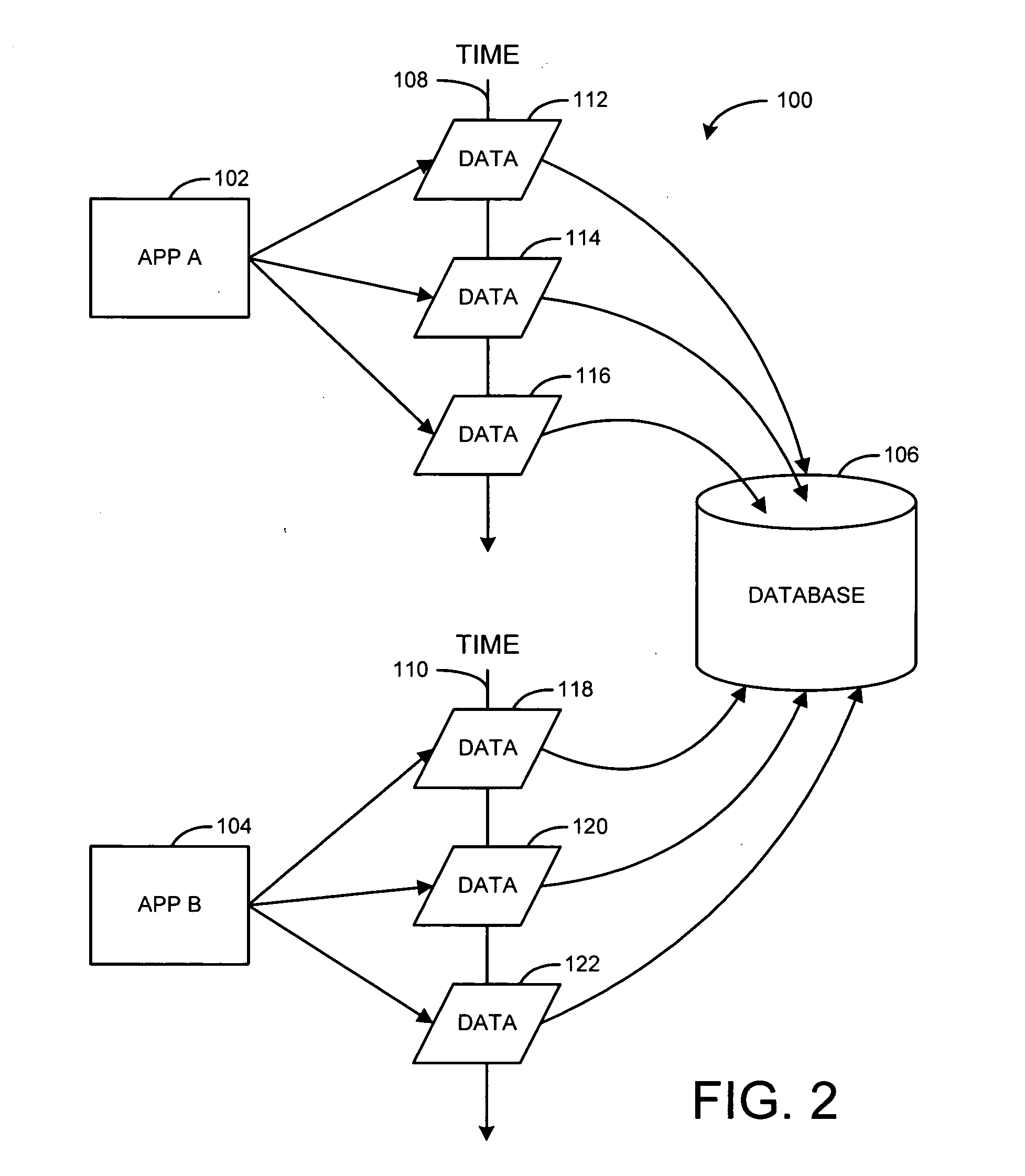
Patents
Literature
1722 results about "Data restoration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
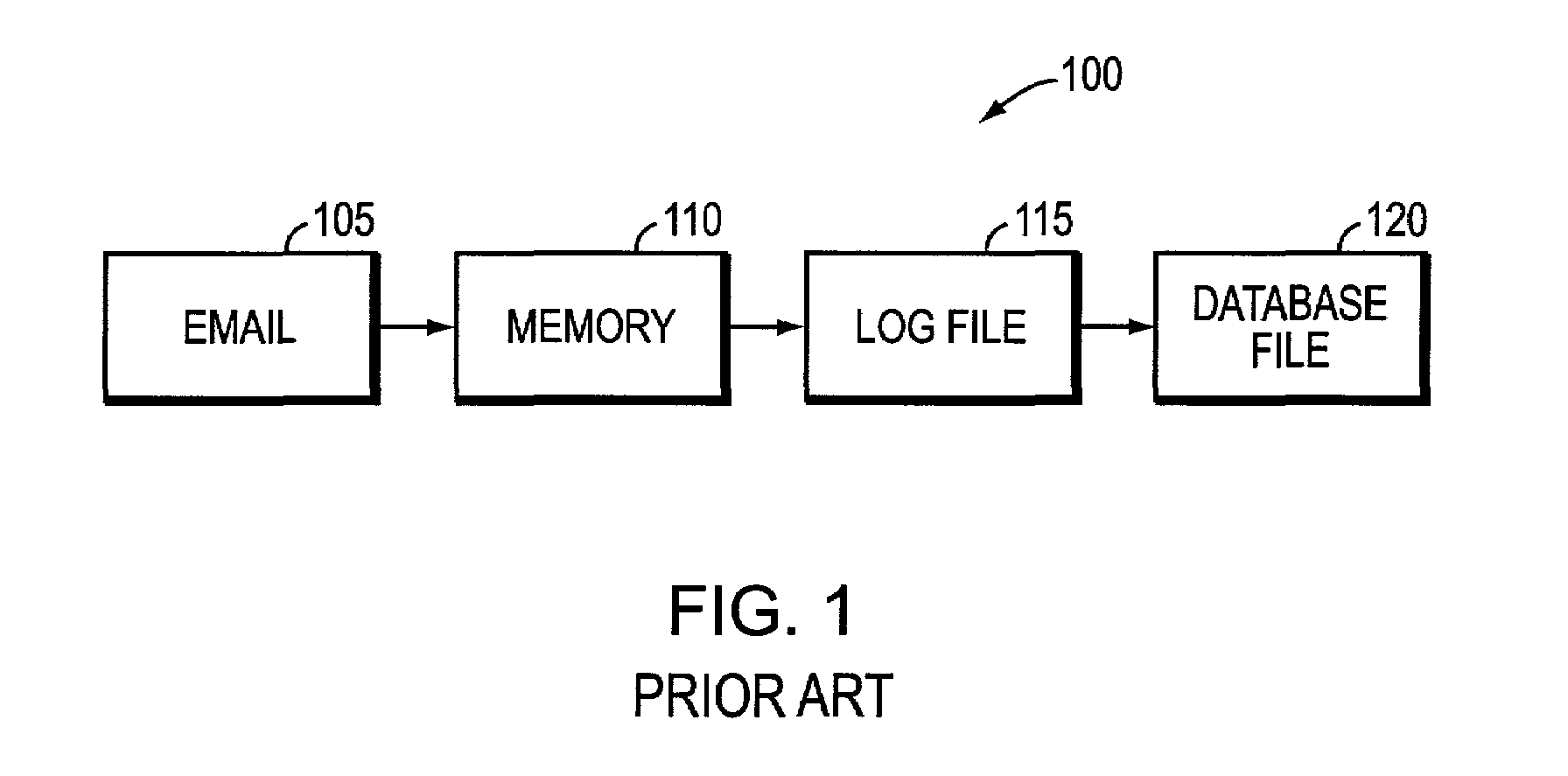
Data restoration techniques. The approach used to restore data depends on what information was lost or damaged, how much data was affected, how the incident happened, the software used to create the data backup, the backup target media and other factors. Some backup software enables users to restore lost files themselves.
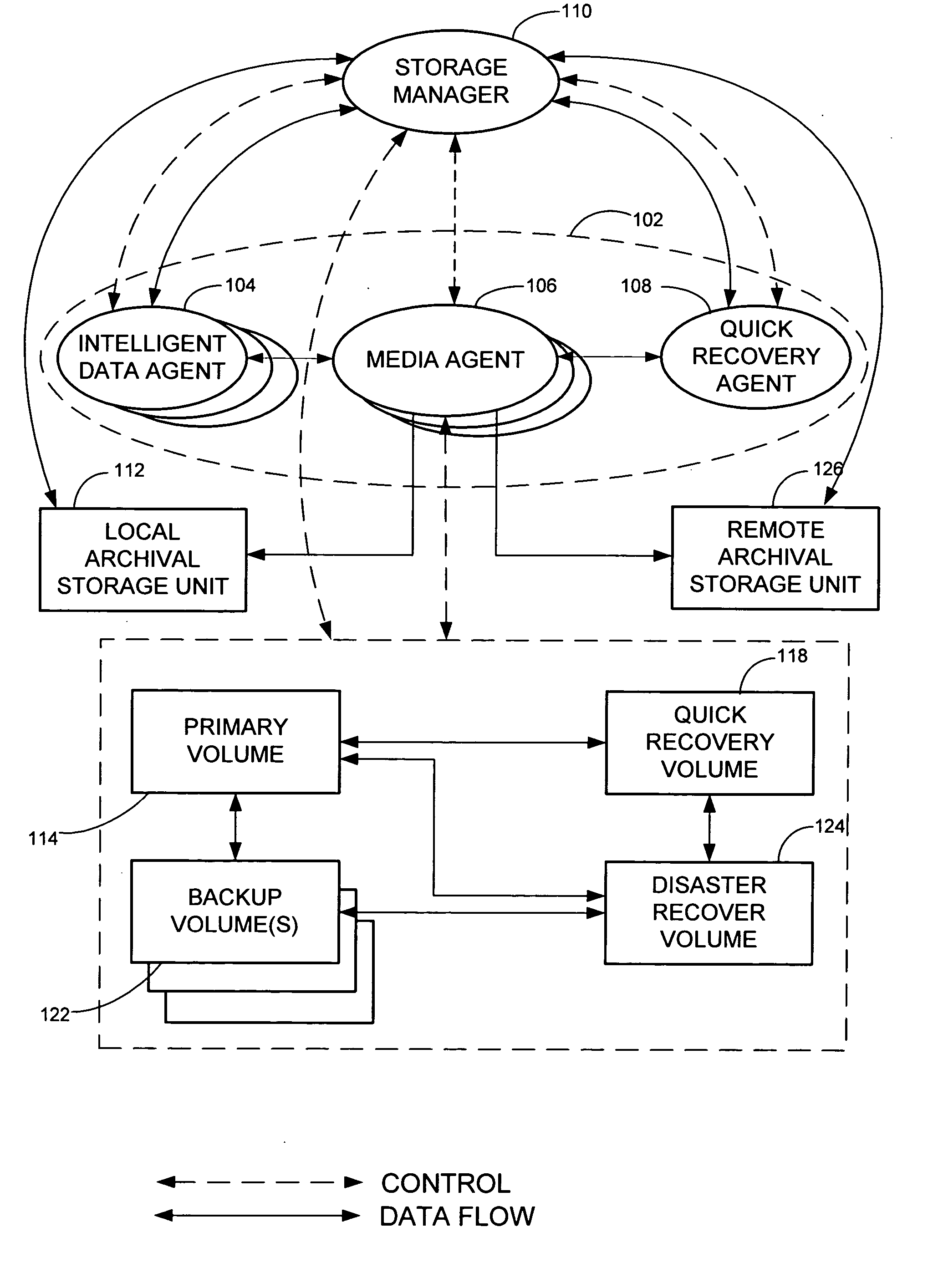
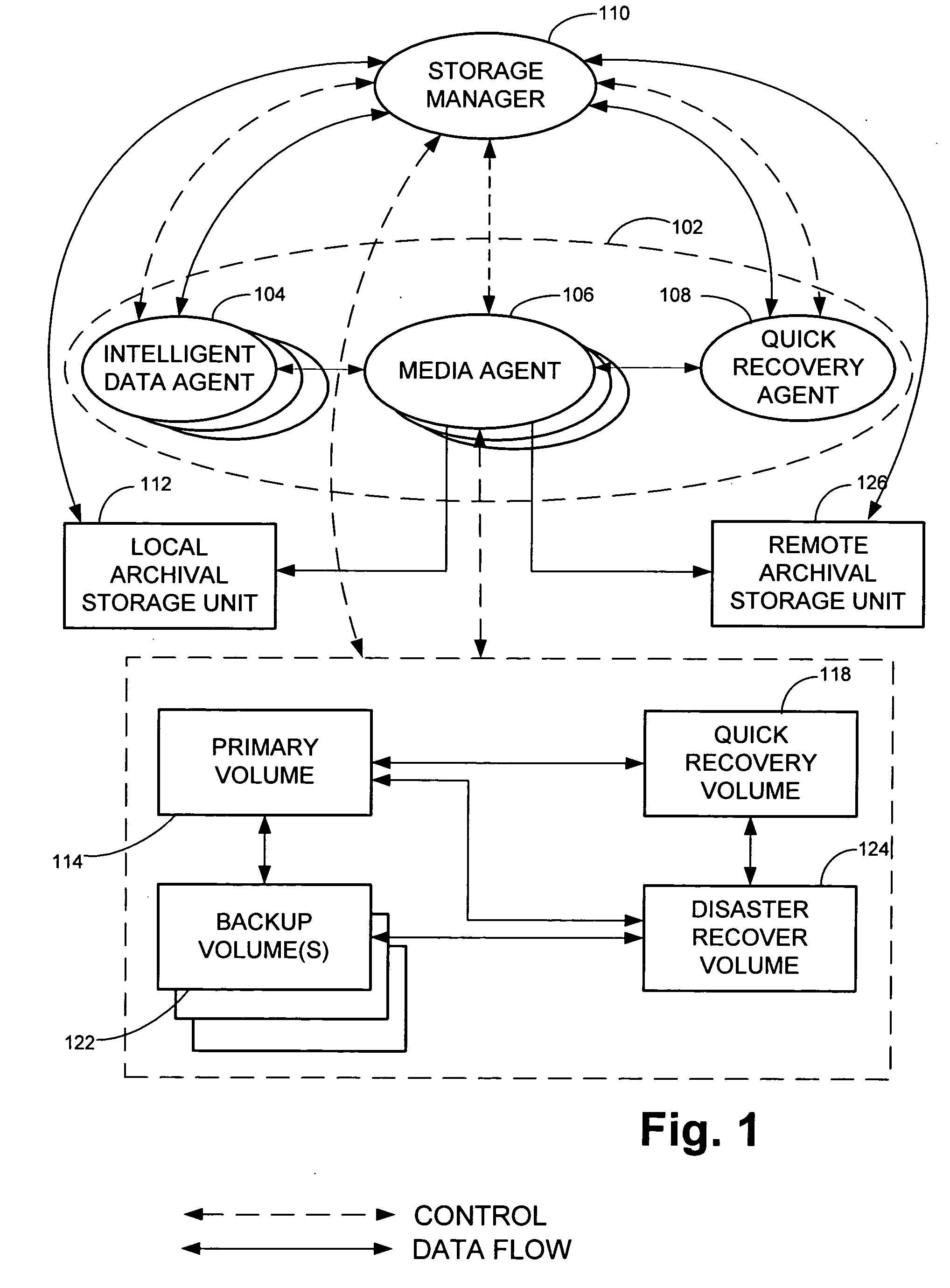
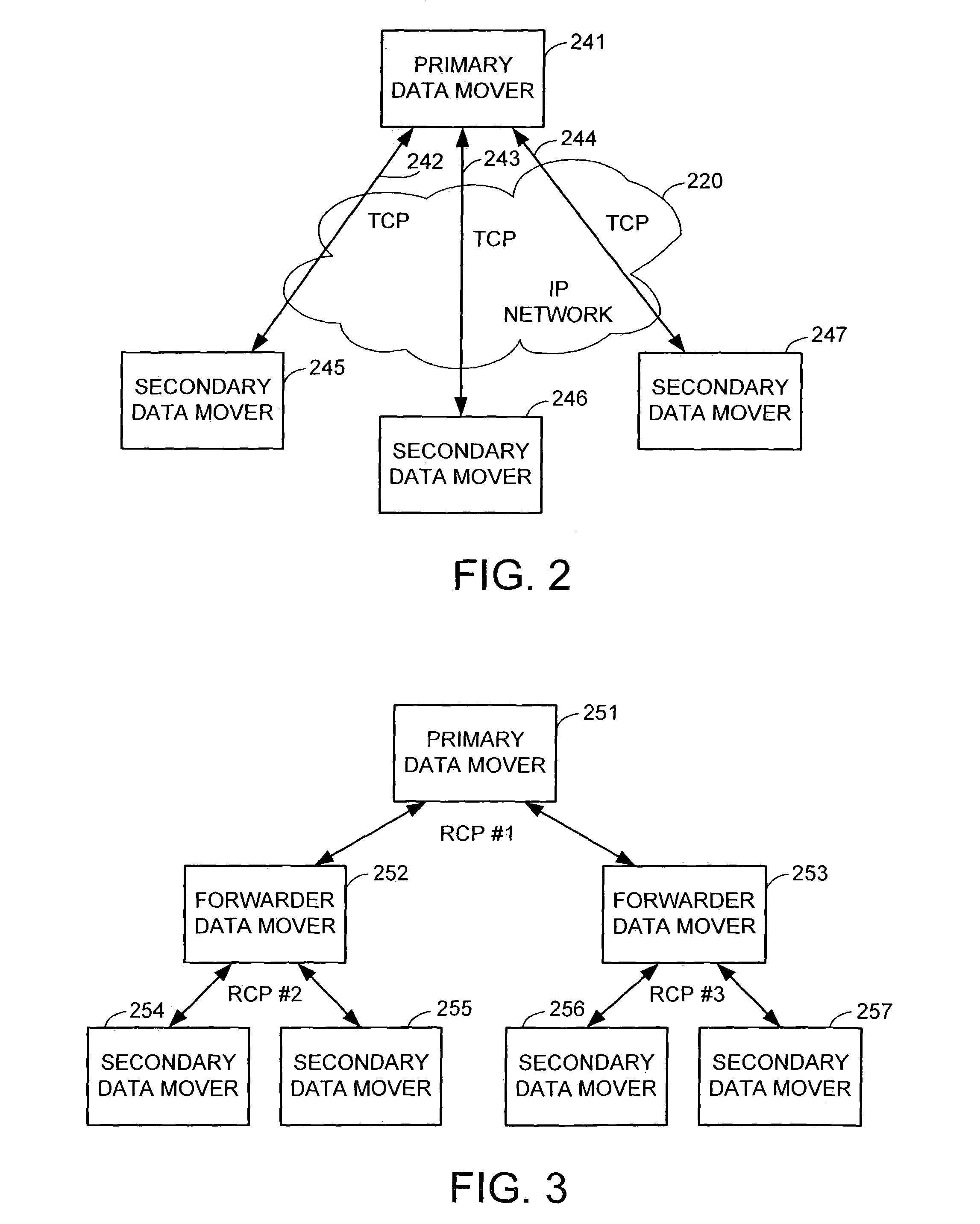
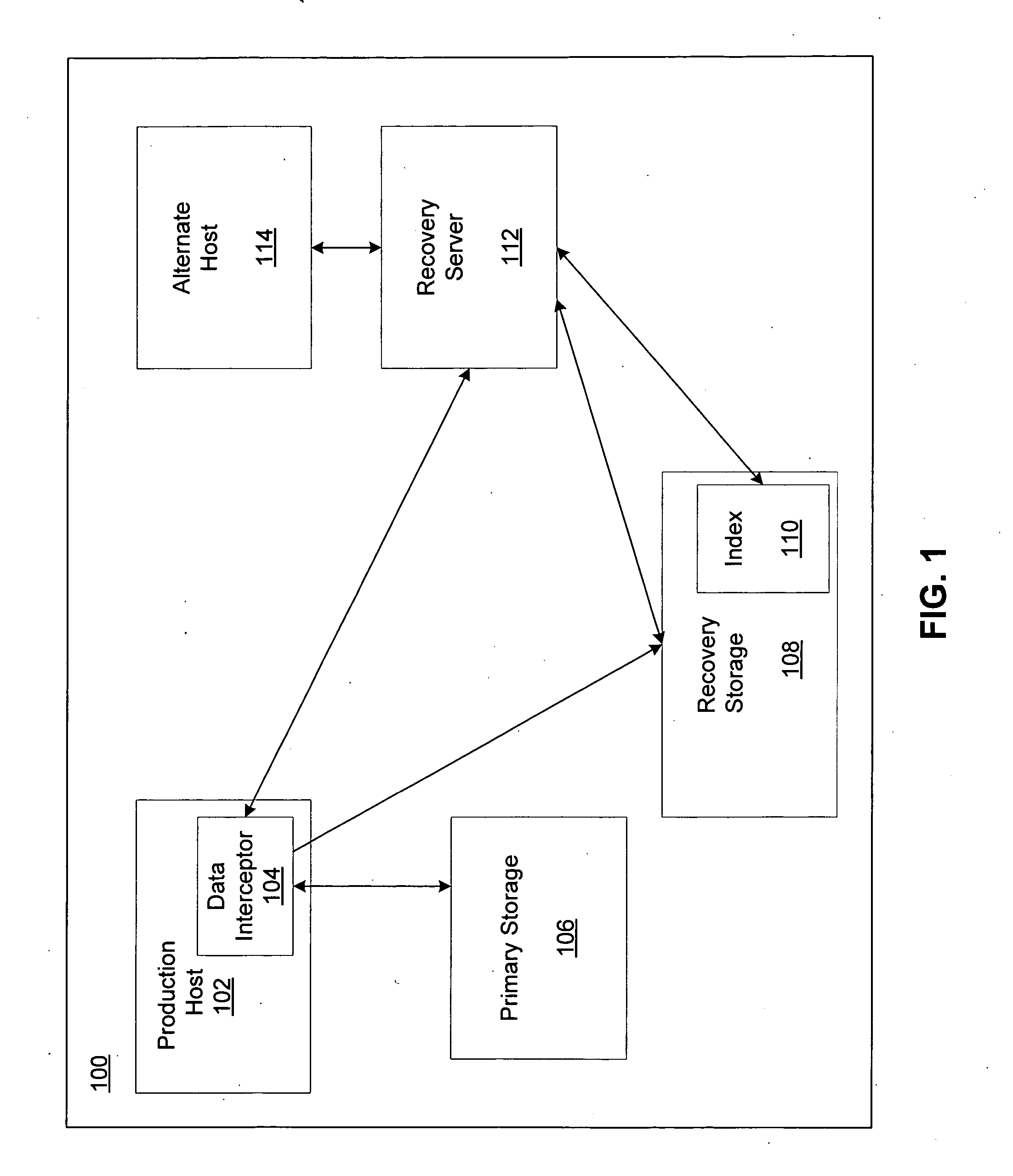
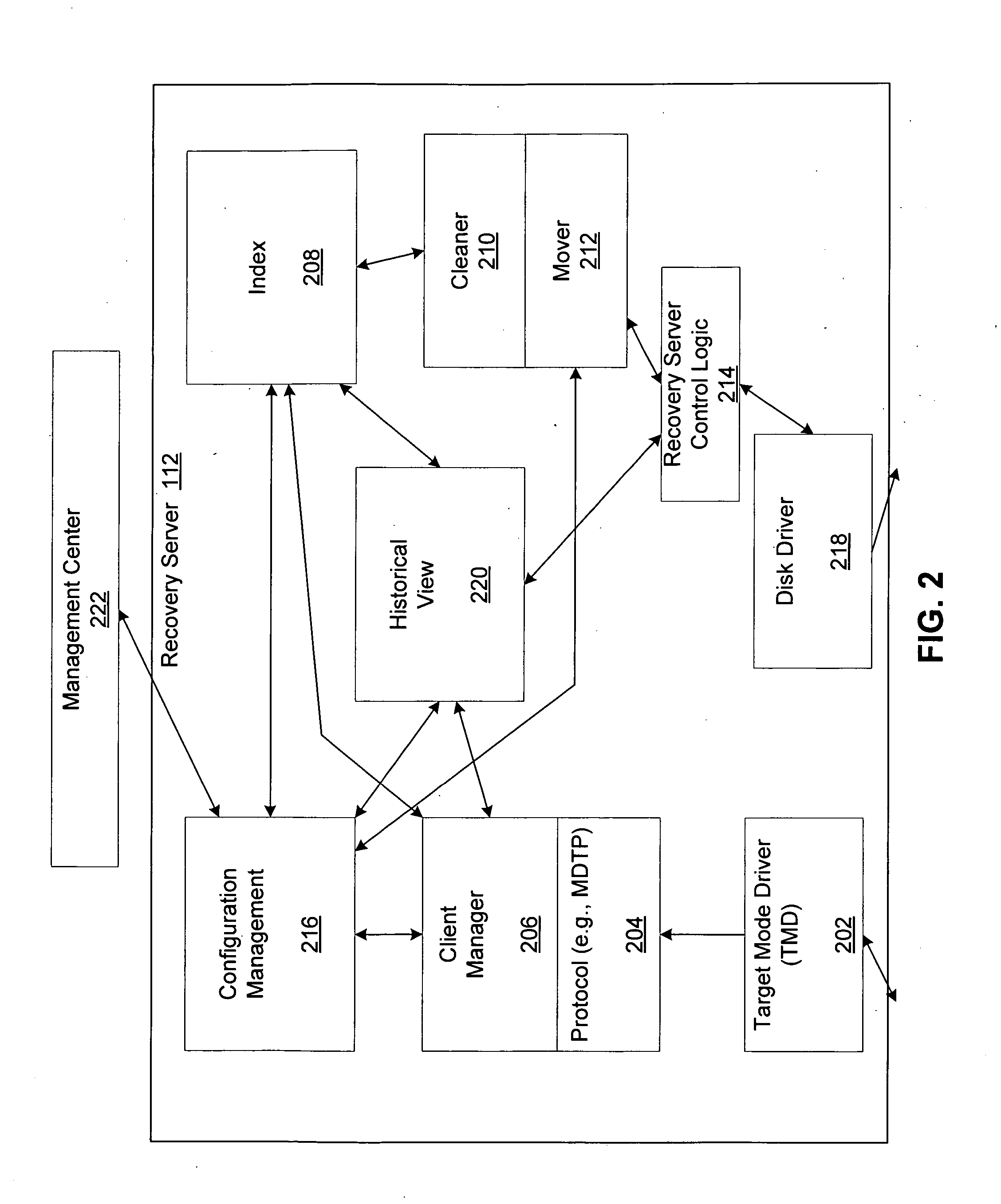
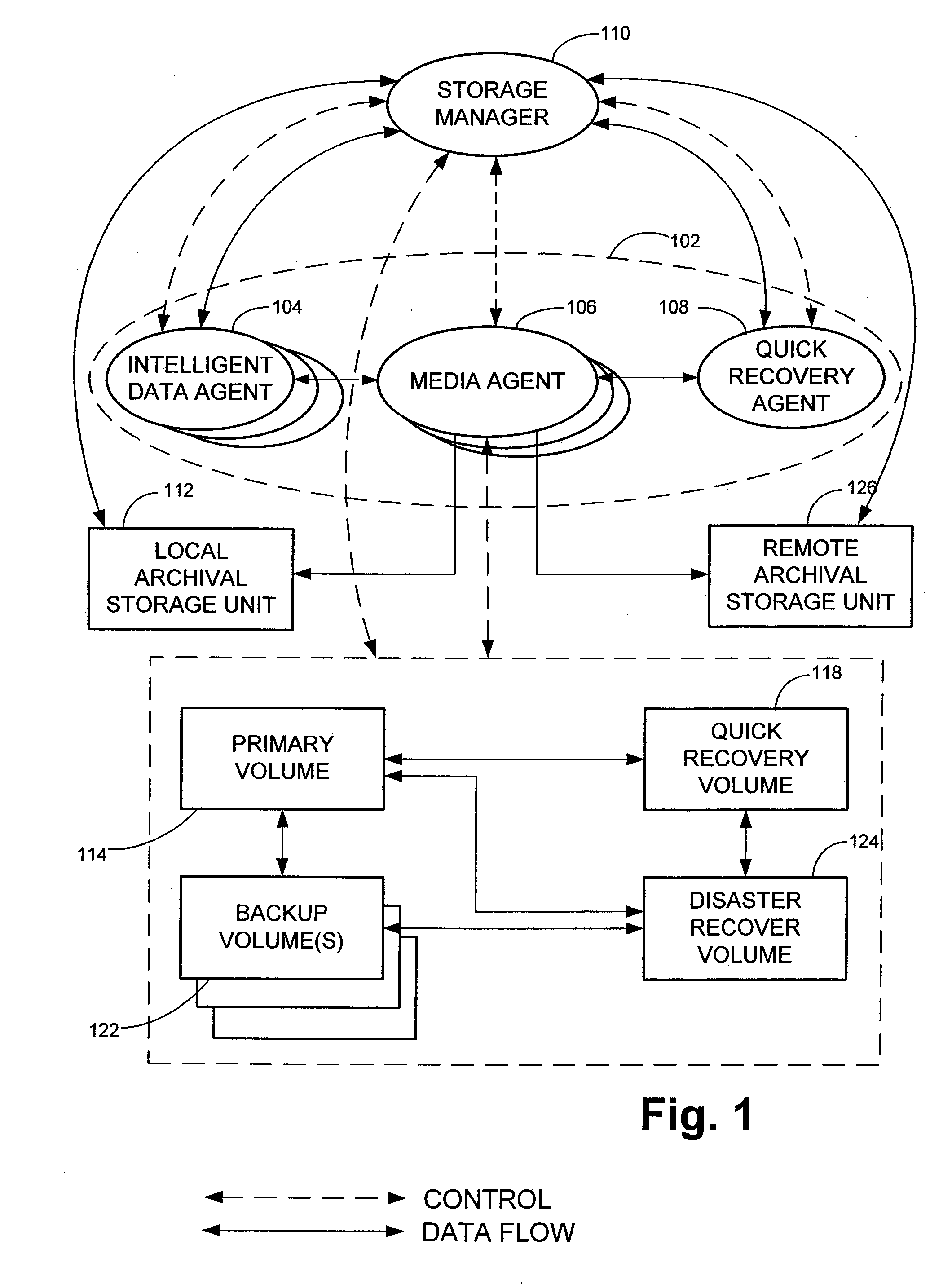
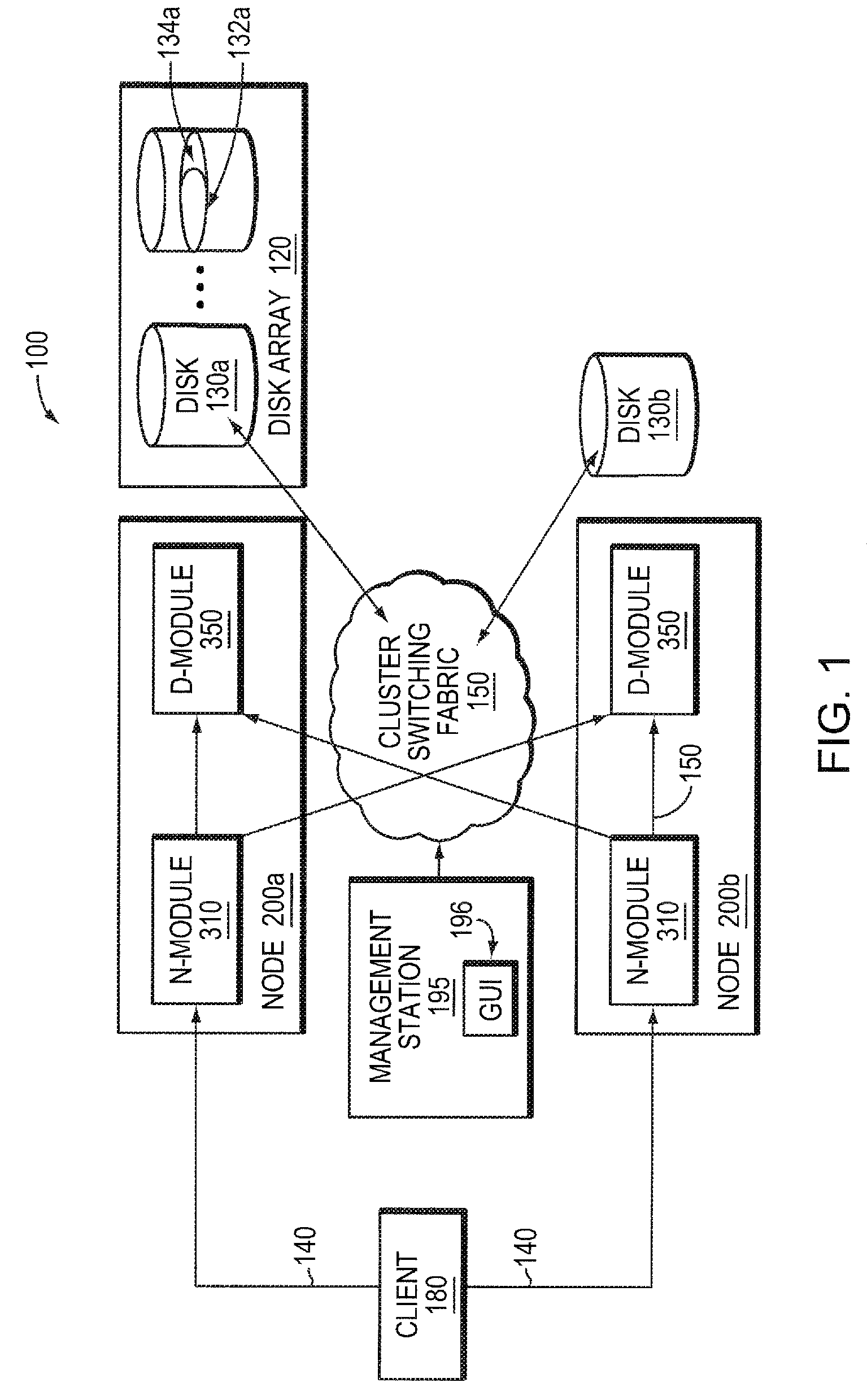
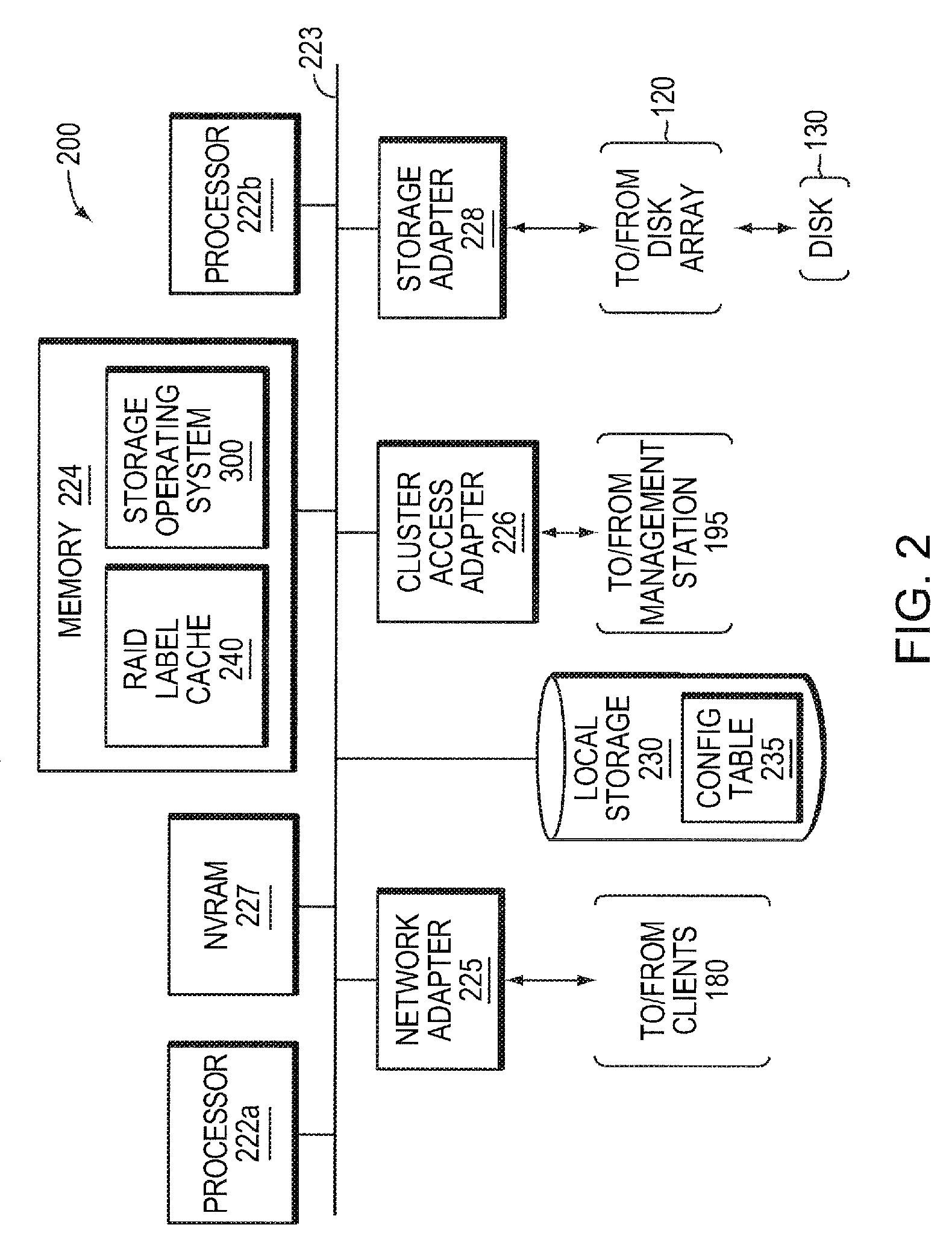
Remote disaster data recovery system and method
InactiveUS20050039069A1Error detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsInternet trafficArchival storage
The present invention provides computer systems, methods, and software products enabling the creation and maintenance of disaster recovery volumes having a reduced impact with regard to network traffic over a communications network. A disaster recovery volume is generally created at a local archival storage unit including therein at least one storage medium constituting the disaster recovery volume. The medium constituting the disaster recovery volume is associated with the primary volume thereby allowing the storage medium constituting the disaster recovery volume to be relocated to a remote archival storage unit at a remote location without compromising the association between the primary volume and the disaster recovery volume. Incremental changes to the primary volume may then be communicated and incorporated in to the disaster recovery relocated to the remote location.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
System and method for creating a point-in-time restoration of a database file
InactiveUS7373364B1Overcome disadvantagesAvoid data lossData processing applicationsError detection/correctionFile systemDatabase file
The present invention provides a method for generating a point-in-time restoration of database files and associated log files by utilizing a snapshot feature of the file system storing the files. At regular intervals, snapshots, which produce read-only copies of the files, are taken along with backups of the associated log files. To restore to a given point-in-time, the snapshot and stored log files are transferred to the active file system. In a second embodiment, all log files associated with snapshots taken after the selected snapshot are also restored.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Data recovery with internet protocol replication with or without full resync
ActiveUS7275177B2Data processing applicationsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPrimary sitesFile system
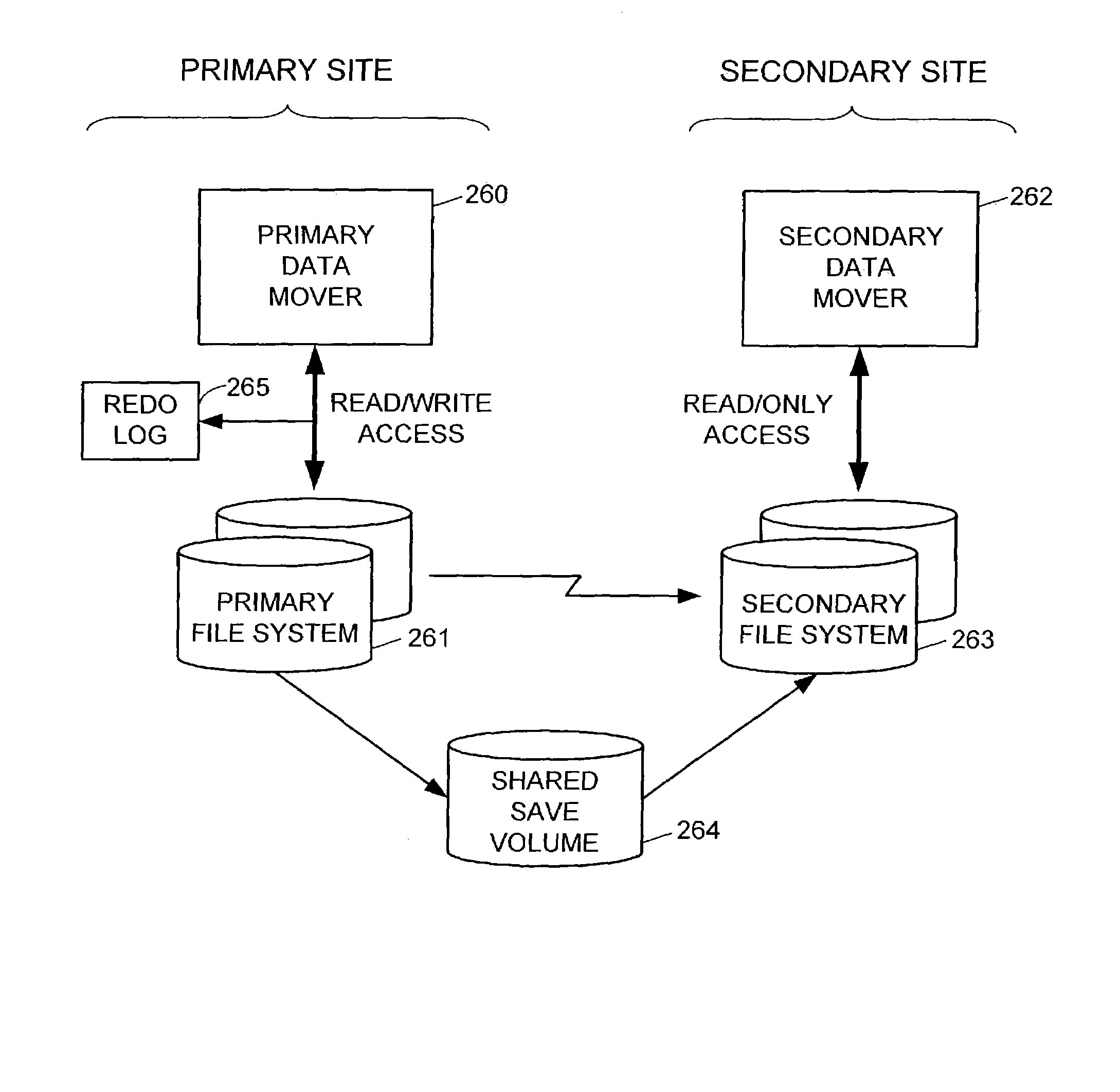
In an asynchronous remote copy system, a primary site keeps a list of data blocks for which changes have been made to a primary file system and transmitted to a secondary file system at a secondary site. When the primary site becomes inoperative, the secondary site begins read / write access to the secondary file system and keeps a snapshot copy of the restart point. Once the primary site becomes operative, the primary file system is restored to the state of the secondary file system at the restart point by using the list of data blocks for obtaining from the snapshot copy the data of the blocks for which changes had been made to the primary file system after the restart point. Then the primary file system is synchronized to the secondary file system, and read / write access is switched back from the secondary file system to the primary file system.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
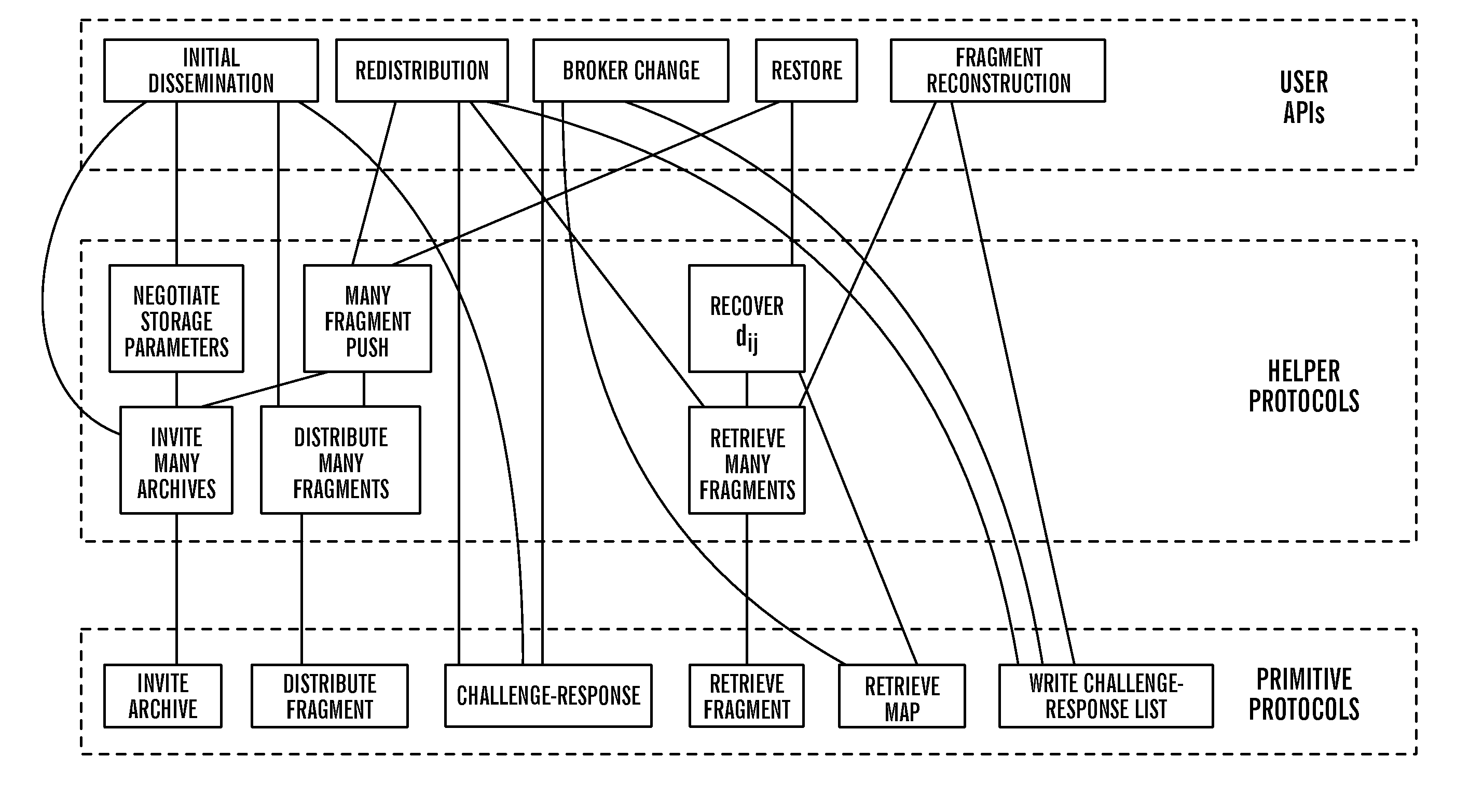
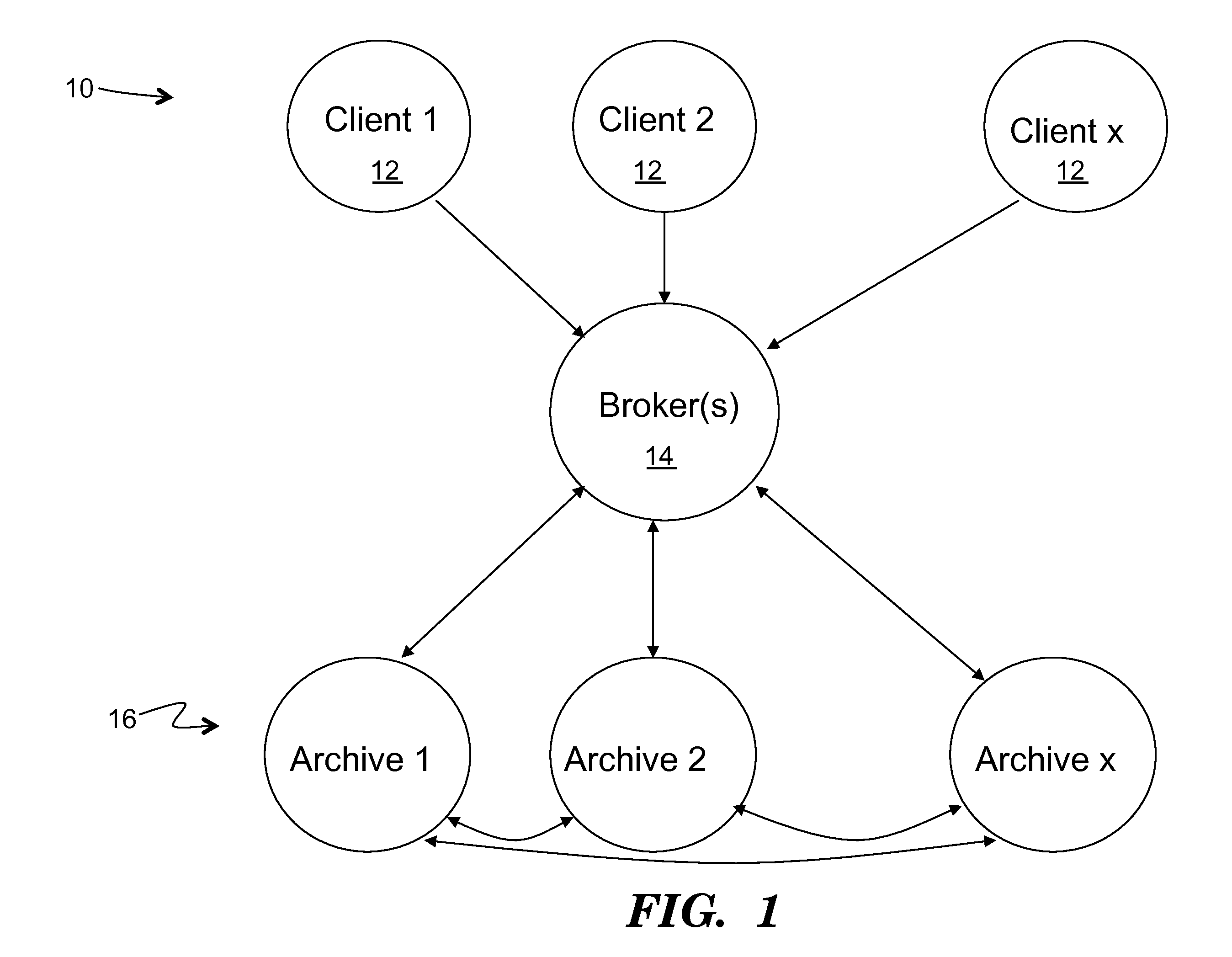
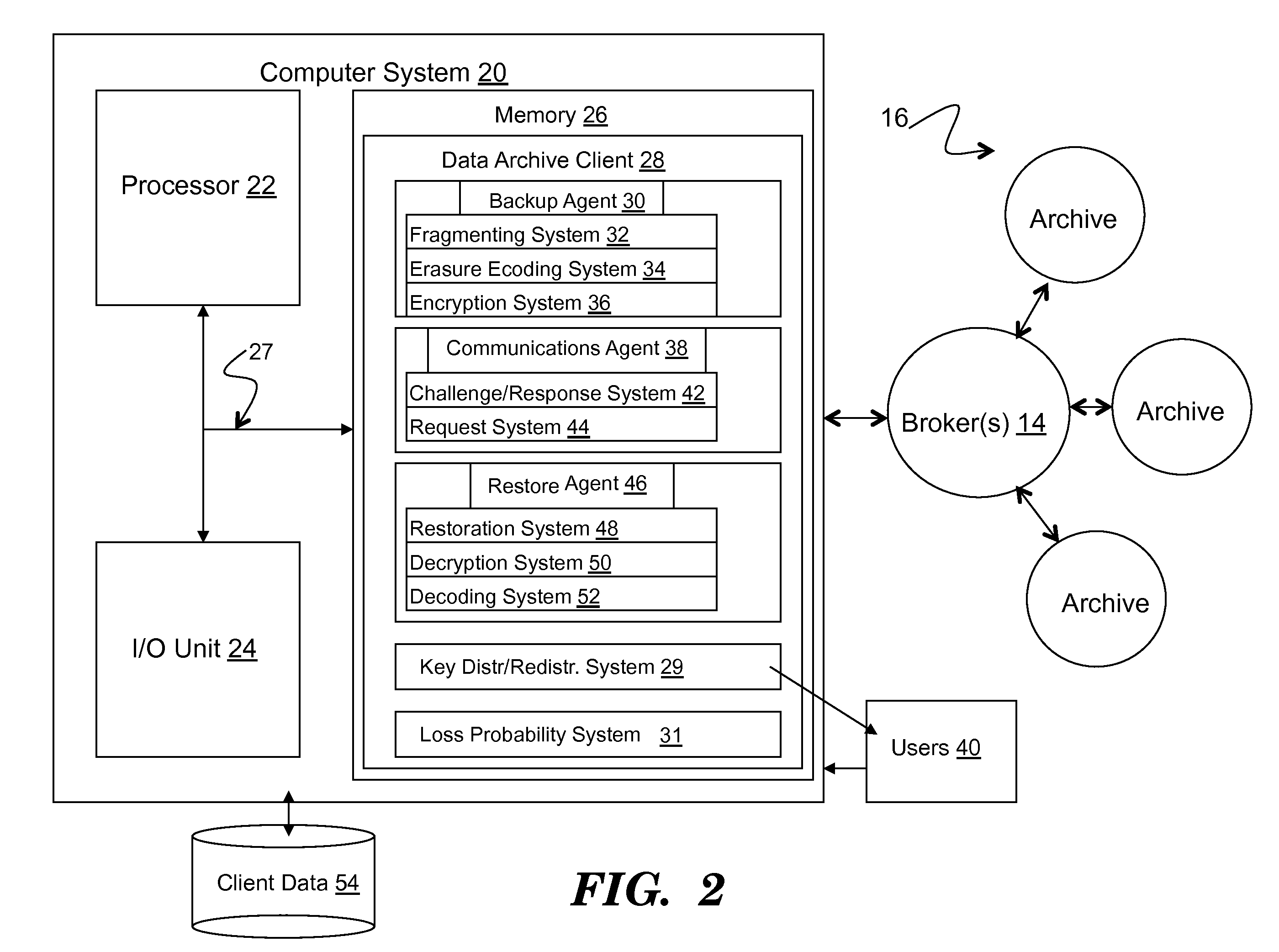
Method to support privacy preserving secure data management in archival systems
InactiveUS20100037056A1Digital data information retrievalUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyPrivacy preserving
An infrastructure for archiving data among a client, a broker, and a plurality of archives, wherein the client comprises: a backup agent configured to fragment and erasure encode the data to create a set of erasure encoded data fragments; a communications agent configured to communicate the erasure encoded data fragments to the broker, issue a challenge for a challenge / response protocol to the broker, and to request data from the archives; and a restore agent configured to combine the data fragments obtained from the broker upon a data restore request.
Owner:ALTAVAULT
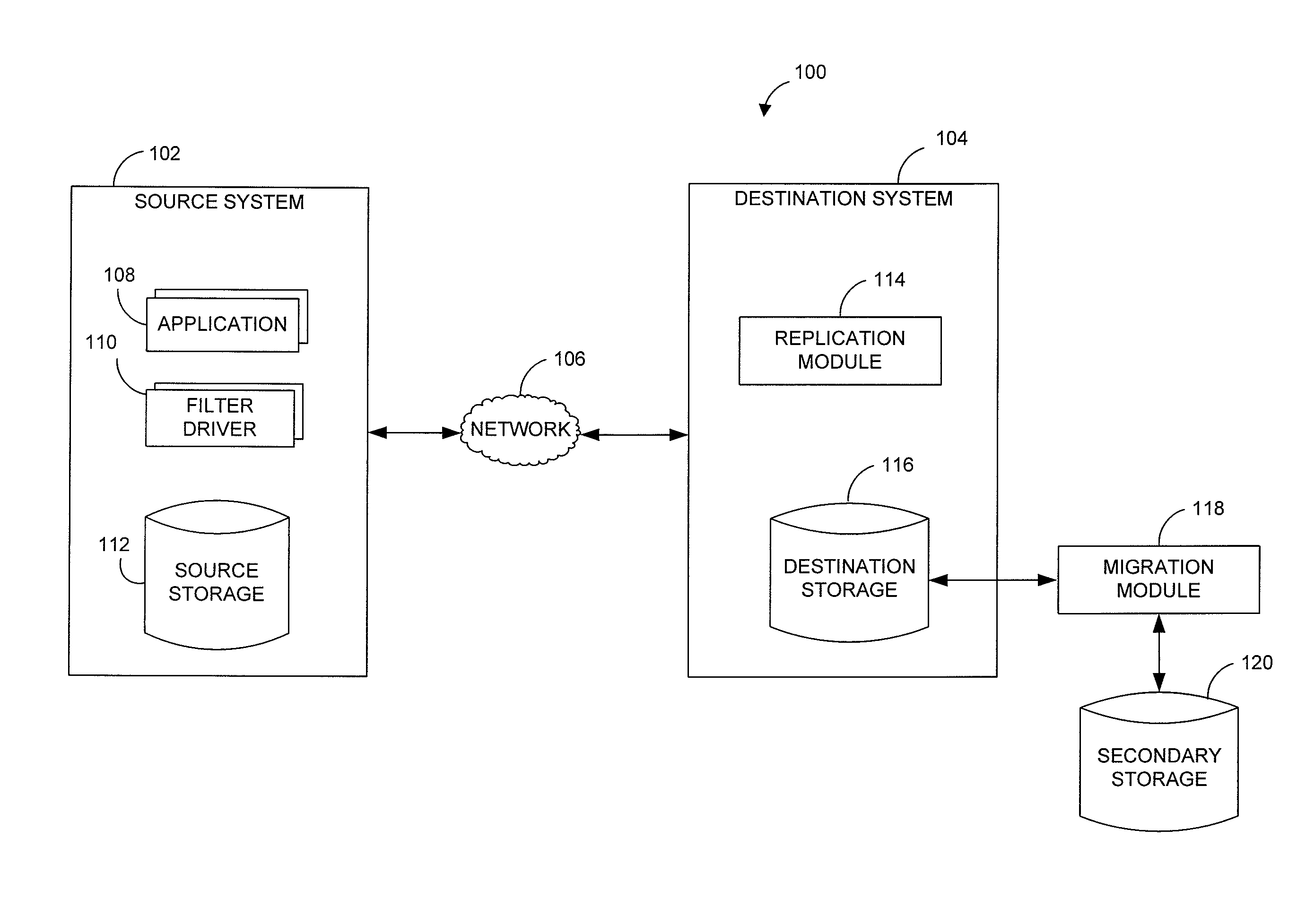
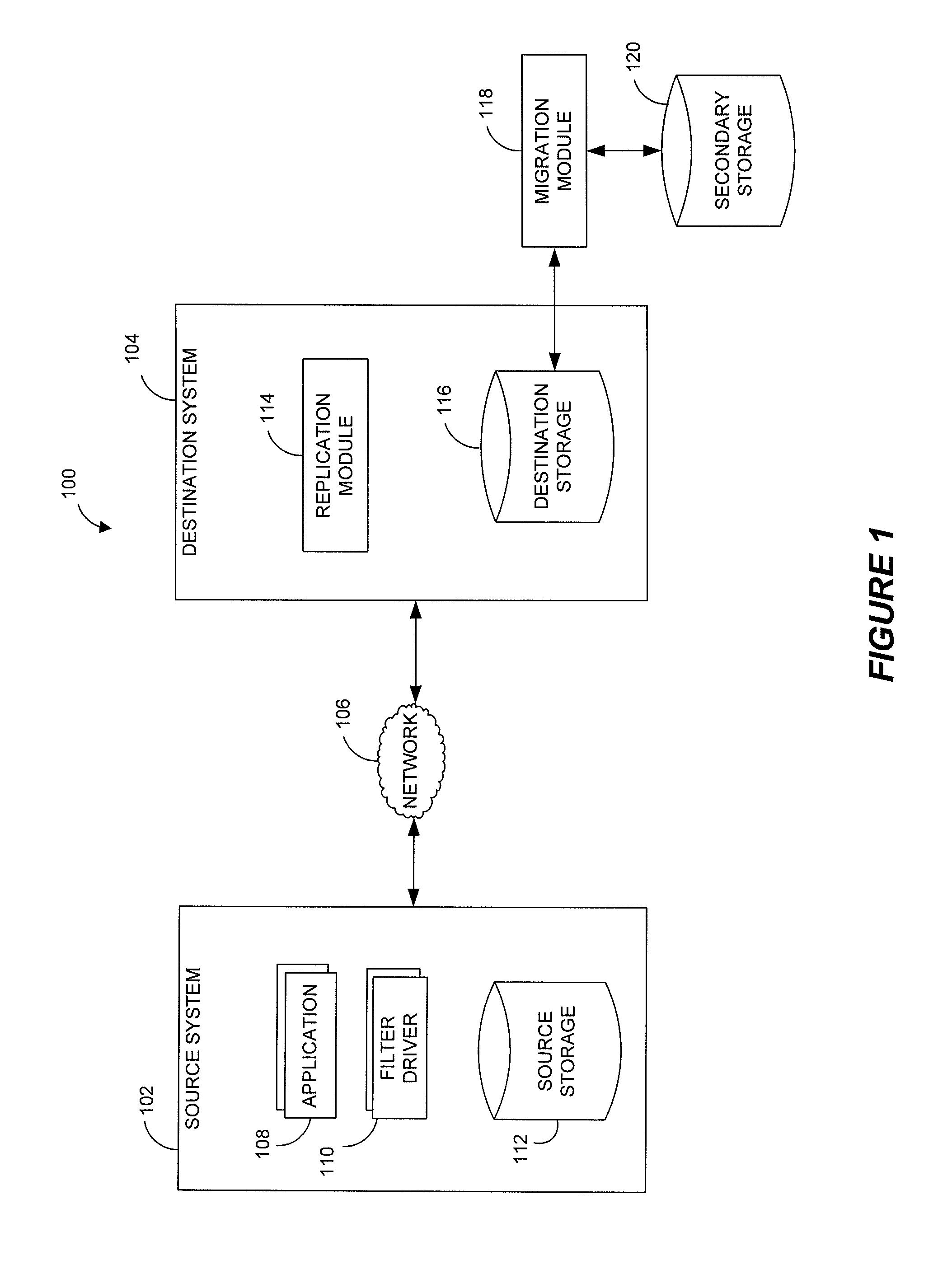
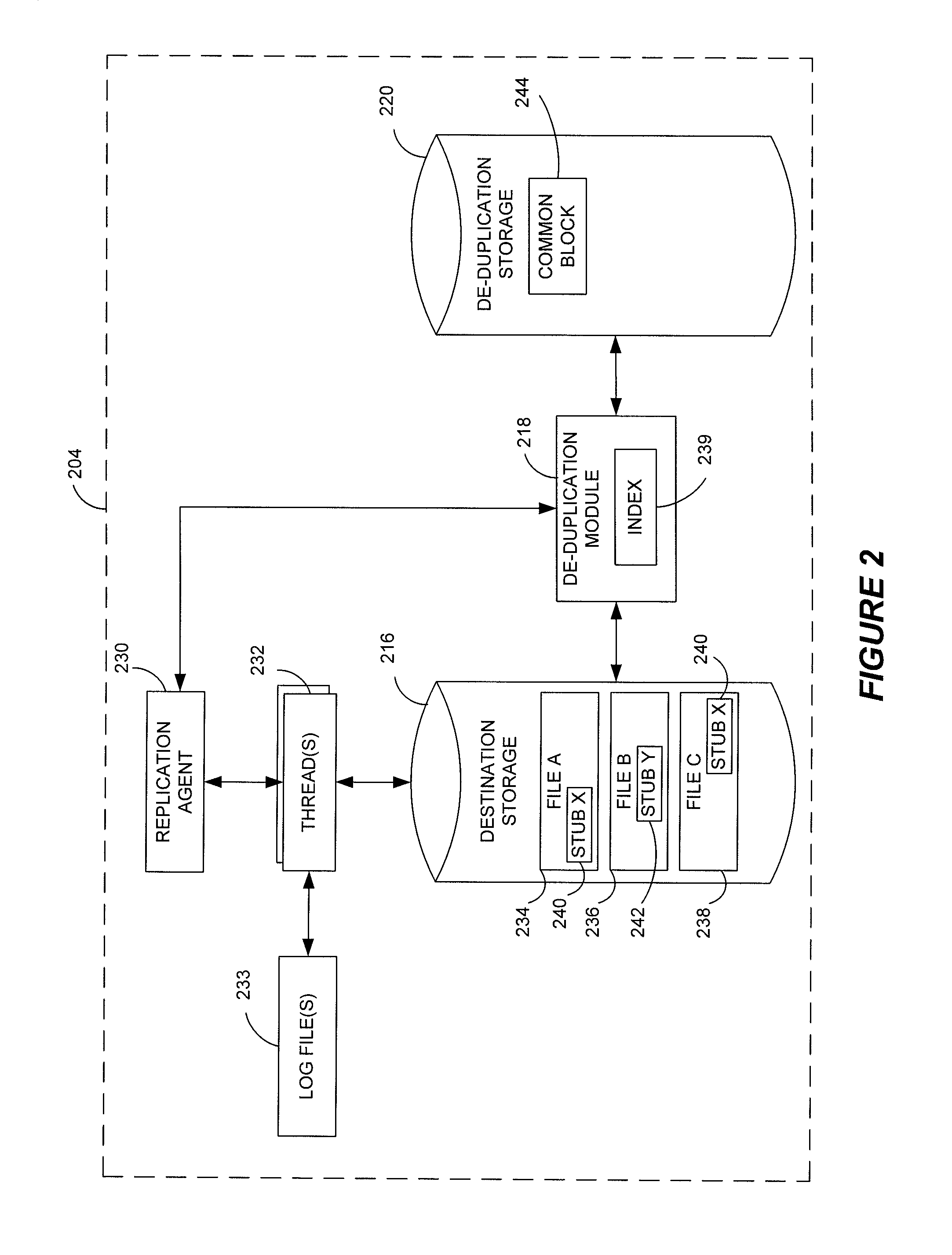
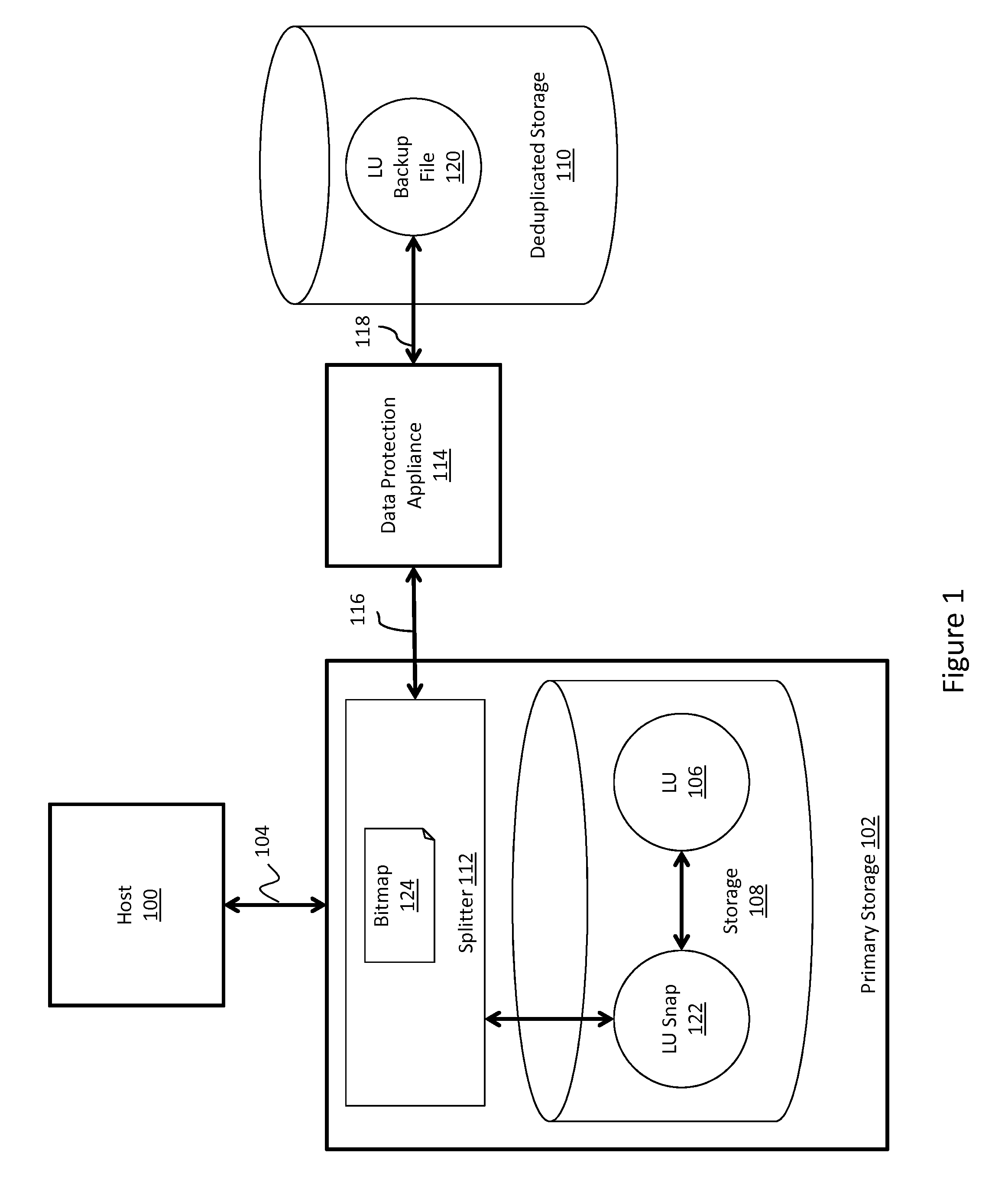
Data restore systems and methods in a replication environment
ActiveUS8352422B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData managementGoal system
Stubbing systems and methods are provided for intelligent data management in a replication environment, such as by reducing the space occupied by replication data on a destination system. In certain examples, stub files or like objects replace migrated, de-duplicated or otherwise copied data that has been moved from the destination system to secondary storage. Access is further provided to the replication data in a manner that is transparent to the user and / or without substantially impacting the base replication process. In order to distinguish stub files representing migrated replication data from replicated stub files, priority tags or like identifiers can be used. Thus, when accessing a stub file on the destination system, such as to modify replication data or perform a restore process, the tagged stub files can be used to recall archived data prior to performing the requested operation so that an accurate copy of the source data is generated.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
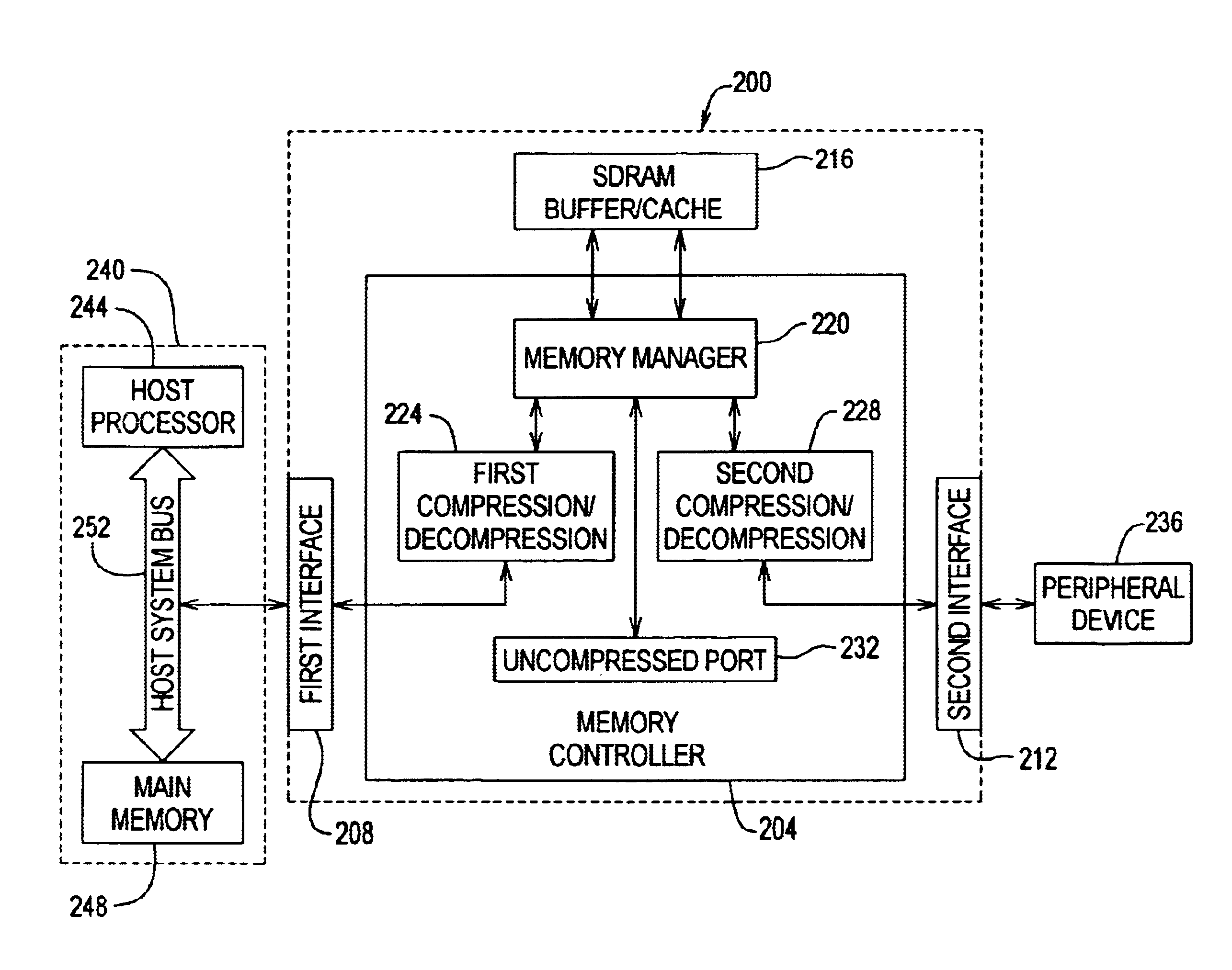
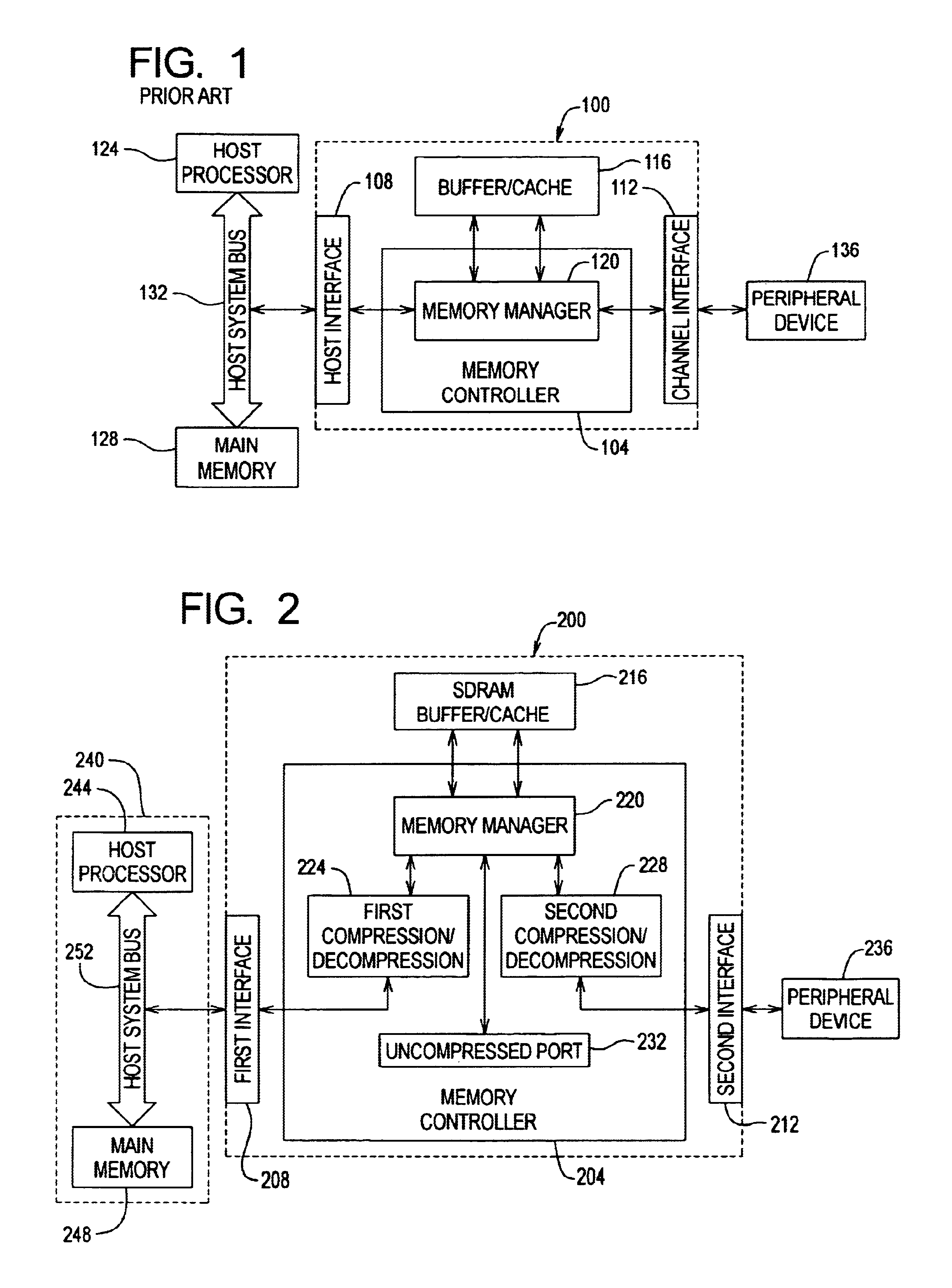
Method and apparatus for using data compression as a means of increasing buffer bandwidth
InactiveUS6883079B1Increase effective bandwidthEffective bandwidth of memoryMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersData compressionMemory controller
A method and apparatus for increasing the bandwidth of a memory controller system are provided. According to the invention, data received at an interface of a memory controller system is compressed in the memory controller by a compression engine for storage in associated memory. The address of the data written to memory is maintained in a memory controller. When data is read from the memory for provision to an interface of the memory controller, the memory manager retrieves the data from memory and provides it to a decompression engine. The decompression engine restores the data to its original, uncompressed form. The data is then provided to the appropriate interface.
Owner:MAXTOR
Approach for optimizing restores of deduplicated data
InactiveUS20110218969A1Reduce the amount of processingImprove efficiencyError detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsData fileClient data
Various techniques for improving the performance of restoring deduplicated data files from a server to a client within a storage management system are disclosed. In one embodiment, a chunk index is maintained on the client that tracks the chunks remaining on the client for each data file that is stored to and restored from the storage server. When a specific file is selected for restore from the storage server to the client, the client determines if any local copies of this specific file's chunks are stored in files already existing on the client data store. The file is then reconstructed from a combination of these local copies of the file chunks and chunks retrieved from the storage server. Therefore, only chunks that are not stored or are inaccessible to the client are retrieved from the server, reducing server-side processing requirements and the bandwidth required for data restore operations.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for automatically and dynamically optimizing application data resources to meet business objectives
ActiveUS20050015641A1Provide flexibilityMinimize impactEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionSpecial data processing applicationsQuality of serviceData availability
A system and method to automatically and dynamically optimize available resources to meet application data availability and business objectives. In one embodiment, a backup and data recovery system continually and dynamically adjust to the backup and recovery or restore process depending on the customer's environment, workload, and business objectives. Acceptable tolerance of downtime due to recovery and backup impacts the customer's business or system operation. From this high-level business requirement, the present system determines the backup and recovery plan details. The present system accepts application data availability policies based on business objectives, and devises, executes and refines a resource optimal backup and recovery strategy required to deliver the desired quality of service in the environments that have dynamically changing application workloads, business objectives, and hardware / software infrastructure technologies. In addition, the present system performs backups outside blocked windows to minimize the impact on the customer's system.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
System, method, and program product for saving a submitted form of a web page
InactiveUS6950980B1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsOperational systemApplication software
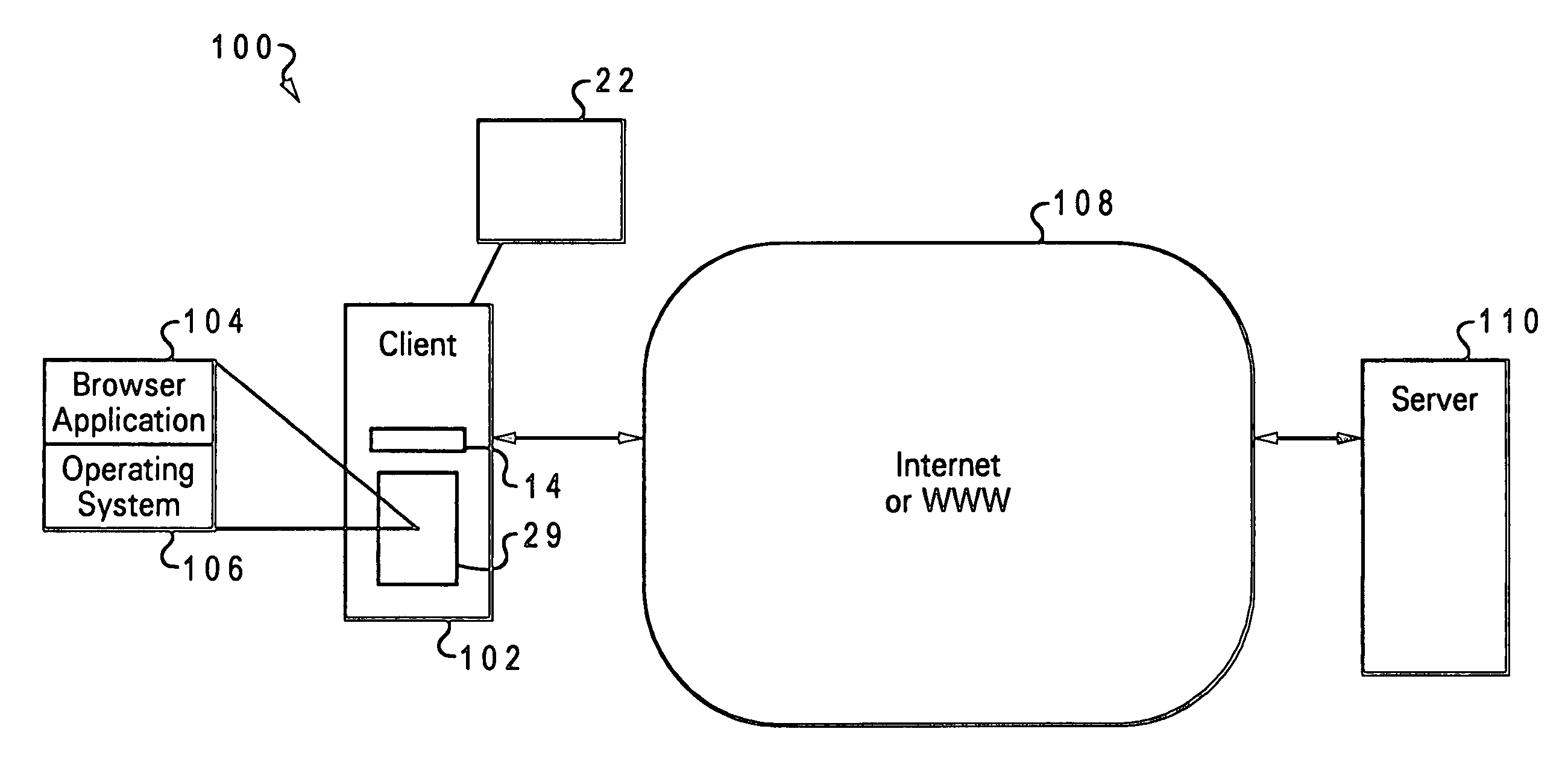
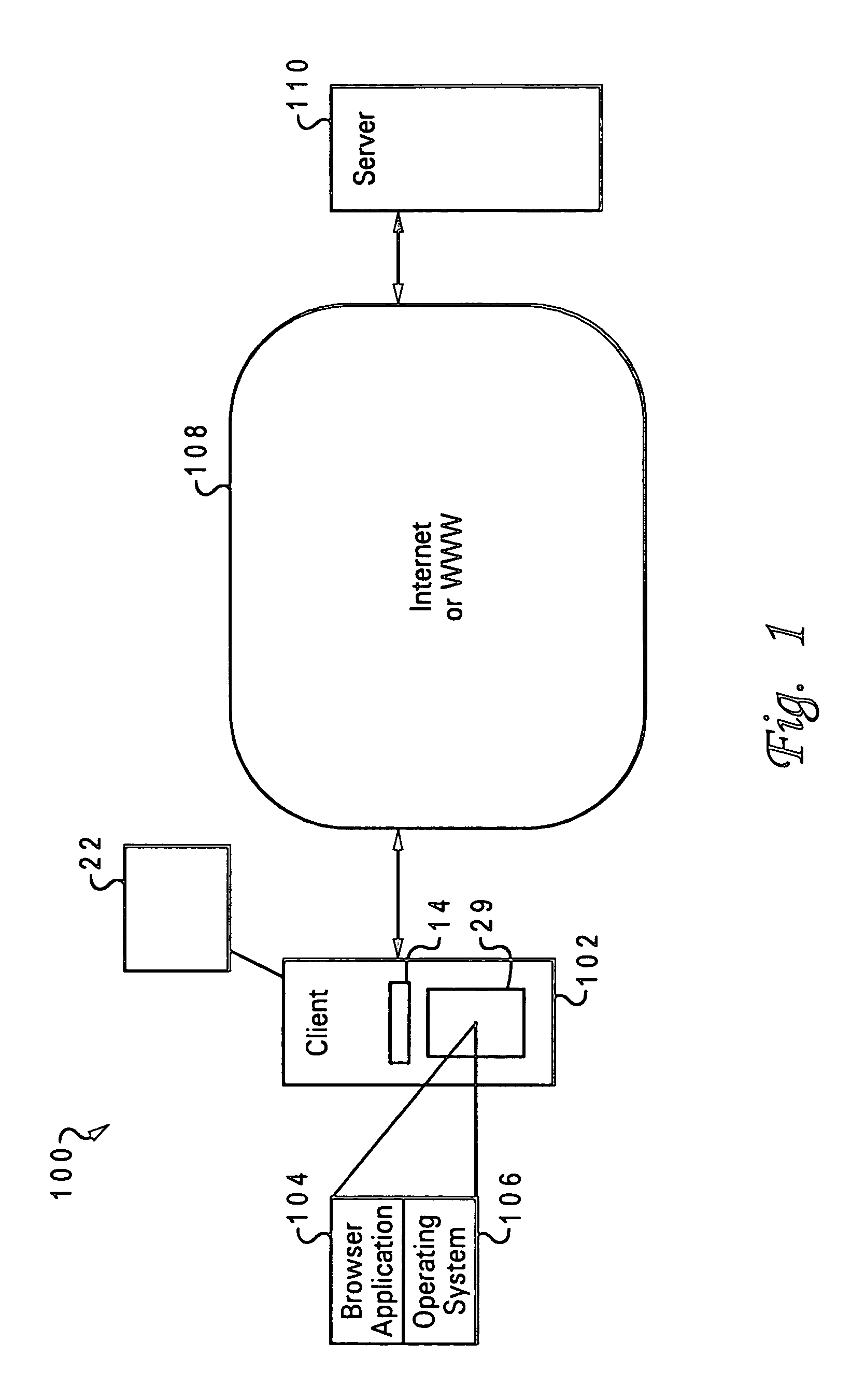
A system, method, and program product enables saving a submitted form of a web page. A browser application receives from a user data for a form in a web page. Upon the submission of the form with the data to a server system hosting the web page, an address of the web page, the data provided from the user for the form, and at least one field identifier for associating the data to at least one respective field of the form, are saved into a volatile memory of the client. The address, the data, and the at least one field identifier remain stored in the volatile memory system after the browser application is closed. When the user opens the browser that had been dosed and again requests retrieval of the web page, the browser retrieves from the server the web page that is at the address stored in the volatile memory. The browser restores the form of the web page with the data stored in the volatile memory. The browser calls a clipboard operation of an operating system on which the client system operates to save the address of the web page, the data for the form, and the one or more field identifiers, into the volatile memory. If the data for the form is successfully submitted to the server and the browser receives another request for a next web page from the user, the browser application erases, if required, the data from the volatile memory system.
Owner:IBM CORP
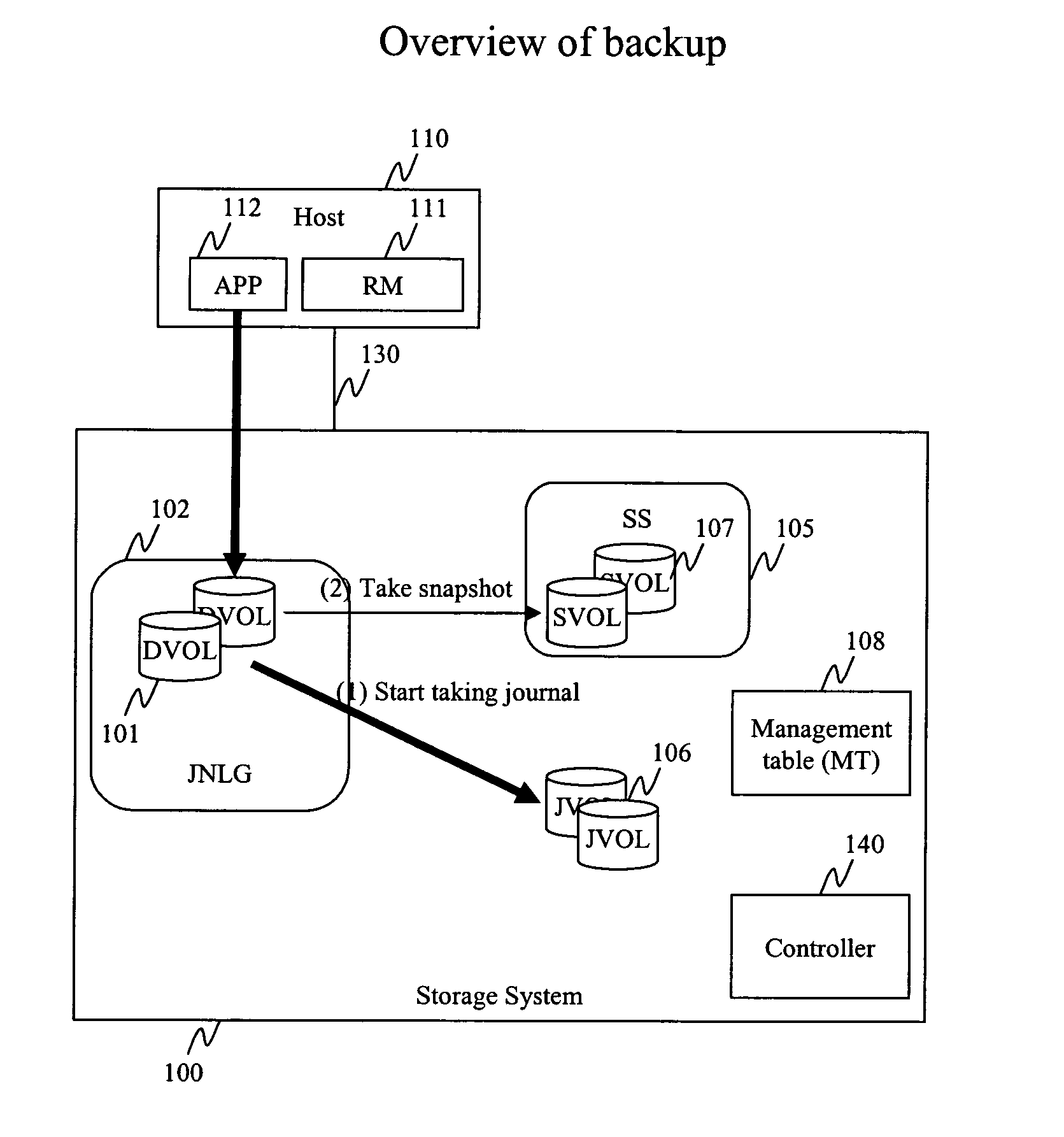
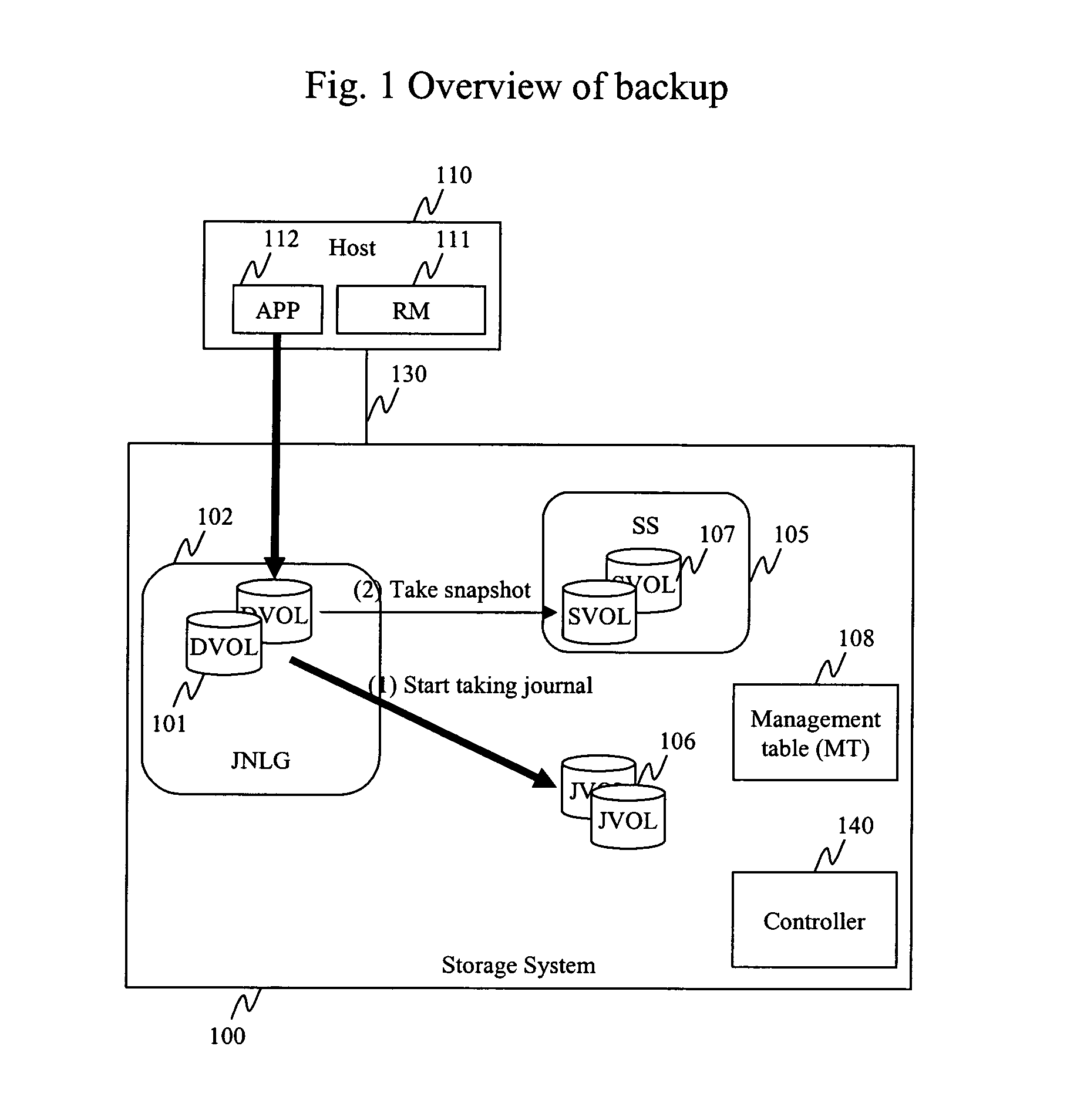
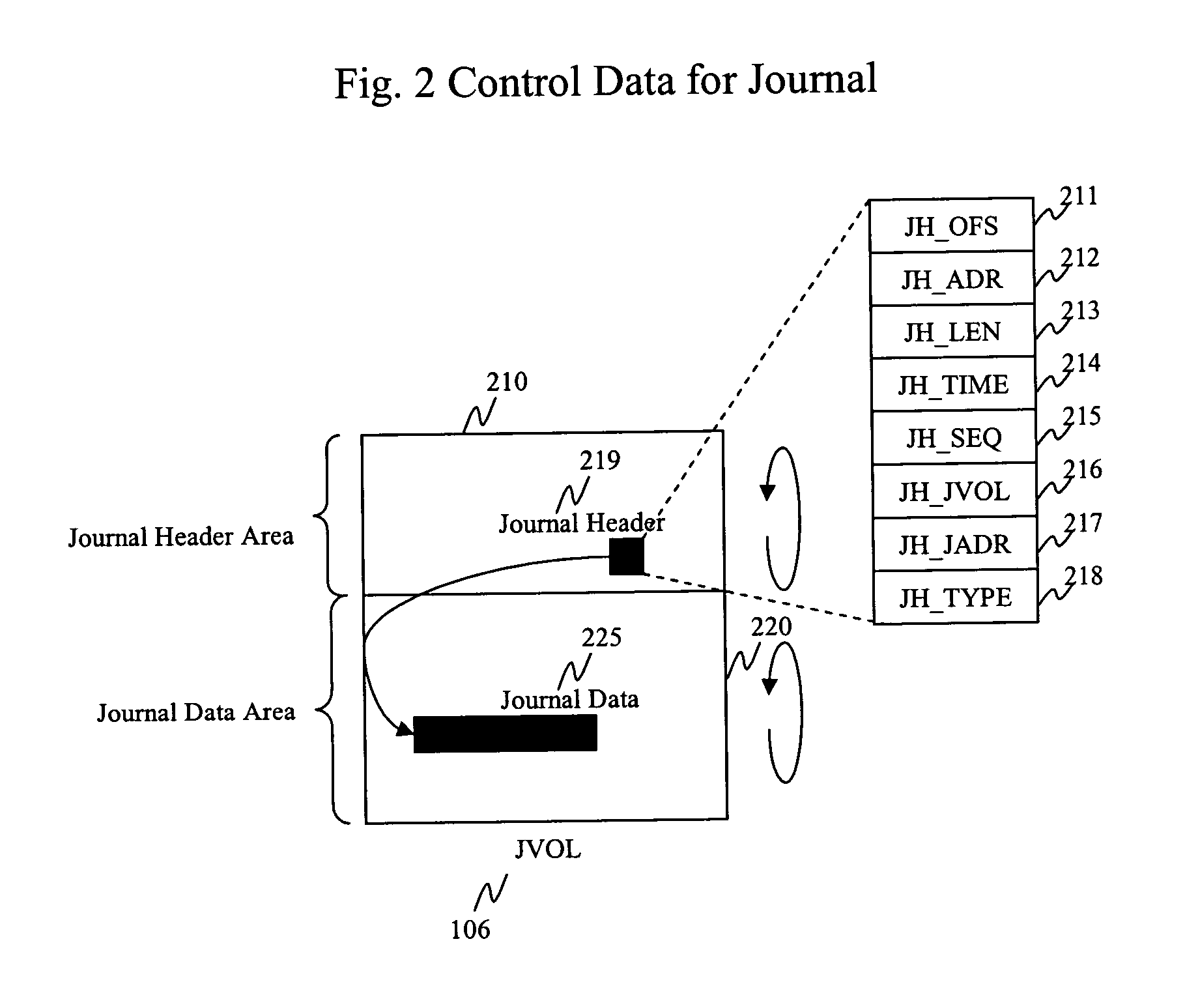
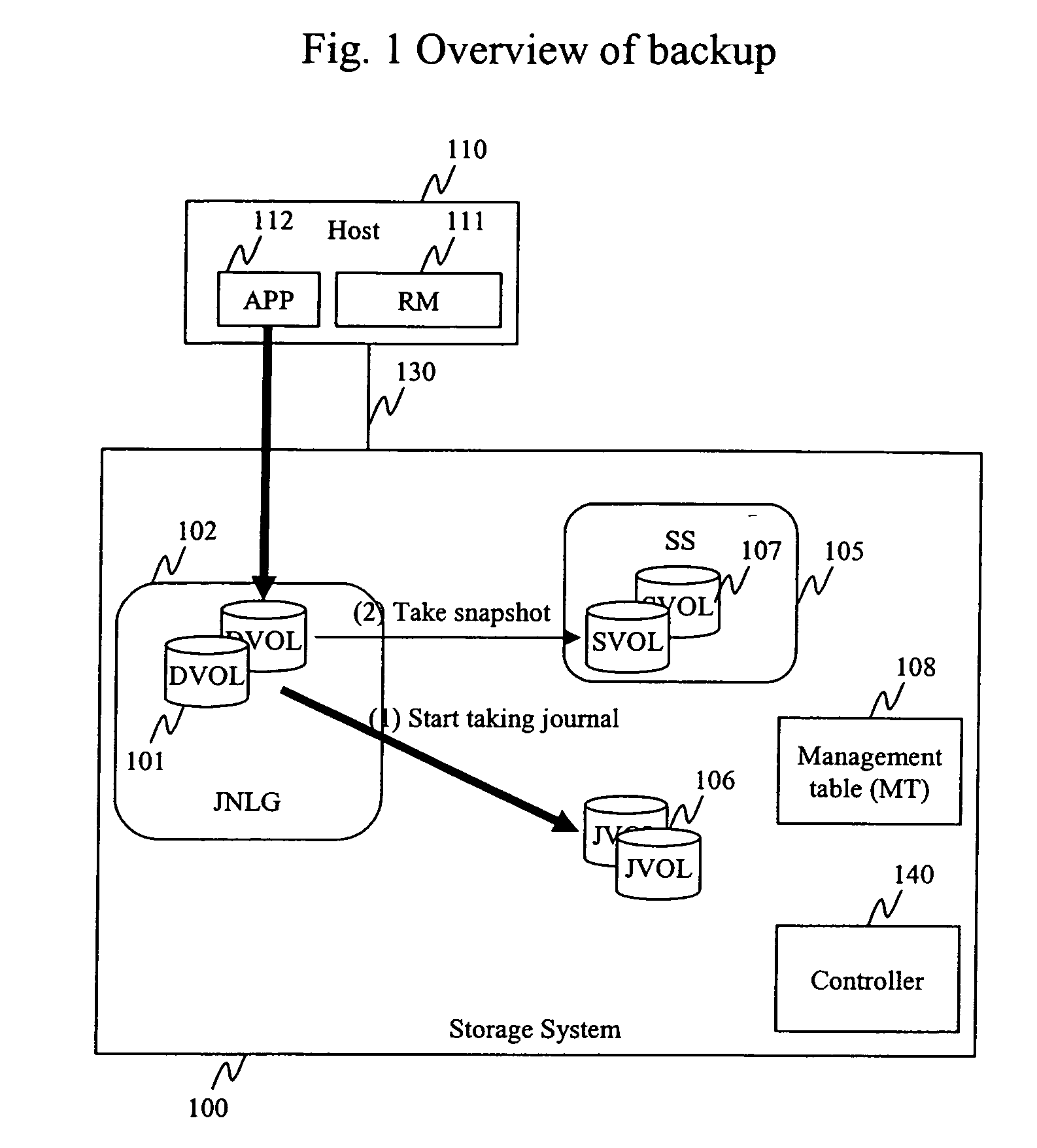
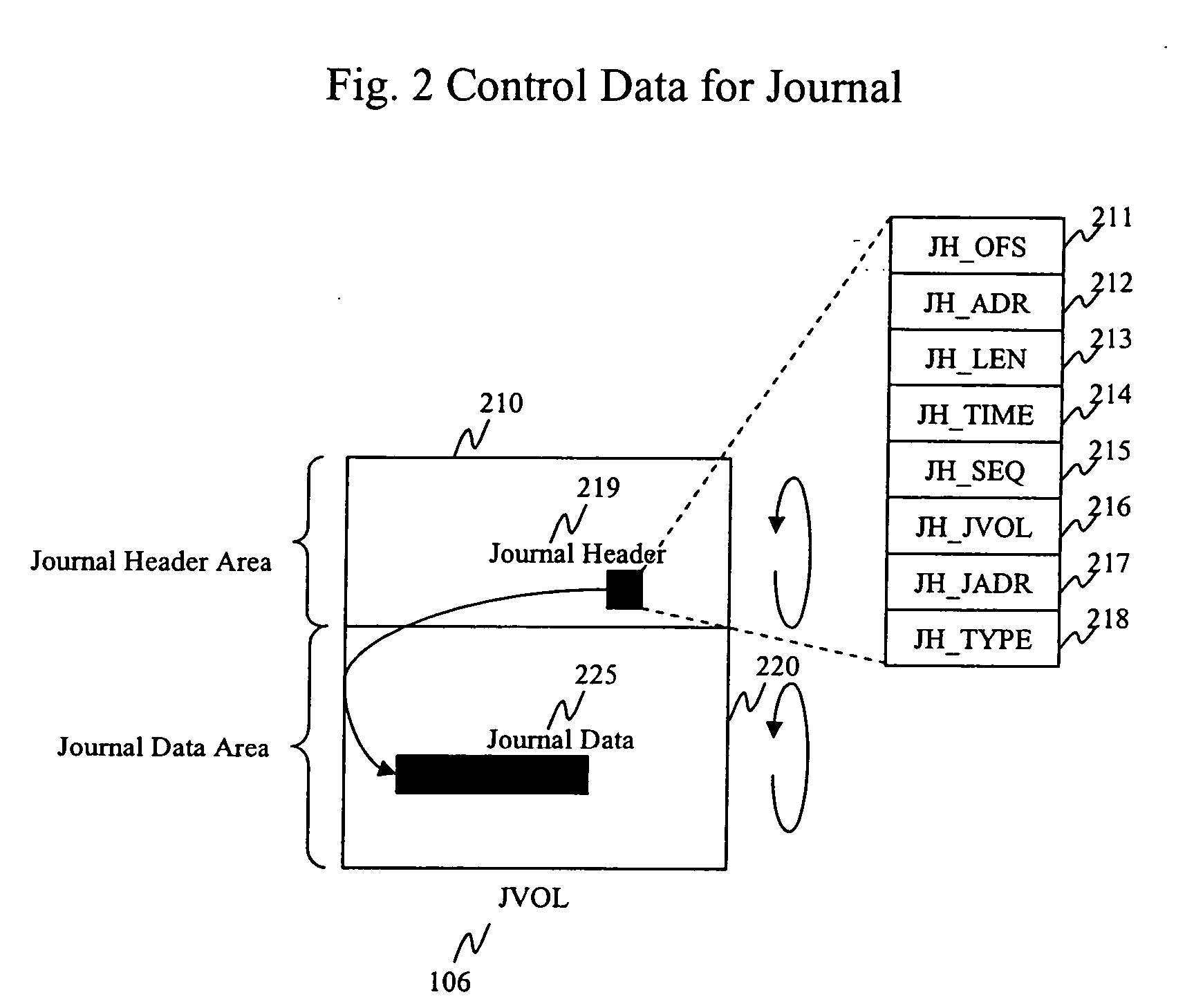
Method and apparatus for data recovery using storage based journaling
InactiveUS20050015416A1Resume normal operationError detection/correctionMemory systemsSystem maintenanceComputer science
A storage system maintains a journal and a snapshot of one or more data volumes. Two journal entry types are maintained, an AFTER journal entry and a BEFORE journal entry. Two modes of data recovery are provided: “fast” recovery and “undo-able” recovery. A combination of both recovery modes allows the user to quickly recover a targeted data state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
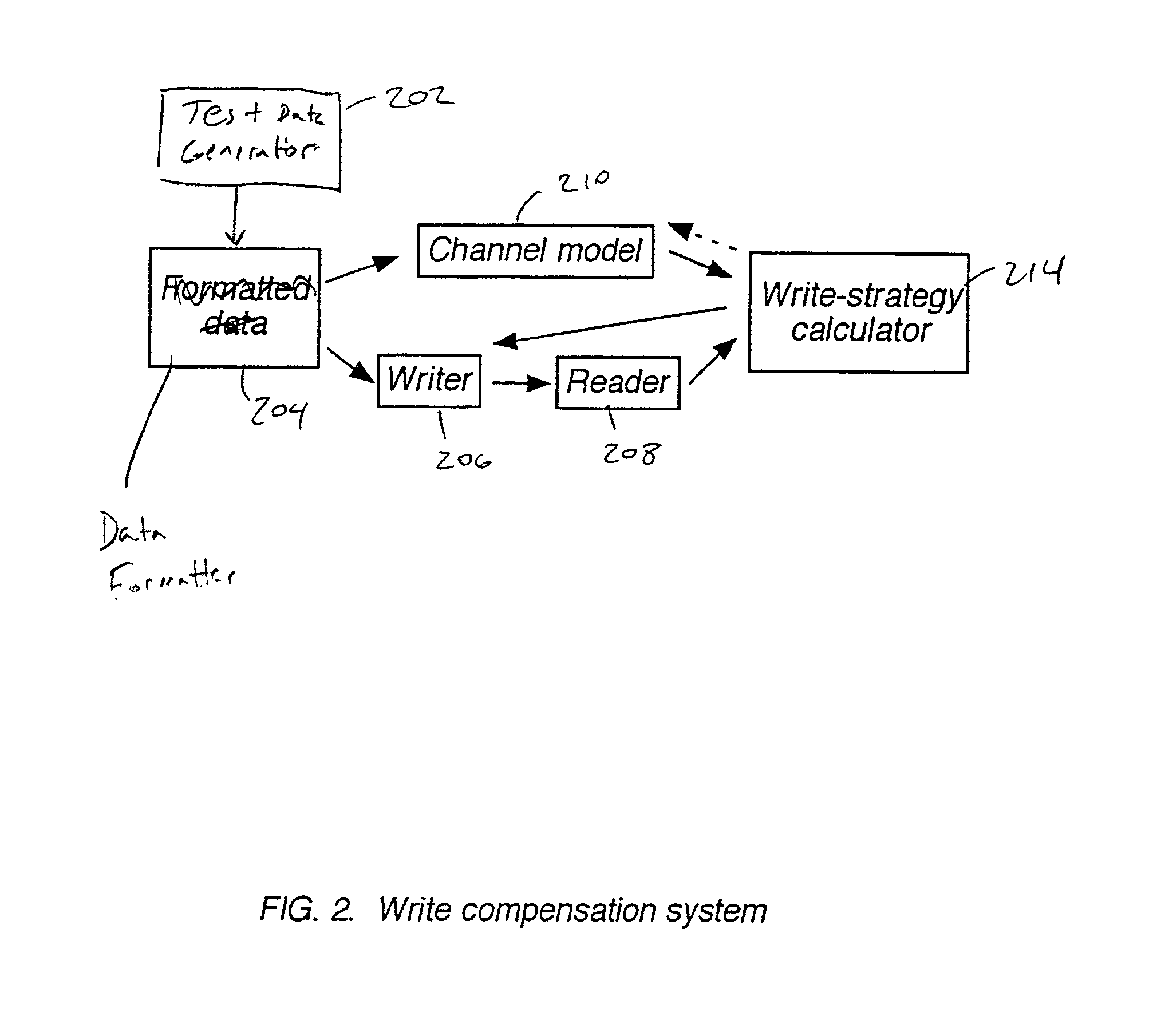
Write compensation for data storage and communication systems
InactiveUS20020126604A1Television system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersCommunications systemChannel sensitivity
Methods and systems for write compensation for optimizing the performance of a data storage or communication channel are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method comprises determining channel sensitivity to modifications in write signal parameters, detecting systematic errors in a read signal recovered from data written with a first set of write parameters, and adjusting the write signal parameters by an amount determined from the channel sensitivity such that the systematic errors are reduced when data are written with the adjusted write parameters.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
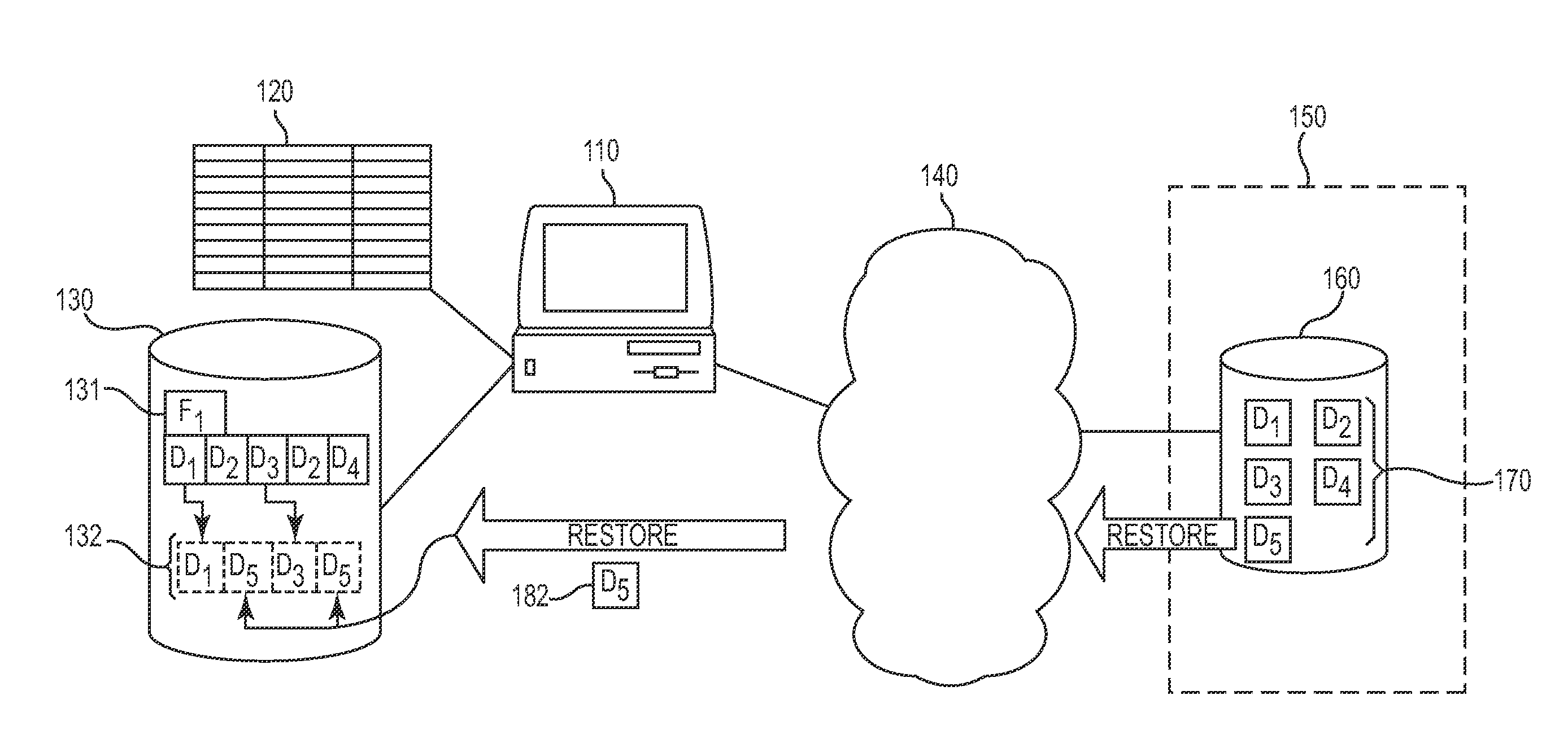
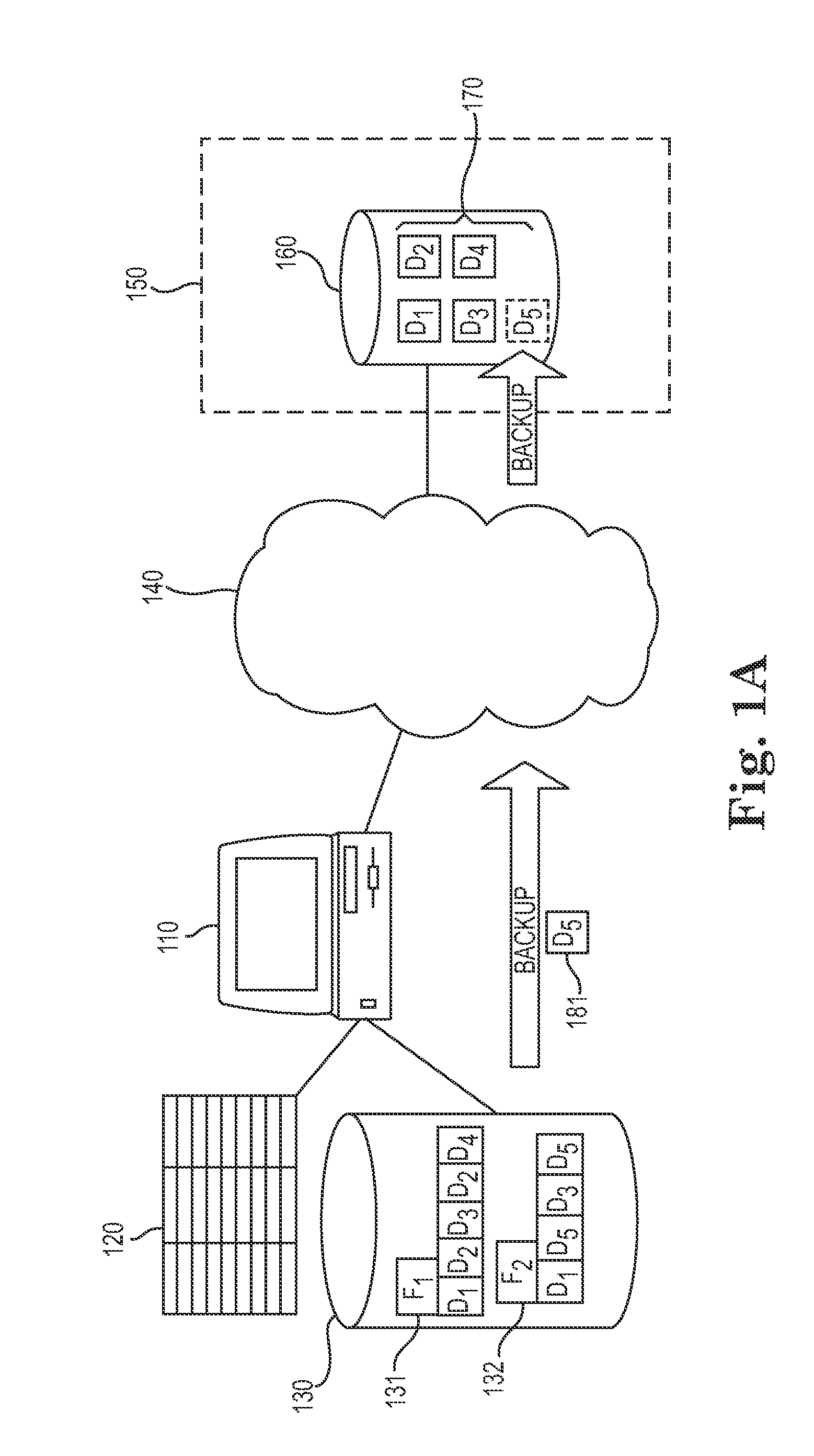
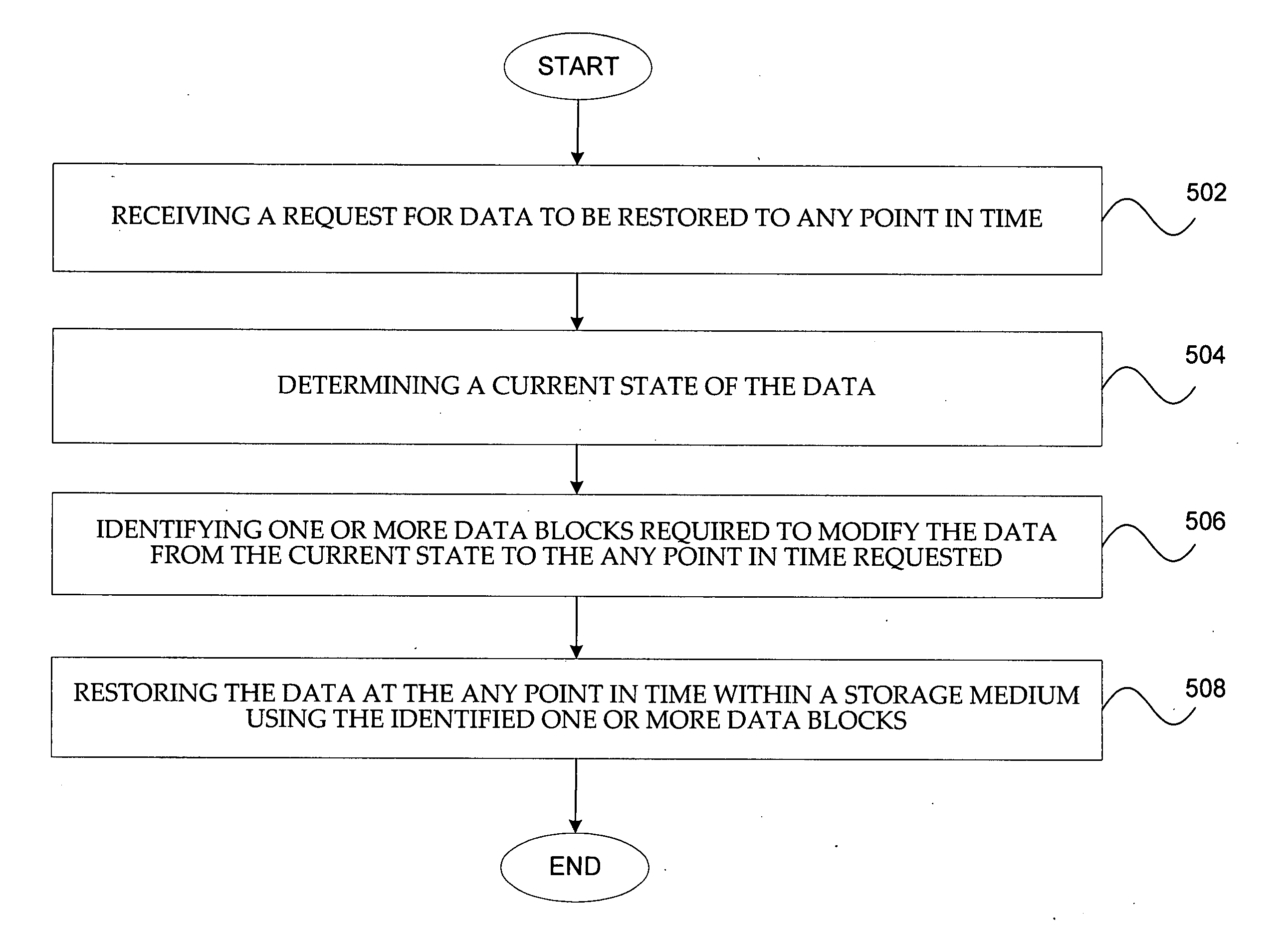
Systems and methods for optimizing restoration of stored data
ActiveUS20060047996A1Optimizing restoration of stored dataError detection/correctionData miningData restoration
A system and method is provided for optimizing restoration of stored data. A request for data to be restored to any point in time is received. A current state of the data is determined. One or more data blocks required to modify the data from the current state to the any point in time requested are identified. The data at the any point in time is restored within a storage medium using the identified one or more data blocks.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
System and method for maintaining a backup storage system for a computer system
ActiveUS7844577B2Digital data processing detailsRedundant operation error correctionComputerized systemApplication software
A backup computer storage system that protects and / or recovers data on a primary computer storage system is disclosed. The backup computer system may be used to backup databases, files, and / or applications. In some embodiments, the backup system may be used to backup an image of the primary computer system. In other embodiments, the backup system may be used to backup one or more databases. In some embodiments of the present invention, the backup system replicates an image of data that is on a primary computer system. The backup system may also be used to restore data from the backup system to the primary computer system. In some embodiments, the backup system may restore data to a database while non-affected portions of the database are available and can be used. In some embodiments, the backup system records all transactions in real time without overwriting any previously stored backup data. In some embodiments of the present invention, the backup system maintains historical and / or chronological information related to the backed up data.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Remote disaster data recovery system and method
InactiveUS20100114837A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsTraffic capacityComputerized system
The present invention provides computer systems, methods, and software products enabling the creation and maintenance of disaster recovery volumes having a reduced impact with regard to network traffic over a communications network. A disaster recovery volume is generally created at a local archival storage unit including therein at least one storage medium constituting the disaster recovery volume. The medium constituting the disaster recovery volume is associated with the primary volume thereby allowing the storage medium constituting the disaster recovery volume to be relocated to a remote archival storage unit at a remote location without compromising the association between the primary volume and the disaster recovery volume. Incremental changes to the primary volume may then be communicated and incorporated in to the disaster recovery relocated to the remote location.
Owner:PRAHLAD ANAND +5
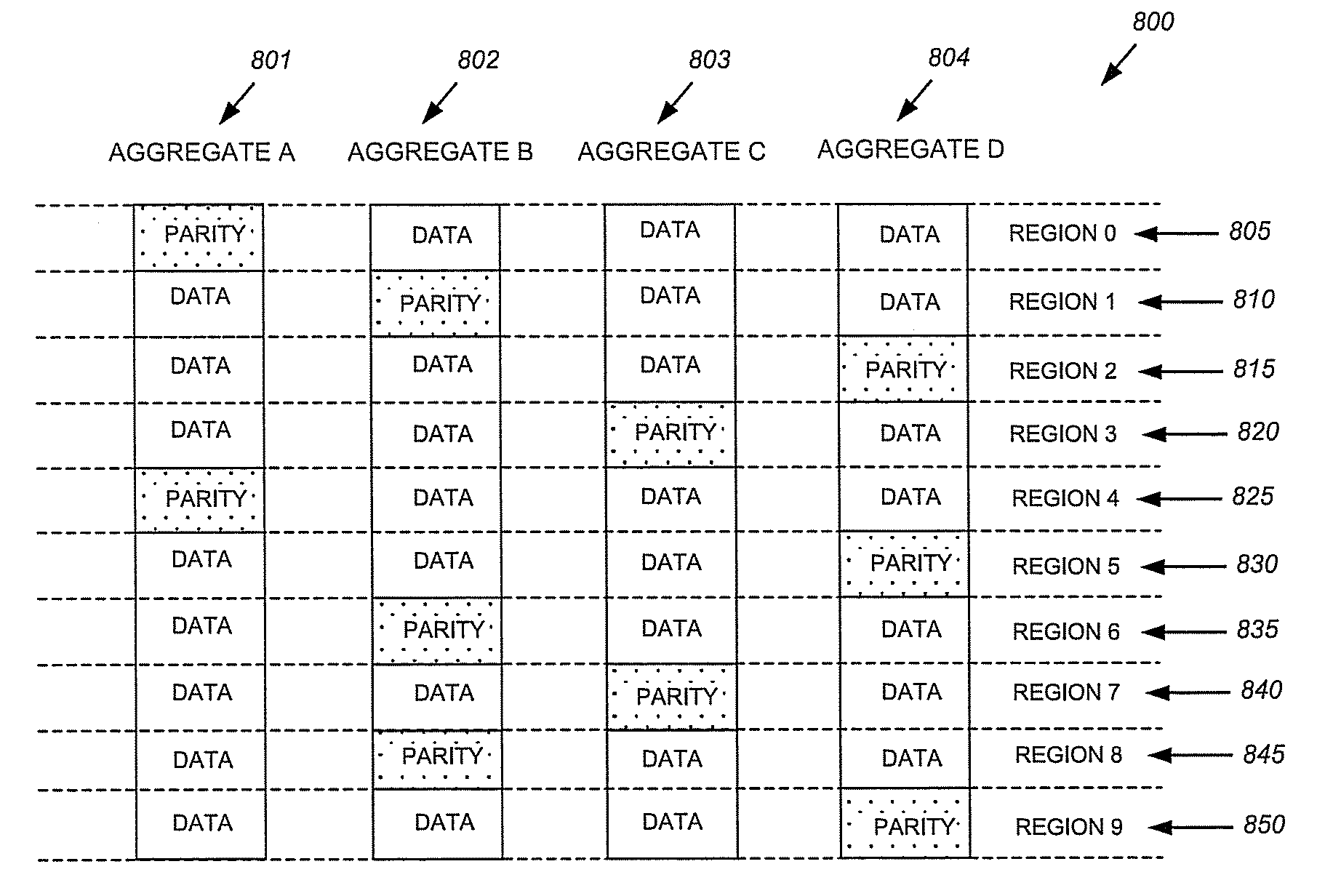
System and method for redundancy-protected aggregates
ActiveUS8495417B2Overcome disadvantagesRedundant data error correctionMemory systemsClient-sideData storing
The present invention provides a system and a method for utilizing a parity protection module to back up data on striped aggregates. Specifically, the system computes parity data for data stored at a particular location of each of a plurality of constituent aggregates, and stores the parity on one of the constituent aggregates that is a parity owner for that particular location of data. In the event one of the constituent aggregates fails, new data may still be accessed by the system (the striped aggregates), both to write new data, and to read data stored on the failed aggregate. In particular, the parity protection module allows clients to read data from a failed aggregate by running a reverse parity computation, which may also be used to restore the data to the failed aggregate.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
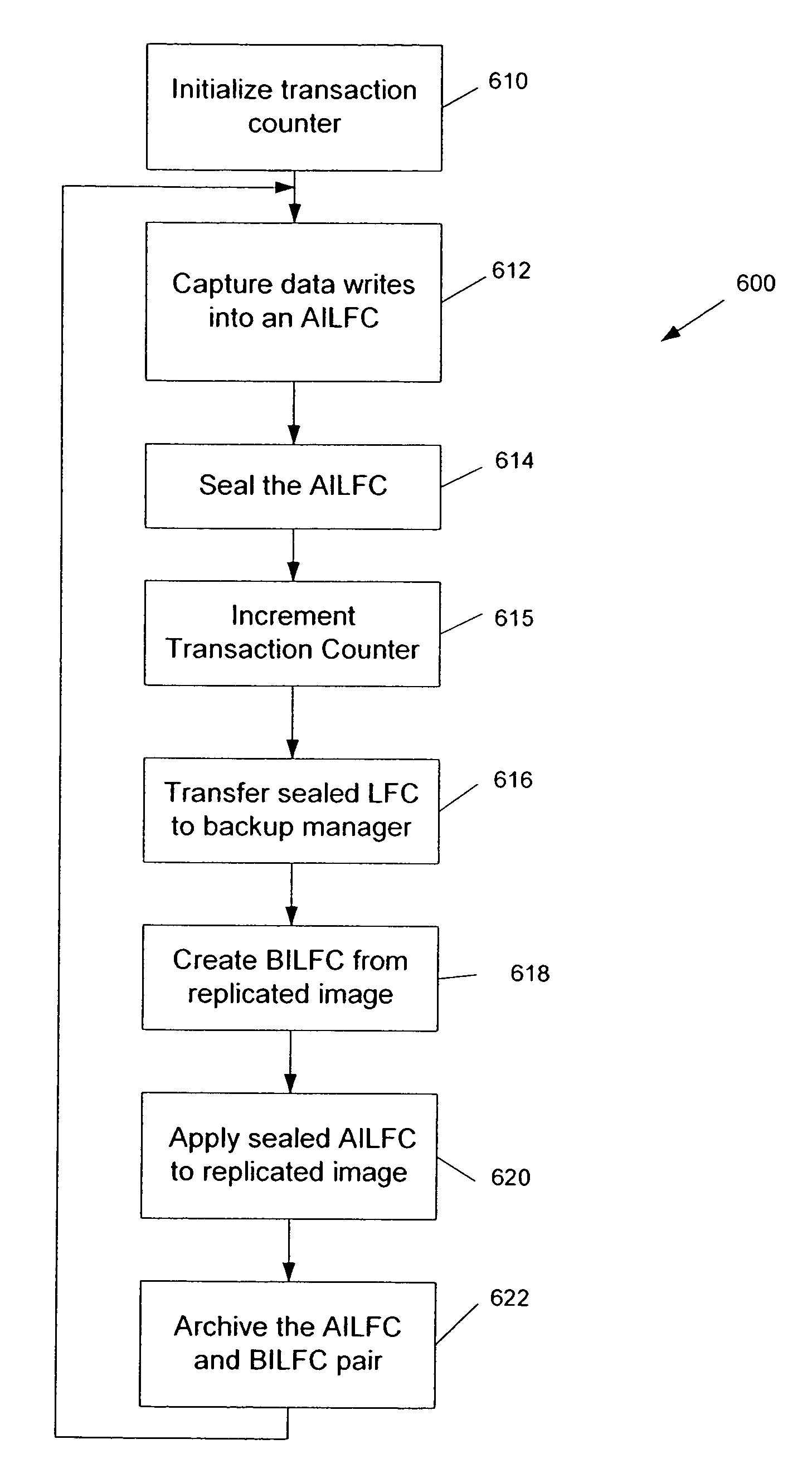
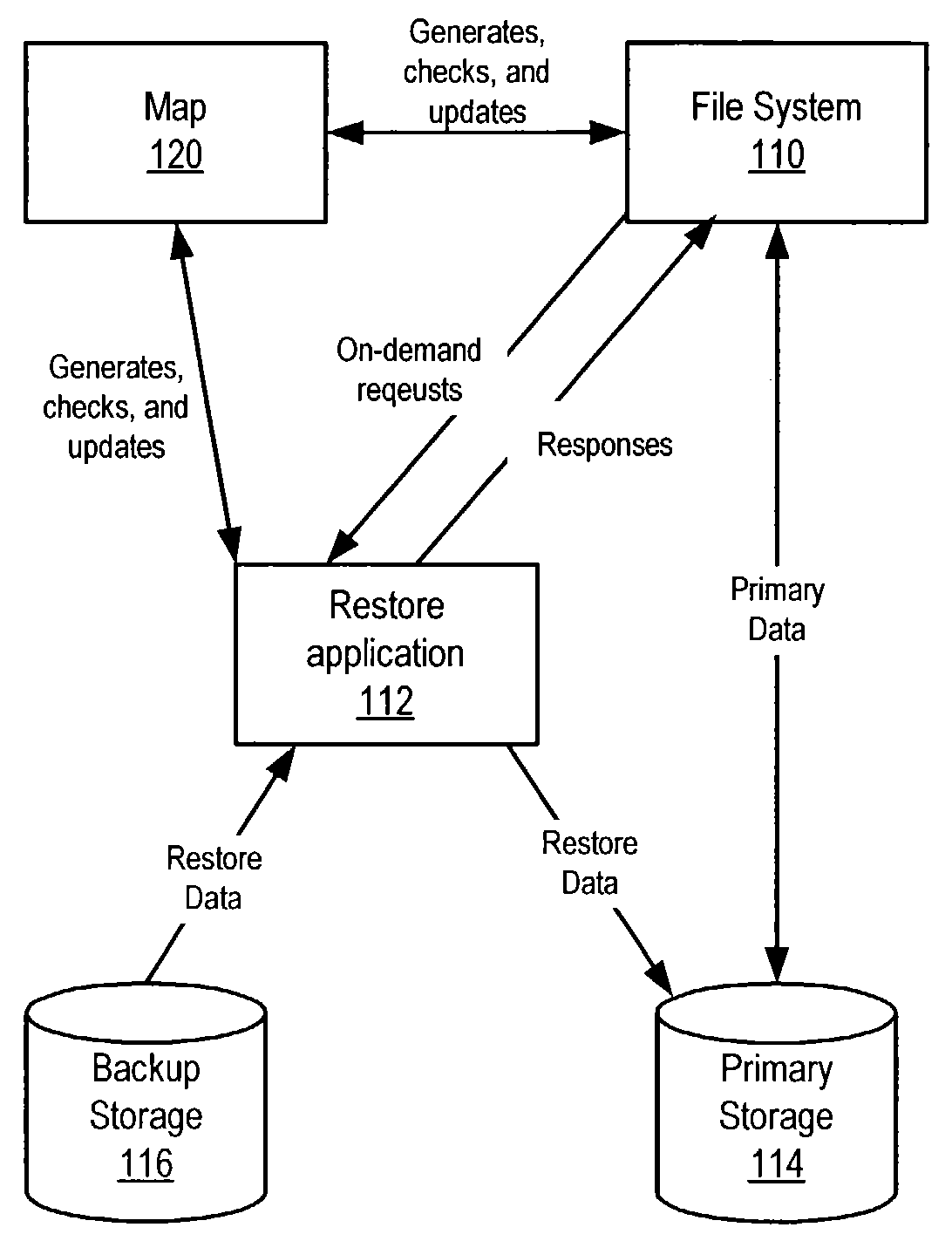
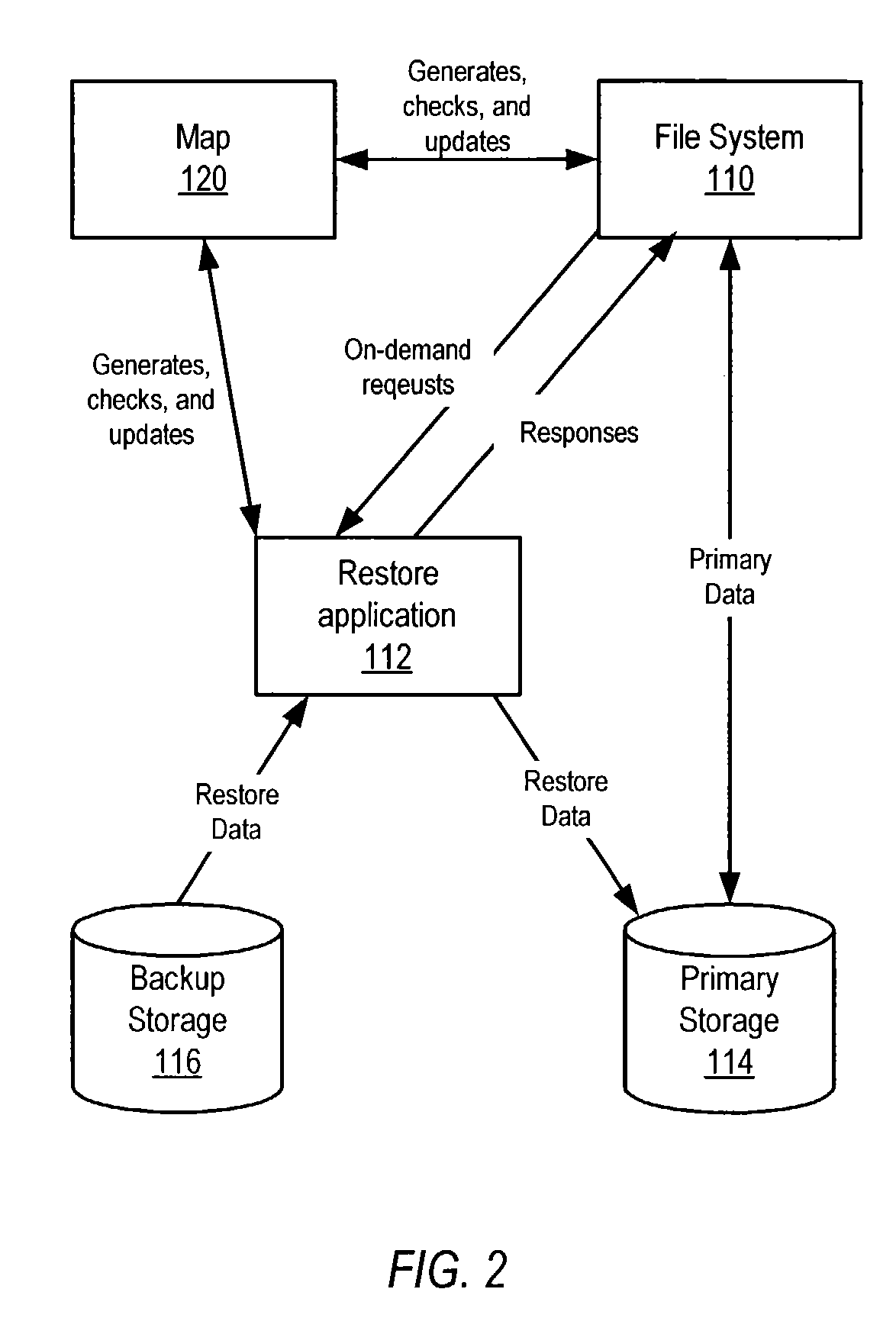
Data restore mechanism
ActiveUS7024527B1Limited or no impact on the applicationError detection/correctionMemory systemsPosition dependentBackup
System and method for performing restores from backups while applications are active and accessing the data being restored. A map correlating destination locations on primary storage to source locations on backup storage for files to be restored may be generated. A restore of the files from the backup storage to the primary storage may be started. During the restore, one or more blocks of data of a file needed by an application may be determined. The map may be accessed to determine if the blocks have been restored. If the blocks have not been restored, the blocks may be restored from the backup storage to the primary storage. The restored blocks of data are accessible by the application while the restore is in progress. The map may be updated to indicate blocks of data that have been restored to the primary storage.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
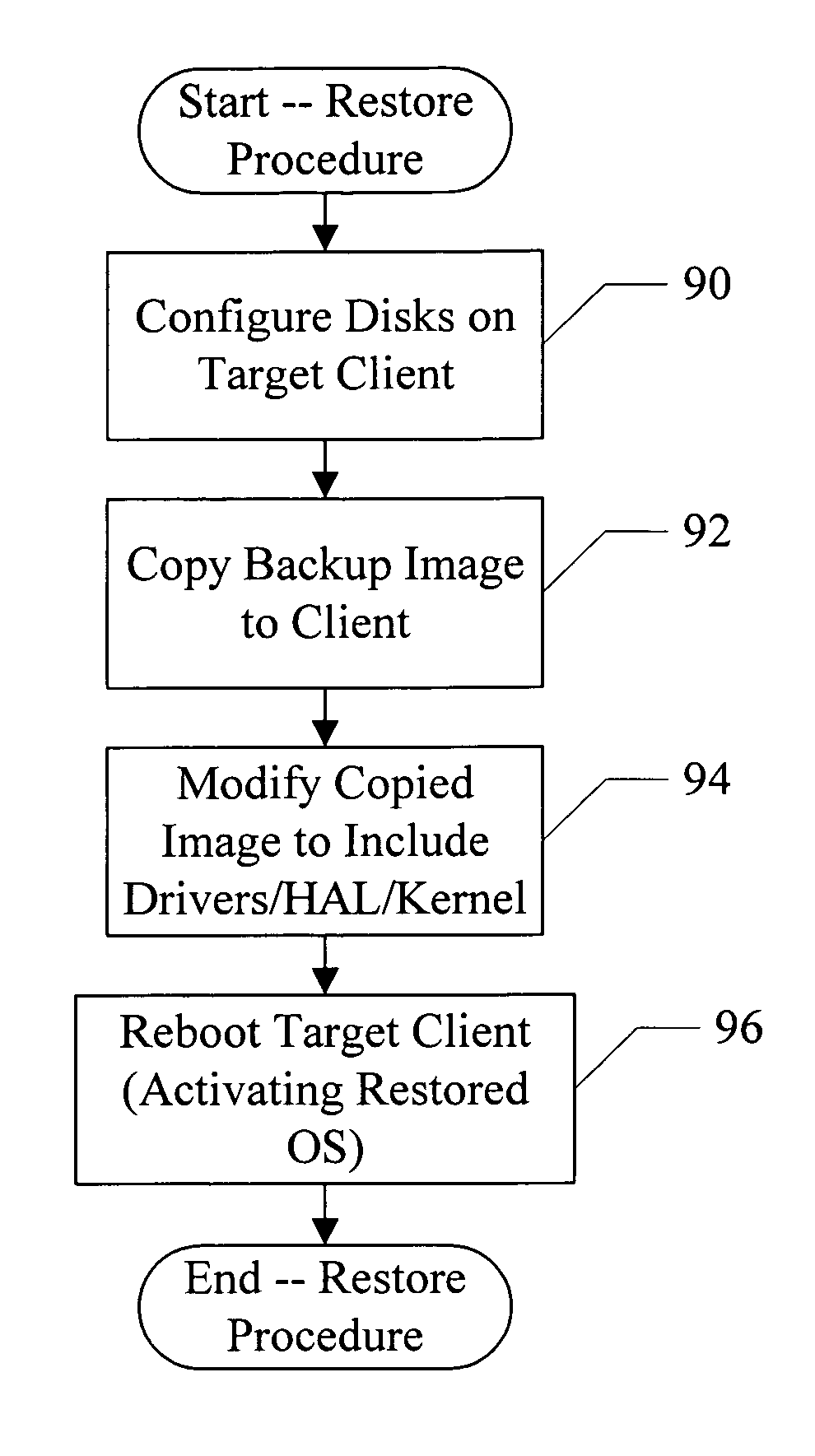
Restore of data to a computer system having different hardware
In some embodiments, a computer accessible medium comprises a plurality of instructions which, when executed: cause a modification of an image of files created from a computer system having first hardware; and cause the image to be copied to a computer system having second hardware different from the first hardware. A difference between the first hardware and the second hardware necessitates that the modification of the image be performed. For example, the difference may indicate that a different device driver is to be included in the image, or that HAL or kernel code is to be changed. A similar method of modifying the image and copying the image is also contemplated.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
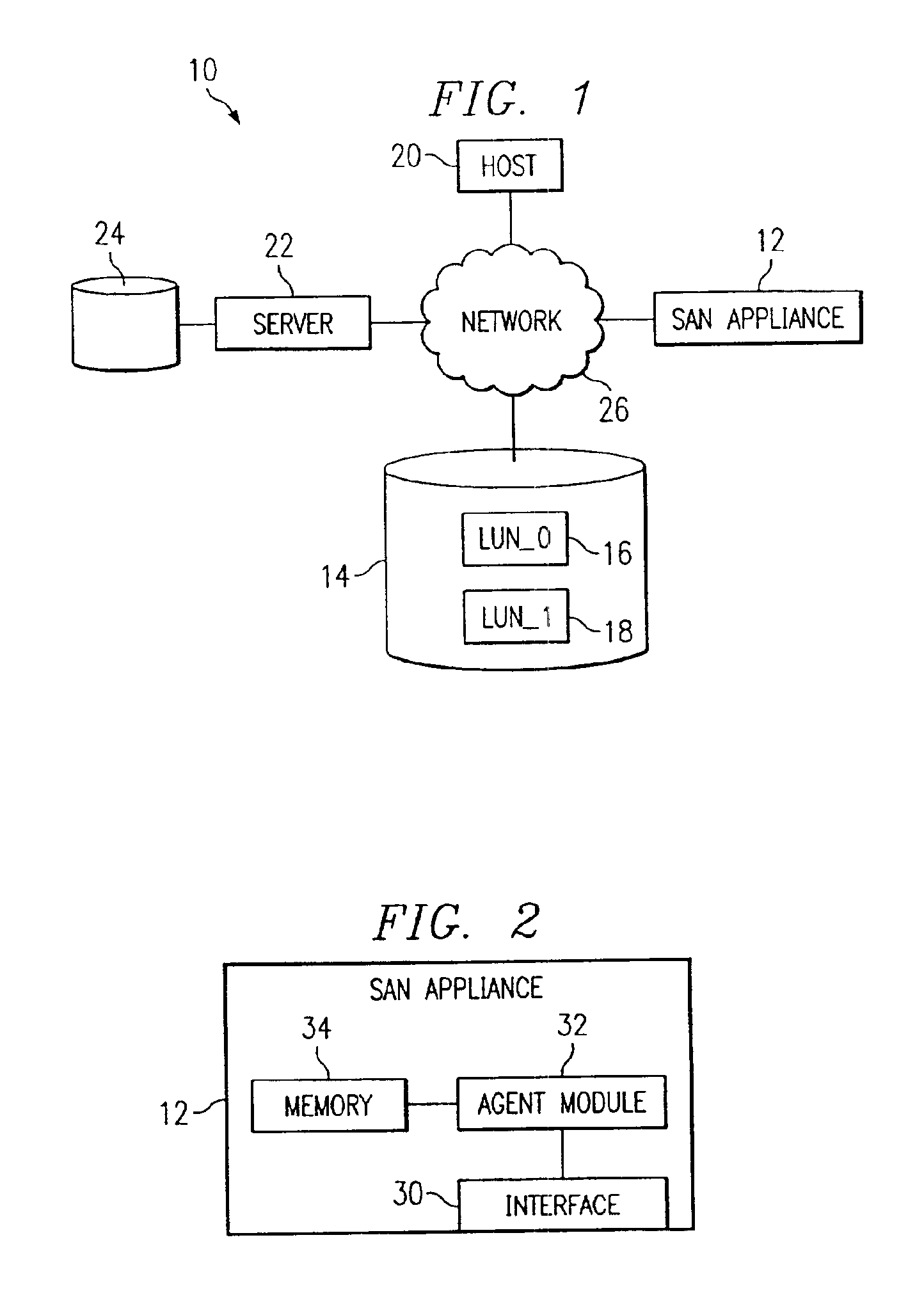
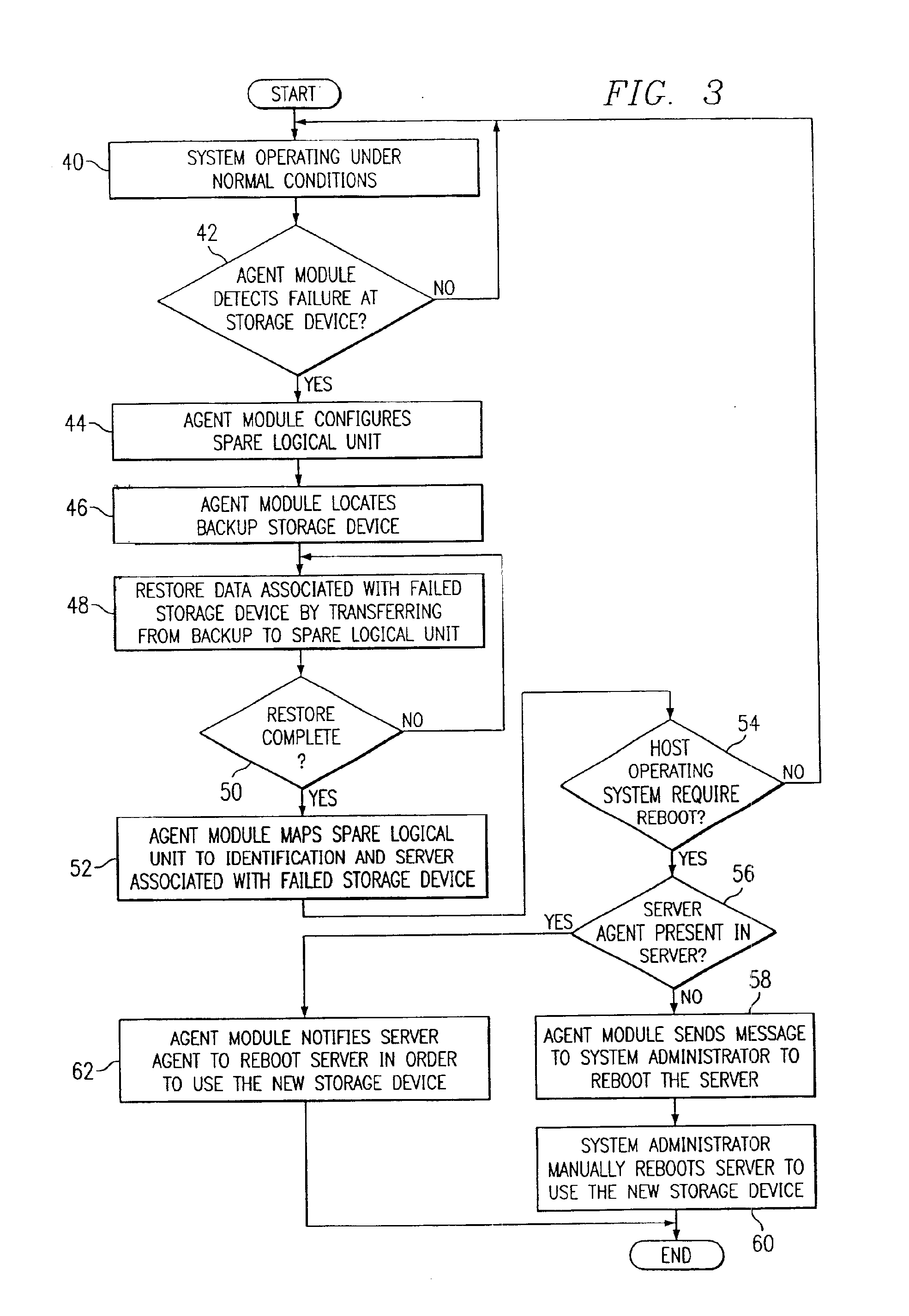
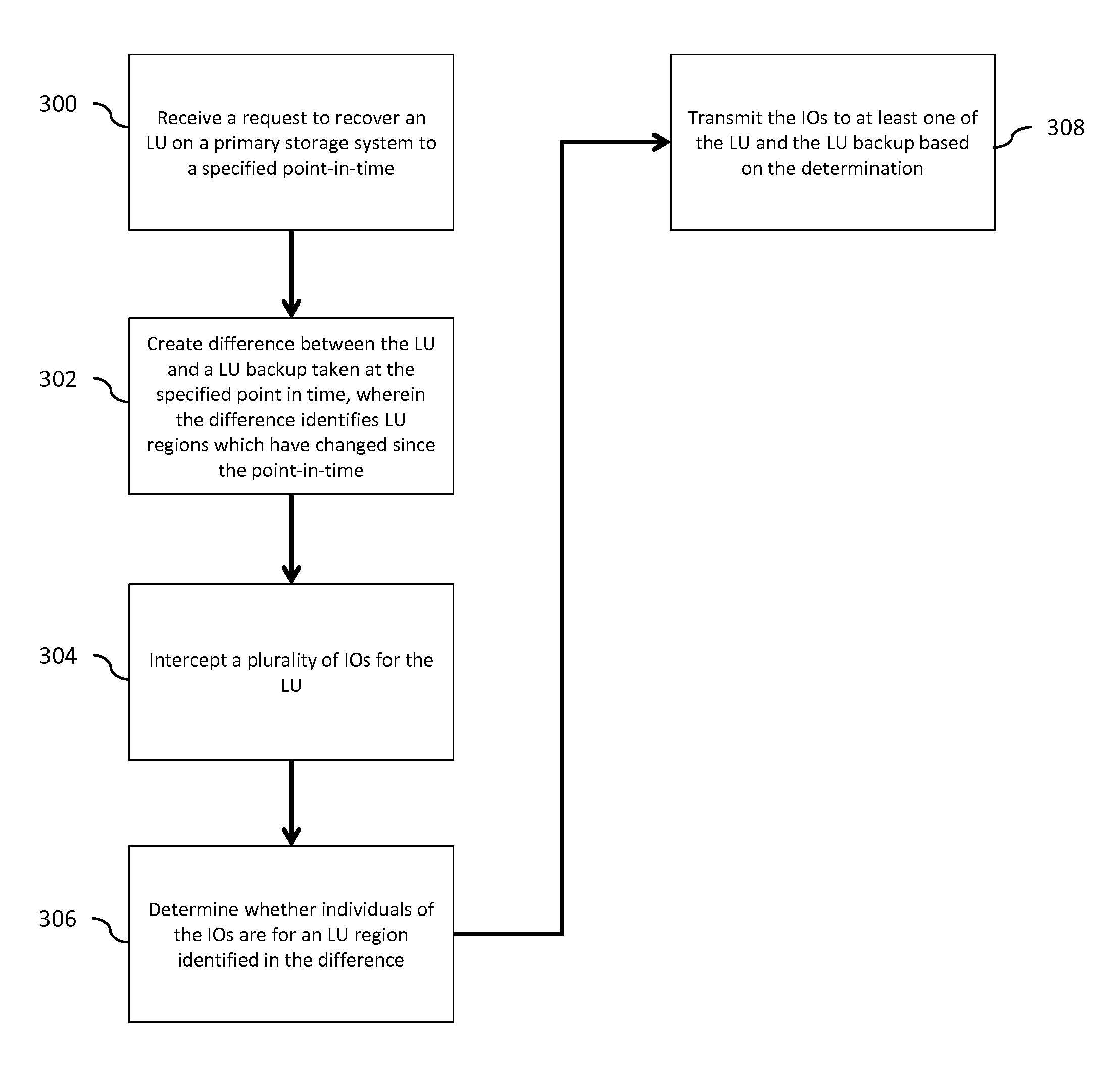
System and method for providing automatic data restoration after a storage device failure
InactiveUS6880101B2Eliminate and reduce disadvantageEliminate and reduce and problemRedundant operation error correctionRedundant hardware error correctionDevice failureOperating system
A system and method for providing automatic data restoration after a storage device failure are disclosed. An agent module detects a failure at a logical unit located at a primary storage device. The agent module locates backup data from the failed logical unit that is stored on a backup storage device and transfers the backup data from the backup storage device to a spare logical unit located on the primary storage device. The agent module then maps the spare logical unit to an address associated with a host in response to detecting the failure at the logical unit.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
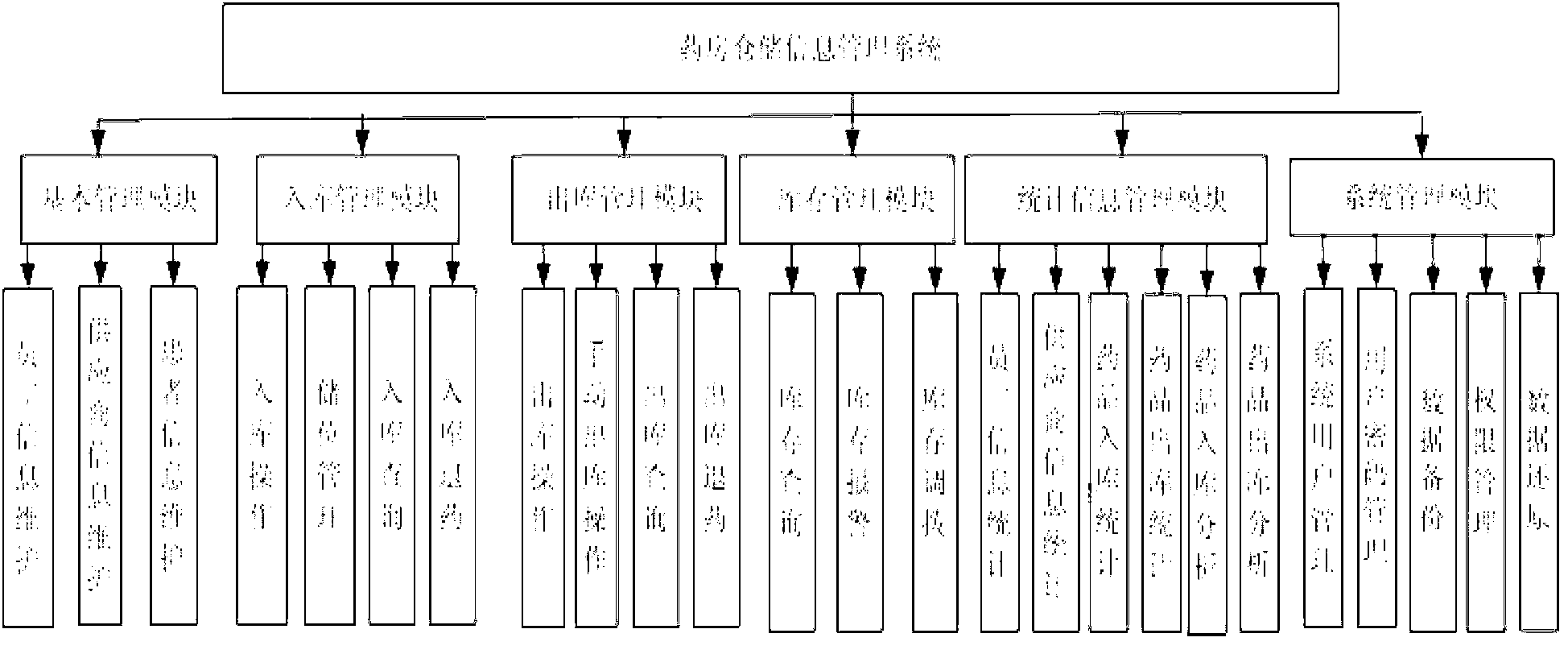
Drug storage information managing system for pharmacy
InactiveCN102708529AGuaranteed real-timeImprove storage efficiencyData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsSystems managementStatistical analysis
The invention provides a drug storage information managing system for pharmacy, comprising a basic information managing module, an in-storage managing module, an out-storage managing module, an inventory managing module, a statistic information managing module and a system managing module, wherein the basic information managing module is used for maintaining and managing the staff information, maintaining and managing the information of pharmaceutical suppliers, and maintaining and managing the patient information; the in-storage managing module is used for managing in-storage operation, storage location, in-storage query and in-storage drug-return; the out-storage managing module is used for managing manual out-storage operation, out-storage query and out-storage drug-return; the inventory managing module is used for managing inventory query, inventory alarm and inventory transfer function; the statistic information managing module is used for managing the statistic of the staff information, the statistic of the information of suppliers, the statistic of the in-storage drug, the statistic and analysis of the in-storage drug, the statistic of the out-storage drug, and the statistic and analysis of the out-storage; and the system managing module is used for managing the system users, the user passwords, the data backup, the data restoration and the authority. After adopting the drug storage information managing system for the pharmacy, the pharmacy management is automated and normalized and becomes scientific, and the whole efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
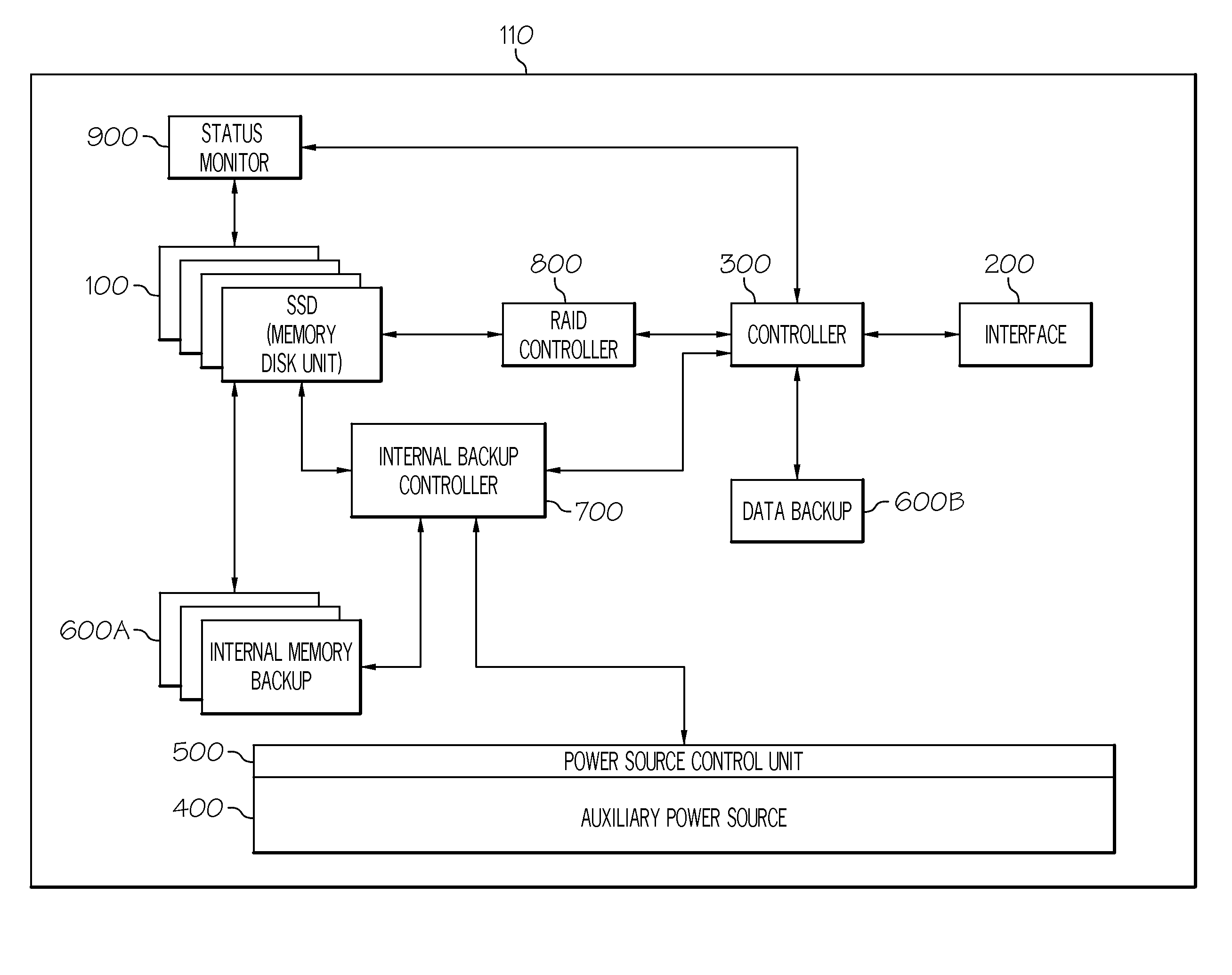
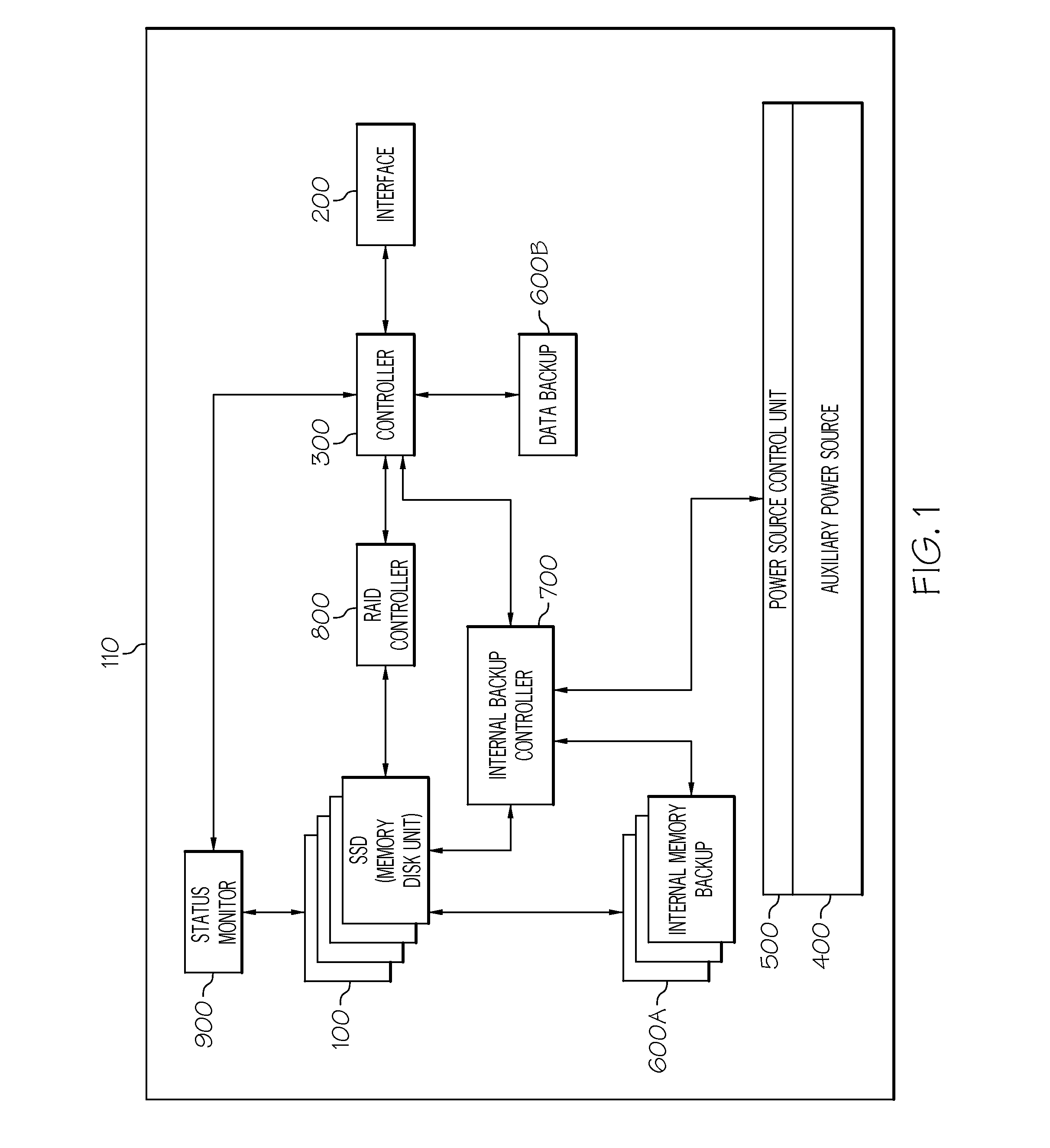
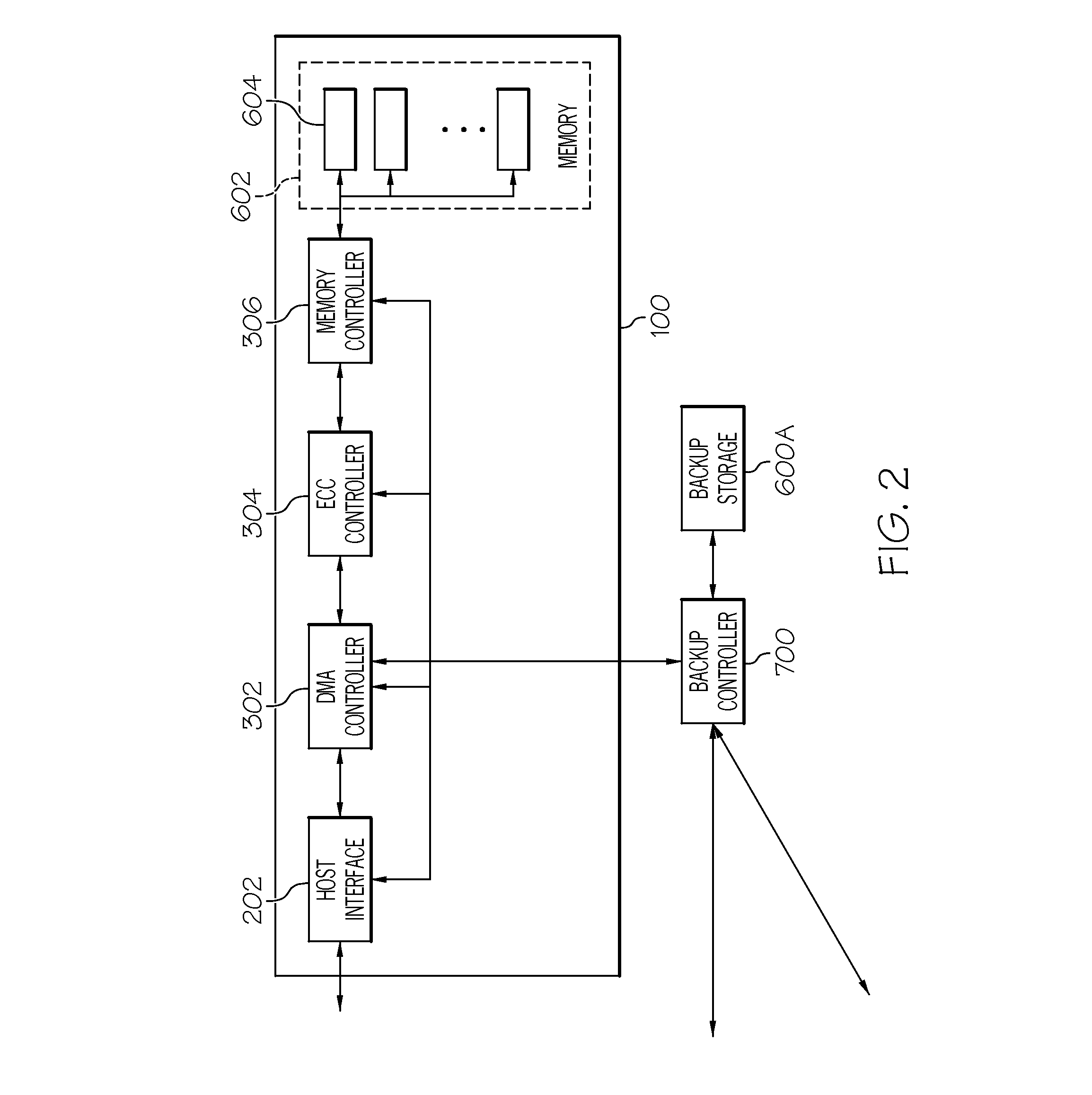
Alarm-based backup and restoration for a semiconductor storage device
ActiveUS20120210163A1Low-speed data processing speedMemory loss protectionRedundant data error correctionLow speedSemiconductor storage devices
Embodiments of the present invention provide backup and restoration functions for a storage device of a PCI-Express (PCI-e) type that support a low-speed data processing speed for a host. Specifically, embodiments of this invention provide backup and restoration functions for one or more (i.e., a set of) semiconductor storage devices (SSDs). In general, the present invention provides an alarm unit and a secondary power supply coupled to a backup controller. The backup controller is coupled to a backup storage device. When a primary power supply is deactivated (e.g., fails), an alarm unit and the secondary power supply is activated. In response to this activation, the backup controller will backup any data stored on any SSDs of the storage system (as well as any data stored in main memory of the storage system or in main memory of any host server connected thereto). When the primary power supply is reactivated, the secondary power supply (and the alarm unit) is deactivated, and all data backed up is restored to its original source.
Owner:TAJIN INFO TECH CO LTD
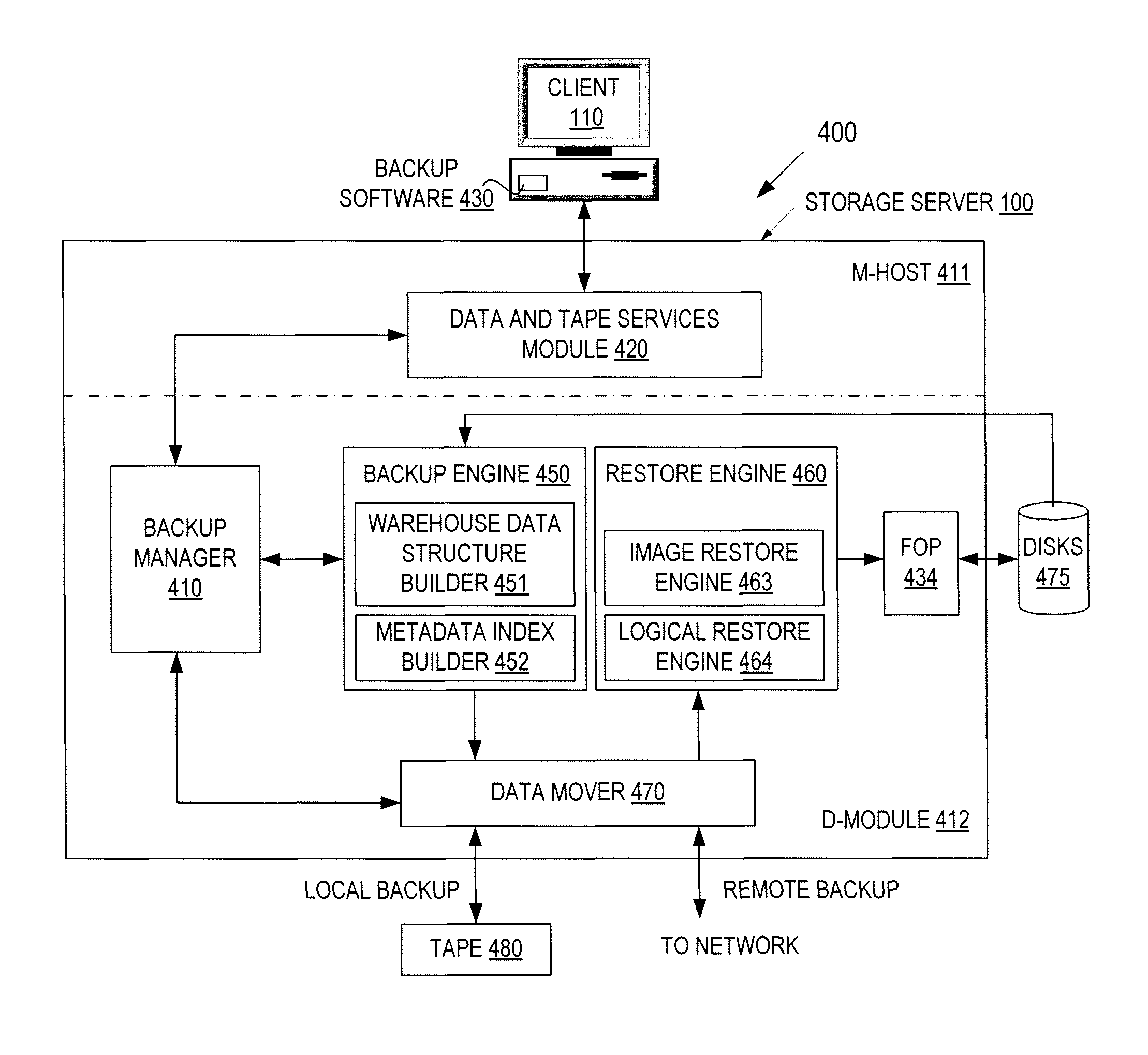
Single file restore from image backup by using an independent block list for each file
Image-based data restoration restores an entire image of a volume or selective files. A restore engine receives a request to restore data from a backup image that includes a plurality of data blocks and metadata describing attributes of the data blocks. In response to the request, the restore engine determines a restore mode. If it is determined to be a logical restore mode, the restore engine restores a file by retrieving the metadata associated with the file and the data blocks that are pointed to by the metadata. If it is determined to be an image restore mode, the restore engine restores an entire image of the volume by using the data blocks in the backup image without using the metadata.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
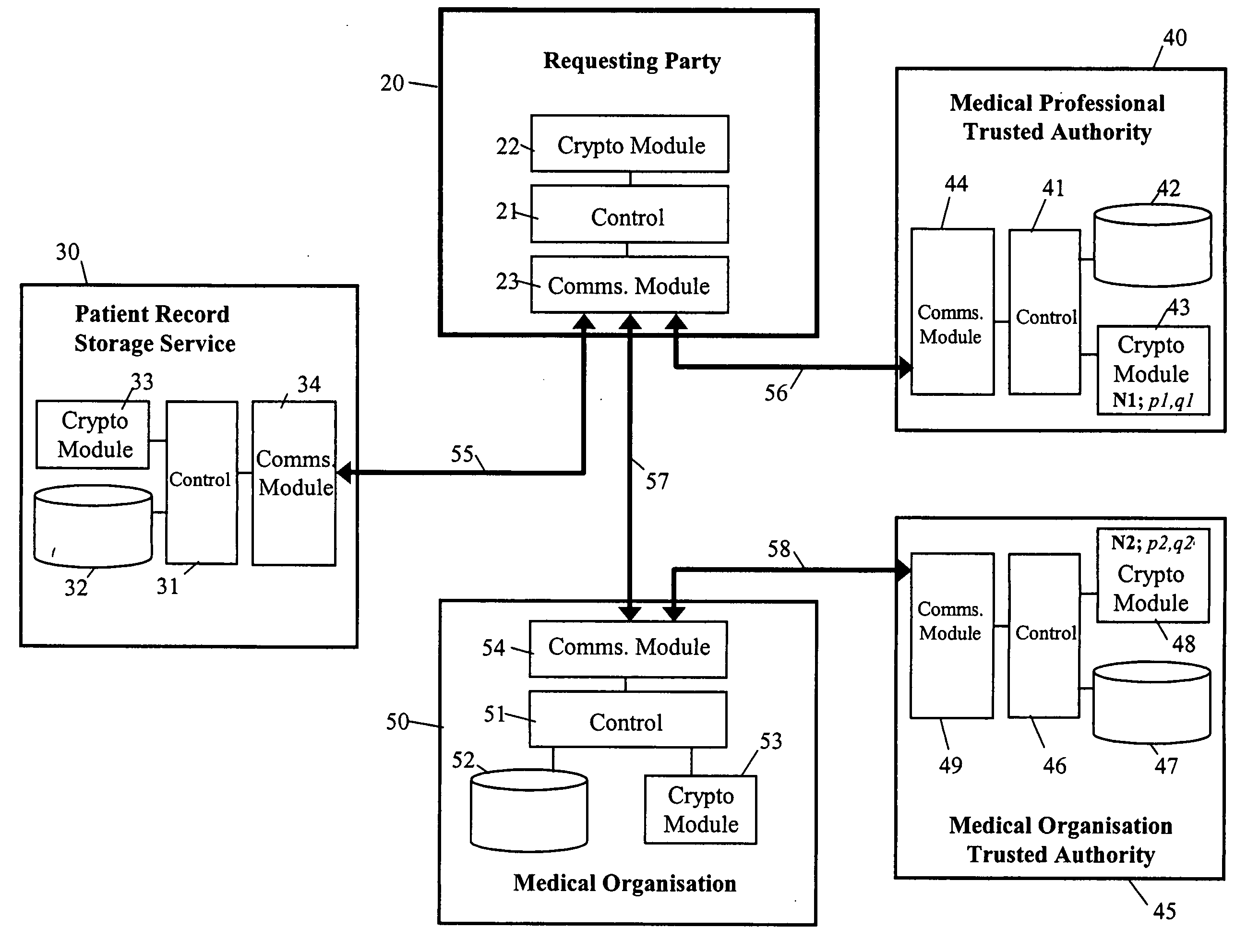
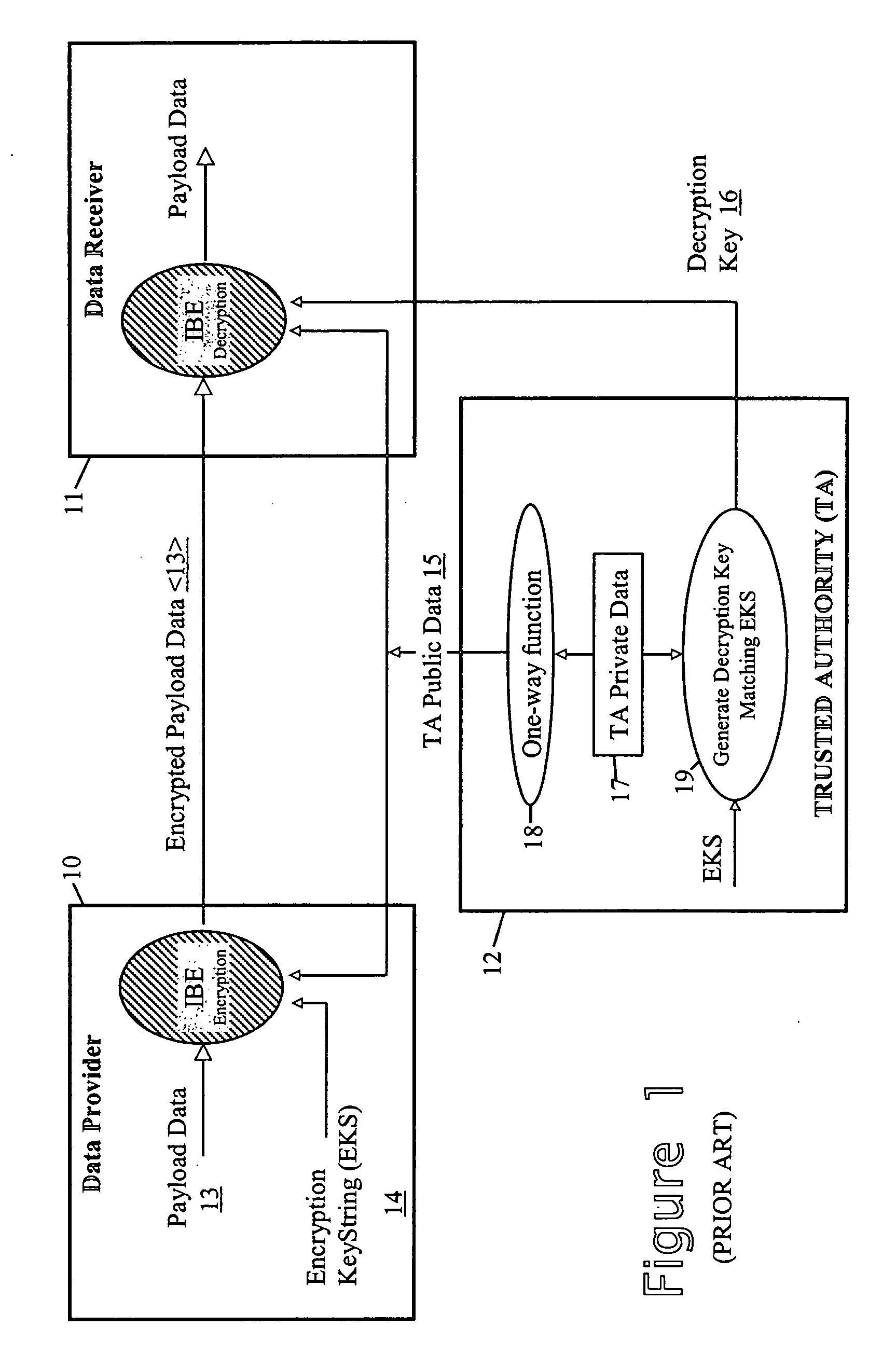
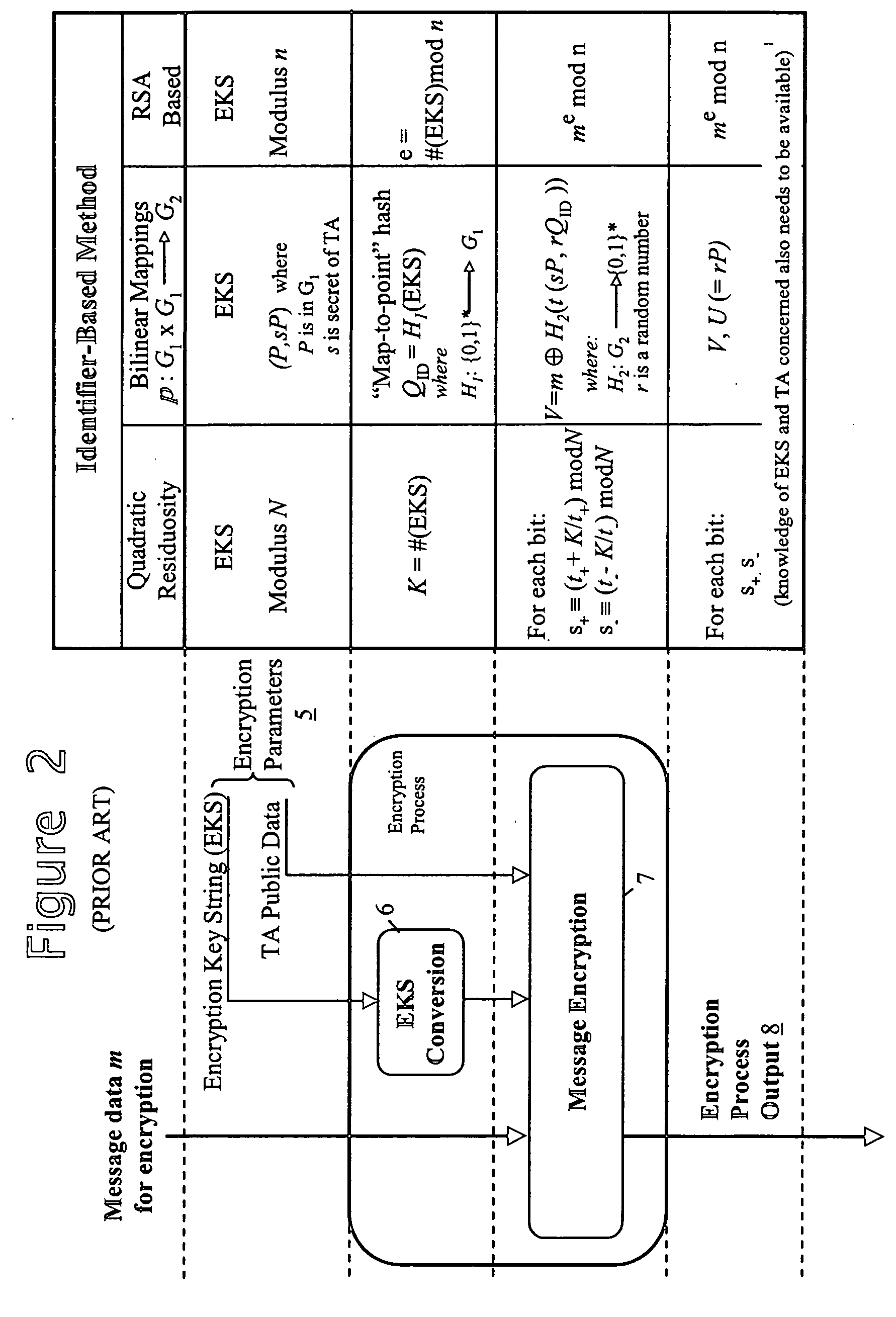
Secure data provision method and apparatus and data recovery method and system
InactiveUS20050010760A1Eliminate needDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionTrusted authorityData set
To control access to target data whilst relieving the data provider of policing obligations, the data provider provides the target data in encrypted form to a requesting party as part of a data set with which first and second trusted authorities are associated in a non-subvertible manner. Recovery of the target data in clear by the party requires the first trusted authority to verify that a specific individual is a professional accredited with it, the second trusted authority to verify that a particular organisation is accredited with it, the particular organisation to verify that the specific individual is engaged by it, and at least one of the particular organisation and the first trusted authority to verify that the party is the specific individual. Various ways of encrypting the target data are provided, the preferred ways being based on Identifier-Based Encryption schemas.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method, medium and system for recovering data using a timeline-based computing environment
InactiveUS20050216527A1Simple and intuitive graphical representationSimple technologyData processing applicationsProgram control using stored programsSpammingImproved method
The present description discloses a technique for recovering data using a timeline-based computing environment. Data items of the application are periodically saved for recovery such that the saved data items can be used to recover the application at a point in time when the items are saved. As a result, a search through a time-based computing environment is provided to recover the application at different points in time. The application with the saved data items can then be recovered at a designated point in time. Each saved data item can also be indexed with metadata, which are used to conduct a search to generate a list of data items according to a match between the indexed metadata and a user selected variable. Moreover, when the application is a communication client having multiple messages, an index data to indicate whether a message in the communication client is spam is saved. Using this index data, a search that includes or excludes the spam messages can then be conducted. Thus, using a timeline-based computing environment, an improved method and system of recovering data that is more user friendly, effective, and manageable is thus provided.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
In-vehicle apparatus and service providing system
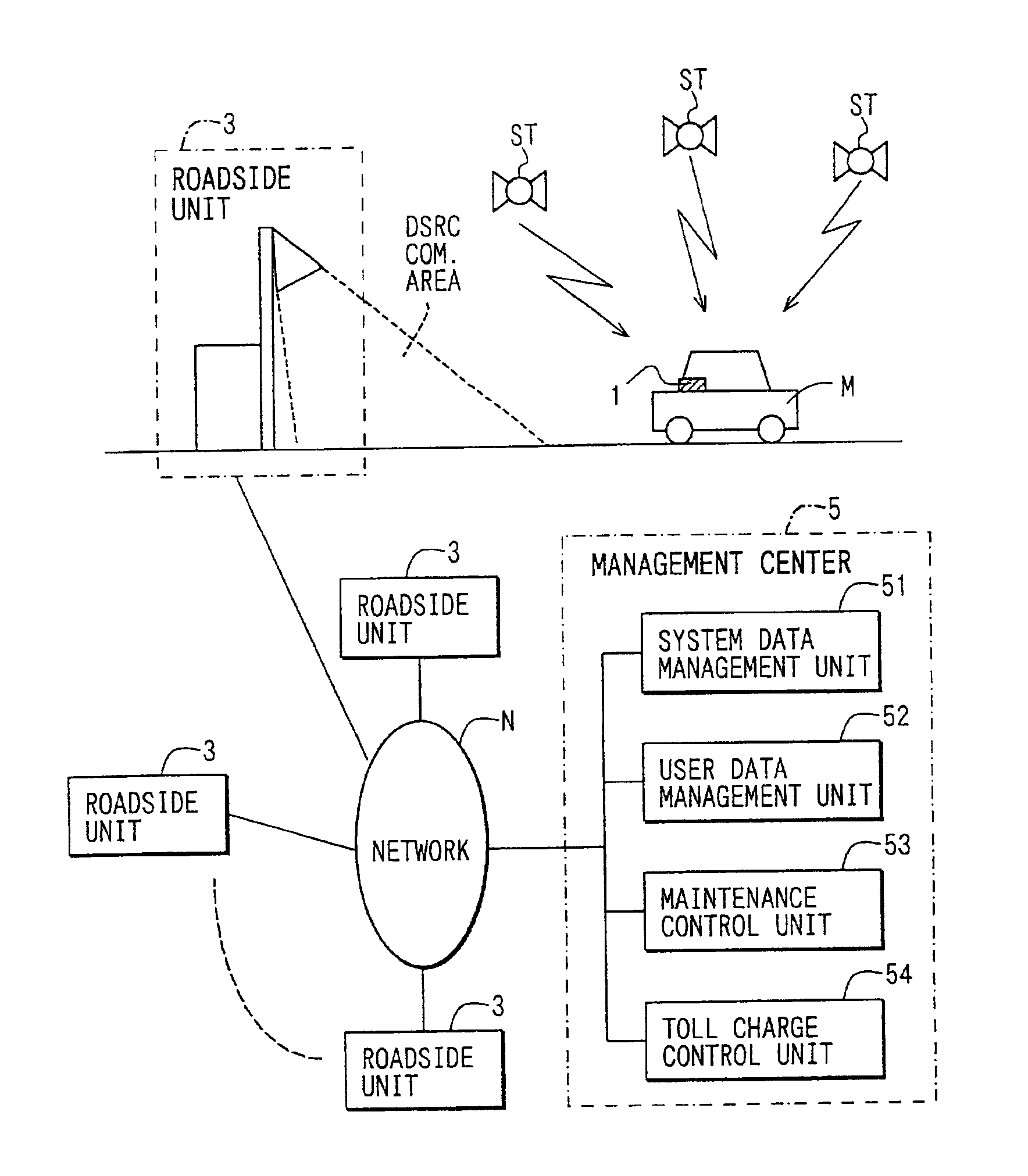
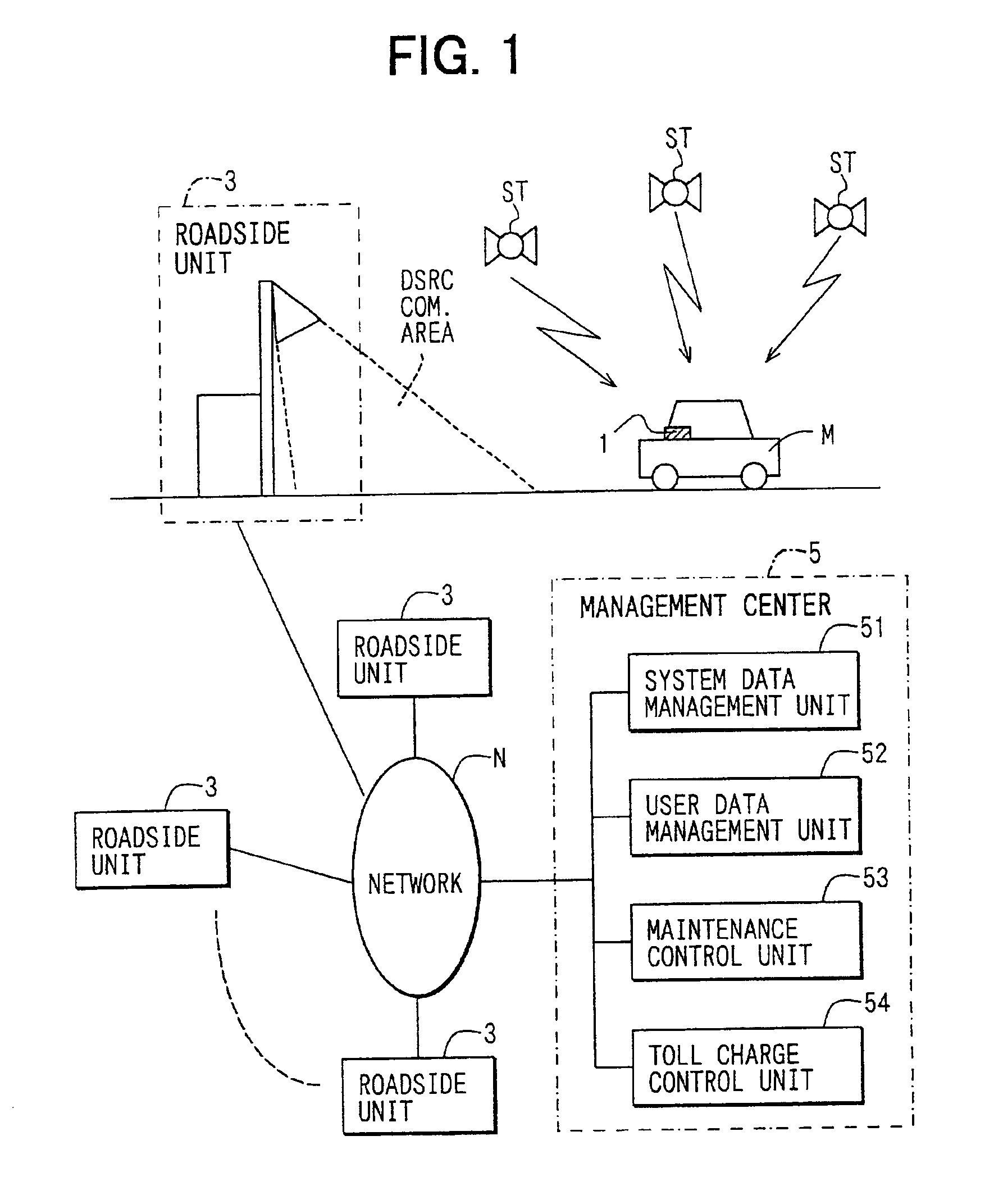
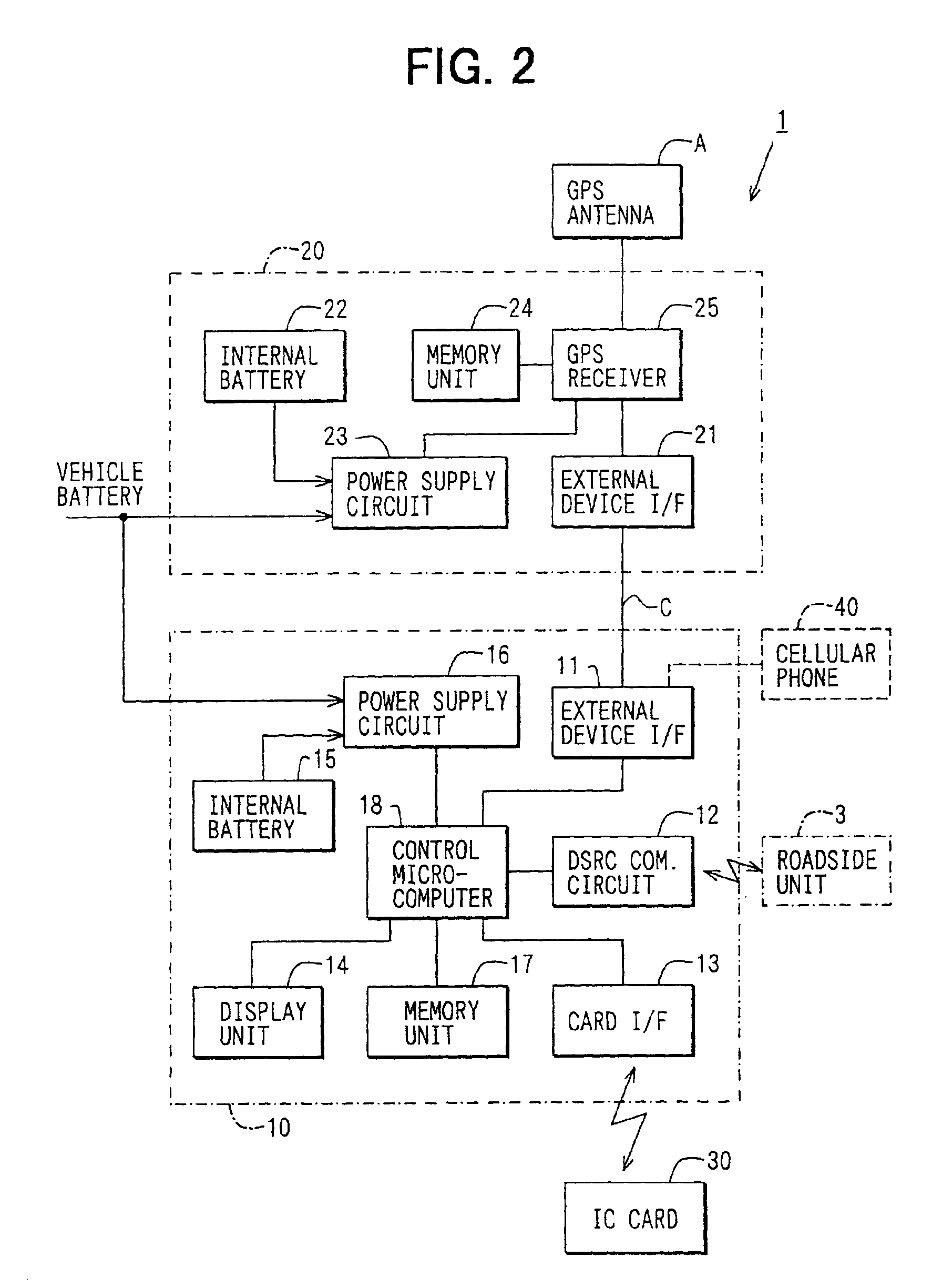
InactiveUS6937162B2Avoid illegal operationVehicle testingTicket-issuing apparatusLocation detectionService provision
If acquisition of measured position and time data (position / time) from a position detection unit fails, a “GPS OFF mode” is set, and the latest position and time data is stored as start data. Thereafter, when the position and time data is obtained successfully, and the operation is recovered from the “GPS OFF mode”, the “GPS OFF mode” is cancelled. Also, the obtained position and time data (restoration data) is stored. Monitor data is formed from the start data and the restoration data. The monitor data is transmitted to a management center through road-vehicle communication. Also, history data of the position and time stored in the position detection unit during the “GPS OFF mode” is read. If the history data satisfies the toll charging condition, the toll charging data is formed and is transmitted to the management center.
Owner:DENSO CORP
System and method for redundancy-protected aggregates
ActiveUS20100180153A1Overcome disadvantagesRedundant data error correctionRedundant operation error correctionClient-sideData storing
The present invention provides a system and a method for utilizing a parity protection module to back up data on striped aggregates. Specifically, the system computes party data for data stored at a particular location of each of a plurality of constituent aggregates, and stores the parity on one of the constituent aggregates that is a parity owner for that particular location of data. In the event one of the constituent aggregates fails, new data may still be accessed by the system (the striped aggregates), both to write new data, and to read data stored on the failed aggregate. In particular, the parity protection module allows clients to read data from a failed aggregate by running a reverse parity computation, which may also be used to restore the data to the failed aggregate.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method and apparatus for data recovery using storage based journaling
ActiveUS20060149798A1Digital data processing detailsError detection/correctionSystem maintenanceDatabase
A storage system maintains a journal and a snapshot of one or more data volumes. Two journal entry types are maintained, an AFTER journal entry and a BEFORE journal entry. Two modes of data recovery are provided: “fast” recovery and “undo-able” recovery. A combination of both recovery modes allows the user to quickly recover a targeted data state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
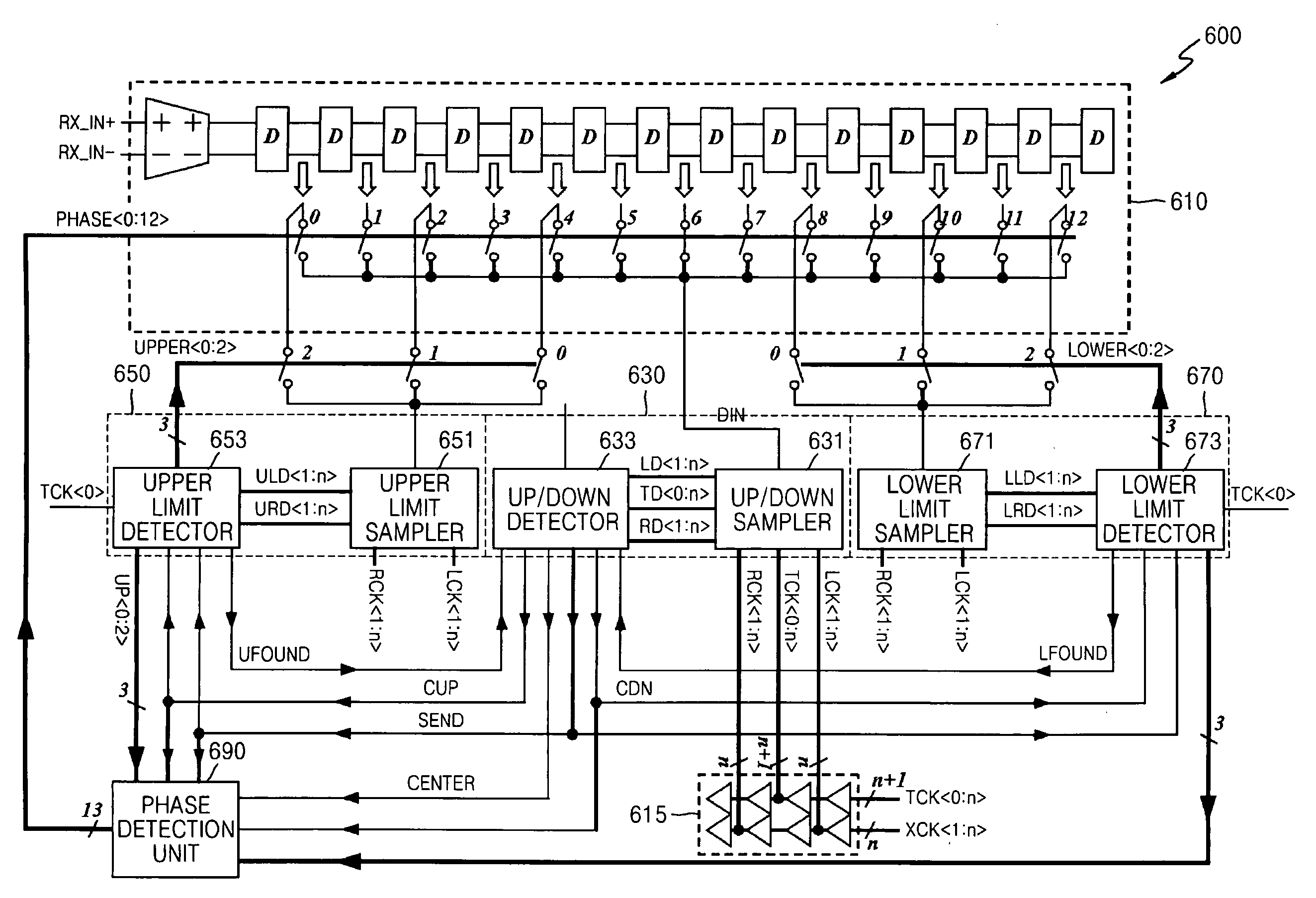
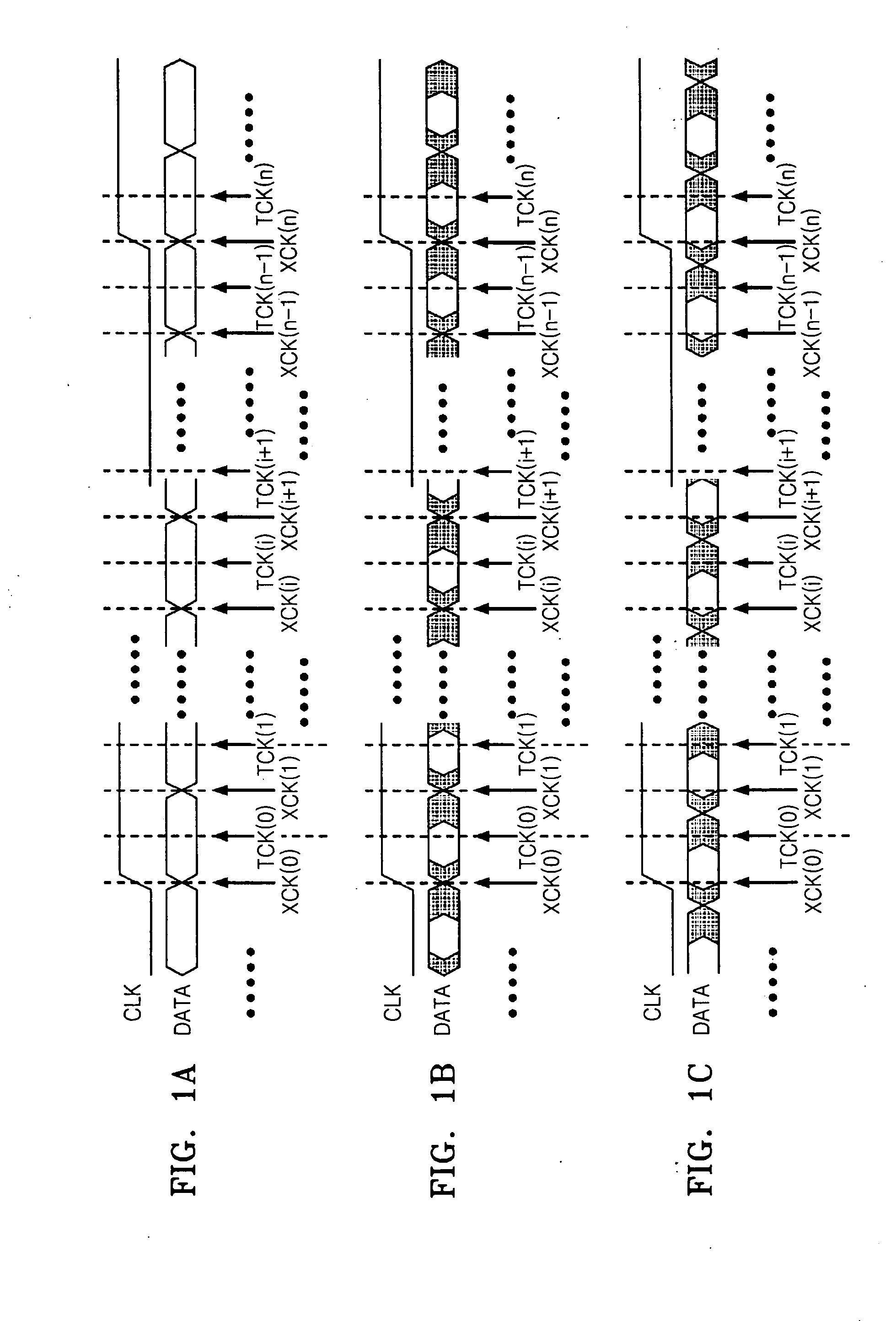
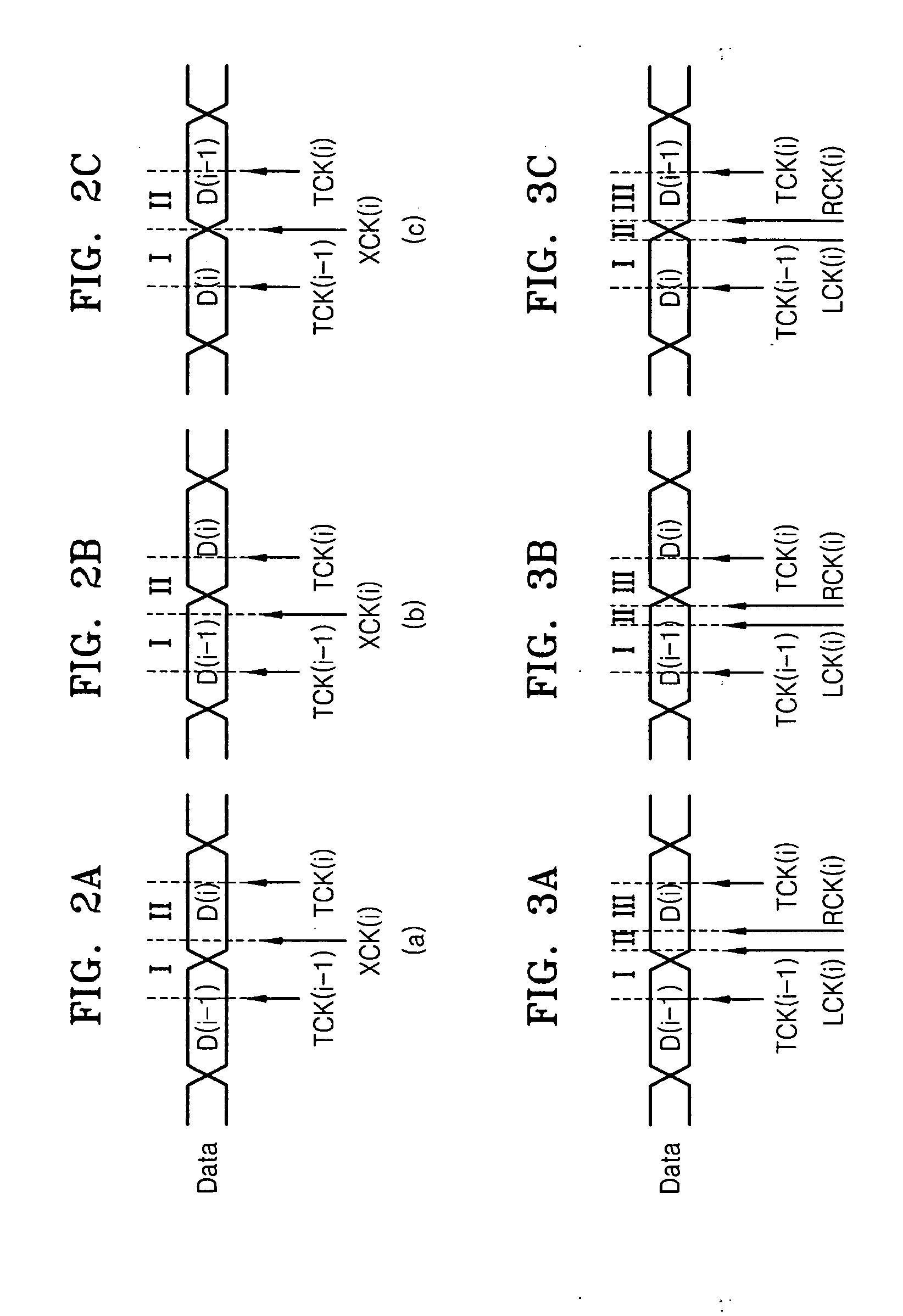
Deskewing method and apparatus, and data reception apparatus using the deskewing method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070297551A1Pulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionLower limitData signal
Deskewing method and apparatus, and a data reception apparatus using the deskewing method and apparatus, in which the deskewing apparatus includes an up / down detection unit, a lower limit detection unit, an upper limit detection unit, a phase detection unit, and a buffer unit. The up / down detection unit samples a received data signal in response to a data sampling clock signal, a first edge sampling clock signal, and a second edge sampling clock signal and determines in which of first through third areas of the data signal the logic level of the data signal transitions by using the result of the sampling, wherein the data sampling clock signal, the first edge sampling clock signal, and the second edge sampling clock signal are sequentially activated. The lower limit detection unit detects a lower limit of the first area if the logic level of the data signal transitions in the first area. The upper limit detection unit detects an upper limit of the third area if the logic level of the data signal transitions in the third area. The phase detection unit determines a delay amount indicating the amount by which the data signal is to be delayed according to the upper limit detected by the upper limit detection unit and the lower limit detected by the lower limit detection unit. The buffer unit delays the data signal by the delay amount determined by the phase detection unit. The deskewing apparatus can optimize data sampling by efficiently reducing data skew. In addition, the deskewing apparatus can minimize data restoration errors by reducing an accumulation of jitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
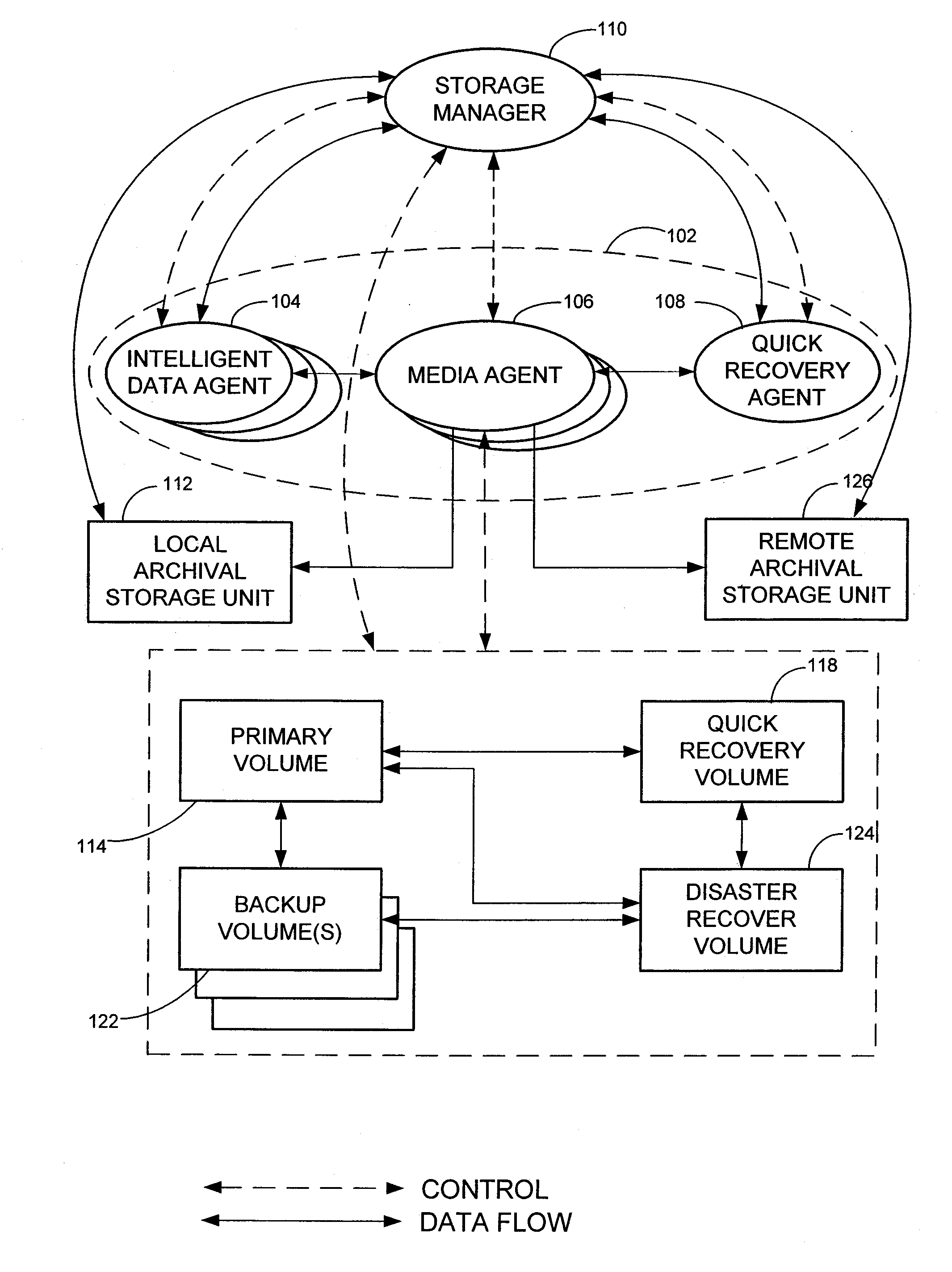
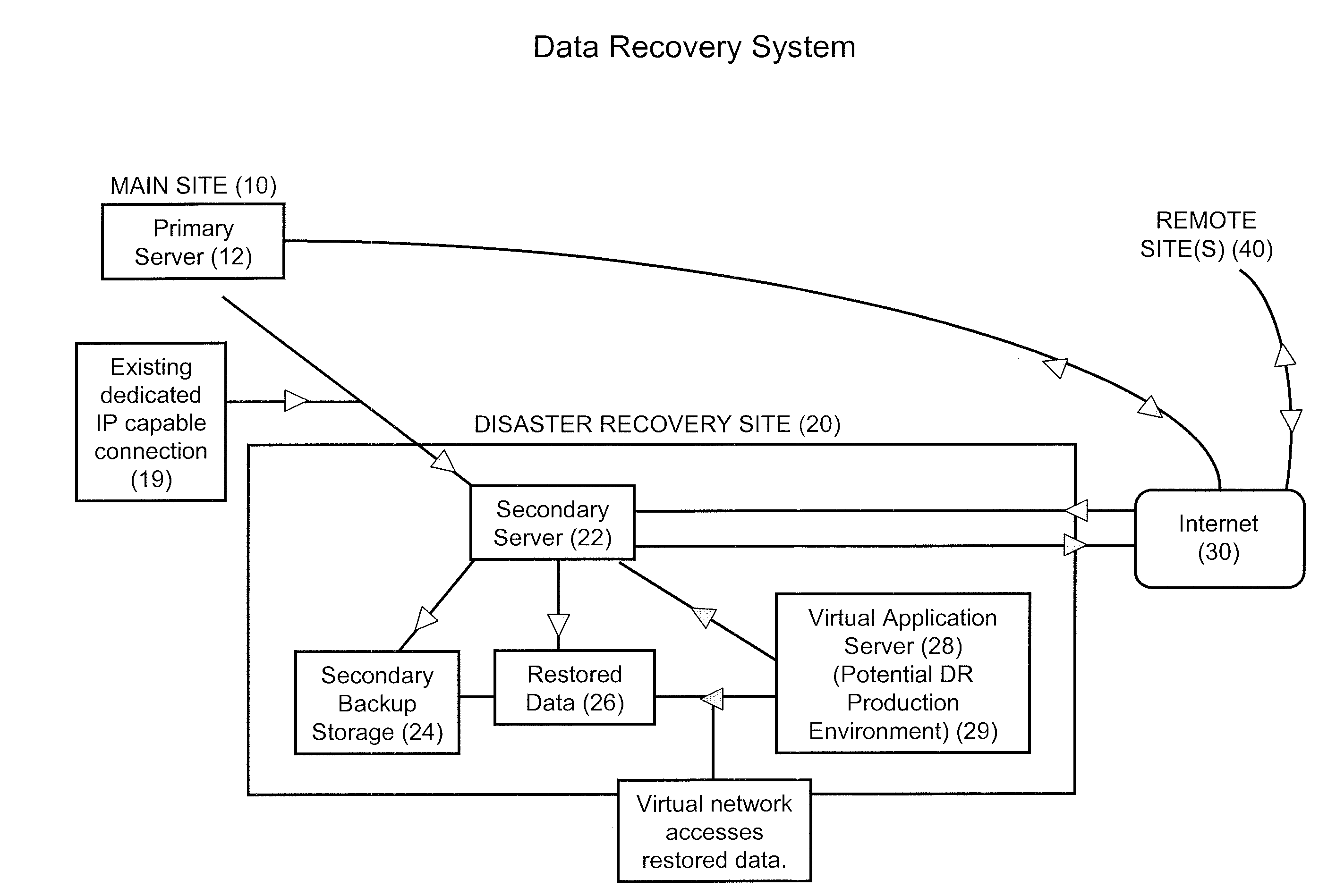
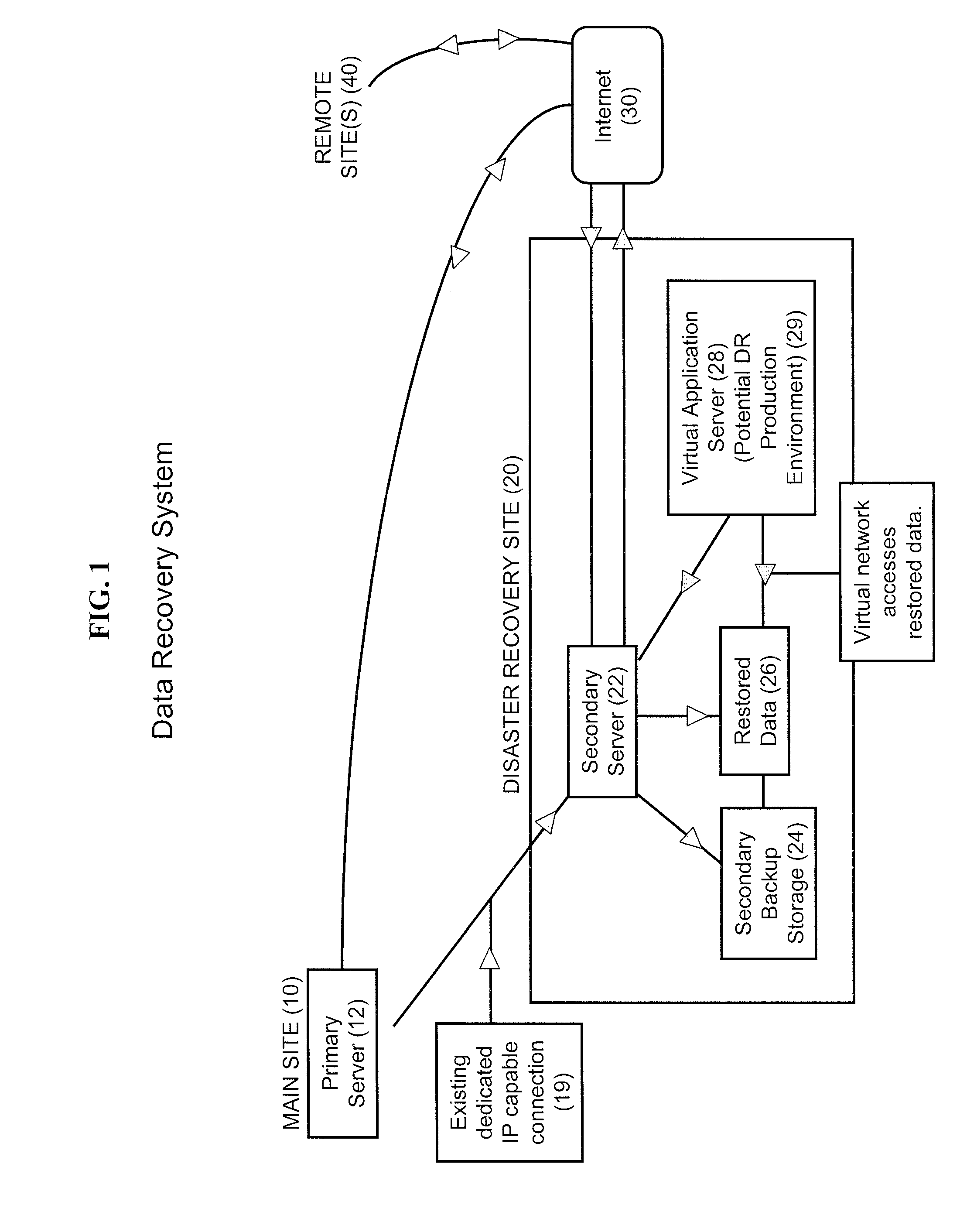
Data Recovery Systems and Methods
Nearline disaster recovery (“nearline DR”) storage systems and methods that permit the use of previously restored stored data from a near time period by virtual applications operating off a backup storage location during the period of disaster recovery at a primary site. This is generally referred to as a “nearline DR storage process.”
Owner:LEWIS RICE & FINGERSH LC
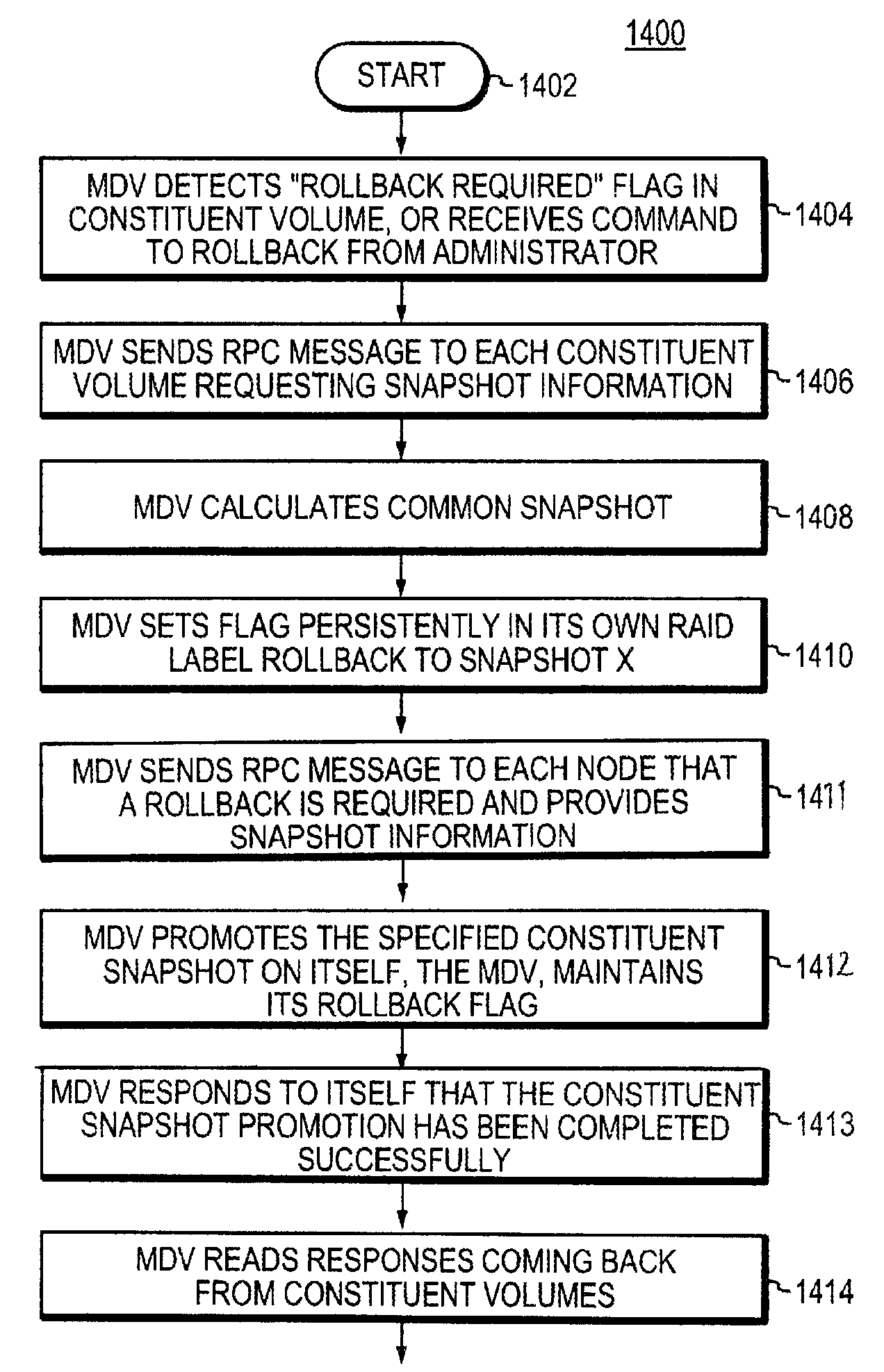
Method and system for promoting a snapshot in a distributed file system
ActiveUS7827350B1Simple and efficient snapshot promotionSimple and efficient promotionDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionRAIDDistributed File System
A method and system for promoting a snapshot in a distributed striped volume system is provided. A master volume server is configured with a rollback process such that when it is determined that a rollback is required, the master volume server sets a flag persistently in its own raid label on disk. After the persistent flag is set, the master volume server determines a “common snapshot,” and starts the process of sending RPC messages to each node hosting constituent volumes instructing each constituent volume to roll back to the identified snapshot. When the nodes receive this message a flag is set in the own raid label of each constituent volume and the volume then promotes the particular snapshot. If the master volume server has not received a successful response from each node that the snapshot promotion was successful within a specified time period, there is a retry. The common snapshot is then used as the active file system, thus providing data recovery for the striped volume set.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Concurrent data recovery and input/output processing
ActiveUS9535800B1Input/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionBackupInput/output
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com