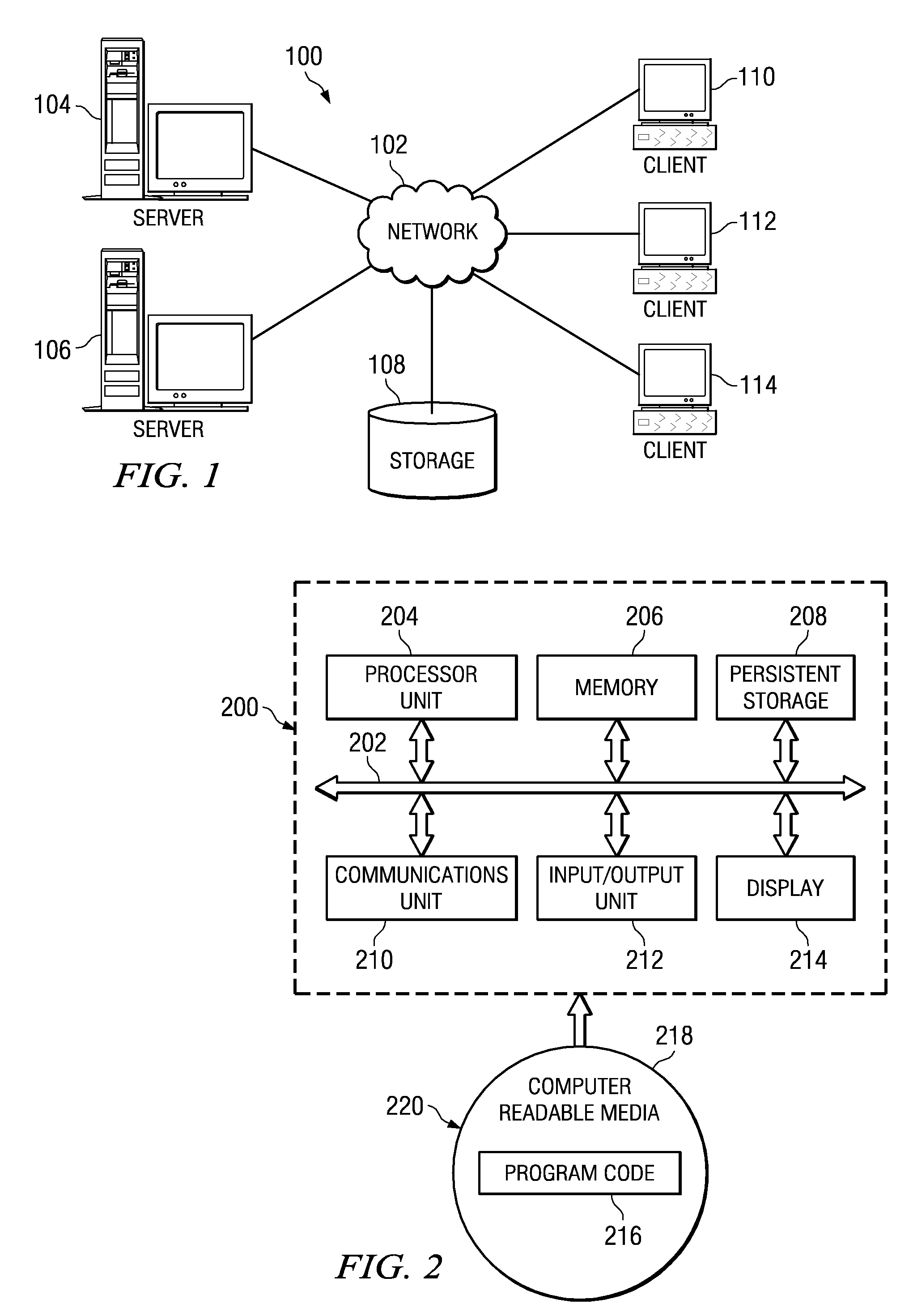
Patents
Literature
347 results about "Time to live" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Time to live (TTL) or hop limit is a mechanism that limits the lifespan or lifetime of data in a computer or network. TTL may be implemented as a counter or timestamp attached to or embedded in the data. Once the prescribed event count or timespan has elapsed, data is discarded or revalidated. In computer networking, TTL prevents a data packet from circulating indefinitely. In computing applications, TTL is commonly used to improve the performance and manage the caching of data.
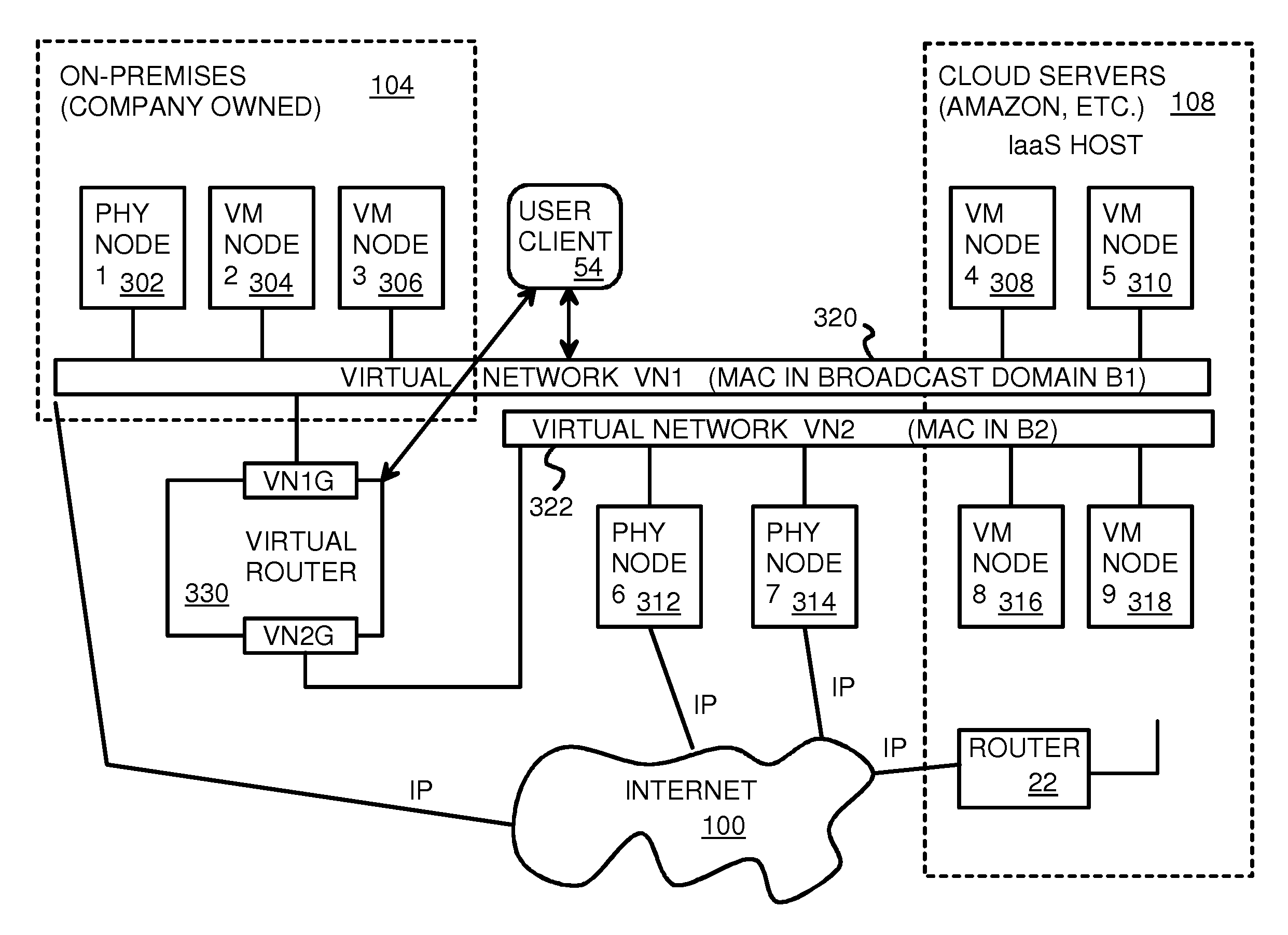
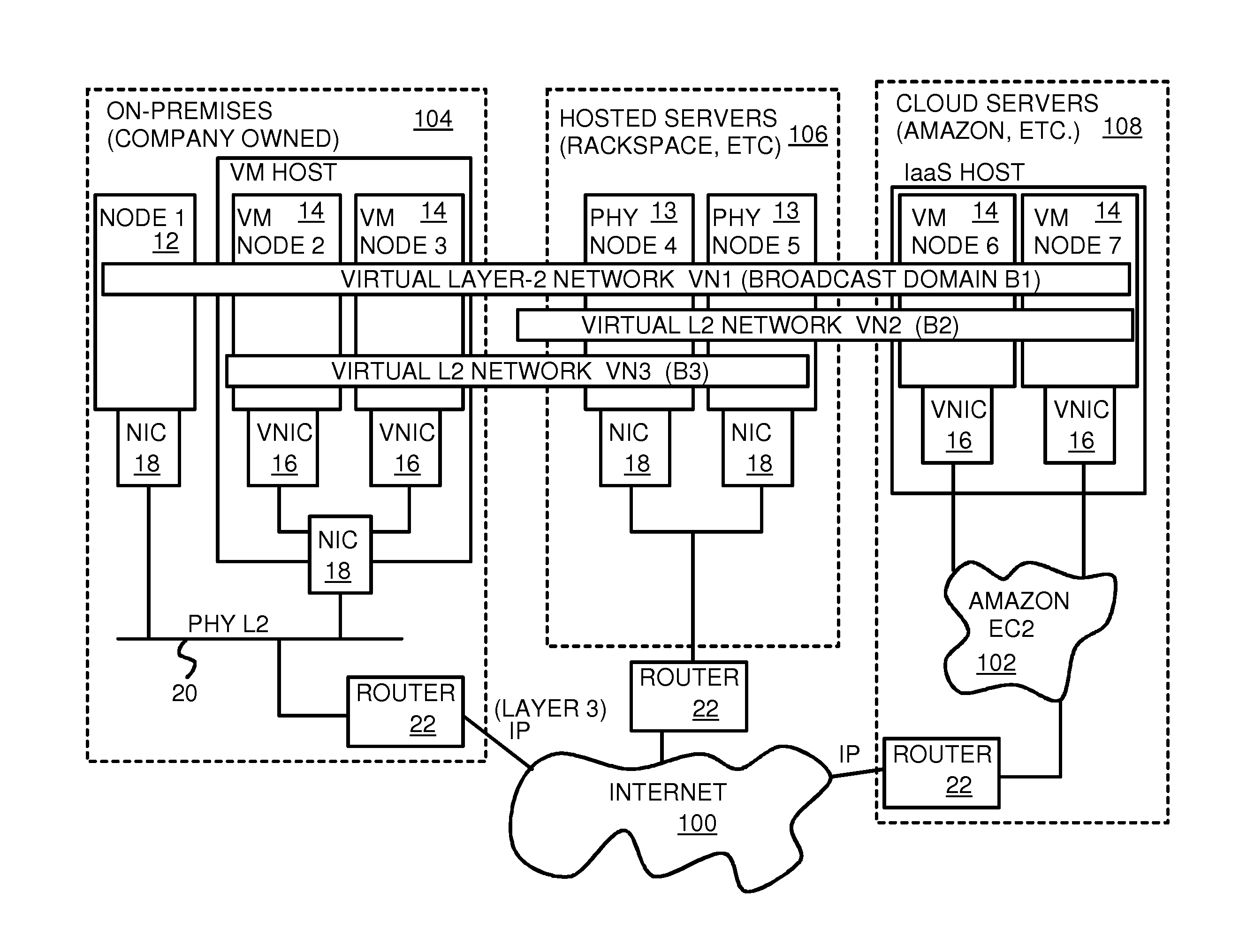
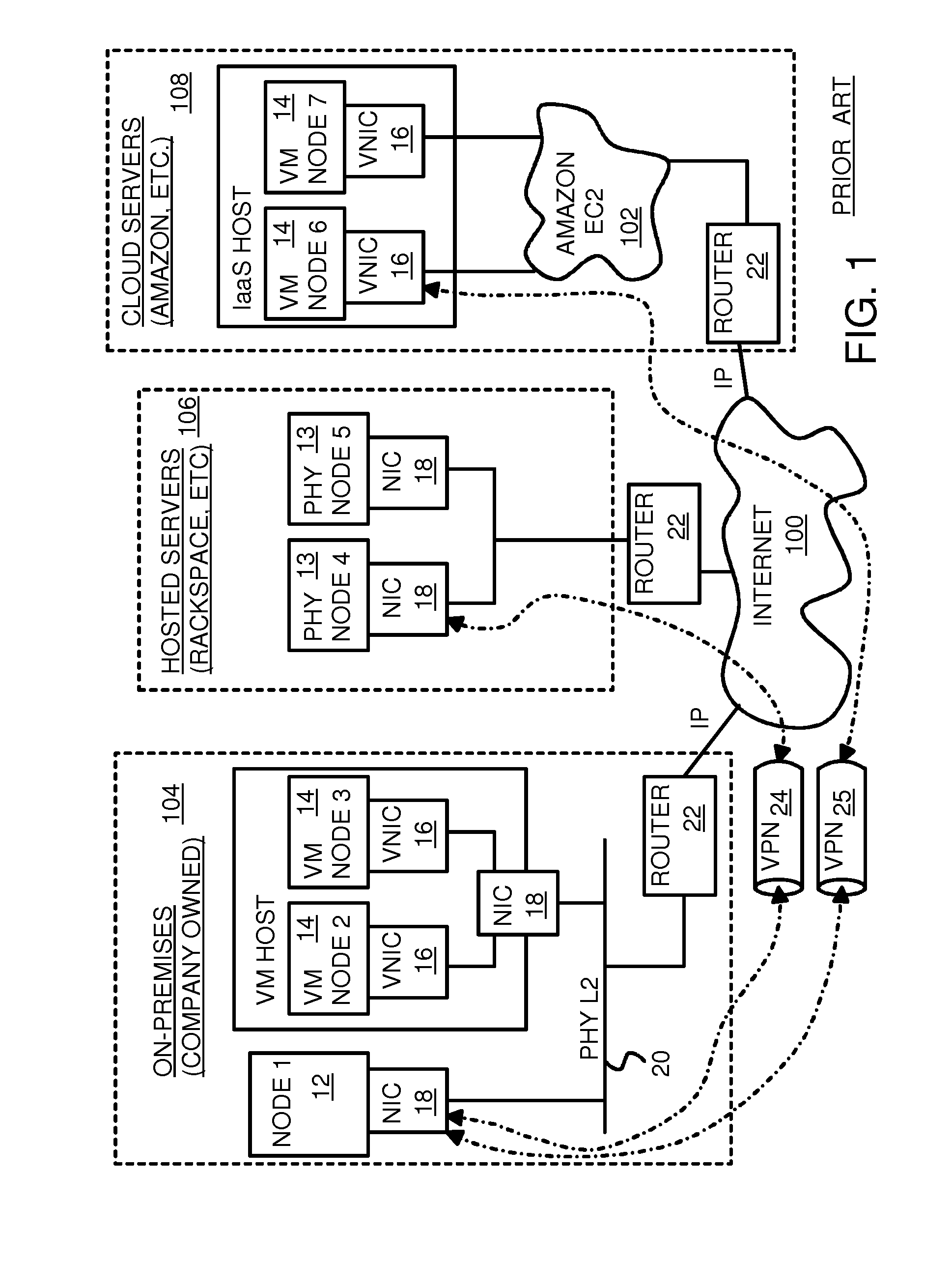
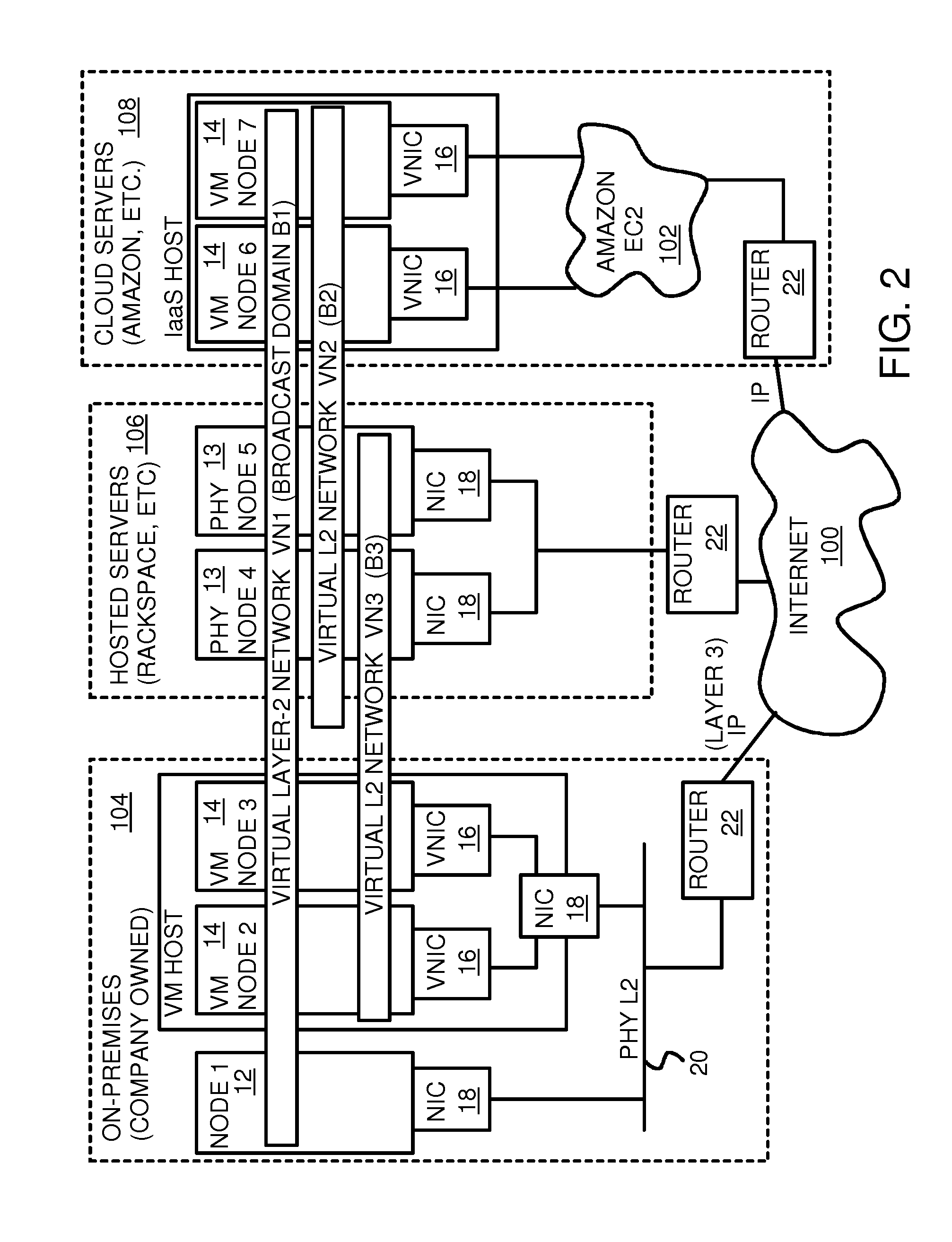
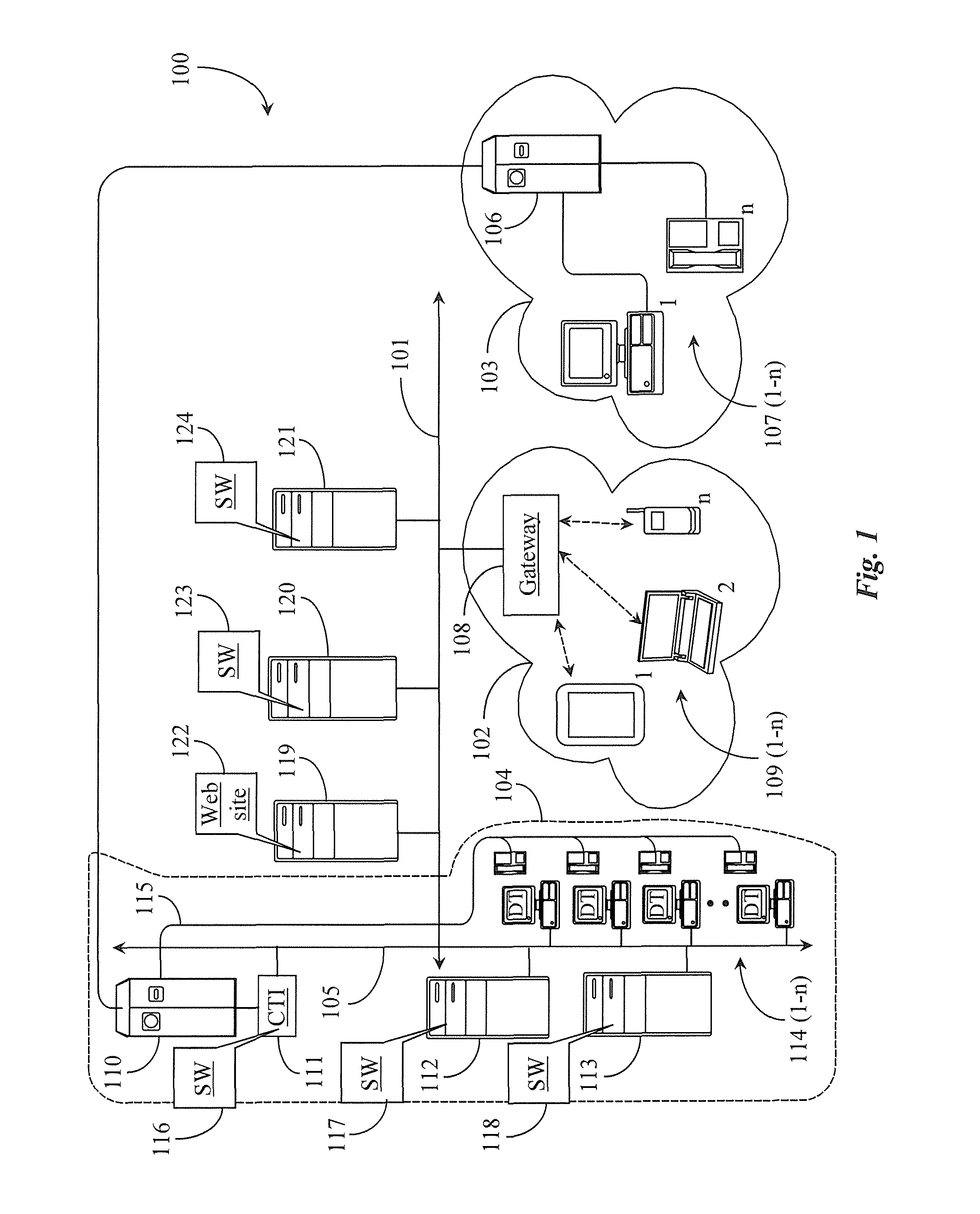
Fully distributed routing over a user-configured on-demand virtual network for infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) on hybrid cloud networks
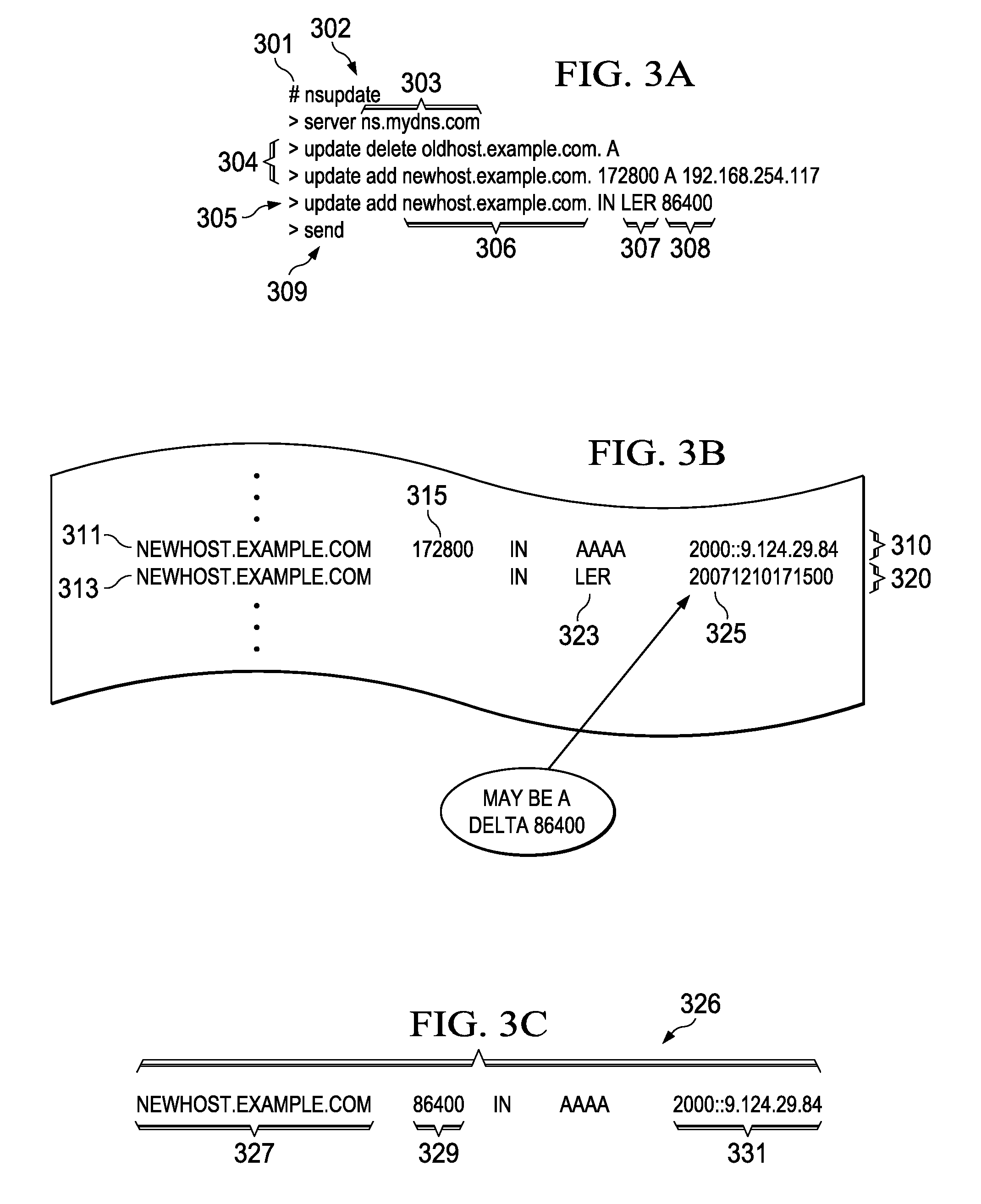
A layer-3 virtual router connects two or more virtual networks. Virtual networks are overlaid upon physical networks. Each virtual network (VN) is a layer-2 network that appears to expand an organization's LAN using virtual MAC addresses. The network stack forms a virtual-network packet with a virtual gateway MAC address of the virtual router to reach a remote virtual network. A VN device driver shim intercepts packets and their virtual MAC and IP addresses and encapsulates them with physical packets sent over the Internet. A VN switch table is expanded to include entries for nodes on the remote virtual network so that all nodes on both virtual networks are accessible. A copy of the VN switch table is stored on each node by a virtual network management daemon on the node. A Time-To-Live field in the virtual-network packet is decremented for each virtual hop and a checksum recalculated.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
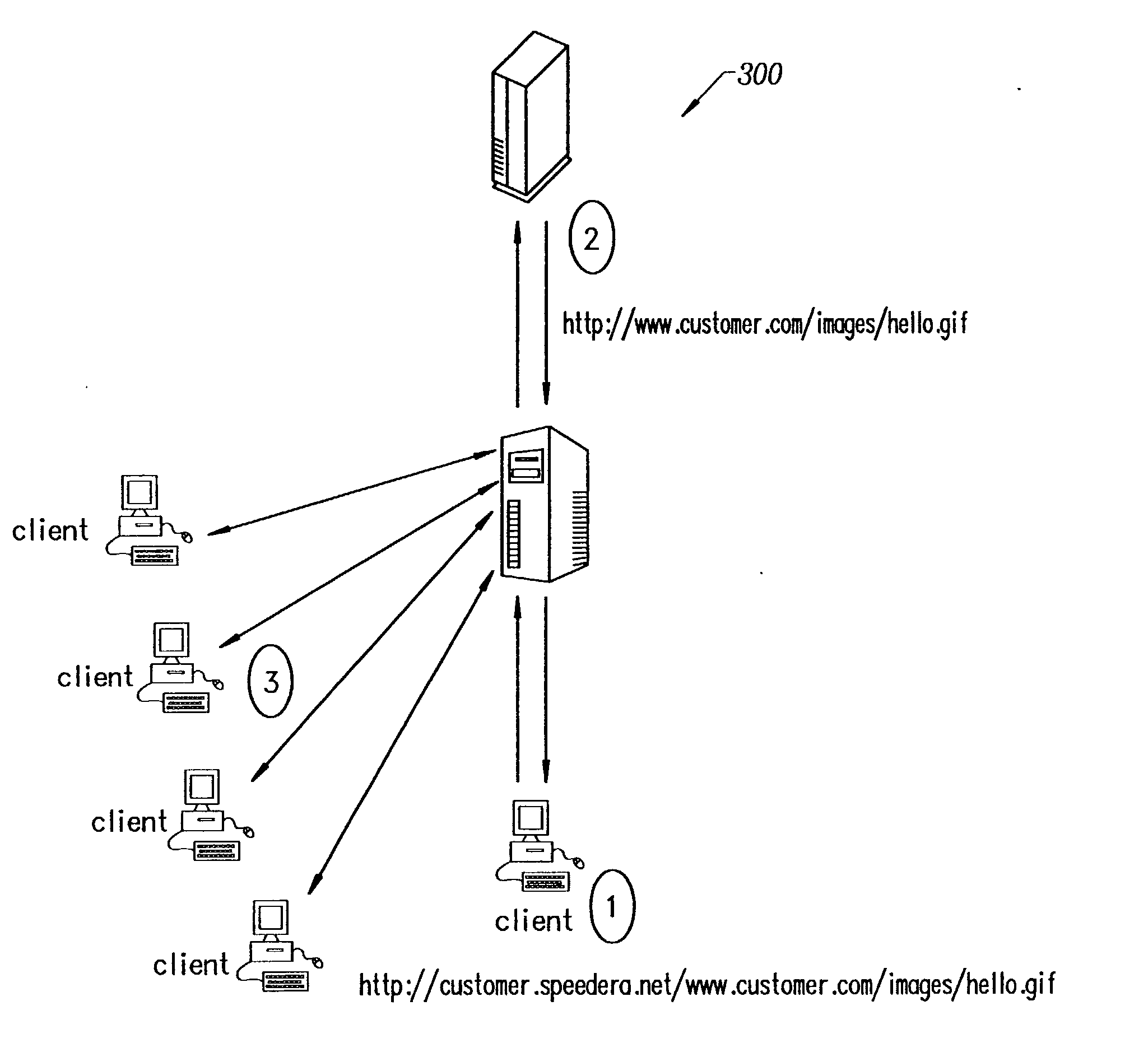
Secure content delivery system
InactiveUS20030097564A1Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsUser identity/authority verificationExpiration TimeRelevant information
A secure streaming content delivery system provides a plurality of content servers connected to a network that host customer content that can be cached and / or stored, e.g., images, video, text, and / or software. The content servers respond to requests for customer content from users. The invention load balances user requests for cached customer content to the appropriate content server. A user makes a request to a customer's server / authorization server for delivery of the customer's content. The authorization server checks if the user is authorized to view the requested content. If the user is authorized, then the authorization server generates a hash value using the authorization server's secret key, the current time, a time-to-live value, and any other information that the customer has configured, and embeds it into the URL which is passed to the user. A content server receives a URL request from the user for customer content cached on the content server. The request is verified by the content server creating its own hash value using the customer server's secret key, the current time, a time-to-live value, and any other related information configured for the customer. If the hash value from the URL matches the content server's generated hash value, then the user's request is valid and within the expiration time period and the content server delivers the requested content to the user.
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
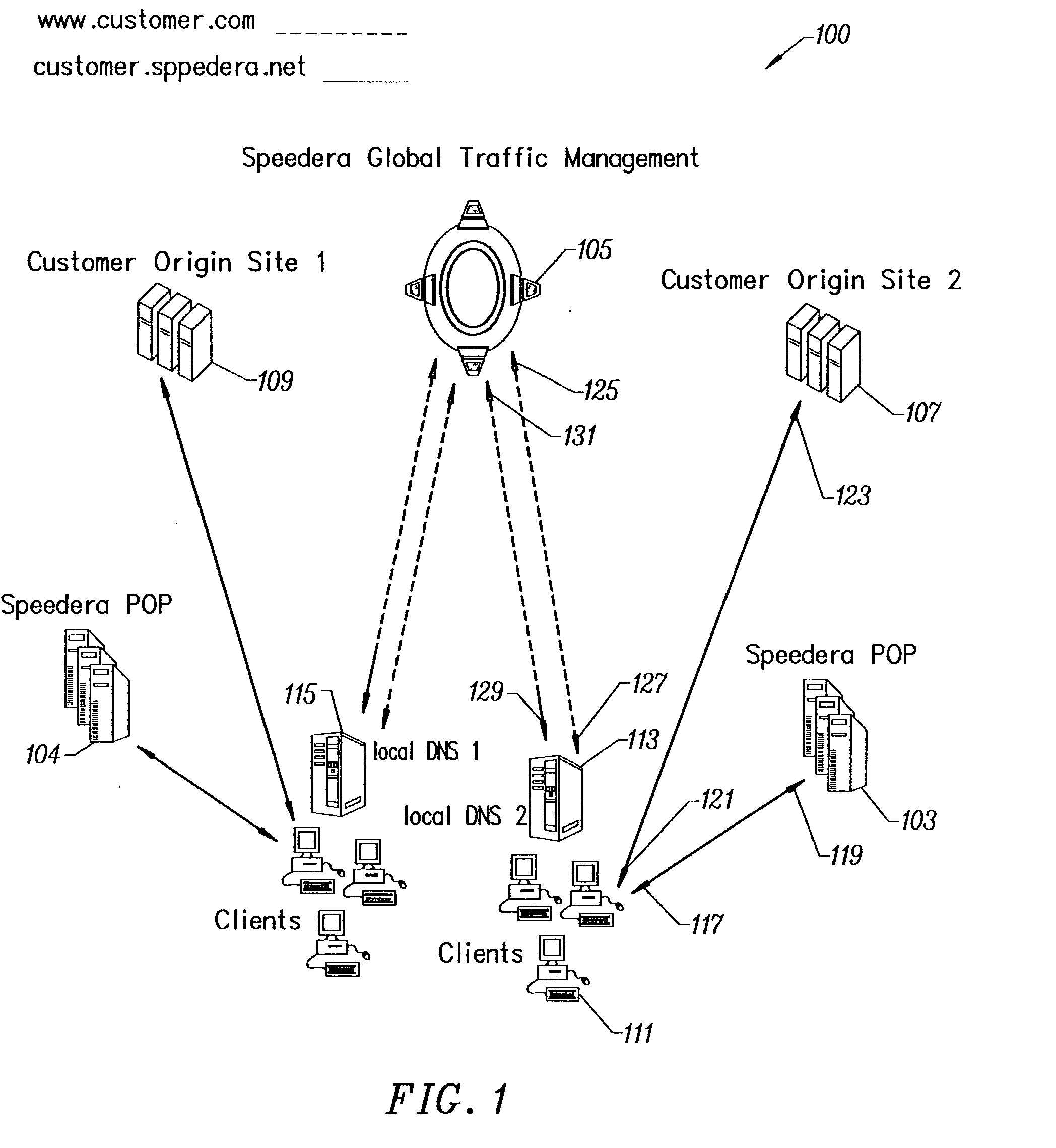
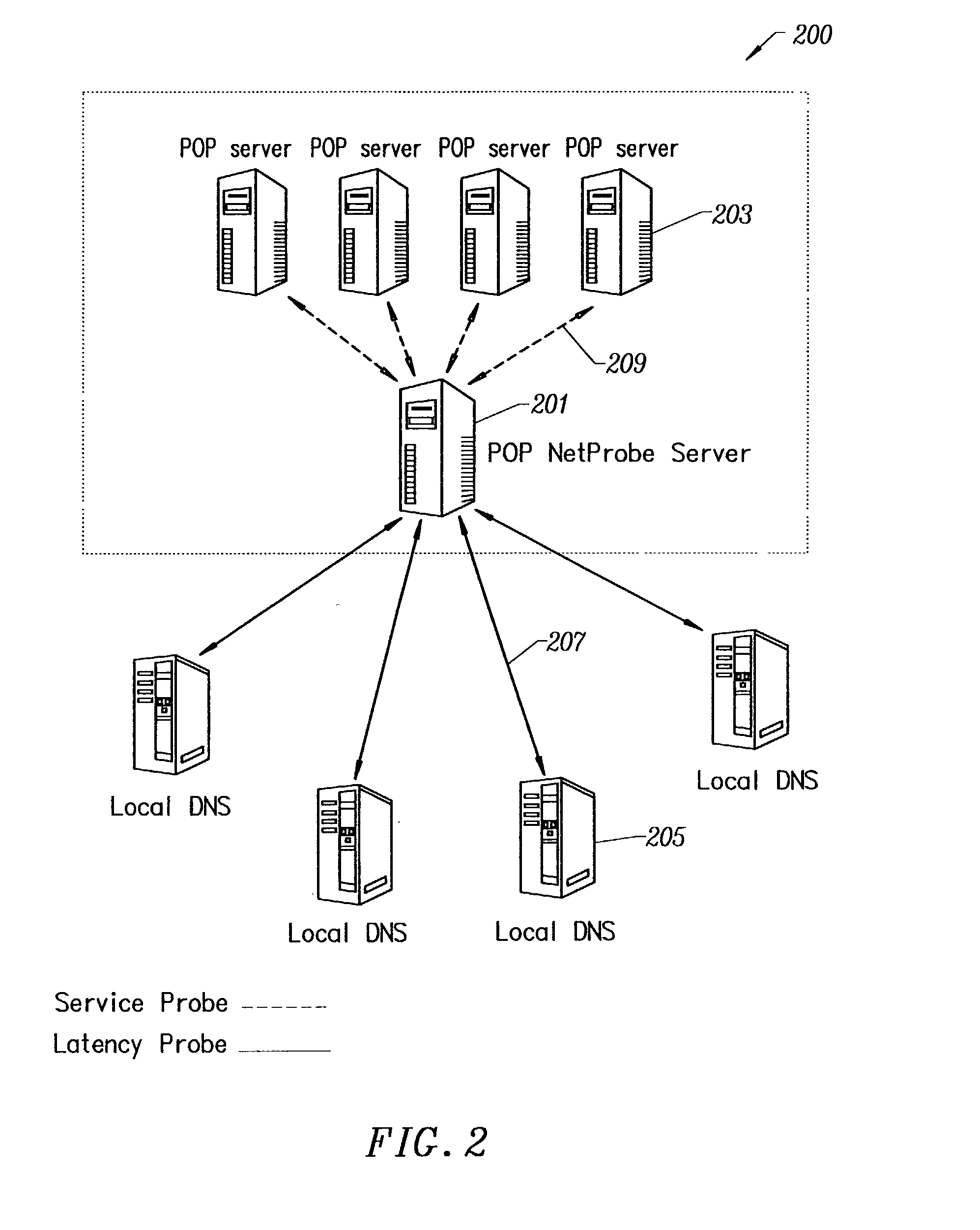
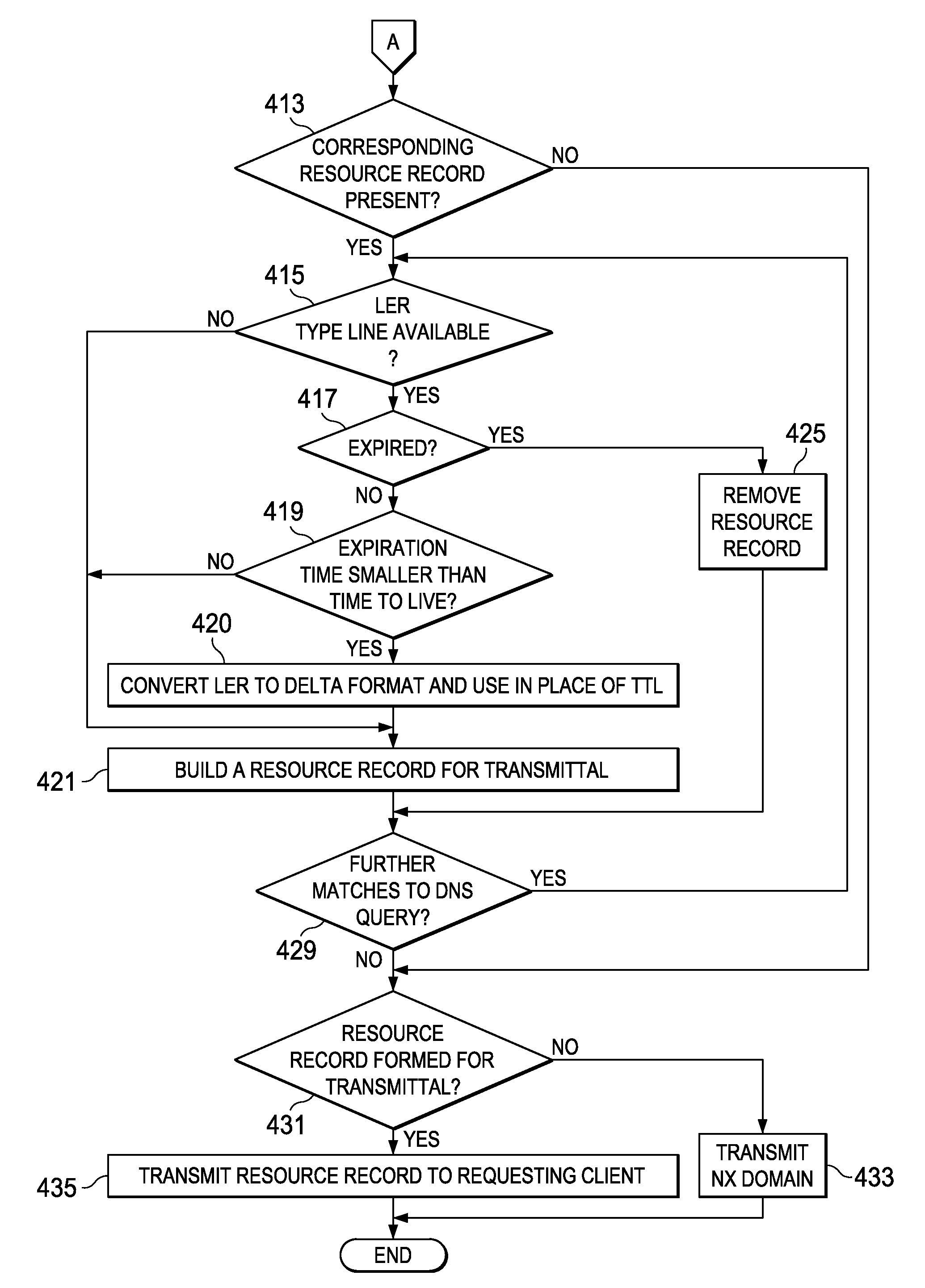
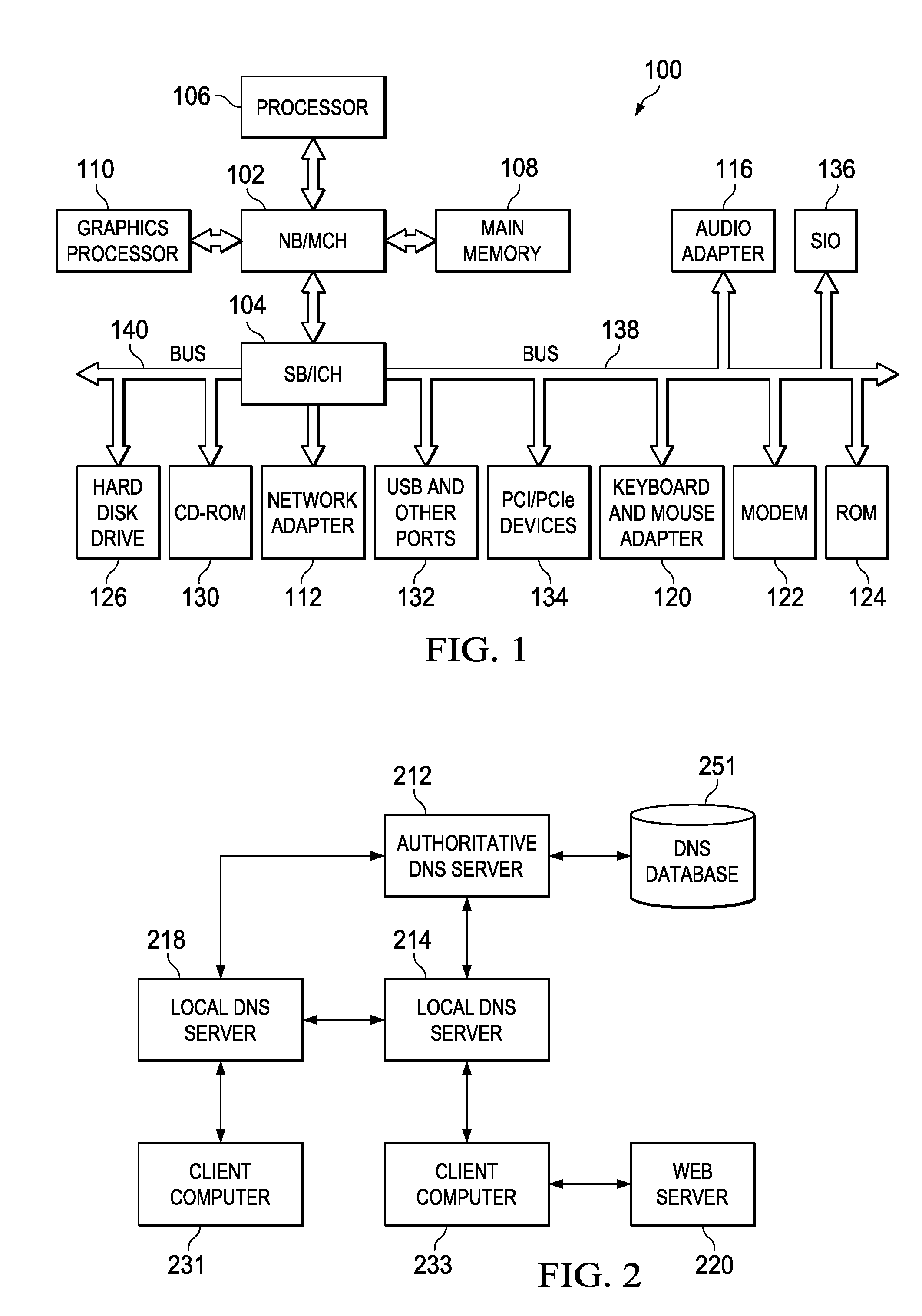
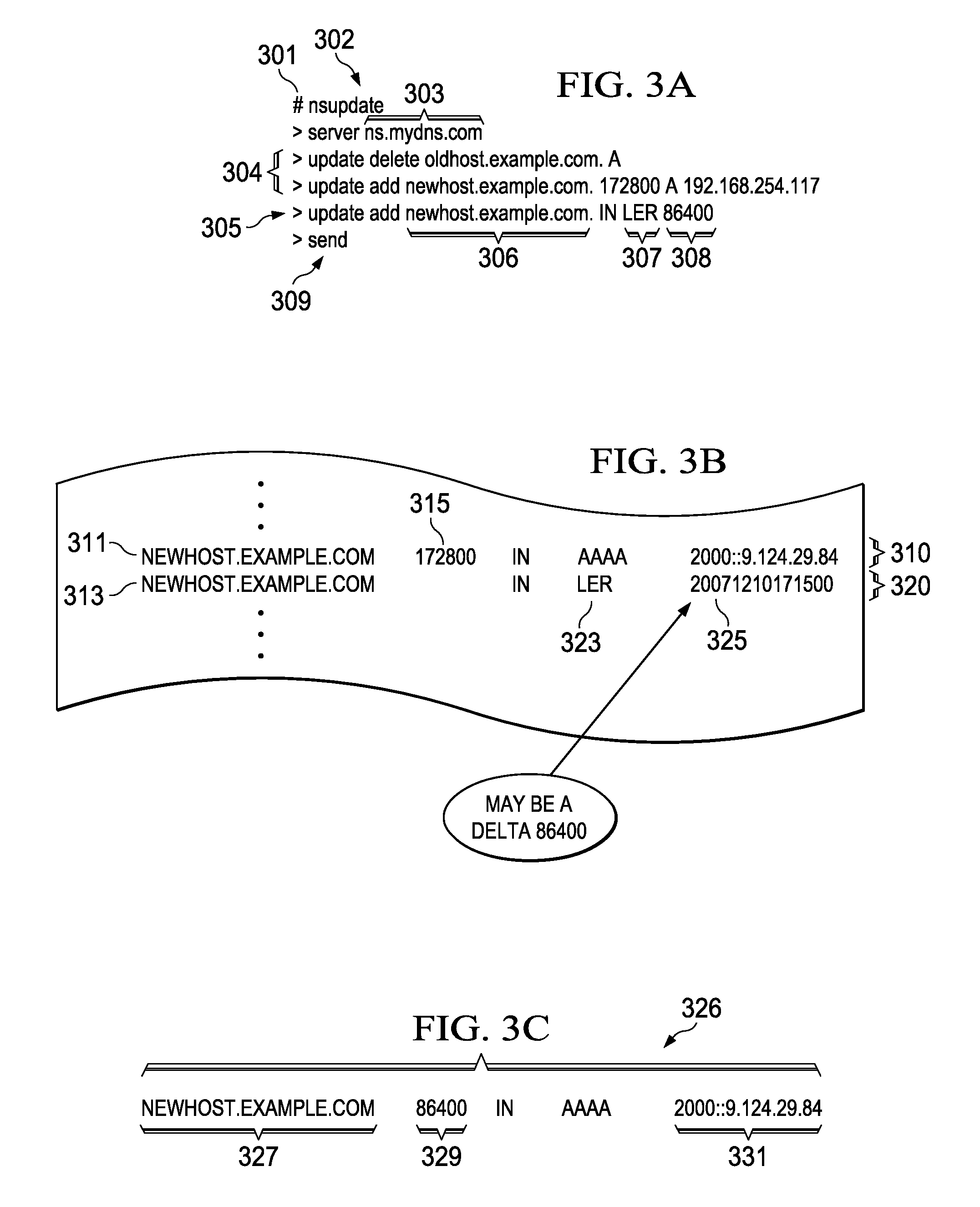
Dynamic expiration of domain name service entries
Disclosed is a computer implemented method and computer program product for transmitting a resource record to a requesting computer. An authoritative domain name server receives a DNS query from a requesting computer at a name server. The authoritative domain name server looks up the resource record based on the DNS query, wherein the resource record is associated with an epochal time and a time to live. The authoritative domain name server transmits the resource record response based on the epochal time.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Virtual machine based network carriers
InactiveUS20070079307A1Environment safetyTransmissionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData packData set
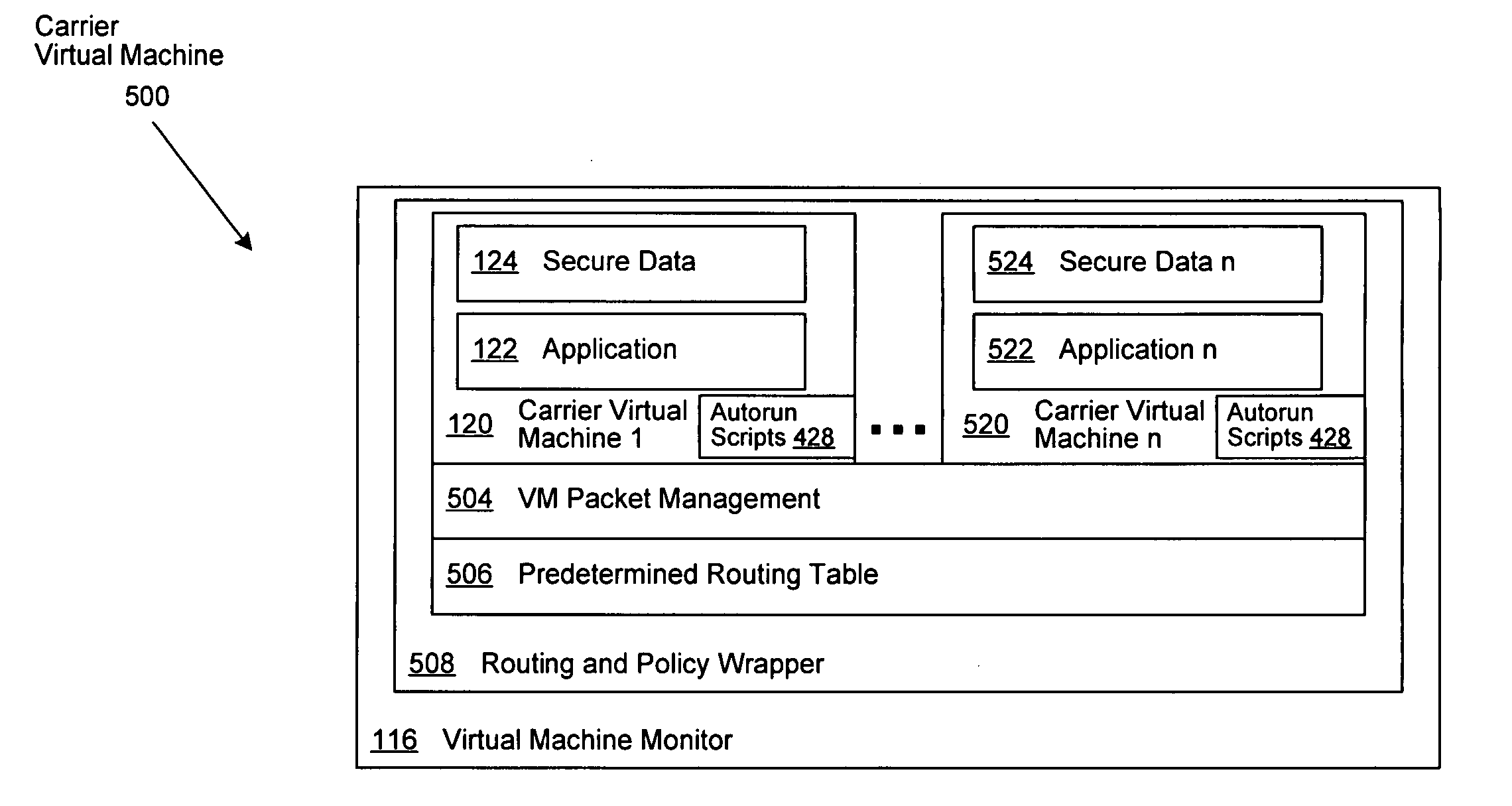
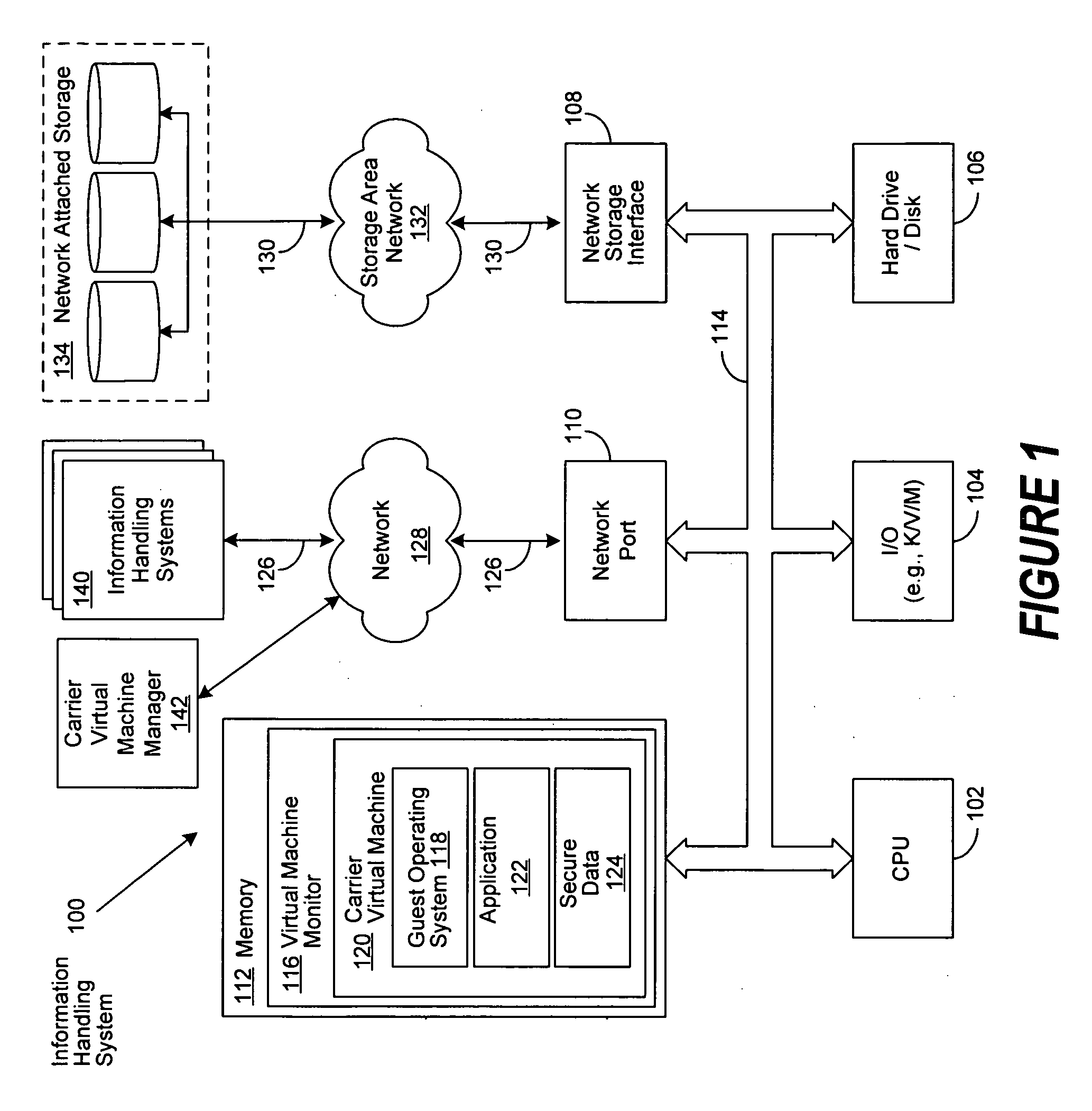
A system and method is disclosed for the secure transfer of data by carrier virtual machines between participating physical hosts through a virtual network (VNET) implemented on one or more internal and / or external networks. The method of the invention can provide additional security controls, comprising parameters that may include, but are not limited to, time-to-live (TTL), access control lists (ACLs), usage policies, directory roles, etc. Additionally, access to one or more of a plurality of carrier virtual machine payloads by security groups, individual access, subdivided individual access, and MIME-like subdivision of a VM-encapsulated payload may be controlled, thereby providing the carrier VM the ability to carry many secured payloads. In addition, VM packets, a group of packets, a single VM, or subpackets within a VM between network endpoints, or at a predetermined intermediary network point, may be quarantined to realize further security. Individual or combinations of these functionalities on carrier virtual machines, and by extension, application and / or one or more sets of secure data may be implemented.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
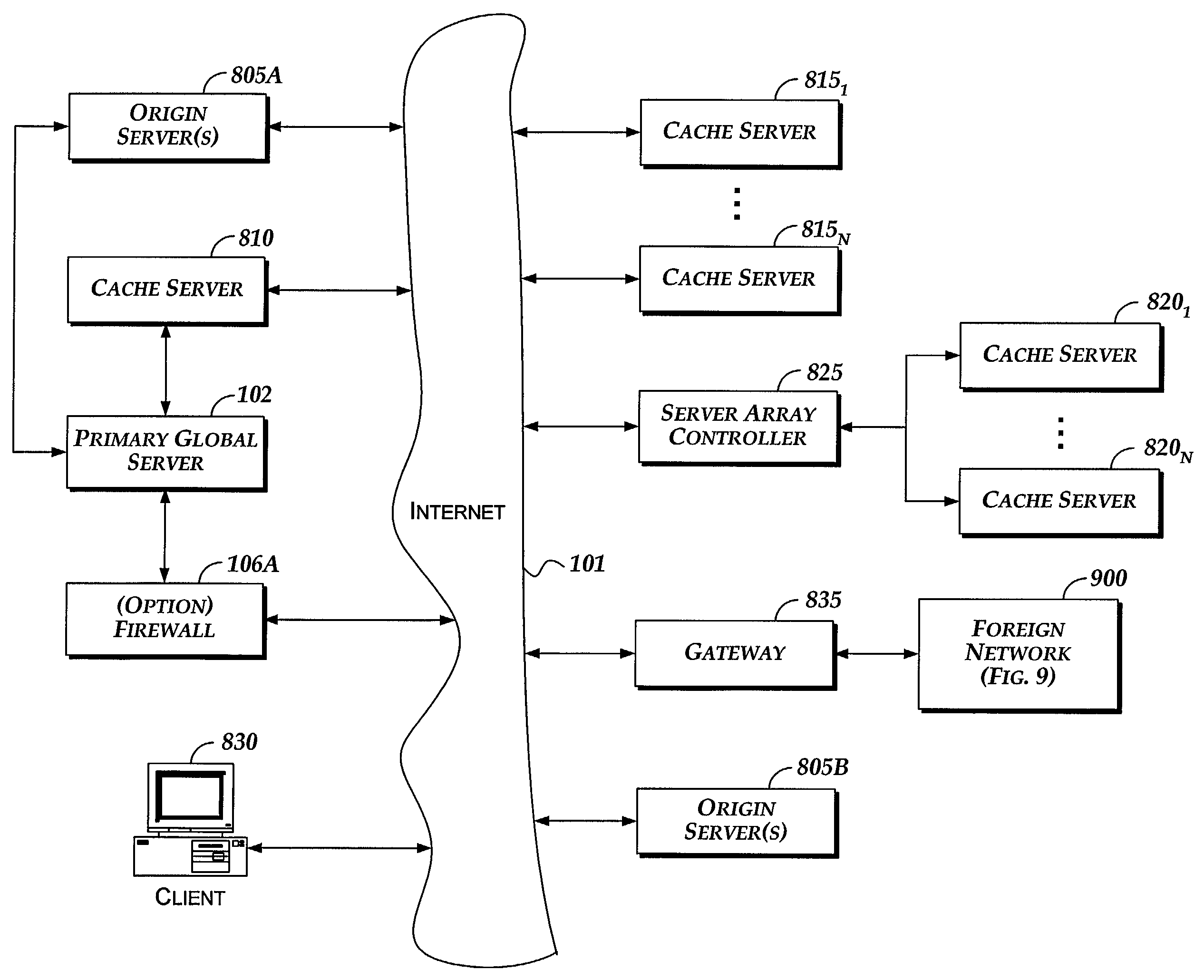
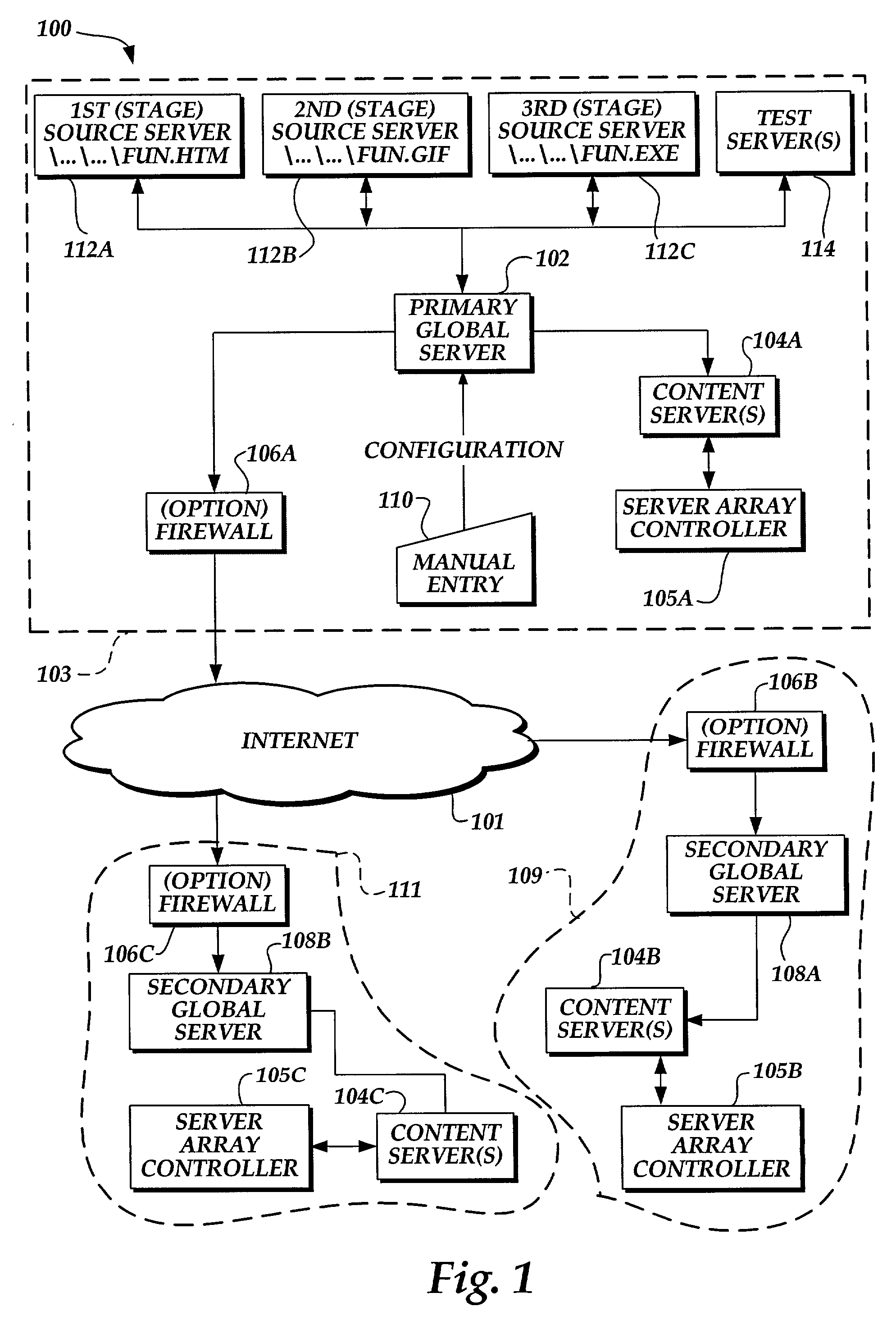
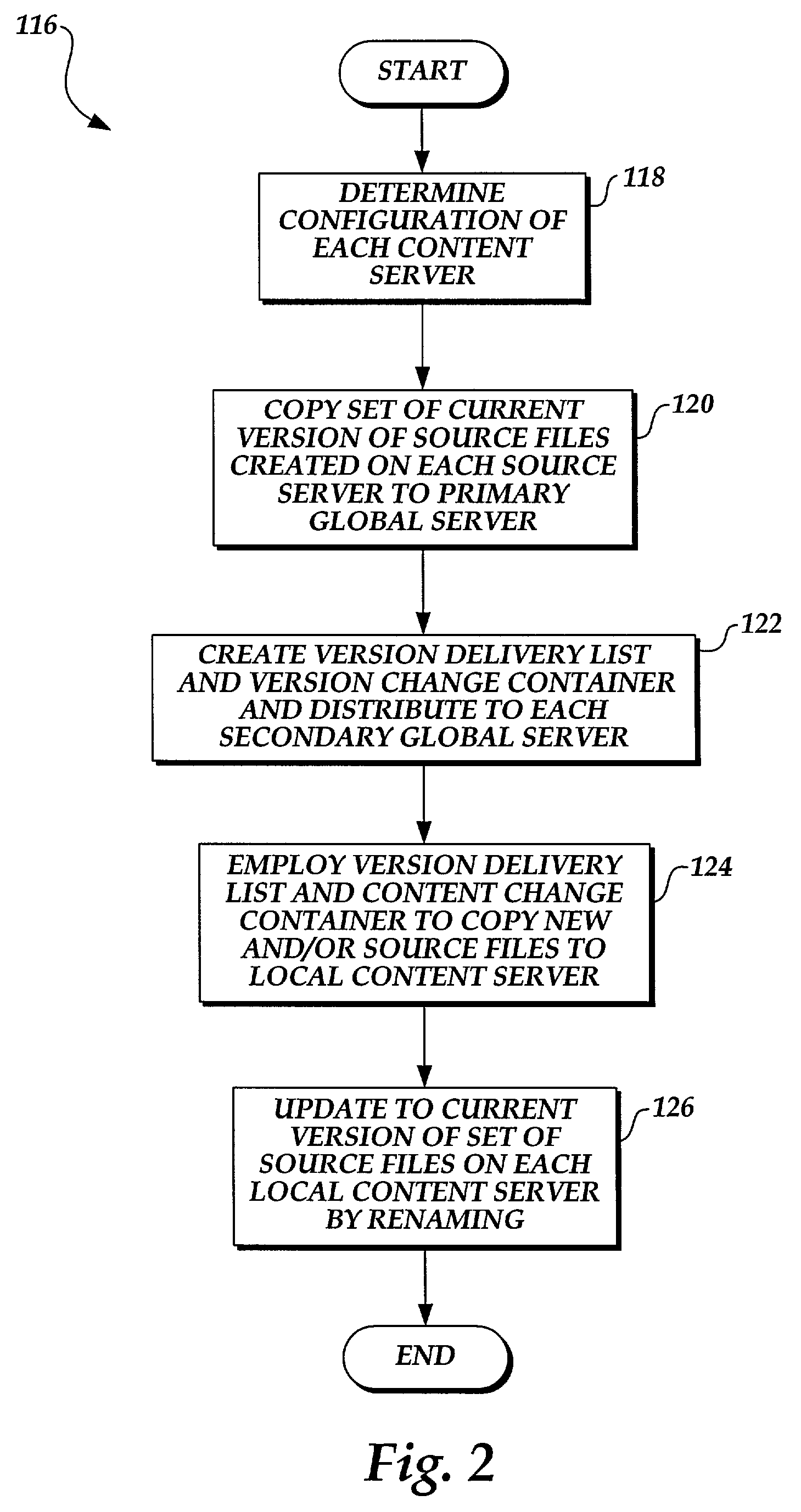
Method and system for automatically updating content stored on servers connected by a network
InactiveUS7113962B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalCache serverNetwork connection
A system and computer implementable method for updating content on servers coupled to a network. The method includes updating an origin server with a version of files used to provide content, retrieving data that indicates an action to be performed on one or more cache servers in conjunction with updating the origin server, and performing the action to update entries in the one or more cache servers. Each entry in each cache server is associated with a subset of the content on the origin server and may include an expiration field and / or a time to live field. An example of a subset of content to which a cache entry may be associated is a Web page. Cache servers are not required to poll origin servers to determine whether new content is available. Cache servers may be pre-populated using push or pull techniques.
Owner:F5 NETWORKS INC
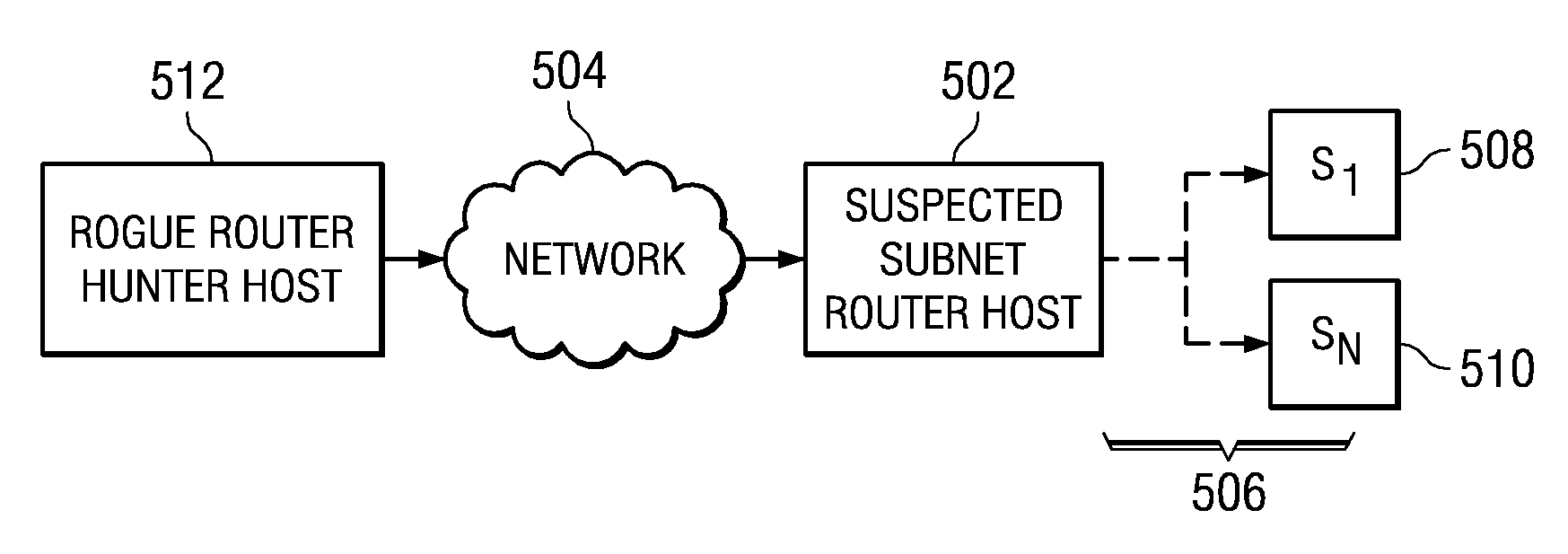
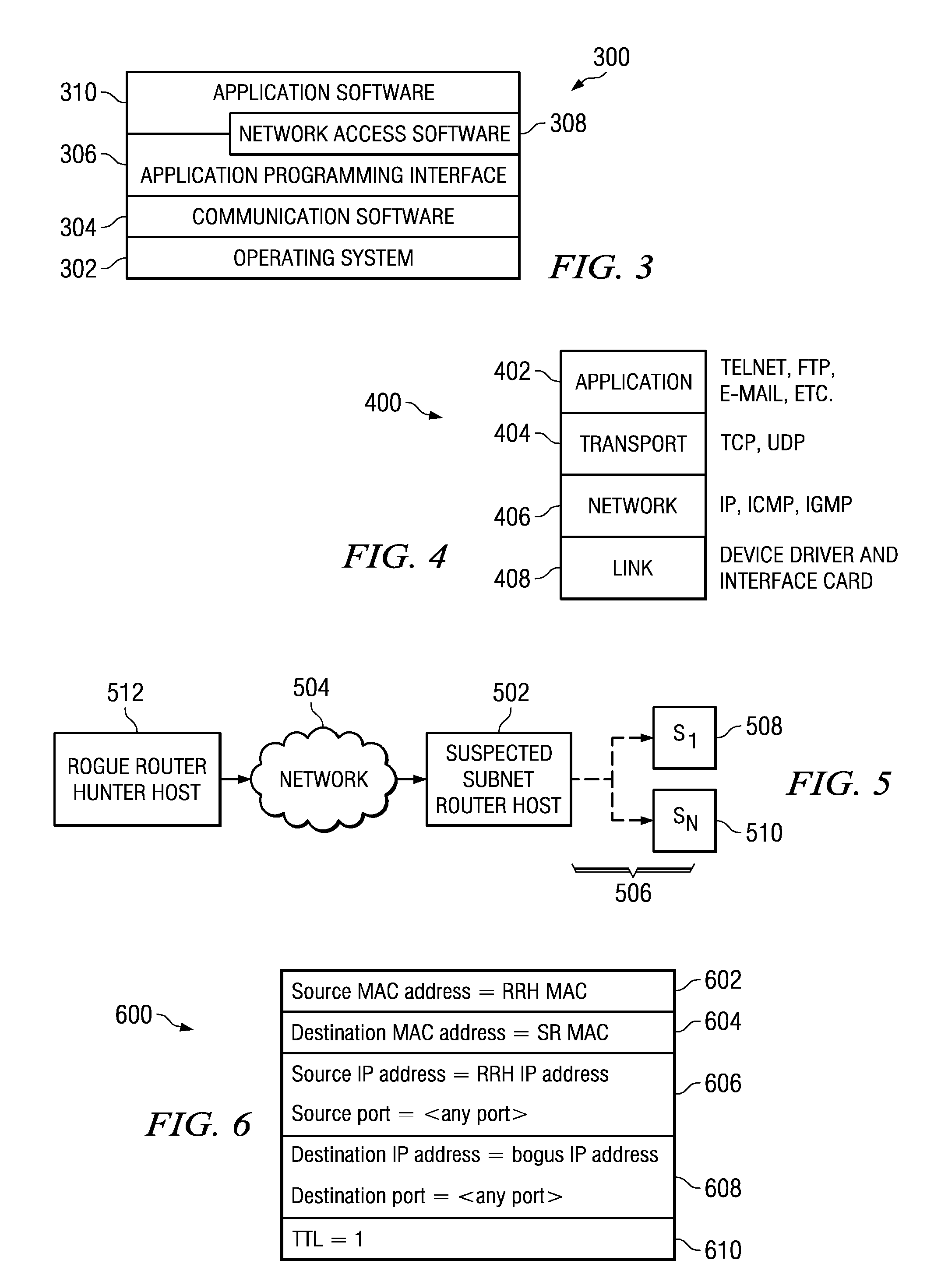
Rogue router hunter
InactiveUS7991877B2Digital computer detailsPlatform integrity maintainanceData processing systemTime limit
A computer implemented method, data processing system, and computer program product for discovering an unauthorized router in a network. The process in the illustrative embodiments first obtains a physical address of a suspected router or destination device. A data packet is created which comprises at least a destination media access control field, a destination internet protocol field, and a time-to-live field, wherein the destination media access control field comprises the physical address of the destination device, wherein the destination internet protocol field comprises a bogus internet protocol address, and wherein the time-to-live field comprises a value indicating the data packet has exceeded a time limit. The data packet is sent to the destination device using the physical address in the destination media access control field. If a time exceeded message is received from the destination device, the destination device is determined to be enabled for routing.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Fully Distributed Routing over a User-Configured On-Demand Virtual Network for Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) on Hybrid Cloud Networks
A layer-3 virtual router connects two or more virtual networks. Virtual networks are overlaid upon physical networks. Each virtual network (VN) is a layer-2 network that appears to expand an organization's LAN using virtual MAC addresses. The network stack forms a virtual-network packet with a virtual gateway MAC address of the virtual router to reach a remote virtual network. A VN device driver shim intercepts packets and their virtual MAC and IP addresses and encapsulates them with physical packets sent over the Internet. A VN switch table is expanded to include entries for nodes on the remote virtual network so that all nodes on both virtual networks are accessible. A copy of the VN switch table is stored on each node by a virtual network management daemon on the node. A Time-To-Live field in the virtual-network packet is decremented for each virtual hop and a checksum recalculated.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
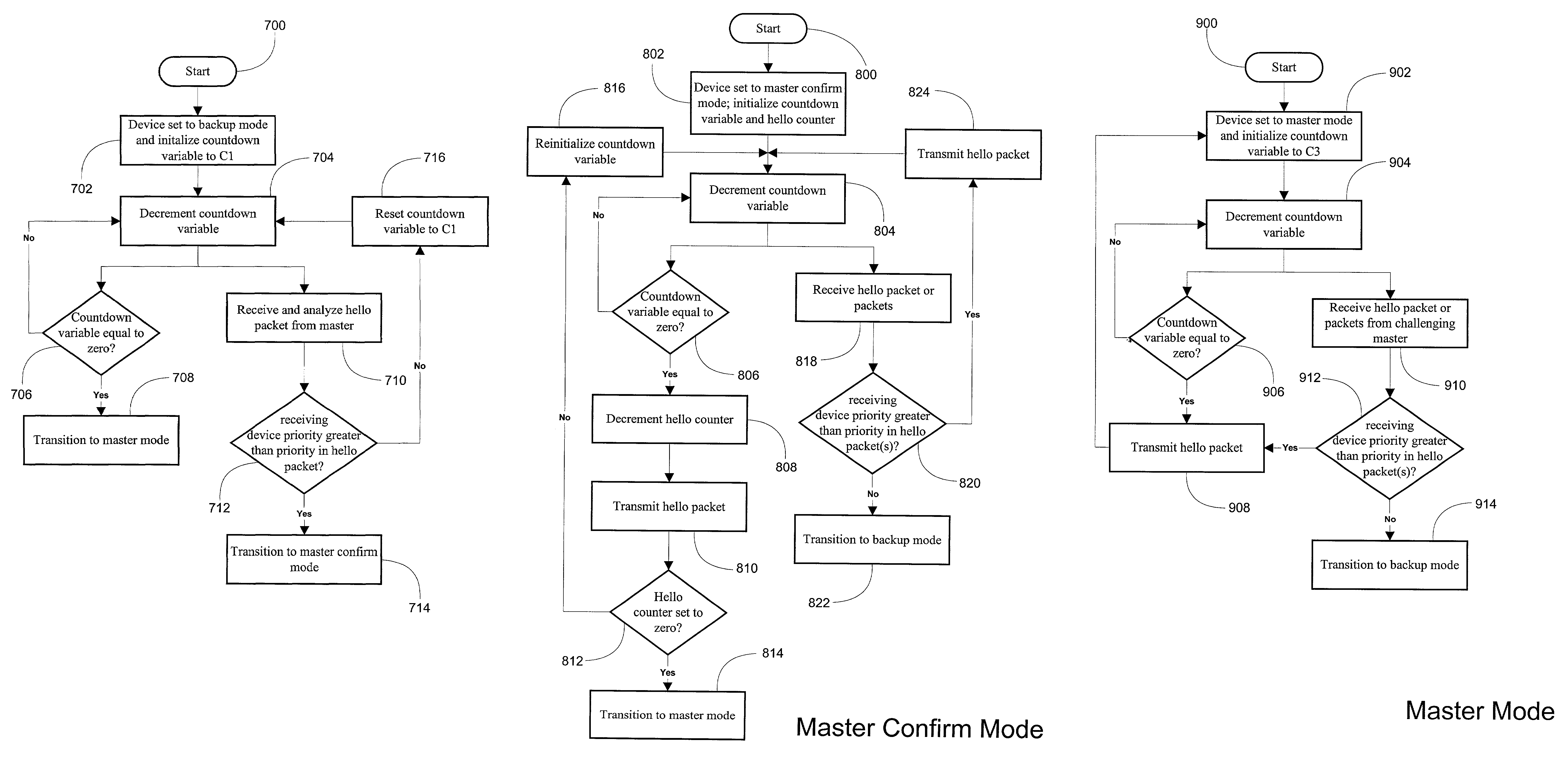
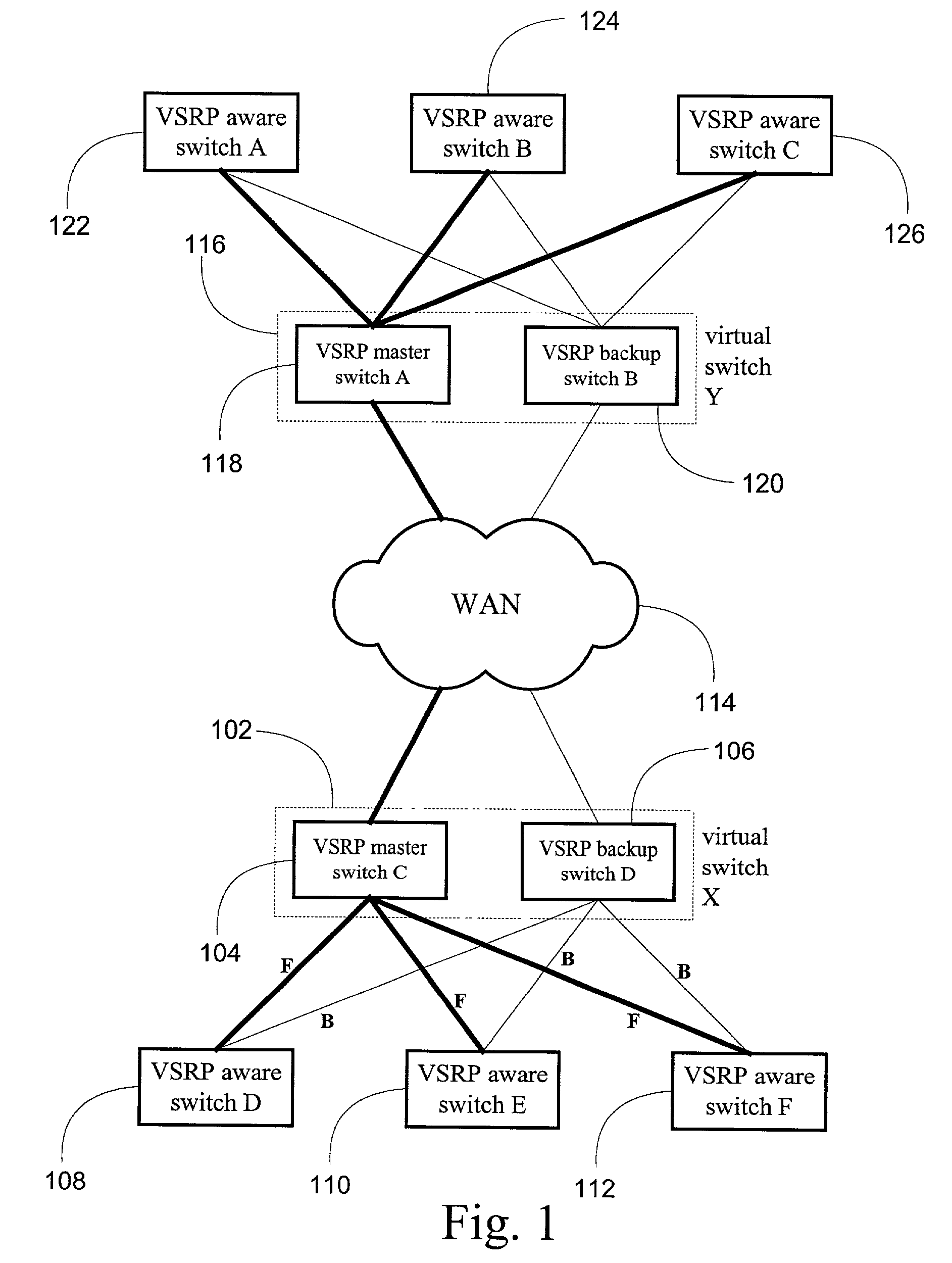
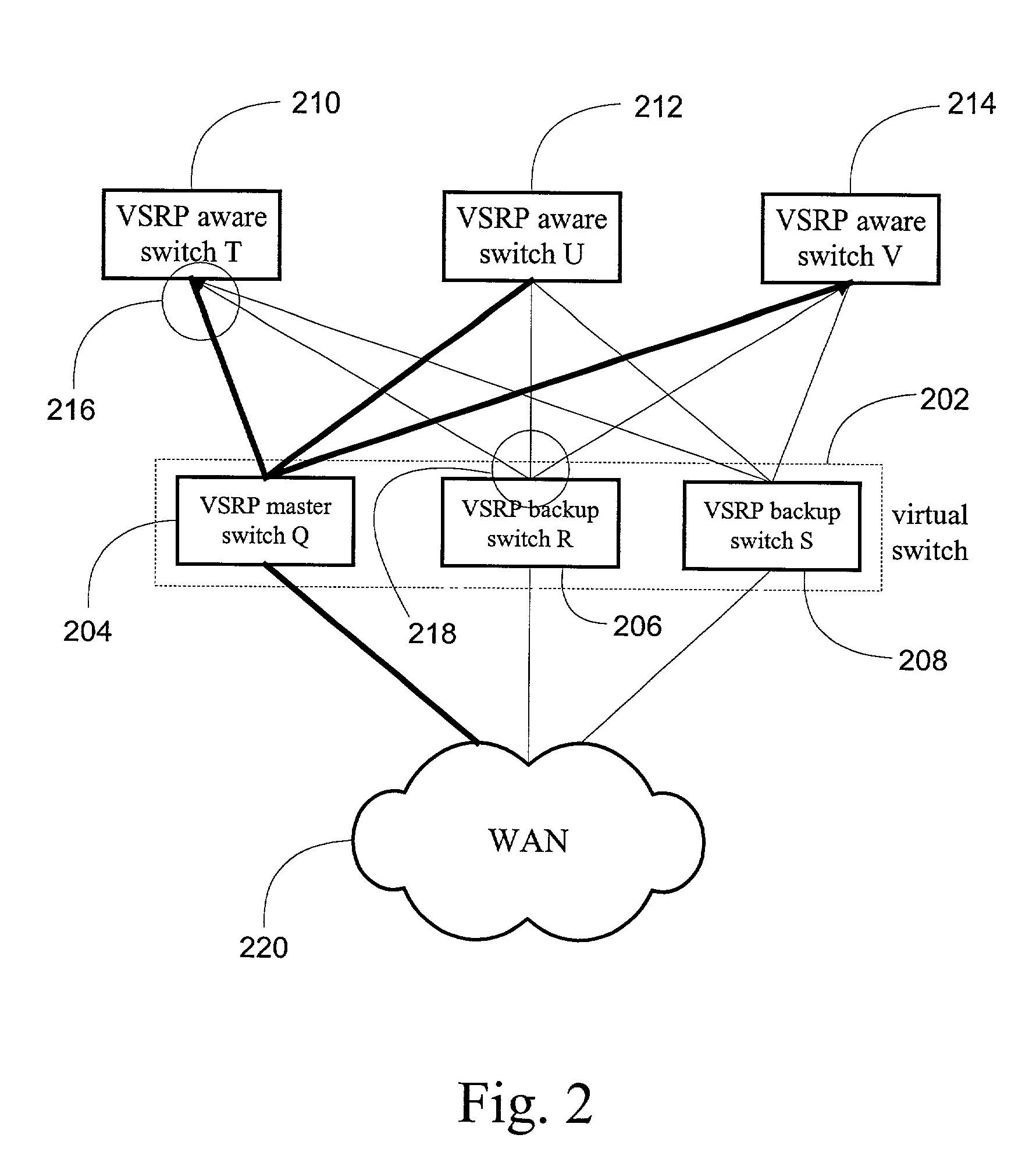
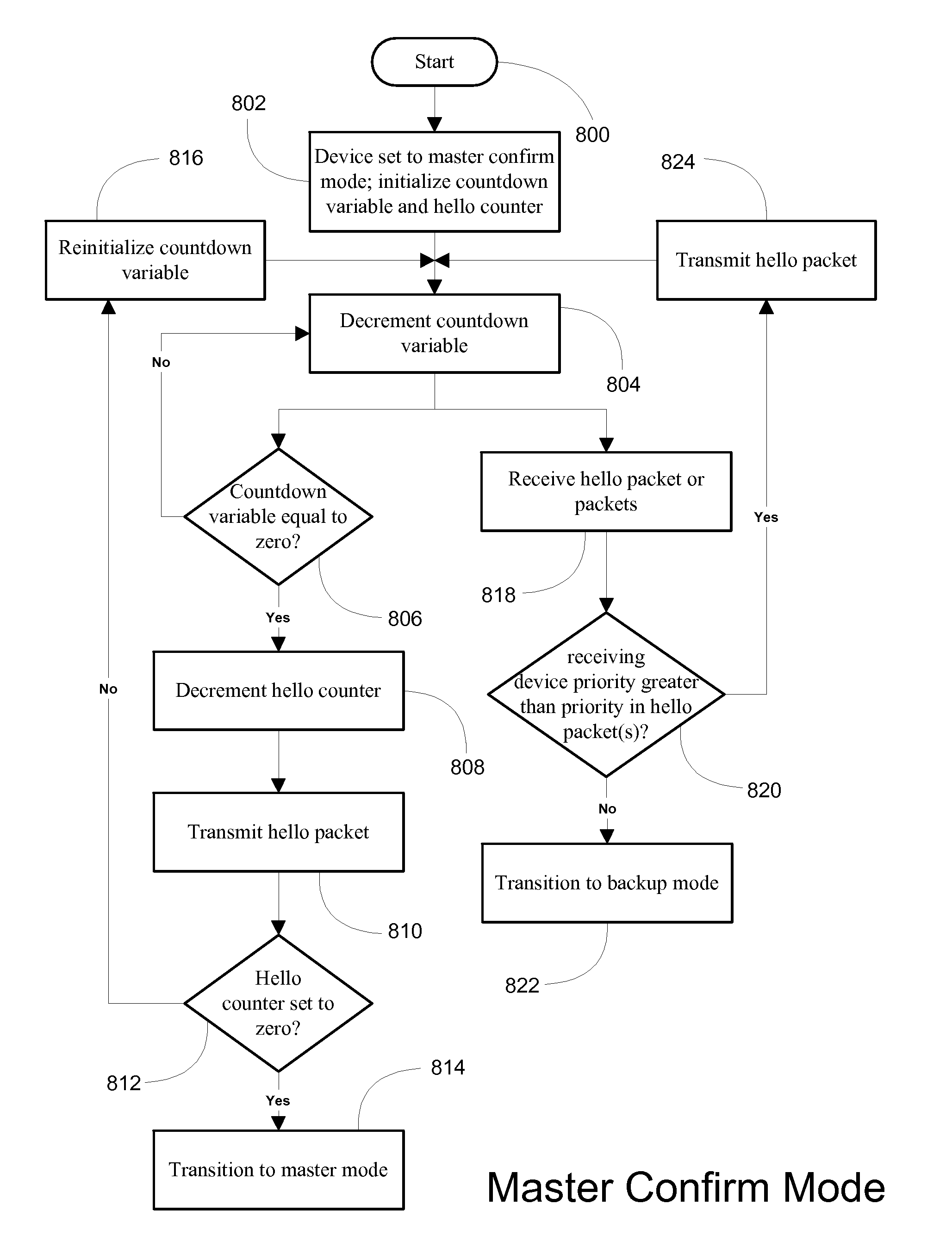
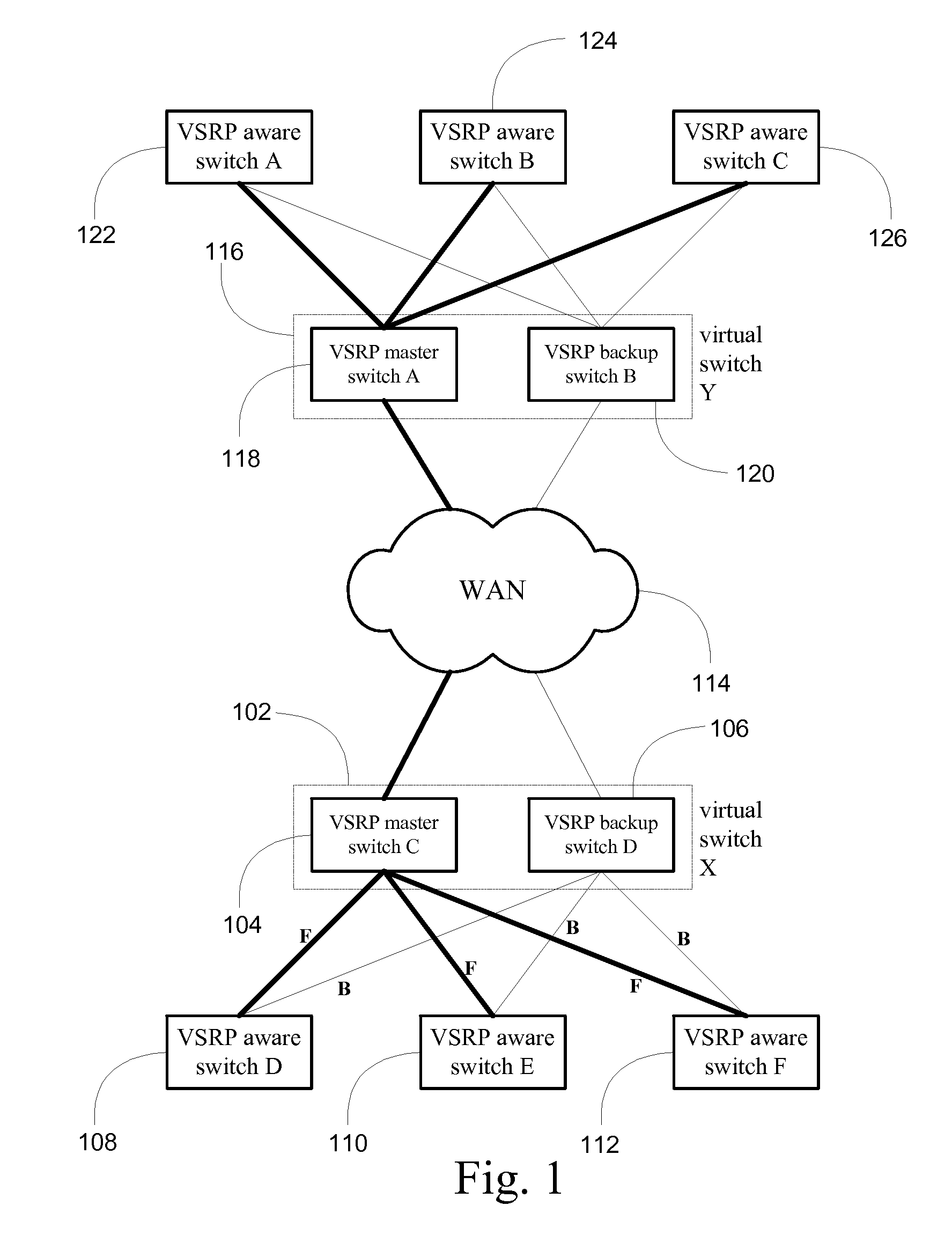
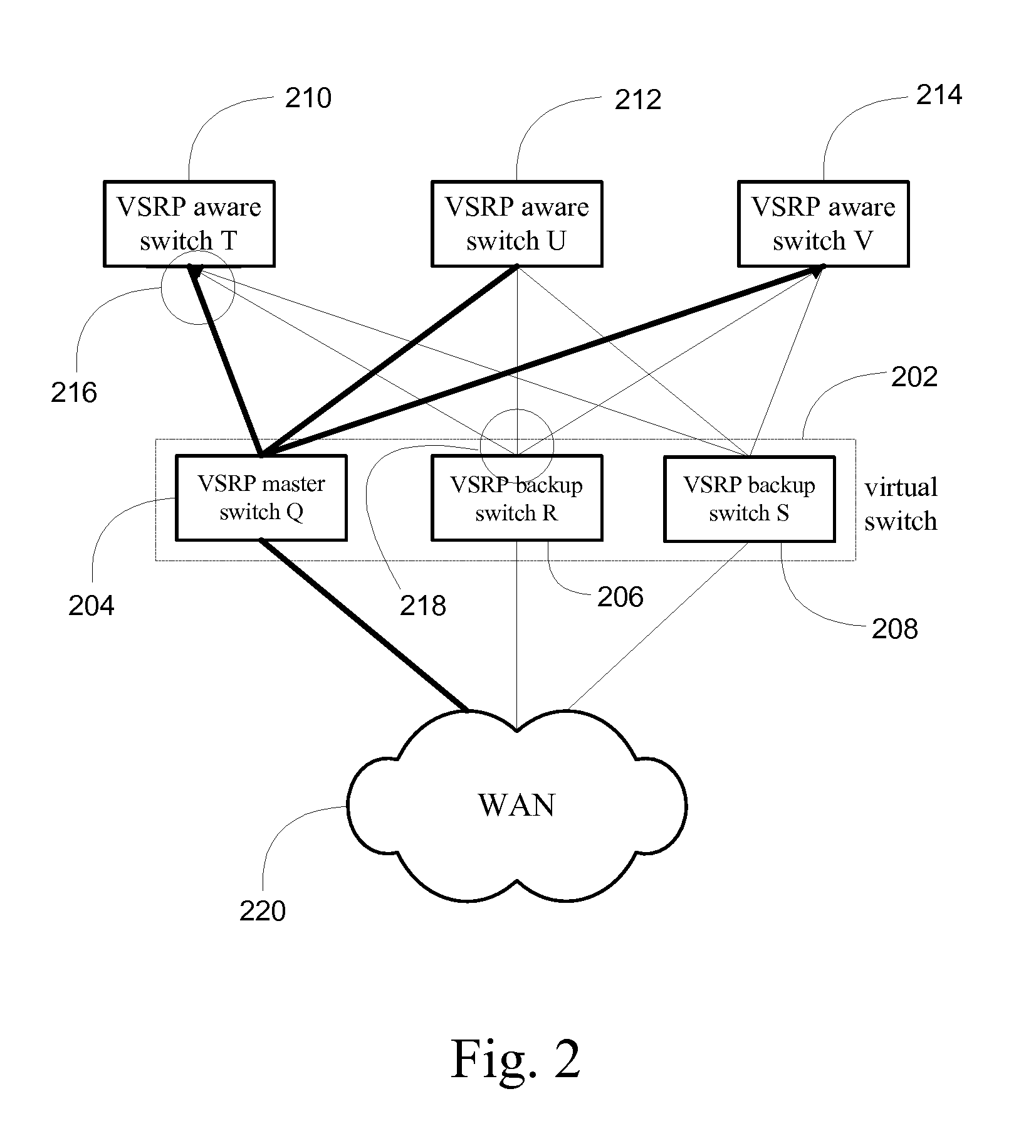
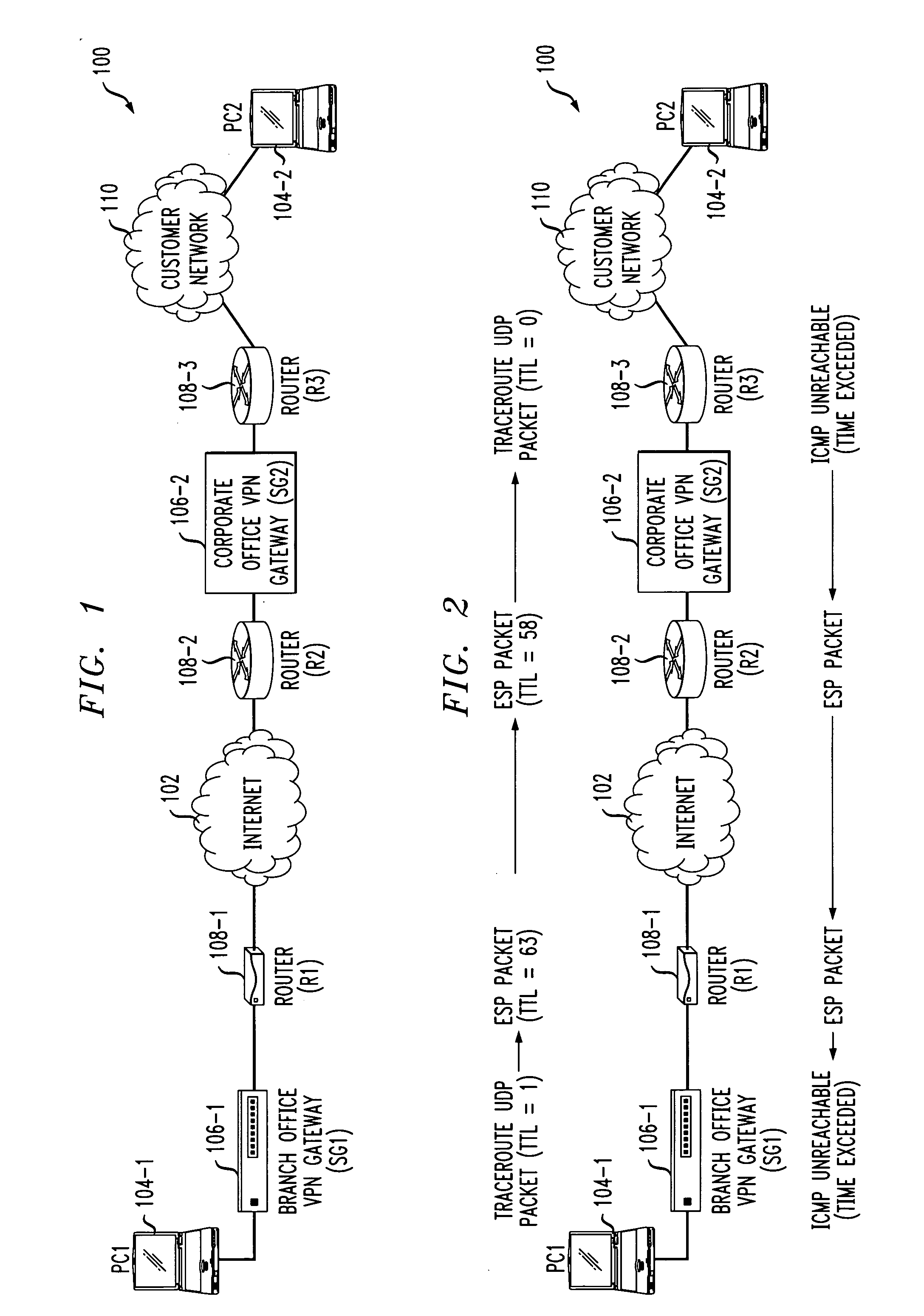
System and method for providing network route redundancy across Layer 2 devices
ActiveUS7209435B1Provides redundancyMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTier 2 networkVirtual switch
Systems and methods are described for providing network route redundancy through Layer 2 devices, such as a loop free Layer 2 network having a plurality of switching devices. A virtual switch is coupled to the loop free Layer 2 network, the virtual switch having two or more switches configured to transition between master and backup modes to provide redundant support for the loop free Layer 2 network, the switches communicating their status through use of a plurality of redundancy control packets. The system also includes means for allowing the redundancy control packets to be flooded through the Layer 2 network. The means may include time-to-live data attached to the redundancy control packet which is decremented only when the packets are transferred through devices which are configured to recognize the protocol used in redundancy control packets.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method for providing network route redundancy across layer 2 devices
InactiveUS7558195B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTier 2 networkVirtual switch
Systems and methods are described for providing network route redundancy through Layer 2 devices, such as a loop free Layer 2 network having a plurality of switching devices. A virtual switch is coupled to the loop free Layer 2 network, the virtual switch having two or more switches configured to transition between master and backup modes to provide redundant support for the loop free Layer 2 network, the switches communicating their status through use of a plurality of redundancy control packets. The system also includes means for allowing the redundancy control packets to be flooded through the Layer 2 network. The means may include time-to-live data attached to the redundancy control packet which is decremented only when the packets are transferred through devices which are configured to recognize the protocol used in redundancy control packets.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
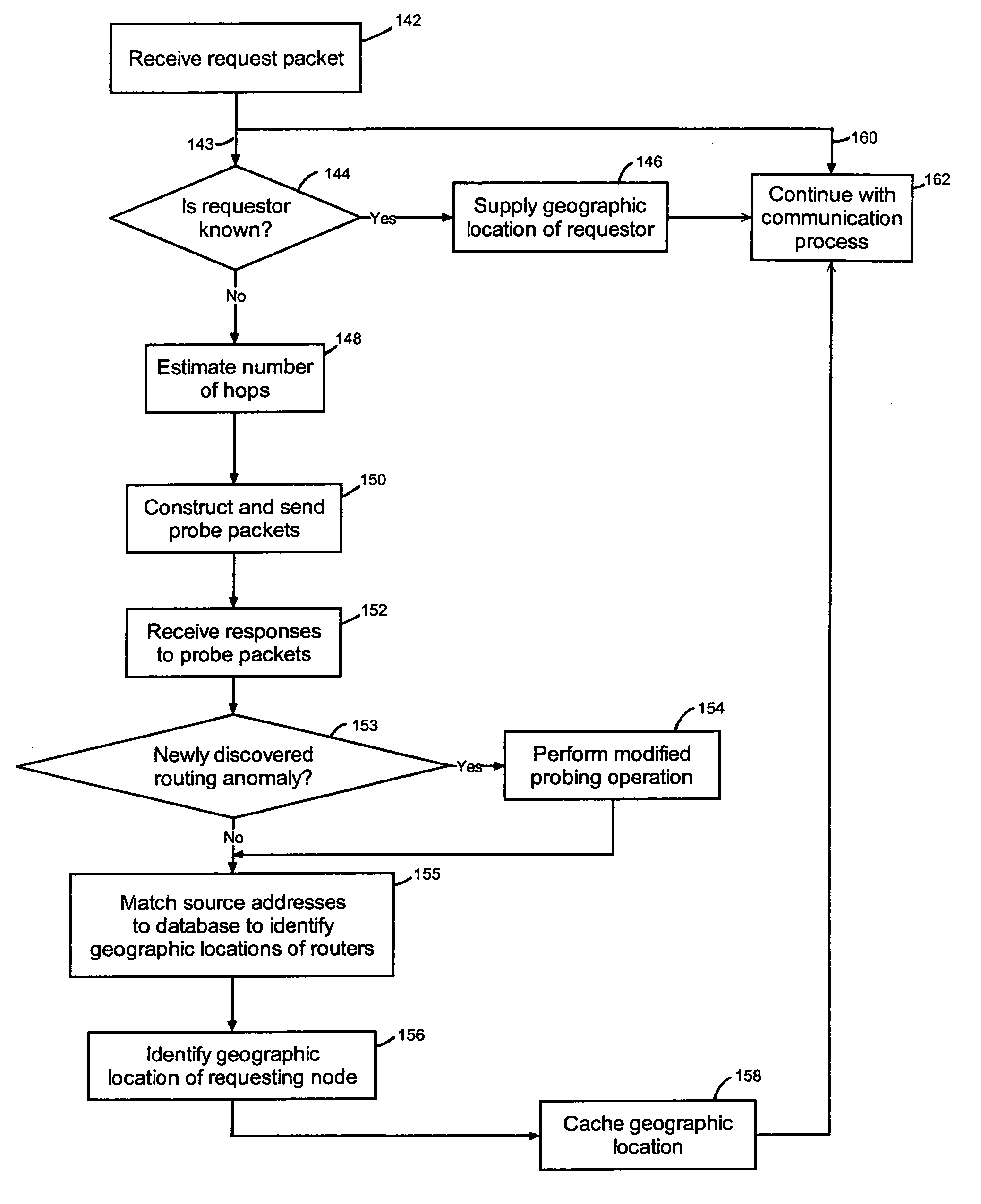
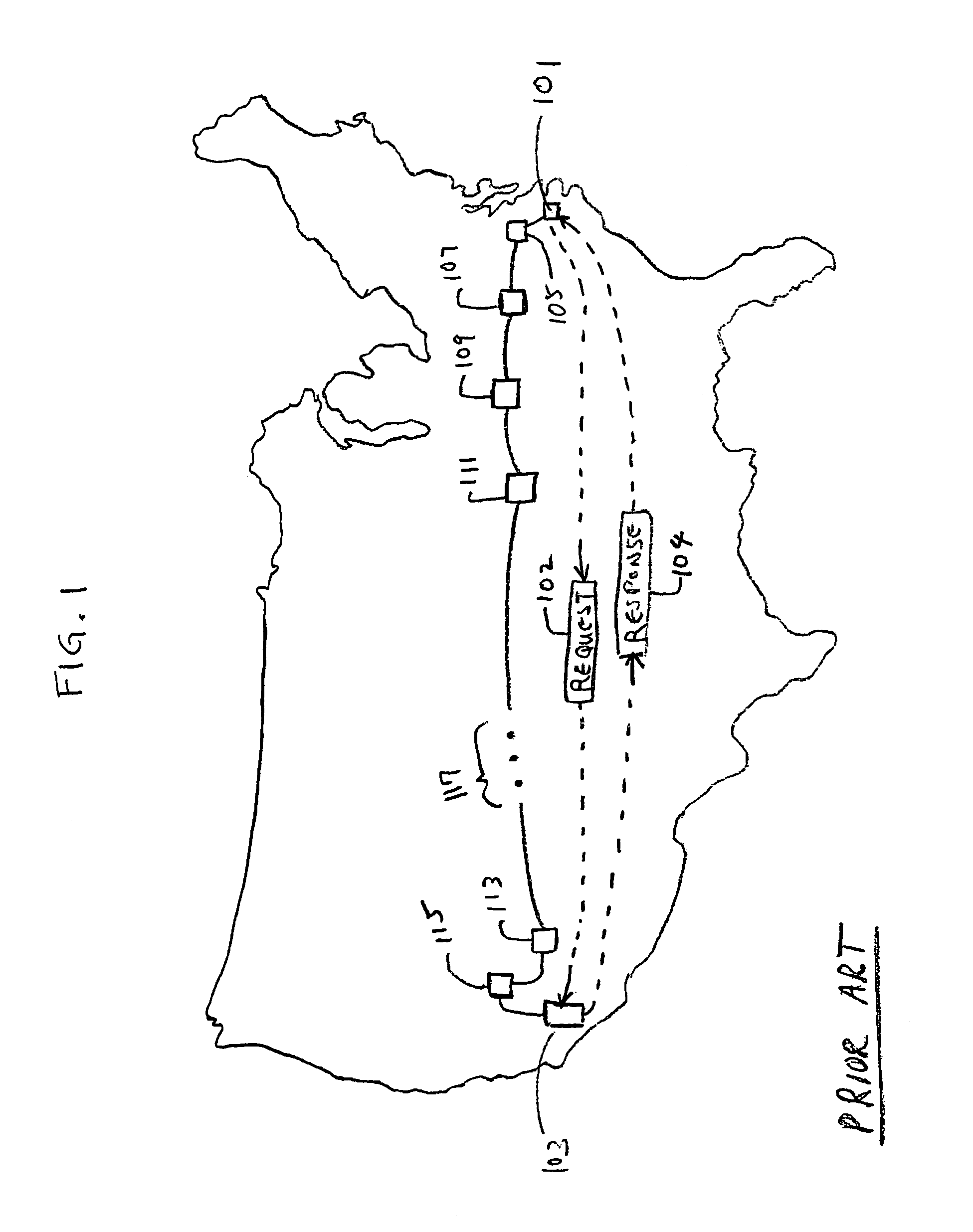
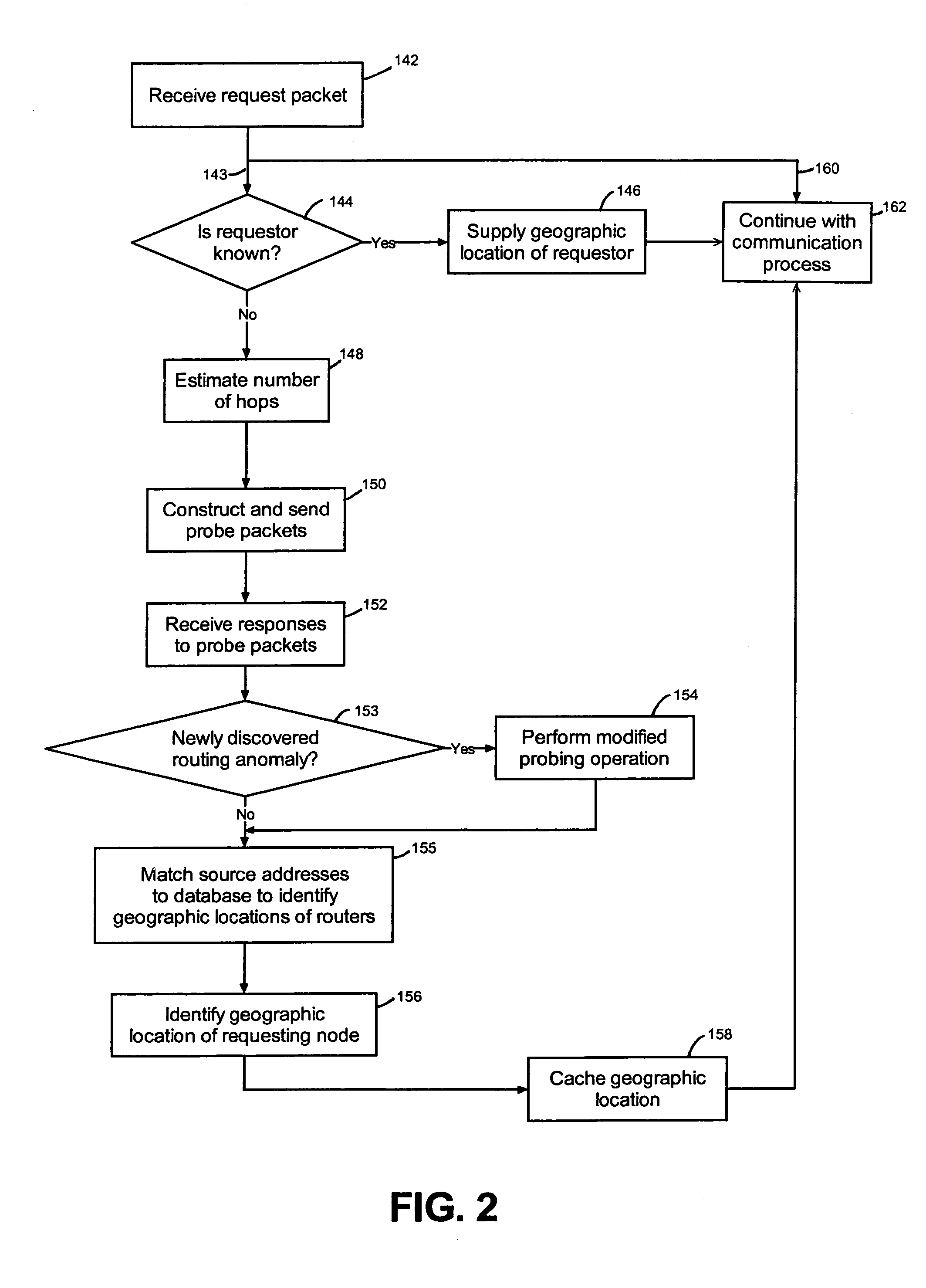
Determining the geographic location of a network device
InactiveUS7200673B1Short maintenance periodProvide informationDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsGeolocationTime to live
Owner:RESOURCE CONSORTIUM LTD LLC
Time-Related Power Systems
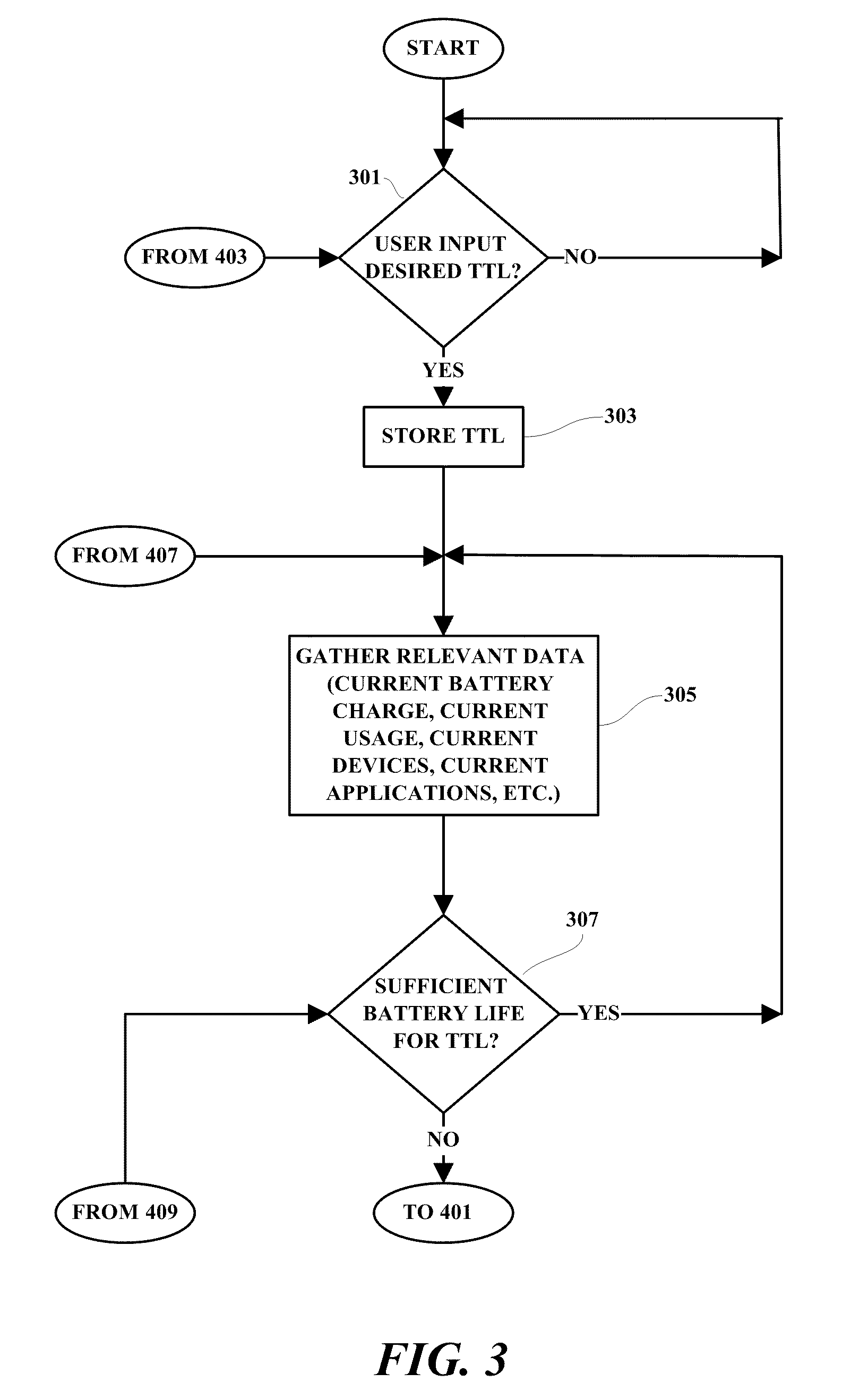
A method, programmed medium and system are disclosed which provide for user-controlled management of power requirements for mobile devices. The system dynamically adjusts power settings according to goals set by the end user. The end user specifies a time-to-live goal in hours, minutes or a predetermined date / time and the power management function continuously monitors and adjusts power components to meet that goal.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fault tolerance approaches for DNS server failures
ActiveUS20100332680A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksDomain nameIndefinite time
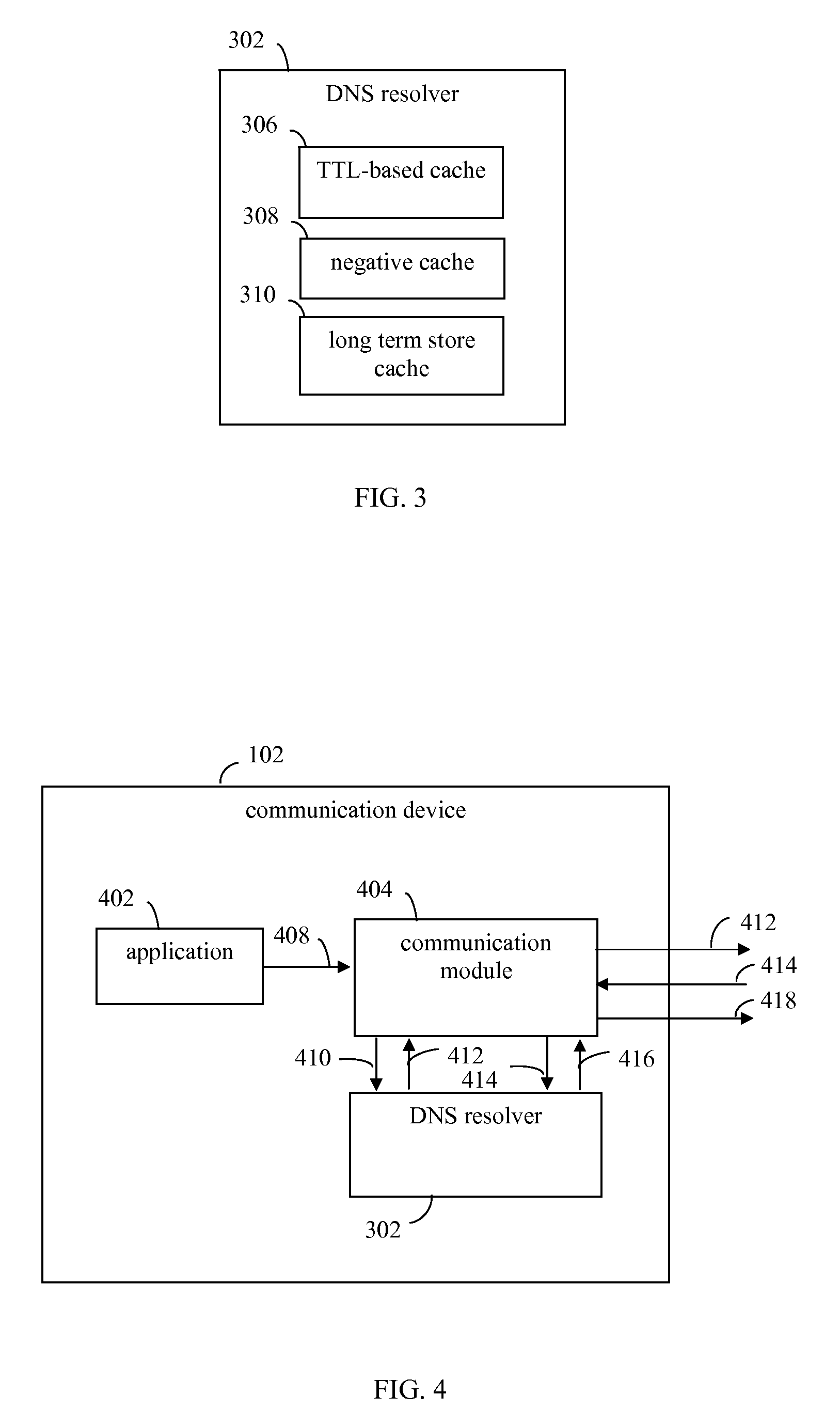
Techniques are provided for handling failures of DNS (domain name system) servers to respond to DNS queries. A DNS resolver is configured to resolve domain names, and includes a time-to-live (TTL)-based cache, a negative cache, and a long term store cache. The TTL-based cache is configured to temporarily store domain names with resolved IP addresses. The negative cache is configured to store negative entries that include information indicating domain names that were failed to be resolved. The long term store cache is configured to store domain names with resolved IP address for an indefinite time period. The caches are accessed in a manner that enables fewer DNS query retries to be performed when a DNS server is non-responsive, to reduce delays and network traffic. Furthermore, the DNS resolver may reduce a number of DNS queries performed the longer the DNS server stays non-responsive.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Path detection in trill networks
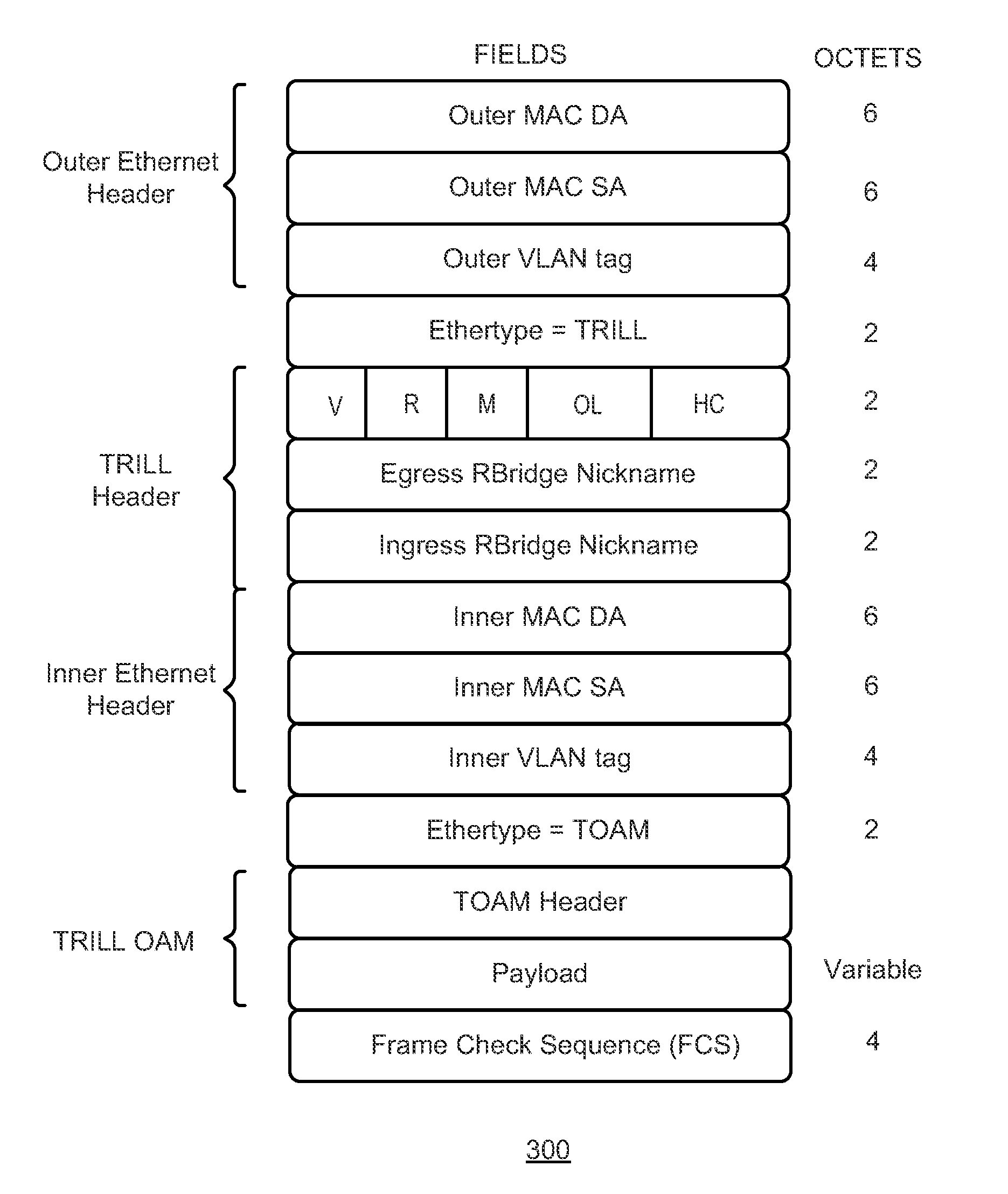
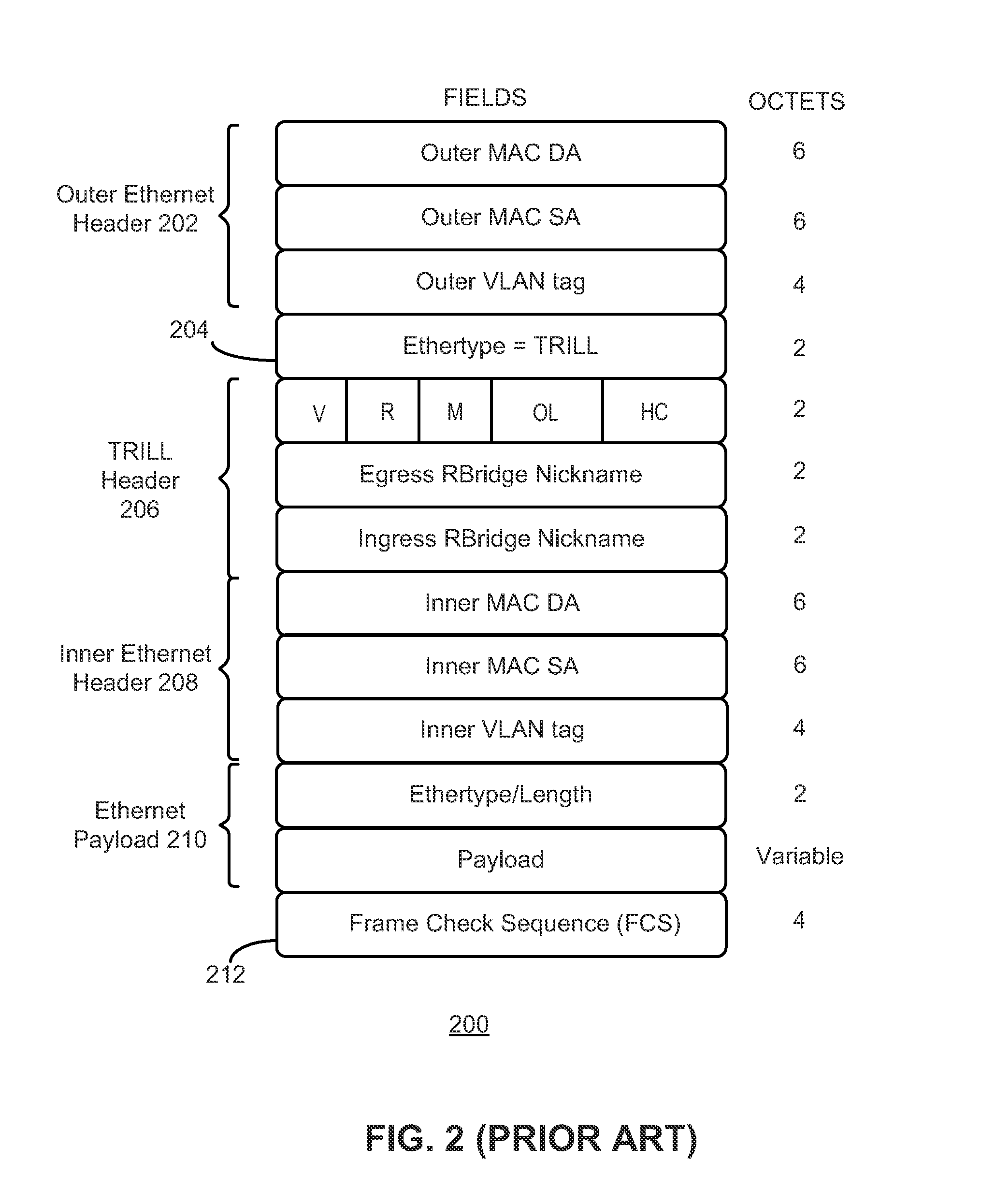
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for detecting a path between two nodes. During operation, the system transmits a network-testing request frame, which includes a time-to-live (TTL) field within a Transparent Interconnection of Lots of Links (TRILL) header, from a source node to a destination node. In response to receiving a network-testing response frame sent from an intermediate node, the system increments the TTL value by 1 and re-transmits the network-testing frame to the destination node. In response to receiving a network-testing response frame sent from the destination node, the system determines a path between the source node and the destination node. The network-testing request or response frames is not processed on an Internet Protocol (IP) layer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dynamic expiration of domain name service entries
InactiveUS20100106833A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDomain nameComputer network
Disclosed is a computer implemented method and computer program product for transmitting a resource record to a requesting computer. An authoritative domain name server receives a DNS query from a requesting computer at a name server. The authoritative domain name server looks up the resource record based on the DNS query, wherein the resource record is associated with an epochal time and a time to live. The authoritative domain name server transmits the resource record response based on the epochal time.
Owner:IBM CORP
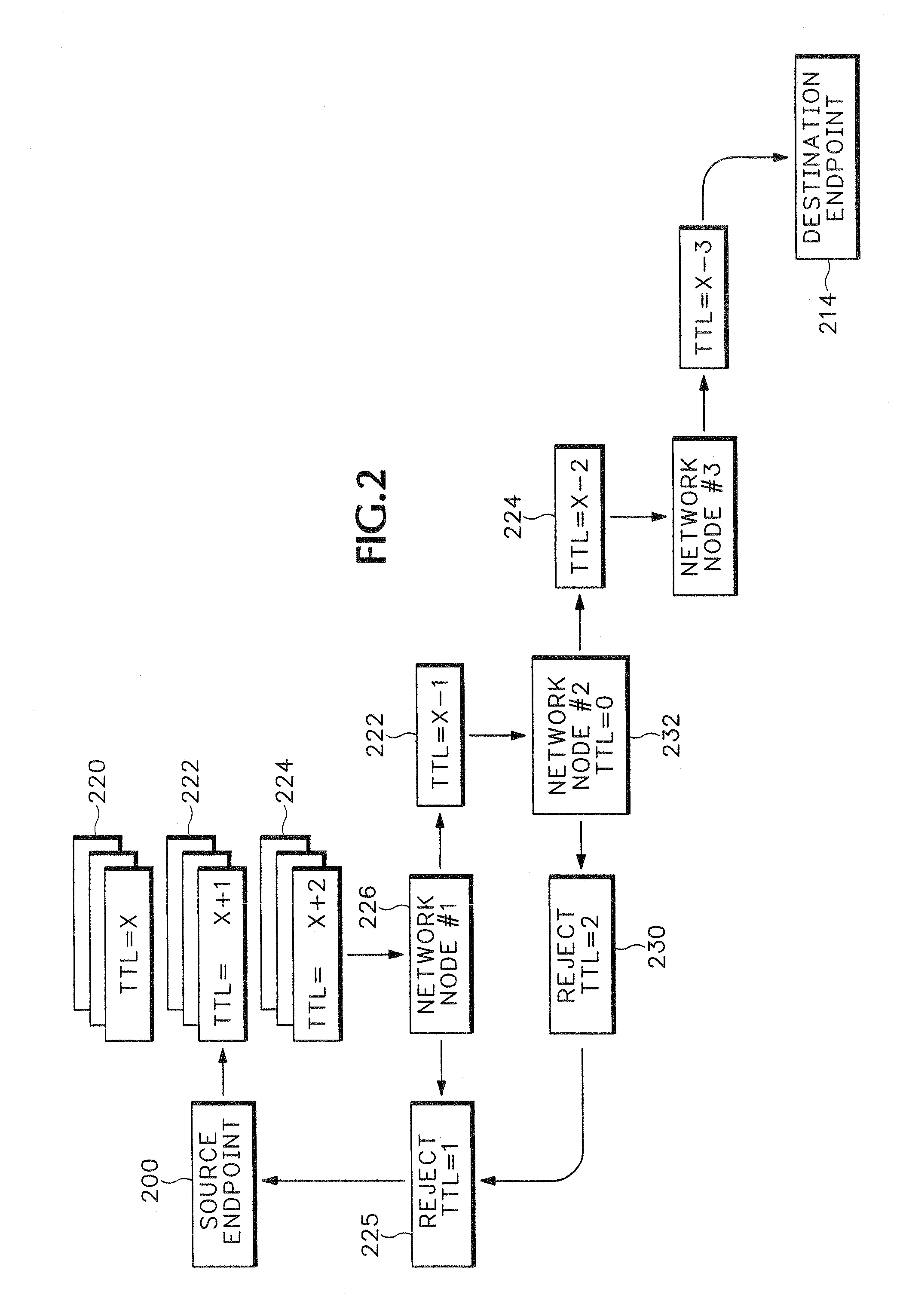
Automatic determination of connectivity problem locations or other network-characterizing information in a network utilizing an encapsulation protocol
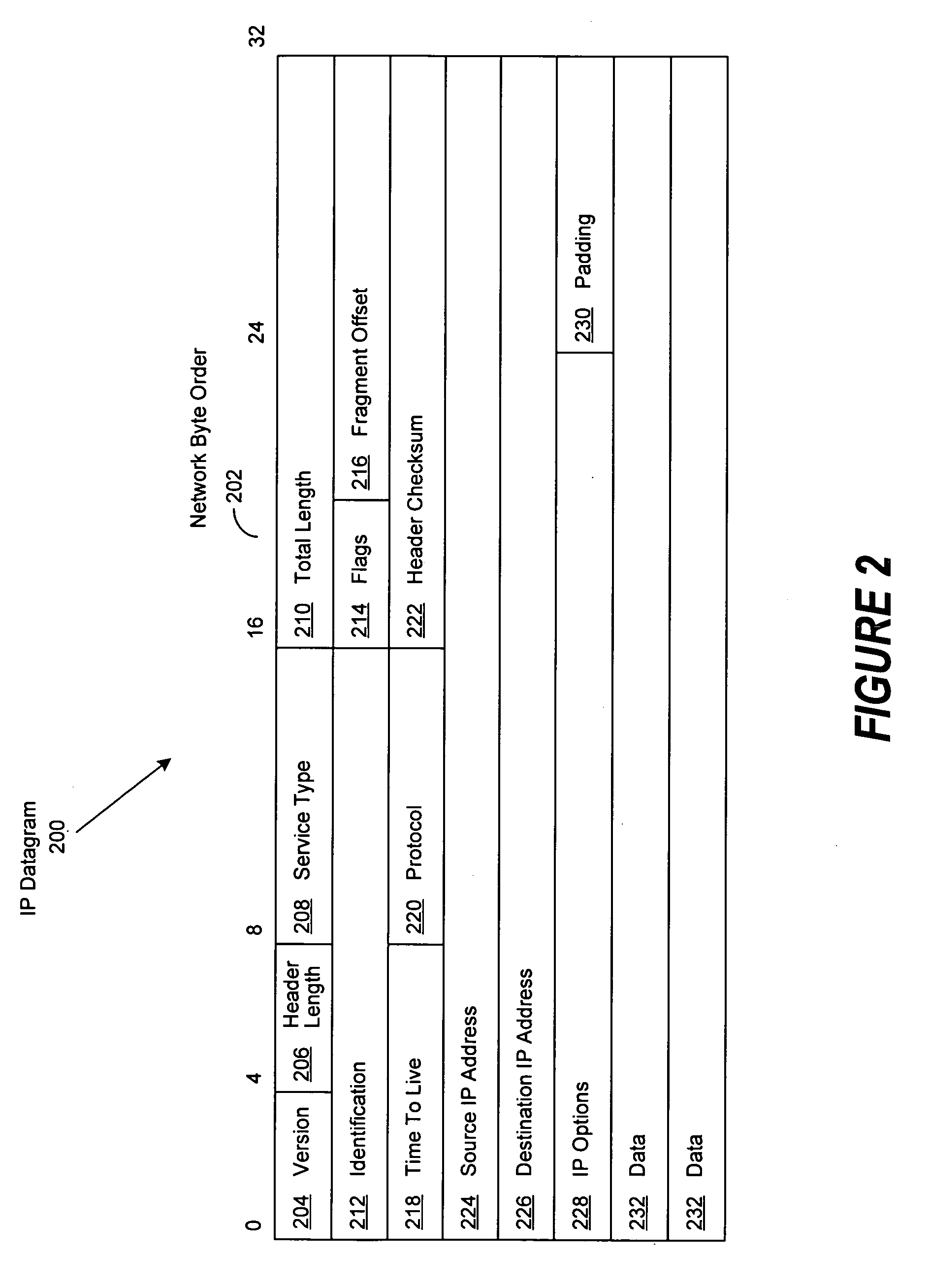
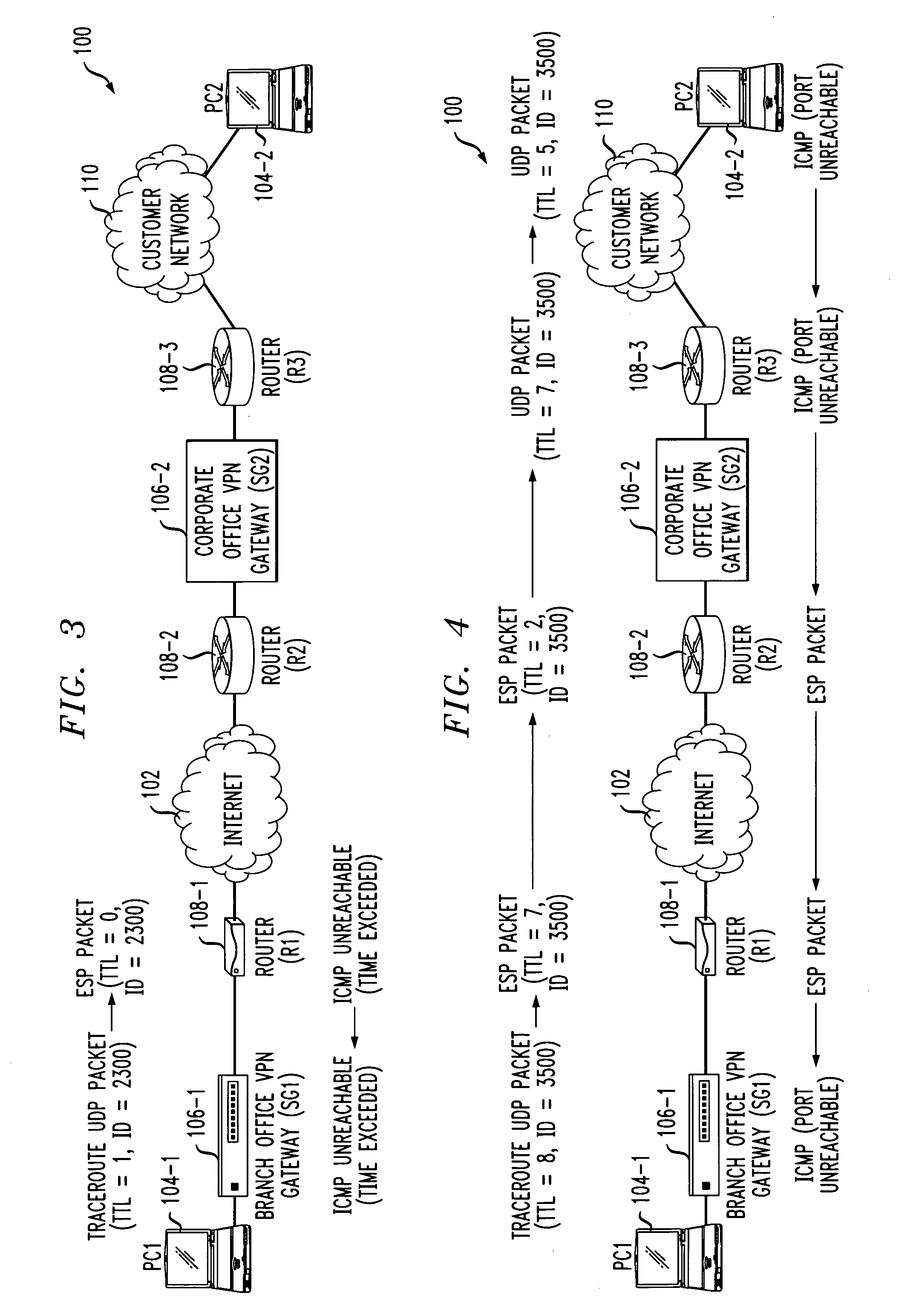
ActiveUS20050207410A1Copying of the TTL value and the identifier may be facilitatedEfficient and accurate mechanismNetworks interconnectionProcessing elementTime to live
Techniques for determining a problem location or otherwise characterizing a network comprising a plurality of processing elements, including at least one processing element associated with performance of a packet encapsulation operation of an encapsulation protocol. The packet encapsulation operation is performed on a test packet to generate an encapsulated packet, the test packet having a time to live (TTL) value and an identifier. In conjunction with performance of the packet encapsulation operation, the TTL value and the identifier of the test packet are copied to a header of the encapsulated packet. The encapsulated packet is transmitted, and a determination is made as to whether a reply packet has been received responsive to transmission of the encapsulated packet. The reply packet, if any, is processed to obtain information utilizable in determining the problem location or otherwise characterizing the network. By way of example, these operations may be repeated, for subsequent test packets with increasing TTL values, until an amount of router hop information sufficient to determine the problem location is obtained.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Communications control for extending the period over which a terminal is able to have an open connection with a host accessible via a packet data network
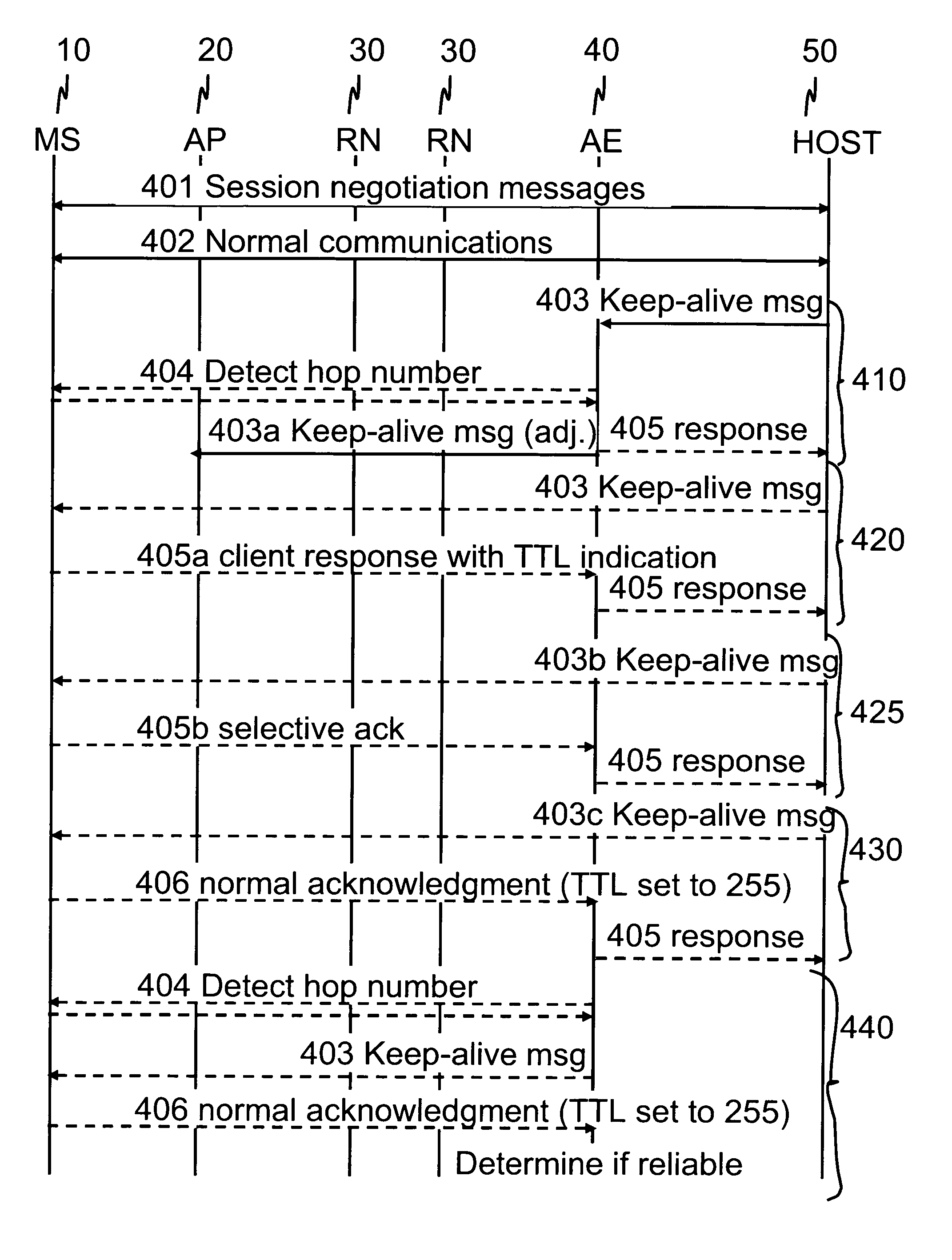
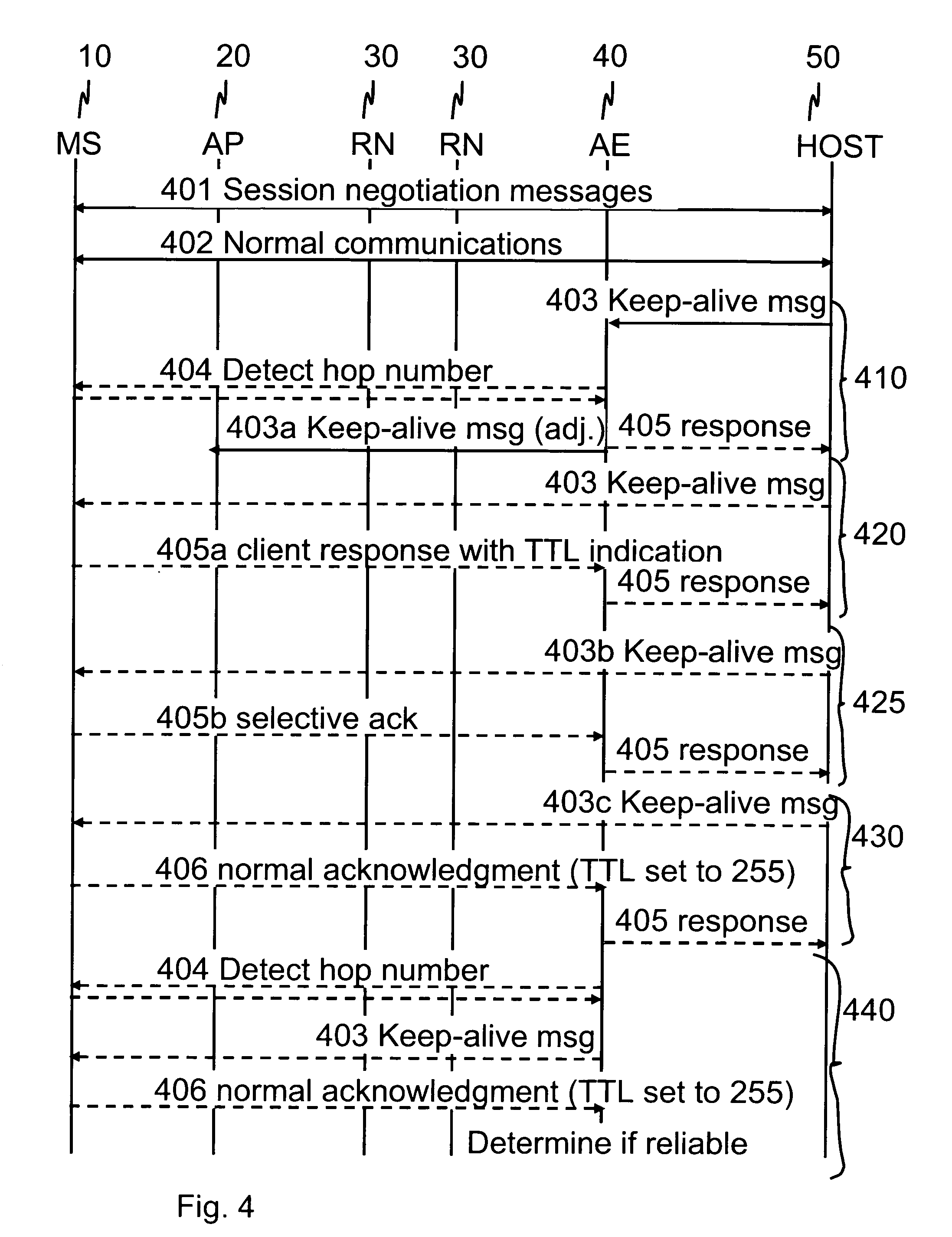
ActiveUS7684346B2Reduce power consumptionExtended maintenance periodError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityThe Internet
A client and a host communicate in a packet data network including a plurality of routing nodes such as routers and firewalls. The host is configured to provide the client with a session and to detect the accessibility of the client by repeatedly sending keep-alive messages to the client. In order to reduce the traffic actually arriving at the client, at least some of the keep-alive message are adjusted such that their routing towards the client will be stopped before the client by storing in a Time-To-Live field specified in the Internet Protocol a value of maximum routing hops defined to correspond with the last routing node before the client on a route from the host to the client. The adaptation of the keep-alive message can also be configured to allow some keep-alive message to reach the client to occasionally test the communication path between the client and server.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
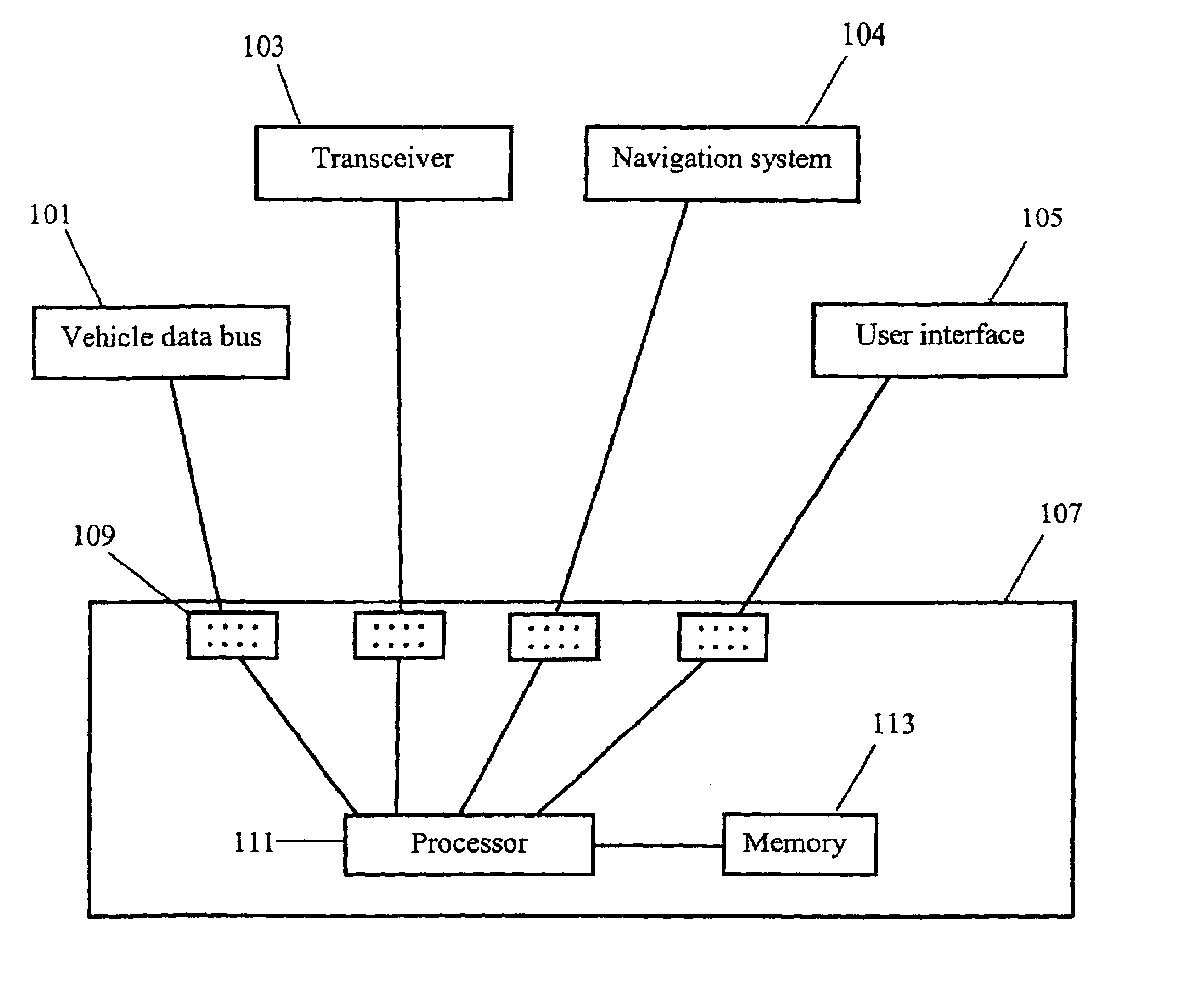
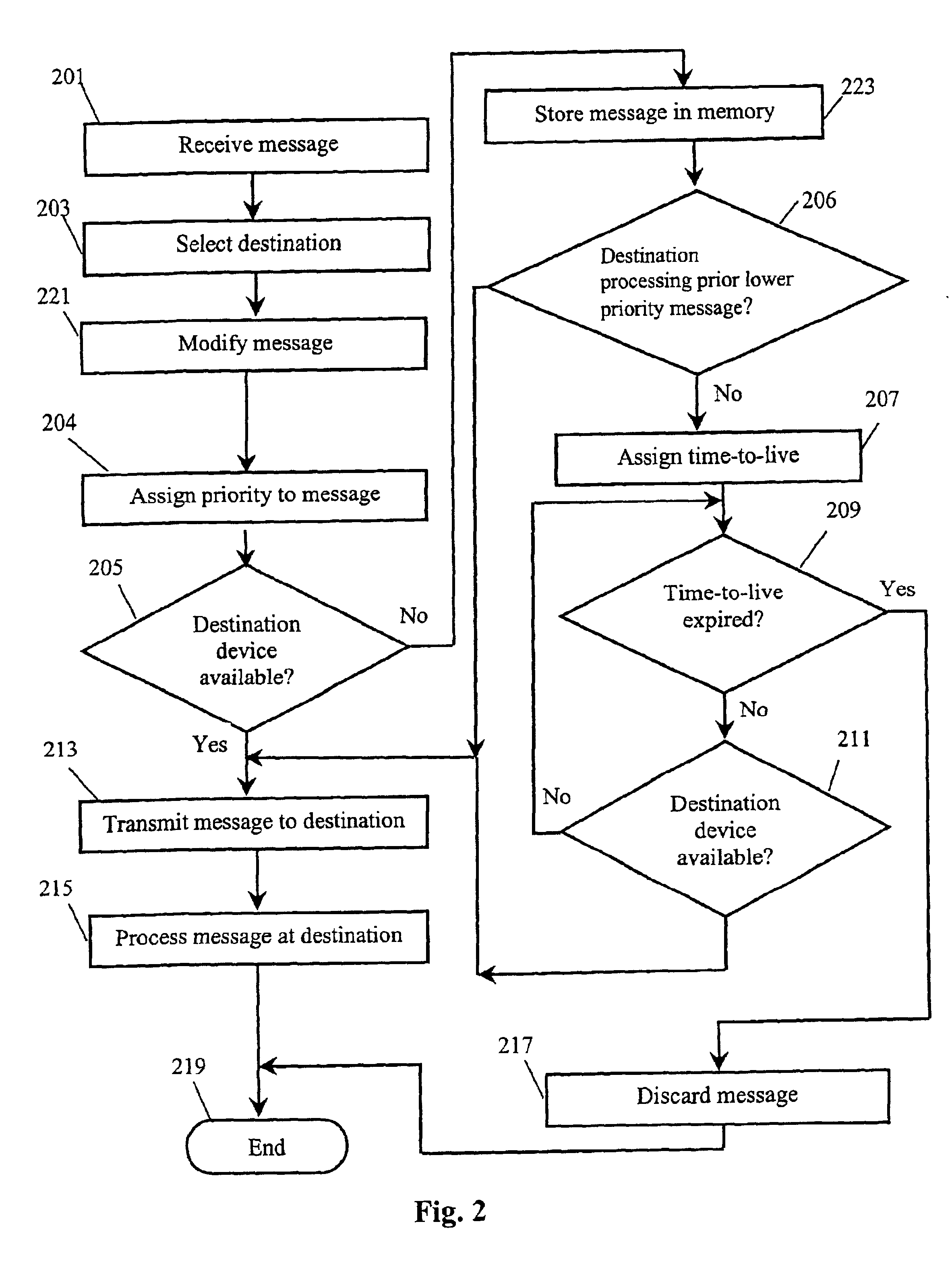
Method and system for communicating telematics messages
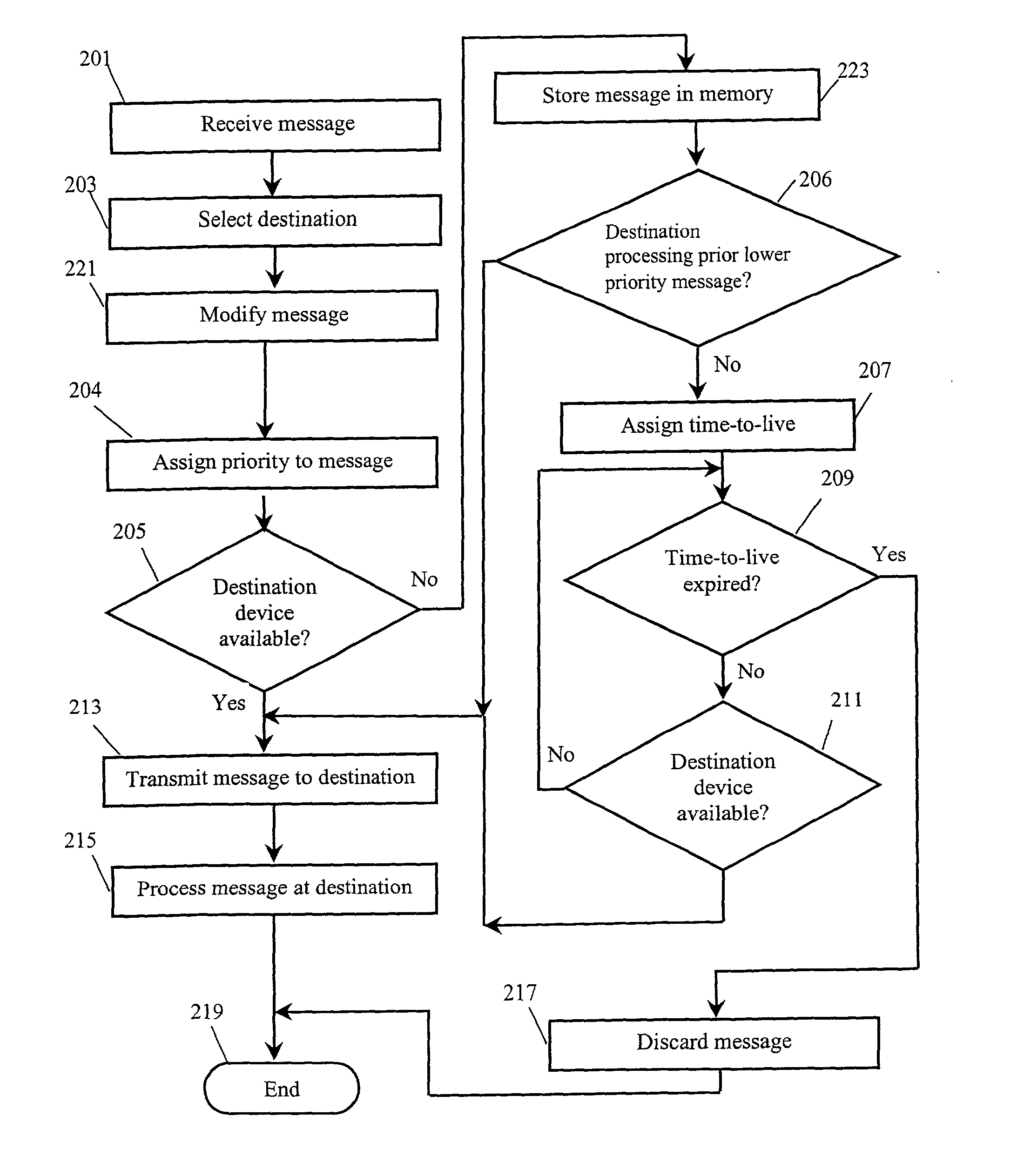
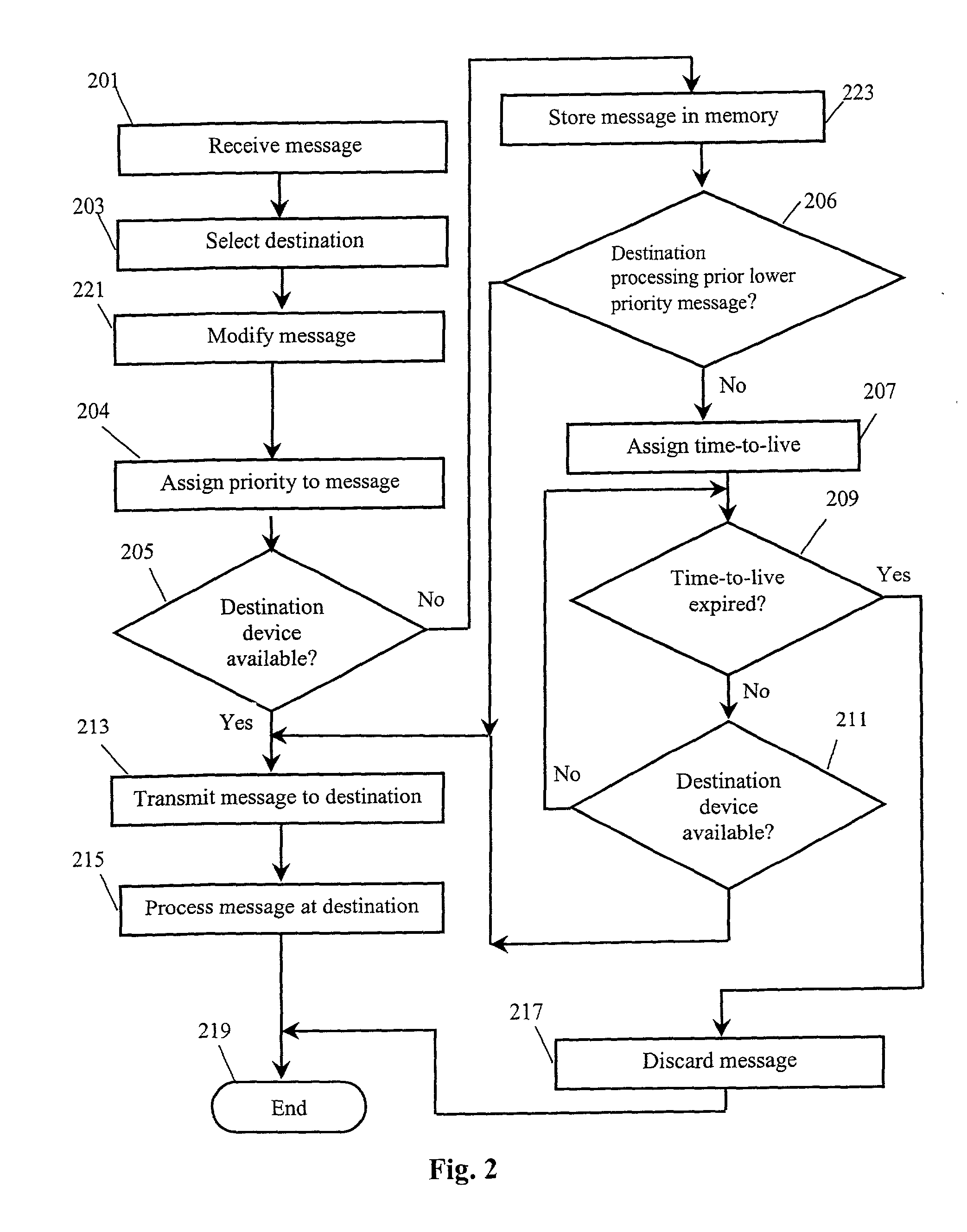
InactiveUS20030083079A1Network traffic/resource managementRoad vehicles traffic controlMessage routingTime to live
Disclosed is a method and system for communicating standardized telematic messages among a plurality of telematic devices. A telematic message is received by a message router from one of the telematic devices. The message router selects a destination device and transmits the message to the destination device, where the message is processed. In one embodiment, the message router determines whether the destination device is available to receive a message before transmitting the message. If the destination device is not available, the message is maintained in memory. In another embodiment, a time-to-live parameter is assigned to the message and the message is removed from memory of the time-to-live expires before the destination device becomes available. In a further embodiment, a priority parameter is assigned to the message and the processing of a prior message is interrupted if a new message is received that has a higher priority parameter than the previously received message.
Owner:ENT SERVICES DEV CORP LP
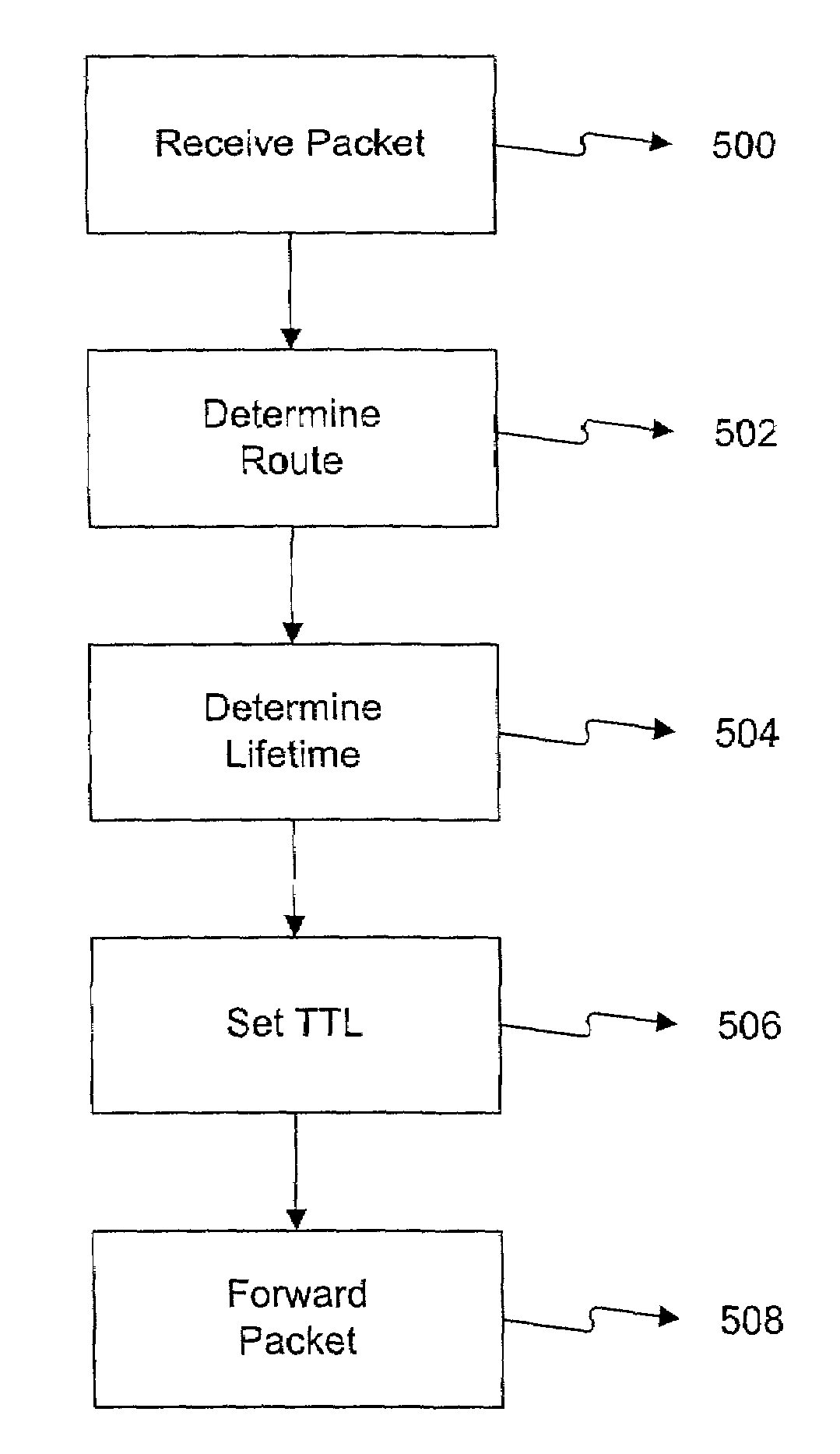
Automatic setting of time-to-live fields for packets in an ad hoc network
The present invention helps increase the reliability, throughput, and ease-of-configuration for data networks. The invention sets “time-to-live” (“TTL”) values for packets which may be routed through a network within a router based on a selected route, rather than by a host computer or using a fixed pre-configured value. Upon receiving an incoming data packet from a host computer, a TTL value is set which tailored to network conditions and the route selected. The data packet is then routed within the network using the tailored TTL and is discarded more quickly than if a large default value were used.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
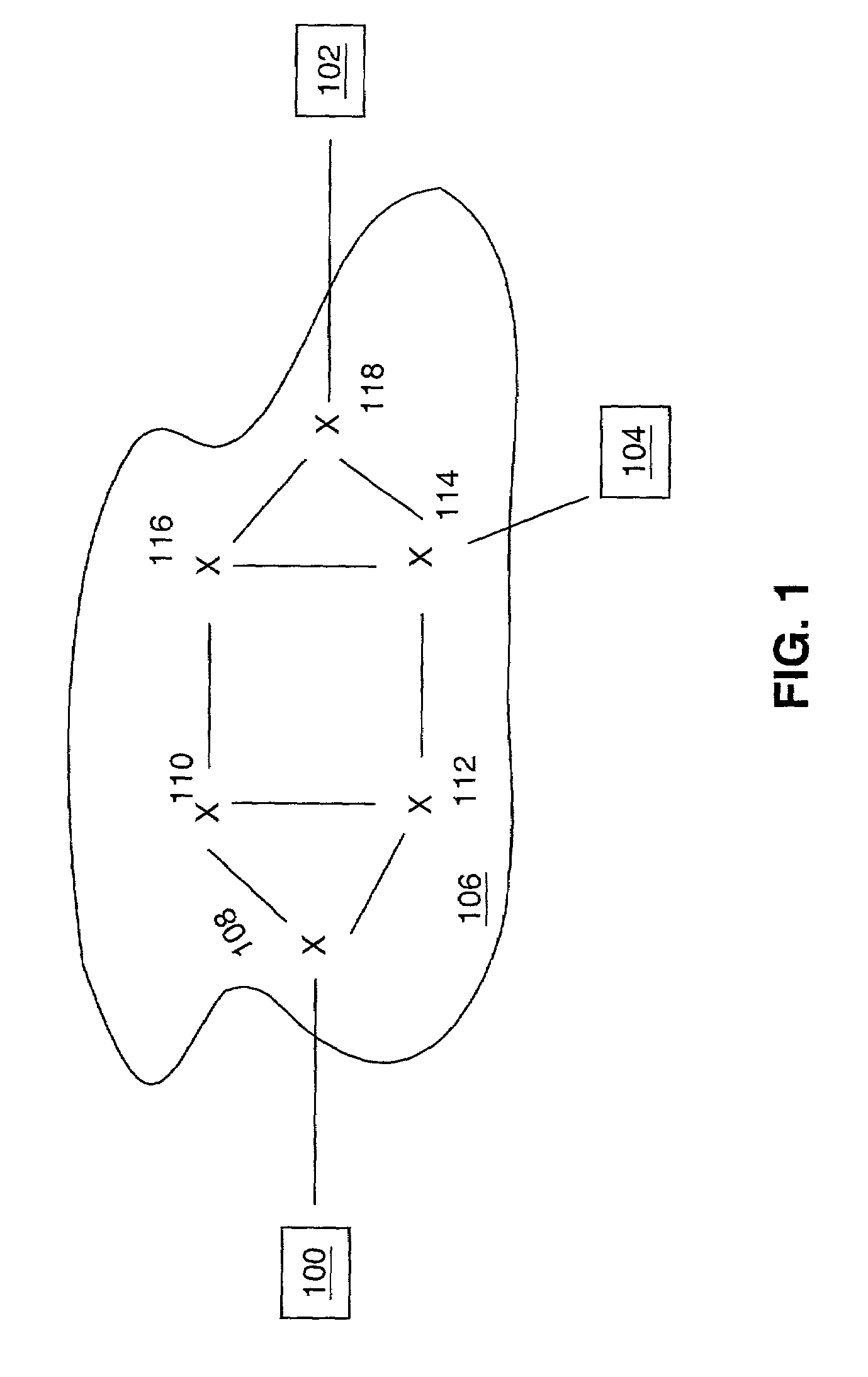
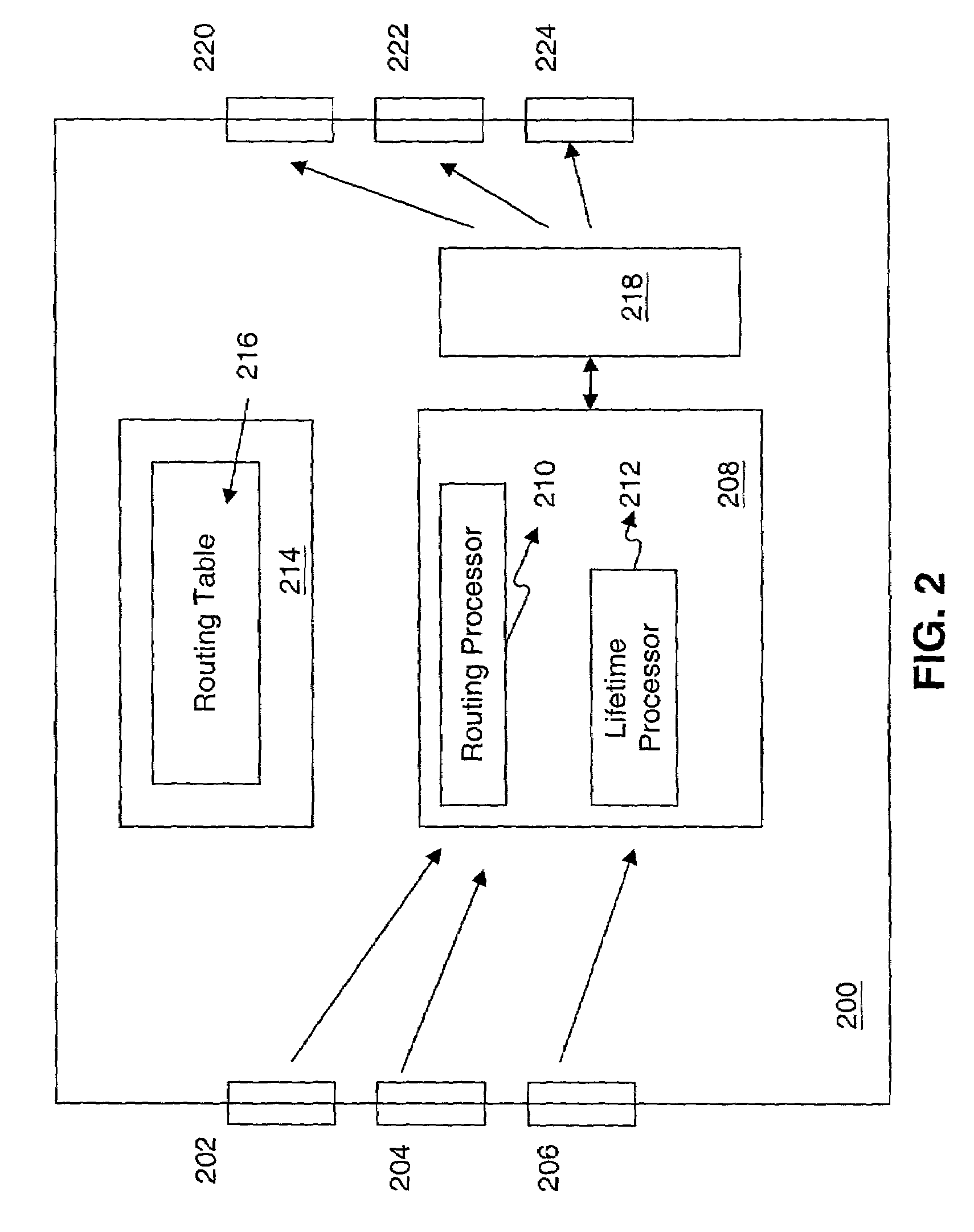
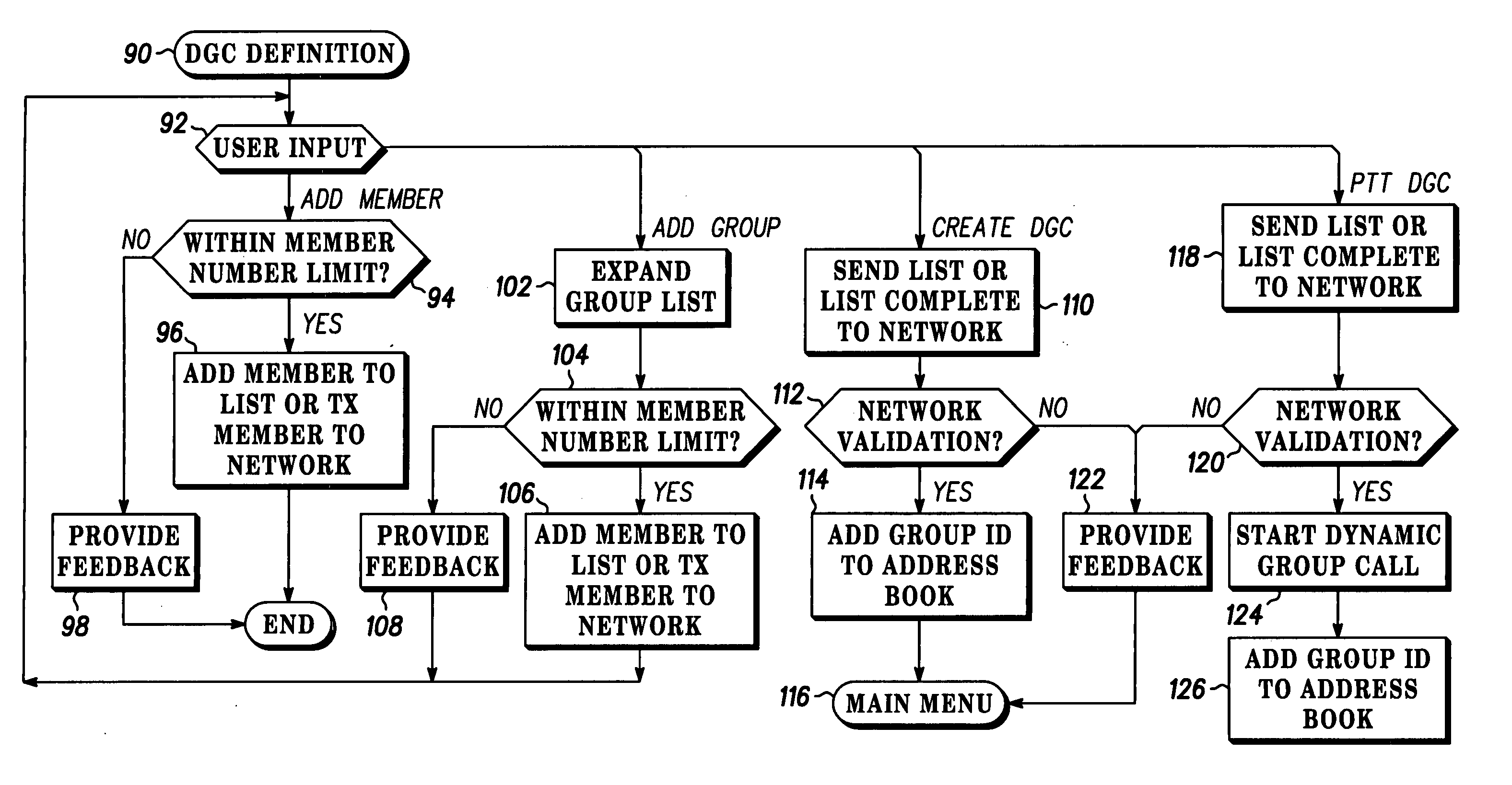
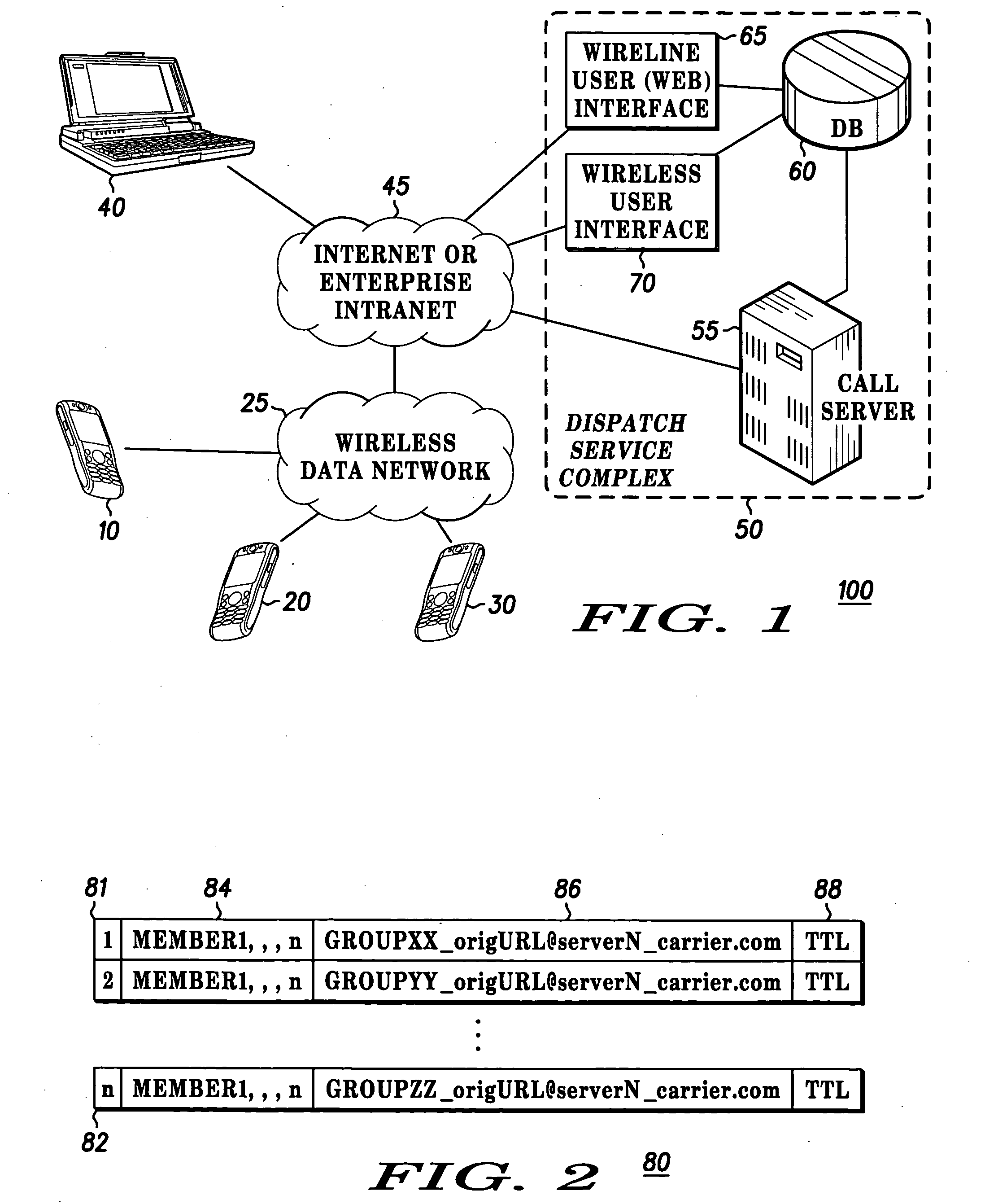
Method for dynamic group call
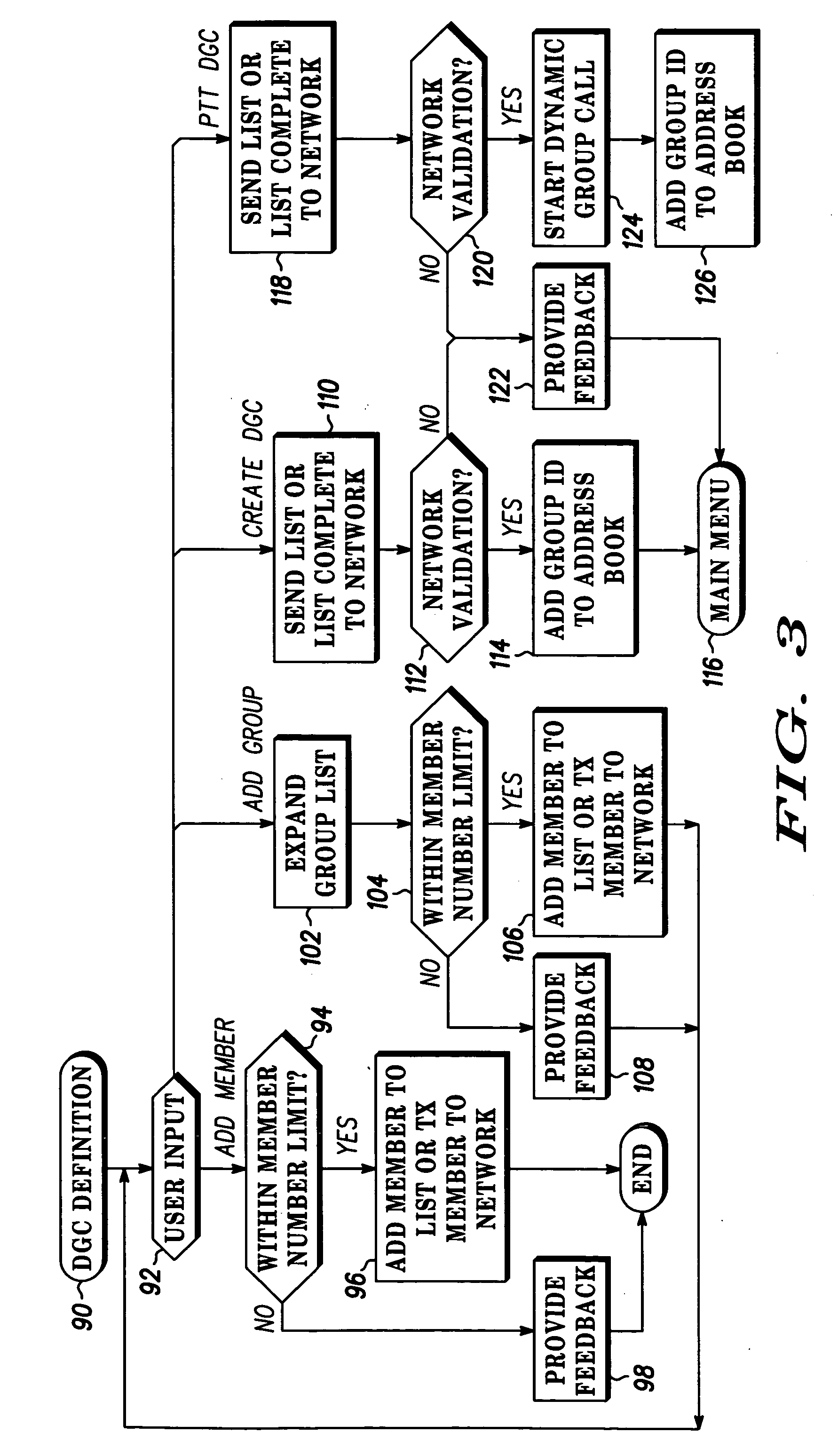
ActiveUS20050192041A1Special service for subscribersBroadcast service distributionTime to liveWireless
A method for providing dynamic group call among a group of users both wireless (10-30) and wireline (40) places the selectability of the call in the hands of an originating user (10). An originating user (10) may make a fixed number of entries (80). The originating user (10) can create a dynamic group call, add a group call list for later execution, add a member to the group call list, or create a dynamic group call list and immediately execute a group call (92). The method for dynamic group call also provides for selecting a time to live for each group call entry (81) in database (60). This parameter time to live is directly selectable by the originating user (167) or the server. In addition, any member to a previous or existing group call may rejoin or reestablish the dynamic group call (220).
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Method and system for communicating telematics messages
InactiveUS6871067B2Network traffic/resource managementRoad vehicles traffic controlMessage routingComputer science
Disclosed is a method and system for communicating standardized telematic messages among a plurality of telematic devices. A telematic message is received by a message router from one of the telematic devices. The message router selects a destination device and transmits the message to the destination device, where the message is processed. In one embodiment, the message router determines whether the destination device is available to receive a message before transmitting the message. If the destination device is not available, the message is maintained in memory. In another embodiment, a time-to-live parameter is assigned to the message and the message is removed from memory of the time-to-live expires before the destination device becomes available. In a further embodiment, a priority parameter is assigned to the message and the processing of a prior message is interrupted if a new message is received that has a higher priority parameter than the previously received message.
Owner:ENT SERVICES DEV CORP LP
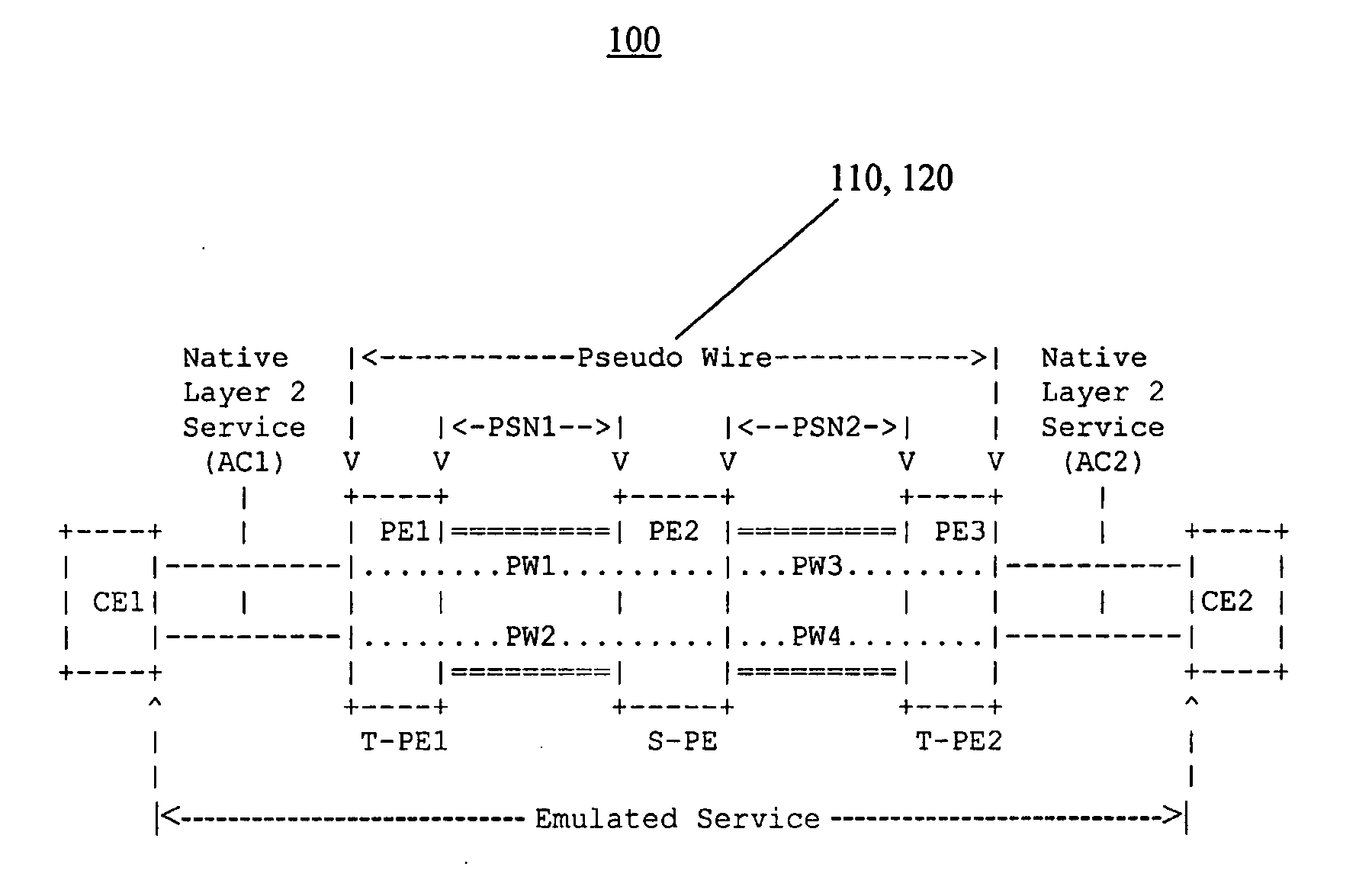
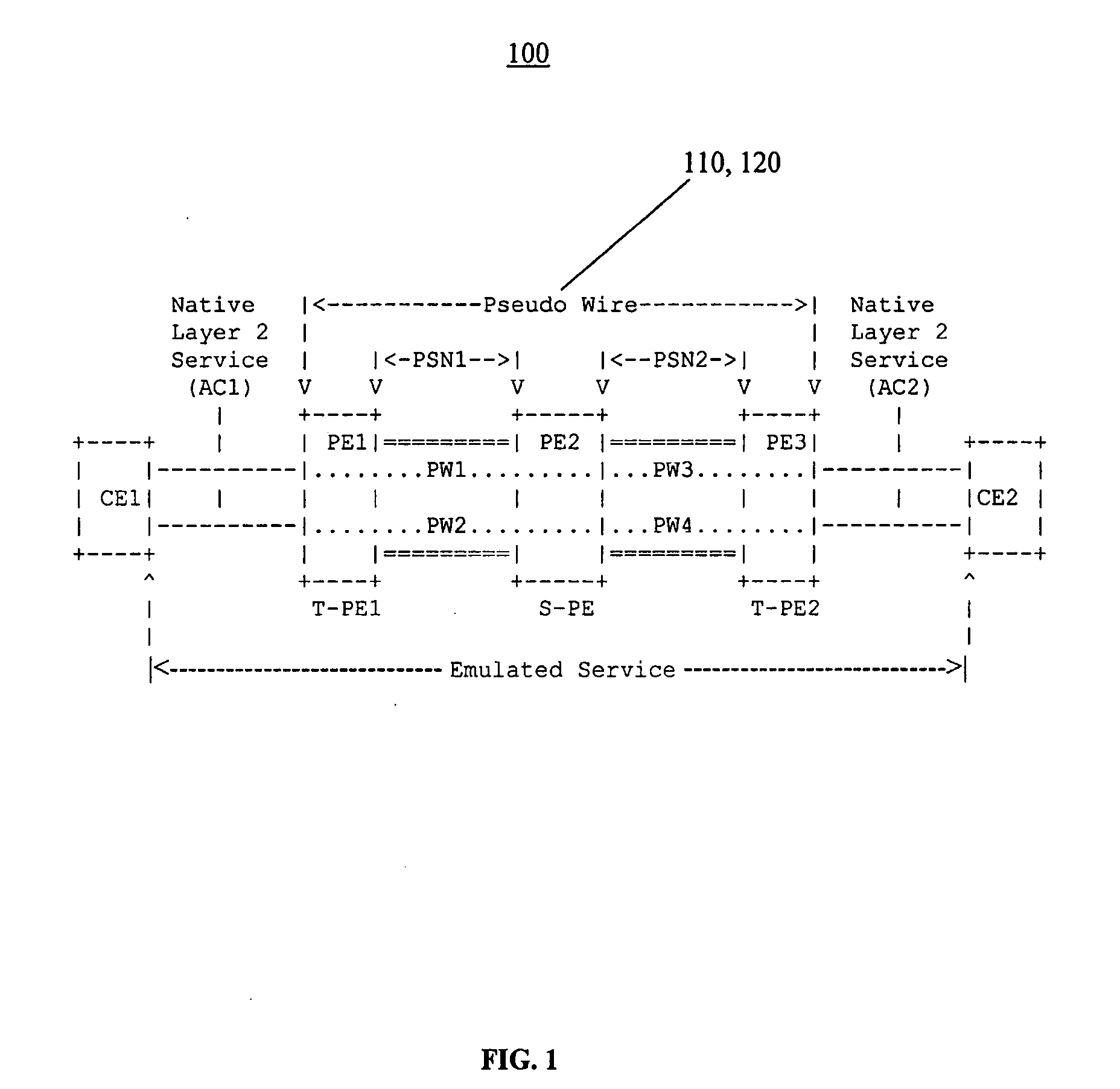
Method and system for verifying connectivity of multi-segment pseudo-wires
ActiveUS20080279110A1Confirming connectivityError preventionTransmission systemsTime to liveProvider Edge
A method for testing connectivity of a multi-segment pseudo-wire (“MS-PW”) in a network, the method comprising: sending an echo request message from a first provider edge (“PE”) device to a second provider edge (“PE”) device for a section of the multi-segment pseudo-wire (“MS-PW”) between the first provider edge (“PE”) device and the second provider edge (“PE”) device; the echo request message being identified as such by a control word contained therein; an inner label of the echo request message having a time-to-live (“TTL”) value set to a number of segments in the section; the time-to-live (“TTL”) value for determining whether the control word is to be inspected as it traverses the section; upon the echo request message arriving at the second provider edge (“PE”) device, the second provider edge (“PE”) device recognizing the echo request message as such by inspecting the control word contained therein; and, receiving an echo reply message from the second provider edge (“PE”) device in response to the echo request message, the echo reply message confirming connectivity of the section.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
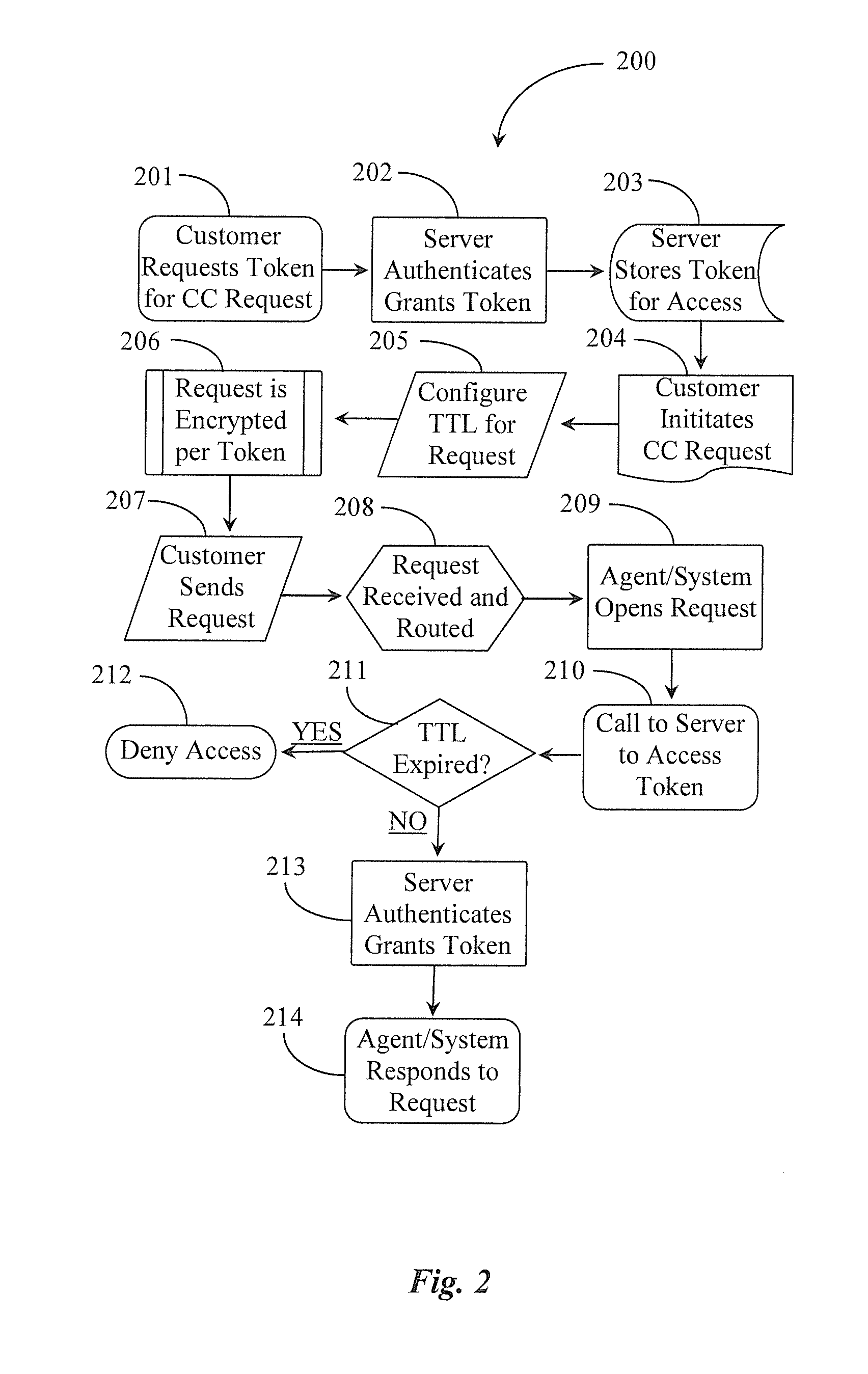
System and method for controlling lifespan of interaction requests
ActiveUS8824664B1Special service for subscribersManual exchangesHuman–computer interactionCommunication device
An apparatus for controlling lifespan of interaction requests includes a processor and a memory, the memory storing instructions that when executed by the processor cause the processor to detect when an interaction request is being initiated for send from a communications appliance, server, or system, activate an interface on the appliance, server, or system for configuring a time to live (TTL) for the interaction request, cause, via the configuration, the interaction request to expire if not answered within the TTL life span, and cause, via the configuration, the TTL constraint applied to the interaction request to be lifted if the interaction is answered within the TTL life span.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES INC
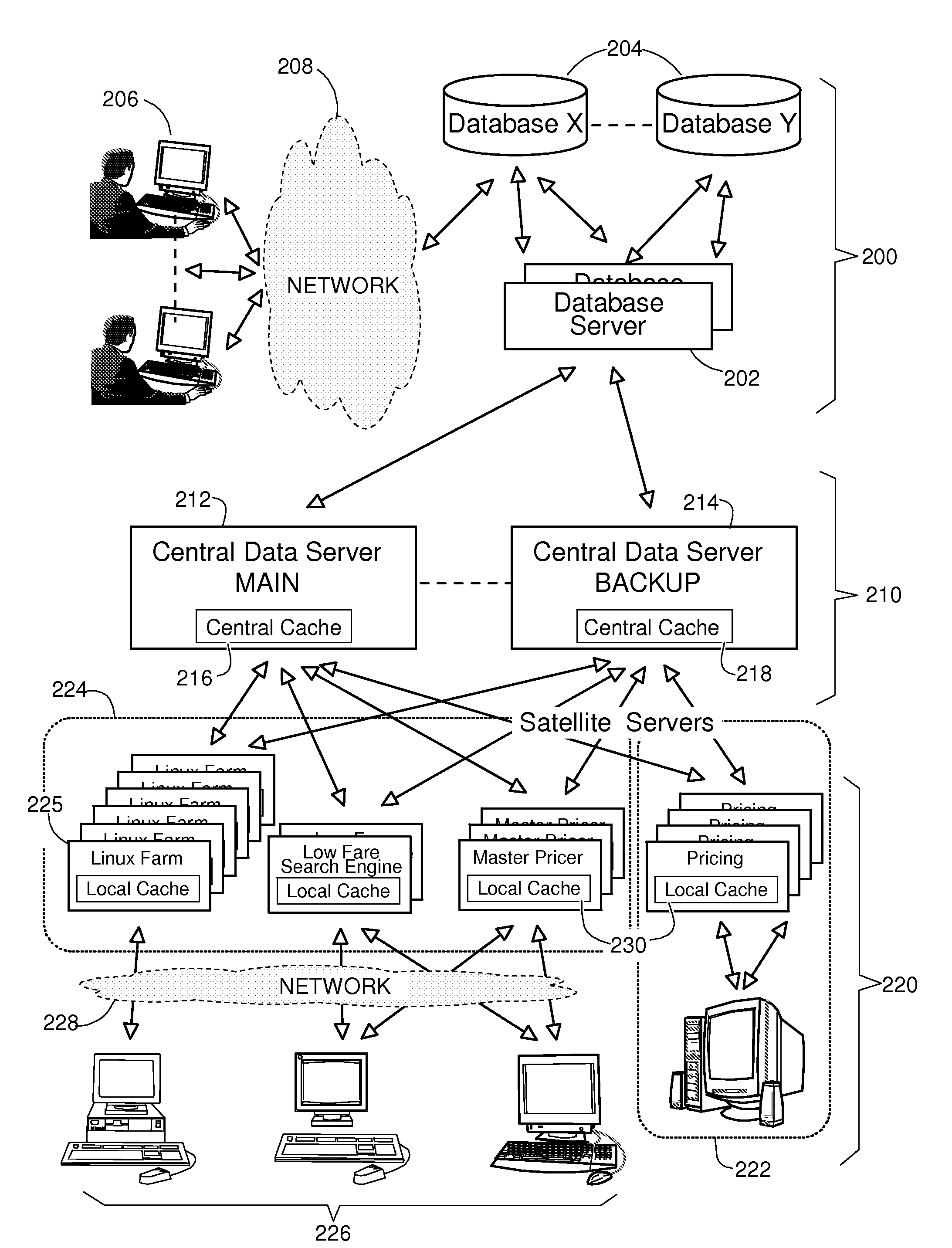
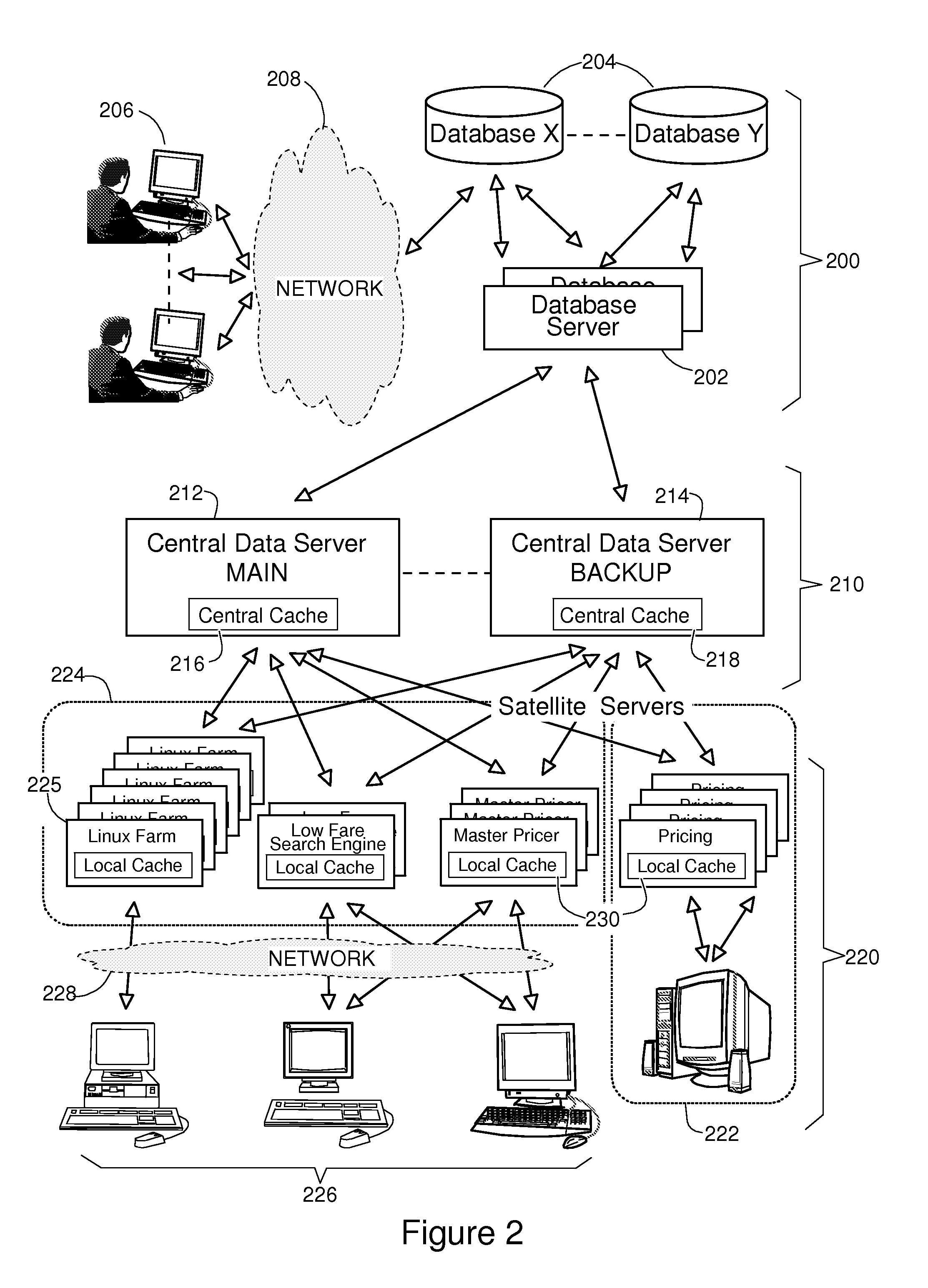
System and Method to Maintain Coherence of Cache Contents in a Multi-Tier System Aimed at Interfacing Large Databases
ActiveUS20080235292A1Improve the level ofFrequent updateDigital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationDatabase serverApplication software
A method and a system for maintaining coherence of cache contents in a multi-tiered architecture of servers are described. This includes a front tier of satellite servers, each operating a local cache, and a middle tier of central servers each operating a central cache. Central servers interface with databases through database servers to retrieve the data elements used to construct objects and store them in central caches. Once constructed, objects are attributed a time-to-live (TTL) and stored in central caches then, forwarded to the satellite servers where they are stored in local caches before being delivered to the software applications that have requested them. They are invalidated when outdated and reconstructed from a central server from where they are forwarded to all central caches and to the local caches where they are needed.
Owner:AMADEUS S
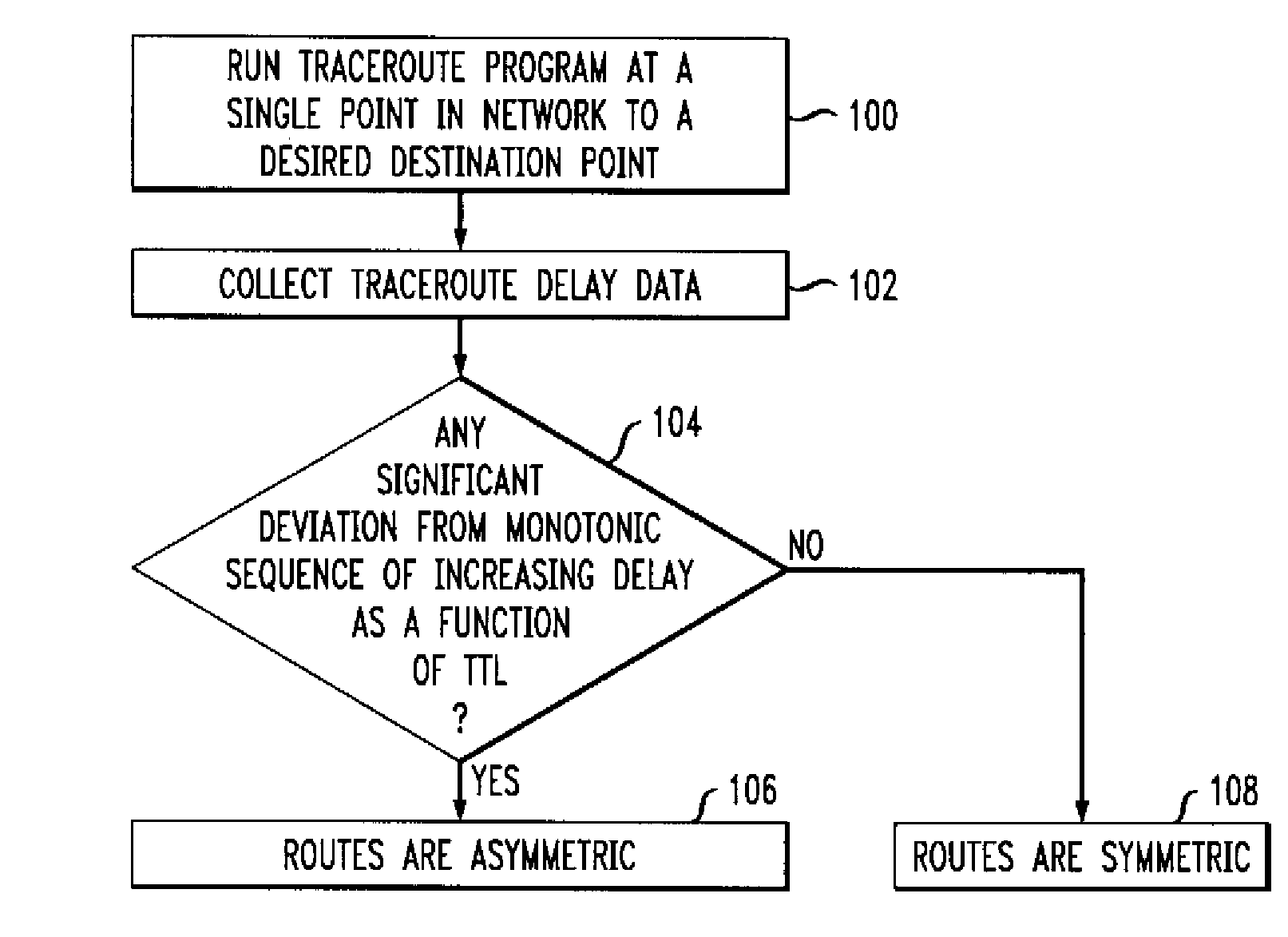
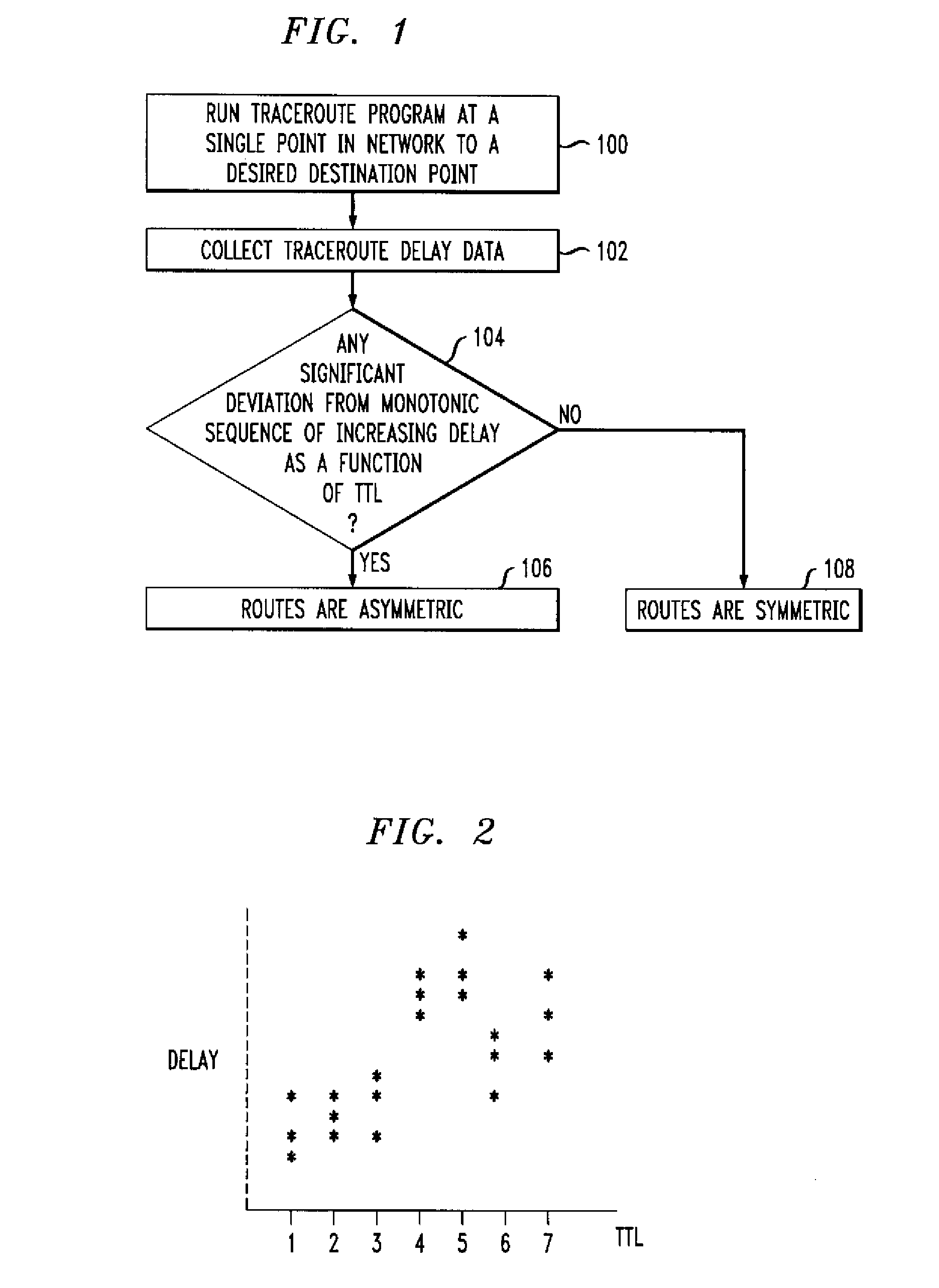
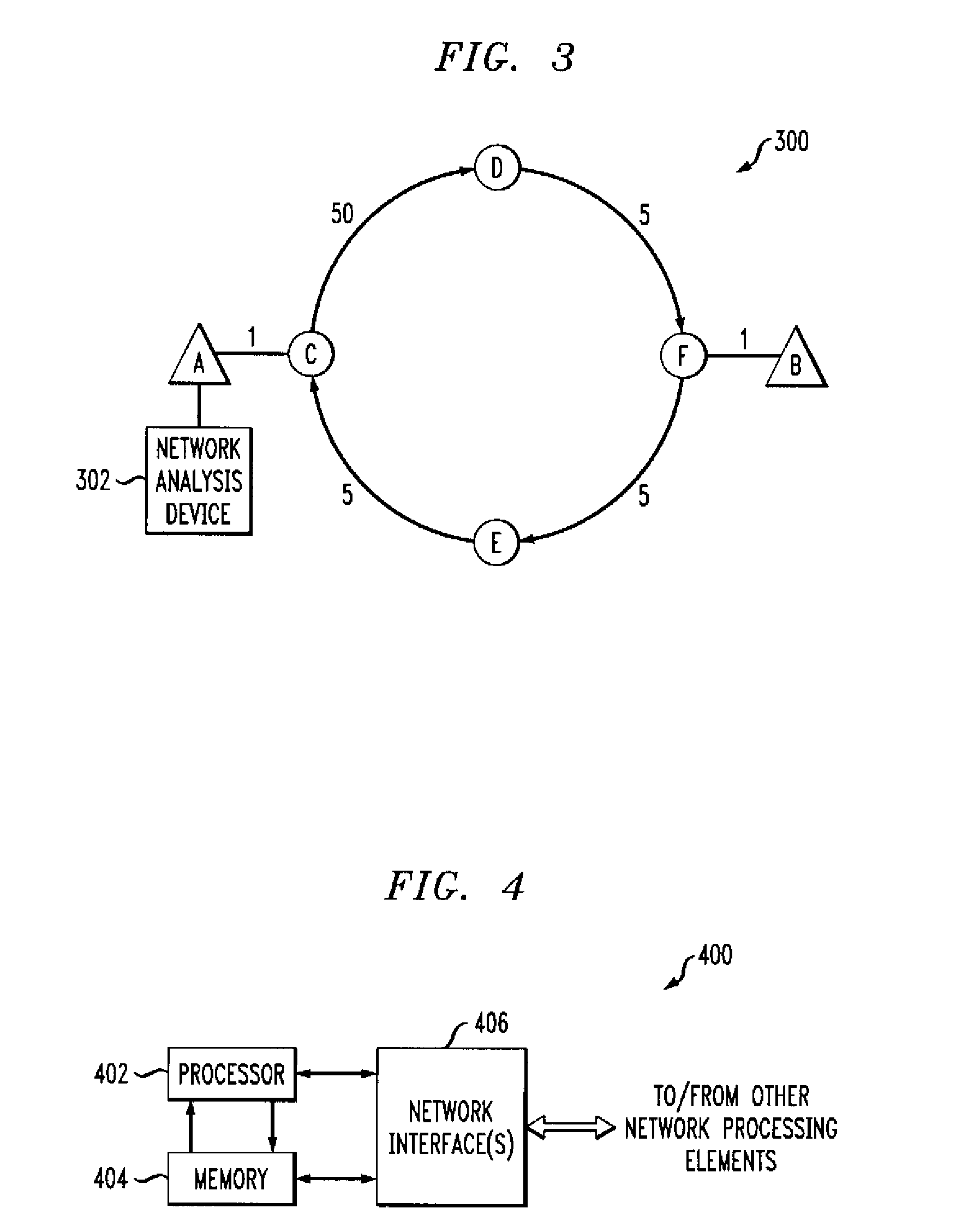
Detection of Asymmetric Network Routes
ActiveUS20080205292A1Easy to determineImprove approachData switching by path configurationTime to liveAsymmetry
Route asymmetry is detected in a network by running a route tracing program to trace routes between a first element of the network and a second element of the network. The route tracing program need be run at only a single network element, such as the first network element. Forward and reverse routes between the first and second network elements are identified as asymmetric if performance data from the route tracing program indicates a significant deviation from an expected monotonic characteristic as a function of time-to-live values of respective packets transmitted by the route tracing program.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Computer system capable of fast failover upon failure
InactiveUS20050198327A1Extension of timeFast failoverMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPrimary sitesComputerized system
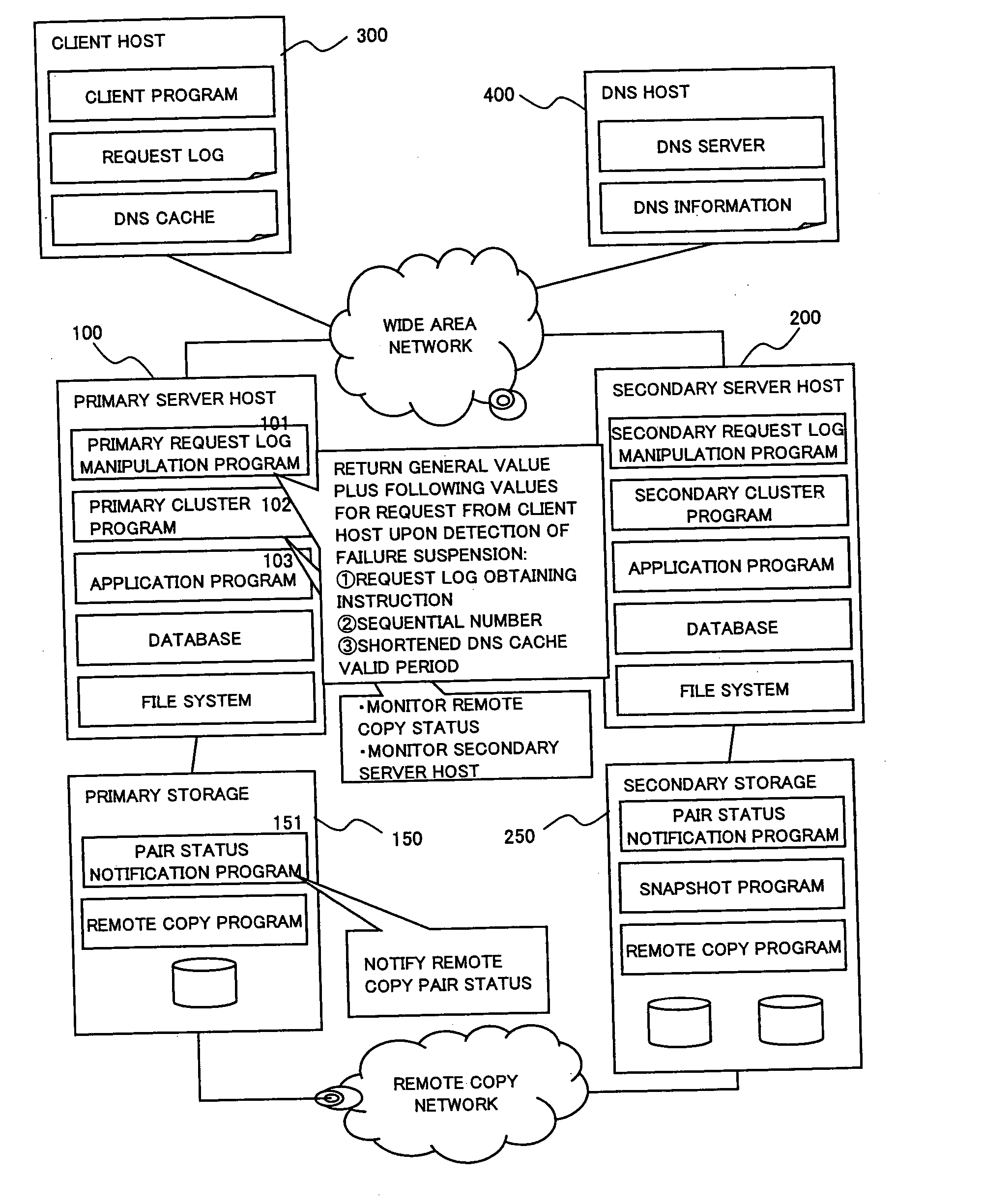
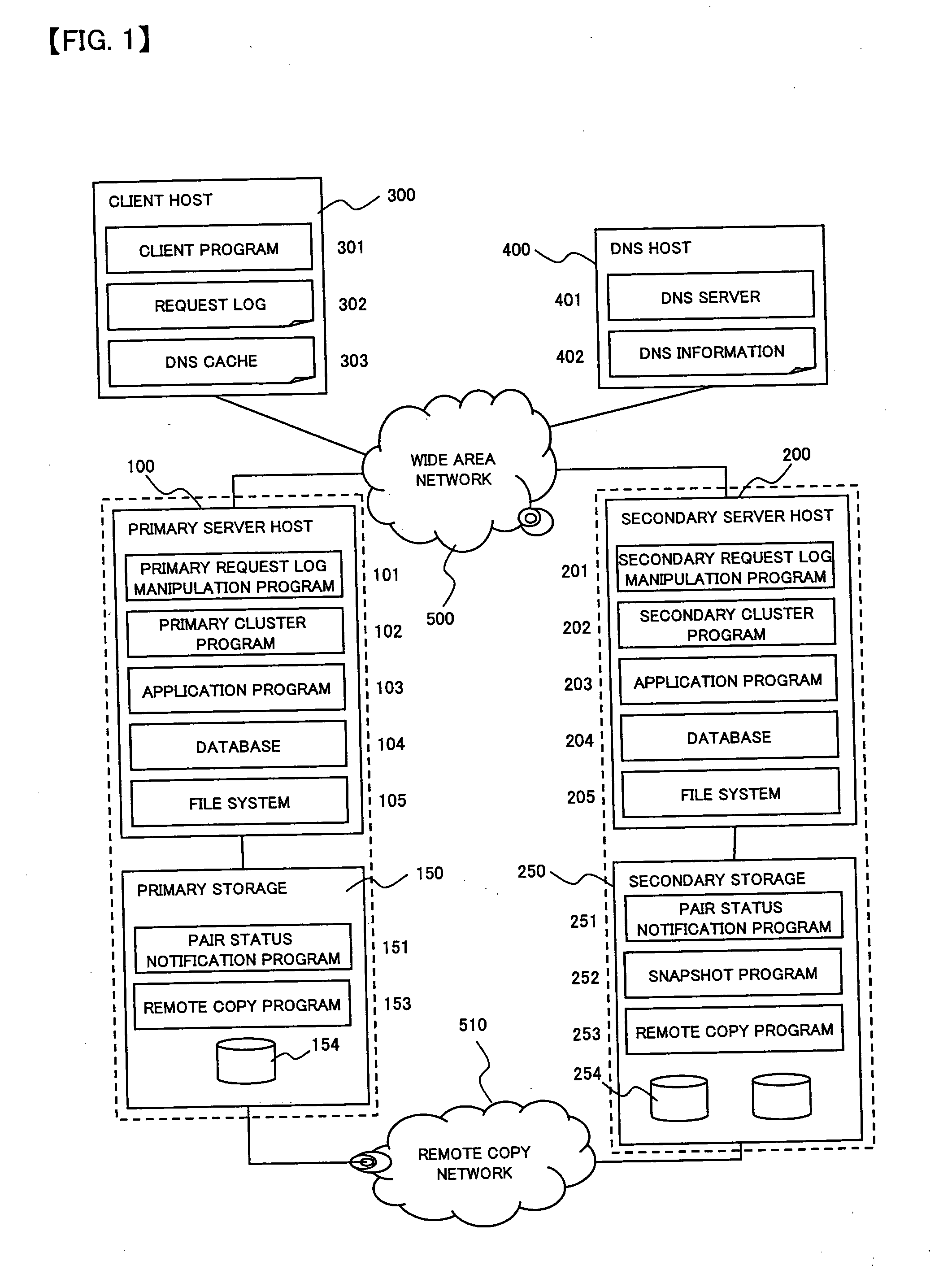
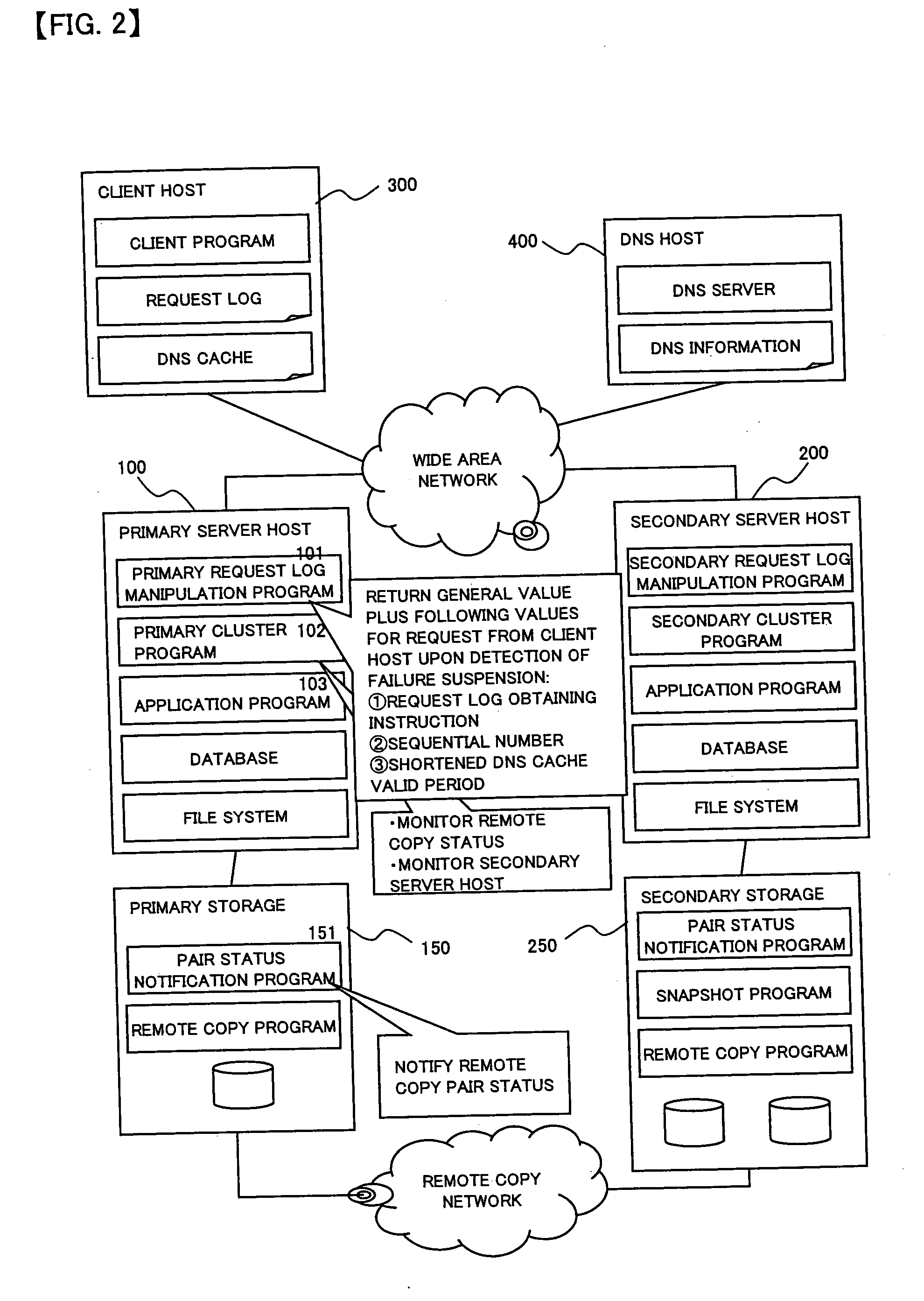
To provide a computer system capable of fast failover so that a service is stopped only for a brief period of time from a failure in a first site. The computer system includes a primary site for regular operation and a secondary site that operating when the primary site fails. A primary storage and a secondary storage have a synchronization unit to make contents stored in the primary storage and contents stored in the secondary storage identical to each other. A client has a cache for recording address information (e.g. DNS) that gives the client an access to the server from which the service is provided and information that defines a time to live of the address information. A first server has a primary request log processing unit, which instructs the client to shorten the recorded time to live of the address information when communication with the secondary site is detected to be impossible.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
IP Time to Live (TTL) field used as a covert channel
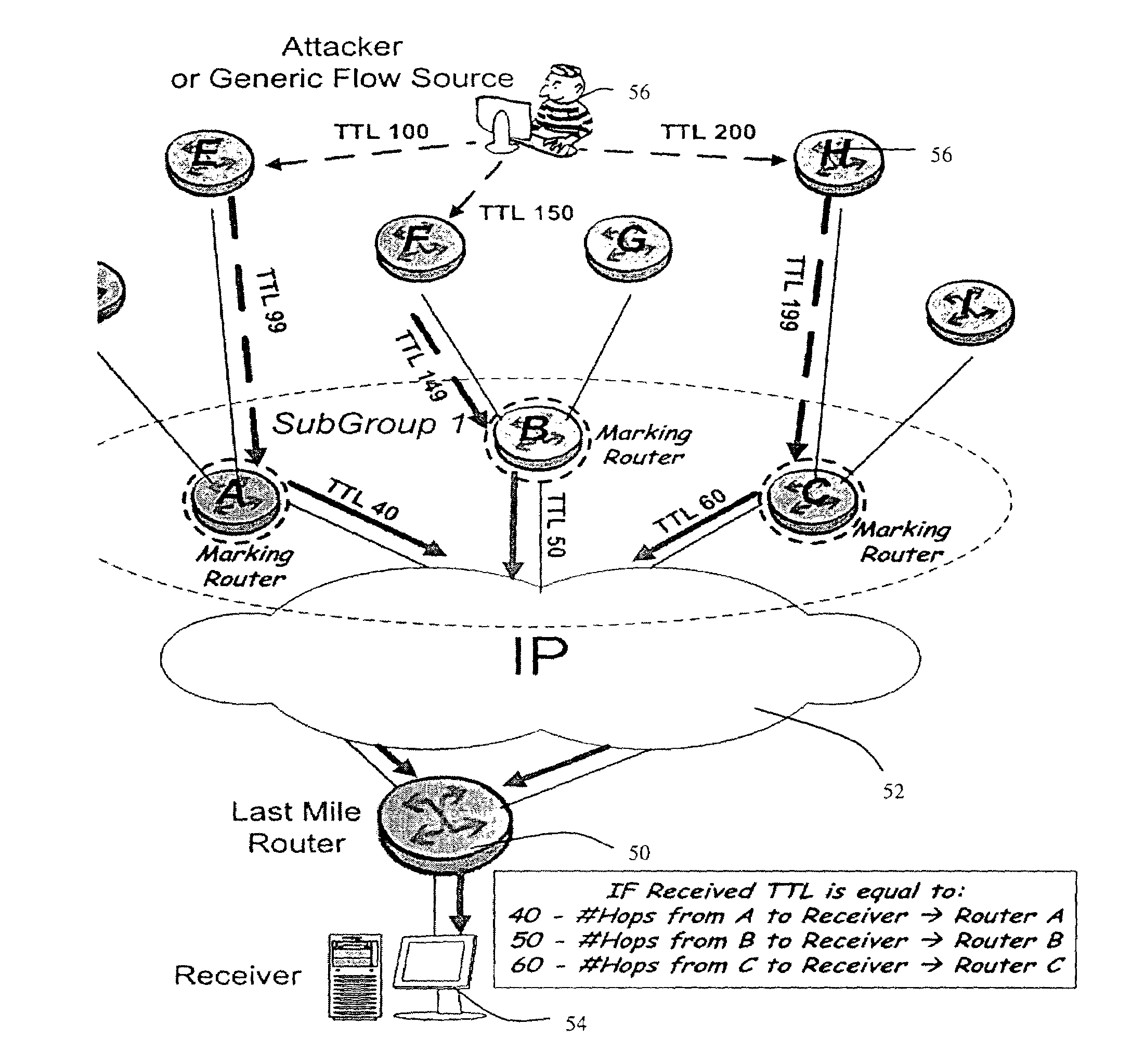
The Time to Live (TTL) field in an IP header is used as a covert channel in a communication system. More particularly the TTL field can be used to selectively mark packets with unique identifiers as they pass through an upstream station on their way to a downstream station. In this way the source of a traffic flow at least within a particular domain can be absolutely identified. This method of performing a traceback operation doesn't utilize additional resources as it relies on functionality which already exists in the system.
Owner:RPX CORP
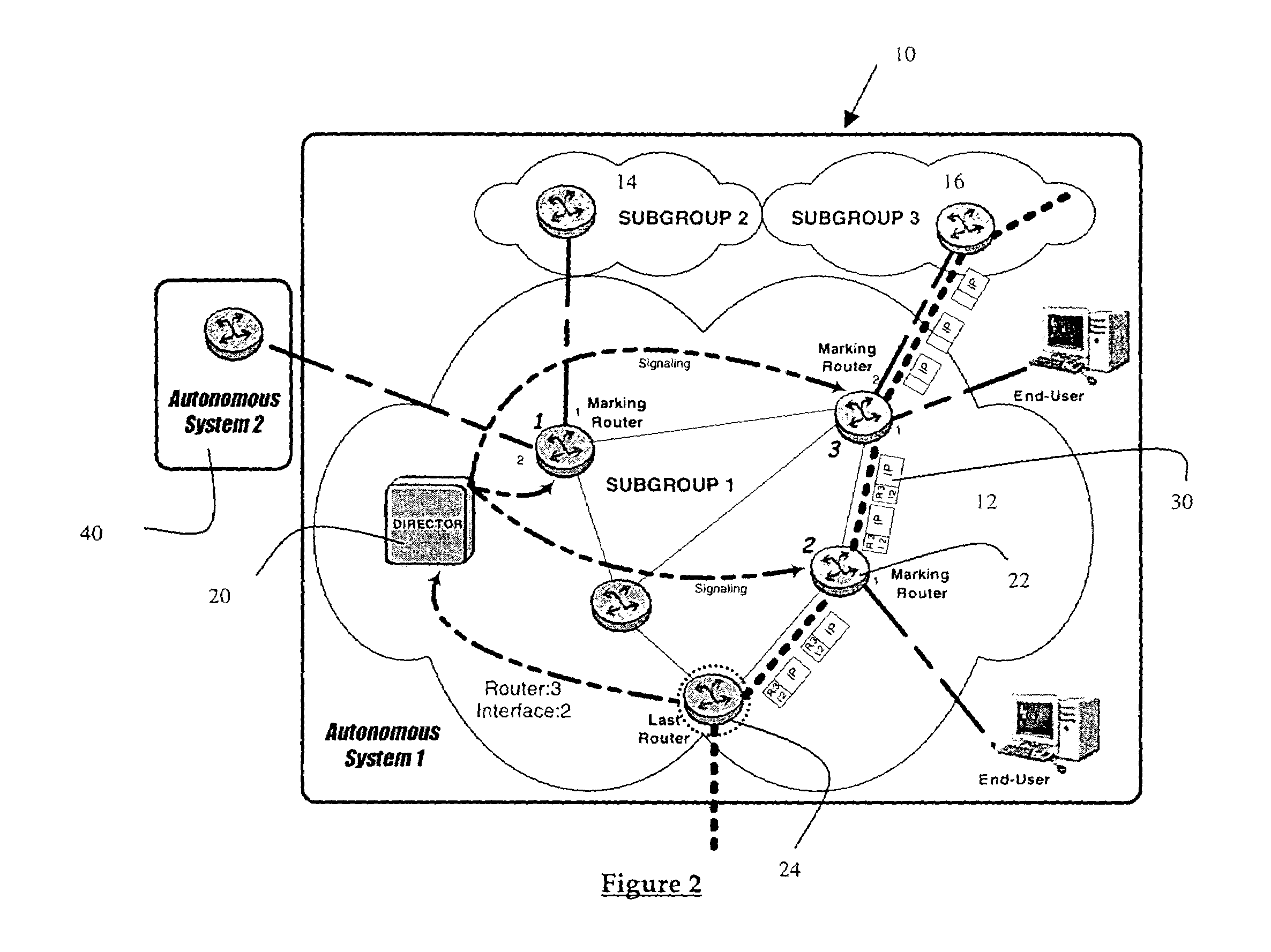
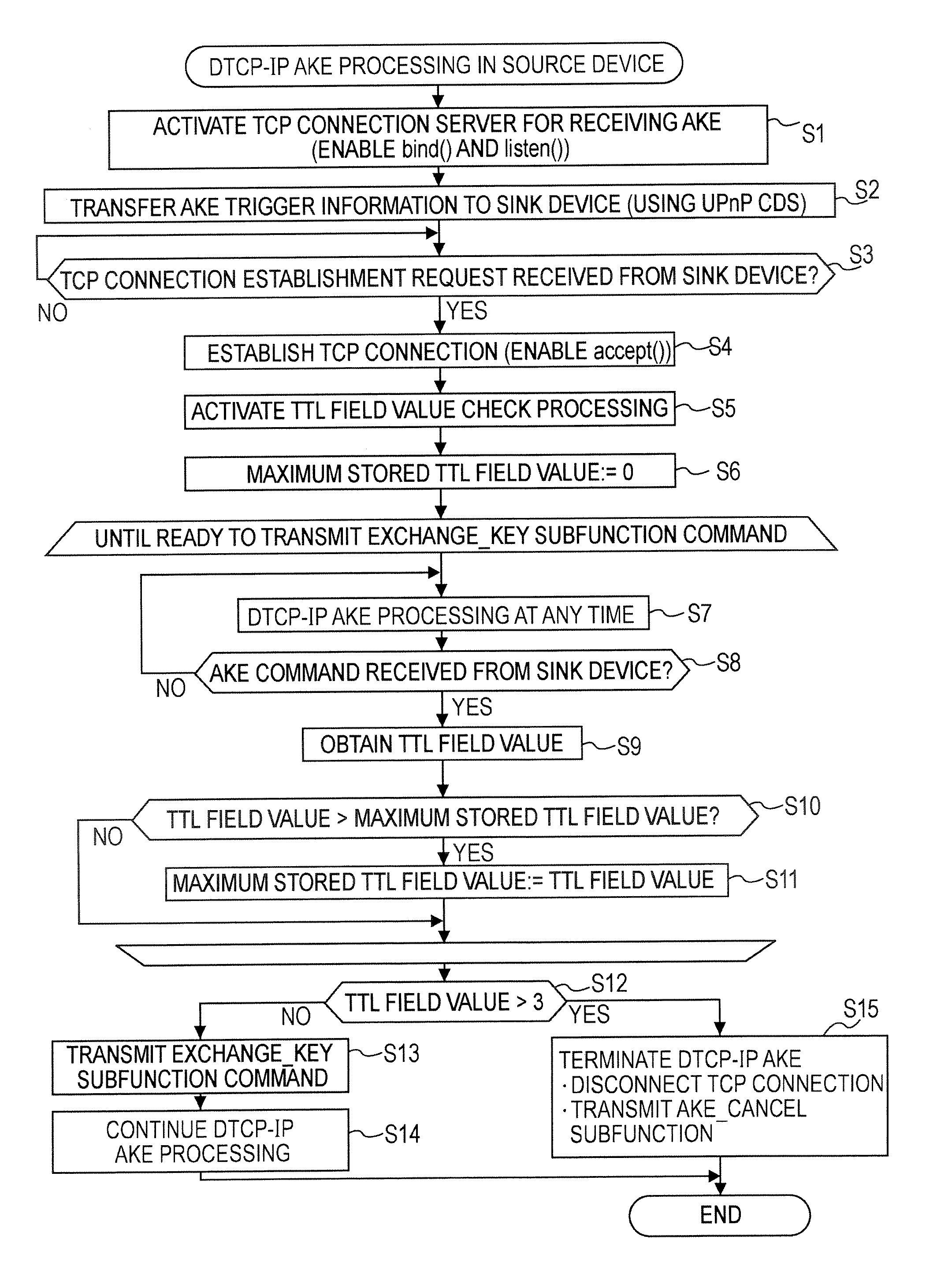
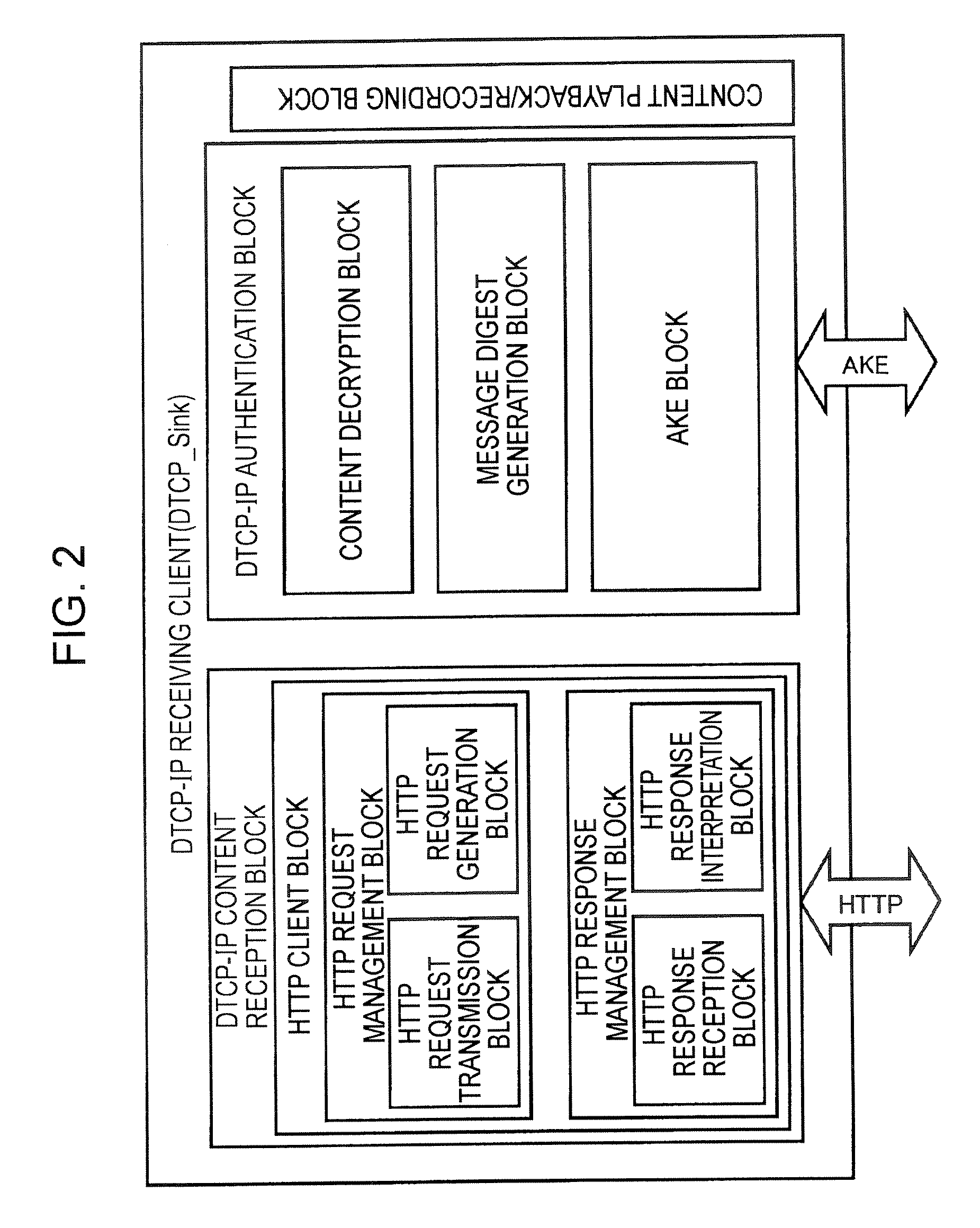
Information communication system, information communication apparatus and method, and computer program
InactiveUS20070022195A1Effect is exertedReduce in quantityKey distribution for secure communicationMemory loss protectionCommunications systemTime to live
In an information communication system, information communication devices exchange an IP packet over IP networks. When performing a predetermined packet exchanging procedure in which the number of router hops is limited to a predetermined control value or less, each of the information communication devices monitors Time-To-Live values designated in the headers of IP packets received over a period of time from the start of the predetermined packet exchanging procedure to immediately before the end of the predetermined packet exchanging procedure to continuously update the maximum Time-To-Live value of the monitored Time-To-Live values, and checks whether the maximum Time-To-Live value does not exceed the control value.
Owner:SONY CORP
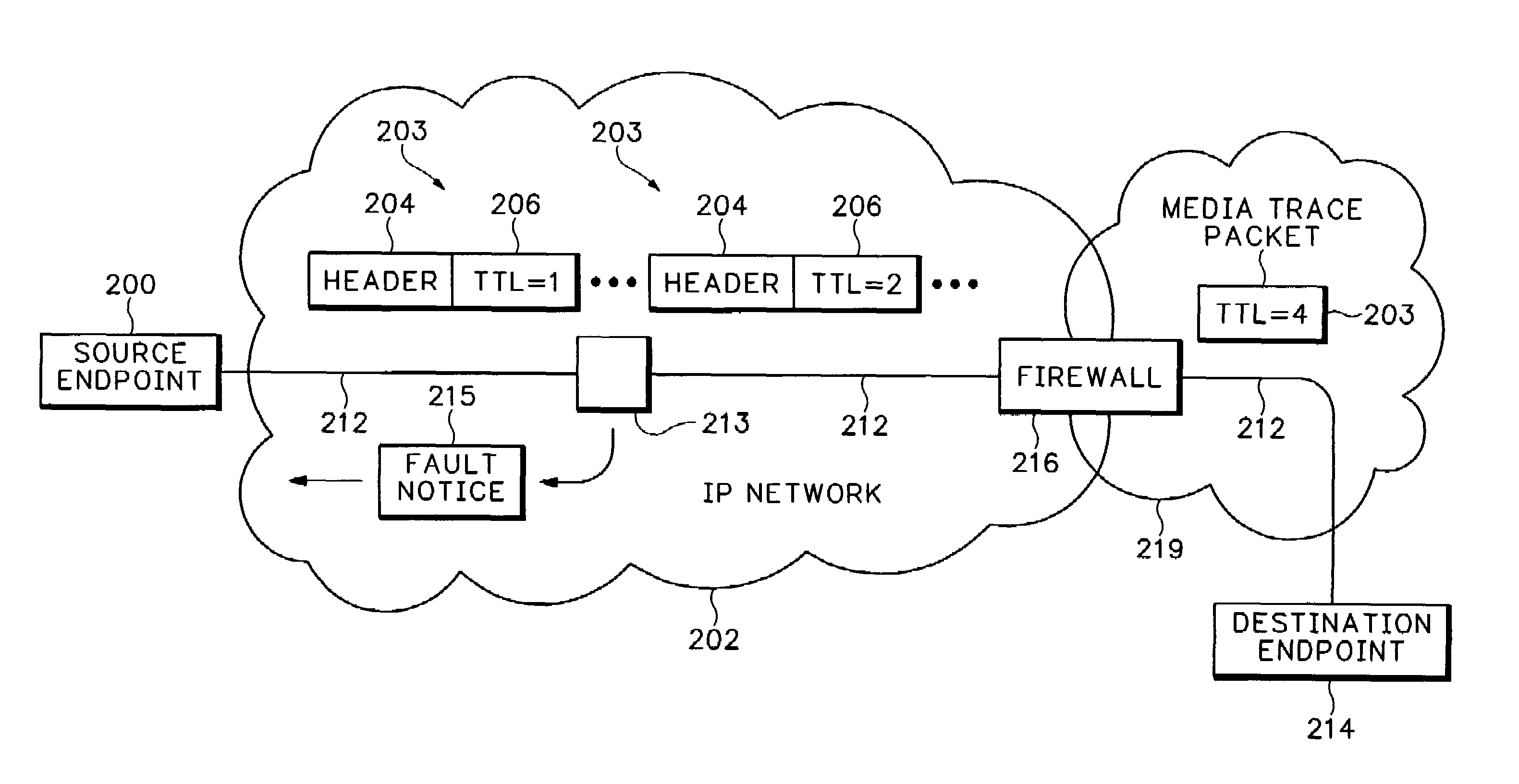
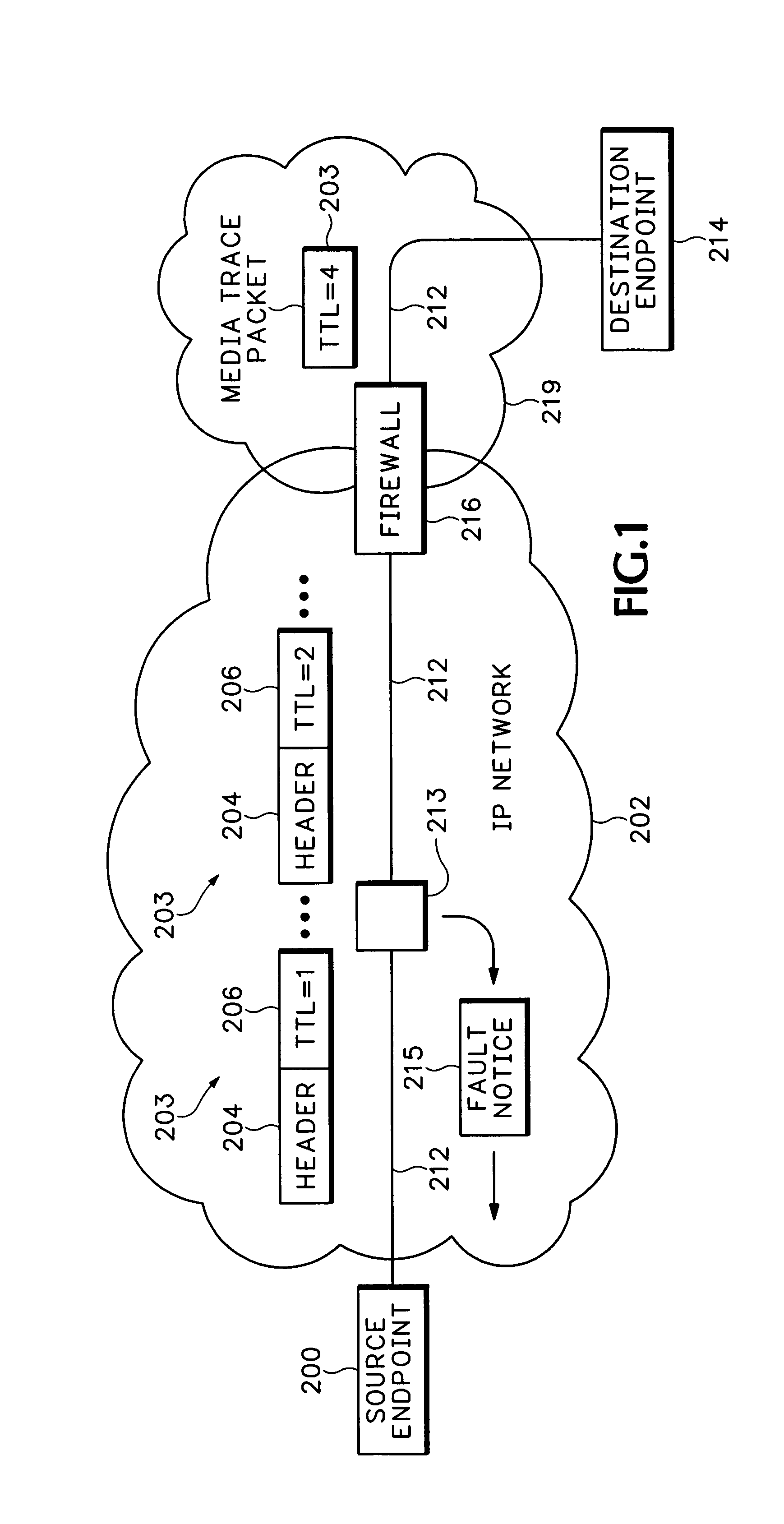
Method and apparatus for analyzing a media path for an internet protocol (IP) media session
Time To Live (TTL) values are modified in media packets to intentionally cause rejection of the media packets at intermediate nodes in a media path. Rejection notices caused by the TTL modified media packets are then analyzed to isolate Quality of Service (QoS) problems in the media path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Systems and methods for dynamically expanding load balancing pool
The present application is directed towards systems and methods for configuring and applying autoscaling to a service group of an intermediary device for a domain based server. All the IP addresses resolved by the domain name of the server and that are determined as up will automatically become members of the service group. The resolver monitor will resolve the server's domain name based on the TTL (Time to Live) value in the address record or whenever the appropriate command is executed. Each time the domain is resolved, if there is a change in the number of IP addresses resolved, then the members of the service group will shrink or expand based on the number of IP addresses resolved
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Systems and Methods for Subscriber Profile Management
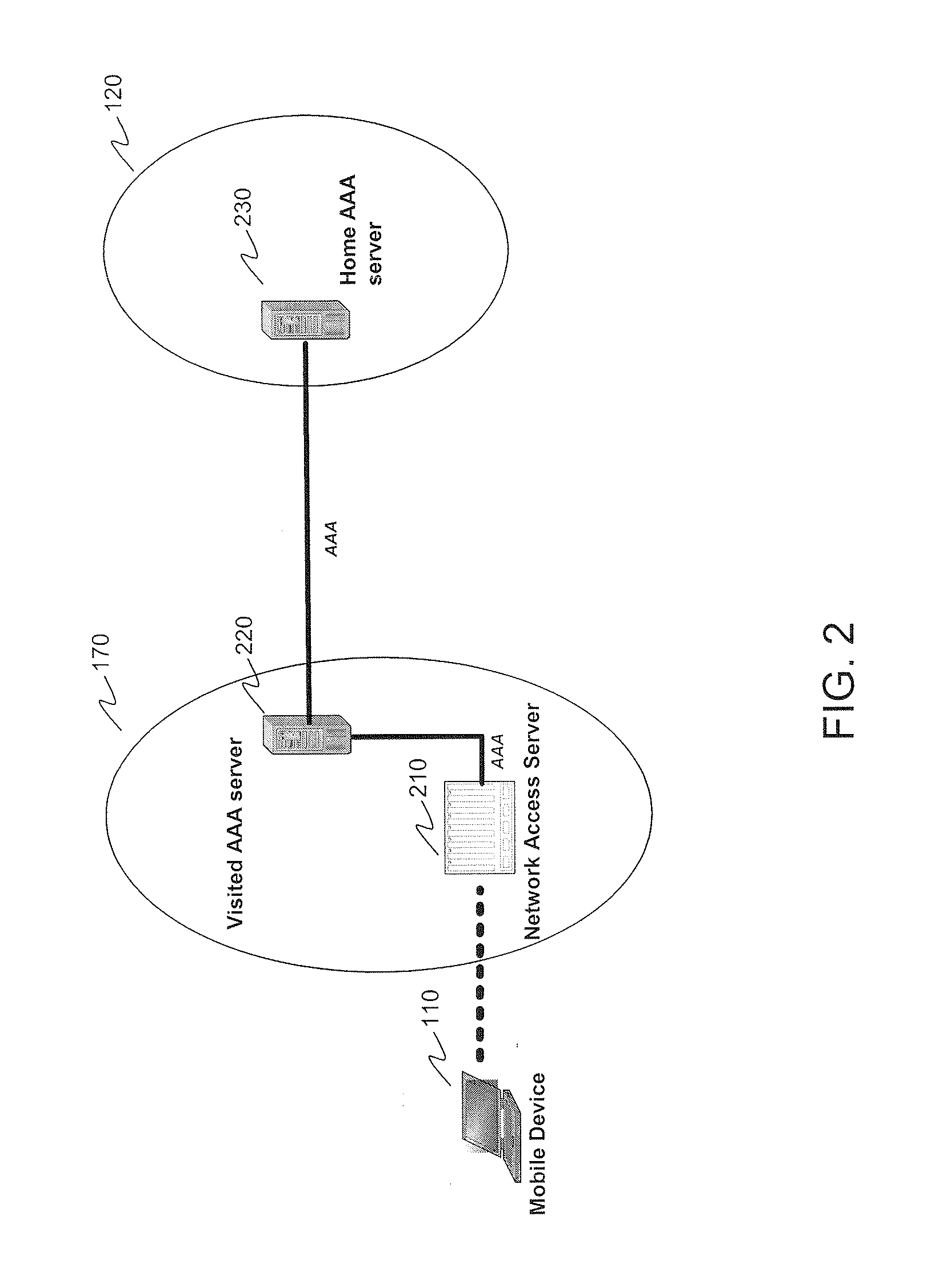
ActiveUS20110124313A1Facilitate seamless roamingAccounting/billing servicesUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionMobile deviceProfile management
Systems and methods subscriber profile management to facilitate seamless roaming of mobile devices from one network to another. A subscriber profile management system is provided that includes a time to live (“TTL”) generator that generates a TTL limit for a subscriber based on usage characteristics of the subscriber. The subscriber profile management system further includes an administration module that administers TTL limits, TTL limit database that store TTL limits, a subscriber profile database that stores subscriber profiles, a usage measurement database that stores usage measurements, and a TTL limit reference module that administers TTLs when a subscriber profile and TTL limit are transmitted. The invention further includes a series of methods that support seamless roaming capabilities of a subscriber throughout visited networks without the need to continually make proxy calls to re-authenticate a subscriber.
Owner:AMDOCS CANADIAN MANAGED SERVICES INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com