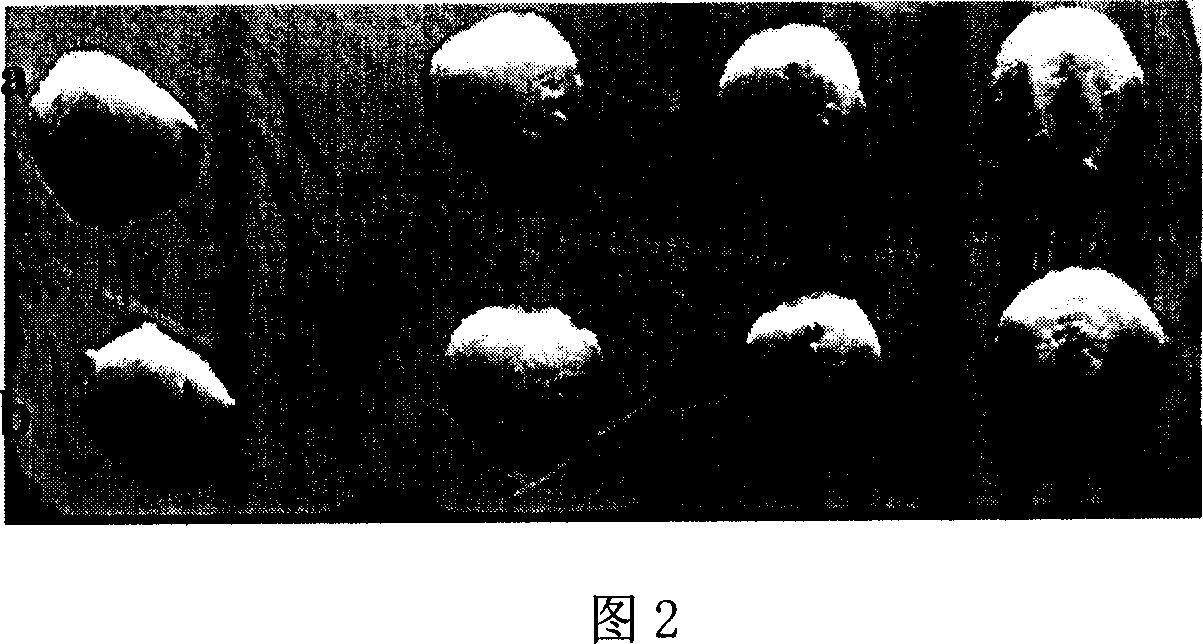
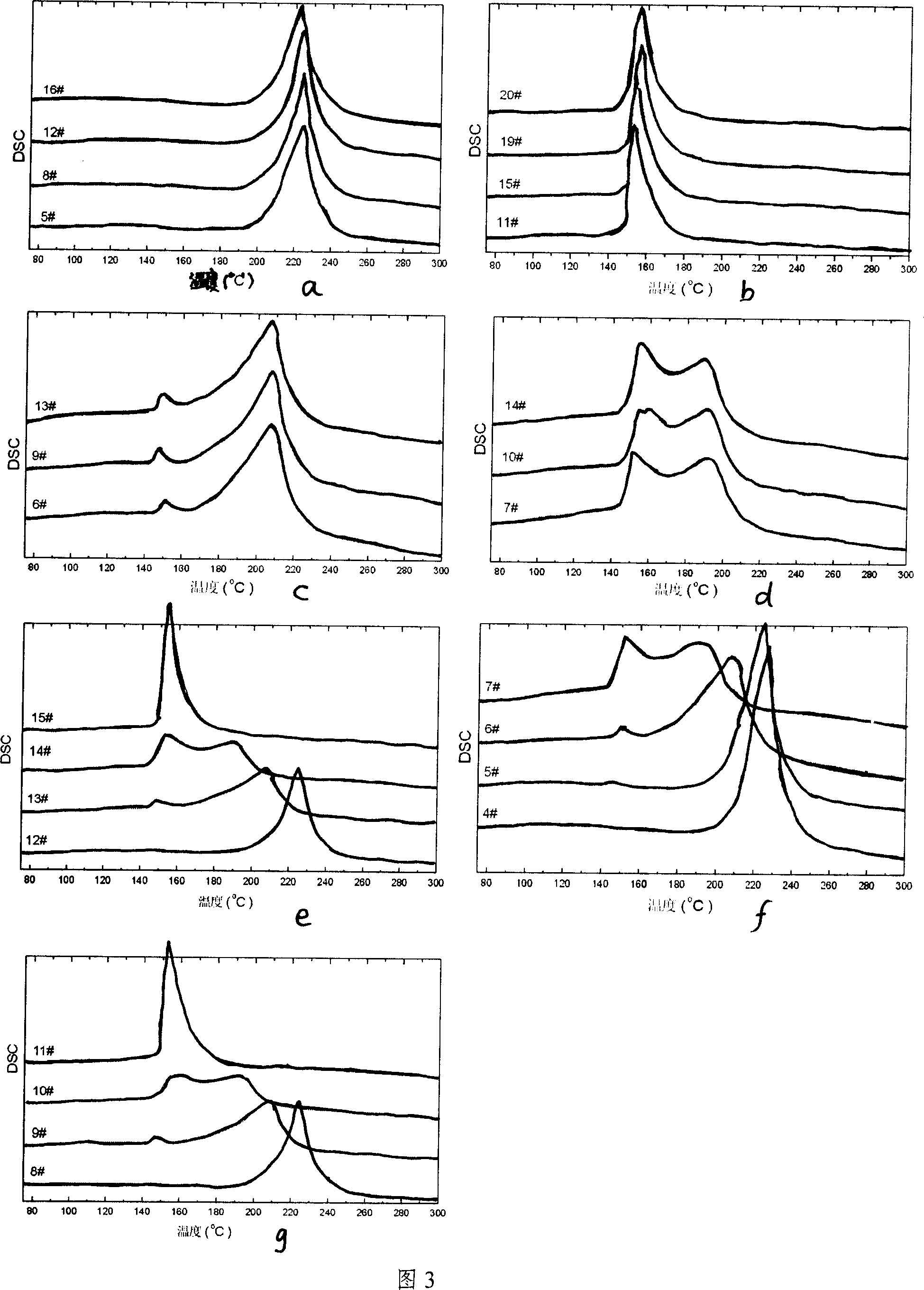
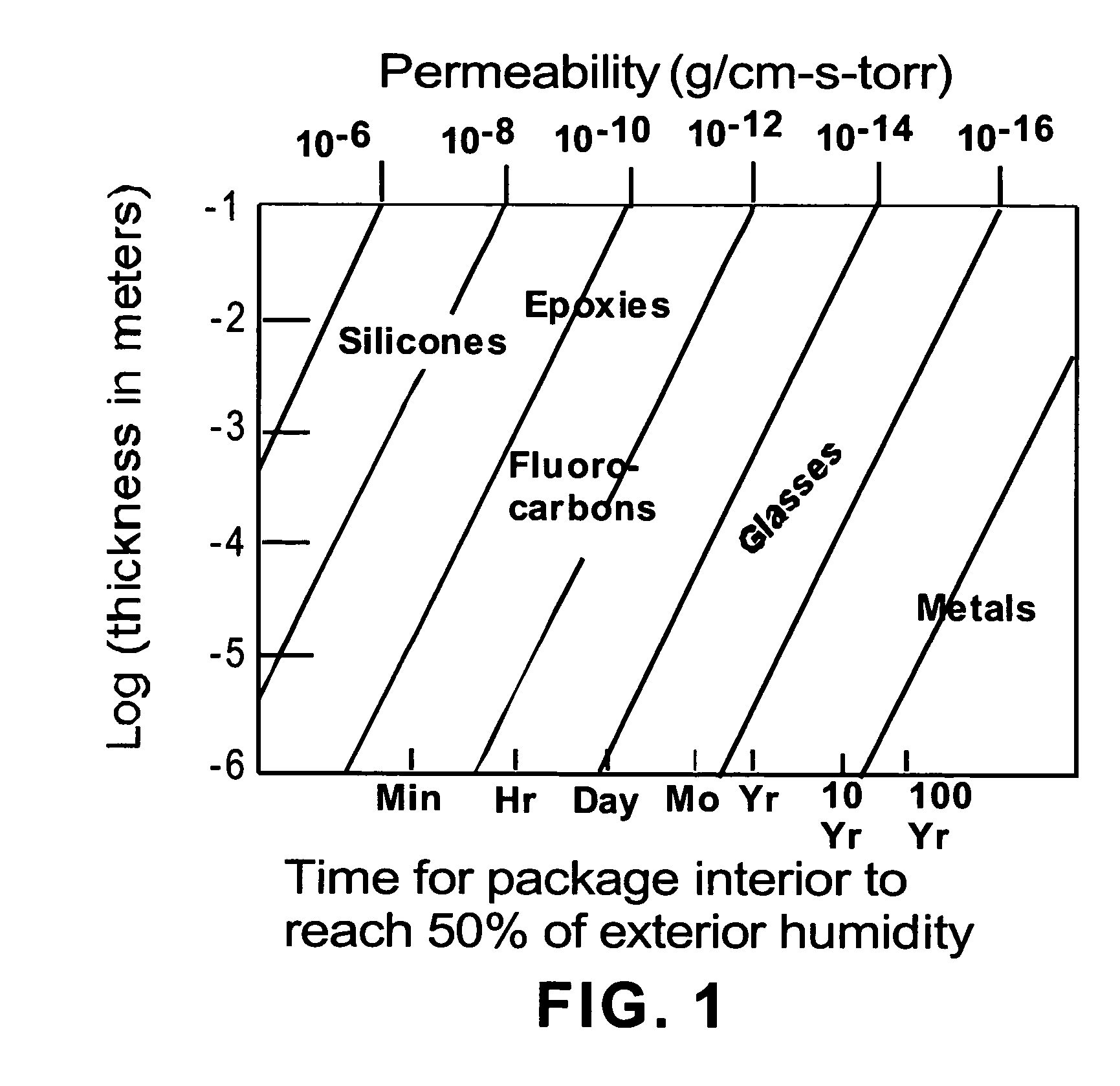
Patents
Literature
990 results about "Solder alloy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solder alloys are metallic materials that are used to connect metal workpieces. This is achieved by melting the alloy and then cooling it down. The choice of specific alloy depends on its melting point, chemical reactivity, mechanical properties, toxicity, and other properties.
Solder ball and method for producing same
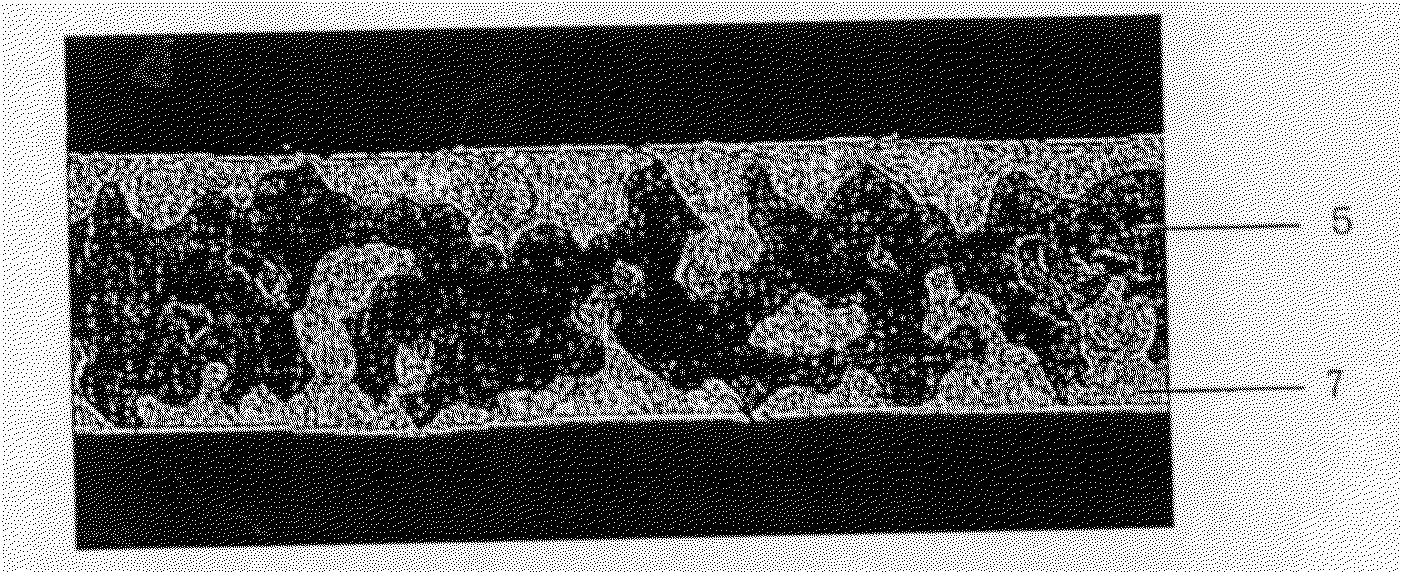
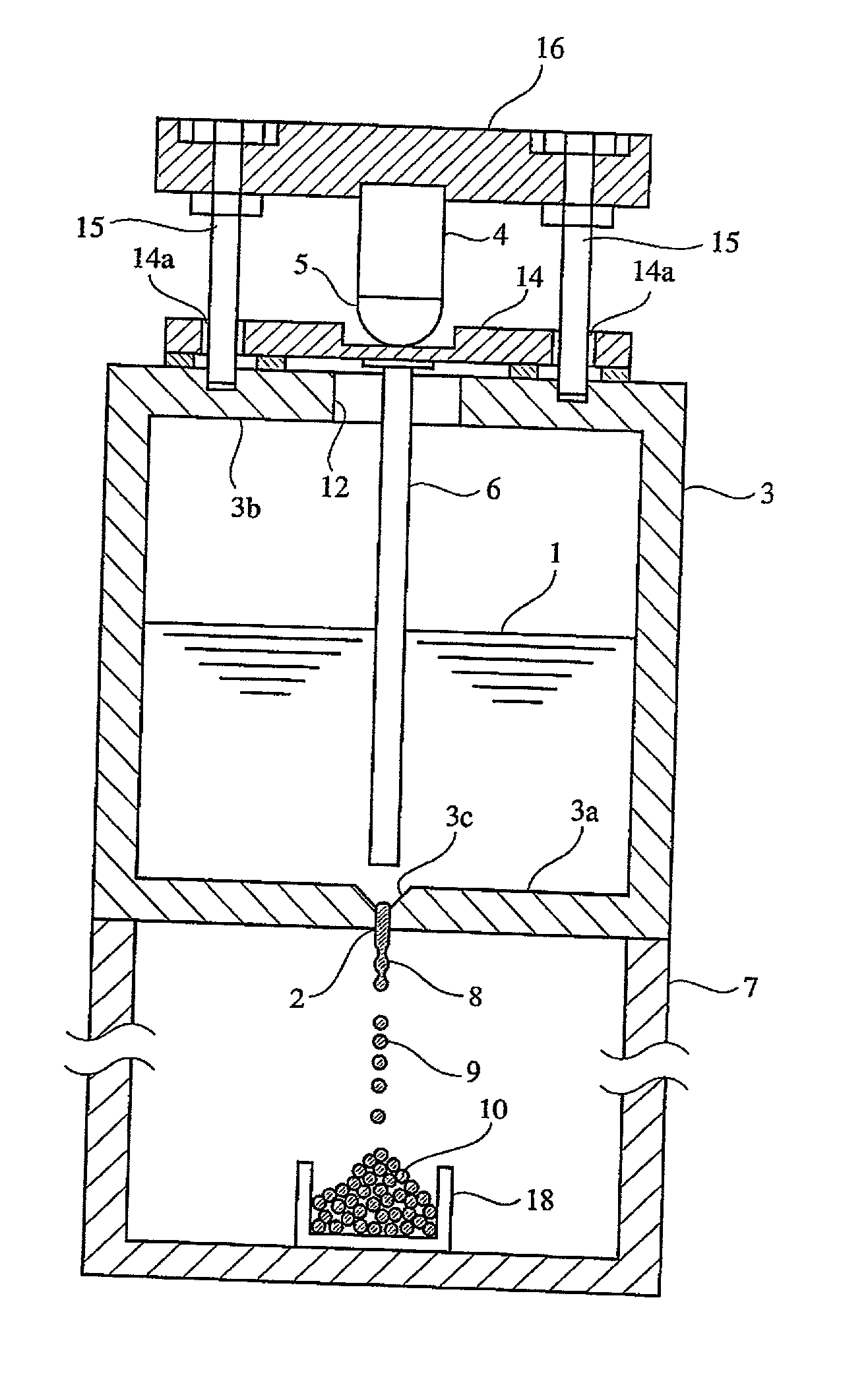
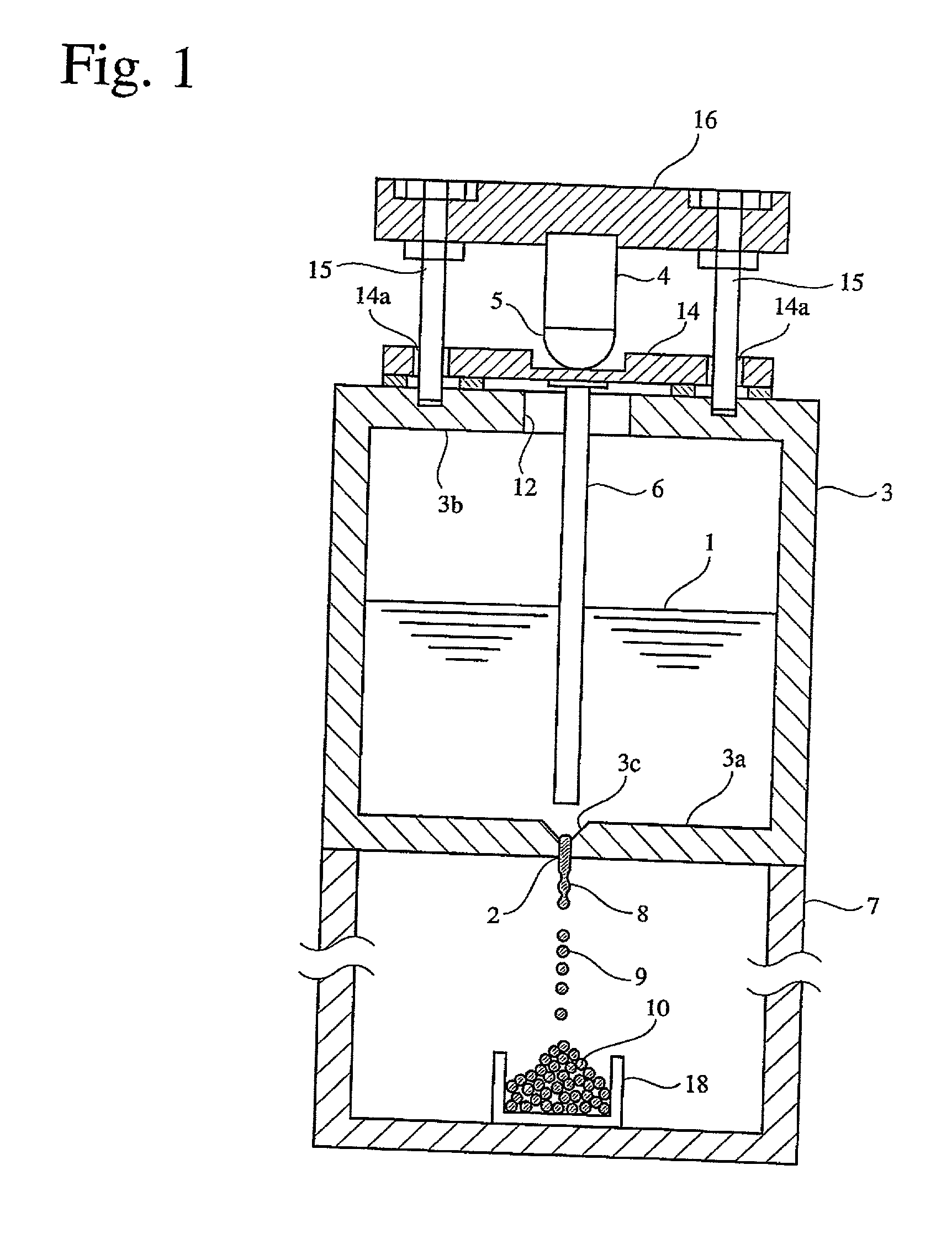
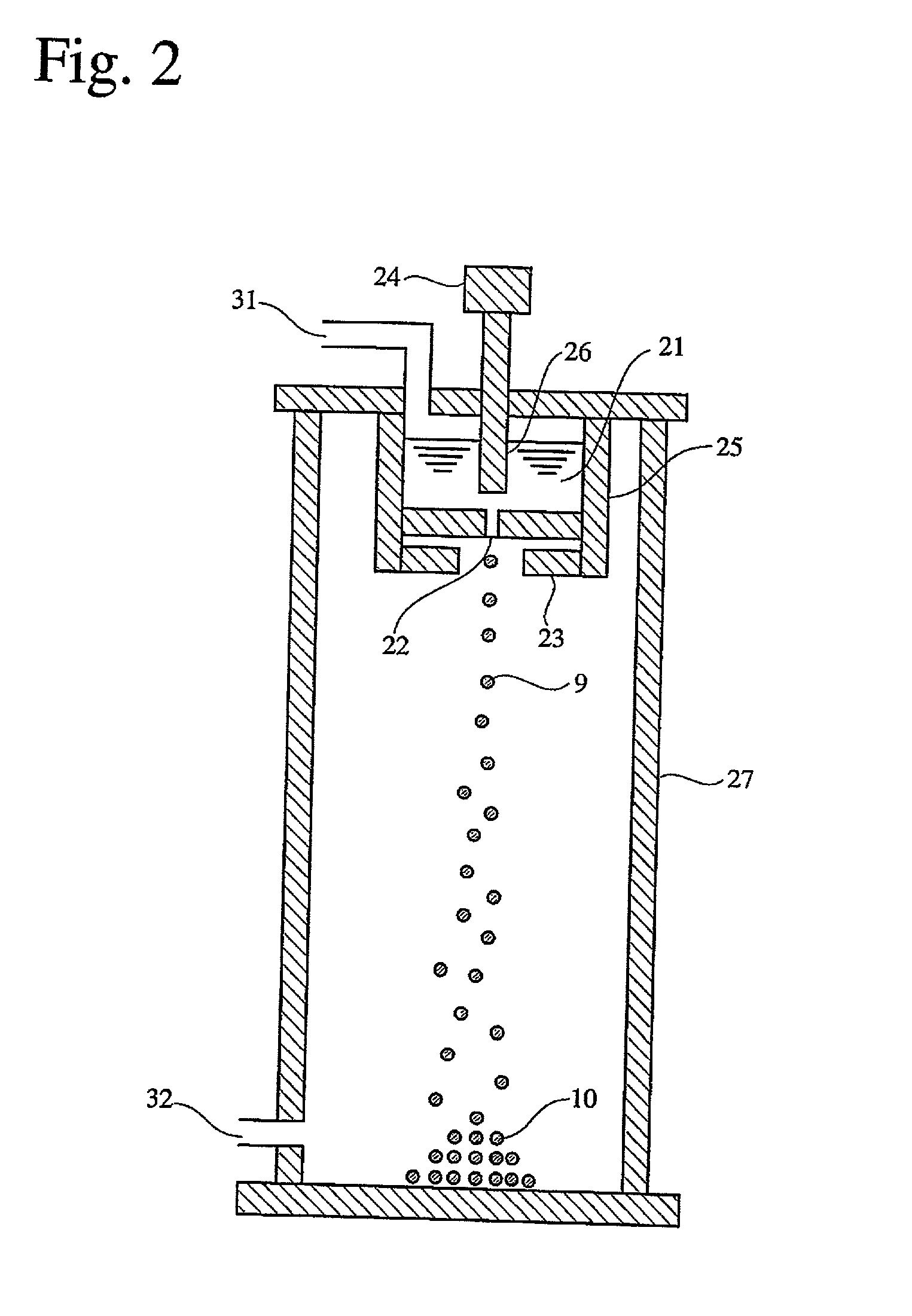
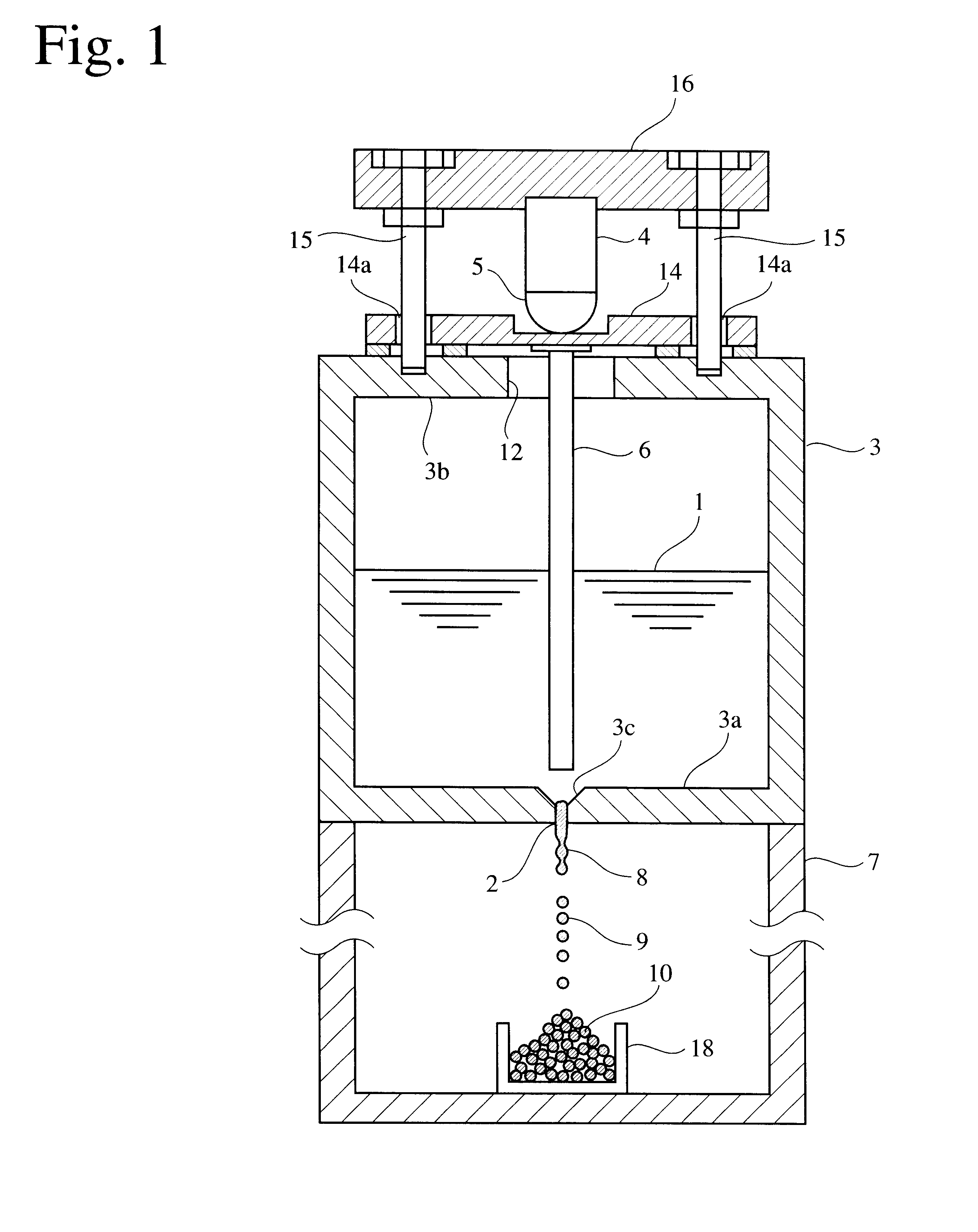
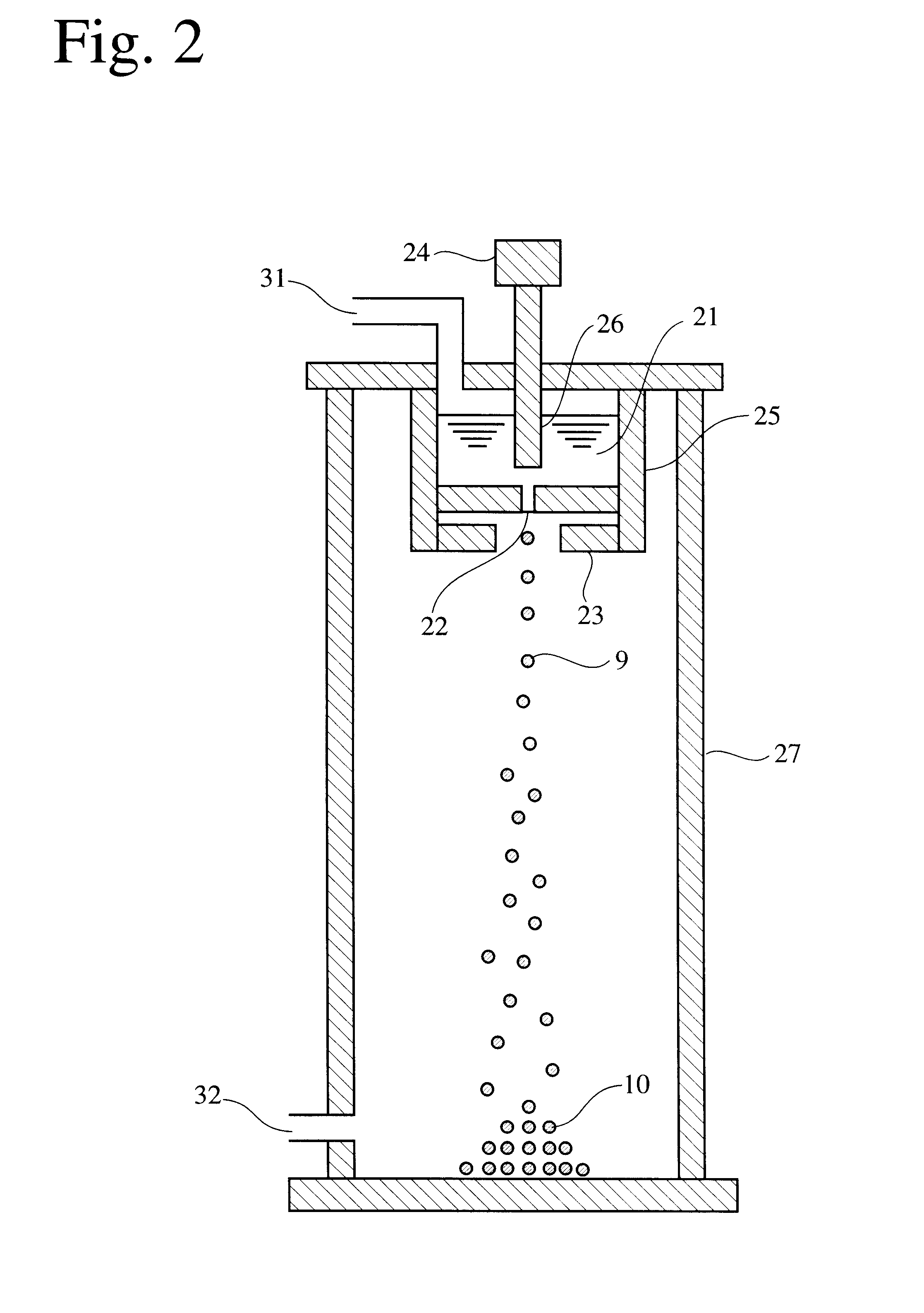
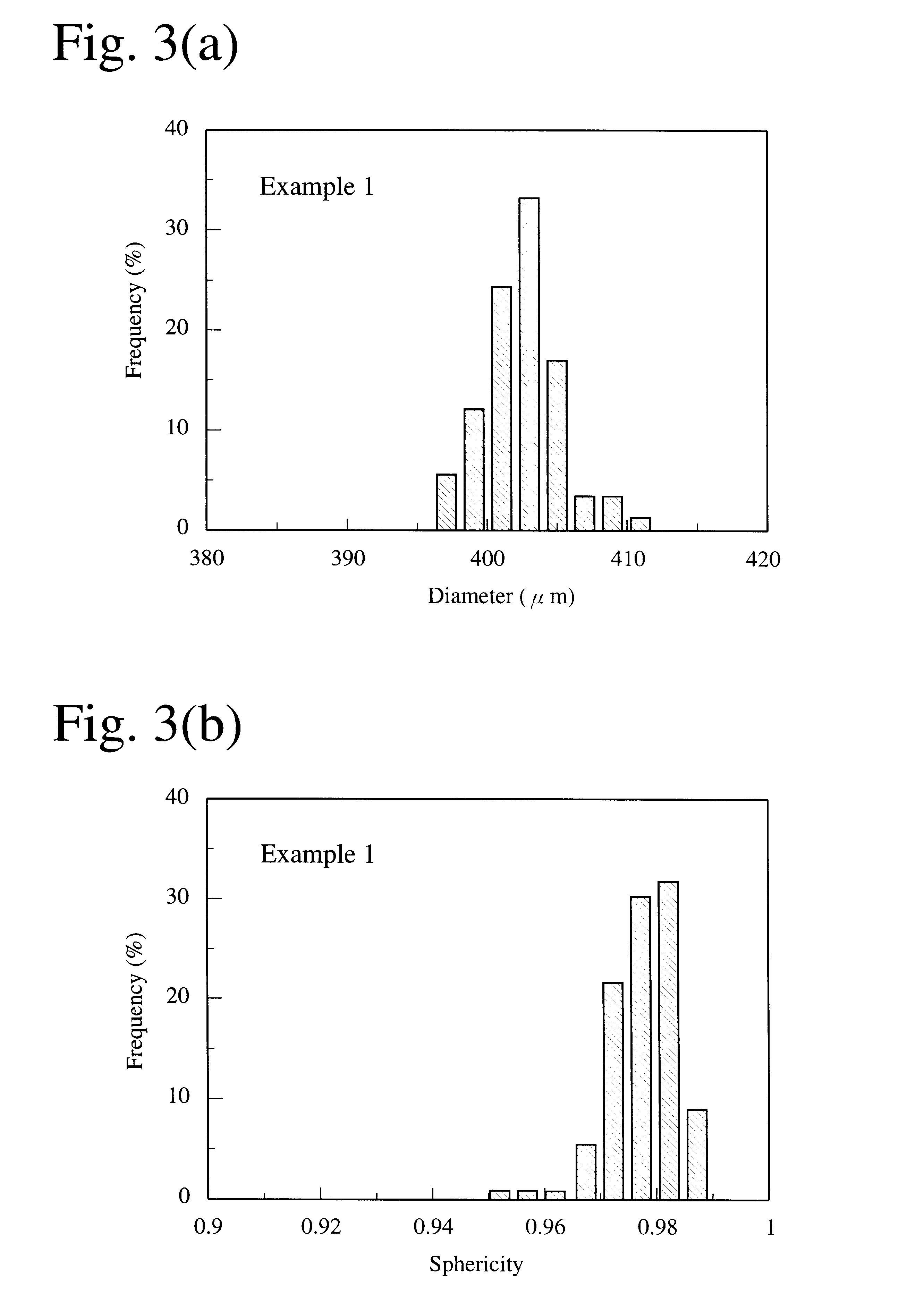
InactiveUS20020051728A1High degree of sphericityNarrow dimension distributionPrinted circuit assemblingTransportation and packagingCrucibleSolder ball
A solder ball having a diameter of 1.2 mm or less, a dispersion of a diameter distribution of 5% or less and sphericity of 0.95 or more, an area ratio of the maximum dendrite being 80% or less of a cross section including a center of the solder ball, comprises a first additional element of 0.5-8 mass% of Ag and / or 0.1-3 mass % of Cu, and 0.006-10 mass %, in total, of at least one second additional element selected from the group consisting of Bi, Ge, Ni, P, Mn, Au, Pd, Pt, S, In and Sb, the balance being substantially Sn. The solder ball is produced by a uniform droplet-spraying method comprising the steps of vibrating a melt of a solder alloy in a crucible under pressure to force the melt to drop through orifices of the crucible; permitting the melt dropping through the orifices to become spherical droplets in a non-oxidizing gas atmosphere; and rapidly solidifying them.
Owner:DUKSAN HI METAL
Silver-free tin-bismuth-copper leadless solder and preparation method
ActiveCN1927525AGood solder wettabilityImprove antioxidant capacityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaShielding gasIngot
The invention relates to a tin-base leadless solder without silver, and relative production. Wherein, it comprises Bi at 7.5-60% (without 7.5%), Cu at 0.1-3.0%, and the left is tin; and it also can contain Zn, Ni, P, Ge, Ga, In, Al, La, Ce, Sb, Cr, Fe, Mn, or Co while the total amount of micro alloy element is not higher than 1.0%. And the production comprises that in protective gas or vacuum, smelting middle alloy Sn-Cu10; then smelting into leadless solder alloy ingot which can be used as solder directly or be made into bar band, wire plate or powder. The inventive solder has low cost while its fusion point can be controlled between 140 and 230Deg. C. And it has strong anti-oxidization and anti-corrosion properties.
Owner:BEIJING COMPO ADVANCED TECH
Lead free solder alloy and its preparation method
InactiveCN1570166ARight melting pointLow costWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMaterials scienceTin
The invention relates to a lead-free solder alloy for welding the electronic elements and its manufacturing method. The lead-free solder alloy is characterized in that the main components are Sn, Ag, Cu, and Ni, and In, Bi, Pd, P, Ge, Ga, Se, Te, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Tm are added selectively. The preparation method is characterized by taking Sn, Ag, Cu, Ni and the additional elements in proportion and smelting them at the temperature of 1300 C. to 1500 C. to obtain the intermediate alloy by using water glass covering process; melting the residual Sn and the intermediate alloy at the temperature of 300 C. to 350 C. by using water glass covering process, and casting the molten materials into alloy pig and soldering tin rod at the temperature of between 250 C. and 350 C.. The lead-free solder alloy provided by the invention can be used for welding the Ag and Pd noble metal electronic element.
Owner:邓和升
Metal seal packaging for organic light emitting diode device
InactiveUS7202602B2Suppress permeation of moistureImprove life performanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDesiccantLight-emitting diode
A metal sealed organic light emitting diode device comprising a lid, containing a recessed portion to accommodate large quantity of getter / dessicant, a band of metal stack at the perimeter over which is laid a band of low temperature melting solder alloy, pre-tinned subsequently, and a substrate. The substrate containing organic light emitting diode at the central area with a band of metal stack at the perimeter. The lid and the substrate are placed together in substantial alignment such that the pre-tinned low melting solder band of the lid contacts the metal stack of the substrate and thermally sealed in a controlled atmosphere. Multiples of substrates are sealed with a single lid containing multiplicity of recessed portions with multi-segmented metal stack and pre-tinned solder band to derive a large area device.
Owner:ORGANIC LIGHTING TECH
Lead-free solder alloy
InactiveUS6319461B1Low melting pointImprove wettabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCeramicBonding strength
A lead-free solder alloy substantially contains Sn and Ti, and has a temperature of a liquidus line of not greater than 400° C. The lead-free solder alloy contains no toxic lead and has sufficient bonding strength to oxide materials such as glass and ceramics.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Modification of pb-free solder alloy compositions to improve interlayer dielectric delamination in silicon devices and electromigration resistance in solder joints
InactiveUS20090197114A1Good mechanical integrityImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesPrinted circuit manufactureDielectricSilicon
A solder joint comprising a solder capture pad on a substrate having a circuit; and a lead free solder selected from the group comprising Sn—Ag—Cu solder and Sn—Ag solder adhered to the solder capture pad; the solder selected from the group comprising between 0.1 to 2.0% by weight Sb or Bi, and 0.5 to 3.0% Ag. Formation of voids at an interface between the solder and the solder capture pad is suppressed, by including Zn. Interlayer dielectric delamination is suppressed, and electromigration characteristics are greatly improved. Methods for forming solder joints using the solders.
Owner:SHIH YUAN +5
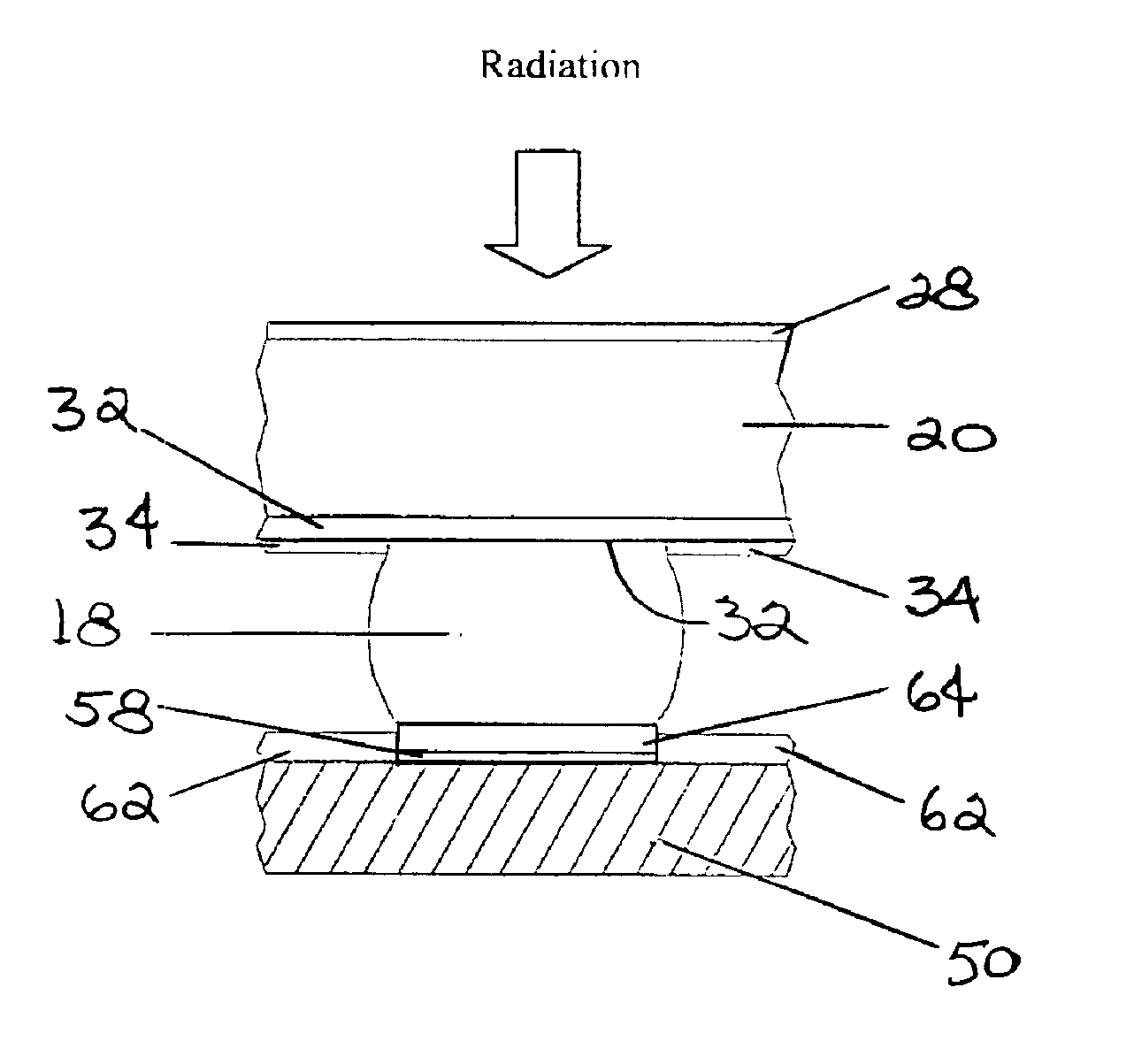
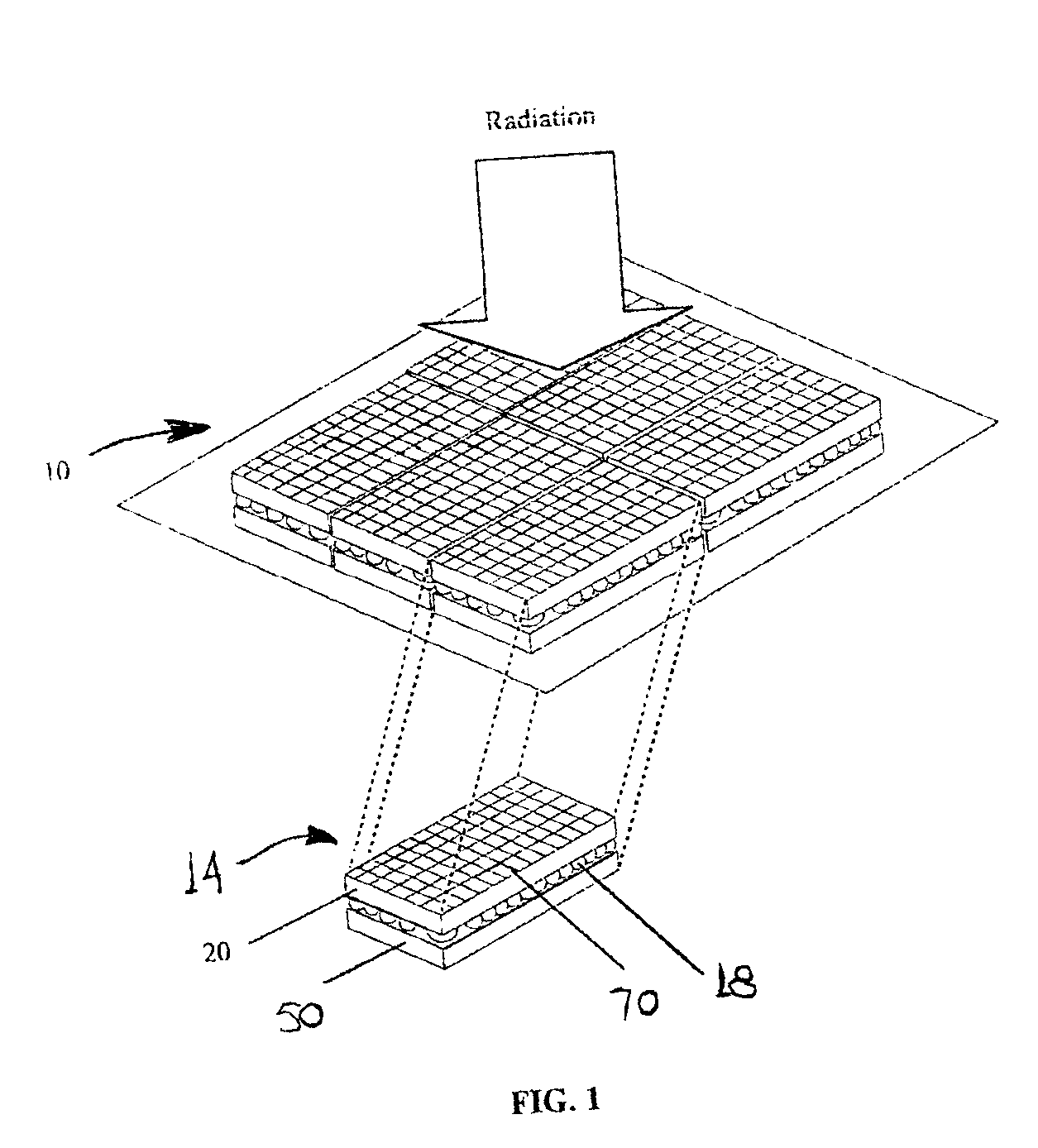
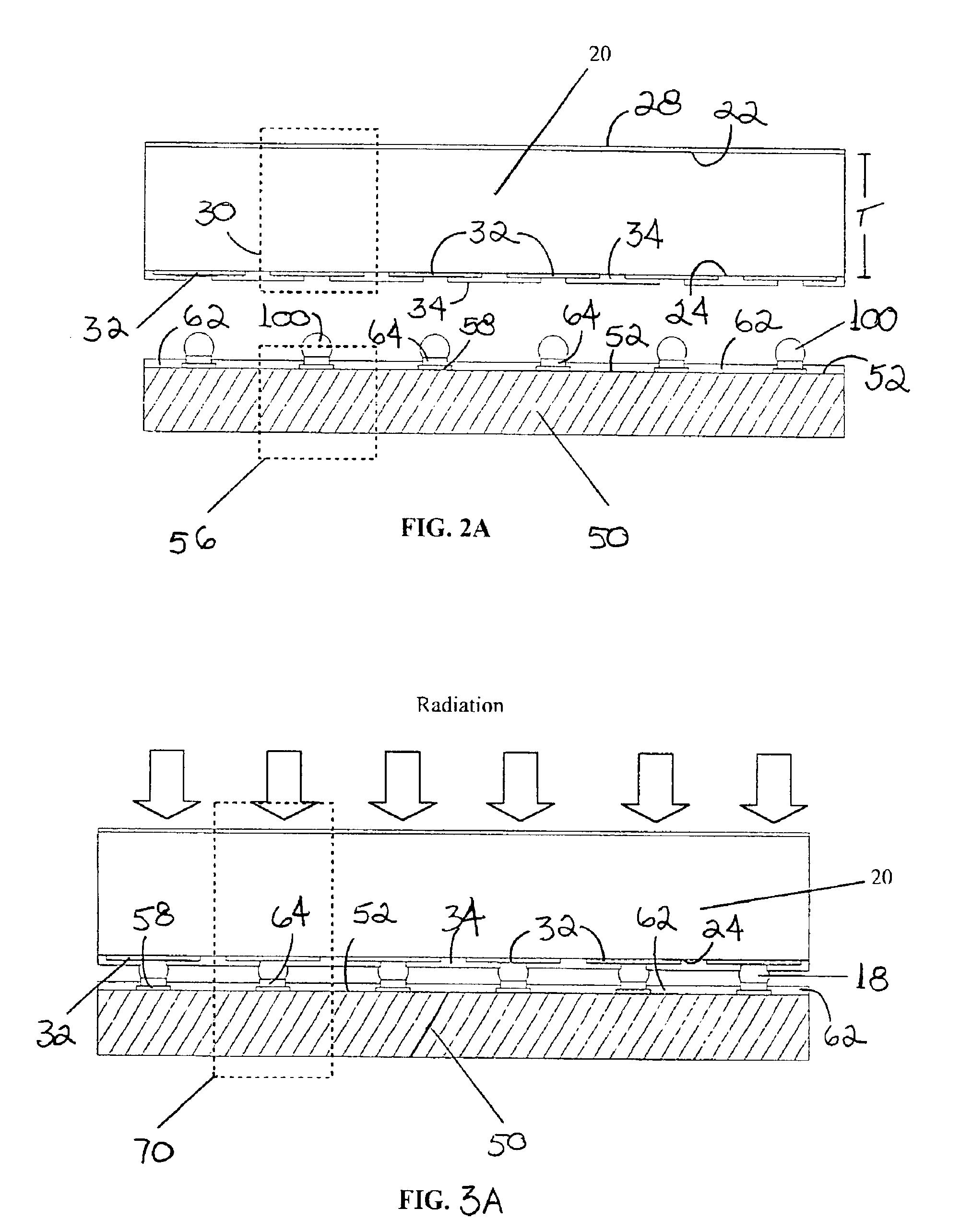
Low temperature, bump-bonded radiation imaging device
InactiveUS6933505B2Reliable and high yieldIncrease productionSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOSSoft x ray
An x-ray and gamma-ray radiant energy imaging device is disclosed having a temperature sensitive semiconductor detector substrate bump-bonded to a semiconductor CMOS readout substrate. The temperature sensitive, semiconductor detector substrate utilizes Tellurium compound materials, such as CdTe and CdZnTe. The bump bonds are formed of a low-temperature, lead-free binary solder alloy having a melting point between about 100° C. and about 180° C. Also described is a process for forming solder bumps utilizing the low-temperature, lead-free binary solder alloy, to prevent damage to temperature sensitive and potentially brittle detector substrate when assembling the imaging device.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
Bonding Material for Semiconductor Devices
ActiveUS20130134591A1Improve reliabilityFew voidPorous dielectricsLayered productsMetallurgyInternal bond
A semiconductor device is provided which has internal bonds which do not melt at the time of mounting on a substrate. A bonding material is used for internal bonding of the semiconductor device. The bonding material is obtained by filling the pores of a porous metal body having a mesh-like structure and covering the surface thereof with Sn or an Sn-based solder alloy.
Owner:SENJU METAL IND CO LTD
Solder stripping agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101962776AReduce pollutionSolution to short lifeConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalNitric oxideTin
The invention discloses a solder stripping agent, which is prepared from the following components: 500 to 650g / L of 70 percent nitric acid, 50 to 70g / L of hydrochloric acid, 4.3 to 8.6g / L of ferric nitrate or 2.9 to 5.8g / L of ferric trichloride or 4.8 to 9.7g / L of ferric chloride hexahydrate, 0.5 to 25g / L of organic acid complexing agent, 1 to 50g / L of water-soluble organic amine, 1 to 10g / L of organic corrosion inhibitor for copper, 1 to 2g / L of stabilizing agent, 1 to 5g / L of surfactant, and 0.1 to 1g / L of small molecular alcohol. The solder stripping agent can quickly strip solder or solder alloy layers thoroughly, basically cannot generate or generates little salt mist containing nitric oxides in the stripping process, and has the advantages of small silt amount, long service life of stripping solution, no strong corrosion on copper at a bottom layer, bright substrate and the like.
Owner:济南德锡科技有限公司
Composite solder alloy preform
ActiveUS20110220704A1High remelting temperatureSolid-state devicesWelding/cutting media/materialsMelting temperatureMetal
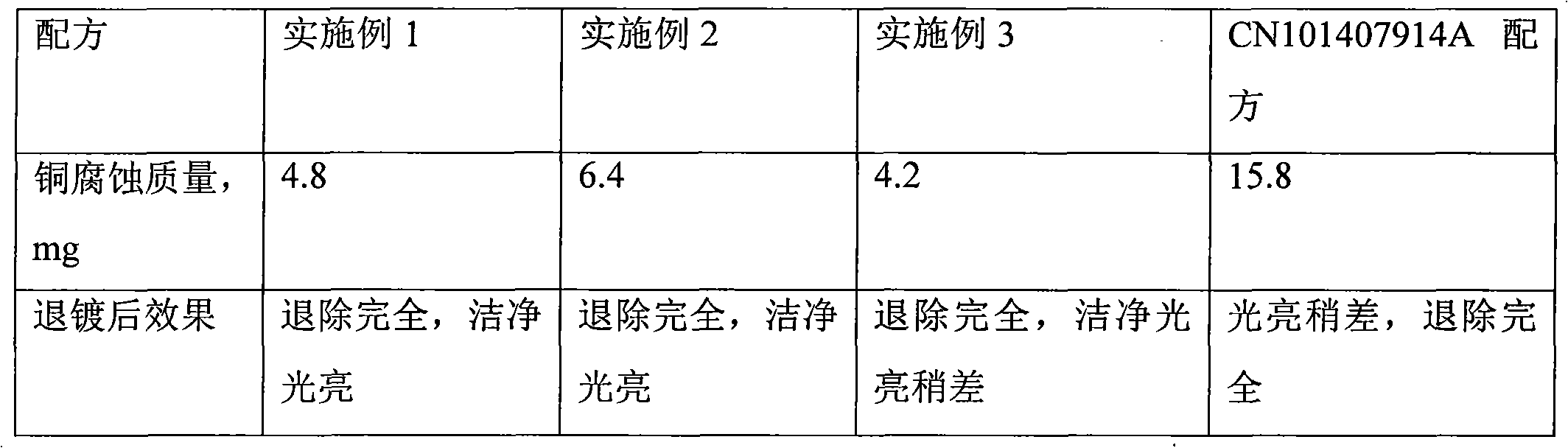
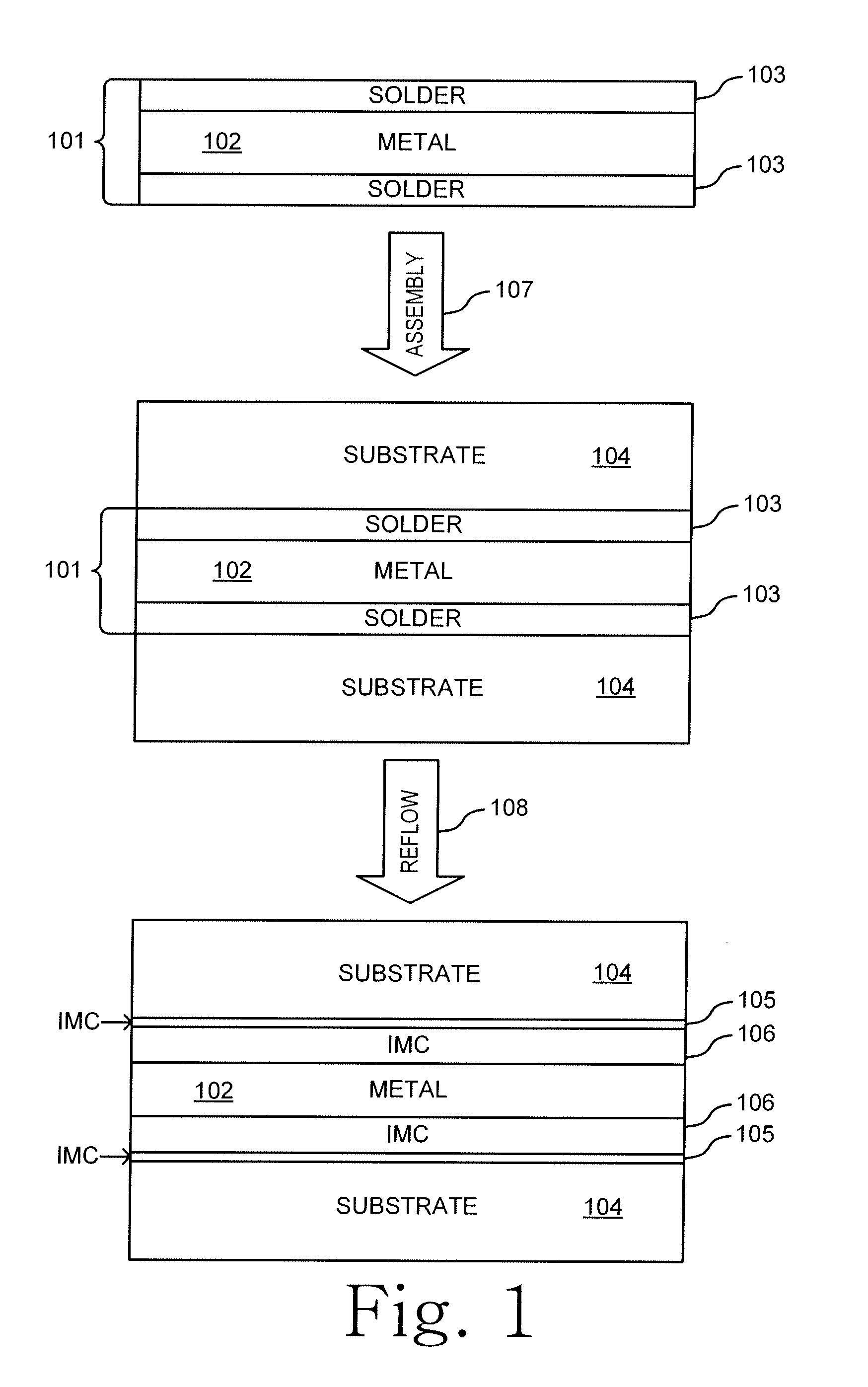
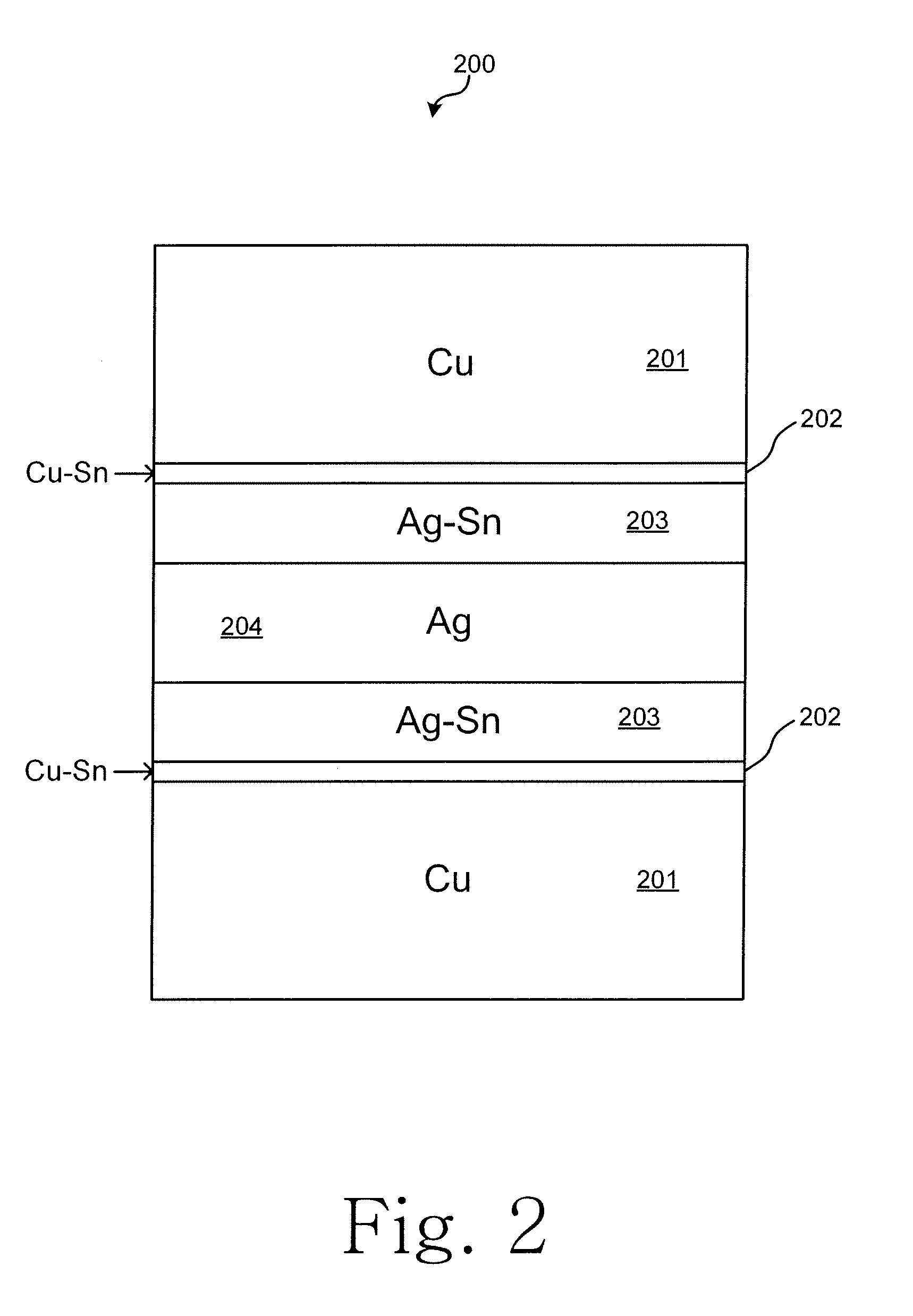
Various embodiments of the invention provide laminate composite preform foils for high-temperature Pb-free soldering applications. The laminate composite preform foil is composed of a high-melting, ductile metal or alloy core layer and a low-melting solder coating layer at either side of the core layer. During soldering, the core metal, liquid solder layer, and substrate metals react and consume the low-melting solder phase to form high-melting intermetallic compound phases (IMCs). The resultant solder joint is composed of a ductile core layer sandwiched by the IMCs layers at substrate sides. The joint has a much higher remelt temperature than the original melting temperature of the initial solder alloy coating, allowing subsequent mounting of packaged devices.
Owner:INDIUM CORPORATION
Solder ball and method for producing same
InactiveUS6517602B2High degree of sphericityNarrow distributionPrinted circuit assemblingTransportation and packagingCrucibleSolder ball
A solder ball having a diameter of 1.2 mm or less, a dispersion of a diameter distribution of 5% or less and sphericity of 0.95 or more, an area ratio of the maximum dendrite being 80% or less of a cross section including a center of the solder ball, comprises a first additional element of 0.5-8 mass % of Ag and / or 0.1-3 mass % of Cu, and 0.006-10 mass %, in total, of at least one second additional element selected from the group consisting of Bi, Ge, Ni, P, Mn, Au, Pd, Pt, S, In and Sb, the balance being substantially Sn. The solder ball is produced by a uniform droplet-spraying method comprising the steps of vibrating a melt of a solder alloy in a crucible under pressure to force the melt to drop through orifices of the crucible; permitting the melt dropping through the orifices to become spherical droplets in a non-oxidizing gas atmosphere; and rapidly solidifying them.
Owner:DUKSAN HI METAL
Glass fixture-joined glass article and joint structure using this
ActiveUS20050112291A1Reduced strengthReduce crackingLiquid surface applicatorsAntenna connectorsSilver pasteFrit
The present invention is intended to provide a glass article with a metal member joined thereto in which an electroconductive coating film is formed on at least a part of the surface of the glass article by baking a silver paste that includes Ag particles and a glass frit, a joining plane of the metal member is fixed onto the electroconductive coating film with a lead-free solder alloy containing Sn as a main component, and the lead-free solder alloy contains at least 1.5 mass % of Ag, which prevents the appearance of the electroconductive coating film and the bonding strength from degrading. Furthermore, in the present invention, when using a metal member having at least two joining planes, the total area of the joining planes is set within a range of 37 mm2 to 50 mm2, which allows high bonding strength between the glass article and metal member to be maintained while using the lead-free solder alloy. Moreover, in the present invention, the volume of the lead-free solder alloy to be provided on each joining plane is set to be 1.0 to 2.0 times the product of the area of the joining plane concerned and the thickness of the lead-free solder alloy, which prevents cracks from occurring in the glass article.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
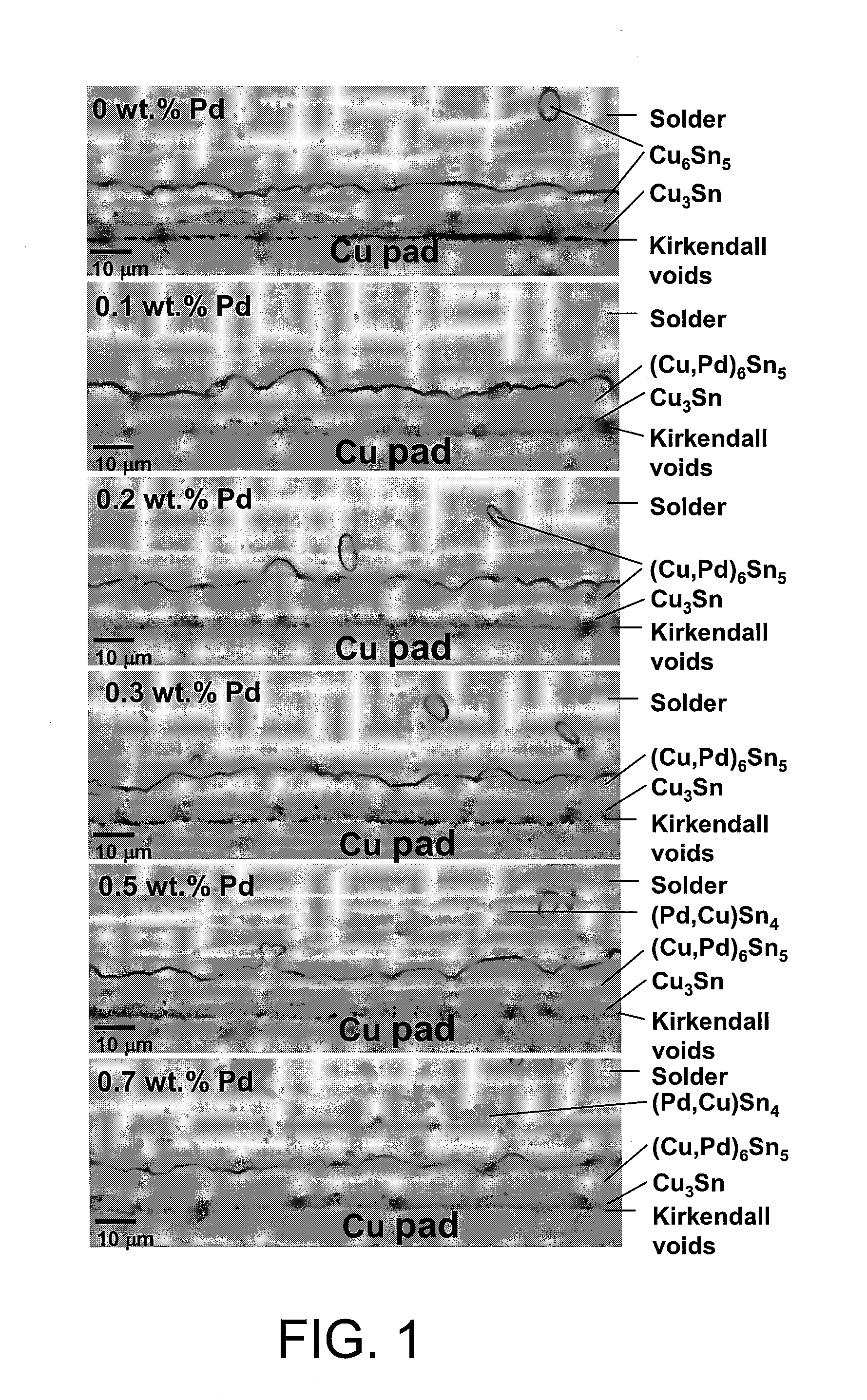
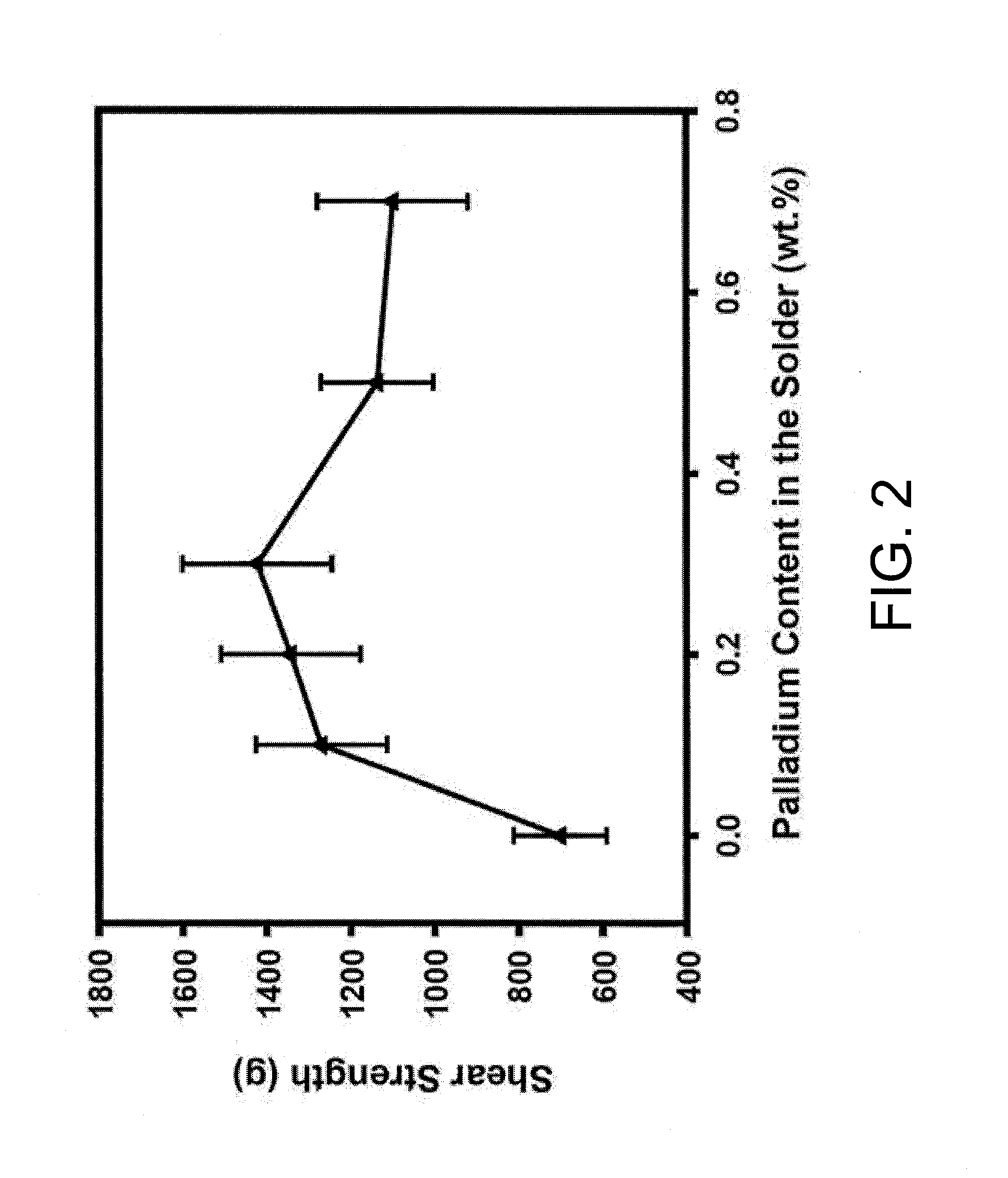
Method for suppressing kirkendall voids formation at the interface between solder and copper pad
InactiveUS20130153646A1QuantityImprove propertiesWelding/cutting media/materialsPrinted circuitsSurface finishMechanical reliability
The embodiment of the present invention relates to a method for suppressing Kirkendall voids formation in a solder joint. A solder alloy doped with 0.1˜0.7 weight percent (wt. %) of palladium (Pd) is utilized. Before soldering, the solder alloy is disposed on a copper (Cu) pad, possibly treated with a surface finish. Subsequently, the solder alloy is joined with the Cu pad, so as to form the solder joint with a Cu / Cu3Sn / (Cu,Pd)6Sn5 / solder structure. The formation of Kirkendall voids at the Cu / Cu3Sn interface is greatly suppressed in the presence of Pd in the solder. As the amount of Pd doped is minimal, the properties and the processing conditions for soldering are not changed to a large extent, and the mechanical reliability of the solder joint is significantly improved. Therefore, the present invention is suitable for the microelectronic packaging applications.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Solder alloy
Owner:爱尔发加热有限公司
Method and equipment for breaking down and reclaiming electronic components and solder of discarded circuit board
InactiveCN1600458AReduce damage rateHigh split rateSolid waste disposalPrinted circuitsRecovery methodElectronic component
Owner:张杰
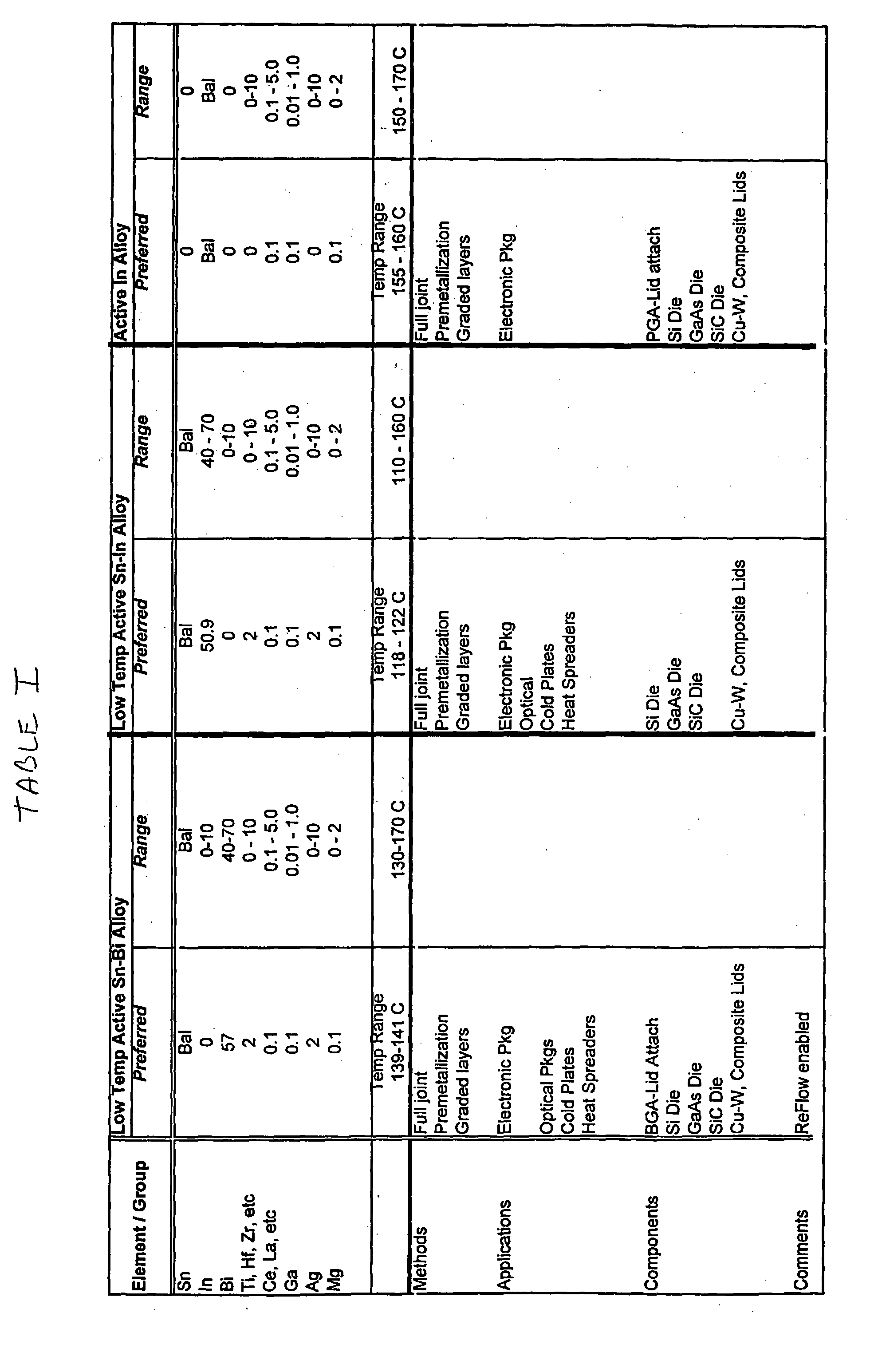
Electronic Package Formed Using Low-Temperature Active Solder Including Indium, Bismuth, and/or Cadmium
InactiveUS20070228109A1Increase concentrationHigh-strength, high-thermal conductivity jointsCooking-vessel materialsExhaust apparatusIndiumNiobium
An active solder alloy, an electronic device package including the active solder alloy bonding an electronic device to a substrate, and a method of forming high-strength joints by soldering using the solder alloy. The alloy contains up to about 10% by weight of an element or a mixture of elements selected from the group consisting of titanium, zirconium, hafnium, vanadium, niobium, or tantalum; between about 0.1 and 5% by weight of an element or a mixture of elements selected from the group of the lanthanides (rare earths); between about 0.01 and 1% by weight of gallium up to about 10% by weight of silver; up to about 2% by weight of magnesium; and a remainder consisting of tin, bismuth, indium, cadmium, or a mixture of two or more of these elements. The alloy enables low-temperature (less than about 180° C.) soldering within relatively narrow melting ranges (less than about 10° C.).
Owner:S BOND TECH
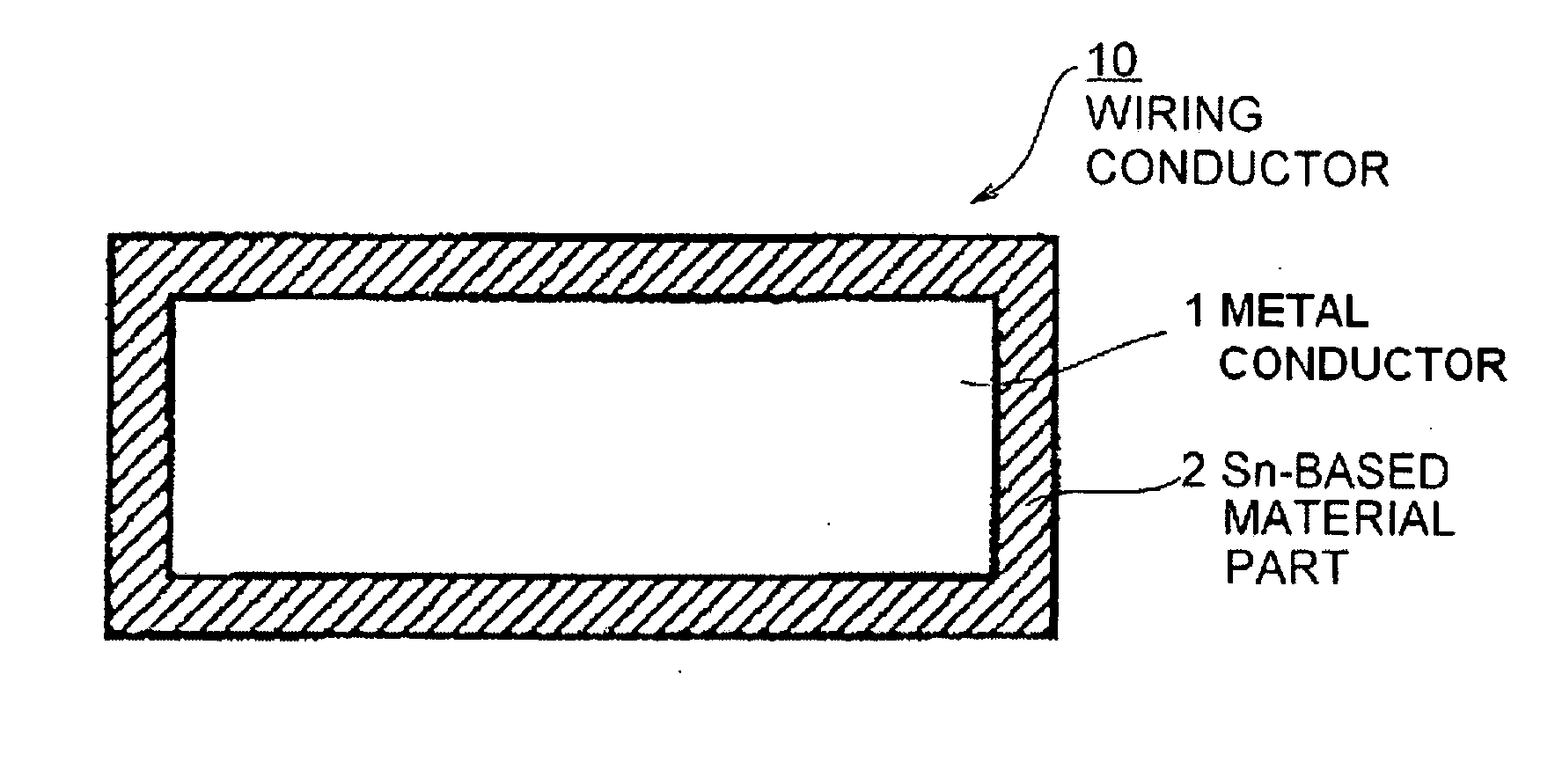
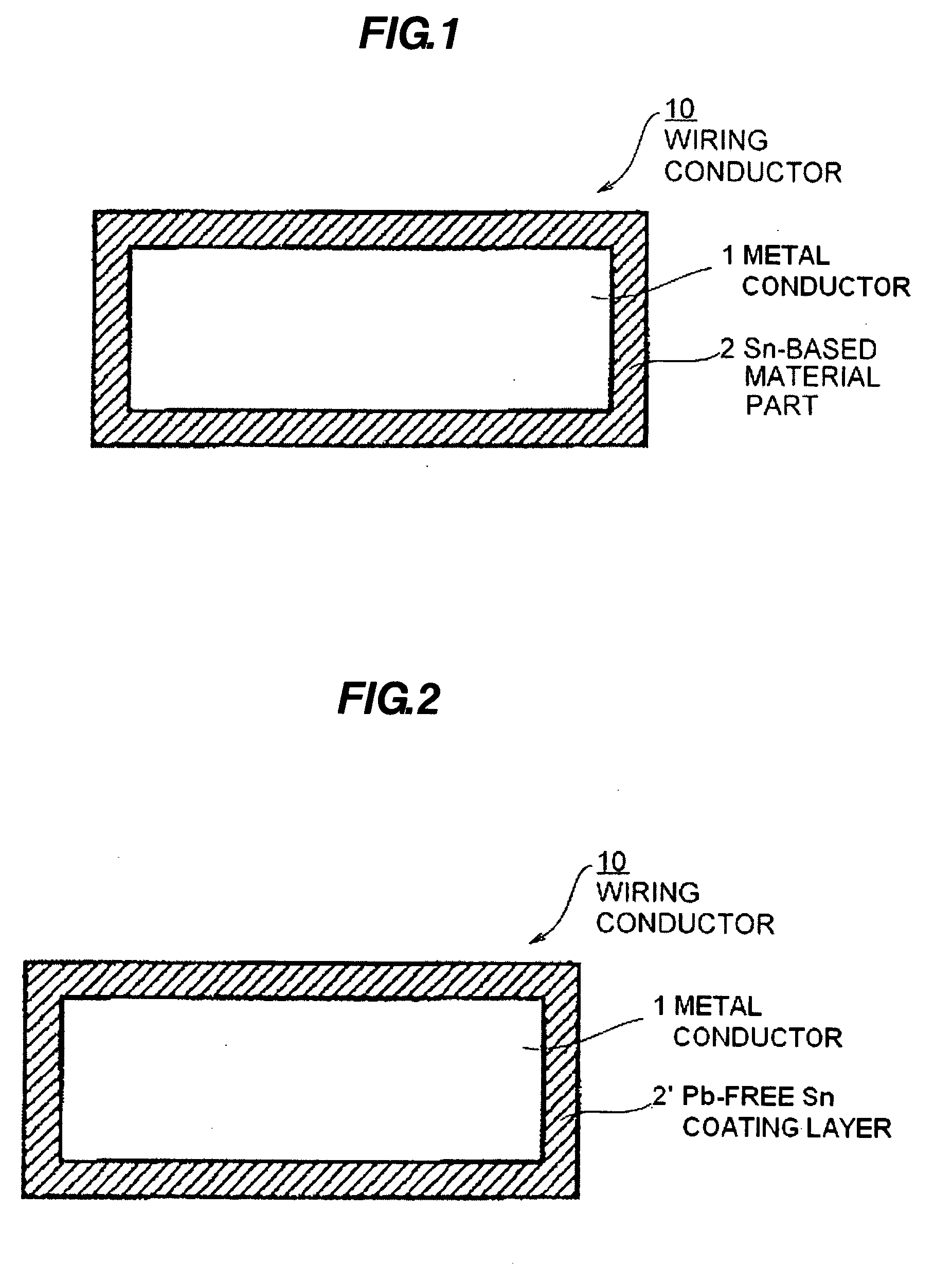
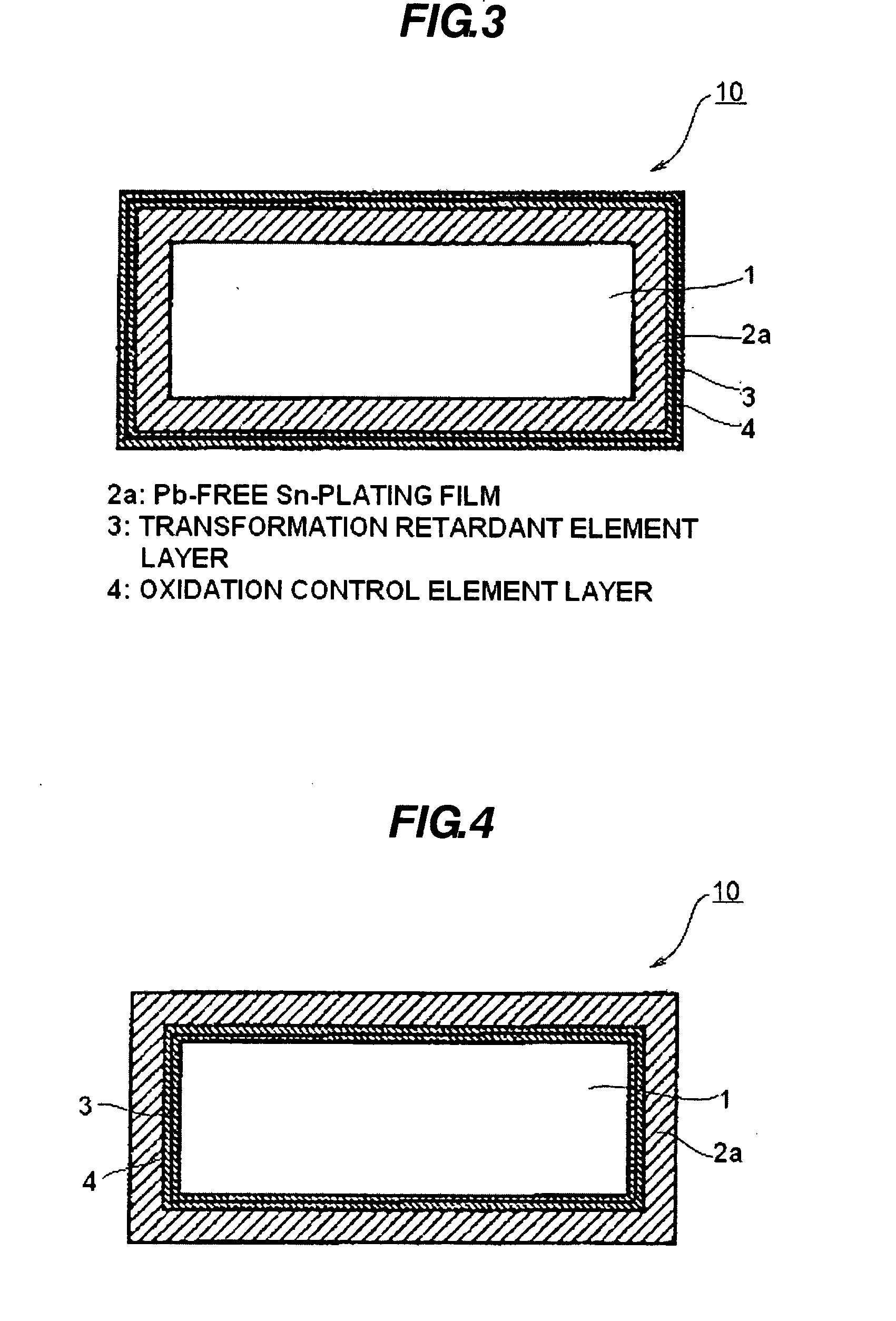
Pb-free sn-based material, wiring conductor, terminal connecting assembly, and pb-free solder alloy
InactiveCN101096730AImprove connection reliabilityReduce stressPrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit manufactureElectrical conductorBase metal
A Pb-free Sn-based material part of a wiring conductor is provided at least at a part of a surface the wiring conductor, and the Sn-based material part includes a base metal doped with a transformation retardant element and an oxidation control element. The transformation retardant element is at least one element selected from a group consisted of Sb, Bi, Cd, In, Ag, Au, Ni, Ti, Zr, and Hf. The oxidation control element is at least one element selected from a group consisted of Ge, P, Zn, Kr, Cr, Mn, Na, V, Si, Al, Li, Mg and Ca. The wiring conductor is reflow processed, such that at least one of the Sn, the transformation retardant element and the oxidation control element is diffused to form an alloy.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
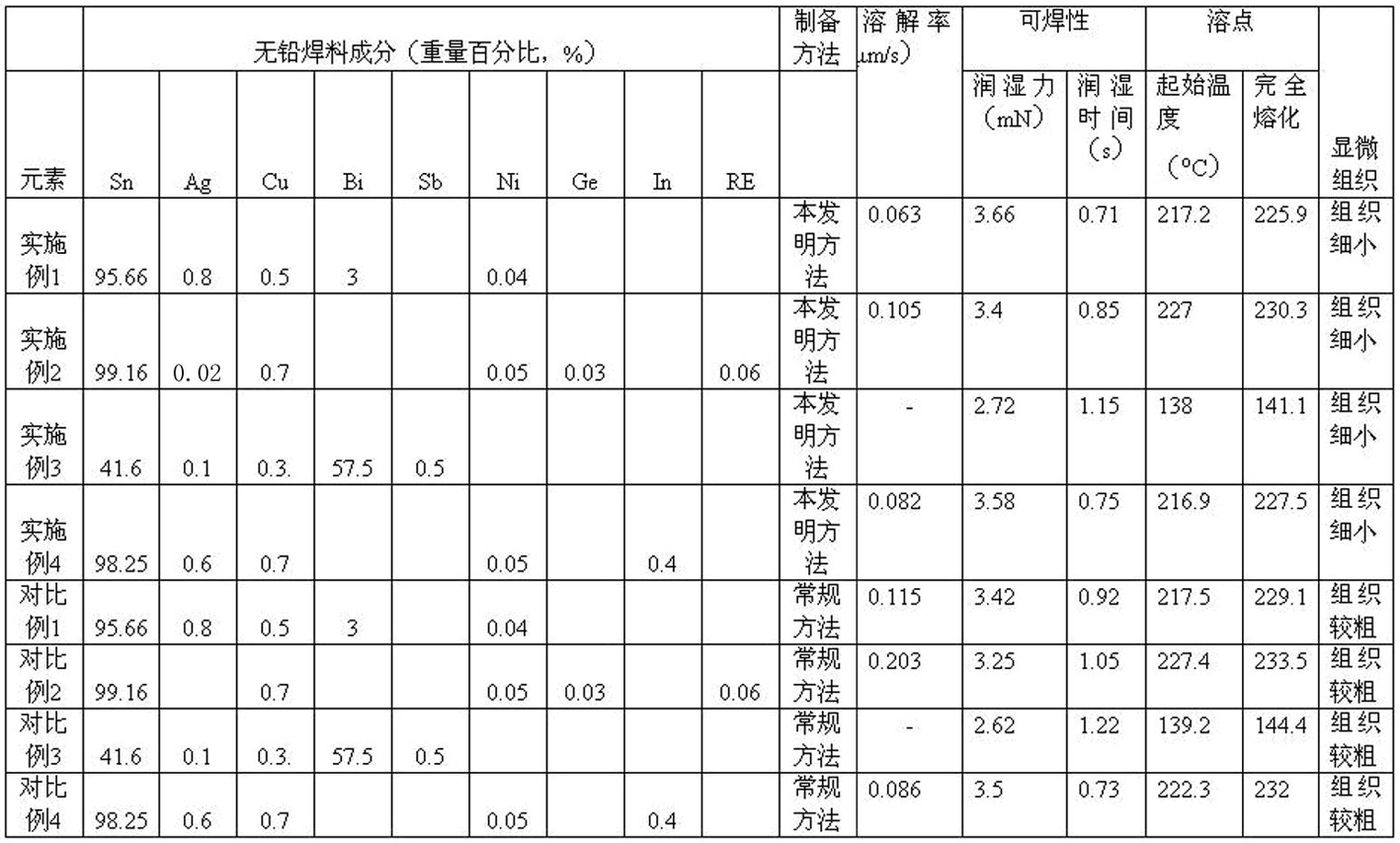
Low-silver lead-free solder alloy and preparation method and device thereof
InactiveCN102029479AImprove unevennessNo segregationWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaElectronic packagingMetal
The invention relates to a low-silver lead-free solder alloy and a preparation method and a used device thereof. The low-silver lead-free solder alloy consists of the following components in percentage by weight: more than 0 and less than or equal to 1 percent of Ag, 0.2 to 1 percent of Cu, 0 to 59 percent of Bi, 0 to 0.07 percent of Ni, 0 to 0.7 percent of Sb, 0 to 0.06 percent of Ge, 0 to 1 percent of Ga, 0 to 0.1 percent of RE and the balance of Sn. The solder prepared by the invention does not contain harmful metal Pb and meets the national requirement of electronic packaging environmental-friendly use; in addition, the quick cooling and vibration combined preparation method is adopted, so that the melting range is effectively reduced, the alloy is quickly solidified, structure non-uniformity is improved, component uniformity and structure refinement are ensured while oxidation is reduced, and a product has the characteristics of fine structure, low copper dissolution rate and high wettability and oxidation resistance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
Electrically conductive compositions comprising non-eutectic solder alloys
Transient liquid phase sintering compositions comprising one or more high melting point metals and one or more low melting temperature alloys are known in the art as useful compositions for creating electrically and / or thermally conductive pathways in electronic applications. The present invention provides transient liquid phase sintering compositions that employ non-eutectic low melting temperature alloys for improved sintering and metal matrix properties.
Owner:ORMET CIRCUITS
Pb-free Sn-based material, wiring conductor, terminal connecting assembly, and Pb-free solder alloy
InactiveUS20070295528A1Suppress oxidationSuppress structureConductive layers on insulating-supportsContact member assembly/disassemblyElectrical conductorMetal
A Pb-free Sn-based material part of a wiring conductor is provided at least at a part of a surface the wiring conductor, and the Sn-based material part includes a base metal doped with a transformation retardant element and an oxidation control element. The transformation retardant element is at least one element selected from a group consisted of Sb, Bi, Cd, In, Ag, Au, Ni, Ti, Zr, and Hf. The oxidation control element is at least one element selected from a group consisted of Ge, P, Zn, Kr, Cr, Mn, Na, V, Si, Al, Li, Mg and Ca. The wiring conductor is reflow processed, such that at least one of the Sn, the transformation retardant element and the oxidation control element is diffused to form an alloy.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE
Solder alloy, solder paste, and electronic circuit board
ActiveUS9221132B2Low costEasy to oxidizePrinted circuit assemblingComponent plug-in assemblagesIndiumTin-silver-copper
A solder alloy is a tin-silver-copper solder alloy containing tin, silver, copper, nickel, antimony, bismuth, and indium, and substantially does not contain germanium, wherein relative to the total amount of the solder alloy, the silver content is more than 0.05 mass % and less than 0.2 mass %, and the antimony content is 0.01 mass % or more and less than 2.5 mass %.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC
Solder alloy, use of the solder alloy and method for processing, particularly repairing, workpieces, particularly gas turbine components
InactiveUS20070175546A1High strengthHigh melting pointWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRheniumNiobium
A solder alloy and a multi-component soldering system, to the use of the same, and to a method for repairing gas turbine components are described herein. The solder alloy based on nickel includes the following elements: nickel (Ni), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), molybdenum (Mo), aluminum (Al), tantalum (Ta), niobium (Nb), yttrium (Y), hafnium (Hf), palladium (Pd), boron (B) and silicon (Si). The multi-component soldering system includes the solder alloy and additionally at least one additive material. The additive materials include the following elements: nickel (Ni), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), molybdenum (Mo), aluminum (Al), tantalum (Ta), titanium (Ti), rhenium (Re), iron (Fe), niobium (Nb), yttrium (Y), hafnium (Hf), palladium (Pd), carbon (C), zirconium (Zr), boron (B) and silicon (Si). A specific mixing of solder alloy and additive materials produces a multi-component soldering system that may be specifically adapted to the material of the component to be repaired, the mixture ratio of solder alloy and additive materials being freely selectable. The repair method is based on high-temperature diffusion soldering using the solder alloy hereof or the multi-component soldering system hereof.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
Structure, materials, and methods for socketable ball grid
InactiveUS6300164B1Improve fatigue lifeReduce failurePrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufacturePolymer resinAdhesive
A socketable ball grid array structure is disclosed which comprises mechanically rigid (compared to solder alloys) balls coated with noble contact metals joined to the chip carrier terminals by means of a novel electrically conducting adhesive. Because of the nature of the filler that includes conducting particles with a fusible coating and the appropriate selection of the polymer resin used in the adhesive, the balls are attached to the module in a compliant and resilient manner while leaving the majority of the bottom surface of the balls pristine. The array of balls can therefore be plugged into mating sockets in a printed circuit board forming a demountable contact. This facilitates easy removal of the socketable BGA from a board for repair or upgrade purposes as well as allows ease of plugging and unplugging of these BGA's into test and burn-in boards.
Owner:IBM CORP
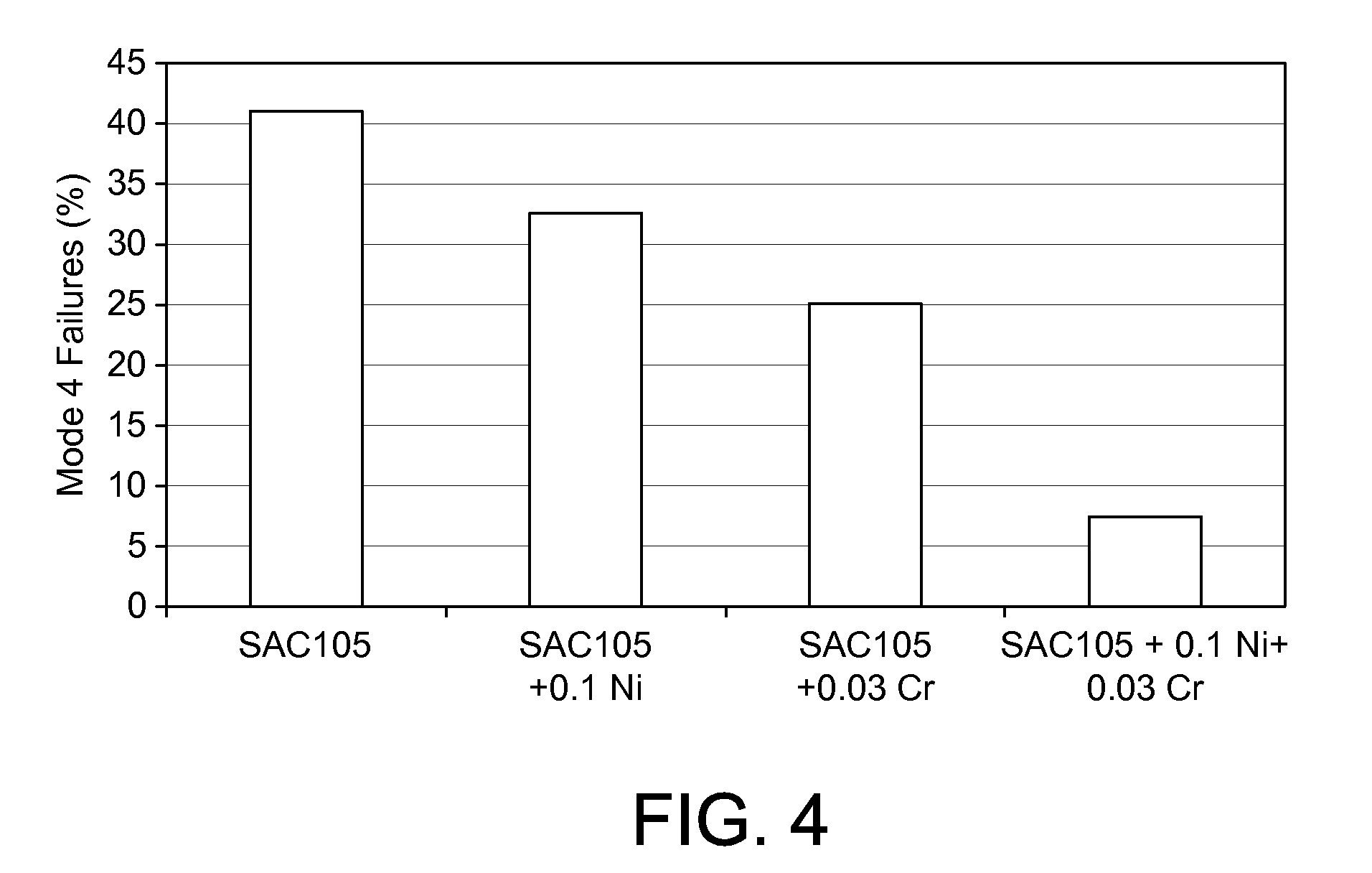
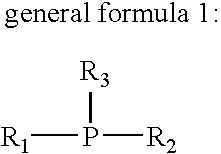
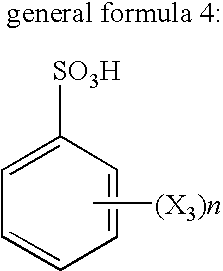
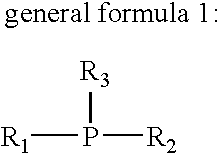
Solder alloy
An alloy suitable for use in a ball grid array or chip scale package comprising from 0.05-1.5 wt. % copper, from 0.1-2 wt. % silver, from 0.005-0.3 wt % nickel, from 0.003-0.3 wt % chromium, from 0-0.1 wt. % phosphorus, from 0-0.1 wt. % germanium, from 0-0.1 wt. % gallium, from 0-0.3 wt. % of one or more rare earth elements, from 0-0.3 wt. % indium, from 0-0.3 wt. % magnesium, from 0-0.3 wt. % calcium, from 0-0.3 wt. % silicon, from 0-0.3 wt. % aluminium, from 0-0.3 wt. % zinc, from 0-2 wt. % bismuth, from 0-1 wt. % antimony, from 0-0.2 wt % manganese, from 0-0.3 wt % cobalt, from 0-0.3 wt % iron, and from 0-0.1 wt % zirconium, and the balance tin, together with unavoidable impurities.
Owner:FRY S METALS INC
Flux for soldering and circuit board
InactiveUS20060147683A1High bonding strengthSuppress DiffuseBlast furnace componentsBlast furnace detailsSolventCopper complex
A flux contains resin having film forming ability, activator, solvent, and at least one complex selected from silver complex and copper complex. The flux is used when soldering is performed onto a circuit having electroless nickel plating or further having gold plating on the electroless nickel plating. Allowing a barrier layer of silver or copper to deposit on the surfaces of lands suppresses the diffusion of nickel into the melted solder alloy during soldering, and also prevents phosphorous concentration. This improves the bonding strength of soldering and suppresses the reduction deposition of silver and / or copper to portions other than circuit patterns.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC
Lead-free solder alloy, solder ball and electronic member, and lead-free solder alloy, solder ball and electronic member for automobile-mounted electronic member
ActiveUS20090304545A1Improve impact resistanceAvoid fracturesPrinted circuit assemblingWelding/cutting media/materialsSolder ballIntermetallic
A lead-free solder alloy exhibiting good performance in impact resistance and vibration resistance. Also provided are a solder ball using such a lead-free solder alloy, and an electronic member having a solder bump using such a lead-free alloy. Specifically, the lead-free solder alloy consists of 1.0 to 2.0% by mass of Ag, 0.3 to 1.0% by mass of Cu, 0.005 to 0.1% by mass of Ni and the balance including Sn and unavoidable impurities. In an Sn—Ag—Cu based solder joint portion on a Cu electrode, a Cu3Sn intermetallic compound layer is formed directly on the Cu electrode, and then a Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound layer is formed thereon. A Cu atomic site in the Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound layer is replaced by Ni having a smaller atomic radius than Cu to thereby reduce strain in the Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound layer, thus enabling impact resistance and vibration resistance to be improved therein.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD +1
Lead free solder paste and application thereof
ActiveCN101232967ADamage causedAvoid short circuitPrinted circuit assemblingWelding/cutting media/materialsDicarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
A solder paste composed of solder alloy powder and flux, the volume expansion rate of which is 0.5% or less when the solder alloy is melted, and the flux contains bisphenol A type epoxy resin and a hardening agent selected from carboxylic anhydrides and dicarboxylic acids agent, the solder paste can be used for high temperature solder applications. In terms of mass%, the solder alloy has the following alloy composition: 70-98 mass% of Bi; 0-0.5% of Ag, Cu, Sb, In, Zn, Ni, Cr, Fe, Mo, P, Ge and One or more elements selected from Ga; the balance is composed of Sn.
Owner:SENJU METAL IND CO LTD +1
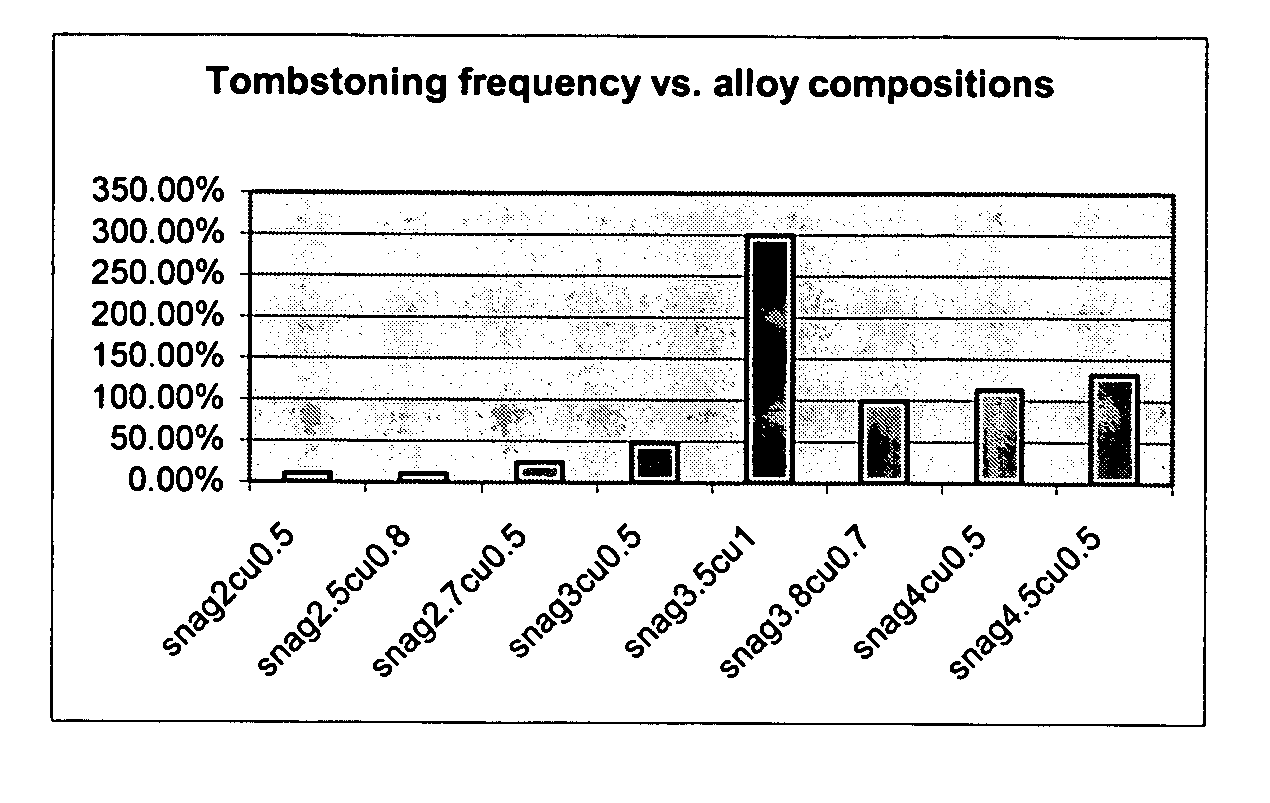
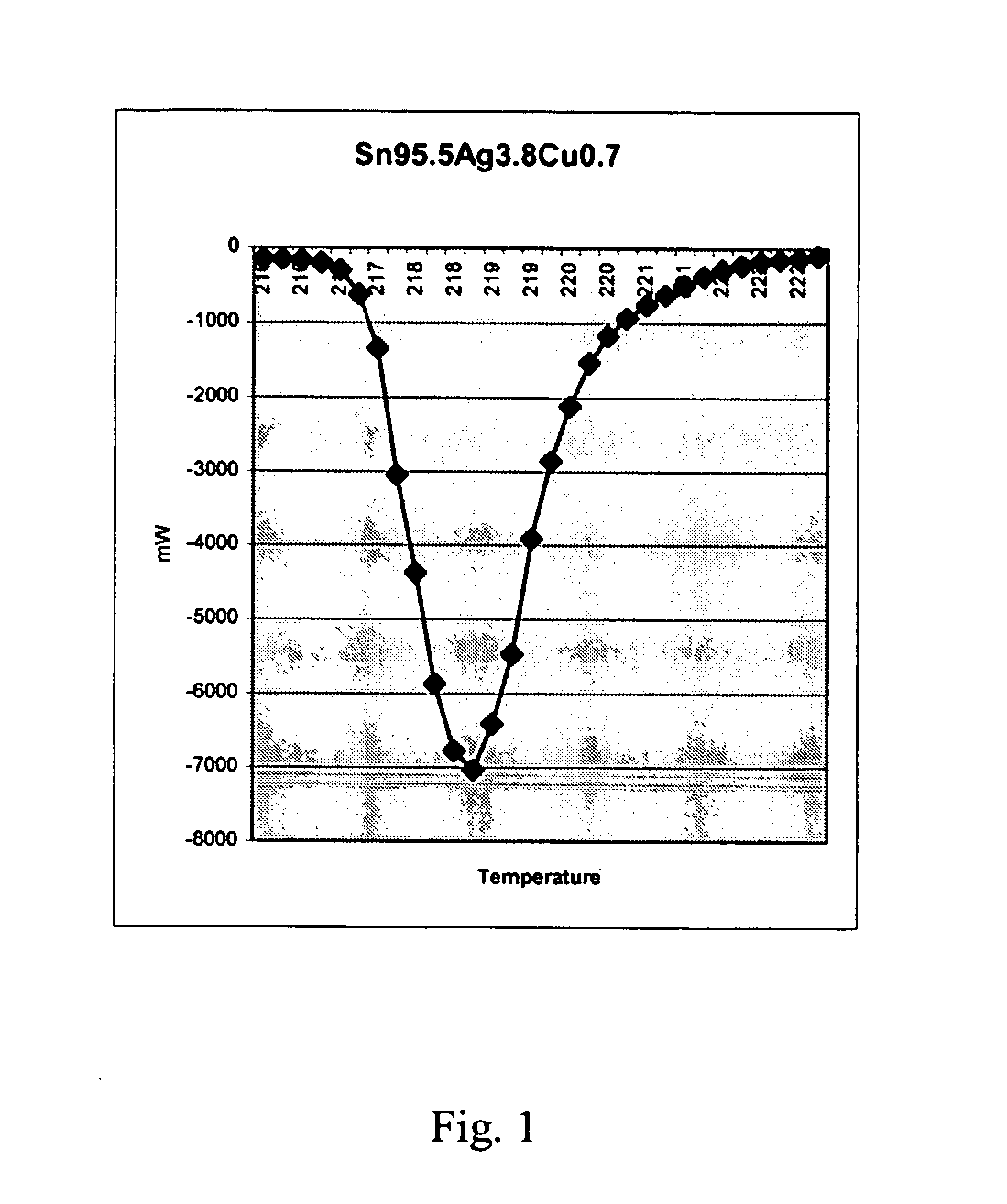
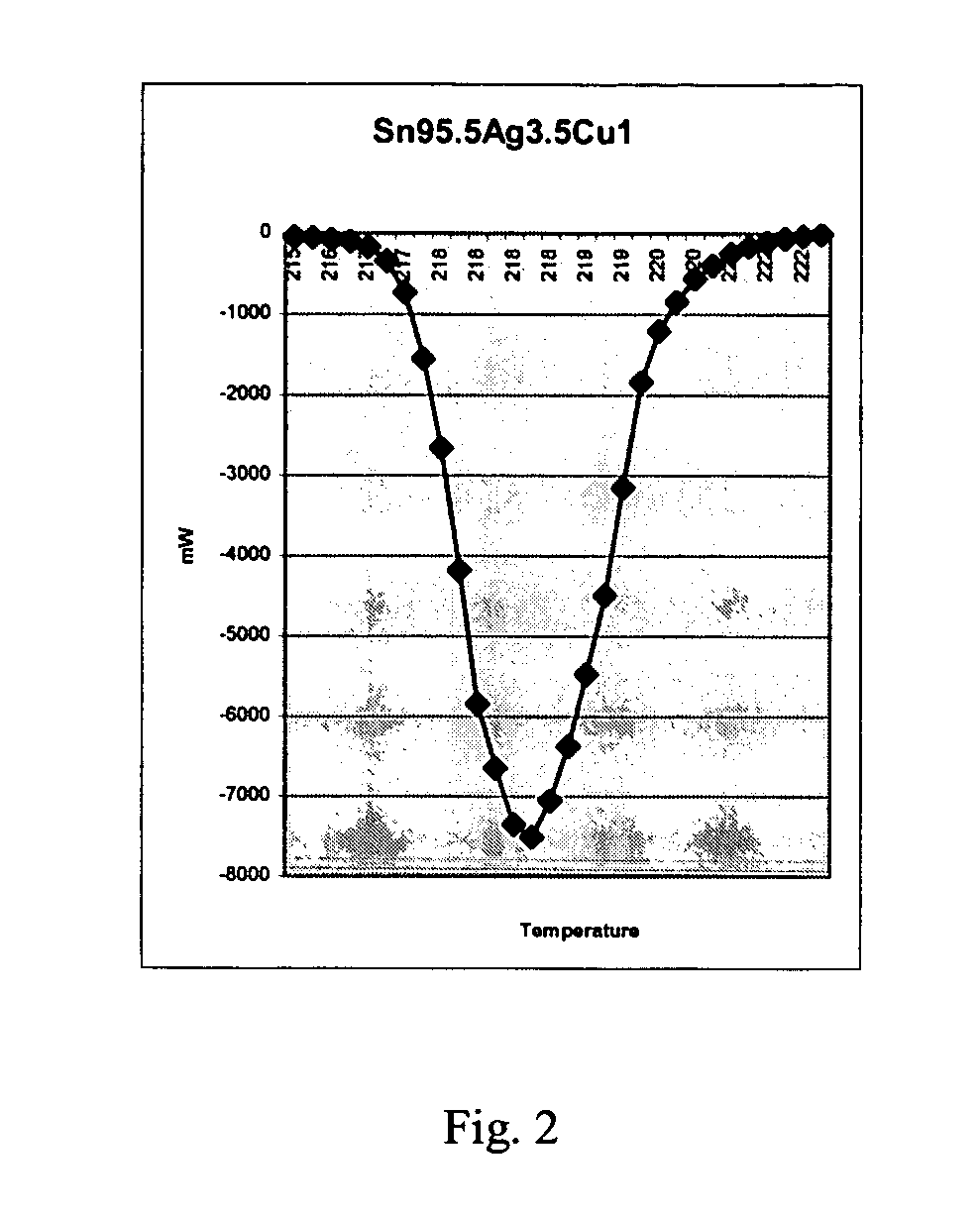
Anti-tombstoning lead free alloys for surface mount reflow soldering
InactiveUS20050100474A1Reducing tombstoning effectPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSurface mountingCopper
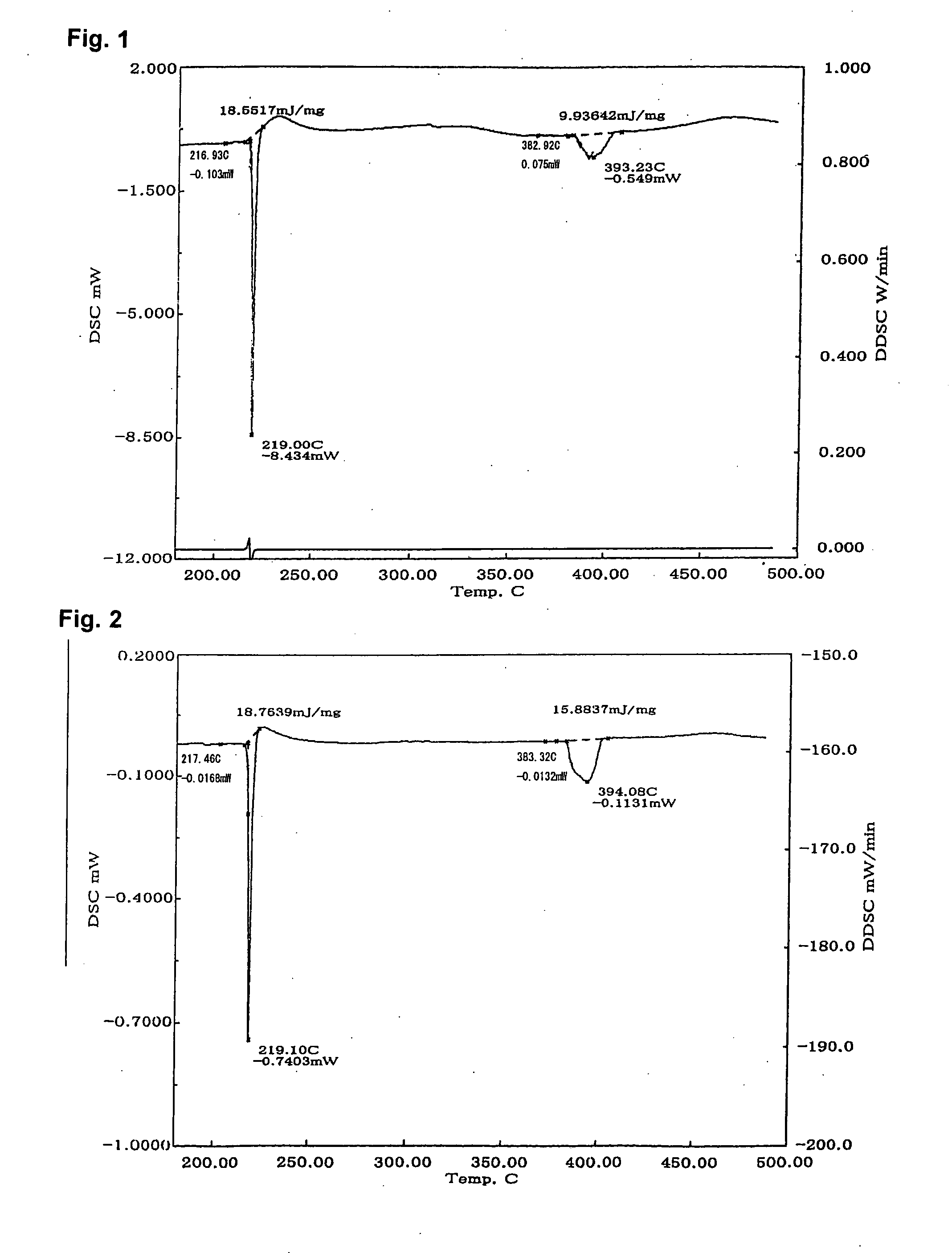
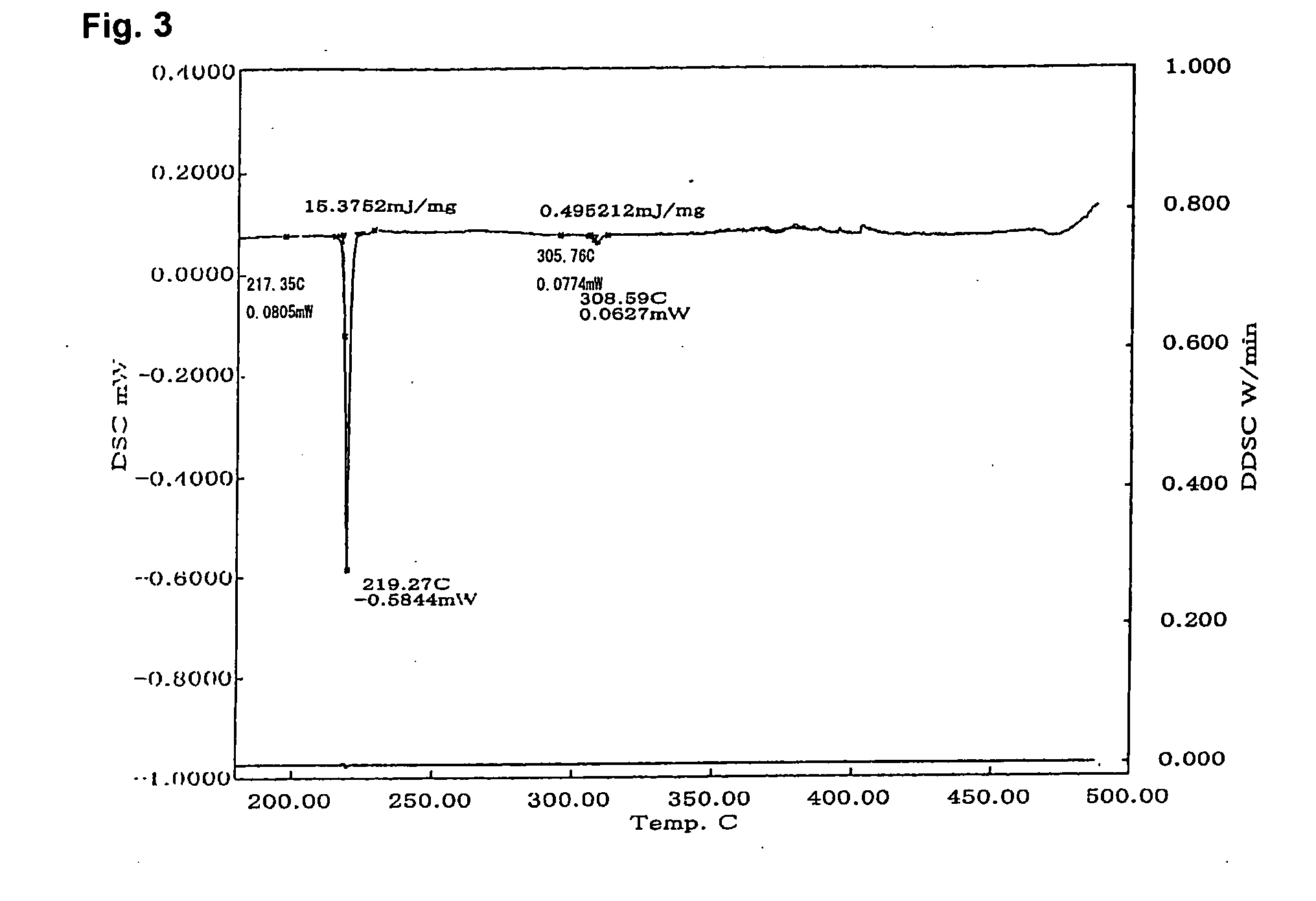
A lead-free solder alloy composition comprising tin, silver and copper, and a process for reflow soldering for minimizing tombstoning frequency are disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the lead-free Sn—Ag—Cu solder alloys for minimizing the tombstoning effect of the present disclosure display high mass fraction during melting and prolonged melting as shown by a widened DSC peaks, that allows for a balanced surface tension on both ends of the chip component to develop. In accordance with further aspects of this exemplary embodiment, the alloys display a mass fraction of solid during melting greater than 20% and a DSC peak width greater than 8° C. using a 5° C. / min scan rate. In accordance with further aspects of this exemplary embodiment, the alloy comprises on a weight basis Ag 1-4.5%, Cu 0.3-1% balanced with Sn.
Owner:INDIUM CORPORATION
Method to form bump in bumping technology
InactiveUS20020127836A1Low costFree of ChargeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesContact padSolder ball
A new method and processing sequence is provided for the creation of interconnect bumps. A layer of passivation is deposited over a contact pad and patterned, creating an opening in the layer of passivation that aligns with the contact pad. A layer of UBM metal is deposited over the layer of passivation, the layer of UBM is overlying the contact pad and limited to the immediate surroundings of the contact pad. The central surface of the layer of UBM is selectively electroplated after which a layer of solder or solder alloy is solder printed over the electroplated surface of the layer of UBM. A solder flux or paste is applied over the surface of the solder printed solder compound or solder alloy. Flowing of the solder or solder alloy creates the solder bump of the invention.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Solder Paste
ActiveUS20090220812A1Correct position deviationPrinted circuit aspectsPrinted circuit manufacturePowder mixtureSufficient time
High-temperature solders having a higher melting point than solder alloys used for soldering of printed circuit boards are used for internal bonding of electronic parts, but high-temperature solders which are free from Pb have not been developed. There exist high-temperature solders which comprises Sn balls and Cu balls and which perform bonding through the formation of an intermetallic compound without melting to form a single-phase structure, but they have poor wettability to the lands of a printed circuit board or electrodes of electronic parts and have not been used.A solder paste according to the present invention is provided by mixing flux with a powder mixture of Sn powder or an Sn based lead-free solder powder with Cu or Ag powder which has Ni plating formed on its surface. Although the solder paste performs bonding by means of an intermetallic compound without melting to form a single phase structure, the Ni plating acts as a barrier which retards the formation of the intermetallic compound so as to leave enough time to permit wetting of the lands of a printed circuit board or electrodes of an electronic part.
Owner:SENJU METAL IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com