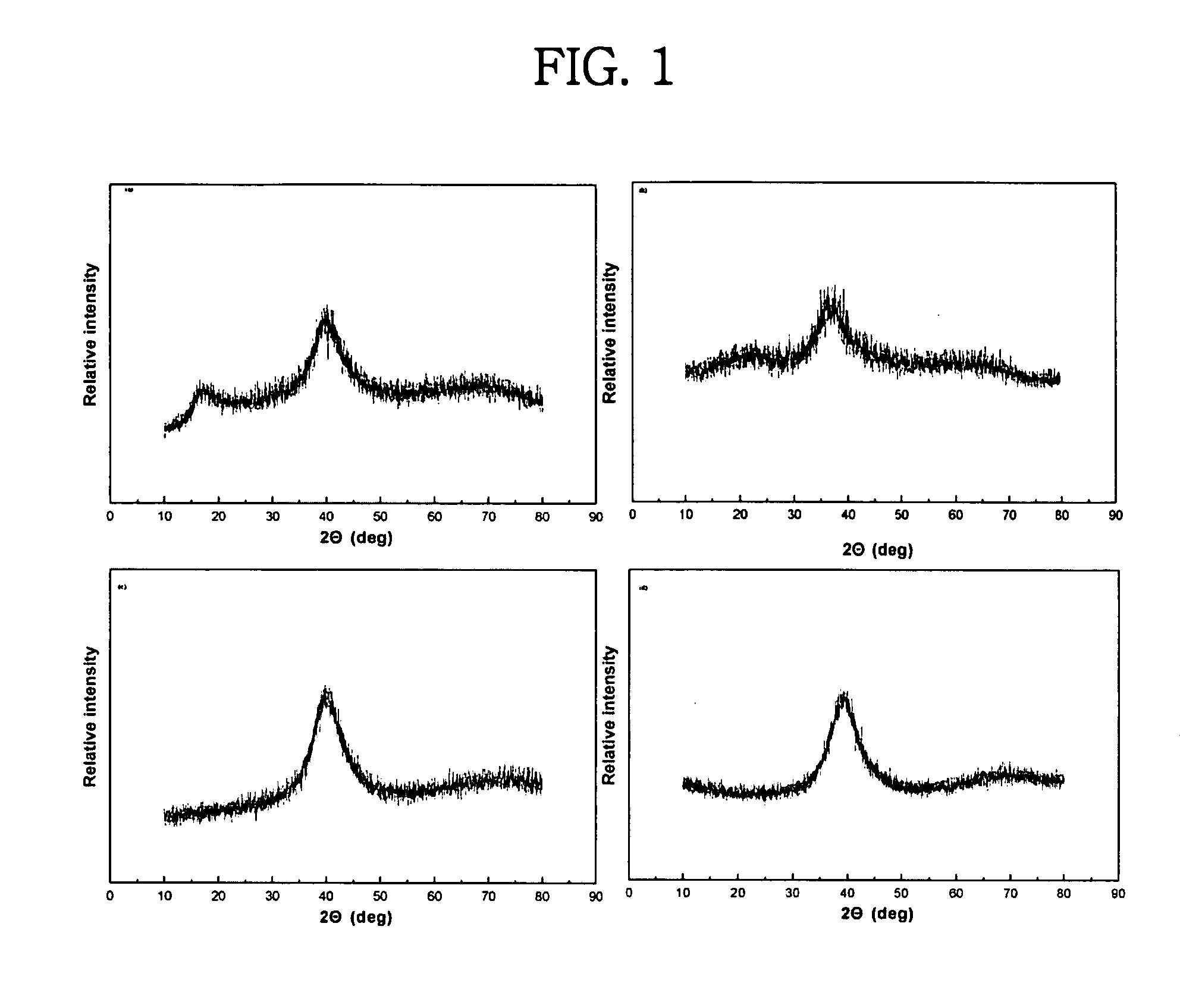
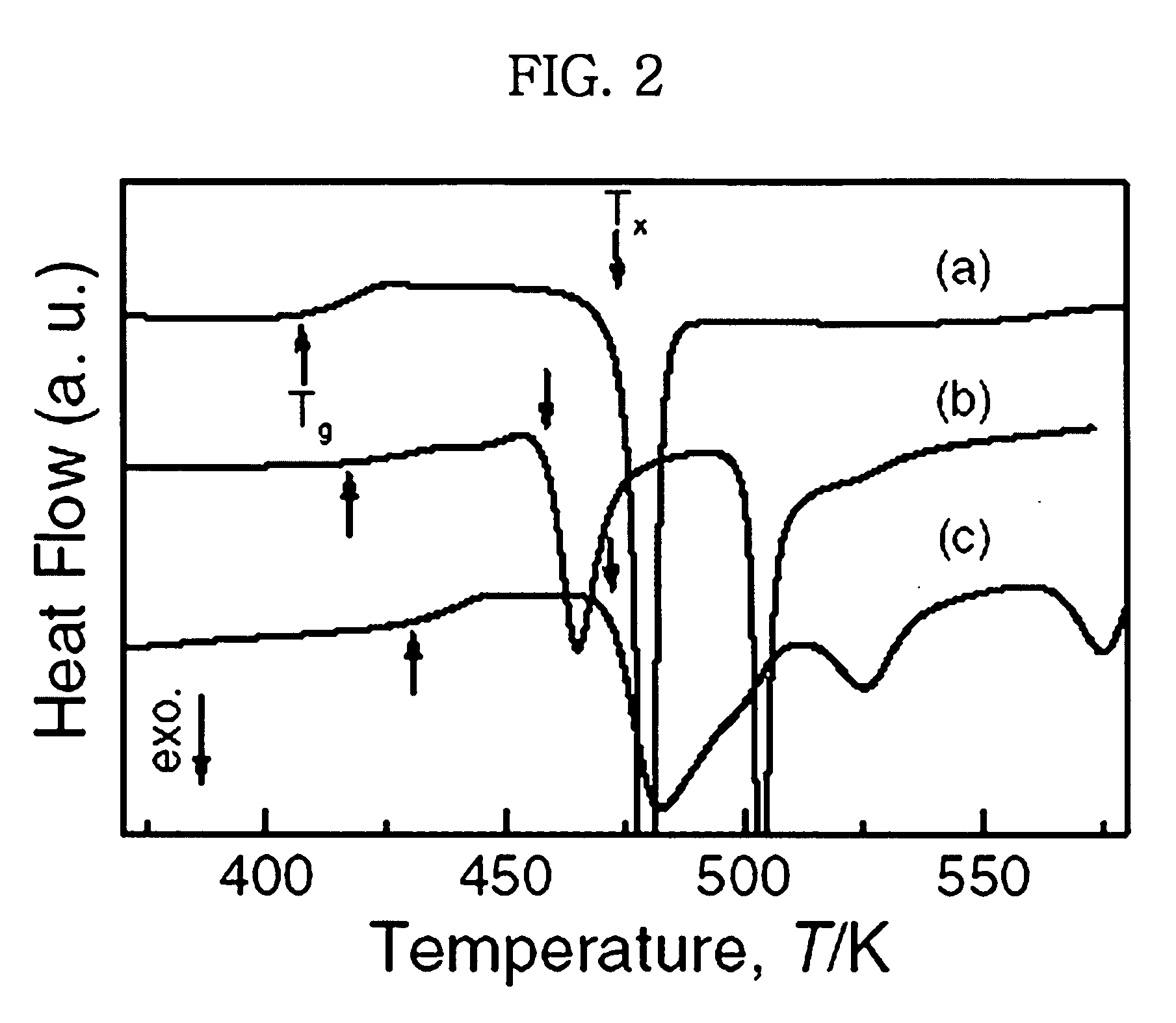
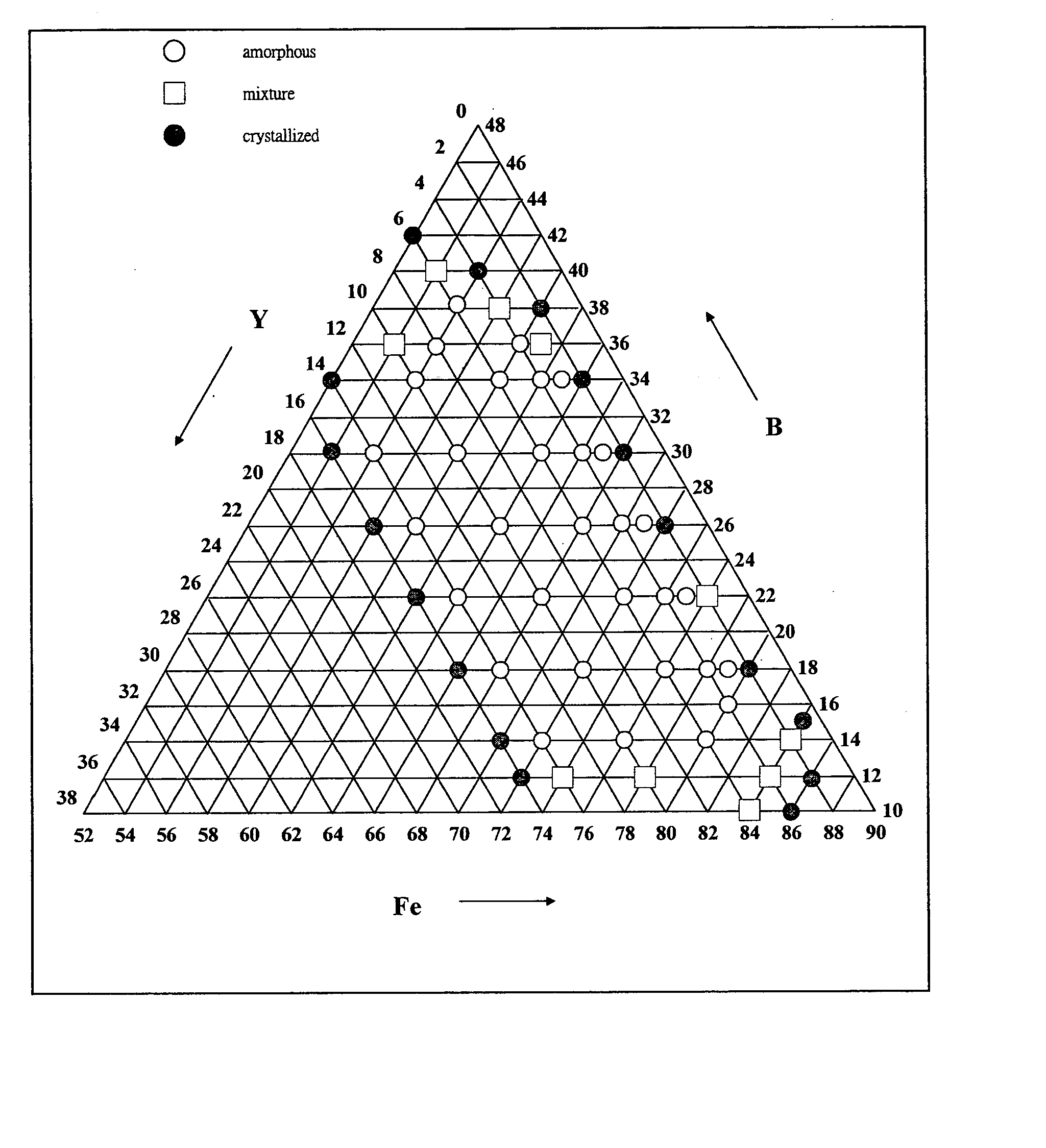
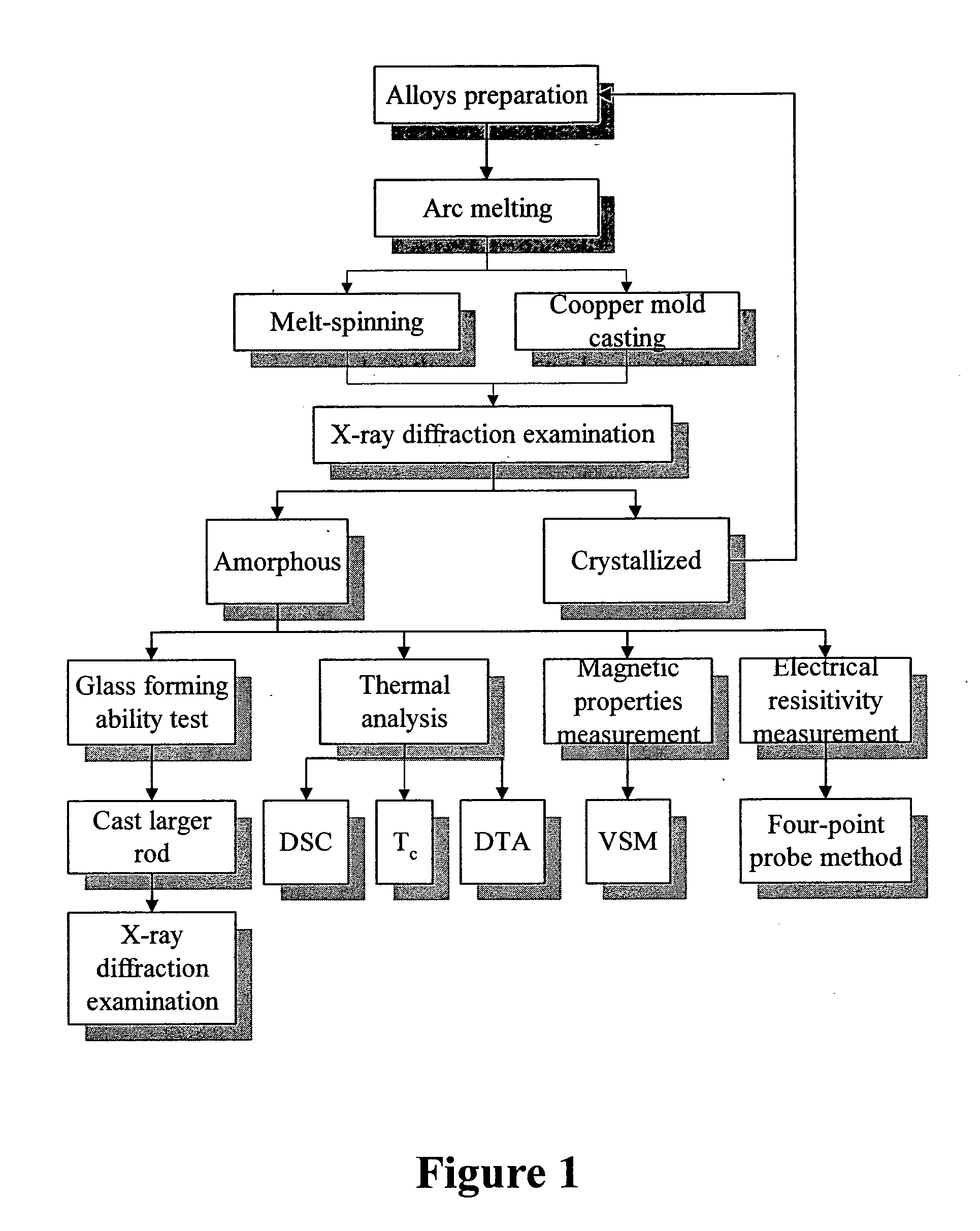
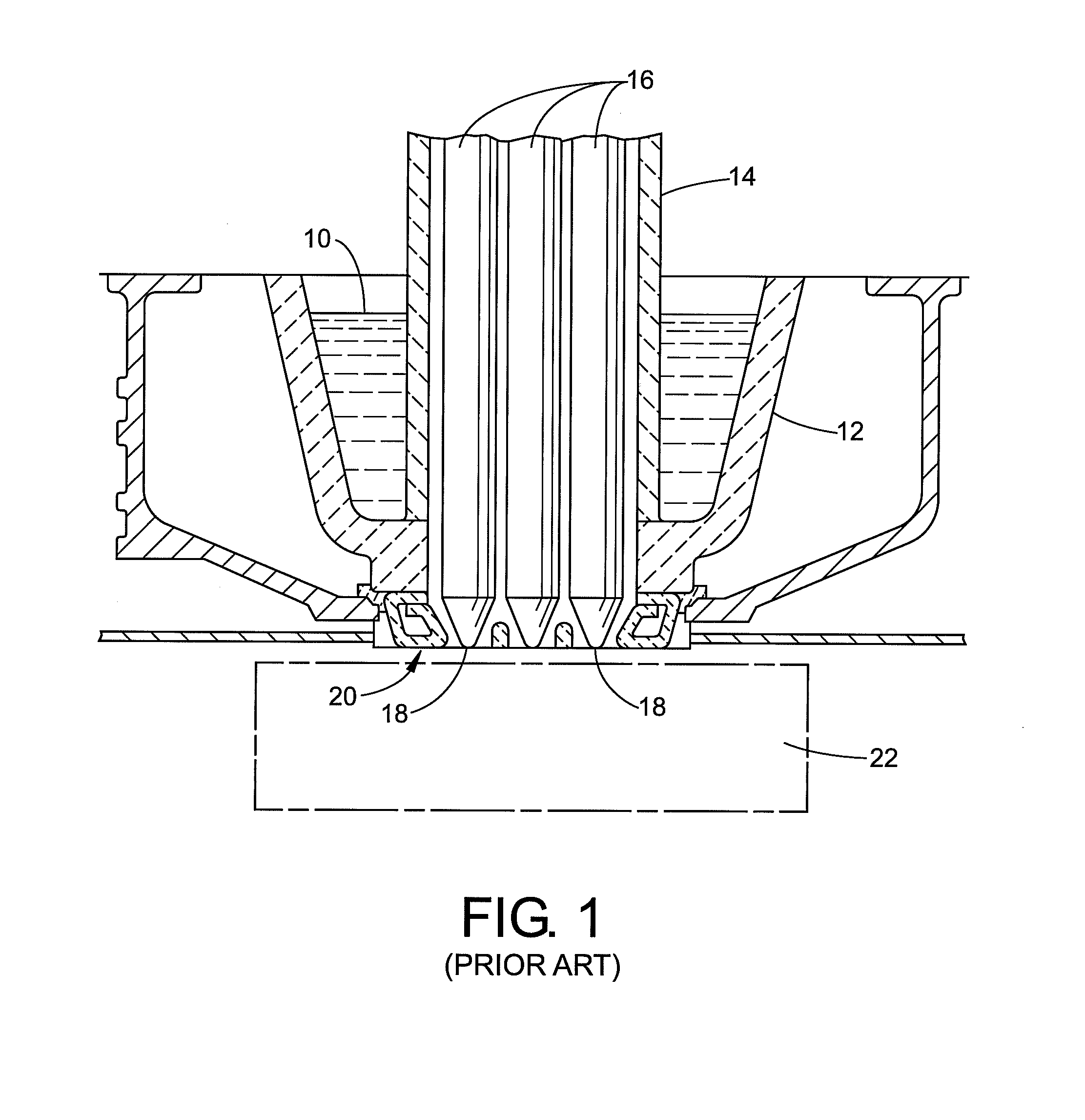
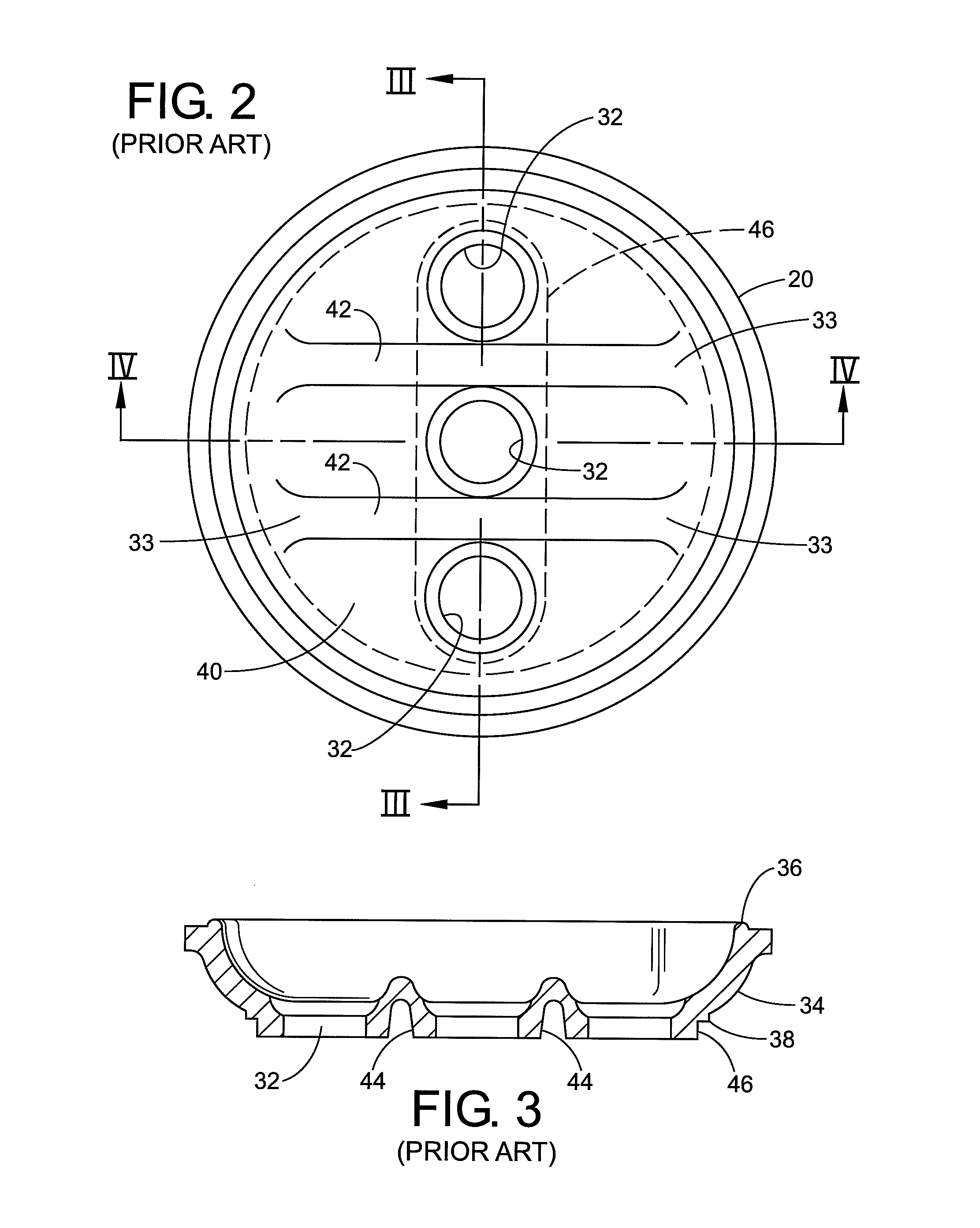
Patents
Literature
1276 results about "Glass forming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single phase rare earth oxide-aluminum oxide glasses
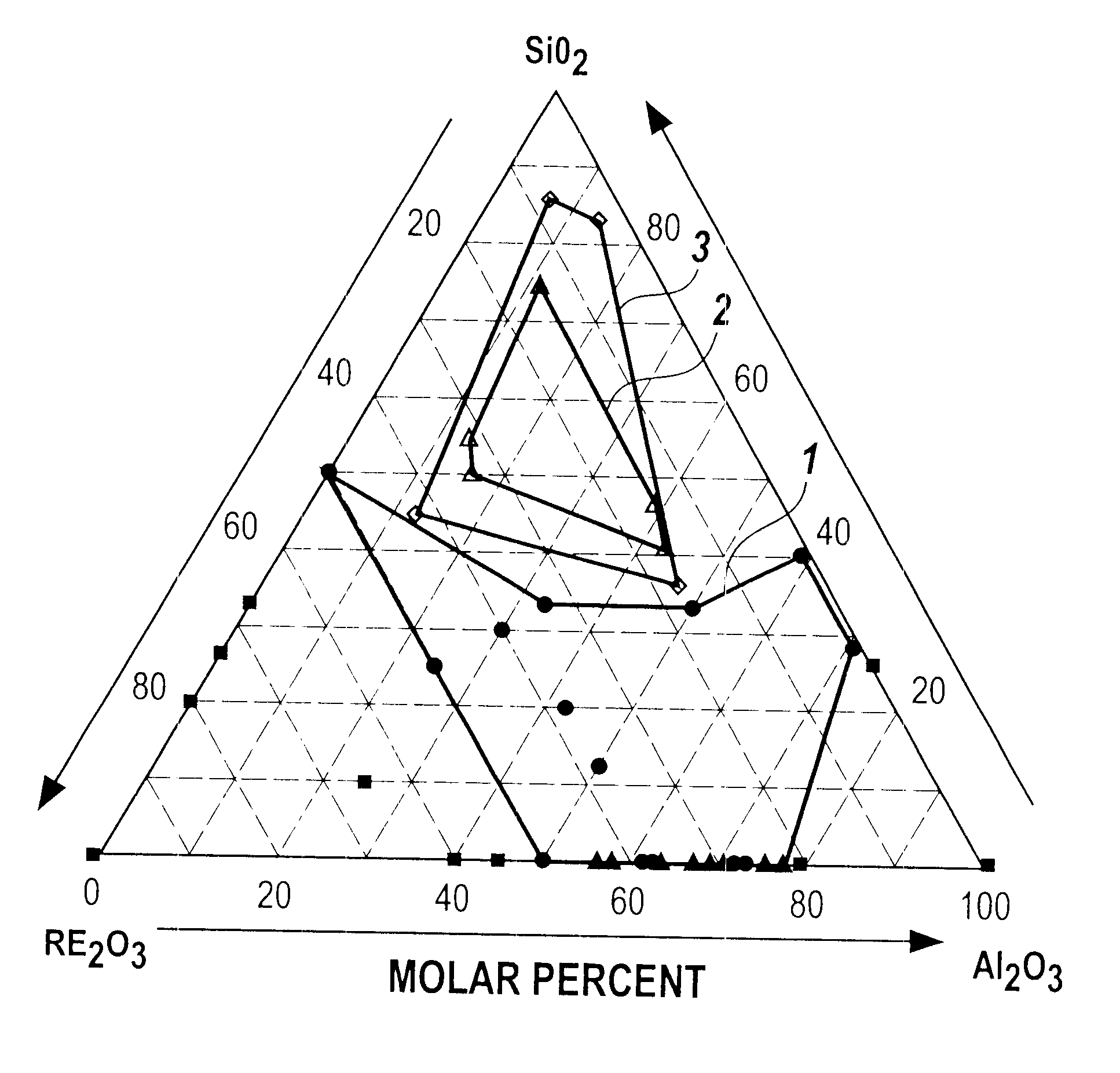
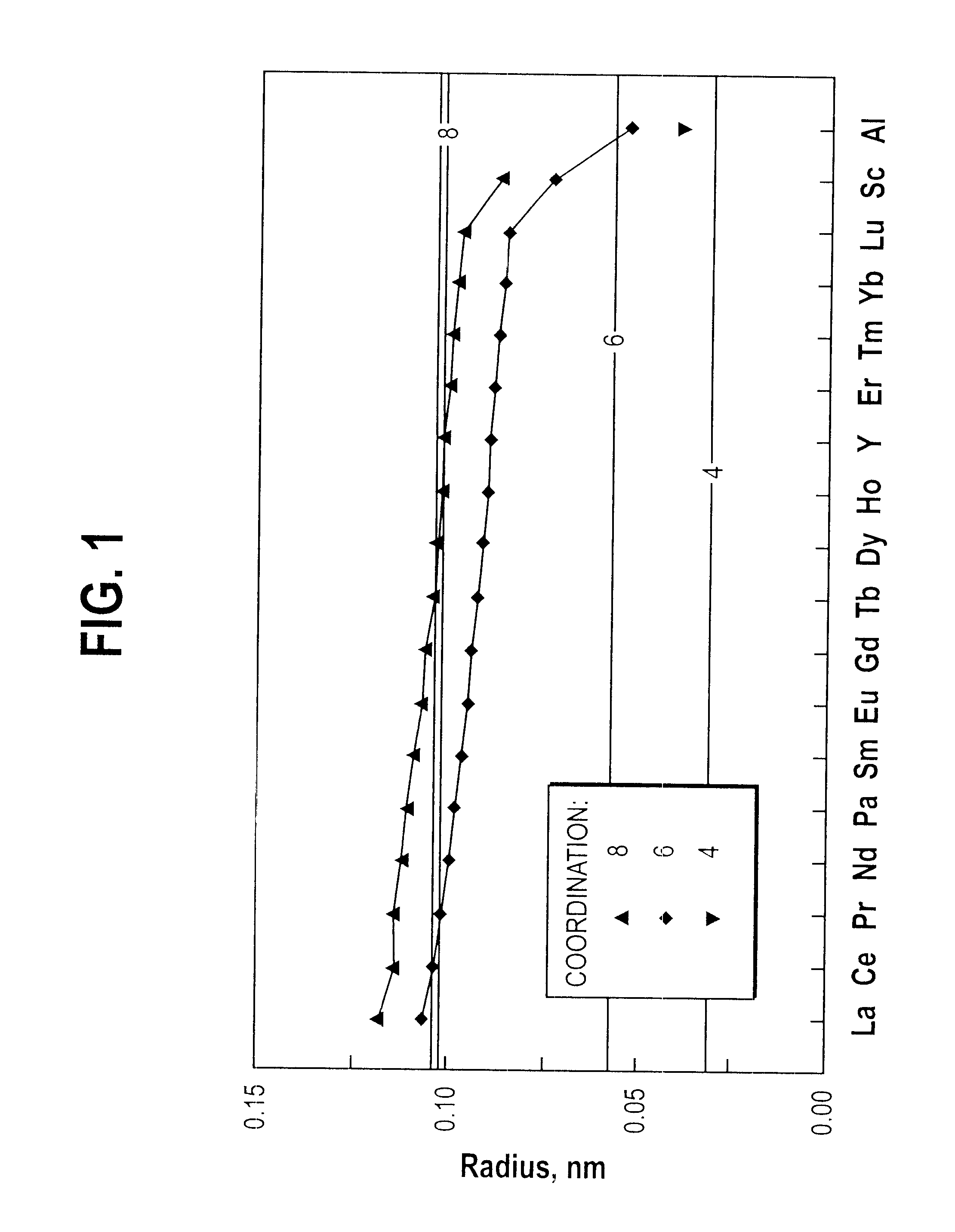
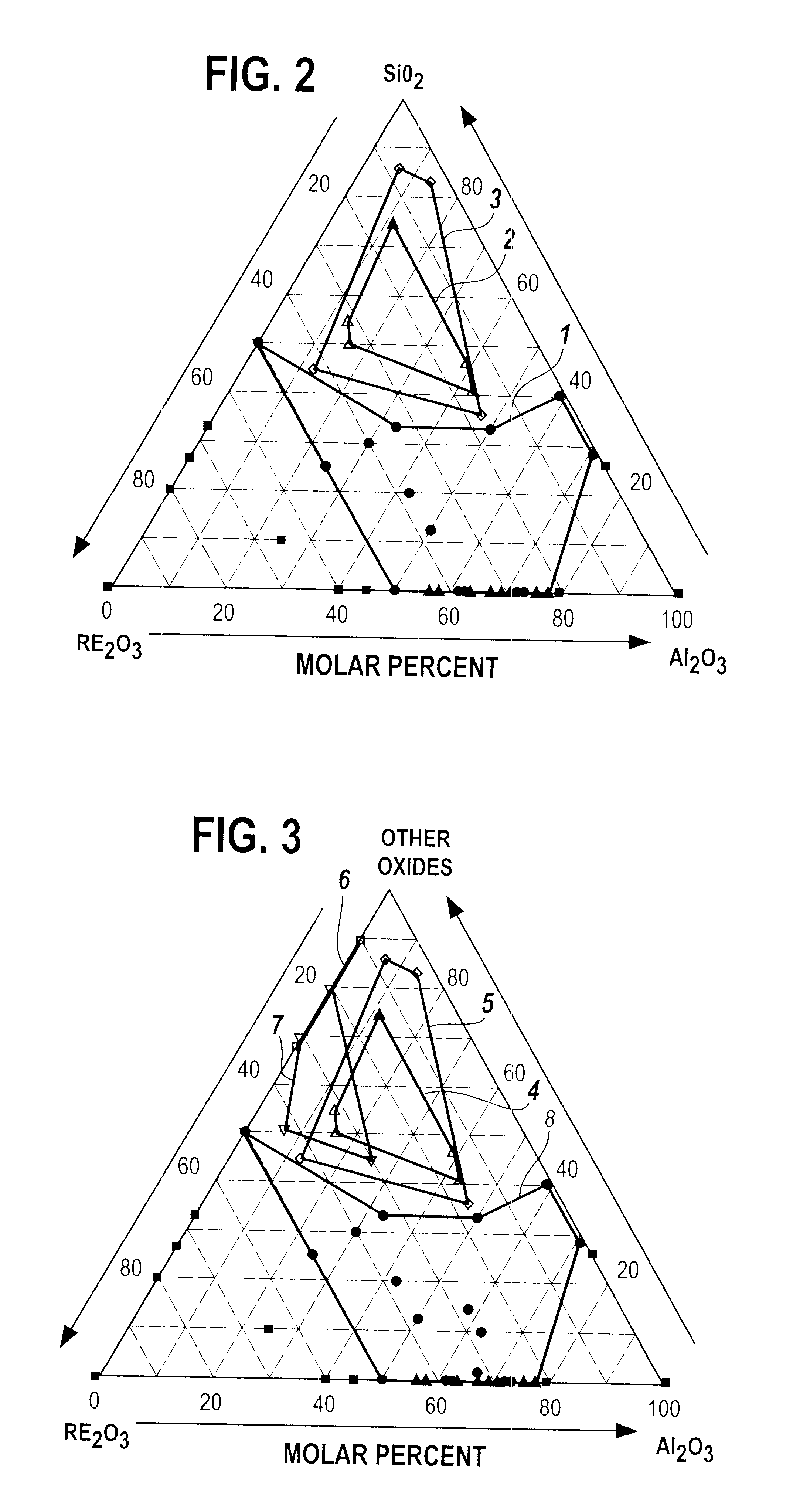
A bulk single phase glass comprising 23 molar % to 50 molar % rare earth oxides, RE203, and 50 molar % to 77 molar % aluminum oxide, A12O3 is provided. The glass contains at least 50 molar % of Al2O3+RE2O3 and smaller amounts of oxide glass forming agents and other oxides than are found in prior art glasses. The addition of small amounts of lanthanum oxide, La2O3, prevents phase separation. The single phase glass is useful for optical applications such as lasers and optical amplifiers.
Owner:CONTAINERLESS RES
Coated powder particles for producing three-dimensional bodies by means of a layer constituting method
InactiveUS20060251535A1Good storage stabilityHigh distinctnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingOrganic solventLaser light
The invention relates a powder material consisting of coated particles for a powder-based rapid generative prototyping methods, in particular by compressing a 3D binder. Said powder material consists of individual plastic, metal and / or ceramic particles and / or granules. A coating essentially consists of an adhesive agent which can be activated by a liquid binder, light or laser light, and of sinterable or glass-forming fine-grained material. Said invention also relates to a method for compressing 3D binder with the aid of an organic solvent having a water content less than 45% and to sintered bodies, in particular for moulding or precision mechanical engineering, which are fixed to each other by sintering or glass formation from a fine grained material.
Owner:PFEIFER ROLF +2
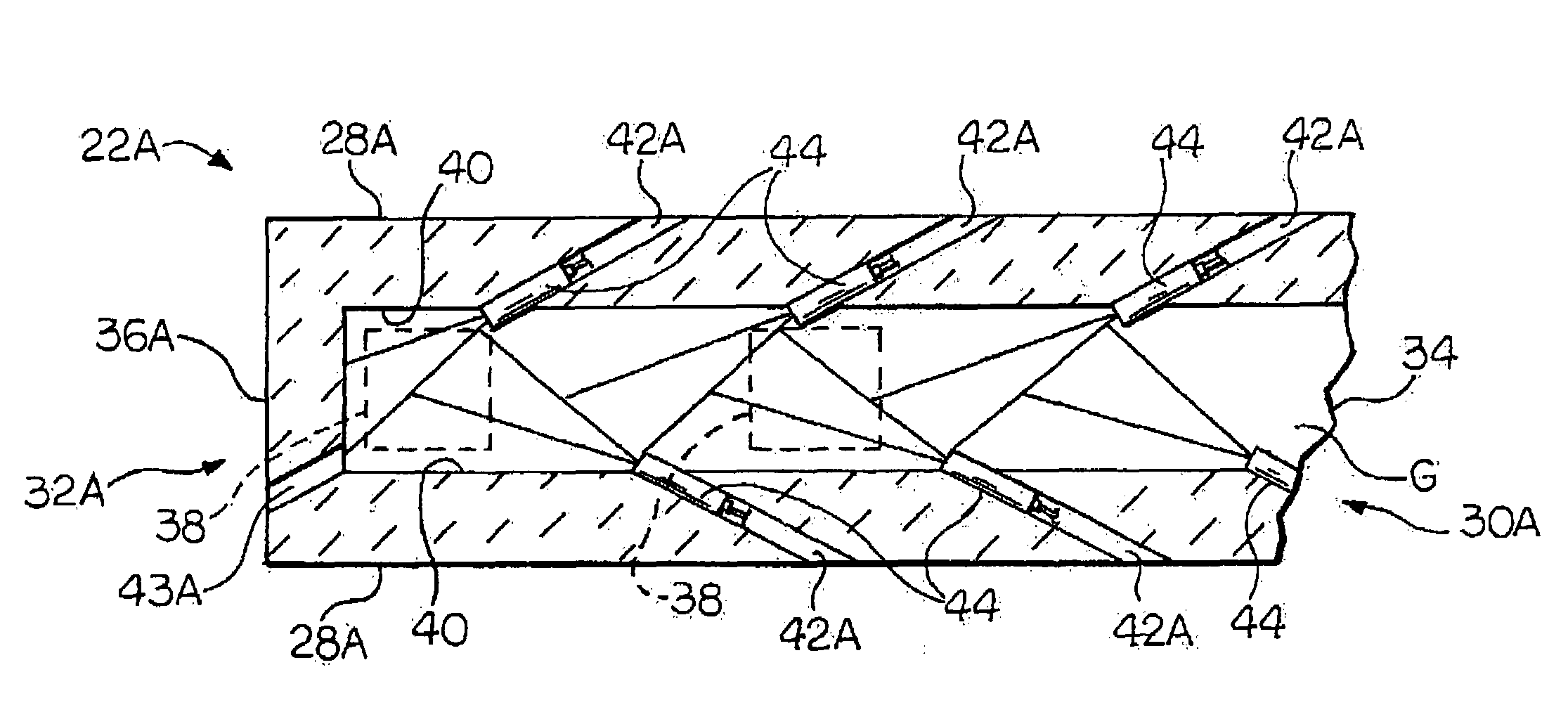
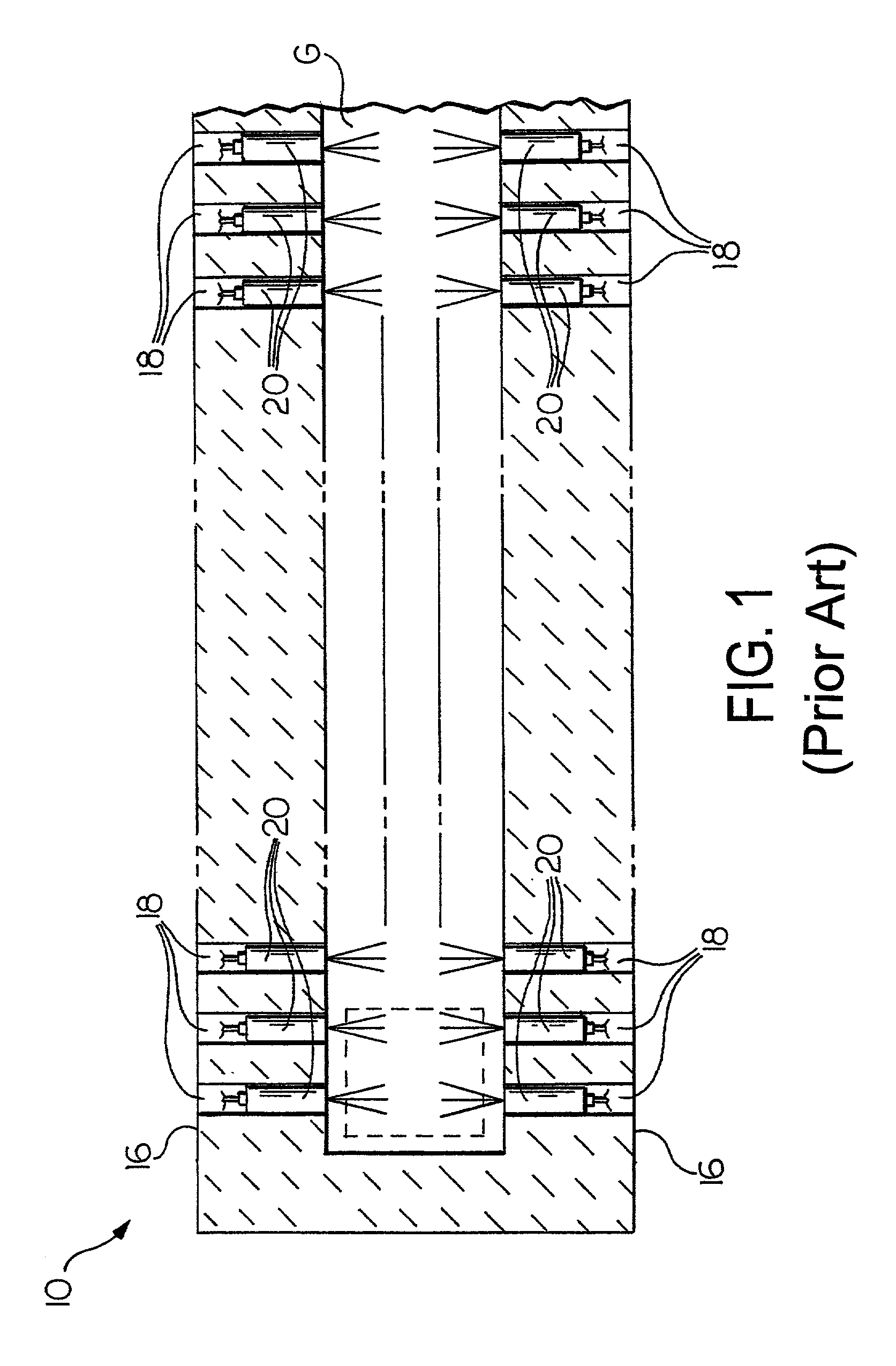
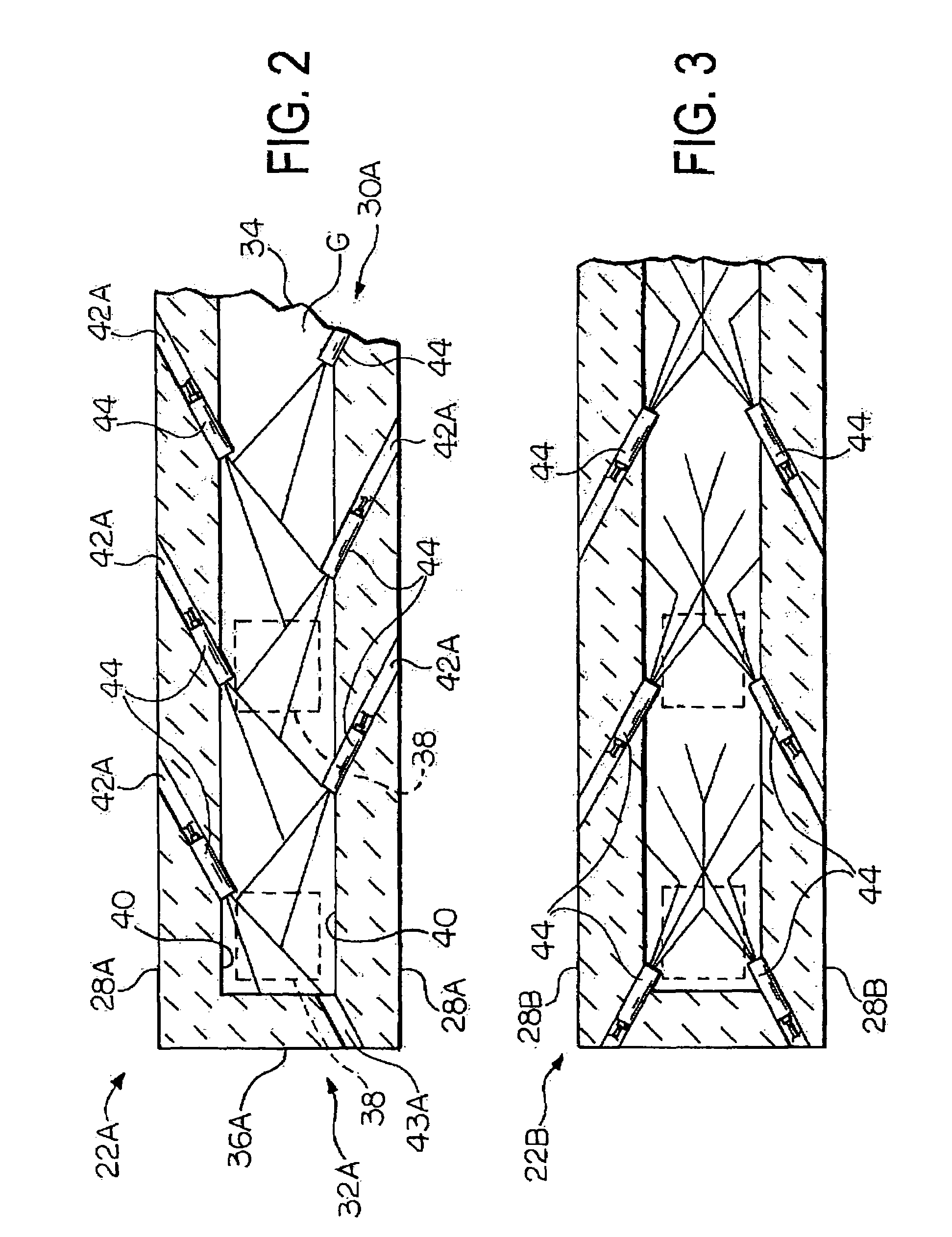
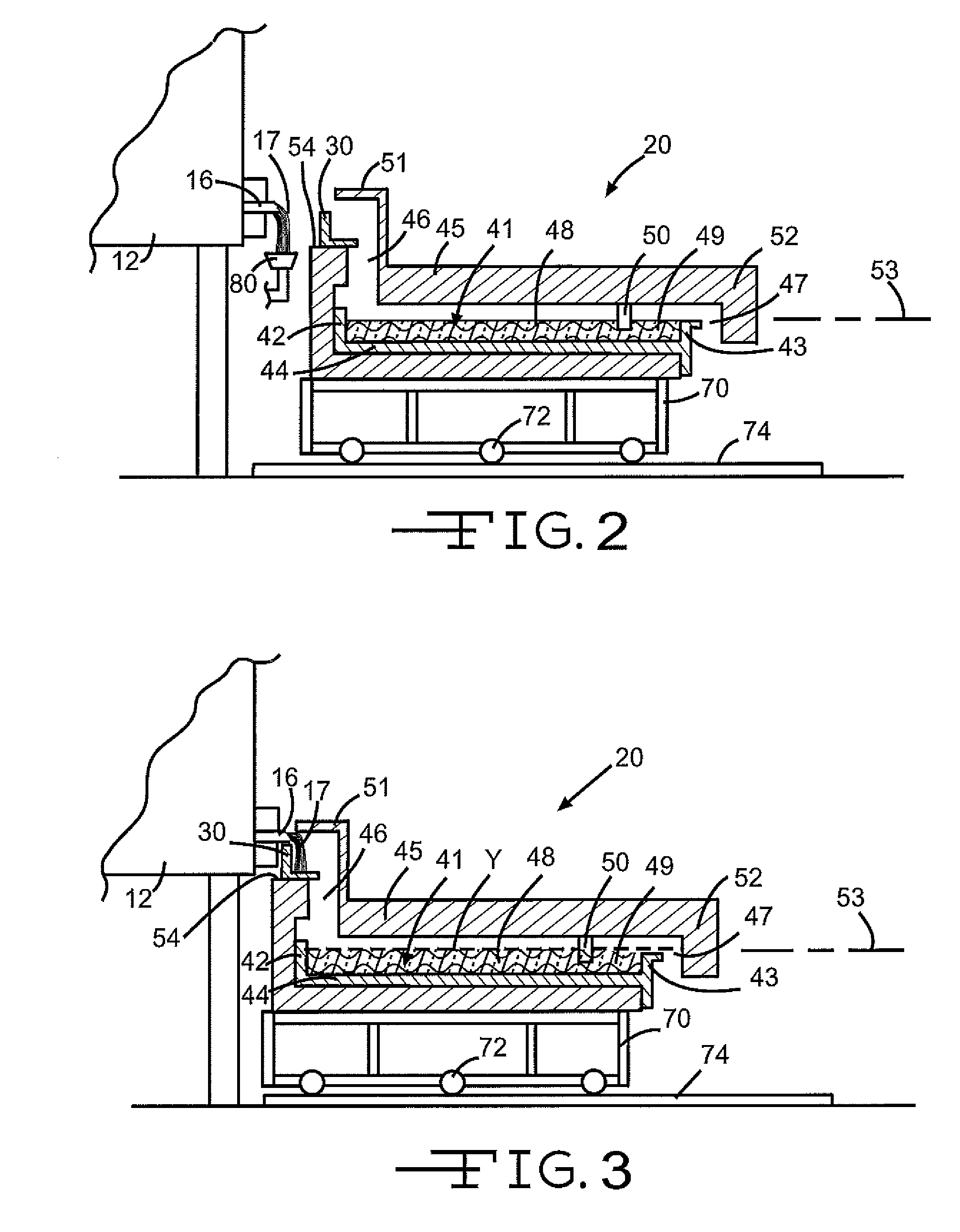
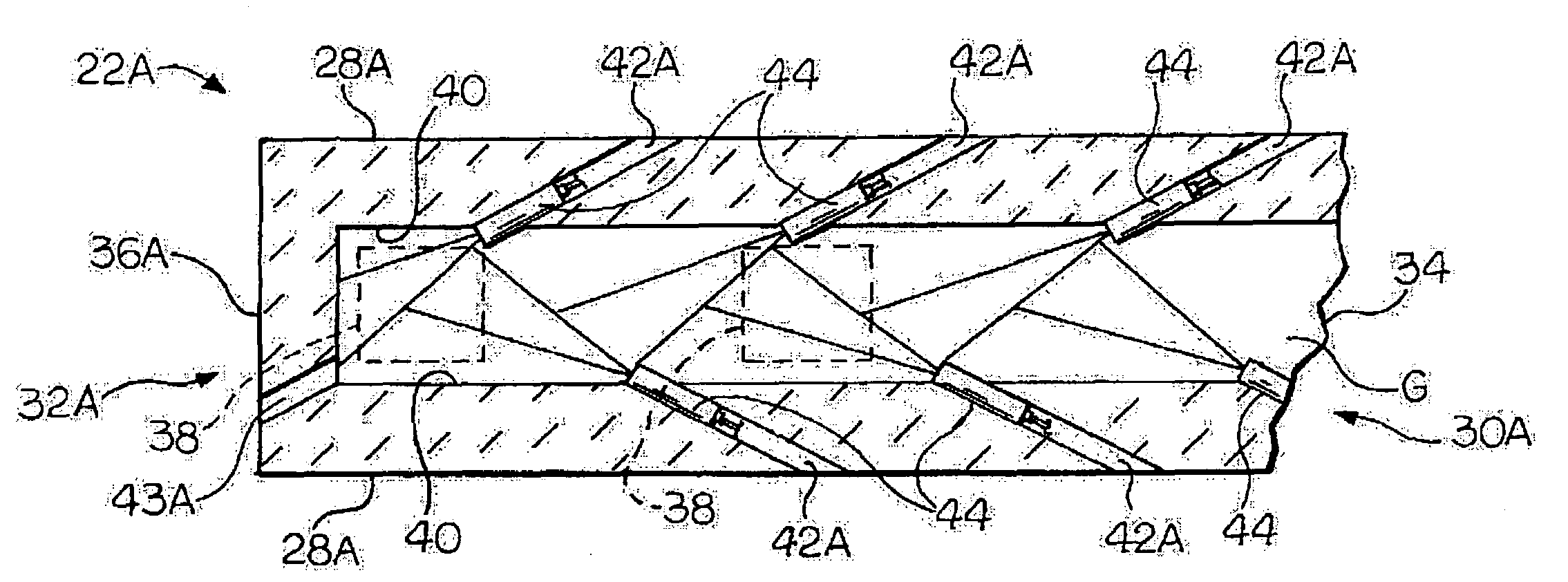
Overflow downdraw glass forming method and apparatus
ActiveUS20060016219A1Process can be modifiedMinimizing thickness variationGlass furnace apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementThermal creepEngineering
The present invention significantly modifies “The Overflow Process”. It includes a method and apparatus for measuring glass flow rate and maintaining a constant glass flow rate. It also embodies design features and methods that support and stress the forming apparatus in a manner such that the deformation that results from thermal creep is corrected, thus minimizing the effect of the thermal creep on the thickness variation of the glass sheet. The present invention also embodies design features that change the process from a single step (combined flow distribution and cooling) to a two step process; step one being flow distribution and step two being cooling.
Owner:CORNING INC
Oxygen-fired front end for glass forming operation
A front end for a glass forming operation comprises an open channel and at least one burner. The channel has at least one surface. The surface has at least one hole therein. The burner is oriented in the hole at an acute angle relative to the surface. In another embodiment of the invention, the channel has a top and a pair of sidewalls each having a surface. At least one hole is in at least one of the surfaces. The hole is at an acute angle relative to at least one surface. The burner is an oxygen-fired burner. In yet another embodiment of the invention, the top and sidewalls each have a super structure surface constructed of refractory material. The channel has an upstream end and a downstream end. At least one of the surfaces has a plurality of holes therein. The burners extend at an acute angle relative to at least one surface and in a plane extending between the upstream end and the downstream end and perpendicular to at least one surface. Oxygen-fired burners extend axially through corresponding holes.
Owner:OCV INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
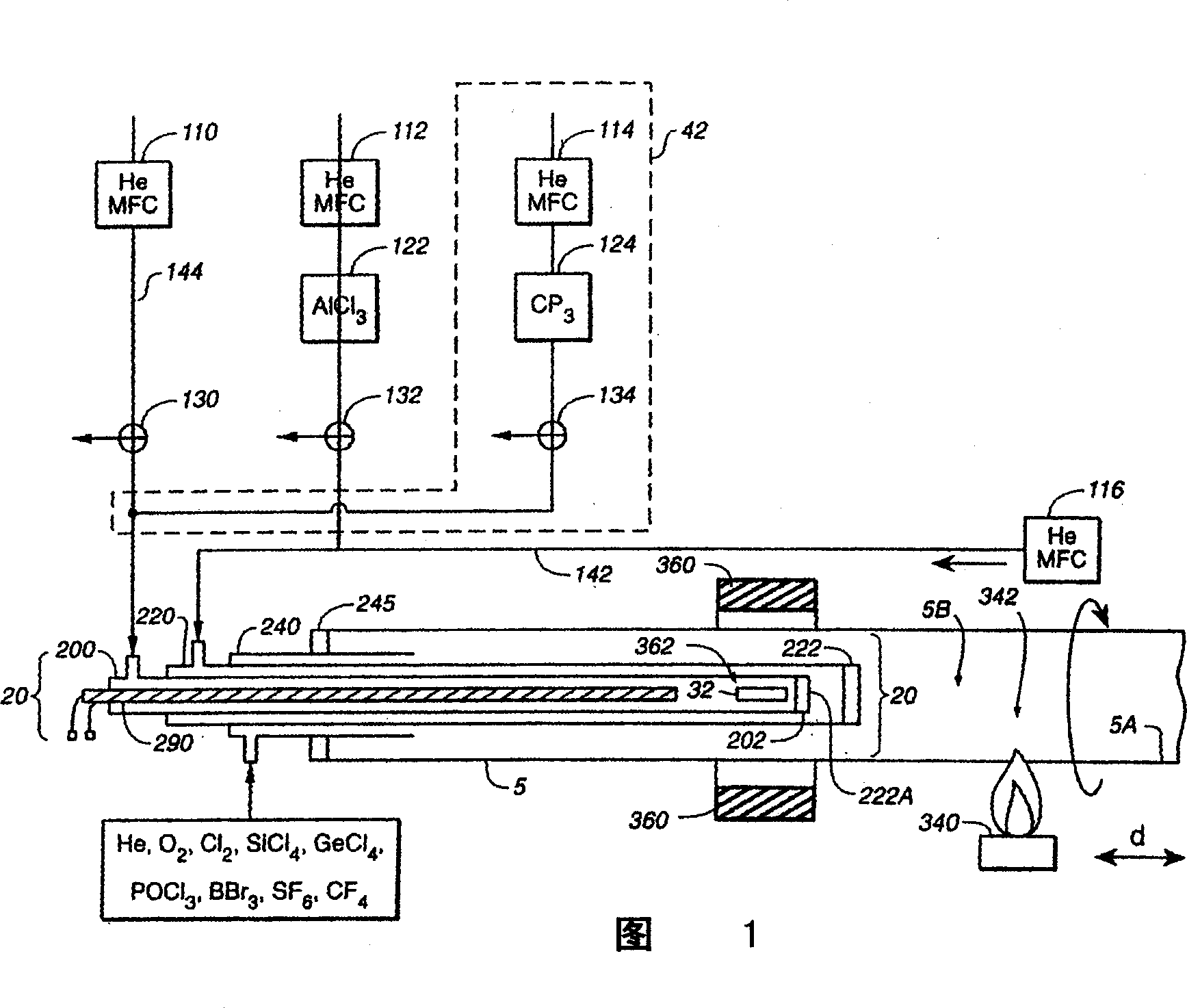
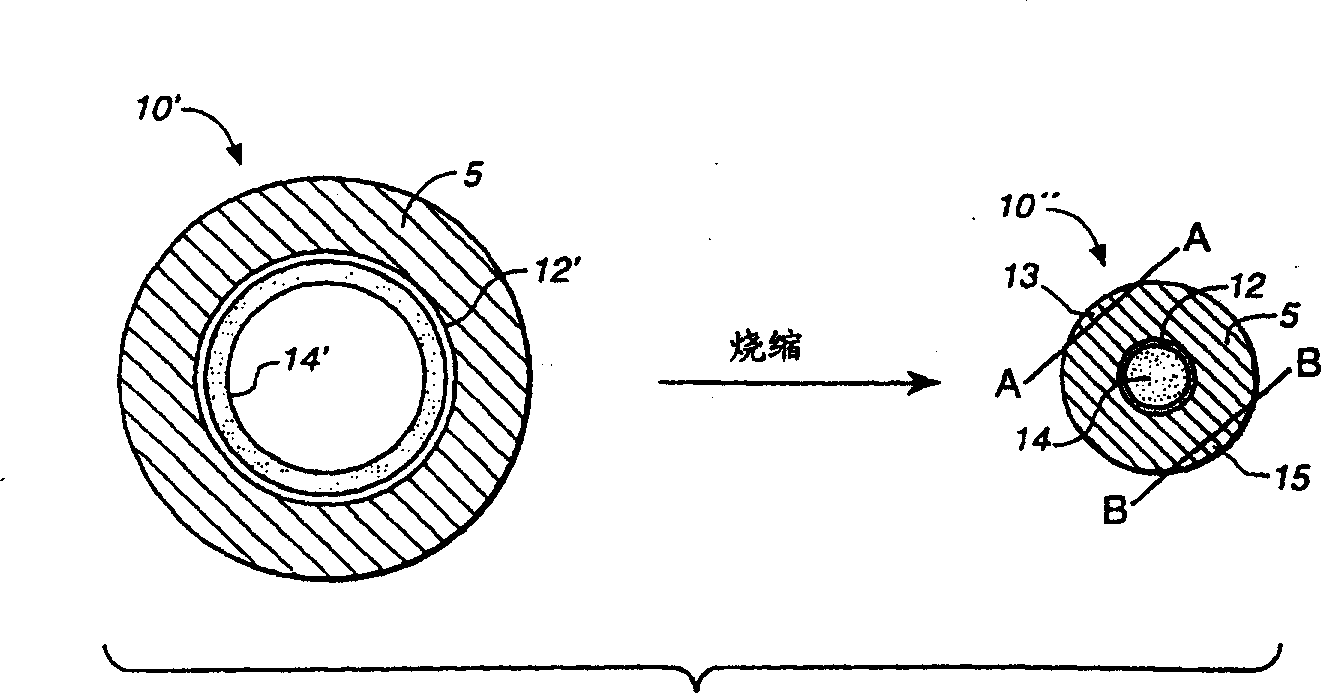
Method and apparatus for manufacturing a rare-earth metal doped optical fiber preform
InactiveCN1307544AHigh pump power absorptionSmall numerical apertureGlass deposition burnersOptical light guidesHigh concentrationGlass forming
A method and apparatus is disclosed for the manufacture of an optical fiber preform having incorporated therein a comparatively high concentration of rare earth metal dopant material, and which thus can be drawn and processed into an optical fiber having low numerical aperture, low core attenuation, and high pumping power absorption. The high concentrations of rare earth metal dopant material are accomplished through a ''hybrid vapor processing'' (HVP) method or a ''hybrid liquid processing'' (HLP) method, either being practiced in combination or independently of one another. The HVP method involves the vaporization of a rare earth metal halide by the exposure thereof to a sufficiently elevated temperature, independently, or contemporaneously with the transport of the resultant rare earth metal halide laden vapor, into a glass-forming oxidation reaction zone on a flowing stream of essentially an unreactive inert gas, such as helium. According to the HLP method, a first amount of rare earth metal dopant is provided according to the HVP method and / or other vapor source of rare earth metal dopant which is mixed with glass-forming vapors to form a deposited soot layer on the internal surface of a glass tube. The soot-deposited tube is then impregnated with a dopant solution comprising, a second amount of rare earth metal dopant. The tube is then thermally collapsed resulting in an optical preform with an enhanced amount of rare earth metal dopant incorporated at a comparatively high concentration. The apparatus comprises means, such as tubes, for introducing the rare earth metal dopant as a vapor, formed from a solid state form of the dopant, into the main glass deposition tube separately from glass-forming material vapors and oxygen for the reaction within the main tube.
Owner:JDS单相公司
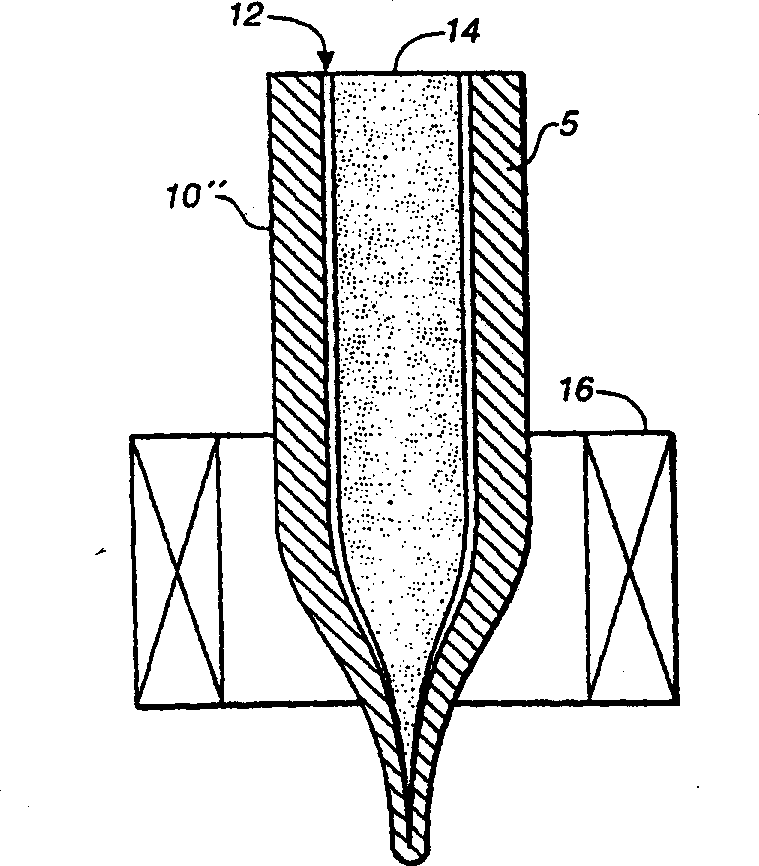
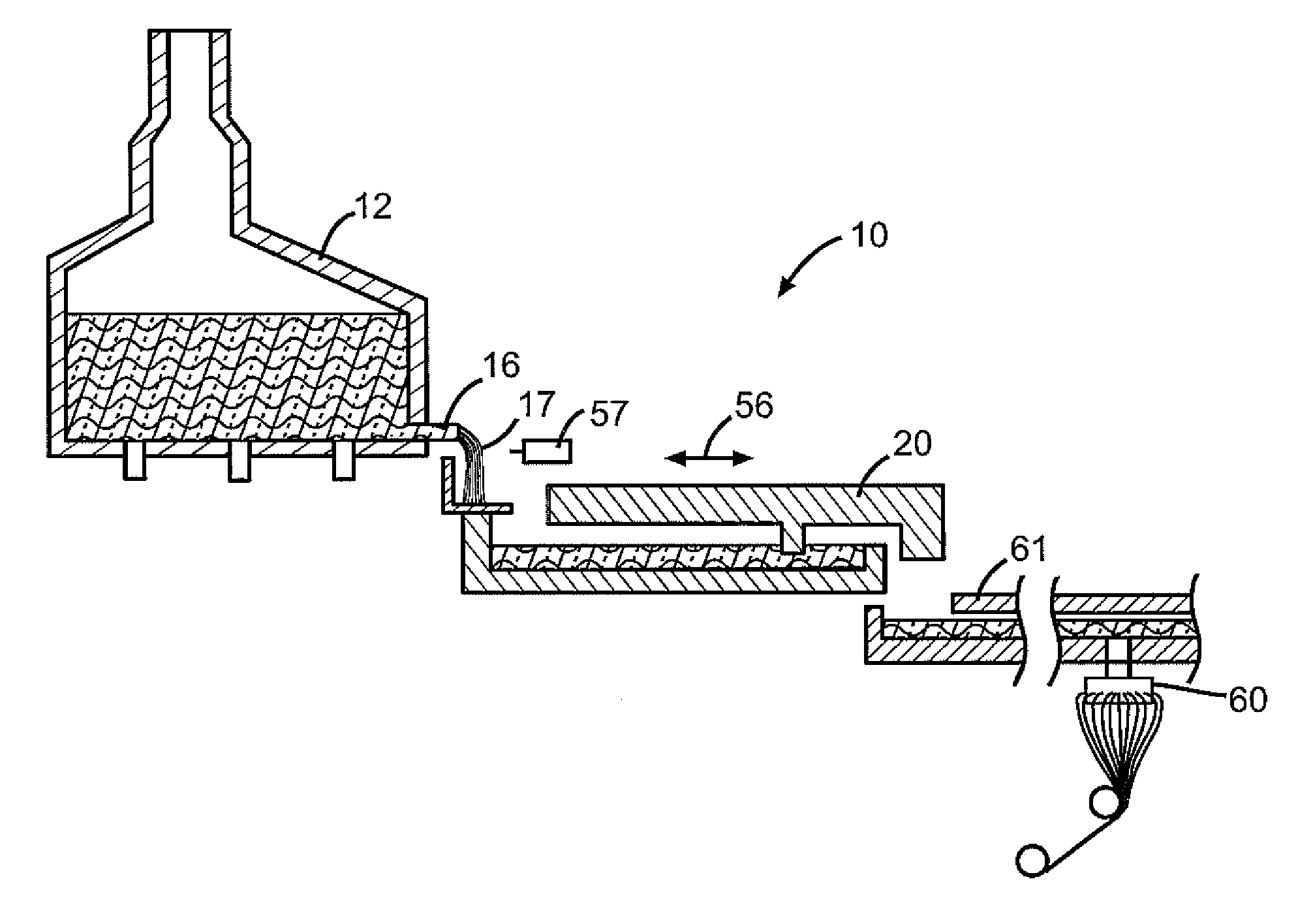
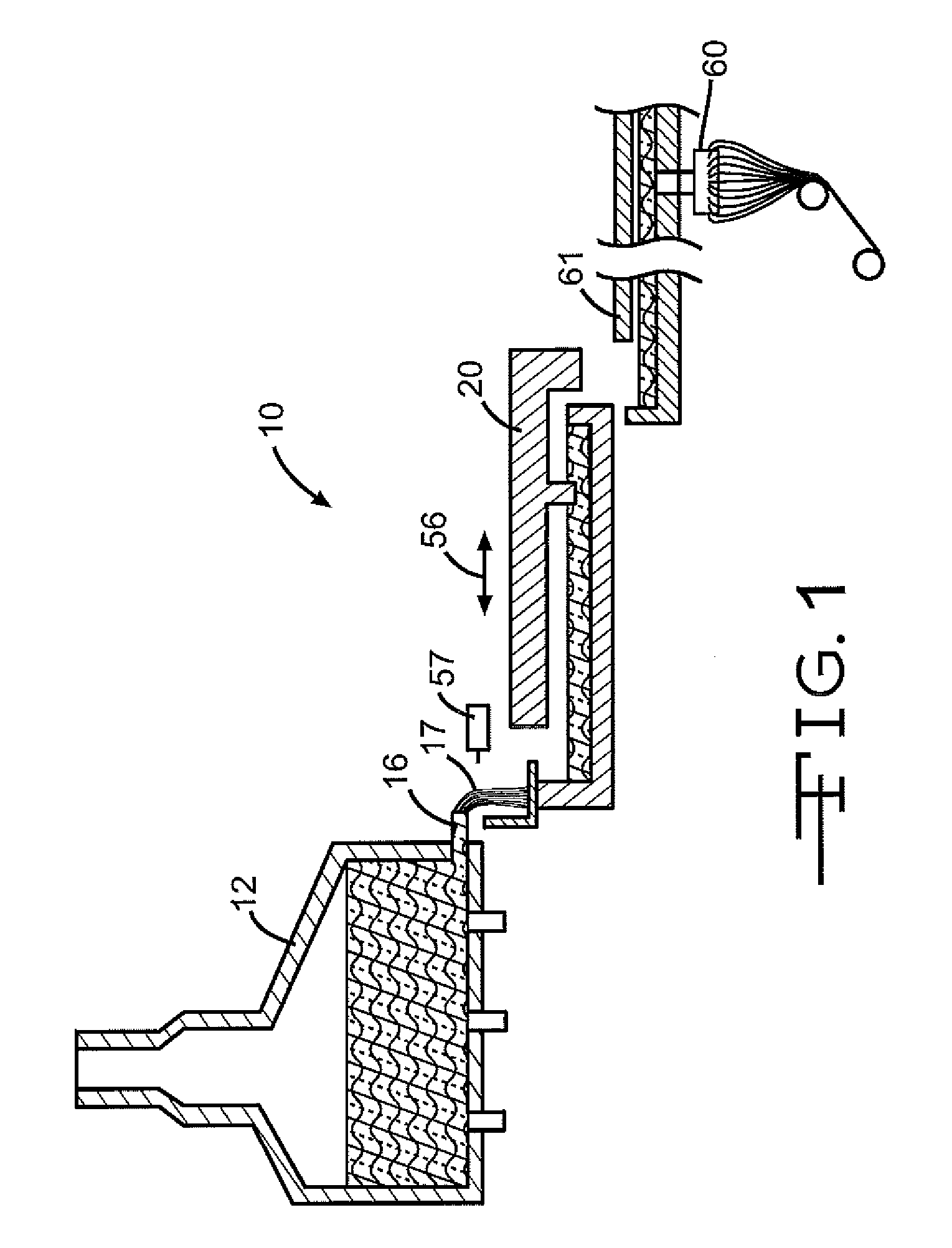
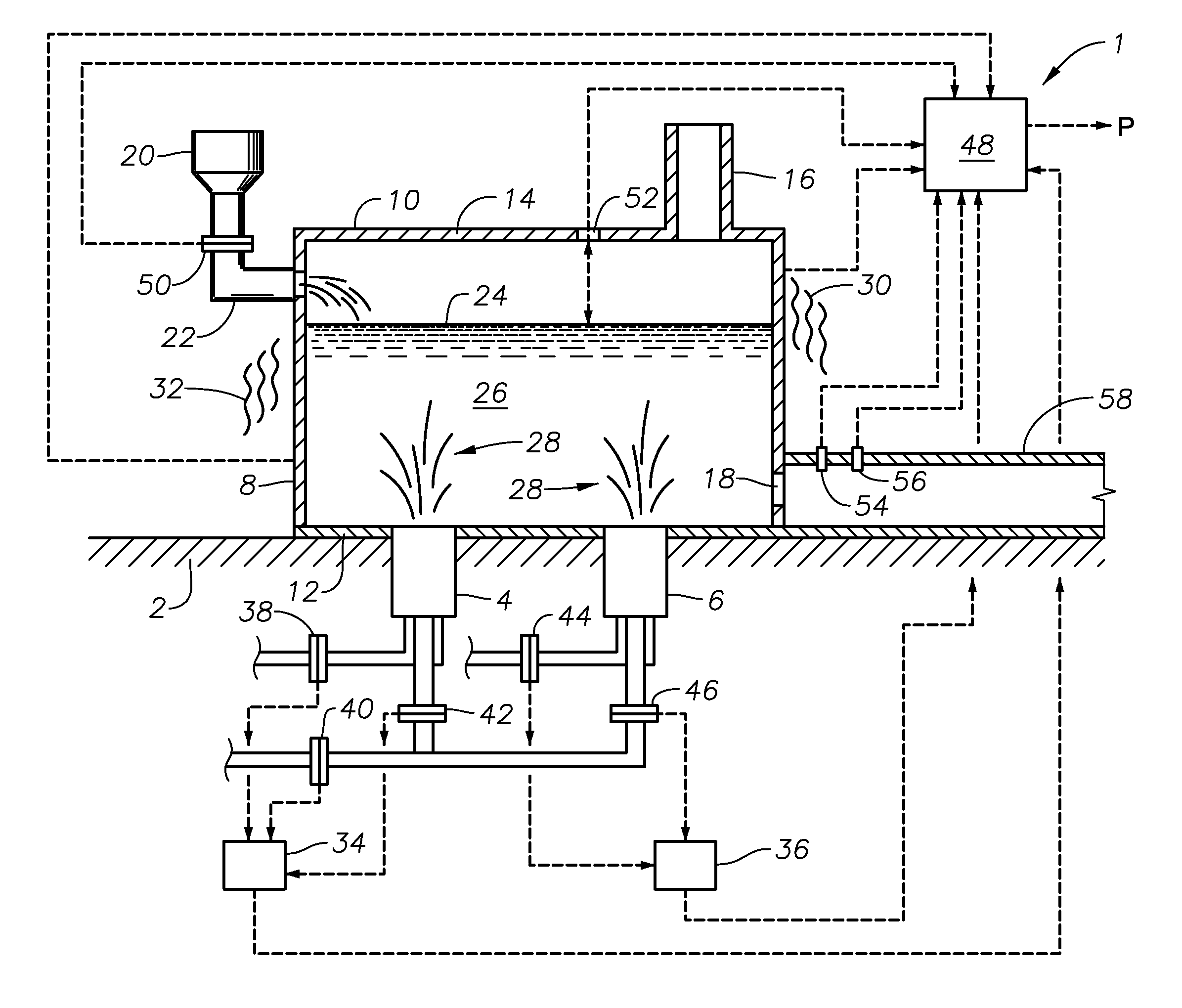
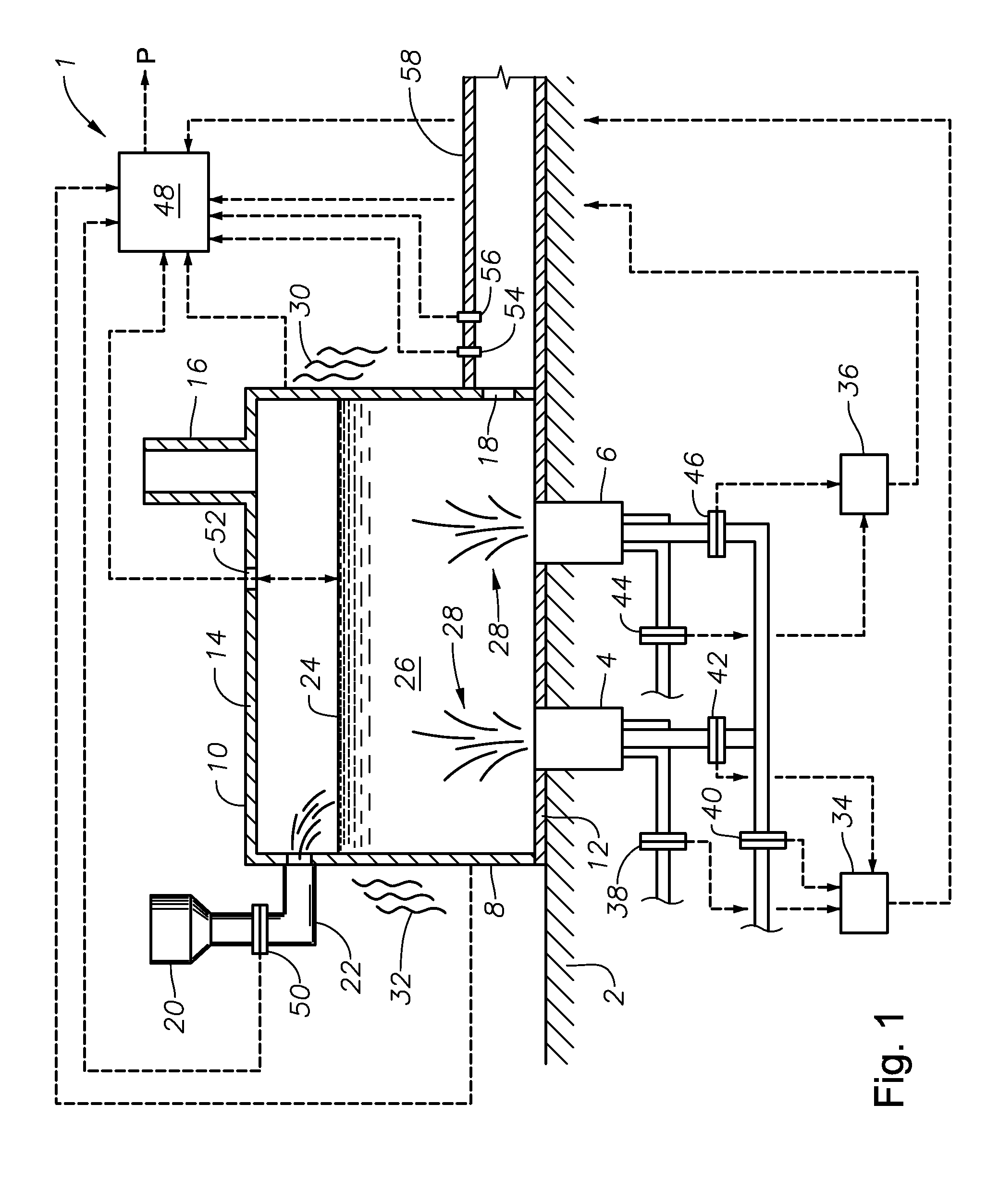
Molten glass delivery and refining system
Methods and apparatus for refining and delivering a supply of molten glass include melting a supply of glass in a melter and discharging a stream of molten glass. A refining section is provided to refine the molten glass discharged by the melter and to deliver the molten glass downstream to a glass forming apparatus. The refining section is mounted for movement into and out of contact with the stream of molten glass to connect and disconnect the glass forming apparatus with the stream of molten glass.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Methods of using a submerged combustion melter to produce glass products
A method comprises flowing an oxidant and a fuel into a submerged combustion burner in a glass tank furnace, the glass tank furnace receiving a feed of glass forming material and producing molten glass, the burner and furnace comprising a melting system. The melting system has a variable system vibration and / or oscillation due to the nature of submerged combustion. One method includes predicting a value of at least one property, such as viscosity, of the molten glass using the variable system vibration and / or oscillation.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Low heat capacity gas oxy fired burner
A front end for a glass forming operation including an open channel and at least one burner. The channel surface has at least one burner port and a burner oriented in the burner port at an acute angle relative to the channel surface. The surface may be a top, side or end wall and the burner port is at an acute angle relative to the surface of the wall.
Owner:OCV INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
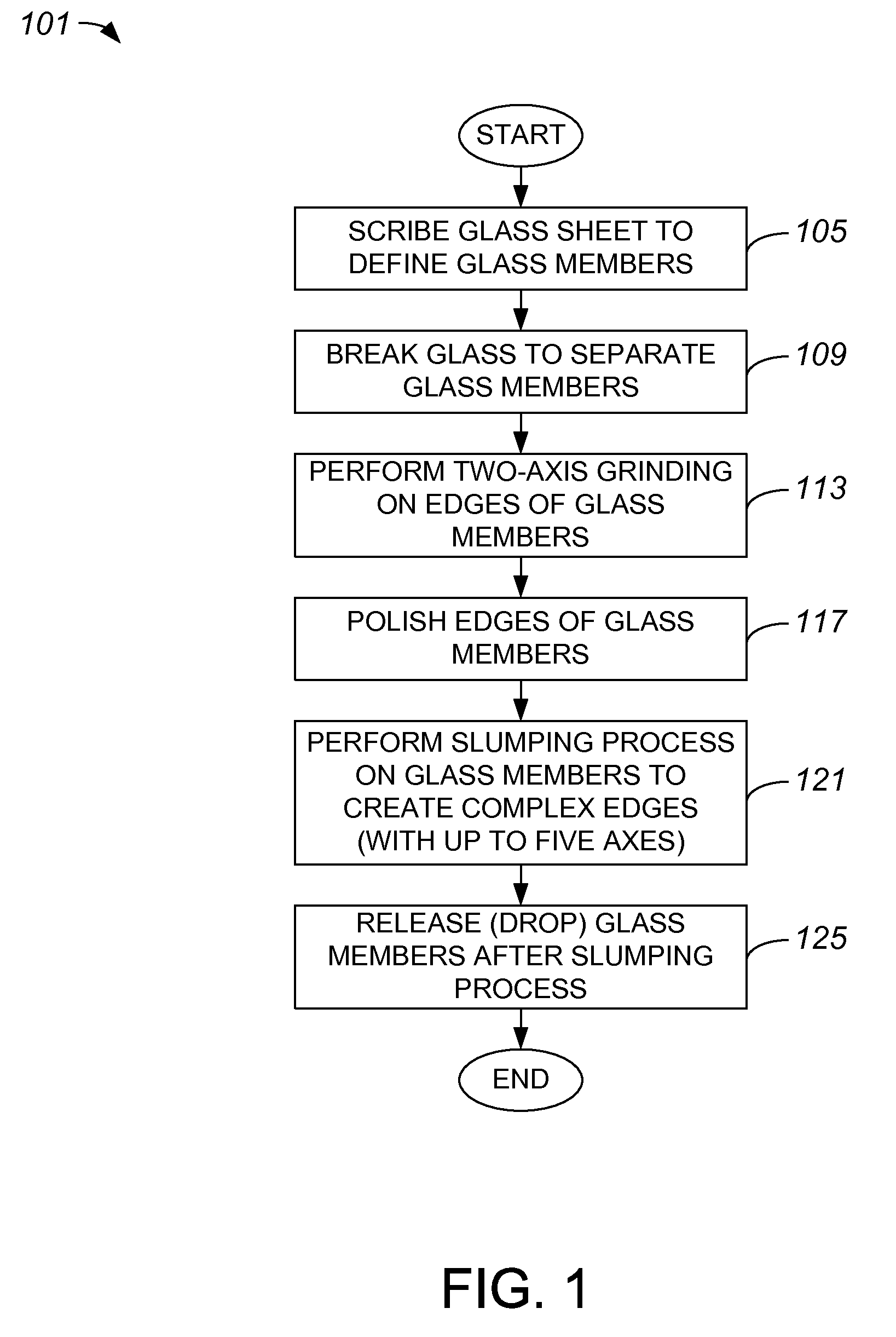
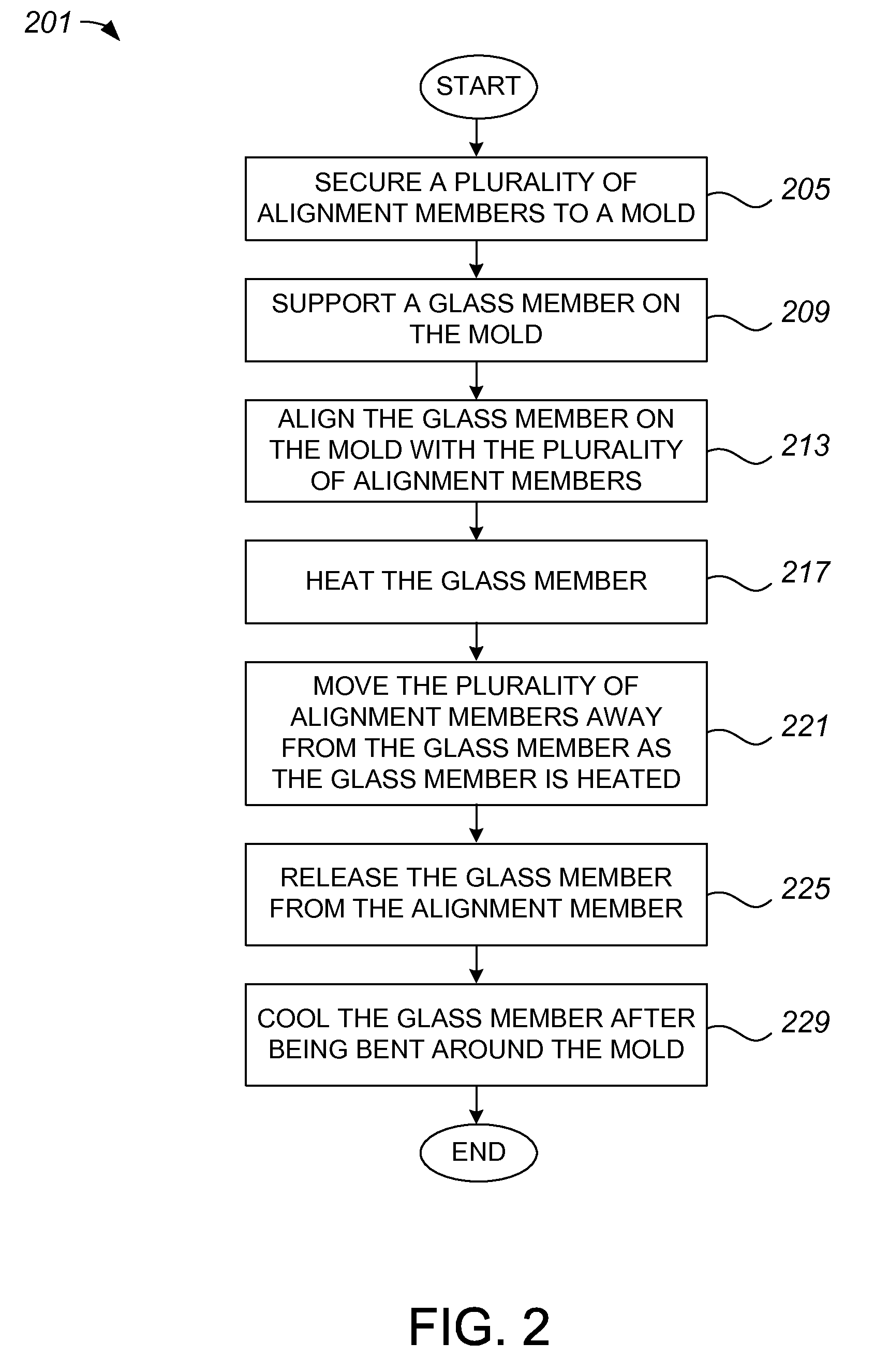
Pre-Processing Techniques to Produce Complex Edges Using a Glass Slumping Process
ActiveUS20110072856A1Effectively be molded into a complex geometryEdge grinding machinesGlass transportation apparatusPre treatmentGlass forming
Apparatus, systems and methods for forming complex edges on a glass member through the use of a glass slumping process are disclosed. According to one aspect of the invention, a method of forming a complex edge in a glass forming process includes grinding an edge of a glass member and polishing the edge of the glass member. Grinding the edge of the glass member causes the edge of the glass member to have a first level of complexity. The method also includes performing a slumping process on the glass member. Performing the slumping process causes the edge of the glass member to have a second level of complexity that is more complex than the first level of complexity.
Owner:APPLE INC
Sheet width control for overflow downdraw sheet glass forming apparatus
InactiveUS20050183455A1Minimize distortionKeep widthBlowing machine gearingsGlass furnace apparatusFlat glassManufactured apparatus
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical transparent film and sputtering target for forming optical transparent film
InactiveUS6528442B1Reduced particle formationImprove adhesionConductive layers on insulating-supportsVacuum evaporation coatingTectorial membraneSputtering
To provide an optically transparent film containing 0.01 to 20% by weight glass forming oxide consisting of Nb2O5, V2O5, B2O3, SiO2, and P2O6; 0.01 to 20% by weight Al2O3 or Ga2O3; and 0.01 to 5% by weight hard oxide of ZrO2 and TiO2 as required; balance being ZnO, and a sputtering target for forming such a film. This sputtering target reduces occurrence of particles during sputtering, decreases the number of interruption or discontinuance of sputtering to improve production efficiency, and forms a protective film for optical disks with large transmittance and low reflectance.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Method and apparatus for characterizing a glass ribbon
InactiveUS20070140311A1Quality improvementReduce shapingThermometer detailsGlass forming apparatusImage resolutionSpace resolution
A method and apparatus for measuring the temperature and / or displacement of a glass ribbon formed in a downdraw glass forming process, and measured across width of the ribbon. Temperature and displacement measurements may advantageously be performed simultaneously with a high degree of spatial resolution by a measurement assembly which does not contact the glass ribbon. Temperature measurements may be performed across substantially the entire width of the ribbon. Data developed by the measurement assembly may be used in an automated feedback loop to control the glass ribbon forming conditions.
Owner:CORNING INC
Overflow Downdraw Glass Forming Method and Apparatus
InactiveUS20070068197A1Reduce unevennessEfficient degradationBlowing machine gearingsGlass furnace apparatusFlat glassThermal creep
The present invention discloses improved methods and apparatus for forming sheet glass. In one embodiment, the invention introduces a counteracting force to the stresses on the forming structure in a manner such that the thermal creep which inevitably occurs has a minimum impact on the glass flow characteristics of the forming structure.
Owner:CORNING INC
Burner injection system for glass melting
A burner for melting glass forming batch material includes a burner assembly constructed and arranged with a first passage for providing a fuel stream and a second passage for providing an oxidant stream, the first and second streams coacting to produce a supersonic combustion jet flame penetrable into glass melt. A method for melting glass forming batch material is also provided and includes providing a fuel stream; providing an oxidant stream; mixing the fuel and oxidant streams with sufficient force for providing a supersonic combustion jet flame; directing the supersonic combustion jet flame to contact the glass forming batch material; and penetrating the glass forming batch material to a select depth with the supersonic combustion jet flame.
Owner:LINDE AG
Method for reducing corrosion
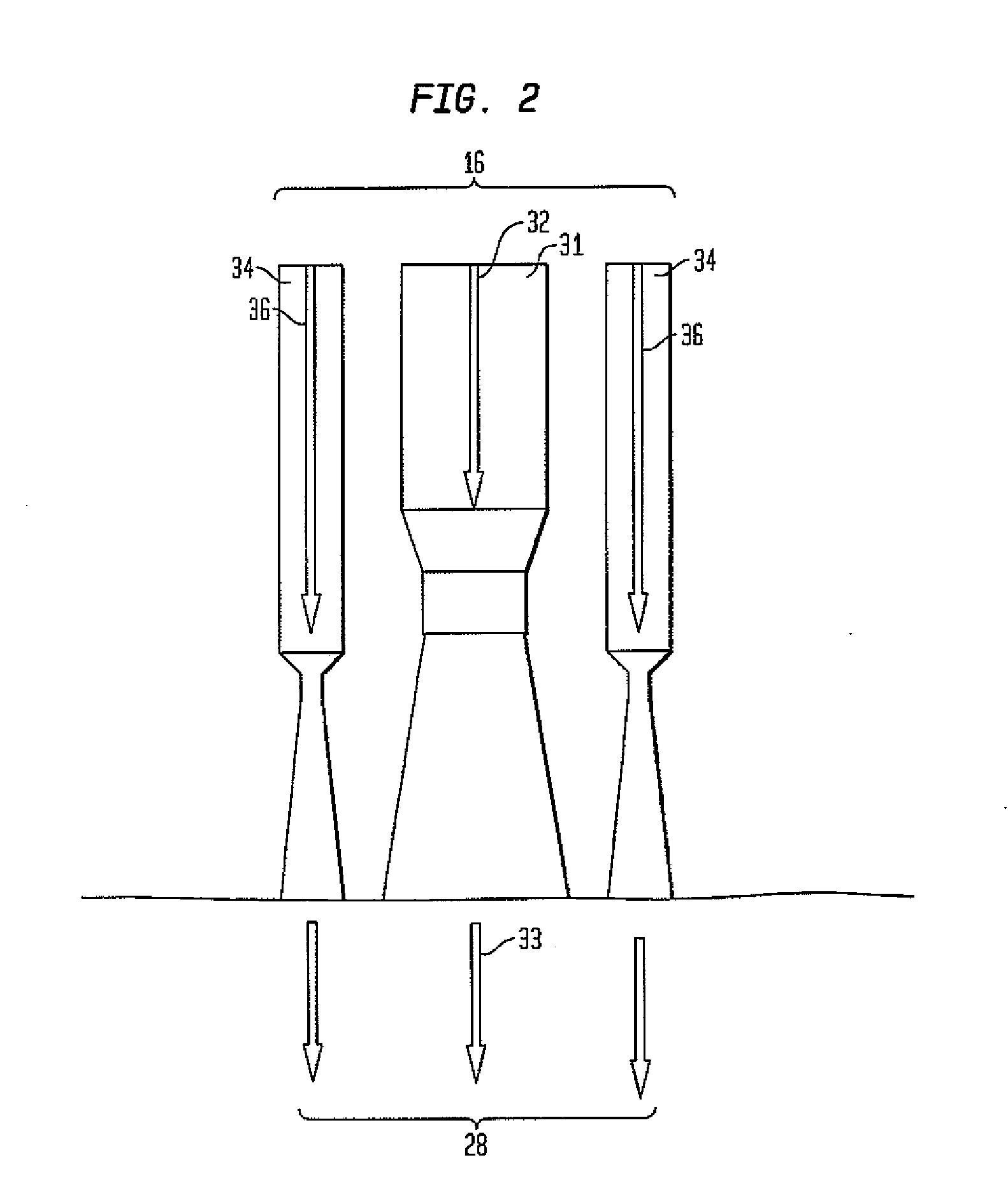
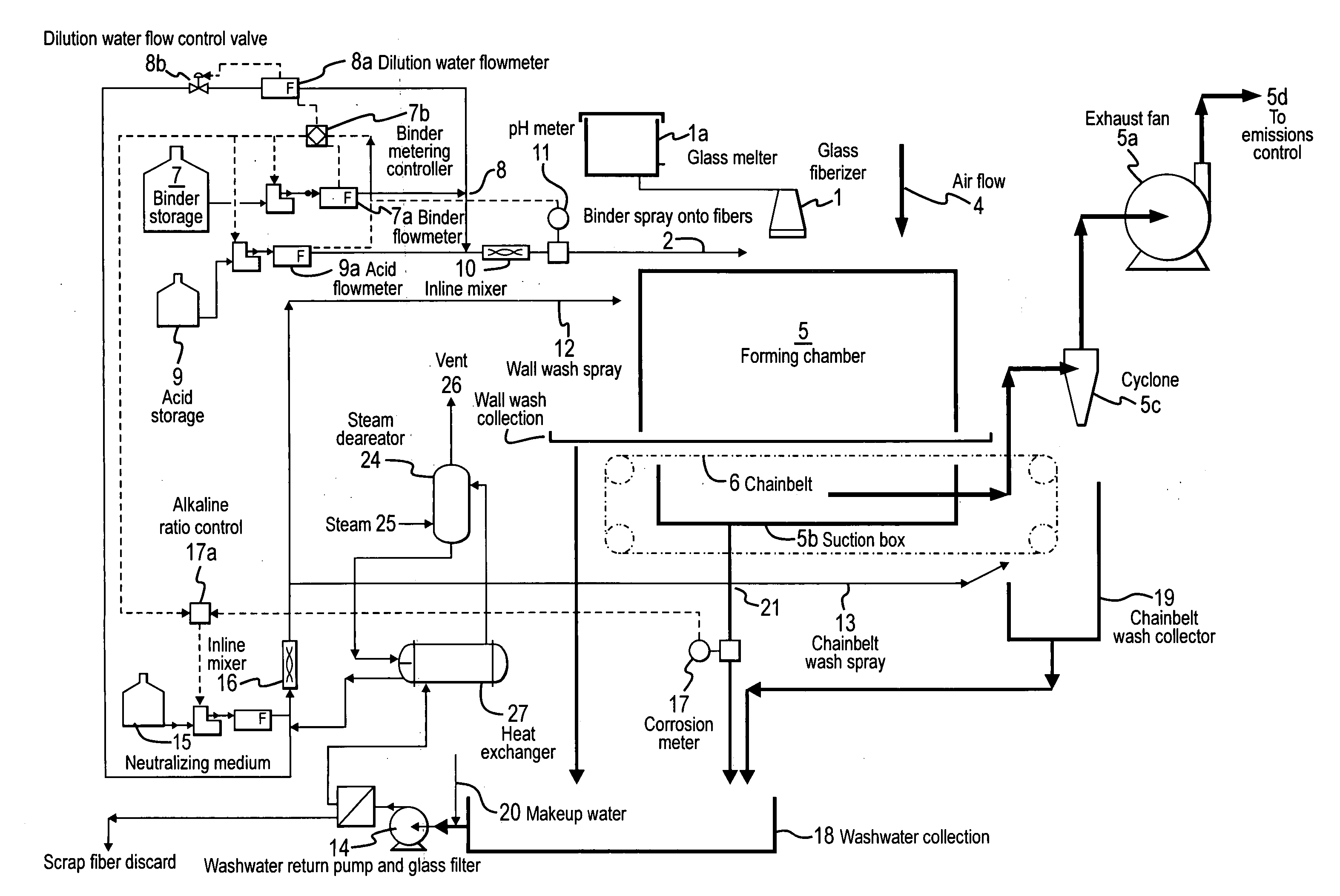
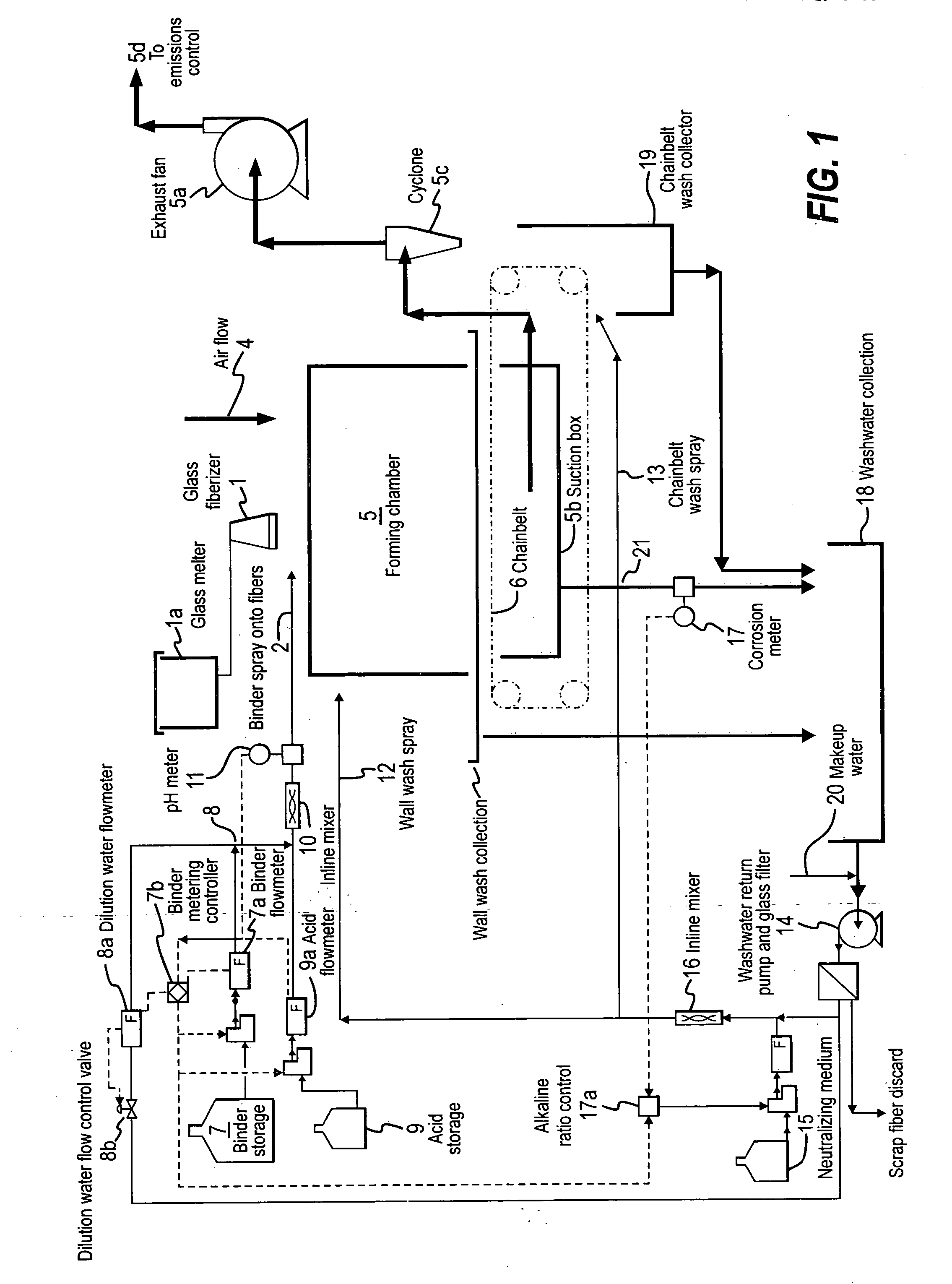
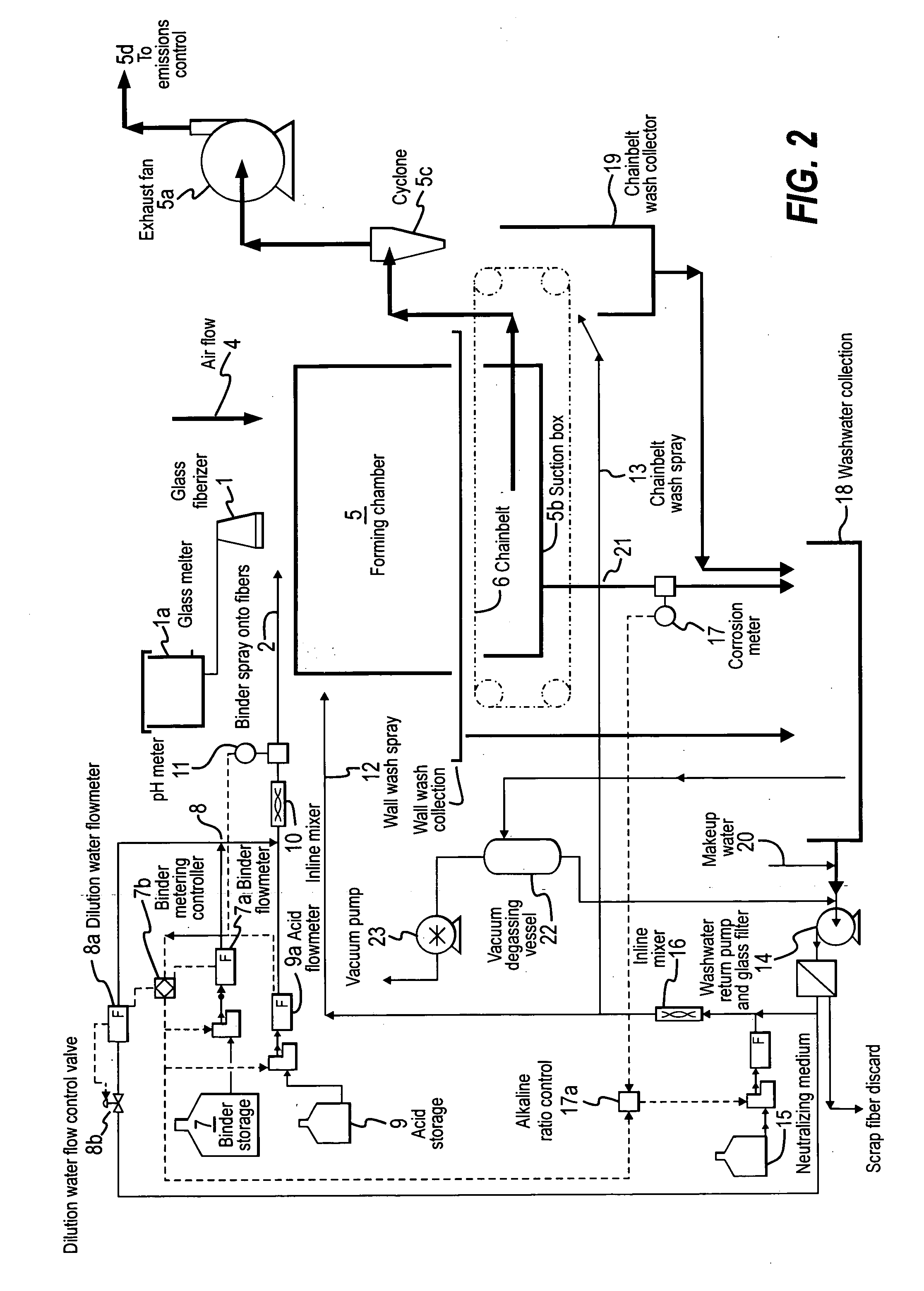
InactiveUS20060198954A1Limiting amount of downtimeAvoid damageGlass making apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsGlass fiberWash water
A method for reducing corrosion of a wash water system for glass forming lines, by using a corrosion meter, is provided. Also provided is a fiberglass manufacturing process that utilizes the method.
Owner:FRECHEM BART SHANNON +2
Overflow downdraw glass forming method and apparatus
InactiveUS6997017B2Facilitate faster and uniform flowIncrease rangeGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusEngineeringFlow augmentation
The forming apparatus of the present invention preferably includes an orifice on top of the trough. The uniquely shaped orifice substitutes for the weirs as the controlling entity for glass thickness. The orifice is designed such that as it deforms, it maintains a linear flow characteristic with respect to its length. As the orifice is made larger by the applied stress, the percentage width increase is the same over its length and consequently the percentage flow increase is the same over the length of the orifice. In another embodiment, the present invention provides an adjustment to change the flow characteristics of the trough to compensate for the degradation of the forming trough during an extended production run. A flow control plug can be inserted into the trough, such that flow dynamics can be altered during hot operation by insertion, removal or position adjustment of the flow control plug.
Owner:CORNING INC
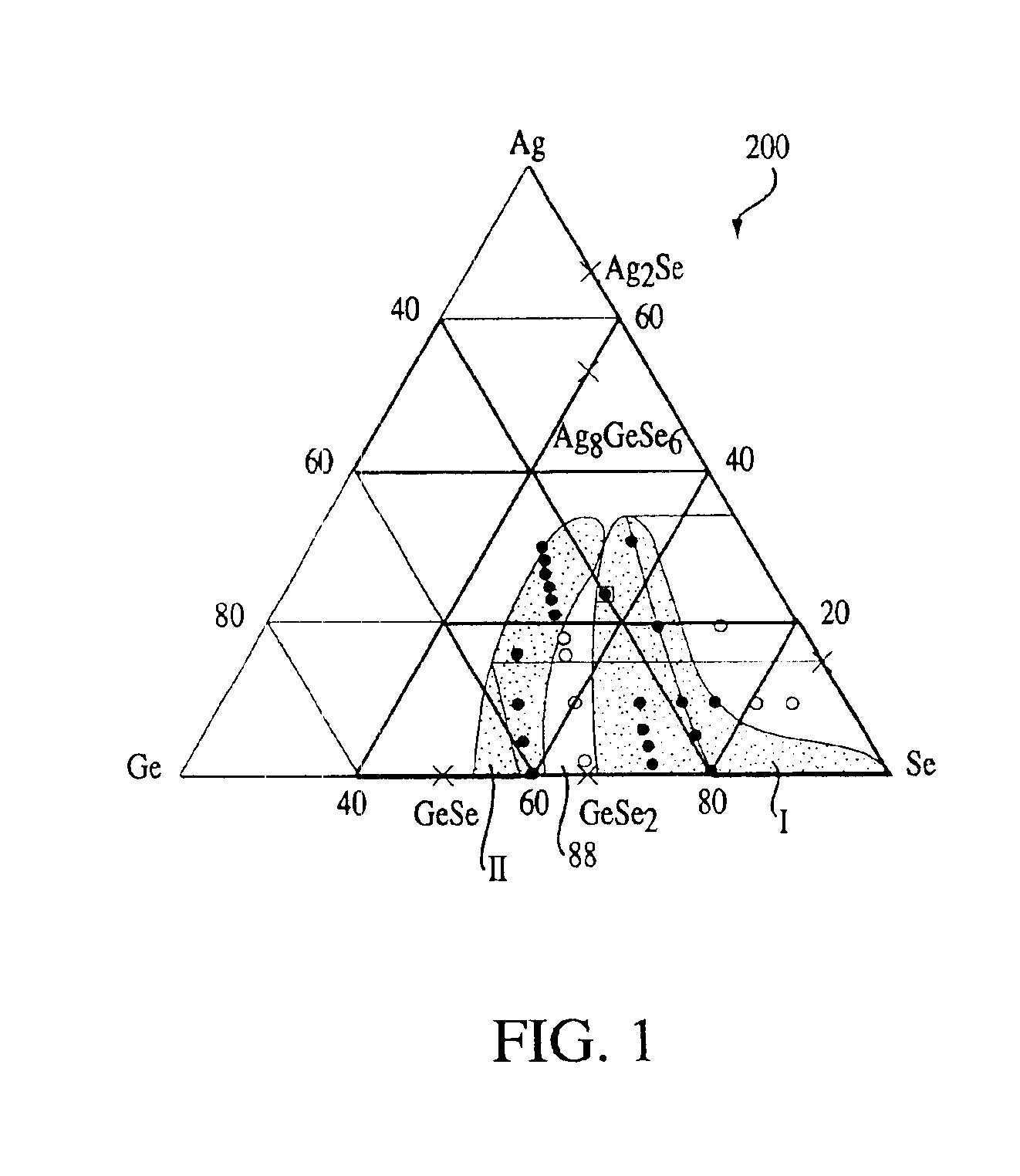
Stoichiometry for chalcogenide glasses useful for memory devices and method of formation
InactiveUS6888155B2High glass transition temperatureRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVitrificationChalcogenide glass
A method of forming resistance changing elements with improved operational characteristics for use in memory devices and the resulting structures are disclosed. A chalcogenide glass having the formula (Gex1Se1-x1)1-y1Agy1, wherein 18≦x1≦28, or the formula (Gex2Se1-x2)1-y2Agy2, wherein 39≦x2≦42, and wherein in both the silver is in a concentration which maintains the germanium selenide glass in the glass forming region is used in a memory cell. The glass may also have a glass transition temperature (Tg) near or higher than typical temperatures used for fabricating and packaging memory devices containing the memory cell.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Coated powder particles for producing three-dimensional bodies by means of a layer constituting method
InactiveUS7722802B2High distinctnessGood storage stabilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingOrganic solventShell molding
The invention relates a powder material consisting of coated particles for a powder-based rapid generative prototyping methods, in particular by compressing a 3D binder. Said powder material consists of individual plastic, metal and / or ceramic particles and / or granules. A coating essentially consists of an adhesive agent which can be activated by a liquid binder, light or laser light, and of sinterable or glass-forming fine-grained material. Said invention also relates to a method for compressing 3D binder with the aid of an organic solvent having a water content less than 45% and to sintered bodies, in particular for moulding or precision mechanical engineering, which are fixed to each other by sintering or glass formation from a fine grained material.
Owner:PFEIFER ROLF +2
Overflow downdrawn glass forming method and apparatus
InactiveUS6889526B2Reduce unevennessEfficient degradationGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusThermal creepEngineering
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical glass, glass gob for press-molding, optical part, process for producing glass shaped material and process for producing optical part
An optical glass having a high light transmittance, a high refractive index and excellent production stability, which contains at least one of CaO and SrO together with SiO2, B2O3, La2O3, Nb2O5, TiO2 and BaO, having a composition that substantially contains, by weight %, 1 to 18% of SiO2, 3 to 24% of B2O3, provided that the ratio of content of B2O3 to the content of SiO2 (B2O3 / SiO2) is over 1, 10 to 50% of La2O3, 1 to 30% of Nb2O5, 1 to 30% of TiO2, over 6% but not more than 25% of BaO, less than 7% of CaO, 6% or less of SrO, 0 to 13% of MgO, provided that the total content of BaO, CaO, SrO and MgO is 40% or less, 0 to 15% of ZnO, 0 to 15% of ZrO2, 0 to 10% of Al2O3, 0 to 20% of Gd2O3, 0% or more but less than 2% of Y2O3, 0 to 5% of Yb2O3, 0 to 18% of Ta2O5, 0 to 20% of Bi2O3, 0 to 10% of GeO2, 0% or more but less than 2% of Sb2O3, and 0% or more but less than 2% of SnO2, and having a refractive index (nd) of over 1.8, Abbe's number (νd) of 28 to 40 and a density of 4.2 g / cm3 or more.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Methods of vitrifying waste with low melting high lithia glass compositions
InactiveUS6258994B1Reduce pointsReduce the temperatureSludge treatmentSolid waste disposalAlkali metal oxideRadioactive agent
The invention relates to methods of vitrifying waste and for lowering the melting point of glass forming systems by including lithia formers in the glass forming composition in significant amounts, typically from about 0.16 wt % to about 11 wt %, based on the total glass forming oxides. The lithia is typically included as a replacement for alkali oxide glass formers that would normally be present in a particular glass forming system. Replacement can occur on a mole percent or weight percent basis, and typically results in a composition wherein lithia forms about 10 wt % to about 100 wt % of the alkali oxide glass formers present in the composition. The present invention also relates to the high lithia glass compositions formed by these methods. The invention is useful for stabilization of numerous types of waste materials, including aqueous waste streams, sludge solids, mixtures of aqueous supernate and sludge solids, combinations of spent filter aids from waste water treatment and waste sludges, supernate alone, incinerator ash, incinerator offgas blowdown, or combinations thereof, geological mine tailings and sludges, asbestos, inorganic filter media, cement waste forms in need of remediation, spent or partially spent ion exchange resins or zeolites, contaminated soils, lead paint, etc. The decrease in melting point achieved by the present invention desirably prevents volatilization of hazardous or radioactive species during vitrification.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS
Overflow downdrawn glass forming method and apparatus
InactiveUS6895782B2Reduce unevennessGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusFlat glassThermal creep
The present invention alters the flow path at the inlet of the sheet glass forming apparatus to improve quality. The bottom of the downcomer pipe is preferably shaped to alter the character of the vortex flow in the quiescent flow zone between the pipes. In another embodiment, a bead guide provides hydraulic stresses that are in opposition to the surface tension stress and thus reduces the influence of surface tension on the formation of thick beads on the edges of the sheet. The present invention also measures the temperature of the glass by immersing thermocouples in the glass, at locations where any defects caused by the immersion are in the glass that forms the unusable edges of the sheet. In another embodiment, the support structure for the trough is altered to substantially reduce the aging of the trough due to thermal creep.
Owner:CORNING INC
Overflow downdraw glass forming method and apparatus
InactiveUS7681414B2Reduce unevennessEfficient degradationBlowing machine gearingsGlass furnace apparatusFlat glassThermal creep
The present invention discloses improved methods and apparatus for forming sheet glass. In one embodiment, the invention introduces a counteracting force to the stresses on the forming structure in a manner such that the thermal creep which inevitably occurs has a minimum impact on the glass flow characteristics of the forming structure.
Owner:CORNING INC
Glass-forming die and method
InactiveUS20060213632A1Easy to controlImprove uniformityGlass drawing apparatusFoundry mouldsTemperature controlEngineering
Glass-forming die, such as a parsain-forming or bottle-forming die, includes a die body having a molding surface with a curved contour to form at least a portion of a glass bottle or other article to be made. The die body has one or more cooling passages inside the body wherein the cooling passages is / are non-linear (non-straight) along at least a portion of their length to improve temperature control of the die during the glass forming operation. To this end, the cooling passages are curved in a manner to generally follow the curved contour along at least a portion of the length of the curved contour, and may include heat radiating or turbulating elements in the cooling passage. The glass-forming die alternately, or in addition, can include integral cooling fins, ribs or other heat radiating element on one or more exterior regions of the die.
Owner:HOWMET CORPORATION
Optical fiber fixing member and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6240235B1Easy alignmentImprove accuracyGlass pressing apparatusCoupling light guidesEngineeringMachining
The optical fiber fixing member made of glass, especially optical fiber guide block, is conventionally produced by a mechanical processing. However, the mechanical processing has problems that a production cost becomes high and mass-production is difficult. The problems above can be solved by the present invention providing a method for producing an optical fiber fixing member comprising: disposing a glass shaping preform whose plane view resembles to the plane view of the molded article and whose faces to be positioned in the pressurizing direction during press-molding assumes planes or outwardly convex curved surfaces, in a mold having a cavity of a given shape; and heating the glass shaping preform up to a temperature at which the glass shaping preform can be mold-shaping and thereby press-molding it into a molded article having at least one edge formed of a free surface.
Owner:HOYA CORP +1
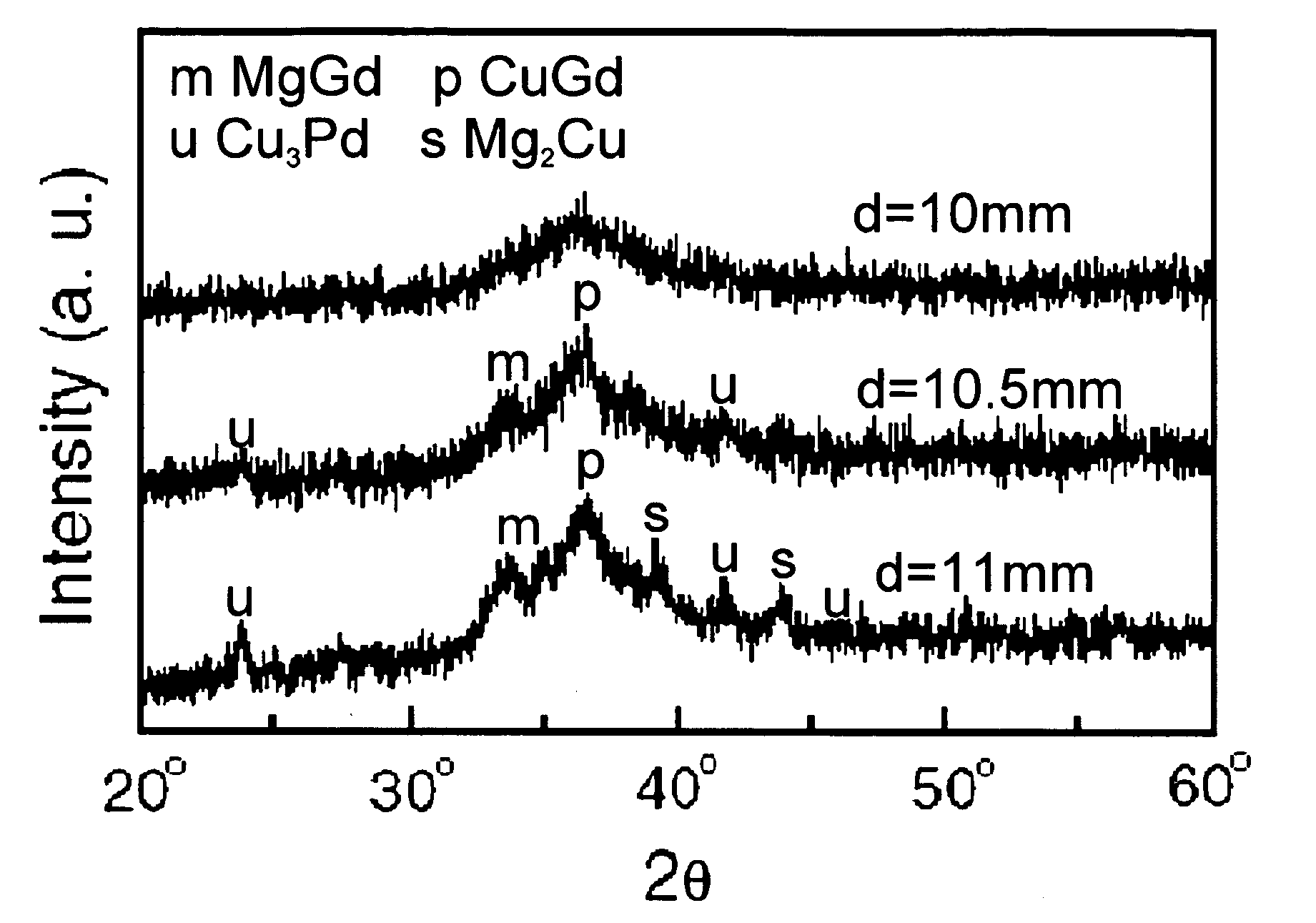
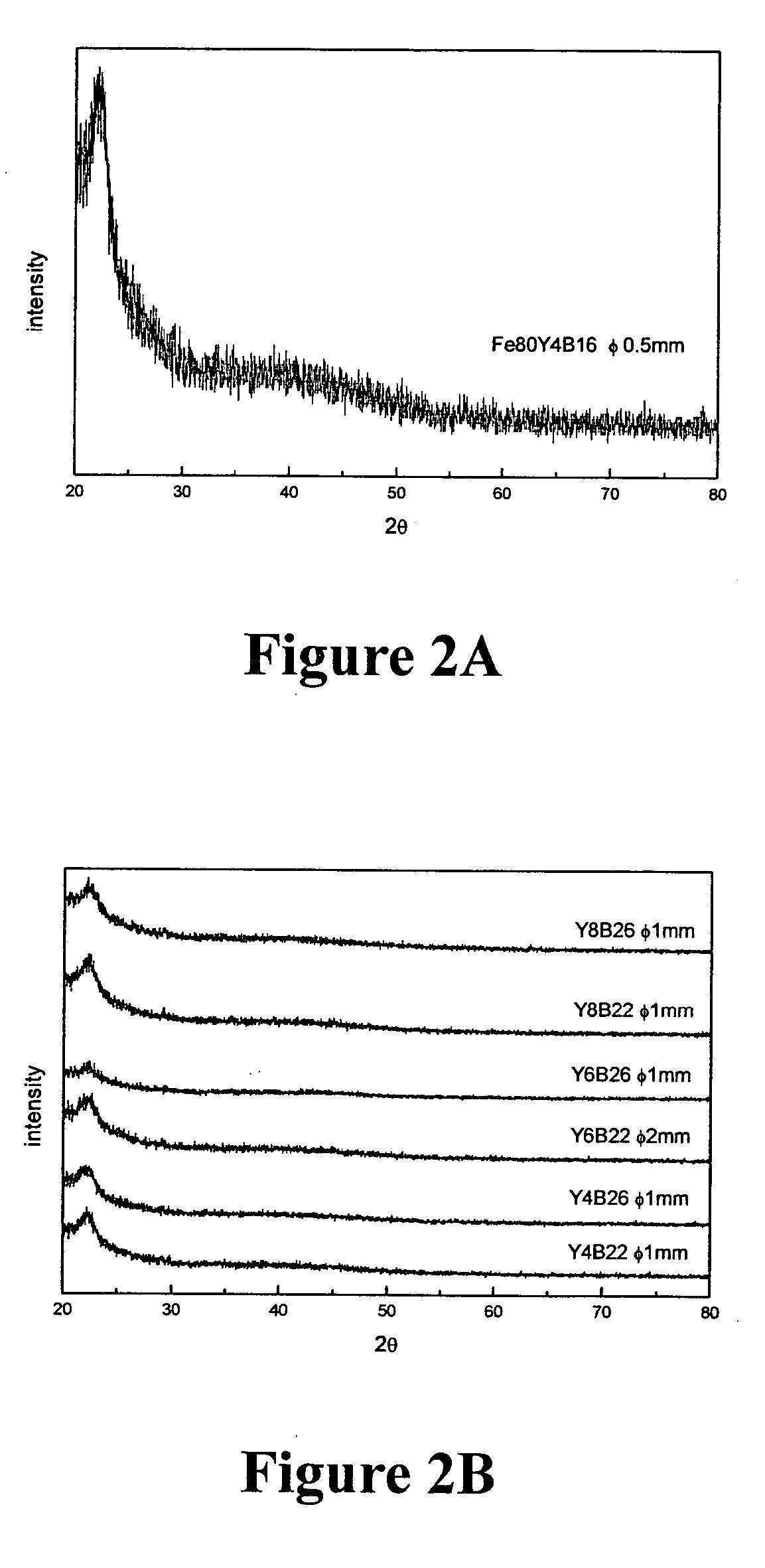
Magnesium based amorphous alloy having improved glass forming ability and ductility
Disclosed is a magnesium based amorphous alloy having a good glass forming ability and ductility. The Mg based amorphous alloy has a composition range of Mg100-x-yAxBy where x and y are respectively 2.5≦x≦30, 2.5≦y≦20 in atomic percent. Here, A includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Cu, Ni, Zn, Al, Ag, and Pd, and B includes at least one element selected from the group consisting of Gd, Y, Ca, and Nd.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ternary and multi-nary iron-based bulk glassy alloys and nanocrystalline alloys
InactiveUS20050263216A1High glass forming abilityIncreased electrical resistivityMagnetic materialsAmorphous phaseAtomic radius
Disclosed in this invention is a family of ternary and multi-nary iron-based new compositions of bulk metallic glasses which possess promising soft magnetic properties, and the composition selection rules that lead to the design of such new compositions. The embodiment alloys are represented by the formula MaXbZc, where M represents at least one of ferromagnetic elements such as iron and may partly be replaced by some other substitute elements; X is an element or combinations of elements selected from those with atomic radius at least 130% that of iron and in the mean time is able to form an M-rich eutectic; and Z is an element or combinations of elements selected from semi-metallic or non-metallic elements with atomic radius smaller than 86% that of iron and in the meantime is able to form an M-Z eutectic; a, b, c are the atomic percentage of M, X, Z, respectively, and a+b+c=100%. When 1%<b<15% and 10%<c<39%, the alloys show a bulk glass forming ability to cast amorphous ribbons / sheets at least 0.1 mm in thickness. When 3%<b<10% and 18%<c<30%, the alloys show a bulk glass forming ability to cast amorphous rods at least 1 mm in diameter. The amorphous phase of these as-cast sheets / rods is at least 95% by volume. This invention also discloses the existence of nano-crystalline phase outside of the outer regime of the bulk glass forming region mentioned above.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
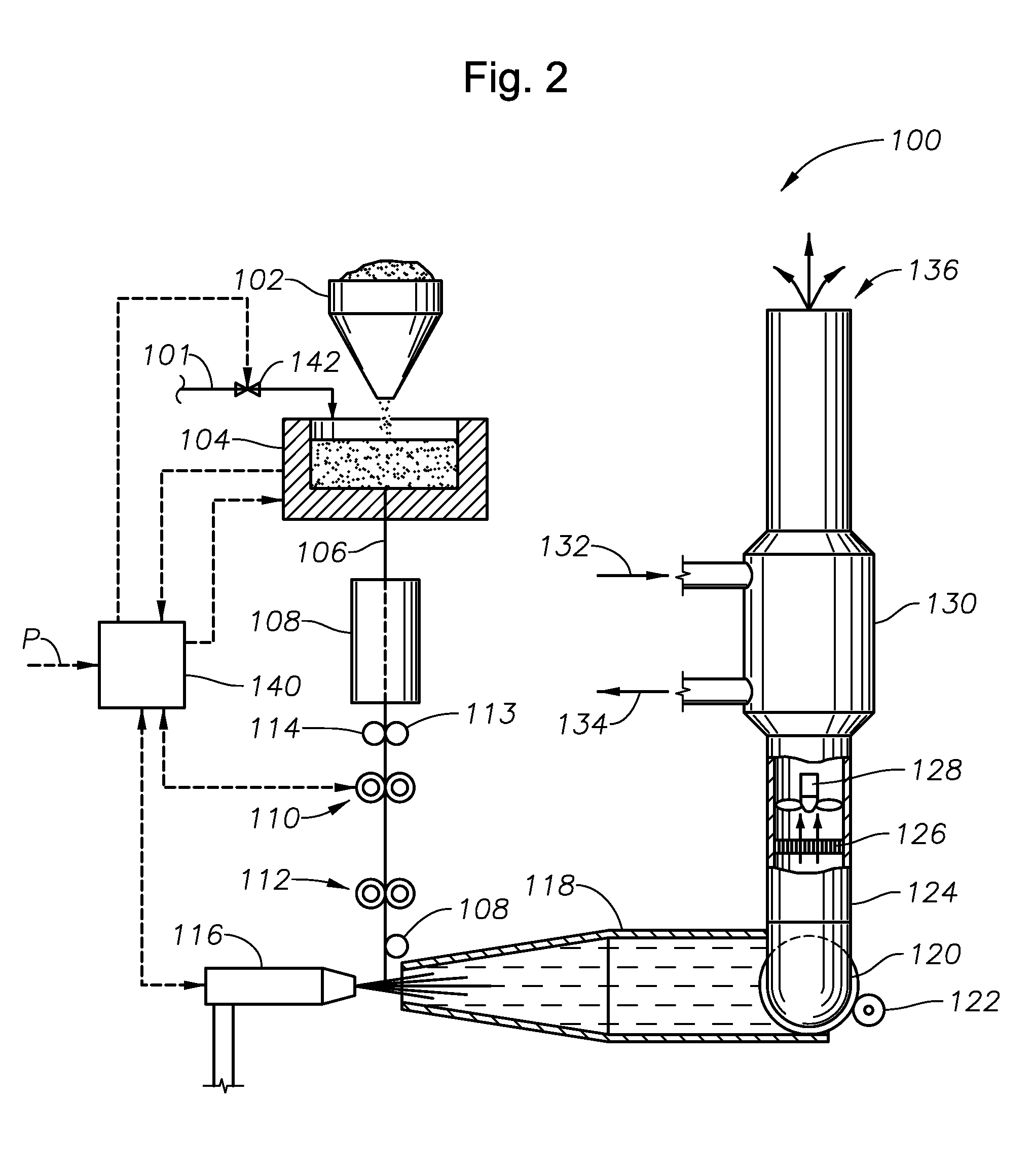
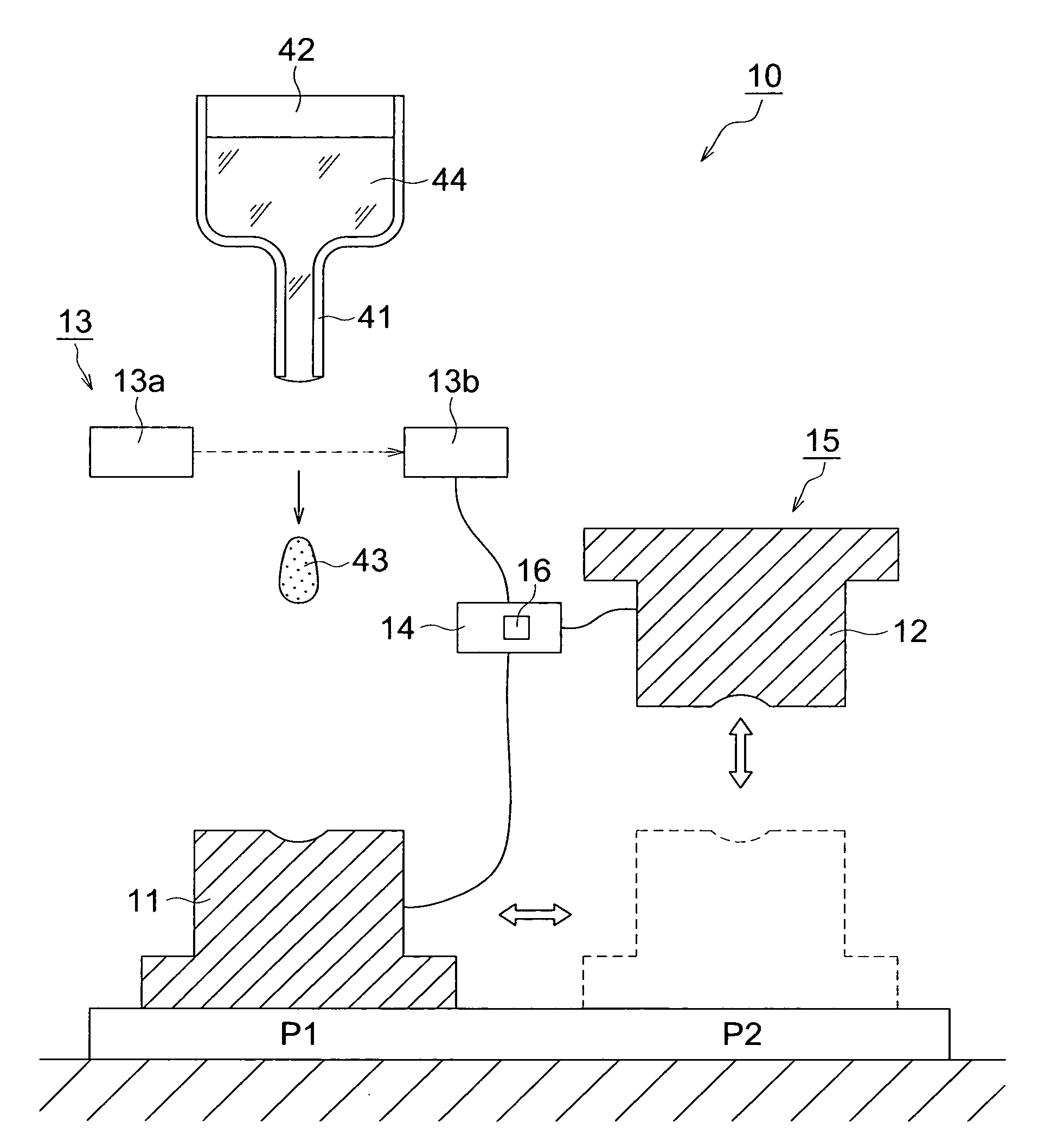
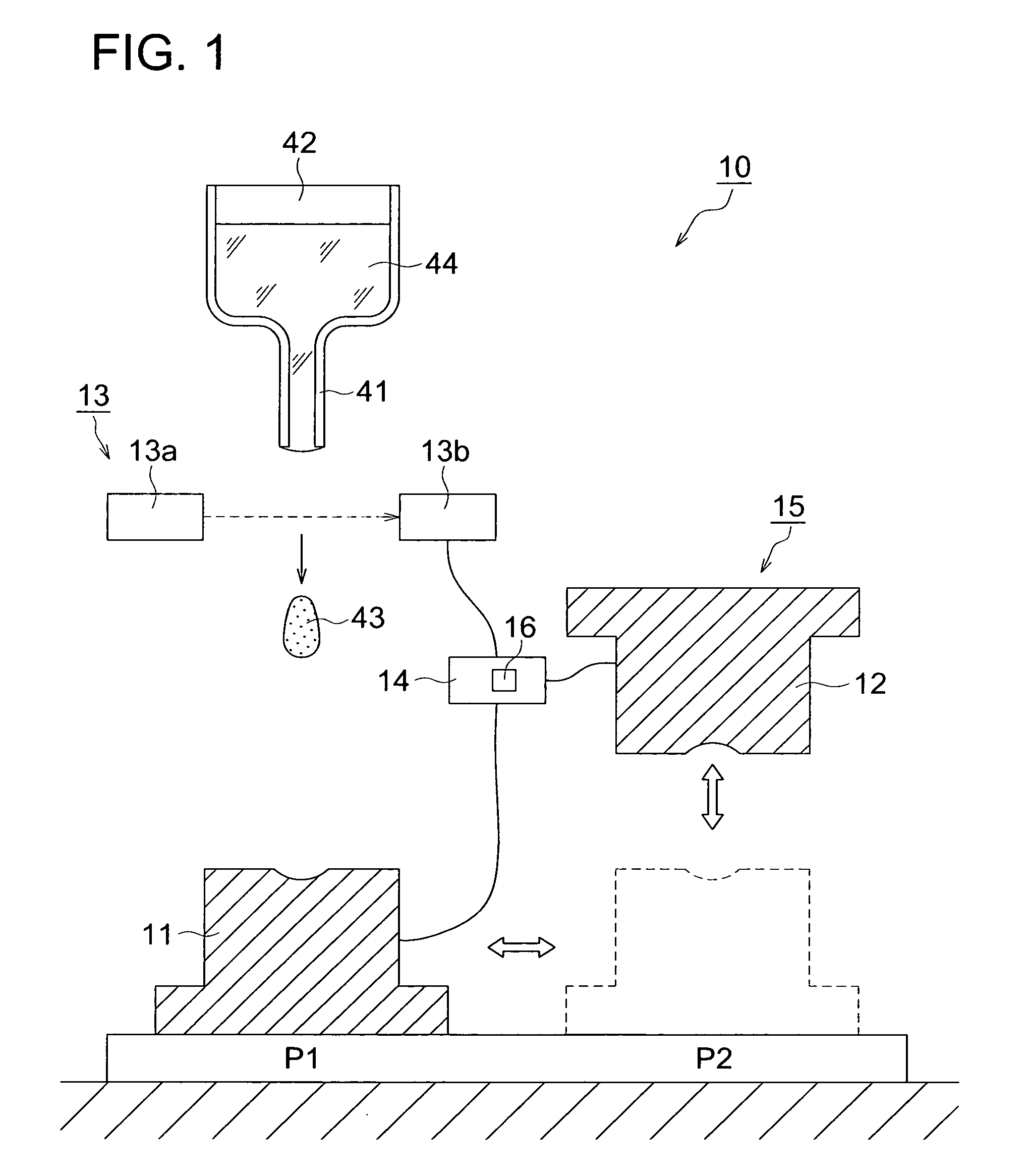
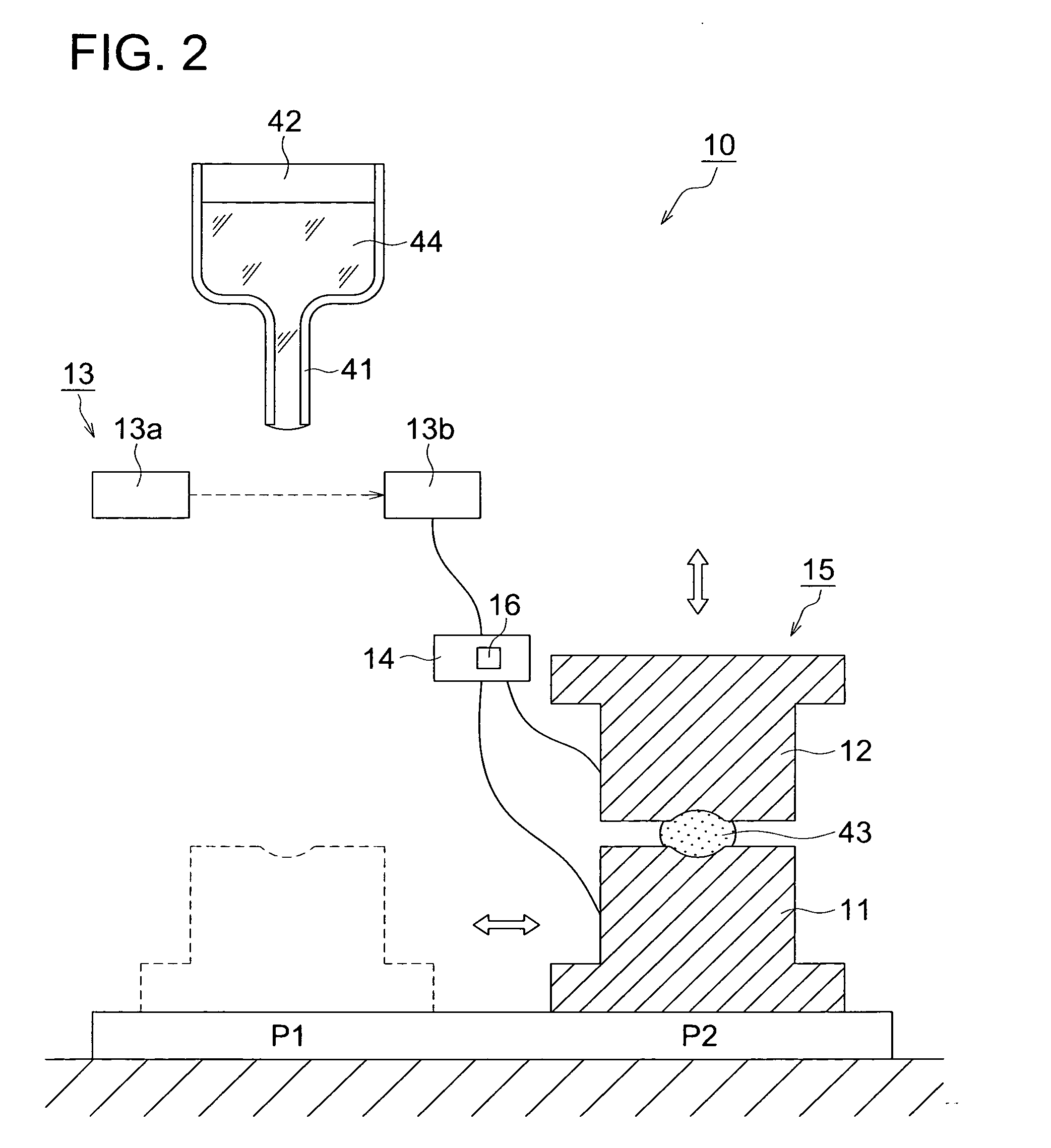
Manufacturing method of glass molded body, manufacturing apparatus of glass molded body, and glass molded body
InactiveUS20100120601A1Quality improvementImprove accuracyGlass pressing apparatusSensitive elementsShell moldingManufactured apparatus
A process for producing a glass molding, in which a glass molding of stable quality can be efficiently produced through minimizing of temperature fluctuation of molten glass drops at pressure molding operation; and an apparatus for production of a glass molding used in this process. Molten glass drops are fed into an inferior die by causing the molten glass drops to fall from above toward the inferior die. The arrival of molten glass drops having fallen at a given location is detected, and pressurization of the molten glass drops by means of molding dies is initiated upon the passage of a given time since the detection.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Molding device of glass molding articles
ActiveCN104556644AReduce CooldownReduce molding cycle timeGlass reforming apparatusVacuum pressureMaterials science
The invention relates to a molding device of glass molding articles. More specifically, the molding device of the glass molding articles comprises a pre-heating mechanism contacted with a mold body in a non-load state for pre-heating, a discharge cooling line provided with a cooling water line is formed at an outlet side of a molding chamber, the cooling time in the molding chamber is shortened, the whole molding period time of glass with a curved surface portion is further shortened, a plurality of suction holes into which vacuum pressure flows are formed at the bottom of a lower mold of the mold body, vacuum pressure absorption materials flowing into the suction holes are employed during molding motions, the glass with the excellent curved surface portion is molded, an inlet side of the molding chamber is provided with a vacuum mechanism for vacuum treatment of the mold body, and the molding device can be applied to the molding of infrared glass optical lenses.
Owner:DAEHO TECH CO LTD
Glass forming apparatus
According to a first embodiment, a refractory orifice ring of a glass forming apparatus is provided. The orifice ring includes an annular side wall and a base wall. At least one discharge hole is formed in the base wall. The discharge hole includes a top opening and a bottom opening, wherein the top opening has a surface area greater than a surface area of the bottom opening.
Owner:PYROTECK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com