Structure and method for lead free solder electronic package interconnections
a technology of electronic package and structure, which is applied in the direction of soldering apparatus, semiconductor/solid-state device details, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of encapsulant walls being large, chip blm becoming molten, and subsequent reflow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
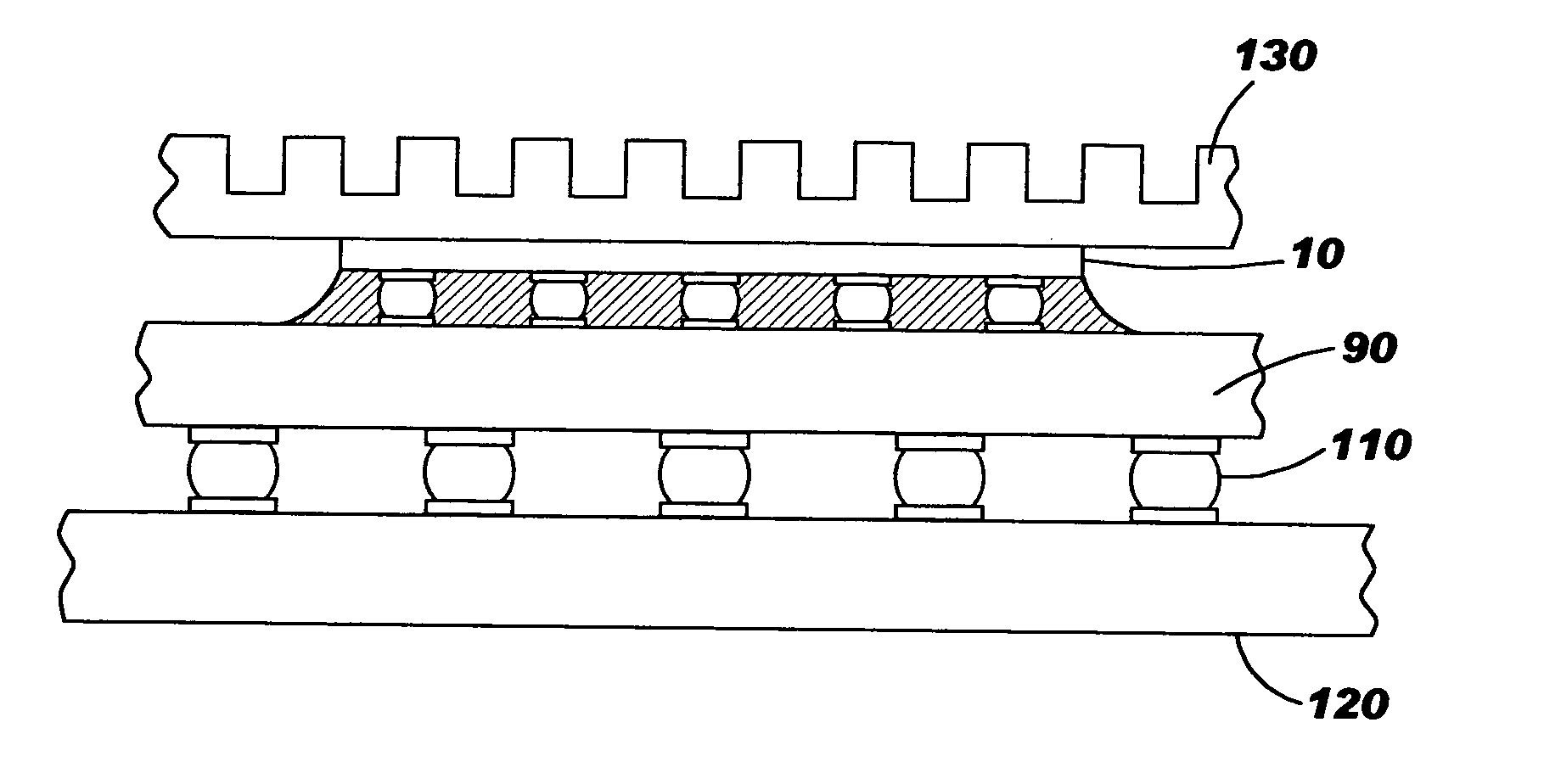
[0032] In the present invention a Sn / Ag off-eutectic lead free solder composition is provided having between about 52.0-95.0 weight % Sn and between about 48.0-5.0 weight % Ag and having inter-metallics with a melting temperature greater than 250° C. The term “inter-metallic” has its ordinary meaning of a compound with two or more metals.
[0033] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention a 72Sn / 28Ag (weight %) solder alloy is used which has a liquidus temperature of approximately 400° C. A chip join C4 reflow cycle with a peak temperature of approximately 355-375° C., with adequate dwell time typically about 1-4 minutes, will suffice to create a homogenous lead free C4 solder alloy interconnection. A homogenized solder alloy interconnection has a uniformly distributed inter-metallic phase structure.
[0034] During the subsequent second level join / assembly process, the maximum peak temperature is approximately 250° C. This temperature will create a pasty two-phase inter-metalli...
second embodiment
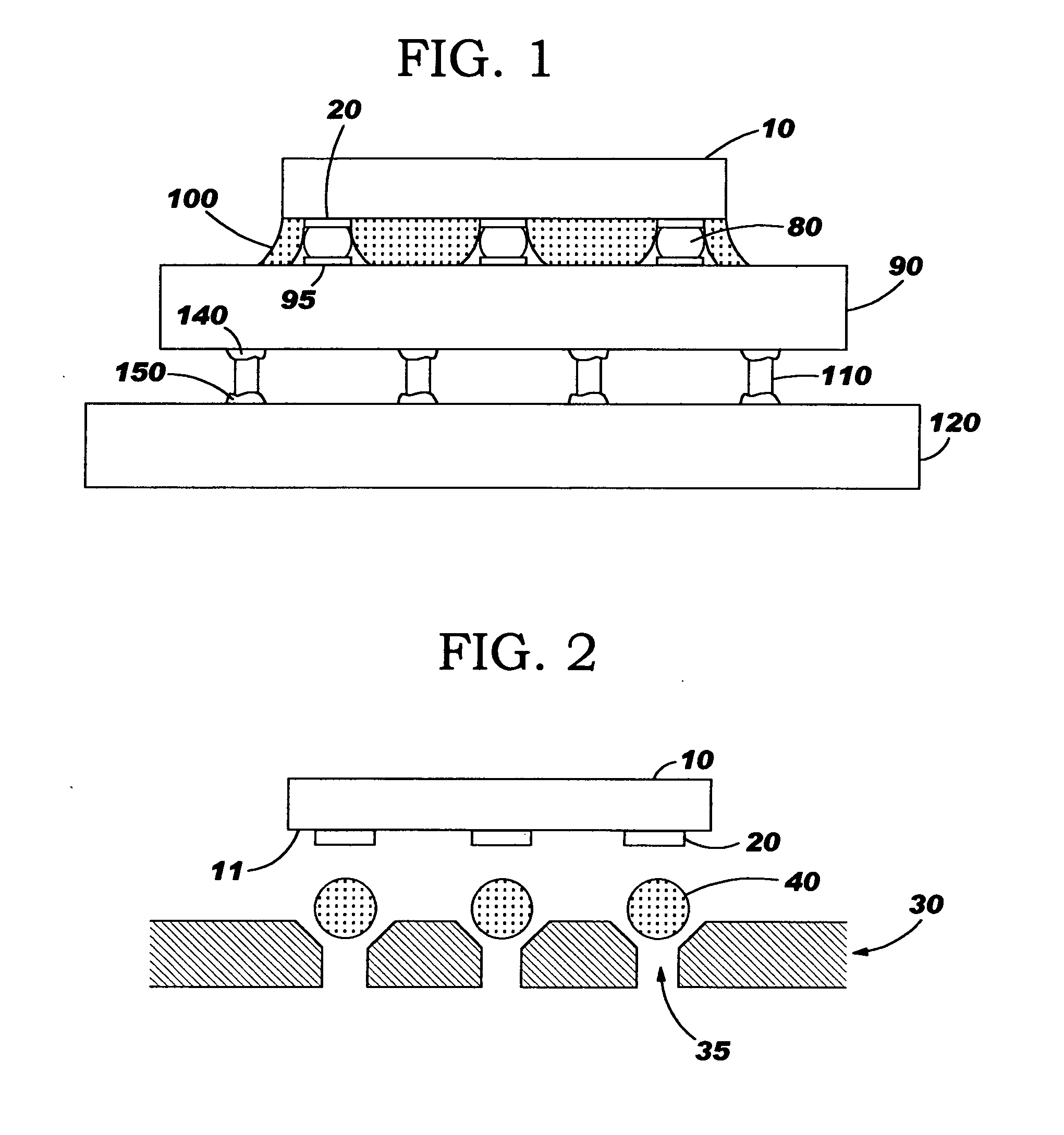
[0038] In the present invention a Sn / Cu off-eutectic lead free solder composition of between about 84.0-99.3 weight % Sn and between about 16.0-0.7 weight % Cu and having inter-metallics with a melting temperature greater than 250° C.
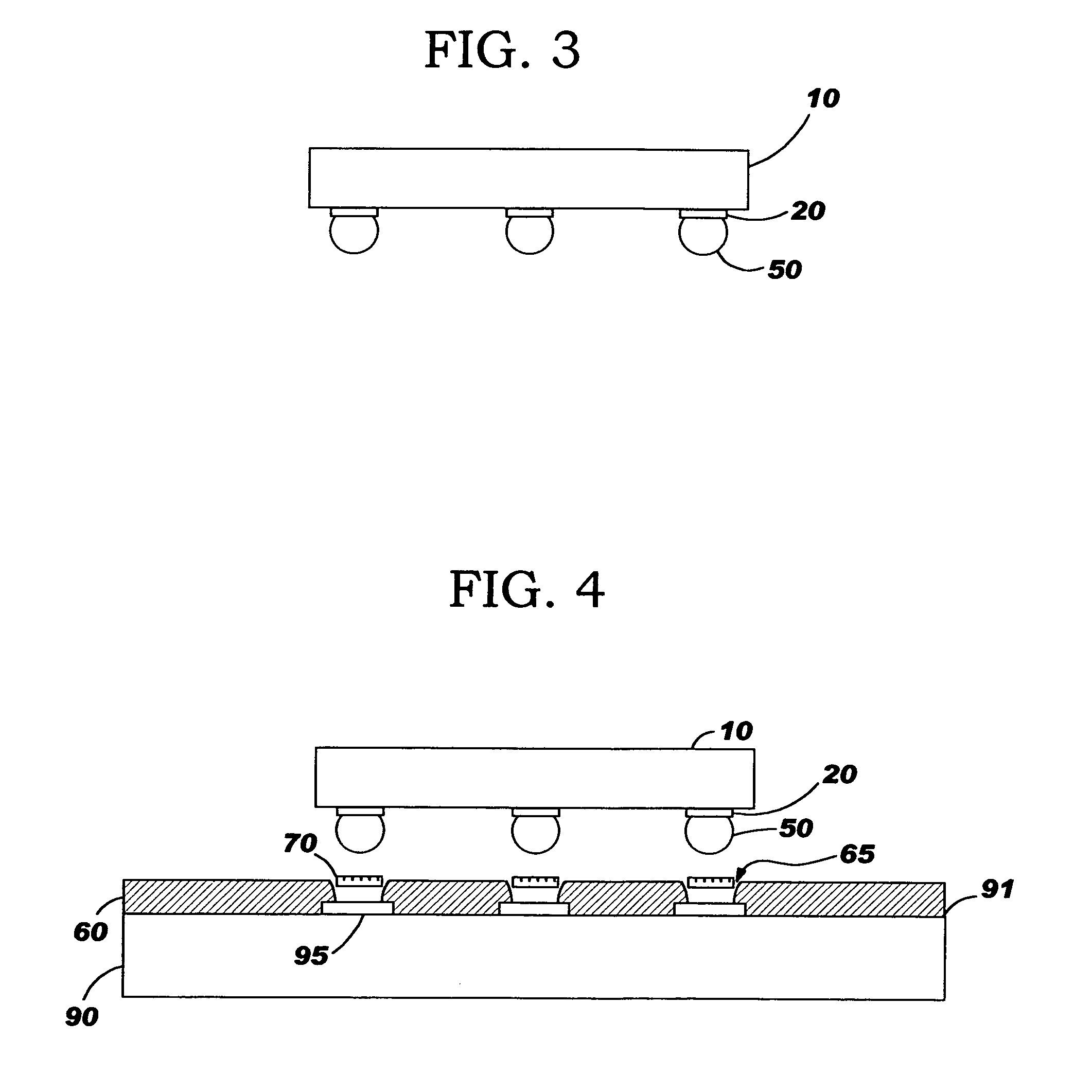
[0039] In a preferred embodiment of the present invention a 84Sn / 16Cu (in weight %) solder alloy is used which has a liquidus temperature of approximately 500° C. A chip C4 reflow cycle with a peak temperature of approximately 350-375° C., with adequate dwell time typically about 1-4 minutes, will suffice to create a homogenized C4 solder alloy interconnection. Then during the subsequent second level join / assembly process, the maximum peak temperature is approximately 250° C. This temperature will create a pasty two-phase inter-metallic structure in the C4 solder alloy interconnect, comprised of approximately 72 weight % liquid phase, and approximately 28 weight % solid phase. This alloy structure will restrict the expansion of the C4 interconnections a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| liquidus temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| liquidus temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com