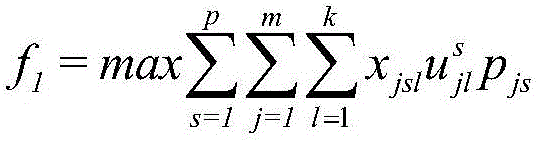Patents
Literature
165 results about "Primary sites" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
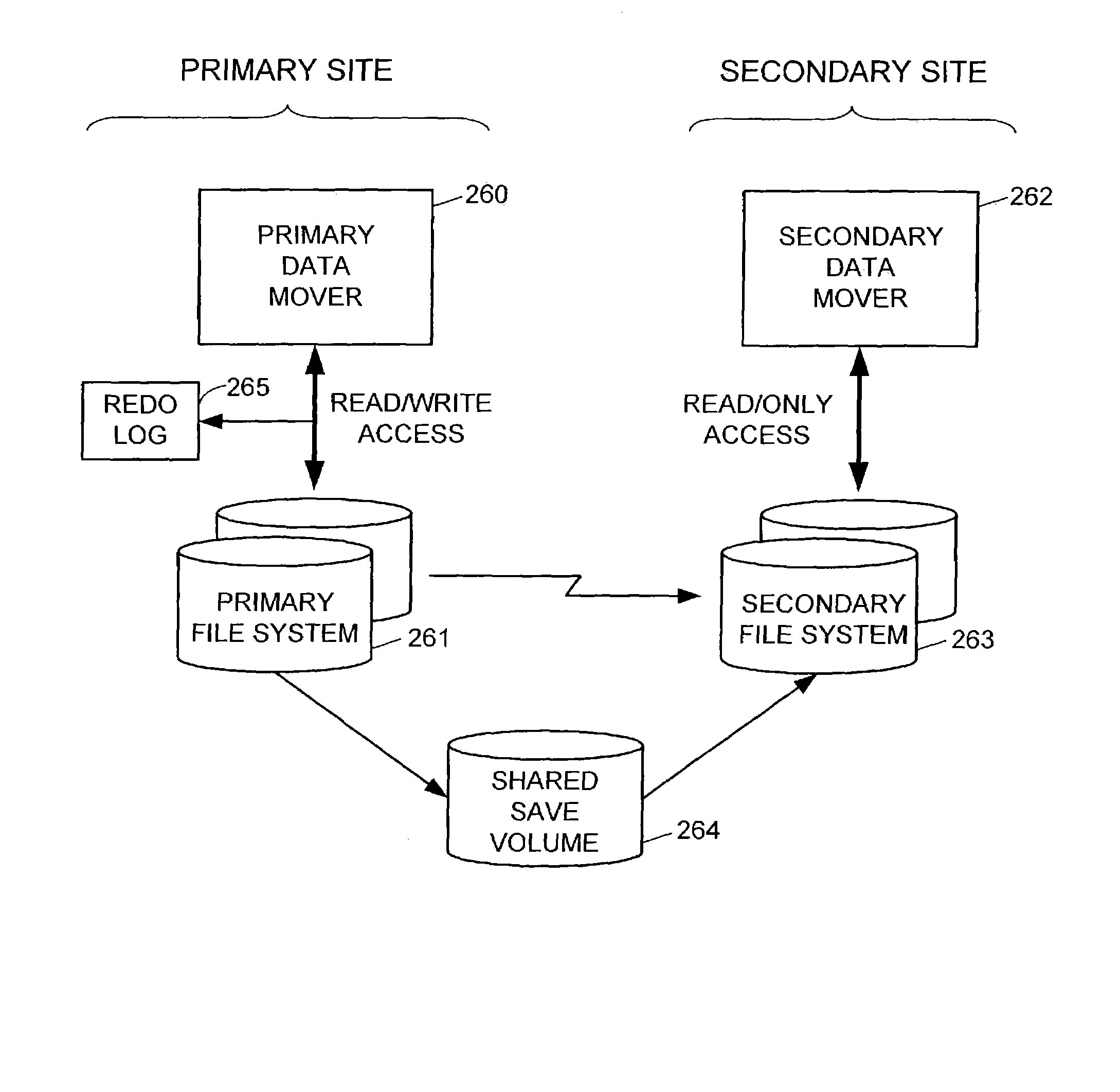
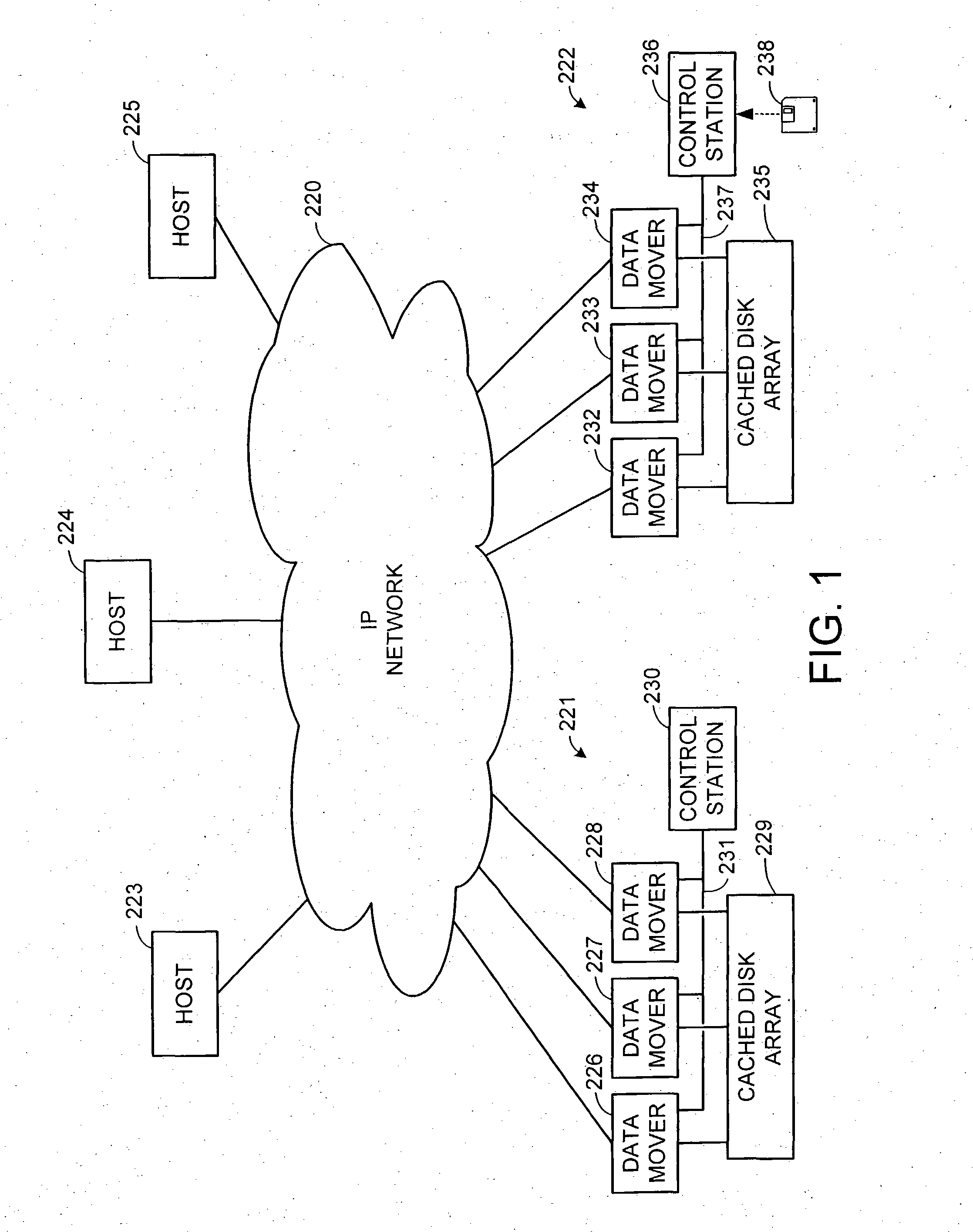
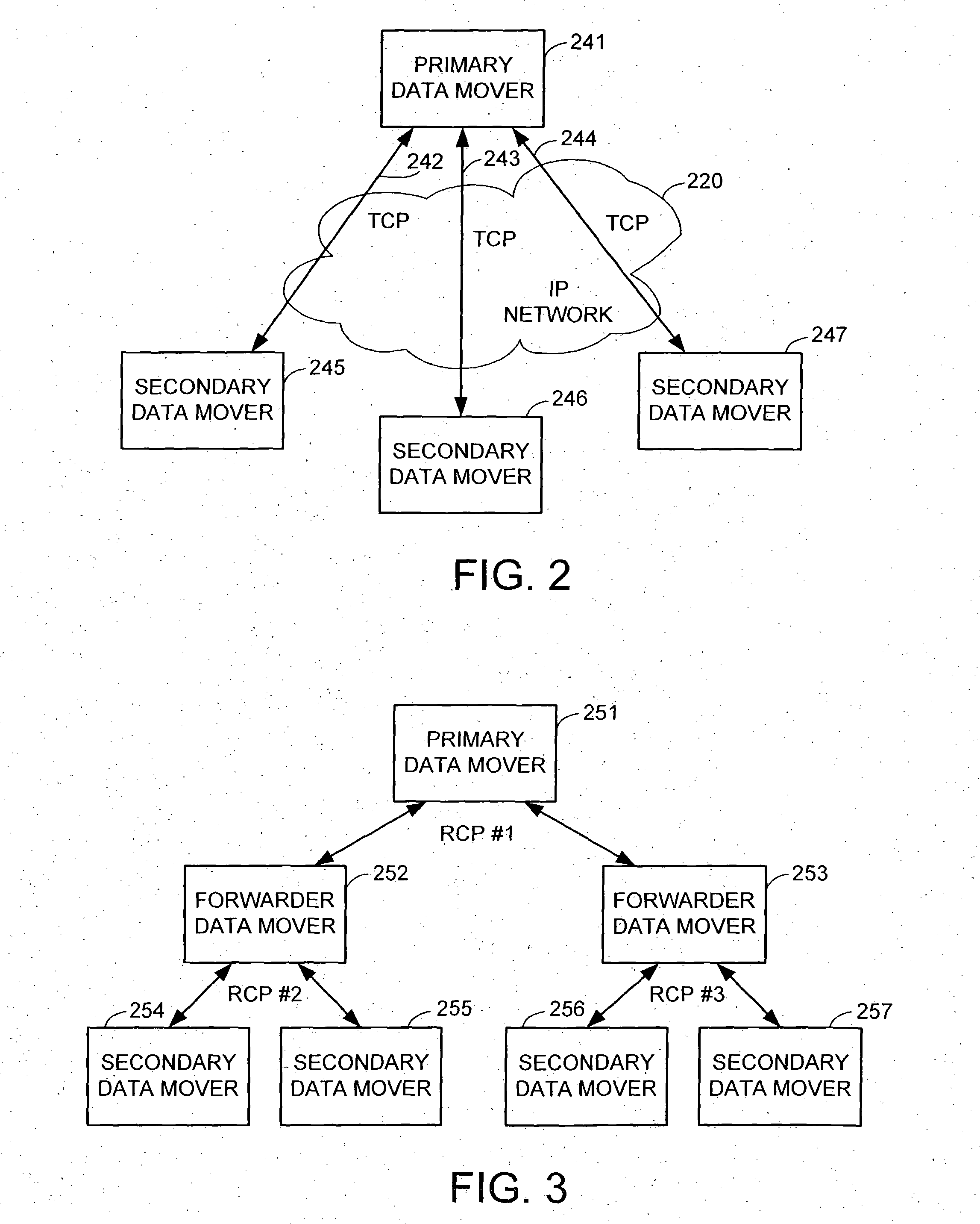
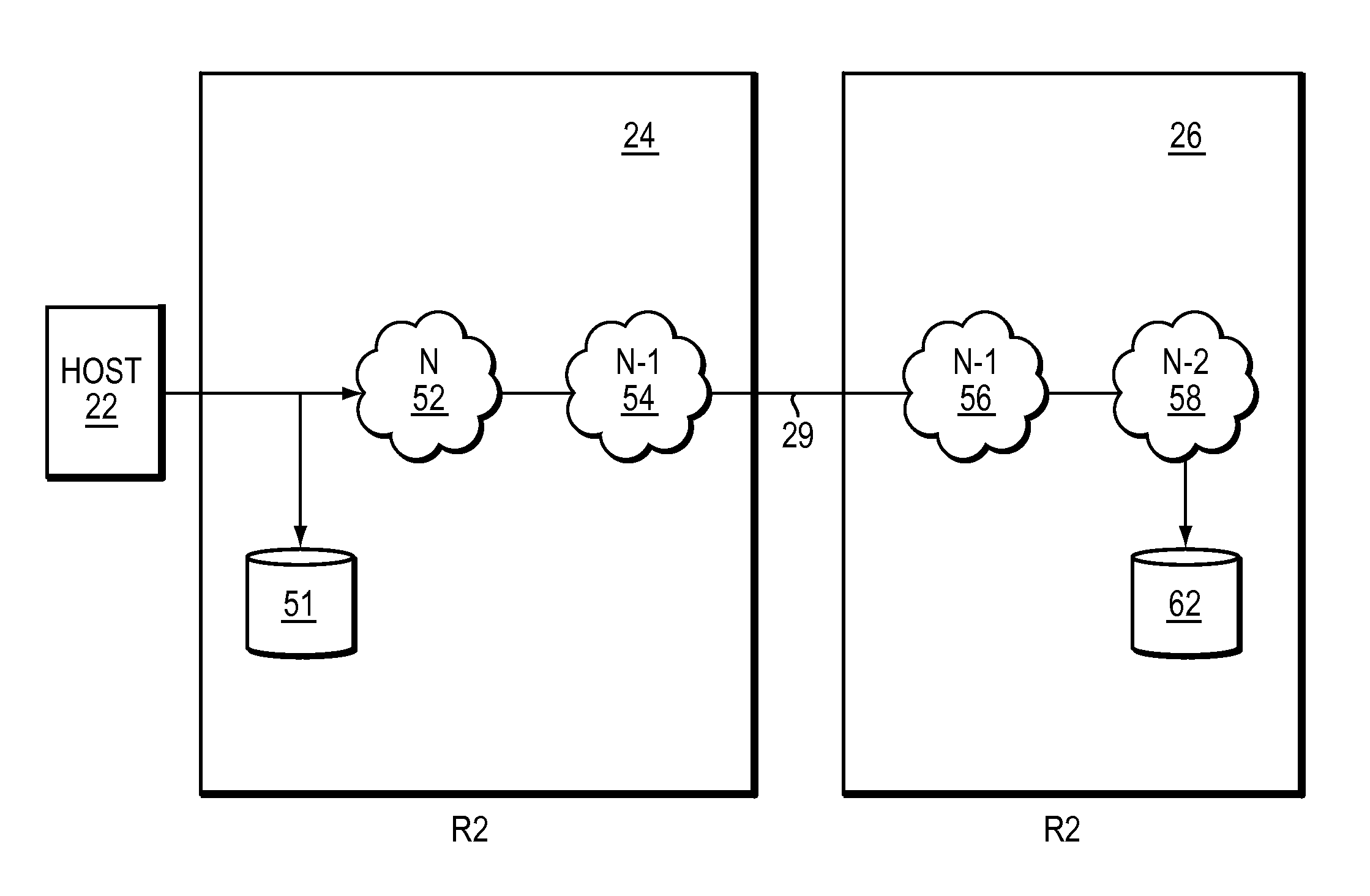
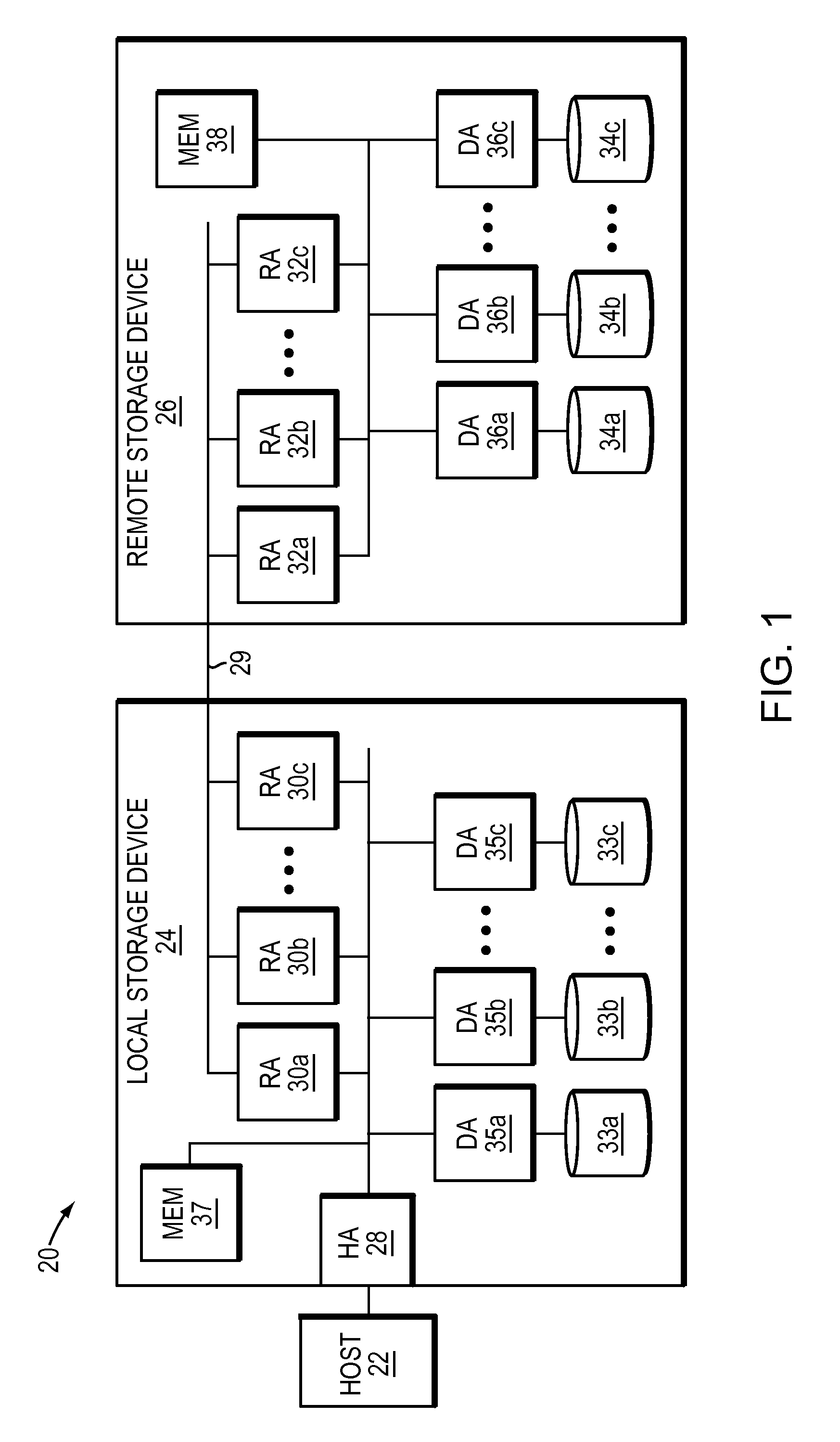
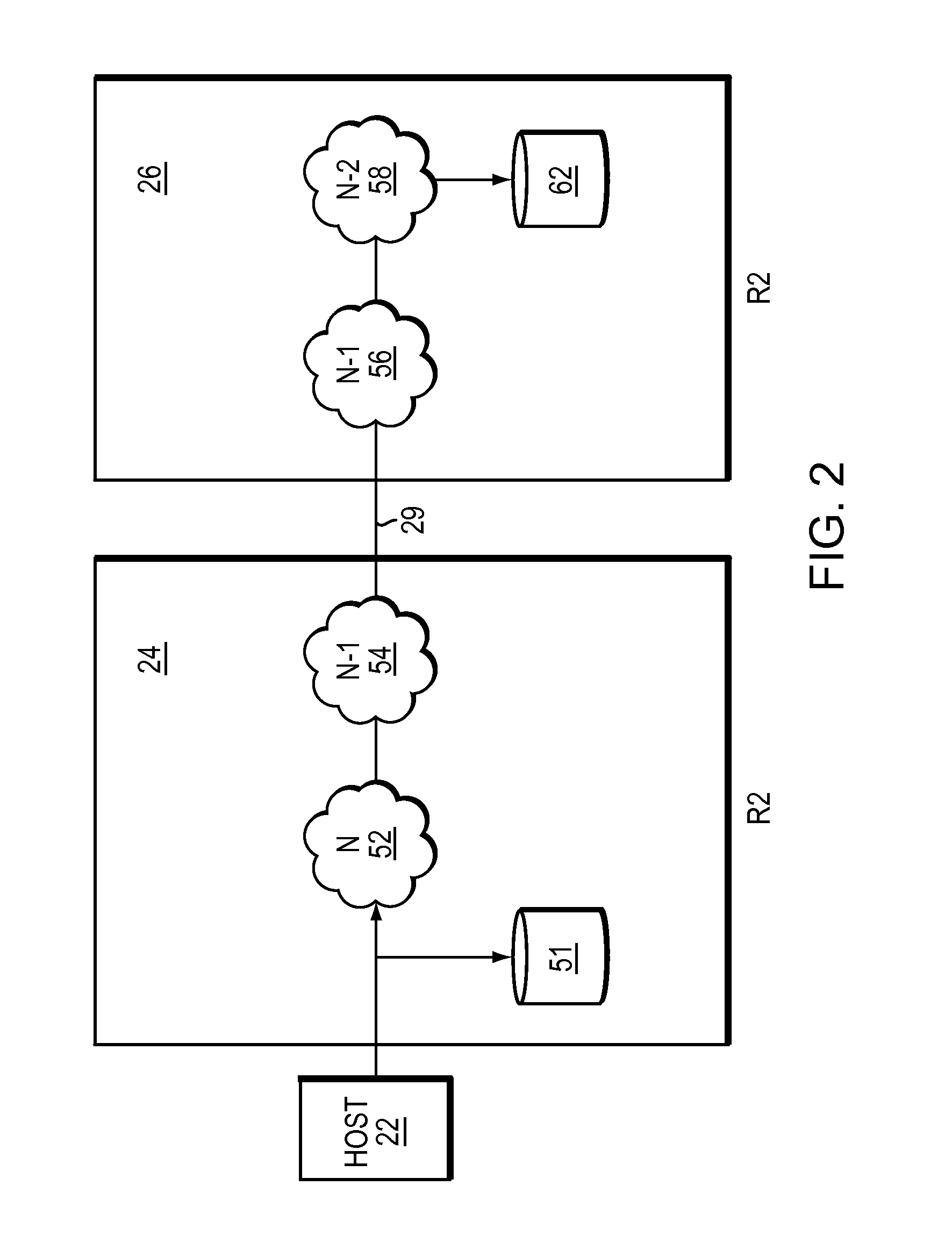
Data recovery with internet protocol replication with or without full resync
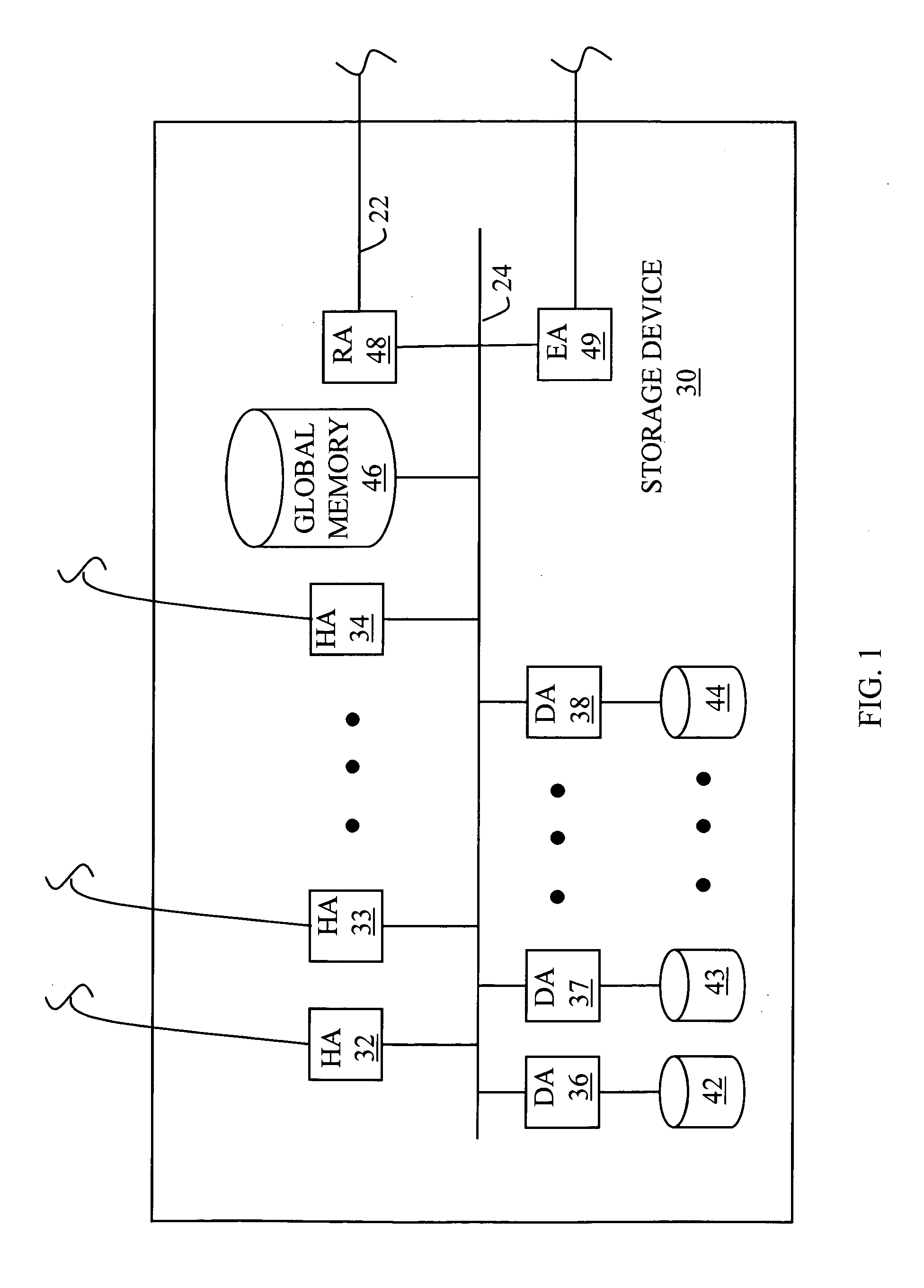
ActiveUS7275177B2Data processing applicationsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPrimary sitesFile system
In an asynchronous remote copy system, a primary site keeps a list of data blocks for which changes have been made to a primary file system and transmitted to a secondary file system at a secondary site. When the primary site becomes inoperative, the secondary site begins read / write access to the secondary file system and keeps a snapshot copy of the restart point. Once the primary site becomes operative, the primary file system is restored to the state of the secondary file system at the restart point by using the list of data blocks for obtaining from the snapshot copy the data of the blocks for which changes had been made to the primary file system after the restart point. Then the primary file system is synchronized to the secondary file system, and read / write access is switched back from the secondary file system to the primary file system.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Data recovery with internet protocol replication with or without full resync
ActiveUS20050015663A1Data processing applicationsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPrimary sitesFile system
In an asynchronous remote copy system, a primary site keeps a list of data blocks for which changes have been made to a primary file system and transmitted to a secondary file system at a secondary site. When the primary site becomes inoperative, the secondary site begins read / write access to the secondary file system and keeps a snapshot copy of the restart point. Once the primary site becomes operative, the primary file system is restored to the state of the secondary file system at the restart point by using the list of data blocks for obtaining from the snapshot copy the data of the blocks for which changes had been made to the primary file system after the restart point. Then the primary file system is synchronized to the secondary file system, and read / write access is switched back from the secondary file system to the primary file system.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
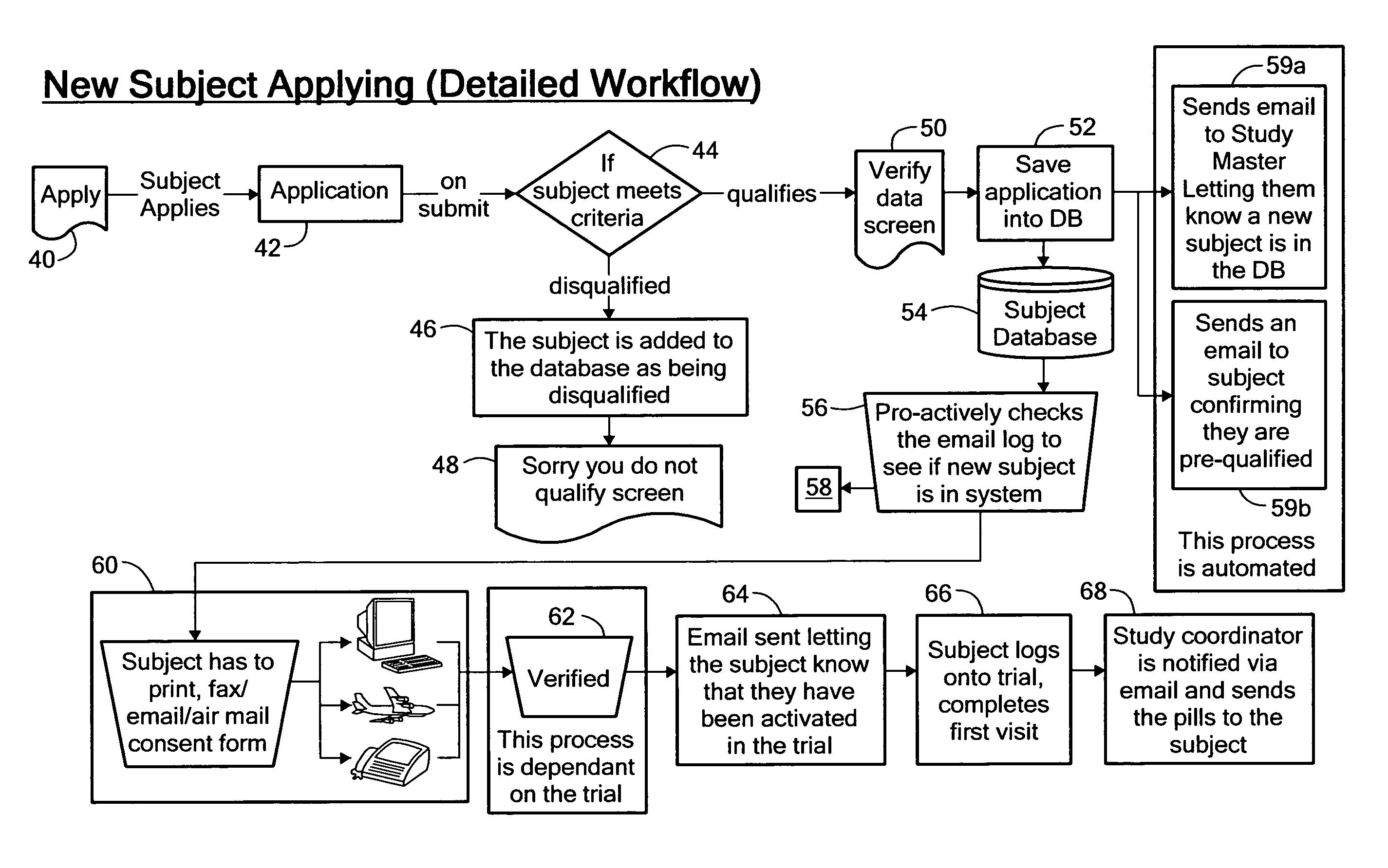
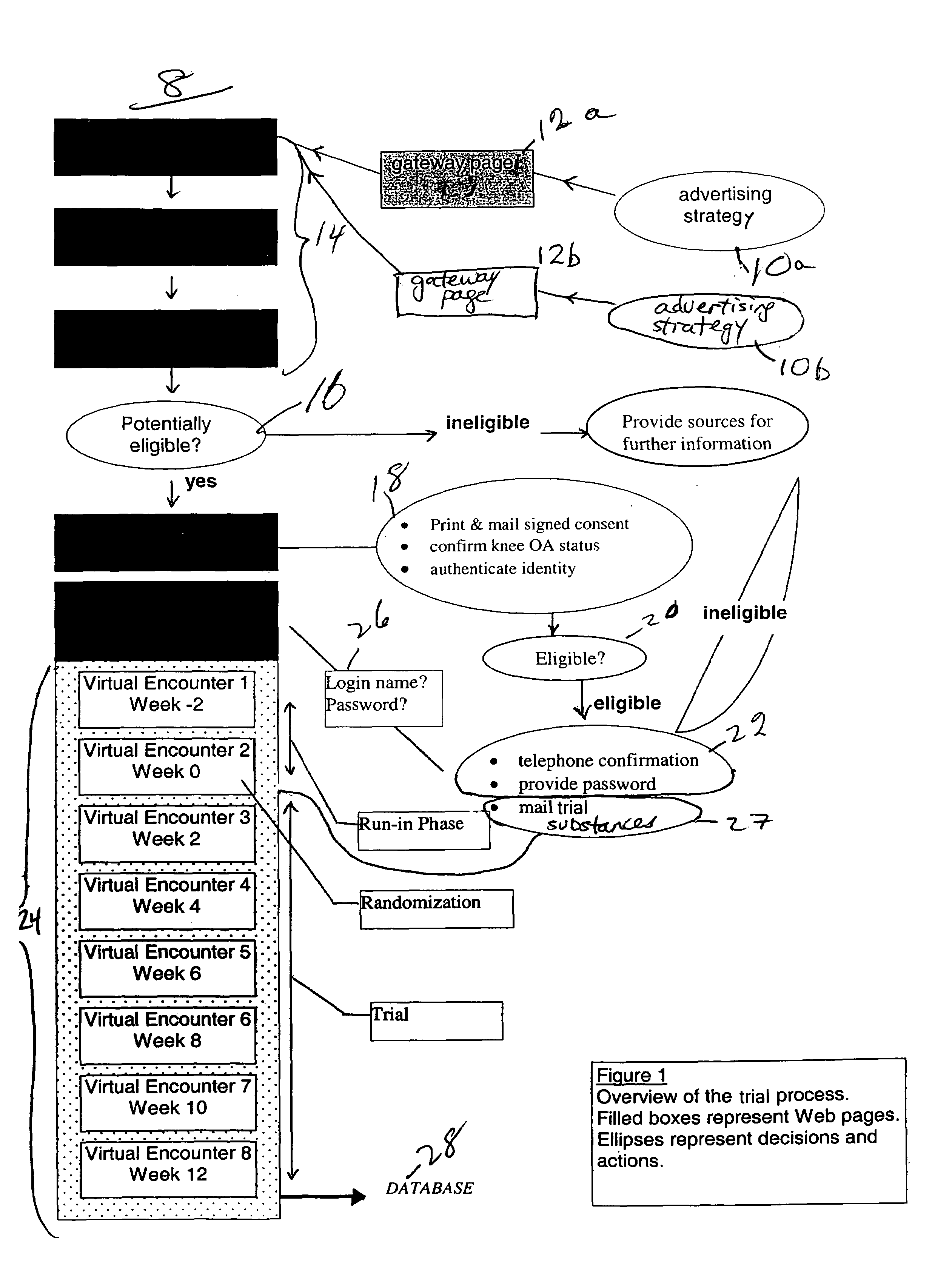
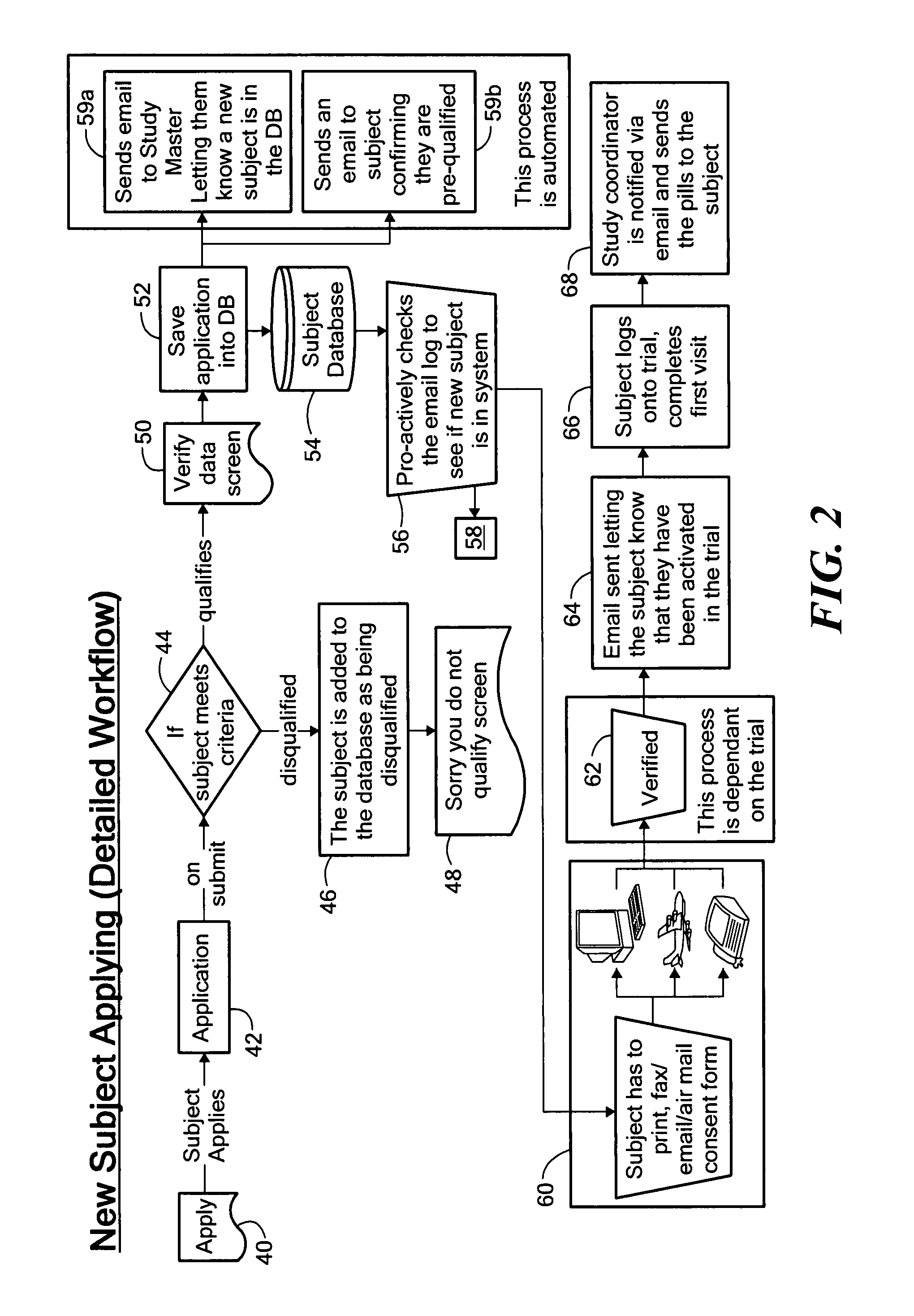
Method for conducting clinical trials over the internet
InactiveUS7251609B1Data processing applicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionSubstance usePrimary sites
The invention encompasses a method of conducting a clinical trial of a test substance from a primary site, via the internet. The internet is used in various phases of a clinical trial, including: recruiting and screening for candidates who are eligible to participate in a clinical trial of a test substance using the internet; obtaining, directly from a participant at a remote site, personal information as well as information allowing a determination of any effect(s) of the test substance on the participant after use (e.g., by evaluation forms completed and transmitted over the internet); compiling data from multiple participants.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
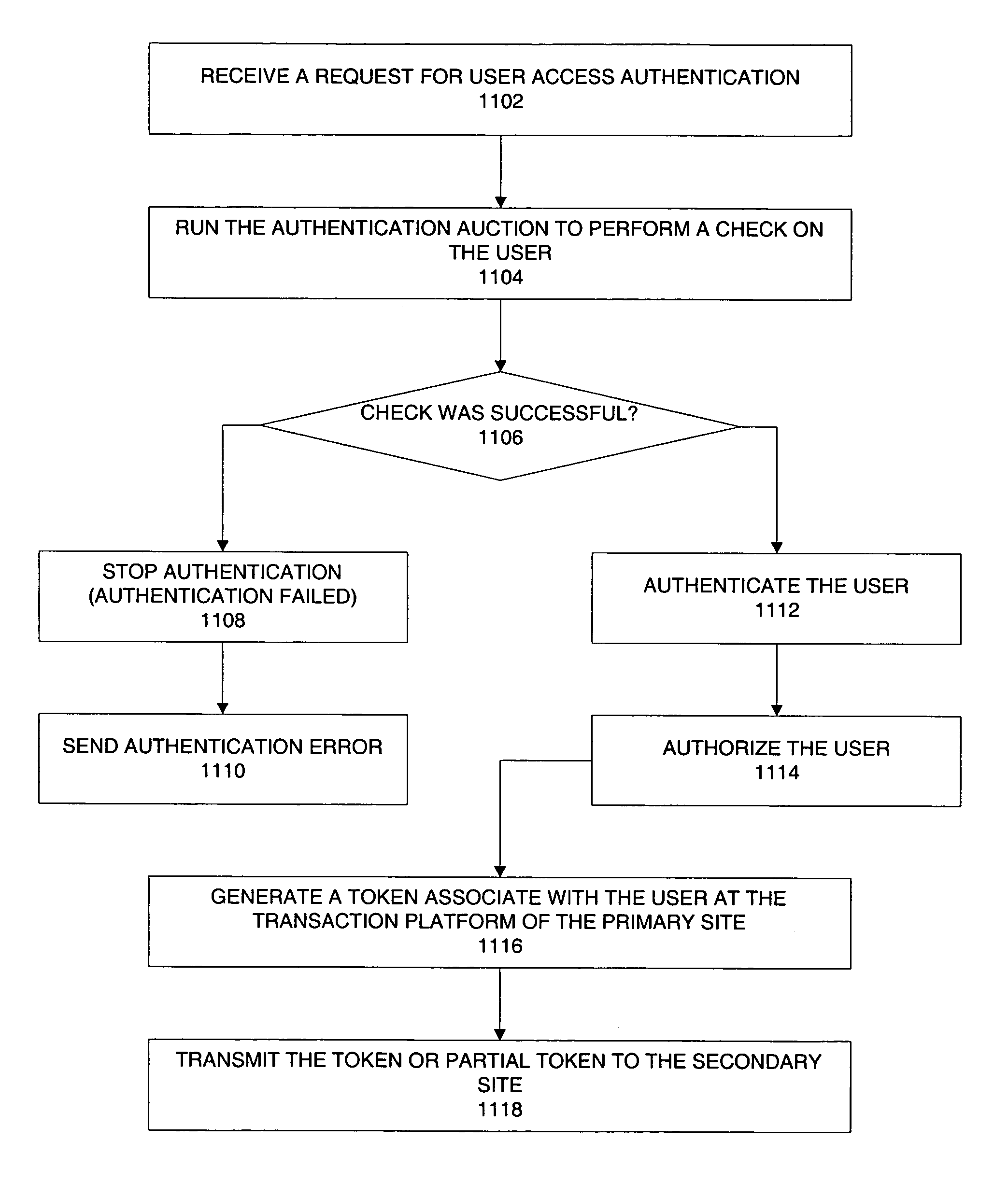
Method and apparatus to authenticate and authorize user access to a system
ActiveUS7769998B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPrimary sitesInternet privacy
A method, apparatus, and system are provided for authenticating and authorizing user access to a system. According to one embodiment, a request for authentication and authorization of a user is received from a secondary site on behalf of the user who is seeking to access a primary site via the secondary site via a computer network. The request includes information relating to the user. The user information is then verified for authenticity, including determining whether the user satisfies the criteria for obtaining authentication and authorization as defined by the primary site. If the criteria are satisfied, a token, associated with the user, is generated at the primary site. A portion of the token is transmitted from the primary site to the secondary site on behalf of the user to permit the user to access the primary site via the secondary site, via the computer network.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
Application of virtual servers to high availability and disaster recovery soultions
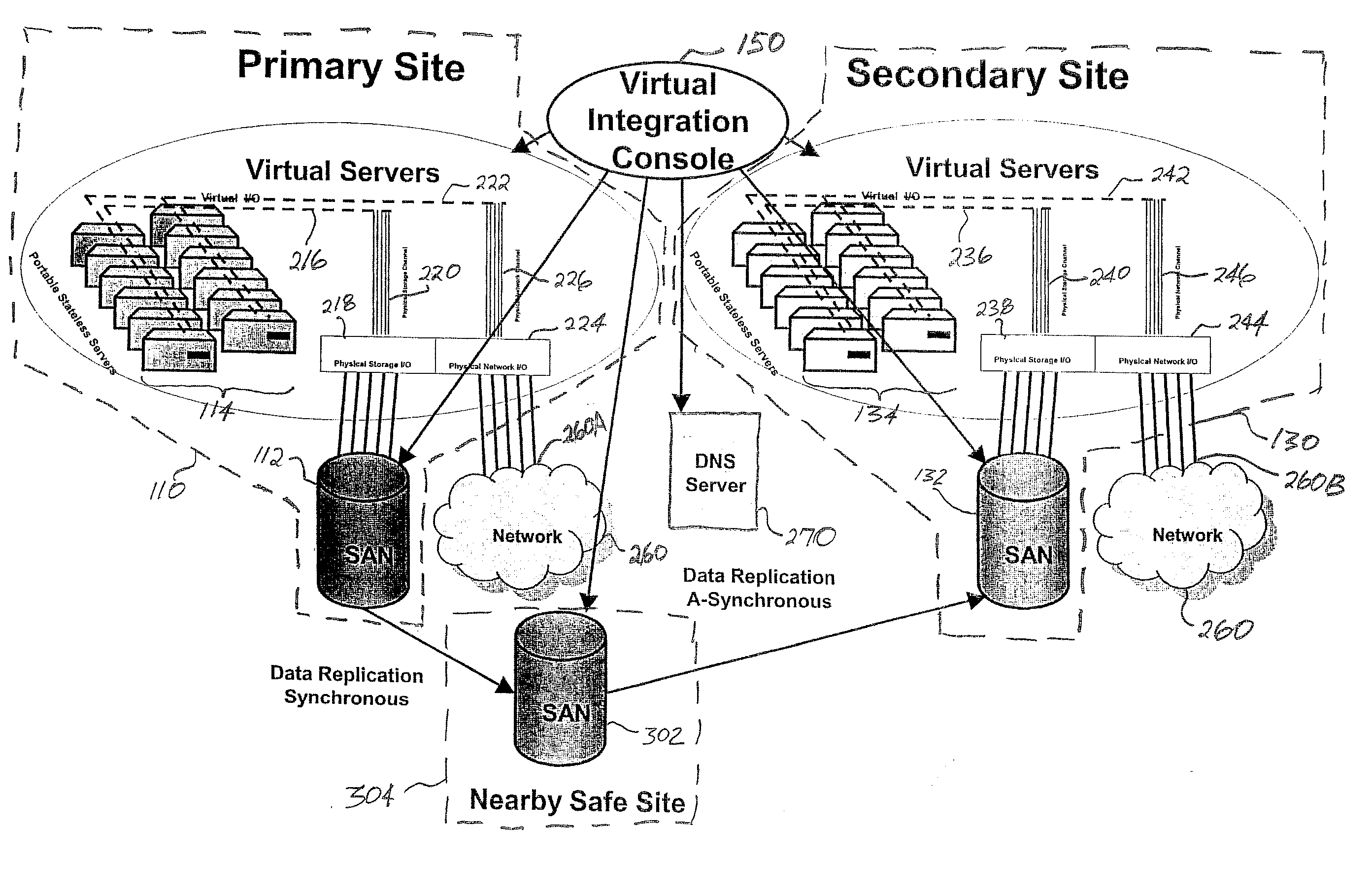
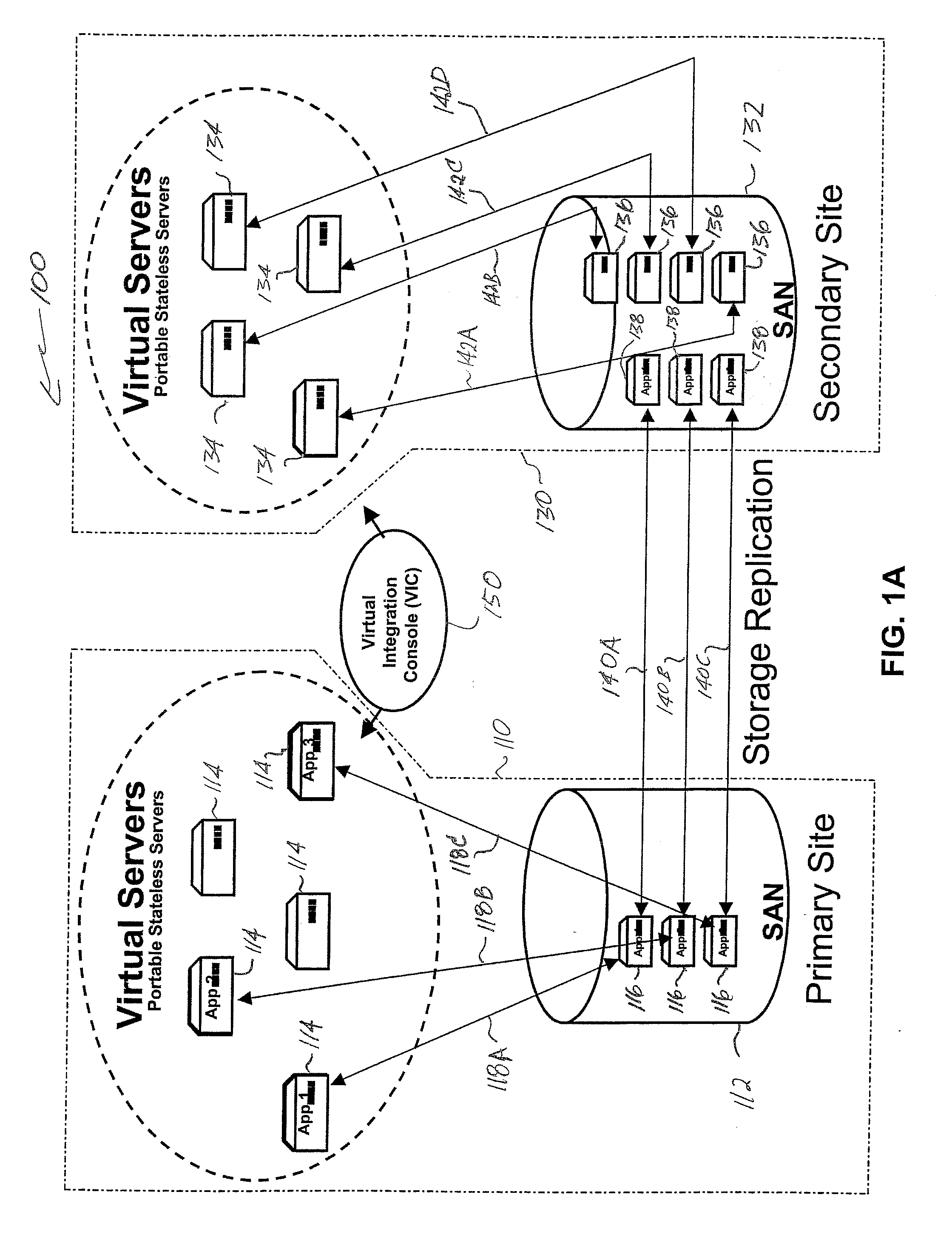
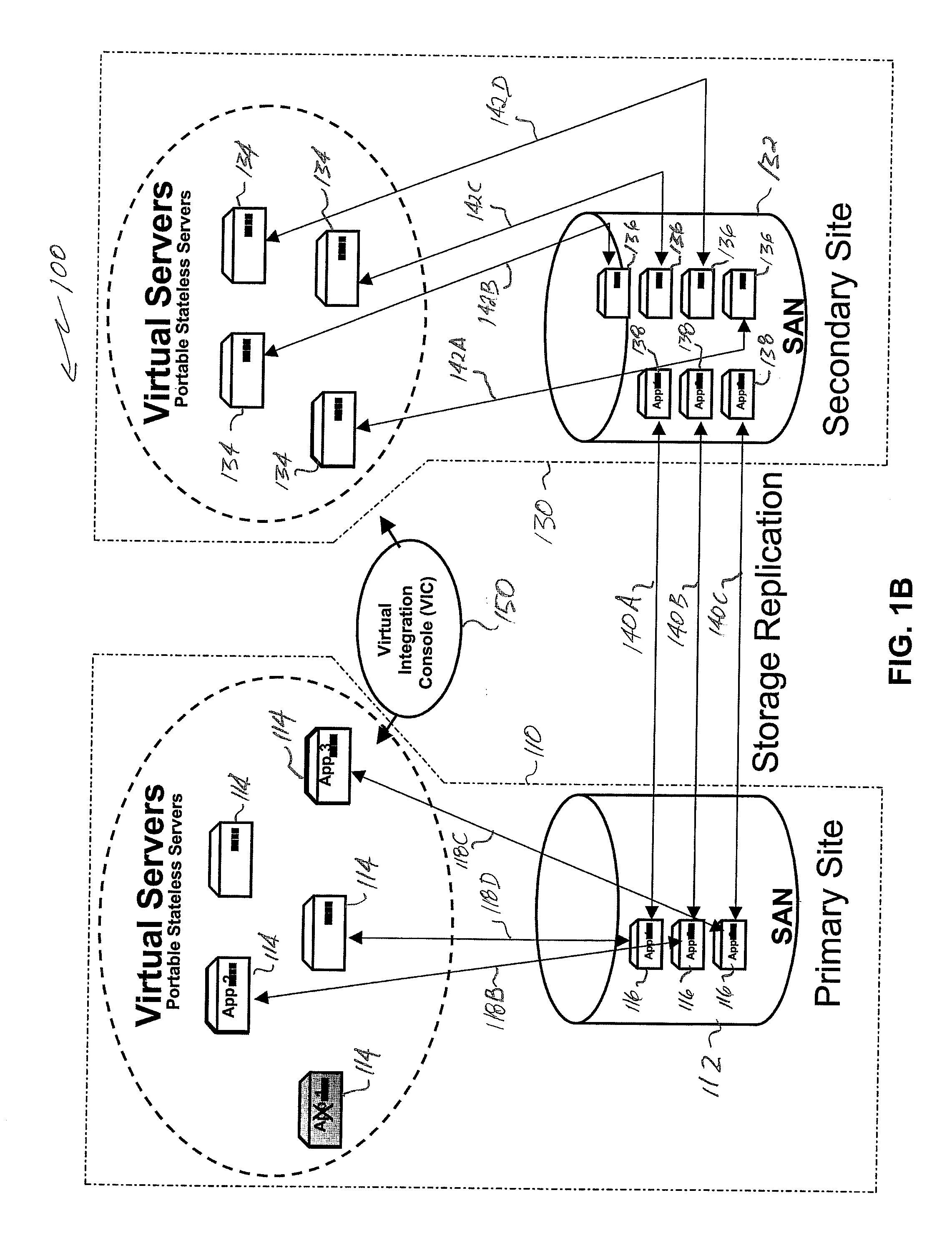
InactiveUS20070078982A1Improve availabilityHigh dataError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtualizationStorage area network
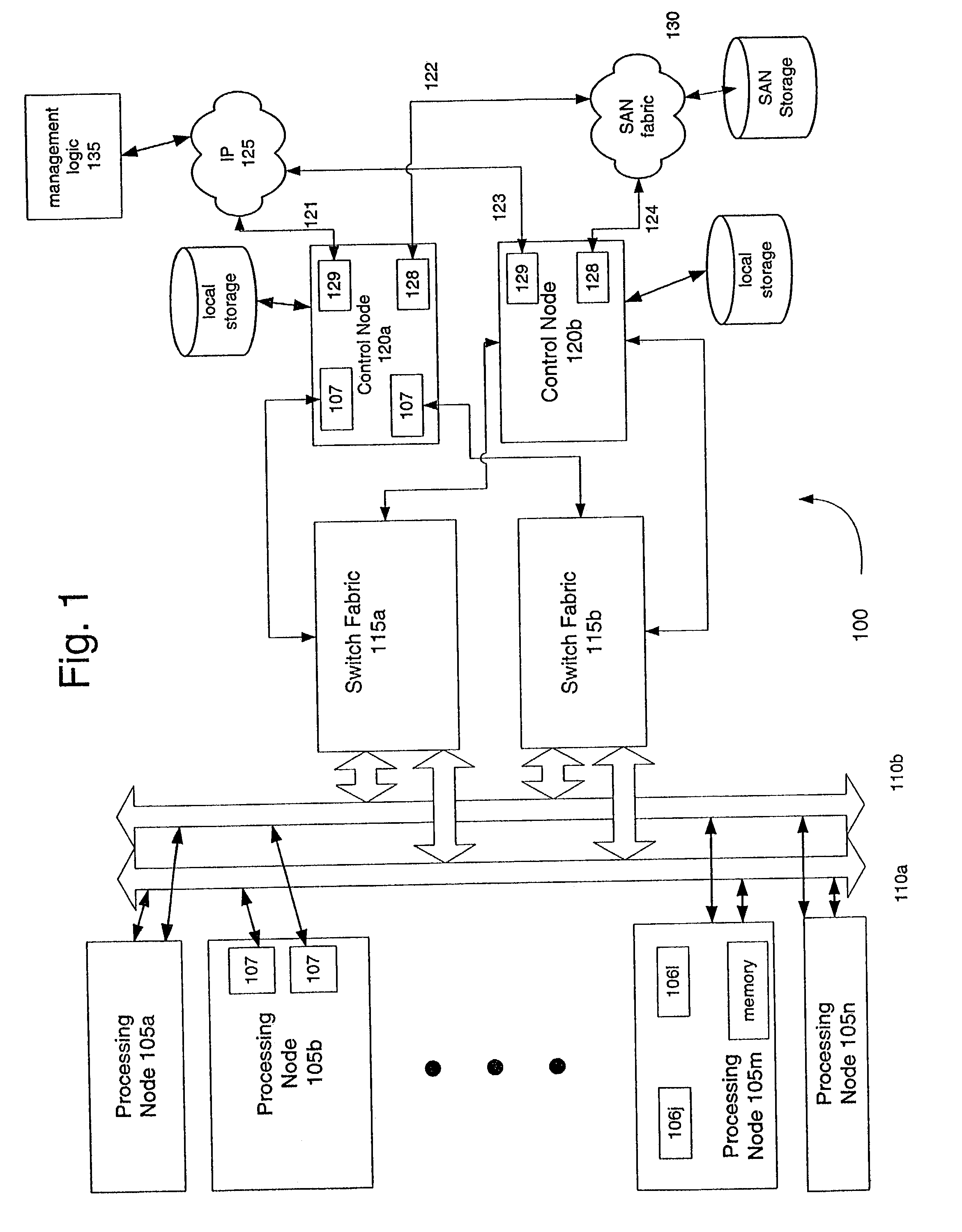
Server virtualization technology is applied to virtualize and encapsulate all unique information of a server as an image that is stored on a storage area network at one site and replicated on a storage area network at another site to provide high availability of system resources and data recovery capabilities. In one embodiment, a virtualized server system (100) includes a primary site (110), a secondary site (130), and a computer executable control application (150). The primary site (110) includes a storage area network (112), at least one primary virtual server platform (114), and at least one primary virtual server stored as at least one image (116) on the storage area network (112). The control application (150) directs replication of the primary virtual server image (116) onto a storage area network (132) at the secondary site (130) to create a corresponding replicated virtual server image (138). The control application (150) also monitors operation of the primary virtual server platform (114) and associates the replicated virtual server image (138) with a secondary virtual server (134) at the secondary site (130) in the event that a problem is detected with the primary site virtual server (114).
Owner:LEIDOS INNOVATIONS TECH INC
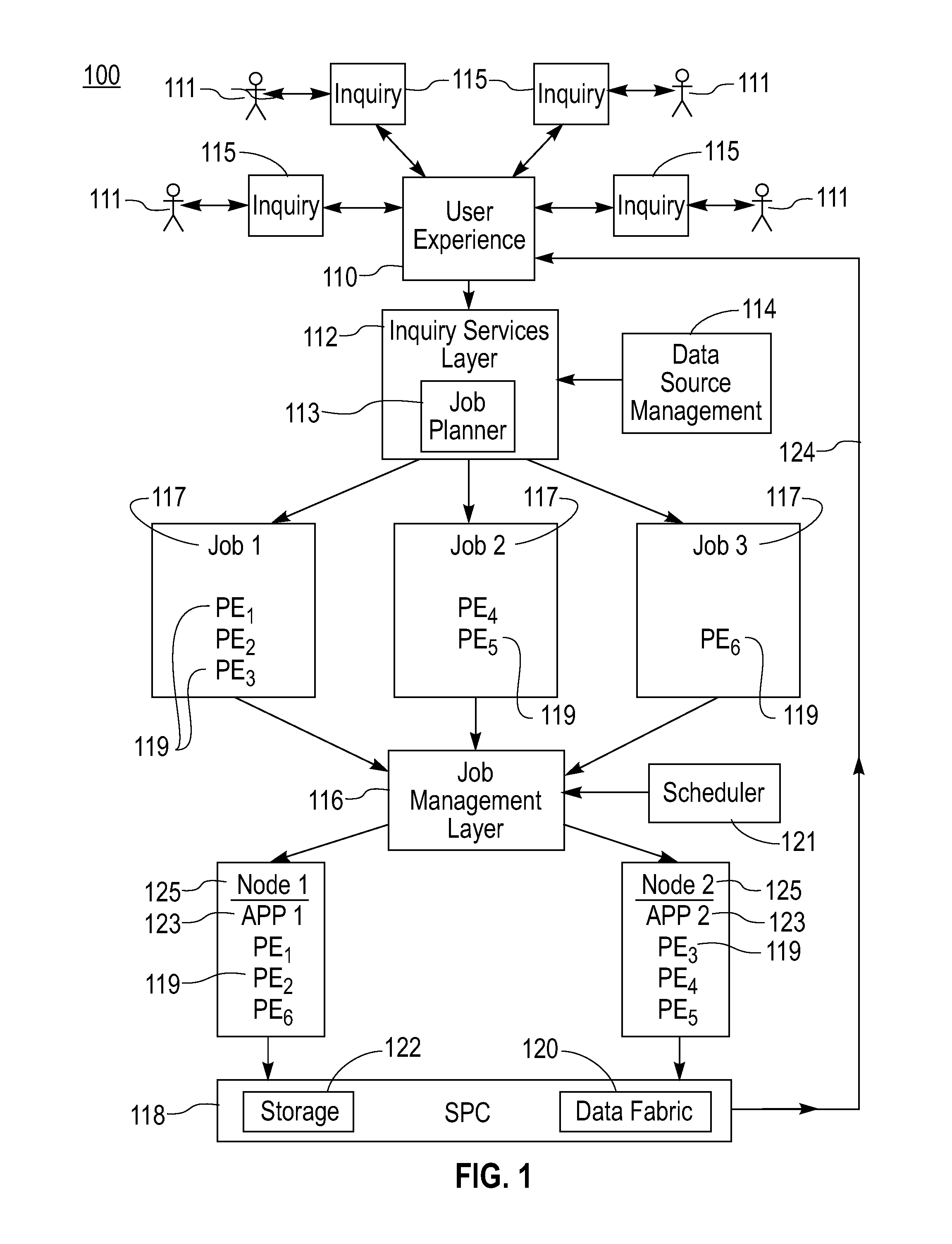
Mechanism for Recovery from Site Failure in a Stream Processing System
InactiveUS20080256384A1Describe wellCompensation differenceFault responseData processing systemPrimary sites
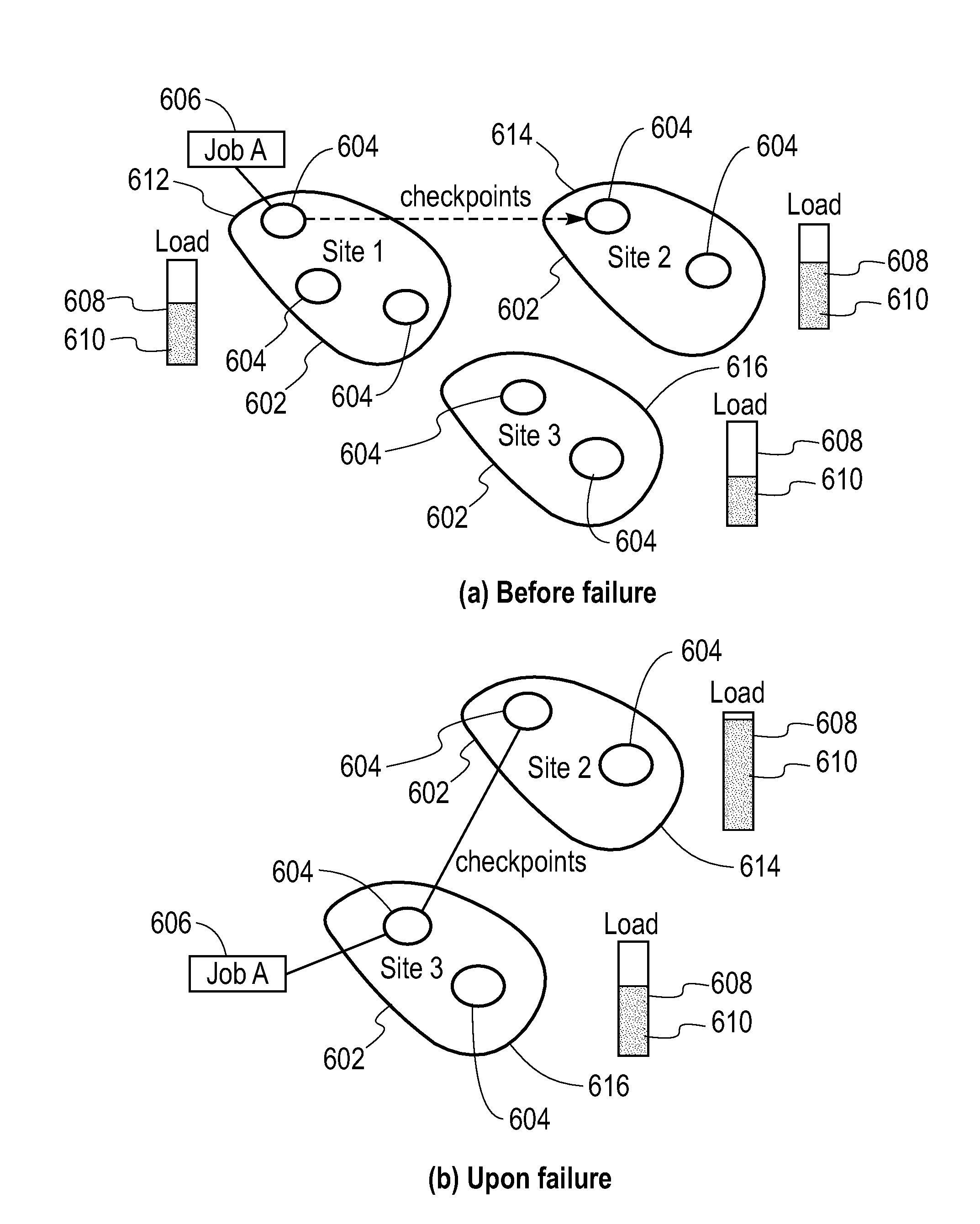
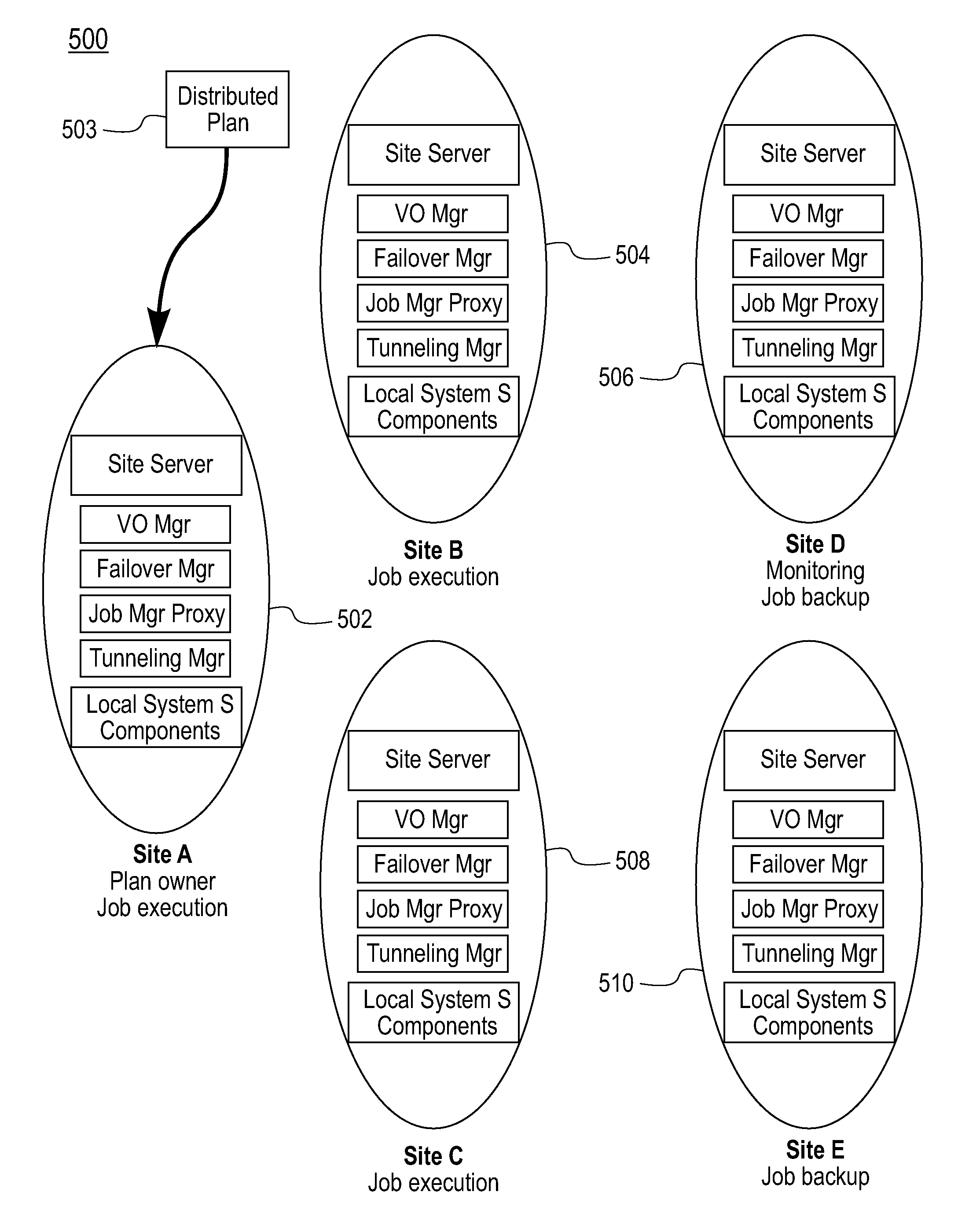
A failure recovery framework to be used in cooperative data stream processing is provided that can be used in a large-scale stream data analysis environment. Failure recovery supports a plurality of independent distributed sites, each having its own local administration and goals. The distributed sites cooperate in an inter-site back-up mechanism to provide for system recovery from a variety of failures within the system. Failure recovery is both automatic and timely through cooperation among sites. Back-up sites associated with a given primary site are identified. These sites are used to identify failures within the primary site including failures of applications running on the nodes of the primary site. The failed applications are reinstated on one or more nodes within the back-up sites using job management instances local to the back-up sites in combination with previously stored state information and data values for the failed applications. In additions to inter-site mechanisms, each one of the plurality of sites employs an intra-site back-up mechanism to handle failure recoveries within the site.
Owner:IBM CORP
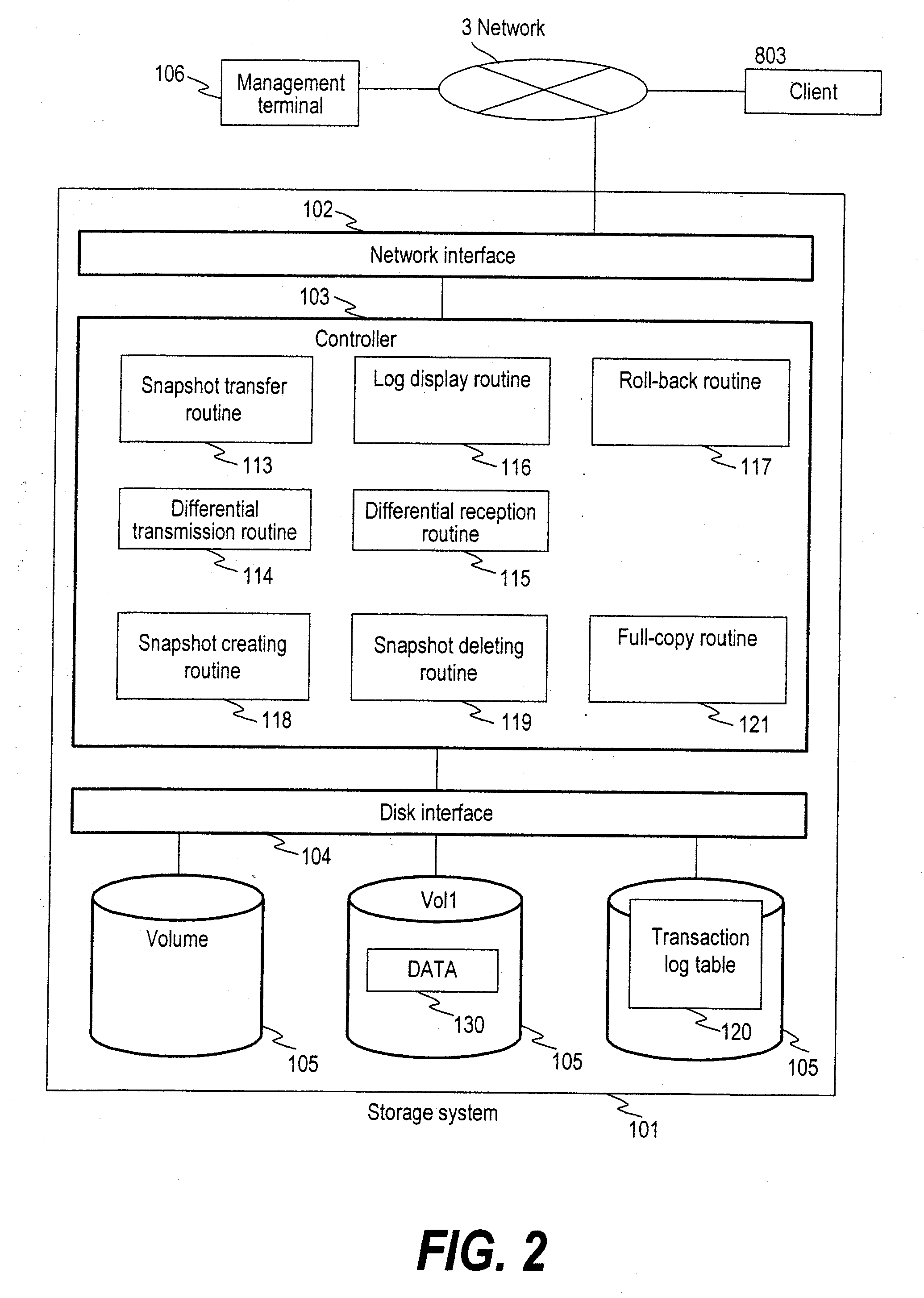
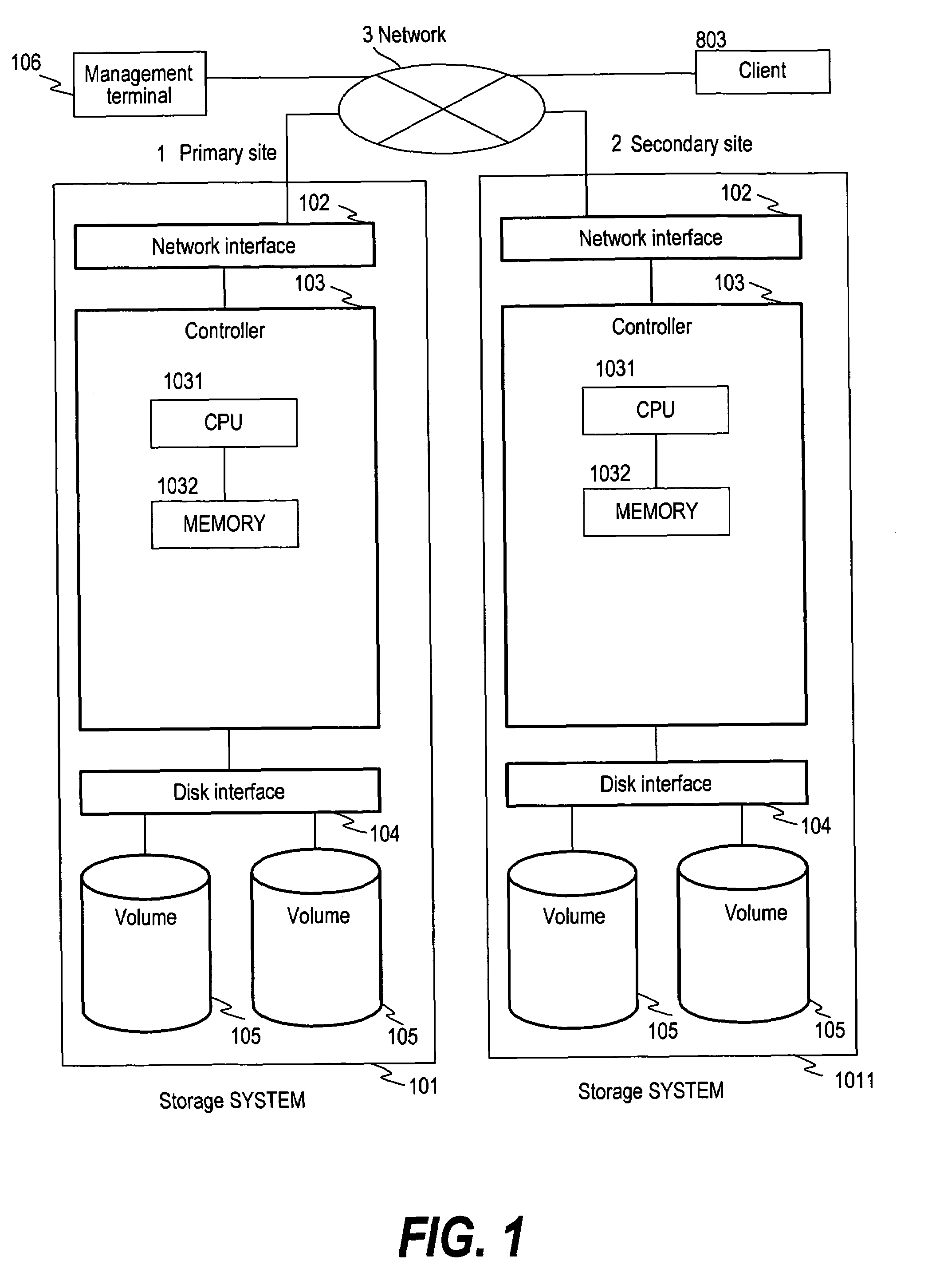
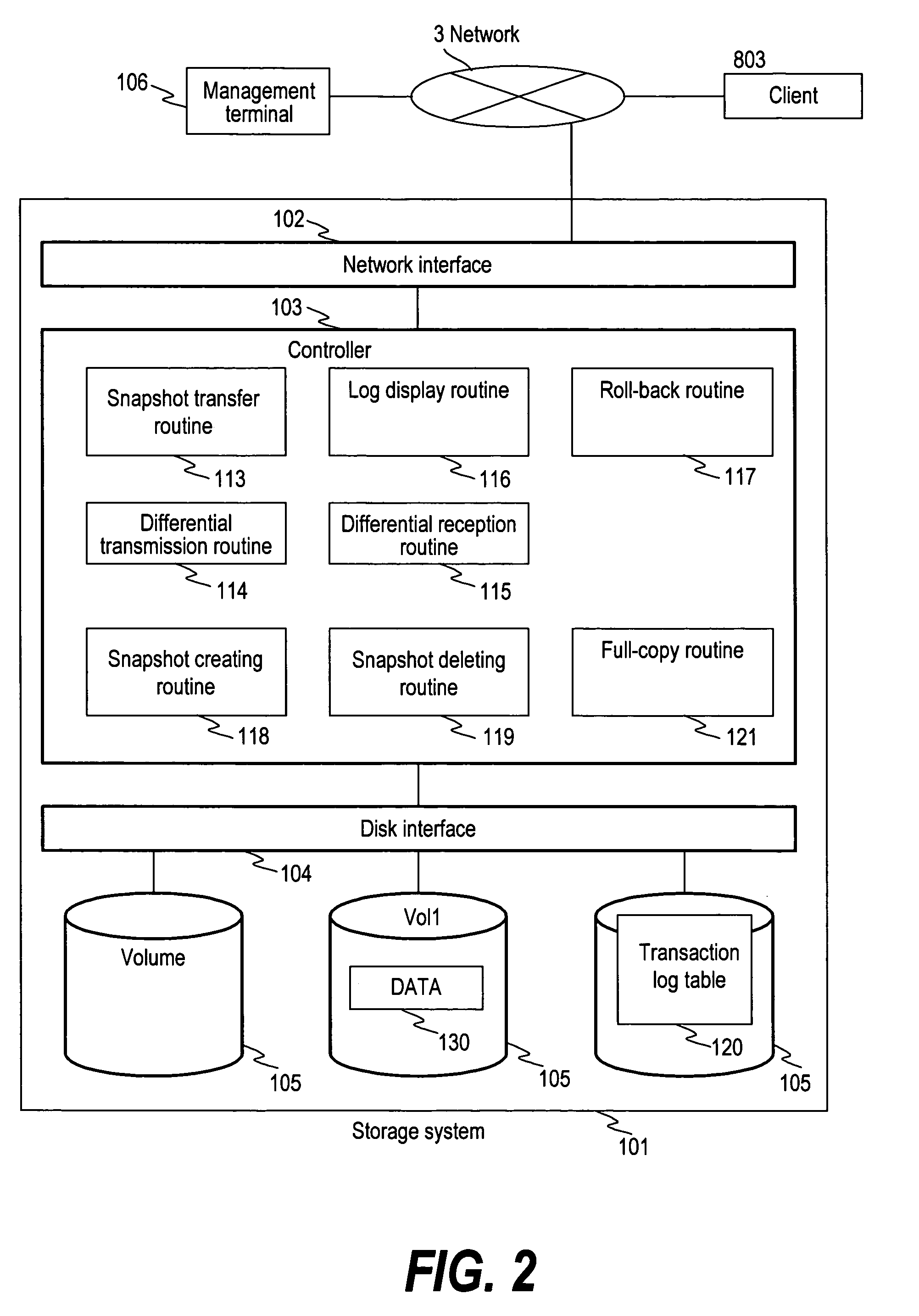
Method for rolling back from snapshot with log
InactiveUS20090044046A1Reduce copying timeFast copyRedundant operation error correctionPrimary sitesSecondary site
High speed differential copy can be implemented in the fail-back after disaster recovery when the data of the primary site is protected safely. When a restore command is issued, the common snapshots of the snapshots of the primary site and the secondary site are extracted as the base snapshot by comparing the log tables of the primary site and secondary site. The volume of the primary site is rolled back with the extracted snapshots. The latest snapshot of the volume of the secondary site is transmitted to the primary site and it is applied to the volume of the primary site to synchronize the volumes of the primary site and the secondary site.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Incremental update control for remote copy
ActiveUS20030158869A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsPrimary sitesCommunication link
There is provided a method, system and program storage device for asynchronously transmitting one or more incremental database updates from a primary volume at a primary site to a remote volume at a remote site, the primary site and the remote site interconnected by at least one communication link, the method, system and program storage device comprising: destaging modified data to the primary volume for a current database update and updating one or more bits in a first bitmap at the primary site that indicate one or more tracks on the primary volume that are to be overwritten with the modified data; transferring the first bitmap to a second bitmap at the primary site for indicating the modified data that is to be transmitted to the remote volume at the remote site for the current database update; and synchronizing the primary volume at the primary site with the remote volume at the remote site for the current database update by transmitting the modified data to the remote volume as indicated by one or more bits in the second bitmap, wherein the one or more incremental database updates at the primary volume of the primary site are decoupled from transmission of the one or more incremental database updates to the remote volume at the remote site.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Extent commands in replication
ActiveUS8977826B1Input/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionPrimary sitesComputer science
A method, system, and computer program product for ordering a plurality of data IO captured at a primary site to be applied at a secondary site, comprising removing the one or more extent level portions from the captured data IO, determining if the one or more extent level portions are time sequenced to overwrite a portion of data of the data IO, based on a determination that the portion data is to be overwritten, removing the overwritten portion of data from the plurality of the data IO and ordering the one or more extent level portions to be applied at the secondary site before the captured data IO.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
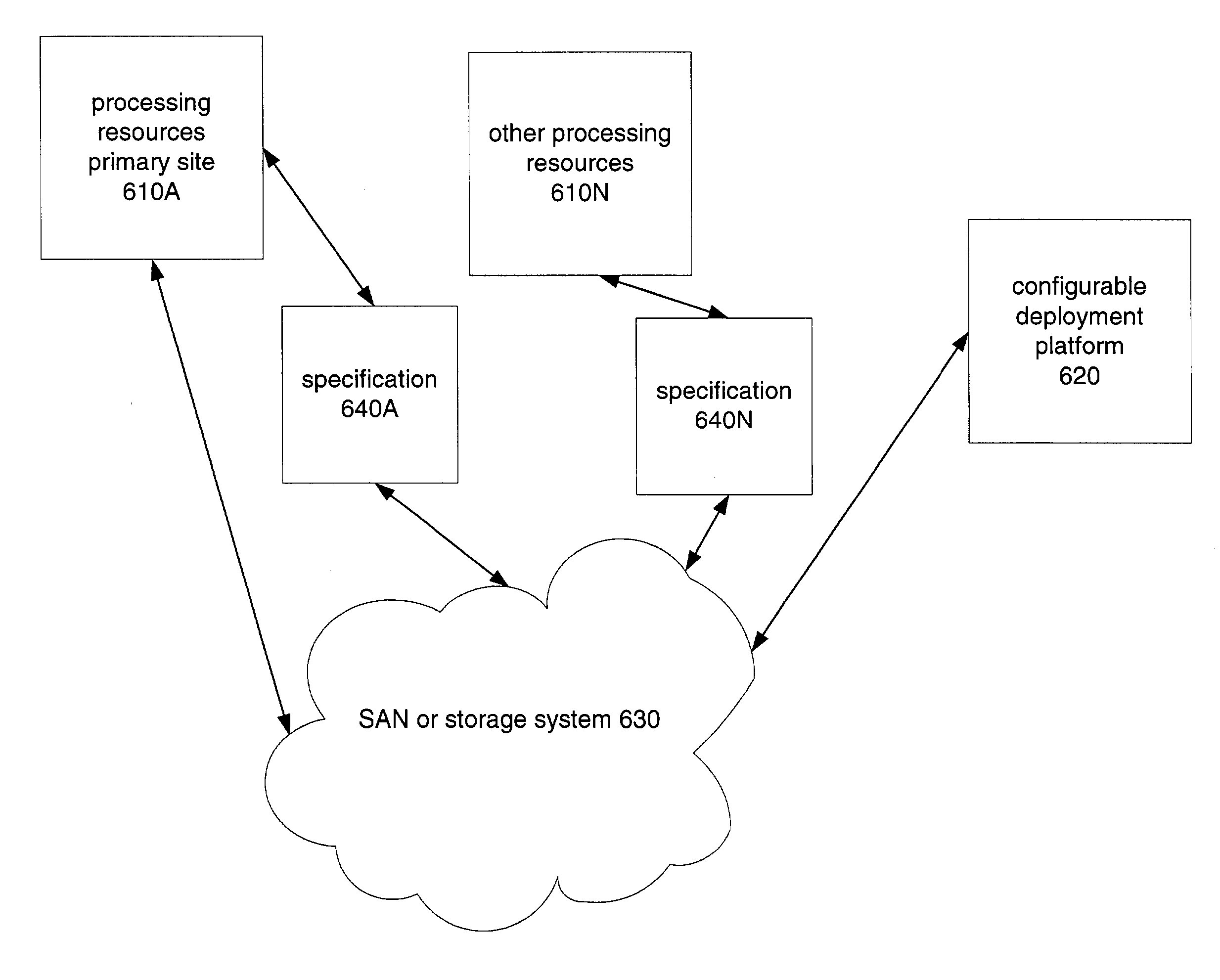
Disaster recovery for processing resources using configurable deployment platform
A system and method for disaster recovery for processing resources using configurable deployment platform. A primary site has a configuration of processing resources. A specification of the configuration of processing resources of the primary site is generated. The specification is provided to a fail-over site that has a configurable processing platform capable of deploying processing area networks in response to software commands. Using the specification, software commands are generated to the configurable platform to deploy processing area network corresponding to the specifications.
Owner:EGENERA
Remote activity monitoring
InactiveUS20050080895A1Undesirable operationUndesirable split brain operation can be avoidedError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsPrimary sitesActivity monitoring
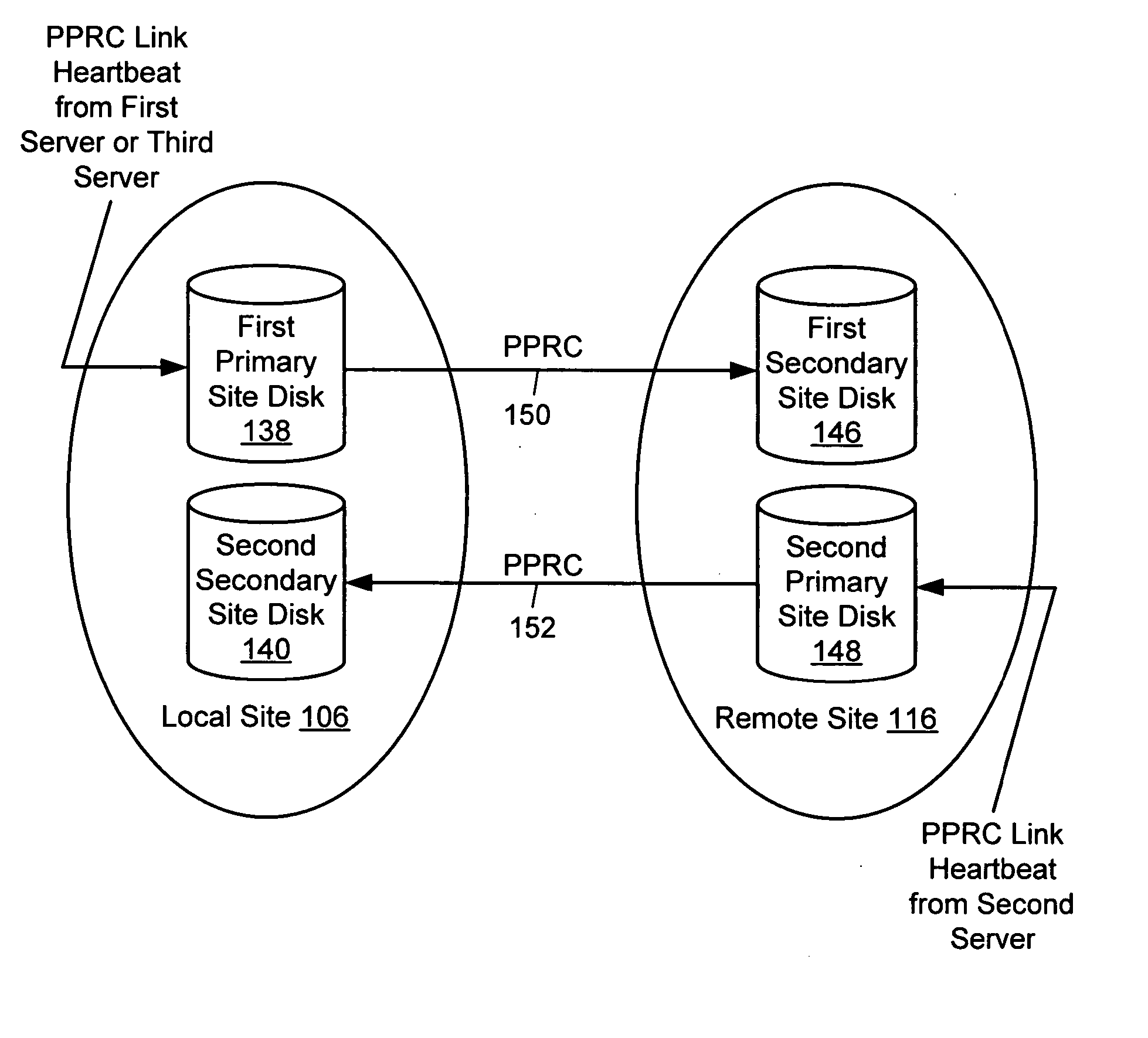
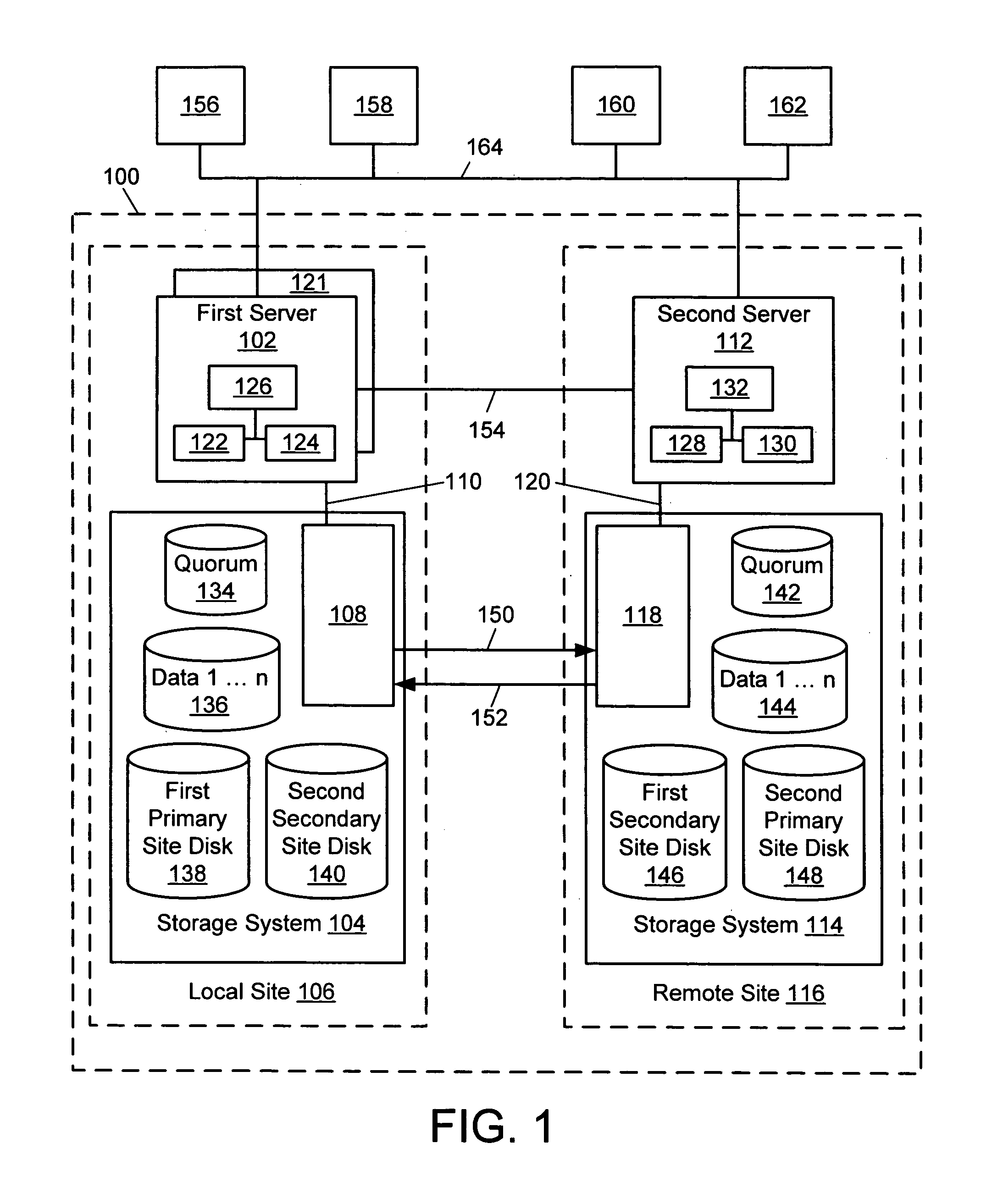
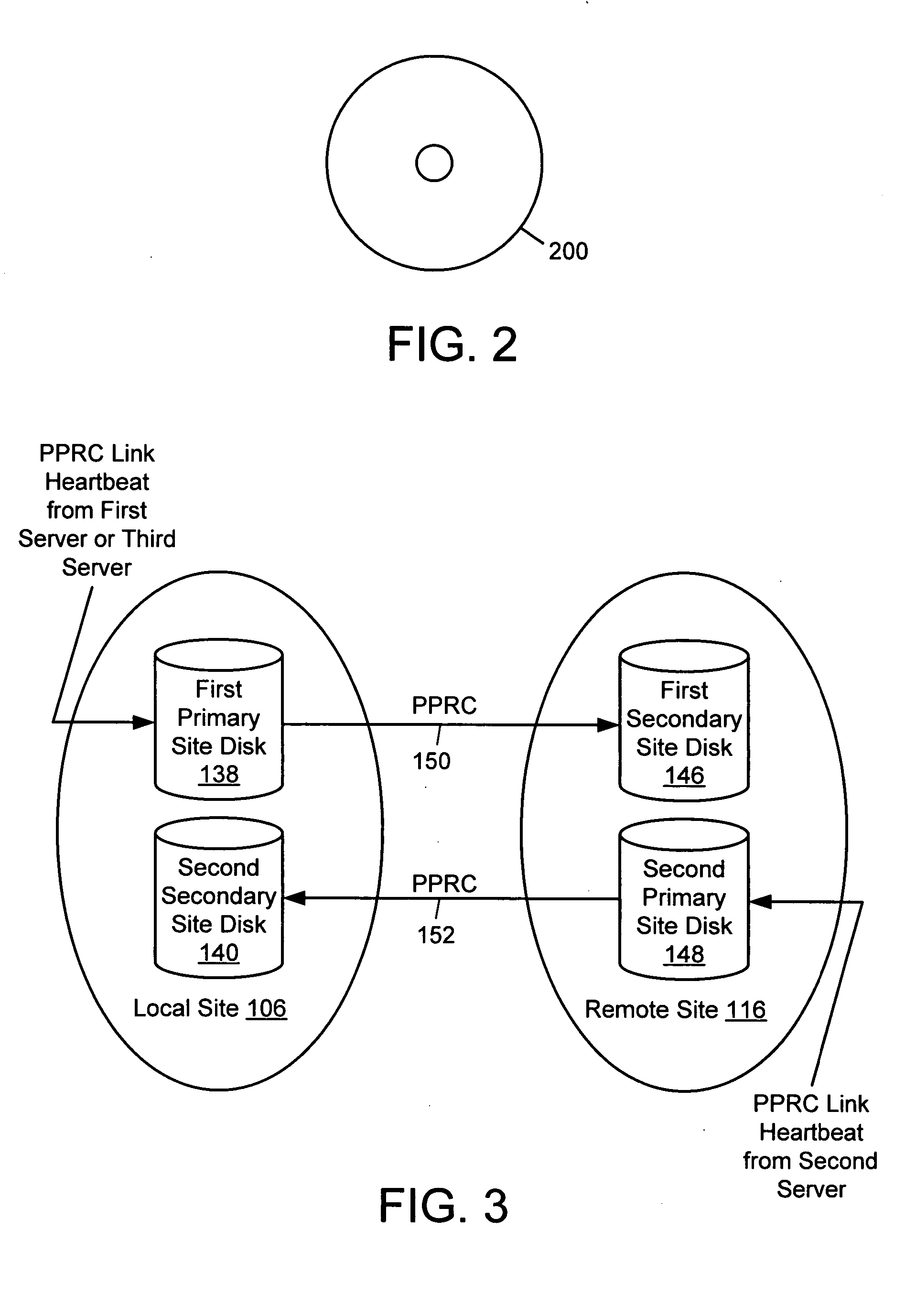
A method for remotely monitoring activity includes generating first server heartbeat information at a first server at a local site, and storing the first server heartbeat information in a first primary site disk at the local site. The method also includes sending the first server heartbeat information from the first primary site disk, to a first secondary site disk at a remote site. The method further includes receiving information from a second secondary site disk at the local site, and determining if the information received from the second secondary site disk includes updated heartbeat information.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data processing system
ActiveUS20070033437A1Promote recoverySolve the lack of balanceData processing applicationsMemory systemsData processing systemPrimary sites
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Data processing system
InactiveUS7328373B2Promote recoverySolve the lack of balanceData processing applicationsMemory systemsData processing systemTransfer procedure
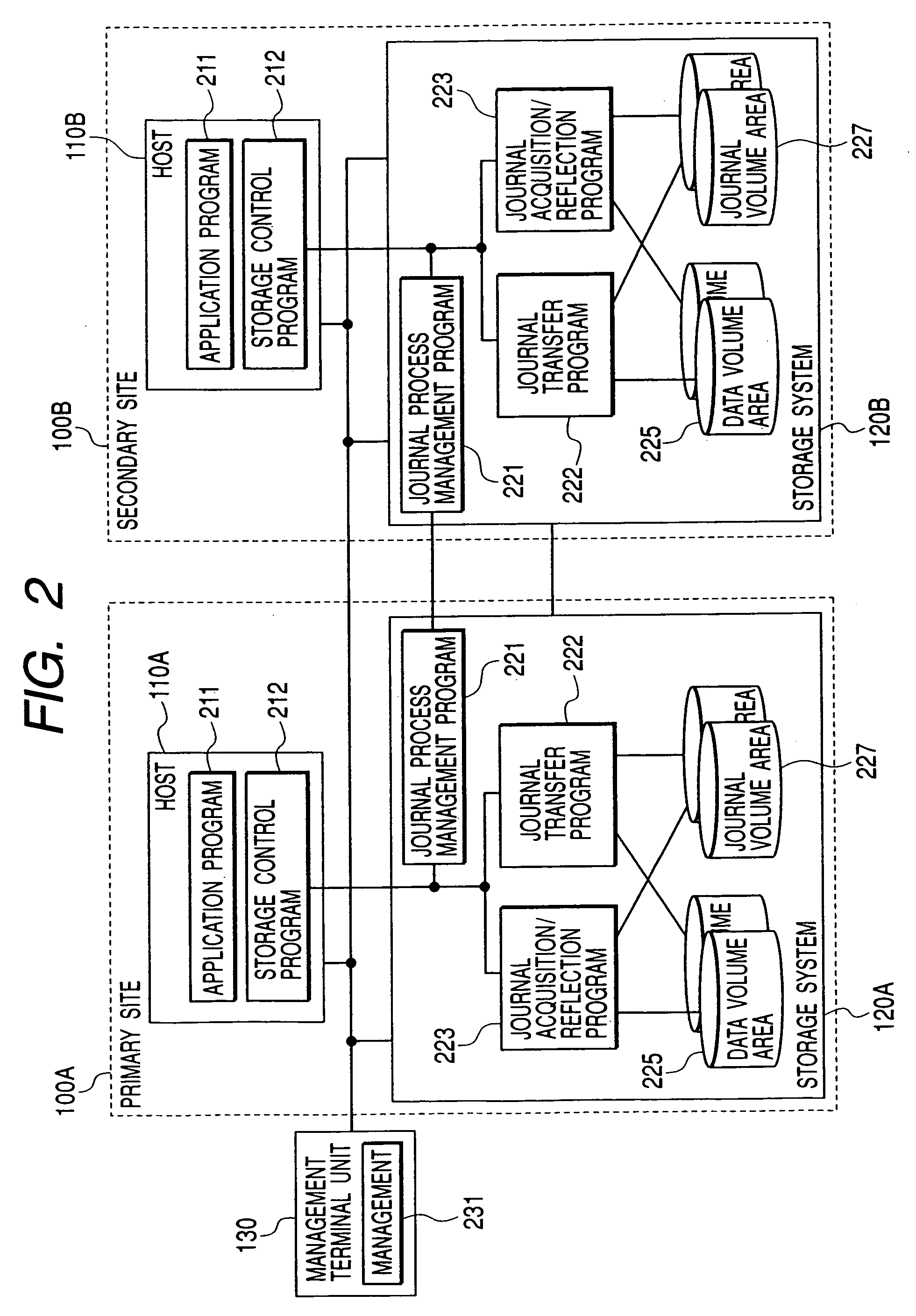
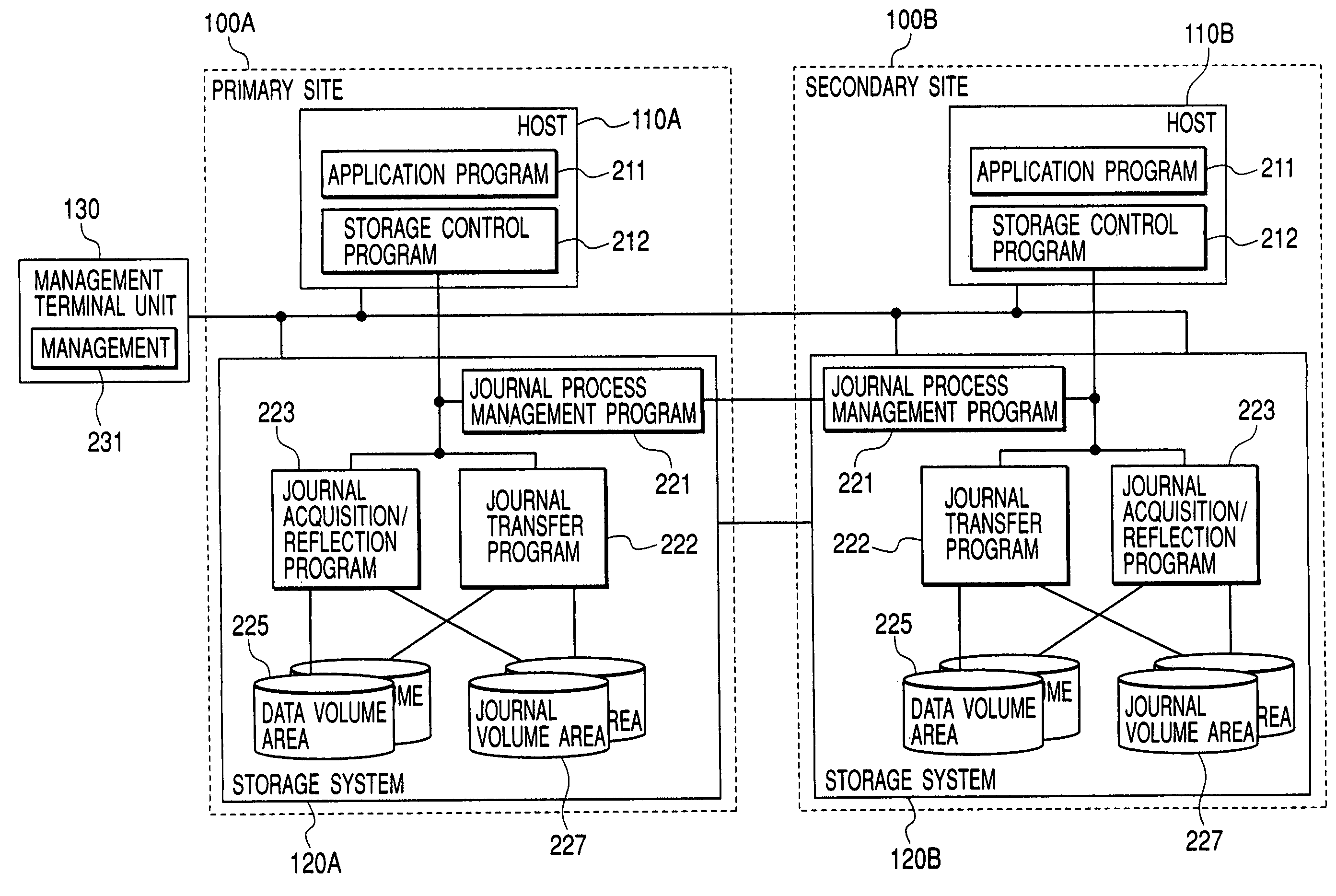
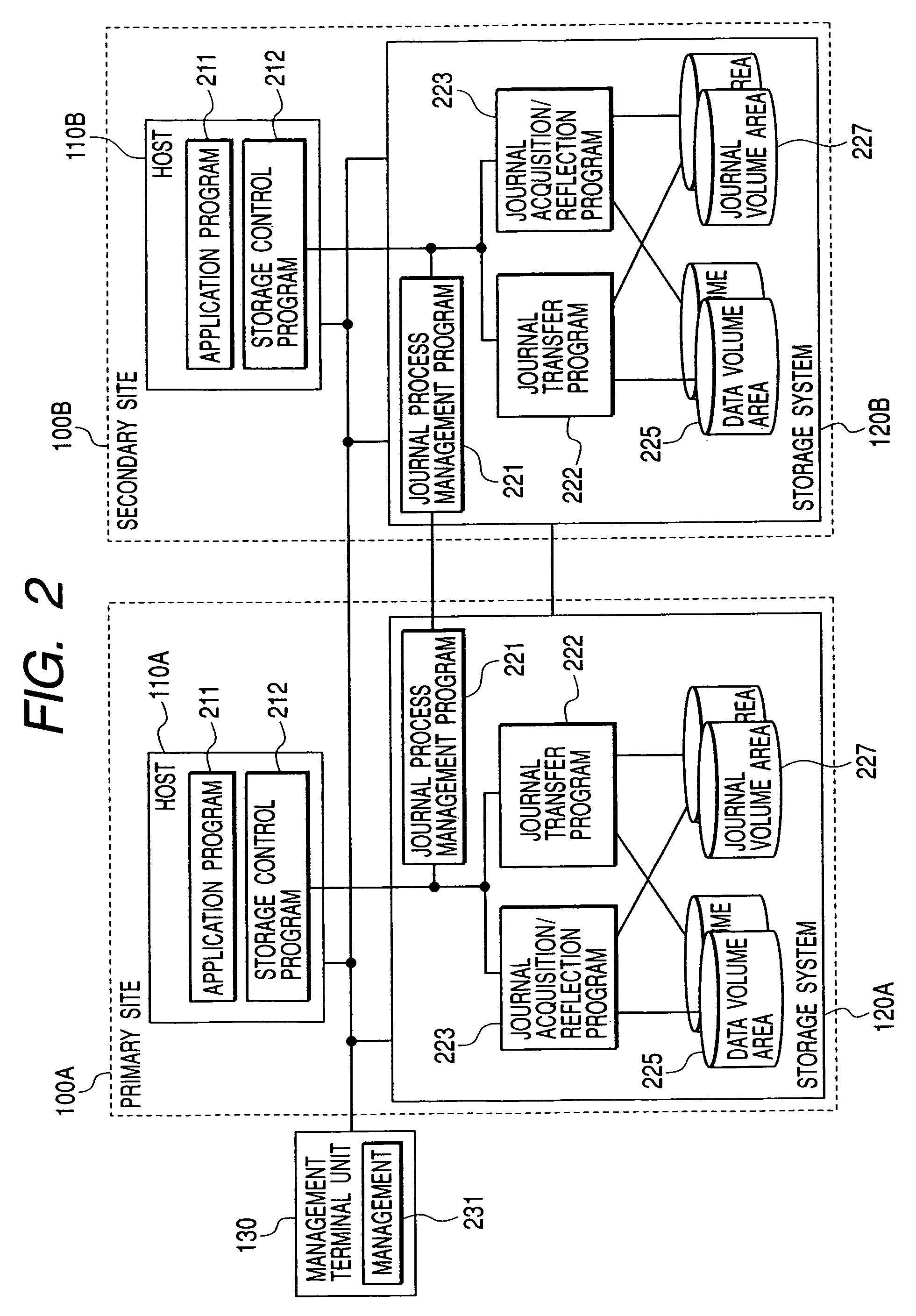
In a data processing system Saving a primary site and a secondary site, storage systems are connected to each other via a communication line, data update history is recorded in a storage device as a journal in the primary site, and the journal is transferred to the secondary site via the communication line. During such transfer, loads will not concentrate to a specific volume, by switching the volume that stores the journal in the primary site, while, by switching the transfer-destination volume of the journal in the secondary site.With such arrangement, in a data processing system, it is possible to ensure data consistency in a plurality of sites and prevent the system throughput capacity from being deteriorated without applying loads to a host and a network, and without causing load concentration on a specific storage device that is caused as a result of data update or recovery operations.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method for rolling back from snapshot with log
InactiveUS7428657B2Reduce copying timeFast copyMemory systemsRedundant hardware error correctionPrimary sitesSecondary site
High speed differential copy can be implemented in the fail-back after disaster recovery when the data of the primary site is protected safely. When a restore command is issued, the common snapshots of the snapshots of the primary site and the secondary site are extracted as the base snapshot by comparing the log tables of the primary site and secondary site. The volume of the primary site is rolled back with the extracted snapshots. The latest snapshot of the volume of the secondary site is transmitted to the primary site and it is applied to the volume of the primary site to synchronize the volumes of the primary site and the secondary site.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
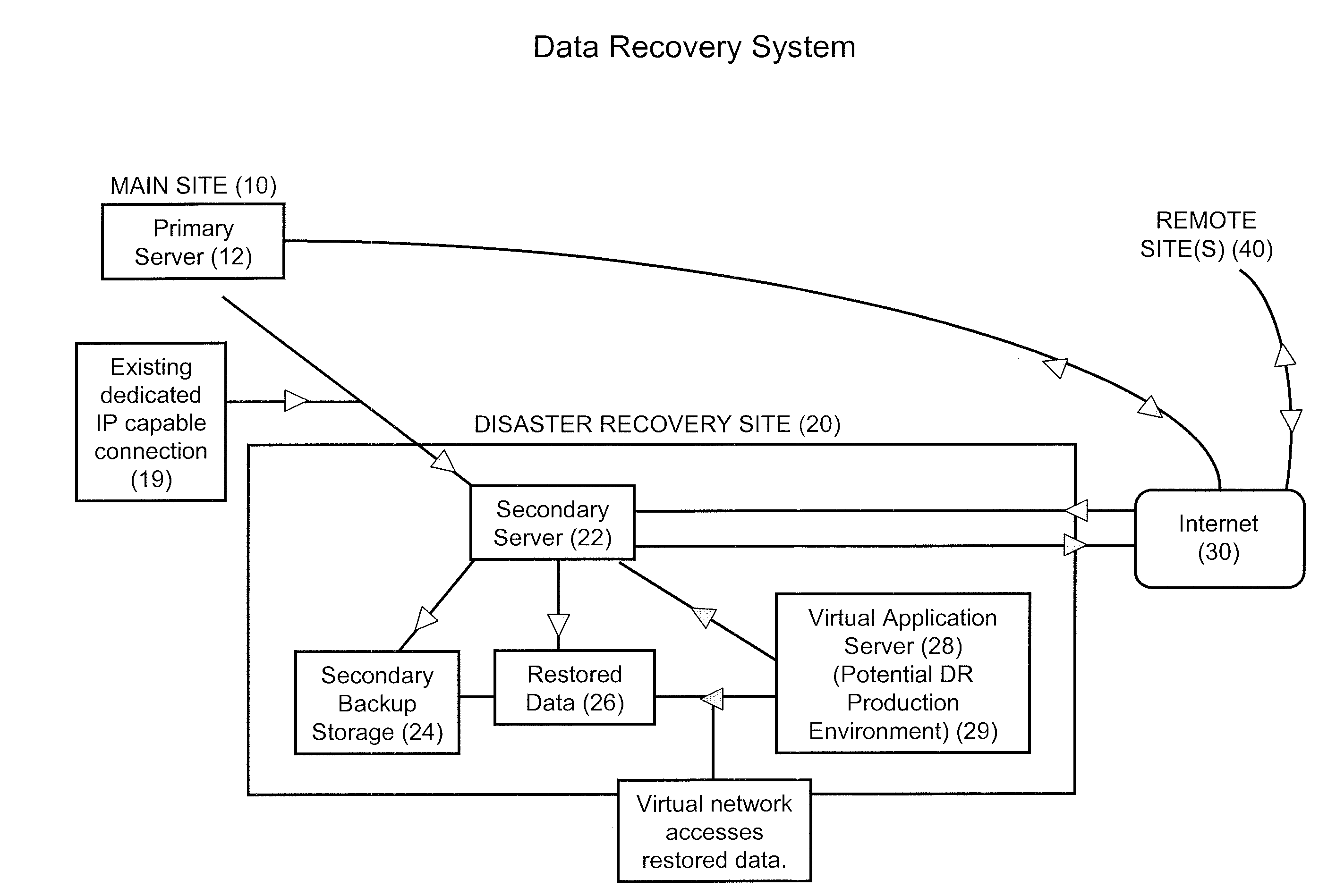
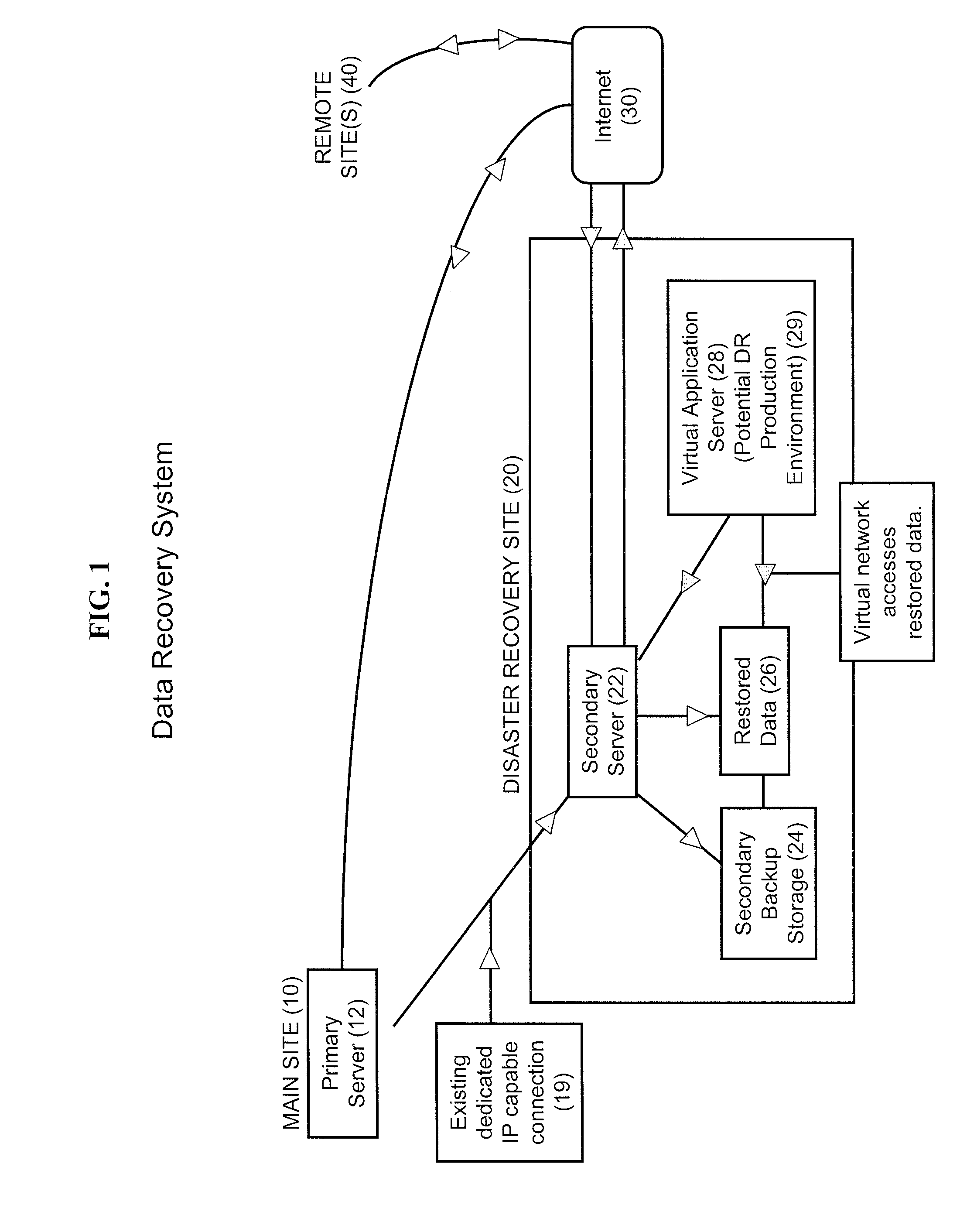
Data Recovery Systems and Methods
Nearline disaster recovery (“nearline DR”) storage systems and methods that permit the use of previously restored stored data from a near time period by virtual applications operating off a backup storage location during the period of disaster recovery at a primary site. This is generally referred to as a “nearline DR storage process.”
Owner:LEWIS RICE & FINGERSH LC
Methods and Apparatus for Effective On-Line Backup Selection for Failure Recovery in Distributed Stream Processing Systems
InactiveUS20080253283A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPrimary sitesSystem recovery
A failure recovery framework to be used in cooperative data stream processing is provided that can be used in a large-scale stream data analysis environment. Failure recovery supports a plurality of independent distributed sites, each having its own local administration and goals. The distributed sites cooperate in an inter-site back-up mechanism to provide for system recovery from a variety of failures within the system. Failure recovery is both automatic and timely through cooperation among sites. Back-up sites associated with a given primary site are identified. These sites are used to identify failures within the primary site including failures of applications running on the nodes of the primary site. The failed applications are reinstated on one or more nodes within the back-up sites using job management instances local to the back-up sites in combination with previously stored state information and data values for the failed applications. In additions to inter-site mechanisms, each one of the plurality of sites employs an intra-site back-up mechanism to handle failure recoveries within the site.
Owner:IBM CORP
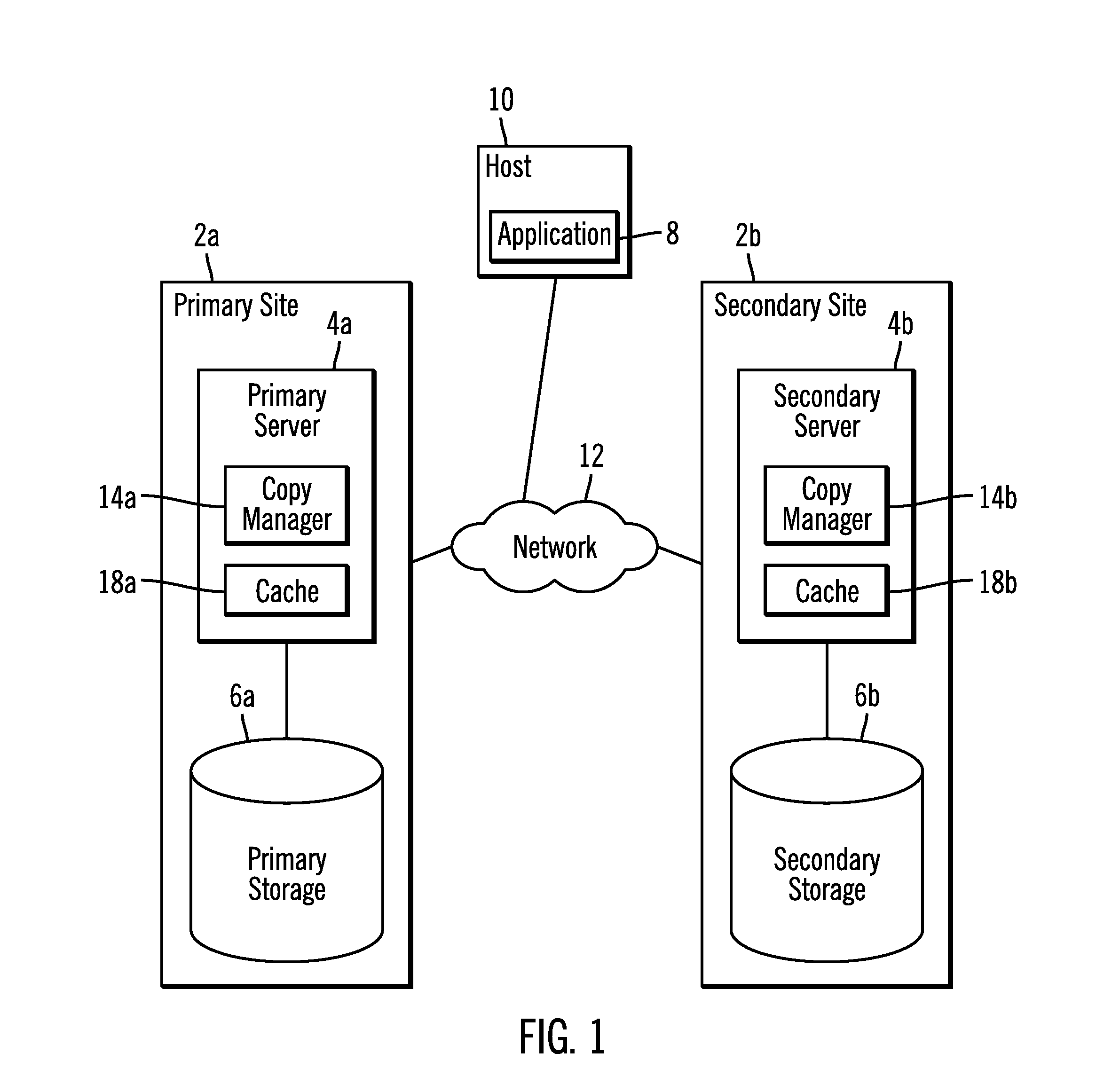
Synchronizing performance requirements across multiple storage platforms
Synchronization of data layouts and resource utilizations at one or more remote replica sites with the workload and data tiering decisions being made at the primary site allows for an efficient and effective workload support transfer in the event of site failover from a primary site to a remote site. Relevant data access information about workload being supported at the primary site is collected and from that raw information, characterized data access information is generated that condenses the raw data access information or otherwise provides relevant encapsulated information about the raw data access information. The characterized data access information is transmitted to the one or more remote sites allowing each remote site to make its own independent decisions on how best to utilize its available resources to match the performance requirements currently being supported by the primary site.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
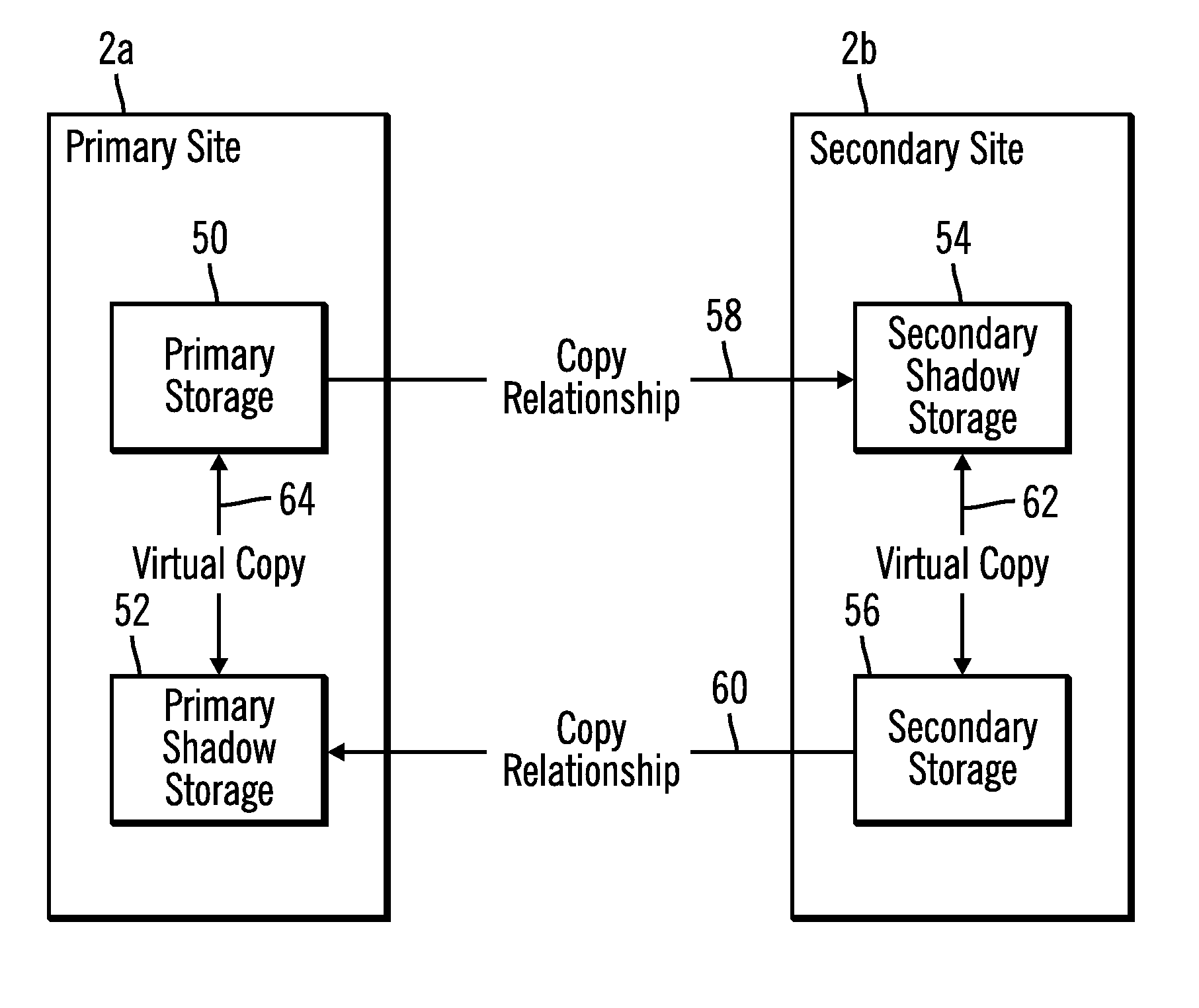
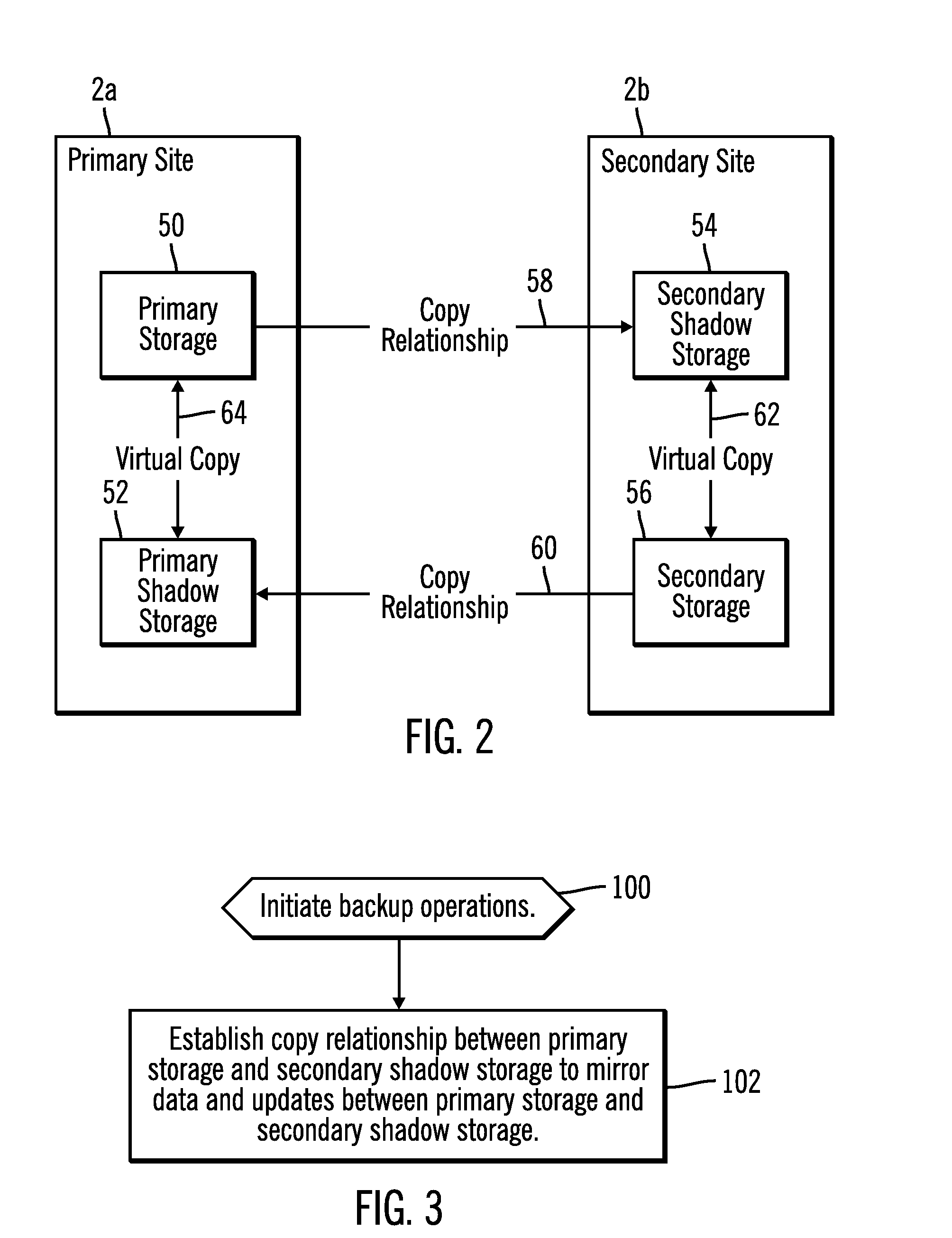
Using virtual copies in a failover and failback environment
ActiveUS20080172572A1Program control using stored programsRedundant hardware error correctionFailoverPrimary sites
Provided are a method, system, and article of manufacture for using virtual copies in a failover and failback environment. Updates are copied from a primary first storage at the primary site to a secondary first storage at the secondary site during system operations. A second storage is maintained at at least one of the primary and secondary sites. A failover is performed from the primary site to the secondary site after a failure at the primary site. The at least one second storage is used after recovery of the primary site to synchronize the secondary site to the primary site. Only updates made to the secondary site during the failover are copied to or from the at least one second storage in response to the recovery at the primary site.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for disaster recovery of data
ActiveUS20060271815A1Shorten the timeReduce degradationError detection/correctionPrimary sitesData loss
When a public line is used for a remote copy function of storage in a disaster recovery (DR) system, the online performance is degraded due to the increase and decrease of the line utilization rate. Therefore, it is desired to change the remote copy function depending on the line utilization rate. Also, there is the possibility of data loss if disaster occurs during the copy between storage devices. Therefore, it is desired to perform the processing to detect the data status immediately before the occurrence of the disaster. By switching the synchronous transmission and the asynchronous transmission in accordance with the increase and decrease of the response time of the remote copy function between storage devices, the online performance of the primary site can be maintained without being influenced by the line utilization rate, and the data loss can be detected based on the used remote copy function.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
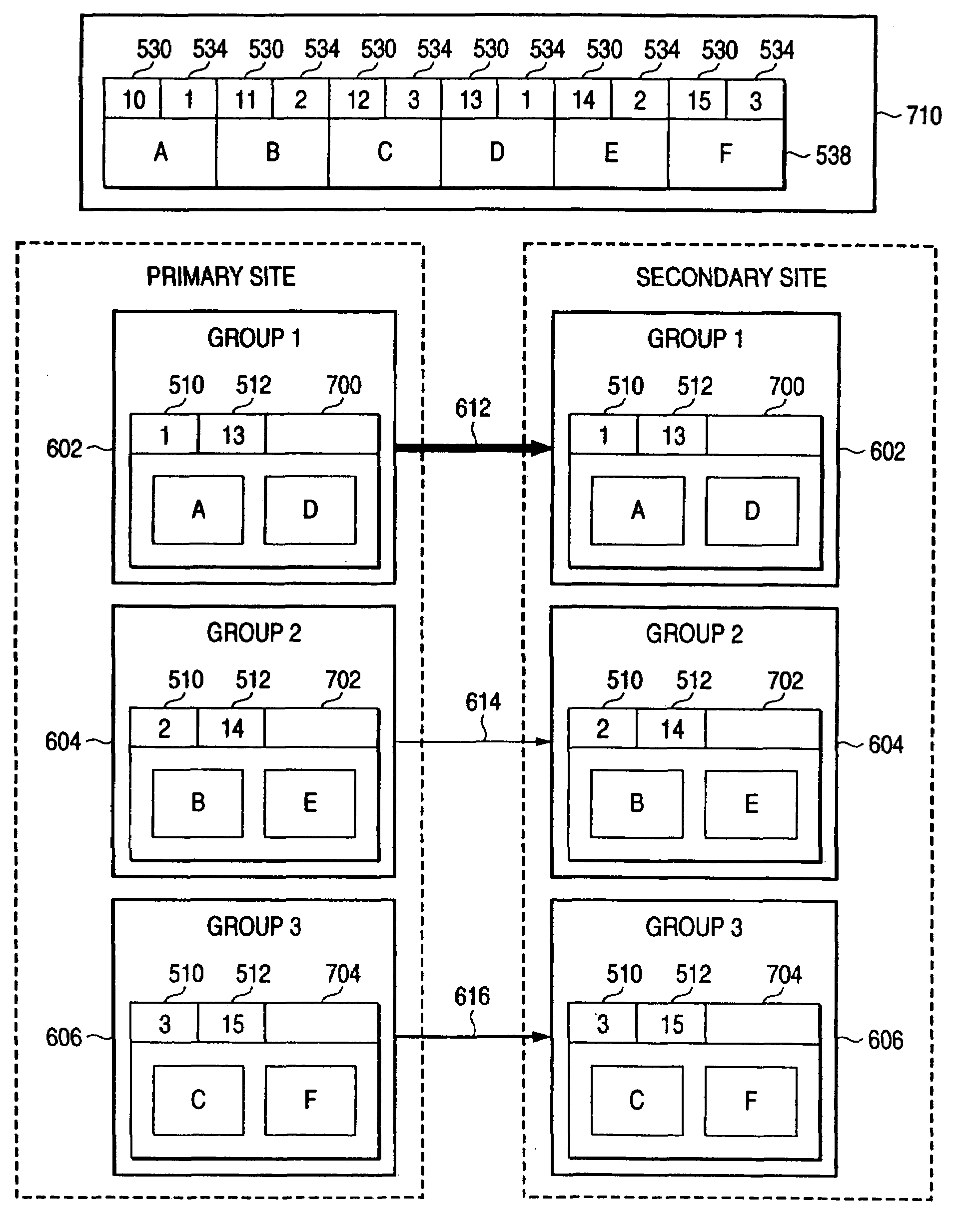
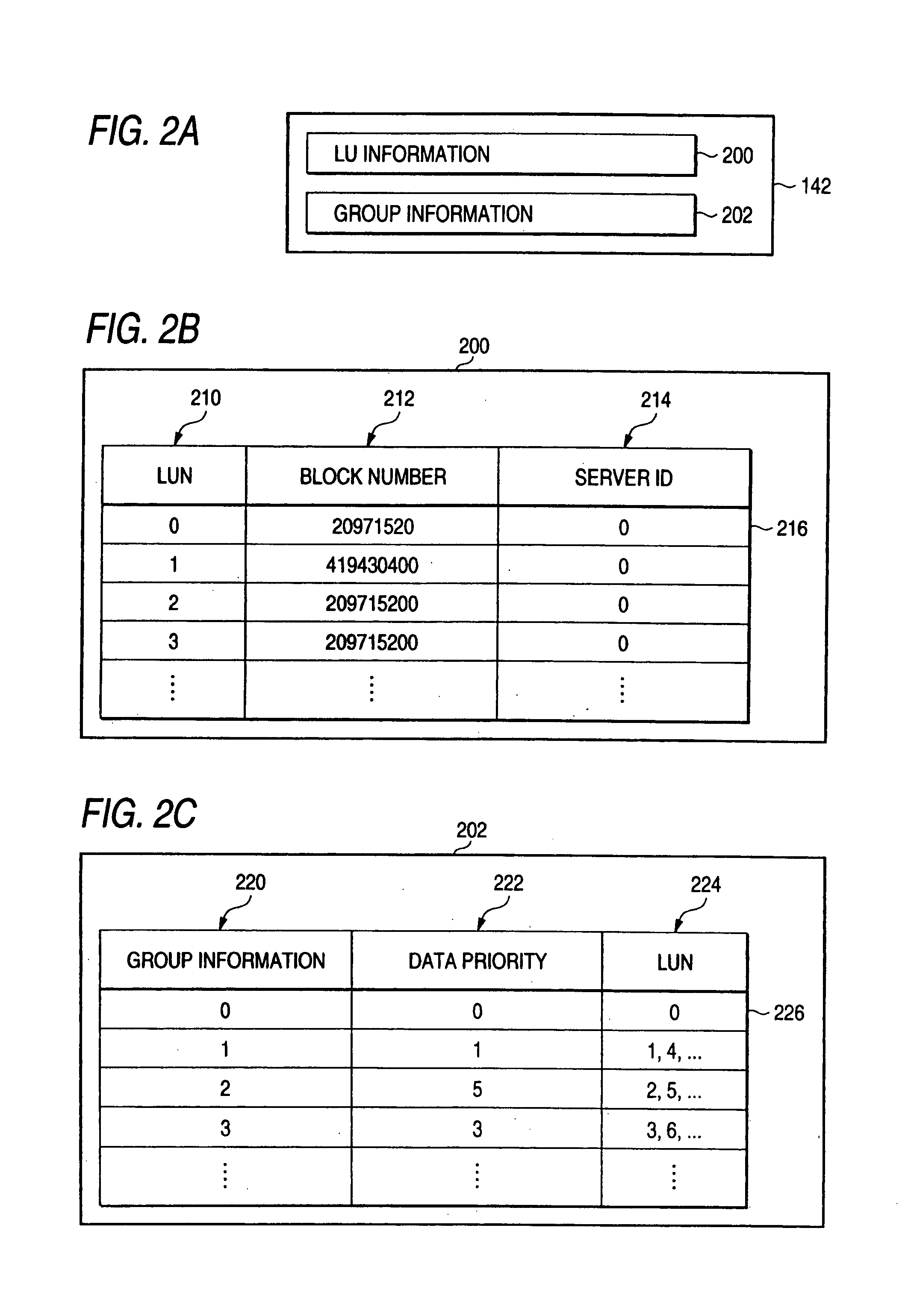
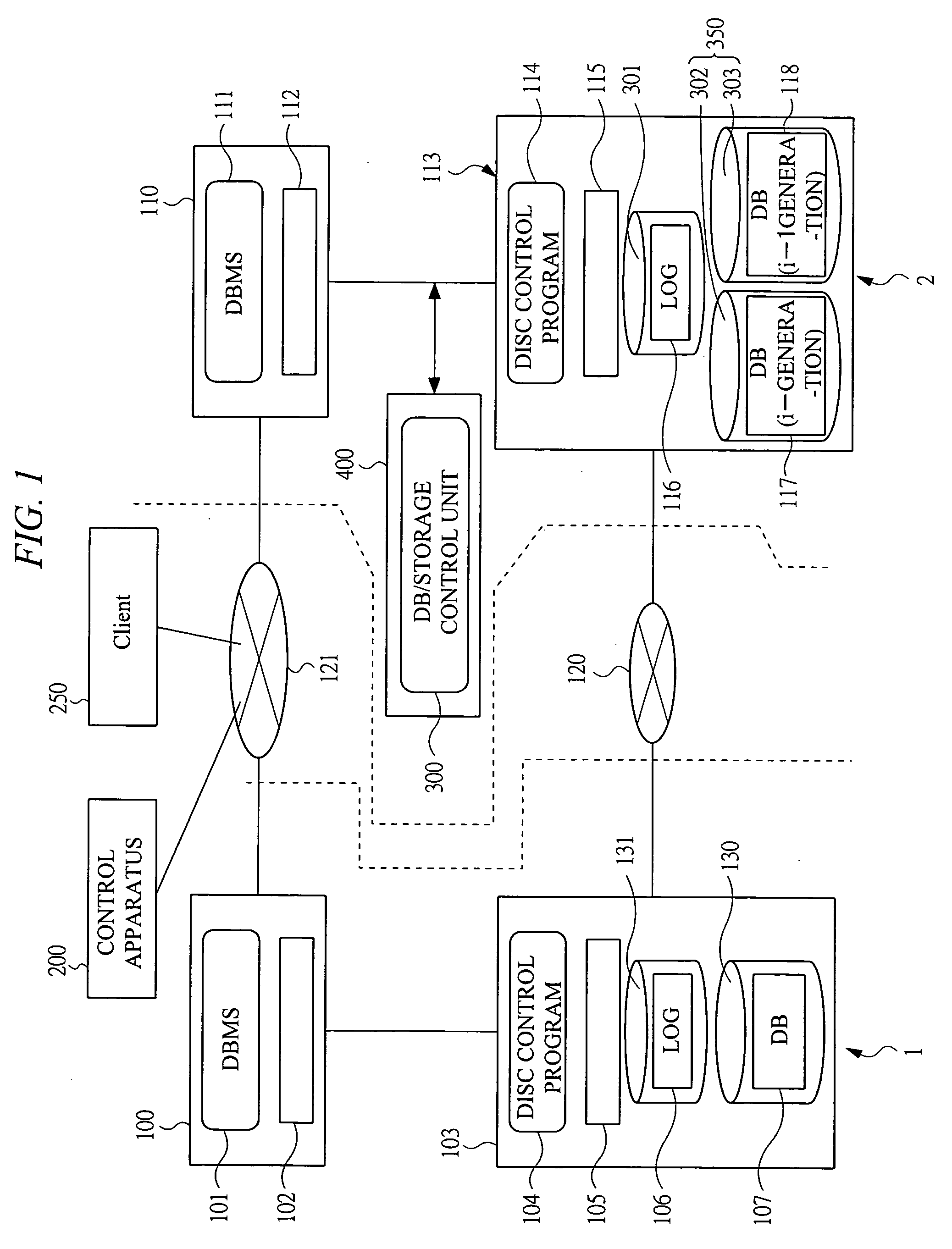
Computer system for recovering data based on priority of the data
ActiveUS7266718B2Input/output to record carriersRedundant operation error correctionManagement unitPrimary sites
In the present invention, there is provided means which sets priorities of DB data for each management unit, means which copies data from a primary site to a secondary site in an order of the data priorities, and means which, when a disaster has occurred in the primary site and recovery of a DB is performed in the secondary site, performs recovery of data in the order of the data priorities to sequentially bring the data to a usable state.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
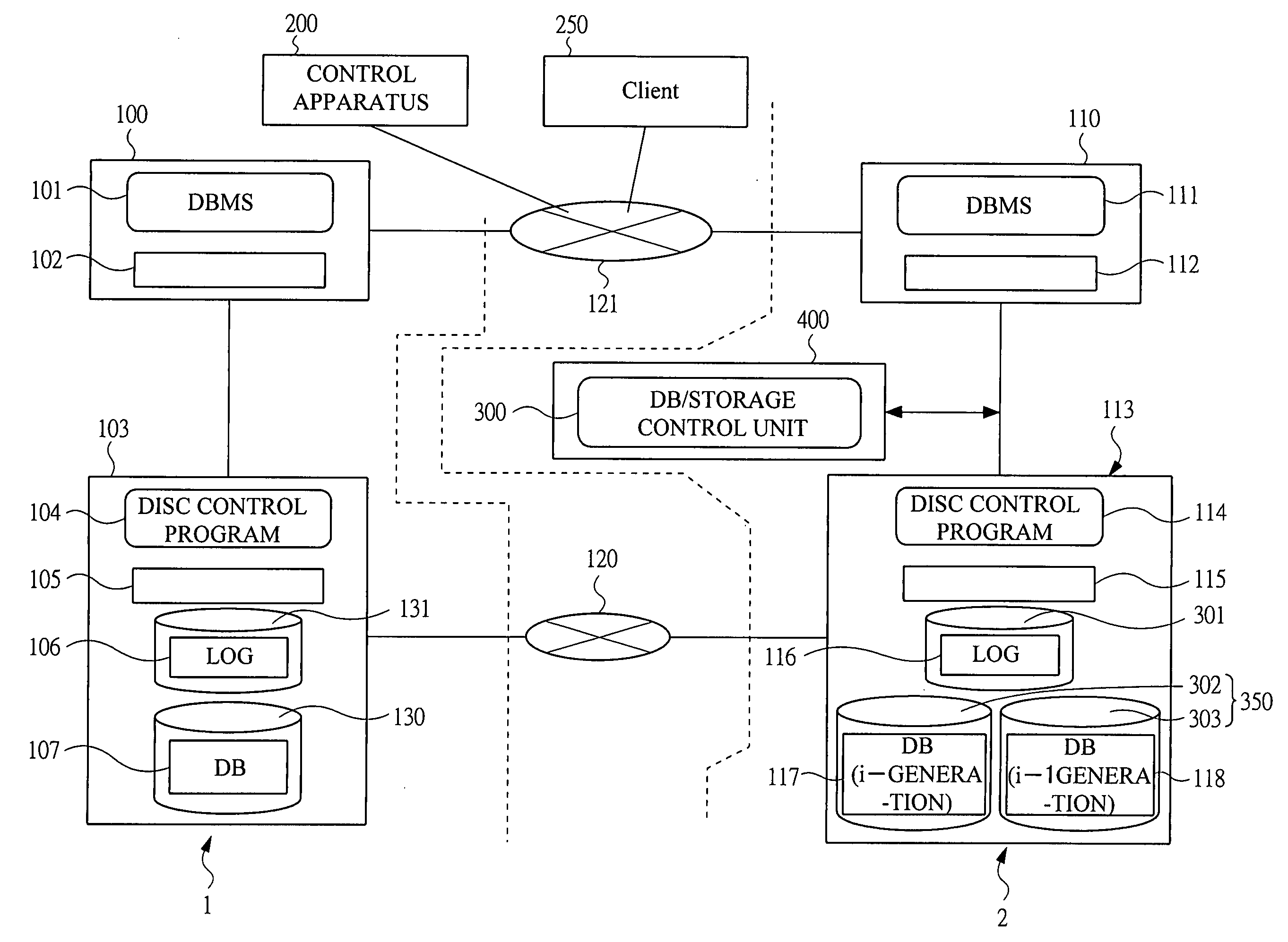
Data duplication method in a disaster recovery system
ActiveUS20060026452A1Increase added valueEasy to prepareRedundant hardware error correctionPrimary sitesDisaster recovery
A recovery of a secondary DB is executed by a log including a update difference of a primary DB, and a command is executed by adding the command to the log and analyzing the log by a secondary site. An operation command execution in the secondary site is applied to the DB having the consistency in the transaction at the same timing as a primary site or an intended timing, by transferring and executing the operation command via the log. In the case that the command is constituted by a snap shot generating instruction, a plurality of volumes of a mirror set forming a secondary storage apparatus are set to a pair state and the secondary DB is written in each of the volumes and synchronized, and the mirror set is set to a split state after the synchronization is finished, whereby a secondary DB is stored.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
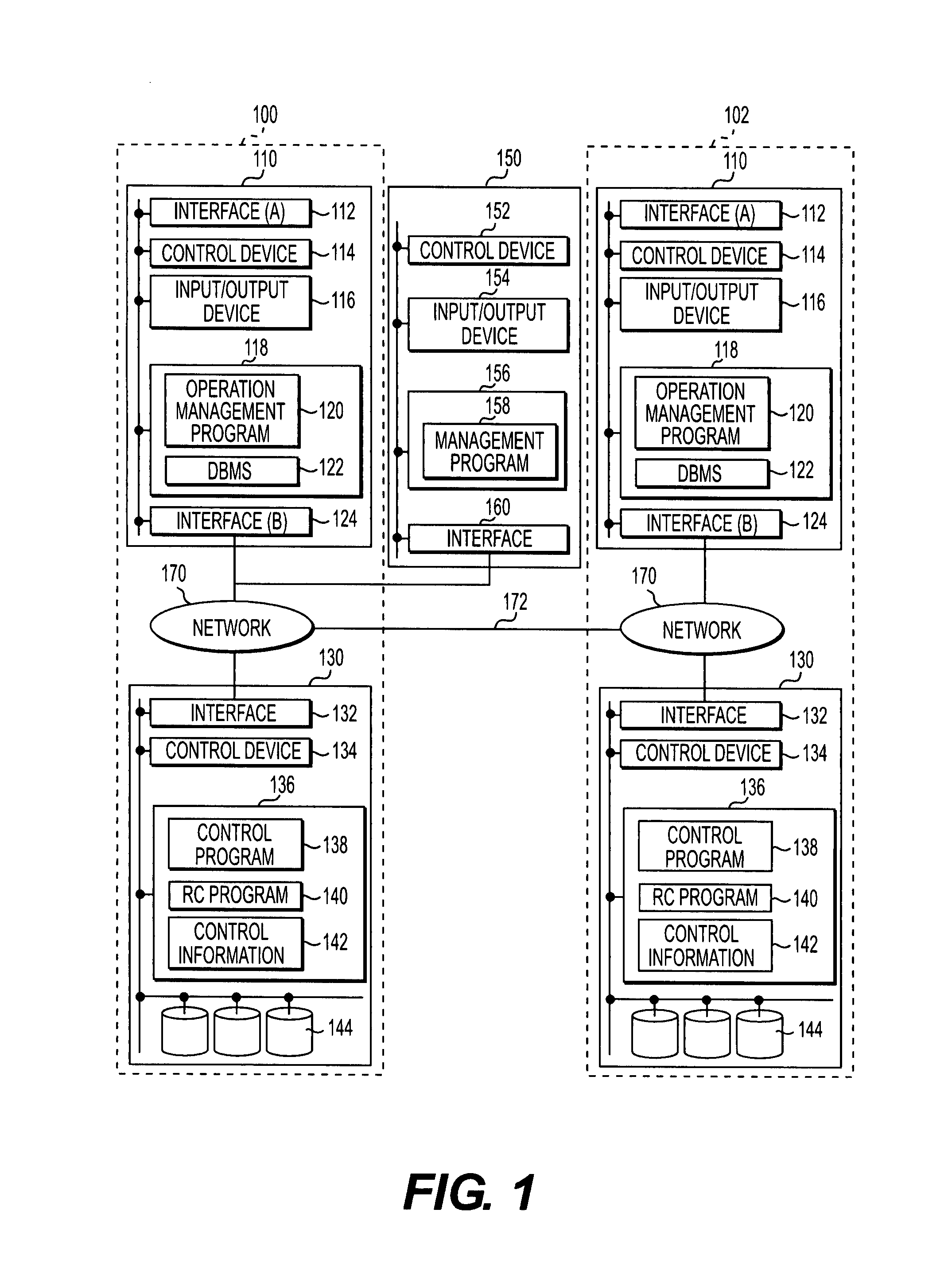
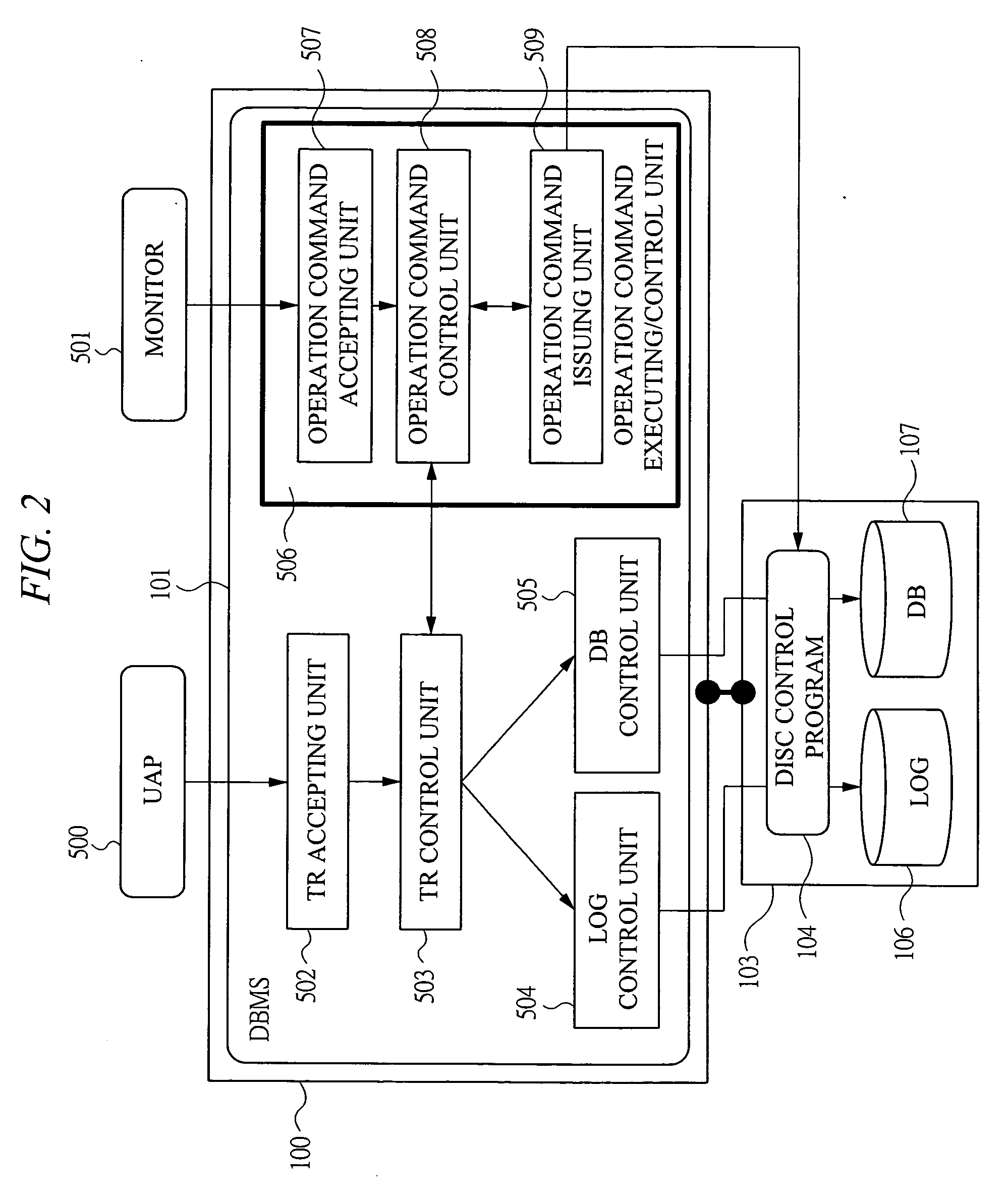
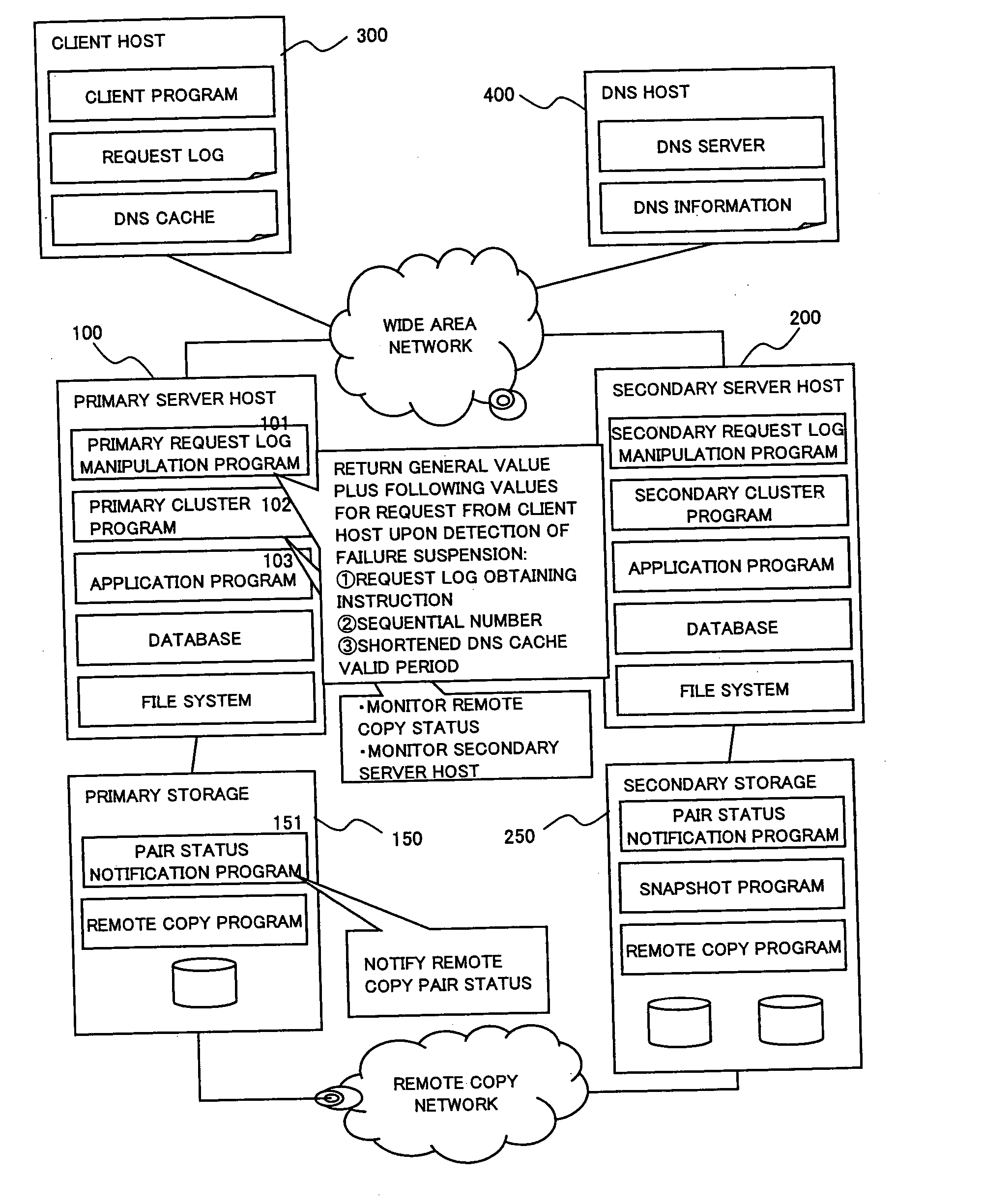
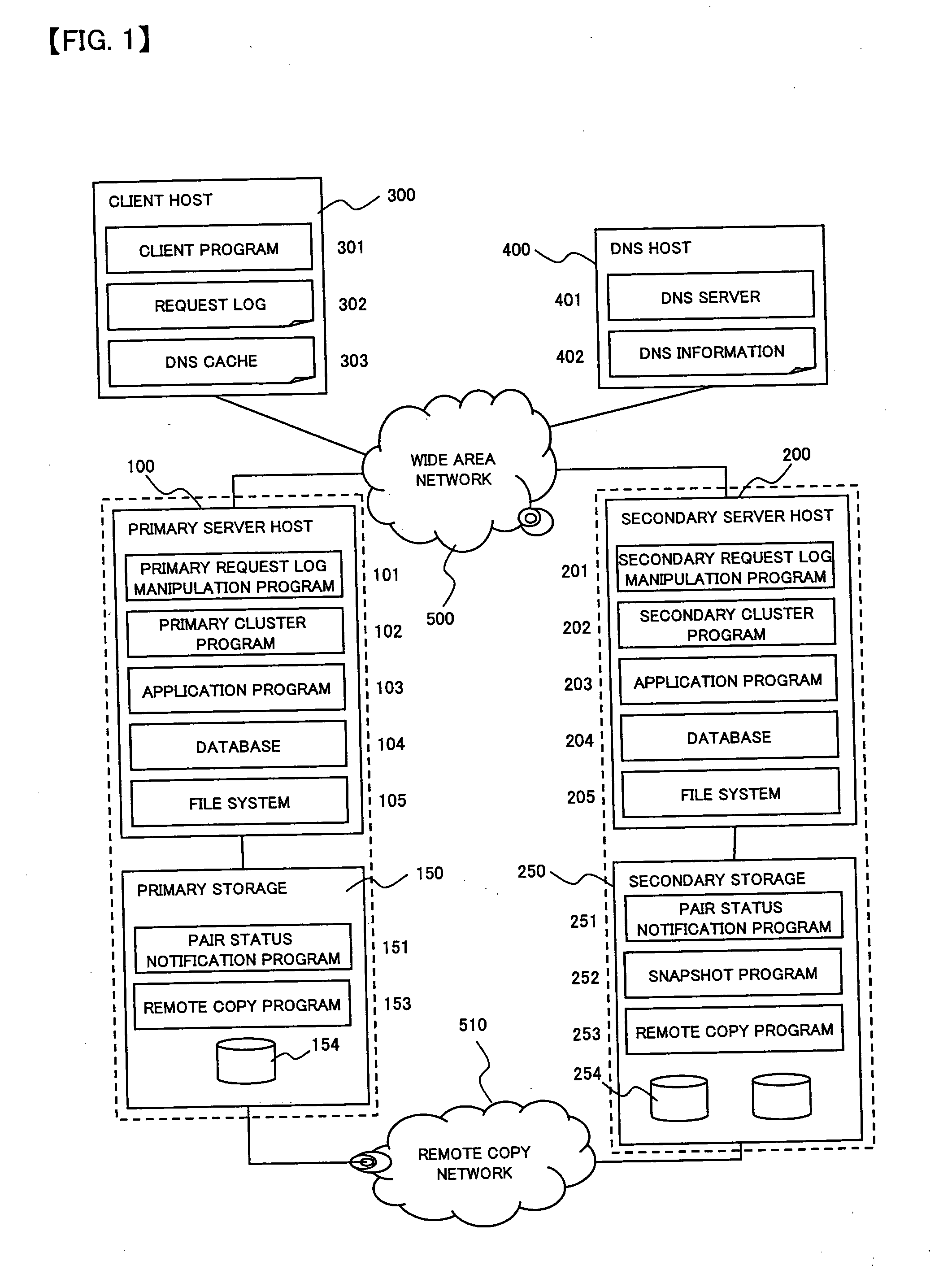
Computer system capable of fast failover upon failure
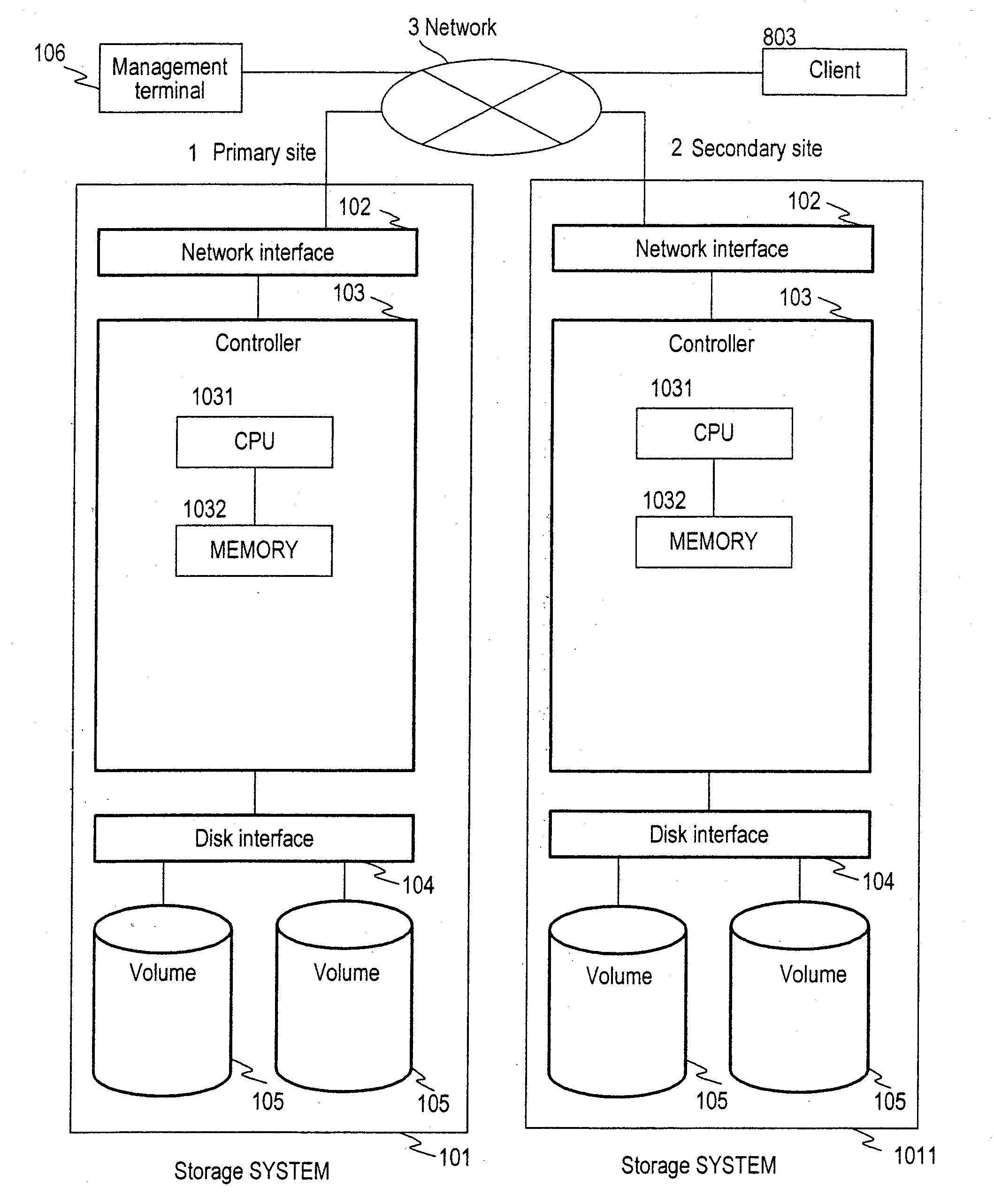
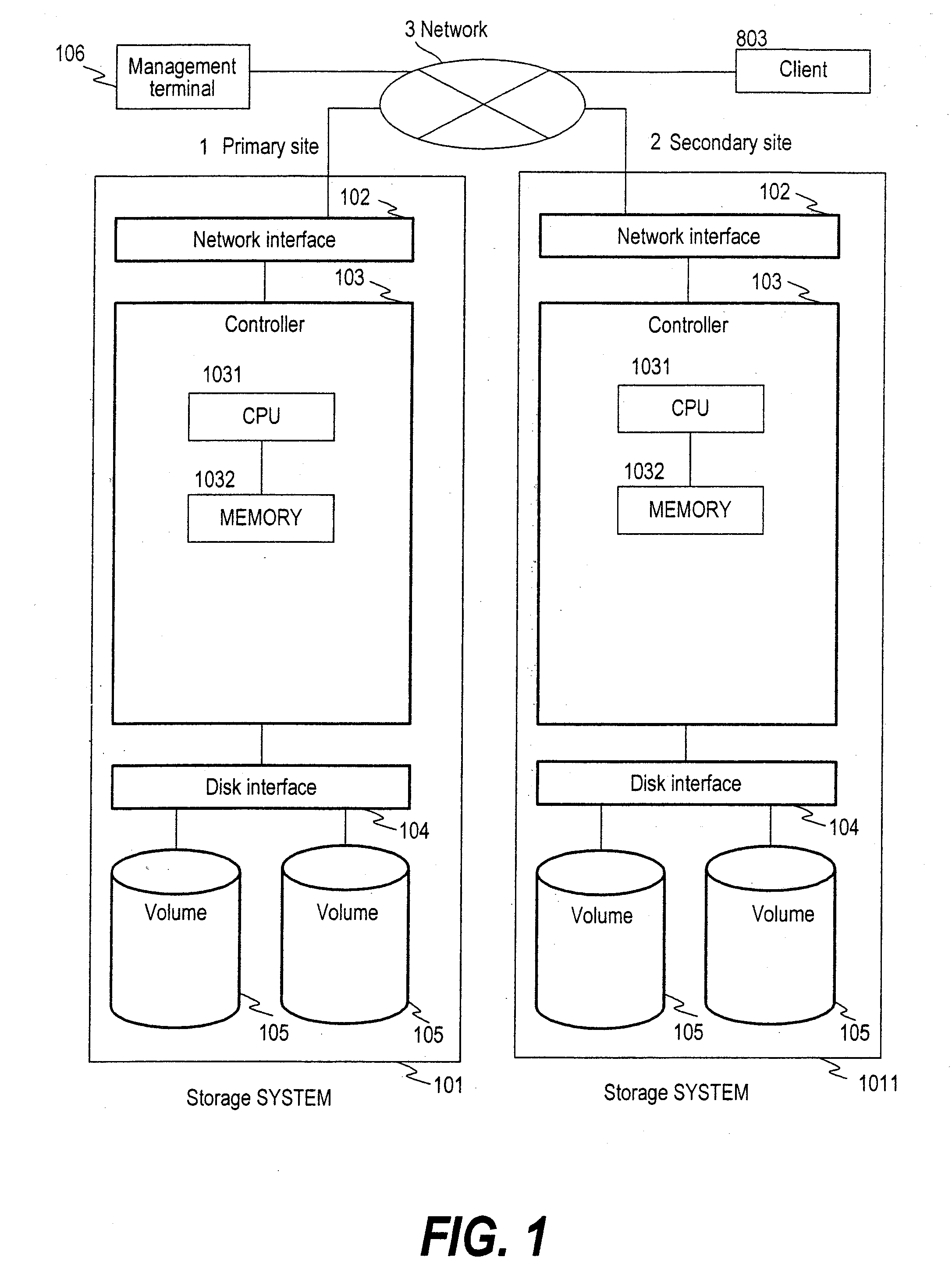
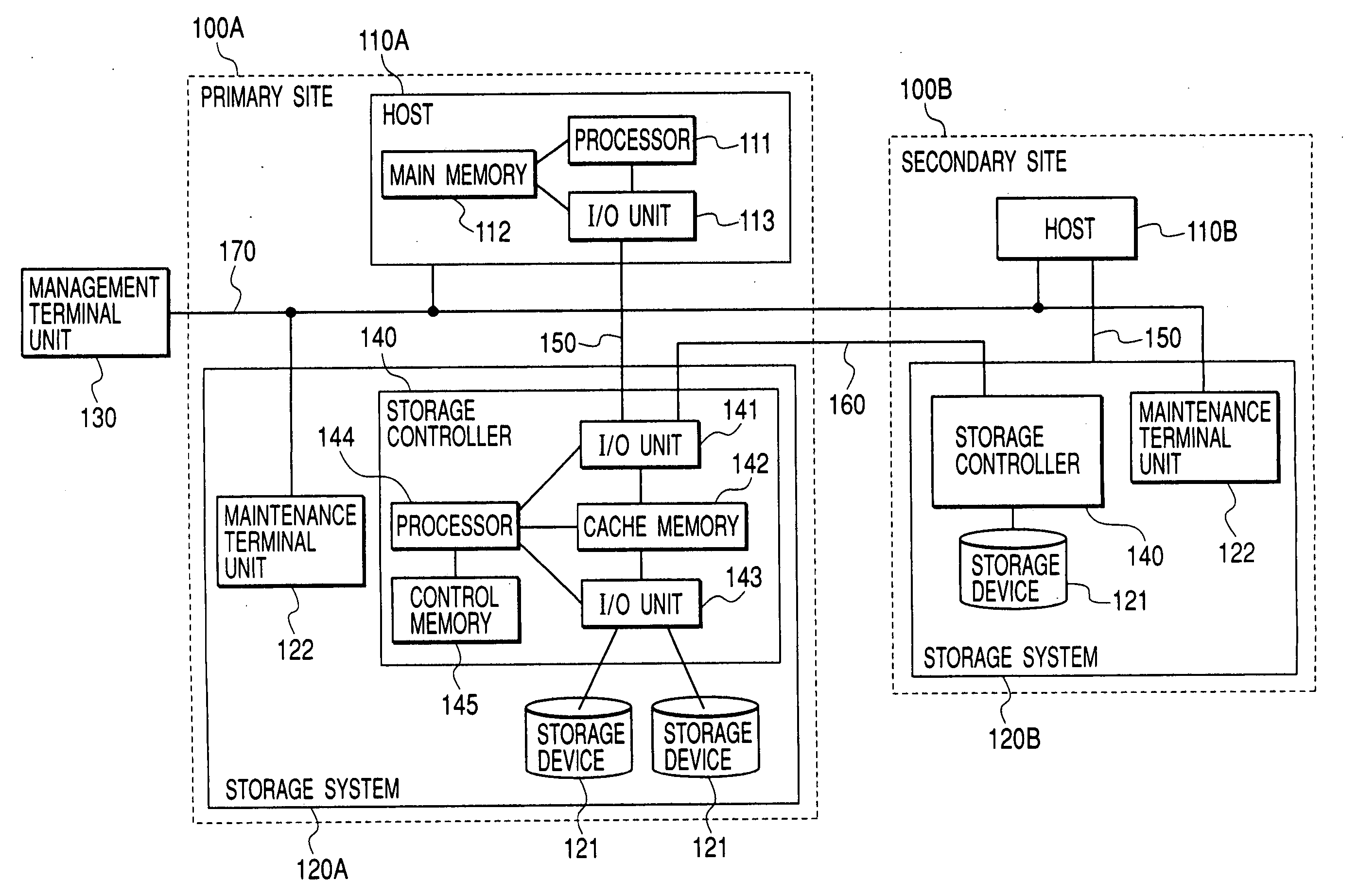
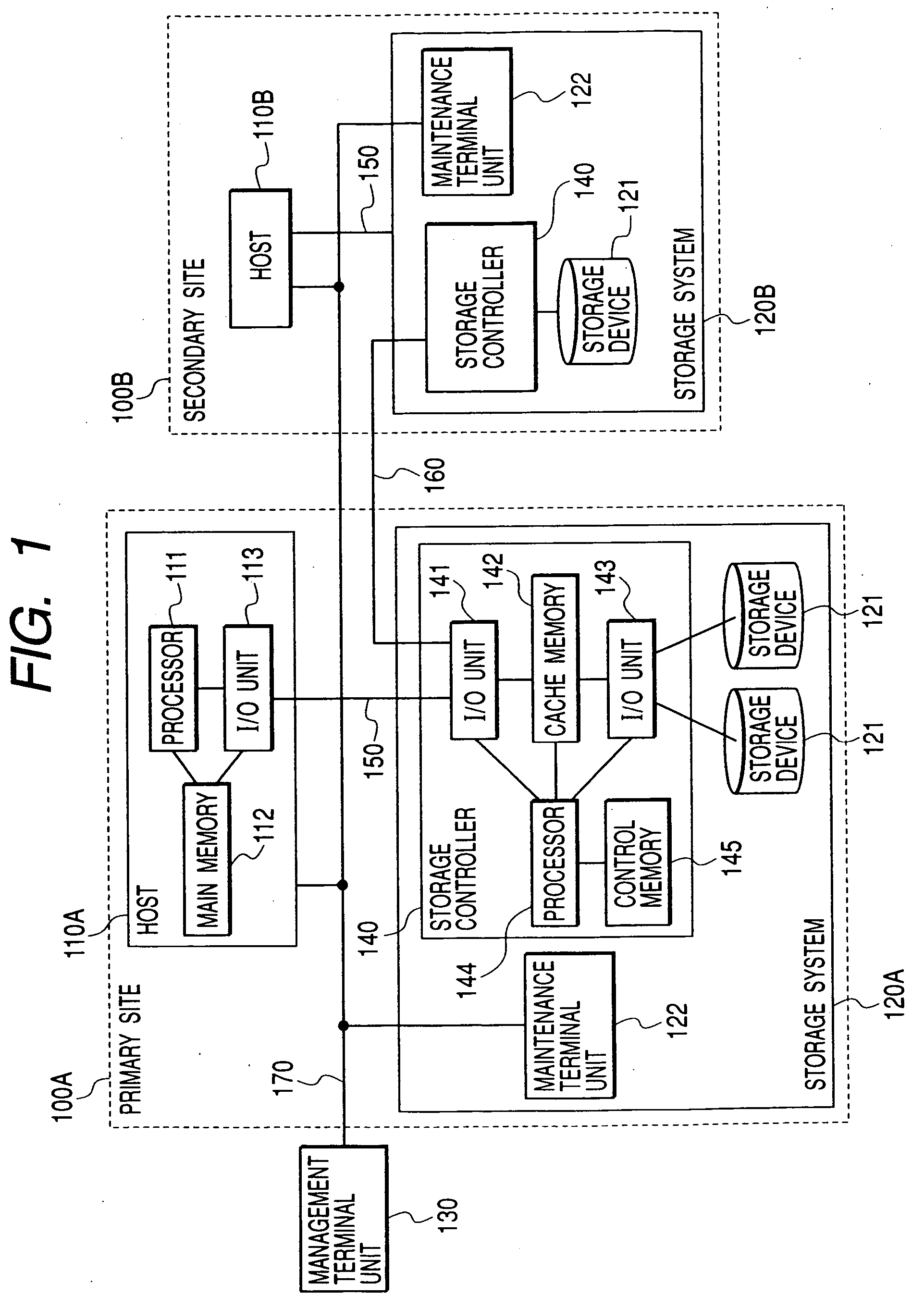
InactiveUS20050198327A1Extension of timeFast failoverMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPrimary sitesComputerized system
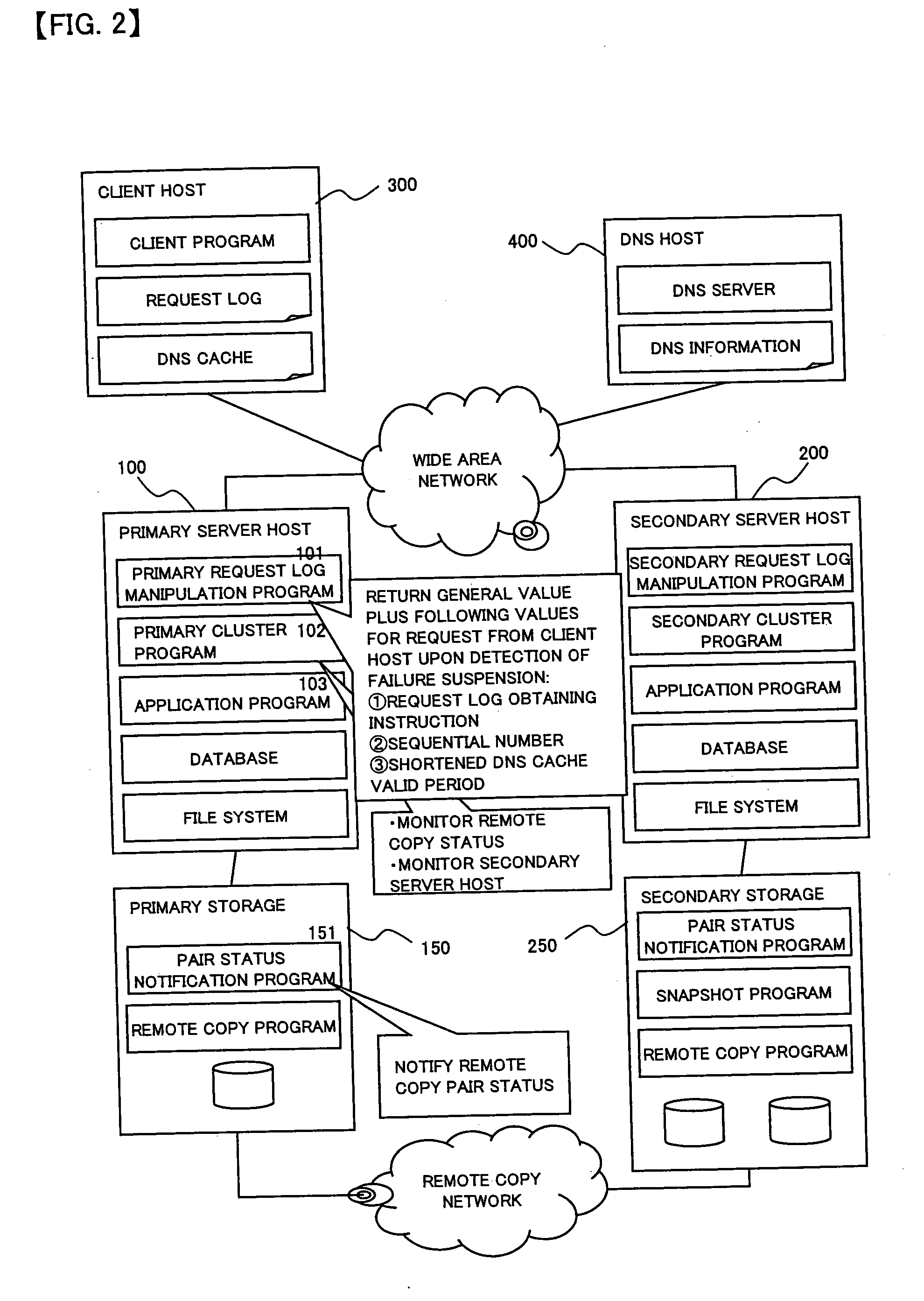
To provide a computer system capable of fast failover so that a service is stopped only for a brief period of time from a failure in a first site. The computer system includes a primary site for regular operation and a secondary site that operating when the primary site fails. A primary storage and a secondary storage have a synchronization unit to make contents stored in the primary storage and contents stored in the secondary storage identical to each other. A client has a cache for recording address information (e.g. DNS) that gives the client an access to the server from which the service is provided and information that defines a time to live of the address information. A first server has a primary request log processing unit, which instructs the client to shorten the recorded time to live of the address information when communication with the secondary site is detected to be impossible.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for reproducing configuration of a computer system in a remote site
InactiveUS20060230103A1Shorten the overall cycleMinimize damageError detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsPrimary sitesComputerized system
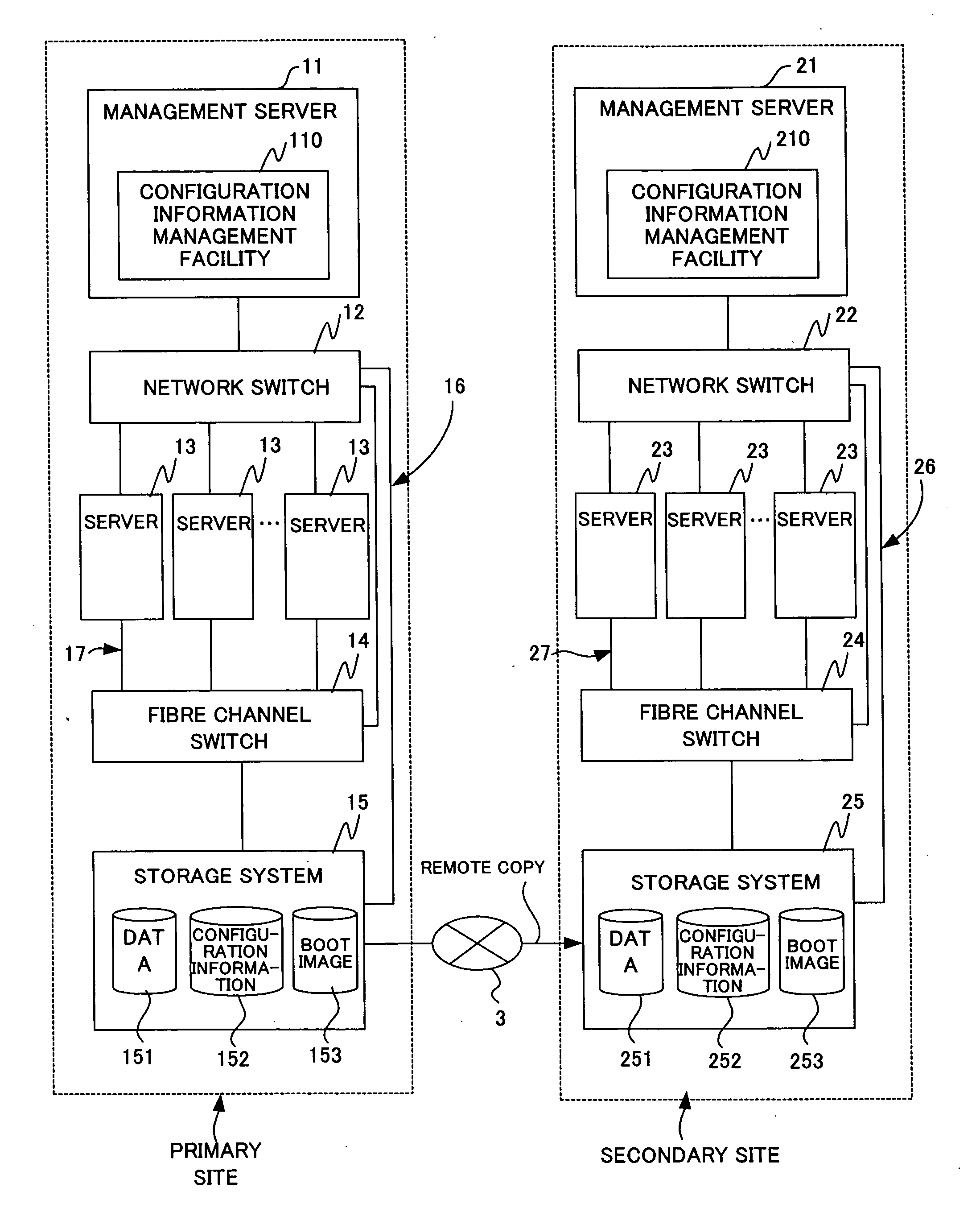
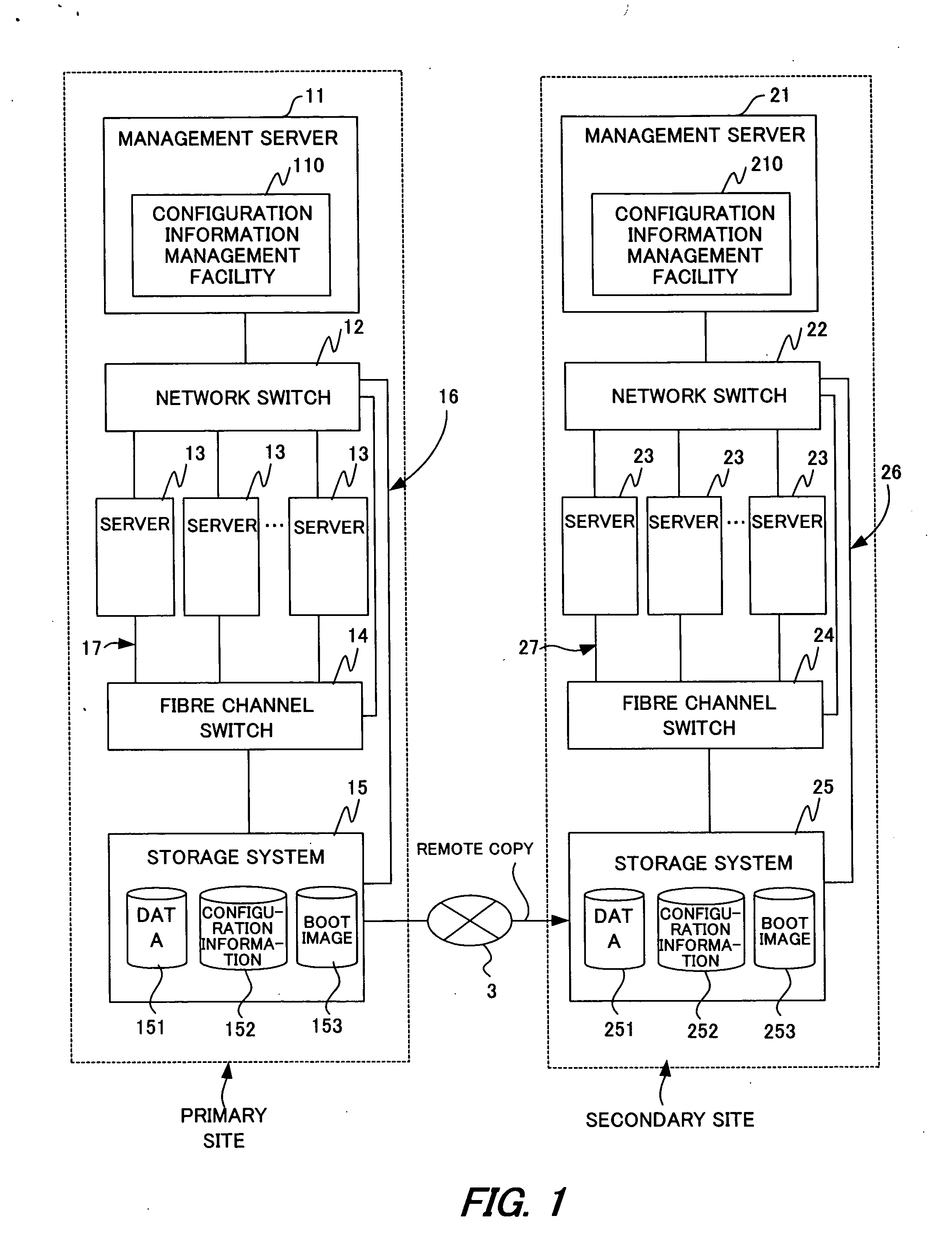
A computer system that has formerly handled a service is quickly reproduced with another computer system to resume the service immediately. The association relations between services run by a primary site (1) and primary site servers (13) are collected. The association relations between the primary site servers (13) and a primary site storage system (15) are collected. The association relation between the storage system (15) of the primary site (1) and a storage system (25) of a secondary site (2) is collected. The association relations between the primary site services and the primary site servers (13), the association relations between the primary site servers (13) and the primary site storage system (15), and the association relation between the primary site storage system (15) and the secondary site storage system (25) are copied as configuration information from the storage system (15) of the primary site (1) to the secondary site (2). On the secondary site (2), based on the copied configuration information of the primary site.(1), services of the primary site (1) are assigned to servers (23) of the secondary site (2), and the secondary site servers (23) to which the services are assigned are associated with the storage system (25) of the secondary site (2) to reproduce the primary site (1) on the secondary site (2).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
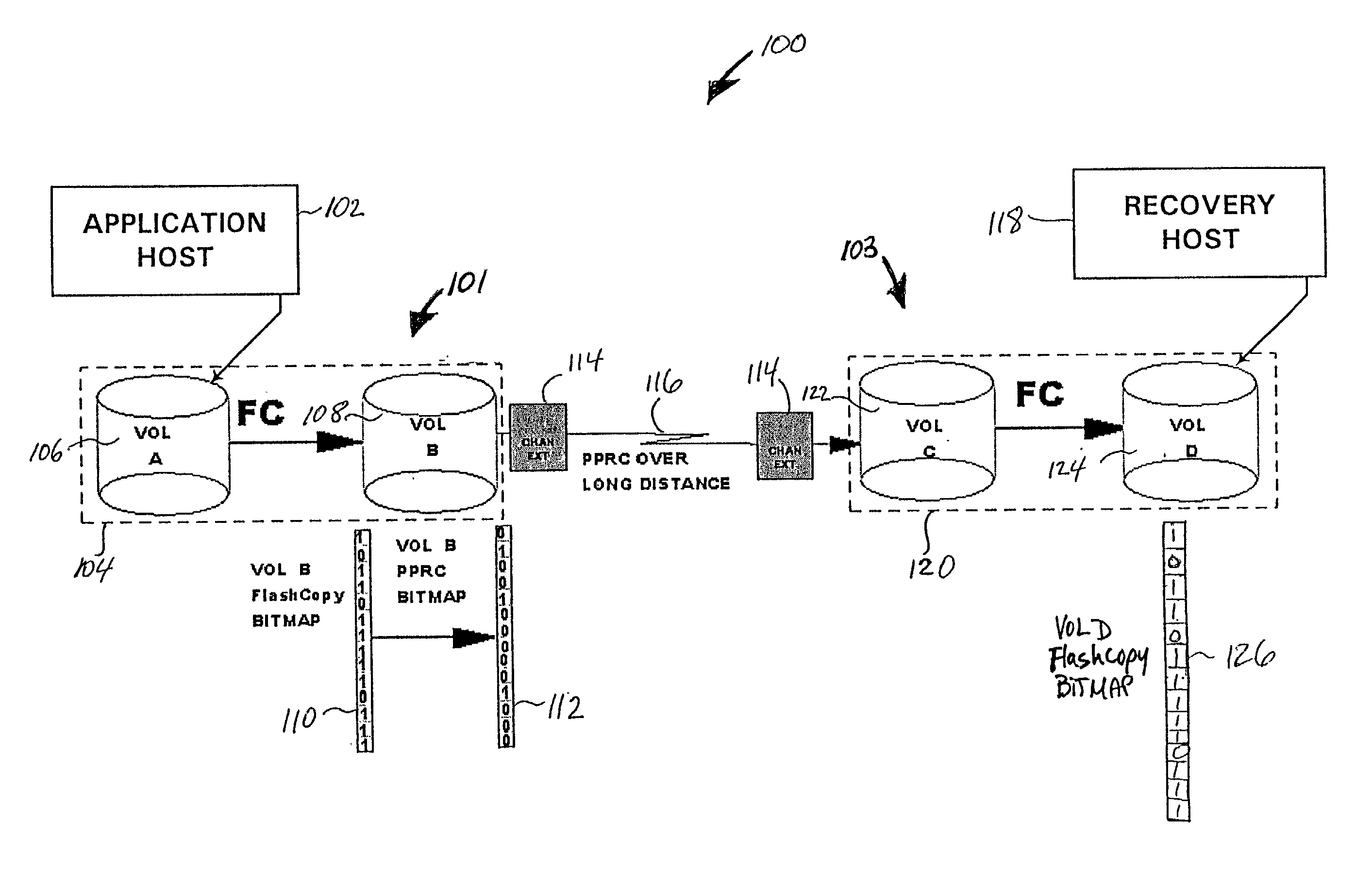
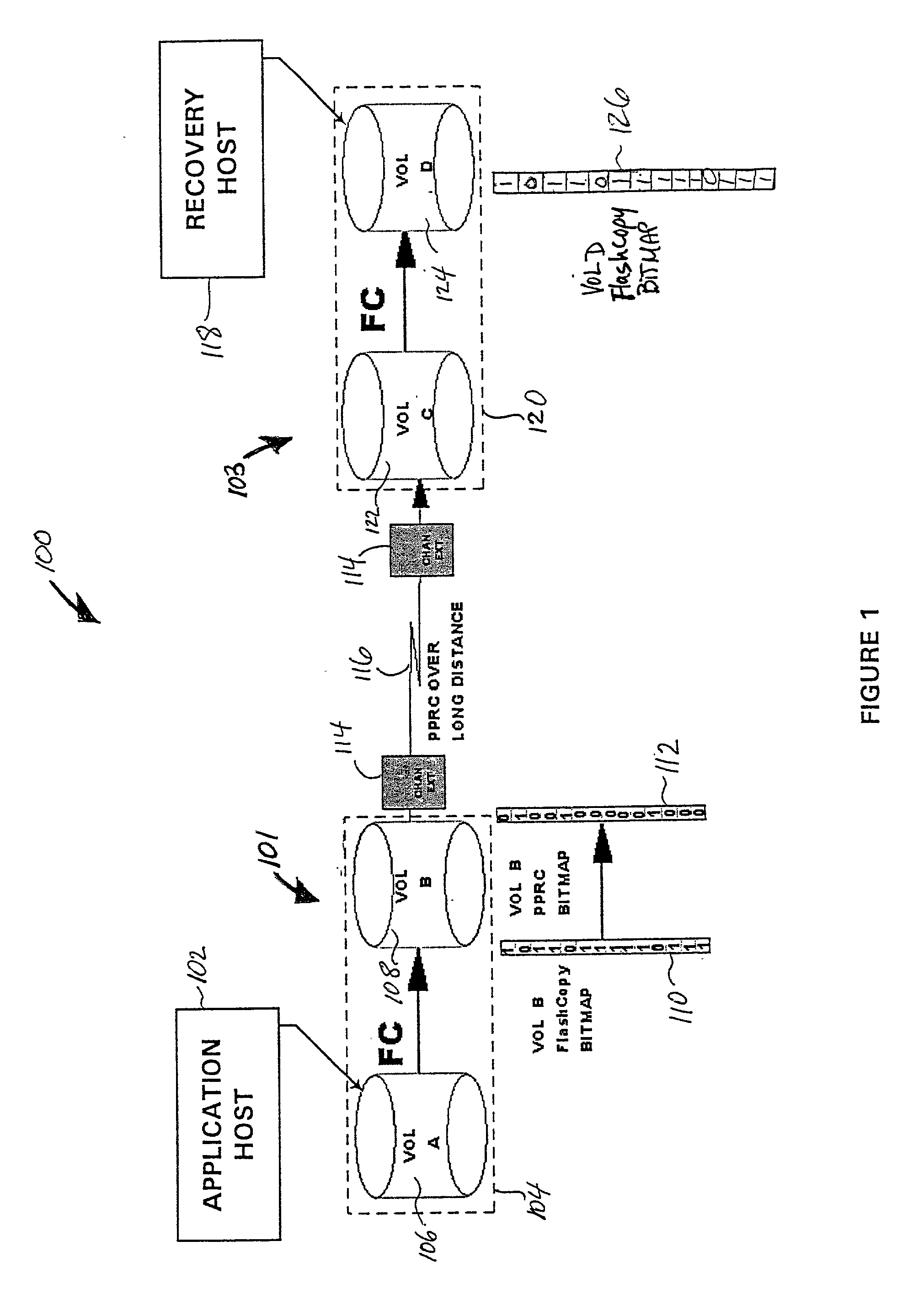
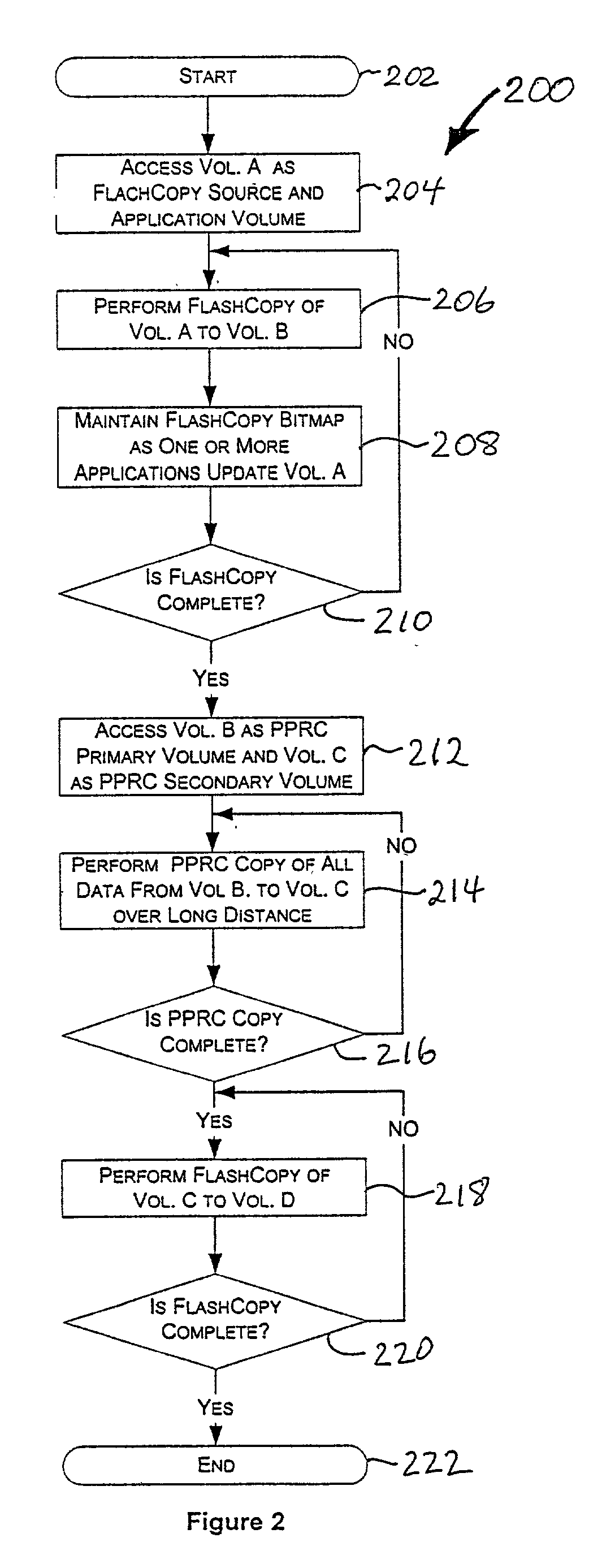
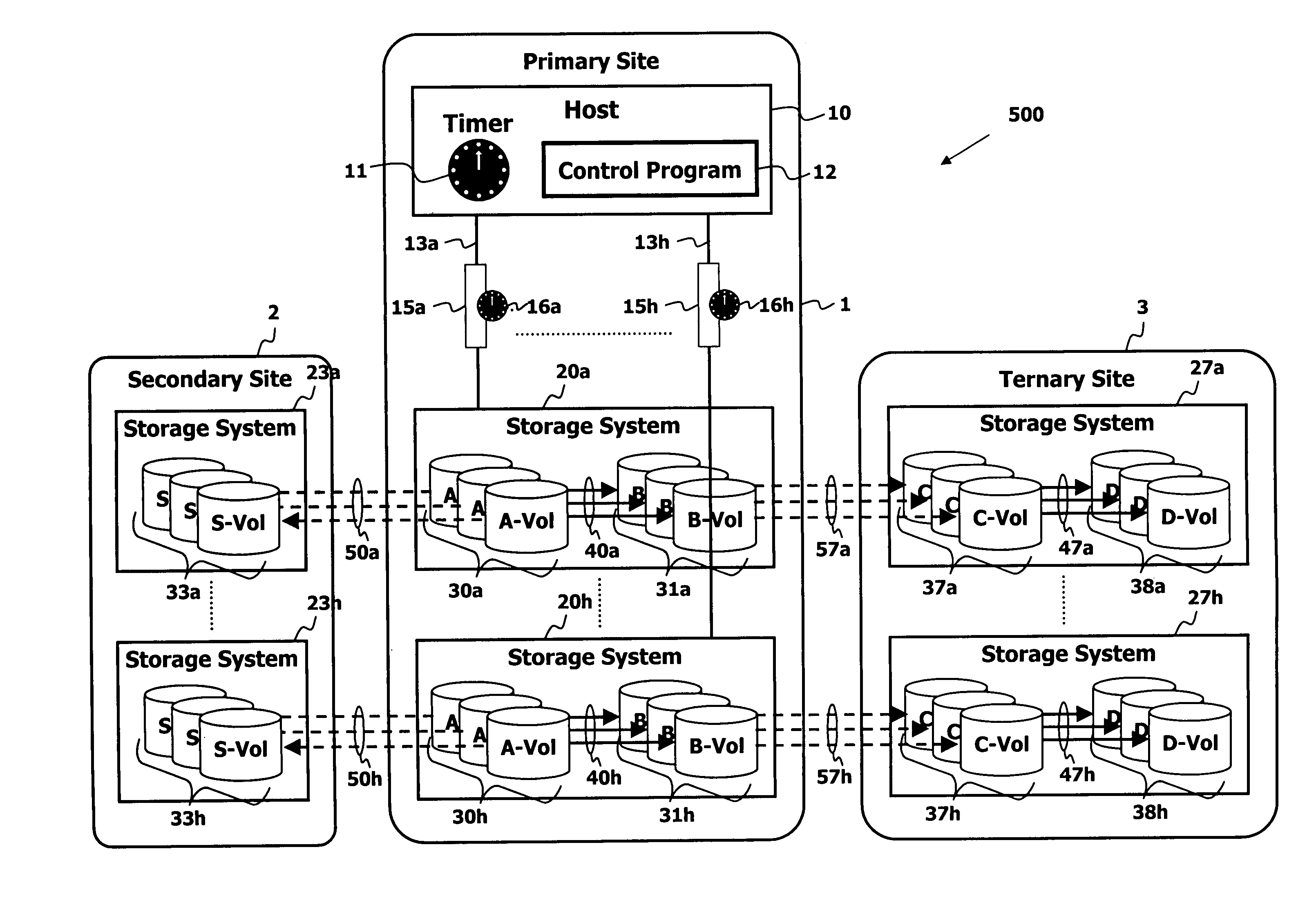
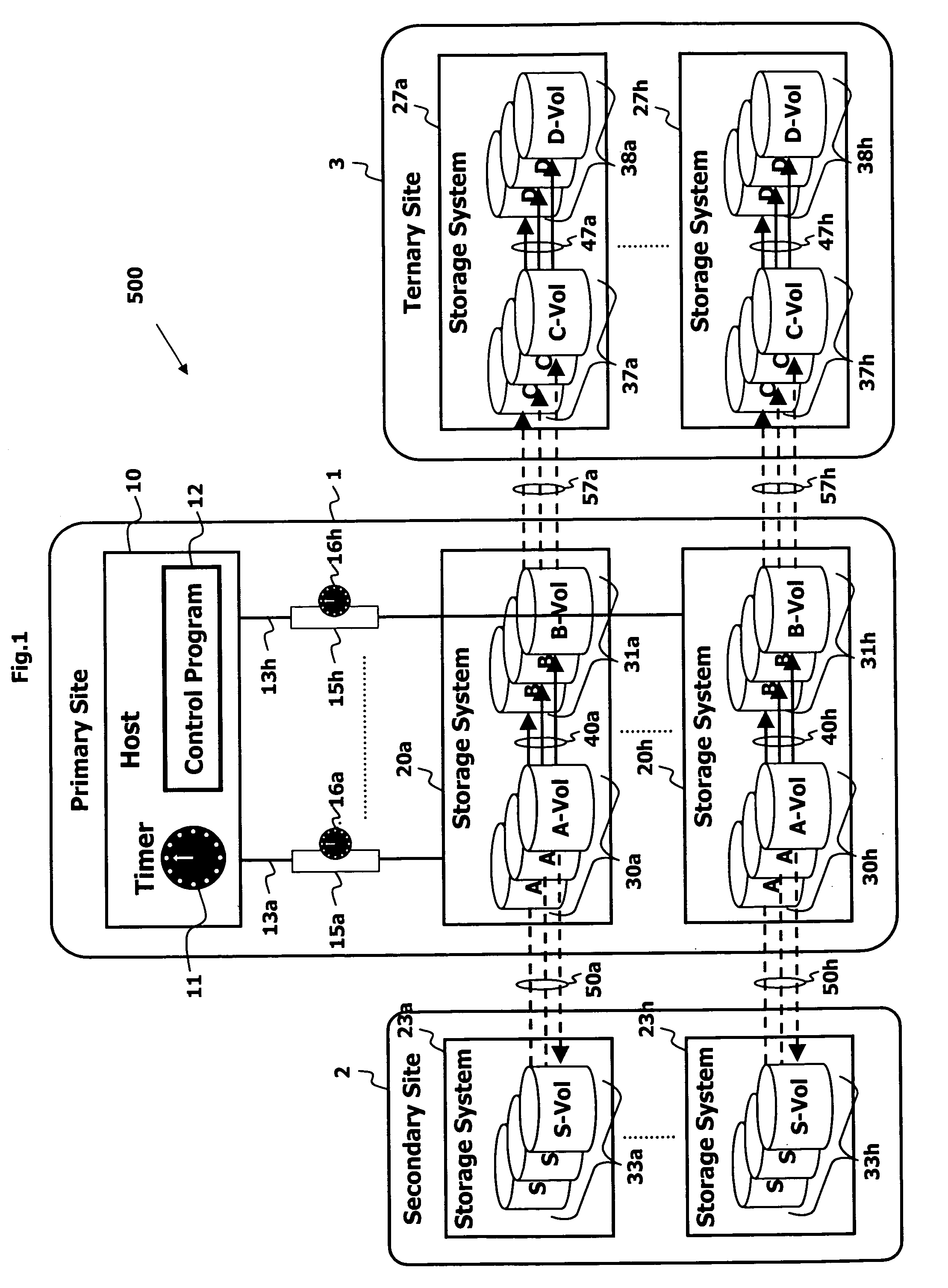
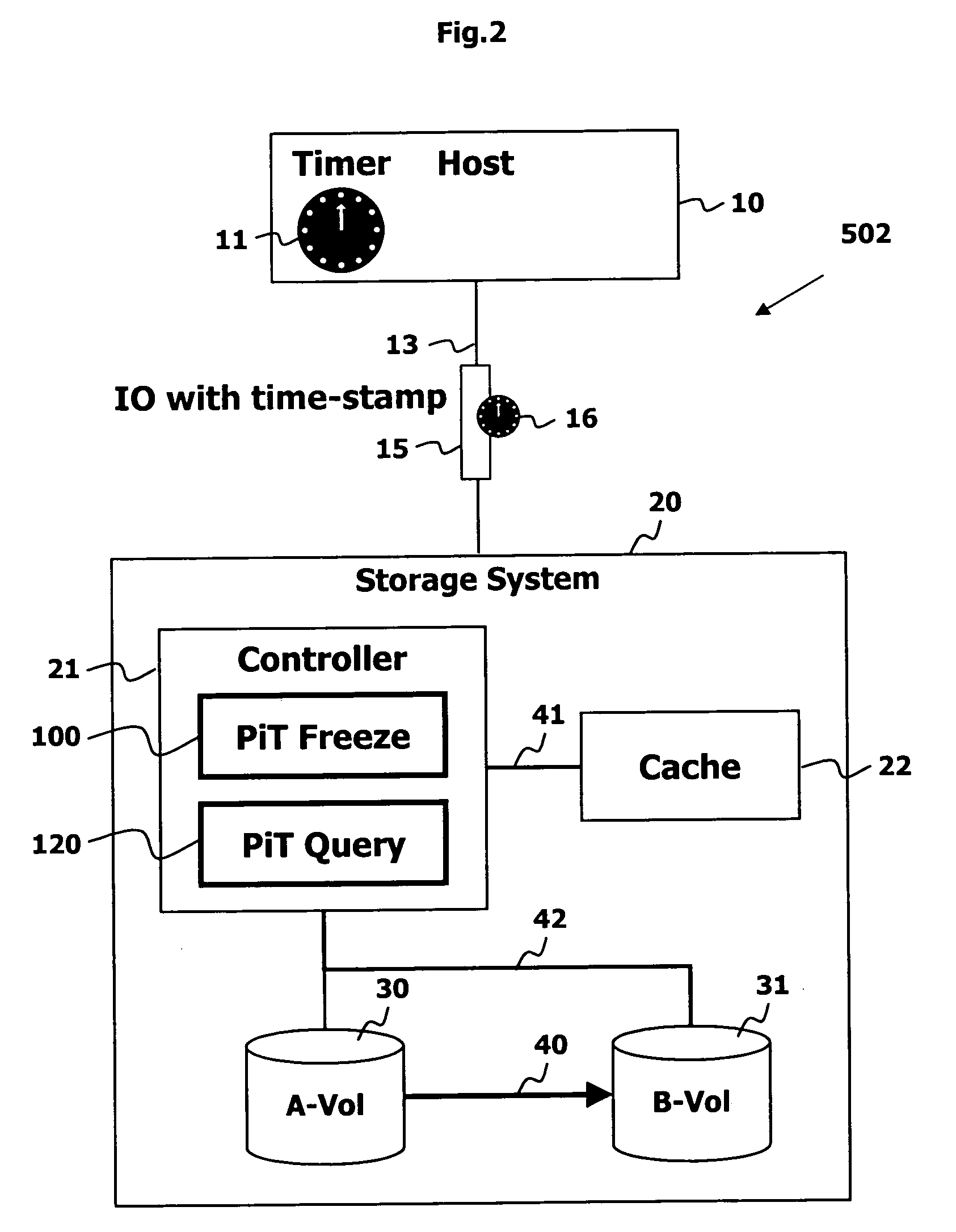
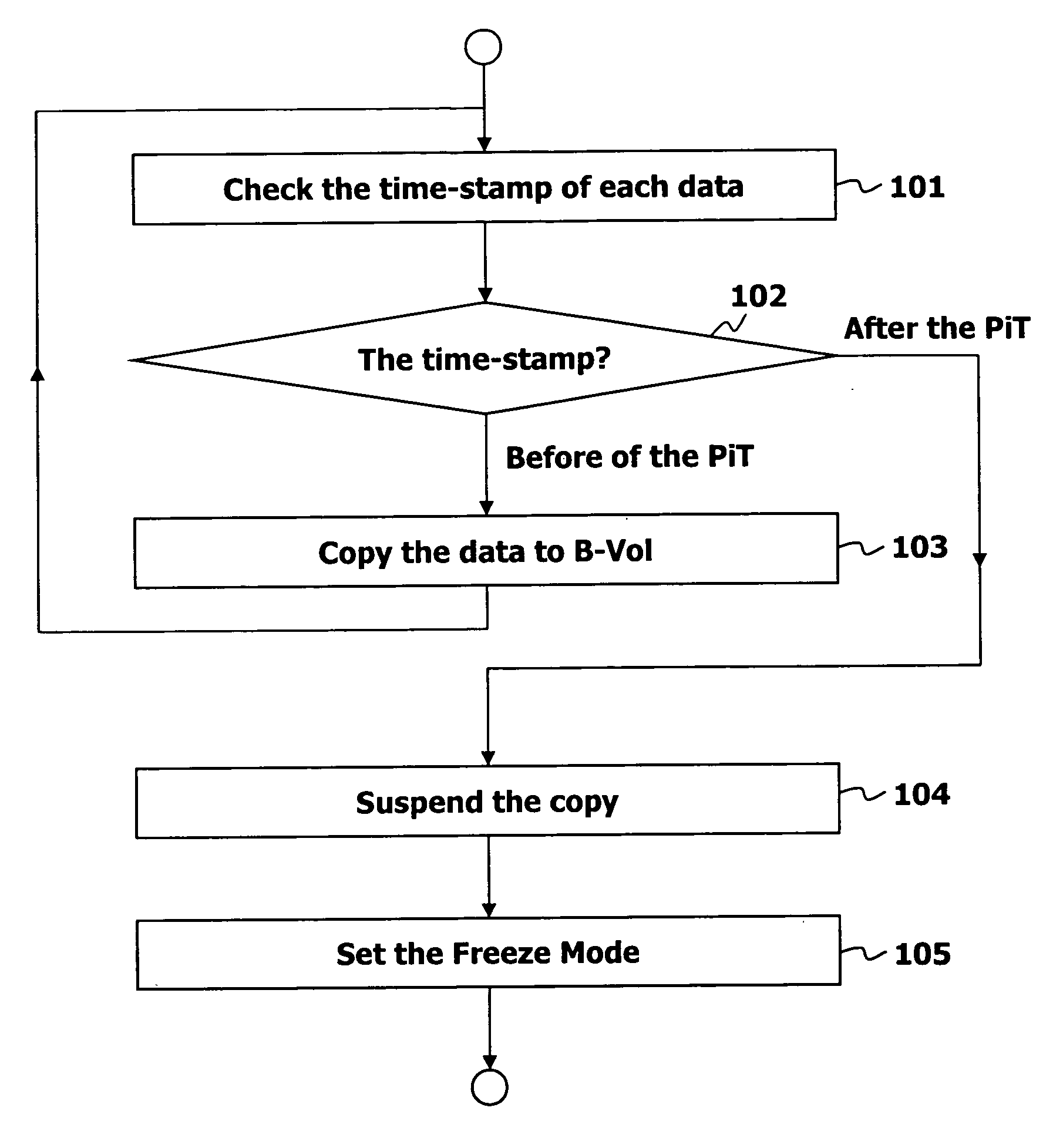
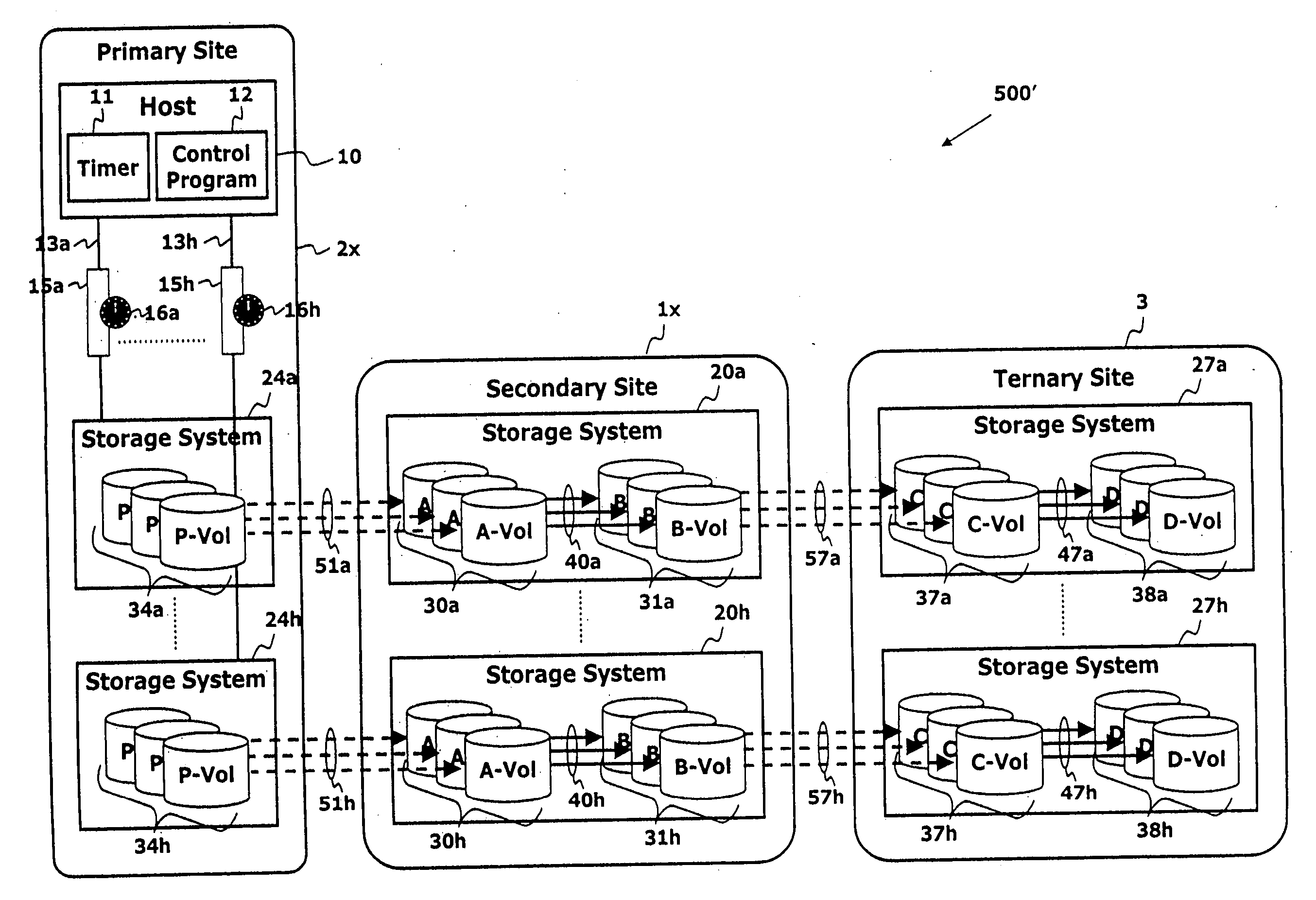
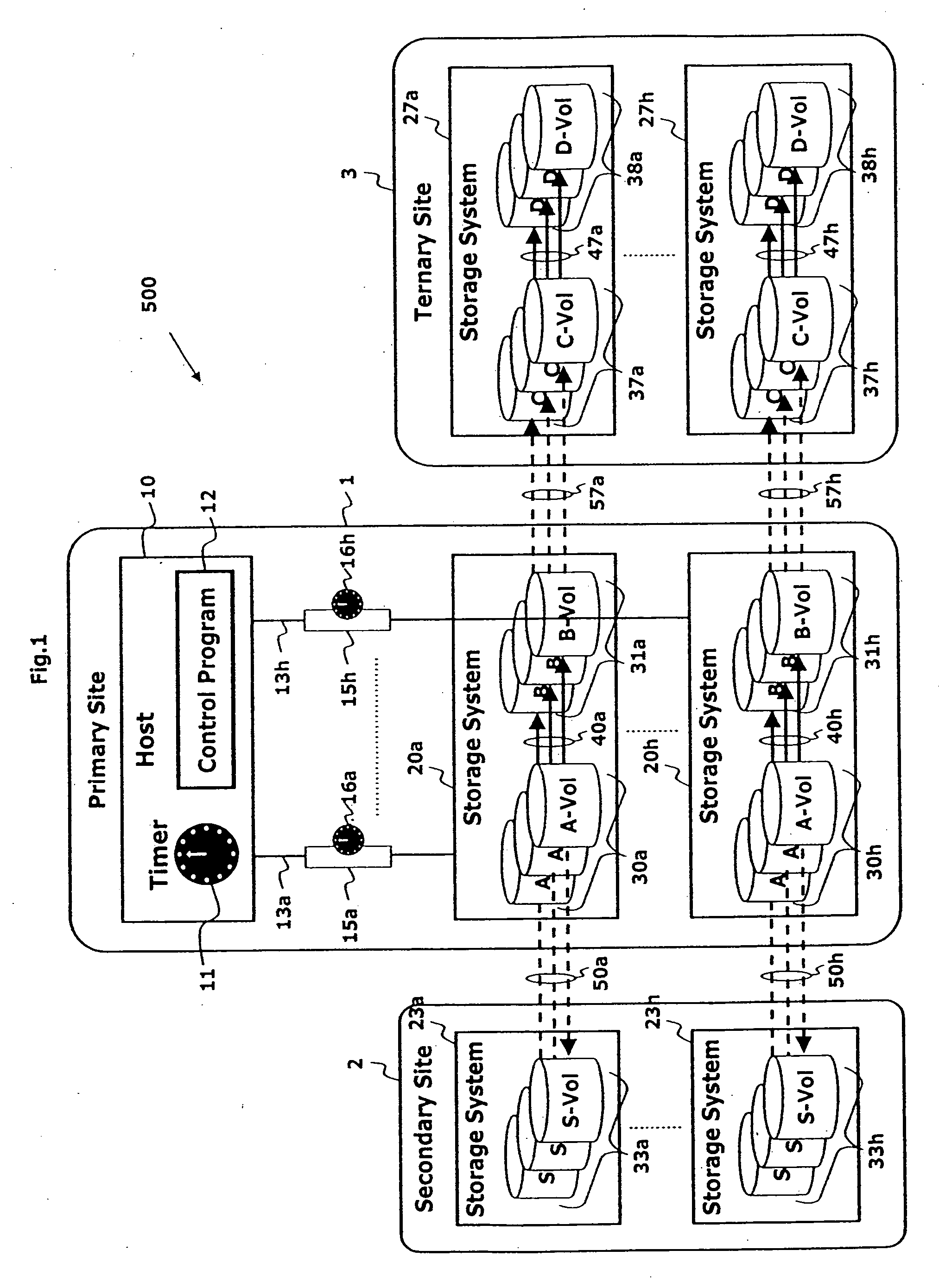
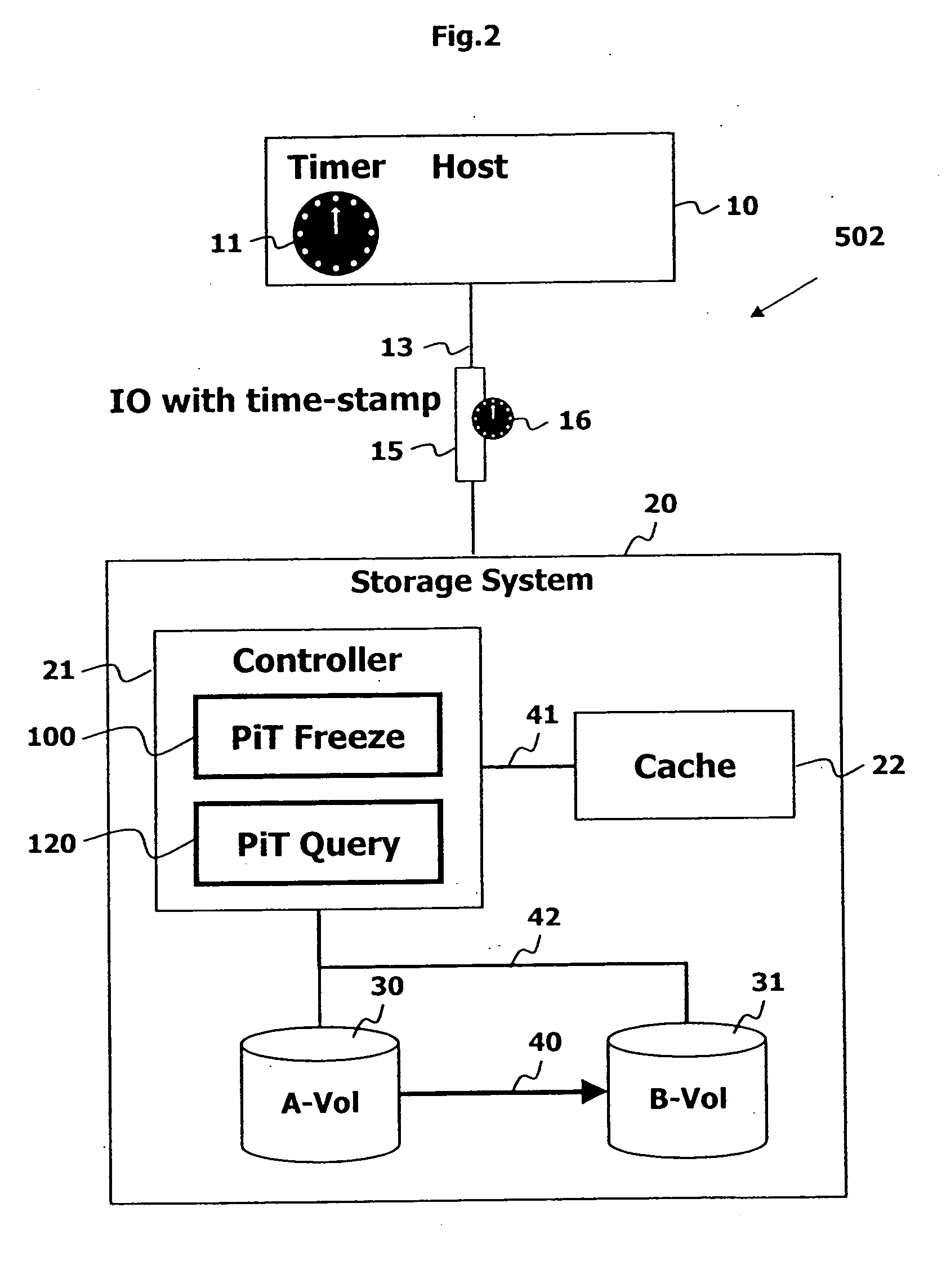
Point in time remote copy for multiple sites
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Point in time remote copy for multiple sites
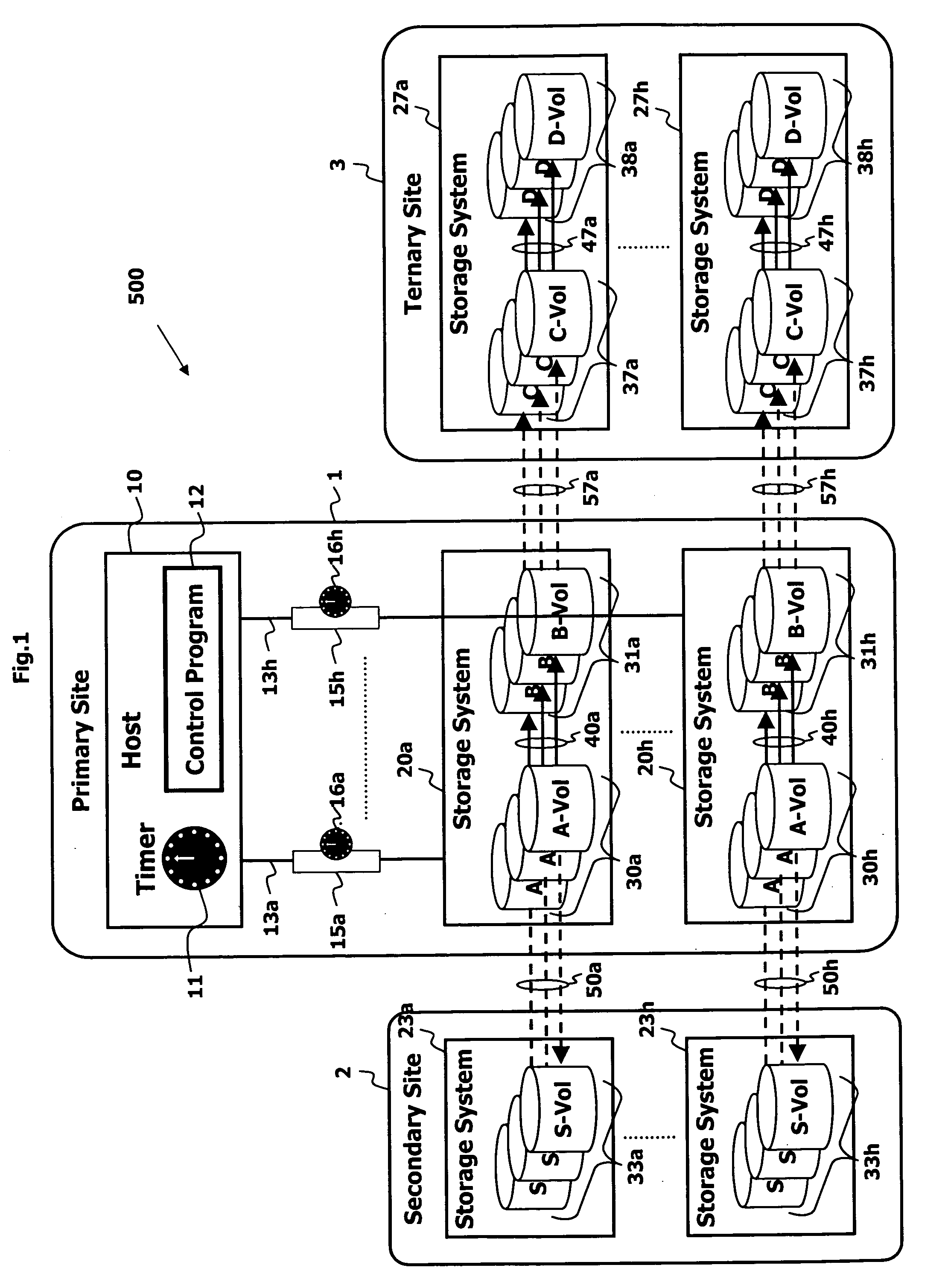
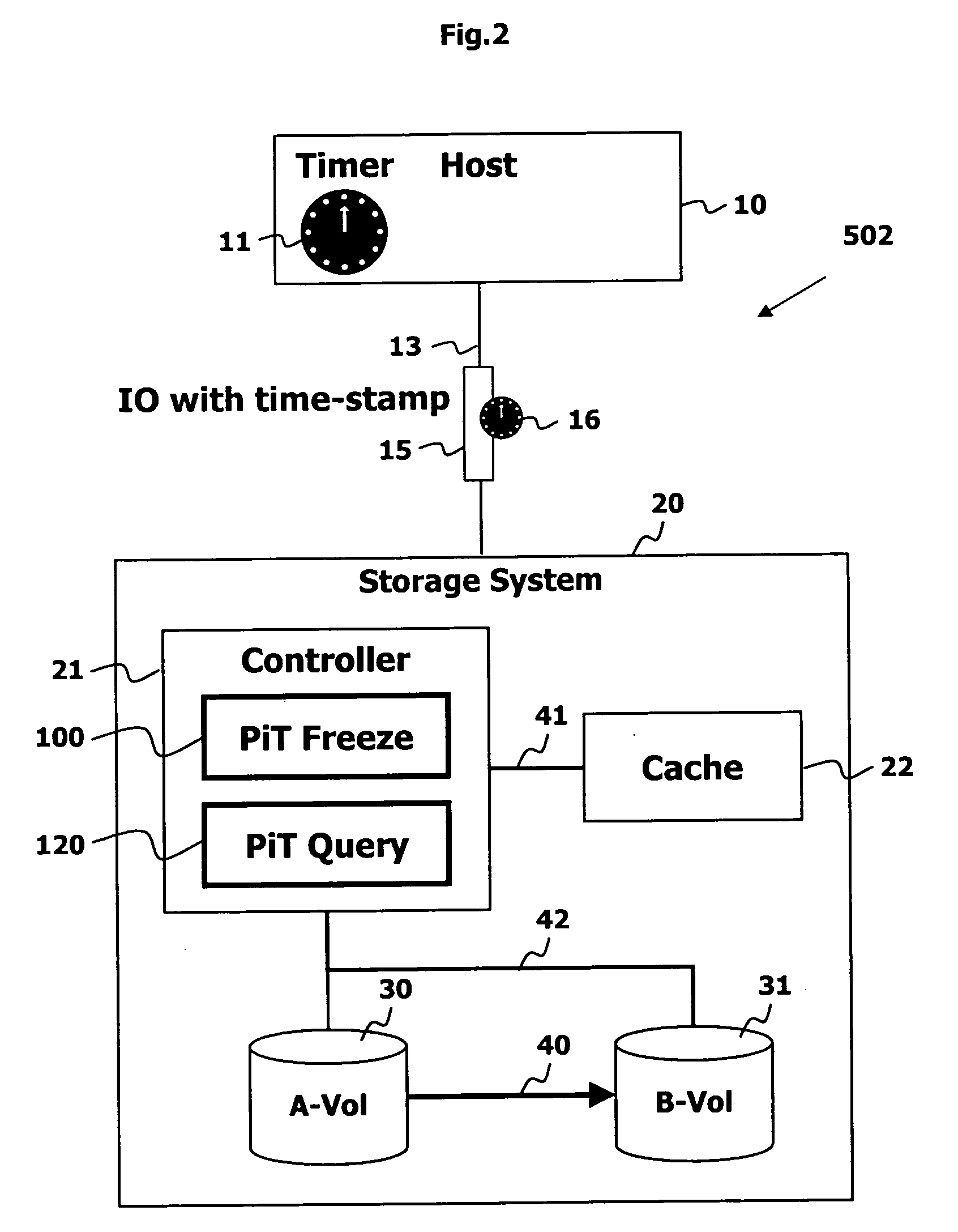
A method for copying data to multiple remote sites includes transmitting data from a first volume in a primary storage system to a back-up volume provided in a secondary storage system. The primary storage system is located at a primary site, and the secondary storage system is located at a first remote site from the primary site. The data from the first volume in the primary storage system is copied to a second volume in the primary storage system using a point in time (PiT) as a reference point of time for the copying. The second volume is provided with a first time consistent image of the first volume with respect to the reference point of time. The data from the second volume in the primary storage system is transferred to a third volume in a ternary storage system at a second remote site. The third volume is provided with a second time consistent image of the second volume with respect to the reference point of time, where the second time consistent image is a mirror image of the first time consistent image. The data from the third volume is transferred to a fourth volume in the ternary storage system. The fourth volume is provided with a third time consistent image. In the ternary storage, either of the third volume or fourth volume can always keep time consistent image of the first volume.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Storage system and back-up method for storage system
ActiveUS20050223170A1Reduce storageReduce data transfer timeData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersPrimary sitesDisk array
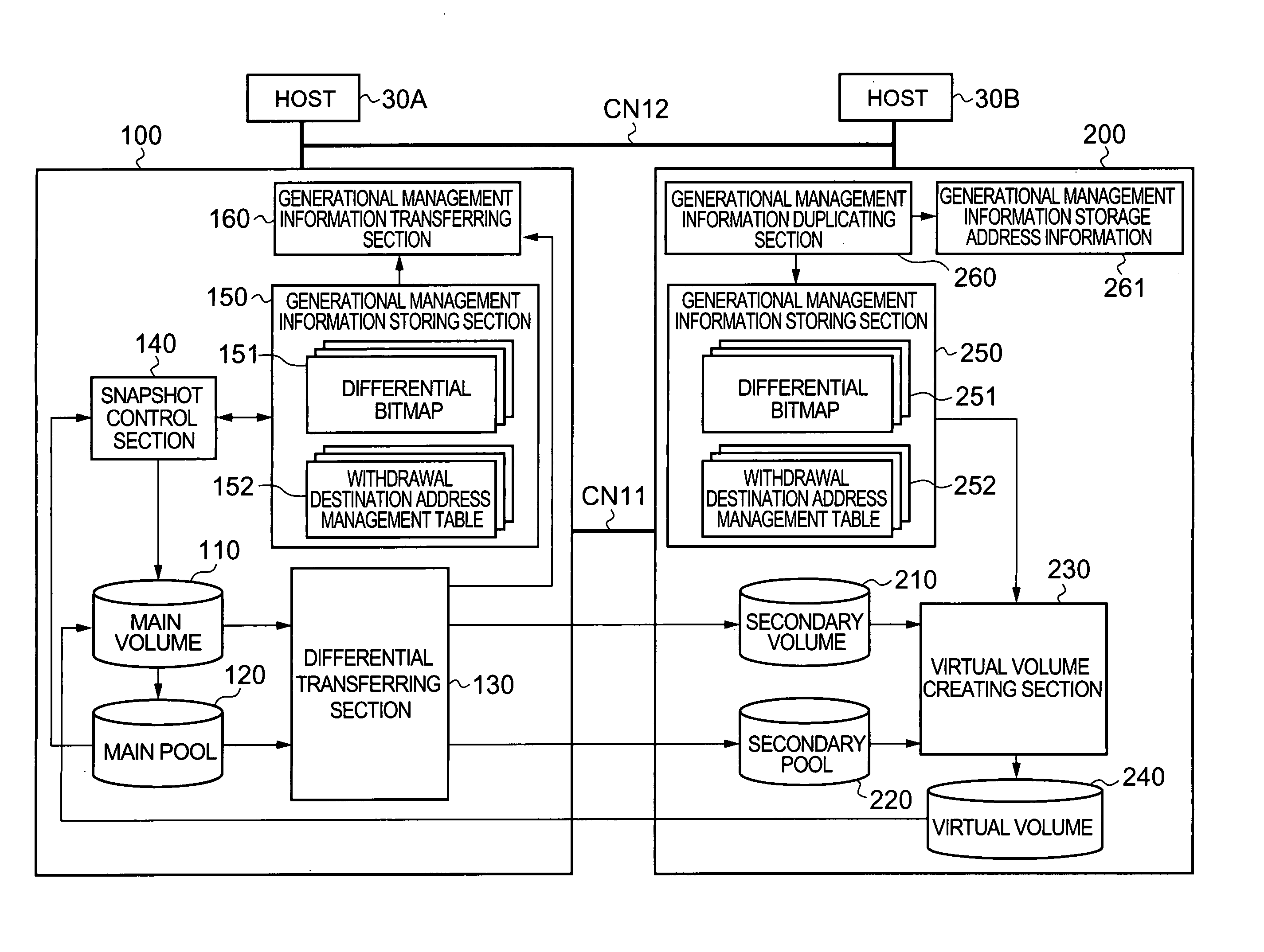
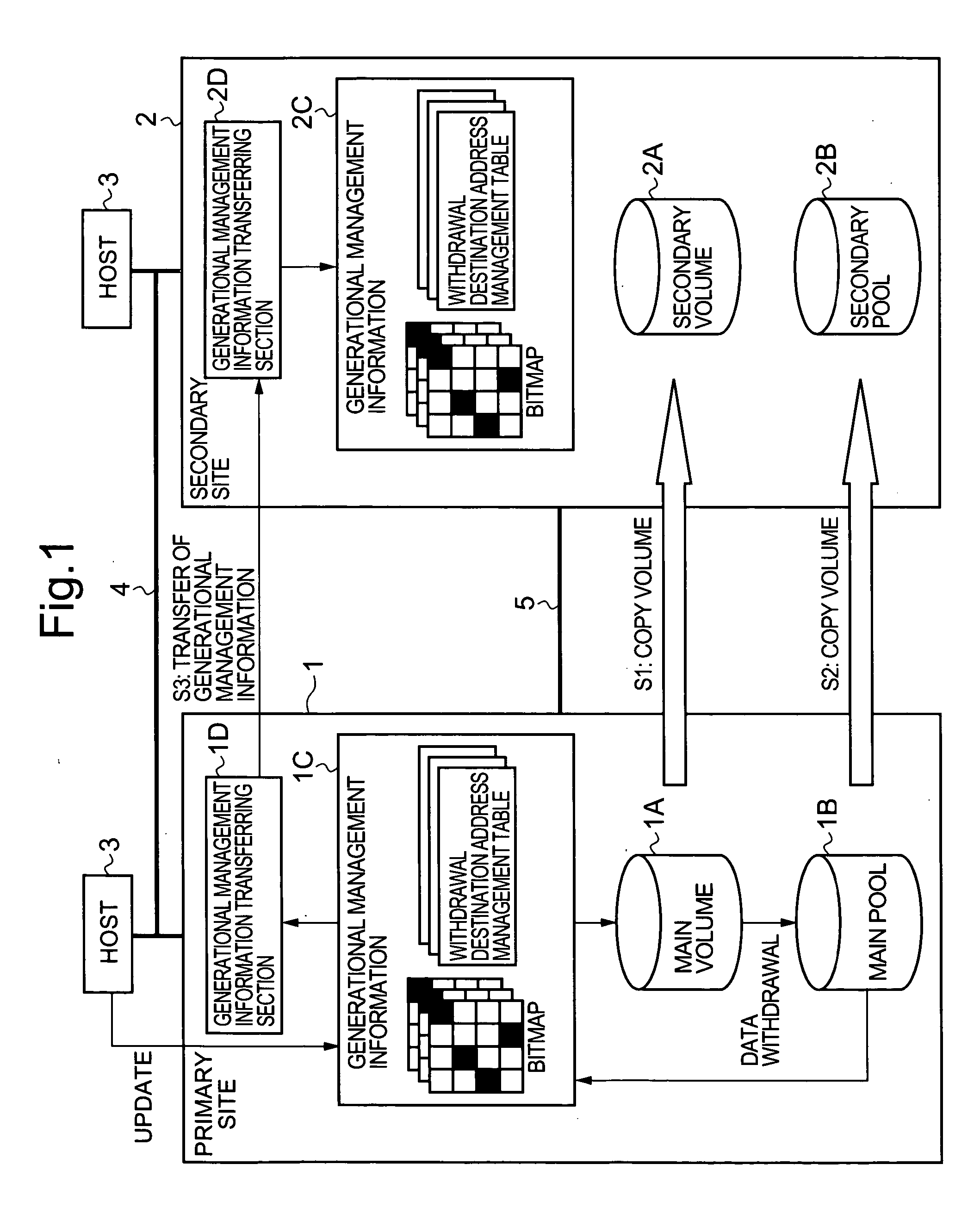
The present invention provides a storage system whereby it is also possible to back up the generational management information of a copy source disk array device. The disk array device of the primary site manages back-up data of a main volume, in a plurality of generations, by means of differential snapshots. The differential data of the main volume and the main pool is transferred from the primary site to the secondary site, at a prescribed timing. The secondary site holds the secondary volume, which is a copy of the main volume, and a secondary pool which is a copy of the main pool. The primary site also transfers the generational management information to the secondary site. The generational management information may also comprise a differential bitmap table and a withdrawal destination address management table. The secondary site holds a copy of the generational management information. Thereby, it is possible to back up the whole of the data, including the generational management information, and hence protection against failure is improved.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
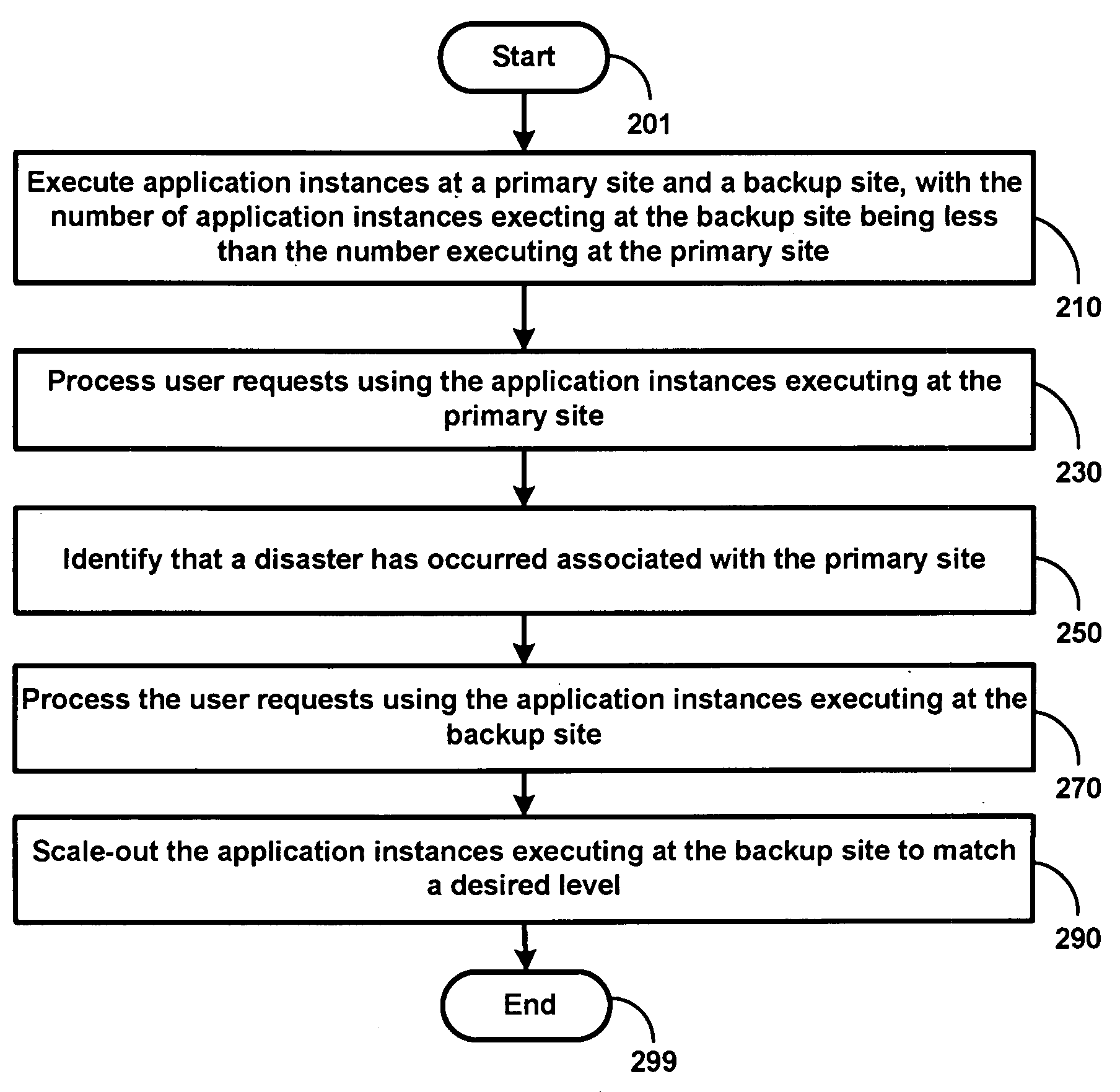
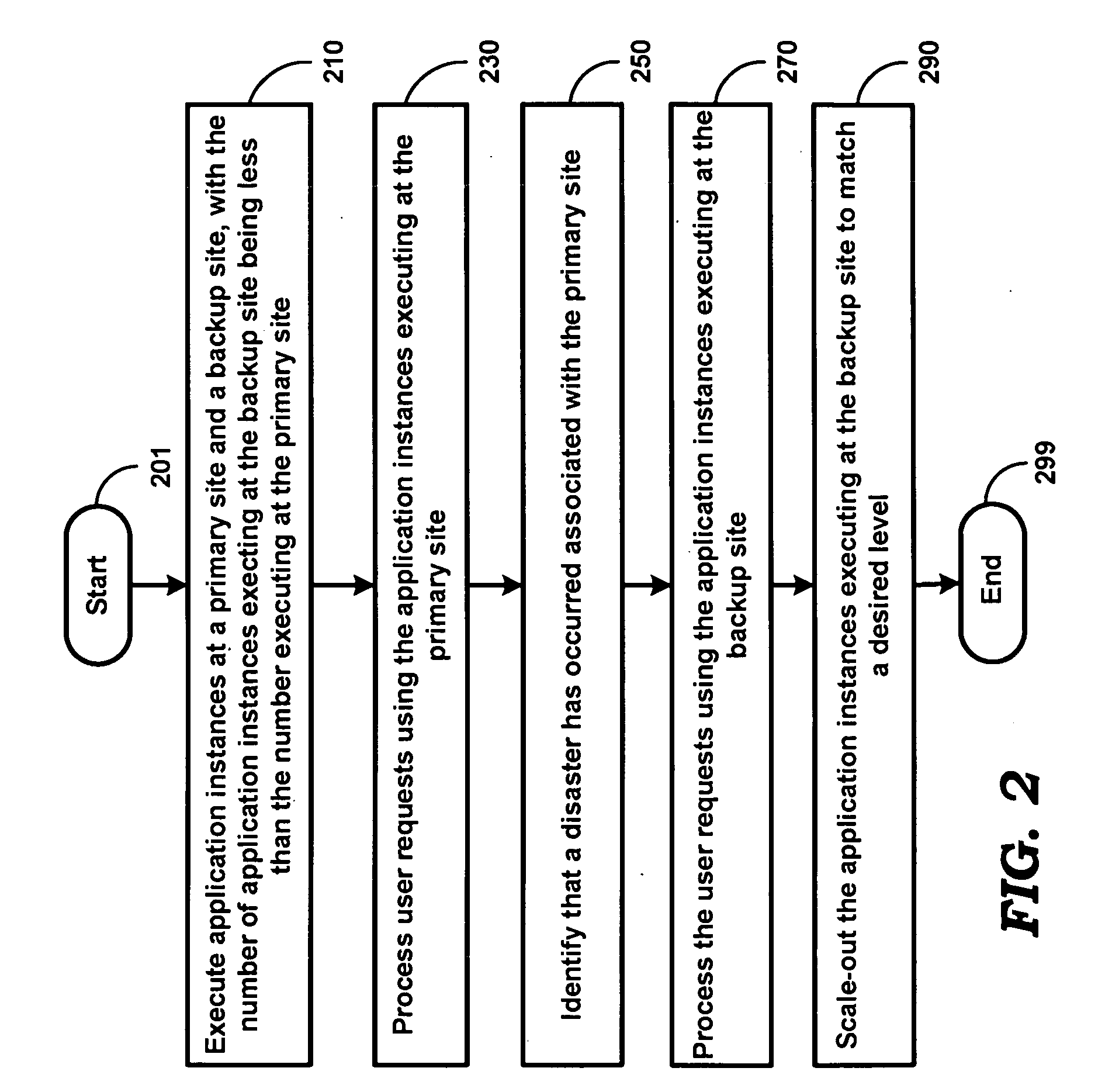
Reducing recovery time for business organizations in case of disasters
An aspect of the present invention reduces the recovery time for business organizations in case of disasters. In one embodiment, a disaster recovery system containing a primary site and a backup site (implemented as a cluster) is maintained. Application instances are executed in both the primary site and the backup site, with the number of instances executed on the backup site being fewer than that executed on the primary site. During normal operation, user requests received are processed using only the instances executing in the primary site, while the instances executing in the backup site are used in a standby state. On identifying that a disaster has occurred, the user requests received immediately after identification of the disaster are processed using only the instances executing in the backup site. The cluster at the backup site is then scaled out to add application instances until a desired level / percentage is achieved.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
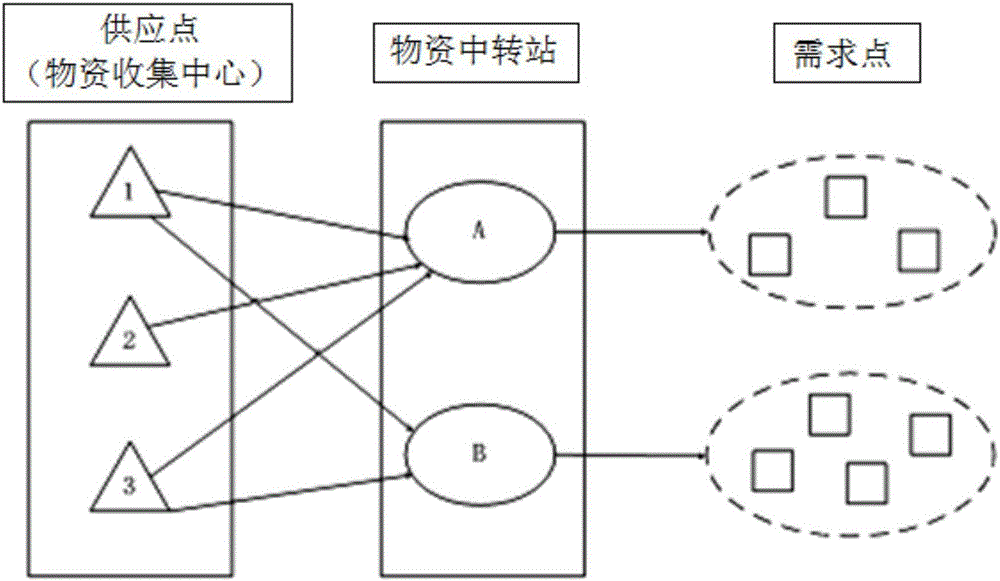
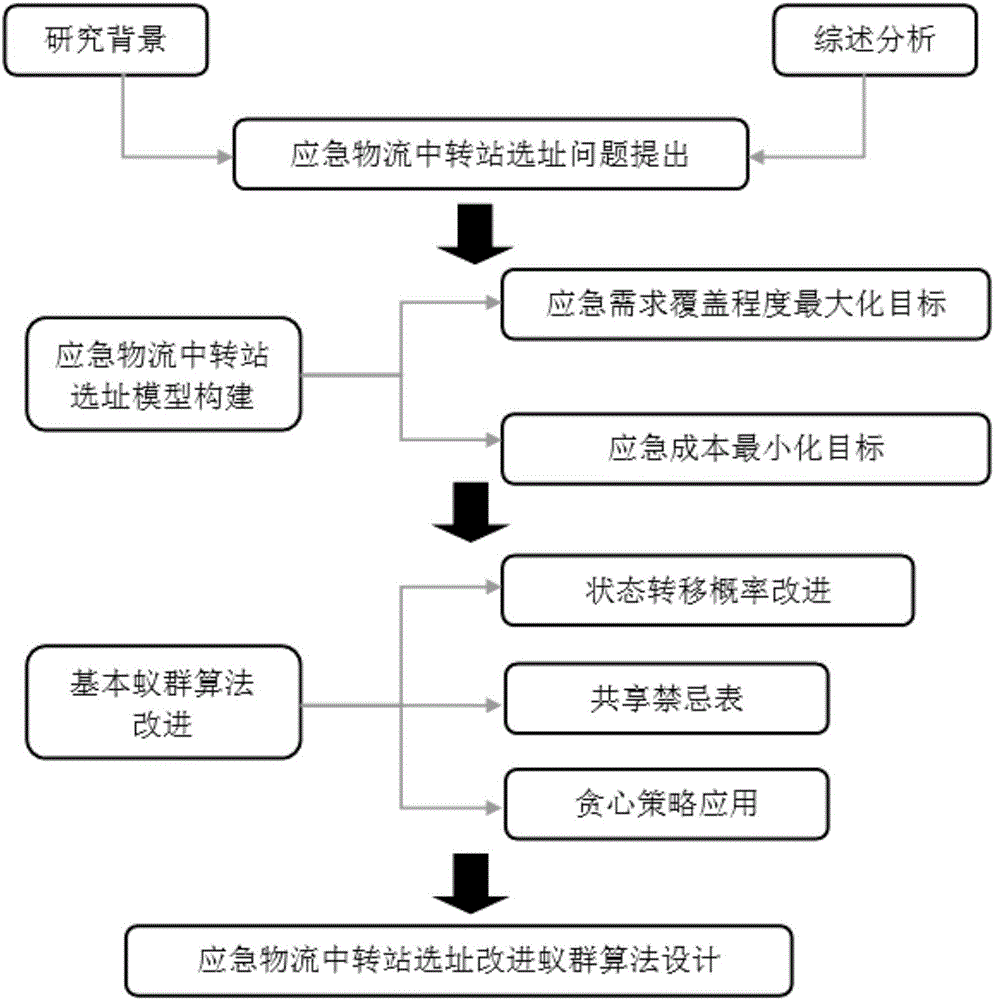
Emergency logistic transfer station site selection method based on improved ant colony algorithm
ActiveCN105787595AState Transition Probability ImprovementForecastingArtificial lifePrimary sitesGreedy algorithm
The invention discloses an emergency logistic transfer station site selection method based on an improved ant colony algorithm. The method comprises the steps of: constructing a multi-target optimizing model with an maximum emergency demand coverage degree and minimum emergency cost serving as a target, and combining constraint conditions of the optimizing model to determine the number of the temporary transfer stations; combining the clustering ant colony algorithm and a greedy algorithm to solve the multi-target optimizing model, successively performing clustering analysis on coverage situations of disaster points under each disaster level, determining grouping of the disaster points and making a primary site selection scheme of the transfer stations; evaluating the unselected transfer stations, replacing the primary selected transfer station with the transfer station of a maximum evaluation value, performing transfer station repositioning until the site selection scheme does not change; and outputting the final transfer station site selection scheme. According to the invention, the ant colony algorithm is improved on the application of the state transition probability, the sharing tabu table and the greedy algorithm idea, the convergence rate and the solving quality are increased and a theoretical basis is provided for the optimizing of the emergency logistic transfer station site selection.
Owner:TAIHUA WISDOM IND GRP CO LTD
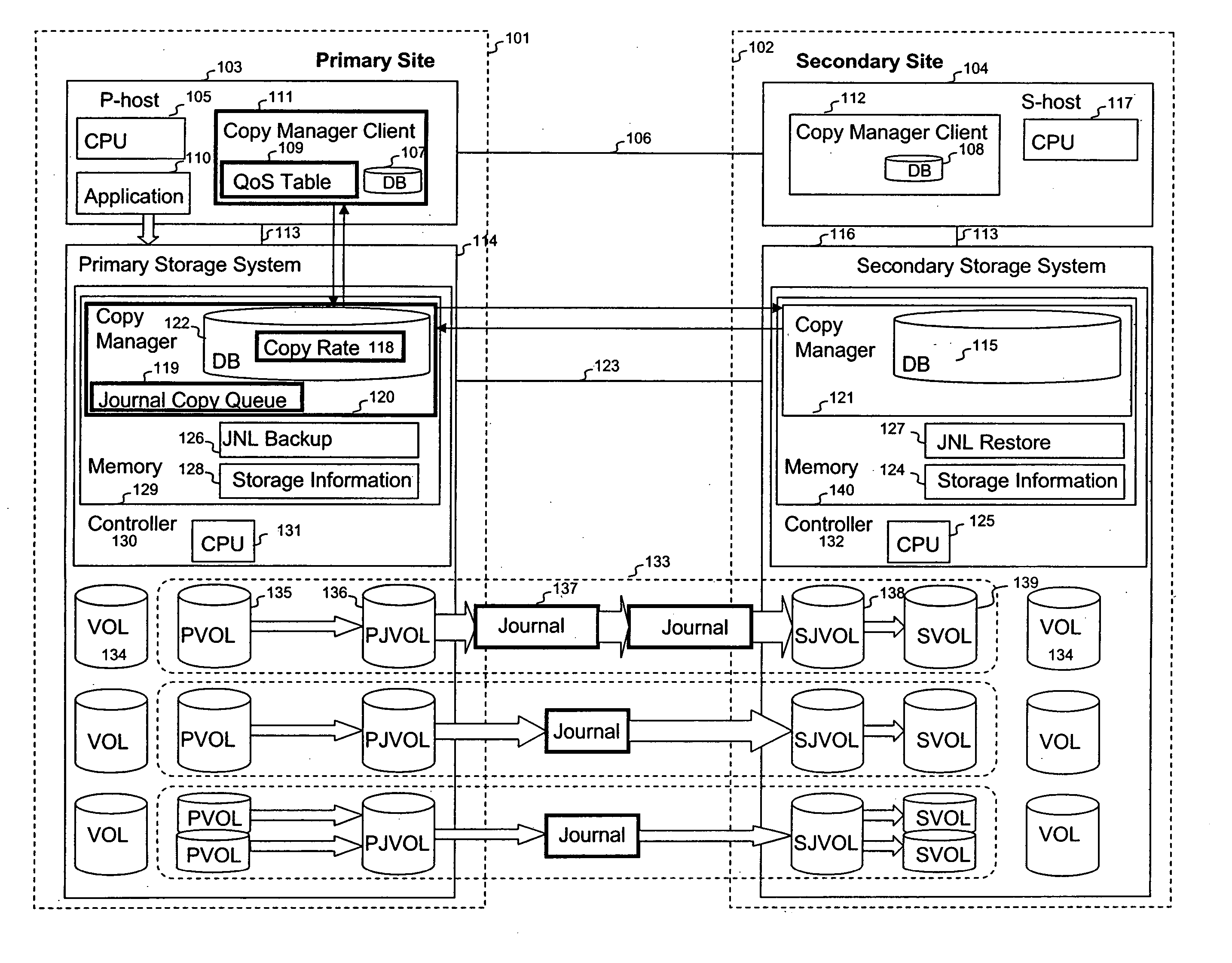
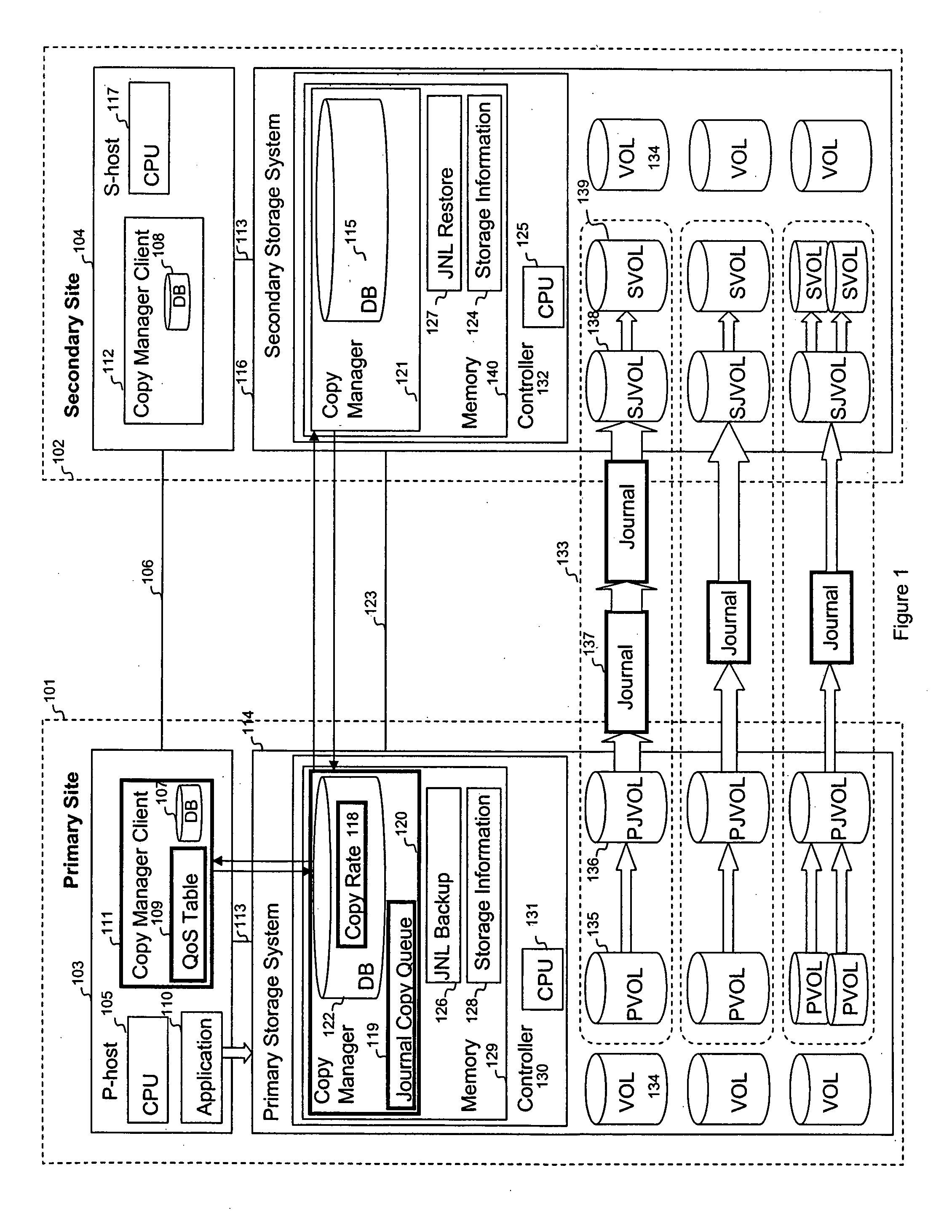
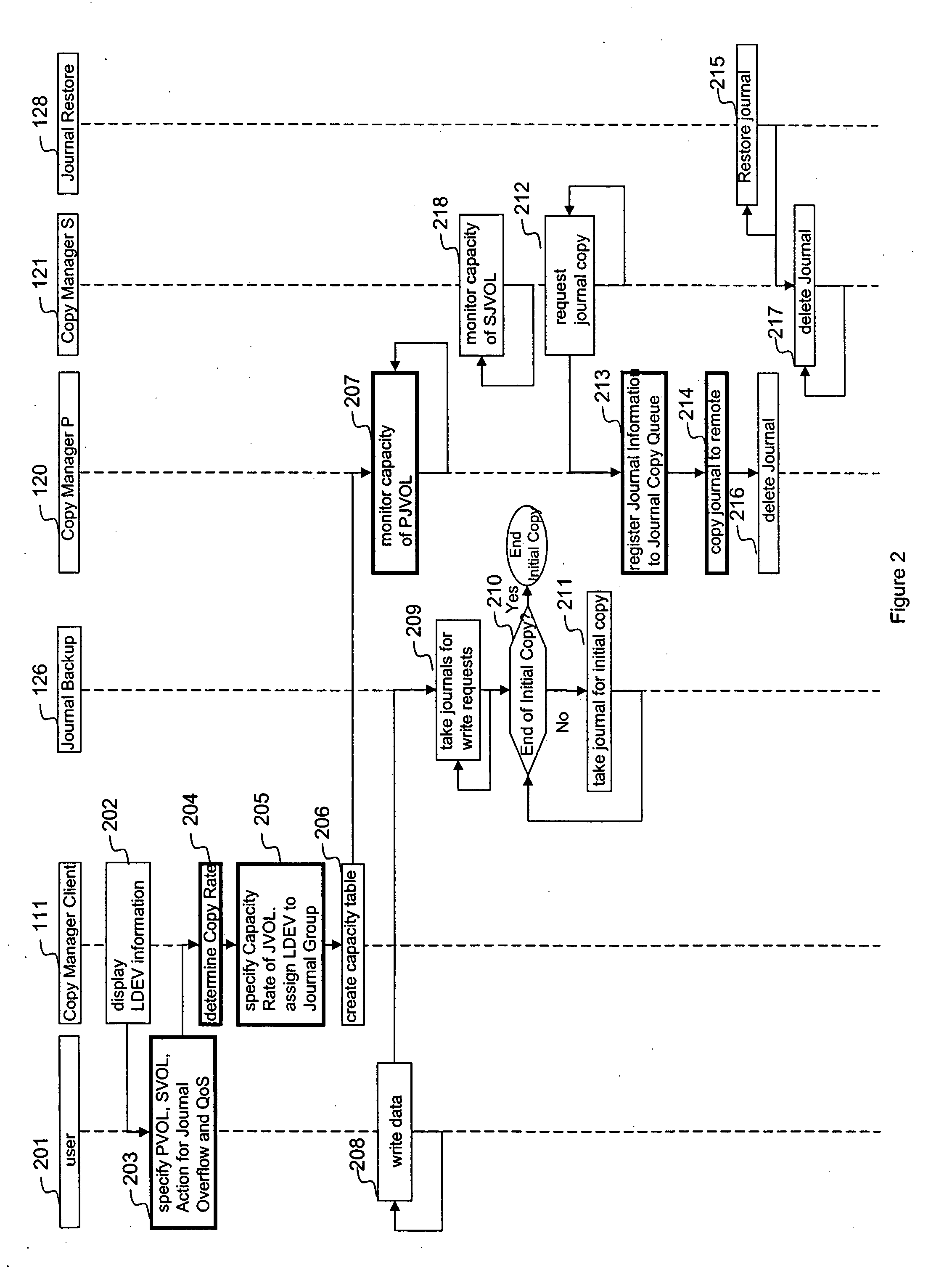
Quality of service for remote copy operations in storage systems
InactiveUS20060095696A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionQuality of servicePrimary sites
A system is provided for storage of journal data from a primary site to a secondary site with a predefined quality of service. In one implementation, the primary storage system stores information for updating data stored on the primary disk array in the form of a history of updates made to the data. The primary storage system is configured to transfer this journal information to the secondary storage system. The user can specify the quality of service desired using a variety of measures, for example, a recovery point objective or a recovery time objective. In response, a copy manager within one of the storage systems determines the capacity of the various primary and secondary volumes, and determines the copy rate available, typically dependent upon the bandwidth between the primary and secondary systems. The copy manager then copies journal data to the remote site where it is stored.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Point in time remote copy for multiple sites
A method for copying data to multiple remote sites includes transmitting data from a first volume in a primary storage system to a back-up volume provided in a secondary storage system. The primary storage system is located at a primary site, and the secondary storage system is located at a first remote site from the primary site. The data from the first volume in the primary storage system is copied to a second volume in the primary storage system using a point in time (PiT) as a reference point of time for the copying. The second volume is provided with a first time consistent image of the first volume with respect to the reference point of time. The data from the second volume in the primary storage system is transferred to a third volume in a ternary storage system at a second remote site. The third volume is provided with a second time consistent image of the second volume with respect to the reference point of time, where the second time consistent image is a mirror image of the first time consistent image. The data from the third volume is transferred to a fourth volume in the ternary storage system. The fourth volume is provided with a third time consistent image. In the ternary storage, either of the third volume or fourth volume can always keep time consistent image of the first volume.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com