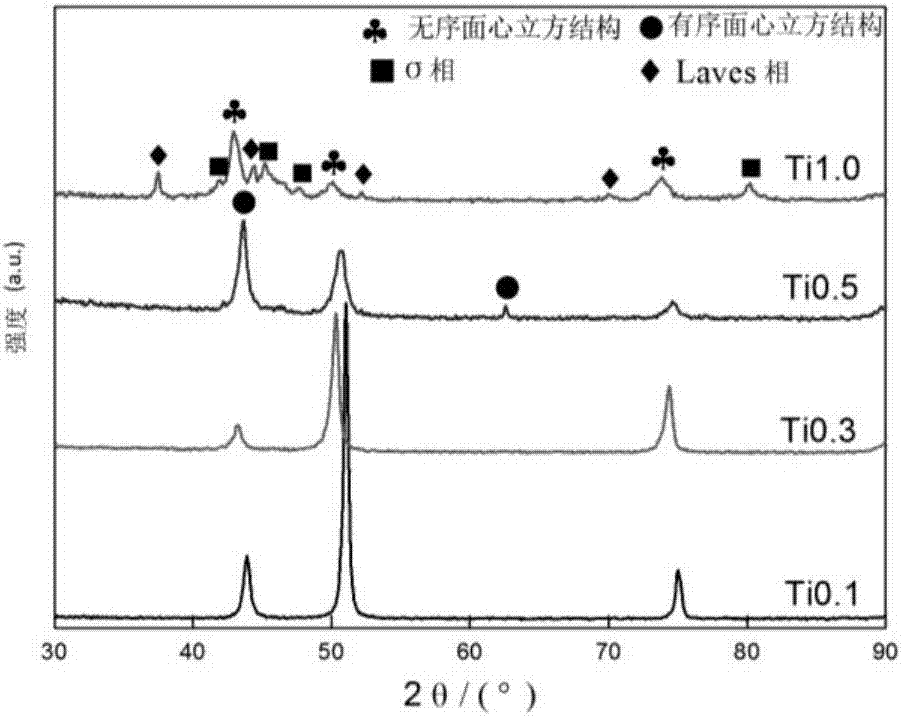
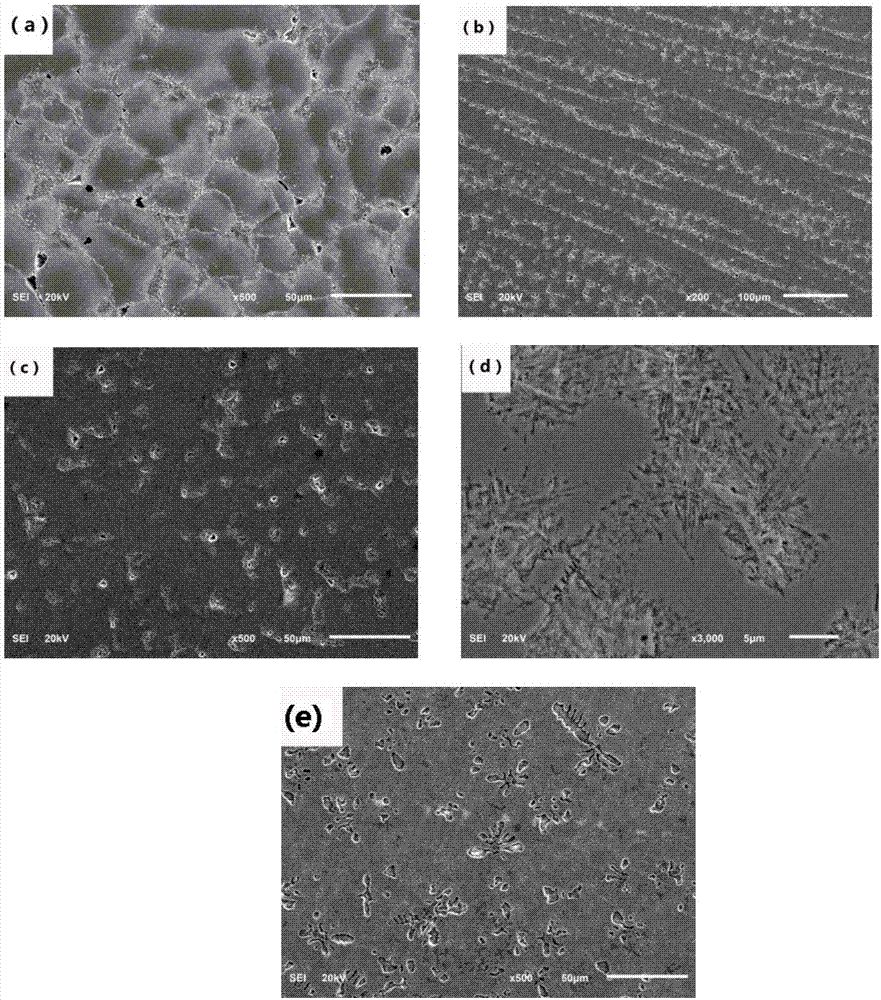
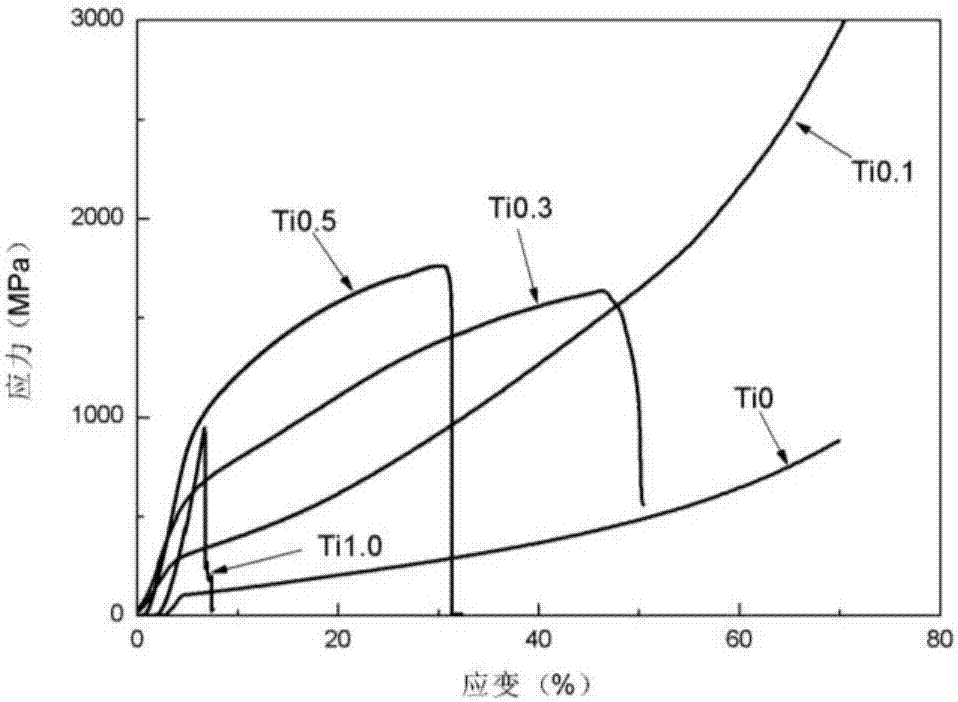
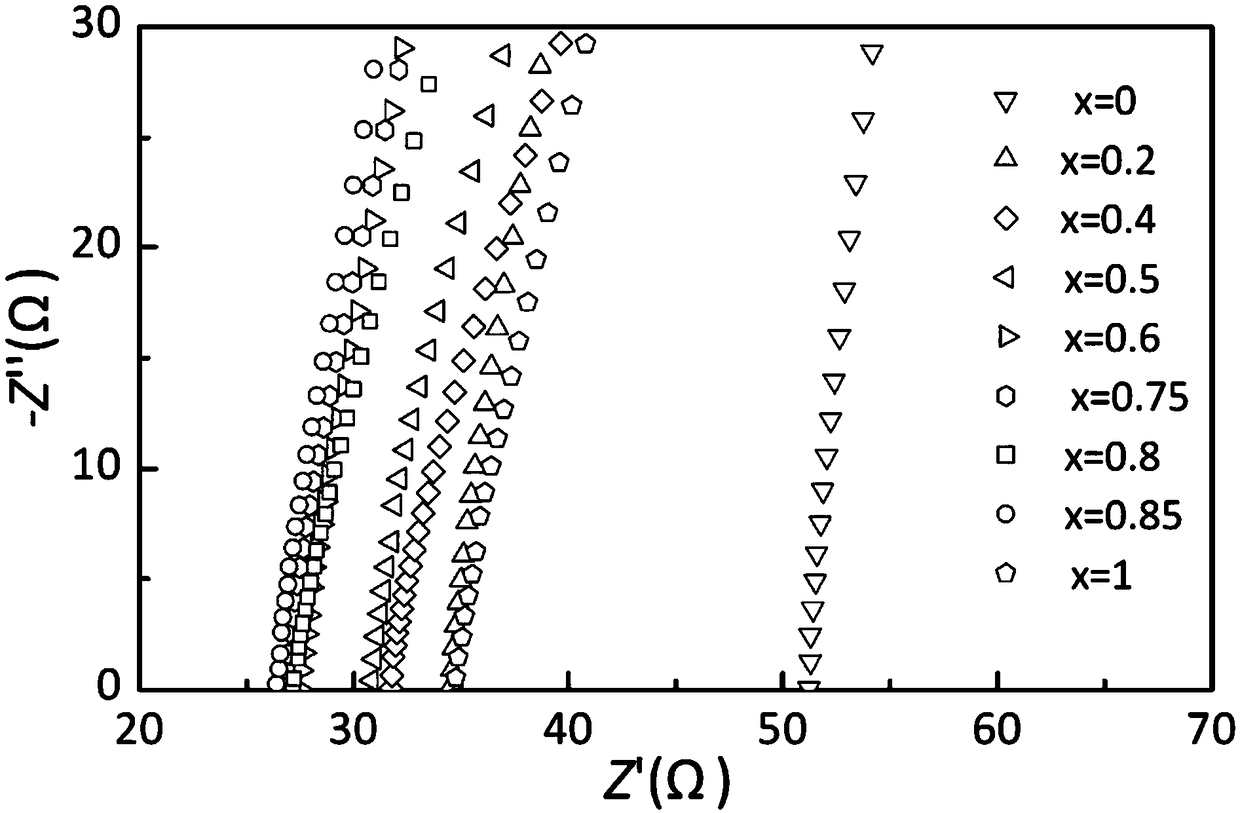
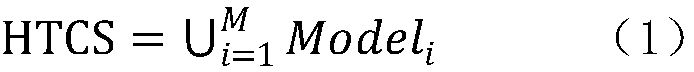Patents
Literature
70 results about "Atomic radius" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atoms, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the boundary of the surrounding shells of electrons. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. Three widely used definitions of atomic radius are: Van der Waals radius, ionic radius, and covalent radius.
N-type carrier enhancement in semiconductors
InactiveUS8178430B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantCharge carrier
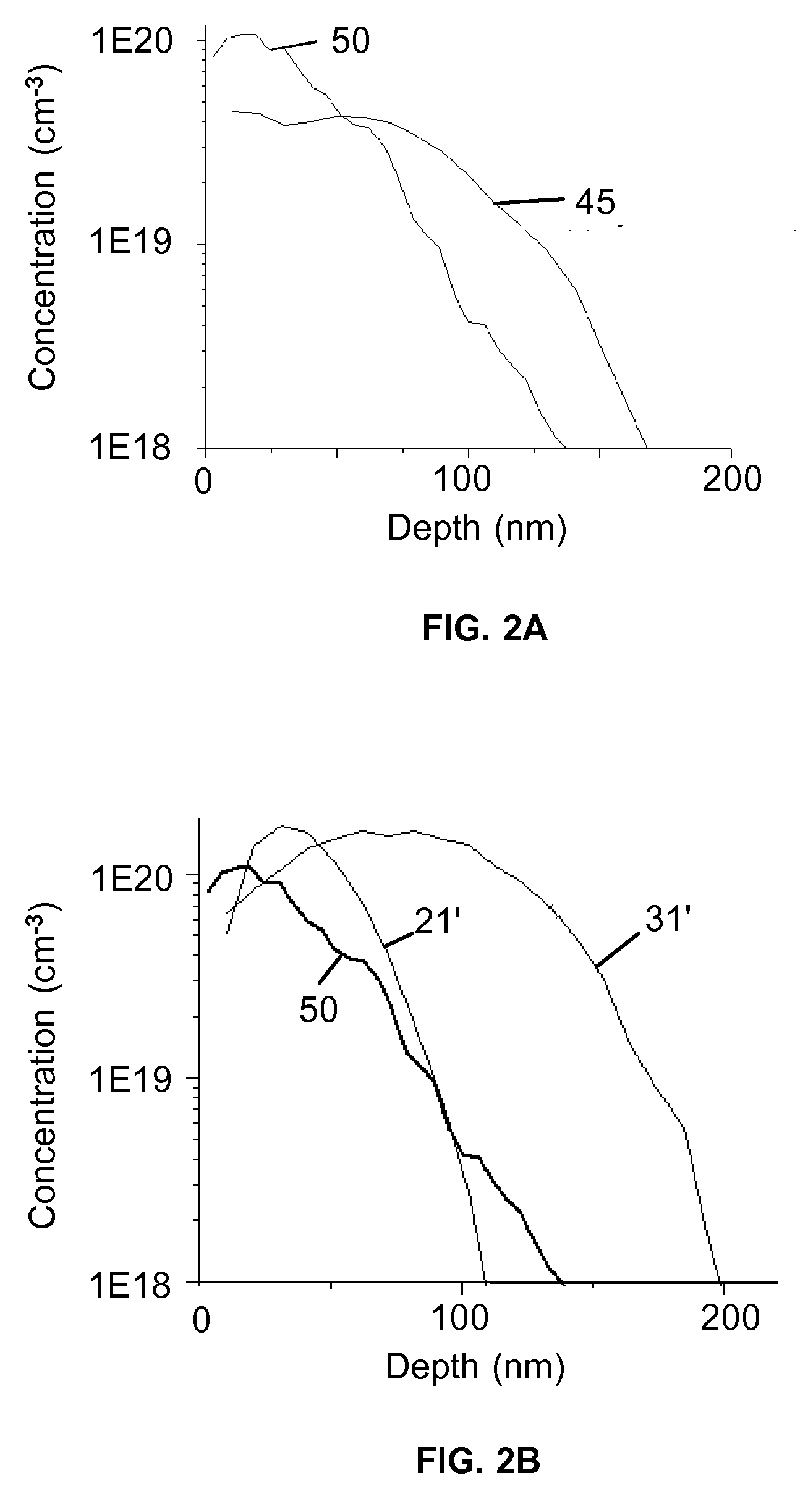
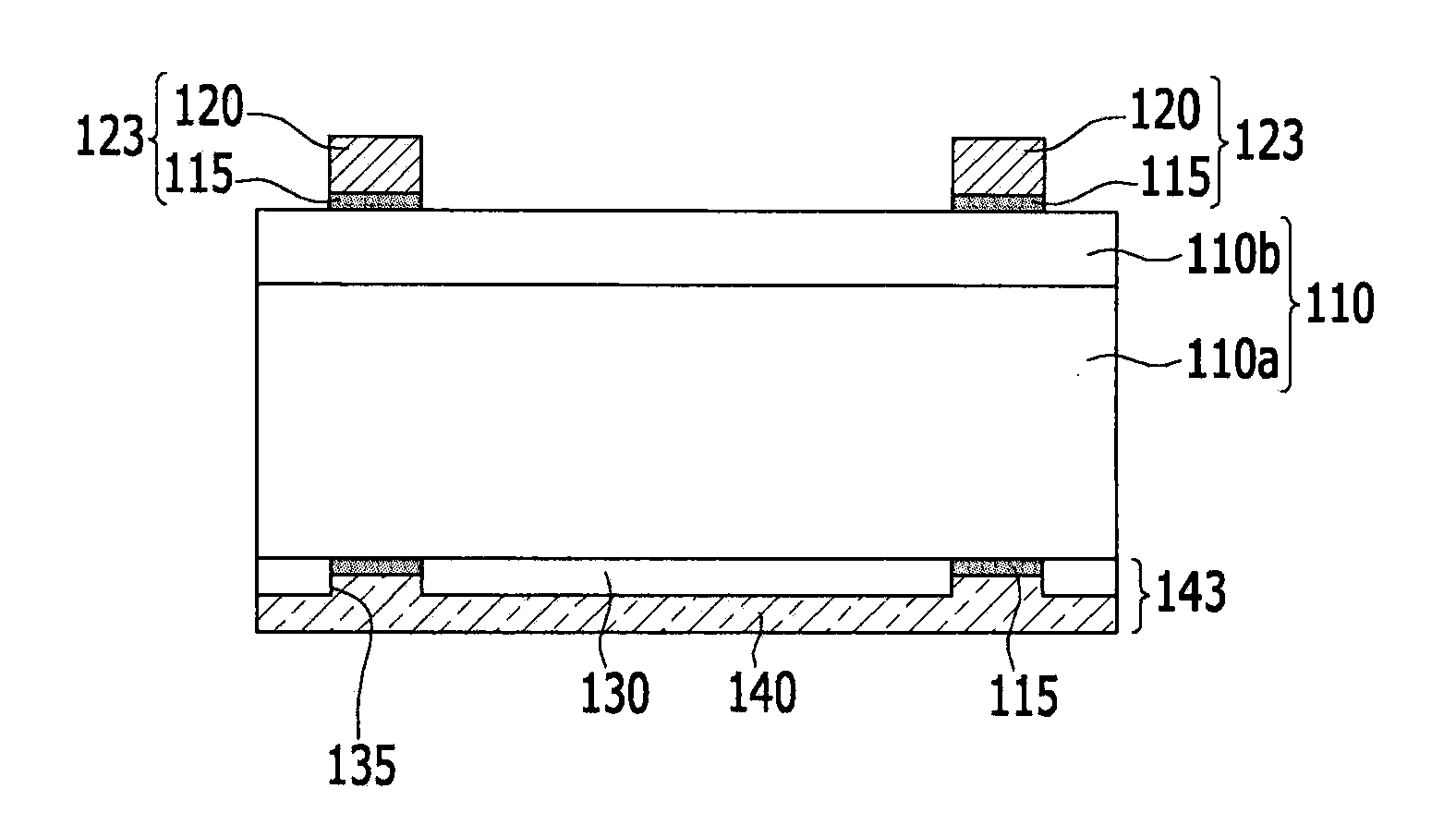
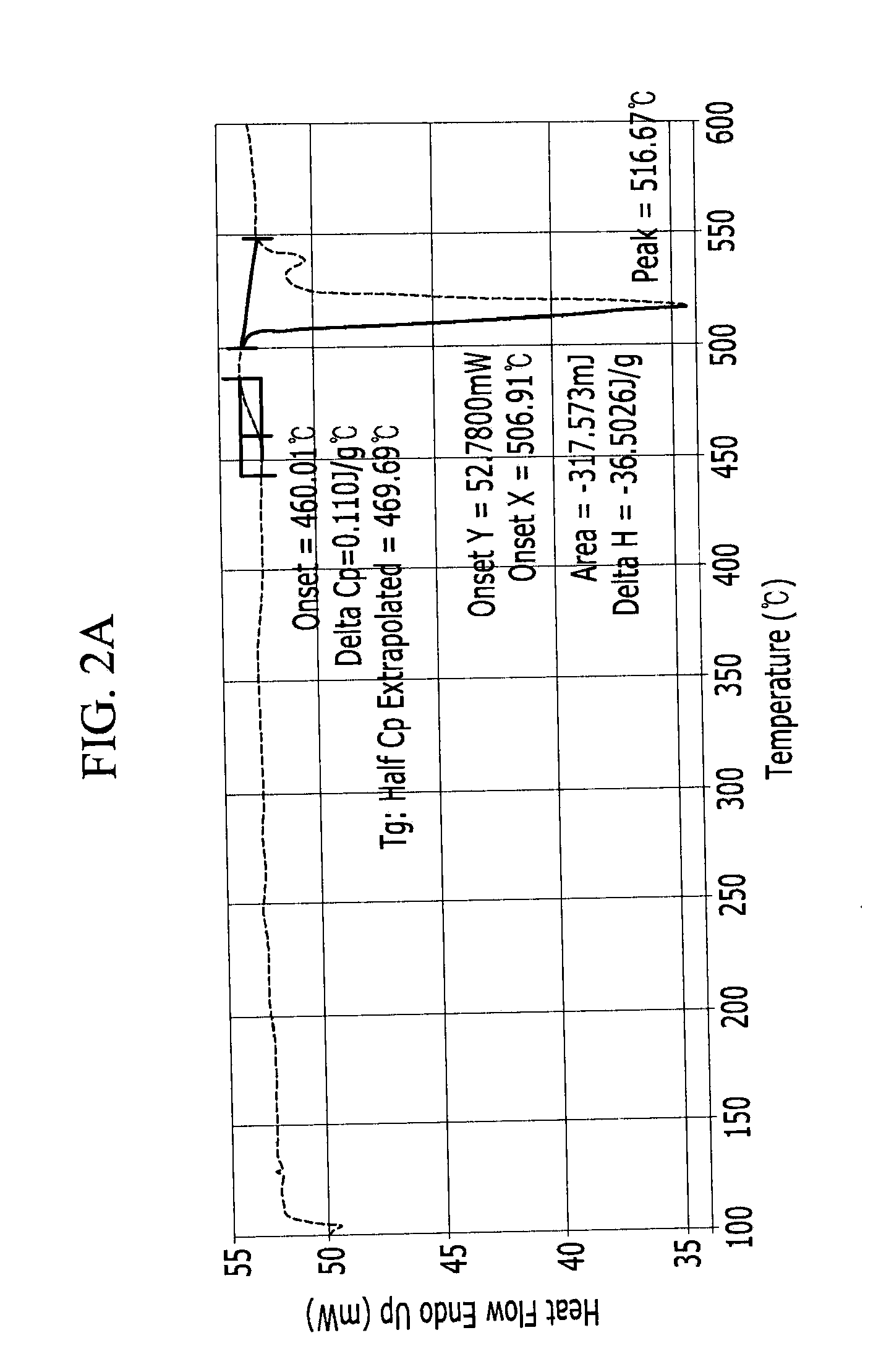
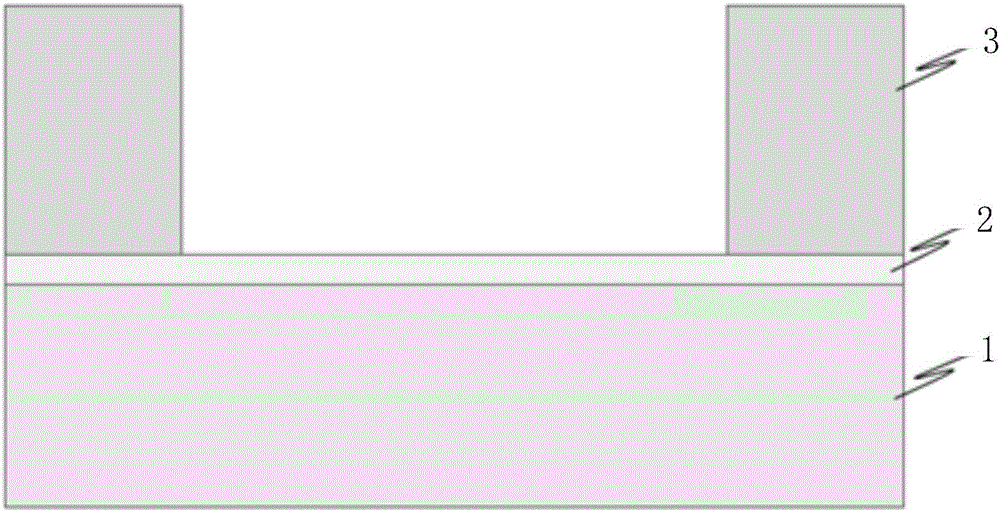
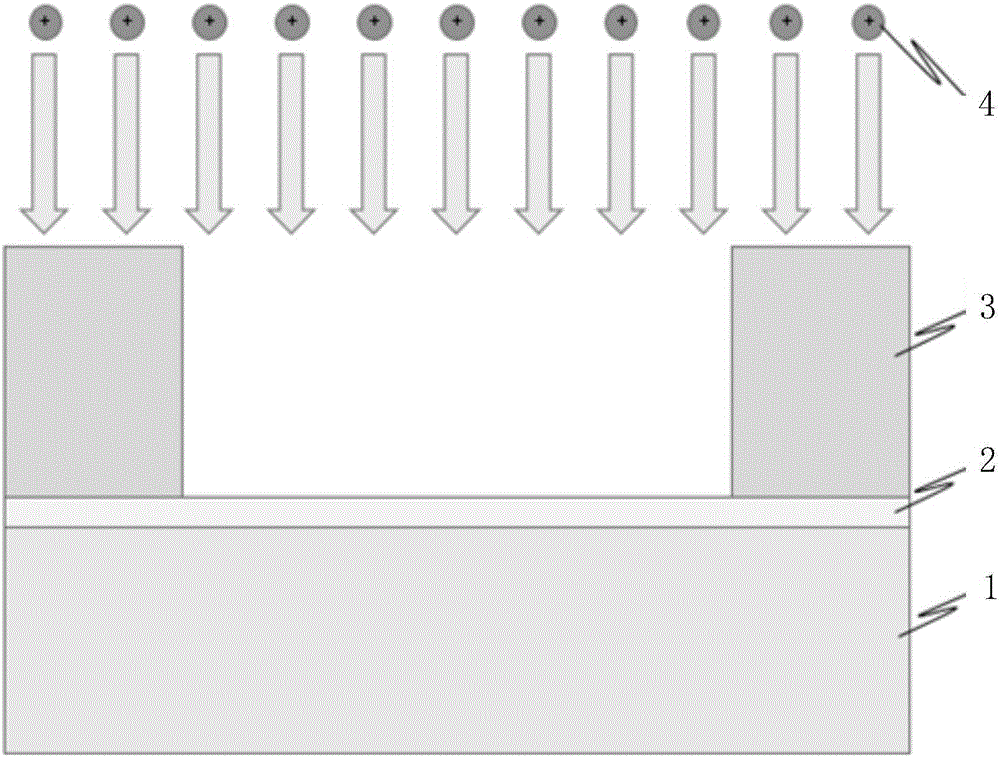
A method for generating n-type carriers in a semiconductor is disclosed. The method includes supplying a semiconductor having an atomic radius. Implanting an n-type dopant species into the semiconductor, which n-type dopant species has a dopant atomic radius. Implanting a compensating species into the semiconductor, which compensating species has a compensating atomic radius. Selecting the n-type dopant species and the compensating species in such manner that the size of the semiconductor atomic radius is inbetween the dopant atomic radius and the compensating atomic radius. A further method is disclosed for generating n-type carriers in germanium (Ge). The method includes setting a target concentration for the carriers, implanting a dose of an n-type dopant species into the Ge, and selecting the dose to correspond to a fraction of the target carrier concentration. Thermal annealing the Ge in such manner as to activate the n-type dopant species and to repair a least a portion of the implantation damage. Repeating the implantation and the thermal annealing until the target n-type carrier concentration has been reached.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
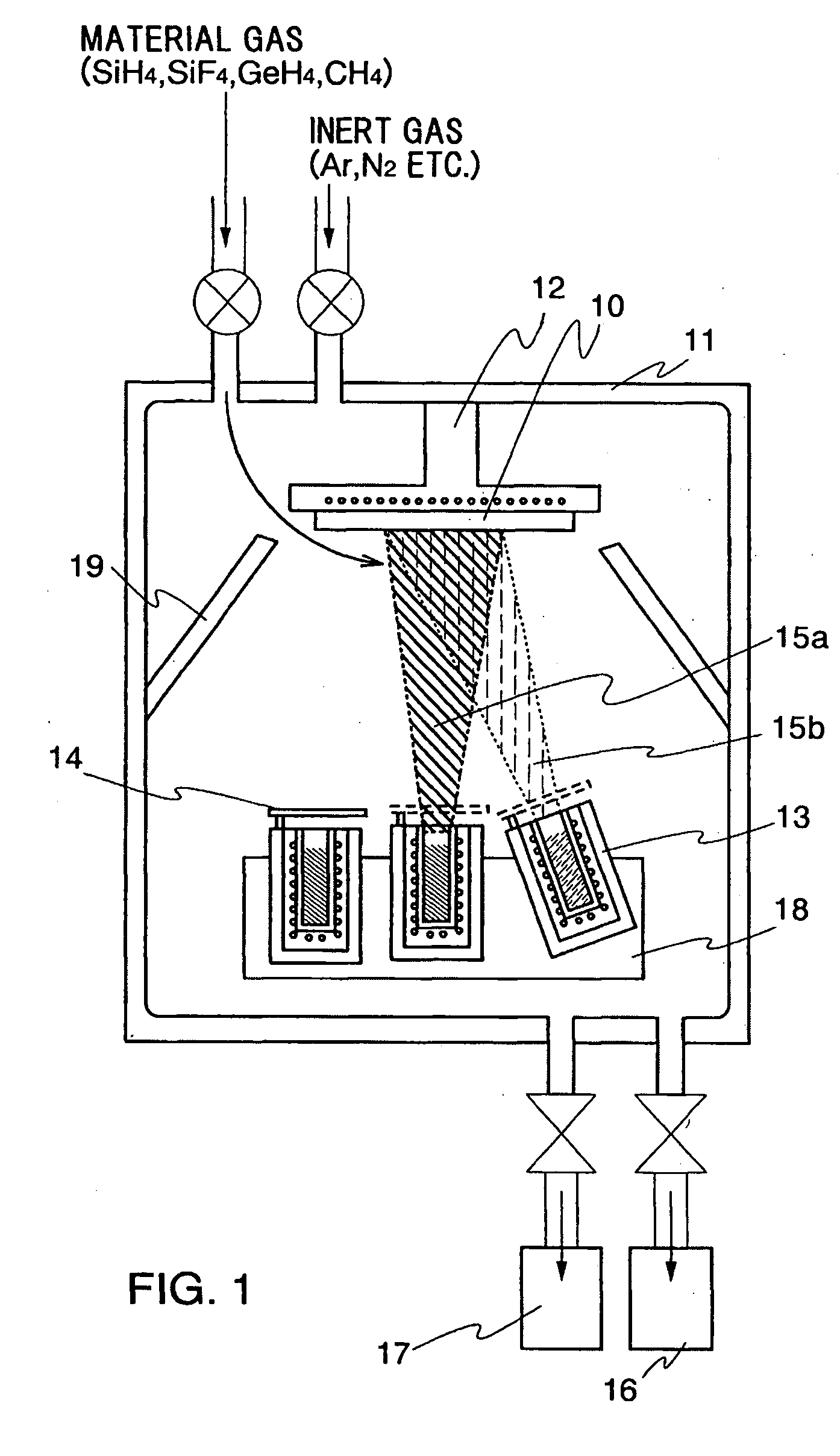
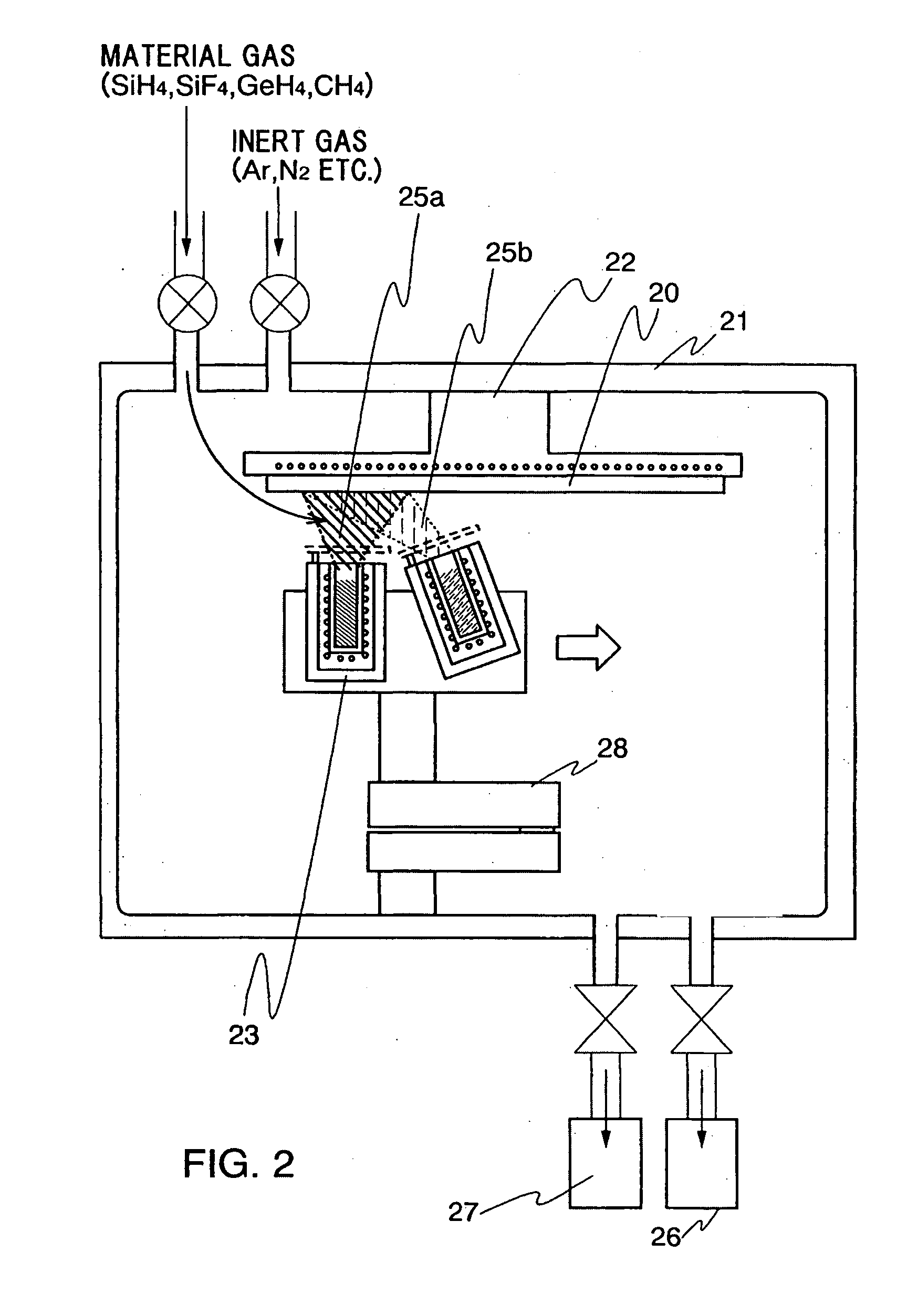
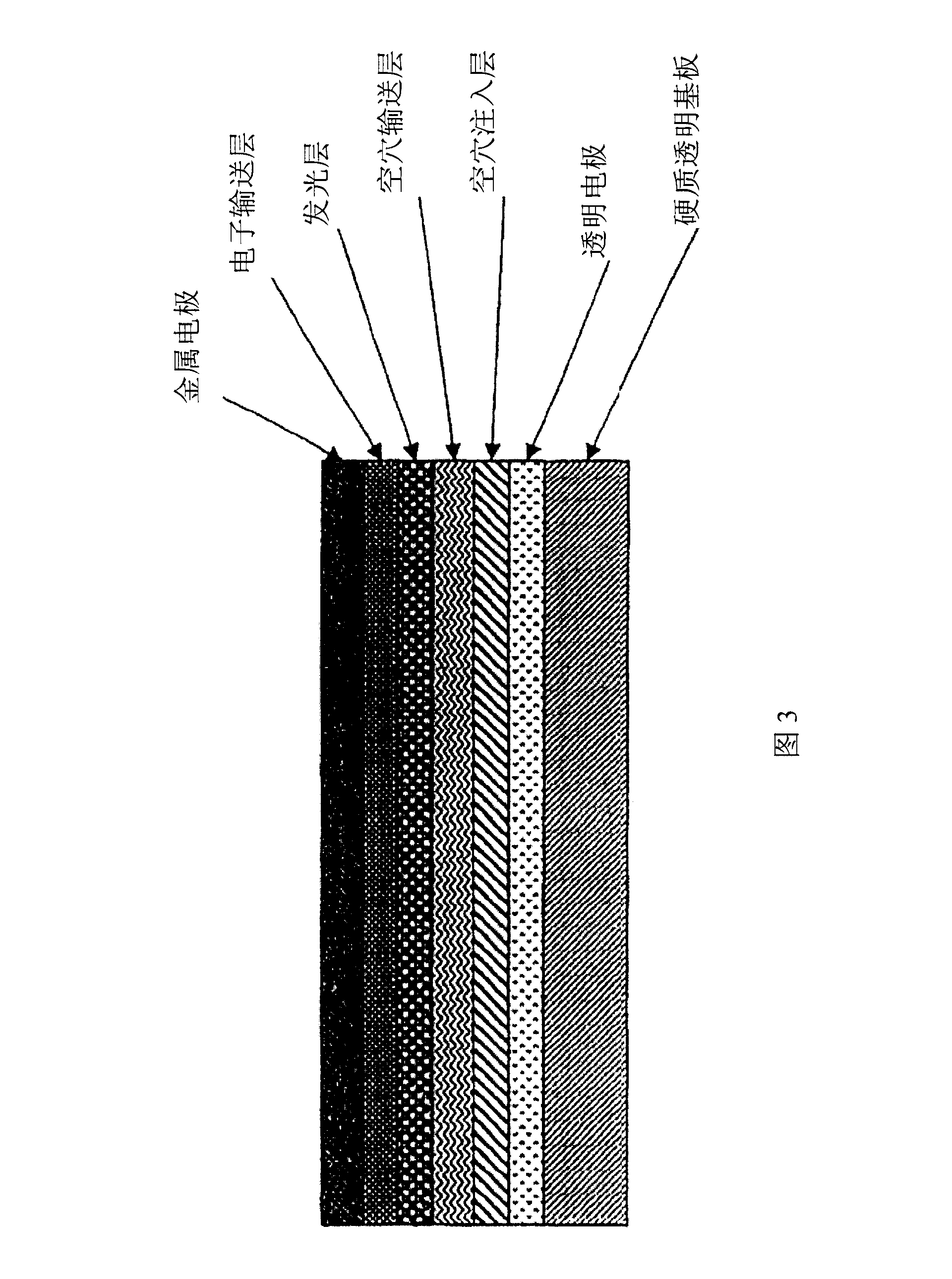
Light-emitting device, film-forming method and manufacturing apparatus thereof, and cleaning method of the manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS20050016462A1Small surface areaGas discharge is preventedElectroluminescent light sourcesVacuum evaporation coatingSilanesMetallurgy
This invention provides a new film forming method in which, on the occasion that pressure is decreased by pressure decreasing means which was connected to a film forming chamber, and a film is formed by evaporating an organic compound material from a deposition source in the film forming chamber, minute amounts of gas (silane series gas) which comprises smaller particles than particles of the organic compound material, i.e., a material with a smaller atomic radius are flowed, and the material with a small atomic radius is made to be included in an organic compound film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electronics device, semiconductor deivce, and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050045891A1Show reliableDeterioration of propertyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceAtomic radius
It is an object of the present invention to provide a high reliable EL display device and a manufacturing method thereof by shielding intruding moisture or oxygen which is a factor of deteriorating the property of an EL element without enlarging the EL display device. In the invention, application is used as a method for forming a high thermostability planarizing film 16, typically, an interlayer insulating film (a film which serves as a base film of a light emitting element later) of a TFT in which a skeletal structure is configured by the combination of silicon (Si) and oxygen (O). After the formation, an edge portion or an opening portion is formed to have a tapered shape. Afterwards, distortion is given by adding an inert element with a comparatively large atomic radius to modify or highly densify a surface (including a side surface) for preventing the intrusion of moisture or oxygen.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
CMOS transistors with stressed high mobility channels
InactiveUS20120037998A1Improve mobilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSCharge carrier
A p-type field effect transistor (PFET) having a compressively stressed channel and an n-type field effect transistor (NFET) having a tensilely stressed channel are formed. In one embodiment, a silicon-germanium alloy is employed as a device layer, and the source and drain regions of the PFET are formed employing embedded germanium-containing regions, and source and drain regions of the NFET are formed employing embedded silicon-containing regions. In another embodiment, a germanium layer is employed as a device layer, and the source and drain regions of the PFET are formed by implanting a Group IIIA element having an atomic radius greater than the atomic radius of germanium into portions of the germanium layer, and source and drain regions of the NFET are formed employing embedded silicon-germanium alloy regions. The compressive stress and the tensile stress enhance the mobility of charge carriers in the PFET and the NFET, respectively.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
Electronics device, semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7446336B2Show reliableDeterioration of propertyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide a high reliable EL display device and a manufacturing method thereof by shielding intruding moisture or oxygen which is a factor of deteriorating the property of an EL element without enlarging the EL display device.In the invention, application is used as a method for forming a high thermostability planarizing film 16, typically, an interlayer insulating film (a film which serves as a base film of a light emitting element later) of a TFT in which a skeletal structure is configured by the combination of silicon (Si) and oxygen (O). After the formation, an edge portion or an opening portion is formed to have a tapered shape. Afterwards, distortion is given by adding an inert element with a comparatively large atomic radius to modify or highly densify a surface (including a side surface) for preventing the intrusion of moisture or oxygen.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
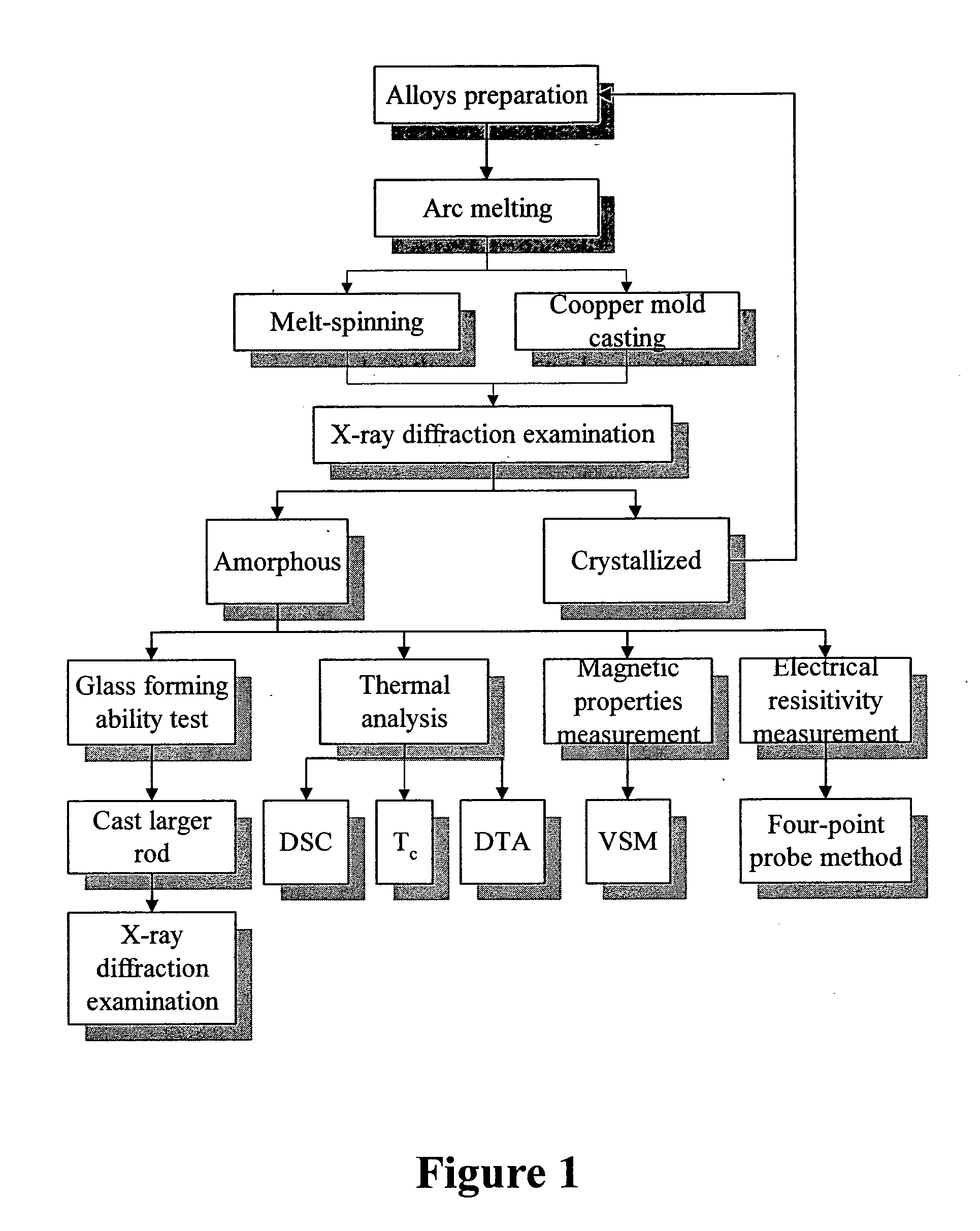
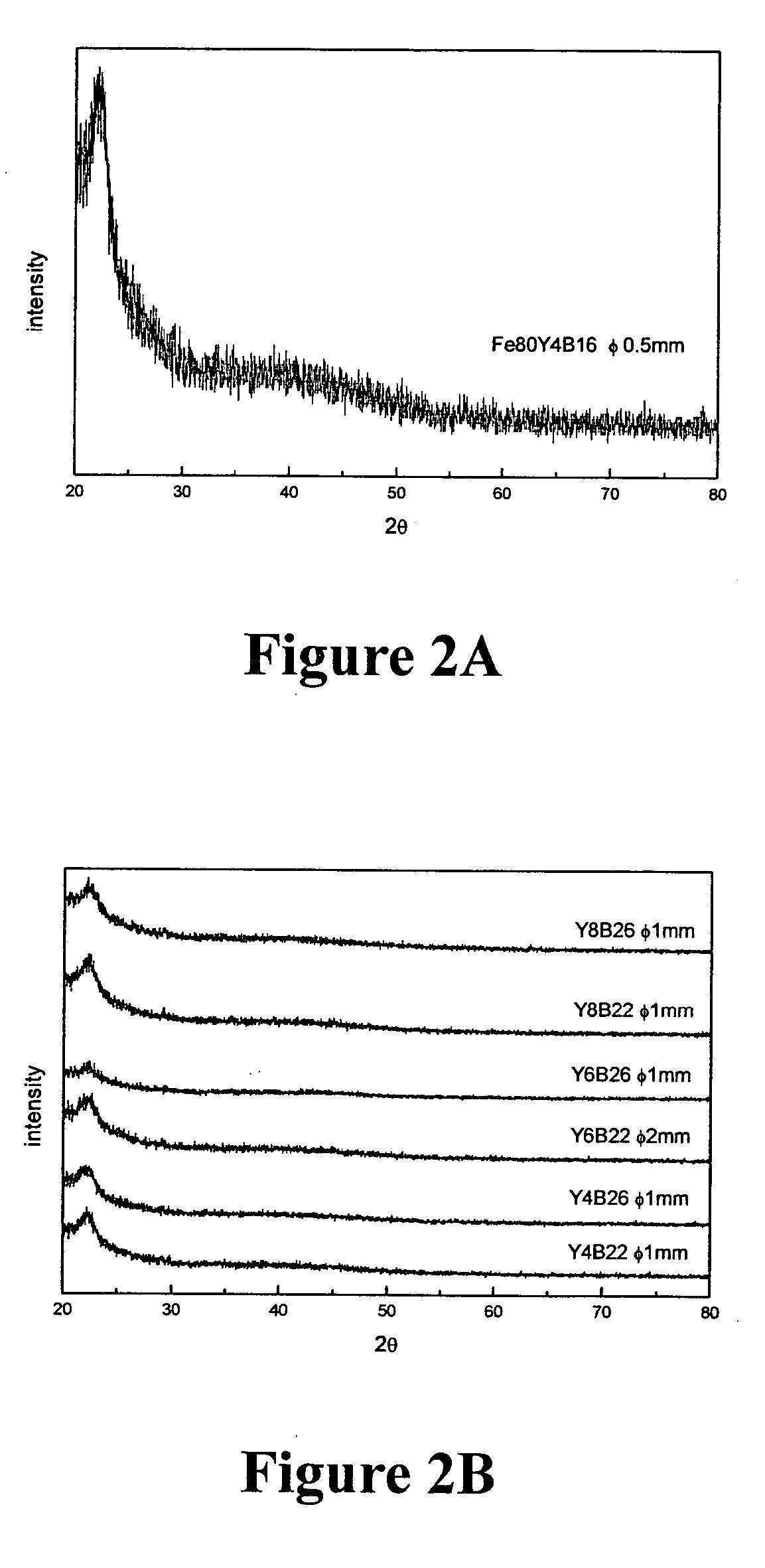
Ternary and multi-nary iron-based bulk glassy alloys and nanocrystalline alloys
InactiveUS20050263216A1High glass forming abilityIncreased electrical resistivityMagnetic materialsAmorphous phaseAtomic radius
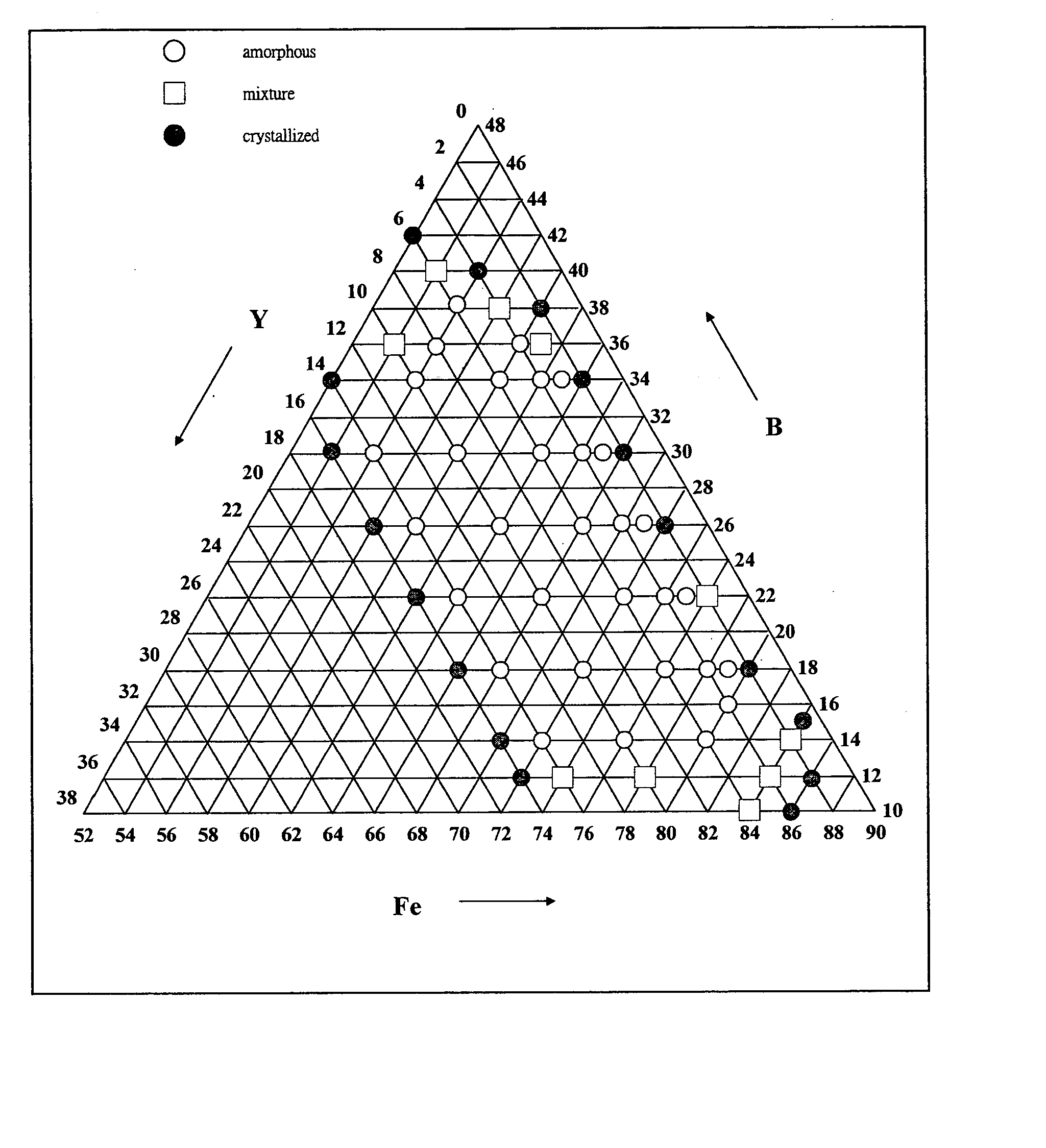
Disclosed in this invention is a family of ternary and multi-nary iron-based new compositions of bulk metallic glasses which possess promising soft magnetic properties, and the composition selection rules that lead to the design of such new compositions. The embodiment alloys are represented by the formula MaXbZc, where M represents at least one of ferromagnetic elements such as iron and may partly be replaced by some other substitute elements; X is an element or combinations of elements selected from those with atomic radius at least 130% that of iron and in the mean time is able to form an M-rich eutectic; and Z is an element or combinations of elements selected from semi-metallic or non-metallic elements with atomic radius smaller than 86% that of iron and in the meantime is able to form an M-Z eutectic; a, b, c are the atomic percentage of M, X, Z, respectively, and a+b+c=100%. When 1%<b<15% and 10%<c<39%, the alloys show a bulk glass forming ability to cast amorphous ribbons / sheets at least 0.1 mm in thickness. When 3%<b<10% and 18%<c<30%, the alloys show a bulk glass forming ability to cast amorphous rods at least 1 mm in diameter. The amorphous phase of these as-cast sheets / rods is at least 95% by volume. This invention also discloses the existence of nano-crystalline phase outside of the outer regime of the bulk glass forming region mentioned above.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
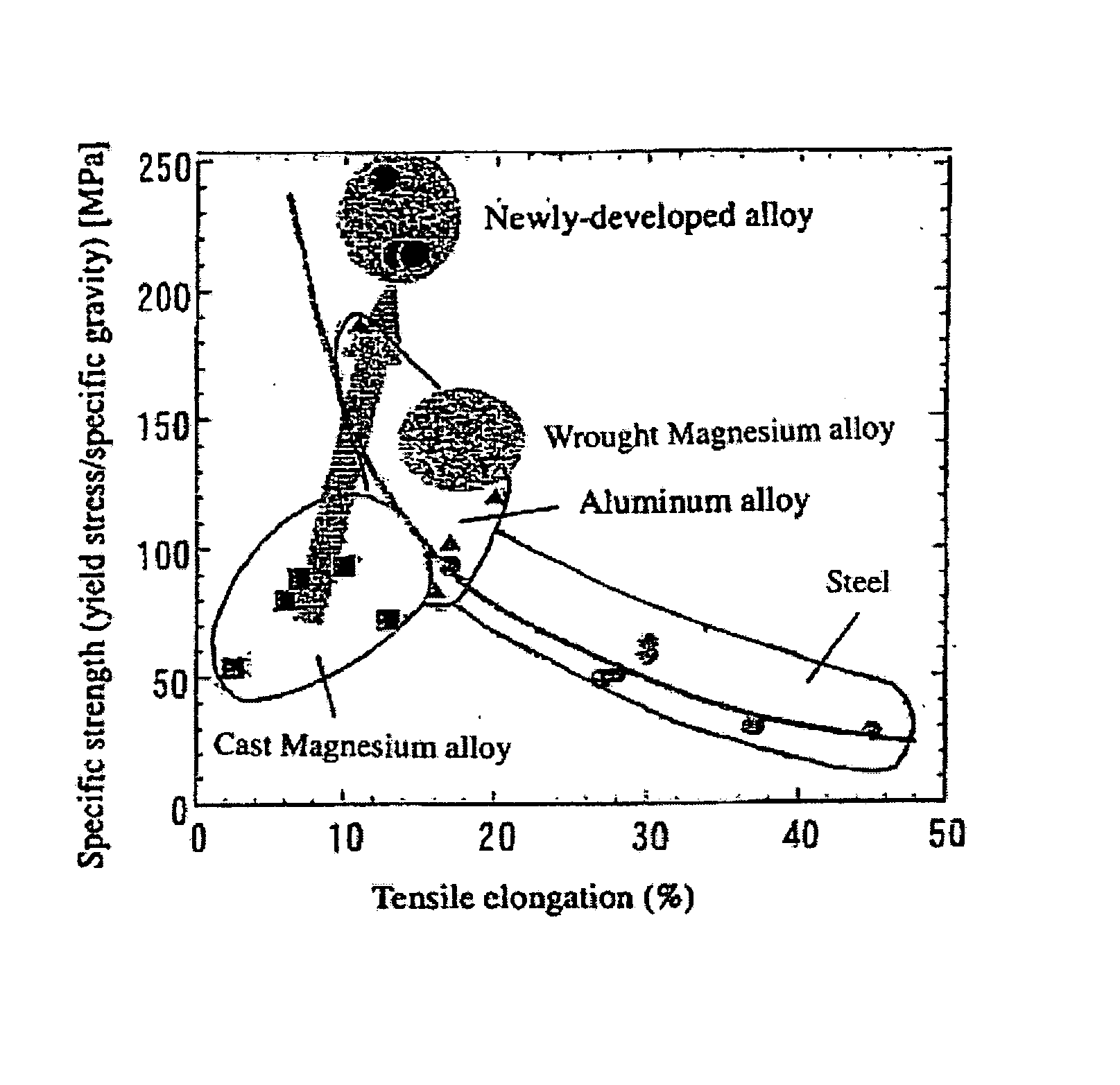
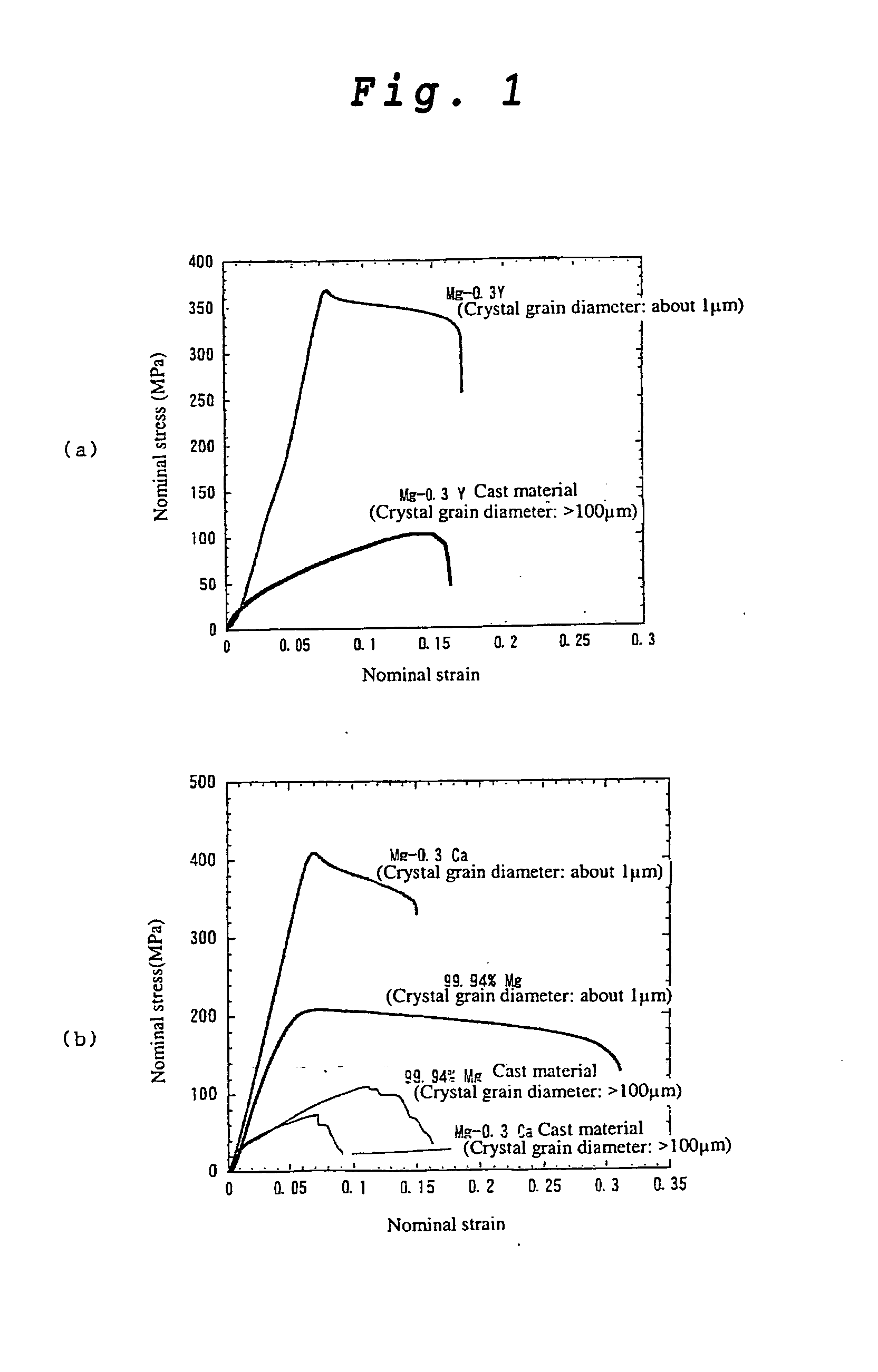
Magnesium Alloy Exhibiting High Strength and High Ductility and Method for Production Thereof
A magnesium alloy exhibiting high strength and high ductility, characterized in that it comprises 0.03 to 0.54 atomic % of certain solute atoms belonging to 2 Group, 3 Group or Lanthanoids of the Periodic Table and having an atomic radius larger than that of magnesium and the balanced amount of magnesium, and has a fine crystal grain structure wherein solute atoms having an average crystal grain diameter of 1.5 μm or less and being unevenly present in the vicinity of crystal grain boundaries at a concentration being 1.5 to 10 times that within crystal grains, wherein an atom selected from the group consisting of Ca, Sr, Ba, Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Th, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu can be used as the above solute atom; and a method for producing the magnesium alloy. The above magnesium alloy is novel and achieves high strength and high ductility at the same time.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
High-specific-strength high-plasticity refractory high-entropy alloy and preparing method thereof
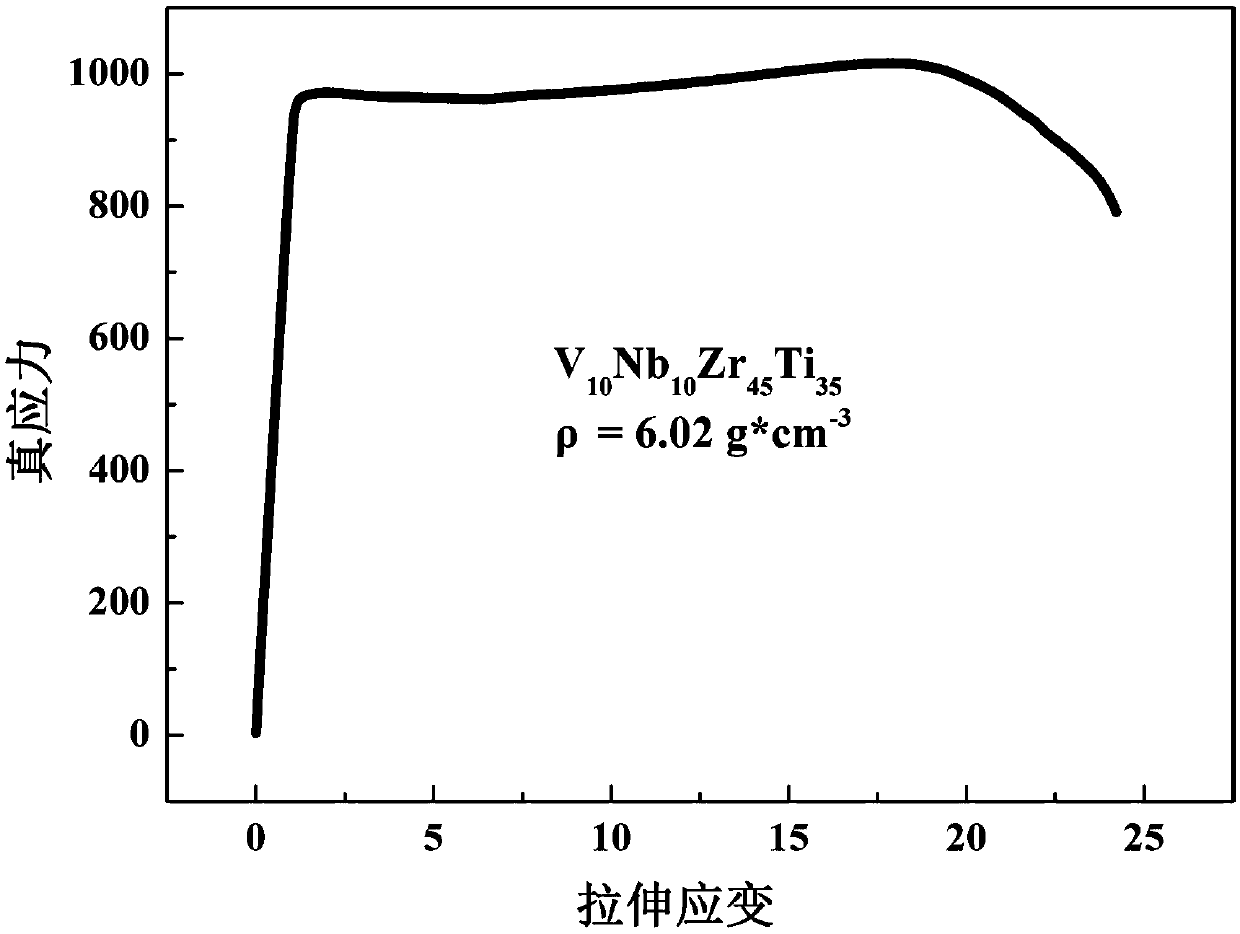
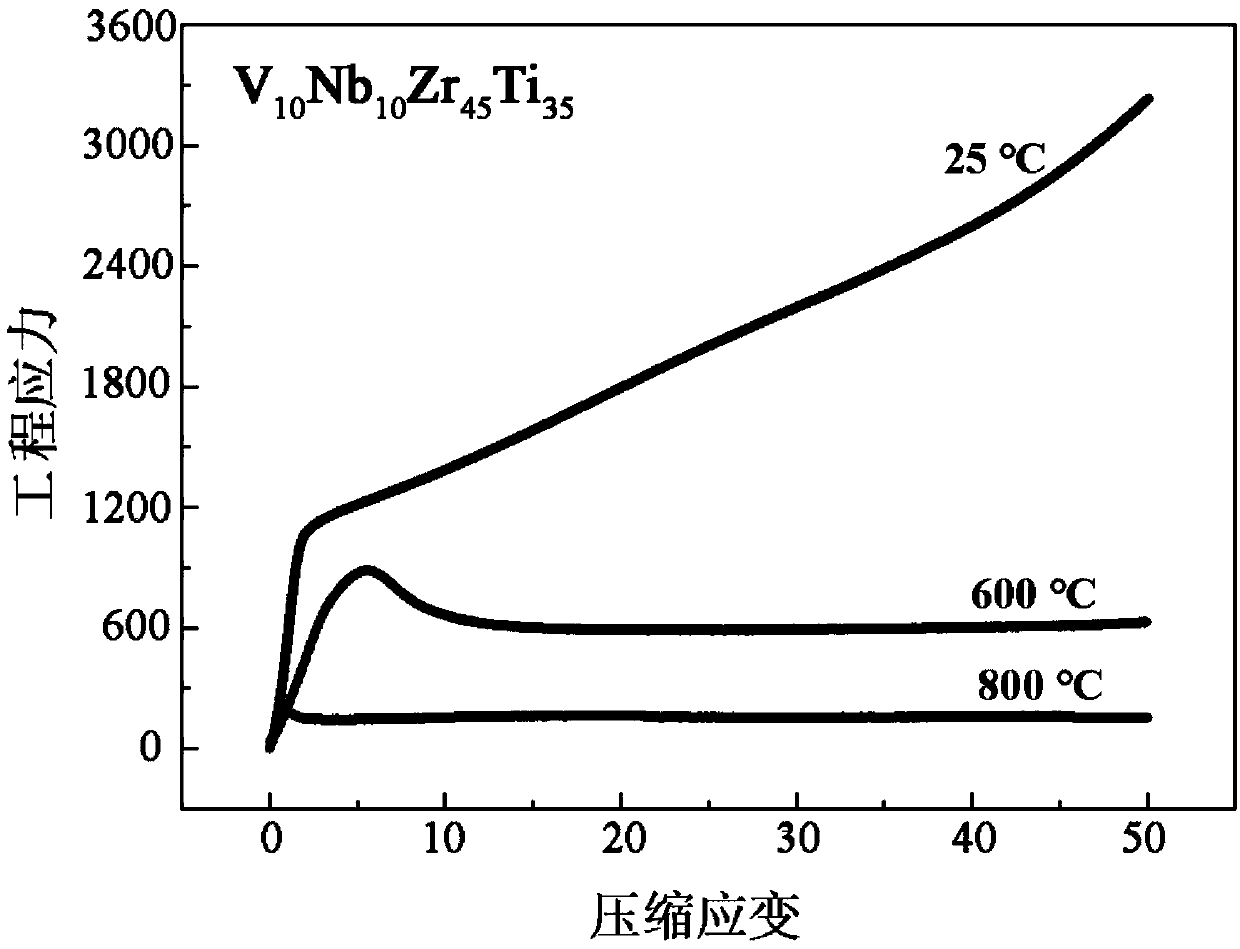
The invention relates to a high-specific-strength high-plasticity refractory high-entropy alloy and a preparing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of metal materials. The expression isVaNbbZrcTidMeNfPg, wherein M, N, P can be the elements such as Cr, Al, Ni, Fe, Si, O, B, C, and N; a is no less than 15% and no more than 20%, b is no less than 15% and no more than 25%, c is no lessthan 30% and no more than 50%, d is no more than 30% and no less than 50%, e is no less than 0 and no more than 5%, f is no less than 0 and no more than 5%, g is no less than 0 and no more than 5%, and the sum of a, b, c, d, e, f and g is 100%; and meanwhile, the valence electron concentration VEC of the alloy is no less than 4.1 and no more than 4.4, and the atomic radius size difference Delta is no less than 5.5% and no more than 6.4%. The alloy is prepared by various methods, the density of the VaNbbZrcTidMeNfPg alloy is less than 6.5 g*cm<-3>, the room temperature tensile strength is morethan 900 MPa, the plastic deformation is more than 15%, and the high specific strength and high plasticity are achieved; and after the temperature is increased to 600 DEG C, the weakening of the material is not very obvious, after the temperature is increased to 800 DEG C, the material can still maintain a certain strength, and the alloy has a certain storage ability for H2 and can be used in thefield of energy materials.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Hexabasic high-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a hexabasic high-entropy alloy material. The hexabasic high-entropy alloy material is prepared from, by atomic percent, 18.18%-22.22% of Co, 18.18%-22.22% of Cr, 9.1%-11.12% of Cu, 18.18%-22.22% of Fe, 18.18%-22.22% of Ni and 2.17%-18.18% of Ti, wherein the element Ti has the large atomic radius, and the severe lattice distortion effect of the element Ti can effectively enhance a solid solution phase. In addition, the element Ti has the small valence electron concentration and tends to form a compound phase, and therefore the precipitation enhancing function is achieved. An obtained hexabasic CoCrCu0.5FeNiTi0.5 high-entropy alloy has high strength and plasticity, wherein the yield strength is 850 MPa, the compressive strength reaches 1,650 MPa, and meanwhile the plasticity reaches 31.5%. The alloy has good strength and plasticity cooperation, and a preparation method is simple and reliable. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the hexabasic high-entropy alloy material.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lithium ion solid conductor, preparation method thereof and all-solid lithium battery
InactiveCN108899580AIncrease activity spaceImprove conductivitySecondary cellsElectrolyte immobilisation/gelificationElectrical conductorPhysical chemistry
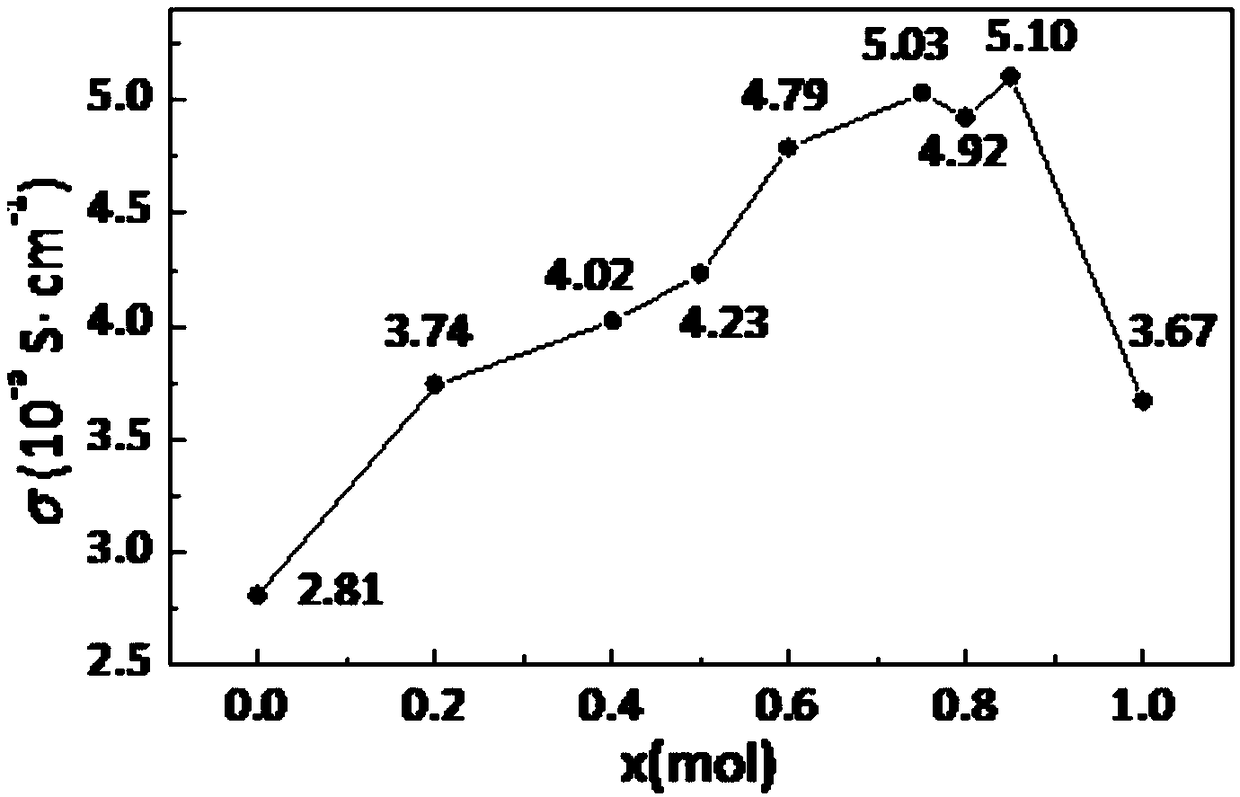
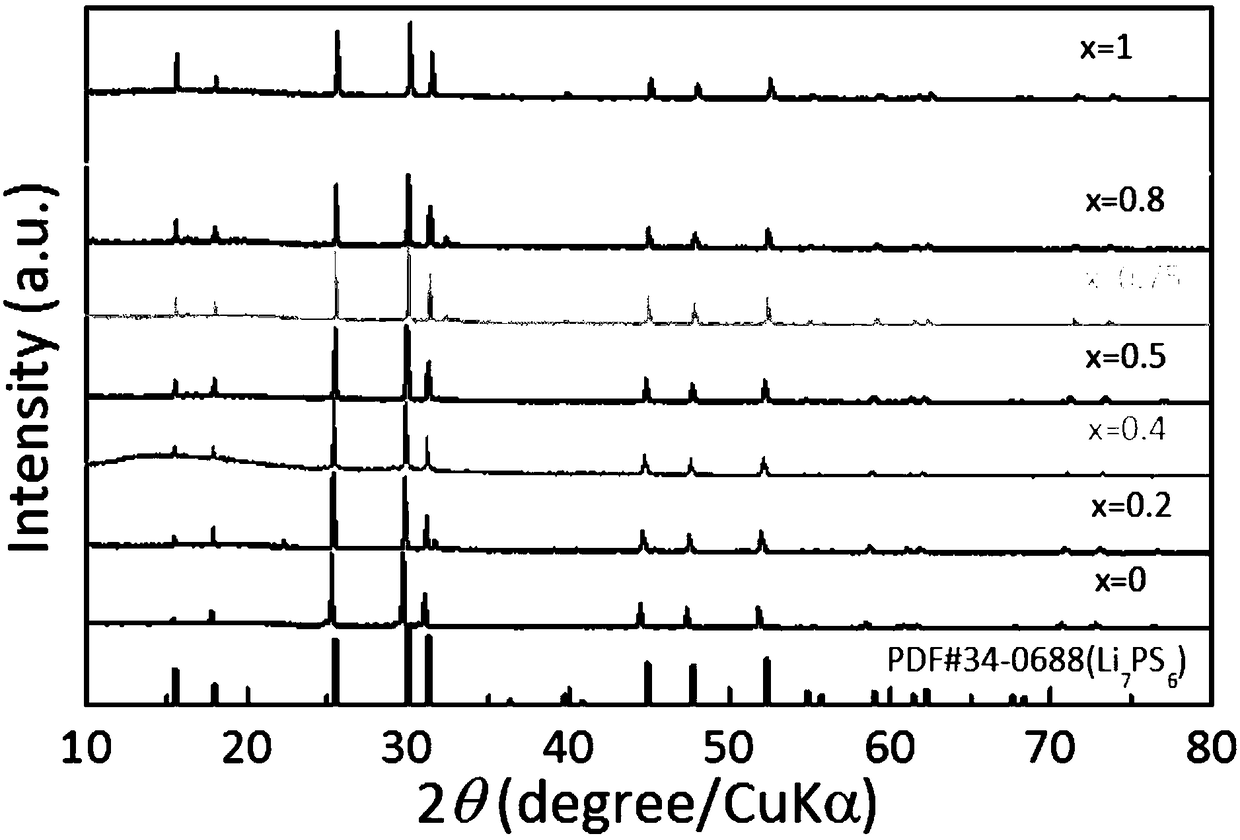
The invention provides a lithium ion solid conductor. The lithium ion solid conductor has a chemical formula (1) as follows: Li6PS5ClzM1-z, wherein M is Br or I, and z is more than or equal to 0.1 butless than 1. In order to solve the problems of widespread chemical instability between an inorganic lithium ion solid conductor material and metal lithium and lower conductivity of lithium ions, thelithium ion solid conductor provided by the invention is characterized in that the chlorine element in a sulfide electrolyte Li6PS5Cl is replaced by the doped halogen elements (Br, I) with larger atomic radiuses so as to acquire a novel sulfide electrolyte Li6PS5ClzM1-z, wherein M is Br or I and z is more than or equal to 0.1 and less than or equal to 1. A lithium ion transmission channel is widened, a multi-dimensional lithium ion transmission channel is formed, an activity space is increased and the conductivity of the lithium ions is promoted. The invention also provides a preparation method for the lithium ion solid conductor and an all-solid lithium battery.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Difluoro-bithiophene polymer as well as preparation method and application thereof to FET (field effect transistor)
ActiveCN106589326AStrong electron-withdrawing propertiesGood planarityOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesPolymer scienceElectron injection
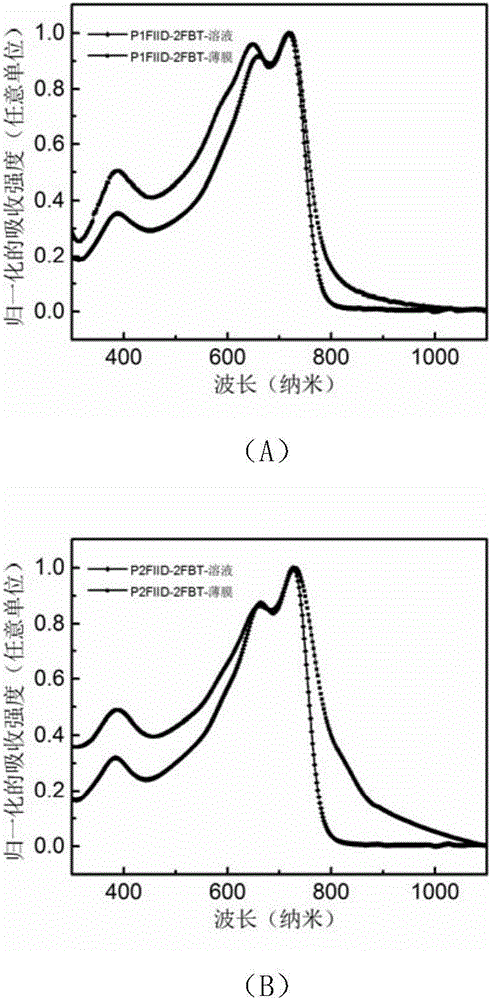
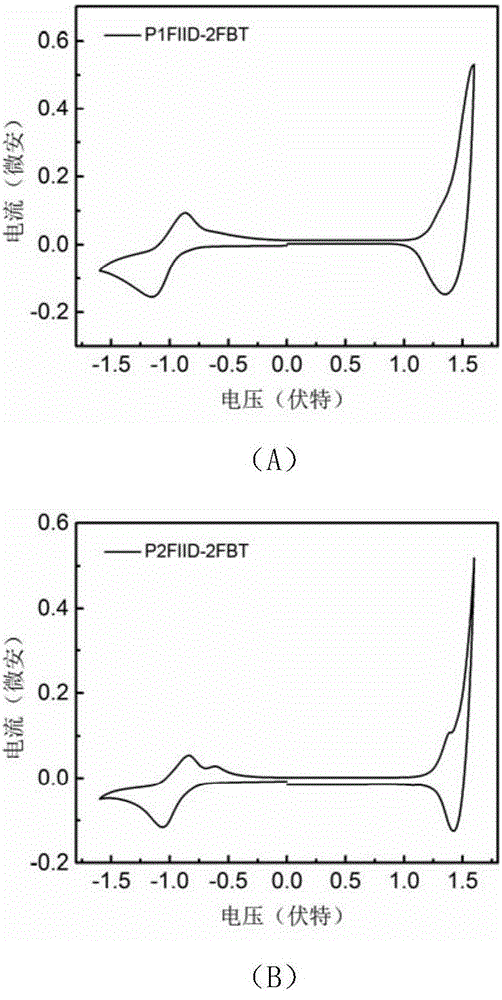
The invention discloses a difluoro-bithiophene polymer as well as a preparation method and application thereof to an FET (field effect transistor). The structural formula of the difluoro-bithiophene polymer is as shown in formula I, wherein n is a natural number ranging from 5 to 100. According to the invention, a fluorine atom is introduced to a thiophene ring to obtain difluoro-bithiophene (2FBT); the fluorine atom has a strong electron-withdrawing property, the atomic radius is small, and the interaction with other atoms such as a hydrogen atom or a sulphur atom is relatively strong, so that the introduction of the fluorine atom can improve the molecular planarity and promote molecular stacking. A polymer taking 2FBT as a donor has relatively low LUMO energy level, and the electron injection of a transport layer is relatively easy, so that the bipolar transfer characteristic can be expressed. The difluoro-bithiophene polymer provided by the invention can be used as a semiconducting material to prepare an OFET (organic field effect transistor). The OFET prepared by taking the difluoro-bithiophene polymer as a semiconducting layer has relatively high migration rate (mu), thereby having a good application prospect in bipolar OFETs.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cu-Ni-Nb ternary alloy film with low resistivity and high chemical inertia and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN102808150AEliminate scattering effectsReduce scatterVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingChemical reactionBlock effect
The invention provides a Cu-Ni-Nb ternary alloy film with low resistivity and high chemical inertia and a preparation process thereof, and belongs to the field of materials. Under the guidance of a cluster model of a stable solid solution, the selection and the addition quantity of alloying elements in the Cu film are determined, and factors such as the enthalpy of mixing, a cluster structure and atomic radius dimension are comprehensively considered, so that the solid solution alloy film with relatively high thermal stability and relatively low chemical reaction activity is formed. By adopting a solid solution structure, resistivity rising caused by mass precipitation of solute elements is avoided; due to the introduction of an element Nb with a large atomic radius, interdiffusion between Cu and surrounding media can be effectively blocked; and due to the proportional addition of the second group of elements Ni, the addition quantity of Nb can be greatly reduced, thereby reducing an electron scattering effect caused by large atom selves to a large extent, facilitating the stabilization of the Cu film and guaranteeing that the resistivity of the Cu film is minimally influenced. The Cu-Ni-Nb ternary alloy film can be expected to simultaneously have a diffusion blocking effect as well as high temperature stability.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Alloy article, product formed of said alloy article, and fluid machine having said product
PendingUS20200290118A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove corrosion resistanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusPump componentsChemical compositionAtomic radius
An objective of the invention to provide an alloy article that exhibits even better mechanical properties and / or even higher corrosion resistance than conventional high entropy articles without sacrificing the attractive properties thereof, a product formed of the alloy article, and a fluid machine having the product. An alloy article according to the invention has a predetermined chemical composition comprising: Co, Cr, Fe, Ni and Ti, each within a range of 5 atomic % or more and 35 atomic % or less; Mo within a range of more than 0 atomic % and less than 8 atomic %; an element with a larger atomic radius than the atomic radiuses of Co, Cr, Fe and Ni within a range of more than 0 atomic % and 4 atomic % or less; and a balance of inevitable impurities.
Owner:PROTERIAL LTD
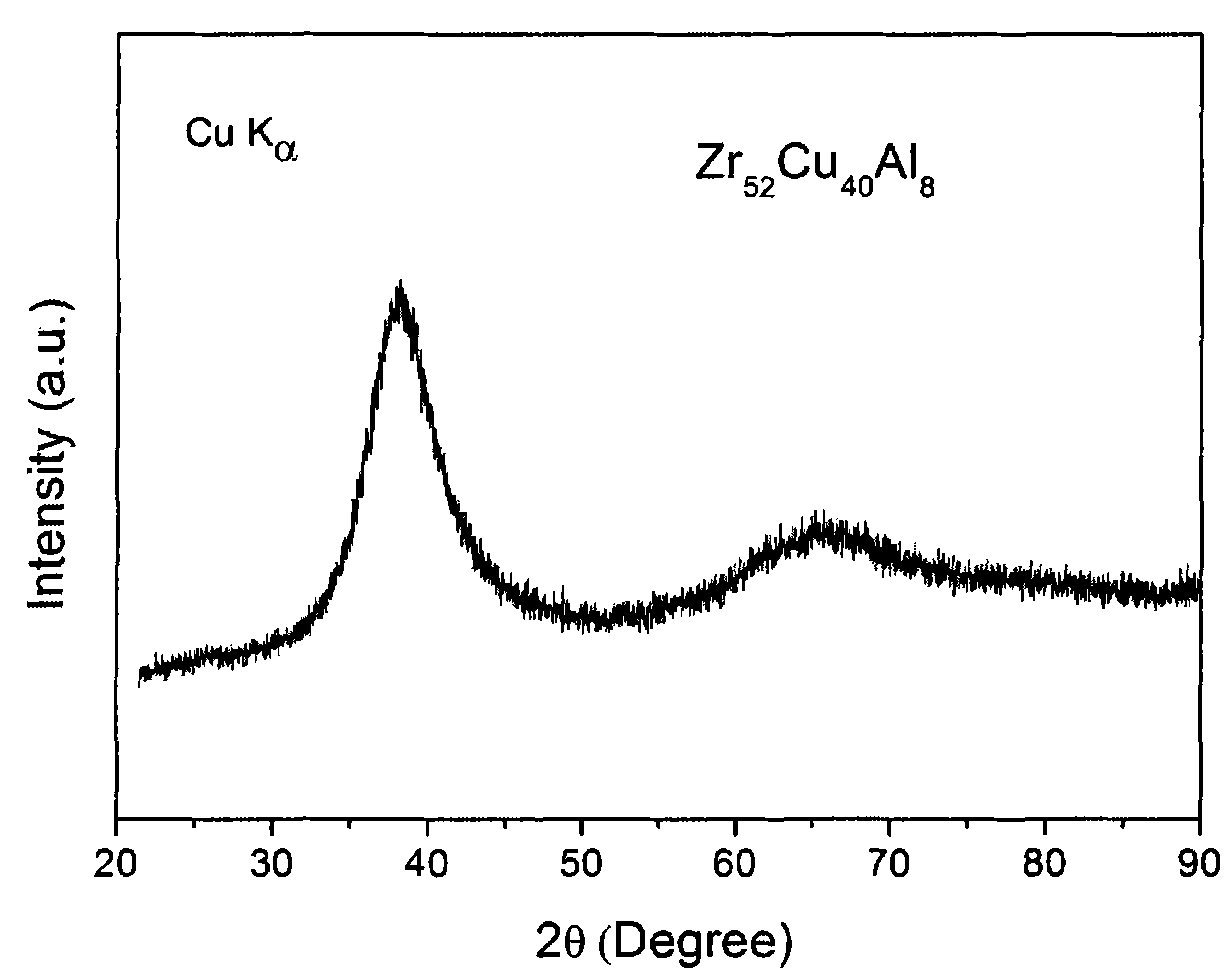
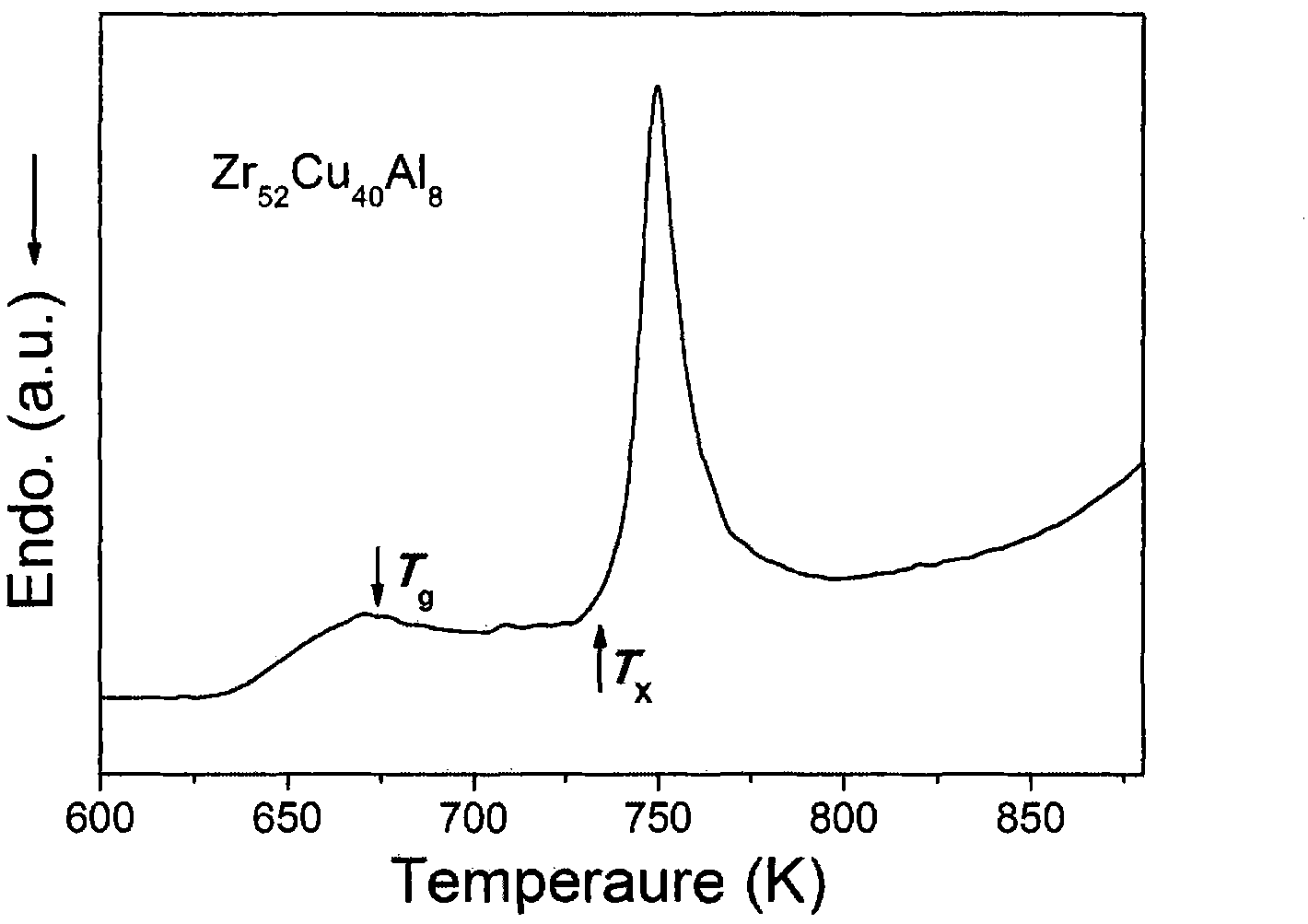
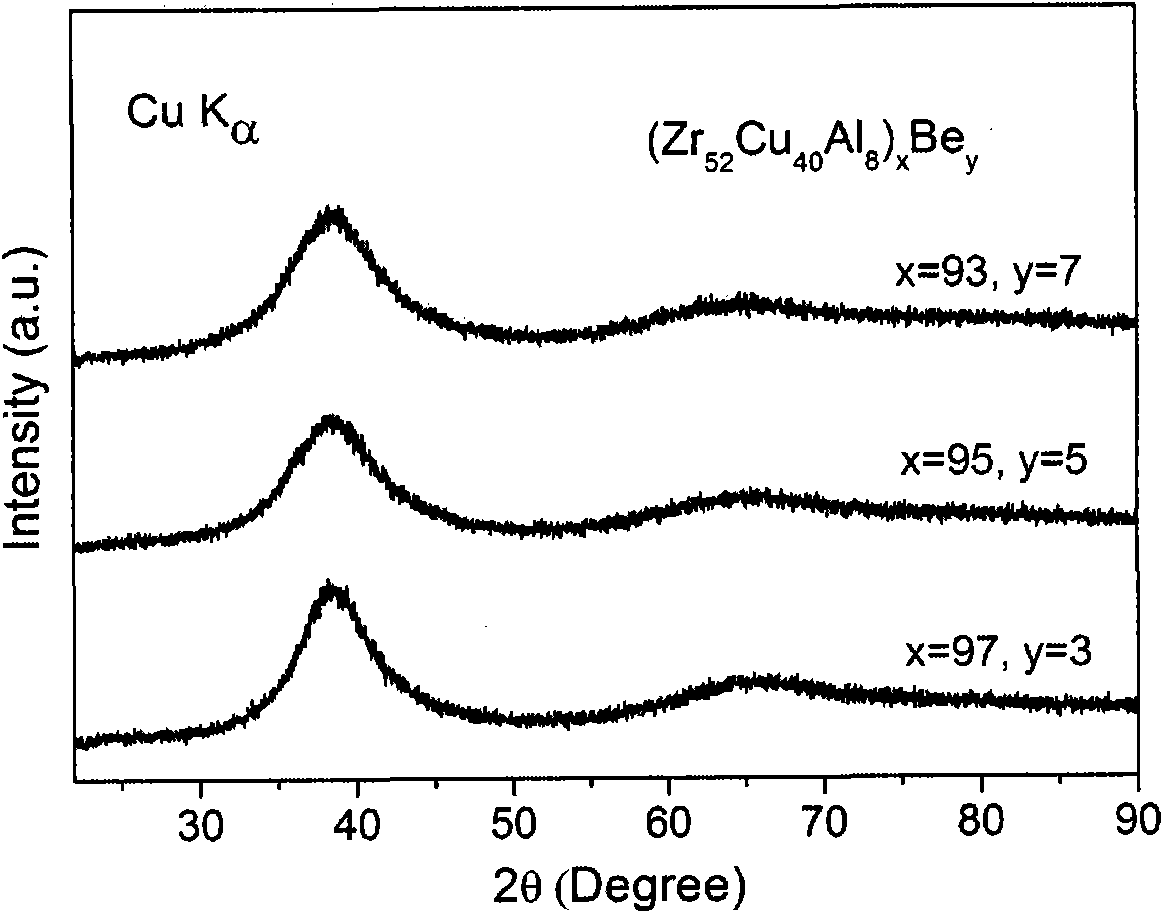
Bulk amorphous alloys of Zr-Cu-Al-Be series and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101886234AStrong industrial applicabilityLarge supercooled liquid regionAlloy elementAtomic radius
The invention relates to bulk amorphous alloys of Zr-Cu-Al-Be series with an extra-wide supercooling liquid phase region. The series of alloys take Zr52Cu40Al8 as basic ingredients, and take the metallic element Be with the minimum atomic radius as the alloying element. The composition of the series of alloy is determined through the following formula: (Zr52Cu40Al8)xBey, wherein x is the molar content of Zr52Cu40Al8, y is the molar content of Be, 80<=x<=100, 0<=y<=20, and x+y=100. The series of alloys can generate bulk amorphous alloys with the critical dimension not less than 3mm, the maximum supercooling liquid phase region reaching 123K and with excellent thermal stability. The series of alloys integrate better glass-forming ability and extra-wide supercooling liquid phase region, and can be widely used in the fields of precise parts, microelectronic components and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Electronics device, semiconductor device, and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080124848A1Show reliableDeterioration of propertyElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
N-type carrier enhancement in semiconductors
InactiveUS20100261319A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantCharge carrier
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Conductive Paste, And Electronic Device And Solar Cell Including An Electrode Formed Using The Same
ActiveUS20120174976A1Reduce charging lossHigh solar efficiencyConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialConductive pasteElectrical battery
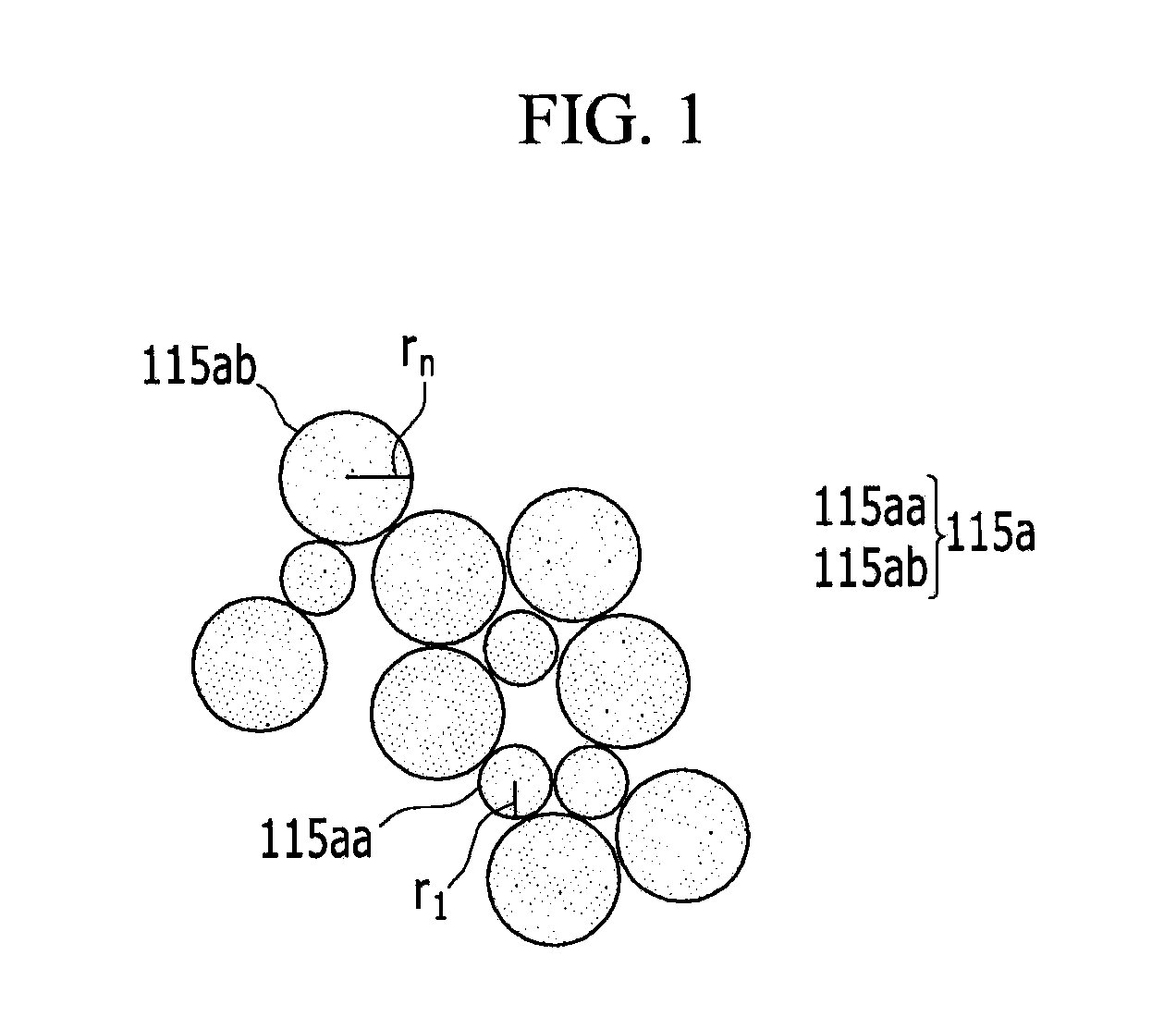
A conductive paste includes a conductive powder, a metallic glass, and an organic vehicle. The metallic glass may be an alloy including a first element with an atomic radius that satisfies the following equation: (r1−rn) / (r1+rn / 2)×100≧9% In the equation, r1 may be an atom radius of the first element, rn may be an atom radius of other elements included in the metallic glass, and n may be an integer ranging from 2 to 10.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
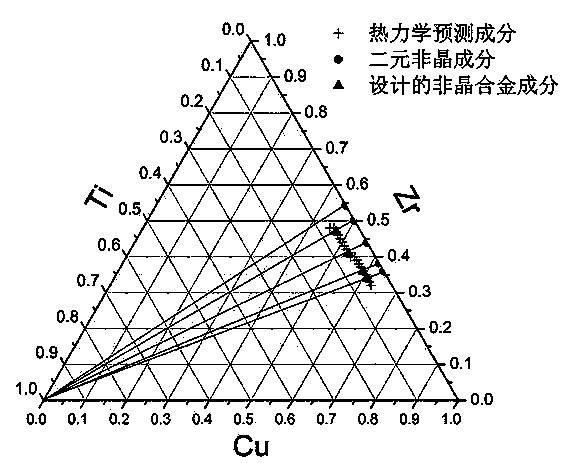
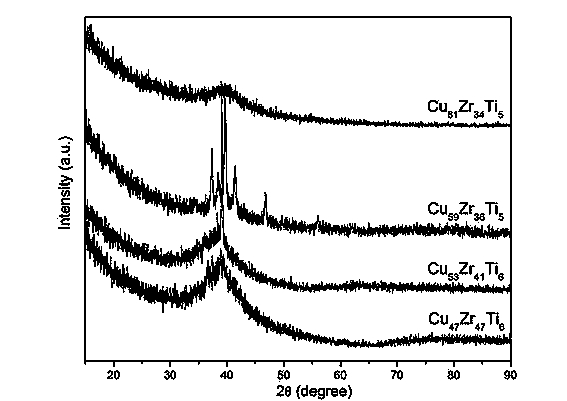
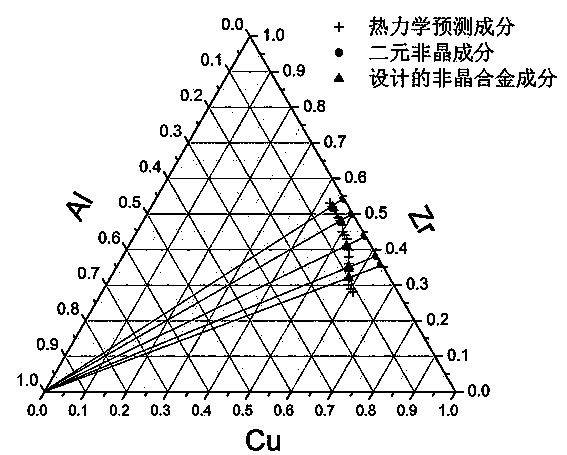
Amorphous alloy composition design method based on thermodynamics factors and structural factors
The invention discloses an amorphous alloy composition design method based on thermodynamics factors and structural factors. The amorphous alloy composition design method comprises the following steps: (1) based on binary block body metal glass, selecting a third component with the principle that the atomic radius difference is about greater than 12%, and connecting a binary amorphous composition point with the third component in a ternary diagram to obtain an atomic structure predicted composition line; (2) based on the binary block body metal glass, calculating the delta Hh.delta Hmix.Sconfig predicted value under different contents of the third component, connecting each minimal value in a ternary alloy diagram to be a line, namely a predicted composition line of thermodynamics; and (3) researching the composition relevance between the alloy at the crossed part of the two predicted composition lines in (1) and (2) and the amorphous forming capacity, and determining the intersection point composition of the two predicted composition lines, namely the amorphous alloy composition of final design. According to the composition design method provided by the invention, the accuracy of amorphous alloy composition design is improved, and the error rate in developing novel amorphous alloys is reduced. The method is simple and clear, and easy to understand and grasp.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Cerium-enriched rare earth permanent magnet applying lanthanum in batches and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107275026ASolve the problems that cannot be applied to rare earth permanent magnetsImprove magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsCeriumAtomic radius
The invention discloses a cerium-enriched rare earth permanent magnet applying lanthanum in batches and a preparation method thereof. The rare earth permanent magnet has the multi-principal-phase structure including a RE-Fe-B principal phase and one or more lanthanum added cerium-enriched principal phases. After component designing, dosing and powder making of the different principal phases are performed separately, alloy powder of the corresponding principal phases is proportionally mixed to be uniform, and then the magnet is prepared through magnetic field compression, sintering and thermal treatment. The problem that a lanthanum element cannot be applied to a rare earth permanent magnet for a long time is solved, and a large number of lanthanum elements can be applied to the rare earth permanent magnet; meanwhile, by adding the lanthanum elements with the large atomic radius into the cerium-enriched principal phase components, the magnetic performance of the cerium-enriched principal phase is kept and improved, so that the performance of the permanent magnet can meet the commercial standard, and massive production and application can be performed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microchannel plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107818902AExtended service lifeHigh gainMutiple dynode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodes manufactureRubidiumIon exchange
The invention relates to a microchannel plate and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of 1) performing bar-tube combination, wiredrawing, plate layout, melting, pressing, mechanical processing and acid cleaning on a core glass bar and a skin glass tube to obtain a microchannel plate blank; 2) performing ion exchange, cleaning, high-temperature reduction and film coating on the microchannel plate blank in molten salt to obtain a microchannel plate, wherein the molten salt comprises rubidium salt and / or cesium salt. According to the invention, ion exchange isperformed on the microchannel plate blank, so that rubidium ions and cesium ions with high atomic weight and large atomic radius replace potassium ions and sodium ions in a reflecting layer, the electron flushing resistant performance of the reflecting layer is improved by the aid of increase in atomic weight of alkali metal ions and a volume congestion effect, so that the service life and the gain performance of the microchannel plate are improved, and the service life and the gain of the microchannel plate are improved by more than 30% and 20% respectively.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core and application thereof
The invention discloses an iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core in the technical field of nano amorphous alloys. The iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core comprises, by weight, 71-75 parts of Fe, 9-15 parts of Si, 12.5-13.5 parts of B, 0.8-1.2 parts of Cu and a promoting material, wherein the promoting material is 2-4 parts of Nb or 0.5-3 parts of Mo. The iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core has the advantages that the use amount of the raw materials is optimized, the Fe is used as the base raw material, the Si and the B which are small in atomic radius are used to promote the formation of the amorphous alloy, the interaction among the Cu, the Nb (or Mo) and the other raw materials is utilized to allow the crystalline grain in the prepared iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core to be fine, a magnetic domain crystal structure is optimized, and accordingly the initial permeability of the iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core in volt-ampere characteristic tests is increased, the volt-ampere characteristic output of the iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core is allowed to be gentle, and the application performance of the iron-based nano amorphous magnetic core in sensors, electronic inductor components or current transformers is optimized.
Owner:贵州鑫湄纳米科技有限公司
Display device
InactiveCN101174053AImprove toughnessEasy to processElectrical apparatusStatic indicating devicesAvogadro constantDisplay device
The invention provides a display device which comes into being through taking advantage of a hard transparent substrate, which has the characteristics of the inorganic glass and the plastics and is good in curve resistance, and laminating various electronic materials used by the display devices. The hard transparent substrate can be obtained through hardening an indurative resin indicated by a general formula (1). The indurative resin has a compact structure part (A) which has a Kp calculated according to a formula (2) ranging from 0.68 to 0.8 and a loose structure part (B) which has a Kp less than 0.68, wherein, the weight ratio of the structure parts (A) / (B) ranges from 0.01 to 5.00. The indurative resin also has a least one unsaturated link, with an average molecular weight ranging from 800 to 60,000. -{(A)-(B)m}n- (1) (m and n are integers greater than 1) Kp=An.Vw.p / Mw (2) (An= Avogadro constant, Vw= van der waals volume, p=density, Mw=molecular weight, Vw=summation of Va, Va=4pi / R3-summation of1 / 3pihi2(3Ra-hi), hi= Ra- (Ra2+di2-Ri2) / 2di, Ra= atomic radius, Ri=radius of bonded atom, and di= interatomic spacing).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CHEMICAL CO LTD
Rolled copper foil and negative electrode of lithium ion secondary battery using same
InactiveCN102899519AExtend your lifeImprove securityElectrode carriers/collectorsSecondary cellsLithiumMetallurgy
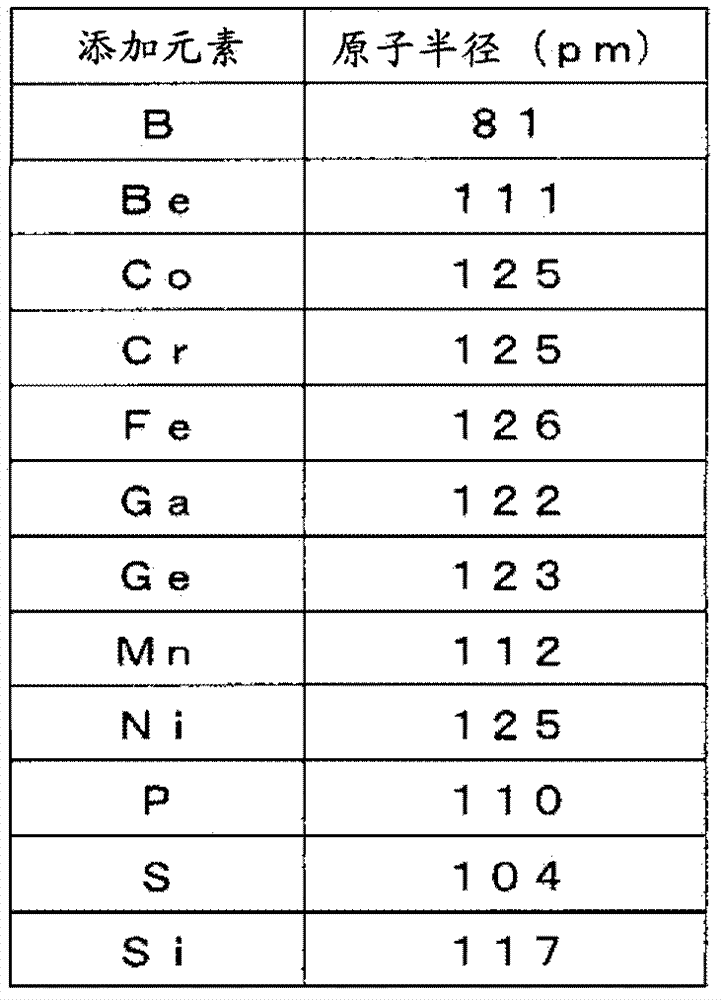
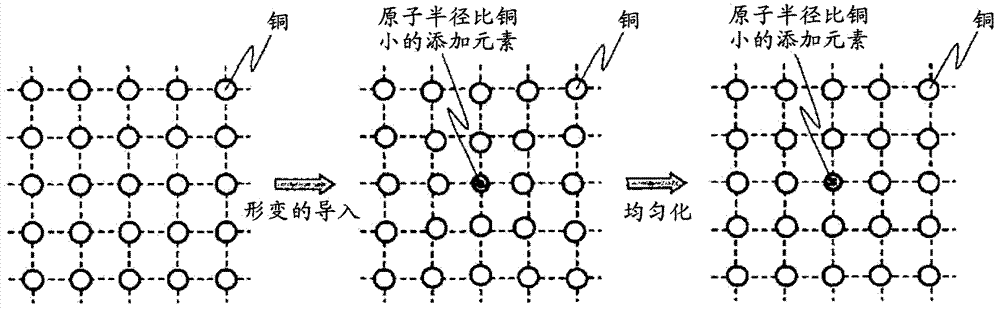
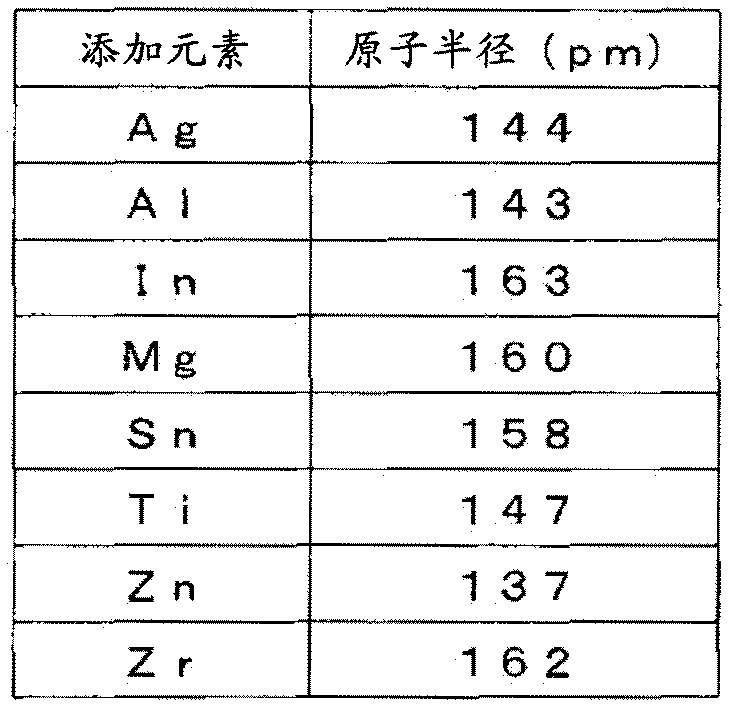
The invention relates to rolled copper foil and a negative electrode of lithium ion secondary battery using the same. The rolled copper foil not only is of high intensity, high heat resistance, high conductive rate and good processing ability and the like, and has high tightness of the resin contained in a negative electrode active material layer without applying coarse processing such as plating of electro-deposition particles on a surface of the copper foil. The rolled copper foil is characterized by comprising a main component of Cu, adding elements A containing one or more elements atomic radius is smaller than that of the Cu, and copper alloy containing unavoidable impurities, wherein variation of the atomic distance is below -0.002pm when a total of (atomic radius difference of each adding element of the adding element A and the Cu) plus (atom% of each adding element) is taken as the variation of atom distance caused by the adding element, and a total quantity of the adding element A is below 1.0 weight%.
Owner:SH COPPER PROD CO LTD
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
ActiveCN106653781ABroaden the wavelength rangeImprove recrystallization recovery abilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal impuritiesAtomic radius
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device. In annealing and re-crystallization technologies, the wavelength range of electromagnetic waves is expanded from a visible light waveband to an infrared light waveband. when the atomic radius of injected impurities is greater than that of semiconductor substrate elements, the annealing process of the infrared waveband, on the basis of a traditional annealing technology, can reach a deeper area under the surface of a silicon chip, and thus, the recrystallization recovery capability of the substrate is improved, crystal lattice displacement of a deep doped area can be reduced, diffusion of metal impurities to the semiconductor substrate is inhibited, and defects of white pixels can be eliminated effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT
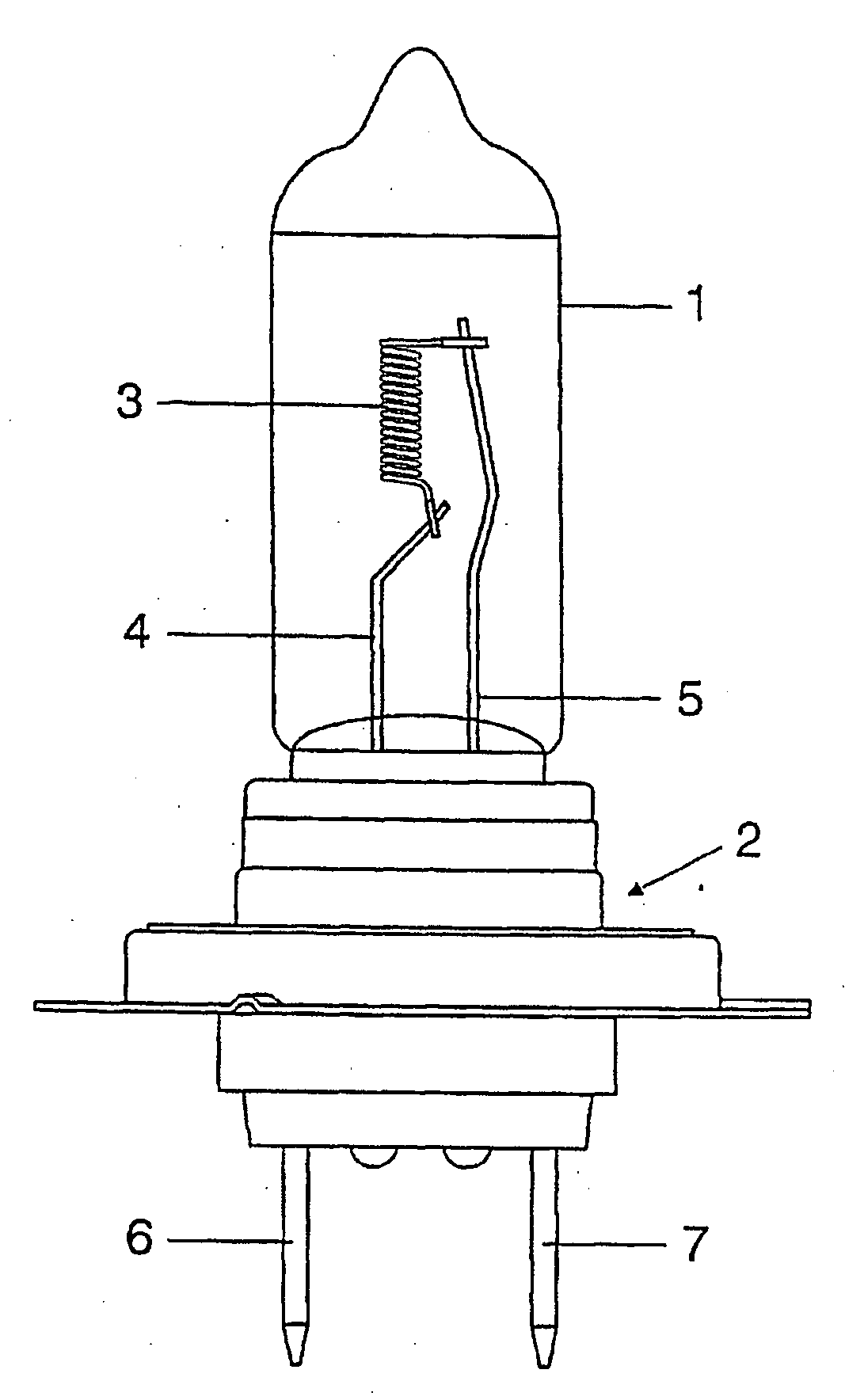
Incandescent Halogen Lamp
InactiveUS20080164813A1Low tungsten evaporation rateAvoid insufficient heatingImage pickup tubesIncandescent lamp energy savingKryptonHalogen
The invention relates to an incandescent halogen lamp, comprising at least one tungsten incandescent filament (3) in a transparent light bulb (1) and a filling in the light bulb (1), which has a halogen component for a halogen recycling process and a noble gas component containing krypton or xenon, whereby the noble gas component comprises at least one further noble gas, the atoms of which have a smaller atomic radius than krypton atoms and the cold filling pressure within the light bulb (1) is greater than or equal to 0.7 Megapascal. Said incandescent halogen lamp is suitable as light source in a curved lamp or as combined day running or position light in a motor vehicle.
Owner:PATENT TREUHAND GESELLSCHAFT FUR ELECTRIC GLUEHLAMPEN MBH
A heuristic high-throughput material simulation calculation optimization method
ActiveCN109635473AGood effectImprove performanceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsComputational simulationAtomic radius
The invention provides a heuristic high-throughput material simulation calculation optimization method, and belongs to the field of material science. The method comprises the following steps: firstly,determining a shared execution mode of all jobs in high-throughput material calculation simulation; Selecting an unexecuted job from the model containing the maximum number of the unexecuted jobs inthe high-throughput material calculation simulation, and executing the job by adopting an independent execution mode; And obtaining the next execution job by using the heuristic information until alljobs in the high-throughput material calculation simulation are executed. According to the method, adjacent relations between different elements in the periodic table of elements and atomic radiuses of the different elements are used as heuristic information, so that the execution efficiency of the high-throughput operation can be greatly improved, and the design time of a new material is greatlyshortened.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
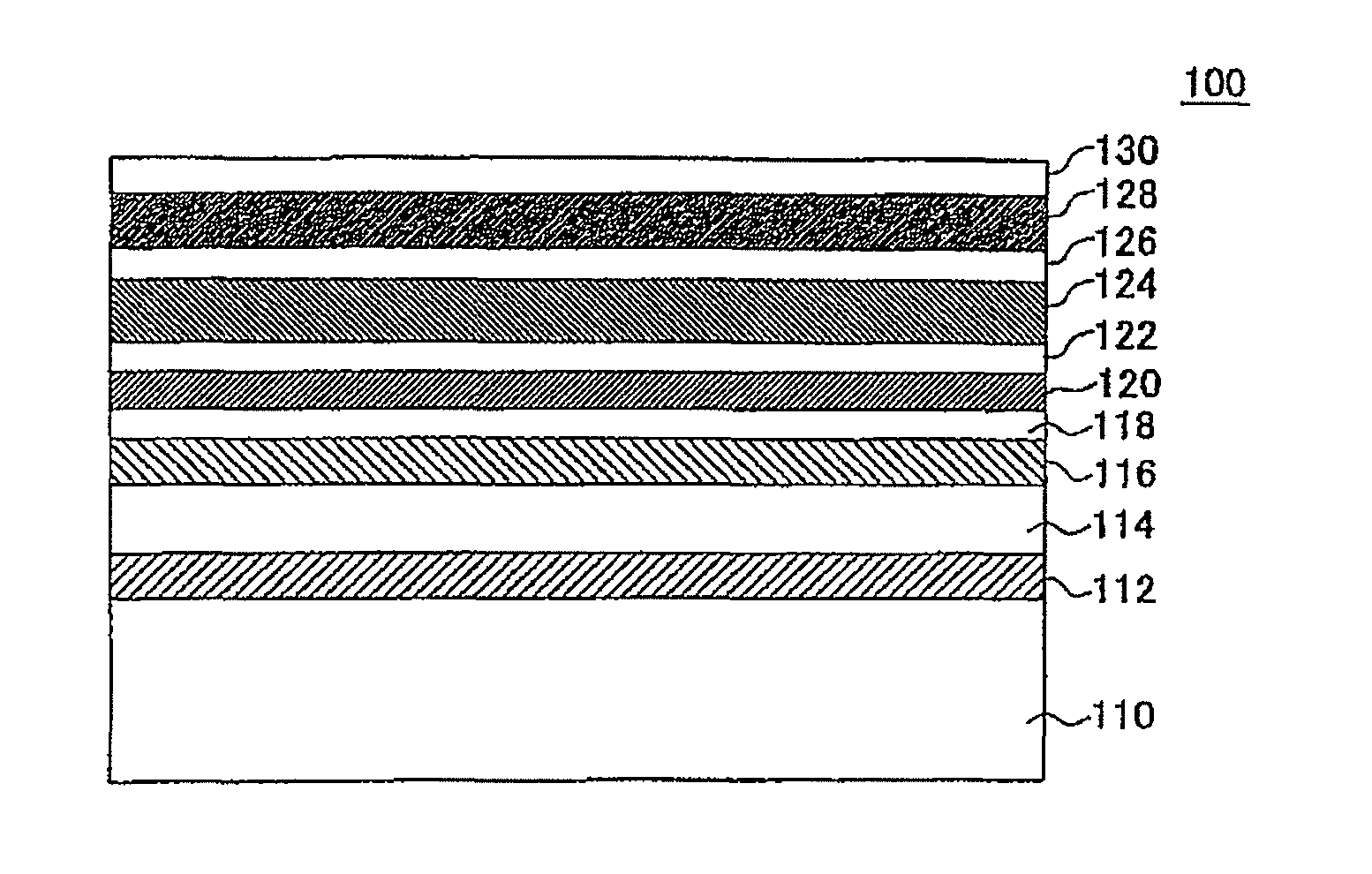
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9159351B2Improve recording densityImprove coercive forceBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageOptoelectronicsAtomic radius
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a substrate, a soft magnetic layer, a pre-underlayer, an underlayer, and a main recording layer serving as a magnetic recording layer. The pre-underlayer contains seed crystal grains that serve as a base for crystal grains of the underlayer, and an addition substance that is added between the seed crystal grains and composed of an element having an atomic radius smaller than that of an element forming the seed crystal grains.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Preparation technology of silicon-carbon composite negative electrode material
InactiveCN108091842AHigh bond energyImprove stabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsCarbon compositesCarbonization
The invention relates to a preparation technology of a silicon-carbon composite negative electrode material. In the preparation technology, a coated modified auxiliary material is used as high-purityindustrial silicon, and a graphite main material is low-ash anthracite. Through innovative adoption of glucose coating carbonization, a coating material is approximately nanocrystalized, so that a coating layer is formed more perfectly and uniformly; fluorocarbon resin is used, fluorine is an element with unique and stable properties, and in the periodic table, fluorine has the strongest electronegativity and the lowest polarizability and has the atomic radius is second only to that of hydrogen; therefore, C-F bonds are very difficultly destroyed by light, heat, electrochemical factors and thelike, F atoms have more negative charges, the adjacent fluorine atoms are mutually exclusive, the fluorine atoms on a fluorine-containing hydrocarbon chain are spirally distributed along C-C bonds ofgraphite, and peripheries of the C-C bonds are surrounded by the fluorine atoms to form a highly-stable three-dimensional protection barrier to protect the stability of the graphite, so that the graphite structure in the charge and discharge process of a lithium battery is improved and the cycle life is increased; the first-time capacity of the industrial silicon is lower by 1500-2000mah / g.
Owner:四川吉瑞德新能源材料有限公司
Semiconductor device with multilayer conductive structure formed on a semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS7012312B2Improve adhesionEasy to integrateSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBond energyDevice material
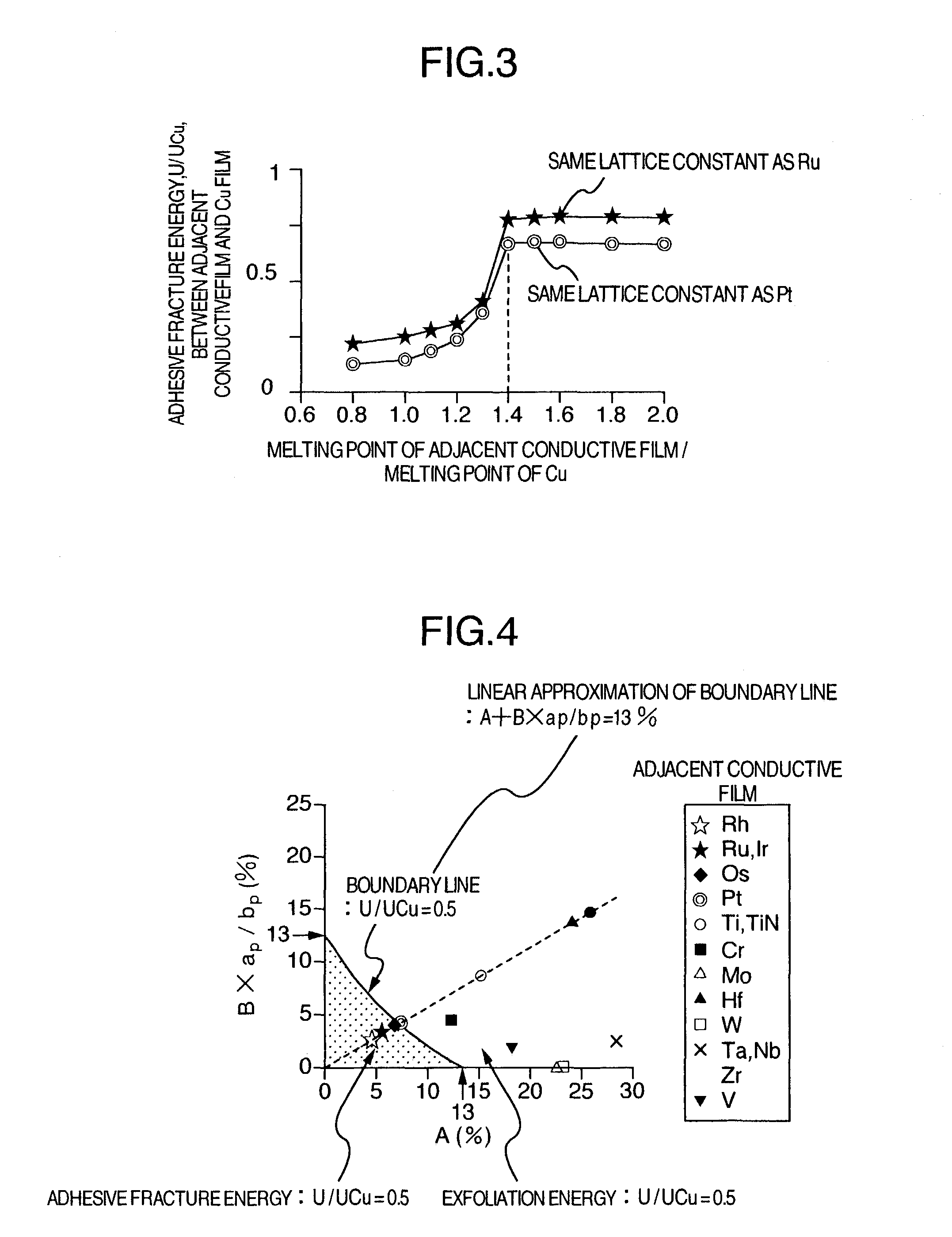
A highly reliable semiconductor device having a multilayer structure including an insulating film, an adjacent conductive film, and a main conductive film in which adhesive fractures, voids and disconnections are unlikely to occur. Regarding main constituent elements of the adjacent conductive film and the main conductive film, lattice mismatching is made small, the melting point the adjacent conductive film is set to be not less than 1.4 times that of the main constituent element of the main conductive film, the adjacent conductive film contains at least one different kind of element, the difference between the atomic radius of an added element and that the atomic radius the adjacent conductive film is set to be not more than 10%, and / or bond energy between the added element and silicon (Si) is not less than 1.9 times that of the main constituent element of the adjacent conductive film and silicon (Si).
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Thermoelectric semiconductor
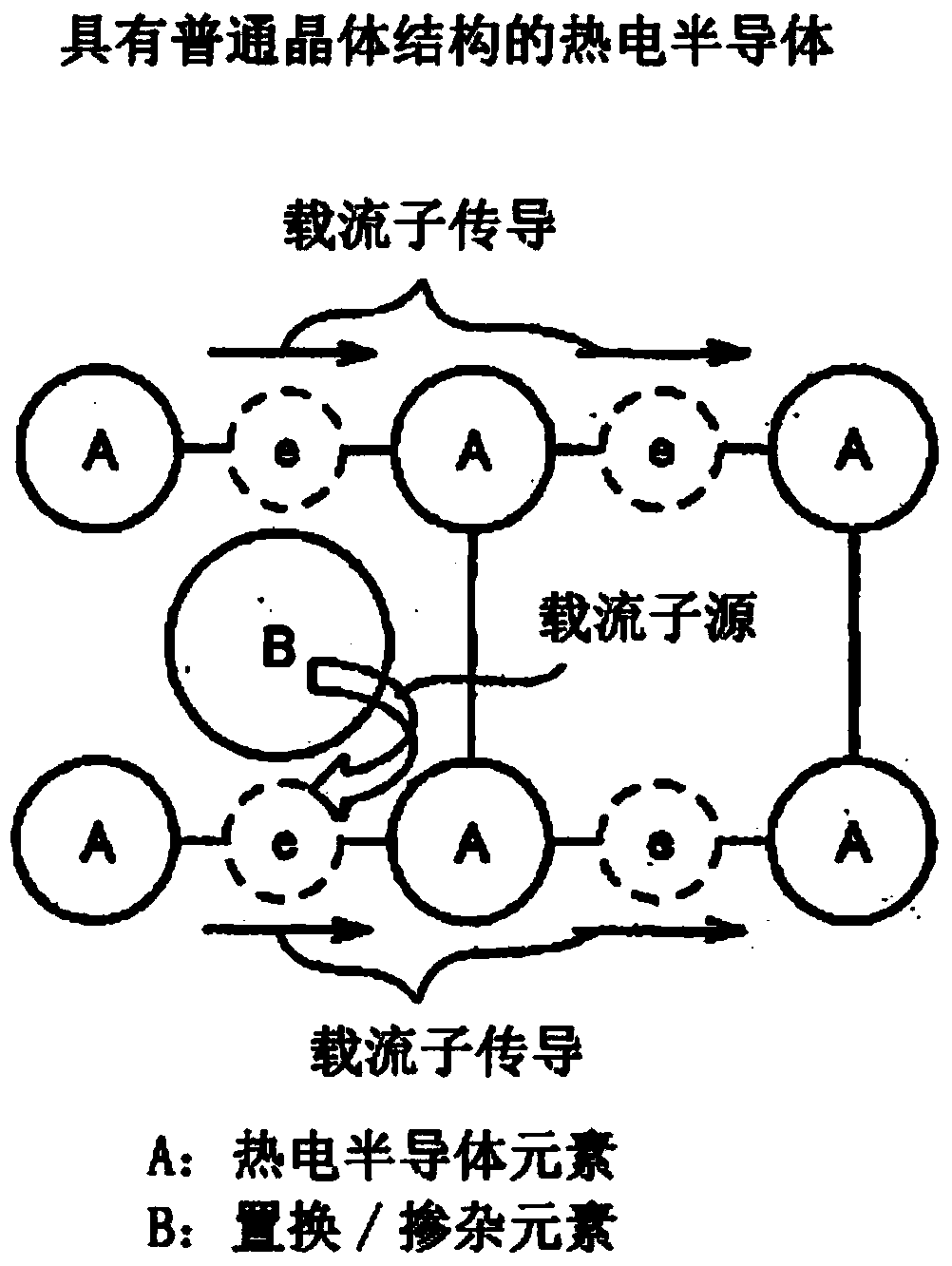
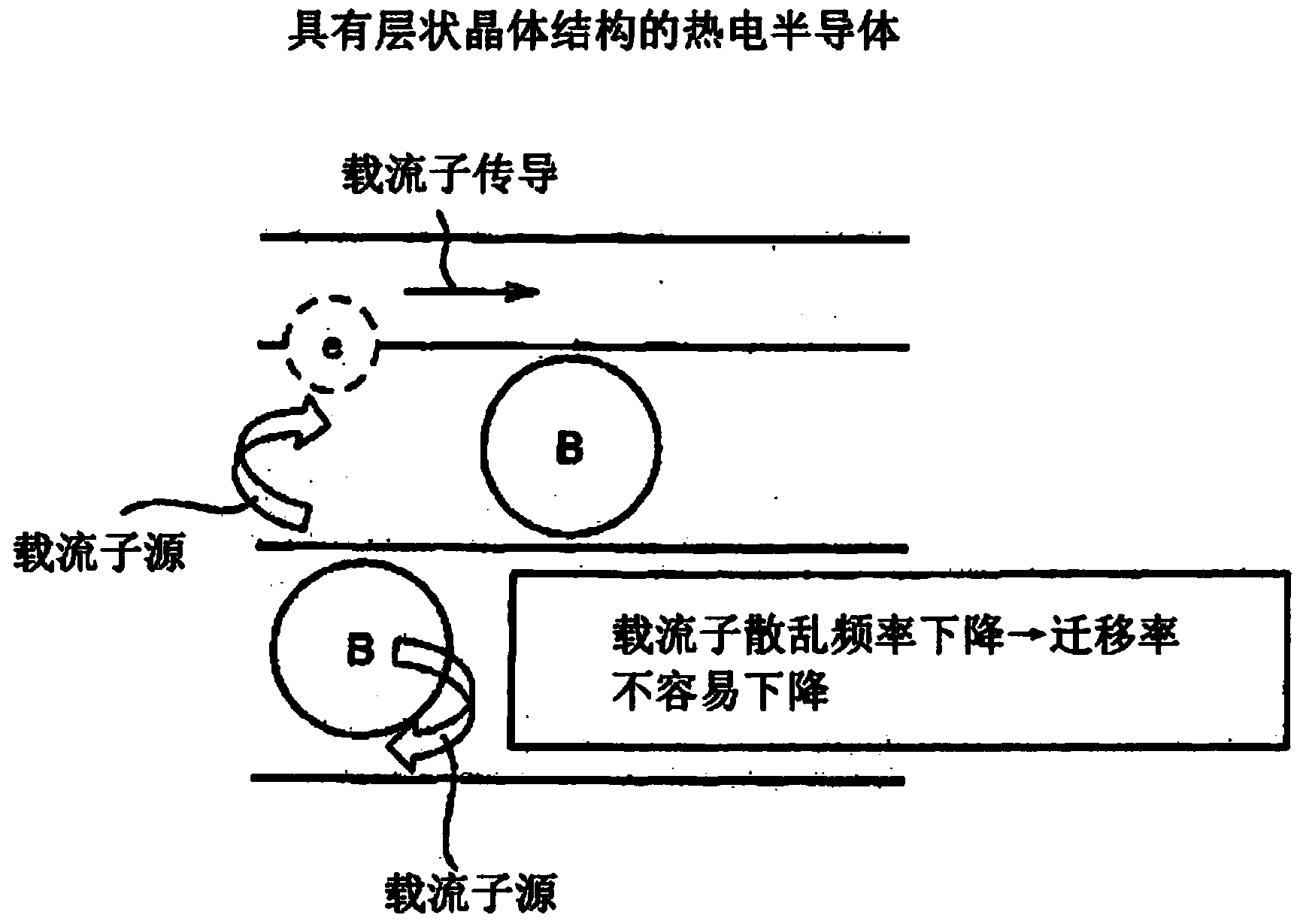
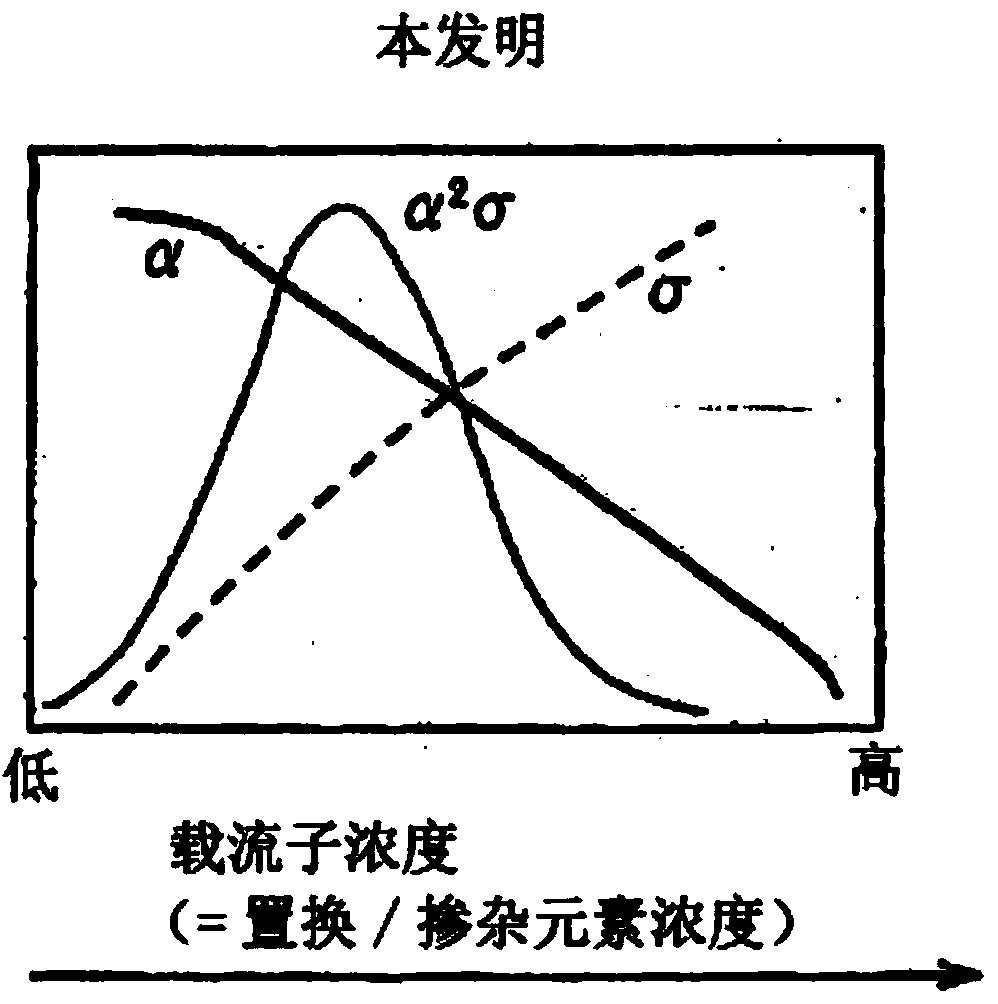
InactiveCN104254928AHigh figure of meritHigh conductivity σSelenium/tellurium compounds with other elementsThermoelectric device junction materialsAtomic radiusSemiconductor
A thermoelectric semiconductor includes a matrix element that forms a matrix, and a dopant element having an atomic radius that is at least 1.09 times as large as the atomic radius of the matrix element.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com