Patents
Literature
210 results about "Data striping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
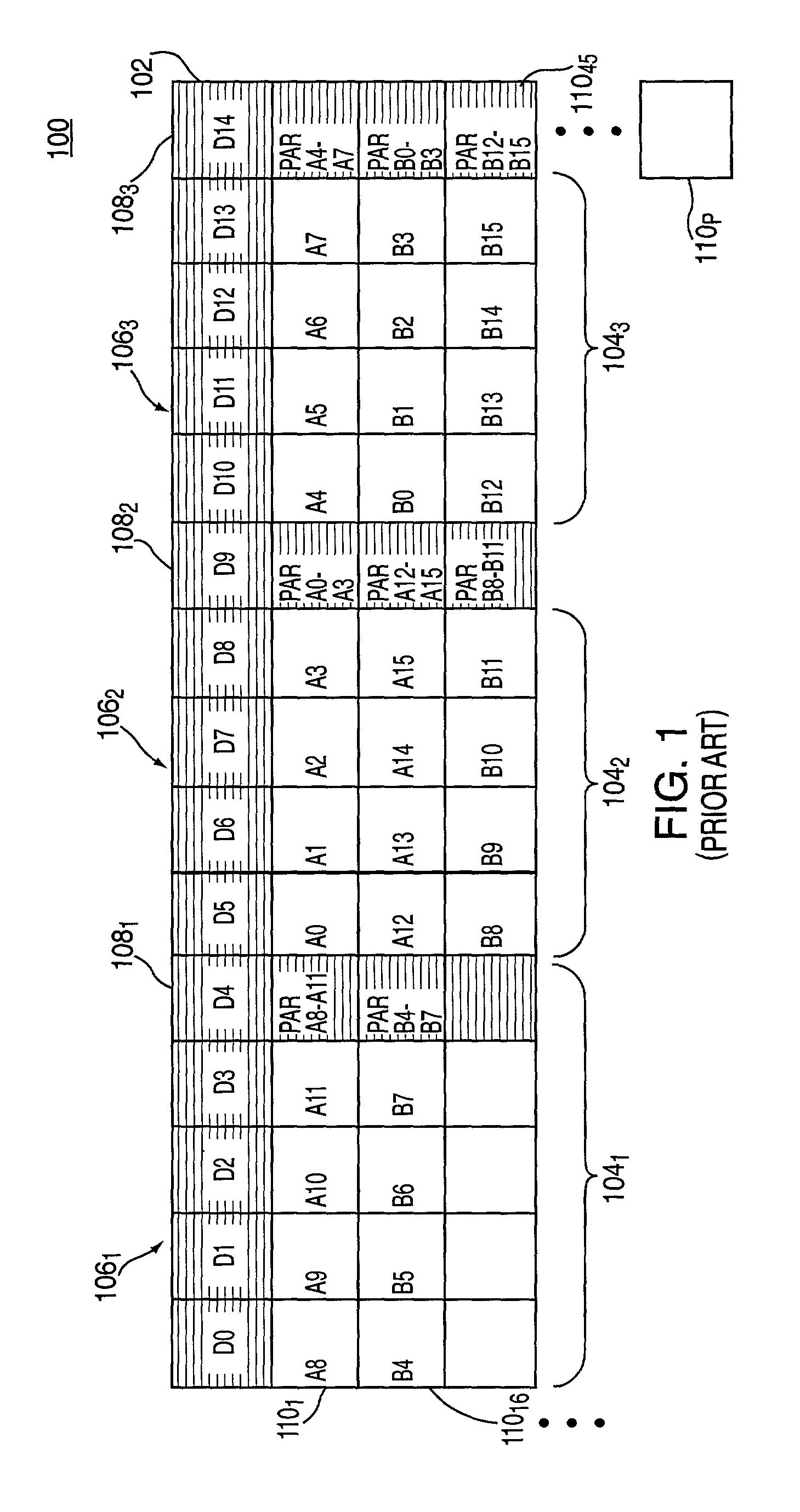
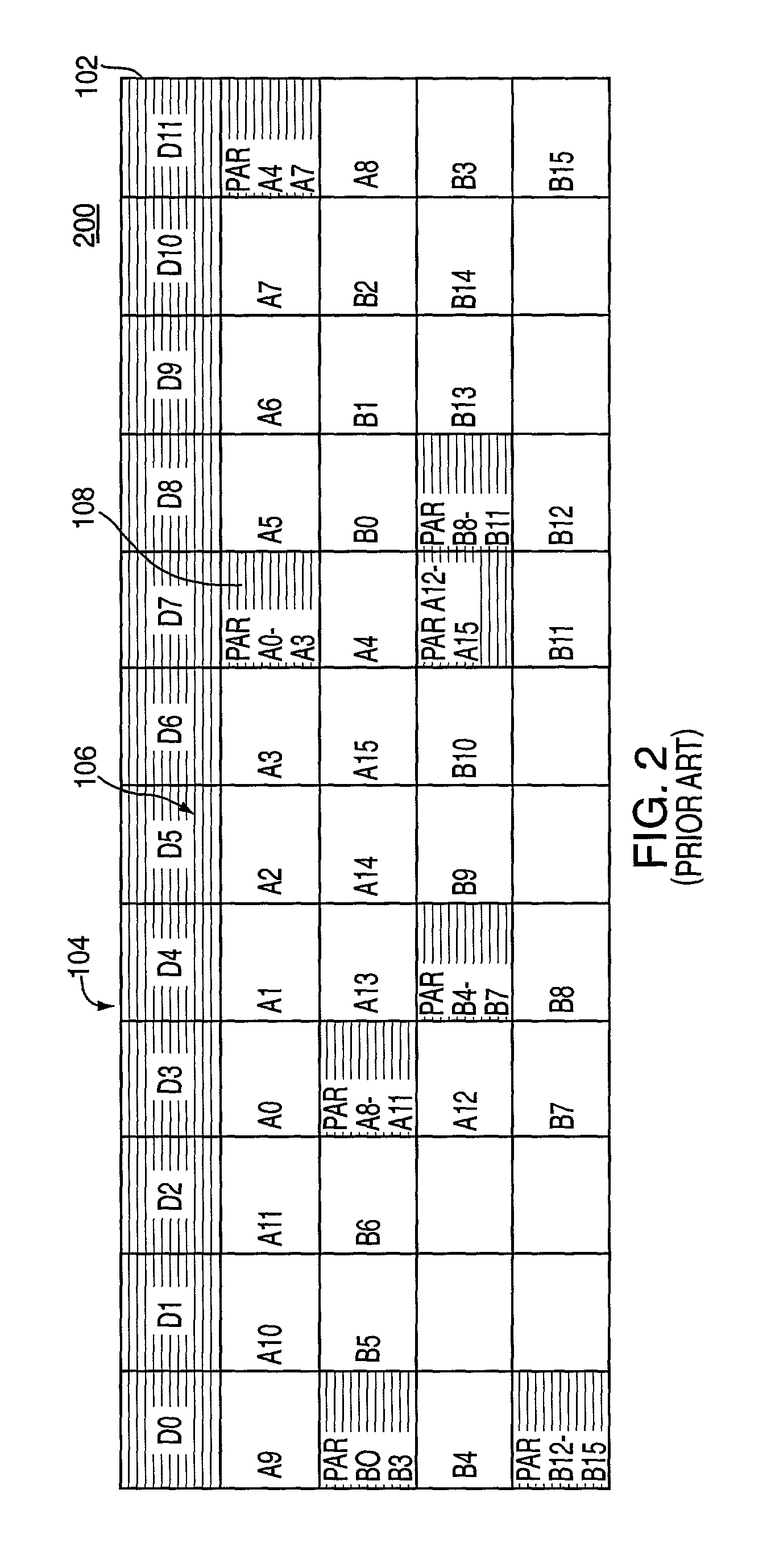
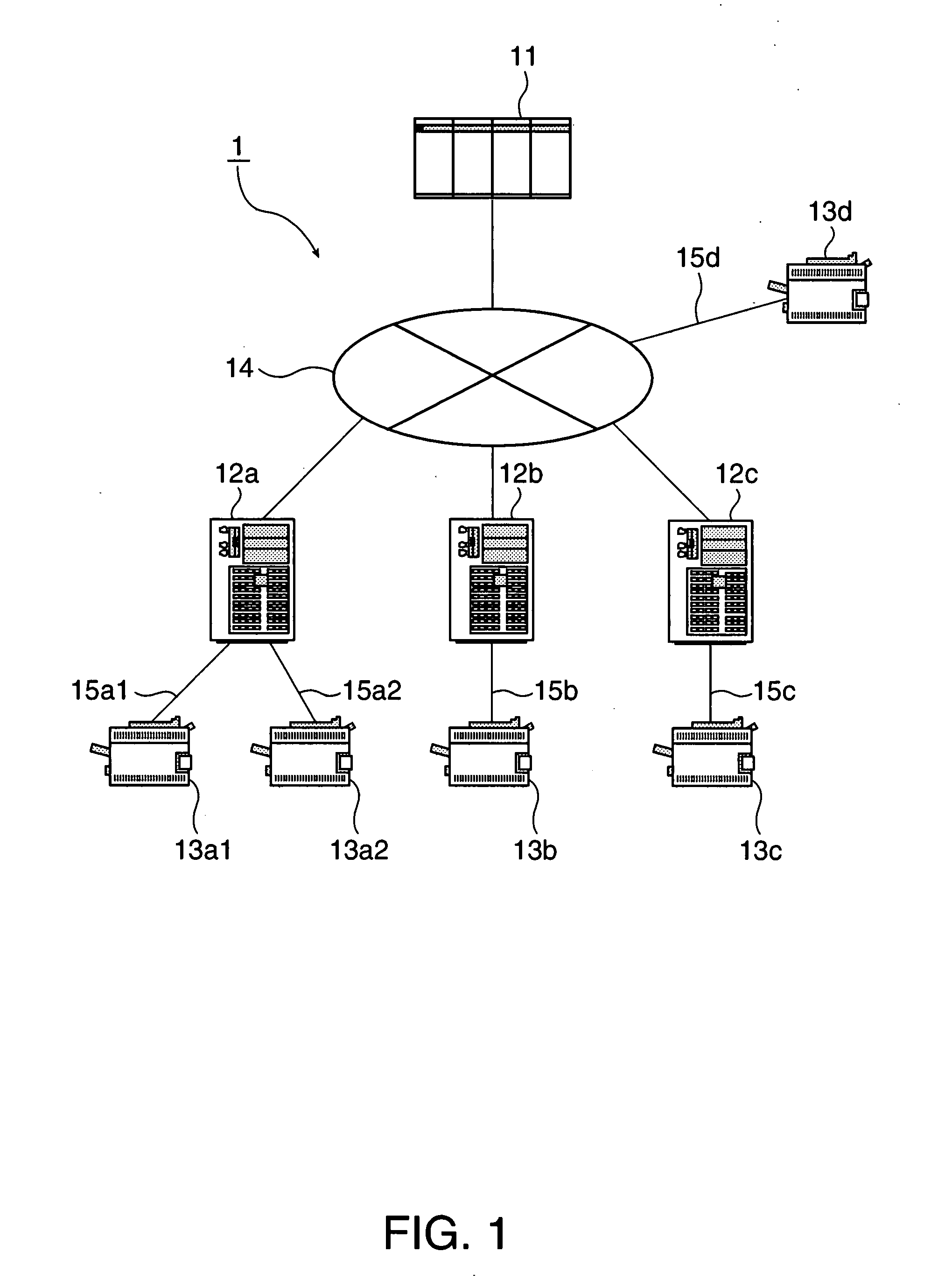
In computer data storage, data striping is the technique of segmenting logically sequential data, such as a file, so that consecutive segments are stored on different physical storage devices. Striping is useful when a processing device requests data more quickly than a single storage device can provide it. By spreading segments across multiple devices which can be accessed concurrently, total data throughput is increased. It is also a useful method for balancing I/O load across an array of disks. Striping is used across disk drives in redundant array of independent disks (RAID) storage, network interface controllers, disk arrays, different computers in clustered file systems and grid-oriented storage, and RAM in some systems.
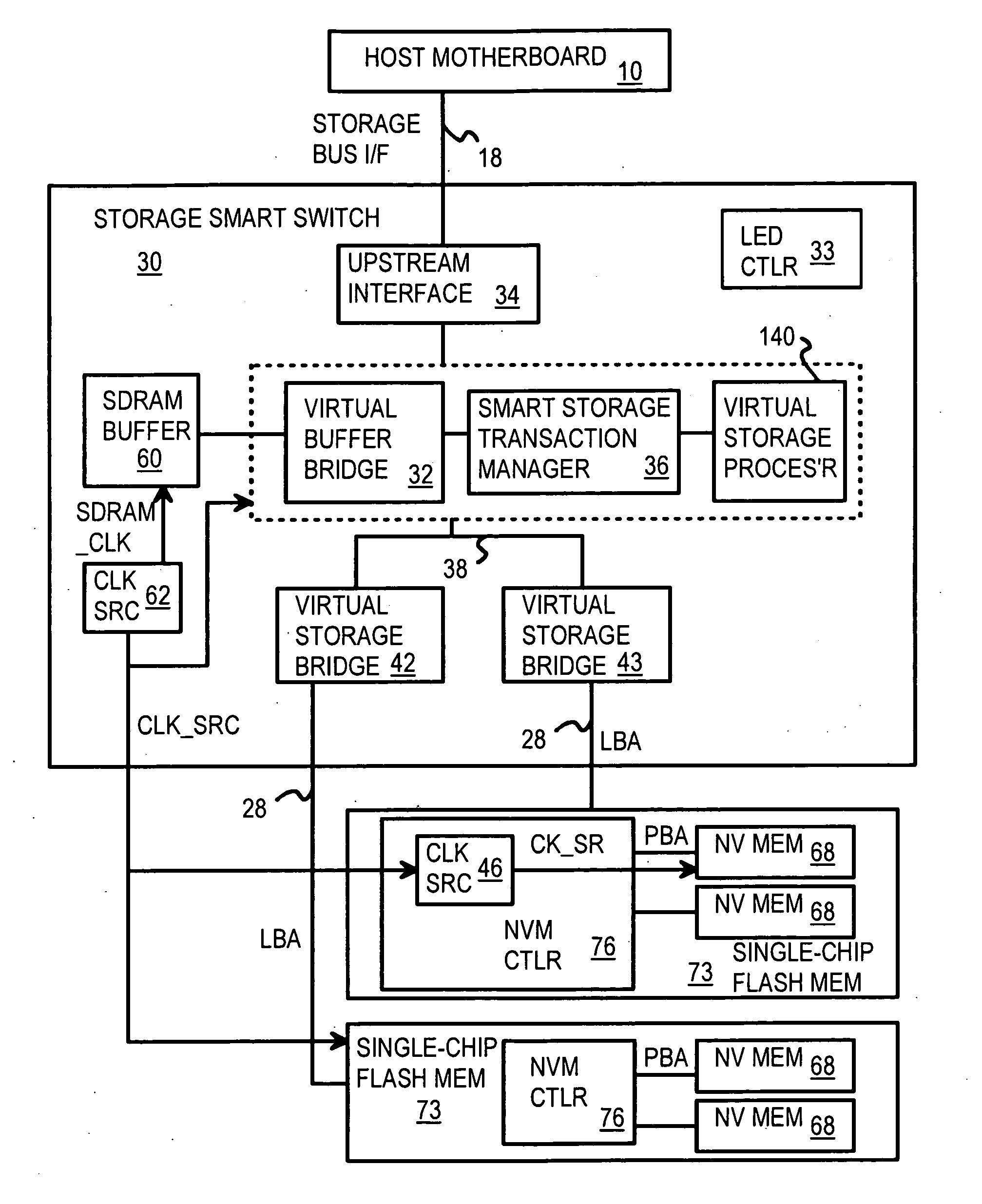
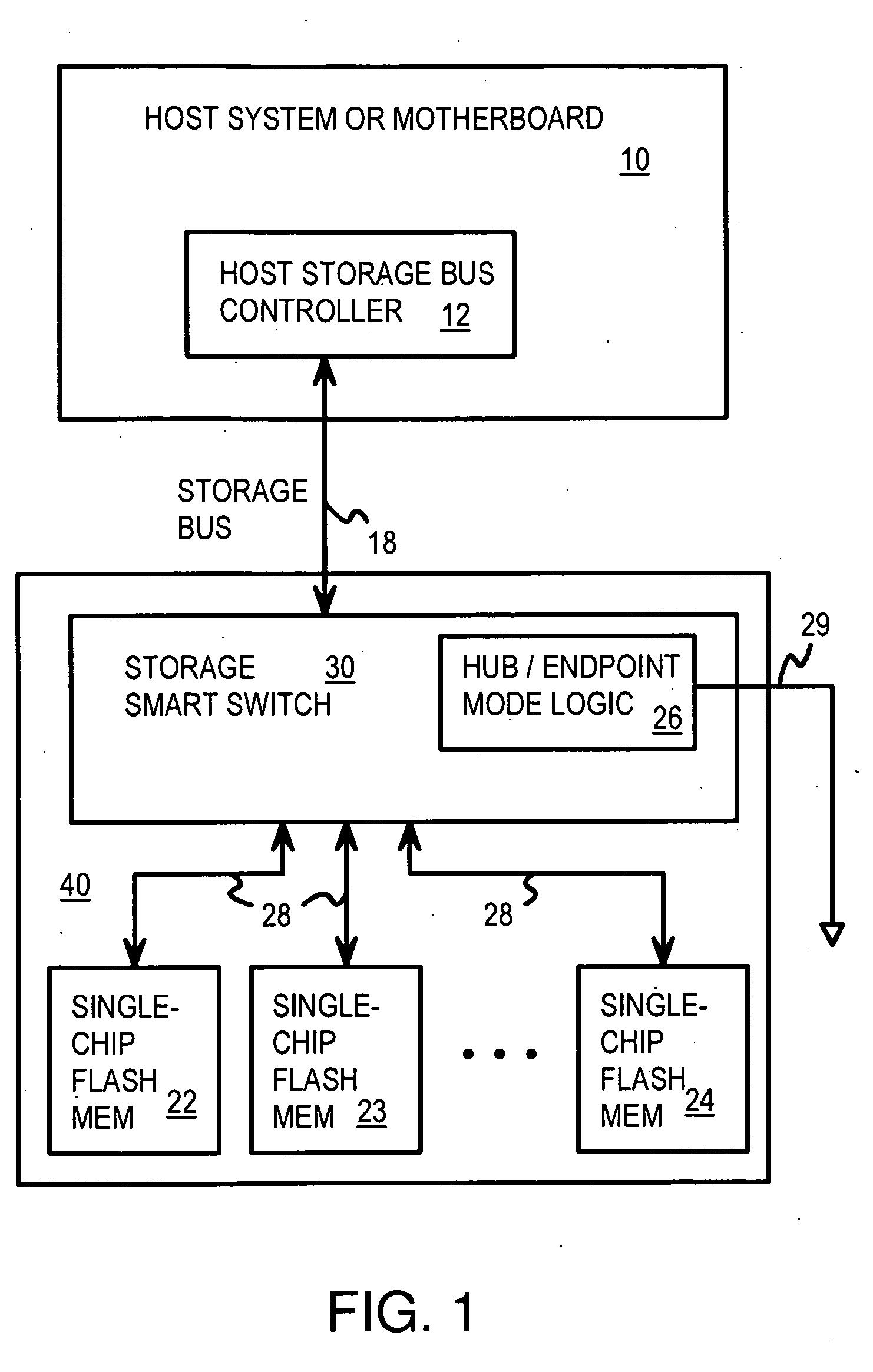
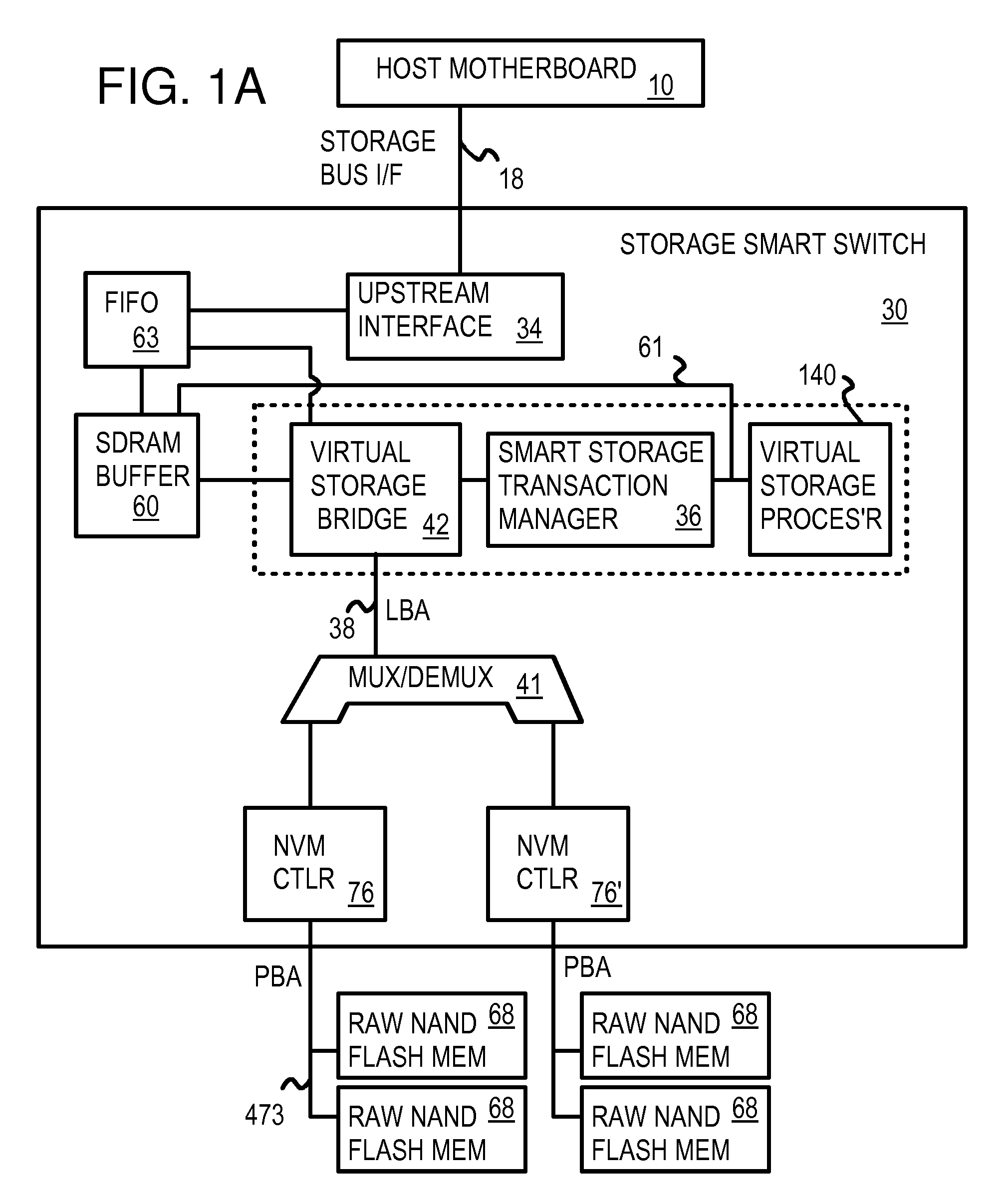
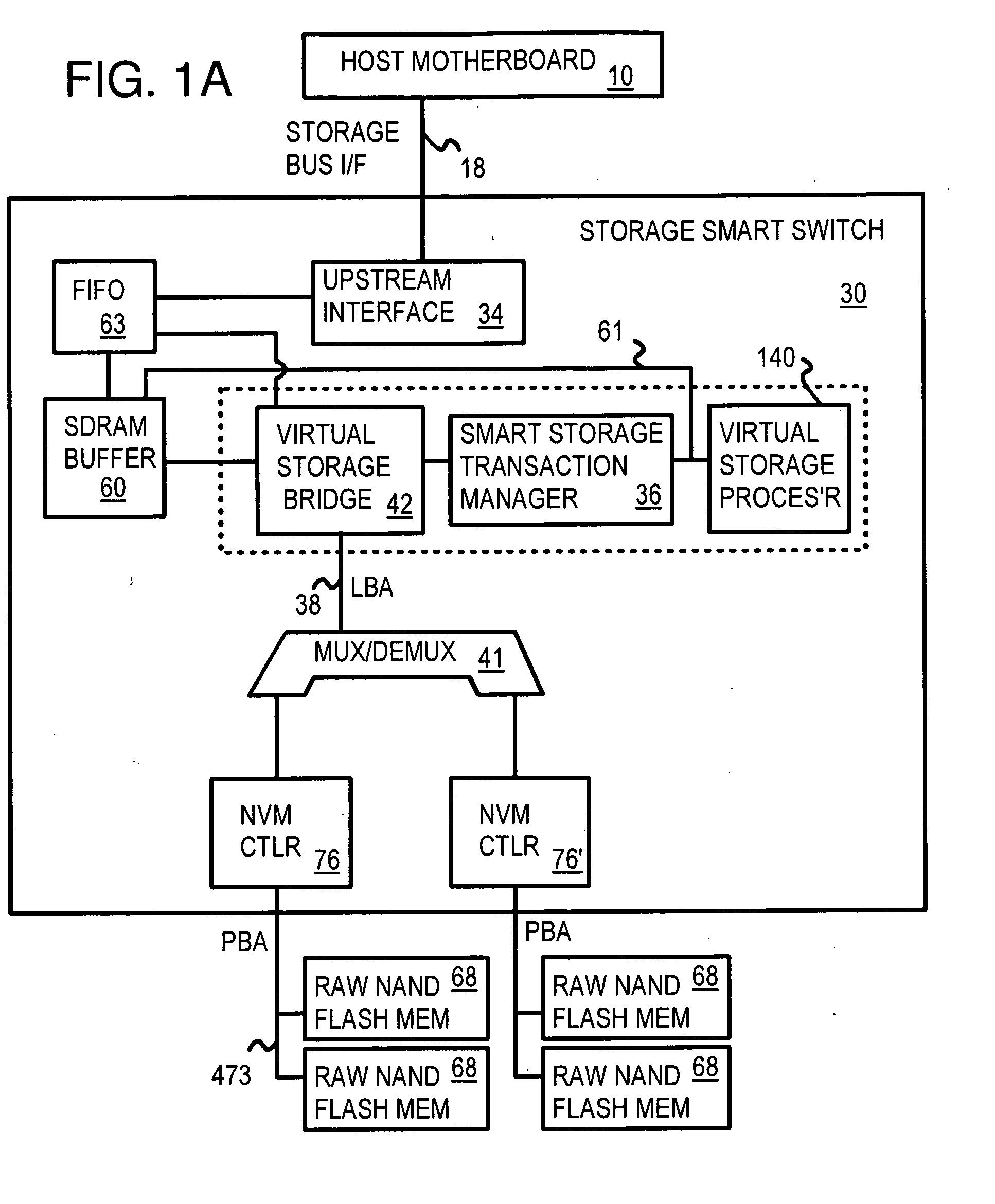
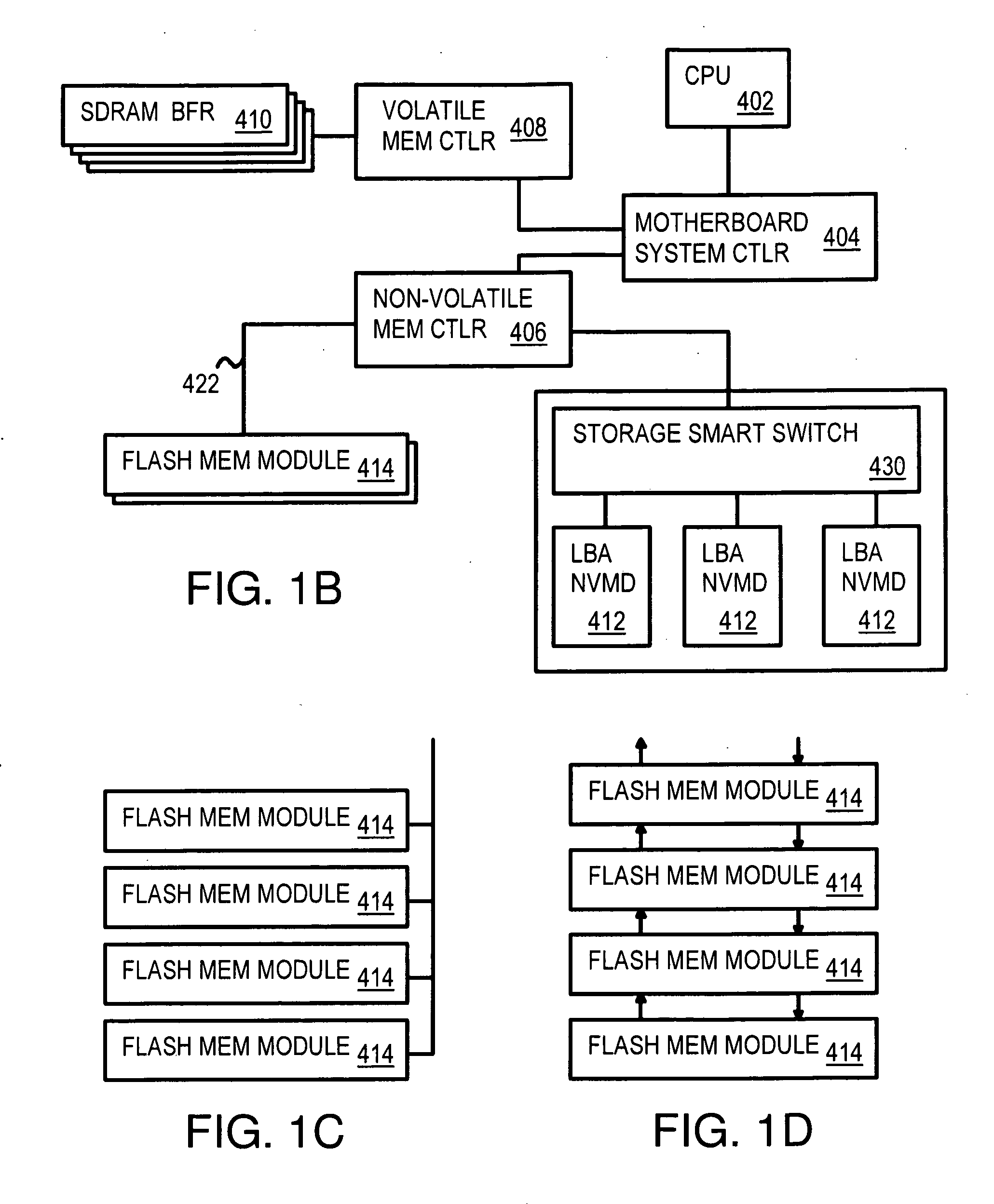
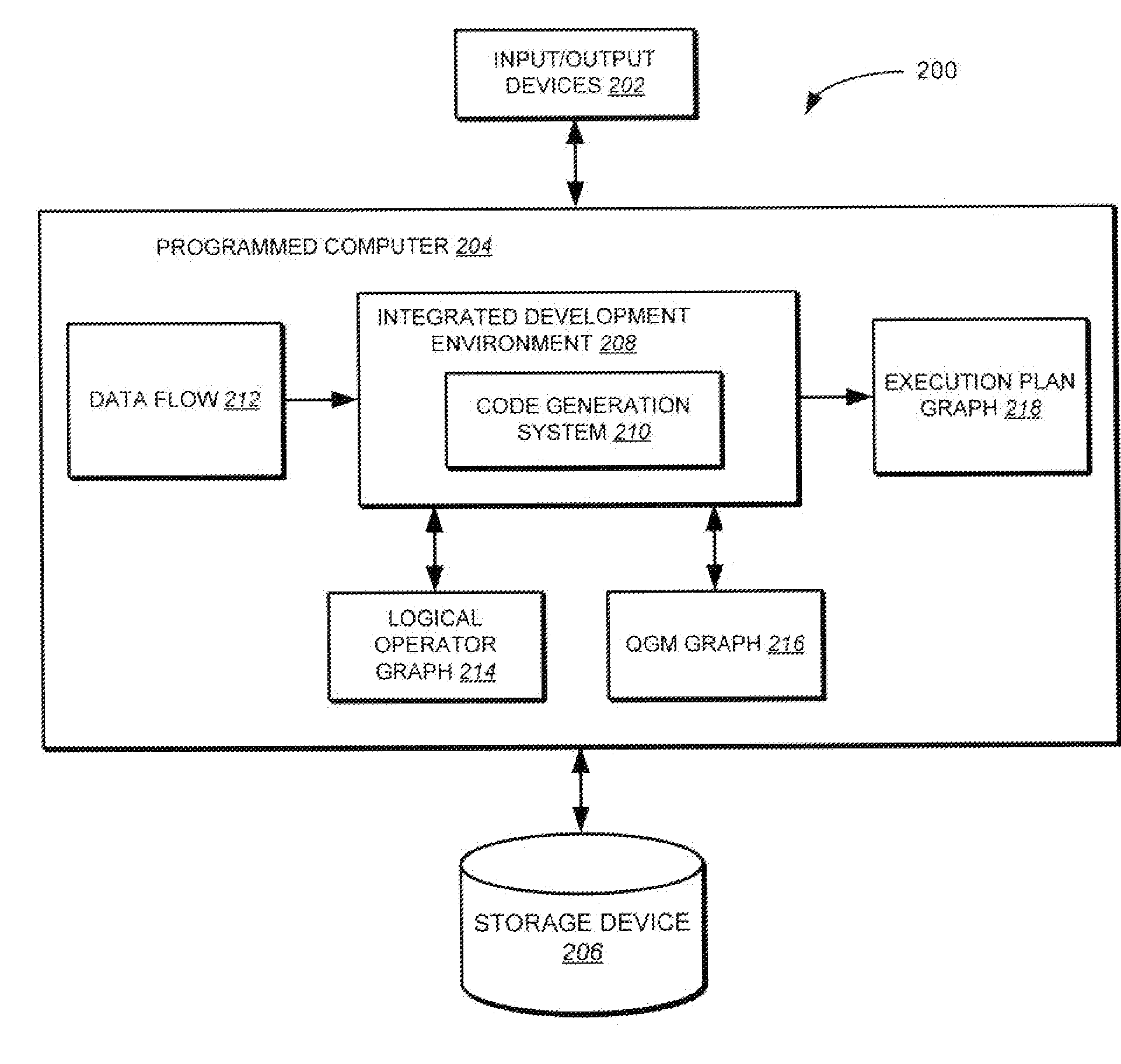
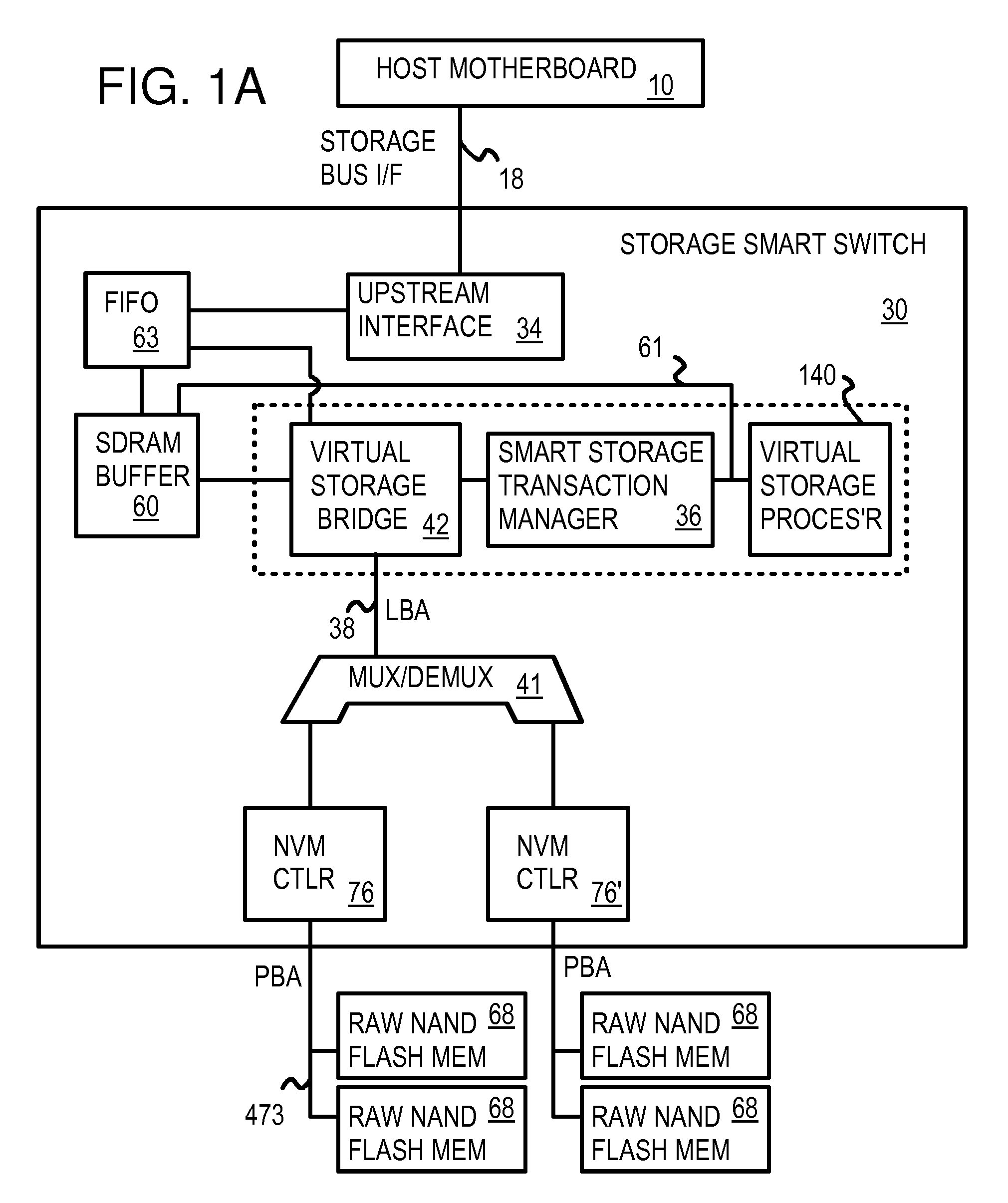
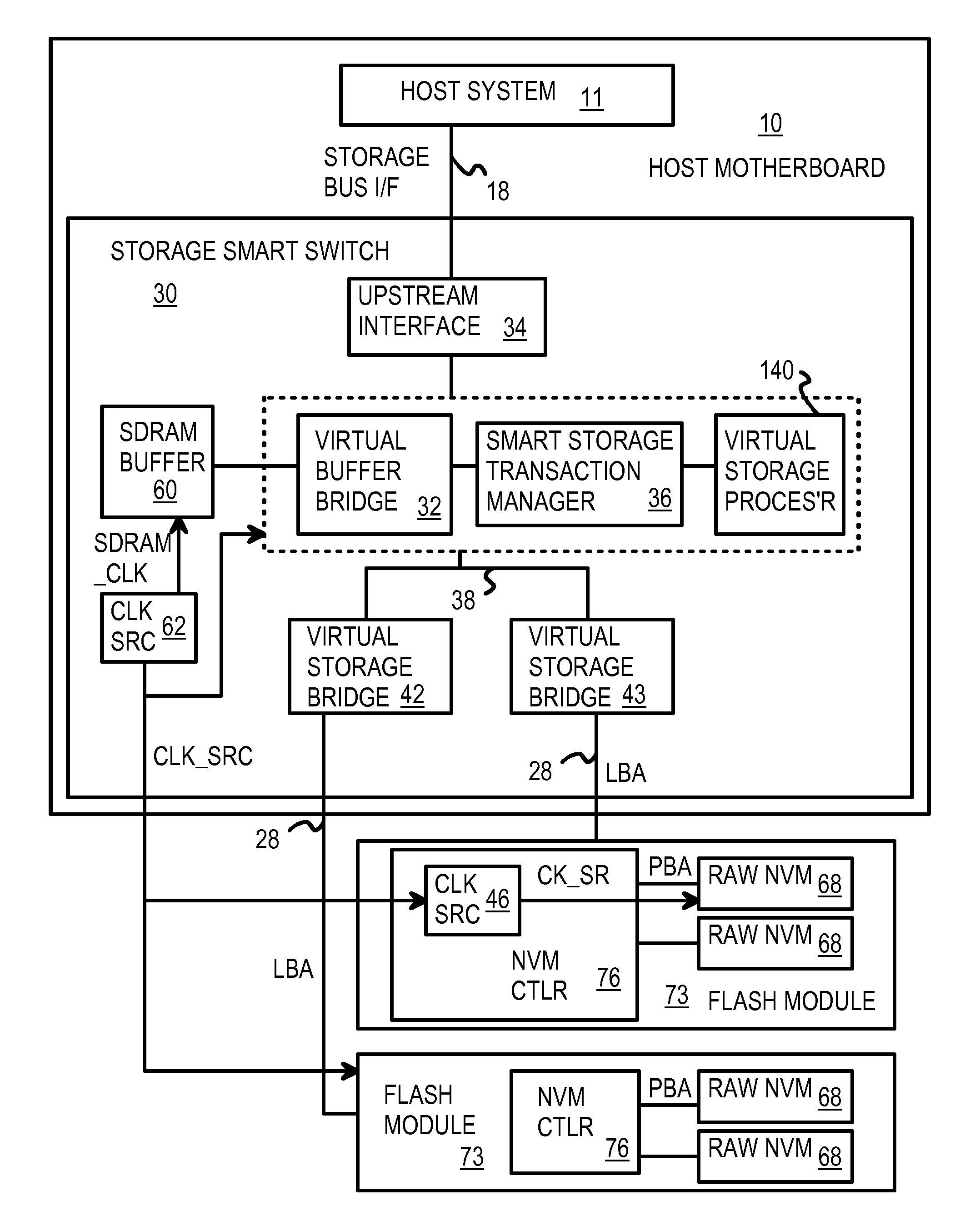
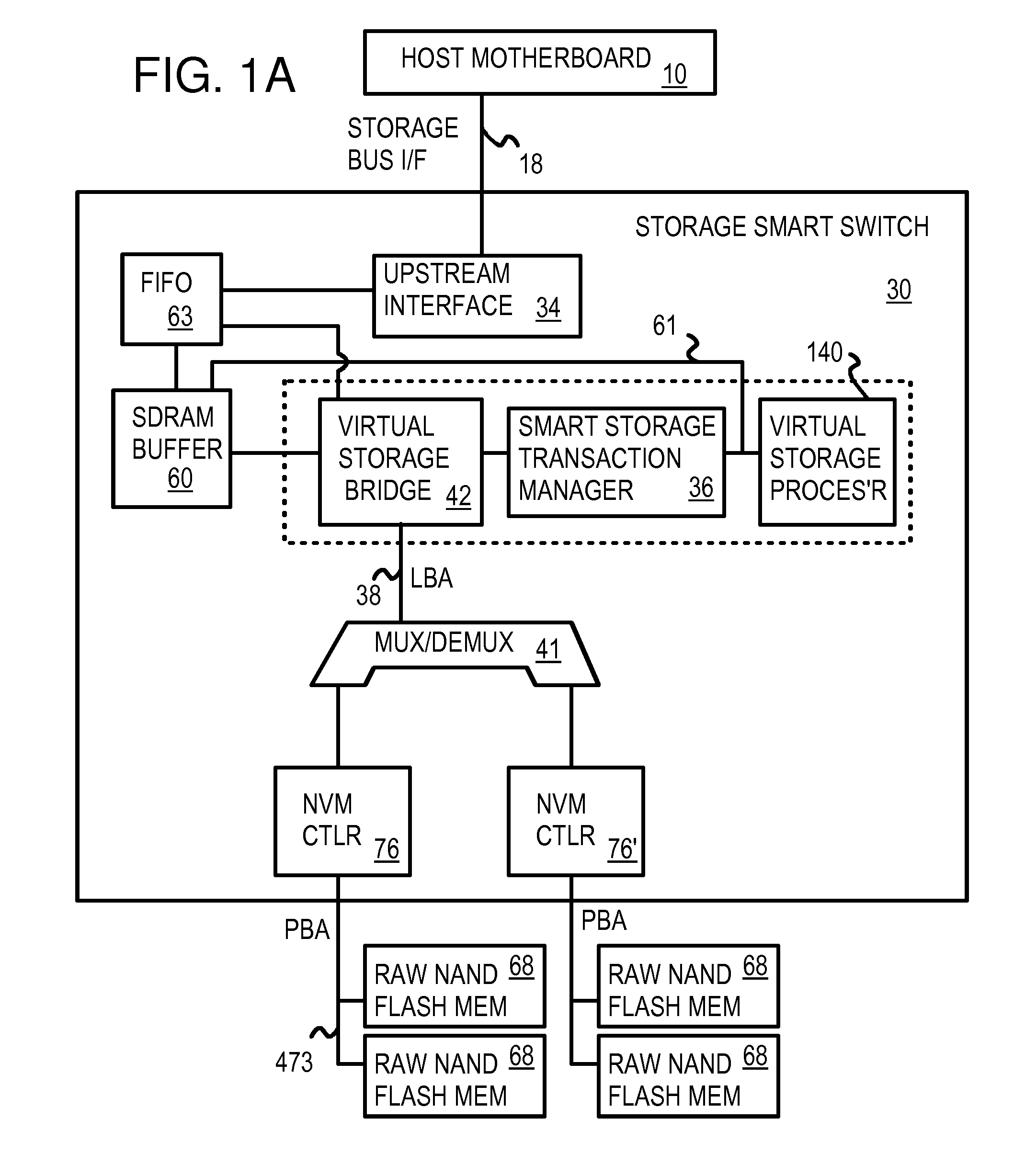
Multi-Level Controller with Smart Storage Transfer Manager for Interleaving Multiple Single-Chip Flash Memory Devices
InactiveUS20080320214A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingSolid-state drive
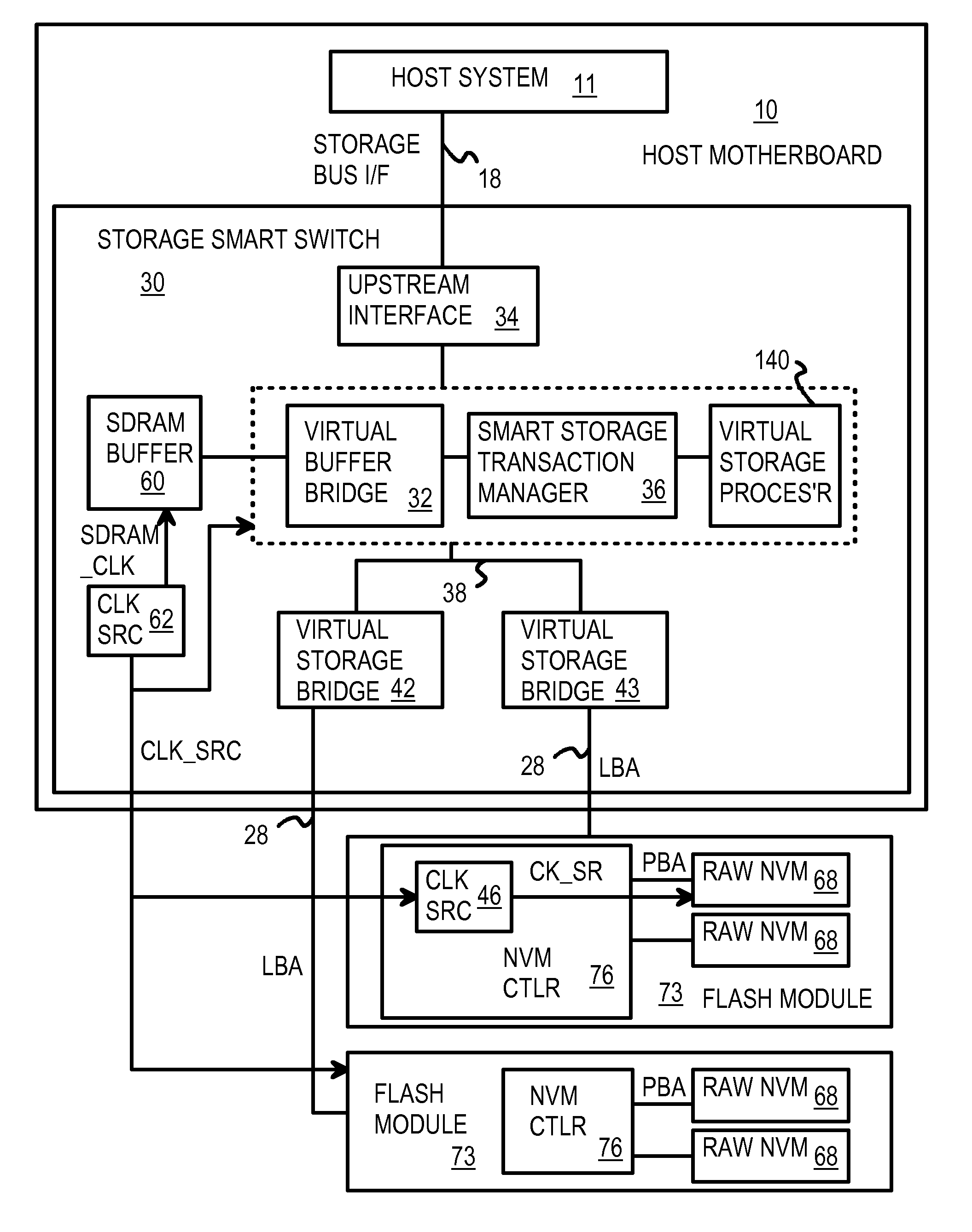
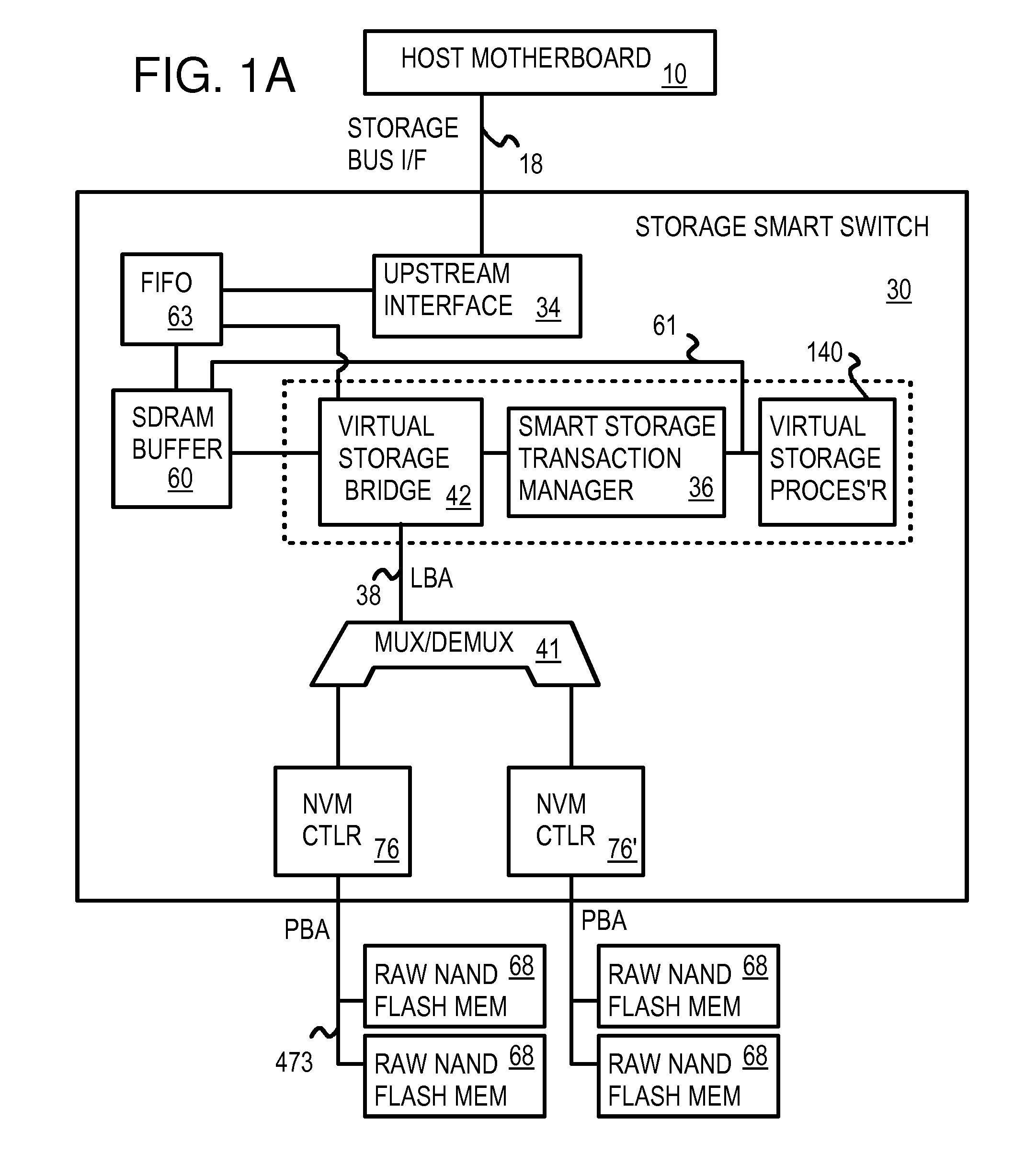
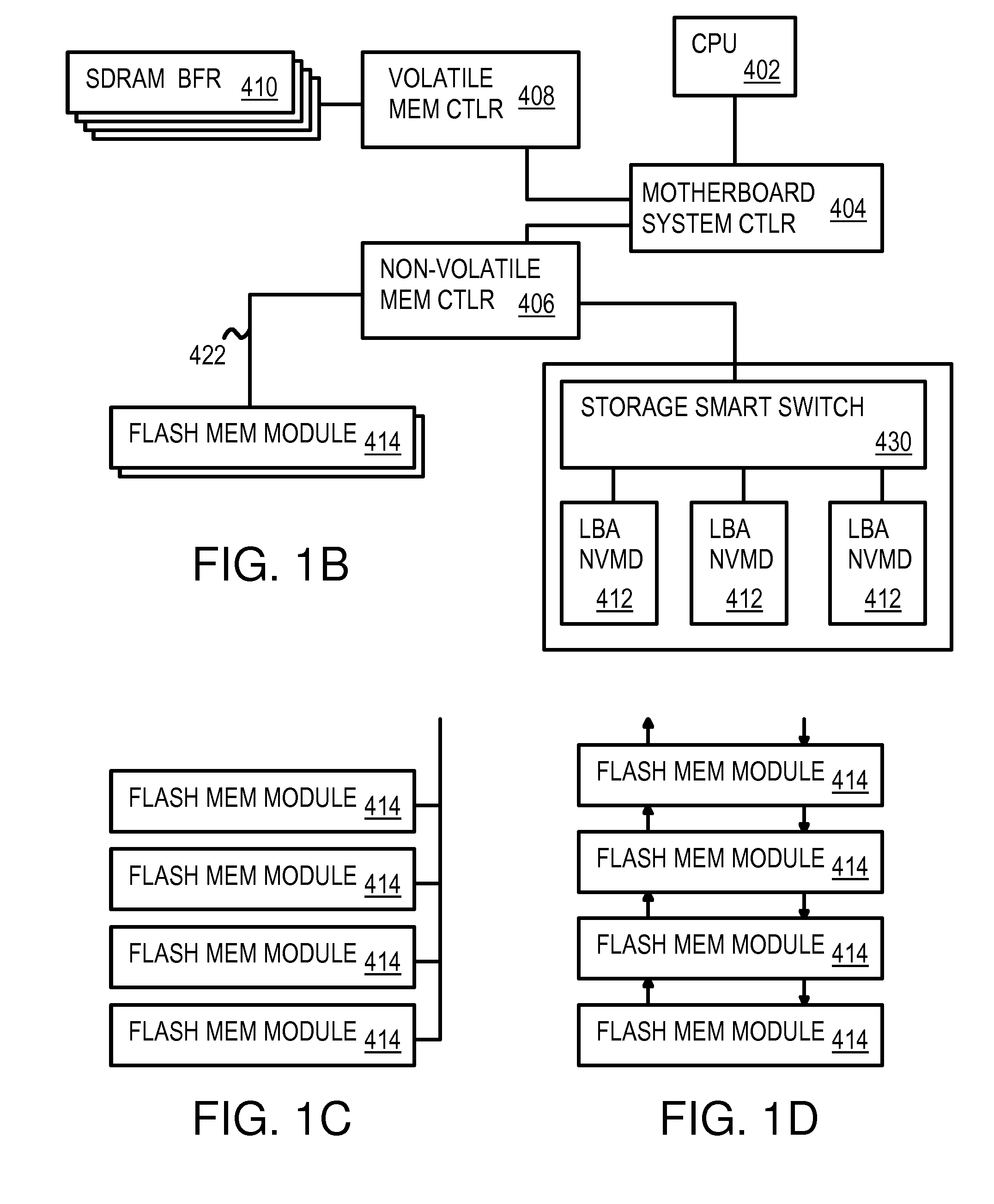
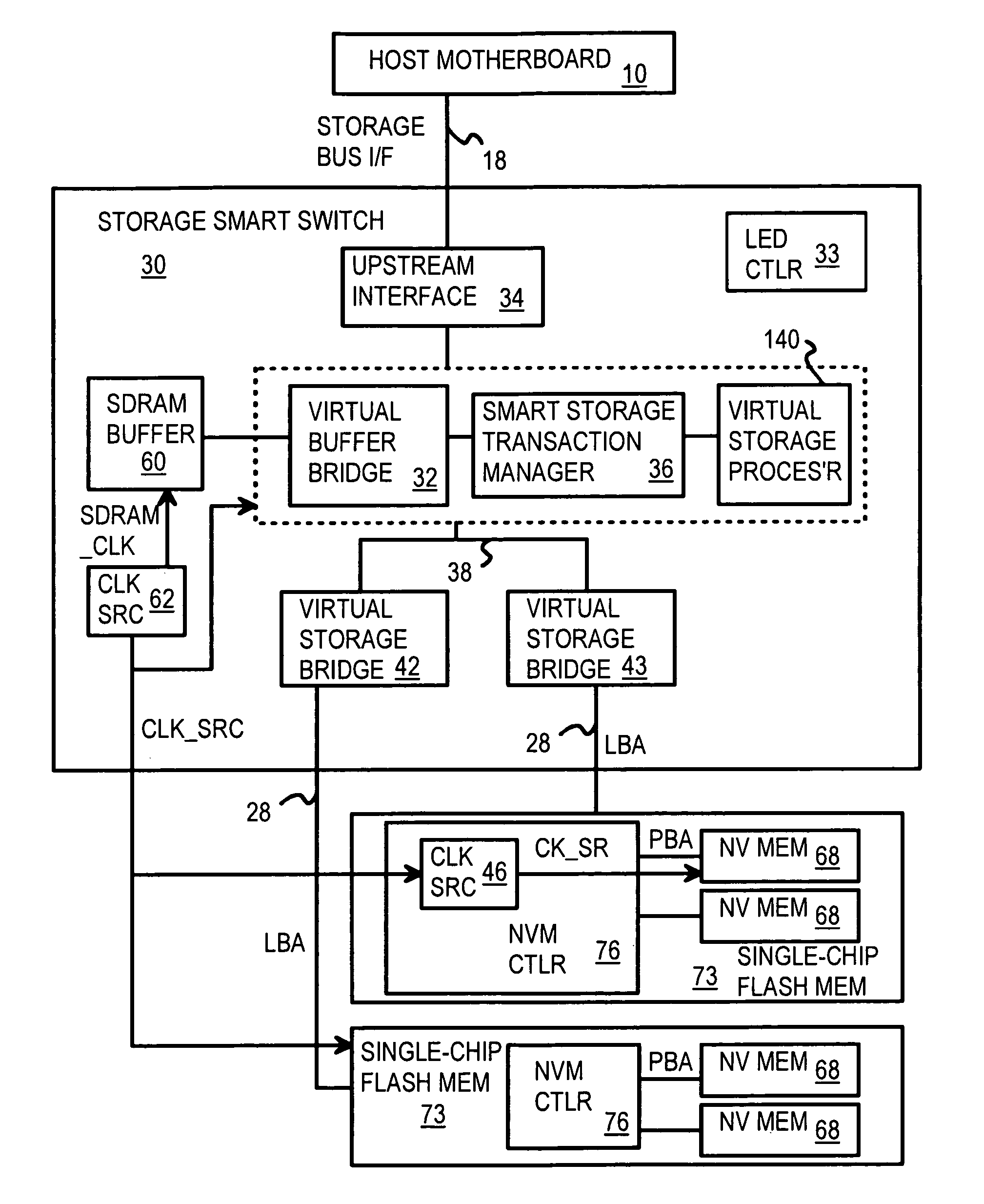
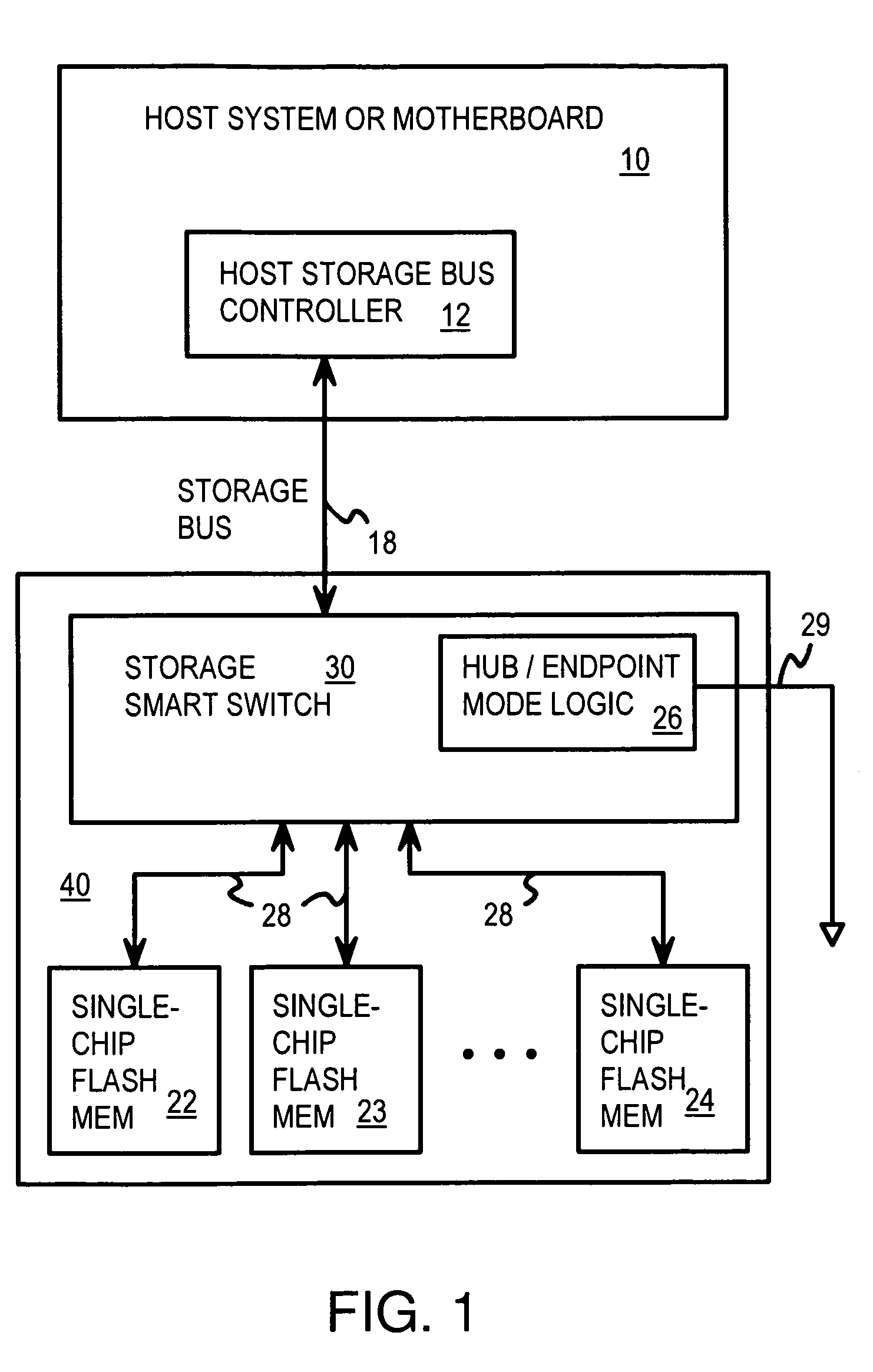
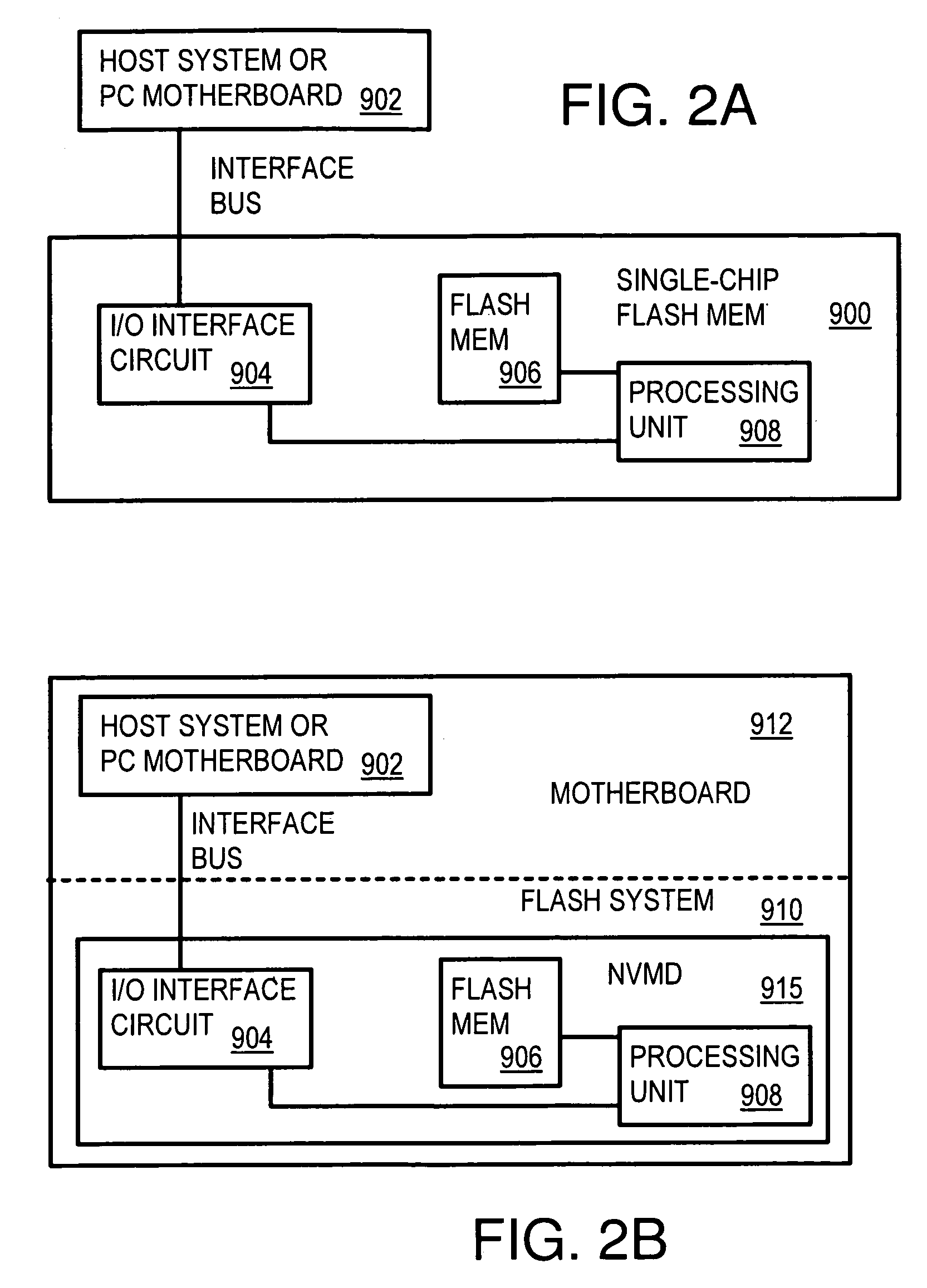
A solid-state disk (SSD) has a smart storage switch with a smart storage transaction manager that re-orders host commands for accessing downstream single-chip flash-memory devices. Each single-chip flash-memory device has a lower-level controller that converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA) that access flash memory blocks in the single-chip flash-memory device. Wear-leveling and bad block remapping are preformed by each single-chip flash-memory device, and at a higher level by a virtual storage processor in the smart storage switch. Virtual storage bridges between the smart storage transaction manager and the single-chip flash-memory devices bridge LBA transactions over LBA buses to the single-chip flash-memory devices. Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the single-chip flash-memory device is controlled at a high level by the smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping may be performed within each single-chip flash-memory device.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
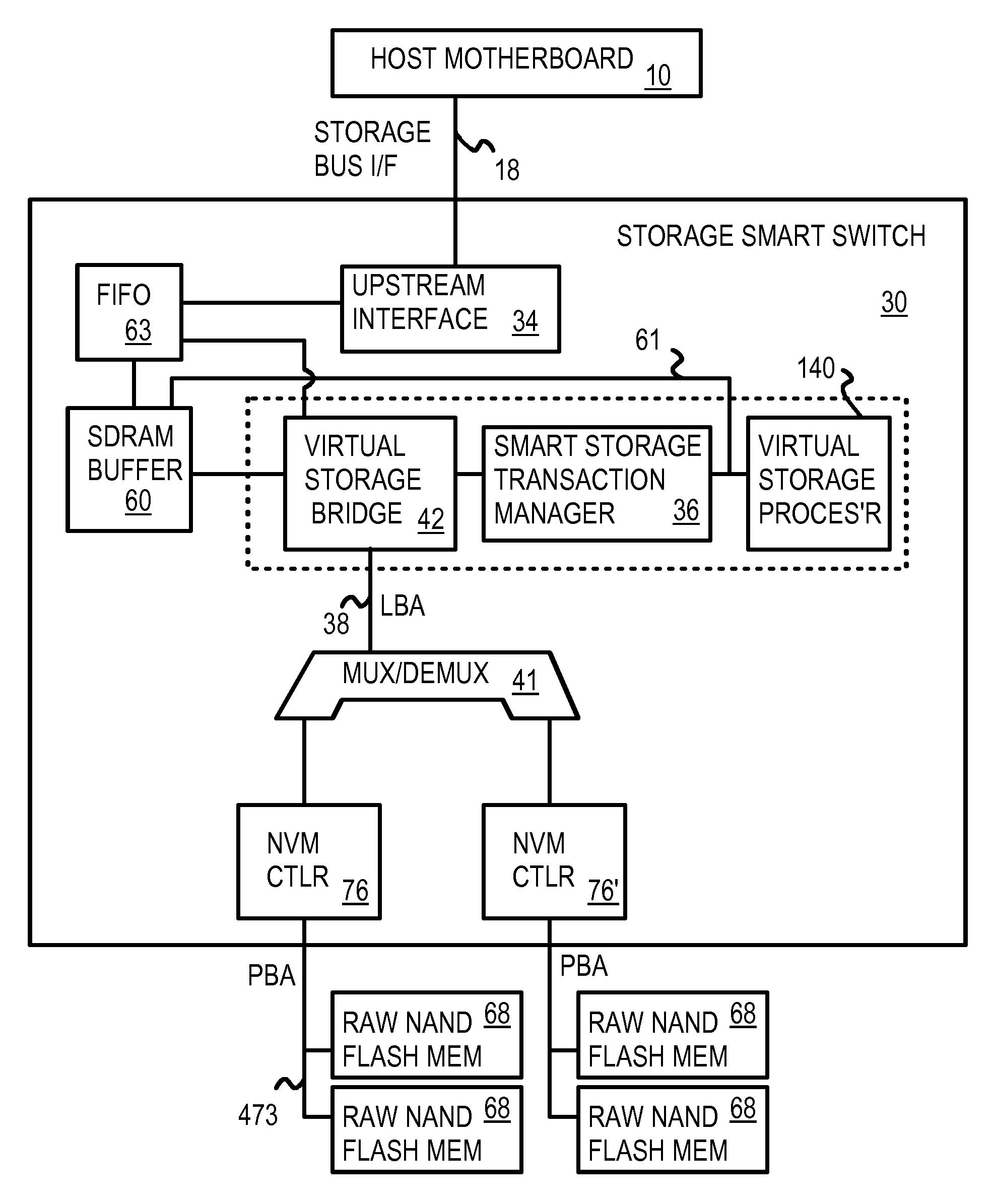
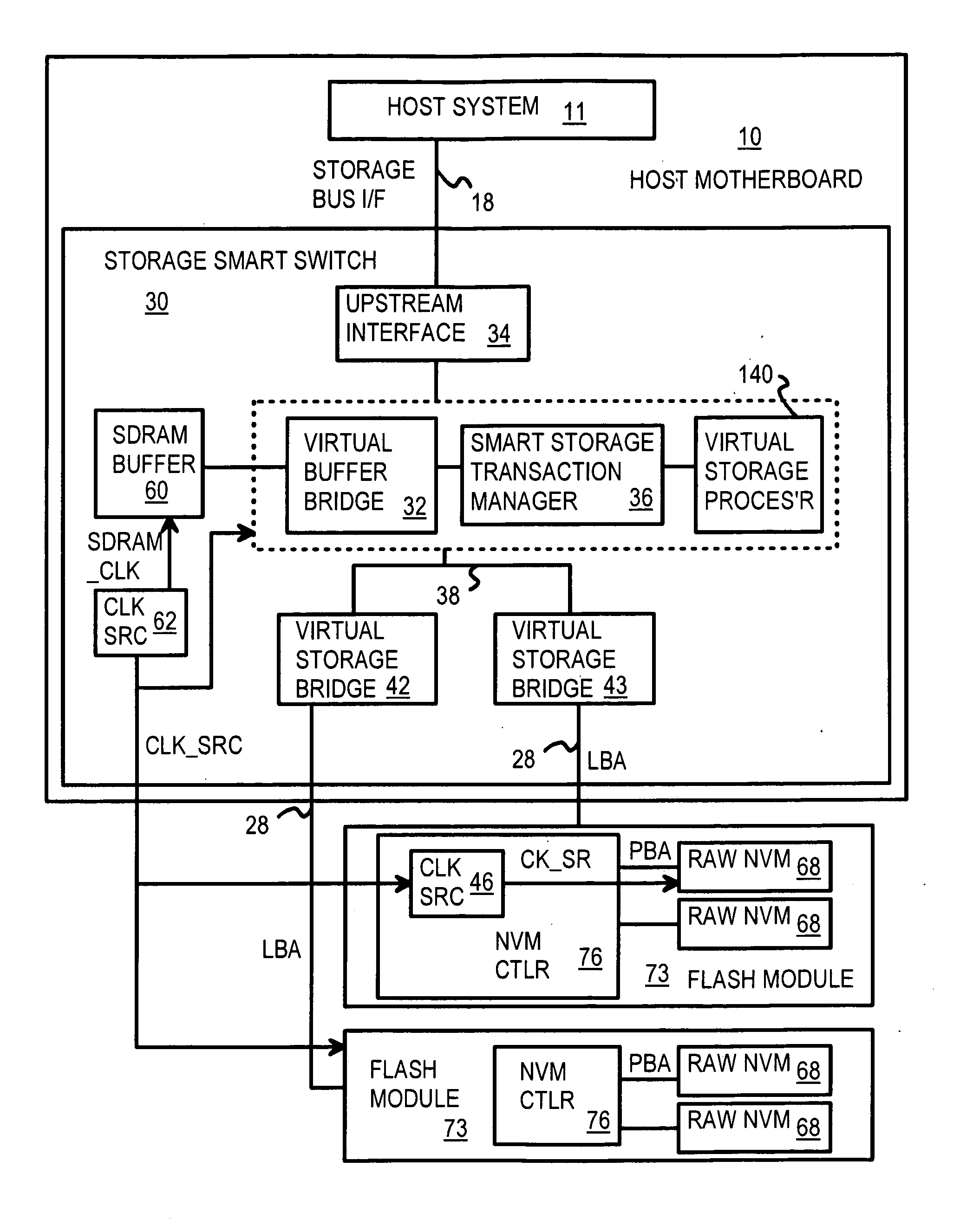
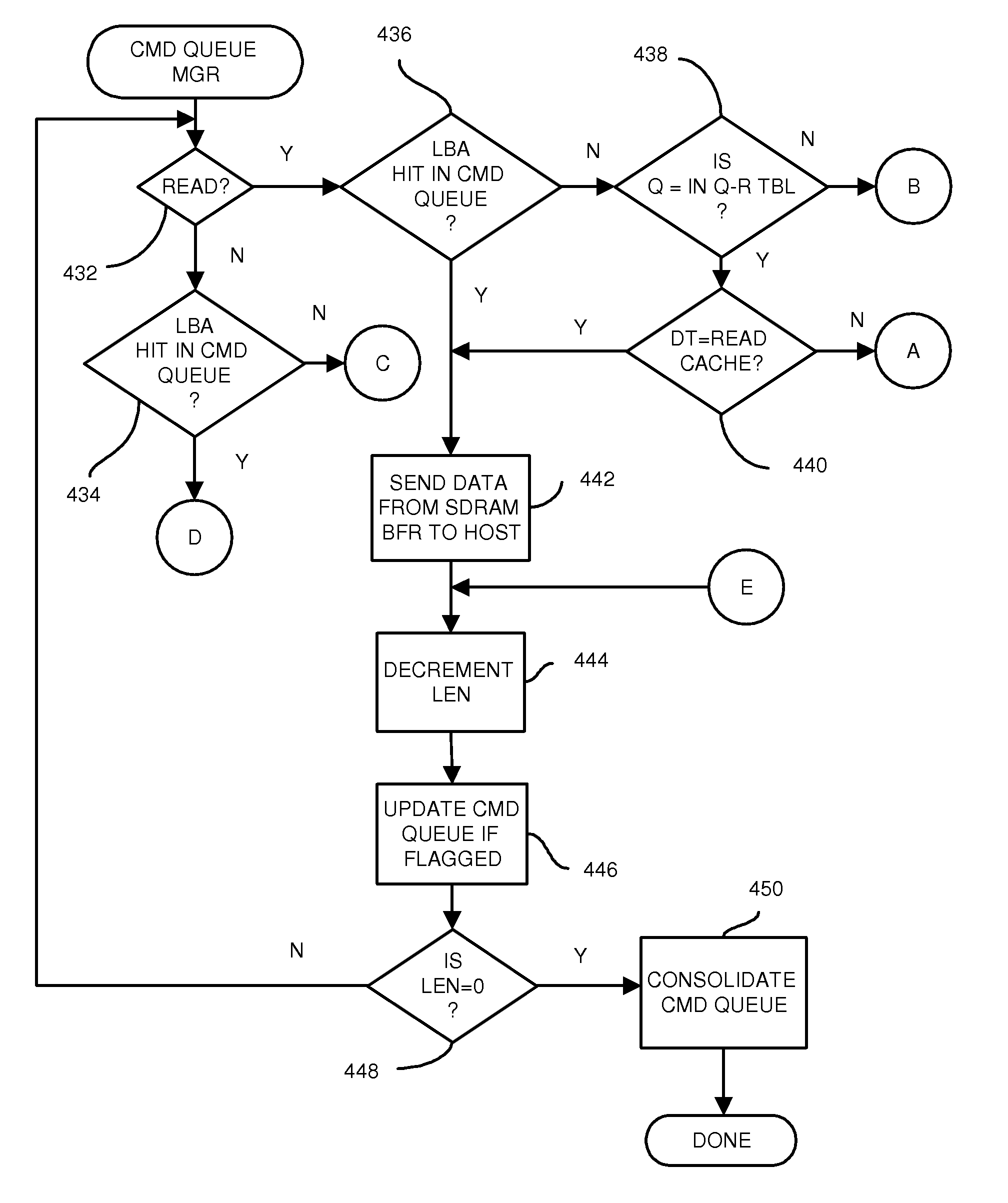
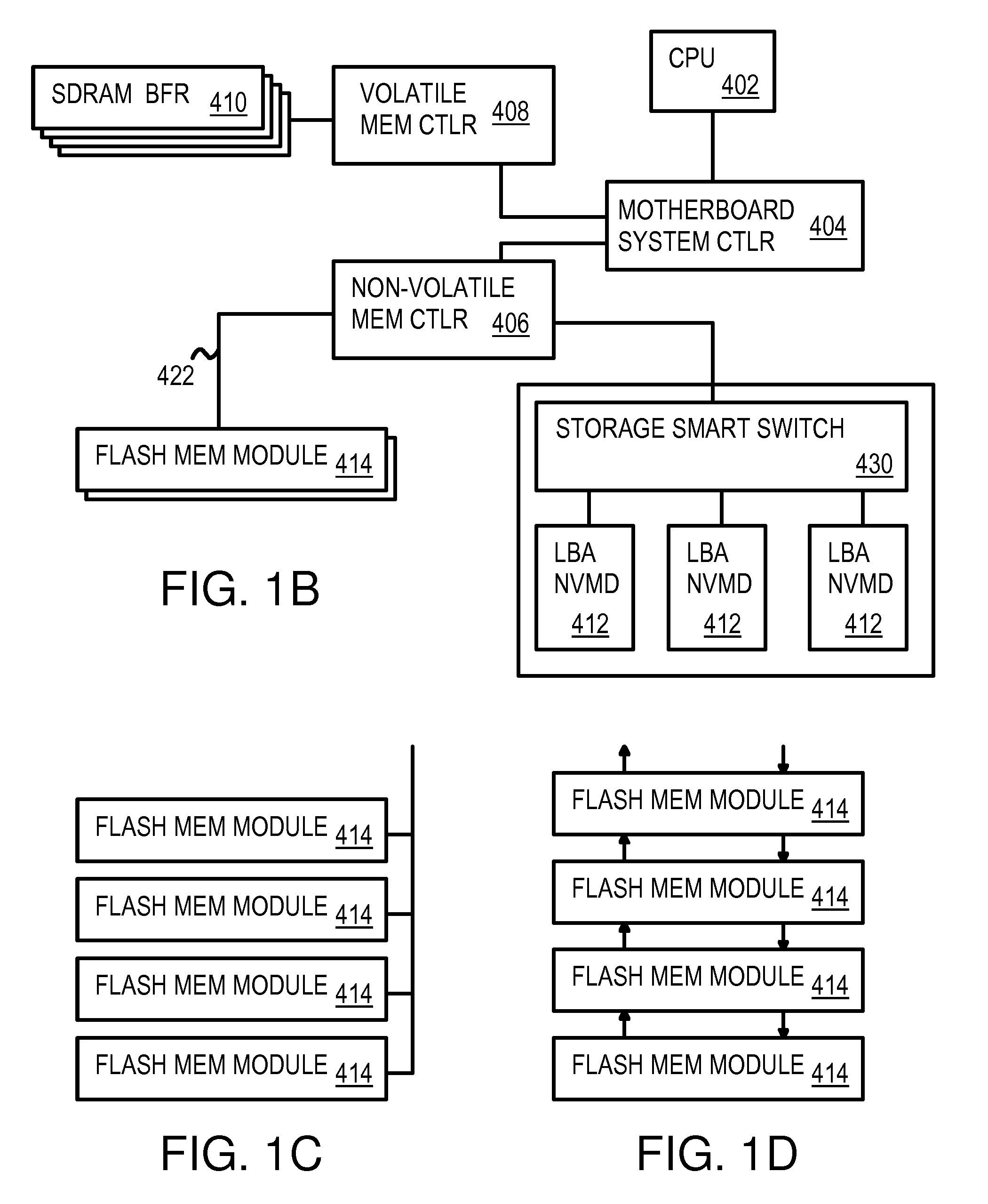
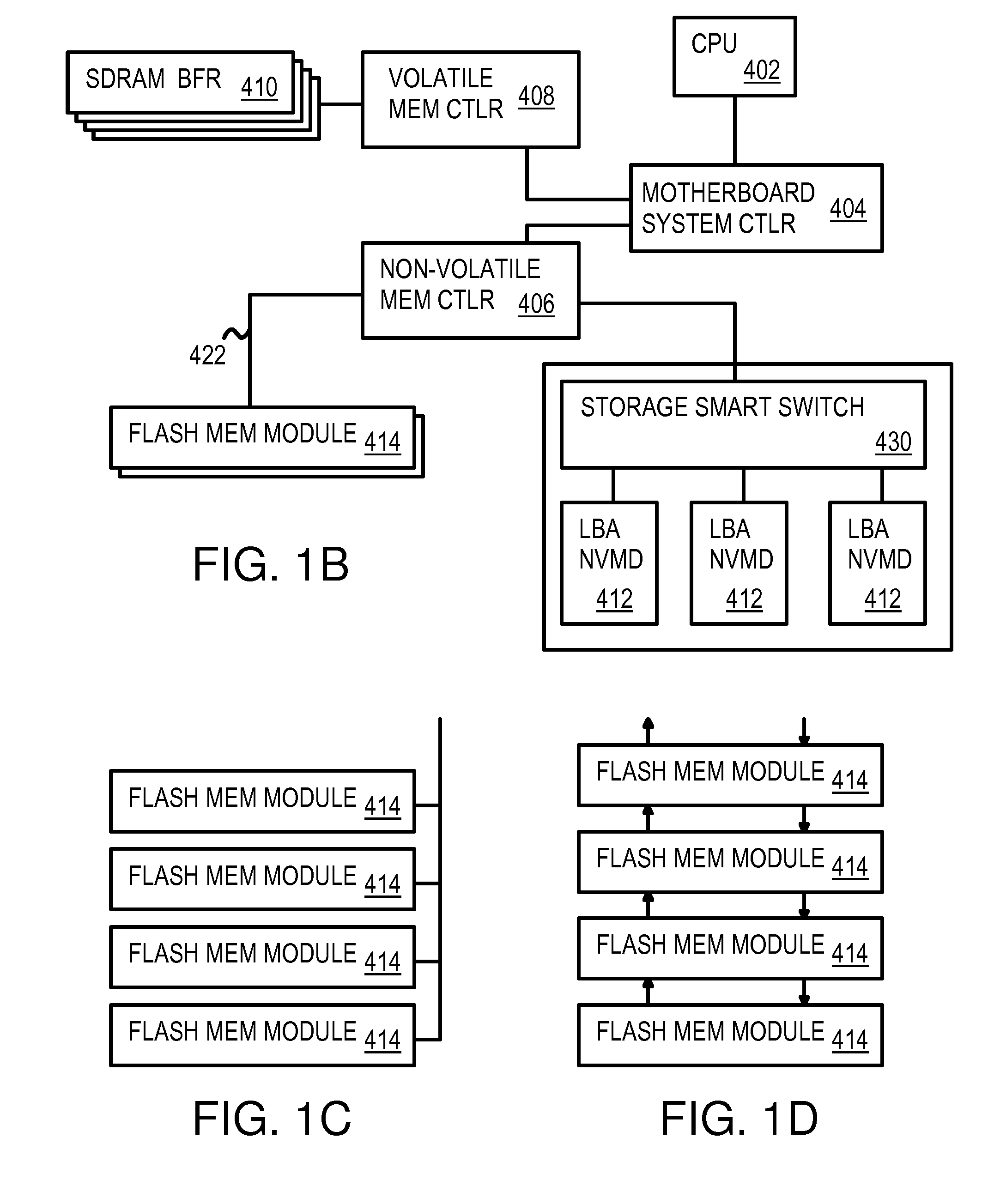
Command Queuing Smart Storage Transfer Manager for Striping Data to Raw-NAND Flash Modules
ActiveUS20090037652A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingHost machine
A flash module has raw-NAND flash memory chips accessed over a physical-block address (PBA) bus by a NVM controller. The NVM controller is on the flash module or on a system board for a solid-state disk (SSD). The NVM controller converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA). Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the flash modules is controlled at a high level by a smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping within a channel may be performed by the NVM controllers. A SDRAM buffer is used by a smart storage switch to cache host data before writing to flash memory. A Q-R pointer table stores quotients and remainders of division of the host address. The remainder points to a location of the host data in the SDRAM. A command queue stores Q, R for host commands.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Command Queuing Smart Storage Transfer Manager for Striping Data to Raw-NAND Flash Modules
InactiveUS20090204872A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingComputer module
A flash module has raw-NAND flash memory chips accessed over a physical-block address (PBA) bus by a NVM controller. The NVM controller is on the flash module or on a system board for a solid-state disk (SSD). The NVM controller converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA). Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the flash modules is controlled at a high level by a smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping within a channel may be performed by the NVM controllers. A SDRAM buffer is used by a smart storage switch to cache host data before writing to flash memory. A Q-R pointer table stores quotients and remainders of division of the host address. The remainder points to a location of the host data in the SDRAM. A command queue stores Q, R for host commands.
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
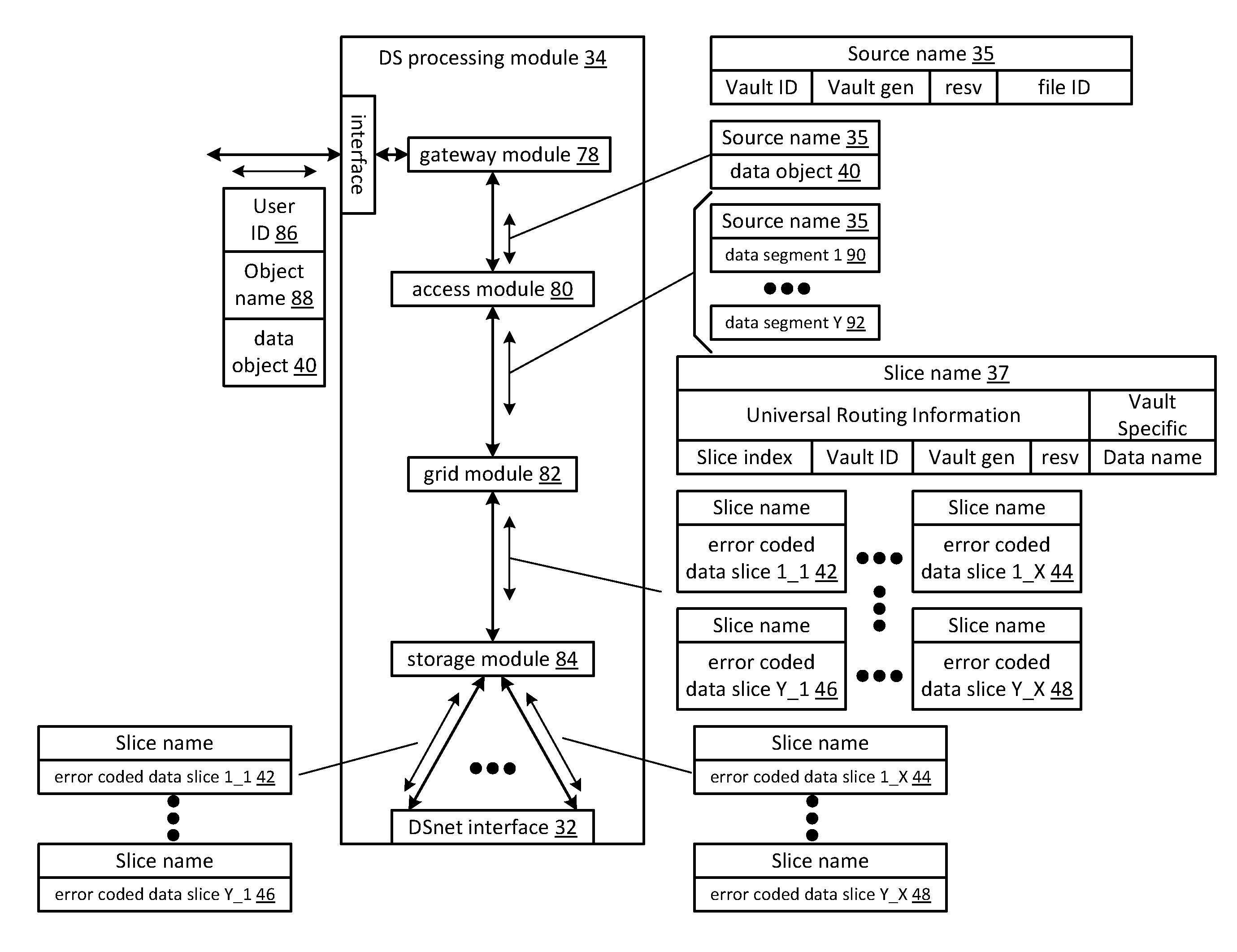
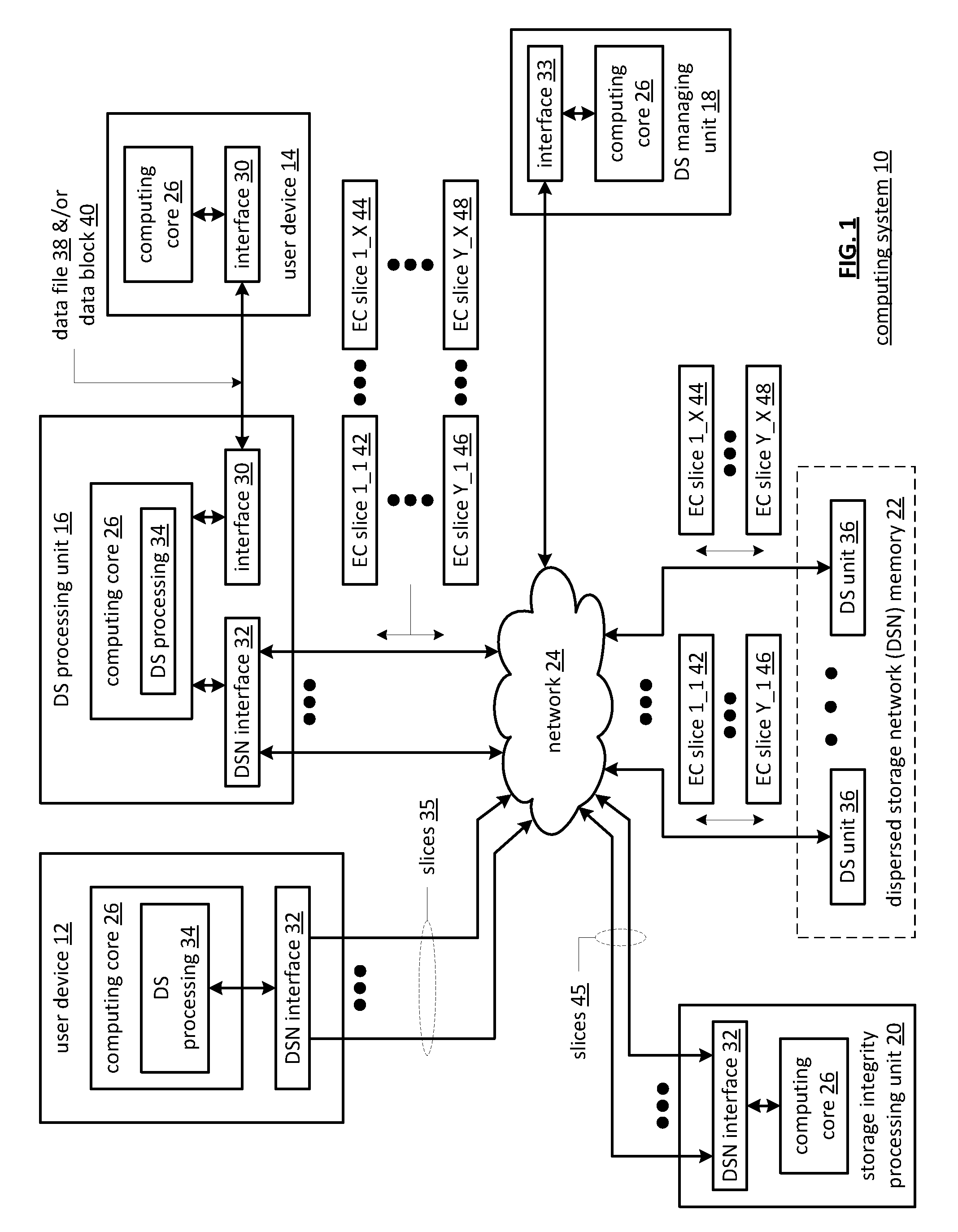
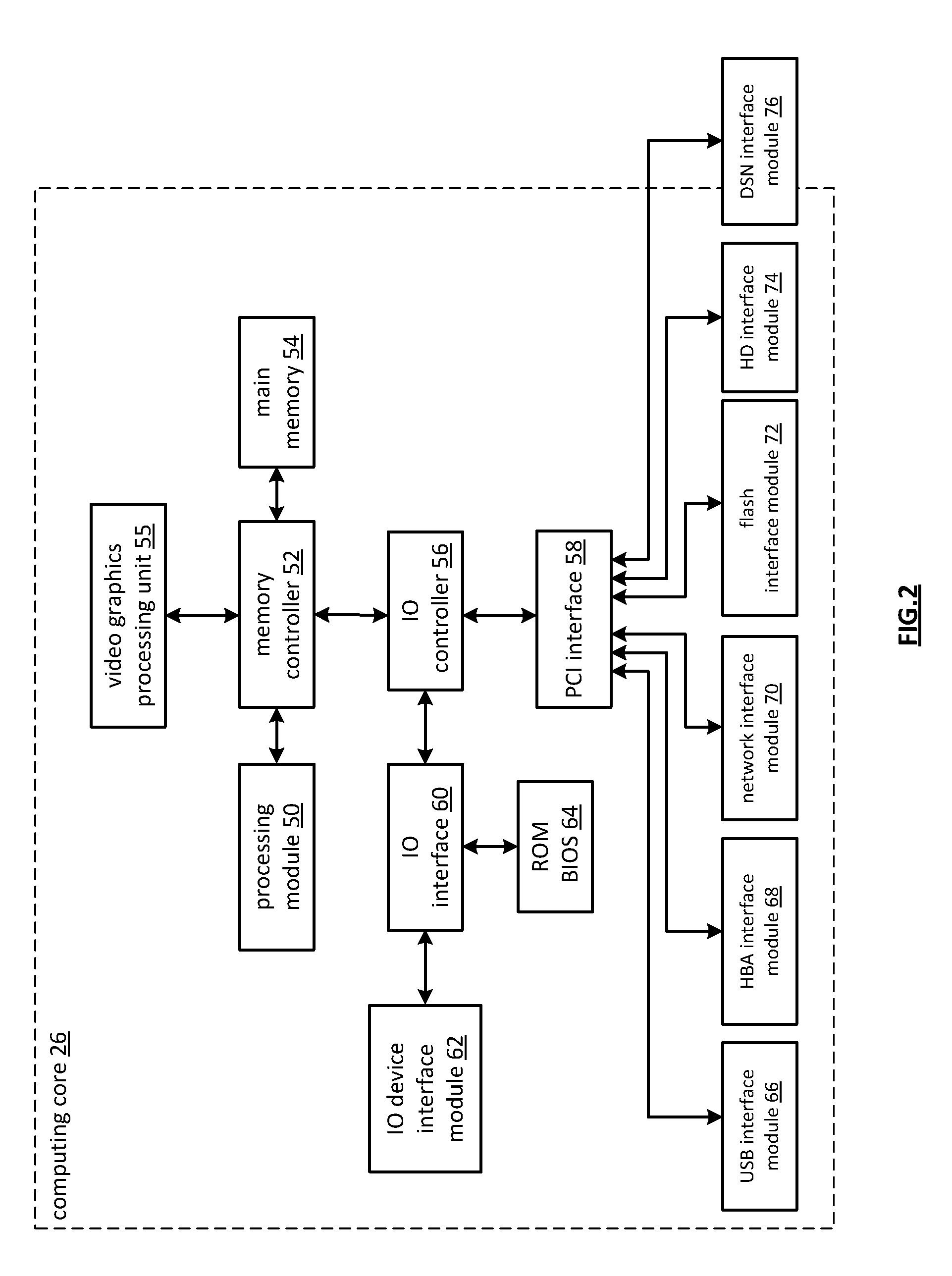
Distributed storage processing module
A dispersed storage (DS) processing module may include a gateway module operable to communicate data and / or corresponding information with a user device and may include an access module operable to segment outbound data of the data into one or more outbound data segments and aggregate one or more inbound data segments into inbound data of the data. The DS processing module may include a grid module operable to encode an outbound data segment of the one or more outbound data segments into a plurality of outbound encoded data slices and decode a plurality of inbound encoded data slices into an inbound data segment of the one or more inbound data segments. The DS processing module may include a storage module operable to output the plurality of outbound encoded data slices to a plurality of DS storage units and receive the plurality of inbound encoded data slices from the plurality of DS storage units.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
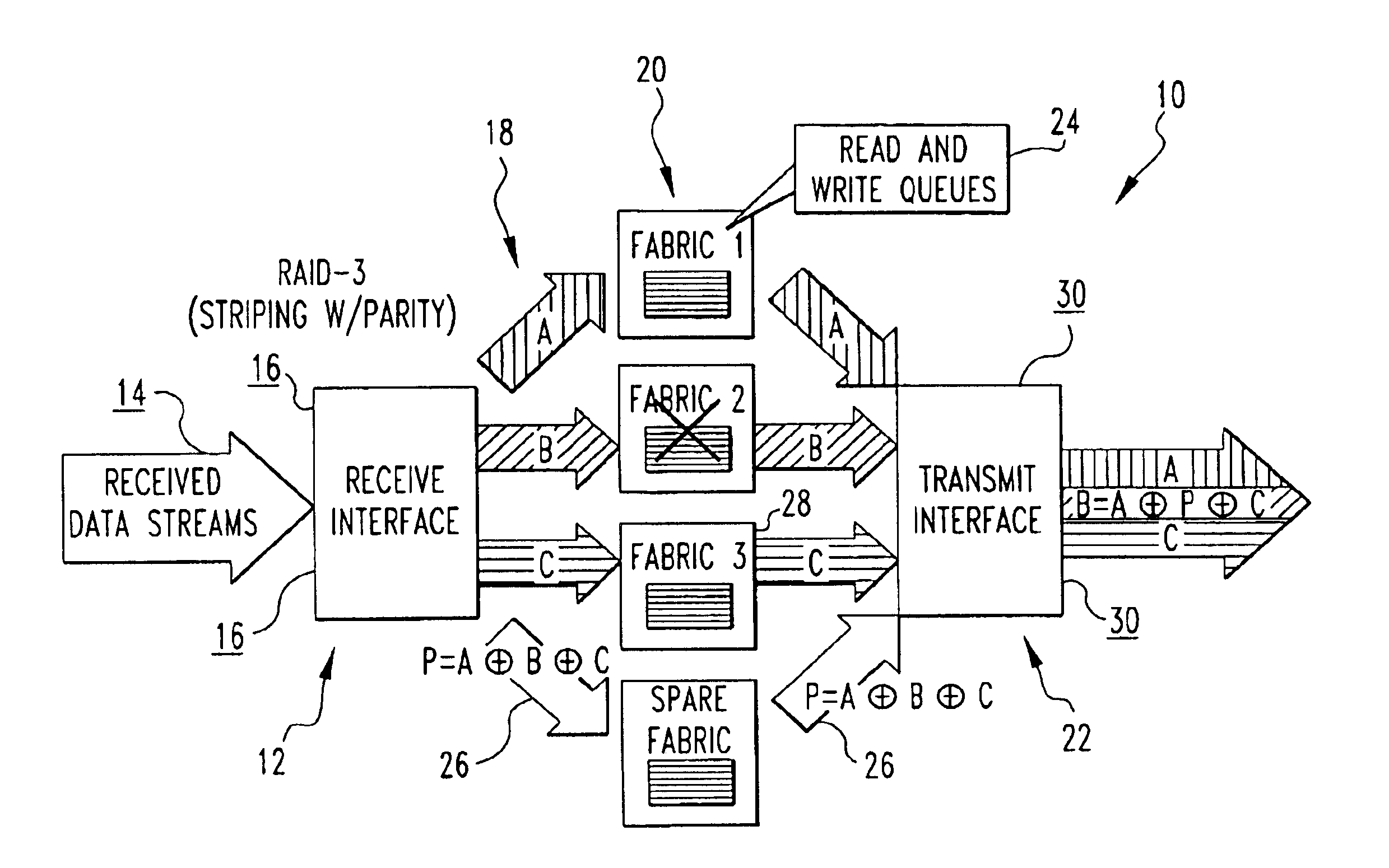
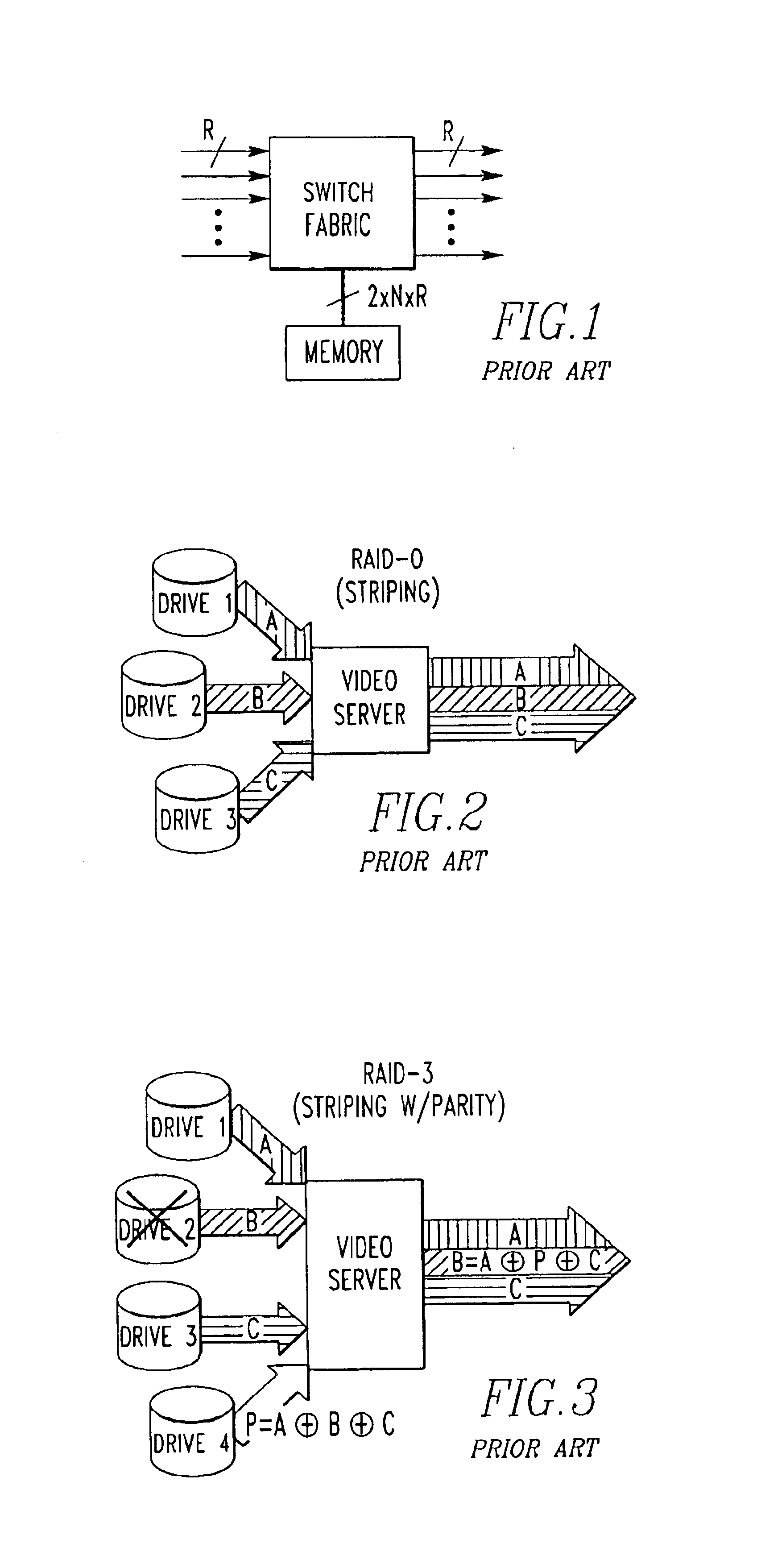
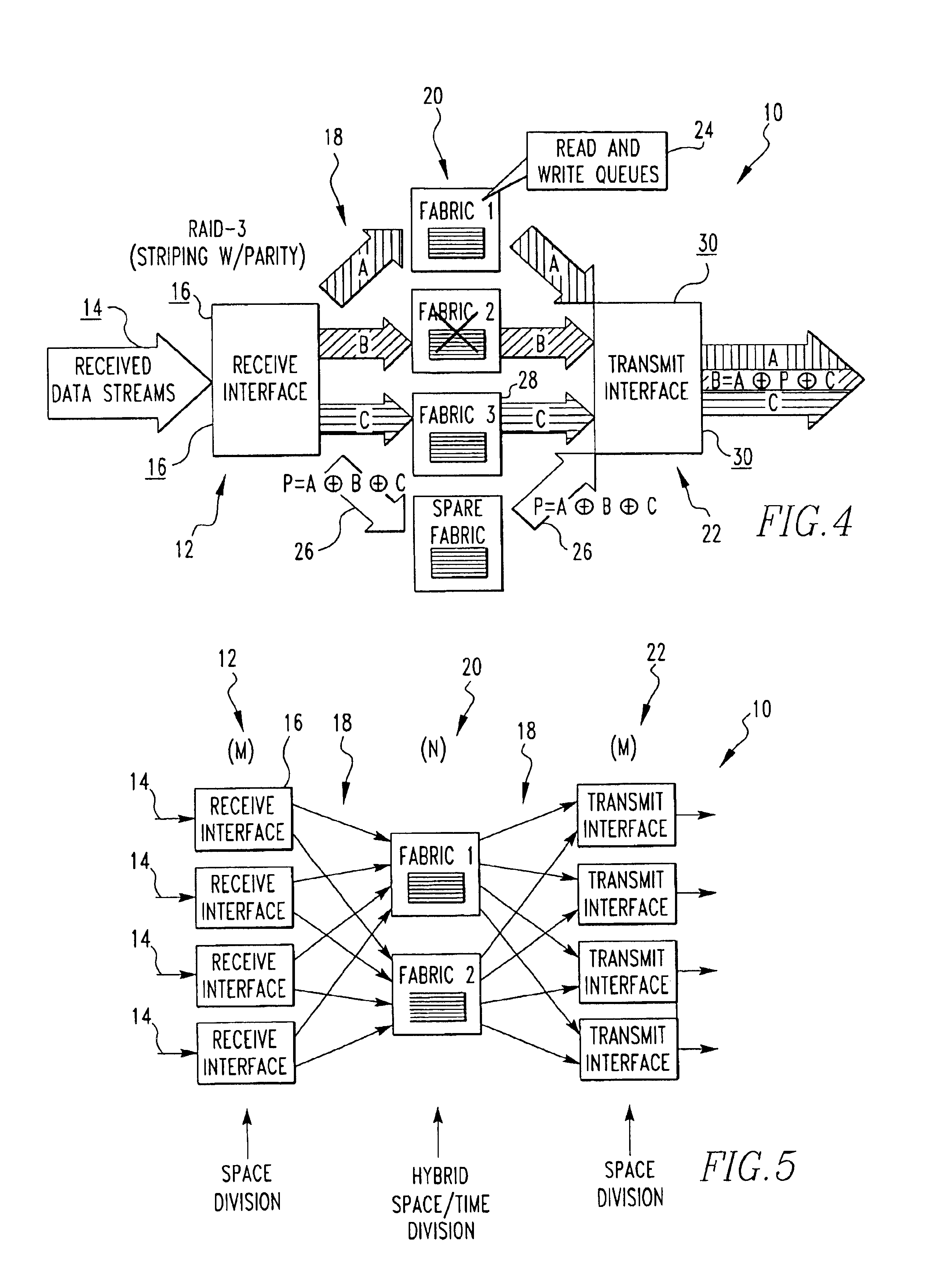
Data striping based switching system
A switching system for a data stream utilizing striping with a parity stripe, so if a fabric of the system fails, the data stream can still be reconstructed with the parity stripe. The system uses receive and transmit interfaces which implement space division, and fabrics which implement hybrid space / time division.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Remote direct memory access with striping over an unreliable datagram transport
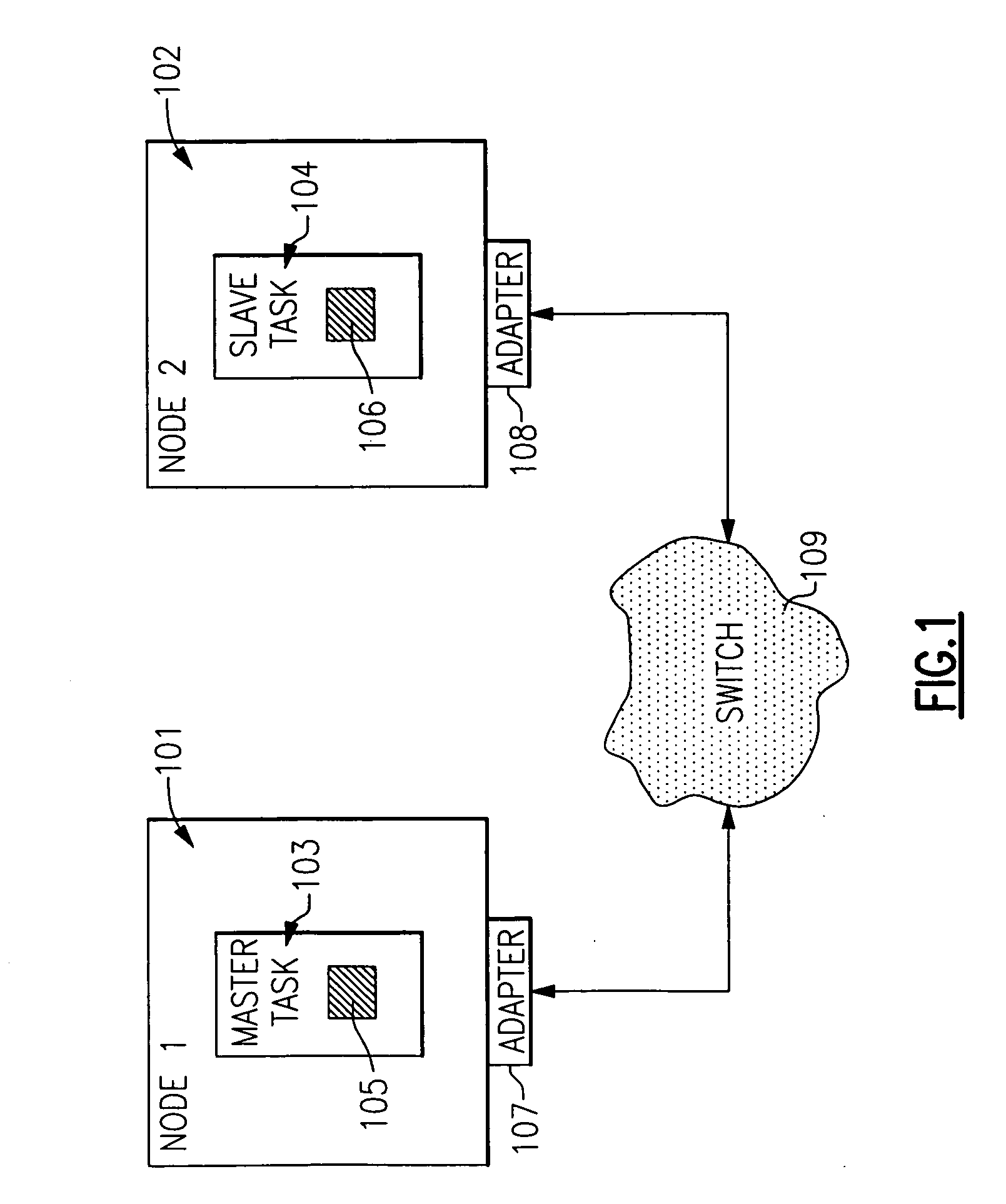
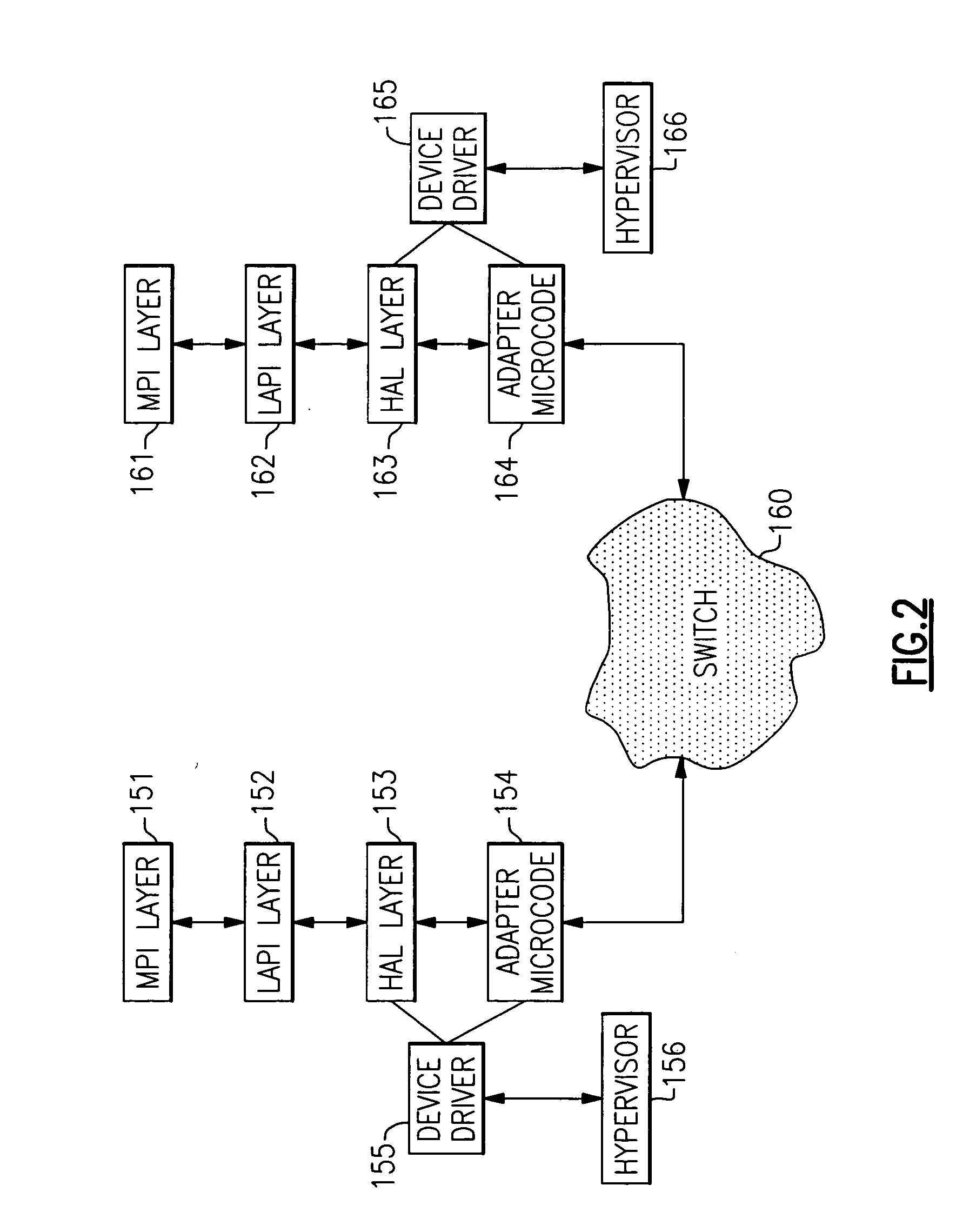
In a multinode data processing system in which nodes exchange information over a network or through a switch, a structure and mechanism are provided which enables data packets to be sent and received in any order. Normally, if in-order transmission and receipt are required, then transmission over a single path is essential to insure proper reassembly. However, the present mechanism avoids this necessity and permits Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) operations to be carried out simultaneously over multiple paths. This provides a data striping mode of operation in which data transfers can be carried out much faster since packets of single or multiple RDMA messages can be portioned and transferred over several paths simultaneously, thus providing the ability to utilize the full system bandwidth that is available.
Owner:IBM CORP
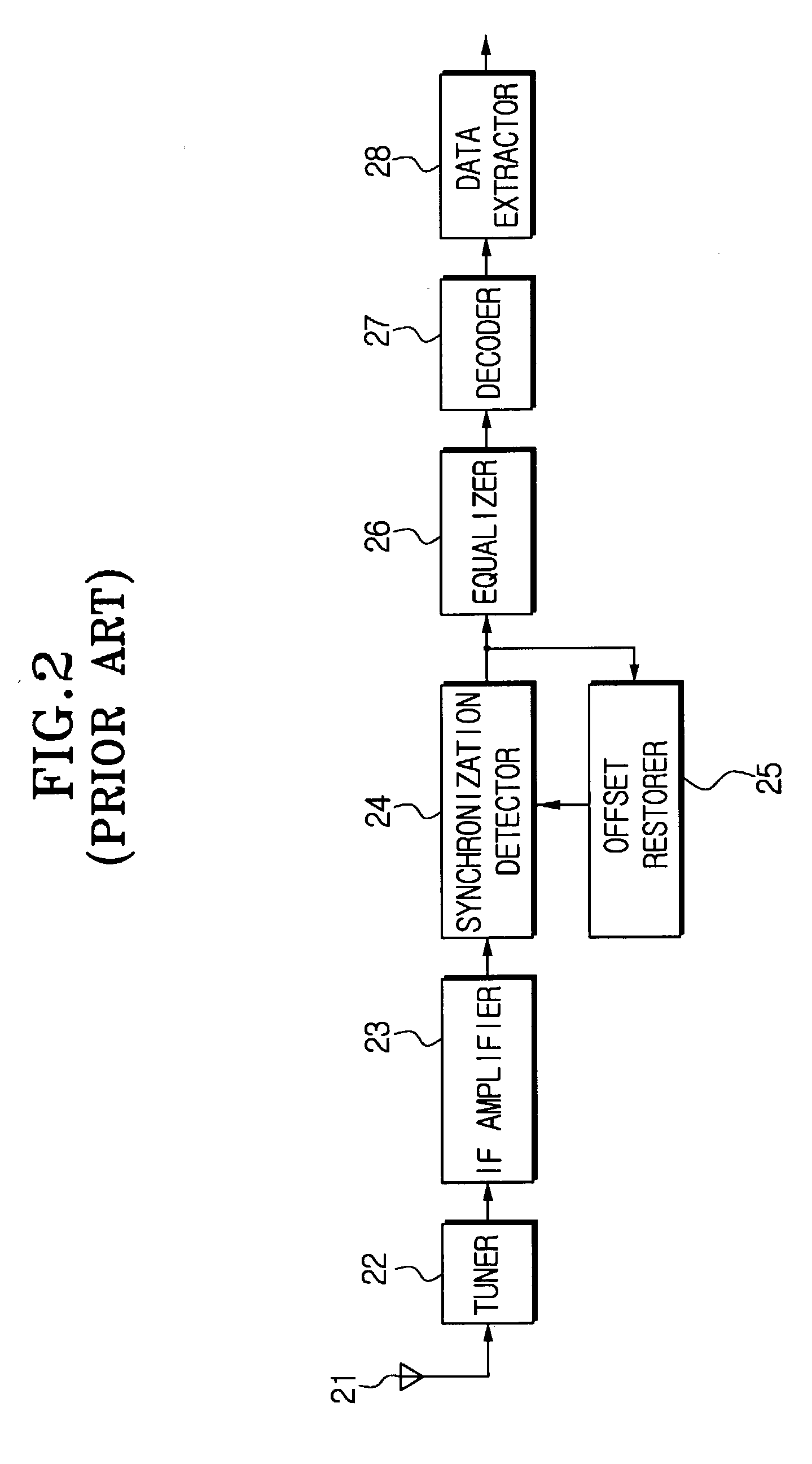
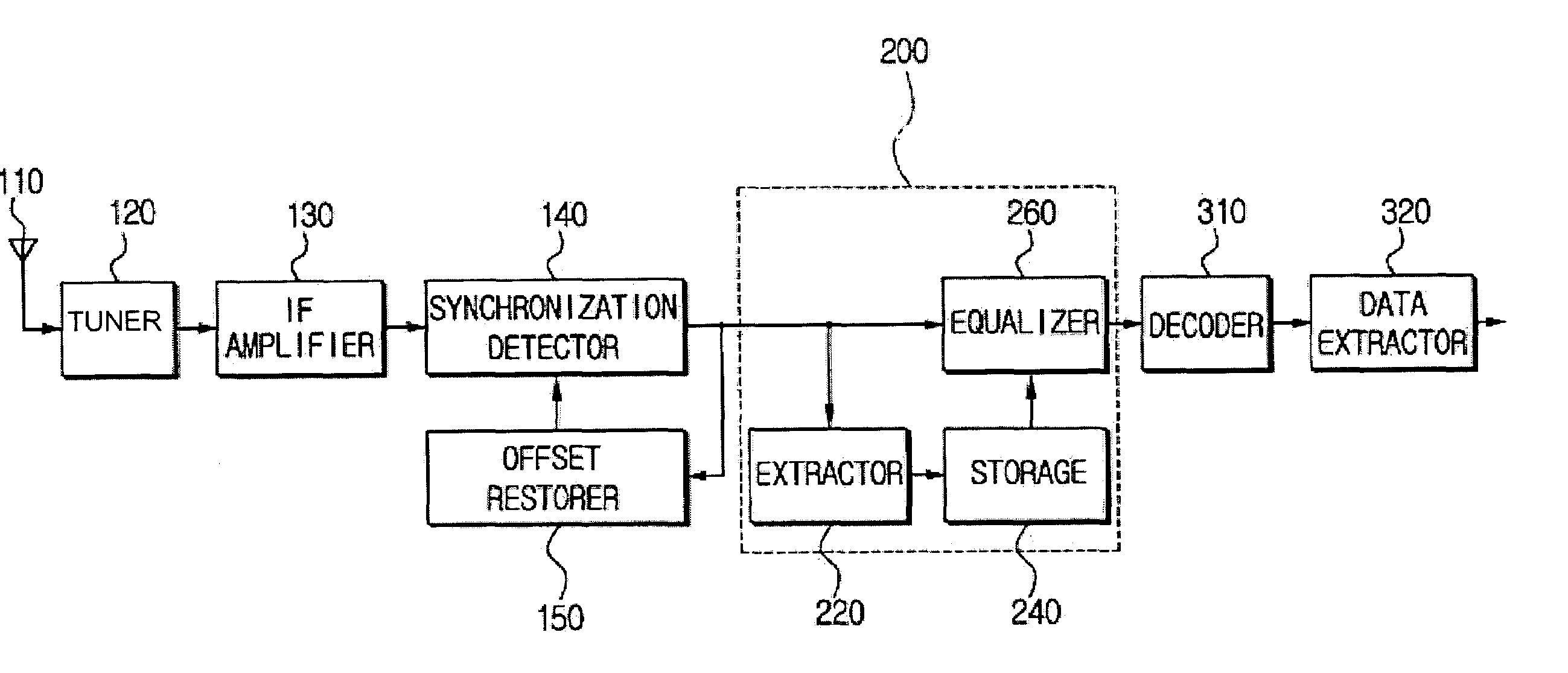
Equalizer for a VSB receiver enabling equalizations using segment synchronization information
InactiveUS20030223519A1Improve uniformityTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksData segmentEqualization
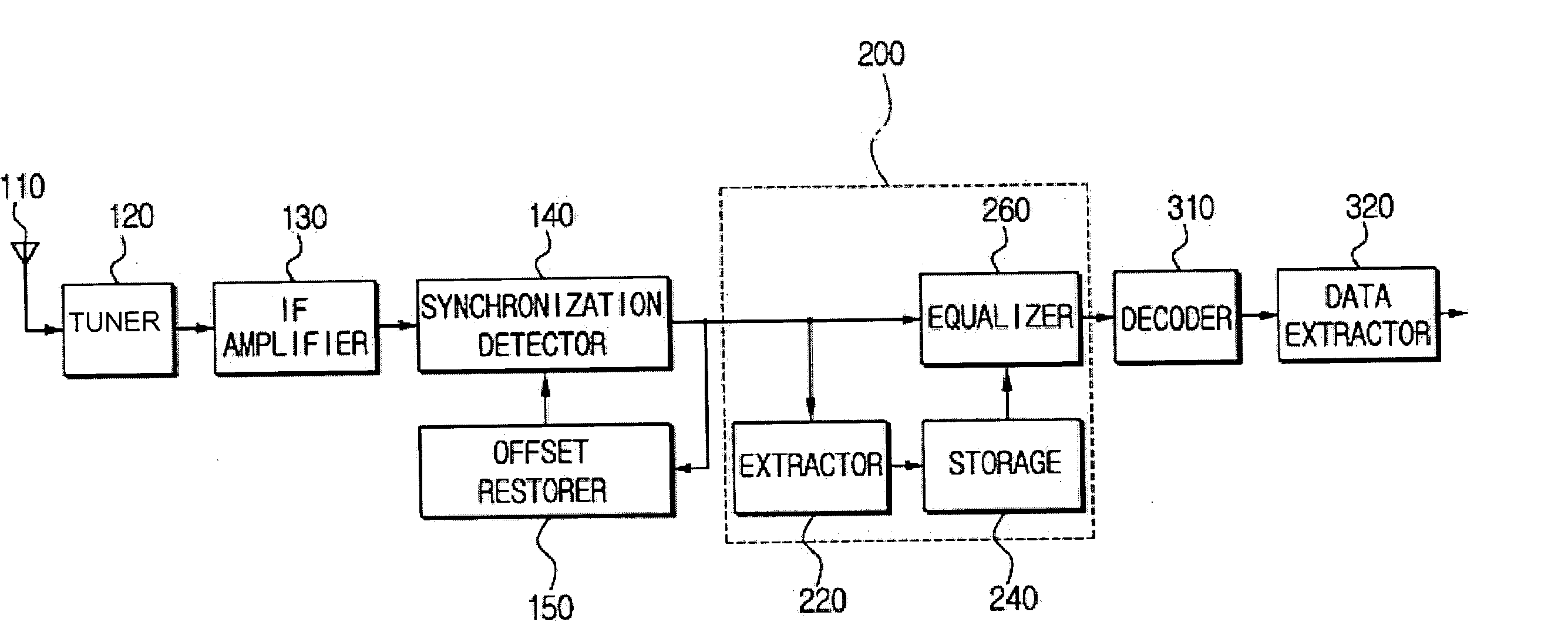
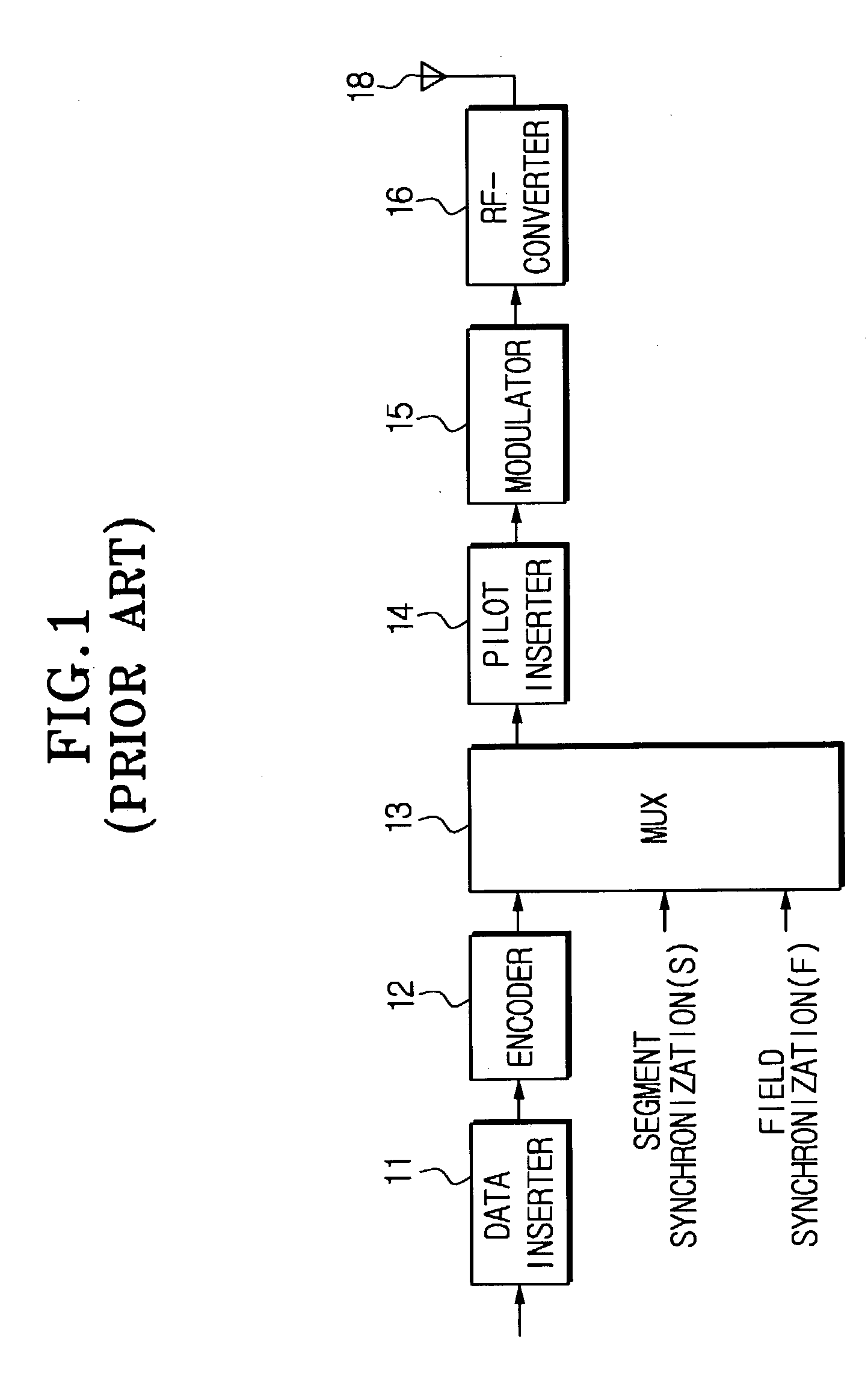
An equalizer for a VSB receiver, which enables equalizations using segment synchronization information, has an extraction unit extracting the segment synchronization information included in the VSB broadcast signal, a storage unit storing the extracted segment synchronization information, and an equalization unit equalizing the VSB broadcast signal based on the segment synchronization information stored in the storage unit. The storage unit stores the segment synchronization information extracted from the extraction unit by field unit or by unit of N data segments within the field according to a channel state. More stable equalizations can be carried out in channel environment changes by storing segment synchronization information by the predetermined number of data segments and equalizing data within a corresponding data segment in a training mode while using the segment synchronization information every matching number of data segments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Archival storage and retrieval system
ActiveUS20140052706A1Digital data processing detailsRedundant data error correctionQuality of serviceData availability
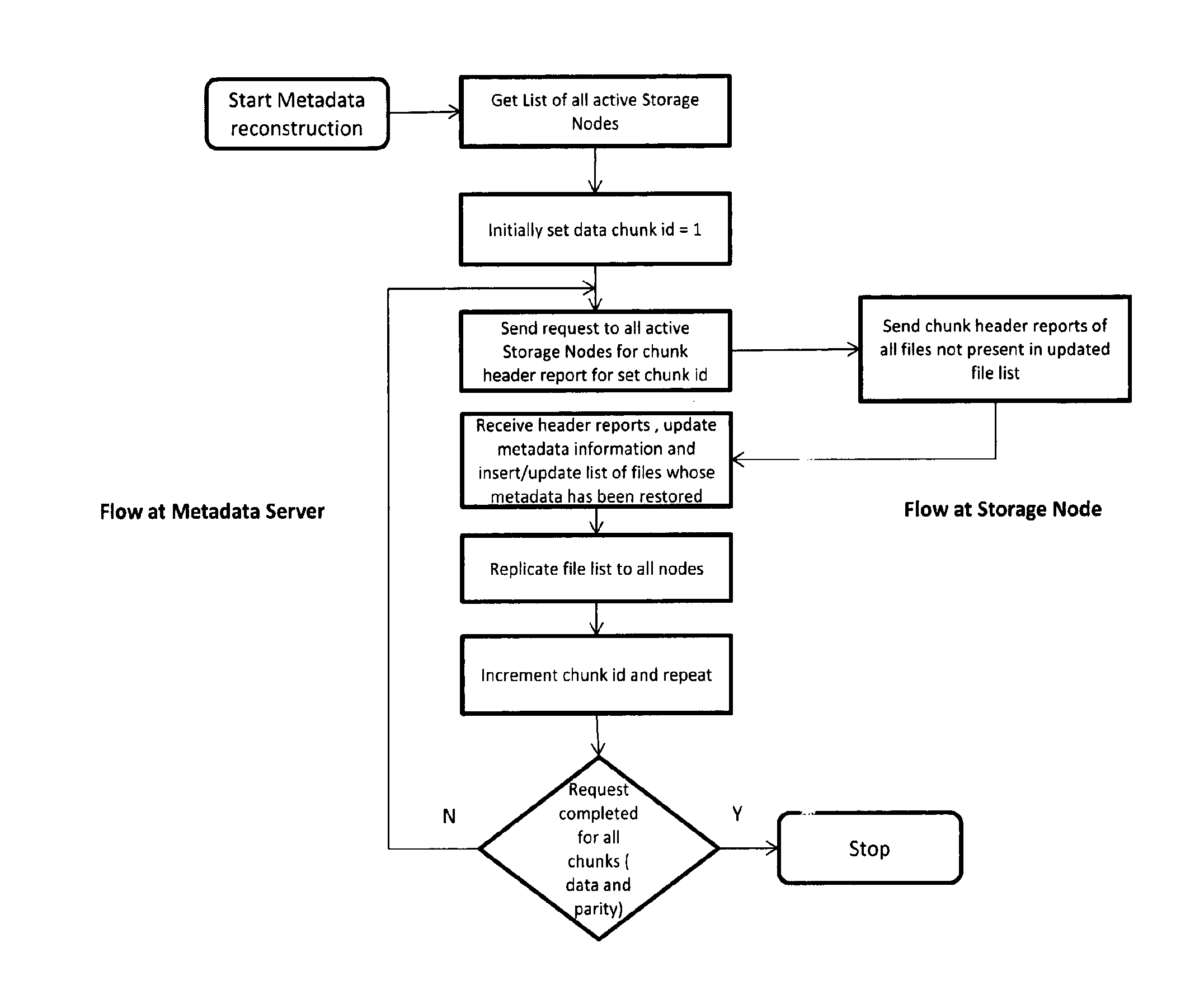
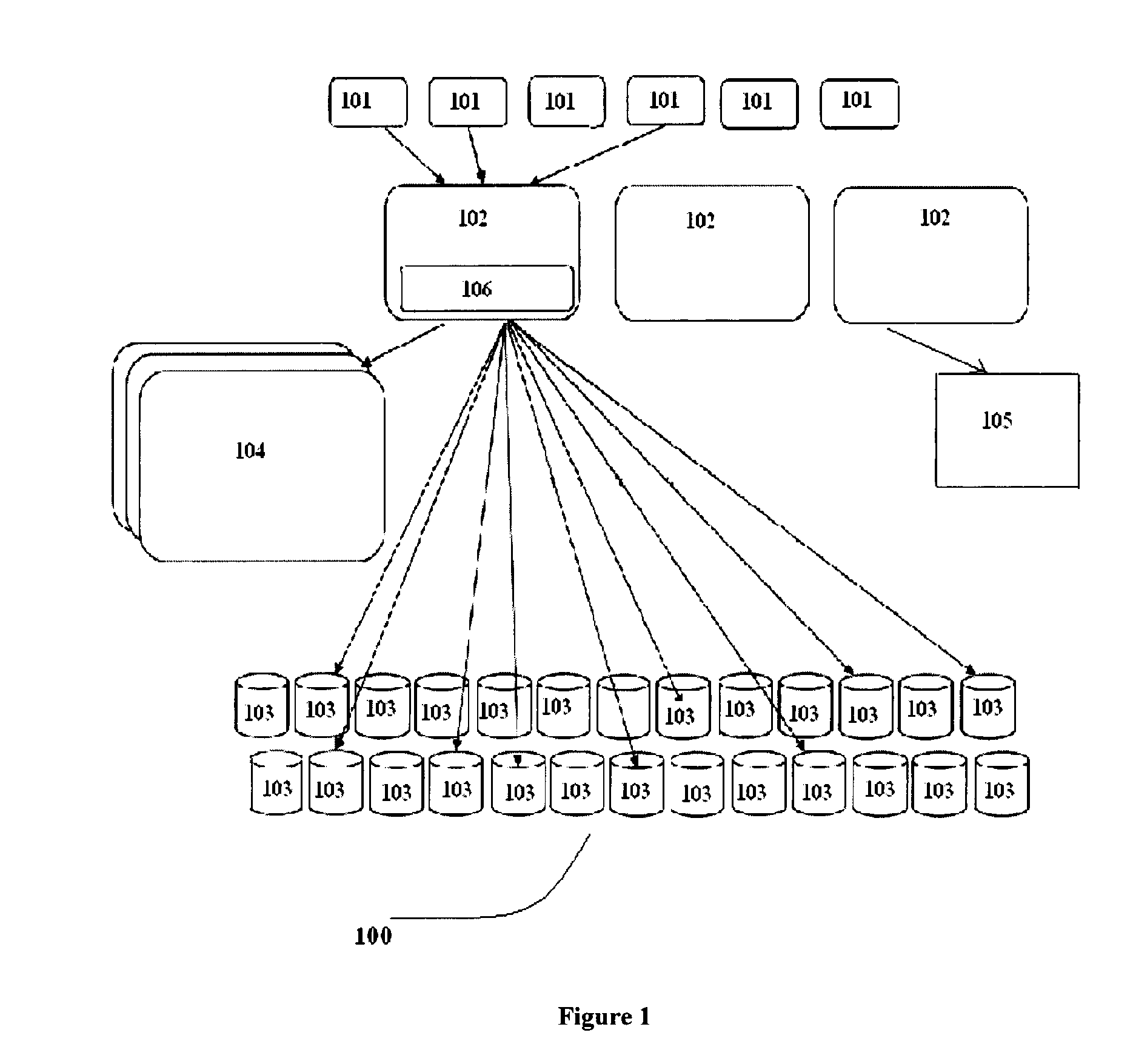
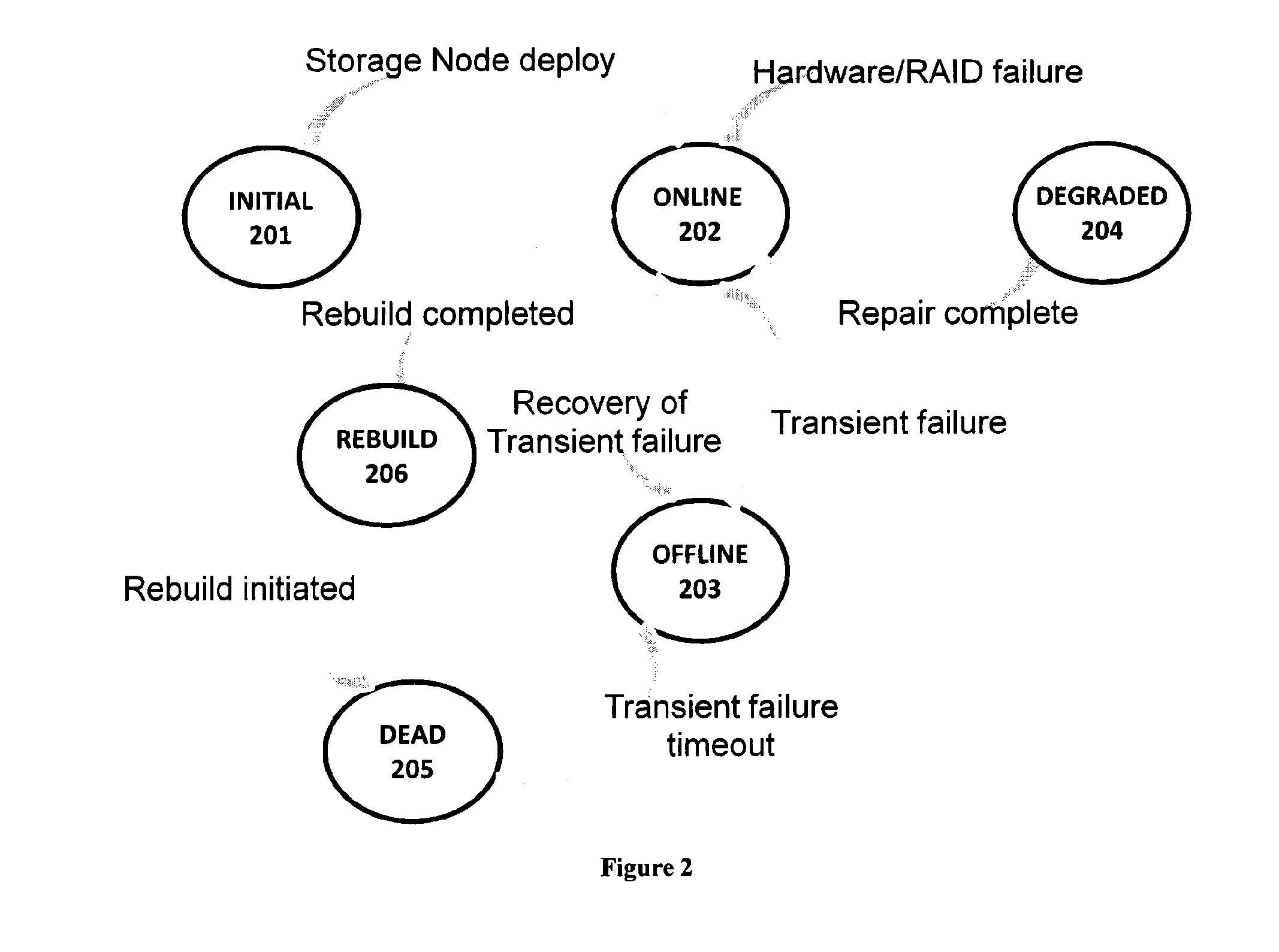
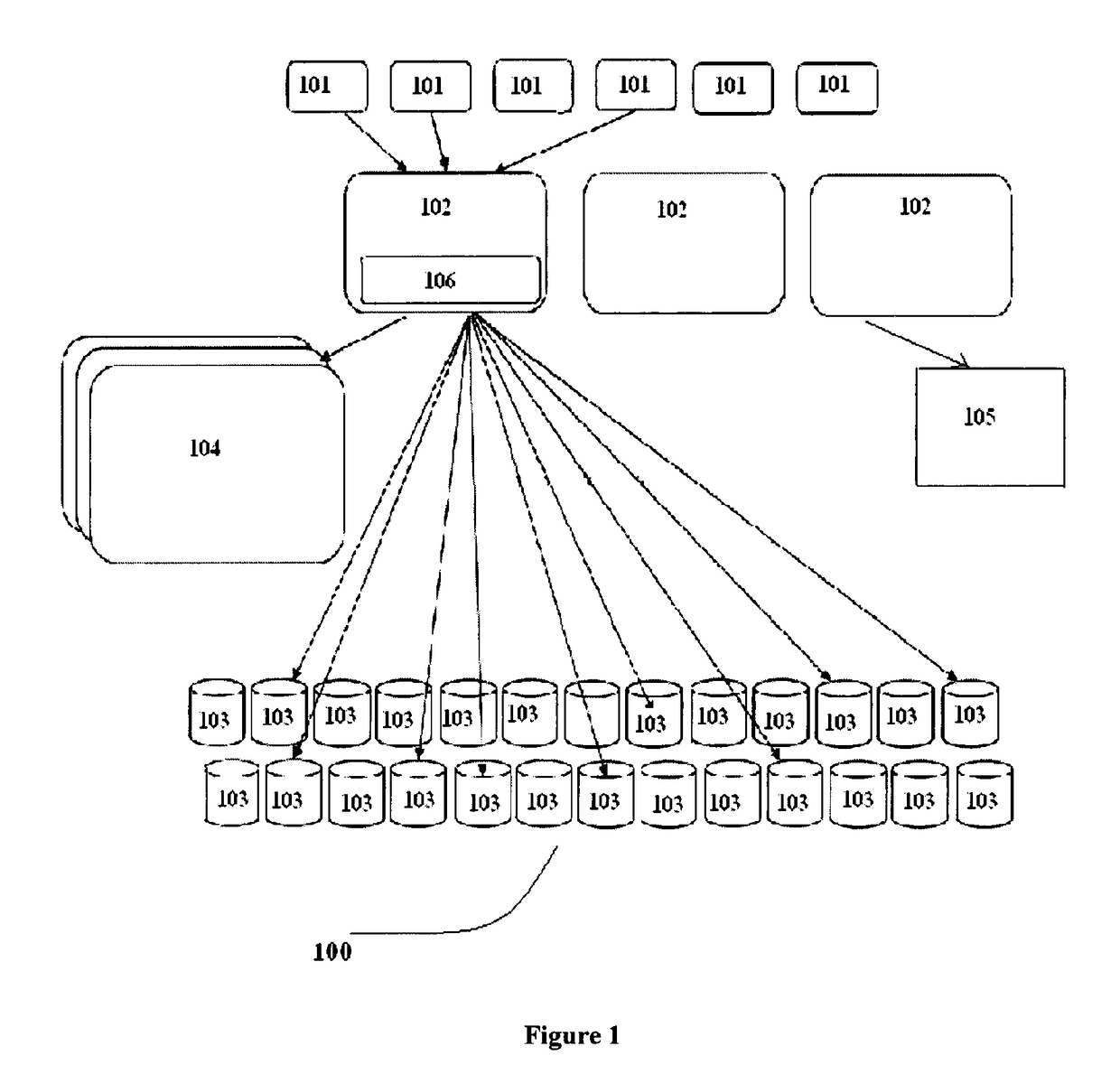
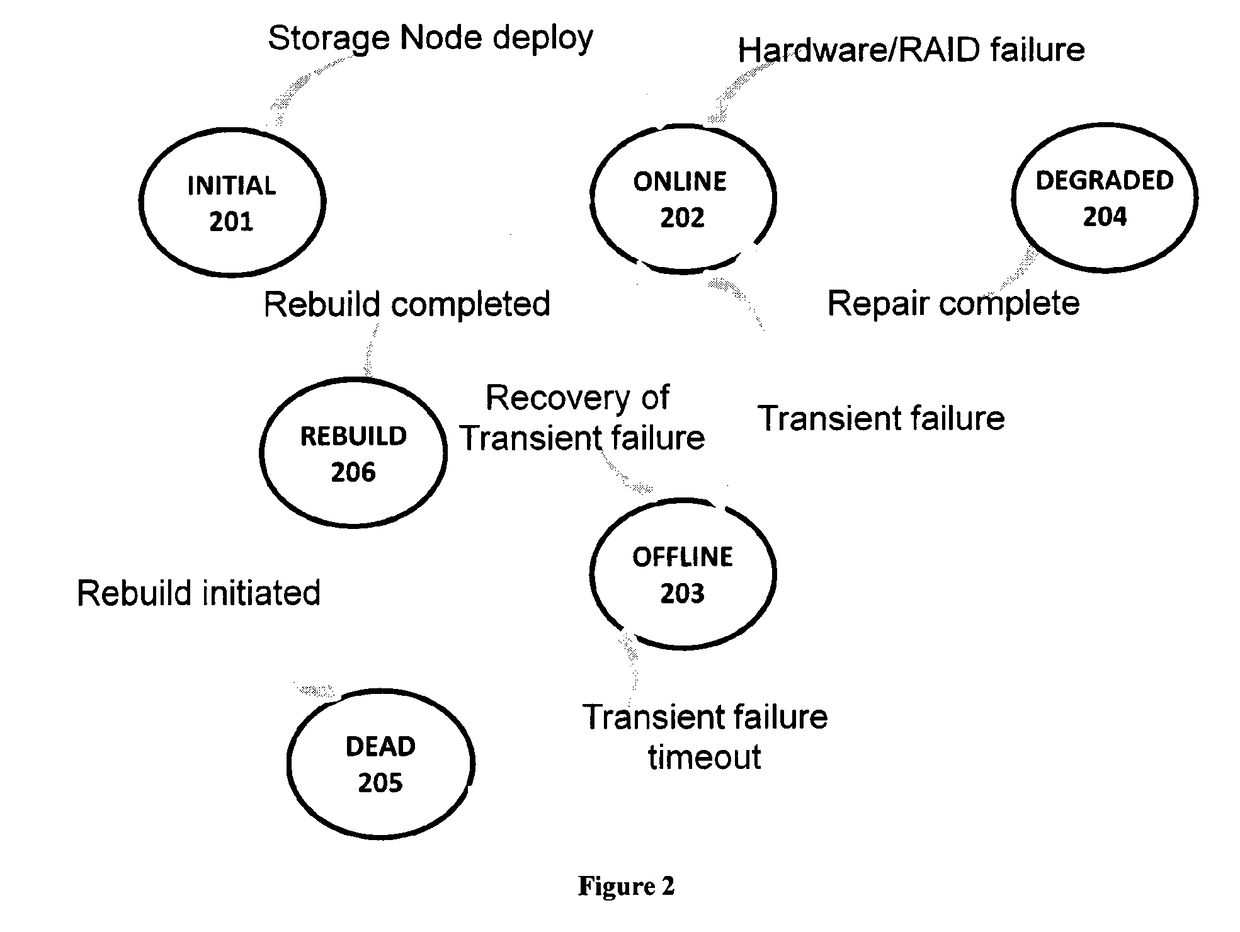
A highly reliable data archival and retrieval method that enables fine grained control over data availability is implemented across a Quality of Service driven archival system, configured to fragment the data into data and parity chunks for storing onto the storage node. The technique employed by the archival system enables files to be read without having need to access any metadata, thereby tolerating complete loss of such metadata. Further, the Quality of Service driven system architecture improves upon the system performance and throughput by means of a storage node regeneration process which ensures balanced load on participating storage node during various storage, retrieval and regeneration operations.
Owner:TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD
Data segmentation, request and transfer method
ActiveUS20110213827A1Network traffic/resource managementConnection managementClient-sideNetwork interface
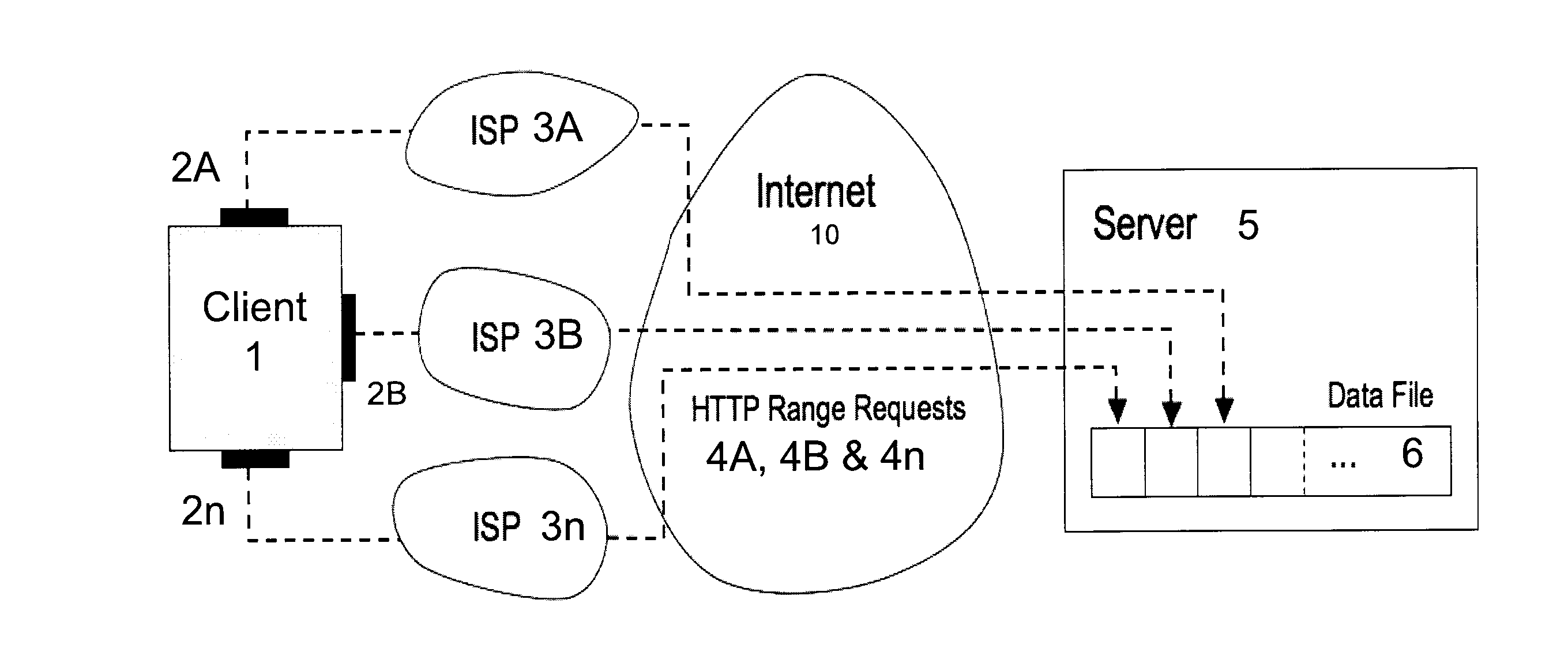
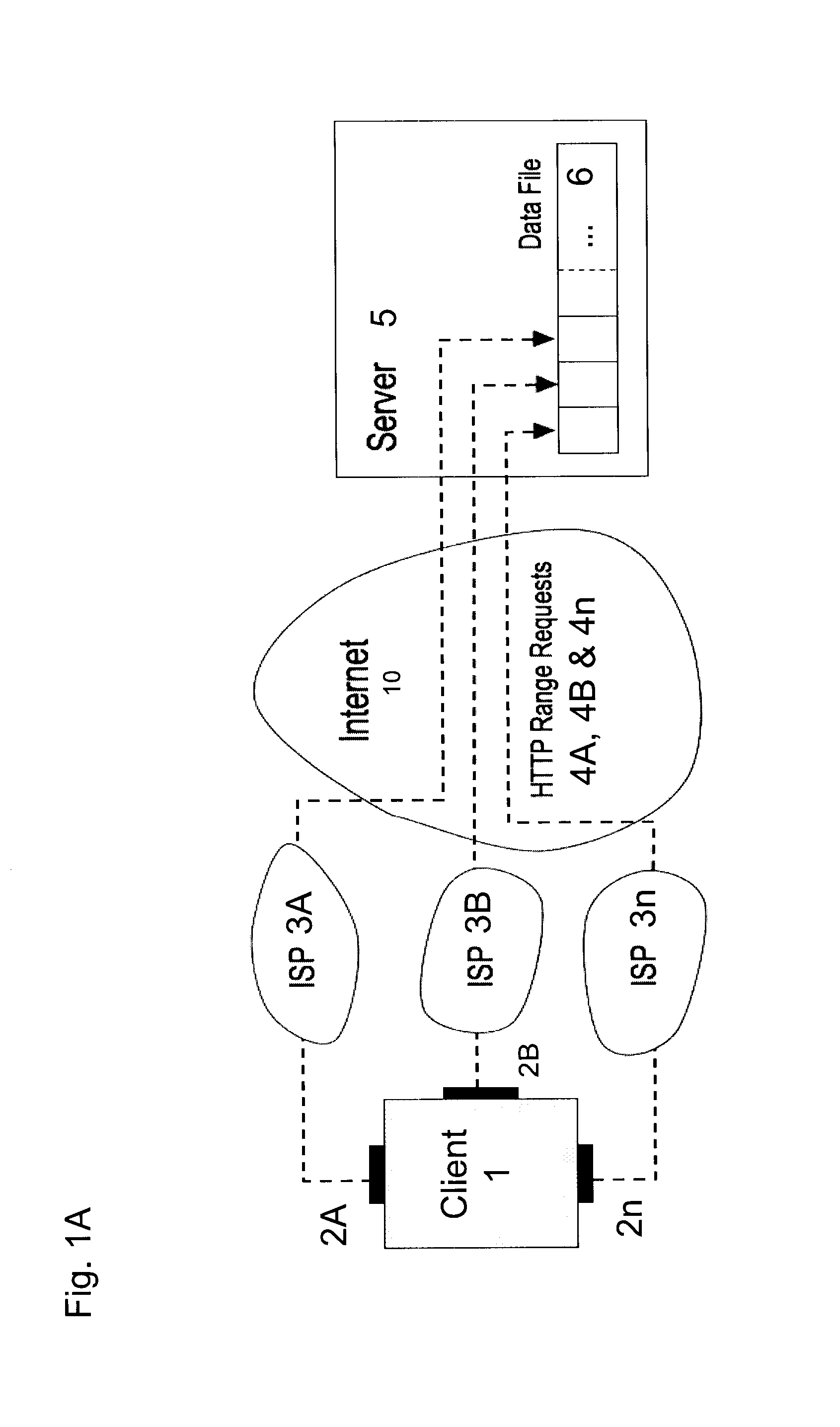
A process for requesting information, the process including generating a plurality of range requests using a client having a plurality of network interfaces, the range requests each corresponding to a data range of a data resource, transmitting, from the client having the plurality of network interfaces, a plurality of range requests to a server via the plurality of network interfaces, receiving, at the client and from the server, a plurality of segments via the plurality of network interfaces such that each segment is received via a network interface which transmitted the corresponding range request, each segment including a portion of the data resource, and reassembling the data resource using the plurality of segments.
Owner:CELERWAY COMM AS
Archival storage and retrieval system
ActiveUS9785498B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsQuality of serviceData availability
A highly reliable data archival and retrieval method that enables fine grained control over data availability is implemented across a Quality of Service driven archival system, configured to fragment the data into data and parity chunks for storing onto the storage node. The technique employed by the archival system enables files to be read without having need to access any metadata, thereby tolerating complete loss of such metadata. Further, the Quality of Service driven system architecture improves upon the system performance and throughput by means of a storage node regeneration process which ensures balanced load on participating storage node during various storage, retrieval and regeneration operations.
Owner:TATA CONSULTANCY SERVICES LTD
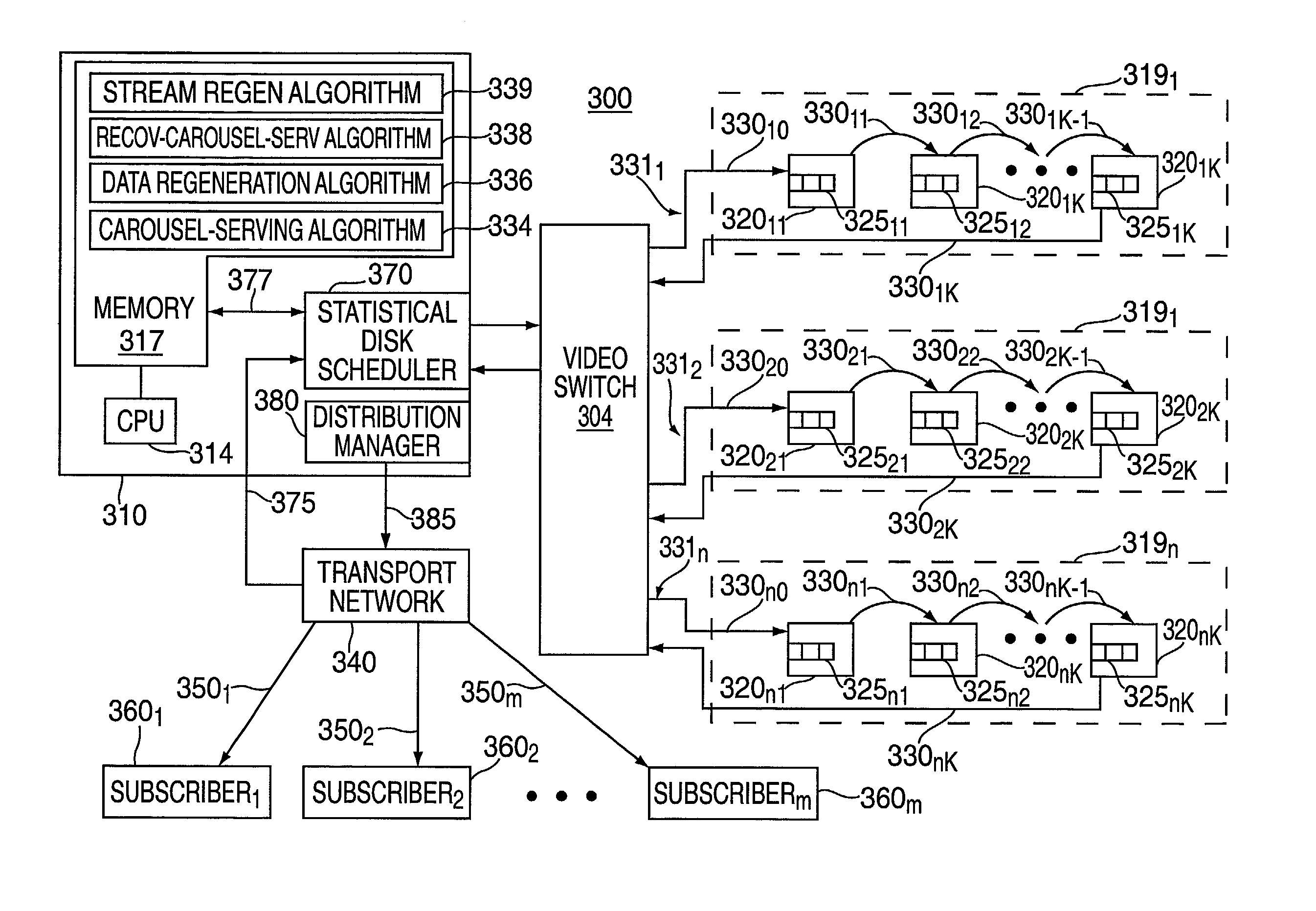
Method for regenerating and streaming content from a video server using RAID 5 data striping
InactiveUS6996742B2Service disruptionMinimize disruptive serviceRedundant data error correctionSelective content distributionRAIDData stream
A method for streaming content striped in RAID 5 format from an array of disk drives to subscribers to minimize disruptive service from a disk drive failure. The method includes accessing content data on an extent-by-extent basis from a plurality of disk drives in an array and streams the content data to the subscribers on an extent-by-extent basis, sequentially, from the plurality of disk drives. Upon detection of an actual disk drive failure the method transitions to a stream regeneration mode of operation, which includes reading the content data substantially simultaneously from all extents in a parity group and regenerating a failed portion of the content data from a failed extent in the parity group corresponding to the failed disk drive. The content data in the parity group is streamed to the subscribers, extent-by-extent, immediately following the regenerating of the content data from the failed extent in the parity group.
Owner:COMCAST IP HLDG I
Command Queuing Smart Storage Transfer Manager for Striping Data to Raw-NAND Flash Modules
InactiveUS20110213921A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical block addressingSolid-state
A flash module has raw-NAND flash memory chips accessed over a physical-block address (PBA) bus by a NVM controller. The NVM controller is on the flash module or on a system board for a solid-state disk (SSD). The NVM controller converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA). Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the flash modules is controlled at a high level by a smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping within a channel may be performed by the NVM controllers. A SDRAM buffer is used by a smart storage switch to cache host data before writing to flash memory. A Q-R pointer table stores quotients and remainders of division of the host address. The remainder points to a location of the host data in the SDRAM. A command queue stores Q, R for host commands.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
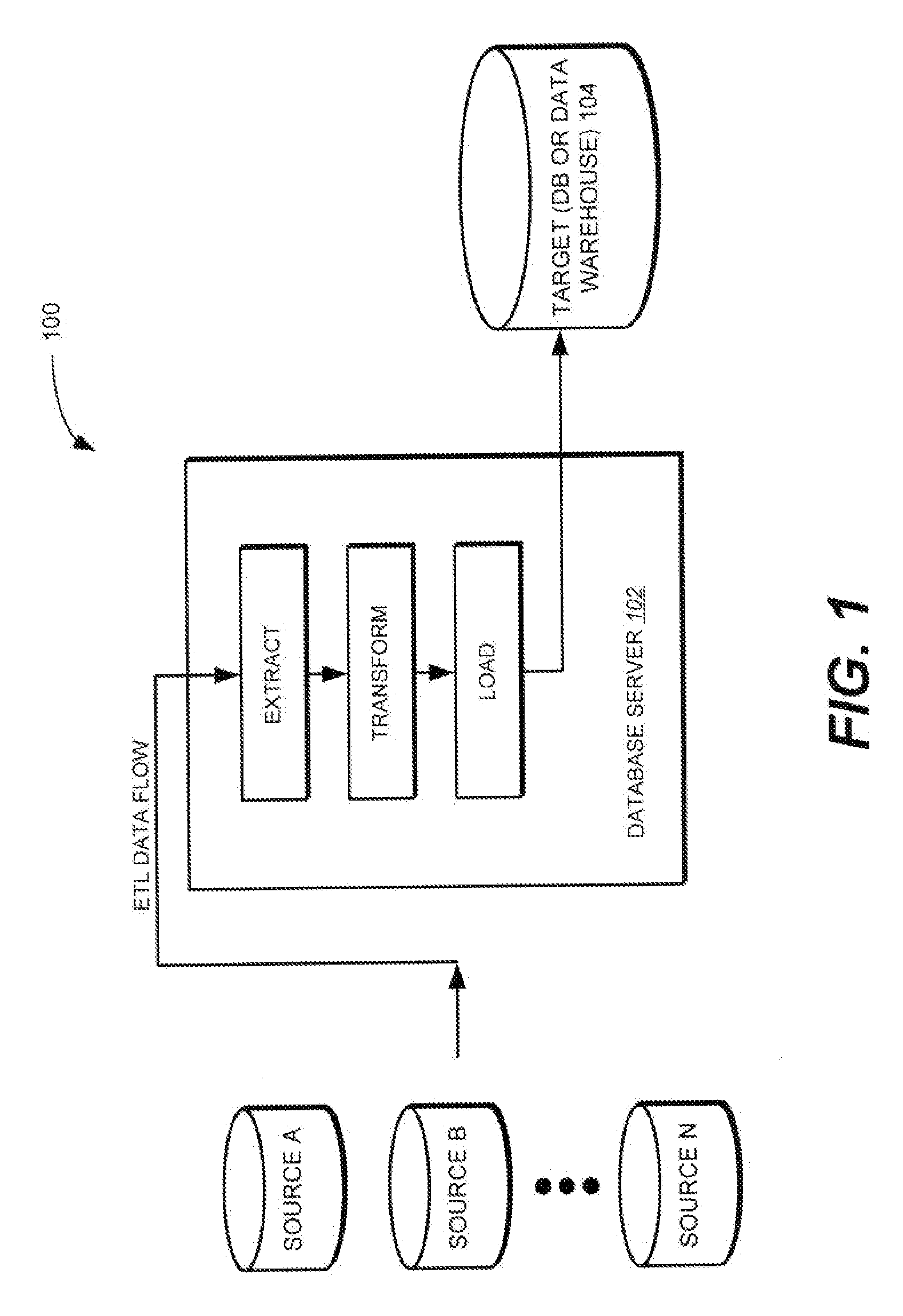
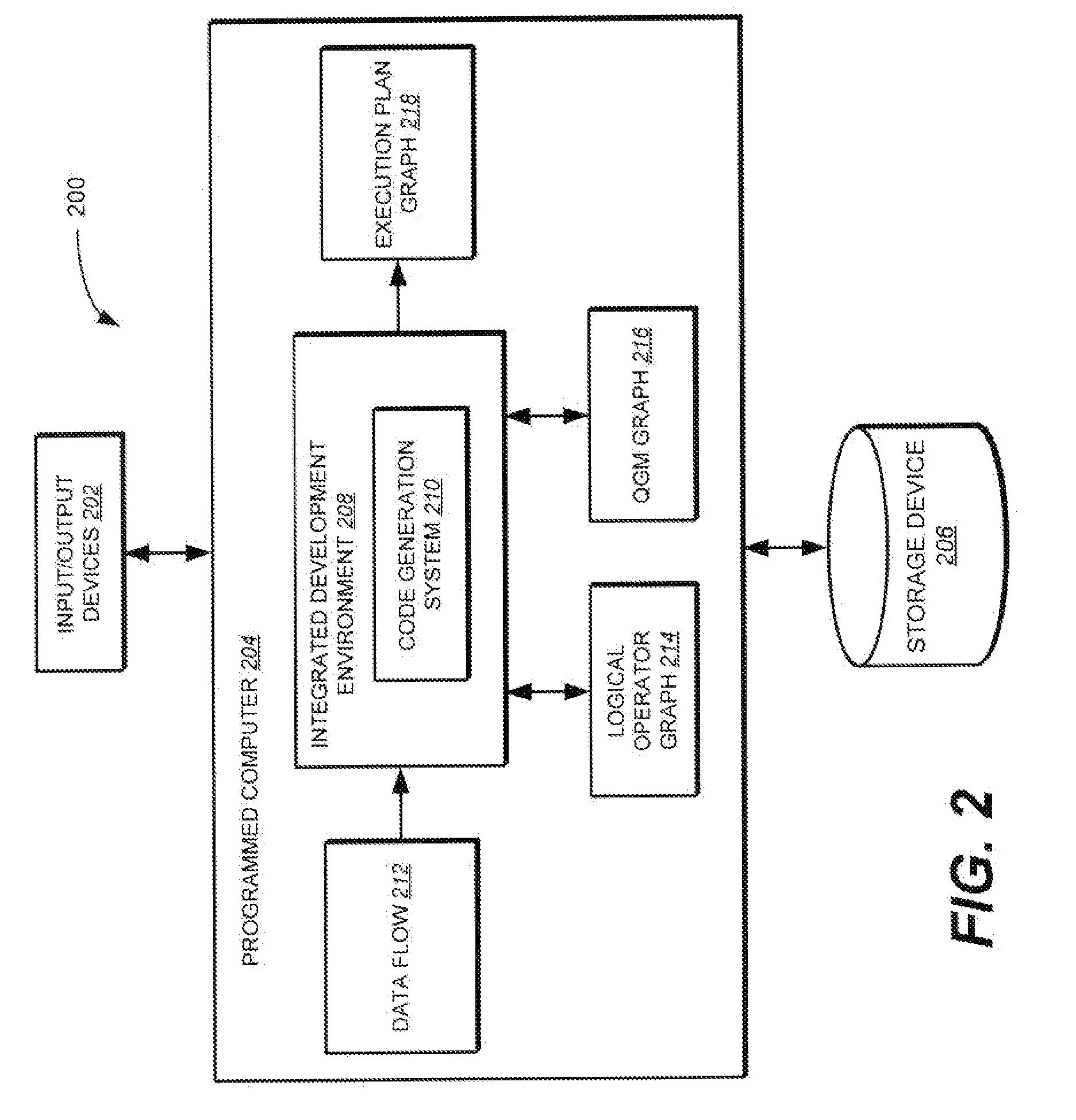
Method and apparatus for modelling data exchange in a data flow of an extract, transform, and load (ETL) process
InactiveUS20080168082A1Good performanceEase of recoveryDigital data processing detailsSoftware designData conversionData exchange
Methods, systems, and computer program products for generating code from a data flow associated with an extract, transform, and load (ETL) process. In one implementation, the method includes identifying a data exchange requirement between a first operator and a second operator in the data flow. The first operator is a graphical object that represents a first data transformation step in the data flow and is associated with a first type of runtime engine, and the second operator is a graphical object that represents a second data transformation step in the date flow and is associated with a second type of runtime engine. The method further includes generating code to manage data staging between the first operator and the second operator in the data flow. The code exchanges data from a format associated with the first type of runtime engine to a format associated with the second type of runtime engine.
Owner:IBM CORP
Command queuing smart storage transfer manager for striping data to raw-NAND flash modules
InactiveUS8037234B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageLogical block addressingComputer science
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Method and Apparatus of Data Segmentation in a Mobile Communications System
ActiveUS20060262811A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionData segmentCommunications system
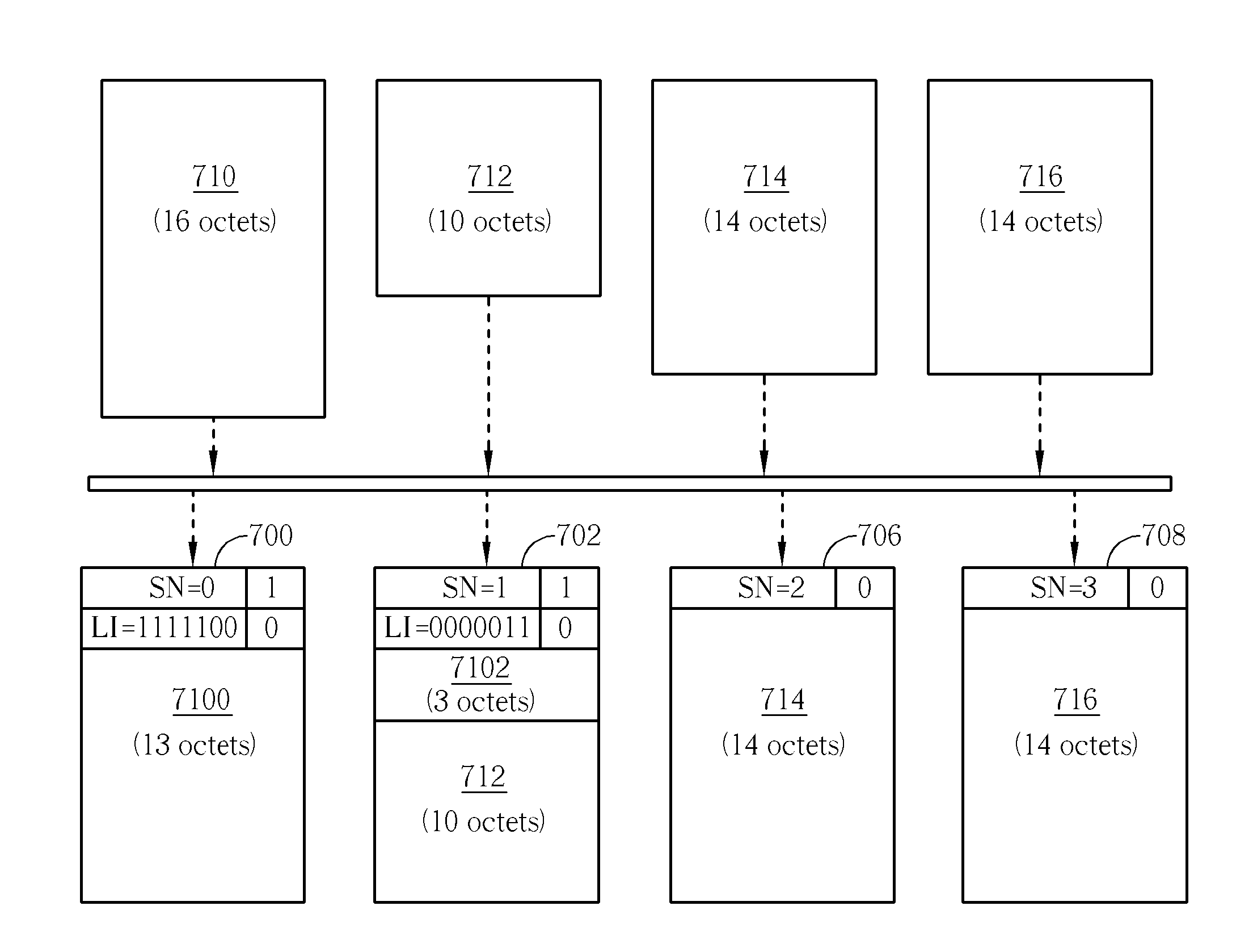
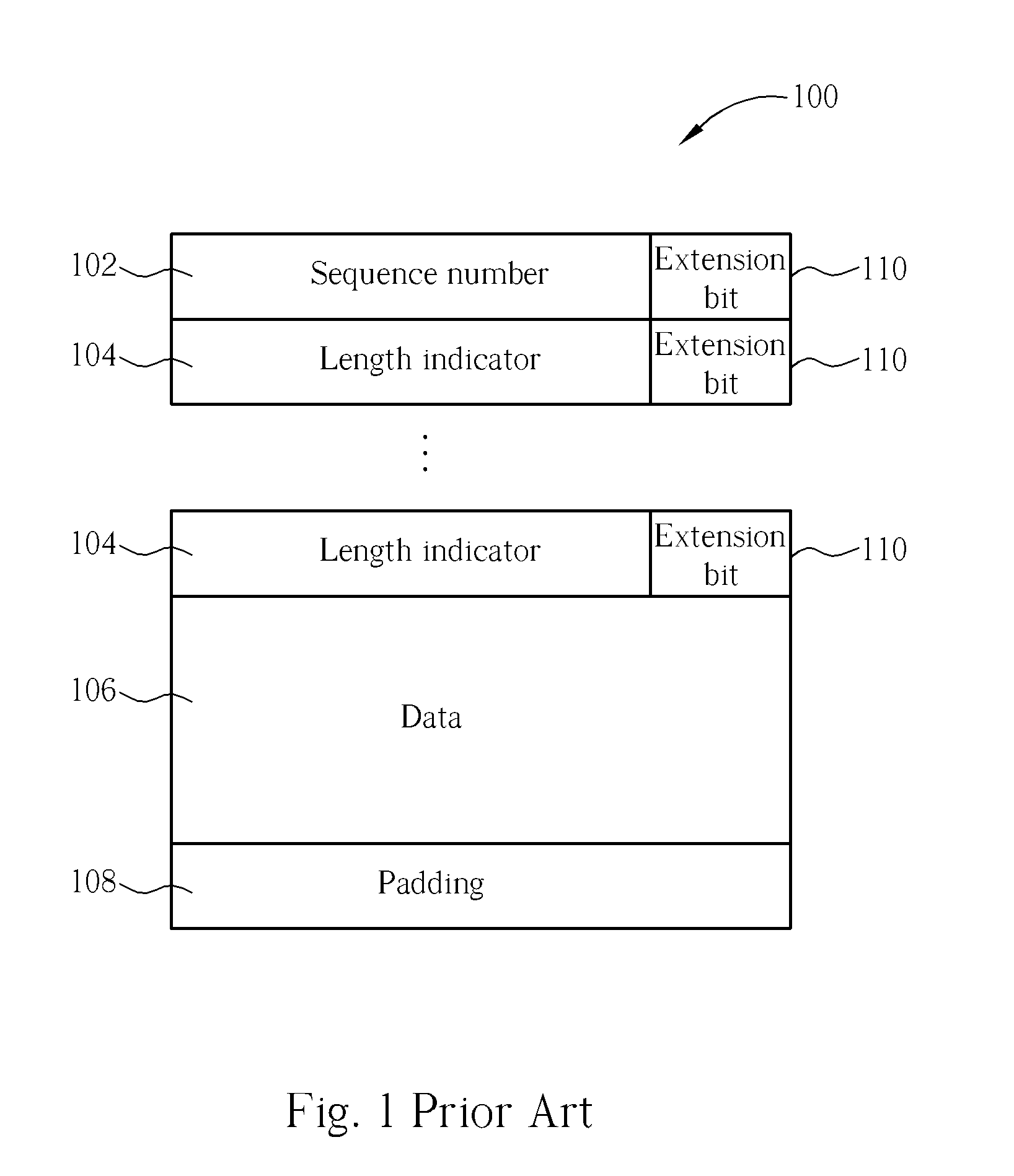
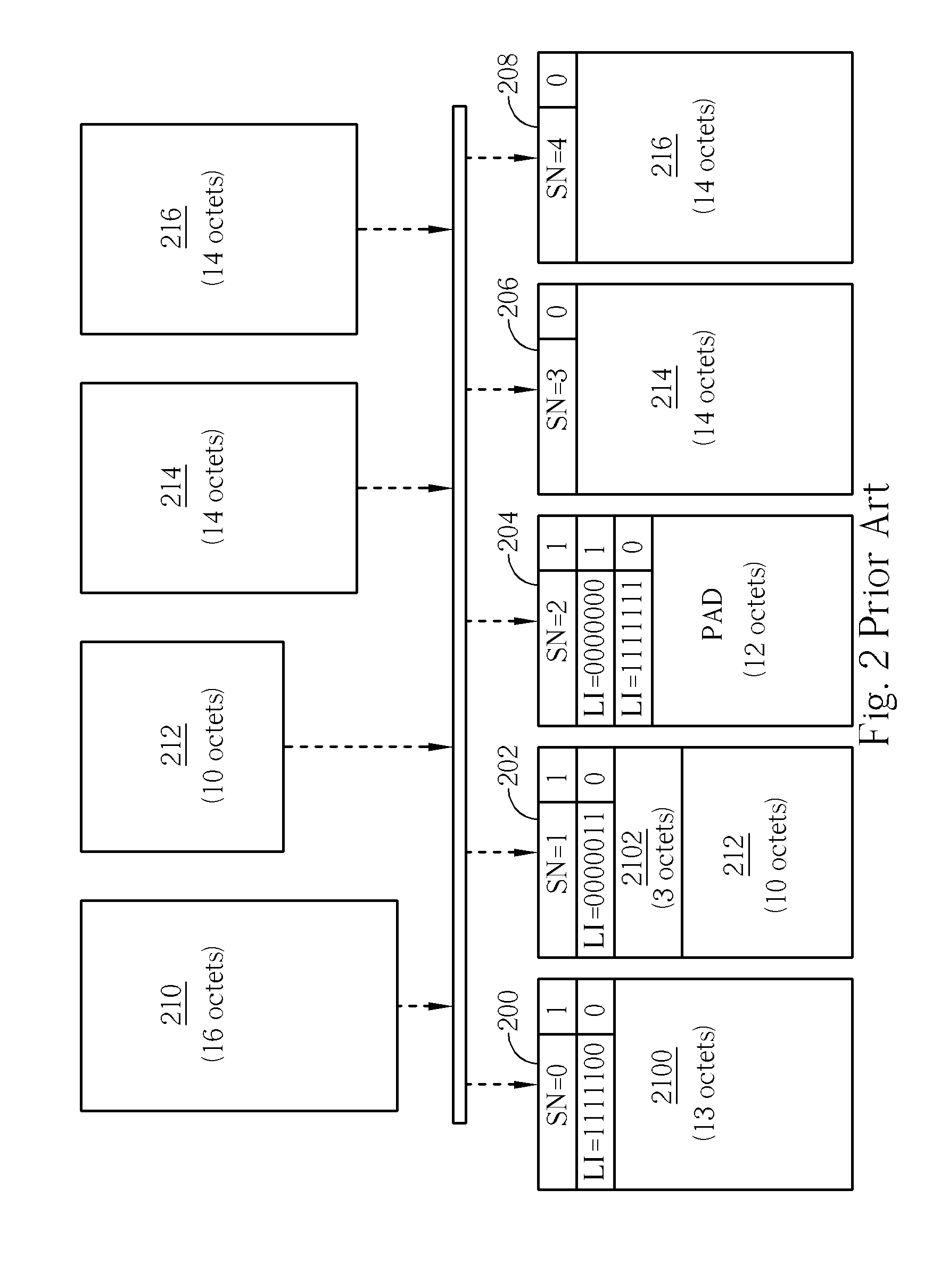
A method of data segmentation in a transmitter of a mobile communications system includes initiating alternate extension bit interpretation, a last data segment of a Service Data Unit exactly ending at an end of a Protocol Data Unit, no Length Indicator in the Protocol Data Unit indicating the end of the Service Data Unit, a length of a next Service Data Unit following the Service Data Unit exactly equaling to a length of a data field of a next Protocol Data Unit following the Protocol Data Unit, and setting a first extension bit of the next Protocol Data Unit to be a specified value for indicating that the next Protocol Data Unit comprises a complete Service Data Unit, which is not segmented, concatenated or padded, and indicating that a Service Data Unit exactly ended in the Protocol Data Unit.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SONIC
Multi-level controller with smart storage transfer manager for interleaving multiple single-chip flash memory devices
InactiveUS8341332B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageLogical block addressingBus
A solid-state disk (SSD) has a smart storage switch with a smart storage transaction manager that re-orders host commands for accessing downstream single-chip flash-memory devices. Each single-chip flash-memory device has a lower-level controller that converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA) that access flash memory blocks in the single-chip flash-memory device. Wear-leveling and bad block remapping are preformed by each single-chip flash-memory device, and at a higher level by a virtual storage processor in the smart storage switch. Virtual storage bridges between the smart storage transaction manager and the single-chip flash-memory devices bridge LBA transactions over LBA buses to the single-chip flash-memory devices. Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the single-chip flash-memory device is controlled at a high level by the smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping may be performed within each single-chip flash-memory device.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Equalizer for a VSB receiver enabling equalizations using segment synchronization information
InactiveUS7218671B2Improve uniformityTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksData segmentEqualization
An equalizer for a VSB receiver, which enables equalizations using segment synchronization information, has an extraction unit extracting the segment synchronization information included in the VSB broadcast signal, a storage unit storing the extracted segment synchronization information, and an equalization unit equalizing the VSB broadcast signal based on the segment synchronization information stored in the storage unit. The storage unit stores the segment synchronization information extracted from the extraction unit by field unit or by unit of N data segments within the field according to a channel state. More stable equalizations can be carried out in channel environment changes by storing segment synchronization information by the predetermined number of data segments and equalizing data within a corresponding data segment in a training mode while using the segment synchronization information every matching number of data segments.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data transmitting/receiving system and method thereof
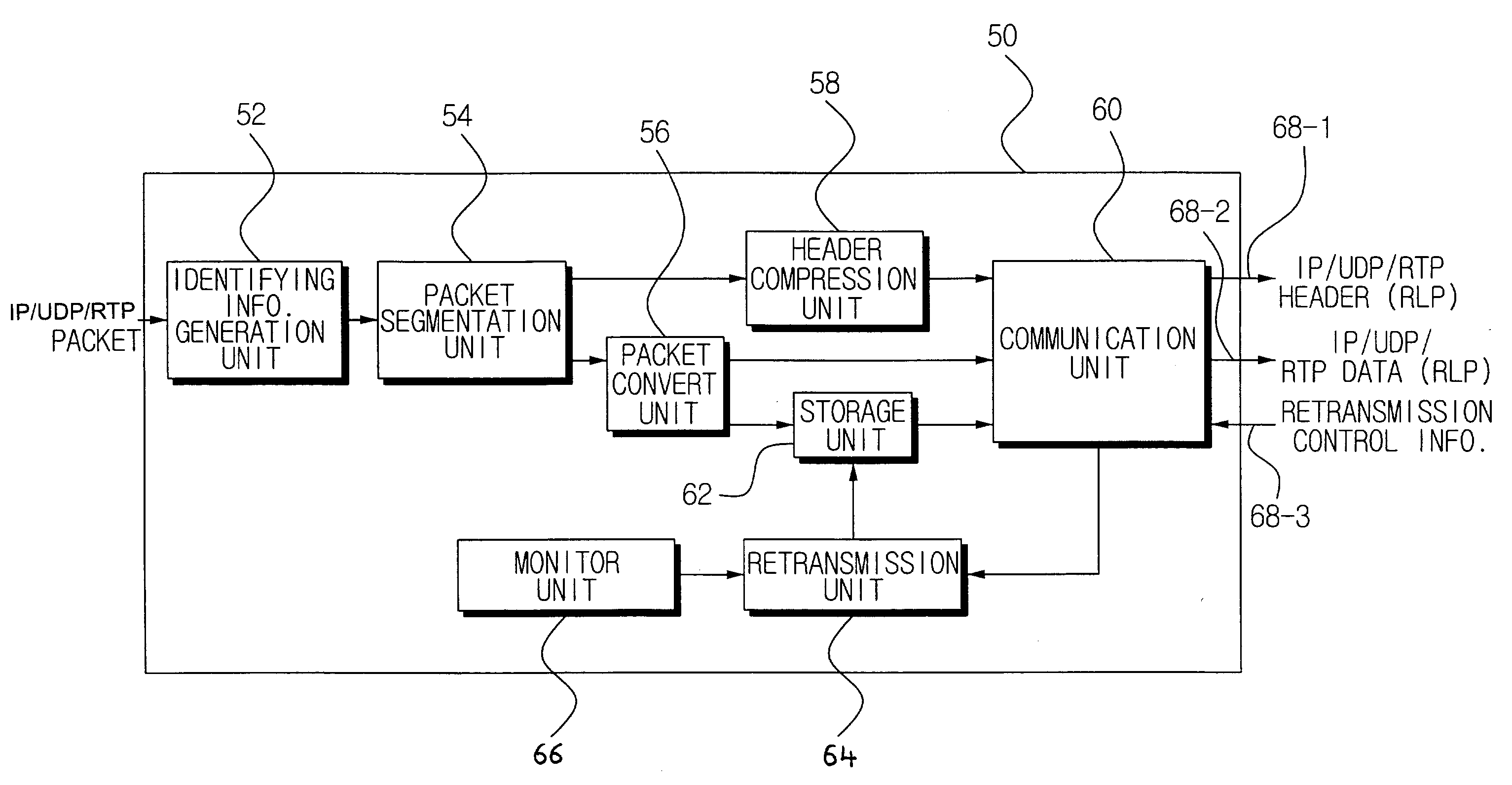
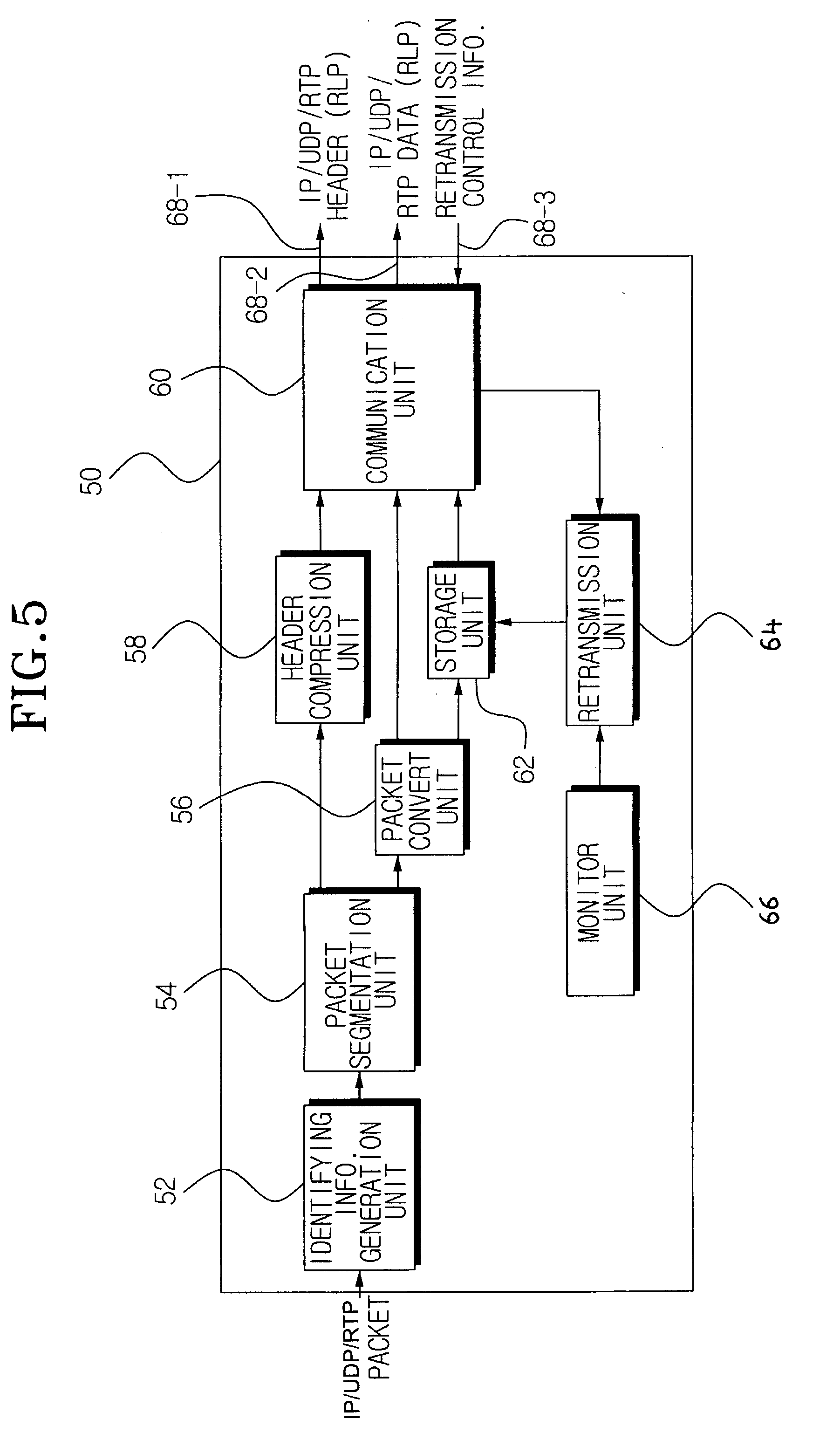
ActiveUS7562277B2Efficient data retransmissionReceived more stablyError prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionData packComputer science
A data transmitting / receiving system adds identifying information to a data packet based on characteristics of the data. The identifying information can be a data type of a payload data of an IP / UDP / RTP packet and / or a temporal data sequence of the payload data. The IP / UDP / RTP packet added with the identifying information is segmented into an IP / UDP / RTP header and IP / UDP / RTP data. The segmented IP / UDP / RTP header and the IP / UDP / RTP data can be transmitted through different channels. A receiver sends retransmission control information based on the added identifying information extracted by the receiver, the retransmission control information providing retransmission time and priority information. A transmitter retransmits reception error occurring IP / UDP / RTP data according to the retransmission control information received by the transmitter. Varying the retransmission times and / or retransmission priority based on the data characteristics, accommodates data retransmission so that data more influential to data restoration in case of loss / damage can be received more stably.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and/or methods for automatically tuning a delivery system for transmission of large, volatile data
ActiveUS20150207851A1Easy to handleImprove throughputMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData streamControl data
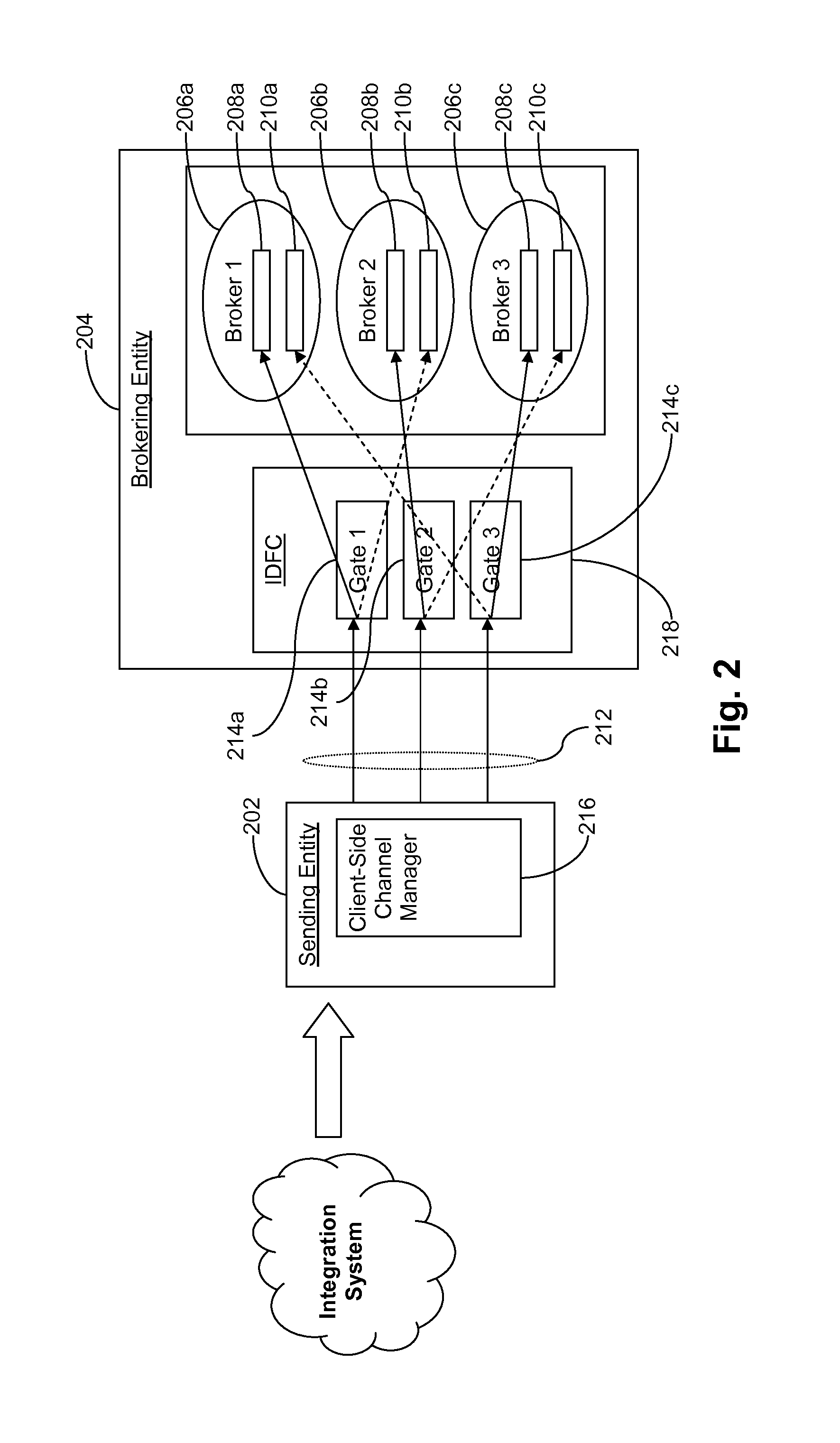
Certain example embodiments relate to the concept of controlling the flow of data by providing an intelligent flow controller / manager, and a client-side component for the selection of a communication channel from a pool, and having these components communicate to regulate data flow through gateways to a broker- and / or other-type secondary stage. Data fragmentation and reassembly can be used to increase performance, e.g., through self-regulating behaviors. Advantageously, reliability is improved by enabling in-memory data persistence, rather than resorting to potentially performance-degrading use of disk storage. The delivery mechanism may be used to deliver data to multiple consumers, providing an end-to-end sender-to-consumer solution that self-regulates to optimize the data flow while still being reliable.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
Update data transmission method, computer program for practicing the method, host device and firmware writing system
ActiveUS20080028387A1Shorten communication timeReduce the amount requiredSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsData connectionData transmission
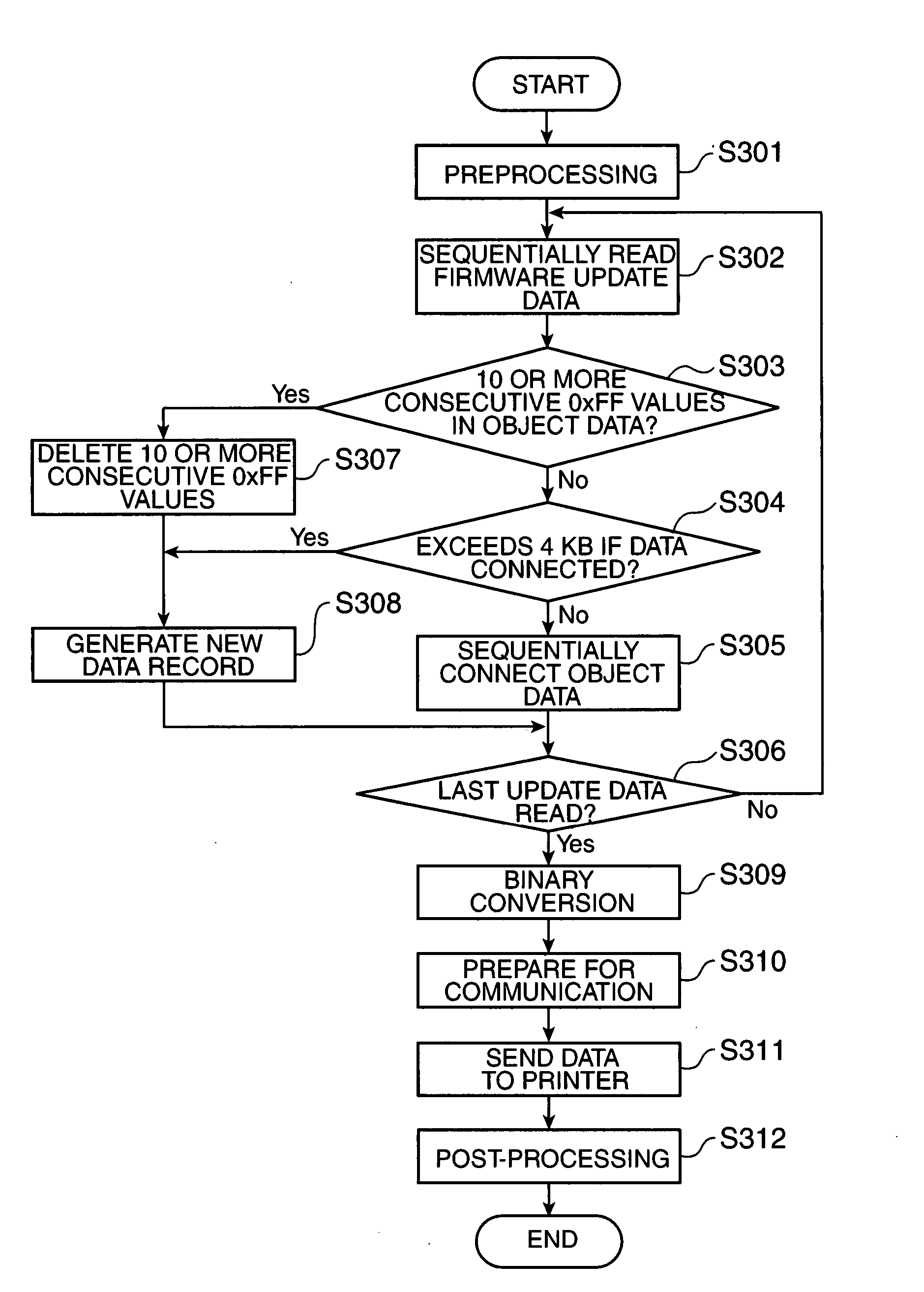
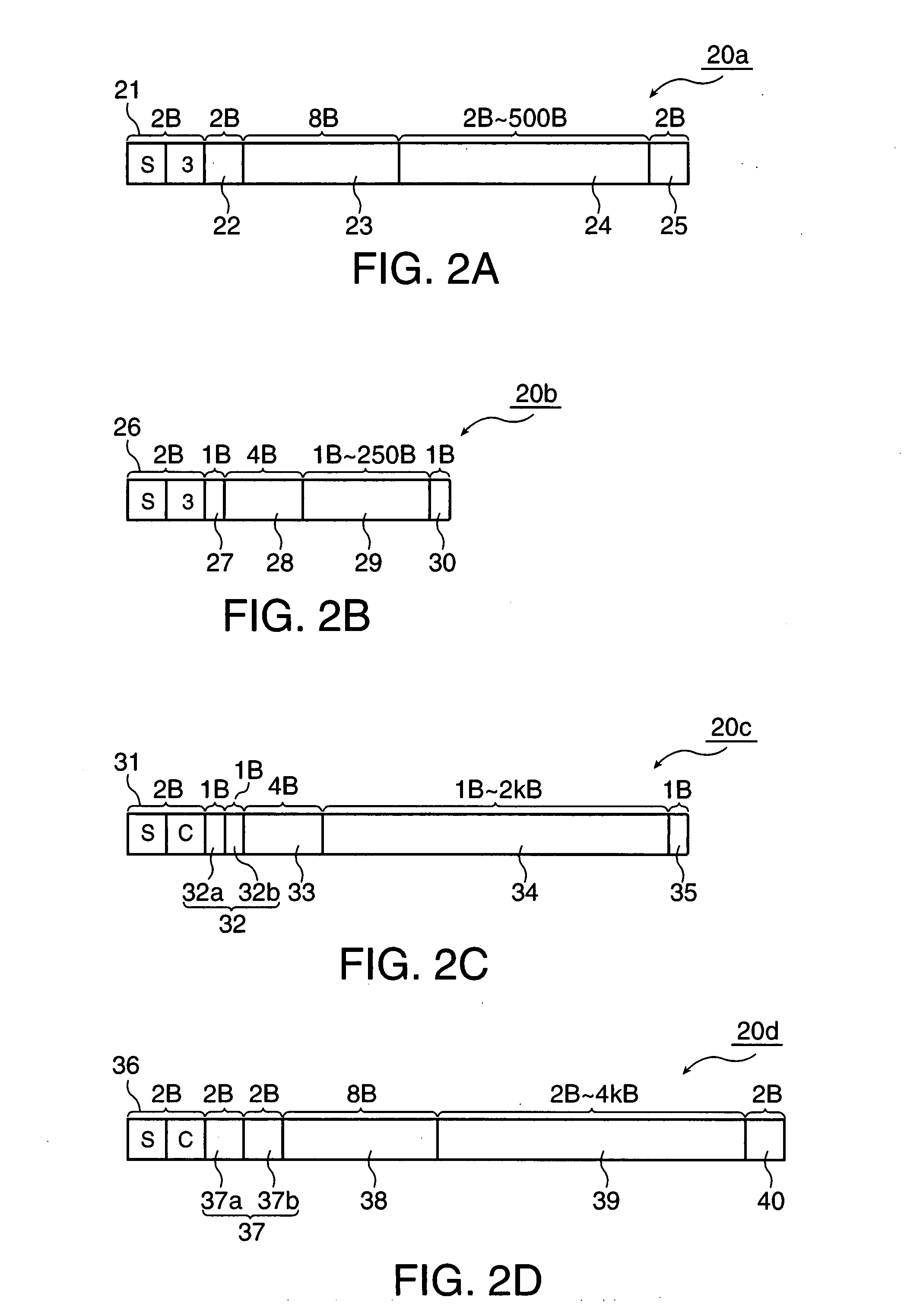
The time required to send firmware update data to a printer or other peripheral device is shortened without changing the communication speed. A server sequentially reads records of source data in a first format, deletes blocks of consecutive blank data that are contained in the object data in records of the first format and are longer than the management data in a second format, and segments the object data before and after the blanks, connects the object data in records of the first format into units of a certain length, generates management data for the segmented object data and generates management data for the connected object data to produce target records in the second format, and sends the update data composed of the target records of the second format to the printer. Records of the first format written in ASCII code are binary converted, and binary records in the second format are sent to the printer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and system for data segmentation
InactiveUS20050114382A1Character and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsData setData element
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
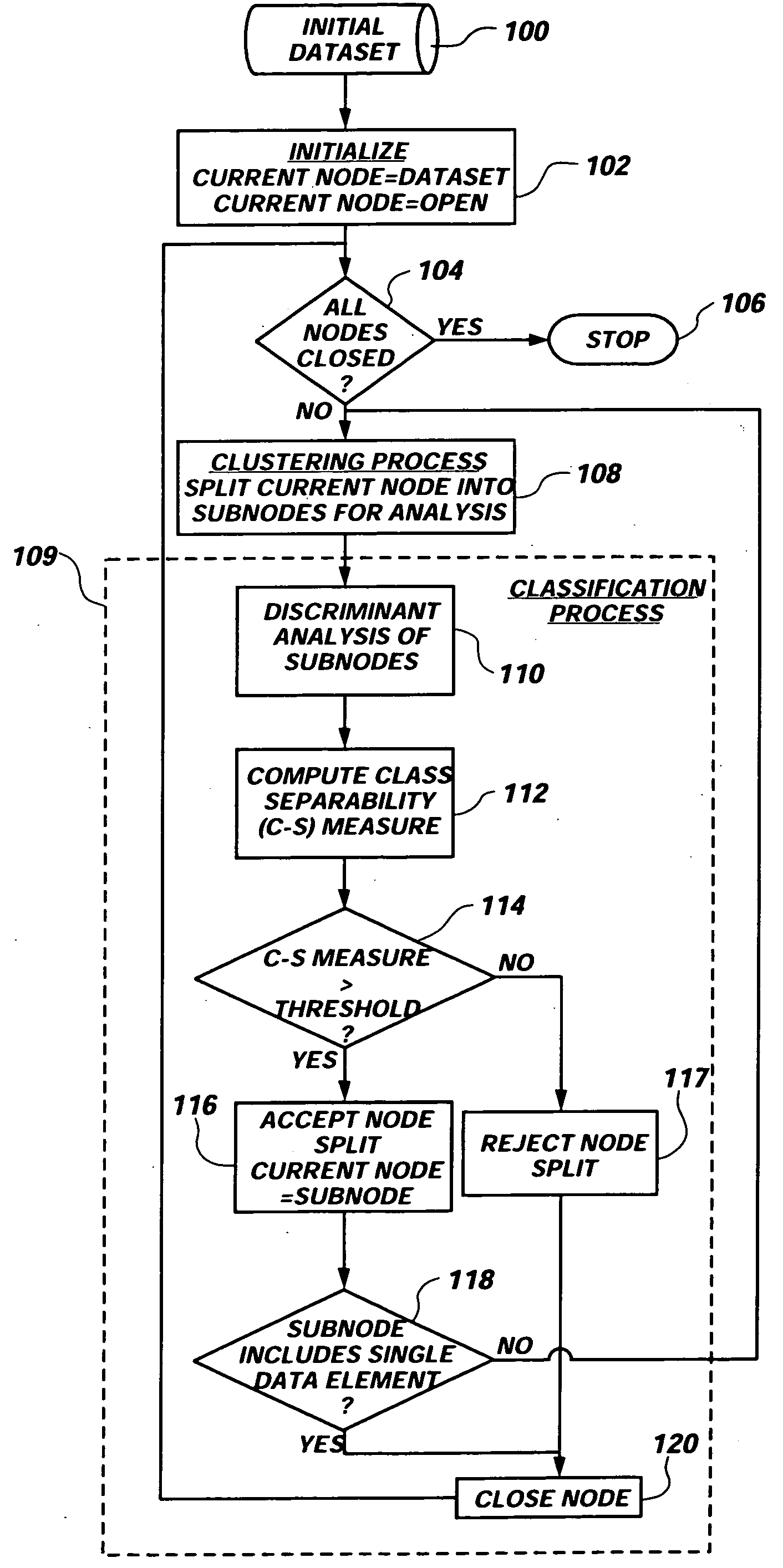
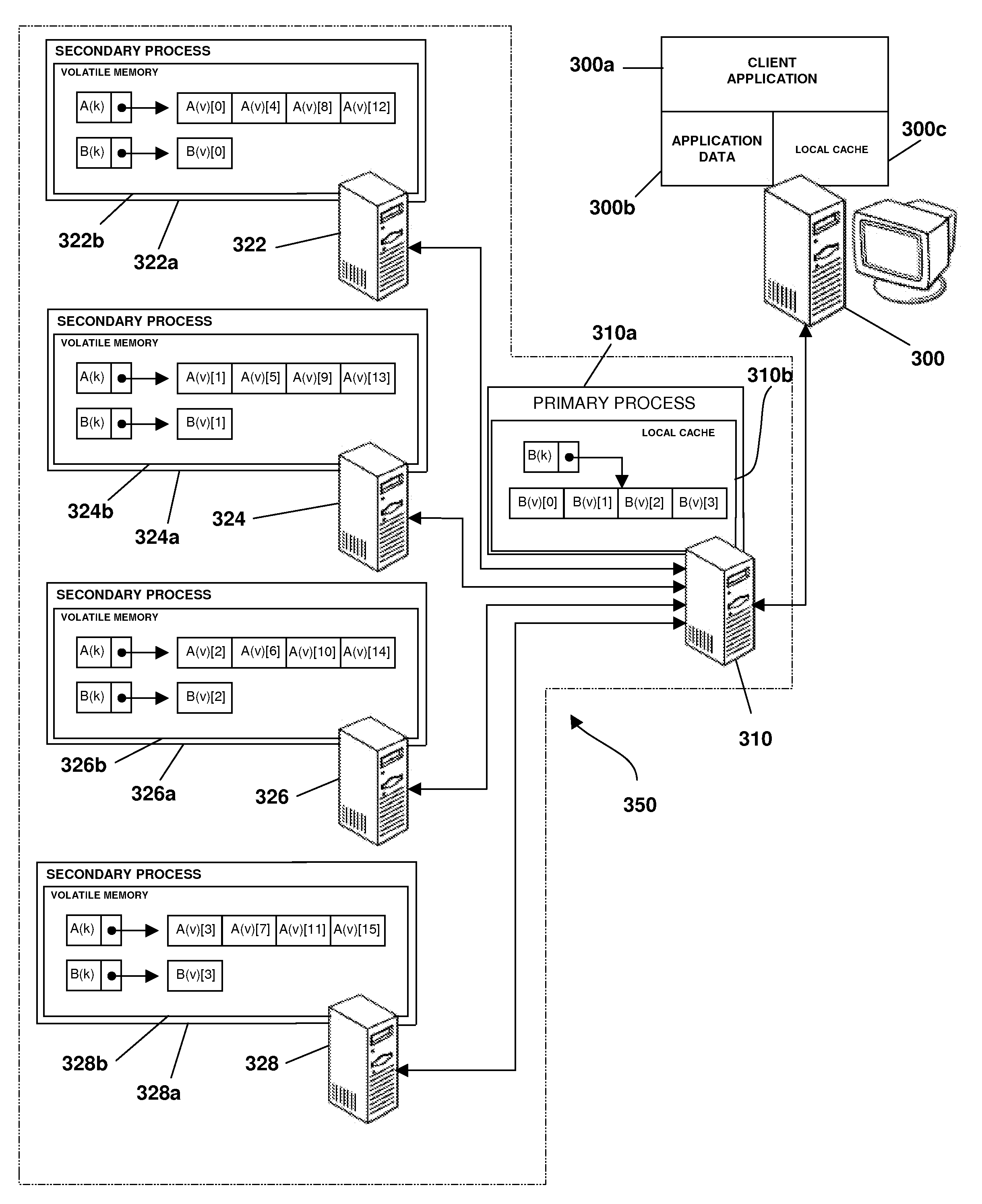
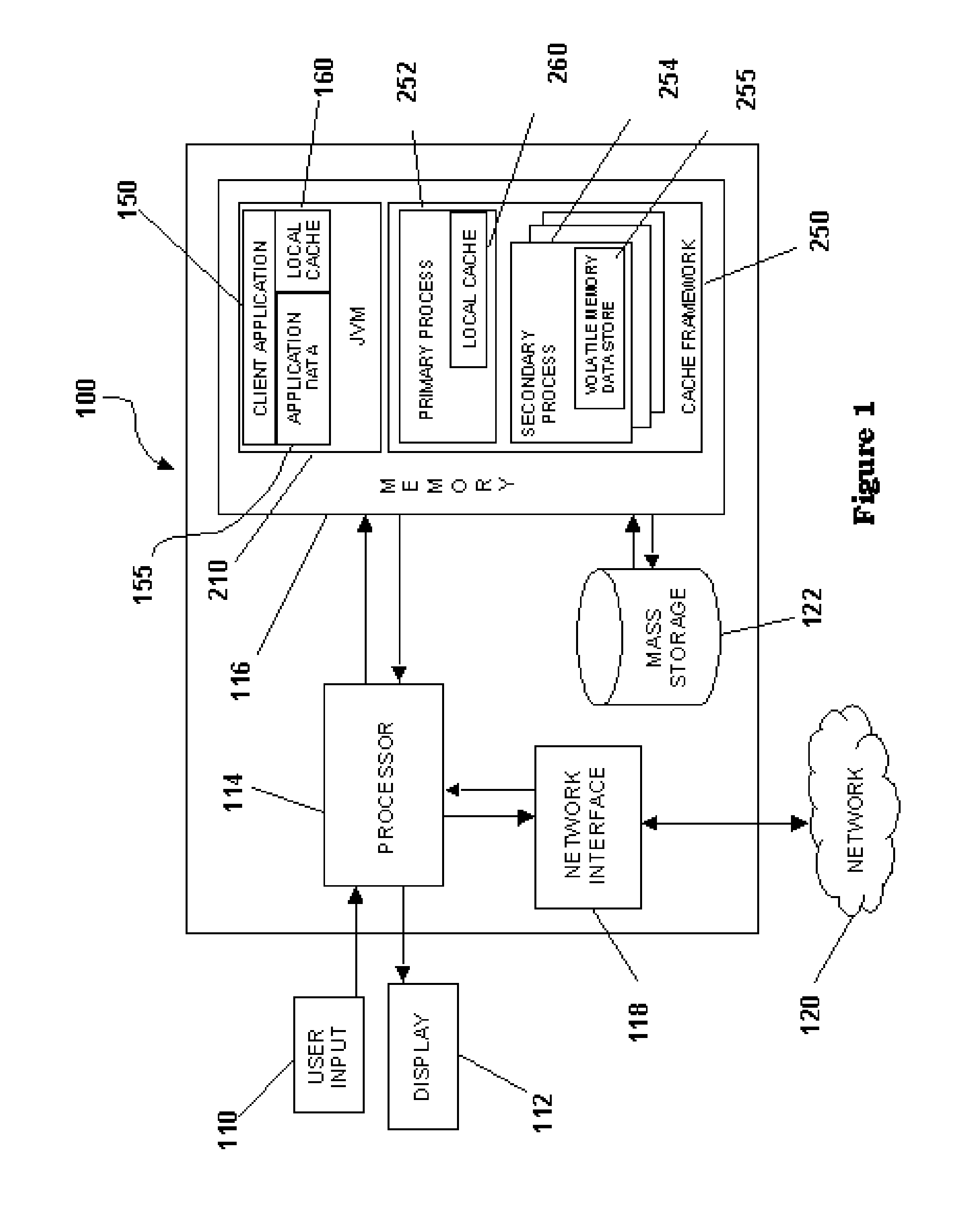
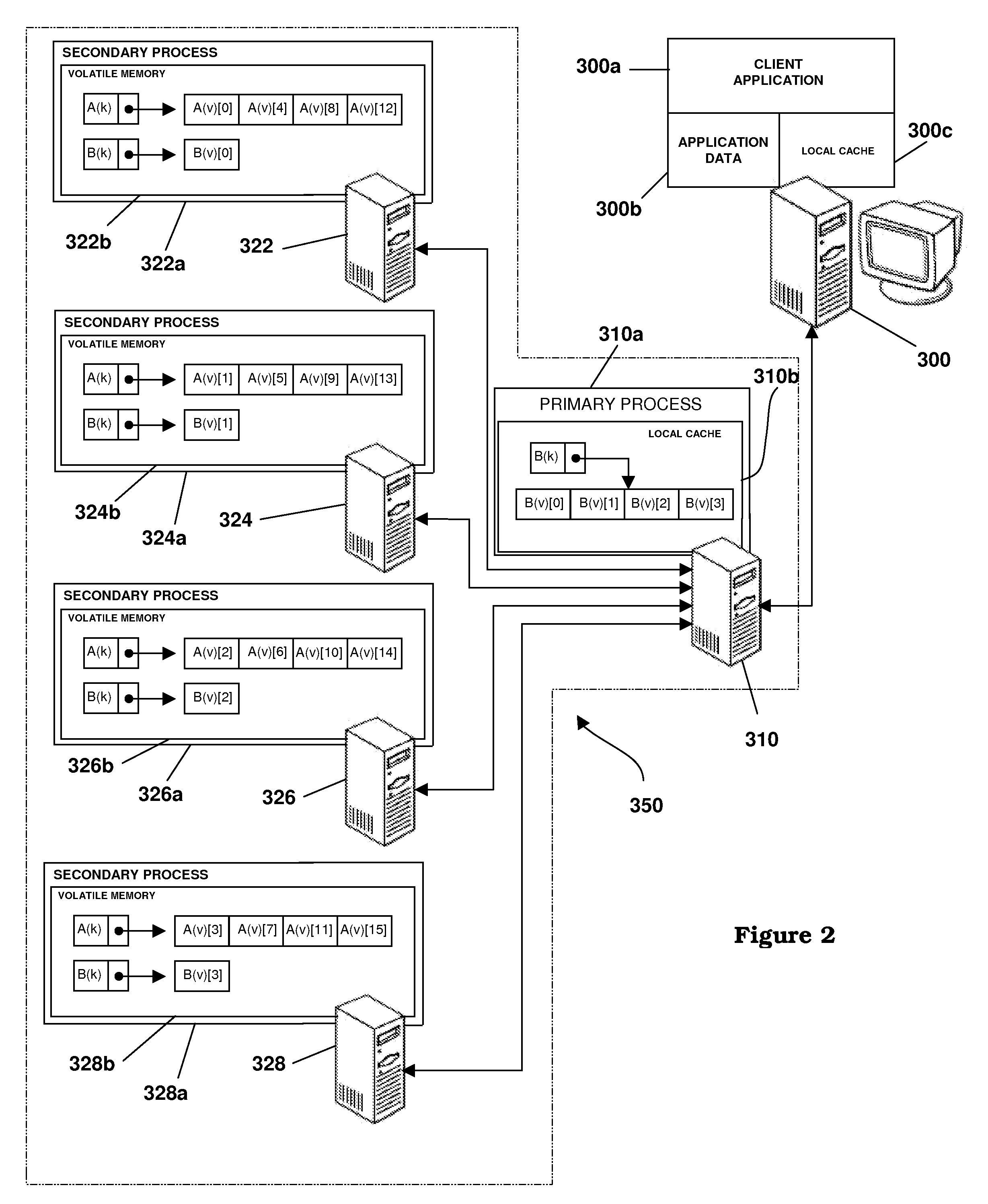
Map Based Striping of Data in a Distributed Volatile Memory Environment
ActiveUS20080126695A1Reduced memory utilizationReduce utilizationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData setData mining
An apparatus, program product and method stripe value data associated with each of a plurality of keyed data sets across a plurality of processes in a data process set and accessing a first keyed data set among the plurality of keyed data sets using at least one of the plurality of processes. Value data is striped by dividing a keyed data set among the plurality of keyed data sets across the plurality of processes in the data process set based on a striping strategy.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
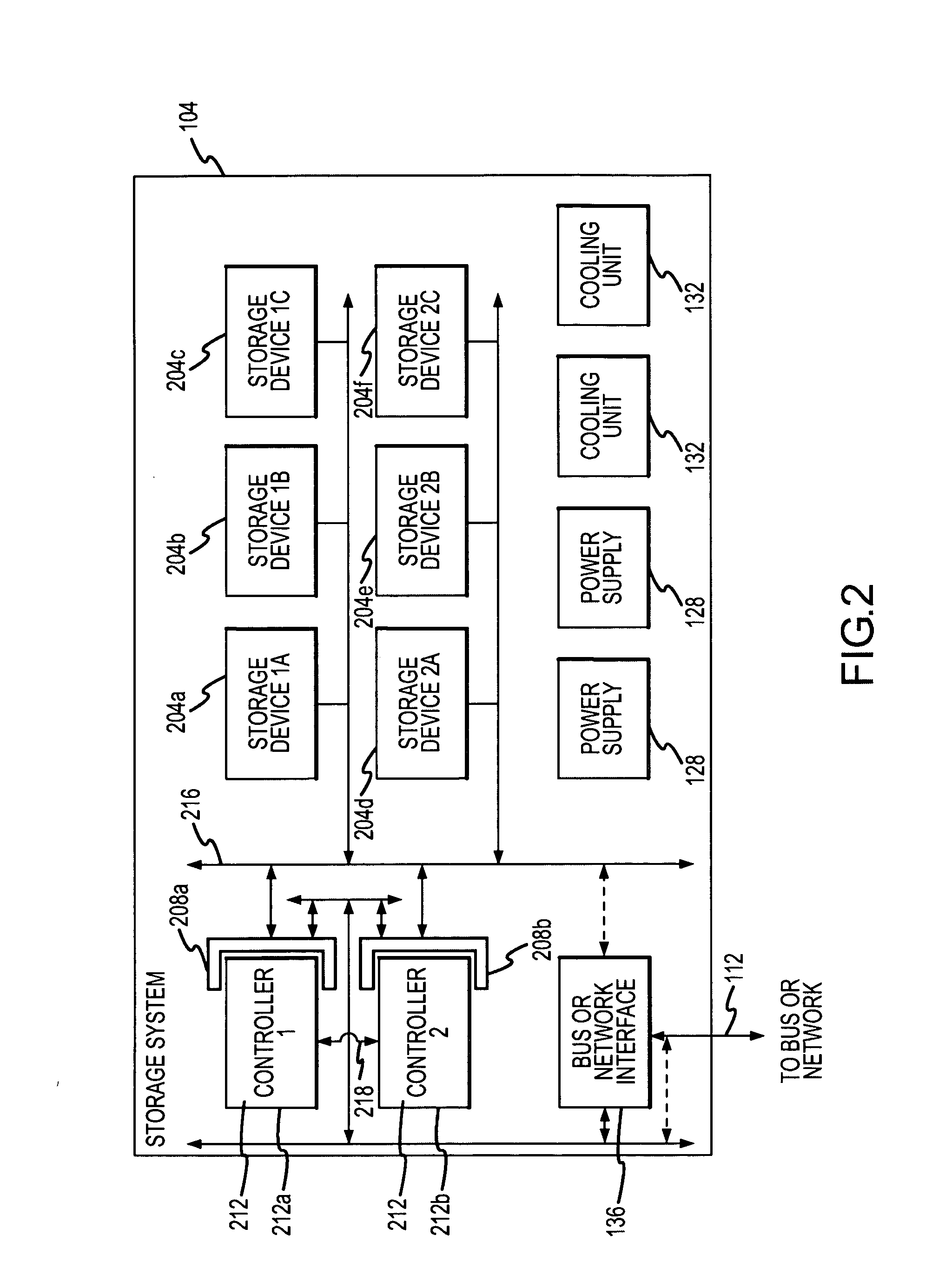
Method and apparatus for mirroring customer data and metadata in paired controllers
InactiveUS20070088975A1Avoid overwritingEasy to operate efficientlyError detection/correctionMemory systemsTerm memoryData store
A data storage system configured for efficient mirroring of data between paired redundant controllers is provided. More particularly, in response to the receipt of customer data from a host for storage, a first controller segments the received customer data into one or more frames of data. In addition, the first controller determines or associates certain metadata for each frame of customer data, and inserts that metadata in the corresponding frame. The frames, including the metadata, are provided to a secondary controller. The secondary controller stores the customer data from a received frame in memory, and stores the corresponding metadata in another location of memory that is indexed to the location where the customer data was stored. The secondary controller may also associate a count value with each frame of data in order to distinguish the most recent frame of data should frames in memory have matching metadata.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
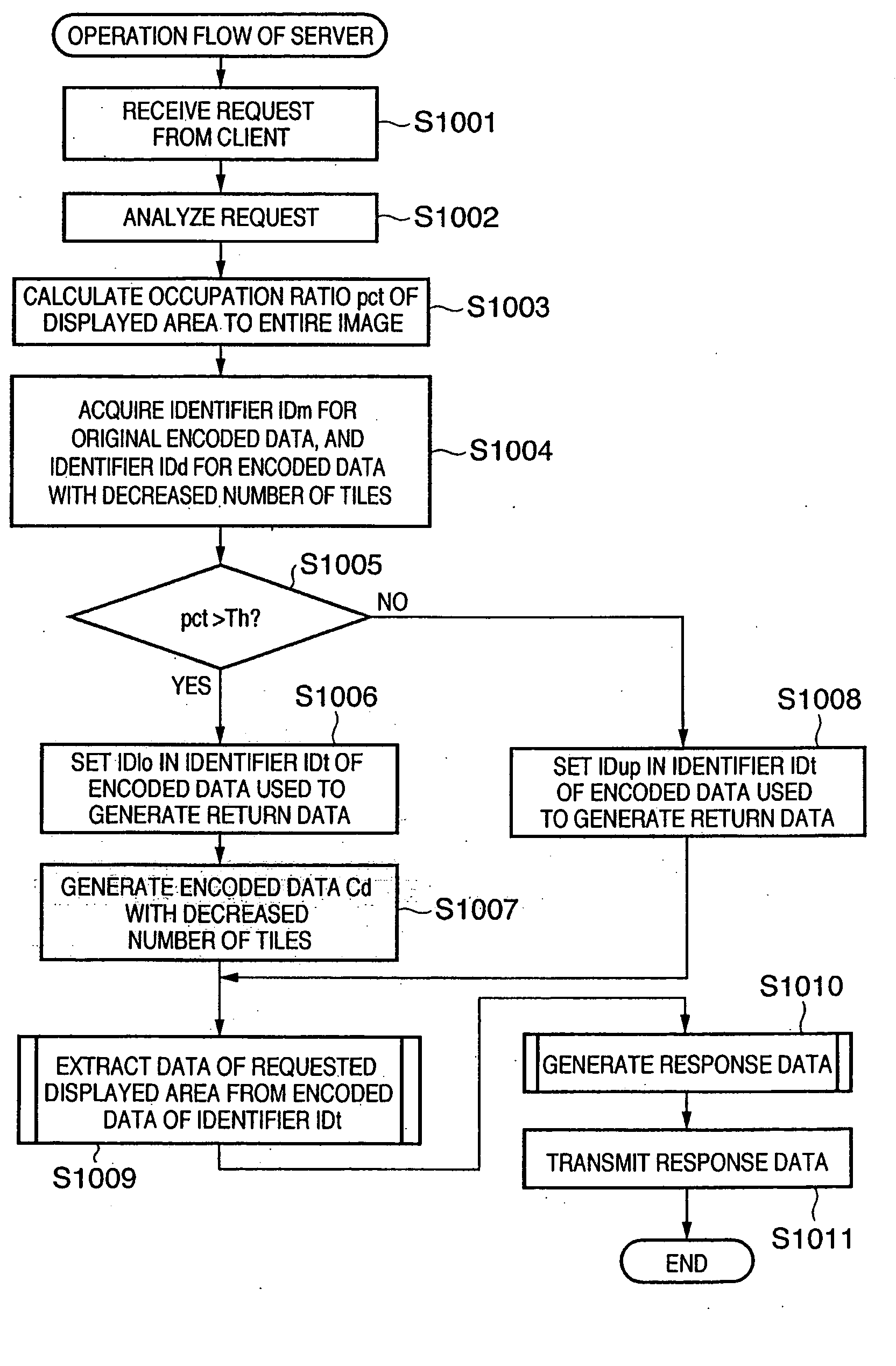
Image processing method and image processing apparatus
ActiveUS20060140494A1Suppress data transferCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingImaging processingImage resolution
There are provided an image processing method and image processing apparatus, which can suitably access a necessary partial image, and can suppress wasteful data transfer by returning data with a small number of tiles for a thumbnail image of a low resolution or the like so as to reduce the number of times of file seek operations, and returning data with a large number of tiles for an image of a high resolution to be returned in response to an enlargement request. To this end, a server encoded data fragmentarily transmits encoded data which is hierarchically encoded by dividing an image into a plurality of tiles in response to a request from a client. The server calculates an occupation ratio of the displayed area of the image requested from the client to the entire image. When the ratio is equal to or lower than a threshold, the server selects encoded data divided to have a larger number of tiles. Otherwise, the server selects encoded data with a smaller number of tiles. The server extracts data corresponding to the displayed area from the selected encoded data, and transmits the extracted data to the client.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for encrypting format-preserved numeric type personally identifiable information
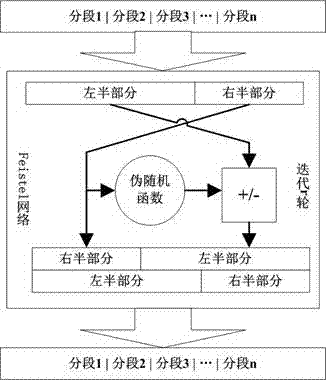
The invention discloses a method for encrypting format-preserved numeric type personally identifiable information (such as ID numbers and bank card numbers). The encryption purpose is achieved on the premise that original formats are kept unchanged. The method comprises the steps of first dividing the personally identifiable information into different data segments according to characteristics of the information and describing element sets of the segments through different integer finite fields; then connecting elements of the segments and inputting the elements into a Feistel network; finally outputting cryptograph data the same as original data in format under the effects of user-defined pseudo-random functions and modulo addition operation and modulo subtraction operation based on specified secret keys. By adopting the method, the possibility that encryption protection is performed on the numeric type personally identifiable information in a database application system is provided.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
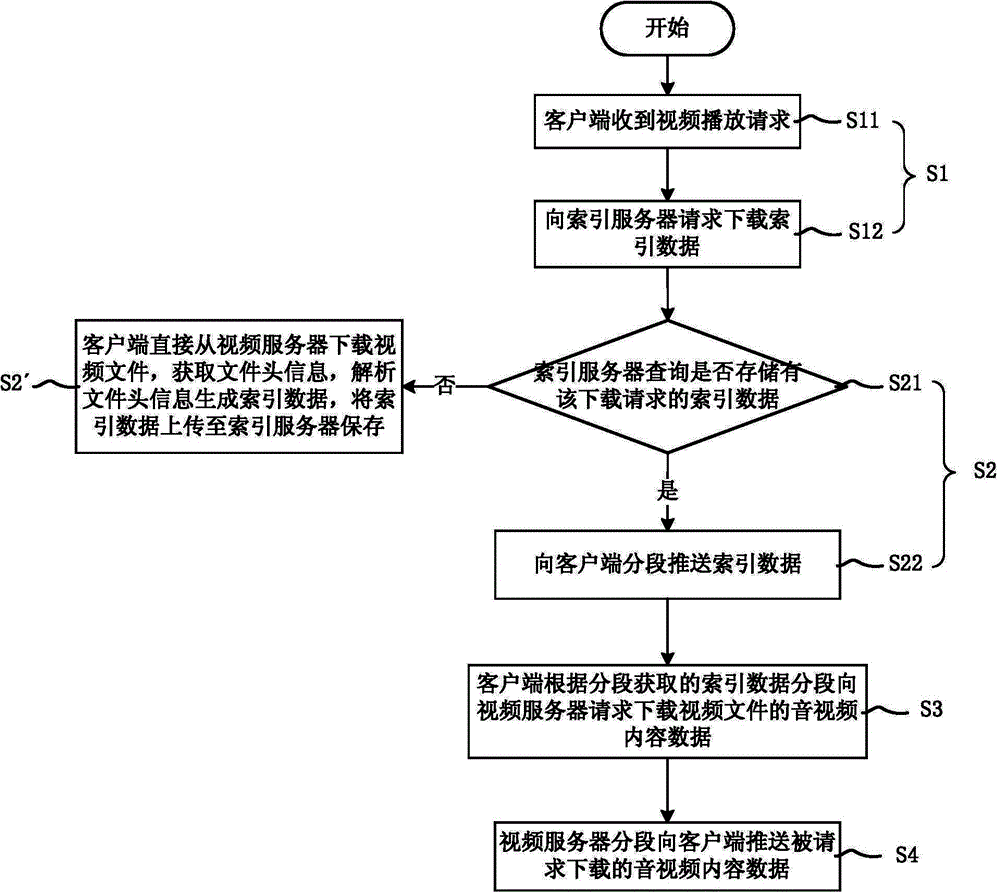
MP4 video on demand data stream transmission method, client side and video on demand system
The invention discloses an MP4 video on demand data stream transmission method, a client side and a video on demand system. The data stream transmission method comprises a first step that the client side sends a request to an index server to download index data according to a video playing request, wherein the index data is analysis data of file header information of a video file stored in the index server; a second step that the index server seizes the index data requested to download, and then pushes the index data to the client side segment by segment; a third step that the client side sends a request to a video server to download audio and video content data according to the acquired index data segments; and a fourth step that the video server pushes the audio and video content data requested to download to the client side segment by segment. When the video file is requested to play, segmented index data is downloaded from the index server, and then the video can be played, so that response speed for video on demand is improved.
Owner:深圳市云帆世纪科技有限公司
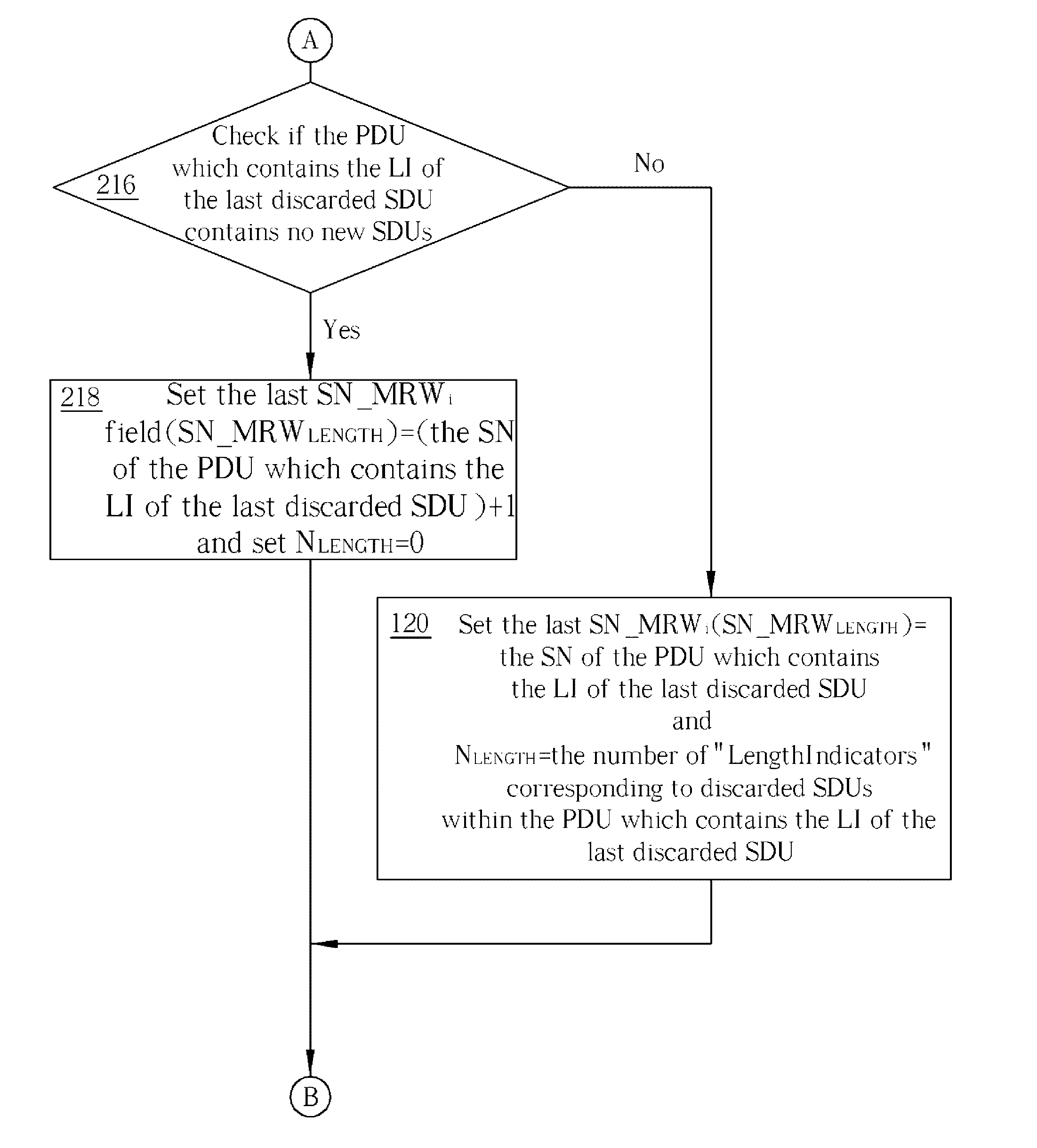
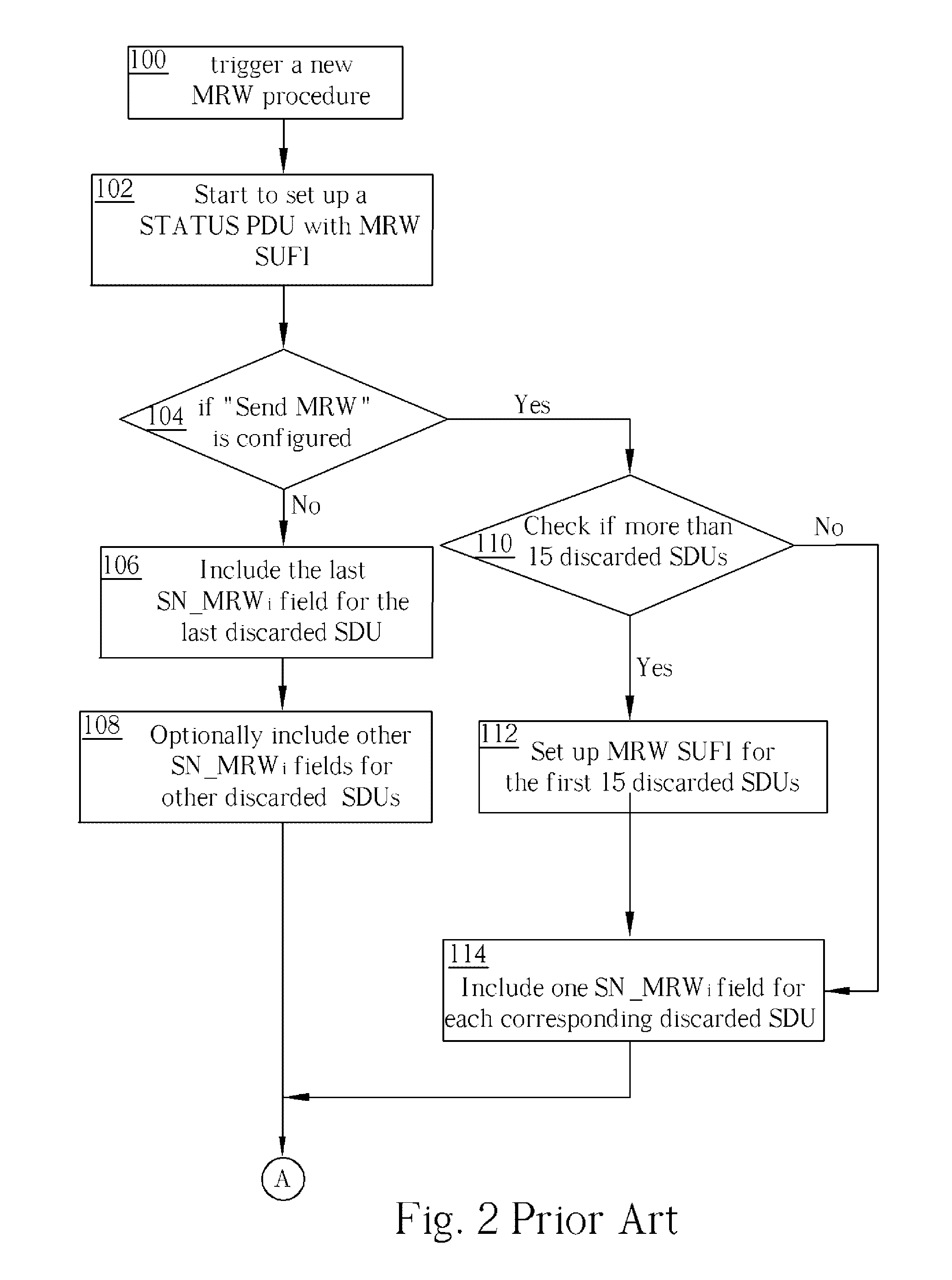
Enhanced SDU Discard Procedure for a Special Data Segmentation in a Wireless Communications System
ActiveUS20060077892A1Eliminate riskError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemProtocol data unit
A method for handling discarding of a sequence of service data units in a communications system is disclosed. The sequence of service data units includes at least a last discarded service data unit (SDU). When a protocol data unit (PDU) containing a length indicator of the last discarded SDU contains no new SDUs, the method includes creating a move receiving window super field (MRW SUFI), setting a NLENGTH field of the MRW SUFI to 0, setting a last sequence number move receiving window field (SN_MRWLENGTH) to a sum of one plus a sequence number (SN) of the PDU containing the length indicator of the last discarded SDU, and issuing the MRW SUFI.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SONIC
Command queuing smart storage transfer manager for striping data to raw-NAND flash modules
InactiveUS8176238B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageLogical block addressingHost machine
A flash module has raw-NAND flash memory chips accessed over a physical-block address (PBA) bus by a NVM controller. The NVM controller is on the flash module or on a system board for a solid-state disk (SSD). The NVM controller converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA). Data striping and interleaving among multiple channels of the flash modules is controlled at a high level by a smart storage transaction manager, while further interleaving and remapping within a channel may be performed by the NVM controllers. A SDRAM buffer is used by a smart storage switch to cache host data before writing to flash memory. A Q-R pointer table stores quotients and remainders of division of the host address. The remainder points to a location of the host data in the SDRAM. A command queue stores Q, R for host commands.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Bluetooth information sending and receiving methods
InactiveCN106571894AIntegrity guaranteedPrevent overflowSignal allocationNear-field systems using receiversData packData transmission
The invention relates to Bluetooth information sending and receiving methods in order to solve the problem that the security of Bluetooth data transmission cannot be guaranteed and the efficiency is low in the prior art. The Bluetooth information sending method of the invention, which is applied to a Bluetooth master computer carrying out communication based on SPP, comprises the following steps: S1, acquiring data, and caching to-be-sent data based on a first-in-first-out mechanism; S2, sub-packaging or packaging the cached to-be-sent data according to the length of the to-be-sent data to get at least one data packet; S3, sending the data packet through an established Bluetooth link. The Bluetooth information receiving method, which is applied to a Bluetooth slave computer carrying out communication based on SPP, comprises the following steps: S4, receiving the data packet through the established Bluetooth link; S5, reading the data in the data packet, and caching the data based on the first-in-first-out mechanism; and S6, sending the cached data to a memory in a segmented way.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDE ELECTRONICS TECH
A forward correcting decoding device and control method
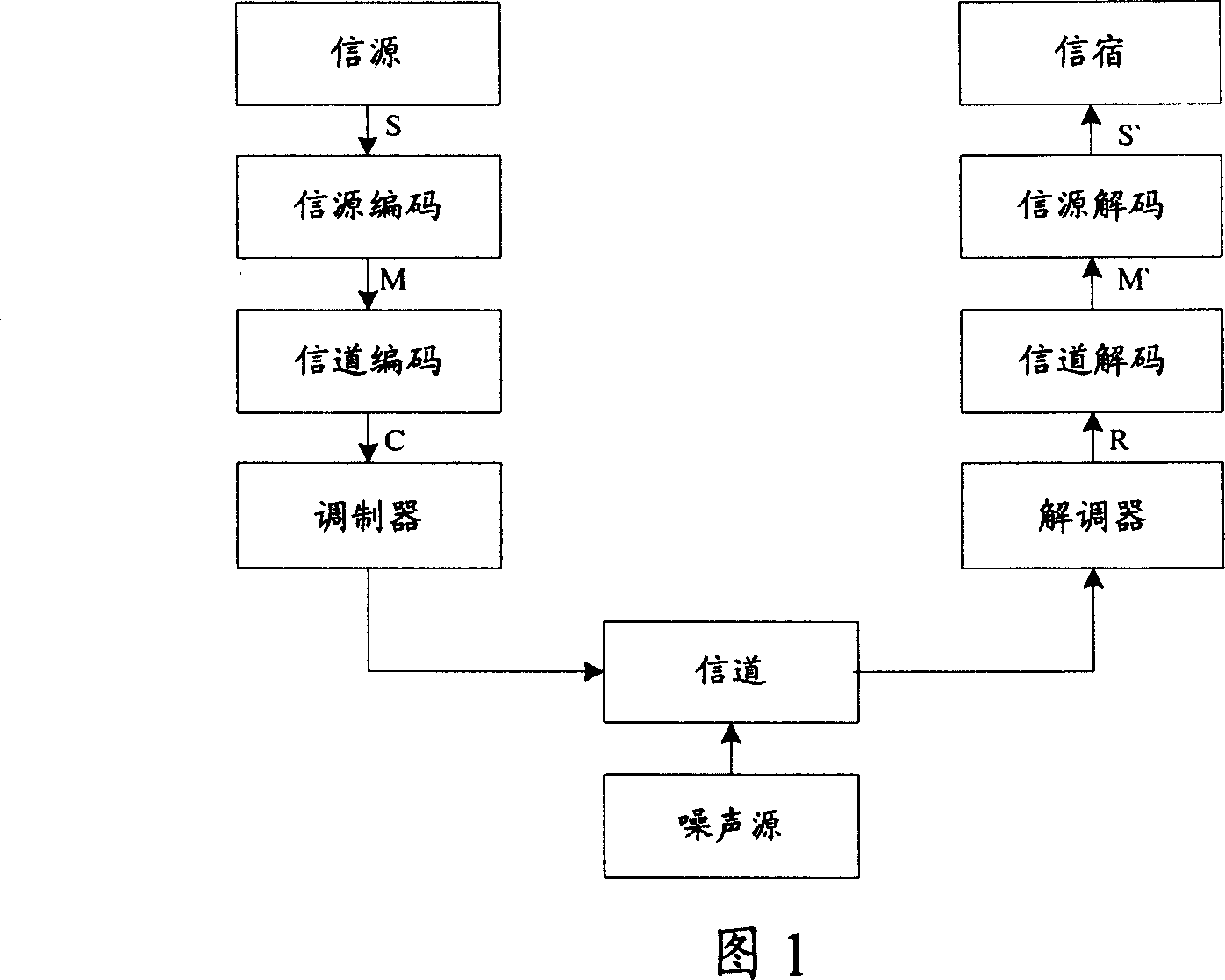
InactiveCN1968036AEliminate Bandwidth LimitationsMeet real-time decoding requirementsError preventionTransmission control/equalisingControl mannerForward error correction
The invention relates to a forward correcting decoder and relative control method, wherein said device comprises forward correct FEC decode circuit, frame data divide module and frame data recombine module; the FEC decode circuit has at least two parallel paths; the frame data divide module receives the frame data transmitted via FEC code method, and divides each frame data via word length sequence; feeds divided data sections into each FEC decode circuit and decodes; the frame data recombine module recombines frame data. The invention can avoid bandwidth limit, in GPON network, to send and decode descending data continuously.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com