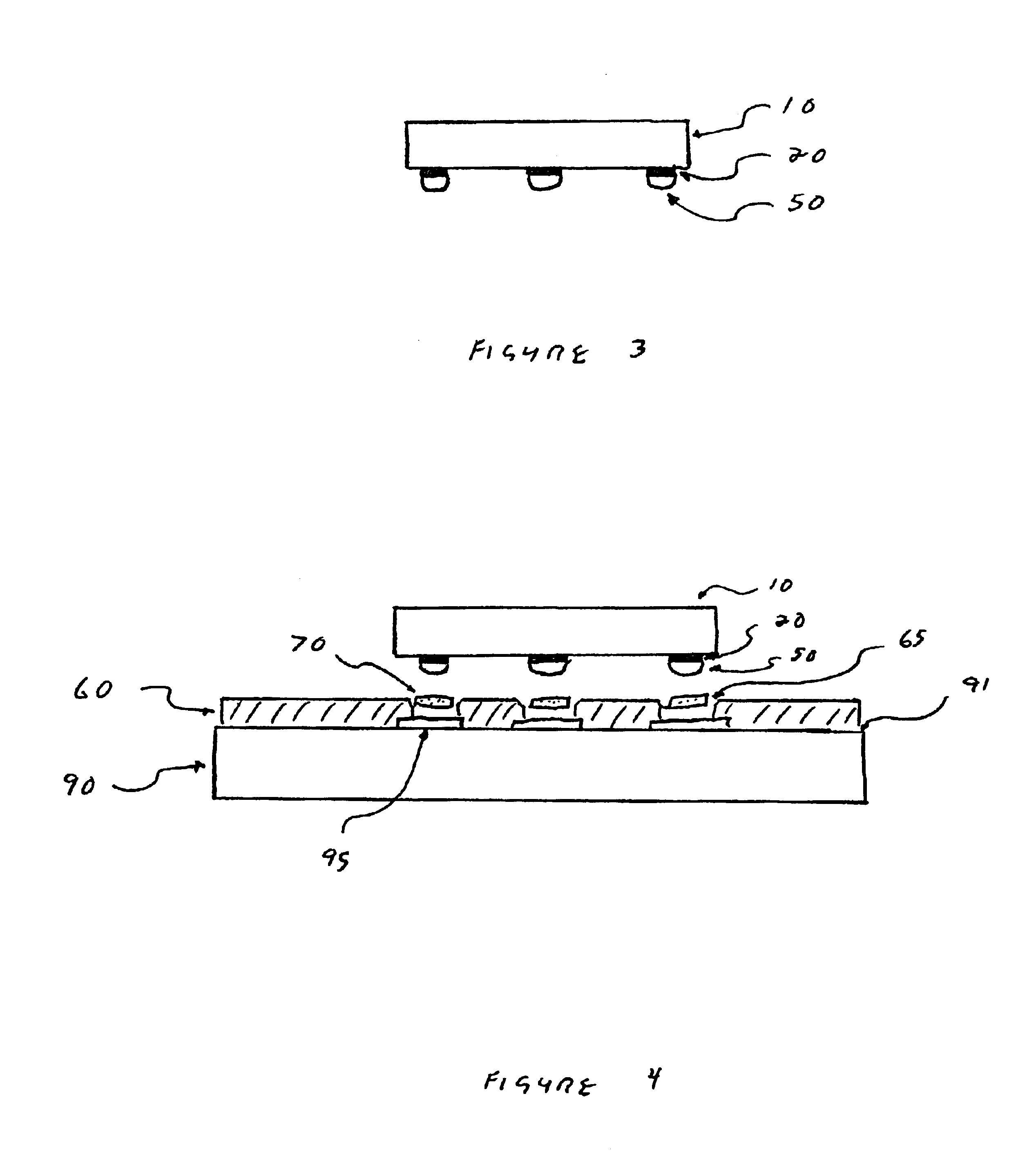
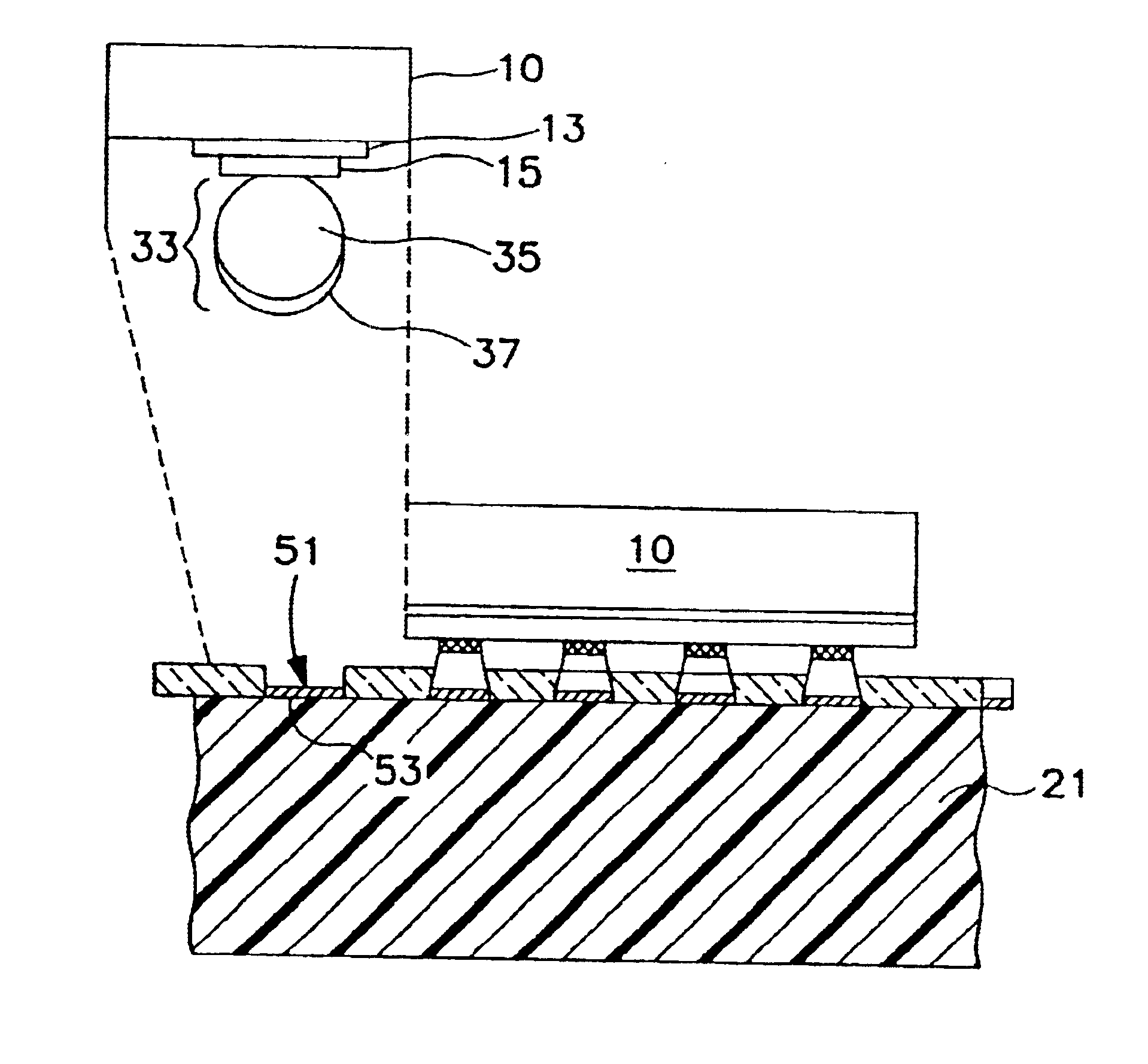
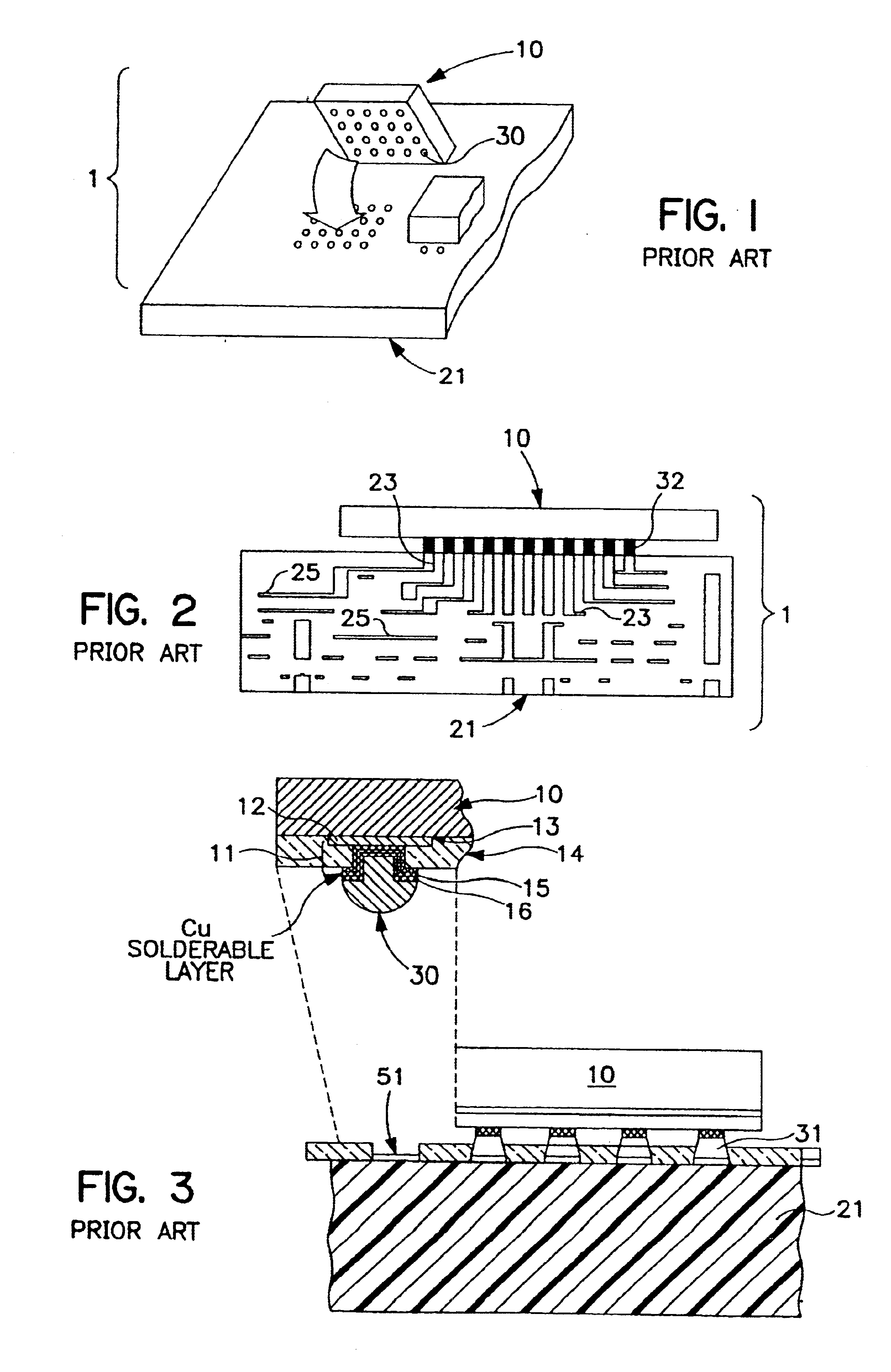
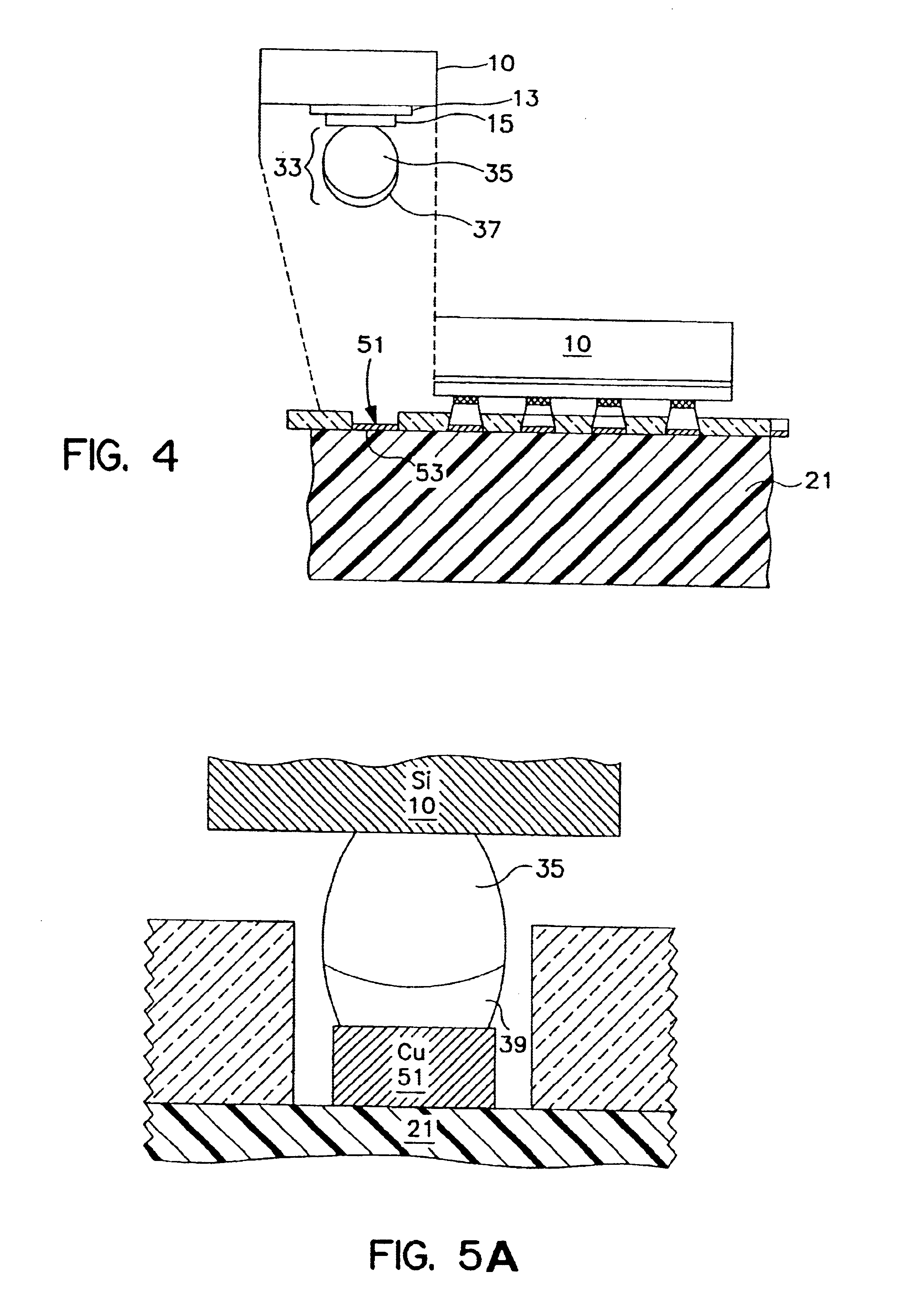
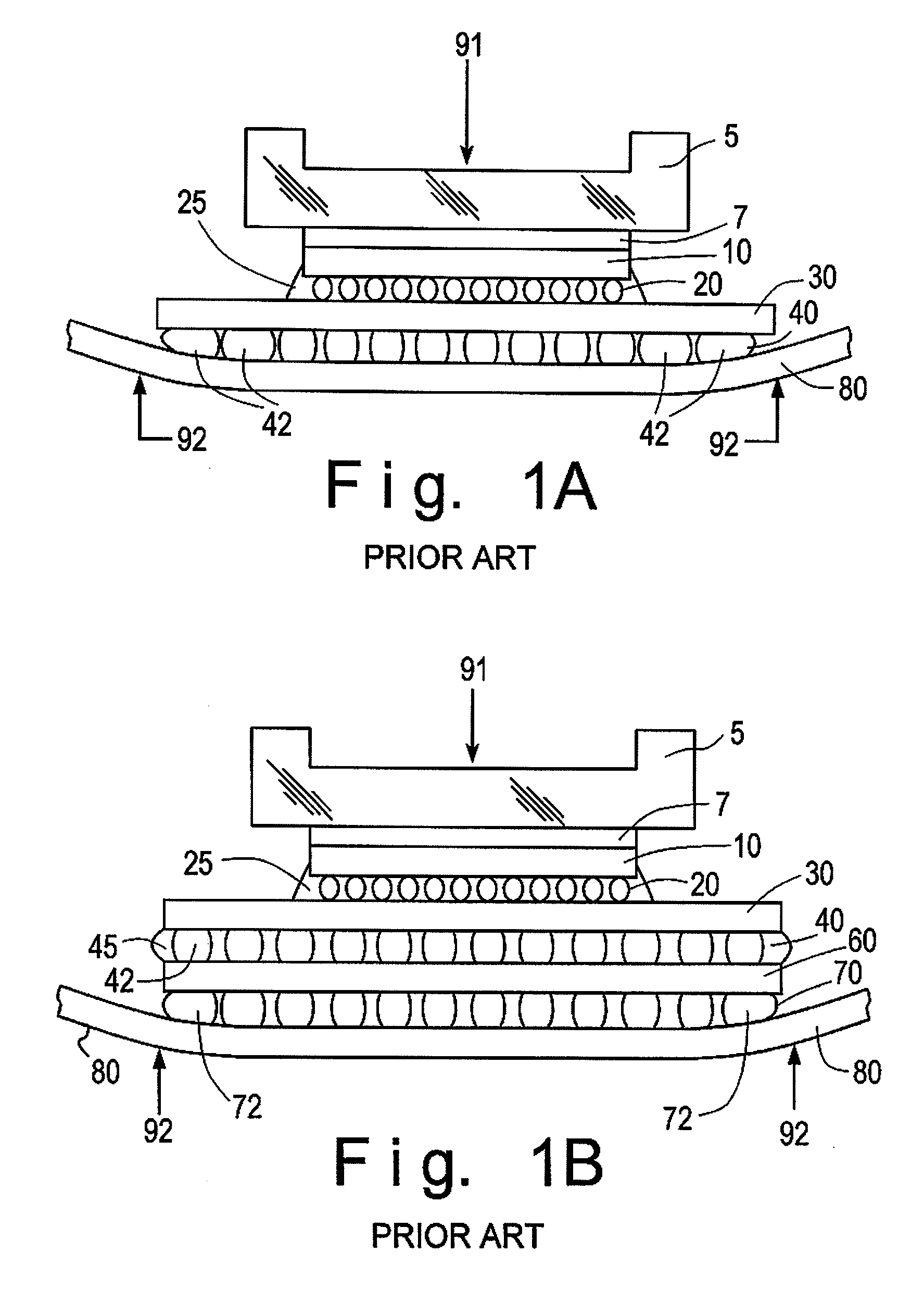
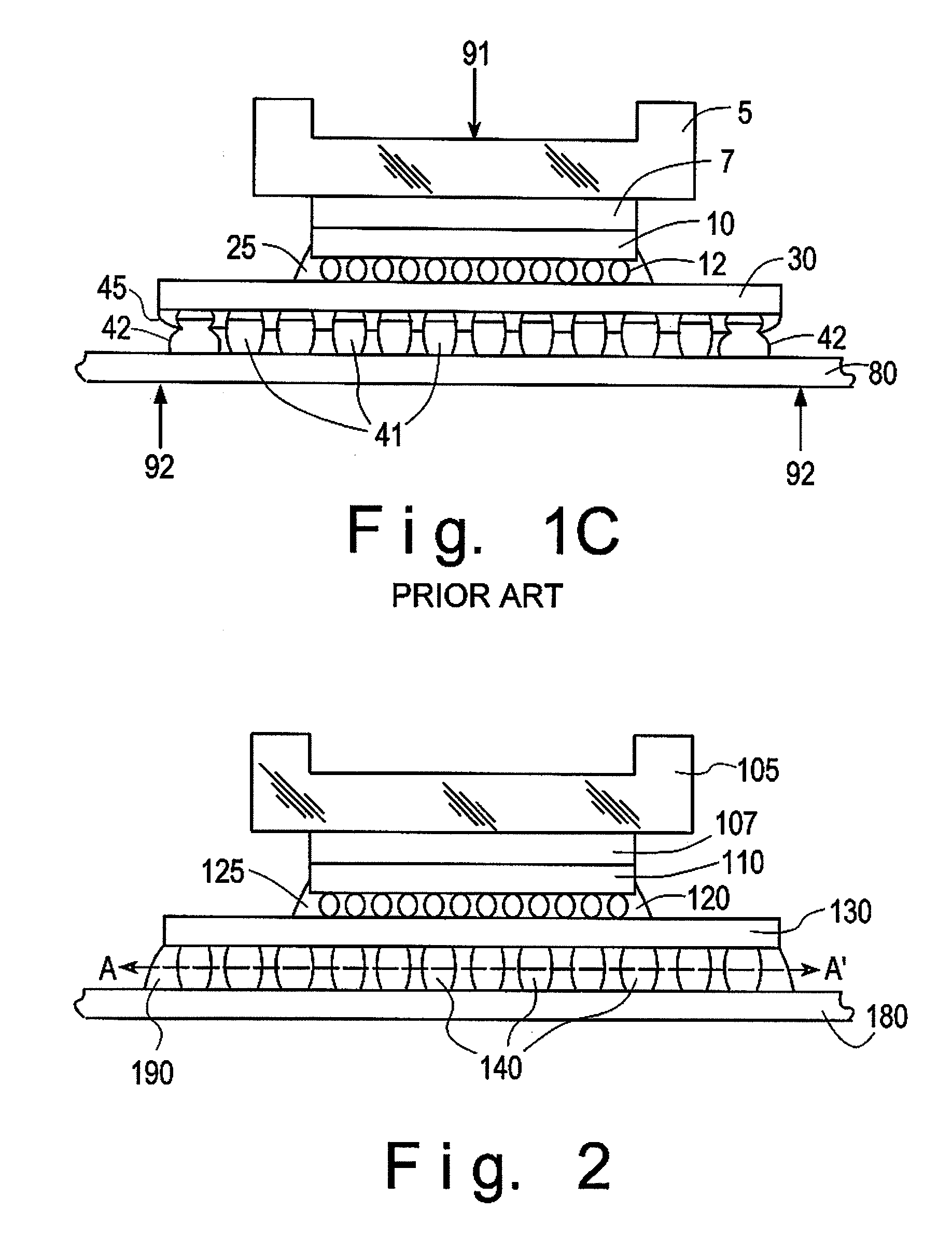
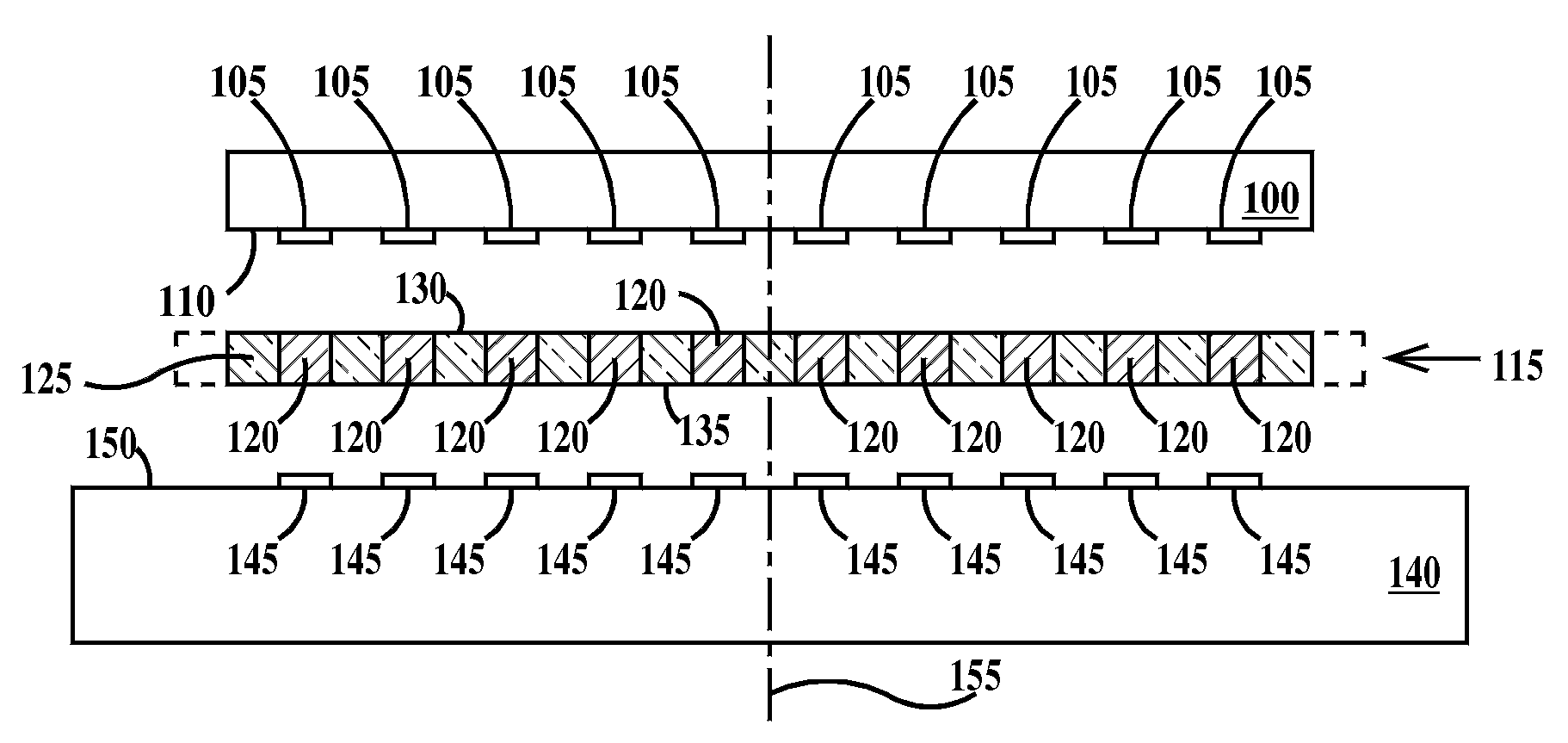
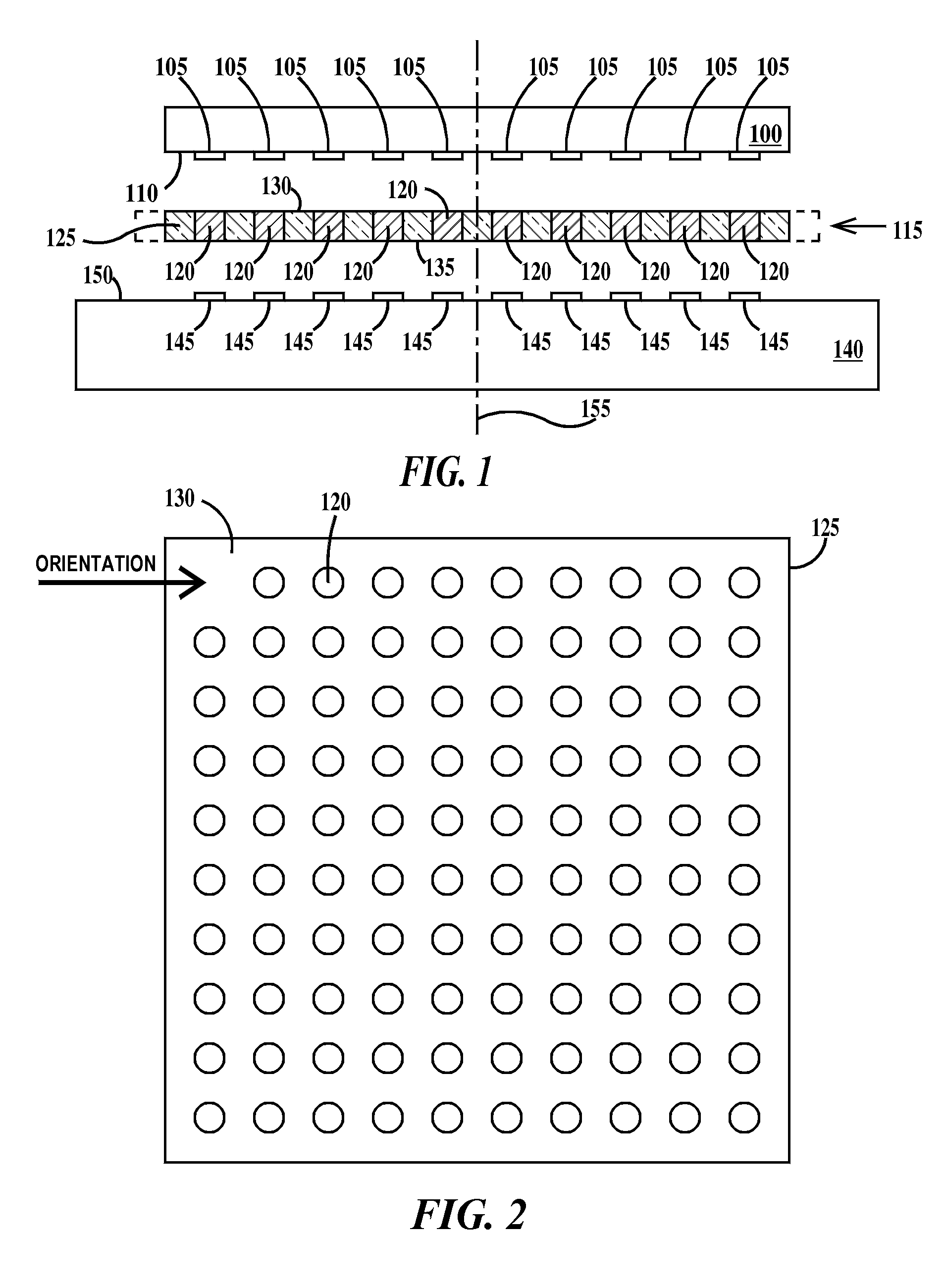
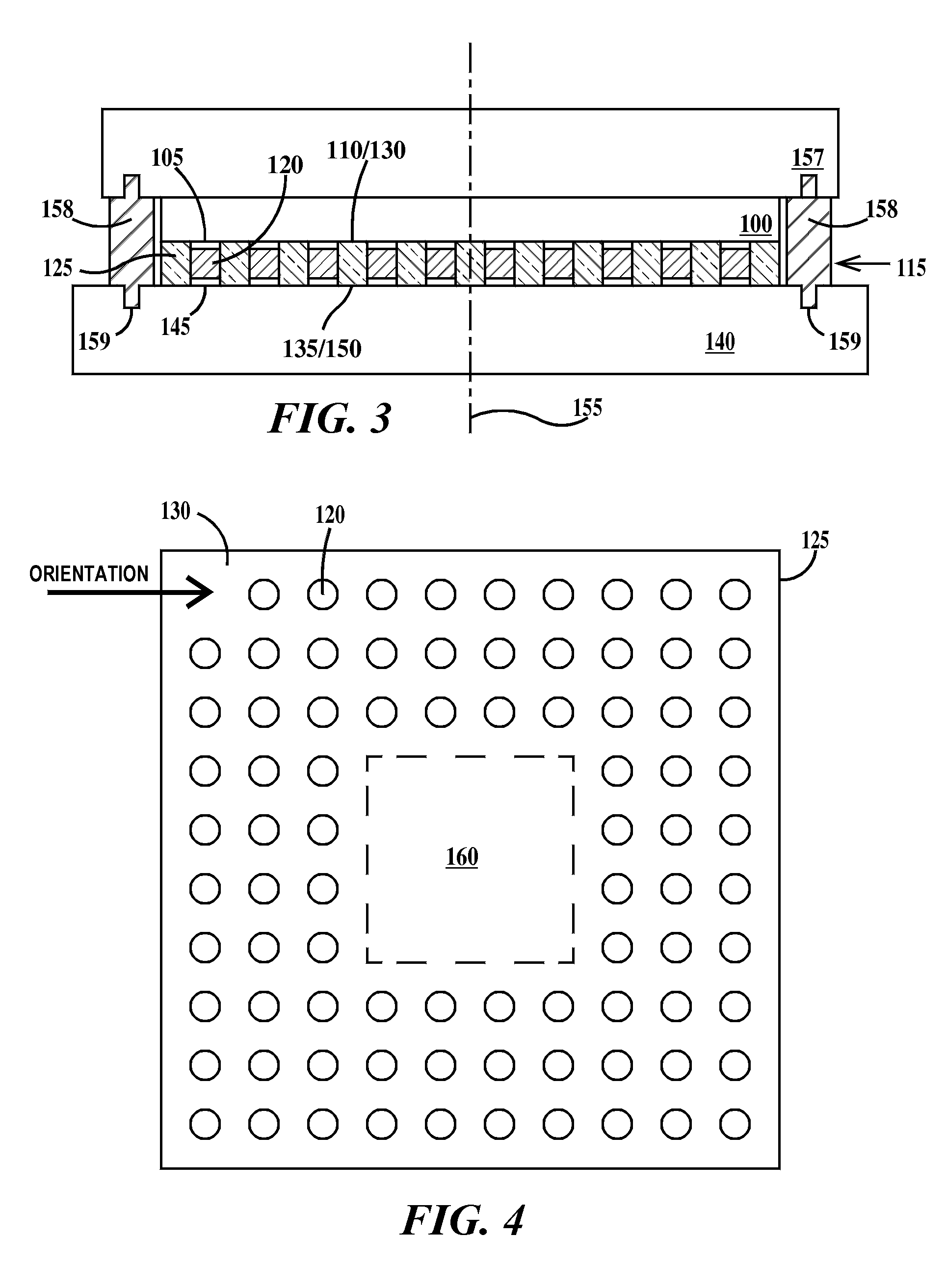
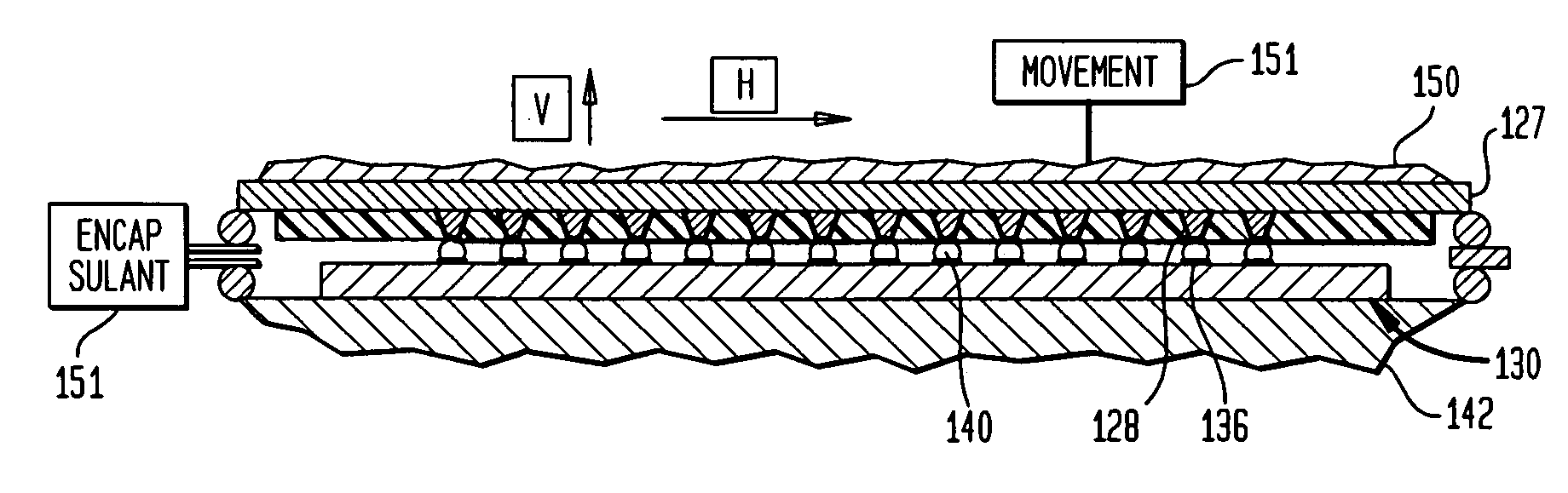
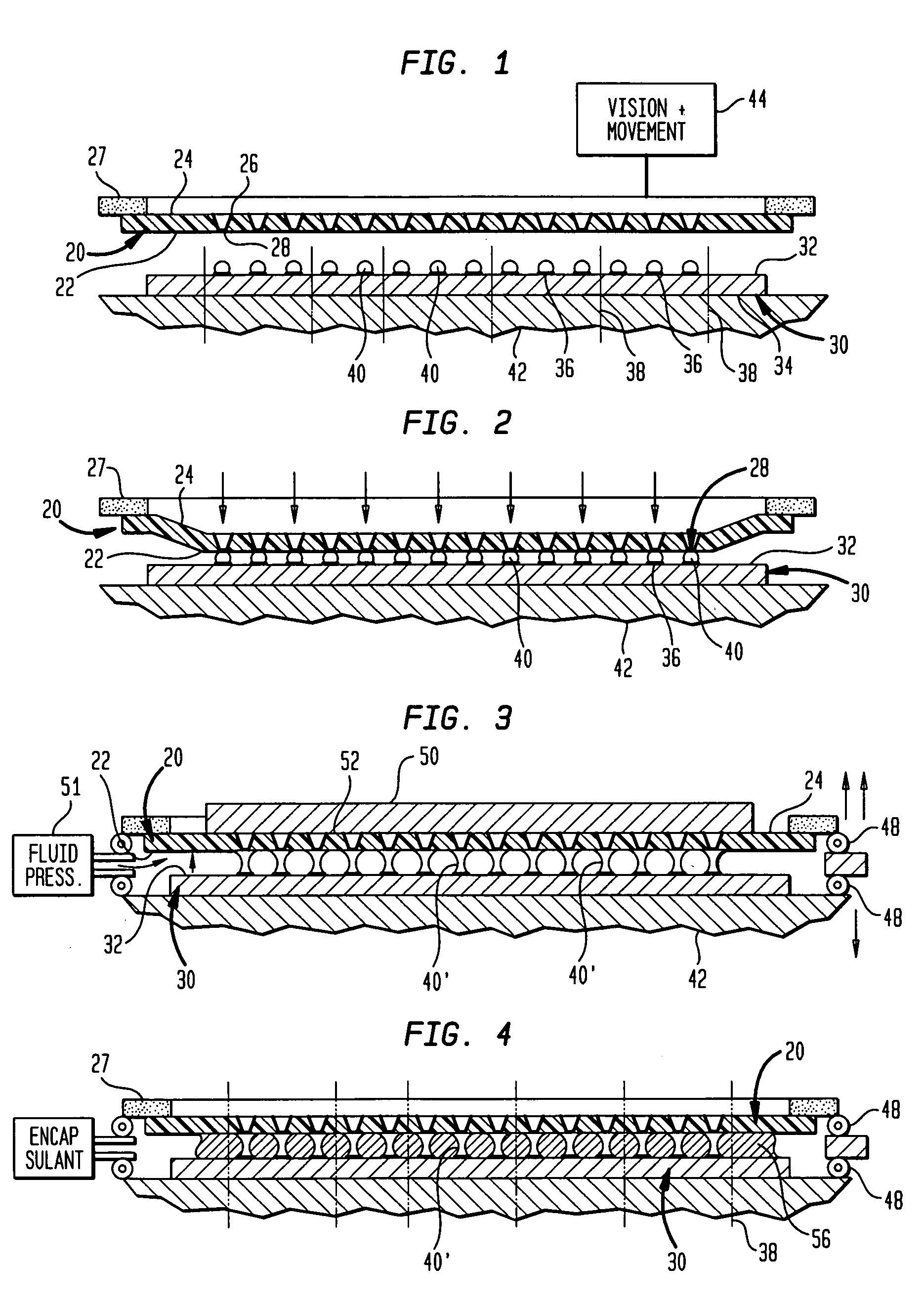
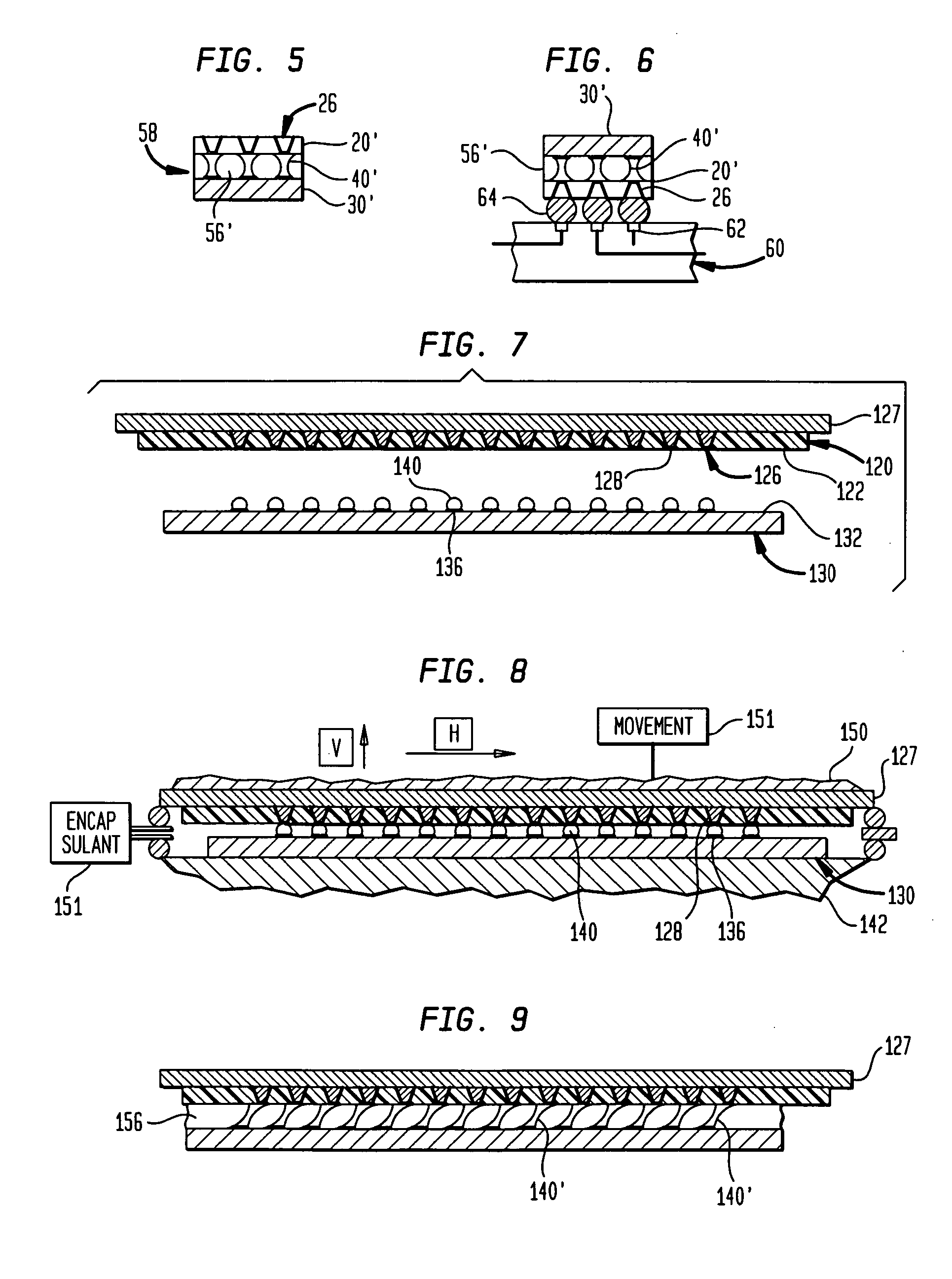
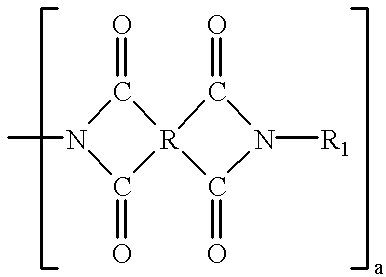
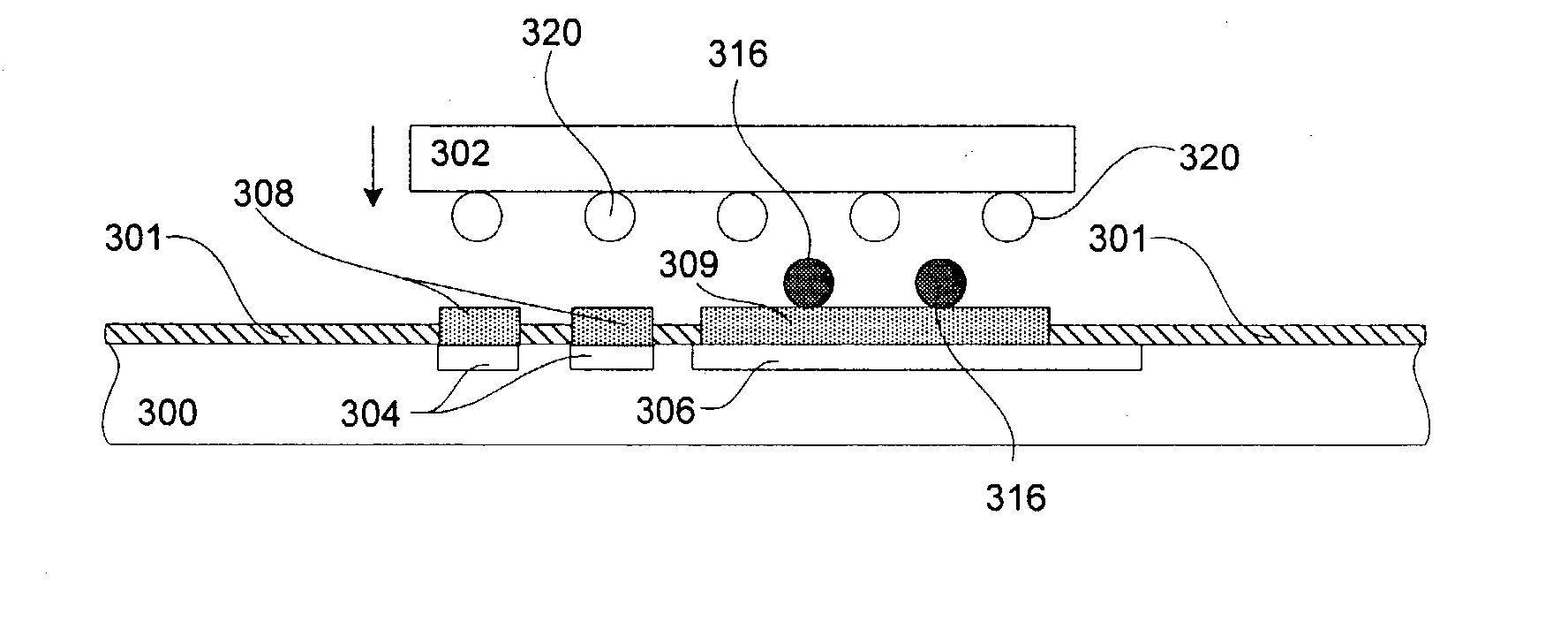
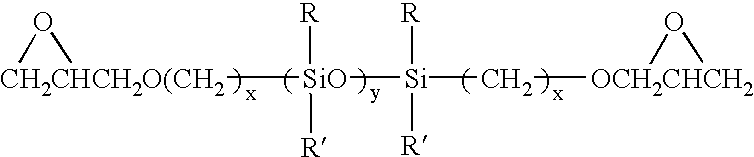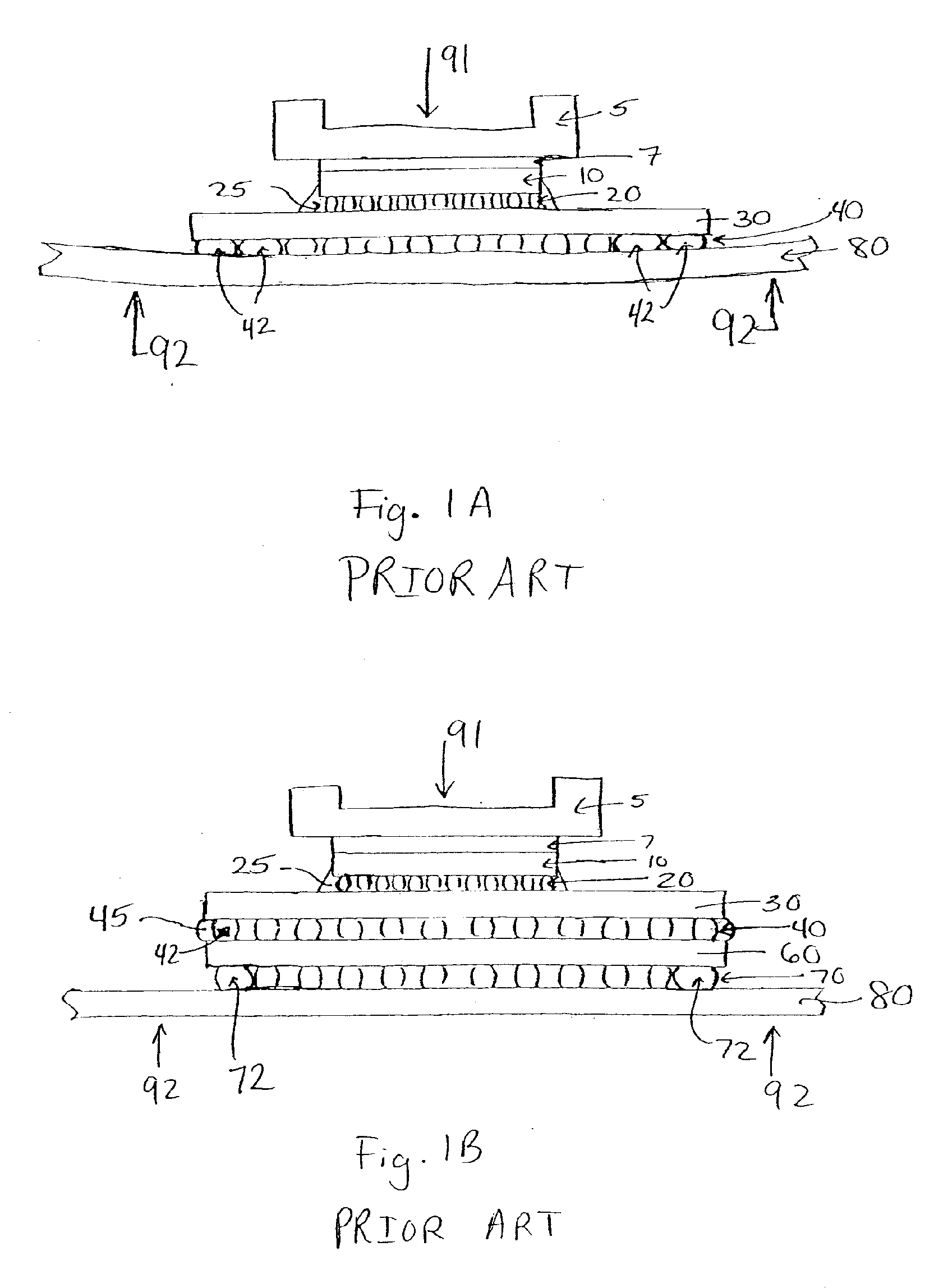Patents
Literature
38 results about "Solder interconnection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
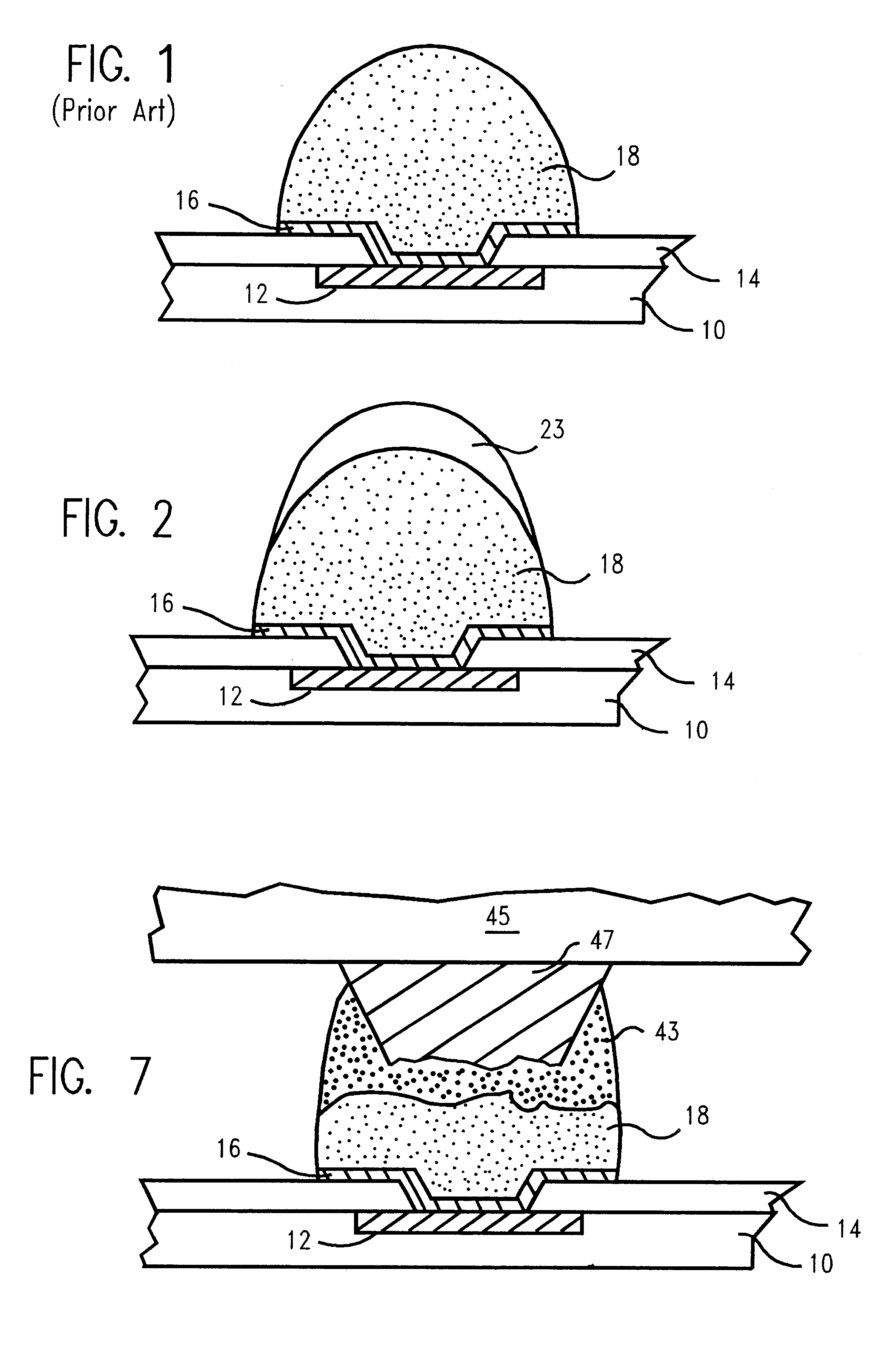
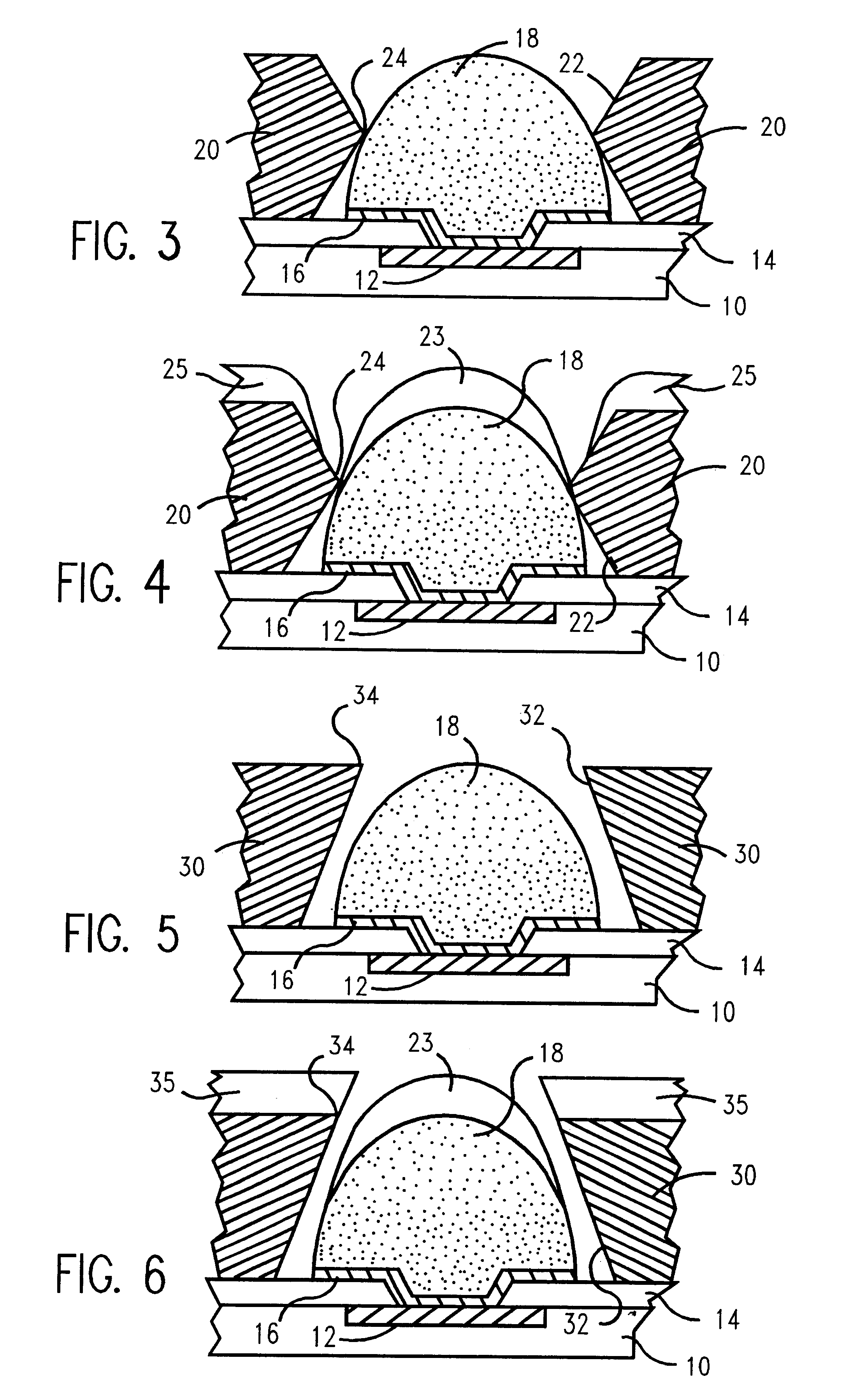
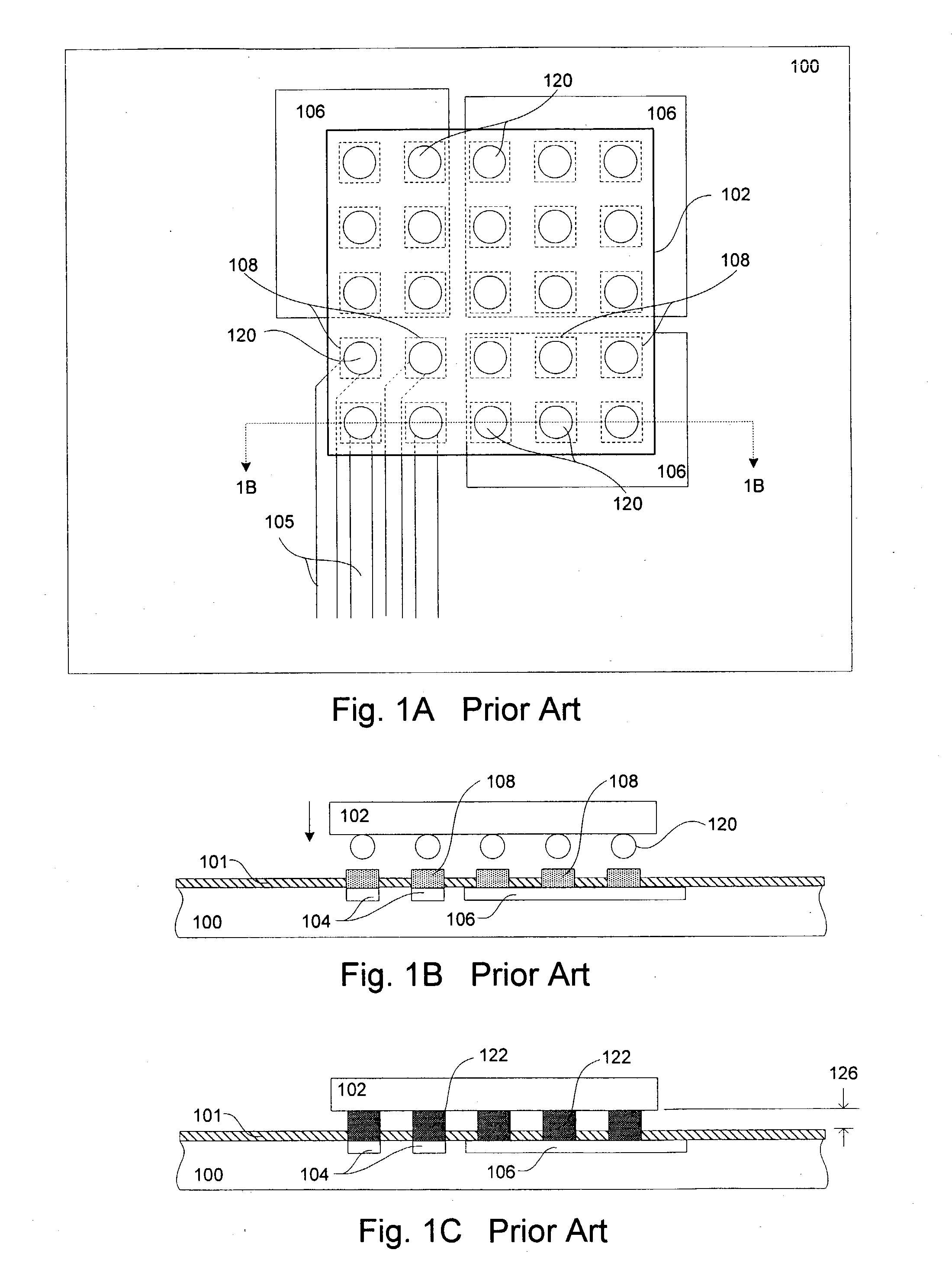
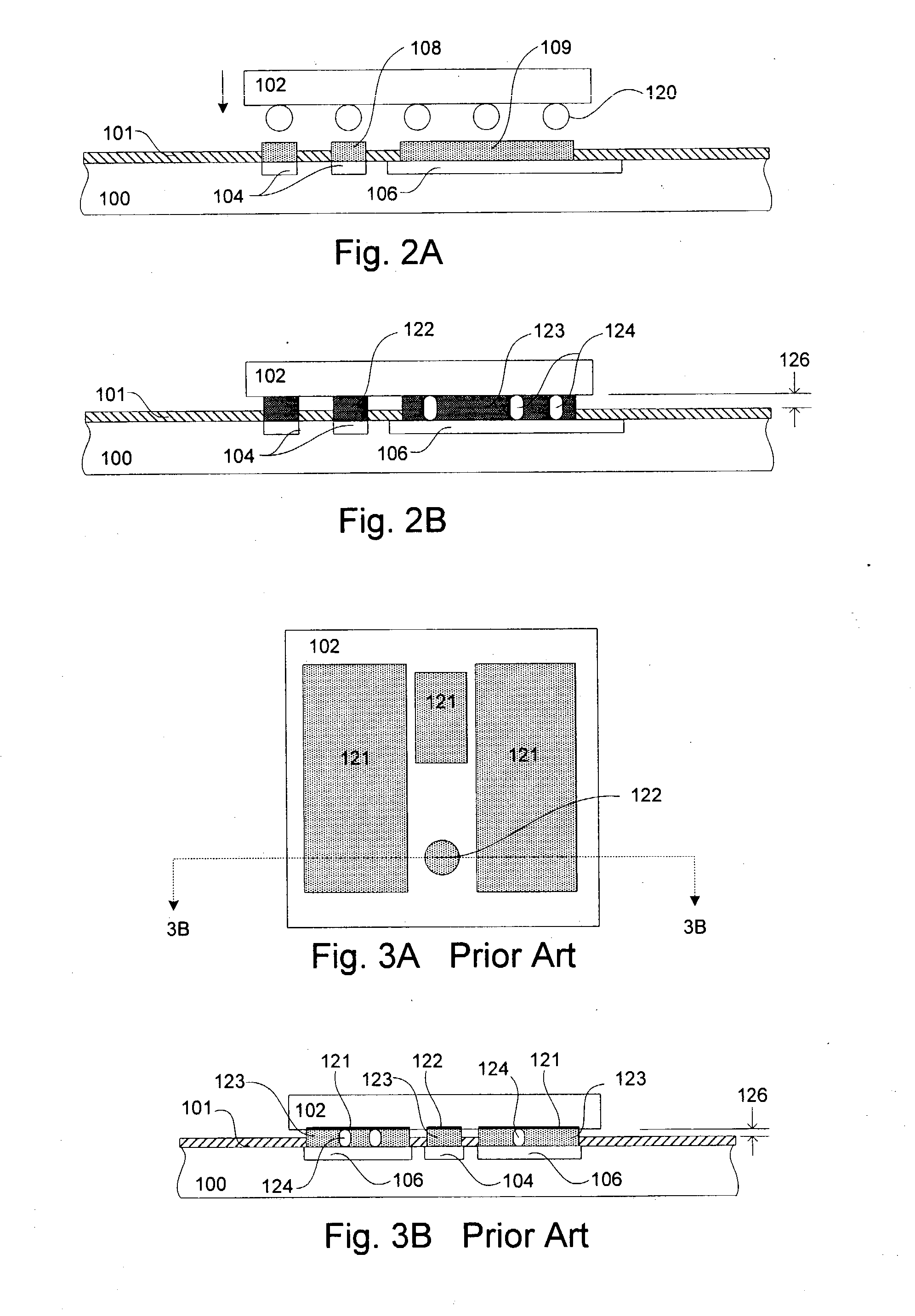
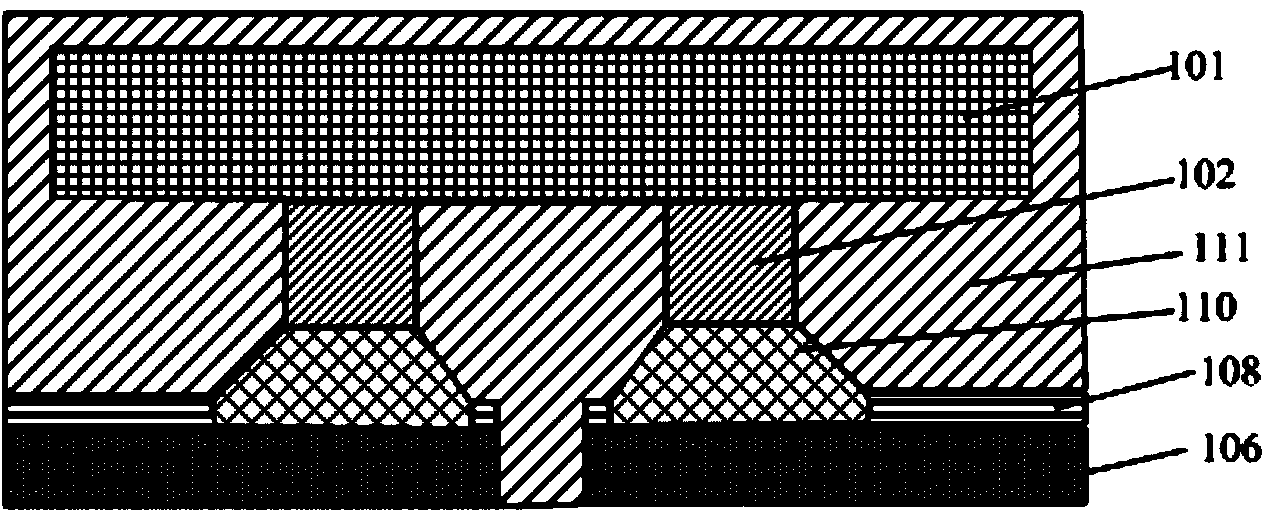
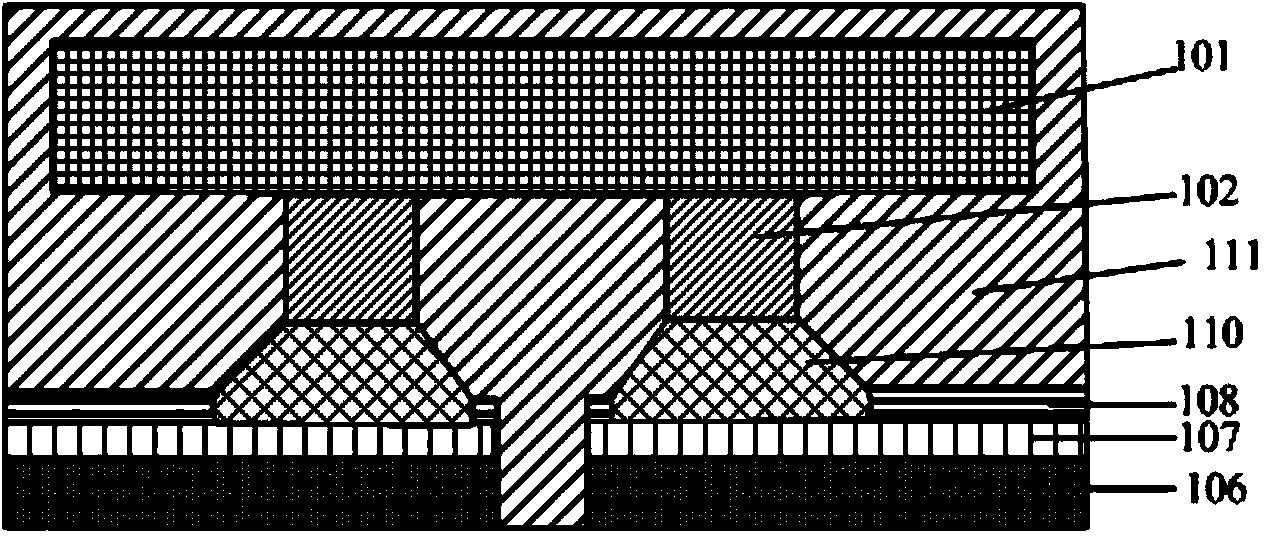
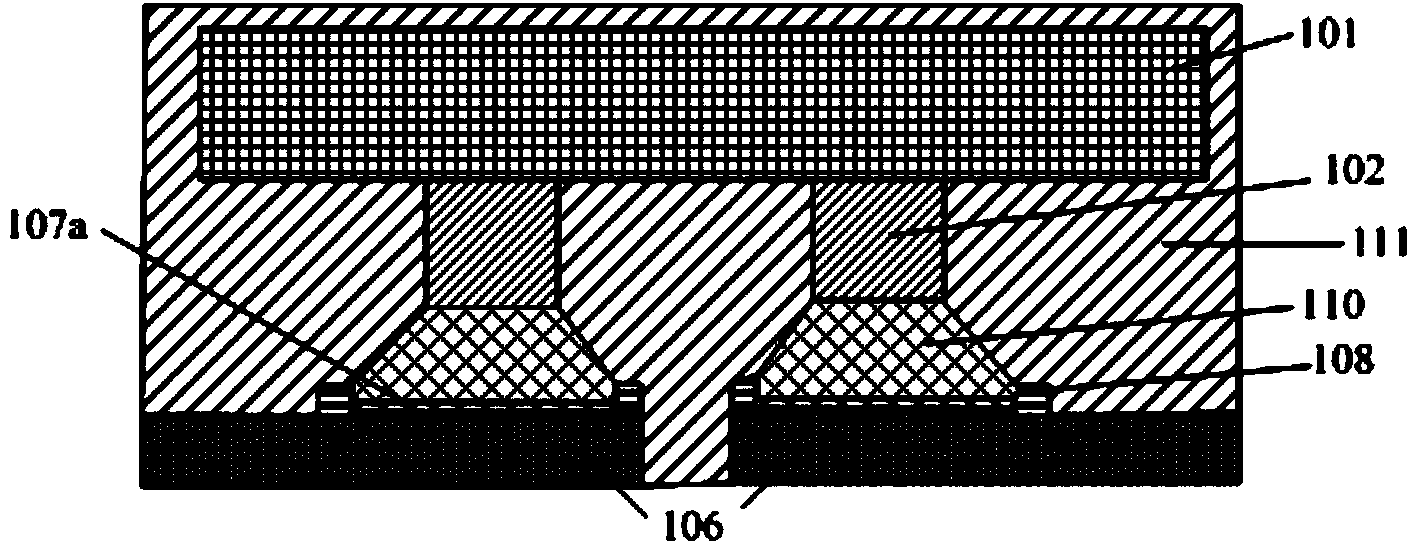
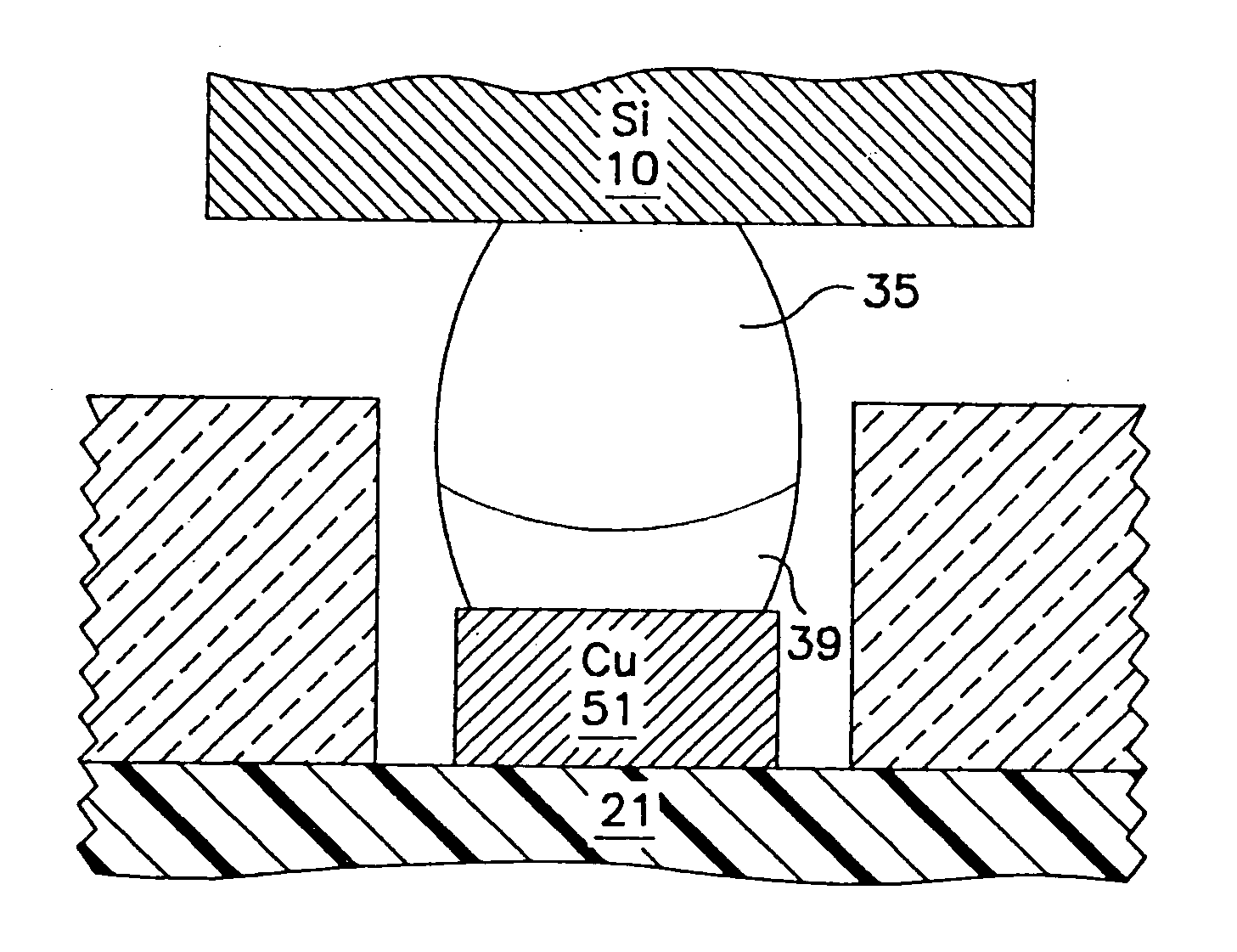
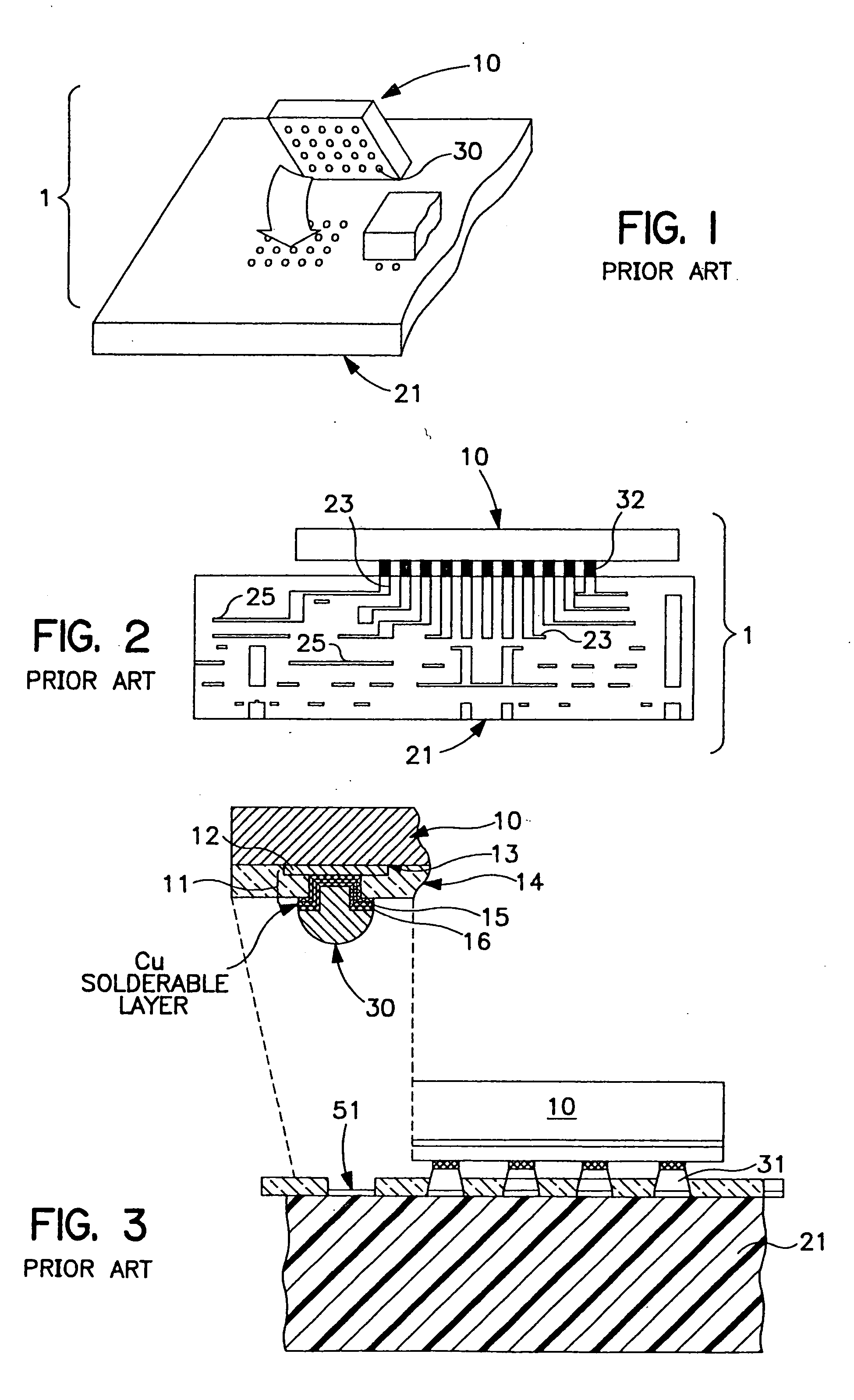
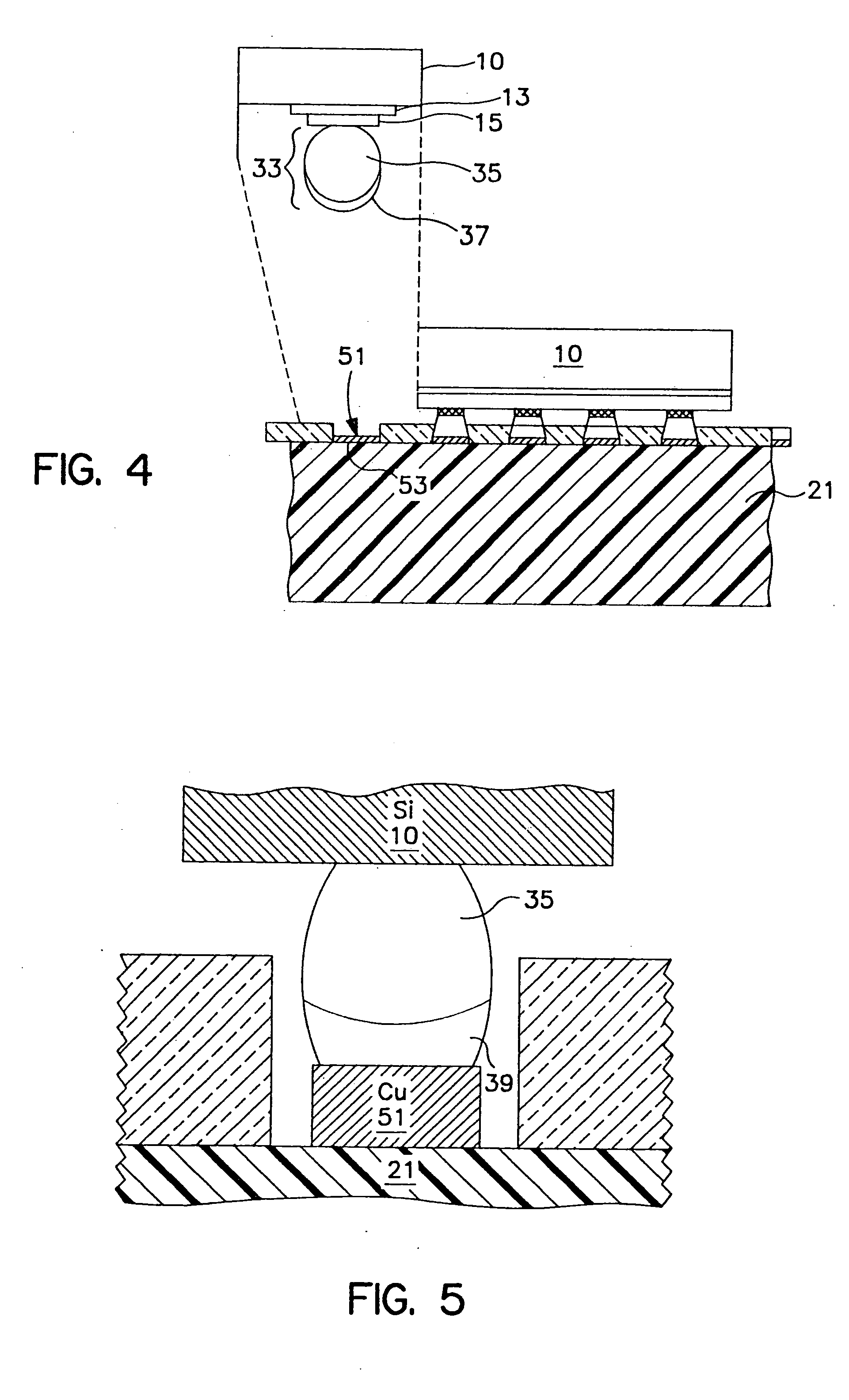
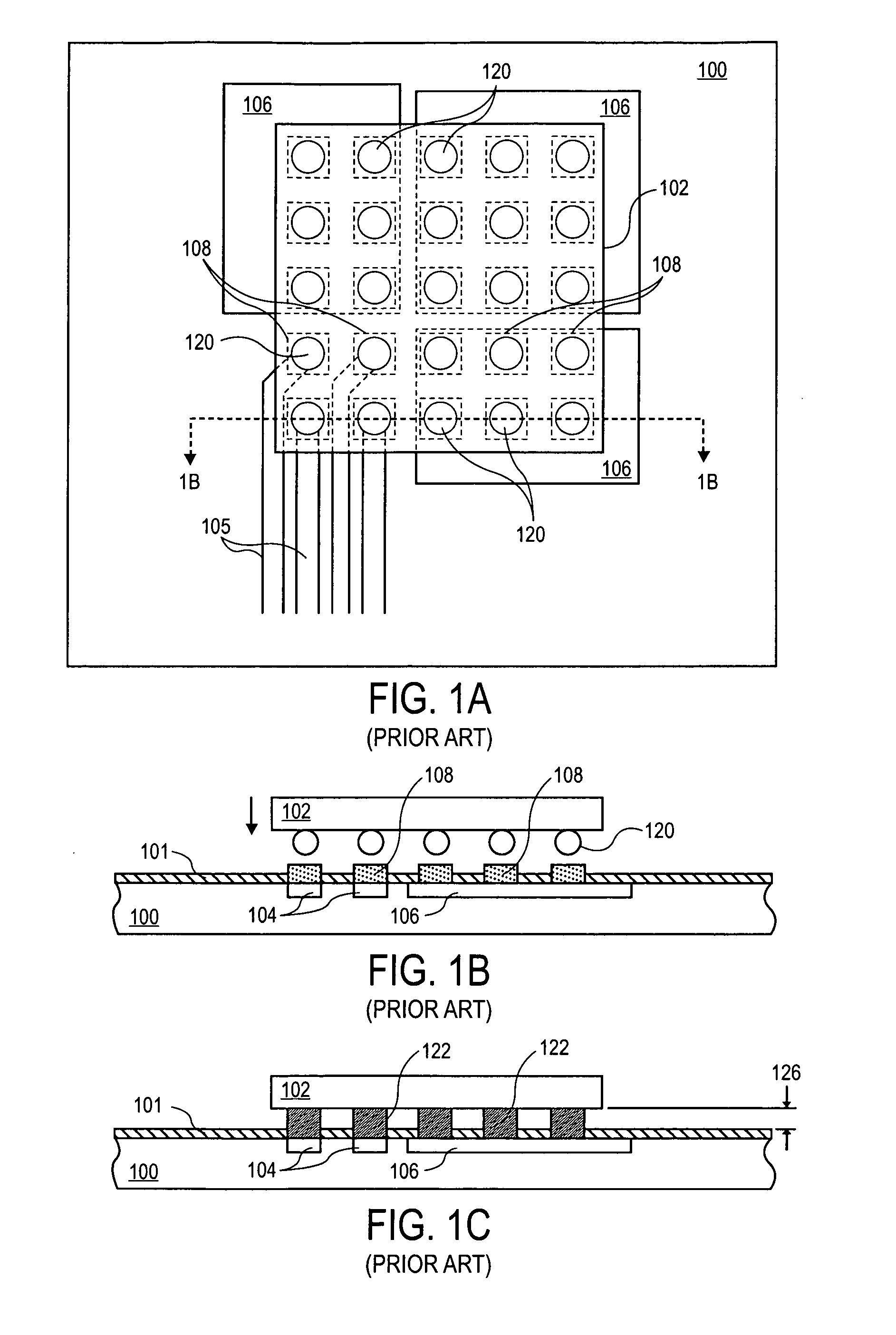
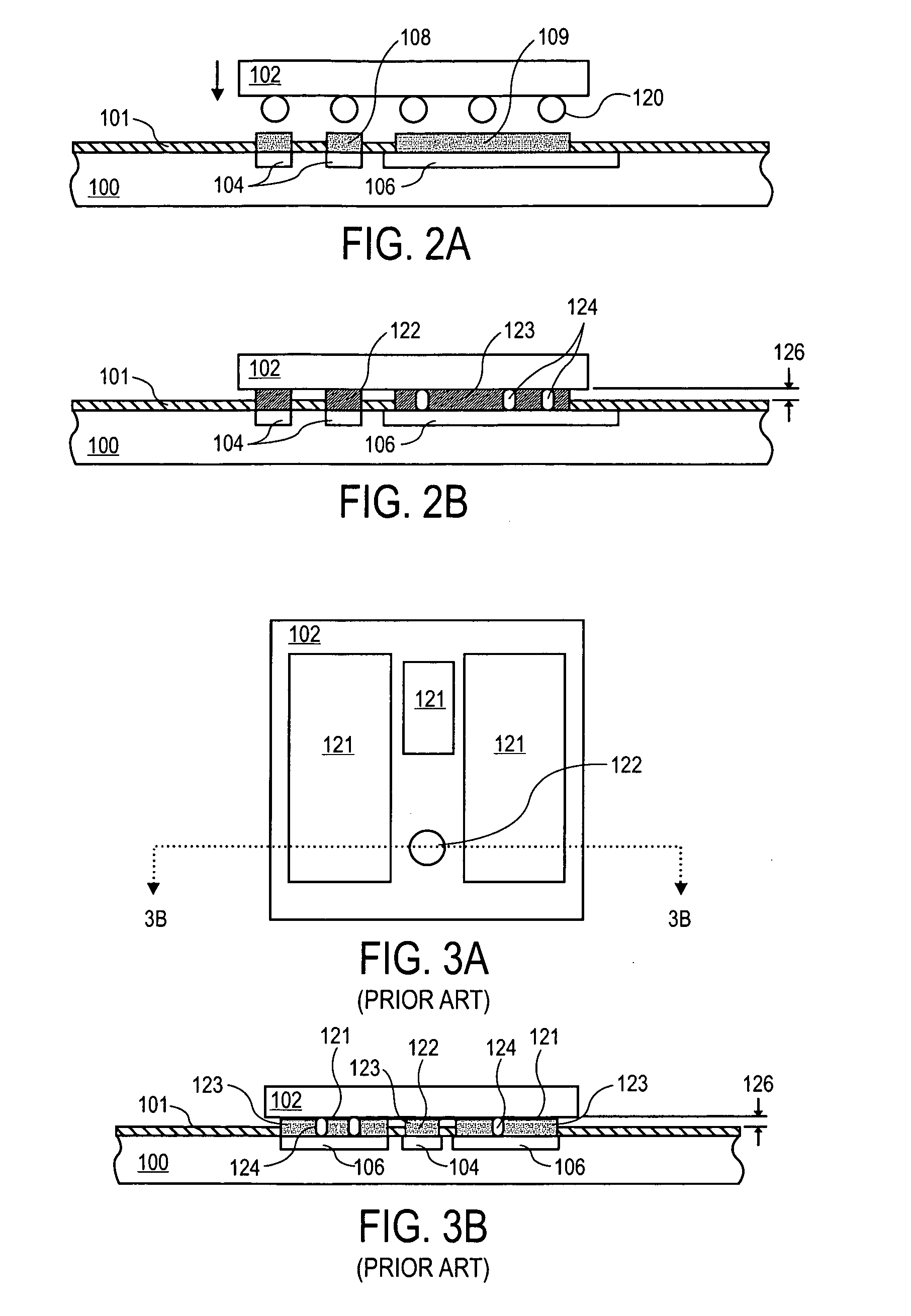
Method for forming reflowed solder ball with low melting point metal cap
InactiveUS6344234B1Reduce the hole diameterMinimal diameterFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTinningIndium
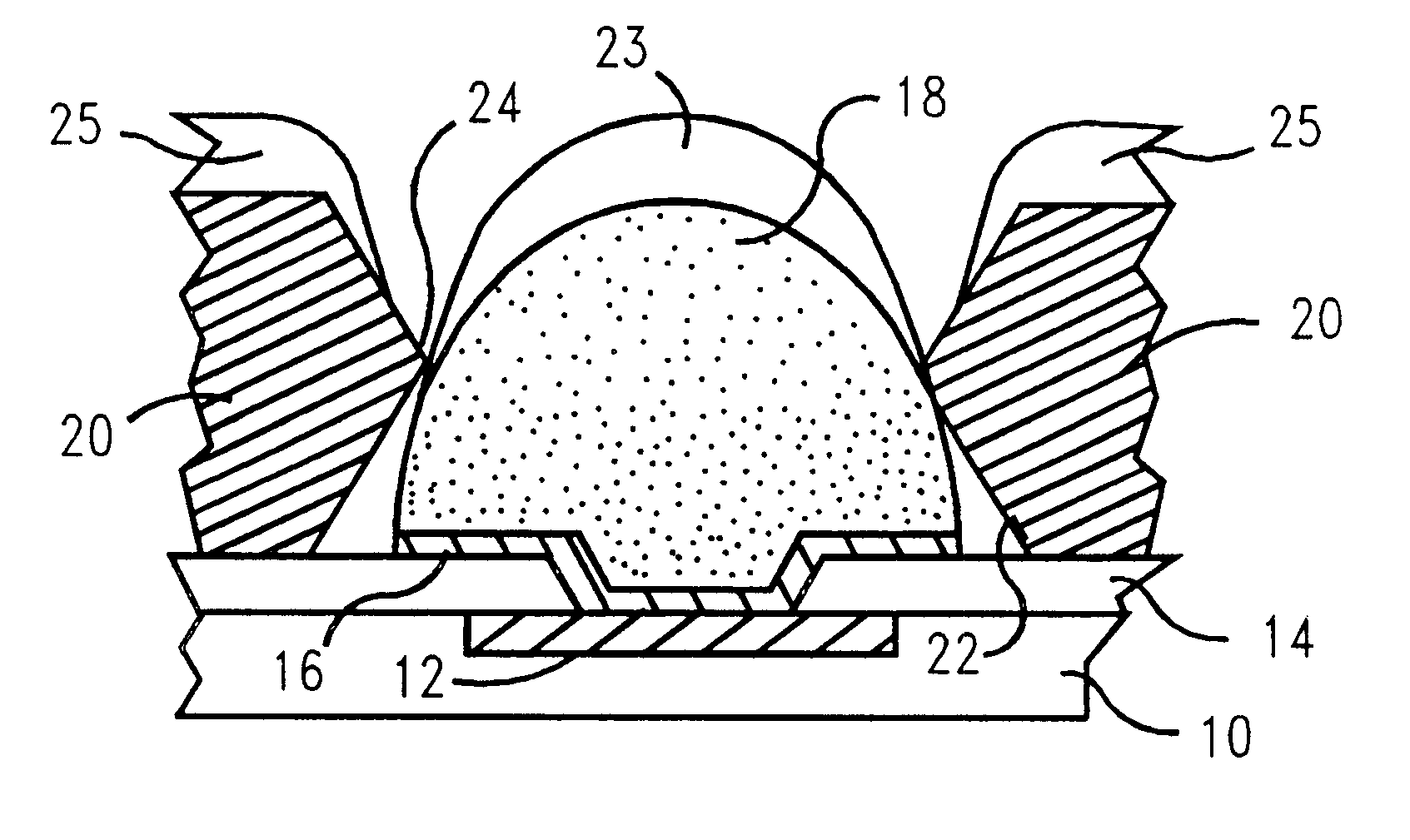
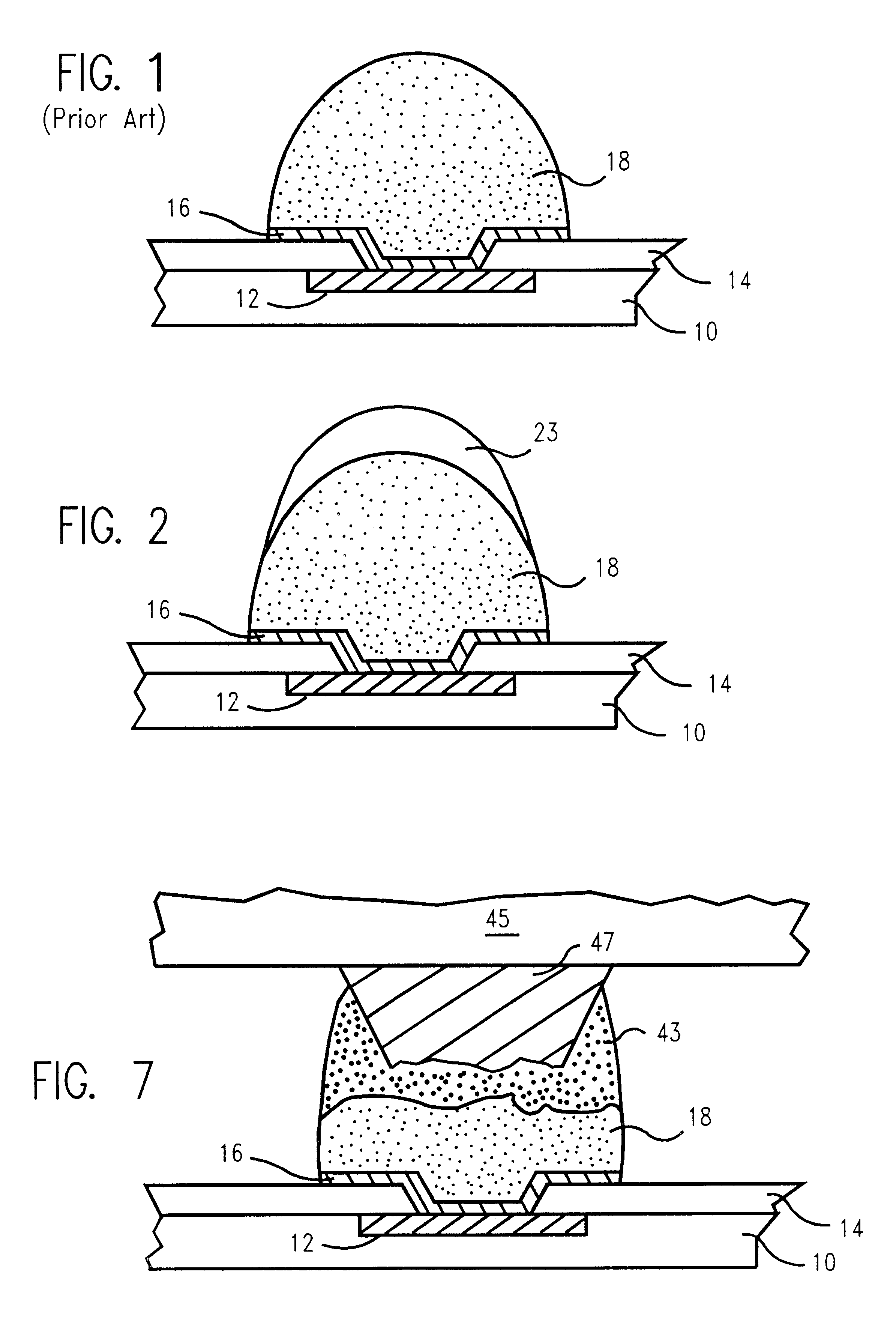
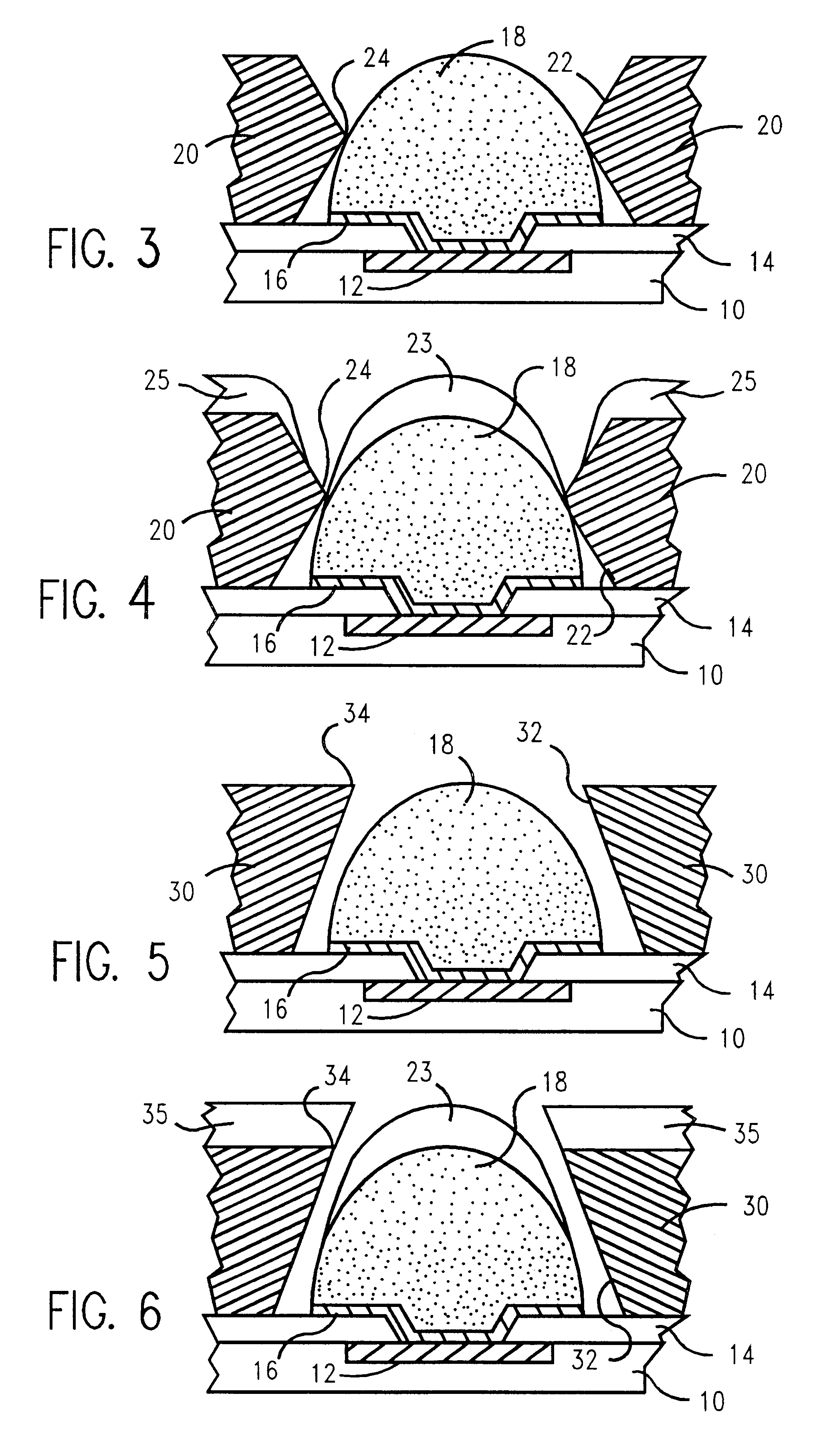
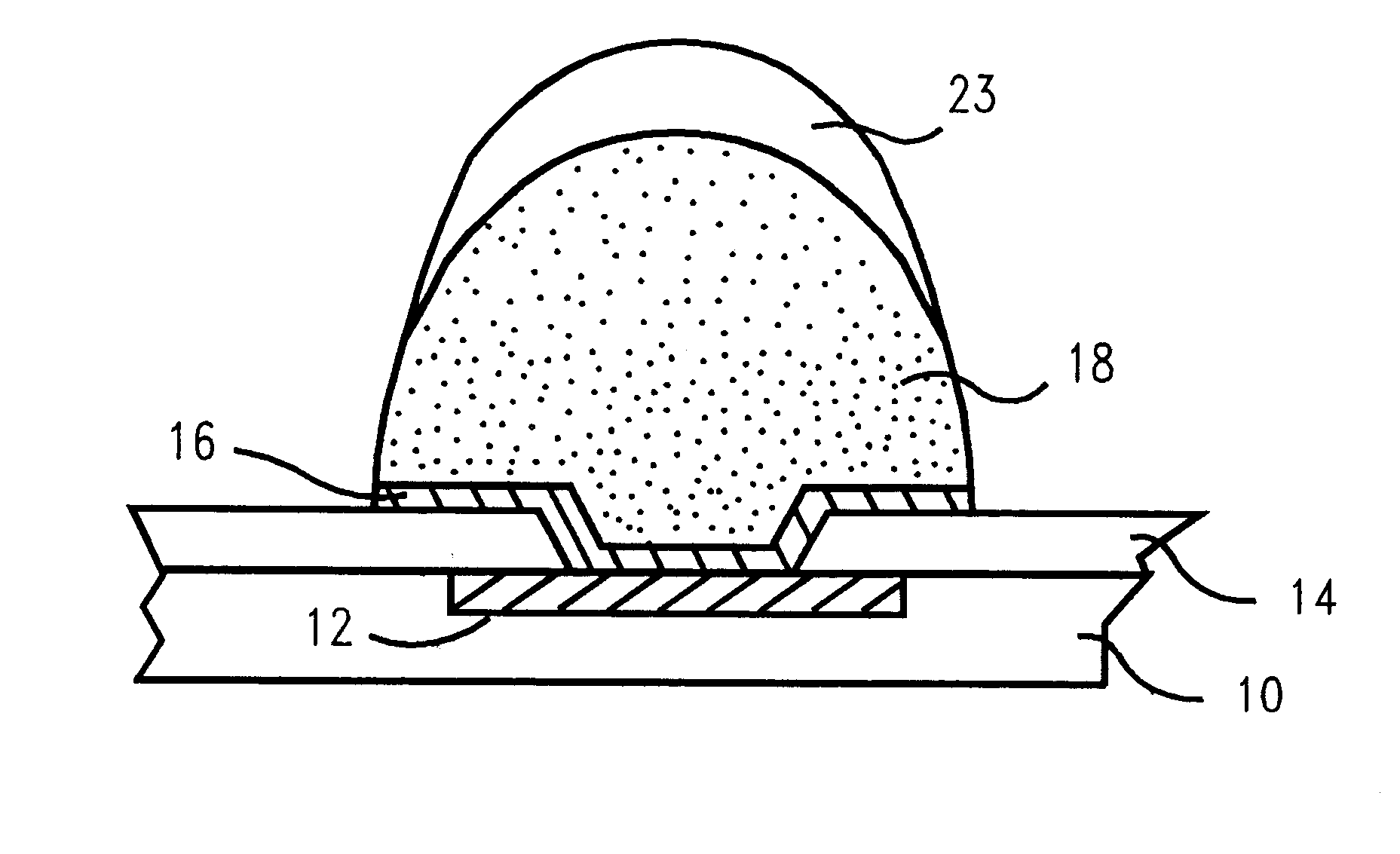
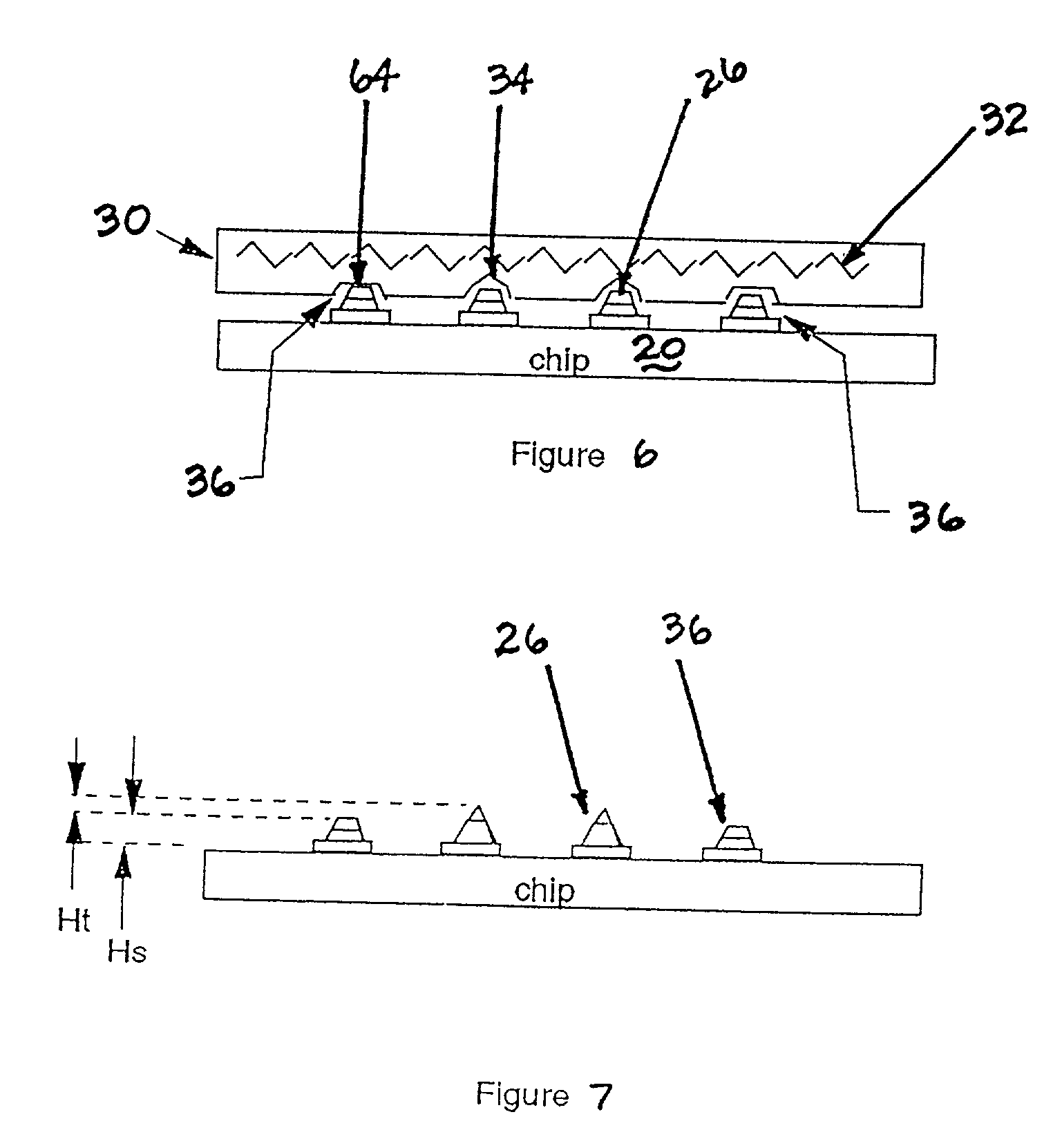
A method and structure for a solder interconnection, using solder balls for making a low temperature chip attachment directly to any of the higher levels of packaging substrate is disclosed. After a solder ball has been formed using standard methods it is reflowed to give the solder ball a smooth surface. A layer of low melting point metal, such as, bismuth, indium or tin, preferably, pure tin, is deposited on the top of the solder balls. This structure results in localizing of the eutectic alloy, formed upon subsequent low temperature joining cycle, to the top of the high melting solder ball even after multiple low temperature reflow cycles. This method does not need tinning of the substrate to which the chip is to be joined, which makes this method economical. It has also been noticed that whenever temperature is raised slightly above the eutectic temperature, the structure always forms a liquid fillet around the joint with copper wires. This liquid fillet formation results in substantial thermal fatigue life improvement for reduced stress at interface; and secondly, provides an easy means to remove chip for the purpose of chip burn-in, replacement or field repairs.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Reflowed solder ball with low melting point metal cap
InactiveUS6259159B1Low costEasy to buildPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureTinningIndium
A method and structure for a solder interconnection, using solder balls for making a low temperature chip attachment directly to any of the higher levels of packaging substrate is disclosed. After a solder ball has been formed using standard methods it is reflowed to give the solder ball a smooth surface. A layer of low melting point metal, such as, bismuth, indium or tin, preferably, pure tin, is deposited on the top of the solder balls. This structure results in localizing of the eutectic alloy, formed upon subsequent low temperature joining cycle, to the top of the high melting solder ball even after multiple low temperature reflow cycles. This method does not need tinning of the substrate to which the chip is to be joined, which makes this method economical. It has also been noticed that whenever temperature is raised slightly above the eutectic temperature, the structure always forms a liquid fillet around the joint with copper wires. This liquid fillet formation results in substantial thermal fatigue life improvement for reduced stress at interface; and secondly, provides an easy means to remove chip for the purpose of chip burn-in, replacement or field repairs.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electrical wiring design for module removal and replacement from organic board
InactiveUS20060200965A1Adversely electrical performancePrinted circuit assemblingSoldering apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
A method and electrical structure for separating electronic components from one another joined by solder interconnections. An electronic module is joined to a substrate via a solder interconnection, whereby the electronic module has an electrical heating component residing within a bottom layer thereof adjacent a solder interconnection. Preferably, a chip carrier is joined to a board whereby the chip carrier has an electrical mesh plane for heating adjacent the solder interconnection. Resistive heat is generated within this electrical heating component either by applying an electrical current to the electrical heating component, or by non-contact inductively heating the layer in which such electrical heating component resides to generate resistive heat within the electrical heating component. The resistive heat is transferred to the solder interconnection to allow for localized melting of the solder interconnection and removal of the electronic components from one another.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Structure and method for lead free solder electronic package interconnections
InactiveUS20050106059A1Printed circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder interconnectionChip carrier
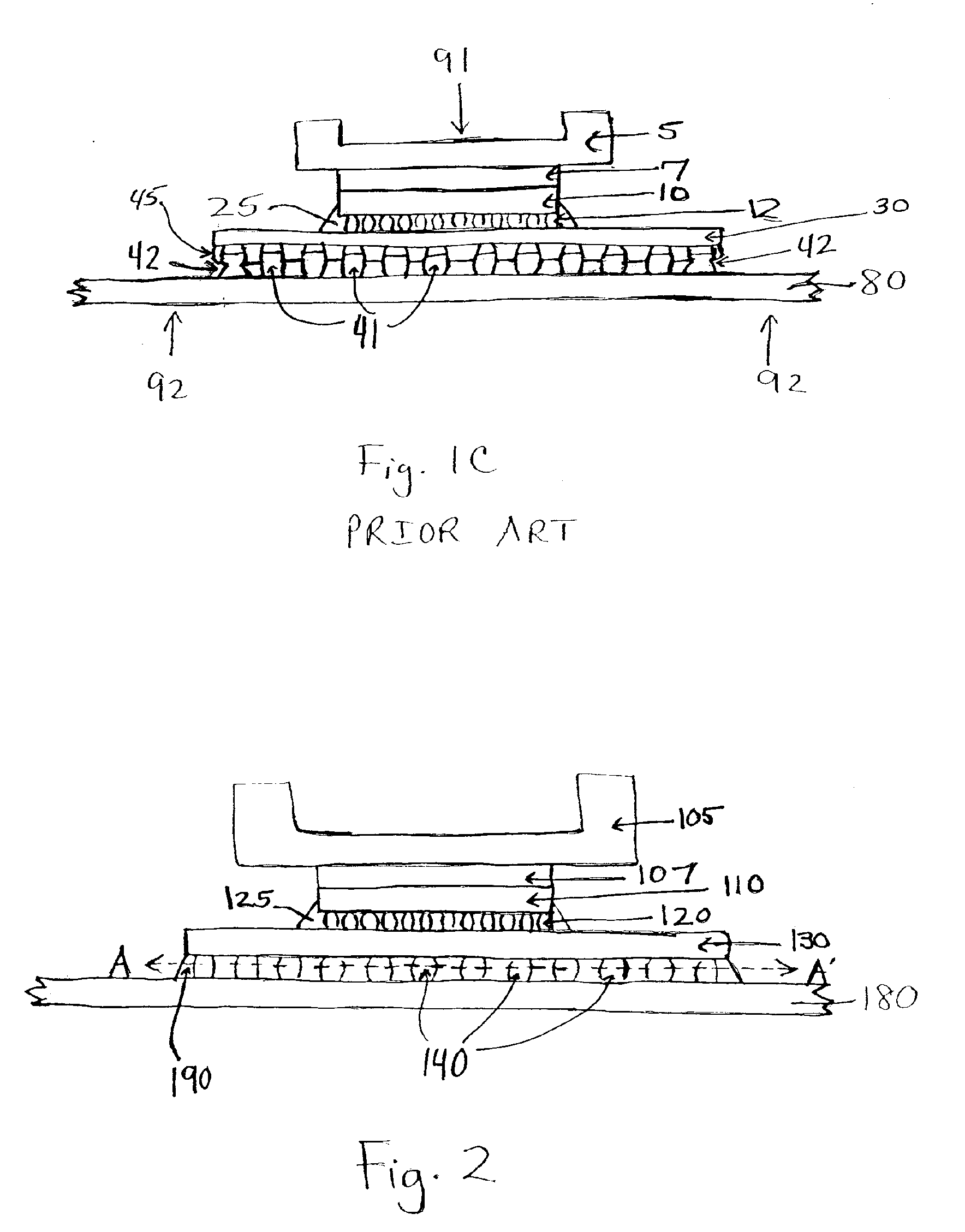
An electronic package having a solder interconnect liquidus temperature hierarchy to limit the extent of the melting of the C4 solder interconnect during subsequent second level join / assembly and rework operations. The solder hierarchy employs the use of off-eutectic solder alloys of Sn / Ag and Sn / Cu with a higher liquidus temperature for the C4 first level solder interconnections, and a lower liquidus temperature alloy for the second level interconnections. When the second level chip carrier to PCB join / assembly operations occur, the chip to chip carrier C4 interconnections do not melt completely. They continue to have a certain fraction of solids, and a lower fraction of liquids, than a fully molten alloy. This provides reduced expansion of the solder join and consequently lower stresses on the C4 interconnect.
Owner:FAROOQ MUKTA G +2
Epoxy-siloxanes based electrically conductive adhesives for semiconductor assembly and process for use thereof
InactiveUS20020127406A1Keep performance stableLow resistivitySolid-state devicesPretreated surfacesEpoxyElectrically conductive adhesive
The invention is directed to improved conductive adhesives for solder-free interconnections in microelectronic assembly processes such as for chip carrier-to-substrate attachment. These adhesives are characterized by low tensile modulus, low resistivity, high adhesion strength, and durability of these properties during reliability stress conditions of thermal shock, thermal aging, and temperature / humidity (85.degree. C. / 85%) exposure of the assembled devices. The adhesives contain a homogeneous solution of a siloxane containing epoxide, a curing agent, a curing catalyst and an organic polymeric or oligomeric additive. A conductive filler is added to the solution forming the filler. Preferred fillers are Ag coated with Pd and Ag coated with Au.
Owner:IBM CORP
Structure and method for lead free solder electronic package interconnections
InactiveUS6854636B2Printed circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder interconnectionChip carrier
An electronic package having a solder interconnect liquidus temperature hierarchy to limit the extent of the melting of the C4 solder interconnect during subsequent second level join / assembly and rework operations. The solder hierarchy employs the use of off-eutectic solder alloys of Sn / Ag and Sn / Cu with a higher liquidus temperature for the C4 first level solder interconnections, and a lower liquidus temperature alloy for the second level interconnections. When the second level chip carrier to PCB join / assembly operations occur, the chip to chip carrier C4 interconnections do not melt completely. They continue to have a certain fraction of solids, and a lower fraction of liquids, than a fully molten alloy. This provides reduced expansion of the solder join and consequently lower stresses on the C4 interconnect.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
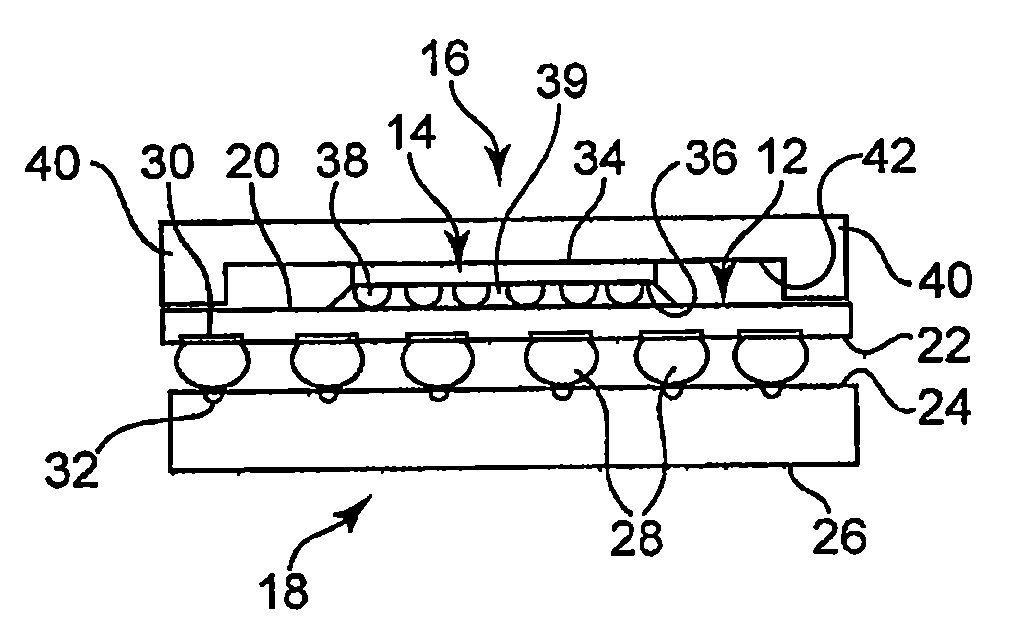
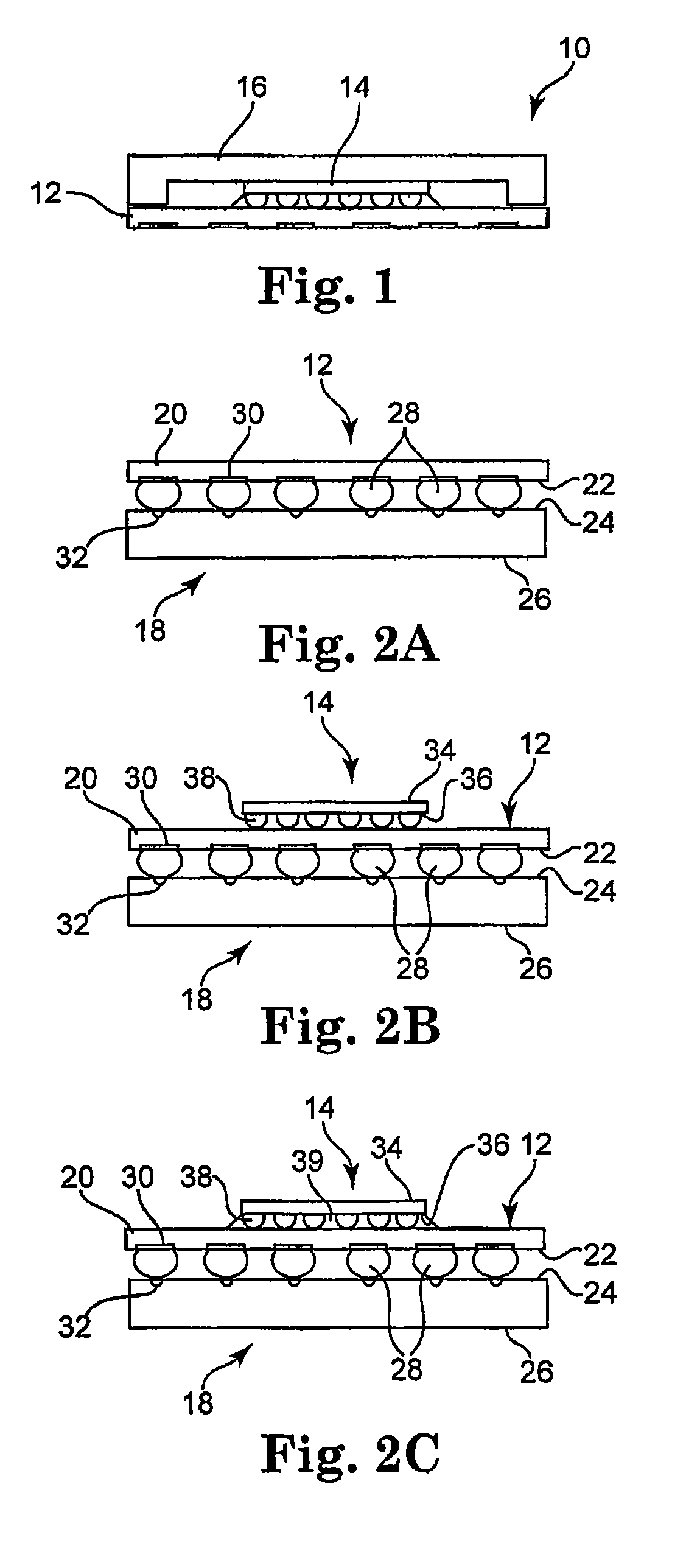
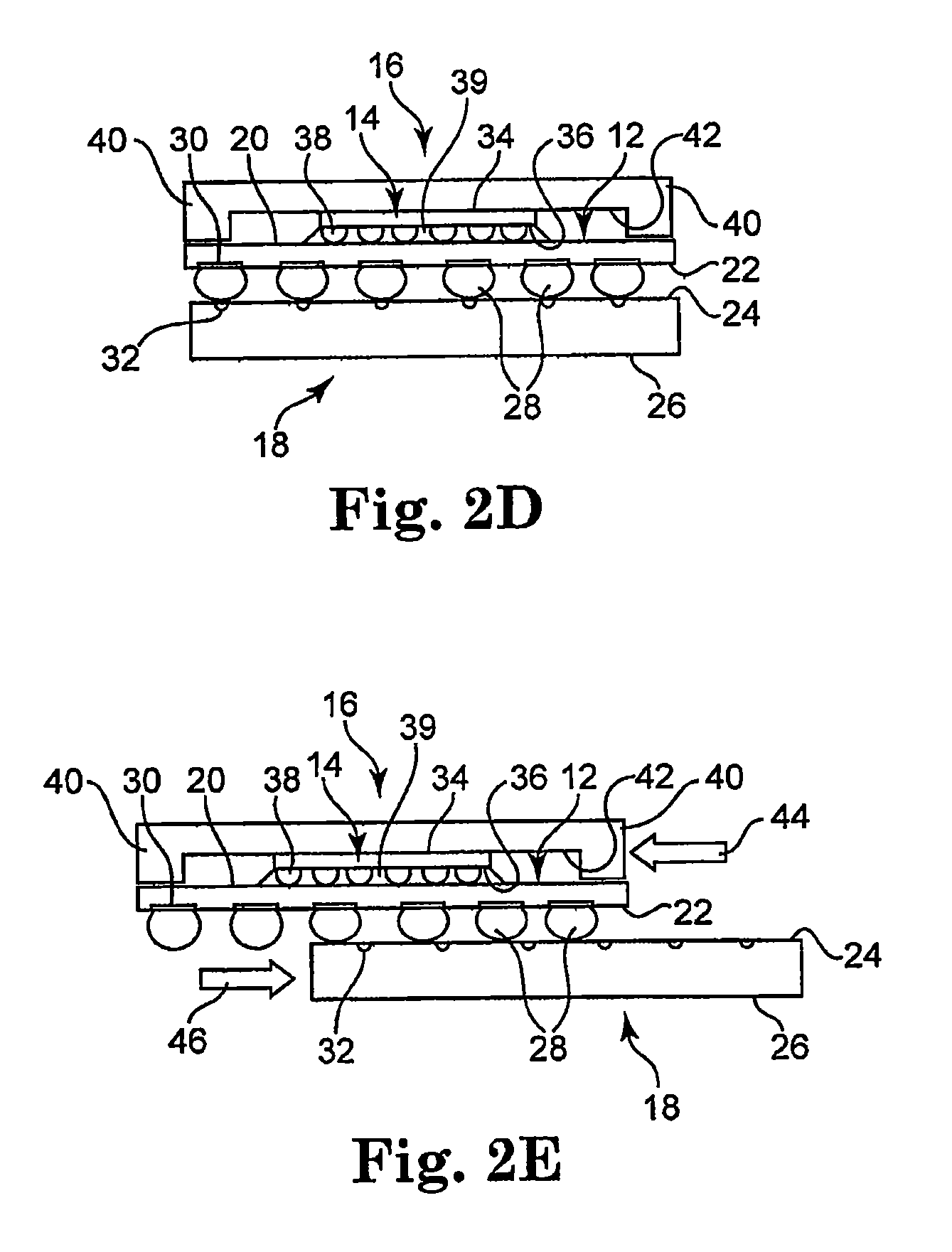
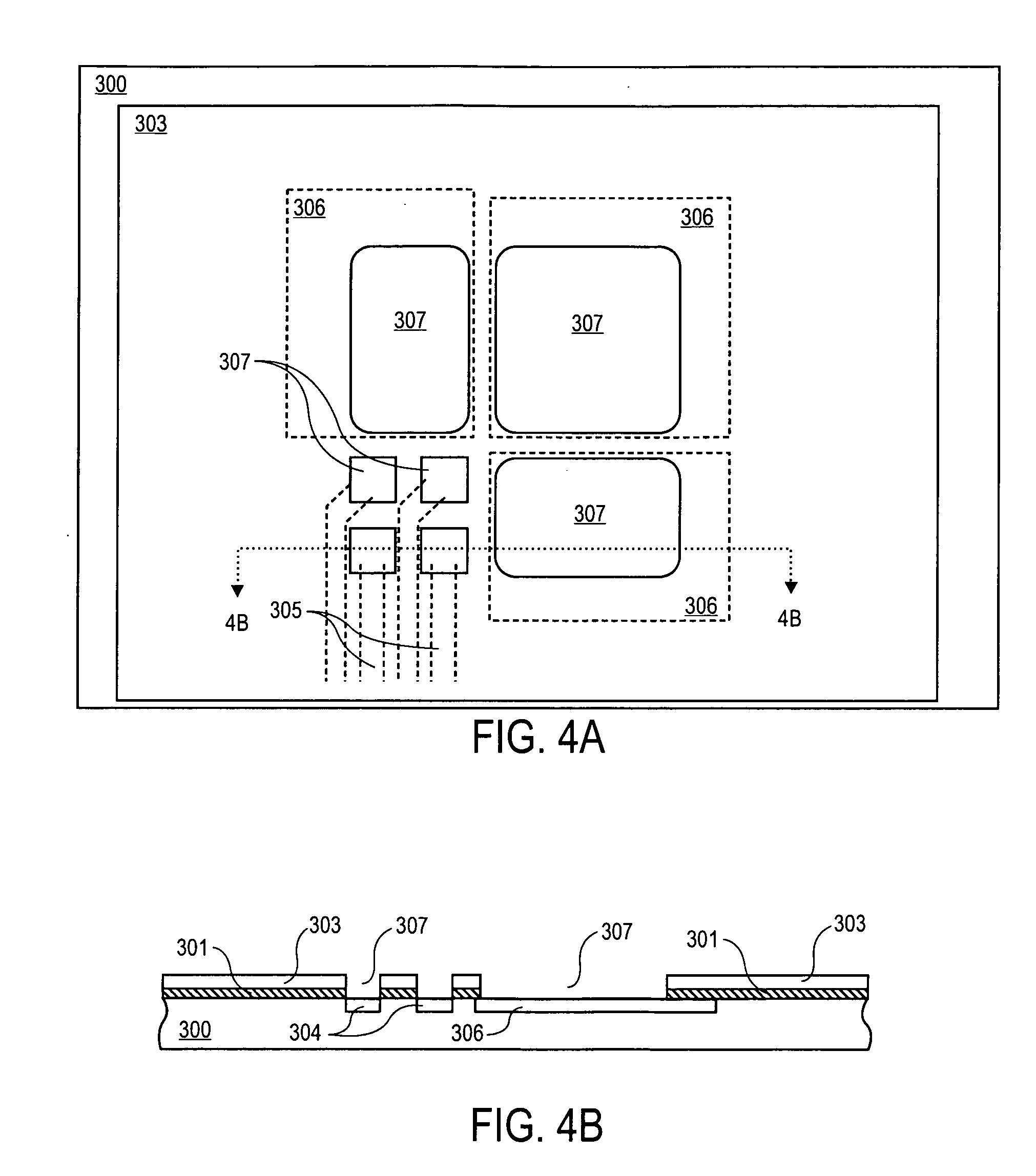
Low temperature solder chip attach structure
InactiveUS6847118B2Improve connection reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSolder ballAlloy
A solder interconnection uses preferably lead-rich solder balls for making a low temperature chip attachment directly to any of the higher levels of packaging substrate. After a solder ball has been formed using standard processes, a thin cap layer of preferably pure tin is deposited on a surface of the solder balls. An interconnecting eutectic alloy is formed upon reflow. Subsequent annealing causes tin to diffuse into the lead, or vice versa, and intermix, thereby raising the melting point temperature of the cap layer of the resulting assembly. This structure and process avoids secondary reflow problems during subsequent processing.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Microelectronic packages with elongated solder interconnections
InactiveUS7078819B2Improve the immunityConvenient registrationPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureThermal fatigueSurface mounting
A soldered assembly for a microelectronic element includes a microelectronic element, solder columns extending from a surface of the microelectronic element and terminals connected to distal ends of the columns. The assembly can be handled and mounted using conventional surface-mount techniques, but provides thermal fatigue resistance. The solder columns may be inclined relative to the chip surface, and may contain long, columnar inclusions preferentially oriented along the lengthwise axes of the columns.
Owner:TESSERA INC
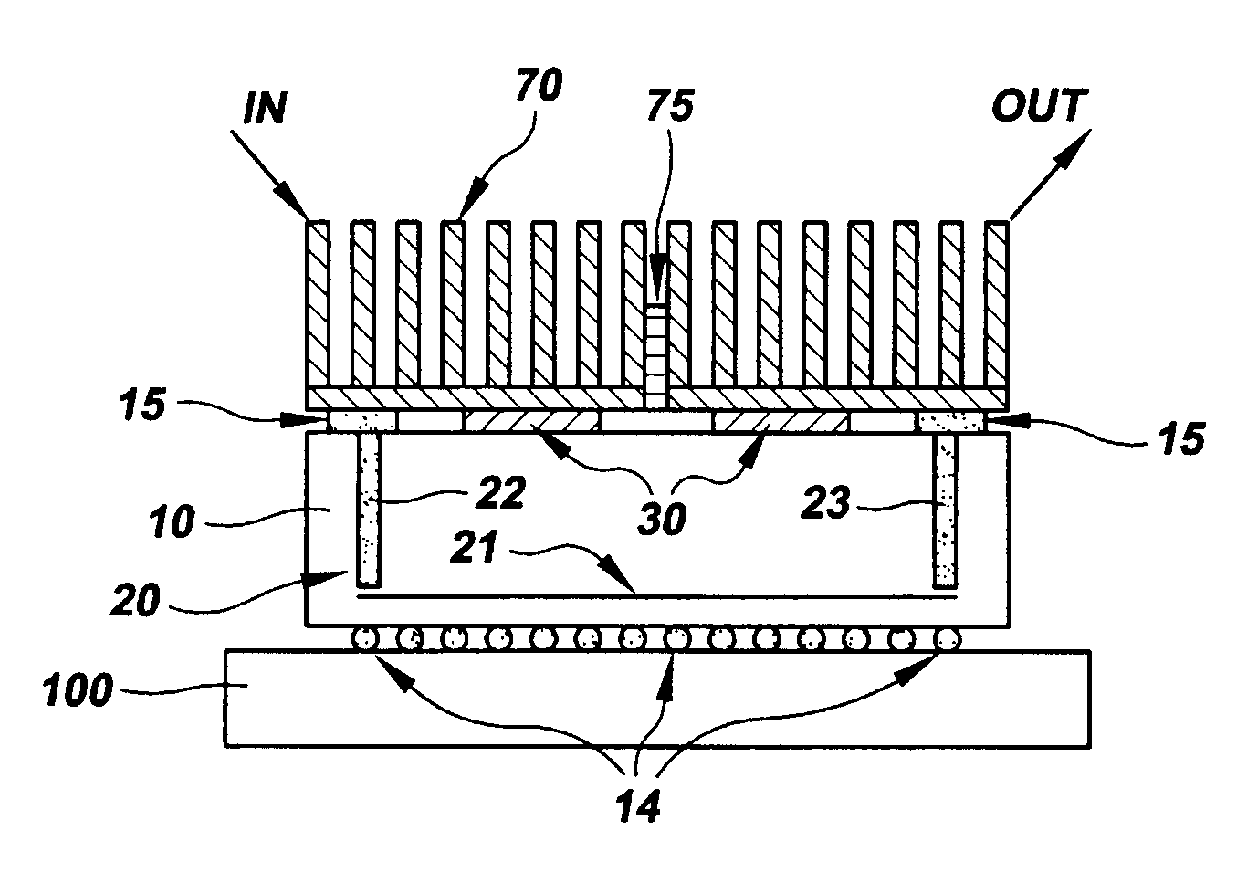
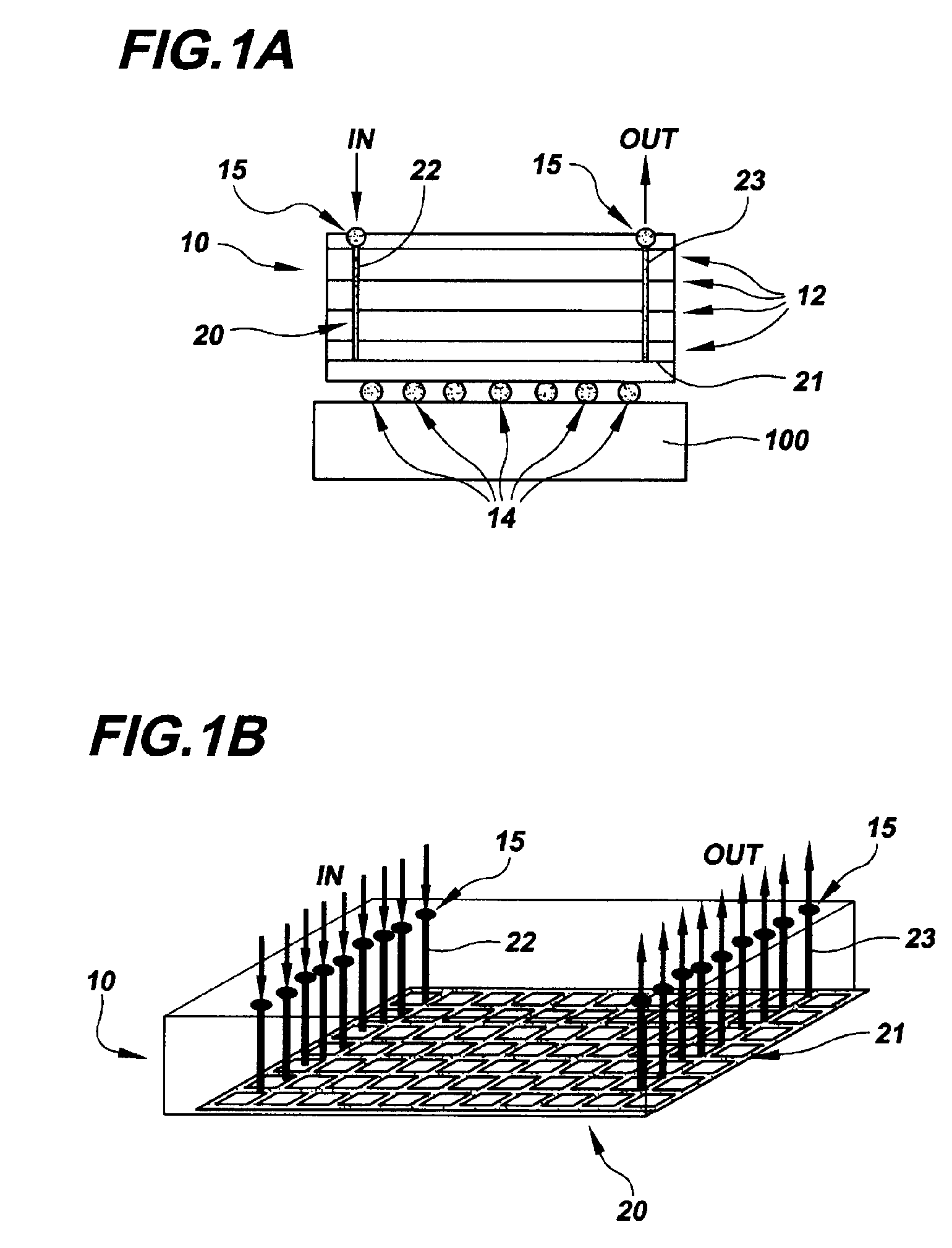
Solder interconnection array with optimal mechanical integrity
InactiveUS20060060636A1Easy to joinAvoid more failuresFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsMechanical integritySolder interconnection
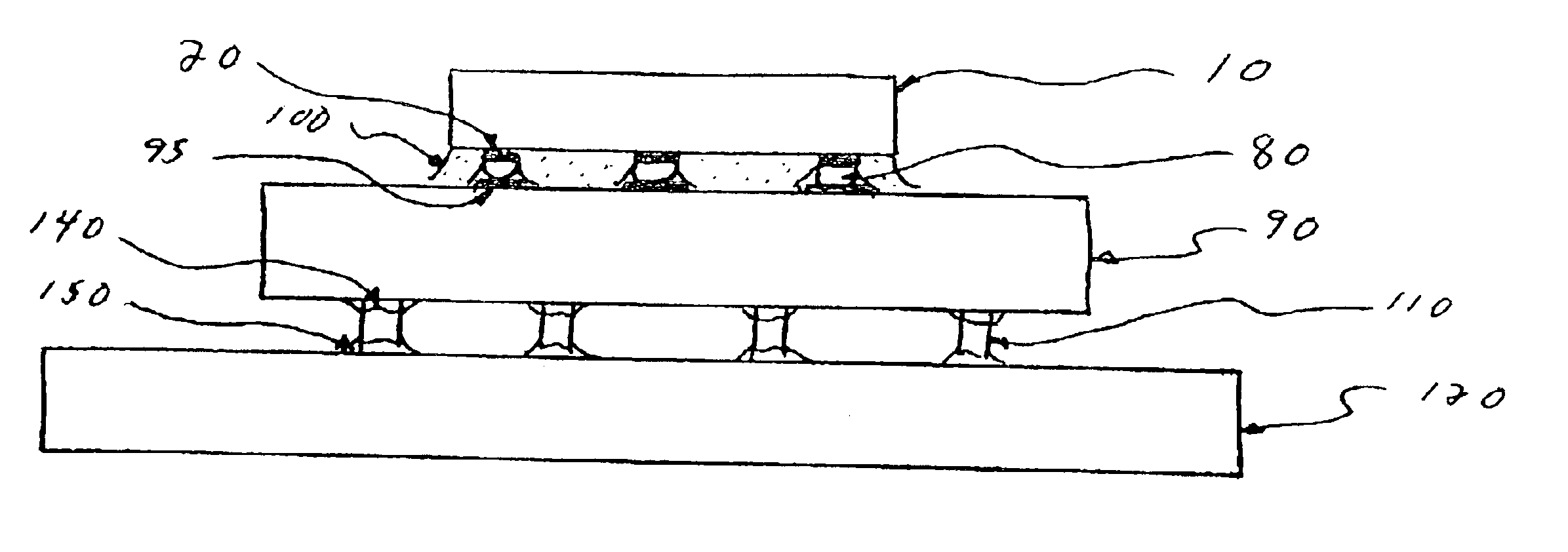
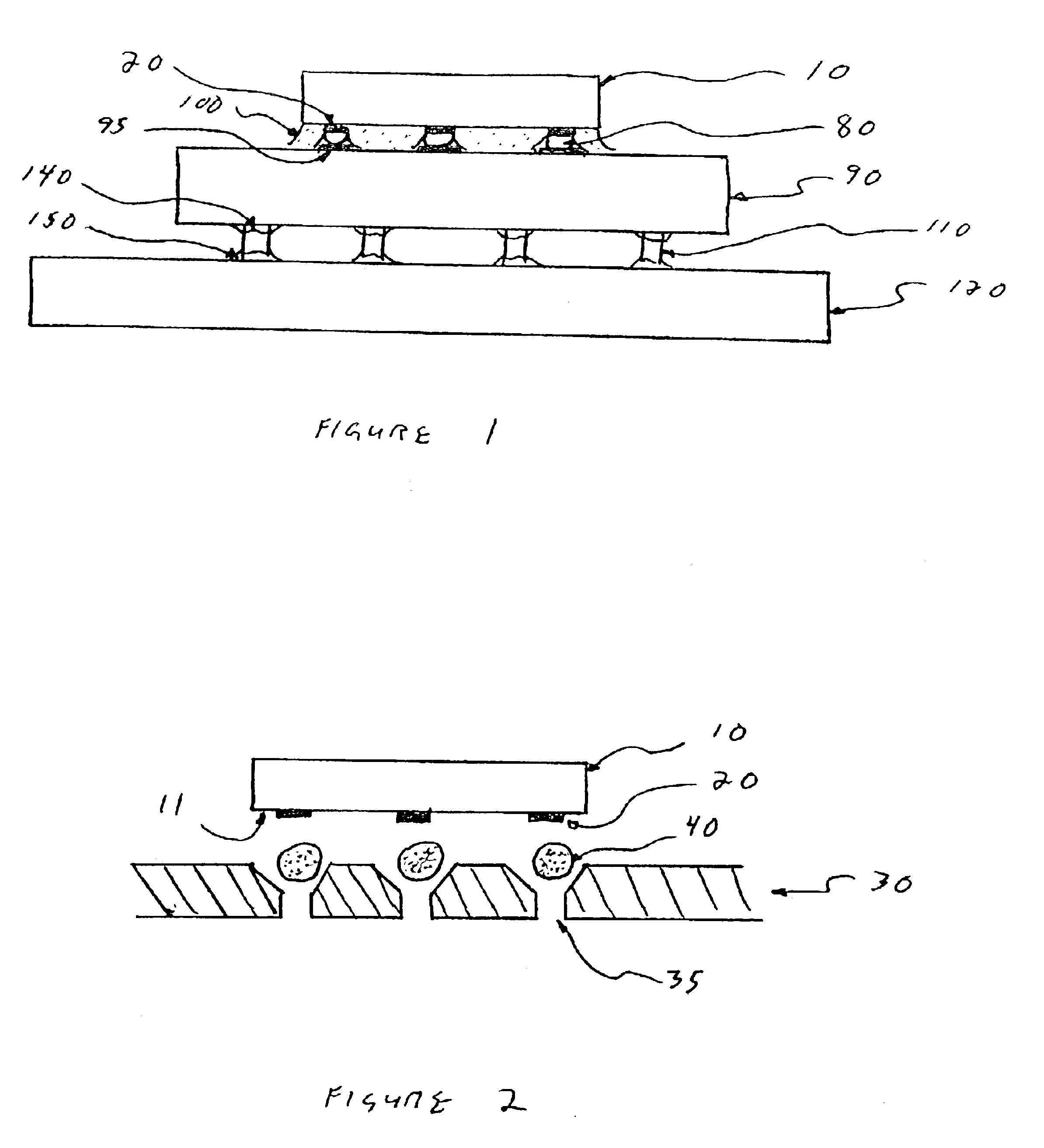
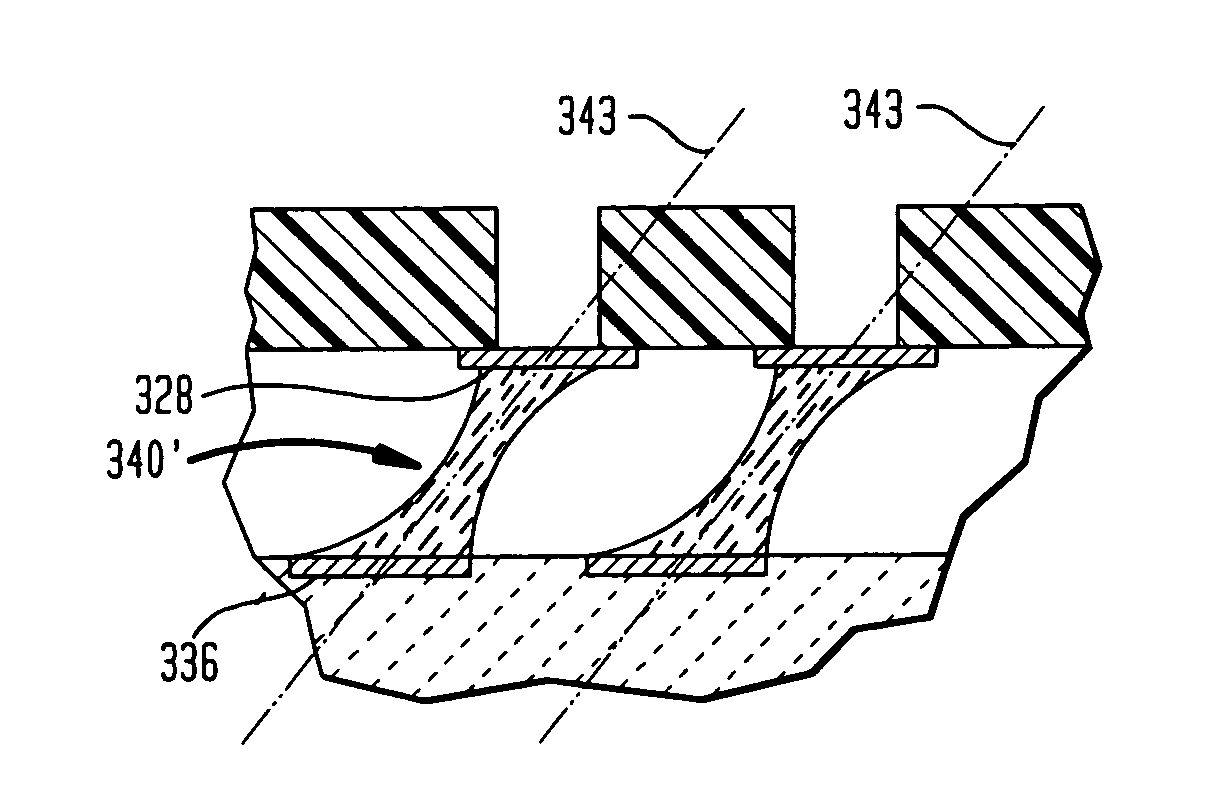
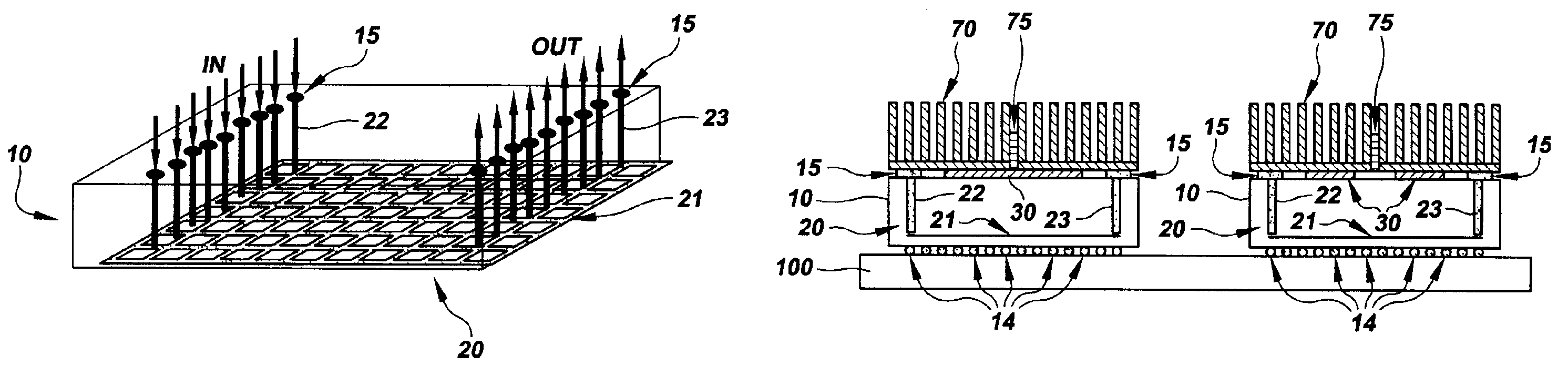
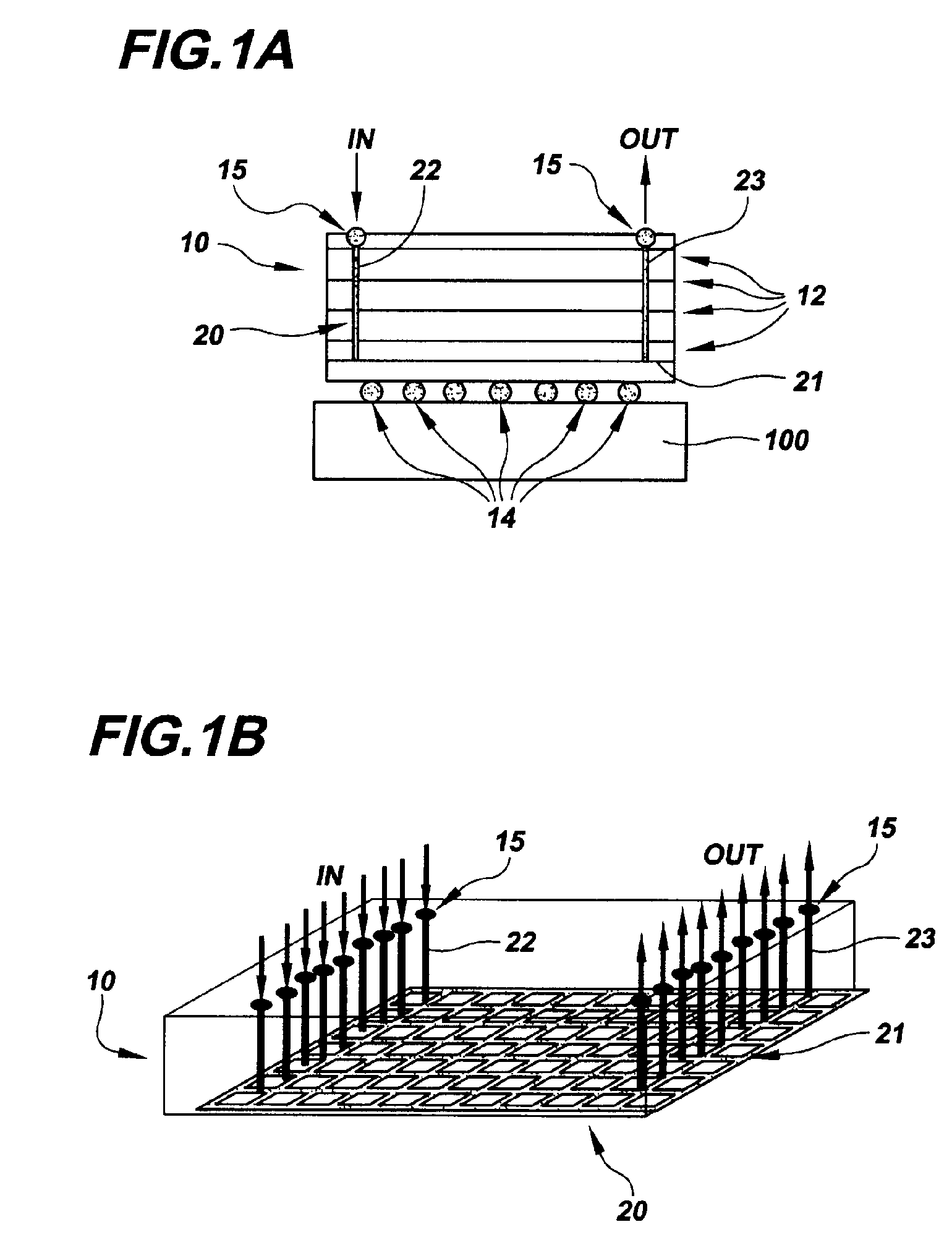
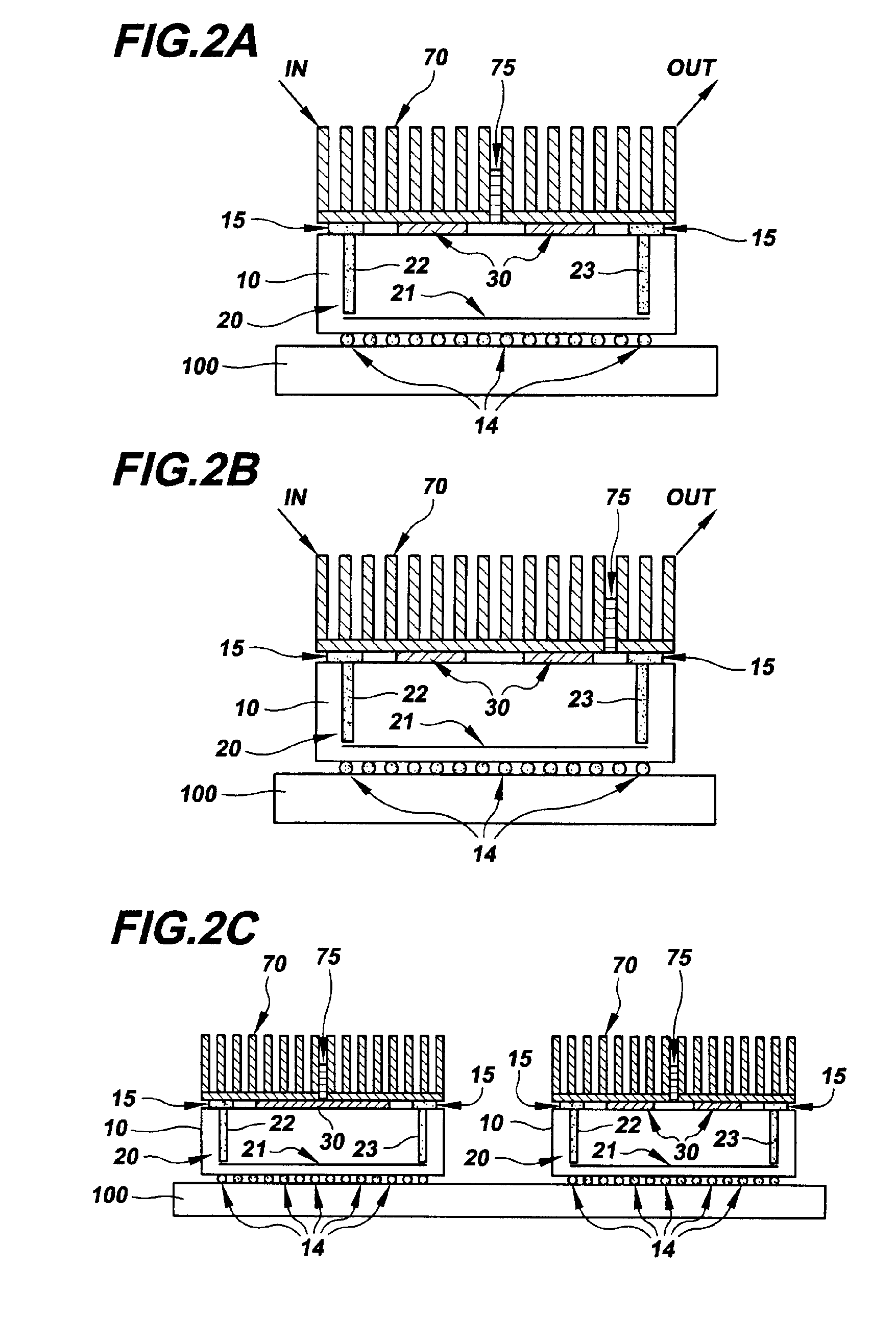
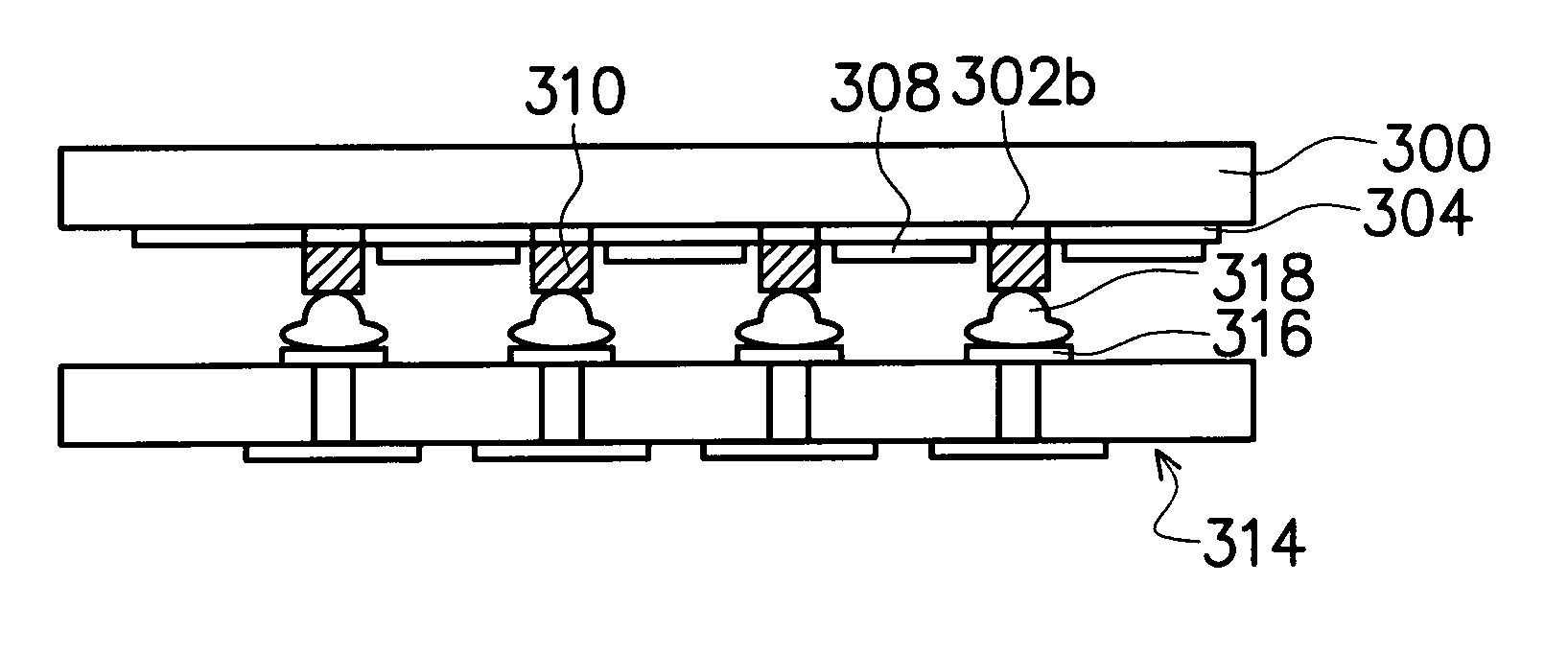
A method for assembling, and the resultant electronic module, includes attaching a chip to a substrate using a first solder interconnection array, and attaching a board to the substrate using a second solder interconnection array, which may be a single-melt or a dual-melt solder array. The second solder interconnection array resides entirely within a space defined between the board and substrate. A creep resistant structure is provided within this space for maintaining the defined space and optimizing integrity of the second solder interconnection array. The creep resistant structure may include an underfill material, balls, brackets, frames, collars or combinations thereof. Wherein the creep resistant structure is an underfill material, it is crucial that the substrate be attached to the board before either entirely encapsulating the second interconnection array with underfill material, or partially encapsulating the second solder interconnection array at discrete locations with underfill material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
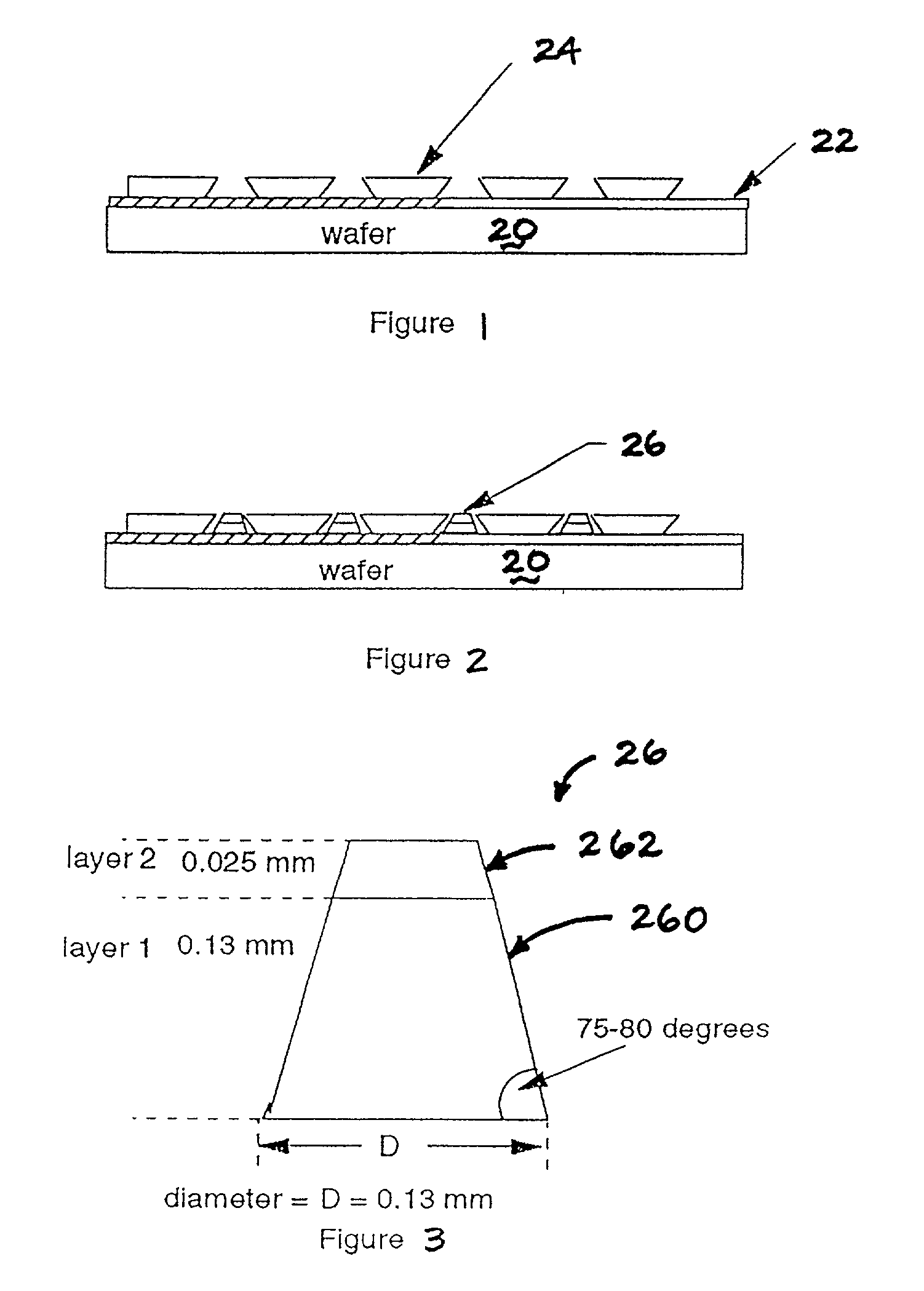
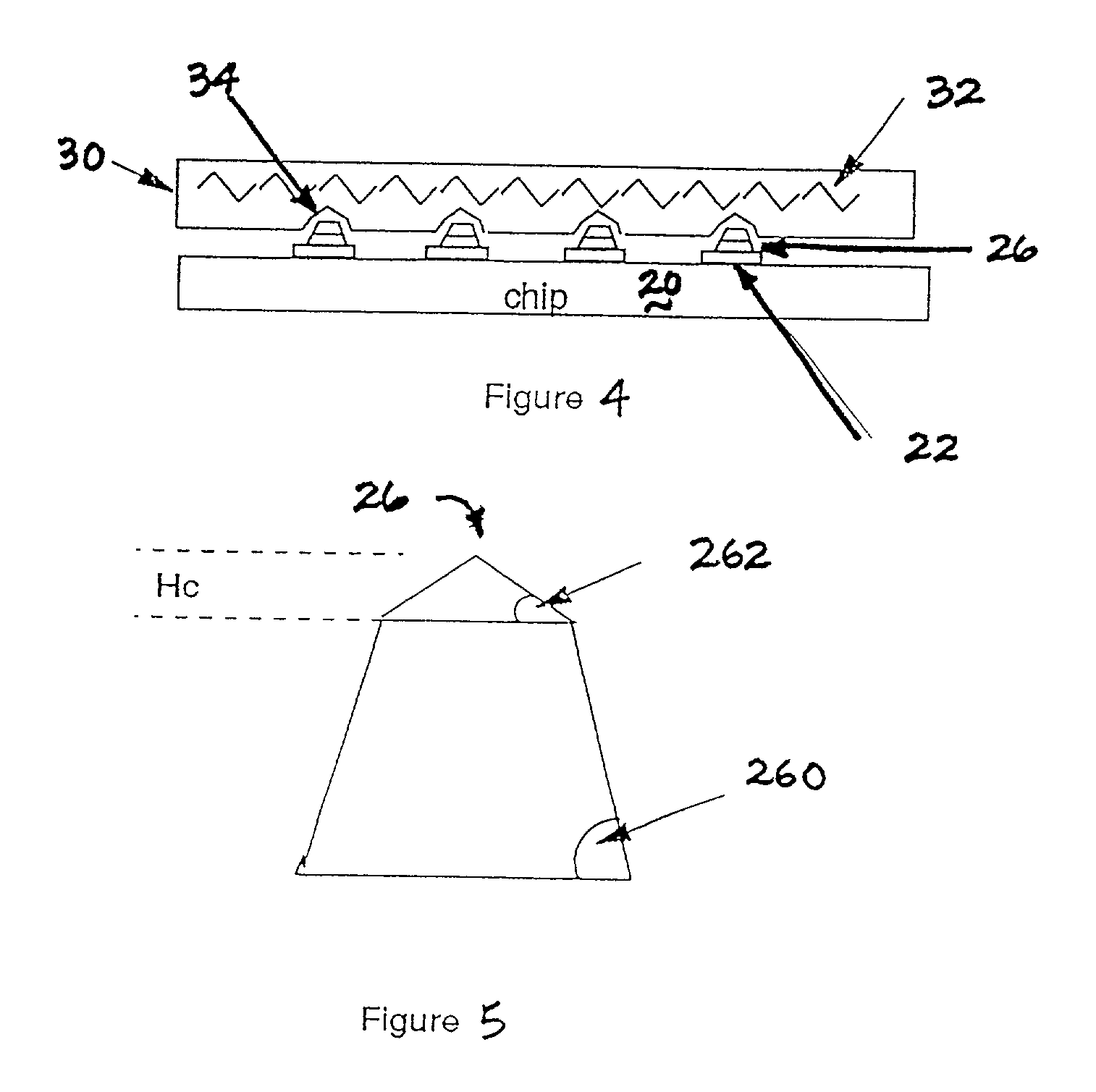
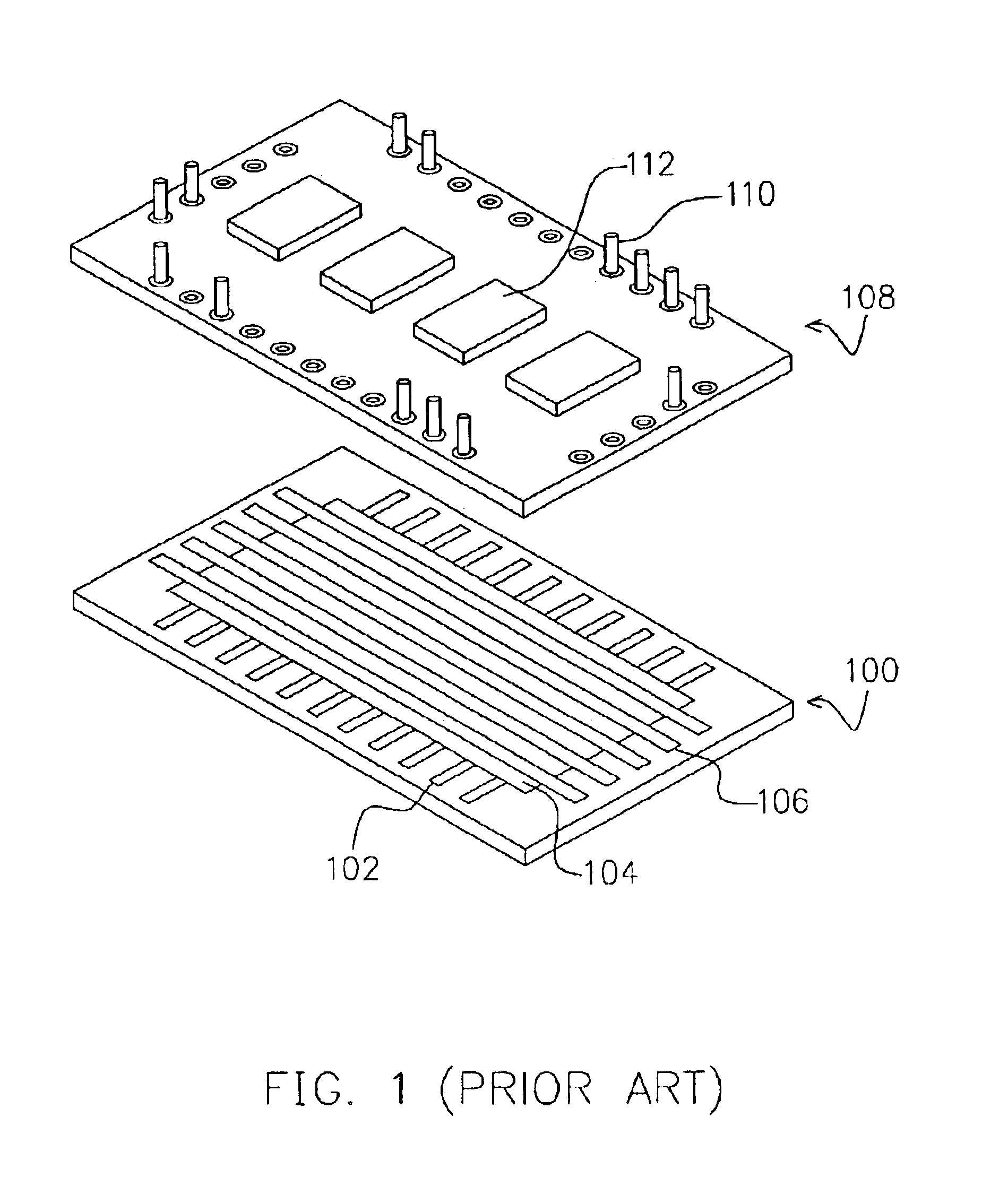
Process for forming cone shaped solder for chip interconnection
InactiveUS20010015495A1Easy to joinPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureRoom temperatureSemiconductor chip
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
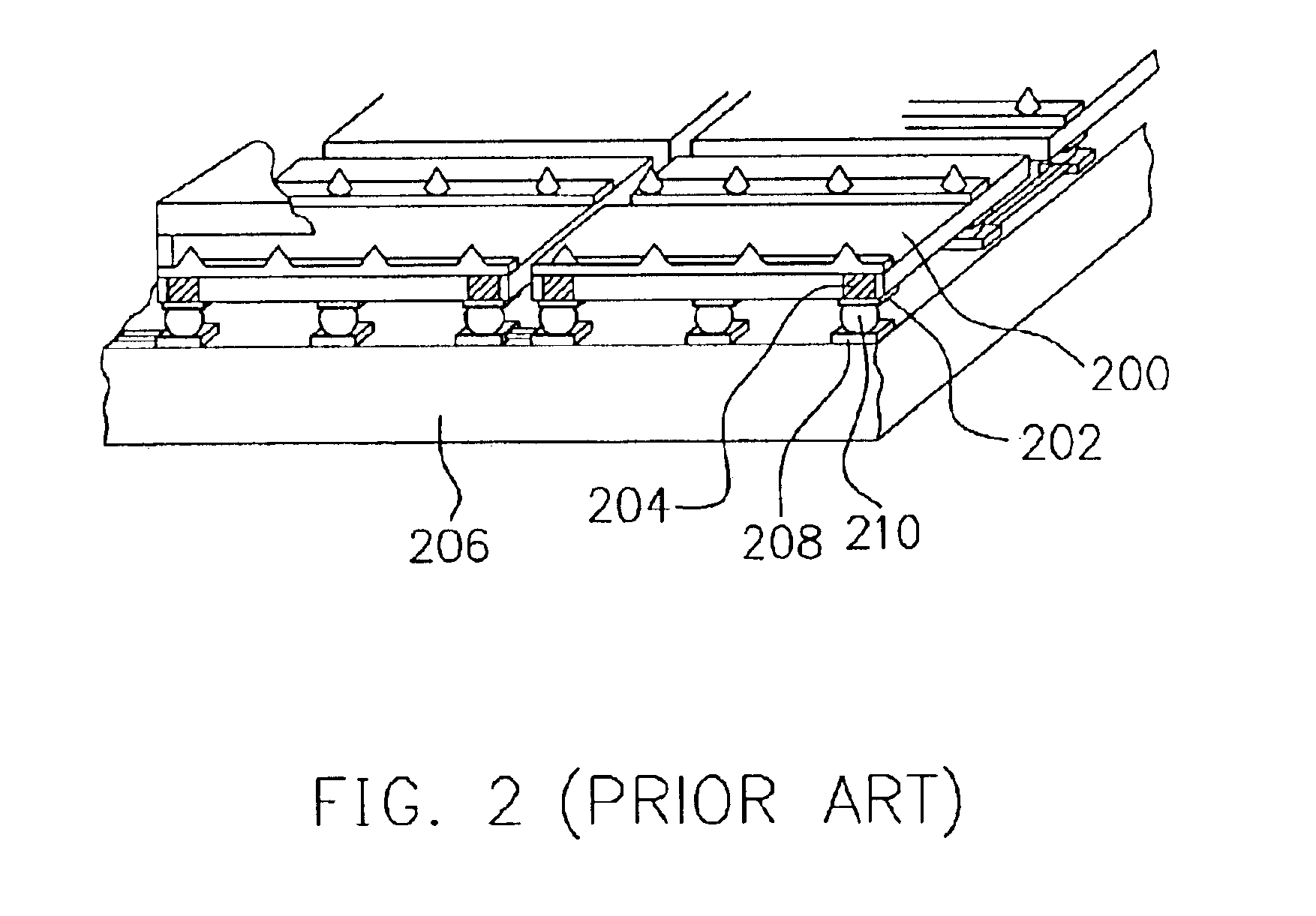
Method for separating electronic component from organic board
InactiveUS7234218B2Adversely electrical performancePrinted circuit assemblingSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceSolder interconnection
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method of fabricating organic electroluminescence panel package
InactiveUS20050003578A1Relieve pressureImprove cooling effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolder interconnectionEngineering
A packaging fabrication for an organic electroluminescence panel is disclosed. The panel comprises a printed circuit board, one or a plurality of OEL panels and a plurality of bumps, wherein the OEL is provided with poly solder interconnections in area array. The printed circuit board is provided with a plurality of solder pads arranged with bumps. One or a plurality of OEL is arranged on the printed circuit board and the poly solder interconnections and bumps are used to electrically connect the OEL with the printed circuit board. Further, the excellent heat dissipation property of the low re-flow temperature of the poly solder interconnections and the ceramic printed circuit board provides packaging fabrication for low temperature low stress OEL.
Owner:RITDISPLAY
Solder interconnection array with optimal mechanical integrity
InactiveUS20080261350A1Easy to joinAvoid more failuresPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureMechanical integrityFilling materials
A method for assembling, and the resultant electronic module, includes attaching a chip to a substrate using a first solder interconnection array, and attaching a board to the substrate using a second solder interconnection array, which may be a single-melt or a dual-melt solder array. The second solder interconnection array resides entirely within a space defined between the board and substrate. A creep resistant structure is provided within this space for maintaining the defined space and optimizing integrity of the second solder interconnection array. The creep resistant structure may include an underfill material, balls, brackets, frames, collars or combinations thereof. Wherein the creep resistant structure is an underfill material, it is crucial that the substrate be attached to the board before either entirely encapsulating the second interconnection array with underfill material, or partially encapsulating the second solder interconnection array at discrete locations with underfill material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method of attaching an integrated circuit chip to a module
InactiveUS20090279275A1Line/current collector detailsFinal product manufactureEngineeringSolder interconnection
A method of attaching an integrated circuit chip to a module and a resultant structure. The method includes placing a solder bump tape between the chip and the module, the solder bump tape including an array of solder columns embedded in a dielectric sheet; aligning and contacting top surfaces of solder columns with respective chip pads of an array of chip pads of the chip and aligning and contacting bottom surfaces of the solder columns with respective module pads of an array of module pads; and reflowing the solder columns to form solder interconnections between chip pads and respective module pads.
Owner:IBM CORP
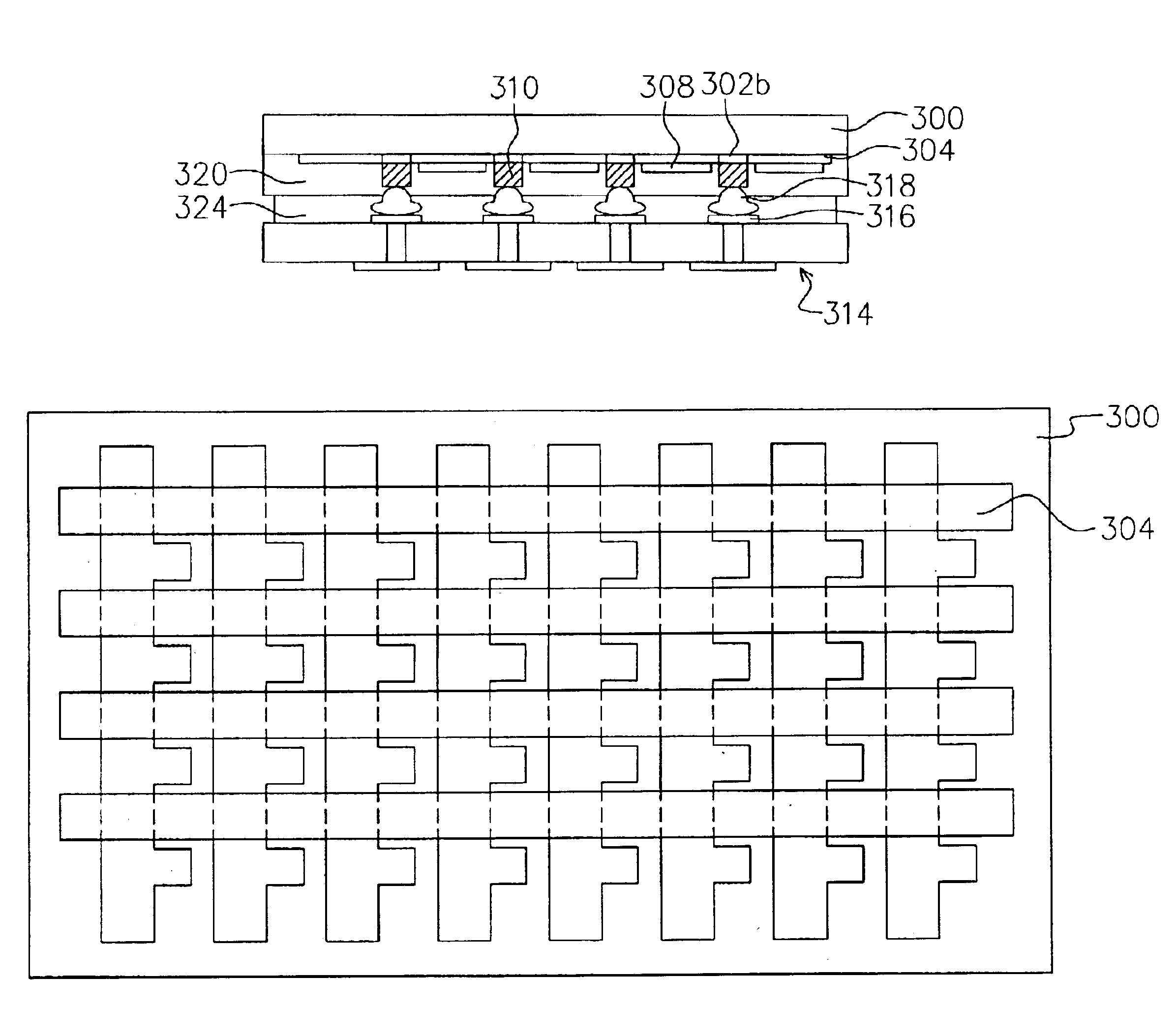
Micro grid array solder interconnection structure for second level packaging joining a module and printed circuit board
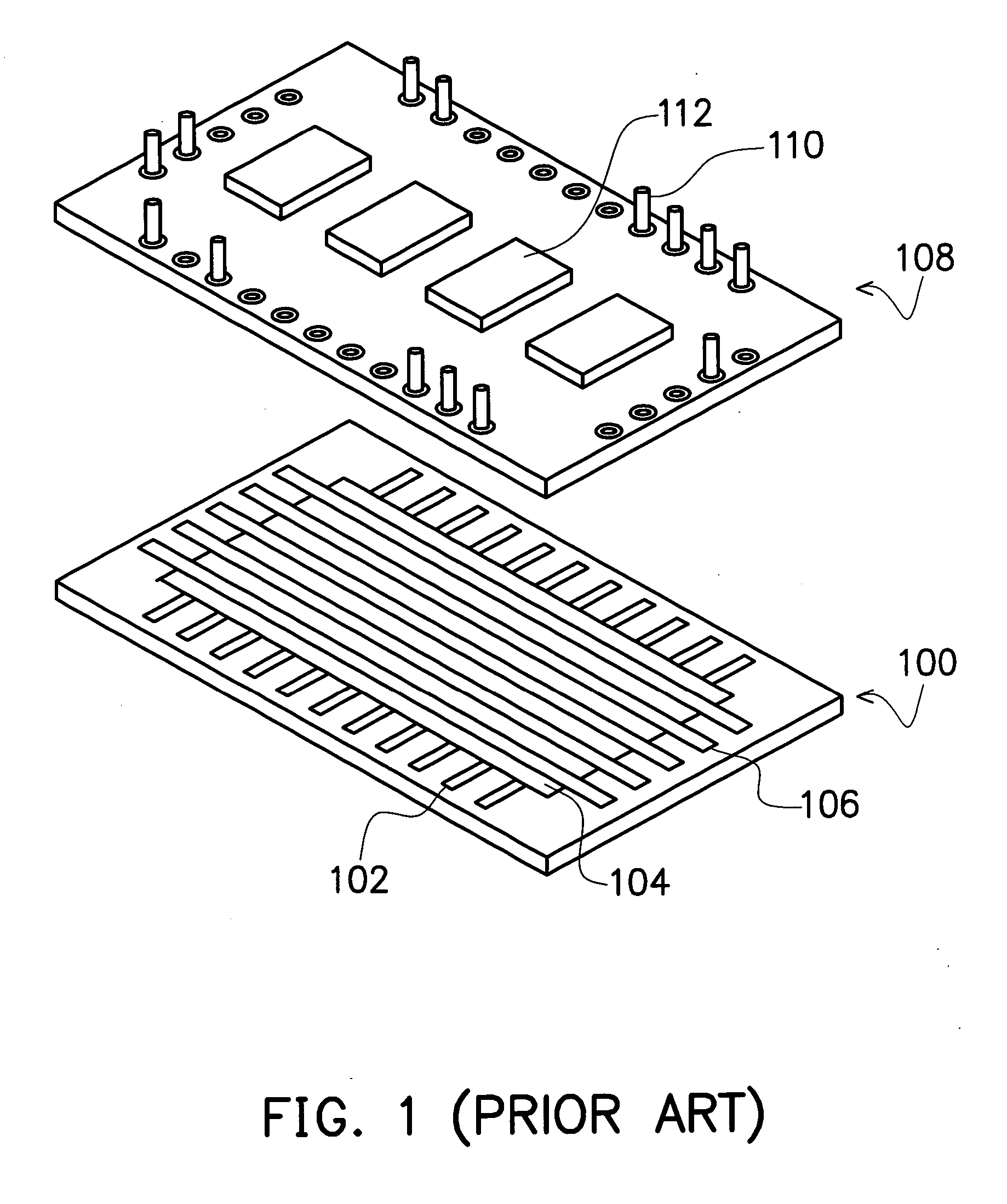
InactiveUS6059173AMinimizes problemIncrease elasticityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSolder interconnectionPrinted circuit board
A solder interconnection between a module and printed circuit board or card is provided by a plurality of solder connections arranged in a micro grid array joining solder wettable pads on a major surface of the module to a corresponding set of solder wettable pads of the printed circuit board or card. The solder connections are column shaped with the height of each connection being at least about 1.4 times the diameter of the connection.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Microelectronic packages with solder interconnections
InactiveUS20060113680A1Relieve pressureImprove fatigue resistancePrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureThermal fatigueSurface mounting
A soldered assembly for a microelectronic element includes a microelectronic element, solder columns extending from a surface of the microelectronic element and terminals connected to distal ends of the columns. The assembly can be handled and mounted using conventional surface-mount techniques, but provides thermal fatigue resistance. The solder columns may be inclined relative to the chip surface, and may contain long, columnar inclusions preferentially oriented along the lengthwise axes of the columns.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Flexible thin film ball grid array containing solder mask
InactiveUS6187610B1Eliminate the problemRelieve pressurePrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder maskSolder ball
An electronic package is provided that includes a flexible polyimide film carrier having electronic circuitry on both of its major surfaces and a plurality of solder interconnection pads on a first major surface; solder mask layers located on both major surfaces, provided that areas between subsequently to be applied individual circuit chips on the first major surface exist that are free from the solder mask; and a plurality of modules attached to the film carrier by the solder balls or bumps. Also provided is a method for fabricating the electronic package that includes reflow of the solder balls or bumps to achieve attachment of the modules.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for improved high current component interconnections
ActiveUS20040216917A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder interconnectionSolder paste
A printed circuit board having at least one conductive region covered in solder paste has preformed solder elements placed on the solder paste in the conductive region. A component package is placed onto the printed circuit board over the conductive region and the solder is reflowed, forming a wide solder interconnection between the component and the conductive region of the printed circuit board.
Owner:INTEL CORP
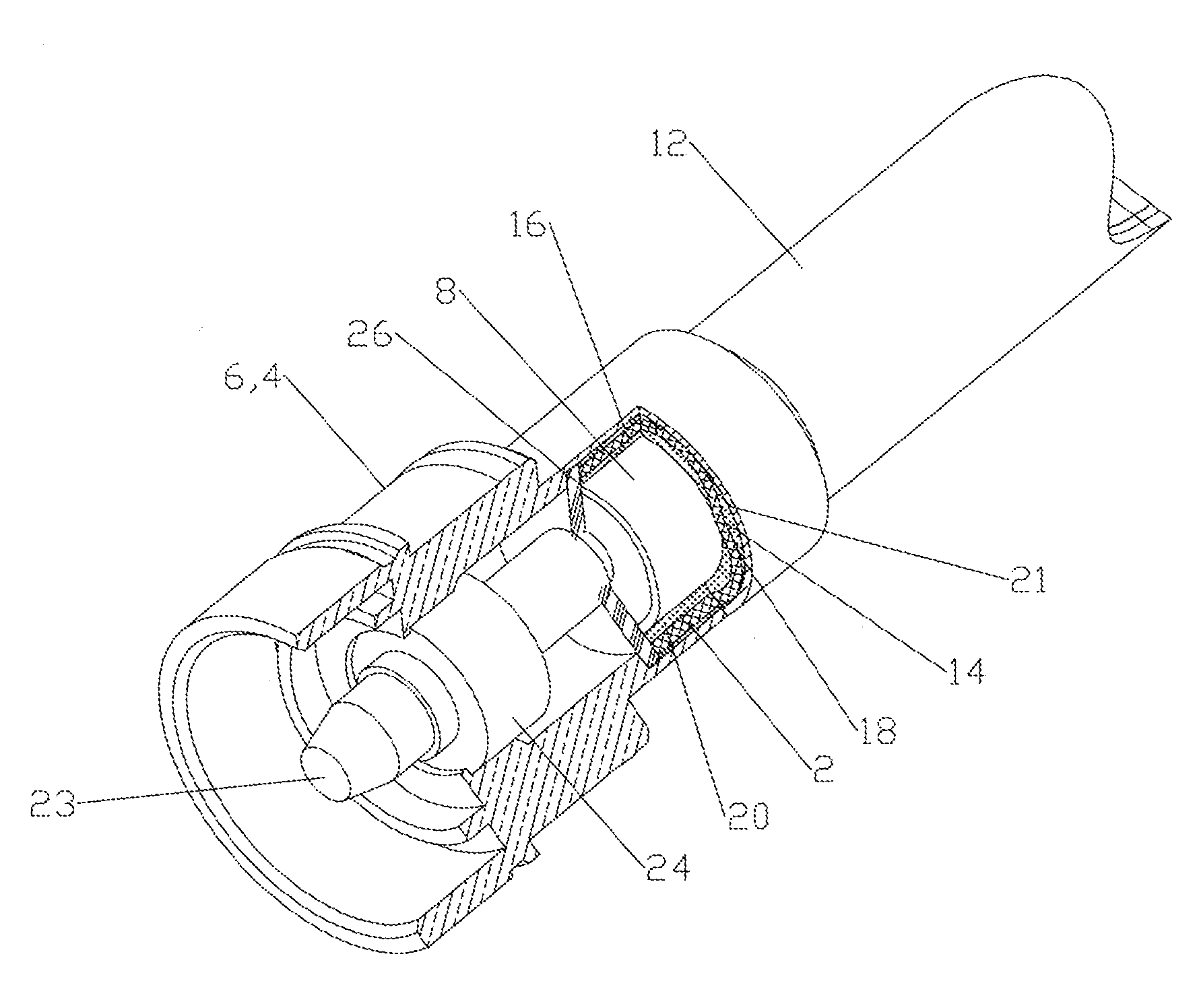
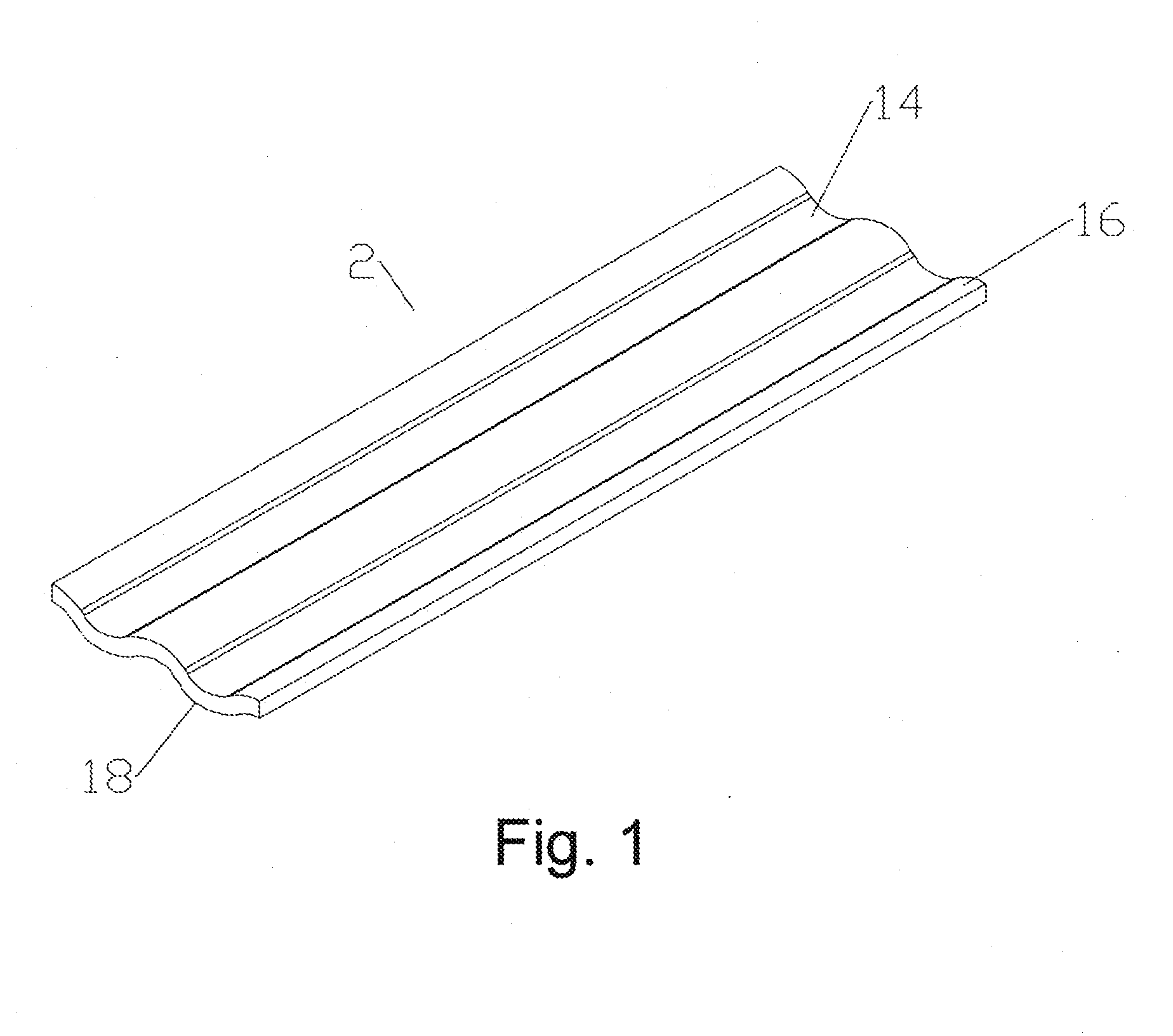
Corrugated Solder Pre-form and Method of Use
InactiveUS20120255991A1Quality improvementSignificant material cost savingLine/current collector detailsElectrically conductive connectionsCoaxial cableElectrical conductor
A solder pre-form for soldering a coaxial cable to a connector body is provided with a plurality of flux grooves on a cable side and a connector side. The solder pre-form may also have a plurality of holes between the cable and connector sides. In a method of use, flux is applied to the flux grooves and the solder pre-form applied to encircle the outer conductor which is then inserted into the connector body and the solder pre-form melted to complete the solder interconnection. Where holes are present, flux may be applied to the connector side, passing through the holes also to the cable side.
Owner:ANDREW LLC
Solder interconnection array with optimal mechanical integrity
InactiveUS7445141B2Easy to joinAvoid more failuresFinal product manufacturePrinted circuit aspectsMechanical integrityFilling materials
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Flip chip semiconductor encapsulation structure
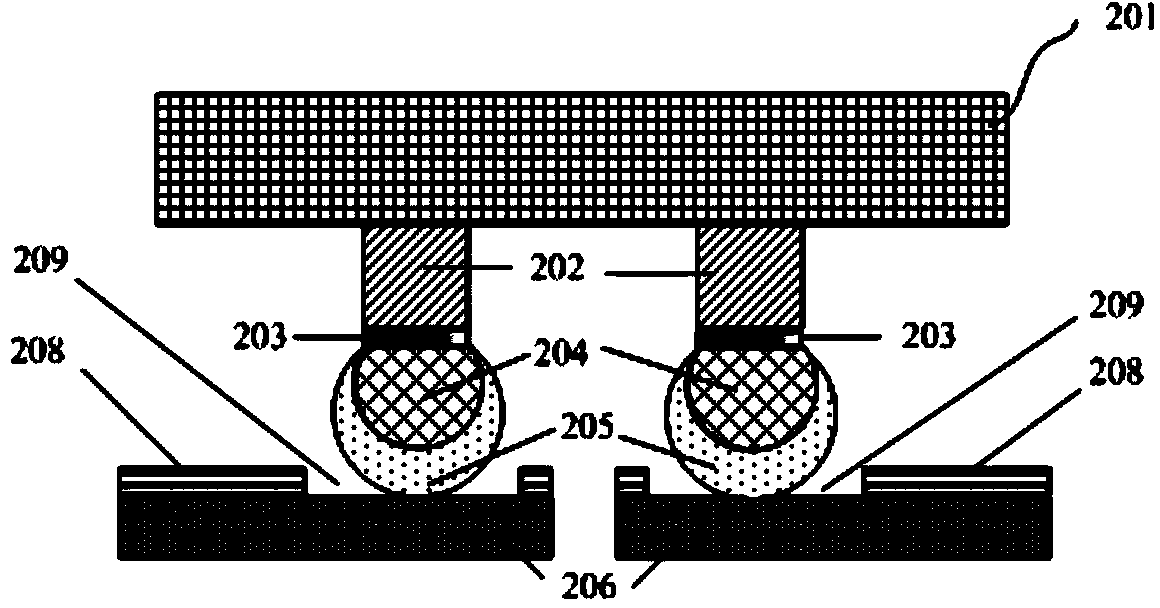
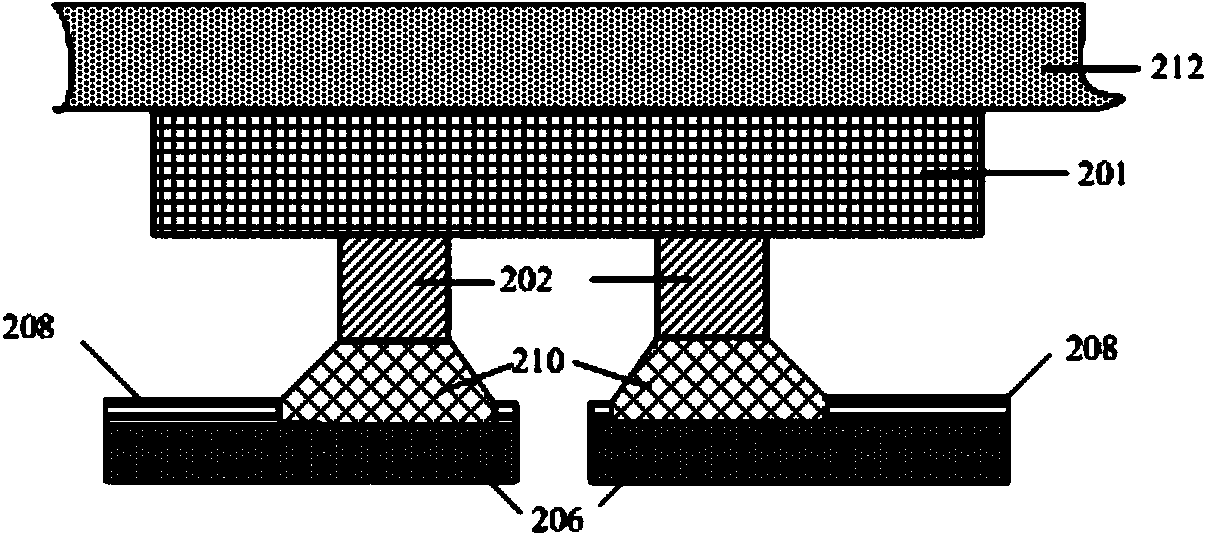
ActiveCN104282637AStop flow awayHigh mechanical strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
The invention discloses a flip chip semiconductor encapsulation structure which comprises a semiconductor chip, multiple copper posts, a lead frame, an insulating layer on the surface of the lead frame, multiple solder interconnection structures and moulding complexing agents. The surface of the semiconductor chip is provided with a pad pattern, and the copper posts are formed on the pad pattern. The insulating layer is provided with an opening, the area of the opening is larger than the cross area of each copper post, and leads on the upper portion of the lead frame are exposed at the opening. The solder interconnection structures are located between the copper posts and the leads exposed at the opening, and the moulding complexing agents are used for encapsulating the assembly. The flip chip semiconductor encapsulation structure enables the semiconductor chip to be firmly coupled on the lead frame, and meanwhile bad contact between the semiconductor chip and the lead frame is prevented.
Owner:NANTONG FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS
Package structure of organic electroluminescence panel
InactiveUS6858874B2Less issueReduce stressSolid-state devicesCircuit arrangements on insulating boardsSolder interconnectionEngineering
A package structure of an OEL panel includes a printed circuit board, at least one OEL panel, and several bumps. Wherein, the OEL panel has several poly solder interconnections arranged in an array structure. The printed circuit board has several solder pads, which are also implemented with bumps. The at least one OEL panel is disposed on the printed circuit board to have the electric connection with the printed circuit board through the poly solder interconnections and the bumps.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Low temperature solder chip attach structure and process to produce a high temperature interconnection
InactiveUS20050109820A1Improve connection reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSolder ballAlloy
A solder interconnection uses preferably lead-rich solder balls for making a low temperature chip attachment directly to any of the higher levels of packaging substrate. After a solder ball has been formed using standard processes, a thin cap layer of preferably pure tin is deposited on a surface of the solder balls. An interconnecting eutectic alloy is formed upon reflow. Subsequent annealing causes tin to diffuse into the lead, or vice versa, and intermix, thereby raising the melting point temperature of the cap layer of the resulting assembly. This structure and process avoids secondary reflow problems during subsequent processing.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
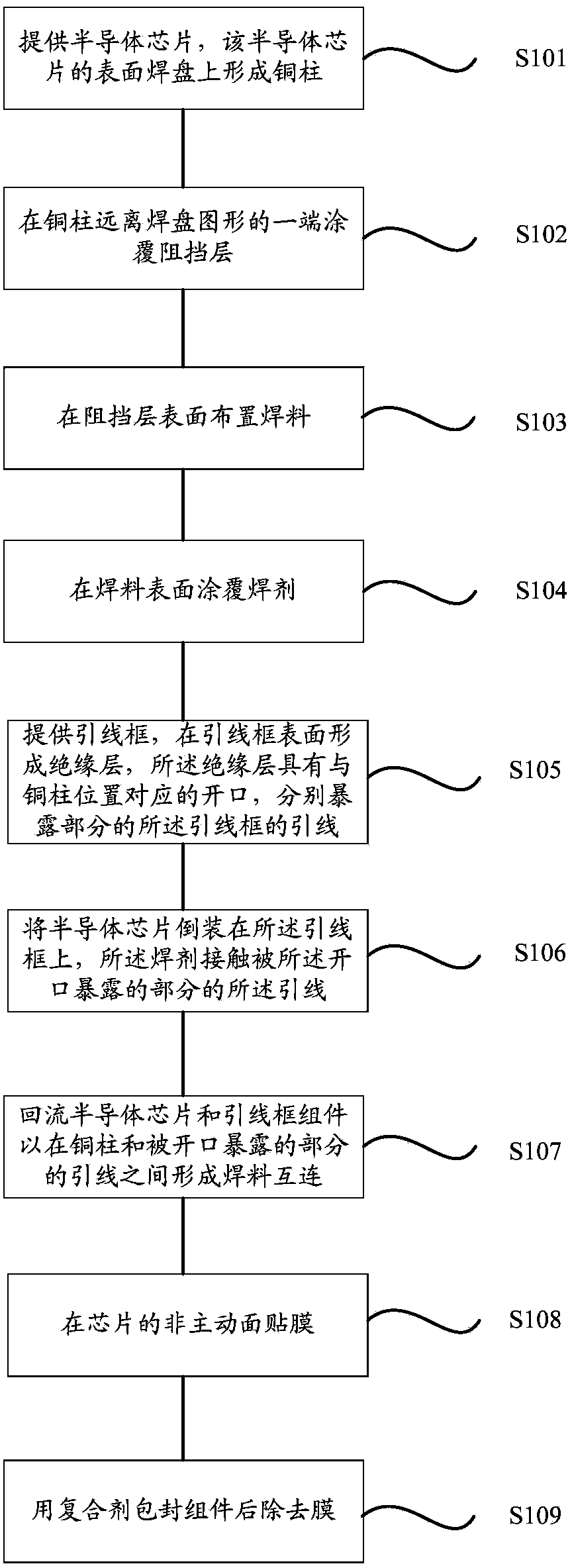
Method of forming flip-chip semiconductor encapsulation device
InactiveCN104392940AImprove cooling effectImprove applicabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
The invention discloses a method of forming a flip-chip semiconductor encapsulation device. The method includes the following steps that: copper columns are formed on a pad pattern of a semiconductor chip, and one end of each copper column, which is far away from the pad pattern, is plated with a barrier layer, and a predetermined amount of solder is distributed on the barrier layers, and the solder is coated with soldering flux; lead frames are provided, and the surfaces of the lead frames are plated with insulating layers, and openings corresponding to the positions of the copper columns, are formed in the insulating layers and expose a part of leads of the lead frames respectively; the semiconductor chip is mounted on the lead frames in a flip manner, and the solder contacts with the exposed leads; when refluxing is performed, the solder is melt, and solder interconnection structures are formed between the copper columns and the exposed leads by means of the soldering flux; and after the refluxing, a film is attached to a non-active surface of the chip, and then, encapsulation is performed, and the film is removed, and therefore, the flip-chip semiconductor encapsulation device can be formed. According to the method, the non-active surface of the chip is not covered with the encapsulation material, so that the formed flip-chip semiconductor device can have an excellent heat dissipation effect.
Owner:NANTONG FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS
Temporary structure to reduce stress and warpage in a flip chip organic package
InactiveUS7538432B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSolder interconnection
A flip chip assembly having reduced stress and warpage comprises a flip chip package including an organic substrate and an integrated circuit chip, a temporary structure having a coefficient of thermal expansion that is substantially similar to a coefficient of thermal expansion of the integrated circuit chip, and a cap member coupled to a top side of the organic substrate. A bottom side of the integrated circuit chip is bonded to the top side of the organic substrate with controlled chip collapse columns. Additionally, a bottom side of the organic substrate is soldered to a top side of the temporary structure with solder interconnections that are applied to a plurality of solder pads on the top side of the temporary structure, the position of the solder pads on the temporary structure mirroring the position of a plurality of solder pads on the bottom side of the organic substrate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Corrugated Solder Pre-form and Method of Use
ActiveUS20140076958A1Quality improvementSignificant material cost savingLine/current collector detailsElectrically conductive connectionsCoaxial cableElectrical conductor
A solder pre-form for soldering a coaxial cable to a connector body is provided with a plurality of flux grooves on a cable side and a connector side. The solder pre-form may also have a plurality of holes between the cable and connector sides. In a method of use, flux is applied to the flux grooves and the solder pre-form applied to encircle the outer conductor which is then inserted into the connector body and the solder pre-form melted to complete the solder interconnection. Where holes are present, flux may be applied to the connector side, passing through the holes also to the cable side.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Contact having soldered interconnection between first and second parts
InactiveUS7891991B2Electrically conductive connectionsCoupling contact membersEngineeringSolder interconnection
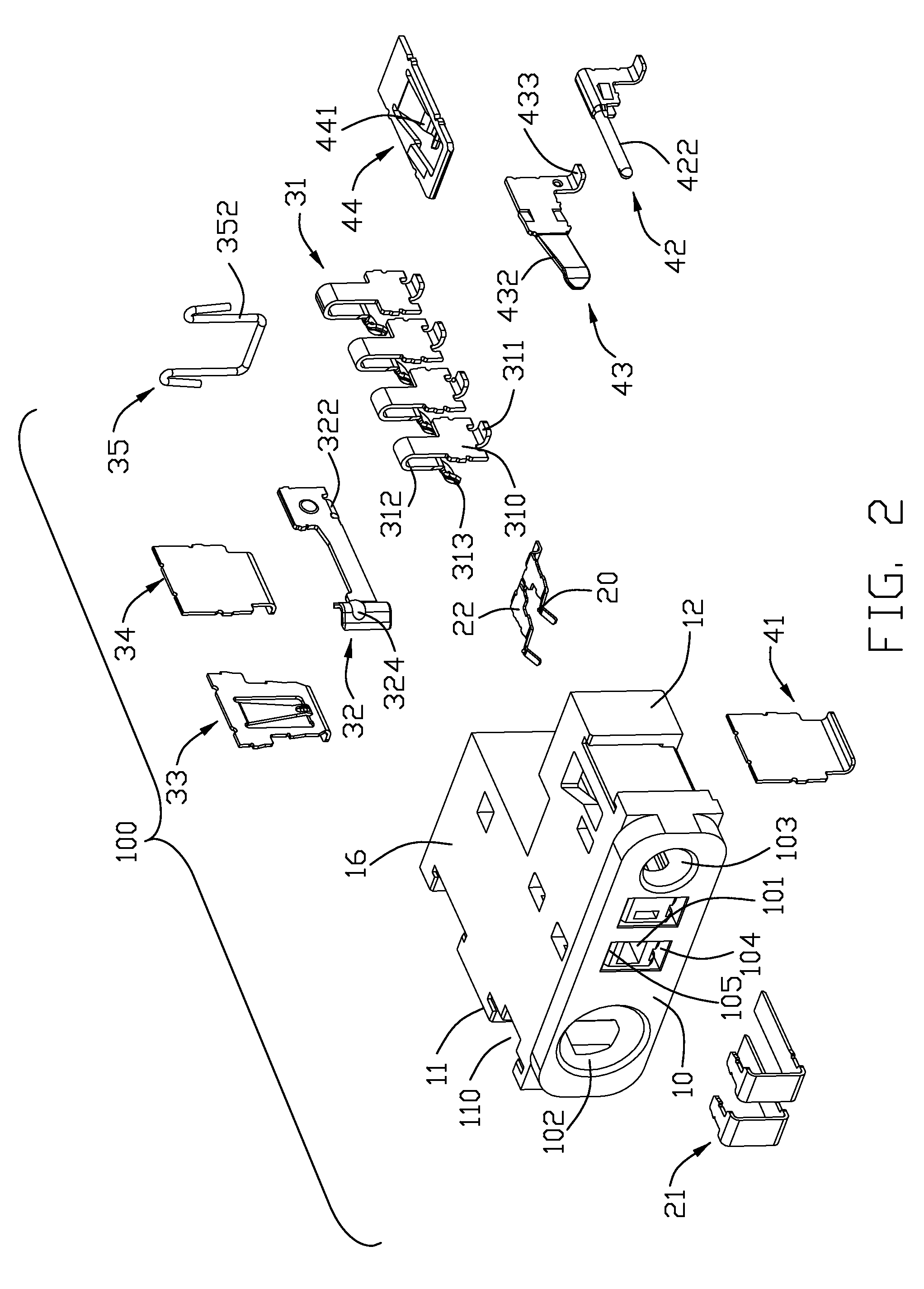
An electrical connector includes an insulting housing, a mating face, a rear face opposite to the mating face, a first receiving groove defined into the mating face and a second receiving groove defined into the rear face, and the two receiving grooves extend towards each other. The first contact includes a contacting contact retained in the first receiving groove and a soldering contact separated from the contacting contact and retained in the second receiving groove, and the contacting contact defines a mating portion exposed to the mating face, and the soldering contact defines a soldering portion exposed out of the housing for mounting onto a printed circuit board and a resilient arm extending into the second receiving groove and soldered to the contacting contact. The separated mating contact and soldering contact are soldered together to provide a secure connection therebetween and a good electronic capability for the electrical connector.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Method for improved high current component interconnections
InactiveUS20050225953A1Printed circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSolder interconnectionSolder paste
A printed circuit board having at least one conductive region covered in solder paste has preformed solder elements placed on the solder paste in the conductive region. A component package is placed onto the printed circuit board over the conductive region and the solder is reflowed, forming a wide solder interconnection between the component and the conductive region of the printed circuit board.
Owner:AMIR DUDI I +1
Method for improved high current component interconnections
InactiveUS20070125833A1Printed circuit assemblingCooking-vessel materialsSolder interconnectionSolder paste
A printed circuit board having at least one conductive region covered in solder paste has preformed solder elements placed on the solder paste in the conductive region. A component package is placed onto the printed circuit board over the conductive region and the solder is reflowed, forming a wide solder interconnection between the component and the conductive region of the printed circuit board.
Owner:AMIR DUDI I +1
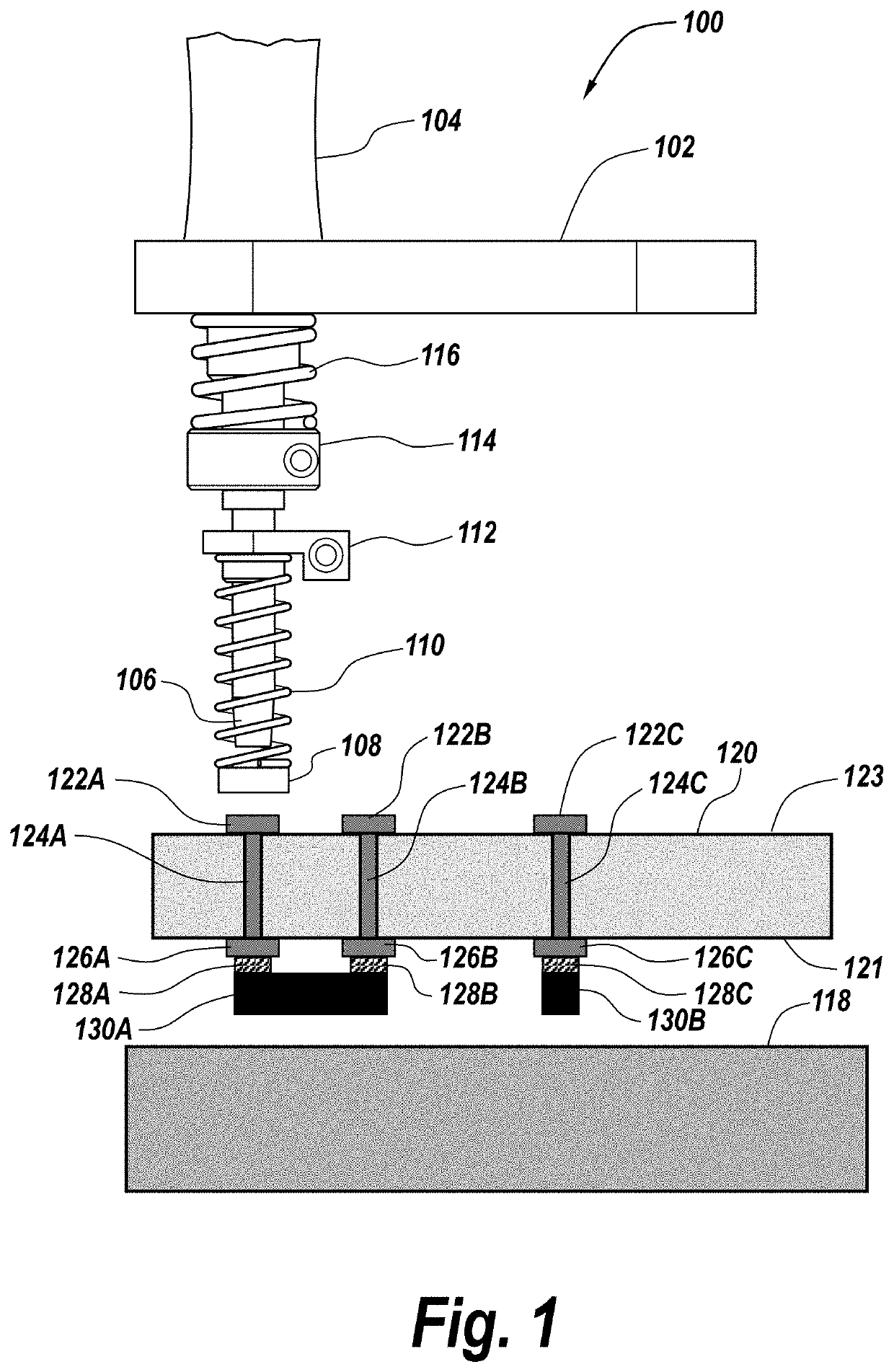
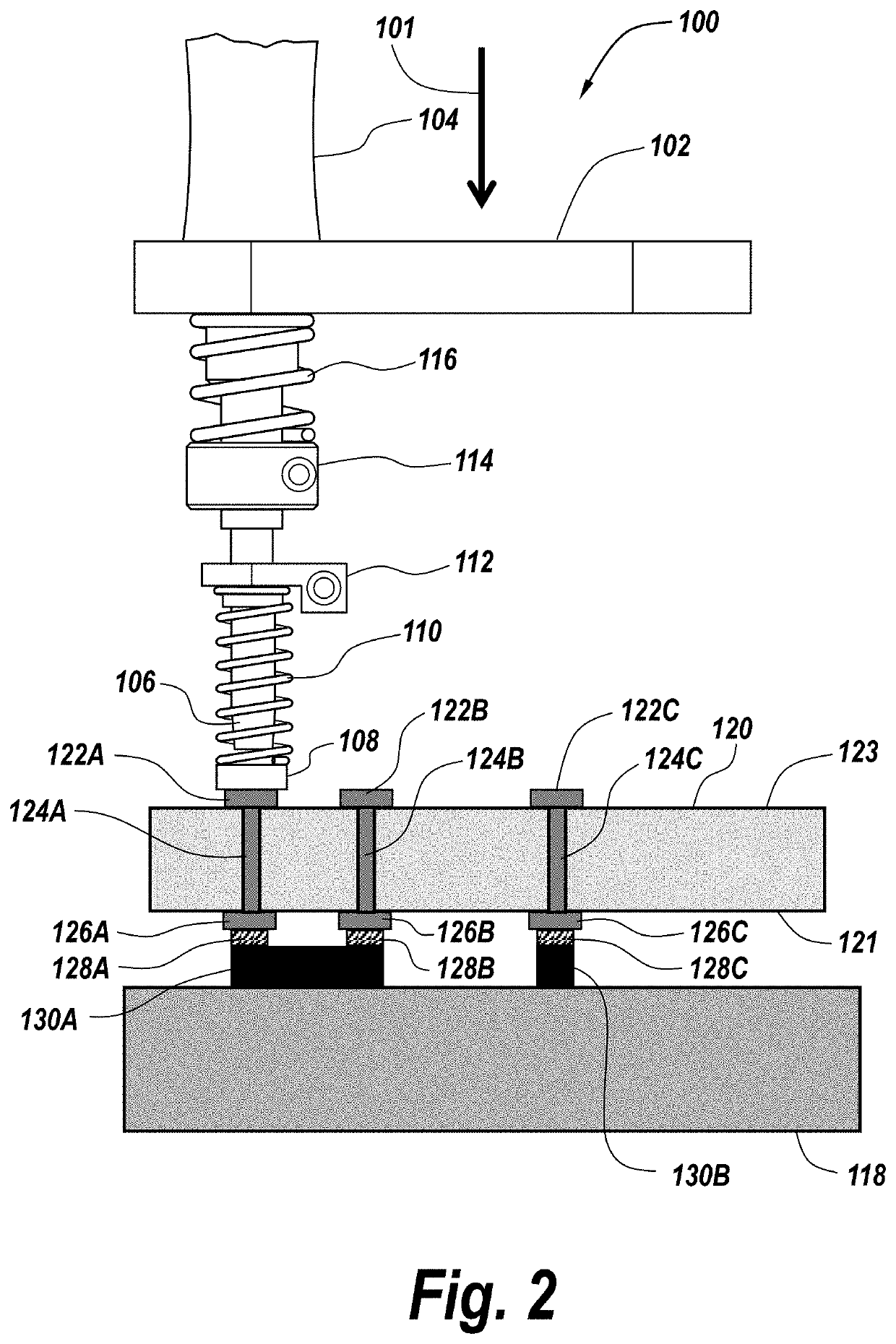
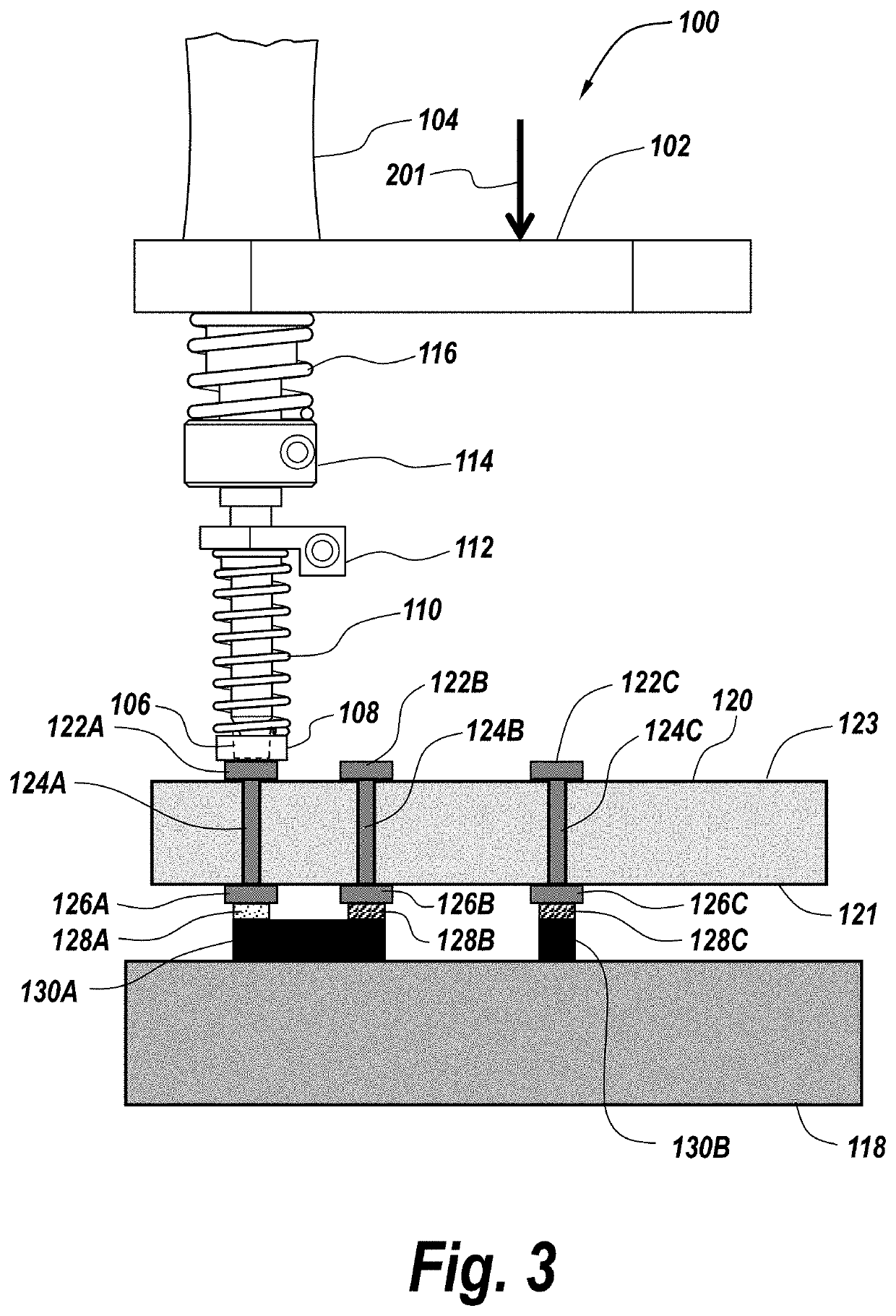
System and method for creating orthogonal solder interconnects
PendingUS20210076505A1Printed circuit assemblingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringSolder interconnection
An apparatus and method for soldering an electrical component to a circuit board includes a stage positioning the circuit board and electrical component in alignment with a solder tip along an axis. A first spring-loaded compression mechanism maintains contact between the circuit board and the electrical component, and a second spring-loaded compression mechanism brings the soldering tip into thermal contact with the circuit board and the electrical component such that solder disposed adjacent to the circuit board and the electrical component melts. When the second spring-loaded compression mechanism removes its applied force such that the soldering tip comes out of contact with the circuit board, the first spring-loaded compression mechanism maintains the contact between the circuit board and the electrical component while the solder cools and solidifies.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com