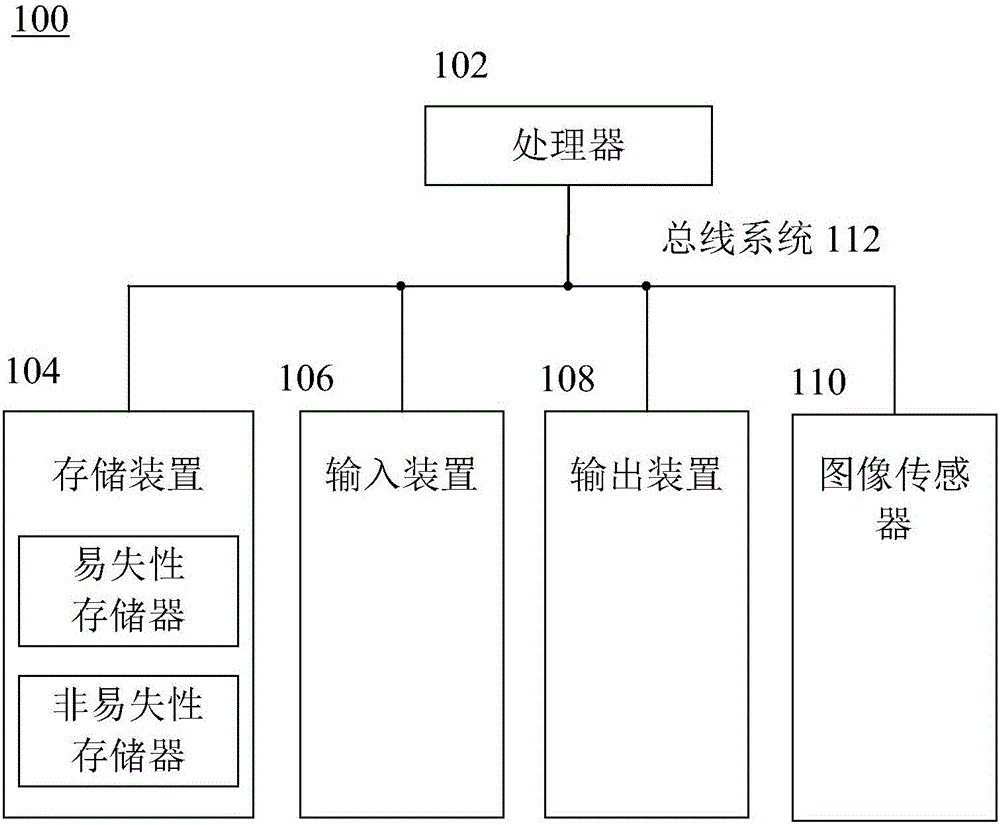
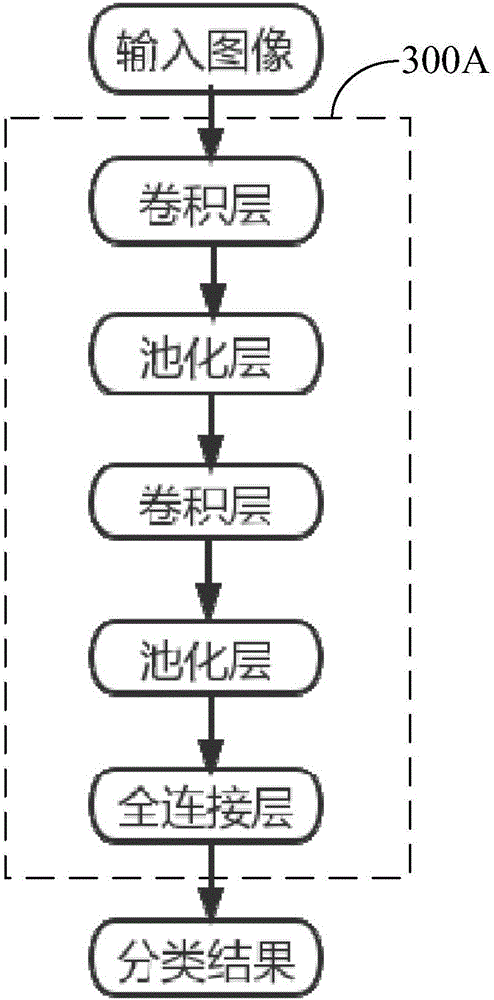
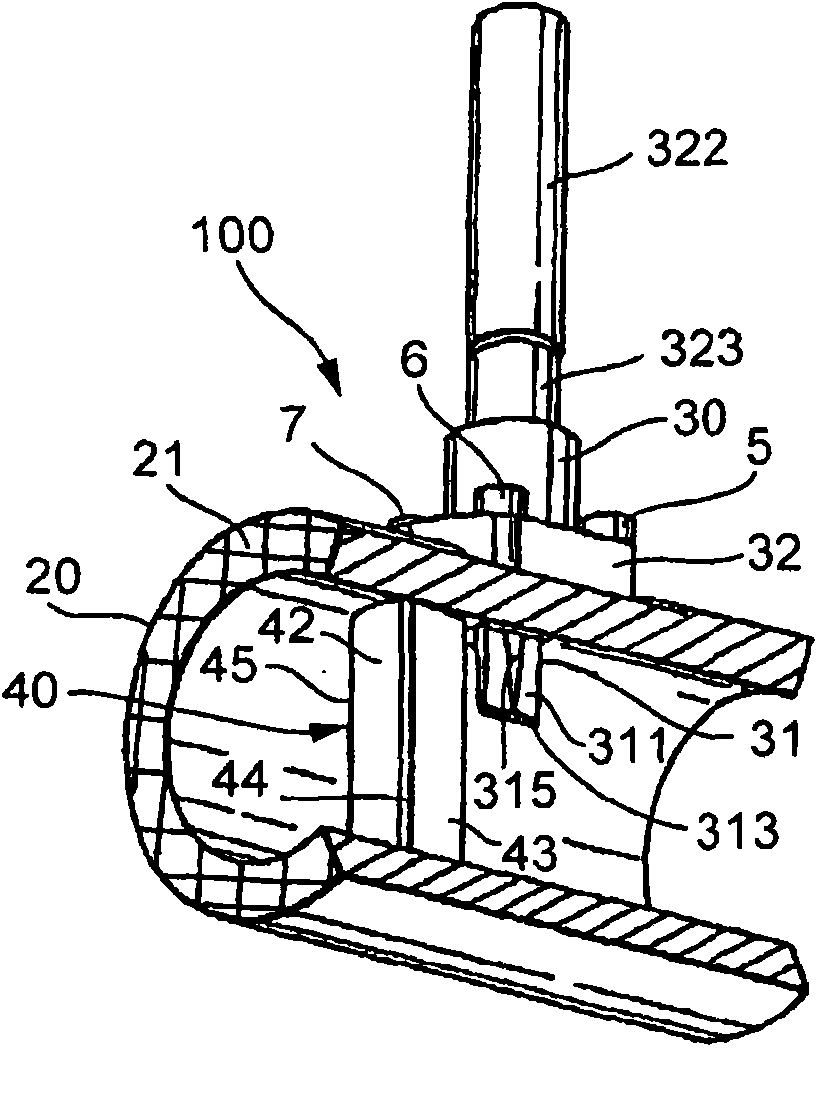
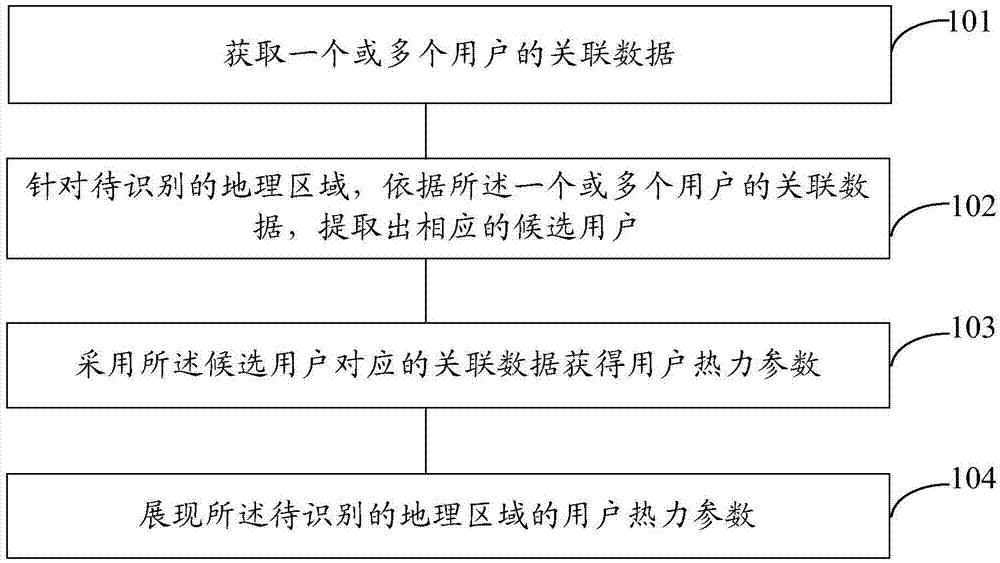
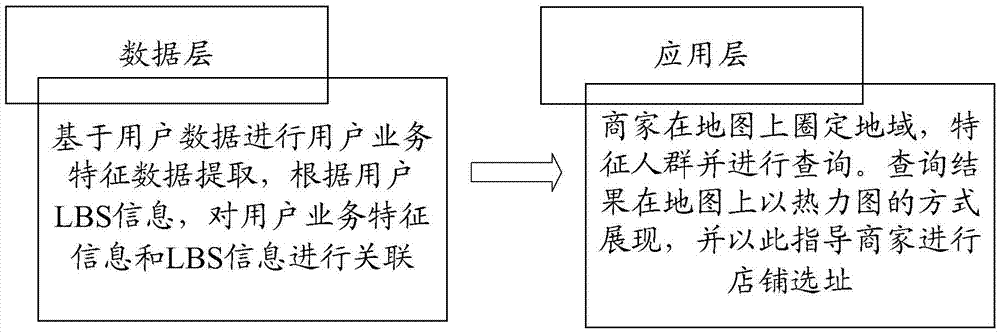
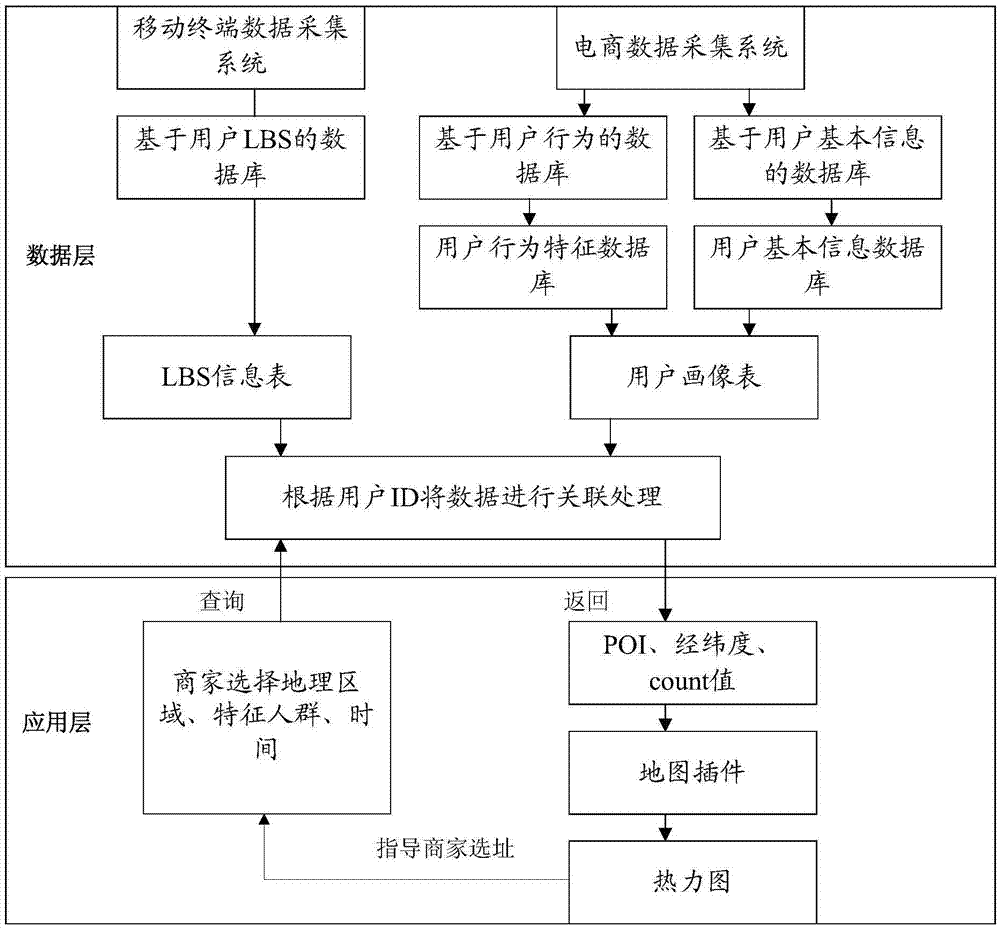
Patents
Literature
118 results about "Thermodynamic state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
For thermodynamics, a thermodynamic state of a system is its condition at a specific time, that is fully identified by values of a suitable set of parameters known as state variables, state parameters or thermodynamic variables. Once such a set of values of thermodynamic variables has been specified for a system, the values of all thermodynamic properties of the system are uniquely determined. Usually, by default, a thermodynamic state is taken to be one of thermodynamic equilibrium. This means that the state is not merely the condition of the system at a specific time, but that the condition is the same, unchanging, over an indefinitely long duration of time.
Method and System for Tank Refilling
ActiveUS20110259469A1Improve performanceLow costCapsCap application using vaccuumAnalytical equationsEngineering
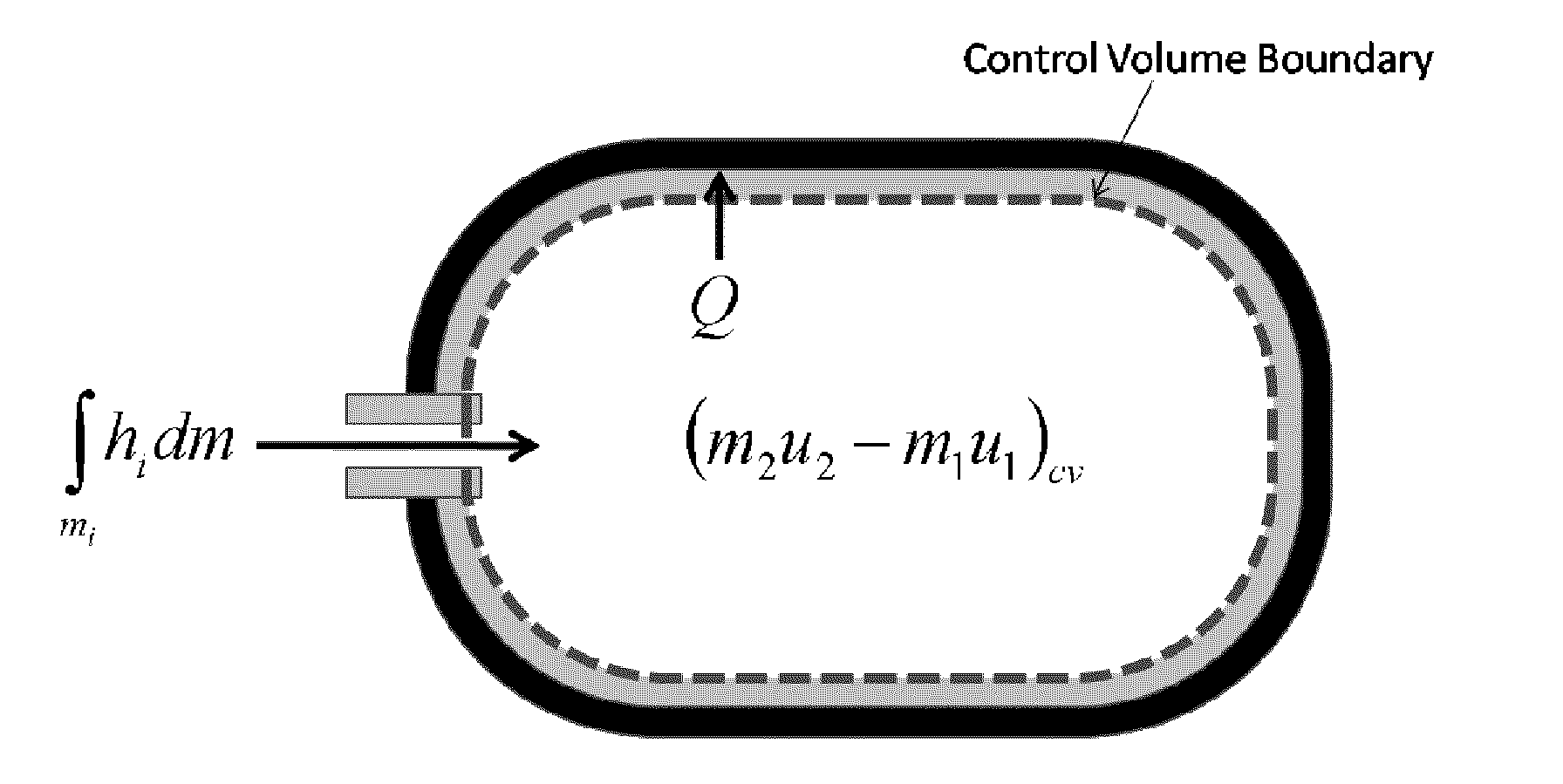
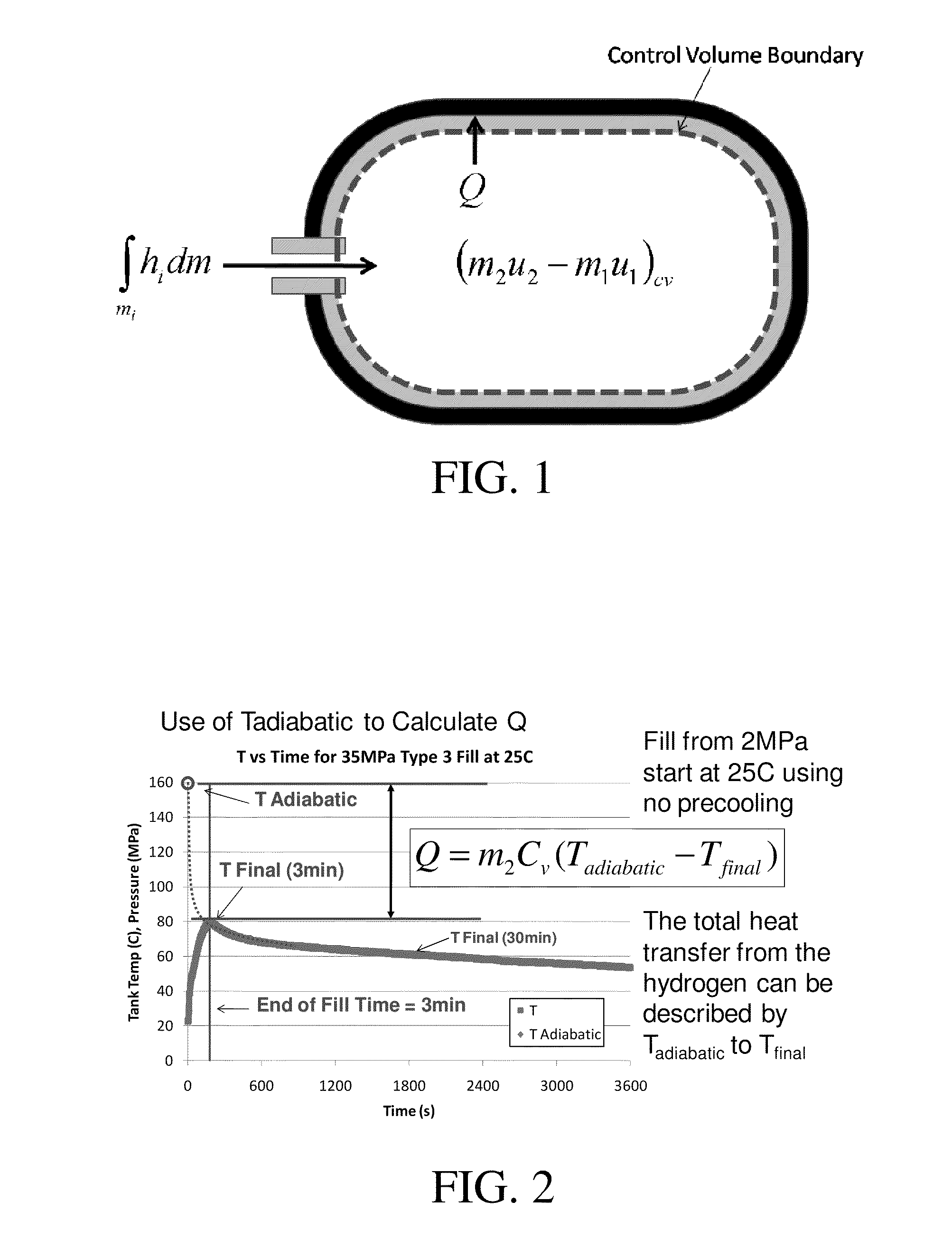
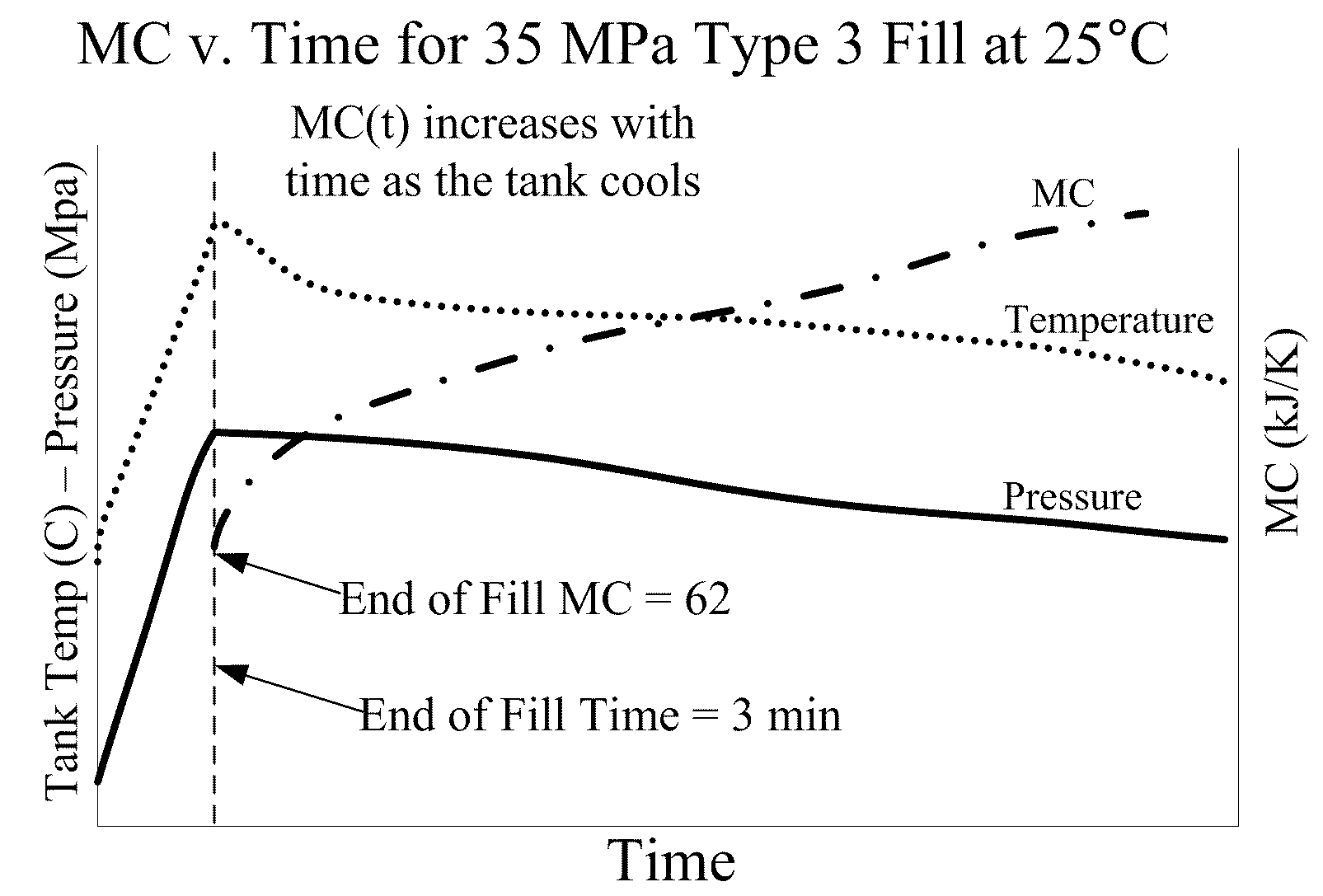
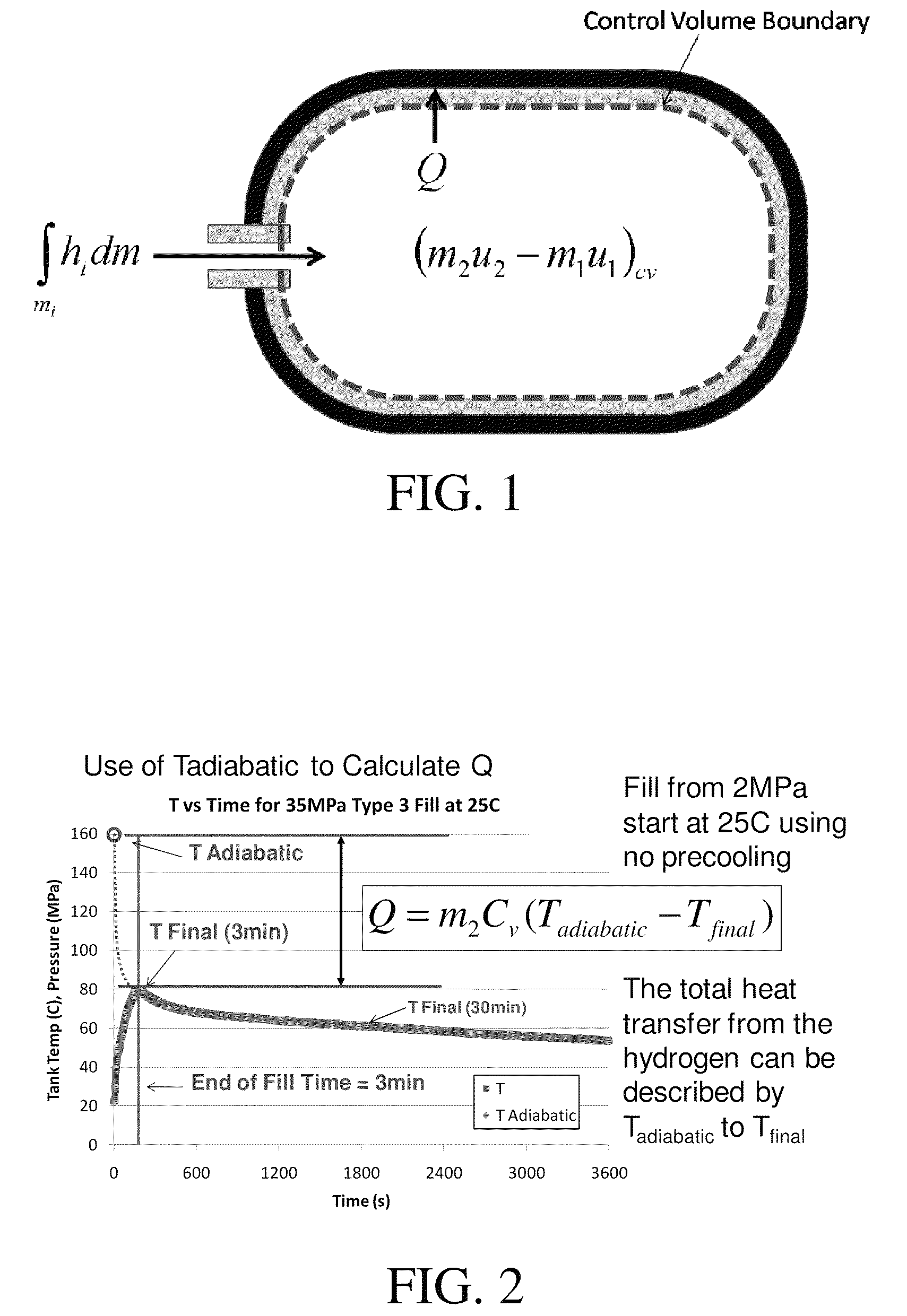
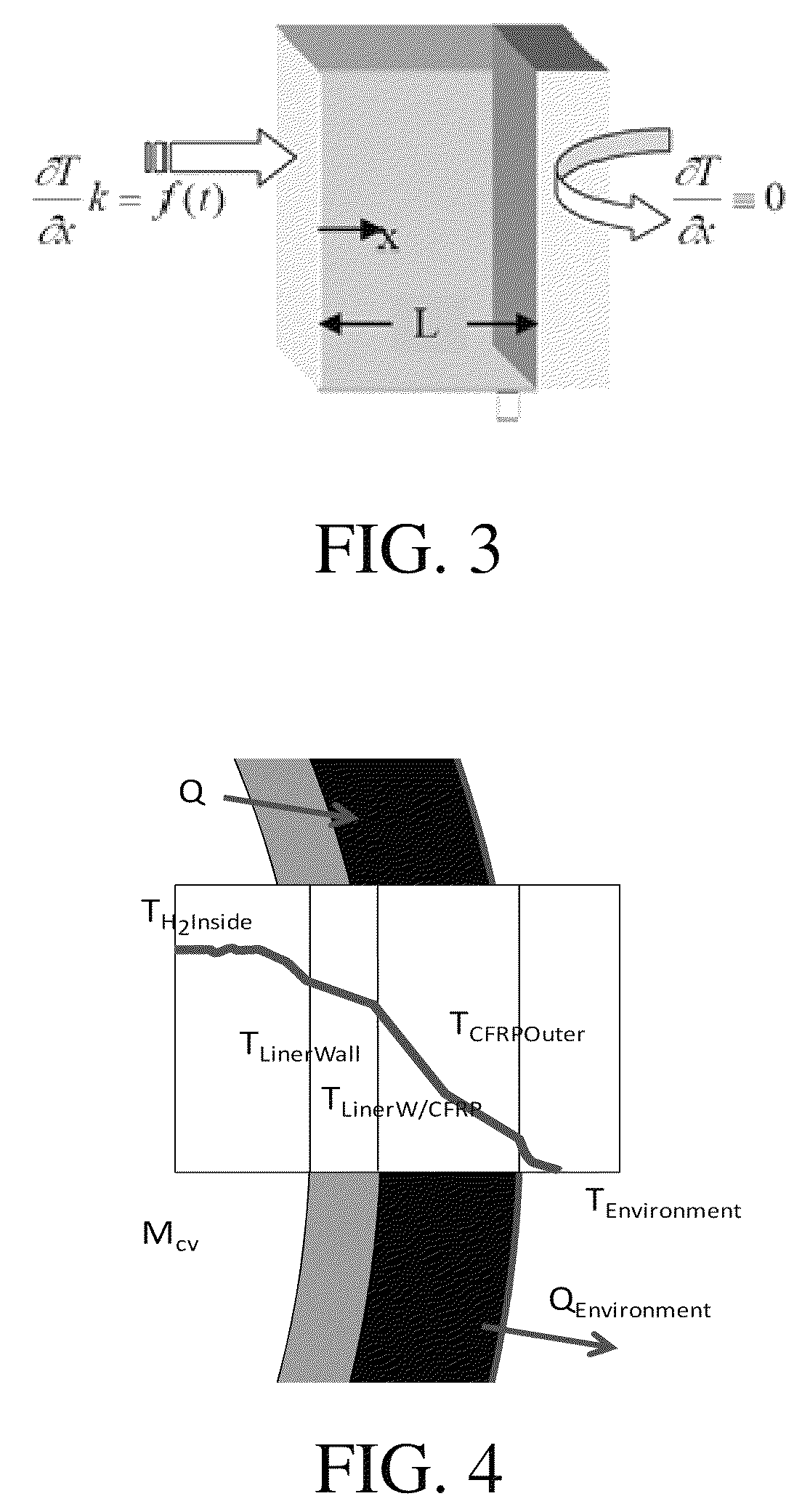
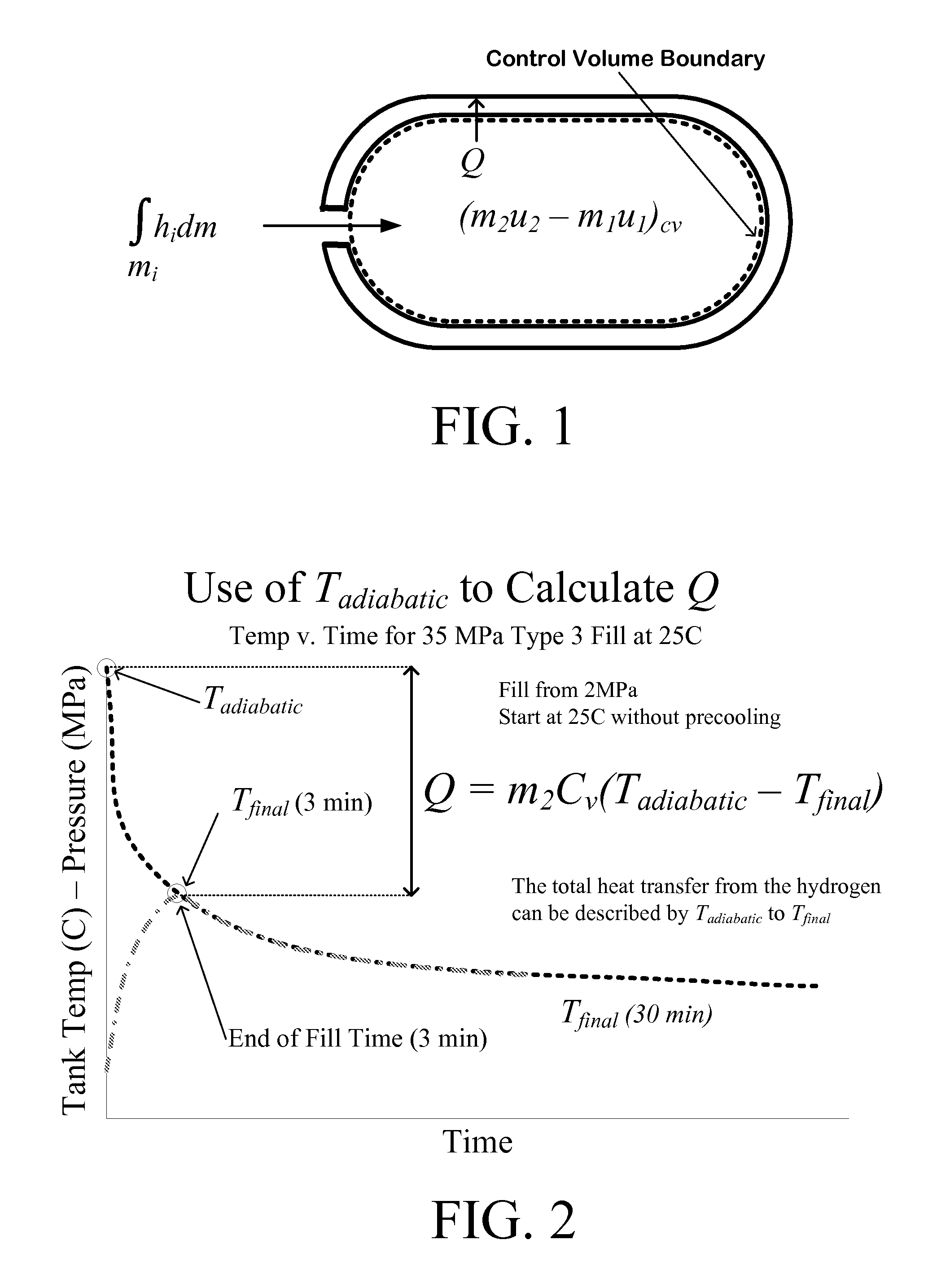
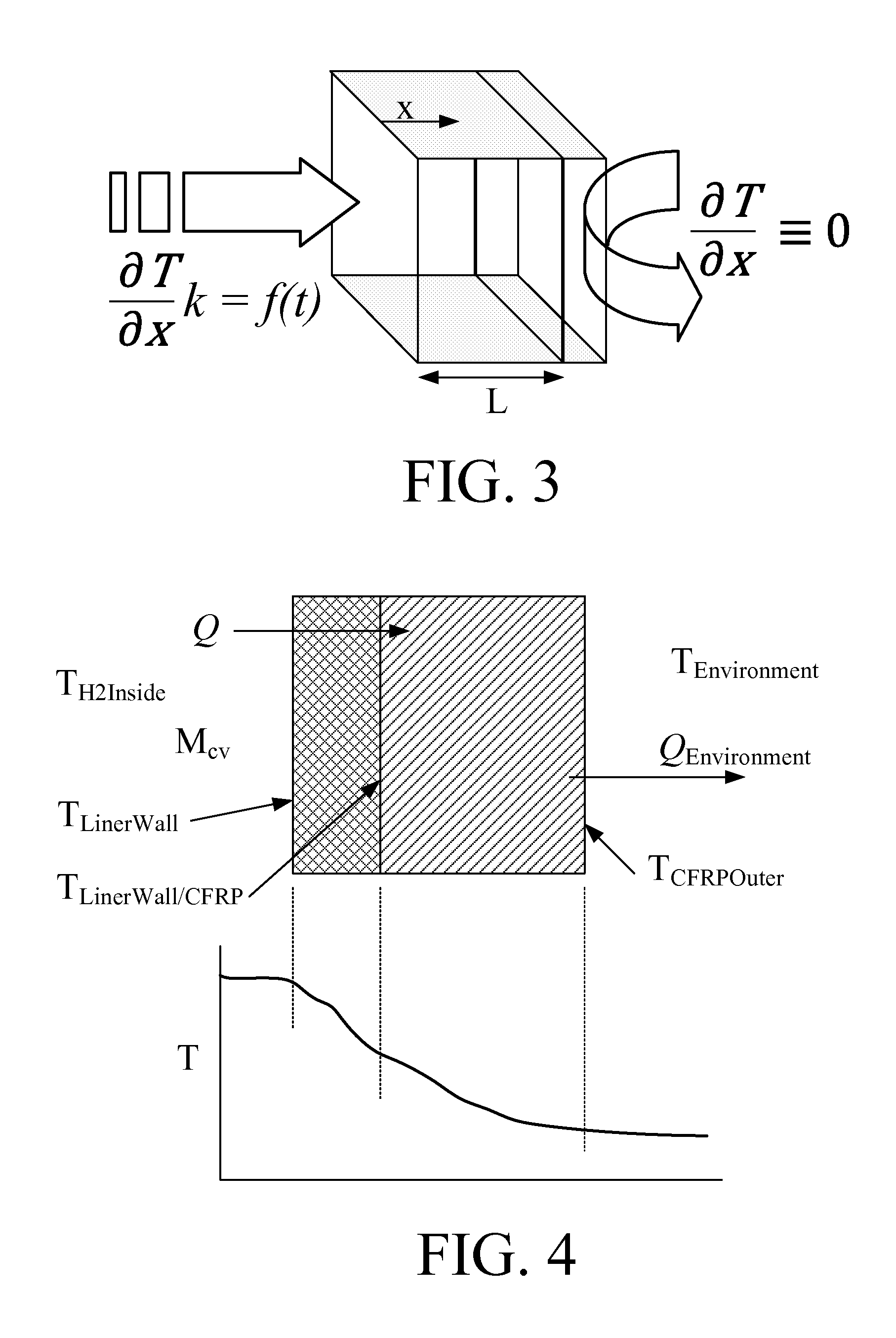
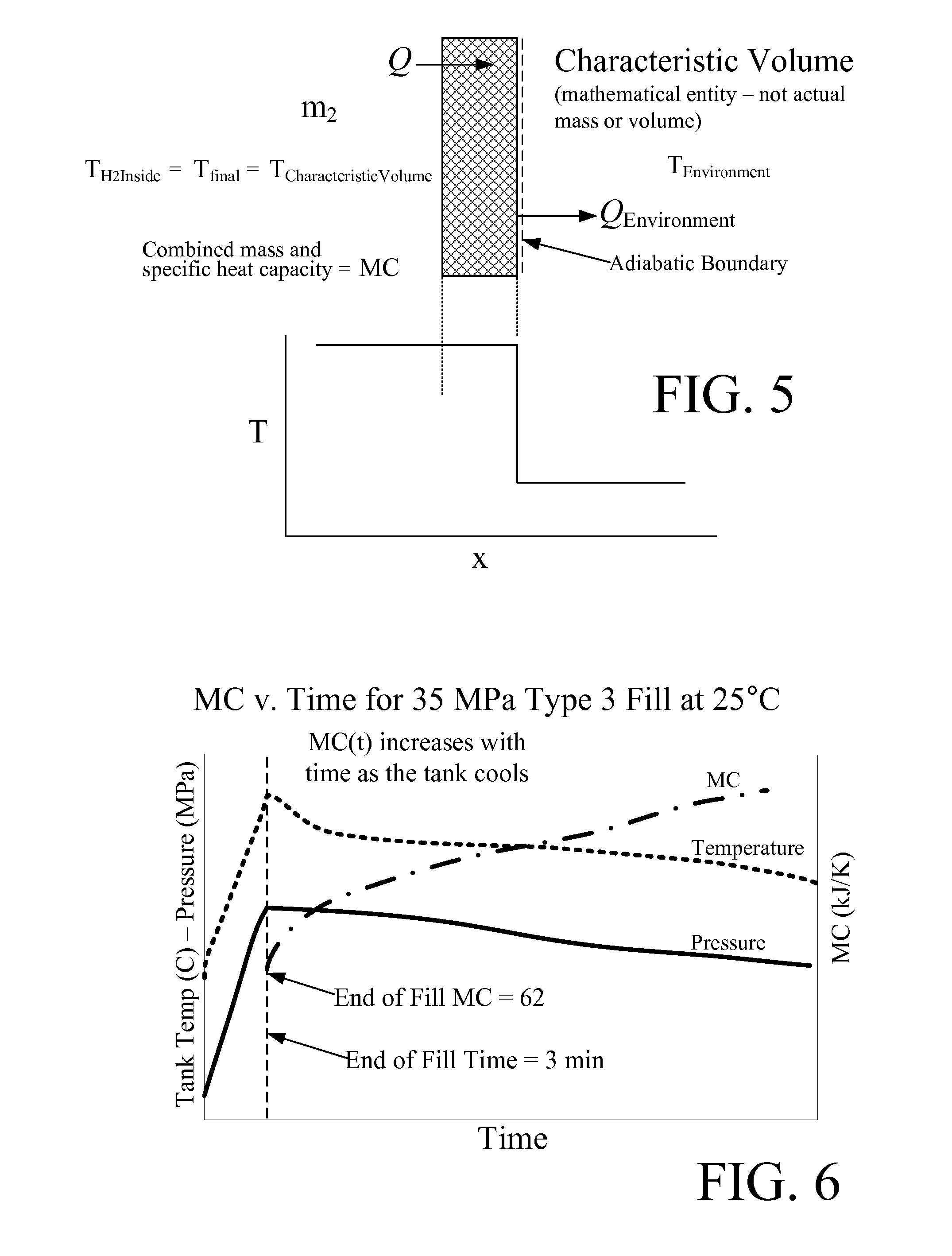
Disclosed is a simple, analytical method that can be utilized by hydrogen filling stations for directly and accurately calculating the end-of-fill temperature in a hydrogen tank that, in turn, allows for improvements in the fill quantity while tending to reduce refueling time. The calculations involve calculation of a composite heat capacity value, MC, from a set of thermodynamic parameters drawn from both the tank system receiving the gas and the station supplying the gas. These thermodynamic parameters are utilized in a series of simple analytical equations to define a multi-step process by which target fill times, final temperatures and final pressures can be determined. The parameters can be communicated to the station directly from the vehicle or retrieved from a database accessible by the station. Because the method is based on direct measurements of actual thermodynamic conditions and quantified thermodynamic behavior, significantly improved tank filling results can be achieved.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
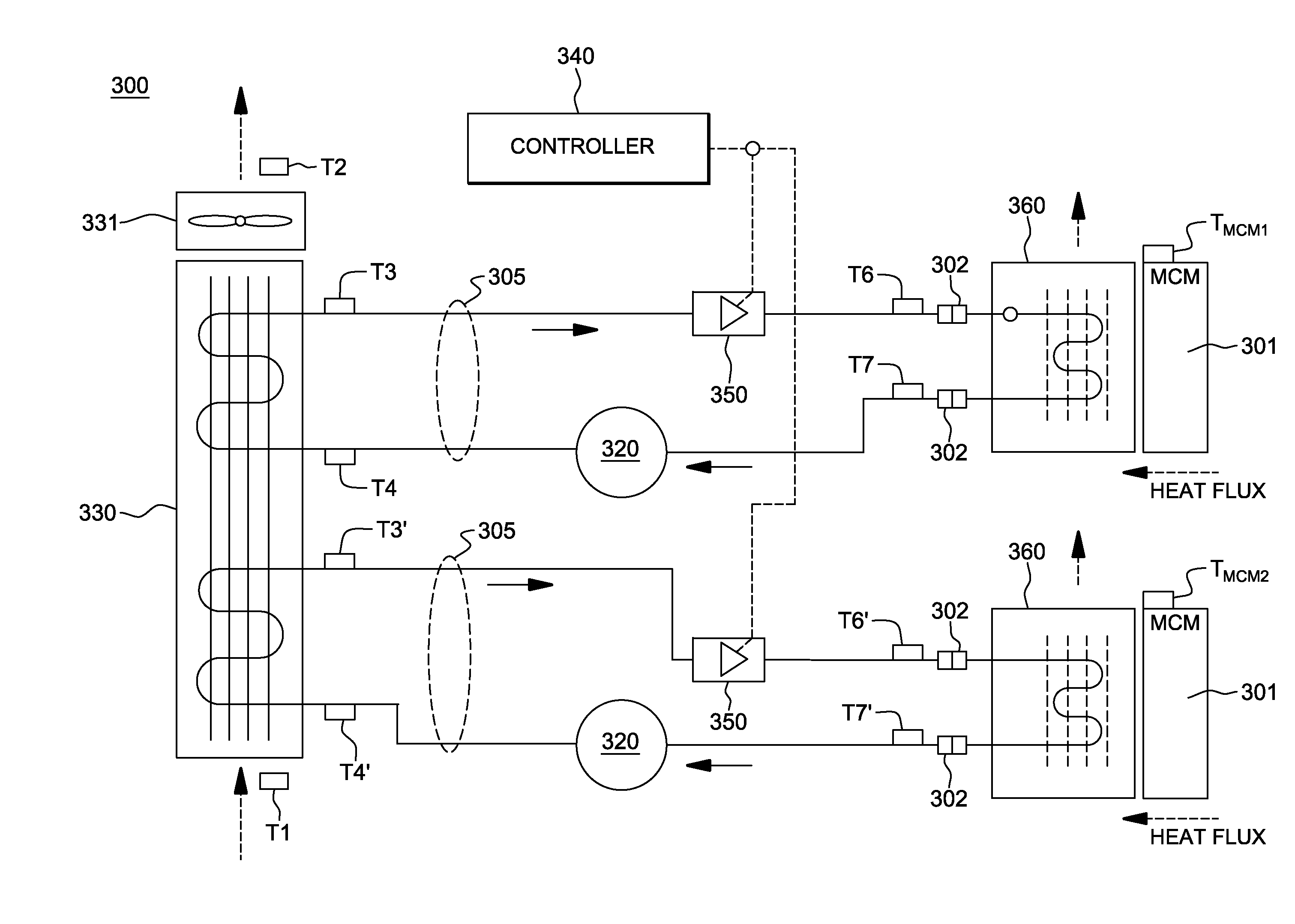
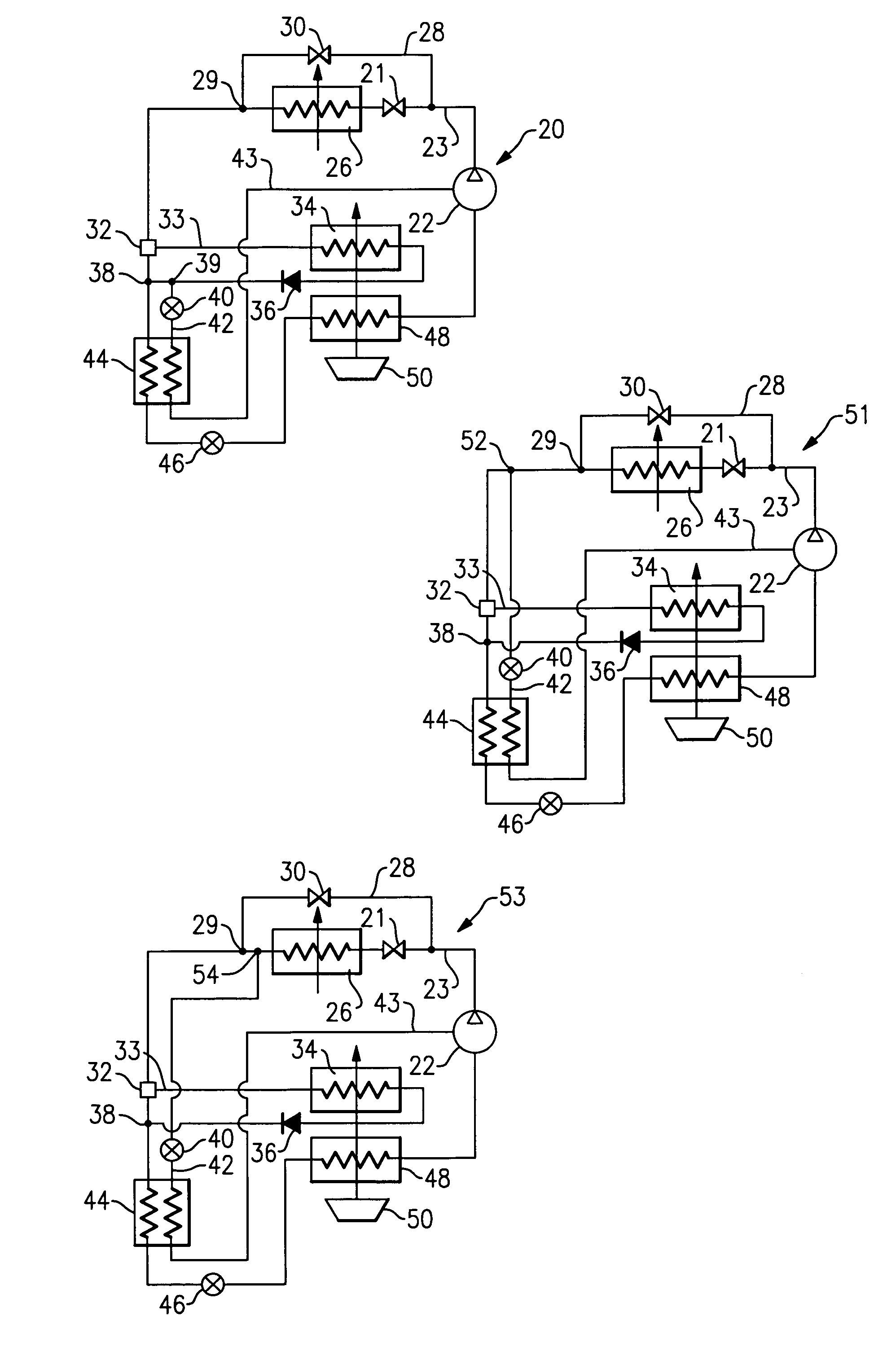
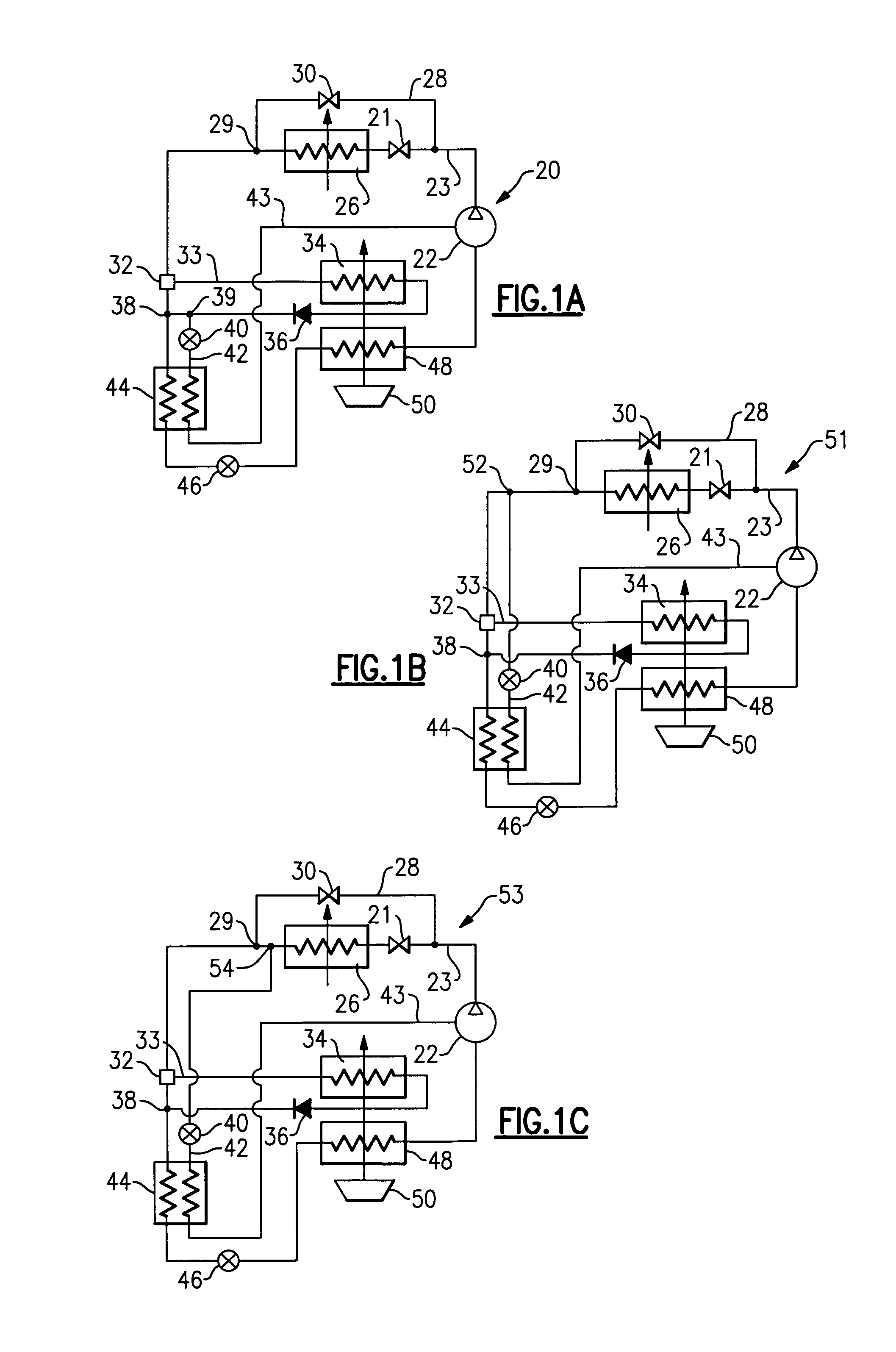
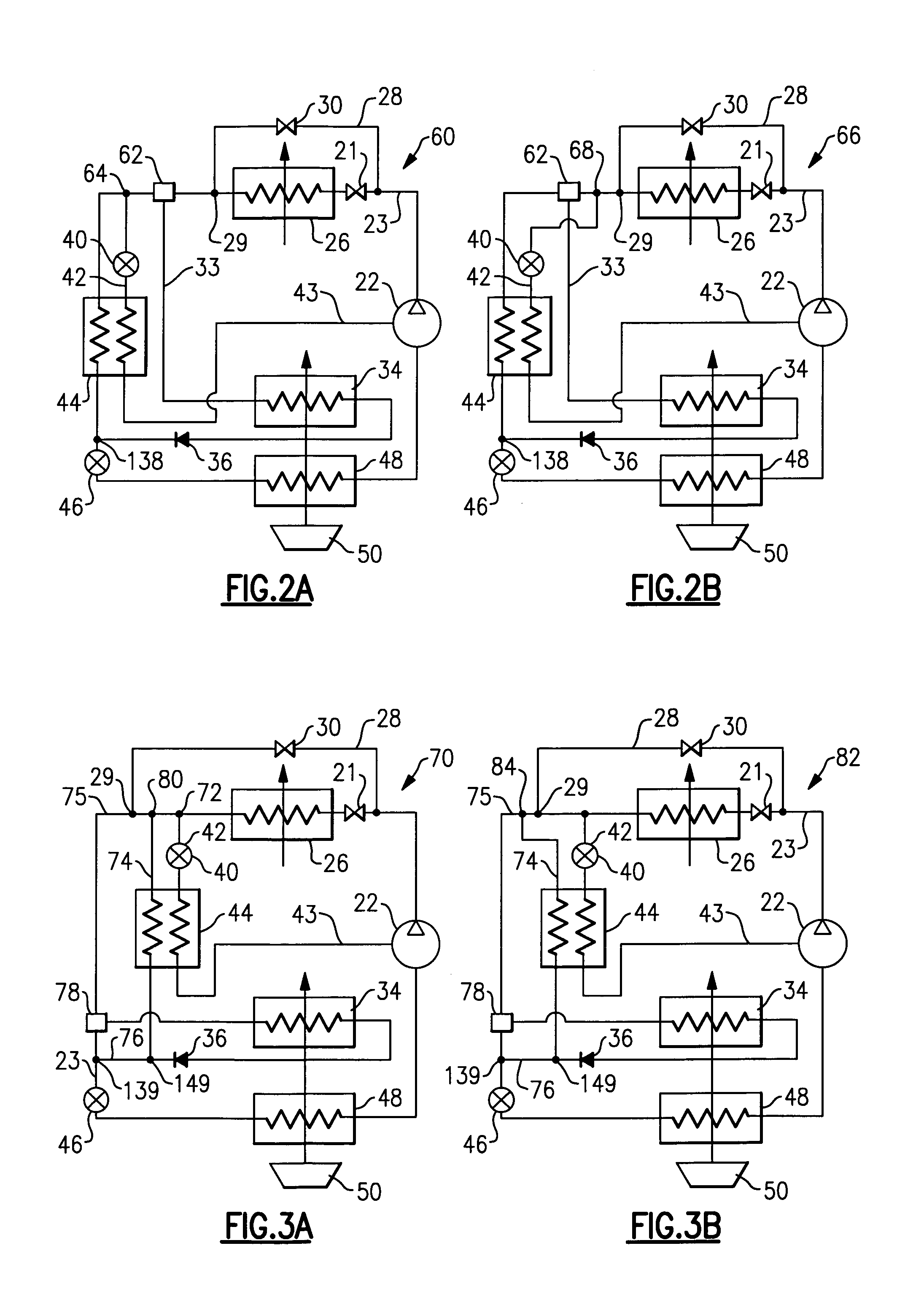
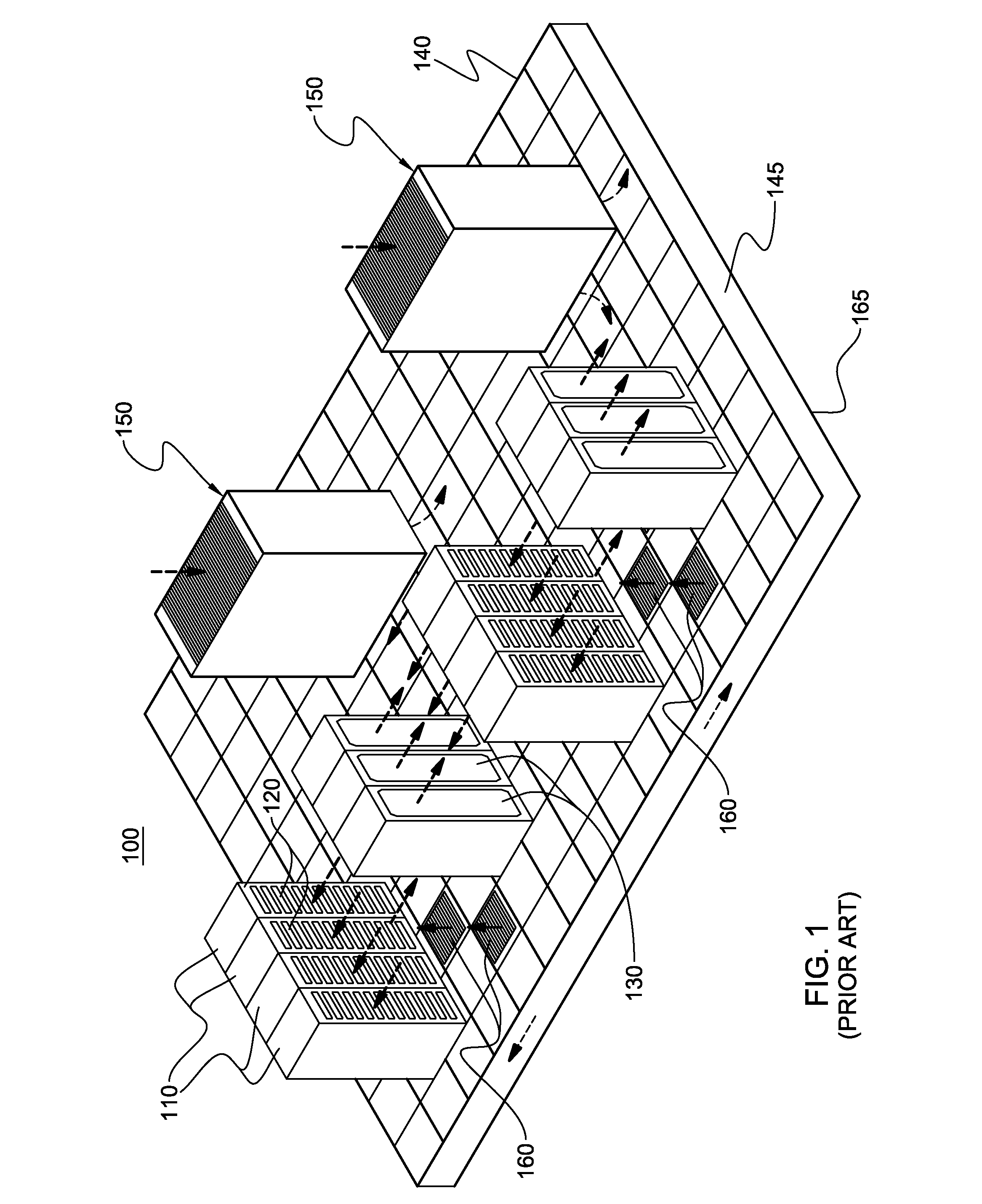
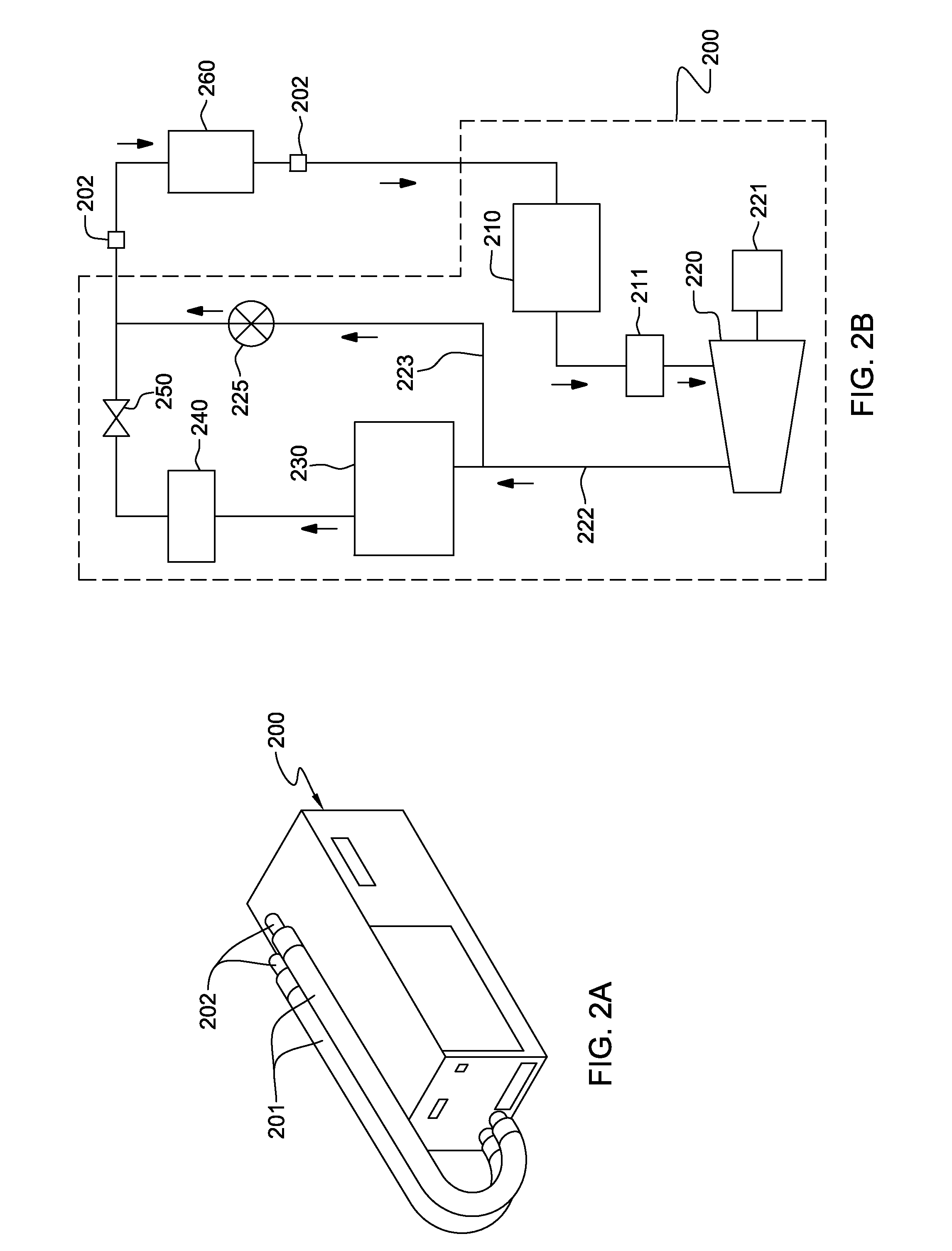
Thermoelectric-enhanced, vapor-compression refrigeration apparatus facilitating cooling of an electronic component
InactiveUS20120111027A1Improve cooling effectOvercomes shortcomingDomestic cooling apparatusMachines using electric/magnetic effectsEngineeringThermodynamic state
Apparatus and method are provided for facilitating cooling of an electronic component. The apparatus includes a refrigerant loop, a compressor coupled to the refrigerant loop, and a controllable thermoelectric array disposed in thermal communication with the refrigerant loop. Refrigerant flowing through the refrigerant loop facilitates dissipation of heat from the electronic component, and the thermoelectric array is disposed with a first portion of the refrigerant loop, residing upstream of the compressor, in thermal contact with a first side of the array, and a second portion of the refrigerant loop, residing downstream of the compressor, in thermal contact with a second side of the array. The thermoelectric array ensures that refrigerant in the refrigerant loop entering the compressor is in a superheated thermodynamic state by transferring heat from refrigerant passing through the second portion to refrigerant passing through the first portion of the refrigerant loop.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thermodynamic diagram showing method and device
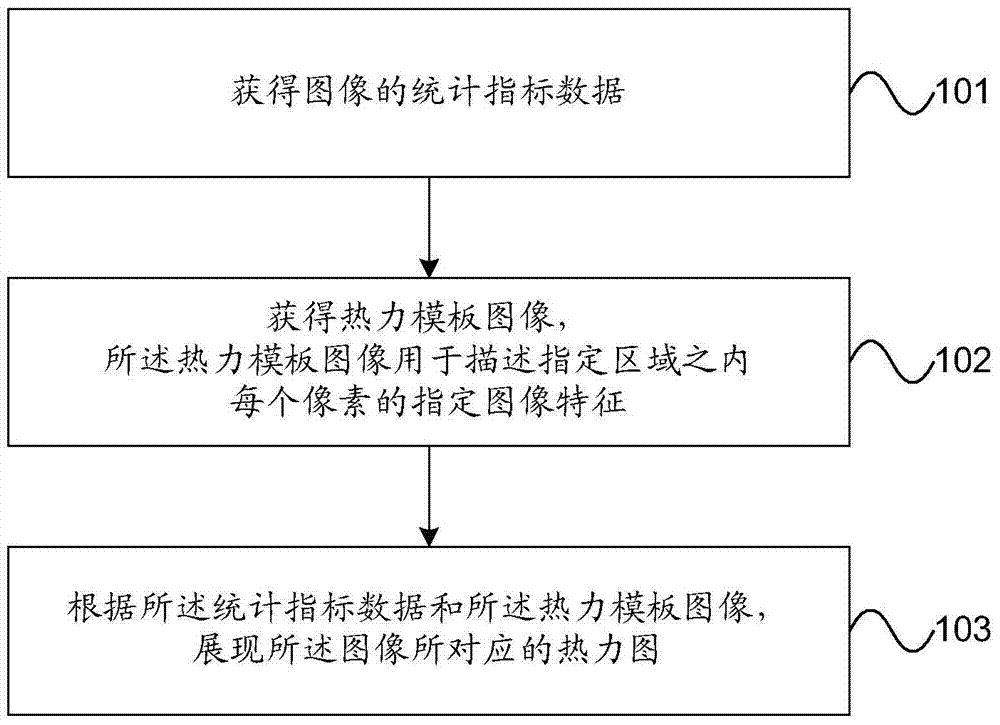
ActiveCN104239617AImprove presentation reliabilityIncrease profitGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionThermodynamic stateDependability
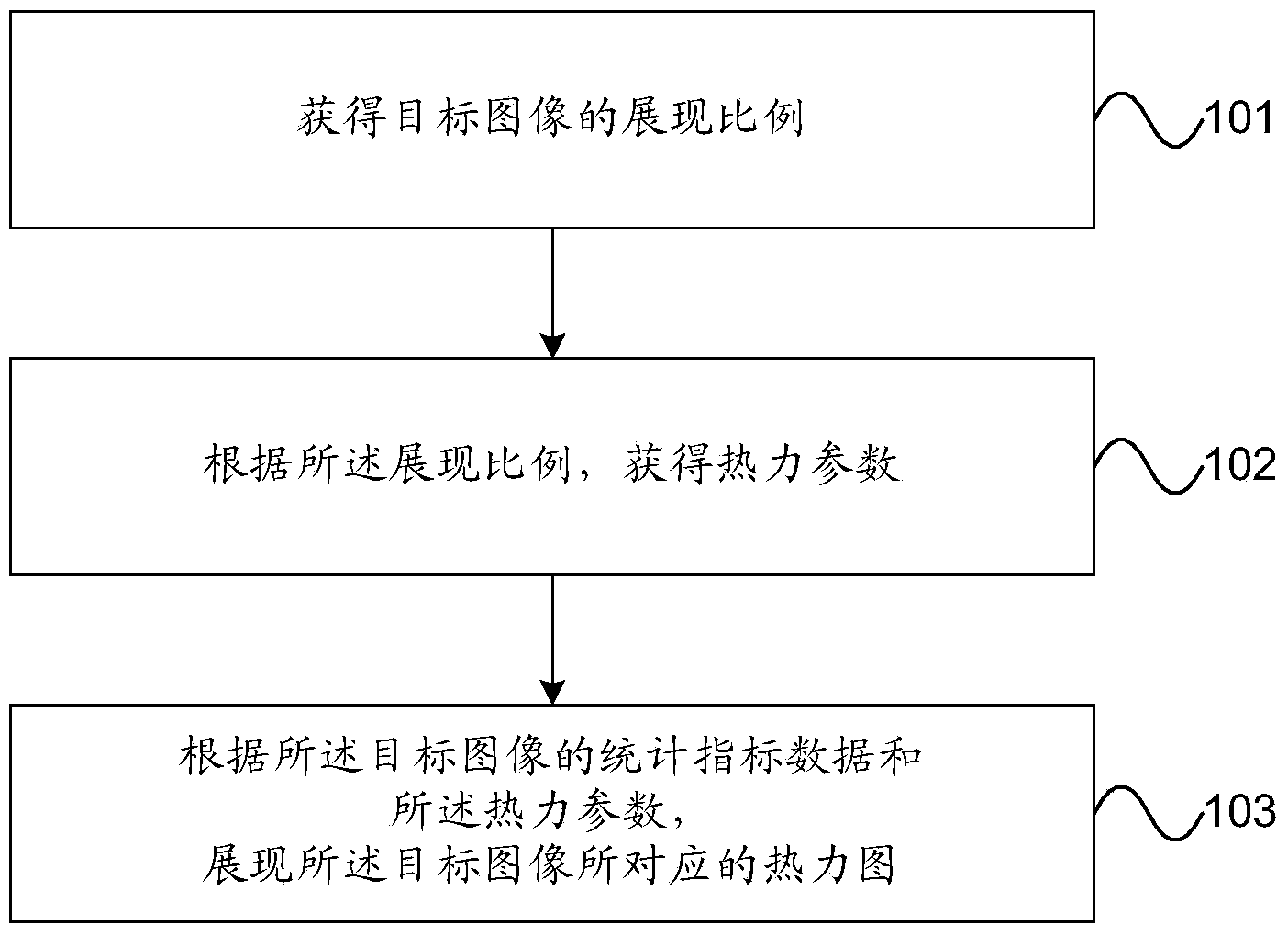
The invention provides a thermodynamic diagram showing method and device. By adopting the embodiment, a showing ratio of a target image is obtained and thermodynamic parameters are further obtained according to the showing ratio so that a thermodynamic diagram corresponding to the target image is shown according to statistical index data of the target image and the thermodynamic parameters; the thermodynamic diagram is shown by adopting the thermodynamic parameters corresponding to the showing ratio of the target image, so that the problems in the prior art that set thermodynamic parameters are adopted so that a distribution condition of the statistical index data of the target image can not be clearly shown by the thermodynamic diagram can be avoided, and thus, the showing reliability of the thermodynamic diagram is improved.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
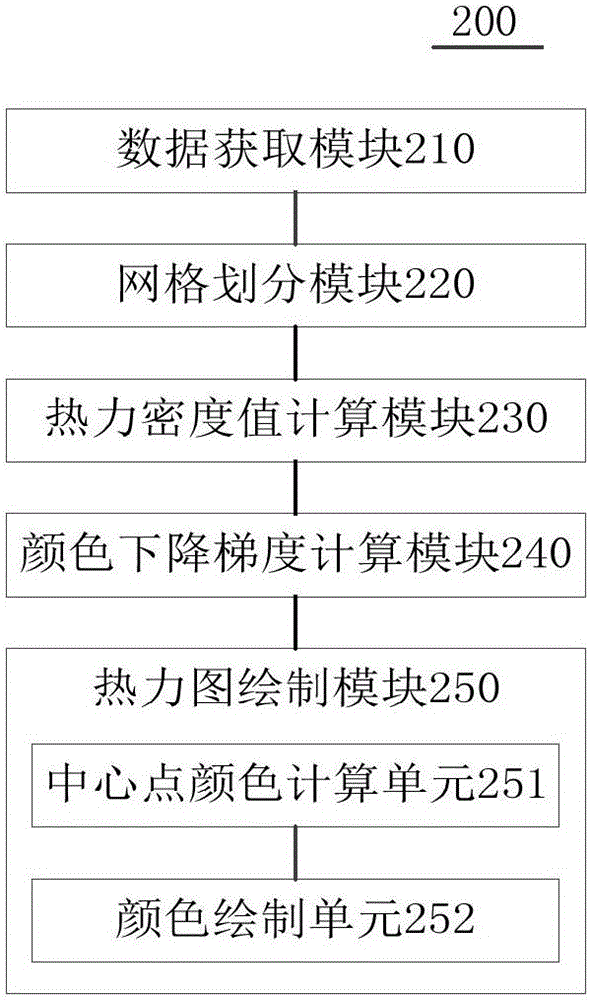
Thermodynamic diagram drawing method and apparatus
The invention provides a thermodynamic diagram drawing method and apparatus and belongs to the image processing field. The method includes the following steps that: a map to be processed and thermodynamic data corresponding to the map are obtained; the map is divided into a plurality of cells; thermodynamic density values corresponding to each cell are calculated according to the thermodynamic data; color descent gradient is calculated according to a preset color shallowest value, a preset color deepest value, a maximum thermodynamic density value and a minimum thermodynamic density value in the thermodynamic density values corresponding to all the cells; and a thermodynamic diagram can be drawn on the map according to the color descent gradient, the thermodynamic density values corresponding to each cell, and the preset color shallowest value.
Owner:JIANFEI INFINITE TECH CO LTD
Indoor attitude estimation method based on thermodynamic map for single image
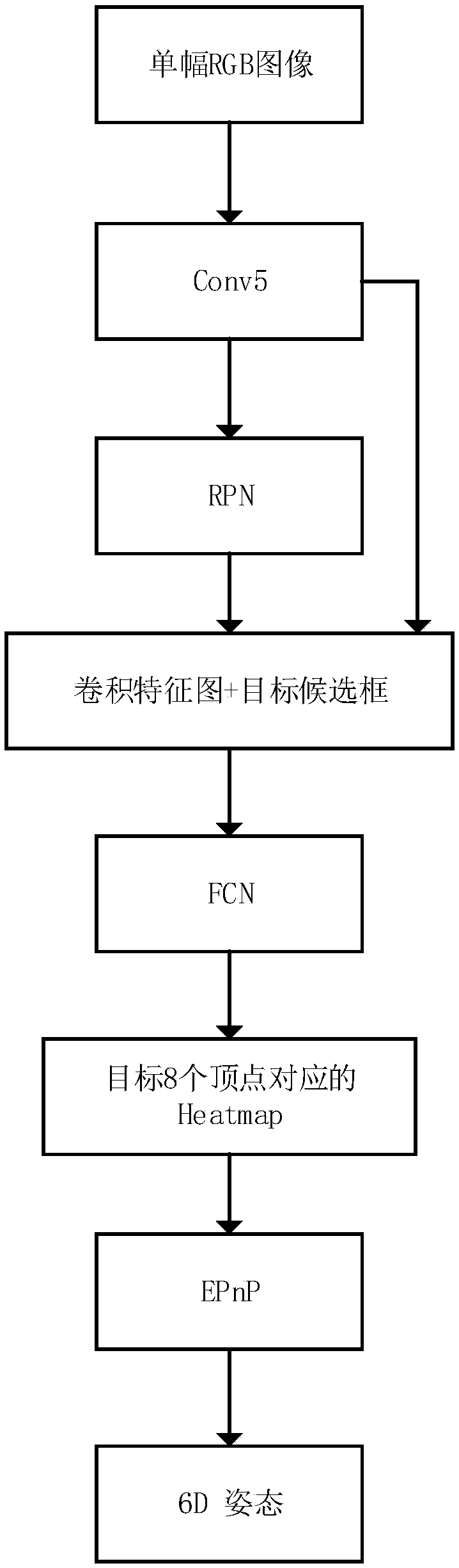
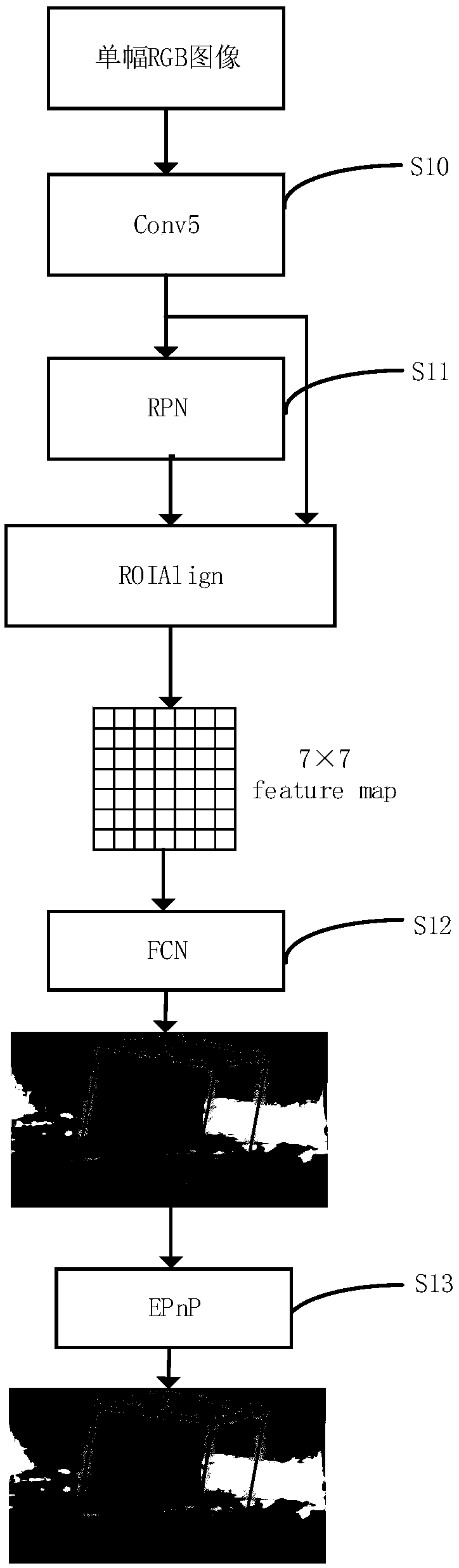
ActiveCN109063301ASlow convergenceFast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesEstimation methodsSingle image
The invention belongs to the field of target attitude estimation, and discloses a single image indoor object attitude estimation method based on thermodynamic map. The object attitude estimation method based on thermodynamic map extracts candidate frames of a plurality of target objects through an RPN network. The thermodynamic images of eight vertices of each object bounding box on two-dimensional images are extracted by full convolution network (FCN), and then the 6D attitude estimation of the object is calculated by using PnP method. ShapeNet is used as CAD model library to synthesize a large amount of training data. The object posture estimation detection technology based on the thermodynamic map adopted by the invention has strong robustness, can estimate the posture of different indoor objects when the background is disorderly indoor scene and the object is partially occluded, has wide application range, is insensitive to light and does not require the object to have obvious texture appearance.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Thermodynamic diagram display method and device
ActiveCN104731894AImprove presentation reliabilityAvoid the problem that the distribution of statistical index data of the image cannot be clearly displayedSpecial data processing applicationsUltrasound attenuationImaging Feature
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Method and system for tank refilling
ActiveUS8783303B2Improve performanceLow costCapsCap application using vaccuumAnalytical equationsEngineering
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Battery SOC determination method and battery management system using method
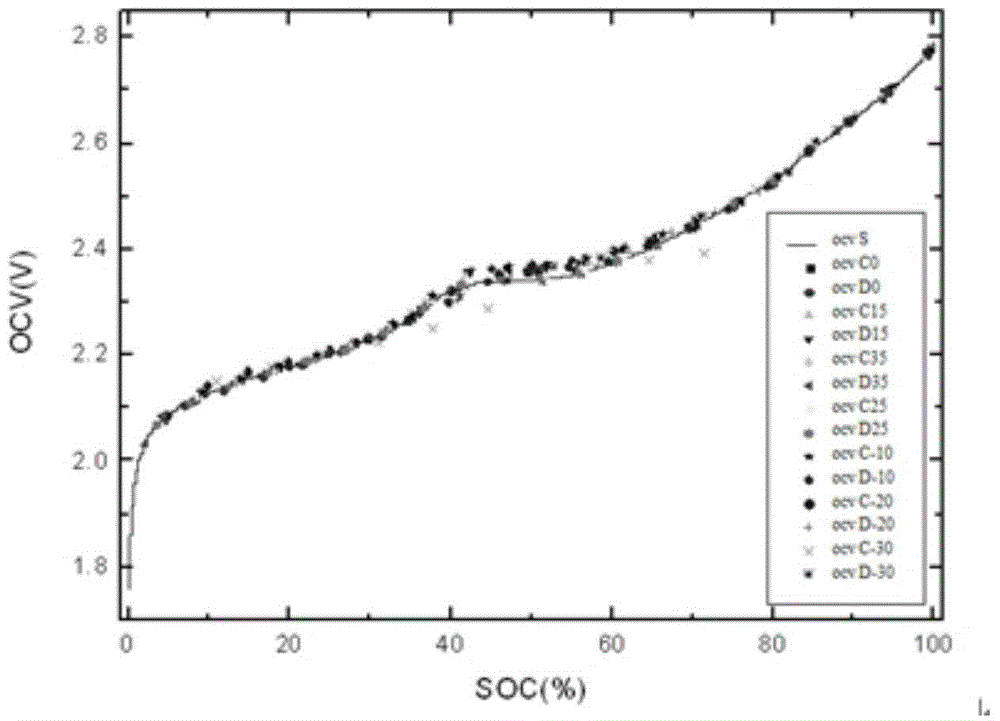
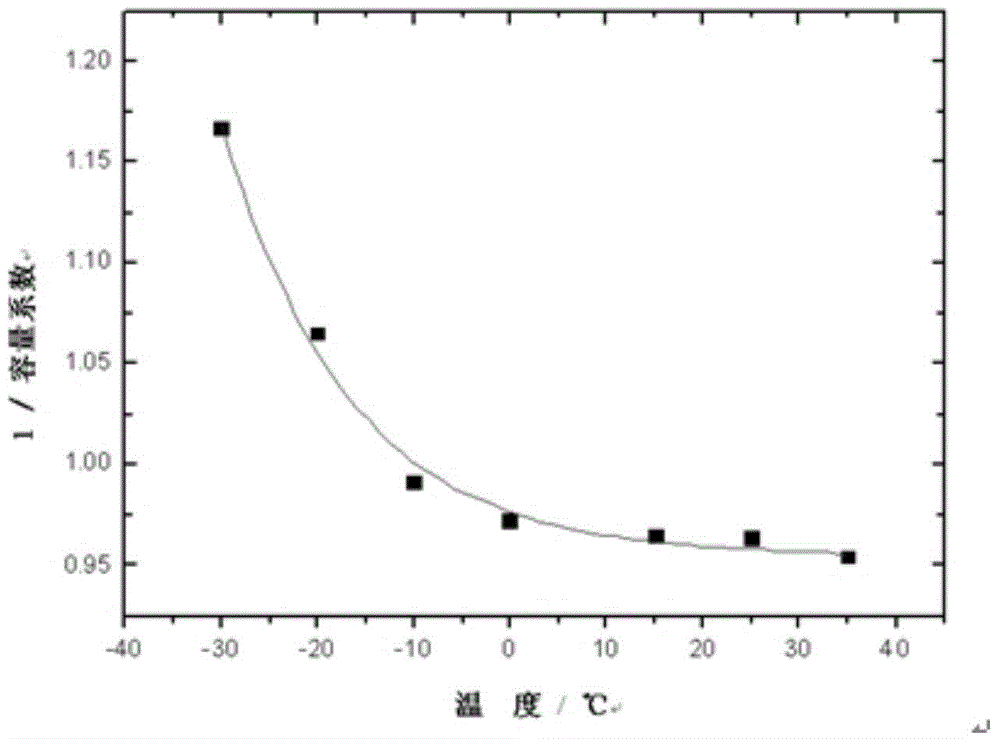
The invention relates to a battery SOC determination method and a battery management system using the method. The battery SOC determination method comprises the steps that open-circuit voltage (OCV) of a battery is measured; the measured open-circuit voltage of the battery is compared with an OCV-SOC curve so that the SOC state of the battery is determined; and the SOC value in the OCV-SOC curve is SOC based on thermodynamic quantity of state.
Owner:MICROVAST
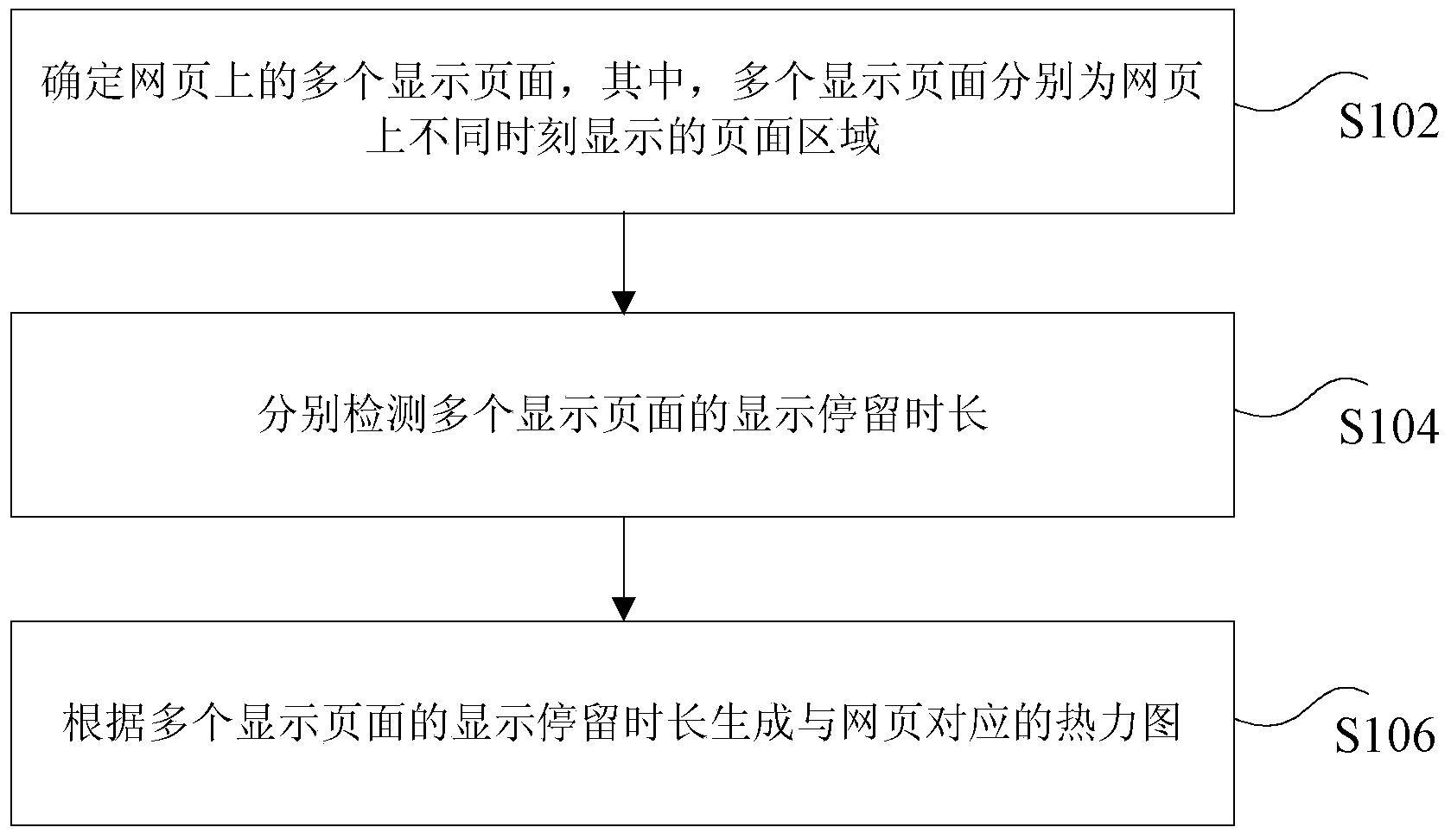
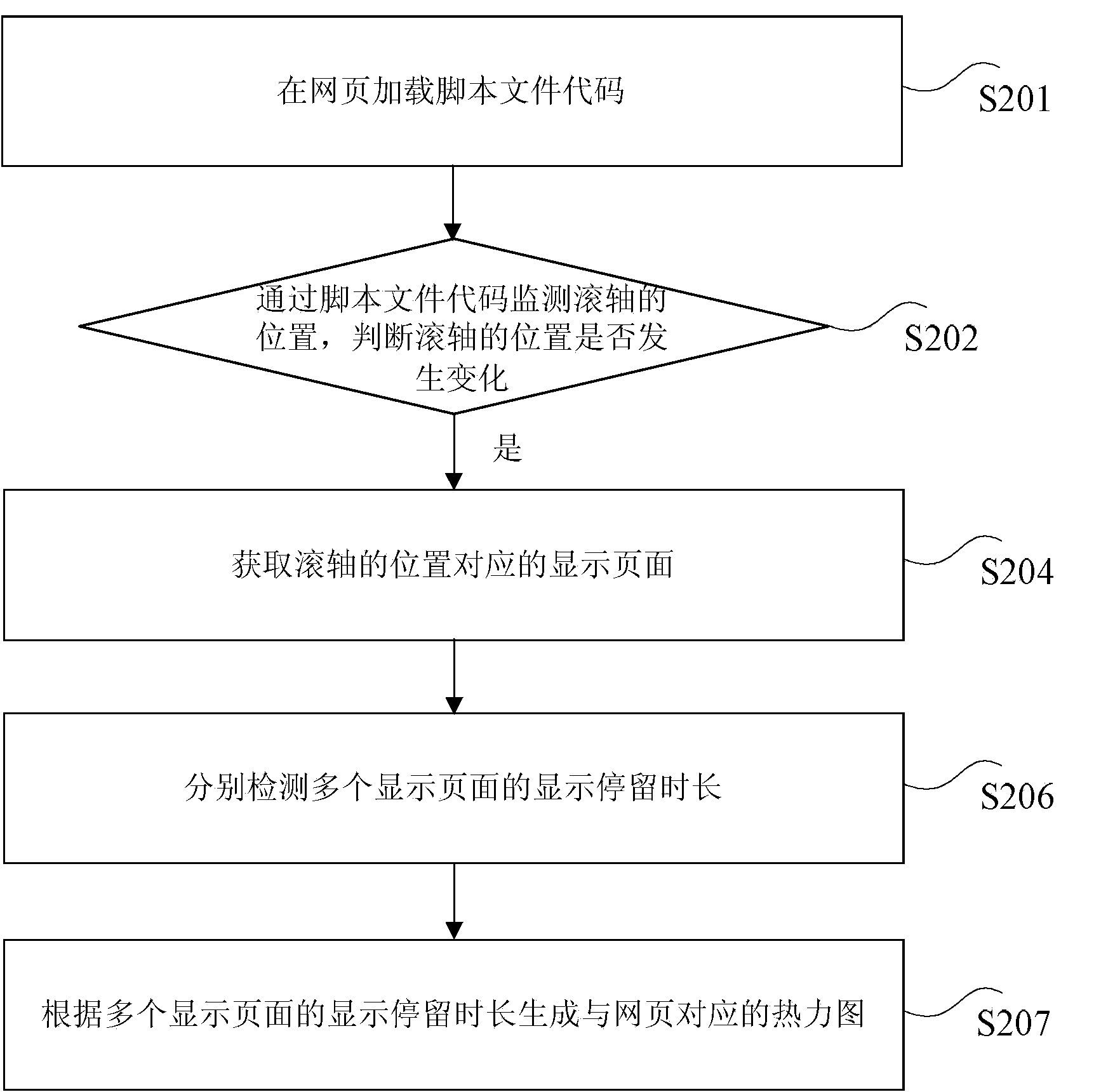
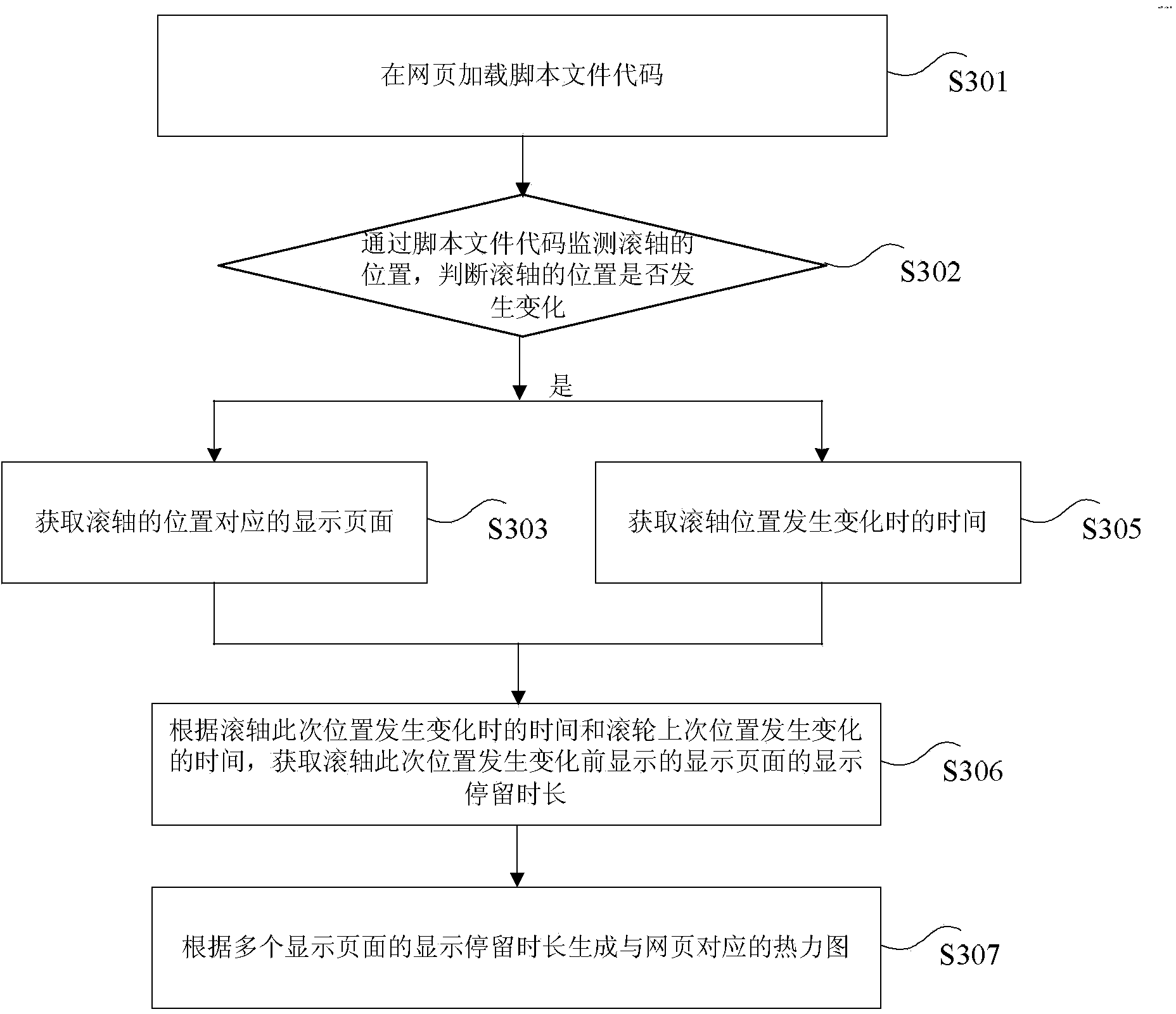
Thermodynamic chart generating method and method
ActiveCN104239042ASpecific program execution arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsThermodynamic stateWeb page
Owner:BEIJING GRIDSUM TECH CO LTD
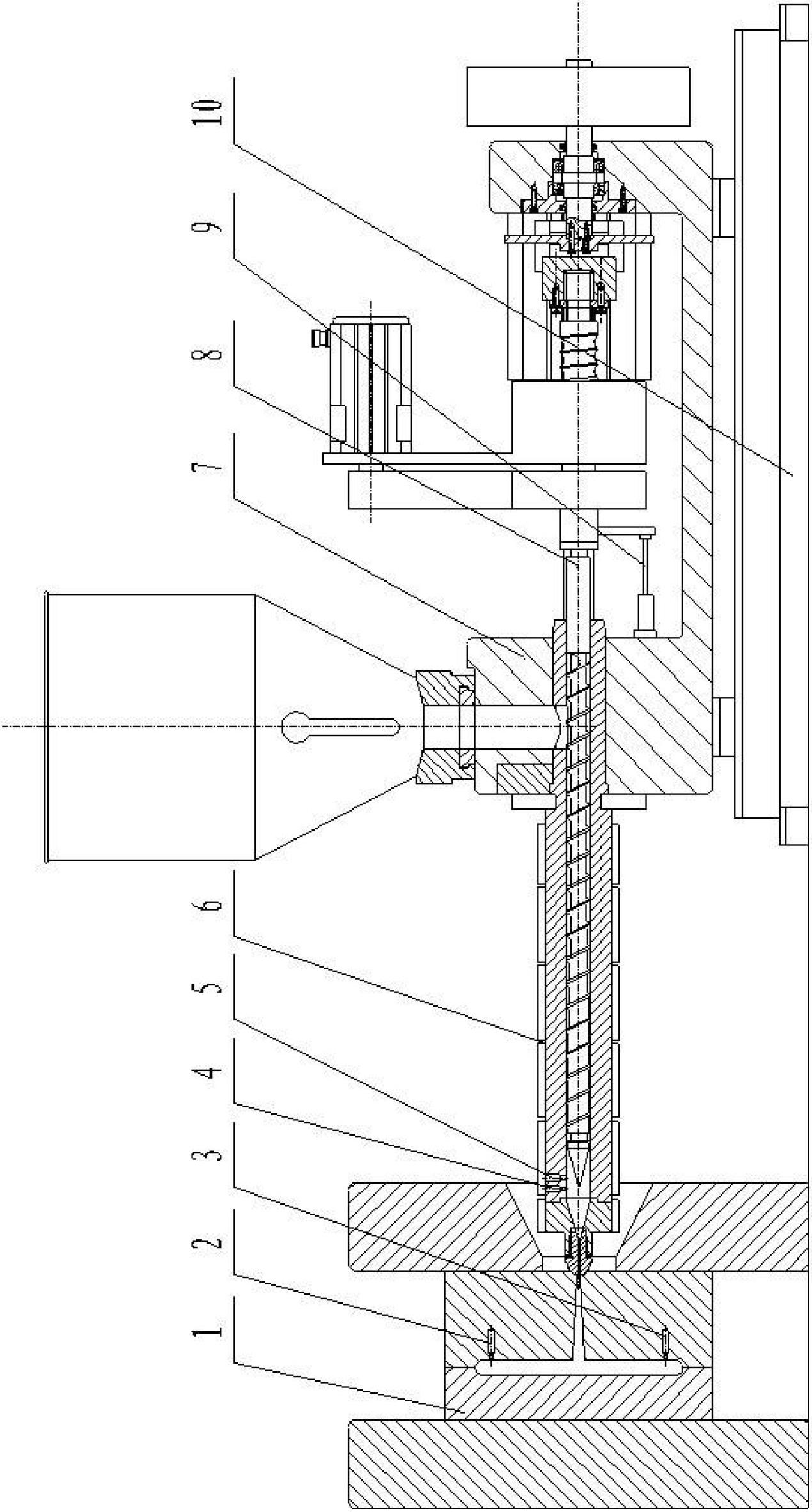
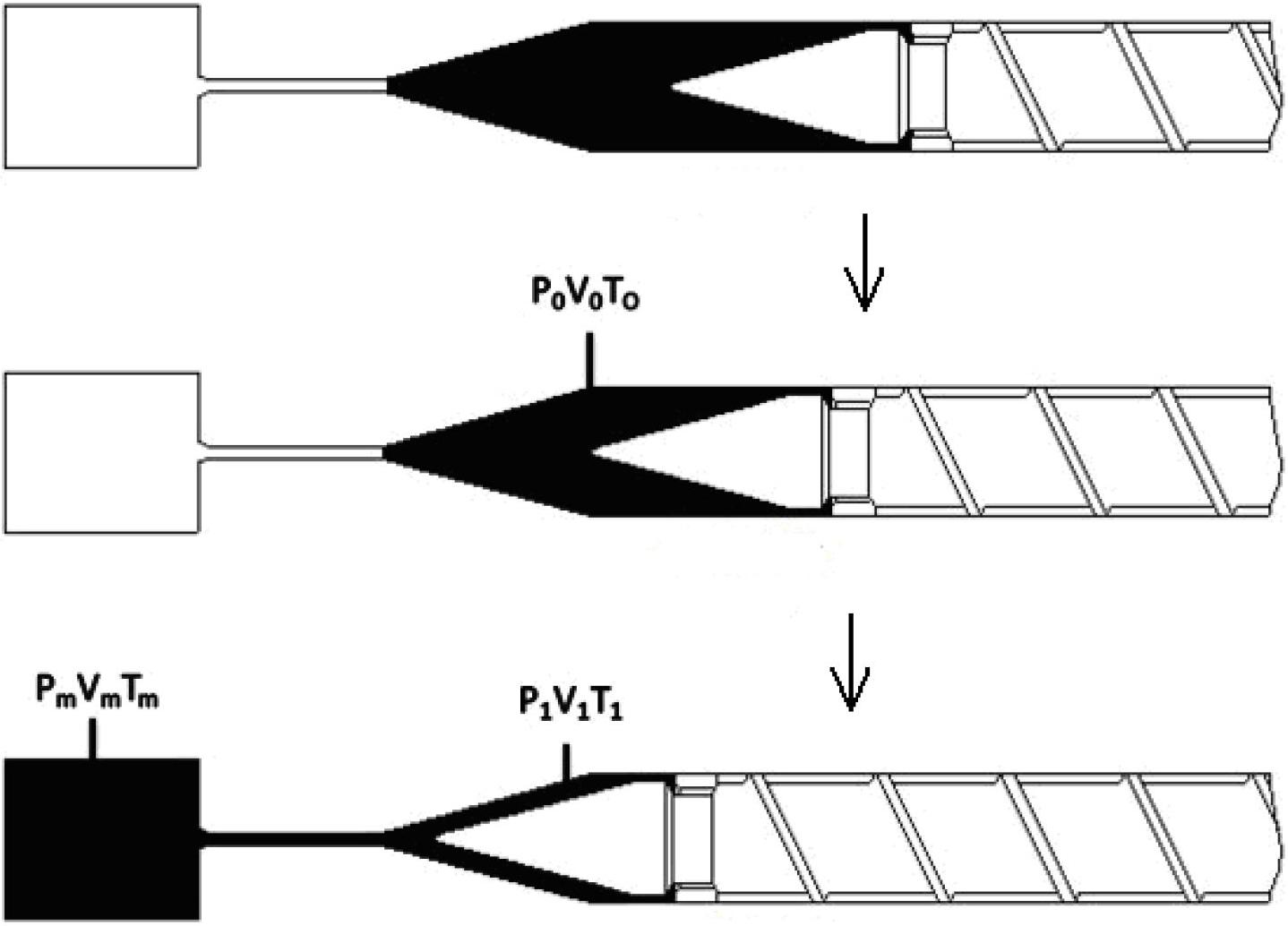
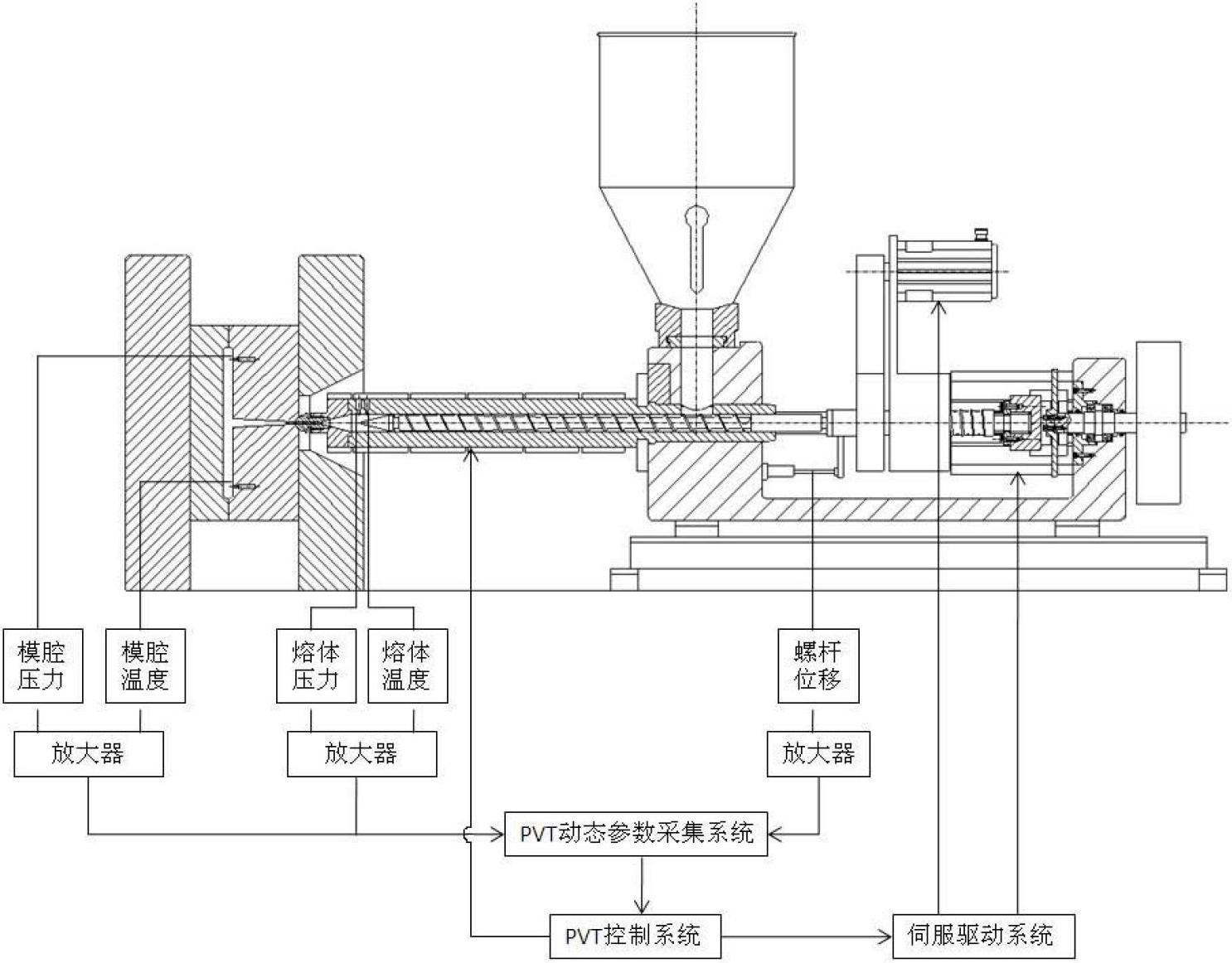
Fully-electric ultra-high speed injection molding PVT (Pressure Volume Temperature) online measurement and control method
The invention discloses a fully-electric ultra-high speed injection molding PVT (Pressure Volume Temperature) online measurement and control method. By using a melt metered through plasticization in a cylinder as an object, a thermodynamic state (P0, T0, V0) of a highly-compressed melt before injection as a control starting point and the thermodynamic state (P1, T1, V1) of the melt in the cylinder after injection molding as a control ending point, through online detection of a PVT relation characteristic of a polymer in an ultra-high speed injection molding process, by depending on a high-pressure control system and a high-response executing mechanism of a fully-electric ultra-high speed injection molding machine and using the PVT relation characteristic of the ultra-high speed injection molded polymer as the guidance, precision control of ultra-high speed injection molding is realized. The fully-electric ultra-high speed injection molding PVT online measurement and control method has the advantages of high control precision and high cost performance.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Vapor-compression refrigeration apparatus with refrgierant bypass and controlled heat load
InactiveUS20120111037A1Easy to moveEasy to maintain temperatureCompression machines with non-reversible cycleRefrigeration devicesThermodynamic stateEngineering
Apparatus and method are provided for cooling an electronic component. The apparatus includes a refrigerant evaporator in thermal communication with the component(s) to be cooled, and a refrigerant loop coupled in fluid communication with the evaporator for facilitating flow of refrigerant through the evaporator. The apparatus further includes a compressor in fluid communication with the refrigerant loop, a refrigerant bypass pipe coupled to the refrigerant loop in parallel fluid communication with the evaporator, and a control valve for controlling refrigerant flow through the evaporator. The control valve is controlled to maintain temperature of the component(s) within a specified temperature range. The apparatus further includes a controllable refrigerant heater associated with the refrigerant bypass pipe for providing an adjustable heat load on refrigerant in the bypass pipe to ensure that refrigerant entering the compressor is in a superheated thermodynamic state.
Owner:IBM CORP
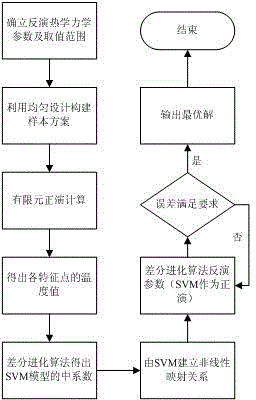
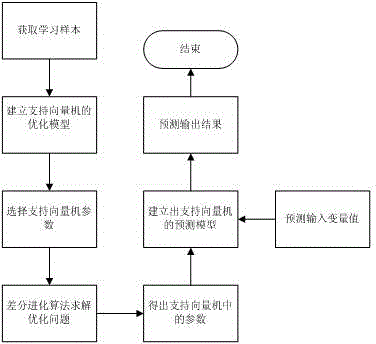
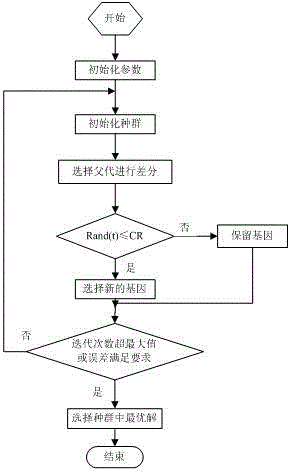
Concrete thermodynamic parameter intelligent recognition method based on support vector machine
InactiveCN103914594AFast recognitionSimple methodGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsUniform designSupport vector regression machine
The invention discloses a concrete thermodynamic parameter intelligent recognition method based on a support vector machine. The method includes firstly determining the range of inverse parameters; designing sample schemes of concrete thermodynamic parameters by an uniform design method; acquiring one temperature value of each feature point in the sample schemes through finite element forward modeling, utilizing the temperature values and corresponding thermodynamic parameters in the sample schemes as study samples, and establishing a support vector machine model; utilizing the differential evolution algorithm to perform global search, searching and acquiring each coefficient of the support vector machine, determining the nonlinear relationship between the inverse parameters and actual temperature values of monitoring points, and establishing a support vector machine prediction model; utilizing the support vector machine prediction model as a forward model, utilizing the differential evolution algorithm to perform global search for the concrete thermodynamic parameters, and searching and acquiring inverse parameters closest to the actual temperature values of the monitoring points as the optimal concrete thermodynamic parameters. The method has the advantages of rapidness in recognition and simpleness.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
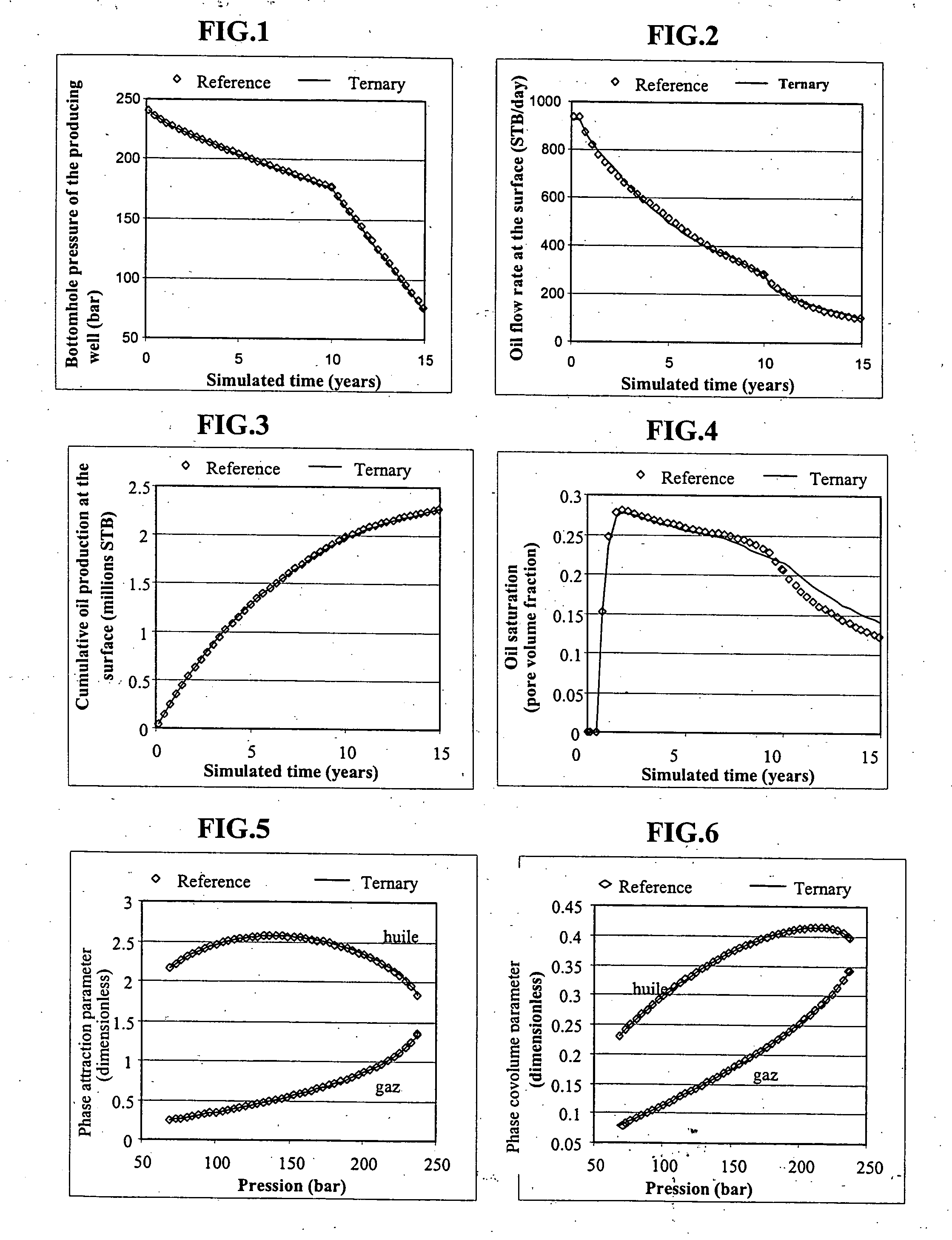
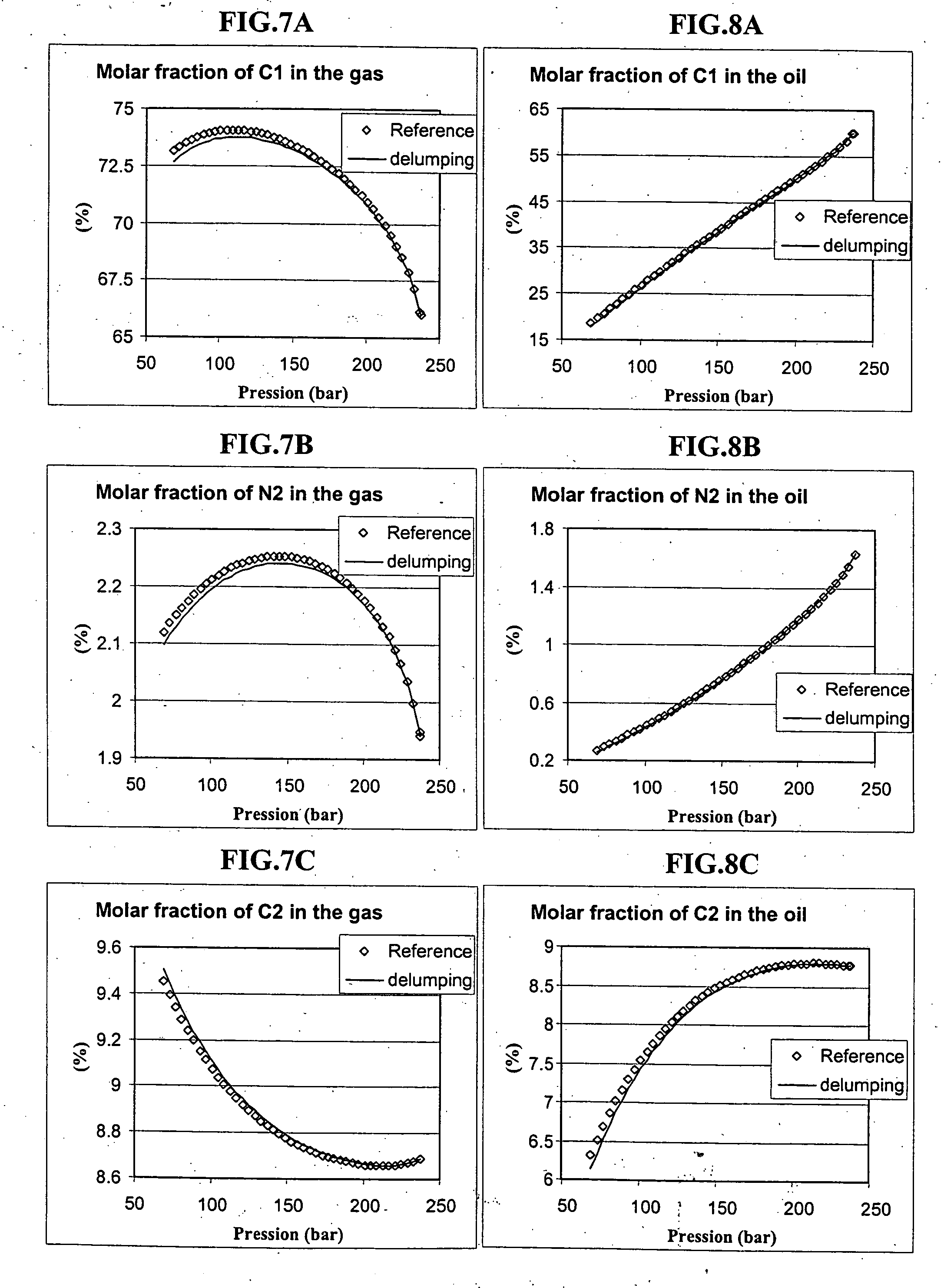
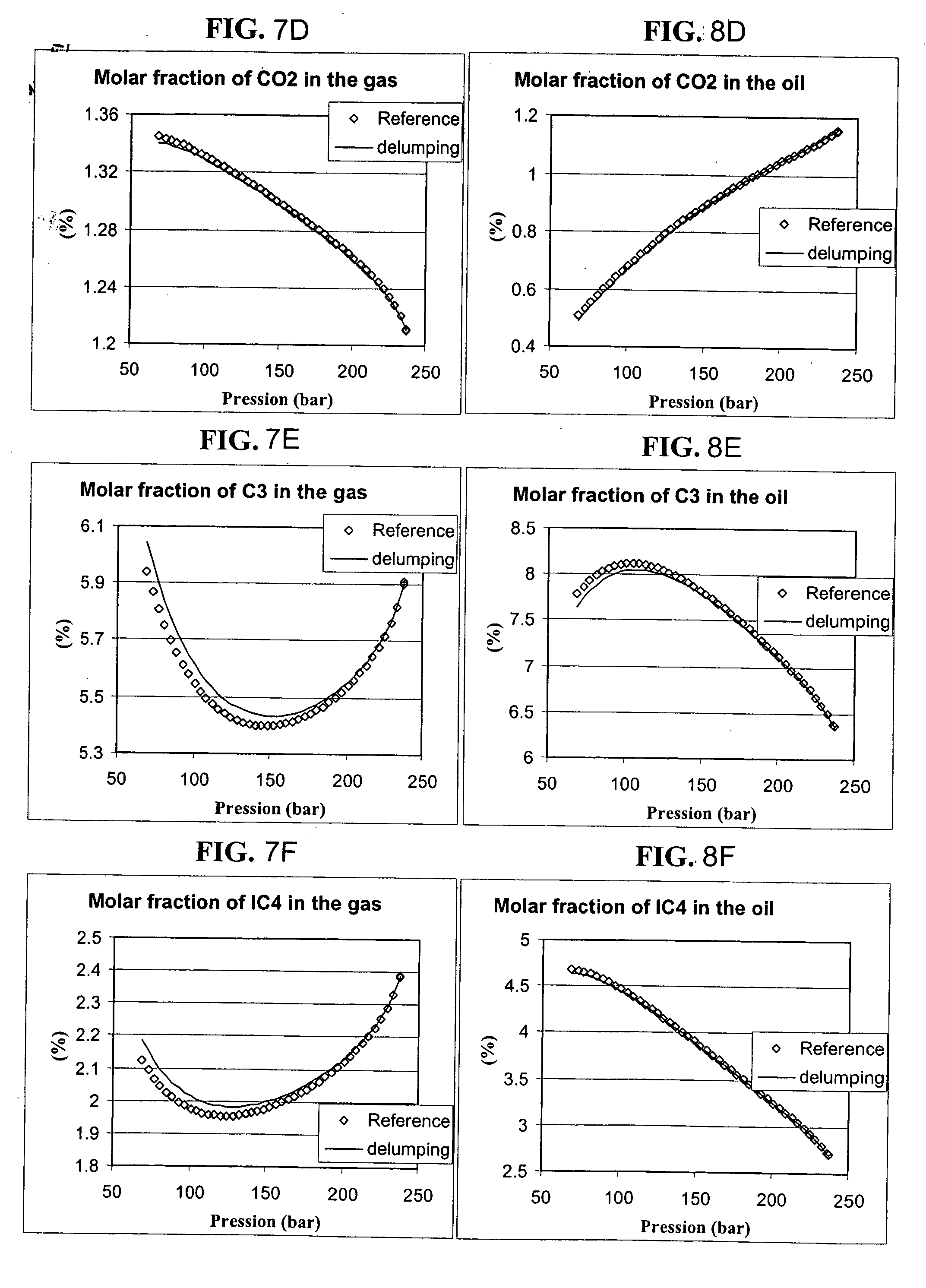
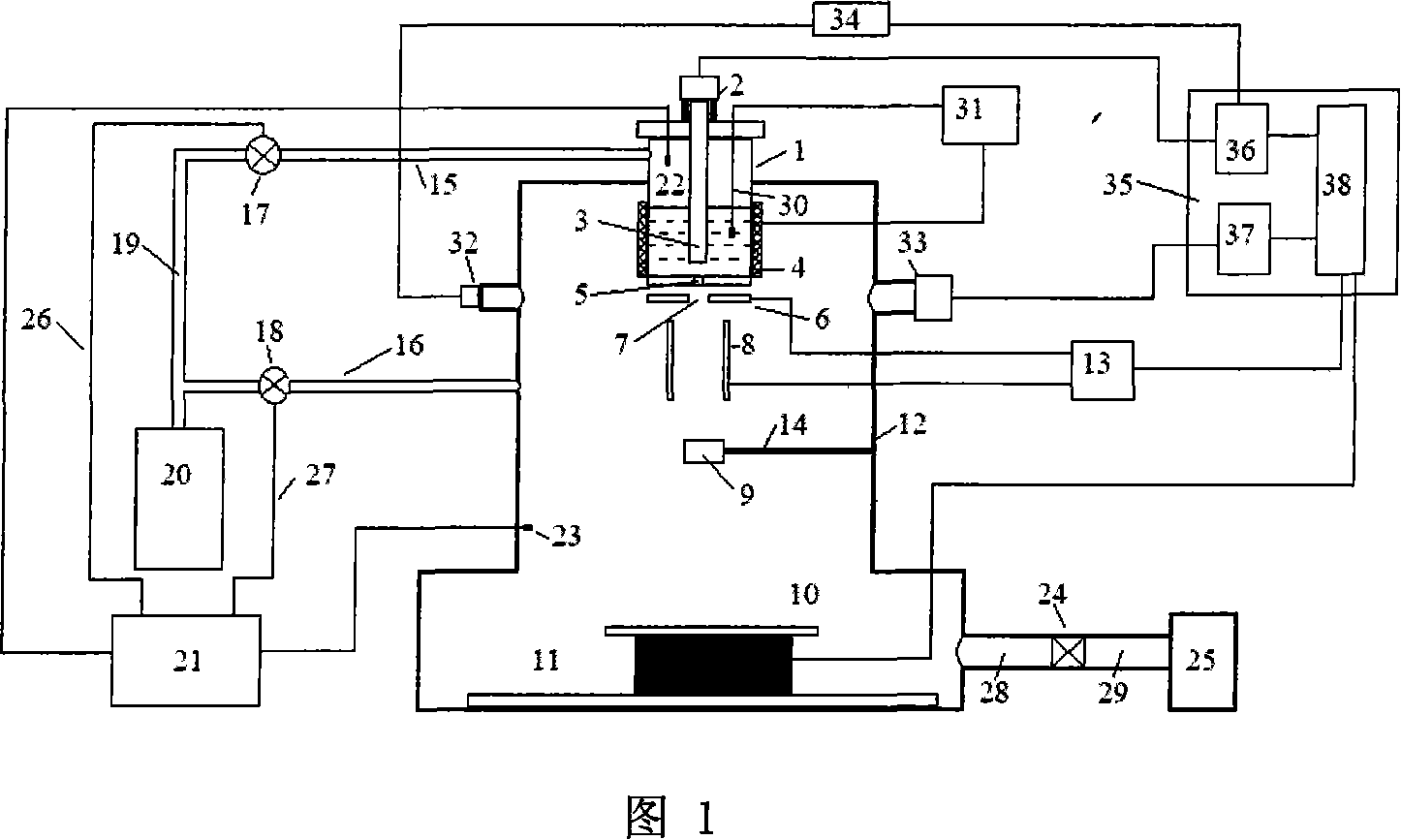
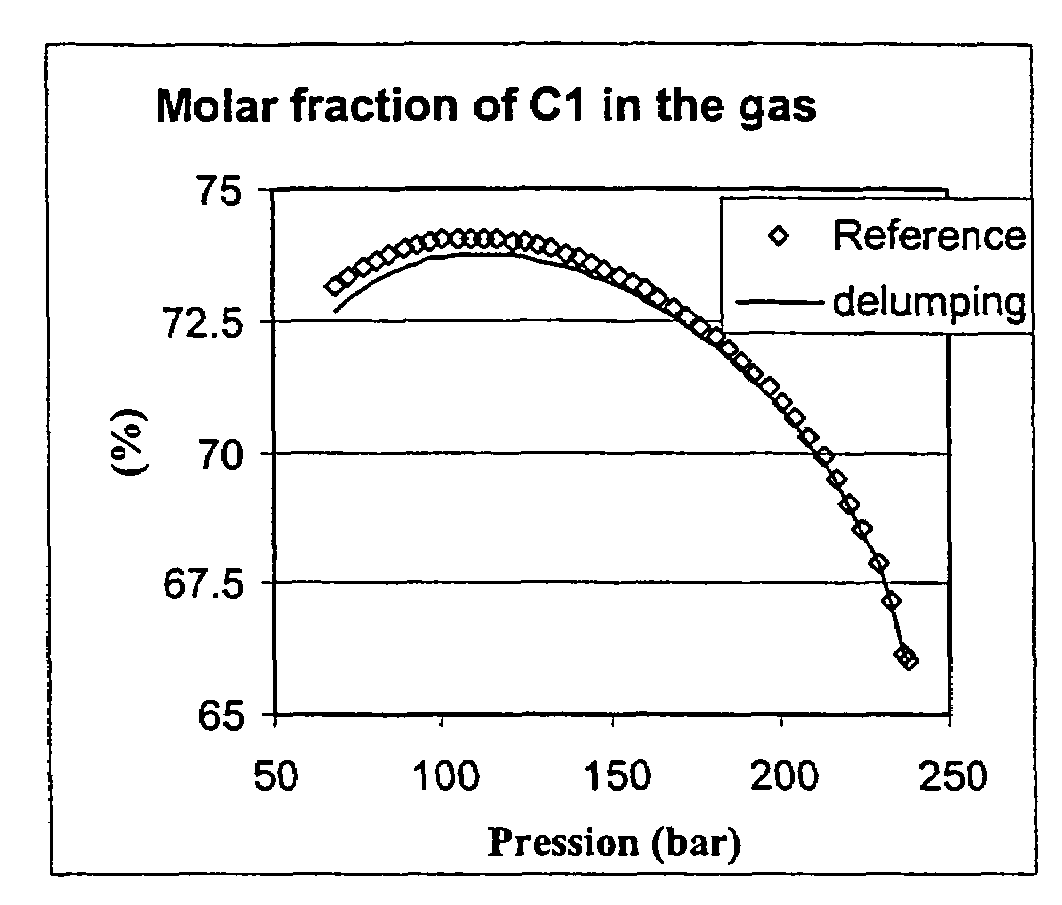
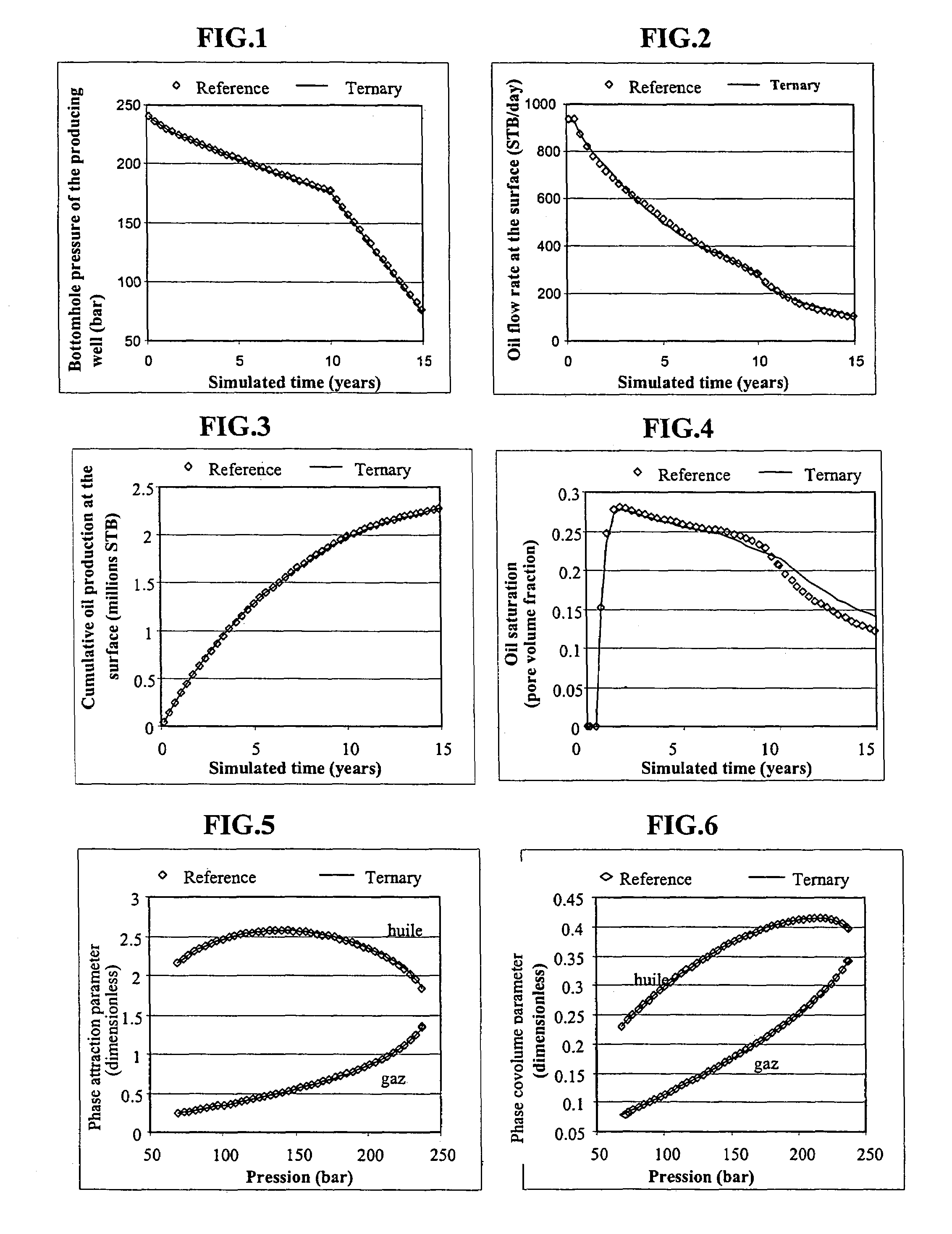
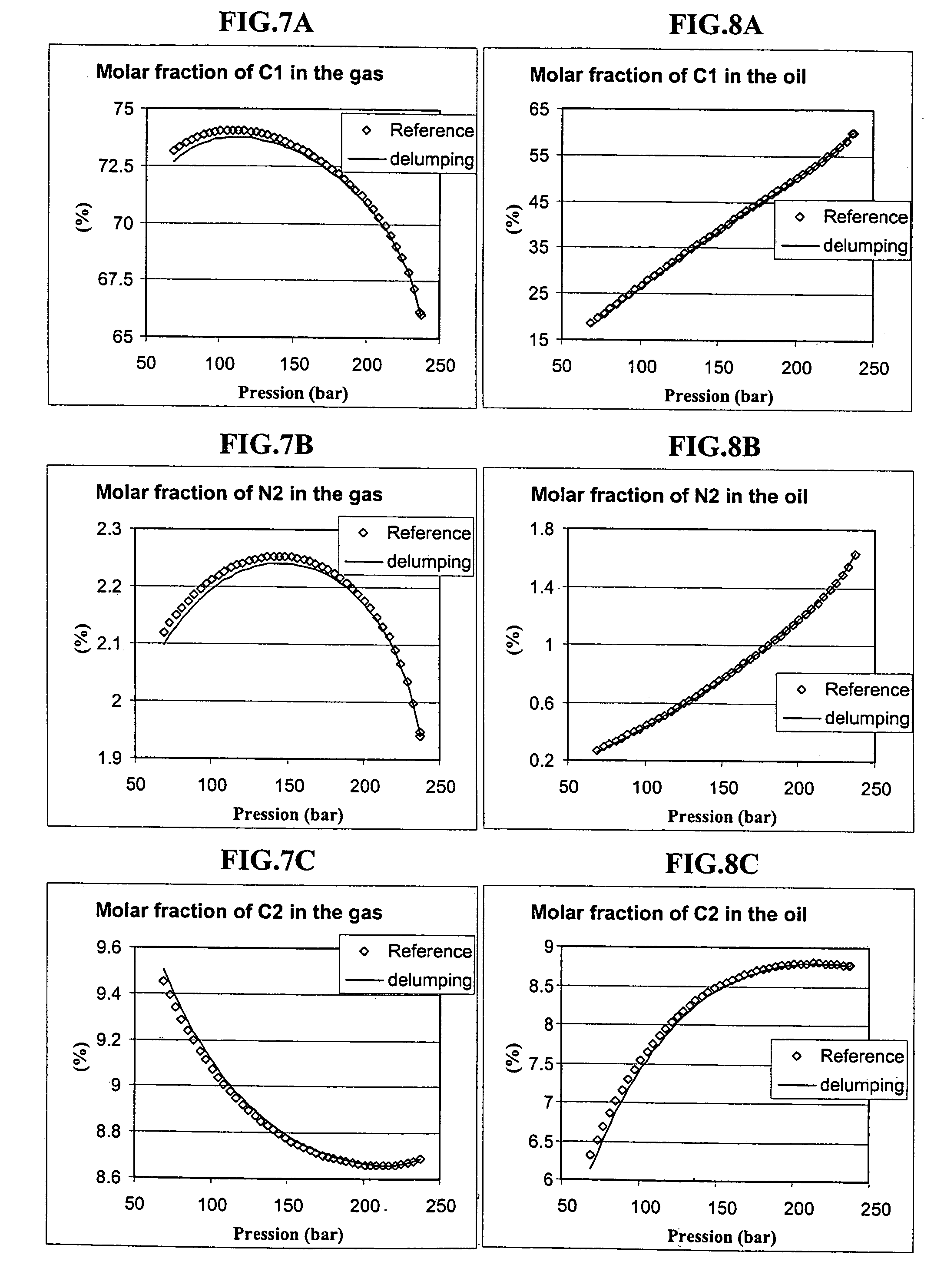
Lumping and delumping method for describing hydrocarbon-containing fluids
ActiveUS20050065759A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDrilling rodsLiquid productMaterial balance
Lumping and delumping method for estimating the properties or the behaviour of liquid and / or vapour hydrocarbon phases from data relative to a reference set consisting of hydrocarbon mixtures in a series of thermodynamic states in a medium. Each one of said hydrocarbon mixtures is grouped into at least three constituents (V, I, H), considering that the gas phases resulting from separation under conditions referred to as surface conditions of each mixture do not contain (H) and that the oil phases under the same conditions do not contain (V). The compositions of the separation products comprising, for the gaseous products, at least V and I in variable proportions and, for the liquid products, at least I and H in variable proportions, are determined by material balance. The at least three-constituent composition of each hydrocarbon mixture of the reference set is then determined by combination of the products resulting from the separation thereof in proportion to the amounts of each separation product. Delumping can then be performed to predict, as a function of time and in at least one thermodynamic zone, a detailed composition of a fluid in the medium. Application: hydrocarbon reservoir fluids for example.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Economized dehumidification system
ActiveUS6986264B1Reduce humidityTemperature controlMechanical apparatusFluid circulation arrangementSystems designEngineering
Various refrigerant system schematics incorporate the ability to bypass refrigerant around a condenser, to selectively provide refrigerant of a desired thermodynamic state to downstream system components, including a reheat coil located downstream of the condenser. In addition, the reheat coil may be utilized in combination, or independently from an economizer cycle, that is also incorporated into the system design. The economizer branch can be configured in a sequential or parallel arrangement relative to the reheat coil. Consequently, a wide spectrum of sensible and latent load demands can be satisfied. Furthermore, various schematics provide distinct benefits and flexibility in unloading and temperature and humidity control, also resulting in system performance and reliability enhancement.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
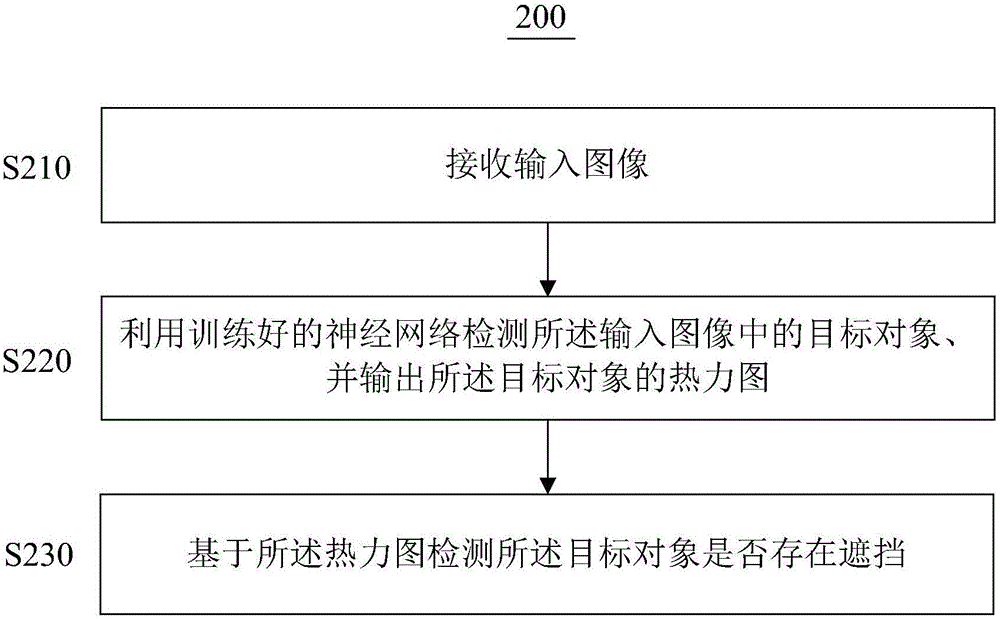
Target object occlusion detection method and target object occlusion detection device
ActiveCN106650662AReduce the difficulty of identificationImprove recognition accuracyBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionThermodynamic state
The invention provides a target object occlusion detection method and a target object occlusion detection device. The target object occlusion detection method comprises steps: input images are received; a well-trained neural network is used to detect a target image in the input images and output a thermodynamic chart of the target object; and based on the thermodynamic chart, whether occlusion exists in the target object is detected. According to the target object occlusion detection method and the target object occlusion detection device provided by the embodiment of the invention, the target object in the input images is converted to the thermodynamic chart based on the well-trained neural network, whether the occlusion exists in the target object is detected through the thermodynamic chart, the target object recognition difficulty can be effectively reduced, and the recognition precision and the stability can be enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING KUANGSHI TECH +1
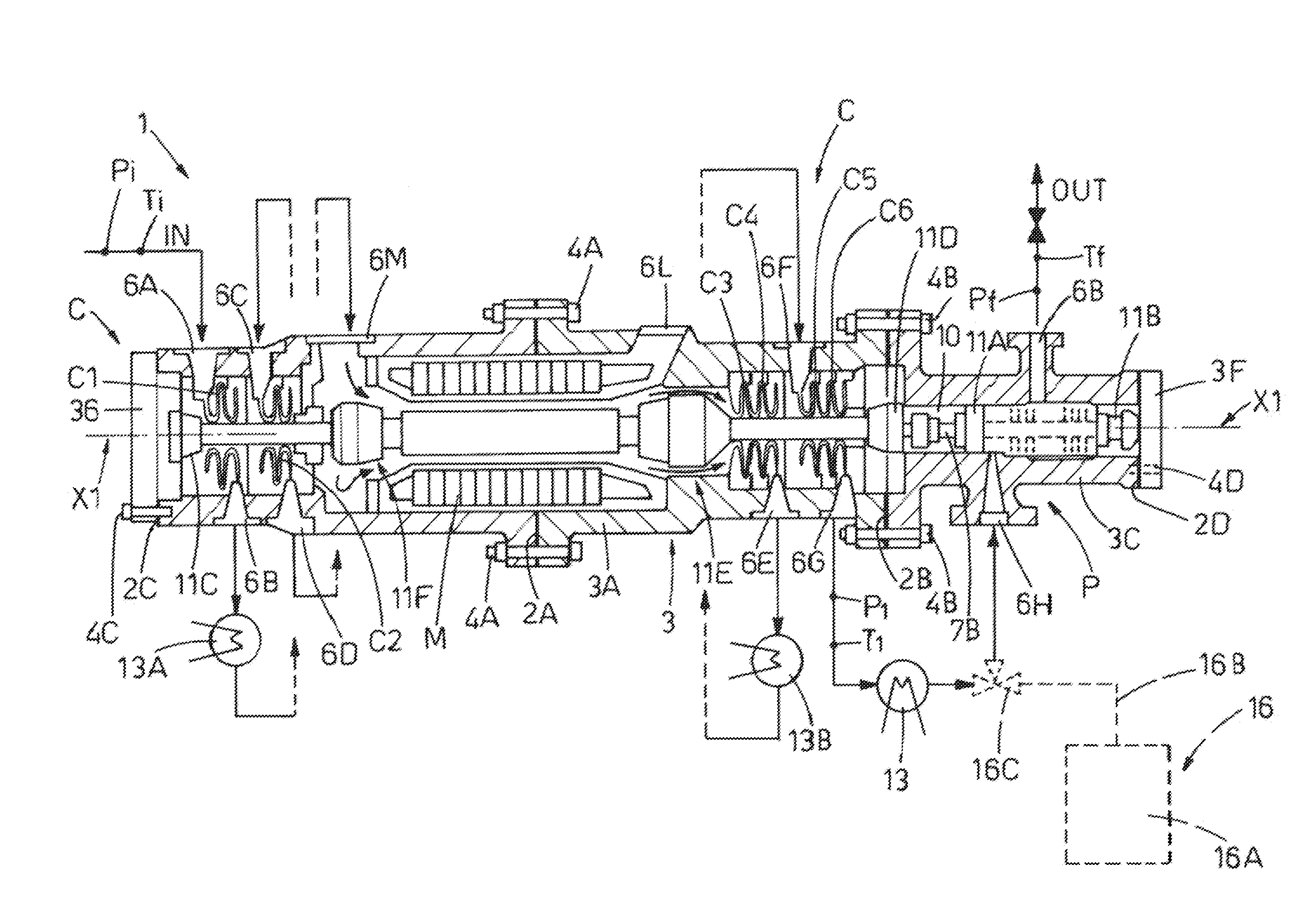
High-pressure compression unit for process fluids for industrial plant and a related method of operation
ActiveUS20110008186A1Overcome problemsSpecific fluid pumpsPositive displacement pump componentsCompression deviceEngineering
An integrated high-pressure compression unit for a process fluid that includes at least a first compression device able to compress the process fluid from a essentially gaseous initial thermodynamic state to an intermediate thermodynamic state, a second compression device connected mechanically to the first compression device and able to compress the process fluid from the intermediate thermodynamic state to a final thermodynamic state, a motor device able to drive the first compression device and the second compression device, and a pressure casing or housing in which at least the said first and second compression devices are mechanically coupled to each other.
Owner:NUOVO PIGNONE TECH SRL
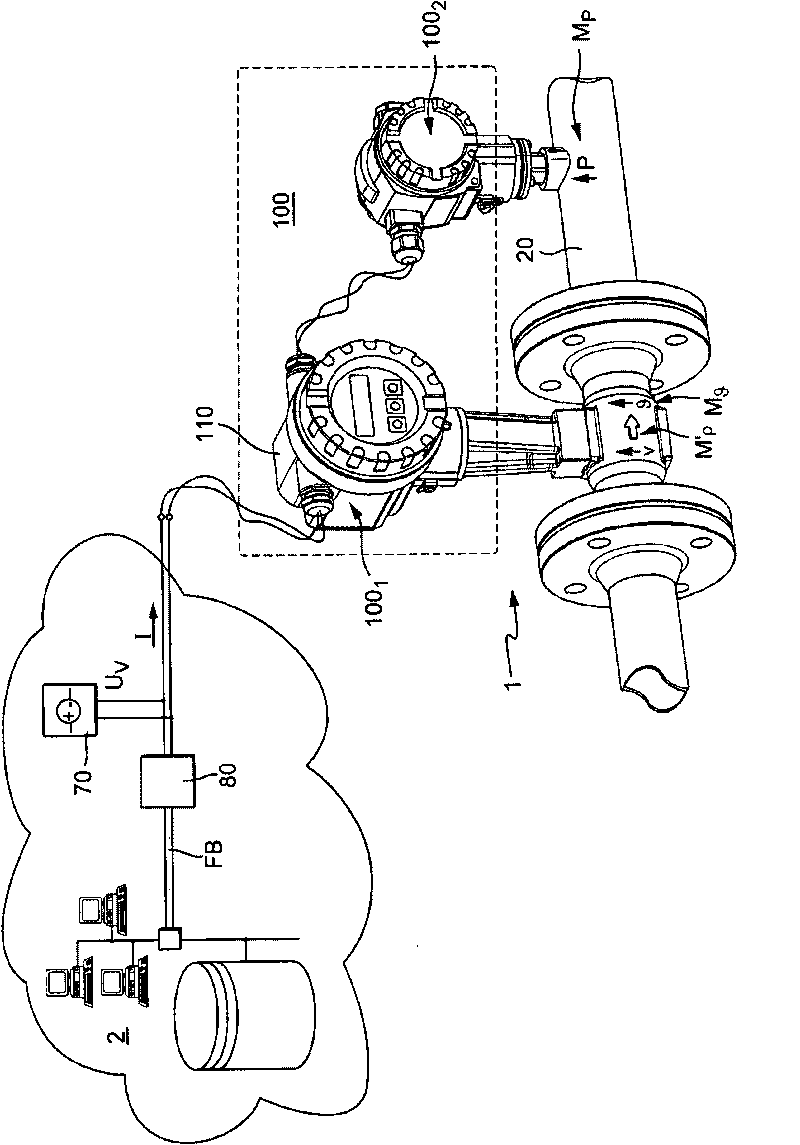
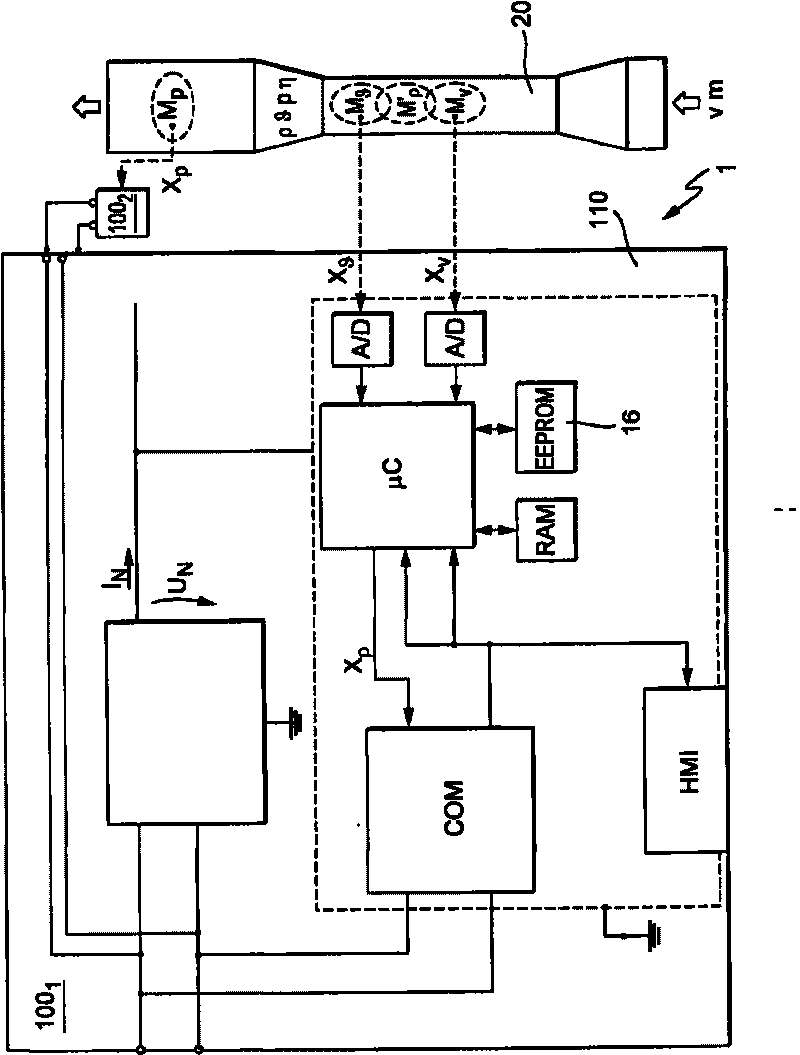
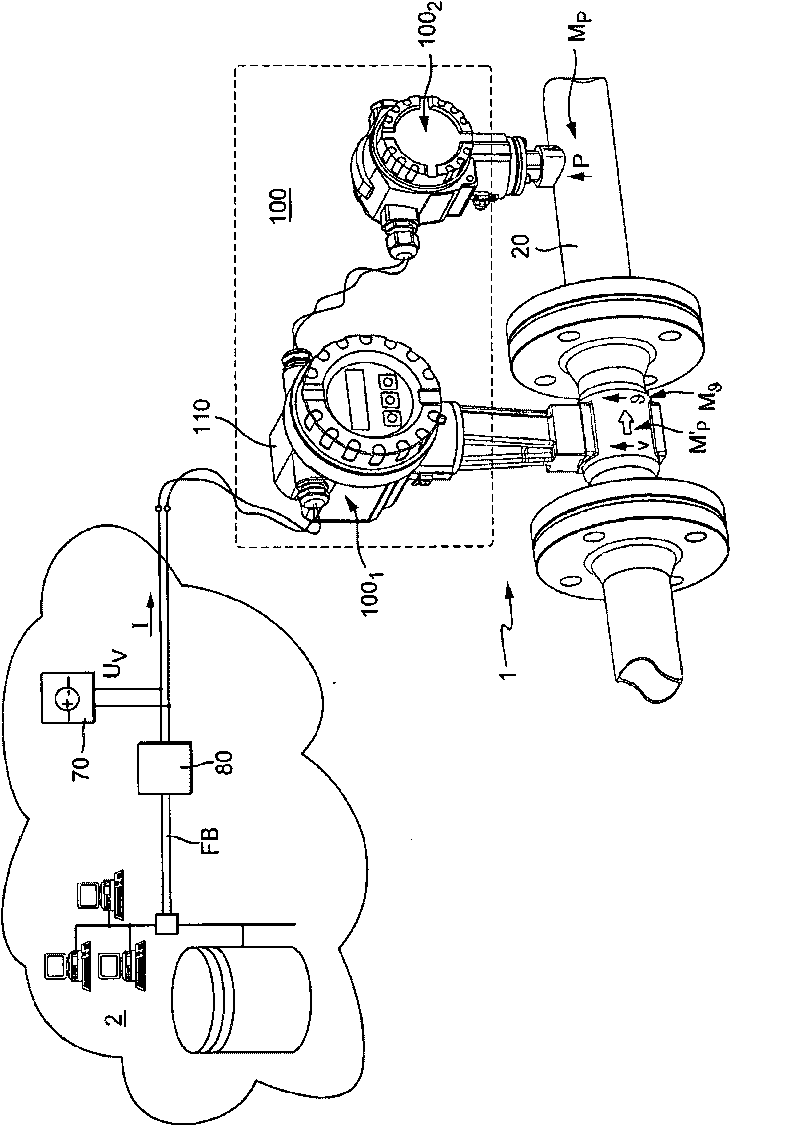
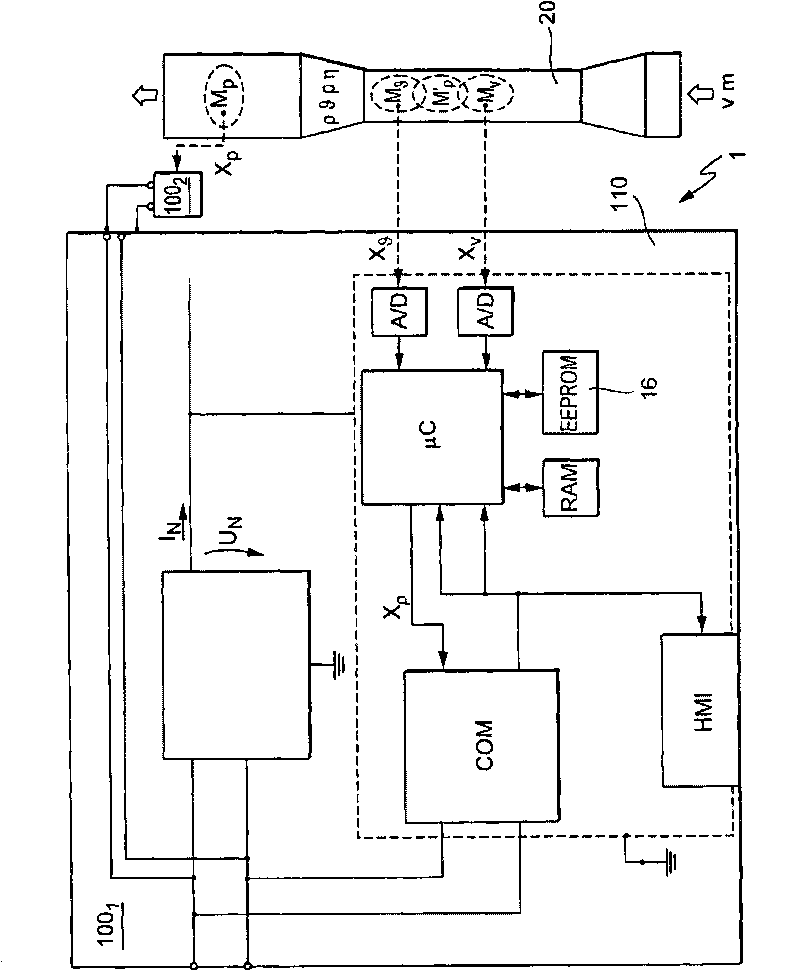
Measuring system for a medium flowing in a process line
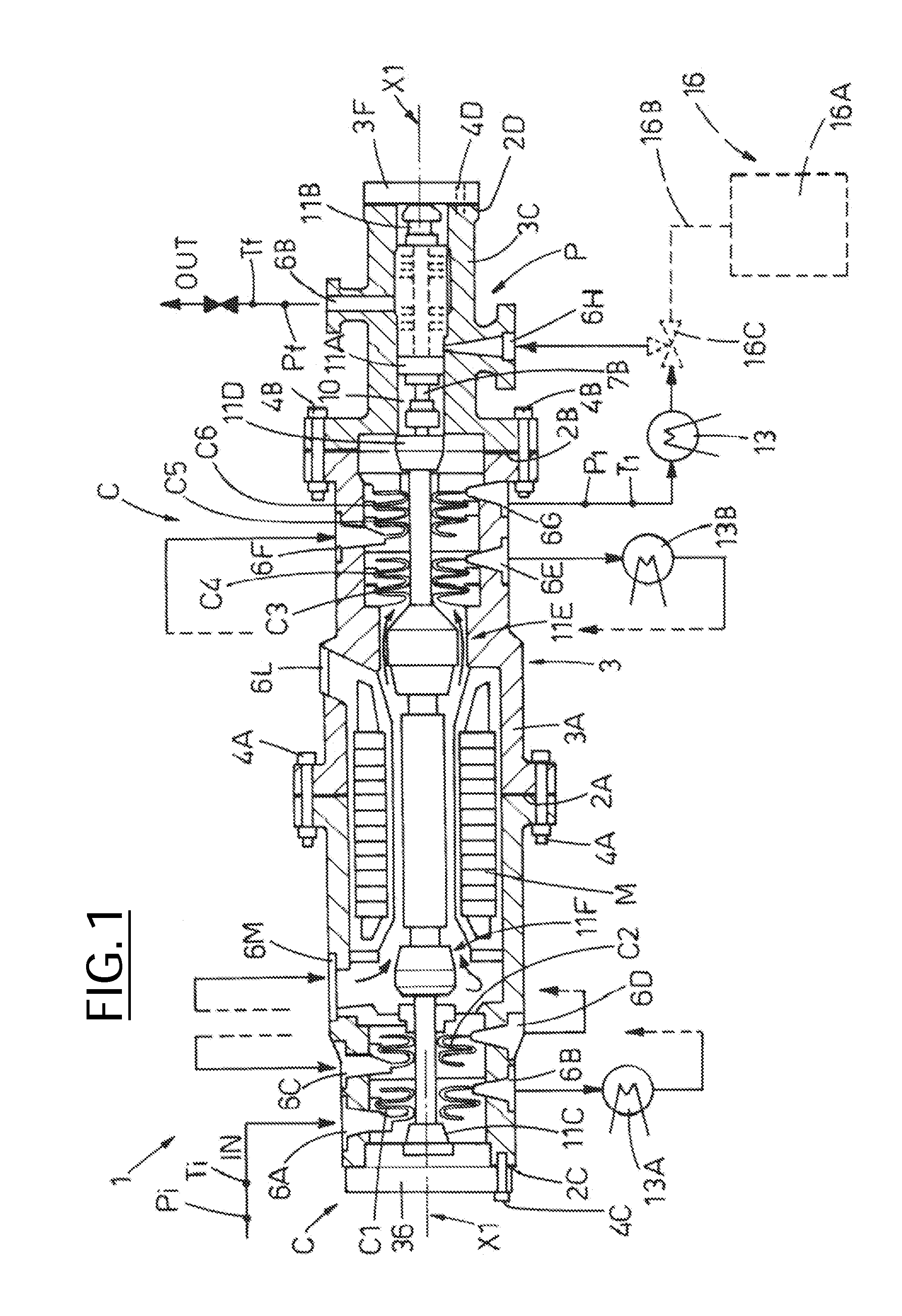
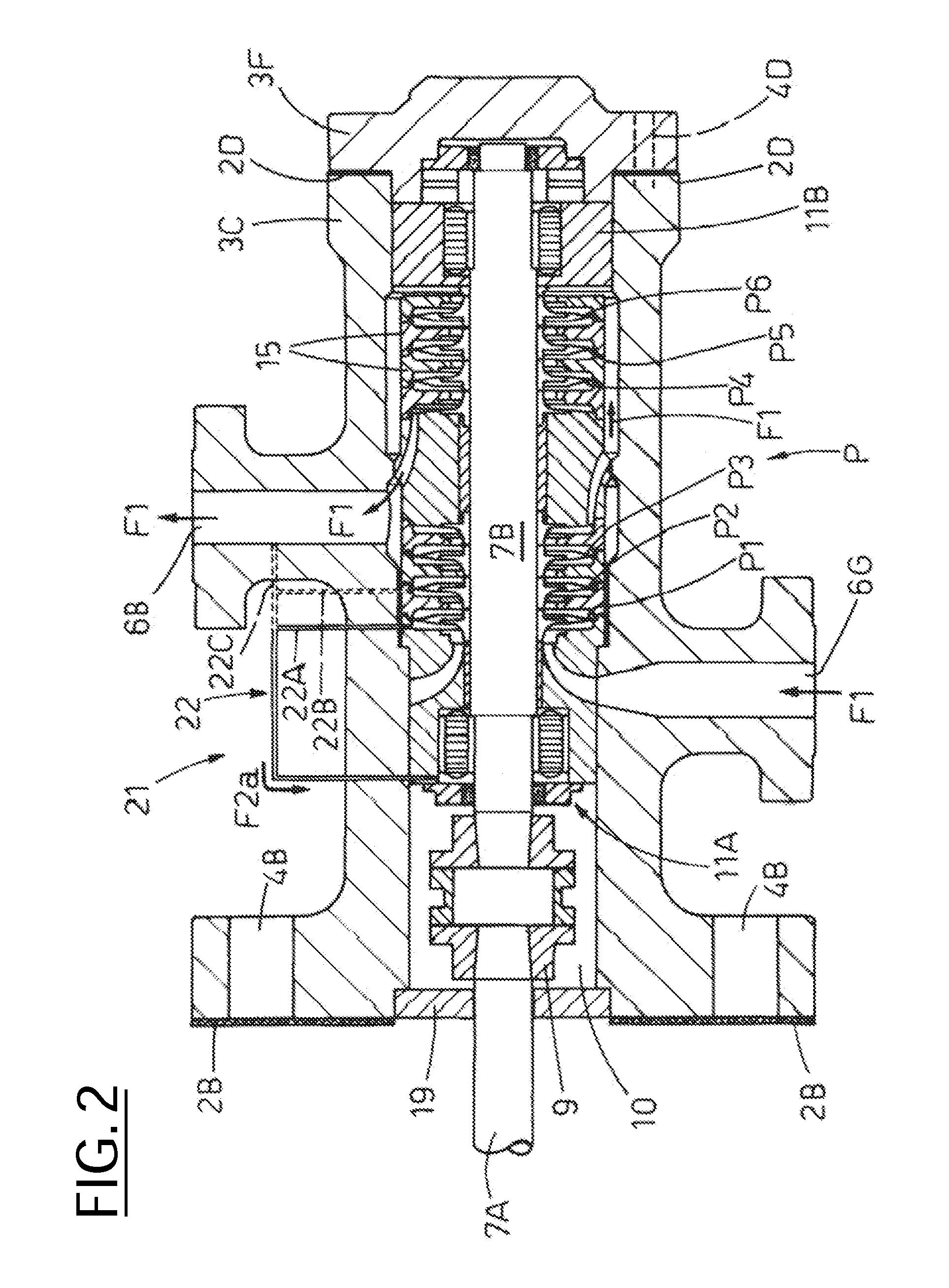
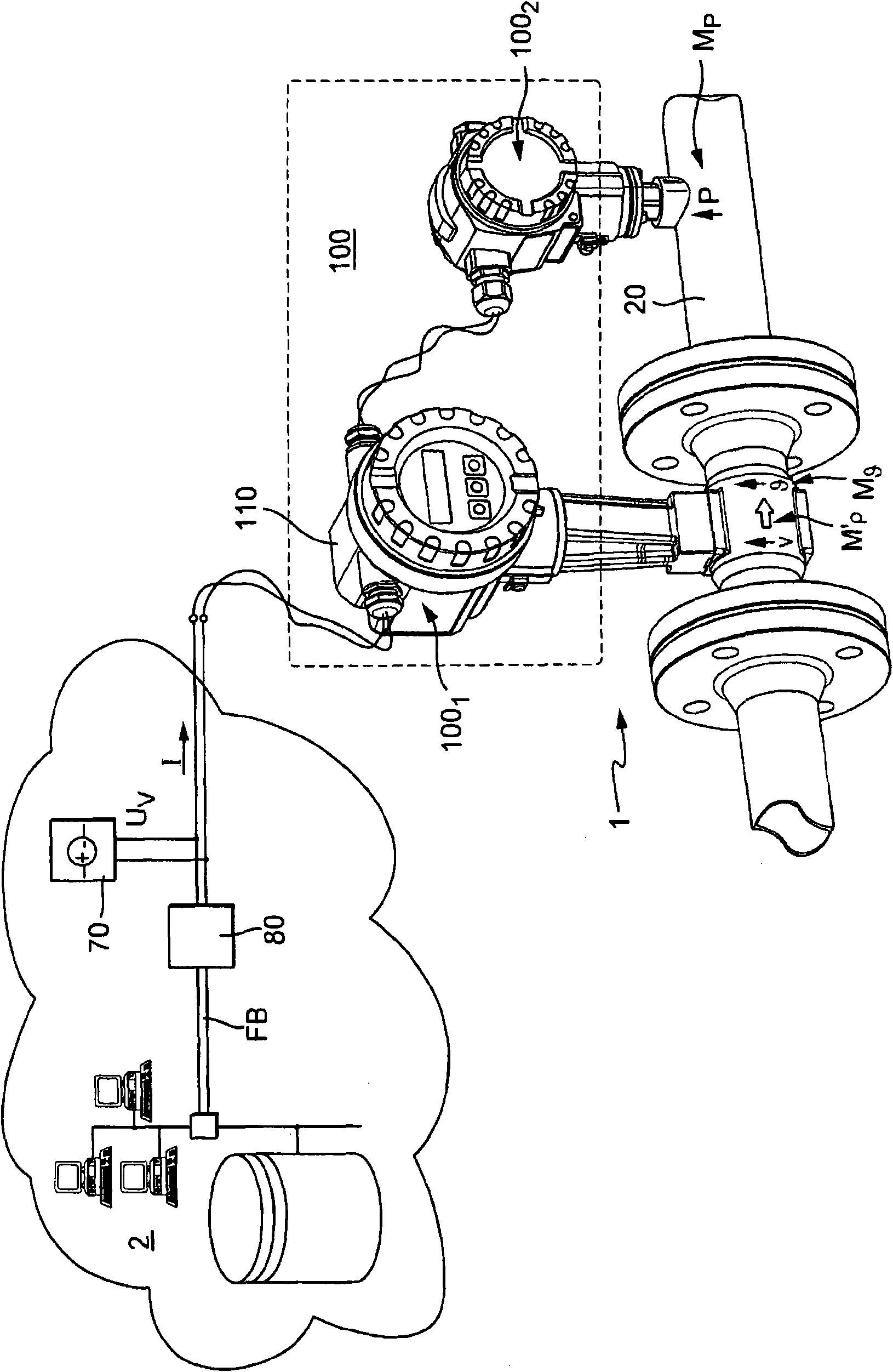
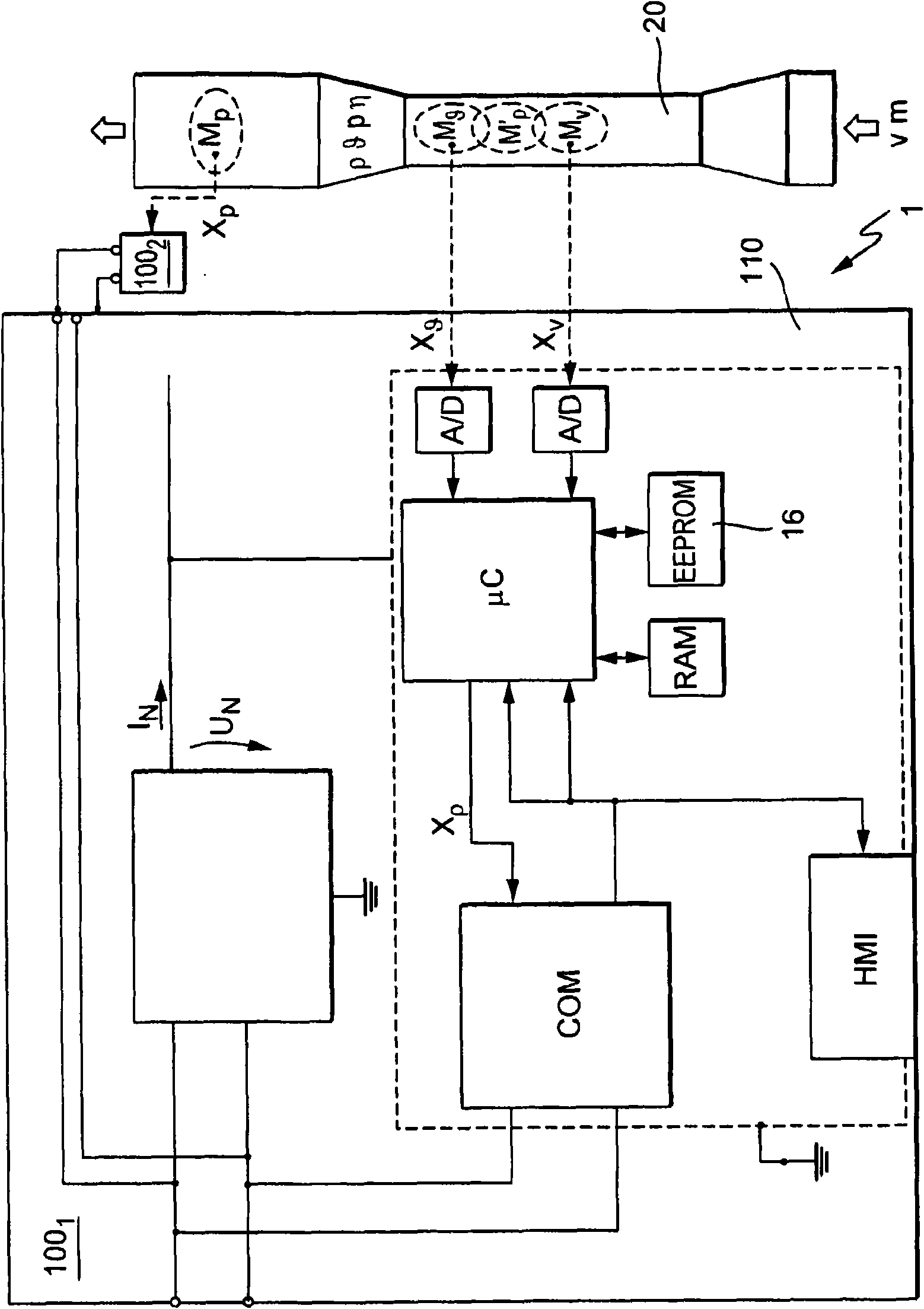
The invention relates to a measuring system for measuring a density of a medium flowing in a process line, said medium being variable regarding its thermodynamic state, especially at least being compressible, along an imaginary axis of flow of the measuring system. The measuring system comprises at least one temperature sensor that is located in a temperature measuring point and that primarily reacts to a local temperature, 9, of a medium flowing past, said temperature sensor supplying at least one temperature measurement signal that is influenced by the local temperature of the medium to be measured, at least one pressure sensor that is located in a pressure measuring point and that primarily reacts to a local, especially static, pressure, p, of a medium flowing past, said pressure sensor supplying at least one pressure measurement signal that is influenced by the local pressure, p, in the medium to be measured, and at least one electronic measuring unit that at least temporarily communicates with at least the temperature sensor and the pressure sensor. The electronic measuring unit generates at least temporarily an especially digital, density value, using the temperature measurement signal and at least the pressure measurement signal, said density value momentarily representing a local density, Rho, which the flowing medium has in an especially stationary, virtual density measuring point that is interspaced from the pressure measuring point and / or the temperature measuring point along the axis of flow at a defined distance.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Thermodynamic presenting method and thermodynamic presenting device for geographical area
ActiveCN106991576AImprove experienceImprove visual effectsMaps/plans/chartsGeographical information databasesPresent methodThermodynamic state
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Thermodynamic diagram processing method and device
ActiveCN104408197AResolution timeSolve the situationWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsThermodynamic statePolymerization
The invention discloses a thermodynamic diagram processing method and device. The method includes acquiring thermodynamic diagram data of a webpage, wherein the thermodynamic diagram at least comprises browse data of the webpage; acquiring a preset time interval; determining the polymerization granularity of the polymerization conducted on the thermodynamic diagram data; forming the thermodynamic diagram data sequence according to the polymerization granularity and the thermodynamic diagram data; sequentially generating a plurality of thermodynamic diagrams according to the time interval and the thermodynamic data sequence, wherein the plurality of thermodynamic diagrams form a dynamic thermodynamic diagram. By means of the method and device, the problem in the prior art that the static thermodynamic diagram can be generated only according to the thermodynamic diagram presentation period, and the change conditions of access data in various time intervals of one period cannot be reflected visually is solved.
Owner:BEIJING GRIDSUM TECH CO LTD
Thermodynamic diagram generation method and device
Embodiments of the invention provide a thermodynamic diagram generation method and device, relates to the field of image processing, and aims at enabling thermodynamic diagrams to continuously and correctly reflect features of areas and enabling changes of image scaling not to influence the continuity and correctness of the thermodynamic diagrams. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing an original image into cells in the current display area of a screen; calculating basic thermal force of a thermodynamic point area of each cell according to statistical data and a thermodynamic weight for generating a thermodynamic diagram; calculating diffusion thermal force suffered by each pixel point in the current display area according to the basic thermal force of the thermodynamic point areas of the cells; obtaining total thermal force of each pixel point in the current display area; and displaying a color corresponding to the total thermal force of each pixel point in the currentdisplay area in the current display area of the original image according to a preset thermodynamic display corresponding relationship, so as to obtain a thermodynamic diagram of the current display area. The method and device are used for generating thermodynamic diagrams.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Thermoelectric-enhanced, vapor-compression refrigeration method facilitating cooling of an electronic component
InactiveUS20120210731A1Machines using electric/magnetic effectsElectrical apparatus contructional detailsEngineeringThermodynamic state
A method is provided for facilitating cooling of an electronic component. The method includes: providing a refrigerant loop configured for refrigerant to flow through the loop; coupling a compressor in fluid communication with the loop, wherein a first portion of the loop resides upstream of a refrigerant inlet of the compressor, and a second portion resides downstream; and disposing a controllable thermoelectric array in thermal communication with the refrigerant loop. The thermoelectric array is disposed with the first portion of the refrigerant loop at least partially in thermal contact with the first side of the array, and the second portion of the loop at least partially in thermal contact with a second side of the array. The array is controlled to ensure that refrigerant in the refrigerant loop entering the compressor is in a superheated thermodynamic state.
Owner:IBM CORP
Measuring system for a medium flowing in a process line
ActiveCN101711351AHigh measurement accuracySpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesSpecific gravity using flow propertiesLine tubingMeasurement point
The invention relates to a measuring system for measuring a density of a medium flowing in a process line, said medium being variable regarding its thermodynamic state, especially at least being proportionally compressible, along an imaginary axis of flow of the measuring system. The measuring system comprises at least one temperature sensor that is located in a temperature measuring point and that primarily reacts to a local temperature, theta, of a medium flowing past, said temperature sensor supplying at least one temperature measurement signal that is influenced by the local temperature of the medium to be measured, at least one pressure sensor that is located in a pressure measuring point and that primarily reacts to a local, especially static, pressure, p, of a medium flowing past, said pressure sensor supplying at least one pressure measurement signal that is influenced by the local pressure, p, in the medium to be measured, and at least one electronic measuring unit that at least temporarily communicates with at least the temperature sensor and the pressure sensor. The electronic measuring unit generates a provisional density value, using the temperature measurement signal and at least the pressure measurement signal, said density value representing a density which the flowing medium only apparently has in a virtual density measuring point that is especially interspaced from the pressure measuring point and / or the temperature measuring point along the axis of flow at a defined distance. The electronic measuring unit further generates at least temporarily at least one especially digital density value, which is different from the provisional density value, using the provisional density value and at least one correctional density value that depends on a flow speed of the medium and on the local temperature prevailing in the temperature measuring point, said correctional value being determined during operation time.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Reduced boiloff cryogen storage
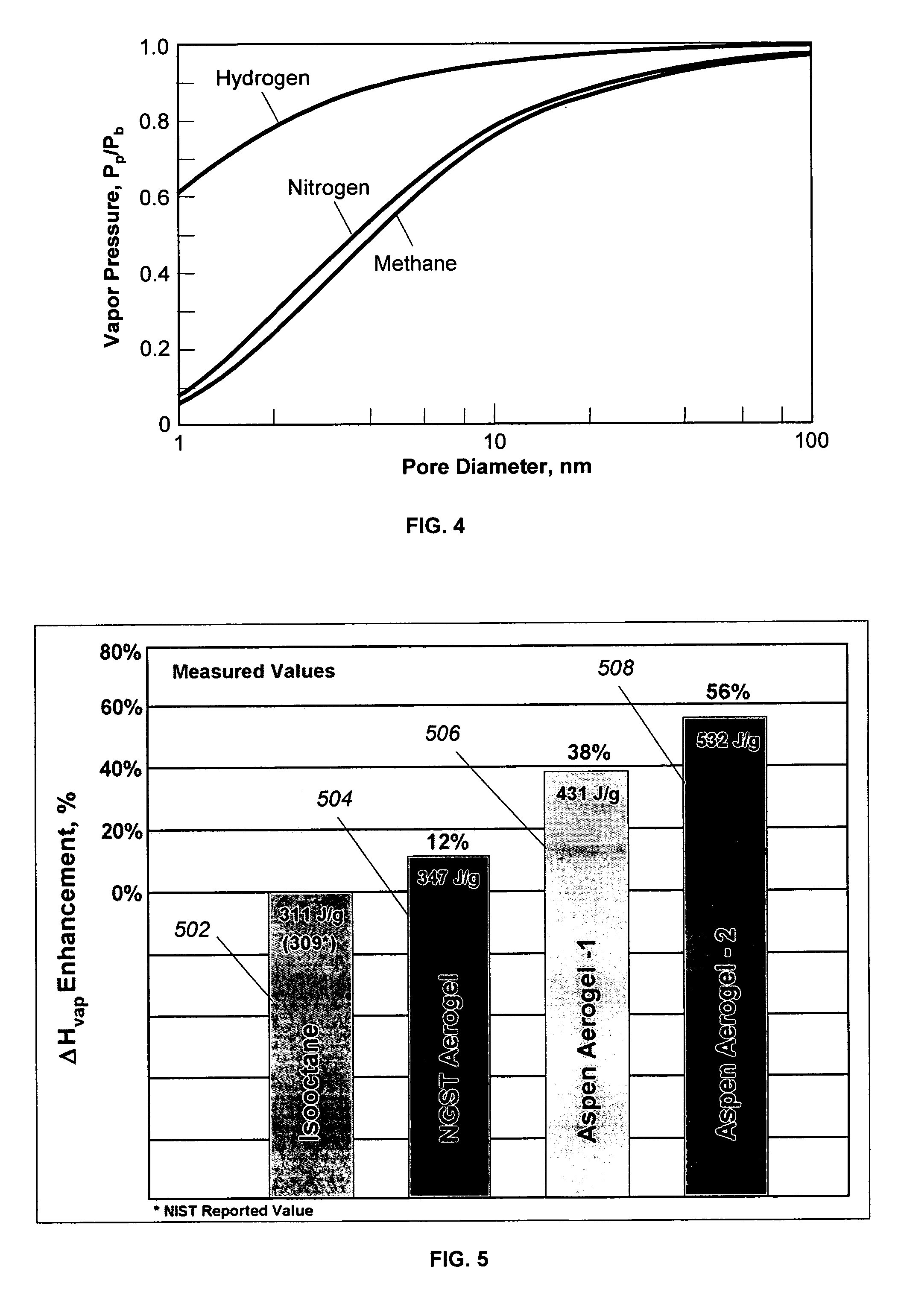
InactiveUS20060218940A1Low vapor pressureReduce leak rateVessel geometry/arrangement/sizeVessel wallsEngineeringHigh surface
A long-term cryogen storage system comprising a storage tank shell substantially filled by a nanoporous material in which a stored cryogen is subject to a dramatically lower boil-off rate than when stored in its bulk state. The nanoporous material provides a storage medium in which the cryogen has a higher surface energy term due to extreme surface curvature provided by the nanopores of the storage medium. As a result, the cryogen exhibits an altered thermodynamic state relative to its bulk fluid state and has a substantially reduced vapor pressure, an effectively higher vaporization enthalpy (ΔHv), and a lower boiloff rate for a given rate of heat leakage through the storage tank shell.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Method and system for tuning a gas turbine and gas turbine including such a system
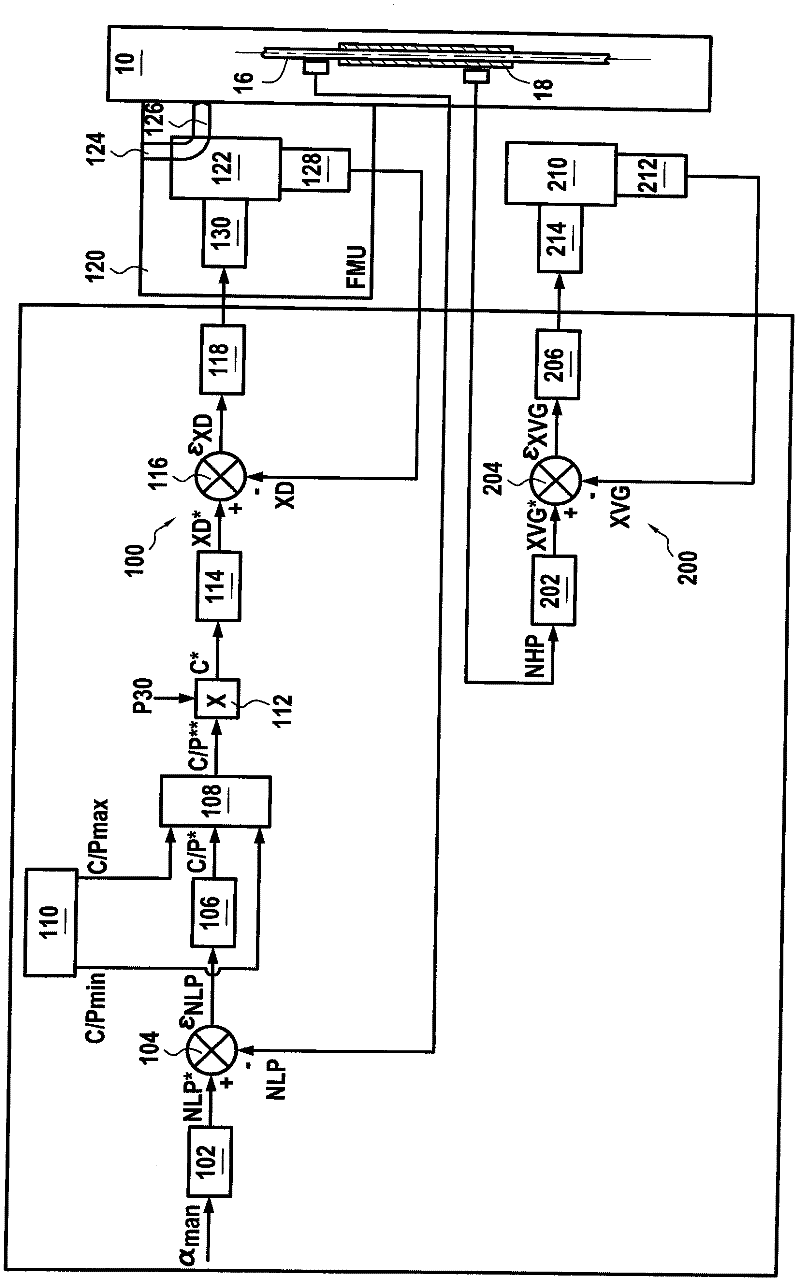
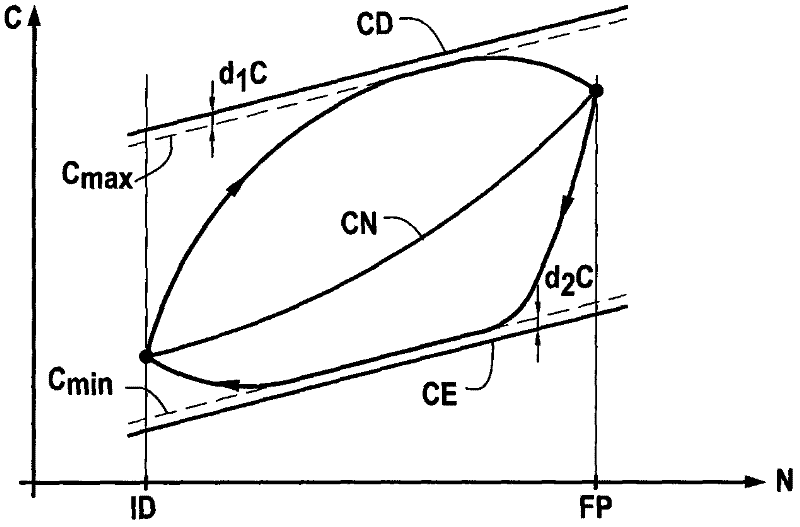
ActiveCN102317600AAcceleration time improvementReduced risk of stallingEfficient propulsion technologiesMachines/enginesCombustion chamberThermodynamic state
The invention relates to a system and to a method for tuning a gas turbine having a compressor system (10) with at least one portion (210) having a variable shape, a combustion chamber and a turbine assembly, wherein said method includes: setting a flow setpoint (C*) for the fuel to be fed into the combustion chamber on the basis of a target mode of the gas turbine, calculating threshold values (C / Pmin', C / Pmax') for maintaining the fuel flow setpoint value within a given range, the threshold values depending on a thermodynamic state of the gas turbine, and controlling the position of the variably-shaped portion by controlling an actuator on the basis of the deviation between position information (XGV) representative of the instantaneous position and setpoint position information (XGV*), the threshold values being adjusted automatically by a real-time calculation on the basis of the instantaneous position information of the variably-shaped portion or the deviation (epsilon XGV) between the detected position information and the setpoint position information.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
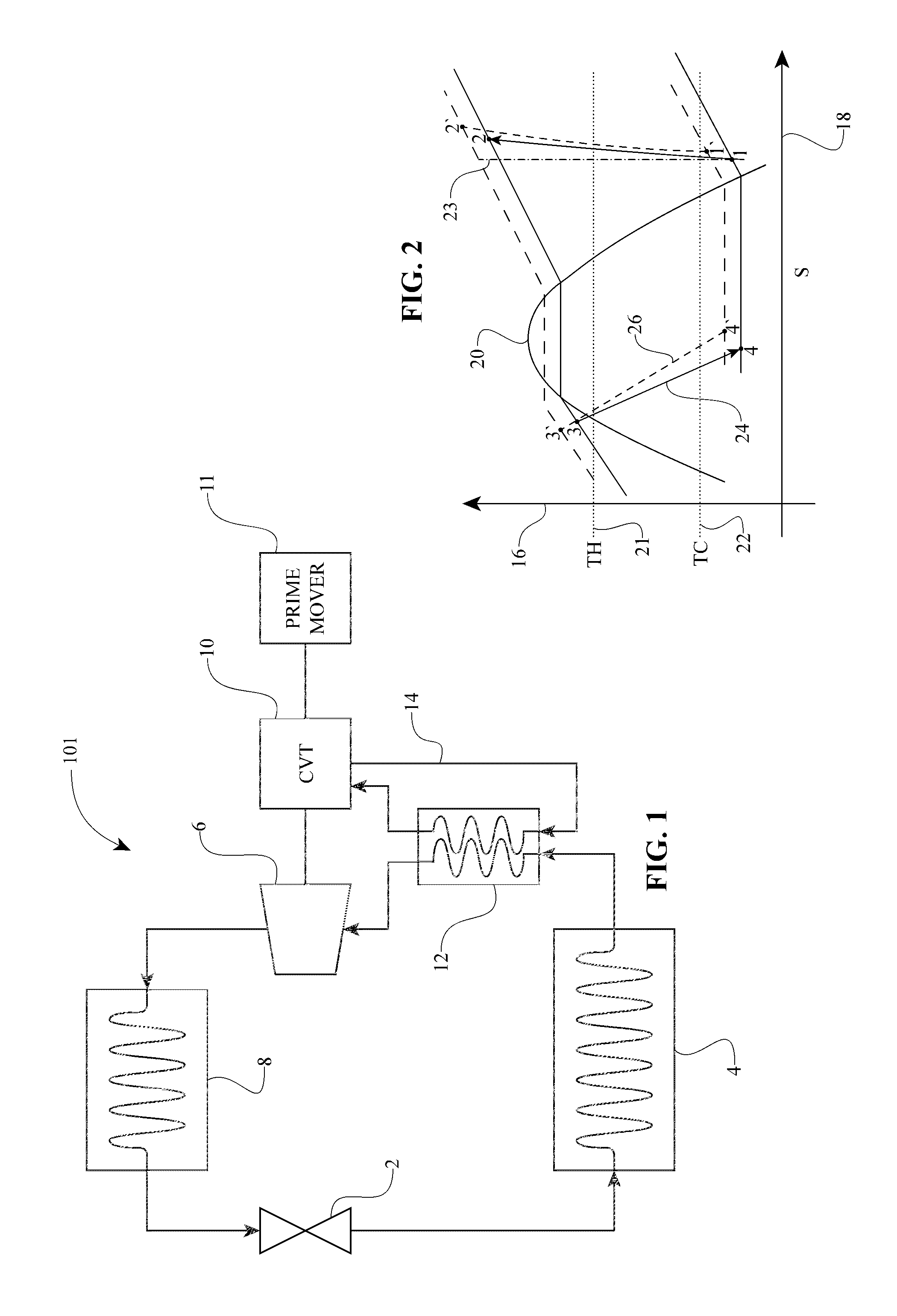
Refrigeration system having a continuously variable transmission
Inventive embodiments are directed to components, subassemblies, systems, and / or methods for a refrigeration system having a compressor operably coupled to continuously variable accessory drive (CVAD). In one embodiment, the refrigerant is adapted to cool the CVAD. In another embodiment, the refrigerant is configured to actuate a change in operating condition of the CVAD. A change in operating condition of the CVAD can be based at least in part on the thermodynamic state, such as pressure or temperature, of the refrigerant. In one embodiment, a skew-based control system is adapted to facilitate a change in the ratio of a CVAD. In another embodiment, a skew-based control system includes a skew actuator coupled to a carrier member. In some embodiments, the skew actuator is configured to rotate a carrier member of a CVT. Among other things, shift control interfaces for a CVT are disclosed.
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Measuring system for a medium flowing in a process line
ActiveCN101730834ASpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectMeasurement pointEngineering
The invention relates to a measuring system for measuring a density of a medium flowing in a process line, said medium being variable regarding its thermodynamic state, along an imaginary axis of flow of the measuring system. The measuring system comprises at least one temperature sensor that primarily reacts to a local temperature, theta, of a medium flowing past, at least one pressure sensor that primarily reacts to a local pressure, p, of a medium flowing past, at least one flow sensor that is located in a flow measuring point and that primarily reacts to a local flow parameter of the medium to be measured, and at least one electronic measuring unit that at least temporarily communicates with at least the temperature sensor, the pressure sensor and the flow sensor. The electronic measuring unit generates at least temporarily at least one density value that momentarily represents a local density, Rho, which the flowing medium has in a virtual density measuring point, using the temperature measurement signal, the pressure measurement signal and the flow measurement signal.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
High-pressure compression unit for process fluids for industrial plant and a related method of operation
ActiveUS8632320B2Overcome problemsSpecific fluid pumpsPositive displacement pump componentsCompression deviceThermodynamic state
Owner:NUOVO PIGNONE TECH SRL
Automatic welding ball packaging metal ball embedding method and apparatus
InactiveCN101140889AUniform sizeImprove controllabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDifferential pressureEngineering
The invention relates to a method and device for Ball Array of the soldered ball in BGA Ball Grid Array Package technology, which belongs to technical field of electronic packing. The invention is to inject the inert gases into the crucible and the vacuum gas tight chamber and makes the crucible and the vacuum gas tight chamber achieve the stable differential pressure by pressure control system, and makes the metal melt ejected from a tiny nozzle of the crucible in the form of laminar jet. The vibration generated from piezoelectric oscillator perturbates the metal jet and makes it fractured into the even liquid drop, and then obtains the real-time size parameters aided by the monitoring system and computer analysis to feedback control the frequency of the oscillator and reduce the difference in size between the generated molten drop and the preset molten drop. The invention can correctly place the even solder ball in the appropriate thermodynamic state on the substrate preconfigured with the positions of the solder ball, which has the advantages of short process flow, good quality of product and greatly lowering the equipment investment.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Lumping and delumping method for describing hydrocarbon-containing fluids
ActiveUS7289943B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDrilling rodsMaterial balanceHydrocarbon mixtures
A lumping and delumping method is useful for estimating the properties or behavior of liquid and / or vapor hydrocarbon phases from data relative to a reference set of hydrocarbon mixtures in a series of thermodynamic states in a medium. Each one of the hydrocarbon mixtures is grouped into at least three constituents (V, I, H), considering that the gas phases resulting from separation under conditions referred to as surface conditions of each mixture do not contain (H) and that the oil phases do not contain (V). The compositions of the separation products are determined by material balance. The at least three-constituent composition of each hydrocarbon mixture is determined by combination of the products resulting from the separation in proportion to the amounts of each separation product. Delumping is performed to predict a detailed composition of a fluid in the medium.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method and System for Tank Refilling
ActiveUS20130269828A1Improve performanceImprove fuel performanceVessel geometry/arrangement/sizeVessel wallsAnalytical equationsThermodynamic state
Disclosed is an improved analytical method that can be utilized by hydrogen filling stations for directly and accurately calculating the end-of-fill temperature in a hydrogen tank that, in turn, allows for improvements in the fill quantity while tending to reduce refueling time. The calculations involve calculation of a composite heat capacity value, MC, from a set of thermodynamic parameters drawn from both the tank system receiving the gas and the station supplying the gas. These thermodynamic parameters are utilized in a series of simple analytical equations to define a multi-step process by which target fill times, final temperatures and final pressures can be determined. The parameters can be communicated to the station directly from the vehicle or retrieved from a database accessible by the station. Because the method is based on direct measurements of actual thermodynamic conditions and quantified thermodynamic behavior, significantly improved tank filling results can be achieved.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com