Patents
Literature
256 results about "Defragmentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
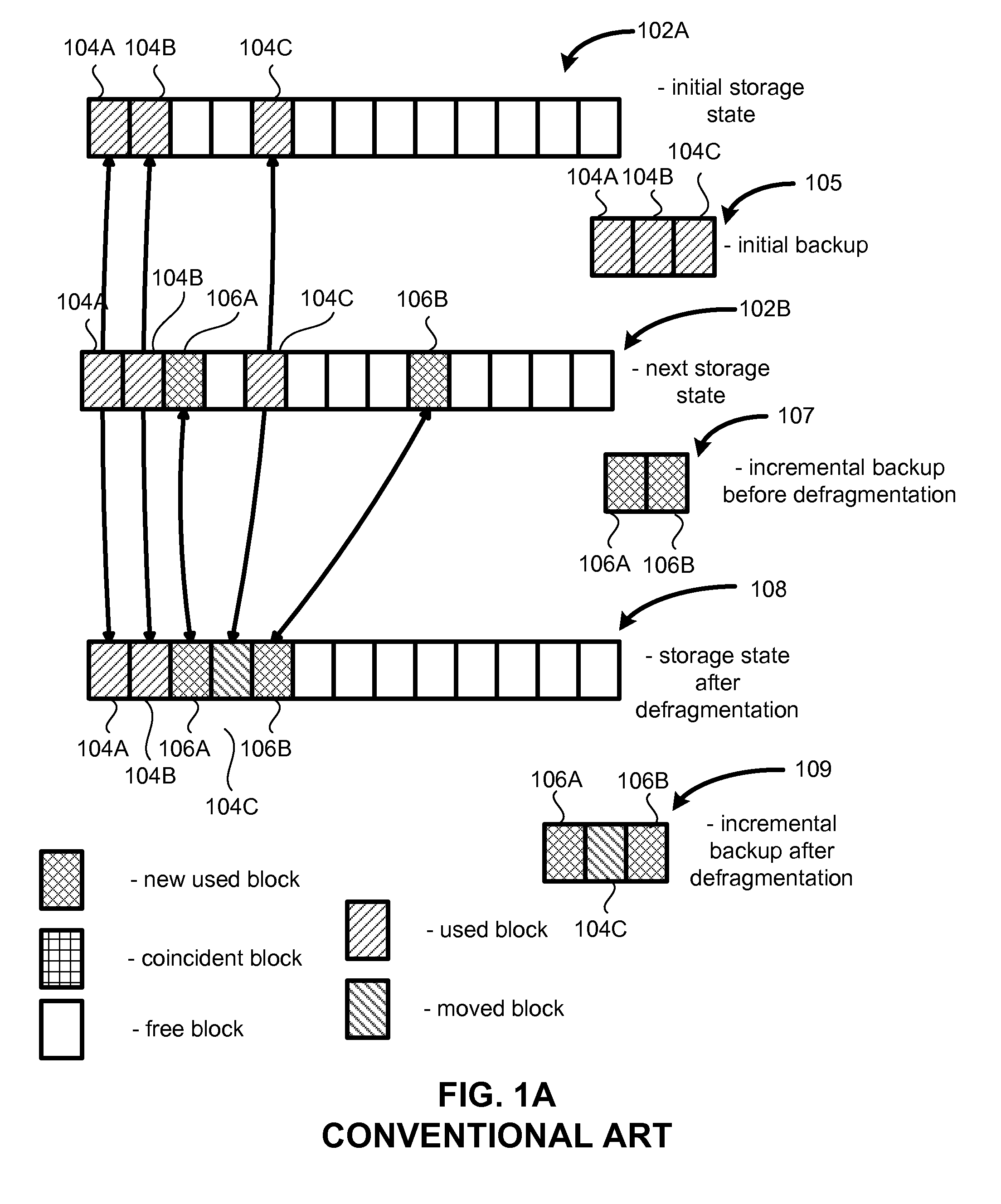
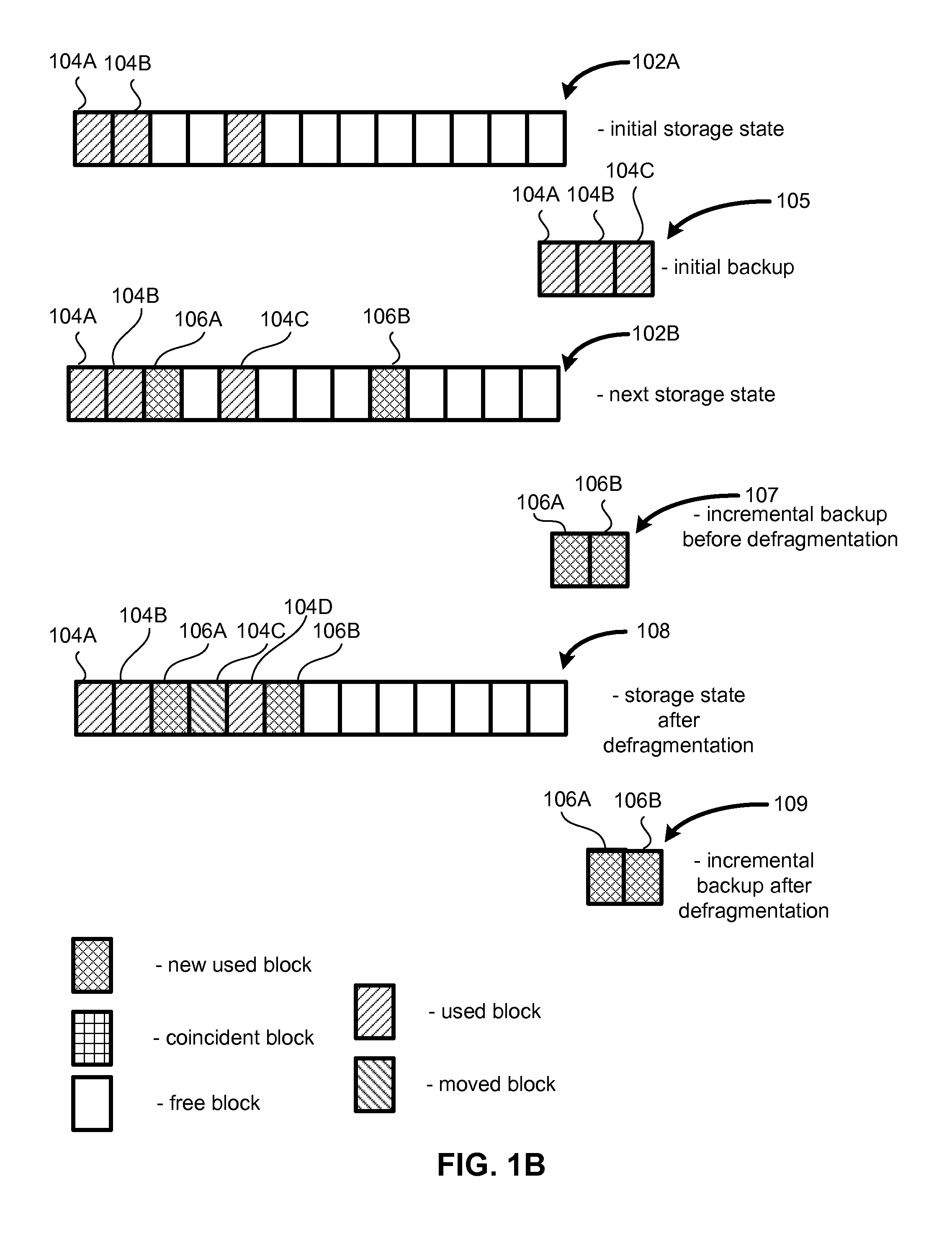
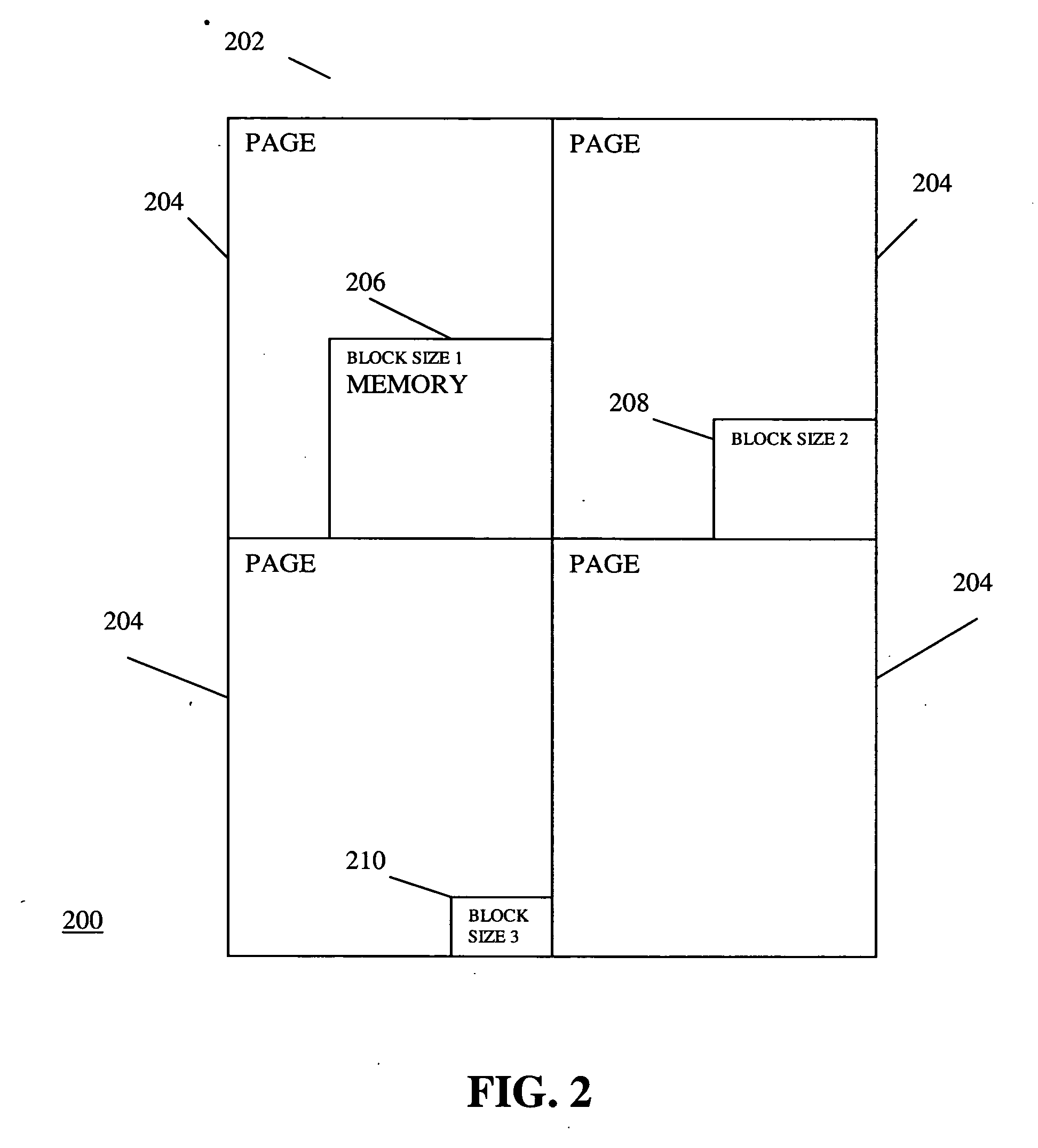
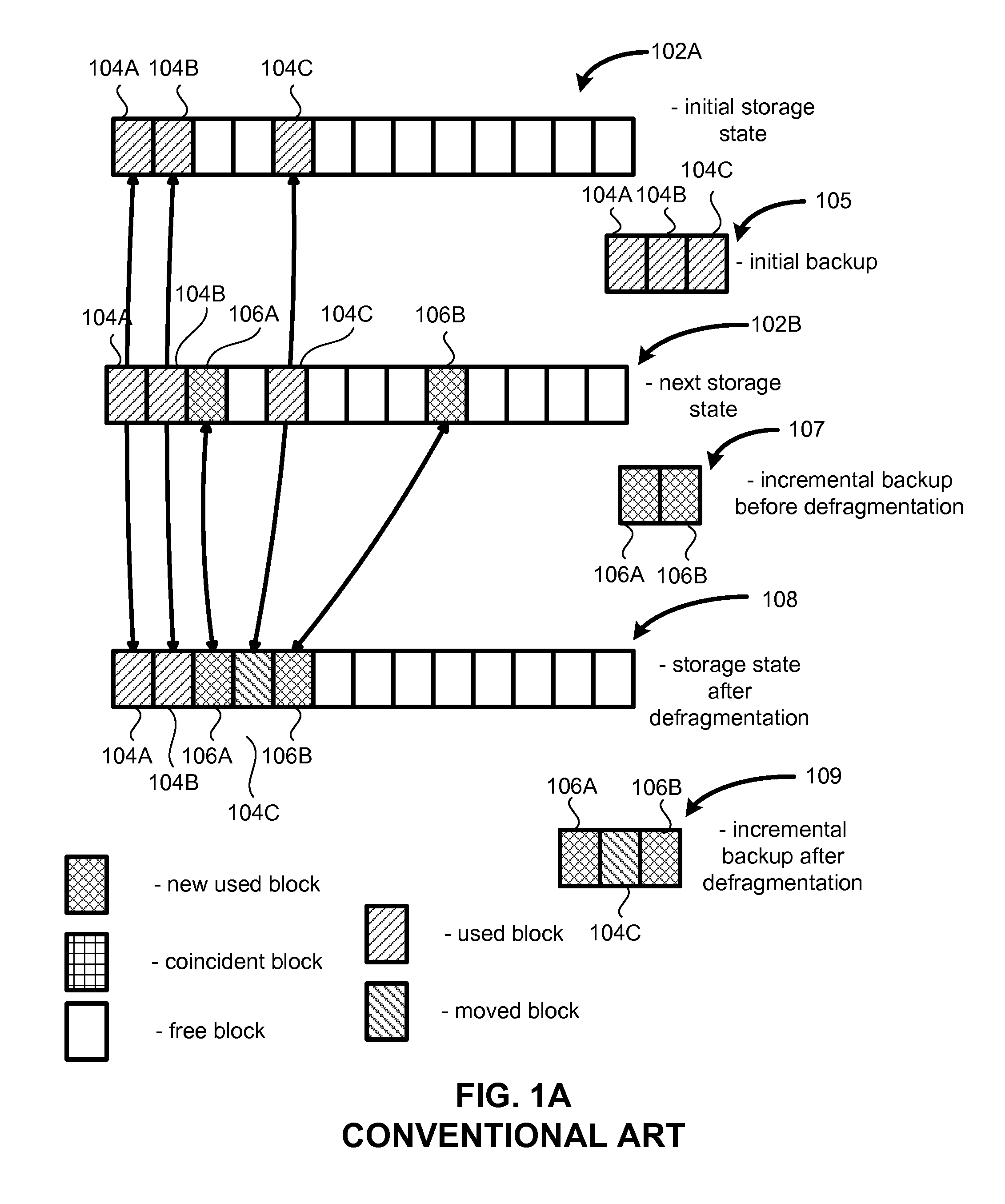
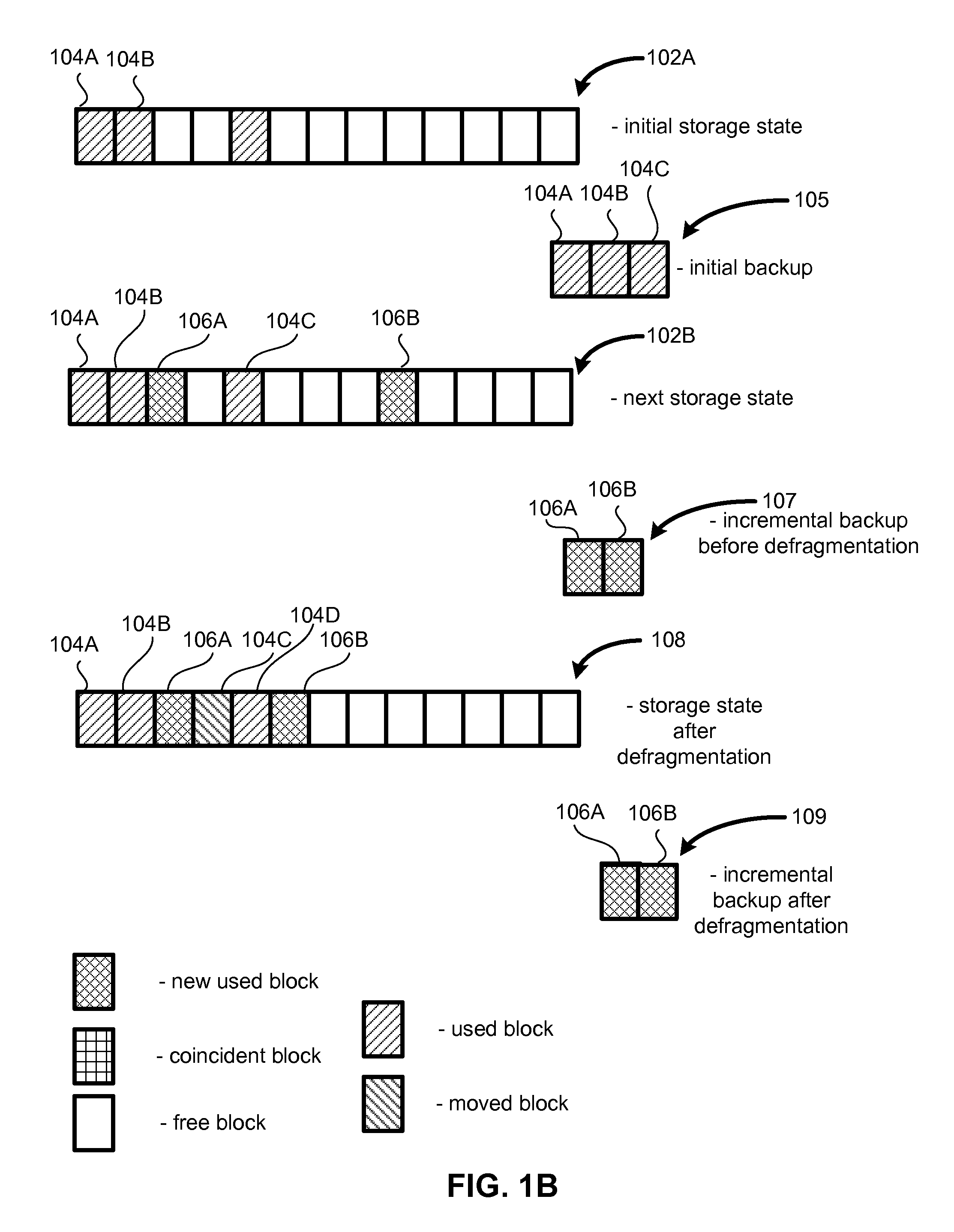
In the maintenance of file systems, defragmentation is a process that reduces the degree of fragmentation. It does this by physically organizing the contents of the mass storage device used to store files into the smallest number of contiguous regions (fragments). It also attempts to create larger regions of free space using compaction to impede the return of fragmentation. Some defragmentation utilities try to keep smaller files within a single directory together, as they are often accessed in sequence.
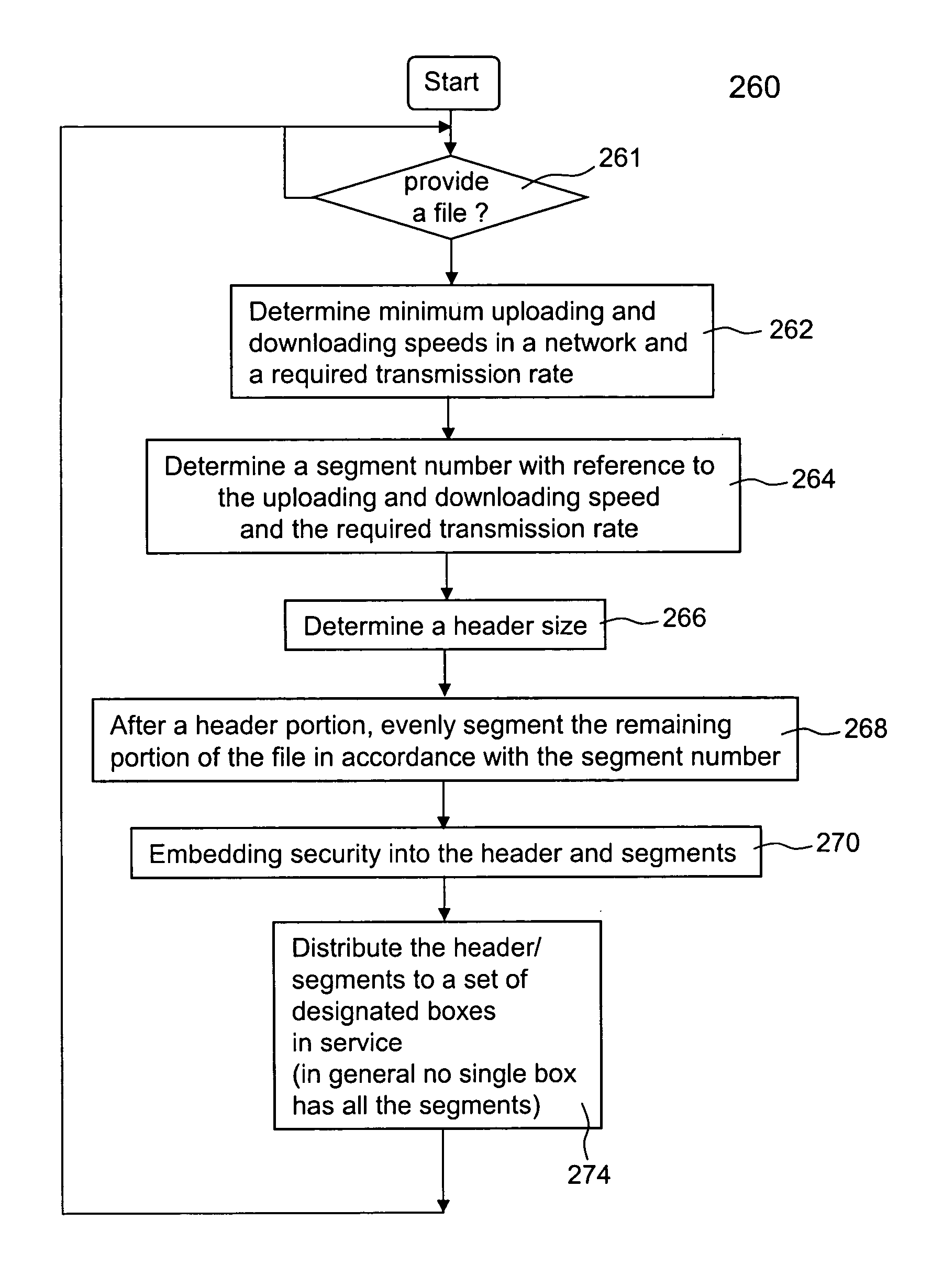
Method for restoring and maintaining solid-state drive performance
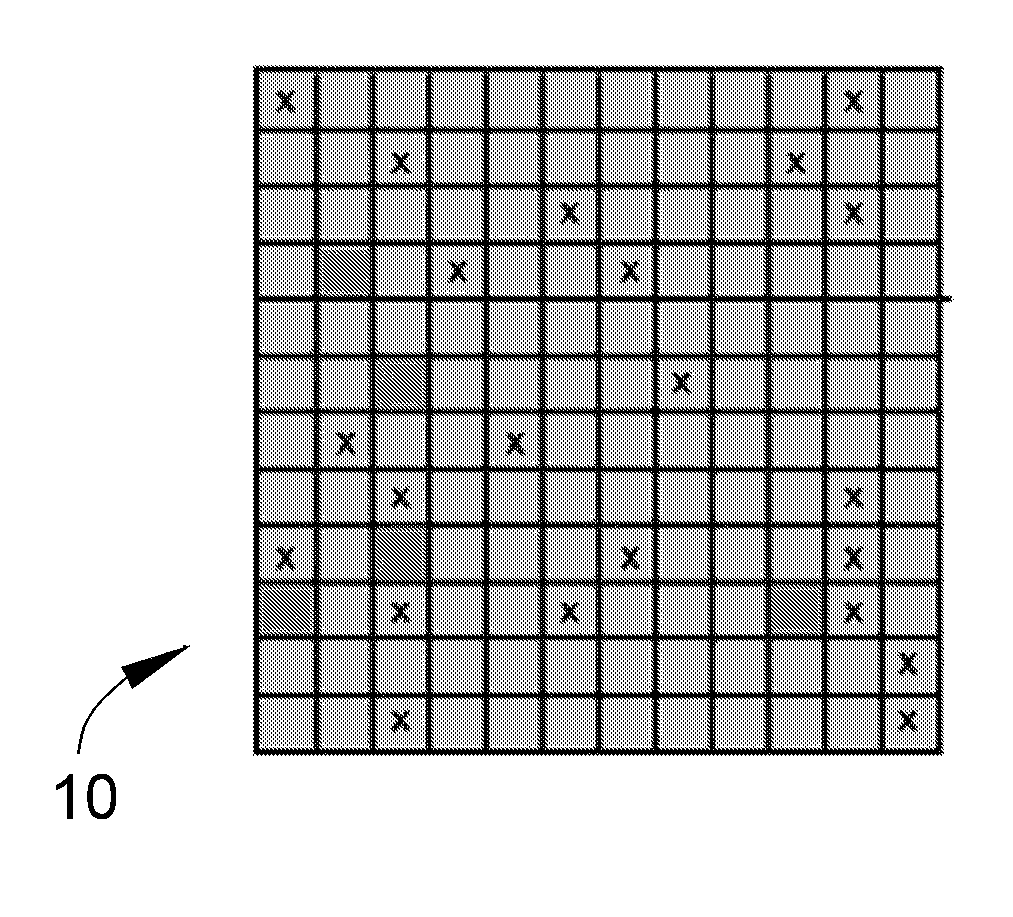
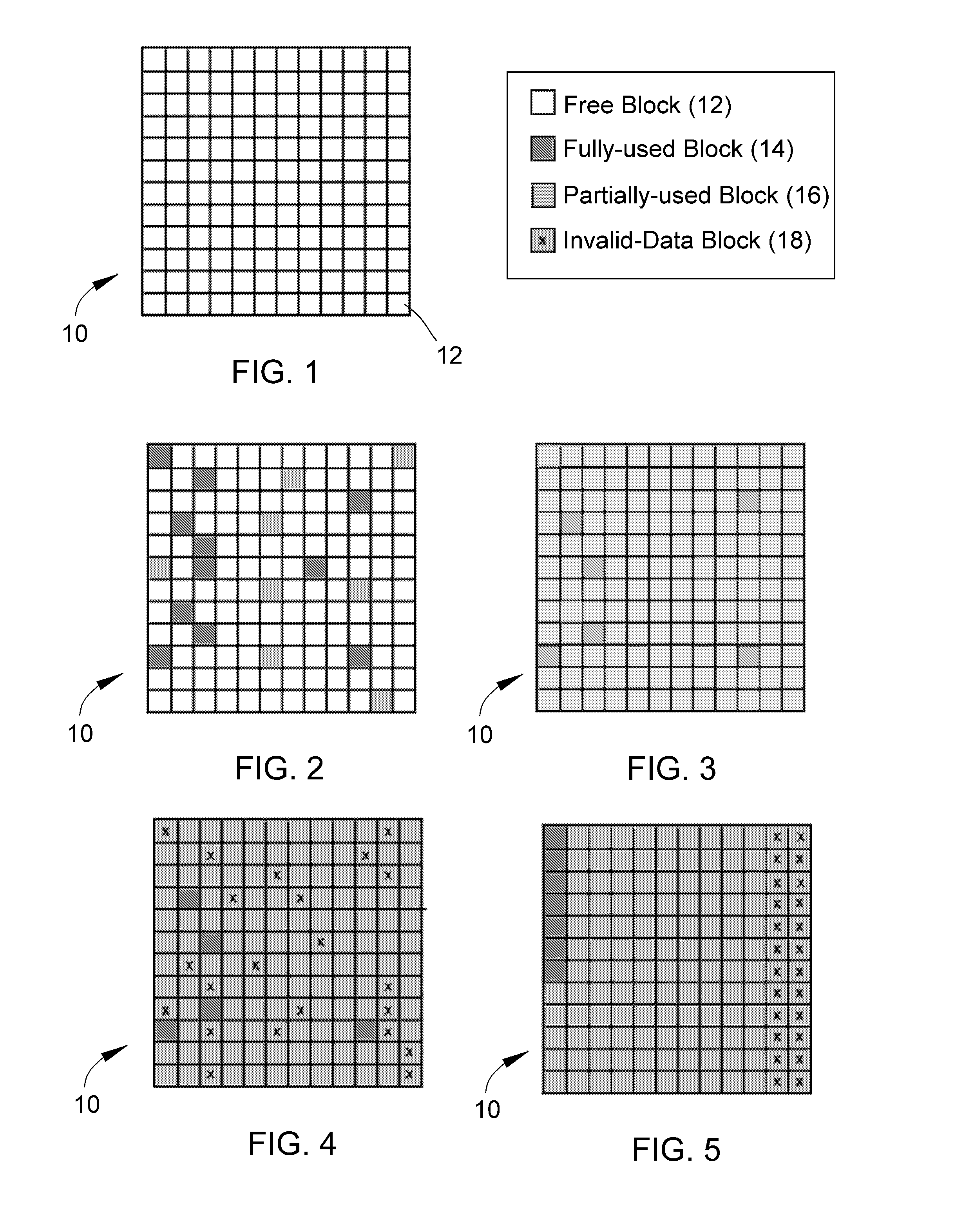
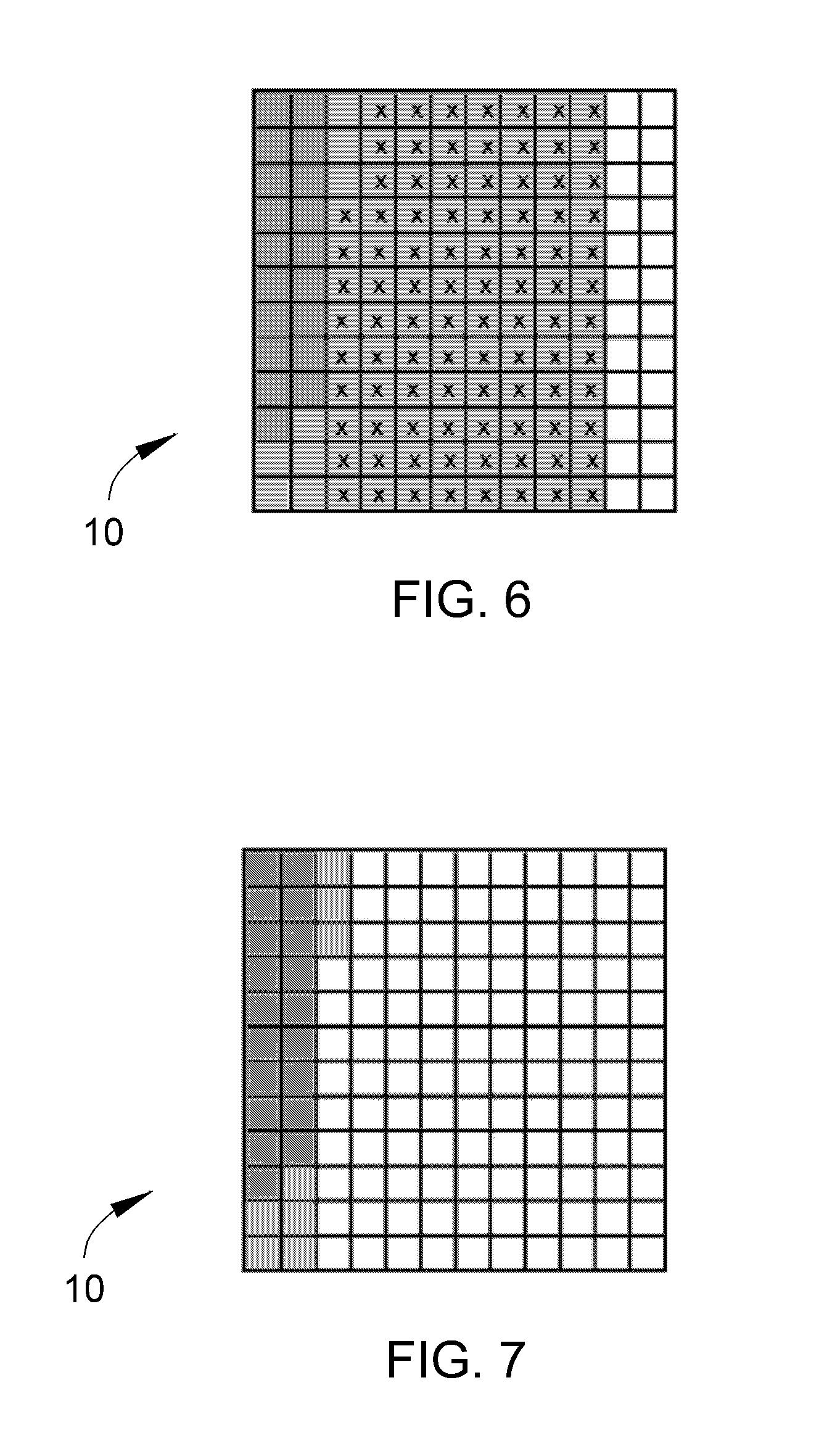
InactiveUS20110119462A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInvalid DataTerm memory
A method of maintaining a solid-state drive so that free space within memory blocks of the drive becomes free usable space to the drive. The drive comprises cells organized in pages that are organized in memory blocks in which at least user files are stored. A defragmentation utility is executed to cause at least some of the memory blocks that are partially filled with data and contain file fragments to be combined or aligned and to cause at least some of the memory blocks that contain only invalid data to be combined or aligned. A block consolidation utility is then executed to eliminate at least some of the partially-filled blocks by consolidating the file fragments into a fewer number of the memory blocks. The consolidation utility also increases the number of memory blocks that contain only invalid memory. All of the memory blocks containing only invalid data are then erased.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
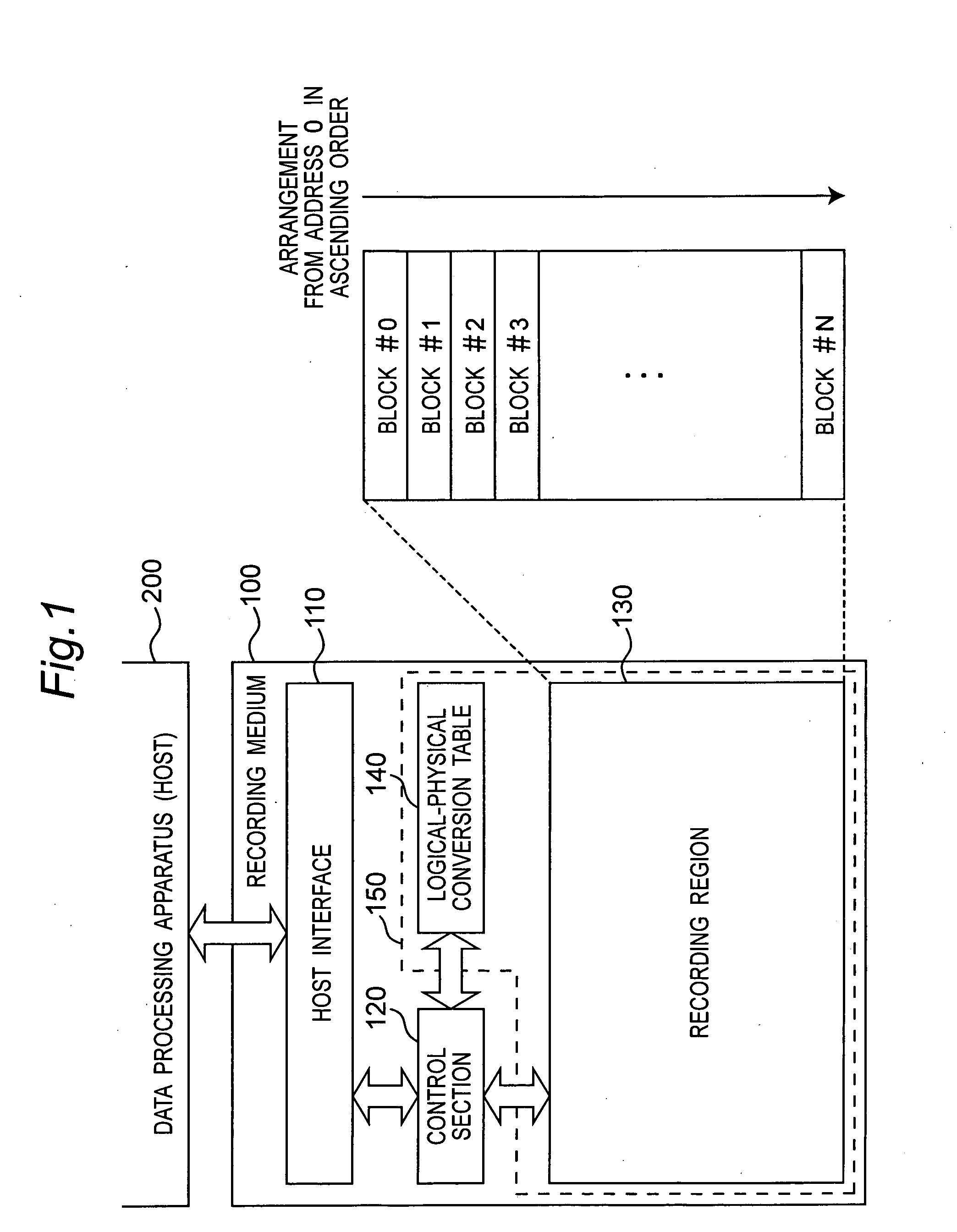
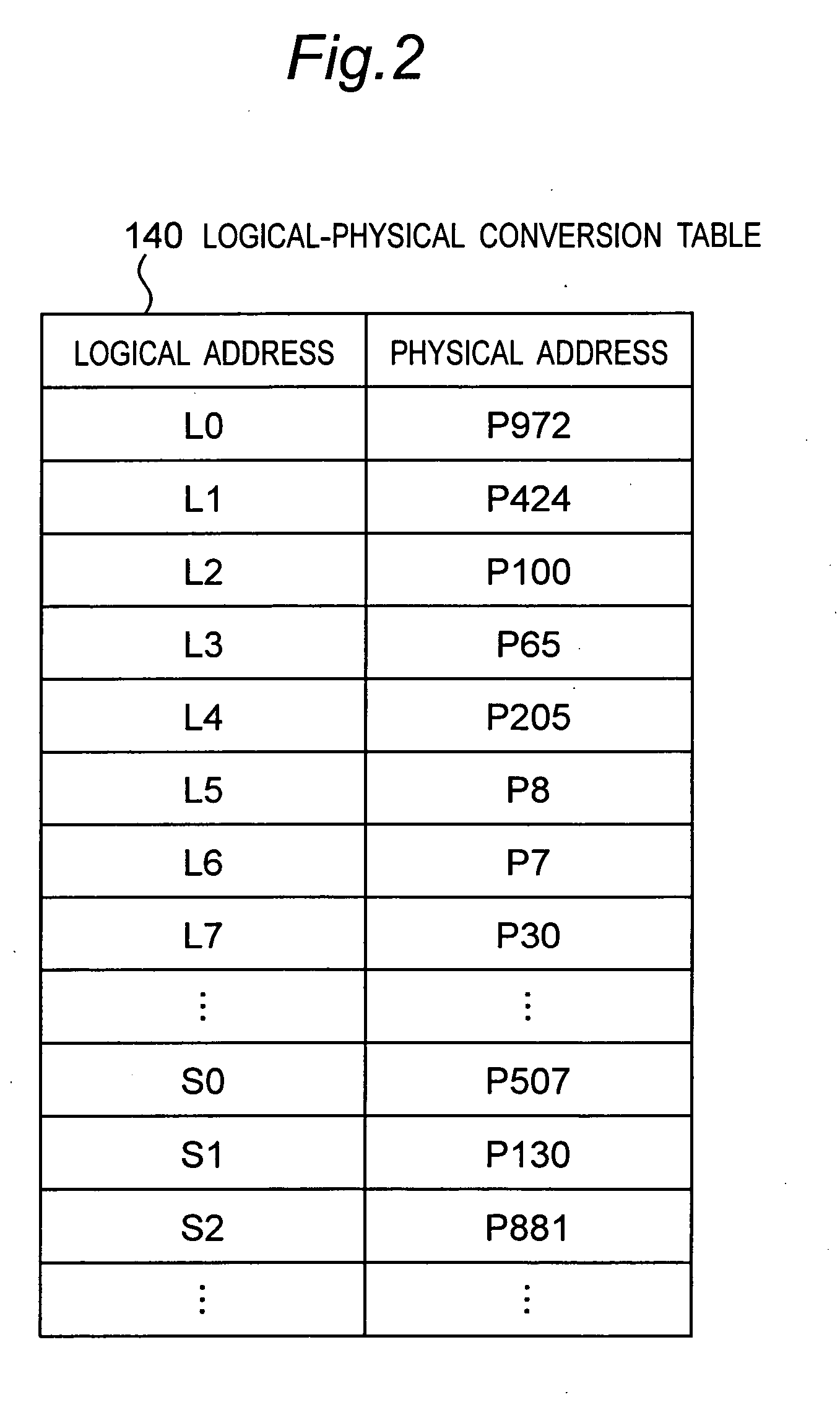
Information recording medium, data processing apparatus and data processing method
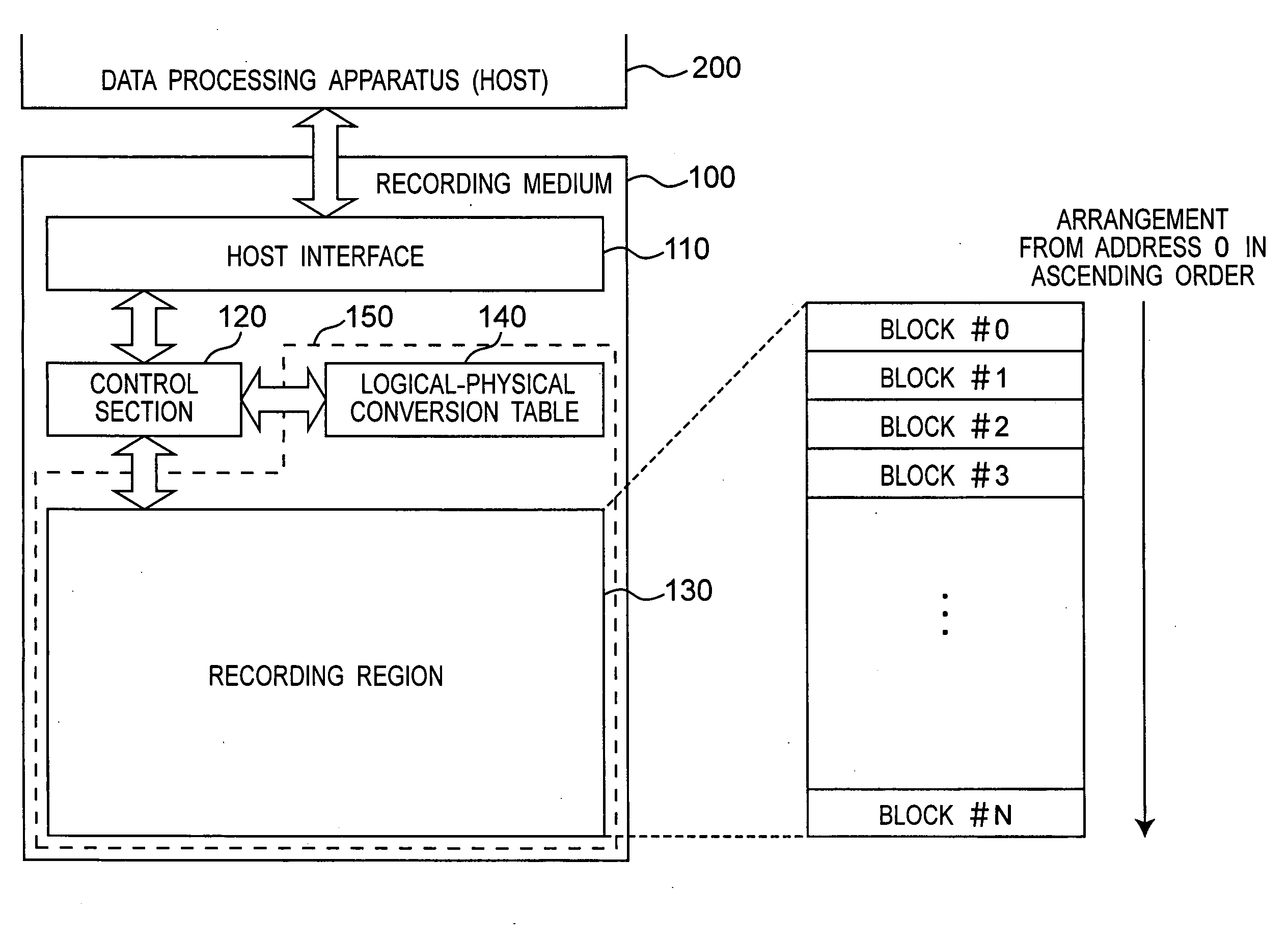
InactiveUS20050231765A1Eliminate data fragmentationIncrease speedDigital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersComputer hardwareRecording media
An apparatus and method which can achieve high-speed data processing and long memory life and is effective to elimination of defragmentation of data, for example, is provided. A recording medium includes a logical-physical conversion table for storing correspondence of a logical address to a physical address of a block in a recording region. The recording medium has a function of replacing correspondence of a logical address to a physical address in the logical-physical conversion table, for a set of logical addresses. A data processing apparatus issues a replace command to the recording medium so that data can be rearranged on a consecutive region in the logical address space, thereby eliminating defragmentaion on the logical address space.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
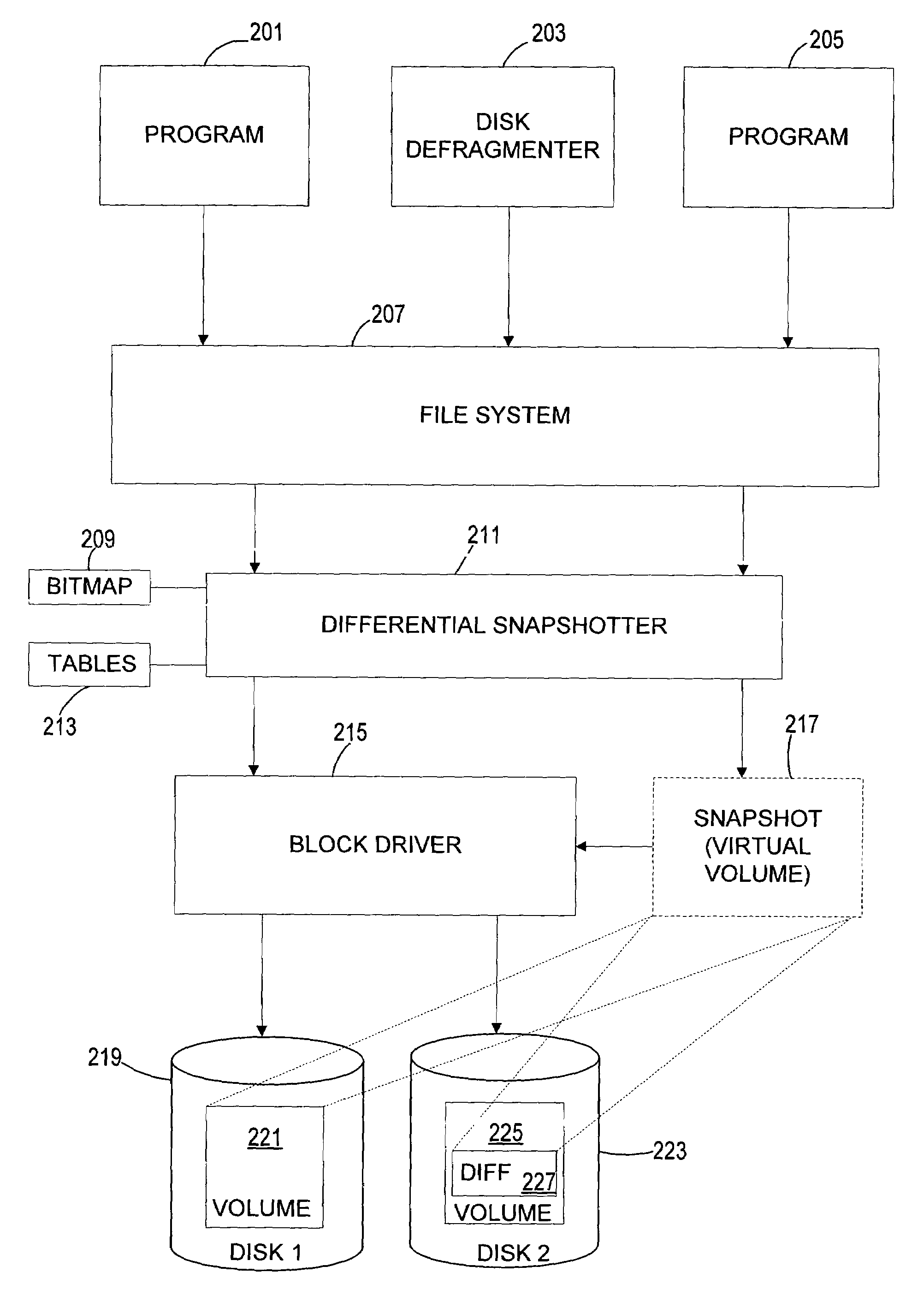
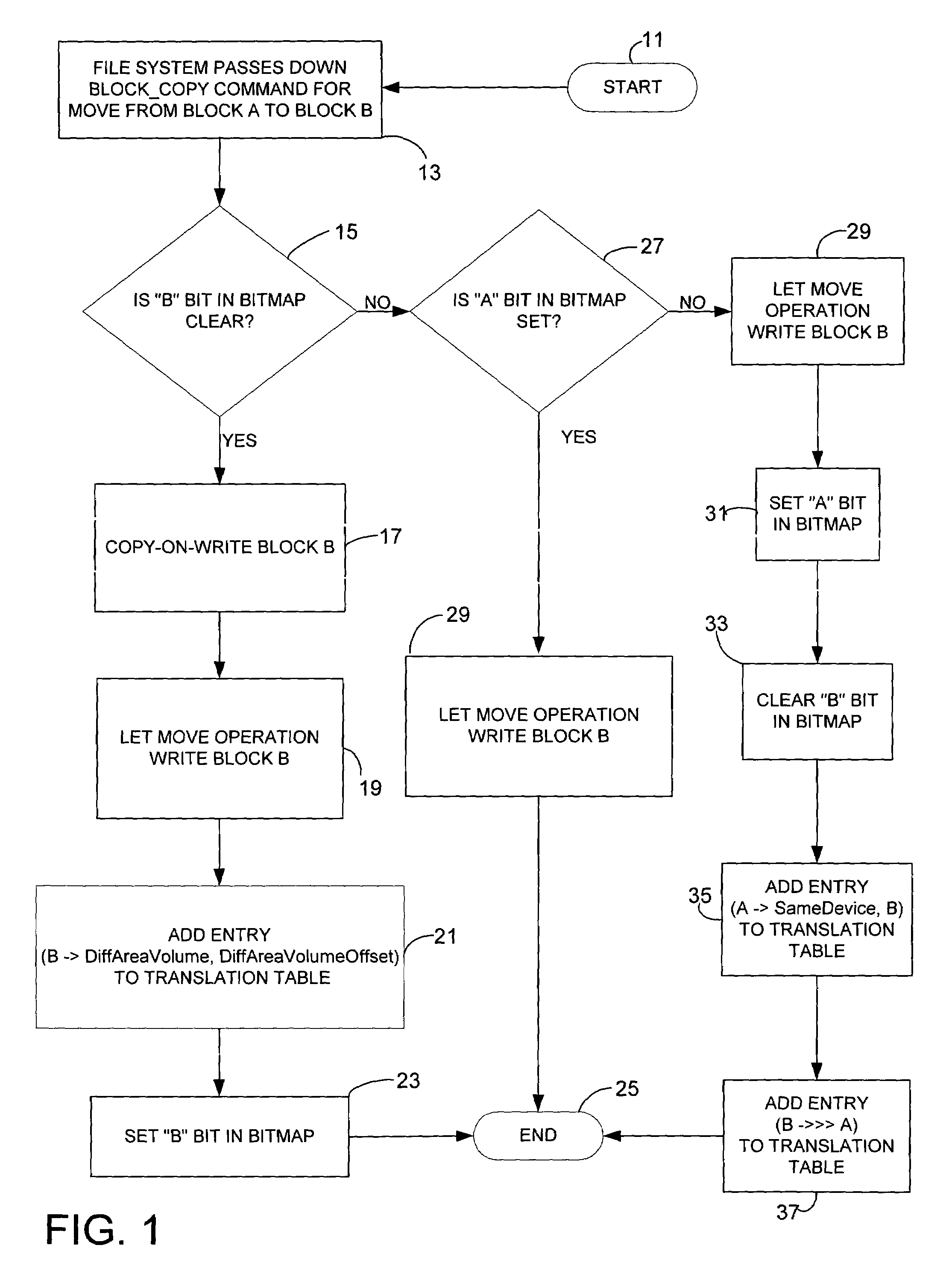
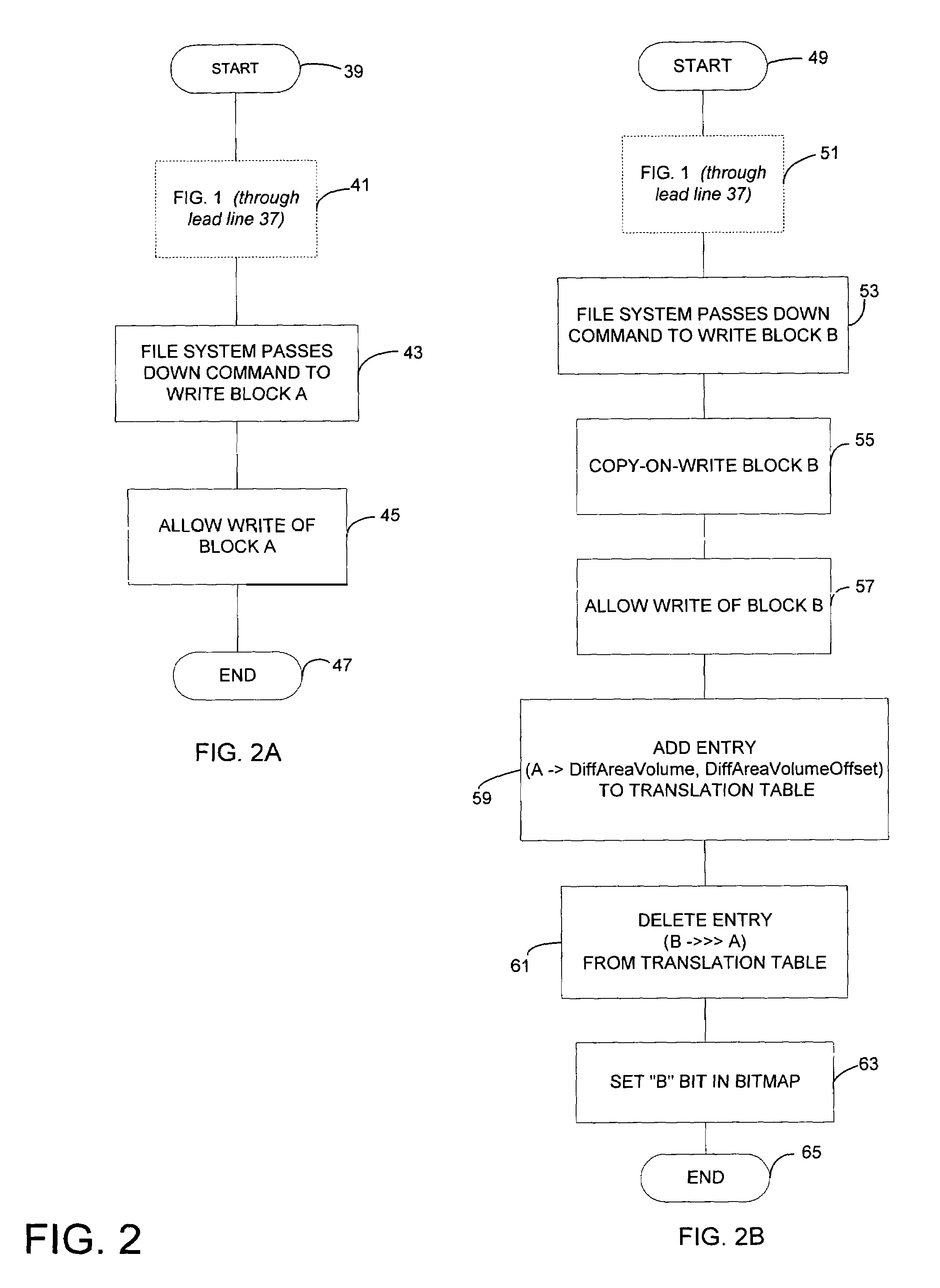
Optimizing defragmentation operations in a differential snapshotter
InactiveUS7664771B2Avoid unnecessary copy-on-write operationInput/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsFile systemTranslation table
A differential snapshot is established and maintained for a set of files stored on a volume. Copy-on-write operations are avoided for logically insignificant moves of blocks, such as the block rearrangements characteristic of defragmentation utilities. A file system passes a block copy command to lower-level drivers that are to inform the snapshotter that a block move operation is not logically meaningful. When the logically insignificant move is of a block whose data forms part of the data captured in the snapshot virtual volume, and when the move is to a block location that is functioning as logical free space, the snapshotter can simply modify its block bitmap and update translation table entries without needing to perform a copy-on-write.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
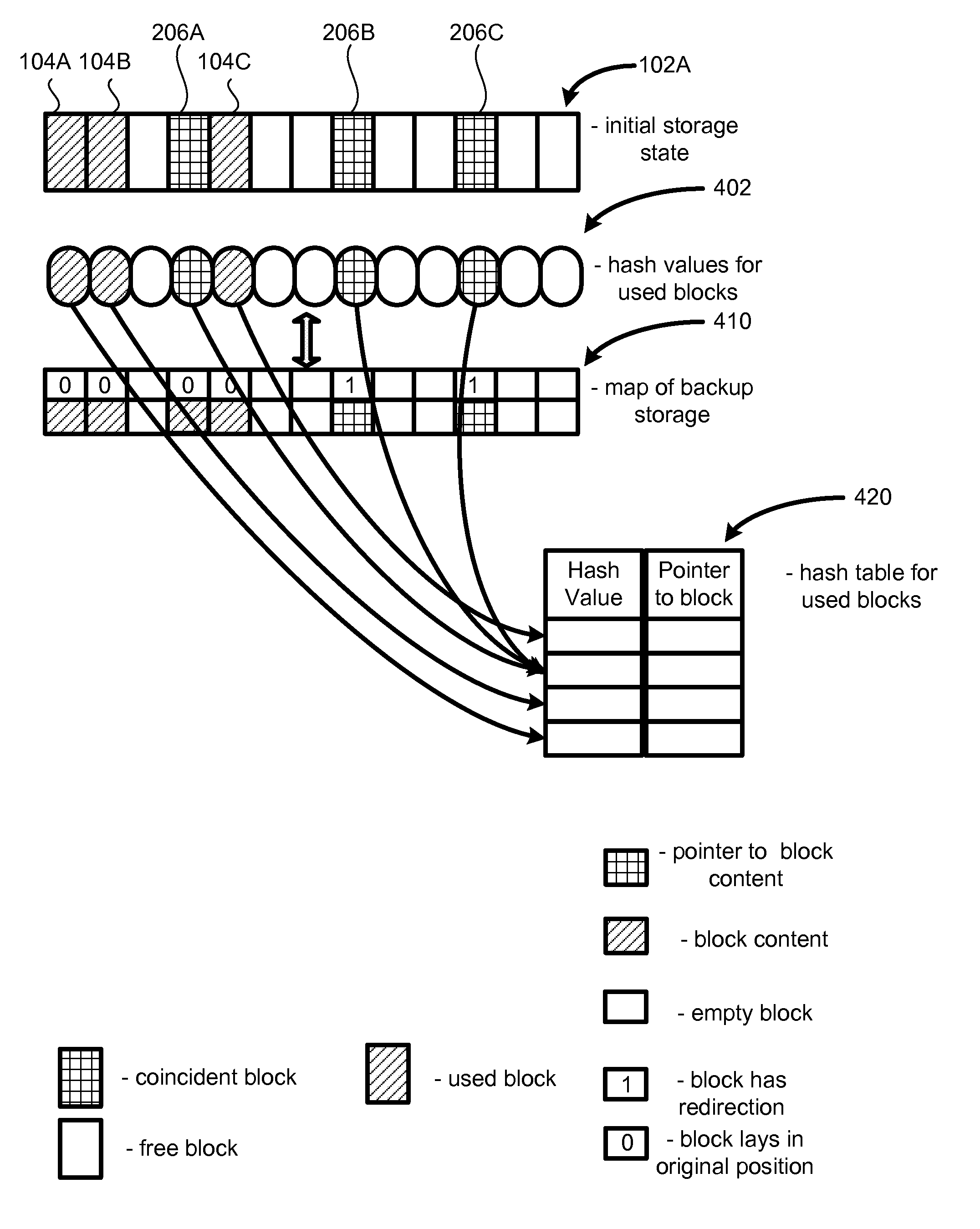
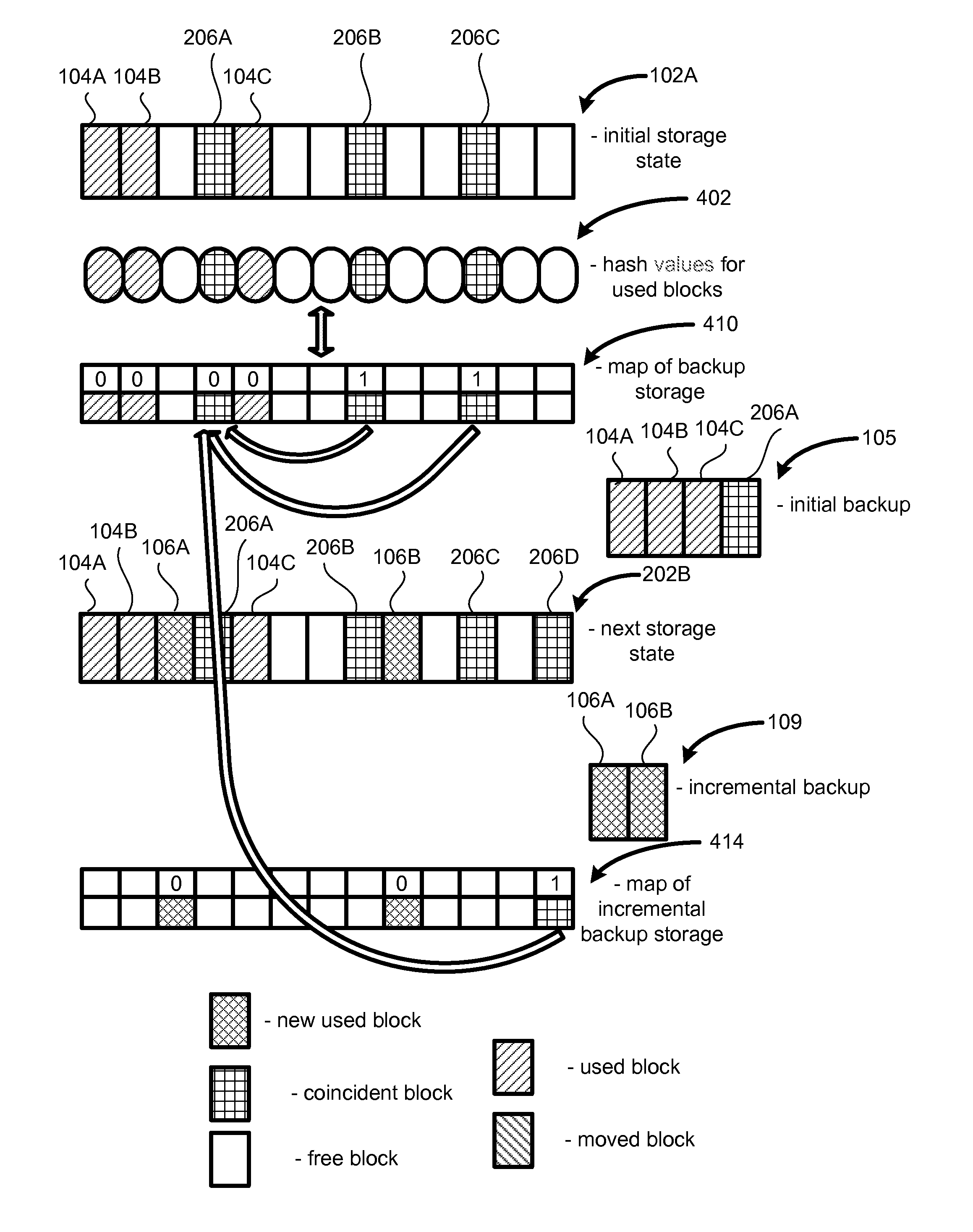
System and method for efficient backup using hashes
ActiveUS7636824B1Easy to useImprove backup efficiencyError detection/correctionMemory systemsHash functionRemovable media
A method, system and computer program product for data backup such that: for each block of a storage device to be backed up to an image, generating a hash function value corresponding to contents of that block; generating a map of links between blocks in the image and corresponding blocks the storage device; using the hash function values to identify blocks of the storage device with identical contents, such that links for the blocks in the storage device with identical contents point to a single block in the image; and modifying the link in the map when a block in the storage is moved (for example, due to defragmentation) but its contents is not altered, so that the link points to the same backed up block.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
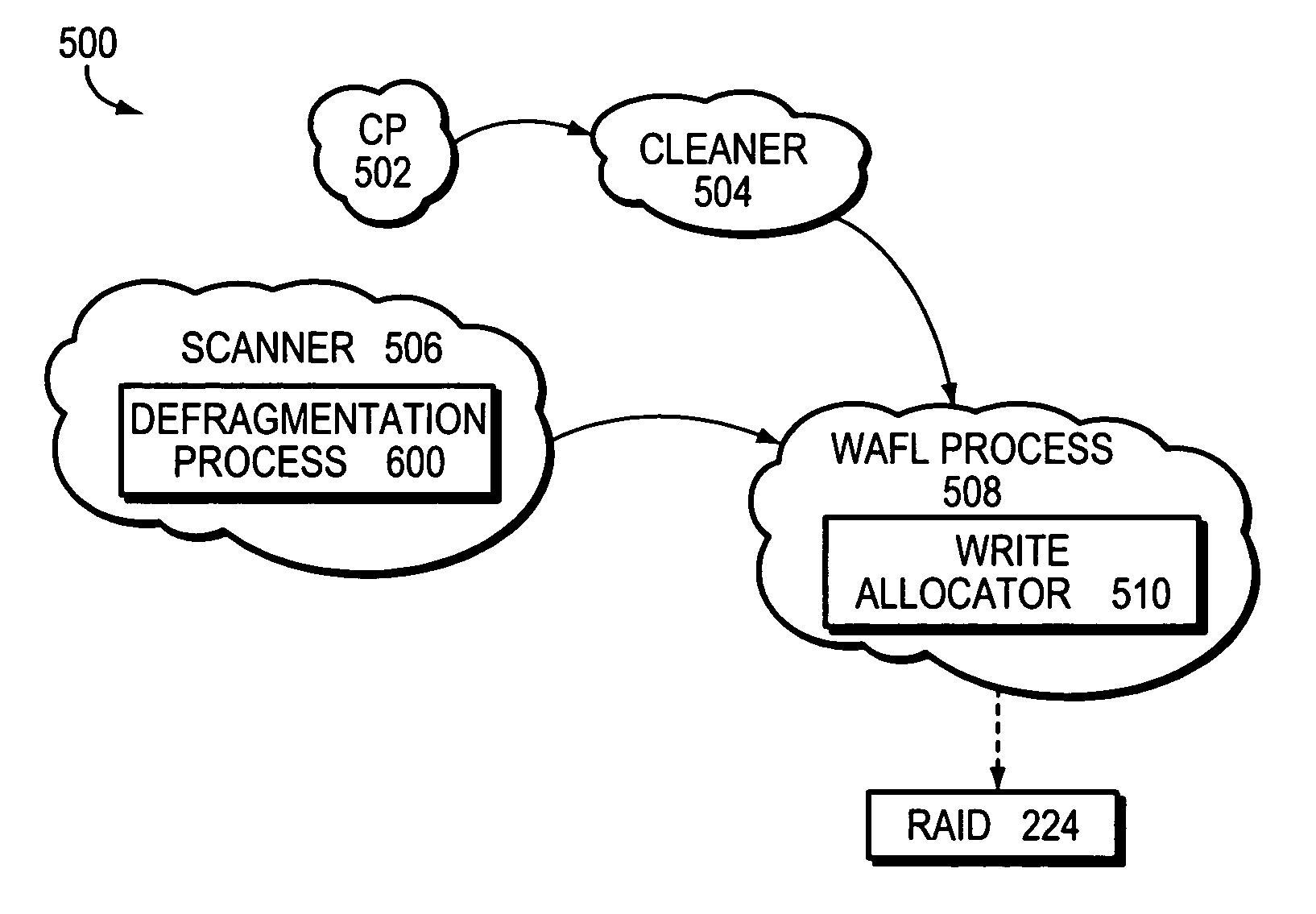
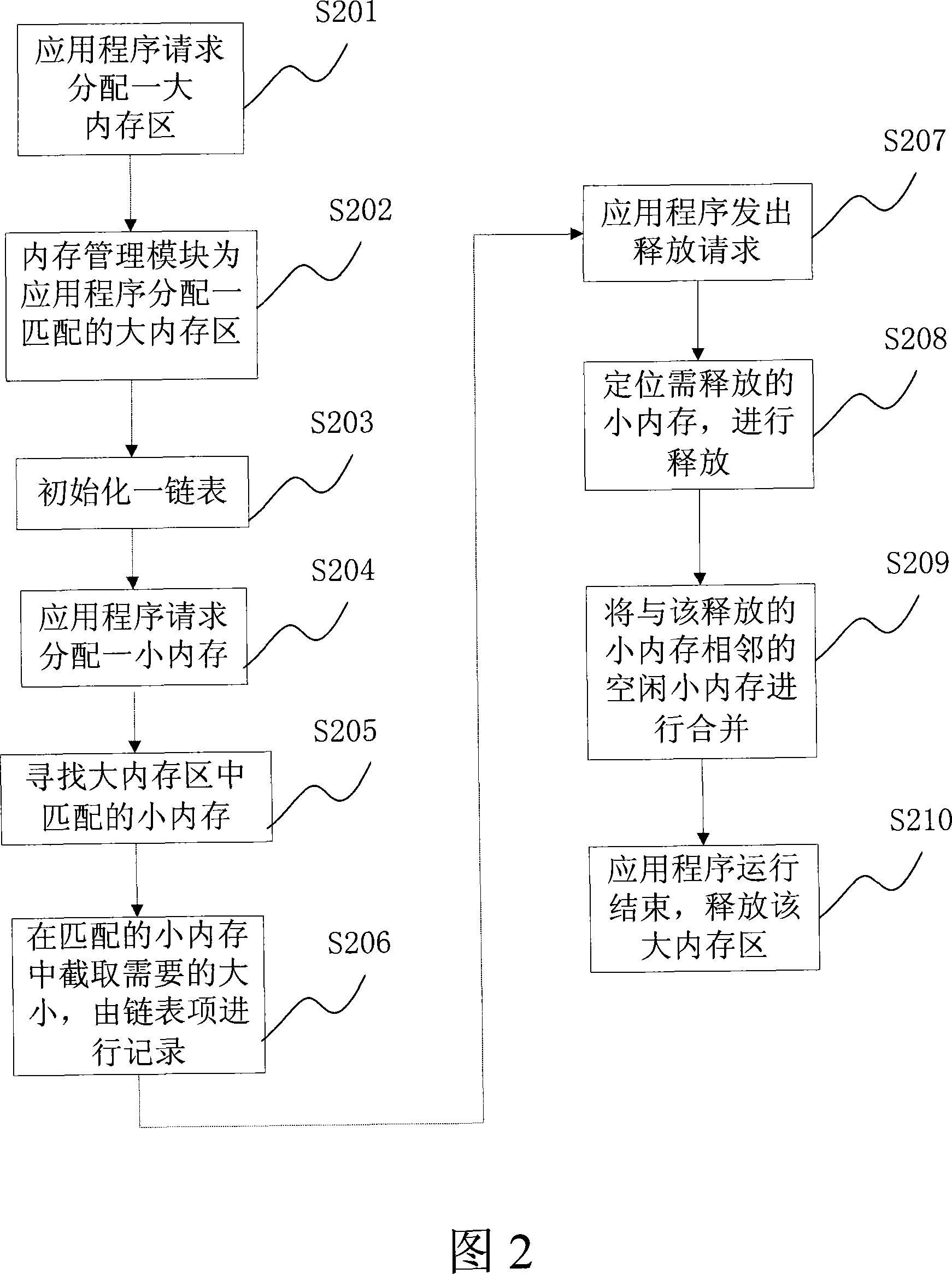
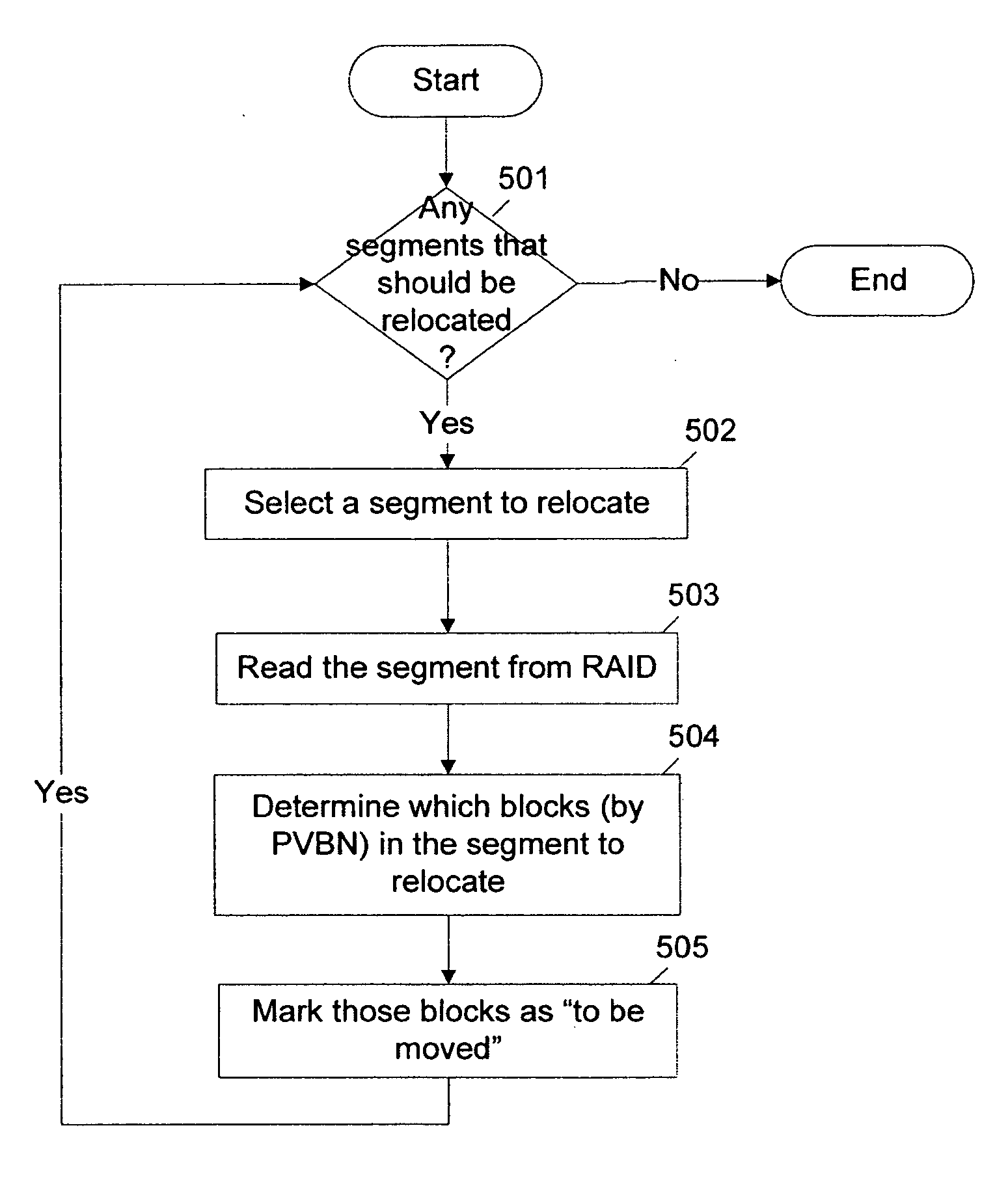
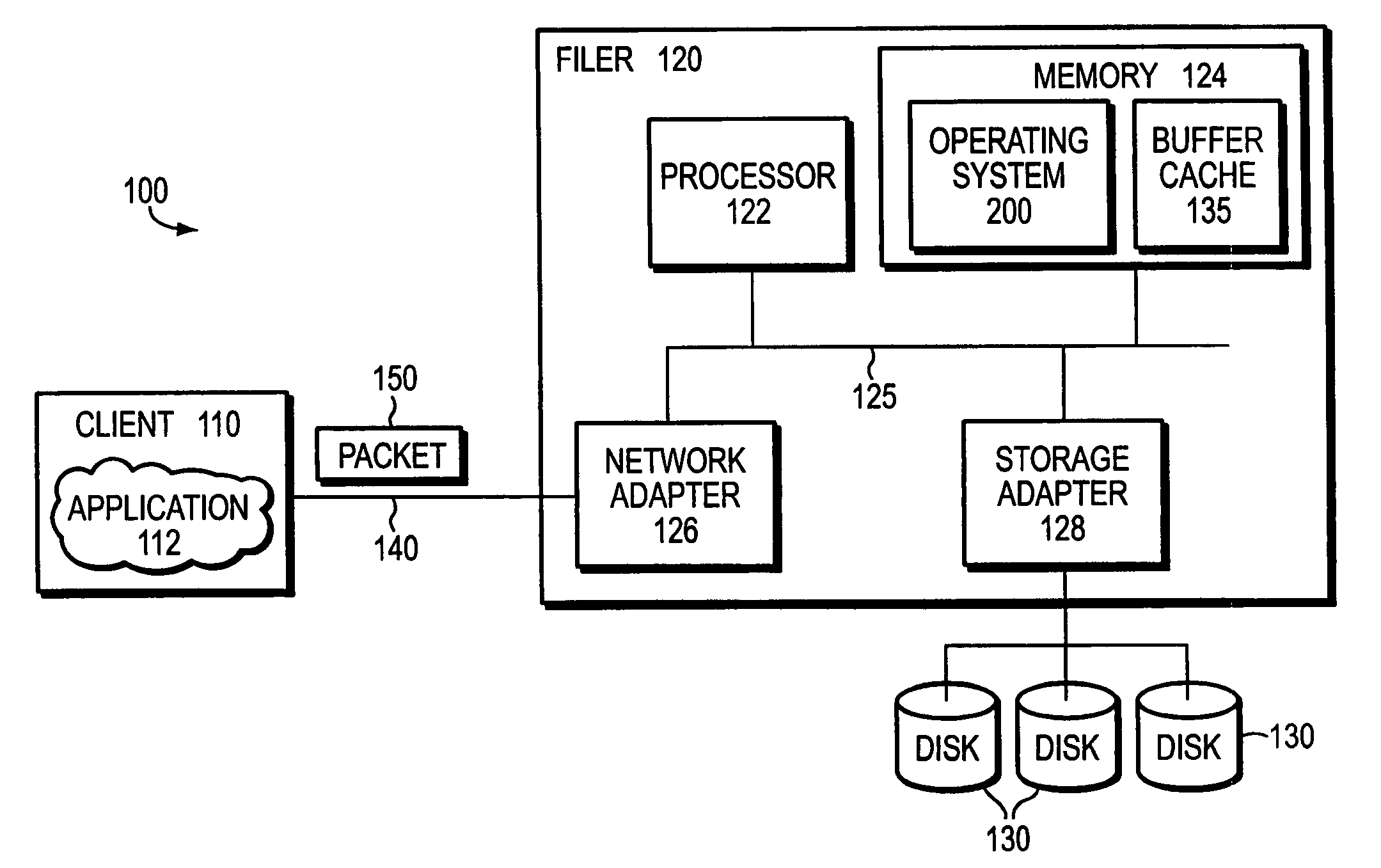
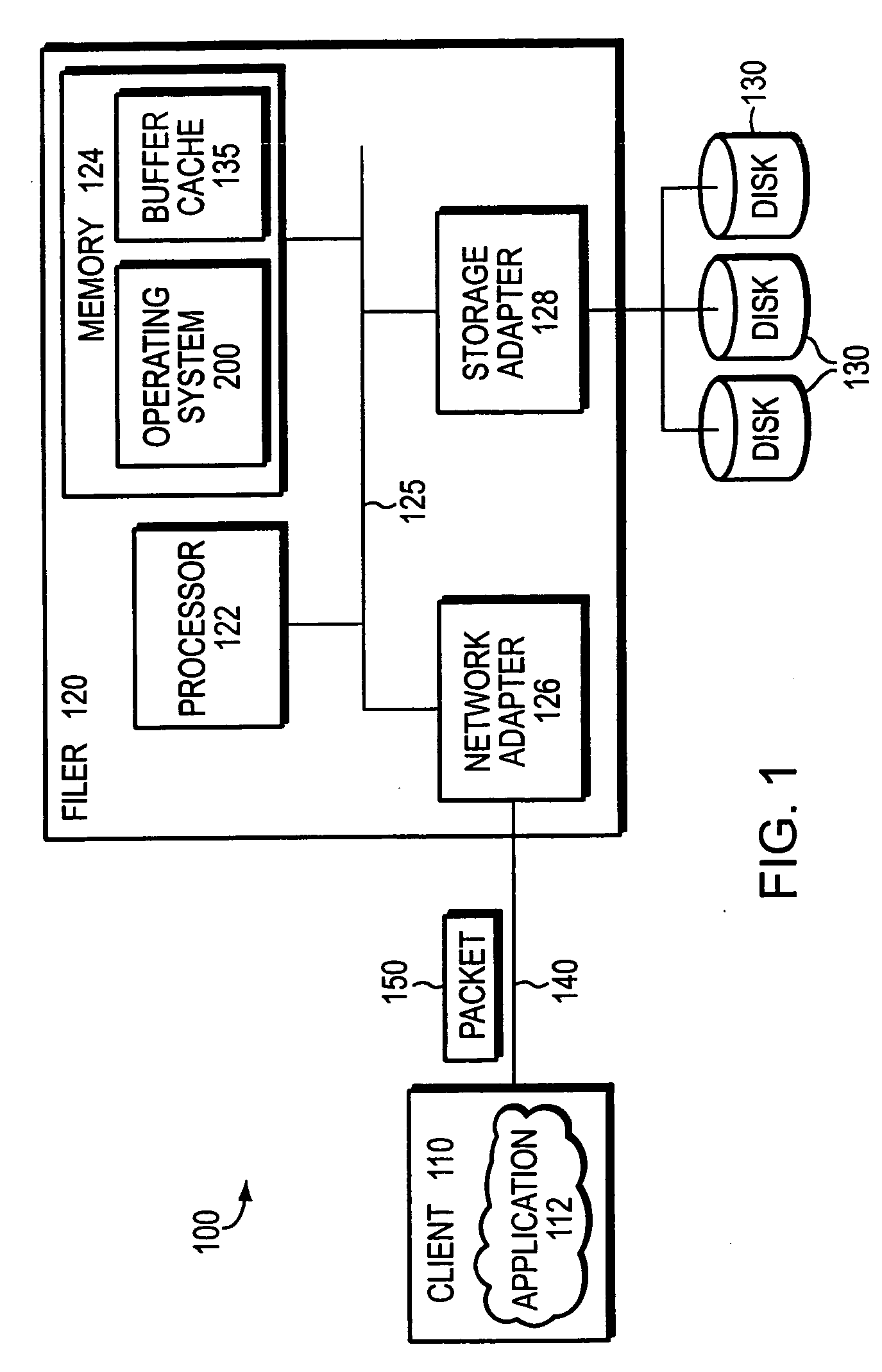
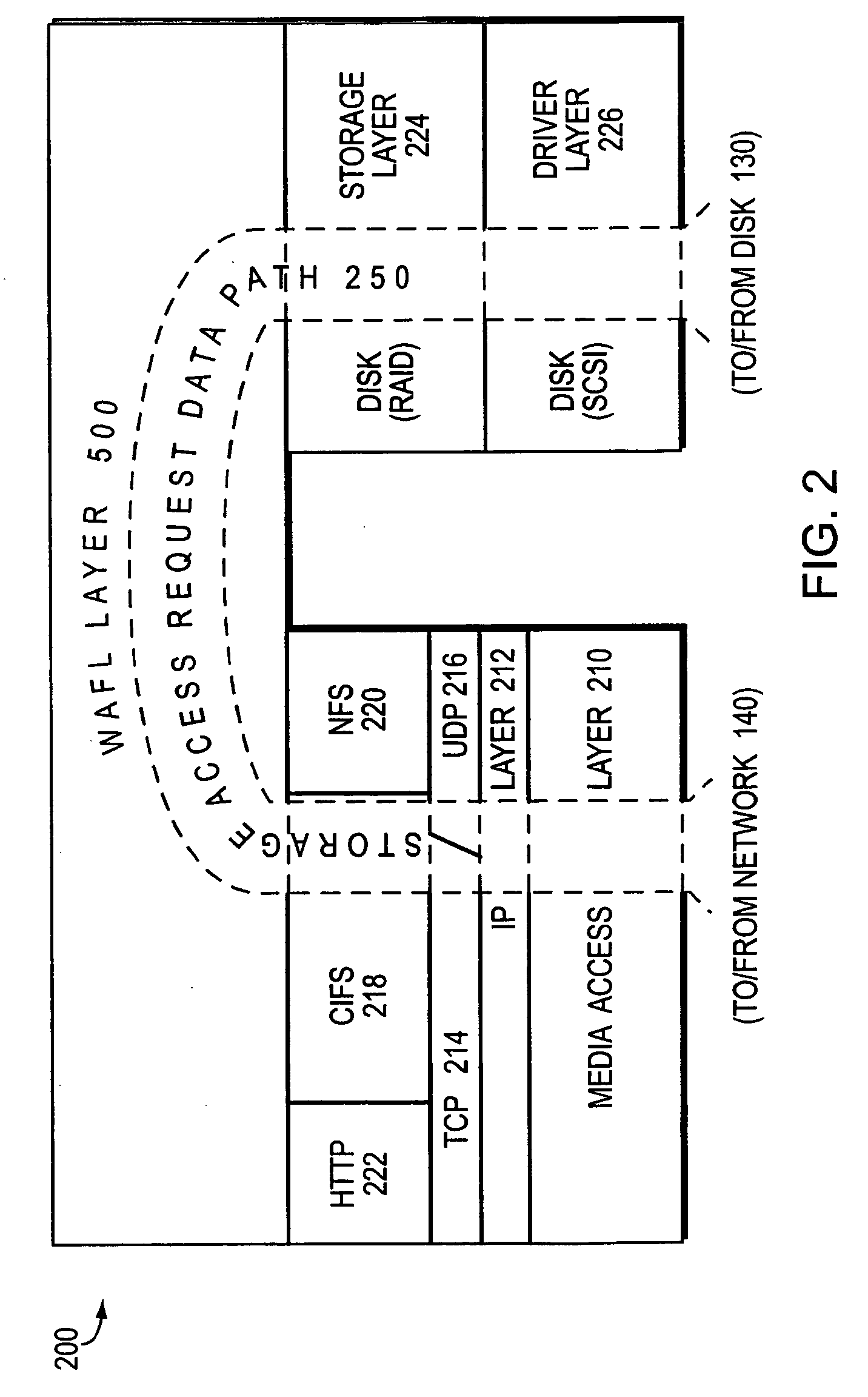
File system defragmentation technique via write allocation
InactiveUS6978283B1Efficiently relocatedPromote fragmentationDigital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersComputer hardwareShard
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
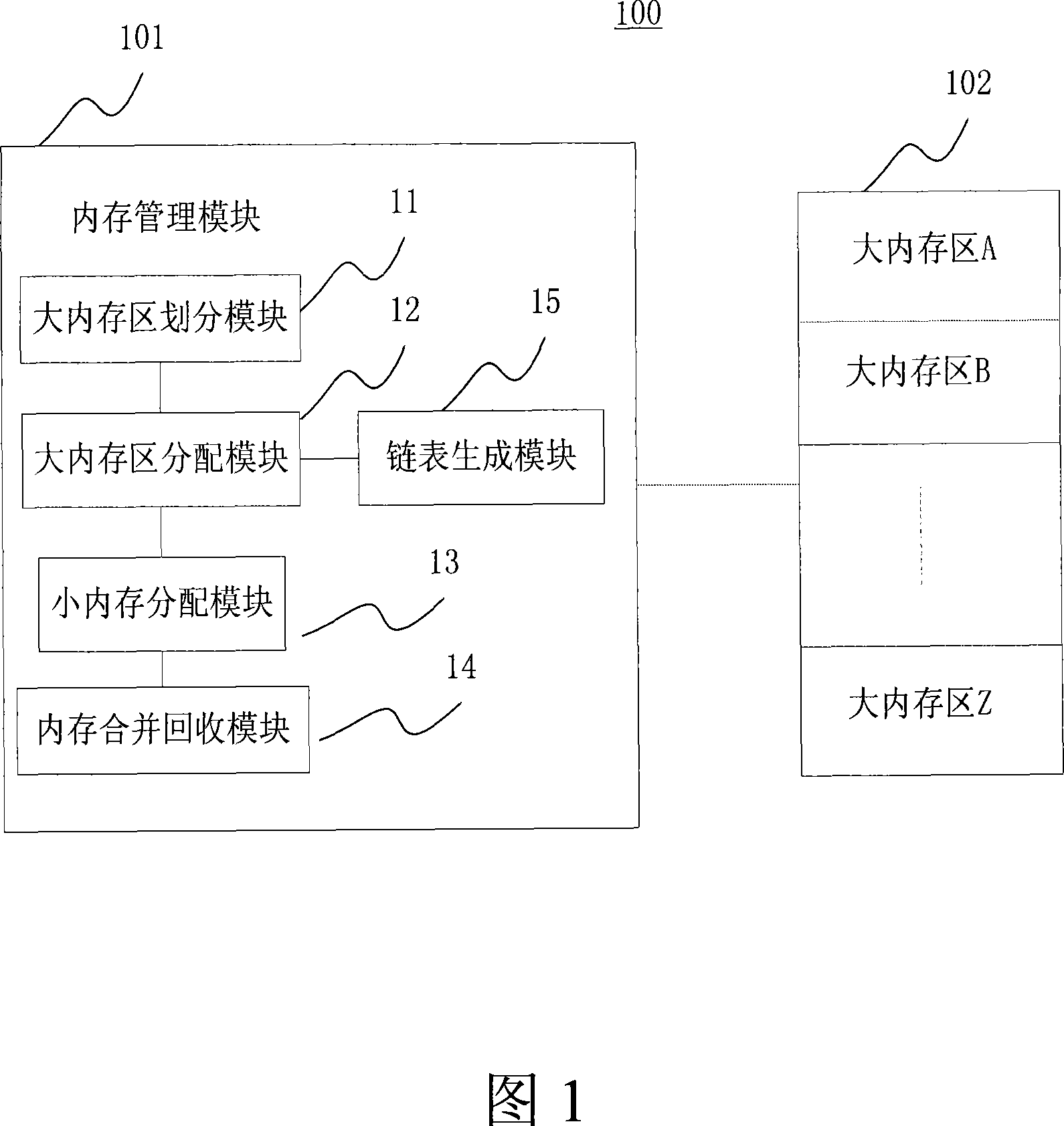
Internal memory managing method and device of embedded system
InactiveCN101221536ASpeed up tidying upNo effect on operationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInternal memoryEmbedded system
The invention discloses a memory management method and a device for an embedded type system. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, a memory is divided into a plurality of large memory zones with unequal memory capacities; secondly, when an application program begins to run, a large memory zone which is matched with a maximum memory requirement value of the application program is allocated for the application program; thirdly, a small memory is allocated for the application program in the matched large memory zone by utilization of heap means; fourthly, when the small memory is released by the application program by utilization of heap means, the small memory is combined with adjacent and free small memories; when the application program stops running, the matched large memory zone is released. The invention avoids a large amount of memory fragmentations, quickens speed of memory fragmentation defrag and avoids the necessity in a memory pool means of calculation of the size and number of each memory which needs for dynamic allocation of each application program.
Owner:ZTE CORP
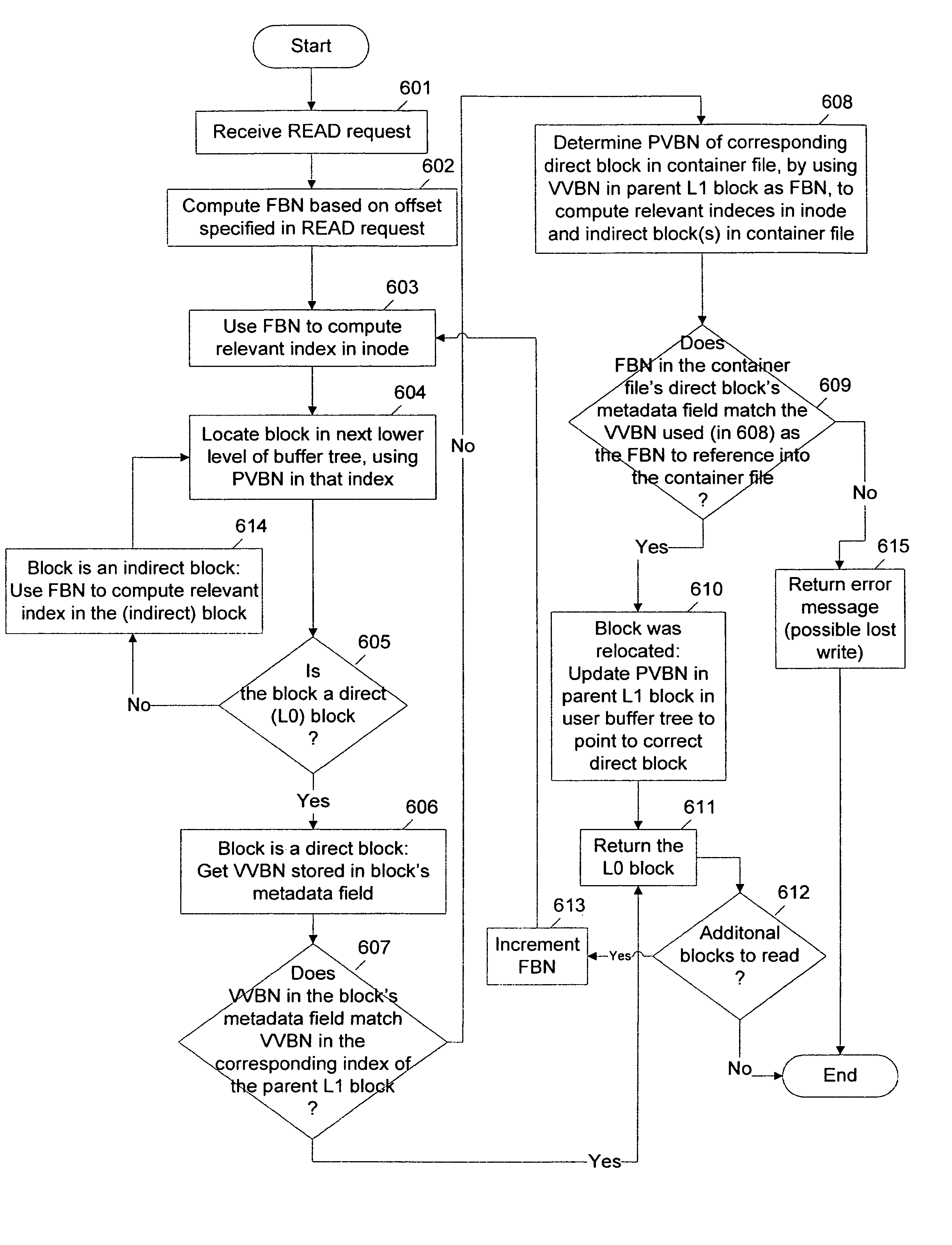
Method and apparatus for defragmentation and for detection of relocated blocks
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Parallel dynamic memory allocation using a nested hierarchical heap
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for dynamically allocating memory using a nested hierarchical heap. A lock-free mechanism is used to access to a hierarchical heap data structure for allocating and deallocating memory from the heap. The heap is organized as a series of levels of fixed-size blocks, where all blocks at given level are the same size. At each lower level of the hierarchy, a collection of N blocks in the lower level equals the size of a single block at the level above. When a thread requests an allocation, one or more blocks at only one level are allocated to the thread. When threads are finished using an allocation, each thread deallocates the respective allocated blocks. When all of the blocks for a level have been deallocated, defragmentation is performed at that level.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
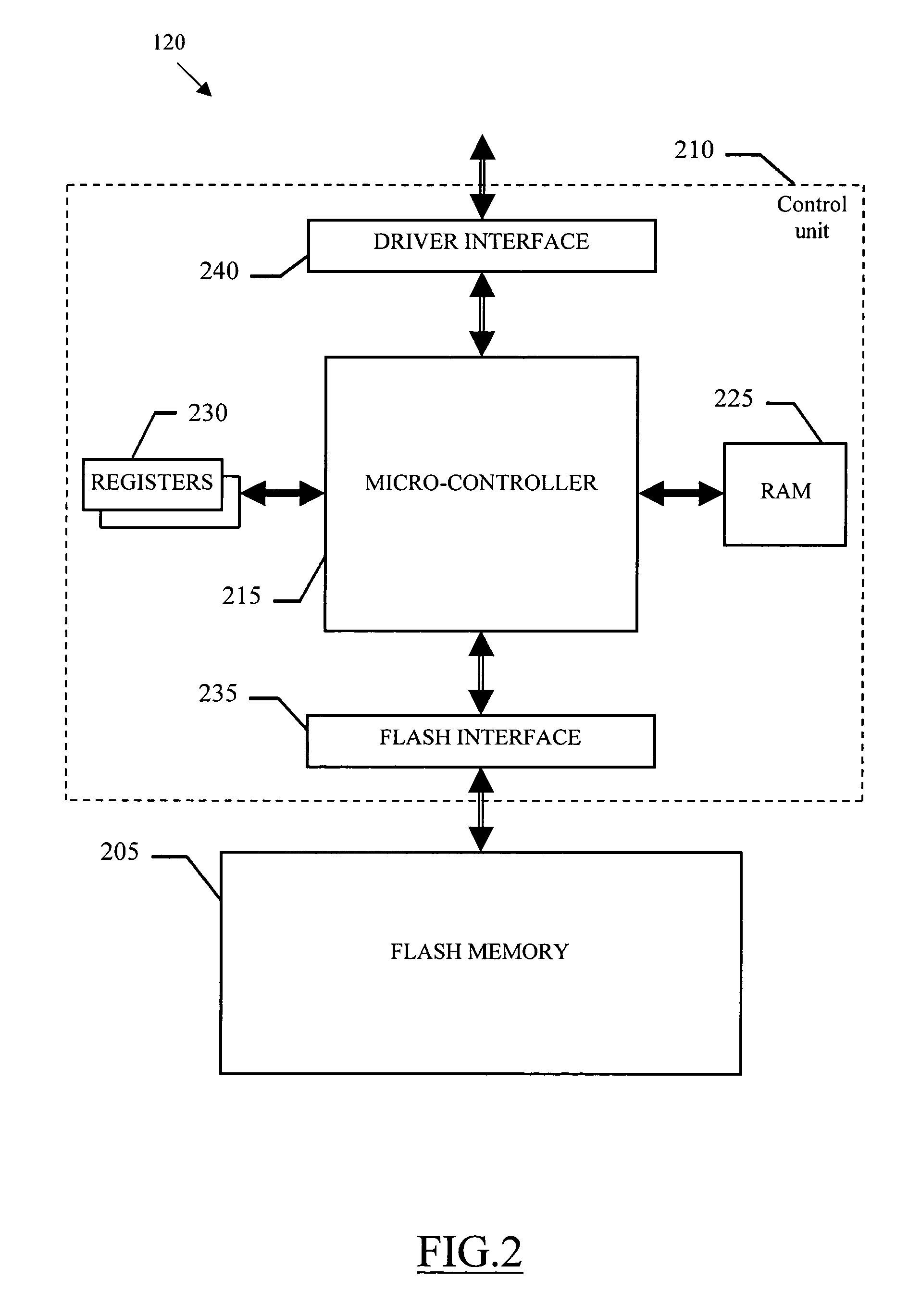
Mass memory device based on a flash memory with multiple buffers
InactiveUS20050021904A1Improve flowMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMass storageLarge capacity
The mass memory device includes a flash memory (205) having a plurality of physical sectors, suitable to be erased individually, each one including a plurality of physical blocks and a method for emulating a random-access logical memory space having a plurality of logical sectors each one including a plurality of logical blocks, the logical sectors being grouped into at least one group. The method includes partitioning a random-access logical memory space into a plurality of logical sectors each one including a plurality of logical blocks, the logical sectors being grouped into at least one group of logical sectors; associating a corresponding data physical sector with each of the logical sectors and associating a plurality of corresponding buffer physical sectors with each group of logical sectors; setting at least one of the buffer physical sectors as an active buffer physical sector; writing each of the logical blocks into one of an available physical block of the corresponding data physical sector if the corresponding data physical sector is not full; and the corresponding active buffer physical sector if the corresponding data physical sector is full; setting another buffer physical sector as active, in response to the active buffer physical sector becoming full; and defragging each data physical sector which is full and associated with a logical sector having at least one logical block stored in the corresponding buffer physical sector which is full.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
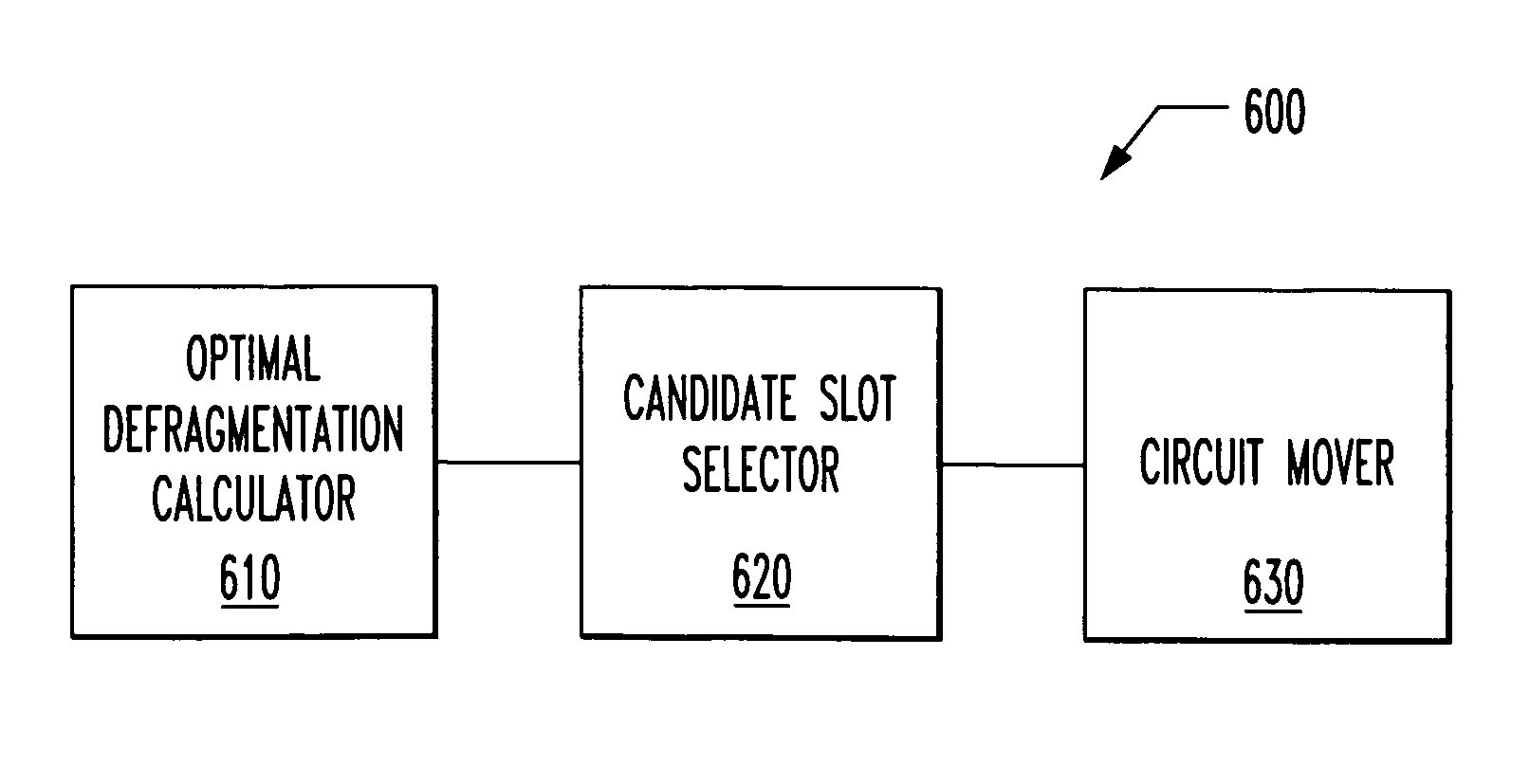
System and method for increasing provisionable bandwidth in time-division multiplexed communication links
ActiveUS7317728B2Free-up bandwidthLow costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsGranularityNetwork management
A system for and method of, increasing provisionable bandwidth in a multiplexed communication link and a network management system incorporating the system or the method. In one embodiment, the system includes: (1) a defragmentation calculator that calculates a defragmentation of the communication link, the defragmentation containing at least one granularity, (2) a candidate slot selector, associated with the defragmentation calculator, that finds reduced cost candidate slots for the at least one granularity and (3) a circuit mover, associated with the candidate slot selector, that identifies target slots into which circuits occupying the candidate slots can be moved.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
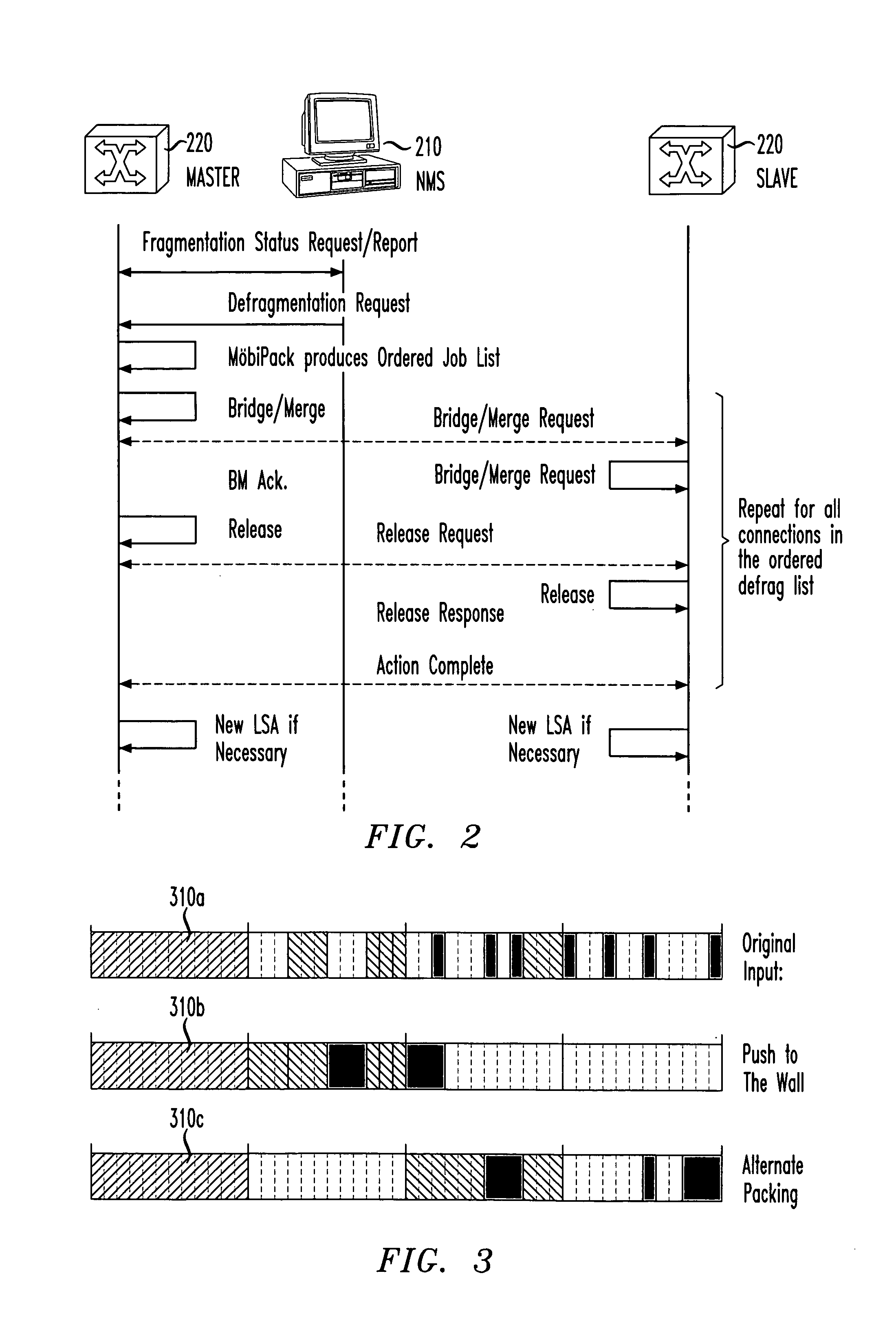
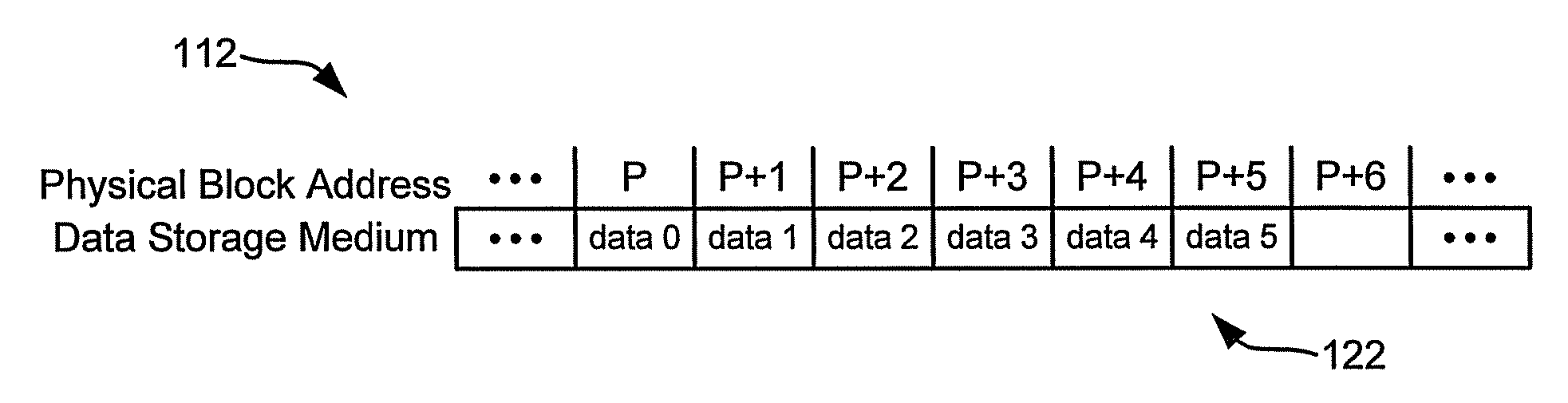
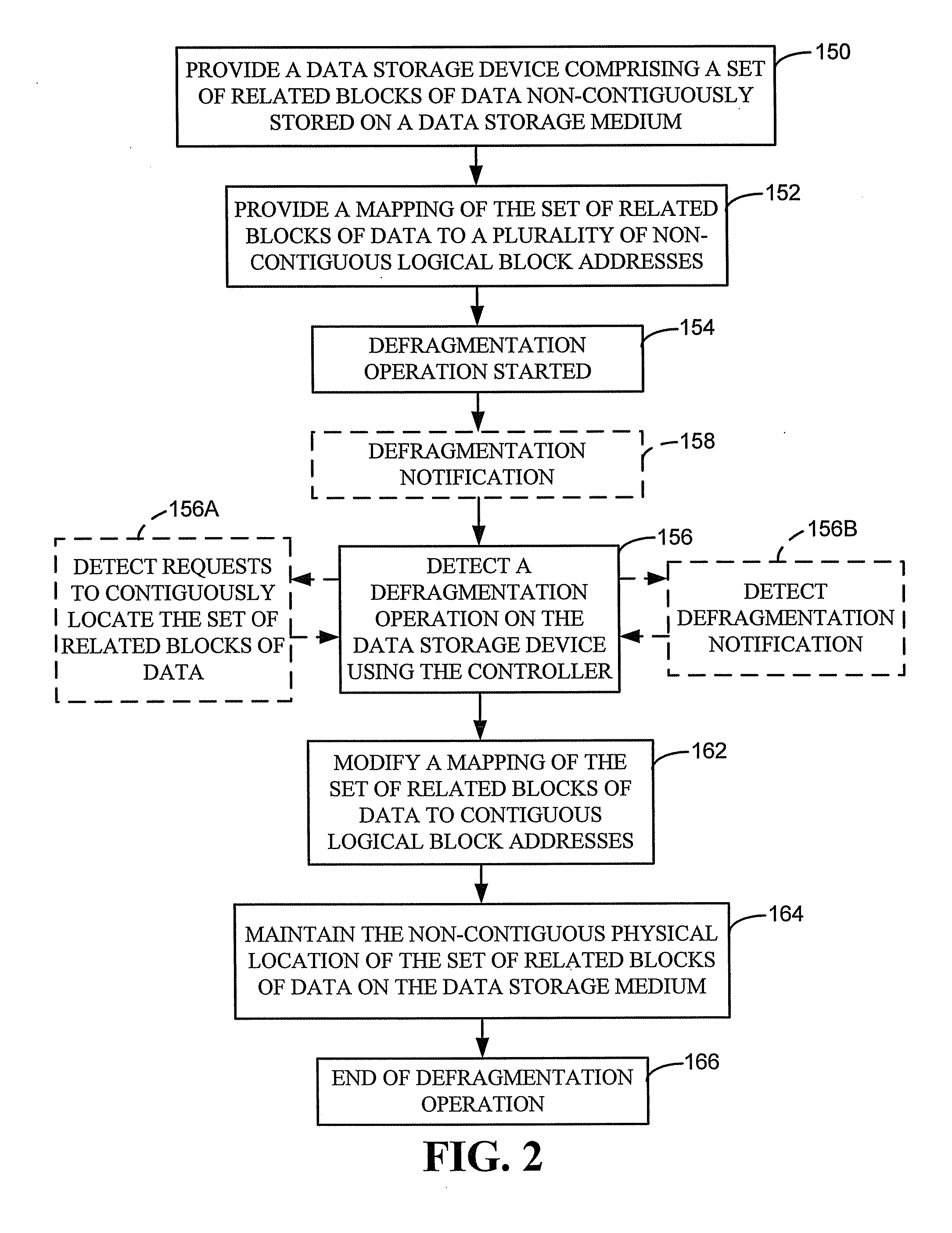
Defragmentation of solid state memory
InactiveUS20100312983A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingLogical block addressingData store
A data storage device includes a solid state data storage medium, a set of related data blocks and a controller. The set of related data blocks are non-contiguously stored on the data storage medium and have an original write sequence. The controller, responsive to a defragmentation request, maps the physical block addresses of the set of related data blocks to contiguous logical block addresses in the original write sequence while maintaining the non-contiguous physical block addresses of the set of related data blocks on the data storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for defragmentation and for detection of relocated blocks
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
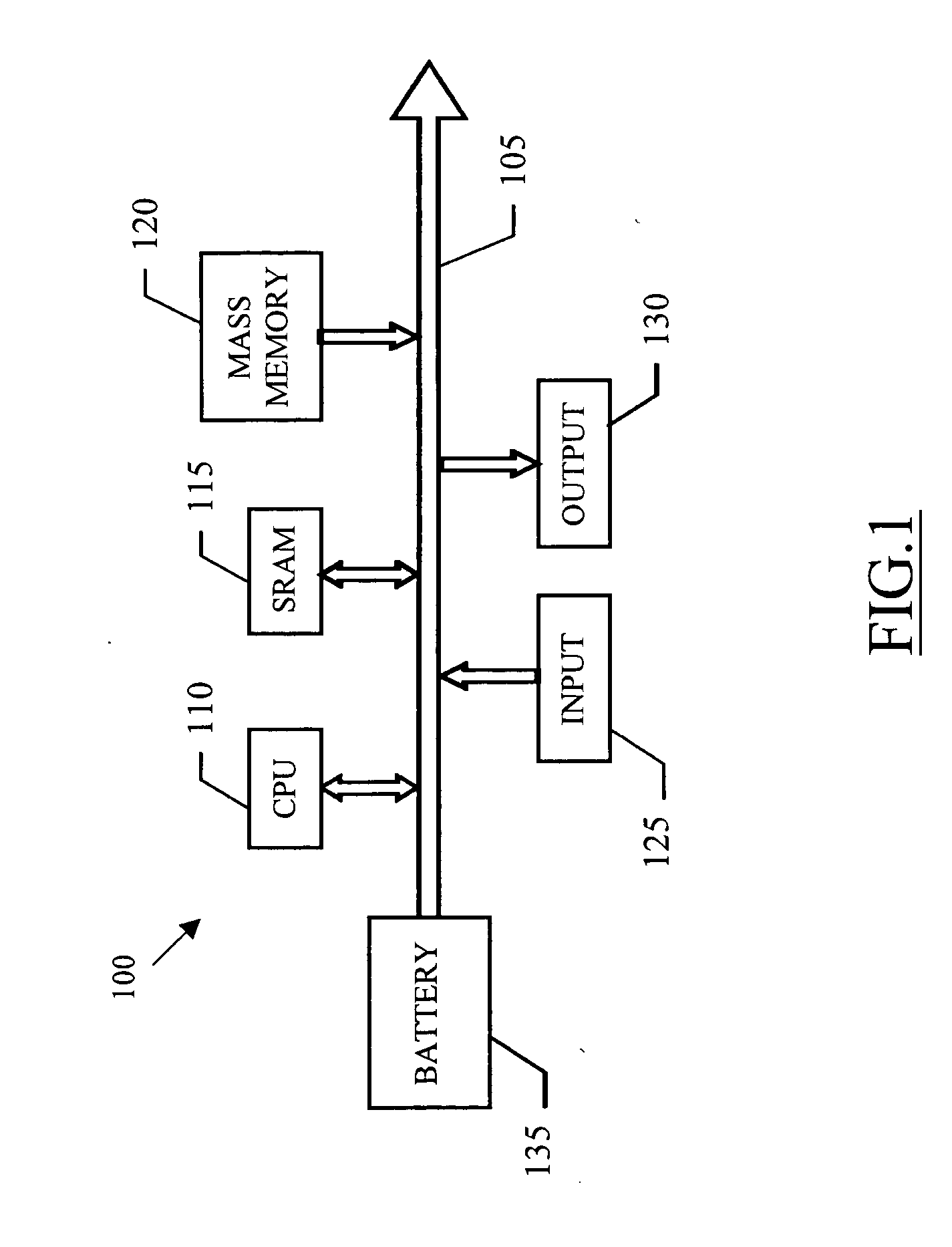
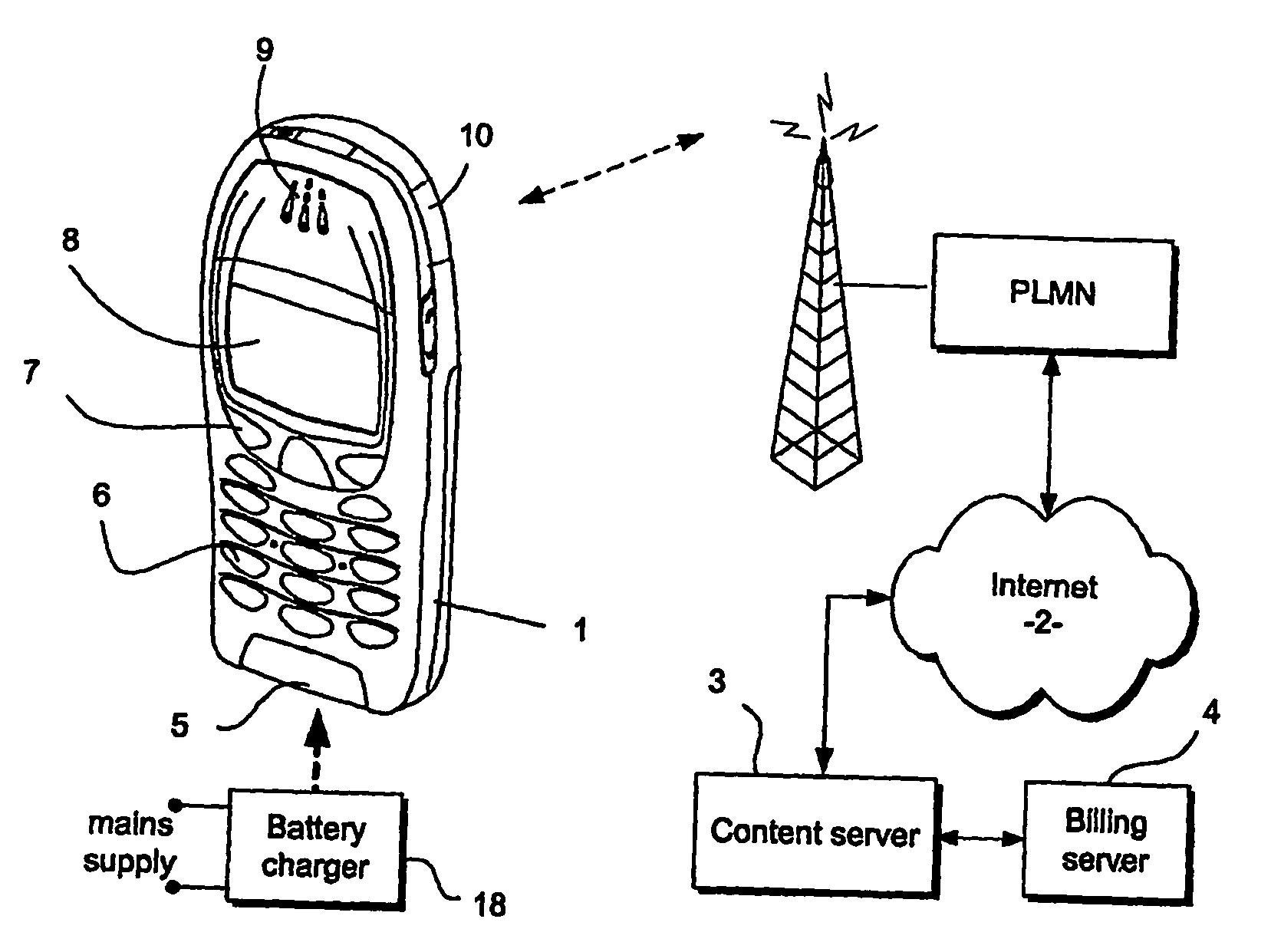
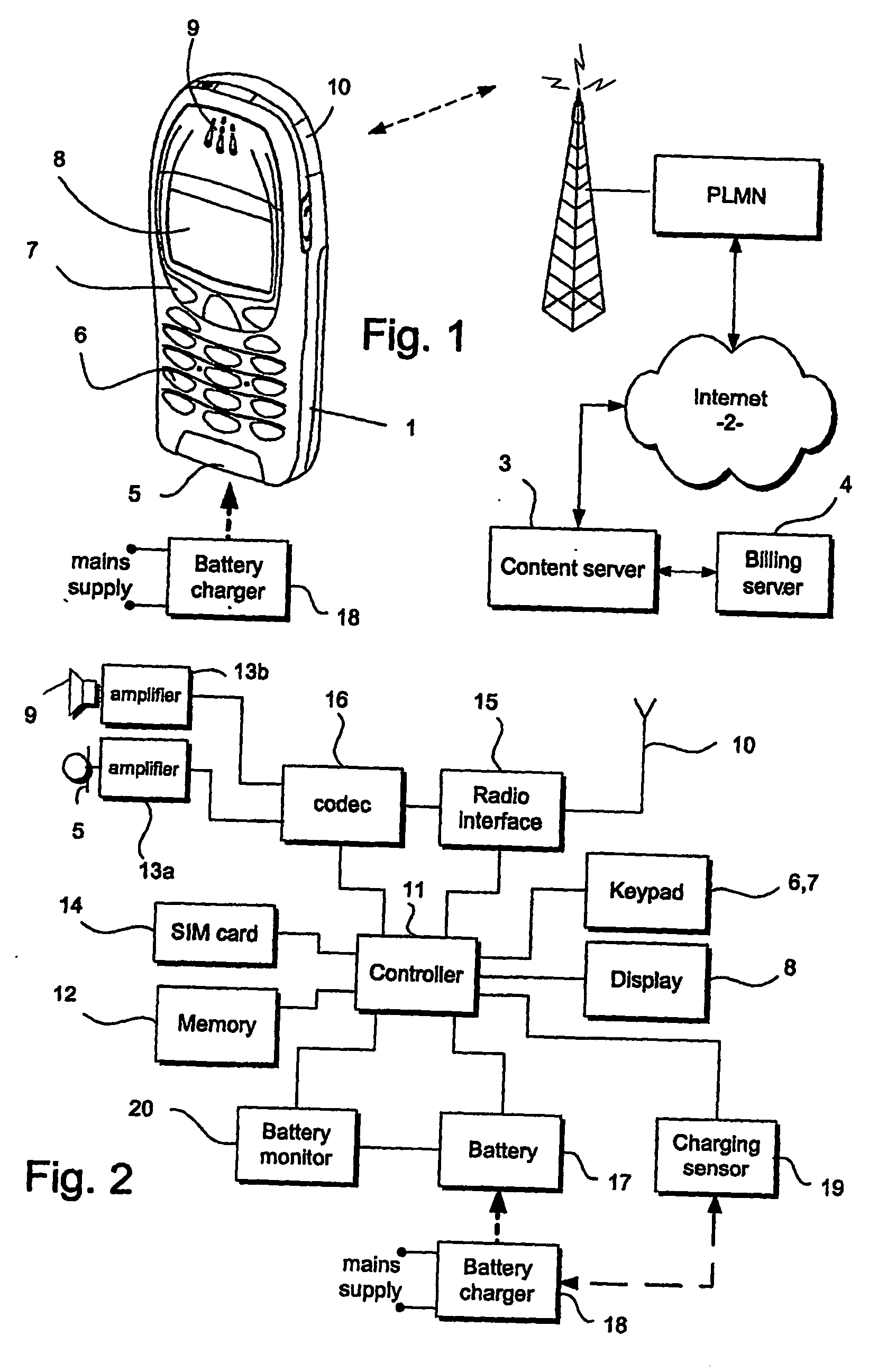
Portable battery driven apparatus
InactiveUS20090164823A1Increase battery capacityDigital data processing detailsElectrical testingBattery chargeElectrical battery
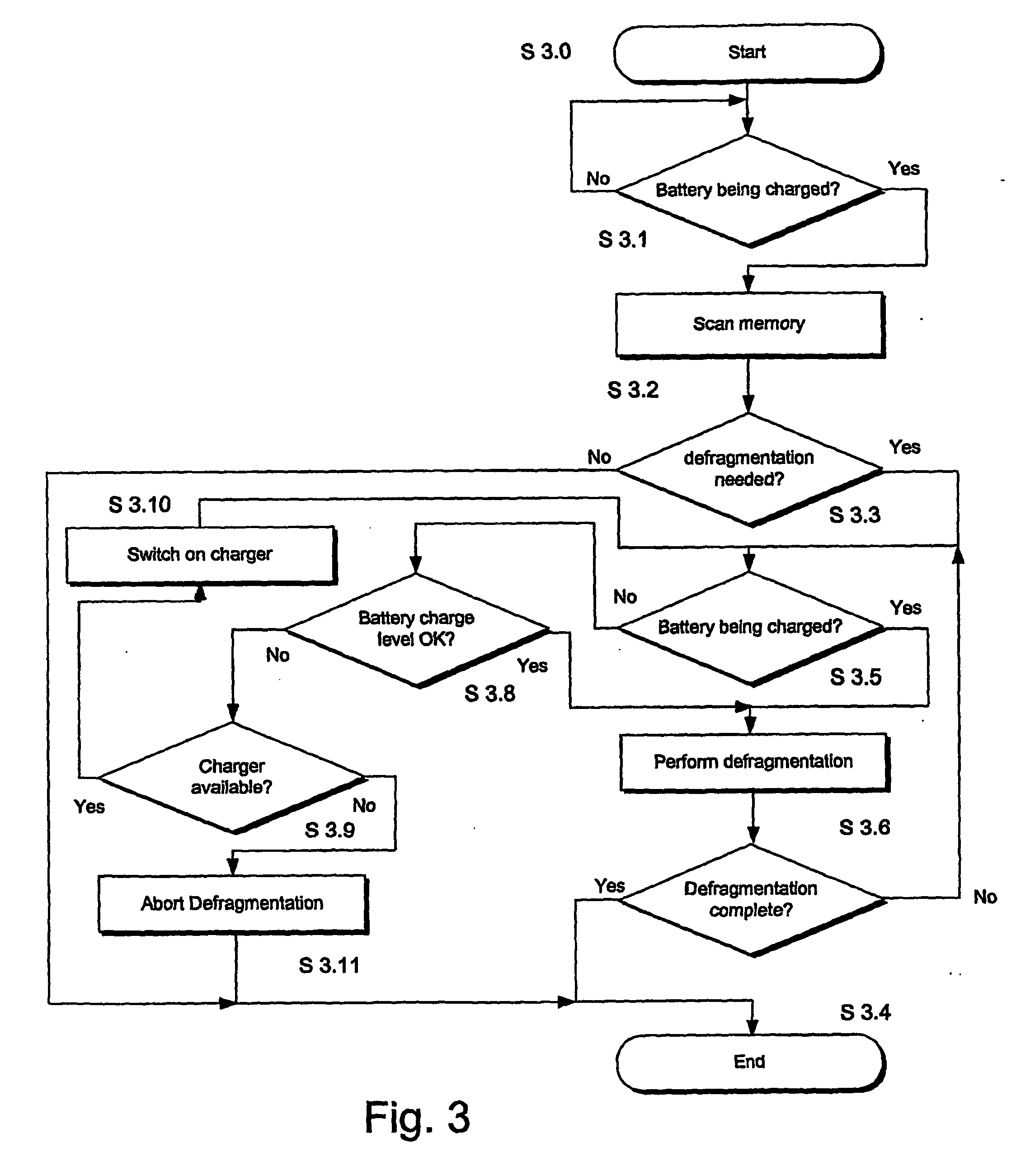
A mobile telephone handset (1) has its circuitry (11) to be driven by a rechargeable battery (17). The handset can to perform a data processing operation such as a download or a memory defragmentation, which requires battery power over a considerable period of time and a battery sensor (20) is coupled to the circuitry for indicating whether the battery has sufficient capability to complete the data operation. The circuitry (11) is configured to cease the data processing operation in the event that the battery is indicated to have insufficient capability to complete the operation. A battery charging sensor (19) indicates when an external battery charger is connected and the download or defragmention process is preferably carried out using the power of the charger rather than the battery.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
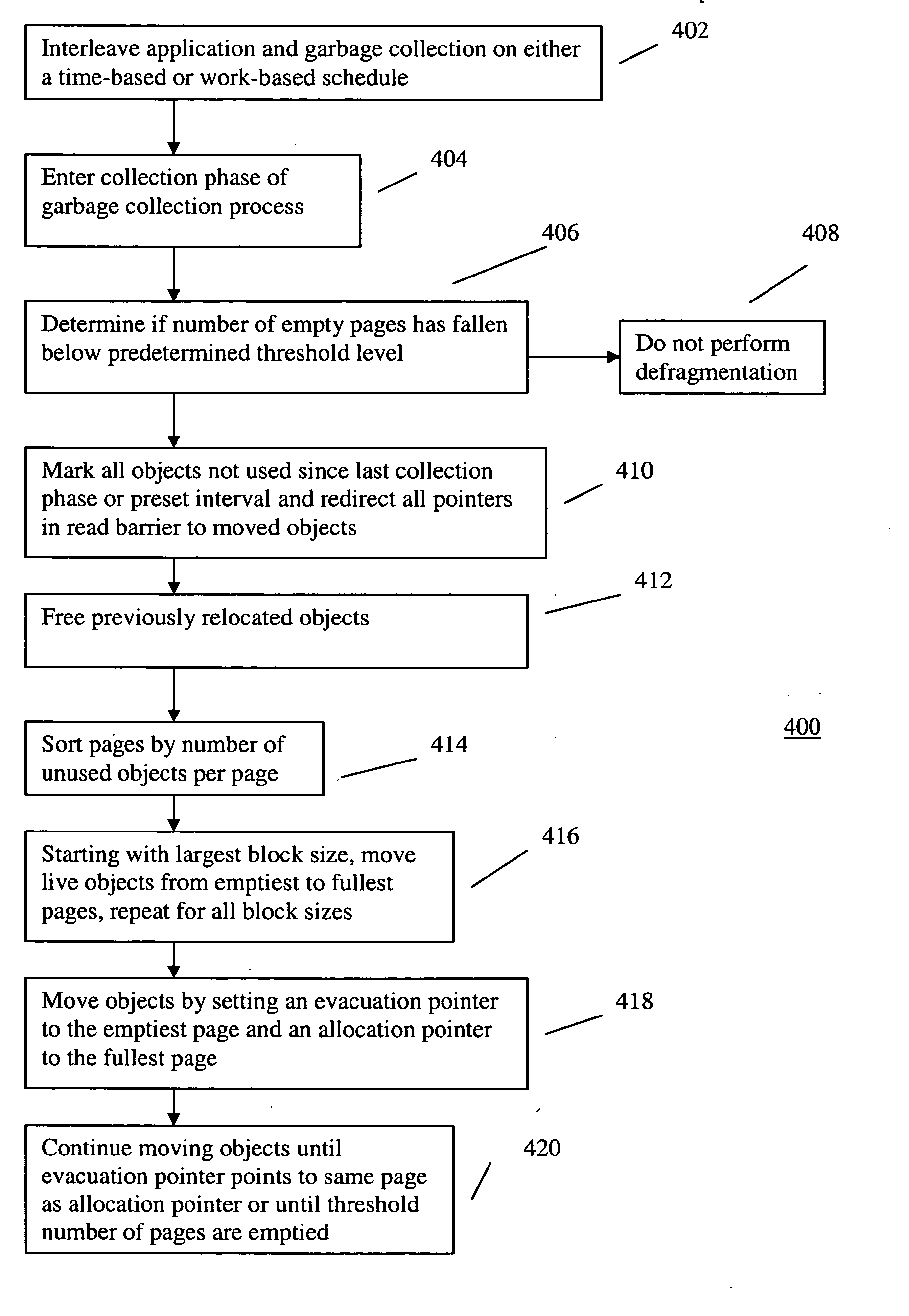
Method and apparatus for dynamic incremental defragmentation of memory
InactiveUS20050149686A1Reduce its software overheadOptimizes the read barrierMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingTerm memory
A garbage collection process for managing a memory includes a defragmentation cycle. The garbage collection process is interleaved with a running application on a time-based or work-based schedule. The memory is divided into pages which are further divided into blocks falling into one of a number of block size classes. Objects that were not used during the last garbage collection phase are marked. Objects that were used are moved from pages containing the least live objects to pages containing the most live objects. Objects of the largest block size classes are moved first and objects of the smallest block size class are moved last. The garbage collection interval can be selected to satisfy desired CPU utilization or memory overhead requirements.
Owner:IBM CORP
File system that manages files according to content
ActiveUS20050193025A1Lower latencyImprove performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemTrade offs
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
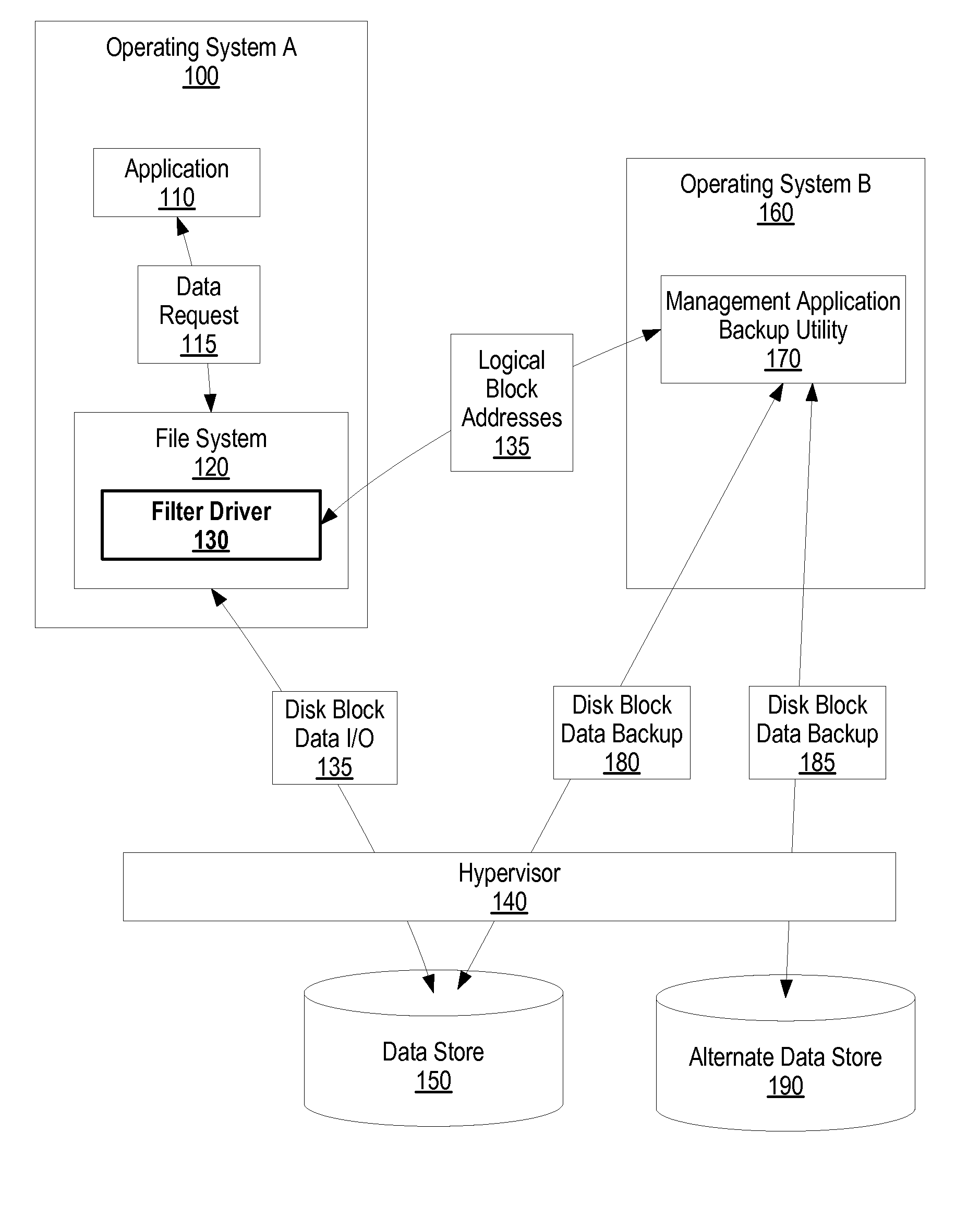
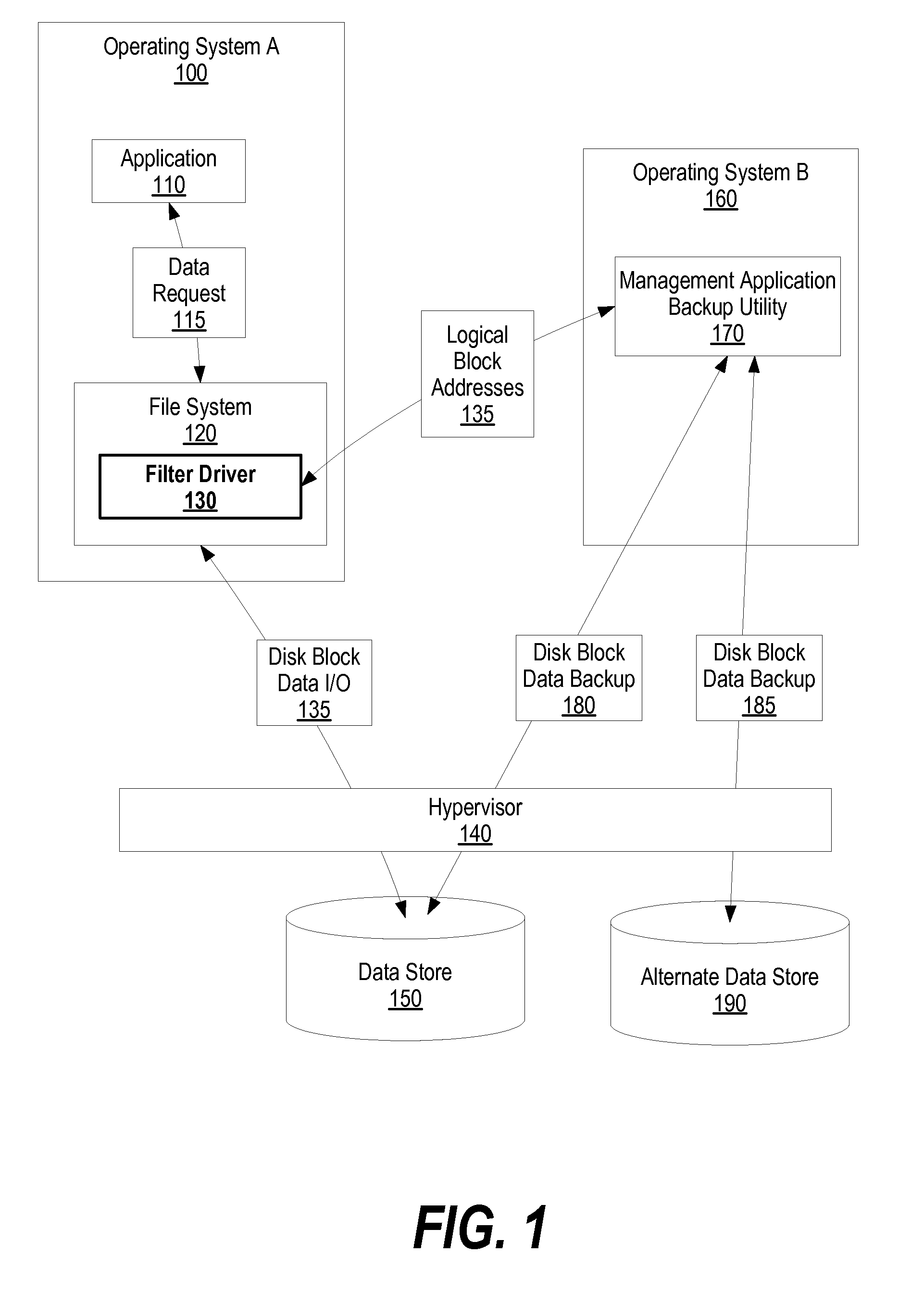
System and Method for Hybrid Virtual Machine Monitor File System Operations
ActiveUS20080154985A1Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsOperational systemApplication software
A system and method for hybrid virtual machine monitor system is provided. A first operating system uses a file system to manage data storage and retrieval within a data storage area. A second operating system, which is not compatible with the first operating system's file system, executes a management application backup utility. The first operating system includes a filter driver that sends logical block addresses, which correspond to data reads / writes, to the management application backup utility. In turn, the management application backup utility uses the logical block addresses to perform operations on the data storage locations. In one embodiment, the management application backup utility performs actions on the data storage area, such as a disk defragmentation, and subsequently sends data location changes to the filter driver. In this embodiment, the filter driver instructs the first operating system's file system to update its translation tables based upon the data location changes.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
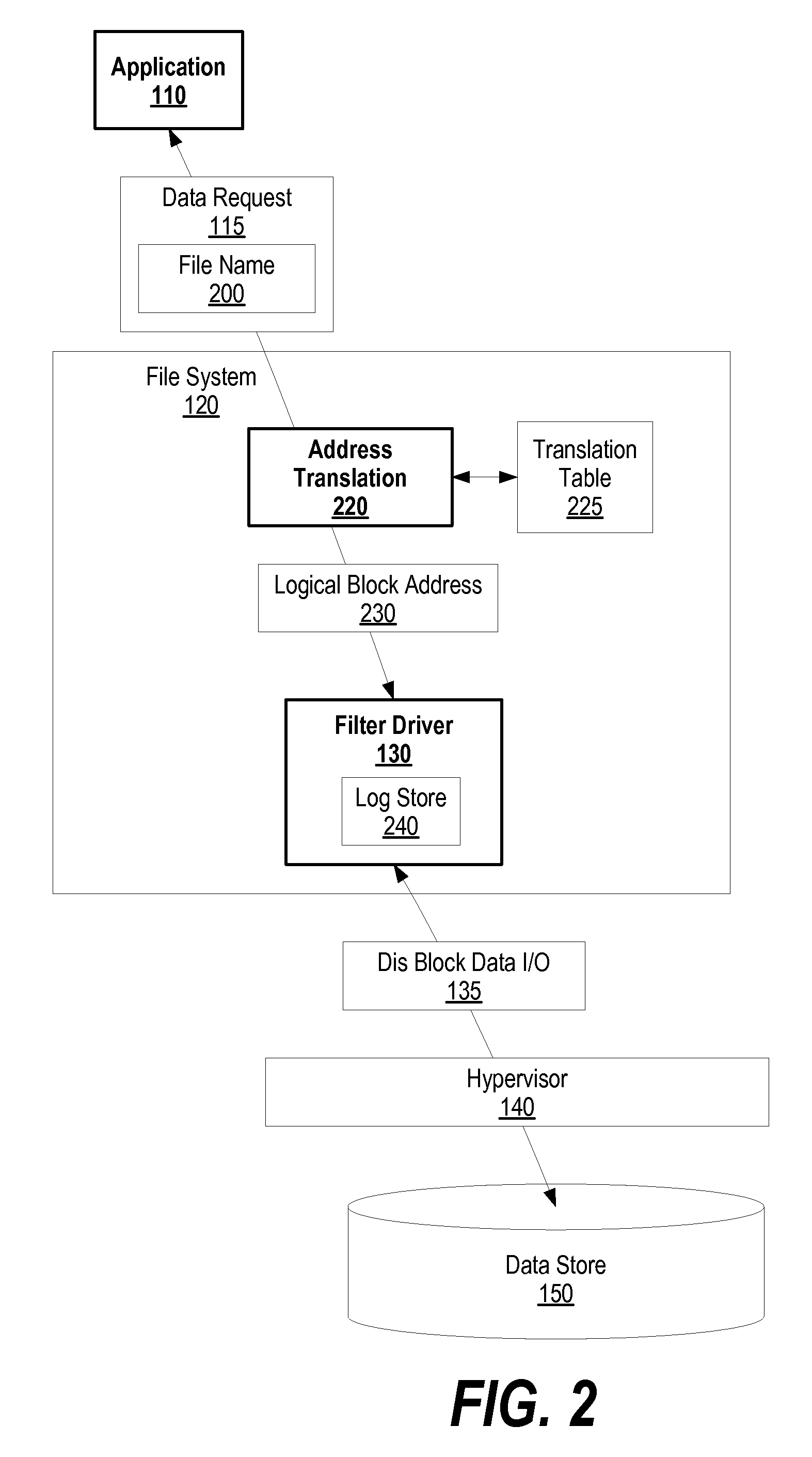
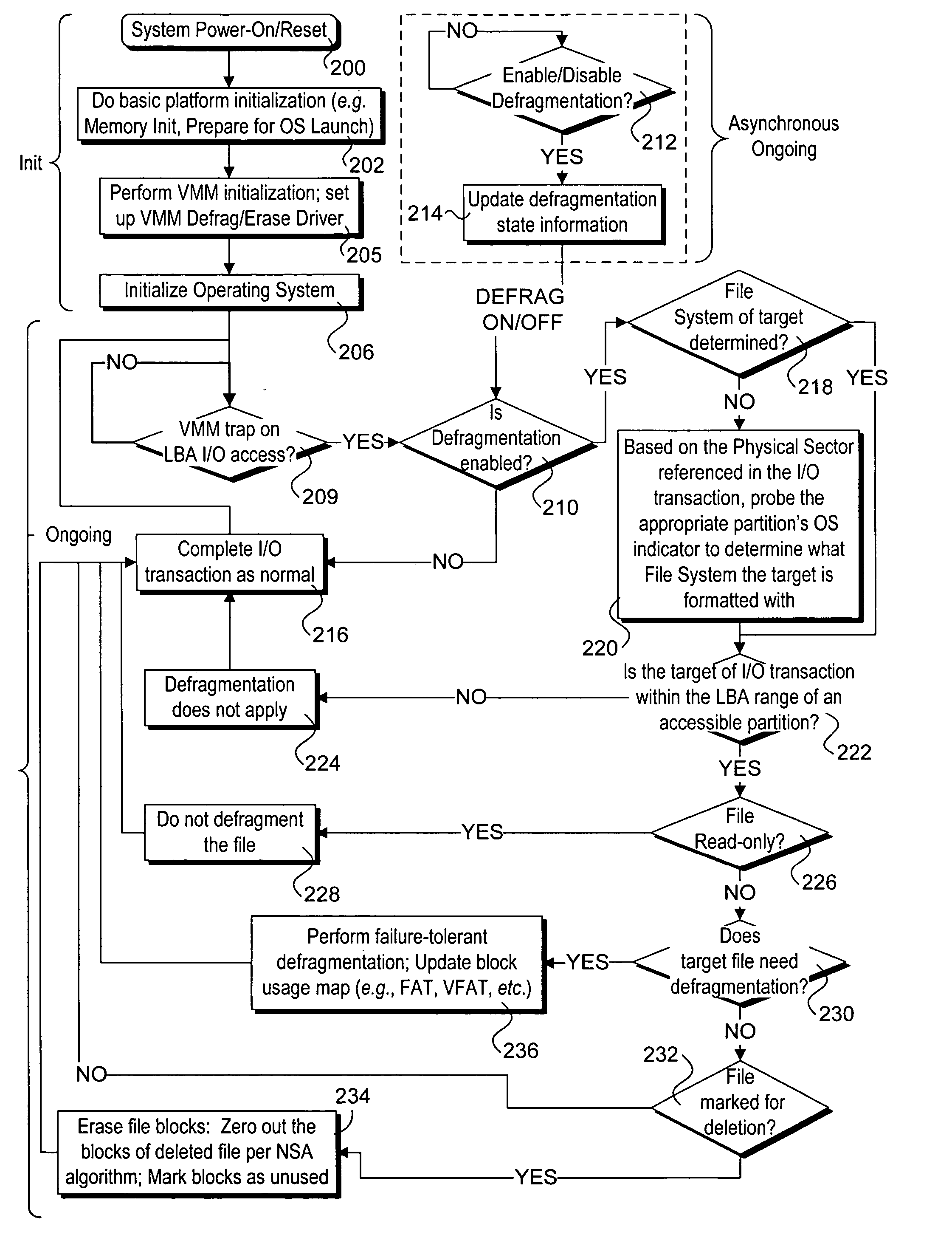
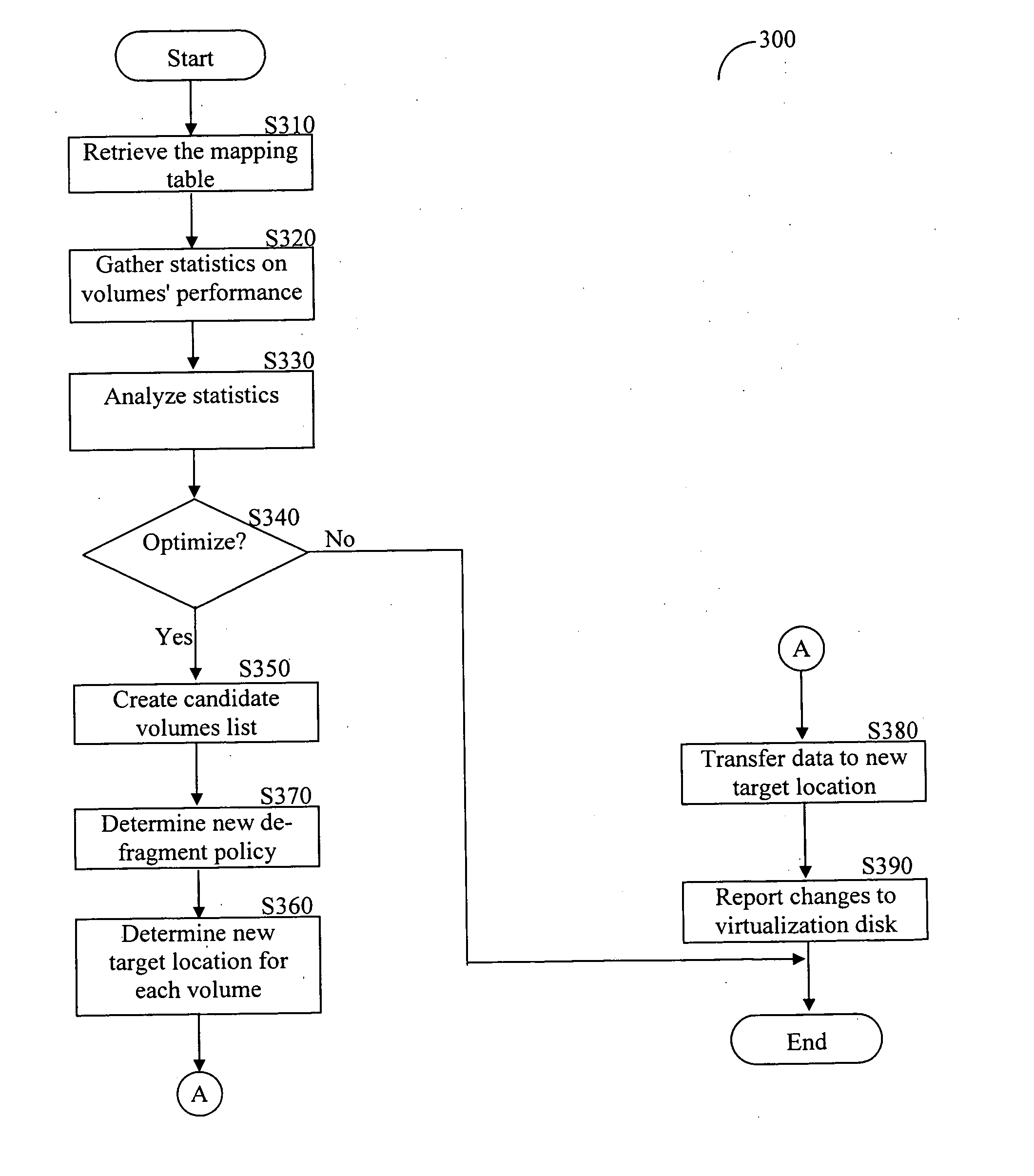
Method and apparatus for ongoing block storage device management
InactiveUS20060149899A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsVirtualizationOperational system
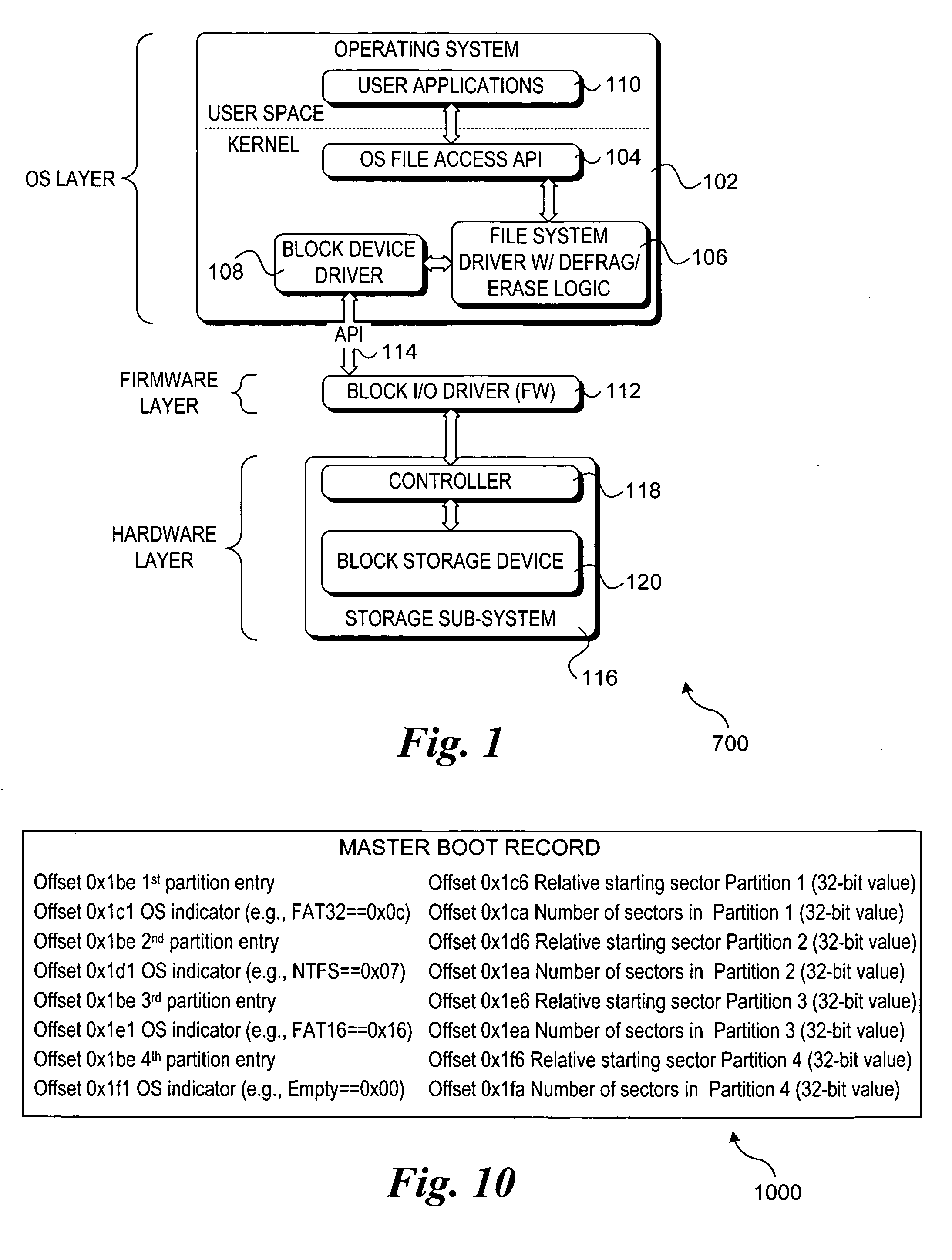
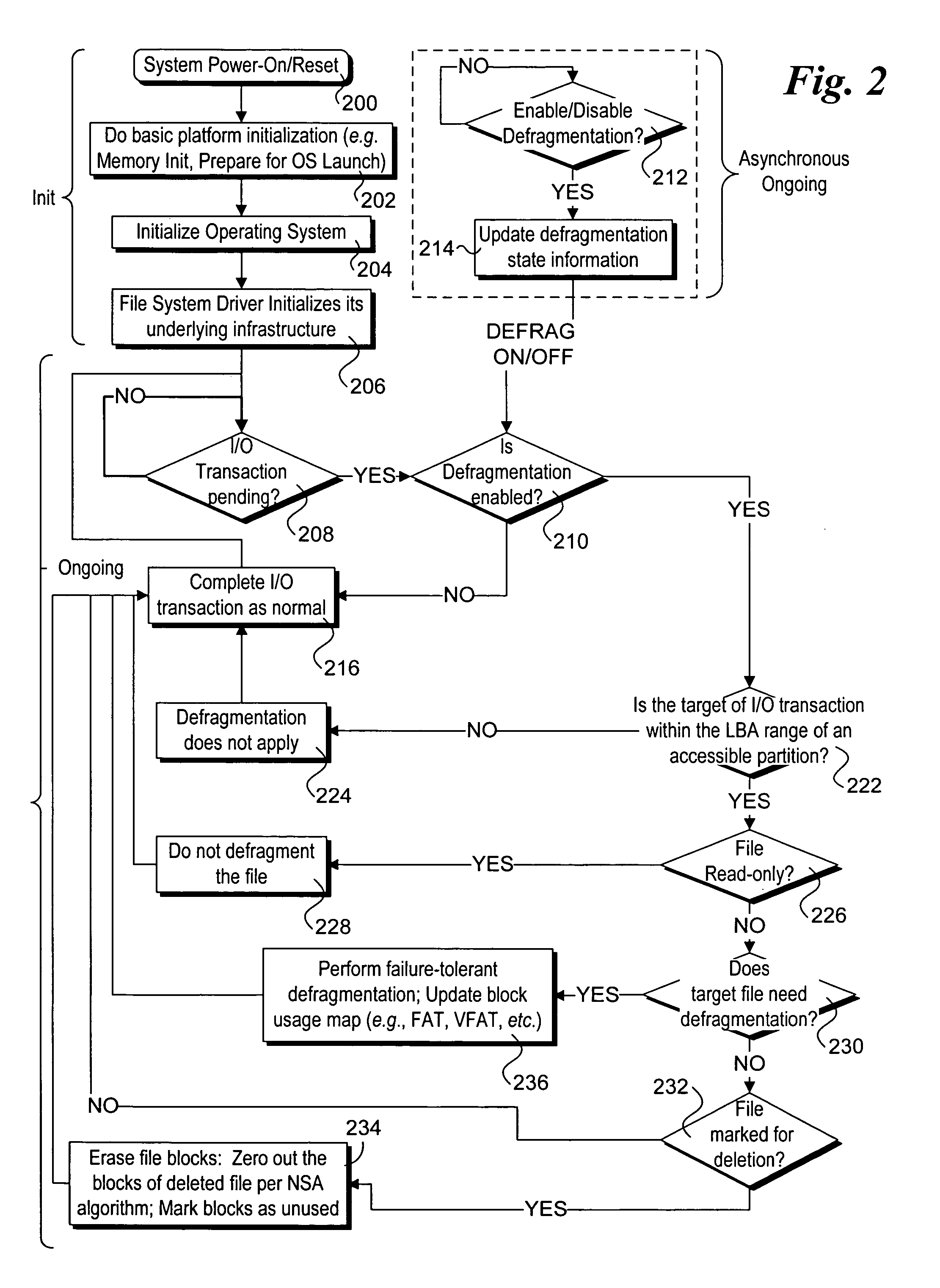
Methods and apparatus for performing ongoing block storage device management operations. Software and / or firmware components are disclosed for performing ongoing block storage device management operations, such as file defragmentation and file erasures, in conjunction with corresponding block input / output (I / O) transactions for block storage devices, such as magnetic disk drives and optical drives. For example, in conjunction with performing a file update (block I / O write), file defragmentation operations are performed on the file. Similarly, block erase operations are performed in conjunction with deleting a file, so as to remove all data artifacts of the file at the same time it is deleted. Components for implementing the block storage device management operations may reside in an operating system layer, a firmware layer, or a virtualization layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Disk drive storage defragmentation system
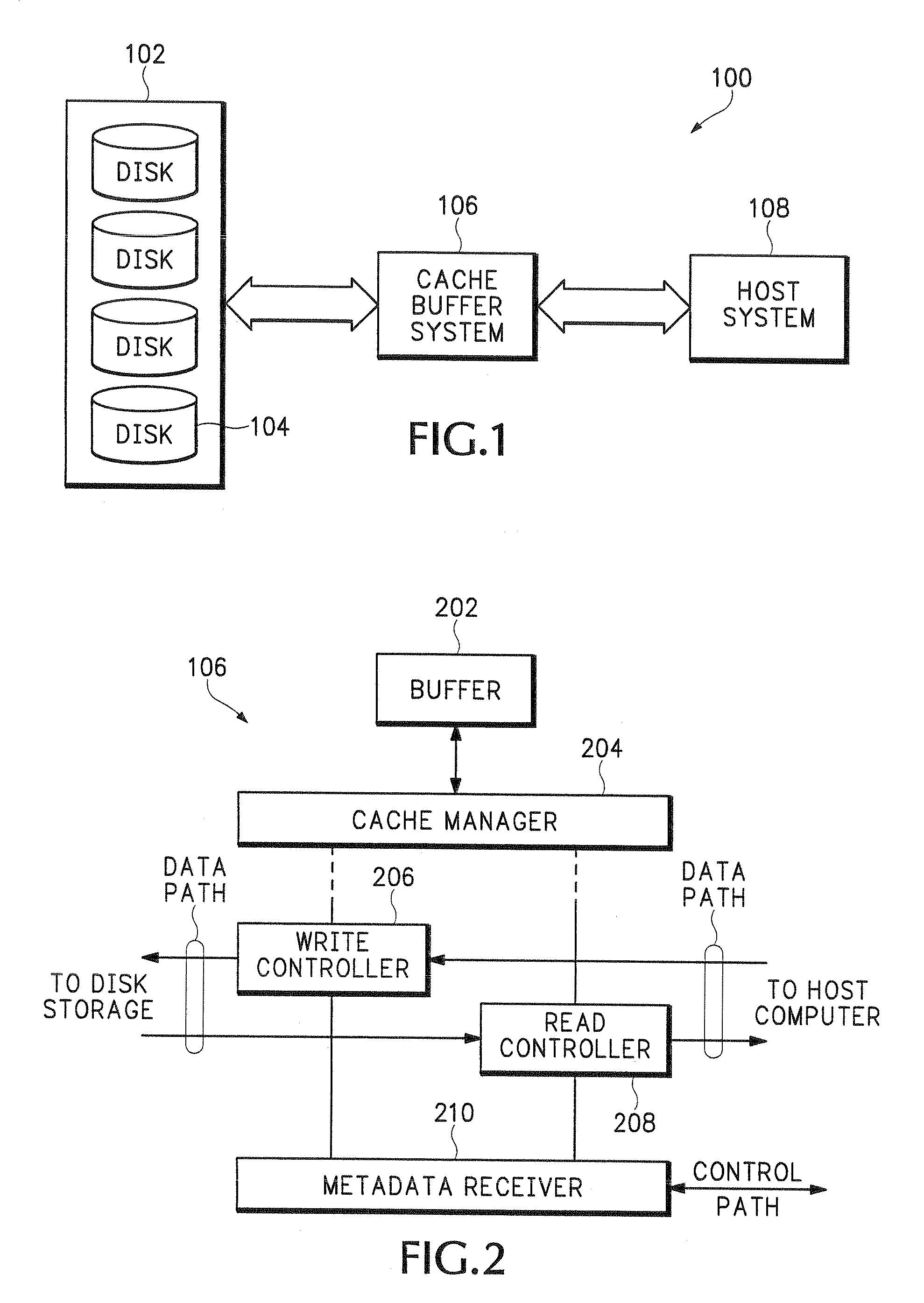
ActiveUS7447836B2Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData accessHost machine
The present invention provides a disk drive storage defragmentation system, comprising providing a cache buffer system coupled to a host system, coupling a disk drive storage system to the cache buffer system, performing a defragmantation process on the disk drive storage system utilizing the cache buffer system and servicing a data access request by the host system from the cache buffer system.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK +1
Fragmentation of a file for instant access
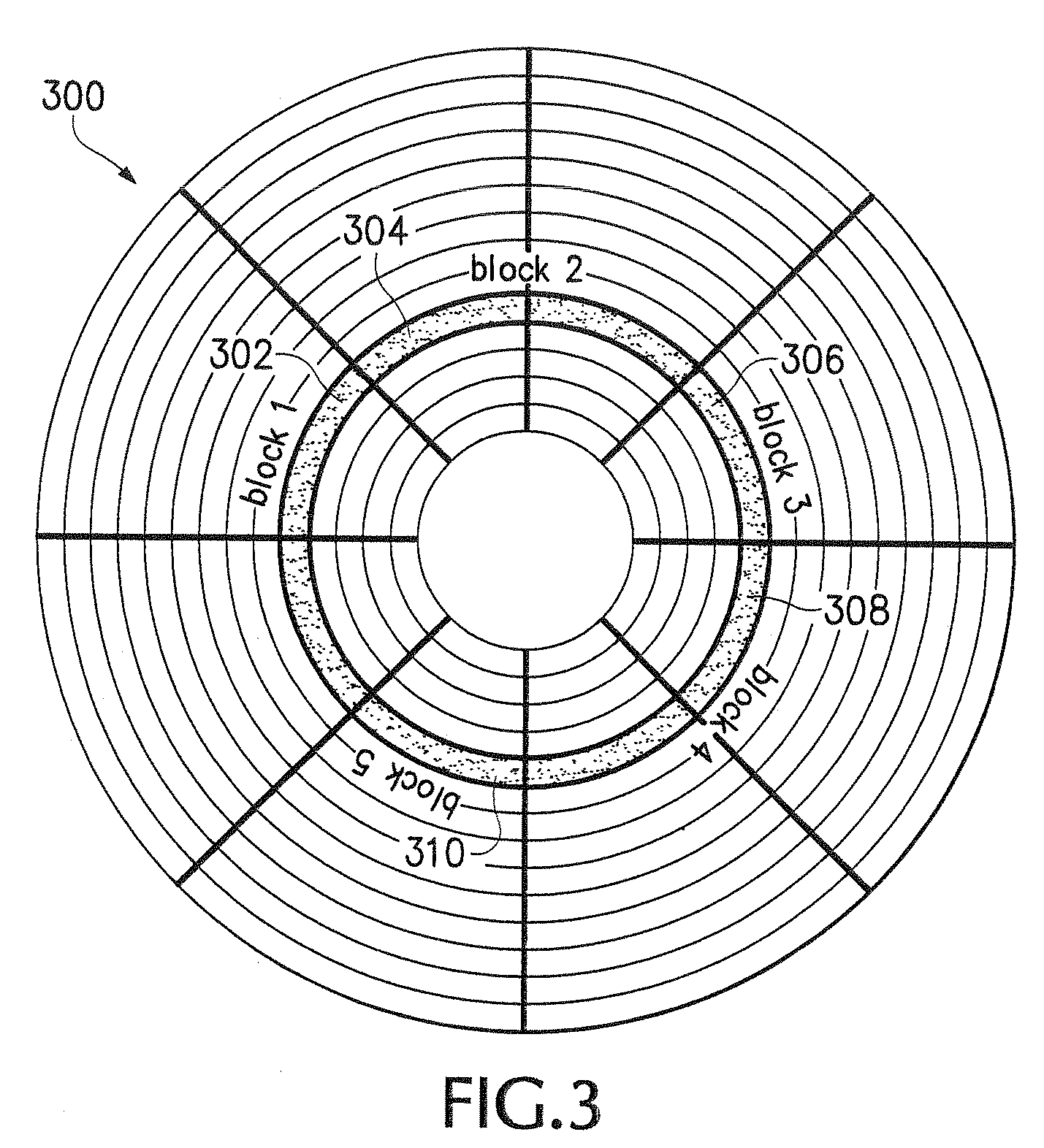
ActiveUS20060206889A1Easy to useEfficient updateDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsDefragmentationShard
Owner:NBCUNIVERSAL
System and method for efficient backup using hashes
ActiveUS7886120B1Easy to useImprove efficiencyError detection/correctionMemory systemsHash functionRemovable media
A method, system and computer program product for data backup such that: for each block of a storage device to be backed up to an image, generating a hash function value corresponding to contents of that block; generating a map of links between blocks in the image and corresponding blocks the storage device; using the hash function values to identify blocks of the storage device with identical contents, such that links for the blocks in the storage device with identical contents point to a single block in the image; and modifying the link in the map when a block in the storage is moved (for example, due to defragmentation) but its contents is not altered, so that the link points to the same backed up block.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST
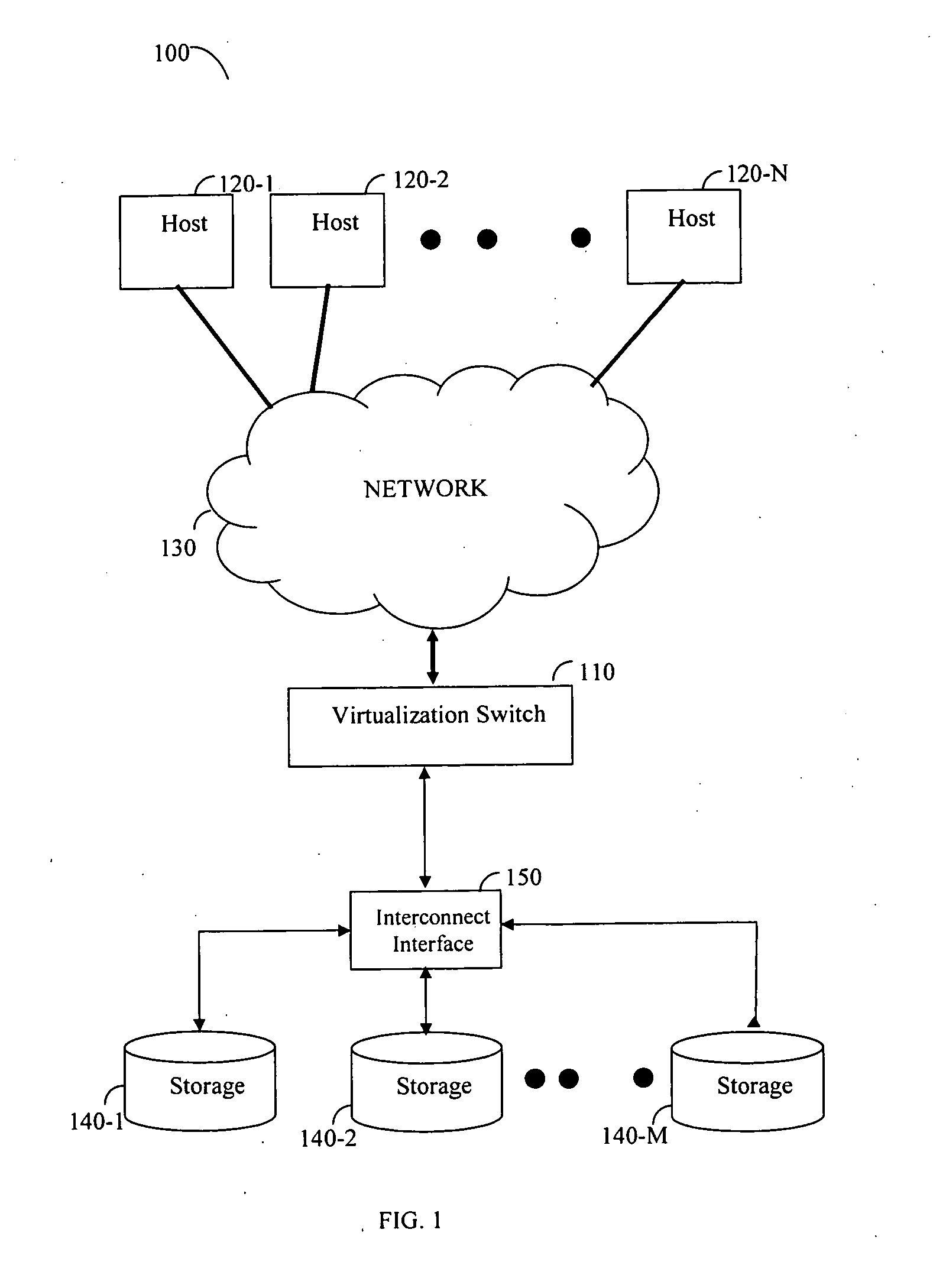
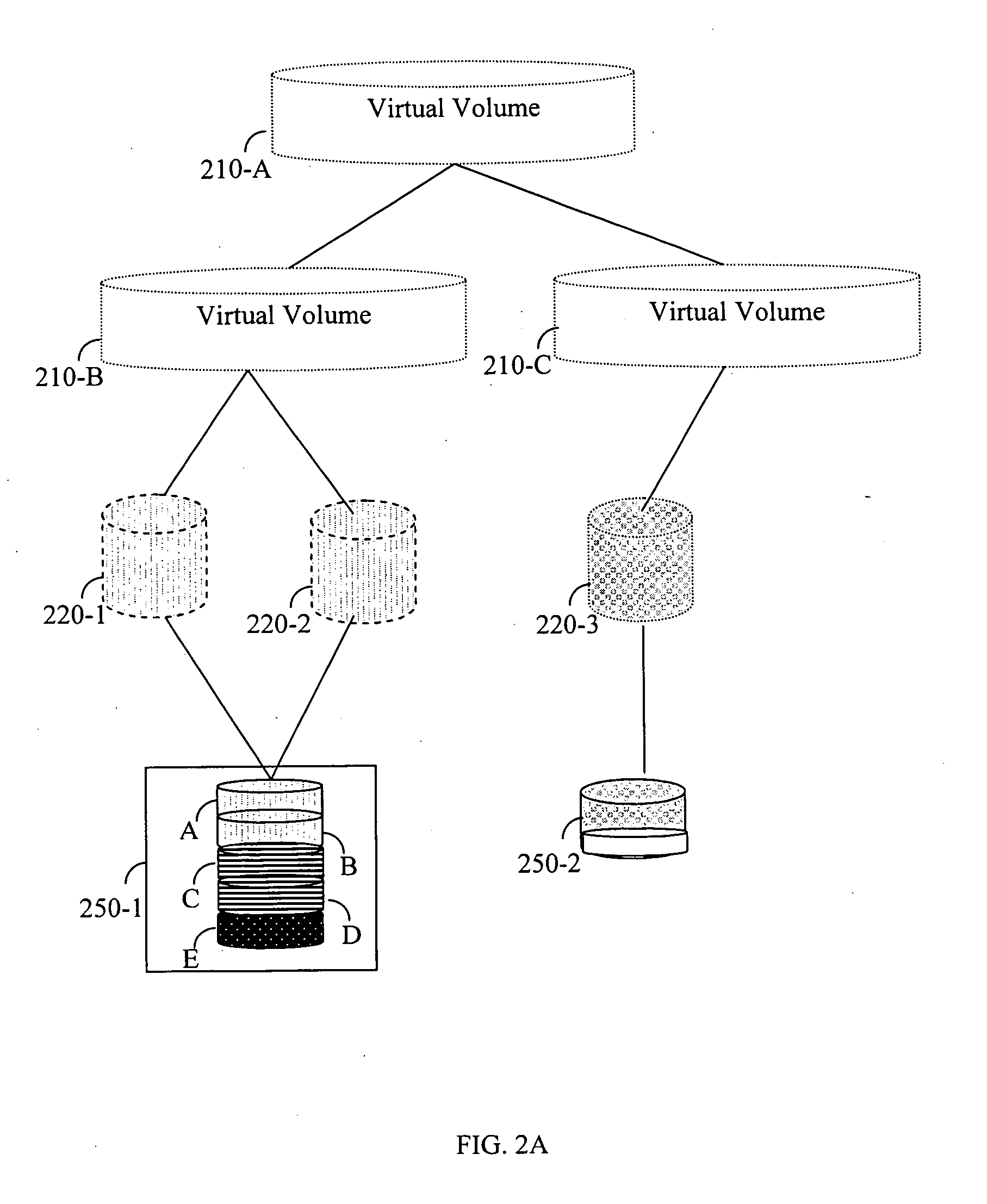
Method for defragmenting of virtual volumes in a storage area network (SAN)
InactiveUS20070113036A1Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingShardStorage area network
A defragmentation method and system to overcome fragmentation of virtual volumes in storage area networks (SANs). The method includes combining and migrating fragments of data spread over multiple storage areas in order to increase storage space utilization and optimize access time to storage. By defragmenting virtual volumes both performance and storage utilization is significantly improved.
Owner:SANRAD INTELLIGENCE STORAGE COMM 2000 +2
File system defragmentation technique via write allocation
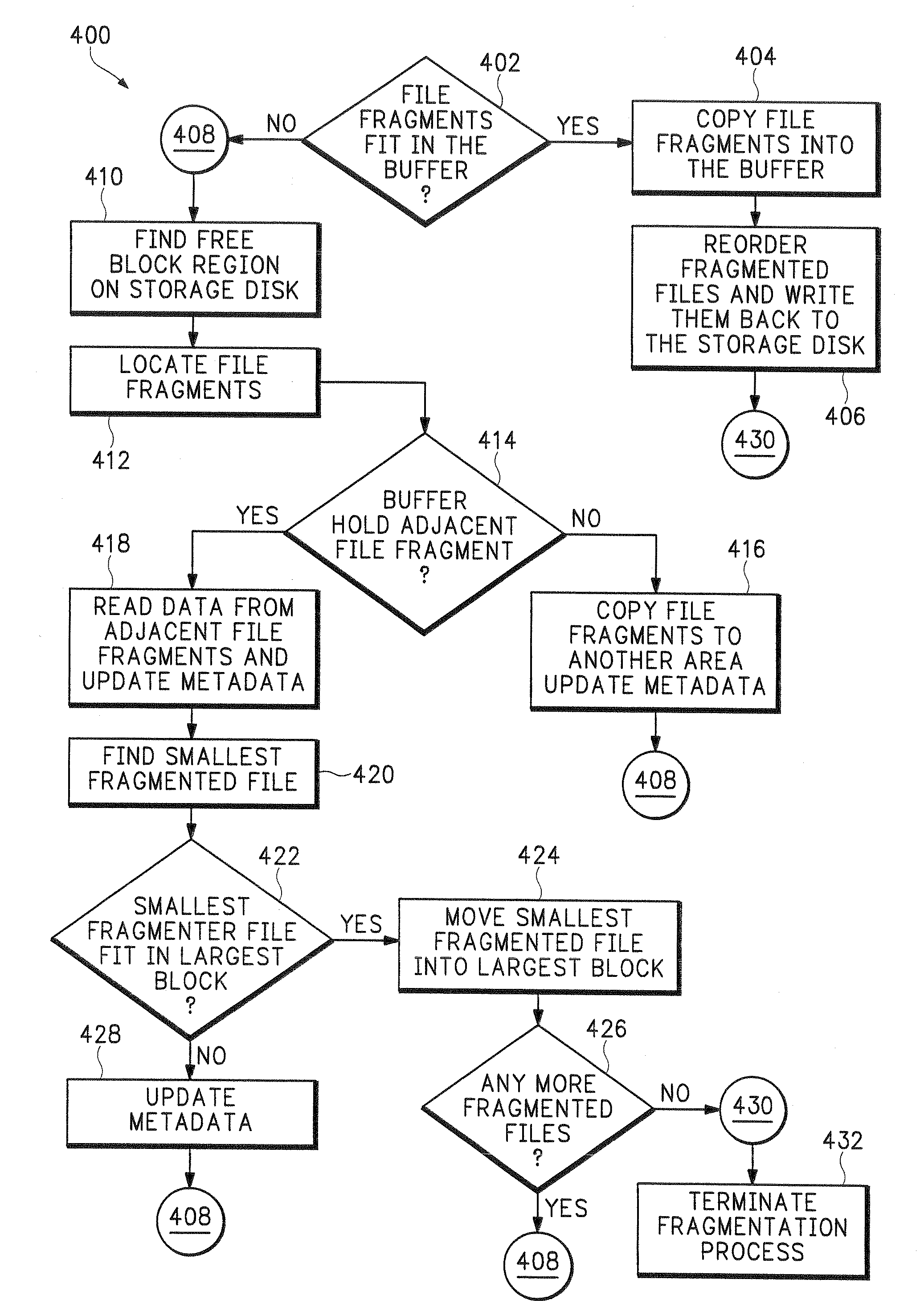
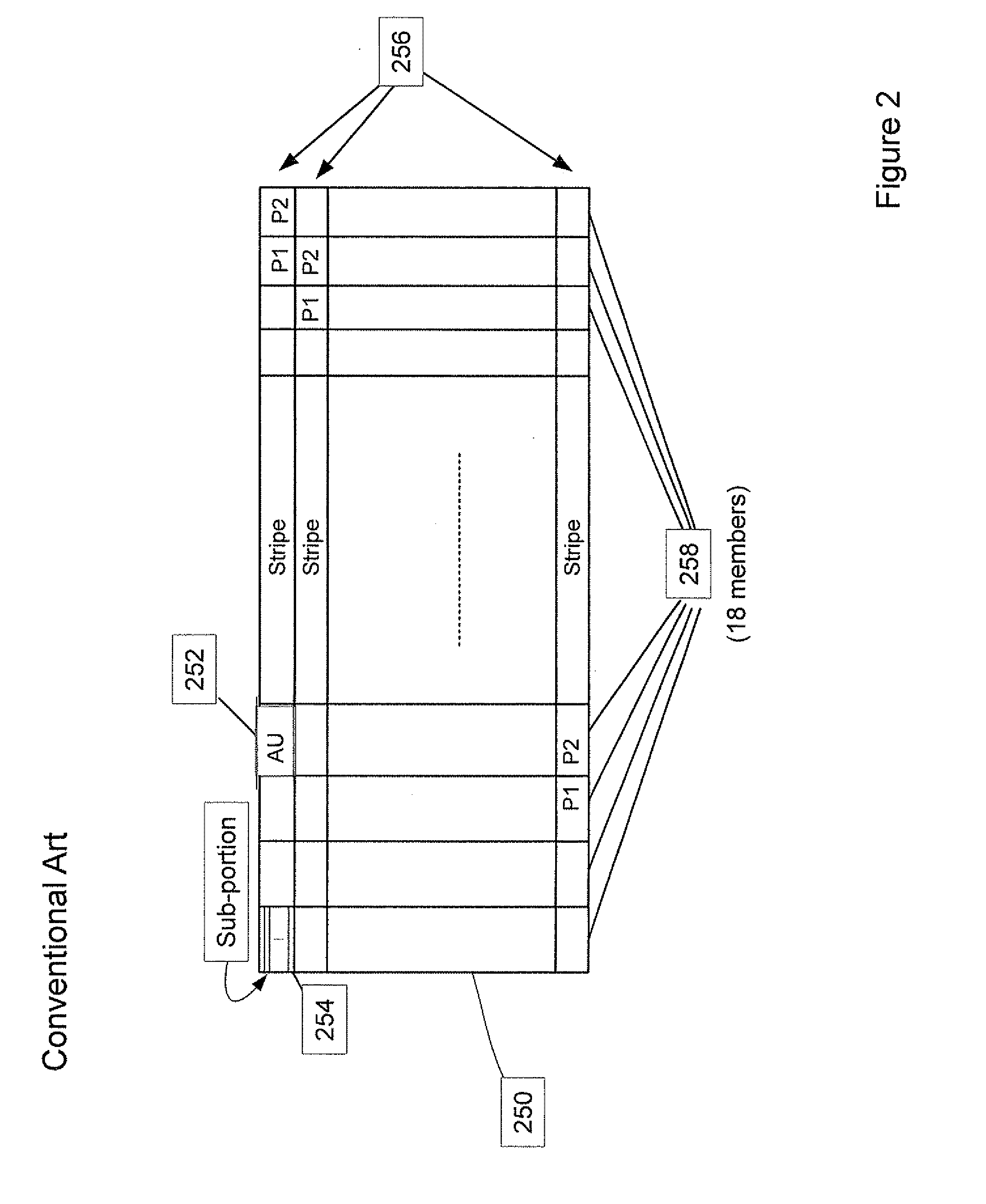
InactiveUS20050187985A1Improved on-disk layoutReduces unnecessary disk input/output operationDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDisk layoutFile system fragmentation
A defragmentation technique determines the extent to which data blocks of a file are fragmented on disks of a computer and, in response, efficiently relocates those blocks if such relocation improves the on-disk layout of the file. Each indirect block of the file is examined and the current layout of the range of pointers referencing the data blocks is determined. In addition, the number of operations needed to retrieve those data blocks from disks is calculated. A potential new layout is then estimated based on an average fullness of the file system. If the potential new layout improves the fragmentation of the current layout, then the data blocks for that range are relocated, if there is sufficient free space on disk. Otherwise, the blocks are not relocated and the current on-disk layout of the file is maintained.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Bandwidth defragmentation systems and methods in optical networks
ActiveUS20120051745A1Avoiding bandwidth fragmentationBetter network utilizationTime-division multiplexOptical multiplexHigh bandwidthHigh probability
The present disclosure provides bandwidth defragmentation systems and methods in optical networks such as Optical Transport Network (OTN), Synchronous Optical Network (SONET), Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH), Ethernet, and the like. In particular, the present invention includes bandwidth defragmentation algorithms that may be used within the context of a signaling and routing protocol to avoid bandwidth defragmentation. As such, the present invention defines a mechanism for computing an end to end path for a connection in a manner that avoids bandwidth fragmentation and provides for better network utilization. For example, the present invention may include a path computation based upon administrative weight and upon fragmentation costs. This may be implemented in existing signaling and routing protocols without changes to existing protocol messages used in topology discovery. Further, the present invention optimizes available bandwidth allowing a higher probability of higher bandwidth request being admitted.
Owner:CIENA
Mass data storage system and method of operating thereof
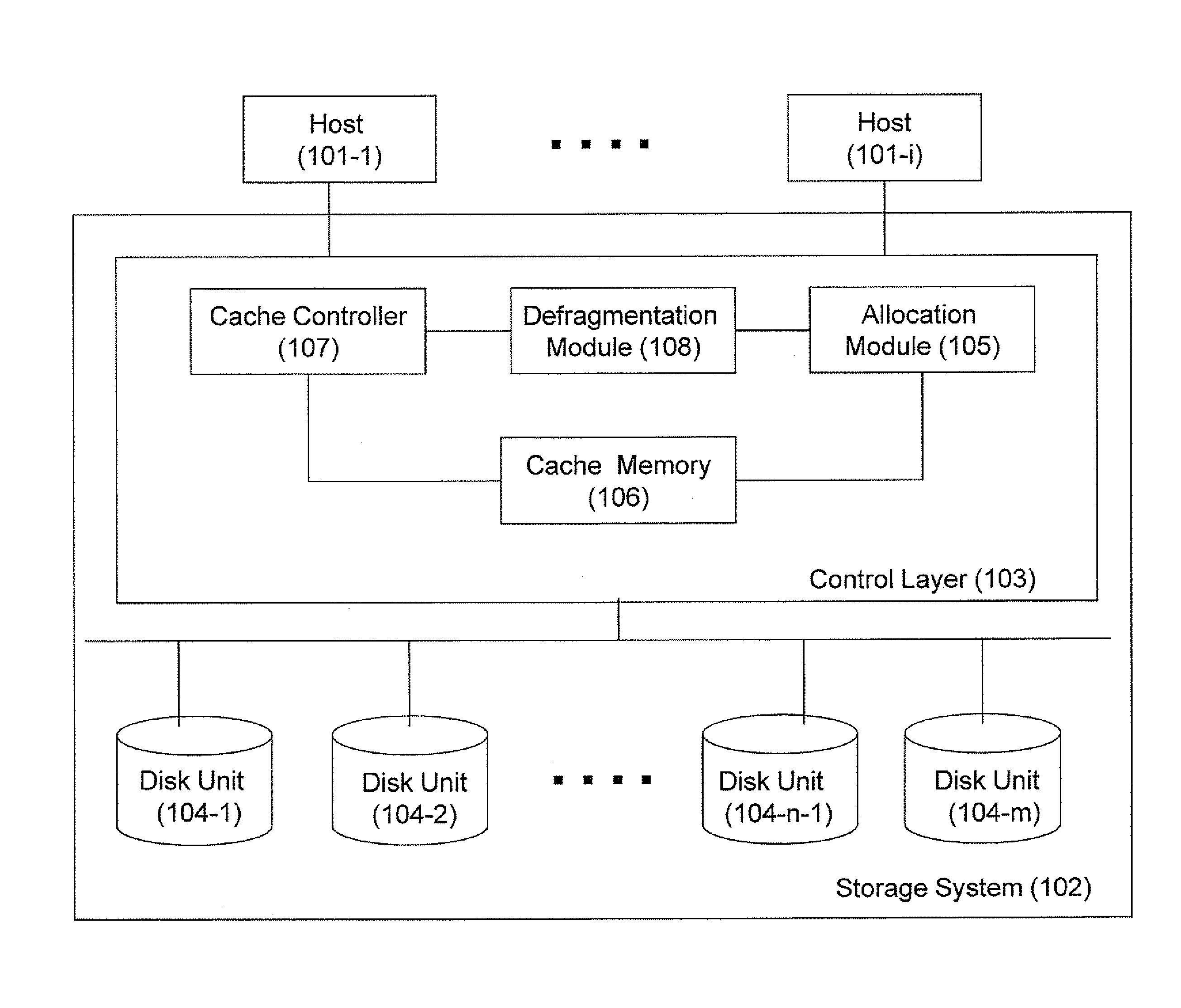
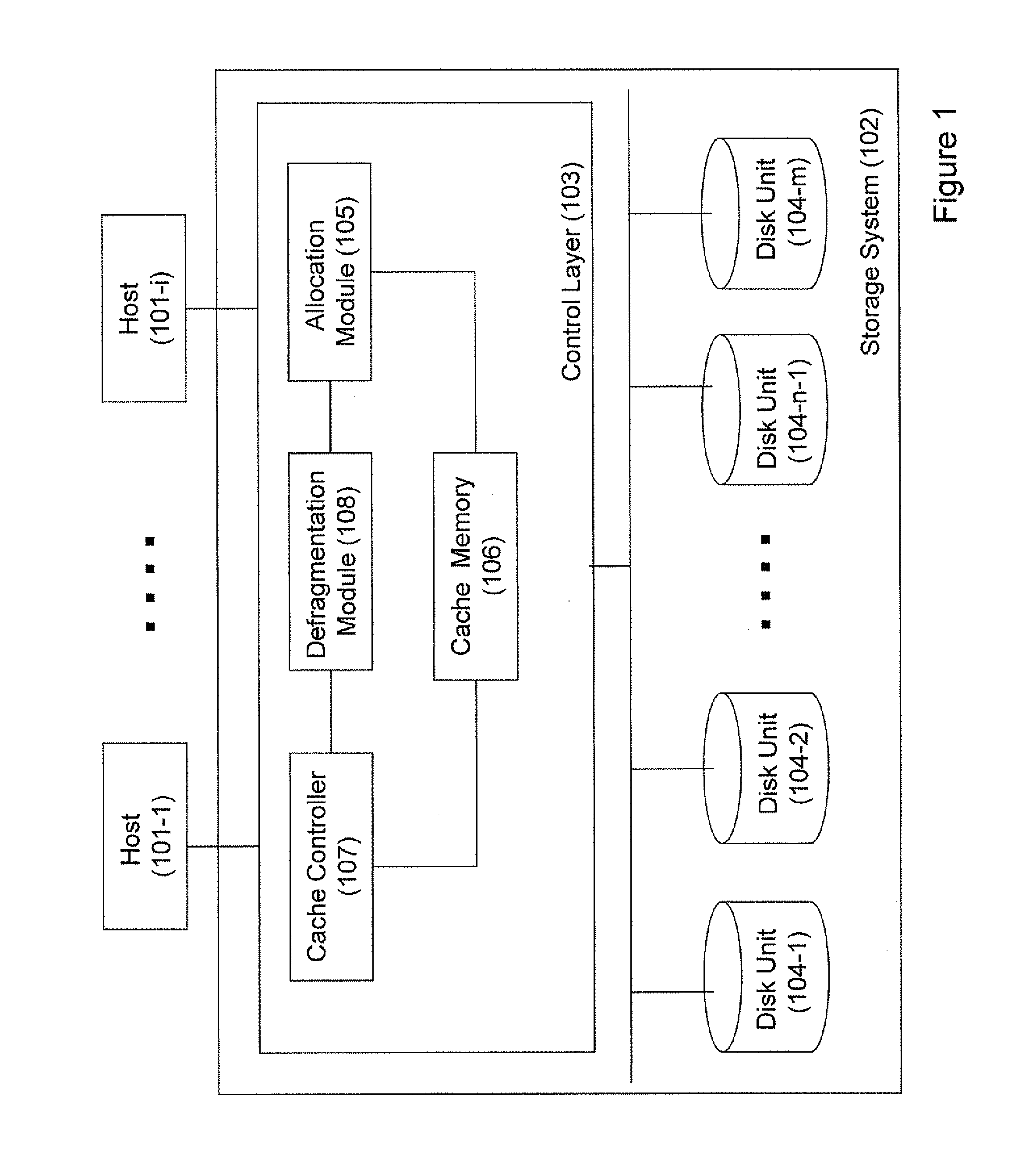
ActiveUS20120117322A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTControl layerManagement process
There are provided a mass storage system comprising a control layer operatively coupled to a physical storage space and operable to interface with one or more clients and to present to said clients a plurality of logical volumes. The method of operating the storage system comprises: dividing one or more logical volumes into a plurality of statistical segments with predefined size; assigning to each given statistical segment a corresponding activity level characterizing statistics of I / O activity with regard to data portions within the given statistical segment, said statistics collected over a plurality of cycles of fixed counting length; and managing one or more data storage processes in the storage system (e.g. a background defragmentation process, a background garbage collection process, a destage management process, etc.) using said activity level.
Owner:INFINIDAT
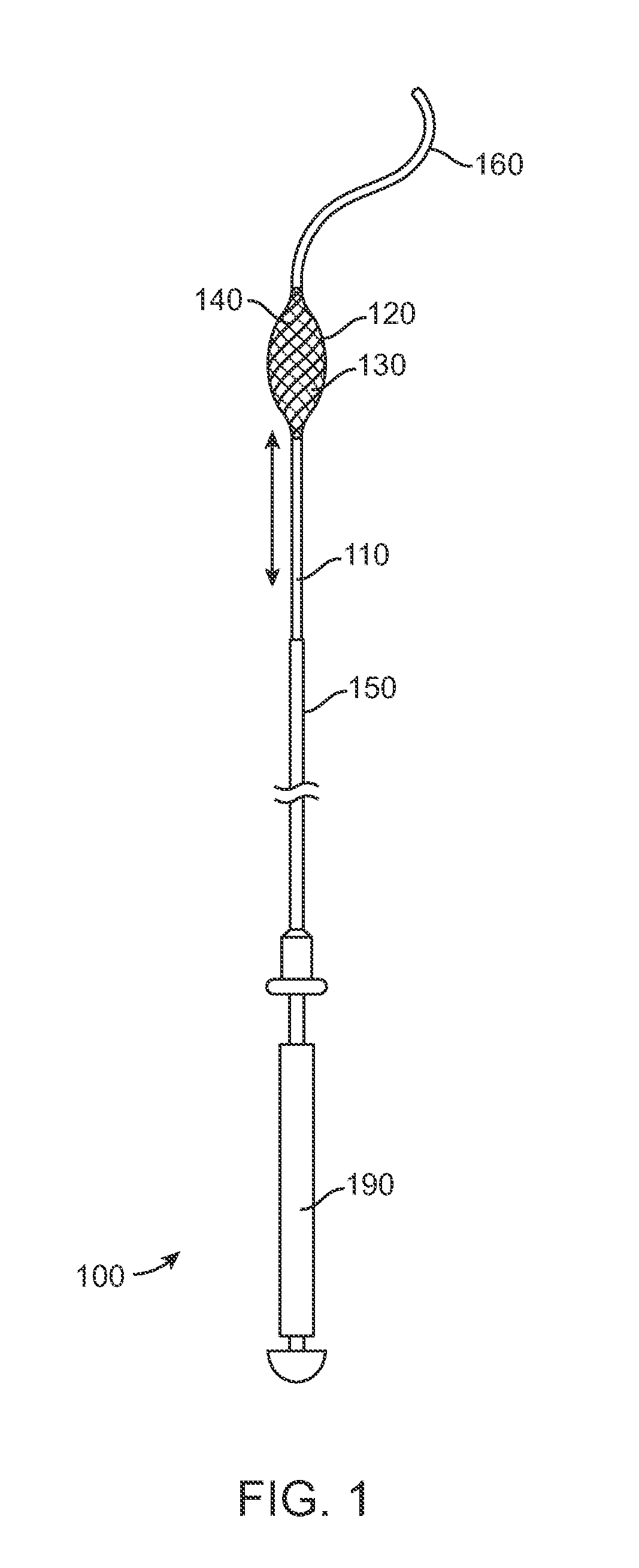
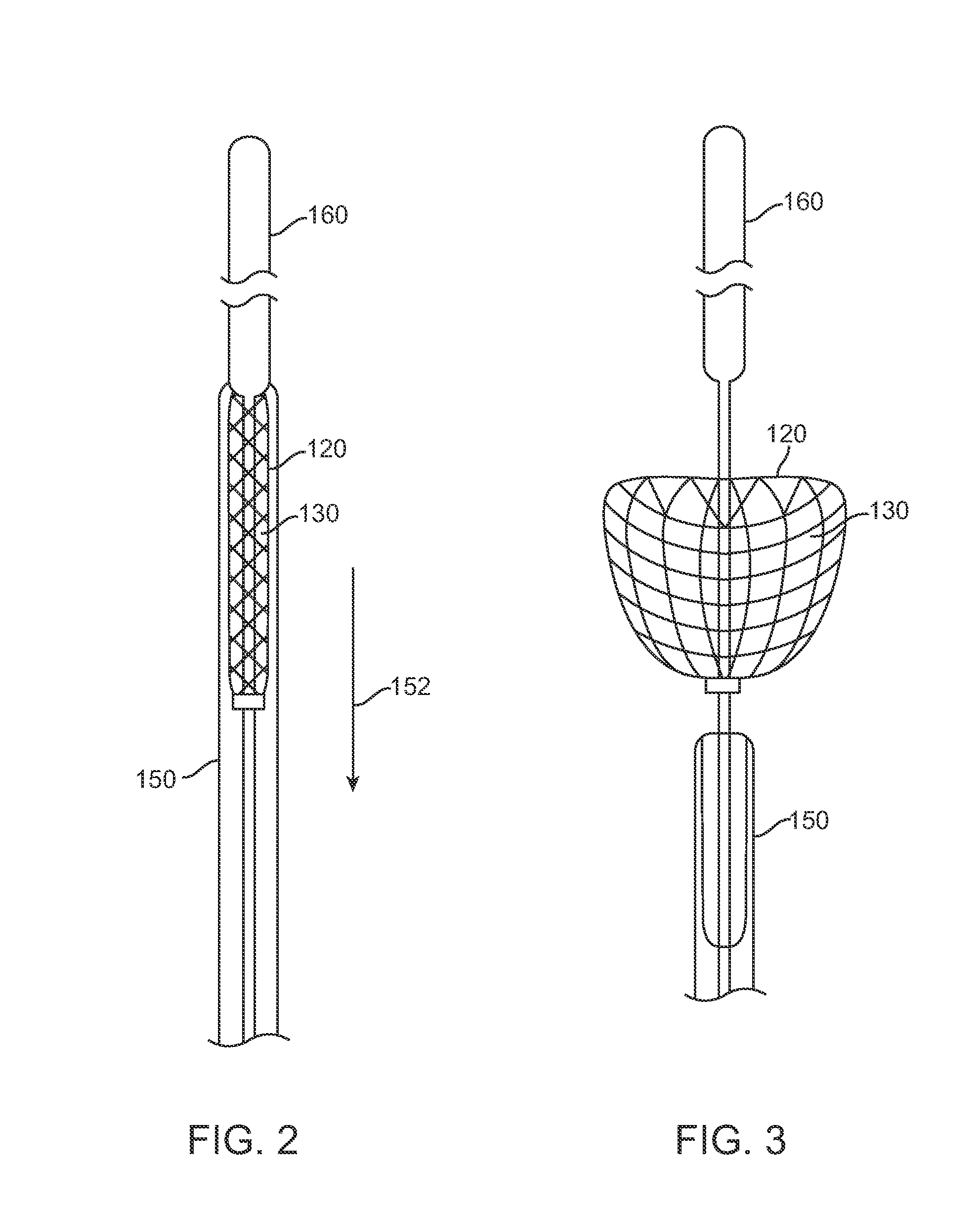
Expandable devices and methods of use
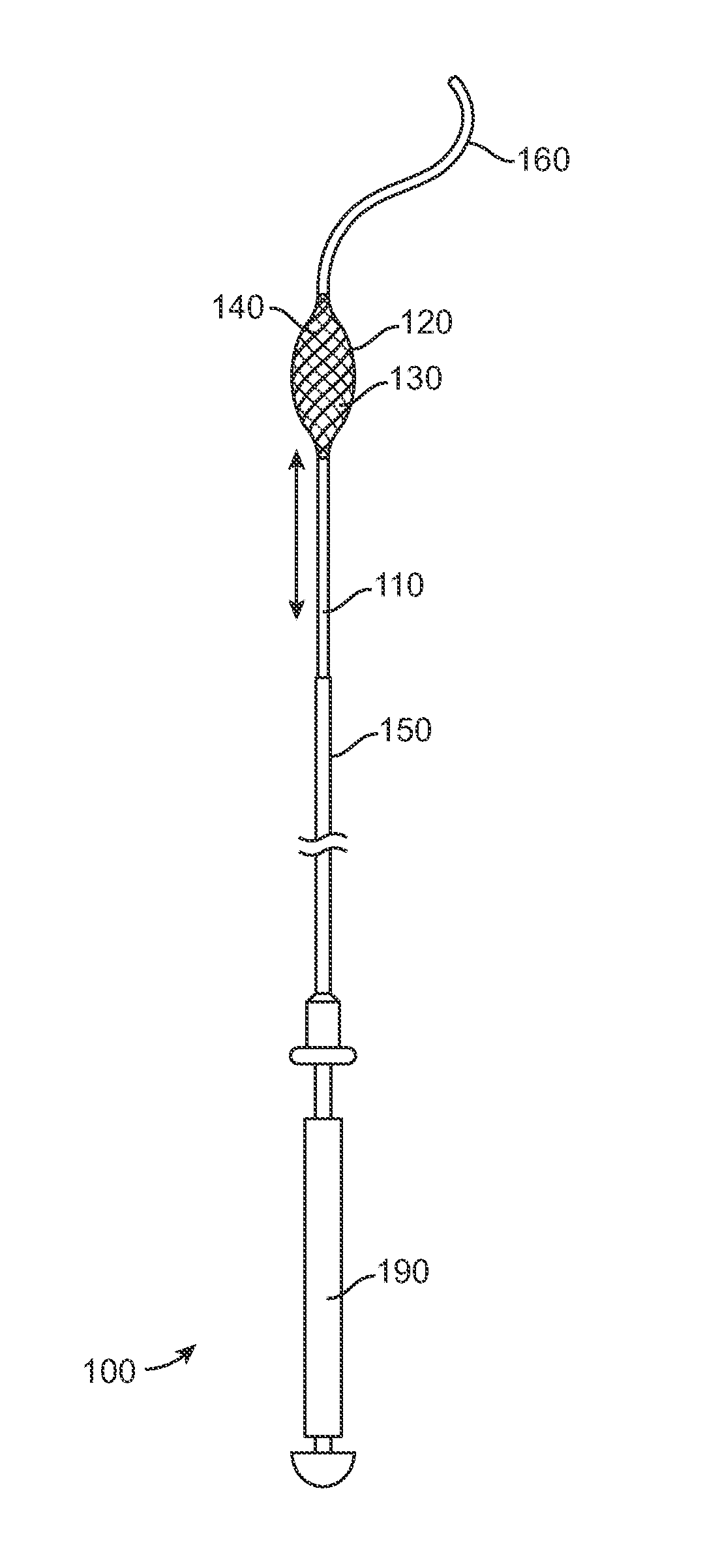
A sieving device and related methods including an expandable sieve mounted on a surgical guide wire. The expandable sieve may be a self-expandable braided filter which is mounted on the guide wire in an axially fixed position, or moveable in one or more directions. The sieving device is deployable in an obstructed ureter, or other body lumen, such as at the beginning of a stone removal procedure, prior to actual stone defragmentation (lithotripsy) phase. The expandable sieve may be set distal to the obstructive stone and expanded to span the entire local ureter cross section in order to retain stone fragments larger than a predetermined size from migrating distally towards the kidney under high irrigation rates / pressures during lithotripsy.
Owner:XENOLITH MEDICAL
Defragmentation of communication channel allocations
InactiveUS20060239272A1Increased bandwidth availabilityNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationCommunication bandwidthDistributed computing
Approaches scheduling and allocation of communication bandwidth across a communication channel provide the opportunity for improved network utilization. According to one embodiment, a method of allocating communication bandwidth among a plurality of network devices scheduling and conducting communication activities within the communication network in a communication network is provided. The method comprises the steps of: a first network device determining allocations of other network devices operating in the communication network; the first network device preempting a scheduled allocation of a second network device; and the first network device scheduling its communication activities on the communication network. Additionally, the first network device can also determine whether a conflict exists between its desired or required allocation and an allocation of the second network device.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Scalable chunk store for data deduplication
ActiveCN102541751ADigital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData streamData mining
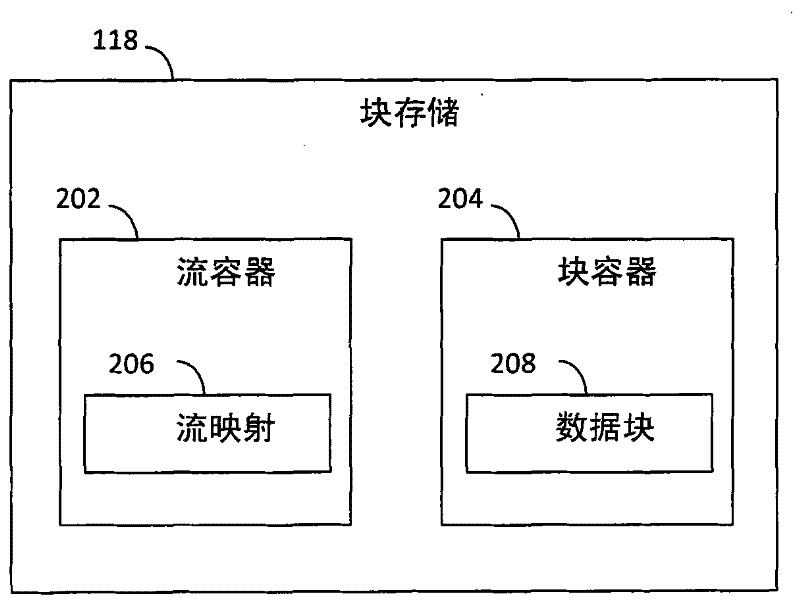
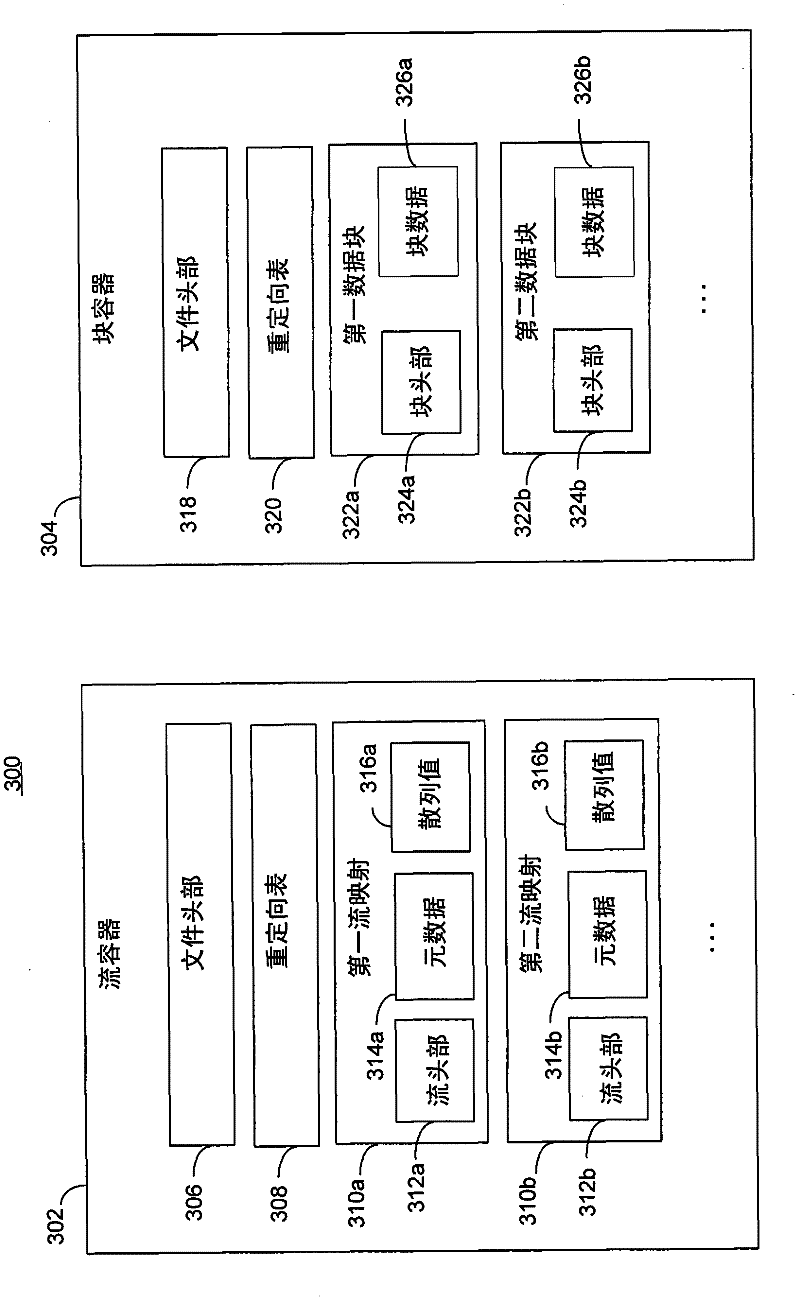
The invention relates to scalable chunk store for data deduplication. Data streams may be stored in a chunk store in the form of stream maps and data chunks. Data chunks corresponding to a data stream may be stored in a chunk container, and a stream map corresponding to the data stream may point to the data chunks in the chunk container. Multiple stream maps may be stored in a stream container, and may point to the data chunks in the chunk container in a manner that duplicate data chunks are not present. Techniques are provided herein for localizing the storage of related data chunks in such chunk containers, for locating data chunks stored in chunk containers, for storing data streams in chunk stores in localized manners that enhance locality and decrease defragmentation, and for reorganizing stored data streams in chunks stores.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Magnetic disk unit, file management system, and file management method
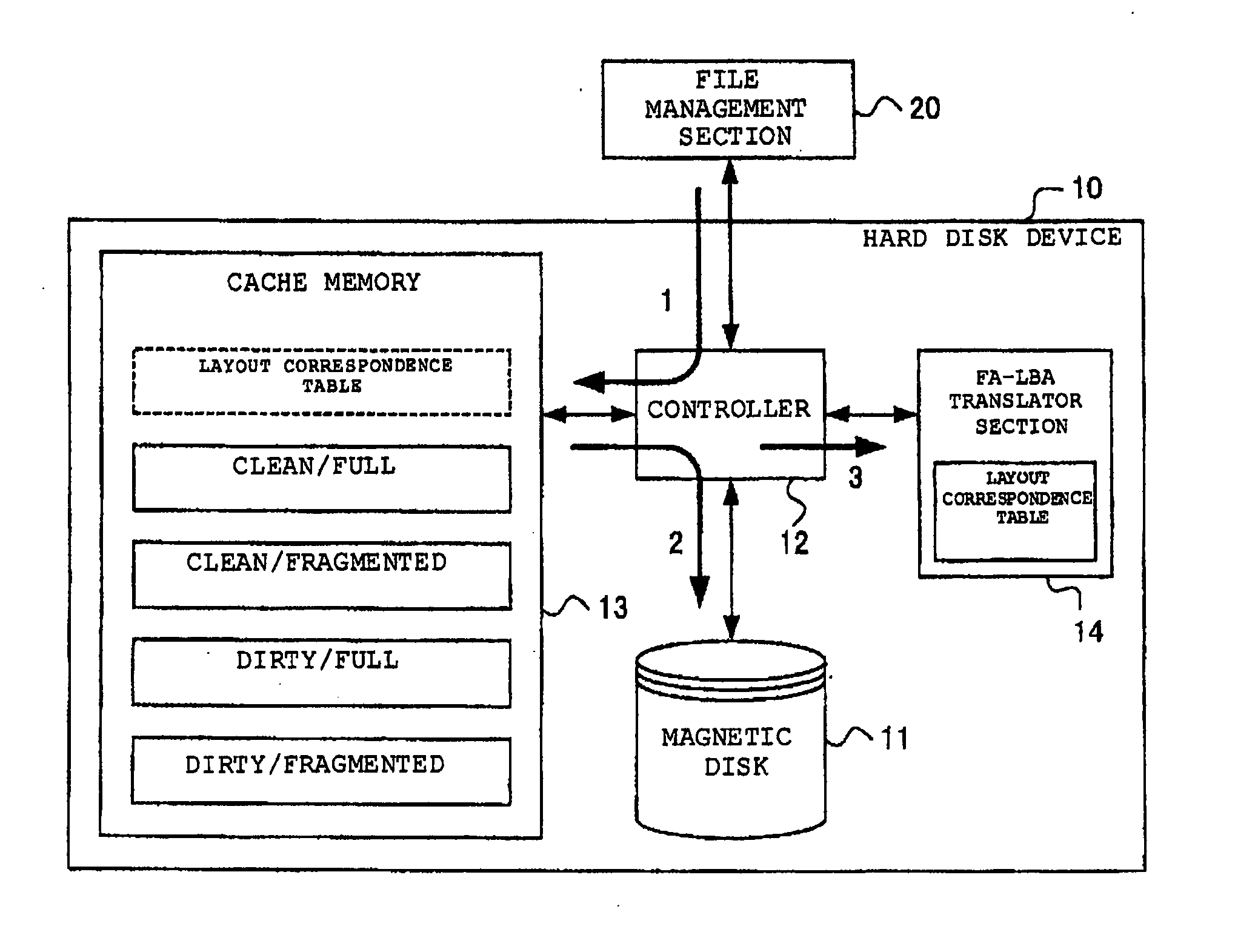
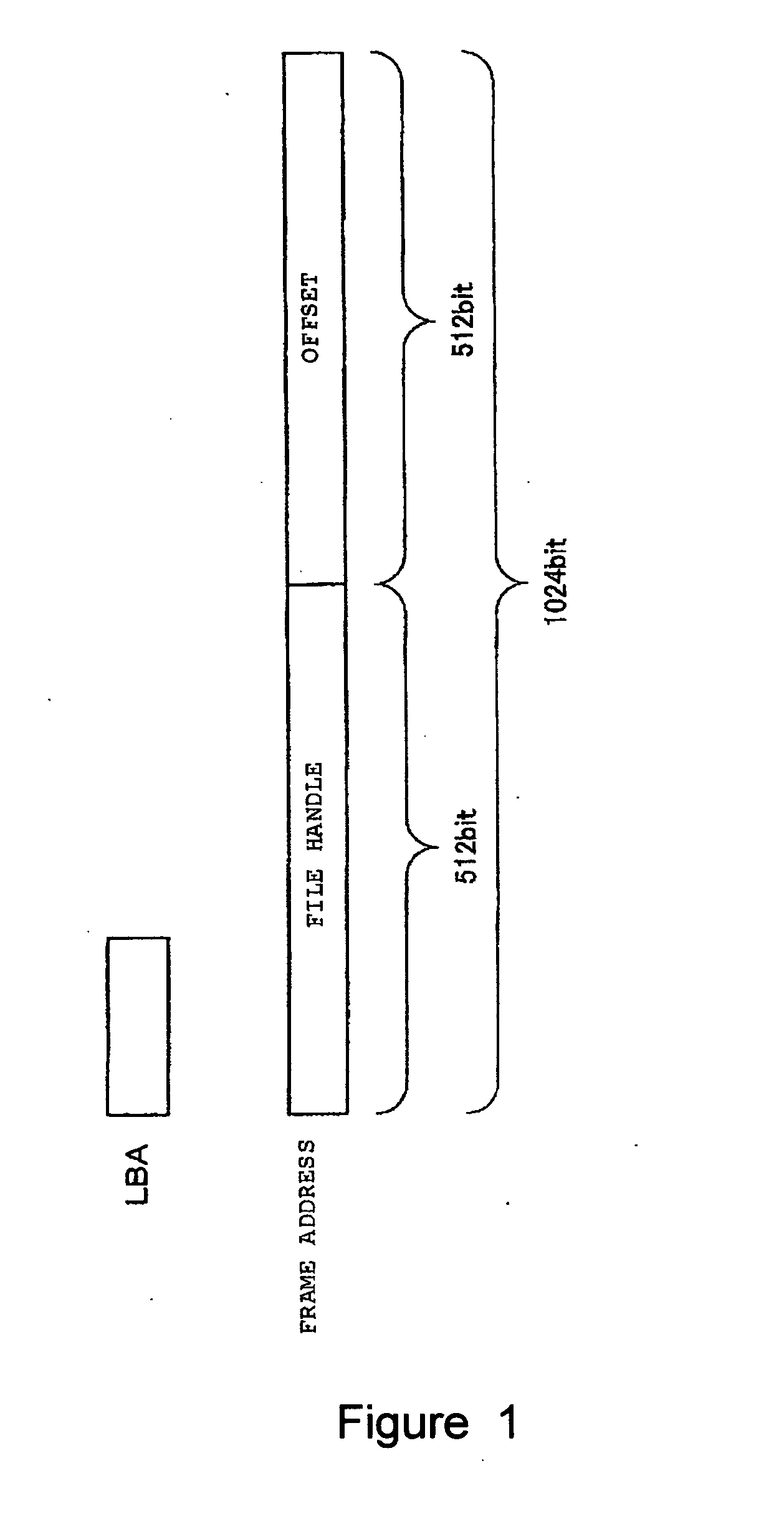
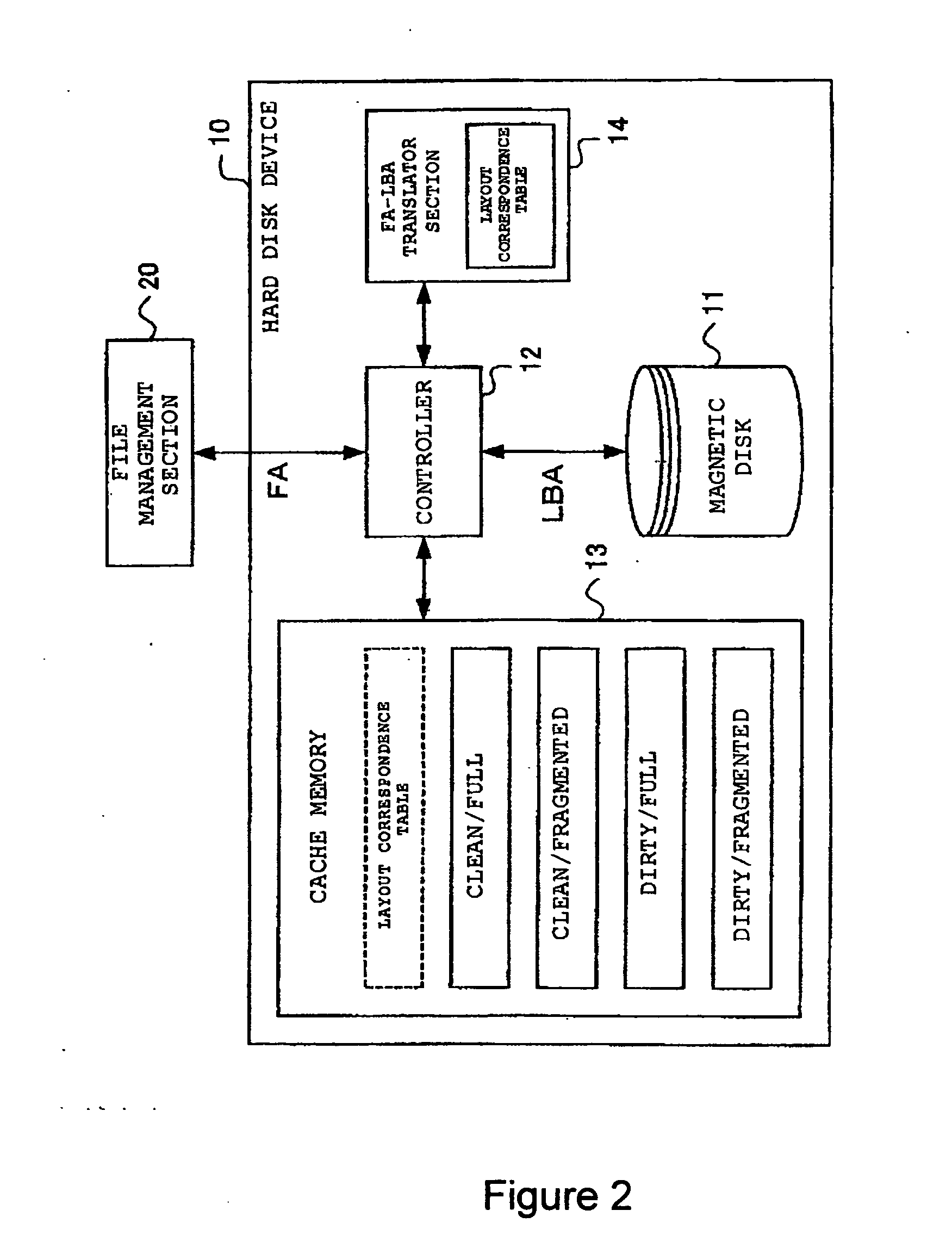
InactiveUS20050021900A1Improve performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationManagement systemDocument management system
A file management system including a hard disk unit and a file management unit. The file management unit manages data to be read and written from and into the hard disk unit such that data in a file is continuous in a predetermined logical address space and specifies a target data requested to be read and written from and into the hard disk unit by a predetermined logical address within the logical address space. The hard disk unit performs processing of reading and writing data after translating the predetermined logical addresses specifying the data requested to be read and written into LBAs. Then the hard disk unit performs defragmentation of data recorded on a magnetic disk based on the predetermined logical addresses.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for retrieving access control information
InactiveUS20070214499A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationAuthentication serverComputer science
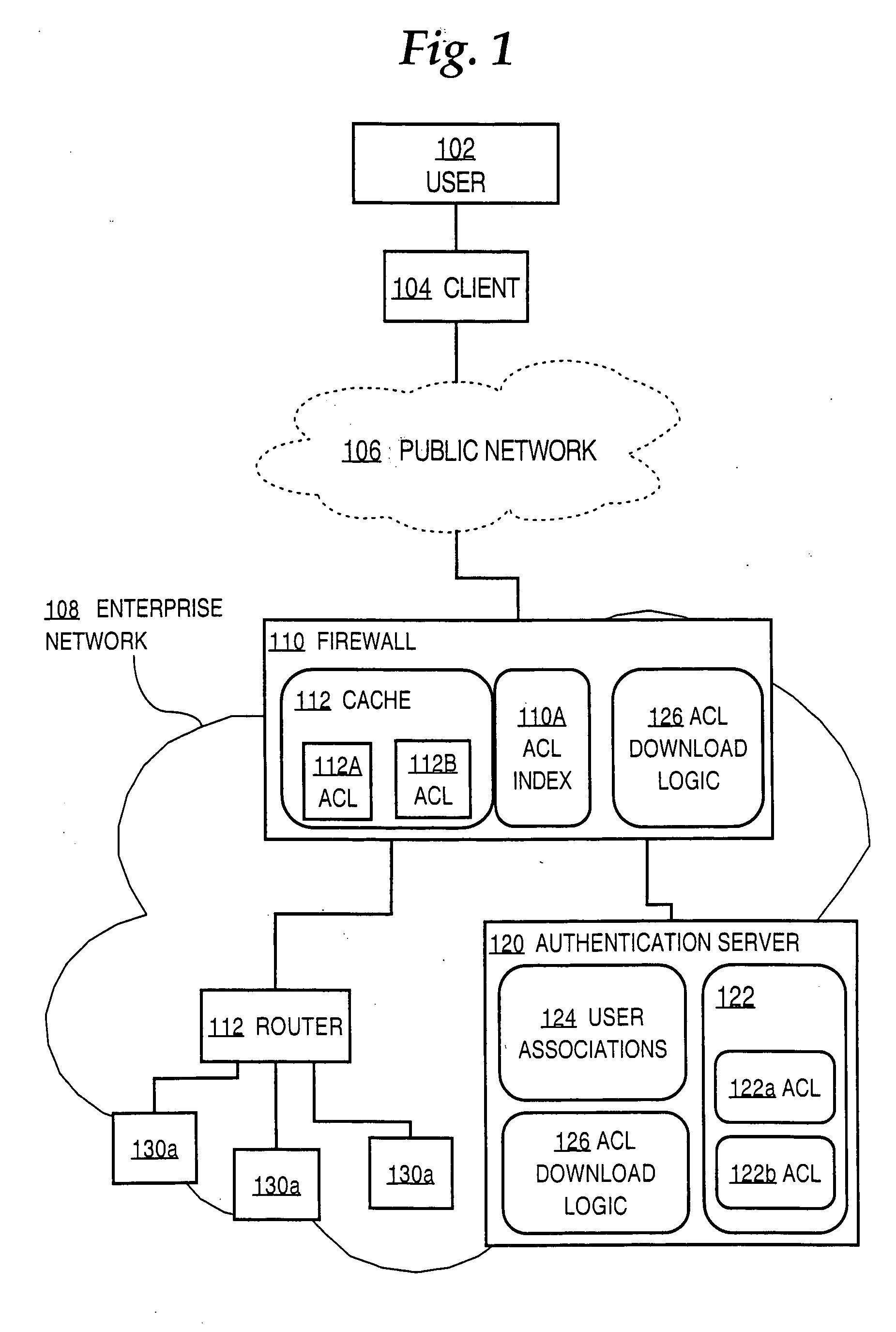
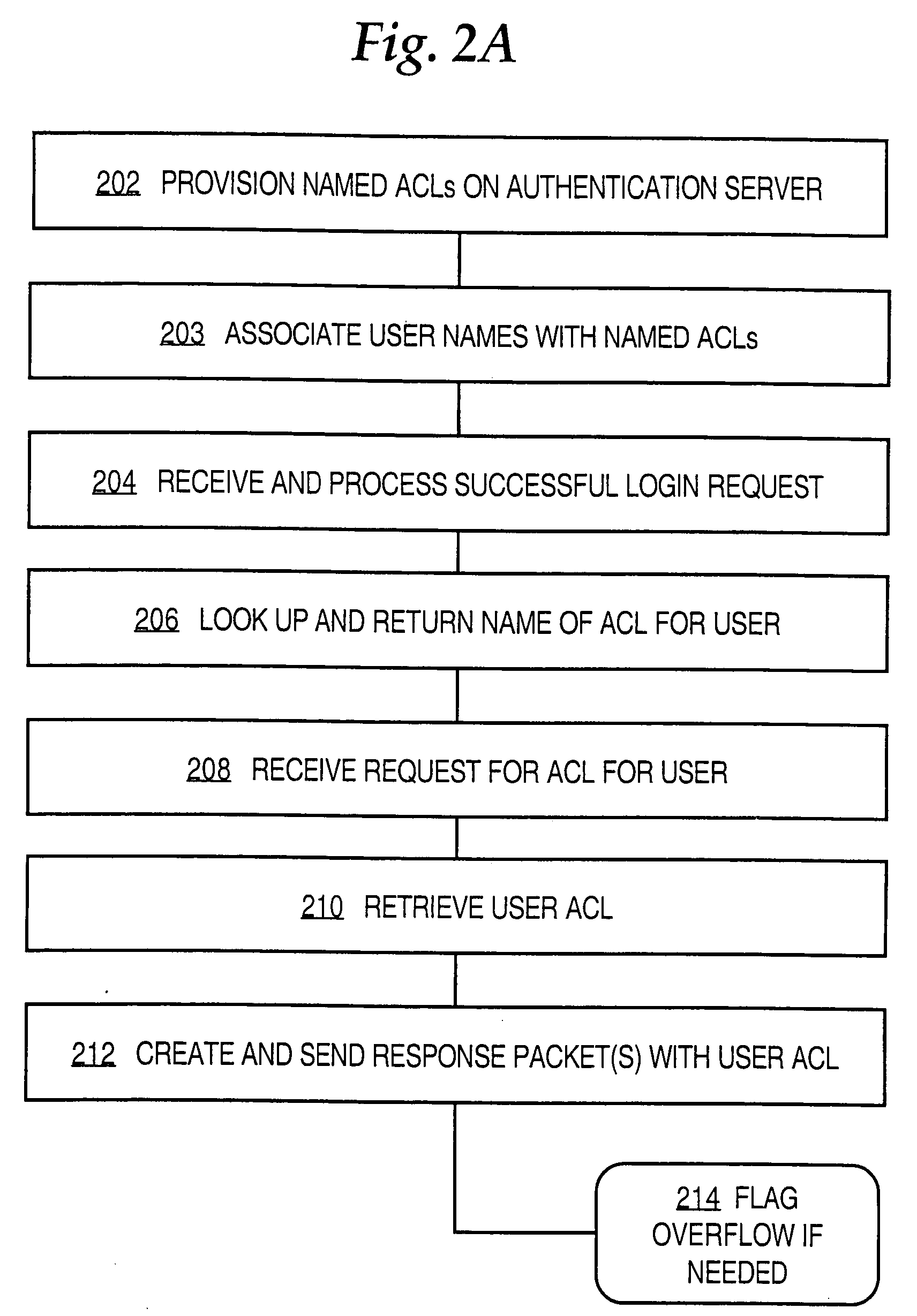
Creating and storing troubleshooting information for providing access control information to a network device involves receiving a provisioning of control lists, and associations of the ACLs to users of the device. During authenticating a user login, a name of a first ACL is provided to the device, selected from among the ACLs based on the associations. A request is received from the device for a first ACL that is associated with a user of the device. The request includes the name of the ACL. The first ACL is sent to the network device in response to the request. Embodiments may use RADIUS for communicating ACLs from an authentication server to a firewall. A de-fragmentation approach enables downloading ACLs that exceed the maximum RADIUS packet size. Using an ACL renaming approach the firewall updates its cache when a user subsequently logs in and the corresponding ACL has changed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for defragmentation in disk storage system
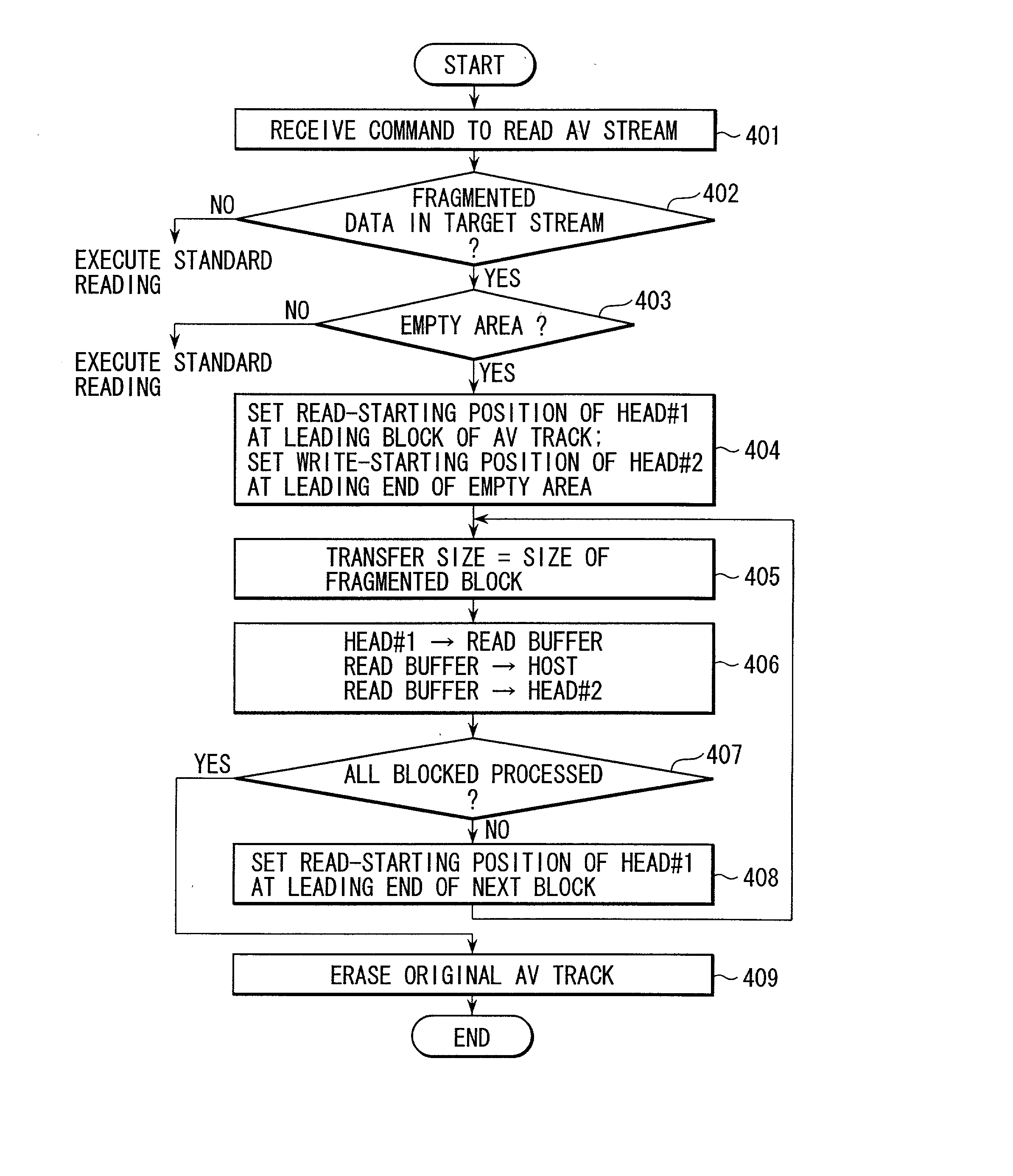
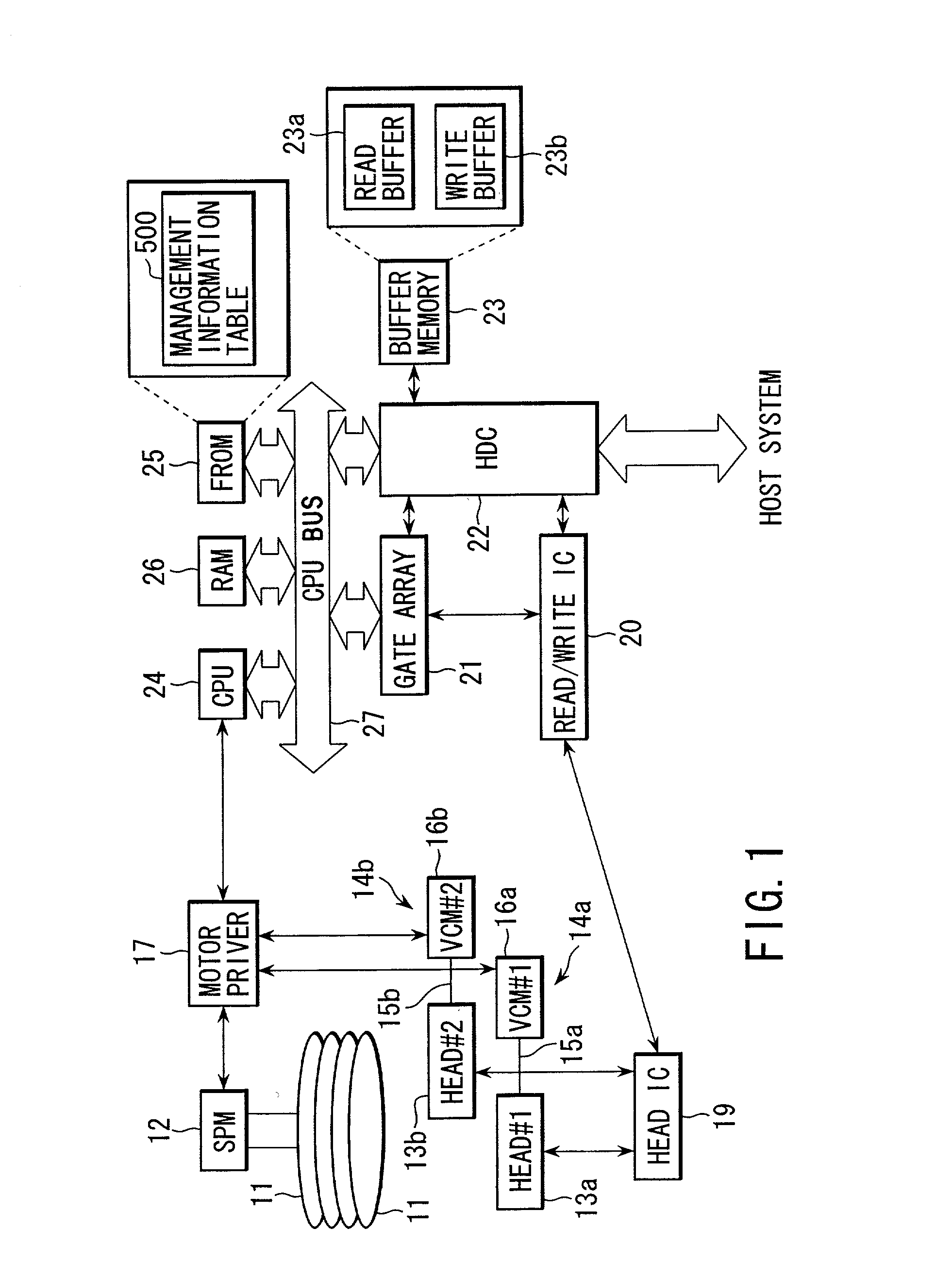
InactiveUS20020129200A1Disc-shaped record carriersInput/output to record carriersSequential dataHost machine
When a host system has requested the reading of sequential data, a CPU incorporated in an HDD determines whether the data is fragmented into a plurality of data blocks on a disk. If the sequential data is fragmented, the CPU executes the control of reading the data from the disk and transferring it to the host system. In parallel with this control, the CPU also executes the control of writing the data read from the disk, to a contiguous area on the disk.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com