Patents
Literature
1171 results about "Burn-in" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
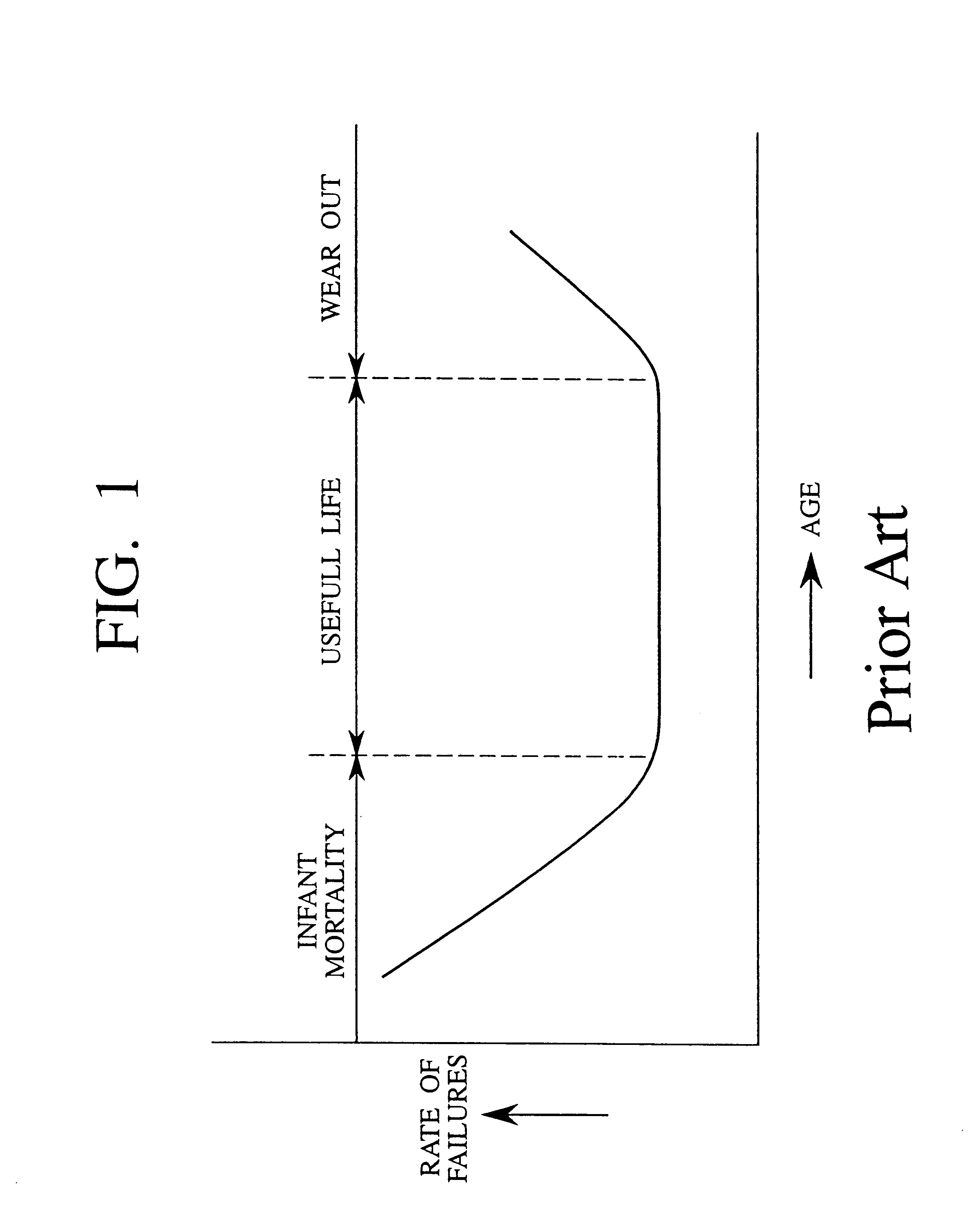
Burn-in is the process by which components of a system are exercised prior to being placed in service (and often, prior to the system being completely assembled from those components). This testing process will force certain failures to occur under supervised conditions so an understanding of load capacity of the product can be established.
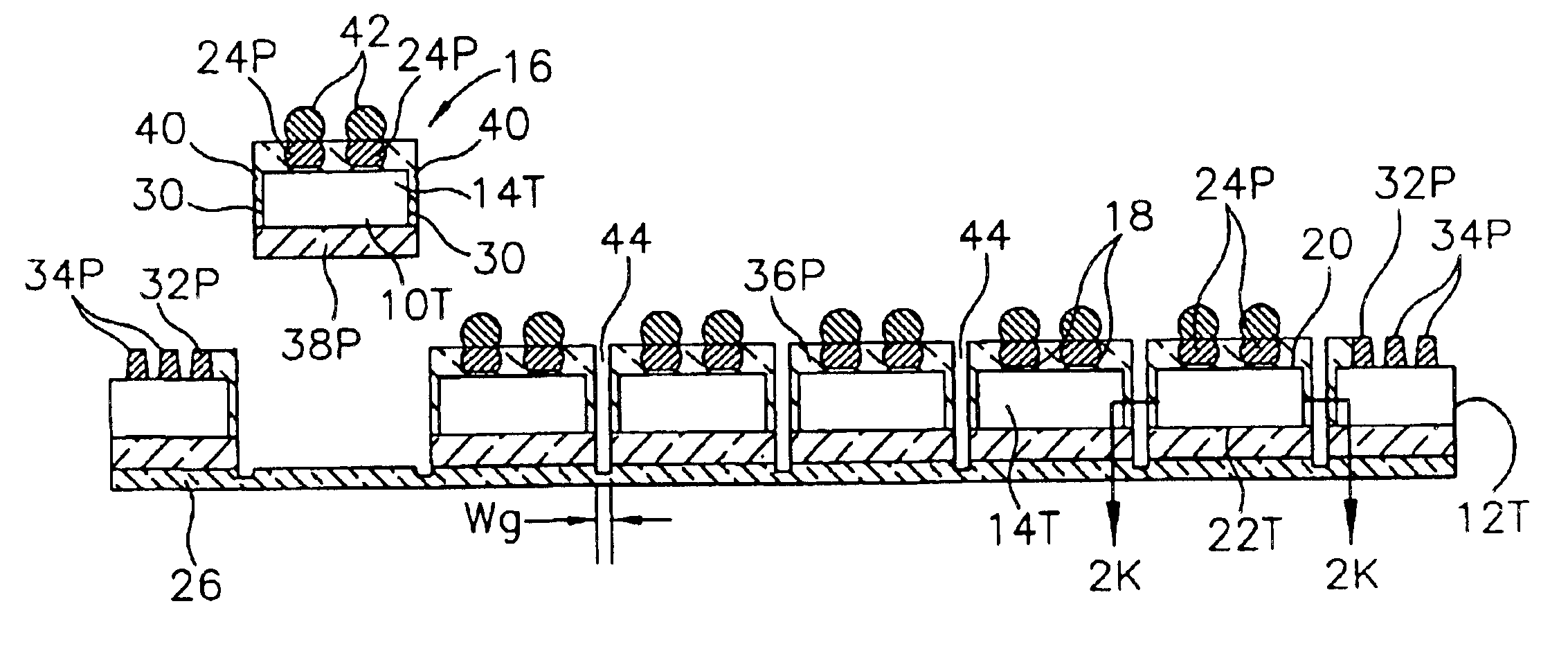
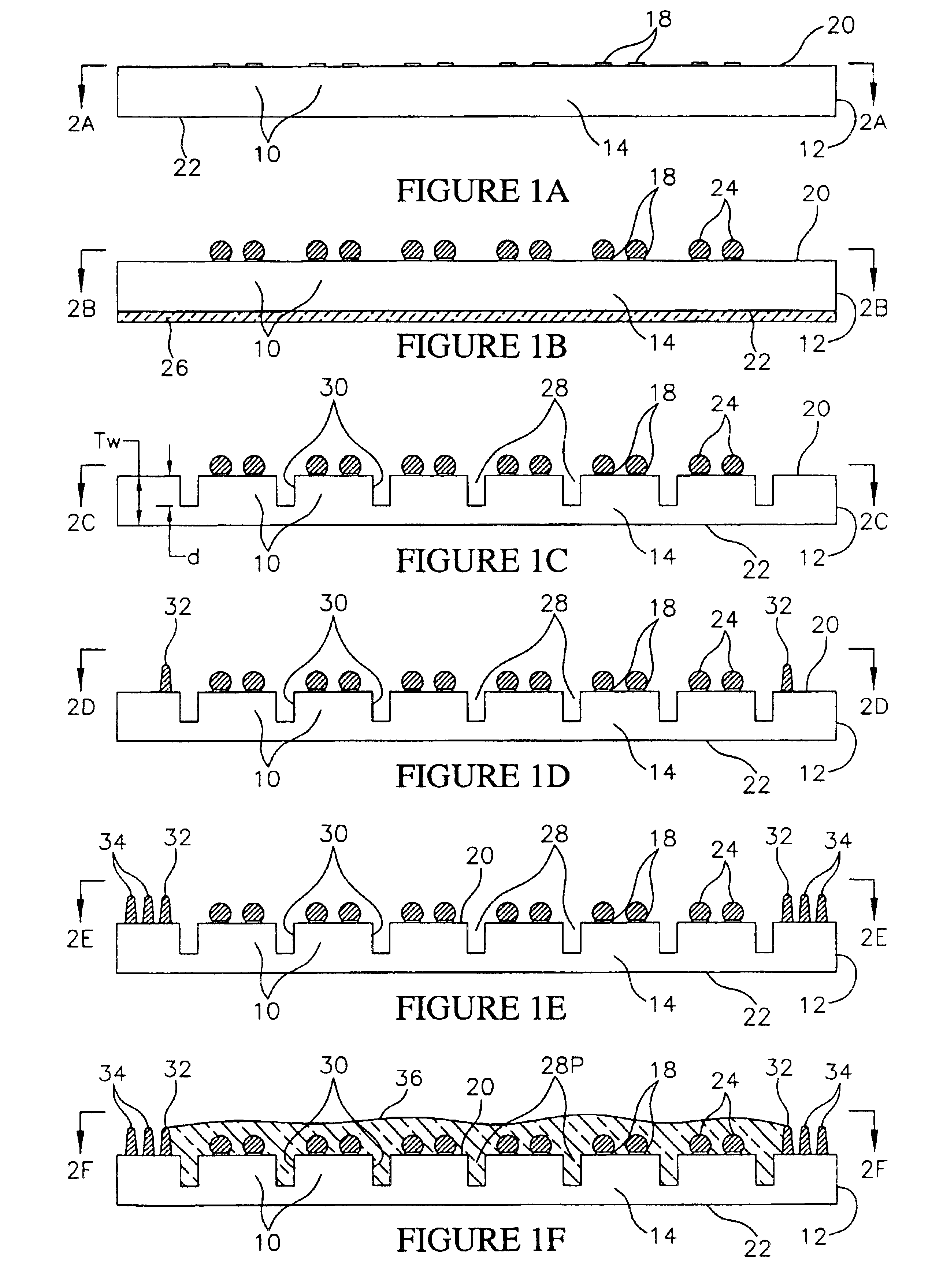
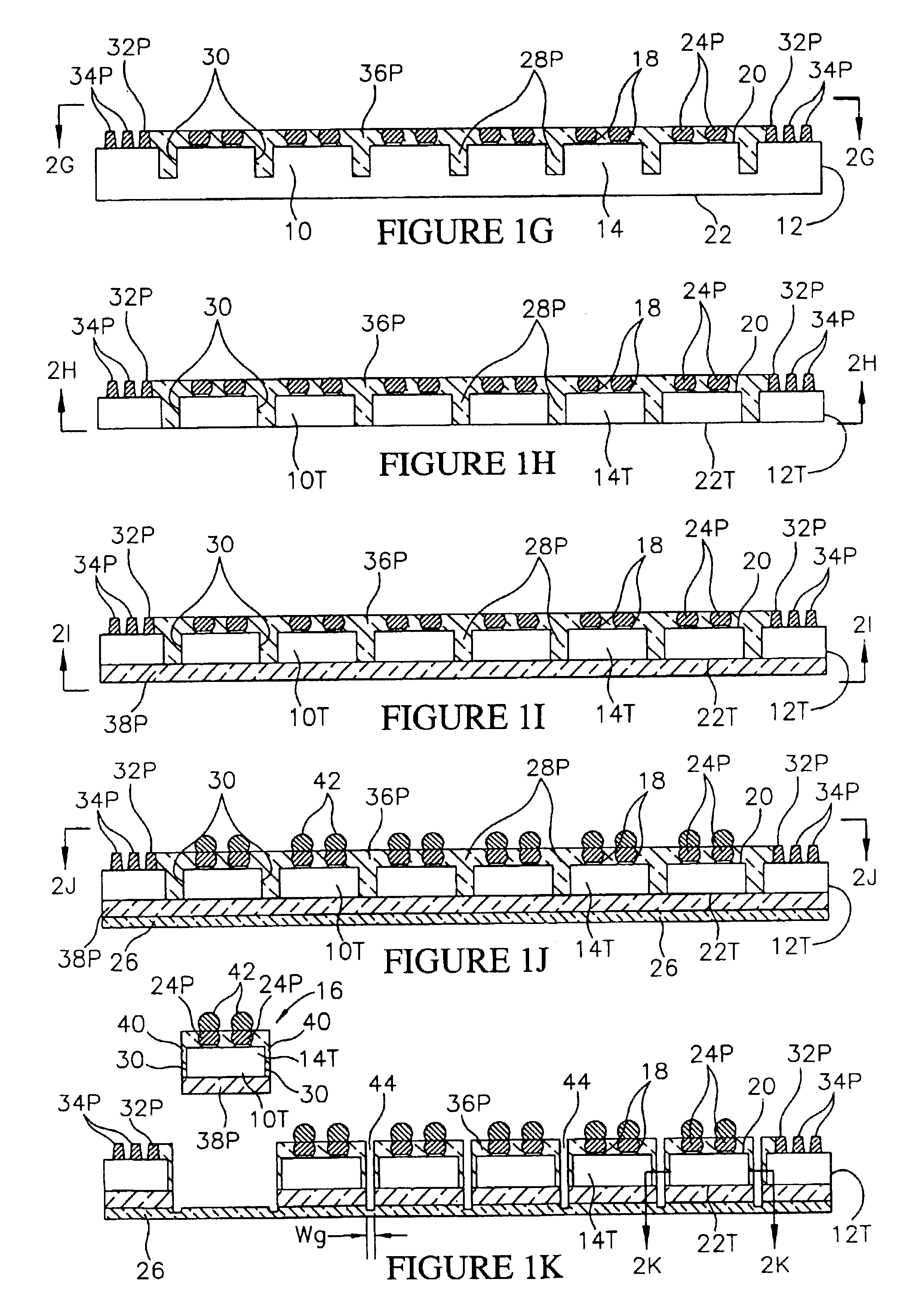
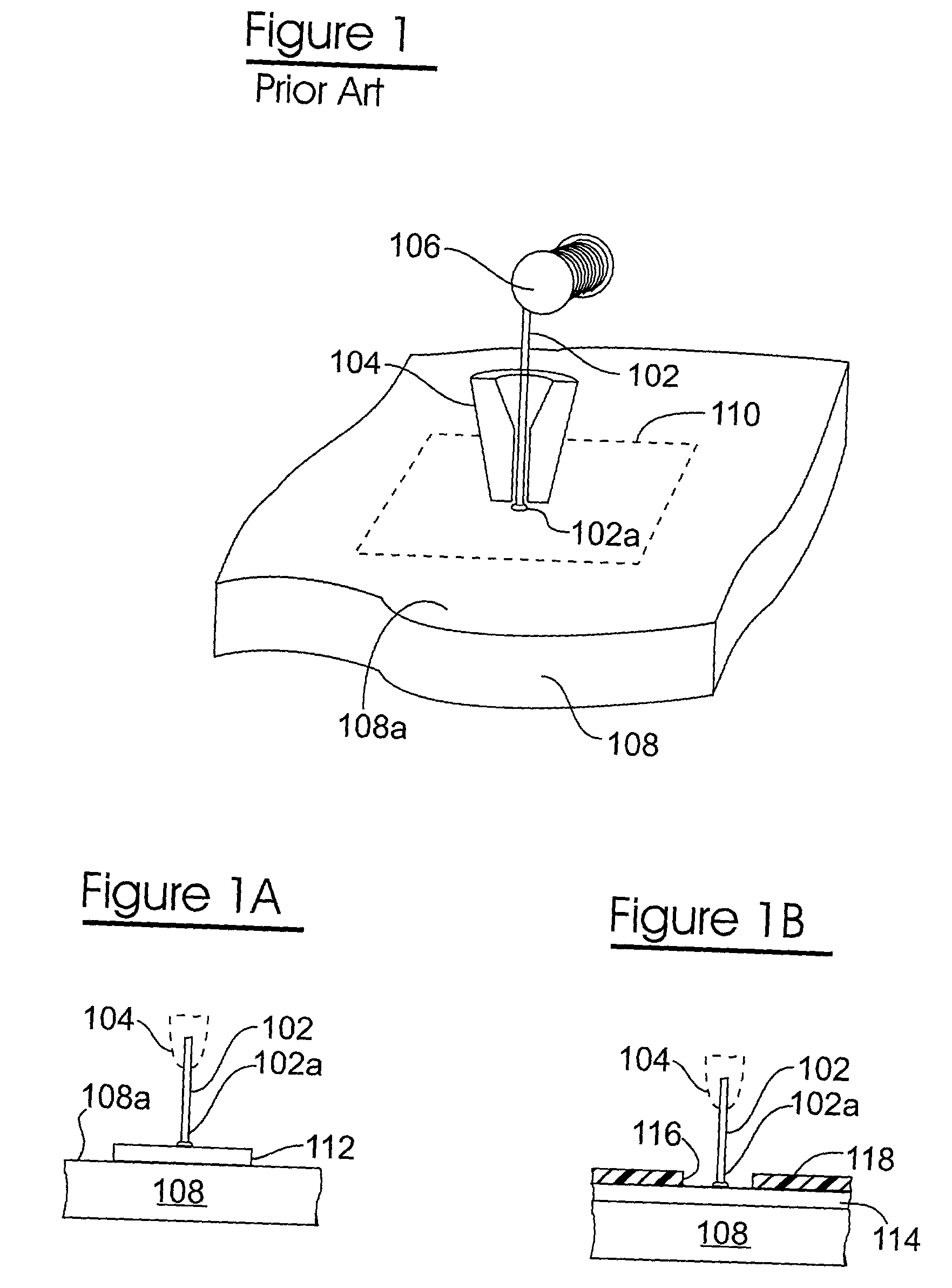
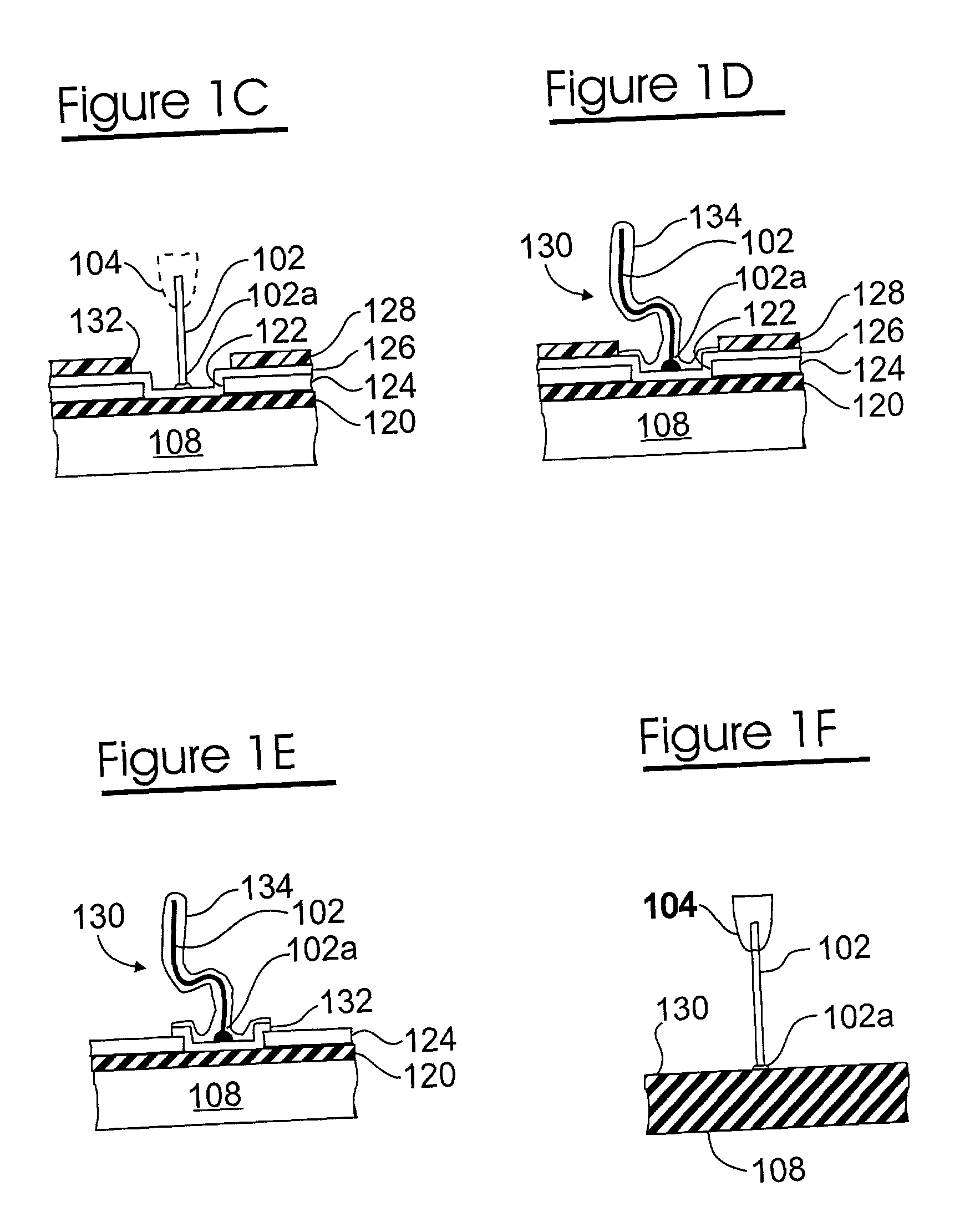
Method for fabricating encapsulated semiconductor components
InactiveUS6908784B1Easy to testAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringPolymer
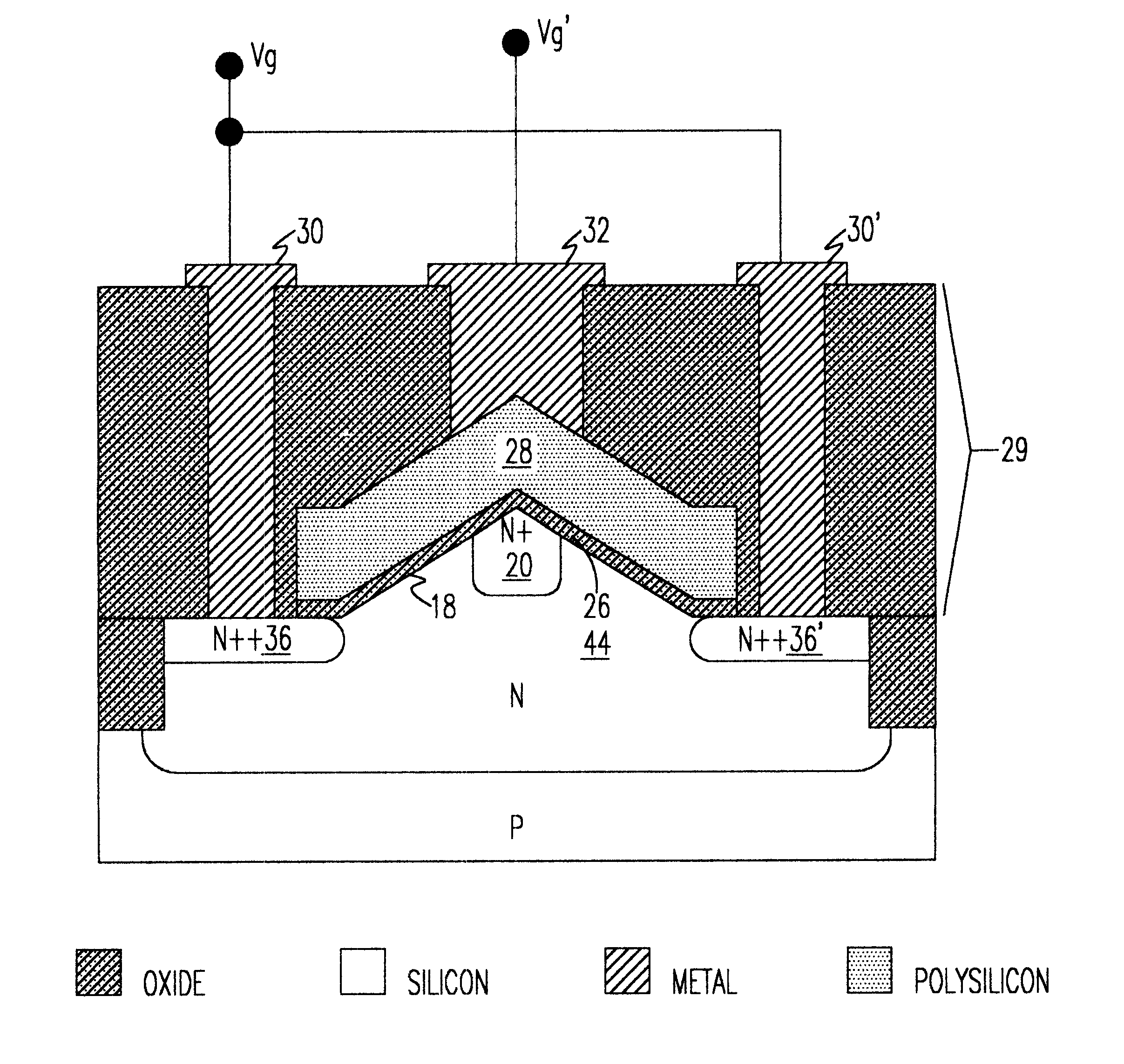
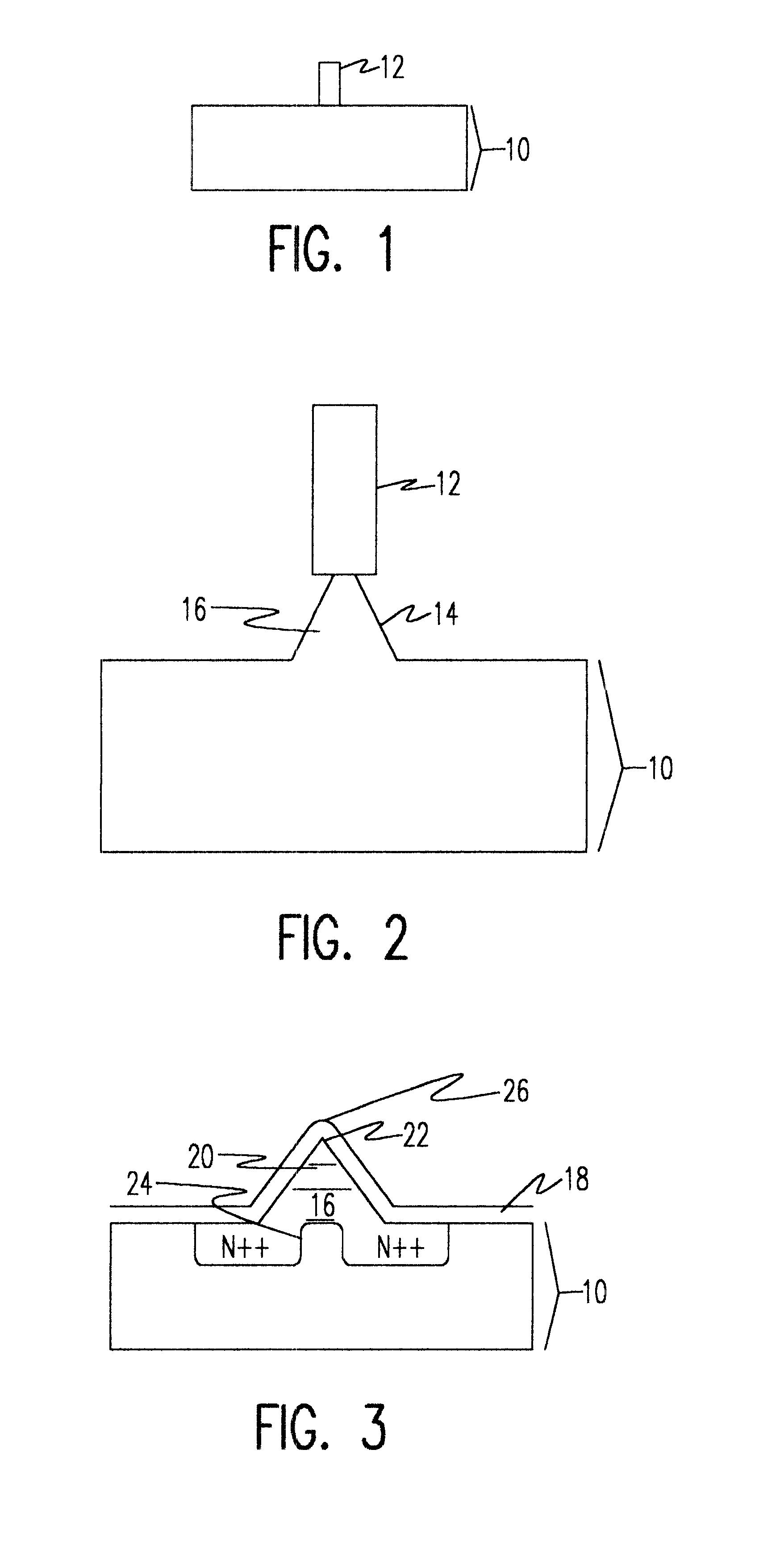
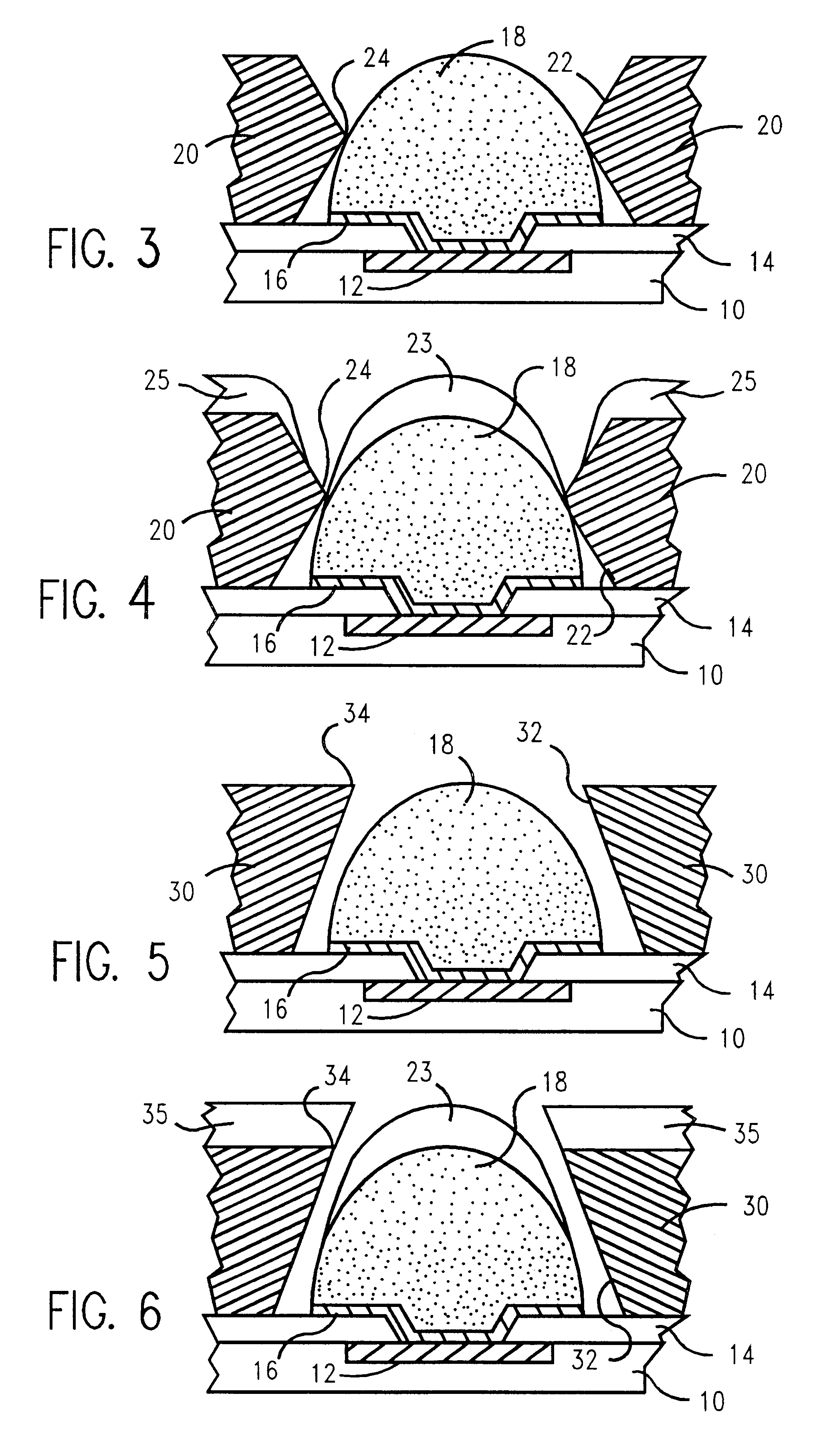
A semiconductor component includes a thinned semiconductor die having protective polymer layers on up to six surfaces. The component also includes contact bumps on the die embedded in a circuit side polymer layer, and terminal contacts on the contact bumps in a dense area array. A method for fabricating the component includes the steps of providing a substrate containing multiple dice, forming trenches on the substrate proximate to peripheral edges of the dice, and depositing a polymer material into the trenches. In addition, the method includes the steps of planarizing the back side of the substrate to contact the polymer filled trenches, and cutting through the polymer trenches to singulate the components from the substrate. Prior to the singulating step the components can be tested and burned-in while they remain on the substrate.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Resilient contact structures formed and then attached to a substrate
InactiveUS20020117330A1Simple technologyCoupling device connectionsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringTopography
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
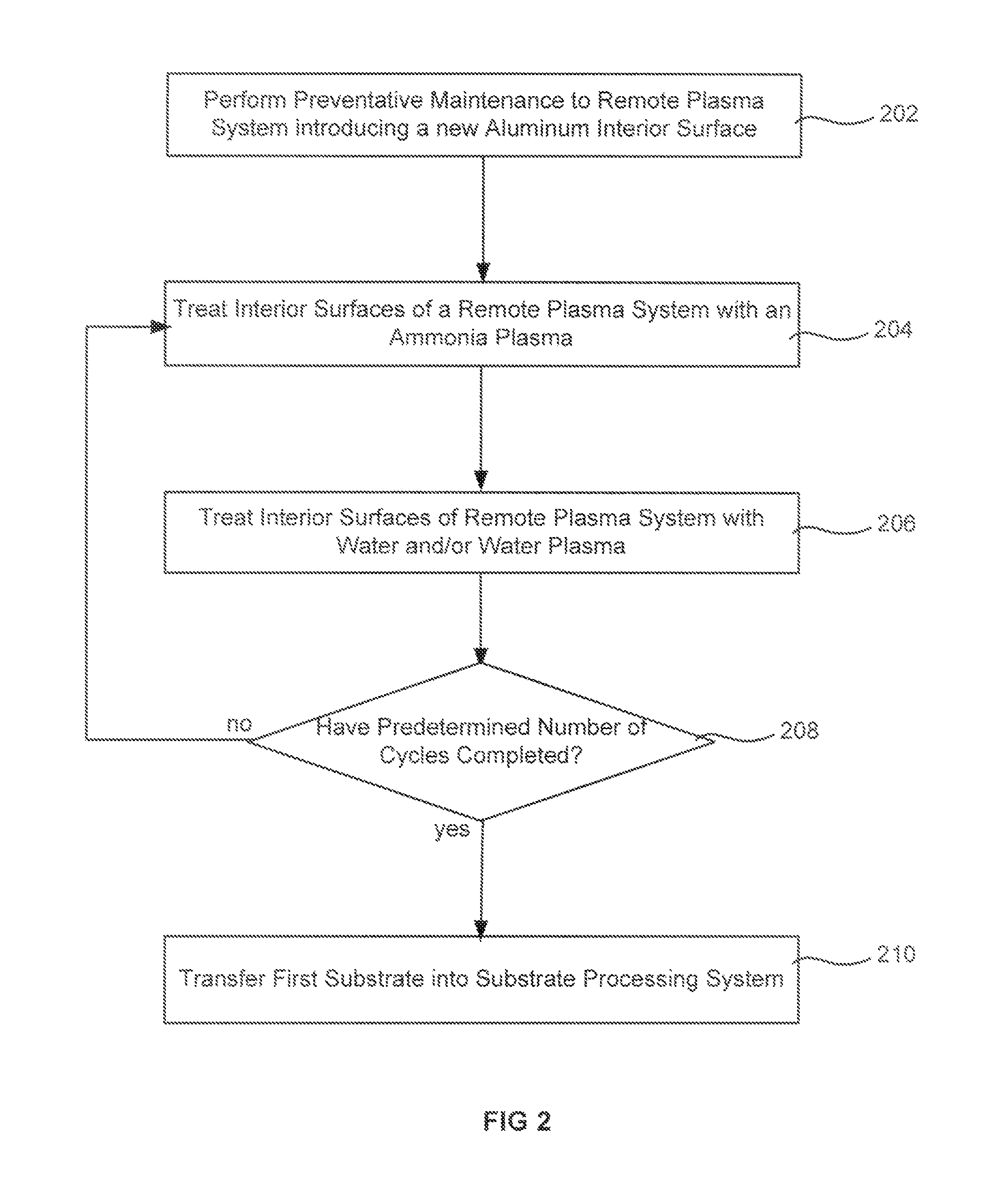
Remote plasma burn-in
InactiveUS8551891B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaHydrogen
Methods of treating the interior of a plasma region are described. The methods include a preventative maintenance procedure or the start-up of a new substrate processing chamber having a remote plasma system. A new interior surface is exposed within the remote plasma system. The (new) interior surfaces are then treated by sequential steps of (1) forming a remote plasma from hydrogen-containing precursor within the remote plasma system and then (2) exposing the interior surfaces to water vapor. Steps (1)-(2) are repeated at least ten times to complete the burn-in process. Following the treatment of the interior surfaces, a substrate may be transferred into a substrate processing chamber. A dielectric film may then be formed on the substrate by flowing one precursor through the remote plasma source and combining the plasma effluents with a second precursor flowing directly to the substrate processing region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
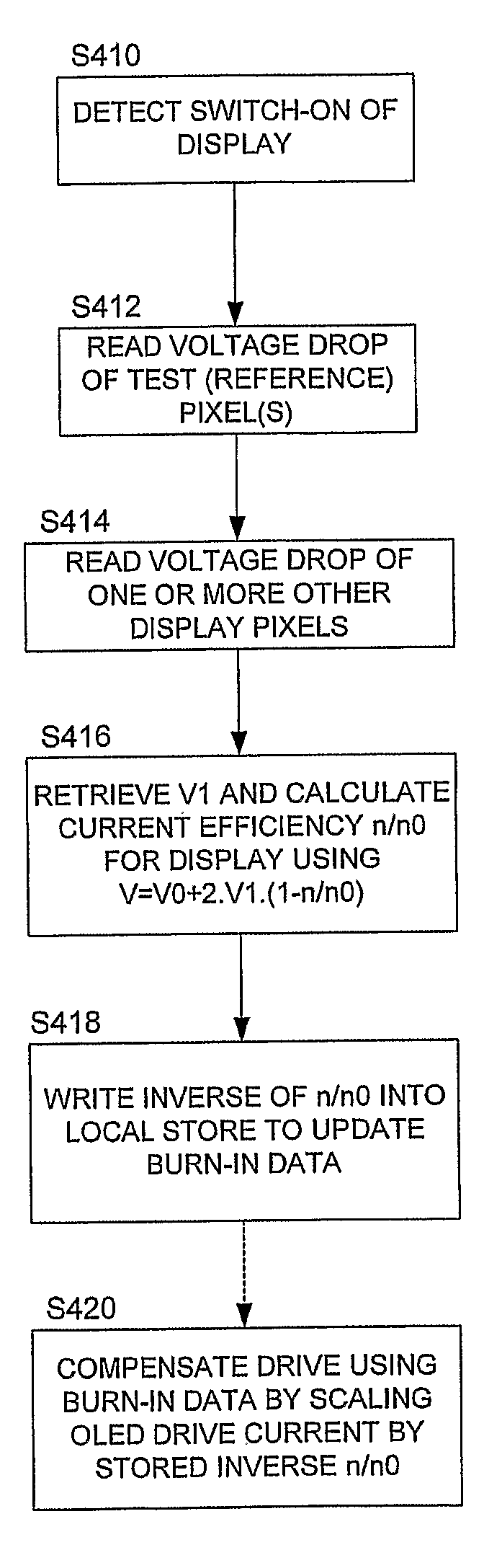
Display Drive Systems
InactiveUS20100026725A1Need to addReduce resistanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceVoltage drop
This invention generally relates to methods, apparatus and computer program code for improved OLED (organic light emitting diode) display drive systems, in particular to compensate for burn-in.A method of compensating an OLED display device for burn-in of pixels of the OLED display, the method comprising: measuring a first voltage drop across at least one test pixel of the display; measuring a second voltage drop across at least one other pixel of the display; determining, from said first and second voltages and a from value (V1) representing a drive voltage increase for a loss in efficiency of said display due to burn-in, an estimated reduction in efficiency of said display due to burn-in; and compensating a drive to said display using said estimated efficiency reduction.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE DISPLAY TECH LTD
Encapsulated semiconductor components and methods of fabrication
InactiveUS20050148160A1Easy to testAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringPolymer
A semiconductor component includes a thinned semiconductor die having protective polymer layers on up to six surfaces. The component also includes contact bumps on the die embedded in a circuit side polymer layer, and terminal contacts on the contact bumps in a dense area array. A method for fabricating the component includes the steps of providing a substrate containing multiple dice, forming trenches on the substrate proximate to peripheral edges of the dice, and depositing a polymer material into the trenches. In addition, the method includes the steps of planarizing the back side of the substrate to contact the polymer filled trenches, and cutting through the polymer trenches to singulate the components from the substrate. Prior to the singulating step the components can be tested and burned-in while they remain on the substrate.
Owner:FARNWORTH WARREN M +2
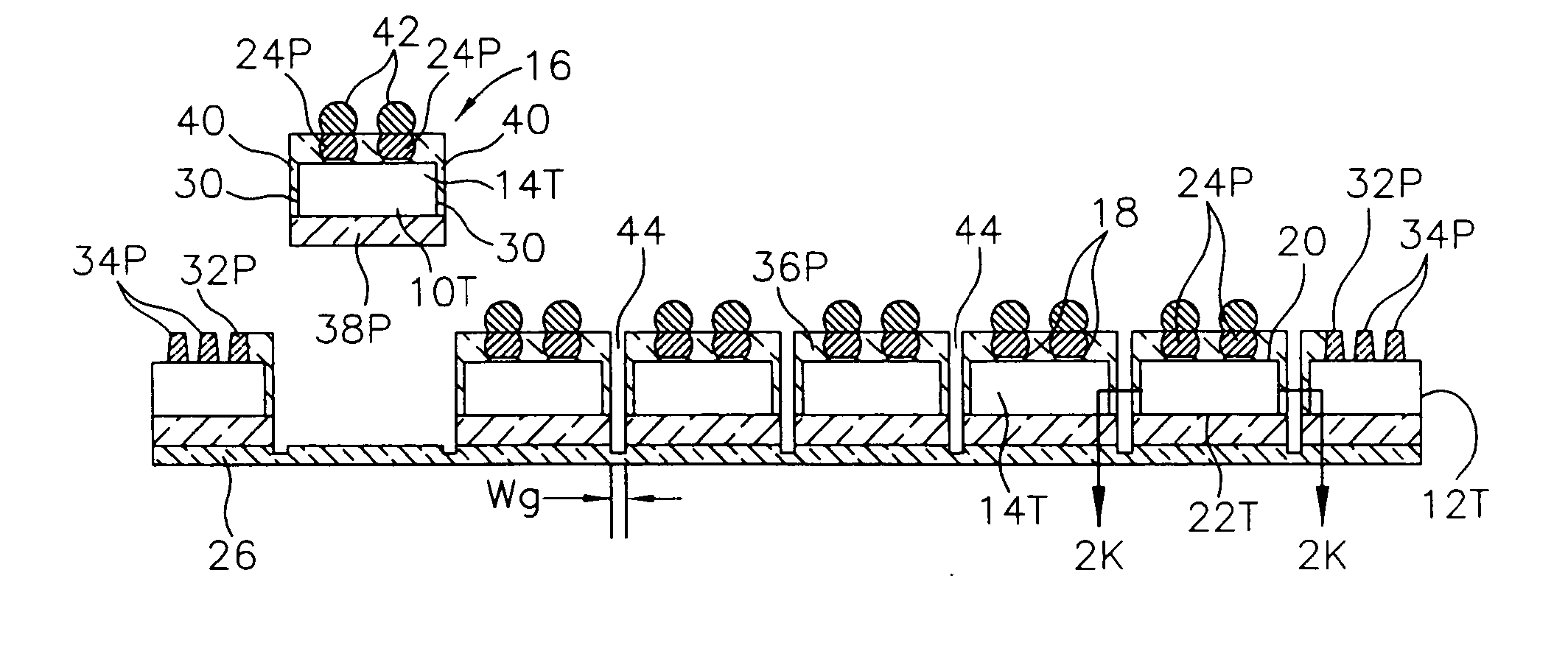
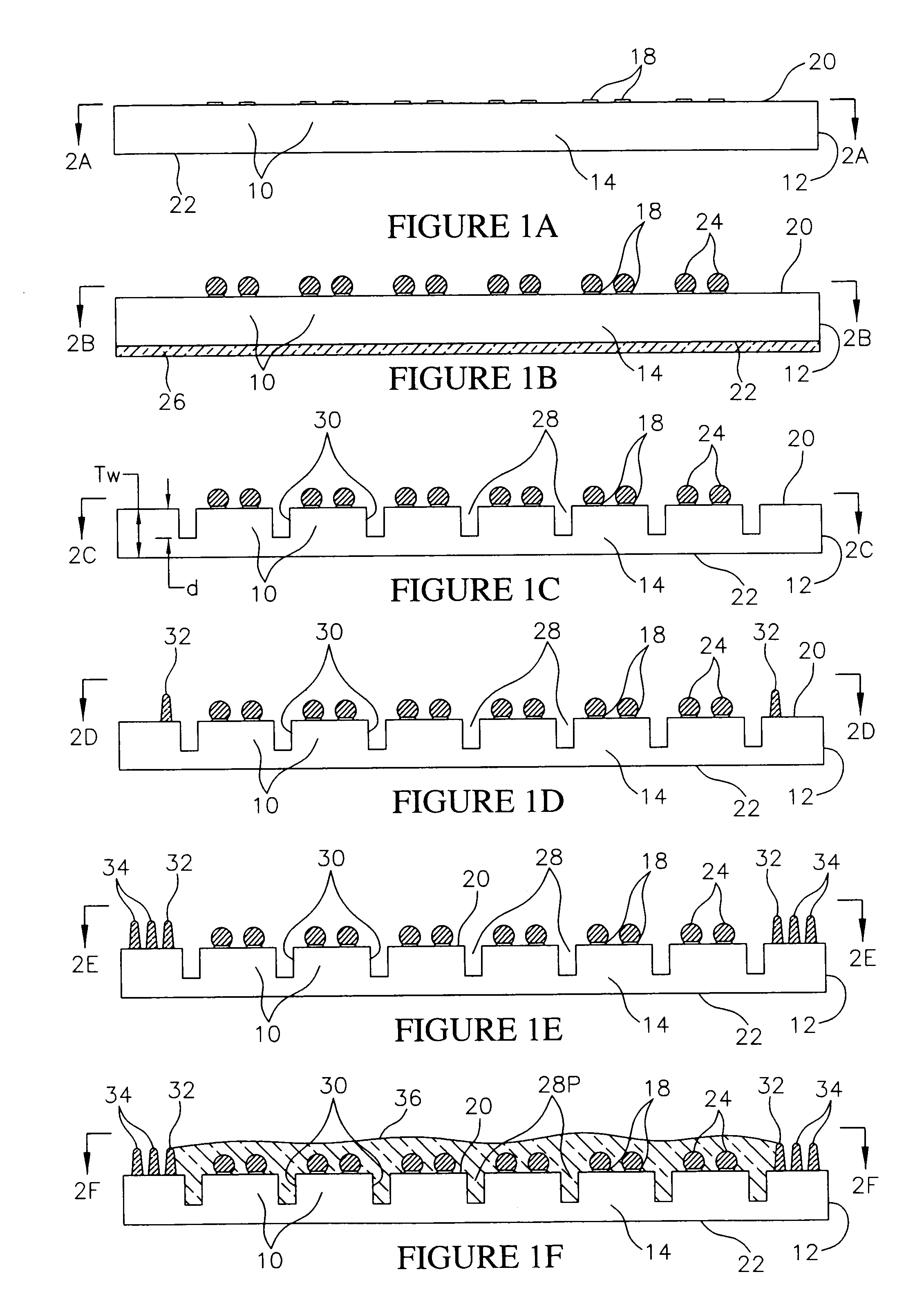
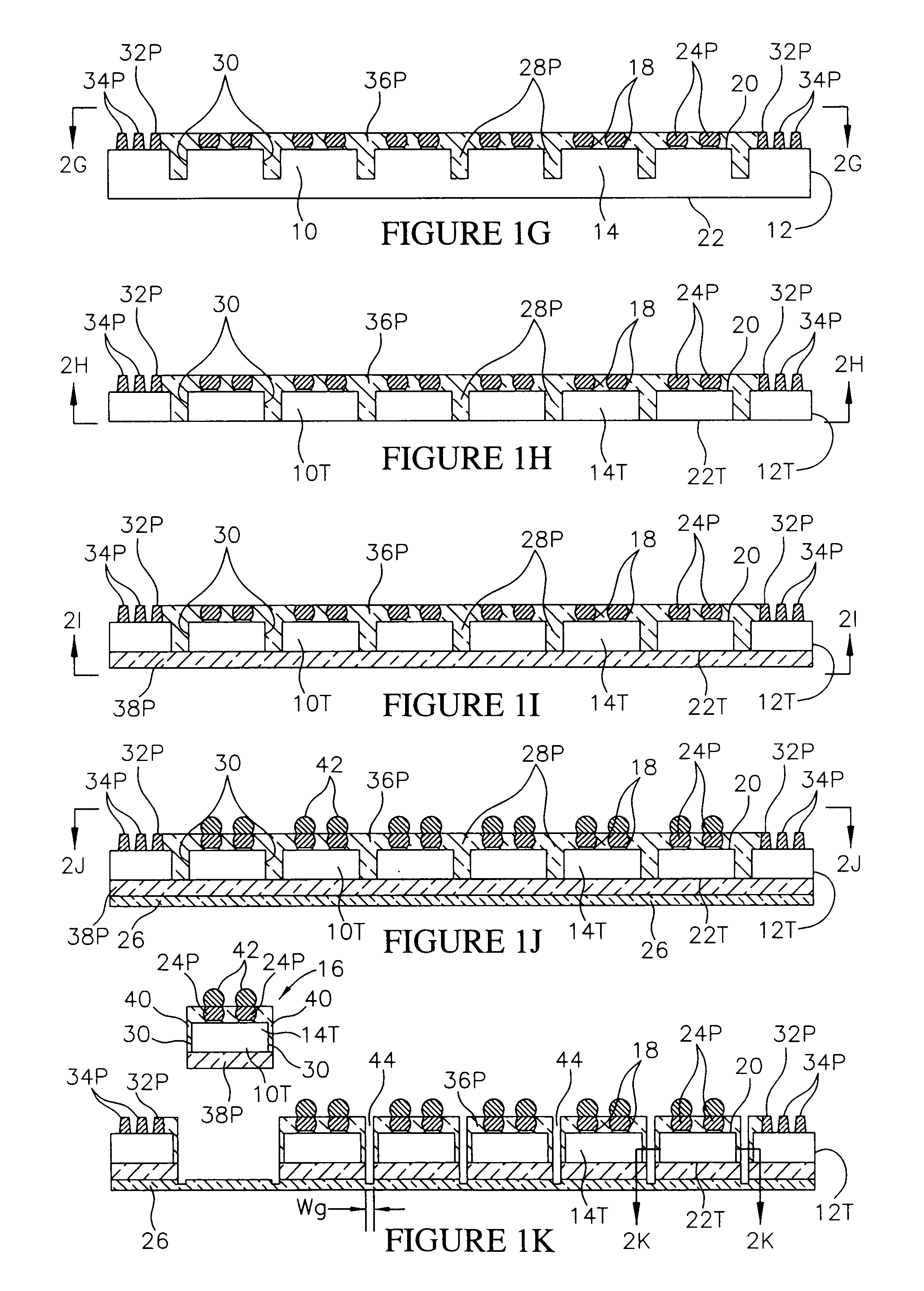
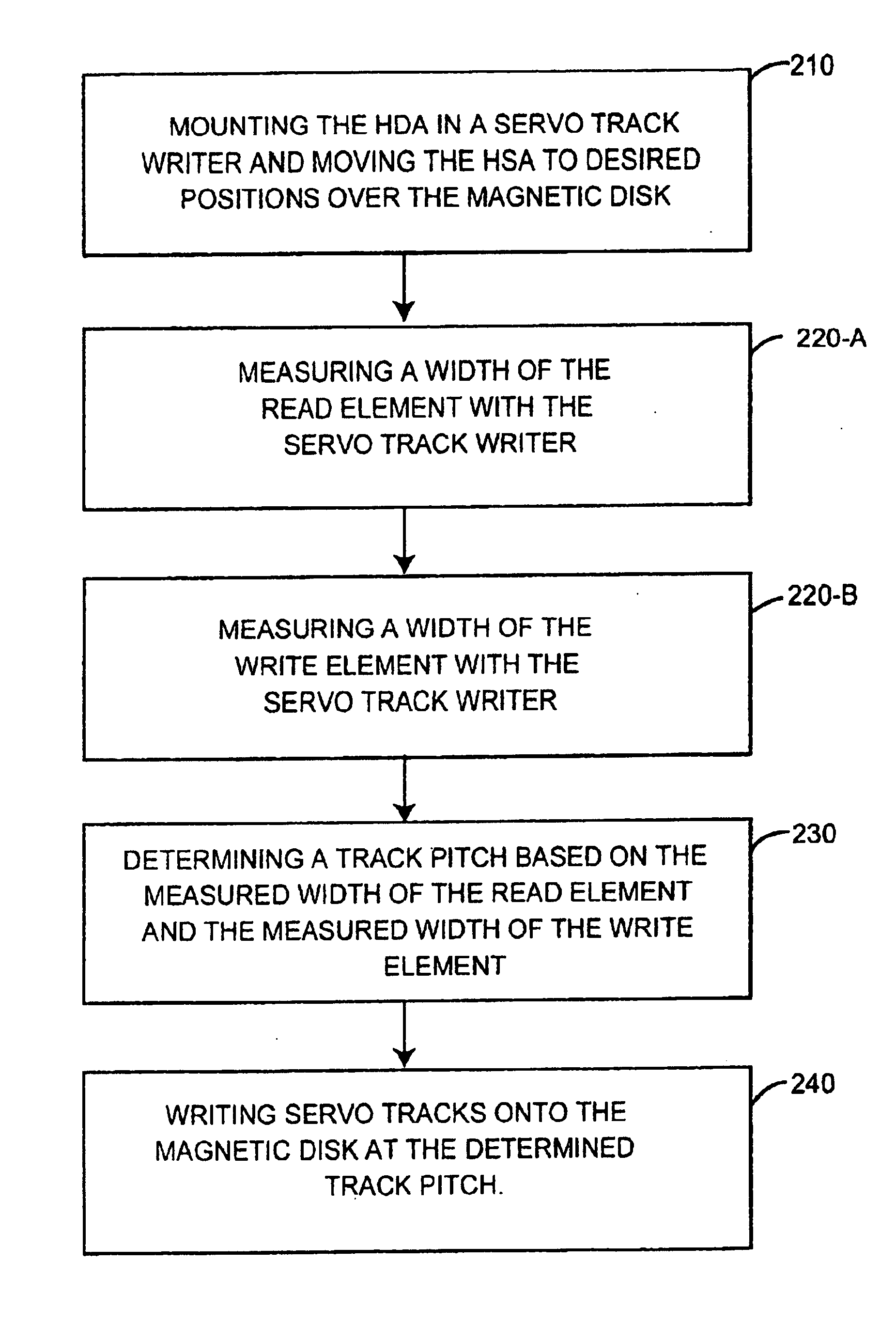
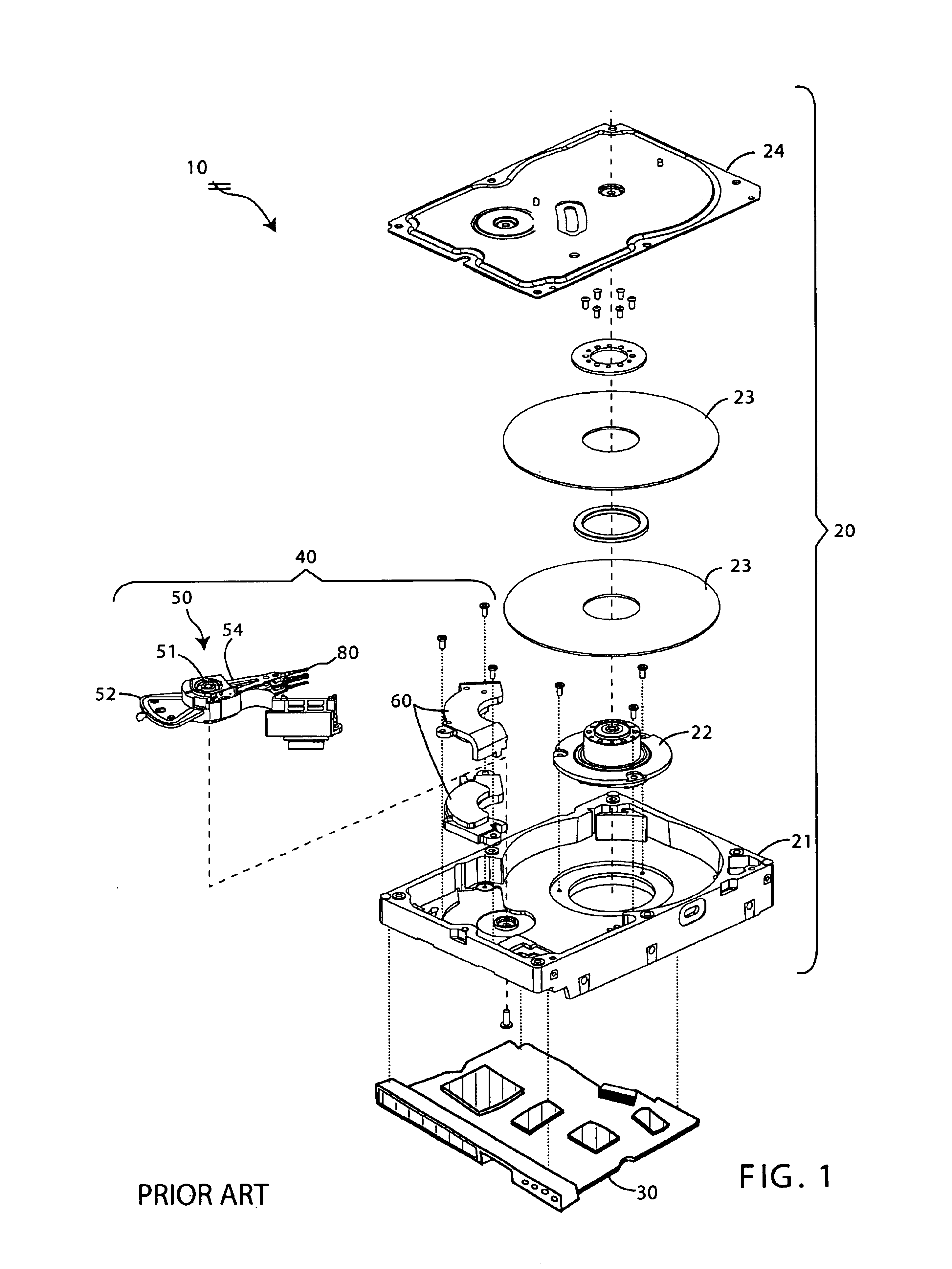
Method of manufacturing and disk drive produced by measuring the read and write widths and varying the track pitch in the servo-writer
A method of manufacturing a disk drive and a disk drive made with such method where the width of the read element and the width of the write element are both measured at servo-writing time and the track pitch of the disk drive is set on the basis of those measurements. Disk drives with superior head width combinations are servo-written with a narrower track pitch in order to have a higher storage capacity. Disk drives with inferior head width combinations are detected before servo-writing so that the disk drive may be servo-written with wider track pitch rather than with a nominal track pitch that results in a subsequent drive failure during initial burn-in (IBI). The heads are used more efficiently in that heads that are more capable are used to their ability and less capable heads that would otherwise be disposed of are used at all. Fewer disk drives are required to be reworked and returned to the servo-writing process.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
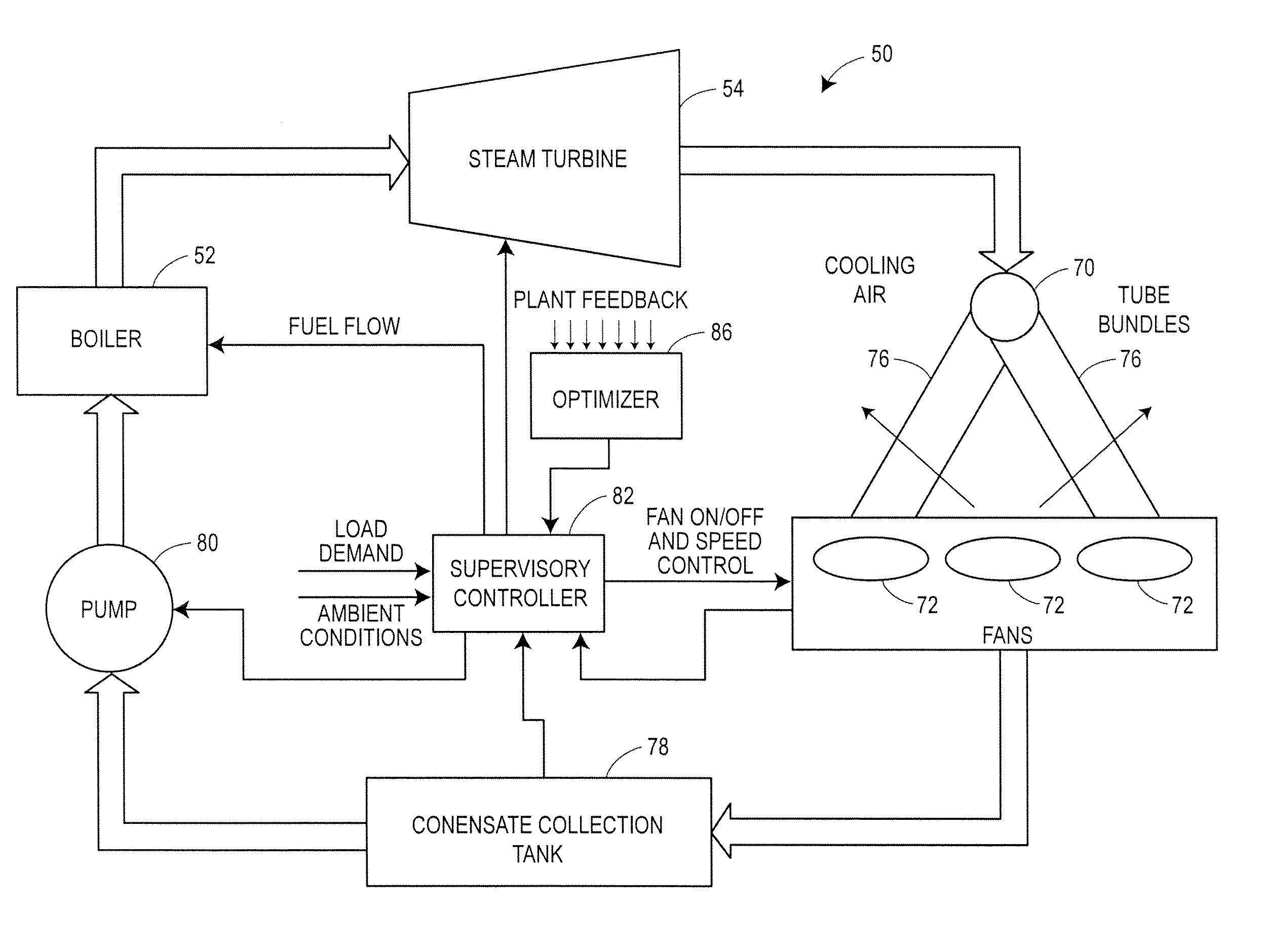
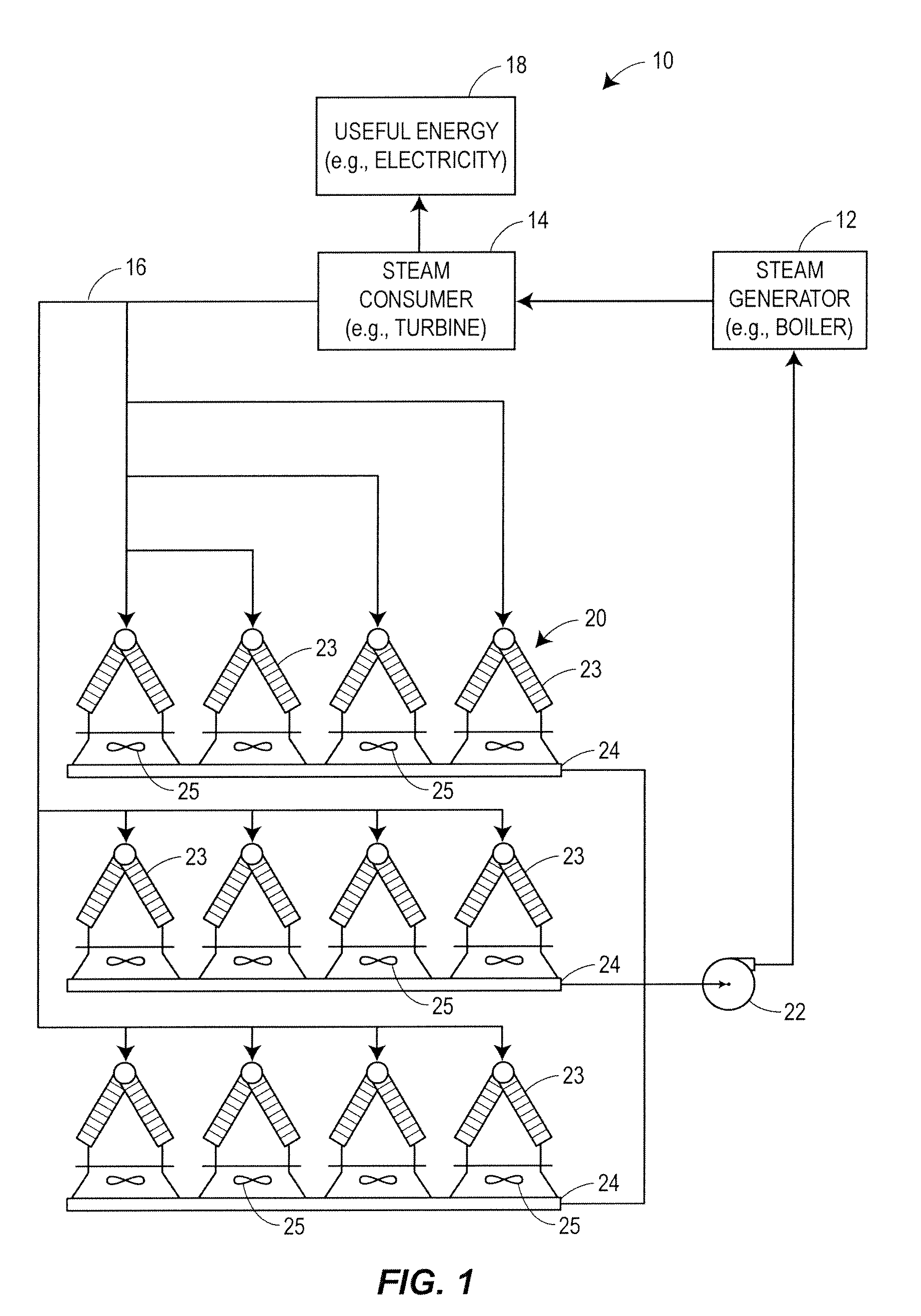
Optimized control of power plants having air cooled condensers
ActiveUS20110066298A1Cost can be reduced and minimizedLow costMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlOperating pointControl variable
An optimization and control system for a utility plant that uses fan based air cooled condensers controls the operation of the power generation system at the plant in conjunction with the operation of the air cooled condensers so as to run the power plant at an optimum operating point associated with minimizing or reducing the cost of each kilowatt-hour of energy or other useful energy produced by the plant. The optimization and control system includes an optimizer having a numerical solver that determines values for a set of control variables associated with an optimal operating point of the plant and an expert system that oversees and modifies the control variable settings prior to providing these settings to a plant controller. The numerical solver uses an objective function and one or more models of plant equipment to determine the operating point of the plant that minimizes the cost per unit of useful energy generated by the plant. As part of determining the optimal plant operating point, the numerical solver may determine the number of fans to run within the air cooled condensers of the plant and / or the speed of the fans to use in the air cooled condensers in conjunction with the amount of fuel to burn in the boiler, the desired temperature of the steam at the input of the steam turbine, etc., all required to produce a given amount of power (load demand) at the particular environmental conditions currently experienced at the plant. The expert system may modify these outputs by determining which fans to actually use at any particular time based on, for example, the availability of or the operational status of the fans, the wear of the fans and fan motors, etc.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
Surgical implement detector utilizing a radio-frequency identification marker
InactiveUS7307530B2Control moreSevere possibilitySurgeryElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingModulation functionEngineering
A radio-frequency surgical implement detection system detects surgical implements in a surgical wound during and at the completion of a surgical procedure. Surgical implements, including surgical sponges or laparotomy pads, gauze pads and metallic surgical instruments, are individually attached to a non battery-powered, encapsulated radio-frequency marker. The marker comprises an integrated chip having a burnt-in memory code, which is broadcast through an antenna using a modulated carrier frequency. The code is received by an interrogating antenna of a detector. The interrogating antenna provides a power pulse, which is received by the antenna of the radio-frequency marker. The power pulse charges a capacitor, which proves power for the read function, carrier frequency modulation function and broadcast function of the integrated chip, permitting each marker-containing implement to be specifically identified.
Owner:FABIAN CARL E
Method of designing an application specific probe card test system
InactiveUS20060273809A1Eliminate needDigital circuit testingOverload protection arrangementsProbe cardOn board
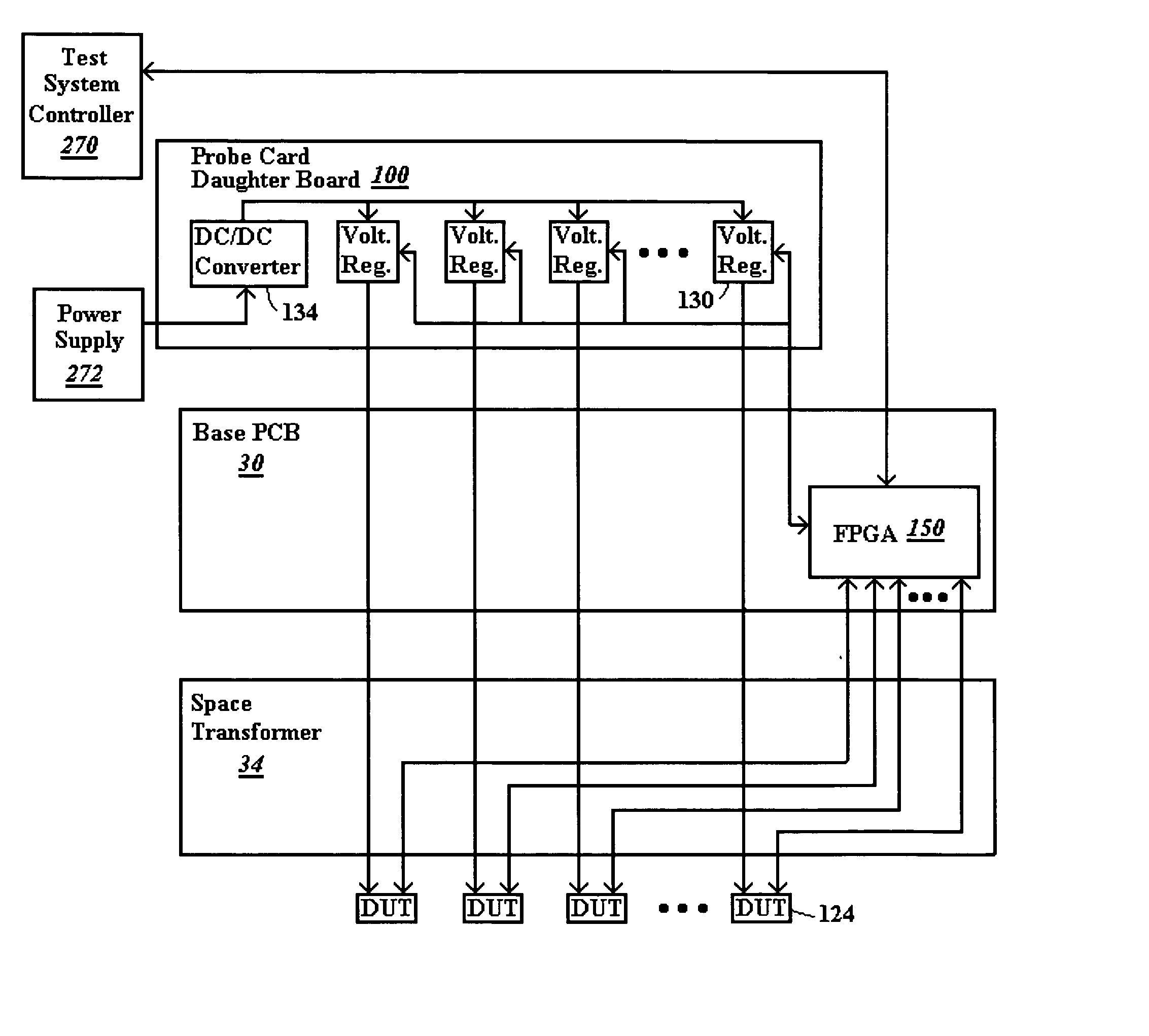
A method is provided for design and programming of a probe card with an on-board programmable controller in a wafer test system. Consideration of introduction of the programmable controller is included in a CAD wafer layout and probe card design process. The CAD design is further loaded into the programmable controller, such as an FPGA to program it: (1) to control direction of signals to particular ICs, even during the test process (2) to generate test vector signals to provide to the ICs, and (3) to receive test signals and process test results from the received signals. In some embodiments, burn-in only testing is provided to limit test system circuitry needed so that with a programmable controller on the probe card, text equipment external to the probe card can be eliminated or significantly reduced from conventional test equipment.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
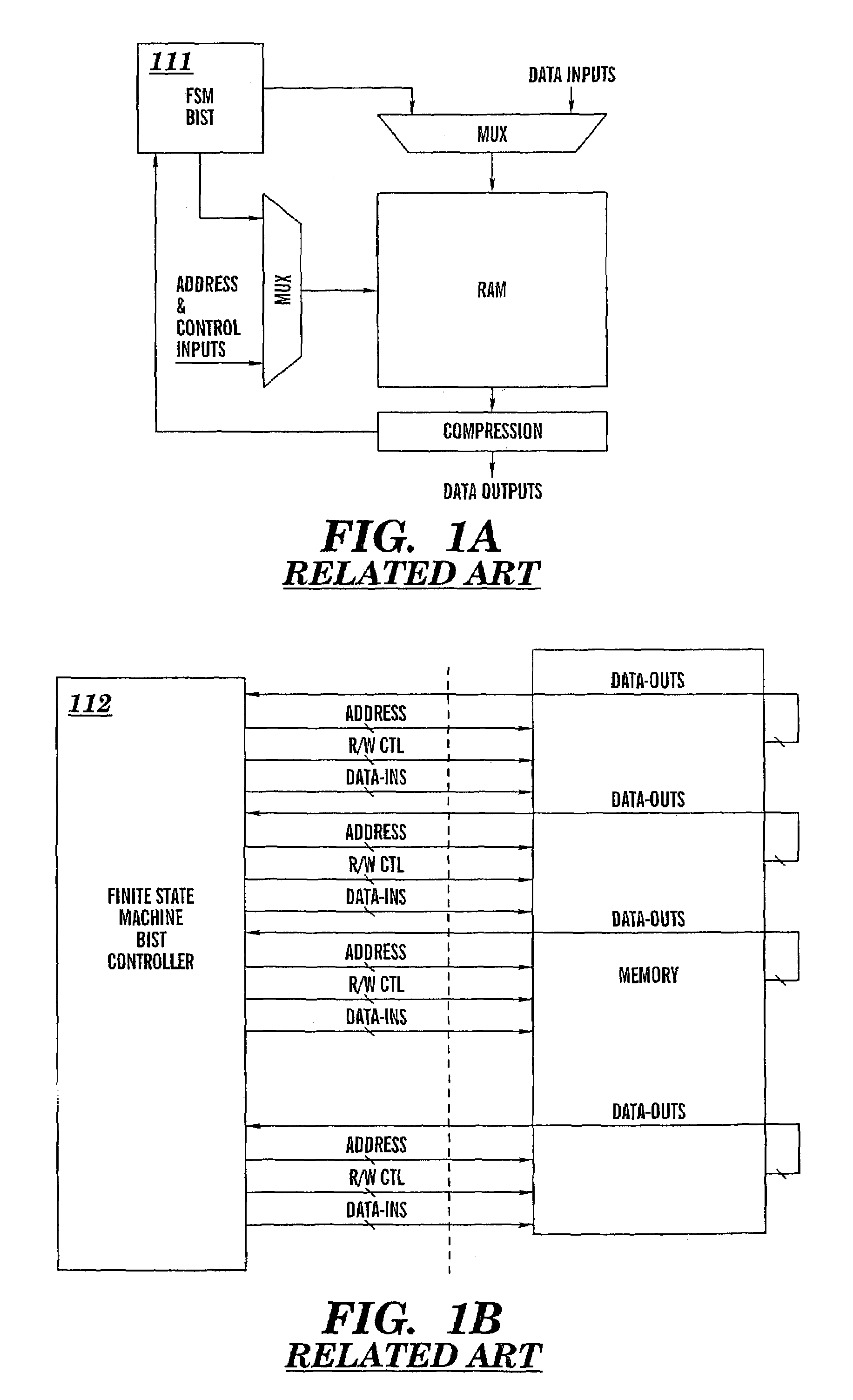
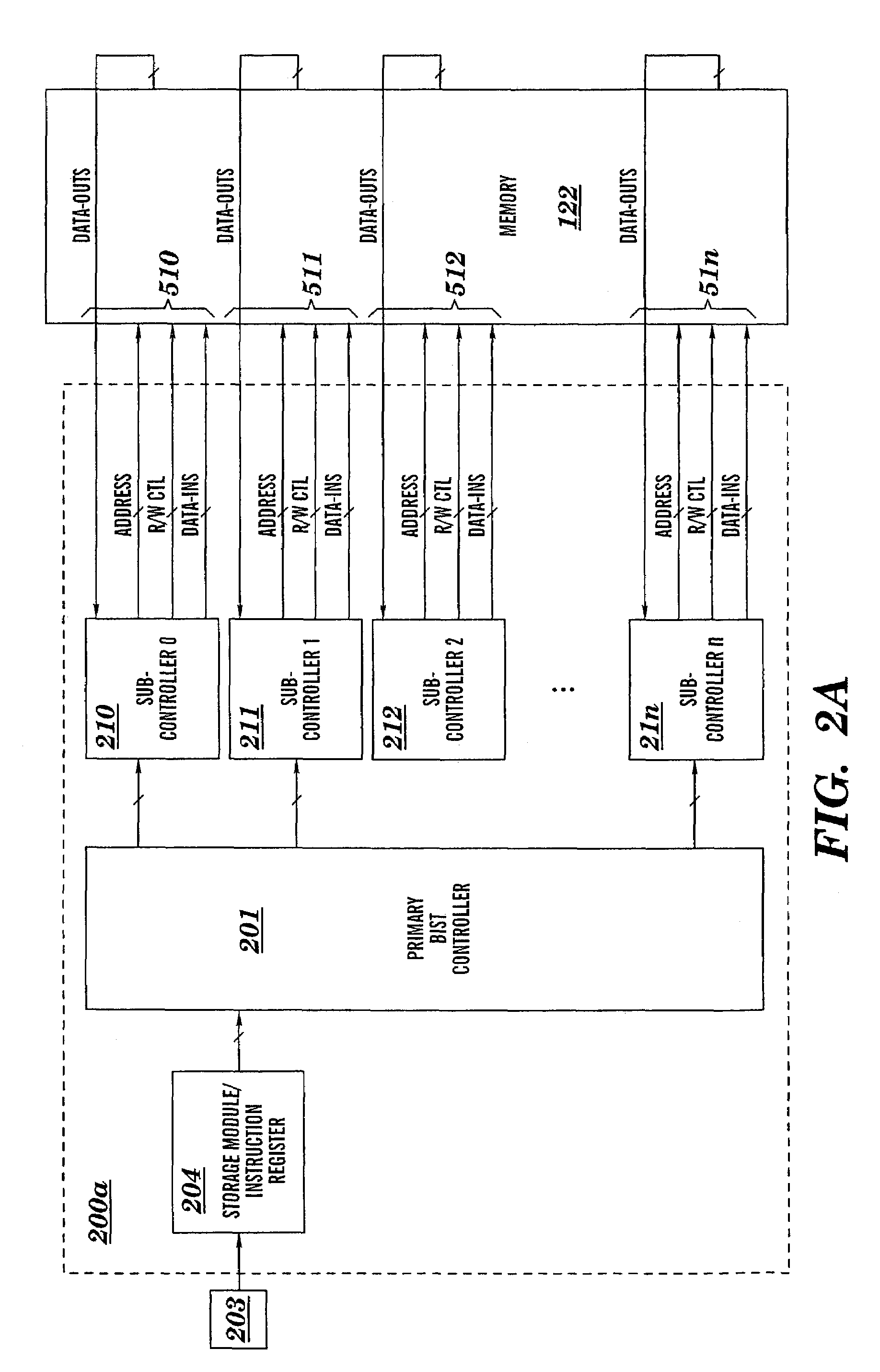
Programable multi-port memory BIST with compact microcode
InactiveUS7168005B2Easy to testIncrease flexibilityElectronic circuit testingFunctional testingAs DirectedMaster controller
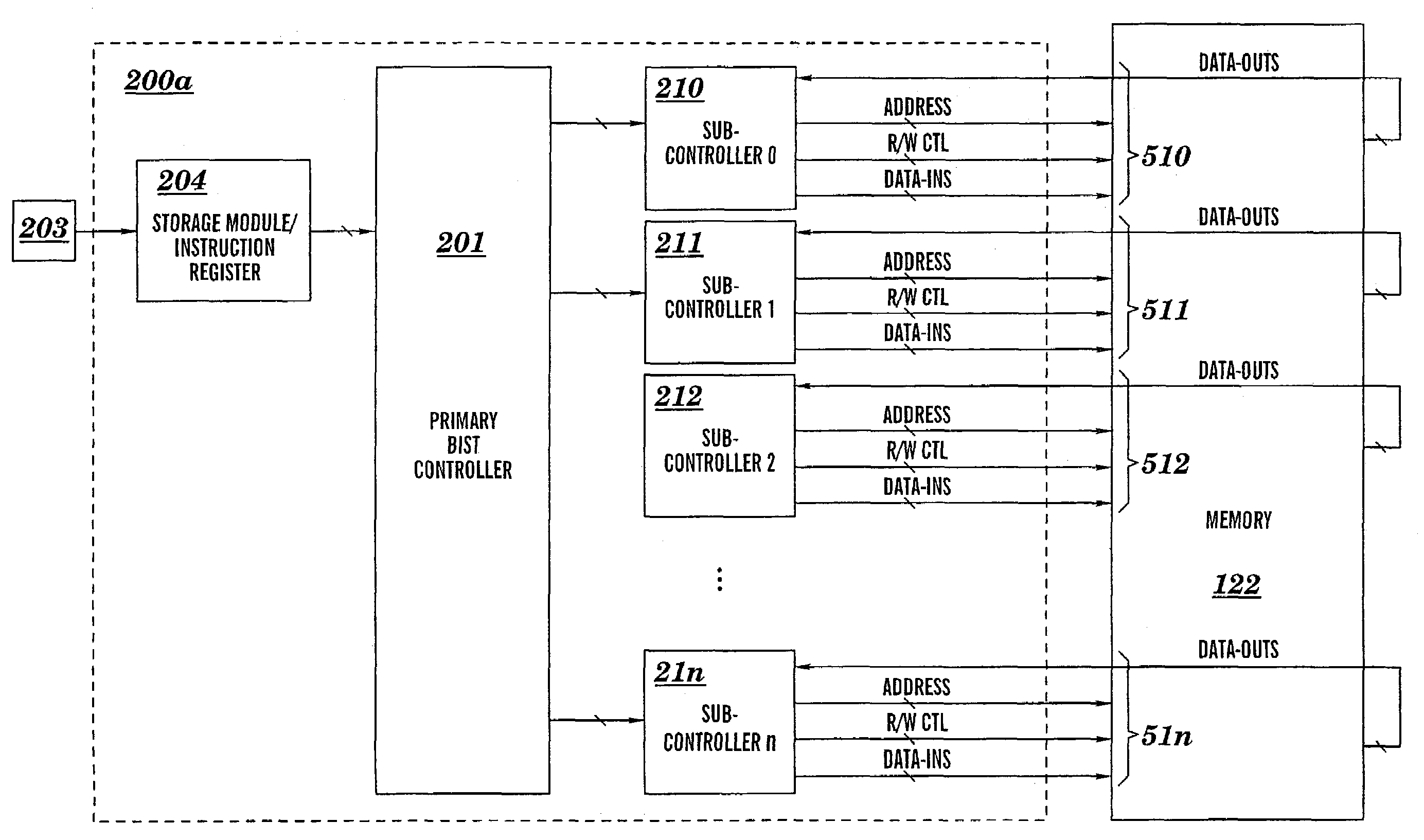
A microcode programmable built-in-self-test (BIST) circuit and method for testing a multiported memory via multiple ports, either simultaneously or sequentially, as directed by a microcode instruction word. The microcode instruction word contains a plurality of executable subinstructions and one bit of information that controls whether the test operations prescribed in the plurality of subinstructions shall be executed in parallel or in series. The executable subinstructions are dispatched by a primary controller to subcontrollers which perform test operations at each port according to the subinstructions. The microcode programable BIST architecture flexibly facilitates the testing of multiple devices, multiported devices, including multiported memory structures and complex dependent multiported memory structures. The BIST supports in-situ testing of the functionality of the memory at wafer, module, and burn-in, as well as system-level testing.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
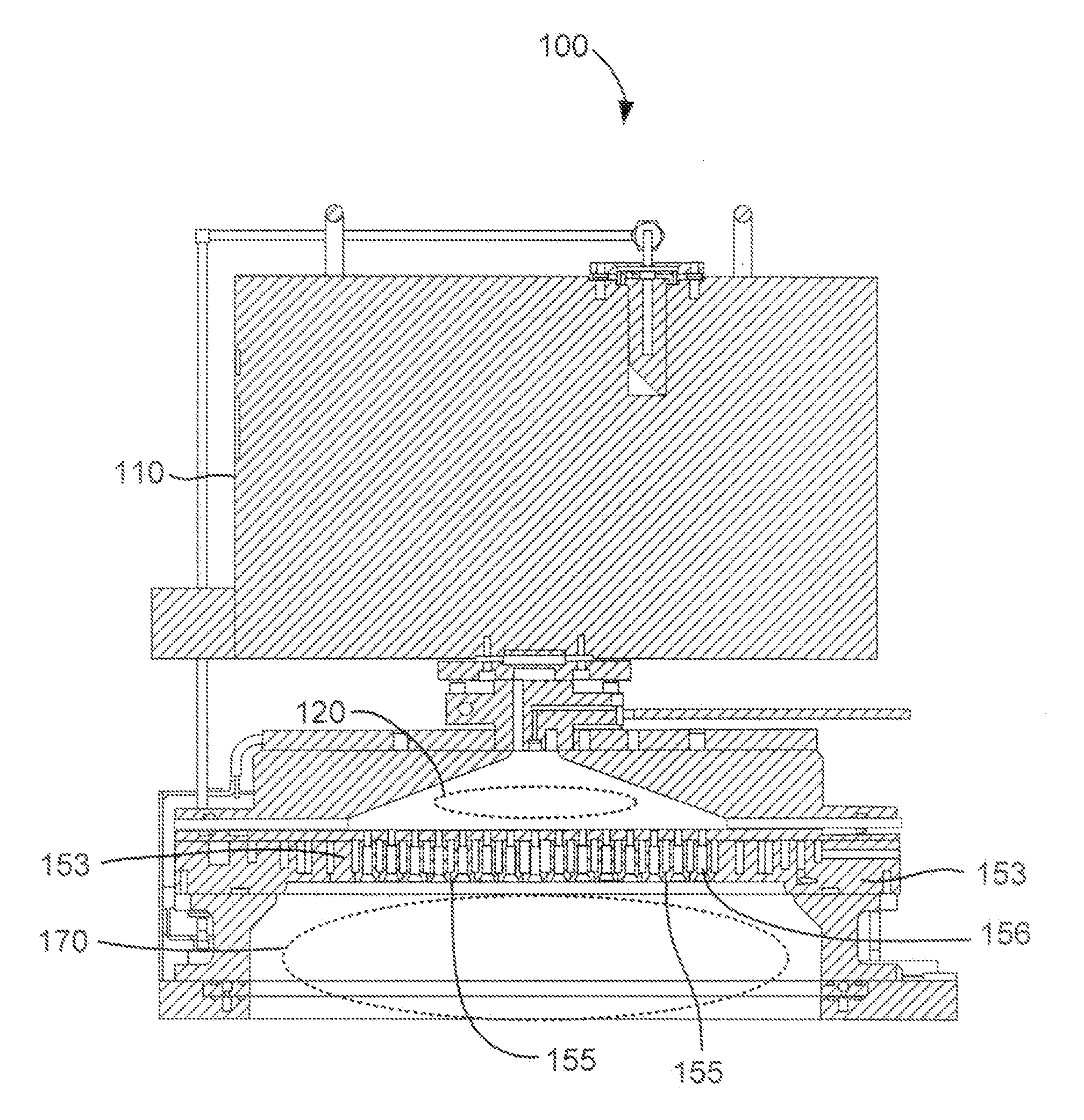
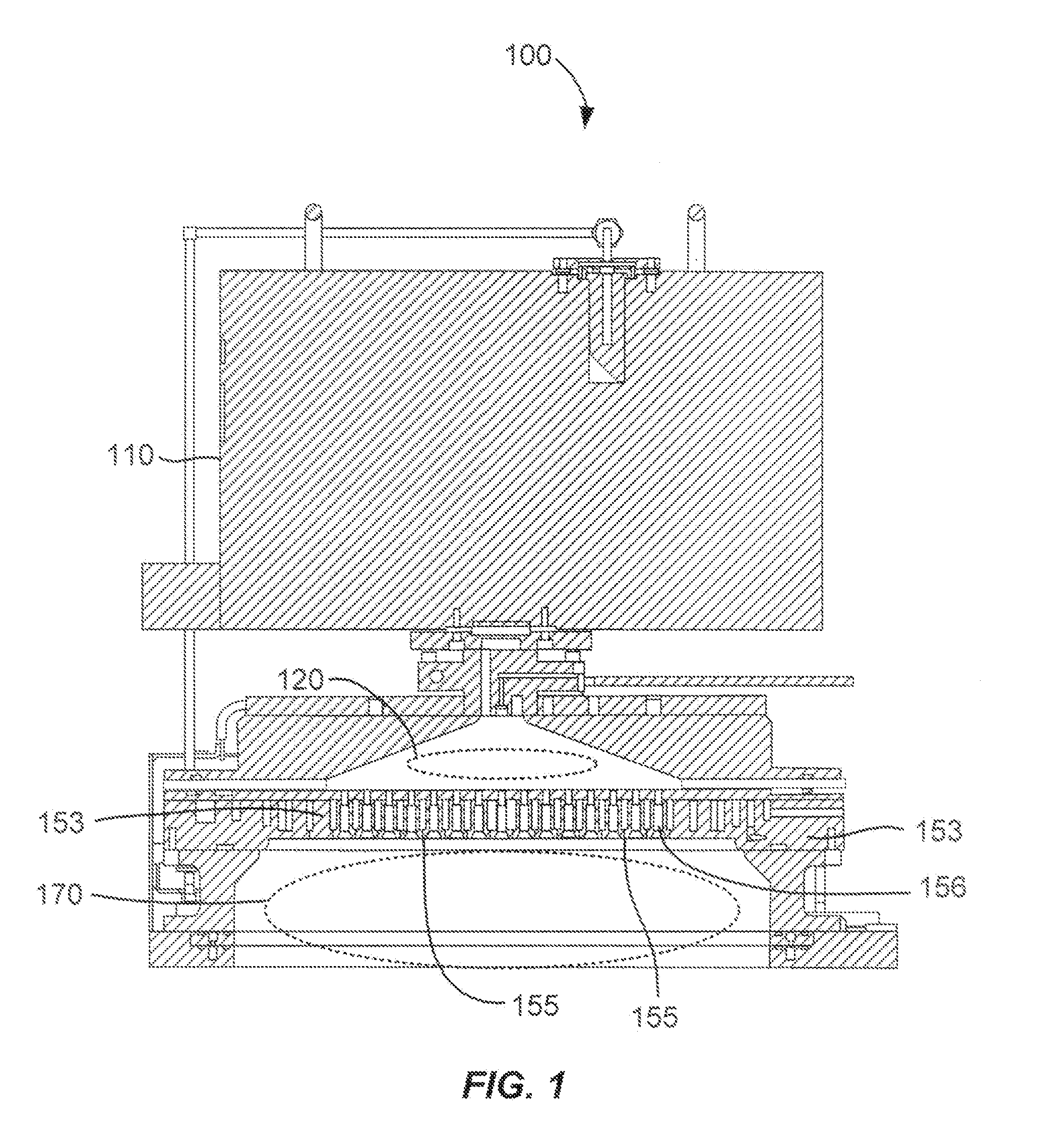
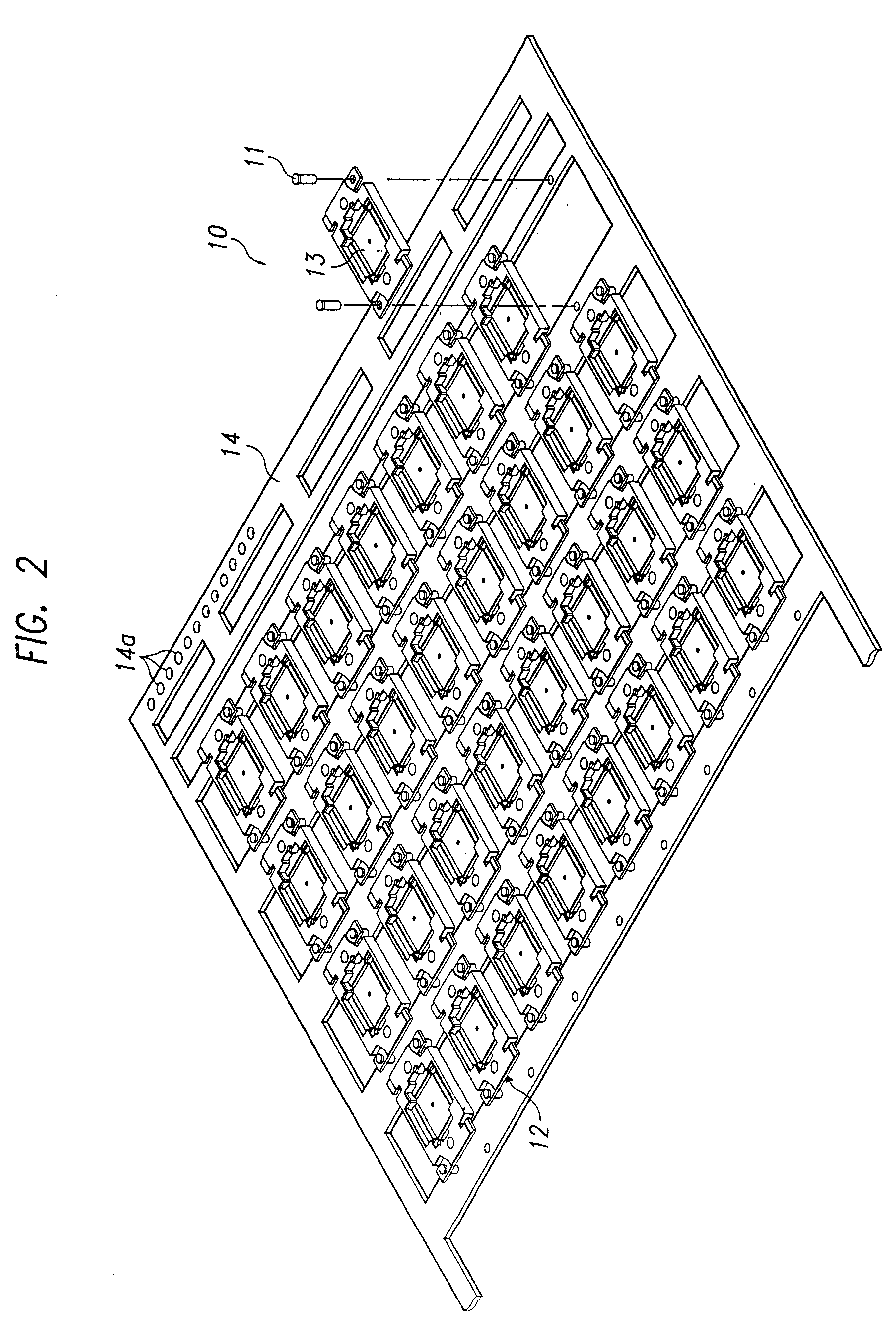
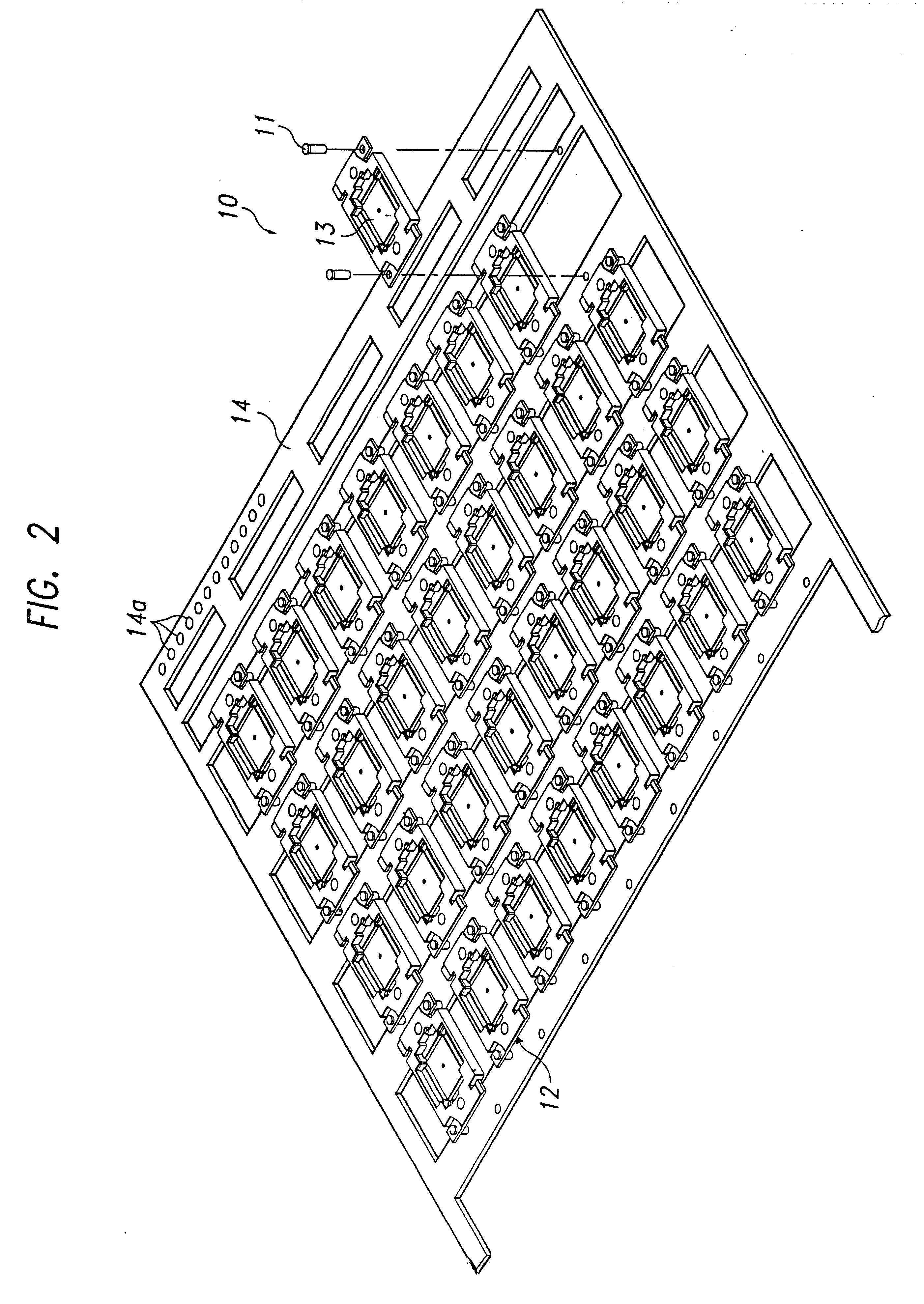
Test and burn-in apparatus, in-line system using the test and burn-in apparatus, and test method using the in-line system
InactiveUS6563331B1Reduced number of stepAvoid excess performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingDevice materialTest phase
An apparatus for testing semiconductor devices allows various testing processes, including a burn-in process, to be performed at the same testing stage. Test trays which contain the semiconductor devices are used throughout an in-line system so that an entire back-end process can be performed without loading / unloading the semiconductor devices between the various tests. The in-line system includes multiple test and burn-in apparatuses as well as a single sorting unit which performs a composite sorting operation after all the testing processes. A method for testing semiconductor devices in the in-line system includes testing the semiconductor devices in the test trays using the test and burn-in apparatus, transferring the test trays to a different testing apparatus for a second testing, and finally sorting the semiconductor devices after all testing processes have been performed based on a final sorting map created by combining test tray maps generated during each of the tests.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
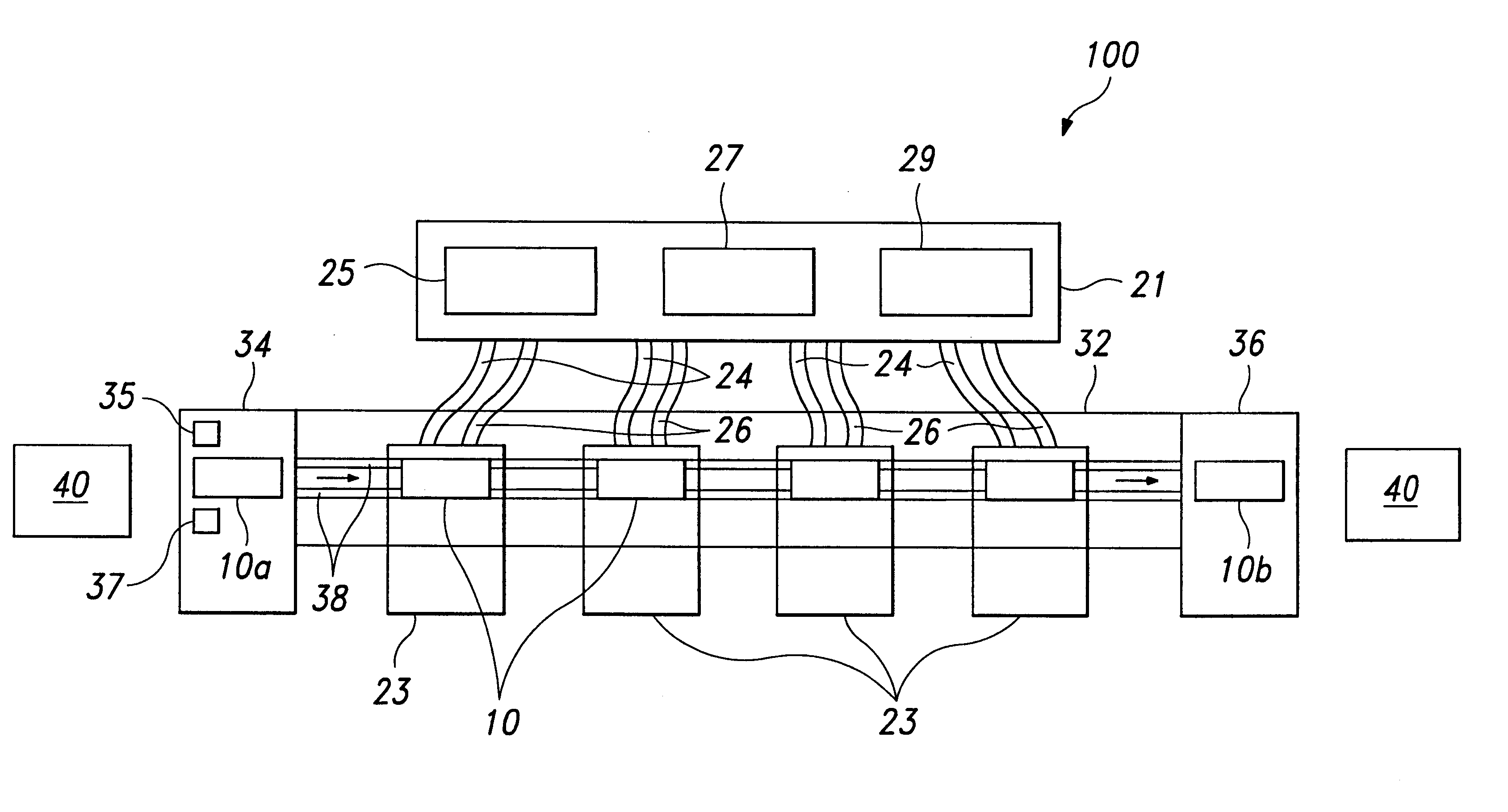
Test and burn-in apparatus, in-line system using the test and burn-in apparatus, and test method using the in-line system
InactiveUS6313652B1Reduced number of stepAvoid excess performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingGeneration processDevice material
A test and burn-in apparatus for semiconductor chip package devices, an in-line system which includes the test and burn-in apparatus, and a test method which employs the in-line system are provided. A test and burn-in apparatus for testing semiconductor devices allows various testing processes, including a burn-in process, to be performed at the same testing stage. The apparatus employs test trays which contain the semiconductor devices. These test trays are used throughout the in-line system so that an entire back-end process can be performed without the need for loading / unloading the semiconductor devices into and from device trays between the various tests. The test and burn-in apparatus according to this invention can therefore occupy less space than the prior art testing apparatuses. The in-line system includes multiple test and burn-in apparatuses as well as a single sorting unit which performs a composite sorting operation after all the testing processes have been performed. Furthermore, the method for testing the semiconductor devices in the in-line system includes testing the semiconductor devices in the test trays using the test and burn-in apparatus, generating a test tray map corresponding to results of the test, transferring the test trays to a different testing apparatus for a second testing and test tray map generation process, and finally sorting the semiconductor devices in the sorting unit after all testing processes have been performed based on a final sorting map created by combining the test tray maps of each of the tests. The benefits of this invention are reduced time and space requirements because neither transferring the devices to device trays between tests nor performing multiple sorting steps are required.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Silicon anti-fuse structures, bulk and silicon on insulator fabrication methods and application
A method and semiconductor structure that uses a field enhanced region where the oxide thickness is substantially reduced, thereby allowing antifuse programming at burn-in voltages which do not damage the standard CMOS logic. The semiconductor device comprises a substrate that has a raised protrusion terminating at a substantially sharp point, an insulator layer over the raised protrusion sufficiently thin to be breached by a breakdown voltage applied to the sharp point, a region comprised of a material on the insulator over the raised protrusion for becoming electrically coupled to the substrate after the insulator layer is breached by the breakdown voltage, and a contact for supplying the breakdown voltage to the substrate. In a second embodiment, the semiconductor device comprises a substrate having a trough formed in a top surface of the substrate, a relatively thick insulator layer over the top surface of the substrate, a relatively thin insulator layer over the trough that is breached by a breakdown voltage applied to the trough, a region comprised of a material on the relatively thin insulator layer over the trough for becoming electrically coupled to the substrate after the relatively thin insulator layer is breached by the breakdown voltage, and a contact for supplying the breakdown voltage to said substrate.
Owner:IBM CORP
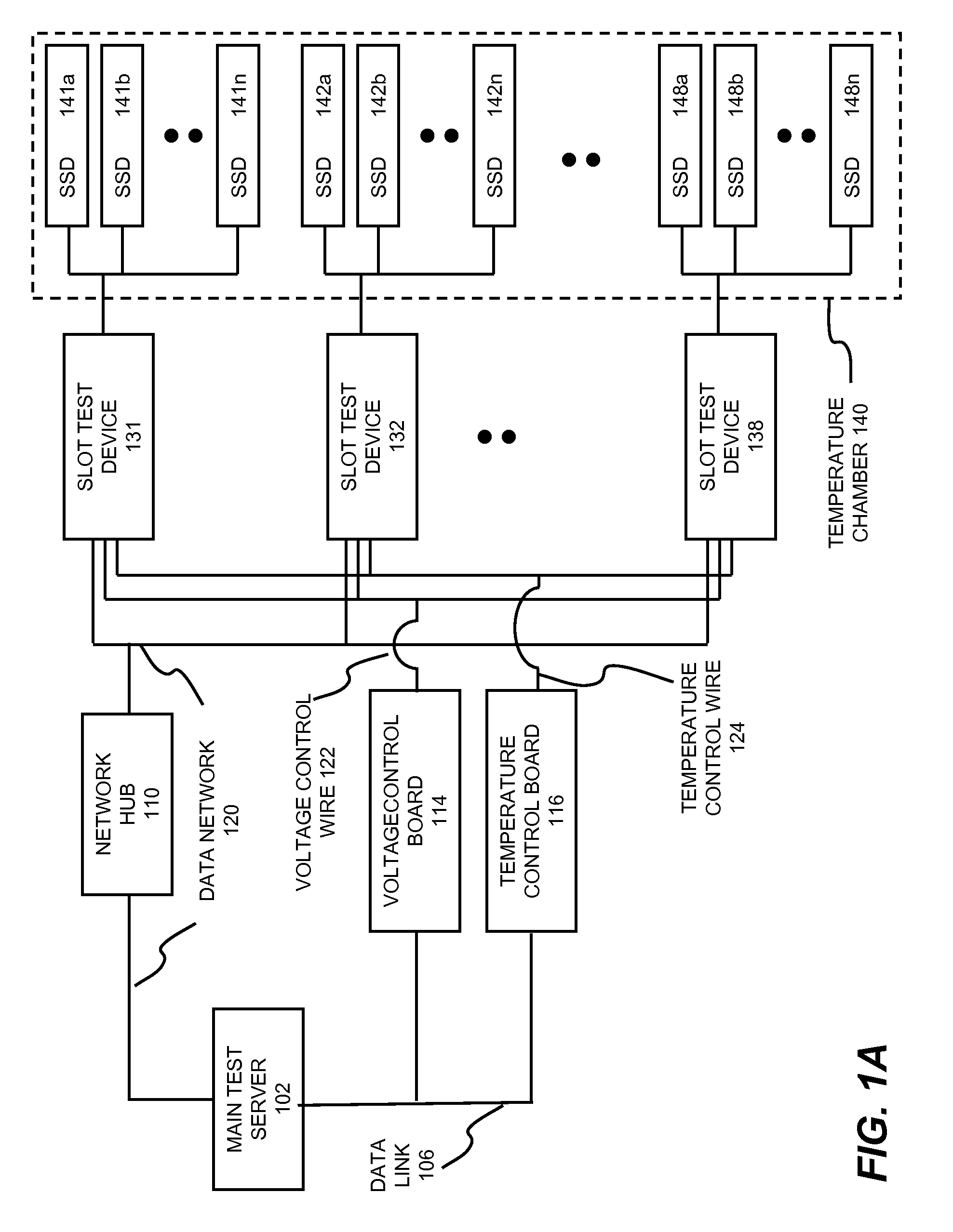
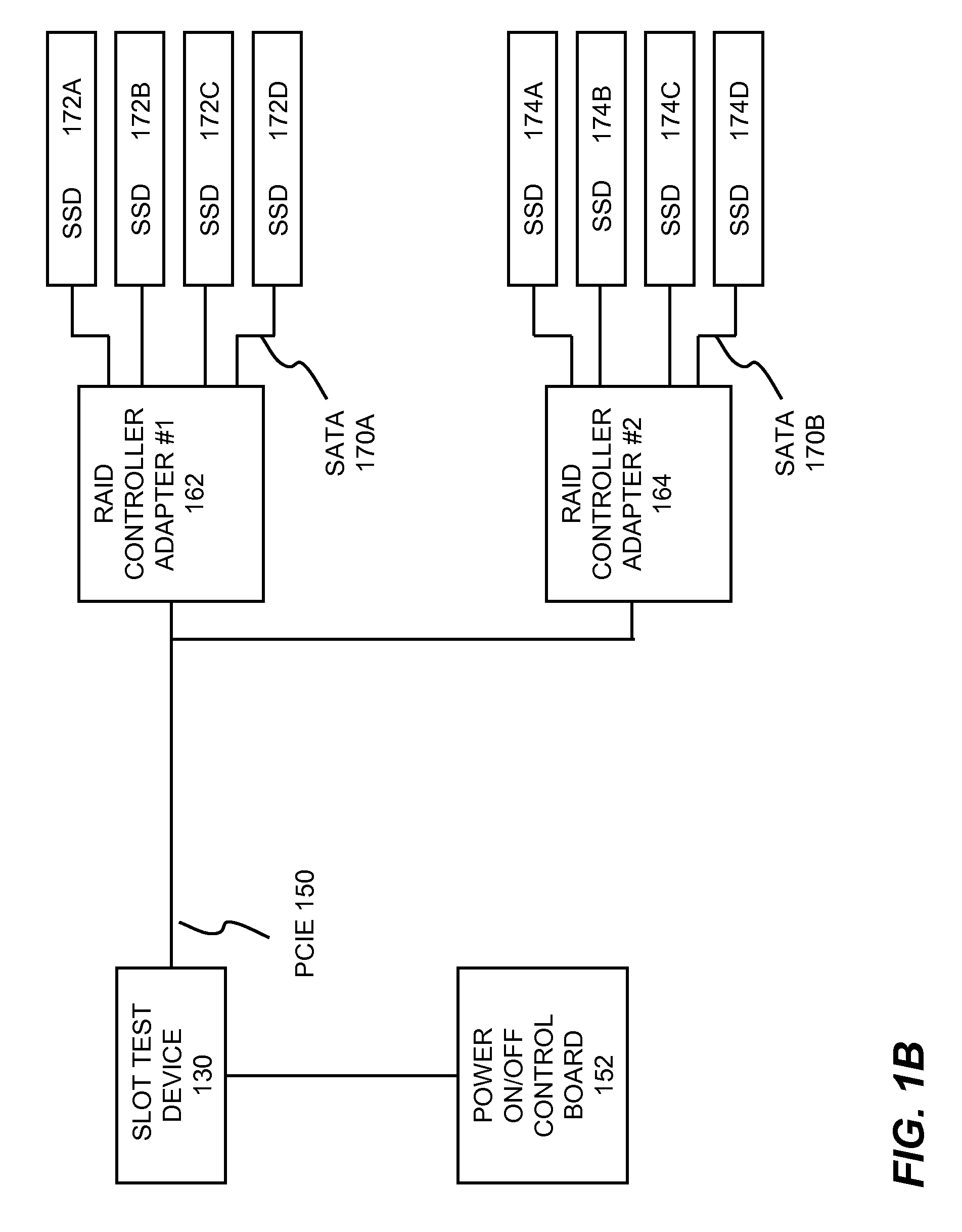
SSD test systems and methods
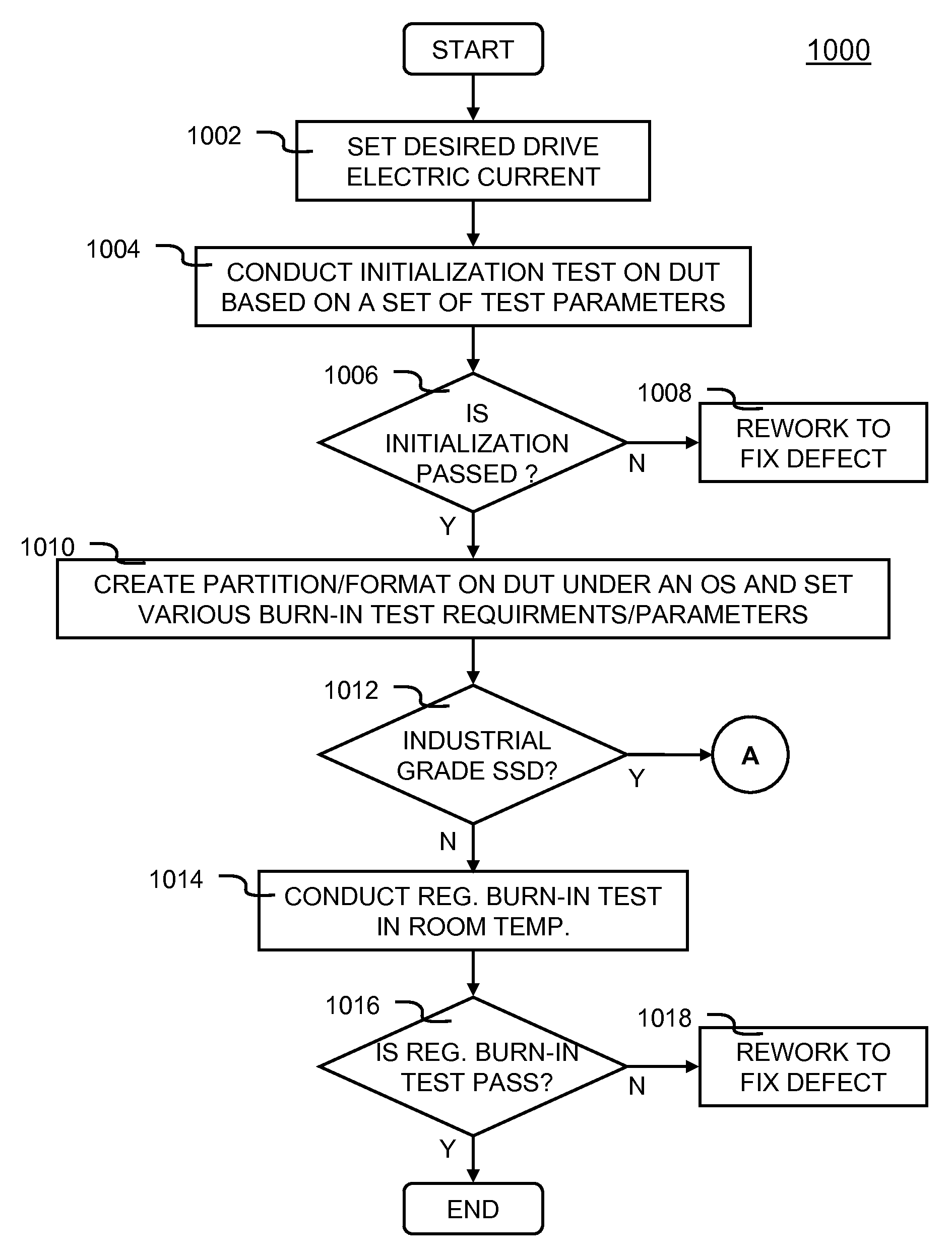
Solid state drive (SSD) testing processes and methods are disclosed. In one embodiment, the SSD testing process comprises: specifying a set of test parameters of firmware, operating system and flash memory for a plurality of SSDs under test (DUTs) in an SSD test system, the set of test parameters includes a model number, a serial number, a desired defective or bad block ratio and a size of the firmware, wherein the model and serial number are configured onto each of the DUTs; performing an initialization test of all of the DUTs based on the specified test parameters to determine a pre-qualified group of the DUTs that passed the initialization test; conducting at least one level of burn-in test for each SSD in the pre-qualified group; conducting at least one level of burn-in test for each SSD in the pre-qualified group; and assigning a quality grade to said each SSD based on which level of the at least one level of burn-in test said each SSD has been tested and passed, wherein the quality grade includes a commercial grade SSD made using at least one Multi-Level Cell flash memory.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
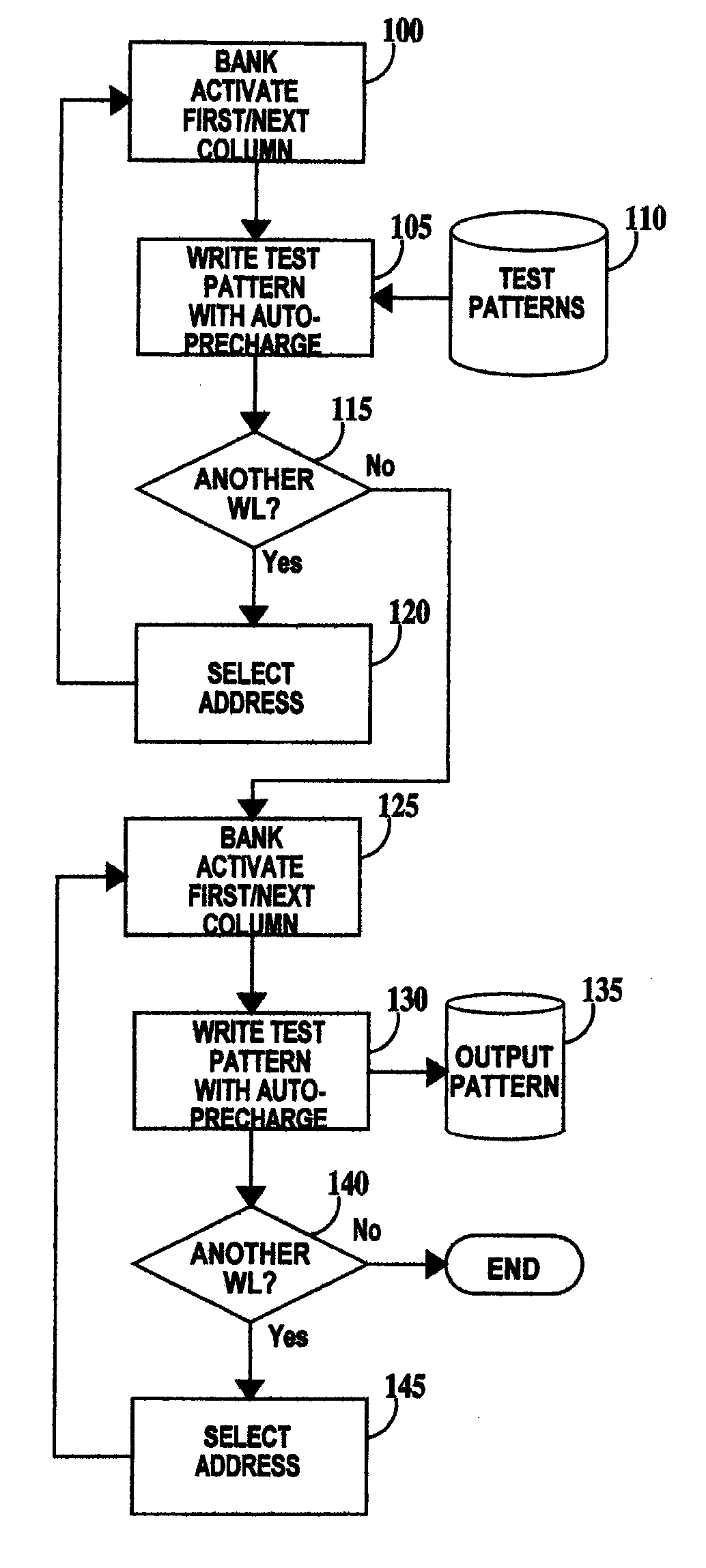
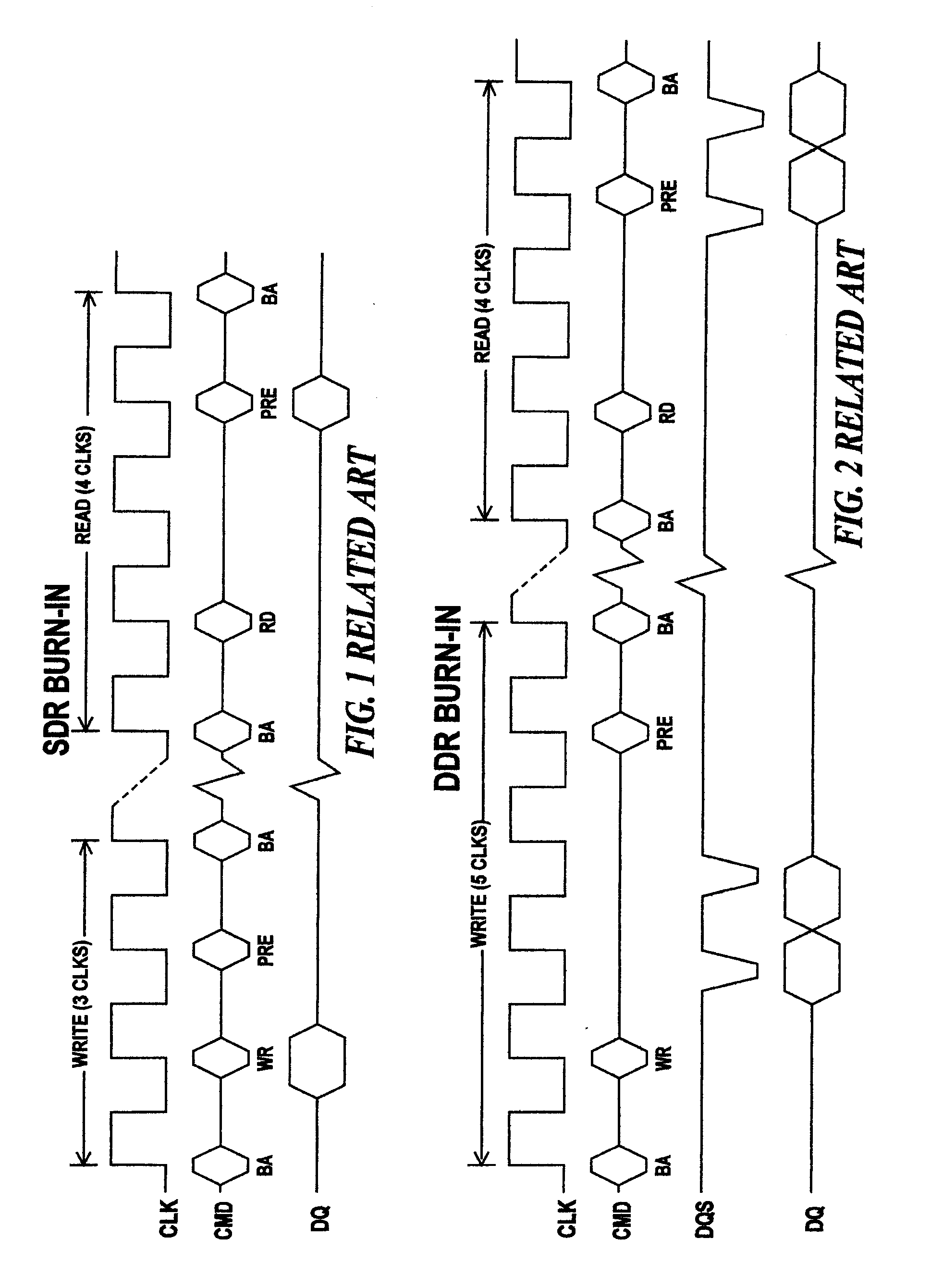
Method for performing a burn-in test
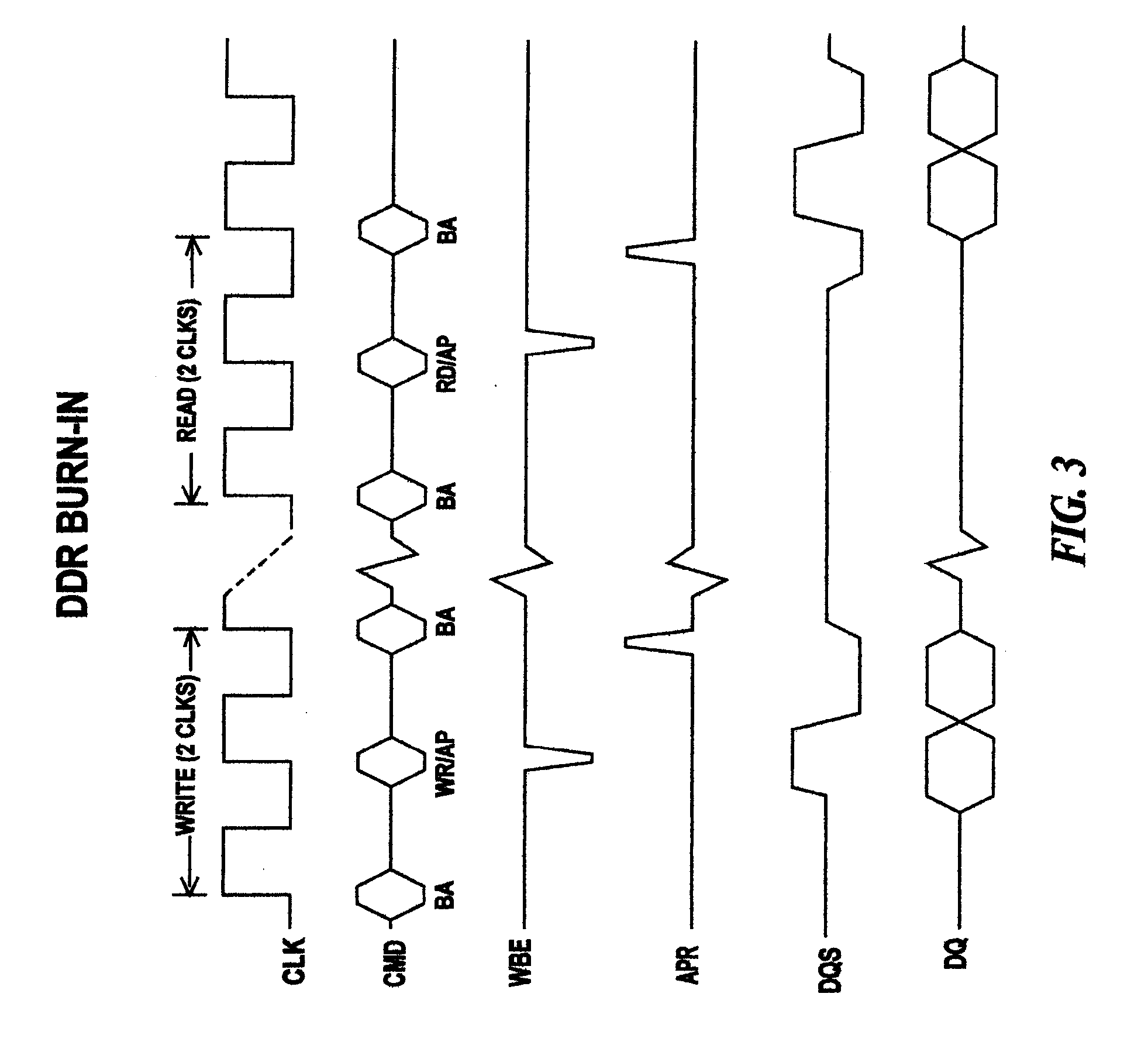
A method for testing a DDR DRAM having a test mode and an operational mode is described. The method including in the order recited: (a) placing the DDR DRAM in test mode; (b) issuing a bank activate command to select and bring up a wordline selected for write of the DDR DRAM; (c) writing with auto-precharge, a test pattern to cells of the DDR DRAM; (d) repeating steps (b) and (c) until all wordlines for write have been selected; (e) issuing a bank activate command to select and bring up a wordline selected for read of the DDR DRAM; (f) reading with auto-precharge, the stored test pattern from cells of the DDR DRAM; and (g) repeating steps (e) and (f) until all wordlines for read have been selected.
Owner:QIMONDA +1
Wafer probe card
InactiveUS6265888B1Electrical measurement instrument detailsFault location by increasing destruction at faultProbe cardSpeed test
An apparatus to heat and test a semiconductor wafer includes a probe card and tests a plurality of die simultaneously at the wafer level. In the present invention, the apparatus heats the wafer to sufficient temperatures to perform burn-in and a speed test. A method of testing the semiconductor allows certain die to be repaired that would otherwise be scrapped in a conventional process where bun-in and other tests are performed on packaged die. The method also eliminates steps associated with handling individually packaged parts, reduces burn-in space and consolidates certain test steps.
Owner:SCS HIGHTECH +1
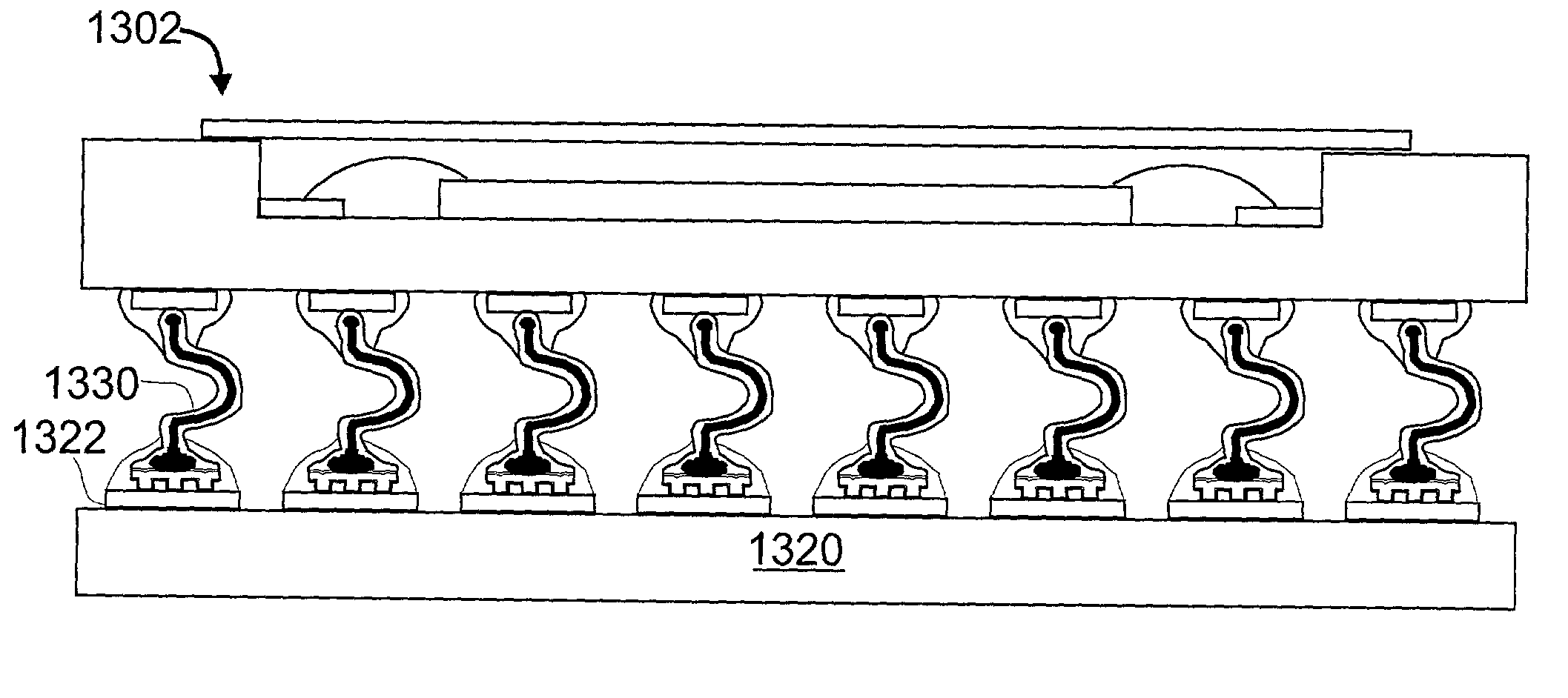
Method and structure of in-situ wafer scale polymer stud grid array contact formation
InactiveUS20020121702A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact formationThermoplastic
Methods and structures of in-situ wafer scale polymer stud grid array (ISWS-PSGA) contact formation on integrated circuit devices, wherein a separate pre-manufactured PSGA substrate is not needed. The methods include injection molding of thermoplastics, transfer-molding of thermoset materials, lamination of polymer films with subsequent in-situ molding / embossing, and forming the PSGA structure directly on the semiconductor wafer. The ISWS-PSGA structure extends across the entire semiconductor wafer, with ISWS-PSGA metallized input / output studs disposed across each of the integrated circuit devices on the wafer. The polymer formed on the wafer surface to create the stud field is extended beyond the perimeter of the wafer, and the polymer film extension is used for temporary connection to an integrated circuit tester, or an integrated circuit test / burn-in system. The extension may further include studs for contacting the tester.
Owner:SIEMENS DEMATIC
System and method for controlling temperature during burn-in
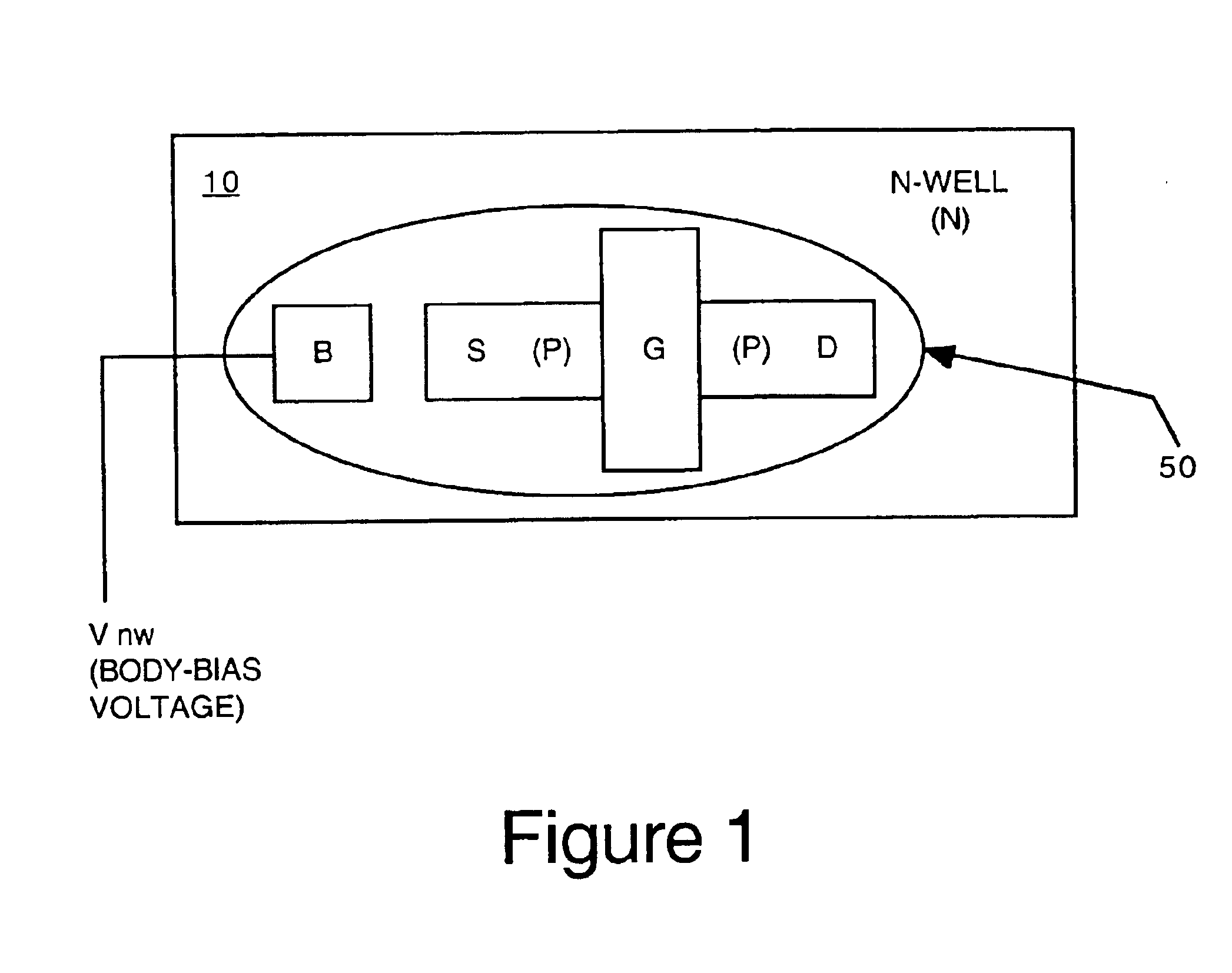
ActiveUS6900650B1Electronic circuit testingFault location by increasing destruction at faultJunction temperatureVoltage
Systems and methods for reducing temperature dissipation during burn-in testing are described. Devices under test are each subject to a body bias voltage. The body bias voltage can be used to control junction temperature (e.g., temperature measured at the device under test). The body bias voltage applied to each device under test can be adjusted device-by-device to achieve essentially the same junction temperature at each device.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
Dynamic burn-in equipment
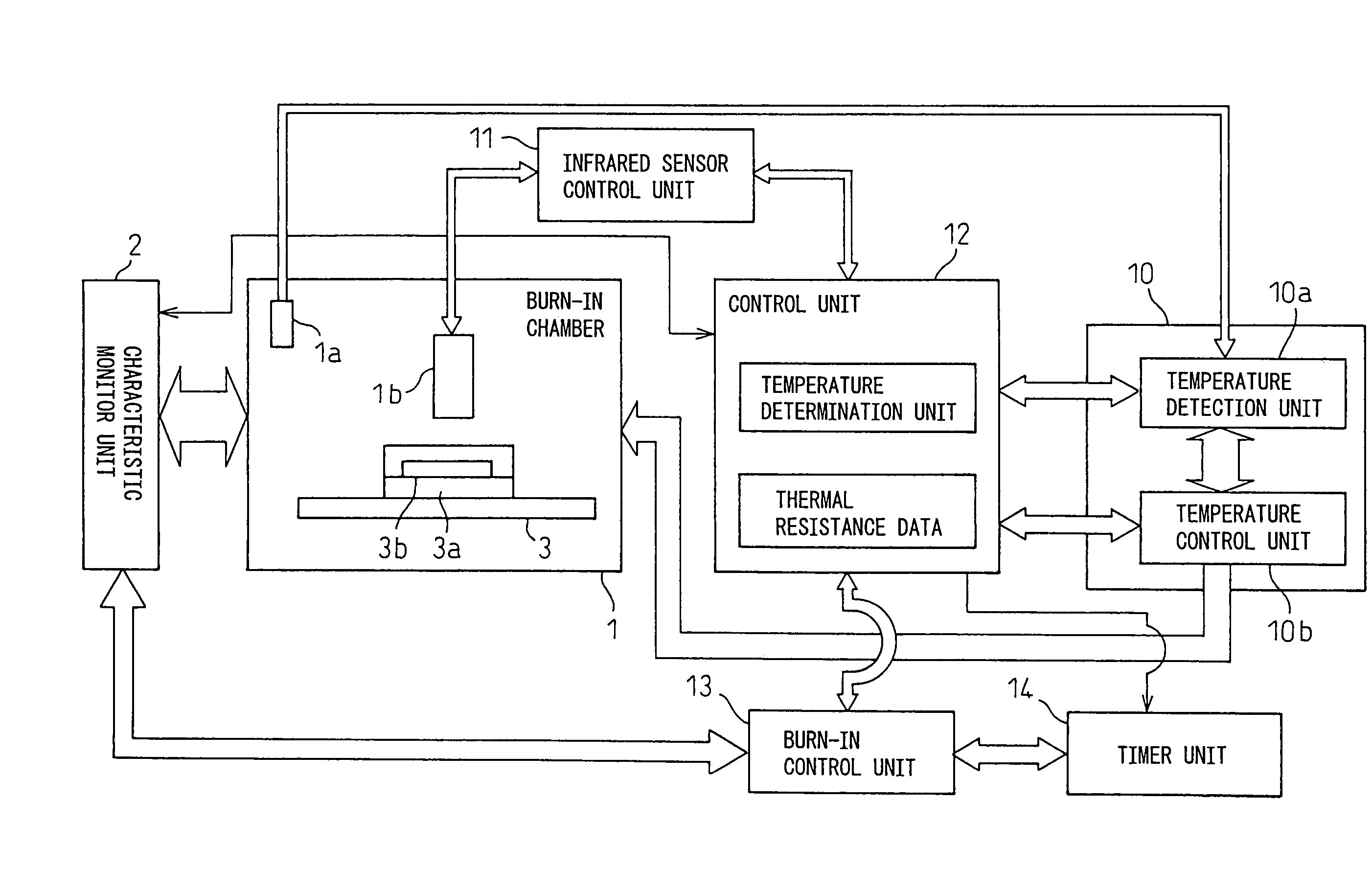
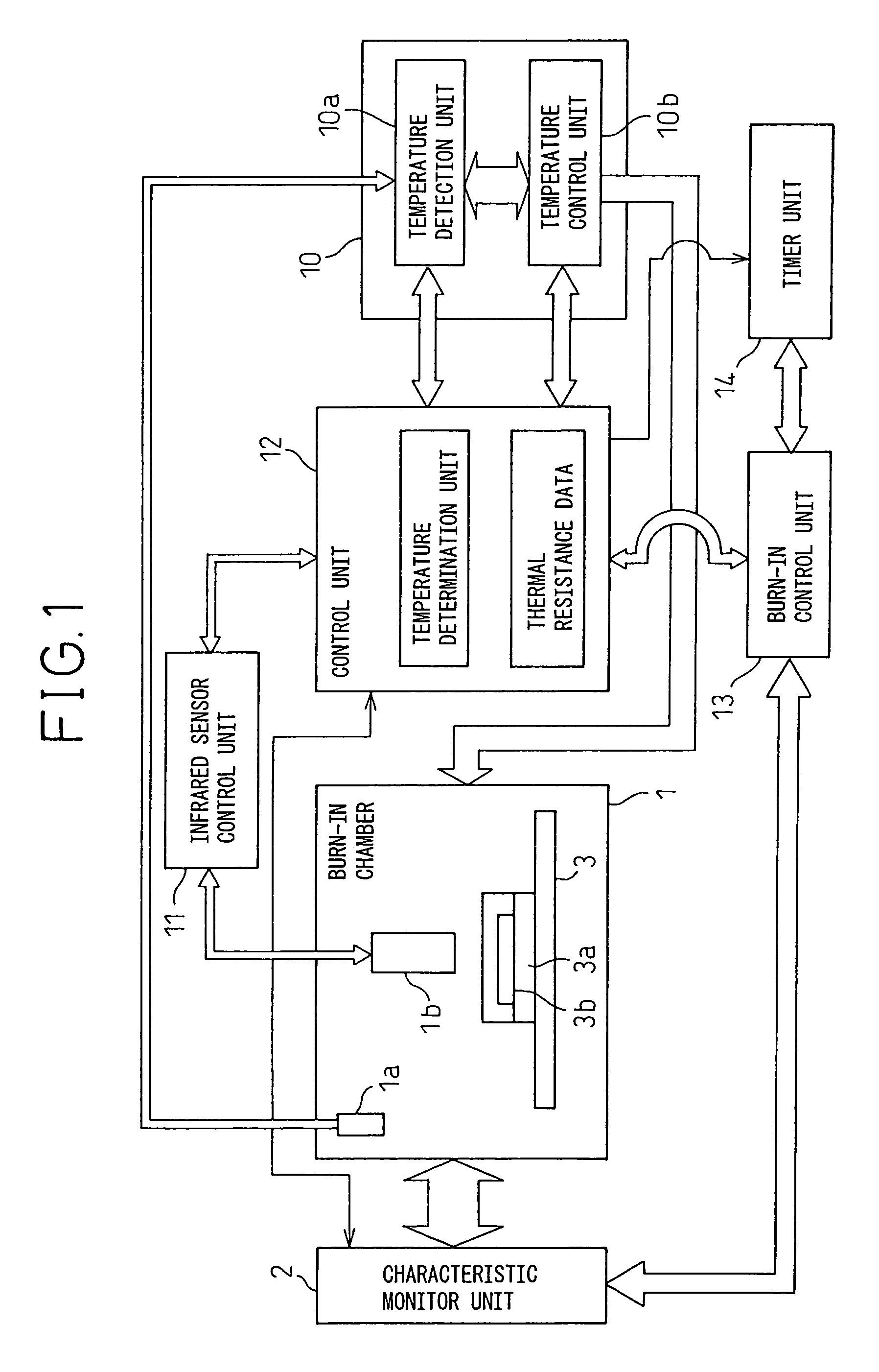
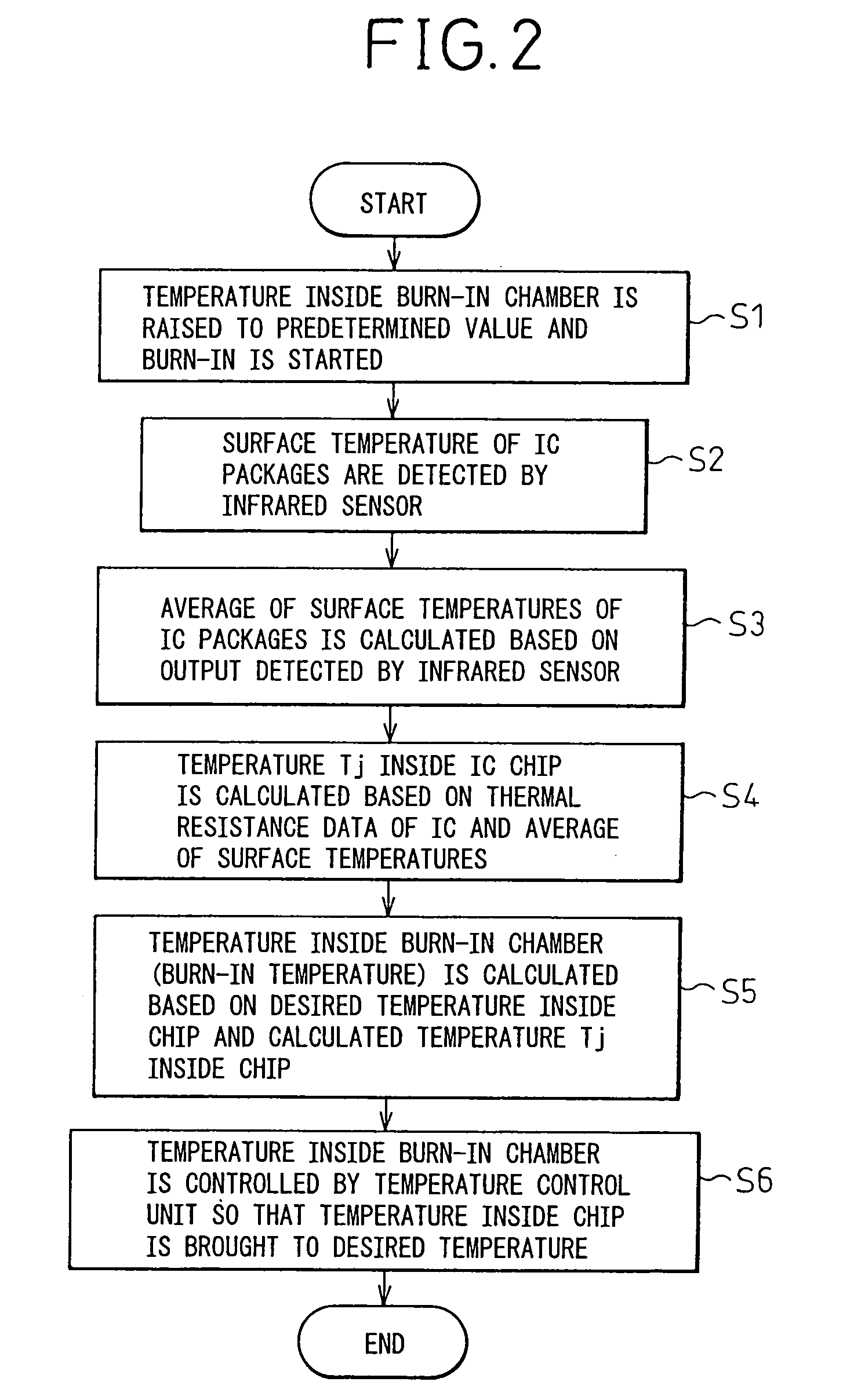
InactiveUS7023229B2Easy to controlFault location by increasing destruction at faultIndividual semiconductor device testingEngineeringInternal temperature
An infrared sensor is provided in a burn-in chamber. The surface temperatures of two or more semiconductor devices are measured by the sensor. A control unit calculates the internal temperatures of the semiconductor devices based on the thermal resistance values of the semiconductor device packages and controls the temperature inside the burn-in chamber so that the average of the internal temperatures is brought to a desired temperature by using a temperature controller. Further, an acceleration coefficient is obtained based on the internal temperatures, a burn-in time is determined based on the acceleration coefficient and a preliminarily given accelerated period, and a burn-in acceleration test is conducted. Moreover, when a defective semiconductor is found, the defective portion of the defective semiconductor device is specified based on the surface temperature distribution of the semiconductor device measured by the infrared sensor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
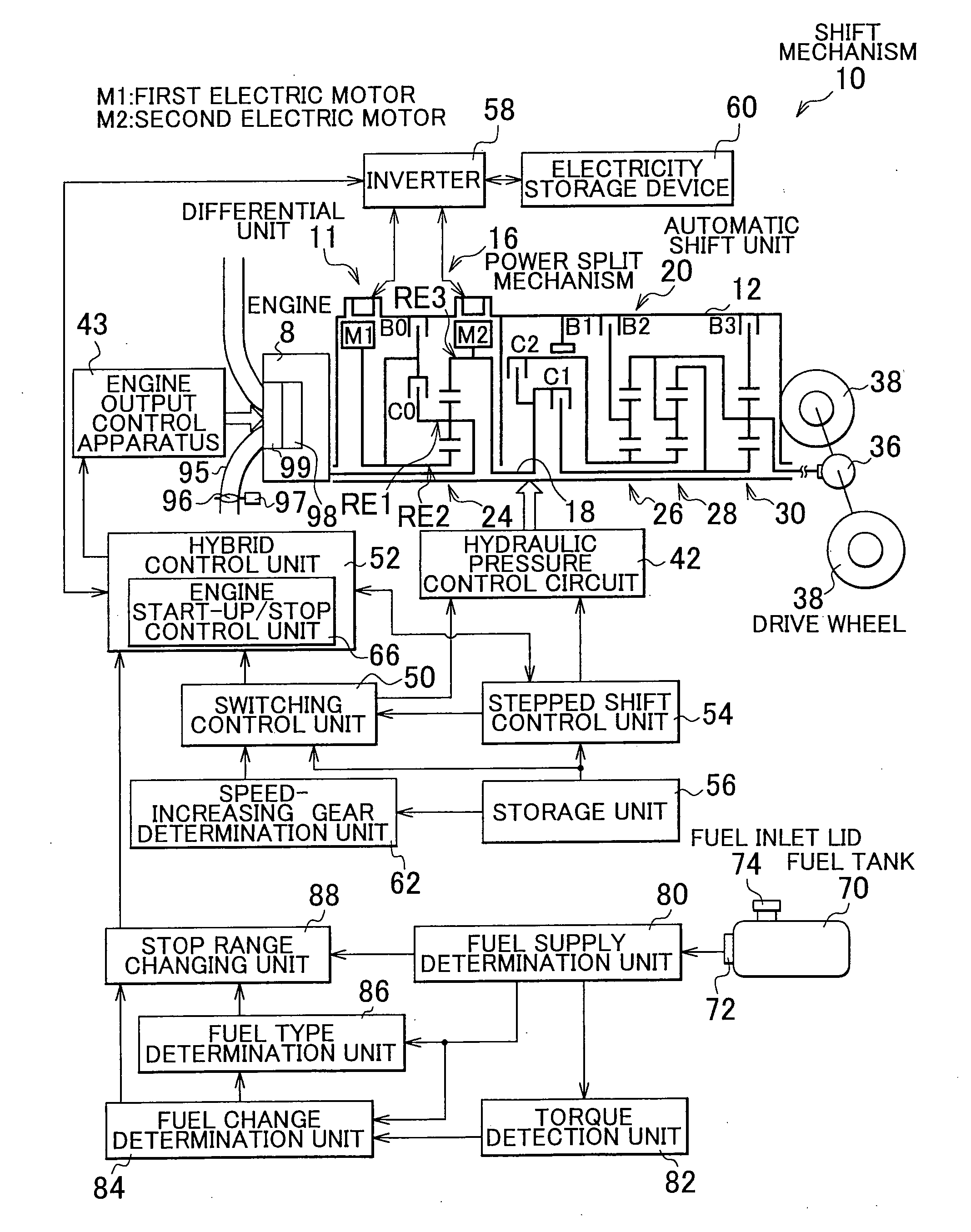
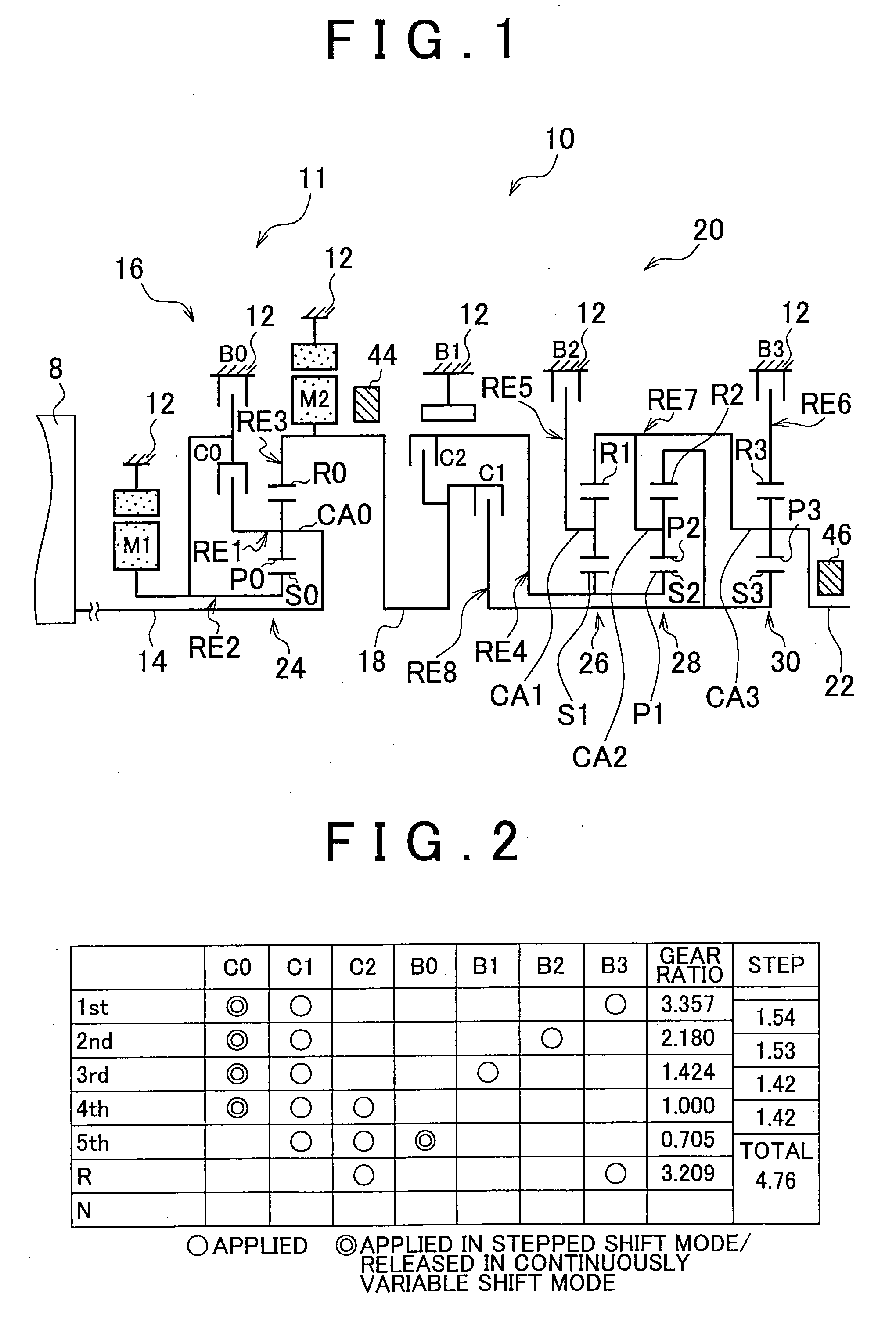
Control apparatus for power transmission system of hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20100138086A1Unfavorable effectDeterioration of start-up performanceHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesFuel typeHybrid vehicle
A stop range changing unit changes an engine stop range, which is a cruise range in which an operation of an engine is stopped, based on a type of fuel that is burned in the engine and that is determined by a fuel type determination unit. Therefore, the engine is stopped or started up under a cruise condition that suits the fuel type. Accordingly, even if start-up performance of the engine varies due to variation of the fuel type, unfavorable effects of the variation in the start-up performance of the engine on a smooth motion of a hybrid vehicle is alleviated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for recovering metal from used Li ion cell
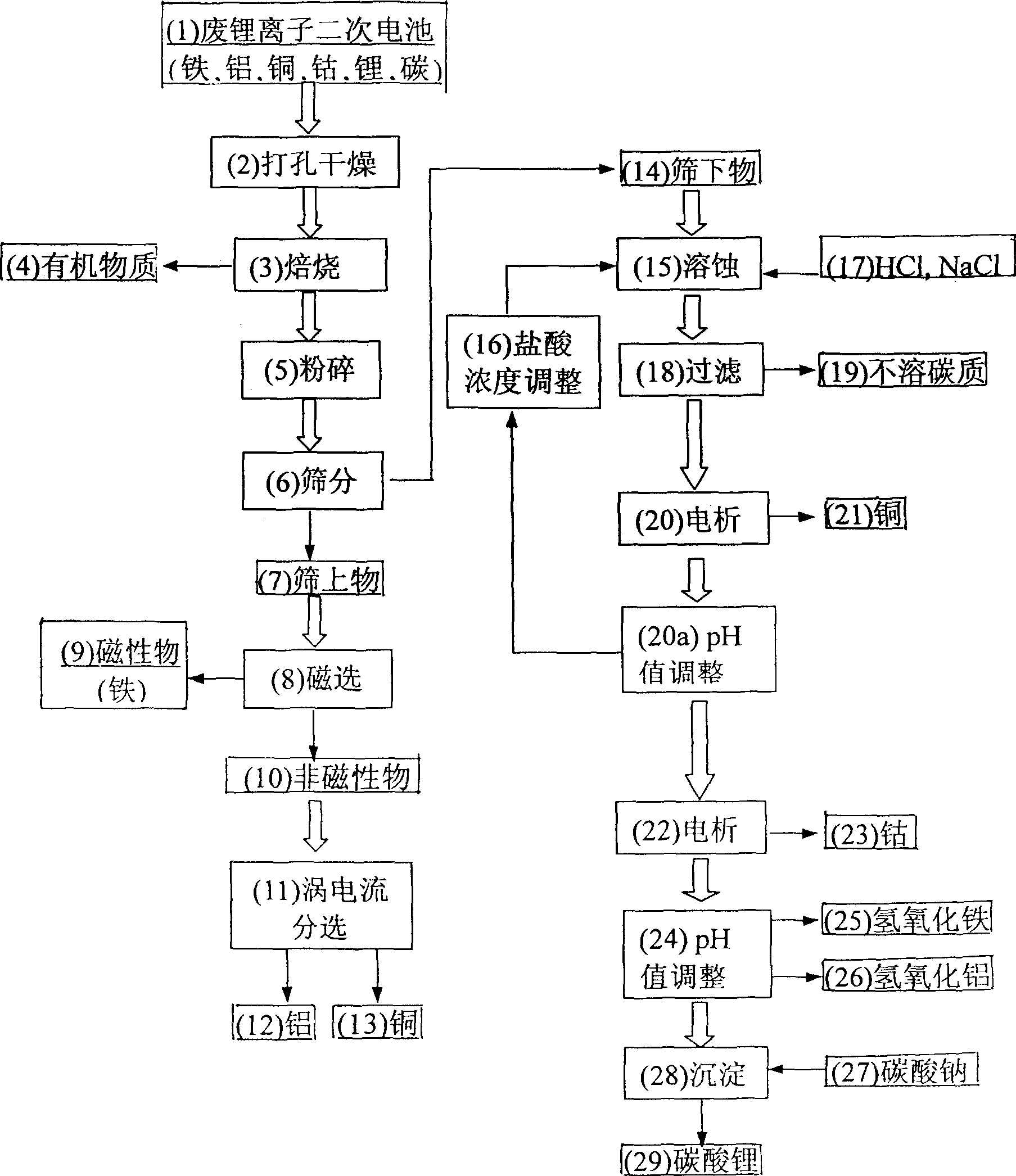
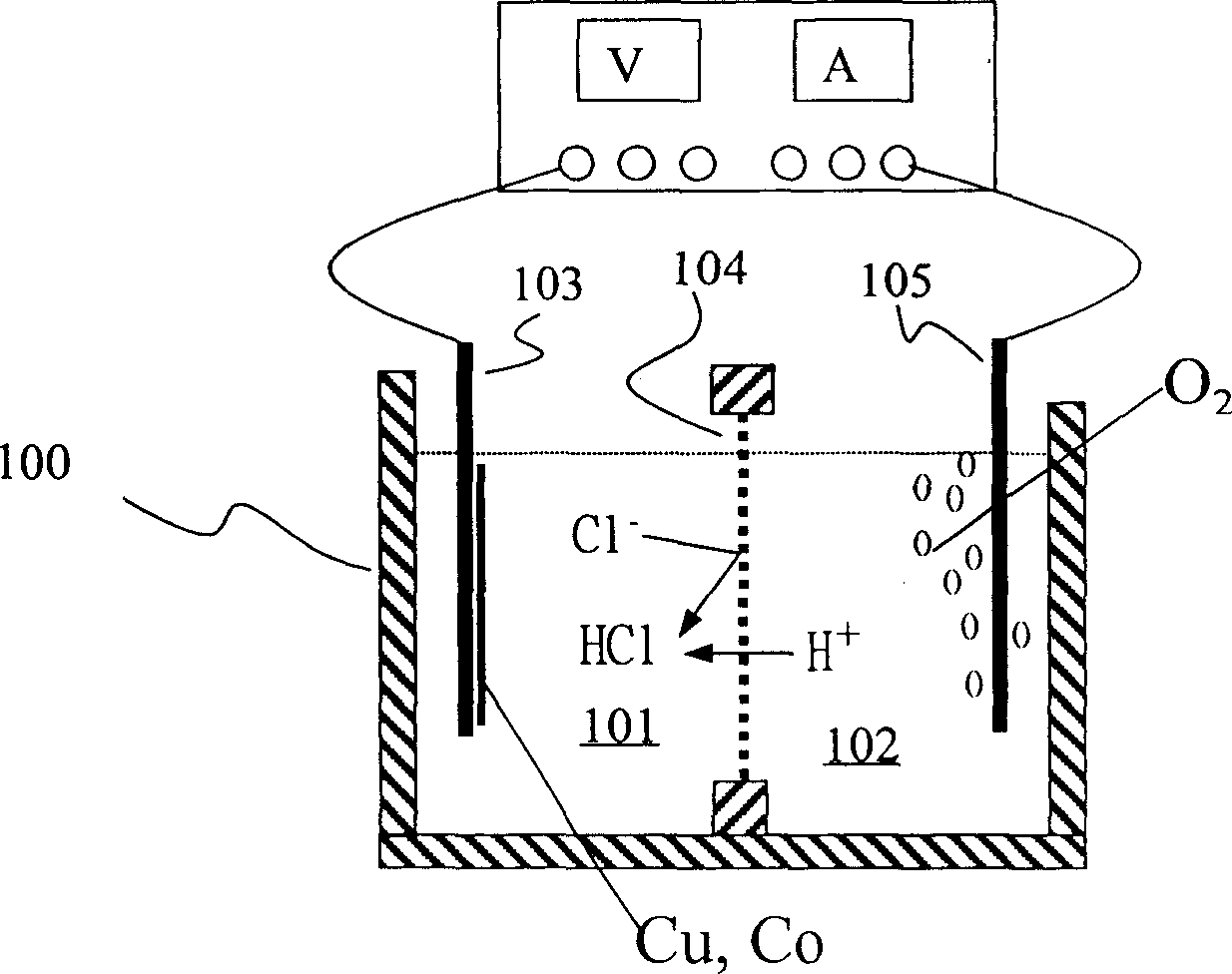
InactiveCN1402376ATo achieve the purpose of separationReduce lossWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingDielectricCopper foil
The invented method includes the physical separation method combining with the preparation procedure of the cleaning wet recycle, providing the features of simple and high purity of the recovered metal. The invention includes following steps. With the disused lithium ion cells being burned in the high-temperature furnace, the organic dielectric is removed. After the smashing and sieving treatment, the oversize material is processed through the magnetic separation and the eddy current sorting so as to obtain the iron case, copper foil and aluminium foil etc. The undersize is processed through the steps of corrosion, filtering and electrolysis so as to obtain copper and cobalt. With carbonic acid radical being added to the solution richen in lithium ion, the high purity carbonate of lithiumis formed so as to recovery lithium.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
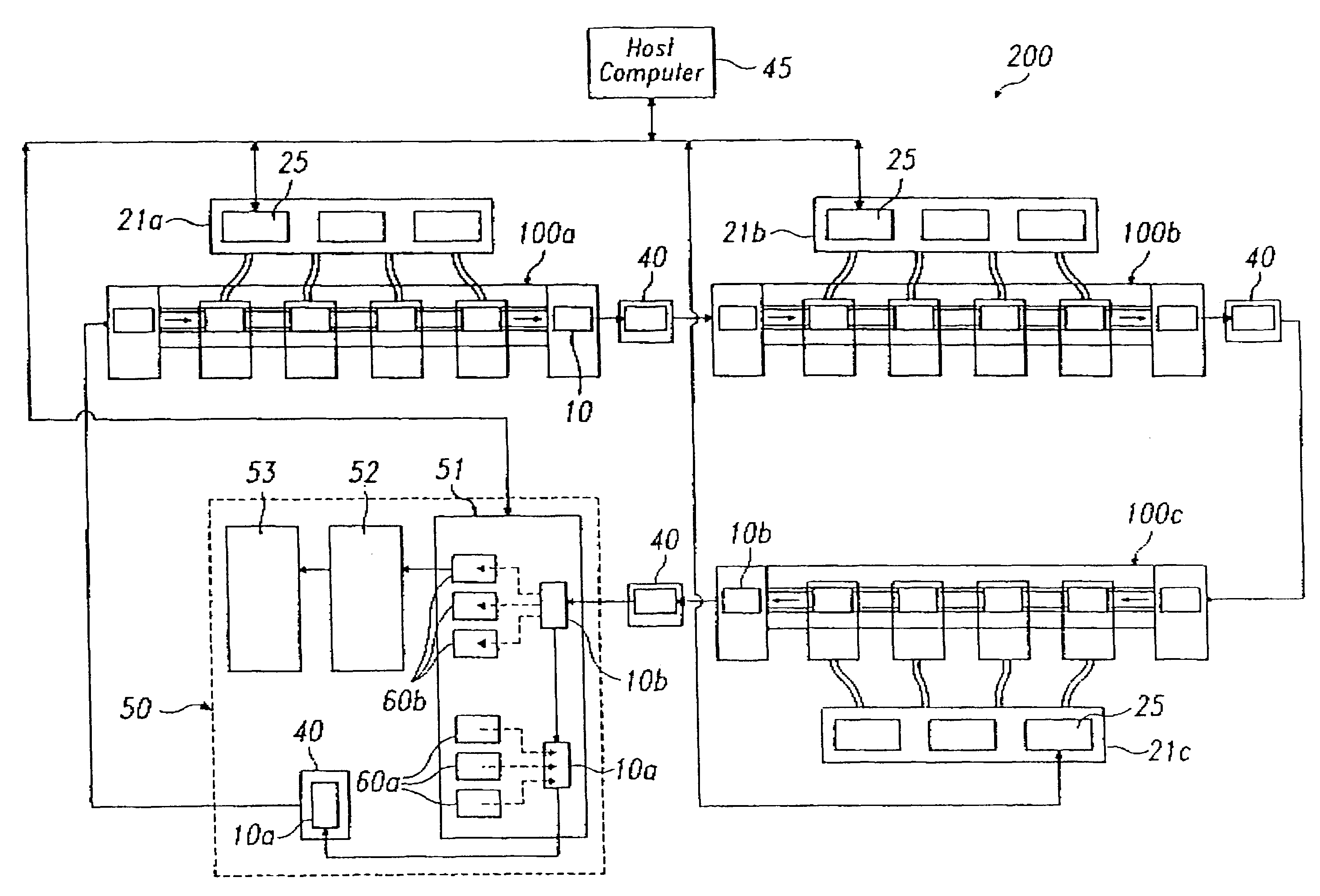
Apparatus for testing hard disk drive
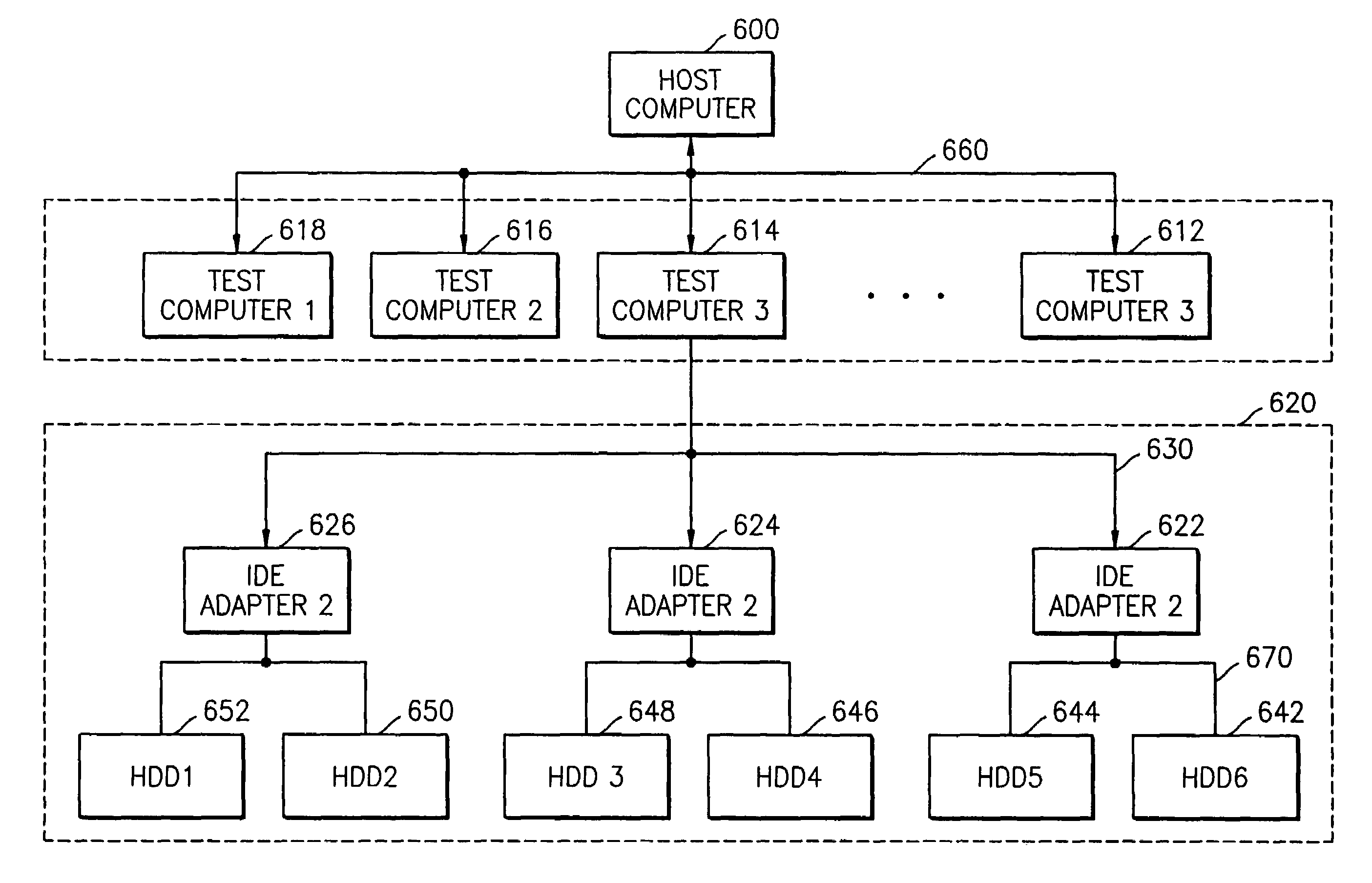
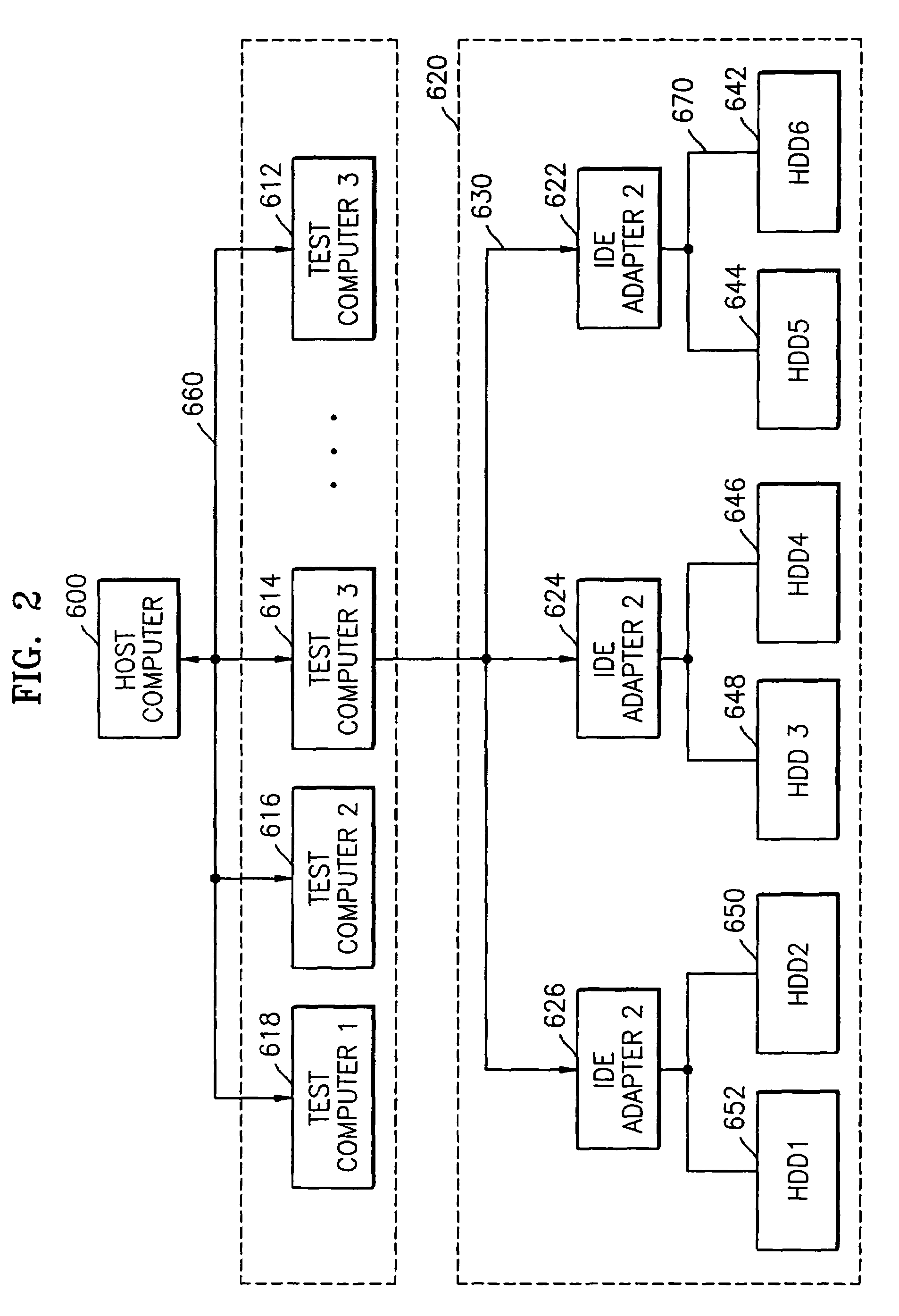
A device testing apparatus, such as a hard disk drive (HDD) testing apparatus, using one host computer to test a plurality of the devices, such as to burn-in test HDDs. A host computer having at least two serial communication ports is communicably connected to power cards which supply operating power to each HDD to be tested. A serial communication exchanger is communicably connected to the serial communication ports of the host computer and to the HDDs, and responds to channel selection instructions issued by the host computer to selectively establish a serial communication channel among HDDs, the power card, and the host computer. The single host computer conducts the testing of the HDDs by communicating with the HDDs via the established serial communication channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method, display apparatus and burn-in reduction device for reducing burn-in on display device
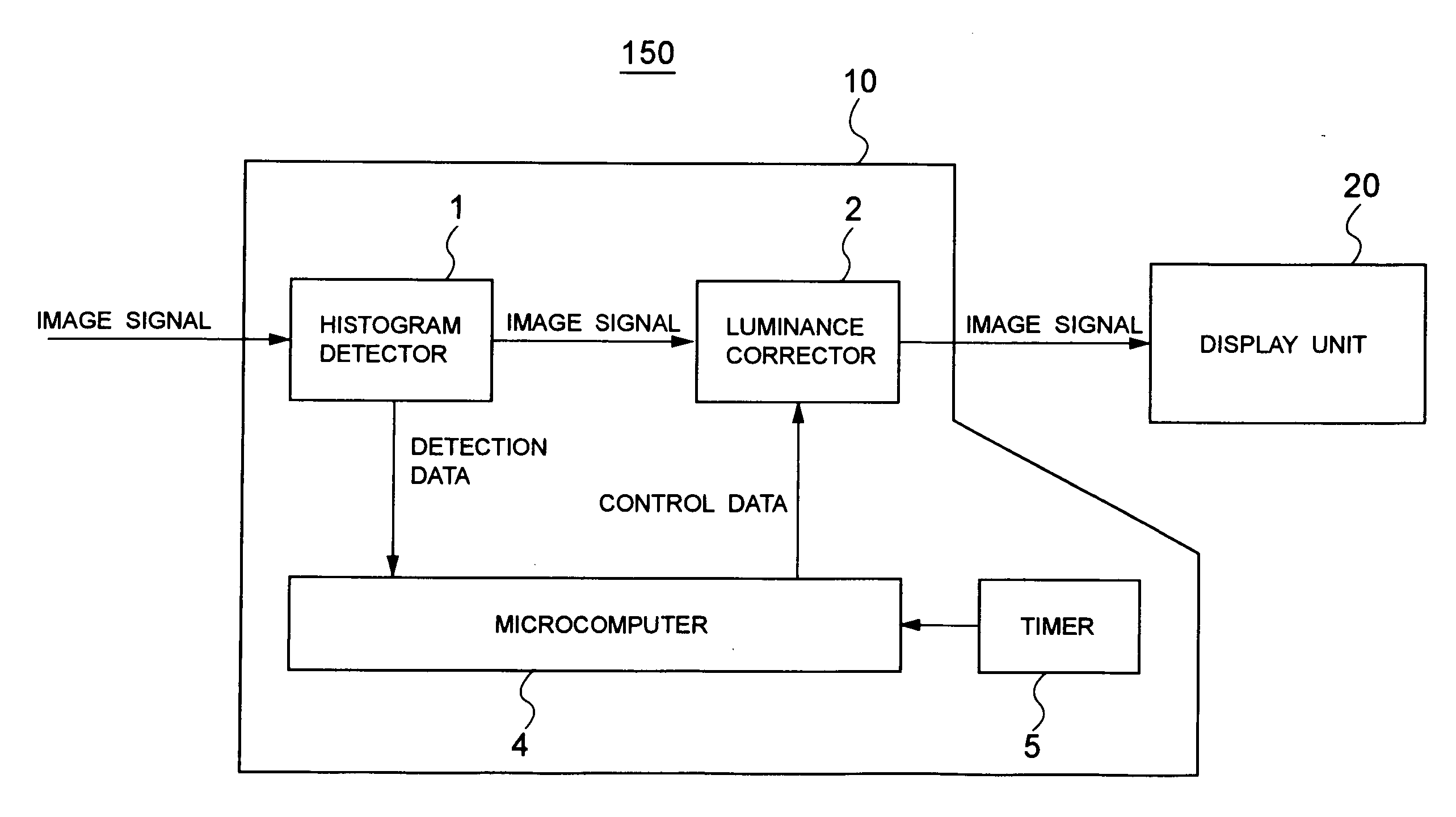
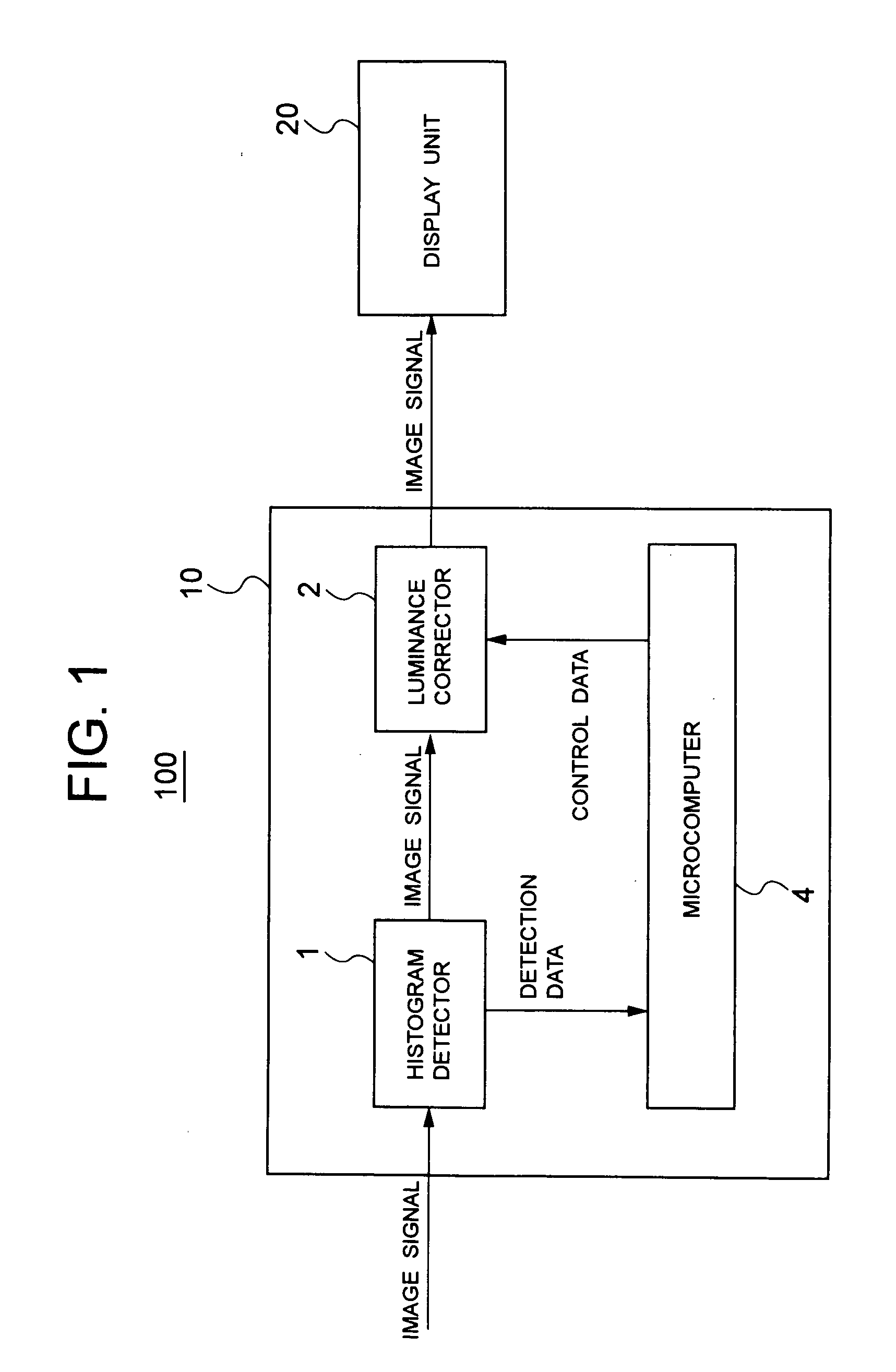
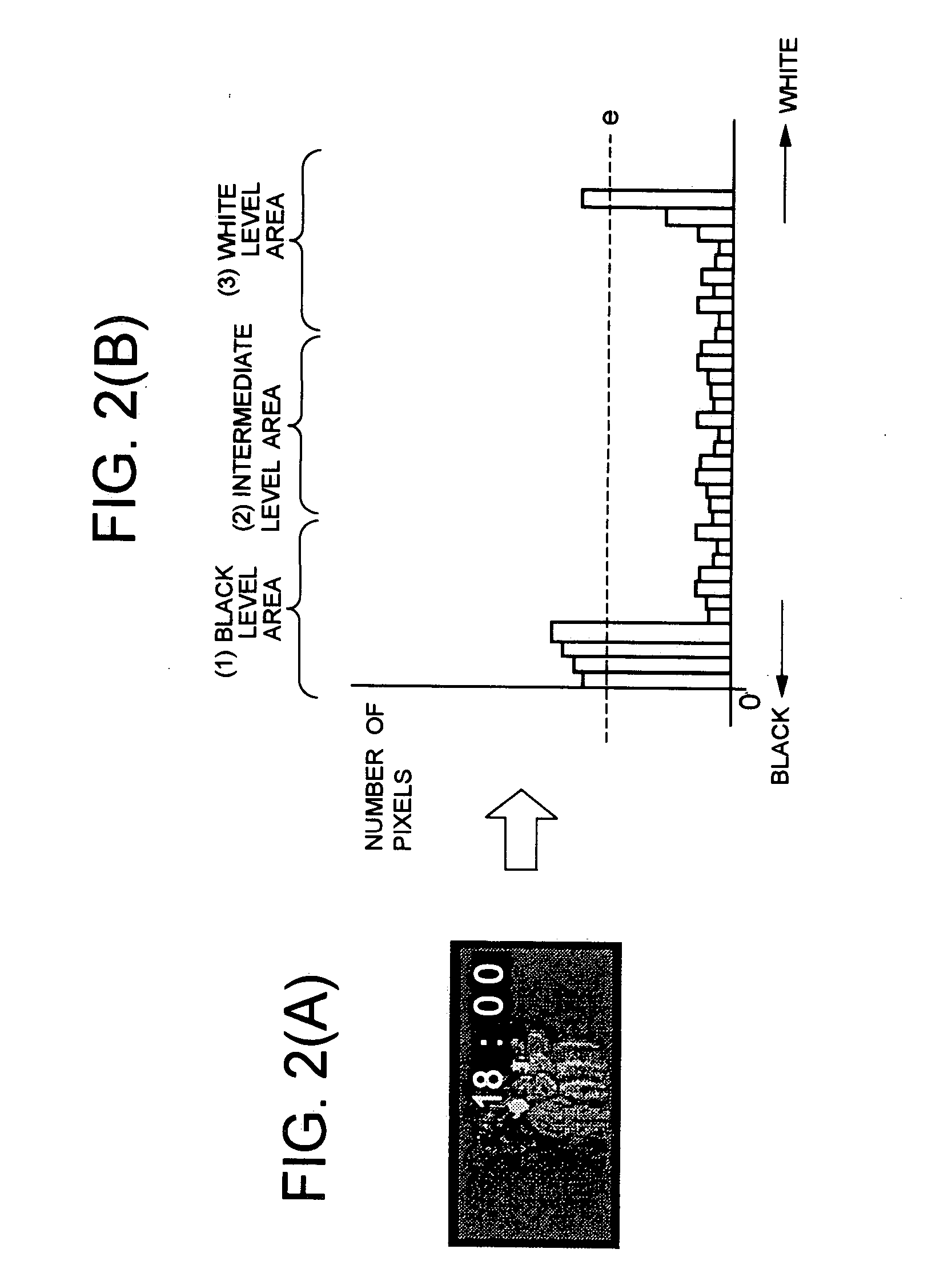
InactiveUS20050212726A1Improve image qualityIncrease the number ofStatic indicating devicesCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceImage signal
Disclosed is a burn-in reduction device capable of favorably reducing burn-in on a screen. The burn-in reduction device comprises luminance level distribution detecting means for detecting a statistical distribution with respect to luminance levels of pixels of an image based on an input image signal; and luminance changing means for changing a luminance level of the input image signal in accordance with the statistical distribution detected by the luminance level distribution detecting means.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Massively parallel interface for electronic circuit
InactiveUS7009412B2Low costShorten the timeElectronic circuit testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectricityEngineering
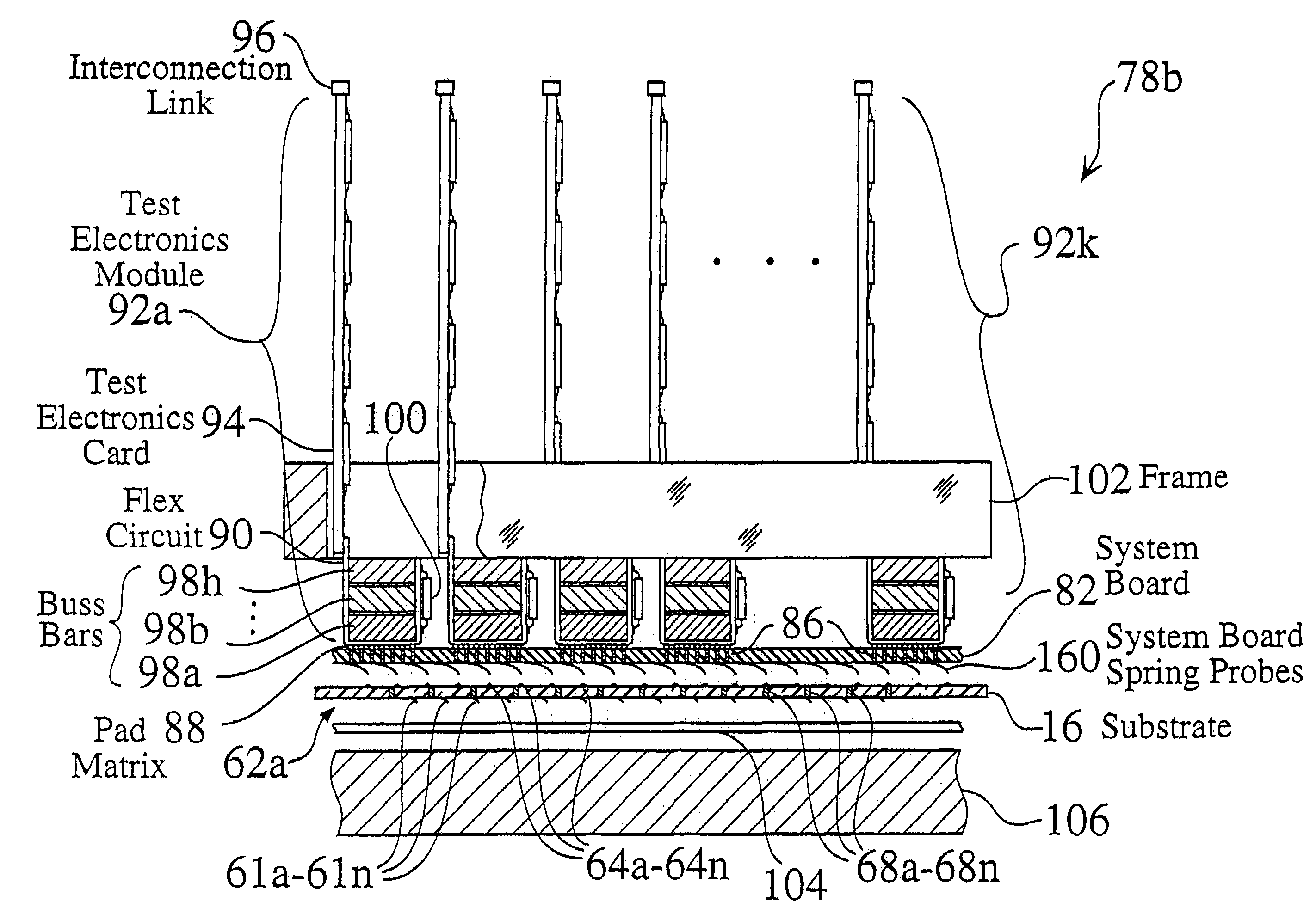
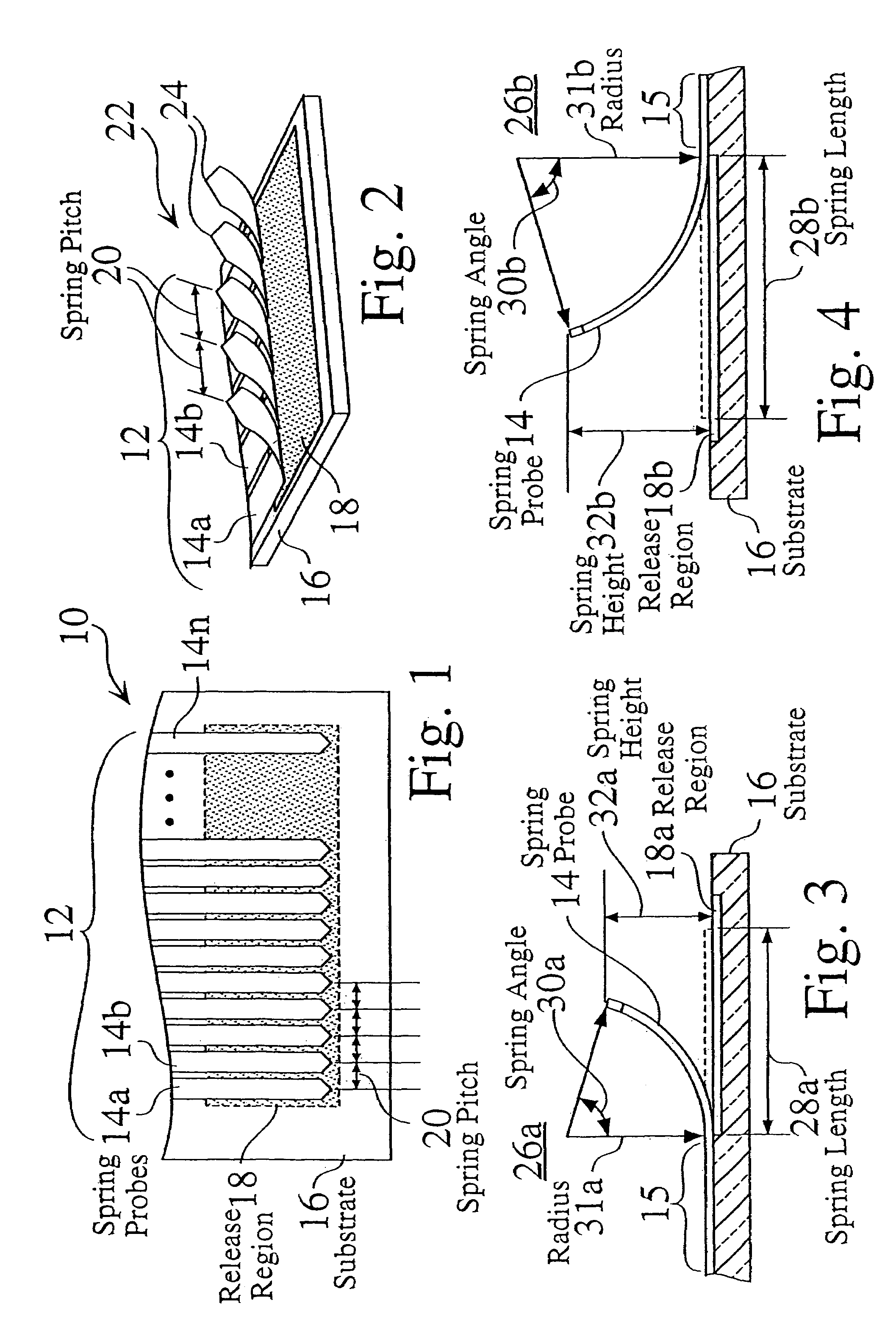
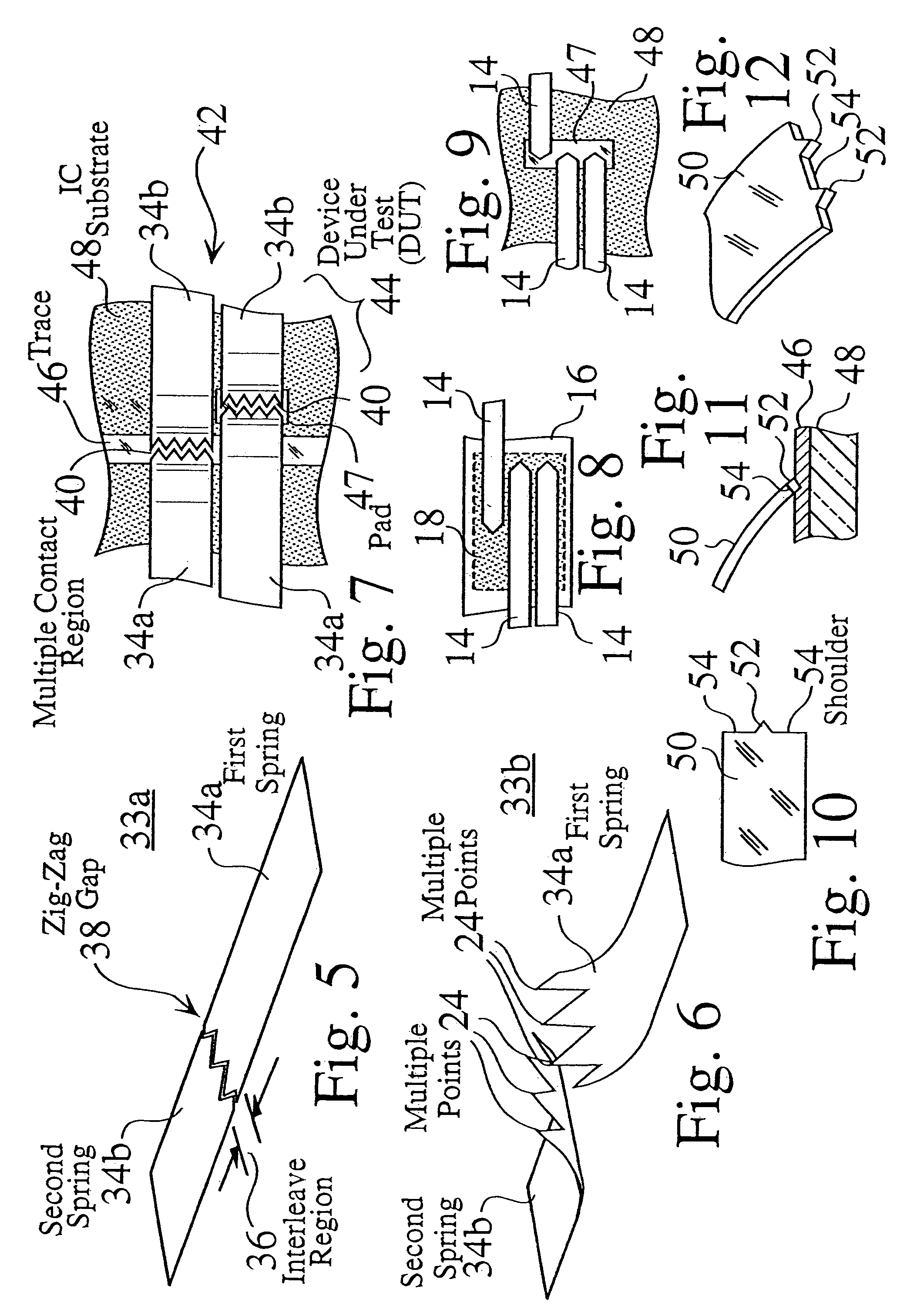
Several embodiments of massively parallel interface structures are disclosed, which may be used in a wide variety of permanent or temporary applications, such as for interconnecting integrated circuits (ICs) to test and burn-in equipment, for interconnecting modules within electronic devices, for interconnecting computers and other peripheral devices within a network, or for interconnecting other electronic circuitry. Preferred embodiments of the massively parallel interface structures provide massively parallel integrated circuit test assemblies. The massively parallel interface structures preferably use one or more substrates to establish connections between one or more integrated circuits on a semiconductor wafer, and one or more test modules. One or more layers on the intermediate substrates preferably include MEMS and / or thin-film fabricated spring probes. The parallel interface assemblies provide tight signal pad pitch and compliance, and preferably enable the parallel testing or burn-in of multiple ICs, using commercial wafer probing equipment. In some preferred embodiments, the parallel interface assembly structures include separable standard electrical connector components, which reduces assembly manufacturing cost and manufacturing time. These structures and assemblies enable high speed testing in wafer form.
Owner:ADVANTEST SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Burn-in test apparatus for BGA packages using forced heat exhaust
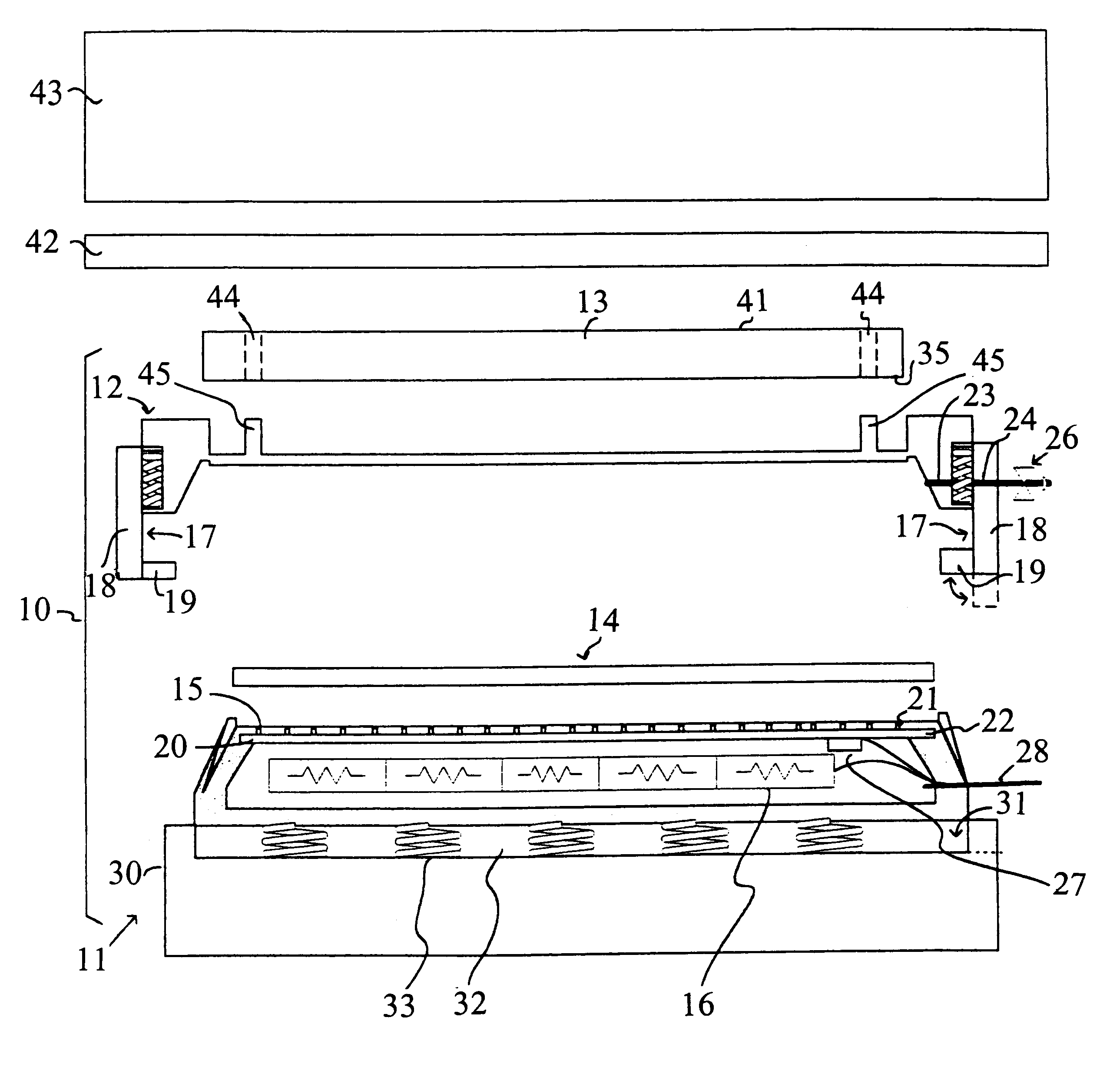
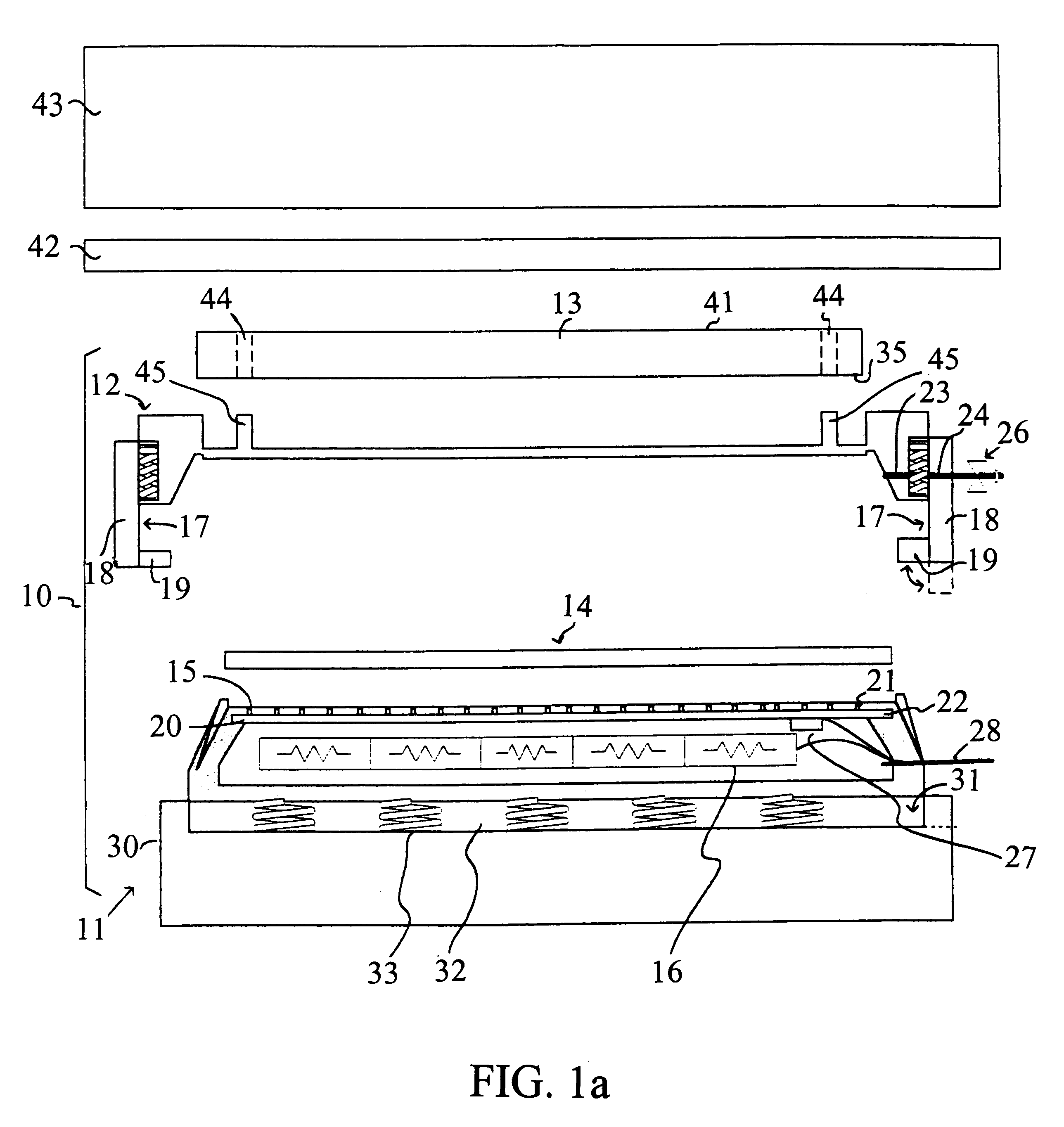
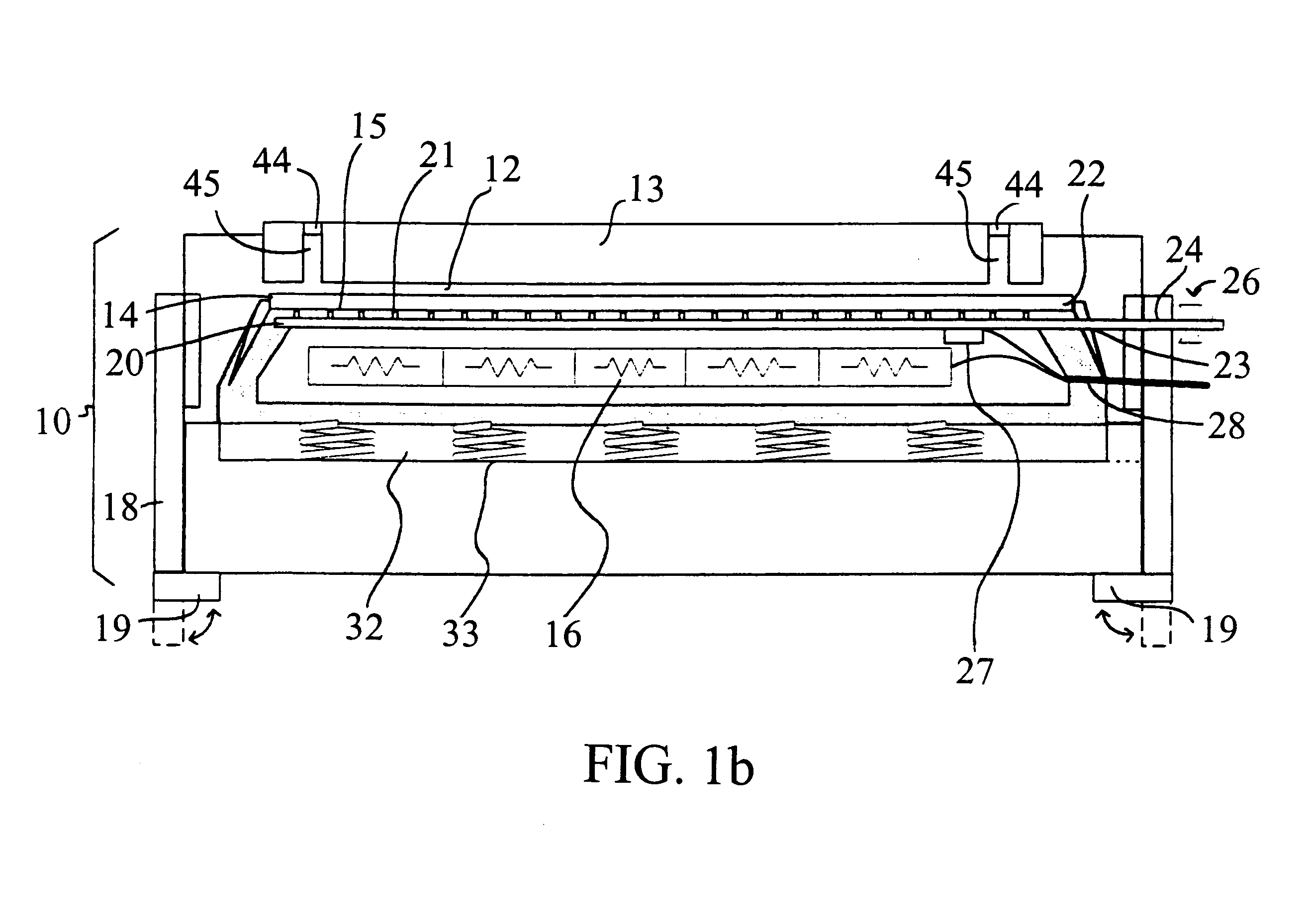
InactiveUS20050179457A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOhmic-resistance electrodesEngineeringForced-air
A forced air heat exhaust type of burn-in test apparatus for packages: A first air supply duct provides air to the burn-in chamber and a second air supply duct provides air to supply tubes that direst air into the test sockets that hold the packages. The test sockets have a structure that allows air ventilation of the conductive balls. Accordingly, the apparatus can control the temperature around the packages as well as the temperature in the burn-in chamber, thus preventing conductive ball-melting.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for forming reflowed solder ball with low melting point metal cap
InactiveUS6344234B1Reduce the hole diameterMinimal diameterFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTinningIndium
A method and structure for a solder interconnection, using solder balls for making a low temperature chip attachment directly to any of the higher levels of packaging substrate is disclosed. After a solder ball has been formed using standard methods it is reflowed to give the solder ball a smooth surface. A layer of low melting point metal, such as, bismuth, indium or tin, preferably, pure tin, is deposited on the top of the solder balls. This structure results in localizing of the eutectic alloy, formed upon subsequent low temperature joining cycle, to the top of the high melting solder ball even after multiple low temperature reflow cycles. This method does not need tinning of the substrate to which the chip is to be joined, which makes this method economical. It has also been noticed that whenever temperature is raised slightly above the eutectic temperature, the structure always forms a liquid fillet around the joint with copper wires. This liquid fillet formation results in substantial thermal fatigue life improvement for reduced stress at interface; and secondly, provides an easy means to remove chip for the purpose of chip burn-in, replacement or field repairs.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Apparatus for testing electronic devices
ActiveUS20070001790A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor operation lifetime testingFunctional testingMicroelectronic circuits
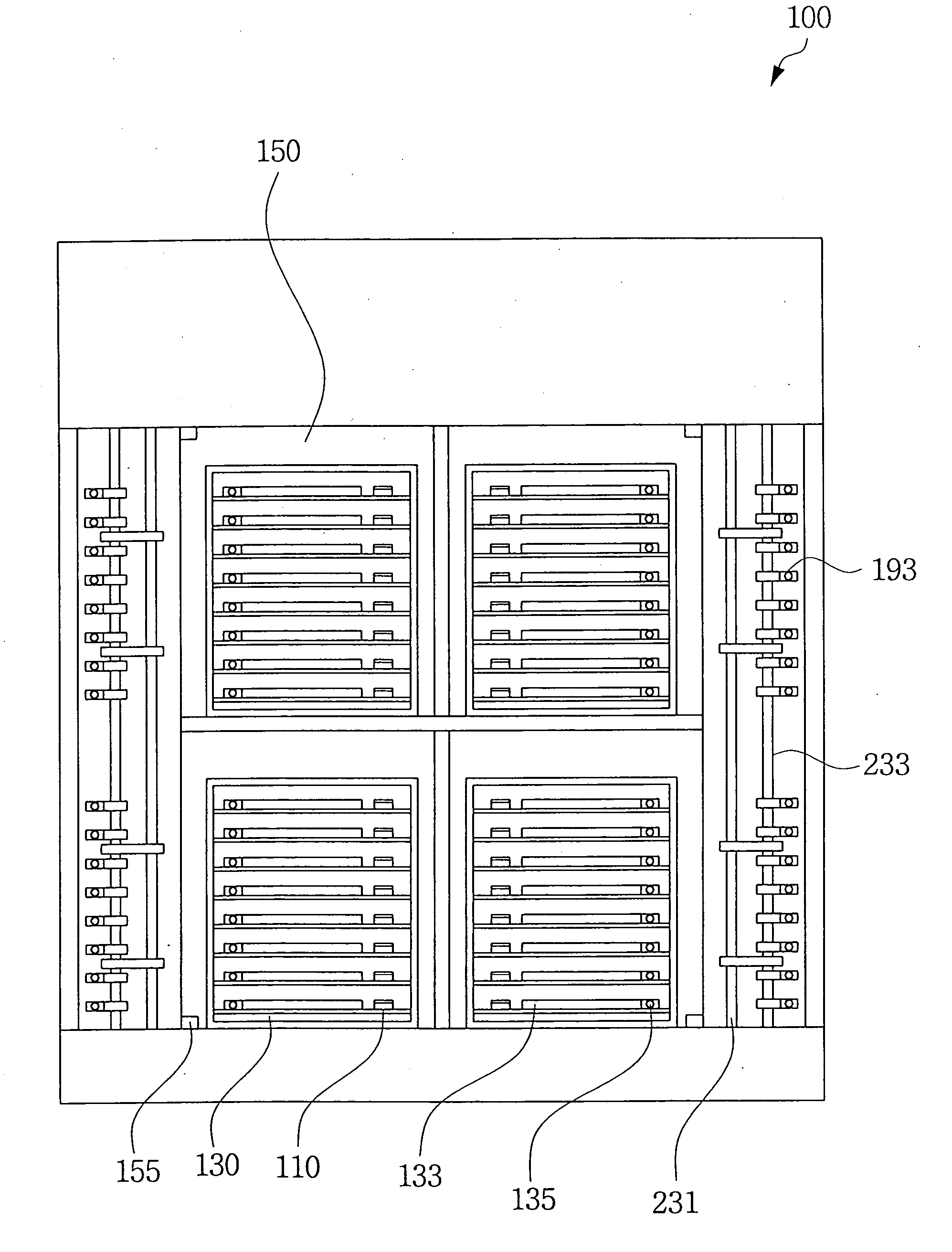
An apparatus is described for burn-in and / or functional testing of microelectronic circuits of unsingulated wafers. A large number of power, ground, and signal connections can be made to a large number of contacts on a wafer. The apparatus has a cartridge that allows for fanning-in of electric paths. A distribution board has a plurality of interfaces that are strategically positioned to provide a dense configuration. The interfaces are connected through flexible attachments to an array of first connector modules. Each one of the first connector modules can be independently connected to a respective one of a plurality of second connector modules, thereby reducing stresses on a frame of the apparatus. Further features include for example a piston that allows for tight control of forces exerted by terminals onto contacts of a wafer.
Owner:AEHR TEST SYST
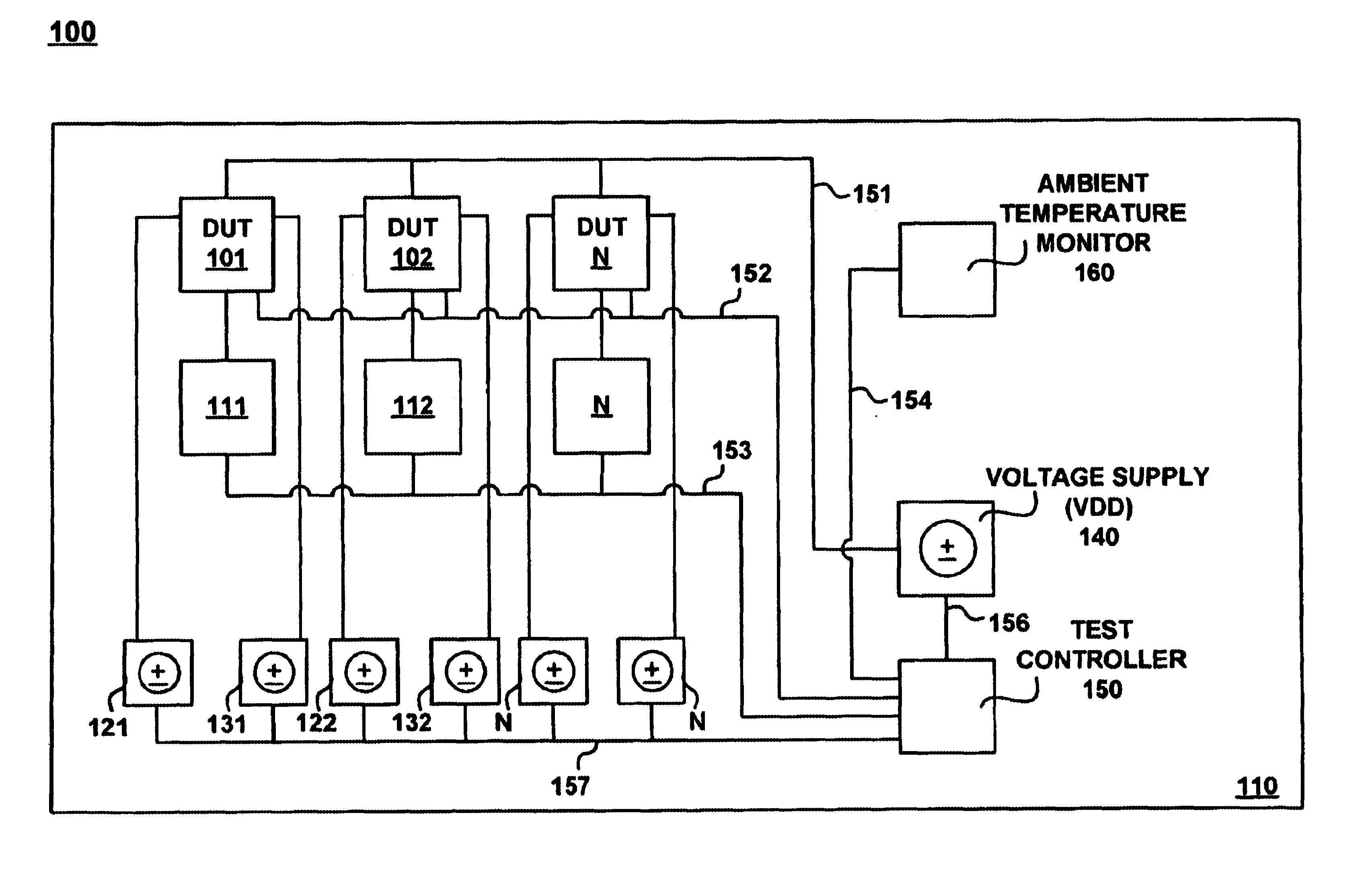
Tester with independent control of devices under test
InactiveUS20020121913A1Electronic circuit testingFault location by increasing destruction at faultTester deviceEngineering
A burn-in tester that provides independent control of the devices under test. The various operating parameters such as temperature, voltage, frequency of operation or test pattern being applied can be independently changed on one device without affecting the operating parameters of the other devices. Thus, e.g., the amount of cooling applied to one device is independent of the amount of cooling applied to another device. In addition, the testing being done on each device may be independently controlled. Thus, a test can be changed on one of the devices under test without affecting the tests being run on any of the other devices. Similarly, the voltage and frequency of operation can be controlled independently to allow for changes to the voltage and / or frequency of one device without affecting those parameters on other devices being tested.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
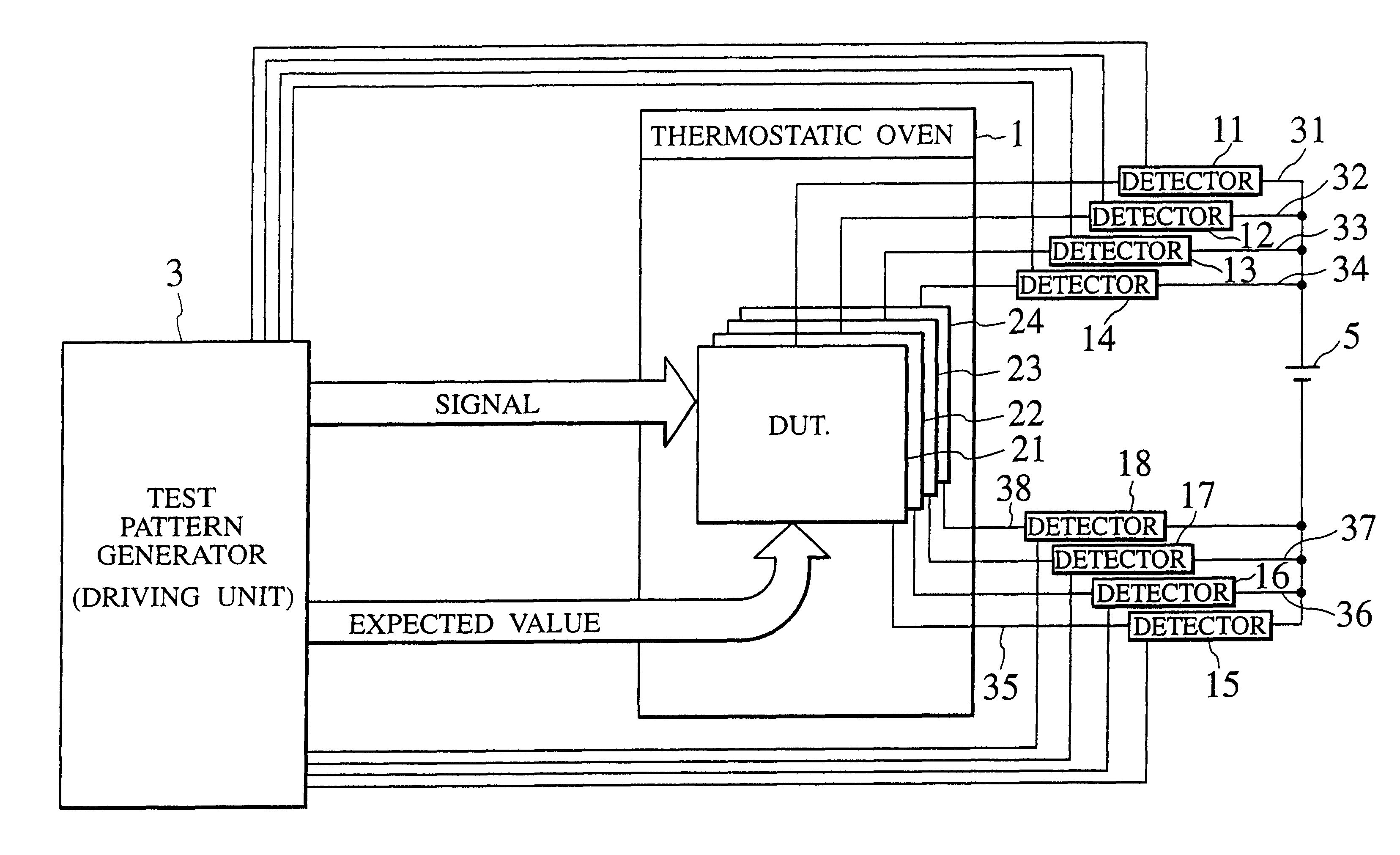
Dynamic burn-in test equipment
InactiveUS6215324B1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingTested timeGround line
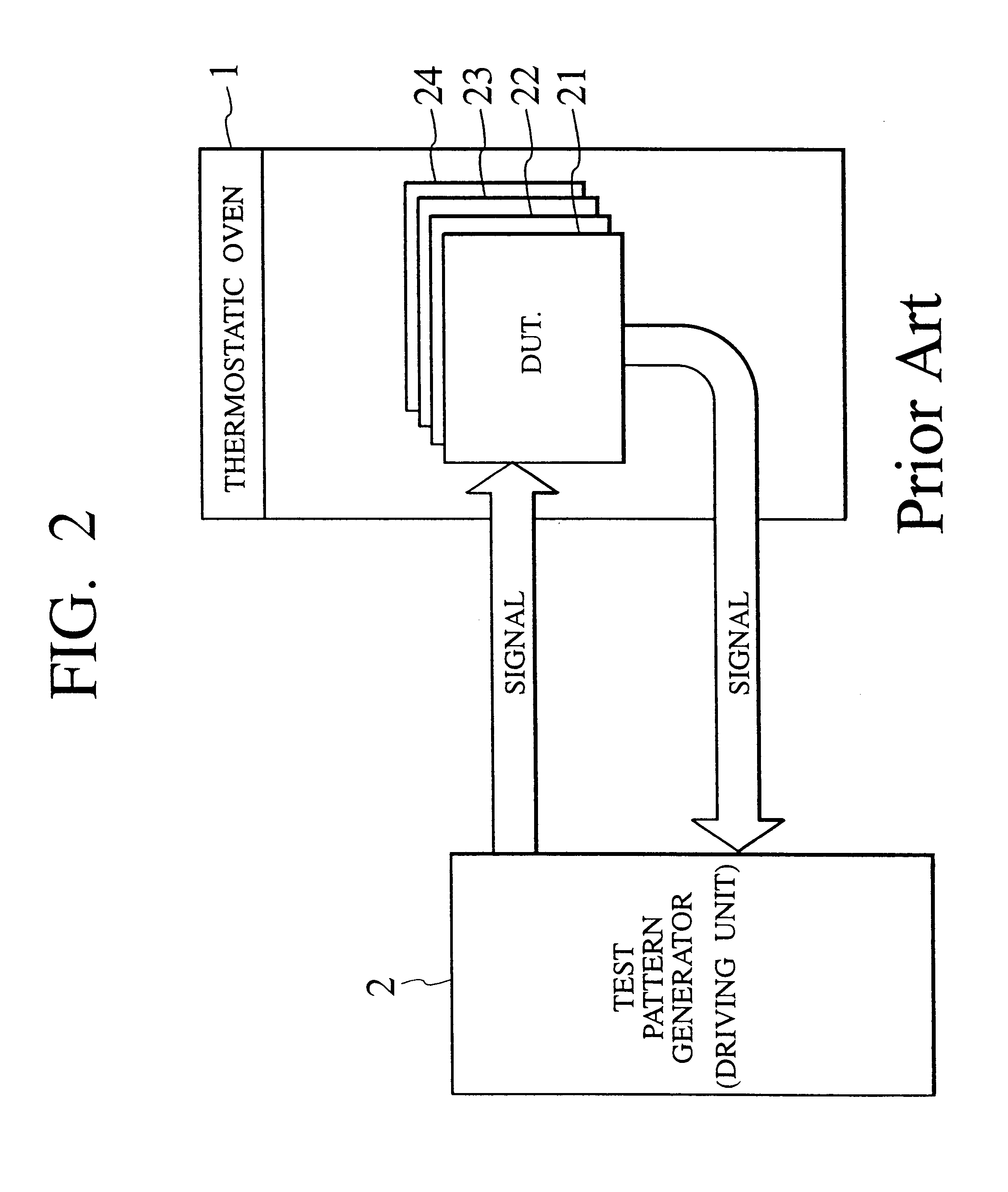
There is provided a dynamic burn-in test equipment being capable of testing a large number of multi-pin LSI chips in a short test time and at a low cost. The dynamic burn-in test equipment includes at least a thermostatic oven for storing DUTs, a driving unit for applying the input signal to the input terminal of each DUT to apply a predetermined expected value to the output terminal of each DUT, a power supply for applying a predetermined power supply voltage to each DUT through a higher level power supply line and a lower level power supply line (ground line), and a current detector arranged on at least one of the higher level power supply line and the lower level power supply line (ground line). The dynamic burn-in test equipment monitors a power supply current to detect a failure.
Owner:NIPPON SCI
Inter-dice signal transfer methods for integrated circuits
InactiveUS7161175B2Good yieldEffectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingDie (integrated circuit)Integrated circuit layout
The present invention discloses novel methods to transfer data between a plurality of integrated circuit dice on a semiconductor wafer. Each individual die contains internal circuits to control data transfer to nearby dice. Wafer level data transfer is achieved by a series of inter-dice data transfers. It is therefore possible to use a small number of small area metal lines to support wafer level parallel processing activities. External connections are provided by a small number of bonding pads on each wafer. The load on each external bounding pad is by far lower than that of prior art wafer level connections. These inter-dice data transfer mechanism also can be programmed to avoid defective circuitry. This invention has been used to support wafer level functional tests and wafer level burn-in tests. A Testing system of the present invention can test thousands of dice in parallel using simple testing equipment. Testing costs for integrated circuits are therefore reduced dramatically. The present application also makes it possible to build large area IC containing multiple dice. Extremely powerful products are realized using parallel processing capability of such multiple die integrated circuits.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com