Patents
Literature
115 results about "Comfort noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
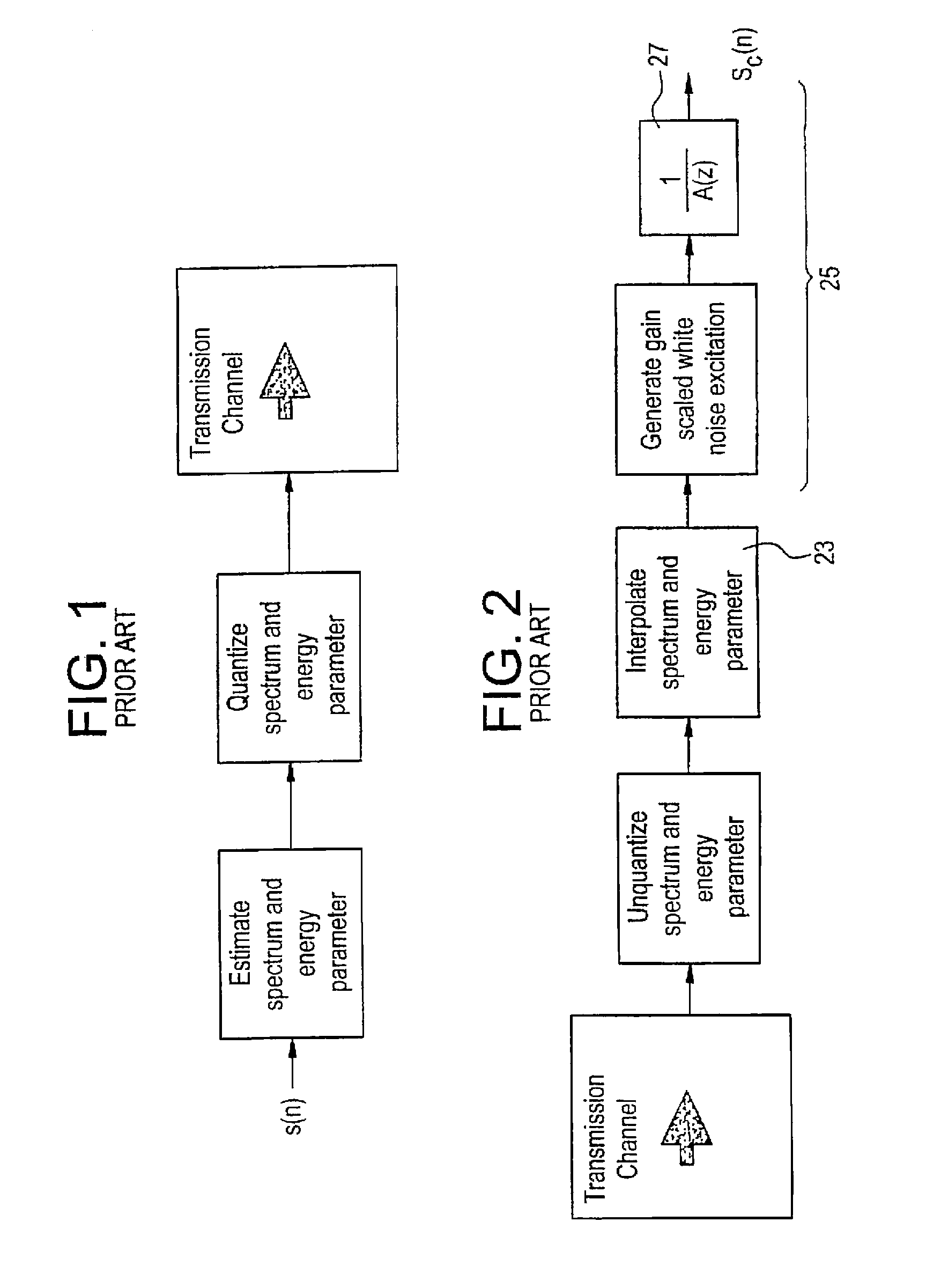
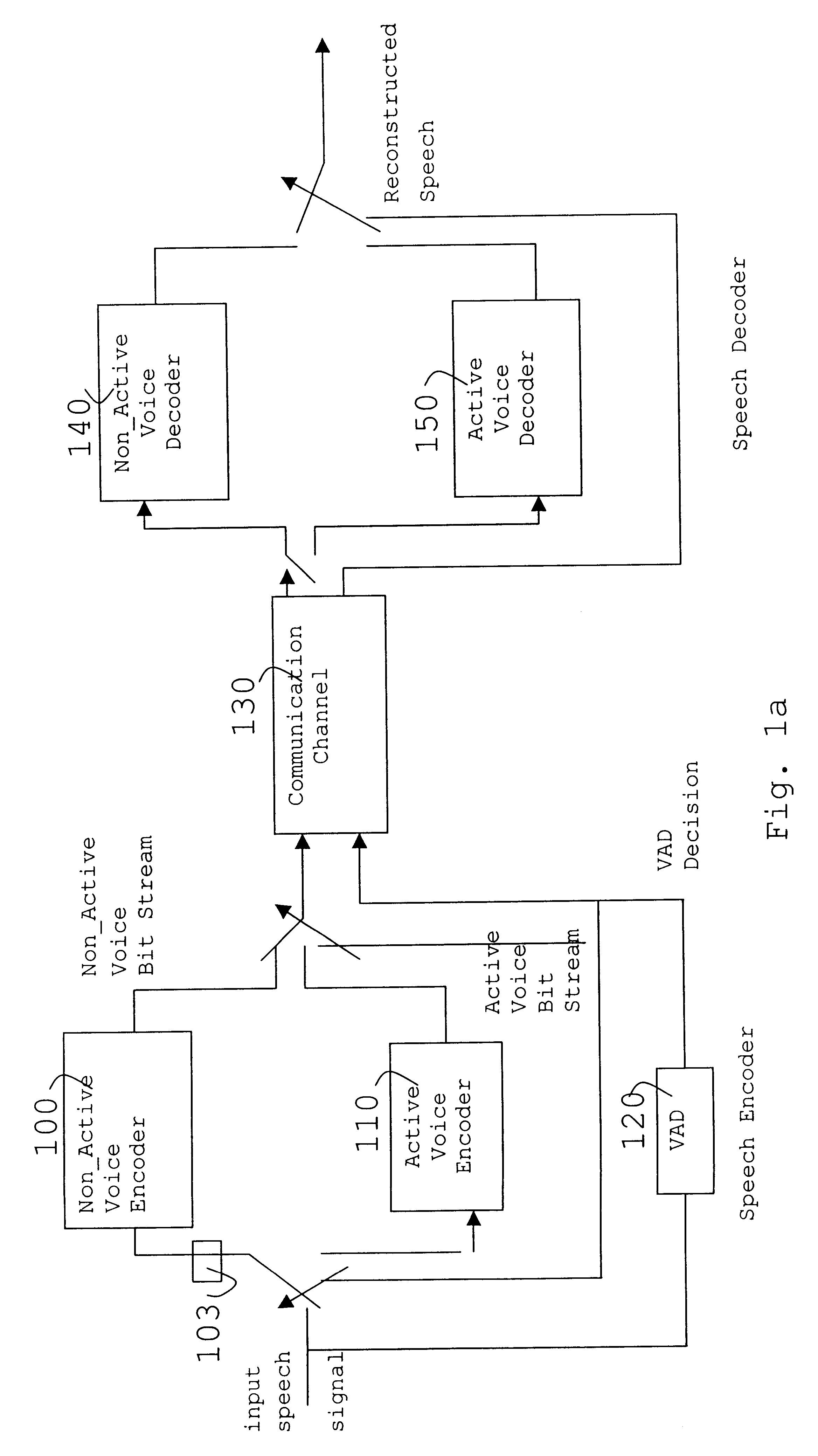
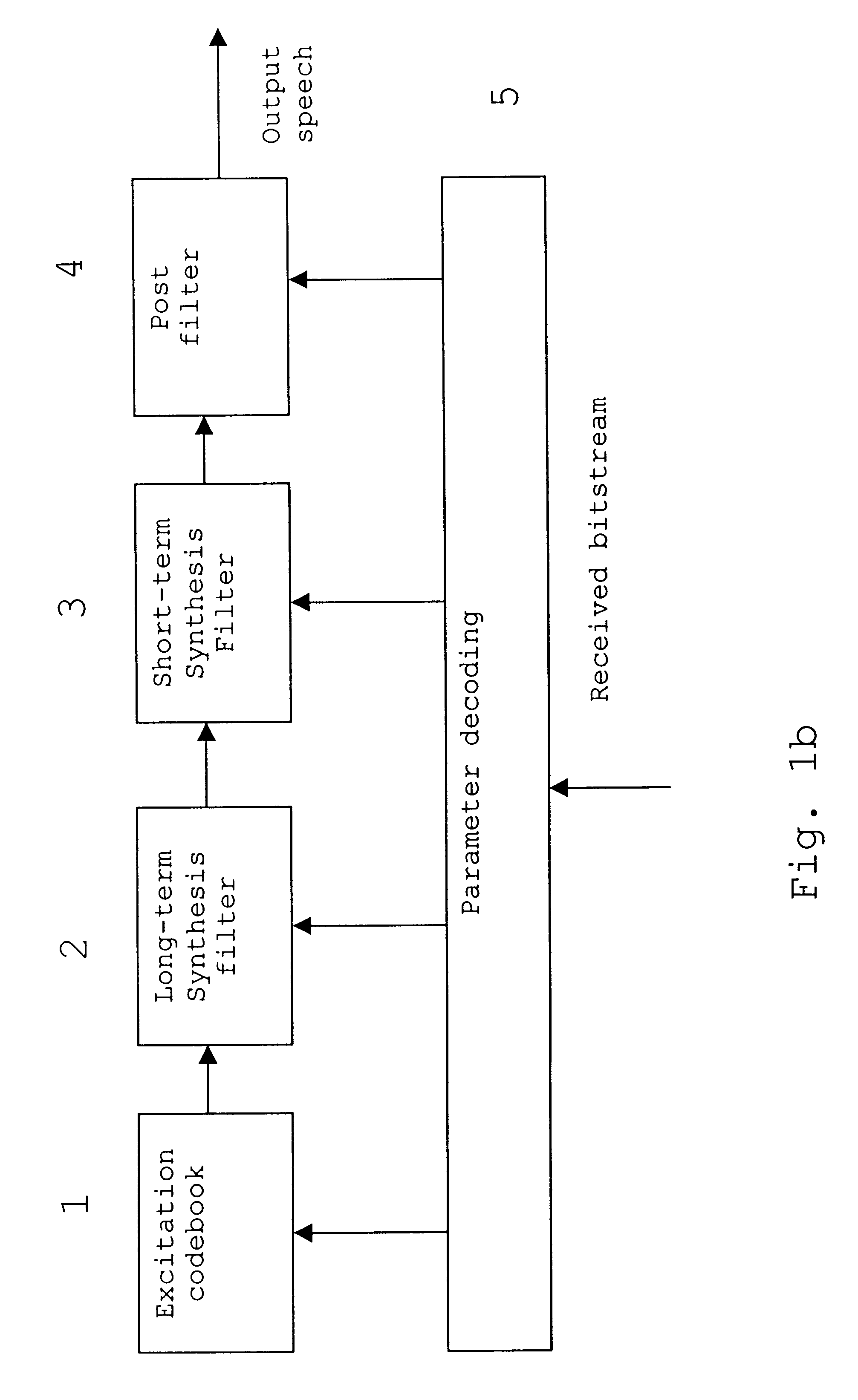
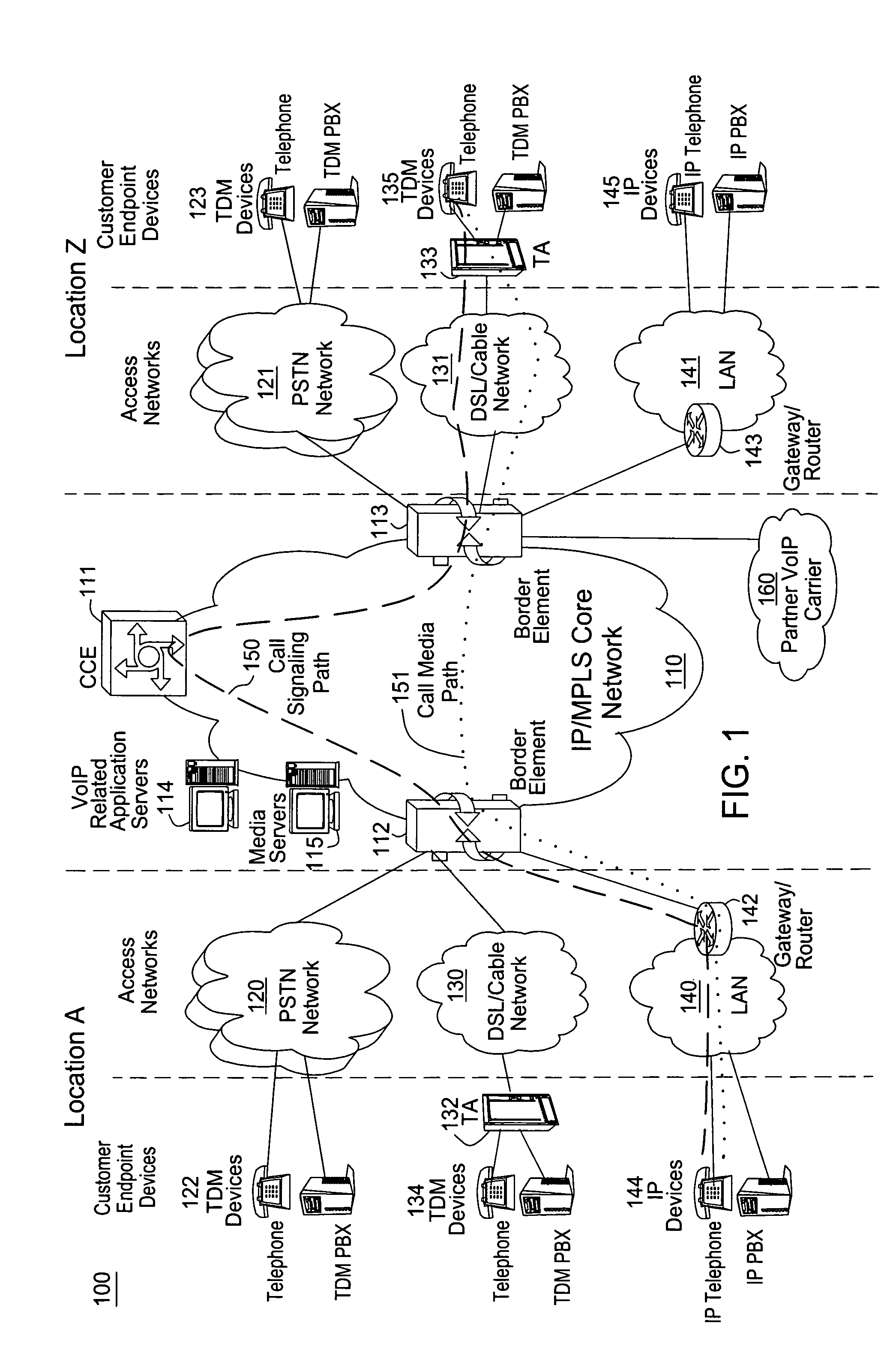
Comfort noise (or comfort tone) is synthetic background noise used in radio and wireless communications to fill the artificial silence in a transmission resulting from voice activity detection or from the audio clarity of modern digital lines.
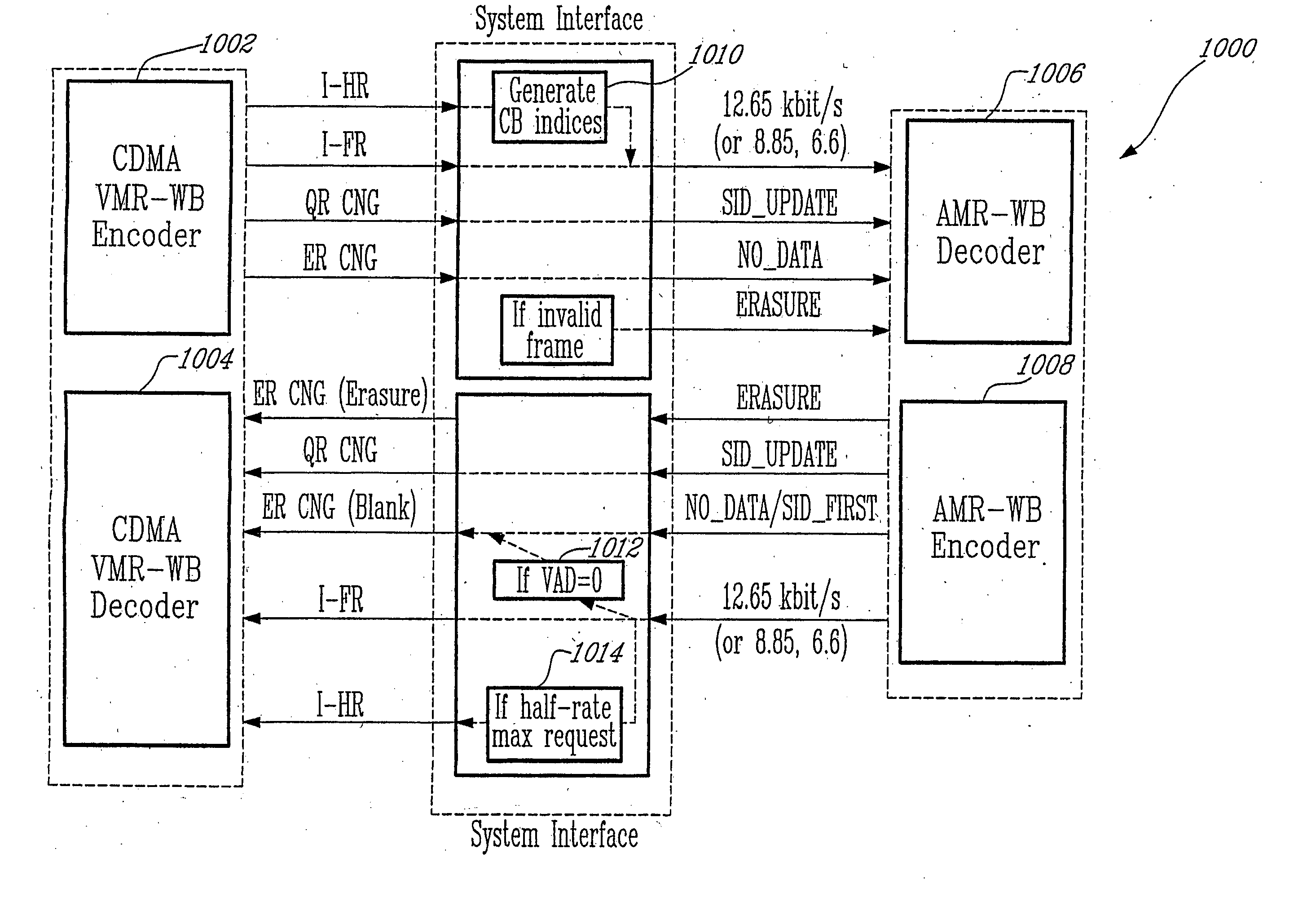
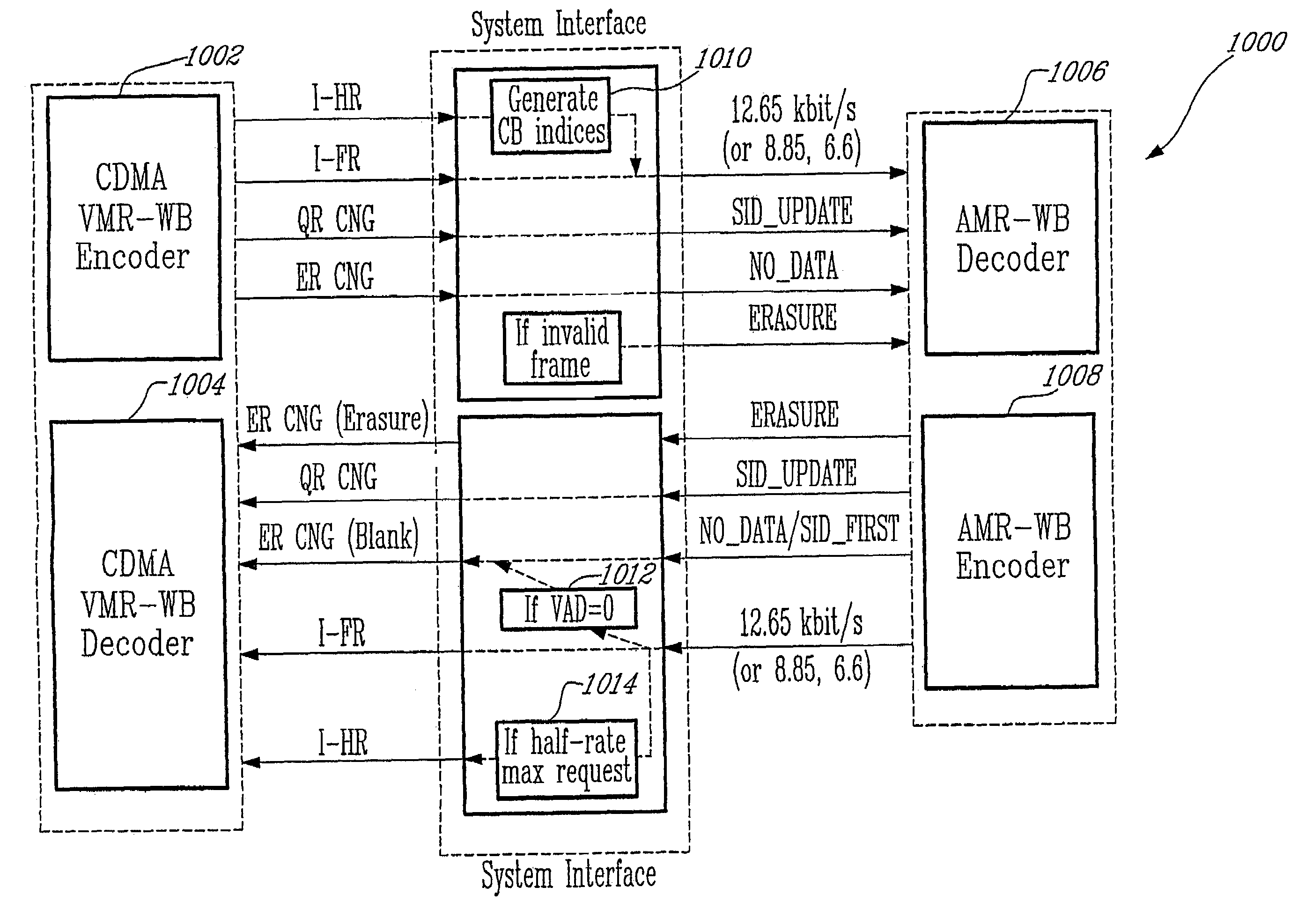
Method for interoperation between adaptive multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) and multi-mode variable bit-rate wideband (VMR-WB) codecs
ActiveUS20050267746A1Improve classificationImprove methodSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementBit allocationFull Rate
A source-controlled Variable bit-rate Multi-mode WideBand (VMR-WB) codec, having a mode of operation that is interoperable with the Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, the codec comprising: at least one Interoperable full-rate (I-FR) mode, having a first bit allocation structure based on one of a AMR-WB codec coding types; and at least one comfort noise generator (CNG) coding type for encoding inactive speech frame having a second bit allocation structure based on AMR-WB SID_UPDATE coding type. Methods for i) digitally encoding a sound using a source-controlled Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codec for interoperation with an adaptative multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, ii) translating a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codecsignal frame into an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame, iii) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame, and iv) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
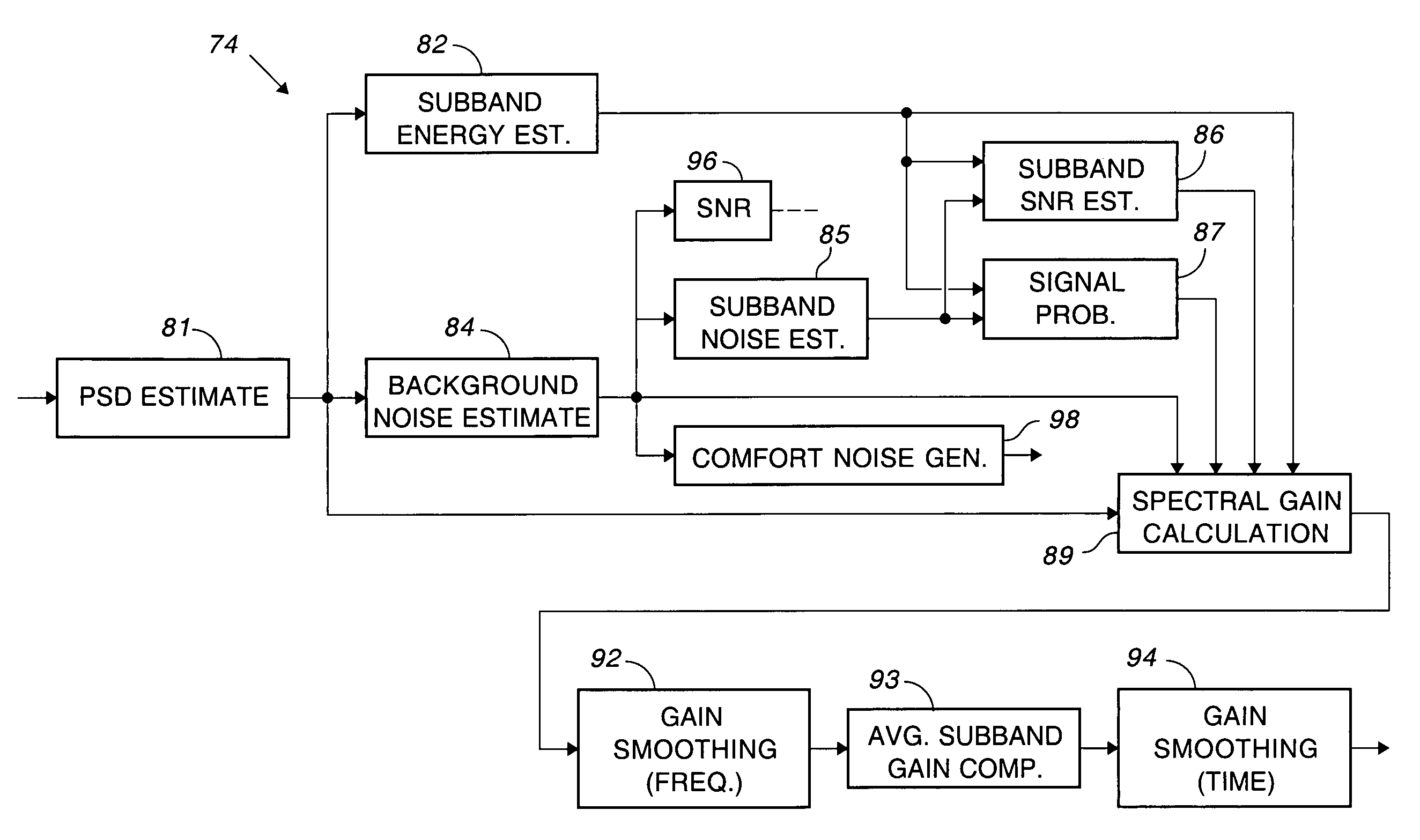
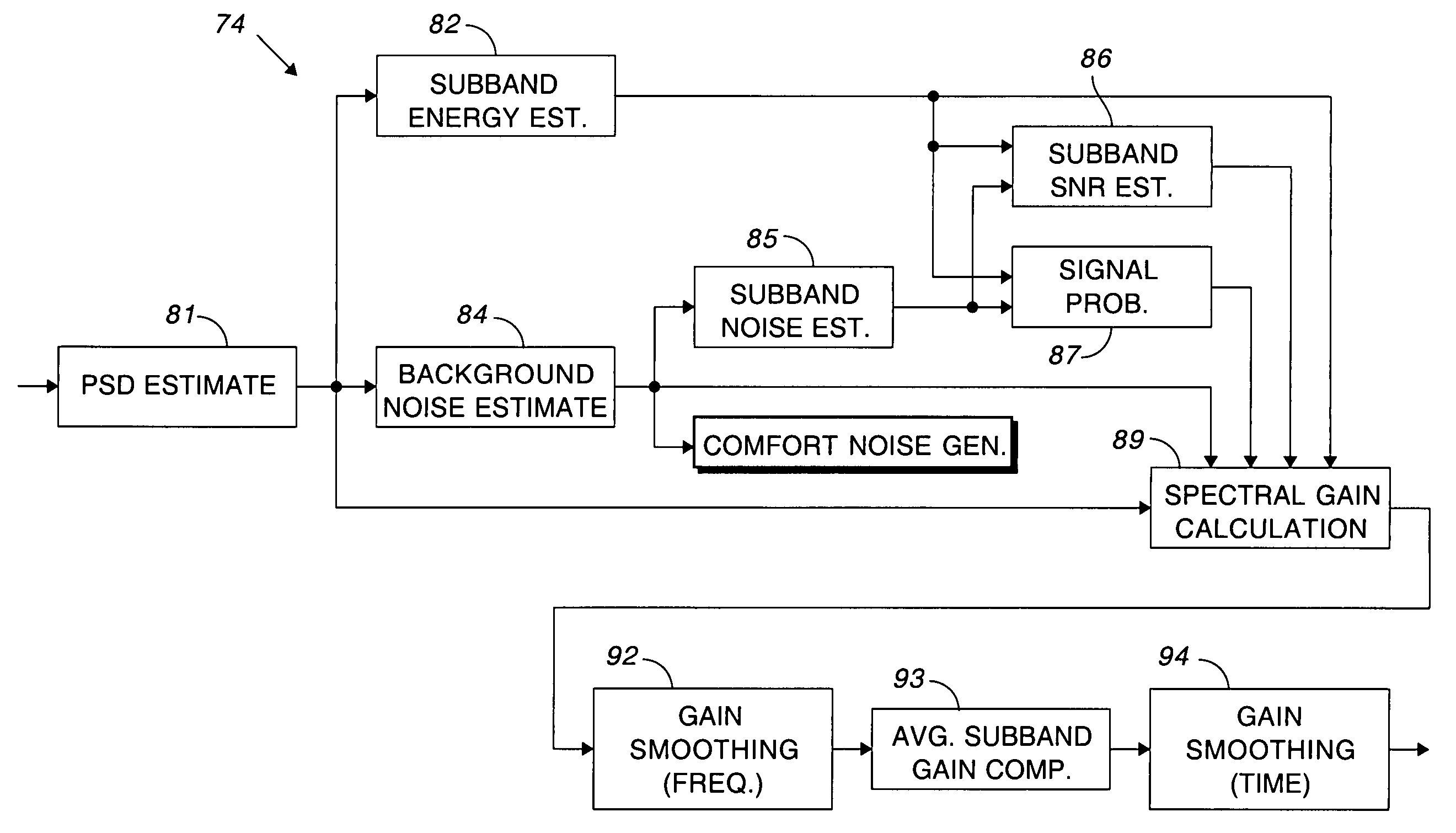
Comfort noise generator using modified doblinger noise estimate
ActiveUS20050278171A1Generate efficientlyEliminates noise pumpingSpeech analysisTime domainComfort noise
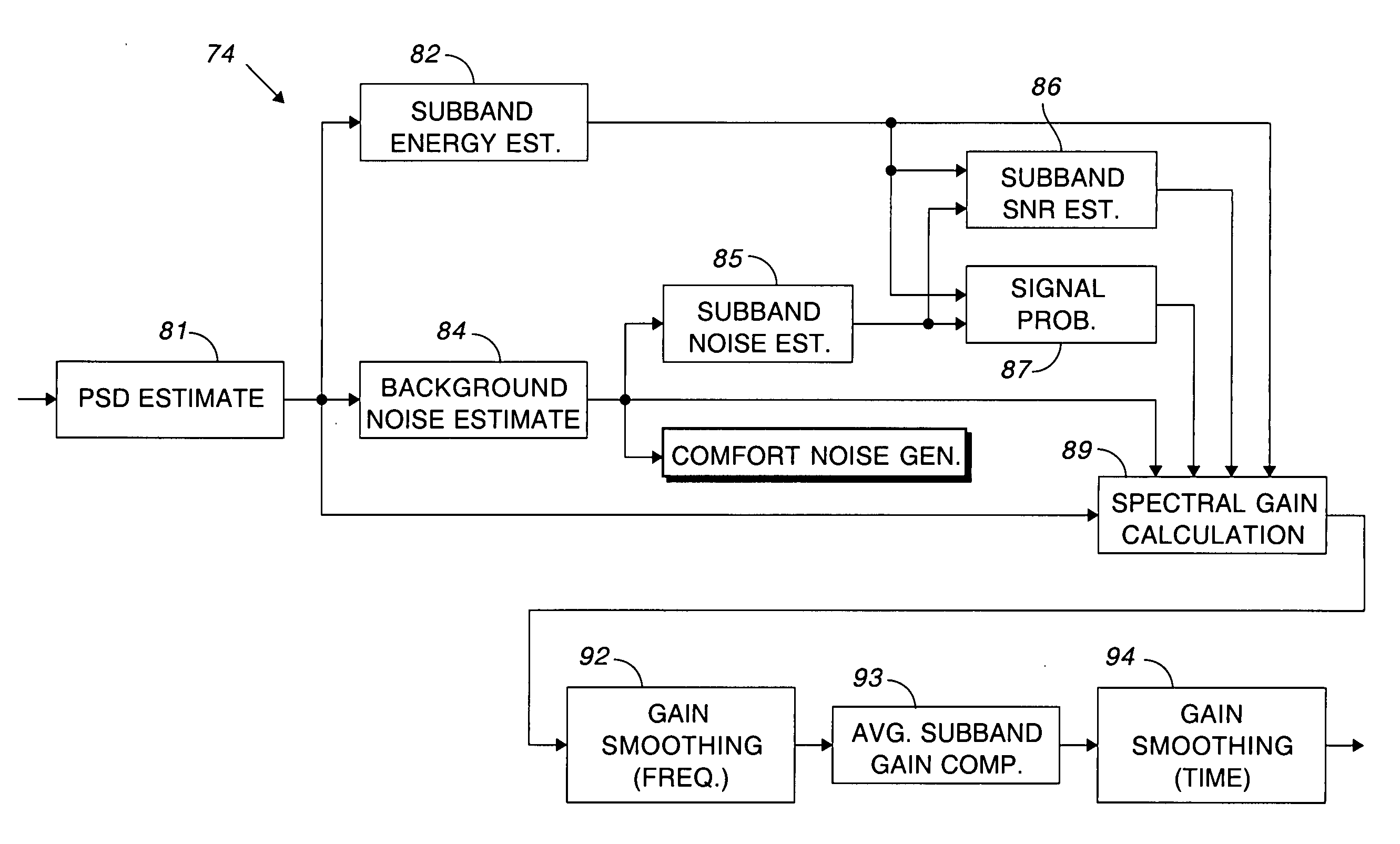
A background noise estimate based upon a modified Doblinger noise estimate is used for modulating the output of a pseudo-random phase spectrum generator to produce the comfort noise. The circuit for estimating noise includes a smoothing filter having a slower time constant for updating the noise estimate during noise than during speech. Comfort noise is smoothly inserted by basing the amount of comfort noise on the amount of noise suppression. A discrete inverse Fourier transform converts the comfort noise back to the time domain and overlapping windows eliminate artifacts that may have been produced during processing.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Method for interoperation between adaptive multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) and multi-mode variable bit-rate wideband (VMR-WB) codecs
InactiveUS7203638B2Improve classificationImprove methodSpeech analysisFluid pressure measurementUltra-widebandBit allocation
A source-controlled Variable bit-rate Multi-mode WideBand (VMR-WB) codec, having a mode of operation that is interoperable with the Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, the codec comprising: at least one Interoperable full-rate (I-FR) mode, having a first bit allocation structure based on one of a AMR-WB codec coding types; and at least one comfort noise generator (CNG) coding type for encoding inactive speech frame having a second bit allocation structure based on AMR-WB SID_UPDATE coding type. Methods for i) digitally encoding a sound using a source-controlled Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codec for interoperation with an adaptative multi-rate wideband (AMR-WB) codec, ii) translating a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) codecsignal frame into an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame, iii) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame, and iv) translating an Adaptive Multi-Rate wideband (AMR-WB) signal frame into a Variable bit rate multi-mode wideband (VMR-WB) signal frame are also provided.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
System and method for adaptive transmission of comfort noise parameters during discontinuous speech transmission
ActiveUS20060293885A1Solve the real problemImprove efficiencySpeech analysisSubstation equipmentCurrent noiseComfort noise
Apparatus is provided that includes at least one entity for transmitting speech signals in a discontinuous transmission mode including transmitting speech frames interspersed with frames including comfort noise parameters during periods of speech pauses. The entit(ies) include a first entity for estimating a current noise value. In addition, the apparatus includes a second entity for selectively controlling a rate at which the frames including comfort noise parameters are transmitted during the periods of speech pauses based upon the estimated current noise value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Noise reduction and comfort noise gain control using bark band weiner filter and linear attenuation
ActiveUS7454010B1Produces no musical artifactLong time constantInterconnection arrangementsSpeech analysisUltrasound attenuationComfort noise
A combination of noise suppression using a Bark band modified Weiner filter and linear noise reduction improves elimination of noise in a telephone. A detector for detecting long, non-speech intervals is coupled to the output of the noise suppresser and controls selection of noise suppression or noise reduction. A gain smoothing filter has a long time constant when noise reduction is used and provides a gradual transition from one level of gain to another. Comfort noise is smoothly inserted by updating the data for generating comfort noise only during detected long, non-speech intervals.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
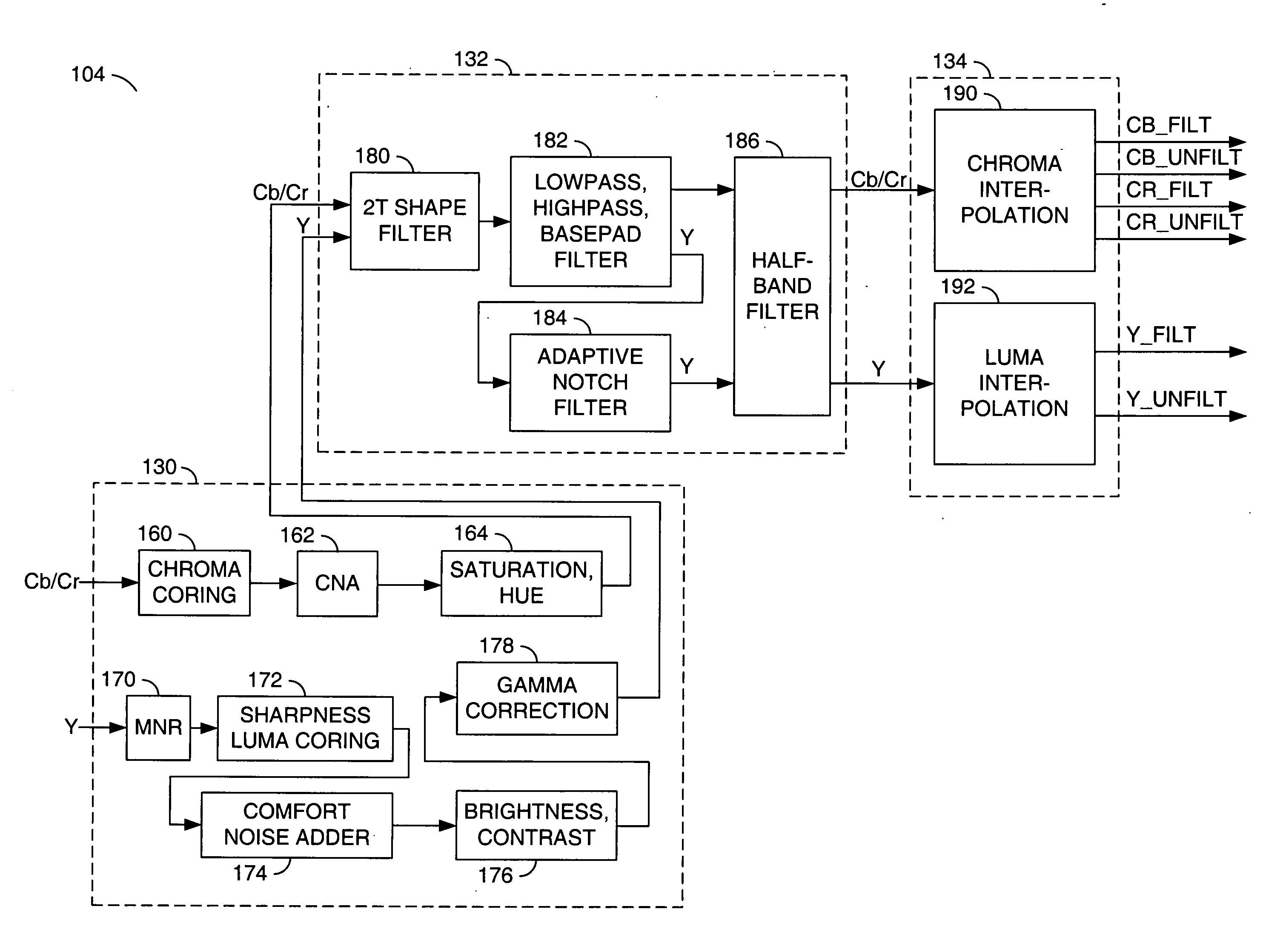
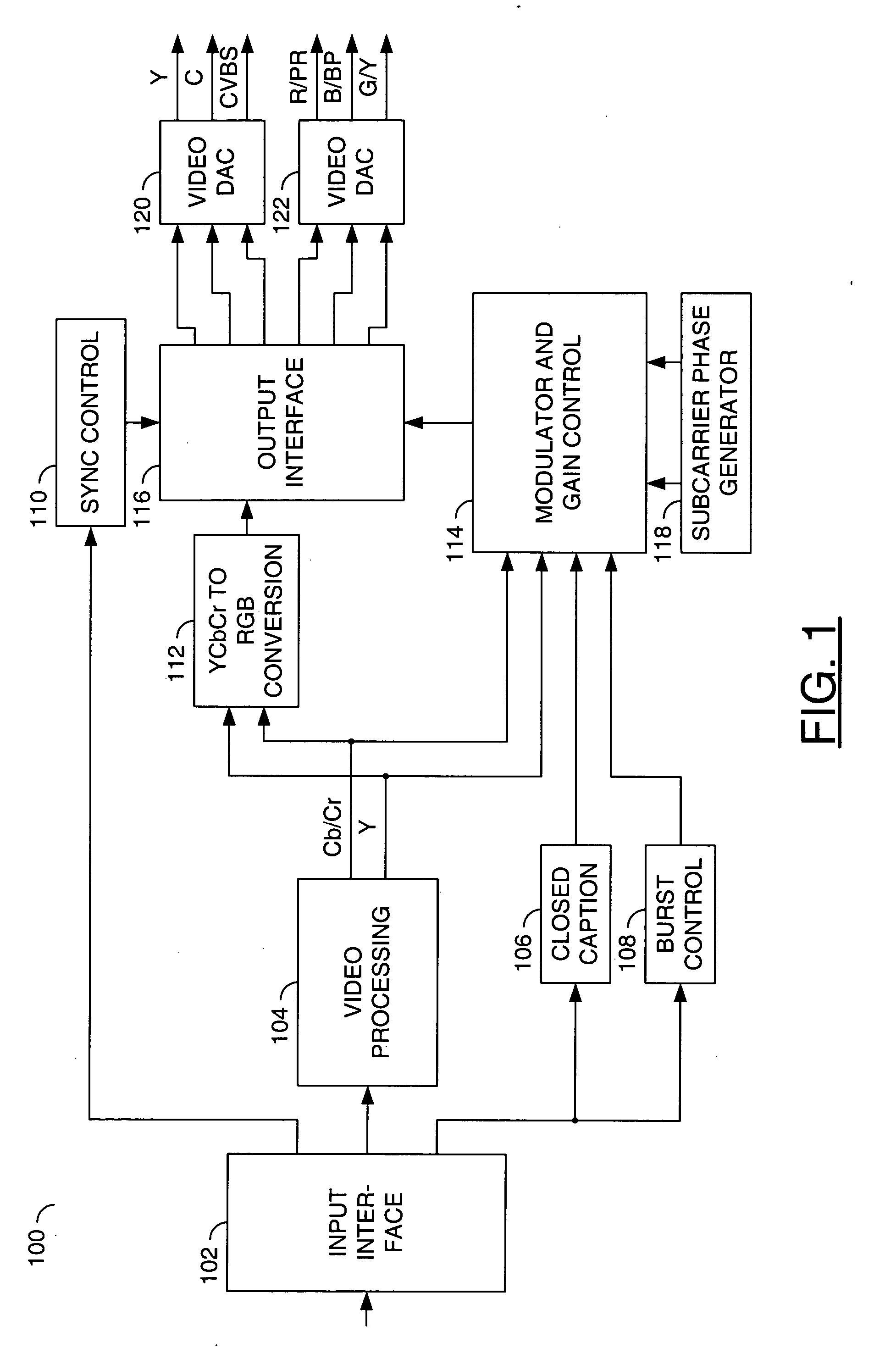
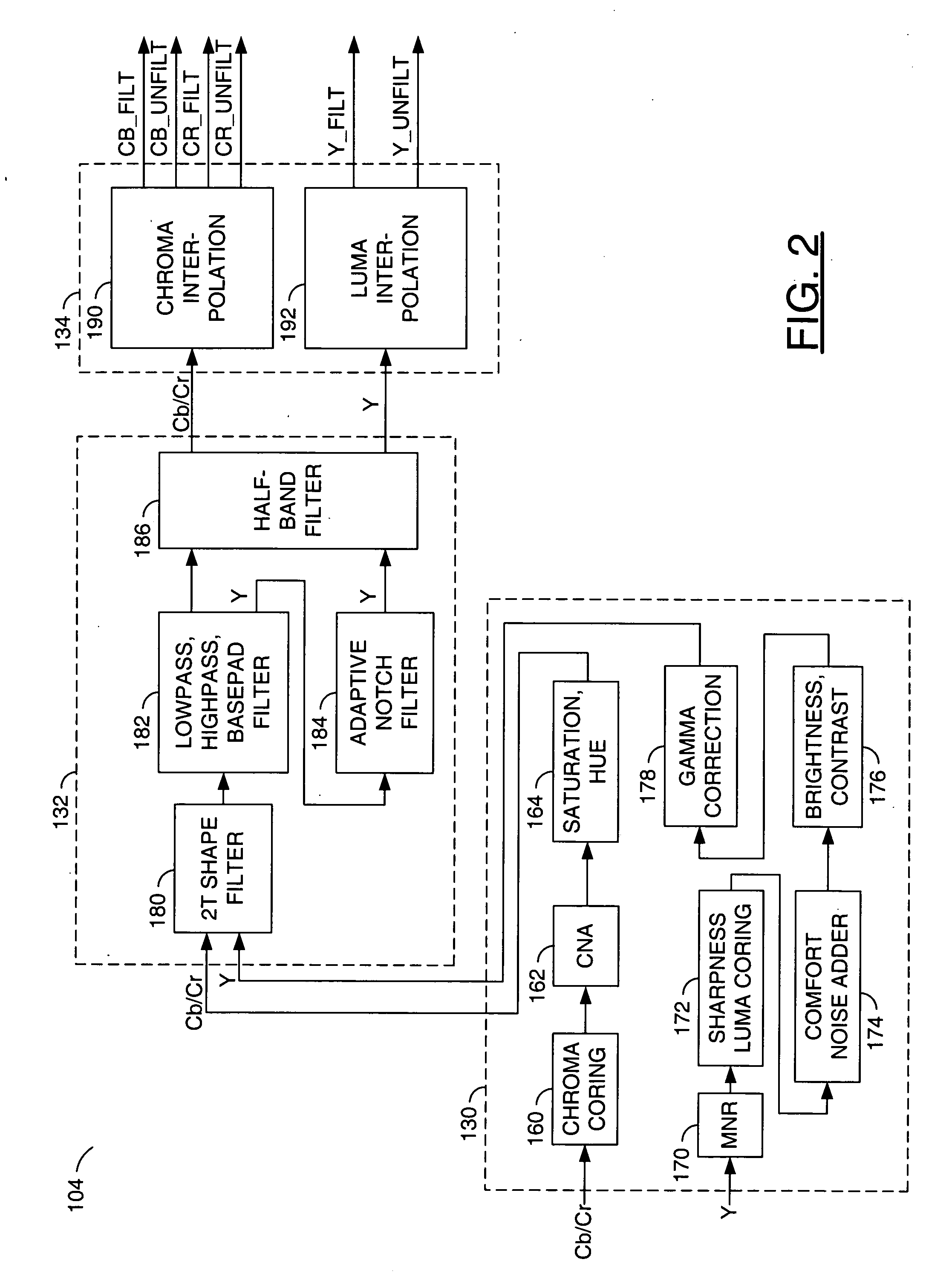
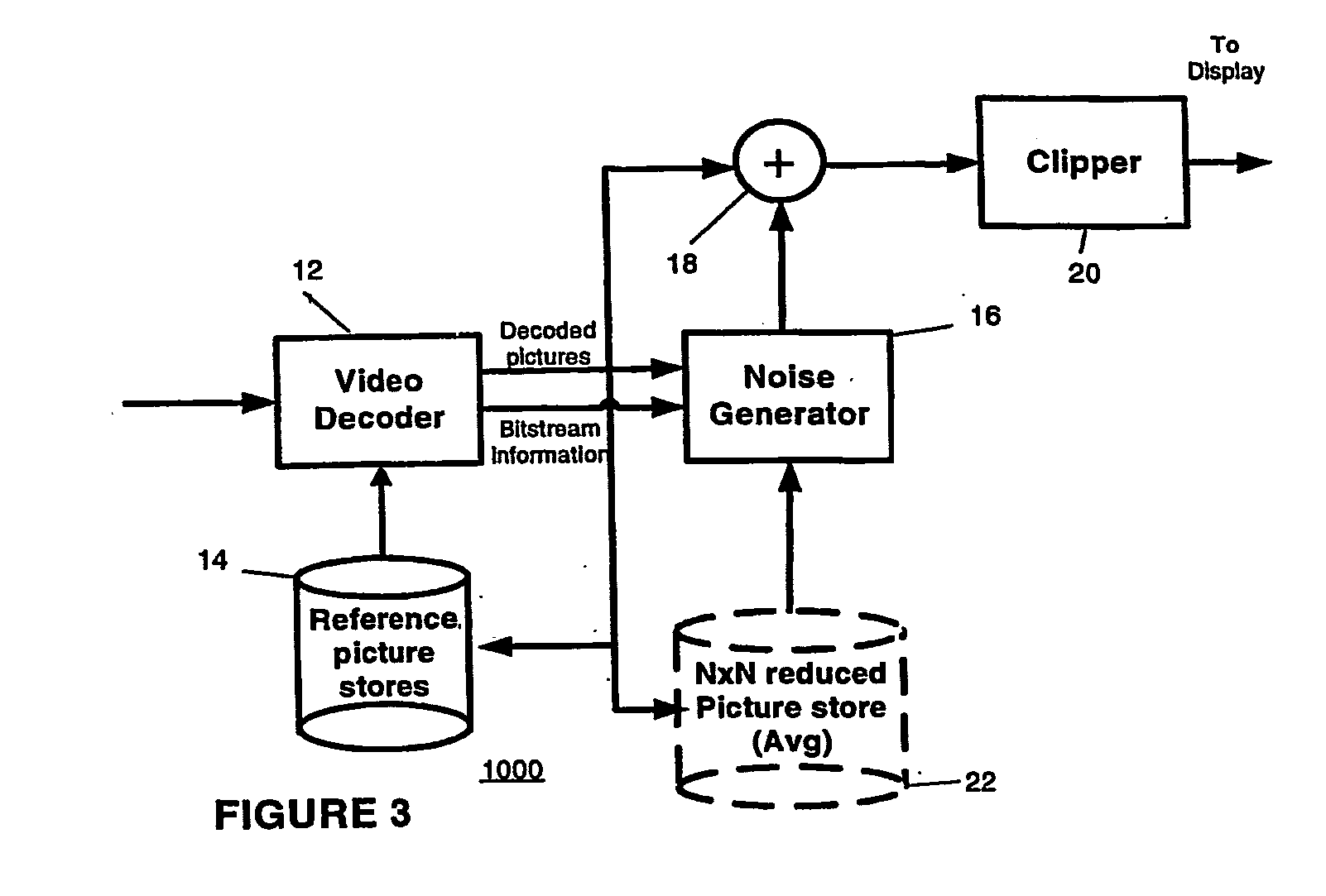
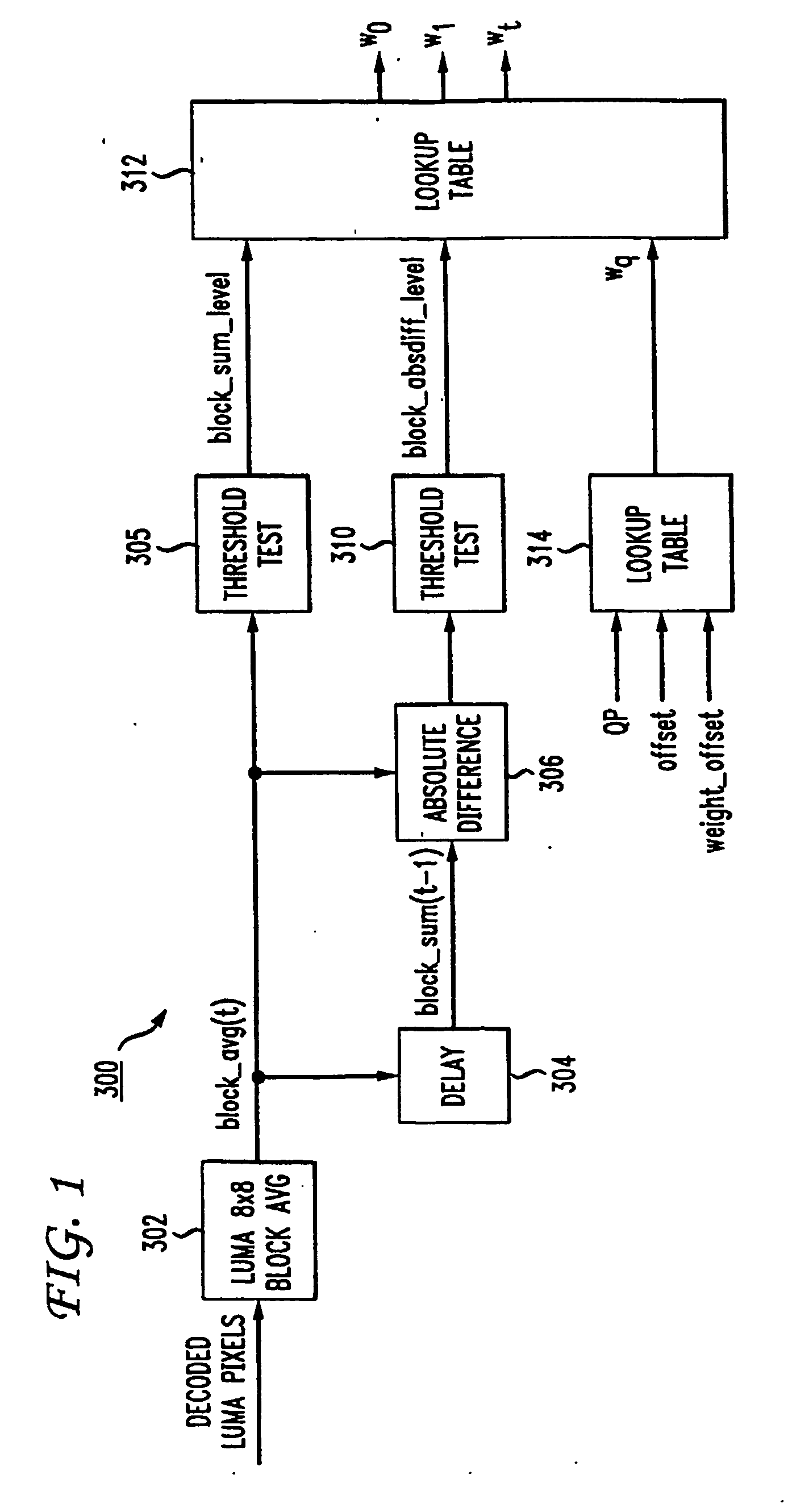
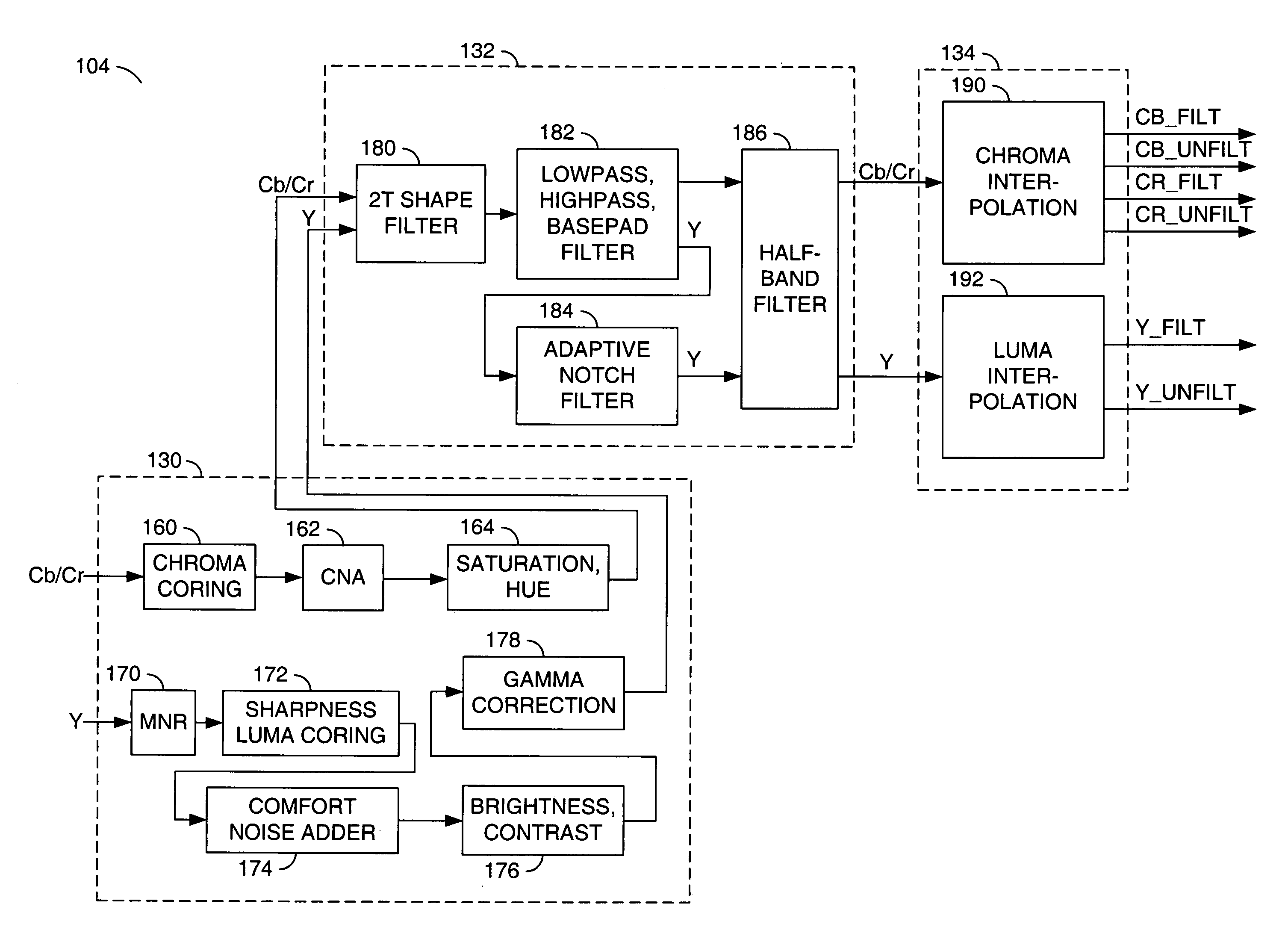
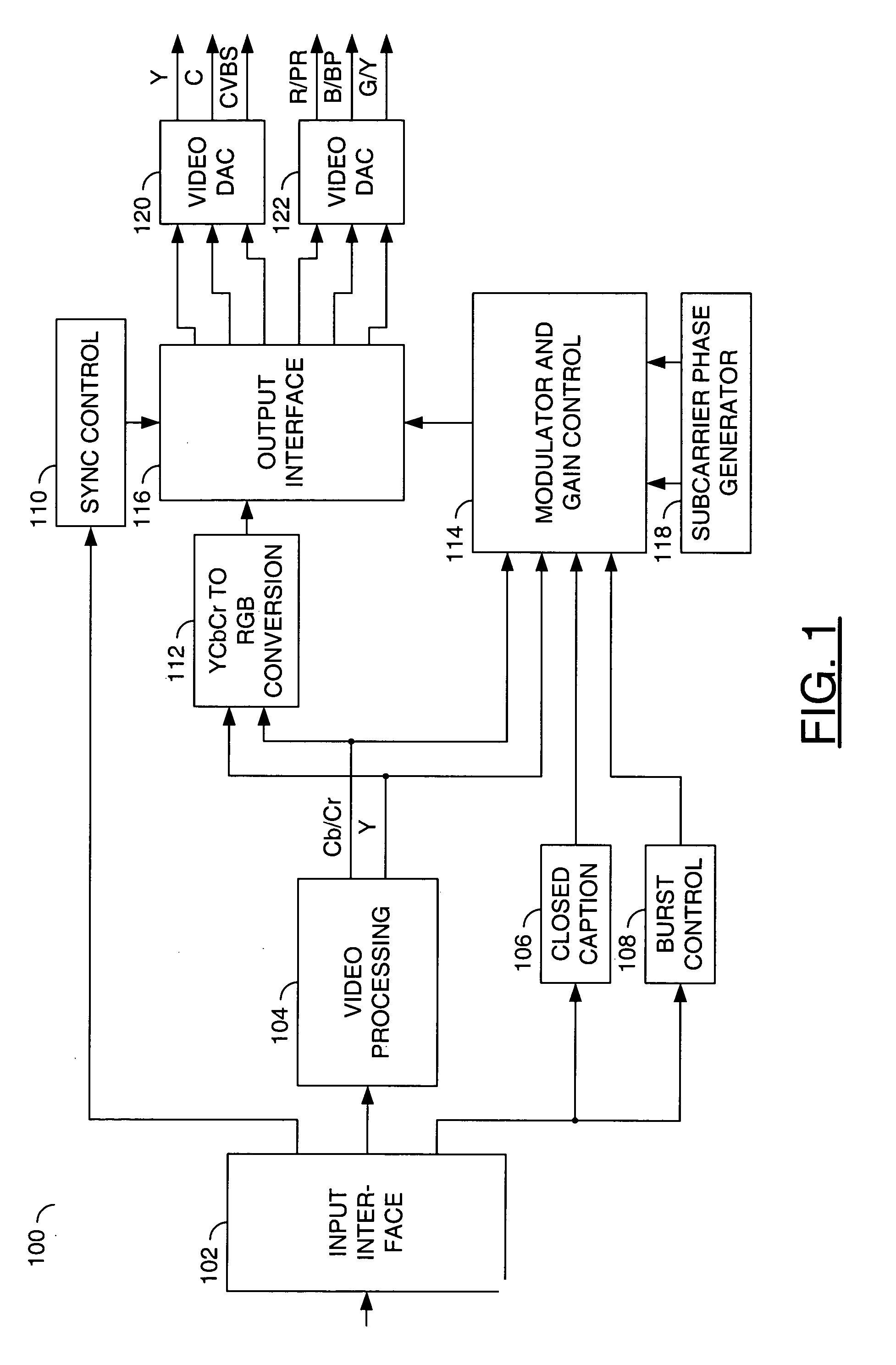
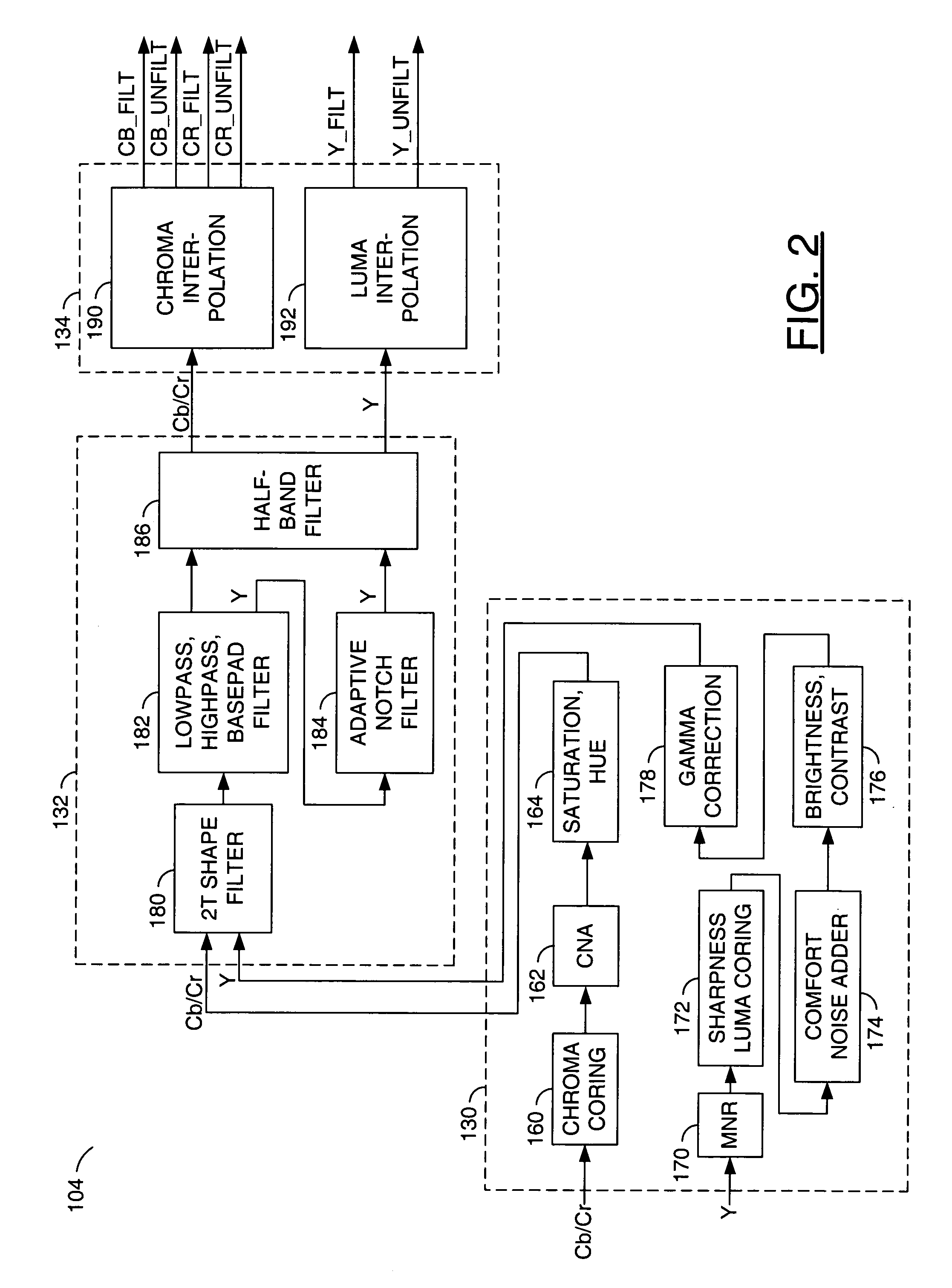
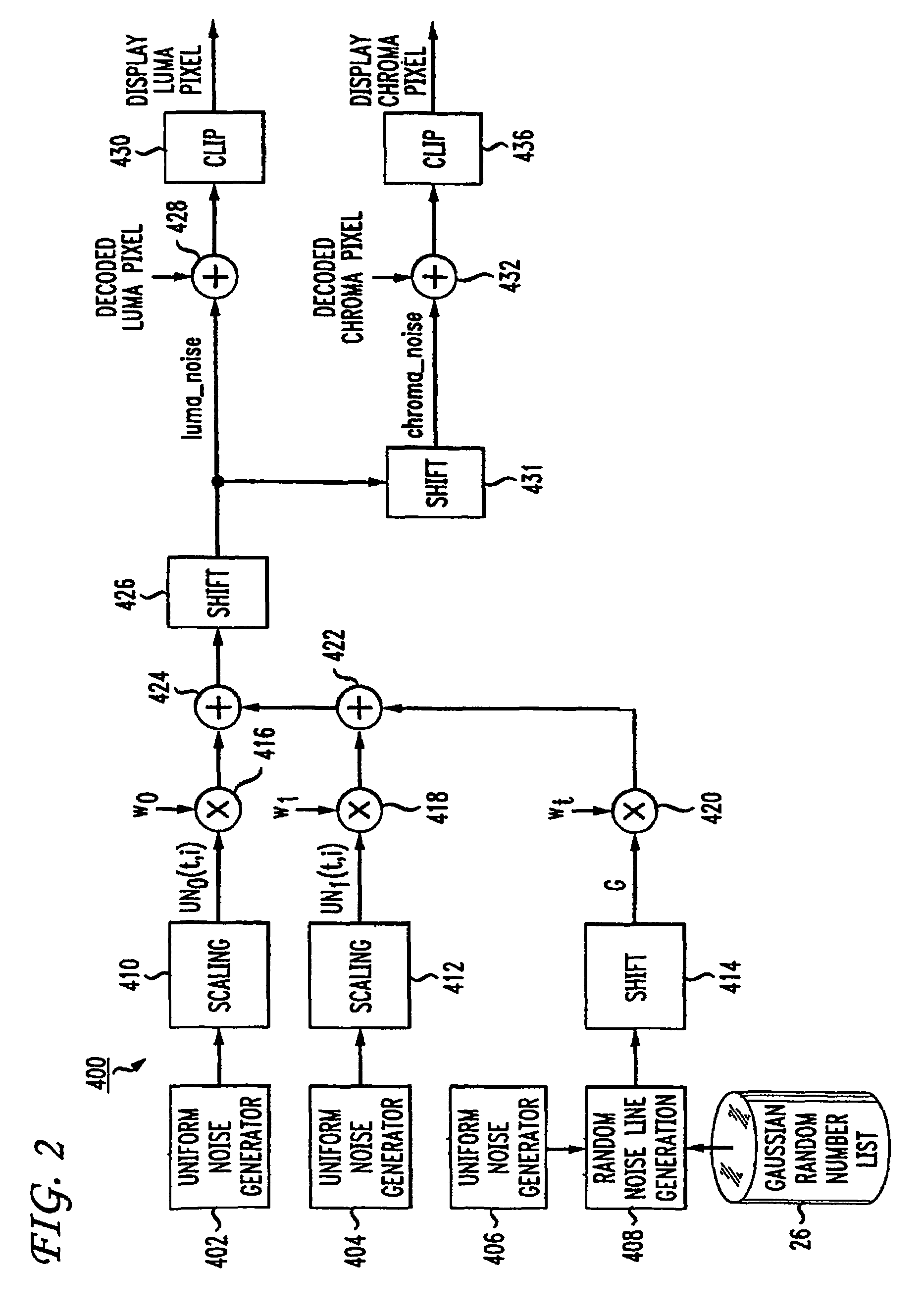
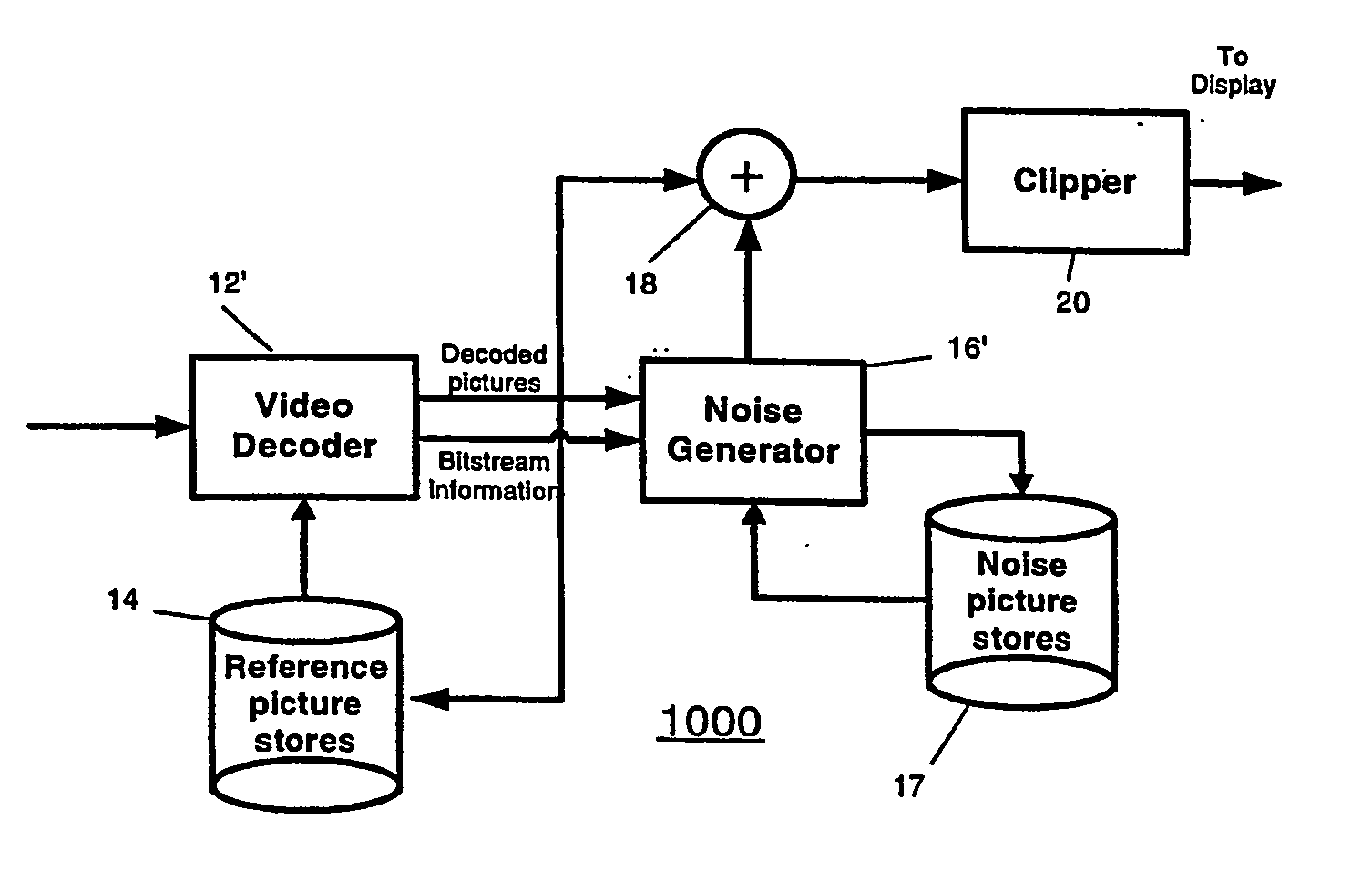
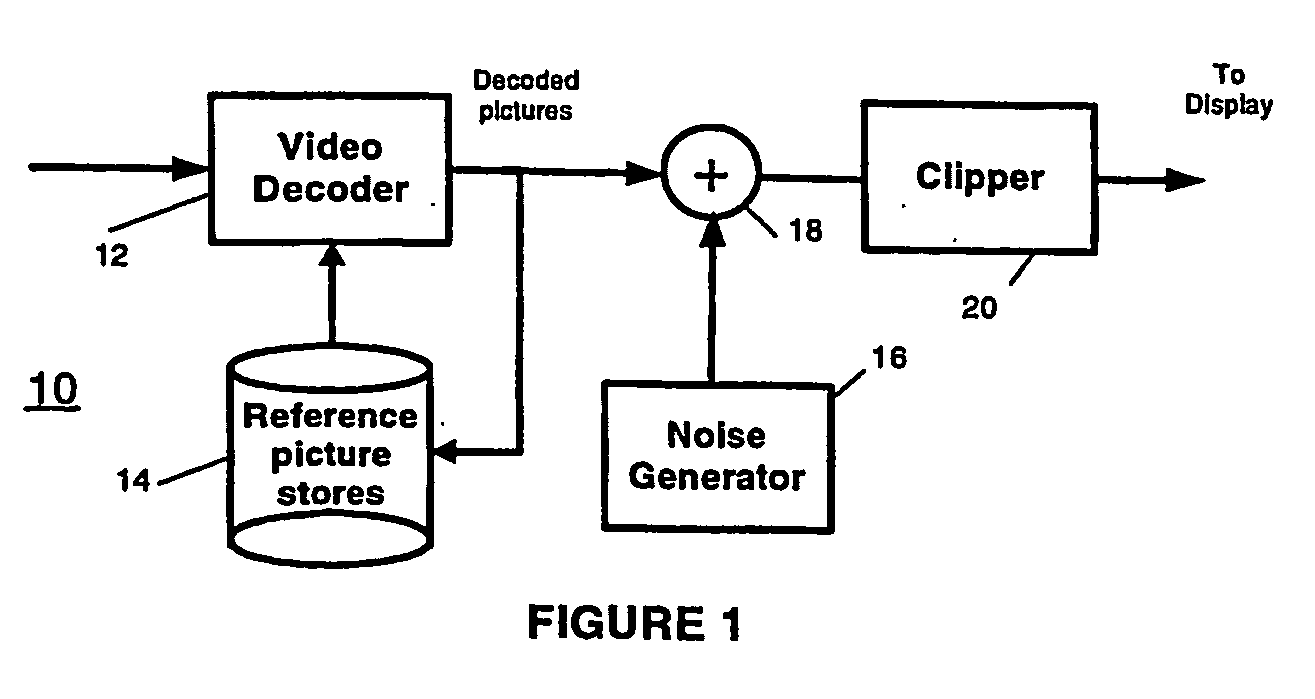
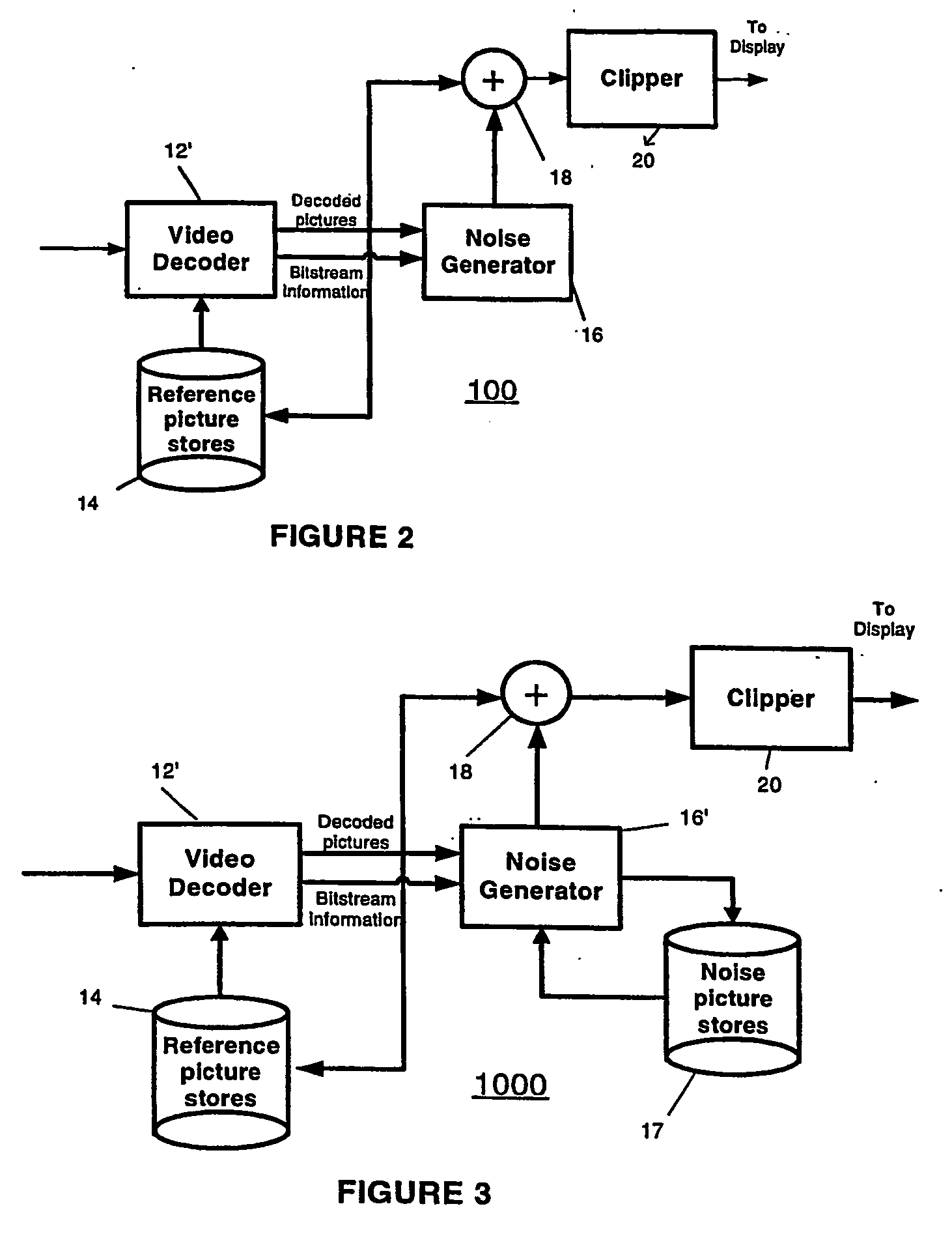
Method and apparatus for masking of video artifacts and/or insertion of film grain in a video decoder
A video decoder comprising (i) a post-processing filter block, (ii) a comfort noise addition block and (iii) a video value / range adjustment block, where the comfort noise addition block is integrated into a video output path of the video decoder. The post-processing filter block may be configured to perform one or more of noise reduction, spatial filtering and temporal filtering on luminance data. The comfort noise addition block may be configured to add comfort noise to the luminance data. The video value / range adjustment block may be configured to adjust one or both of a value and a range of the luminance data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
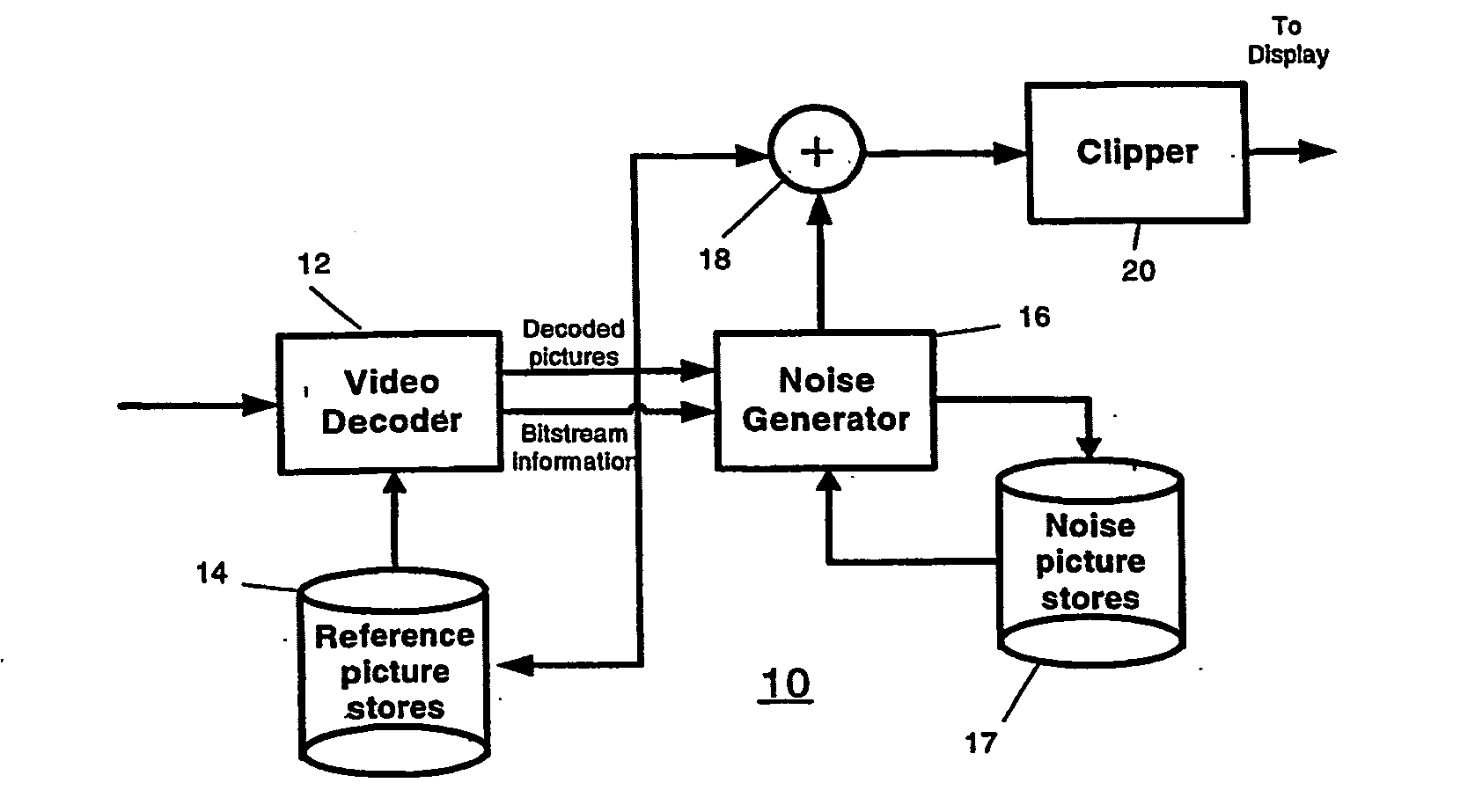
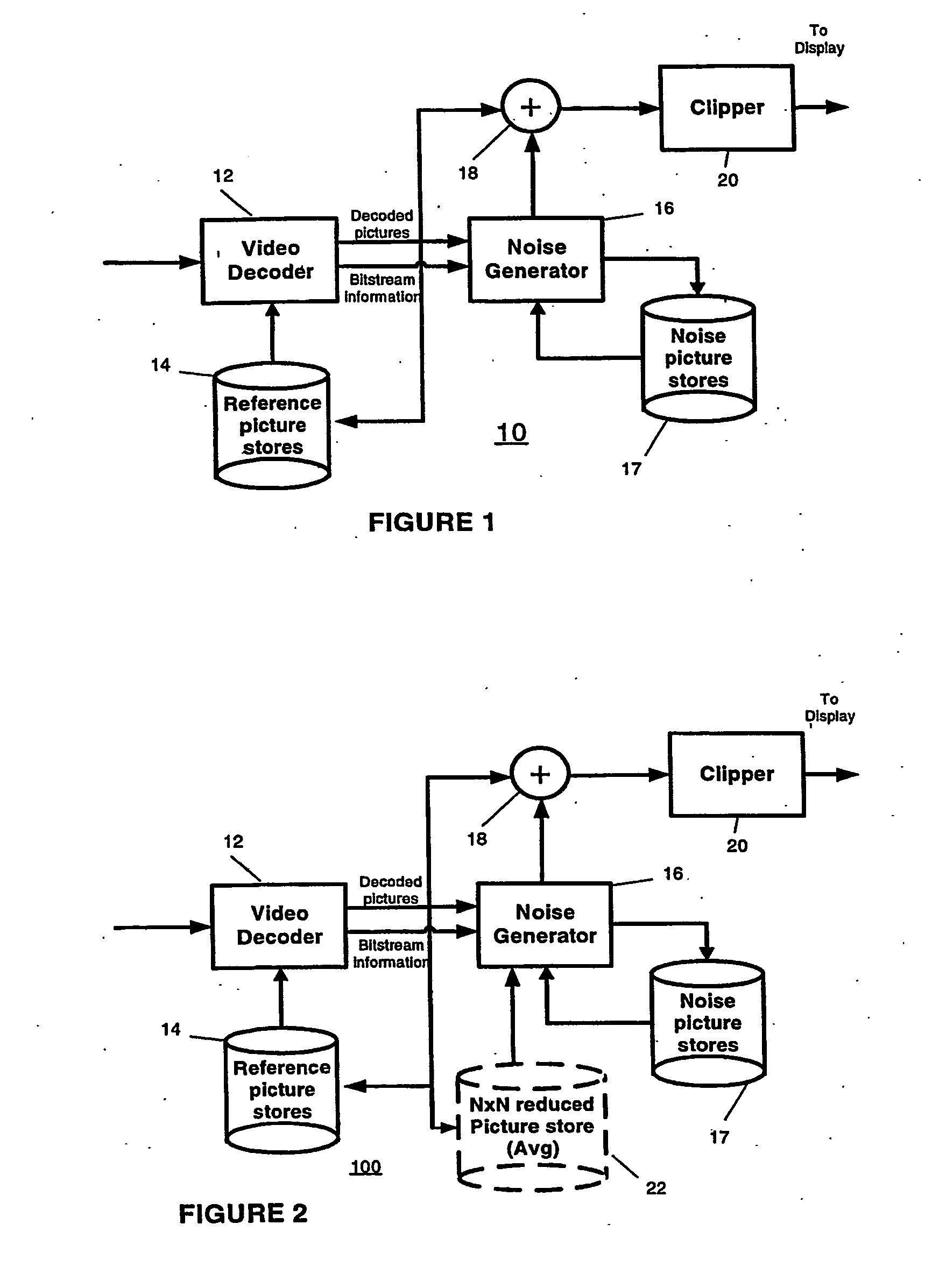
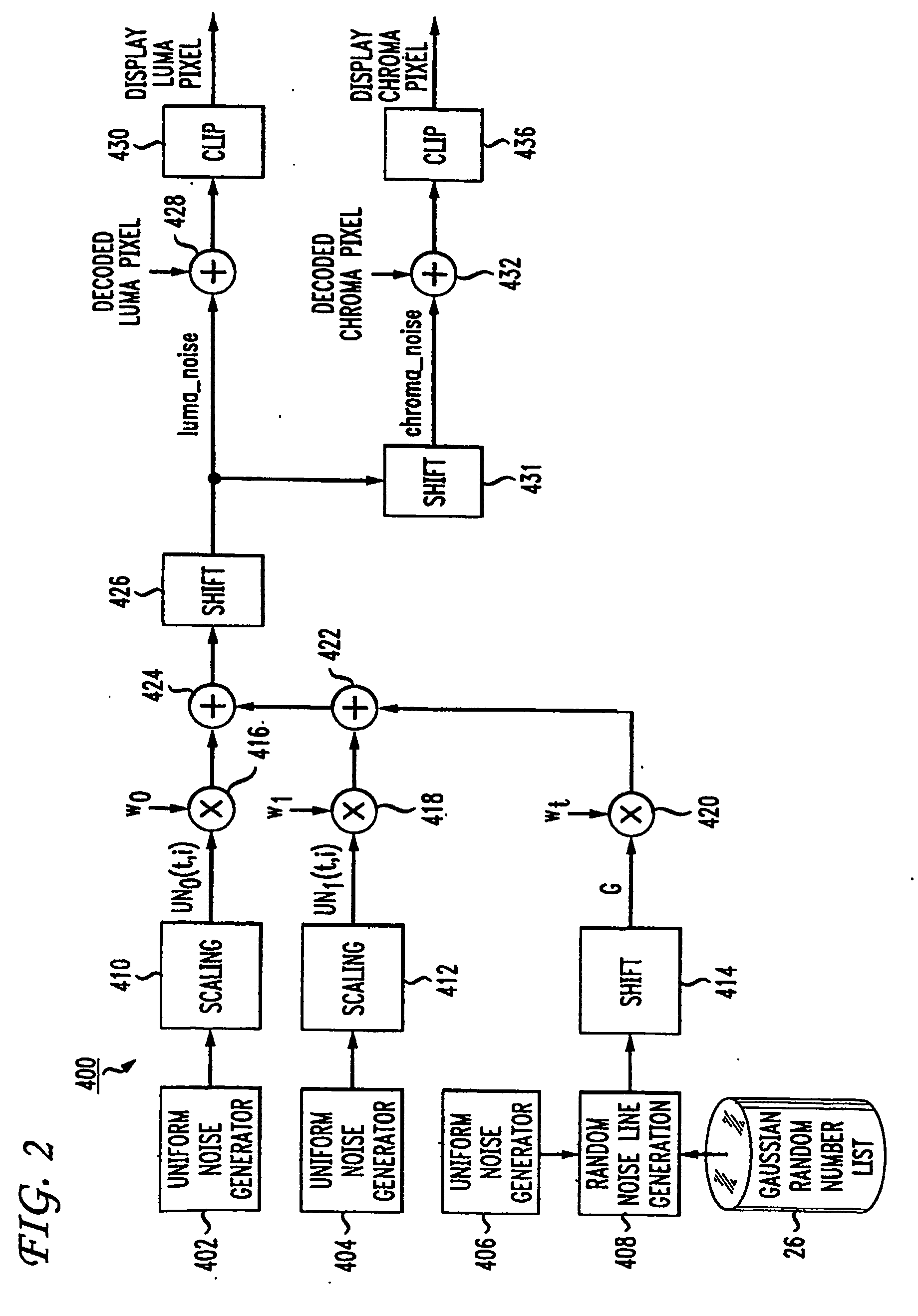
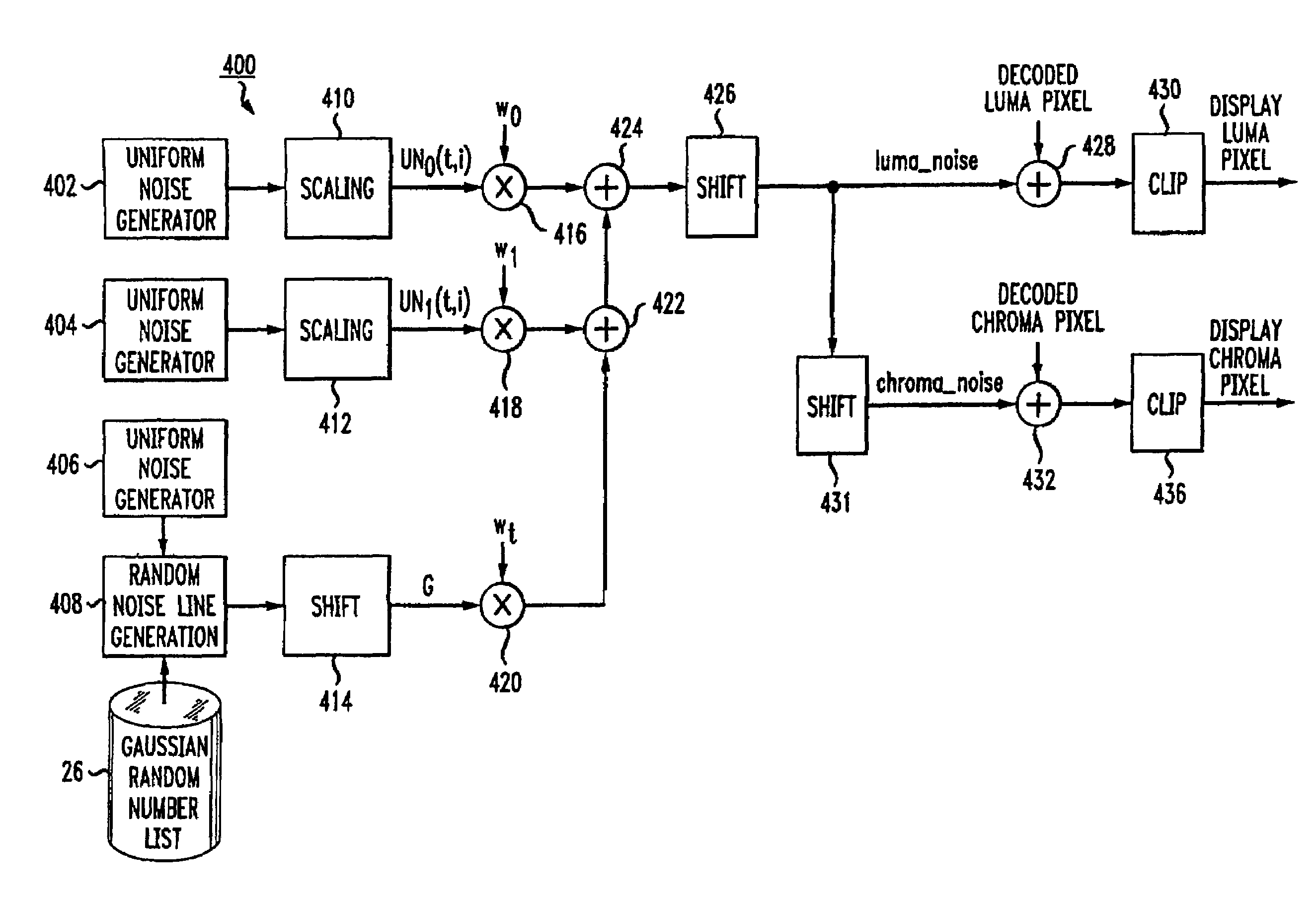
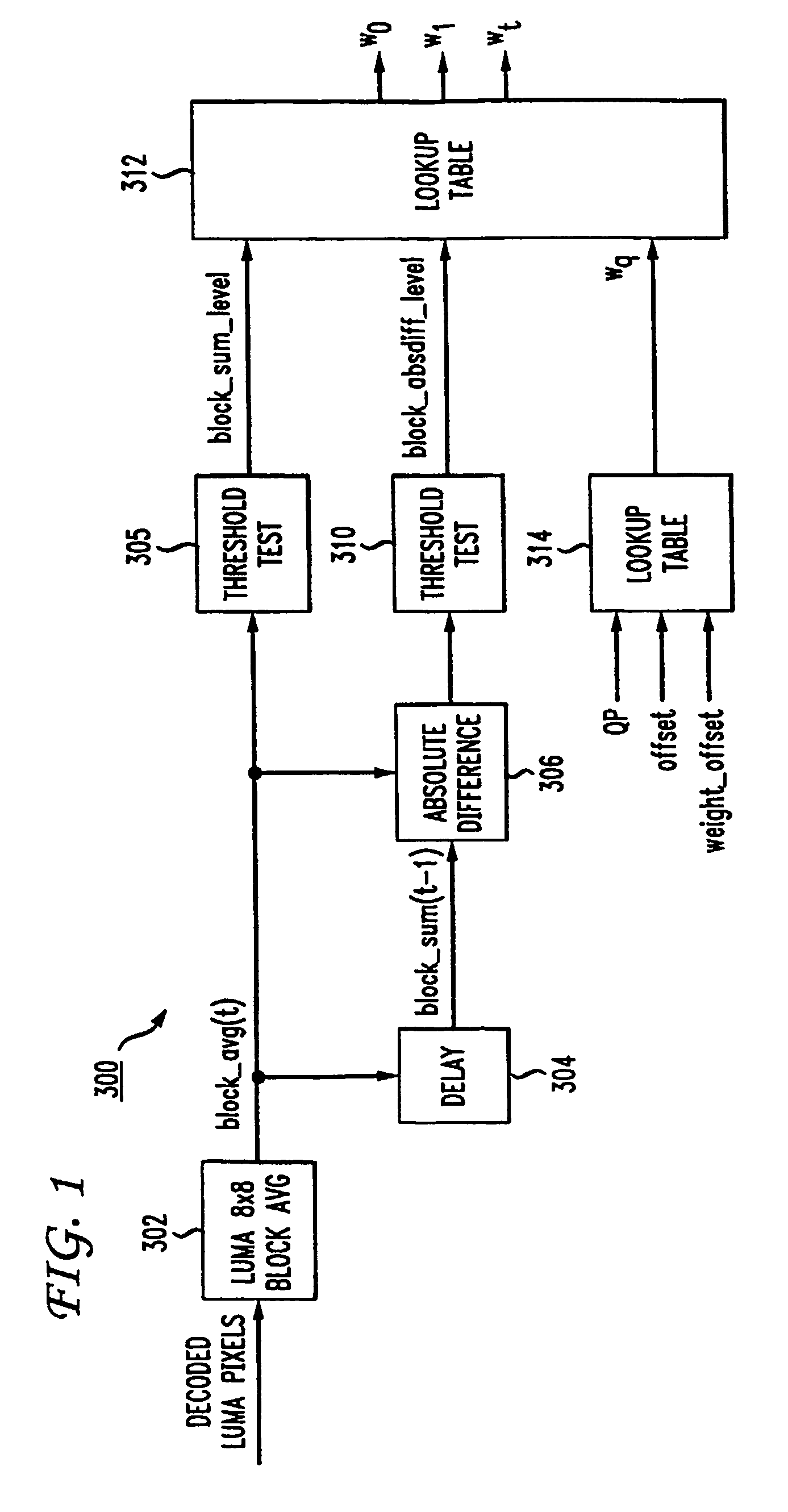
Video comfort noise addition technique
InactiveUS20070047658A1Reduce artifactsSignificant differenceTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionComfort noise
A decoding arrangement for decoding pictures in an incoming video stream includes a noise generator for adding a dither signal containing random noise to the pictures after video decoding, to improve the subjective video quality. The noise generator adds noise to each pixel in an amount correlated to the luminance of at least a portion of the current picture.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
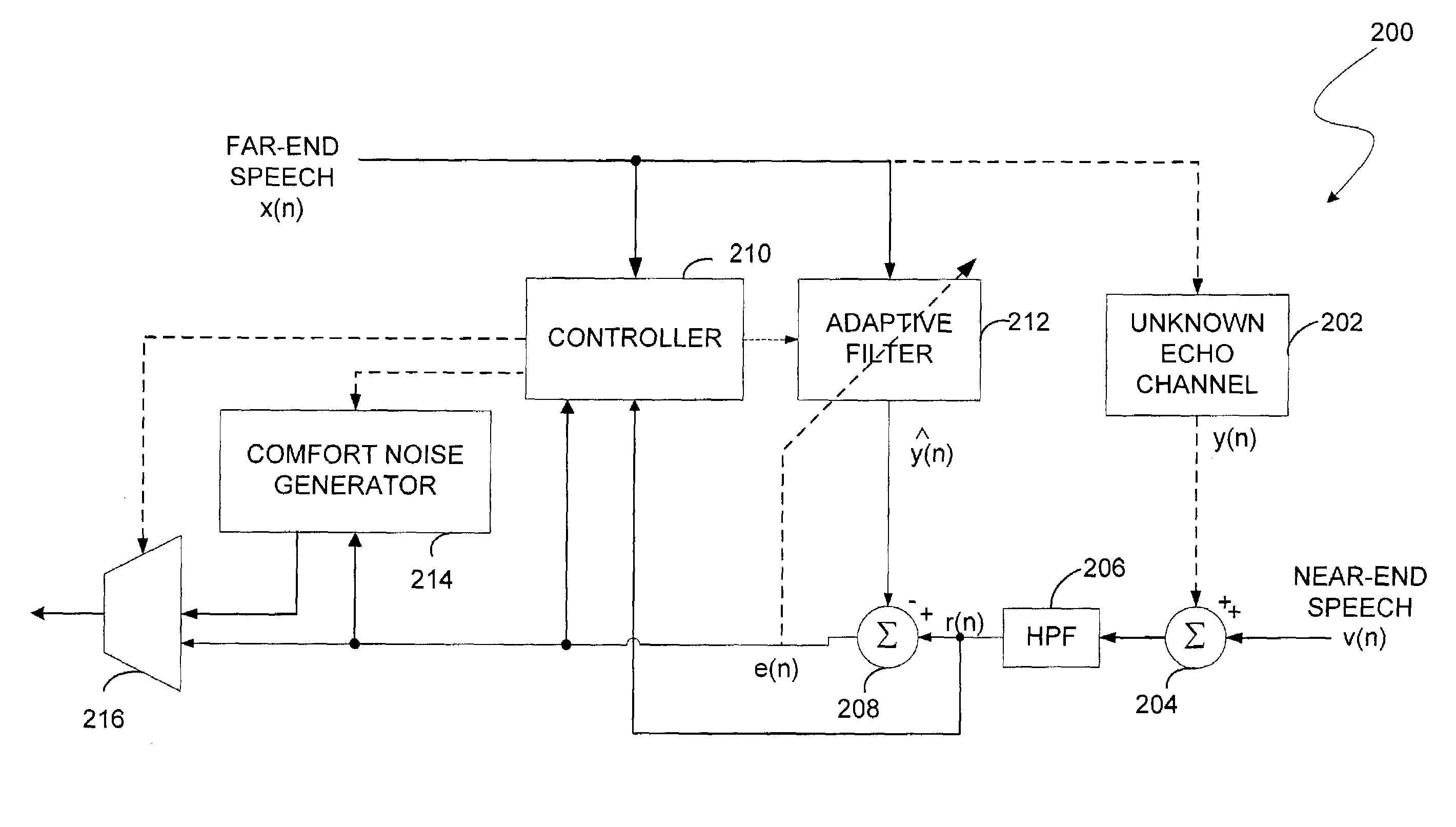
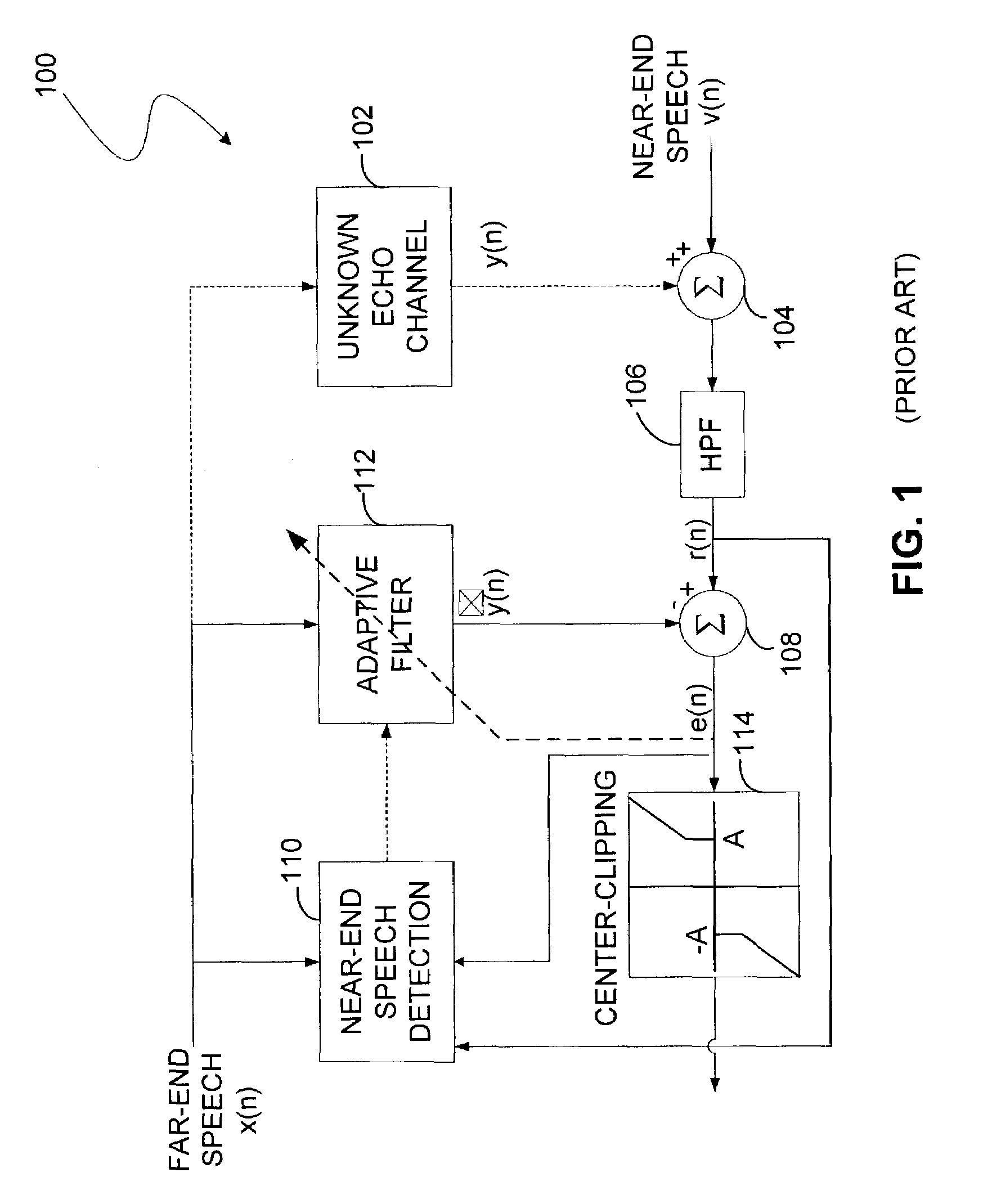
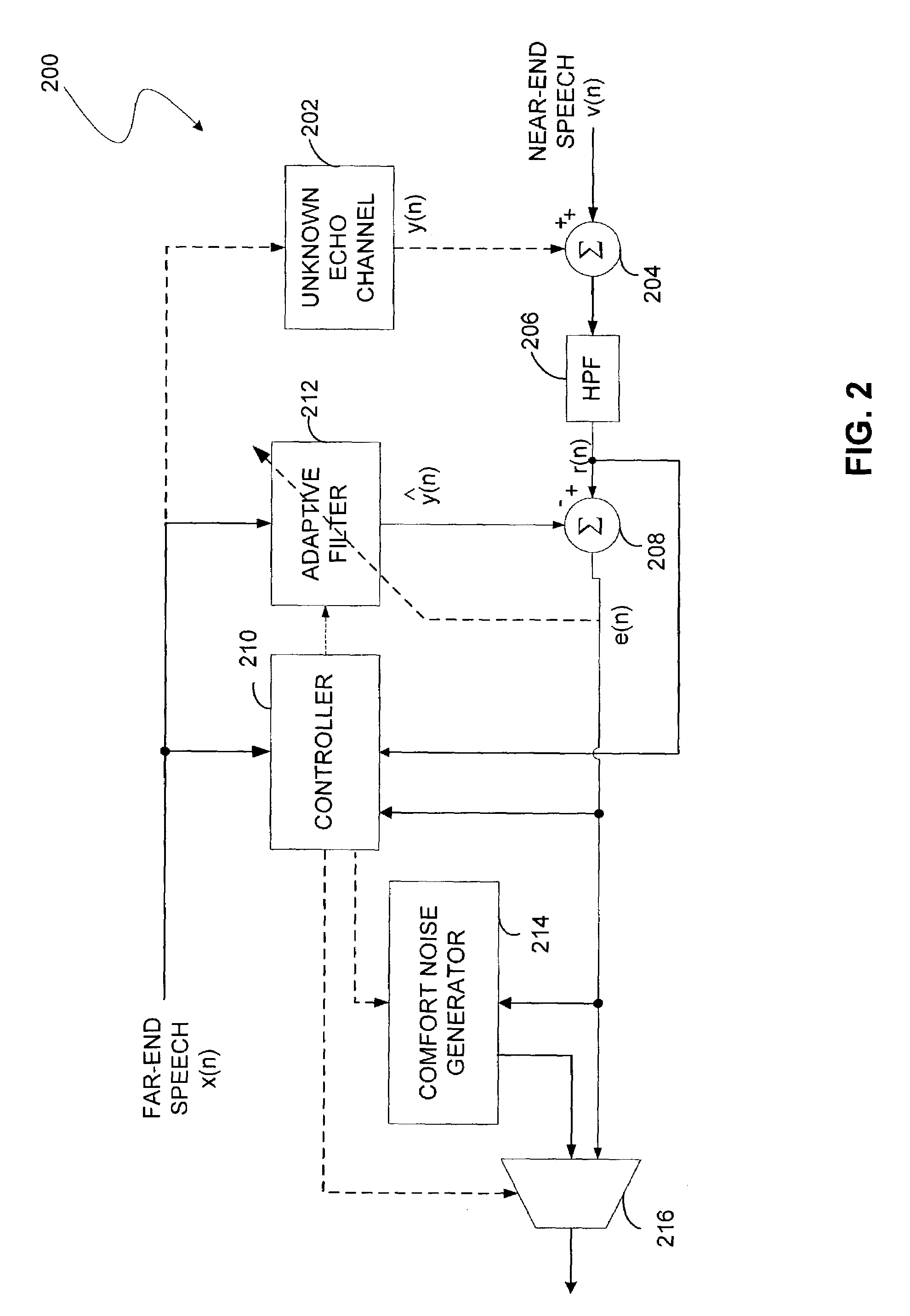
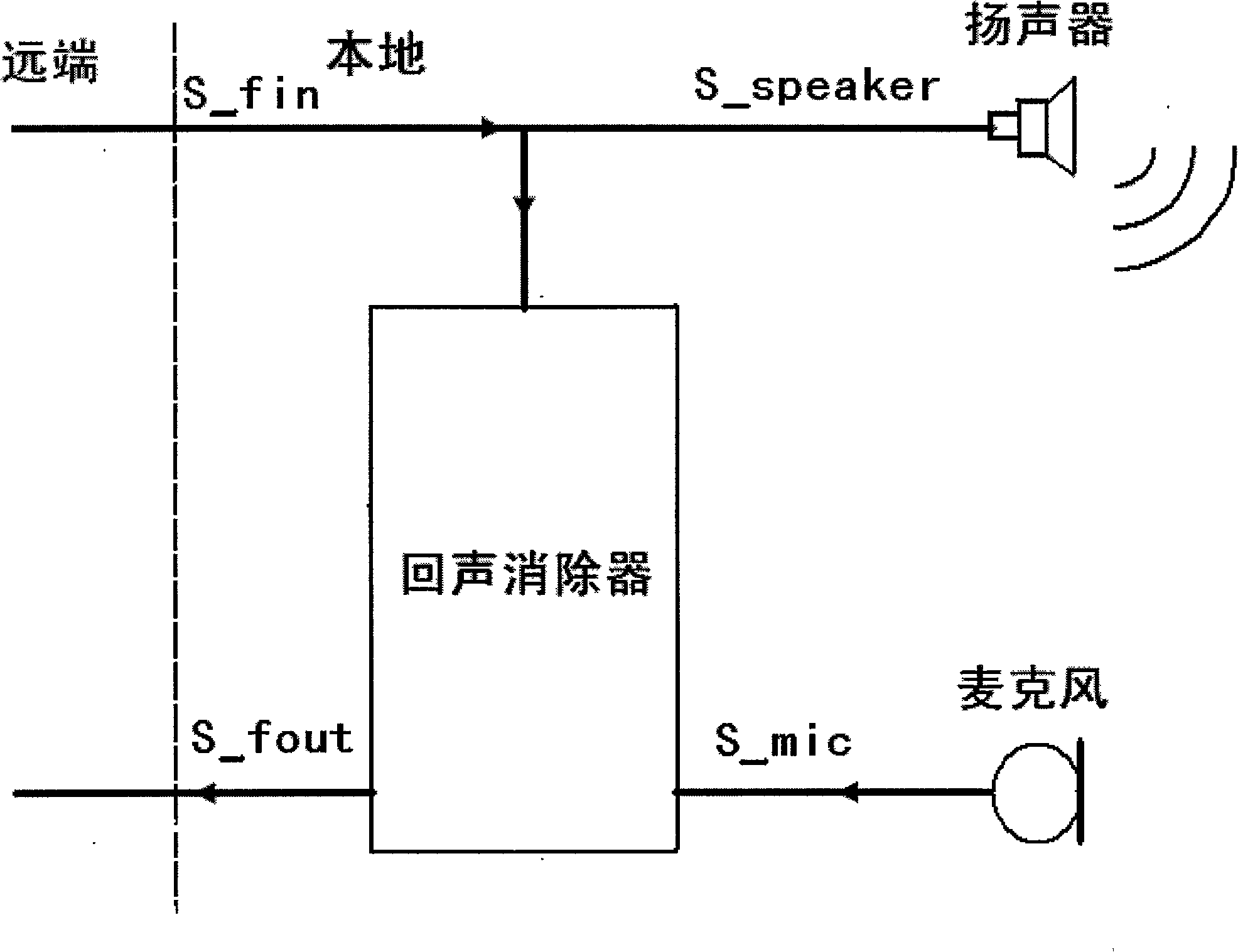
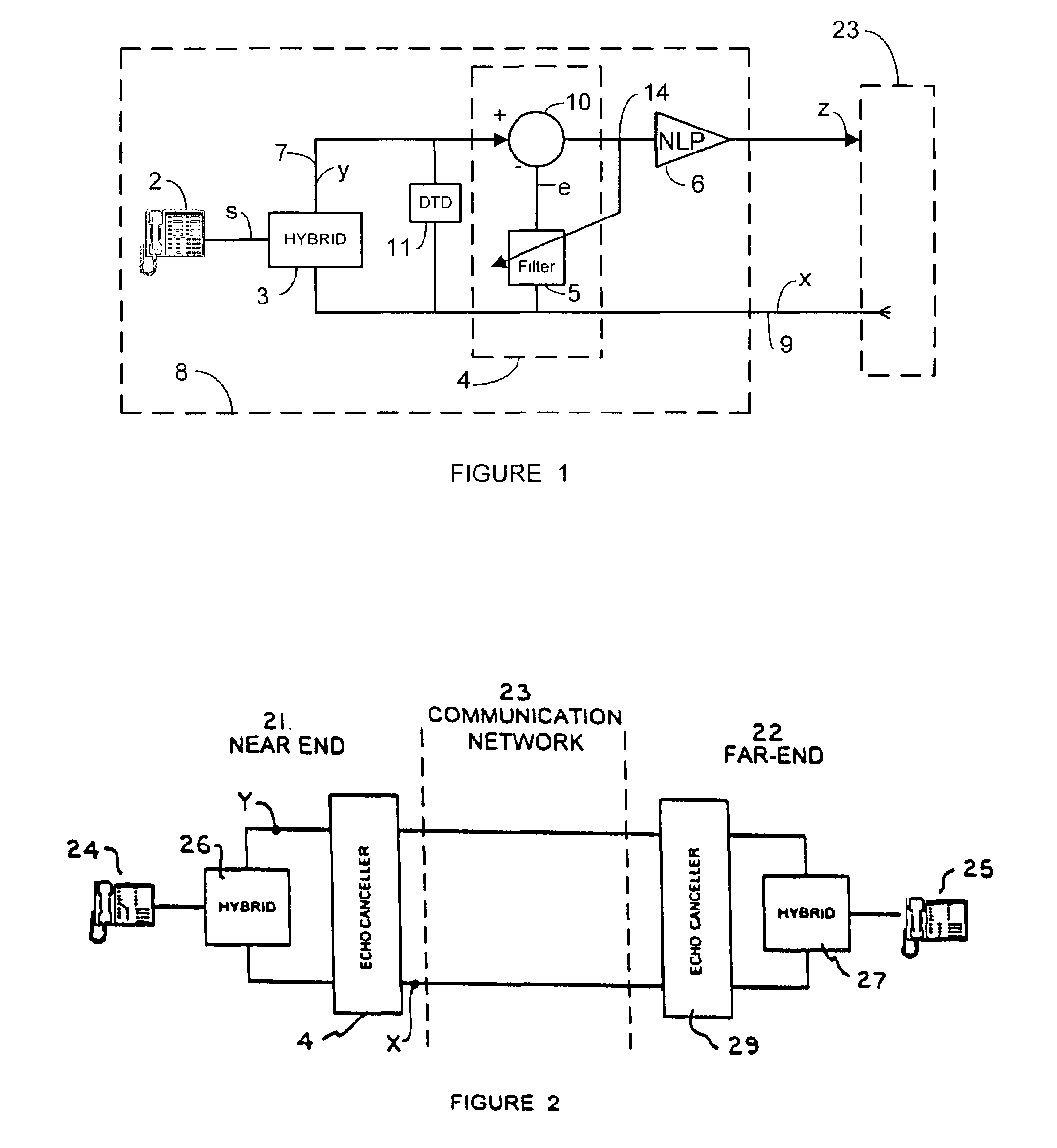
Acoustic echo canceller
InactiveUS7031269B2Limited processing resourceHinder adaptation of filterTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsRadio transmissionComfort noiseProximal point
An apparatus and method for echo cancellation is presented. The echo canceller comprises an adaptive filter that tracks the impulse response of the echo path and produces an estimate of the echo. Filter adaptation is controlled by a controller based on the rate of the far-end speech signal, the rate of the near-end signal, an acoustic loss measure, and a double talk hangover indicator. The controller may also comprise a step size adaptation unit for determining the adaptation step size of the adaptive filter. In addition, the controller may comprise a noise replacement unit, which controls replacement of the echo residual signal with comfort noise to ensure echo is completely rejected when only the far-end speaker is talking.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Technique for bit-accurate comfort noise addition
ActiveUS20070058866A1Reduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComfort noiseCompression artifact
The addition of comfort noise to an image serves to hide compression artifacts. To facilitate comfort noise addition, supplemental information accompanying a video image contains at least one parameter that specifies an attribute regarding comfort noise. Typically, the supplemental information includes parameters that function to turn the comfort noise on and off, as well as to indicate the level of noise to add, based on the expected level of compression artifacts.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
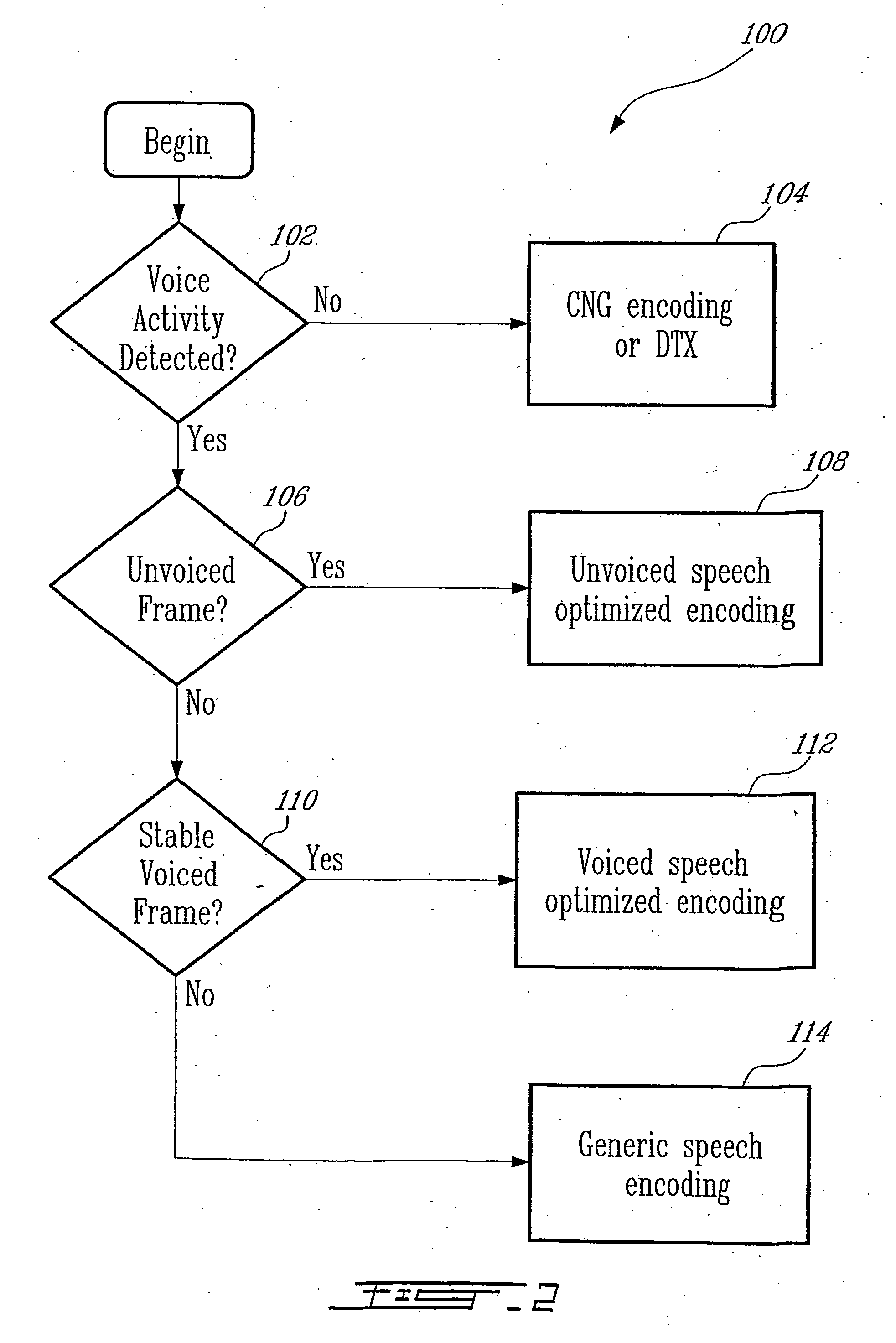
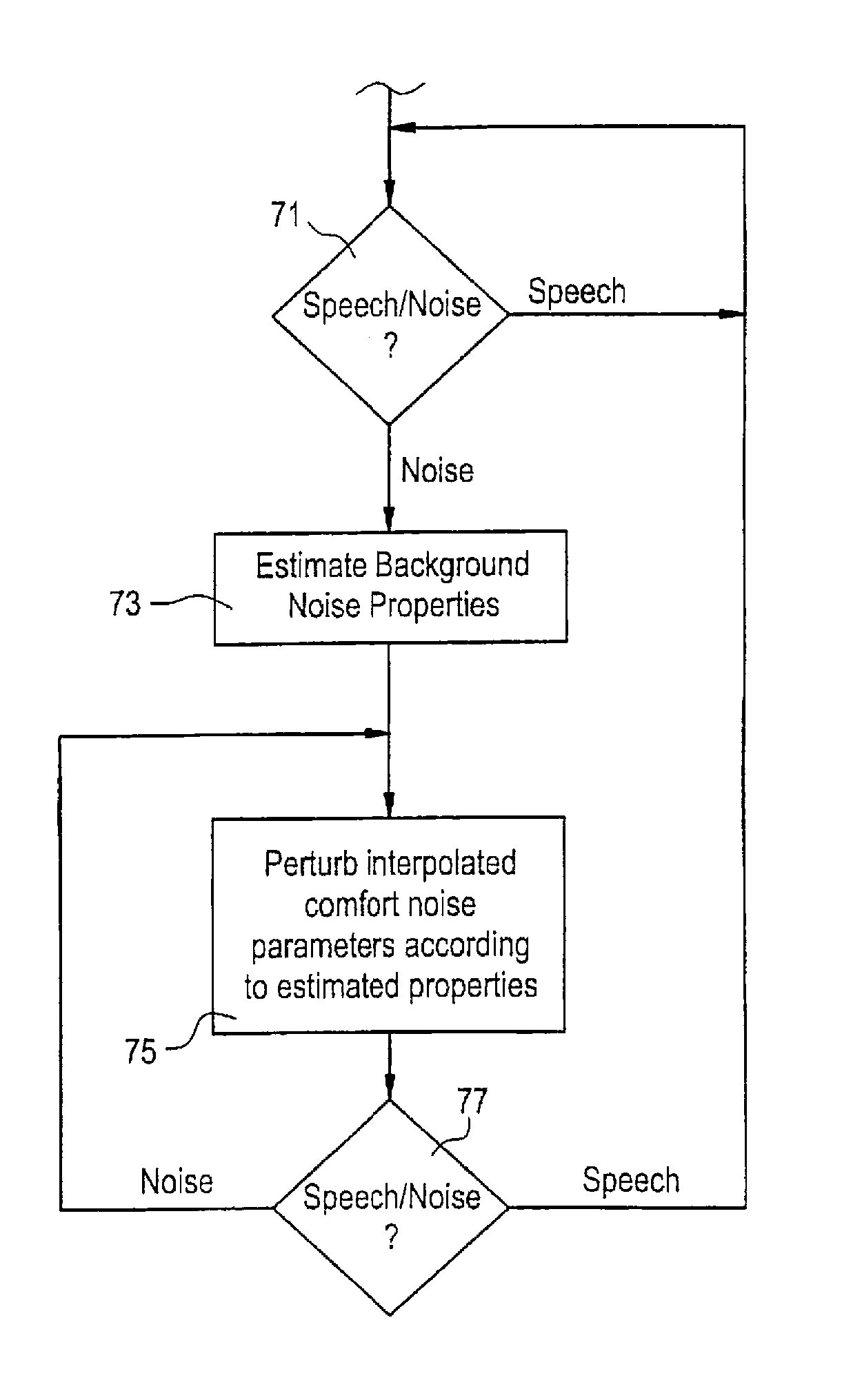
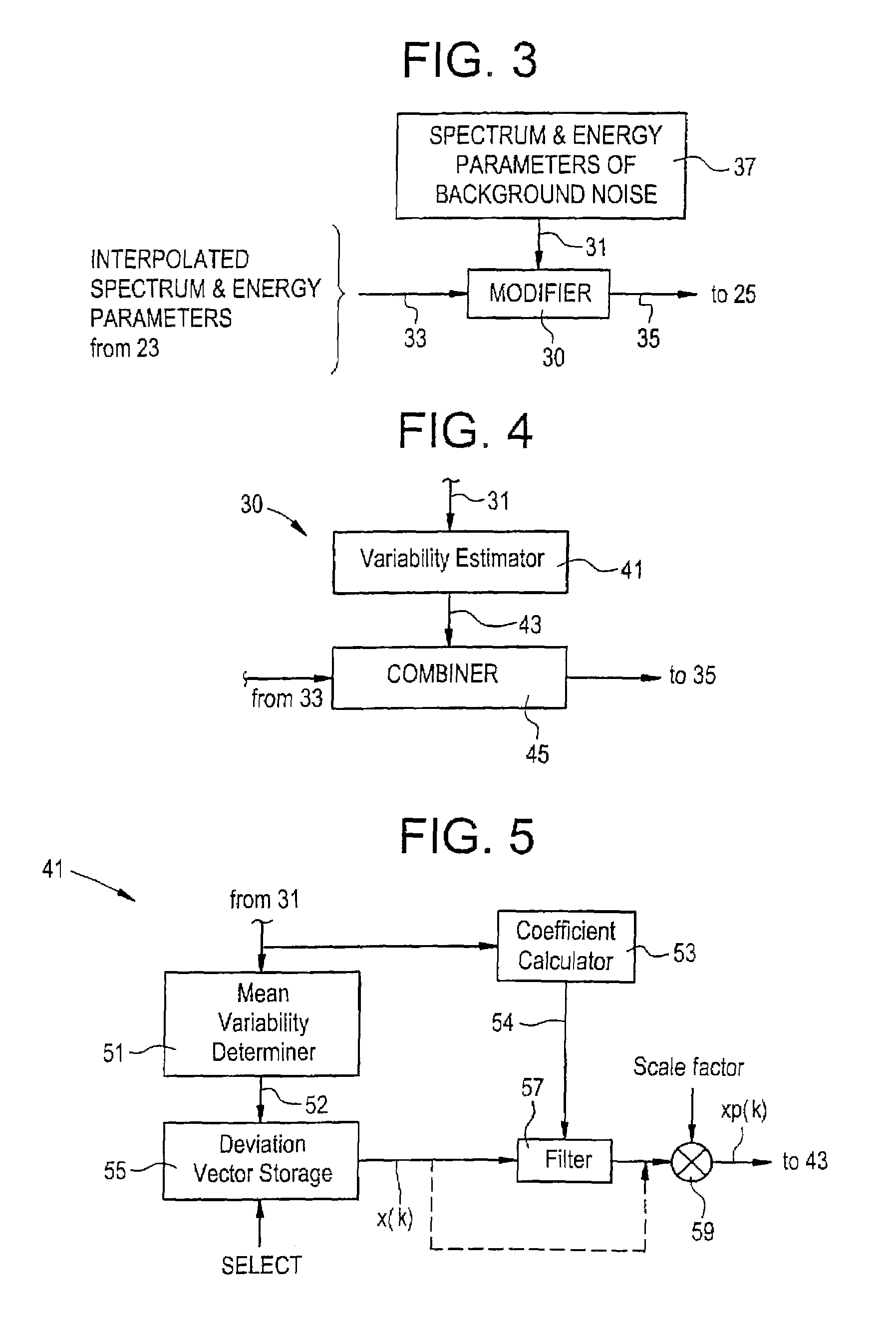
Speech coding with comfort noise variability feature for increased fidelity
The quality of comfort noise generated by a speech decoder during non-speech periods is improved by modifying comfort noise parameter values normally used to generate the comfort noise. The comfort noise parameter values are modified in response to variability information associated with a background noise parameter. The modified comfort noise parameter values are then used to generate the comfort noise.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
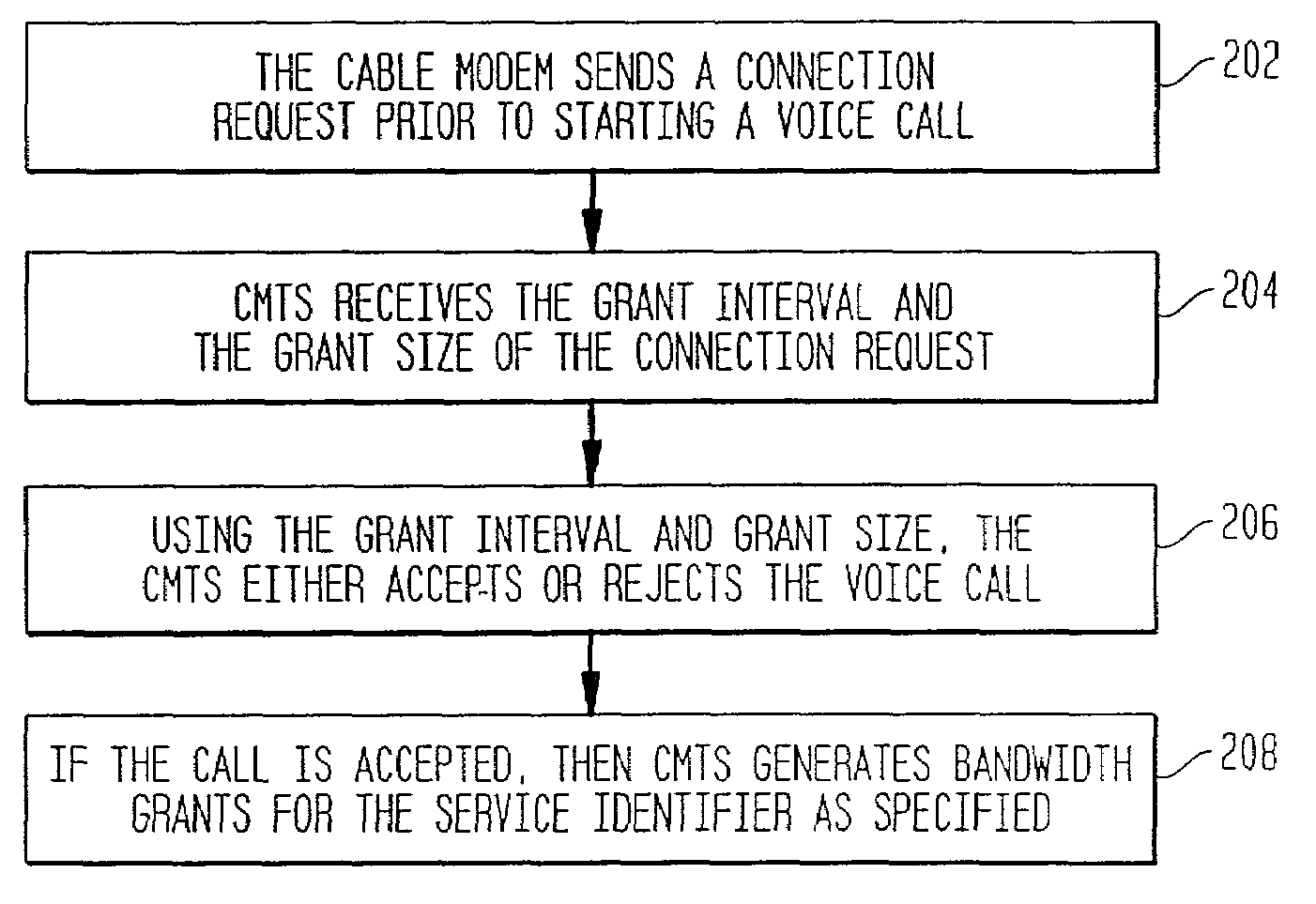
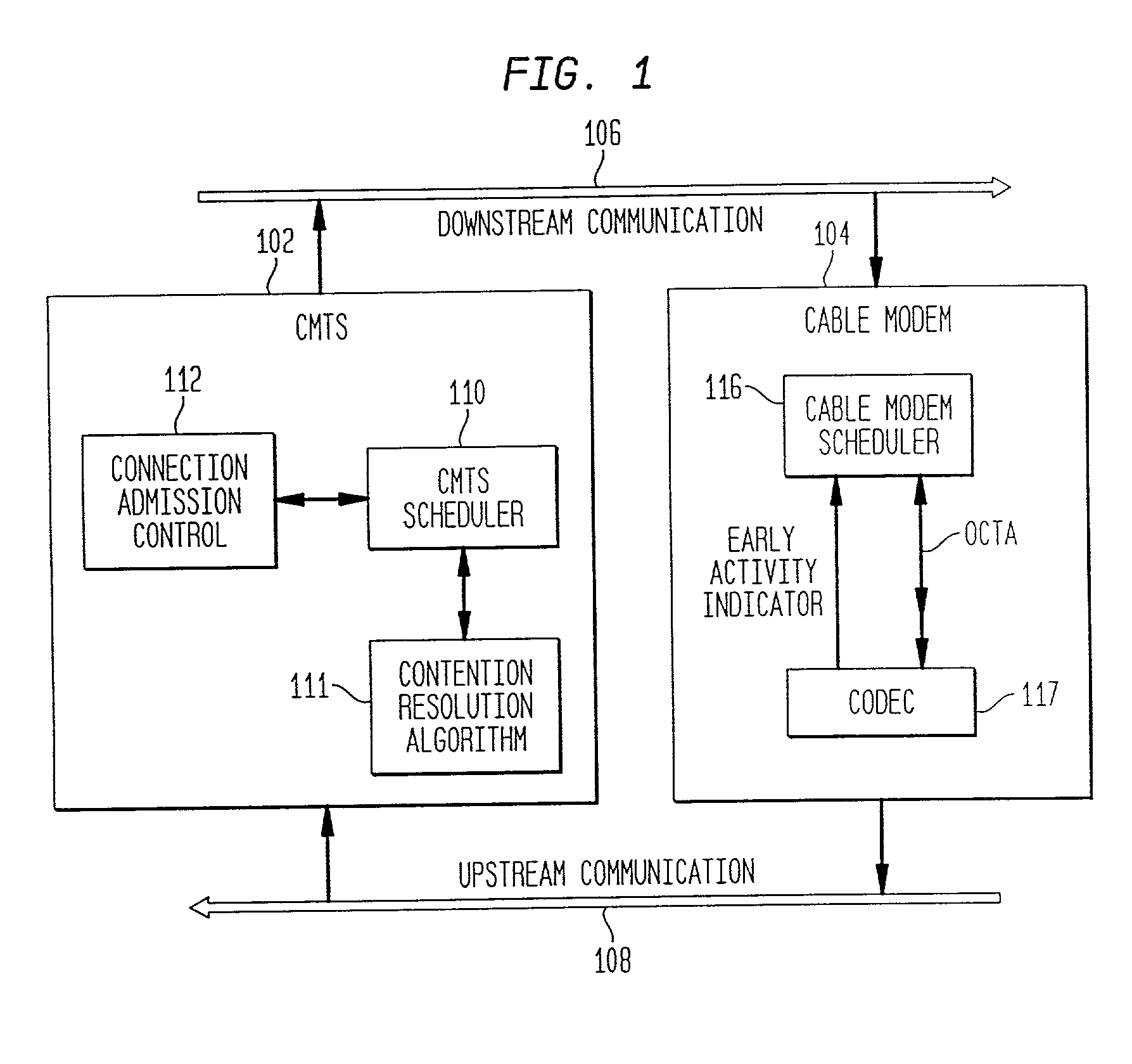
System and method for suppressing silence in voice traffic over an asynchronous communication medium
InactiveUS6993007B2Improve efficiencySignificant bandwidth savingBroadband local area networksNetwork traffic/resource managementComfort noiseAsynchronous communication
A method and system for increasing the efficiency of providing bandwidth for voice traffic to a data provider via asynchronous communication mediums is provided. This is generally accomplished by not transmitting any data during the silence periods and playing out background noise (i.e., comfort noise) at the other end, to obtain significant bandwidth savings.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
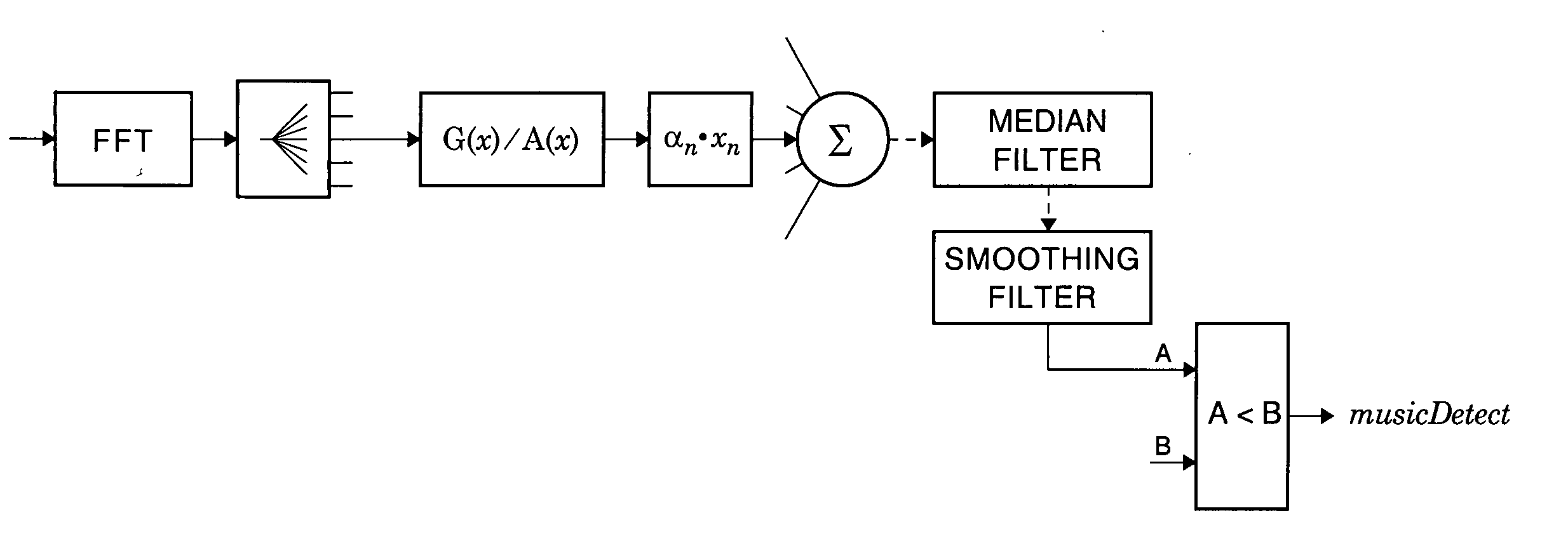
Music detector for echo cancellation and noise reduction
ActiveUS20070136053A1Avoid distortionAvoid noiseElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumComfort noise
An audio signal is divided among exponentially related subband filters. The spectral flatness measure in each subband signal is determined and the measures are weighted and combined. The sum is compared with a threshold to determine the presence of music or noise. If music is detected, the noise estimation process in the noise reduction circuitry is turned off to avoid distorting the signal. If music is detected, residual echo suppression circuitry is also turned off to avoid inserting comfort noise.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
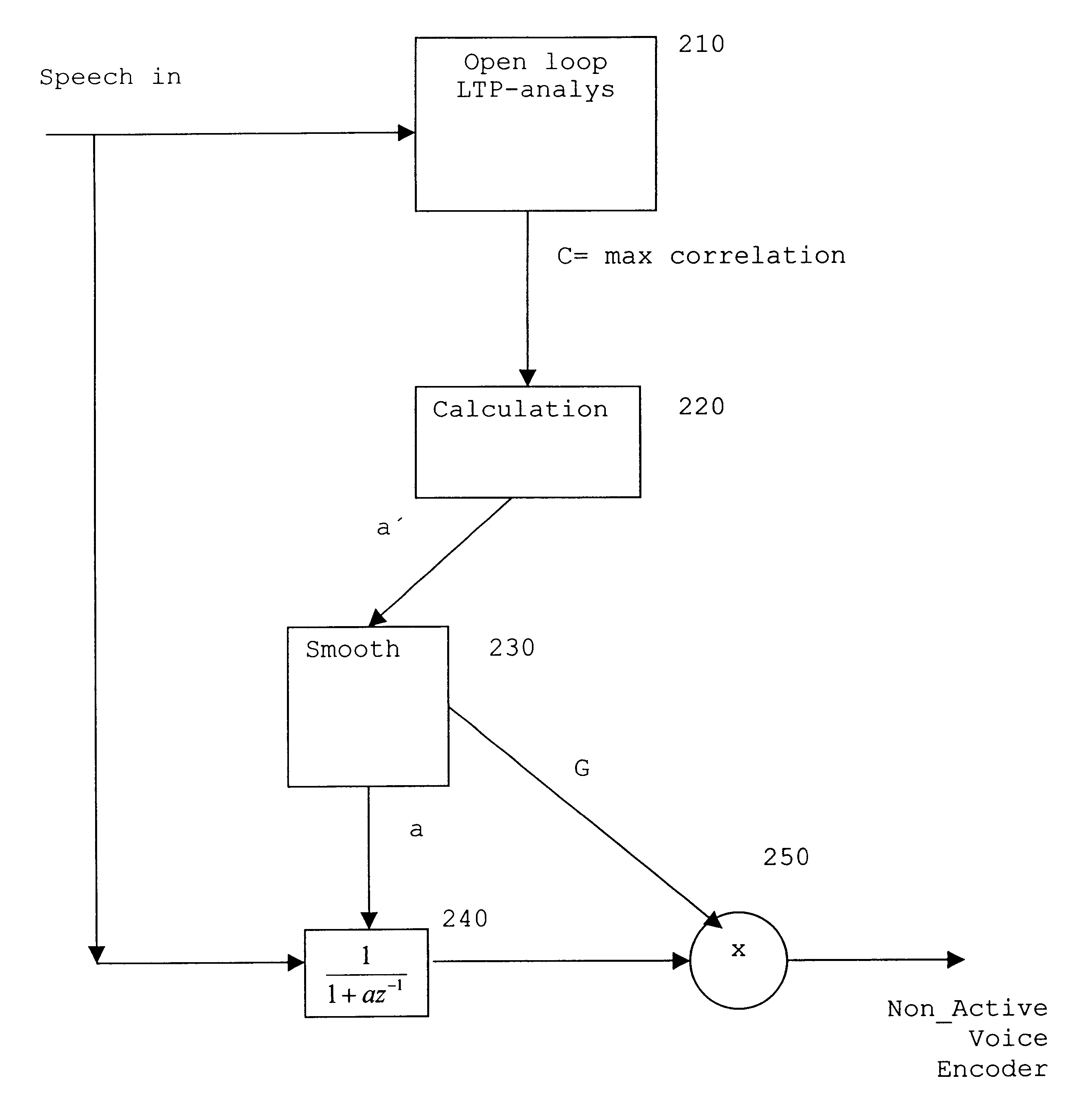
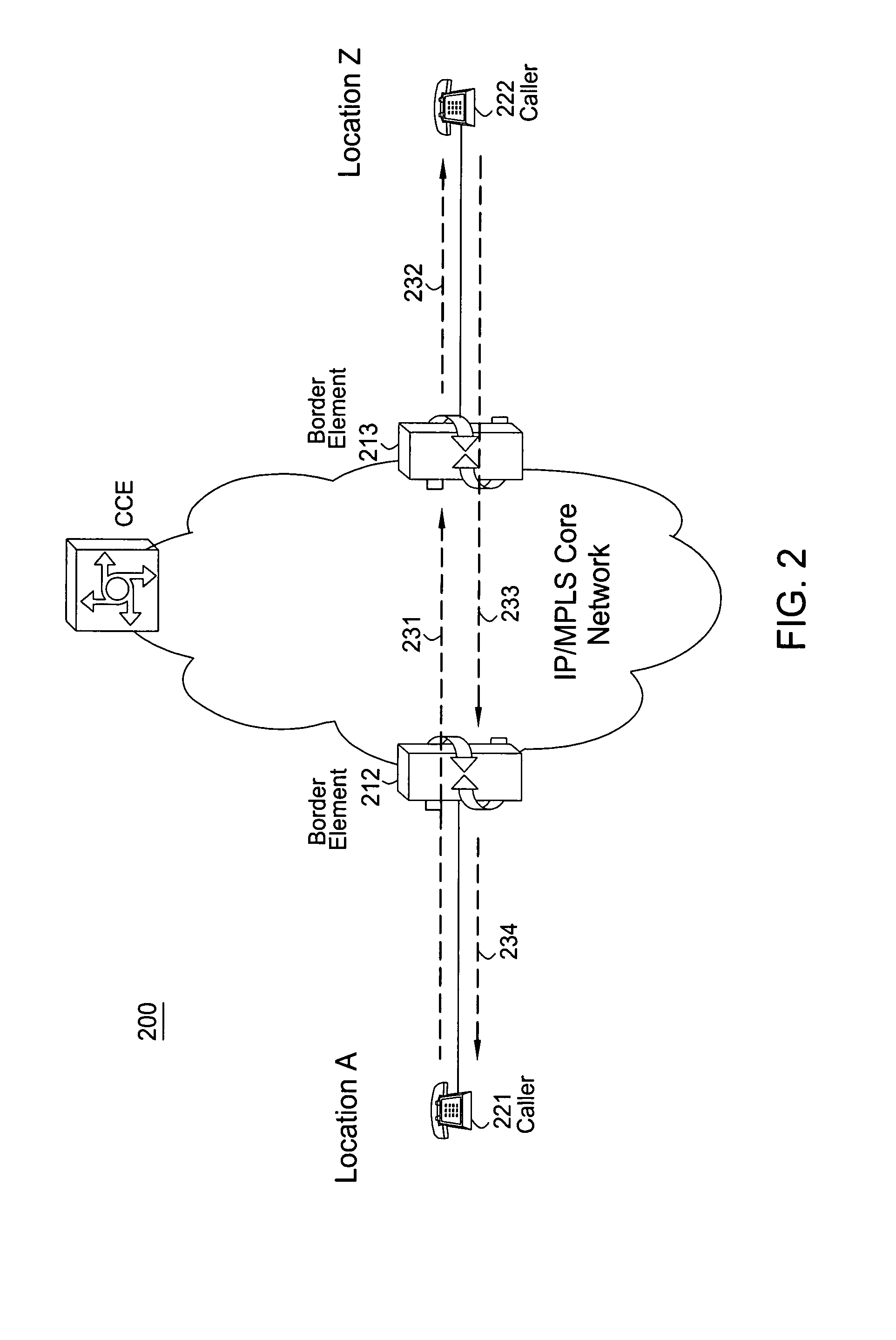
Methods and arrangements in a telecommunications system
InactiveUS6424942B1Quality improvementNo cost in additional bit rateSpeech recognitionTransmissionComfort noiseSpeech sound
A method and arrangement for telecommunication comprises that it is detected (120) whether an incoming signal is speech or background noise, and encoding (100, 110) and transmitting parameters characterising the incoming signal. In or before (103) in the encoding of the background noise, parameters are produced, which represent background noise having increased low frequency components. Thus, the incoming signal can be subjected (103) to a frequency tilting operation. The degree of increasing the low frequency components is determined by the maximum long term correlation of the incoming signal. This method and arrangement provides a better generation of comfort noise, when the input signal comprises low frequency sinusoids, such as engine noise from cars and trams.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
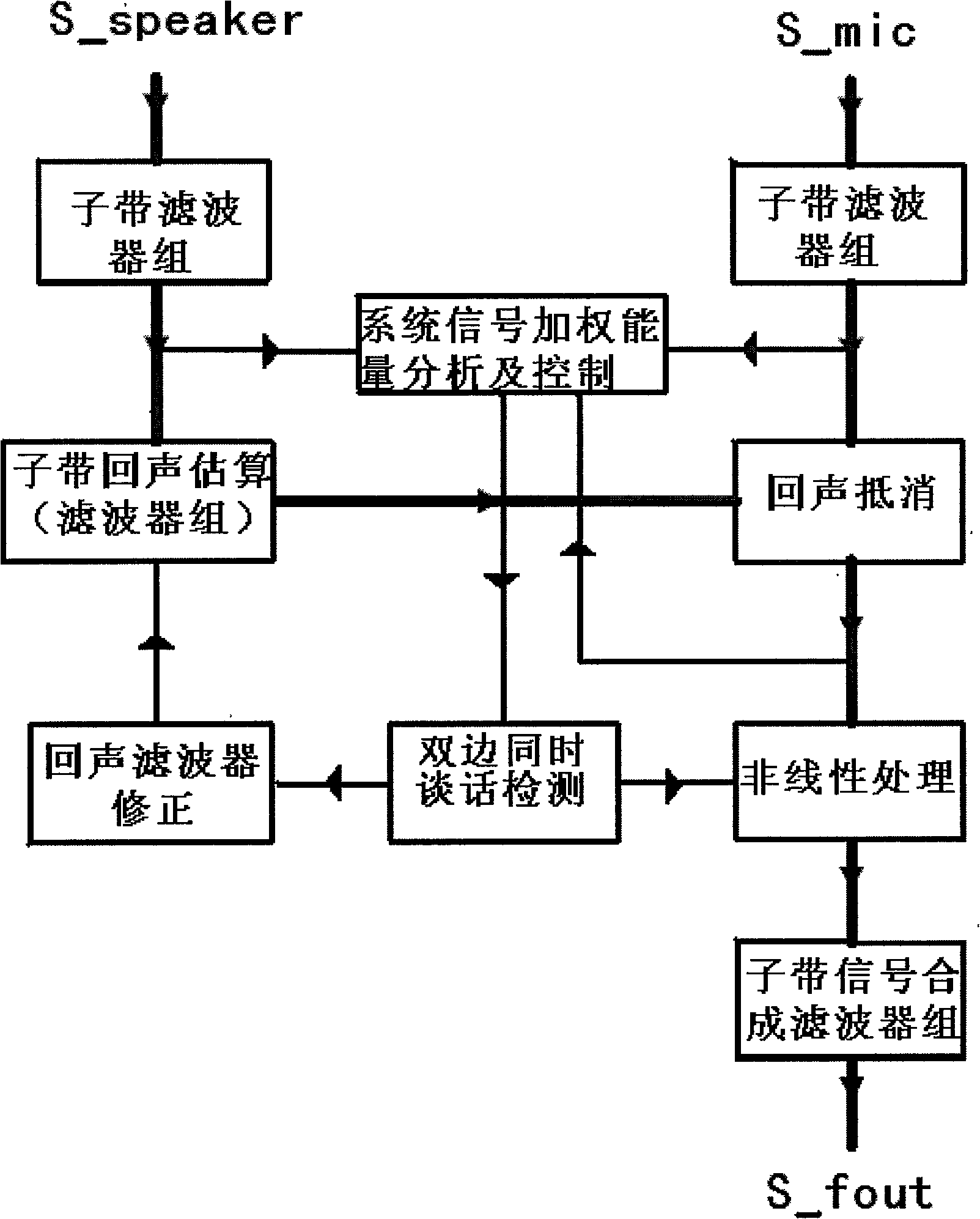
Method of adaptive full duplex full frequency band echo cancellation
ActiveCN101562669AReduce convergence problemsFast convergenceTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFiltrationData treatment
A method of adaptive full duplex full frequency band echo cancellation comprises the following steps of: carrying out filtration by a sub-band filter, carrying out sub-band echo cancellation by a sub-band echo canceller, carrying out weighted energy analysis and control on system signals, carrying out analysis and detection on double talk active state, carrying out coefficient updating on an echo filter, carrying out nonlinear processing on residual echo, and carrying out synthesis on signals of sub-bands. The method further comprises the step of maintaining reference signal and echo signal to be synchronous; after the nonlinear processing is carried out, noise reduction, automatic gain control and comfort noise technique can be added. Owing to adoption of the method of echo cancellation, signals are spilt into sub-bands through filtration, thus reducing correlation among signals of sub-bands, improving convergence problem of adaptive filter, reducing data process load of the system, improving processing efficiency of echo cancellation, realizing full duplex of conversation, improving frequency response of communication audio frequency, improving quality of communication and realizing echo cancellation of full frequency band response.
Owner:南京朗逸锐科电子科技有限公司
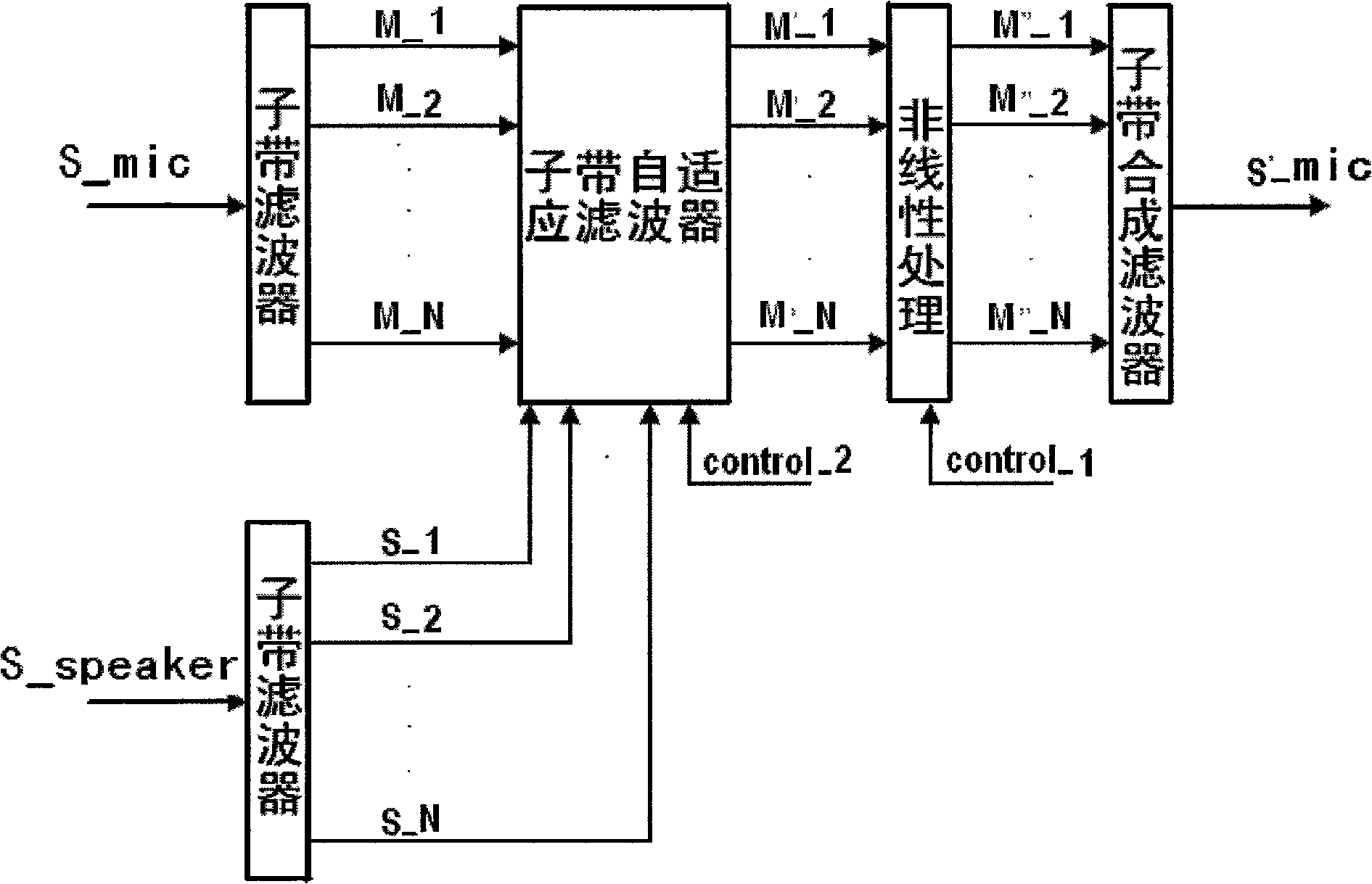
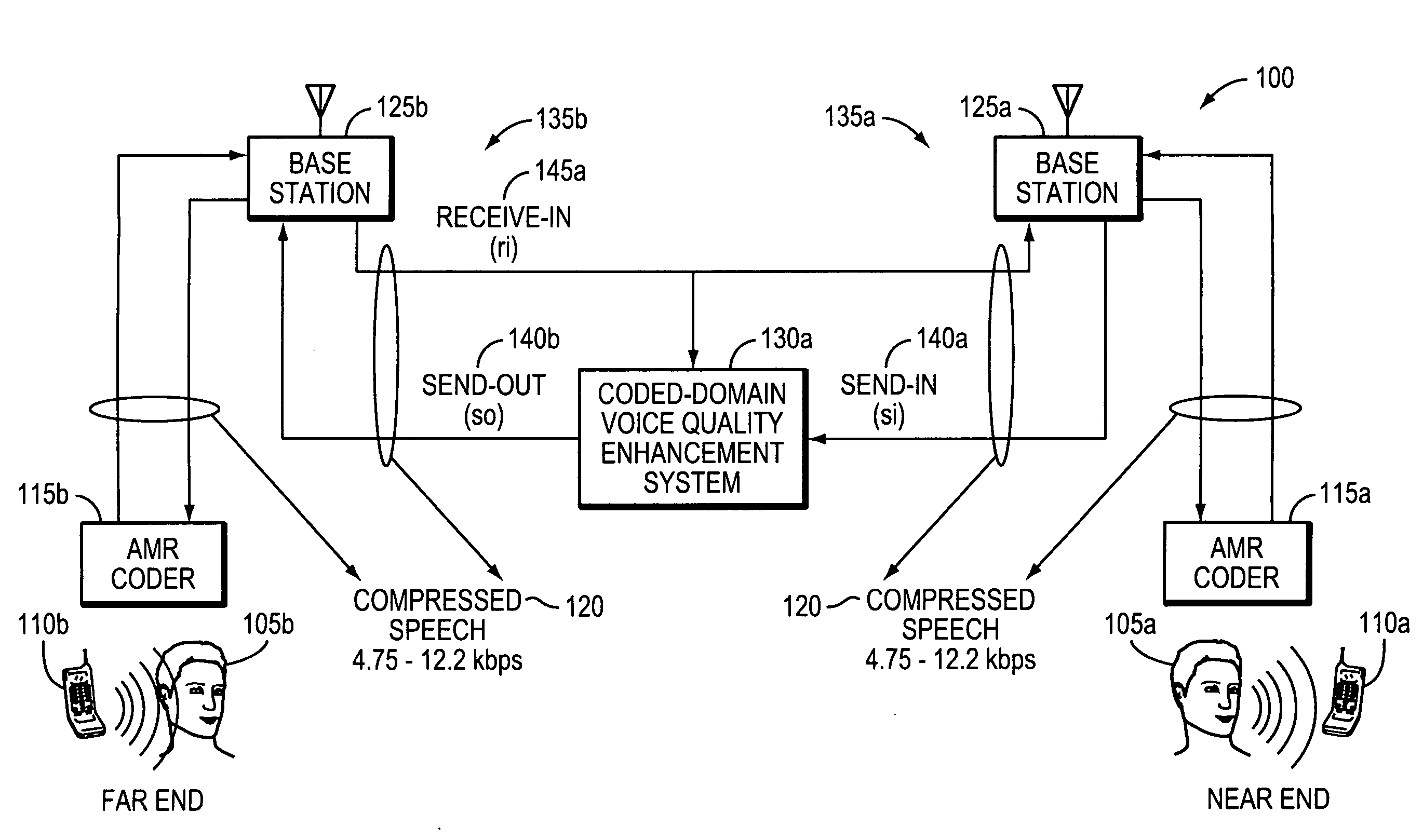
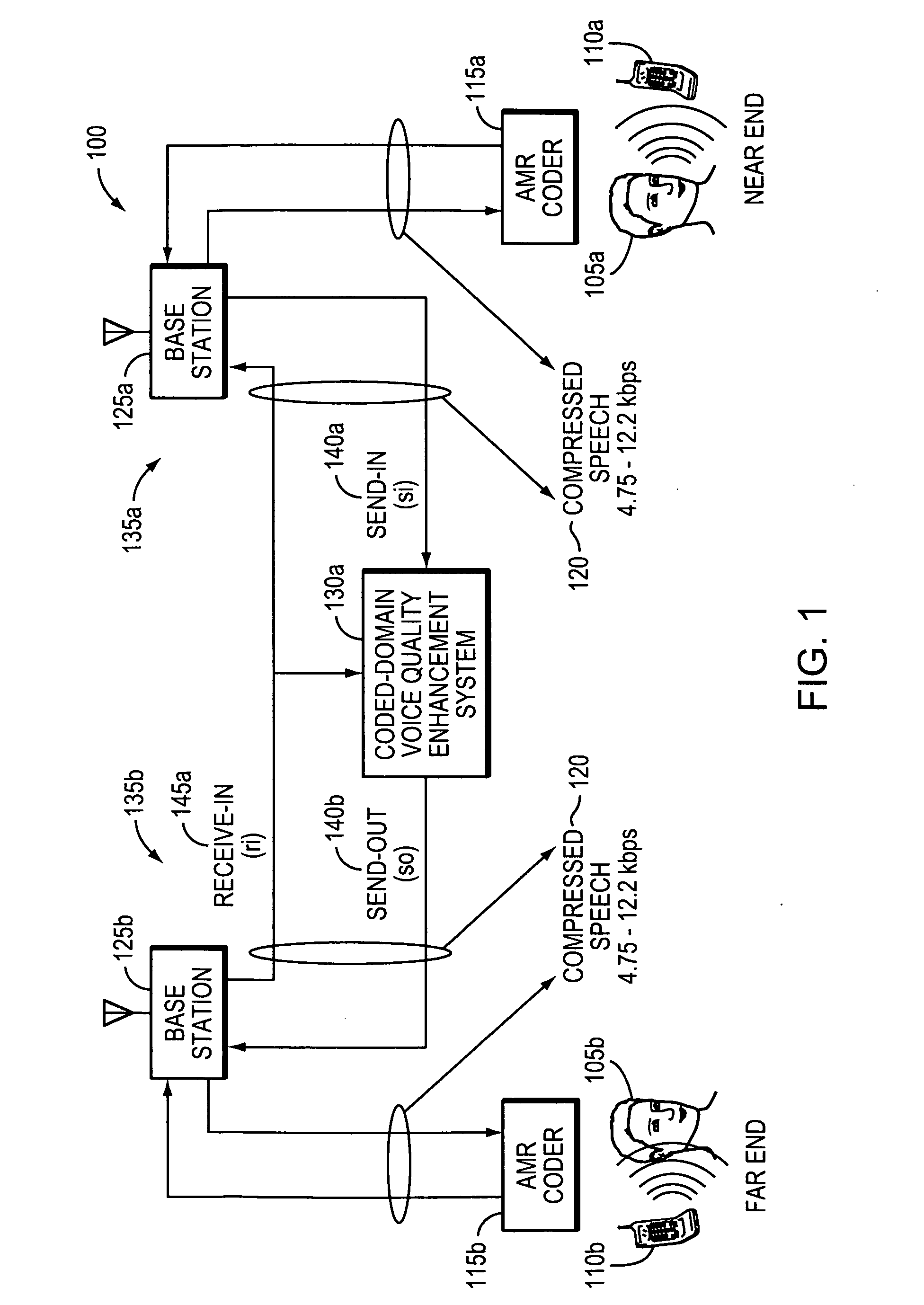
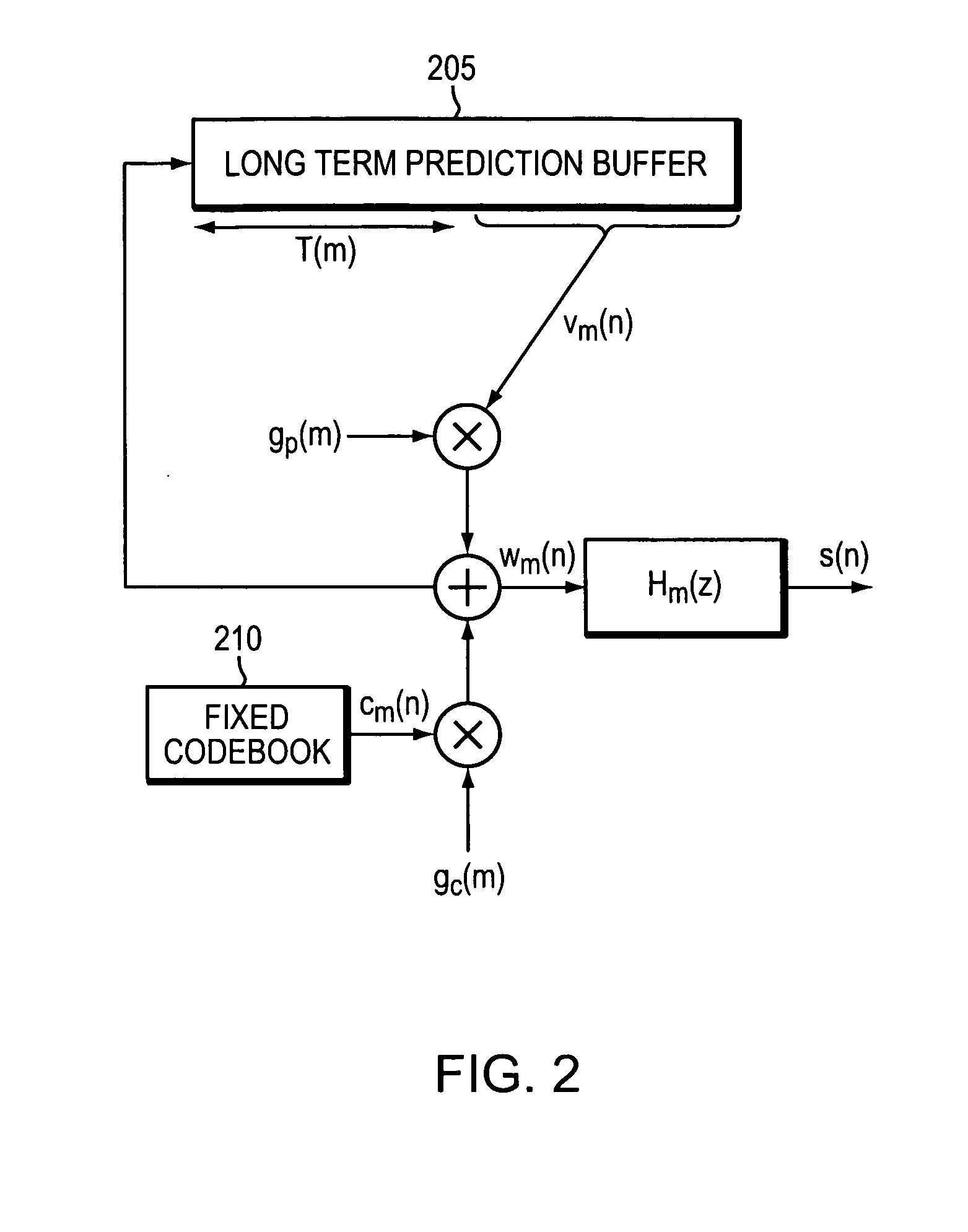
Method and apparatus for controlling echo in the coded domain
InactiveUS20090063142A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsEar treatmentComfort noiseFrequency spectrum
A method and corresponding apparatus for coded-domain acoustic echo control is presented. An echo control problem is considered as that of perceptually matching an echo signal to a reference signal. A perceptual similarity function that is based on the coded spectral parameters produced by the speech codec is defined. Since codecs introduce a significant degree of non-linearity into the echo signal, the similarity function is designed to be robust against such effects. The similarity function is incorporated into a coded-domain echo control system that also includes spectrally-matched noise injection for replacing echo frames with comfort noise. Using actual echoes recorded over a commercial mobile network, it is shown herein that the similarity function is robust against both codec non-linearities and additive noise. Experimental results further show that the echo-control is effective at suppressing echoes compared to a Normalized Least Mean Squared (NLMS)-based echo cancellation system.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Decoding method, speech coding processing unit and a network element
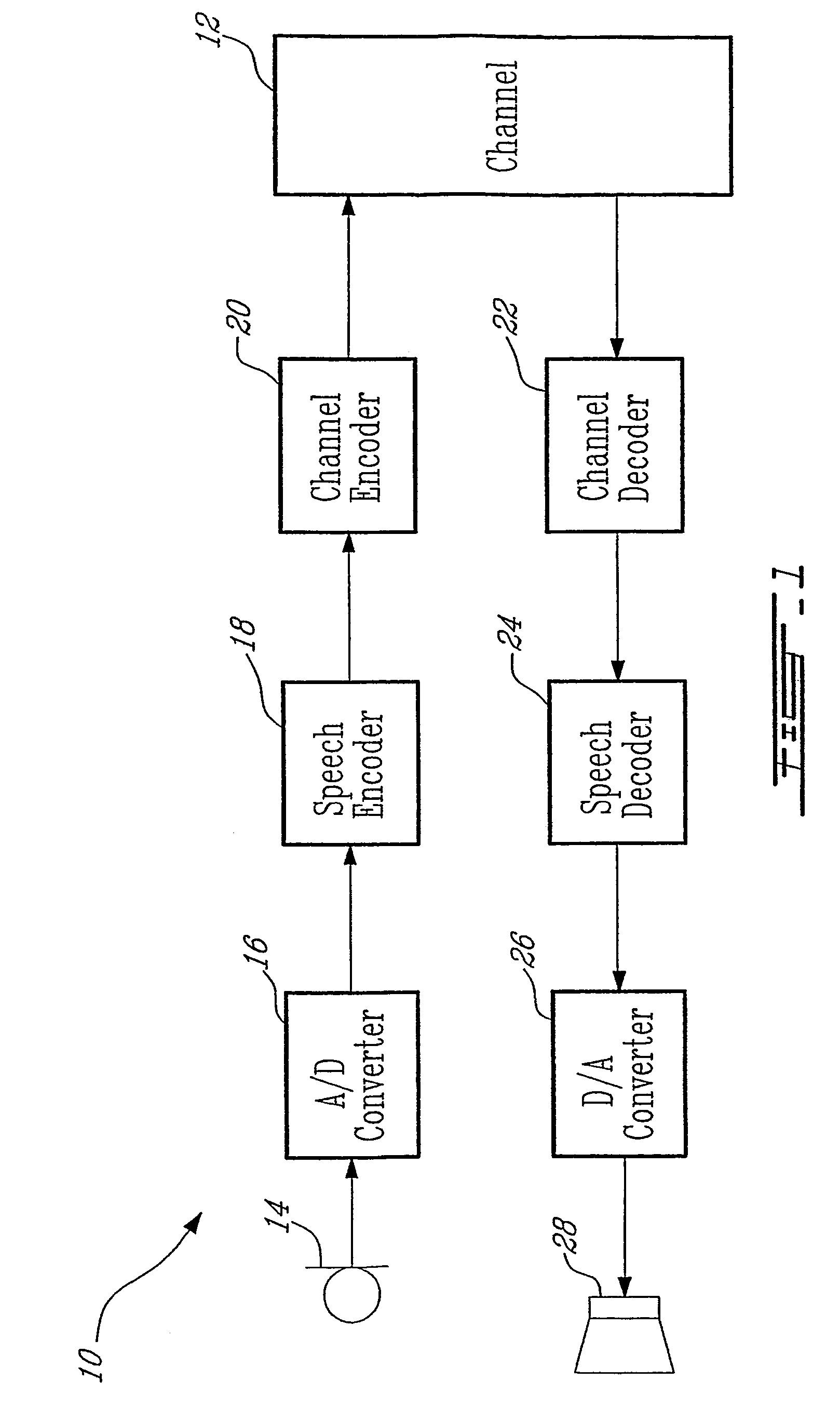
InactiveUS6850883B1Speech analysisRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDecoding methodsComfort noise
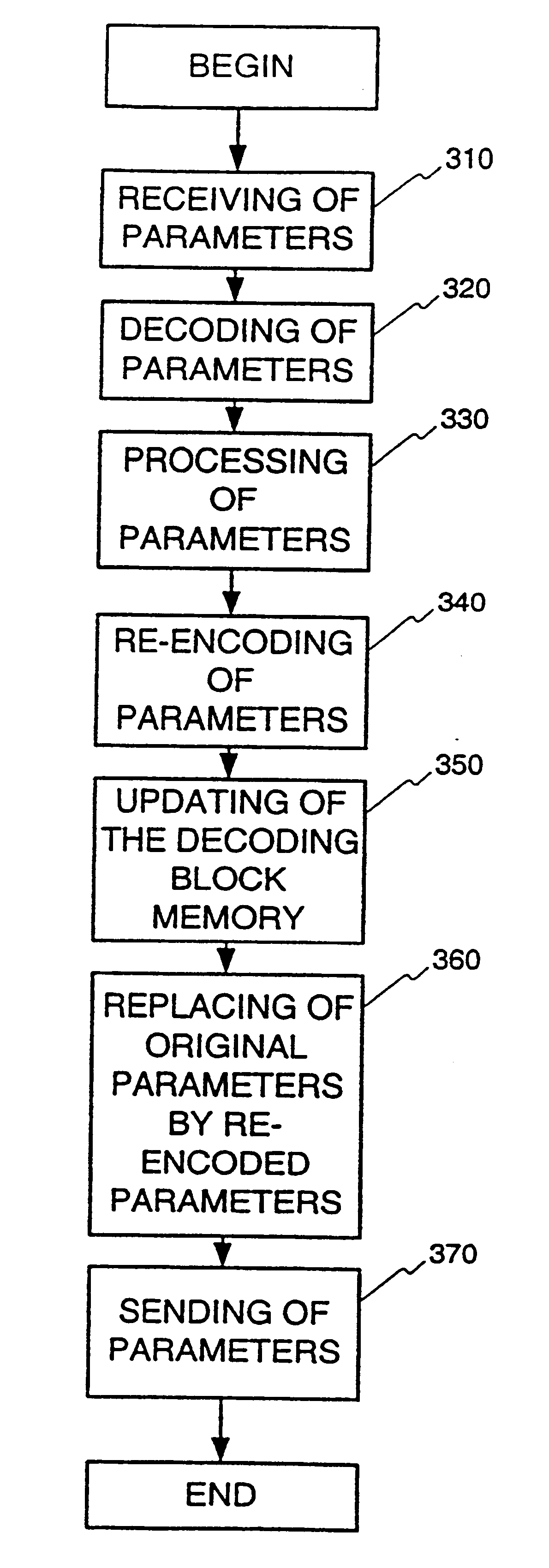
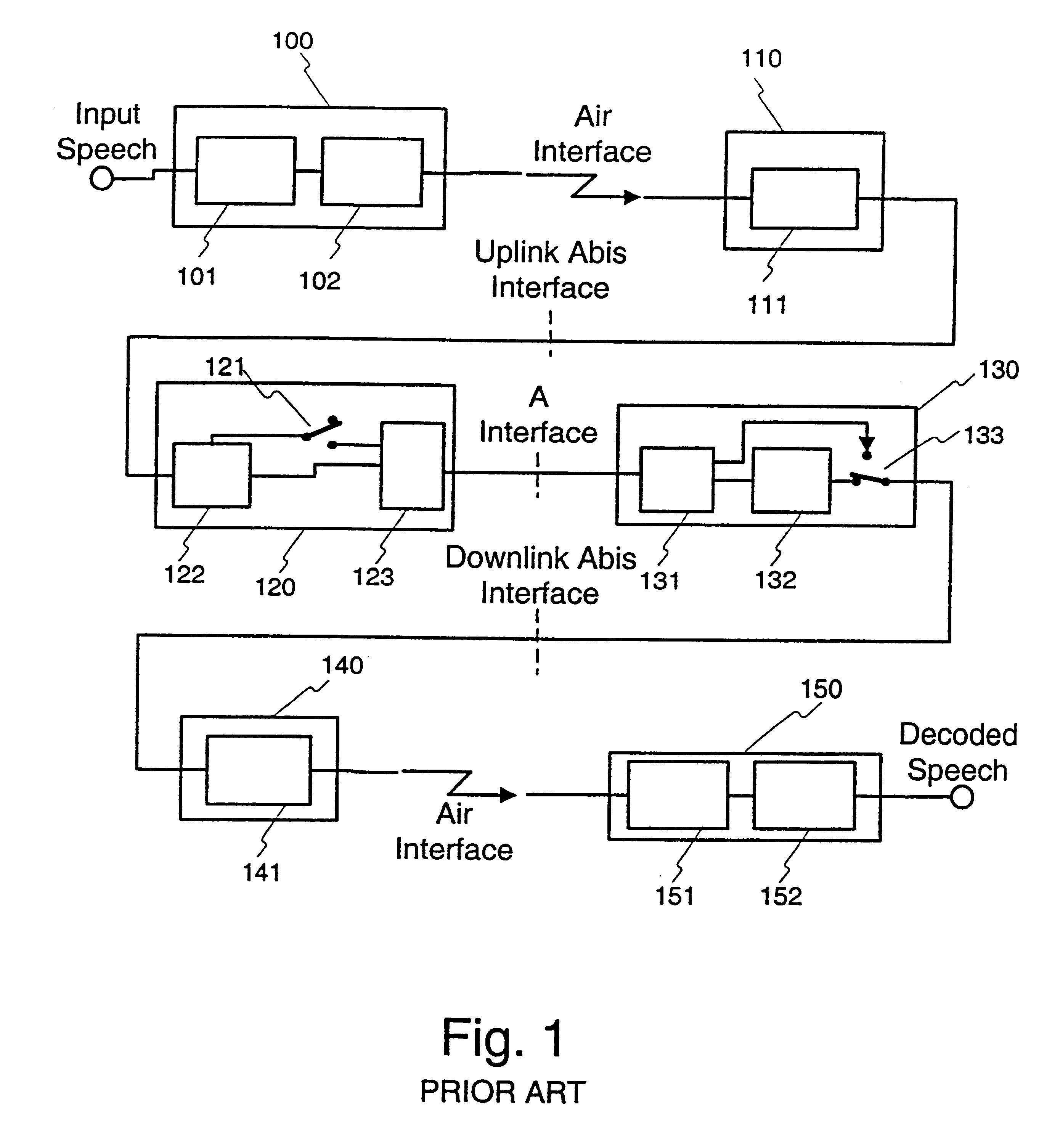
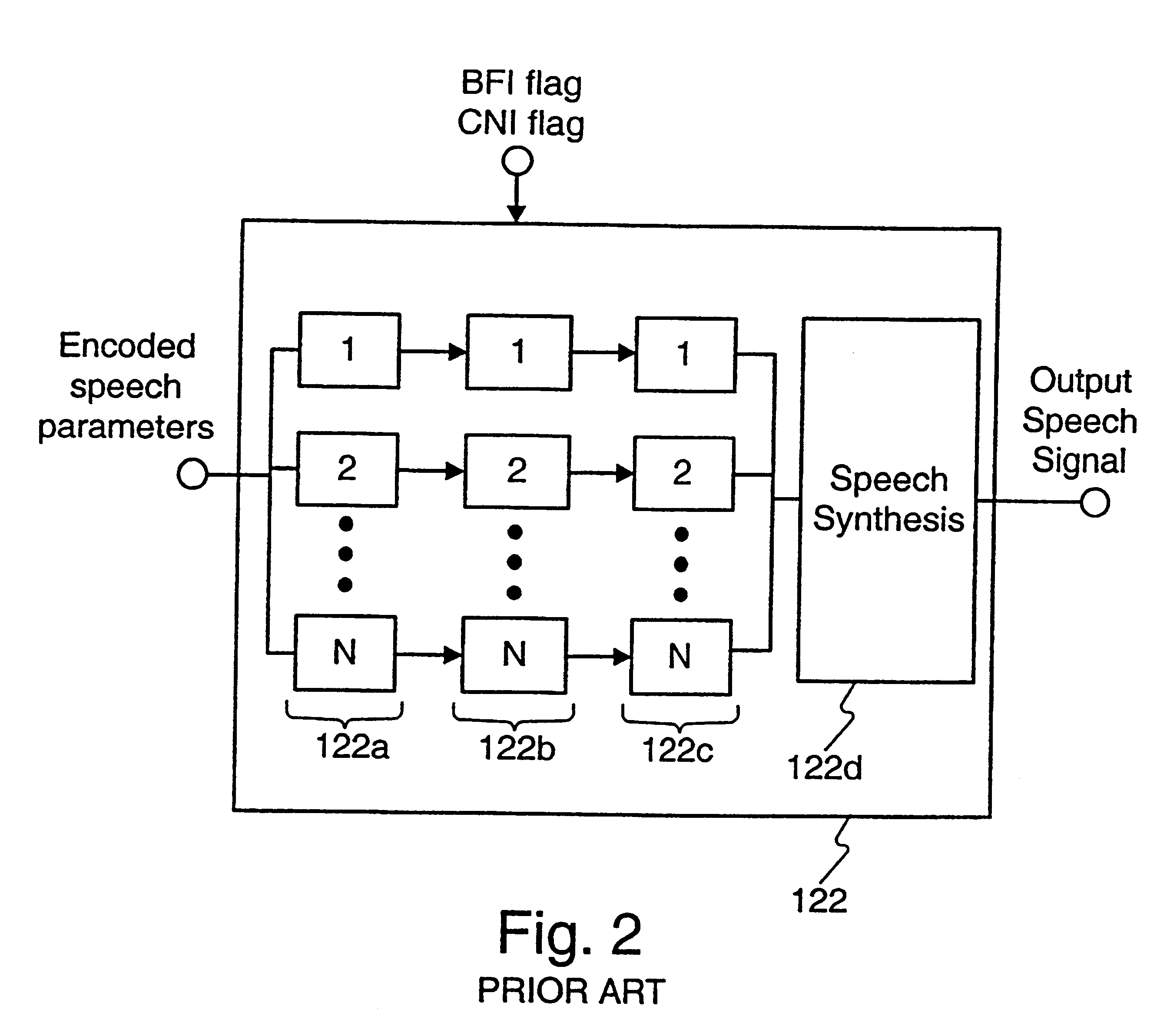
This invention is related to tandem free operation (TFO) in mobile cellular systems. The present invention implements a tandem free operation by using a special feedback loop which makes the decoded parameters available, performs the comfort noise insertion and bad frame handling operations, produces the parameter quantisation indices corresponding to the output of these operations, and synchronises the speech encoders and the speech decoders in the transmission path from the uplink mobile station to the downlink mobile station. This functionality is realized by partly decoding and re-encoding the parameters and synchronising and resetting the quantiser prediction memories in a specific manner. A basic idea of the invention is, that during BFH and CNI processes, a re-encoding block produces models of encoded speech parameters from the BFH / CNI processed speech parameters. These models of encoded speech parameters are then transmitted to the receiving end. The present invention provides a solution to the problem created by predictive, more generally non-stateless encoders in TFO operation.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for masking of video artifacts and/or insertion of film grain in a video decoder
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Technique for bit-accurate comfort noise addition
The addition of comfort noise to an image serves to hide compression artifacts. To facilitate comfort noise addition, supplemental information accompanying a video image contains at least one parameter that specifies an attribute regarding comfort noise. Typically, the supplemental information includes parameters that function to turn the comfort noise on and off, as well as to indicate the level of noise to add, based on the expected level of compression artifacts.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Comfort noise generator using modified Doblinger noise estimate
ActiveUS7649988B2Slow constantSuppression amountTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisFourier transform on finite groupsEngineering
A background noise estimate based upon a modified Doblinger noise estimate is used for modulating the output of a pseudo-random phase spectrum generator to produce the comfort noise. The circuit for estimating noise includes a smoothing filter having a slower time constant for updating the noise estimate during noise than during speech. Comfort noise is smoothly inserted by basing the amount of comfort noise on the amount of noise suppression. A discrete inverse Fourier transform converts the comfort noise back to the time domain and overlapping windows eliminate artifacts that may have been produced during processing.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
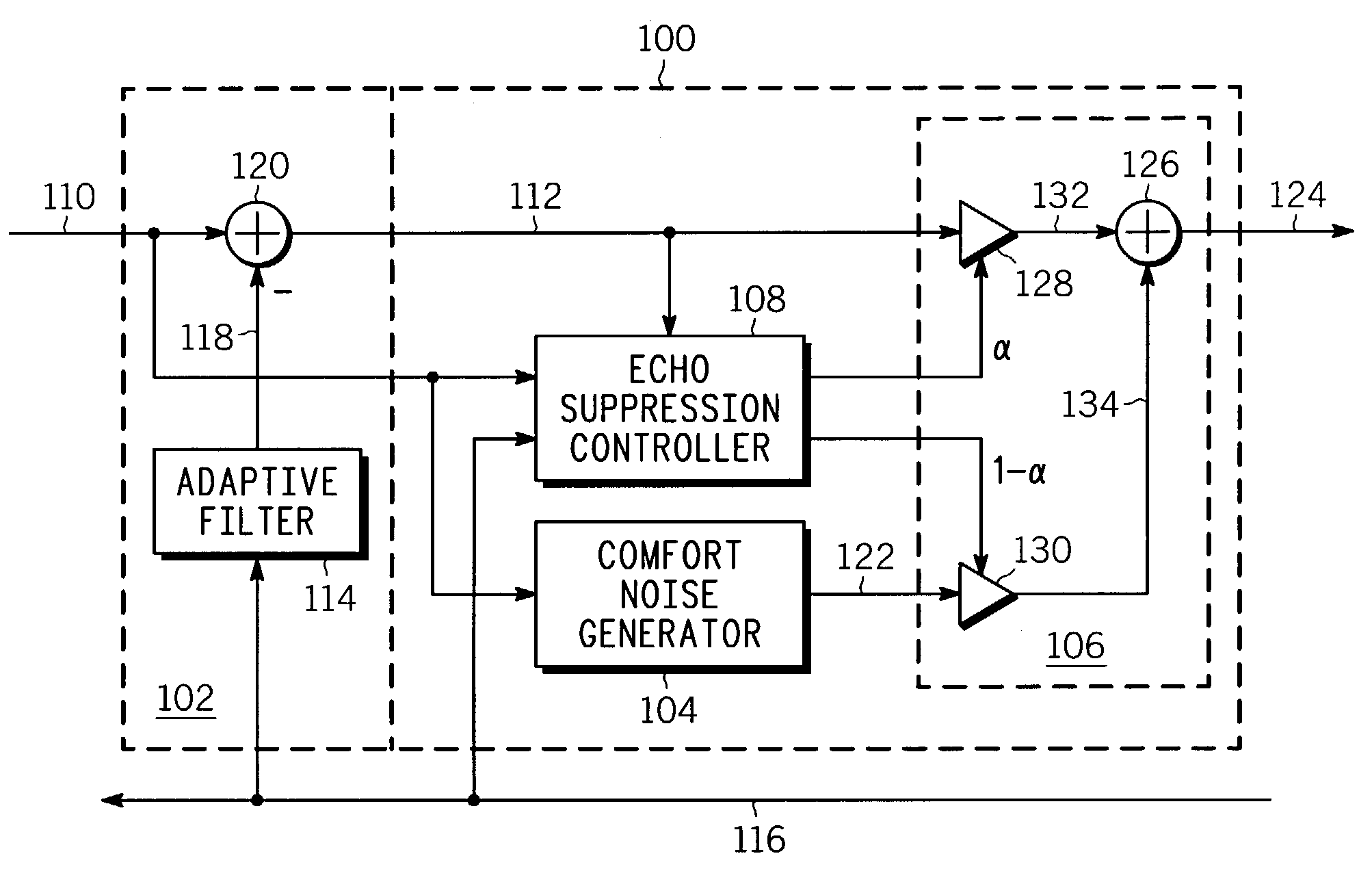
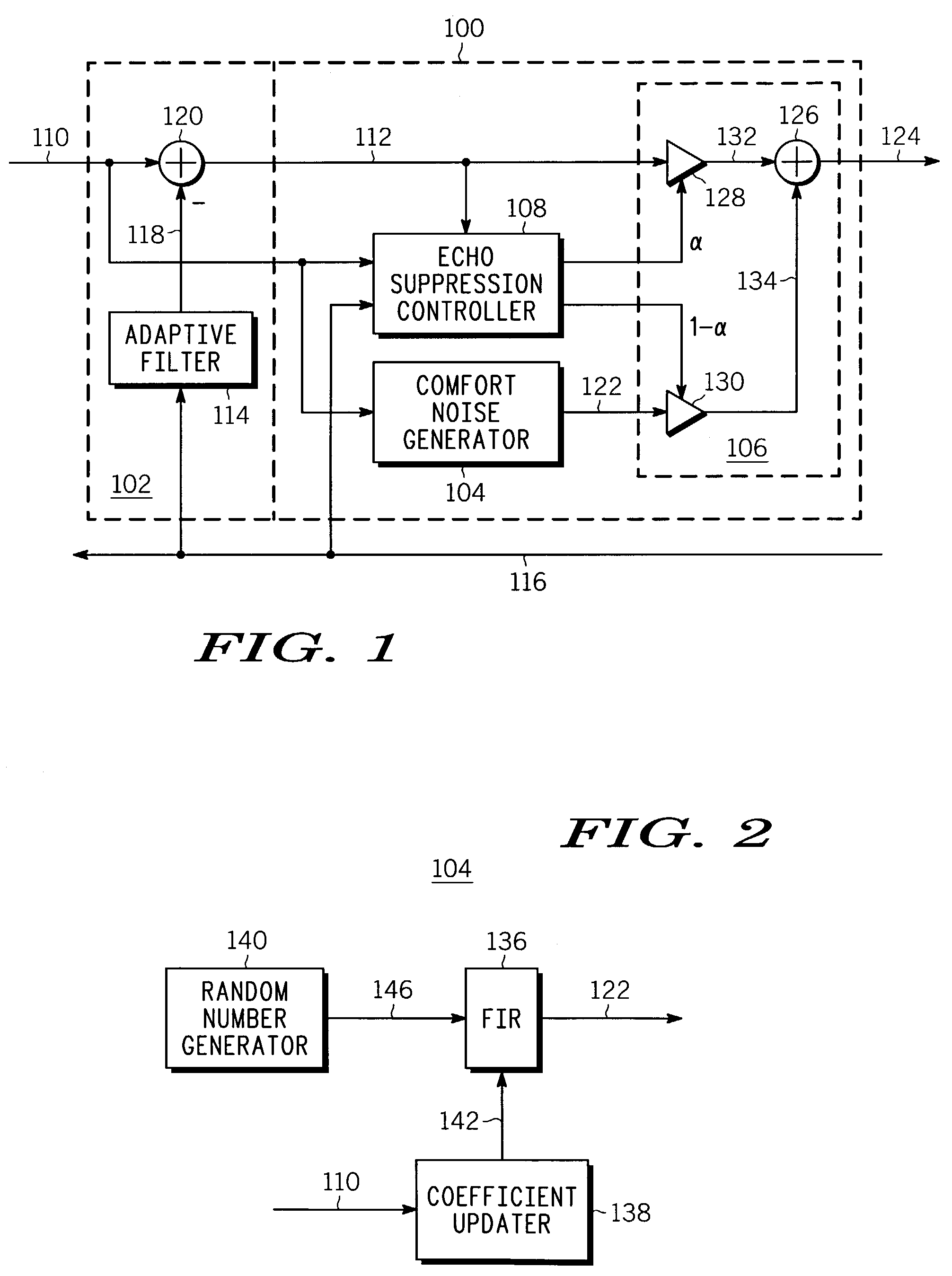
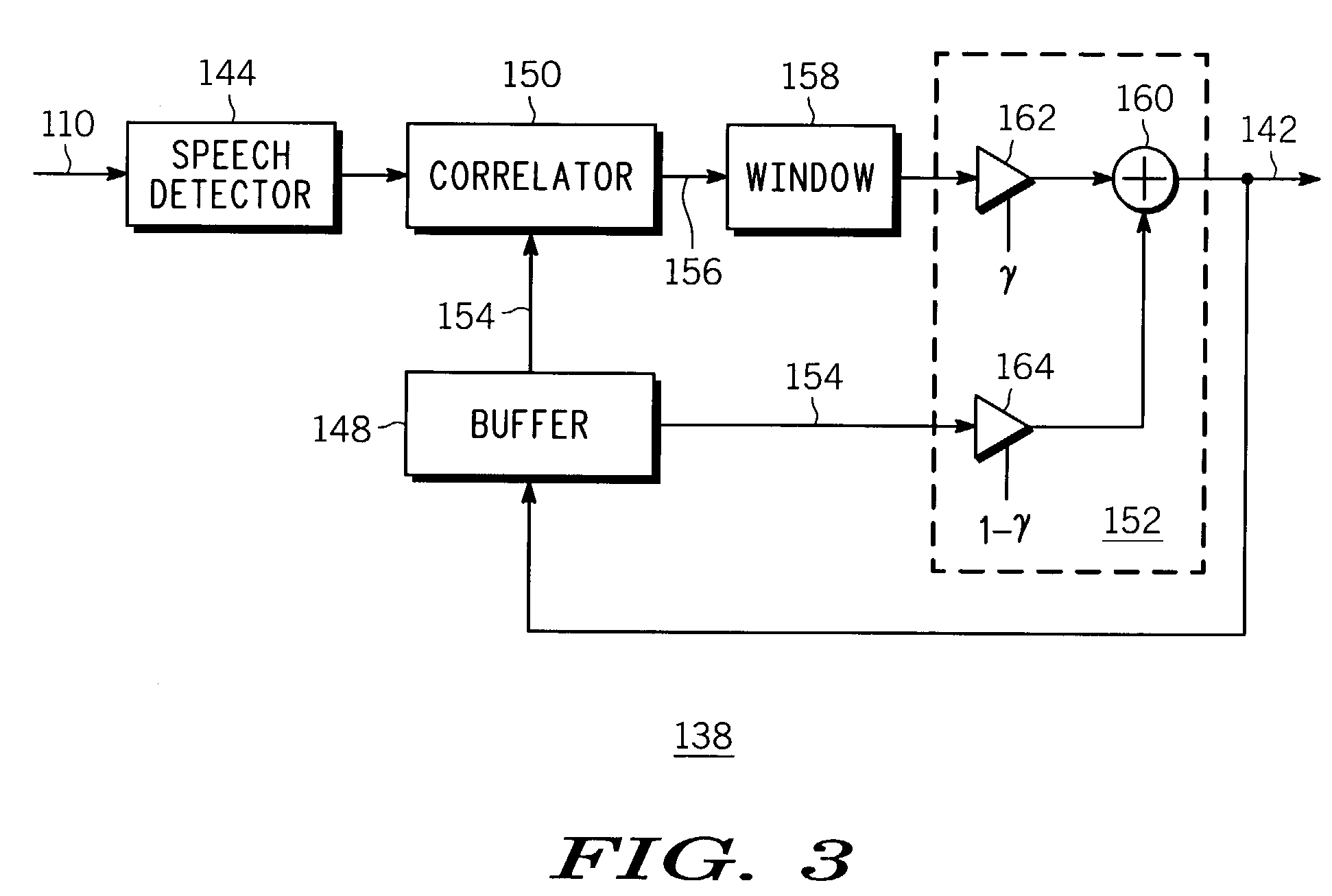
Low-complexity comfort noise generator
A comfort noise generator (104) suitable for use in a communication system includes a finite impulse response (FIR) filter (136), a random number generator (140), and a coefficient updater (138). The coefficient updater (138) determines an updated set of filter coefficients (142) based on the signal frame of the input signal (102). The updated set of filter coefficients (142) is output to the FIR filter (136). The FIR filter (136) shapes a white noise signal (146) supplied by the random number generator (140) to provide a simulated background noise signal, or comfort noise signal (122). The comfort noise signal (122) is selectively output from an echo suppression system or corresponding method to overwrite or suppress reflected residual echoes.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for a subband acoustic echo canceller with integrated voice activity detection
ActiveUS20080306736A1Power managementInterconnection arrangementsComfort noiseFourier transform on finite groups
Methods and systems for a subband acoustic echo canceller with integrated voice activity detection are disclosed and may include adjusting transmit and / or receive powers of wirelessly communicated audio signals based on voice activity detection via subband analysis of the wirelessly communicated audio signals. The receive power may be adjusted by utilizing a reduced duty cycle, or by conveying voice activity detection information via an asynchronous control channel in a Bluetooth application. A plurality of subbands may be generated utilizing a fast Fourier transform, and a first subset of the subbands corresponding to voice activity may be selected and a second subset of the subbands may be selected that corresponds to background noise. The processing of the subsets may be dynamically adjusted due to variations in the voice activity or background noise. Comfort noise may be generated and transmitted at a reduced bandwidth utilizing the second subset of the subbands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for identifying and eliminating echo generated by speech at remote end in SCDMA handset
InactiveCN1917038AAcoustic echo reductionImprove the sound effectTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSpeech analysisComfort noiseSpeech sound
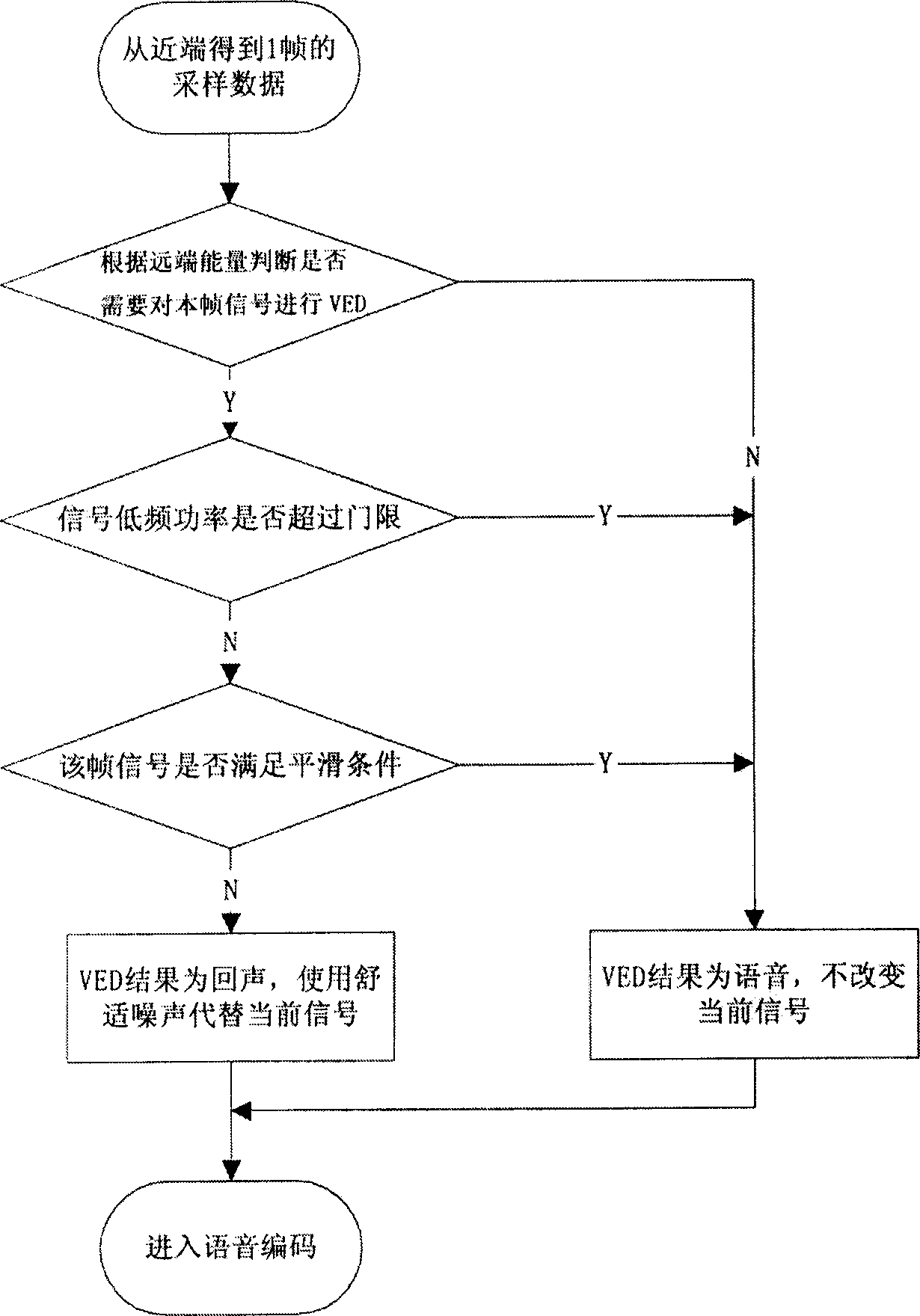
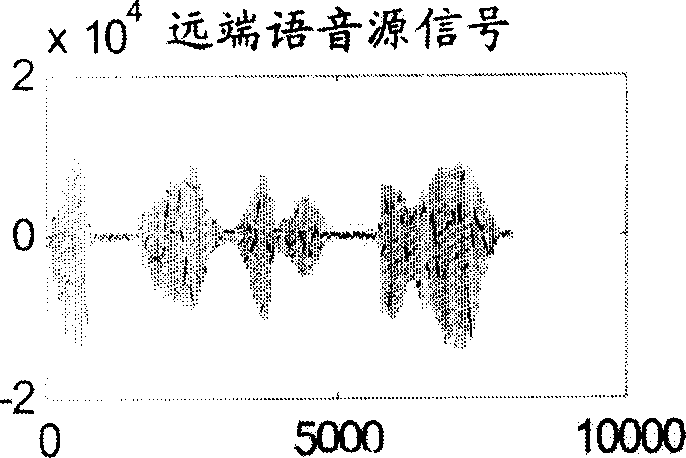
A method for identifying and eliminating echo generated from far end voice in CDMA mobile phone includes obtaining a frame sampling signal at near end to judge whether there is voice at far end or not according last 5-15 frames at far end, detecting voice echo of said frame if it is and calculating low frequency energy of said frame signal to judge out whether only echo is existed or not then carrying out smooth on echo or replace echo by comfort noise signal if echo is existed and not varying current signal if echo is not existed, or otherwise not requiring to carry out detection on voice of said frame at near end and directly coding and transmitting voice.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
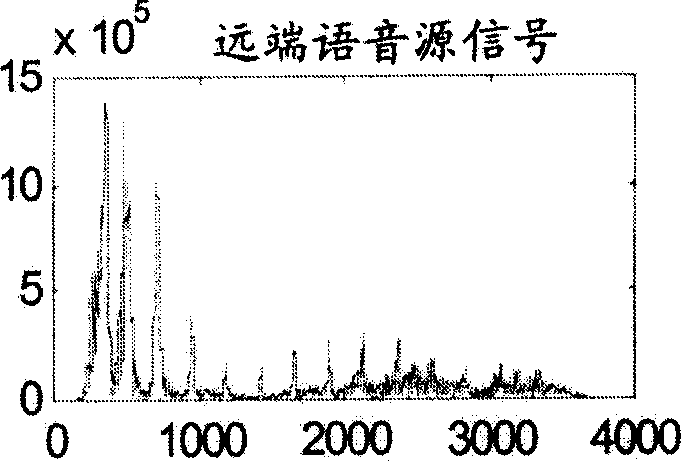
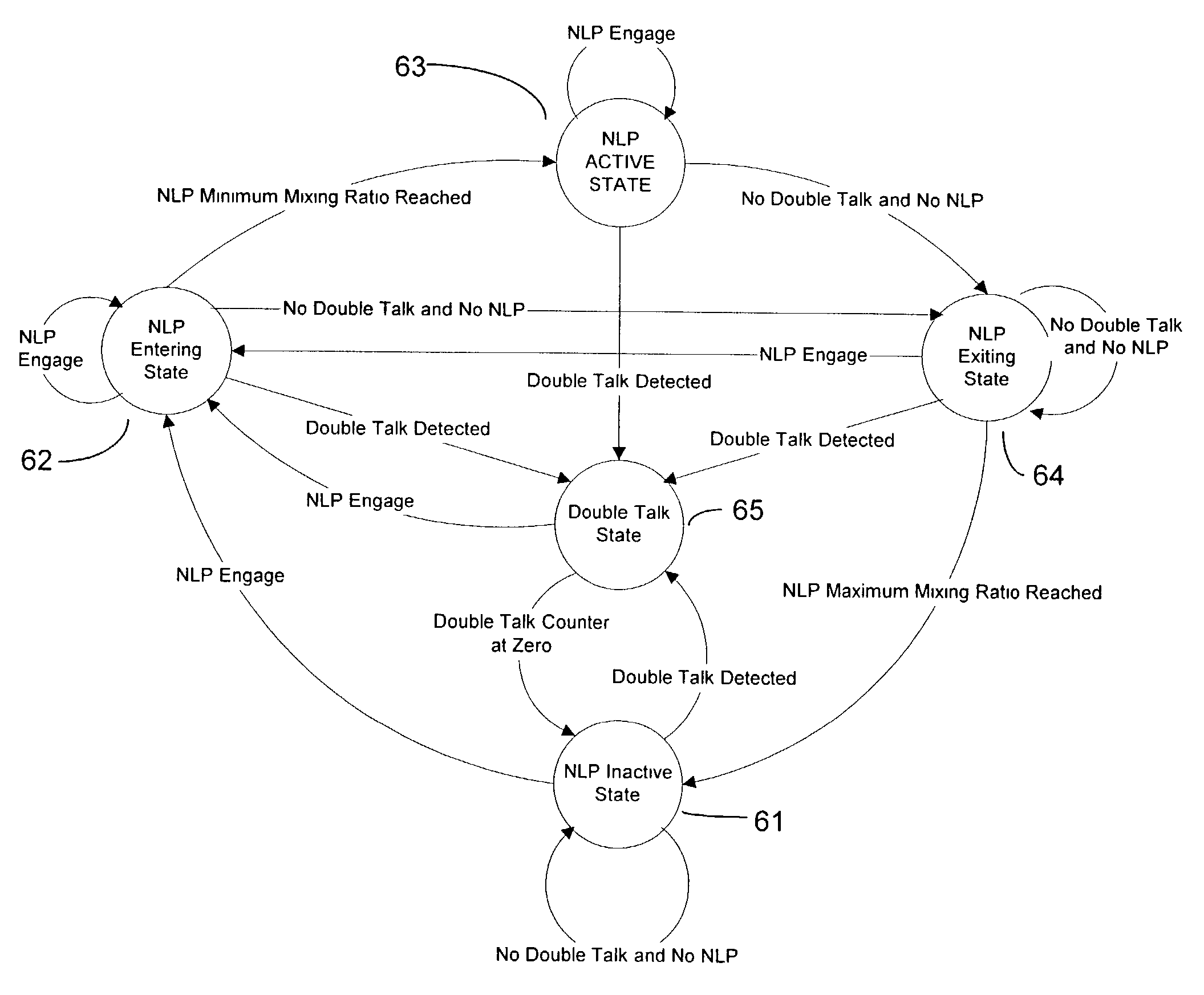
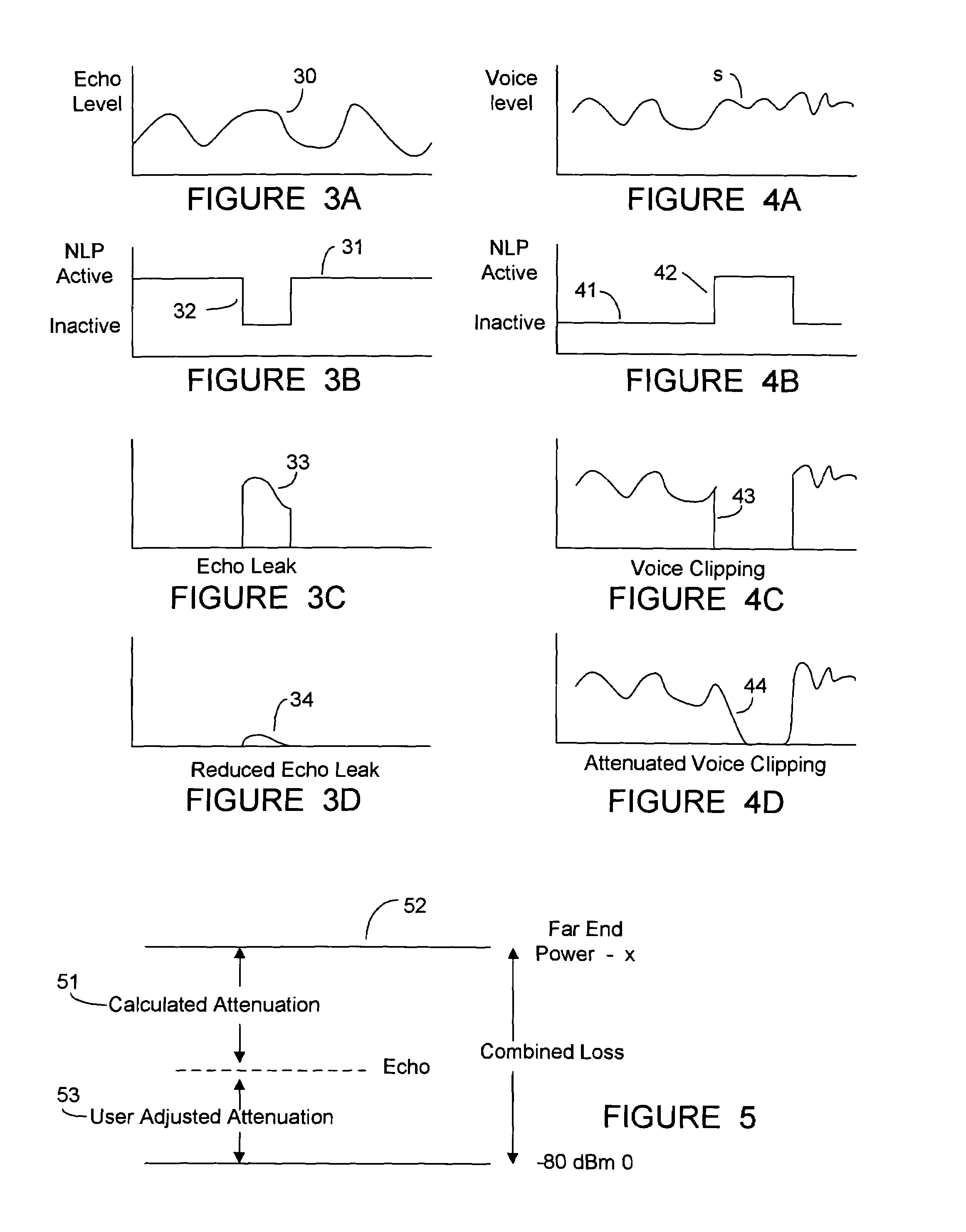
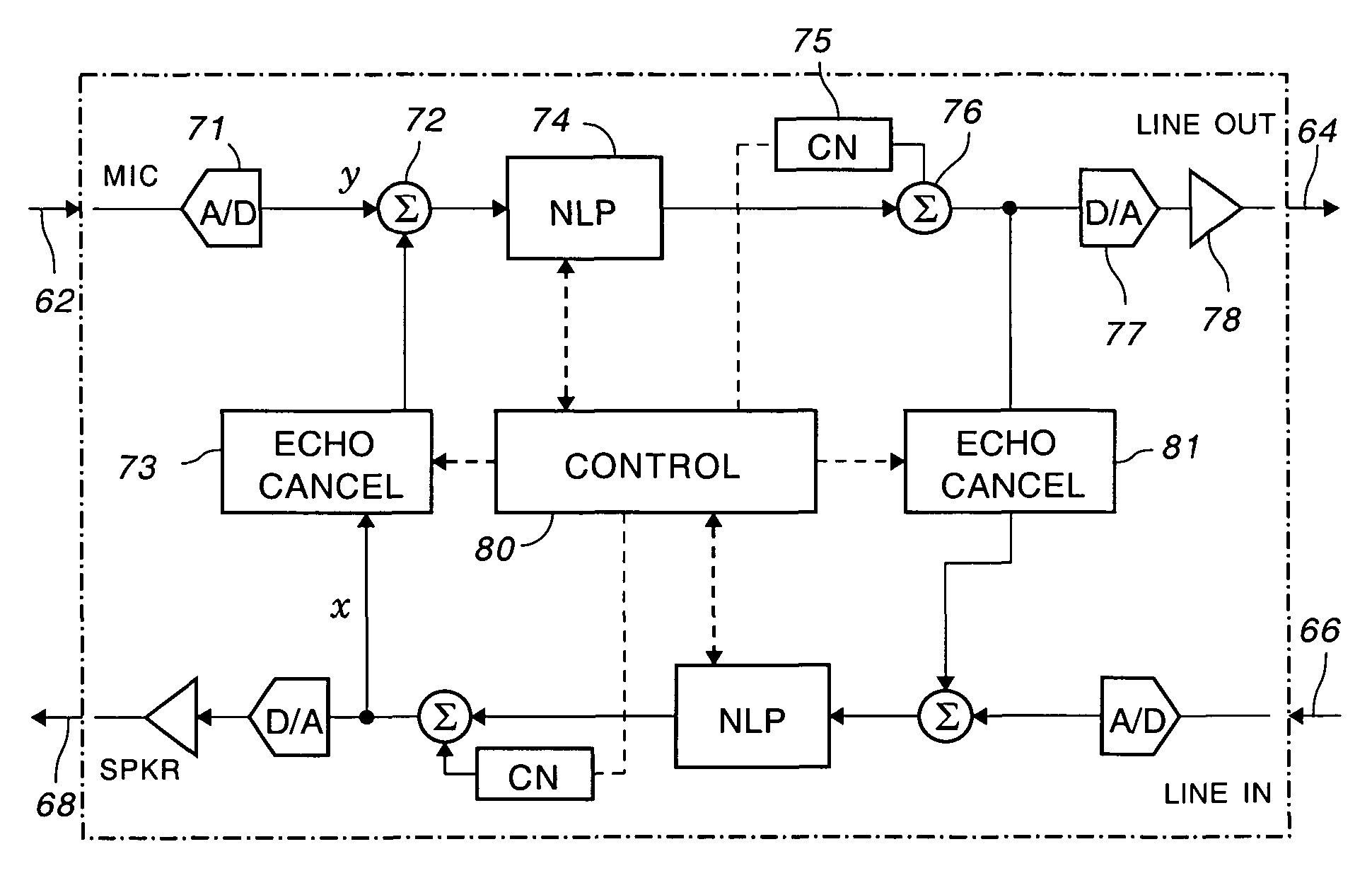
Double talk, NLP and comfort noise
InactiveUS7050576B2Easy accessEcho leak is minimizedTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsSubstations coupling interface circuitsComfort noiseEngineering
A state machine for attenuating the transition into and out of NLP state to reduce voice clipping and to reduce echo leak in a voice over packet signal transmission. The state machine interposes two additional transitional states between the NLP active state and the NLP inactive state to eliminate the sharp transition of NLP activity. An NLP entering state is used to gradually reduce the mixing ratio of echo and voice to attenuate the transition from passage of echo in the NLP inactive state to the suppression of echo in the NLP active state. An NLP exiting state is used to gradually increase (ramping the change) the mixing ratio of echo and voice to attenuate the transition from suppression of echo in the NLP active state to passage of echo in the NLP inactive state. The rate of increase / decrease, the transition rate is determined based upon the signal parameters, including the presence of double talk and a transition rate indicator based unon these factors is generated in software to control the transition rate.
Owner:TELOGY NETWORKS
Video comfort noise addition technique
ActiveUS20060256871A1Reduce artifactsReduce large frame-to-frame differenceTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationSubjective video qualityComfort noise
A decoding arrangement for decoding pictures in an incoming video stream includes a noise generator for adding a dither signal containing random noise to the pictures after video decoding, to improve the subjective video quality. The noise generator adds noise to each pixel in an amount correlated to additive noise of pixels in a prior picture, either a previously displayed picture (i.e., a previously decoded picture to which noise has been added), or a previously decoded picture.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
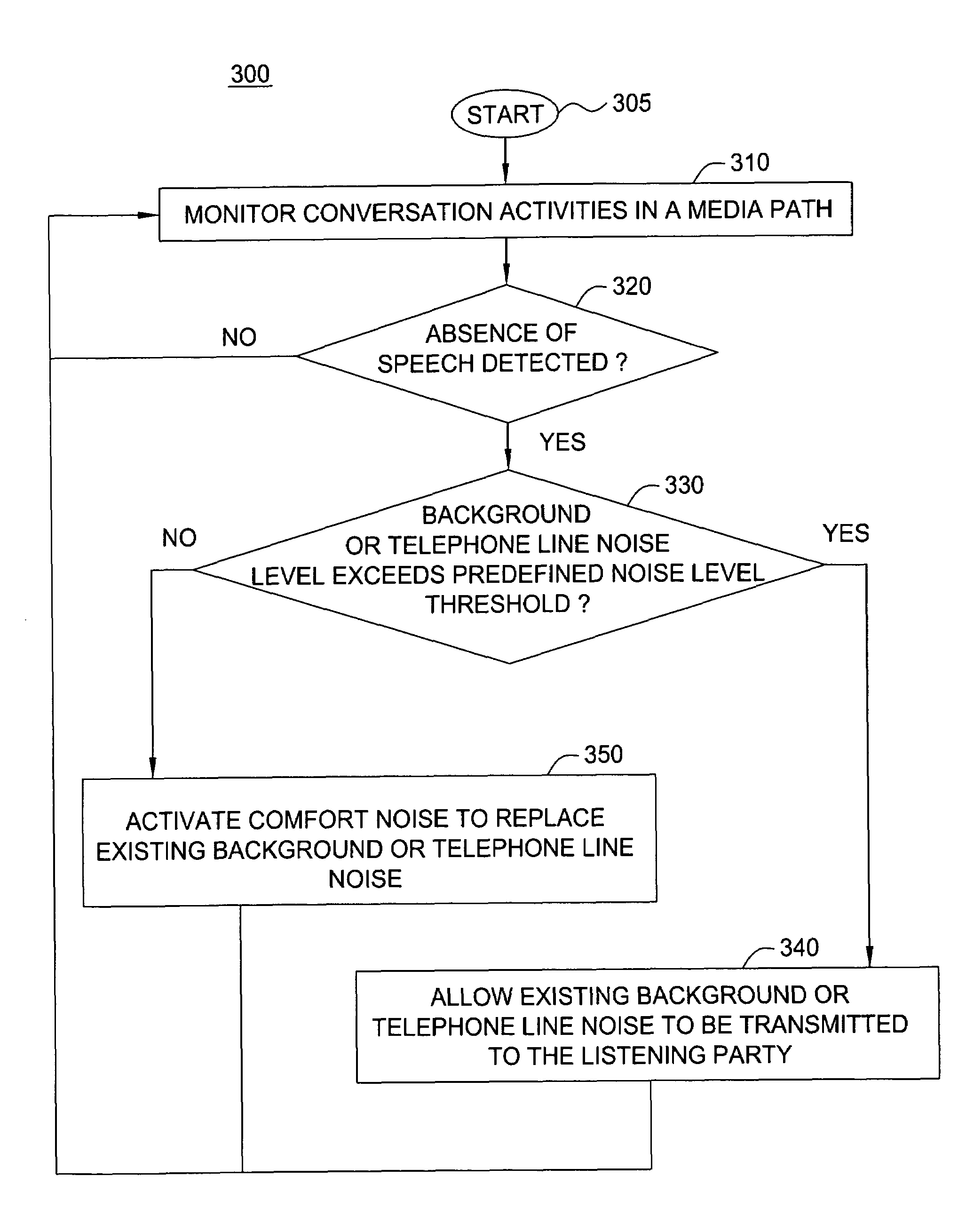
Method and apparatus for dynamically providing comfort noise
A method and apparatus for dynamically enabling the activation and deactivation of comfort noise over a VoIP media path or channel are disclosed. The present method detects all sound levels in the media path and only activates the comfort noise in the absence of sound and when the background noise level or the telephone line noise level is low rather than only in the absence of speech.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
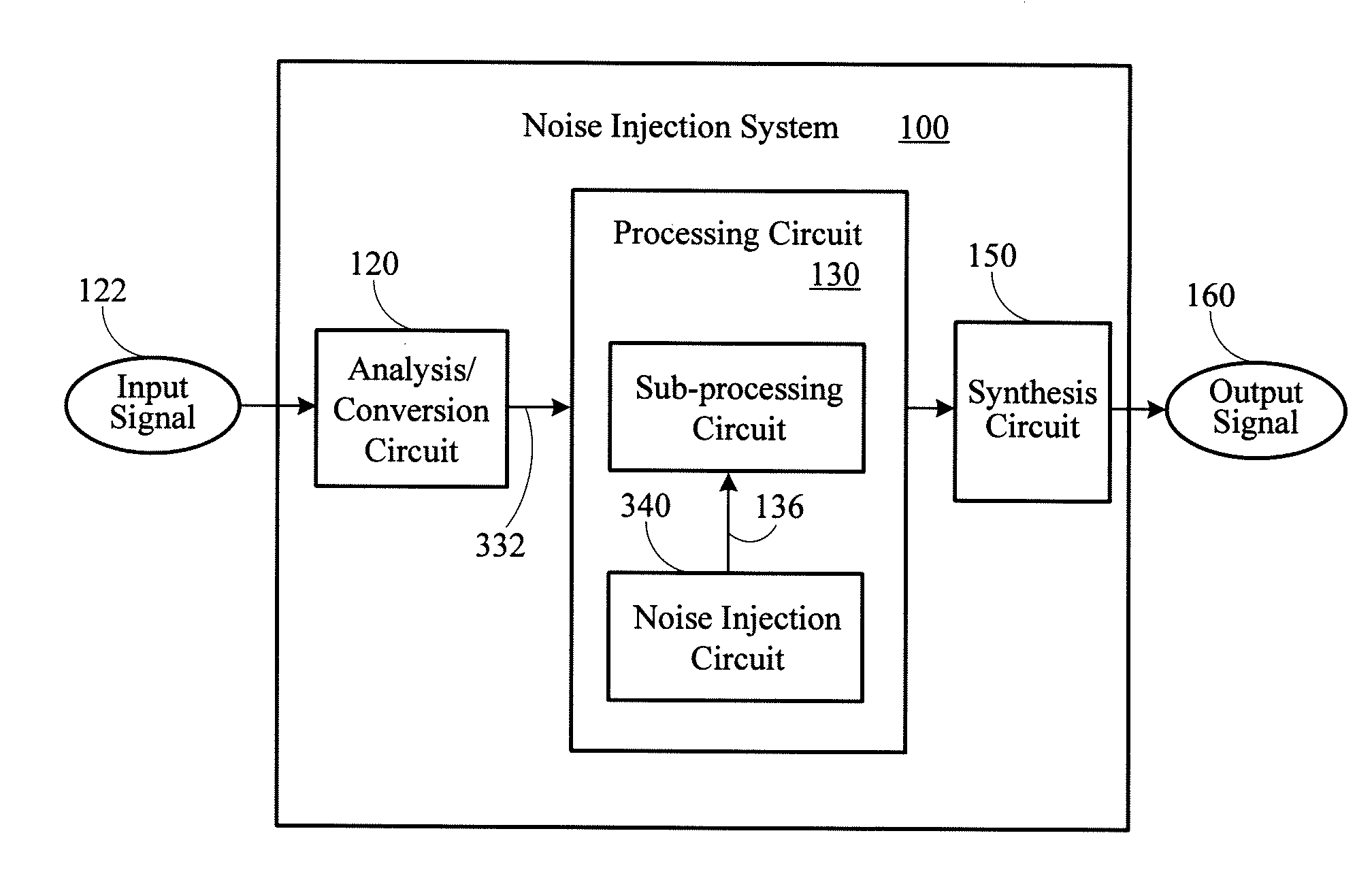
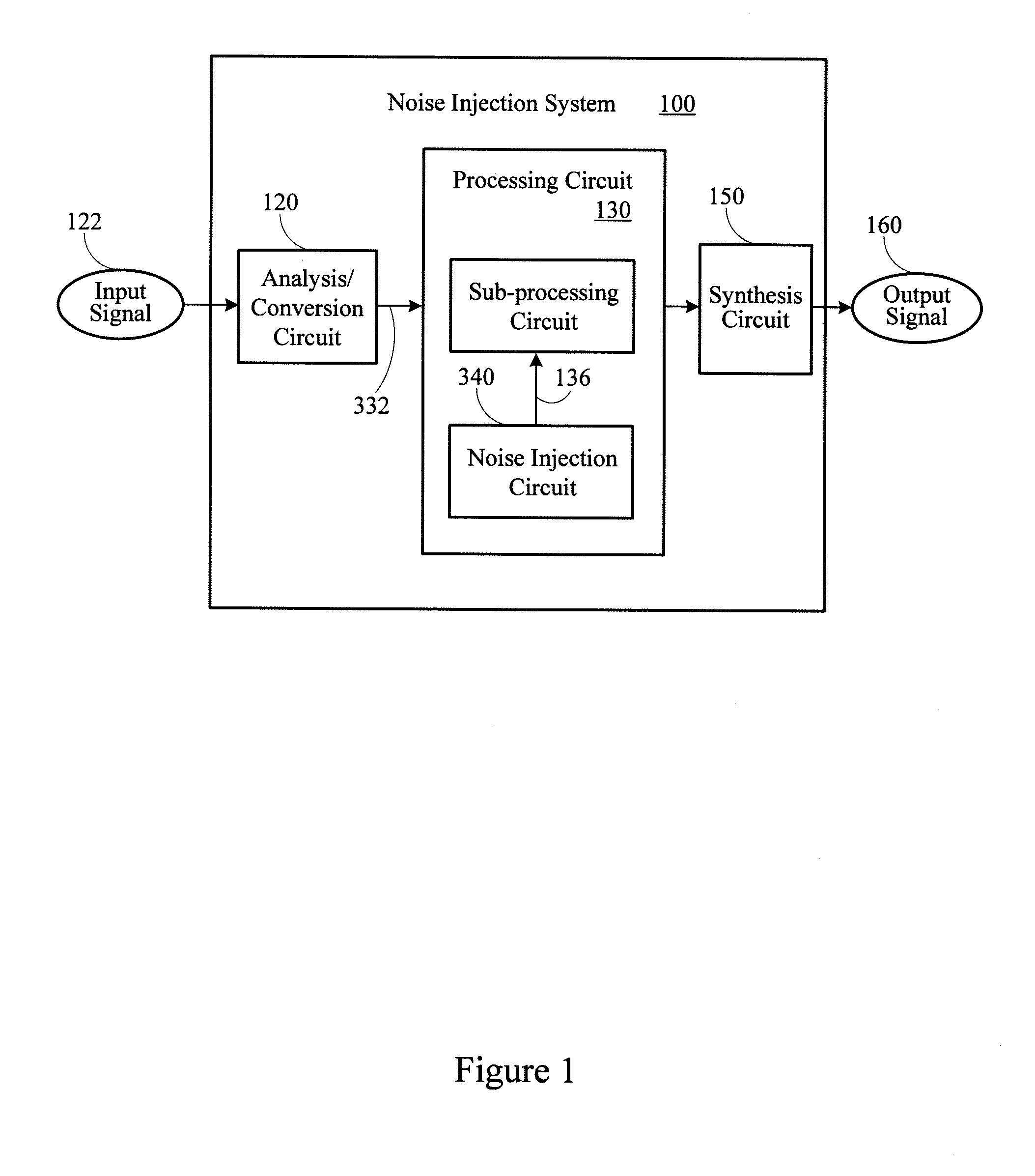
System for comfort noise injection
A noise injection system adds comfort noise to an audio signal. The system includes a background noise estimator that determines a spectral content of a background noise associated with the audio signal. A comfort noise generator generates a comfort noise signal having a random phase. A gain circuit adjusts the comfort noise signal based on the spectral content of the background noise. A combining circuit combines a gain-adjusted comfort noise signal and the audio signal to generate an output signal.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Apparatus and method for controlling noise in a mobile communication terminal
InactiveUS20050021332A1Lower the volumeSuppress noiseSubstation equipmentSpeech recognitionComfort noiseAudio power amplifier
An apparatus and method for controlling a volume of comfort noise in a mobile communication terminal. The mobile communication terminal includes a vocoder for detecting a decoding rate of voice data received after establishing a voice call to output a detection signal and an amplifier for amplifying an output signal of the vocoder. The method comprises the steps of determining whether the decoding rate of the voice data from the vocoder is ⅛, recognizing the voice data as silence period data containing only the comfort noise and providing the vocoder with a control signal to lower a volume of the comfort noise, if the decoding rate of the voice data is ⅛, and controlling a volume of the voice data such that it becomes a volume preset by a user, if the decoding rate of the voice data is not ⅛.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
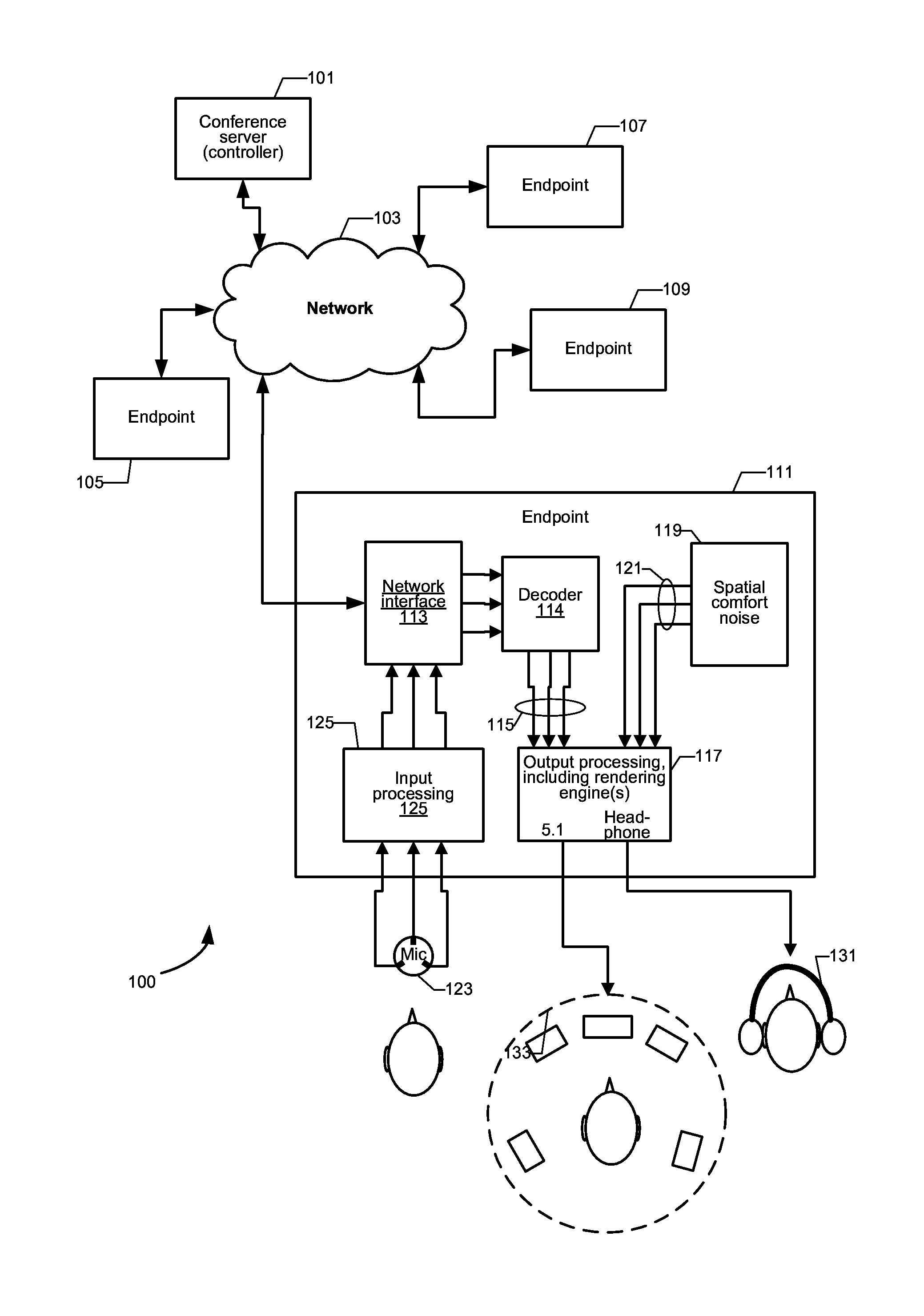
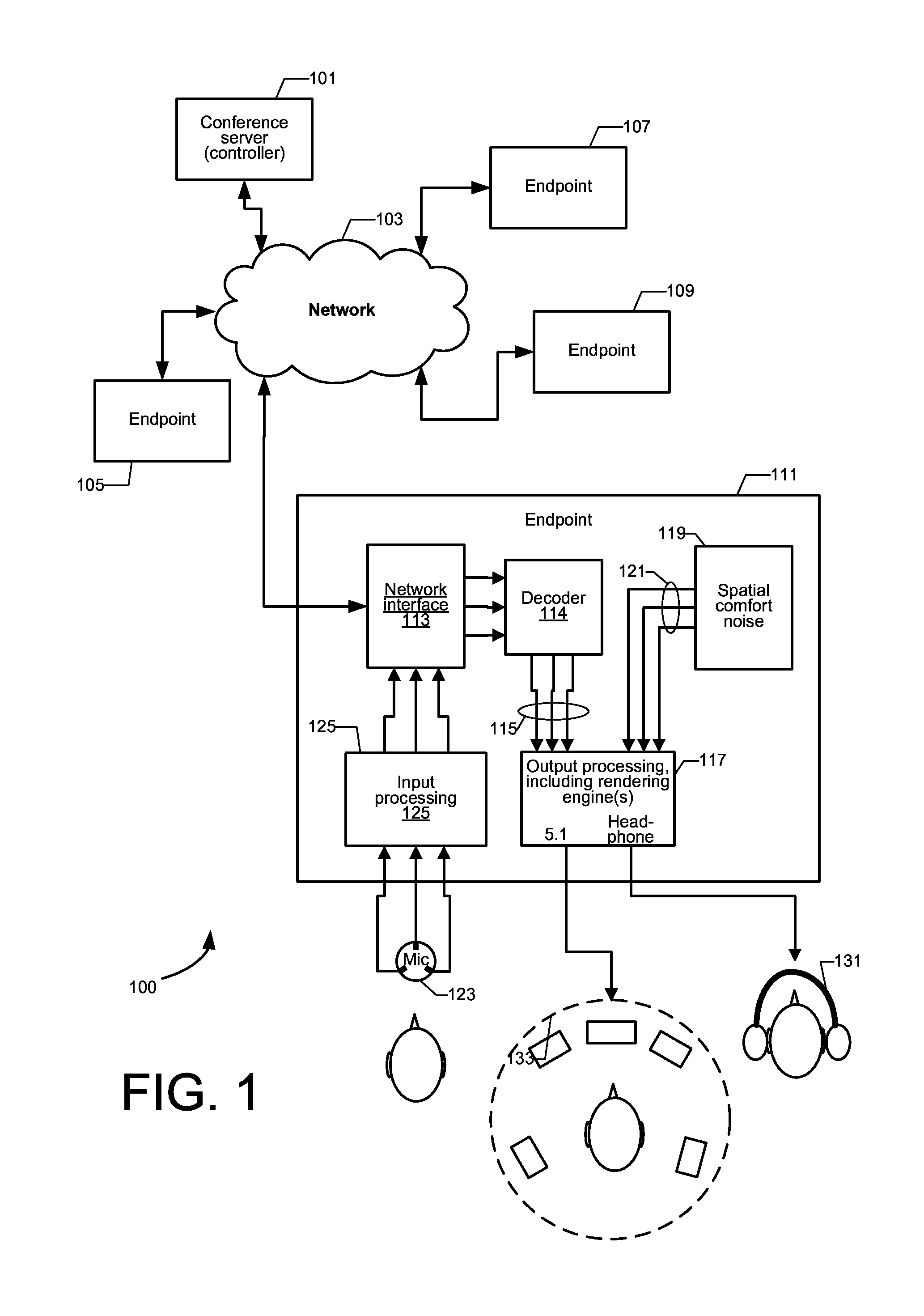
Spatial comfort noise
ActiveUS20160027447A1Avoid complicationsSpeech analysisSpecial service for subscribersComfort noiseAudio signal flow
A method, an apparatus, logic (e.g., executable instructions encoded in a non-transitory computer-readable medium to carry out a method), and a non-transitory computer-readable medium configured with such instructions. The method is to generate and spatially render spatial comfort noise at a receiving endpoint of a conference system, such that the comfort noise has target spectral characteristics typical of comfort noise, and at least one spatial property that at least substantially matches at least one target spatial property. On version includes receiving one or more or more audio signals from other endpoints, combining the received audio signals with the spatial comfort noise signals, and rendering the combination of the received audio signals and the spatial comfort noise signals to a set of output signals for loudspeakers, such that the spatial comfort noise signals are continually in the output signal sin addition to output from the received audio signals.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
Music detector for echo cancellation and noise reduction
An audio signal is divided among exponentially related subband filters. The spectral flatness measure in each subband signal is determined and the measures are weighted and combined. The sum is compared with a threshold to determine the presence of music or noise. If music is detected, the noise estimation process in the noise reduction circuitry is turned off to avoid distorting the signal. If music is detected, residual echo suppression circuitry is also turned off to avoid inserting comfort noise.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
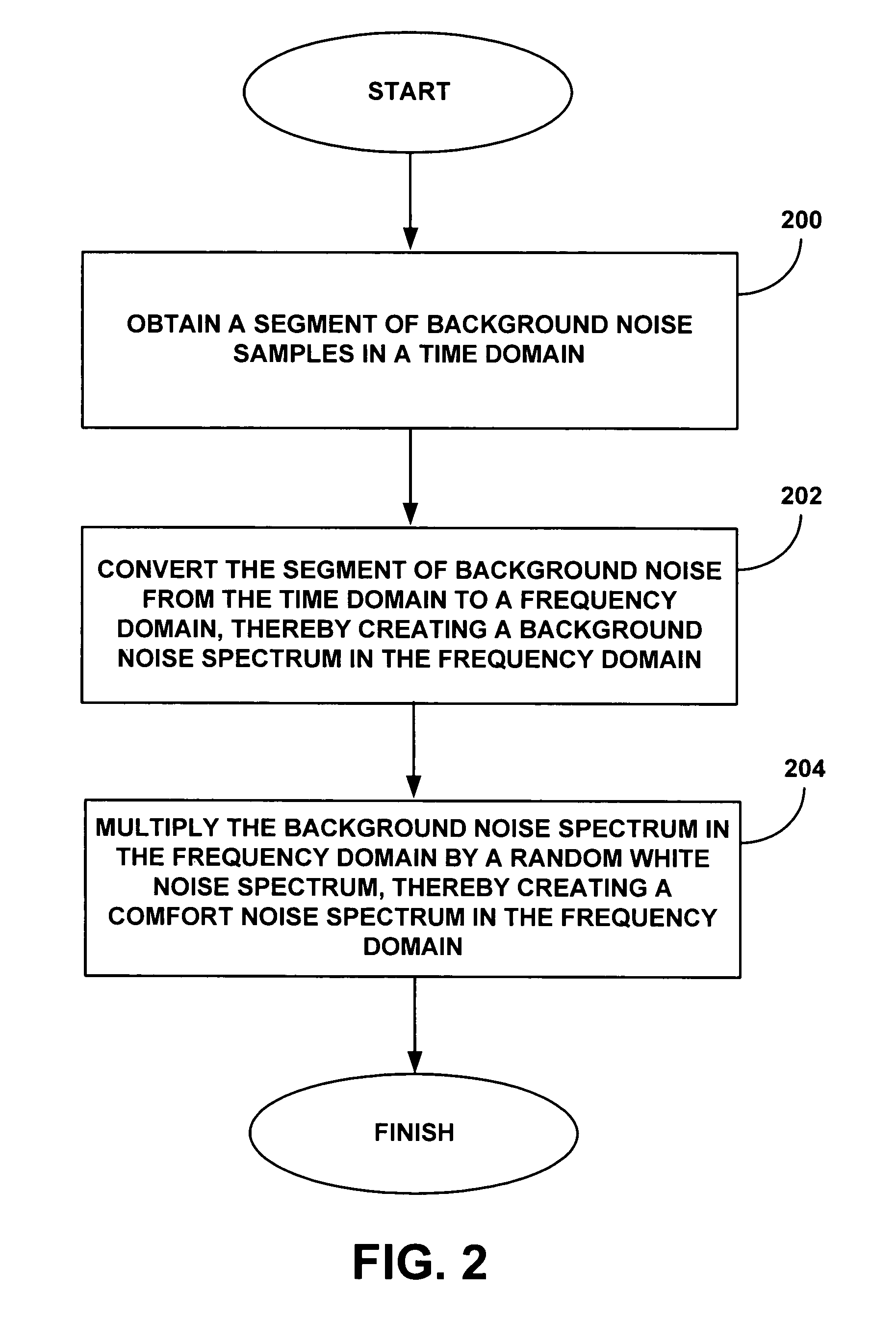
System and method for generating comfort noise
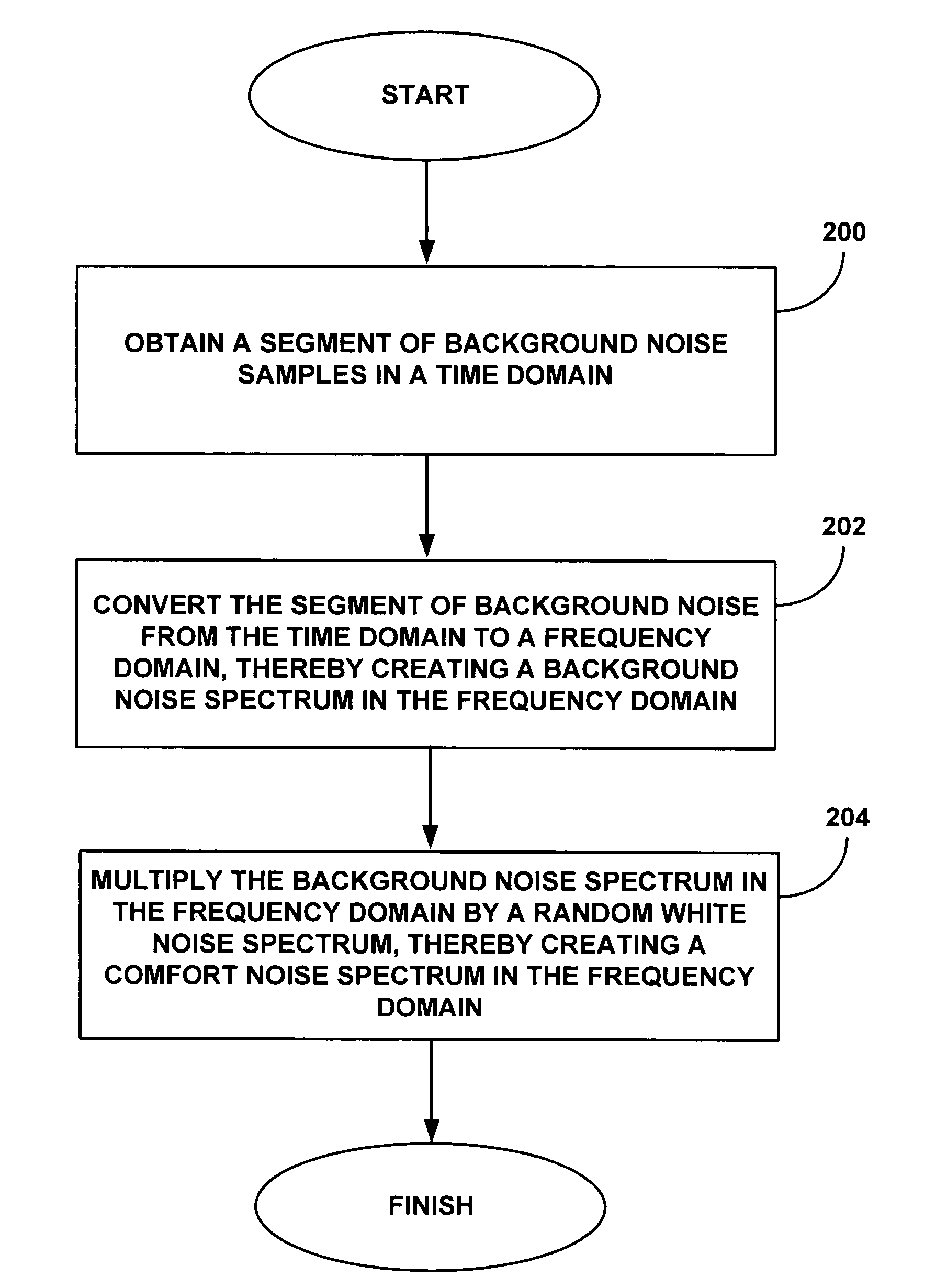
ActiveUS8767974B1Reduce artificial harmonicReduce artificial harmonicsGain controlSpeech analysisTime domainComfort noise
Comfort noise, such as can be used in voice communications can be generated using methods in the frequency domain and / or in the time domain. In various embodiments, a comfort noise spectrum can be generated in the frequency domain as the product of a background noise sample and a random noise sample. In other embodiments, the comfort noise can be generated directly in the time domain as the convolution of a background noise sample and a random noise sample.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com