the speed of the near surface and the stratum speed, and can improve the positioning accuracy.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
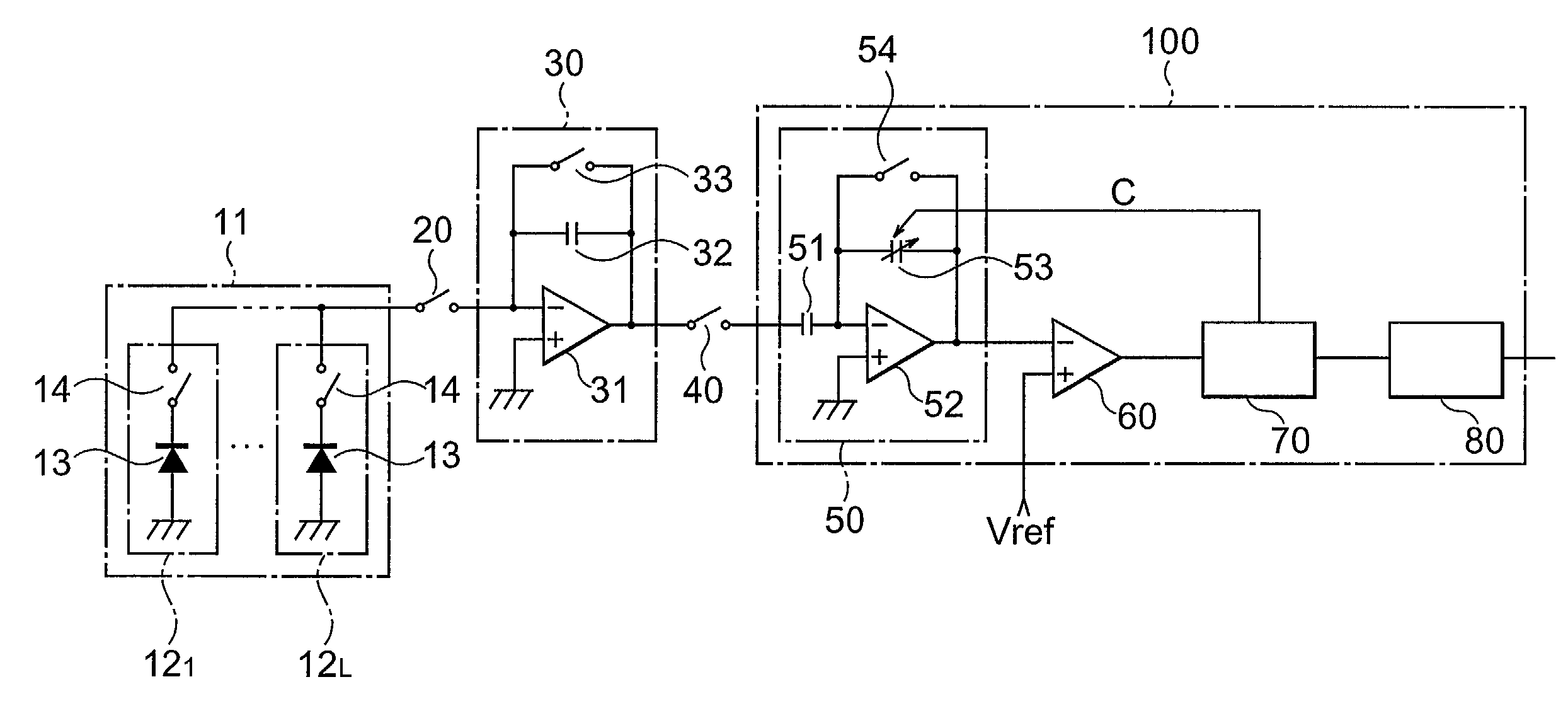
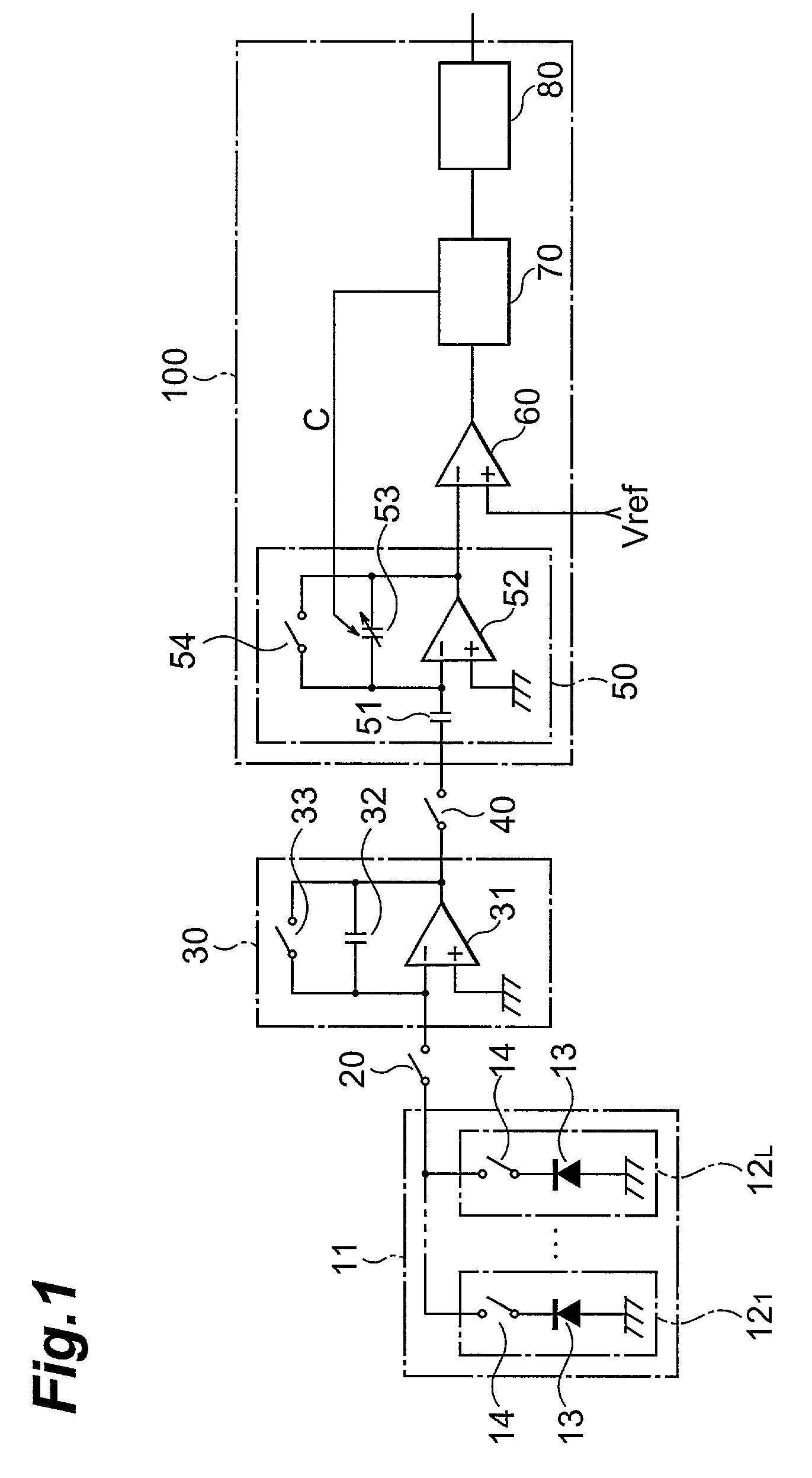
Solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS6977682B2Offset errorImprovement in ratio and suppressionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIntegratorCapacitance
A current signal corresponding to the amount of incident light detected by a photoelectric conversion device 13 is inputted to and integrated by an integrator circuit 30, whereby a voltage signal is outputted from the integrator circuit 30. When a switch 40 is closed, the voltage signal outputted from the integrator circuit 30 is inputted to a capacitor 51 of a variable capacity integrator circuit 50, a change of the voltage signal is inputted to an amplifier 52, and an electric charge corresponding to the change of voltage signal and the capacity value of a variable capacity part 53 flows into the variable capacity part 53. The capacity value of the variable capacity part 53 is controlled by a comparator 60 and a capacity control section 70 such that the value of integrated signal outputted from the variable capacity integrator circuit 50 coincide with a reference value. The capacity control section 70 outputs a first digital signal corresponding to the capacity value of the variable capacity part 53. As a consequence, a solid-state imaging device which is excellent in S / N ratio, yields no offset errors even when its amplifier have offset fluctuations, and has a small circuit scale is obtained.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
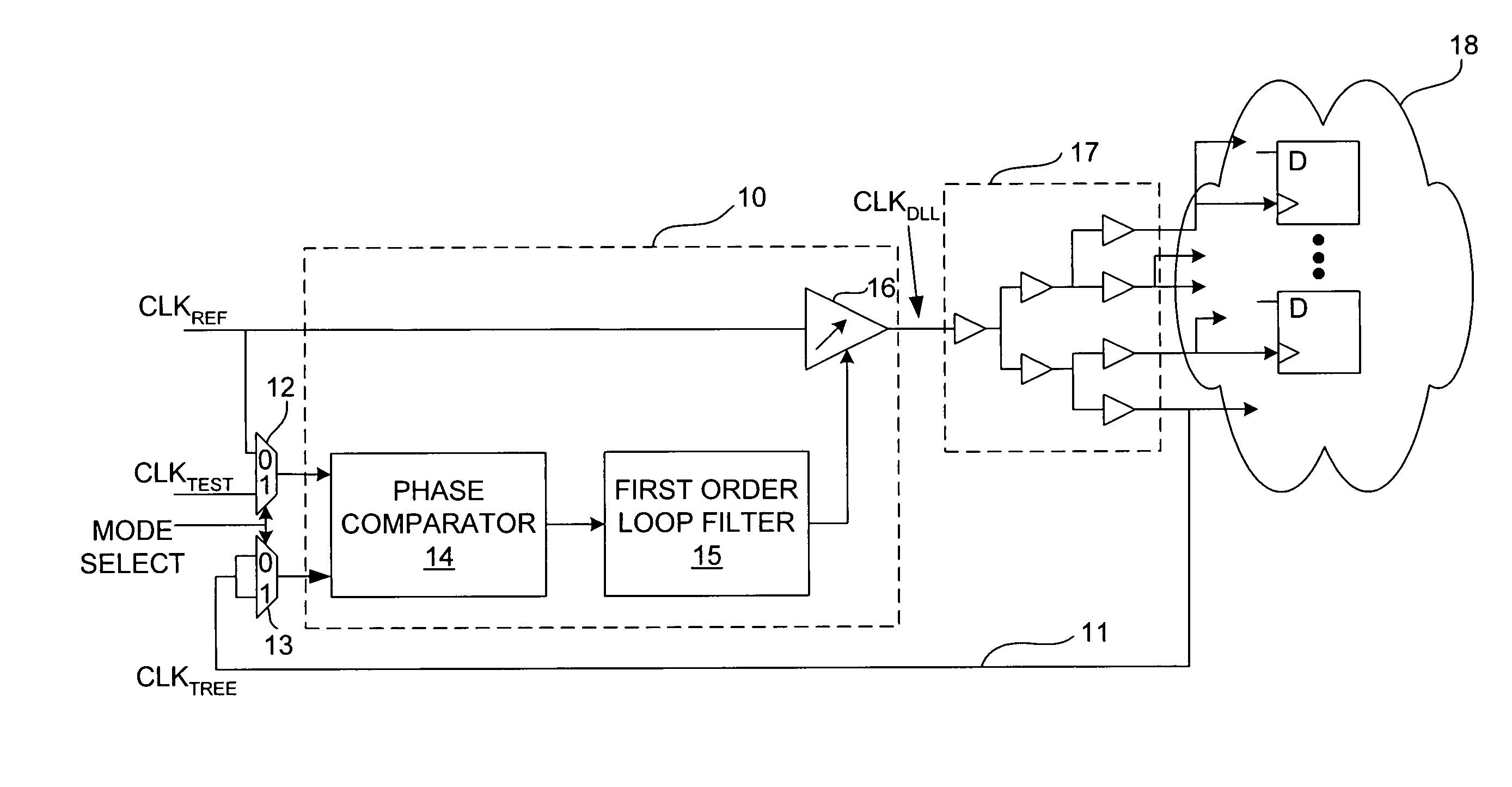
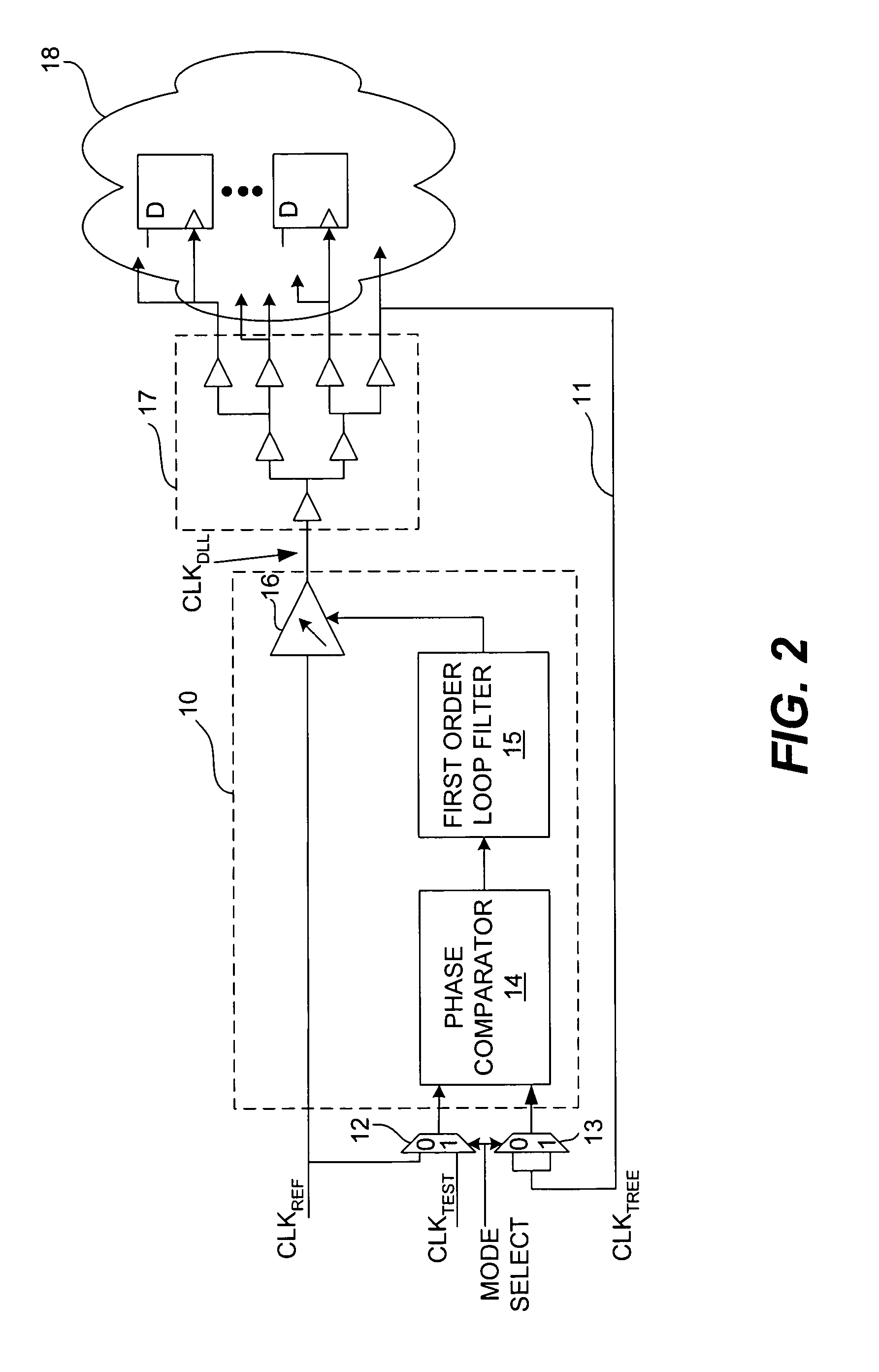
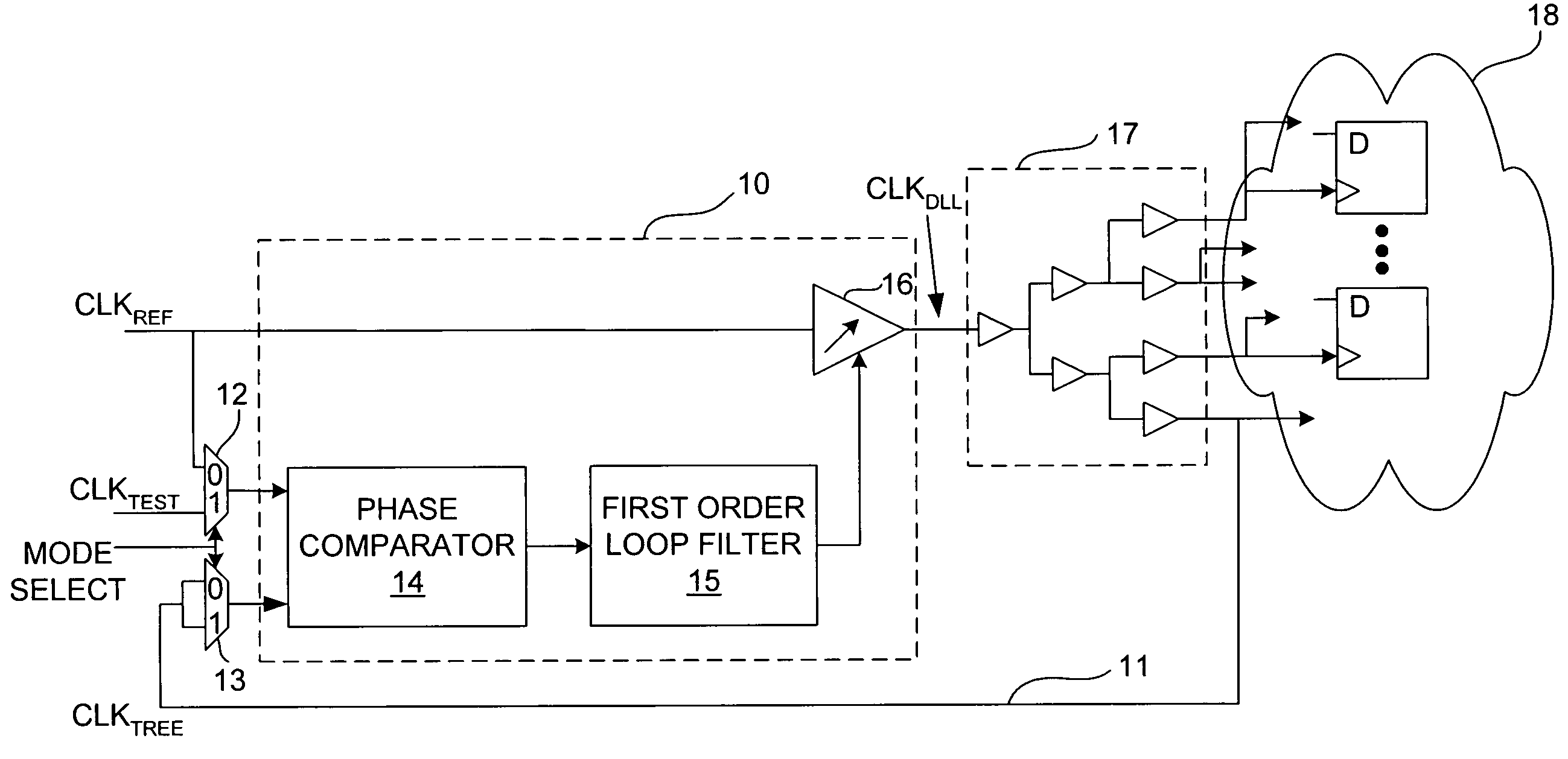
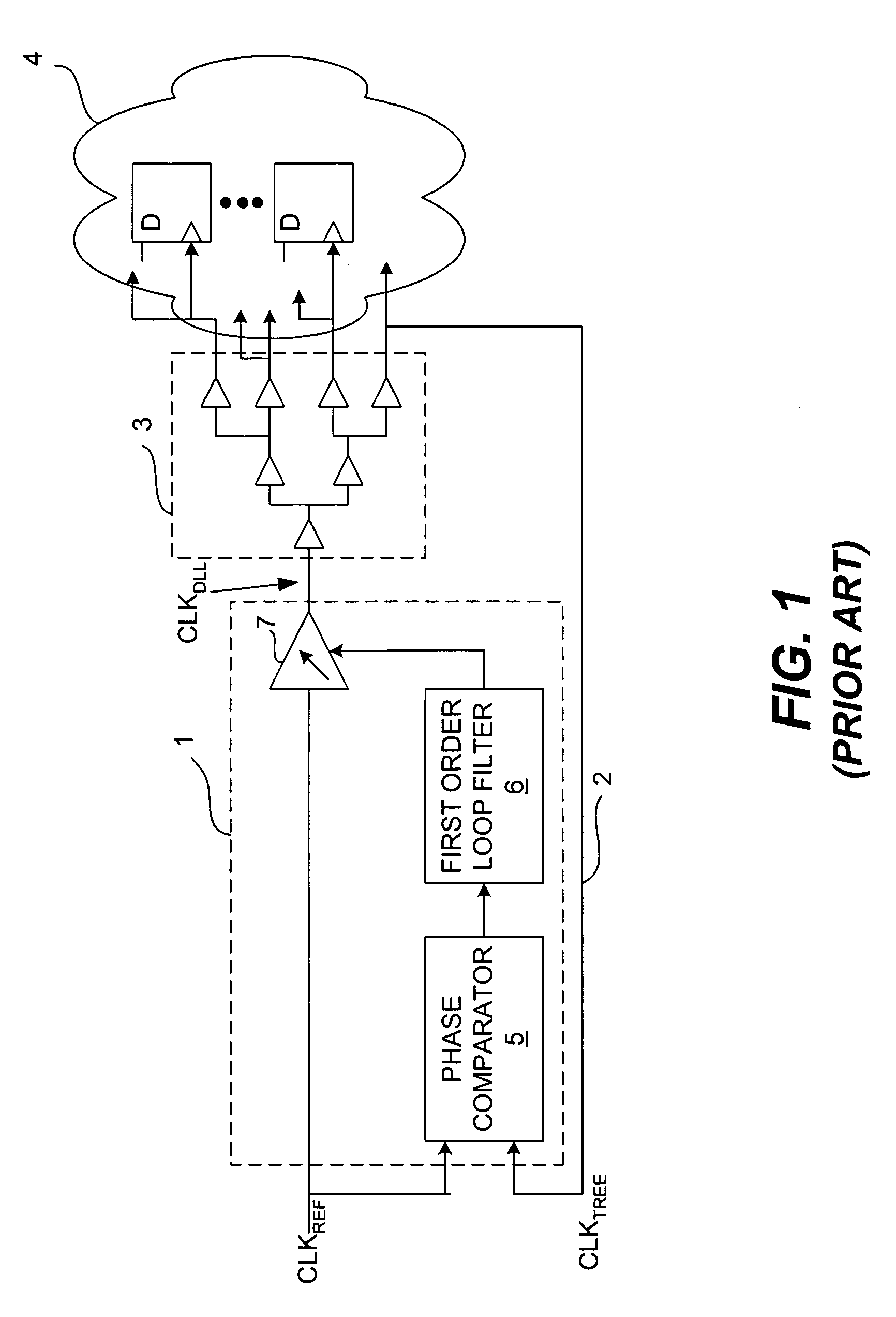
Delay-locked loop and a method of testing a delay-locked loop
ActiveUS6995554B2Offset errorPulse automatic controlElectronic circuit testingPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
A delay-locked loop (DLL) of an integrated circuit (IC) with testing circuitry and a method for testing a DLL. During test mode, a phase comparator of the DLL receives a test clock in place of the reference clock and determines the phase difference between the test clock and the dock fed back to the DLL from a clock buffer tree. A variable delay element of the DLL then shifts the reference clock in time by an amount that depends on that phase difference. The variable delay element can be exercised by varying the phase of the test clock with respect to the reference clock by a known phase offset to cause the variable delay element to produce a range of delays. Whether the variable delay element is functioning properly can be determined by checking whether the phase of the test clock is aligned with the phase of the feedback clock.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
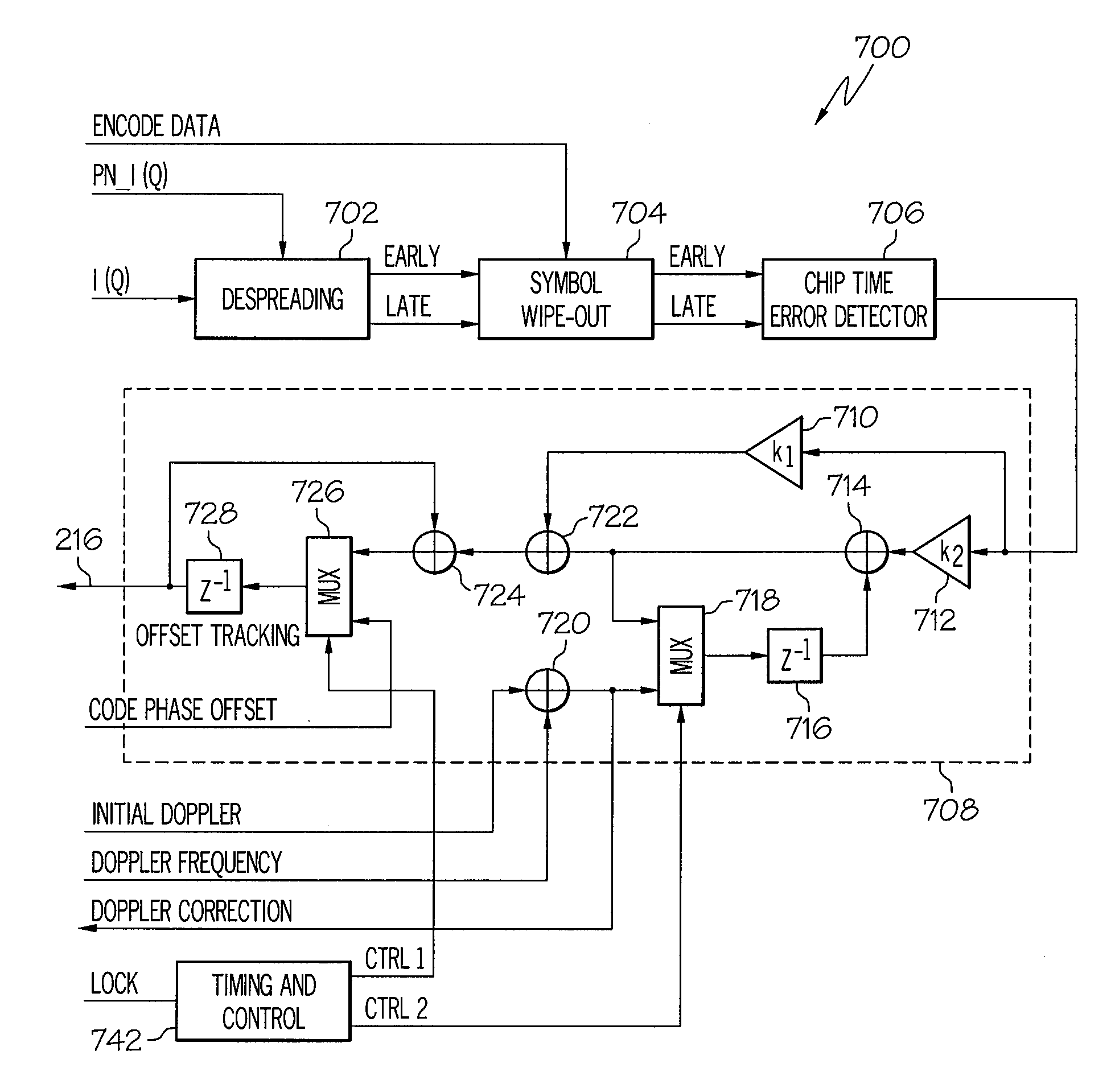
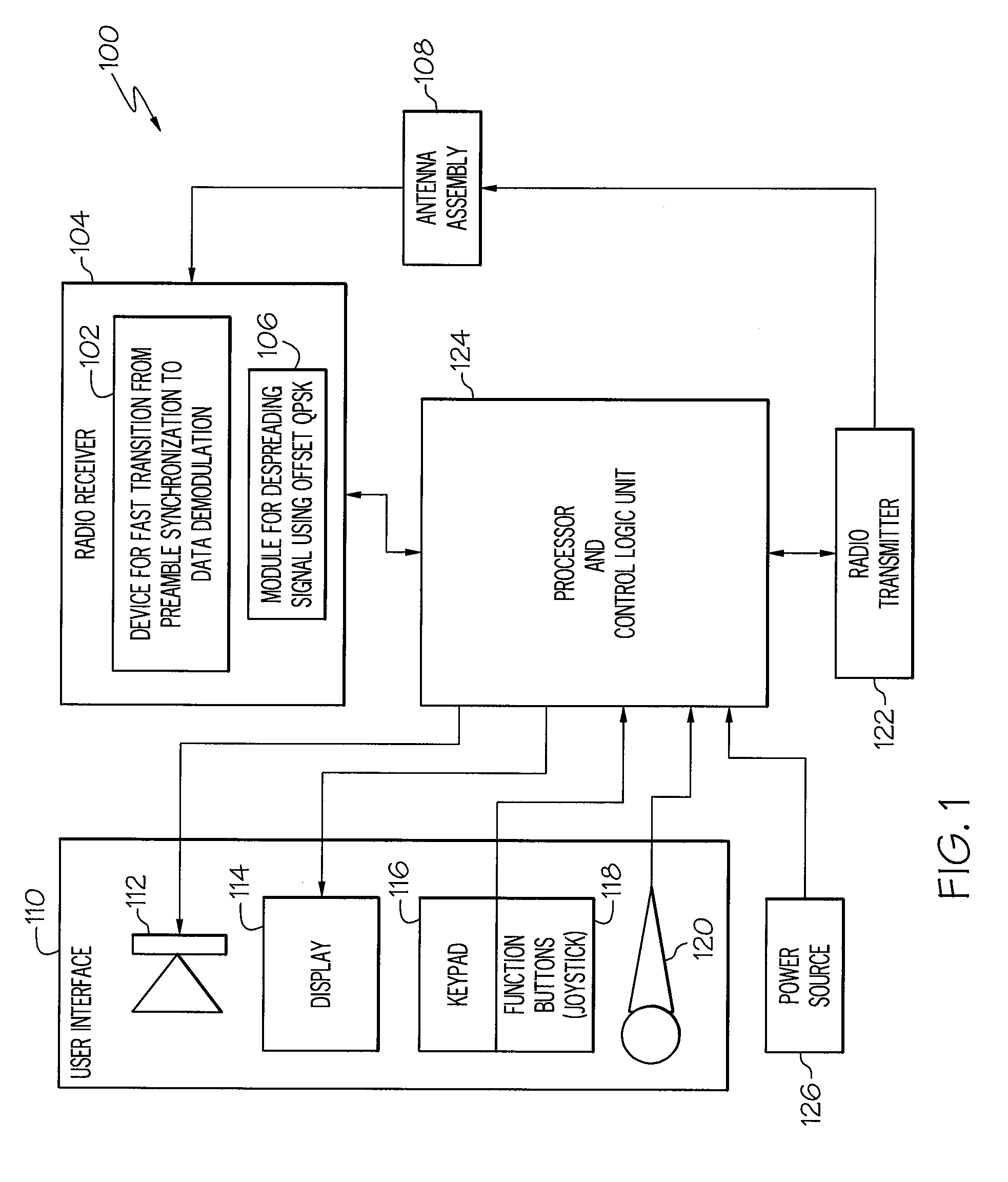
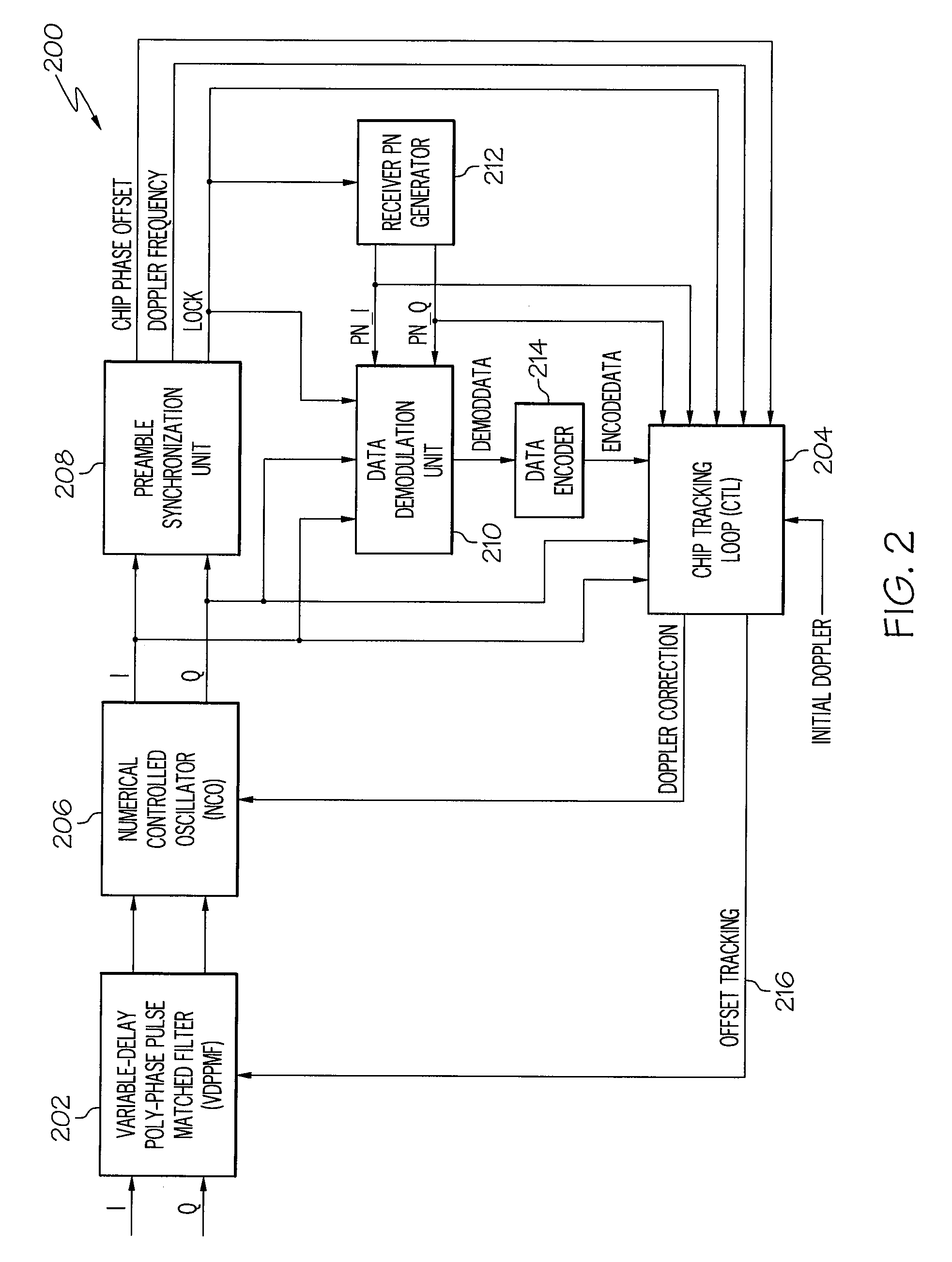
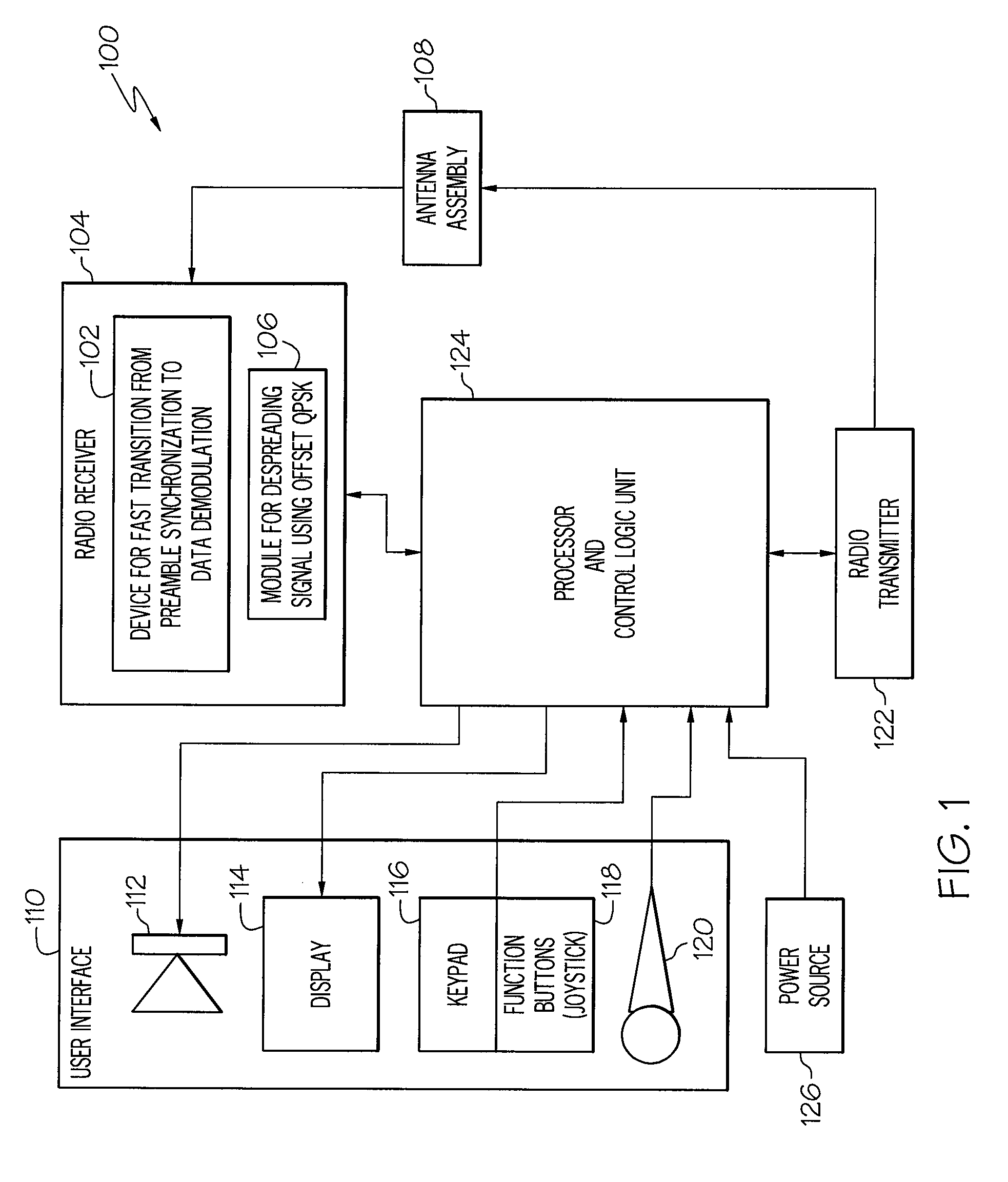
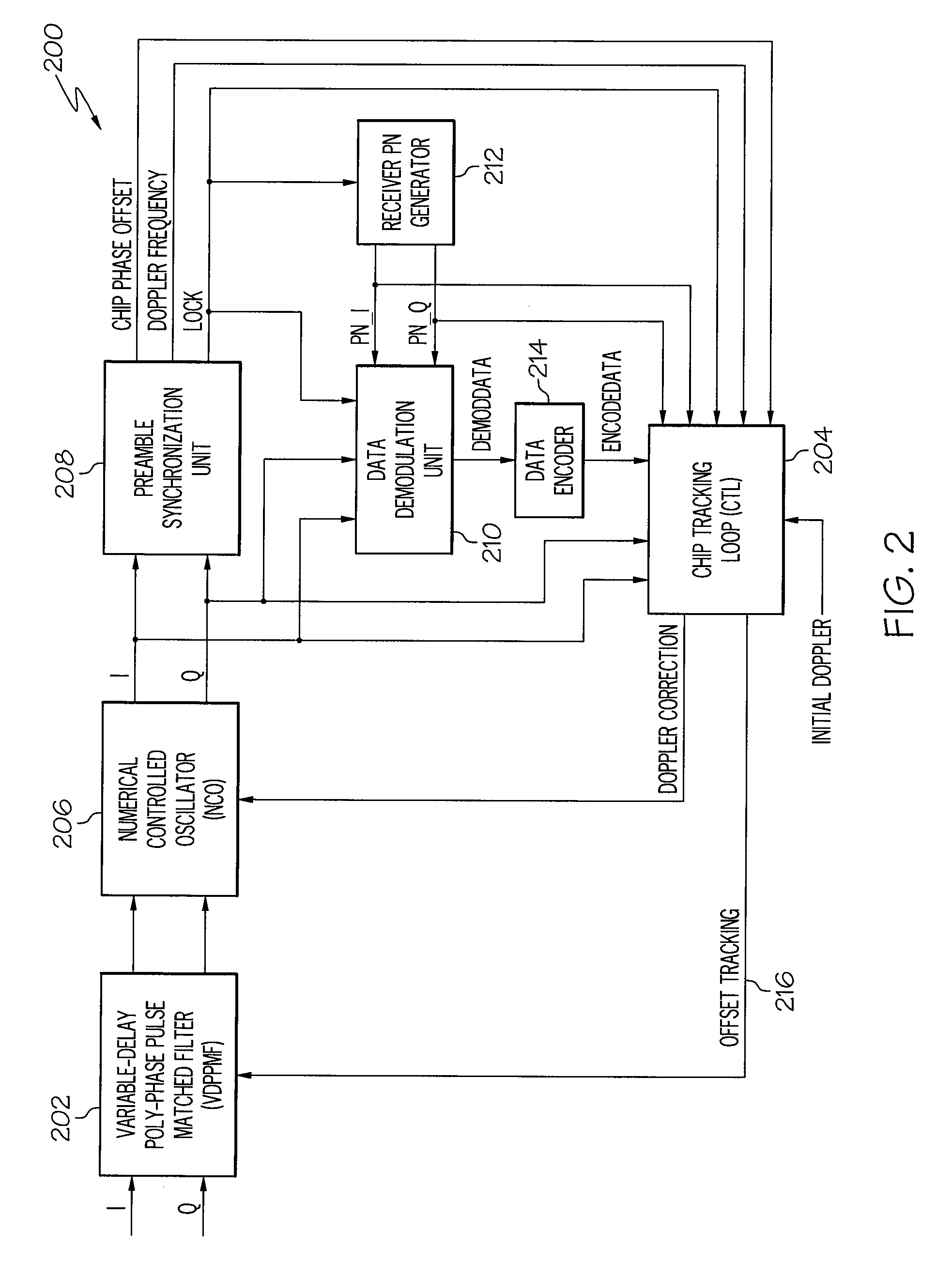
Device and method for fast transition from preamble synchronization to data demodulation in direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communications
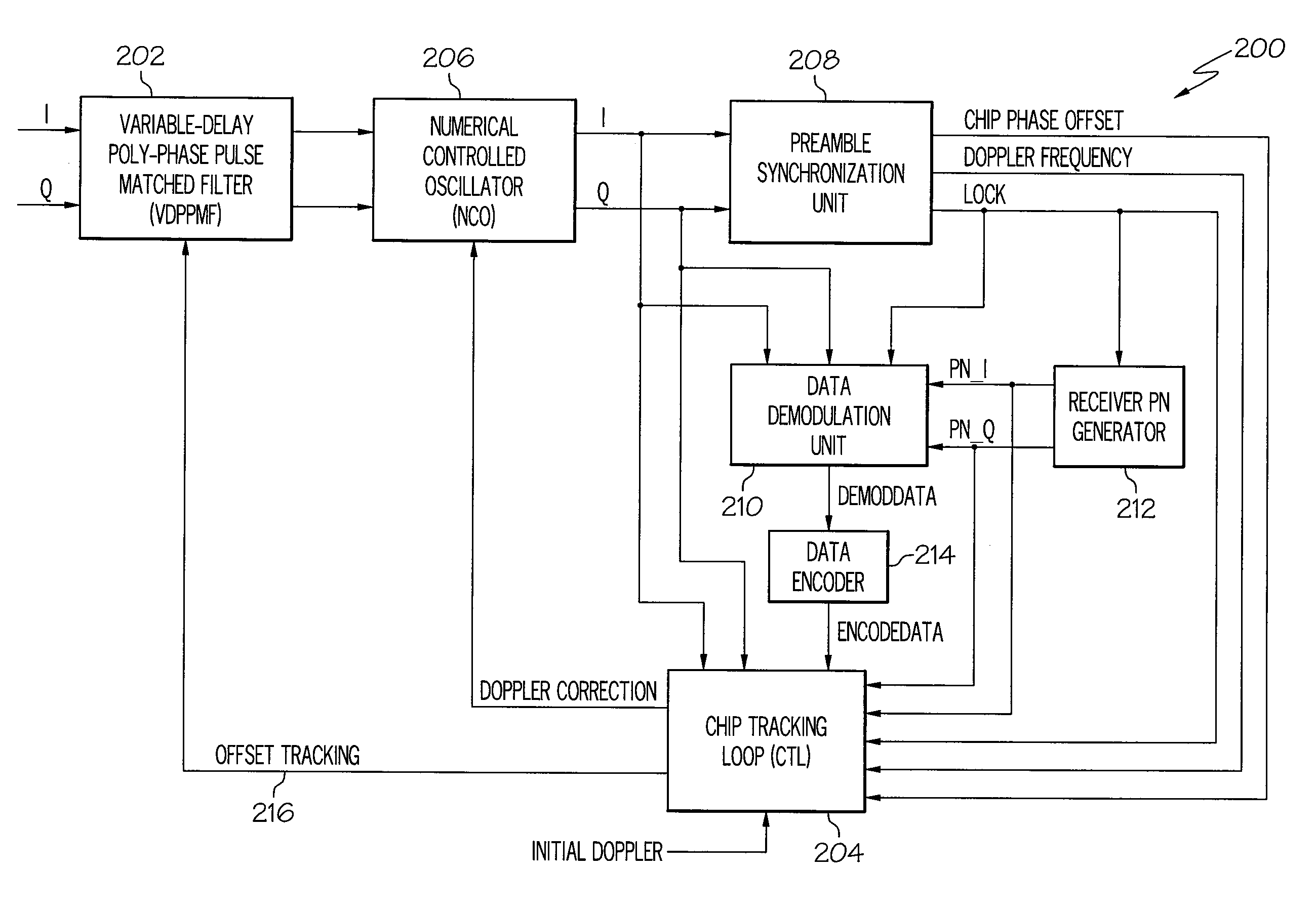
ActiveUS20090180524A1Quick transitionOffset errorTransmissionNumerical controlNumerically controlled oscillator
A device for fast transition from preamble synchronization of a received baseband signal to demodulation of the received baseband signal may include a baseband chip tracking loop to generate an offset tracking value to track any initial chip phase offset and Doppler-caused baseband chip frequency drift associated with the received baseband signal. The device may also include a numerical controlled oscillator to correct any Doppler-caused phase rotation associated with the received signal. The device may additionally include a preamble synchronization unit to detect a preamble of the received baseband signal, and to measure a chip phase offset and a baseband Doppler frequency shift associated with the received baseband signal. The chip phase offset may be used to set an initial chip phase offset value of the chip tracking loop so that the chip tracking loop starts with approximately a zero pull-in error. The baseband Doppler frequency shift may be used to set initial frequency offset values in the chip tracking loop and the numerical controlled oscillator so that both start with substantially near-zero offset errors for substantially immediate demodulation of the received signal. The device may further include an output device to output the data demodulated from the received baseband signal.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
One terminal capacitor interface circuit
ActiveUS20060213270A1Low frequency noiseOffset errorResistance/reactance/impedenceAnalogue conversionCapacitanceEngineering
A one terminal capacitor interface circuit for sensing the capacitance of a capacitor includes a differential integrating amplifier having an input common mode voltage and two summing nodes whose voltage is substantially equal to the input common mode voltage, a switching circuit for charging the capacitor to a first voltage level in a first phase, connecting, in a second phase, the capacitor to one of the summing nodes of the differential amplifier to provide a first output change substantially representative of the difference between the first voltage level and the input common mode voltage, and also representative of the capacitor; charging the capacitor to a second voltage level in a third phase, and connecting, in a fourth phase, the capacitor to the other summing node of the differential amplifier to provide a second output change substantially representative of the difference between the second voltage level and the input common mode voltage, and also representative of the capacitor; the combined first and second output changes representing the capacitance of the capacitor substantially independent of the input common mode voltage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
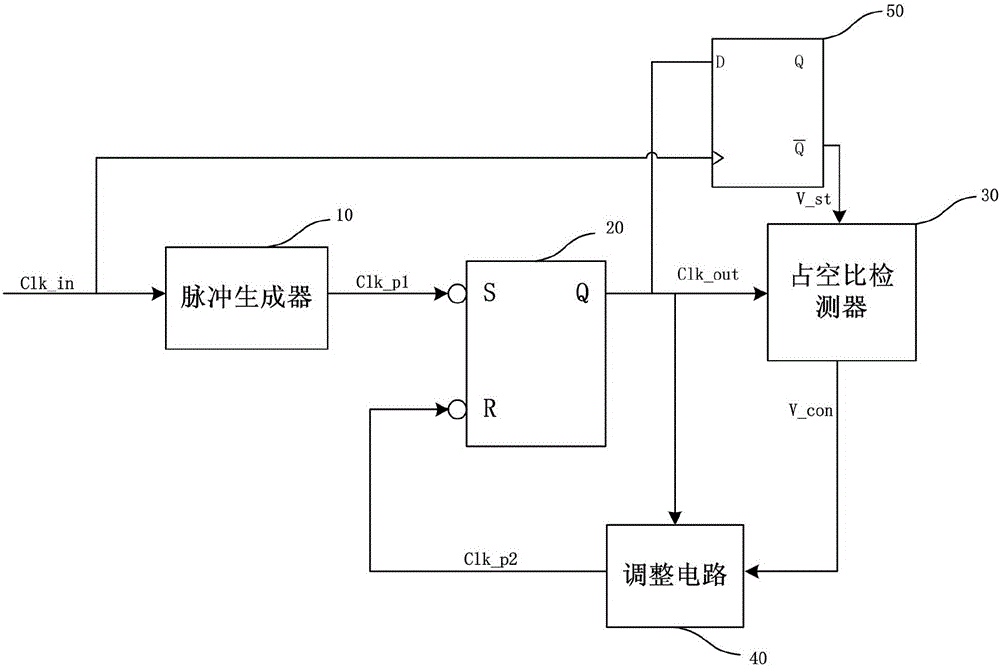
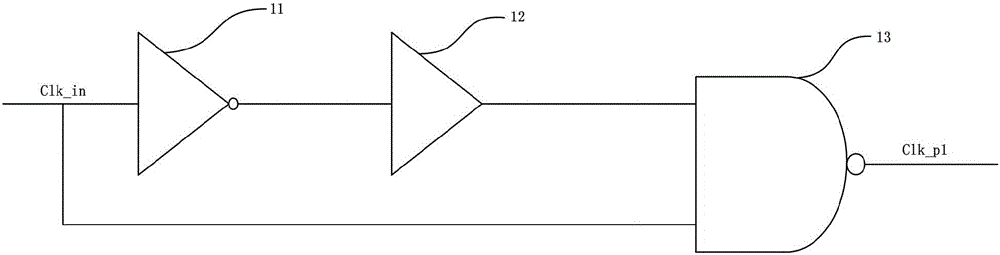
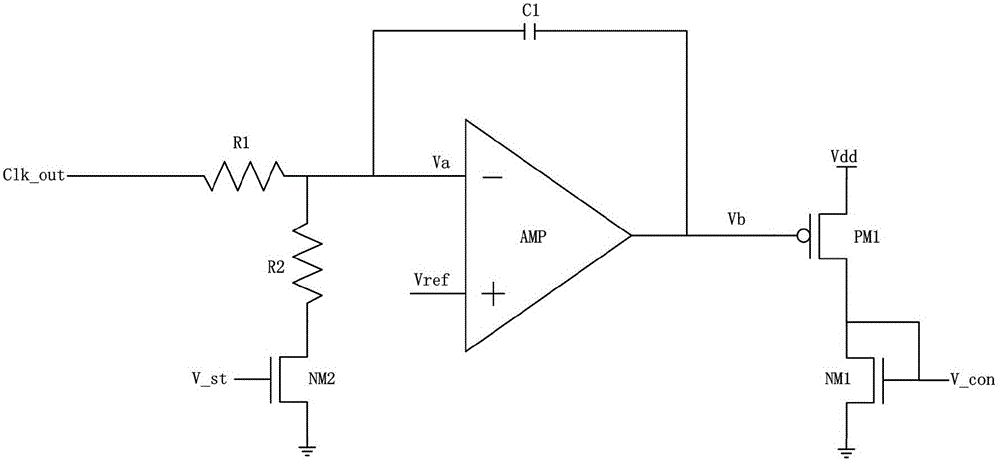
Clock duty ratio adjusting circuit
ActiveCN105811923ASpeed up the boot processLow jitter characteristicsAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsNegative feedbackIntegrator
The invention relates to a clock duty ratio adjusting circuit. The clock duty ratio adjusting circuit comprises a pulse generator, an RS trigger, a duty ratio detector, an adjusting circuit and a D trigger. The pulse generator, the RS trigger and the adjusting circuit are successively connected. The pulse generator is connected to the S input end of the RS trigger; the output end of the RS trigger is connected respectively to the D trigger, the duty ratio detector and the input end of the adjusting circuit; the anti-phase output end of the D trigger is connected to the input end of the duty ratio detector; the output end of the duty ratio detector is connected to the input end of the adjusting circuit; the output end of the adjusting circuit is connected to the R input end of the RS trigger; inputted clock signals are accessed into the pulse generator and the D trigger. According to the invention, an RS trigger is adopted to integrate the edges of a clock. The paths of the duty ratio detector and the adjusting circuit are separate from their output path. The signal outputting path is rather simplified and features low shaking characteristics. The adoption of integrator negative feedback continuous time adjusting enables high accuracy.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
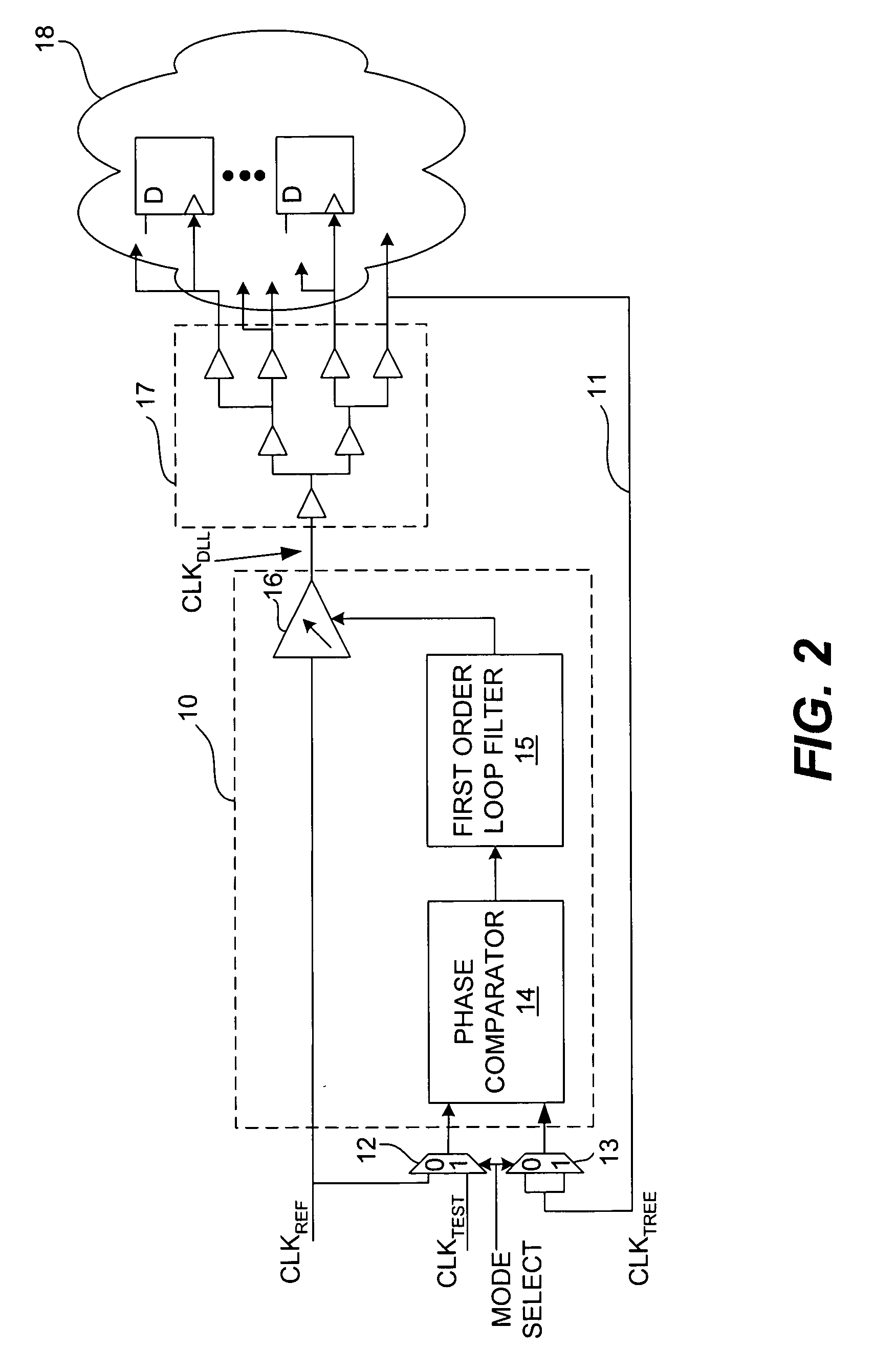
Delay-locked loop and a method of testing a delay-locked loop
ActiveUS20050280407A1Offset errorPulse automatic controlElectronic circuit testingPhase differenceDelay-locked loop
A delay-locked loop (DLL) of an integrated circuit (IC) with testing circuitry and a method for testing a DLL. During test mode, a phase comparator of the DLL receives a test clock in place of the reference clock and determines the phase difference between the test clock and the clock fed back to the DLL from a clock buffer tree. A variable delay element of the DLL then shifts the reference clock in time by an amount that depends on that phase difference. The variable delay element can be exercised by varying the phase of the test clock with respect to the reference clock by a known phase offset to cause the variable delay element to produce a range of delays. Whether the variable delay element is functioning properly can be determined by checking whether the phase of the test clock is aligned with the phase of the feedback clock.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
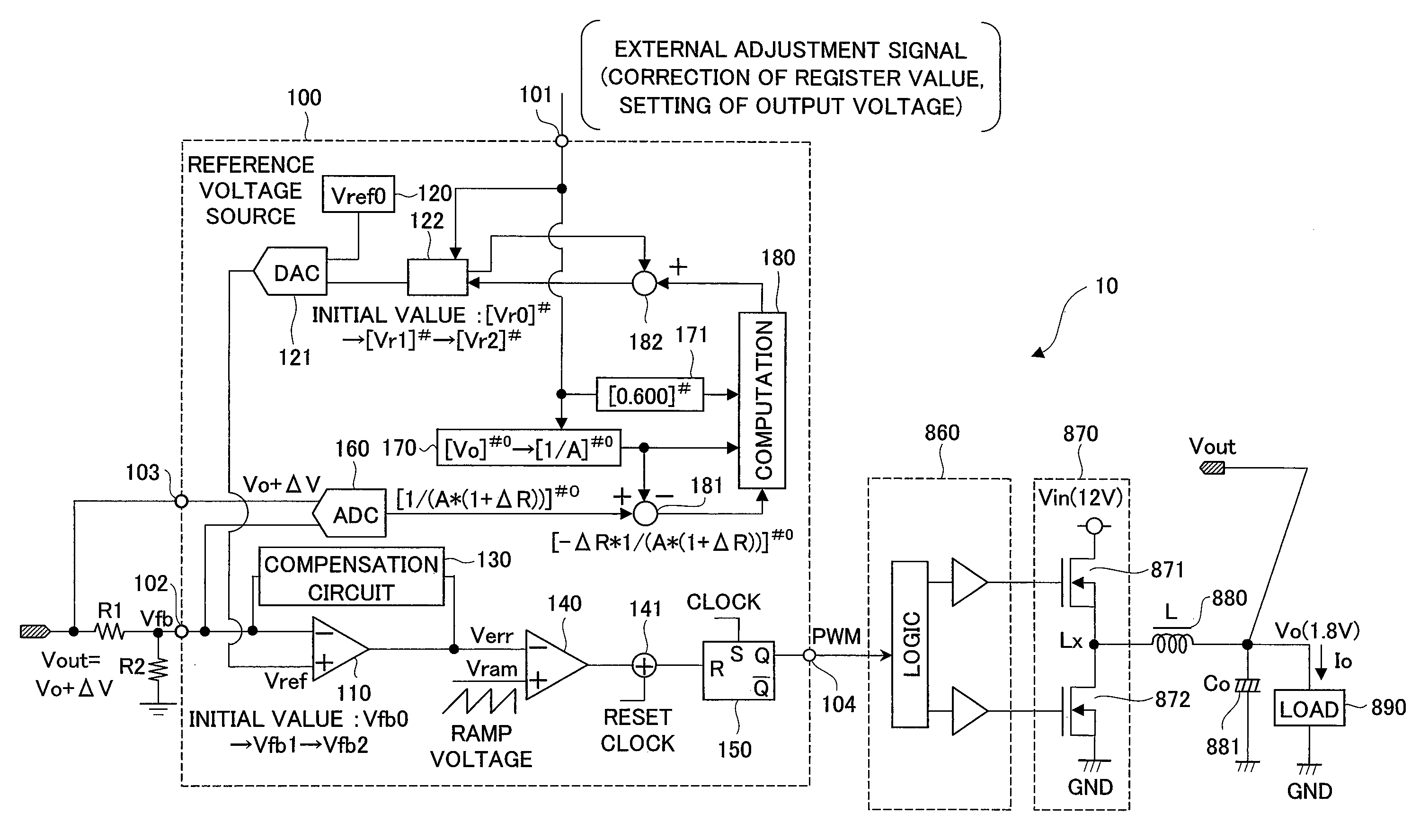
Semiconductor device and power supply using the same
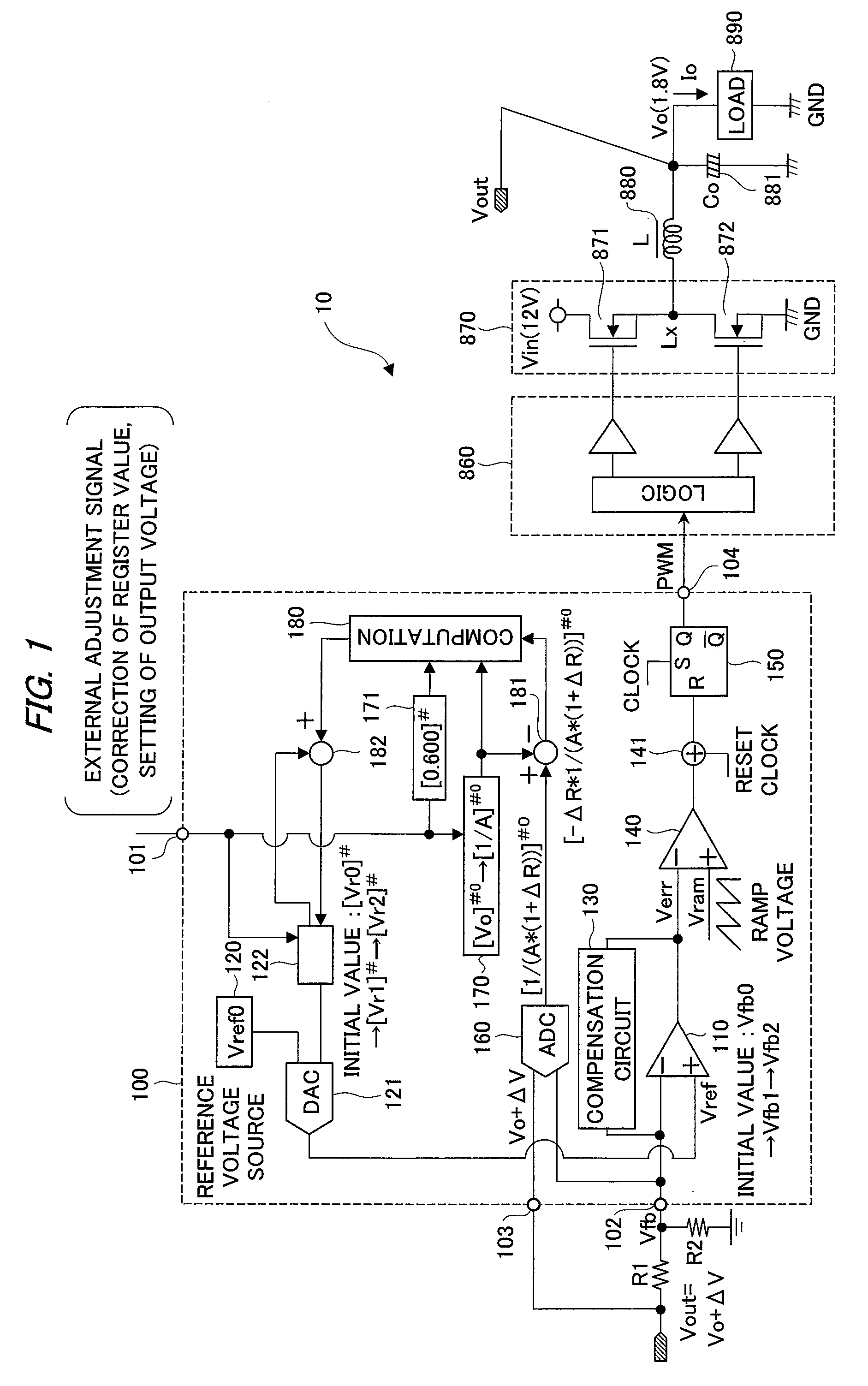
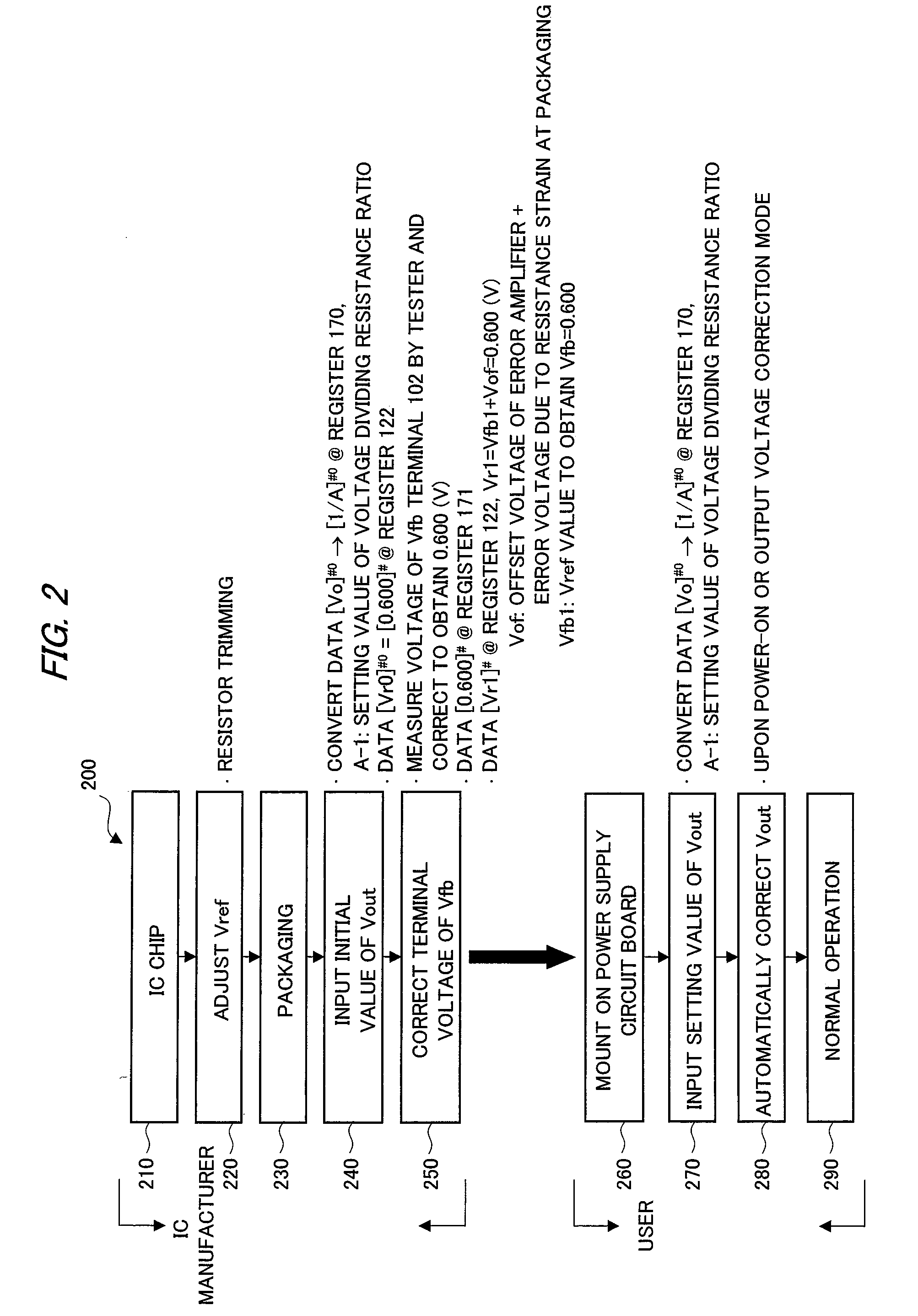
InactiveUS20090243575A1Offset errorStable currentDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalVoltage reference
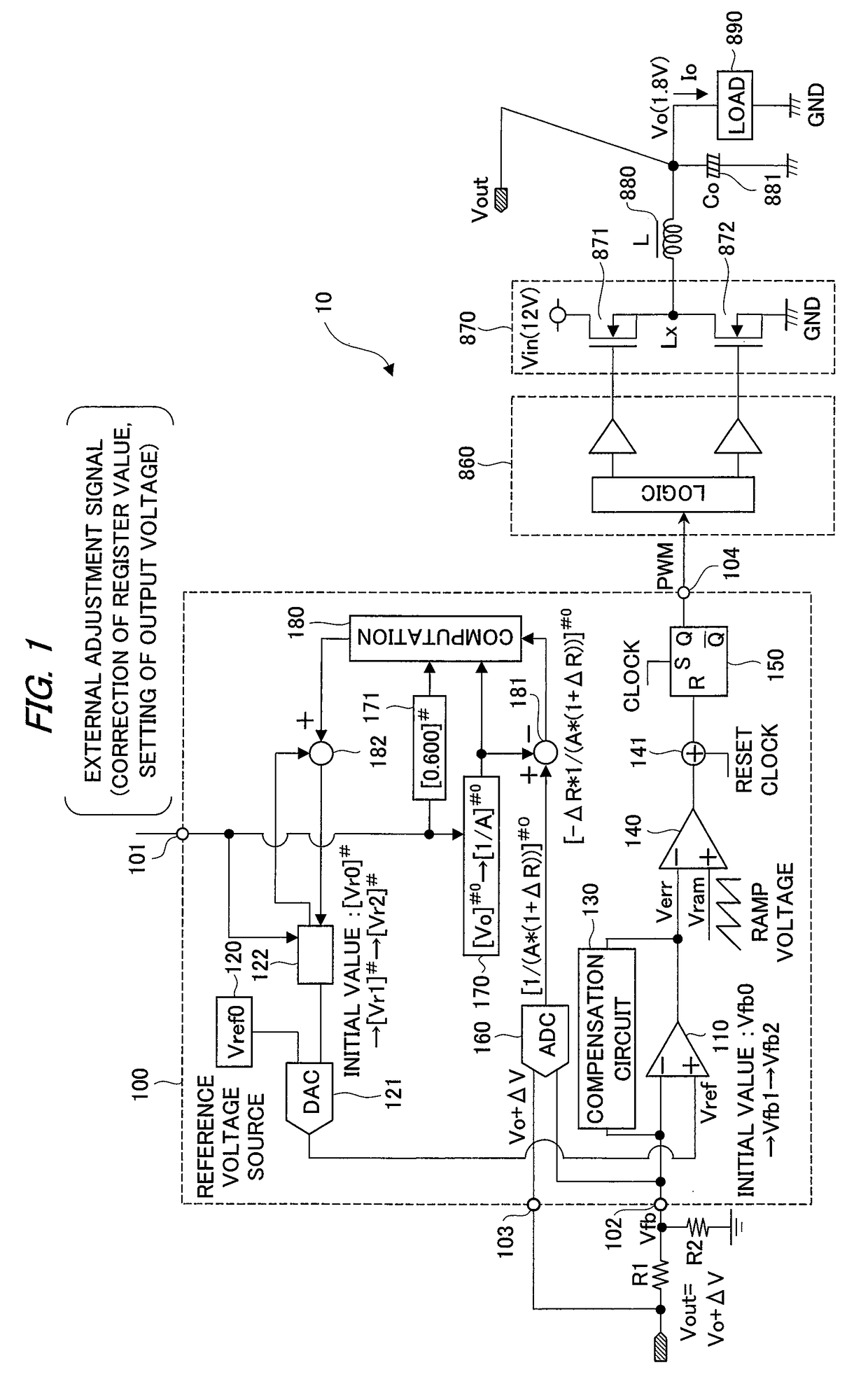
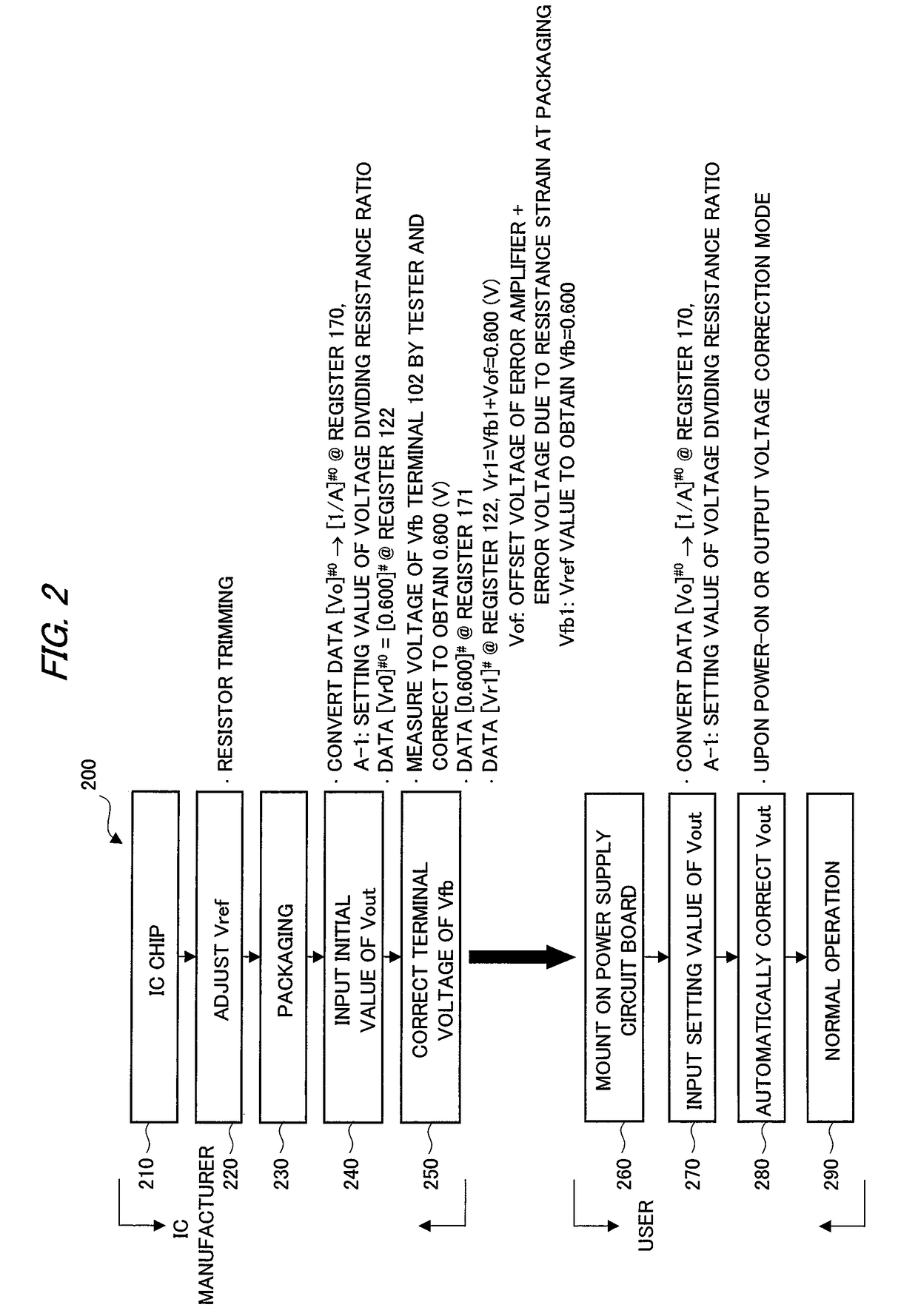
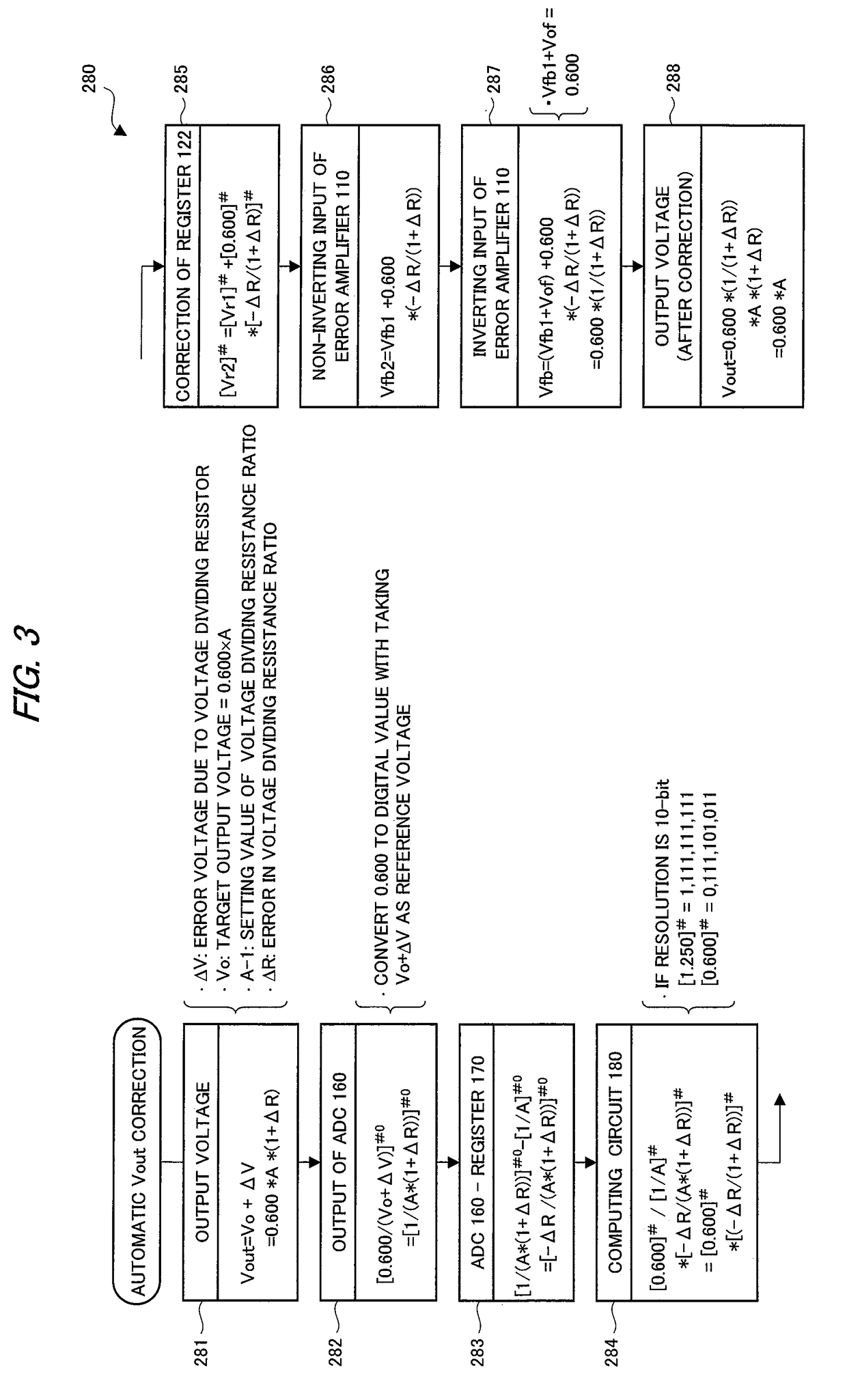
A semiconductor device for control applied to a constant-voltage power supply device includes a digital-analog converter circuit which outputs a reference voltage corresponding to a value of a first register with taking an output voltage of a reference voltage source as a criterial reference voltage, and generates a control signal for driving a power semiconductor device based on an output voltage of an error amplifier which differentially amplifies a feedback voltage obtained by resistive-dividing on an output voltage of the constant-voltage power supply device and the reference voltage. An analog-digital converter circuit which converts the feedback voltage to a digital value with taking the output voltage of the constant-voltage power supply device as a reference voltage is provided, and based on the output, a value of a first register is corrected so as to offset an effect of an error in voltage dividing ratio of a voltage dividing resistor circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
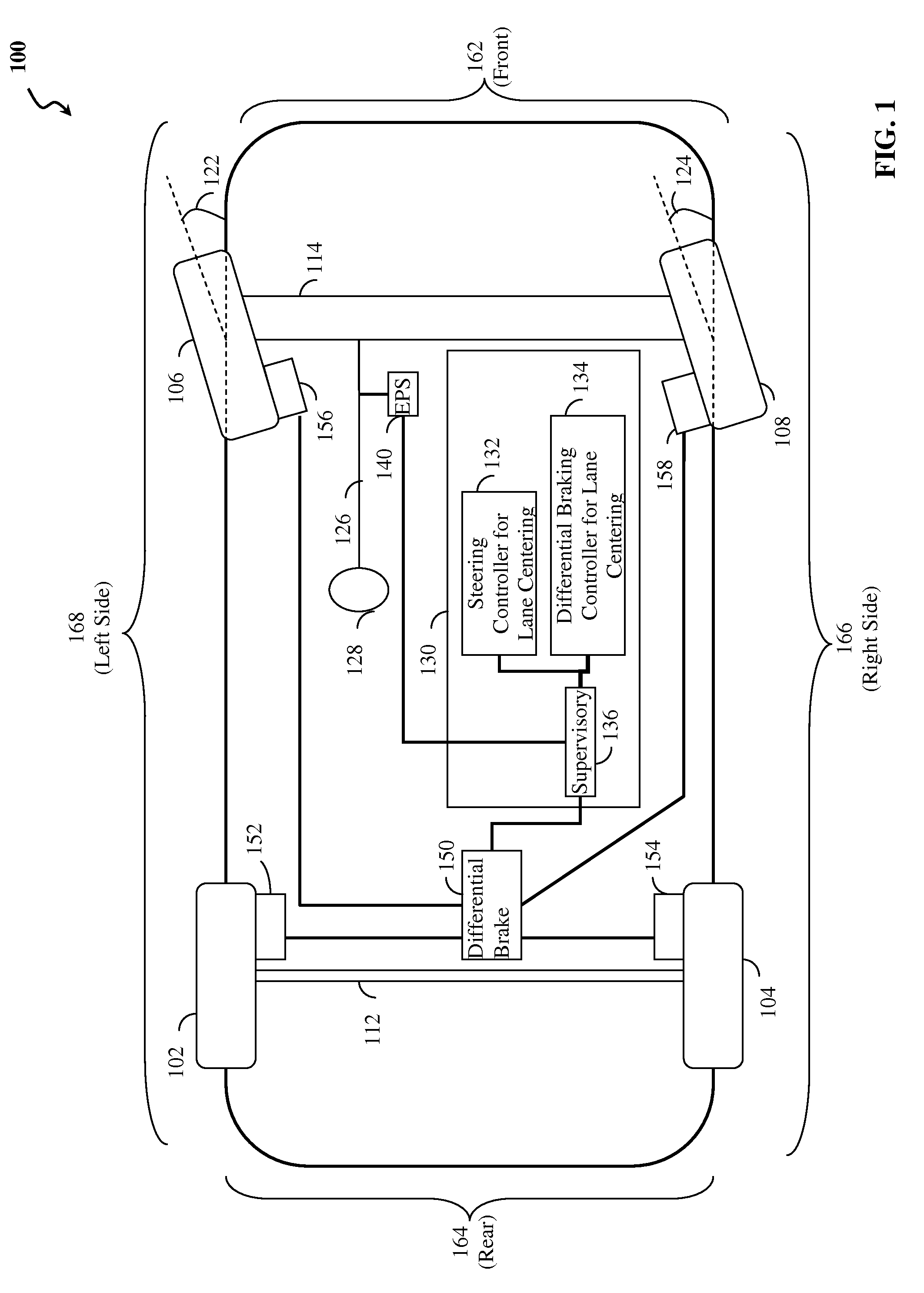
Lane centering fail-safe control using differential braking
ActiveUS8670903B2Minimize the differenceOffset errorVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesElectric power steeringFail-safe
Method, system and non-transitory computer-readable medium for fail-safe performance of a lane centering system. An electrical power steering (EPS) system of a vehicle is monitored for a failure and operation of the lane centering system is switched to a differential braking controller to output differential braking commands to a differential breaking system upon determining that a failure of the EPS system has occurred, where the output braking commands direct the differential braking system to apply force a brake for a wheel of vehicle, such by the applied braking force the vehicle follows a desired path determined for a lane centering operation.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
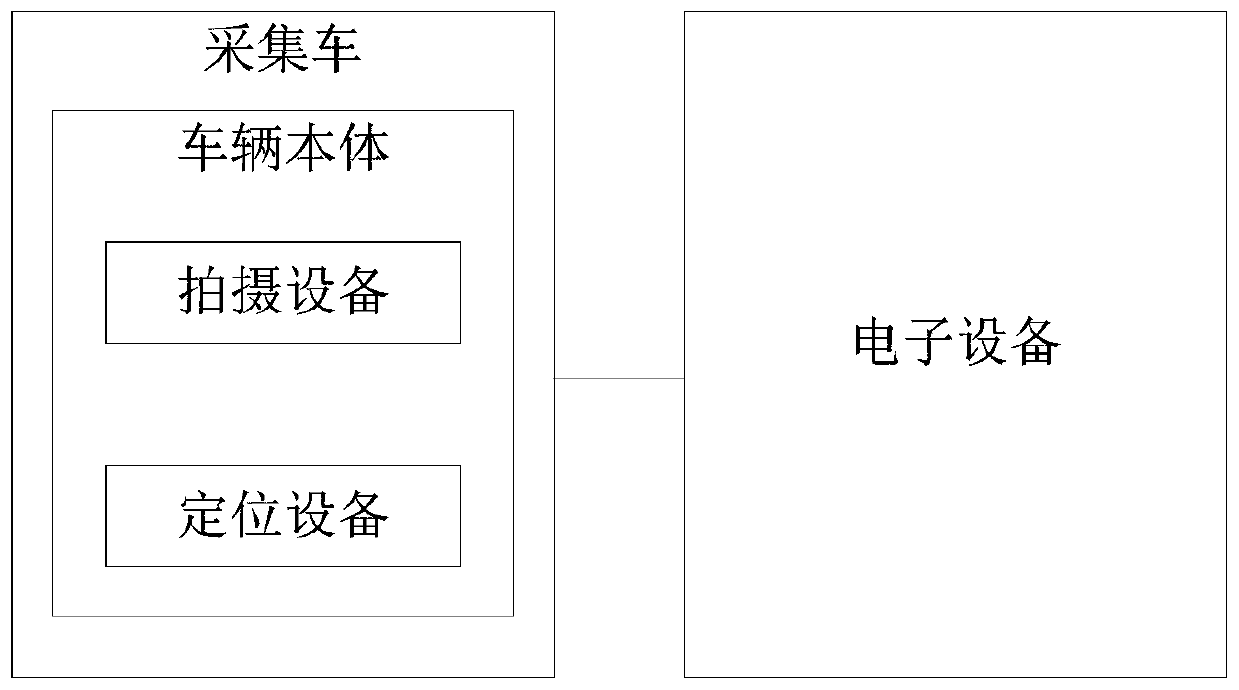
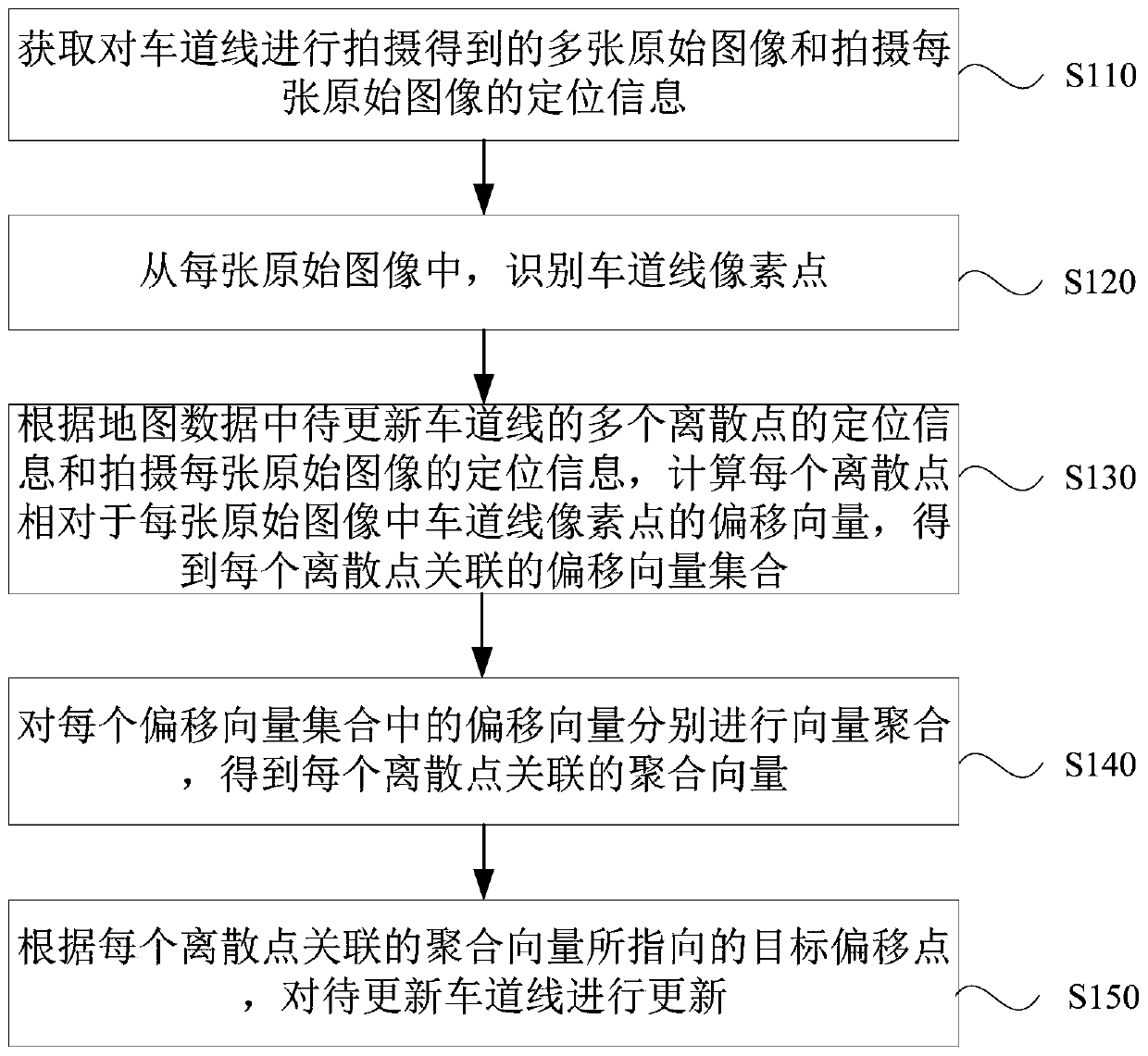
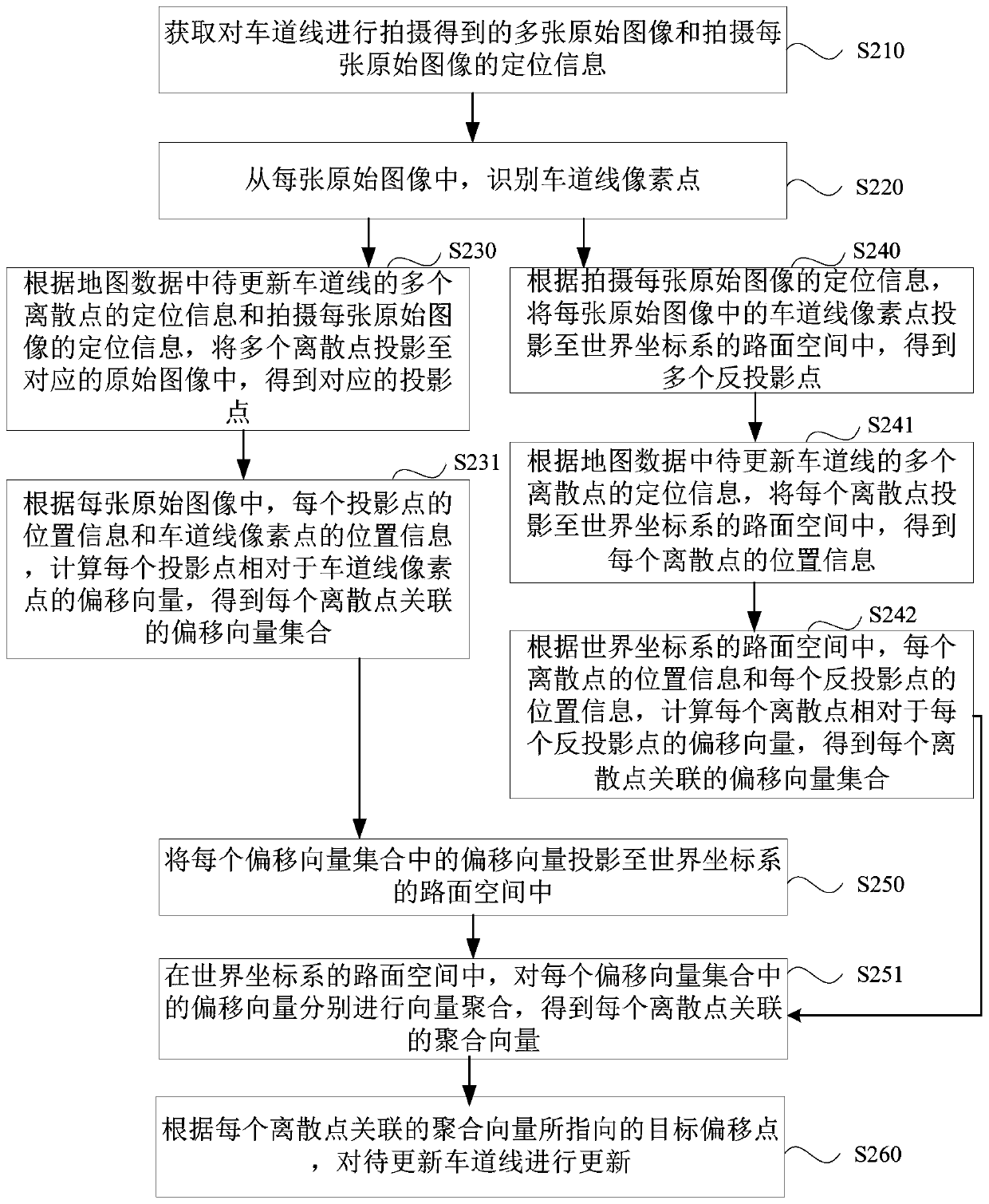
Lane line updating method, device, equipment and system and readable storage medium
ActiveCN110147382AImprove accuracyRaise the spotlightDatabase updatingGeographical information databasesDiscrete pointsComputer science
The embodiment of the invention provides a lane line updating method, device, equipment and system and a readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a plurality of original images obtained by shooting lane lines and positioning information of each shot original image; identifying lane line pixel points from each original image; according to the positioning information of a plurality of discrete points of the lane line to be updated in the map data and the positioning information of each shot original image, calculating an offset vector of each discrete point relative to a lane line pixel point in each original image, and obtaining an offset vector set associated with each discrete point; performing vector aggregation on the offset vectors in each offset vector set to obtain an aggregation vector associated with each discrete point; and updating the lane line to be updated according to the target offset point pointed by the aggregation vector associatedwith each discrete point. According to the method provided by the embodiment of the invention, errors caused by single offset are eliminated, the cost is low, the stability is high, and the occurrenceis high.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
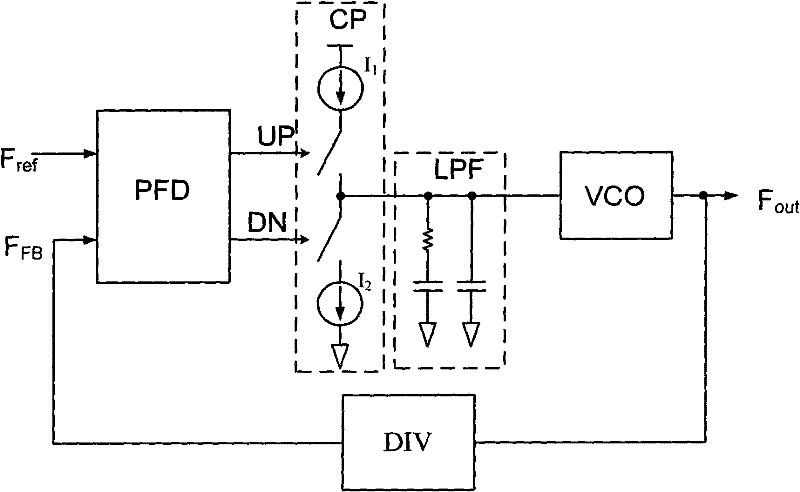
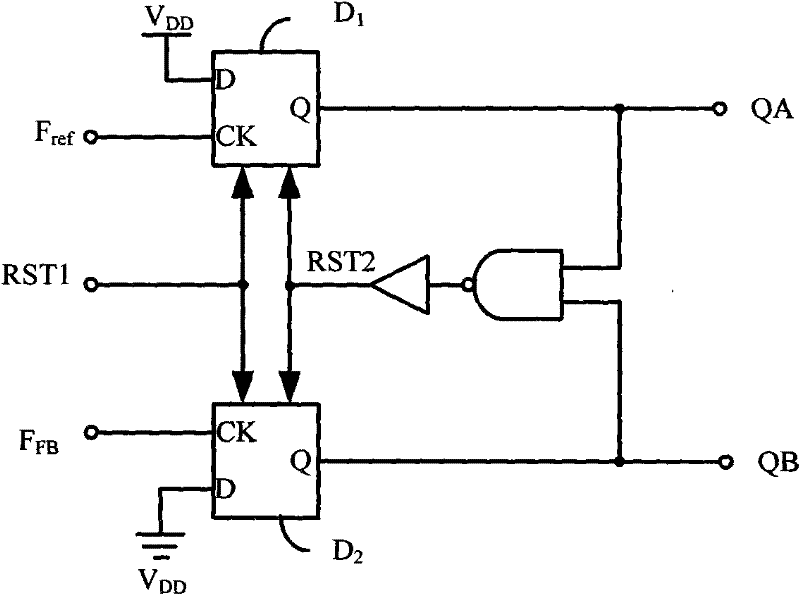
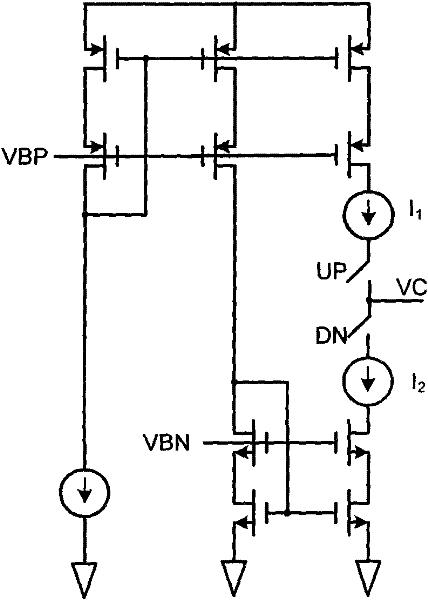
Frequency discrimination phase discriminator and method applying to phase-locked loop
The embodiment of the invention discloses a frequency discrimination phase discriminator. The phase discriminator comprises two D triggers D1 and D2, as well as a nand gate NA1 and a buffer 1, the output ends of the two D triggers D1 and D2 are utilized as an input end of the nand gate; an output end of the nand gate NA1 passes through the buffer 1 to utilize as a second reset terminal RST 2 of the two D triggers, and the output ends of the D trigger D1 and the D trigger D2 can respectively obtain signal Q1 and Q2; and the phase discriminator also comprises a timing control unit, the signals Q1 and Q2 are input signals of the timing control unit, and the timing control unit is used for controlling phase and pulse width of an output signal of the frequency discrimination phase discriminator. The invention also discloses a charge pump phase locked loop applying to the frequency discrimination phase discriminator and a method of a phase locked loop applying to the frequency discrimination phase discriminator. The technical scheme of the phase discriminator and the phase locked loop and the method can effectively avoid an error caused by mismatch charge pump current through a simple circuit structure.
Owner:ARKMICRO TECH
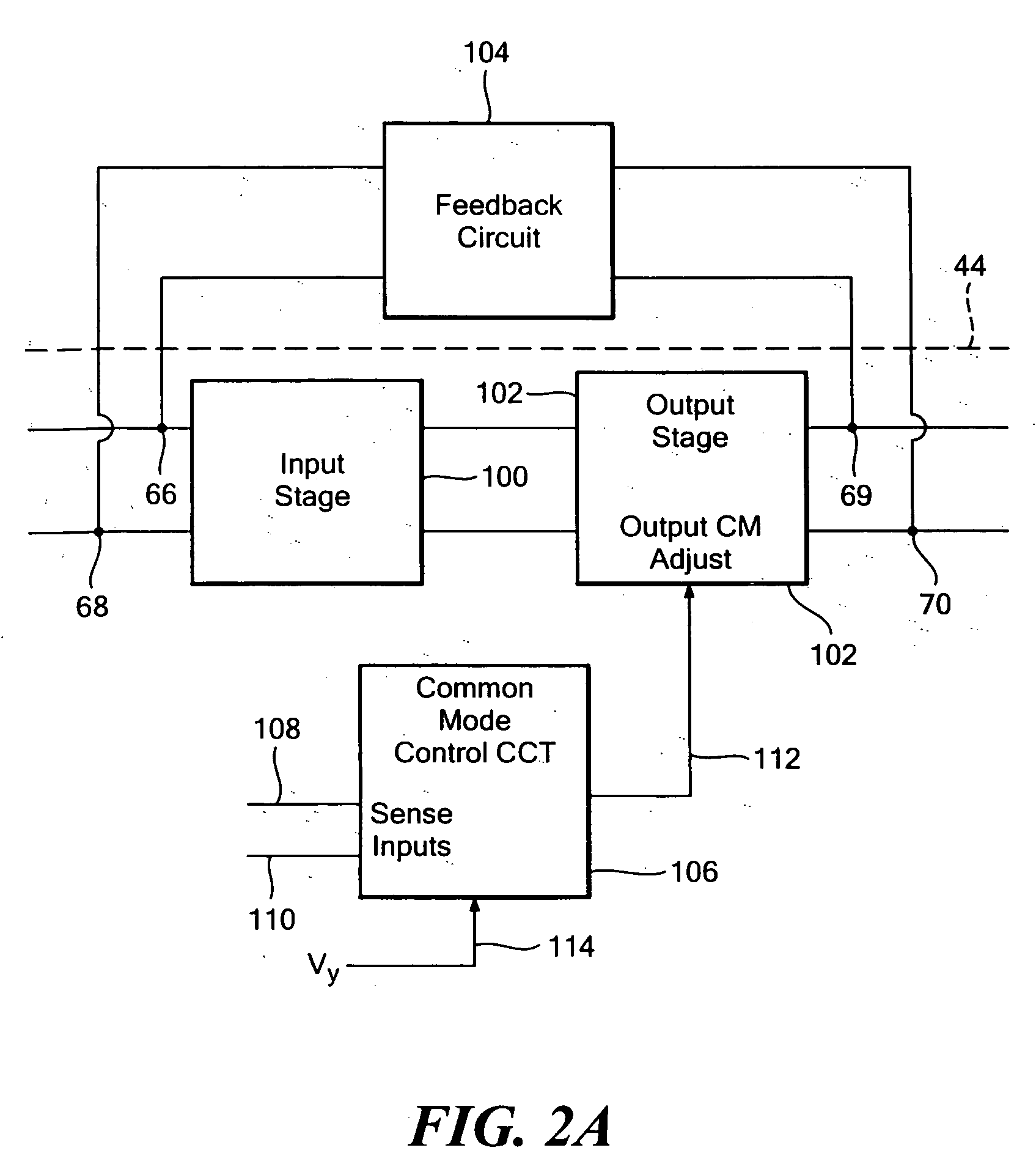
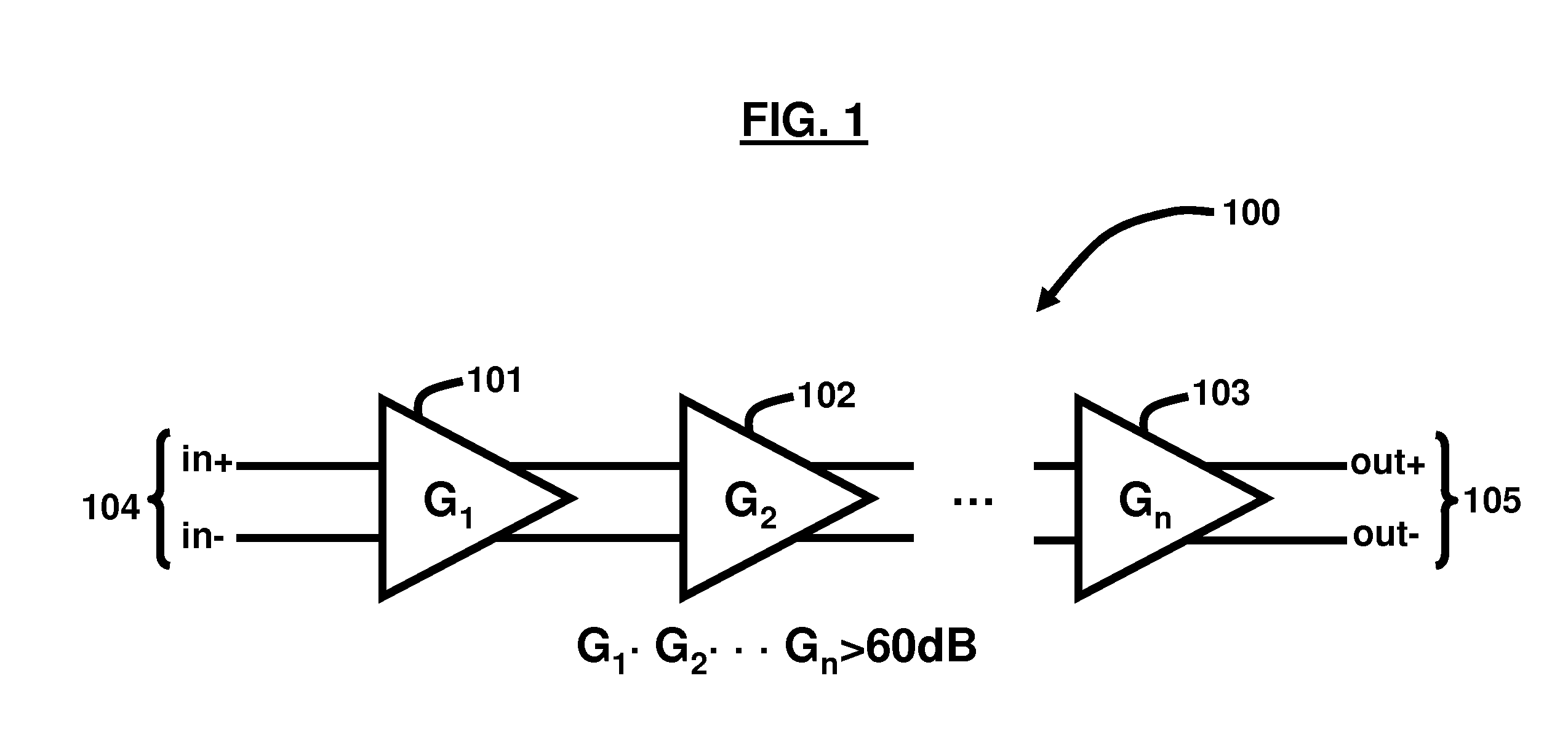
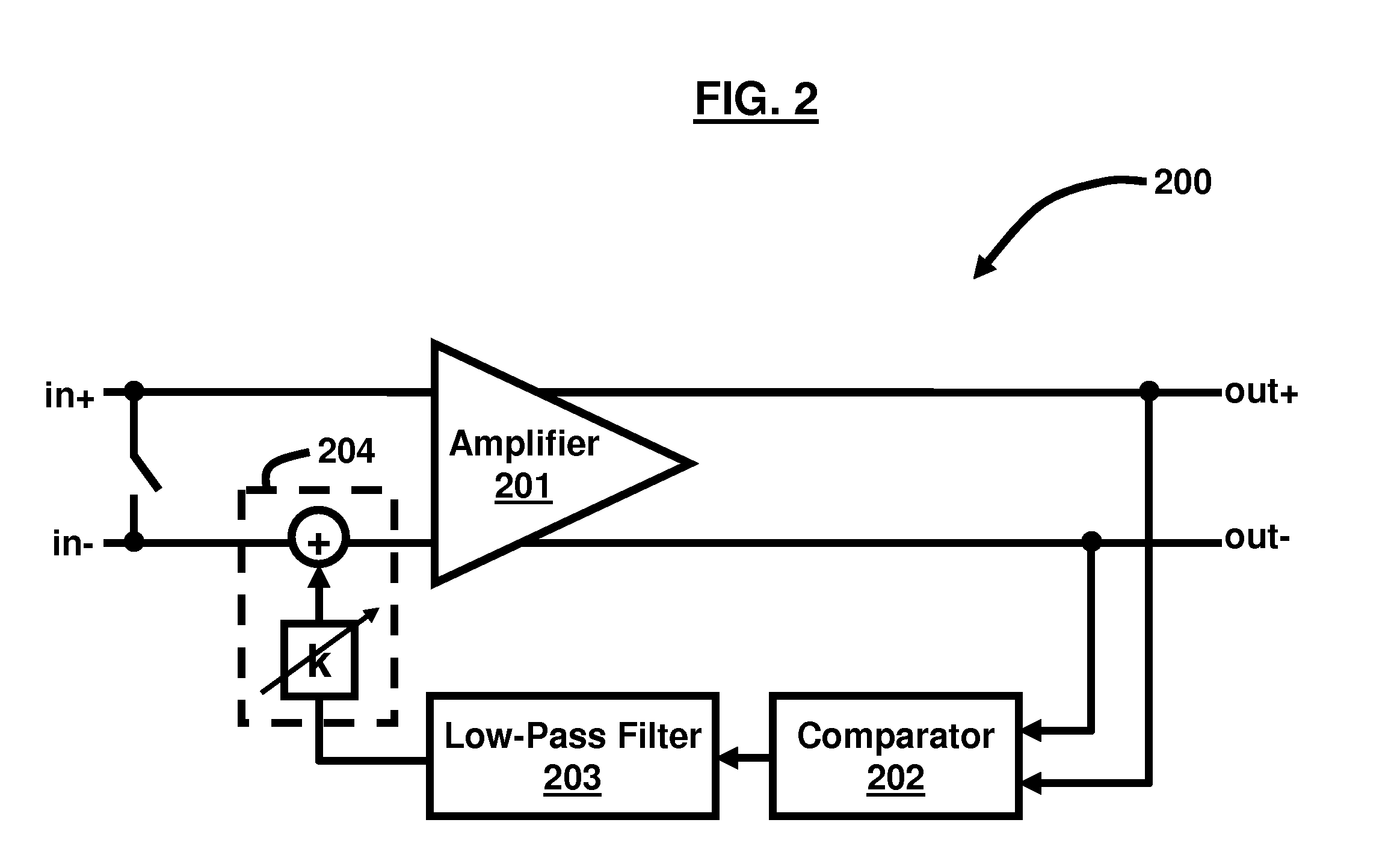
Method and apparatus for DC offset cancellation in amplifiers
ActiveUS20080048773A1Offset errorAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierOffset cancellation
A system, circuit, and method of canceling DC offset errors in cascaded amplifiers comprises arranging a plurality of any of analog voltage and analog current amplifier stages in any of cascaded and parallel configurations; operatively connecting a feedback comparator and digital logic in a feedback path around a given amplifier, wherein the digital logic comprises a finite state machine implementing an adaptive search algorithm comprising fixed switching and modulated switching; operatively connecting a switch at a differential input of the amplifier to short both input terminals of the amplifier; performing fixed switching on binary weighted elements generating discrete analog steps used to vary any of DC offset voltage and current at the input of the amplifier; and performing modulated switching on at least one lower least significant bit (LSB) of all bits used to vary the any of the DC offset voltage and current.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
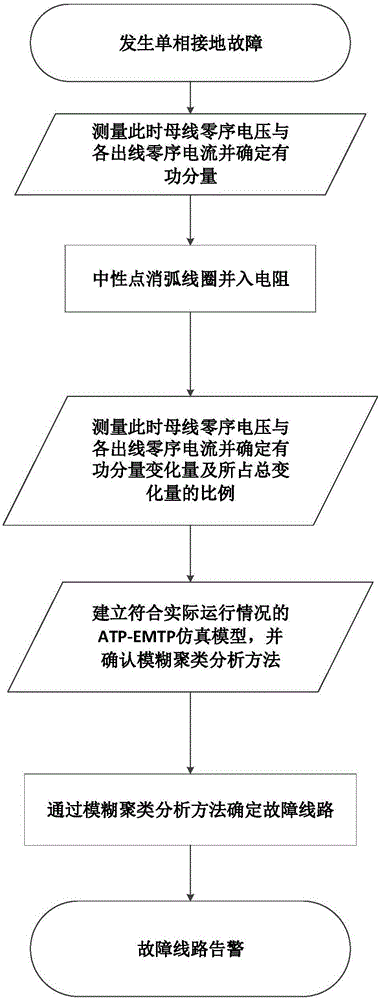
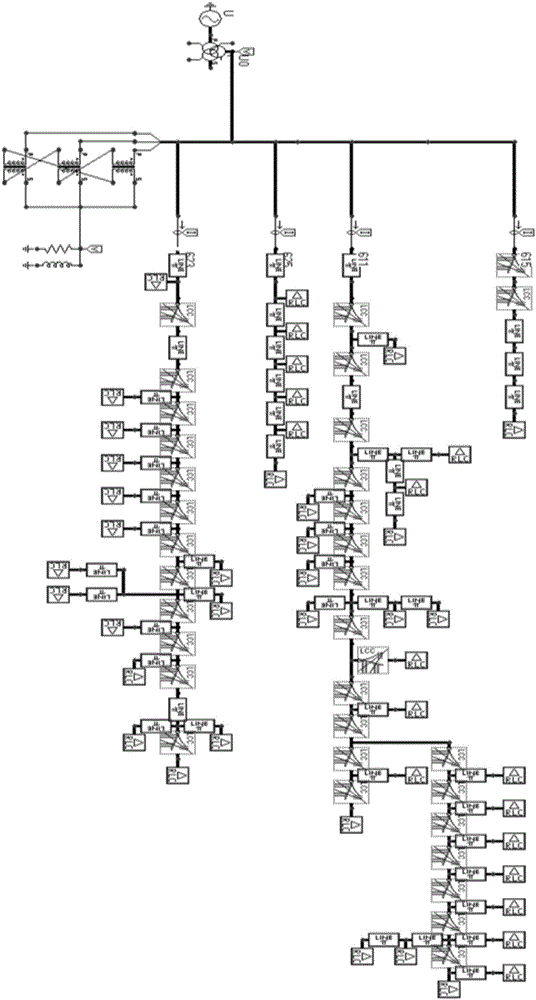
Fuzzy clustering analysis-based power distribution network fault line selection method
ActiveCN106370981AIncrease fault signalImprove line selection accuracyFault locationMeasurement deviceFuzzy clustering analysis
The present invention relates to a fuzzy clustering analysis-based power distribution network fault line selection method. According to the method, the ratio of the variation quantity of the active component of the zero-sequence current of each outgoing line of a power distribution network to the total variation quantity of the active component of the zero-sequence current of the outgoing lines of the power distribution network is calculated; the simulation model of the actual operation of the power distribution network is constructed; and a fault line is determined through using a clustering analysis method. When a single-phase grounding fault occurs on the arc suppression coil grounding system of a neutral point, fault characteristics are not obvious; the grounding mode of the neutral point in the power distribution network is changed, fault signals are amplified, and therefore, line selection accuracy can be improved; a bus-bar potential transformer PT and a current transformer CT are adopted to measure the zero-sequence voltage of a bus-bar and the zero-sequence current of the outgoing lines before and after a resistor is switched; the variation quantity of the active component of the zero-sequence current of each outgoing line of lines is monitored; errors brought by measurement devices such as the current transformer CT of the line can be offset; and high anti-interference performance can be realized.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Semiconductor device and power supply using the same
InactiveUS8120345B2Offset errorDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationControl signalVoltage reference
A semiconductor device for control applied to a constant-voltage power supply device includes a digital-analog converter circuit which outputs a reference voltage corresponding to a value of a first register with taking an output voltage of a reference voltage source as a criterial reference voltage, and generates a control signal for driving a power semiconductor device based on an output voltage of an error amplifier which differentially amplifies a feedback voltage obtained by resistive-dividing on an output voltage of the constant-voltage power supply device and the reference voltage. An analog-digital converter circuit which converts the feedback voltage to a digital value with taking the output voltage of the constant-voltage power supply device as a reference voltage is provided, and based on the output, a value of a first register is corrected so as to offset an effect of an error in voltage dividing ratio of a voltage dividing resistor circuit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
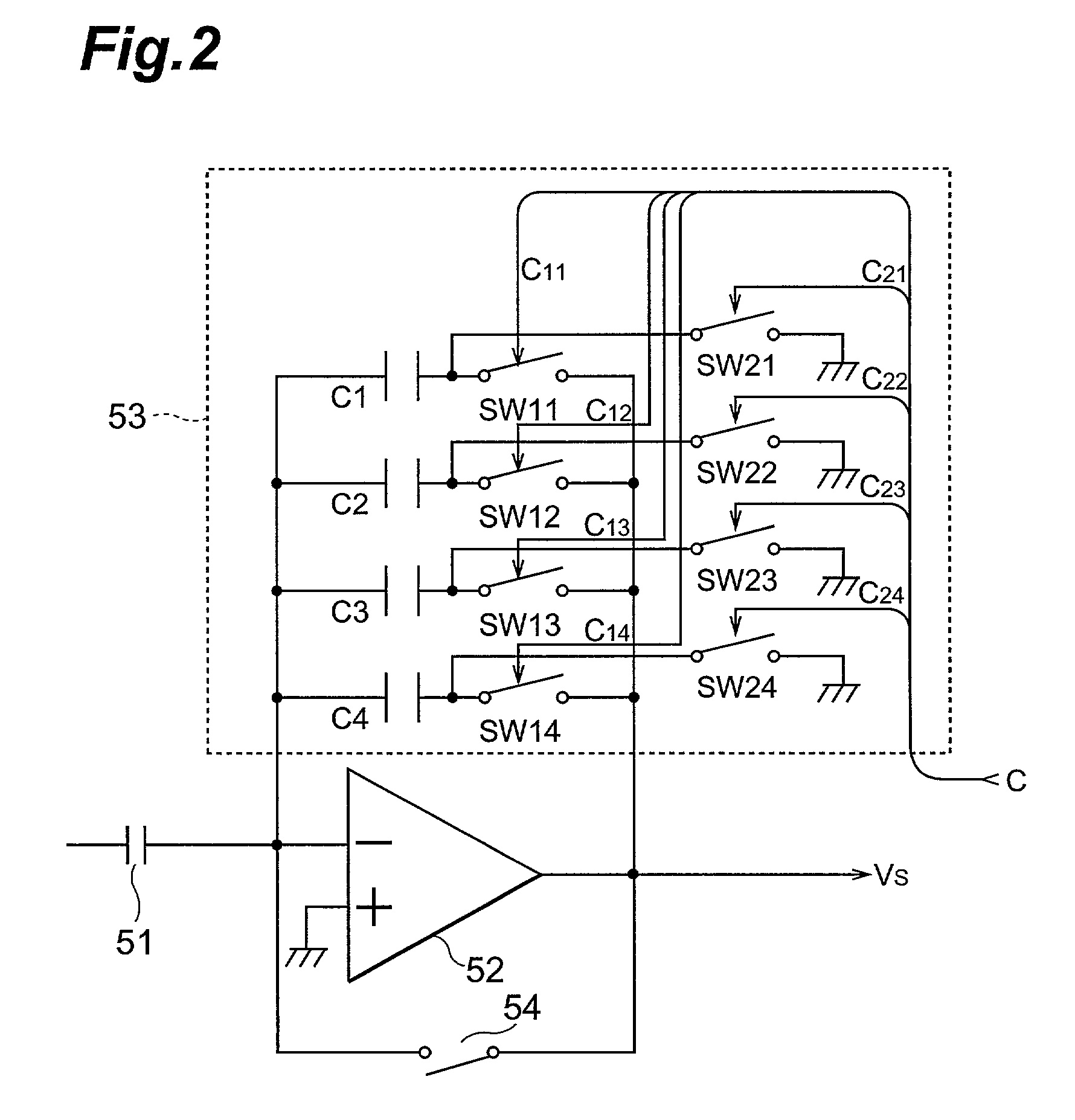
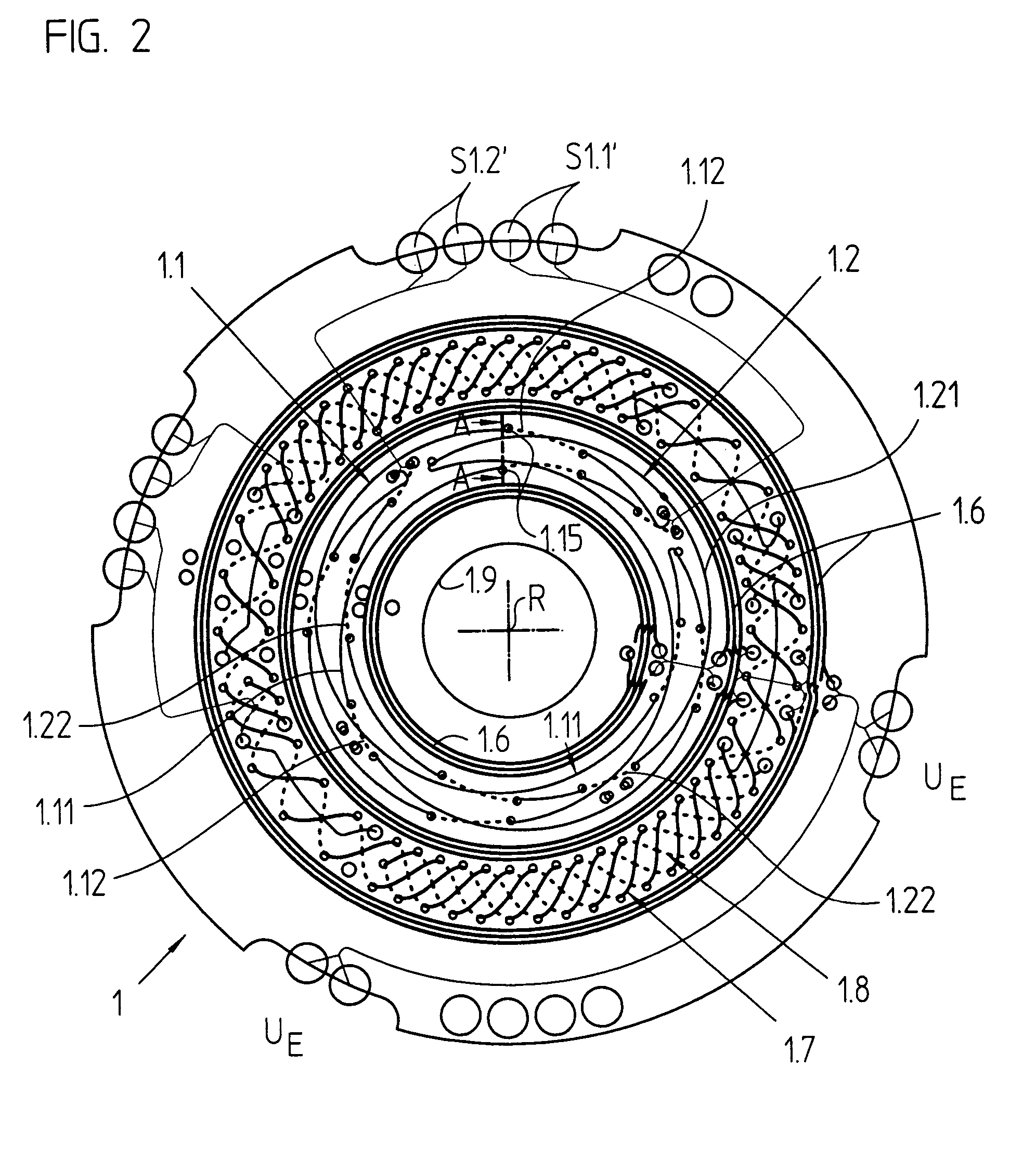
Analog demultiplexer
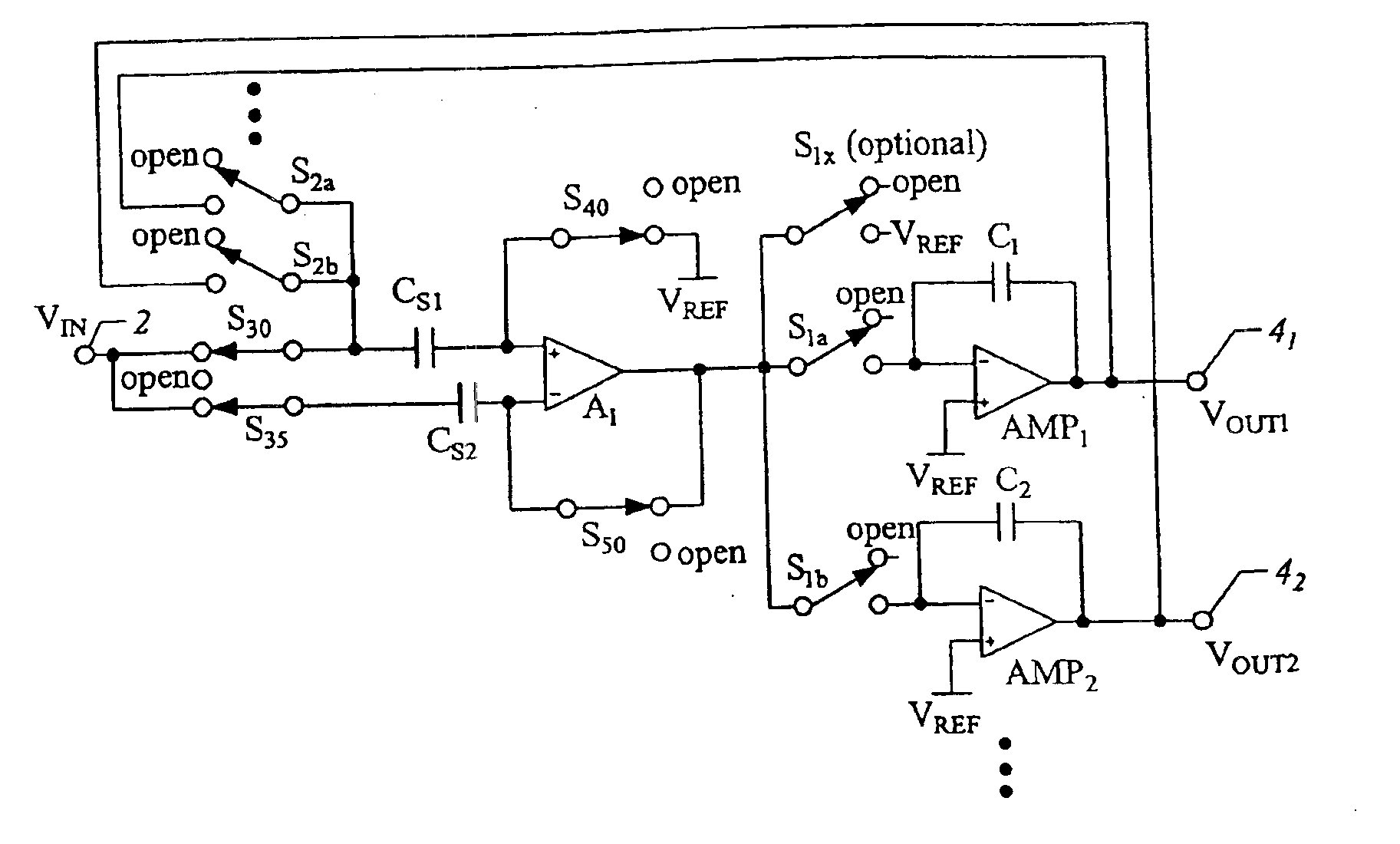
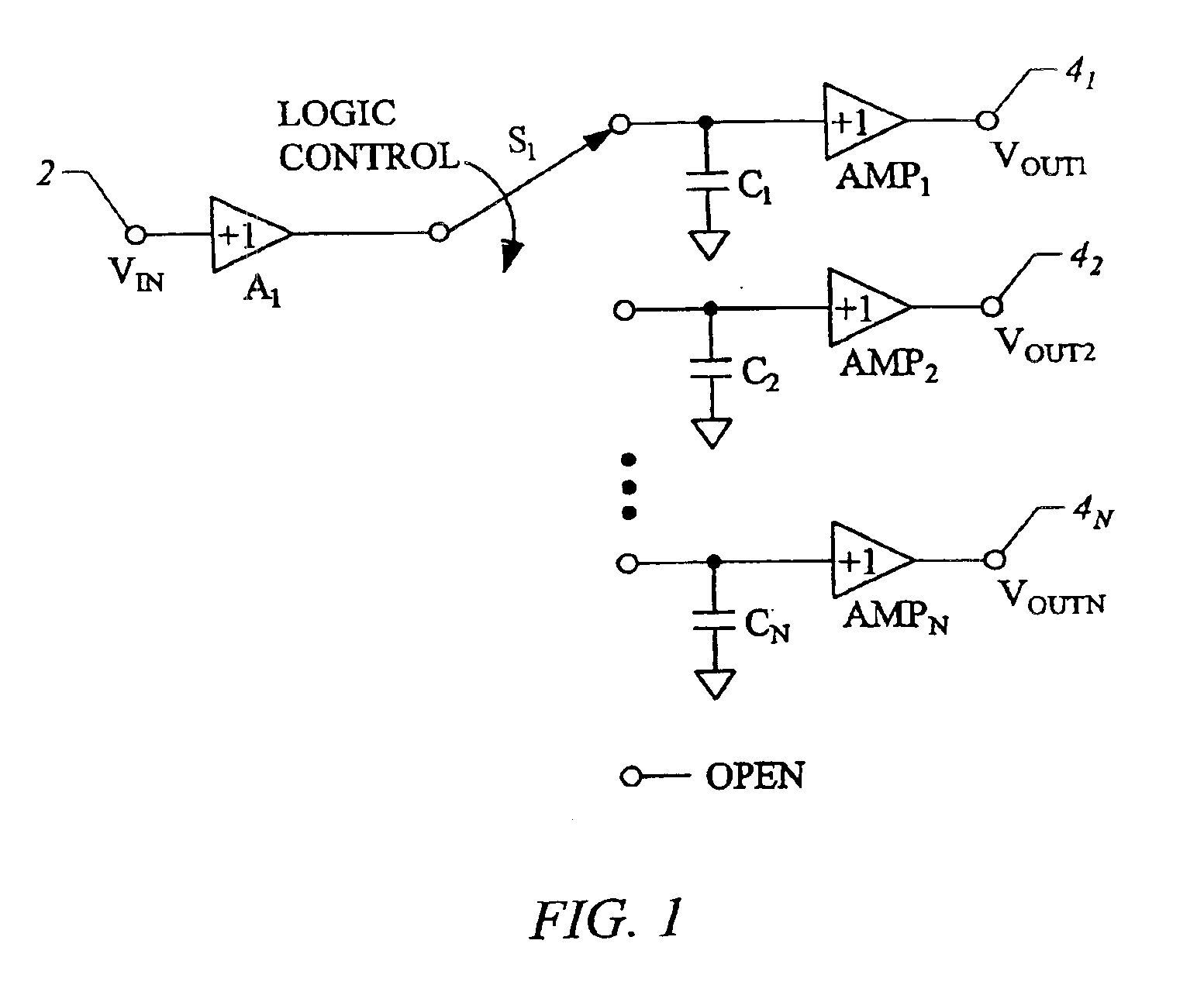
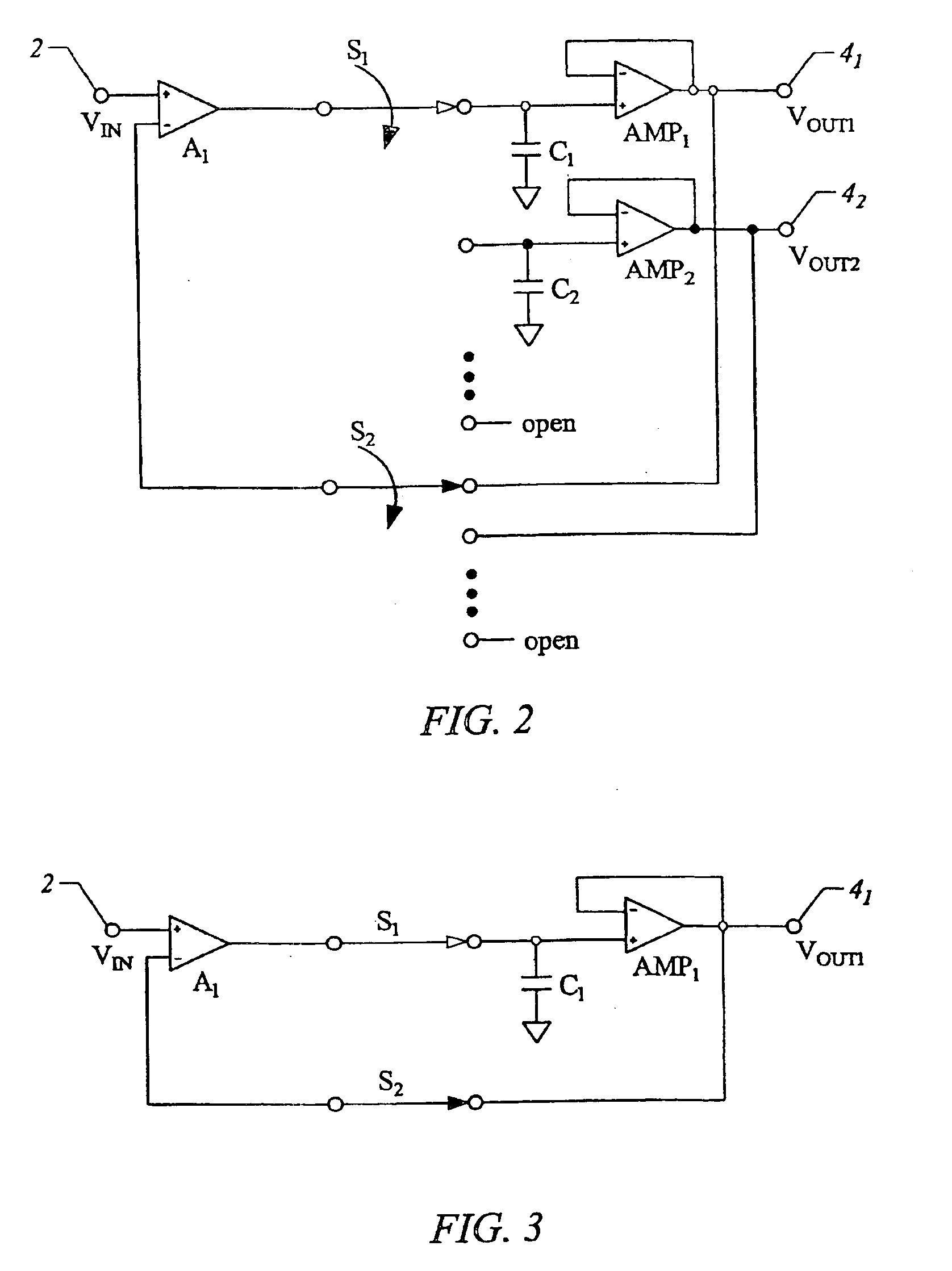
ActiveUS6897800B2Fast switching speedQuick switchTransistorElectric signal transmission systemsVoltage referenceEngineering
The analog demultiplexer (FIG. 6) includes an input amplifier (A1), and output amplifiers (AMP1-AMPN). The output and inverting (−) input of amplifiers (AMP1-AMPN) are connected by a respective capacitor (C1-CN). Switches (S1a, S1b, etc.) connect the output of amplifier (A1) to the inverting input of one of (AMP1-AMPN). Switches (S2a, S2b, etc.) connect the output of one of (AMP1-AMPN) to the non-inverting input of the amplifier A1. Switches (S2a, S2b, etc.) and (S1a, S1b, etc.) open and close together in pairs. With feedback from the output of (AMP1-AMPN) through (A1), the gain and any offset of (AMP1-AMPN) is divided down by the gain of (A1). Amplifier (A1) has capacitors (CS1 and CS2) connected to its inputs. Switch (S50) connects the inverting input of amplifier (A1) to its output, and switch (S40) connects the non-inverting input of (A1) to a voltage reference (VREF) matching (VREF) applied to (AMP2). Switches (S30) and (S35) connect (CS1) and (CS2) to the demultiplexer input (2). In operation, switches (S40, S50, S30 and S35) are initially closed, while switches (S2a, S2b, etc.) are open to charge both capacitors (CS1) and (CS2) and the inputs and output of (A1) to (VREF). Switch (S50) provides feedback to divide down gain errors and offset of (A1). Switches (S30, S35, S40 and S50) are then open, while one of switches (S2a, S2b, etc.) is closed with one switch (S1a, S1b, etc) to drive one of the output voltages (VOUT1-VOUTN). With inputs and outputs of (A1) and the connected (AMP1-AMPN) initially be at (VREF), very little settling time is needed.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Device and method for fast transition from preamble synchronization to data demodulation in direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) communications
ActiveUS8111734B2Quick transitionOffset errorTransmissionNumerical controlNumerically controlled oscillator
A device for fast transition from preamble synchronization of a received baseband signal to demodulation of the received baseband signal may include a baseband chip tracking loop to generate an offset tracking value to track any initial chip phase offset and Doppler-caused baseband chip frequency drift associated with the received baseband signal. The device may also include a numerical controlled oscillator to correct any Doppler-caused phase rotation associated with the received signal. The device may additionally include a preamble synchronization unit to detect a preamble of the received baseband signal, and to measure a chip phase offset and a baseband Doppler frequency shift associated with the received baseband signal. The chip phase offset may be used to set an initial chip phase offset value of the chip tracking loop so that the chip tracking loop starts with approximately a zero pull-in error. The baseband Doppler frequency shift may be used to set initial frequency offset values in the chip tracking loop and the numerical controlled oscillator so that both start with substantially near-zero offset errors for substantially immediate demodulation of the received signal. The device may further include an output device to output the data demodulated from the received baseband signal.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Current mirror for effectively inhibiting power source voltage influence
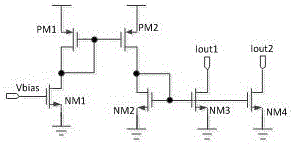
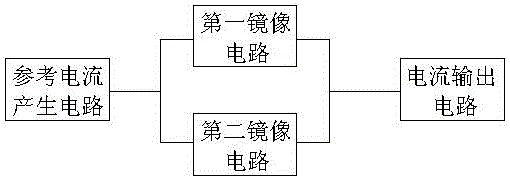
ActiveCN105867518AHigh inhibition ratioOffset errorElectric variable regulationReference currentEngineering
The invention provides a current mirror for effectively inhibiting power source voltage influence. The inhibiting capability of output current on power supply voltage fluctuation can be effectively improved, and the current precision is ensured. The current mirror comprises a reference current generating circuit, a first mirror image circuit, a second mirror image circuit and a current output circuit, wherein the output end of the reference current generating circuit is connected with the input end of the first mirror image circuit and the input end of the second mirror image circuit; the output end of the first mirror image circuit and the output end of the second mirror image circuit output to the current output circuit.
Owner:WUXI PROFESSIONAL COLLEGE OF SCI & TECH
MEMS pressure sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105181217AOffset errorExtended service lifeFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationMems pressure sensorEngineering
The invention relates to an MEMS pressure sensor and a preparation method thereof. The MEMS pressure sensor comprises a pressure sensitive film, at least four front-side voltage dependent resistors and at least four back-side voltage dependent resistors, the pressure sensitive film includes a front side and a back side, each front-side voltage dependent resistor is arranged at the front side of the pressure sensitive film, each back-side voltage dependent resistor is arranged at the back side of the pressure sensitive film, and the front-side voltage dependent resistors and the back-side voltage dependent resistors are electrically connected to form a Wheatstone bridge. The change direction of the resistance, along with the pressure, of the front-side voltage dependent resistor is opposite to that of the resistance, along with the pressure, of the back-side voltage dependent resistor at the corresponding position, so that errors caused by technical conditions and / or external factors of the voltage dependent resistors are offset, and the output stability and precision of the MEMS pressure sensor are improved.
Owner:苏州曼普拉斯传感科技有限公司
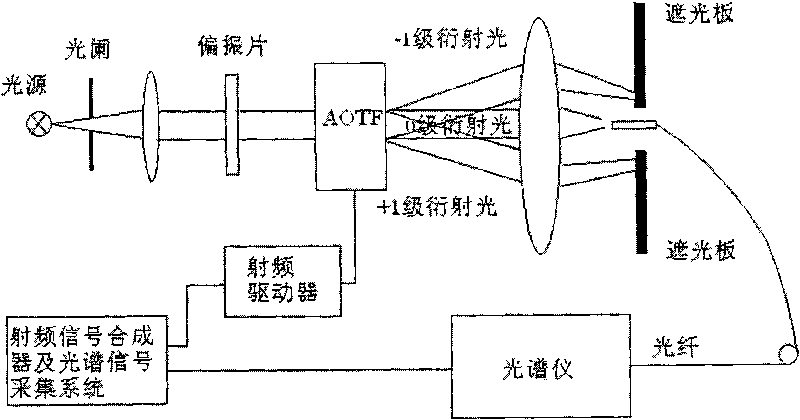
System and method for testing diffraction efficiency of acousto-optic tunable filter
InactiveCN101706361AMeet the densityMeet needsTesting optical propertiesBeam splittingAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a system for testing the diffraction efficiency of an acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF). The system comprises a wavelength tunable laser, a neutral density filter, a diaphragm orifice, a beam splitting mirror, a two-dimensional electric turnplate and an energy meter. The wavelength tunable laser can generate laser beams with continuously adjustable wavelength, the laser beams after passing through the neutral density filter and the diaphragm orifice are split into two beams of lasers with fixed beam splitting ratio by the beam splitting mirror, and the energy of reflecting beams is used as reference energy; transmission beams enter the AOTF, the energy of diffracted light is received when radio-frequency drive is applied to the transmission beams, and energy with direct penetration is received when the drive is not applied to the transmission beams, thereby calculating the diffraction efficiency of the AOTF. Meanwhile, the measurement of an aperture angle can be realized by changing the angle of incident light through the two-dimensional electric turnplate. The device has the characteristics of simple principle and strong operability, can meet the requirement of testing the continuous wavelength of the AOTF and can also enhance the testing accuracy greatly by utilizing reference beams generated by the beam splitting mirror.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
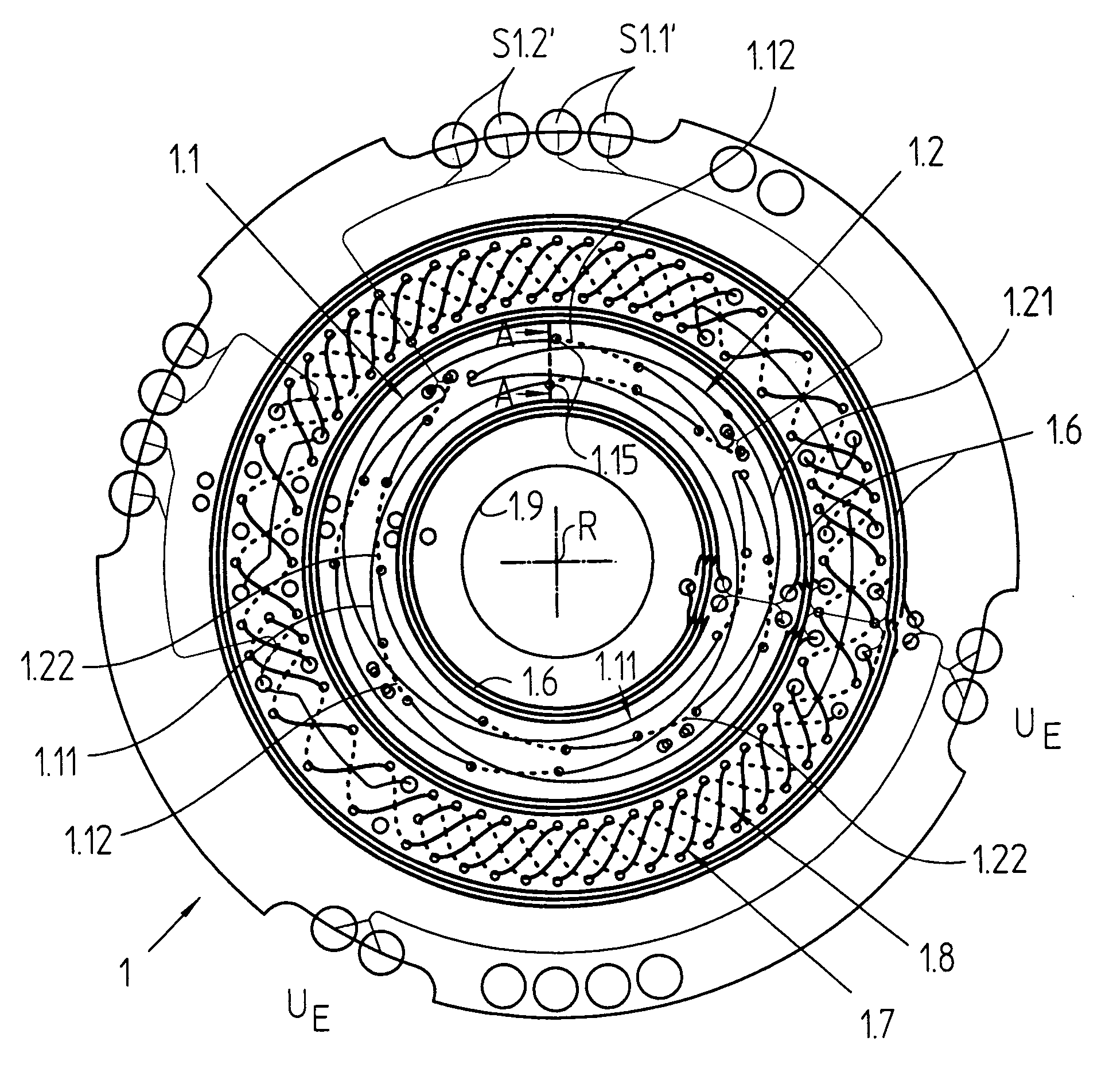
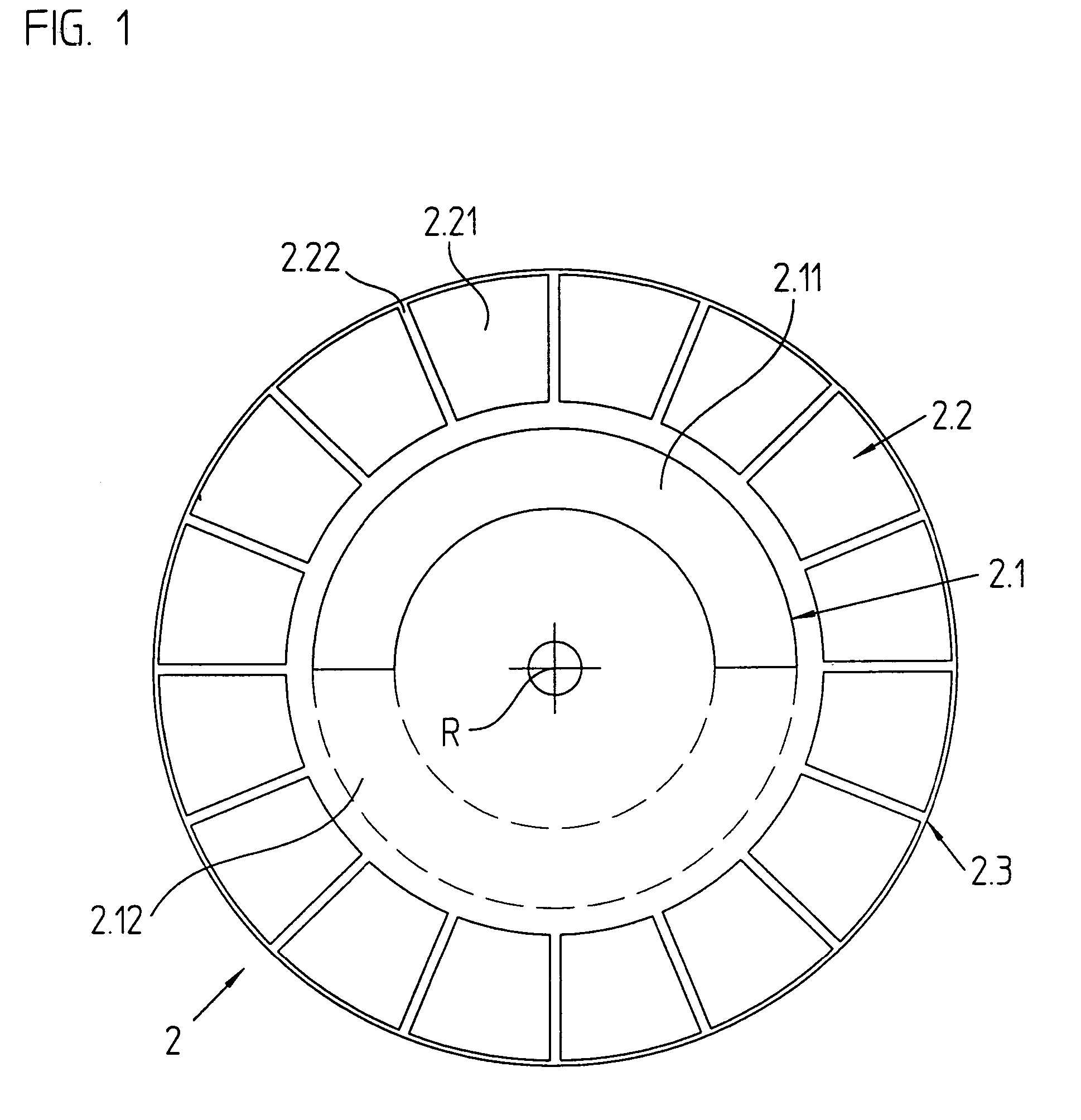
Inductive angle-of-rotation sensor and rotary transducer equipped with the same
ActiveUS7190158B2Error signalOffset errorUsing electrical meansConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyElectrical conductorTransducer
An inductive angle-of-rotation sensor, which is composed of a printed-circuit board, on which an excitation printed conductor and a receiving printed conductor are applied, the receiving printed conductor having a first partial section, which extends in a first plane, and a second partial section, which runs in a second plane. In addition, the inductive angle-of-rotation sensor has a graduation element, which is rotatable in relation to the printed-circuit board and includes a graduation track, which is composed of alternately arranged, electrically conductive and non-conductive graduation regions. The receiving printed conductor supplies an uneven number of signal periods within one rotation relatively to the graduation element. The first partial section of the receiving printed conductor is substantially greater in length than the second partial section. Moreover, a rotary transducer may be equipped with this angle-of-rotation sensor.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
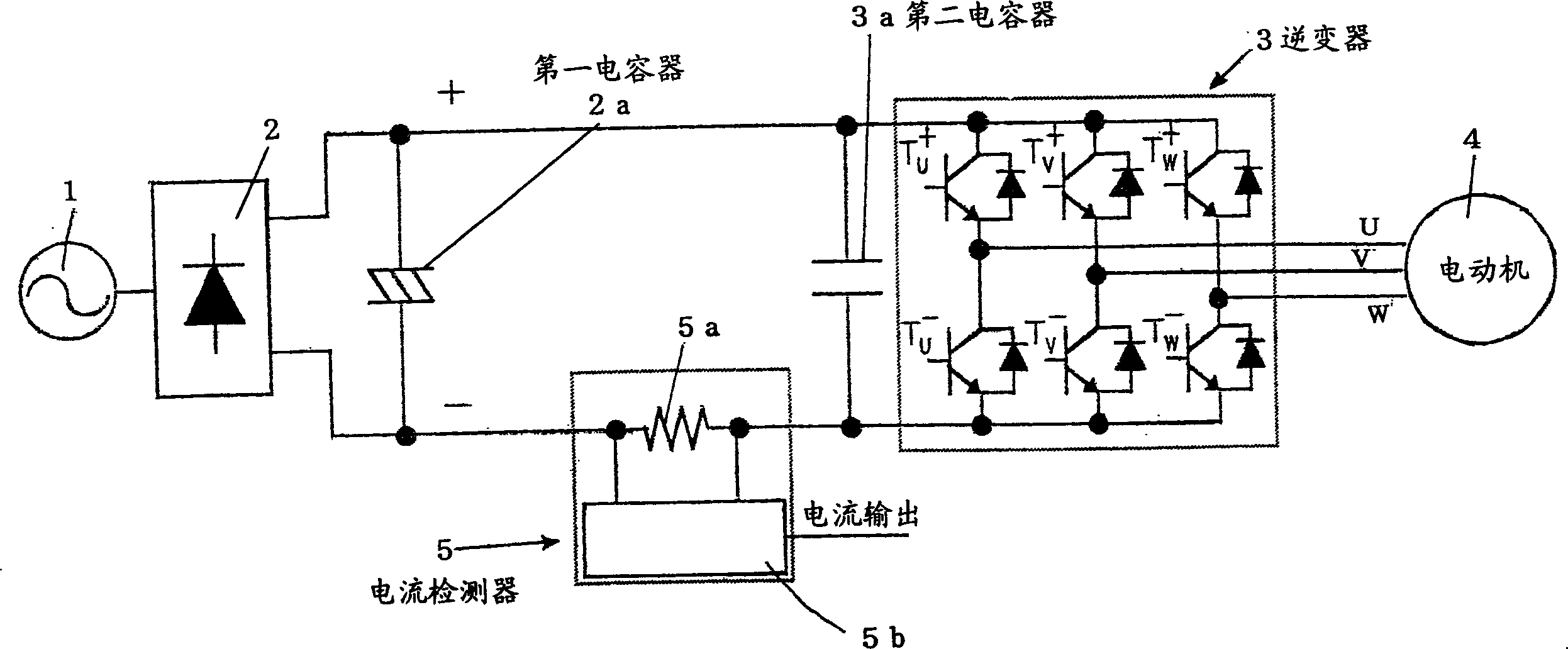
Phase current detector
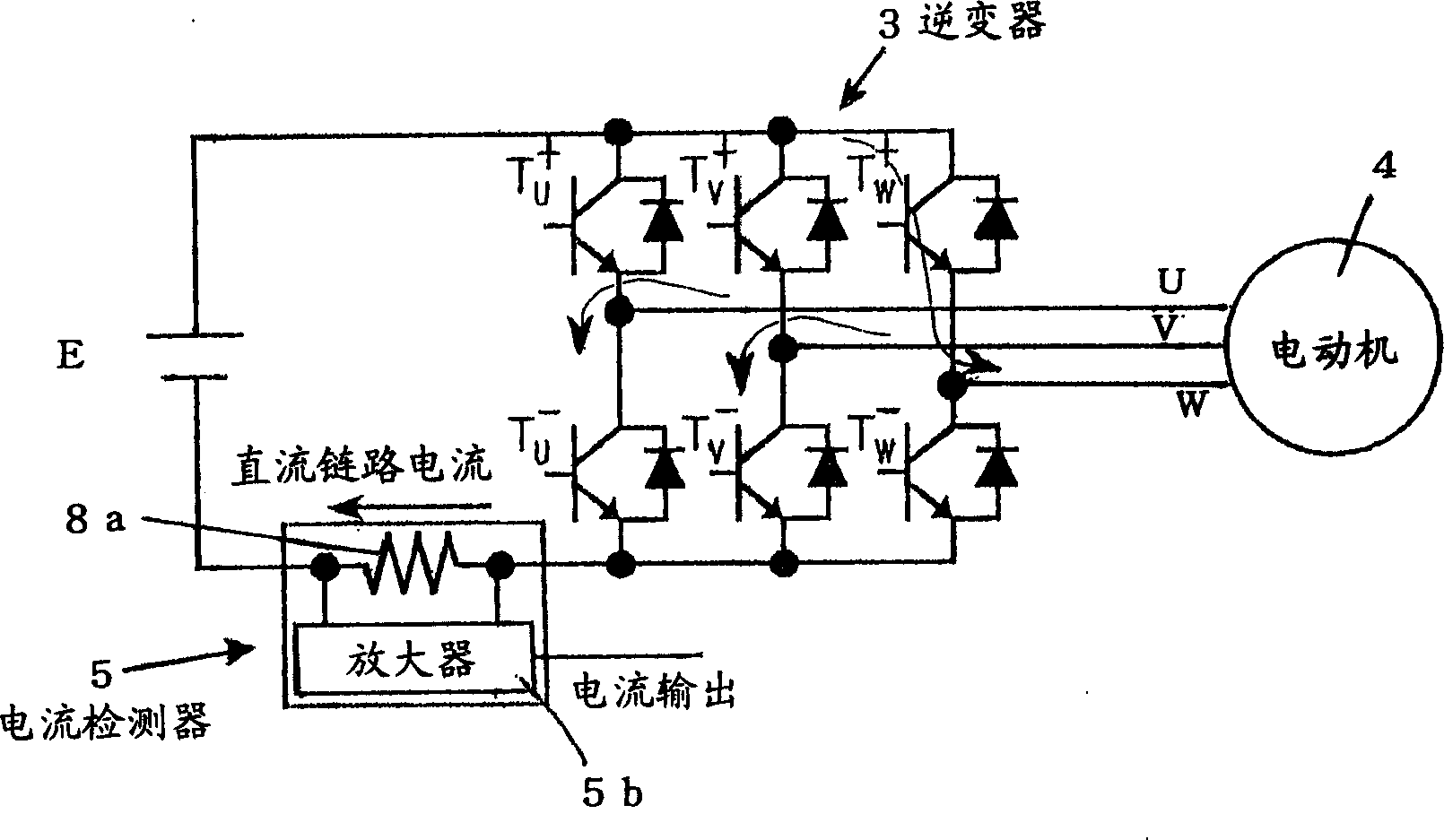
InactiveCN1478319AReduce overshootReduce the effects of ringingElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsPhase currentsCapacitance
A first condenser (2a) is connected between output terminals of a rectifier circuit (2) which receives an AC power (1) as an input, and a three phase inverter (3) is connected in parallel with respect to the first condenser (2a), and output of the three phase inverter (3) is supplied to a motor (4), and a second condenser (3a) is connected in parallel to the input side of the three phase inverter (3), and a current detector (5) is connected between the first condenser (2a) and the second condenser (3a), and a third condenser is connected in parallel to the first condenser (2a) at a position slightly power side with respect to the current detector (5), and the capacitance of the second condenser (3a) is determined as small as possible within the range in which power devices are not destroyed by surge voltage due to switching, therefore, ringing is suppressed, and taking of current is performed rapidly and with high accuracy.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Apparatus for controlling substrate voltage of semiconductor device
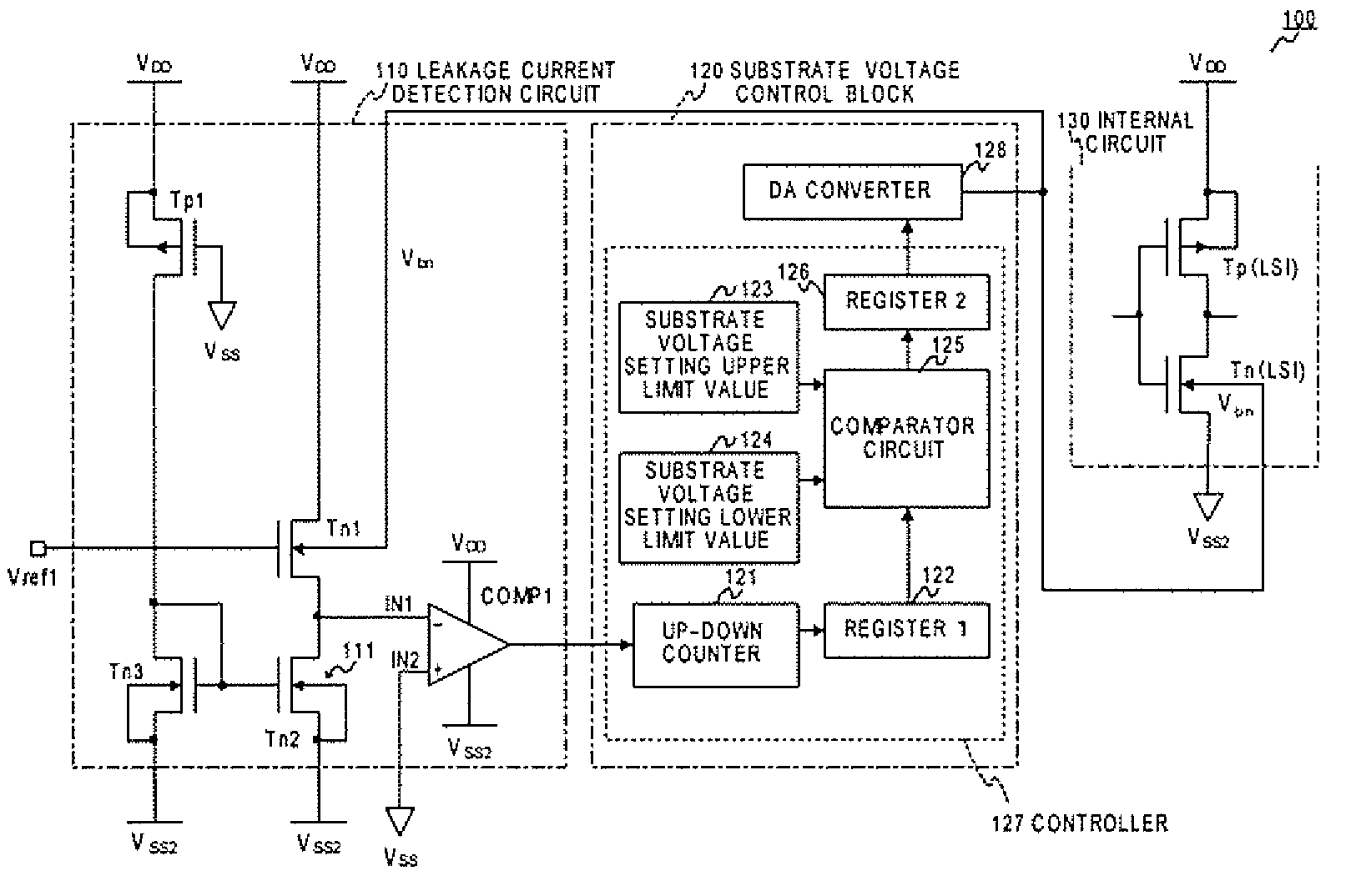
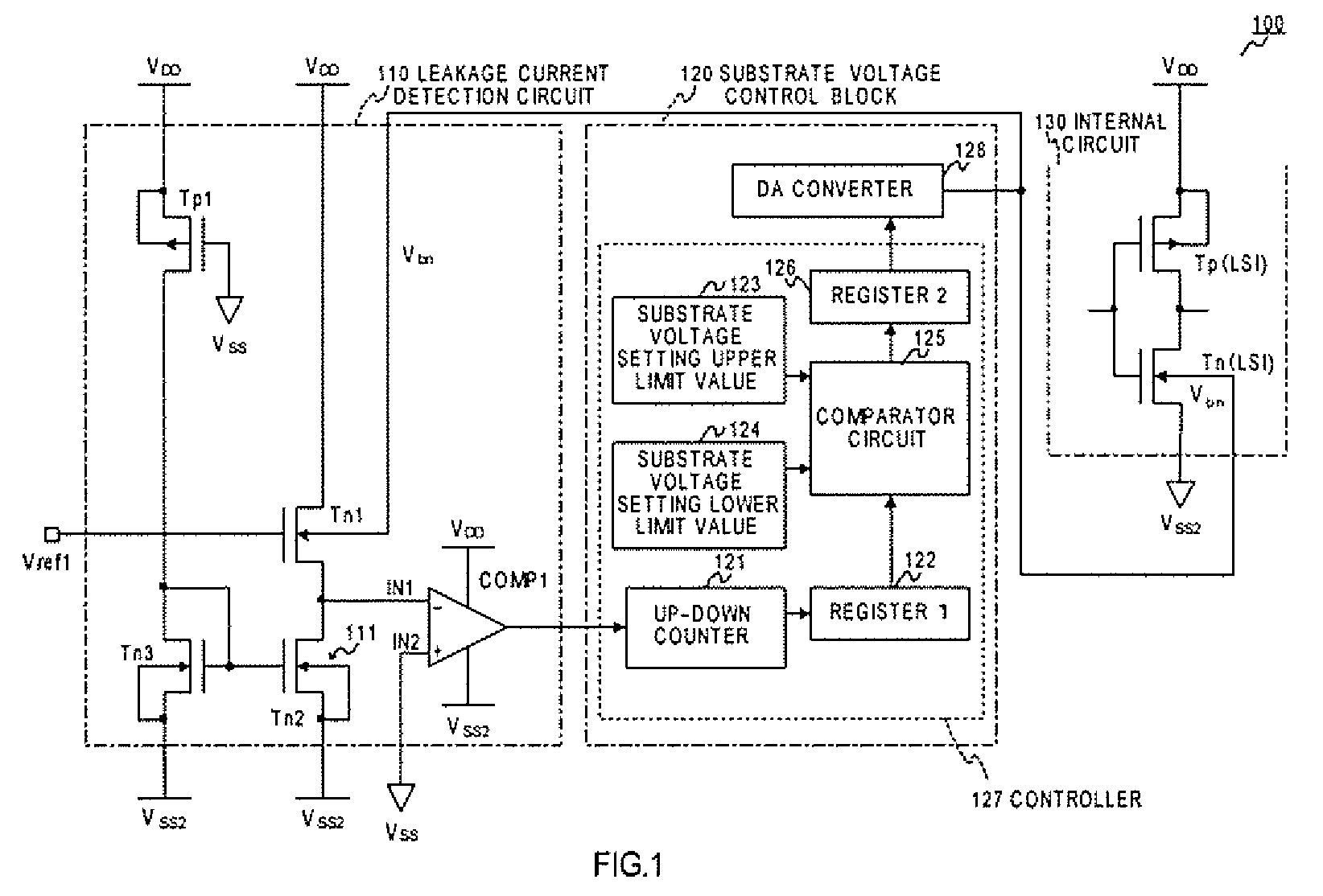
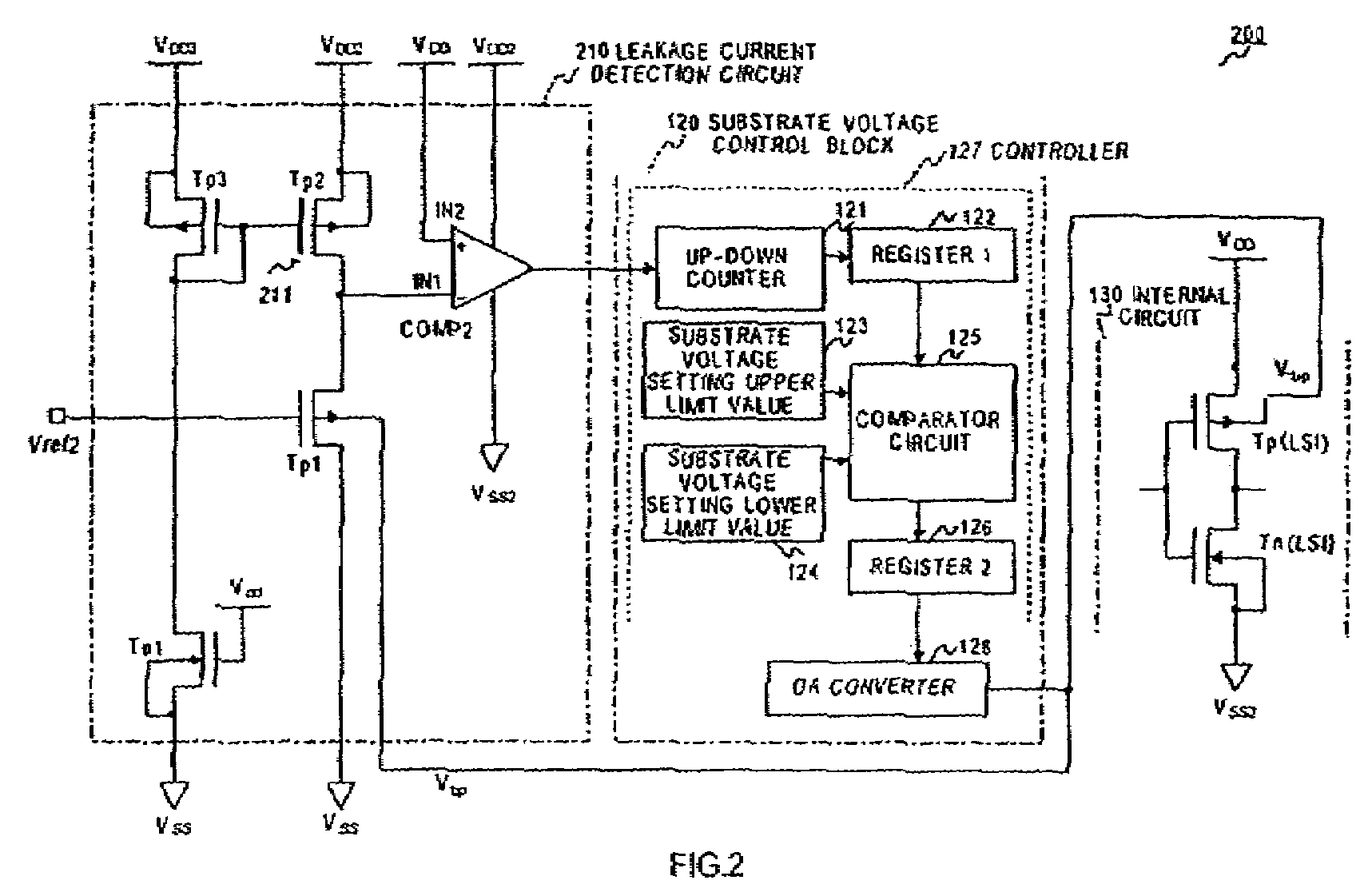
InactiveUS7714601B2High detection sensitivityHigh precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus capable of raising detection sensitivity of a leakage current detection circuit and improving response. A semiconductor integrated circuit apparatus has a substrate voltage control block that supplies a substrate voltage to an internal circuit and controls NchMOS transistor threshold voltage of the internal circuit, and a leakage current detection circuit constituted by a leakage current detection NchMOS transistor supplied with a high potential side supply voltage to a drain, that has a source connected to a constant current source, and that is applied with an arbitrary stabilizing potential to a gate in such a manner that the substrate voltage is controlled by the substrate voltage control block, and a comparator comparing the source potential of the leakage current detection NchMOS transistor and a predetermined reference potential.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
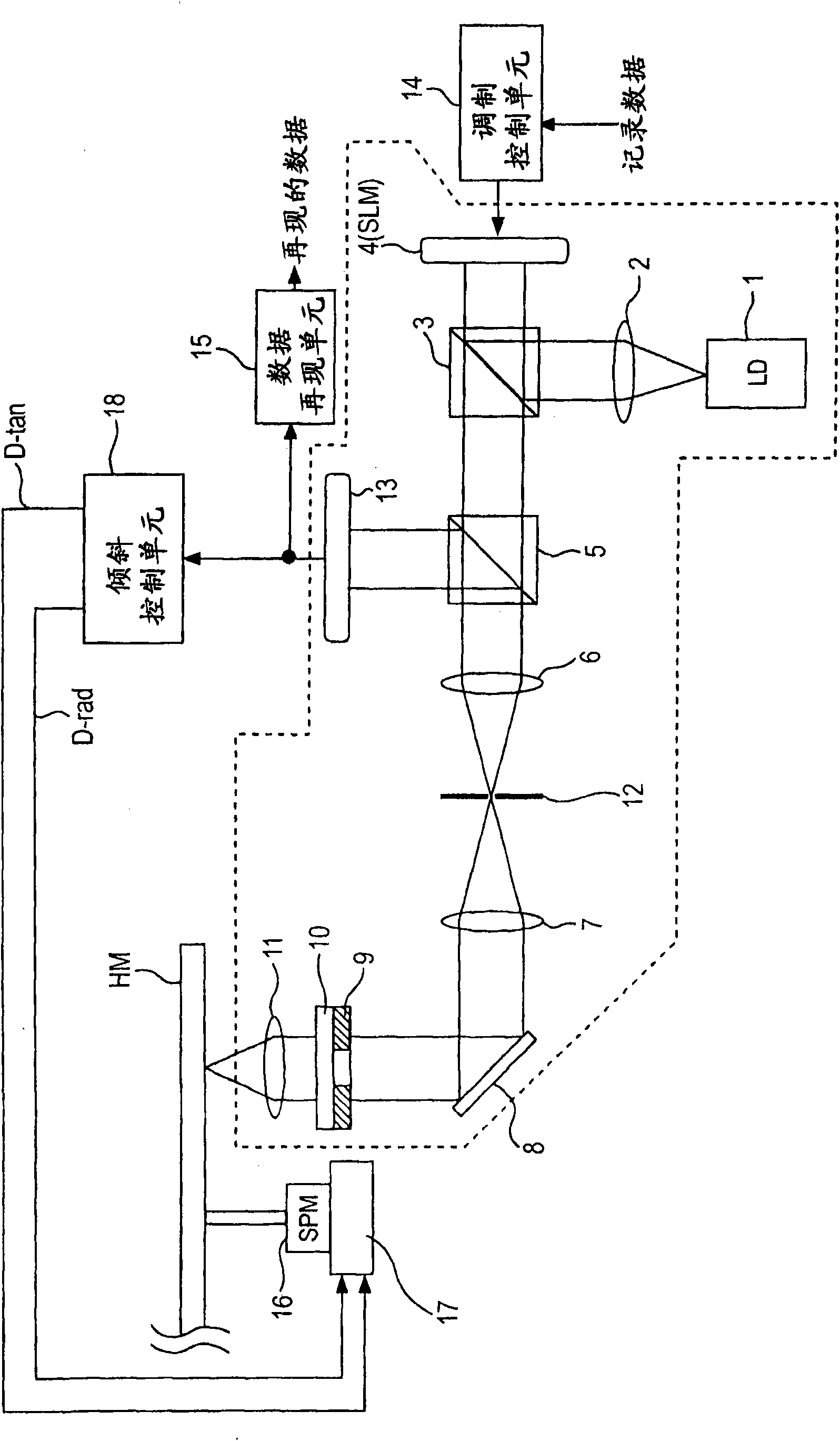
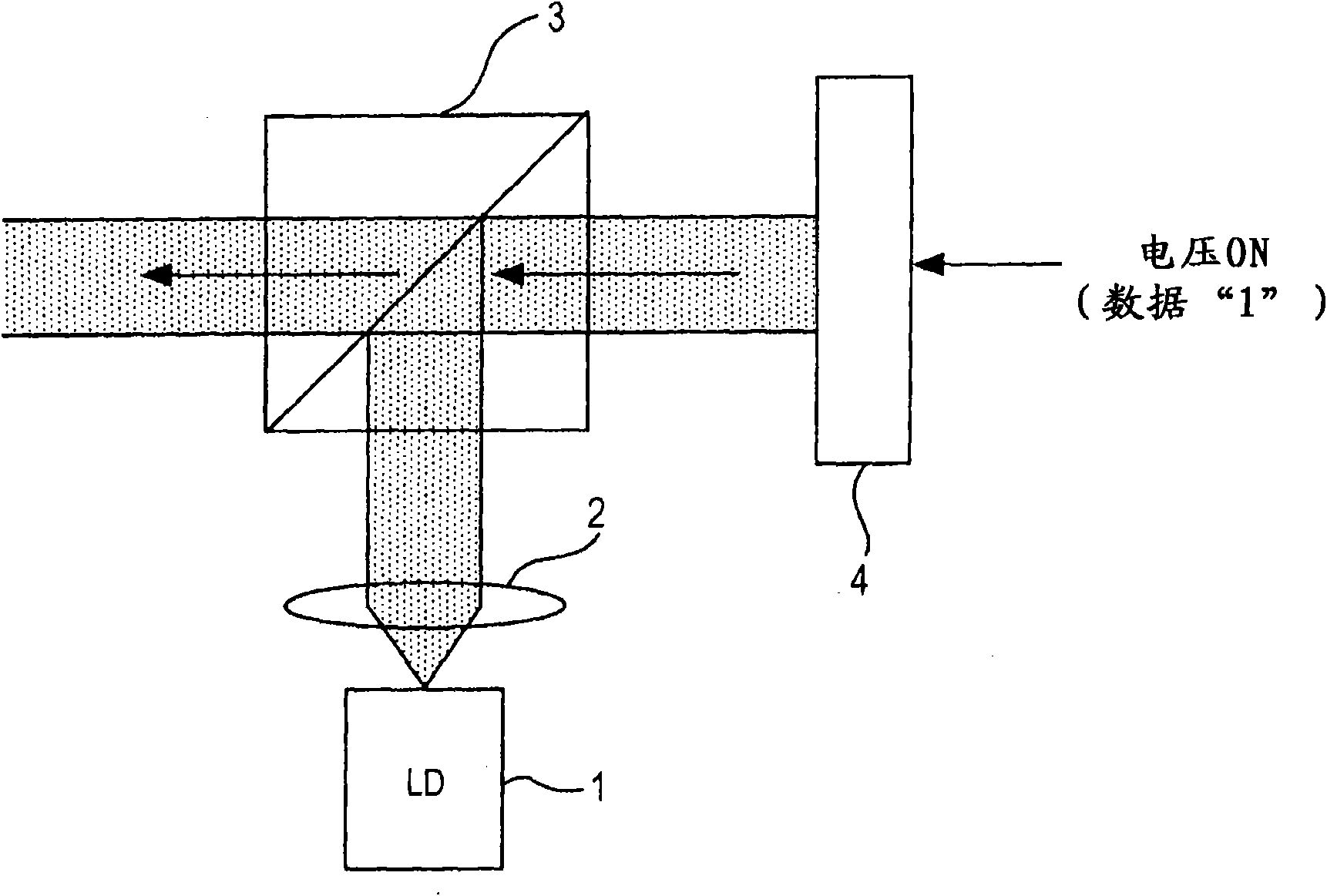
Hologram device, tilt detection method, and tilt correction method
InactiveCN101866659AImplement tilt detectionMiniaturizationRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsOptoelectronicsSignal light
The invention provides a hologram device, a tilt detection method, and a tilt correction method. The hologram device includes: a light source for applying light to a hologram recording medium having a recording layer in which information recording is performed by interference fringes between signal light and reference light; a spatial modulation unit that generates the signal light and / or the reference light and generates a marker light in a predetermined position within an incident surface of the light from the light source by performing spatial light modulation on the light from the light source; a light applying unit that applies the light subjected to spatial light modulation by the spatial light modulation unit to the hologram recording medium via an objective lens; a light receivingunit that receives the light applied via the objective lens through the hologram recording medium; and a tilt detection unit that obtains a tilt error signal representing an error from an ideal angleof a tilt angle as an incident angle of the applied light via the objective lens to an information recording surface of the hologram recording medium based on a result of detection of an error between an ideal light reception position of the marker light in the light receiving unit and a real light reception position of the marker light by the light receiving unit.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
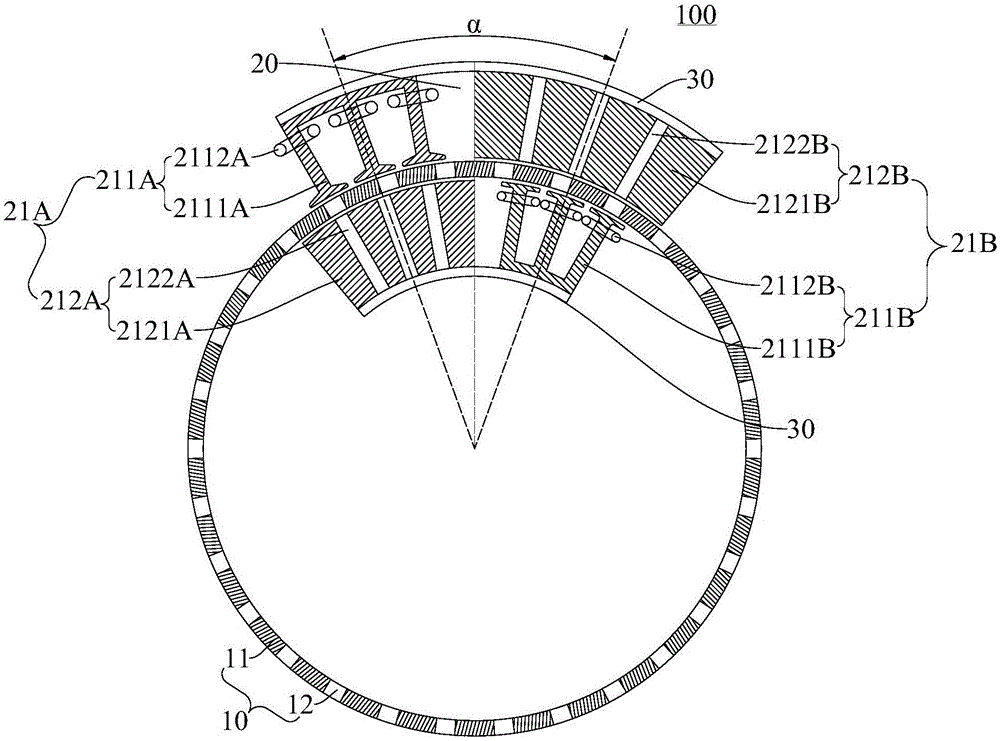
Motor
ActiveCN106374706ASimple structureCompact structureElectric machinesMagnetic circuit stationary partsClosed loopReluctance motor
The invention discloses a motor. The motor comprises a rotatable reluctance rotor and a stator, wherein the reluctance rotor is in a closed loop shape extending in the circumferential direction of the motor; the stator comprises a plurality of stator sections arranged in the circumferential direction of the motor; the number of the stator sections is equal to or smaller than the number of stator sections connected to form the closed loop shape extending in the circumferential direction of the motor; one of the two adjacent stator sections comprises an outer winding excitation stator block located on the outer side of the reluctance rotor in the radial direction of the motor and an inner permanent magnet excitation stator block located on the inner side of the reluctance rotor in the radial direction of the motor; and the other of the two adjacent stator sections comprises an outer permanent magnet excitation stator block located on the outer side of the reluctance rotor in the radial direction of the motor and an inner winding excitation stator block located on the inner side of the reluctance rotor in the radial direction of the motor. The motor provided by an embodiment of the invention is simple and compact in structure, low in material cost, high in system efficiency, suitable for occasions of household appliances, electric vehicles, wind power generation and the like, and wide in application range.
Owner:GUANGDONG WELLING ELECTRIC MACHINE MFG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com