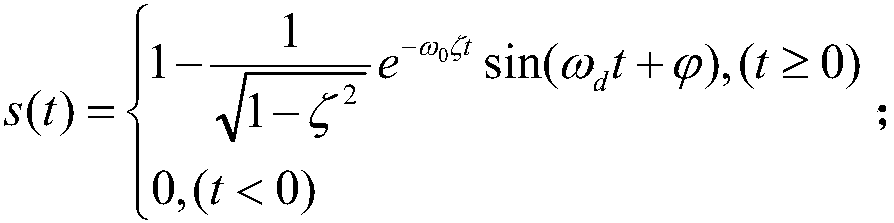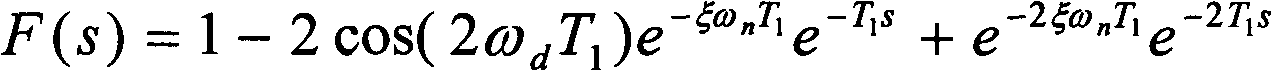Patents
Literature
348 results about "Residual vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
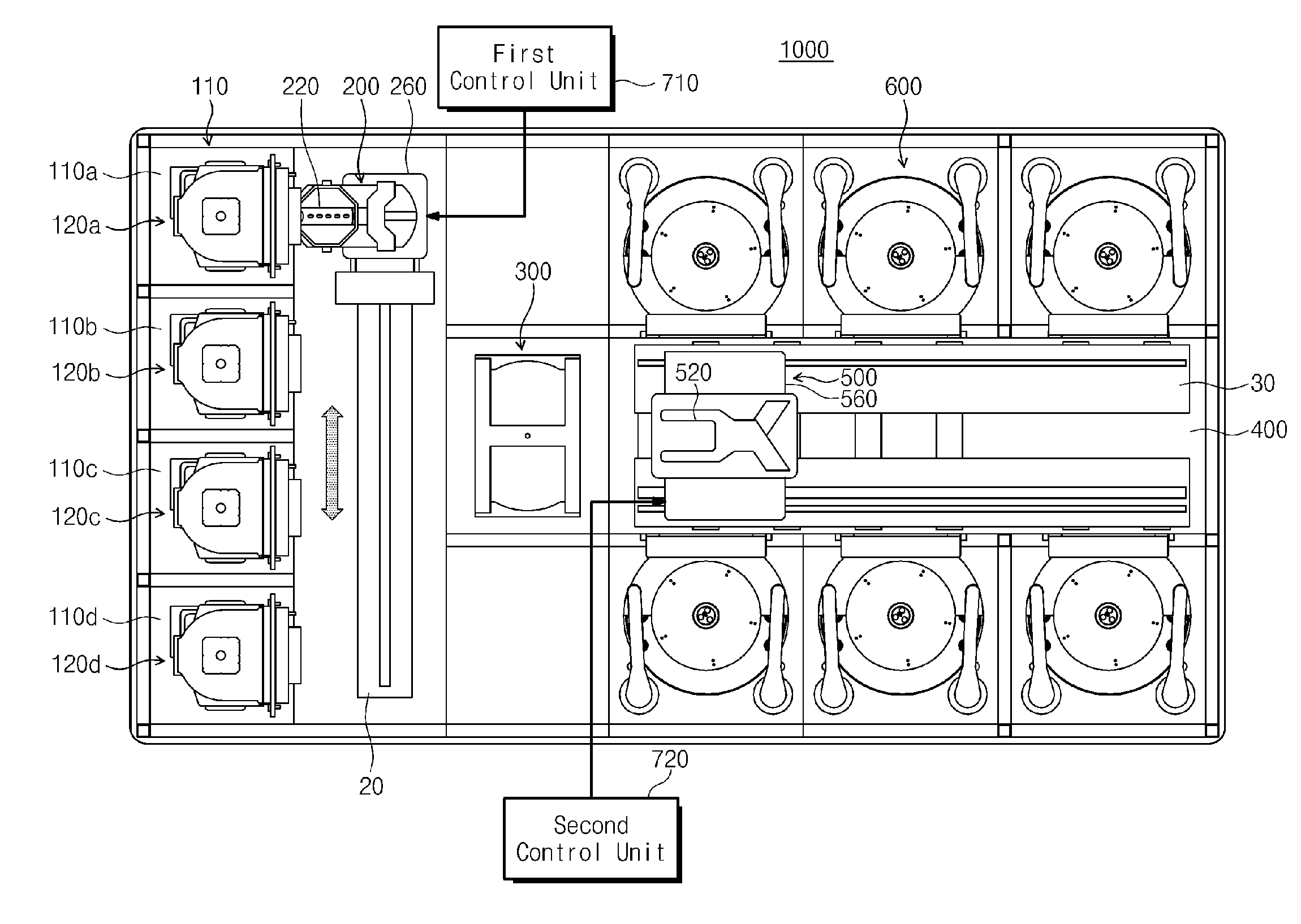
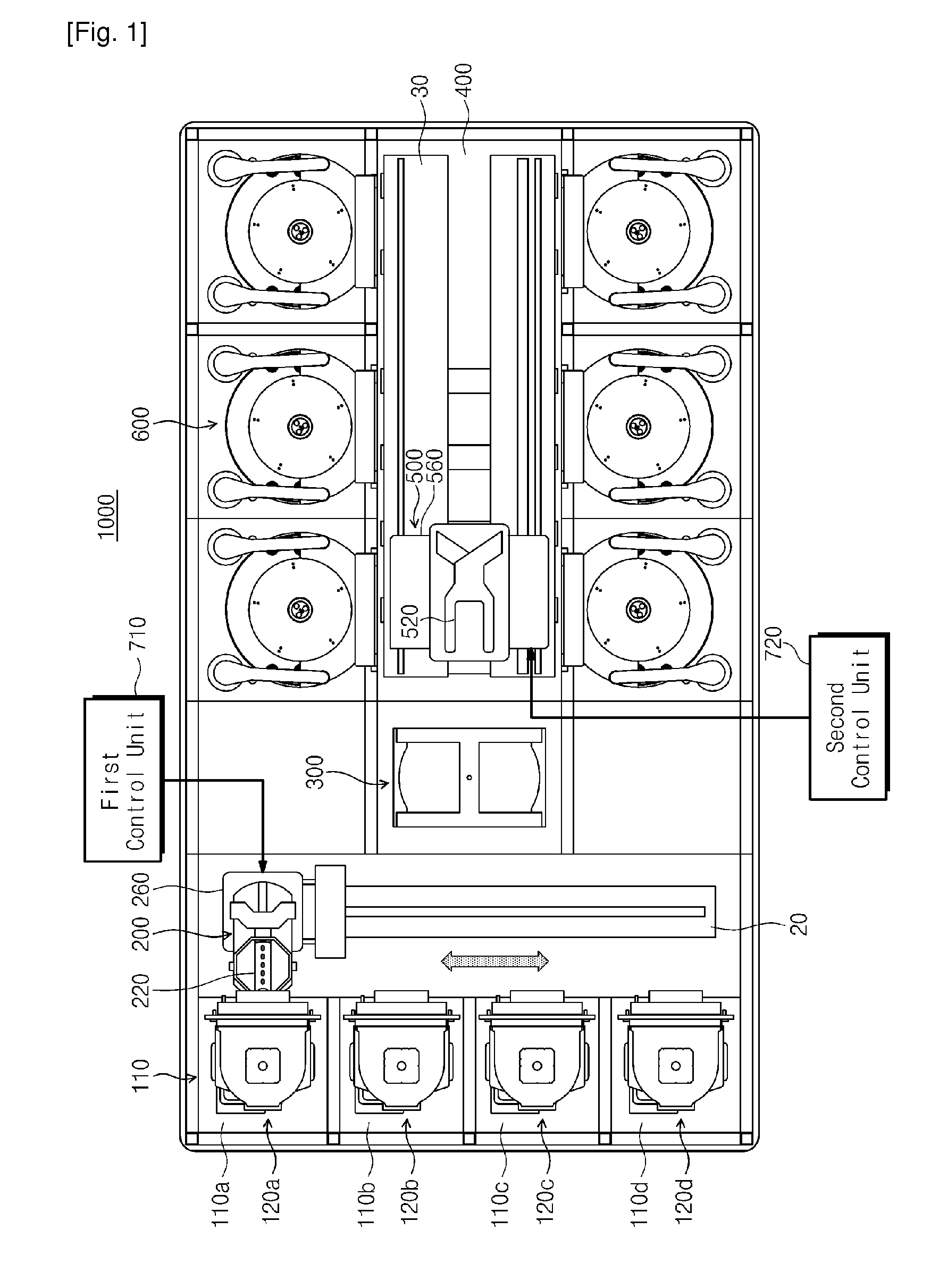
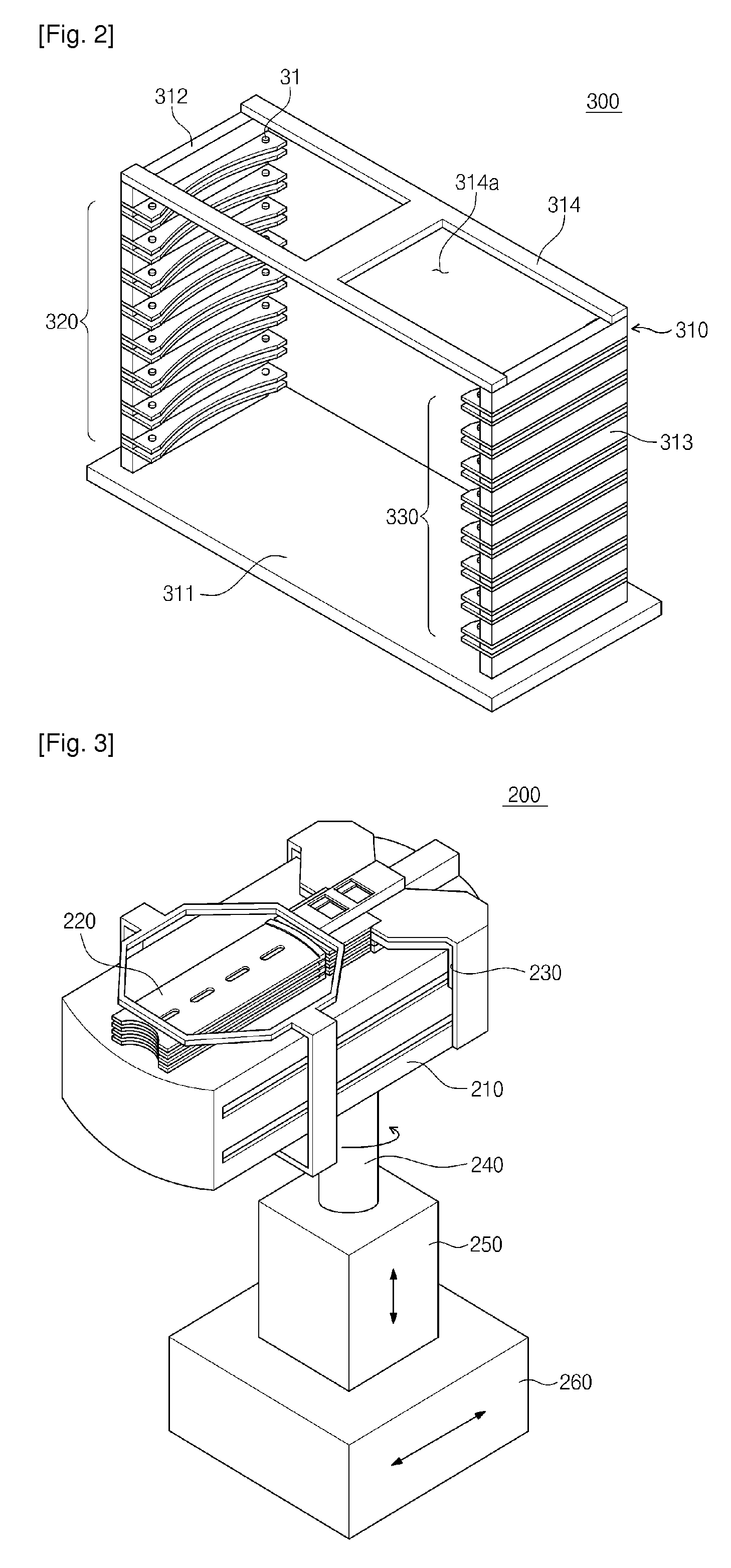
Vibration control apparatus for automotive vehicle
InactiveUS20050049761A1Accurate compensationRapid responseInternal combustion piston enginesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMobile vehicleResidual vibration
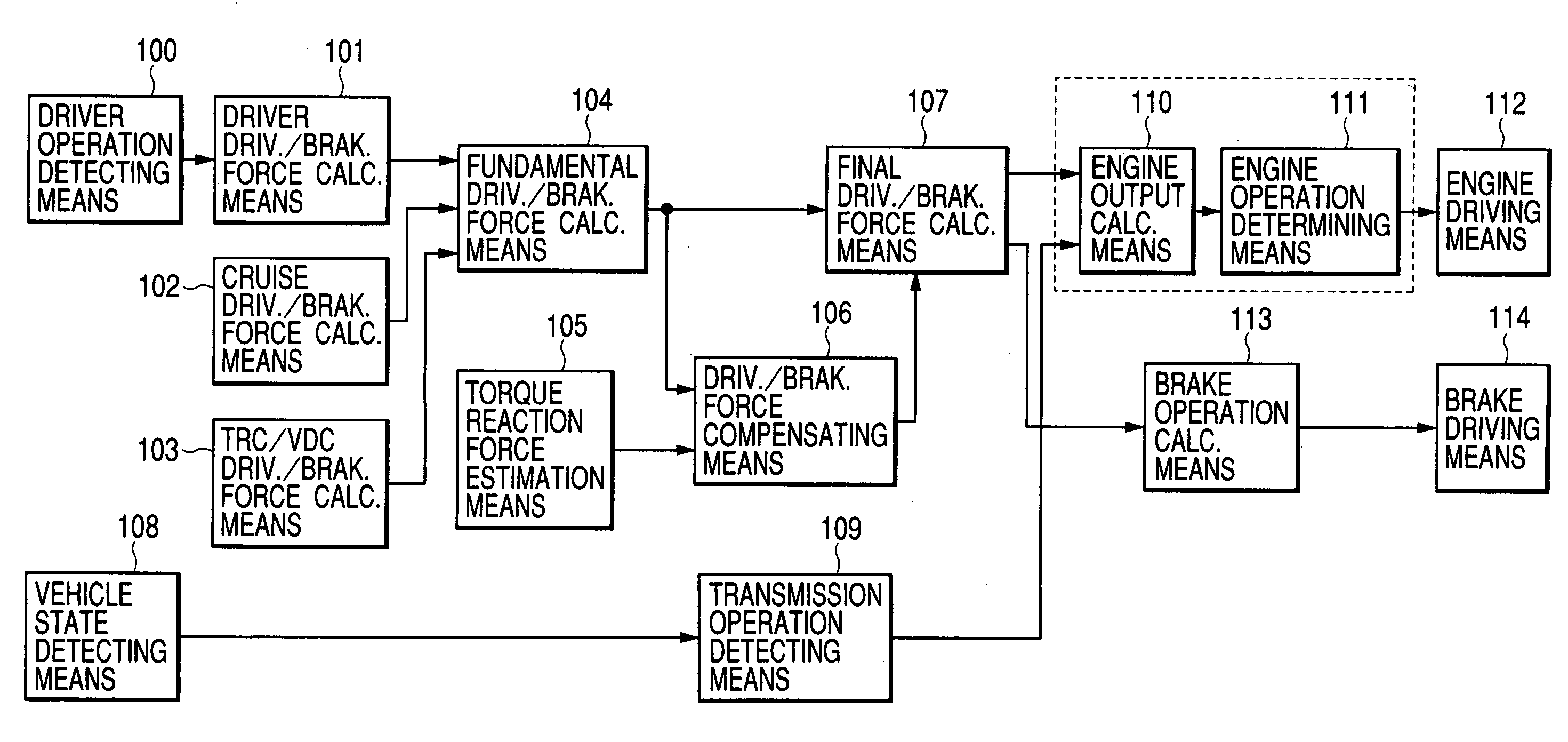
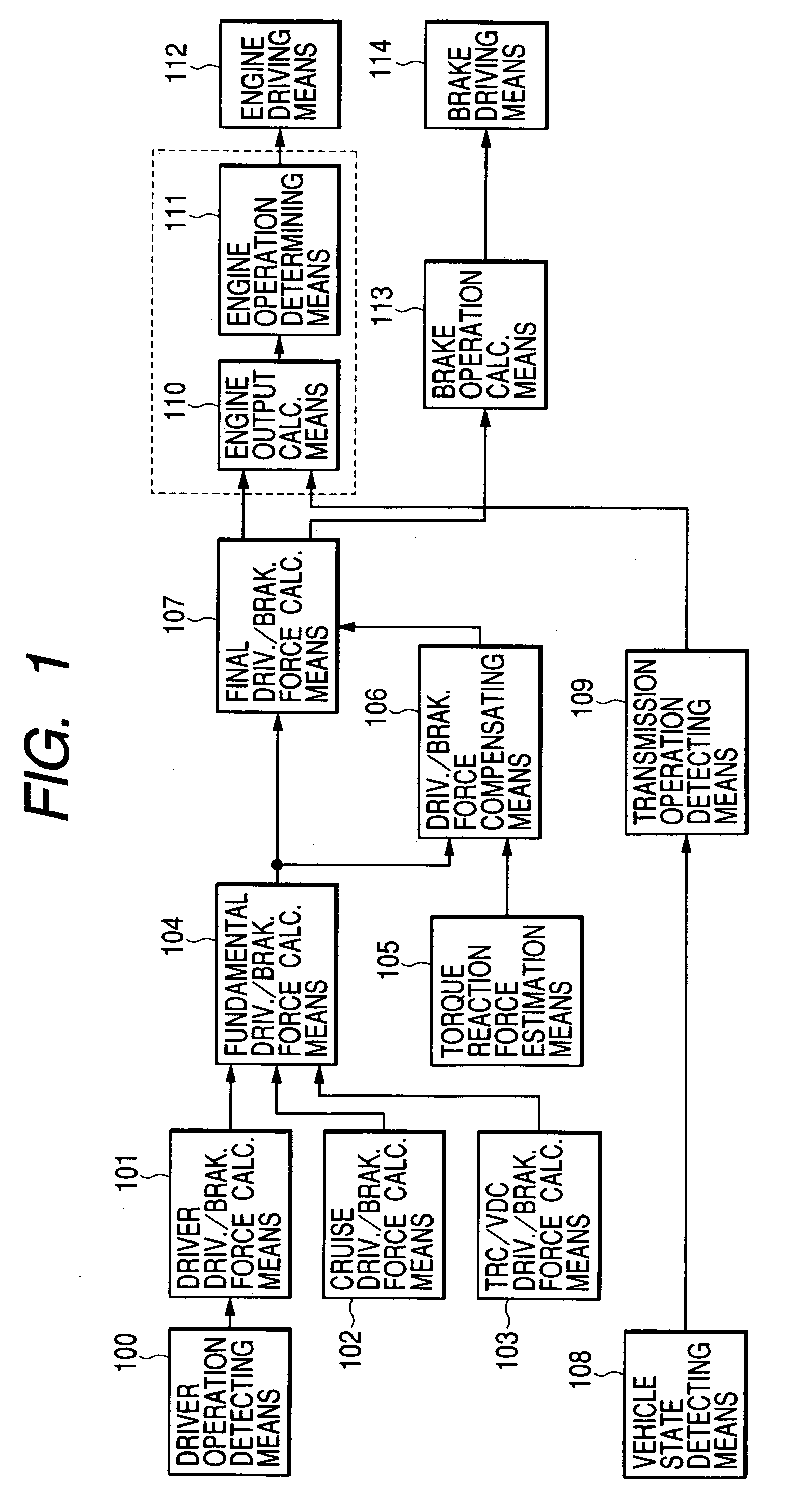
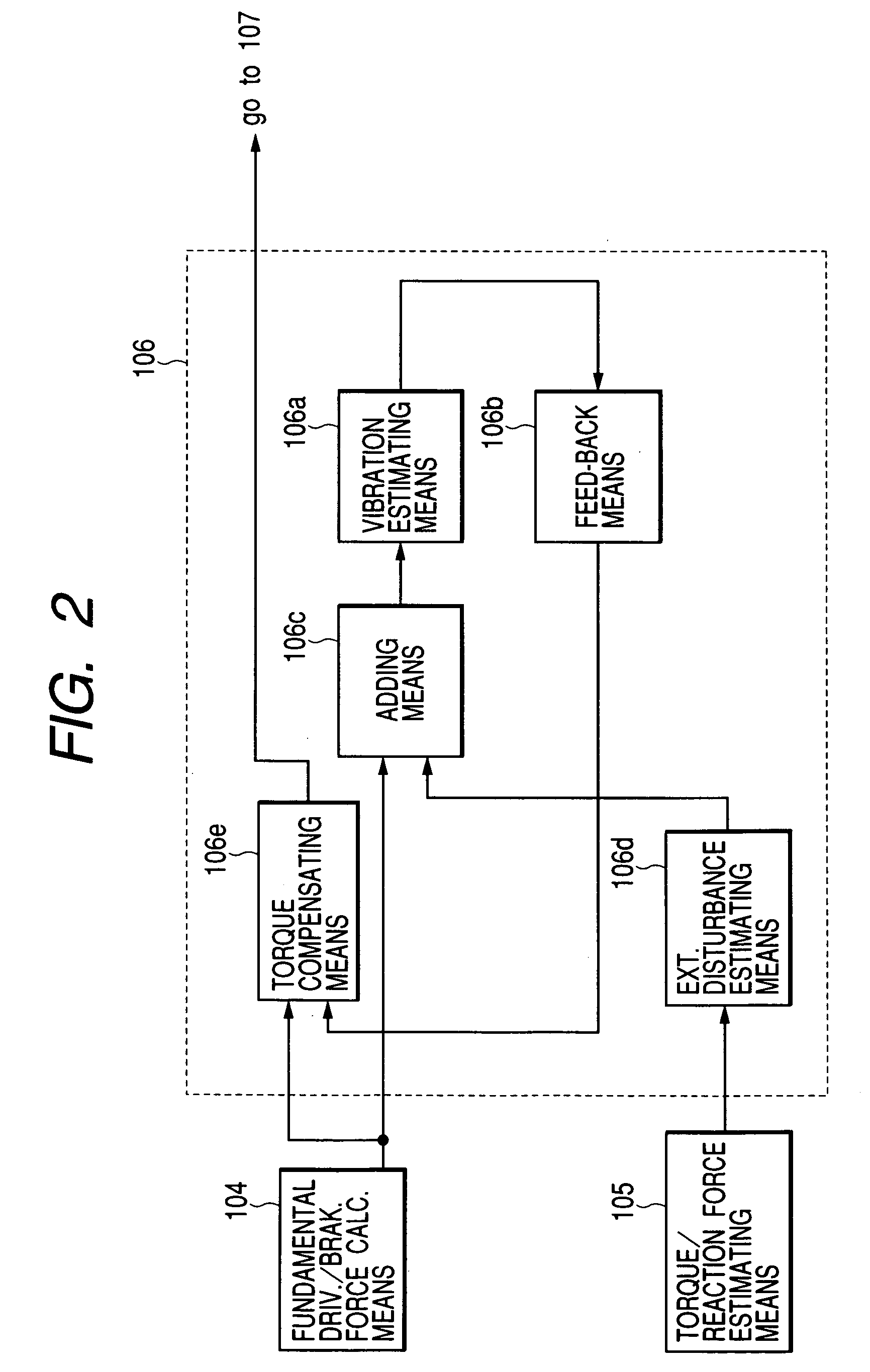
An object of the present invention is to execute an optimum control of vibrations due to a driver's operation of an accelerator pedal, steering wheel and brake pedal. The operation instructions are inputted into a vibration calculating means (kinetic model) comprising a vehicle body model, suspension model and tire model. Conventional kinetic model controlled the suspension in order to suppress the vehicle body vibration. However, in the kinetic model of the present invention, the tire vibration due to a change in the engine output is first absorbed by the suspension, whereby a residual vibration which was not be absorbed yet by the suspension is transferred to the vehicle body. The operation inputs are compensated by the three feed-back loops between the outputs of the above-mentioned three portions and input of the tire portion, giving the highest priority on the vehicle body model.
Owner:DENSO CORP
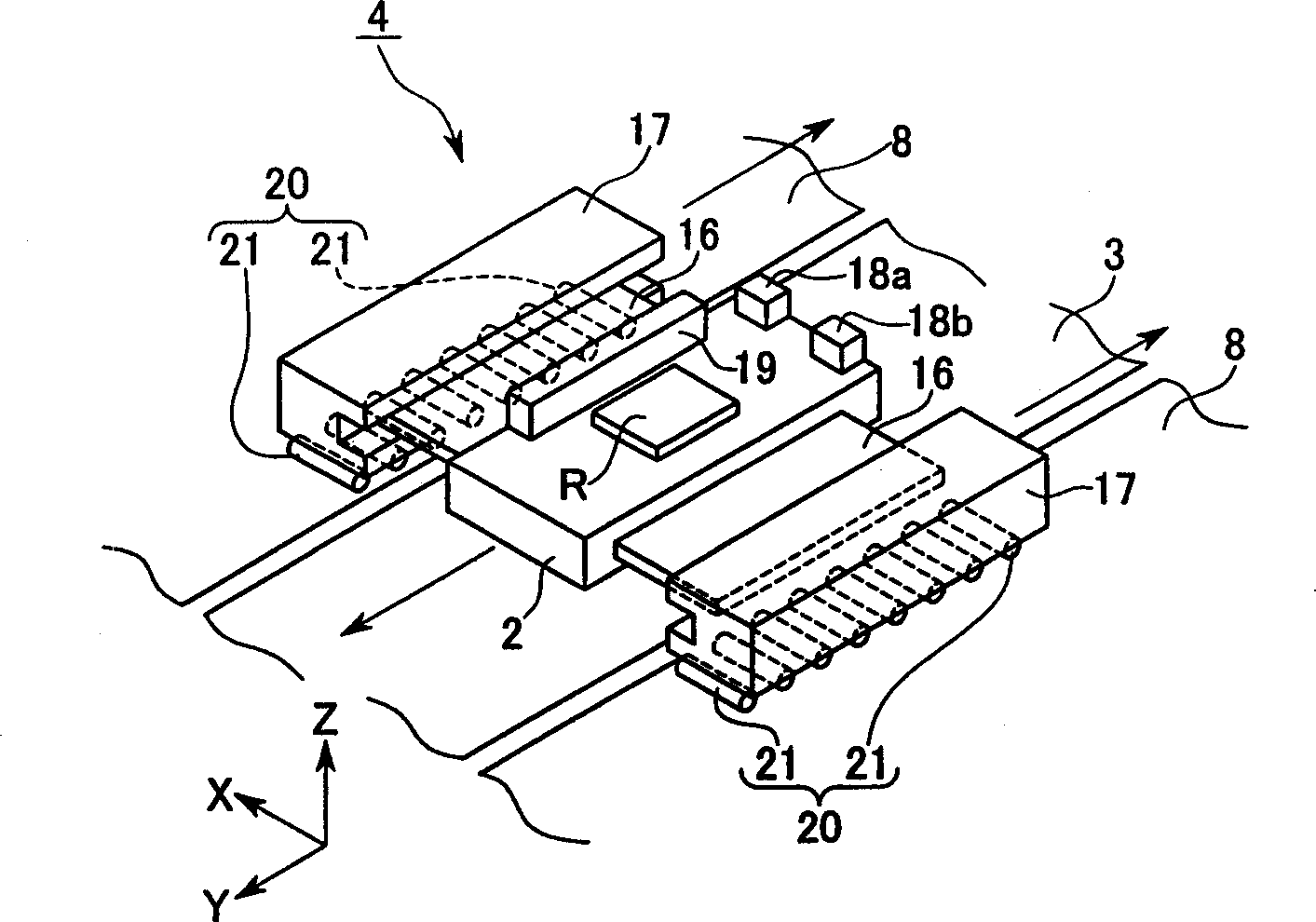
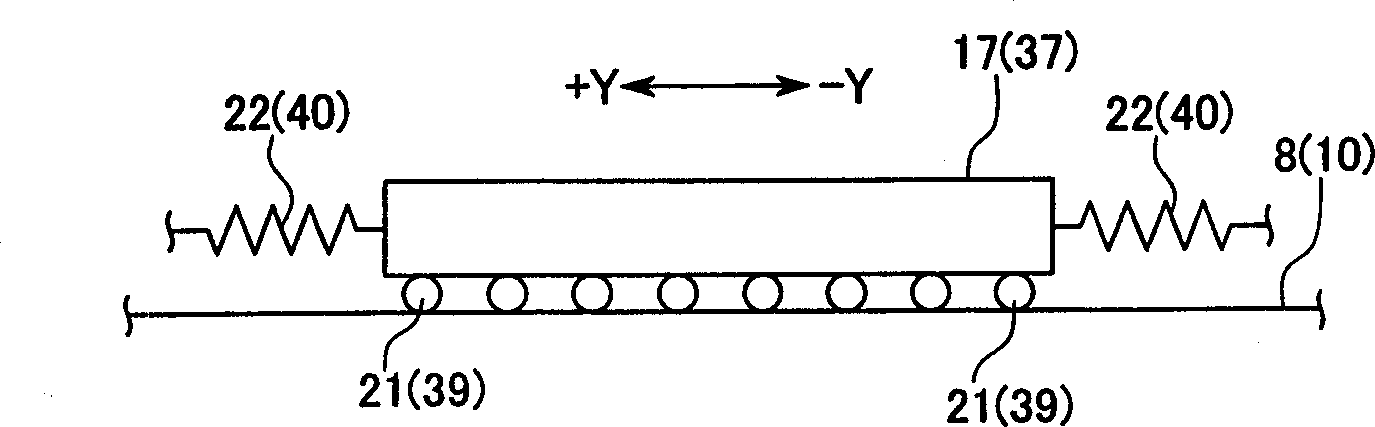
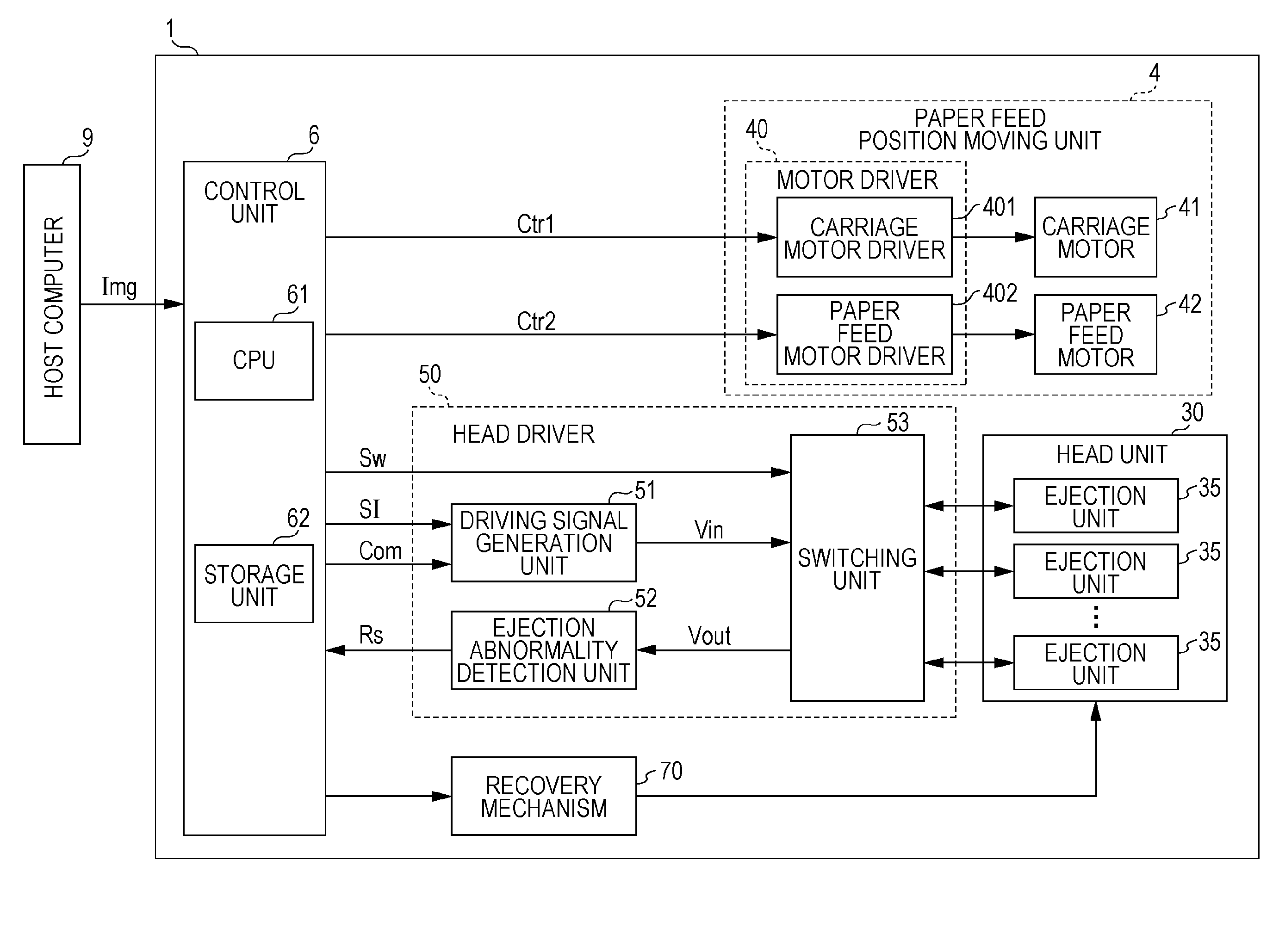
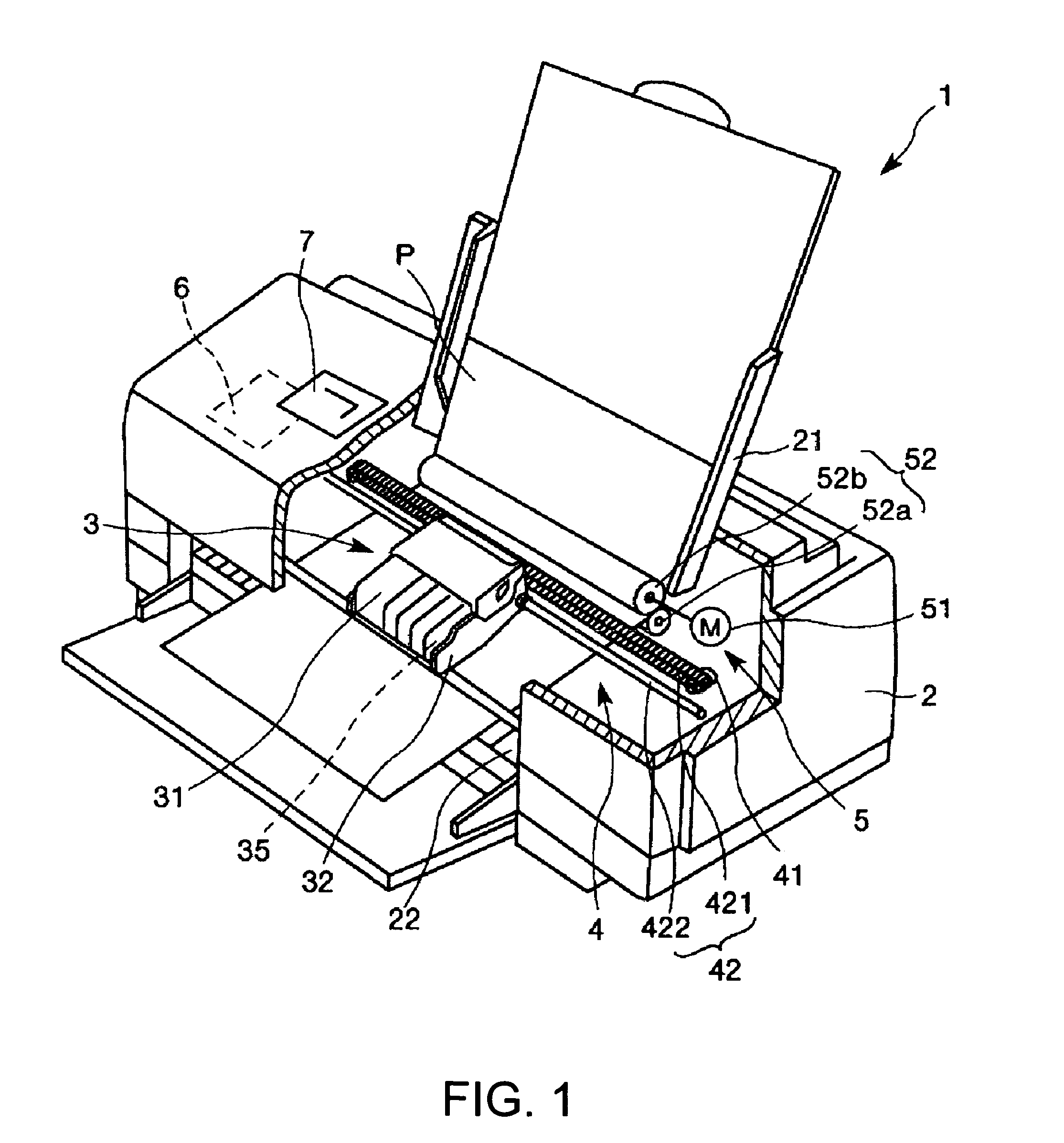
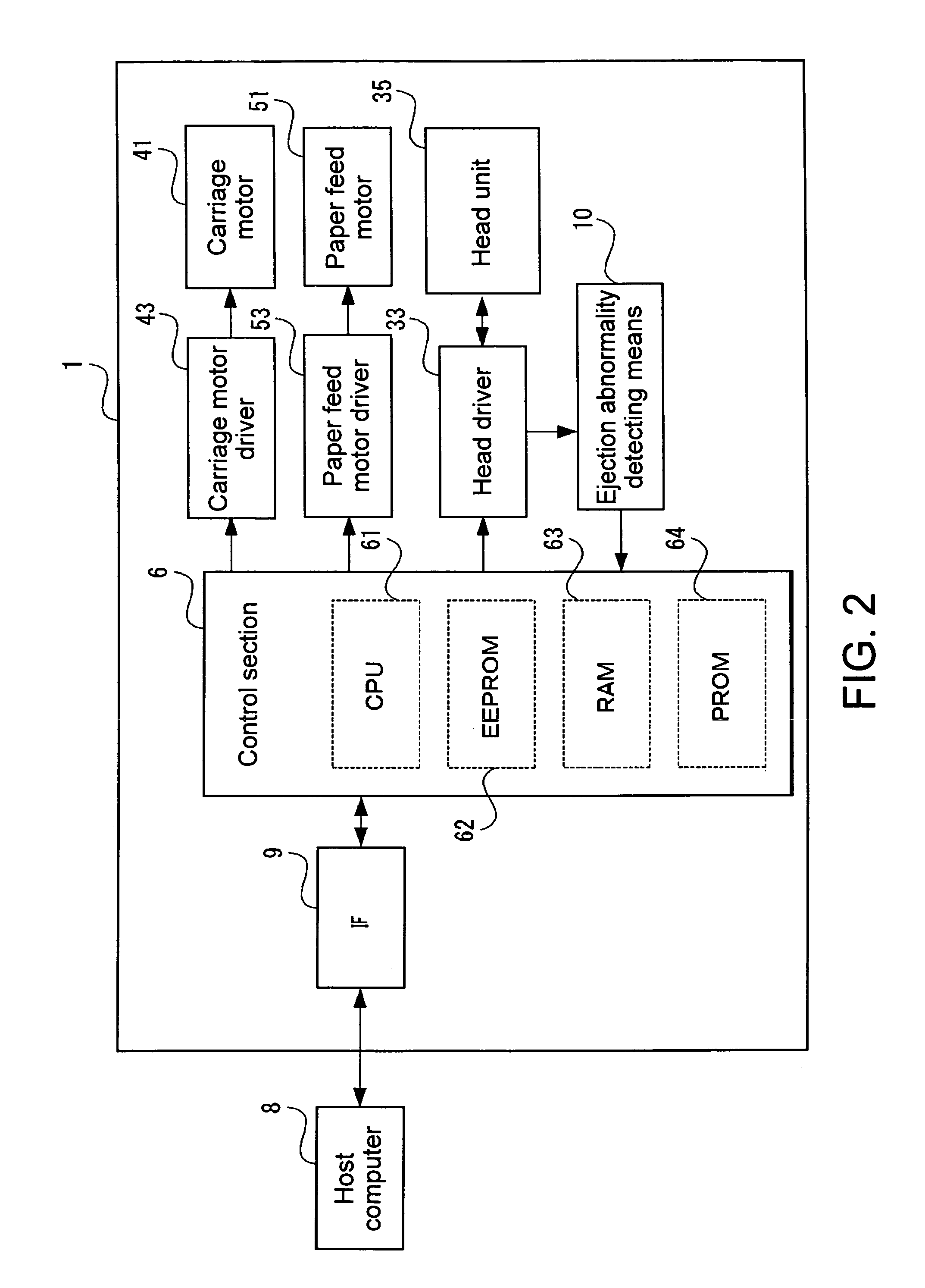
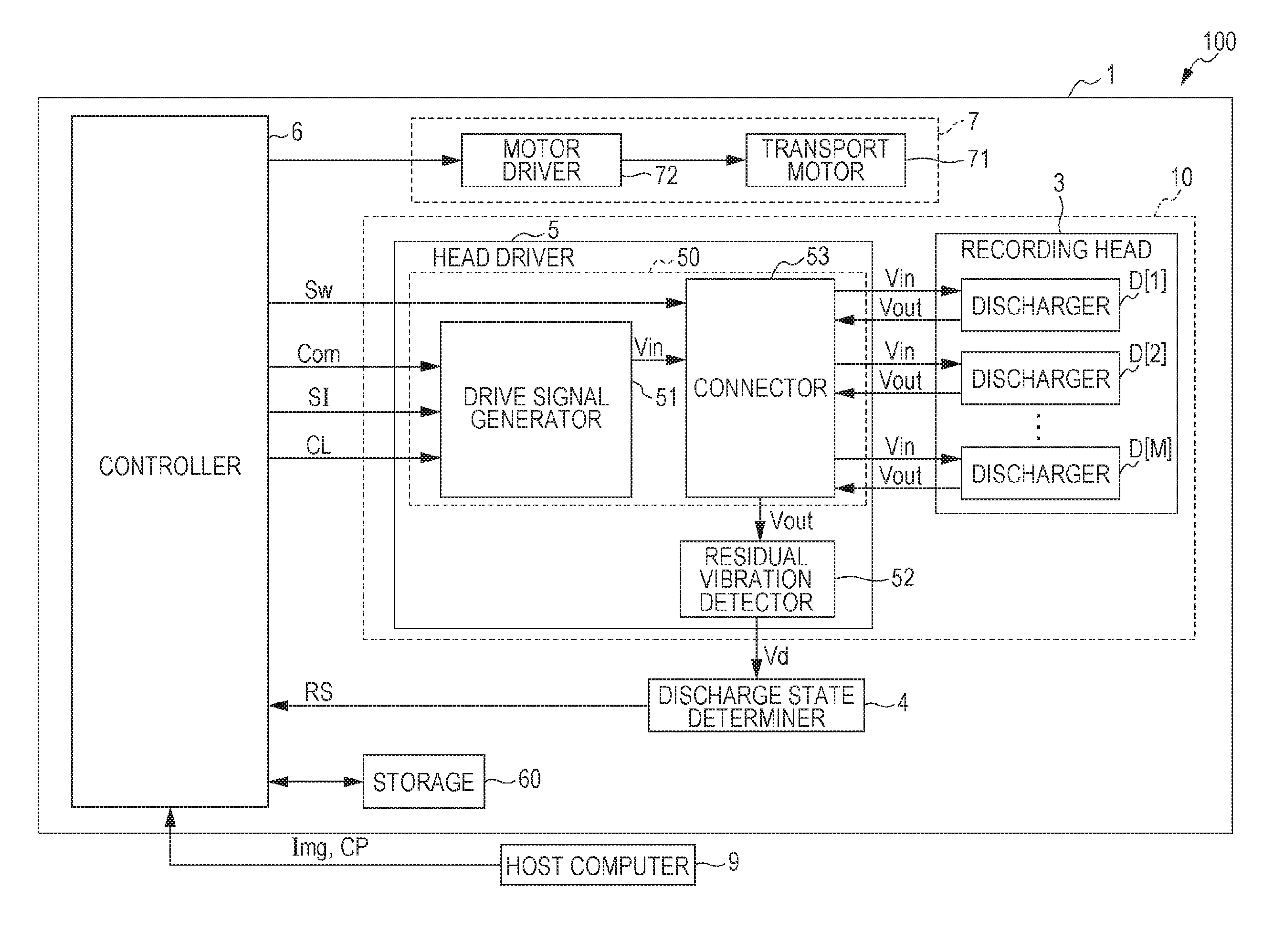
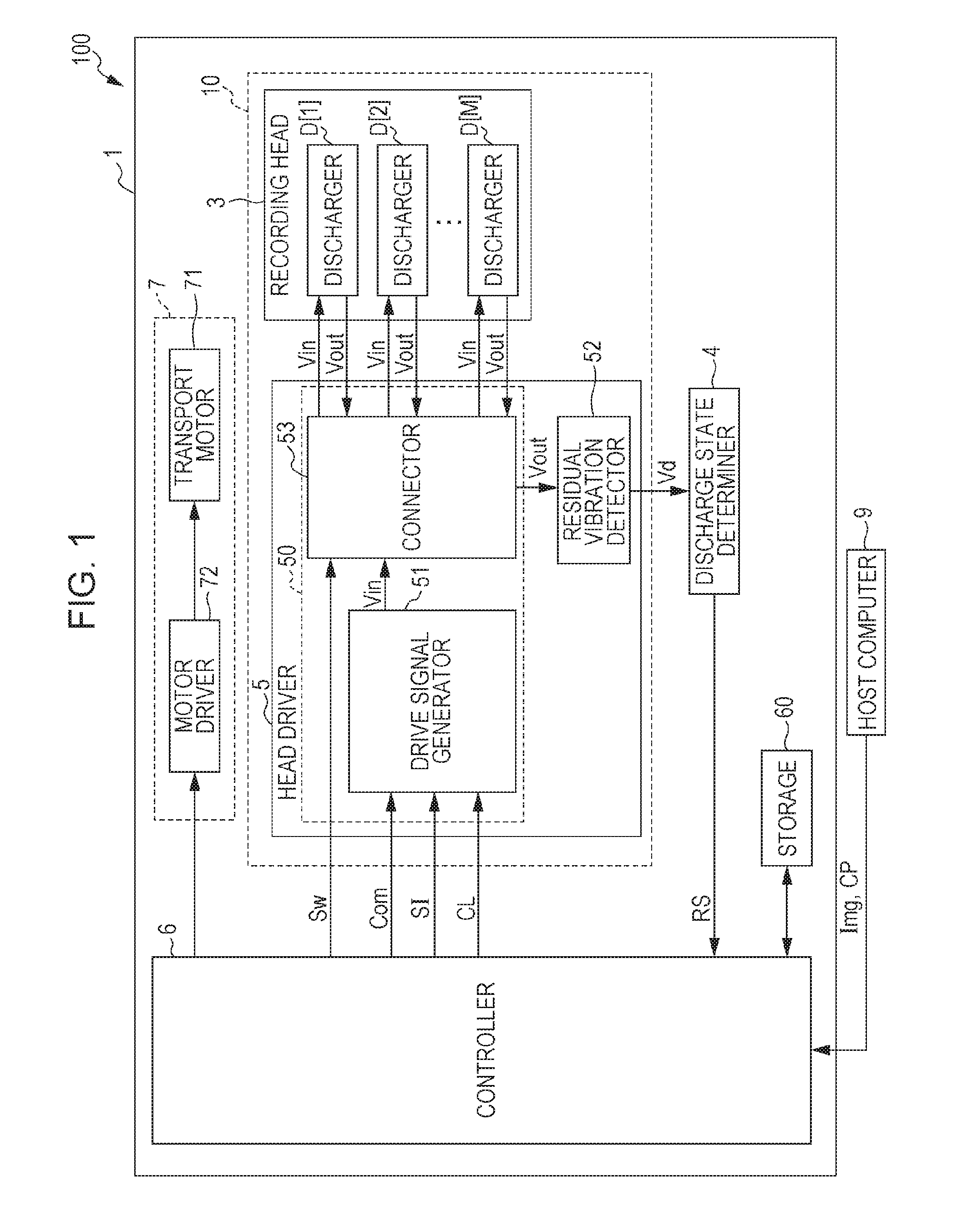
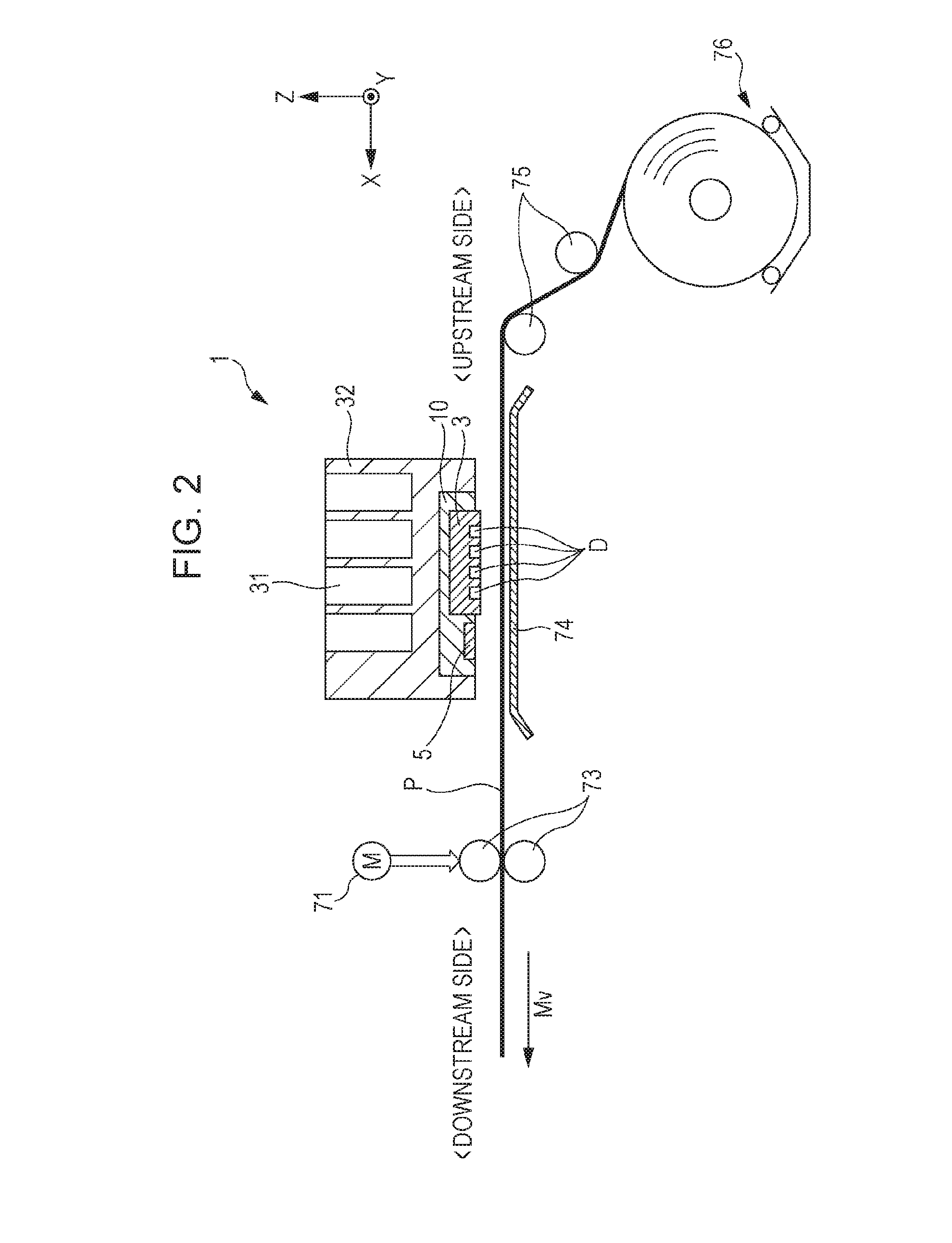
Droplet discharging device and method of detecting discharge abnormality thereof
ActiveUS20050212845A1Accurate detectionSimple structureOther printing apparatusCapacitanceElectricity
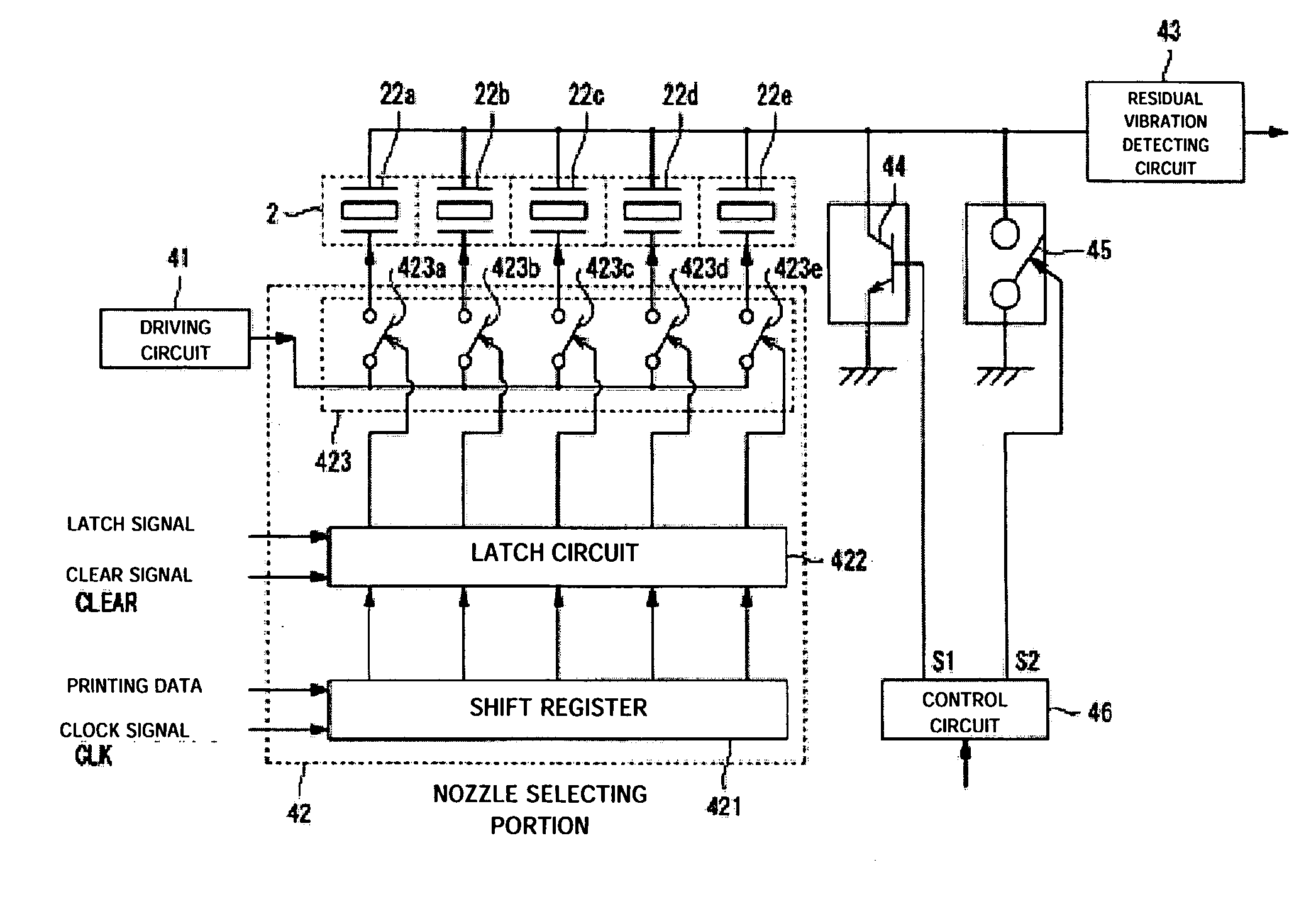
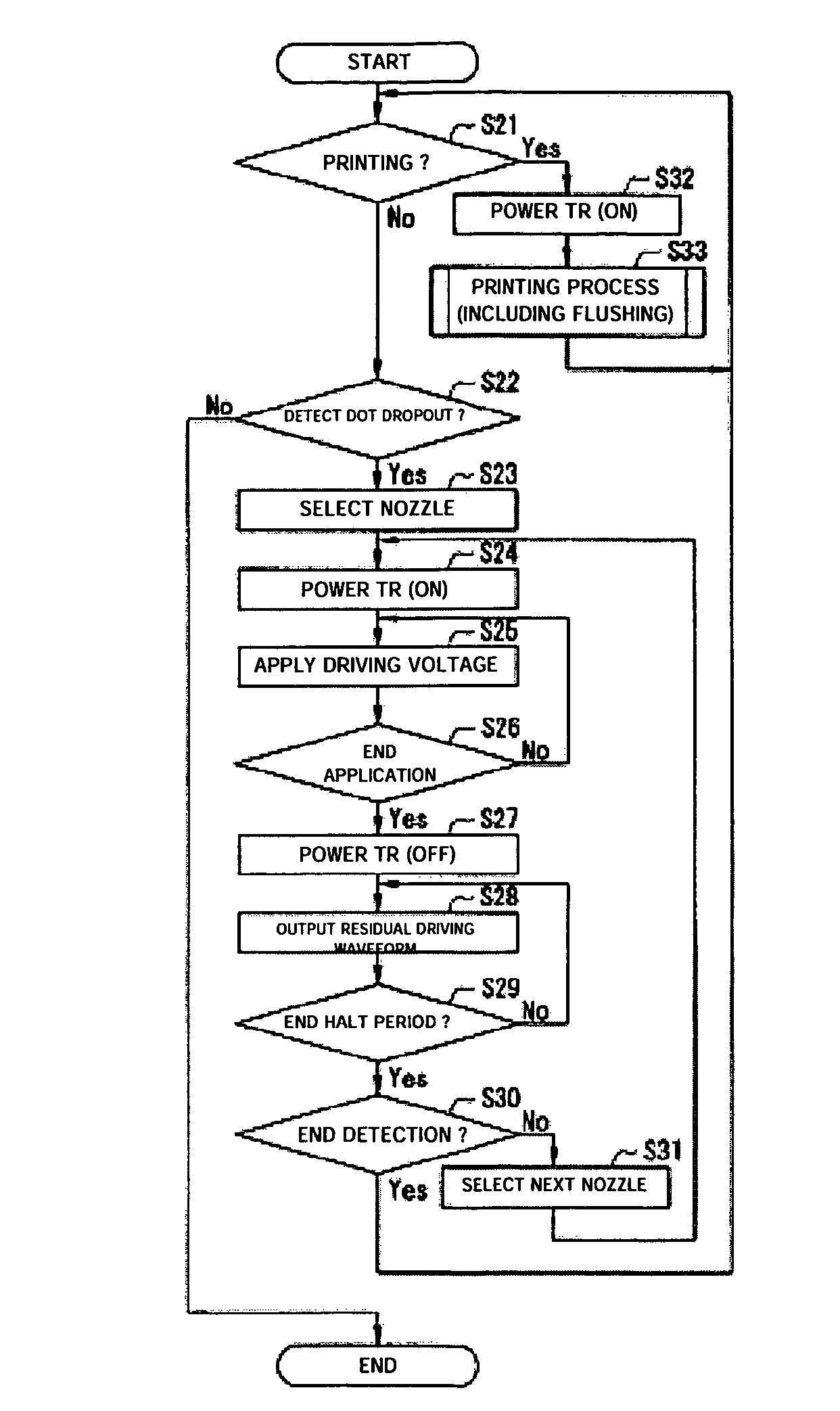
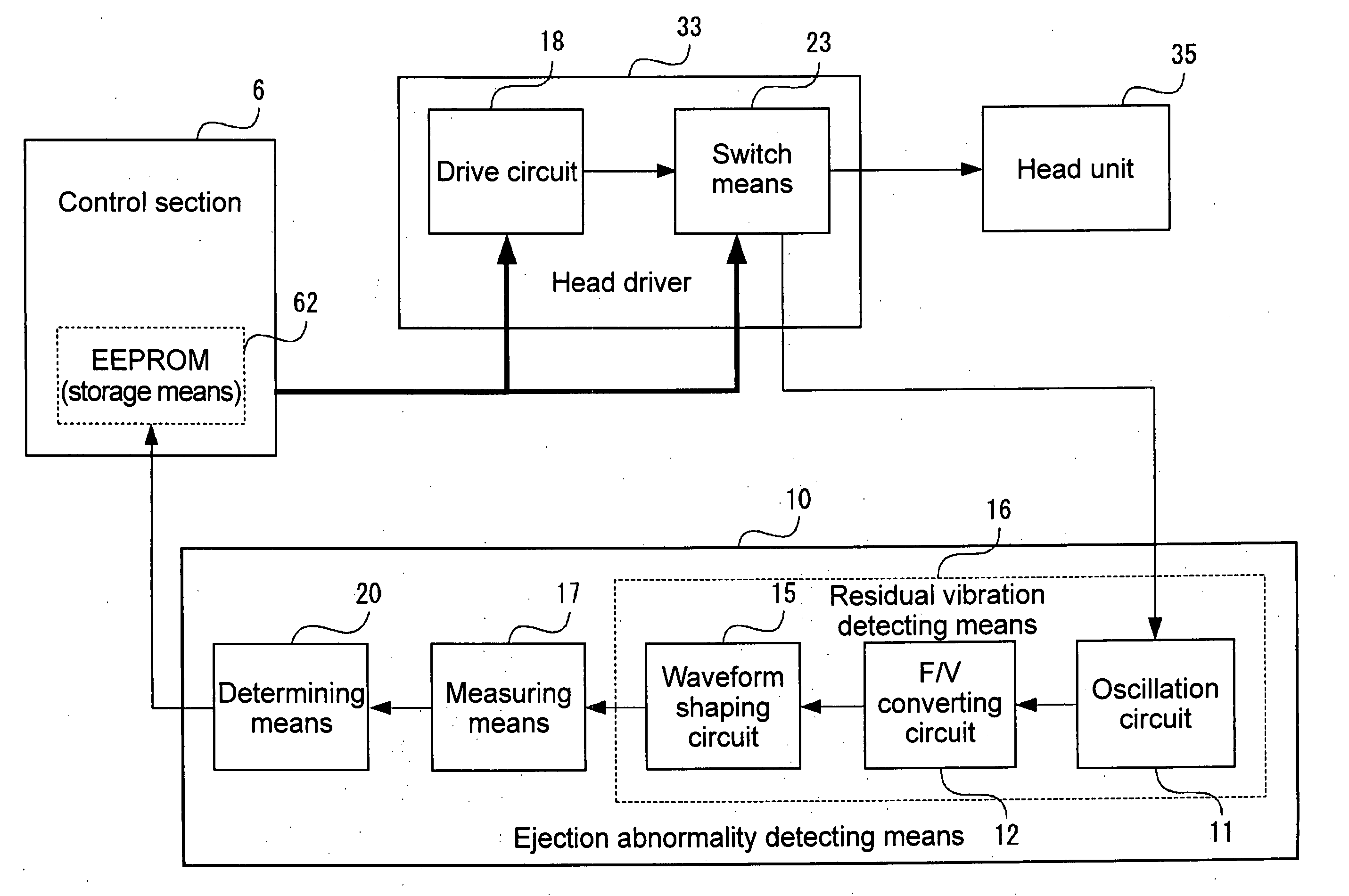
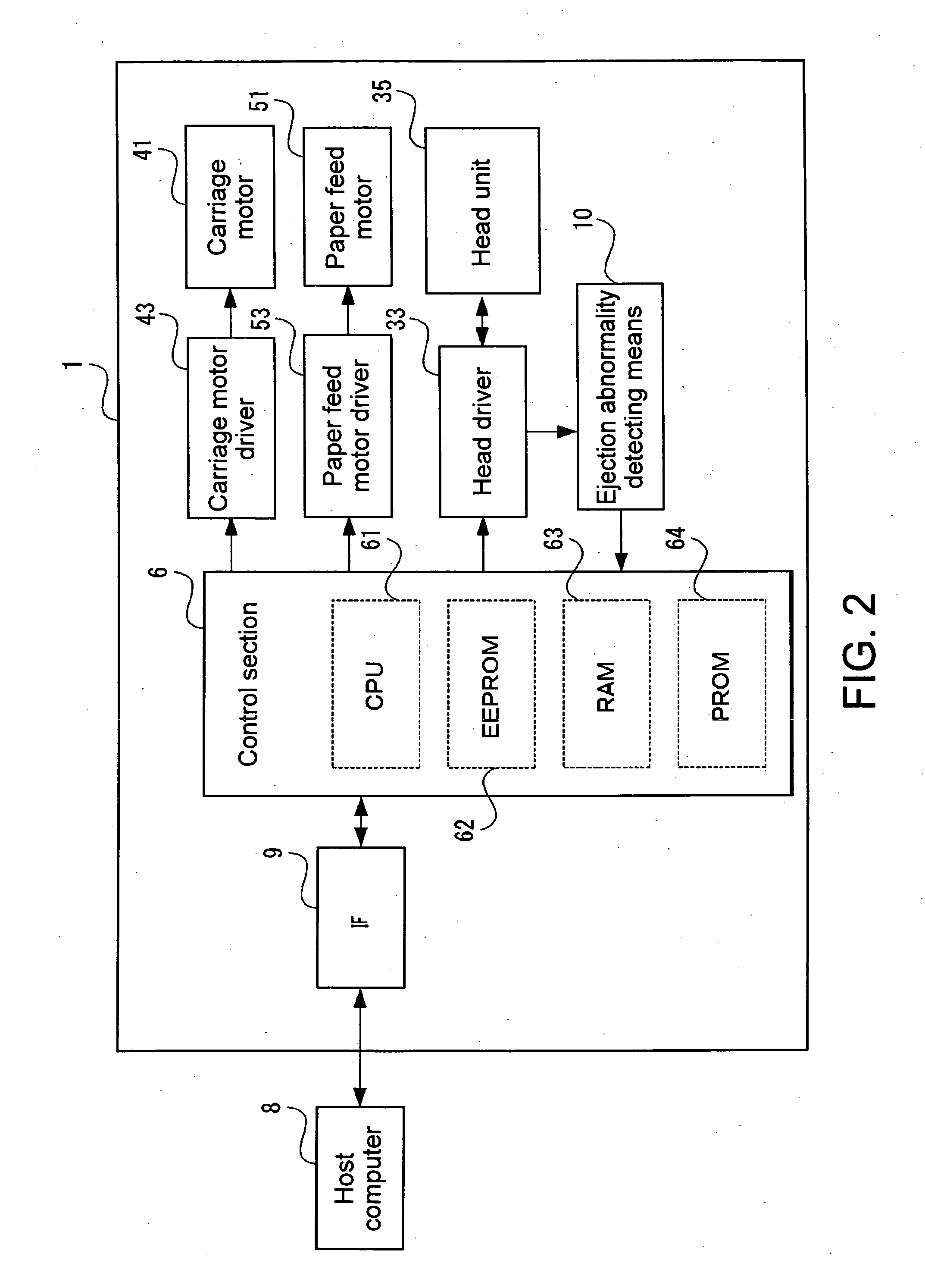
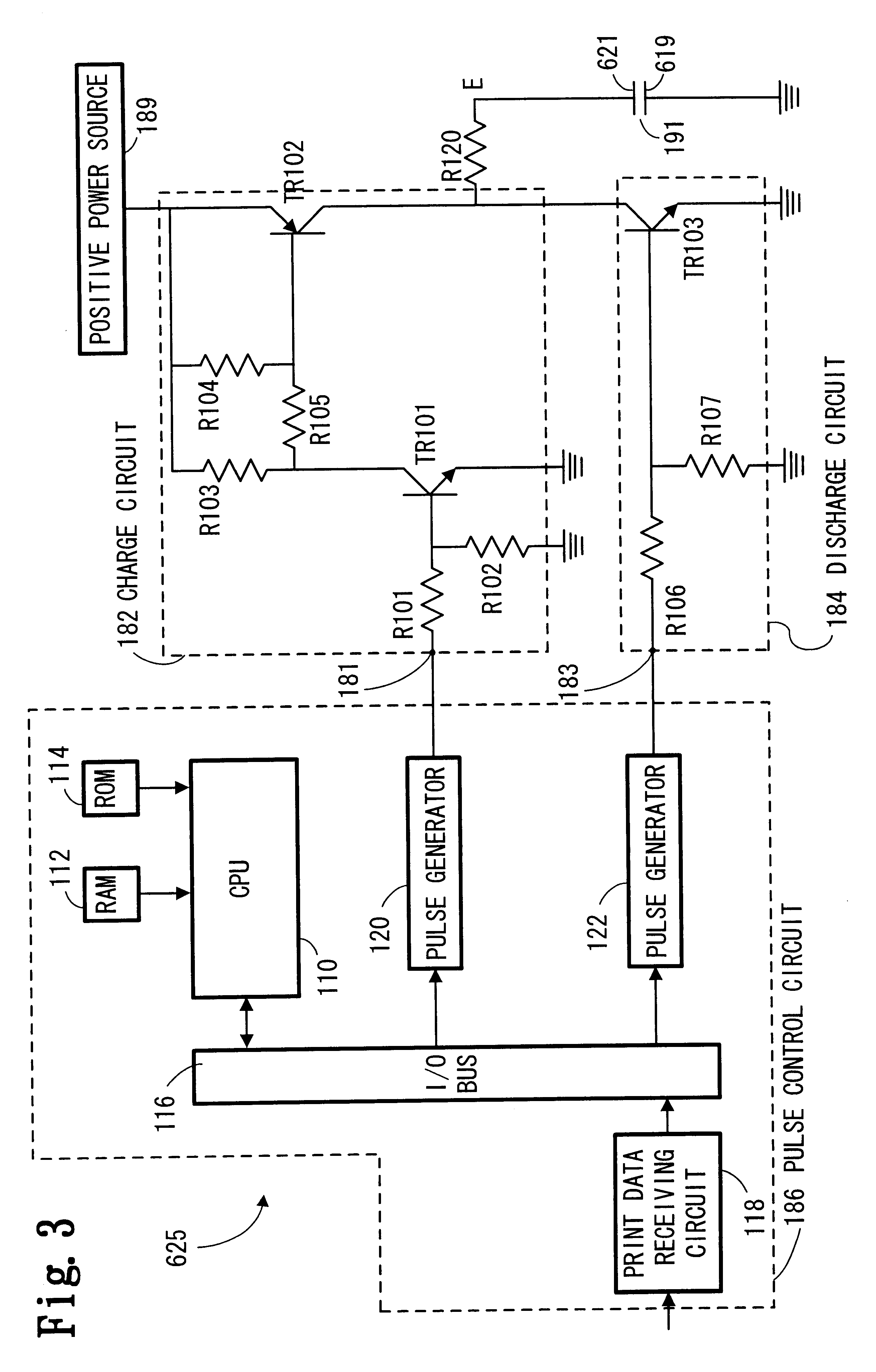
A droplet discharging device is provided which does not require a special sensor (an optical sensor) and can enhance the precision of detecting a discharge abnormality of ink droplets. When printing is to be carried out, a transistor having a large current capacitance is turned on, a driving signal is applied from a driving circuit to piezoelectric actuators, and ink droplets are discharged by corresponding nozzles. Upon detecting a discharge abnormality of the nozzles, one of the piezoelectric actuators corresponding to the nozzles is selected, the transistor is turned off and a switch is turned on. A driving voltage is then applied from the driving circuit to the piezoelectric actuator thus selected in this state. When the application of the driving voltage ends, the switch is turned off. Consequently, a residual vibration detecting circuit detects the electromotive voltage of the piezoelectric actuator by the residual vibration of a vibrating plate.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
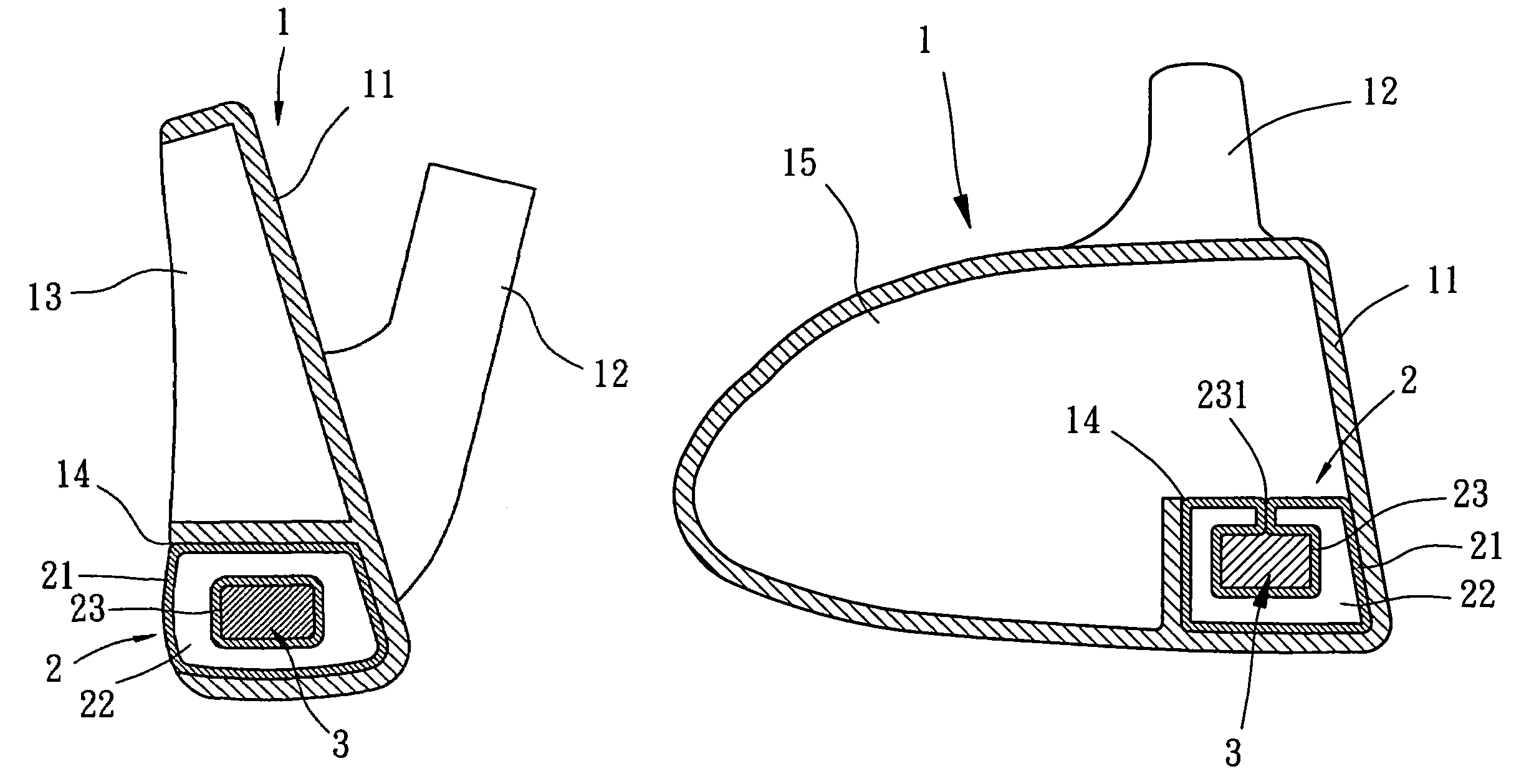
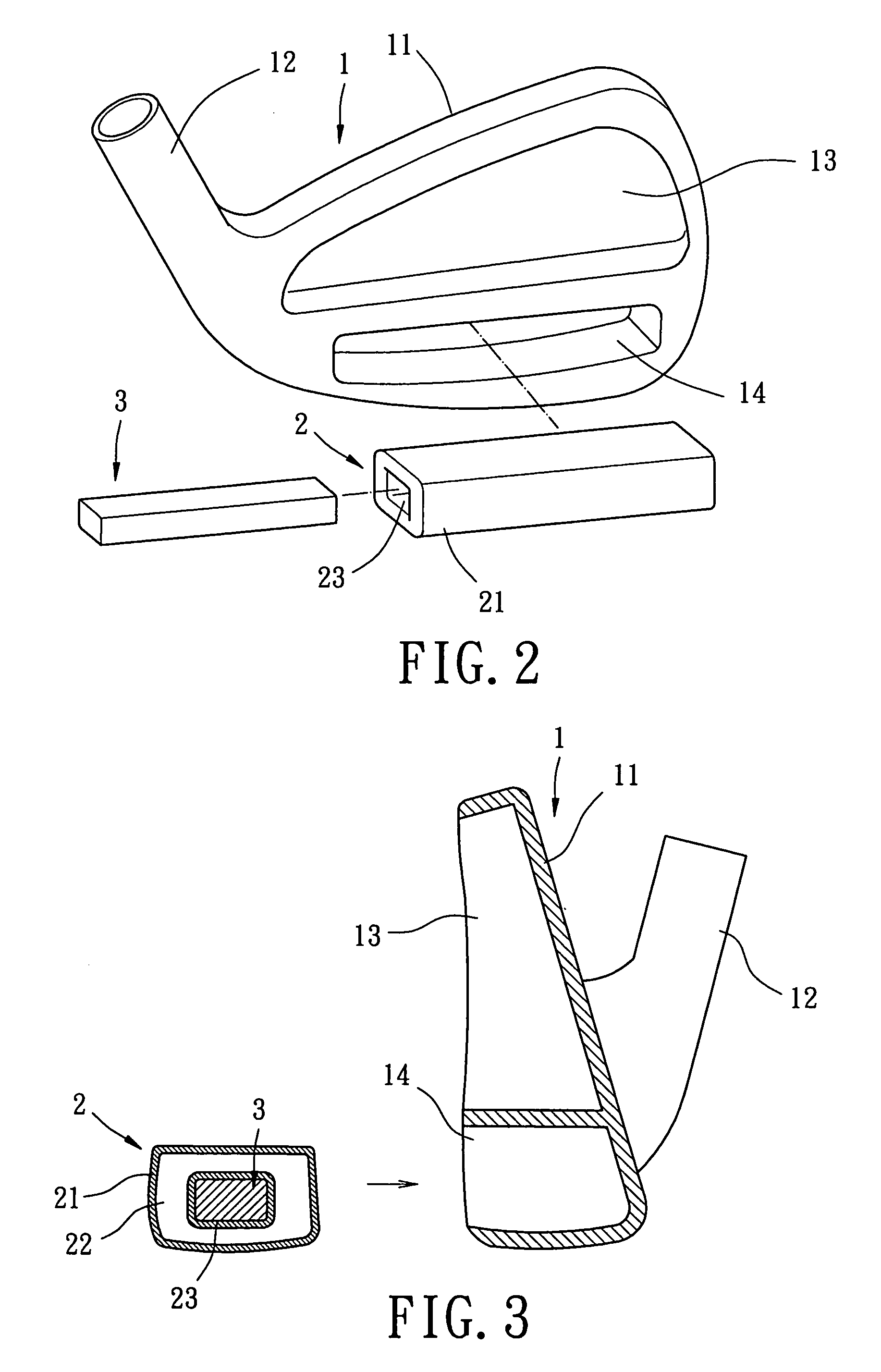
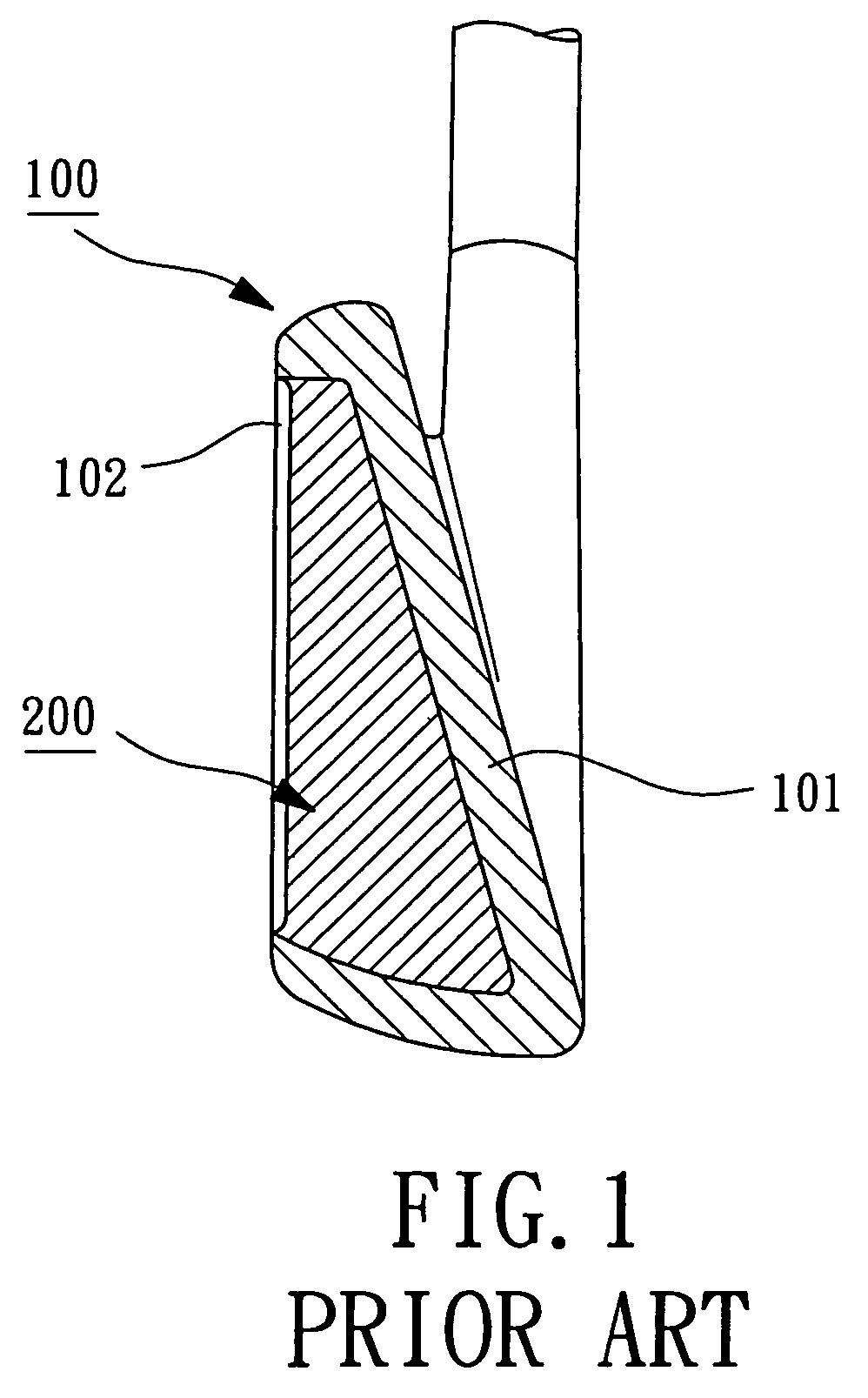
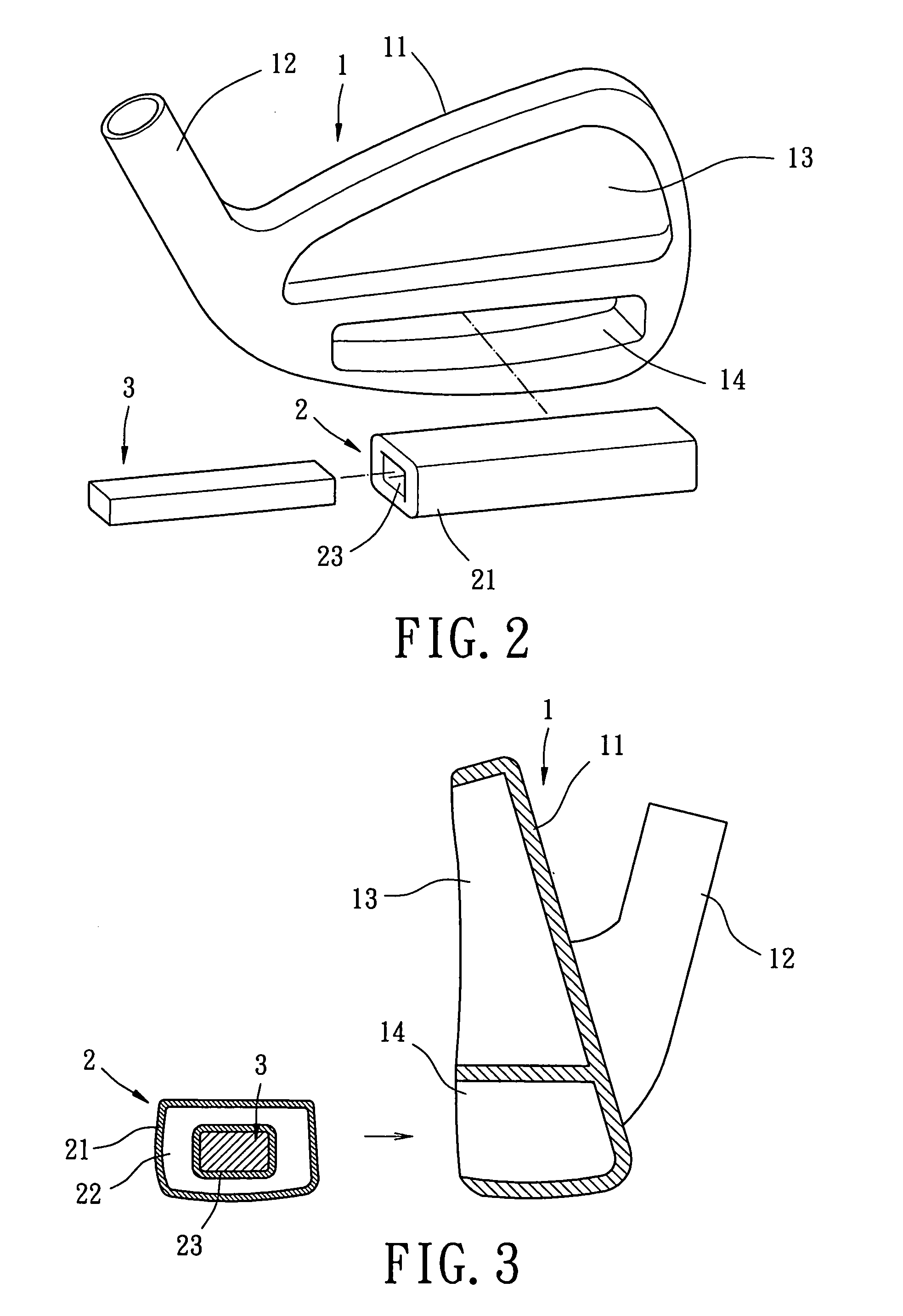
Vibration-absorbing weight system for golf club head
A golf club head includes a body with a striking plate that has a front side for striking a golf ball and a rear side. A vibration-absorbing area is defined behind the striking plate. At least one gas cushion is mounted in the vibration-absorbing area and includes a bladder defining a gas chamber. The bladder is made of an elastomeric material, and the gas chamber is filled with at least one gas to provide the at least one gas cushion with compressibility. The at least one gas cushion includes an engaging section with which at least one weight member is engaged. The at least one weight member and the at least one gas cushion together adjust a center of gravity of the golf club head while absorbing residual vibrations generated as a result of striking a golf ball.
Owner:FUSHENG PRECISION
Liquid ejecting apparatus and control method thereof
InactiveUS20120249638A1Reduce residual vibrationReduce impactOther printing apparatusResidual vibrationPressure generation
A liquid ejecting apparatus includes: a liquid ejecting head, having a pressure chamber filled with a liquid, and a pressure generation element that causes the pressure of the liquid within the pressure chamber to fluctuate that ejects the liquid from a nozzle based on the pressure fluctuation in the liquid within the pressure chamber; a driving waveform generation unit that generates a driving waveform for ejects the liquid; a control unit that causes the liquid ejecting head to execute a flushing operation that discharges the liquid within the pressure chamber; and a residual vibration detection unit that detects a residual vibration in the liquid within the pressure chamber. The control unit calculates a characteristic value in accordance with a characteristic of the liquid based on the residual vibration produced by the flushing operation, and corrects the driving waveform based on the characteristic value.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and apparatus for robust vibration suppression
InactiveUS20070032890A1Useful propertyMore informationVehicle testingRecord information storageTime domainResidual vibration
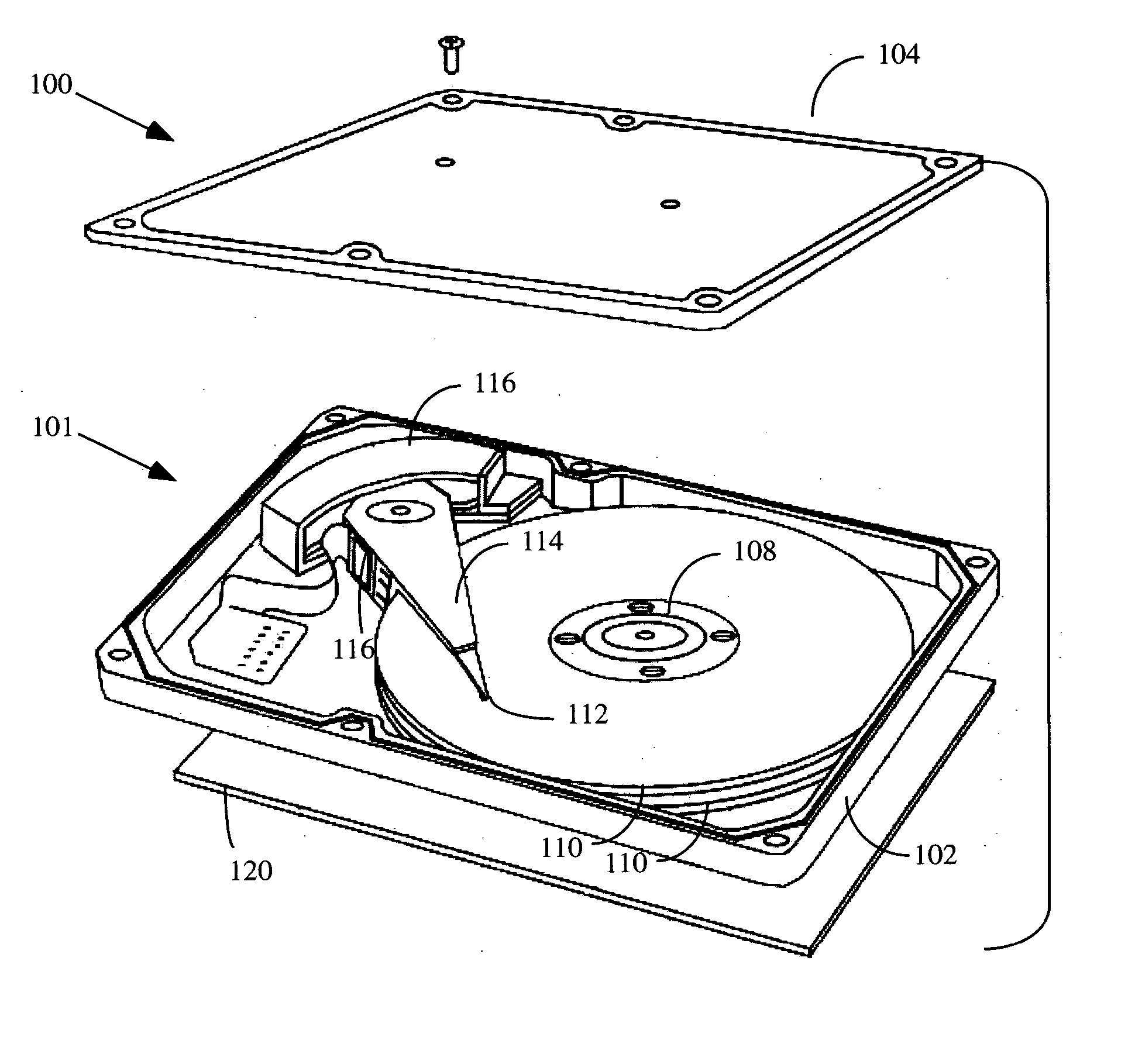
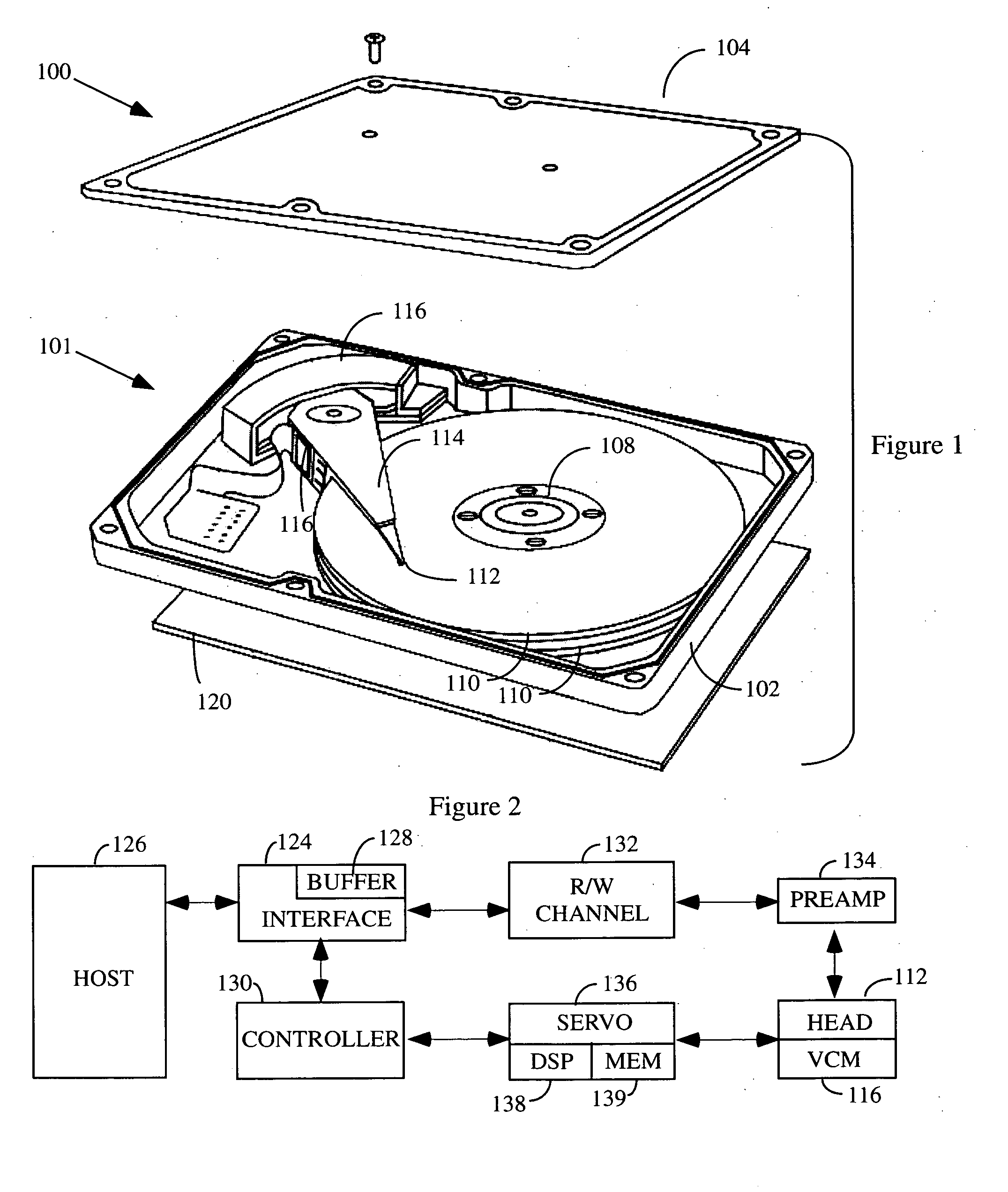
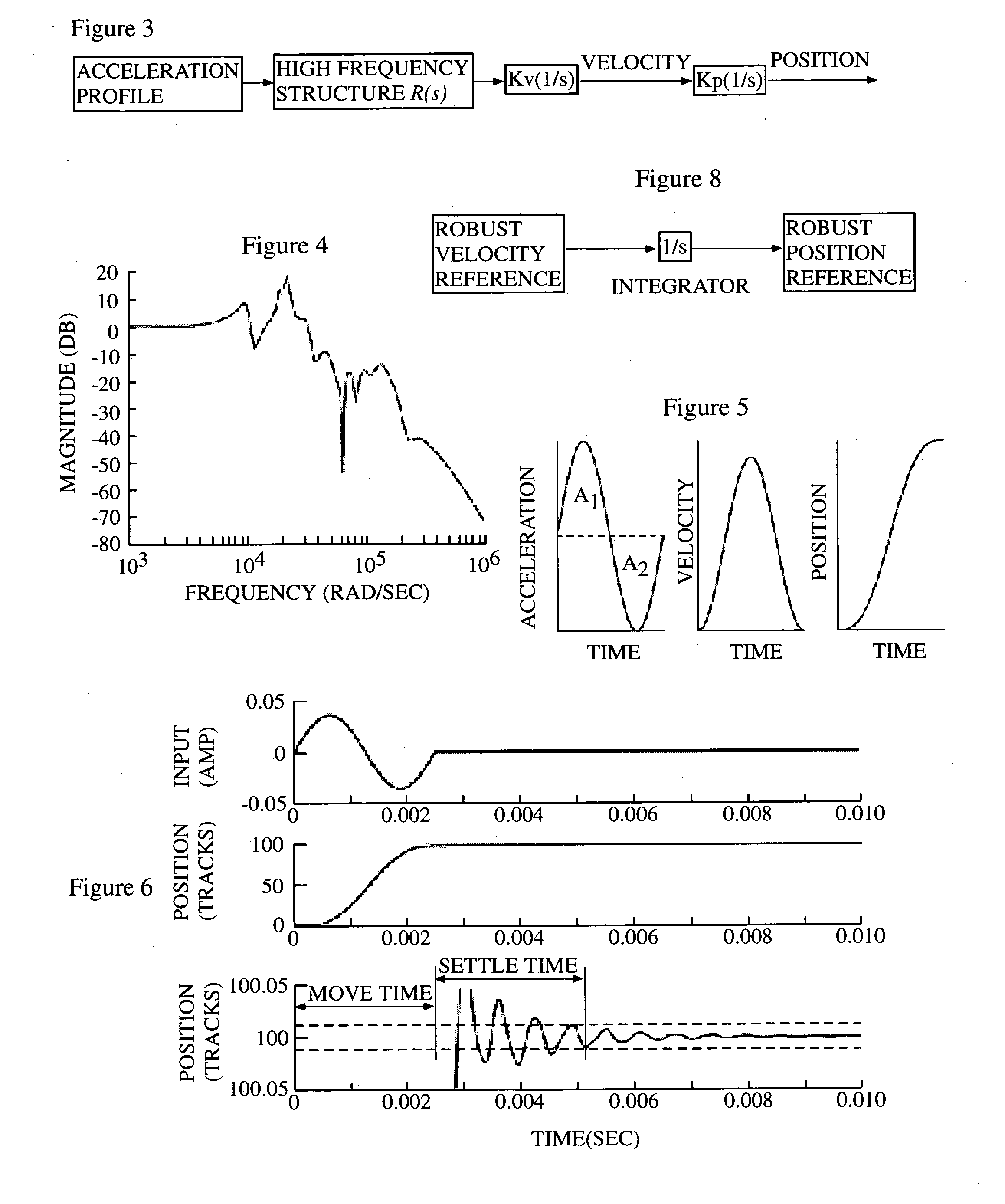
According to a preferred aspect of the instant invention, there is provided a system and method of robust vibration suppression which might be used in many subject matters, but which is preferably used in connection with computer controlled electromechanical devices such as disk drive arms. In a first preferred embodiment, a Gaussian waveform is selected as a velocity profile, with its integral and derivatives providing position and acceleration / jerk profiles respectively. According to another preferred embodiment, the movement velocity profile will be selected to be a member of the prolate spheroid family of waveforms. This family of functions has certain optimal properties with respect to the frequency domain concentration of energy for a given time-domain length time series. The movement of a flexible arm that is performed according to the invention will be one that has minimal or reduced residual vibration after it has reached its destination.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Vibration-absorbing weight system for golf club head
A golf club head includes a body with a striking plate that has a front side for striking a golf ball and a rear side. A vibration-absorbing area is defined behind the striking plate. At least one gas cushion is mounted in the vibration-absorbing area and includes a bladder defining a gas chamber. The bladder is made of an elastomeric material, and the gas chamber is filled with at least one gas to provide the at least one gas cushion with compressibility. The at least one gas cushion includes an engaging section with which at least one weight member is engaged. The at least one weight member and the at least one gas cushion together adjust a center of gravity of the golf club head while absorbing residual vibrations generated as a result of striking a golf ball.
Owner:FUSHENG PRECISION
Robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based on input shaper
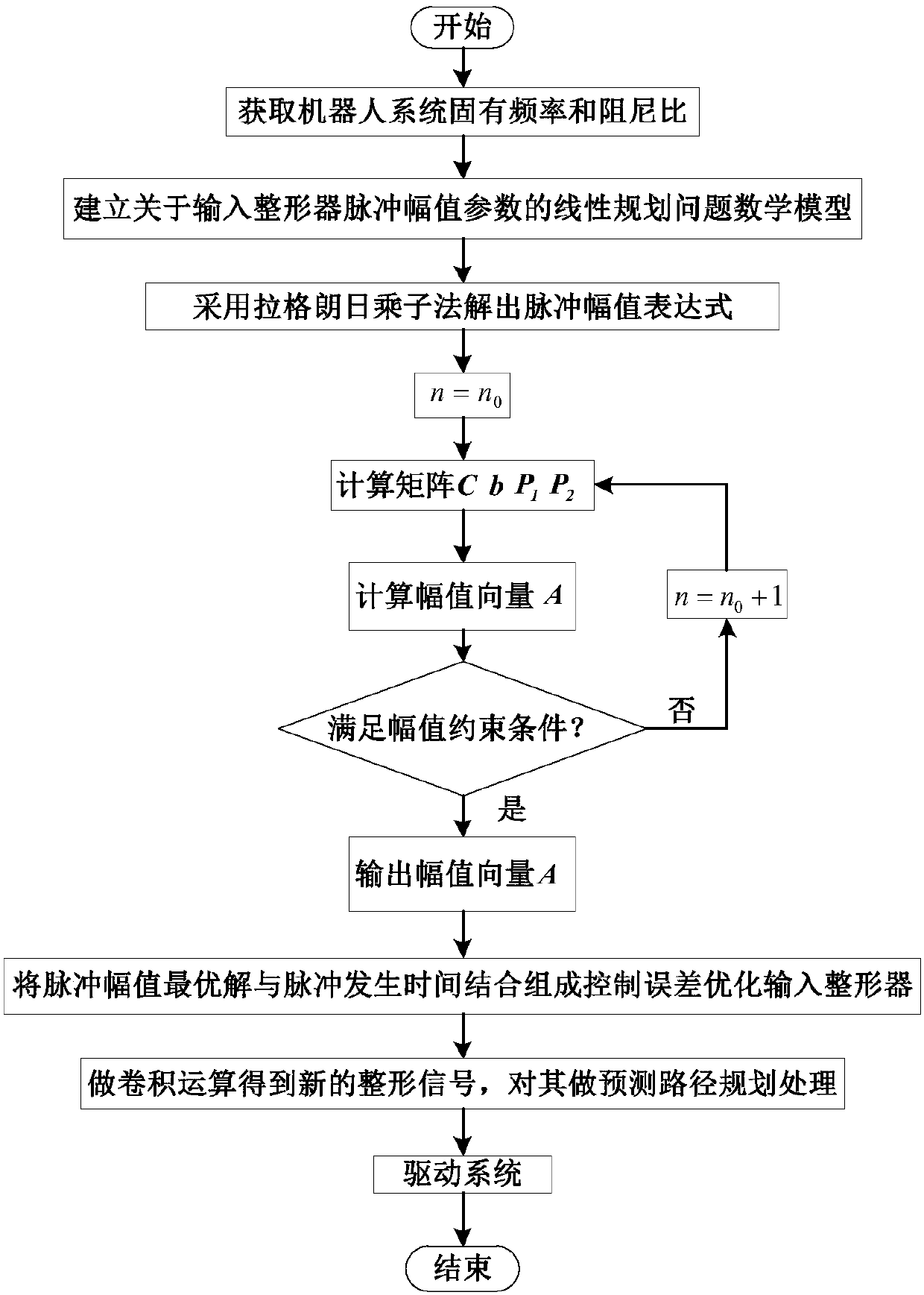
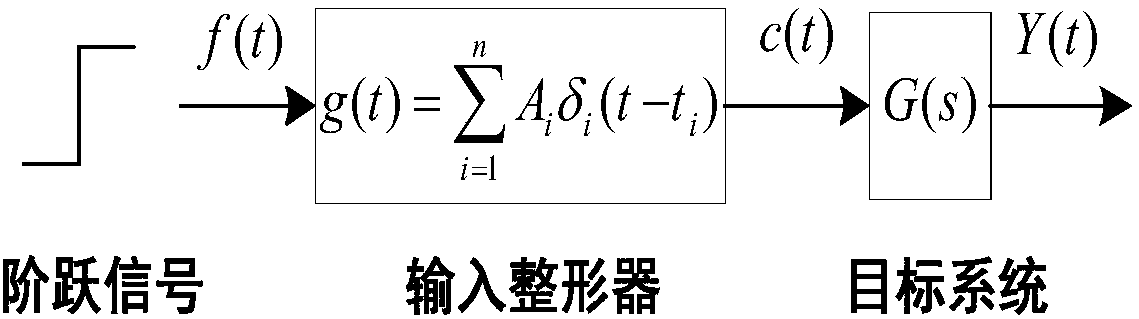
The invention discloses a robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based an input shaper. The robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based the input shaper comprises the steps that firstly, the undamped inherent frequency omega0 and the damping ratio zeta of a robot system are obtained; secondly, a linear programming problem mathematic model about the pulse amplitude parameter of the input shaper is established; thirdly, a pulse amplitude expression is solved through a lagrangian multiplier method, and the optimal solution of the pulse amplitude is workedout through iteration; fourthly, the optimal solution of the pulse amplitude and the pulse generation time are combined to form the control error optimization input shaper; and fifthly, a reference signal and the control error optimization input shaper are subjected to convolution operation, so that a novel shaping signal is obtained, and after a predicted path is planned for the novel shaping signal, the system is driven by the signal to restrain robot tail end residual vibration. According to the robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based the input shaper, the robustness of the input shaper is enhanced, and a process control error and a positioning error are minimized; and the predicted path is planned for the shaped signal, and thus the system lag time caused by input shaping is compensated and reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
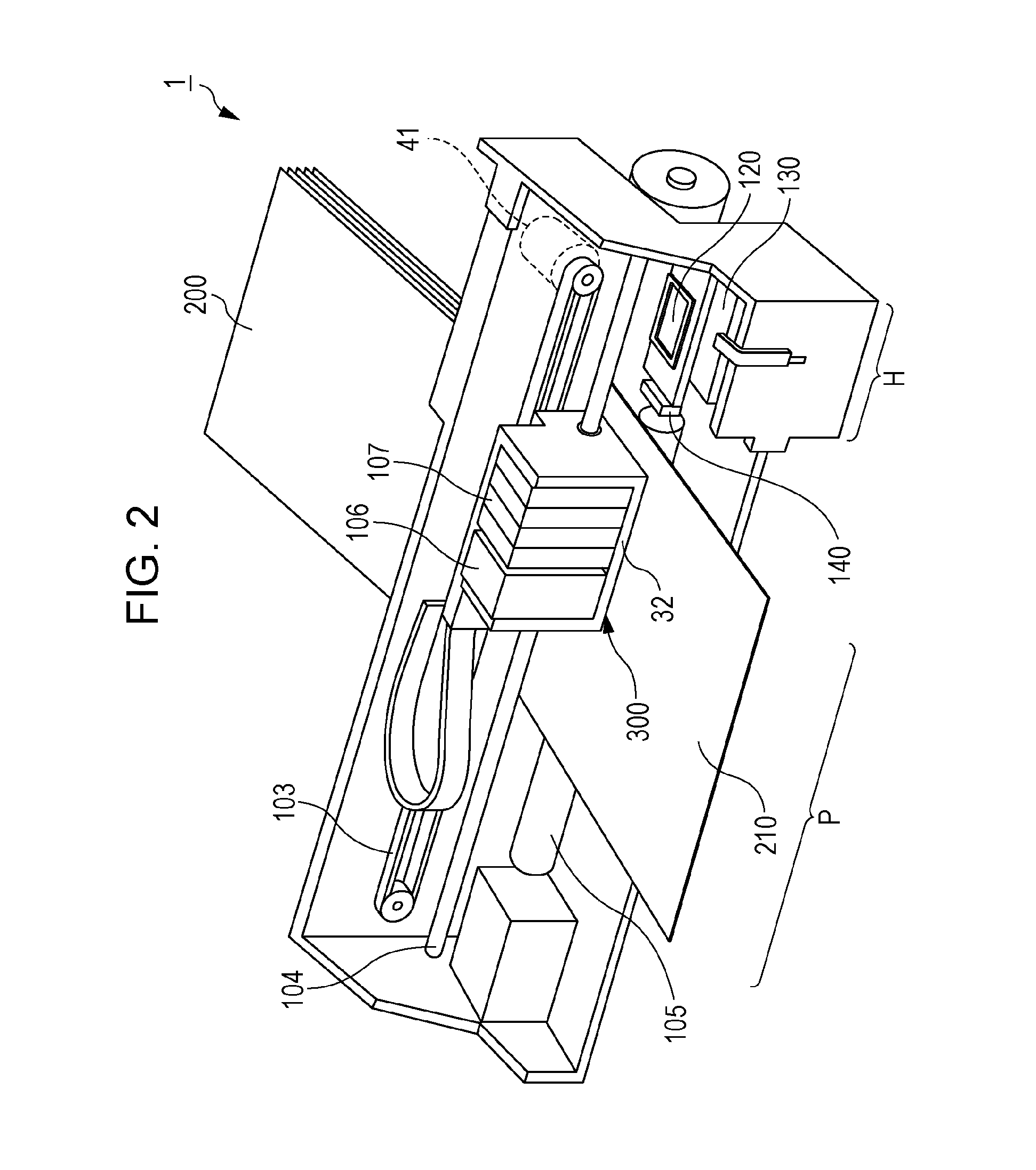
Droplet ejection apparatus and a method of detecting and judging head failure in the same
ActiveUS20050057596A1Eliminate the causeManufacturing costOther printing apparatusResidual vibrationLapse time
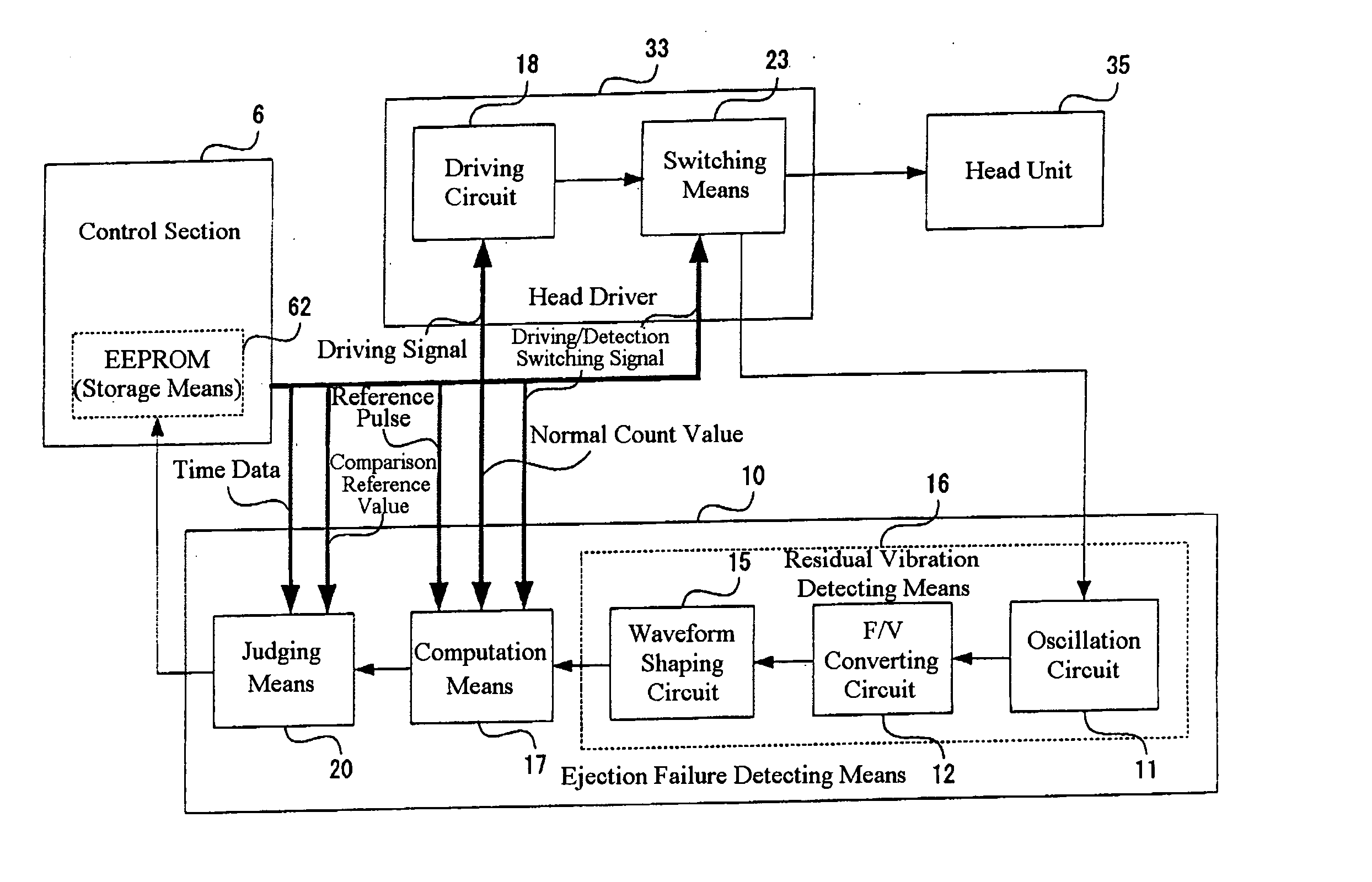
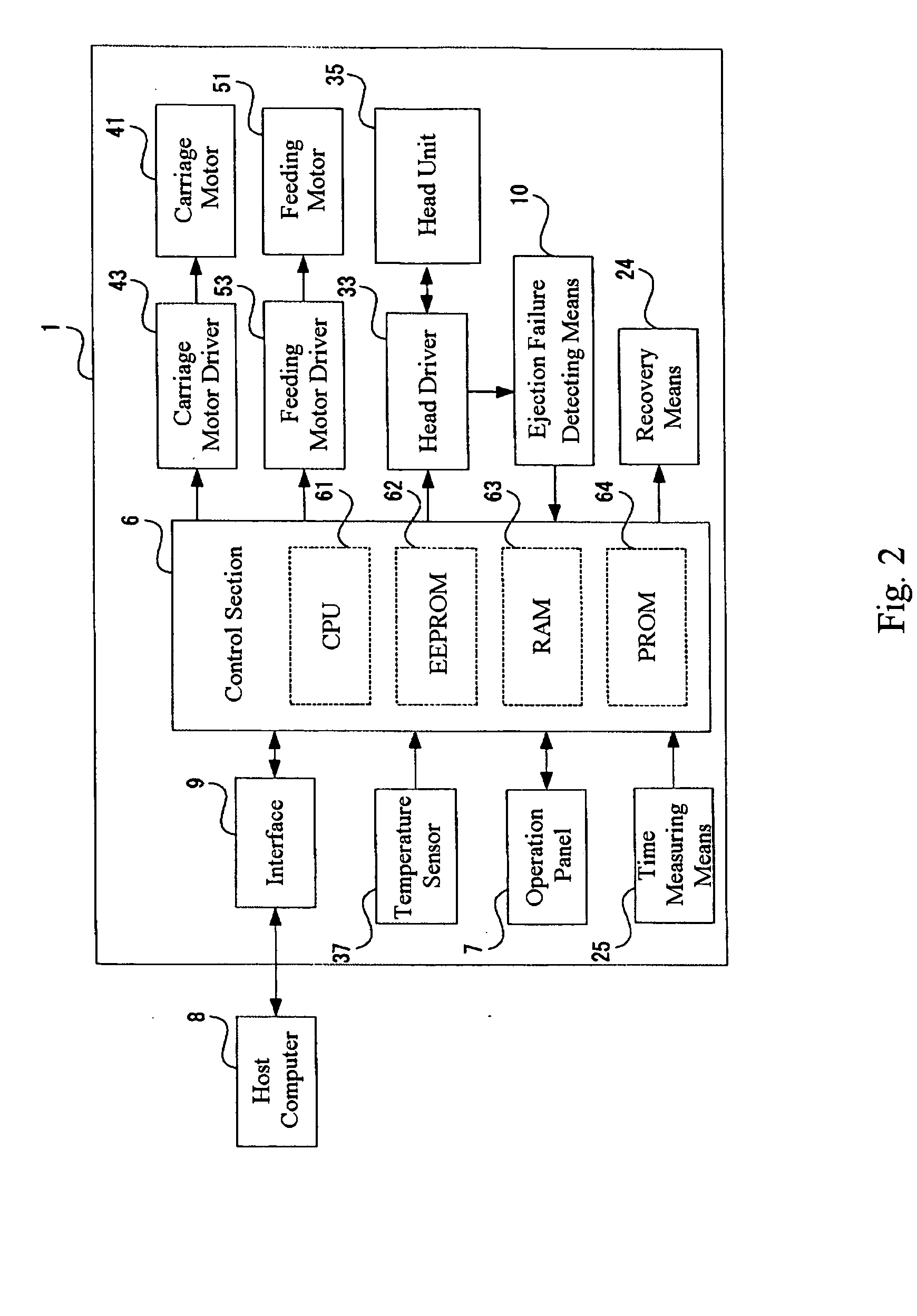
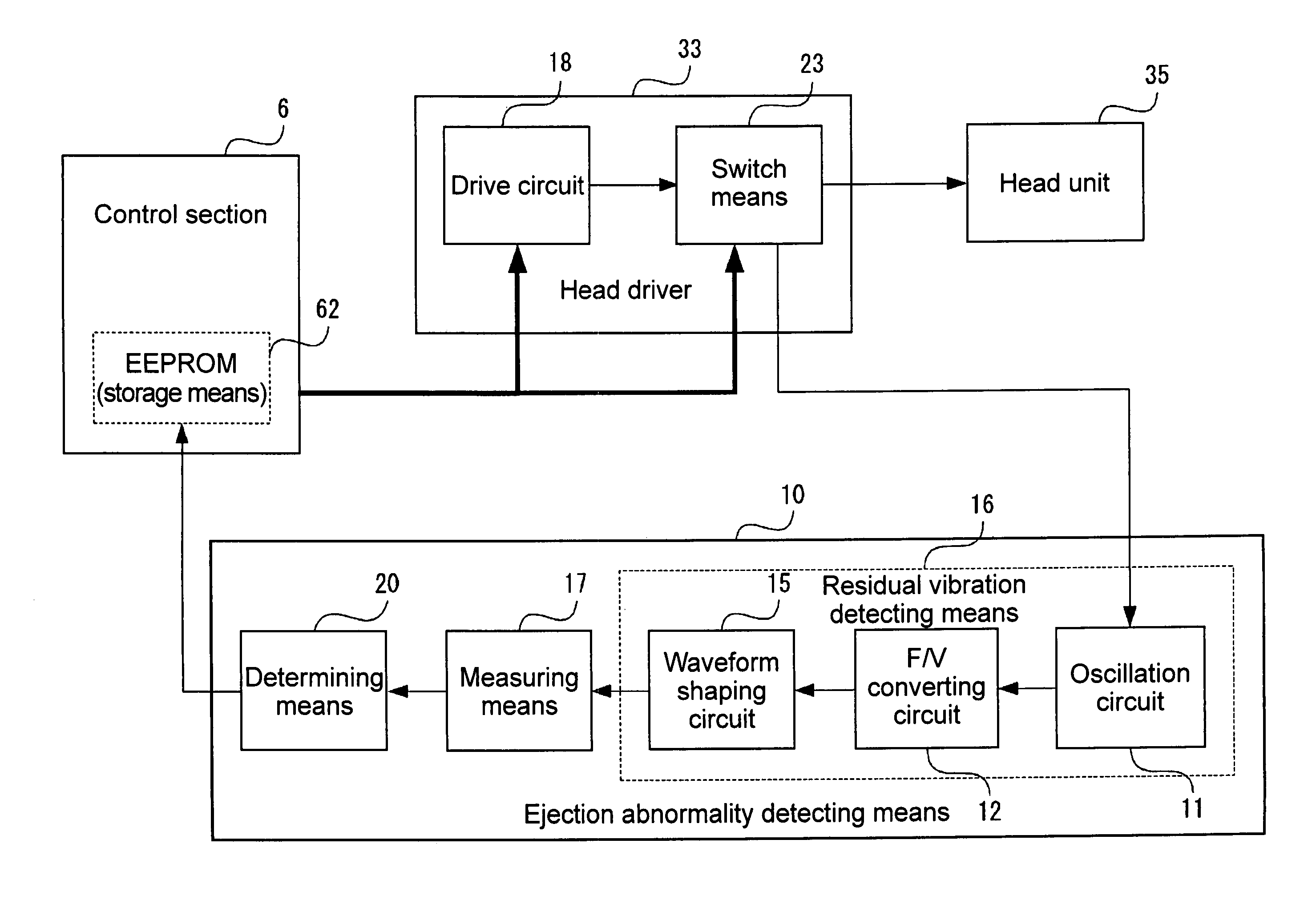
It is an object of the invention to provide a droplet ejection apparatus and a method of detecting and judging a head failure that can detect an ejection failure and carry out appropriate recovery processing according to a cause thereof. The droplet ejection apparatus of the invention includes a plurality of droplet ejection heads, each of the droplet ejection heads including a diaphragm and an actuator which displaces the diaphragm; a driving circuit which drives the actuator of each droplet ejection head; residual vibration detecting means 16 for detecting a residual vibration of the diaphragm displaced by the actuator after the actuator has been driven by the driving circuit; pulse generating means for generating reference pulses; computation means 17 for carrying out a computation for the number of reference pulses generated by the pulse generating means on the basis of the residual vibration of the diaphragm detected by the residual vibration detecting means; time measuring means for measuring a lapsed time since the actuator has been driven by the driving circuit; and head failure judging means 20 for judging a head failure in the droplet ejection heads on the basis of the computation result of the computation means 17 and the lapsed time measured by the time measuring means.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for restraining flexible arm tail end vibration of robot
InactiveCN102636993AImprove travel speedReduce energy consumptionAdaptive controlResidual vibrationControl system
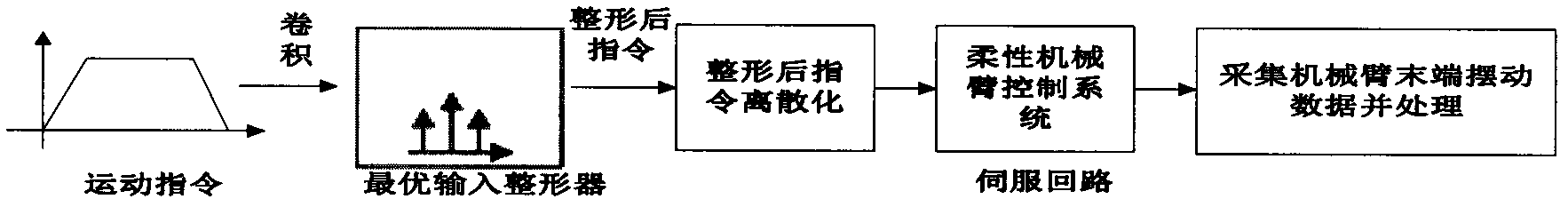
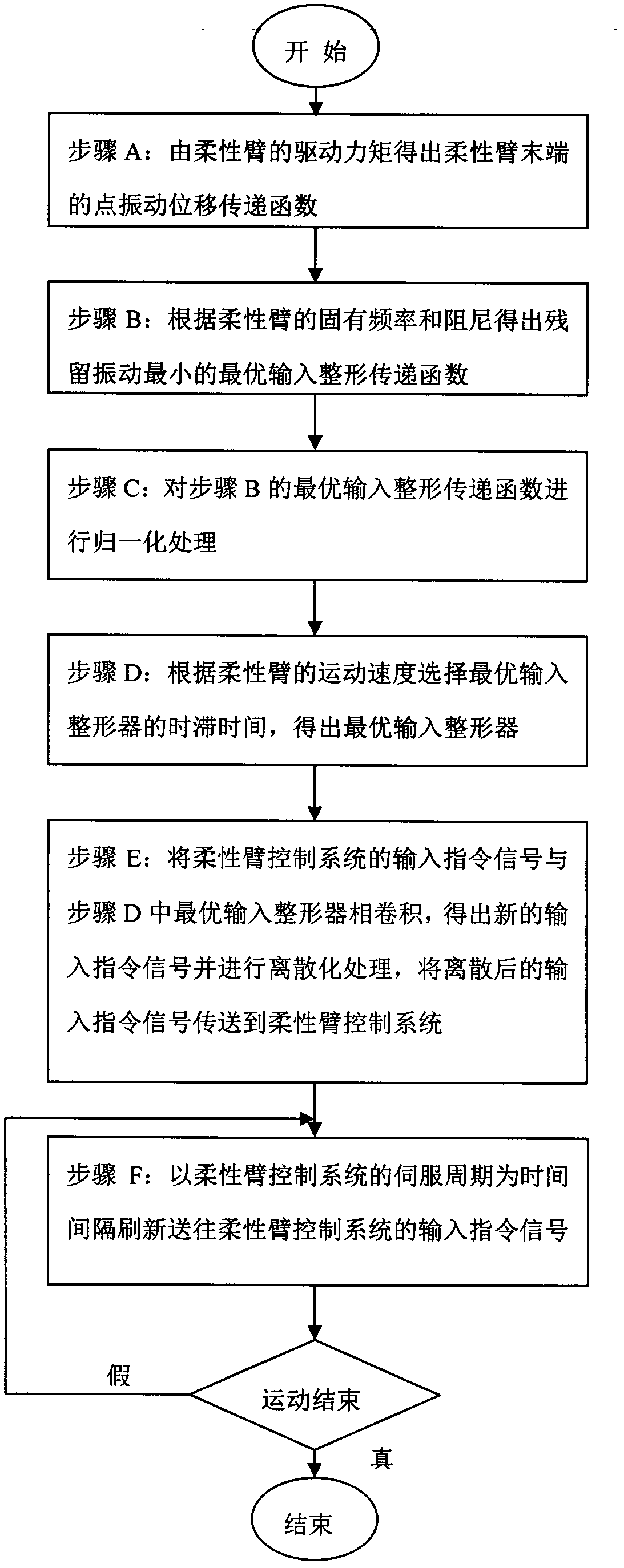
The invention discloses a method for restraining flexible arm tail end vibration of a robot. The method comprises a robot flexible arm, a control system and a processing system for providing a control command signal to the control system. The method comprises the following processing steps of: computing a point vibration displacement transfer function of the tail end of the flexible arm according to driving torque of the flexible arm; computing an optimal input shaping transfer function with smallest residual vibration according to natural frequency and damp of the flexible arm; performing normalization process on the optimal input shaping transfer function; selecting the lag time of an optimal input shaper according to the movement speed of the flexible arm, thus obtaining the optimal input shaper; performing convolution on an input command signal and the optimal input shaper to obtain a new input command signal, discretizing the new input command signal, and transferring the discretized input instruction signal; and refreshing the instruction signal of the control system with the servo cycle serving as the time interval until the end. The method can be used for effectively restraining the vibration at the tail end of the robot flexible arm, improving the follow accuracy and achieving the quick and accurate positioning on the robot flexible arm.
Owner:XUZHOU UNIV OF TECH
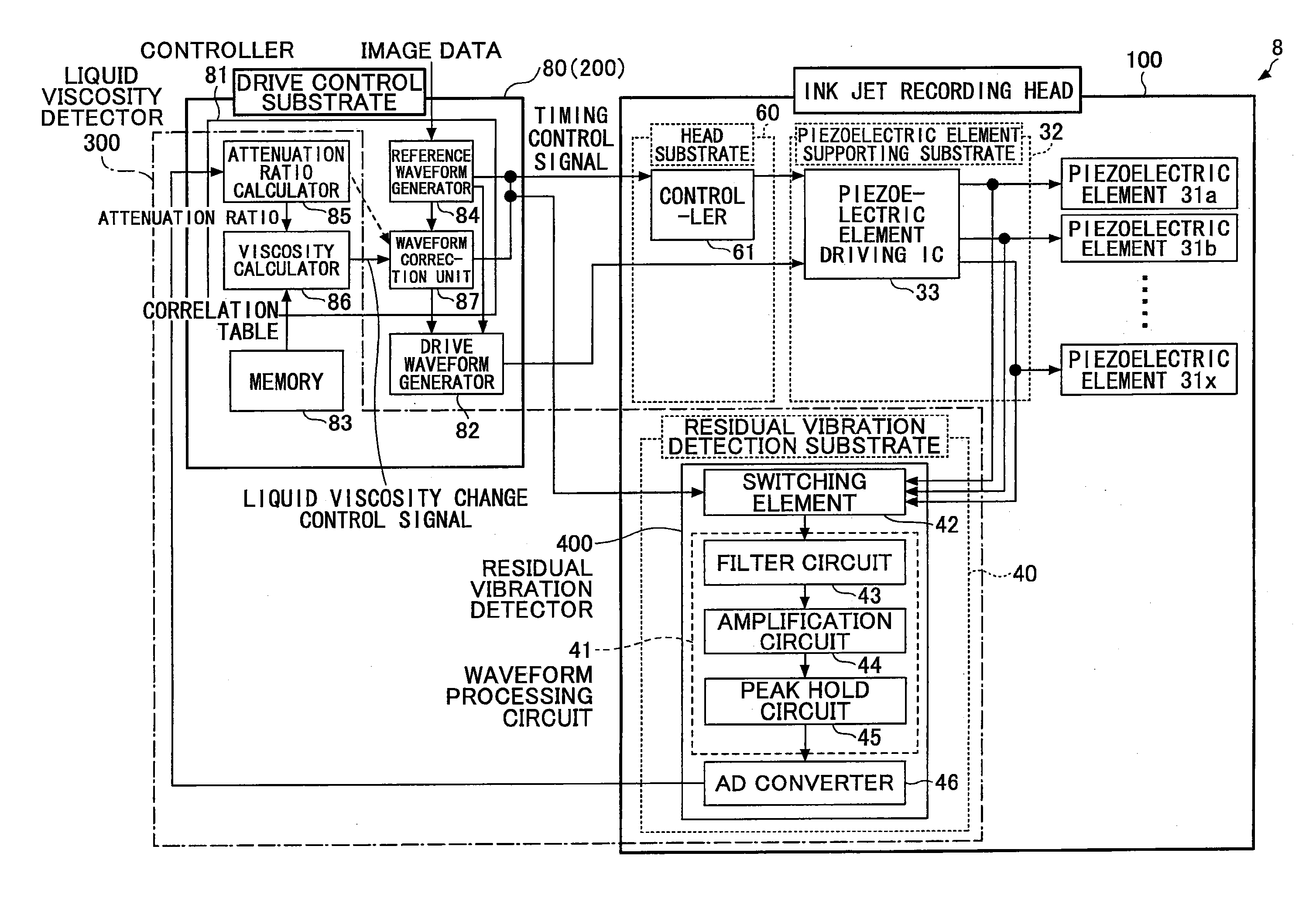
Liquid viscosity detecting method for liquid droplet ejecting device, control method for liquid droplet ejecting device, and liquid droplet ejecting device
A liquid viscosity detecting method is performed in a liquid droplet ejecting device that includes a piezoelectric type droplet ejecting head to which a drive waveform is applied to pressurize a liquid chamber to eject a liquid droplet, a drive waveform generator to apply the drive waveform to the droplet ejecting head, and a residual vibration detector. The method includes detecting, by the residual vibration detector, amplitude values of multiple cycles of a residual vibration waveform occurring within the liquid chamber after the drive waveform is applied; calculating an attenuation ratio based on the amplitude values; and calculating a liquid viscosity in the liquid chamber based on the attenuation ratio.
Owner:RICOH KK
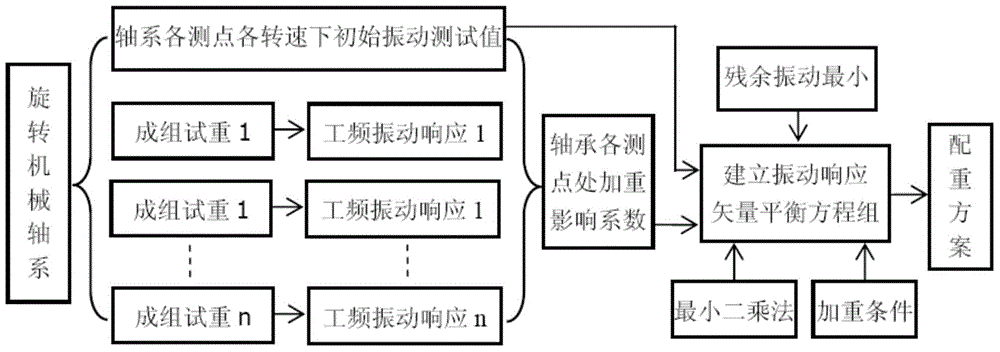
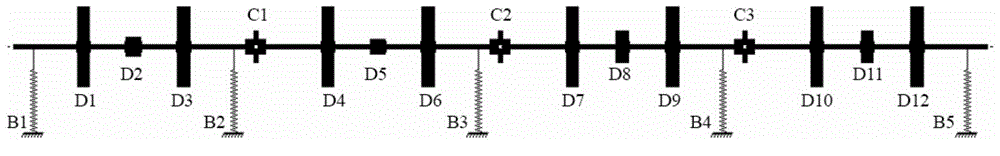
Influence coefficient dynamic balance method on rotating machine with multiple plane, multiple-points and multiple revolving speed shafting
ActiveCN104568313ABig vibrationAvoid the see-saw phenomenonStatic/dynamic balance measurementResidual vibrationDynamic balance
Owner:宁波丰沃增压科技股份有限公司
Droplet discharging device and method of detecting discharge abnormality thereof
A droplet discharging device is provided which does not require a special sensor (an optical sensor) and can enhance the precision of detecting a discharge abnormality of ink droplets. When printing is to be carried out, a transistor having a large current capacitance is turned on, a driving signal is applied from a driving circuit to piezoelectric actuators, and ink droplets are discharged by corresponding nozzles. Upon detecting a discharge abnormality of the nozzles, one of the piezoelectric actuators corresponding to the nozzles is selected, the transistor is turned off and a switch is turned on. A driving voltage is then applied from the driving circuit to the piezoelectric actuator thus selected in this state. When the application of the driving voltage ends, the switch is turned off. Consequently, a residual vibration detecting circuit detects the electromotive voltage of the piezoelectric actuator by the residual vibration of a vibrating plate.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
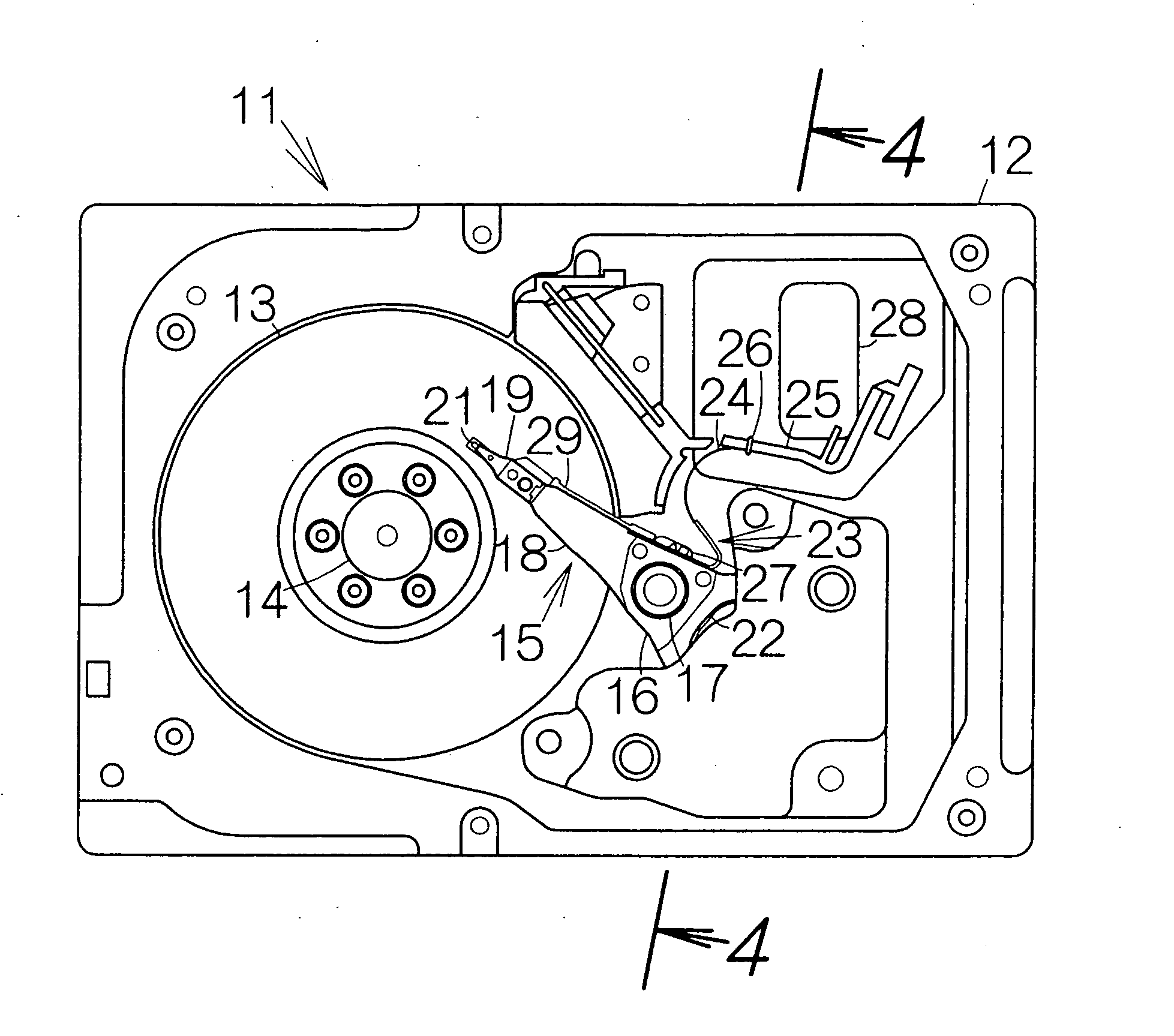
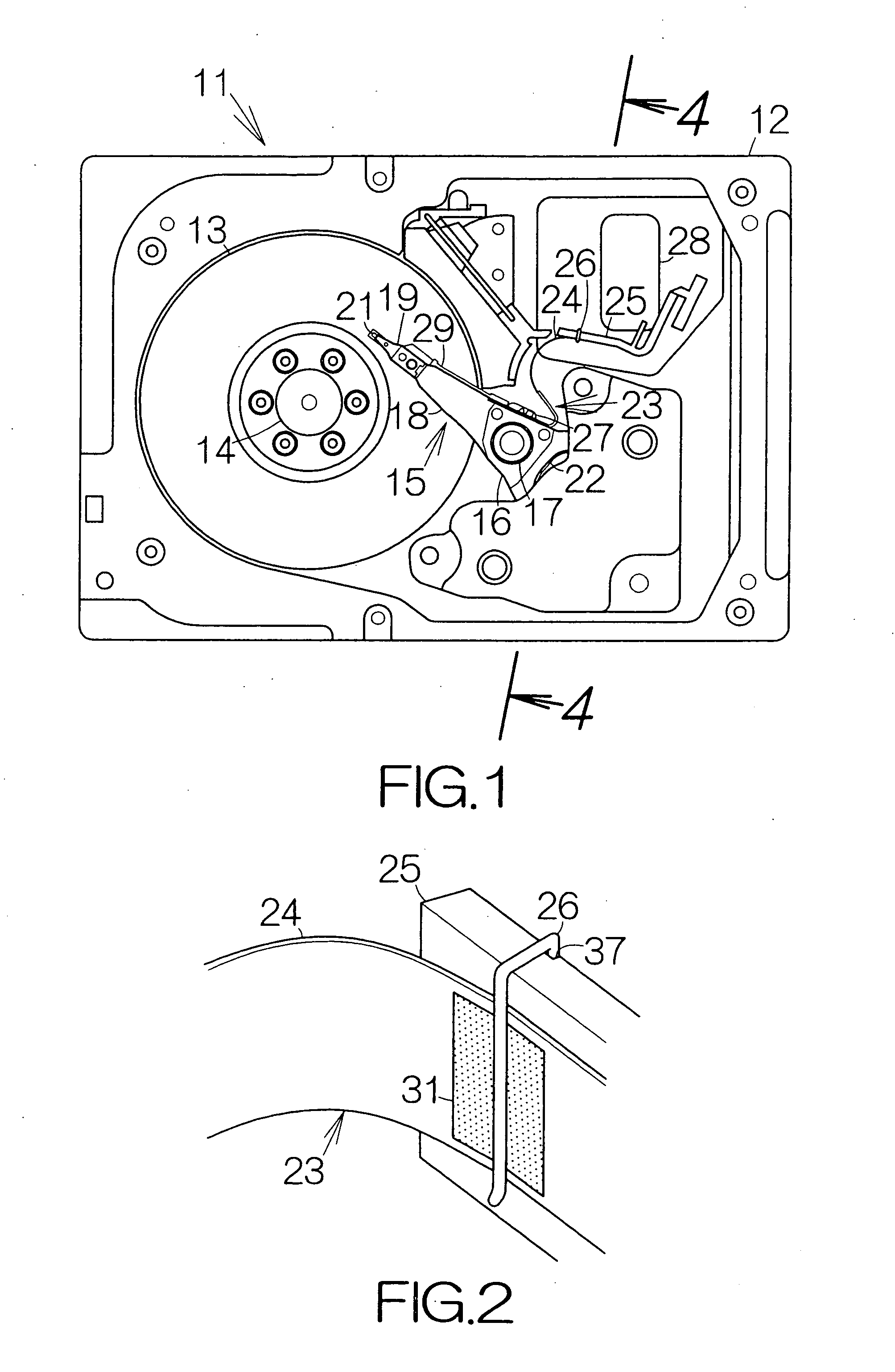
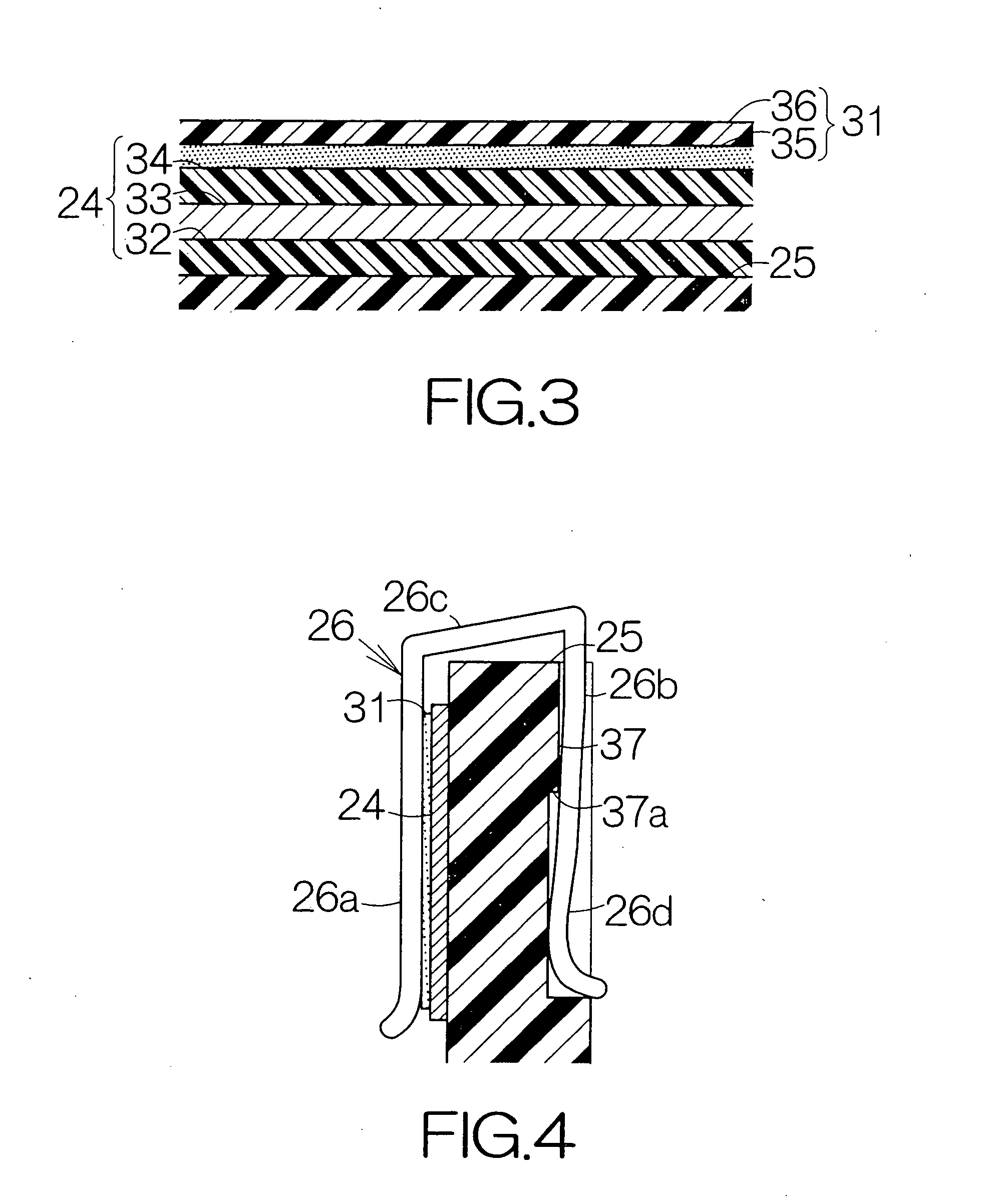
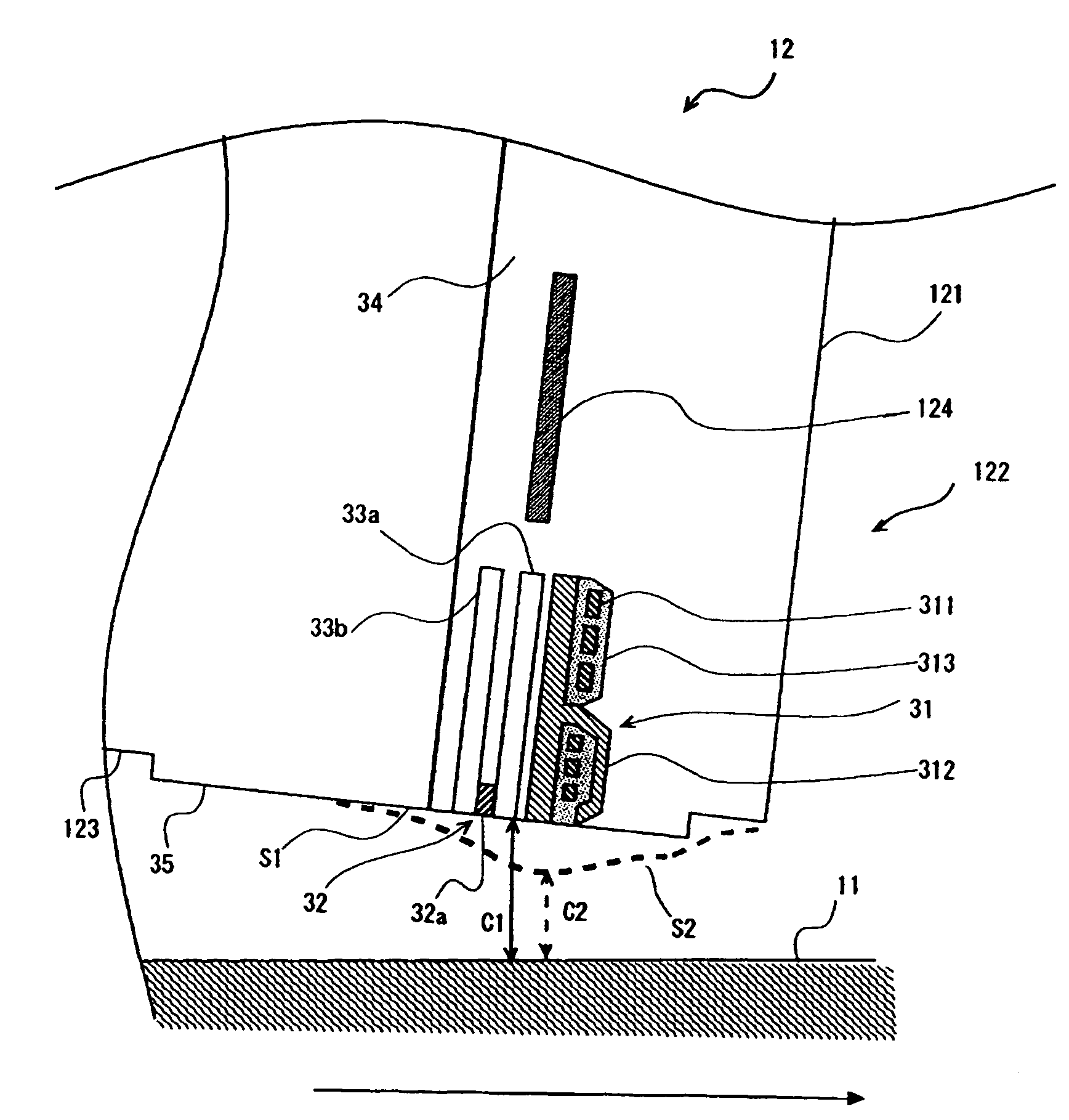
Recording disk drive capable of suppressing vibration of flexible printed circuit board
InactiveUS20070153427A1Vibration of flexibleImprove accuracyLaminating printed circuit boardsRecord information storageResidual vibrationEngineering
A fixing member is spaced from a head actuator by a predetermined distance. A flexible printed circuit board extends at least from the head actuator to the fixing member. The flexible printed circuit board is superposed on the surface of the fixing member. A viscoelastic layer and a protecting layer are overlaid on the surface of the flexible printed circuit board. A clip clips all the fixing member, the flexible printed circuit board, the viscoelastic layer and the protecting layer together. When a head slider is positioned, the head actuator changes its attitude relative to a recording disk. The inertial force based on the rotation causes the first flexible printed circuit board to vibrate when the actuator block stops rotating. The viscoelastic layer serves to absorb this residual vibration of the first flexible printed circuit board. Vibration of the flexible printed circuit board can be suppressed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
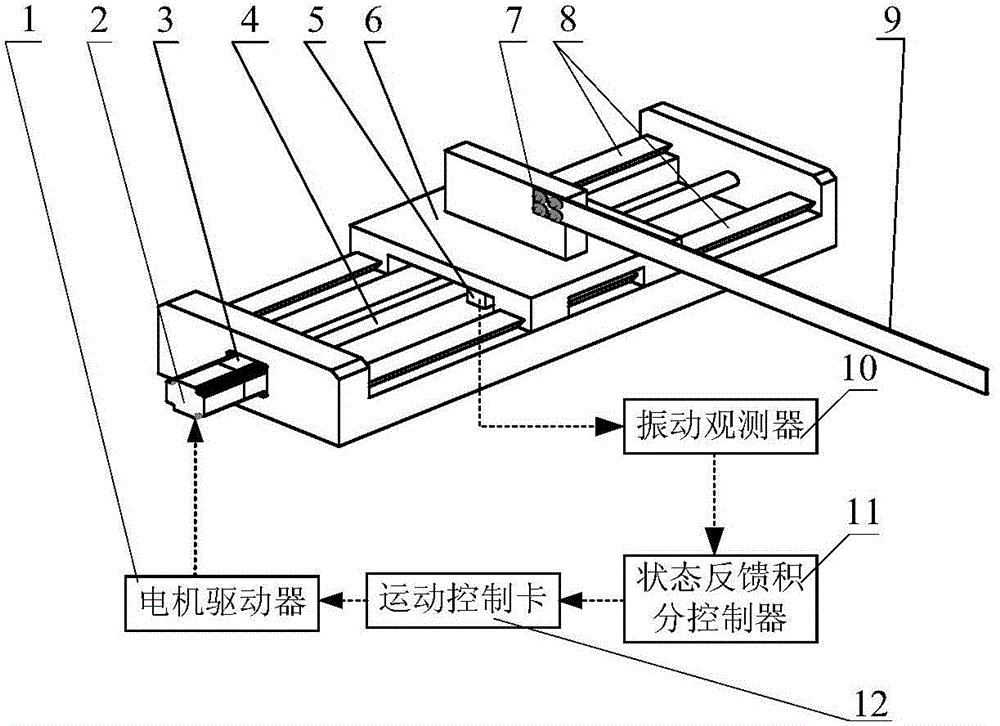
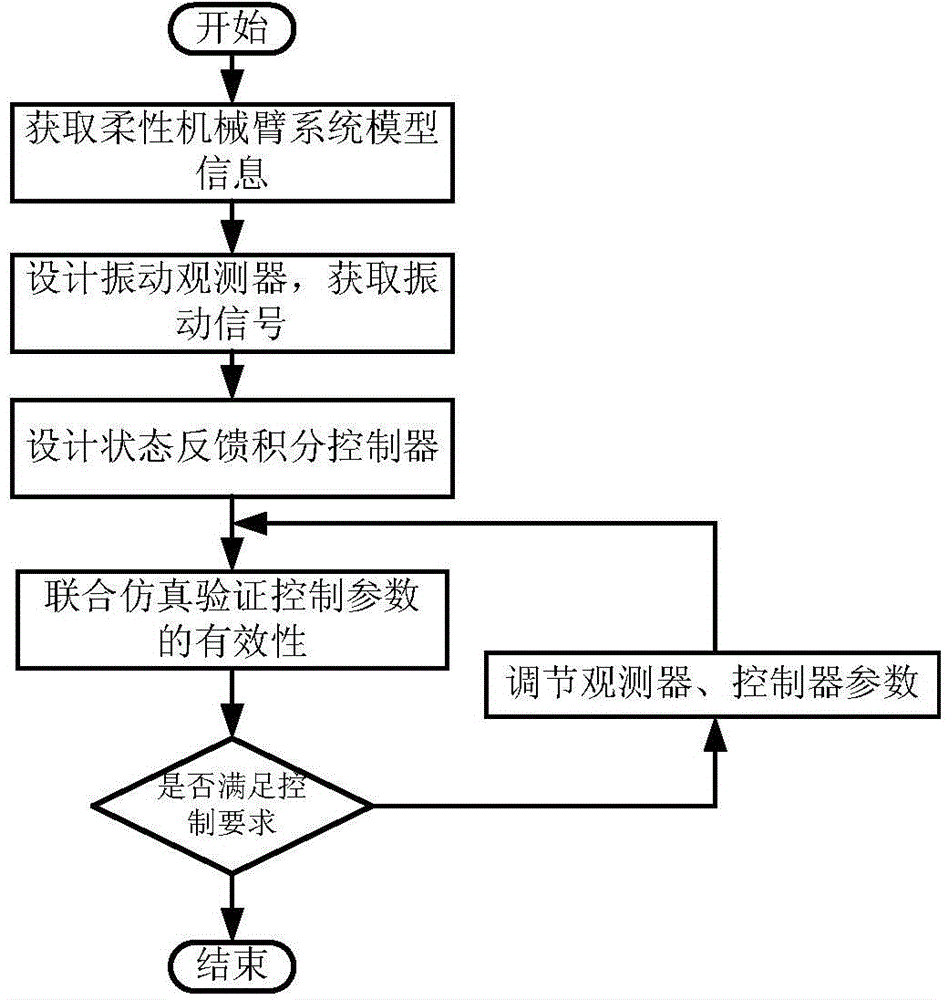
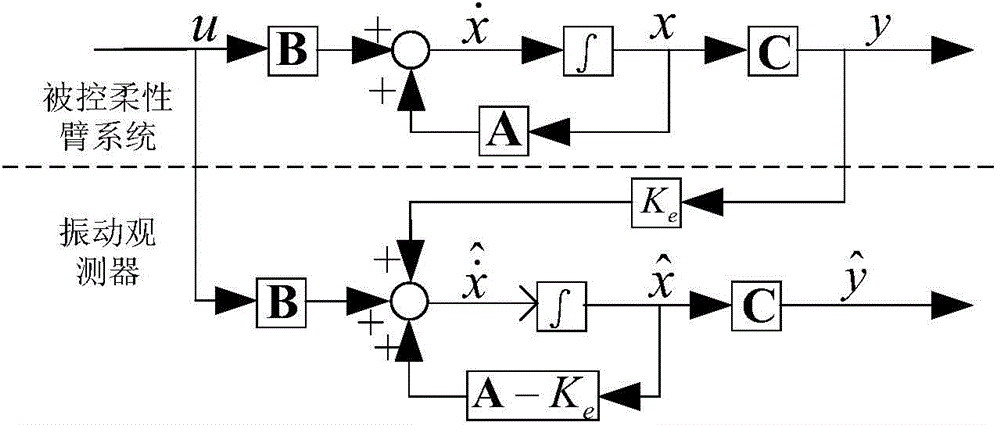
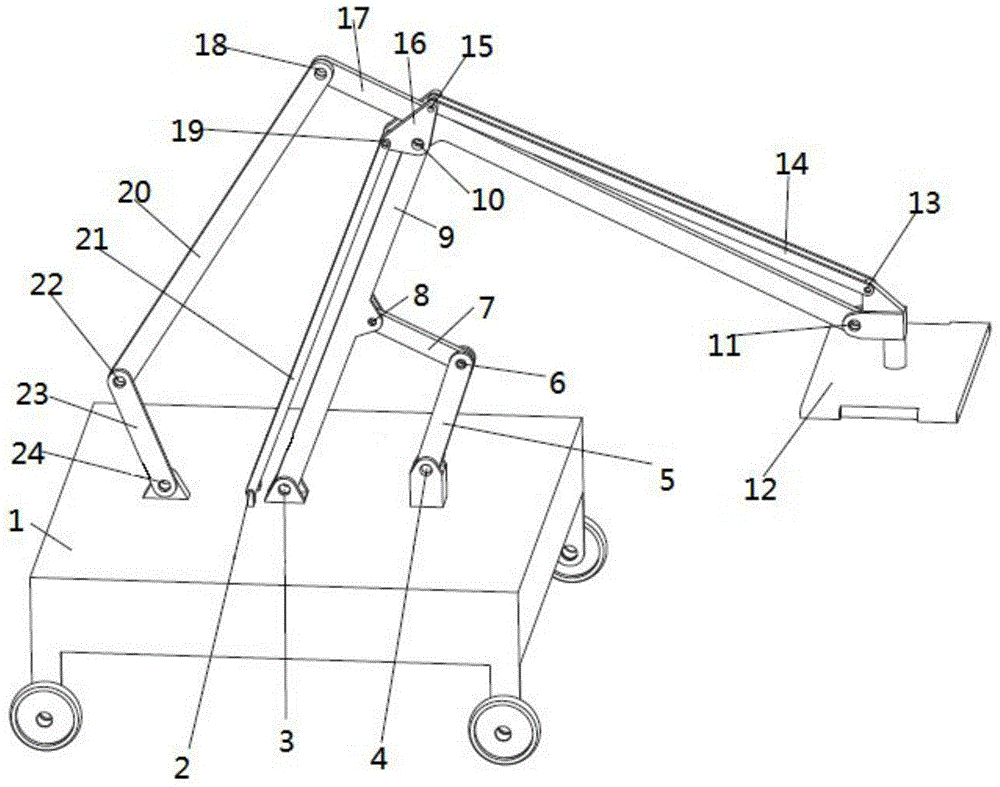
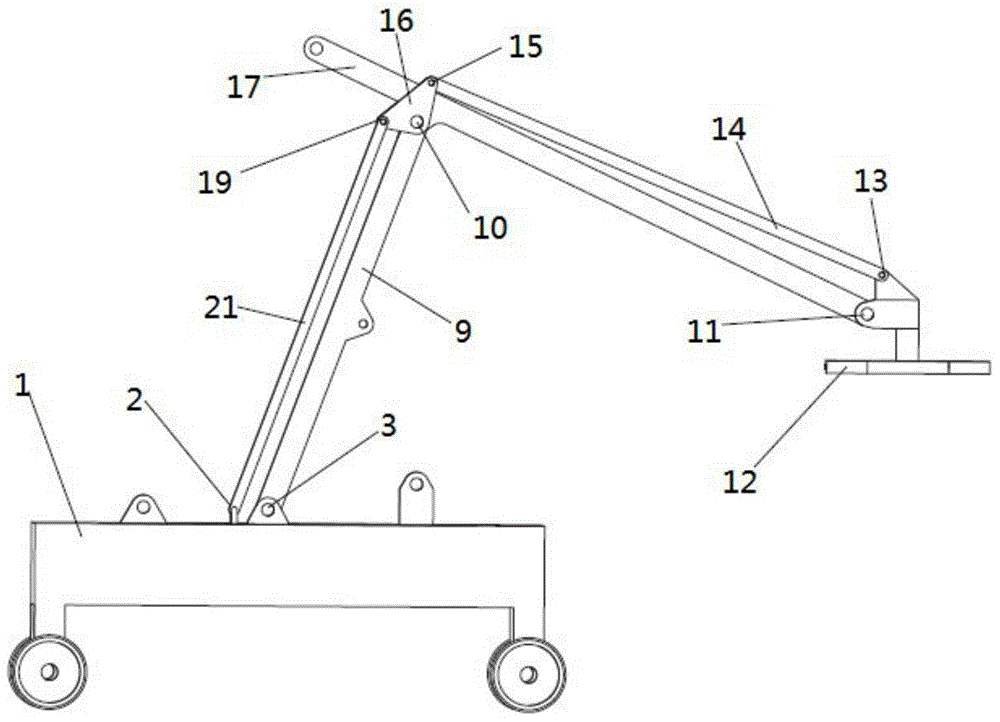
Method for controlling vibration of flexible manipulator based on vibration observer
The invention discloses a method for controlling vibration of a flexible manipulator based on a vibration observer. The method comprises the following steps: 1, establishing a mathematic model of a flexible manipulator system and acquiring model information of the system; 2, designing the vibration observer; 3, designing a state feedback integral controller; 4, adjusting control parameters according to the combined simulation effect; 5, ending the design. When the residual vibration of the tail end of the flexible manipulator is tested and controlled, a vibration signal of the tail end of the flexible manipulator can be obtained without using a sensor in an existing method, the system structure is simplified, and the cost is saved. The state feedback controller with an integral is used at the same time, and unbiased tracked and specified input can be achieved while the dynamic characteristics of the system are effectively adjusted.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Controllable mechanism type two-degrees-of-freedom mobile manipulator
InactiveCN104647336ALarge working spaceImprove stress conditionsManipulatorStress conditionsResidual vibration
The invention relates to a controllable mechanism type two-degrees-of-freedom mobile manipulator. A fourth connecting rod of the manipulator is of a triangular shape; the lower end of a first driving part is connected to a mobile platform and the upper end of the first driving part is connected with one end of a first connecting rod; the other end of the first connecting rod is connected with one end of a second connecting rod; the other end of the second connecting rod is connected with an operation platform; the lower end of a big arm is connected to the mobile platform and the upper end of the big arm is connected with the first end of a fourth connecting rod and simultaneously, the upper end of the big arm is connected to the second connecting rod by a compound hinge; the lower end of the third connecting rod is connected to the mobile platform and the upper end of the third connecting rod is connected with the second end of a fourth connecting rod; one end of a fifth connecting rod is connected with the third end of the fourth connecting rod and the other end of the fifth connecting rod is connected with the operation platform; the lower end of a second driving part is connected to the mobile platform and the upper end of the second driving part is connected with one end of a sixth connecting rod; the other end of the sixth connecting rod is connected to the big arm. According to the invention, the stress condition of the manipulator is improved; the defects of rotational inertia, residual vibration intensity and the like of the manipulator are reduced; moreover, the controllable mechanism type two-degrees-of-freedom mobile manipulator has the advantages of easiness for implementing remote control, reduction of labor intensity of workers and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Measuring instrument
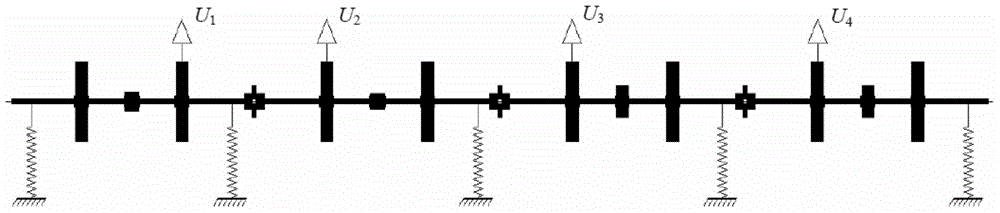
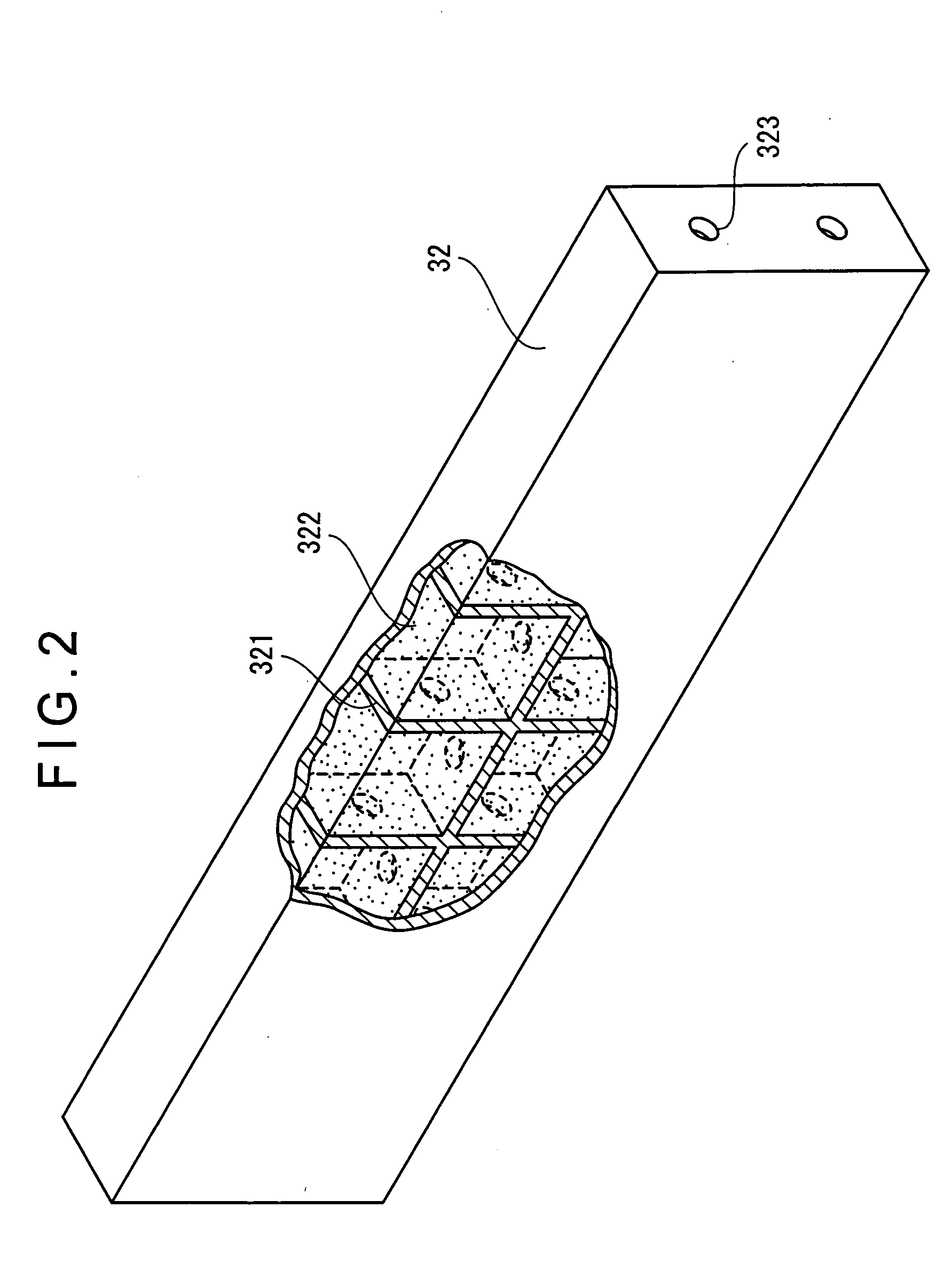
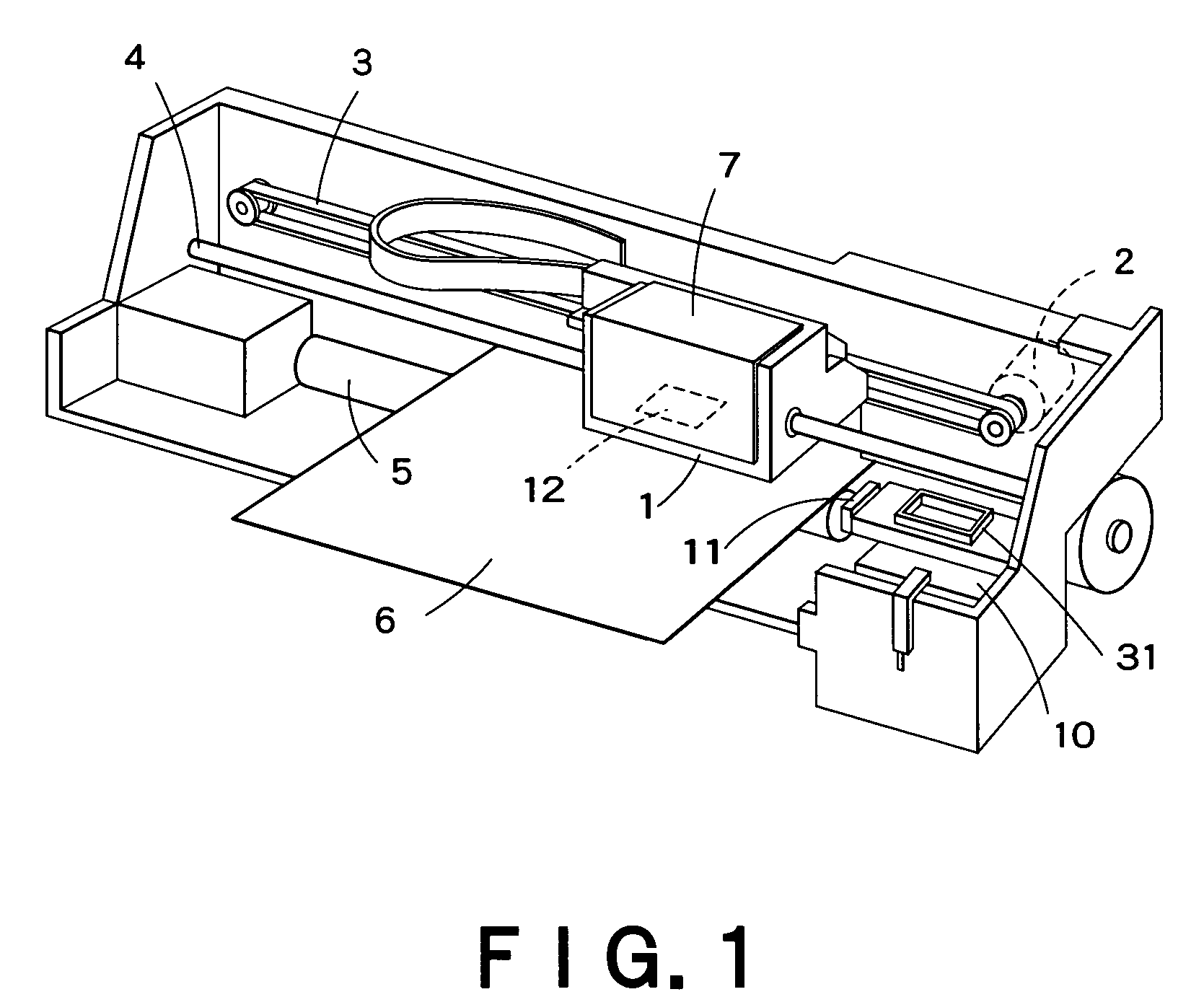
ActiveUS20040250434A1Improve rigidityIncrease vibrationNon-rotating vibration suppressionError compensation/eliminationResidual vibrationMeasuring instrument
At least one assembly of a movable member or a guide member (32) that guides the movement of the movable member out of a plurality of assemblies of a measuring instrument contains a sealed space (322). A filler is filled in the sealed space (322). According to this arrangement, rigidity of the movable member or the guide member (32) can be enhanced. Further, residual vibration generated along with the movement of the movable body can efficiently be attenuated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Droplet ejecting apparatus and ejection abnormality detecting/determining method for a droplet ejecting head
ActiveUS20040227782A1Small sizeSuppress manufacturing costBreathing filtersBreathing masksCapacitanceResidual vibration
A droplet ejecting apparatus and an ejection abnormality detecting / determining method are provided that, depending upon a capacitance change of an actuator after a droplet ejecting operation, measures the period of residual vibration on the vibration plate to thereby enable detection of an ejection abnormality and determination of a cause thereof.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Substrate, stage device, method of driving stage, exposure system and exposure method
InactiveCN1373900AMaintain positional controlAvoid problems such as swayingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusProduction rateResidual vibration
The object stage device (4) includes: a support part (8), which is vibrateably and independently arranged relative to the fixed plate (3); and a reaction force stage (17), which is The resulting reaction force is free to move on the support (8) in said one direction. Thereby, since problems such as shaking due to the reaction force can be avoided, the adjustment time can be shortened, productivity can be improved, and transmission of residual vibration of the support portion to the fixed plate can be suppressed.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Liquid ejection apparatus
ActiveUS20150158293A1Prevent precipitationGood dispersionOther printing apparatusElectricityResidual vibration
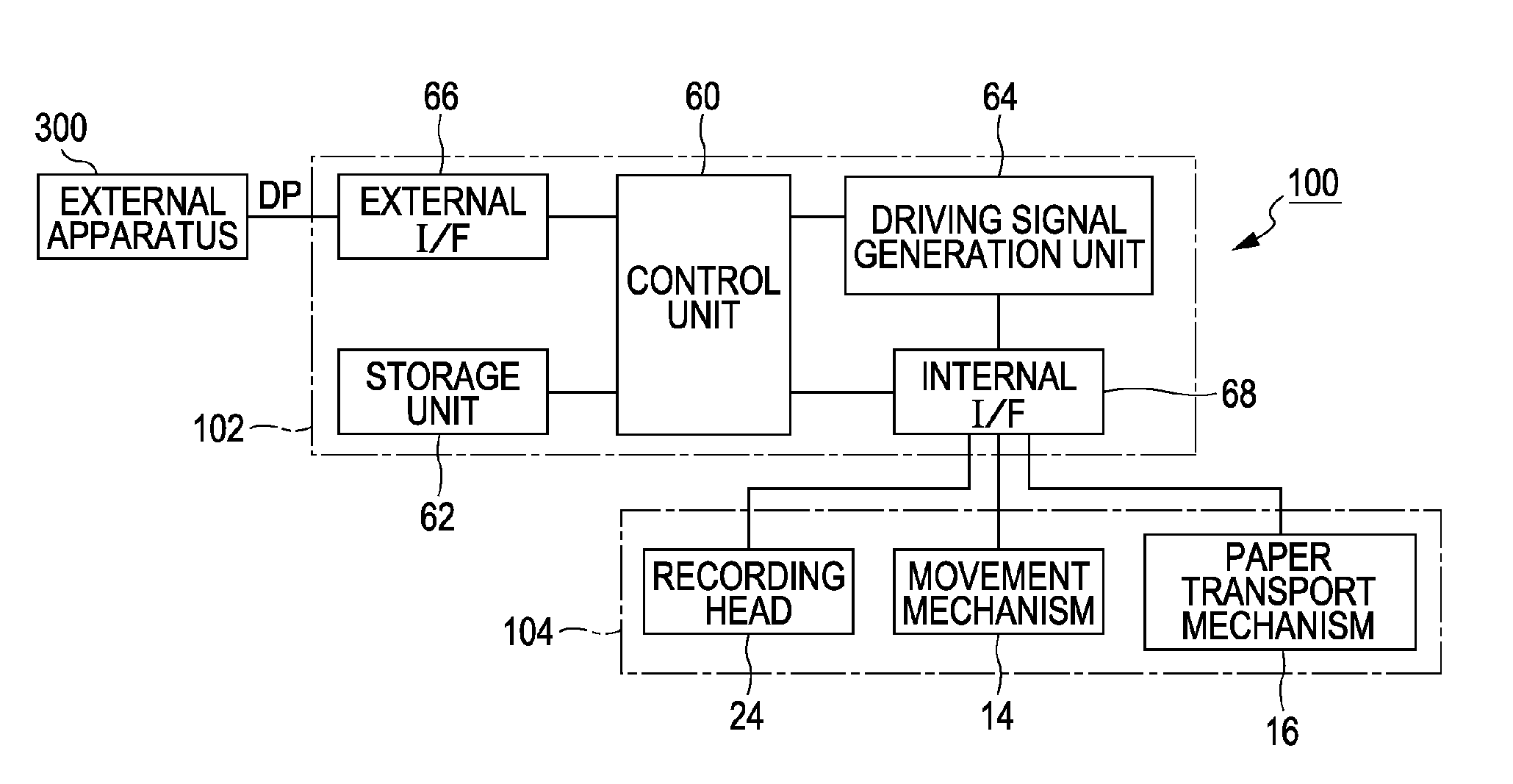
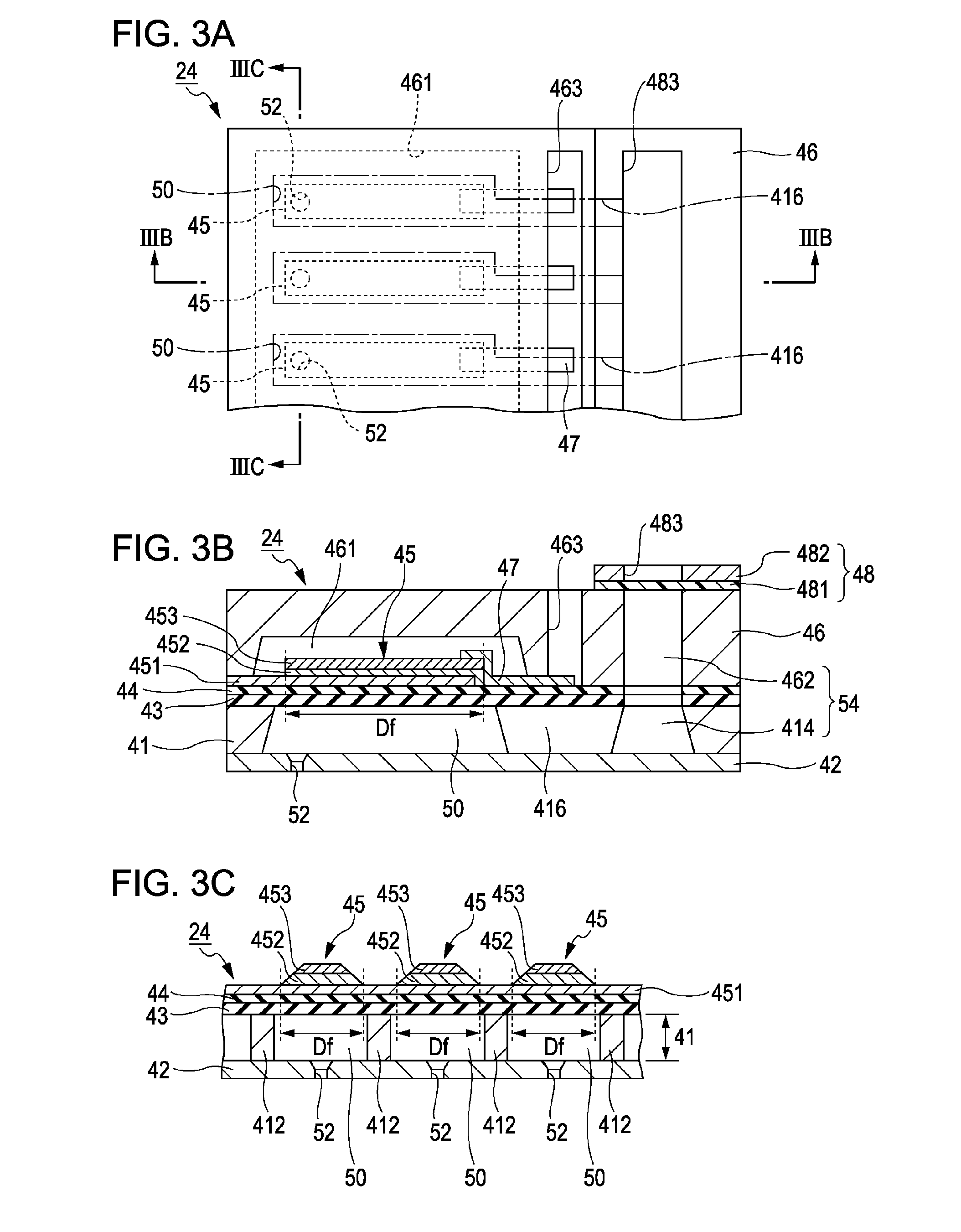
An ink jet printer includes an ejection unit including a nozzle which ejects a liquid containing a pigment; a cavity which communicates with the nozzle; and a piezoelectric element which is provided in the cavity, and a driving signal generation unit which generates a driving signal allowing the piezoelectric element to be displaced such that the cavity expands or is contracted. The ink jet printer includes a detection unit that detects a cycle of a residual vibration waveform of the piezoelectric element which is generated by the driving signal being applied to the piezoelectric element and indicates a value according to change of the pressure inside of the cavity and a determination unit that determines the pigment is settled based on the cycle of the residual vibration waveform detected by the detection unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
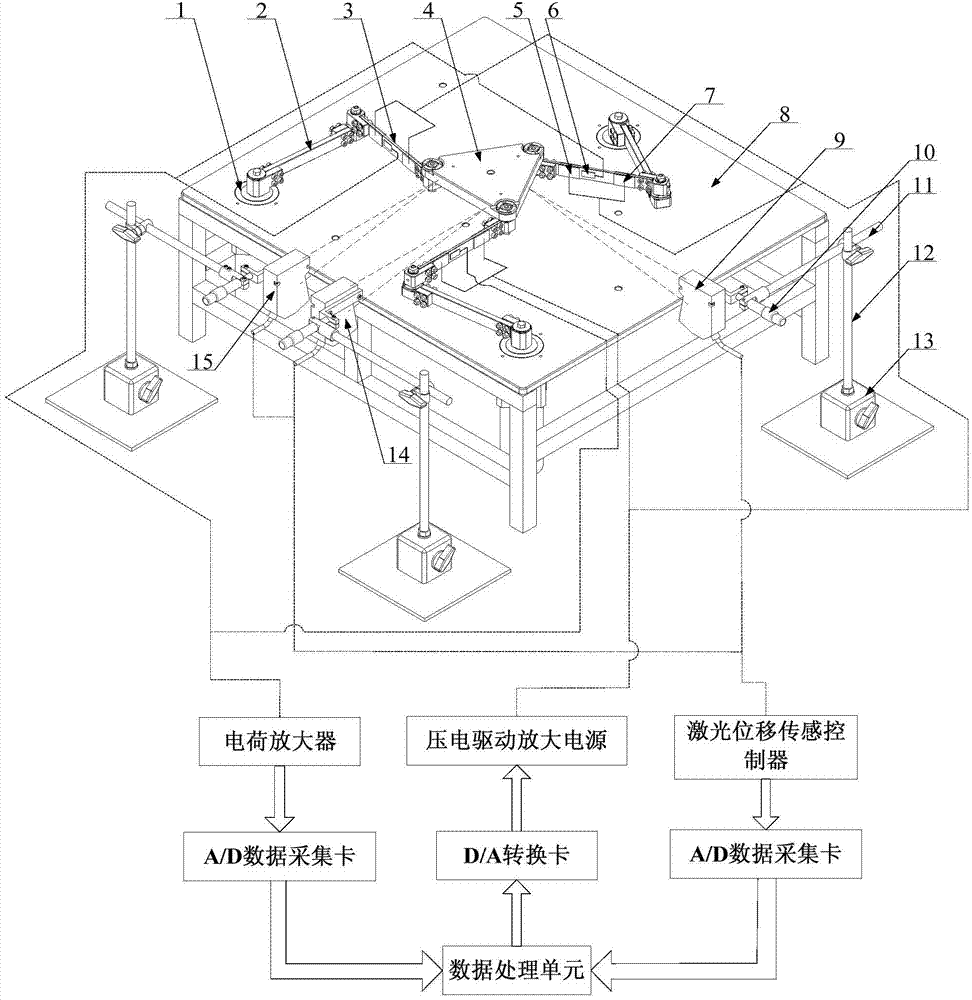
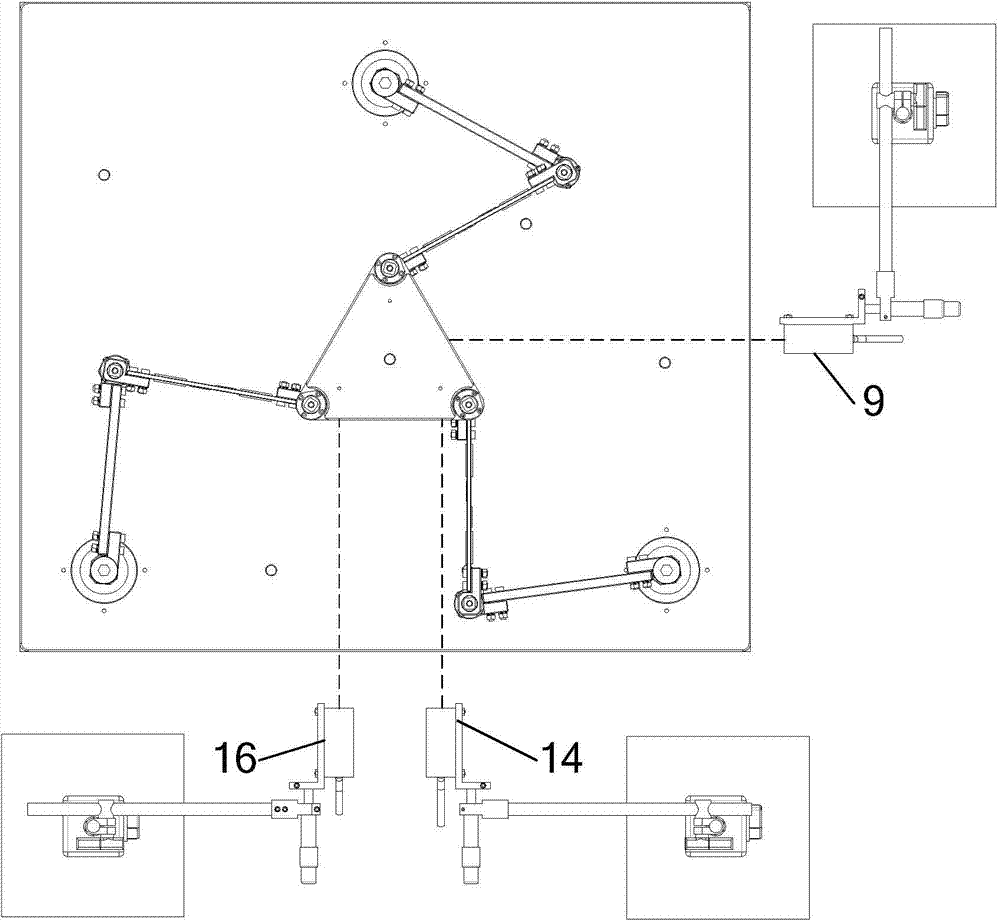
Laser displacement sensor based parallel platform vibration detection control device and method
ActiveCN104760039ANo additional mass added to the structureNo added massProgramme-controlled manipulatorSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementElectricityVibration control
The invention discloses a laser displacement sensor based parallel platform vibration detection control device and method. The device comprises a parallel platform body unit, a vibration detection unit and a vibration control unit. The parallel platform body unit comprises a movable platform, a static platform and three parallel branches. Each parallel branch comprises a motor, a driving rod and a driven flexible rod which are connected successively. A plurality of piezoelectric ceramic piece drivers are pasted on the driven flexible rods. Three laser detection heads are arranged on the periphery of the static platform to be used for detecting the translation displacement and the rotation angle of the movable platform in the horizontal direction. The motors drive the driving rods and the driven flexible rods to locate the movable platform behind the target position, the movable platform has residual vibration, the laser detection head detects vibration signals of the movable platform, the vibration control unit applies the control quantity to the piezoelectric ceramic piece drivers, and accordingly, driving control over the residual vibration of the parallel platforms is achieved. The device and the method have the advantages of being high in measurement accuracy and sampling frequency and quick in dynamic response.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Ink jet apparatus, ink jet apparatus driving method, and storage medium for storing ink jet apparatus control program
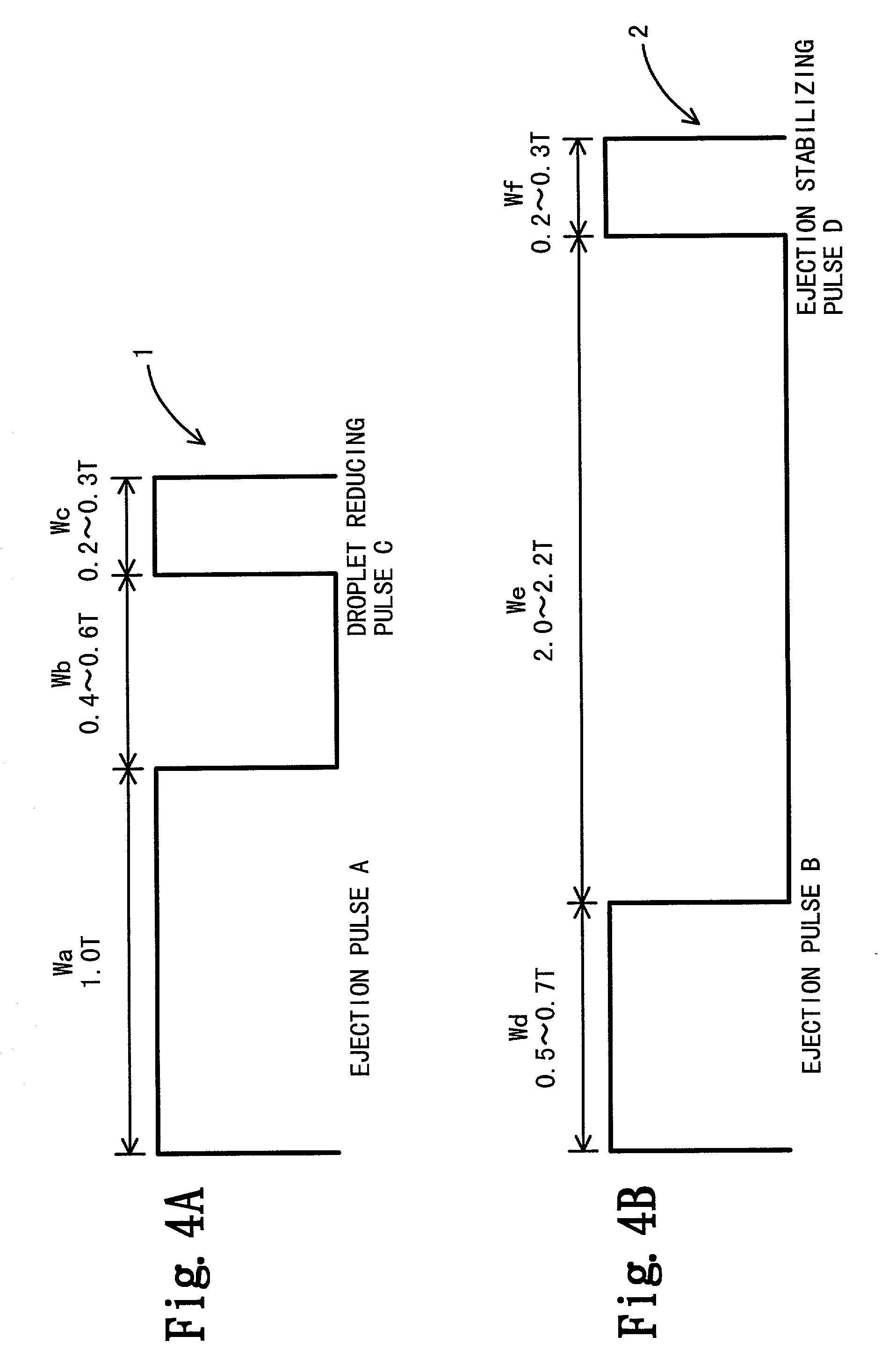
InactiveUS6412896B2Stable ejectionMinimize the differenceInking apparatusOther printing apparatusResidual vibrationElectrical and Electronics engineering
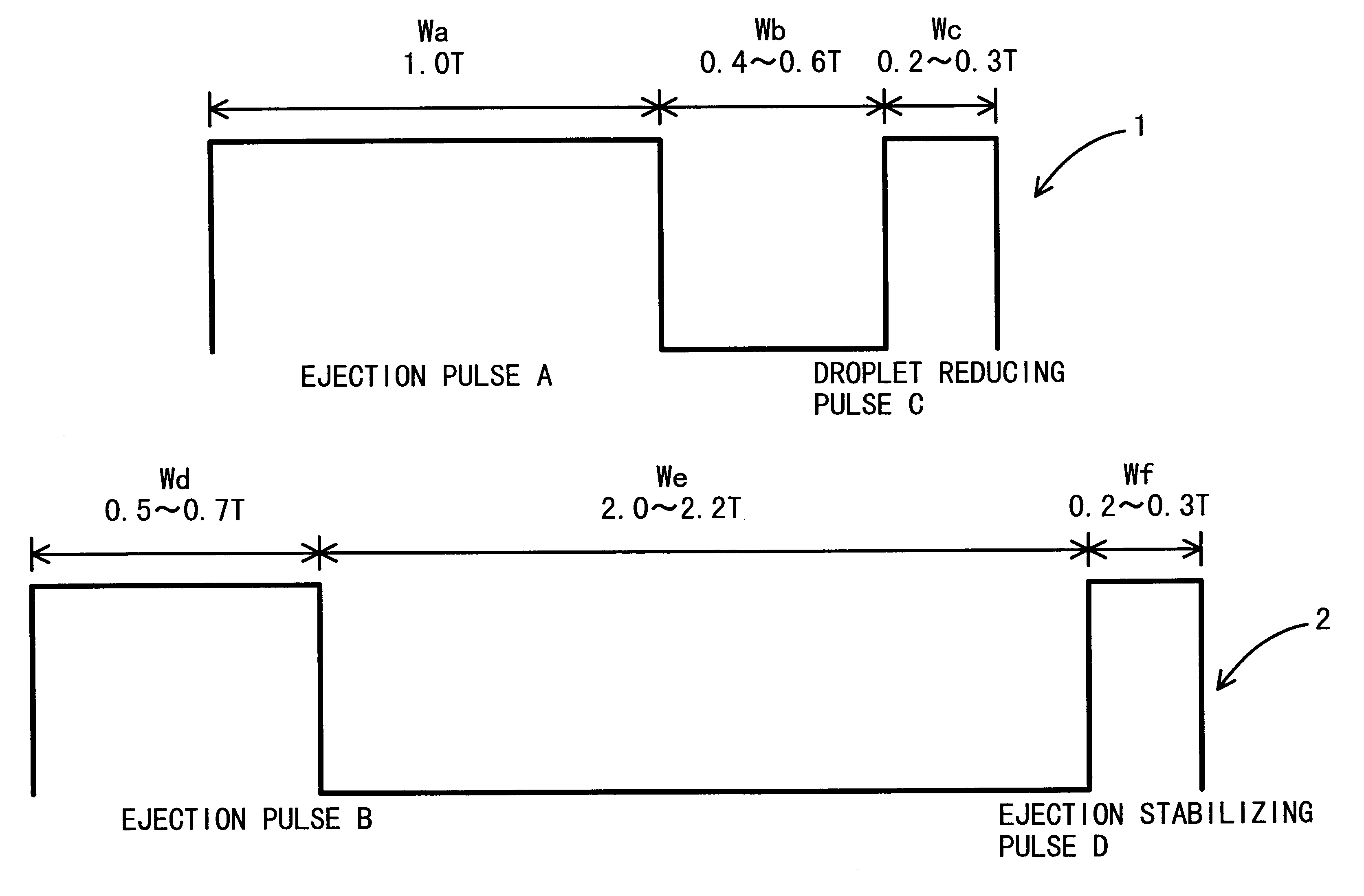
When a dot is formed apart from other dots on a print medium, in response to a discontinuous print command, a first drive waveform is used. The first drive waveform includes an ejection pulse and an ink droplet reducing pulse for retrieving a portion of an ink droplet about to leave the nozzle. When a dot is formed to overlap other dots on a print medium, in response to one of continuous print commands, the second drive waveform is used. The second drive waveform includes an ejection pulse and an ejection stabilizing pulse for suppressing residual vibrations generated by the ejection pulse. By selectively using the first or the second drive waveform, an ink droplet smaller than 20 pl can be ejected stably even at high printing frequencies. As a result, high-quality, high-speed printing can be achieved.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Droplet ejecting apparatus and ejection abnormality detecting/determining method for a droplet ejecting head
ActiveUS7108348B2Small sizeSuppress manufacturing costBreathing filtersBreathing masksCapacitanceResidual vibration
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Ink jet apparatus, ink jet apparatus driving method, and storage medium for storing ink jet apparatus control program
InactiveUS20010024214A1Stable ejectionMinimize the differenceInking apparatusOther printing apparatusResidual vibrationElectrical and Electronics engineering
When a dot is formed apart from other dots on a print medium, in response to a discontinuous print command, a first drive waveform is used. The first drive waveform includes an ejection pulse and an ink droplet reducing pulse for retrieving a portion of an ink droplet about to leave the nozzle. When a dot is formed to overlap other dots on a print medium, in response to one of continuous print commands, the second drive waveform is used. The second drive waveform includes an ejection pulse and an ejection stabilizing pulse for suppressing residual vibrations generated by the ejection pulse. By selectively using the first or the second drive waveform , an ink droplet smaller than 20 pl can be ejected stably even at high printing frequencies. As a result, high-quality, high-speed printing can be achieved.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Liquid storage container
InactiveUS20080012914A1Increase the amount of fluidImprove liquid capacityPrintingResidual vibrationEngineering
To provide a liquid storage container which can prevent a failure that air bubbles are sucked into a liquid guide path even when the amount of liquid remaining in the liquid storage chamber is reduced and which can considerably reduce the amount of liquid discarded without being used. [Solving Means] A liquid storage container 1 includes liquid storage chambers 370 and 430 from which liquid is guided to a liquid-supplying unit 50 through a liquid guide path and a liquid remaining-amount sensor 31 for detecting the presence / absence of the liquid on the basis of variation in residual vibration that occurs when air bubbles enter the liquid guide path. The liquid storage chambers 370 and 430 have concavities 374 and 434 in the bottom walls thereof. Liquid outlets 371 and 432 that communicate with the liquid guide path are formed at the bottom of the concavities 374 and 434, respectively. Therefore, air layers in the liquid storage chambers 370 and 430 are prevented from coming into contact with the liquid outlets 371 and 432, respectively, before the remaining liquid does.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Positioning device and method
A positioning device and method can position a subject of positioning at a higher speed than conventional ones. A positioning device and method for moving a subject of positioning to a desired position, moves the subject of positioning at a desired speed and acceleration, and adjusts the acceleration / deceleration duration of the subject of positioning and the timing of starting the deceleration so as to cancel the residual vibration, in accordance with the vibration period of the residual vibration that occurs immediately after positioning the subject of positioning.
Owner:SONY CORP
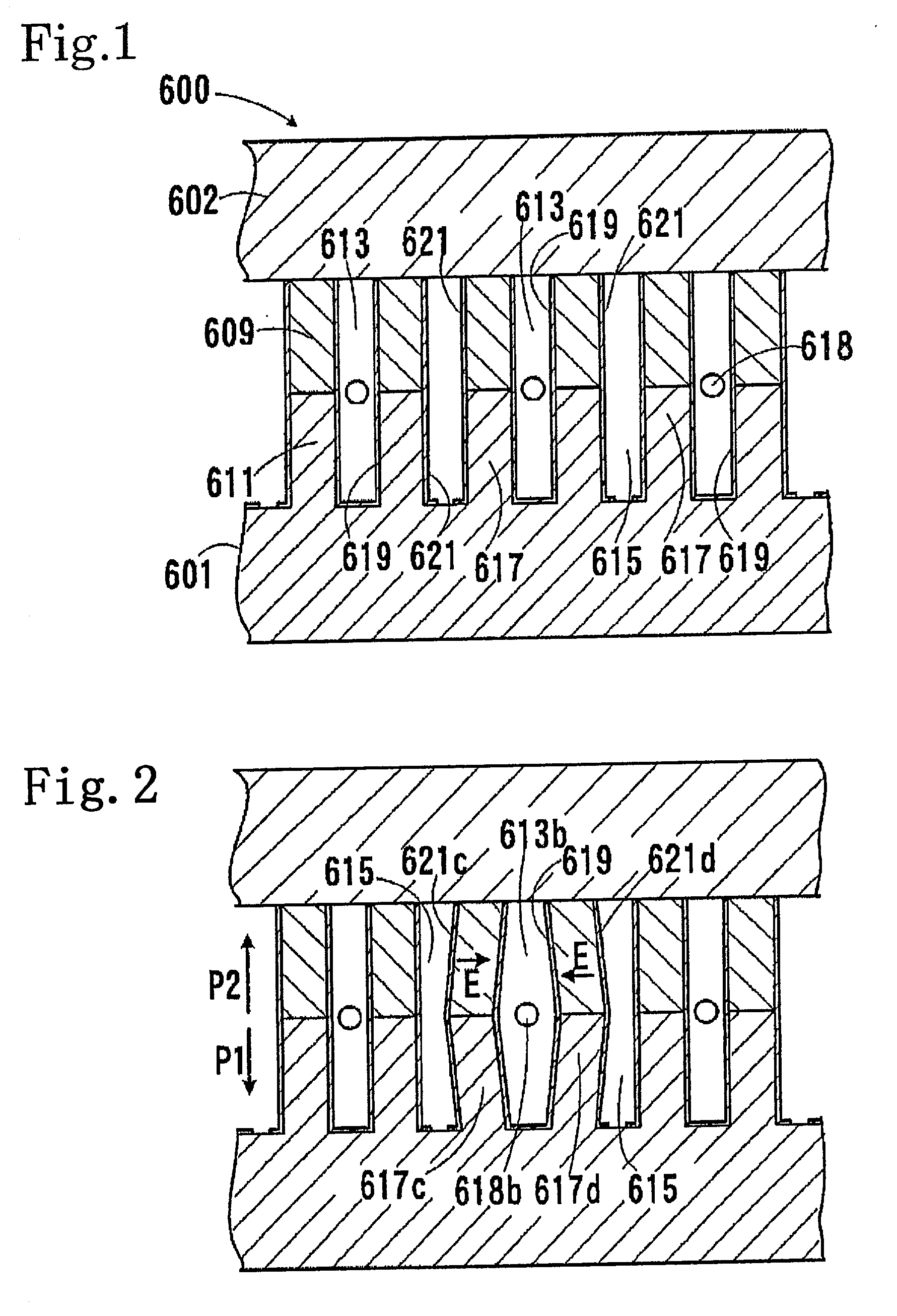
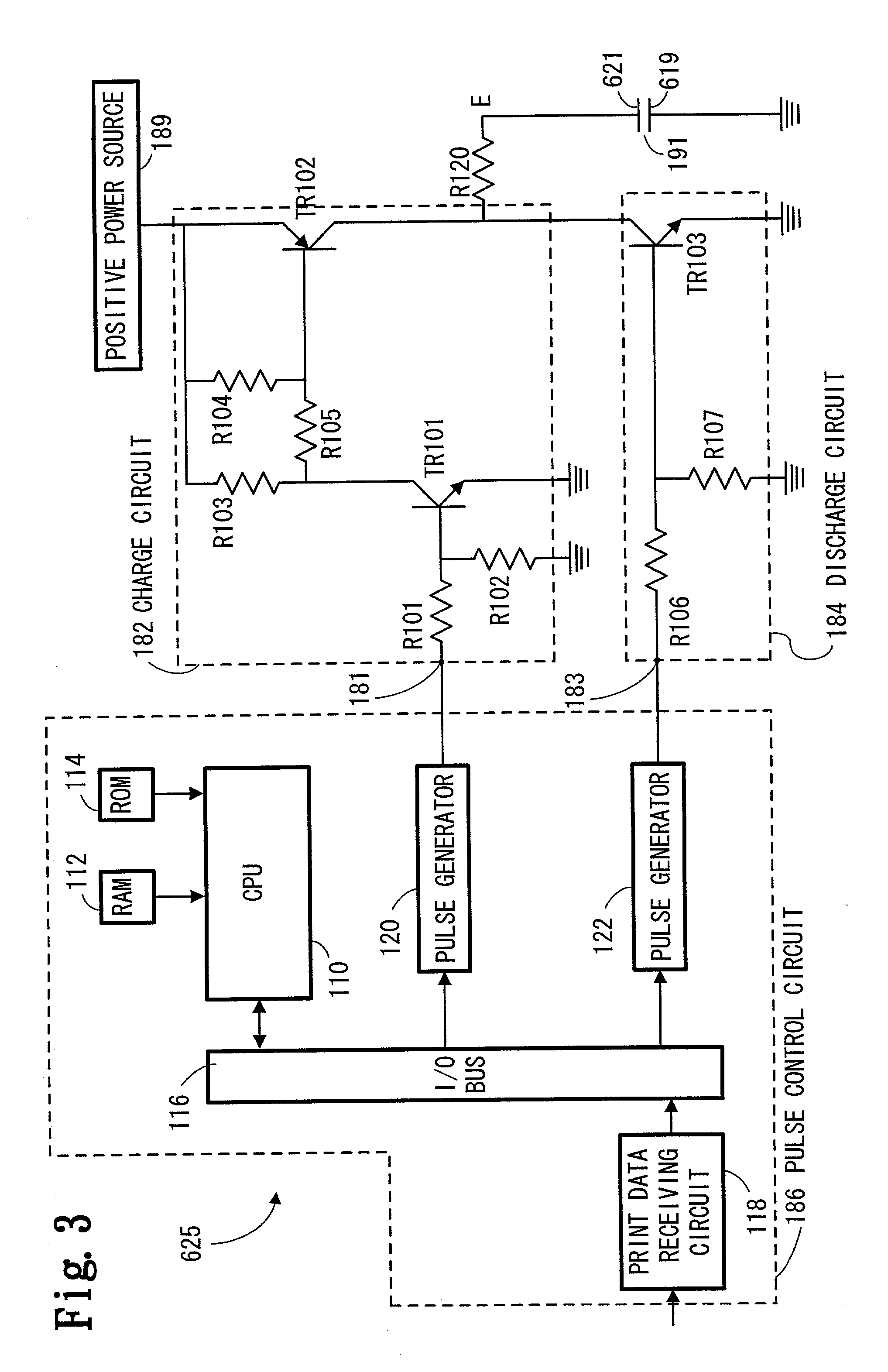
Liquid-detecting device and liquid container with the same
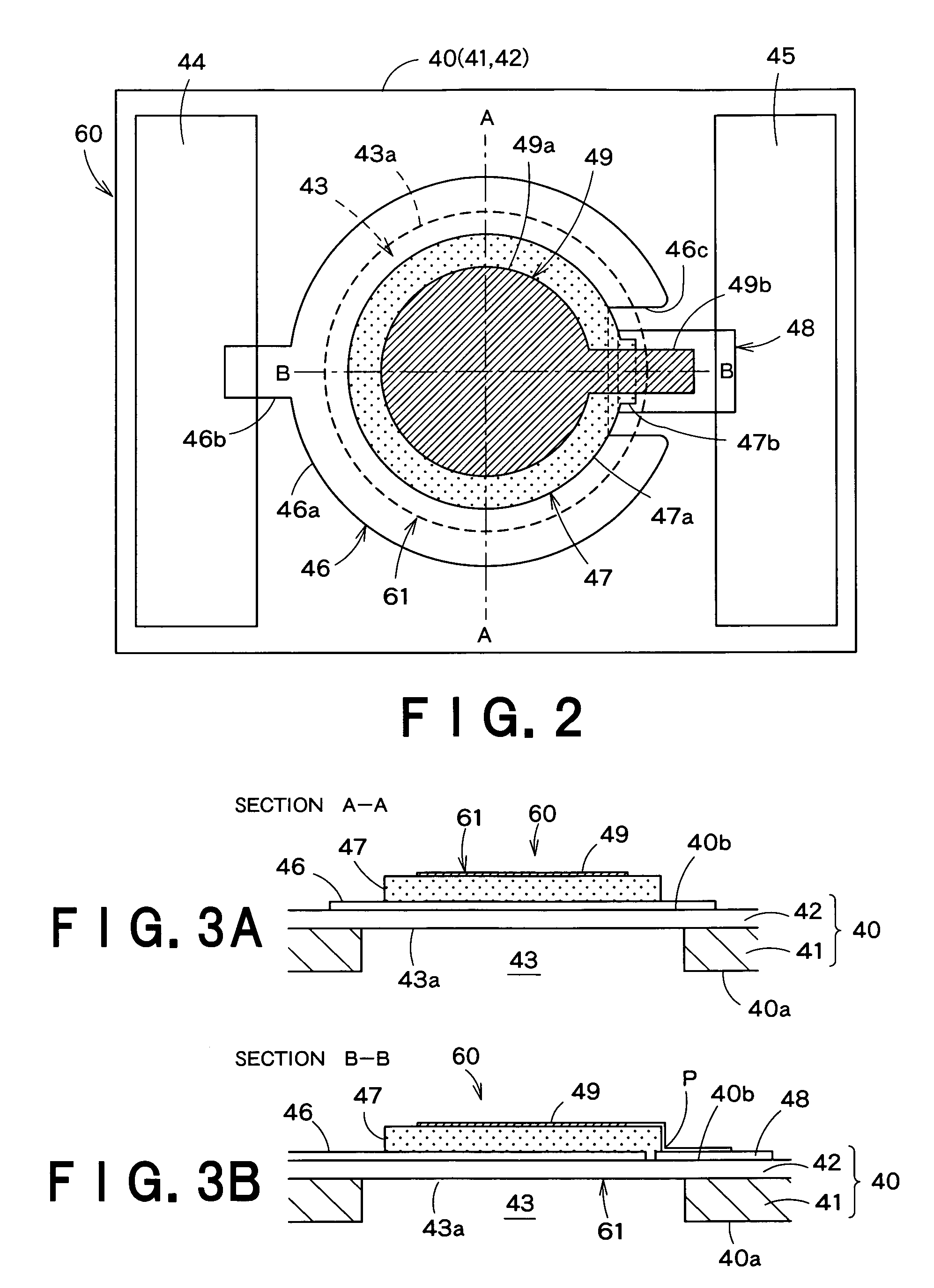
InactiveUS7270386B2Easily and surely detectingAvoid it happening againMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsResidual vibrationEngineering
A first electrode (46) has a main portion (46a) covering almost the overall area of a concavity (43) and including a notch (46c). A piezoelectric layer (47) has a main portion (47a) in a diameter smaller than that of the concavity (43), and the whole thereof is within the concavity area, and almost overall the main portion (47a) excluding the part corresponding to the notch (46c) is laminated on the first electrode (46). An auxiliary electrode (48) extends from the outside of the concavity area into the inside thereof and a part thereof is positioned within the notch (46c) of the first electrode (46) and supports a part of the piezoelectric layer (47). A second electrode (49) has a main portion (49a) laminated on the piezoelectric layer (47) and an extension part (49b) which extends from there and is connected to the auxiliary electrode (48) within the concavity area. The residual vibration state of a vibration part of a liquid-detecting device can be detected easily and surely, and generation of cracks in the piezoelectric layer can be prevented.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Processing-and-manufacturing damping cutting device
InactiveCN107639280AReduce vibrationEasy to cutNon-rotating vibration suppressionShearing machinesResidual vibrationEngineering
The invention provides a processing-and-manufacturing damping cutting device, and relates to the technical field of machining and manufacturing. The processing-and-manufacturing damping cutting devicecomprises a base, the bottom of the base is fixedly connected with the tops of damping feet, the bottoms of the damping feet are fixedly connected with the tops of bottom plates, the top of the baseis fixedly connected with the bottoms of limiting blocks, an installing plate is arranged at the upper portion of the base, and a motor is arranged at the upper portion of the installing plate. According to the processing-and-manufacturing damping cutting device, as a threaded rod is arranged, clamping and fixing of articles required to be processed are convenient, and clamping is more convenientand faster; as limiting rods are arranged, the installing plate is more stable; as nuts are arranged, top supporting of the installing plate is more stable; as damping springs and damping rings are arranged, vibration generated by cutting is greatly reduced; as the damping feet are arranged, residual vibration is buffered and subjected to energy dissipation, and vibration of the cutting device isbetter weakened.
Owner:佘峰
Method of adjusting velocity of transfer member, method of transferring substrate using the method, and substrate-processing apparatus
ActiveUS20110150607A1Improve transmission efficiencyProgramme controlDigital data processing detailsResidual vibrationEngineering
Provided is a method of adjusting a velocity of a transfer arm in a transfer member. The method includes, accelerating the transfer arm from a start point to a first point where a movement velocity reaches a preset reference velocity, dividing a division from the first point to a second point into movement divisions to move the transfer arm in any one of a deceleration motion, an acceleration motion, and a uniform motion according to the respective movement divisions, and decelerating the transfer arm from the second point to a target point. The motion of the transfer arm in the current movement division is different from that in the movement division just before the current movement division. Thus, a different impulse from that in the precedent movement division is applied to a substrate loaded on the transfer arm. Accordingly, the impulse response superposition cancels residual vibration of the substrate, so as to improve transfer efficiency of the transfer member.
Owner:SEMES CO LTD
Liquid discharging apparatus, head unit, control method for liquid discharging apparatus, and control program for liquid discharging apparatus
Provided is a liquid discharging apparatus including a waveform signal generator that generates a drive waveform signal which includes a plurality of waveforms including an inspection waveform; a first discharger including a first piezoelectric element that is displaced by being supplied with a first drive signal; a first switch that is capable of switching whether to supply the first drive signal to the first piezoelectric element for each unit period; and a detector that detects residual vibration occurring in the first discharger after the first drive signal including the inspection waveform is supplied to the first piezoelectric element, in which the first switch stops supply of the first drive signal to the first piezoelectric element during a unit period that precedes one unit period when the first drive signal including the inspection waveform is supplied to the first piezoelectric element during the one unit period.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
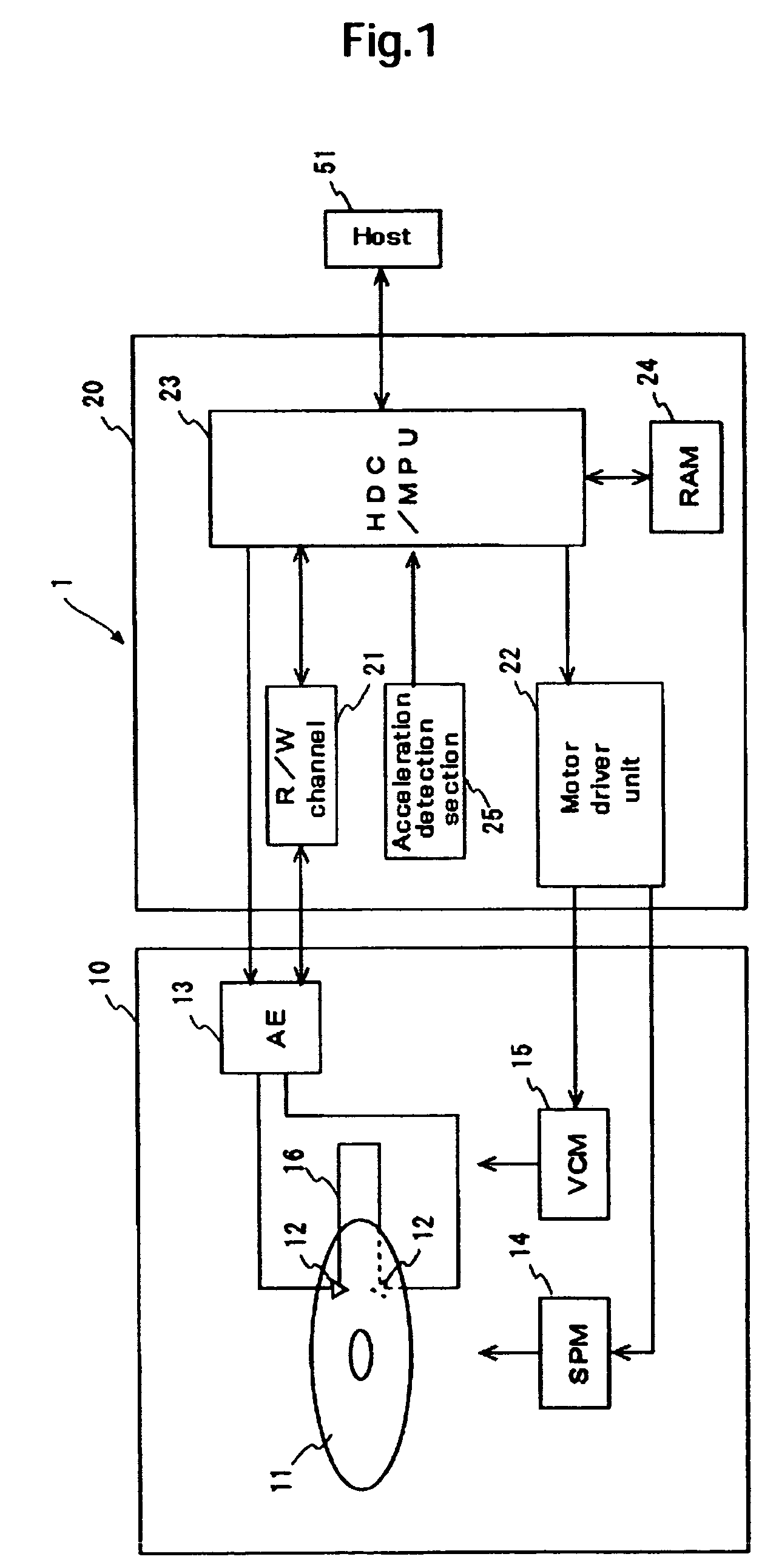
Disk drive and disk drive control method
InactiveUS7616397B2Avoid collisionReduce the probability of collisionDisposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsHard disc driveResidual vibration
Embodiments in accordance with the present invention improve the head characteristic and avoid collisions between a head element section and a recording disk. A hard disk drive according to an embodiment of the present invention performs TFC (Thermal Fly height Control) to adjust the clearance between the head element section and recording disk by means of thermal expansion. A head slider includes a TFC heater. The hard disk drive detects its acceleration and controls the TFC heater in accordance with the detected acceleration, thereby reducing the probability of collision between the head element section and recording disk. Further, the hard disk drive detects residual vibration prevailing after impact application. The heater turns back ON when the residual vibration becomes lower than a reference level.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com