Patents
Literature
2368 results about "Solid-state drive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies as memory to store data persistently, typically using flash memory. It is also sometimes called a solid-state device or a solid-state disk, although SSDs lack the physical spinning disks and movable read-write heads used by the conventional electromechanical storage such as hard drives ("HDD") or floppy disks.
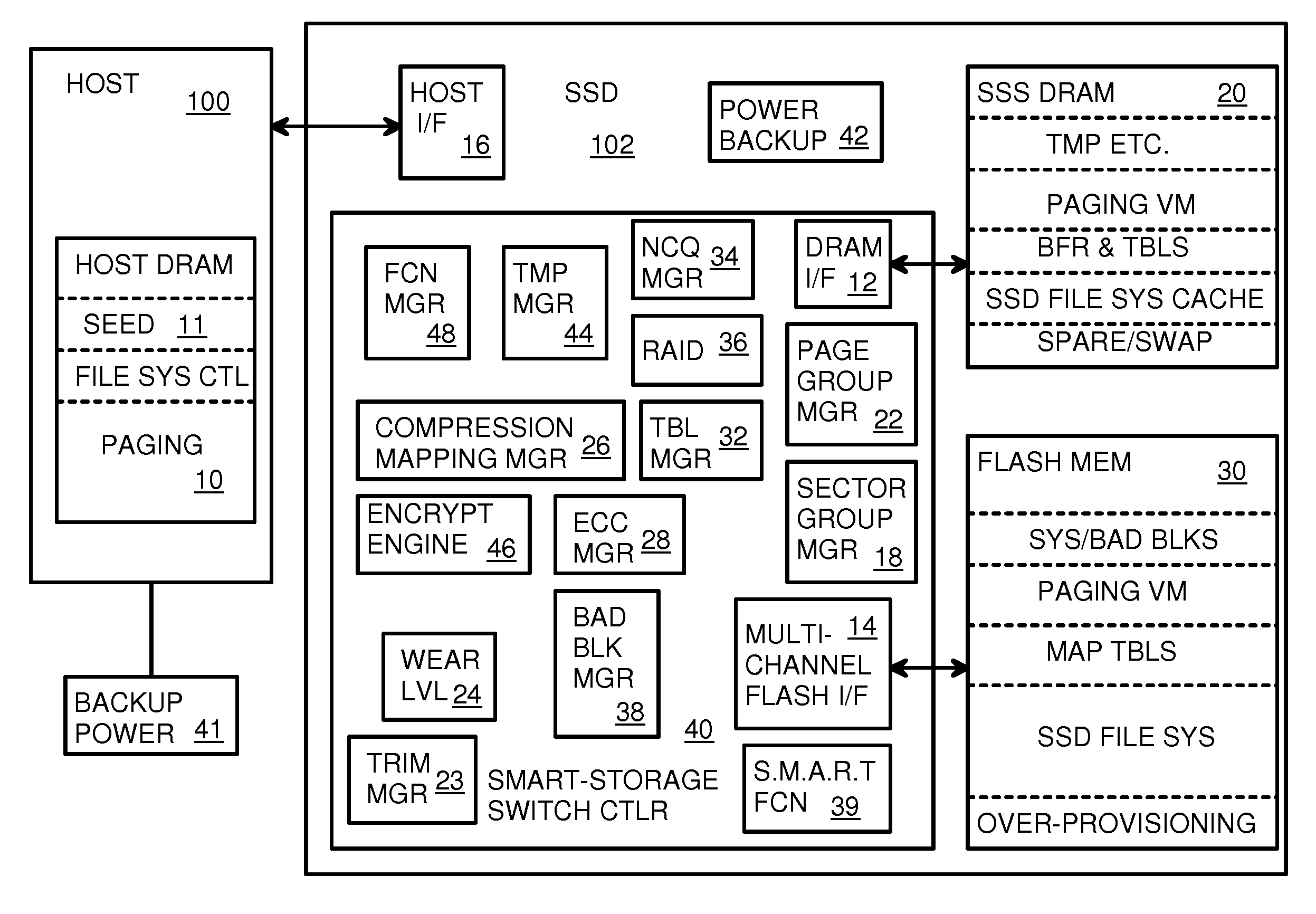
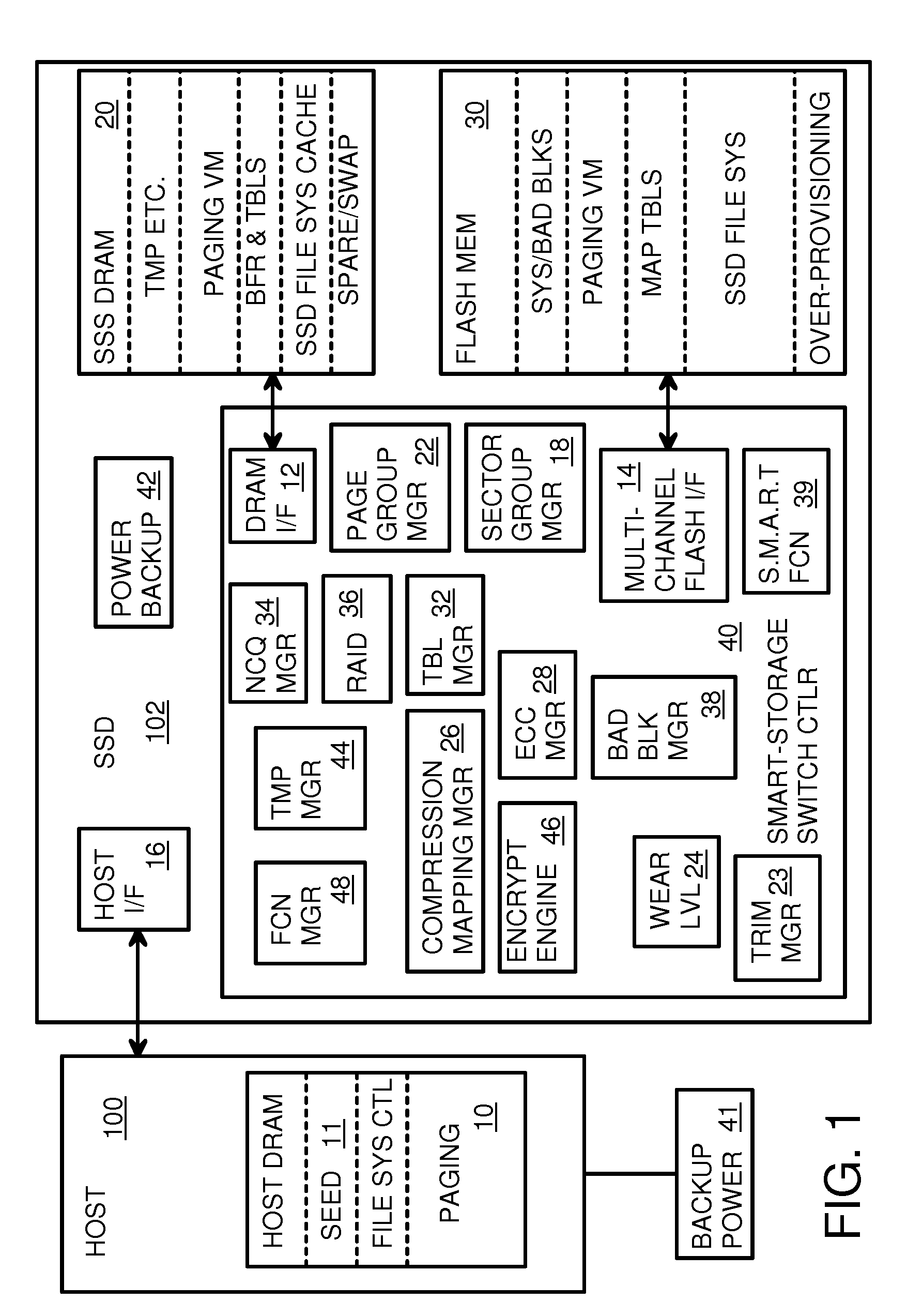
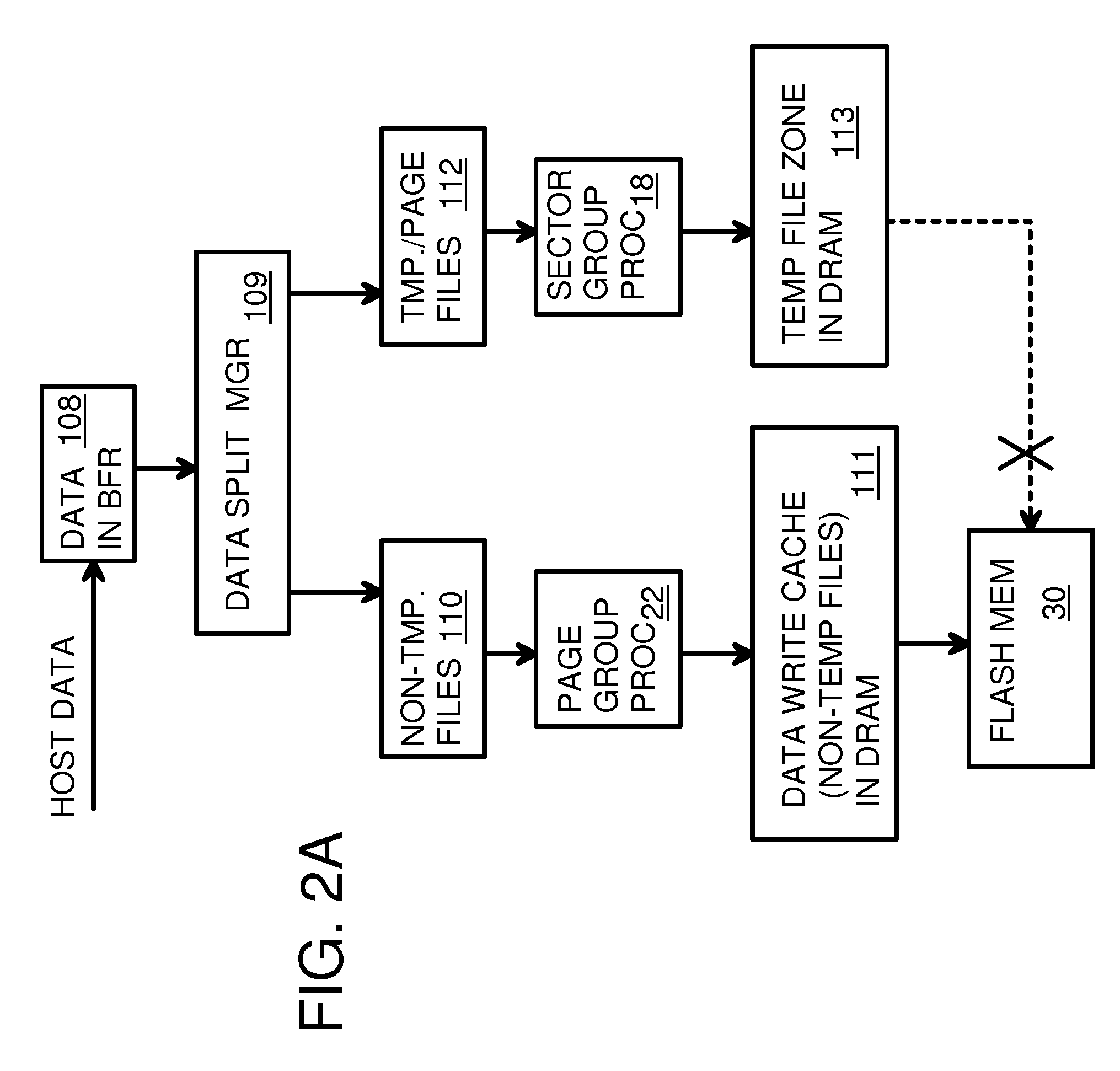
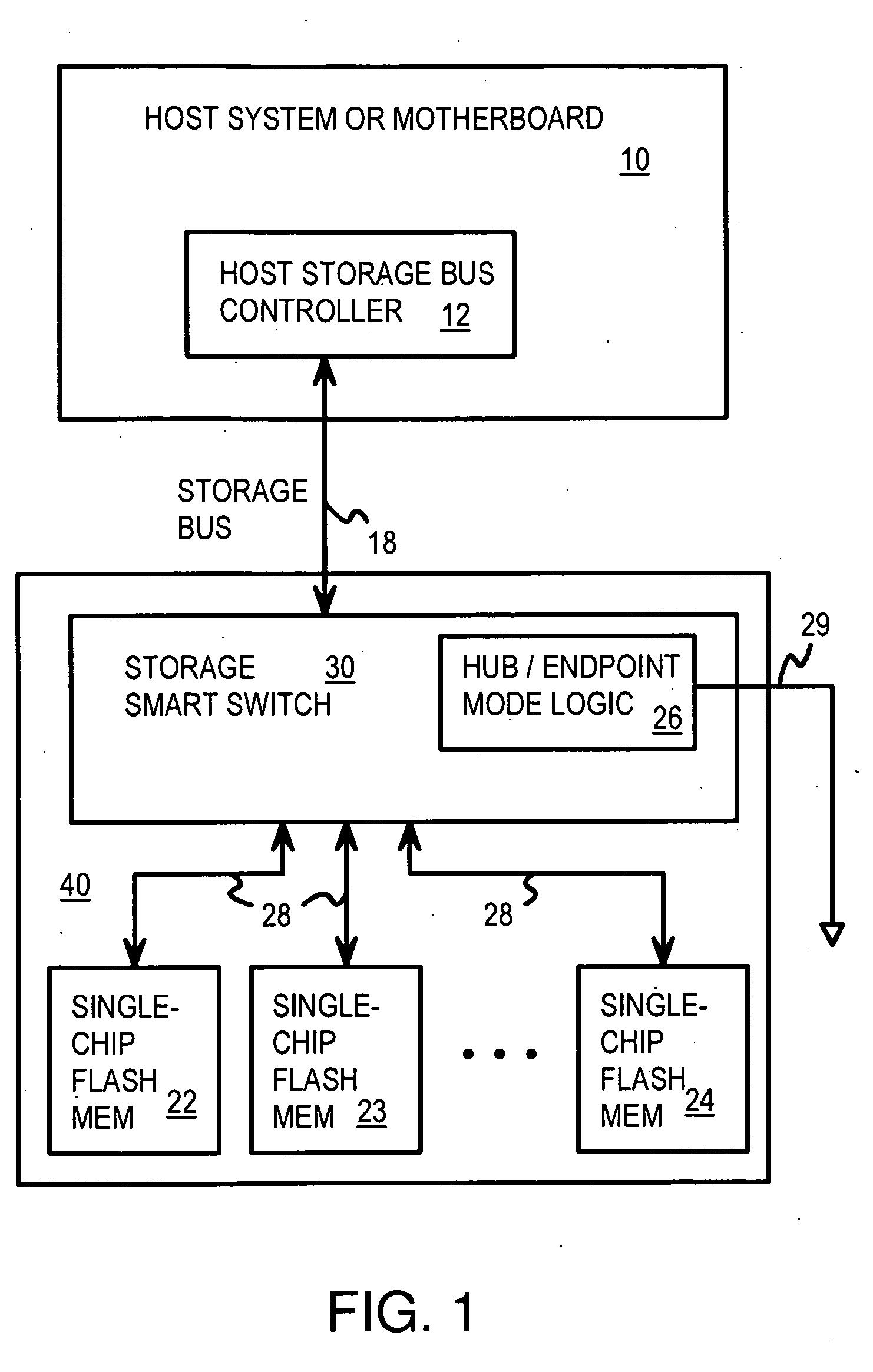
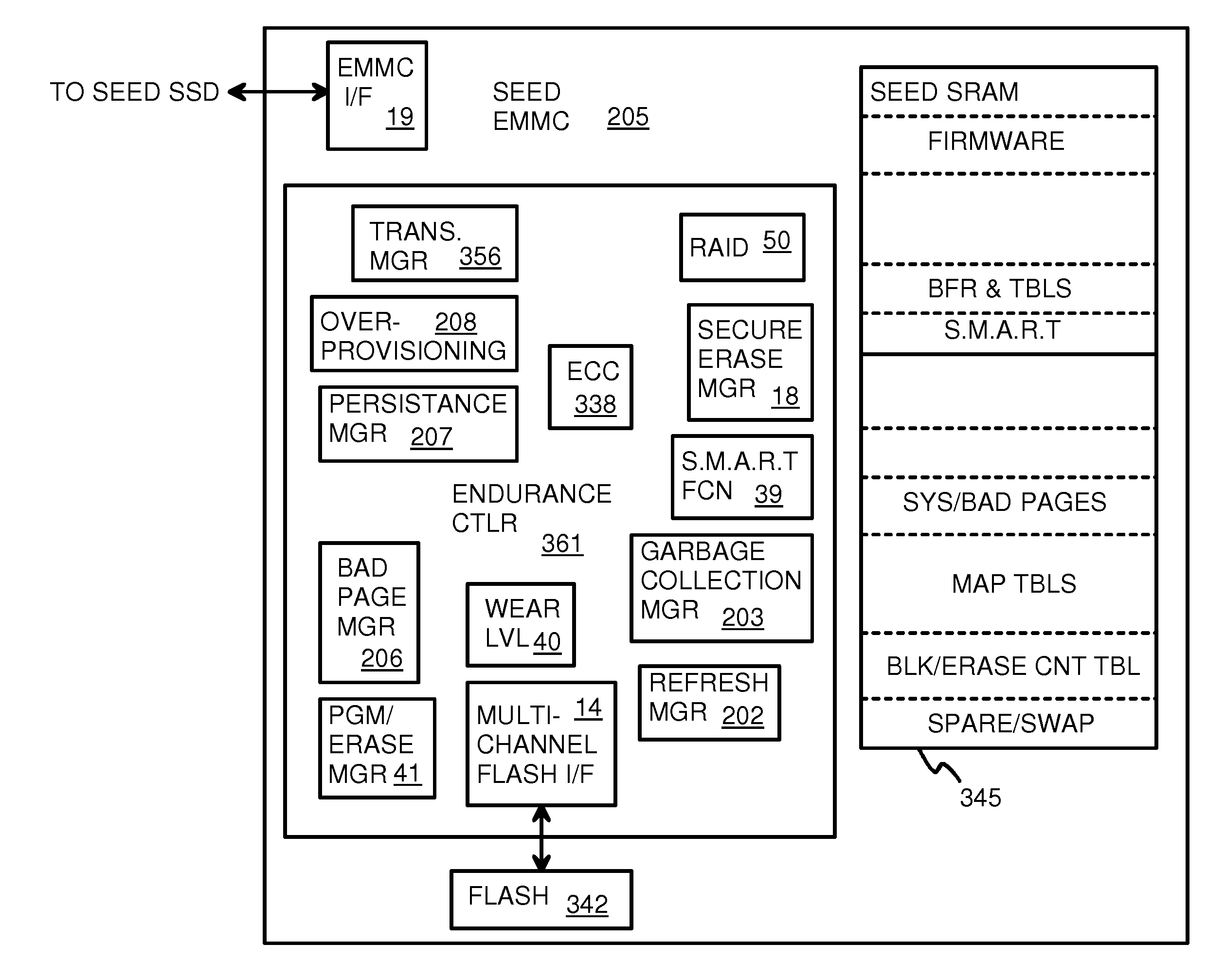
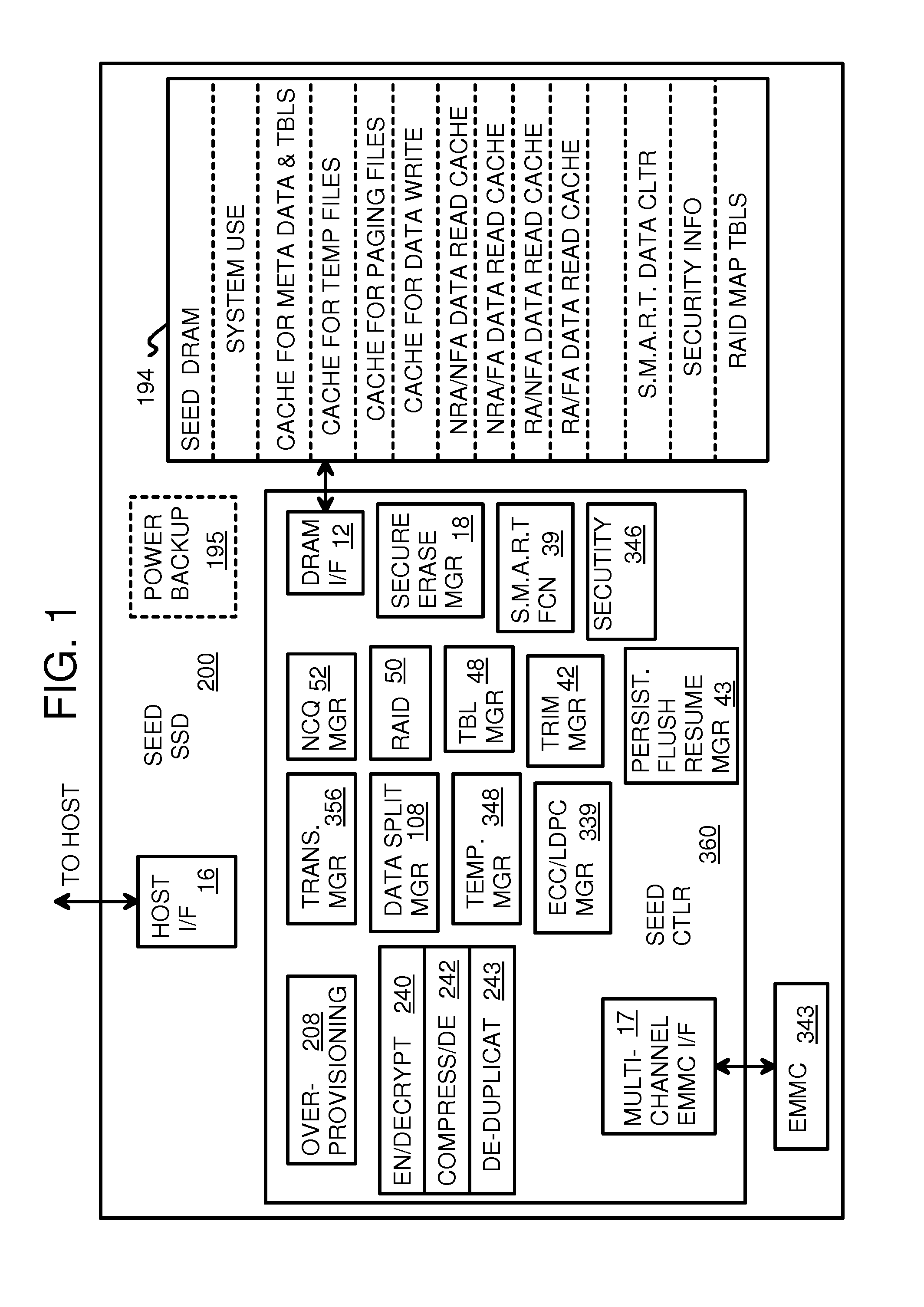
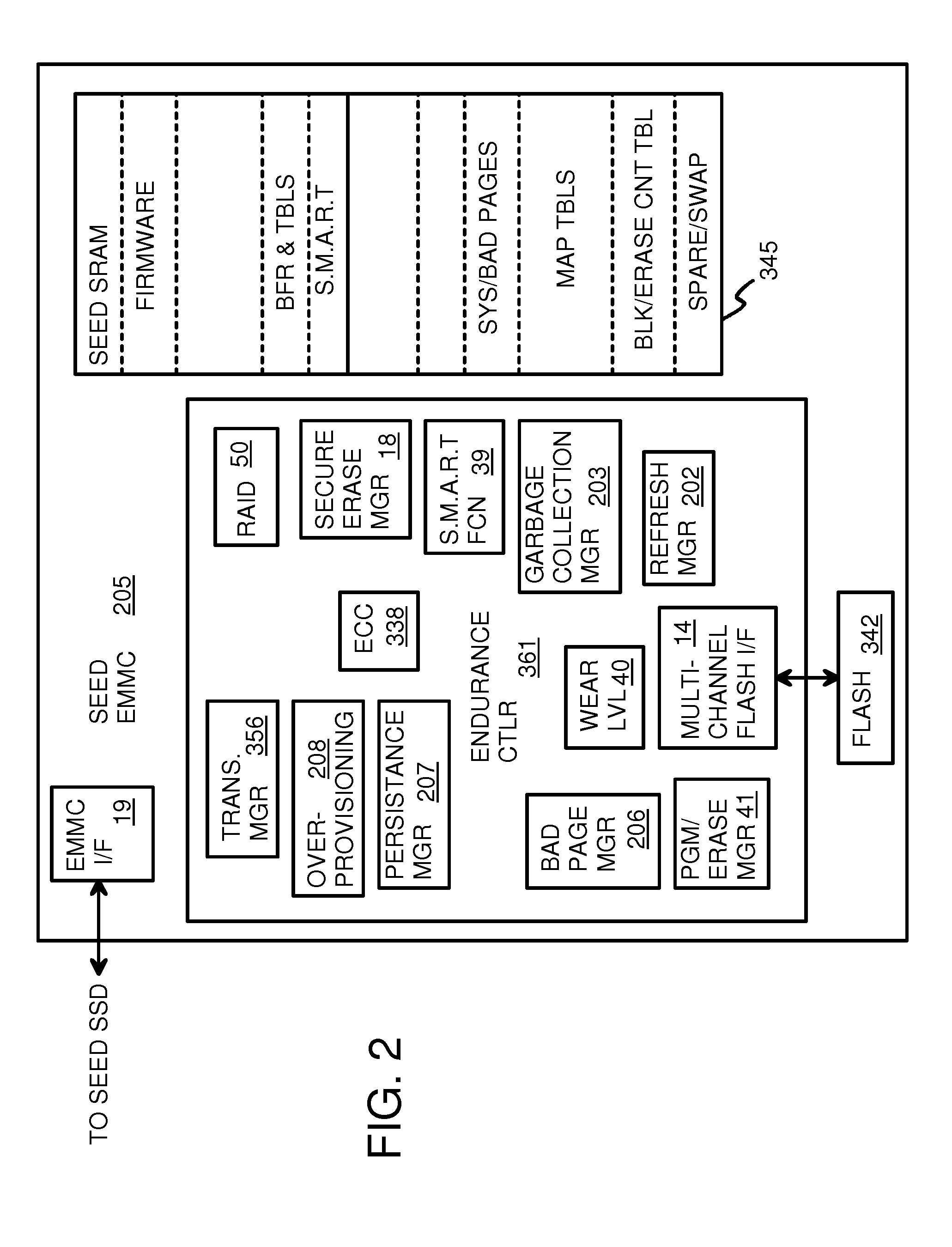
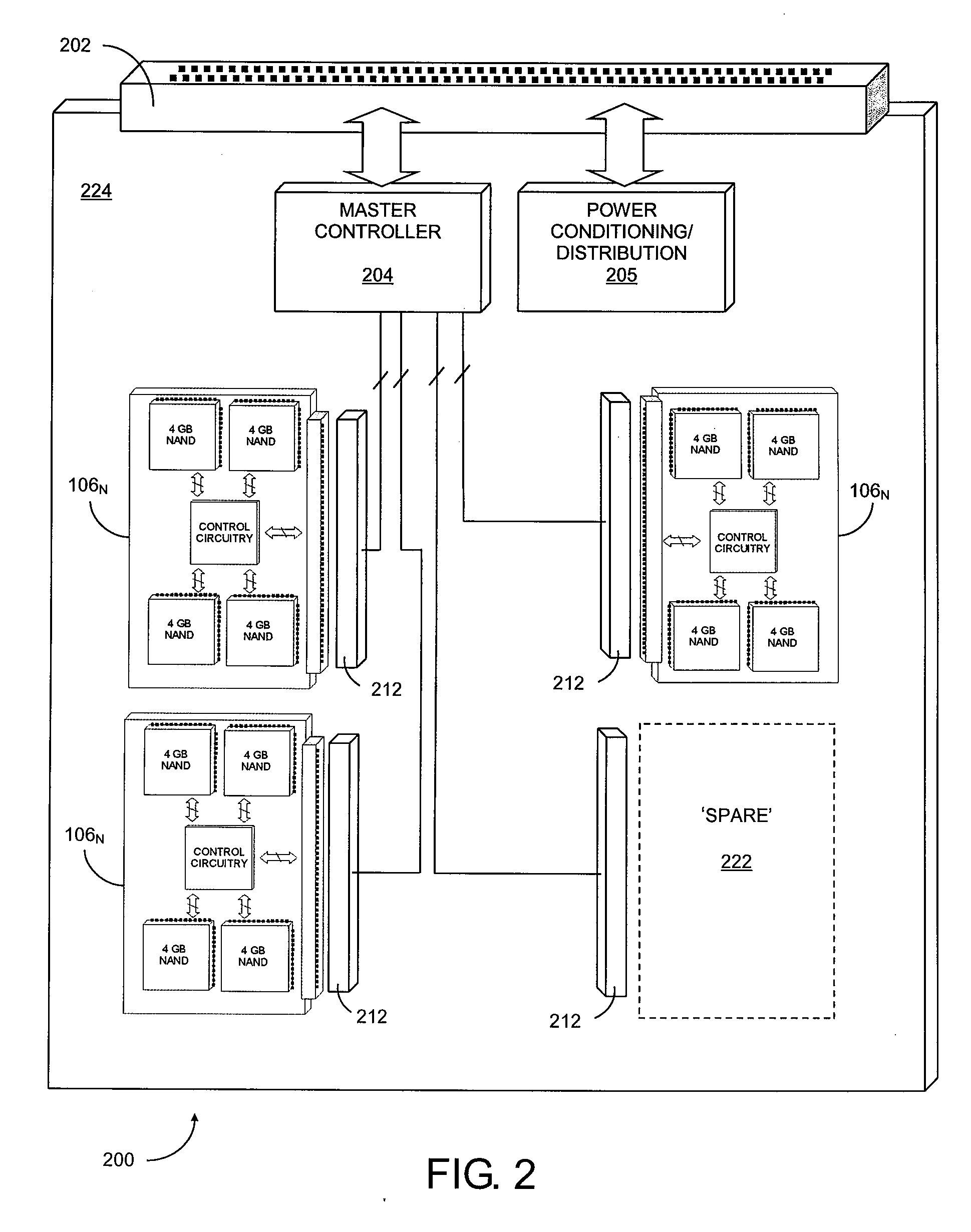
Super-Endurance Solid-State Drive with Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) and Diversion of Temp Files for Reduced Flash Wear
ActiveUS20120284587A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageFilename extensionData file
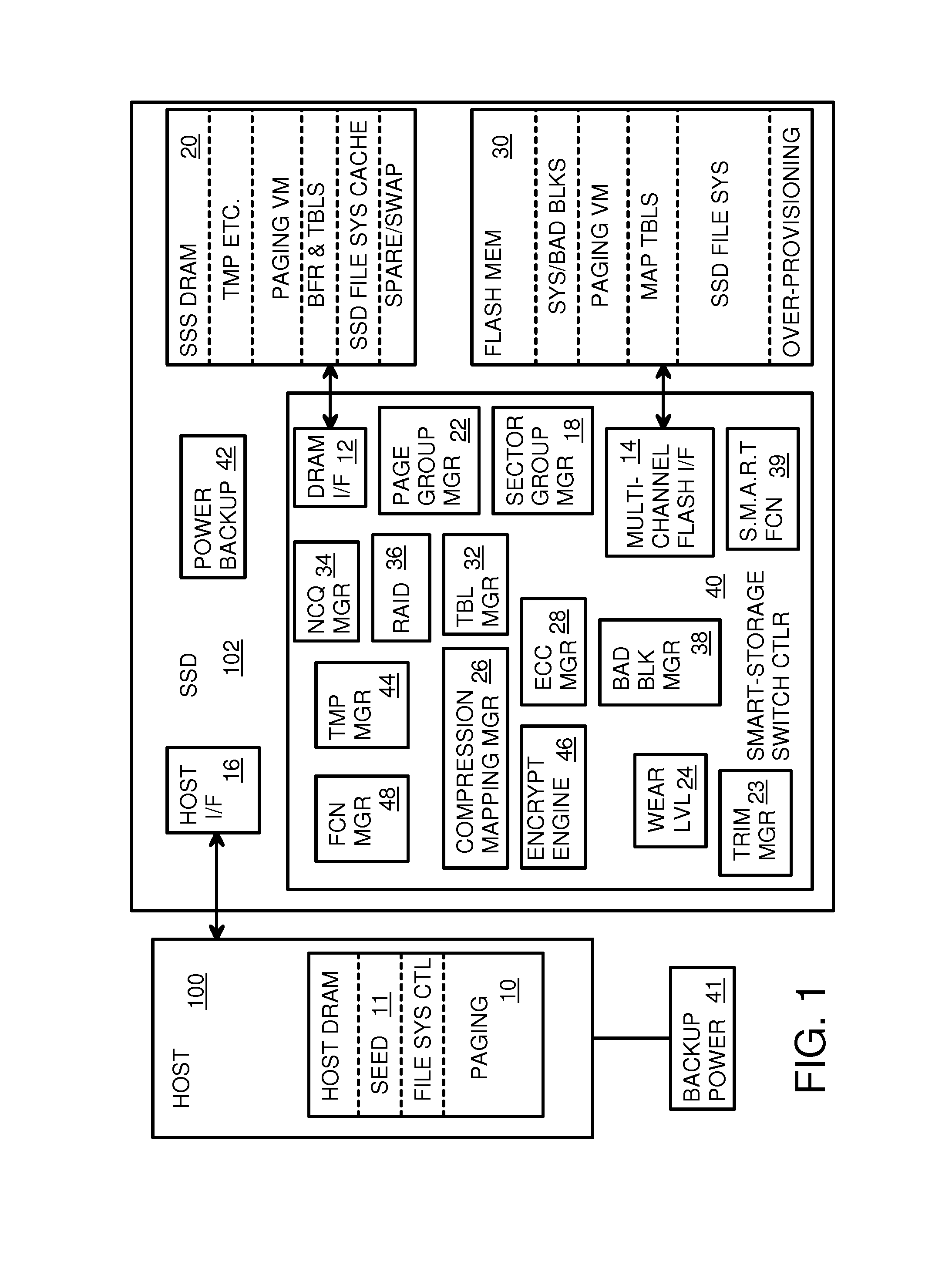
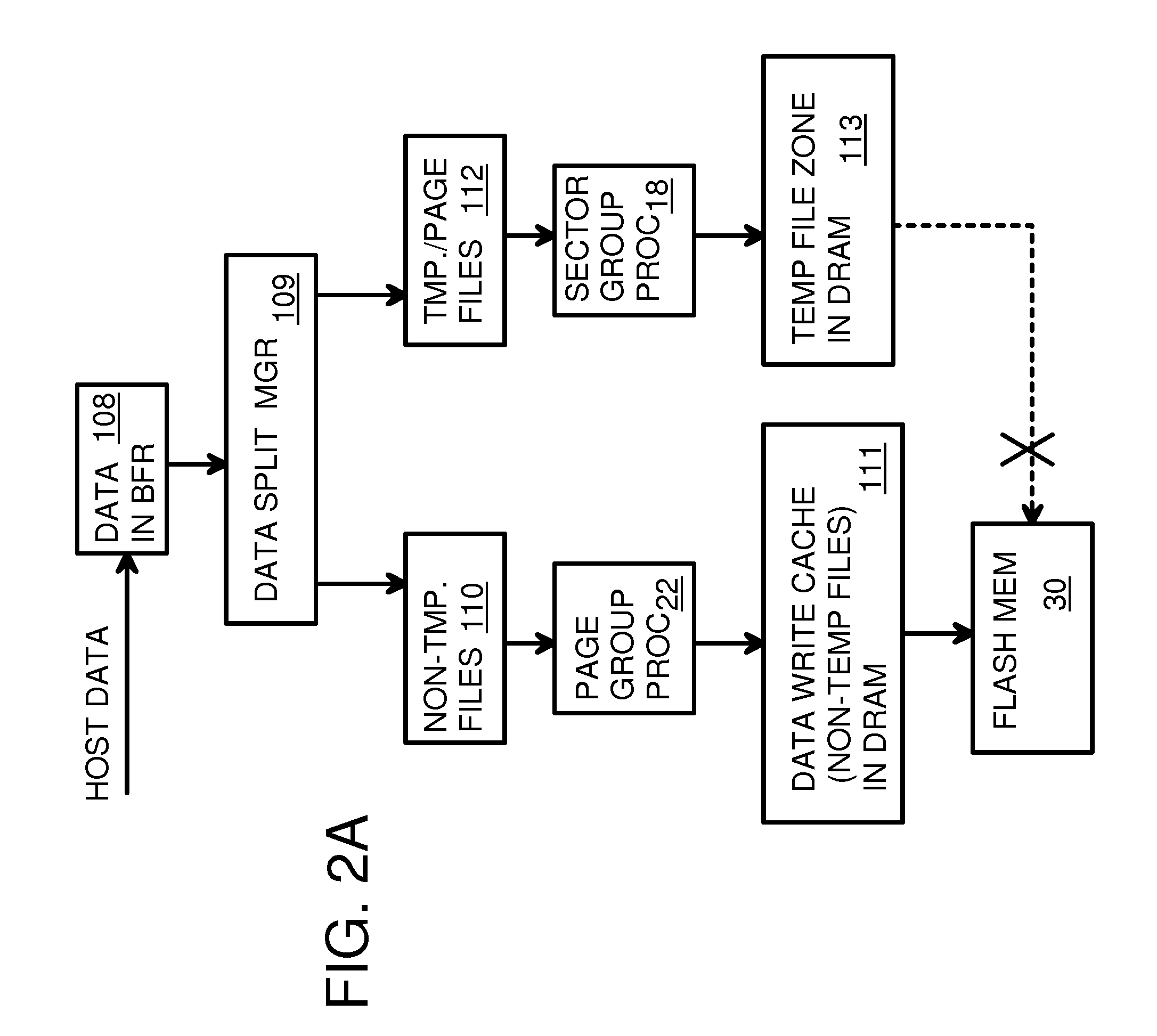
A flash drive has increased endurance and longevity by reducing writes to flash. An Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) is created in a DRAM buffer and provides temporary storage to reduce flash wear. A Smart Storage Switch (SSS) controller assigns data-type bits when categorizing host accesses as paging files used by memory management, temporary files, File Allocation Table (FAT) and File Descriptor Block (FDB) entries, and user data files, using address ranges and file extensions read from FAT. Paging files and temporary files are never written to flash. Partial-page data is packed and sector mapped by sub-sector mapping tables that are pointed to by a unified mapping table that stores the data-type bits and pointers to data or tables in DRAM. Partial sectors are packed together to reduce DRAM usage and flash wear. A spare / swap area in DRAM reduces flash wear. Reference voltages are adjusted when error correction fails.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
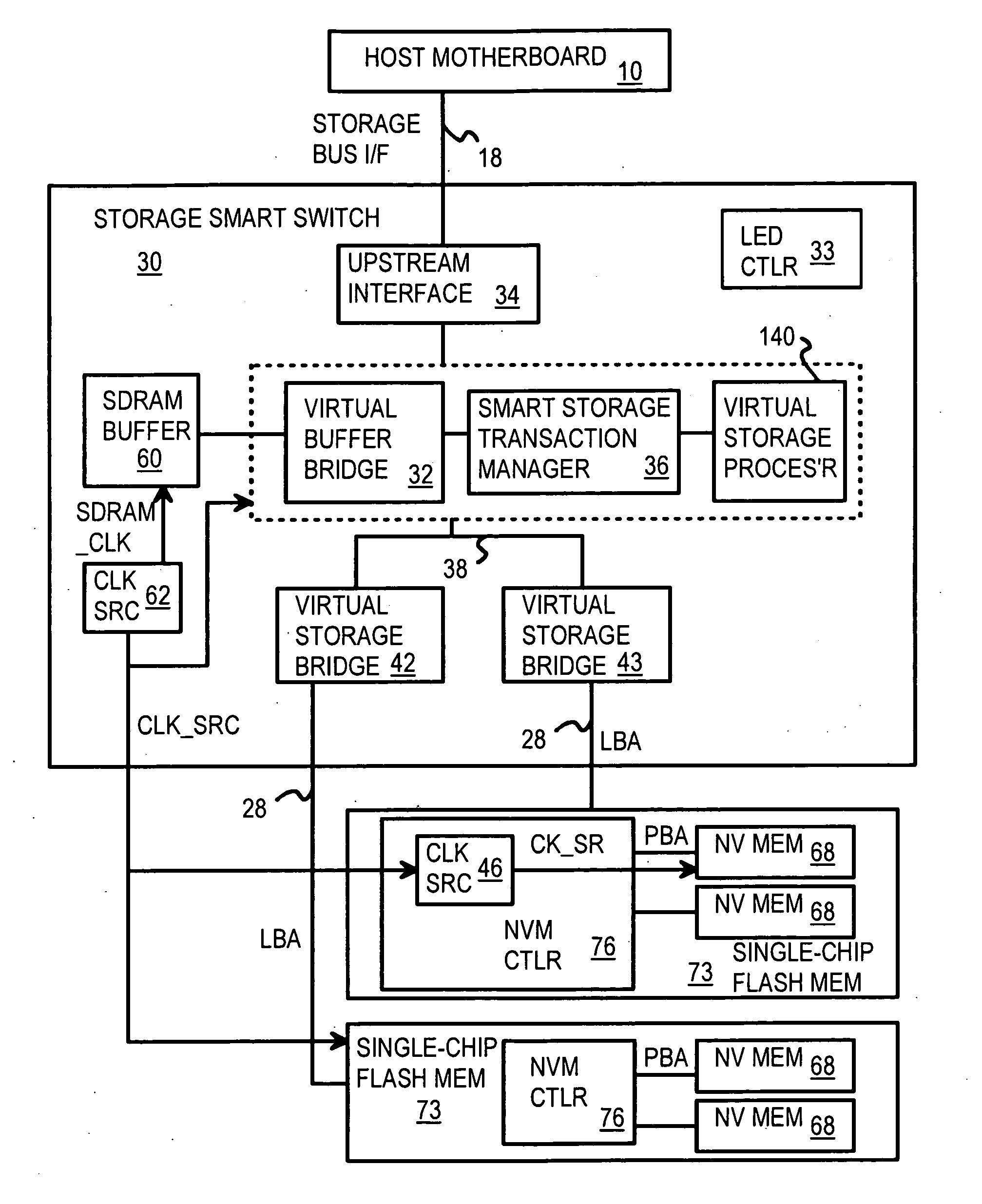
Multi-Level Controller with Smart Storage Transfer Manager for Interleaving Multiple Single-Chip Flash Memory Devices
InactiveUS20080320214A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingSolid-state drive
A solid-state disk (SSD) has a smart storage switch with a smart storage transaction manager that re-orders host commands for accessing downstream single-chip flash-memory devices. Each single-chip flash-memory device has a lower-level controller that converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA) that access flash memory blocks in the single-chip flash-memory device. Wear-leveling and bad block remapping are preformed by each single-chip flash-memory device, and at a higher level by a virtual storage processor in the smart storage switch. Virtual storage bridges between the smart storage transaction manager and the single-chip flash-memory devices bridge LBA transactions over LBA buses to the single-chip flash-memory devices. Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the single-chip flash-memory device is controlled at a high level by the smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping may be performed within each single-chip flash-memory device.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
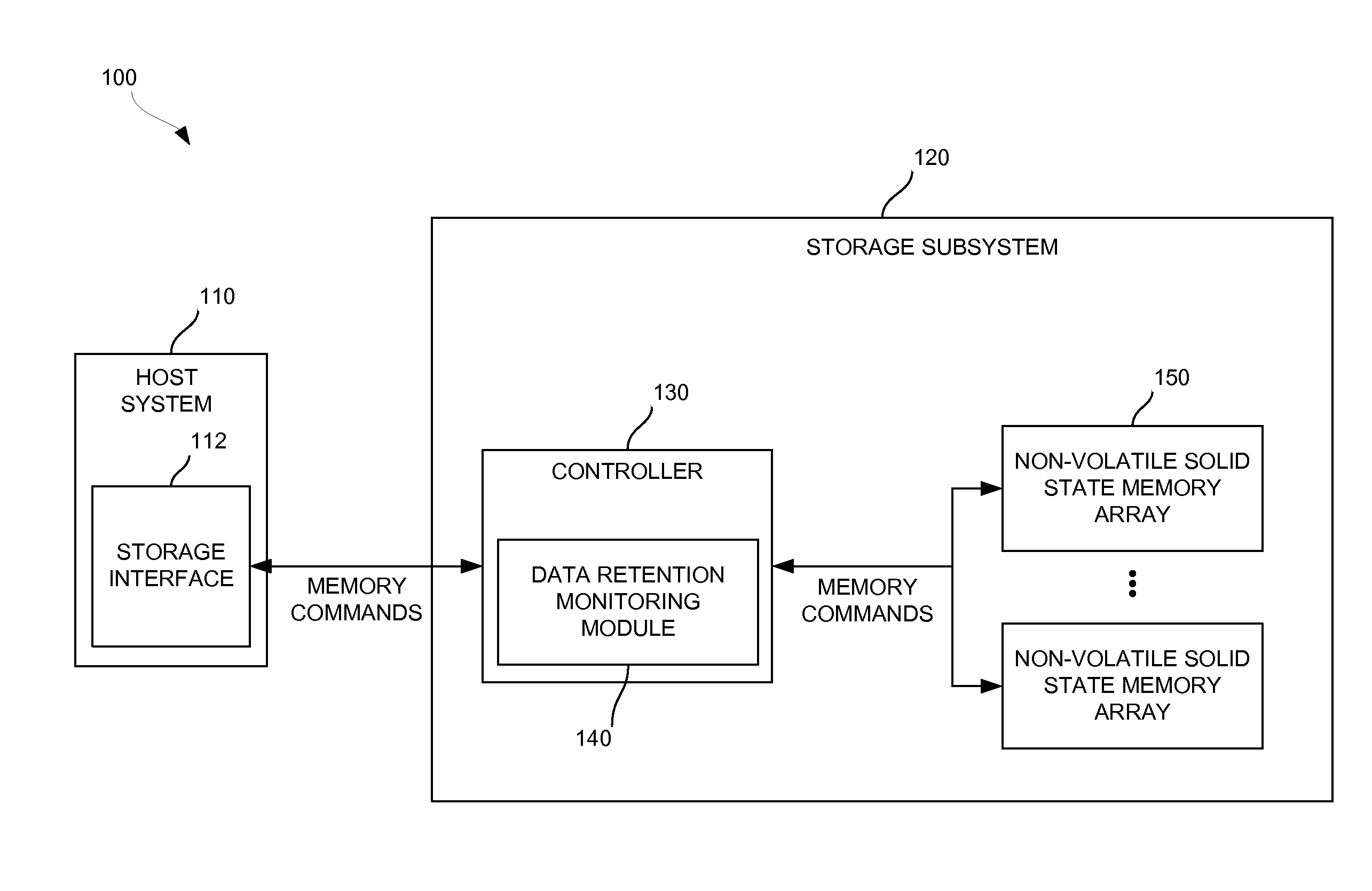
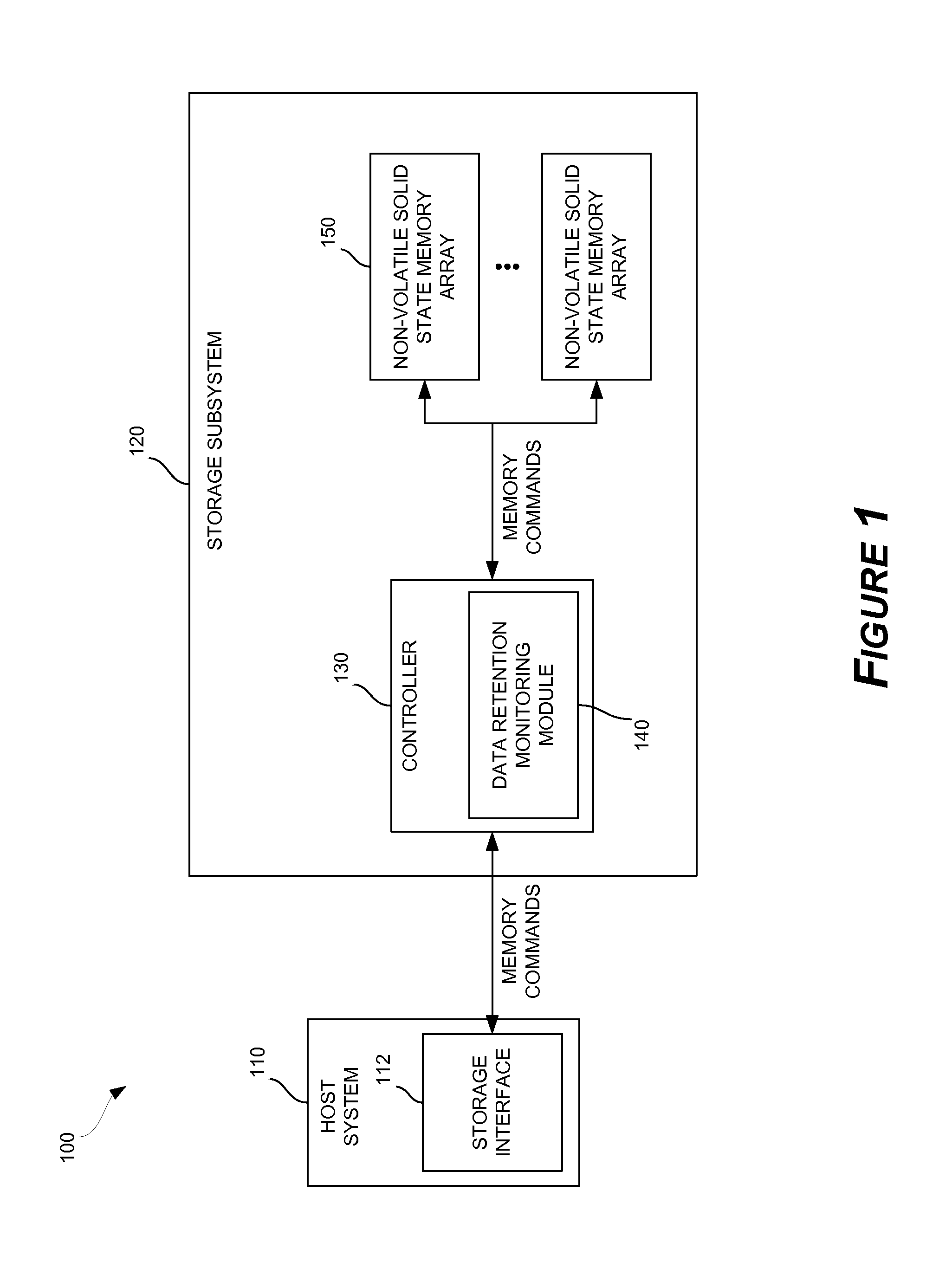
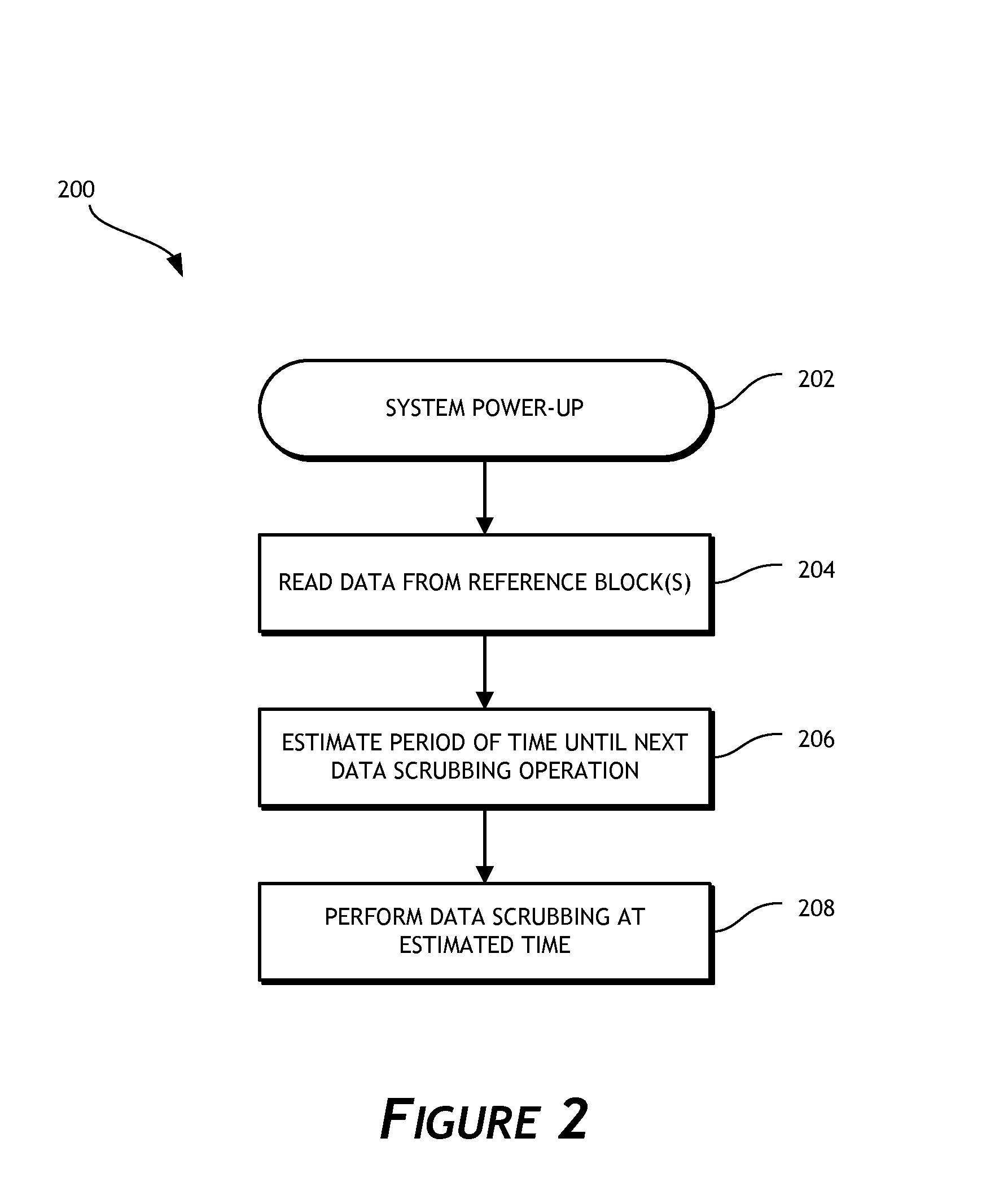
Solid-state drive retention monitor using reference blocks
A solid-state storage retention monitor determines whether user data in a solid-state device is in need of a scrubbing operation. One or more reference blocks may be programmed with a known data pattern, wherein the reference block(s) experiences substantially similar P / E cycling, storage temperature, storage time, and other conditions as the user blocks. The reference blocks may therefore effectively represent data retention properties of the user blocks and provide information regarding whether / when a data refreshing operation is needed.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
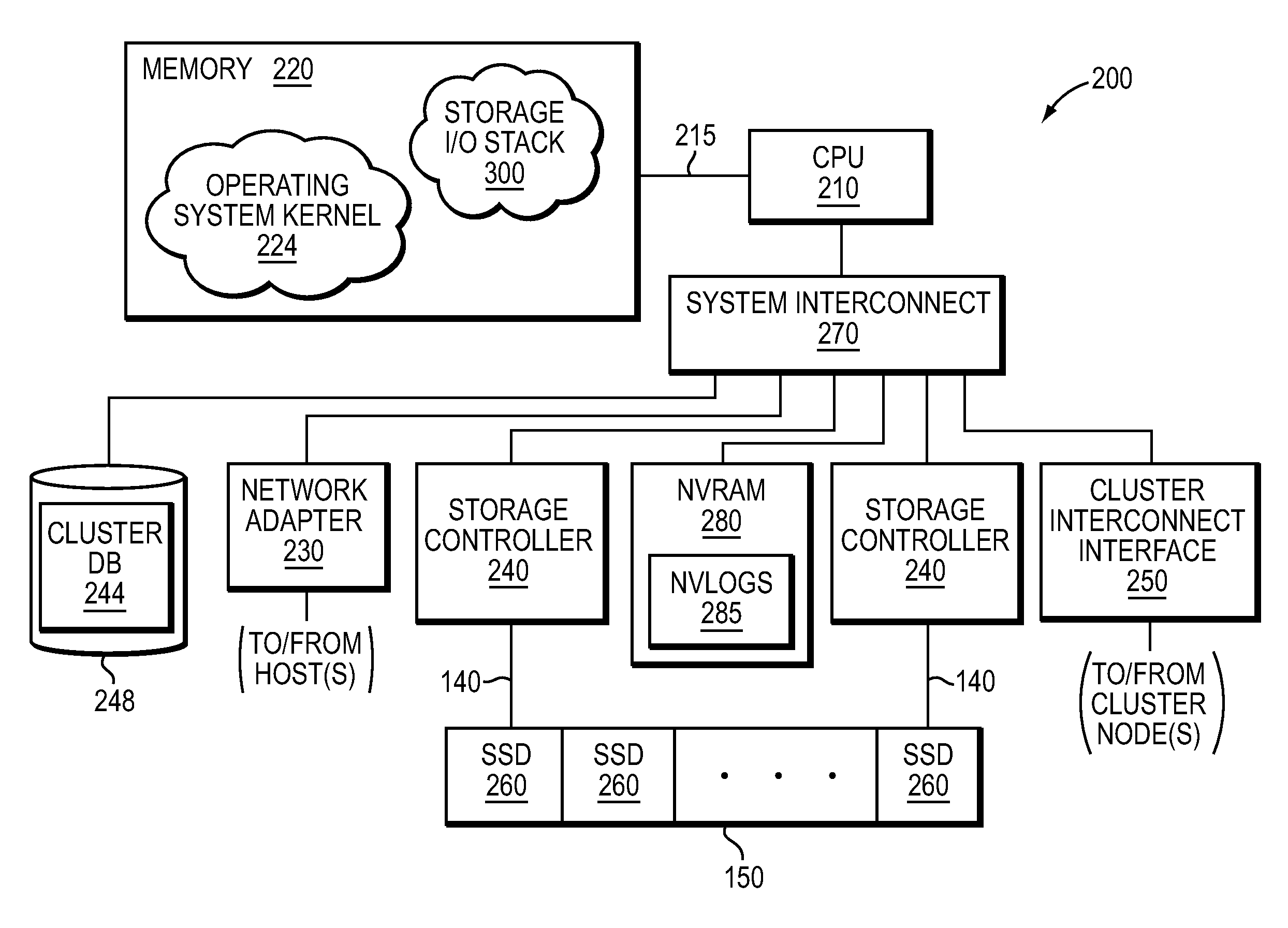
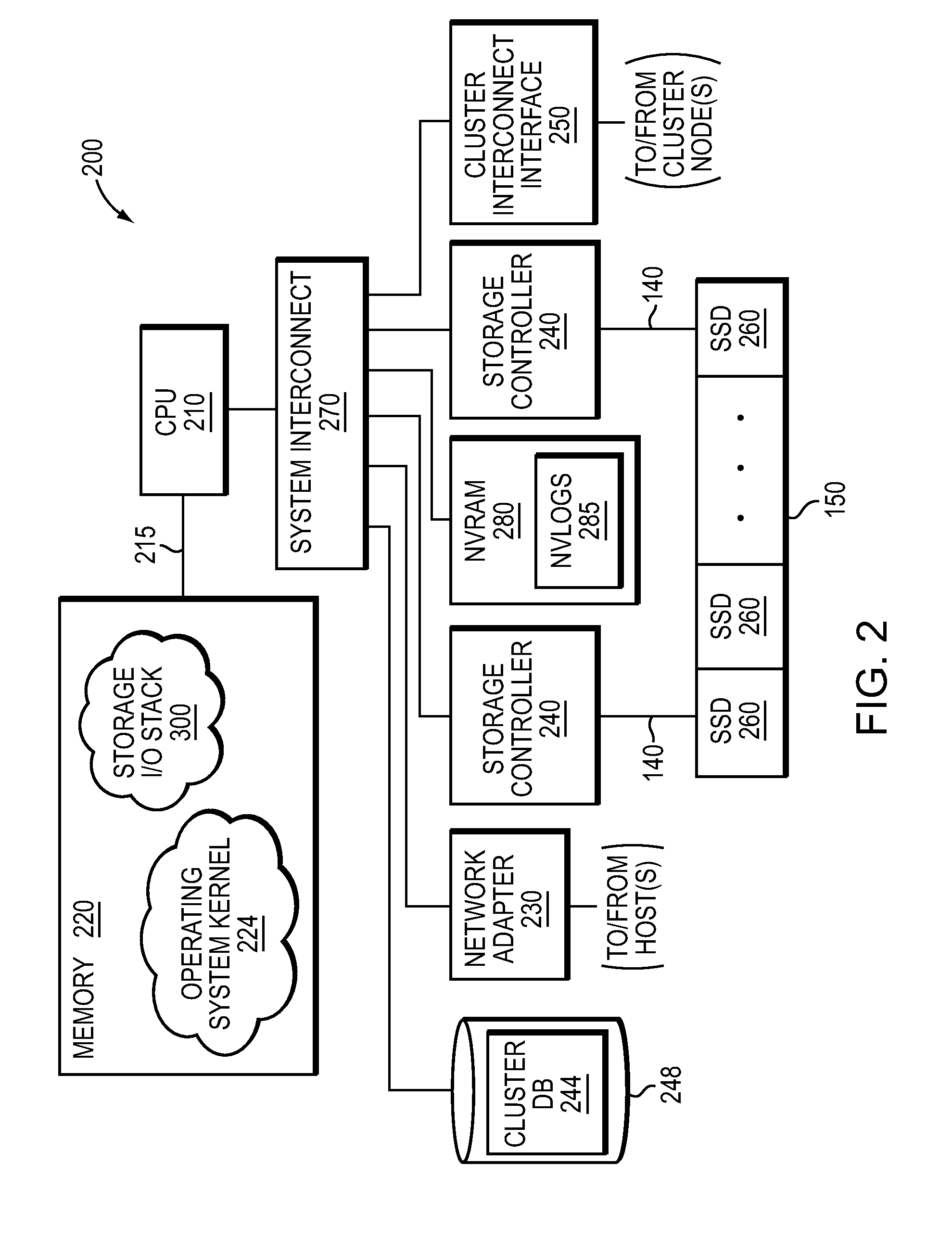
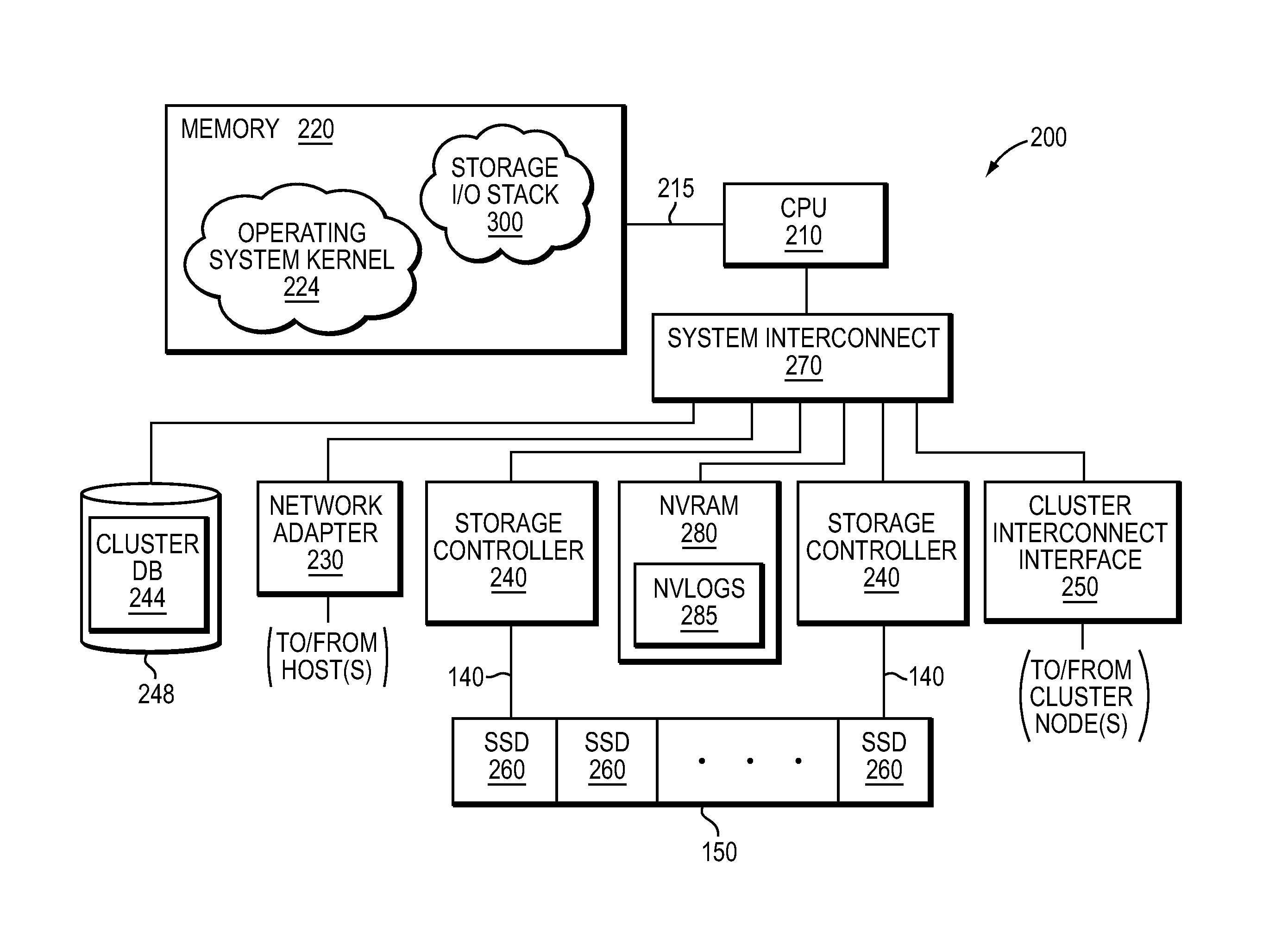
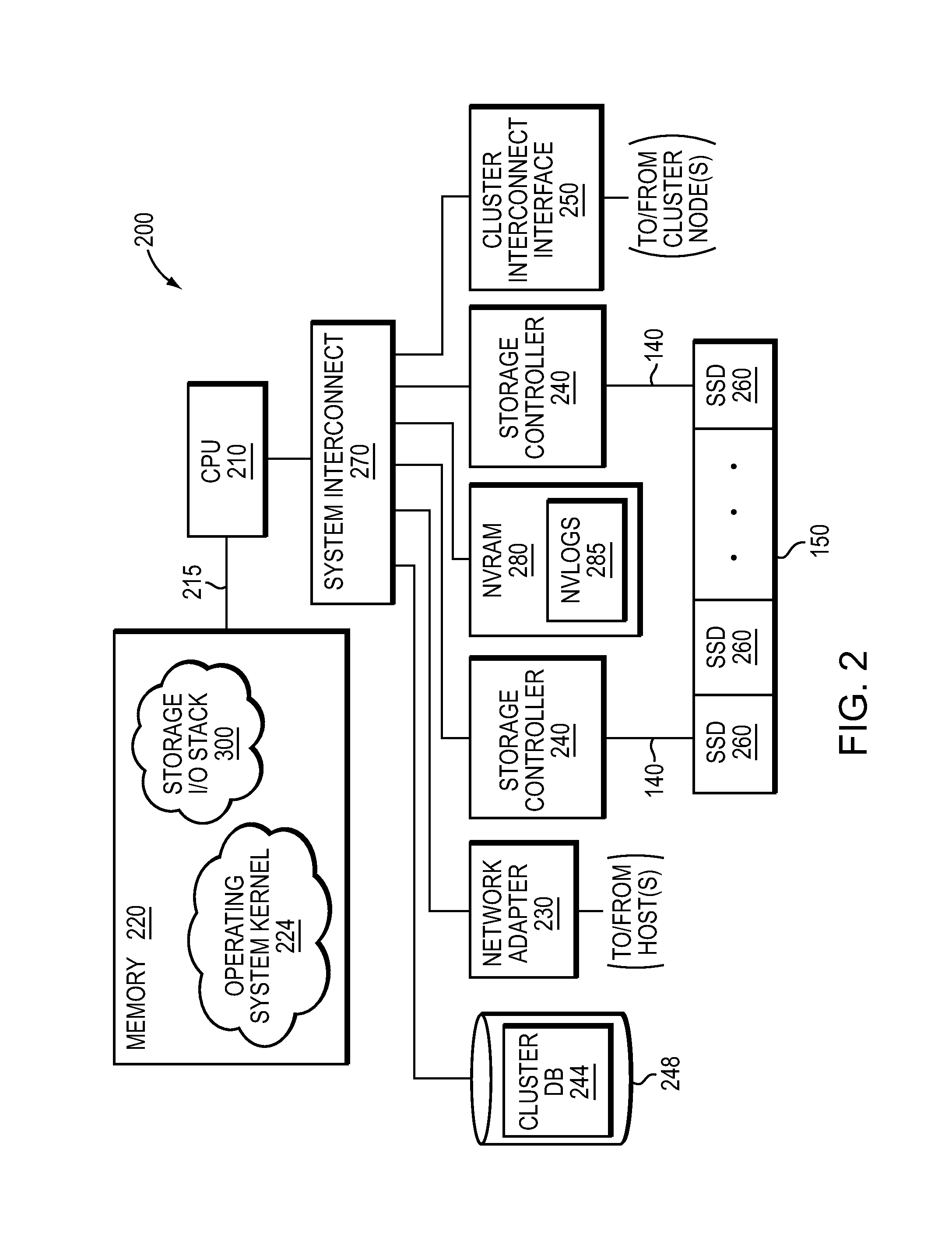
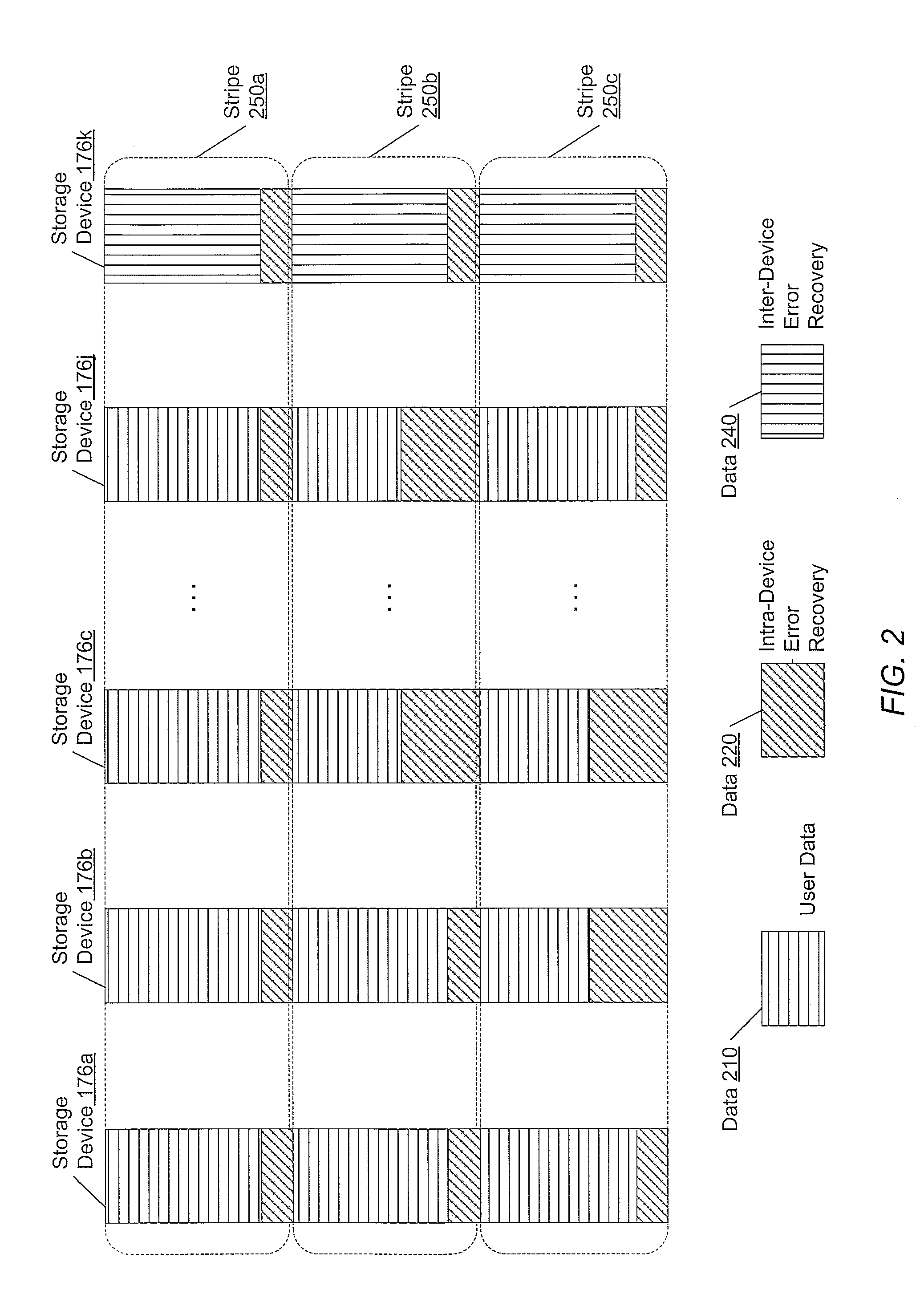
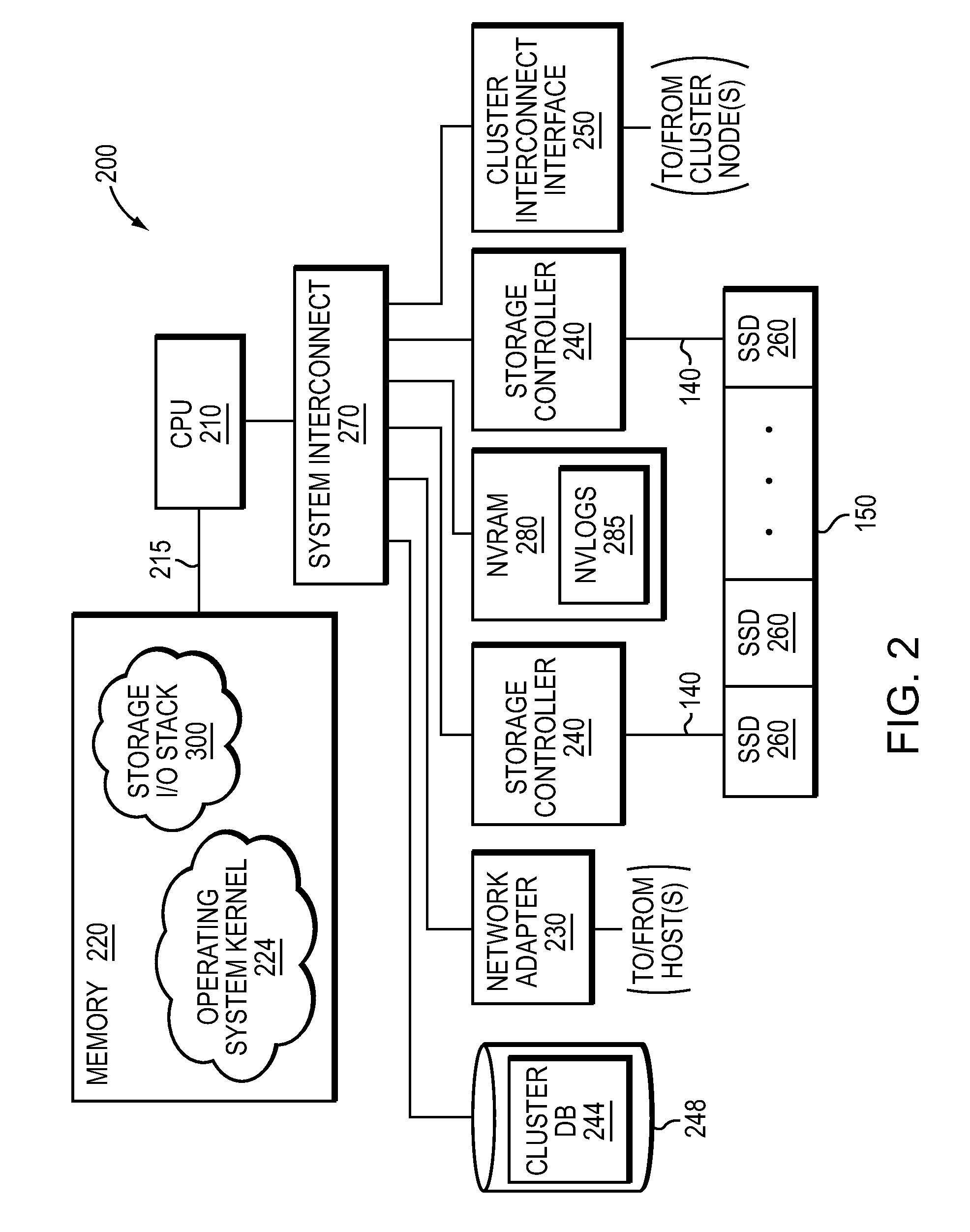
NVRAM caching and logging in a storage system
ActiveUS8898388B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersLatency (engineering)Solid-state drive
In one embodiment, non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM) caching and logging delivers low latency acknowledgements of input / output (I / O) requests, such as write requests, while avoiding loss of data. Write data may be stored in a portion of an NVRAM configured as, e.g., a persistent write-back cache, while parameters of the request may be stored in another portion of the NVRAM configured as one or more logs, e.g., NVLogs. The write data may be organized into separate variable length blocks or extents and “written back” out-of-order from the write back cache to storage devices, such as solid state drives (SSDs). The write data may be preserved in the write-back cache until each extent is safely and successfully stored on SSD (i.e., in the event of power loss), or operations associated with the write request are sufficiently logged on NVLog.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Scheduling of reconstructive I/O read operations in a storage environment
ActiveUS8589625B2Input/output to record carriersError detection/correctionSolid-state storageControl store
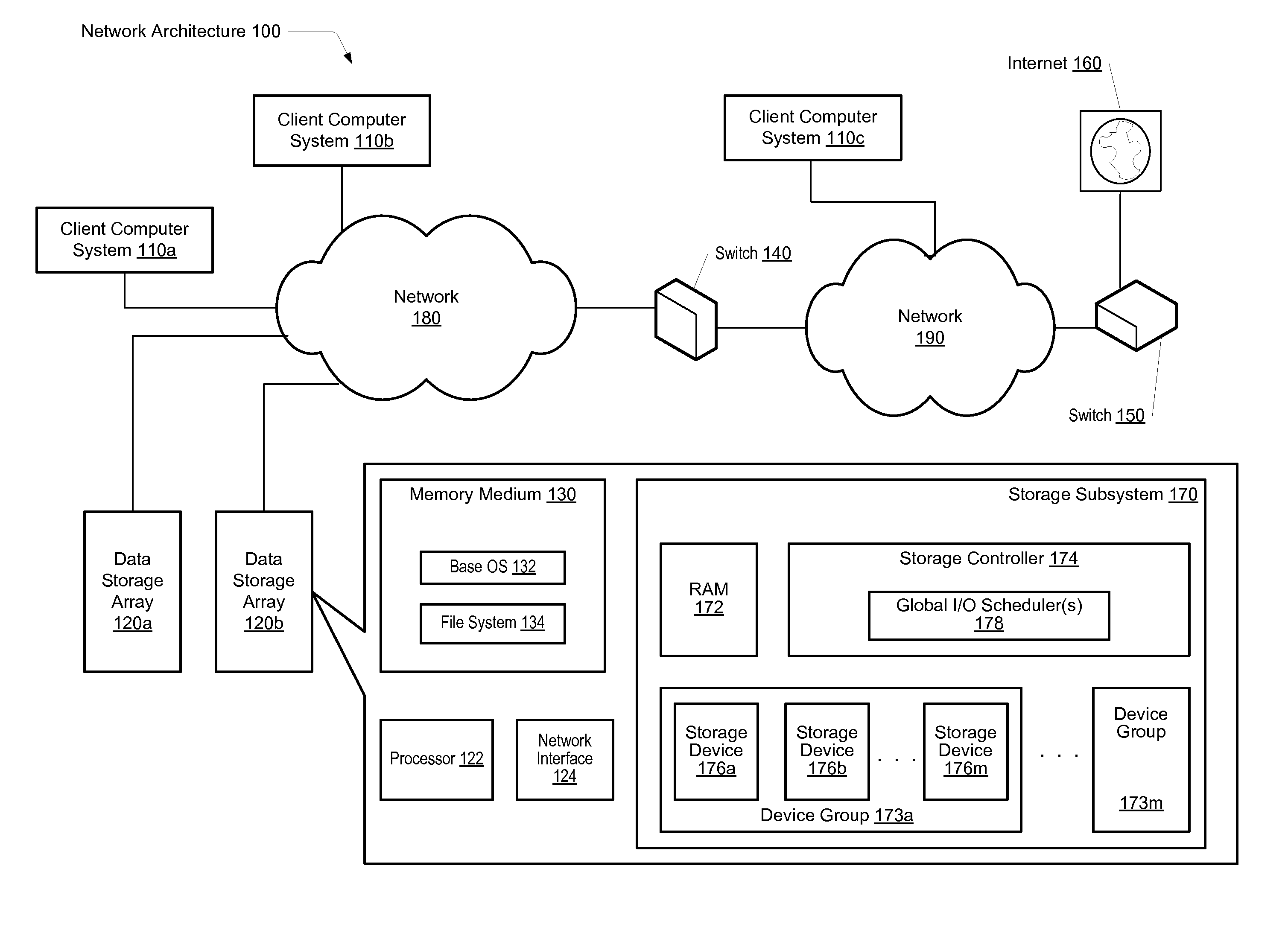
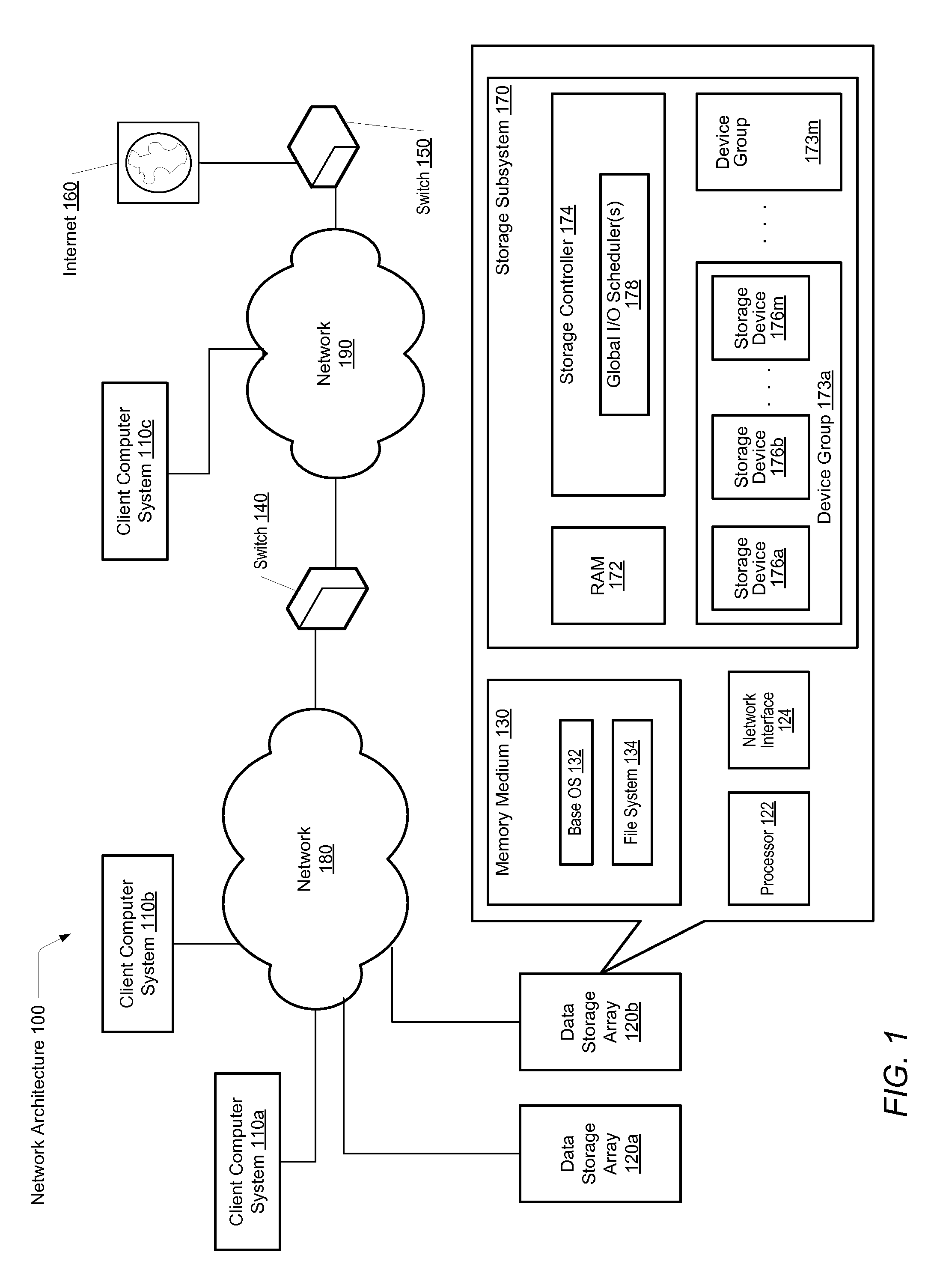
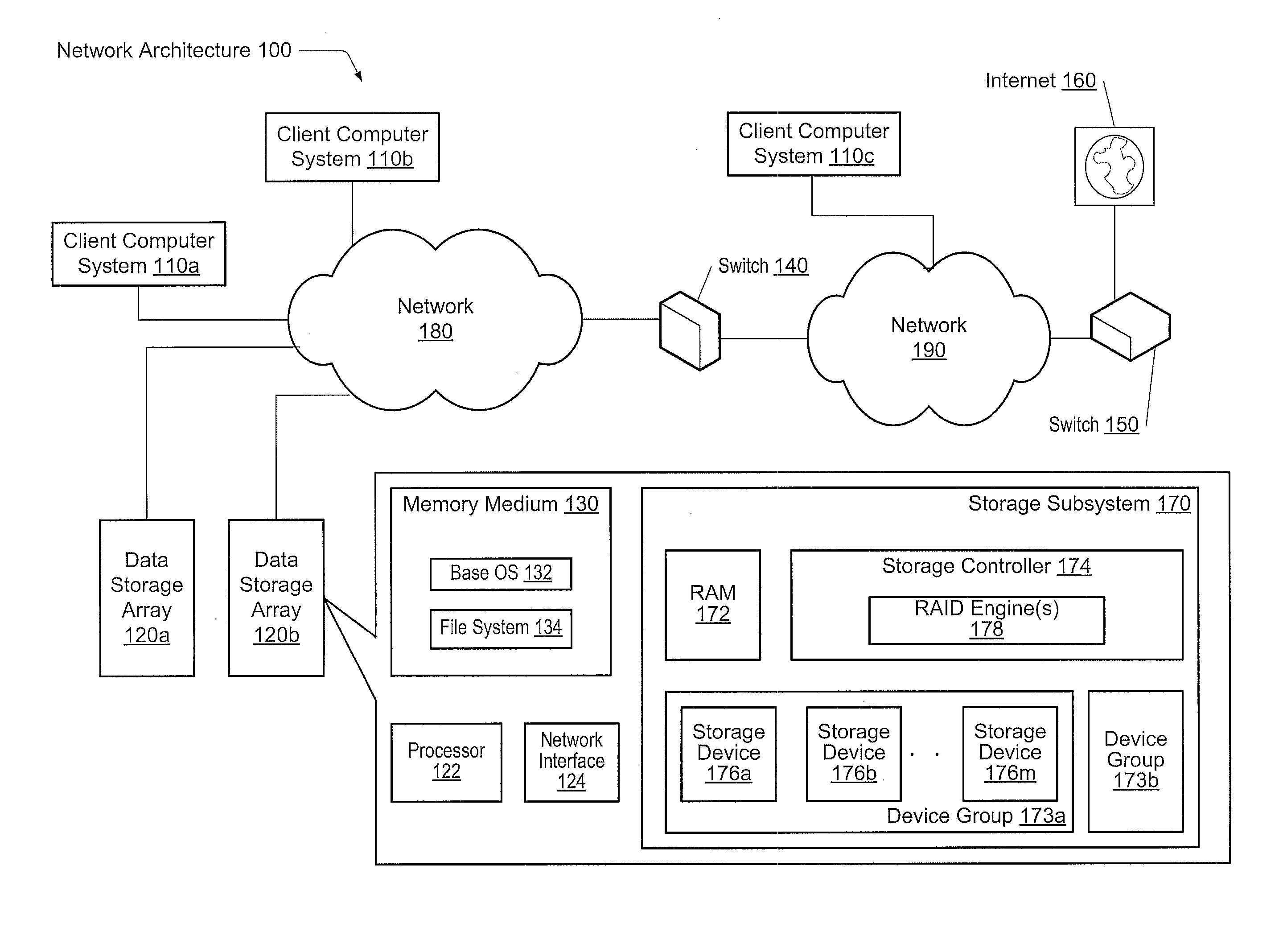
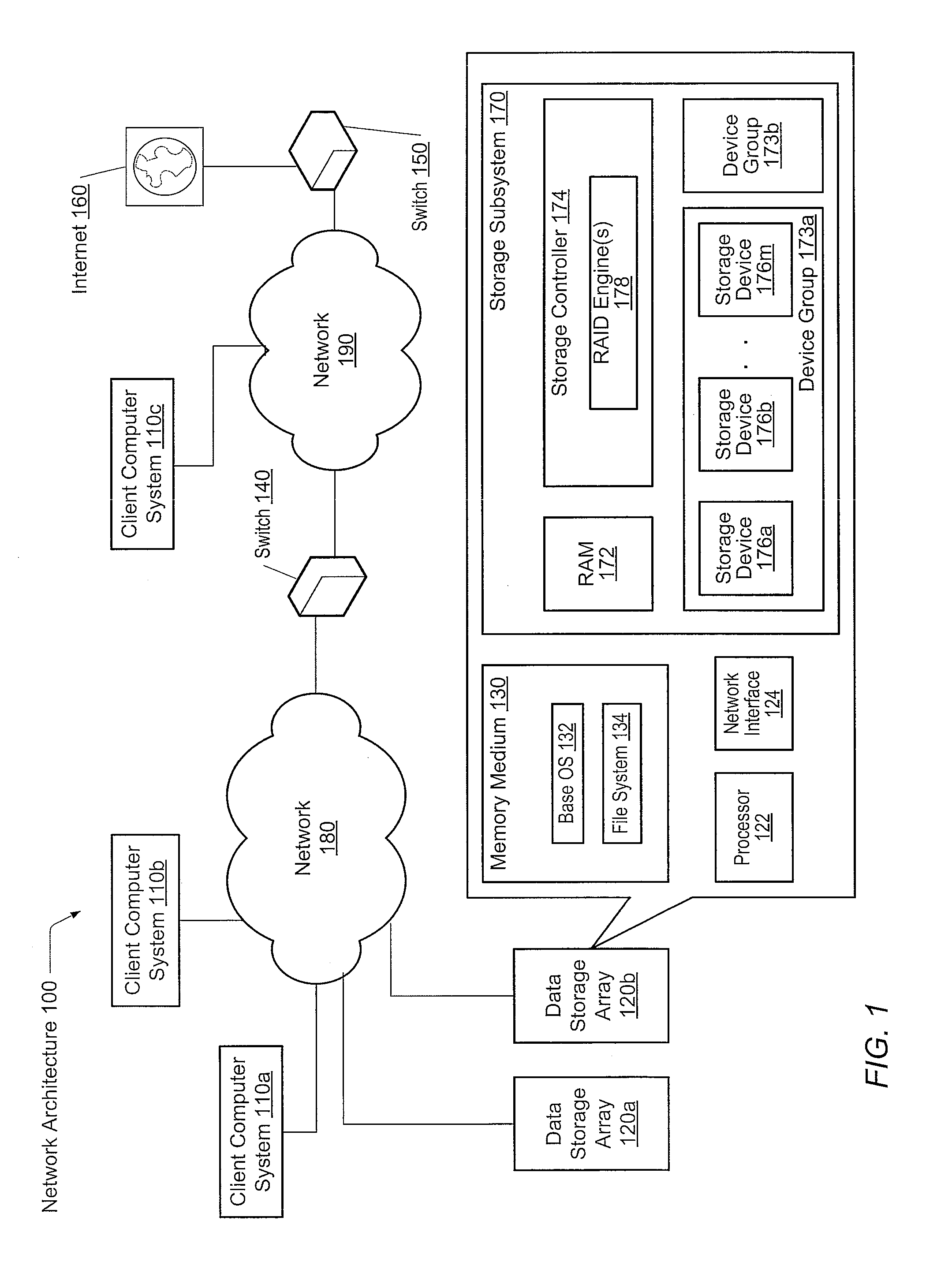
A system and method for effectively scheduling read and write operations among a plurality of solid-state storage devices. A computer system comprises client computers and data storage arrays coupled to one another via a network. A data storage array utilizes solid-state drives and Flash memory cells for data storage. A storage controller within a data storage array comprises an I / O scheduler. The storage controller is configured to receive a read request targeted to the data storage medium, and identify at least a first storage device of the plurality of storage devices which contains data targeted by the read request. In response to either detecting or predicting the first storage device will exhibit variable performance, the controller is configured to generate a reconstruct read request configured to obtain the data from one or more devices of the plurality of storage devices other than the first storage device.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
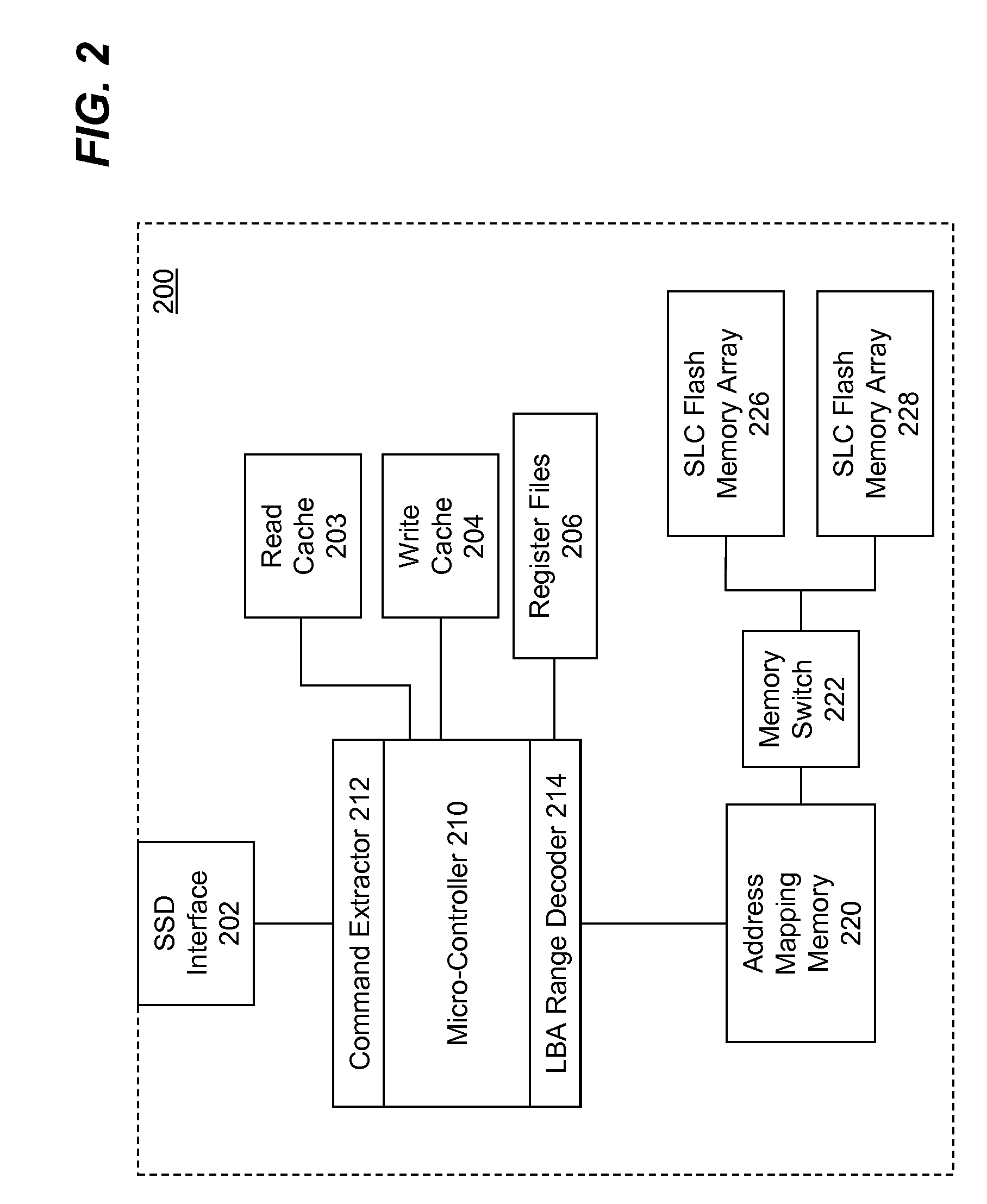
Hybrid SSD Using A Combination of SLC and MLC Flash Memory Arrays
InactiveUS20080215800A1Reduce manufacturing costAcceptable levelMemory architecture accessing/allocationInternal/peripheral component protectionData fileSingle level
Hybrid solid state drives (SSD) using a combination of single-level cell (SLC) and multi-level cell (MLC) flash memory arrays are described. According to one aspect of the present invention, a hybrid SSD is built using a combination SLC and MLC flash memory arrays. The SSD also includes a micro-controller to control and coordinate data transfer from a host computing device to either the SLC flash memory array of the MLC flash memory array. A memory selection indicator is determined by triaging data file based on one or more criteria, which include, but is not limited to, storing system files and user directories in the SLC flash memory array and storing user files in the MLC flash memory array; or storing more frequent access files in the SLC flash memory array, while less frequent accessed files in the MLC flash memory array.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
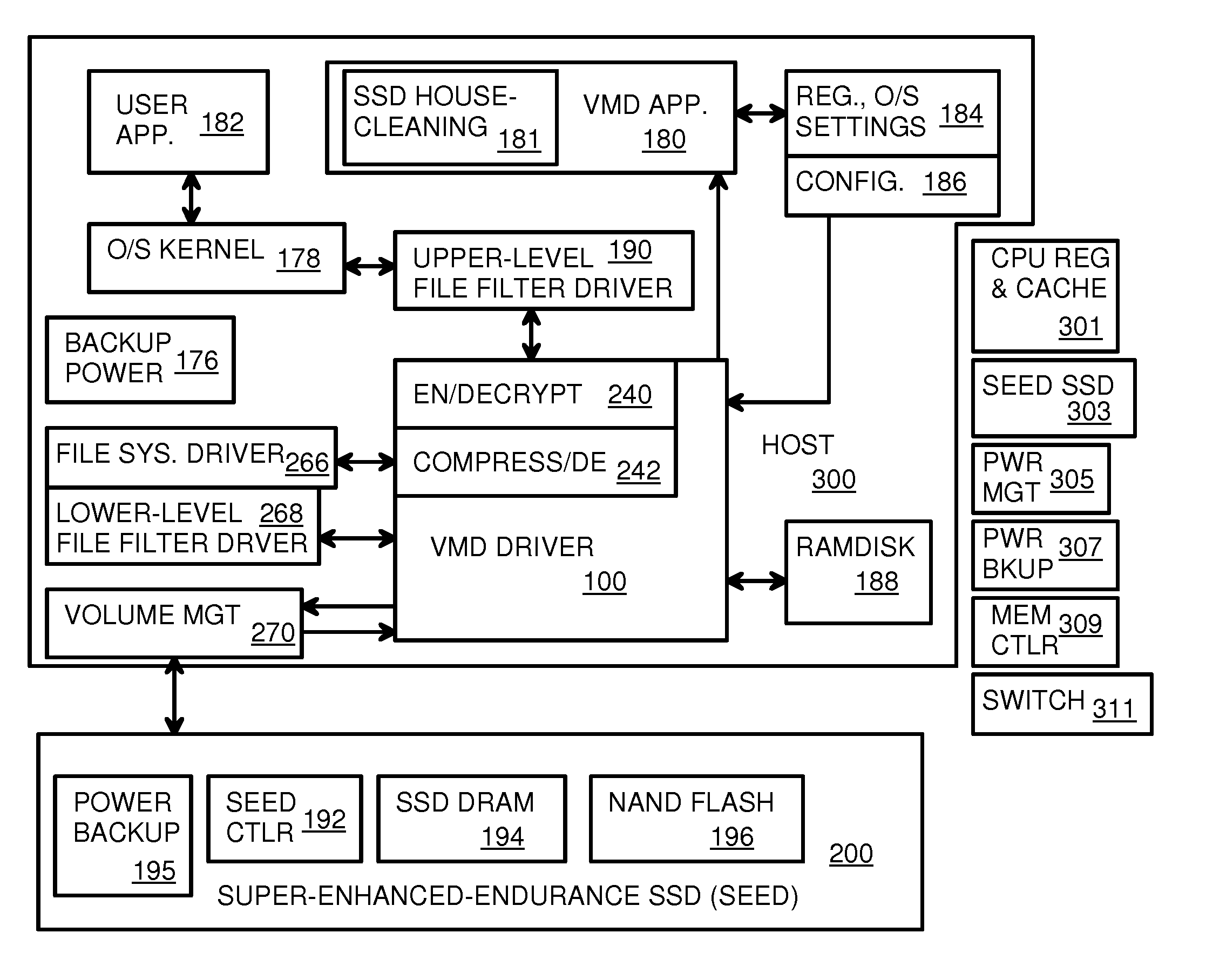
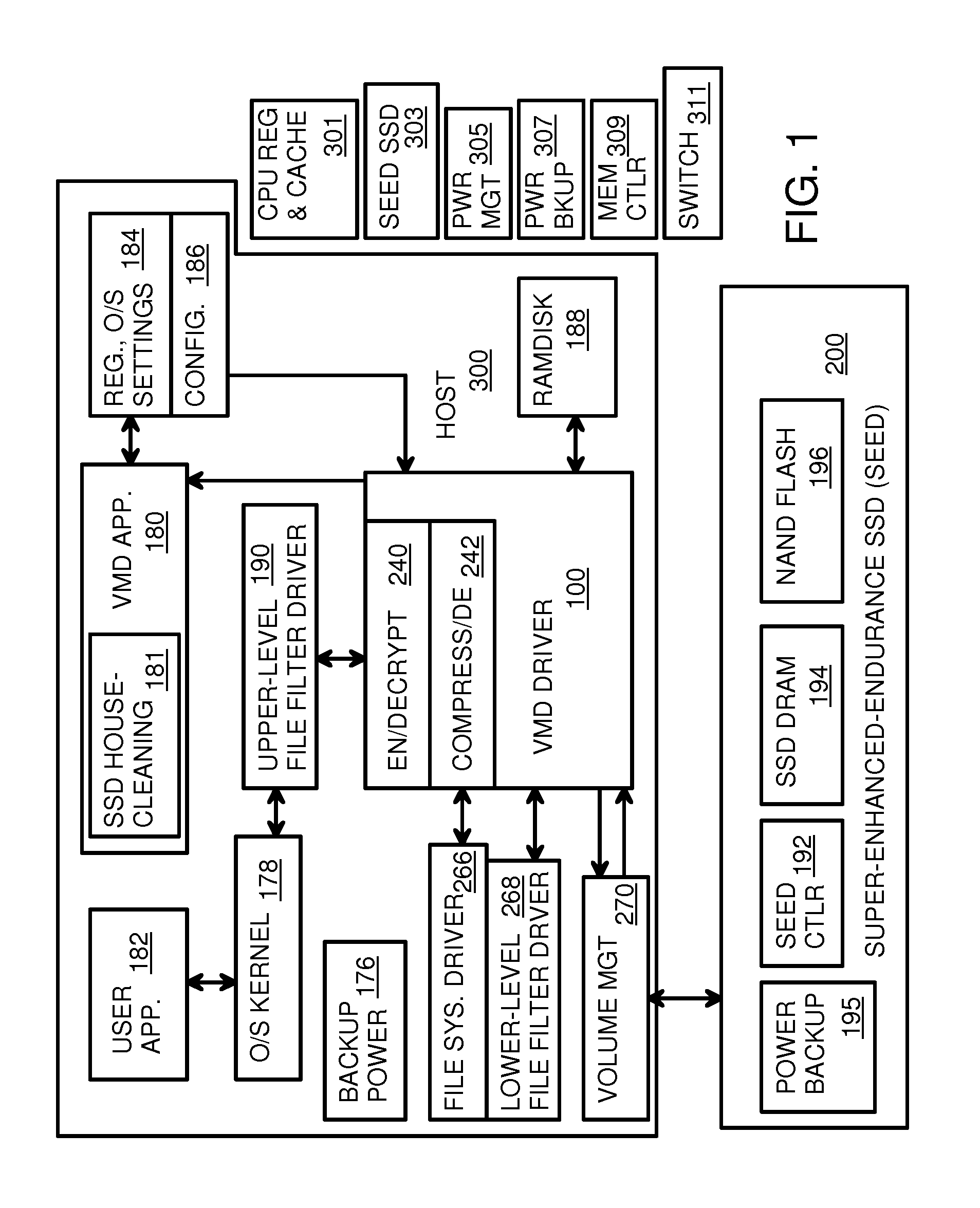
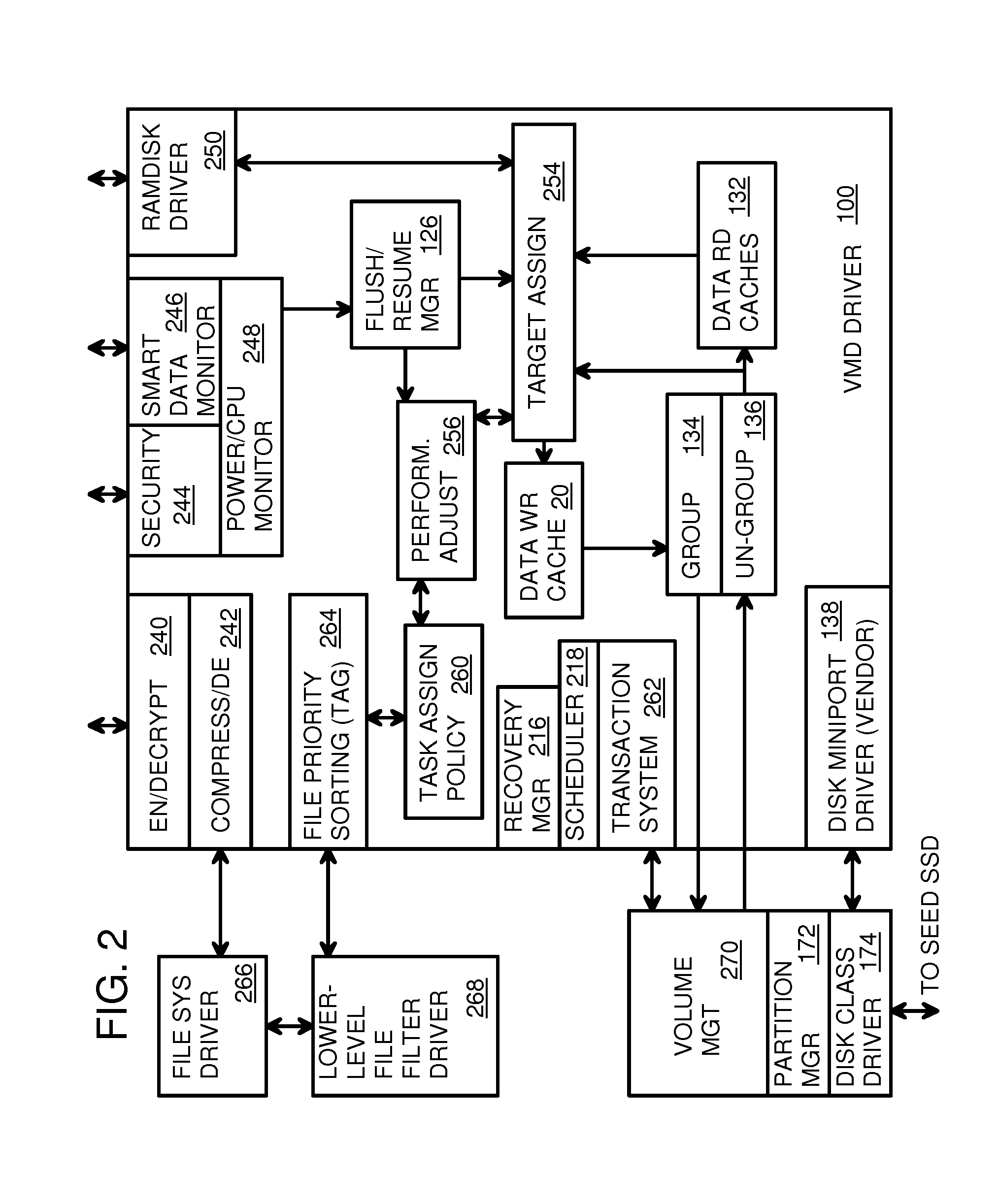
Virtual Memory Device (VMD) Application/Driver with Dual-Level Interception for Data-Type Splitting, Meta-Page Grouping, and Diversion of Temp Files to Ramdisks for Enhanced Flash Endurance
ActiveUS20130145085A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFilename extensionData file
A Virtual-Memory Device (VMD) driver and application execute on a host to increase endurance of flash memory attached to a Super Enhanced Endurance Device (SEED) or Solid-State Drive (SSD). Host accesses to flash are intercepted by the VMD driver using upper and lower-level filter drivers and categorized as data types of paging files, temporary files, meta-data, and user data files, using address ranges and file extensions read from meta-data tables. Paging files and temporary files are optionally written to flash. Full-page and partial-page data are grouped into multi-page meta-pages by data type before storage by the SSD. ramdisks and caches for storing each data type in the host DRAM are managed and flushed to the SSD by the VMD driver. Write dates are stored for pages or blocks for management functions. A spare / swap area in DRAM reduces flash wear. Reference voltages are adjusted when error correction fails.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
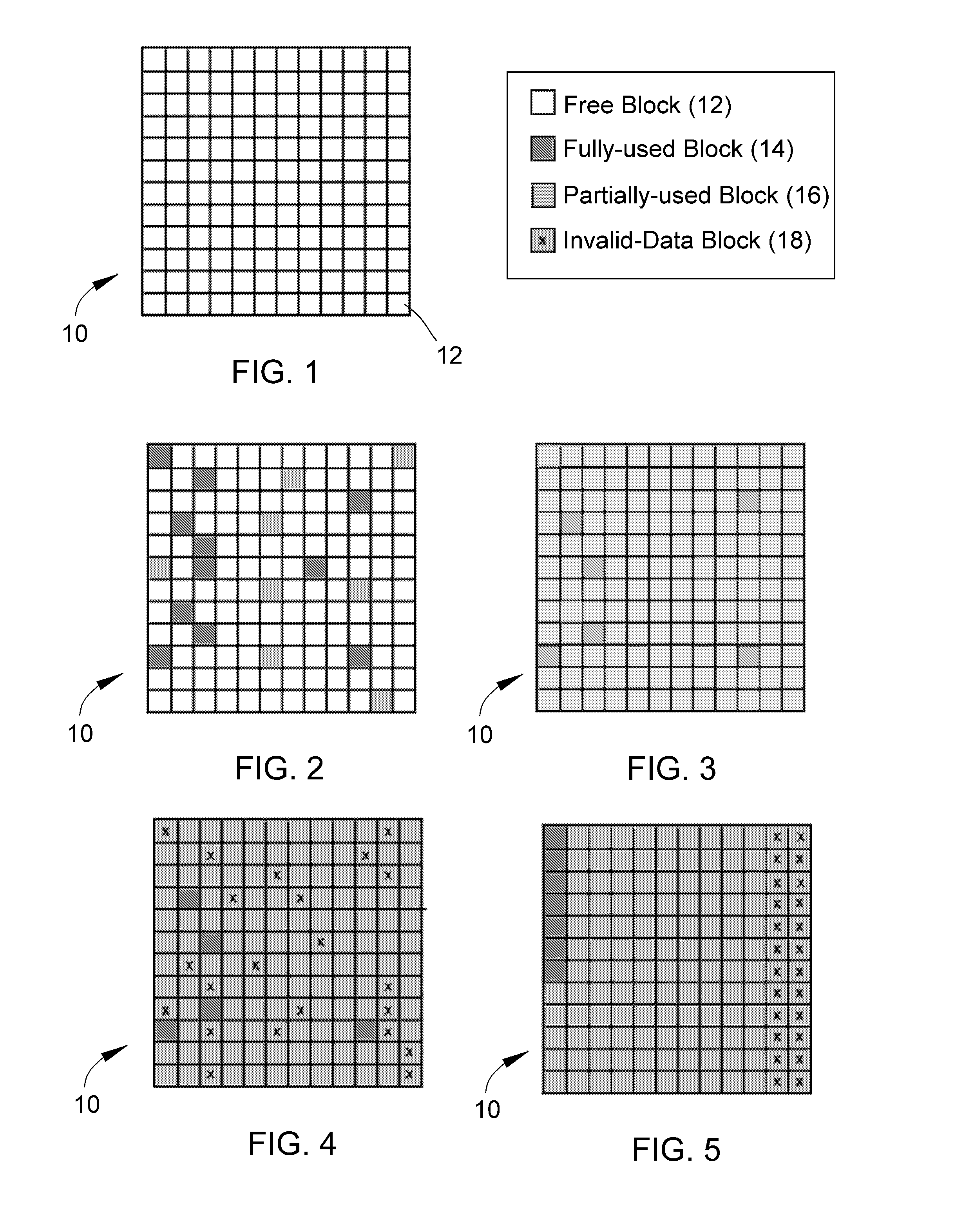
Method for restoring and maintaining solid-state drive performance
InactiveUS20110119462A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInvalid DataTerm memory
A method of maintaining a solid-state drive so that free space within memory blocks of the drive becomes free usable space to the drive. The drive comprises cells organized in pages that are organized in memory blocks in which at least user files are stored. A defragmentation utility is executed to cause at least some of the memory blocks that are partially filled with data and contain file fragments to be combined or aligned and to cause at least some of the memory blocks that contain only invalid data to be combined or aligned. A block consolidation utility is then executed to eliminate at least some of the partially-filled blocks by consolidating the file fragments into a fewer number of the memory blocks. The consolidation utility also increases the number of memory blocks that contain only invalid memory. All of the memory blocks containing only invalid data are then erased.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
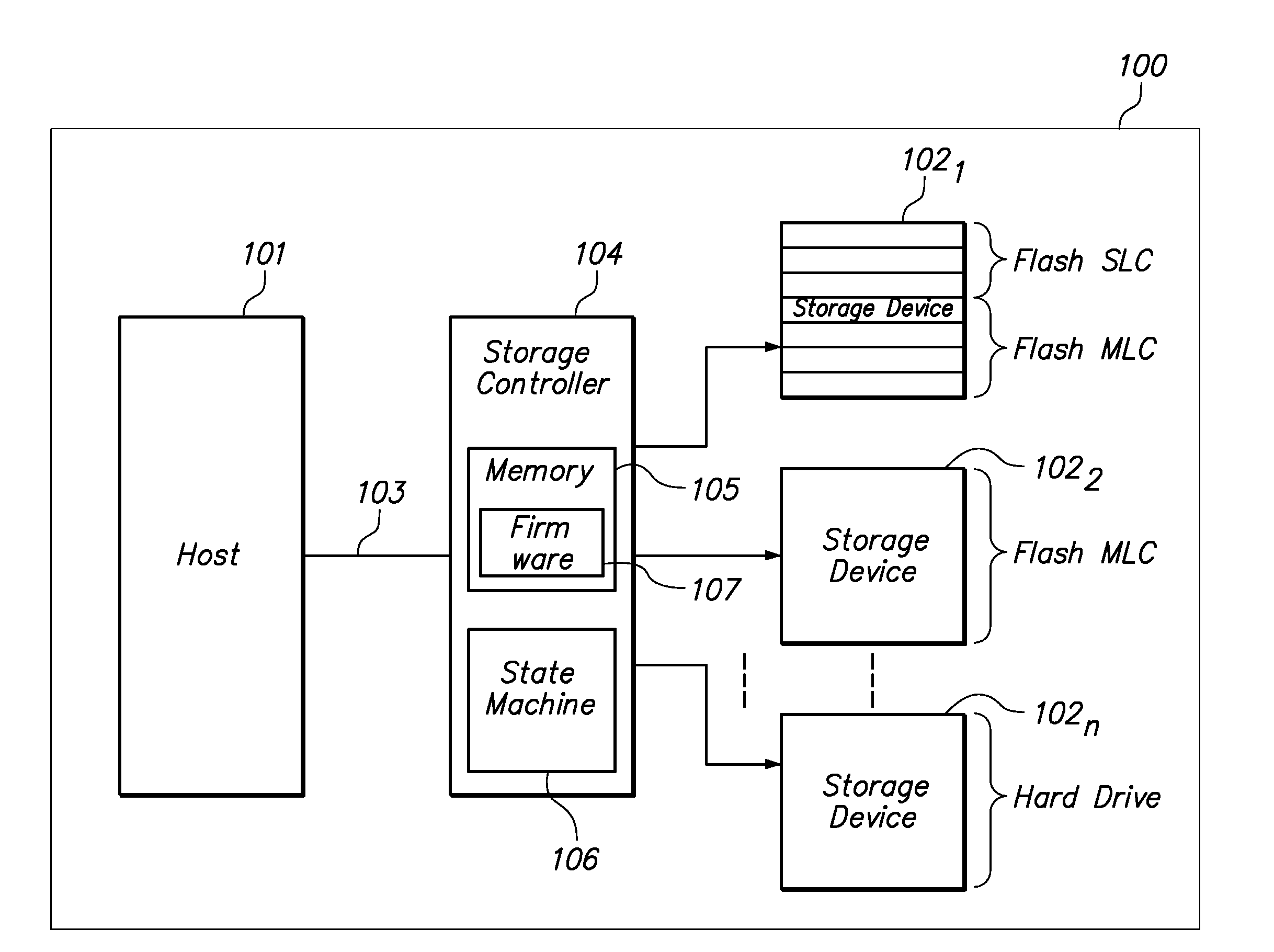
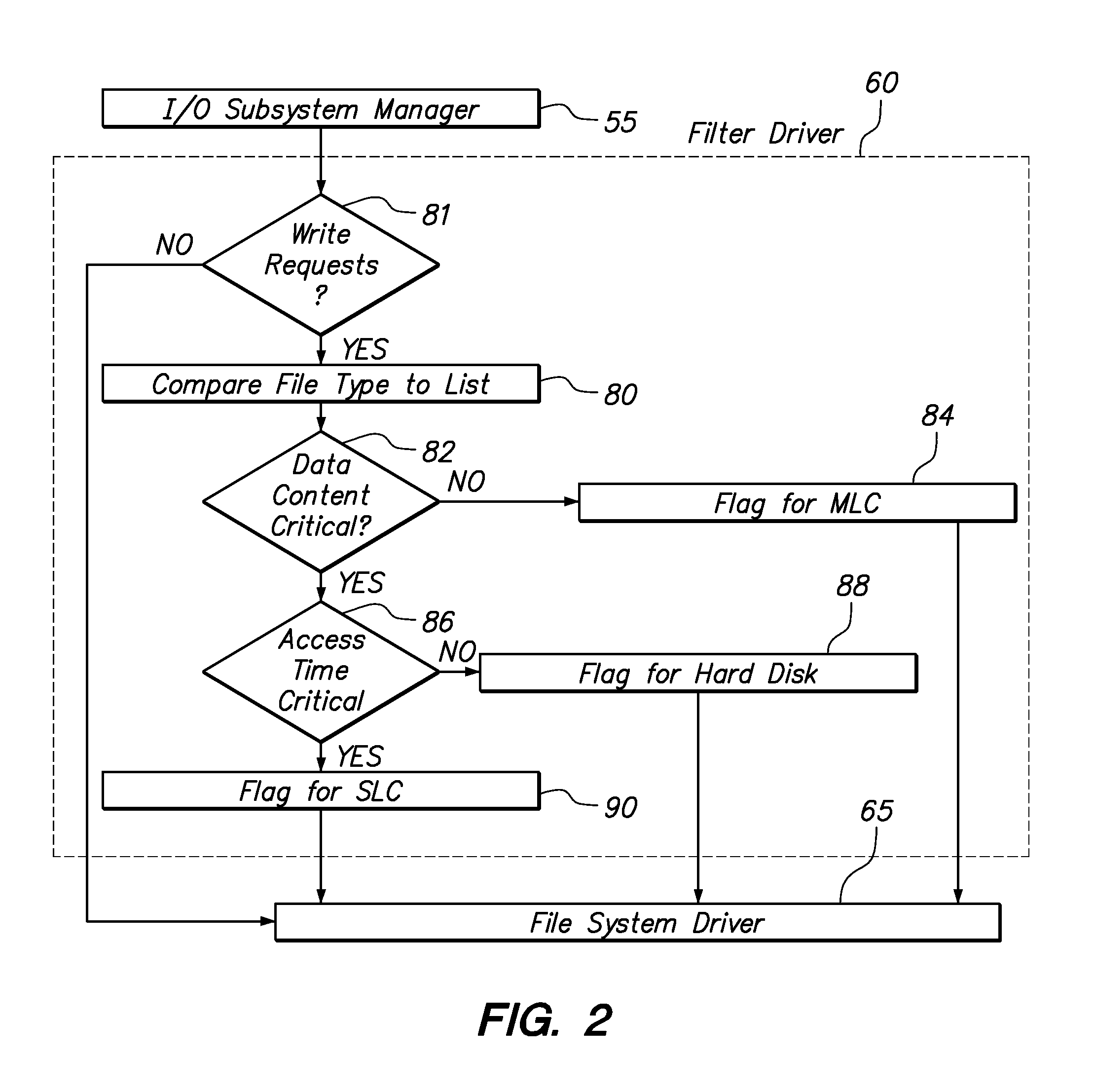
Smart Solid State Drive And Method For Handling Critical Files
InactiveUS20090043831A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingControl storeComputerized system
A method and apparatus for dynamically distributing data to an appropriate storage device based on the significance of the data. In one embodiment the method determines the significance of a data file using the format of the data file. The method also includes identifying a storage device and memory location of the storage device to write the data. In a software implementation, a computer system employs a filter driver and / or a device driver to identify and store data files. In another embodiment, a storage controller includes a state machine that initiates and executes firmware to determine the data file format and also the storage device location.
Owner:MCM PORTFOLIO LLC
Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) and Diversion of Temp Files for Reduced Flash Wear of a Super-Endurance Solid-State Drive
ActiveUS20150106556A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFilename extensionData file
A flash drive has increased endurance and longevity by reducing writes to flash. An Endurance Translation Layer (ETL) is created in a DRAM buffer and provides temporary storage to reduce flash wear. A Smart Storage Switch (SSS) controller assigns data-type bits when categorizing host accesses as paging files used by memory management, temporary files, File Allocation Table (FAT) and File Descriptor Block (FDB) entries, and user data files, using address ranges and file extensions read from FAT. Paging files and temporary files are never written to flash. Partial-page data is packed and sector mapped by sub-sector mapping tables that are pointed to by a unified mapping table that stores the data-type bits and pointers to data or tables in DRAM. Partial sectors are packed together to reduce DRAM usage and flash wear. A spare / swap area in DRAM reduces flash wear. Reference voltages are adjusted when error correction fails.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Methods and systems for data storage using solid state drives
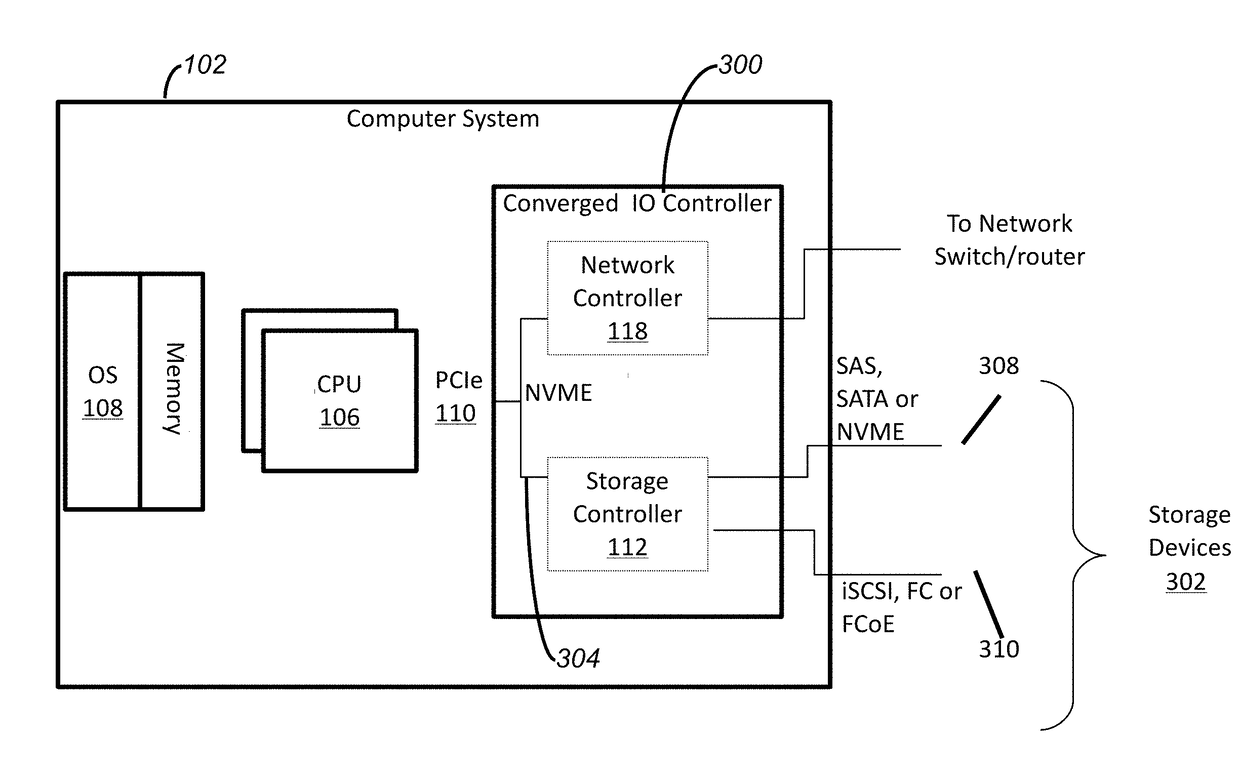
ActiveUS20170177222A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityInput/output to record carriersProgram controlVirtualizationSolid-state drive
Provided herein are methods and systems for improved storage strategies for use of collections of storage resources, such as solid state drives, including in connection with a converged networking and storage node that may be used for virtualization of a collection of physically attached and / or network-connected storage resources.
Owner:DIAMANTI INC
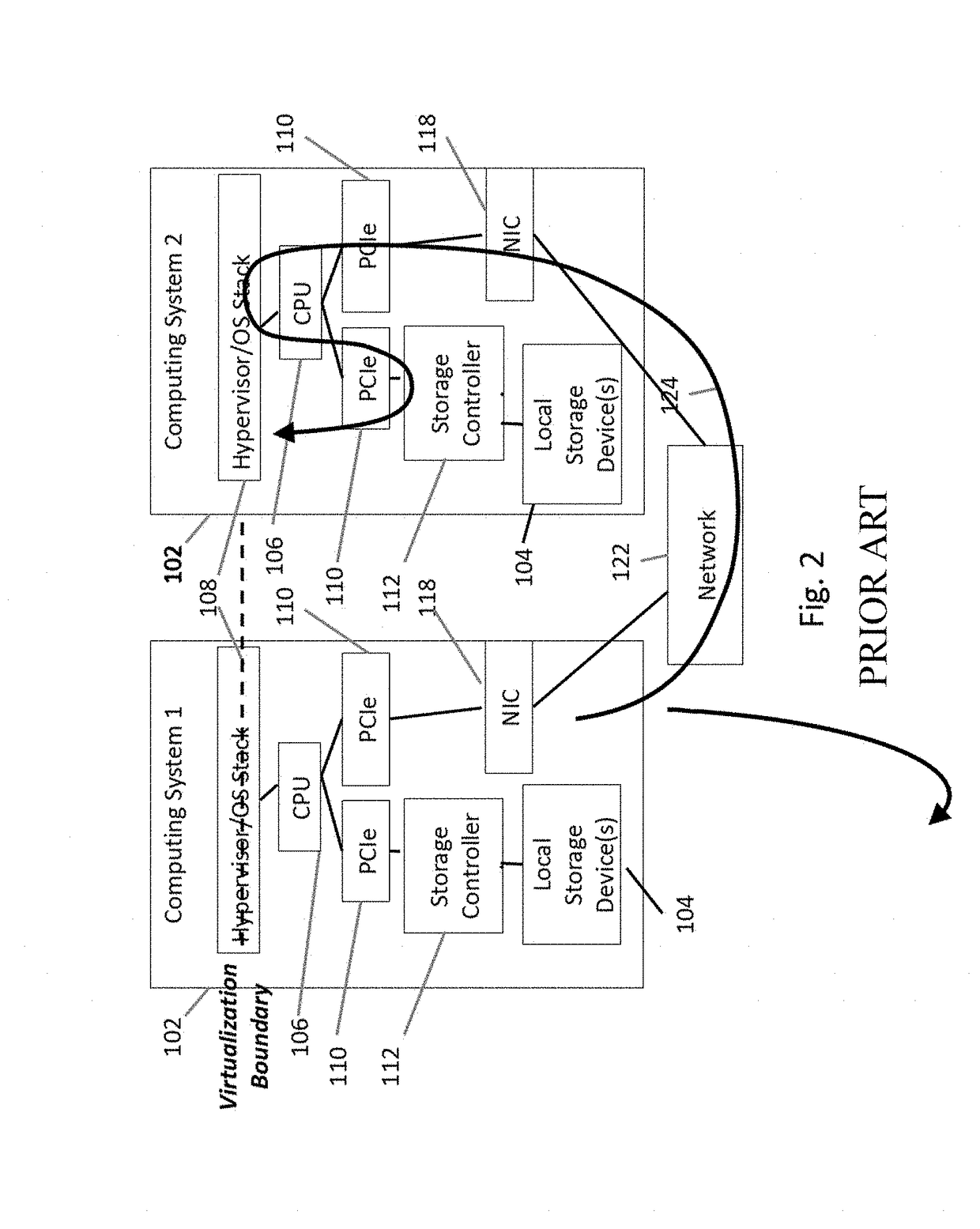
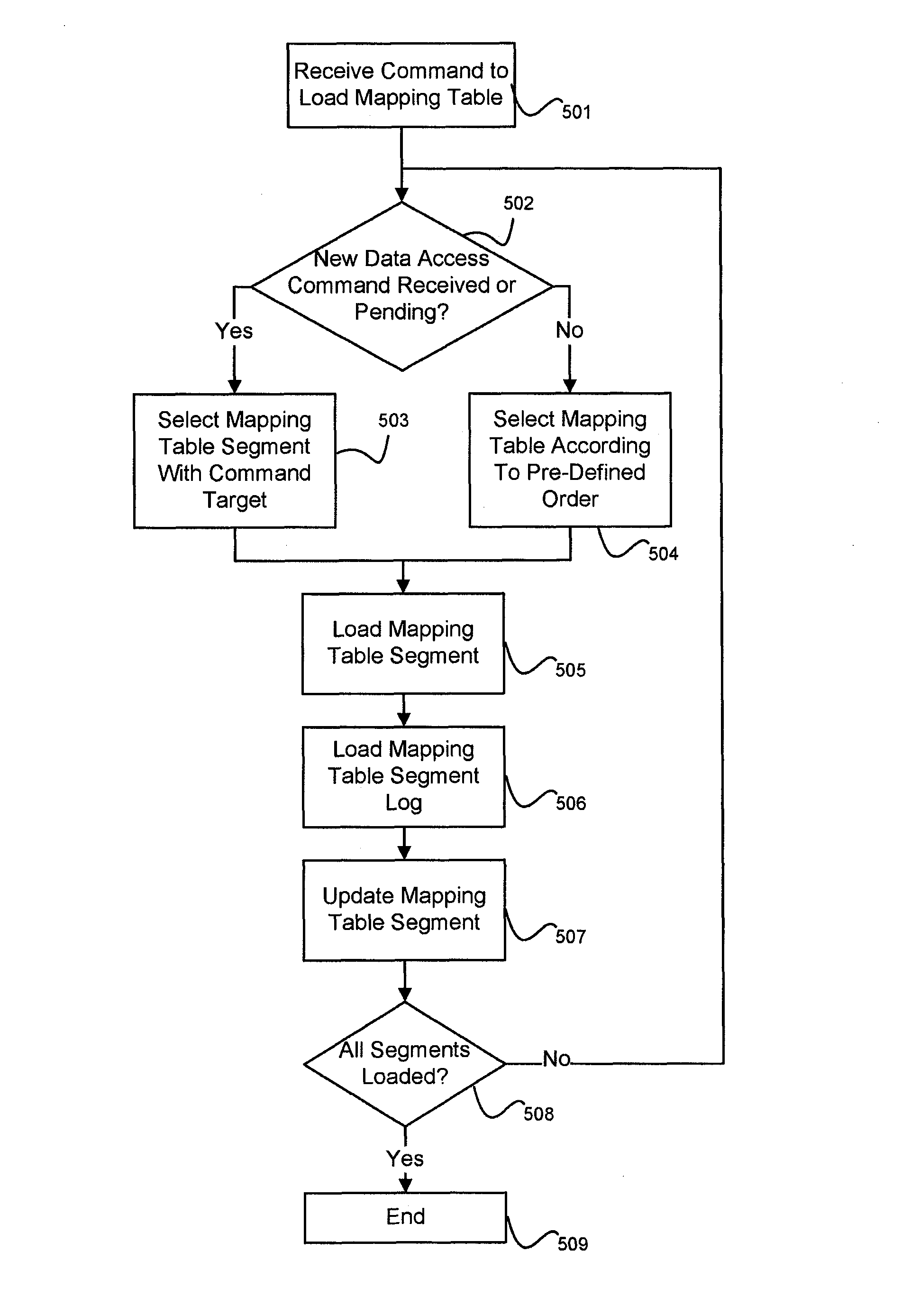
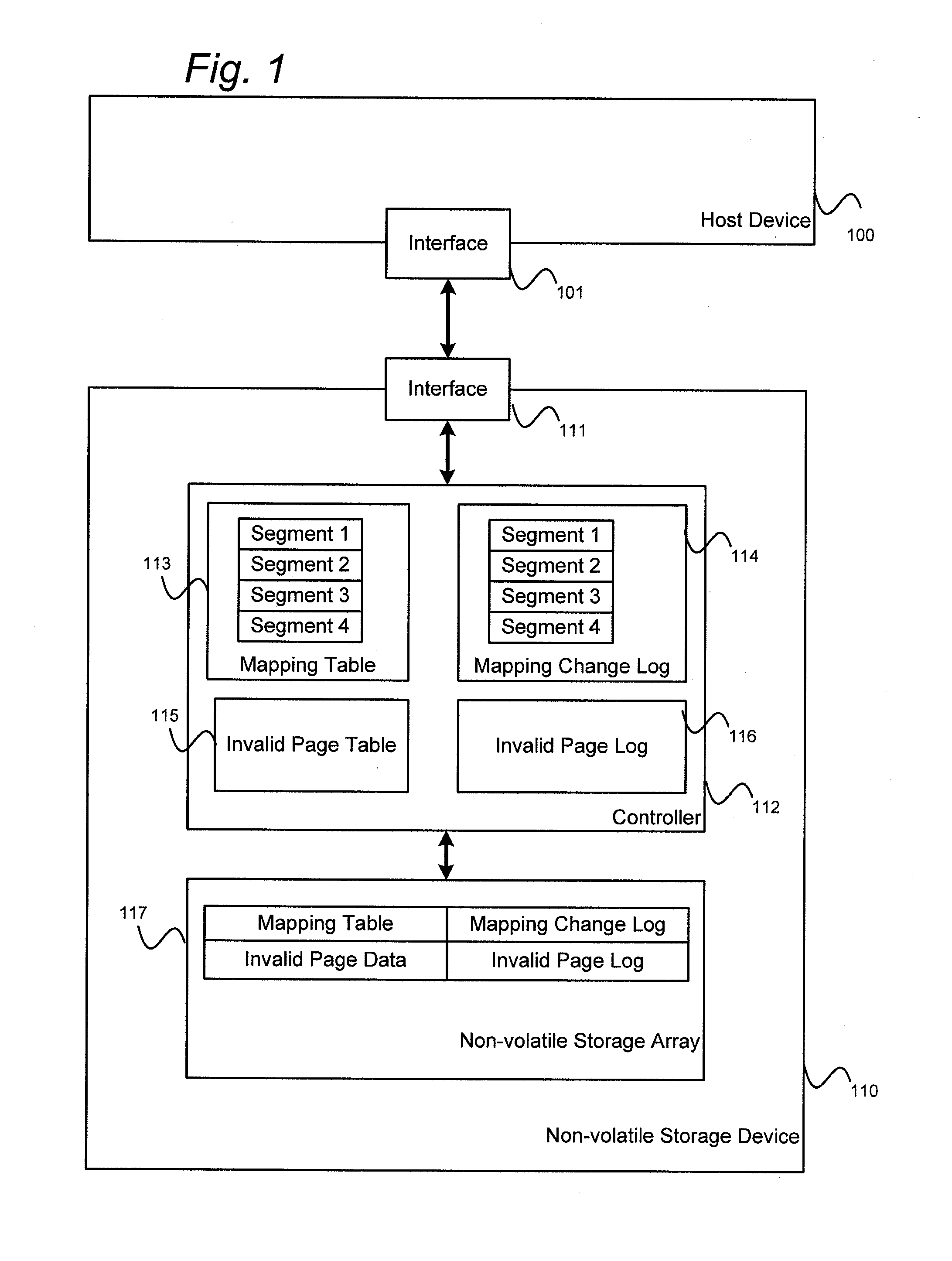
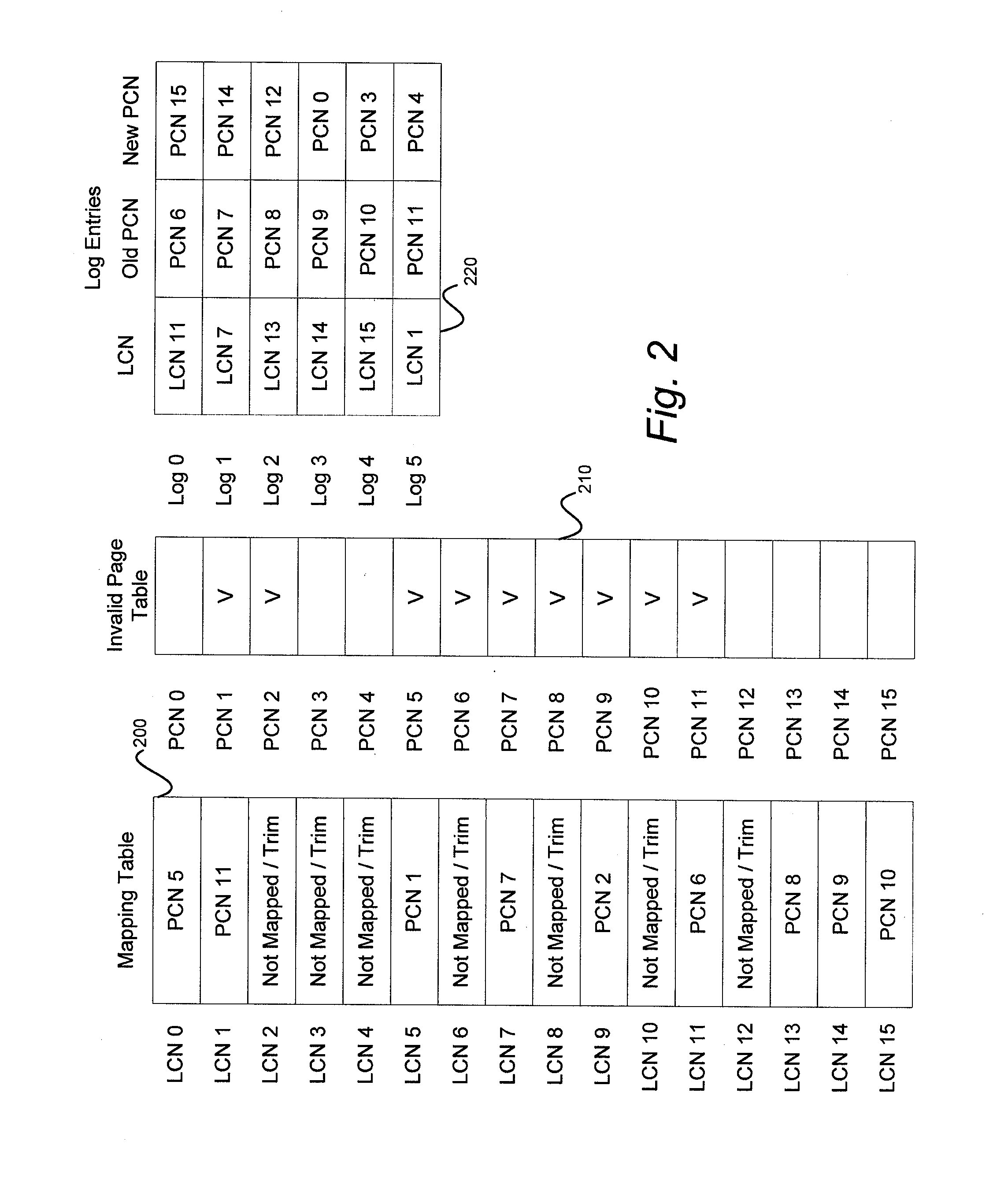
Solid-state drive with reduced power up time
ActiveUS8793429B1Reduce delaysMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTSolid-state driveComputer science
A non-volatile storage system is provided with reduced delays associated with loading and updating a logical-to-physical mapping table from non-volatile memory. The mapping table is stored in a plurality of segments, so that each segment can be loaded individually. The segmented mapping table allows memory access to logical addresses associated with the loaded segment when the segment is loaded, rather than delaying accesses until the entire mapping table is loaded. When loading mapping segments, segments can be loaded according to whether there is a pending command or by an order according to various algorithms.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
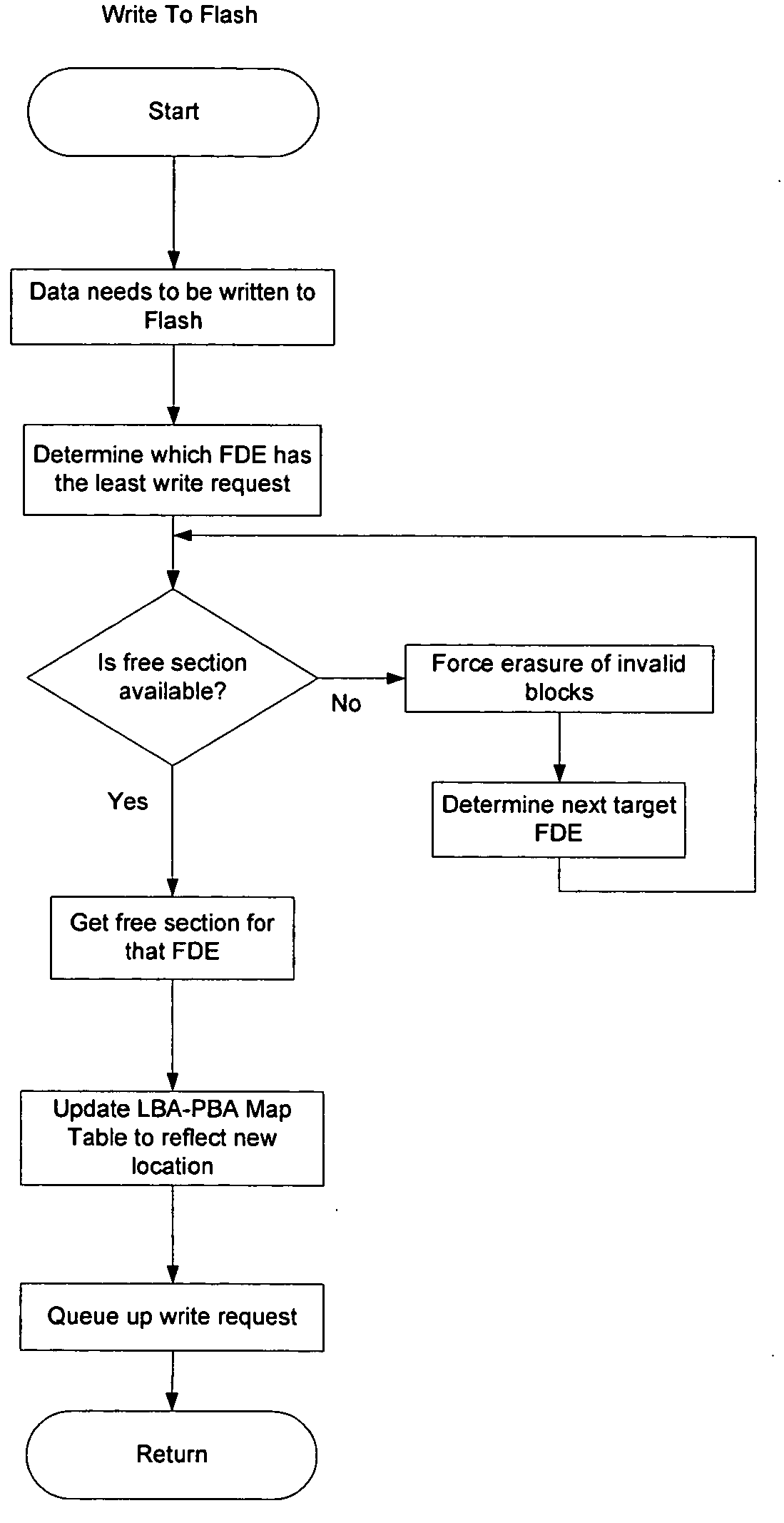
Garbage Collection for Solid State Disks
ActiveUS20110022778A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPage countRefuse collection
Described embodiments provide a method of recovering storage space on a solid state disk (SSD). An index and valid page count are determined for each block of a segment of an SSD. If the valid page count of at least one block in the segment is zero, a quick clean is performed. A quick clean deallocates blocks having zero valid pages and places them in a queue for erasure. Otherwise, a deep clean is performed. A deep clean determines a compaction ratio, N-M, wherein N is a number of partially valid blocks and M is a number of free blocks required to compact the valid data from the N partially valid blocks into M entirely valid blocks. At least one data structure of the SSD is modified to refer to the M entirely valid blocks, and the N partially valid blocks are placed in the queue for erasure.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
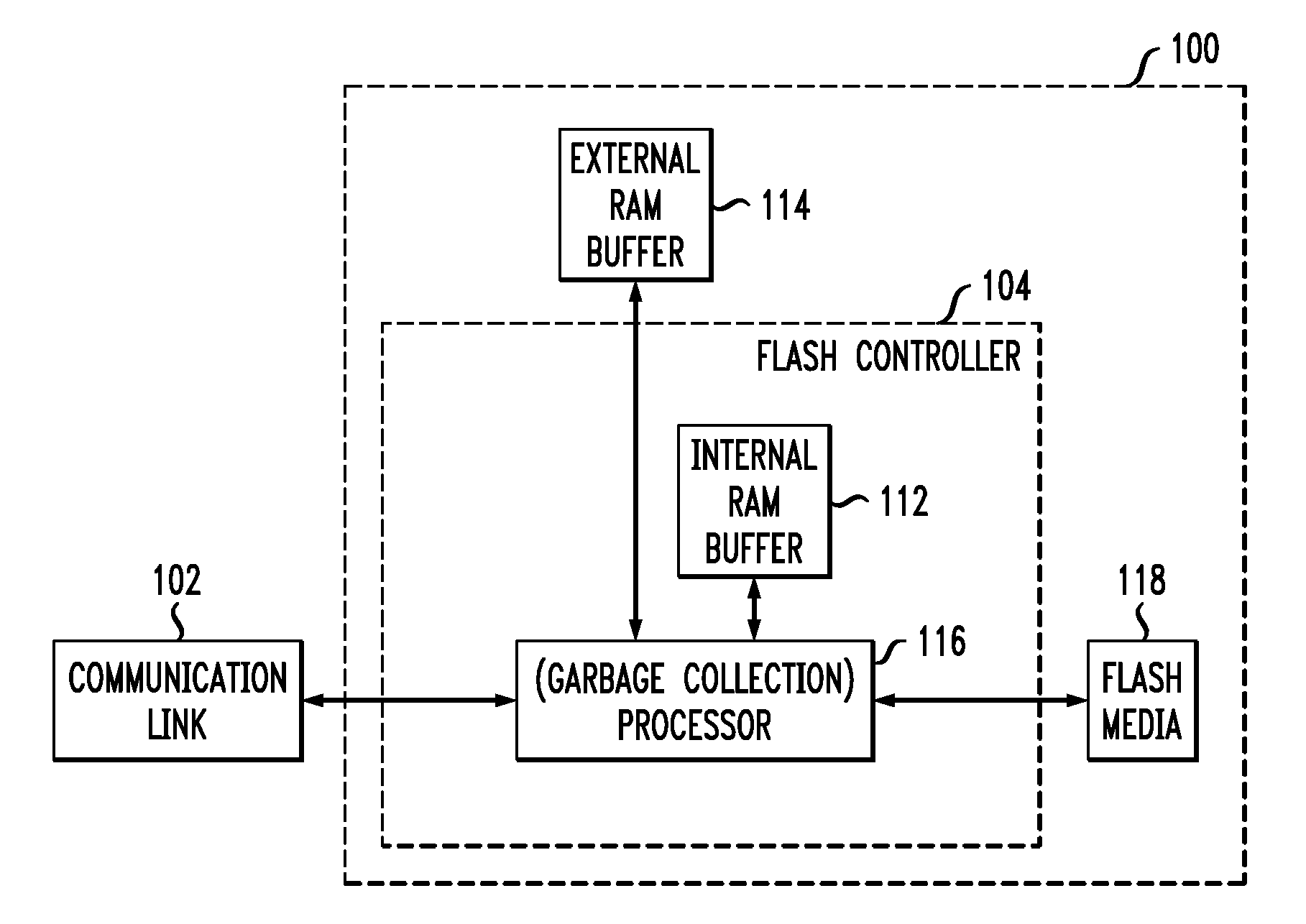
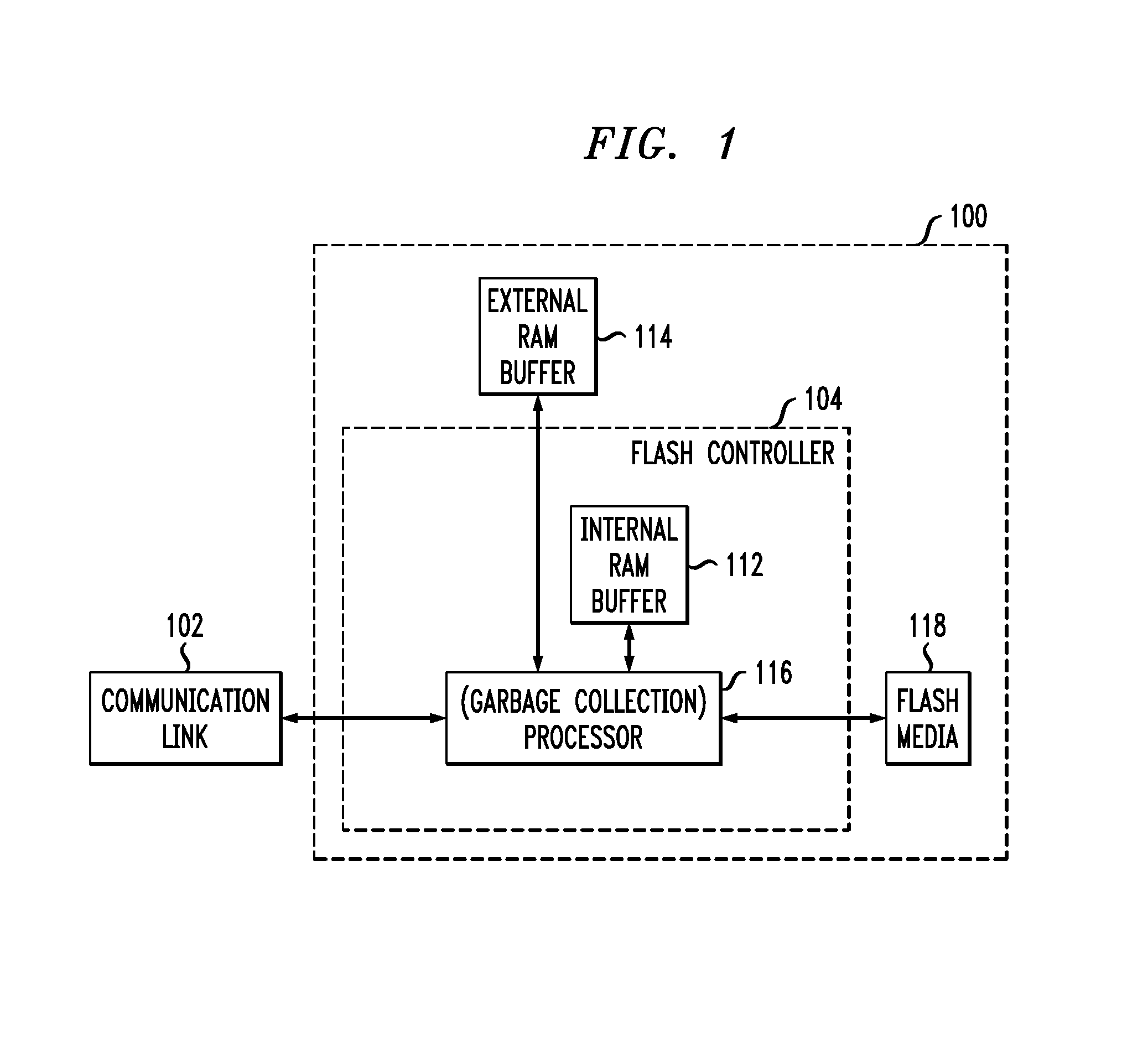
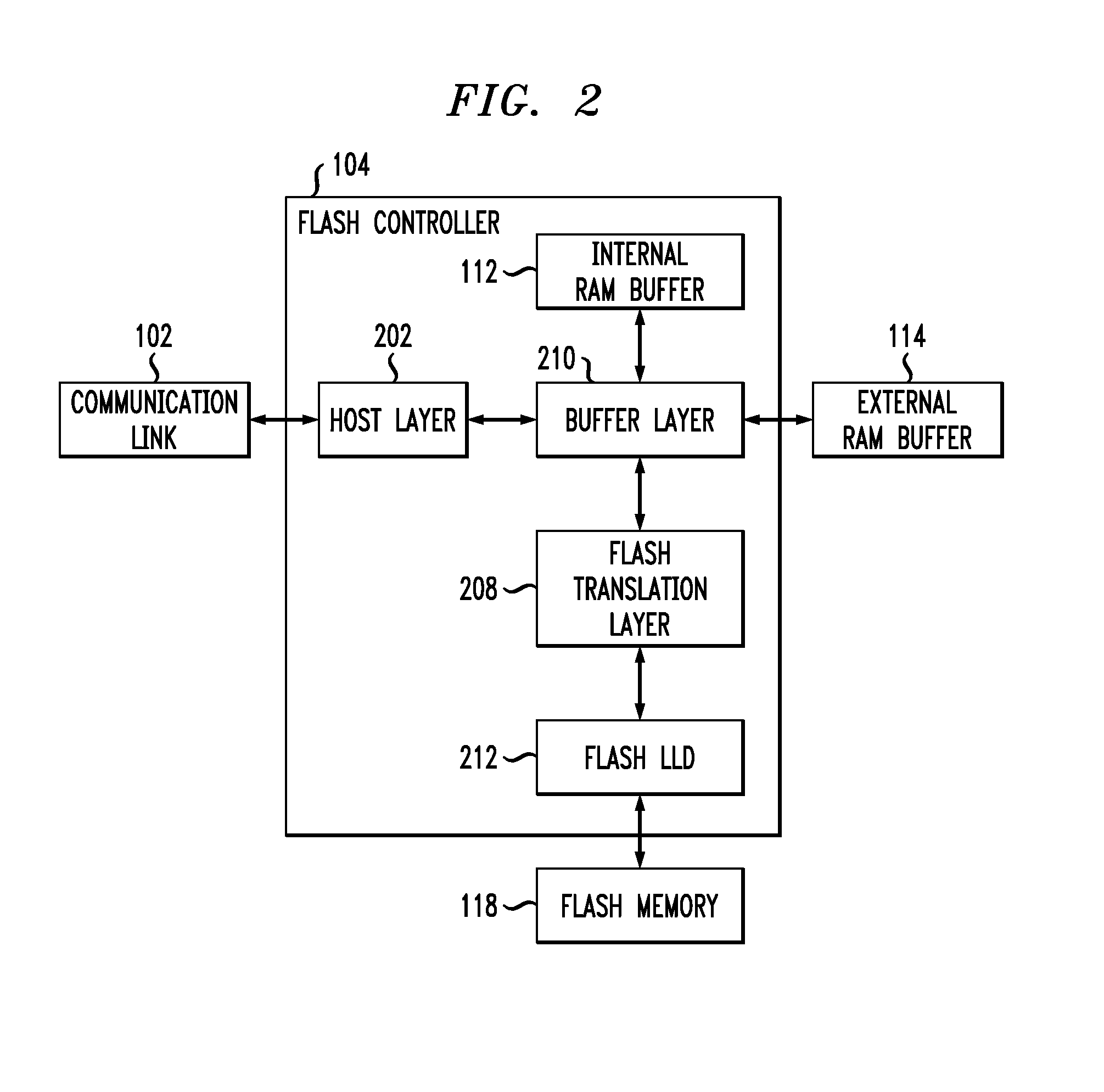
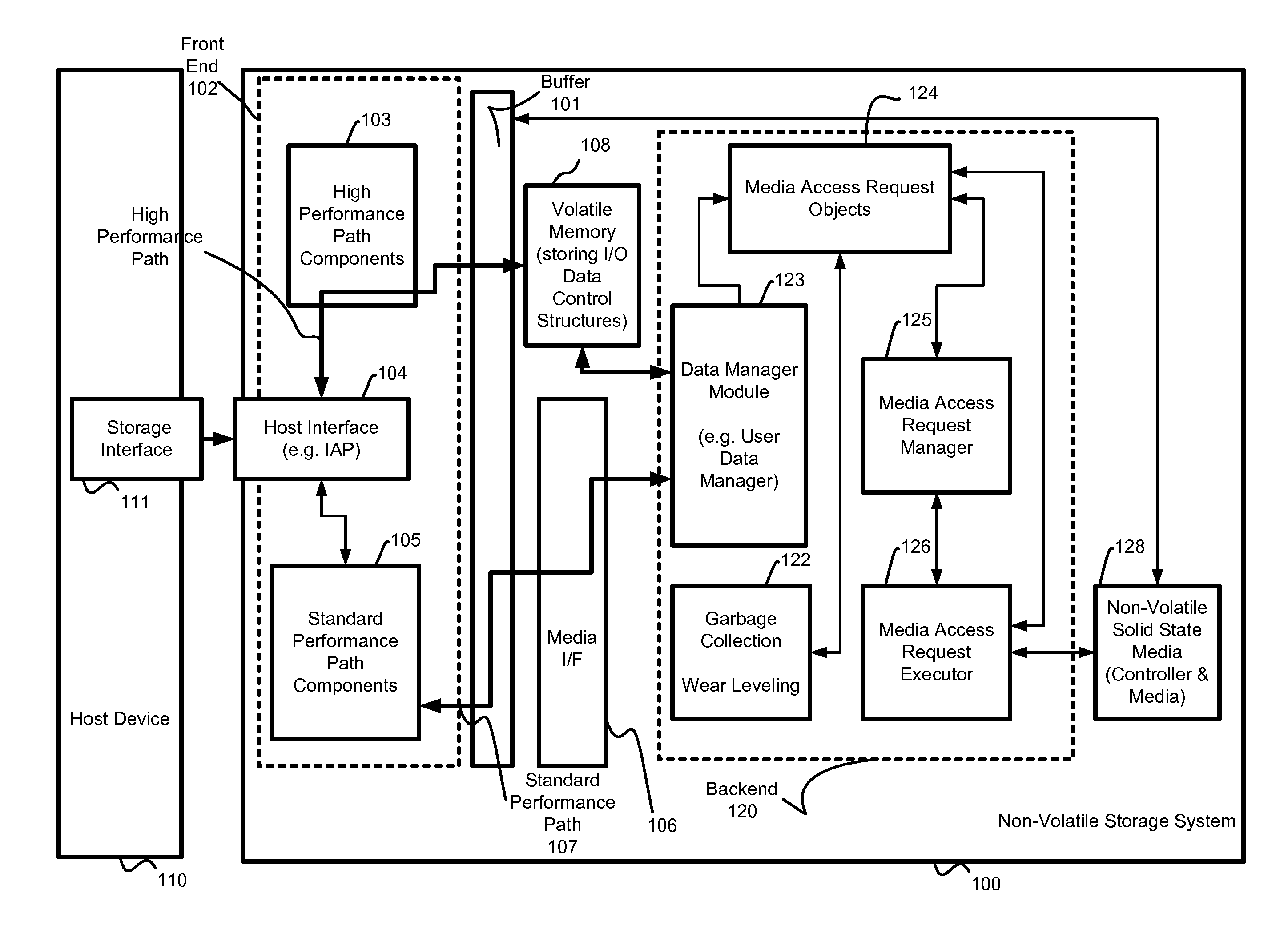
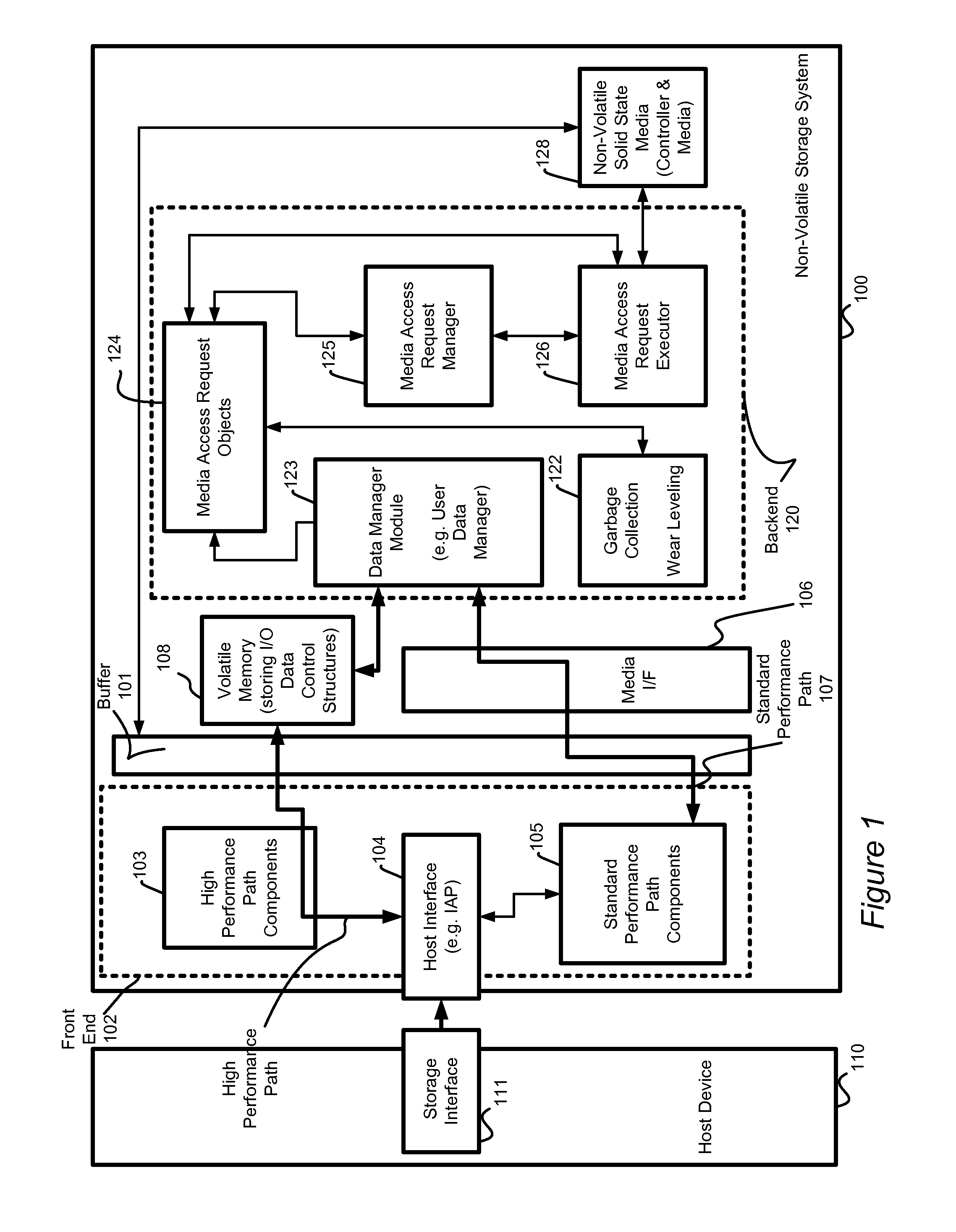
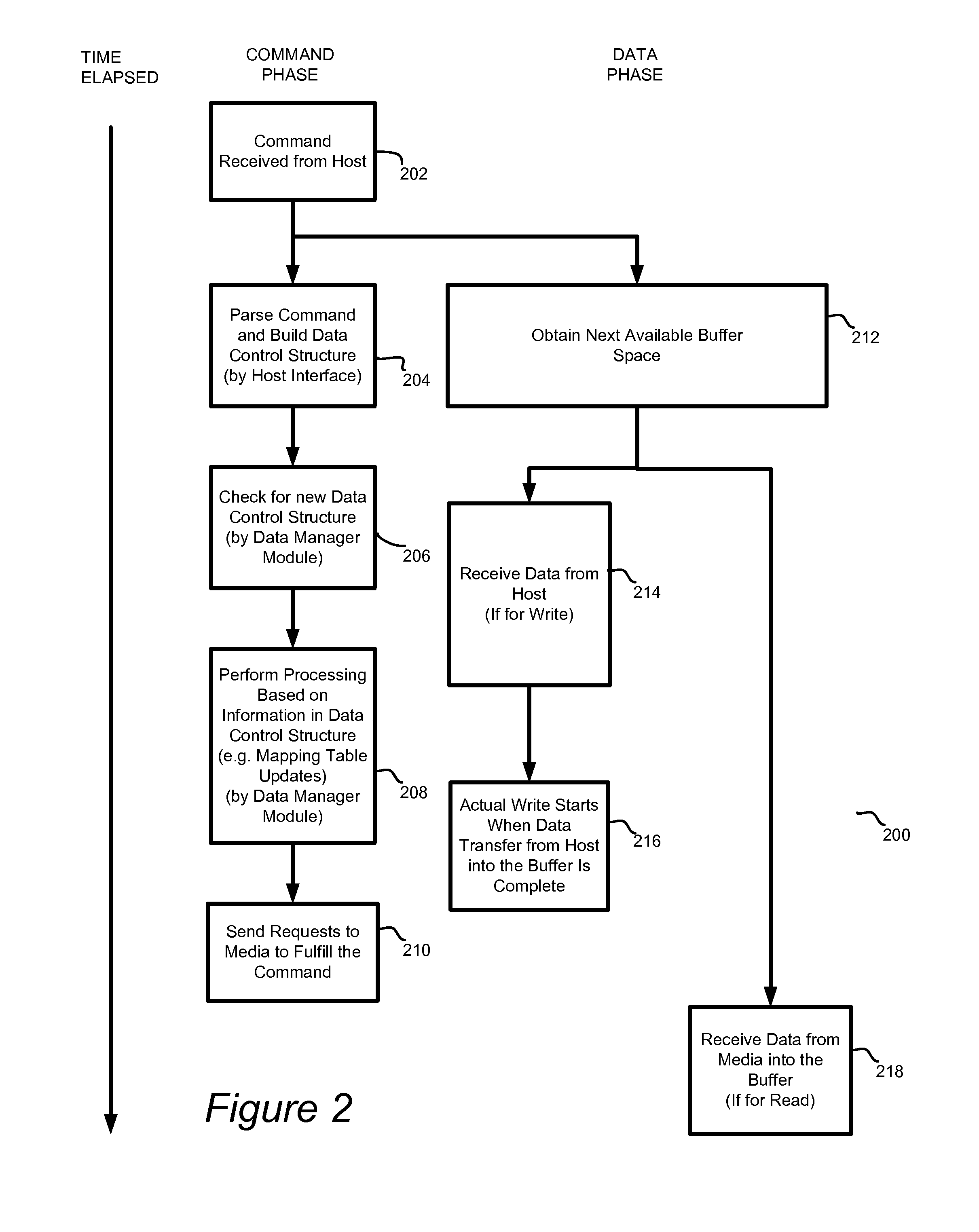
System and method for high performance command processing in solid state drives
ActiveUS8423722B1Improve performanceHigh bandwidthMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsHard disc driveHigh bandwidth
Solid State Drives (SSD) can yield very high performance if it is designed properly. A SSD typically includes both a front end that interfaces with the host and a back end that interfaces with the flash media. Typically SSDs include flash media that is designed with a high degree of parallelism that can support a very high bandwidth on input / output (I / O). A SSD front end designed according to a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) model will not be able to take advantage of the high performance offered by the typical flash media. Embodiments of the invention provide improved management of multiple I / O threads that take advantage of the high performing and concurrent nature of the back end media, so the resulting storage system can achieve a very high performance.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
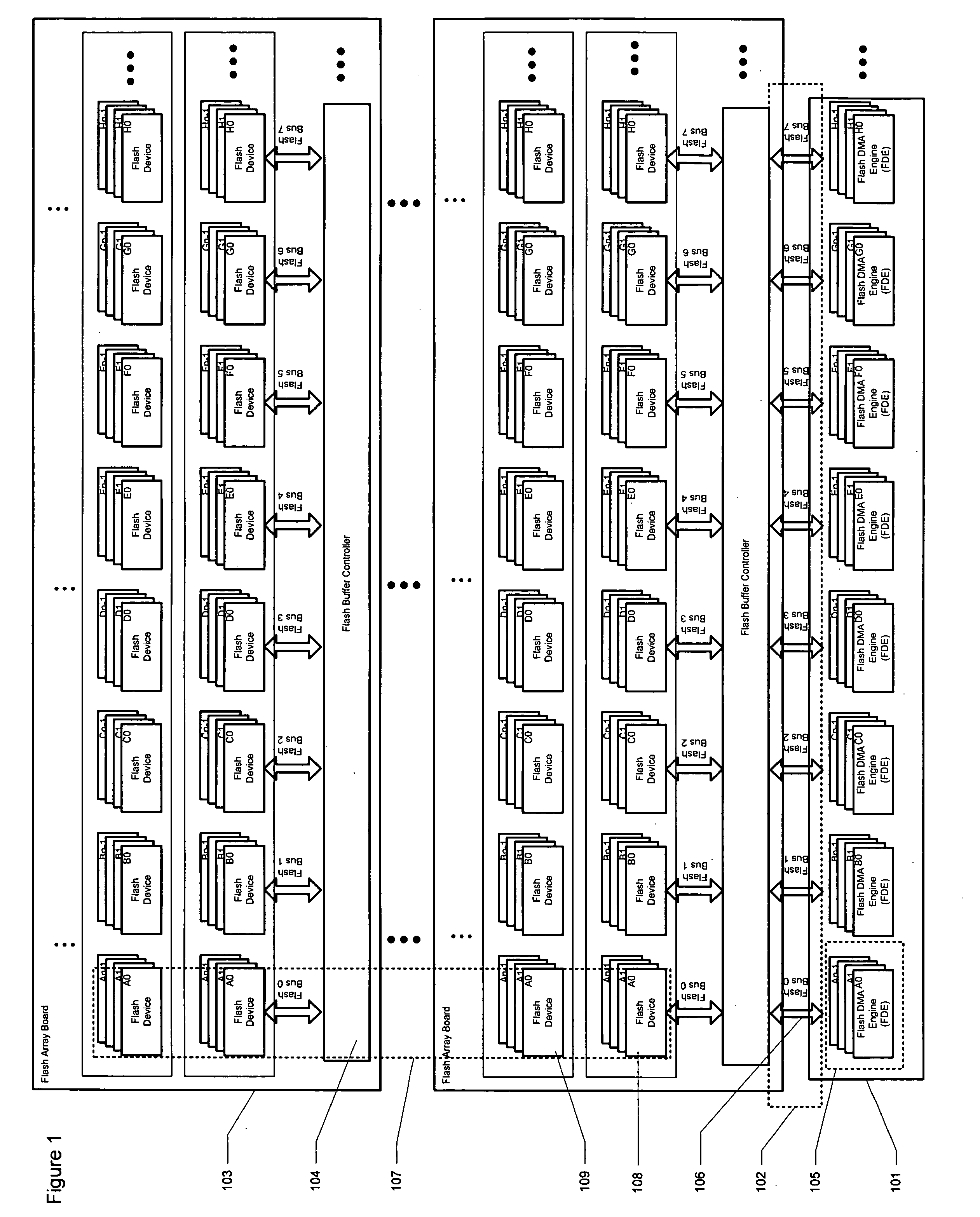
Optimized placement policy for solid state storage devices
InactiveUS20070288686A1Evenly loadedGuarantee efficiencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsSolid-state storageCurrent load
A data storage system is provided comprising several flash arrays in a board and stacking these boards to attain a high-capacity solid state hard drive. A remap table is used to map all logical addresses from a host system to the actual physical addresses where data are stored. The assignments of these physical locations are done in such a way that the load of the system is evenly distributed to its available resources. This would ensure that the storage system will run at its utmost efficiency utilizing its resources properly. To achieve this, the system would make sure that the physical location of data be evenly distributed according to the current load of the system.
Owner:BITMICRO LLC
Set-associative hash table organization for efficient storage and retrieval of data in a storage system
ActiveUS8874842B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersFile systemSolid-state drive
In one embodiment, use of hashing in a file system metadata arrangement reduces an amount of metadata stored in a memory of a node in a cluster and reduces the amount of metadata needed to process an input / output (I / O) request at the node. Illustratively, cuckoo hashing may be modified and applied to construct the file system metadata arrangement. The file system metadata arrangement may be illustratively configured as a key-value extent store embodied as a data structure, e.g., a cuckoo hash table, wherein a value, such as a hash table index, may be configured as an index and applied to the cuckoo hash table to obtain a key, such as an extent key, configured to reference a location of an extent on one or more storage devices, such as solid state drives.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Green eMMC Device (GeD) Controller with DRAM Data Persistence, Data-Type Splitting, Meta-Page Grouping, and Diversion of Temp Files for Enhanced Flash Endurance
ActiveUS20140310574A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersFilename extensionData file
A controller for a Super Enhanced Endurance Device (SEED) or Solid-State Drive (SSD) increases flash endurance using a DRAM buffer. Host accesses to flash are intercepted by the controller and categorized as data types of paging files, temporary files, meta-data, and user data files, using address ranges and file extensions read from meta-data tables. Paging files and temporary files are optionally written to flash. Full-page and partial-page data are grouped into multi-page meta-pages by data type in the DRAM before storage by lower-level flash devices such as eMMC, UFS, or iSSD. Caches in the DRAM buffer for storing each data type are managed and flushed to the flash devices by the controller. Write dates are stored for pages or blocks for management functions. A spare / swap area in DRAM reduces flash wear. Reference voltages are adjusted when error correction fails.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
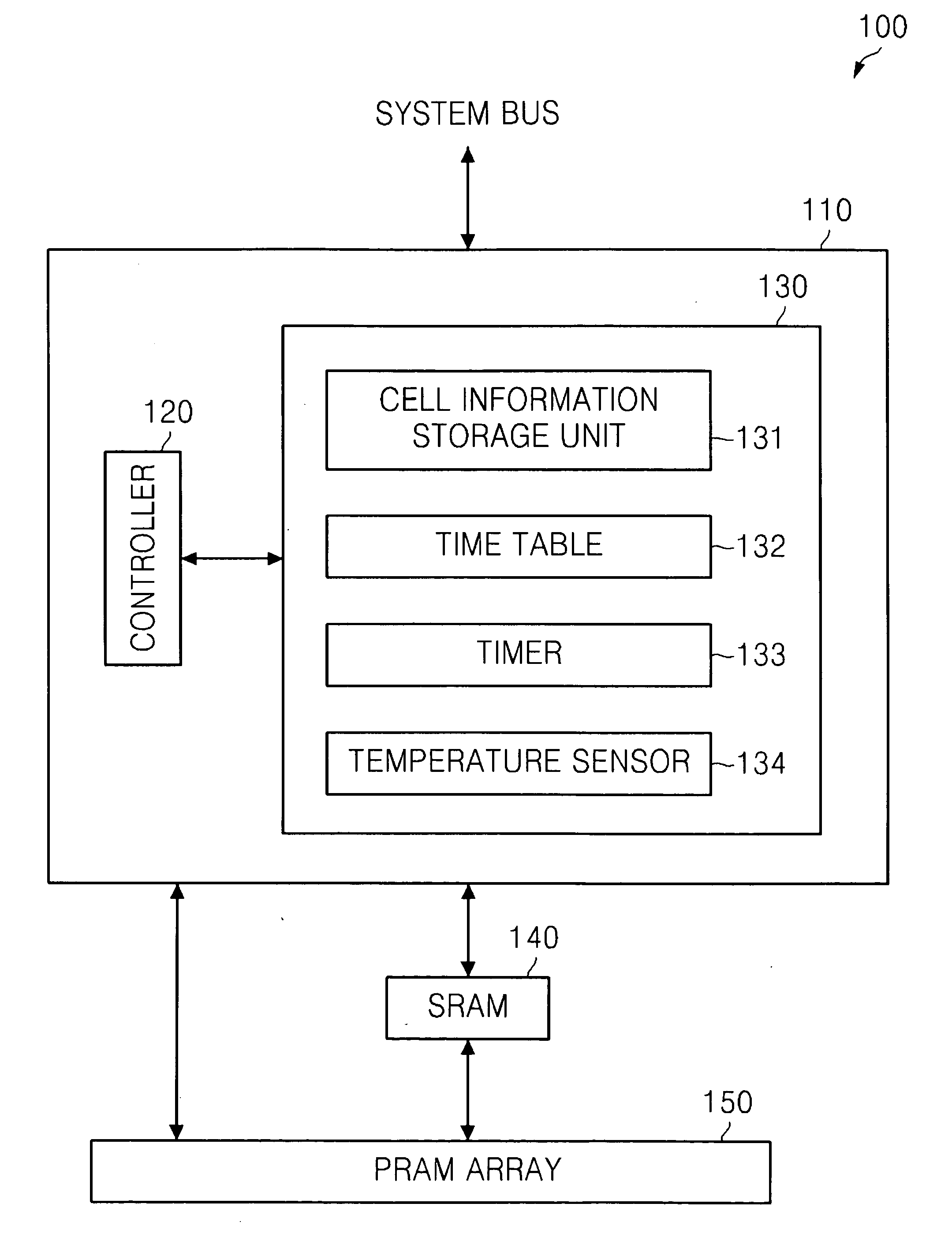
Non-volatile RAM, and solid state drive and computer system including the same
ActiveUS20100259998A1Reduce the likelihood of failureReduce and prevent likelihoodRead-only memoriesDigital storageComputerized systemSolid-state drive
The non-volatile random access memory (RAM) includes a non-volatile RAM array, a buffer configured to buffer data to be programmed in the non-volatile RAM array and configured to buffer data read from the non-volatile RAM array, and a control block configured to read data from at least one of the non-volatile RAM array and the buffer based on whether the data to be read has been stored in the buffer, a temperature when the data was programmed, and a time lapse since the programming of the data.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scaleable and maintainable solid state drive
InactiveUS20090063895A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationRedundant hardware error correctionInternal memoryEngineering
Methods and apparatus for maintaining a solid state disk drive facilitate expansion of storage capacity and maintenance of internal memory storage media, for example, are disclosed. Memory modules are adapted for removable installation in a solid state drive allowing for expansion of drive storage capacity and servicing of failed or worn out memory storage media. Data can be managed to mitigate loss during expansion, maintenance and servicing of the solid state drive.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
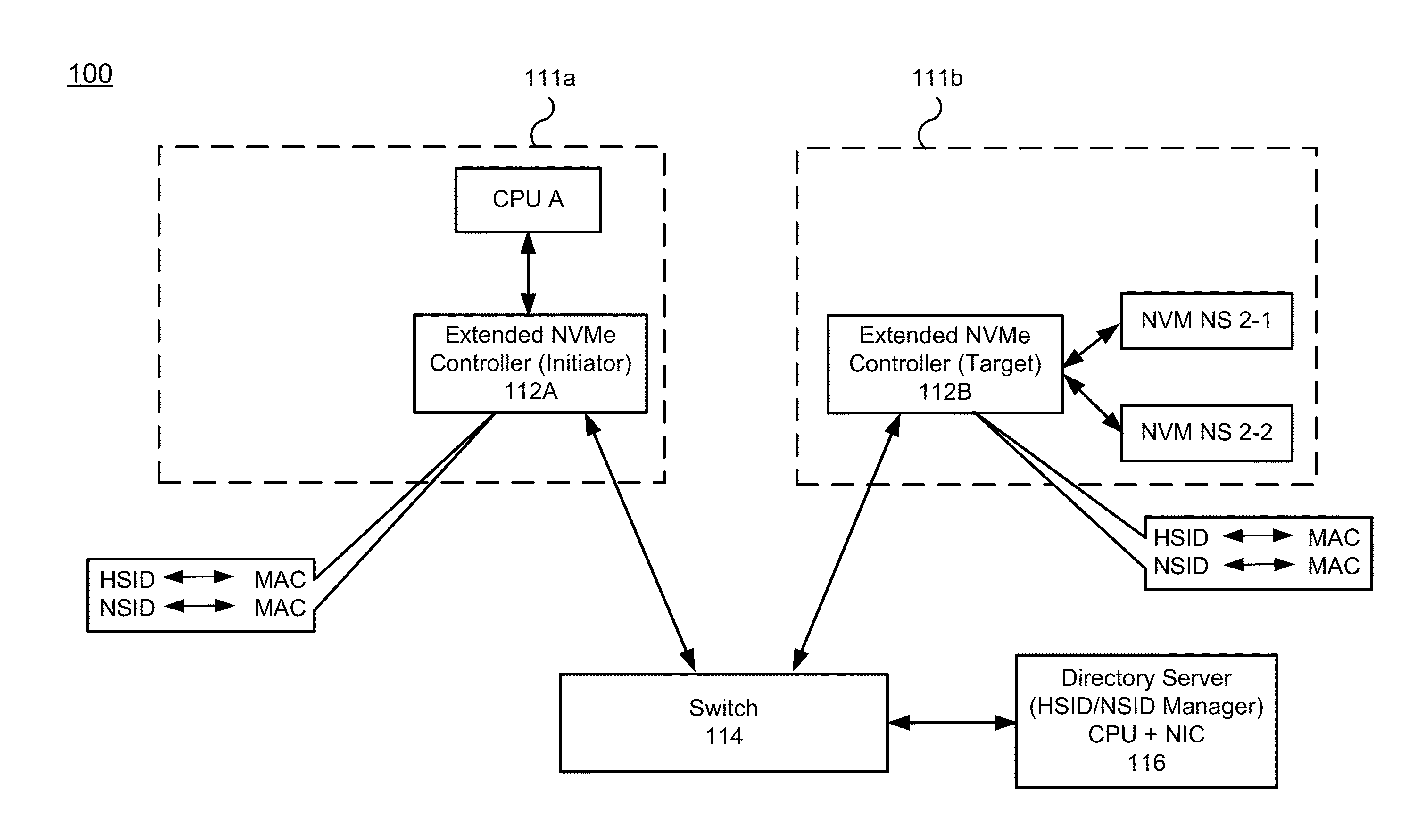
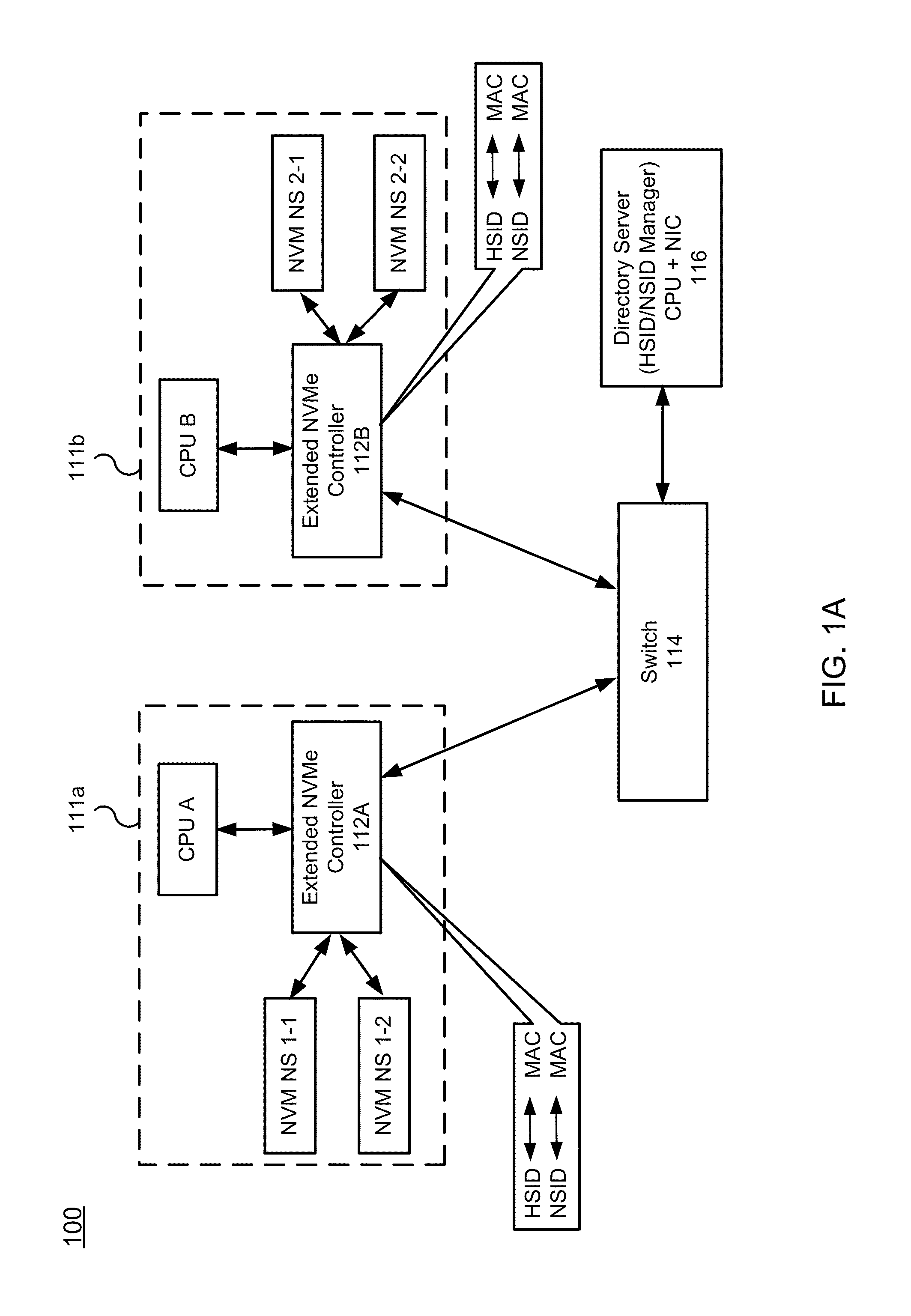
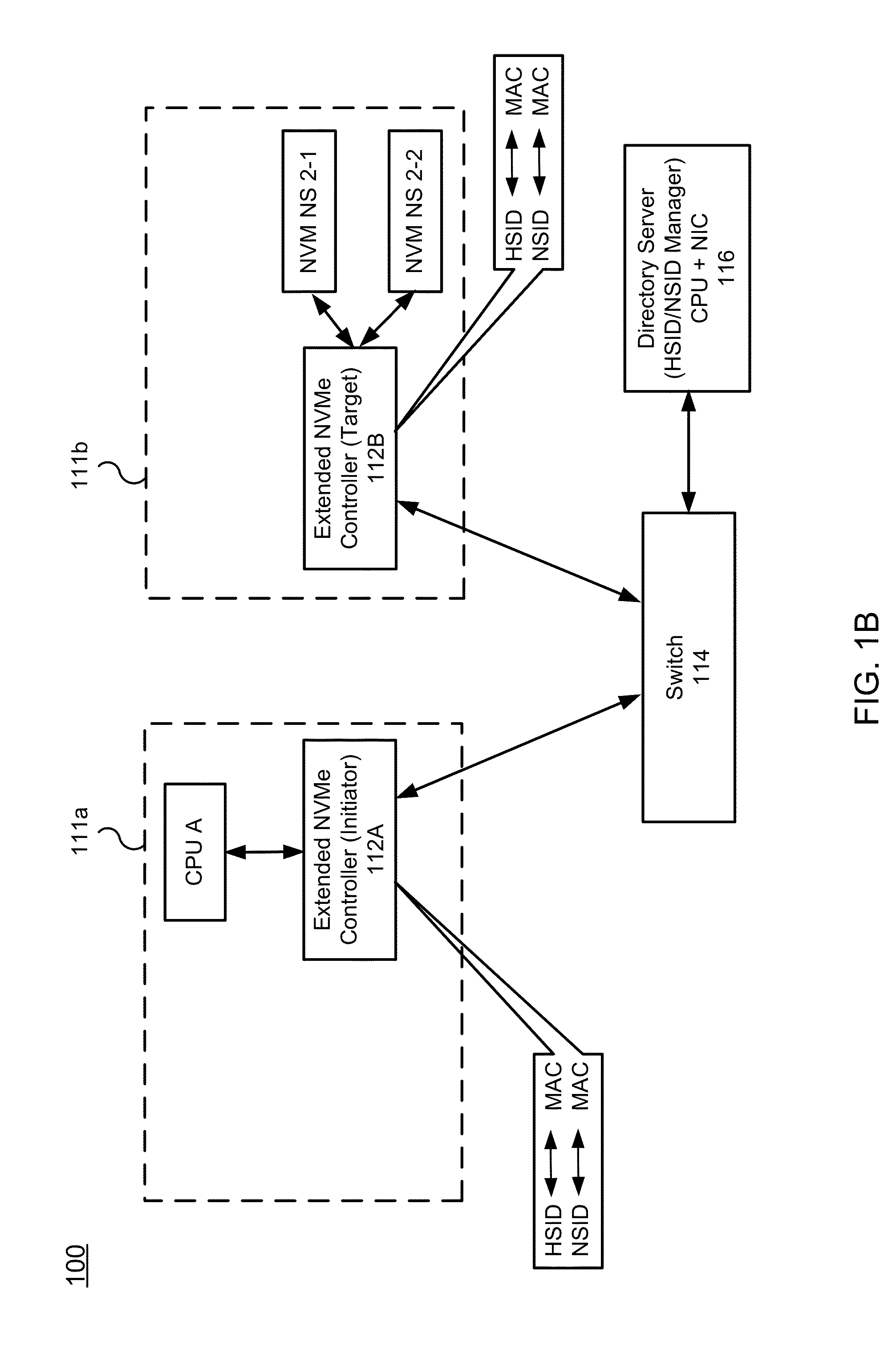
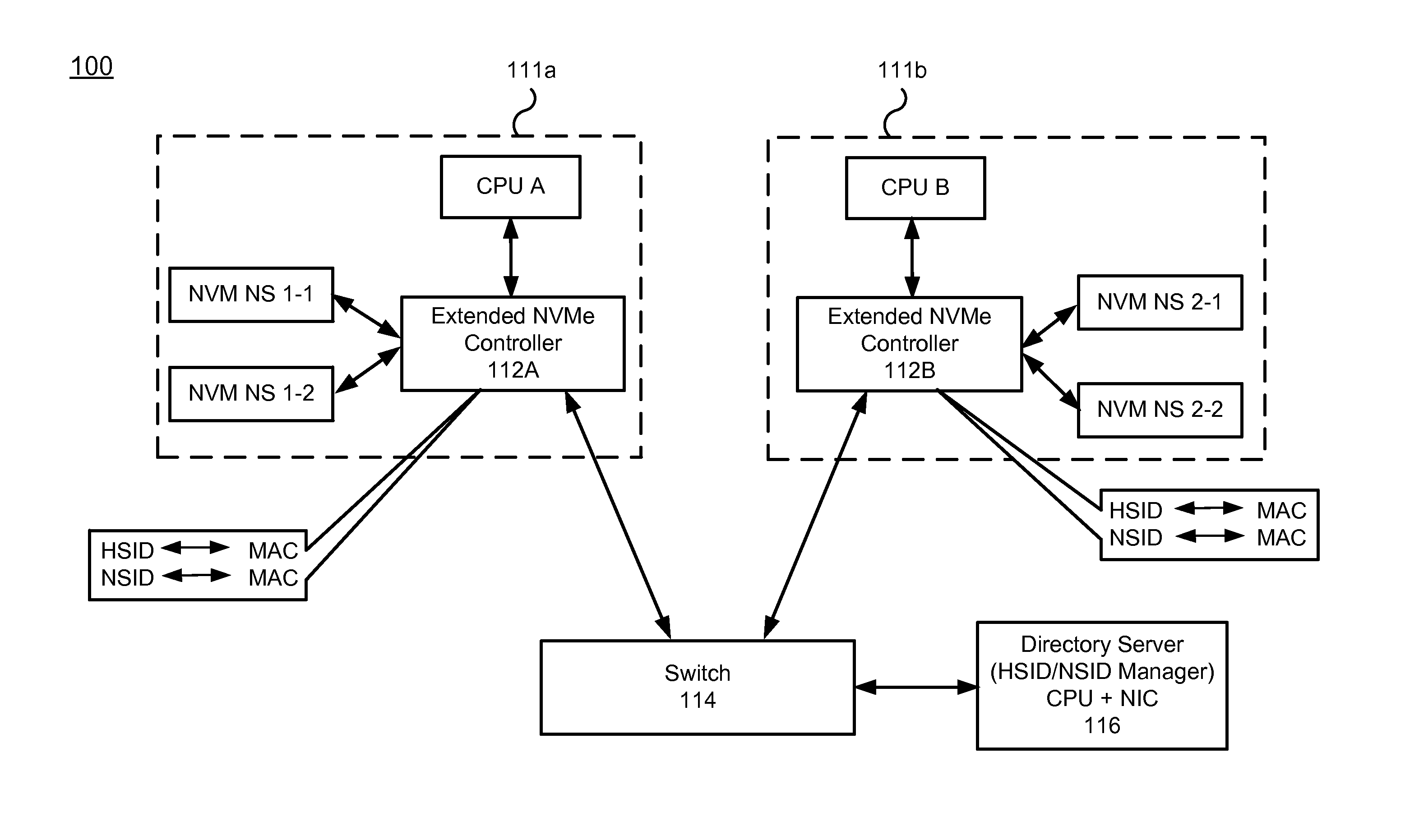
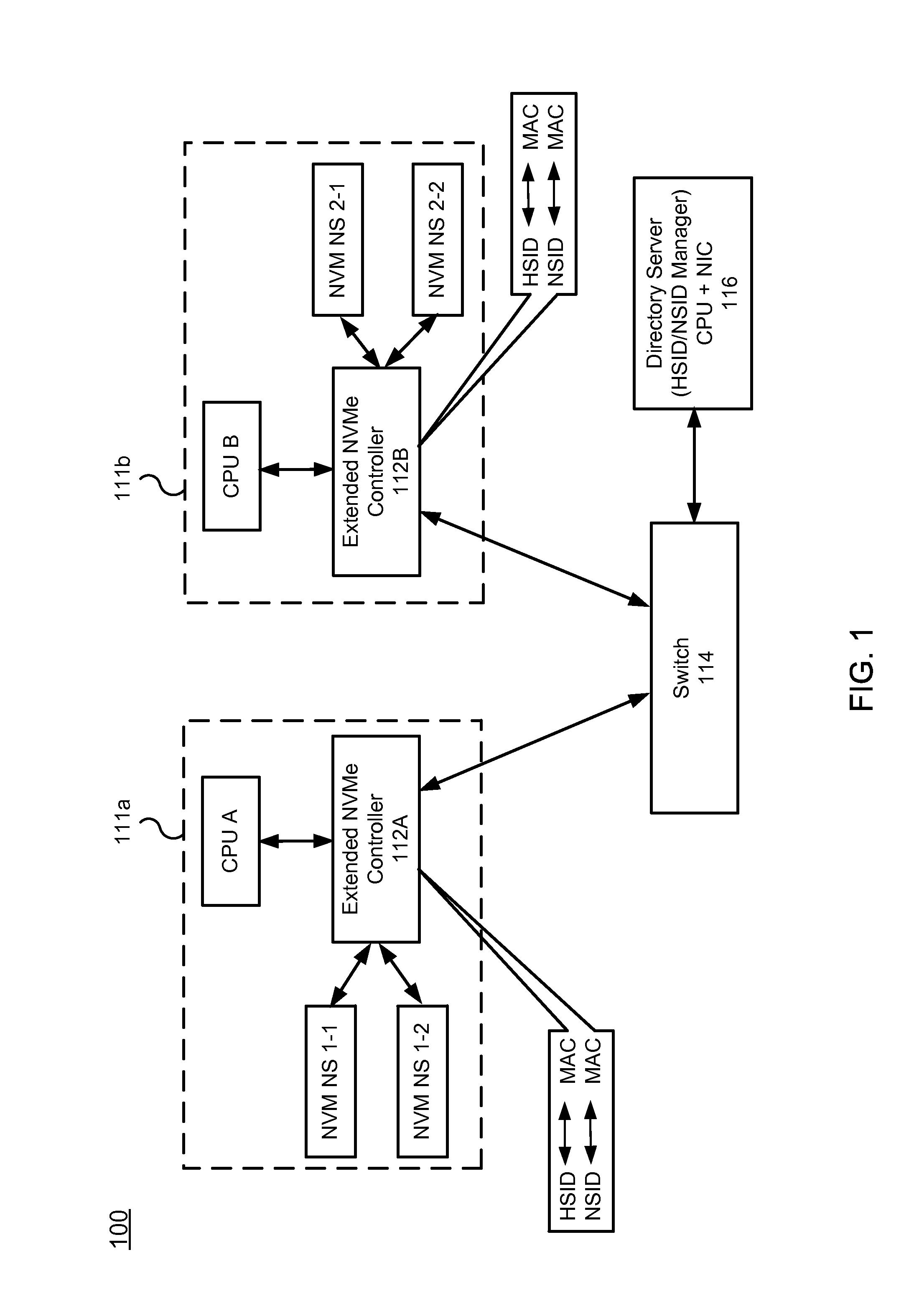
Nvm express controller for remote access of memory and I/O over ethernet-type networks
ActiveUS20160085718A1Input/output to record carriersDigital computer detailsSolid-state driveEthernet frame
A method and system for enabling Non-Volatile Memory express (NVMe) for accessing remote solid state drives (SSDs) (or other types of remote non-volatile memory) over the Ethernet or other networks. An extended NVMe controller is provided for enabling CPU to access remote non-volatile memory using NVMe protocol. The extended NVMe controller is implemented on one server for communication with other servers or non-volatile memory via Ethernet switch. The NVMe protocol is used over the Ethernet or similar networks by modifying it to provide a special NVM-over-Ethernet frame.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
System and method for tolerating a failed page in a flash device
ActiveUS9047214B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationStatic storageWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
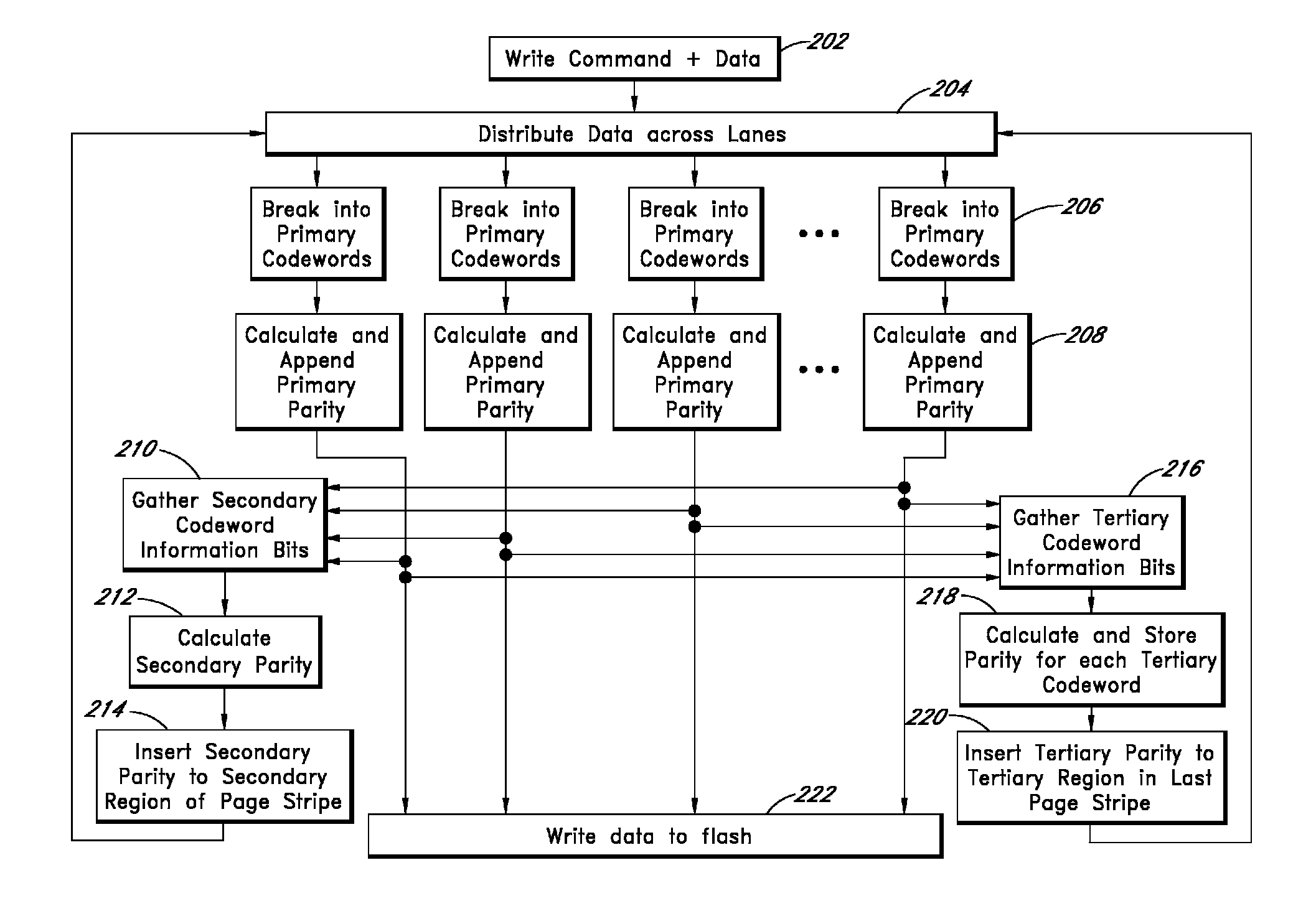
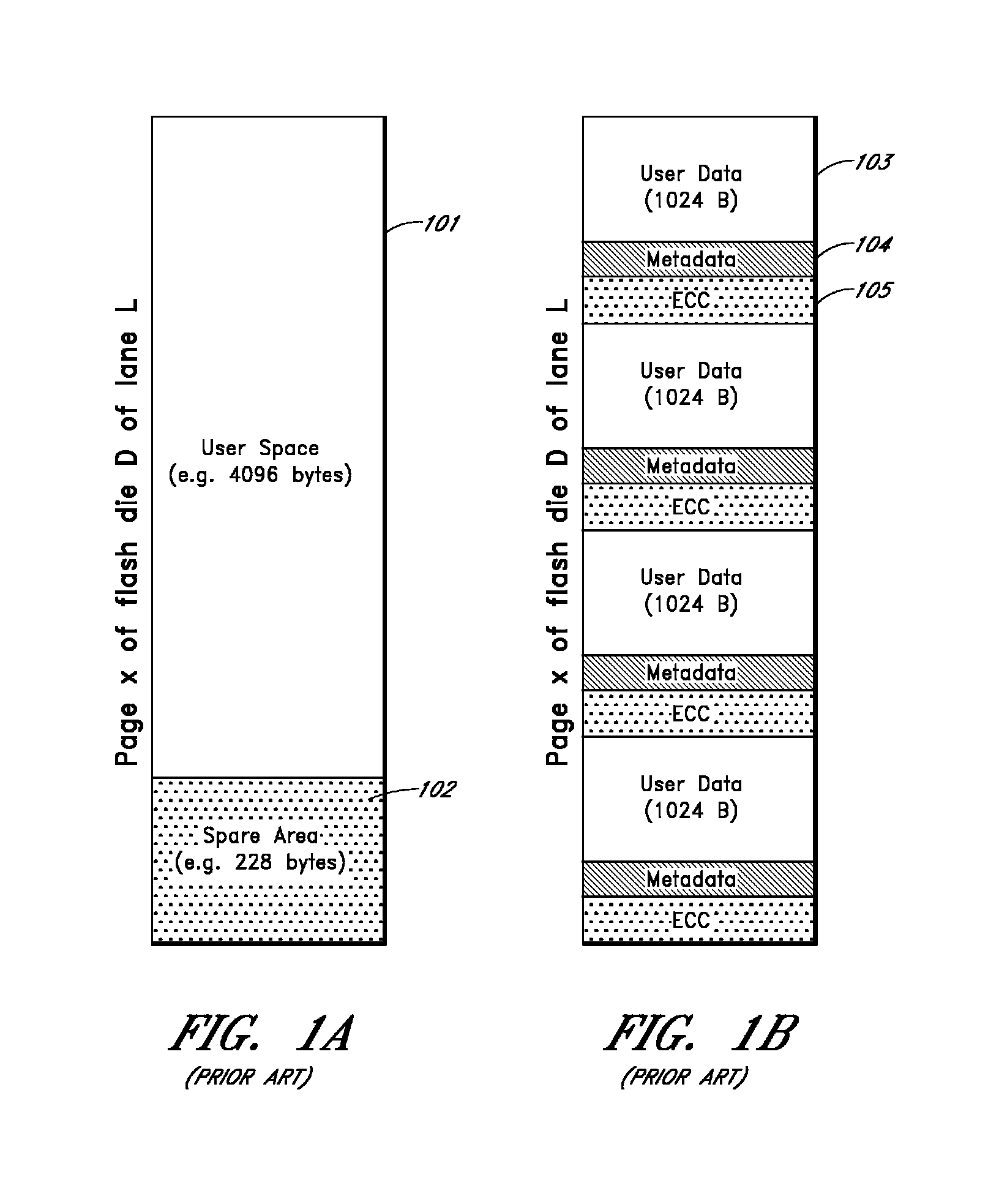
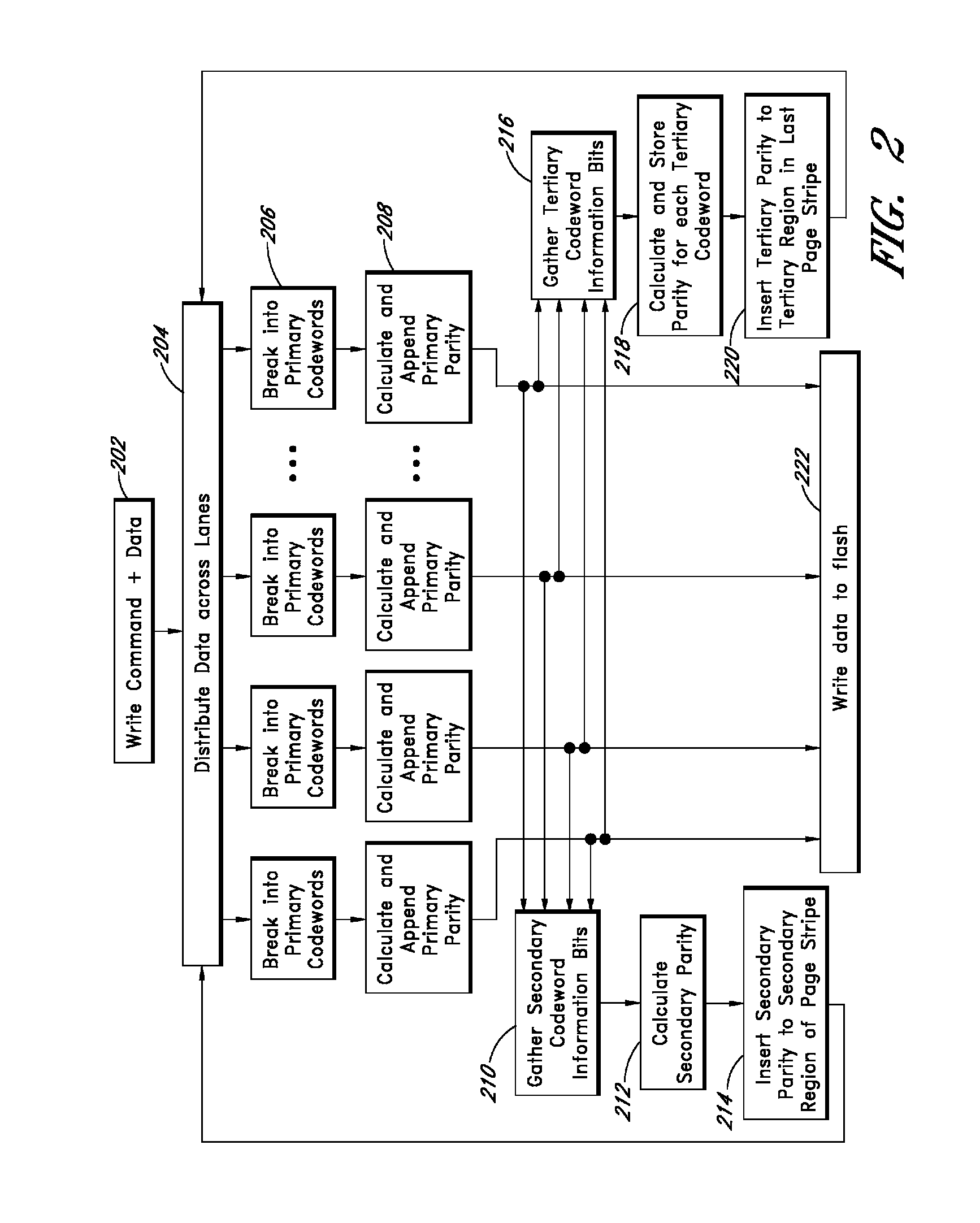
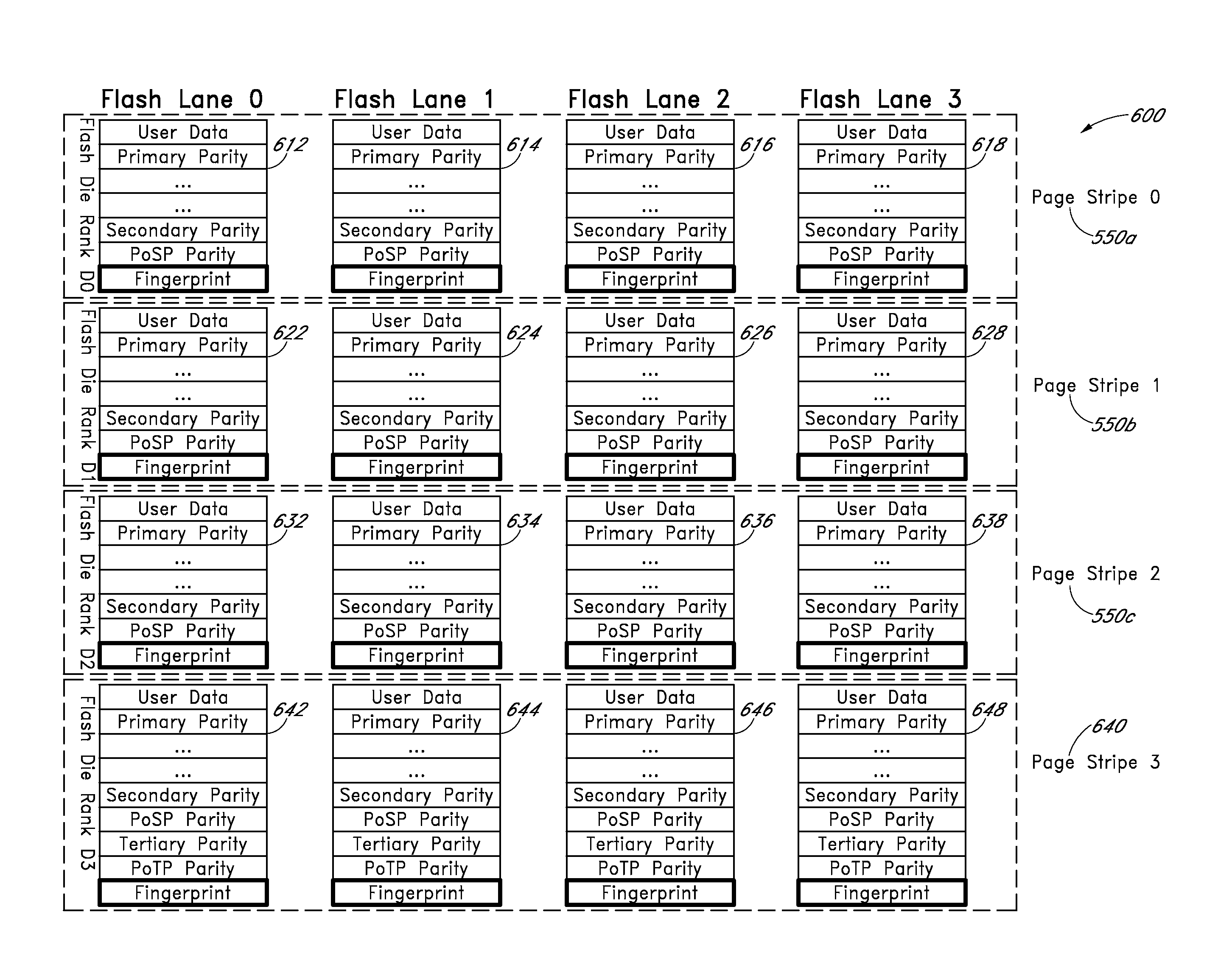
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be implemented using relatively inexpensive MLC Flash for an enterprise storage application. A page is associated with a set of primary ECC codewords, and a page stripe is associated with a set of secondary codewords and primary over secondary parity (PoSP) ECC codewords. Two or more page stripes can form a page grid, wherein the page grid is associated with a group of tertiary ECC codewords, wherein the last page stripe of the page grid has a reduced payload capacity.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
NVM Express Controller for Remote Access of Memory and I/O Over Ethernet-Type Networks
A method and system for enabling Non-Volatile Memory express (NVMe) for accessing remote solid state drives (SSDs) (or other types of remote non-volatile memory) over the Ethernet or other networks. An extended NVMe controller is provided for enabling CPU to access remote non-volatile memory using NVMe protocol. The extended NVMe controller is implemented on one server for communication with other servers or non-volatile memory via Ethernet switch. The NVMe protocol is used over the Ethernet or similar networks by modifying it to provide a special NVM-over-Ethernet frame.
Owner:POINT FINANCIAL
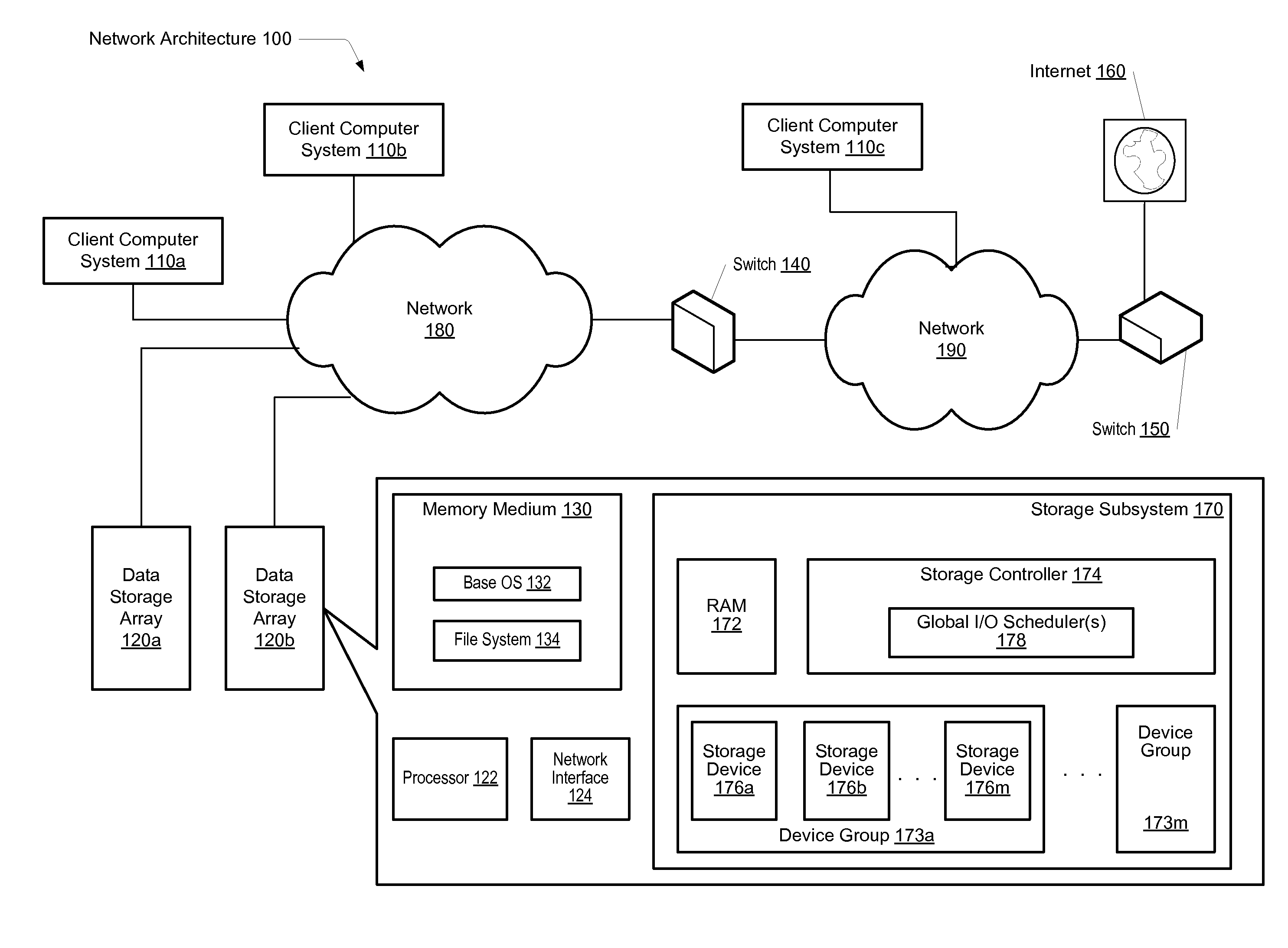
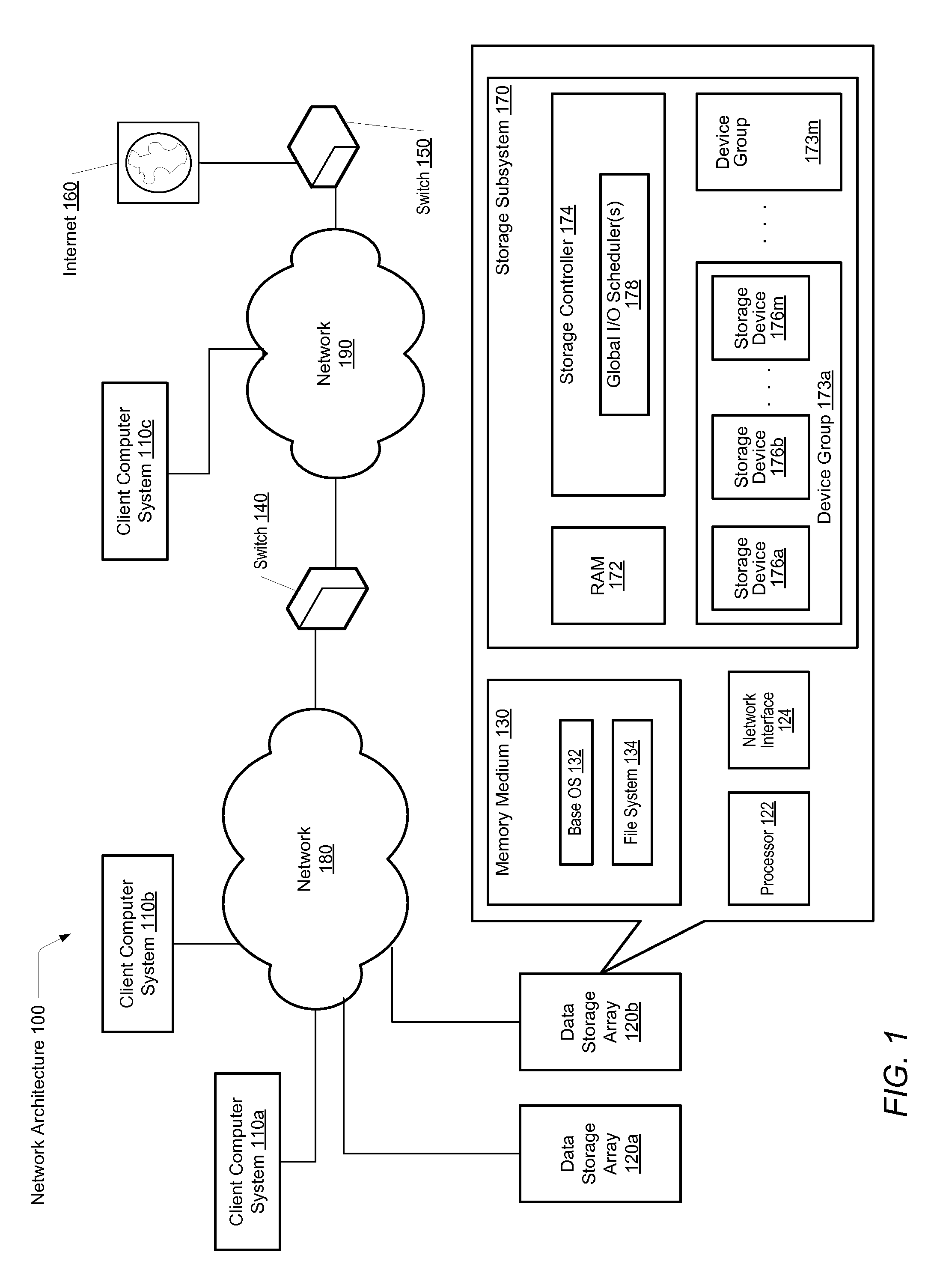
Scheduling of reconstructive I/O read operations in a storage environment
ActiveUS20120066449A1Input/output to record carriersError detection/correctionSolid-state storageControl store
A system and method for effectively scheduling read and write operations among a plurality of solid-state storage devices. A computer system comprises client computers and data storage arrays coupled to one another via a network. A data storage array utilizes solid-state drives and Flash memory cells for data storage. A storage controller within a data storage array comprises an I / O scheduler. The storage controller is configured to receive a read request targeted to the data storage medium, and identify at least a first storage device of the plurality of storage devices which contains data targeted by the read request. In response to either detecting or predicting the first storage device will exhibit variable performance, the controller is configured to generate a reconstruct read request configured to obtain the data from one or more devices of the plurality of storage devices other than the first storage device.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
RAID Enhanced solid state drive
InactiveUS20100049914A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingSolid-state storageRAID
The present invention relates to a solid-state storage subsystem which comprises a plurality of solid state drive designs integrated with a storage processor that provides performance, data integrity and reliability improvements in a standard disk drive form factor with a standard disk drive interface.
Owner:GOODWIN PAUL M
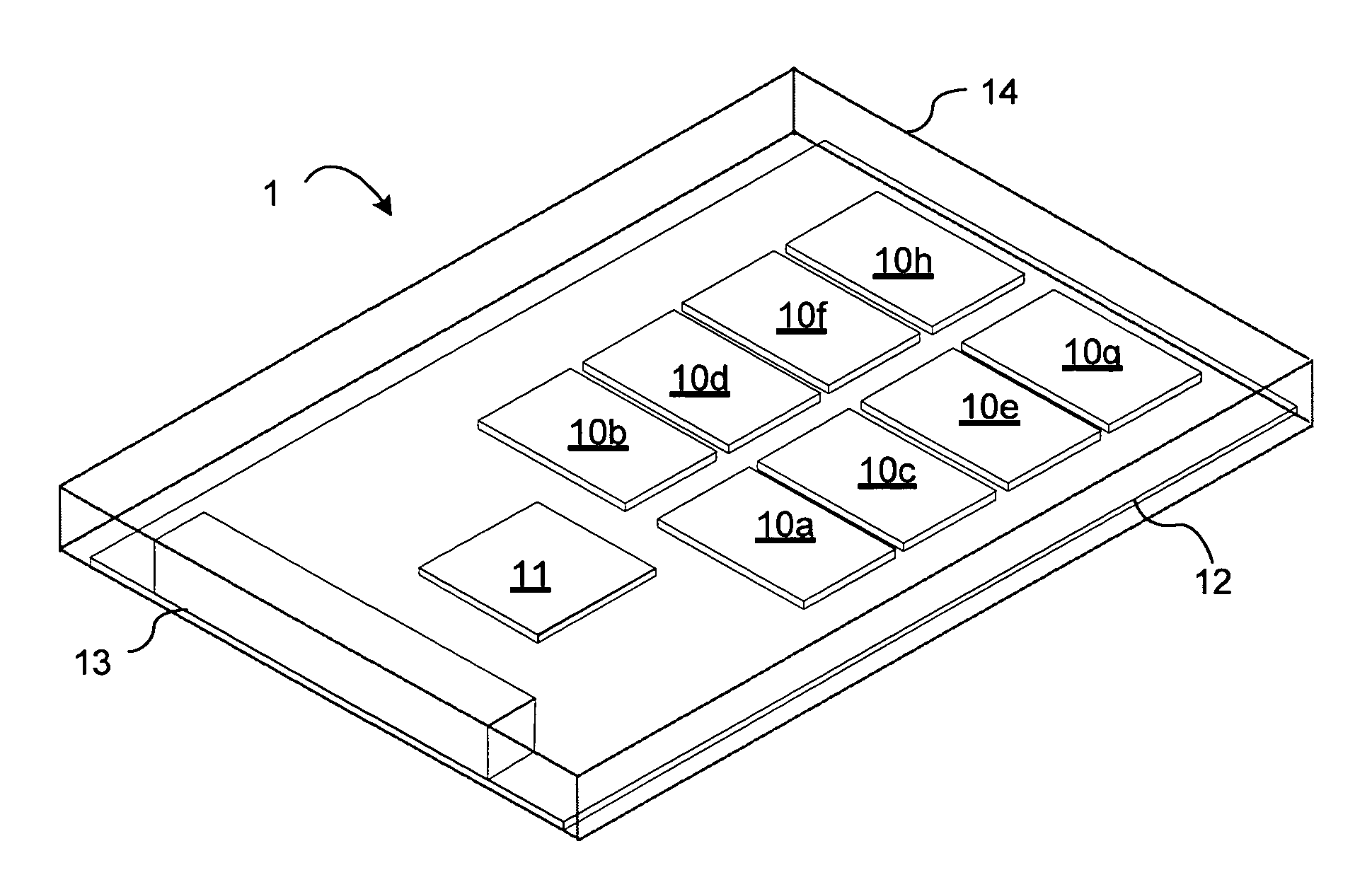
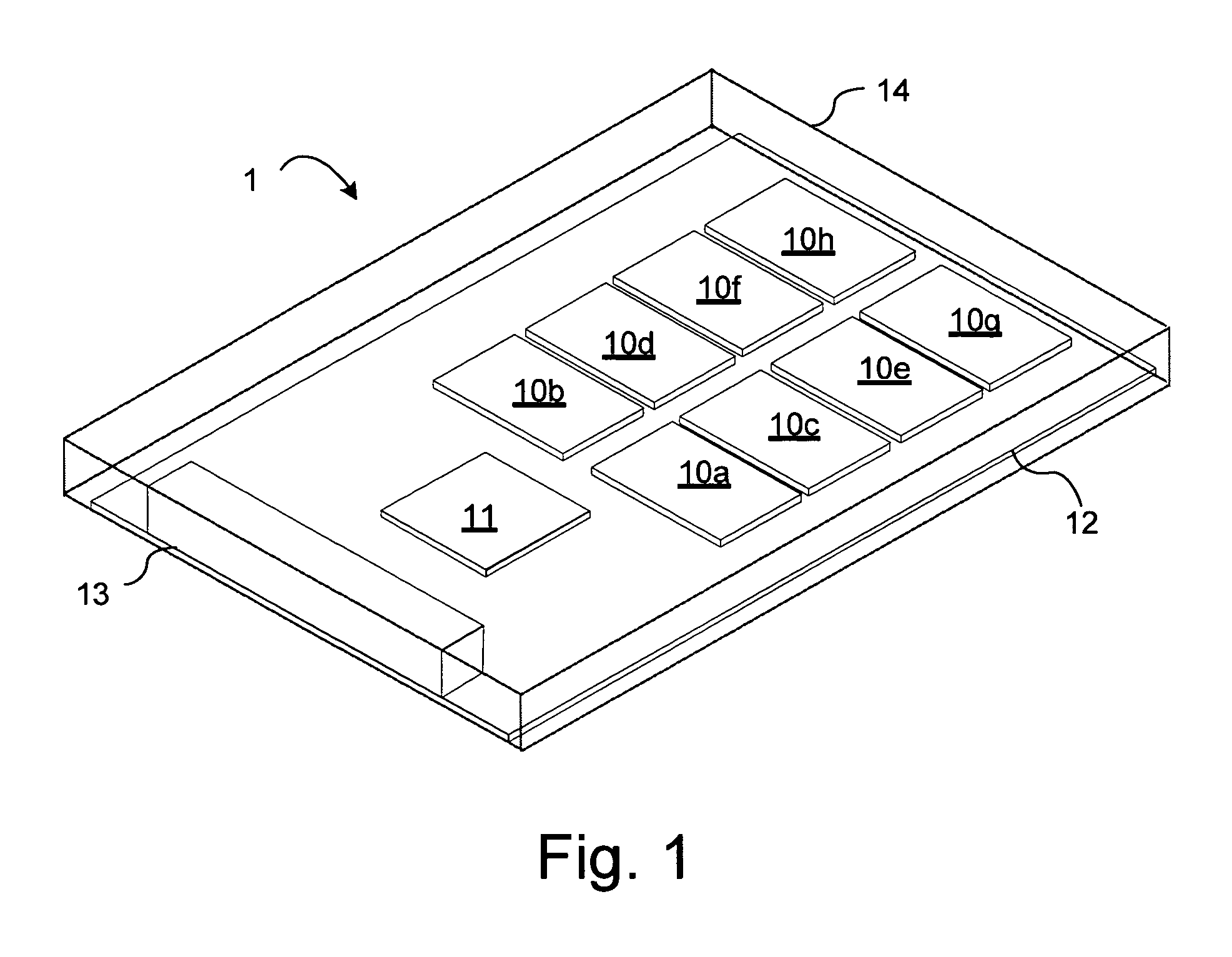
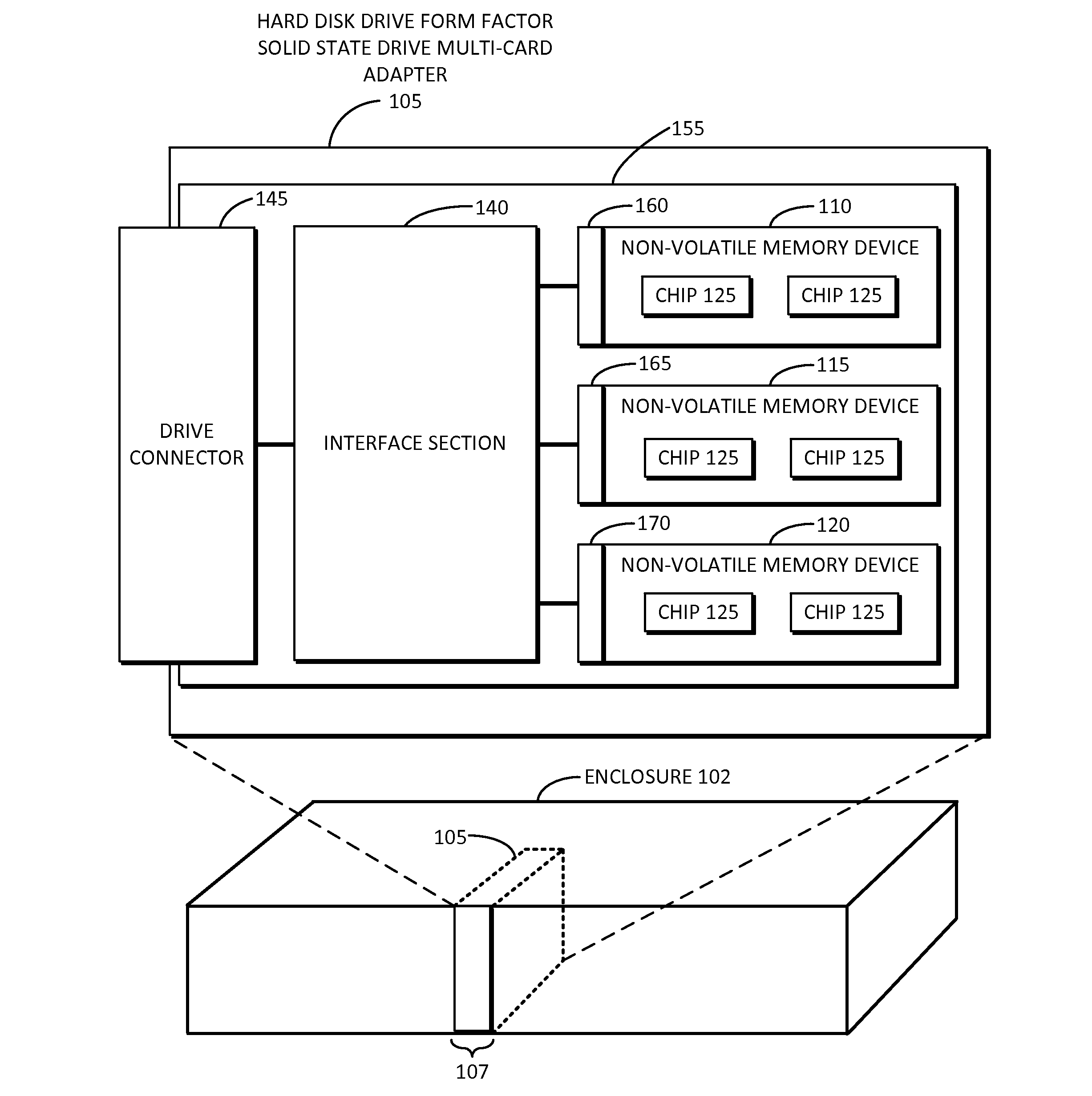
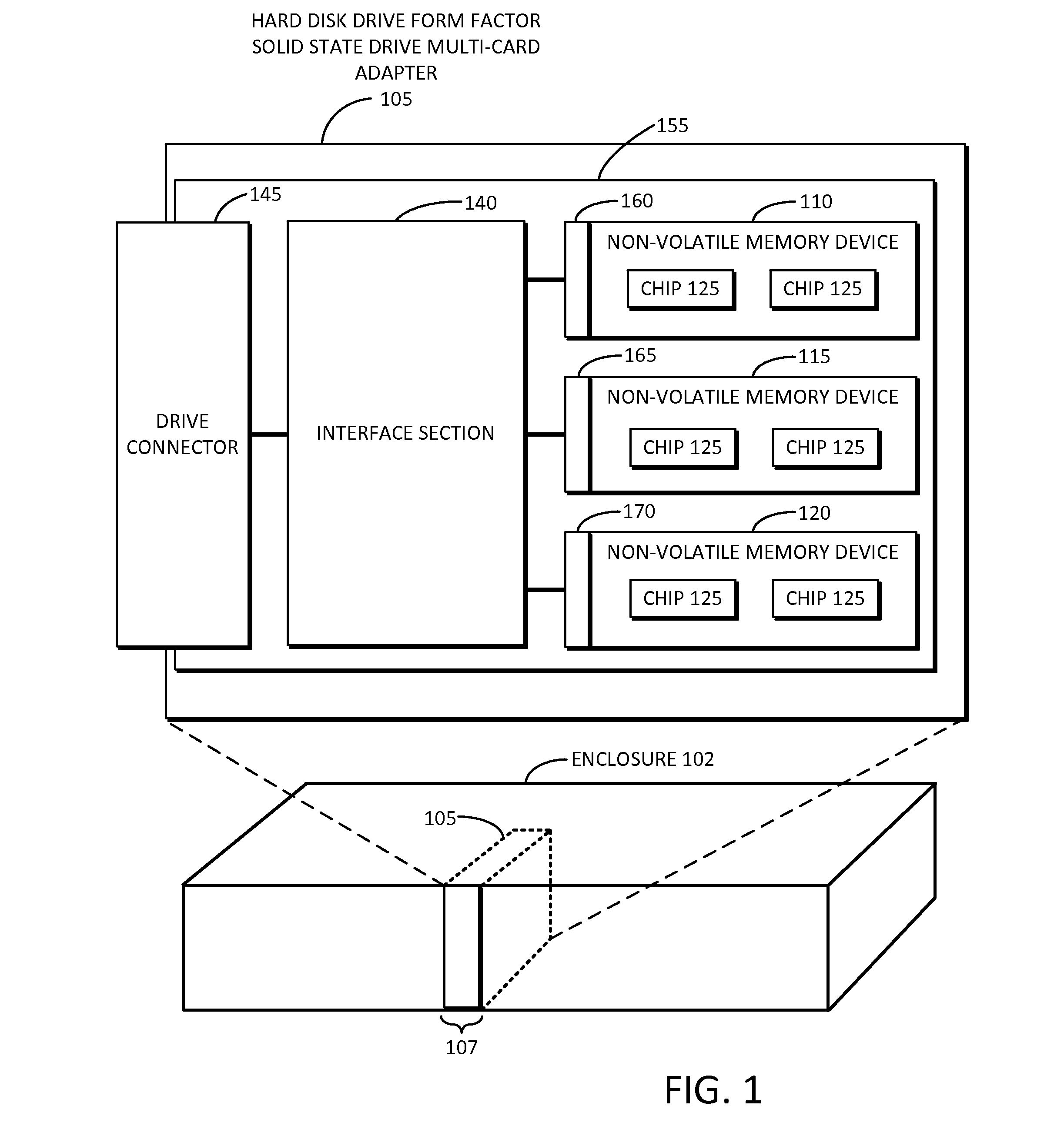
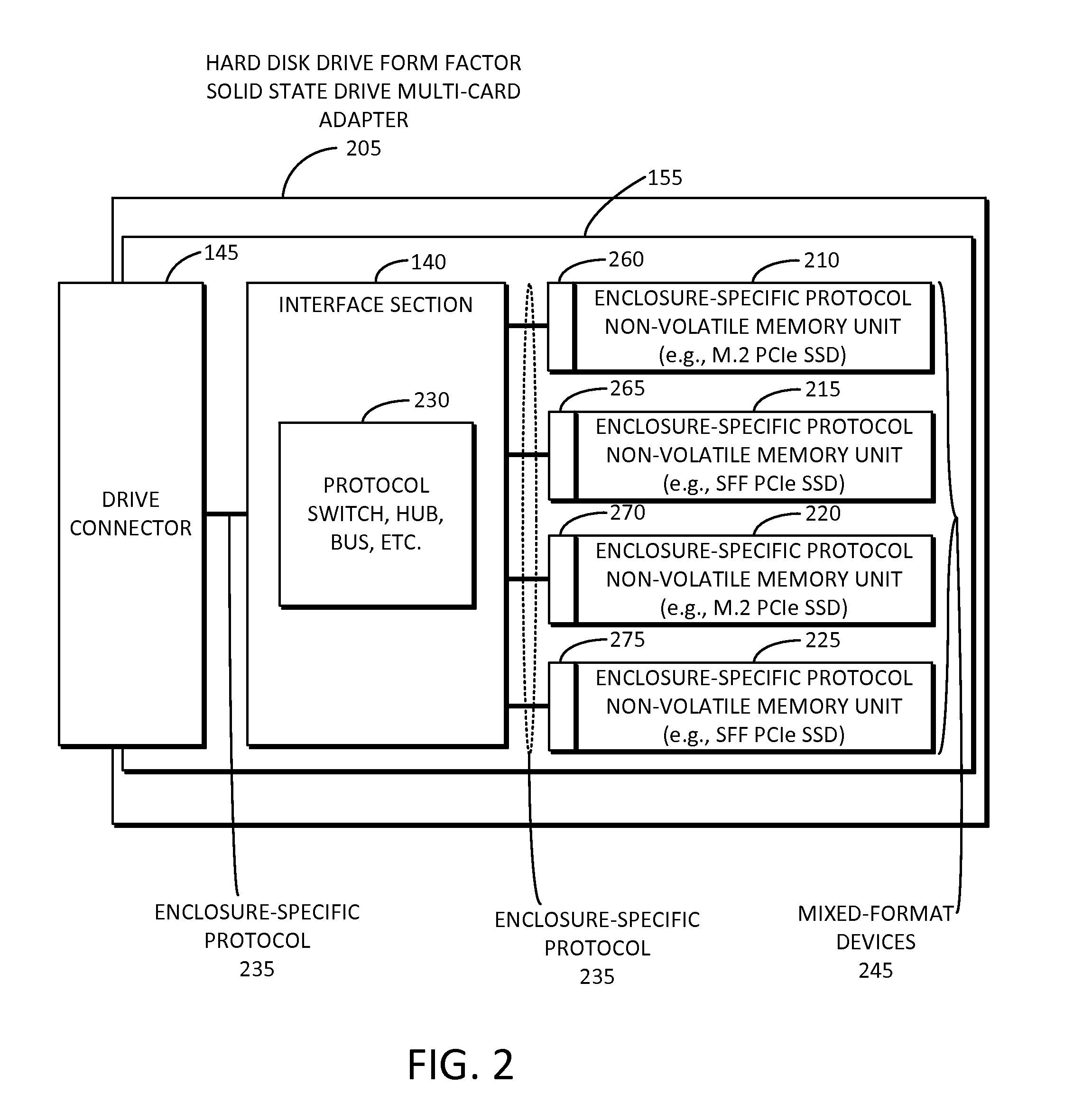
Solid state drive multi-card adapter with integrated processing
Embodiments of the inventive concept include solid state drive (SSD) multi-card adapters that can include multiple solid state drive cards, which can be incorporated into existing enterprise servers without major architectural changes, thereby enabling the server industry ecosystem to easily integrate evolving solid state drive technologies into servers. The SSD multi-card adapters can include an interface section between various solid state drive cards and drive connector types. The interface section can perform protocol translation, packet switching and routing, data encryption, data compression, management information aggregation, virtualization, and other functions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
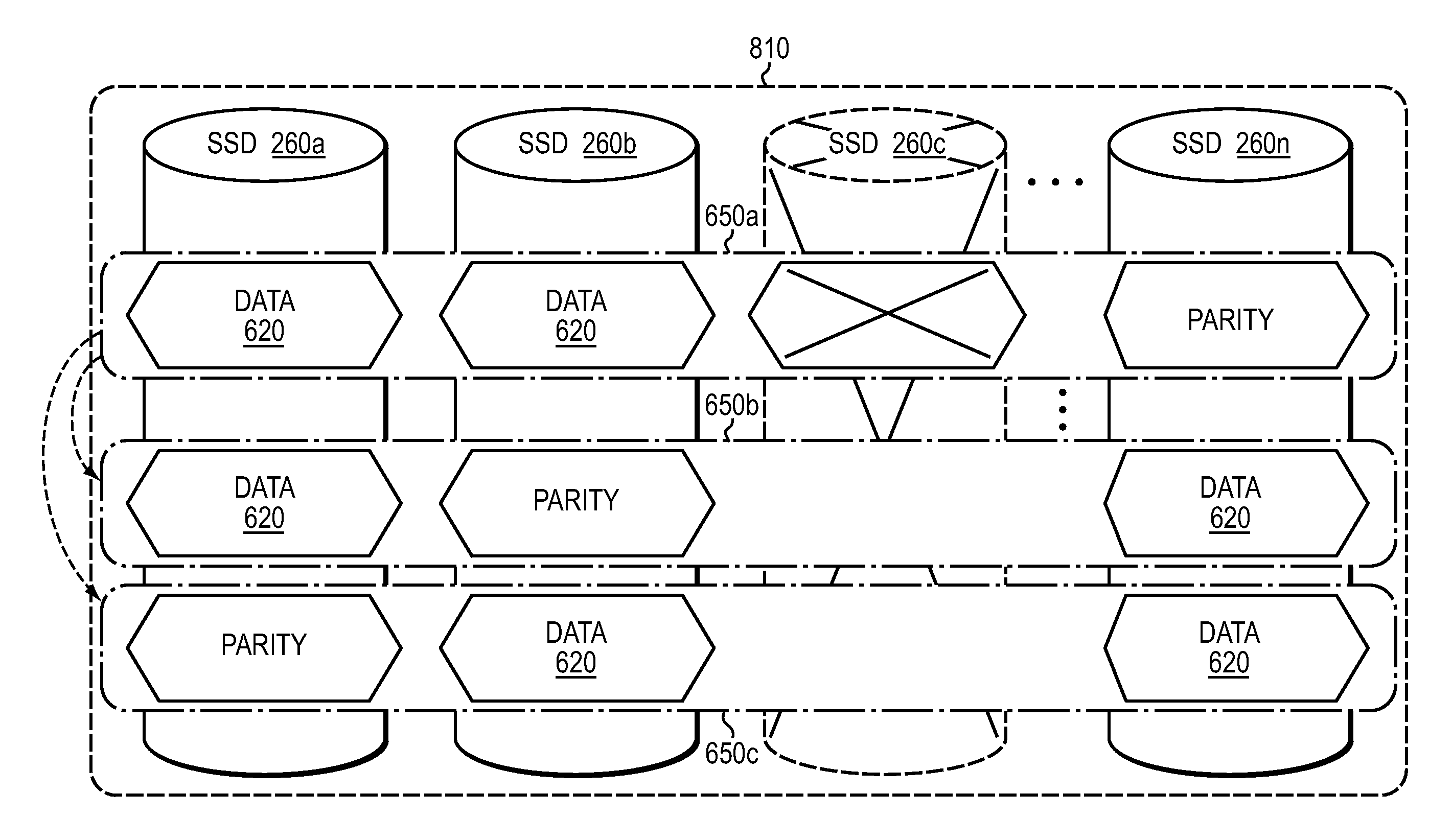
Intra-device data protection in a raid array
A system and method for intra-device data protection in a RAID array. A computer system comprises client computers and data storage arrays coupled to one another via a network. A data storage array utilizes solid-state drives and Flash memory cells for data storage. A storage controller within a data storage array is configured to identify a unit of data stored in the data storage subsystem, wherein said unit of data is stored across at least a first storage device and a second storage device of the plurality of storage devices, each of the first storage device and the second storage device storing intra-device redundancy data corresponding to the unit of data; and change an amount of intra-device redundancy data corresponding to the unit of data on only the first storage device.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
File system driven raid rebuild technique
In one embodiment, a file system driven RAID rebuild technique is provided. A layered file system may organize storage of data as segments spanning one or more sets of storage devices, such as solid state drives (SSDs), of a storage array, wherein each set of SSDs may form a RAID group configured to provide data redundancy for a segment. The file system may then drive (i.e., initiate) rebuild of a RAID configuration of the SSDs on a segment-by-segment basis in response to cleaning of the segment (i.e., segment cleaning). Each segment may include one or more RAID stripes that provide a level of data redundancy (e.g., single parity RAID 5 or double parity RAID 6) as well as RAID organization (i.e., distribution of data and parity) for the segment. Notably, the level of data redundancy and RAID organization may differ among the segments of the array.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Systems and methods for adaptively selecting from among a plurality of error correction coding schemes in a flash drive for robustness and low latency
ActiveUS9183085B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeRedundant data error correctionWrite amplificationLatency (engineering)
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
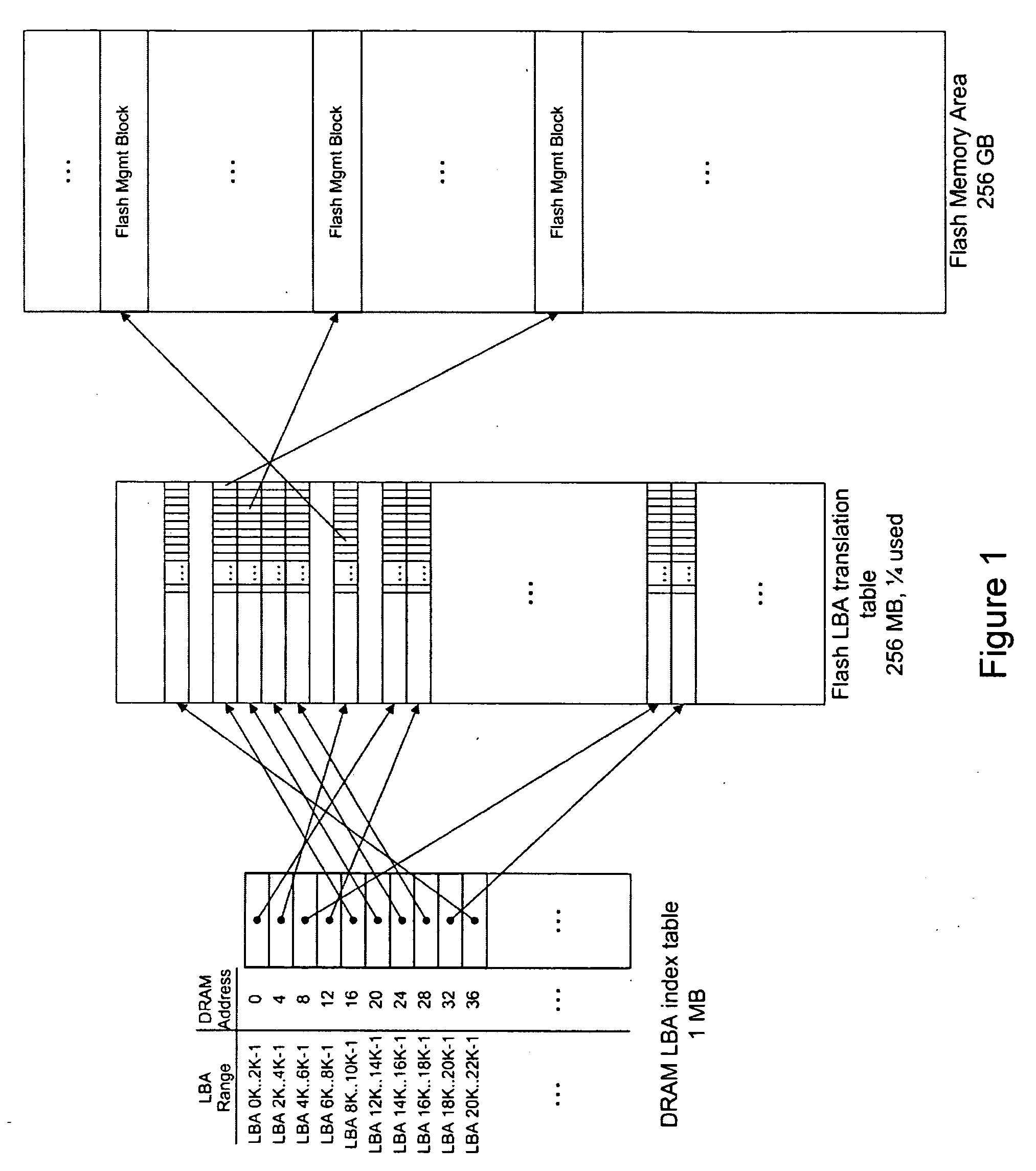
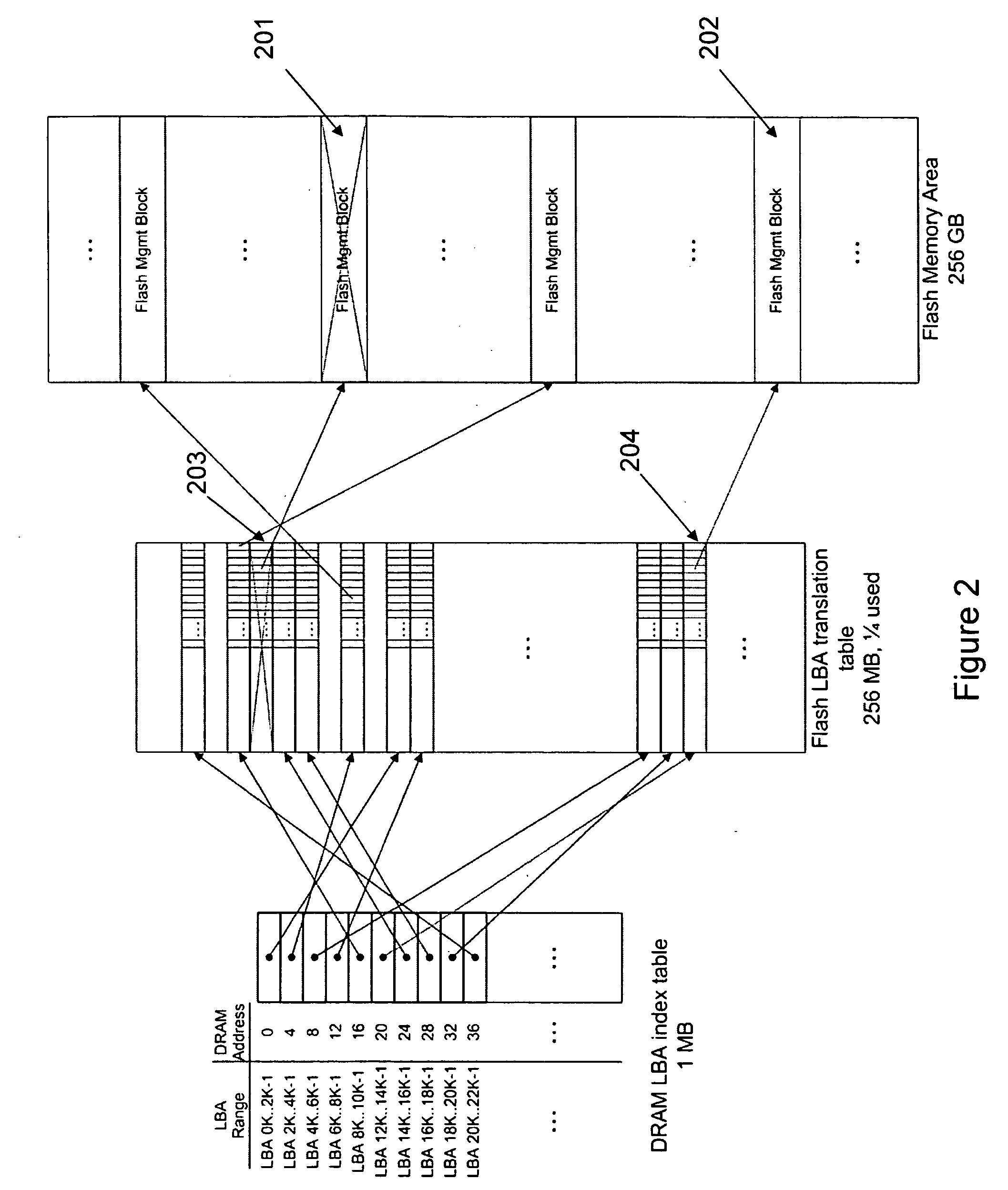
Process and Method for Logical-to-Physical Address Mapping in Solid Sate Disks
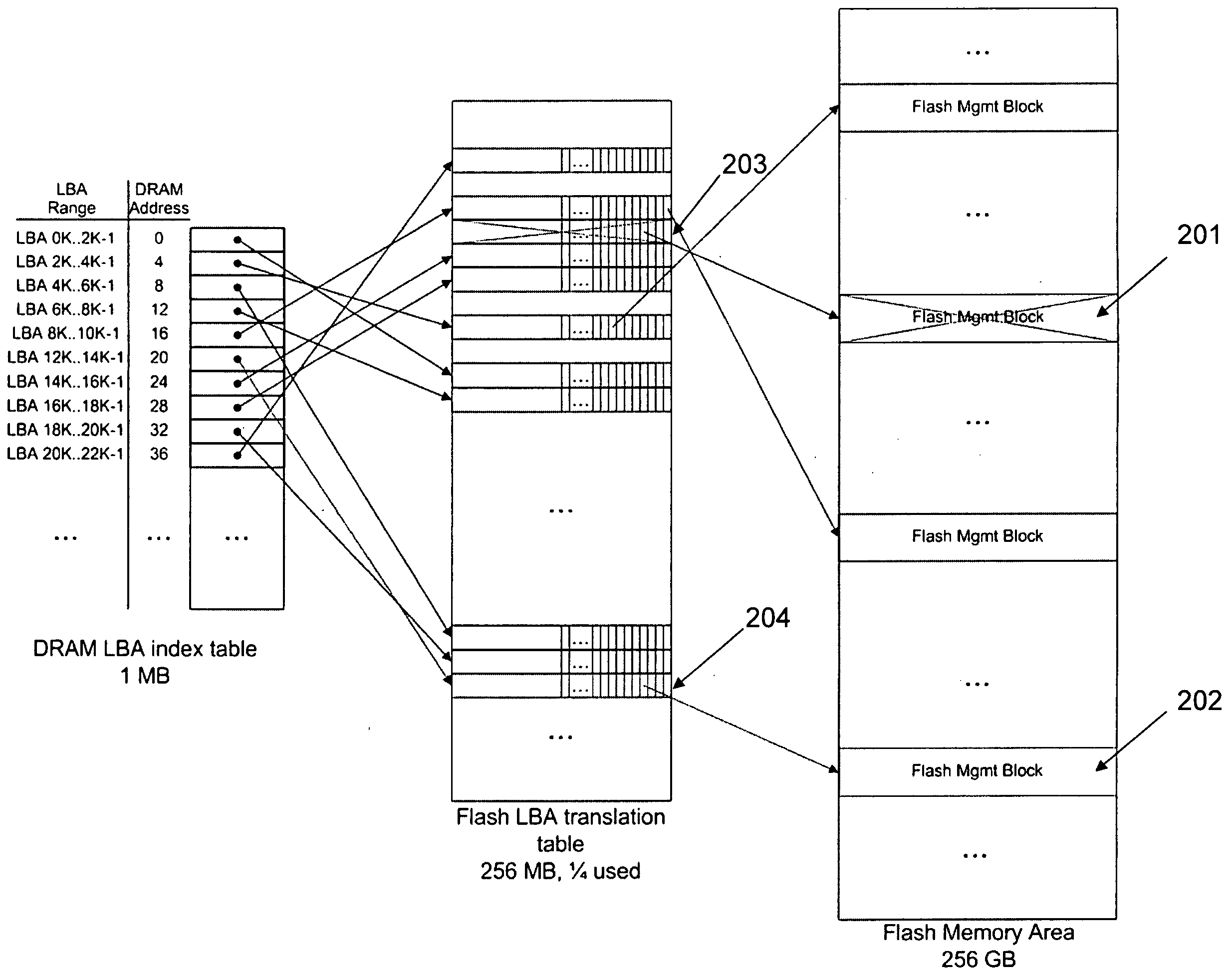
ActiveUS20100030999A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMass storageLogical block addressing
An embodiment of the invention relates to a mass storage device including a nonvolatile memory device with a plurality of memory management blocks and an address translation table formed with pointers to locations of the memory management blocks. A volatile memory device is included with an address index table formed with pointers to the pointers to the locations of the memory management blocks. The address index table is stored in the nonvolatile memory upon loss of bias voltage. Changes to the address translation table are accumulated in the volatile memory and written to the address translation table when at least a minimum quantity of the changes has been accumulated. The changes to the logical block address translation table accumulated in the volatile memory are written to a page in the address translation table after prior data in the page has been updated, written to another page, and then erased.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
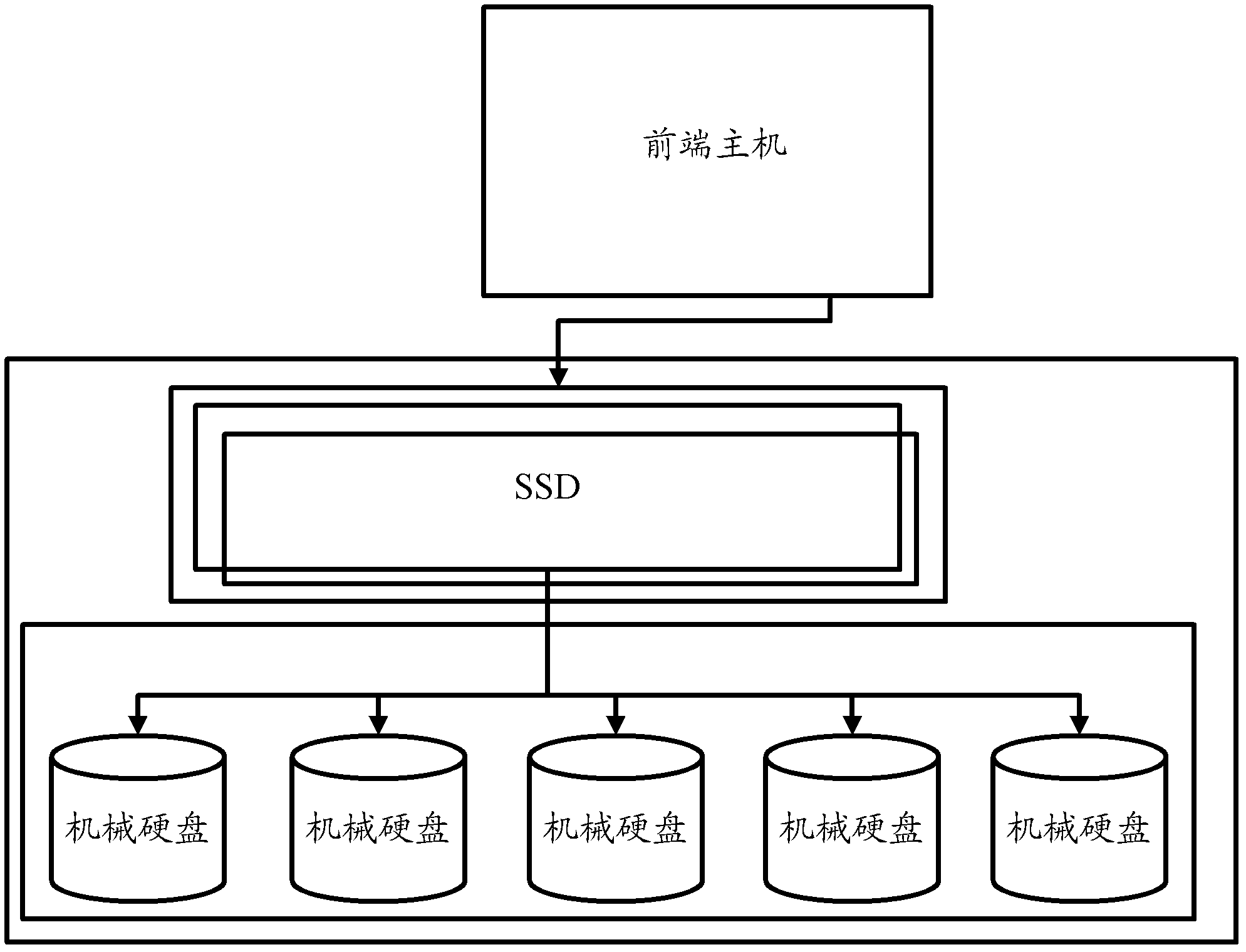
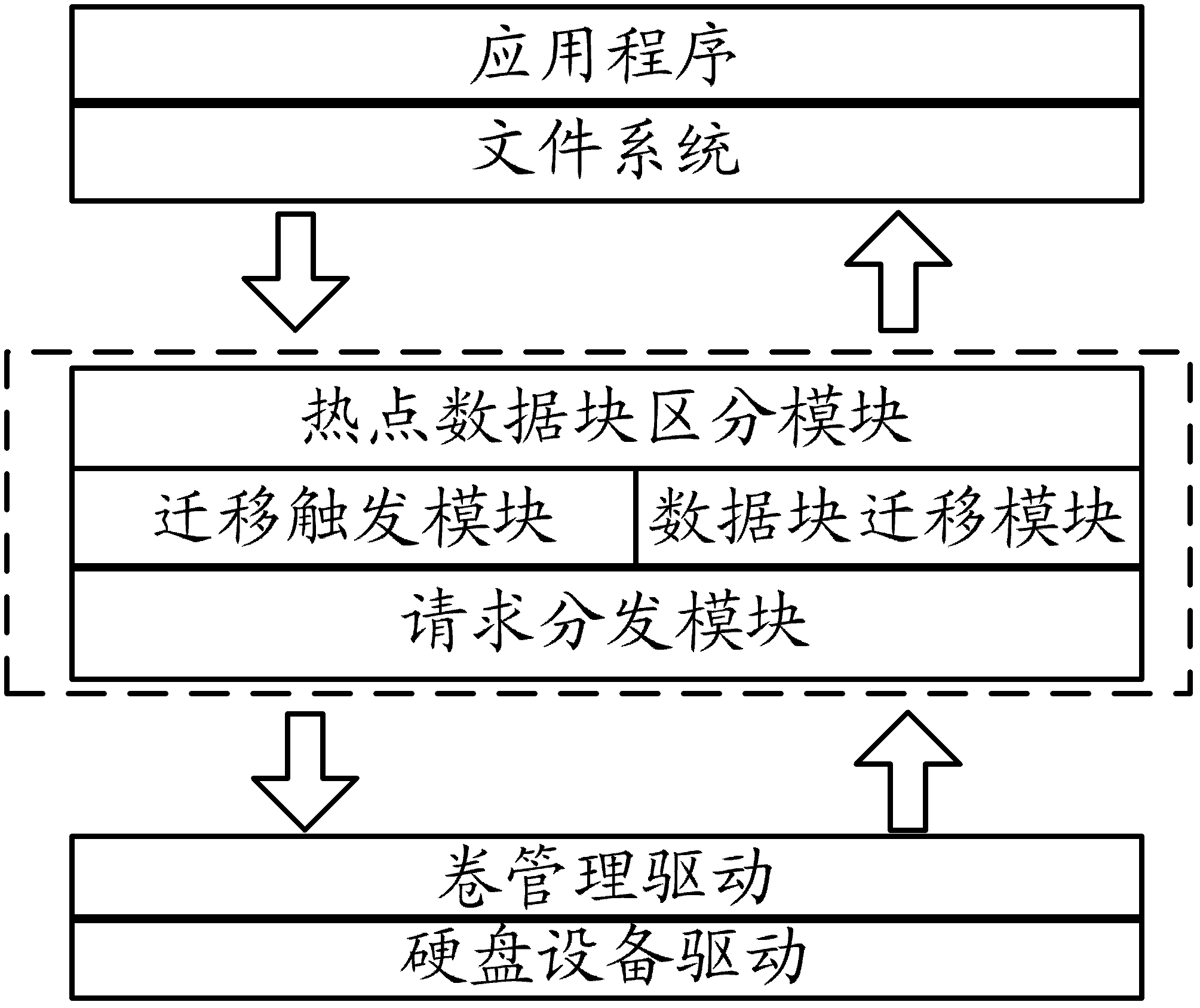
Hybrid storage system and hot spot data block migration method
InactiveCN103186350AGood value for moneyLow costInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-state driveHybrid storage system
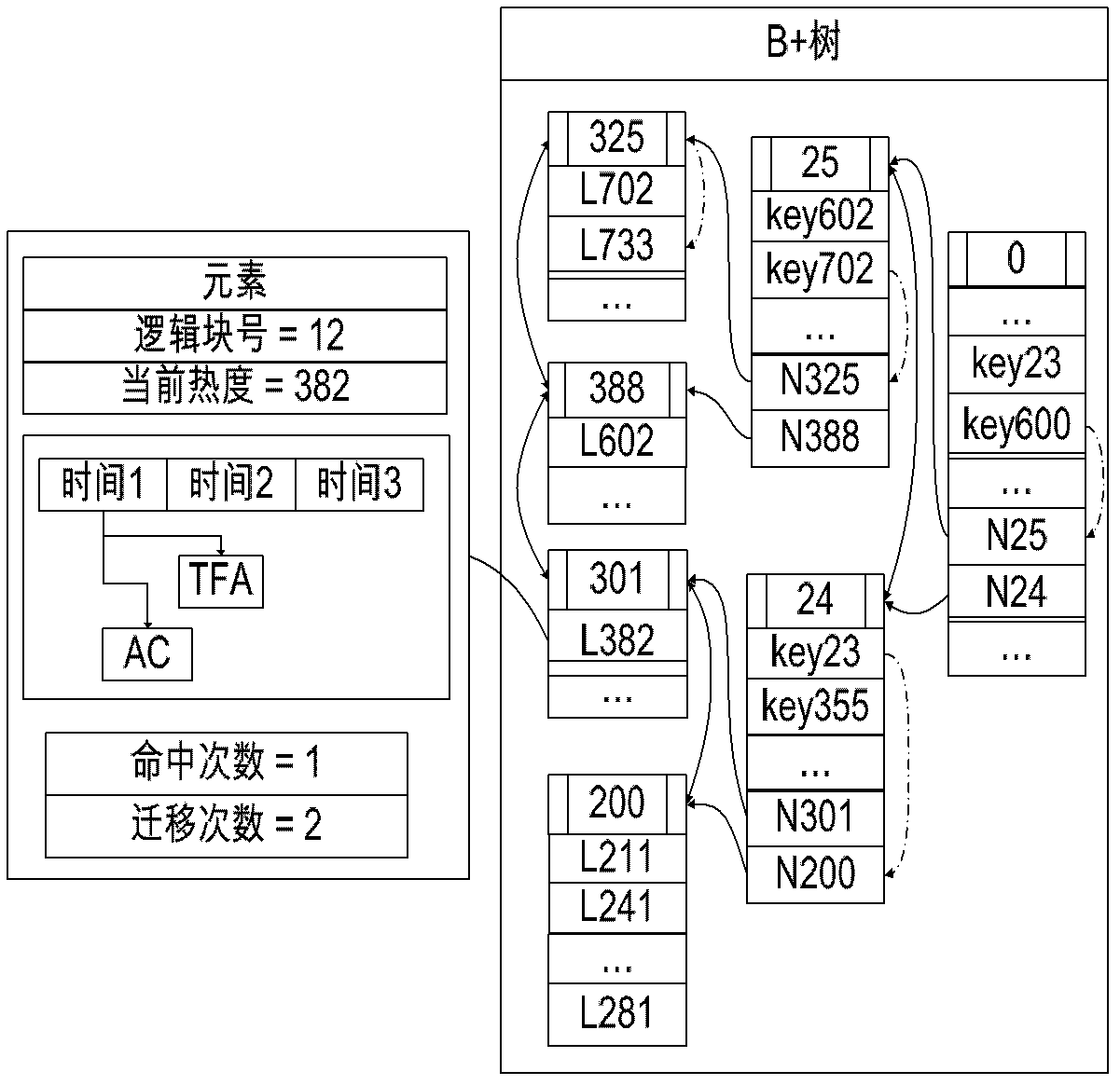
The invention provides a hybrid storage system which comprises at least one solid-state hard disc SSD (solid state drive), at least one mechanical hard disc and a control module, wherein the control module is used for migrating hot spot data blocks in the mechanical hard disc into the SSD, and migrating the non-hot spot data blocks in the SSD into the mechanical hard disc, the hot spot data blocks are data blocks of which the visited frequency is higher than that of other data blocks, and the non hot spot data blocks are data blocks of which the visited frequency is lower than that of others. According to the hybrid storage system and the hot spot data block migration method, provided by the invention, the utilization ratio of the SSD and the performance of the hybrid storage system are effectively enhanced, and meanwhile, the cost of the hybrid storage system is lowered.
Owner:BEIJING FASTWEB TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com