Patents
Literature
3403 results about "Control variable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A control variable (or scientific constant) in scientific experimentation is an experimental element which is constant and unchanged throughout the course of the investigation. Control variables could strongly influence experimental results, were they not held constant during the experiment in order to test the relative relationship of the dependent and independent variables. The control variables themselves are not of primary interest to the experimenter.
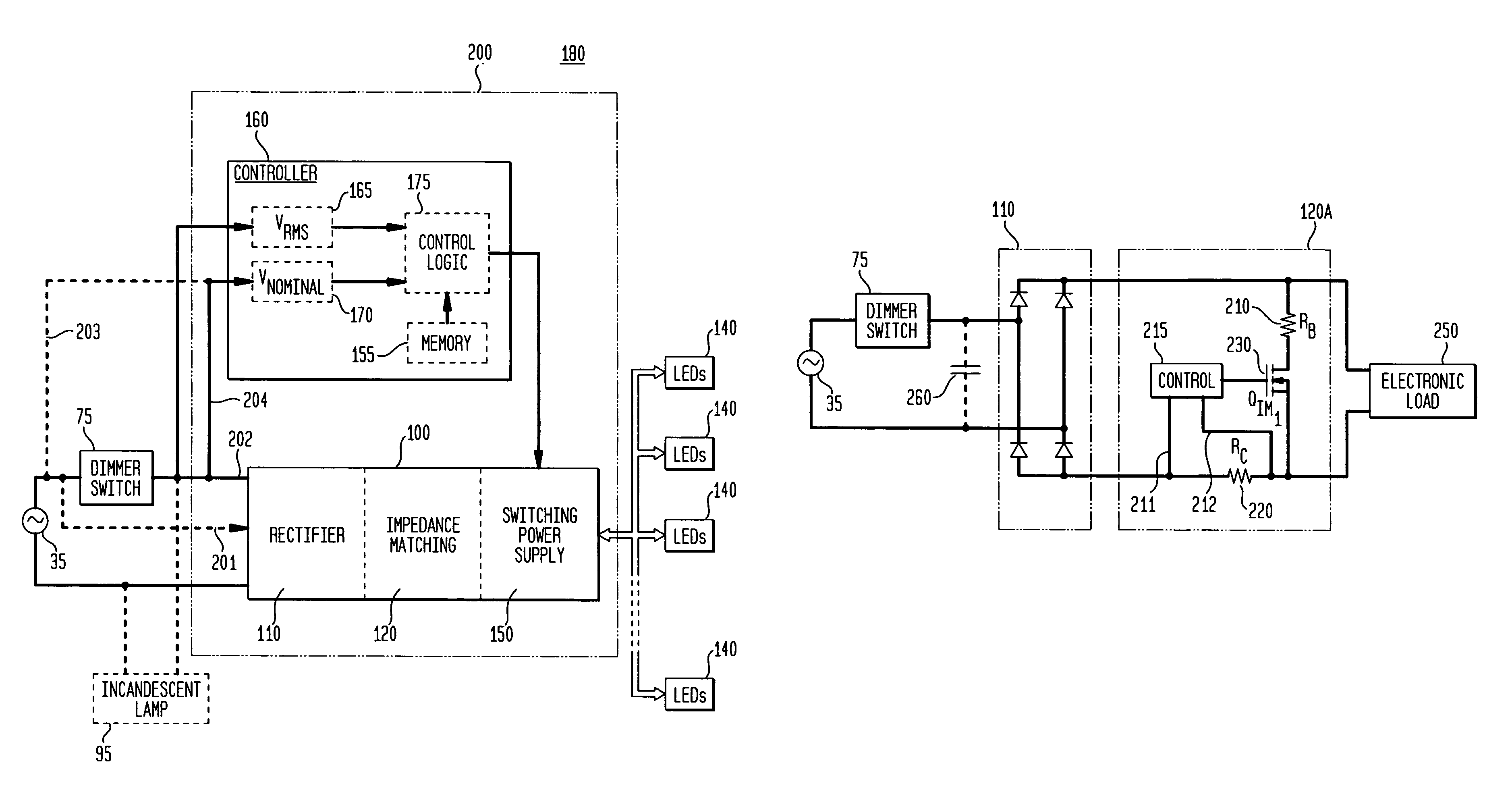
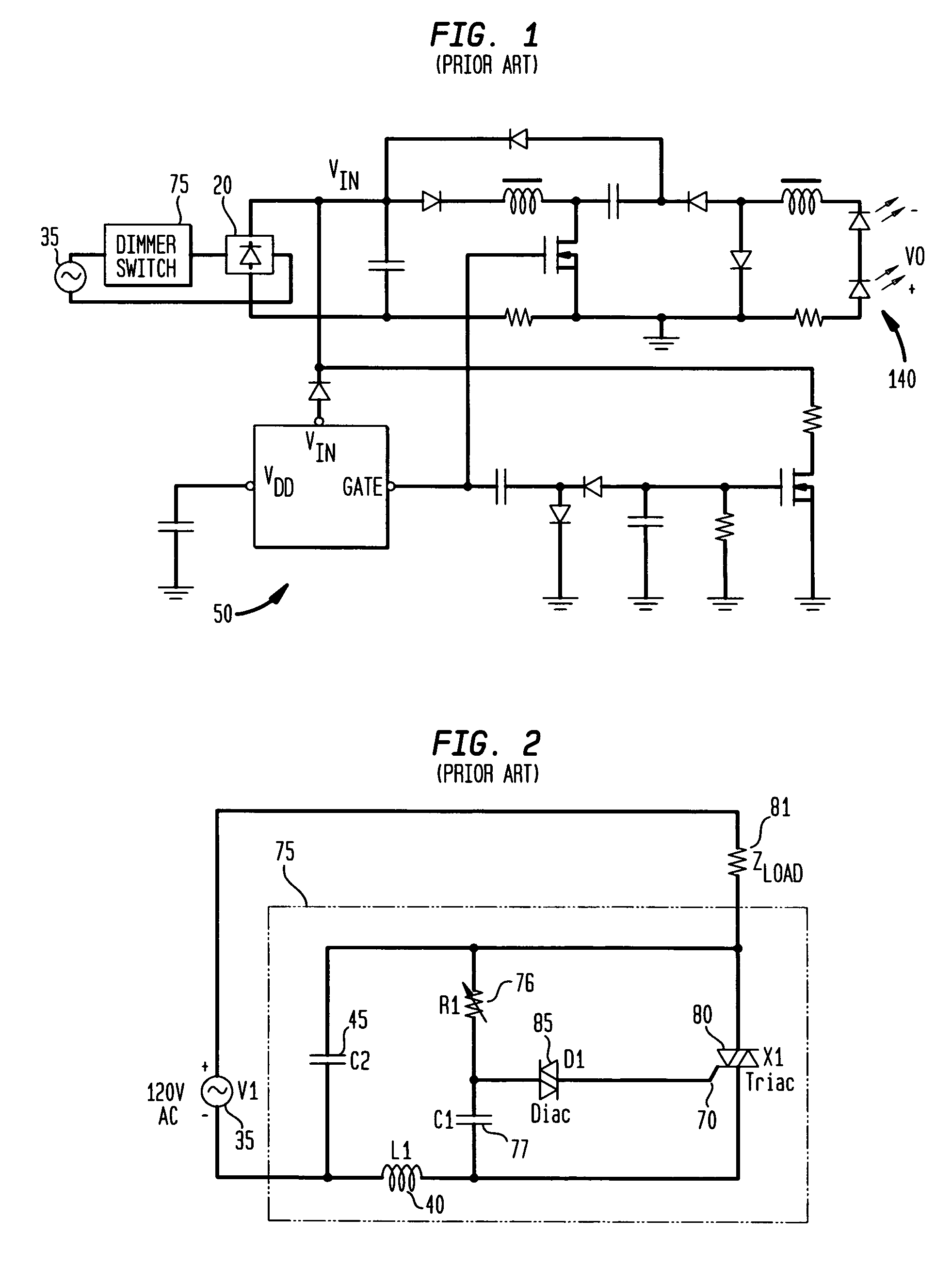
Current regulator for modulating brightness levels of solid state lighting
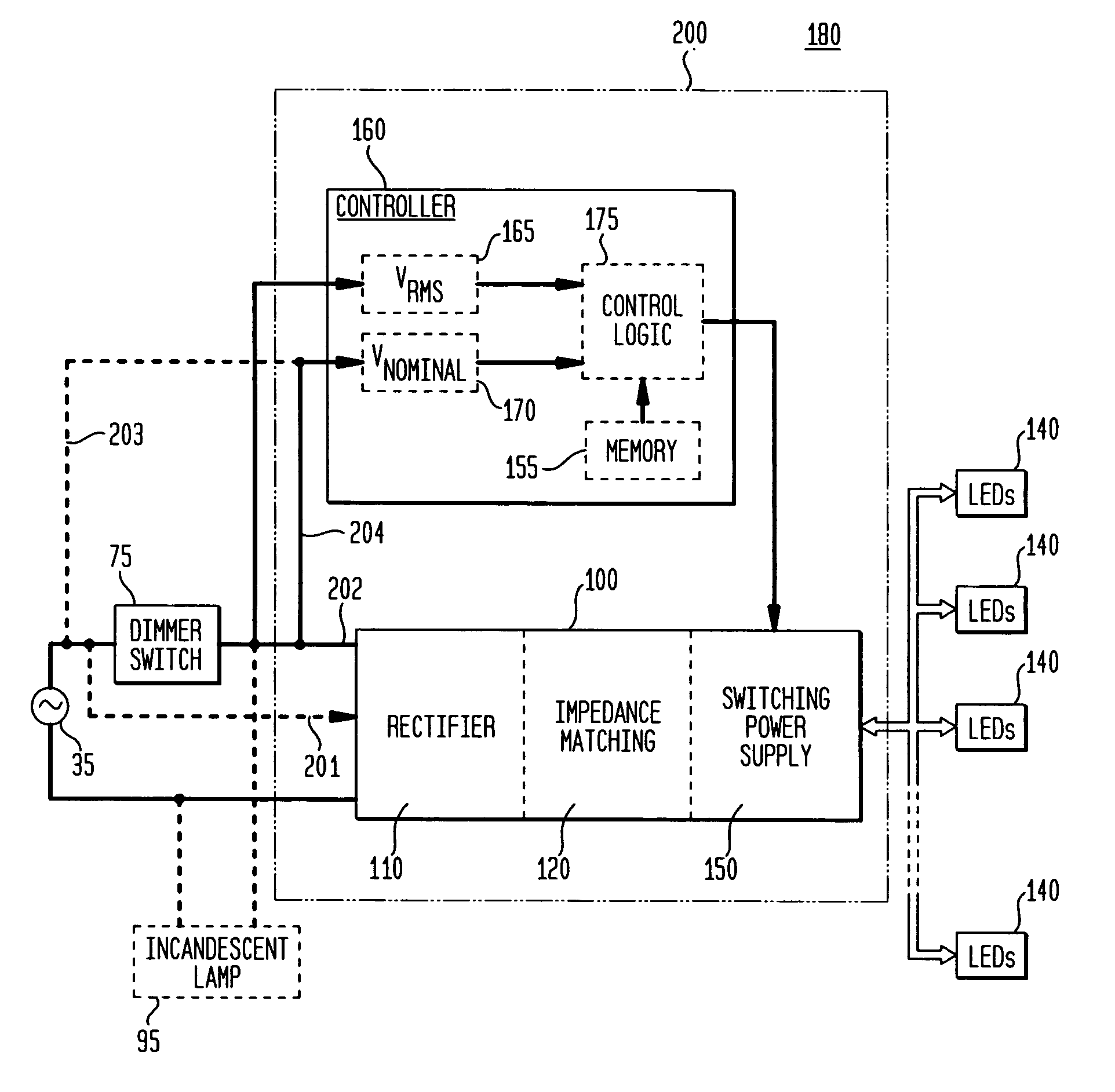
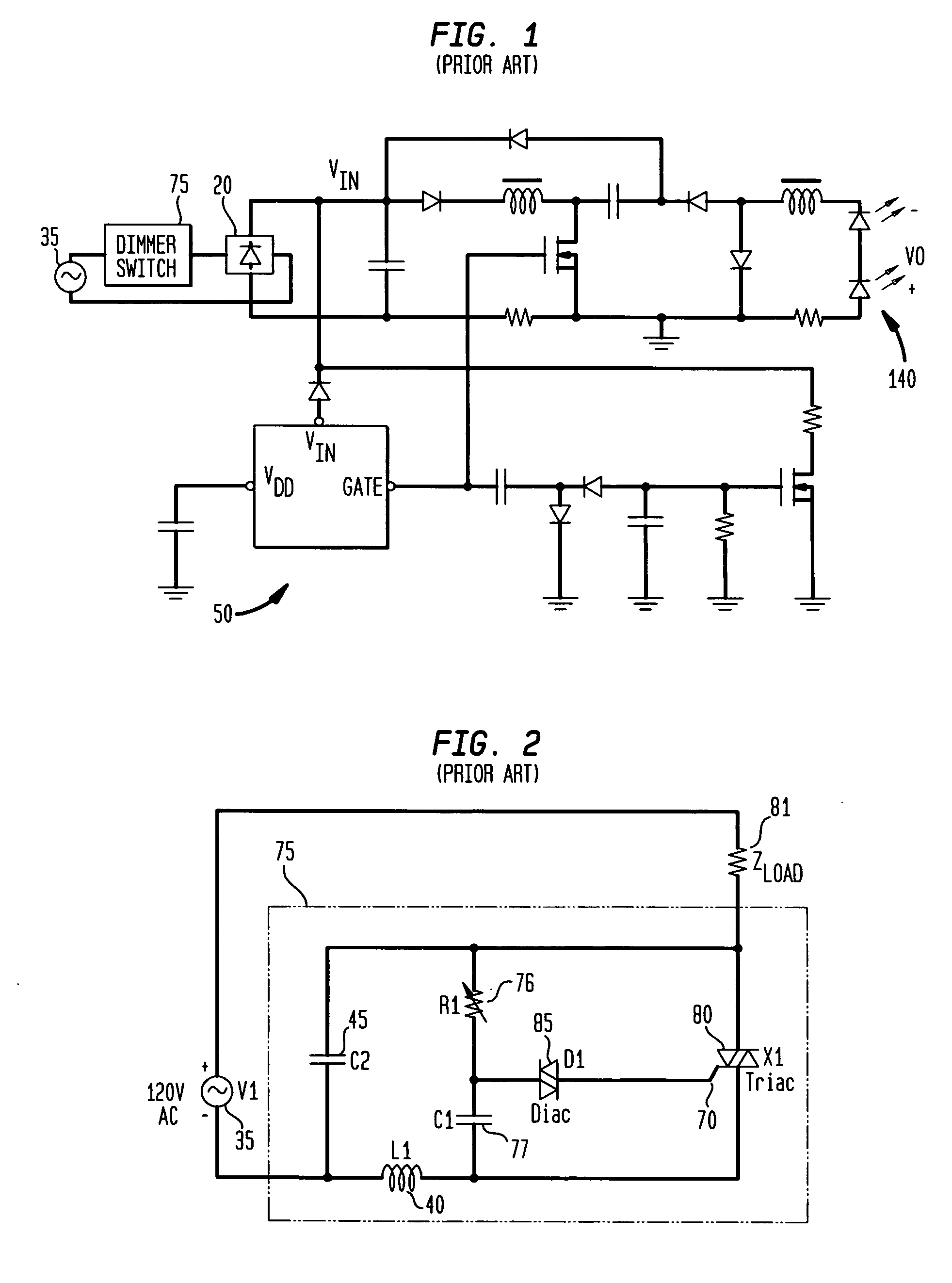
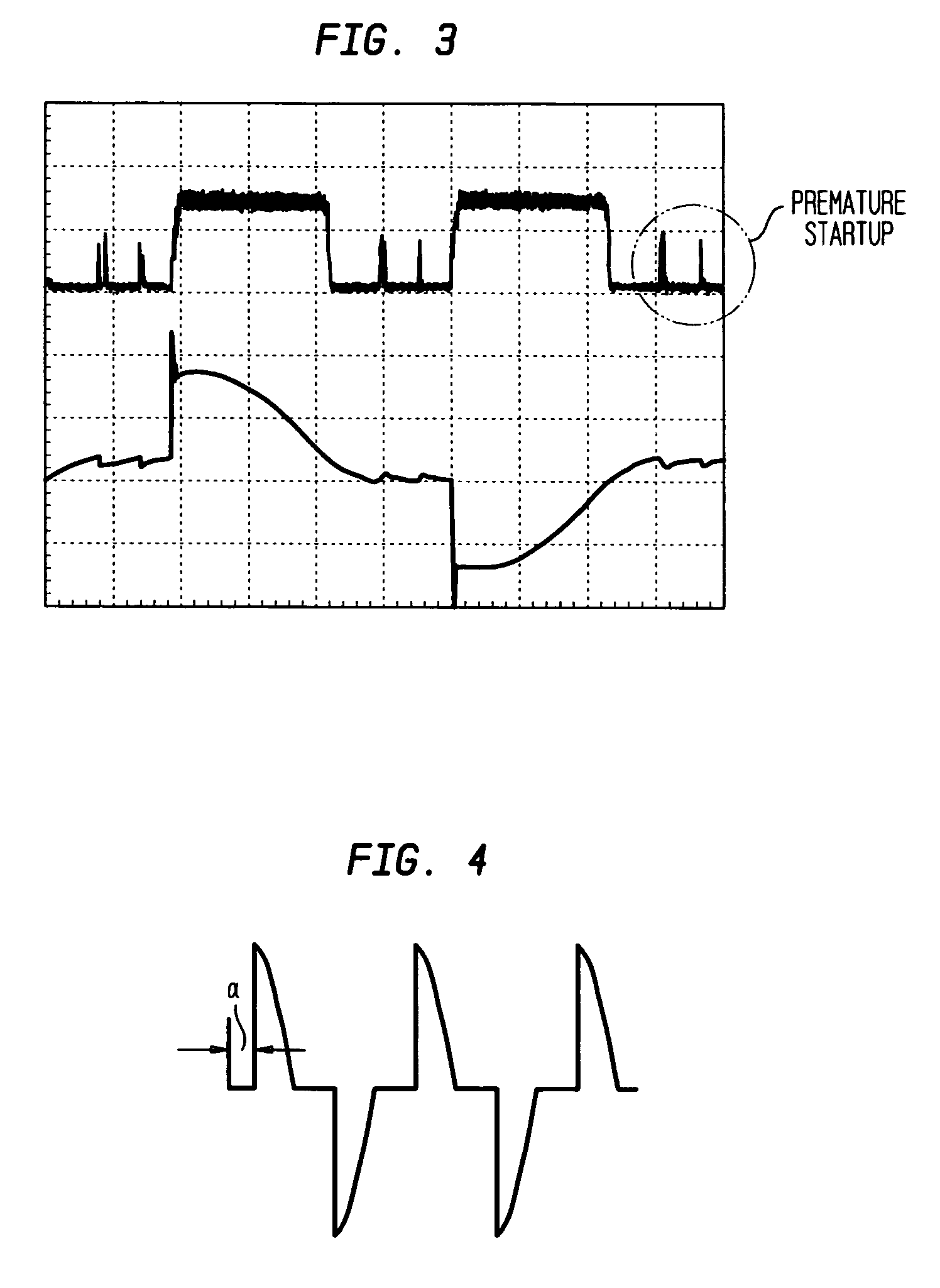
ActiveUS20070182338A1Low component requirementsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesImpedance matchingRoot mean square
An exemplary embodiment provides a current regulator for controlling variable brightness levels for solid state lighting. The current regulator is couplable to a phase-modulating switch, such as a dimmer switch, which is coupled to an AC line voltage. An exemplary current regulator includes a rectifier; a switching power supply providing a first current; an impedance matching circuit; and a controller. The impedance matching circuit is adapted to provide a second current through the phase-modulating switch when a magnitude of the first current is below a first predetermined threshold, such as a holding current of a triac of the phase-modulating switch. The controller is adapted to determine a root-mean-square (RMS) voltage level provided by the phase-modulating switch from the AC line voltage and to determine a duty cycle for pulse-width current modulation by the switching power supply in response to the comparison of the RMS voltage level to a nominal voltage level.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
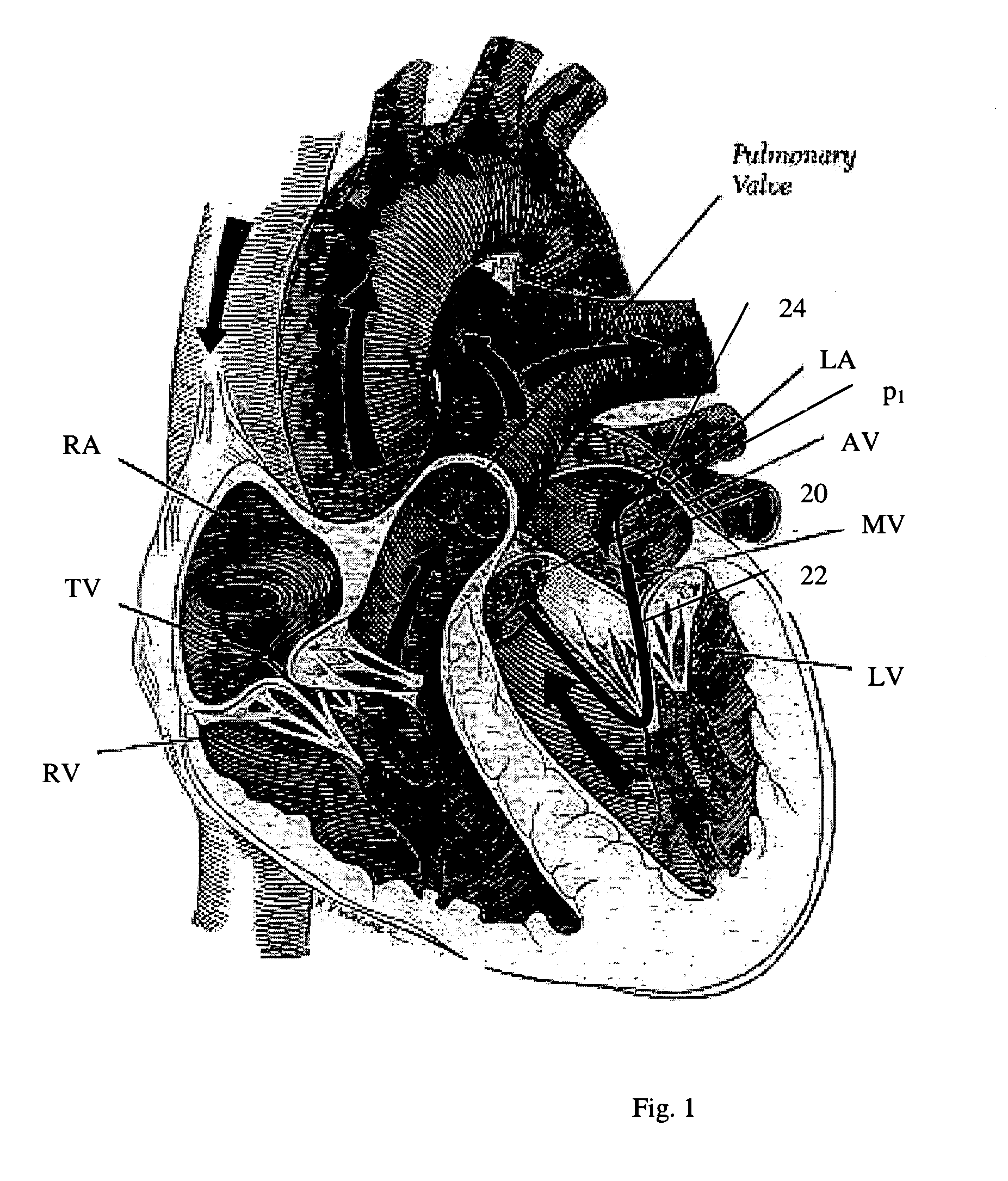
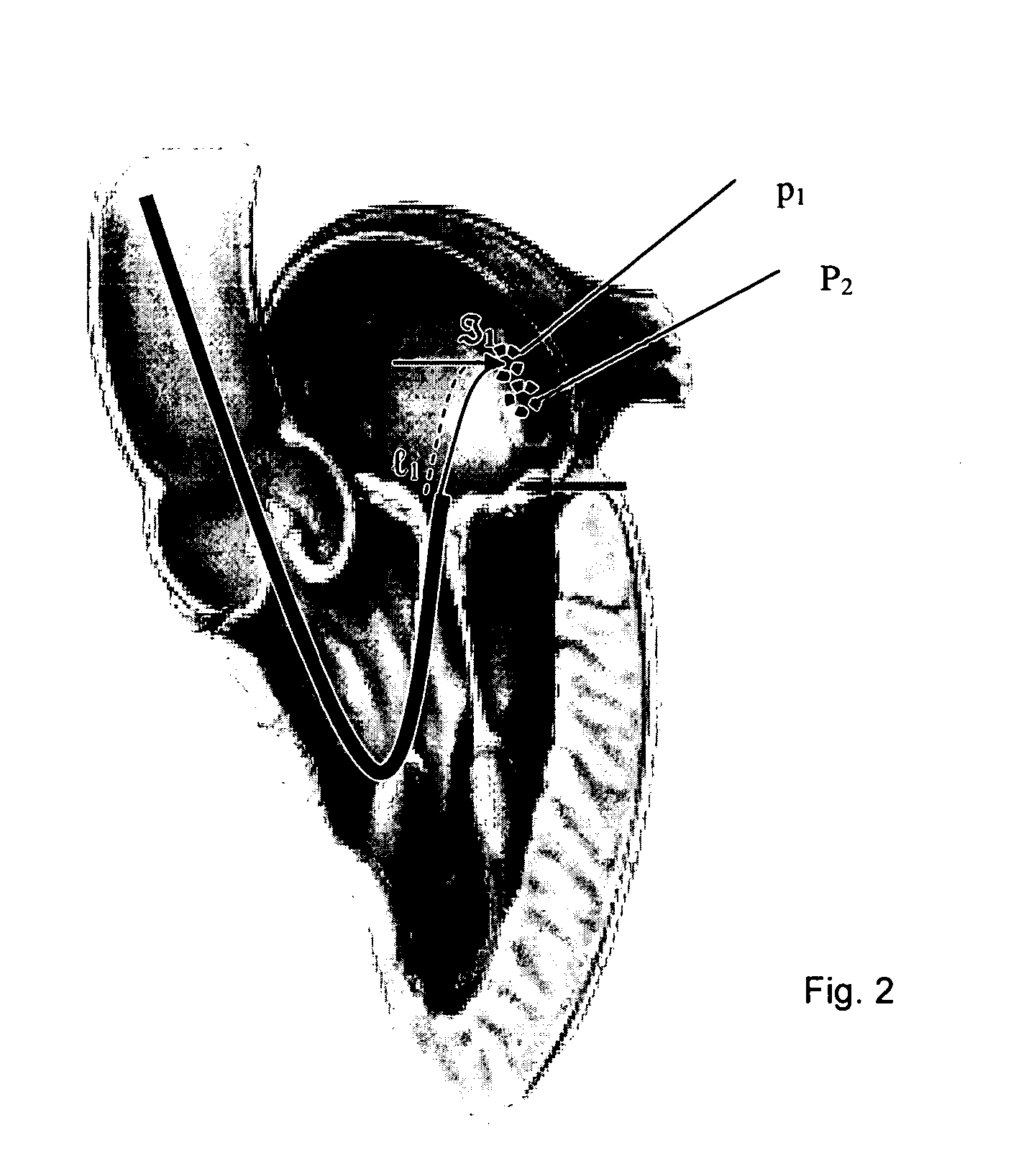
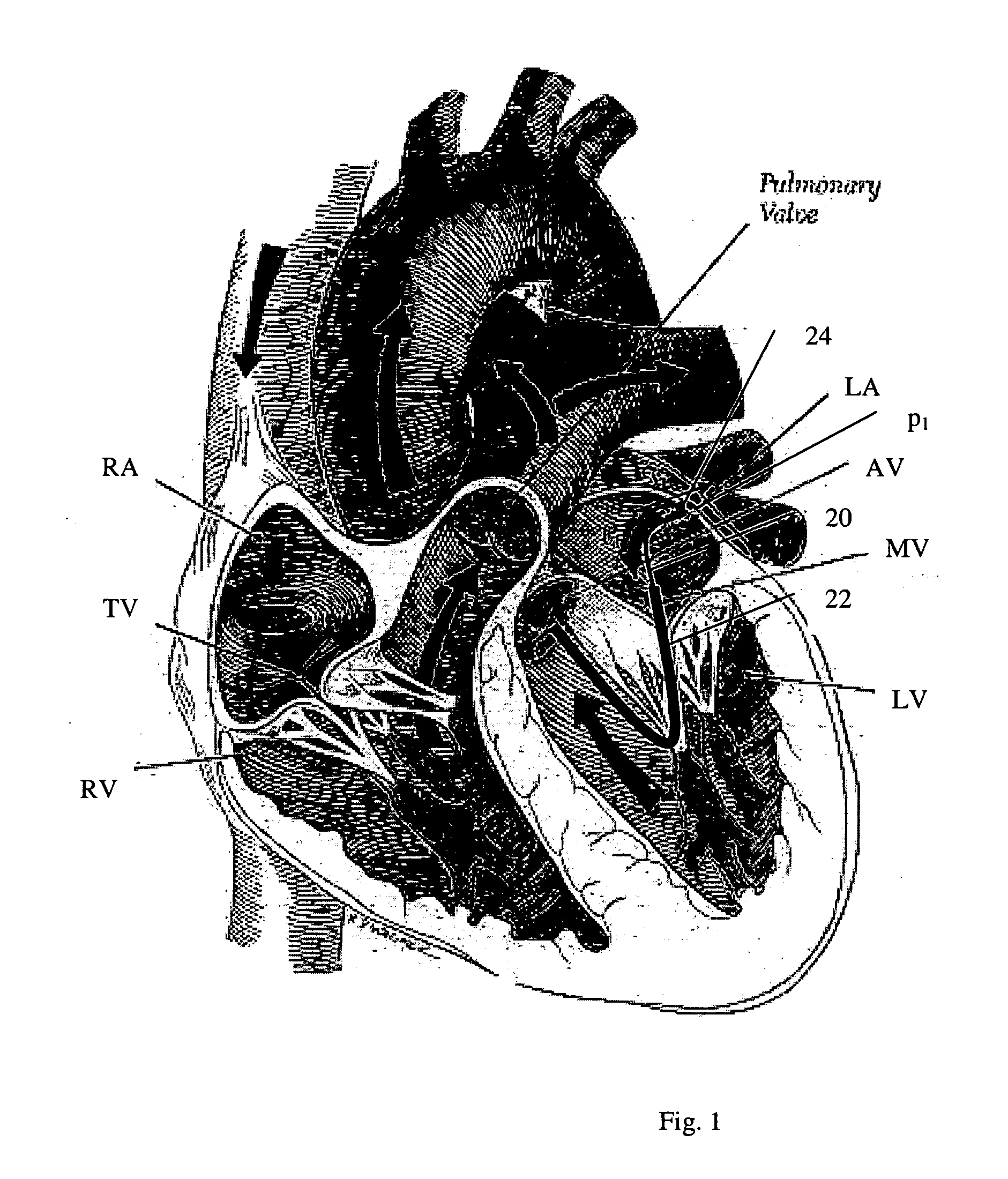
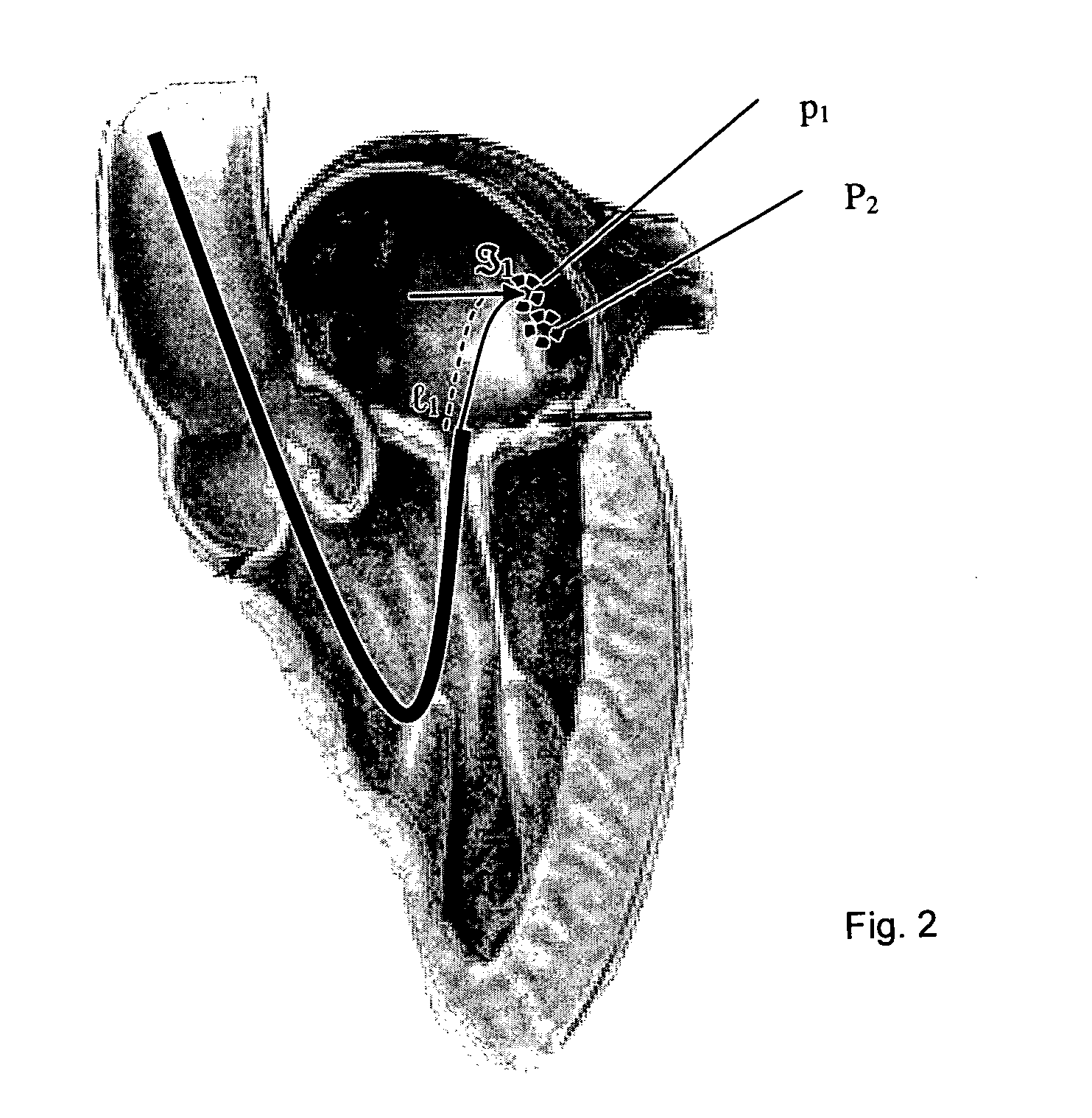
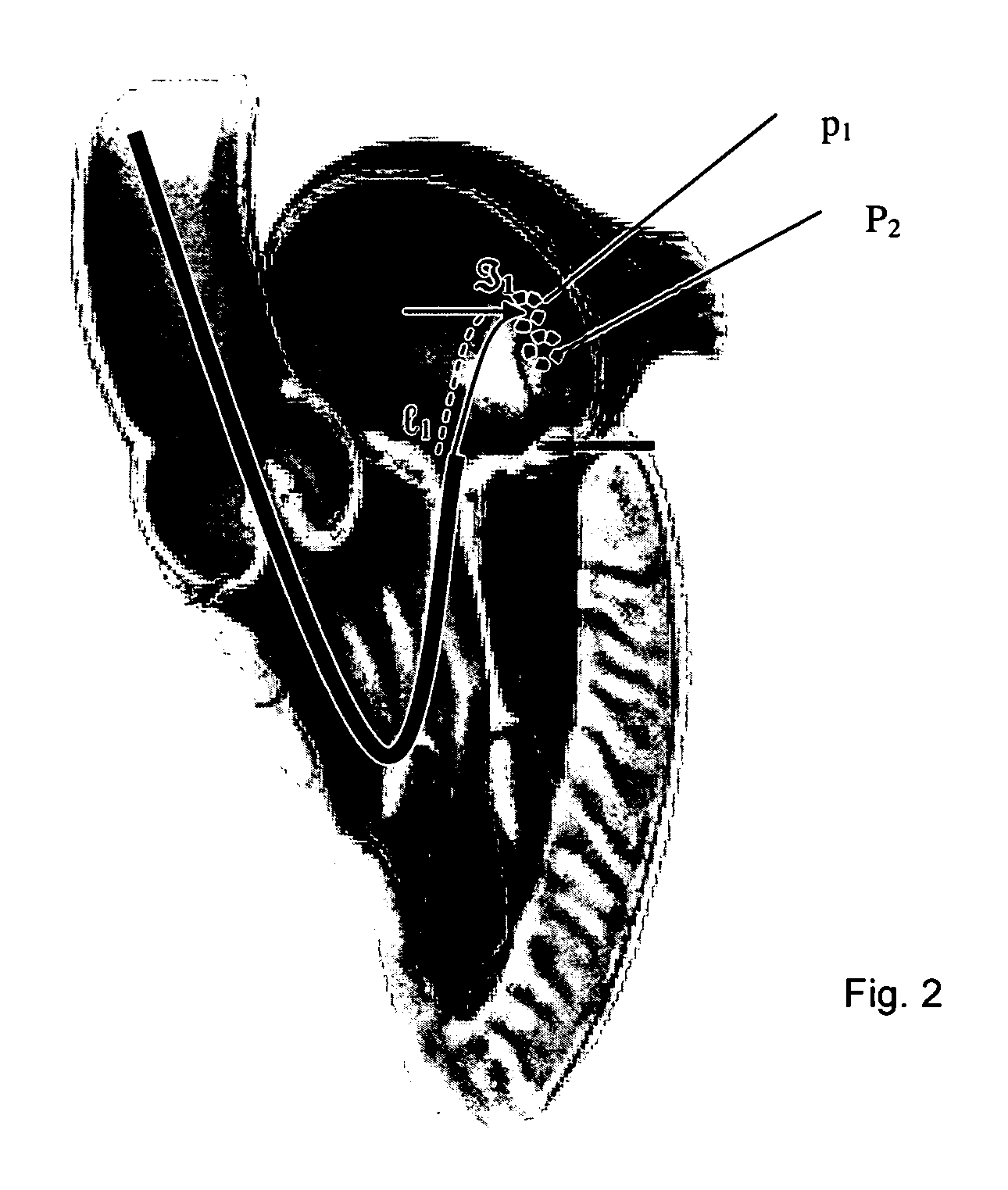
Navigation of remotely actuable medical device using control variable and length
A method of navigating a medical device includes determining the location of a medical device at a point in an operating region in a subject's body, the medical device being responsive to at least one control variable to assume a desired configuration includes storing information representative of the at least one control variable being applied to the medical device at the point, and more preferably storing information representative of the at least one control variable and the device length.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
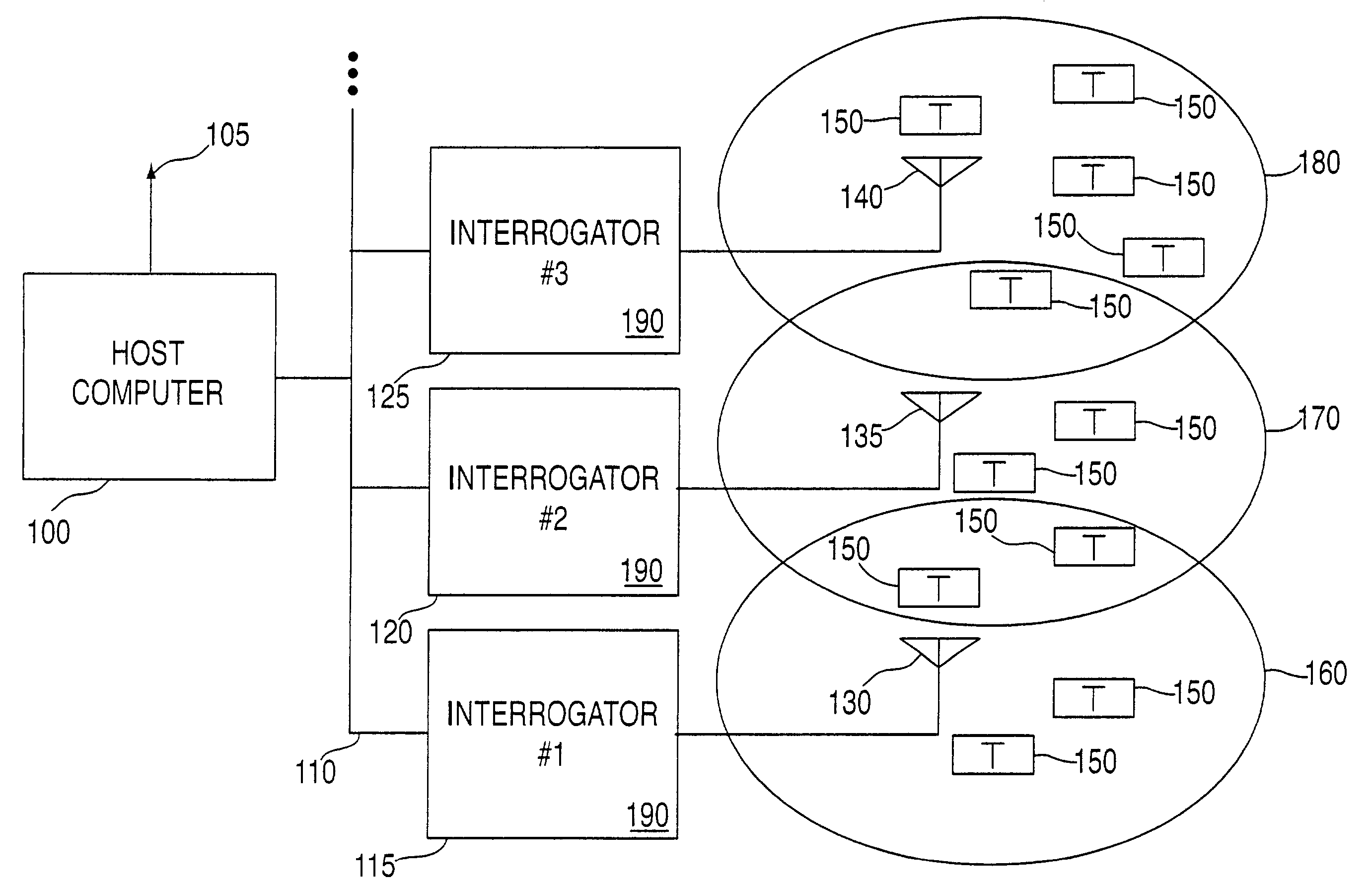
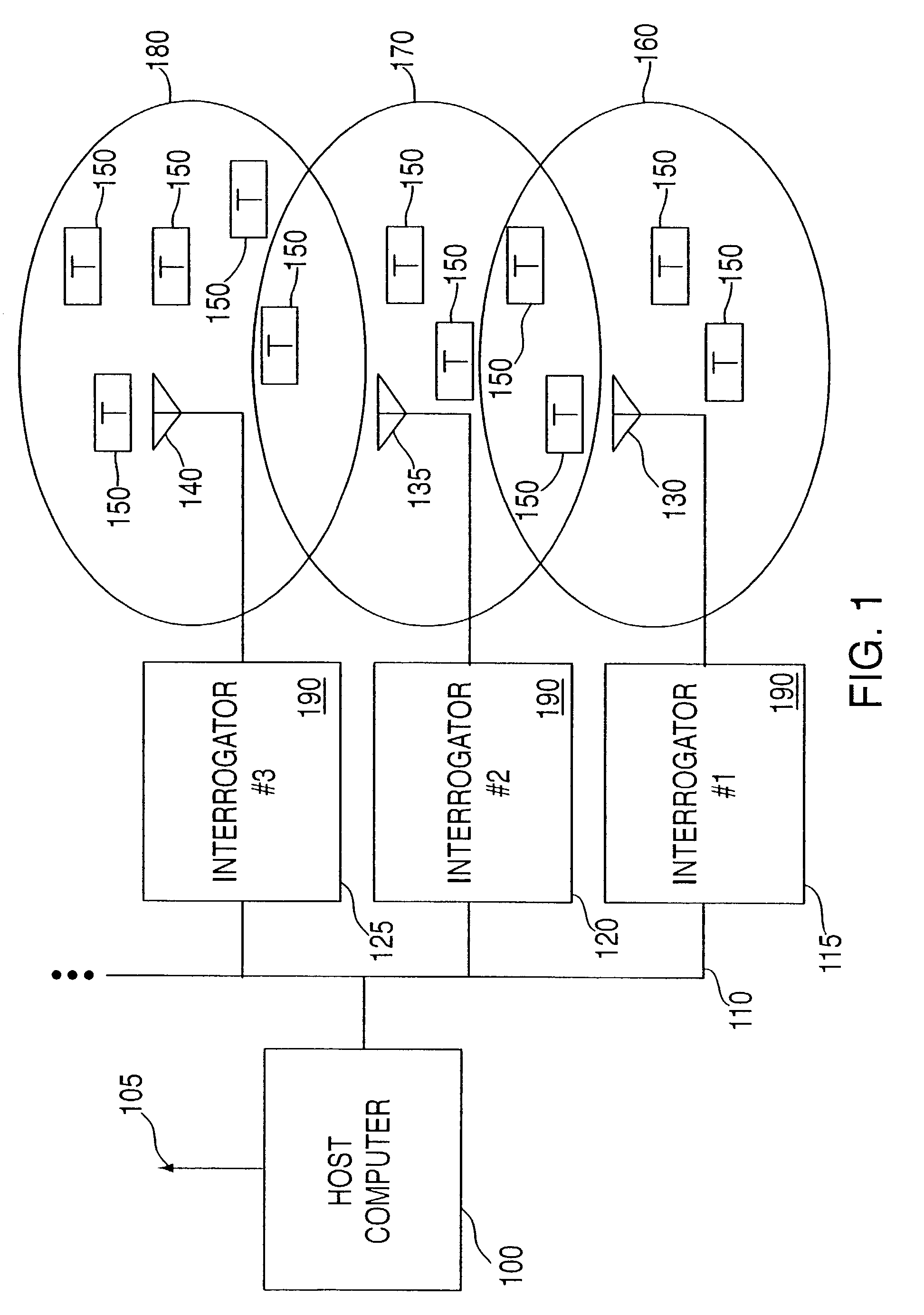
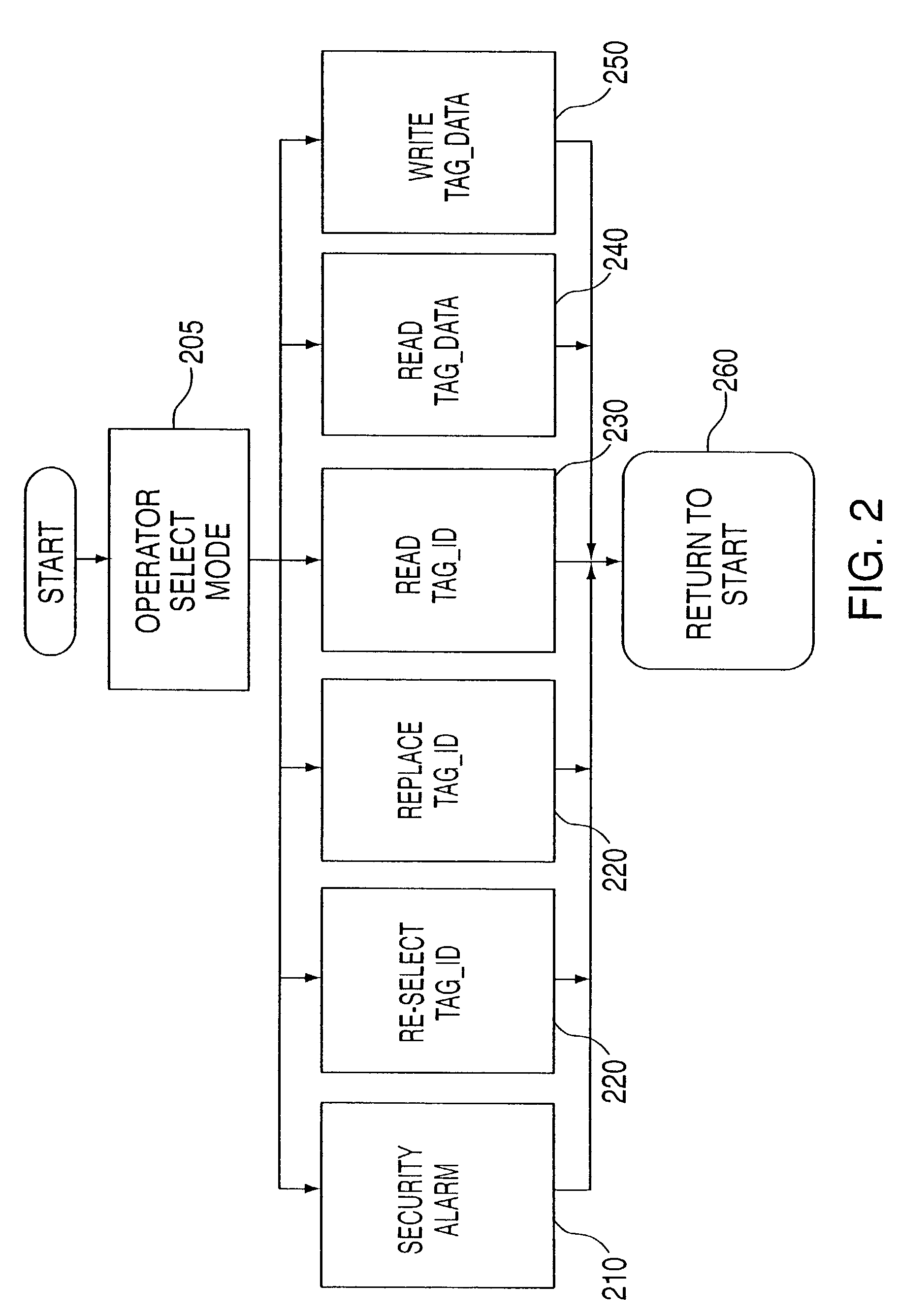
Method and system for communicating with and tracking RFID transponders
ActiveUS7253717B2Reduce the valueMemory record carrier reading problemsCo-operative working arrangementsNear neighborNumber generator
An RFID system and method for communicating between a host computer, one or more interrogators connected to the host computer, and a large body of transponders distributed within an area covered by the interrogators. Each transponder originally has a common identification code, and upon initialization by the host computer internally generates a unique identification code based upon an internally generated random number. The host, through the interrogators, reads each of the identification codes associated with each transponder by iteratively transmitting a read identification code command along with a controlled variable. Each transponder compares the received controlled variable to an internally generated random number, and selectively transmits its identification code based upon the outcome of this comparison. After the completion of each read identification code iteration, the host adjusts the controlled variable based upon the responses received in the previous iteration. Preferably, communications between the interrogators and the transponders are DSSS signals in TDMA format, and the transponders use the random number generator to assign a time slot for transmission of their response. Each interrogator includes an antenna system utilizing a switch matrix to connect multiple antennas having different polarizations, which ensures that all transponders within the range of the interrogator receive the signals from the interrogator. In a further aspect, the interrogators are arranged in groups, each group in nearest neighbor format, to reduce the time for reading the transponders and the emissions generated when more than one interrogator is active at the same time.
Owner:TERRESTRIAL COMMS LLC
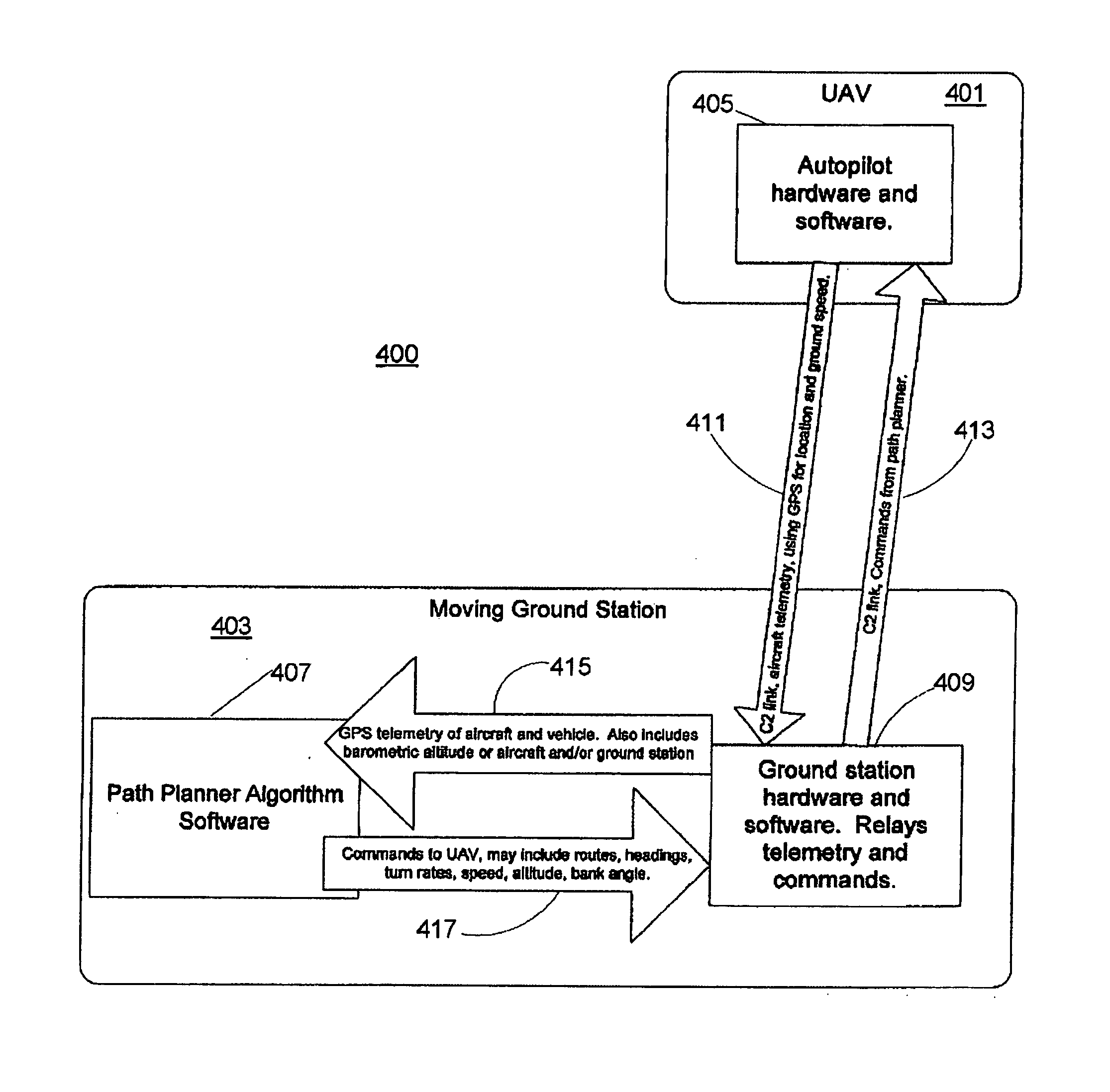
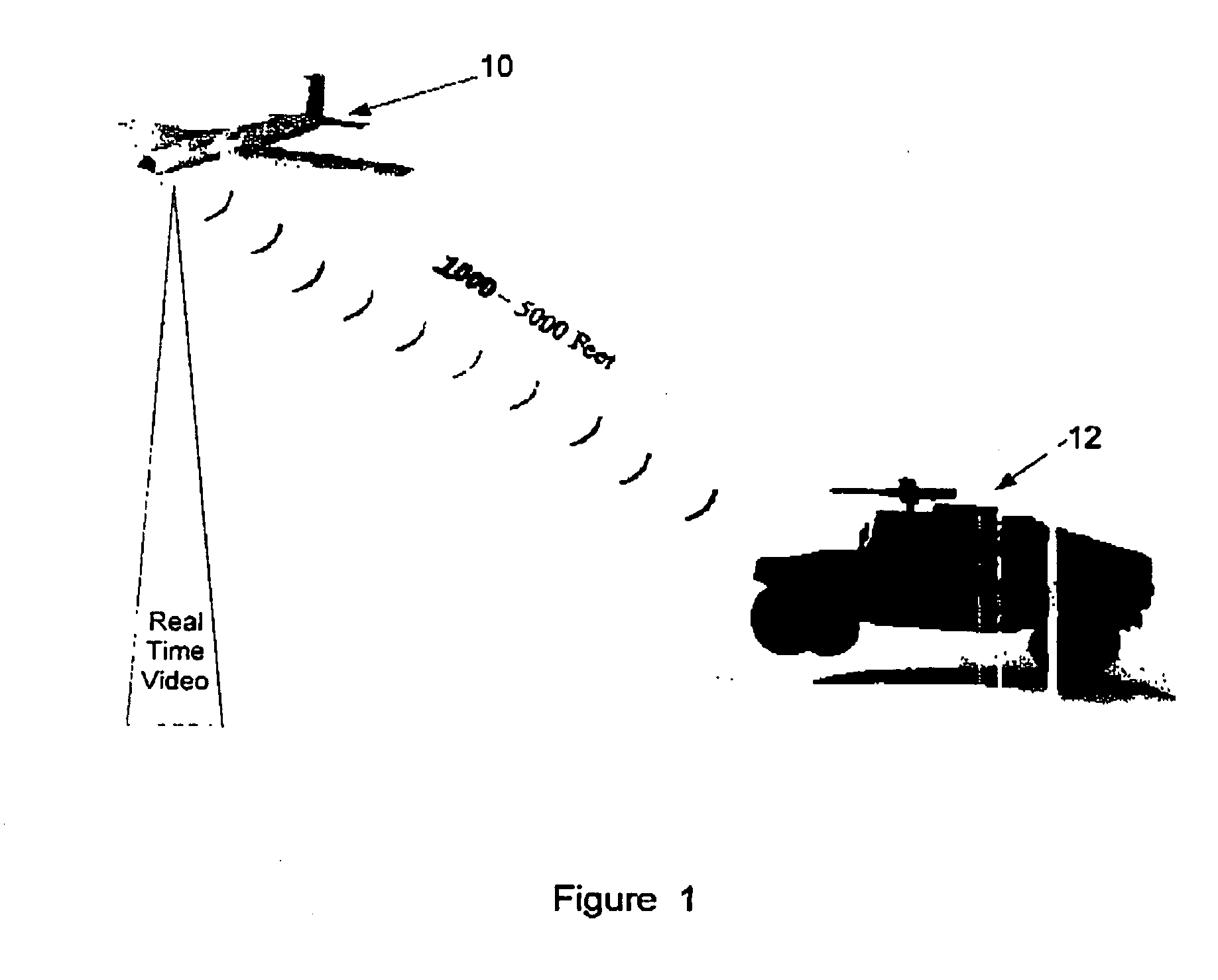
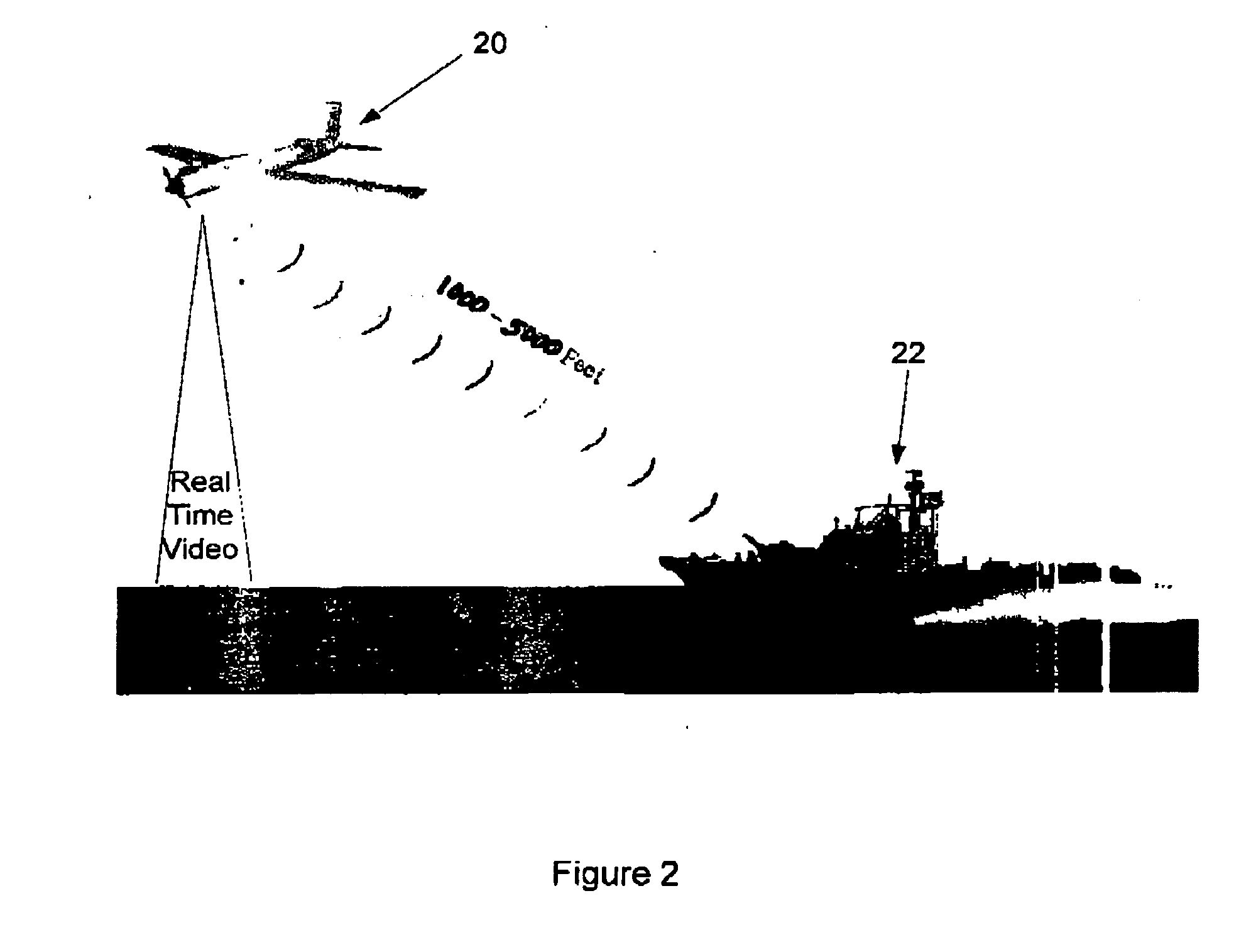
Unmanned vehicle
ActiveUS20060074557A1Aircraft navigation controlInstruments for road network navigationControl variableSoftware
Methods and apparatuses provide surveillance of a convoy. At least one unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) obtains images around the convoy's position to provide information about potential hostile activity while the UAV follows a generally curvilinear path around the convoy as instructed by one of the convoy vehicles. Path planner algorithm software is executed by the controlling convoy vehicle in which position and velocity information regarding the unmanned aerial vehicle and the convoy are processed to determine values of control variables. The determined values are sent to the unmanned aerial vehicle over a wireless communications channel. The path of the surveillance vehicle may be changed in order to provide evasive measures to avoid an attack on the surveillance vehicle by an adversary.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
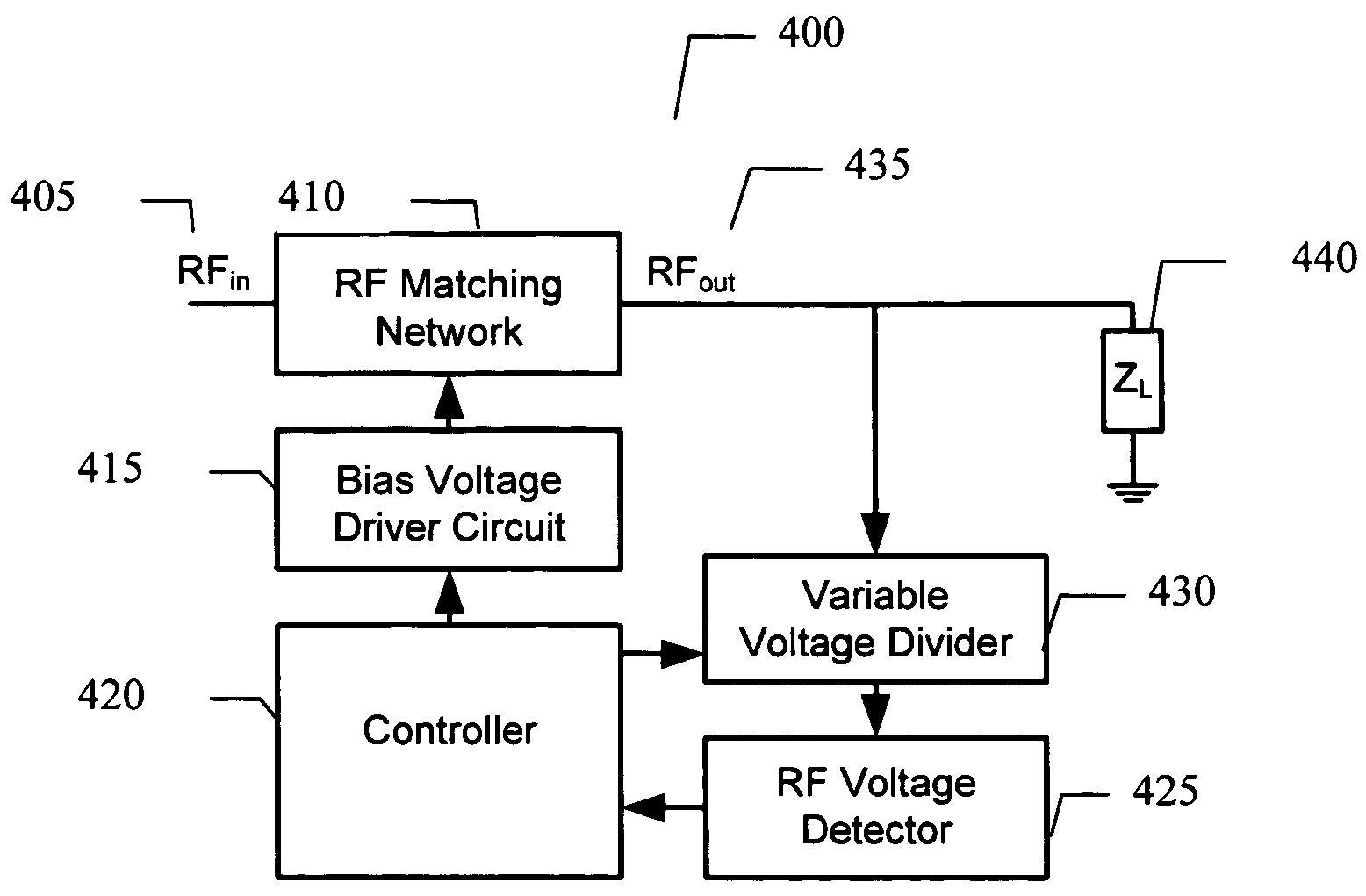
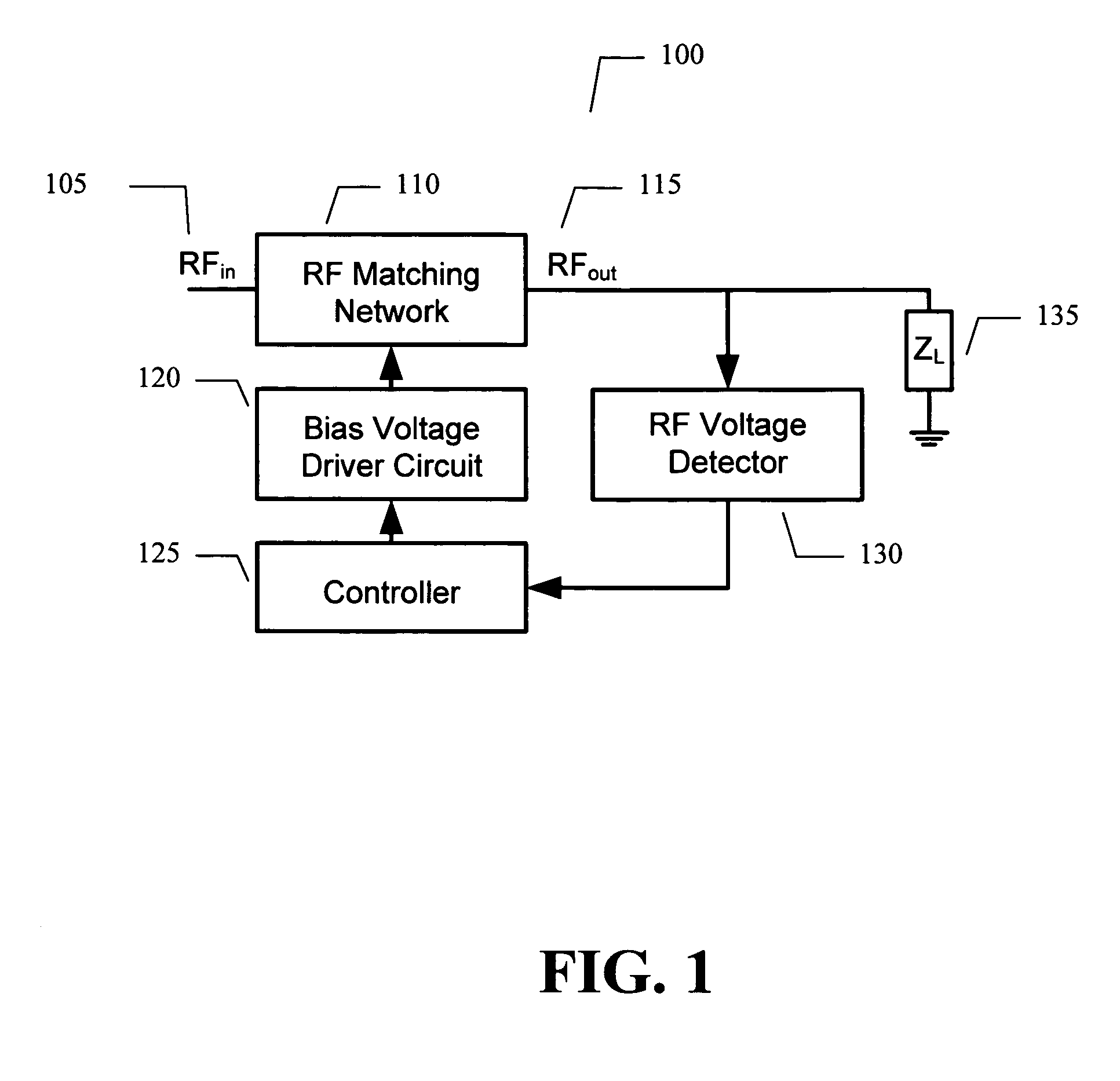
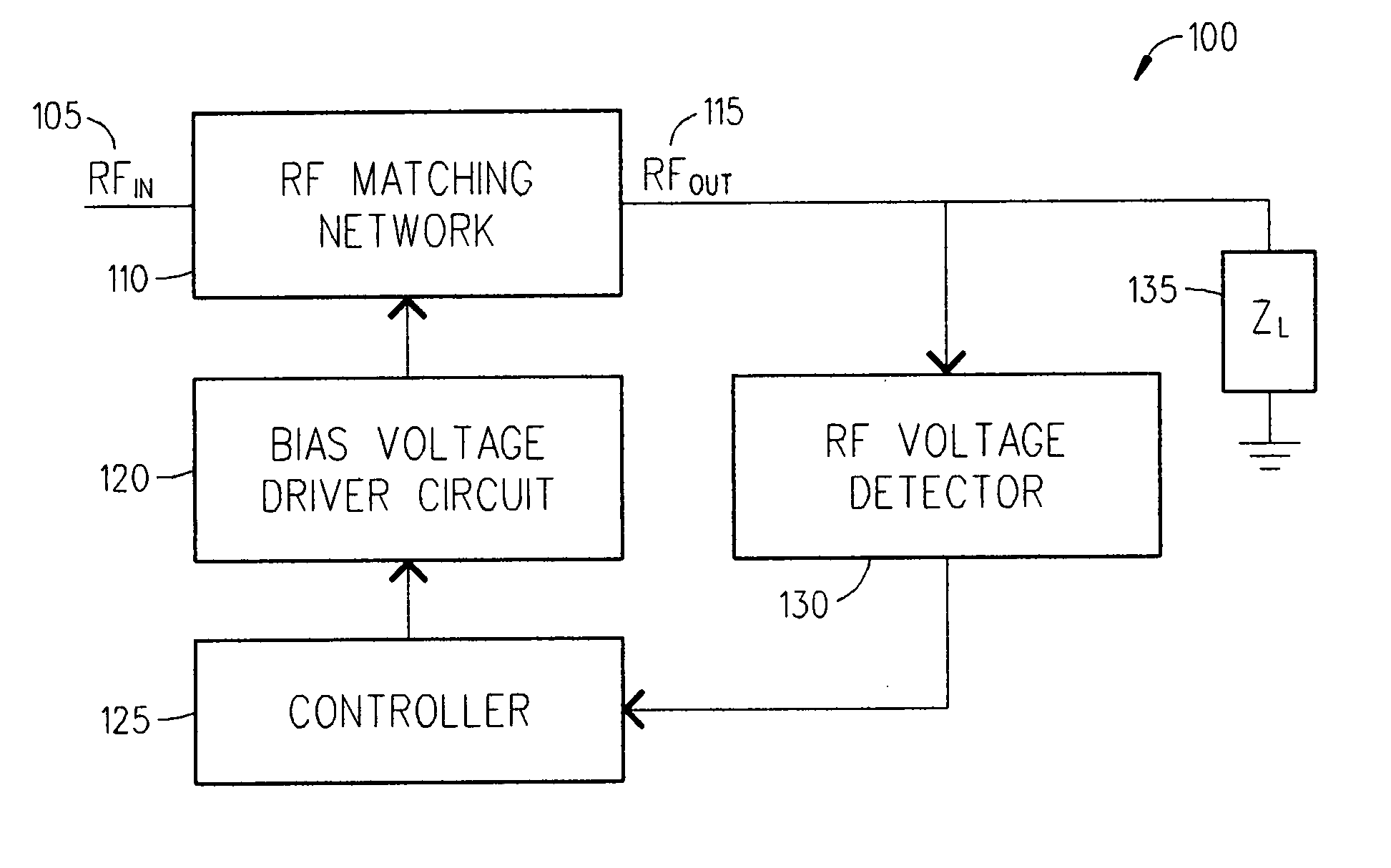
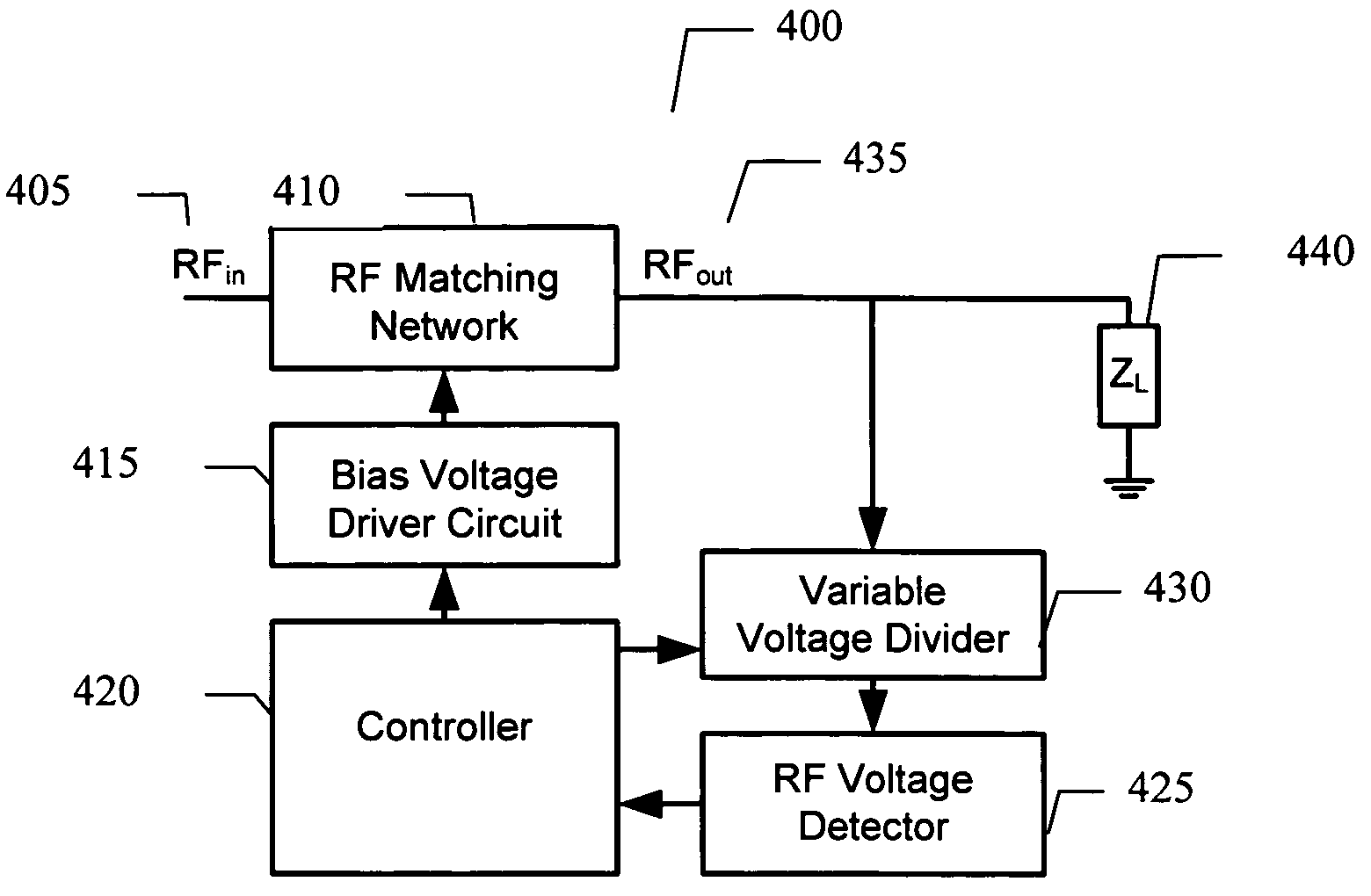
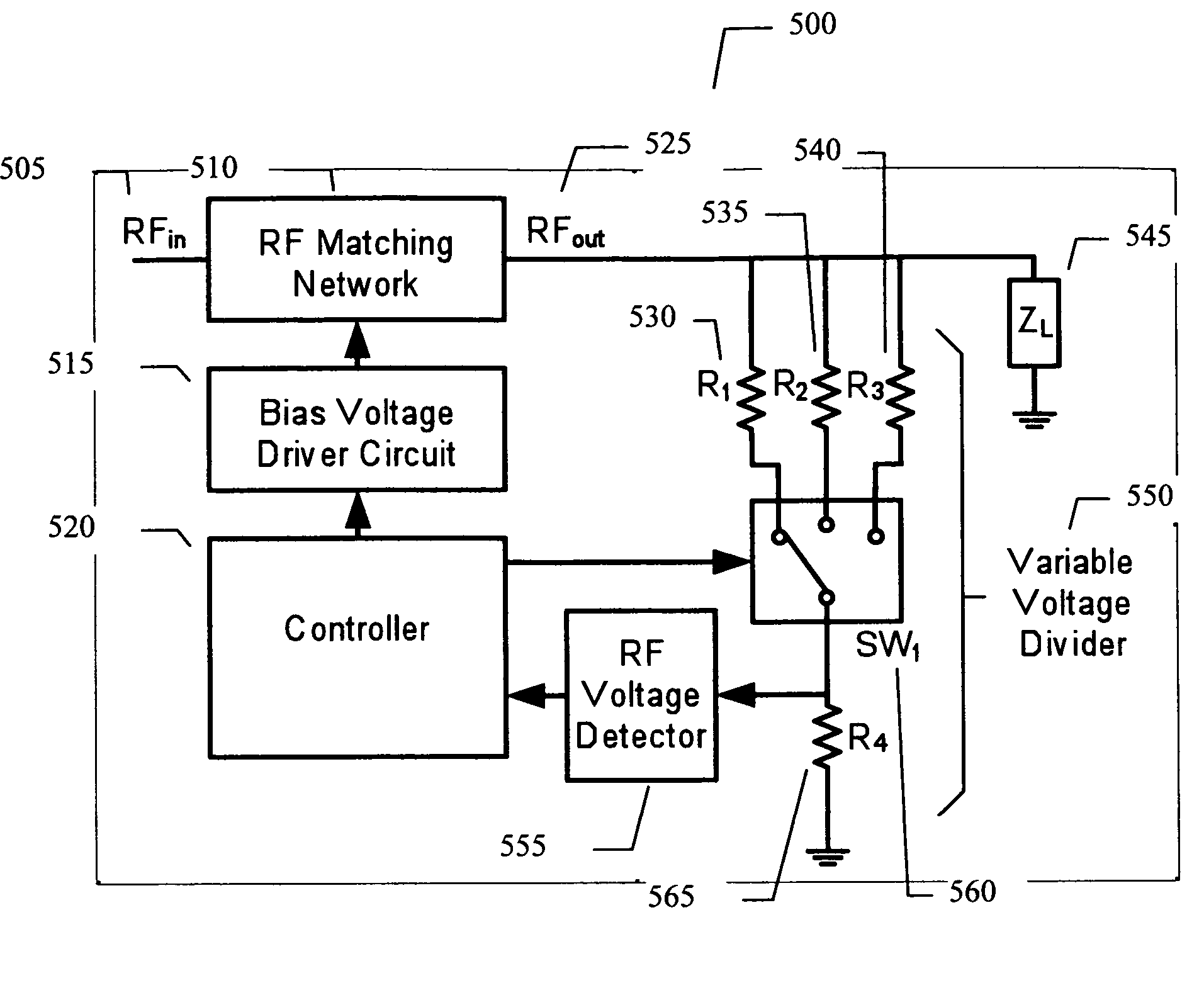
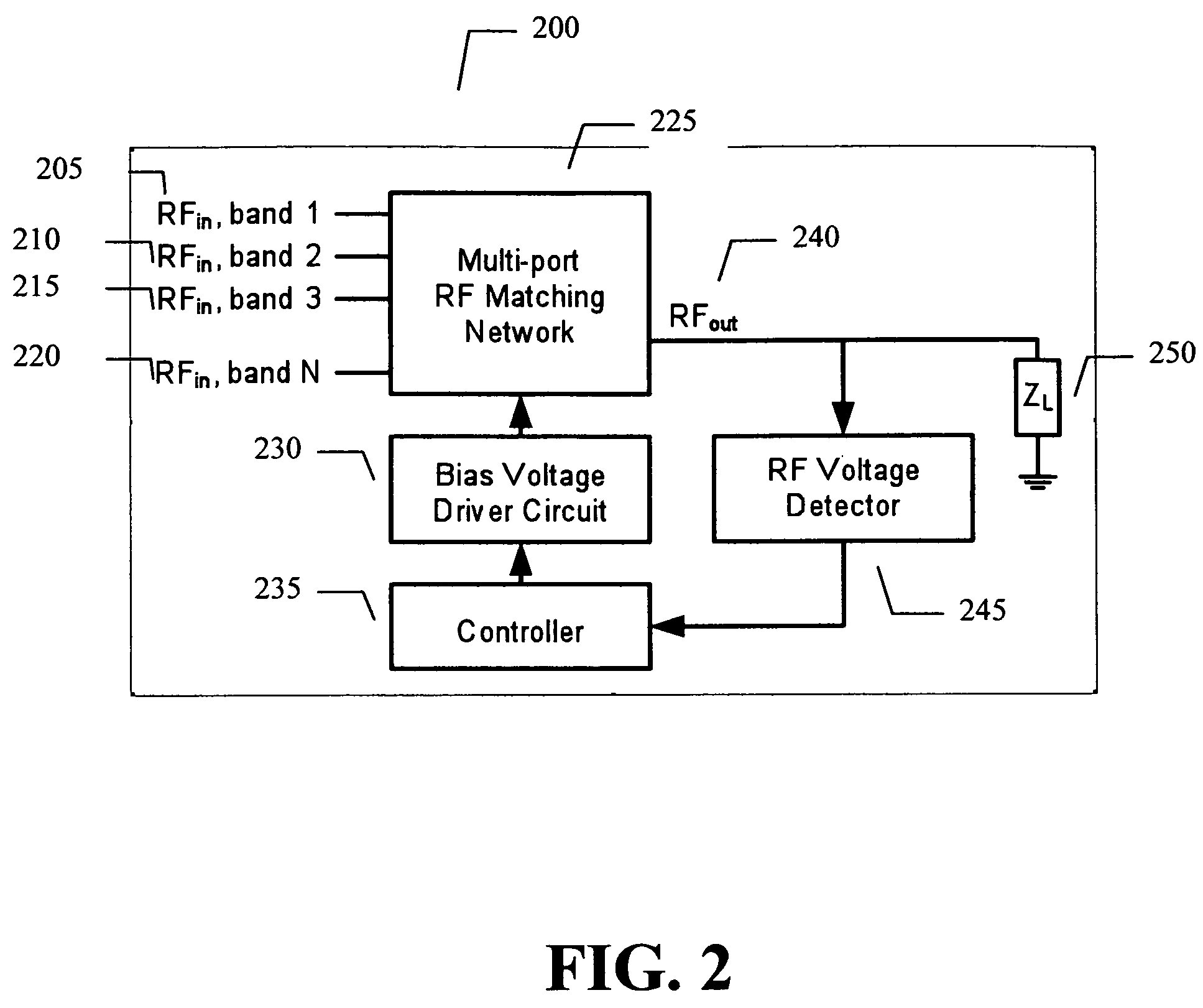
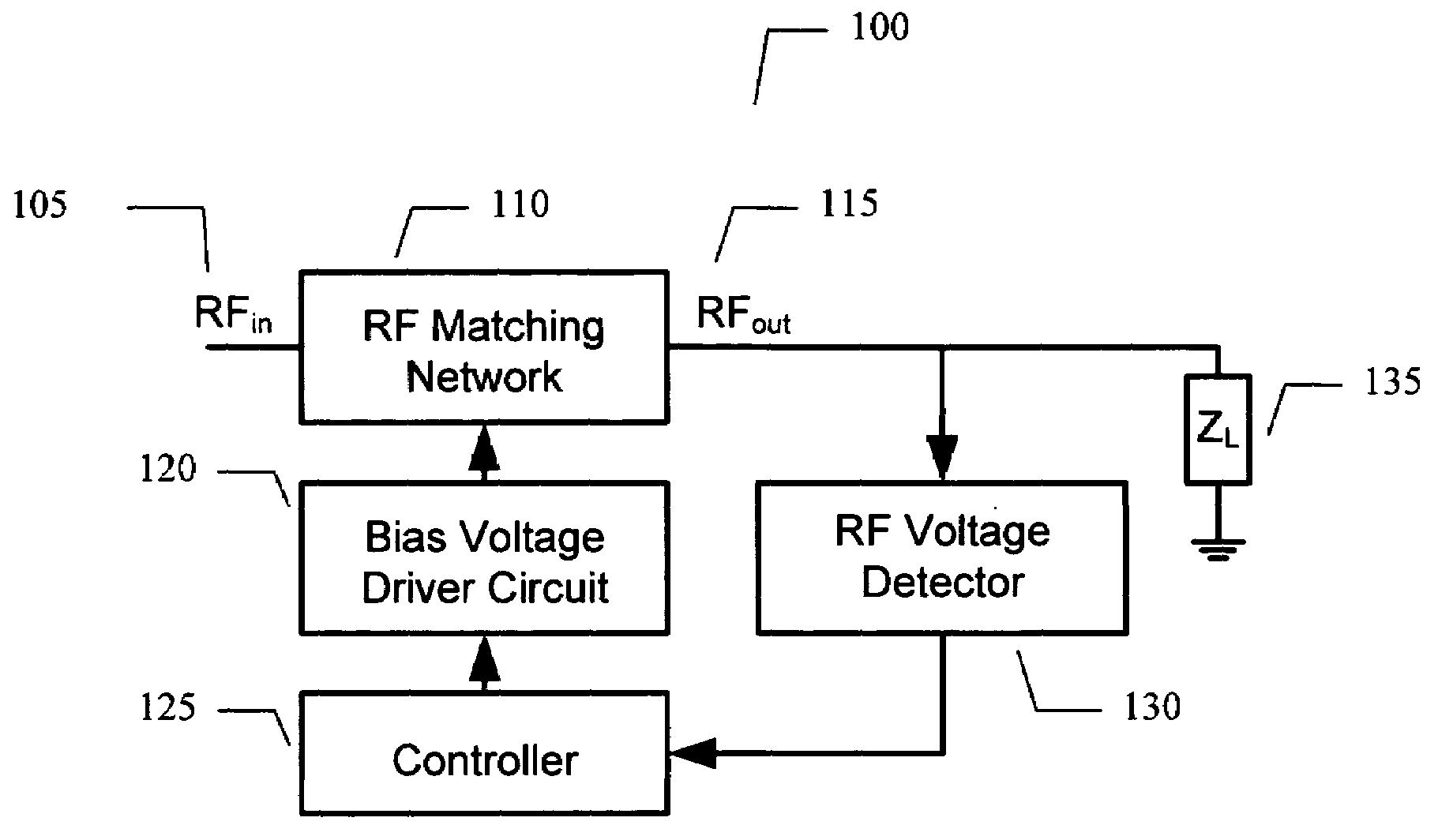
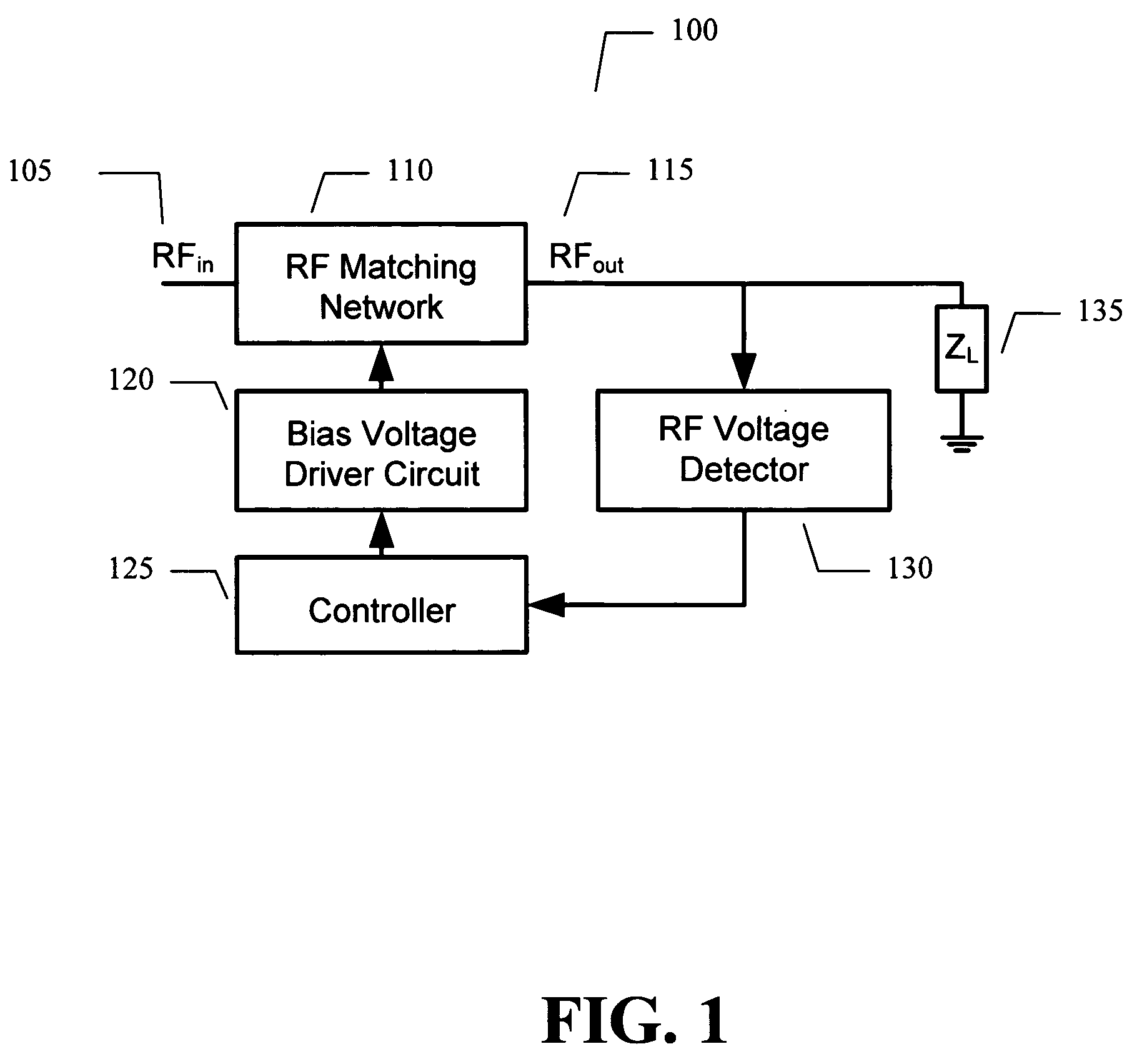
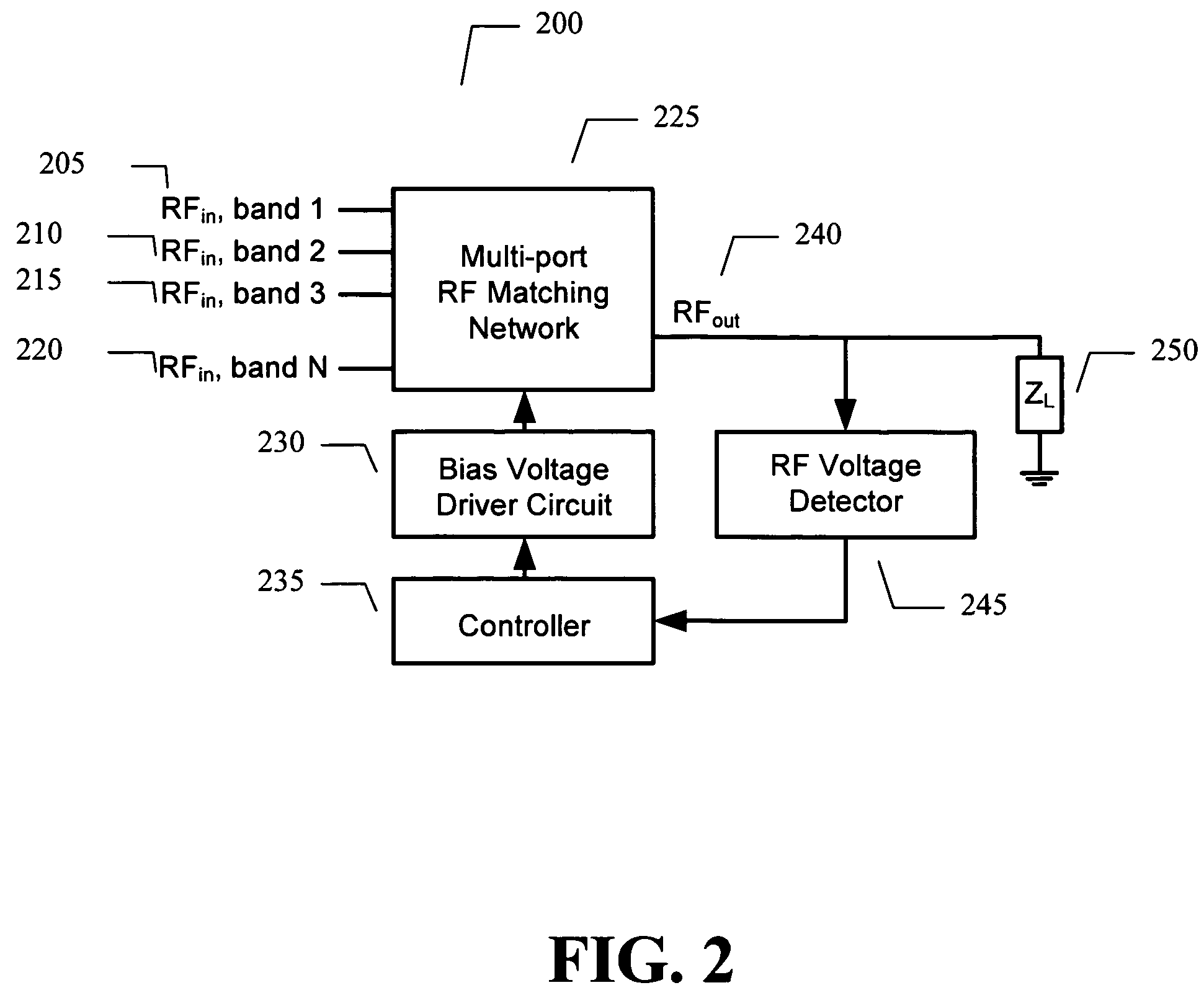
Adaptive impedance matching apparatus, system and method with improved dynamic range
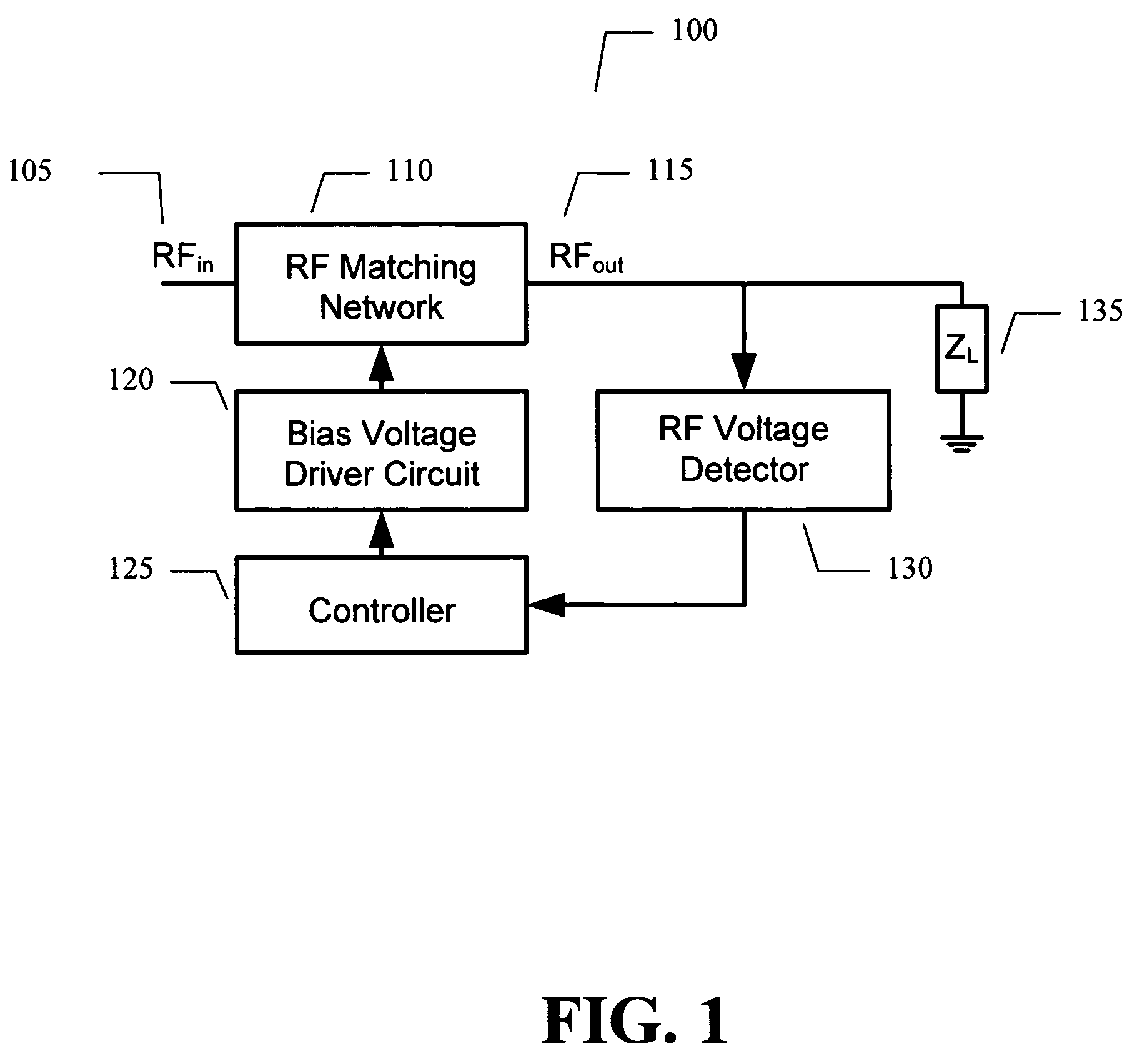
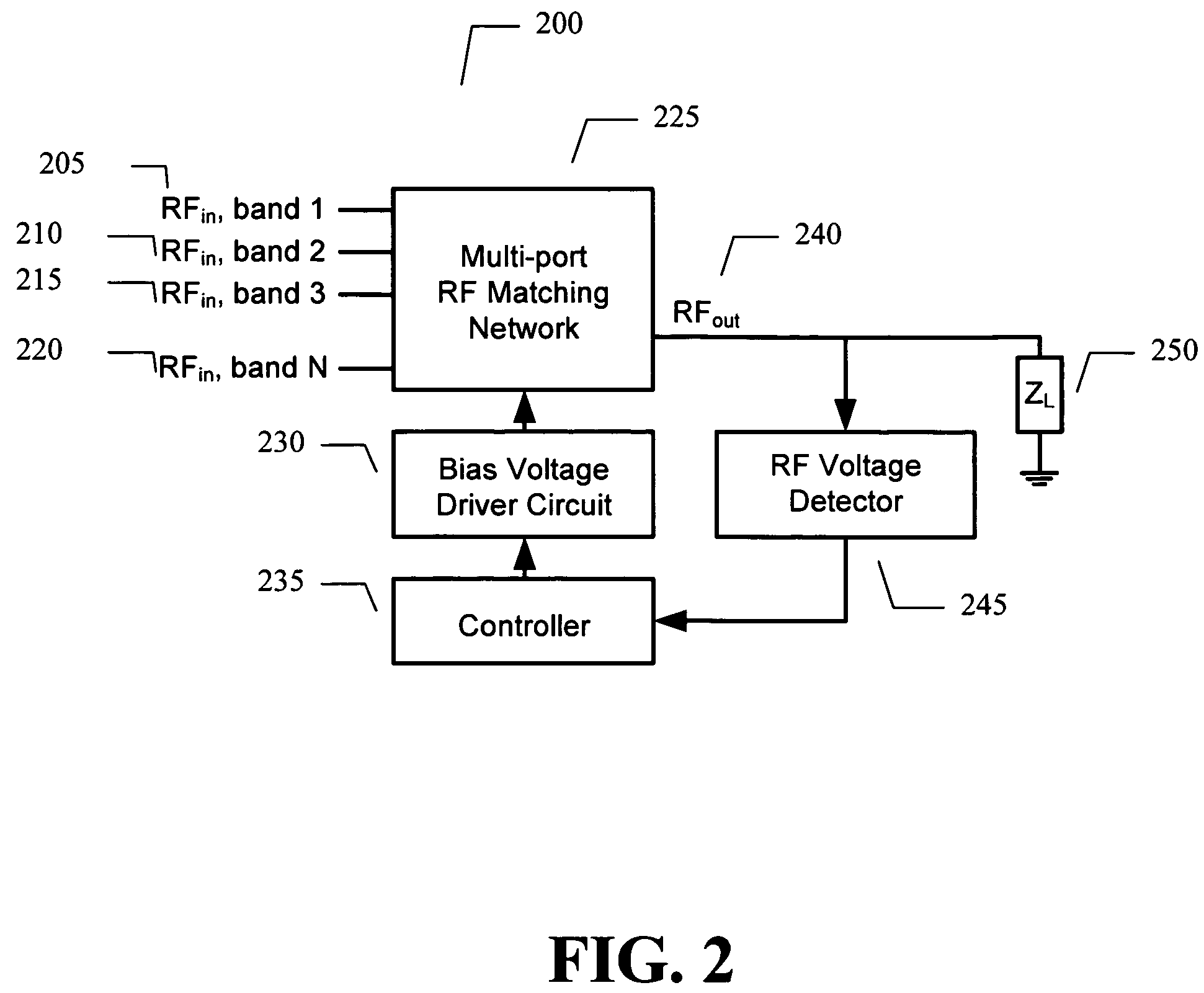
ActiveUS7535312B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasImpedance matchingEngineering
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements, a voltage detector connected to the at least one RF output port via a variable voltage divider to determine the voltage at the at least one RF output port and provide voltage information to a controller that controls a bias driving circuit which provides bias voltage or bias current to the RF matching network, and wherein the RF matching network is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the voltage or current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
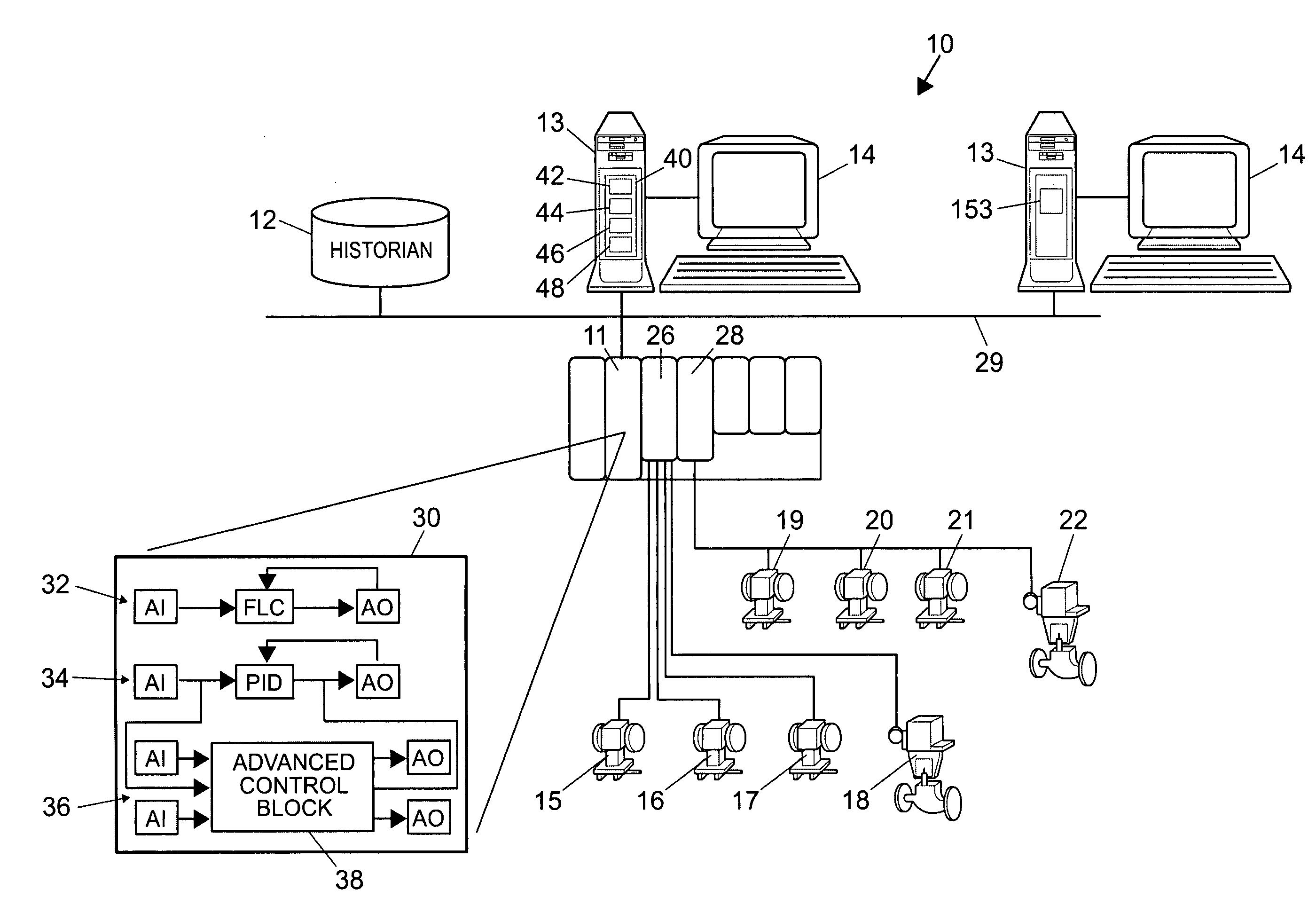
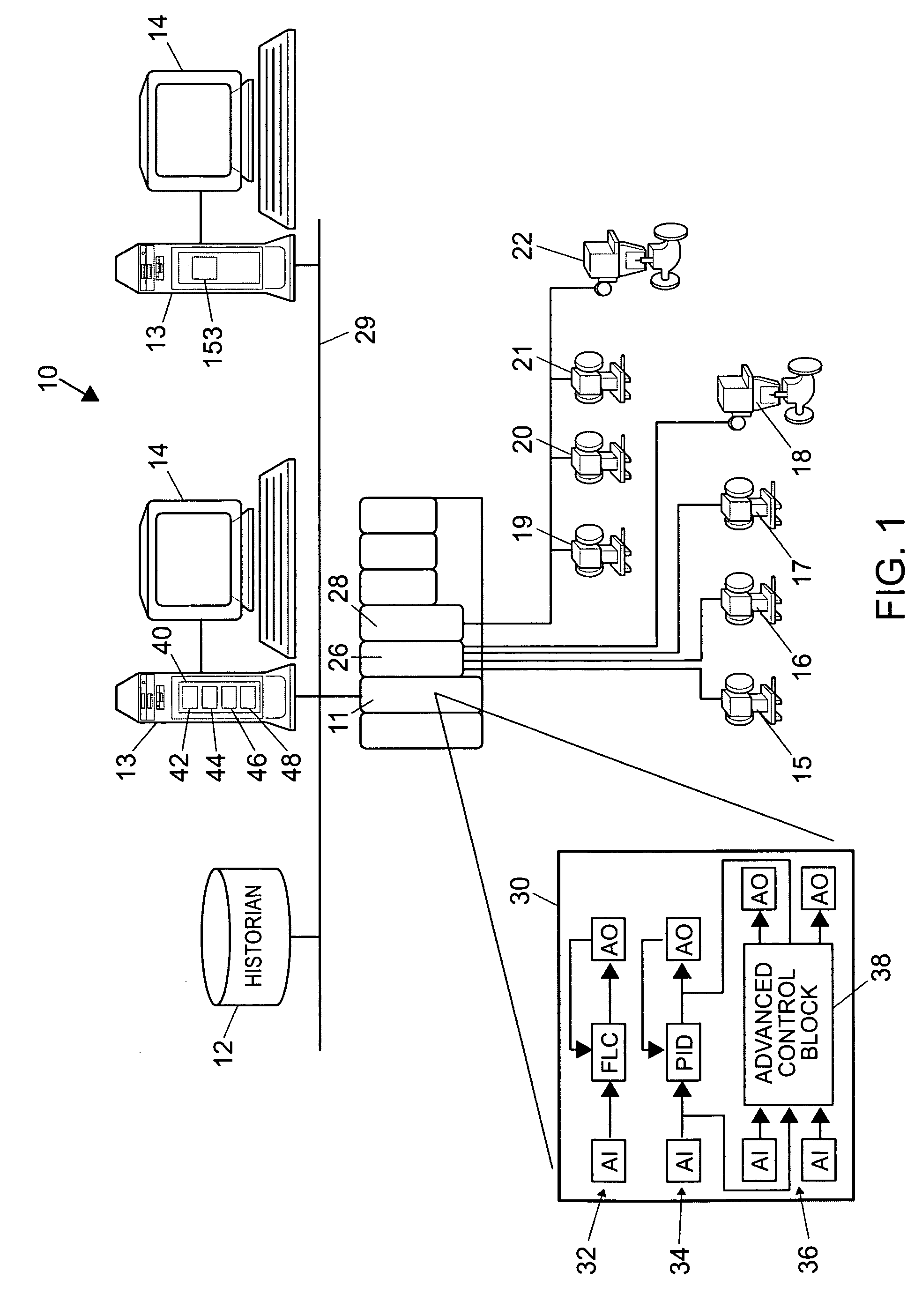
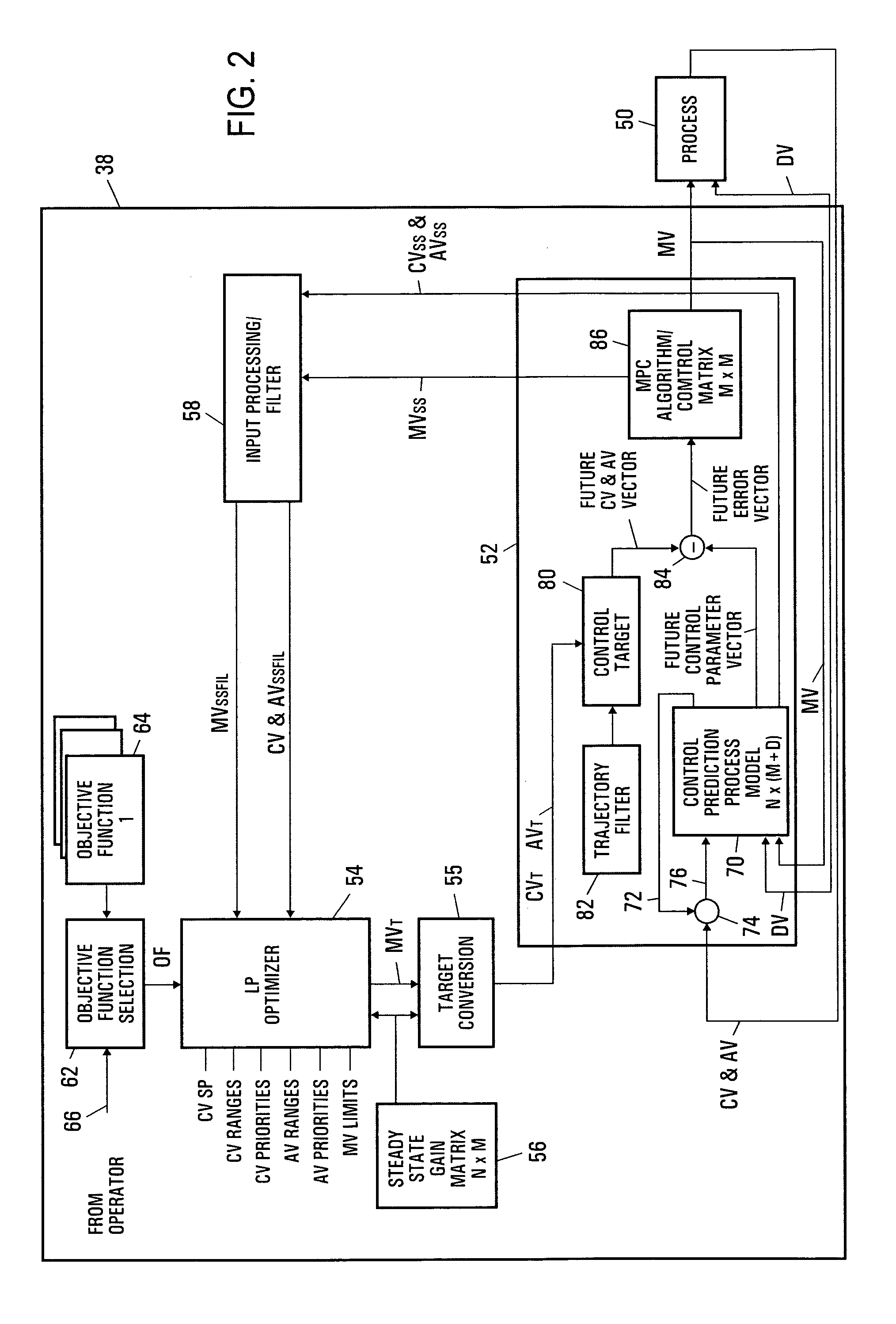
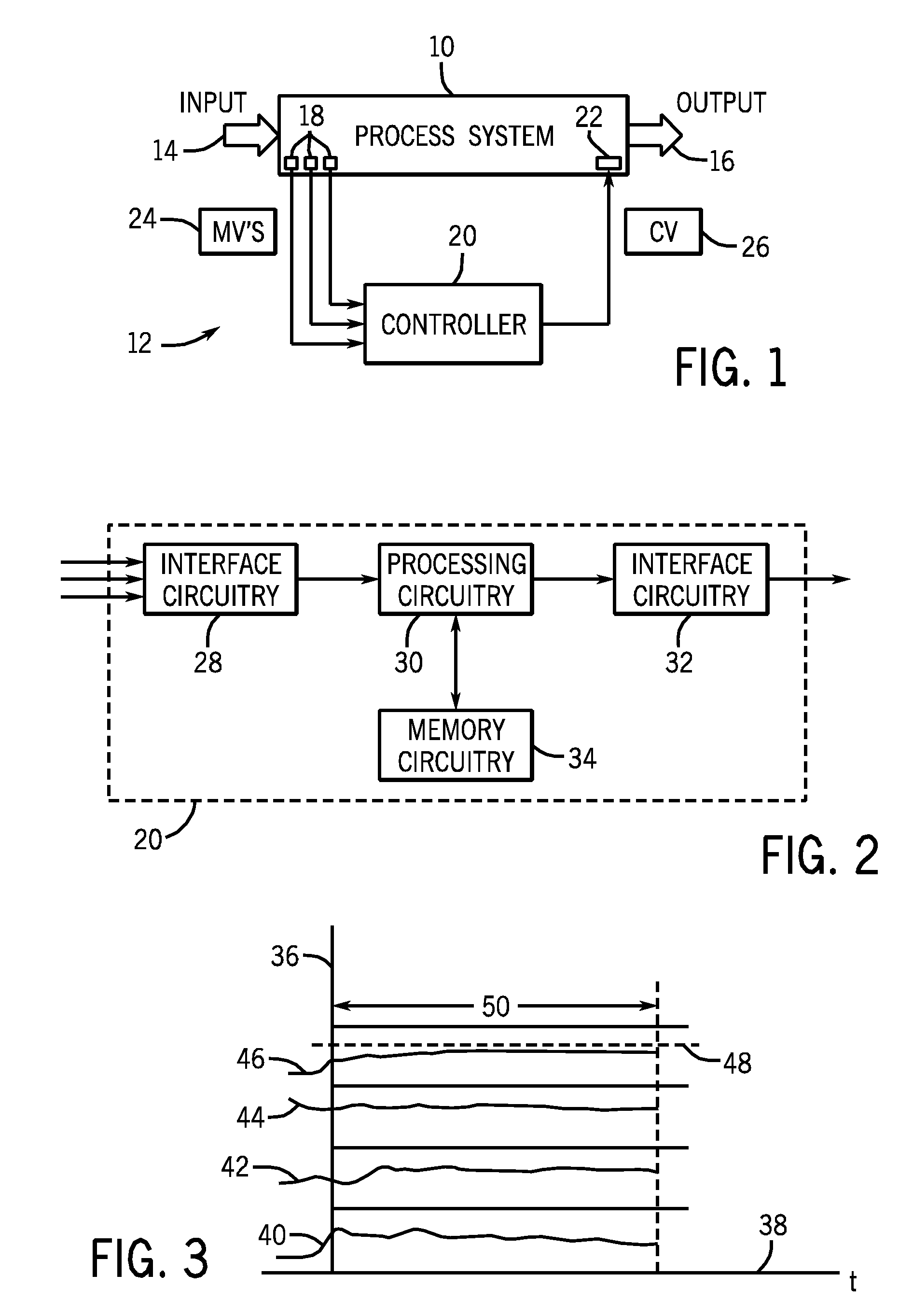
Integrated model predictive control and optimization within a process control system
InactiveUS7376472B2Simple calculationHigh gainData processing applicationsElectric controllersOperating pointControl system
An integrated optimization and control technique integrates an optimization procedure, such as a linear or quadratic programming optimization procedure, with advanced control, such as model predictive control, within a process plant in which the number of control and auxiliary variables can be greater than the number of manipulated variables within the process plant. The technique first determines a step response matrix defining the correlation between changes in the manipulated variables and each of the process variables that are used during optimization. A subset of the control variables and auxiliary variables is then selected to be used as inputs to a model predictive control routine used to perform control during operation of the process and a square M by M control matrix to be used by the model predictive control routine is generated. Thereafter, during each scan of the process controller, the optimizer routine calculates the optimal operating target of each of the complete set of control and auxiliary variables and provides the determined target operating points for each of the selected subset of control and auxiliary variables to the model predictive control routine as inputs. The model predictive control routine determines changes in the manipulated variables for use in controlling the process from the target and measured values for each of the subset of the control and auxiliary variables and the M by M control matrix.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
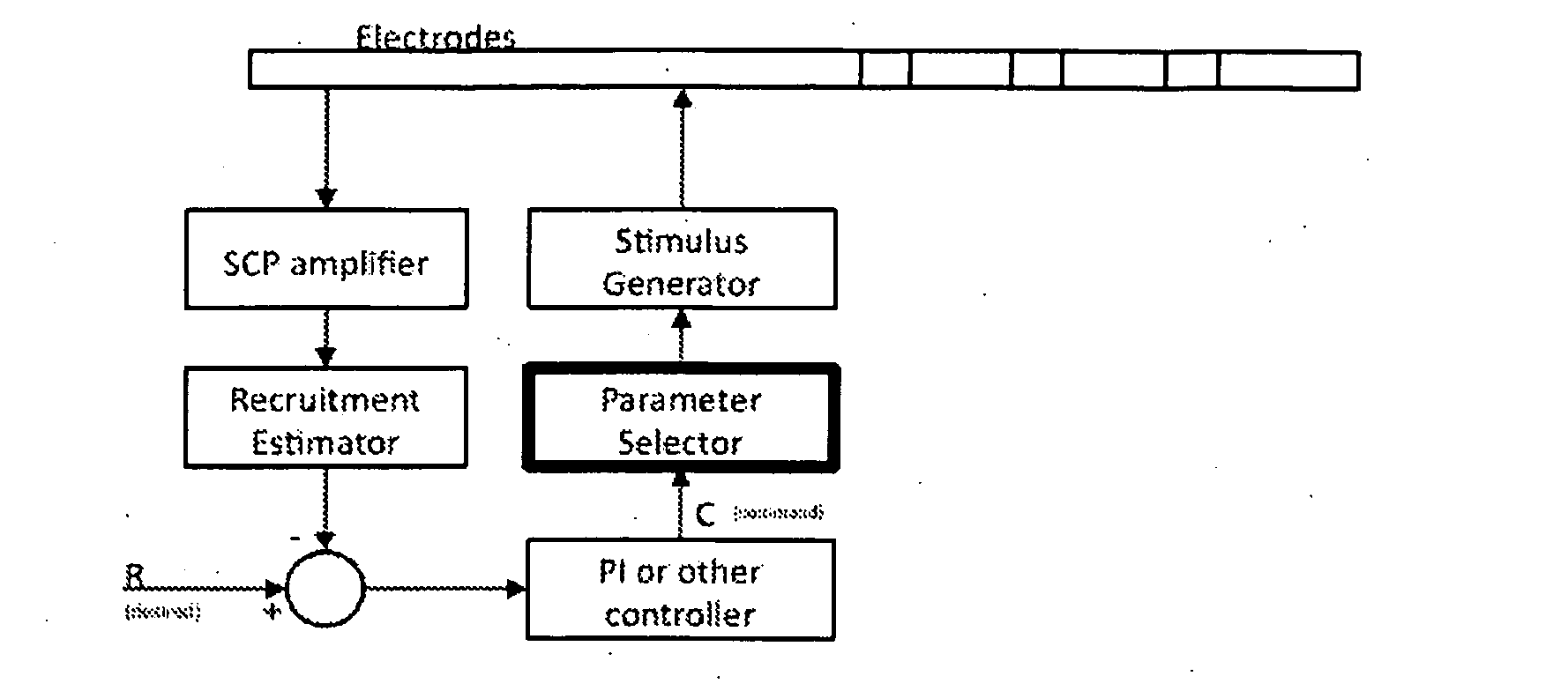
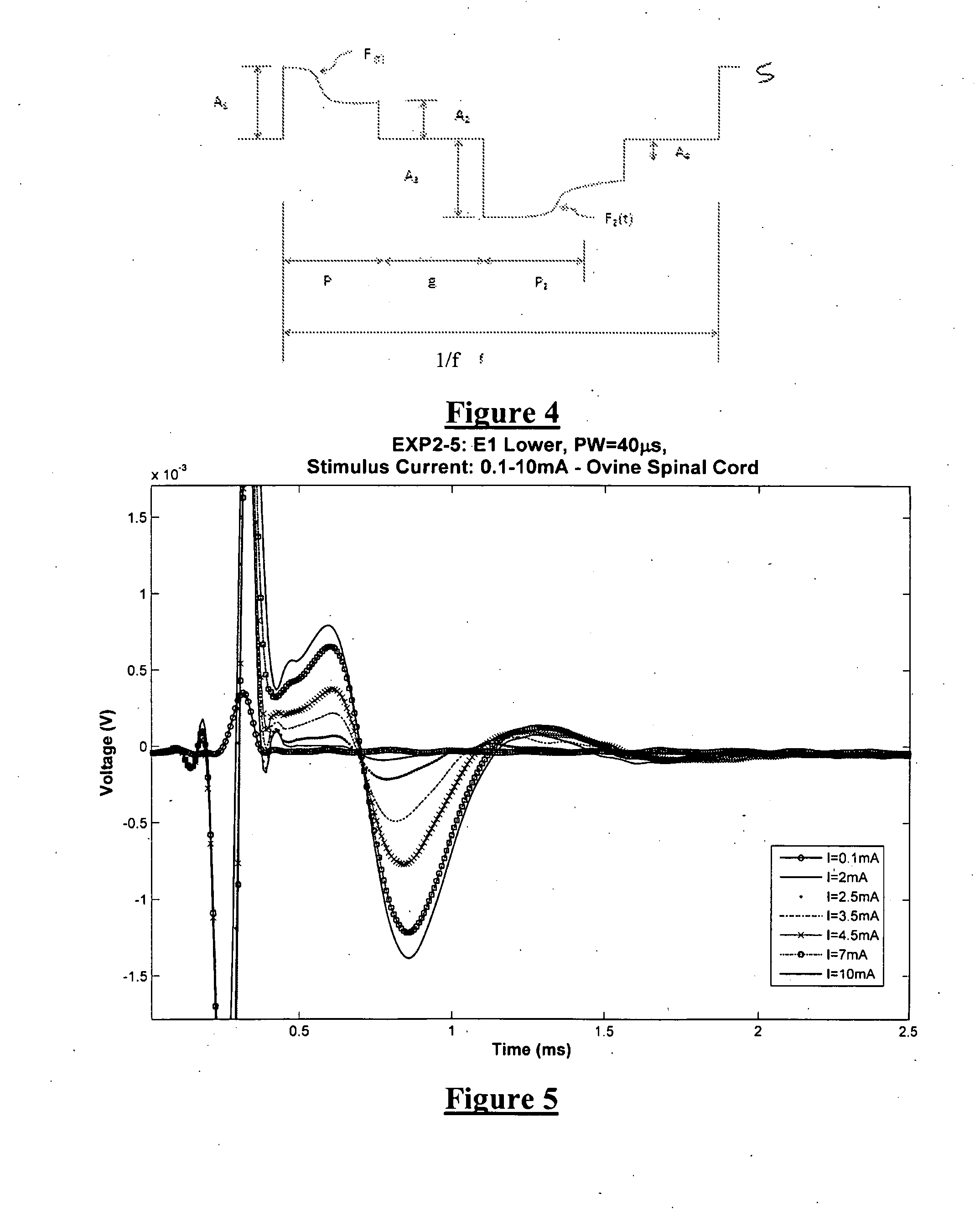
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
ActiveUS20140236257A1Avoid misalignmentControlled levelSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineSpinal cord
An implantable device applies and controls a neural stimulus. The device has a plurality of electrodes, and a stimulus source for providing a stimulus to be delivered from the electrodes to a neural pathway in order to evoke an action potential on the neural pathway, such as the spinal cord. A control unit controls application of a neural stimulus as defined by a set of parameter values and measures via measurement circuitry an evoked neural compound action potential response. The control unit determines from the measured evoked response a feedback variable, and compares it to a therapy map. The therapy map defines a therapeutic relationship of control variable to feedback variable. One or more of the stimulus parameter values are altered to effect the required change in the control variable. This process is performed iteratively to improve alignment of the feedback variable with the therapy map over time.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL
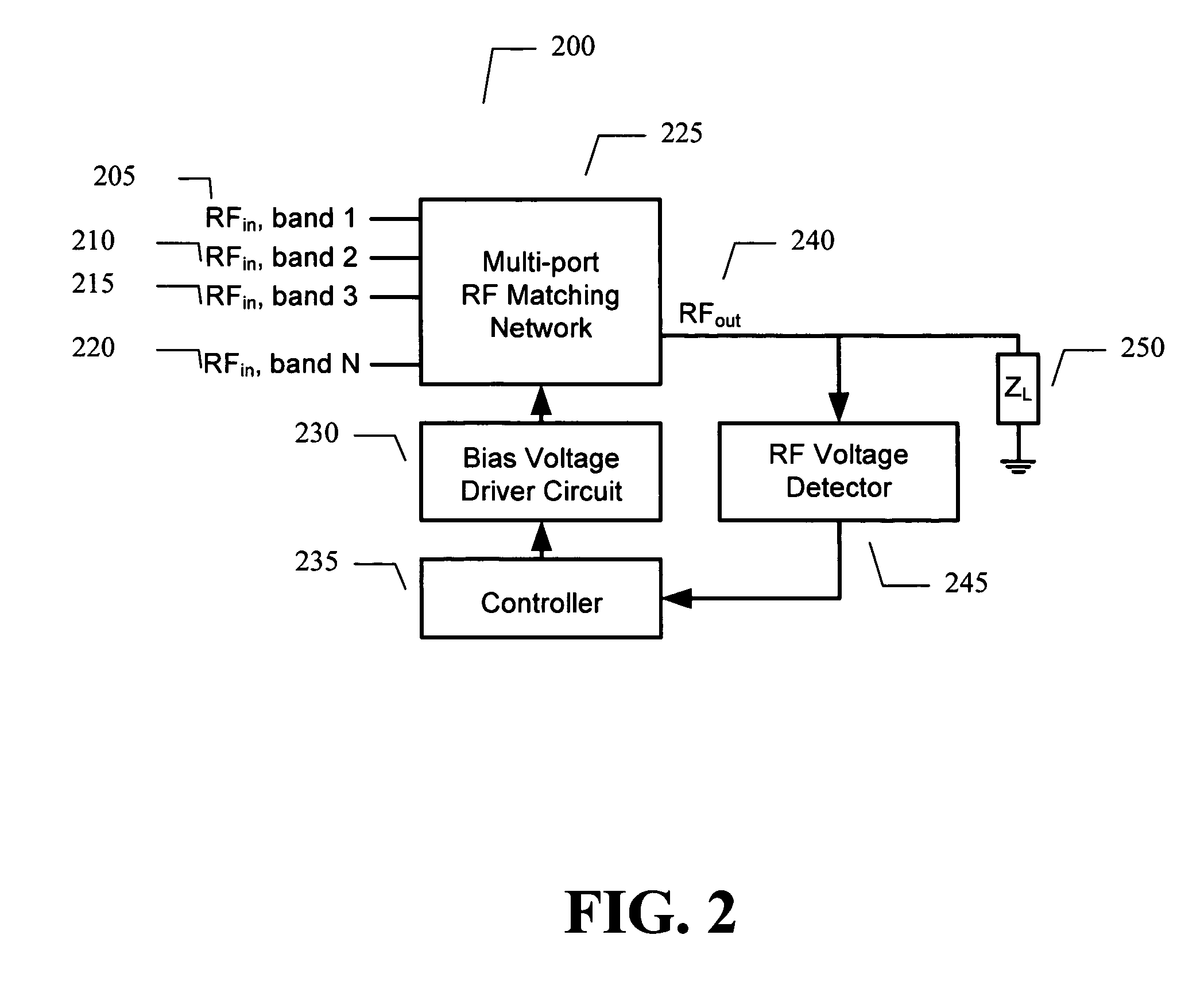
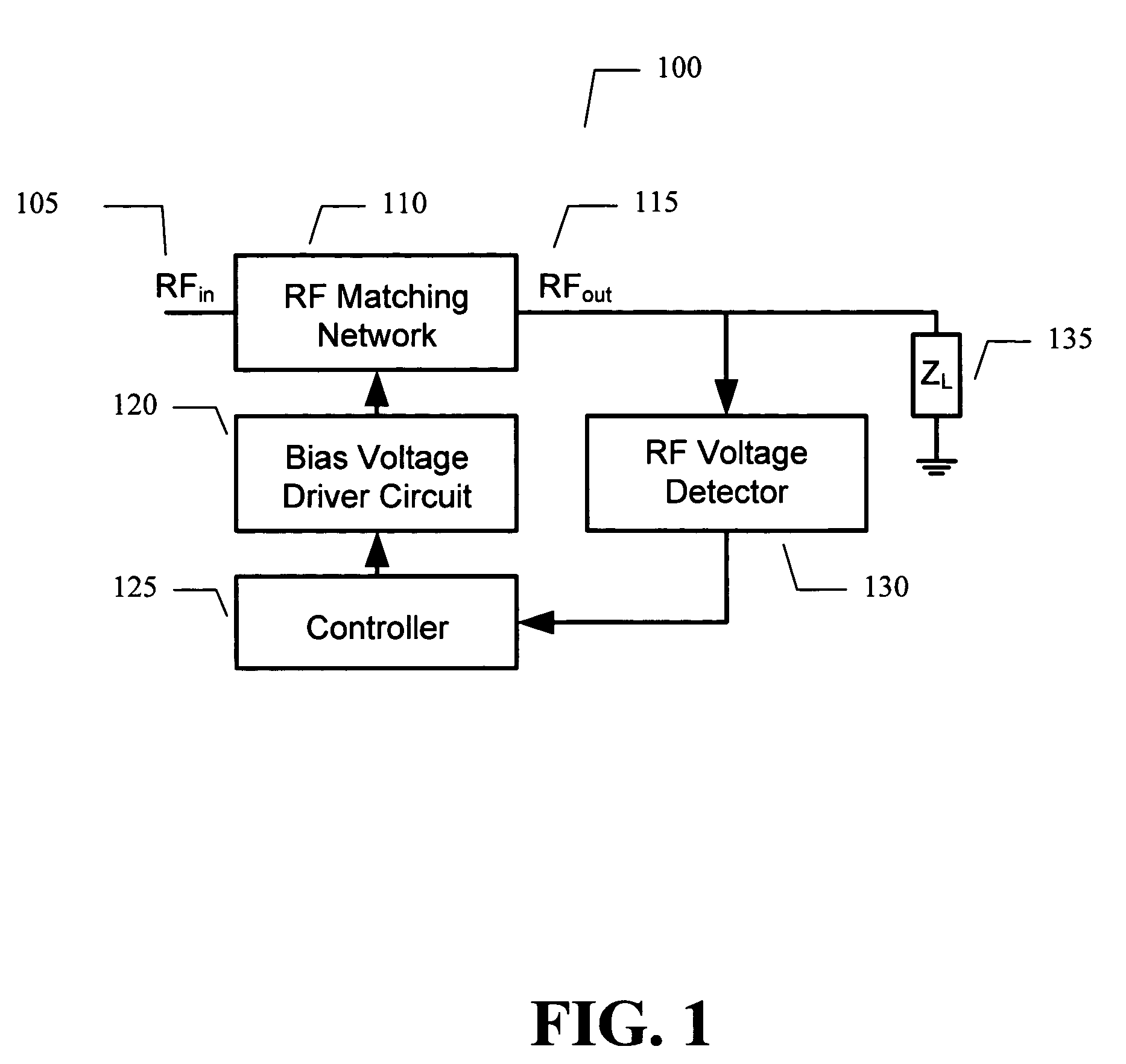
Techniques for improved adaptive impedance matching
ActiveUS20080261544A1Optimal starting positionEasy to determineMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasNetwork connectionImpedance matching
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements; and wherein the RF matching network is tuned to optimize the RF matching network and wherein said tuning is limited by a predetermined number of tuning steps that are taken within a transmit burst and / or limited by the magnitude of each step taken within a transmit burst and / or limited to the steps only being allowed between bursts.
Owner:NXP USA INC
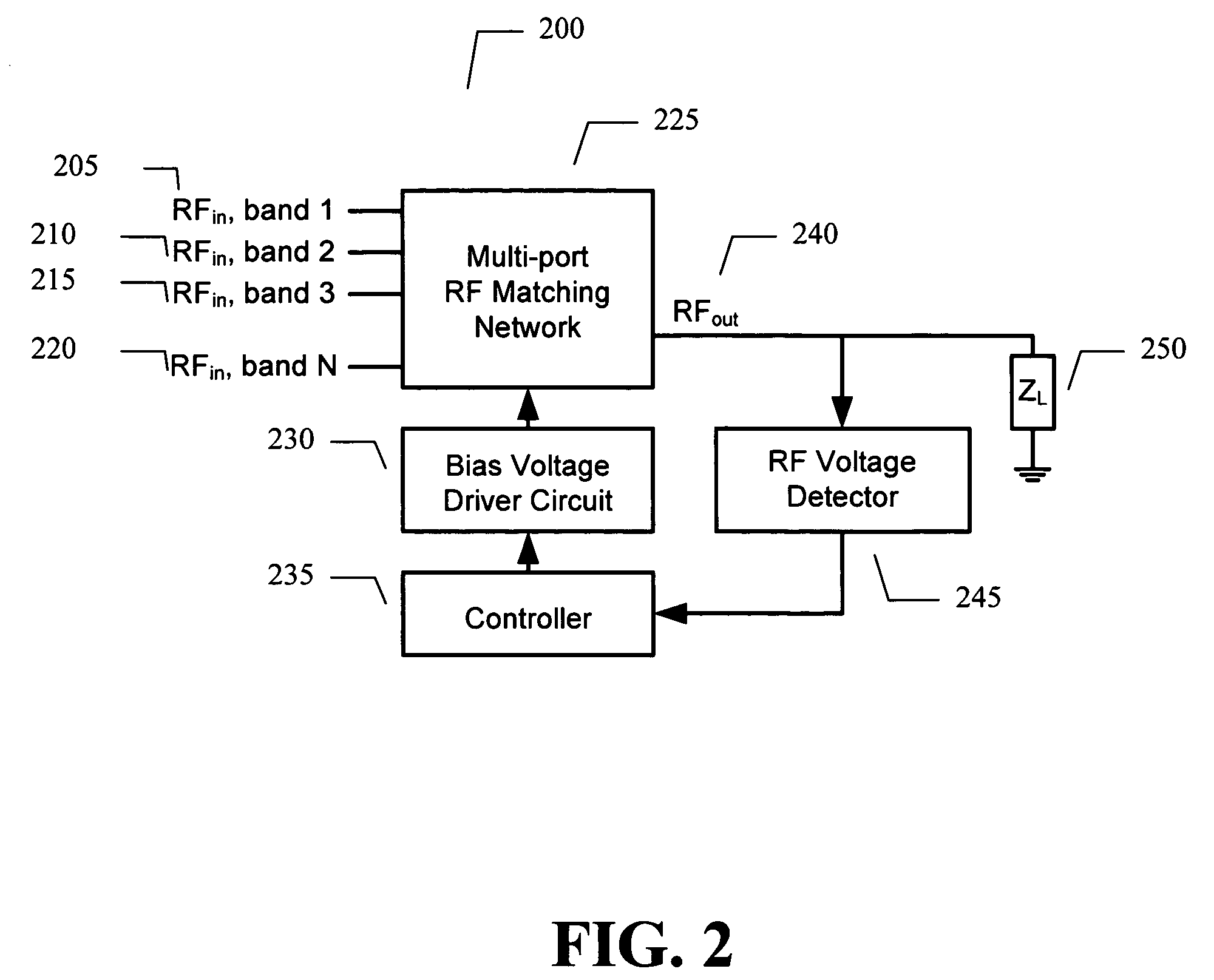
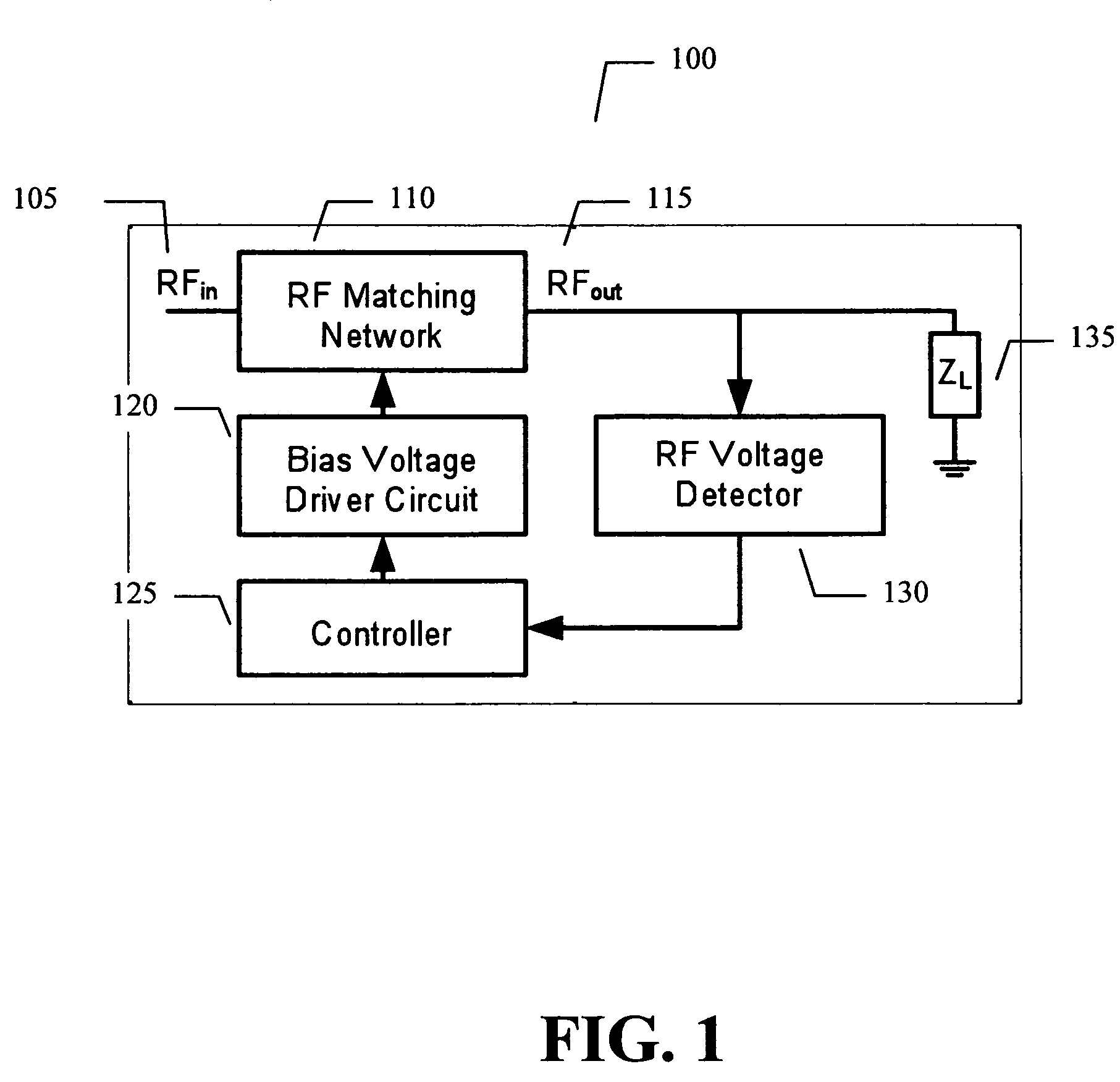
Adaptive impedance matching apparatus, system and method
ActiveUS7714676B2Power maximizationMaximize RF voltagePower managementMultiple-port networksCapacitanceImpedance matching
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements and wherein the RF matching network is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the voltage or current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port. The variable reactive elements may be variable capacitances, variable inductances, or both.
Owner:NXP USA INC
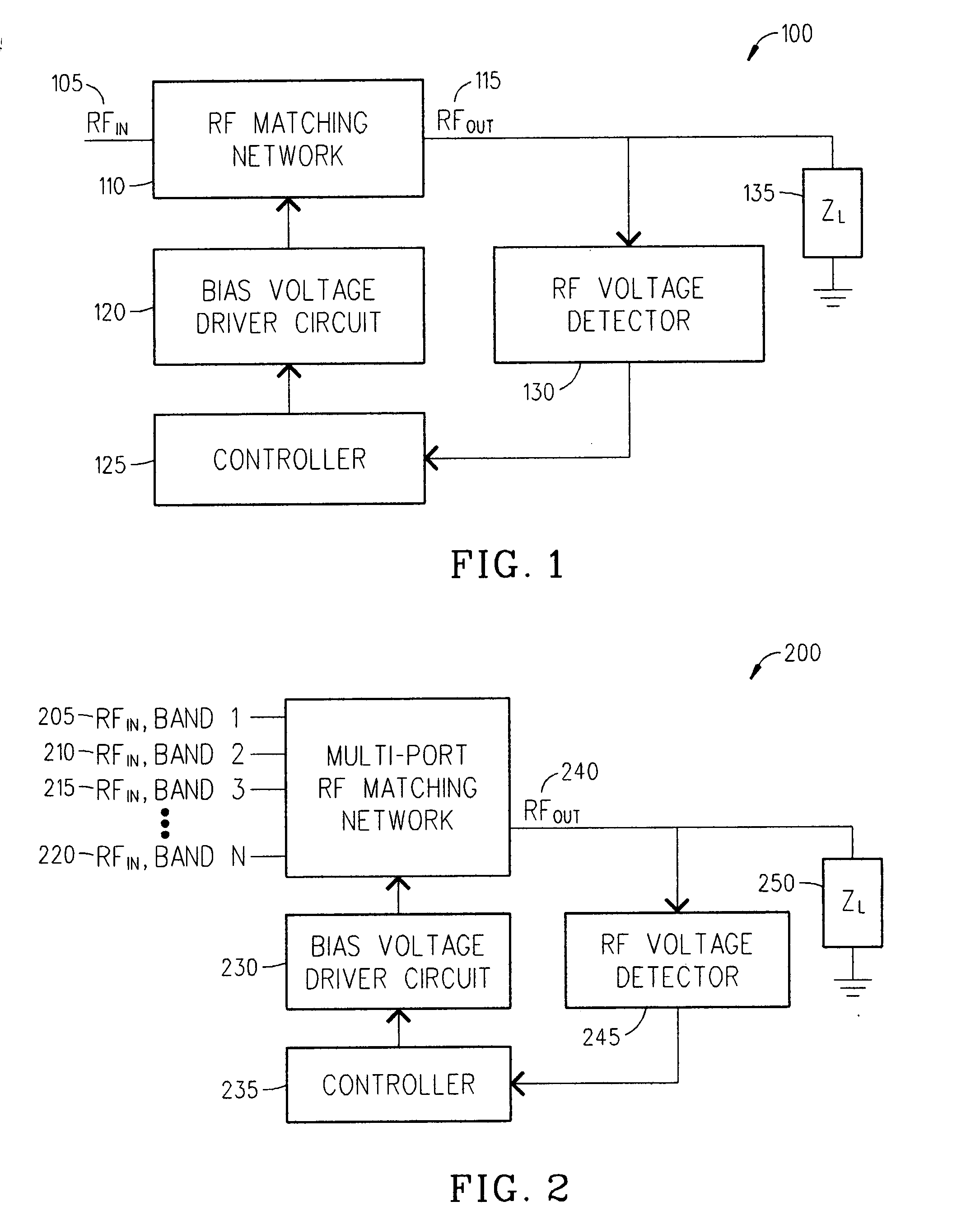
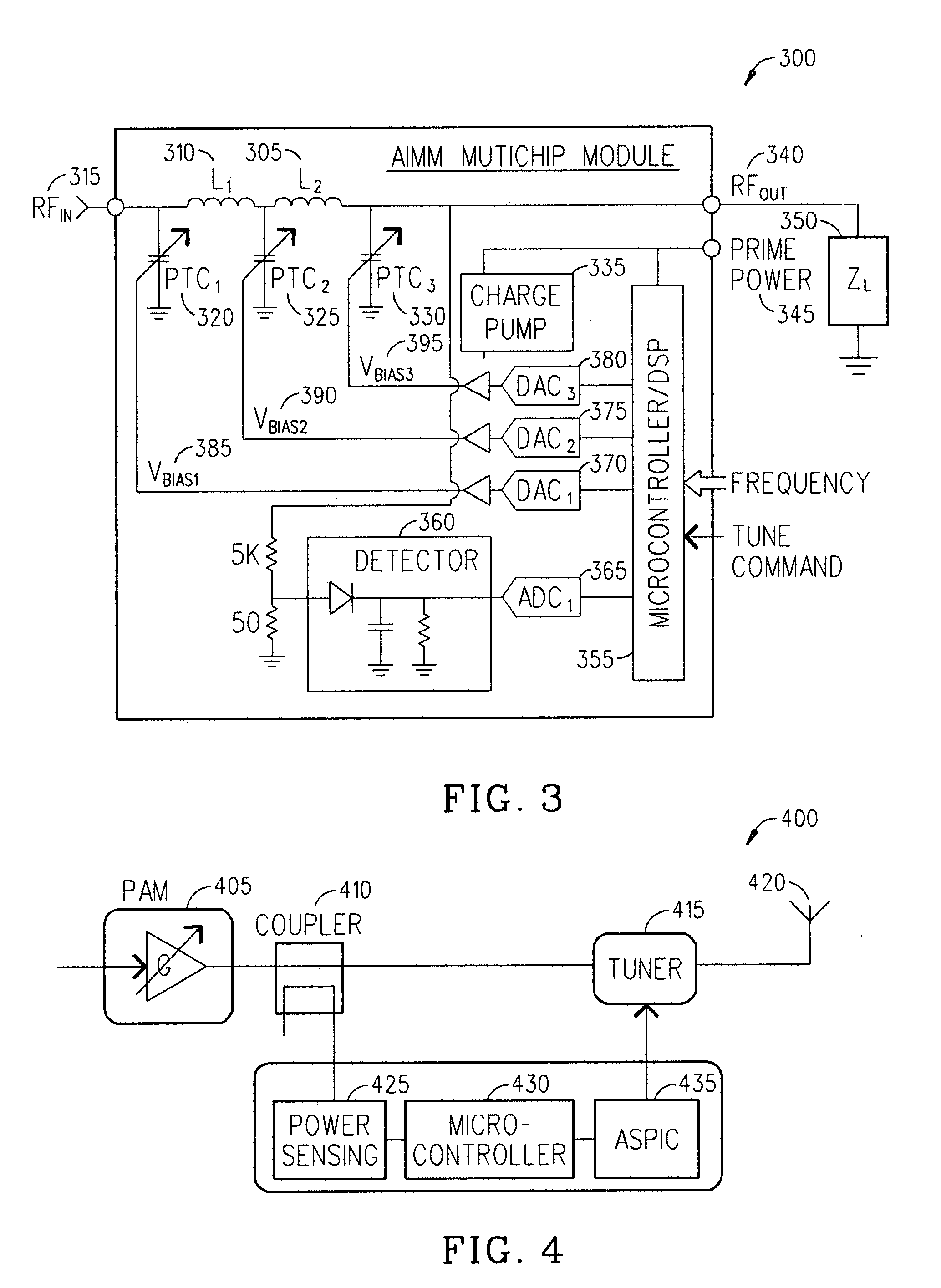
Adaptive impedance matching module
ActiveUS8299867B2Power maximizationMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasImpedance matchingEngineering
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF input port, an RF output port connected to the RF input port via a multichip adaptive impedance matching module (AIMM), and the multichip AIMM comprising one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements, wherein the multichip AIMM is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the bias voltage or bias current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and apparatus for extending the transmission capability of twisted pair communication systems
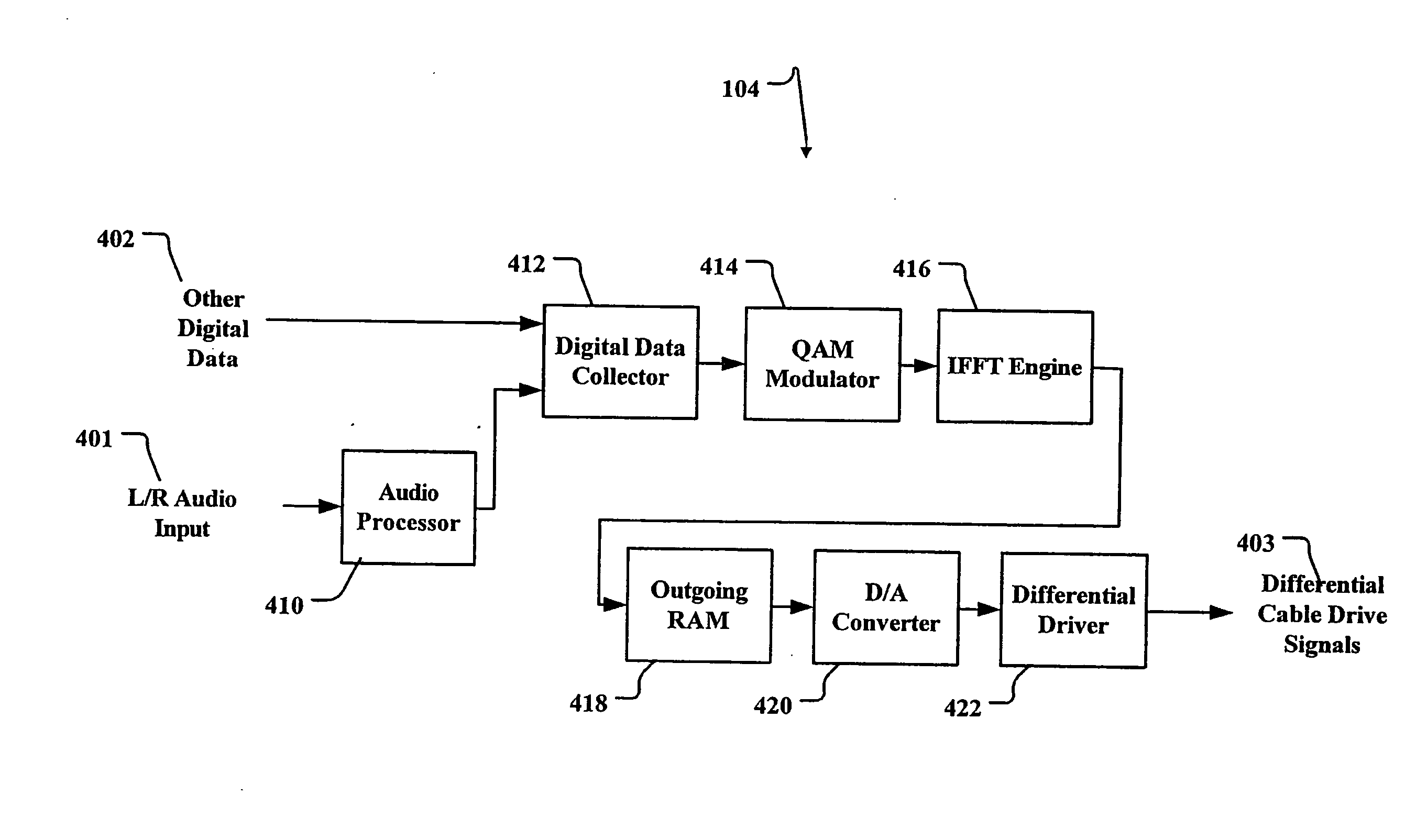
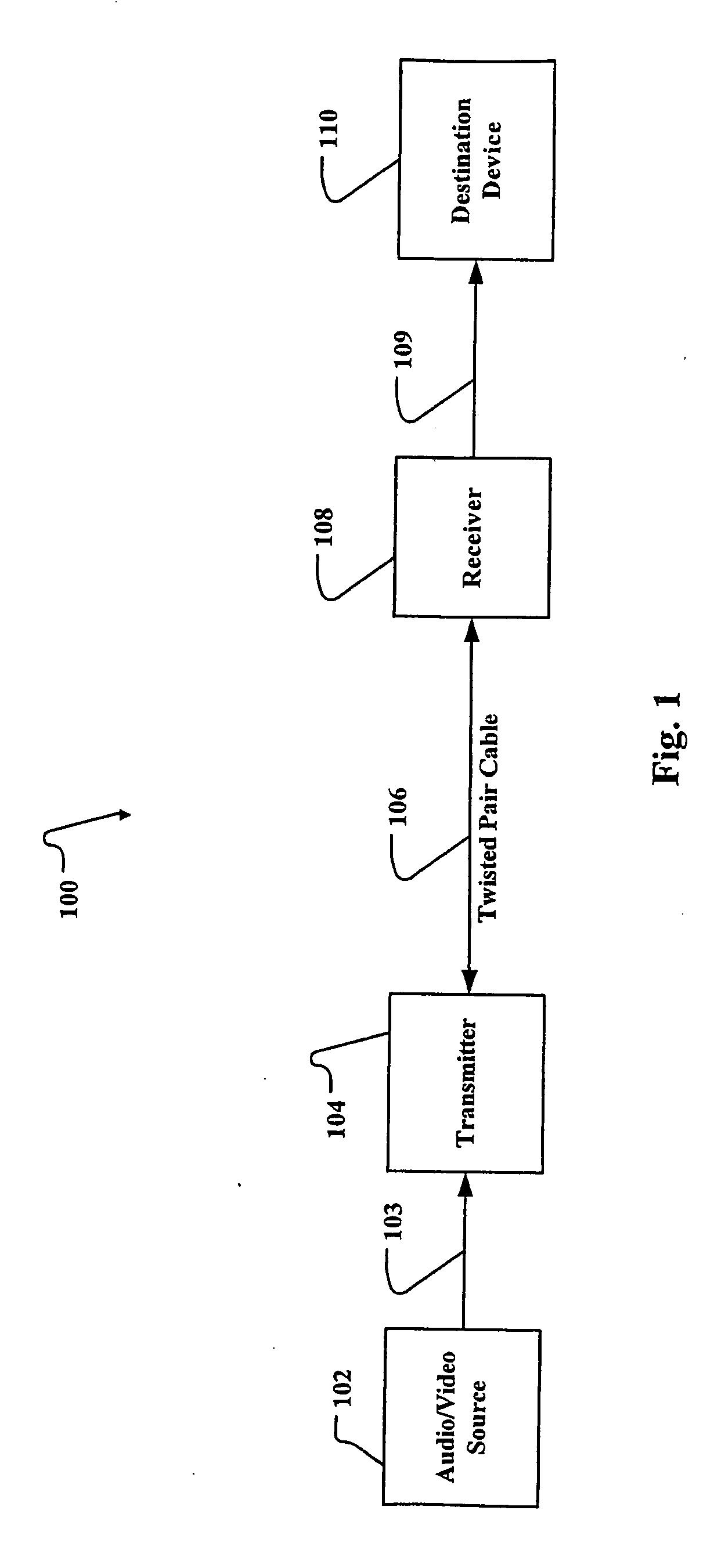
InactiveUS20090059782A1Improve transmission performanceDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemClosed loop feedback
A closed loop feedback system is employed in a receiver to automatically compensate the communication signal from twisted pair cables for AC and DC losses. This is accomplished through the use of a reference pulse signal which is sent along with other digital information. At the receiver, the reference pulse signal is restored to its proper level through a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)-controlled variable compensation amplifier circuit. The received reference signal is compared to a known reference value and the duty cycle of the PWM circuit is adjusted until the proper level reference signal is achieved. Thereafter, the digital signal is extracted. OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) with pilot tones are used to maximize payload while minimizing crosstalk effects. The pilot tones locate the OFDM symbols in time while supplying compensation information concerning the transmission medium.
Owner:RGB SYST INC
Navigation of remotely actuable medical device using control variable and length
A method of navigating a medical device includes determining the location of a medical device at a point in an operating region in a subject's body, the medical device being responsive to at least one control variable to assume a desired configuration includes storing information representative of the at least one control variable being applied to the medical device at the point, and more preferably storing information representative of the at least one control variable and the device length.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
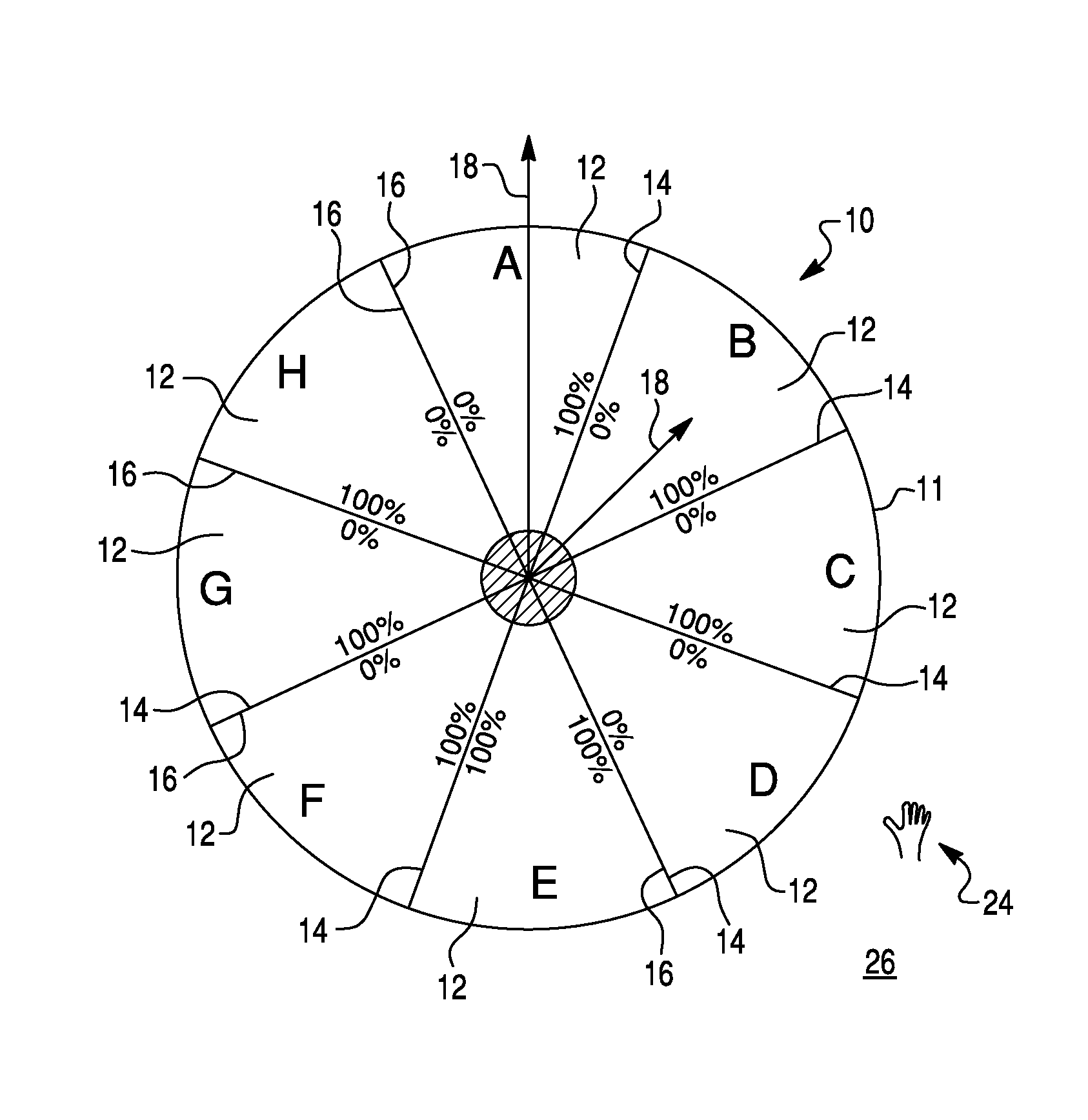
Radial control menu, graphical user interface, method of controlling variables using a radial control menu, and computer readable medium for performing the method
ActiveUS20090187860A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
A graphical user interface for displaying actions of an input device on a display is provided. The interface includes a radial menu having an origin disposed at a center thereof and at least a first wedge defining an area extending outwardly from the origin. The first wedge is associated with a variable that is capable of being set to a value between a predetermined minimum value and a predetermined maximum value. A cursor for indicating a current position of the input device on the display is provided in the interface. The cursor is movable within the first wedge to select a current value of the variable based upon the angular position of the cursor with respect to said origin. A radial menu, computer system, and method are also provided.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
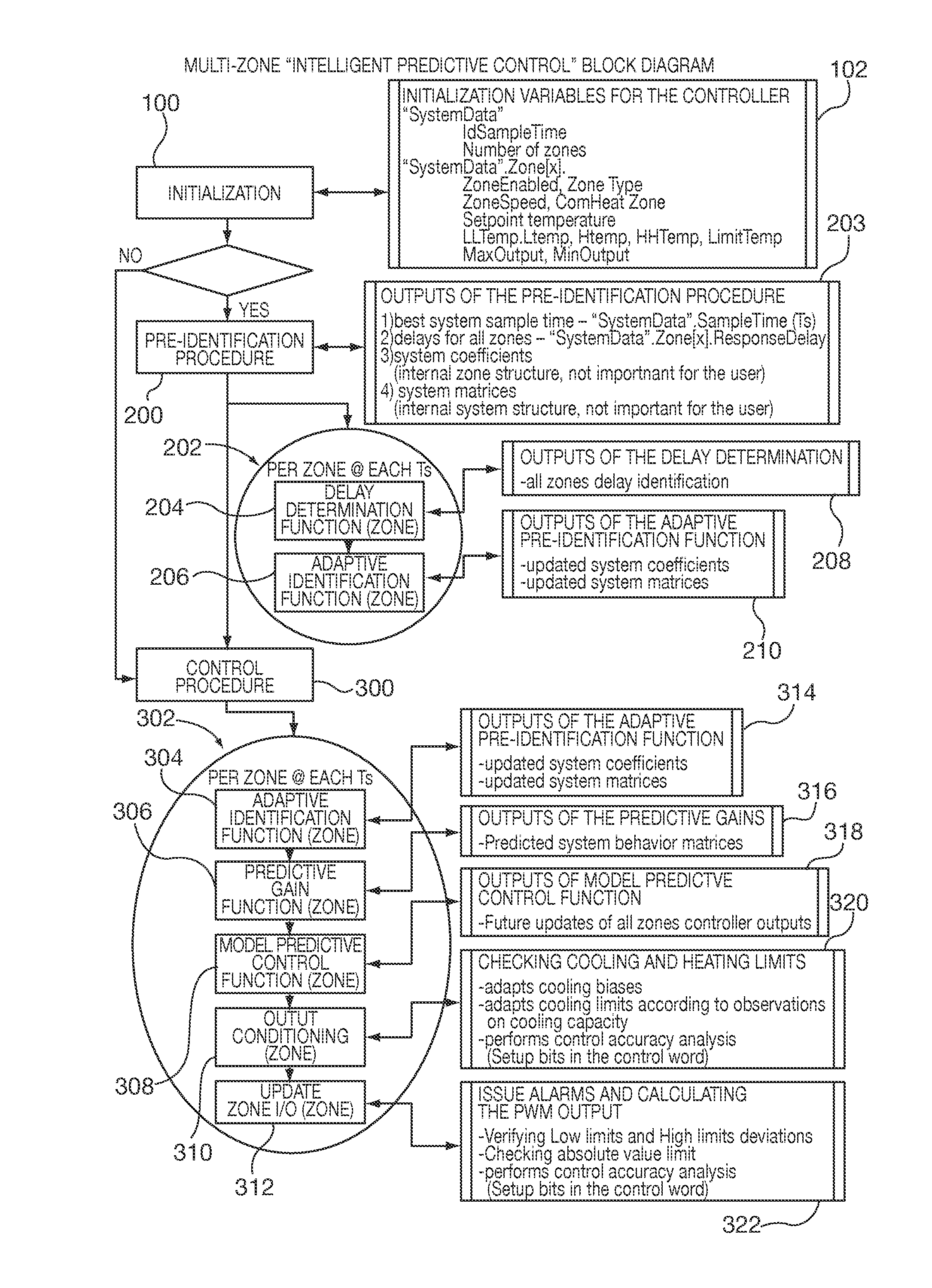
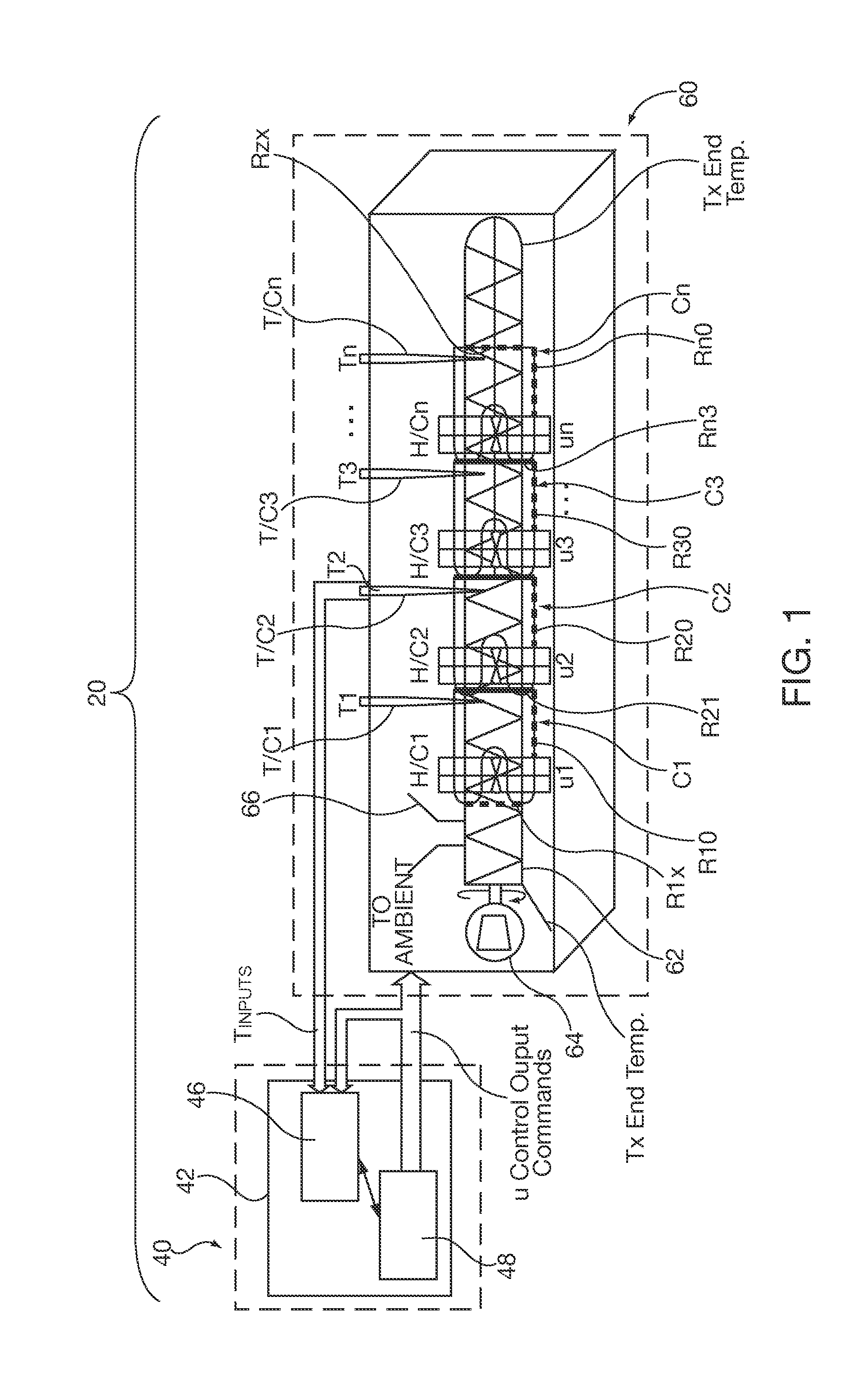
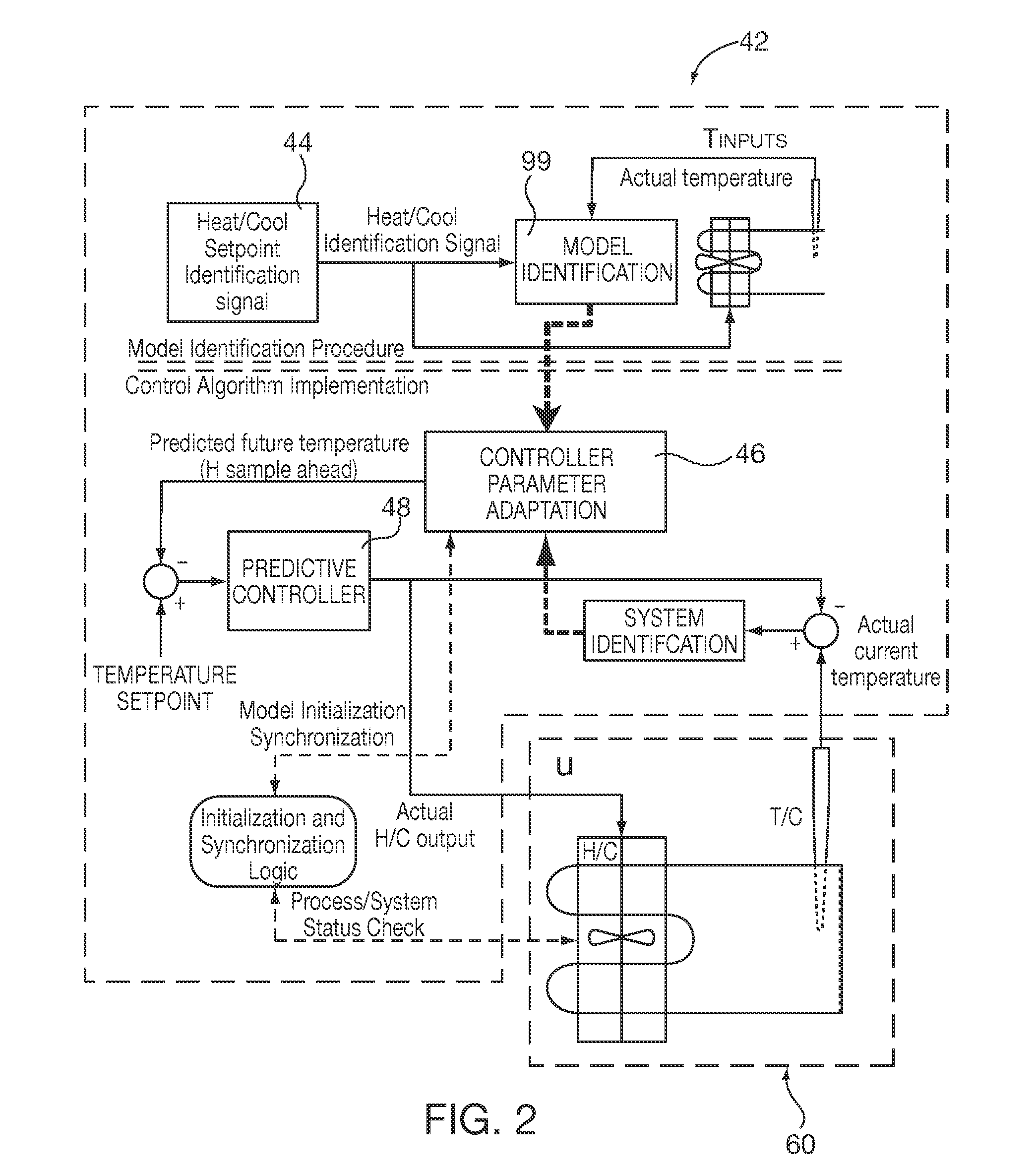
Method and apparatus of a self-configured, model-based adaptive, predictive controller for multi-zone regulation systems
InactiveUS20110022193A1Easy to addPrecise processingSampled-variable control systemsTravelling carriersHorizonPlastic injection molding
A control system simultaneously controls a multi-zone process with a self-adaptive model predictive controller (MPC), such as temperature control within a plastic injection molding system. The controller is initialized with basic system information. A pre-identification procedure determines a suggested system sampling rate, delays or “dead times” for each zone and initial system model matrix coefficients necessary for operation of the control predictions. The recursive least squares based system model update, control variable predictions and calculations of the control horizon values are preferably executed in real time by using matrix calculation basic functions implemented and optimized for being used in a S7 environment by a Siemens PLC. The number of predictions and the horizon of the control steps required to achieve the setpoint are significantly high to achieve smooth and robust control. Several matrix calculations, including an inverse matrix procedure performed at each sample pulse and for each individual zone determine the MPC gain matrices needed to bring the system with minimum control effort and variations to the final setpoint. Corrective signals, based on the predictive model and the minimization criteria explained above, are issued to adjust system heating / cooling outputs at the next sample time occurrence, so as to bring the system to the desired set point. The process is repeated continuously at each sample pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
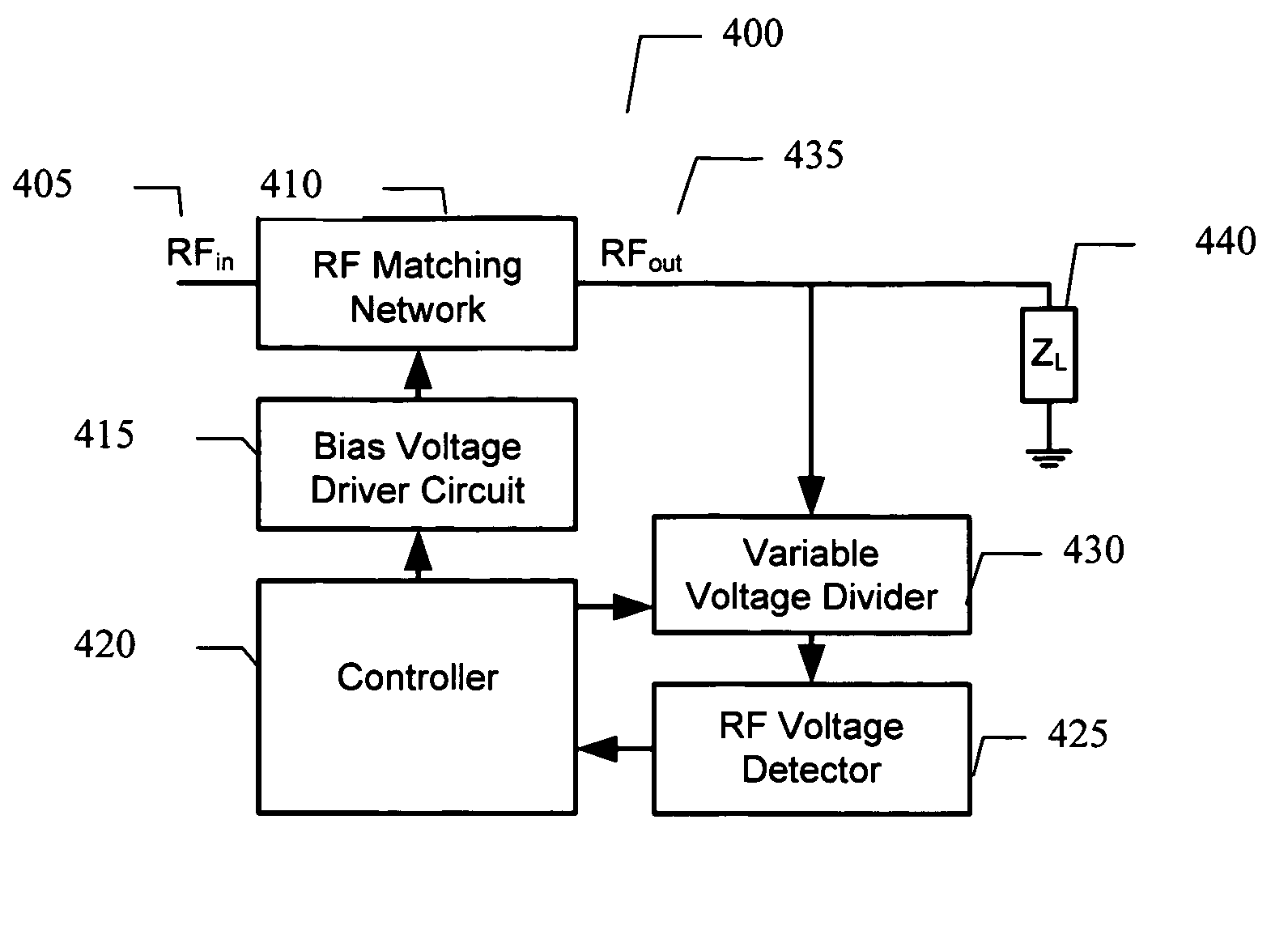
Adaptive impedance matching apparatus, system and method with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS7852170B2Improve dynamic rangeImprove linearityMultiple-port networksAntennas earthing switches associationElectrical resistance and conductanceNetwork connection
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF matching network connected to at least one RF input port and at least one RF output port and including one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements; a voltage detector connected to the at least one RF output port via a variable voltage divider to determine the voltage at the at least one RF output port and provide voltage information to a controller that controls a bias driving circuit which provides voltage or current bias to the RF matching network; a variable voltage divider connected to the voltage detector and implemented using a multi-pole RF switch to select one of a plurality of different resistance ratios to improve the dynamic range of the apparatus; and wherein the RF matching network is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the voltage or current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
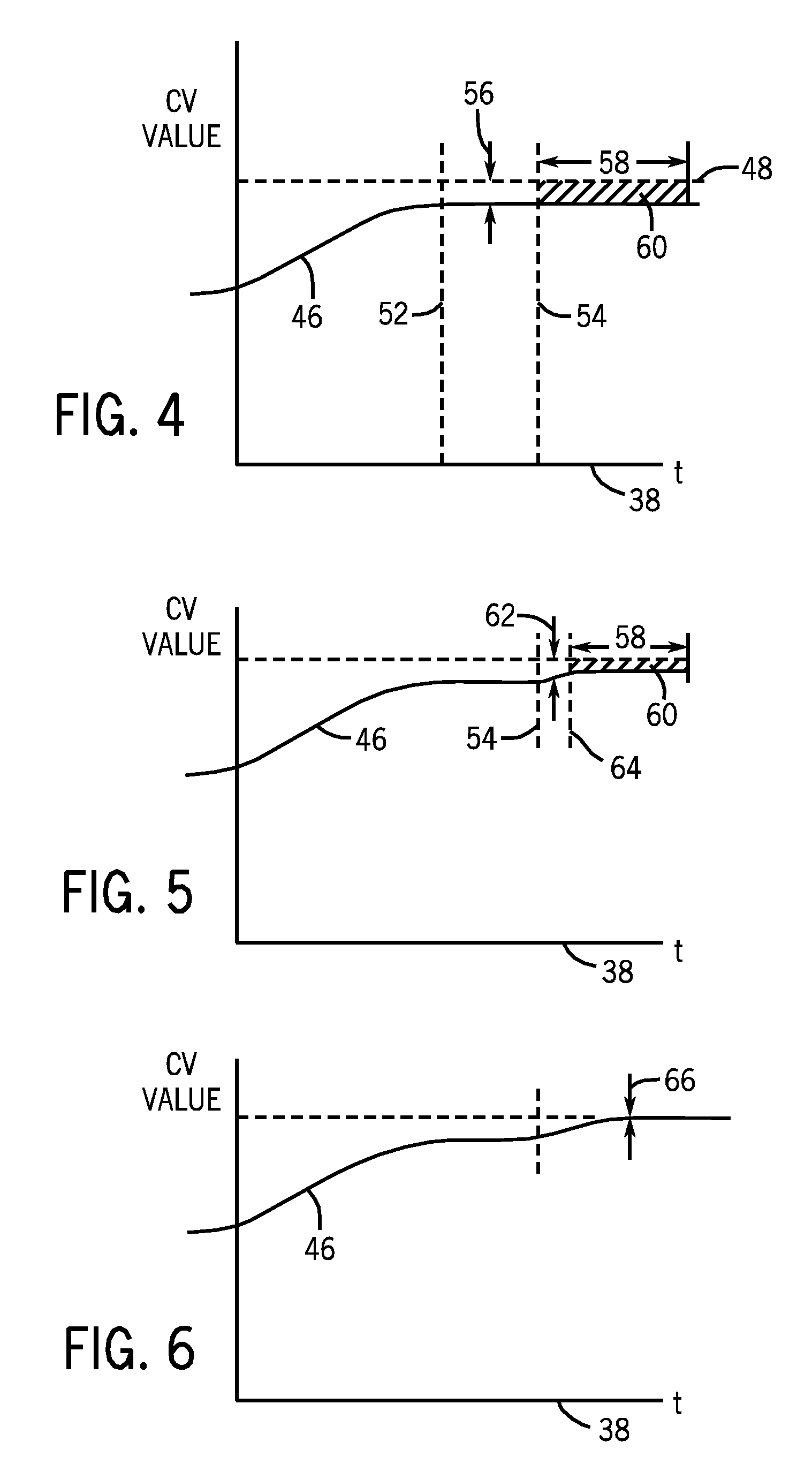
Optimized control of power plants having air cooled condensers
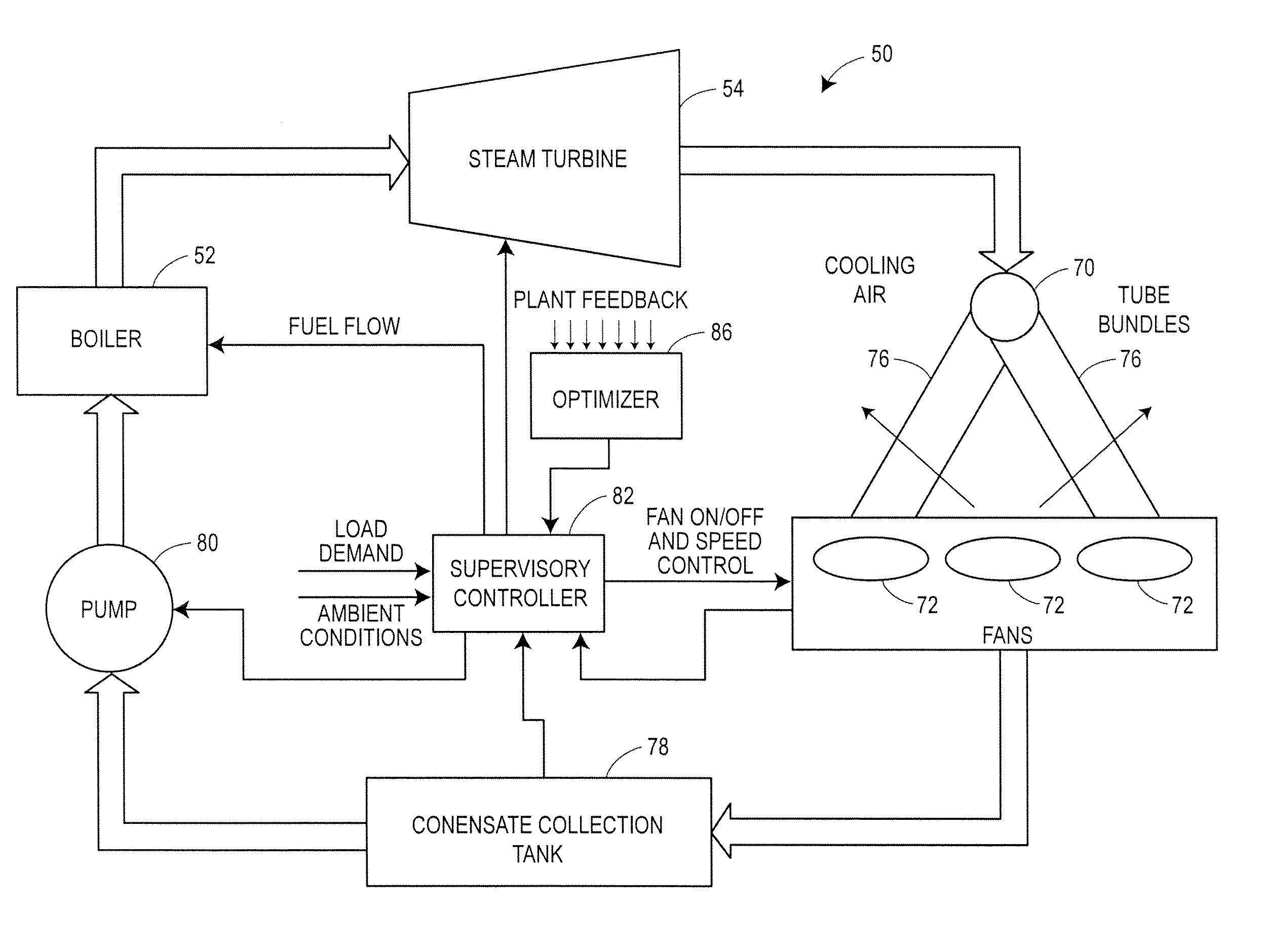
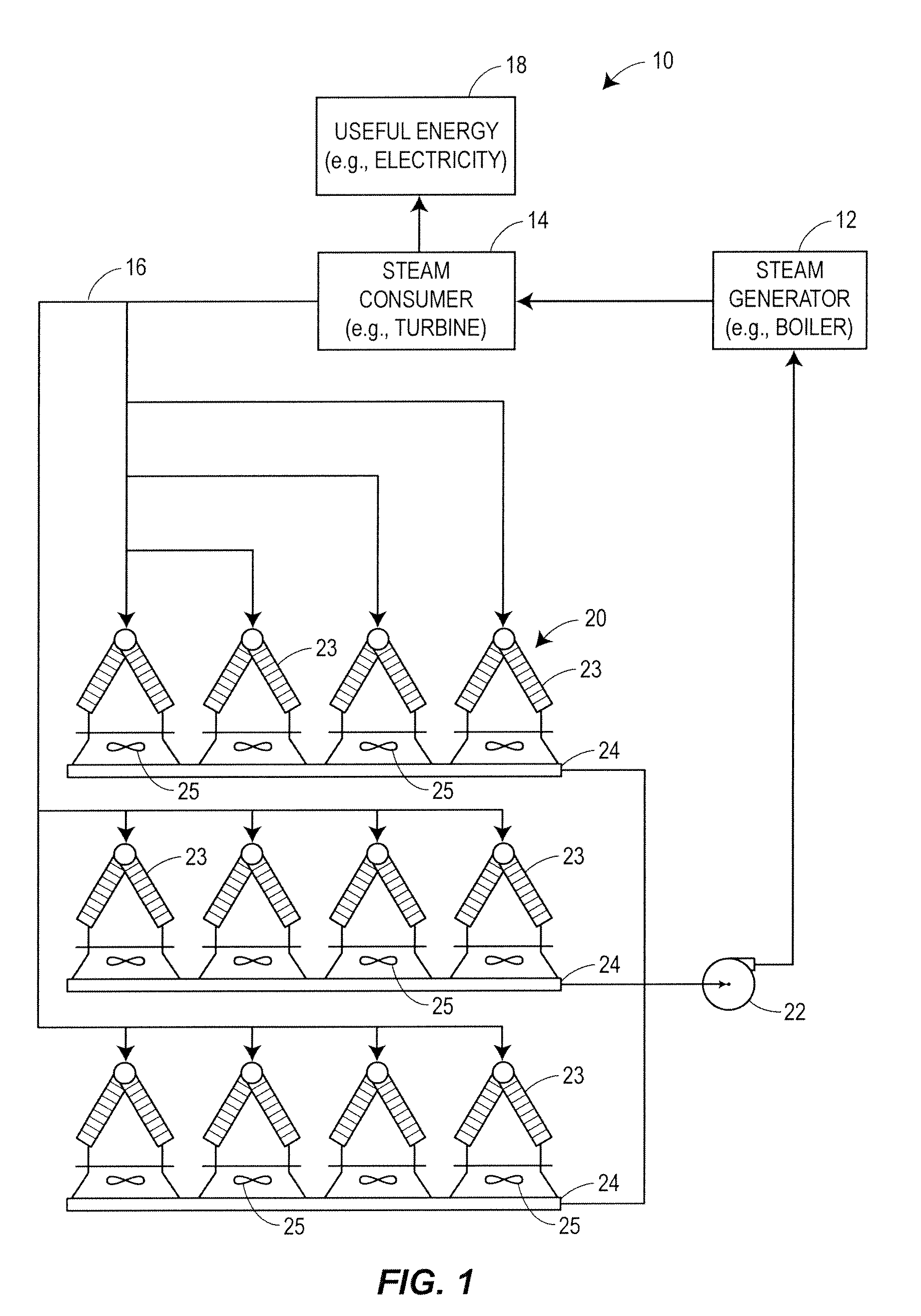
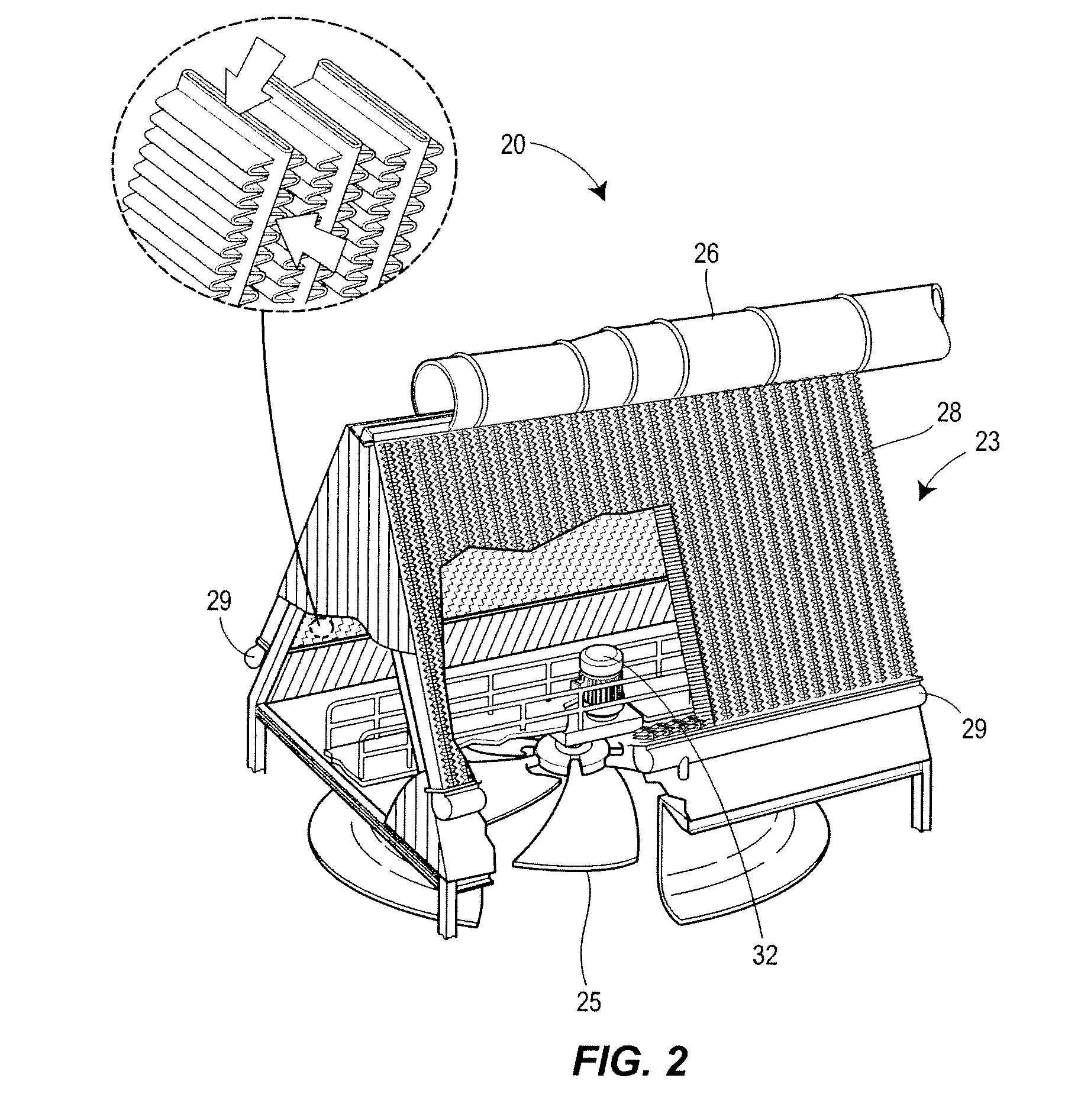
ActiveUS20110066298A1Cost can be reduced and minimizedLow costMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlOperating pointControl variable
An optimization and control system for a utility plant that uses fan based air cooled condensers controls the operation of the power generation system at the plant in conjunction with the operation of the air cooled condensers so as to run the power plant at an optimum operating point associated with minimizing or reducing the cost of each kilowatt-hour of energy or other useful energy produced by the plant. The optimization and control system includes an optimizer having a numerical solver that determines values for a set of control variables associated with an optimal operating point of the plant and an expert system that oversees and modifies the control variable settings prior to providing these settings to a plant controller. The numerical solver uses an objective function and one or more models of plant equipment to determine the operating point of the plant that minimizes the cost per unit of useful energy generated by the plant. As part of determining the optimal plant operating point, the numerical solver may determine the number of fans to run within the air cooled condensers of the plant and / or the speed of the fans to use in the air cooled condensers in conjunction with the amount of fuel to burn in the boiler, the desired temperature of the steam at the input of the steam turbine, etc., all required to produce a given amount of power (load demand) at the particular environmental conditions currently experienced at the plant. The expert system may modify these outputs by determining which fans to actually use at any particular time based on, for example, the availability of or the operational status of the fans, the wear of the fans and fan motors, etc.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
Current regulator for modulating brightness levels of solid state lighting
ActiveUS7902769B2Low component requirementsElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesImpedance matchingRoot mean square
An exemplary embodiment provides a current regulator for controlling variable brightness levels for solid state lighting. The current regulator is couplable to a phase-modulating switch, such as a dimmer switch, which is coupled to an AC line voltage. An exemplary current regulator includes a rectifier; a switching power supply providing a first current; an impedance matching circuit; and a controller. The impedance matching circuit is adapted to provide a second current through the phase-modulating switch when a magnitude of the first current is below a first predetermined threshold, such as a holding current of a triac of the phase-modulating switch. The controller is adapted to determine a root-mean-square (RMS) voltage level provided by the phase-modulating switch from the AC line voltage and to determine a duty cycle for pulse-width current modulation by the switching power supply in response to the comparison of the RMS voltage level to a nominal voltage level.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
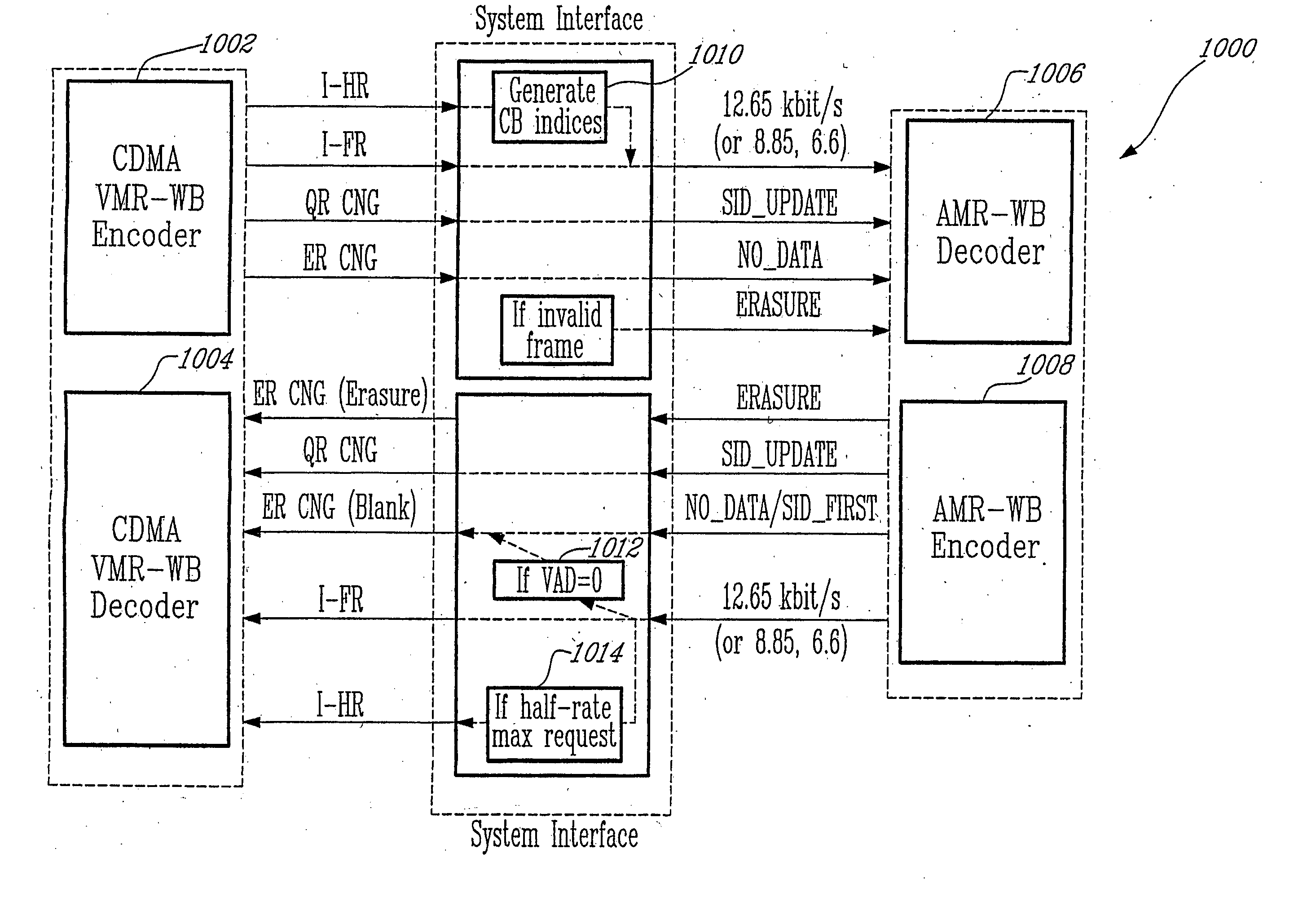
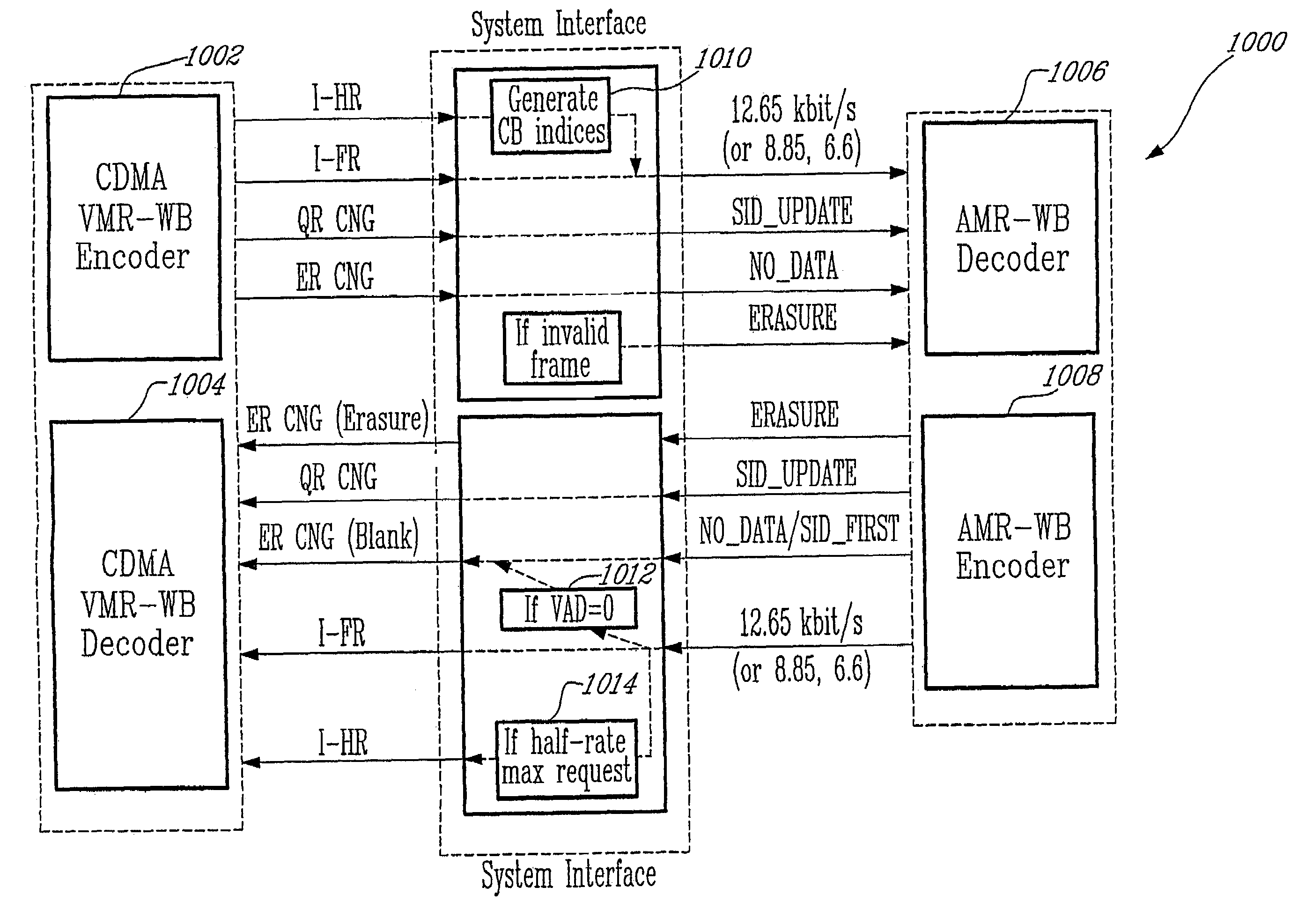
Method for interoperation between adaptive multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) and multi-mode variable bit-rate wideband (VMR-WB) codecs
ActiveUS20050267746A1Improve classificationImprove methodSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementBit allocationFull Rate
A source-controlled Variable bit-rate Multi-mode WideBand (VMR-WB) codec, having a mode of operation that is interoperable with the Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, the codec comprising: at least one Interoperable full-rate (I-FR) mode, having a first bit allocation structure based on one of a AMR-WB codec coding types; and at least one comfort noise generator (CNG) coding type for encoding inactive speech frame having a second bit allocation structure based on AMR-WB SID_UPDATE coding type. Methods for i) digitally encoding a sound using a source-controlled Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codec for interoperation with an adaptative multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, ii) translating a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codecsignal frame into an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame, iii) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame, and iv) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Bicycle rear wheel suspension system with controlled variable shock rate
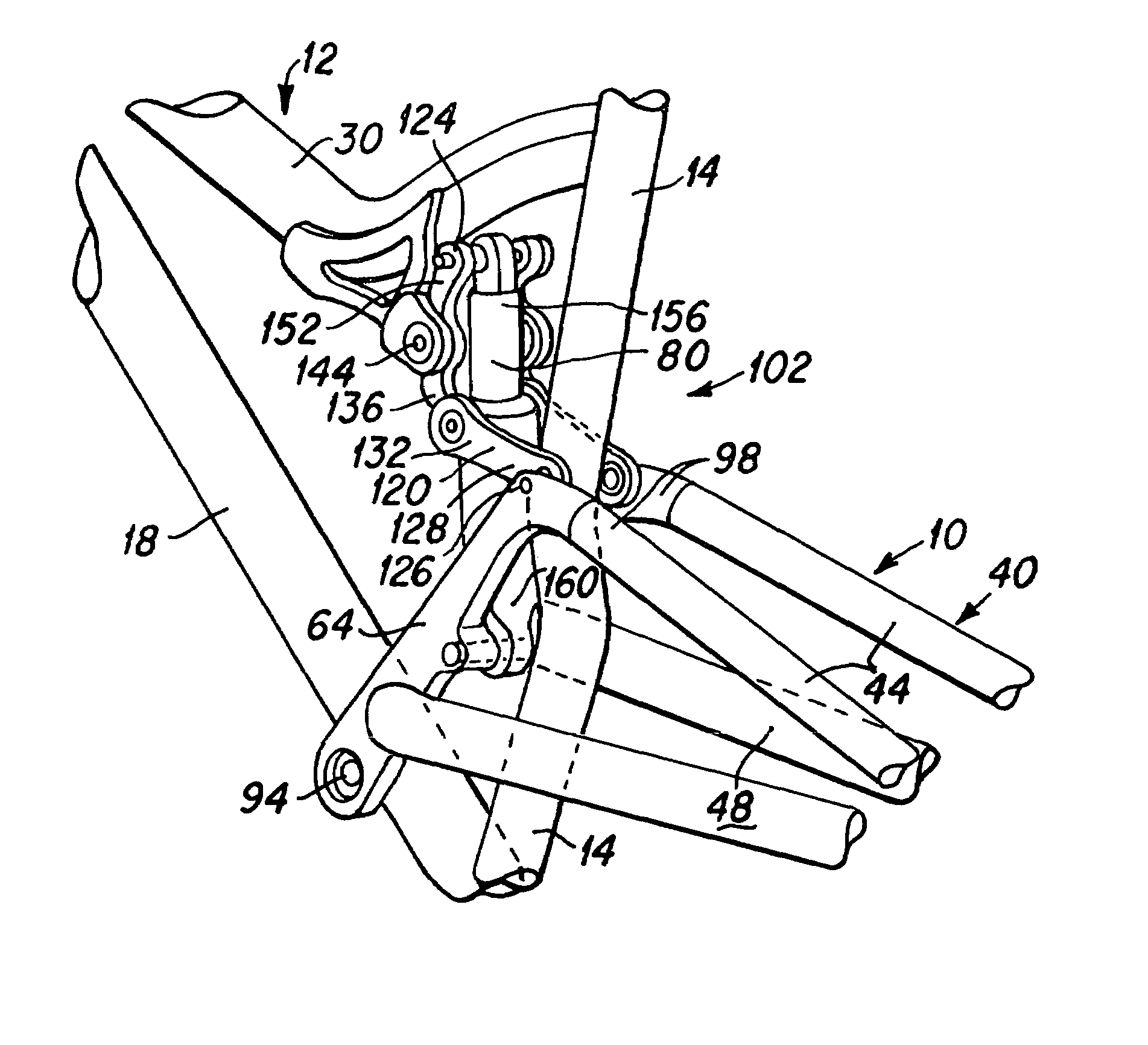
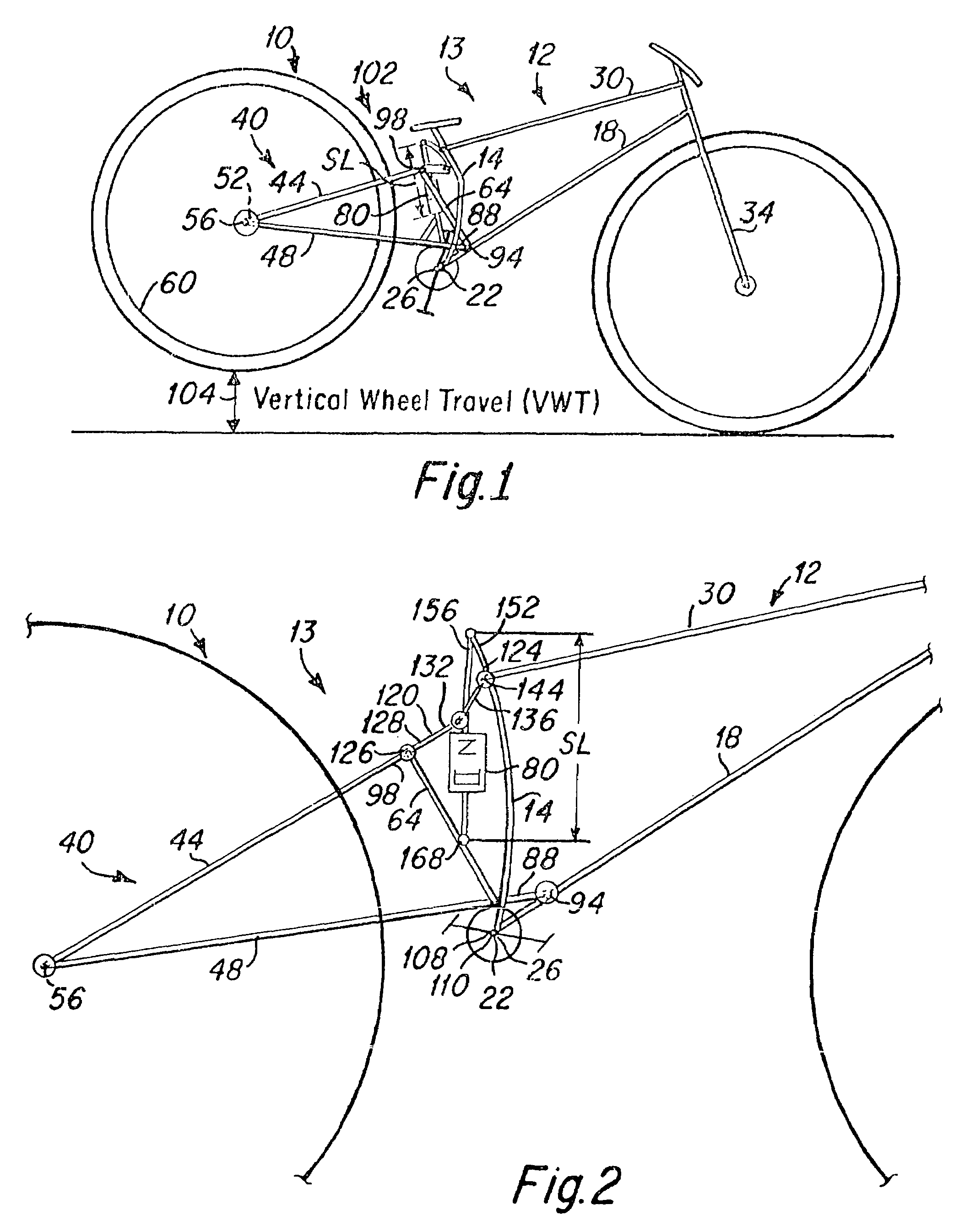
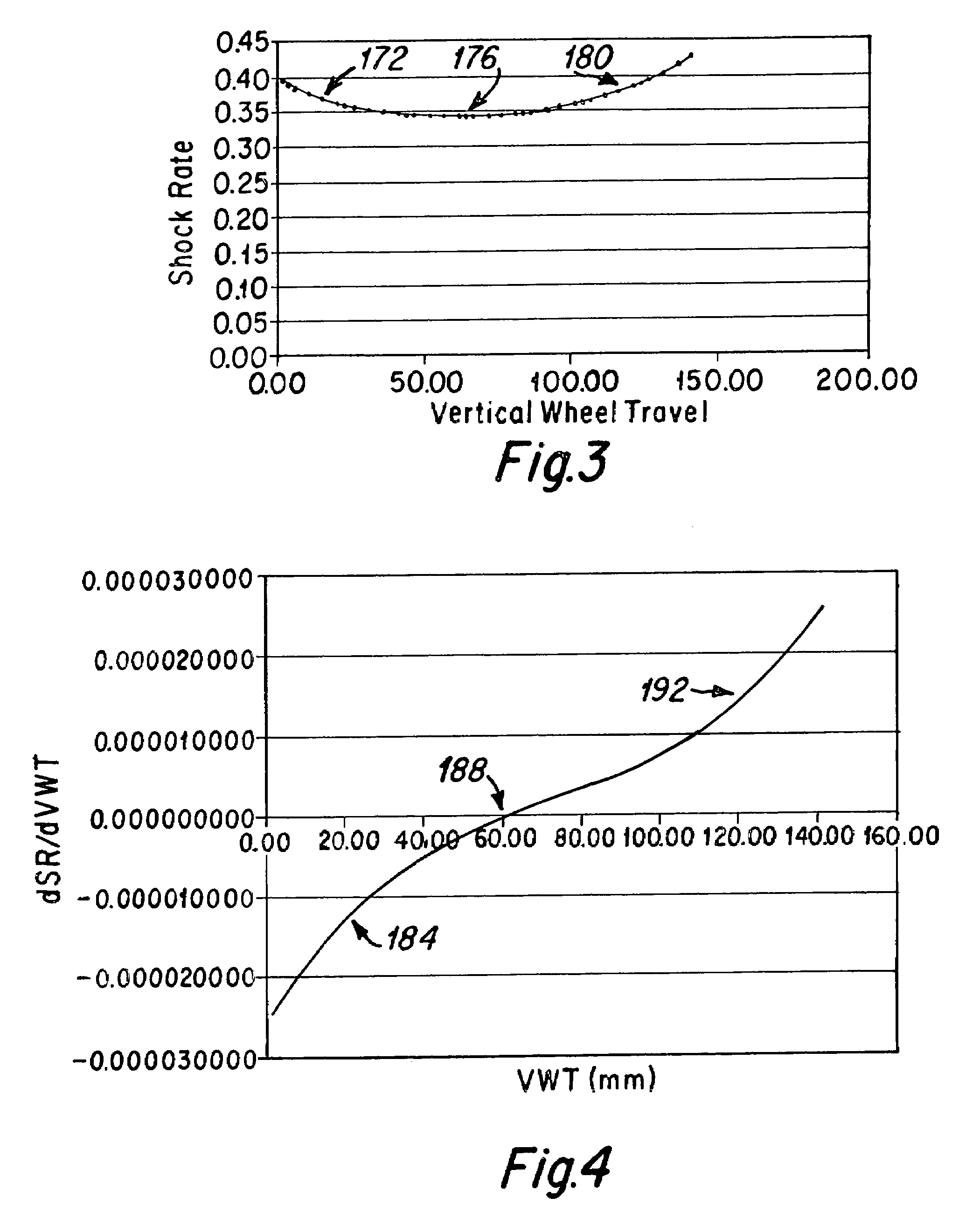
ActiveUS7581743B2Easy to controlGreat tractionPassenger cyclesChildren cyclesVehicle frameEngineering
The present invention is a bicycle including a bicycle frame and a rear wheel suspension system that is attached to the frame. The rear wheel suspension system includes a rear wheel swingarm and a shock absorber that is engaged to the swingarm to control the motion of a rear wheel of the bicycle. A change in the vertical wheel travel (ΔVWT) of the rear wheel is related to a change in the length of the shock absorber (ΔSL), providing a shock rate (SR) according to the relationship:SR=ΔSL / ΔVWT. The shock rate (SR) changes throughout the vertical wheel travel of the rear wheel, such that the change in the shock rate dSR / dVWT has a change in sign as the rear wheel travels through its vertical wheel travel. The shock rate may at first decrease in value and subsequently increase, or initially increase in value and subsequently decrease throughout the vertical wheel travel of the rear wheel. In various exemplary embodiments the swingarm may be attached to the frame at a single pivot point or through a linkage system.
Owner:SANTA CRUZ BICYCLES
Method for interoperation between adaptive multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) and multi-mode variable bit-rate wideband (VMR-WB) codecs
InactiveUS7203638B2Improve classificationImprove methodSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementUltra-widebandBit allocation
A source-controlled Variable bit-rate Multi-mode WideBand (VMR-WB) codec, having a mode of operation that is interoperable with the Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, the codec comprising: at least one Interoperable full-rate (I-FR) mode, having a first bit allocation structure based on one of a AMR-WB codec coding types; and at least one comfort noise generator (CNG) coding type for encoding inactive speech frame having a second bit allocation structure based on AMR-WB SID_UPDATE coding type. Methods for i) digitally encoding a sound using a source-controlled Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codec for interoperation with an adaptative multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, ii) translating a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codecsignal frame into an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame, iii) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame, and iv) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Navigation of remotely actuable medical device using control variable and length
A method of navigating a medical device includes determining the location of a medical device at a point in an operating region in a subject's body, the medical device being responsive to at least one control variable to assume a desired configuration includes storing information representative of the at least one control variable being applied to the medical device at the point, and more preferably storing information representative of the at least one control variable and the device length.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Adaptive impedance matching module
ActiveUS20080122553A1Maximize RF powerMaximize RF voltageMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasImpedance matchingSelf adaptive
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an RF input port, an RF output port connected to the RF input port via a multichip adaptive impedance matching module (AIMM), and the multichip AIMM comprising one or more voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements, wherein the multichip AIMM is adapted to maximize RF power transferred from the at least one RF input port to the at least one RF output port by varying the bias voltage or bias current to the voltage or current controlled variable reactive elements to maximize the RF voltage at the at least one RF output port.
Owner:NXP USA INC
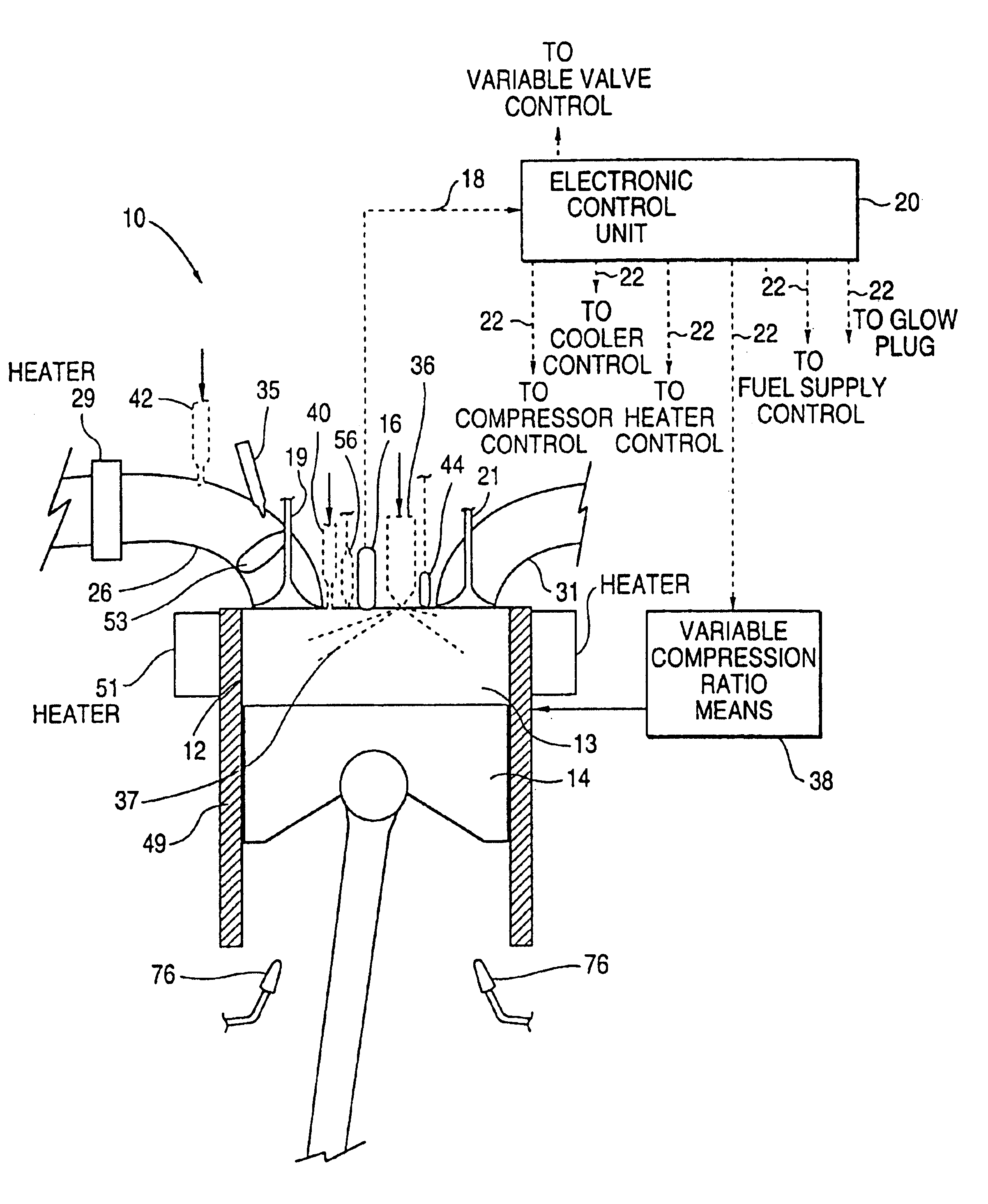
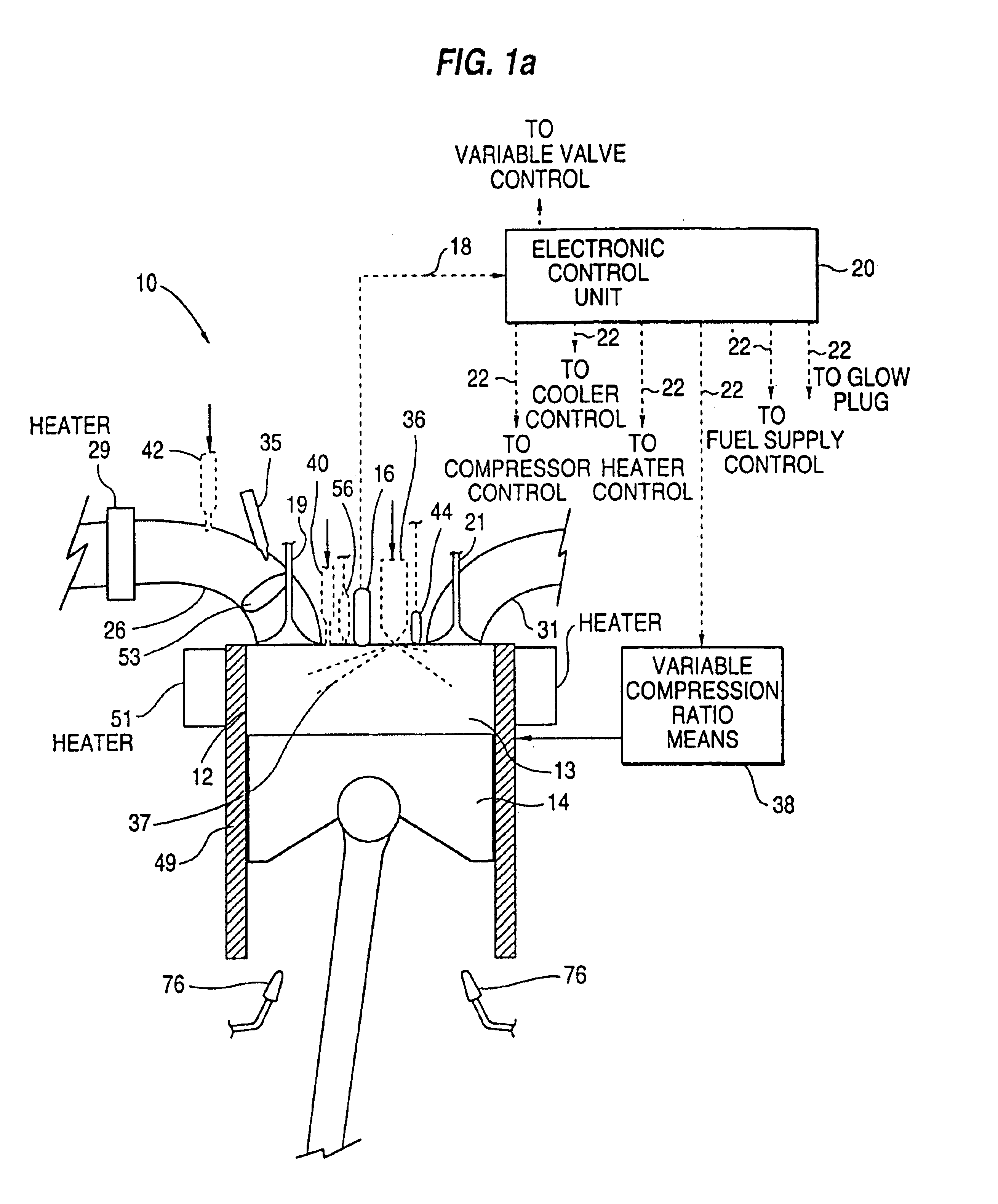
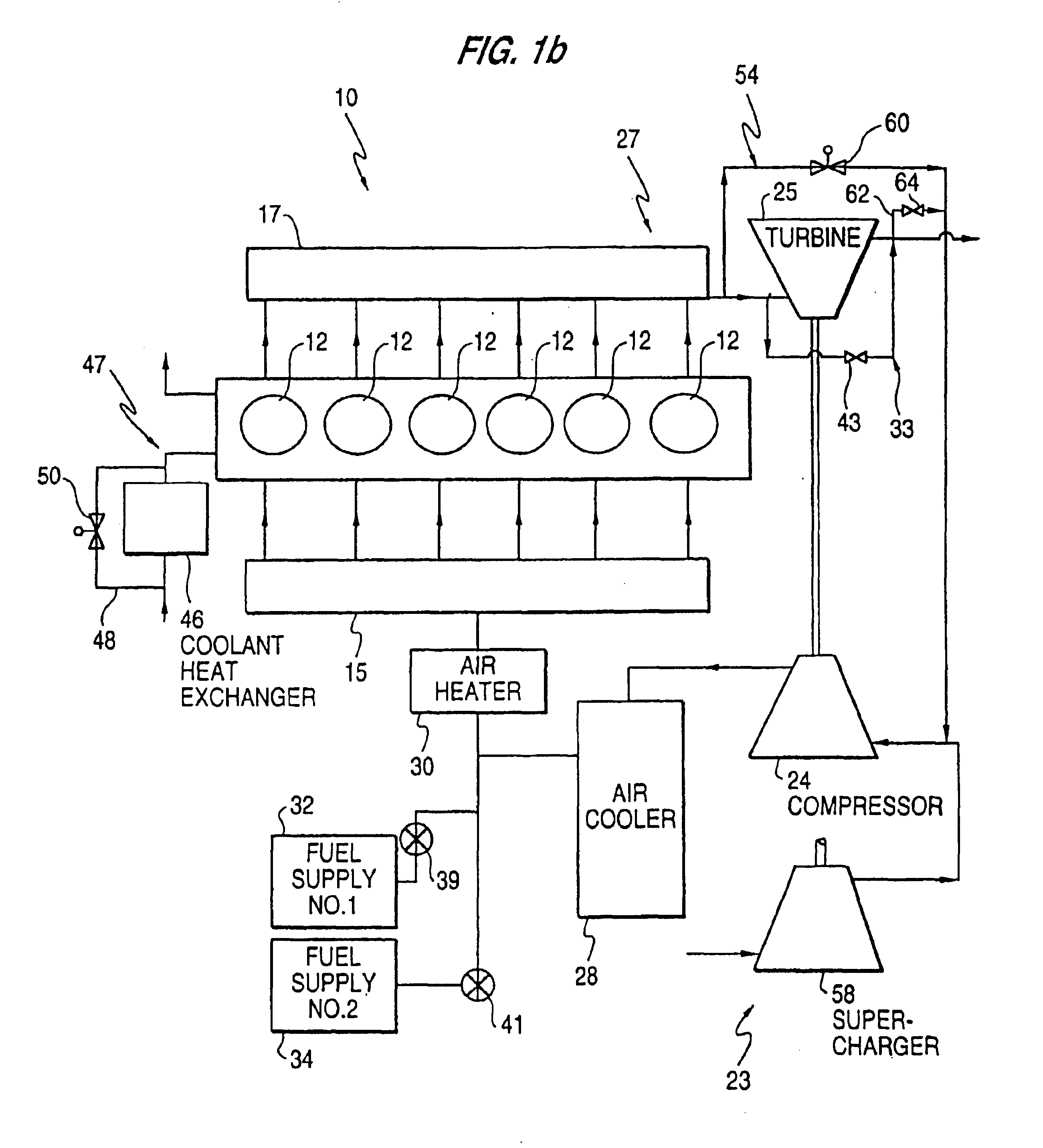
Premixed charge compression ignition engine with optimal combustion control
InactiveUS6915776B2Operate efficiently and effectivelyOvercome deficienciesElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelCombustion noiseControl signal
A premixed charge compression ignition engine, and a control system, is provided which effectively initiates combustion by compression ignition and maintains stable combustion while achieving extremely low nitrous oxide emissions, good overall efficiency and acceptable combustion noise and cylinder pressures. The present engine and control system effectively controls the combustion history, that is, the time at which combustion occurs, the rate of combustion, the duration of combustion and / or the completeness of combustion, by controlling the operation of certain control variables providing temperature control, pressure control, control of the mixture's autoignition properties and equivalence ratio control. The combustion control system provides active feedback control of the combustion event and includes a sensor, e.g. pressure sensor, for detecting an engine operating condition indicative of the combustion history, e.g. the start of combustion, and generating an associated engine operating condition signal. A processor receives the signal and generates control signals based on the engine operating condition signal for controlling various engine components to control the temperature, pressure, equivalence ratio and / or autoignition properties so as to variably control the combustion history of future combustion events to achieve stable, low emission combustion in each cylinder and combustion balancing between the cylinders.
Owner:CUMMINS INC
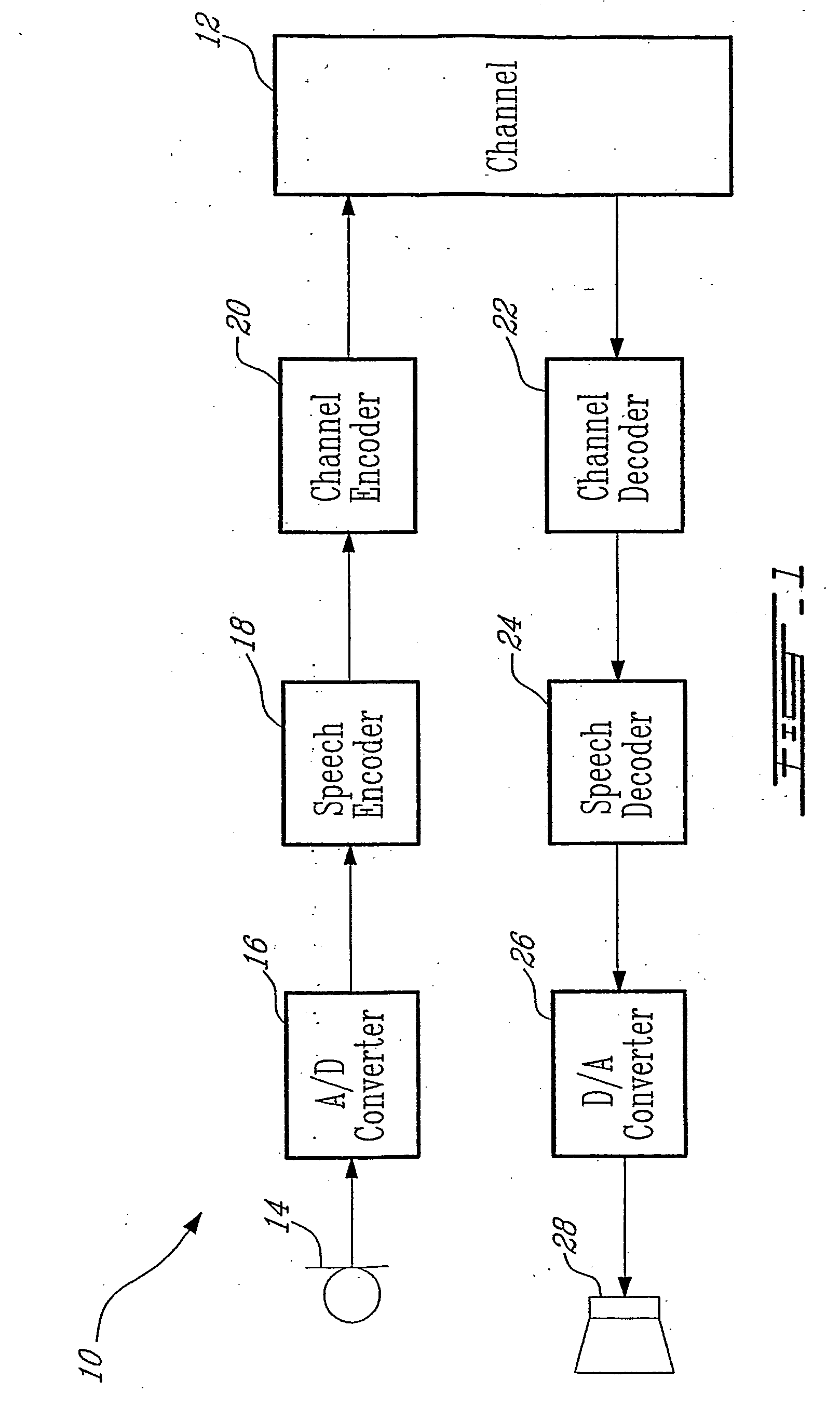
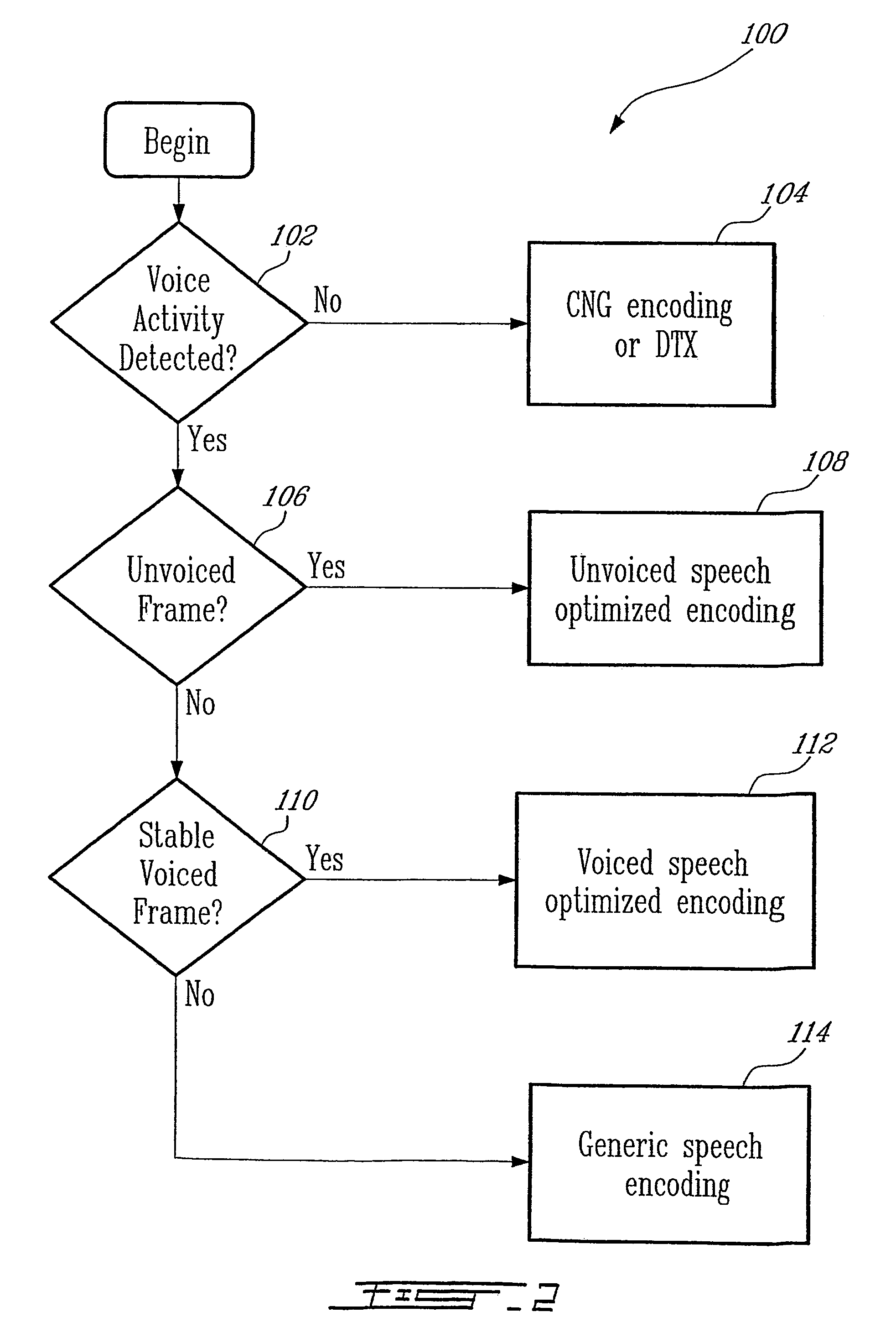
Methods and devices for source controlled variable bit-rate wideband speech coding
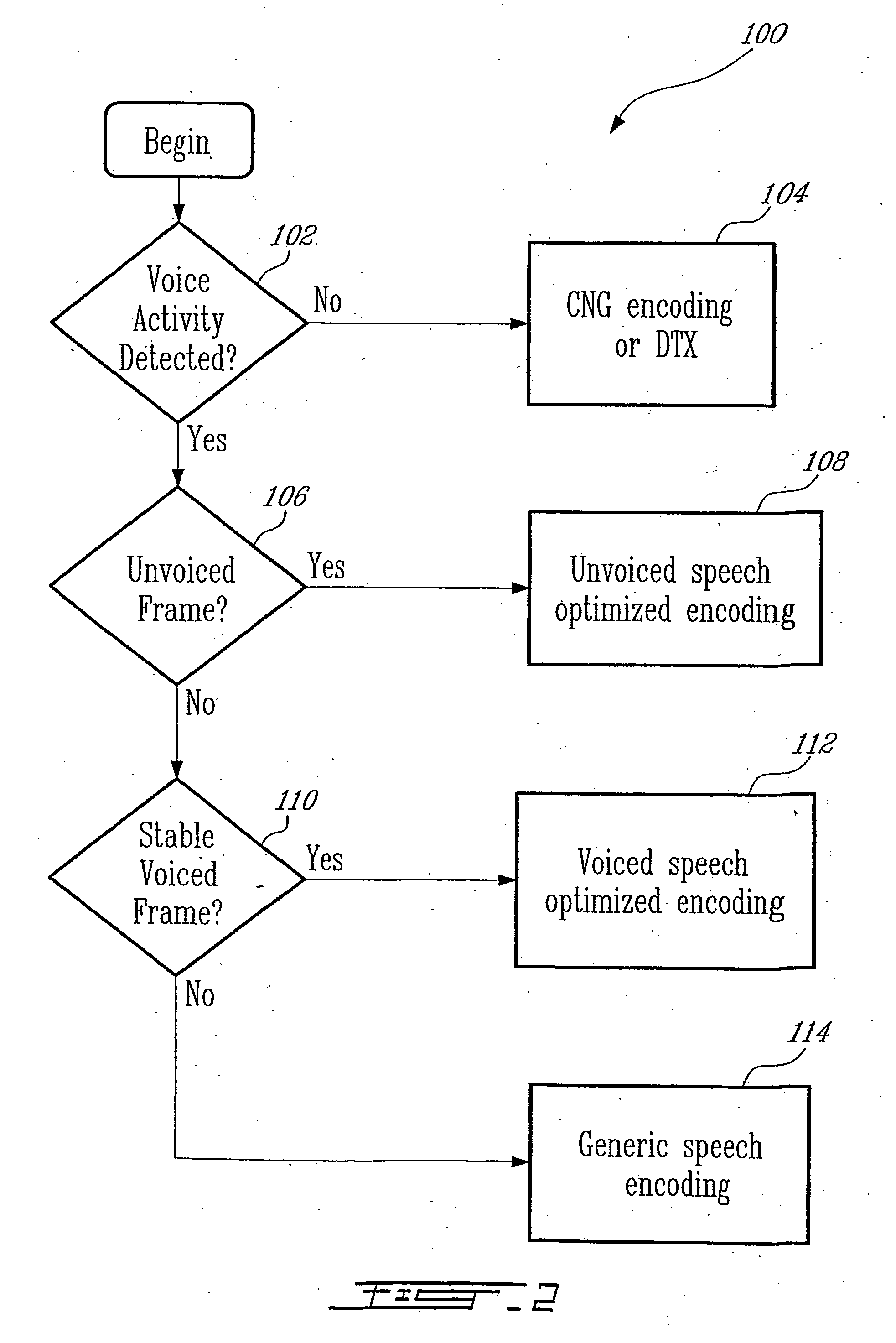
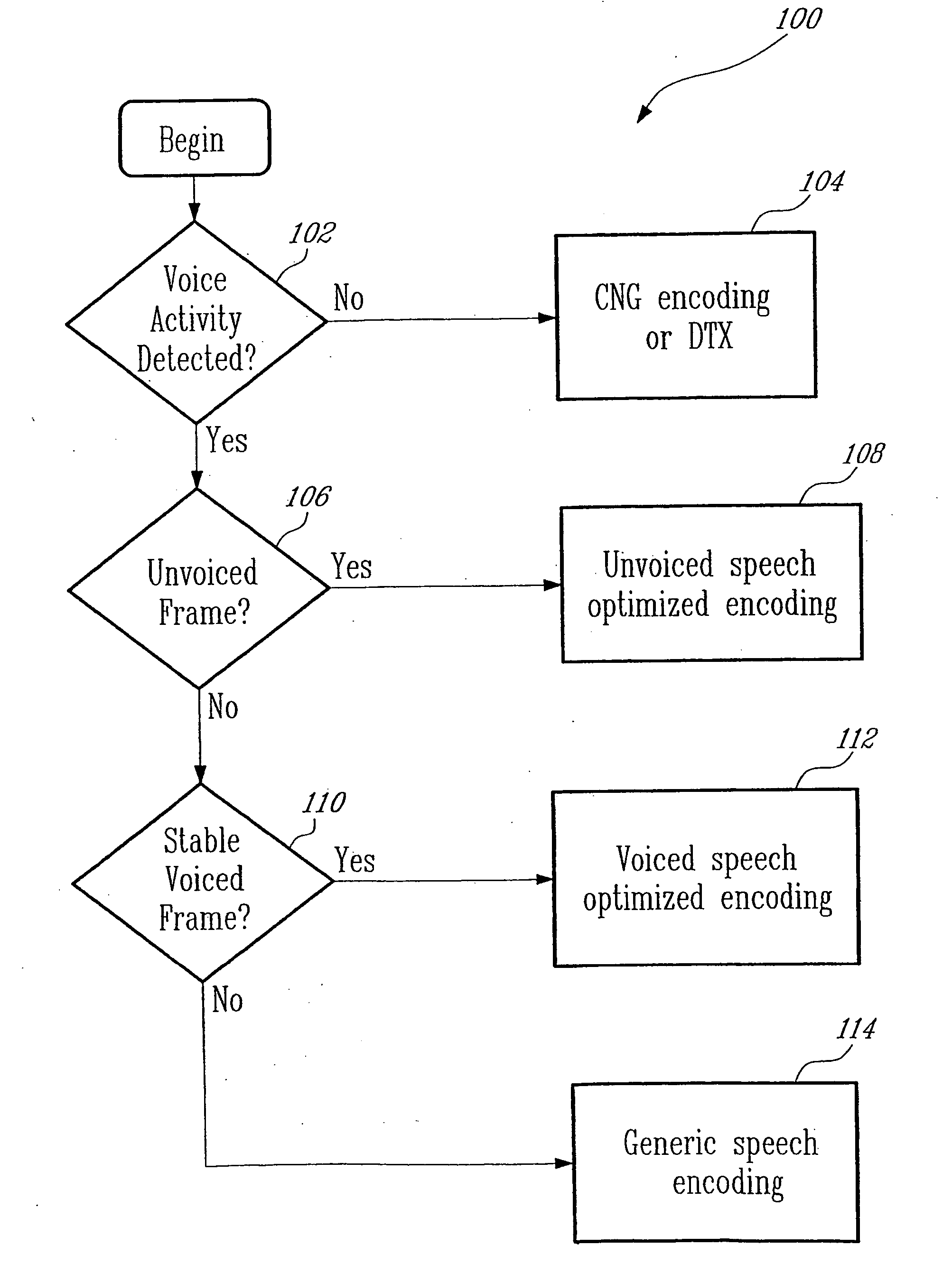
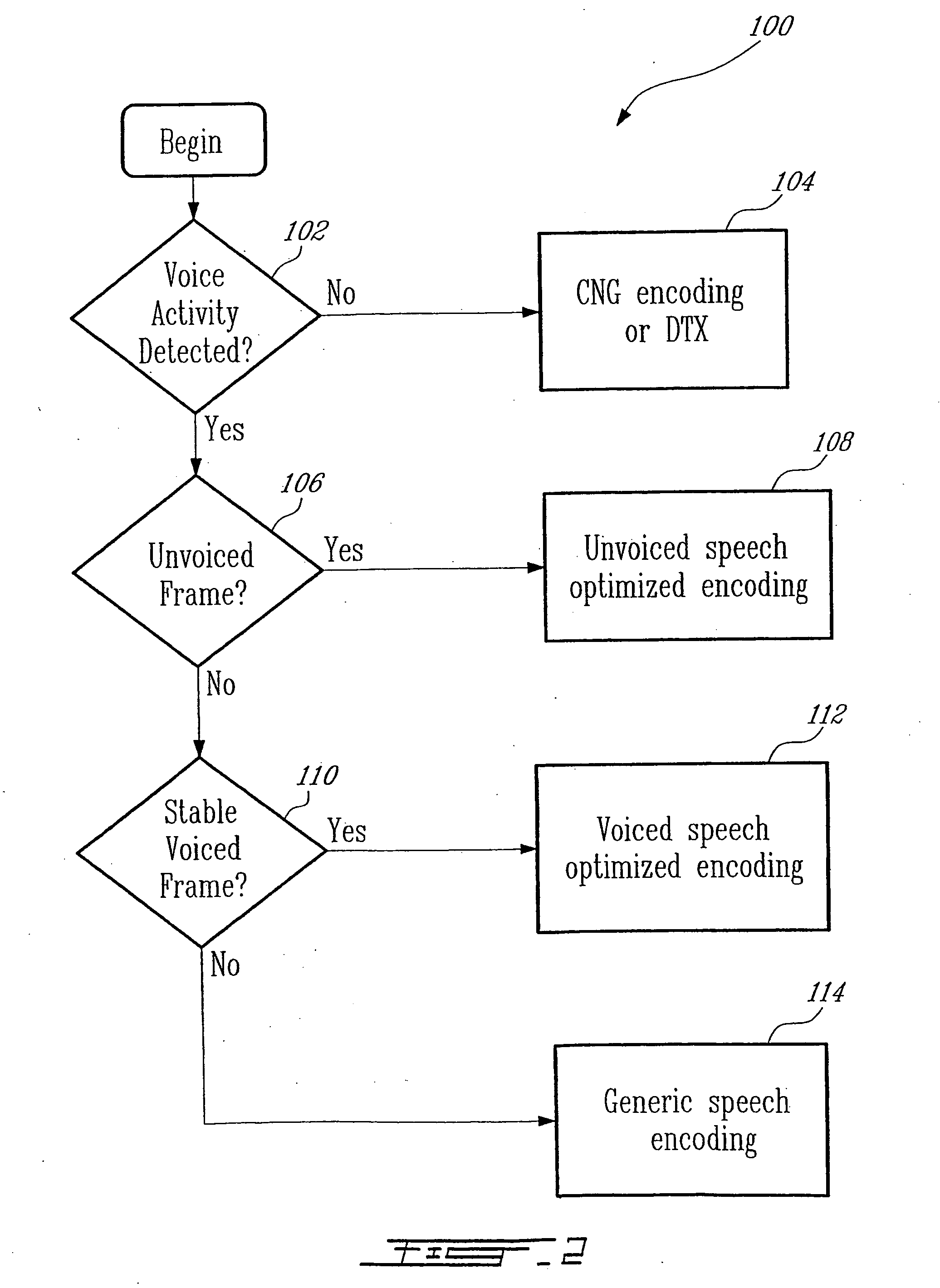
ActiveUS20050177364A1Improve methodImproved signal classificationSpeech analysisControl variableSubjective quality
Speech signal classification and encoding systems and methods are disclosed herein. The signal classification is done in three steps each of them discriminating a specific signal class. First, a voice activity detector (VAD) discriminates between active and inactive speech frames. If an inactive speech frame is detected (background noise signal) then the classification chain ends and the frame is encoded with comfort noise generation (CNG). If an active speech frame is detected, the frame is subjected to a second classifier dedicated to discriminate unvoiced frames. If the classifier classifies the frame as unvoiced speech signal, the classification chain ends, and the frame is encoded using a coding method optimized for unvoiced signals. Otherwise, the speech frame is passed through to the “stable voiced” classification module. If the frame is classified as stable voiced frame, then the frame is encoded using a coding method optimized for stable voiced signals. Otherwise, the frame is likely to contain a non-stationary speech segment such as a voiced onset or rapidly evolving voiced speech signal. In this case a general-purpose speech coder is used at a high bit rate for sustaining good subjective quality.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Model predictive control system and method for reduction of steady state error
ActiveUS8032235B2Reducing steady state errorReduce errorsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingPermeability/surface area analysisHorizonControl system
A technique is disclosed for reducing an error in a controlled variable via model predictive control. A predicted error in the controlled variable is determined for a forward-looking control horizon based upon measured or computed variables. The integral of the predicted error is computed. If the error or the integral exceed a tolerance for a determined time period, the model predictive control algorithm is modified to drive the error or the integral to within a tolerance. The modifications to the control algorithm may include changes to coefficients for terms based upon the error and / or the integral of the error.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Navigation of remotely actuable medical device using control variable and length
A method of navigating a medical device includes determining the location of a medical device at a point in an operating region in a subject's body, the medical device being responsive to at least one control variable to assume a desired configuration includes storing information representative of the at least one control variable being applied to the medical device at the point, and more preferably storing information representative of the at least one control variable and the device length.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
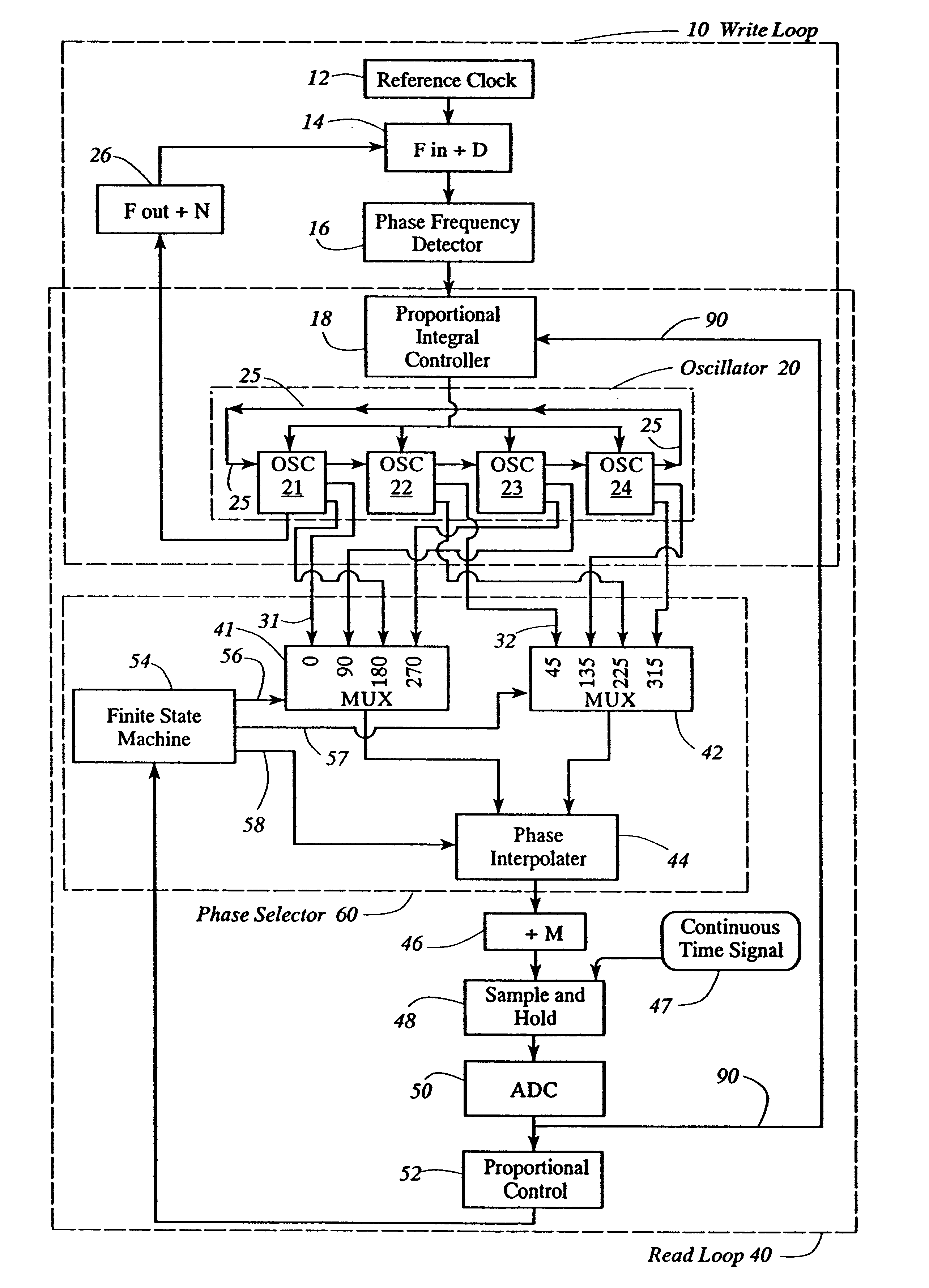
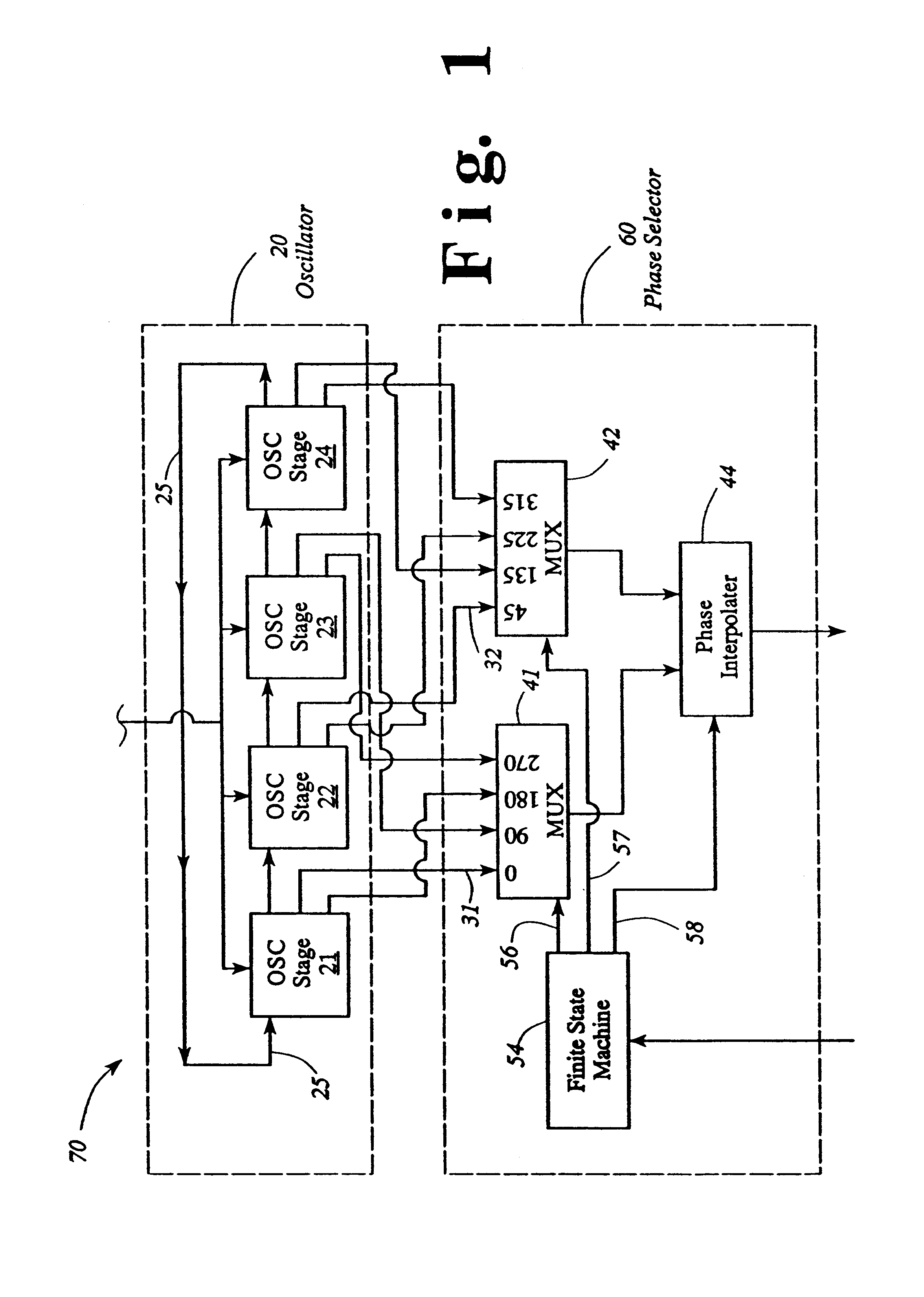
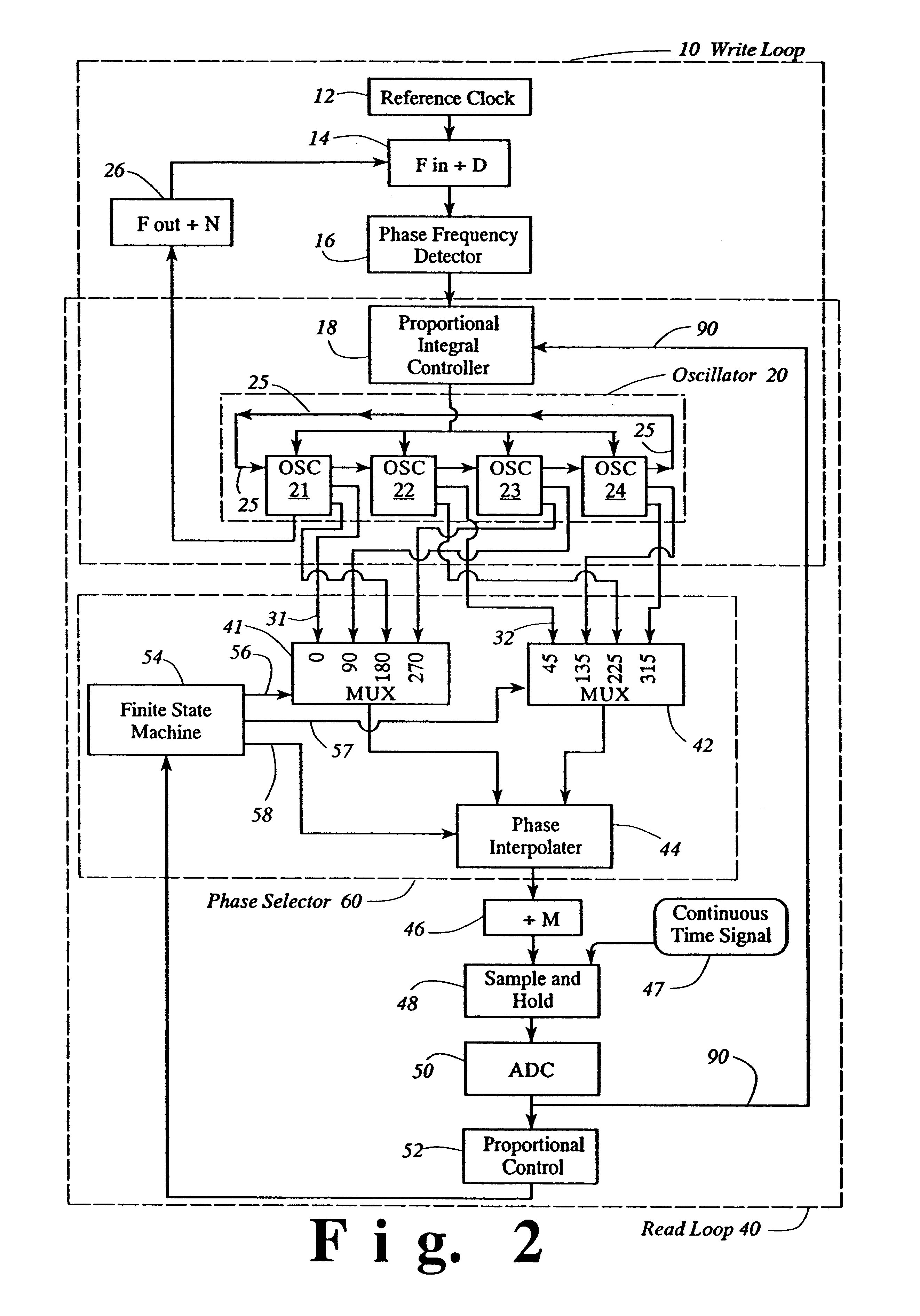
Oscillator with digitally variable phase for a phase-locked loop
InactiveUS6525615B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsPulse automatic controlMultiplexerImproved method
The present invention provides an improved method and apparatus for independently controlling phase and frequency using an oscillator having a plurality of stages in combination with a phase selector within a digitally controlled phase-locked loop, preferably, a read phase locked loop. The present invention provides a digitally controlled variable phase of the read timing loop in read channel integrated circuits associated with data storage devices. The phase selector has a digitally controlled fine interpolator with 12 states for further fine interpolation between at least two multiplexer phase outputs to provide a single phase output selected from a range comprising at least 2pi in selectable variable phase increments of 2pi / 96 radian. The combined oscillator with the phase selector within a phase locked loop controls phase by exact fractional increments of equally space phases of the operating frequency within the phase locked loop, therein controlling phase at all operating frequencies.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Electrically controlled variable thickness plate
InactiveUS6950227B2Easy and economical to manufactureNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectricityVariable thickness
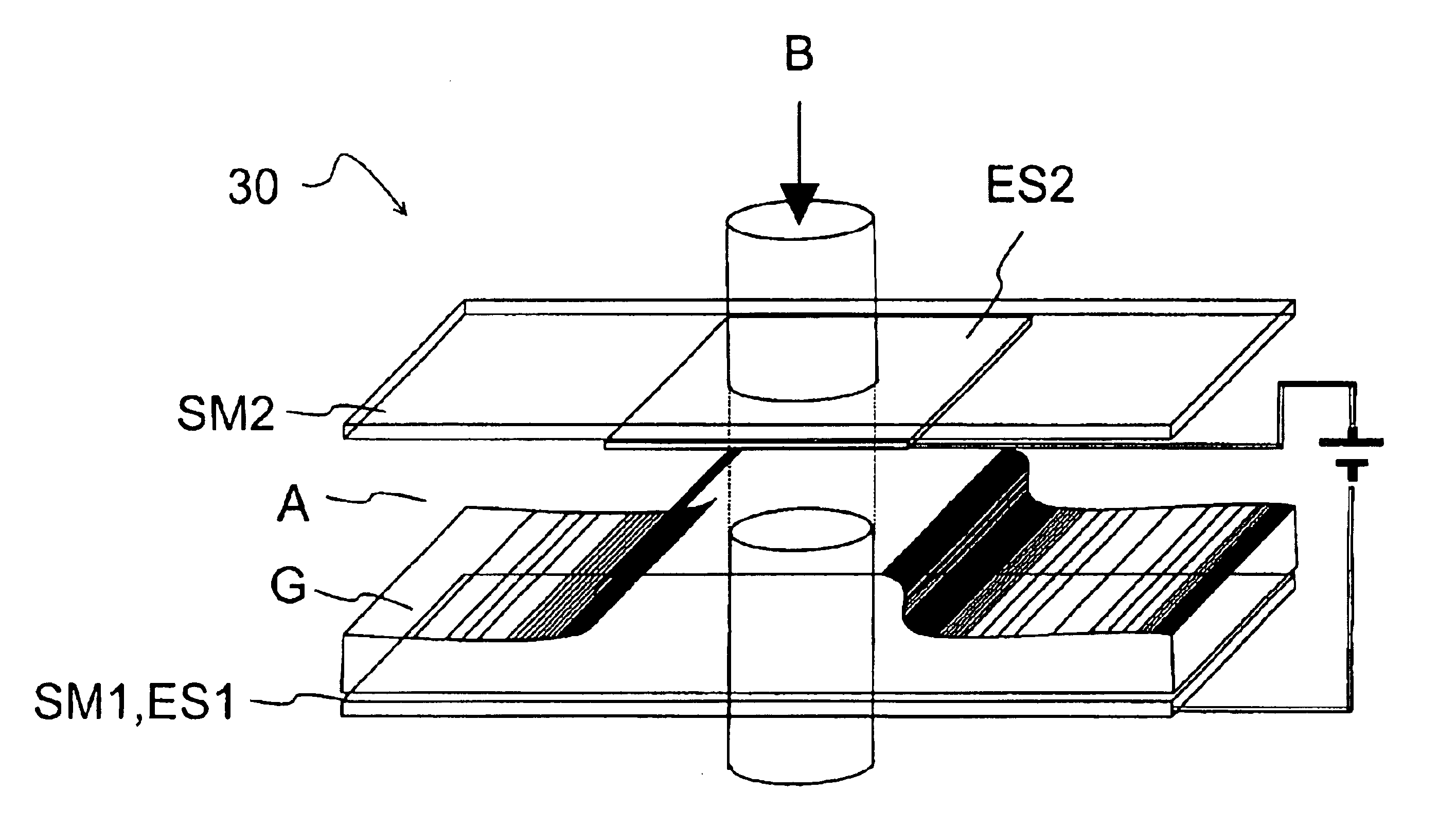
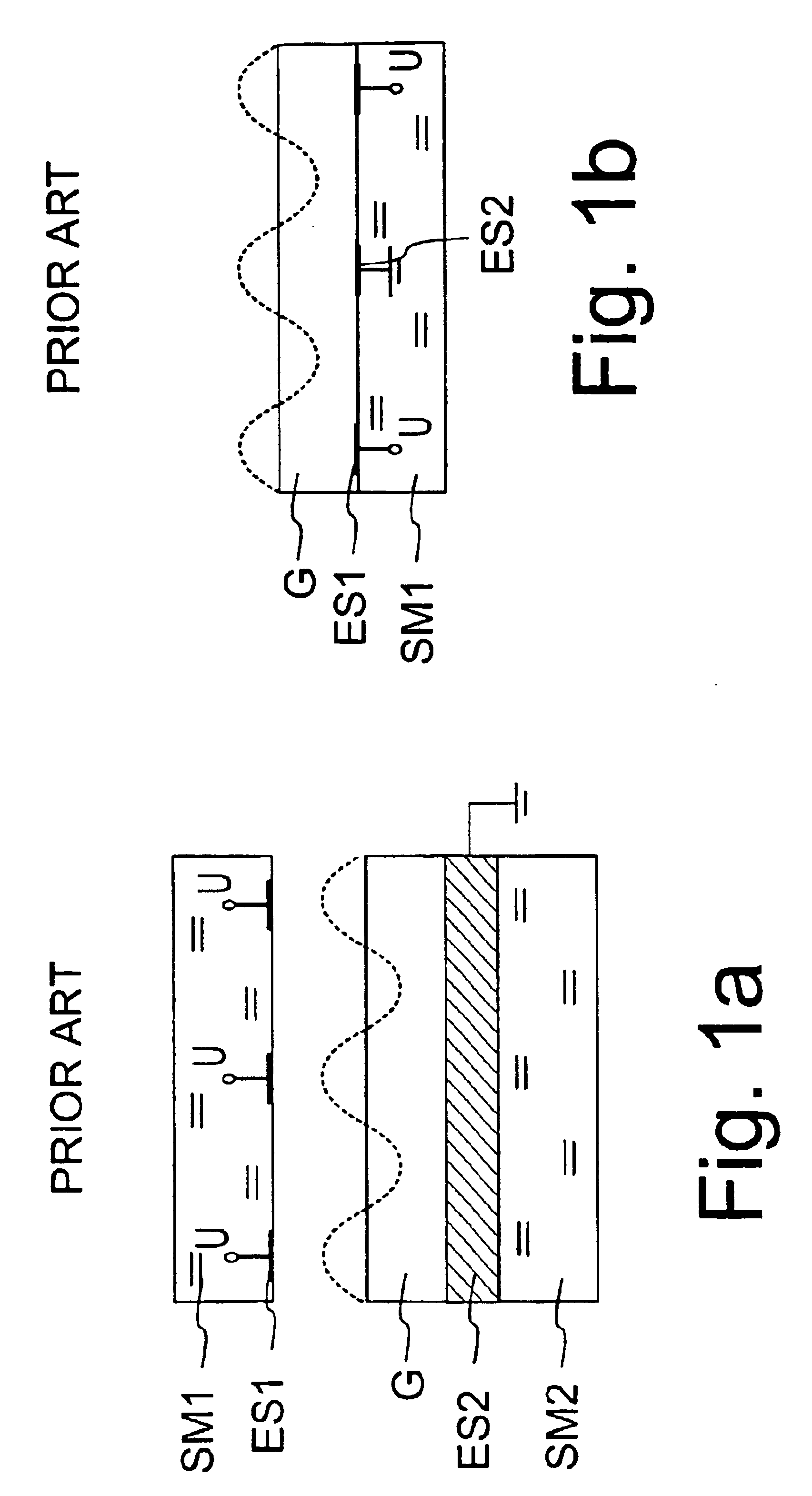
The invention refers to electrically controlled optical switching devices which are based on the use of a layer of dielectric and transparent viscoelastic material (G) located between transparent first (ES1) and transparent second (ES2) electrode structures. According to the invention, the first (ES1) and second (ES2) electrode structures are arranged in a manner that the thickness of the layer of the viscoelastic material (G) can be electrically altered maintaining the thickness of said layer substantially equal. This makes it possible to realize a generic, electrically controlled variable thickness plate (30). The generic variable thickness plate (30) can be further used to create optical switching devices based on a Fabry Perot Interferometer or a Mach-Zehnder Interferometer.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
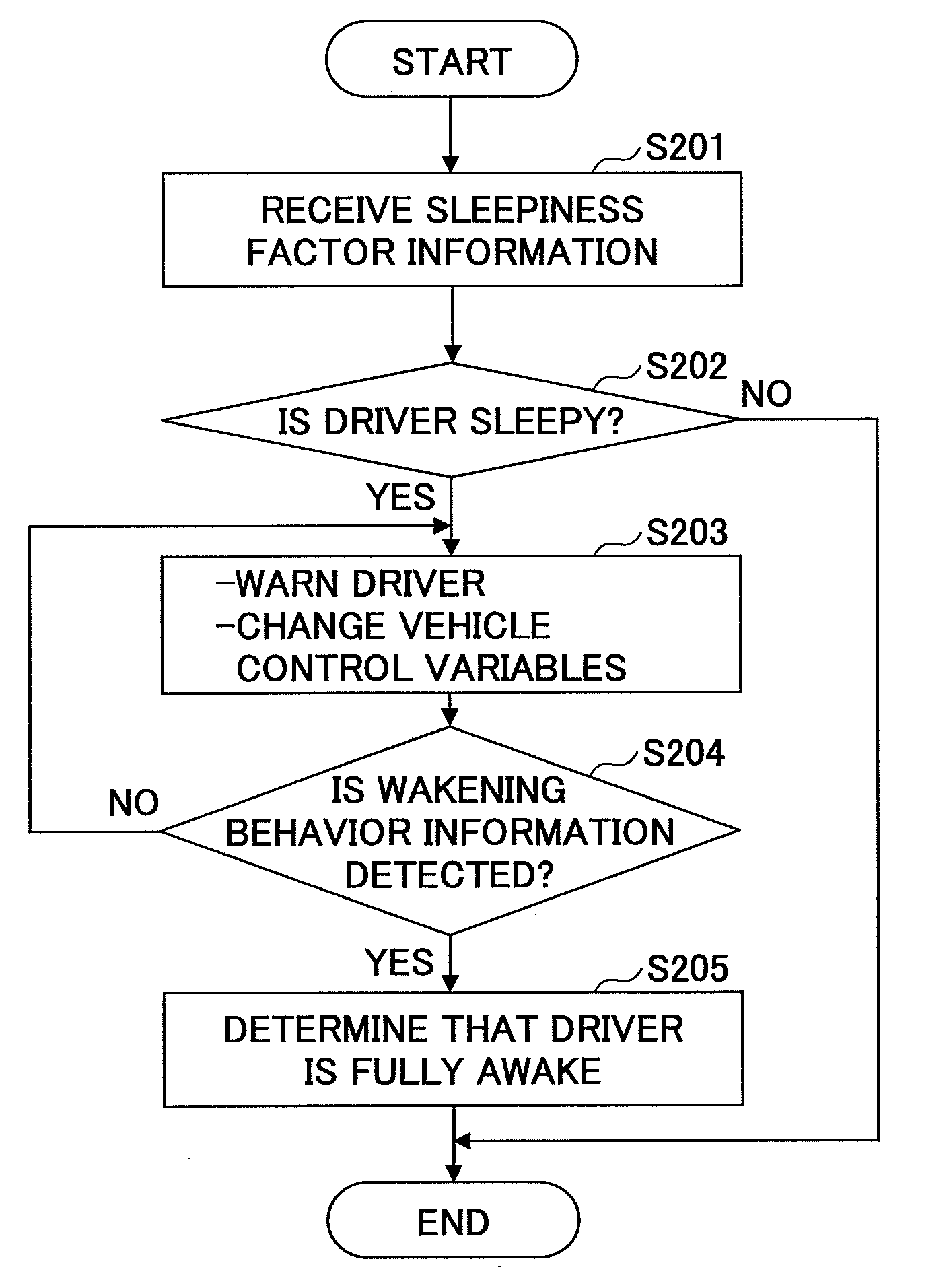
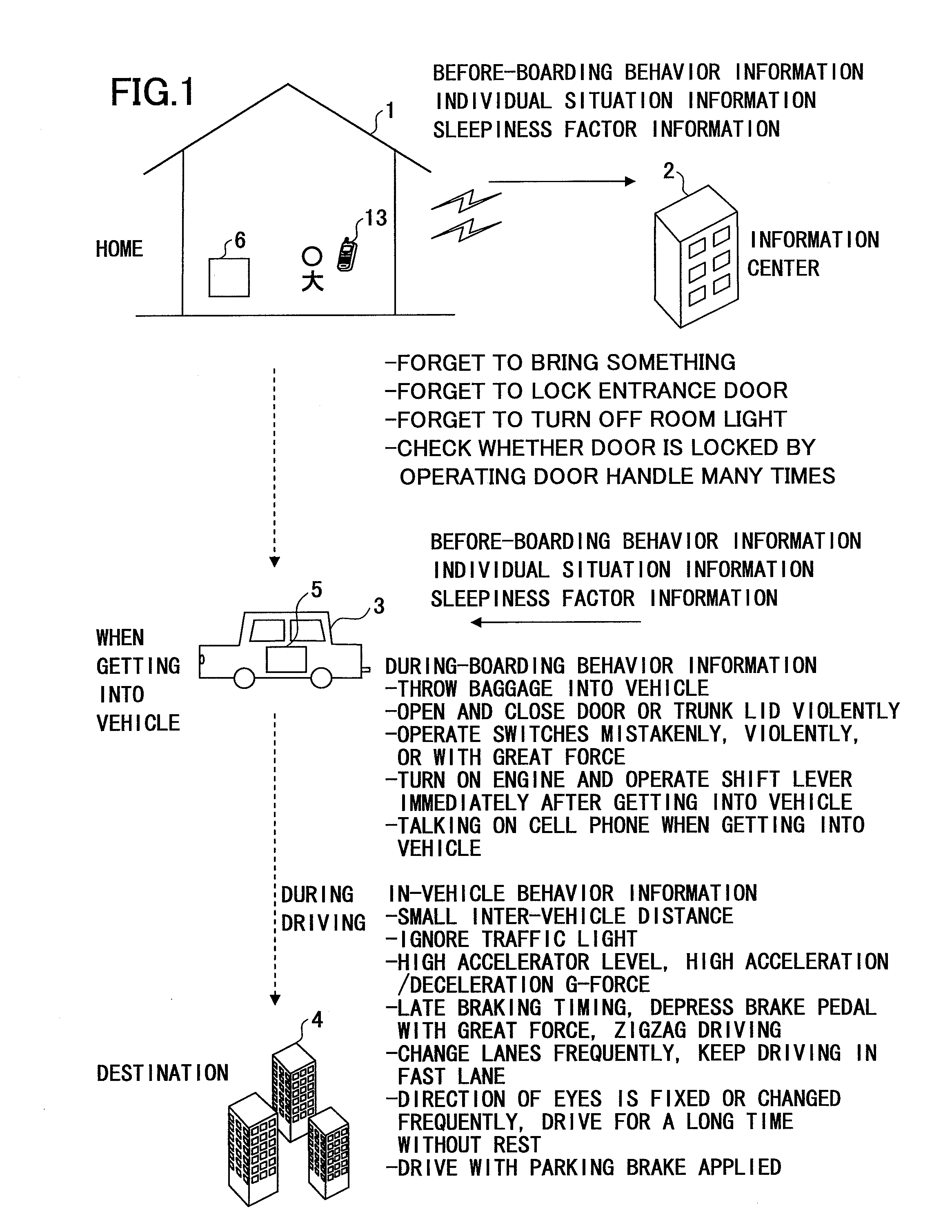
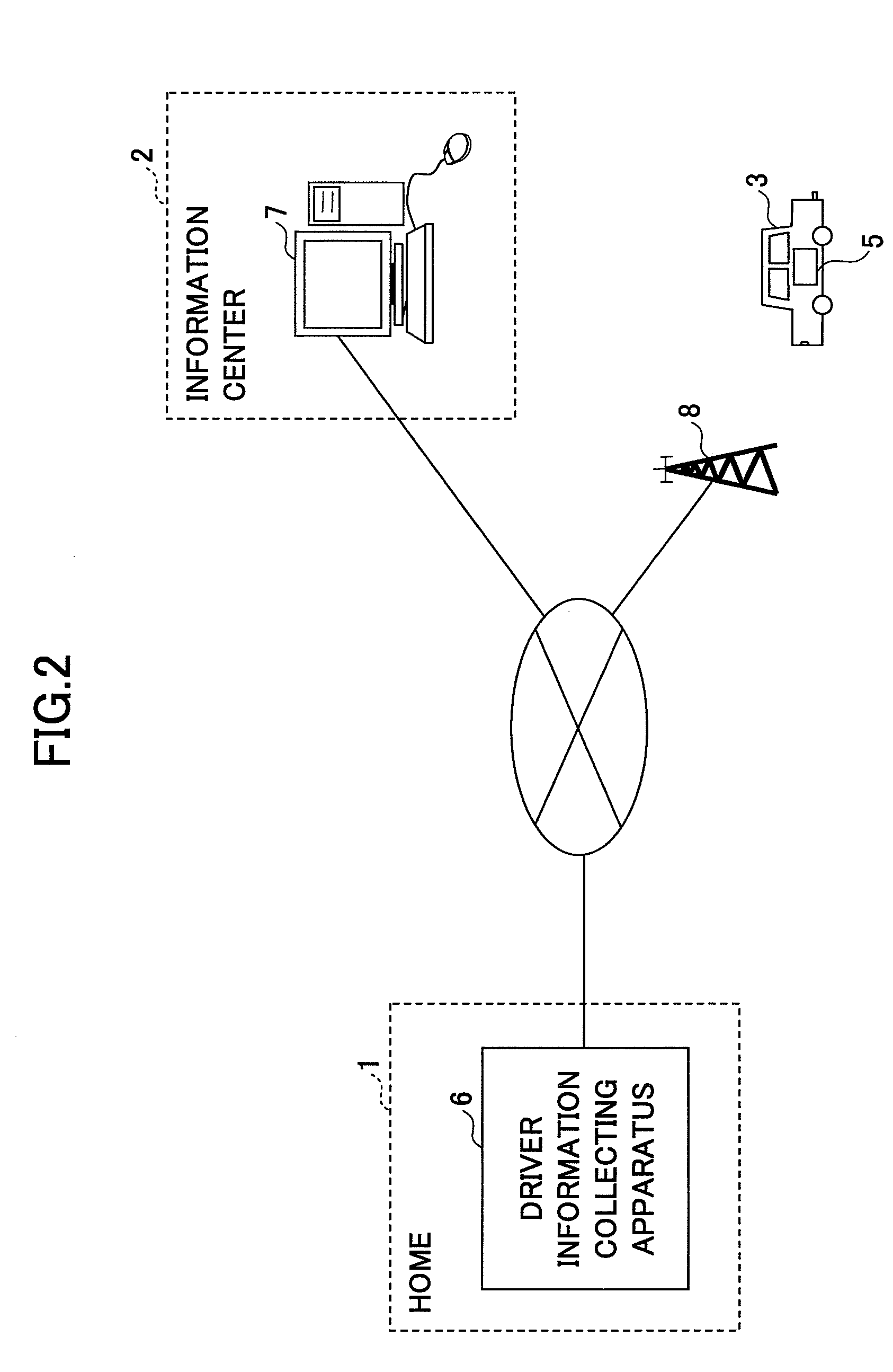
Driver condition estimation apparatus, server, driver information collecting apparatus, and driver condition estimation system
InactiveUS20100030434A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDriver/operatorIn vehicle
A driver condition estimation apparatus 5 estimates condition of a driver. The driver condition estimation apparatus 5 includes a driver condition estimating unit 50a for estimating the condition of the driver before the driver starts driving; and a control variable changing unit 50b for changing control variables of in-vehicle devices based on the condition of the driver estimated by the driver condition estimating unit 50a.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com