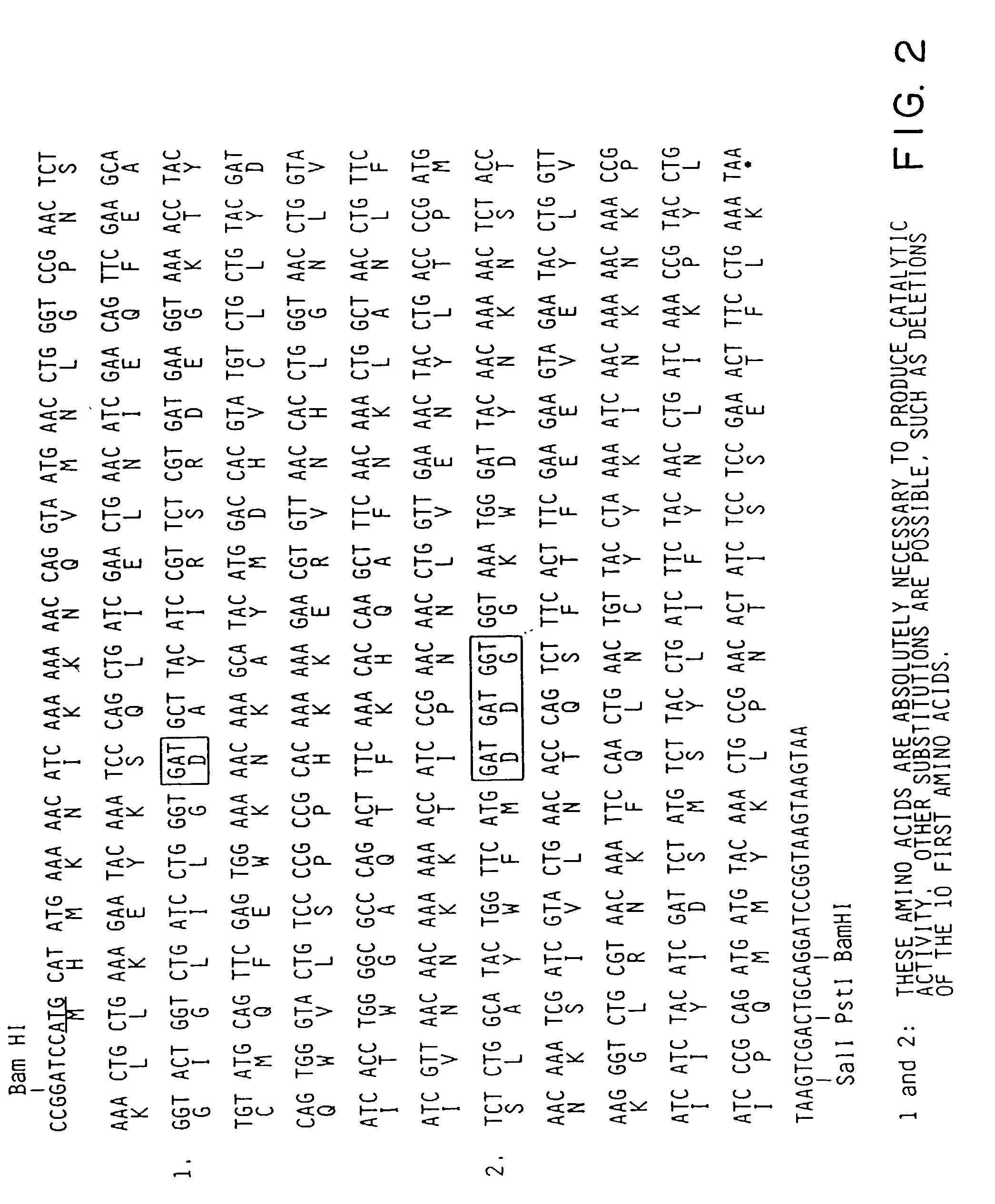
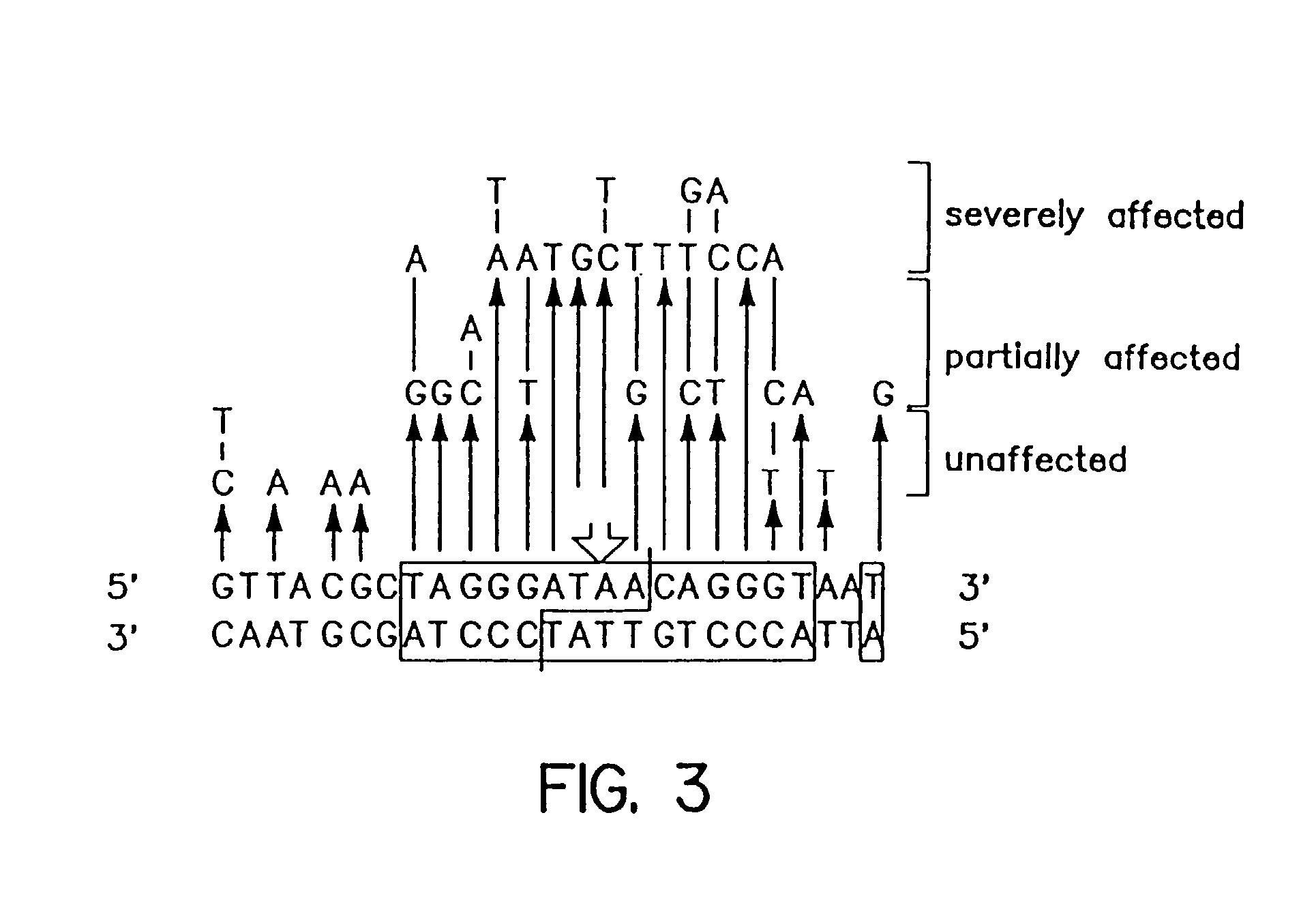
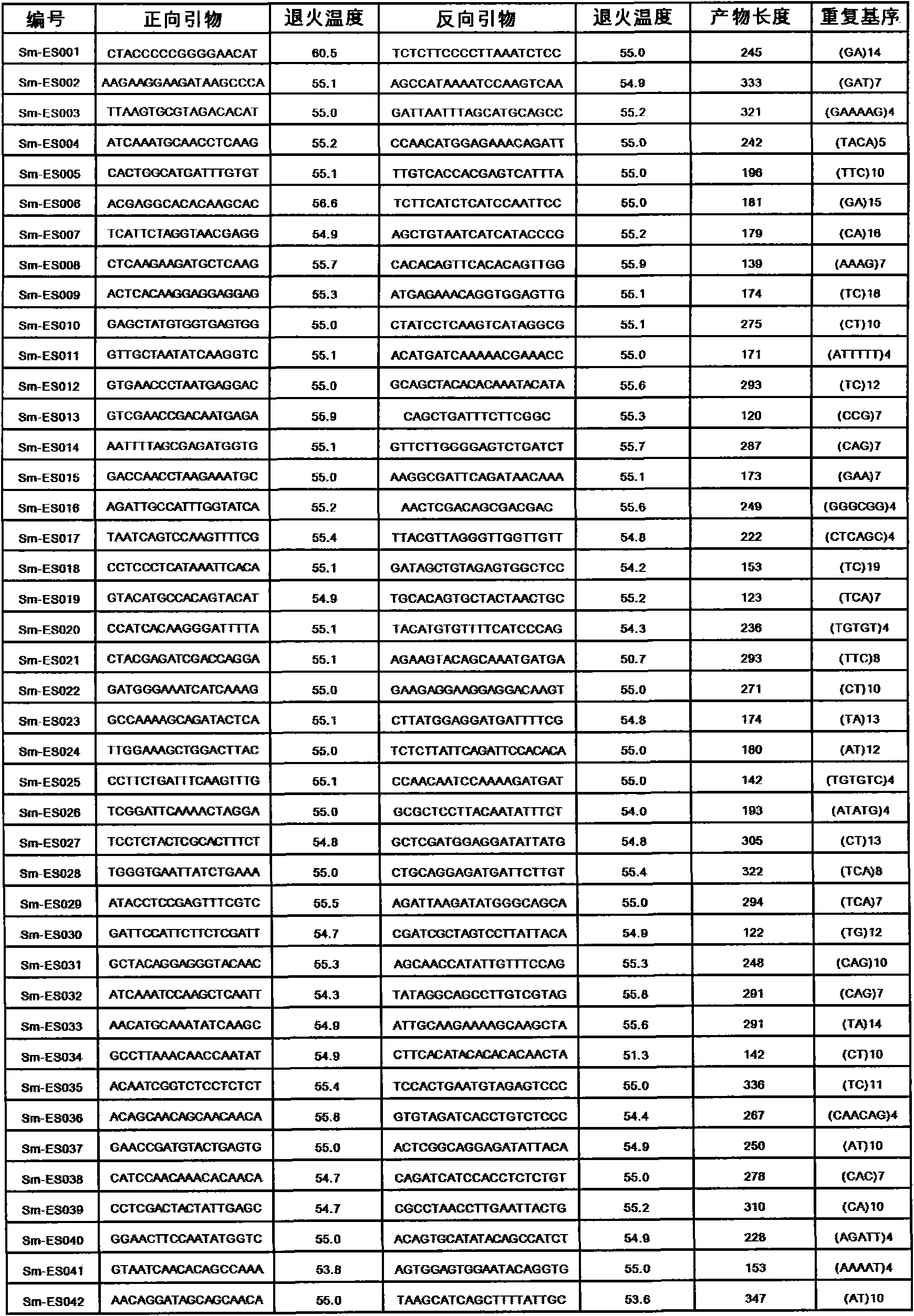
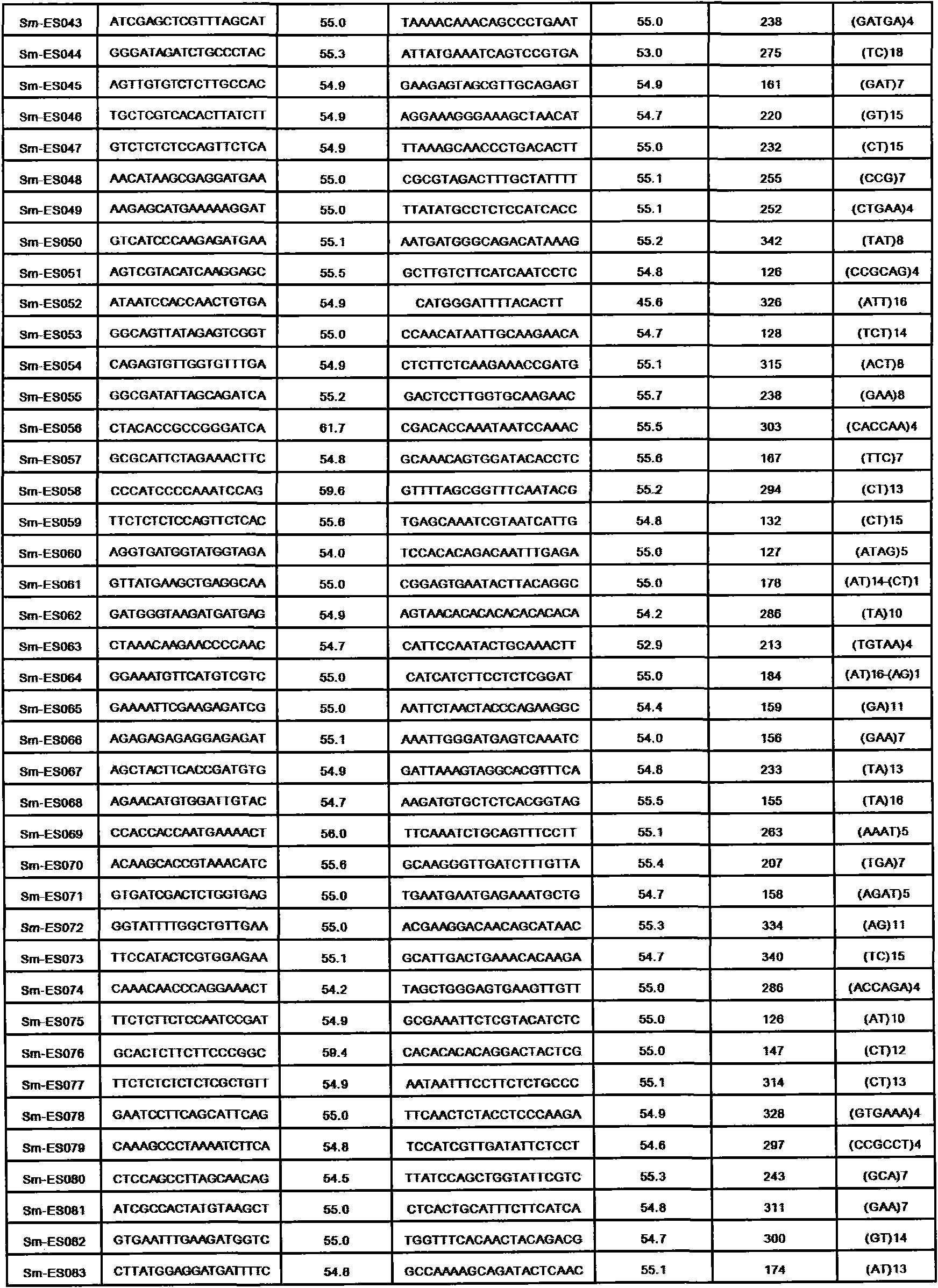
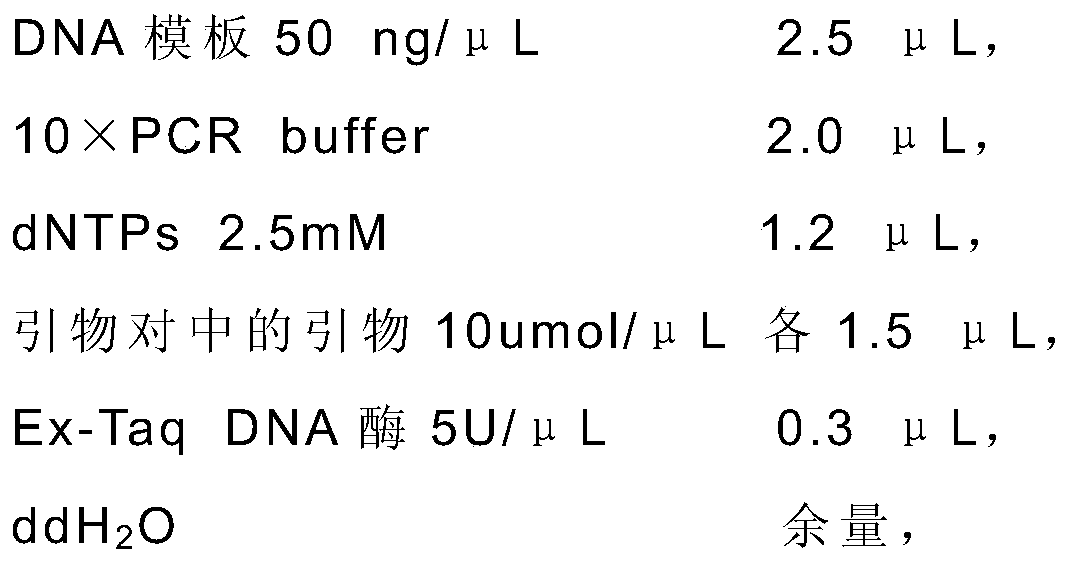
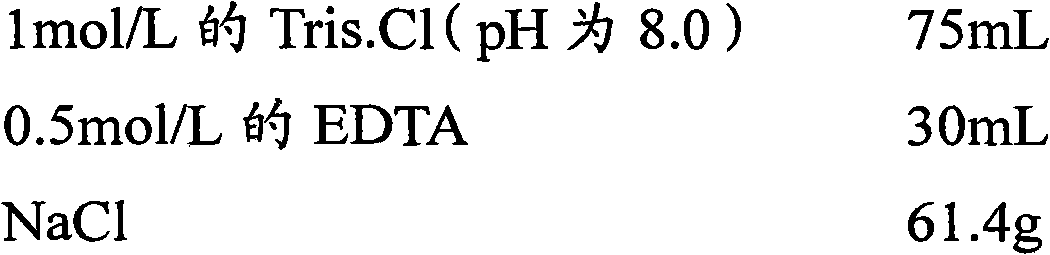Patents
Literature
95 results about "Gene mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene mapping describes the methods used to identify the locus of a gene and the distances between genes. The essence of all genome mapping is to place a collection of molecular markers onto their respective positions on the genome. Molecular markers come in all forms. Genes can be viewed as one special type of genetic markers in the construction of genome maps, and mapped the same way as any other markers.
Rapid screening method for drought-enduring variety of rice at seedling stage
InactiveCN102860199ADrought accurateDrought reliableHorticulture methodsGene mappingScreening method
The invention discloses a rapid screening method for drought-enduring variety of rice at seedling stage, comprising the following steps that: after soil drought processing and drought processing simulated by polyethylene glycol (PEG), variety with strong drought tolerance in two processing methods is screened out. By simultaneously performing soil drought and drought simulated by PEG and conjointly analyzing the result, the defects of two drought processing methods can be simultaneously avoided and the advantages of two methods can be exploited to the full. Thus, the experimental result is accurate and the results of the studies of breeding, group construction, gene mapping and the like of the drought-enduring variety and drought-sensitive variety which are screened out are more credible, and the time and the expenditure of researchers are saved.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark, specific primer and application thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing a salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark. The method mainly comprises the following steps of obtaining and pre-processing a salvia miltiorrhiza EST sequence, screening a SSR locus in the salvia miltiorrhiza EST sequence, designing and synthesizing the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR primer, screening the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR primer and the like. The method excavates the SSR locus aiming at the salvia miltiorrhiza EST and designs the PCR primer according to the flanking sequence of the SSR locus, and on the basis of this, the salvia specificEST-SSR mark system is established; and the method lays a solid foundation for genetic diversity evaluation, genetic relationship or idioplasmatic identification, genetic linkage description, molecular mark auxiliary selection, gene mapping cloning, functional genome analysis, related researches and the like of related species of the salvia miltiorrhiza and the salvia. The invention also discloses the EST-SSR locus specific primer obtained by the method for preparing the salvia miltiorrhiza EST-SSR molecular mark and the application thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data
InactiveUS6909971B2Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGene mappingNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data, which utilizes linkage disequilibrium between genetic markers mi, which are polymorphic nucleic acid or protein sequences or strings of single-nucleotide polymorphisms deriving from a chromosomal region. All marker patterns P that satisfy a certain pattern evaluation function e(P) are searched from the data, each marker mi of the data is scored by a marker score and the location of the gene is predicted as a function of the scores s(mi) of all the markers mi in the data.
Owner:LICENTIA OY
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker chained with pumpkin peel color gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106636393AShorten the timeImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene mappingMolecular breeding
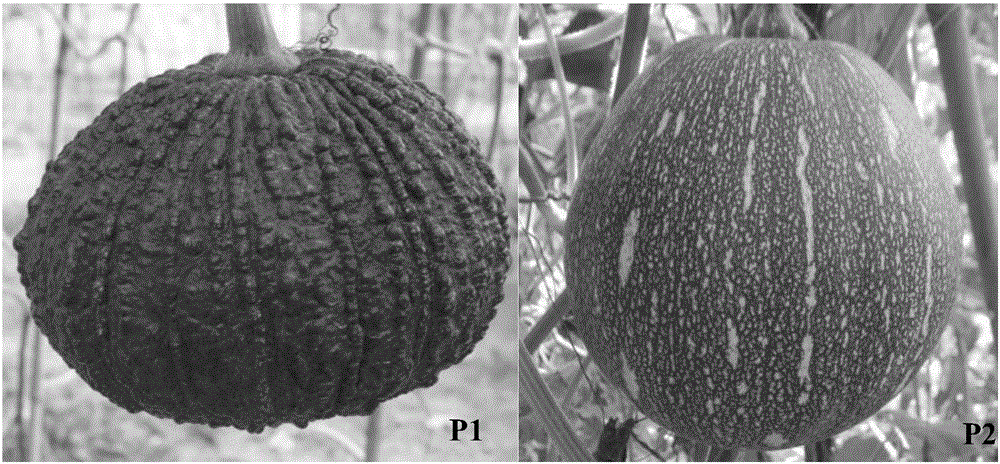
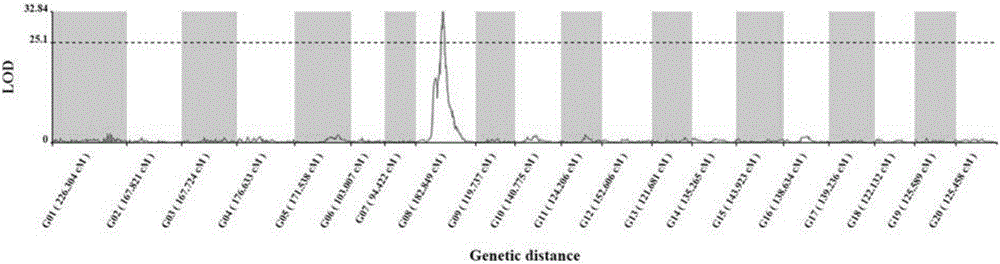
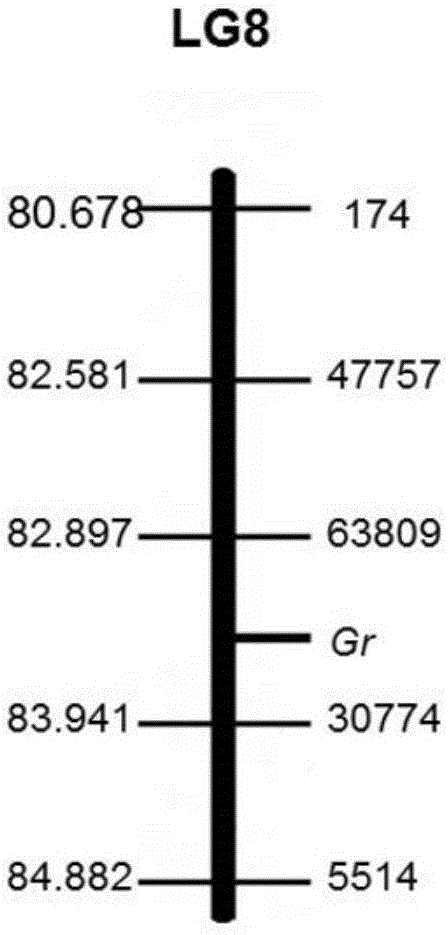
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker chained with a pumpkin peel color gene and an application thereof. A molecular marker 63809 and a molecular marker 30774 obtained by screening are tightly chained with the pumpkin peel color gene, and the genetic distance between the two markers is 1.04cM; the SNP molecular marker can be directly applied to building of a peel color gene molecular marker assisted breeding system. A dCAPS amplification primer designed according to the two molecular markers can be used for improving molecular assisted breeding of pumpkin varieties easily, conveniently and rapidly at a high flux, technical support is provided for pumpkin appearance quality molecular breeding, and meanwhile the conventional gene mapping time is shortened greatly.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Common camellia oleifera SSR molecular marker primers and marking method and application thereof
ActiveCN110144418AFast growthQuick splitMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene mappingRNA extraction
The present invention relates to the technical field of molecular marking and particularly relates to common camellia oleifera SSR molecular marker primers and a marking method and an application thereof. The common camellia oleifera roots are subjected to RNA extraction, sequencing and assembly, MISA is used to search SSR sites, corresponding primers are designed, camellia oleifera genome DNA isused as a material, the designed SSR primers are validated, and the corresponding primers are obtained from the designed 6,738 pairs of the primers. The primers show polymorphism, can successfully distinguish the camellia oleifera materials of different varieties, provide the new molecular markers for molecular marking auxiliary breeding of the camellia oleifera, and provide new ideas for future researches on genetic breeding, genome mapping, gene mapping, species genetic relationship identification, etc.
Owner:QINZHOU UNIV
Breeding method of alien substitution line
The invention relates to a breeding method of an alien substitution line, which can be used for further shifting exogenous beneficial genes to wheat by utilizing a wheat alien substitution line so that an alien translocation line is bred. The alien substitution line has the very important function at the aspects of gene mapping of wheat sibling species, researches on the hereditary feature of an exogenous chromosome in the background of wheat and the evolutionary relationship between the wheat and the sibling species thereof and the like, and a wheat variety with abundant hereditary basis and excellent comprehensive character is selected as a receptor material for breeding the alien substitution line so that the utilization value of the alien substitution line can be enhanced. In addition, a technology system for conveniently and rapidly breeding the alien substitution line is established and also is one of important research subject for enhancing the breeding efficiency of the alien substitution line.
Owner:李祥
Laser microdissection and microarray analysis of breast tumors reveal estrogen receptor related genes and pathways
InactiveCN101965190APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPathway analysisLaser micro dissection
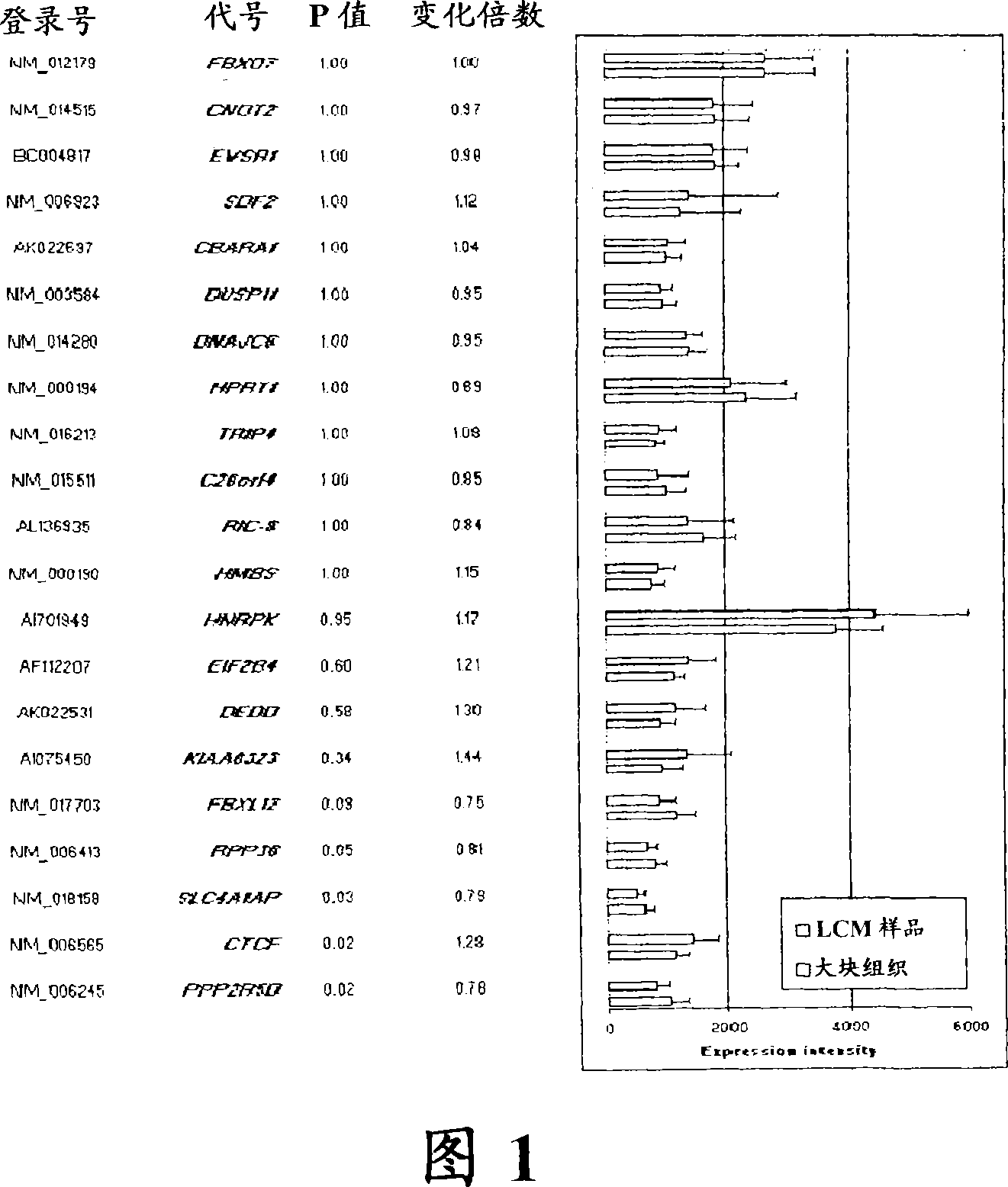
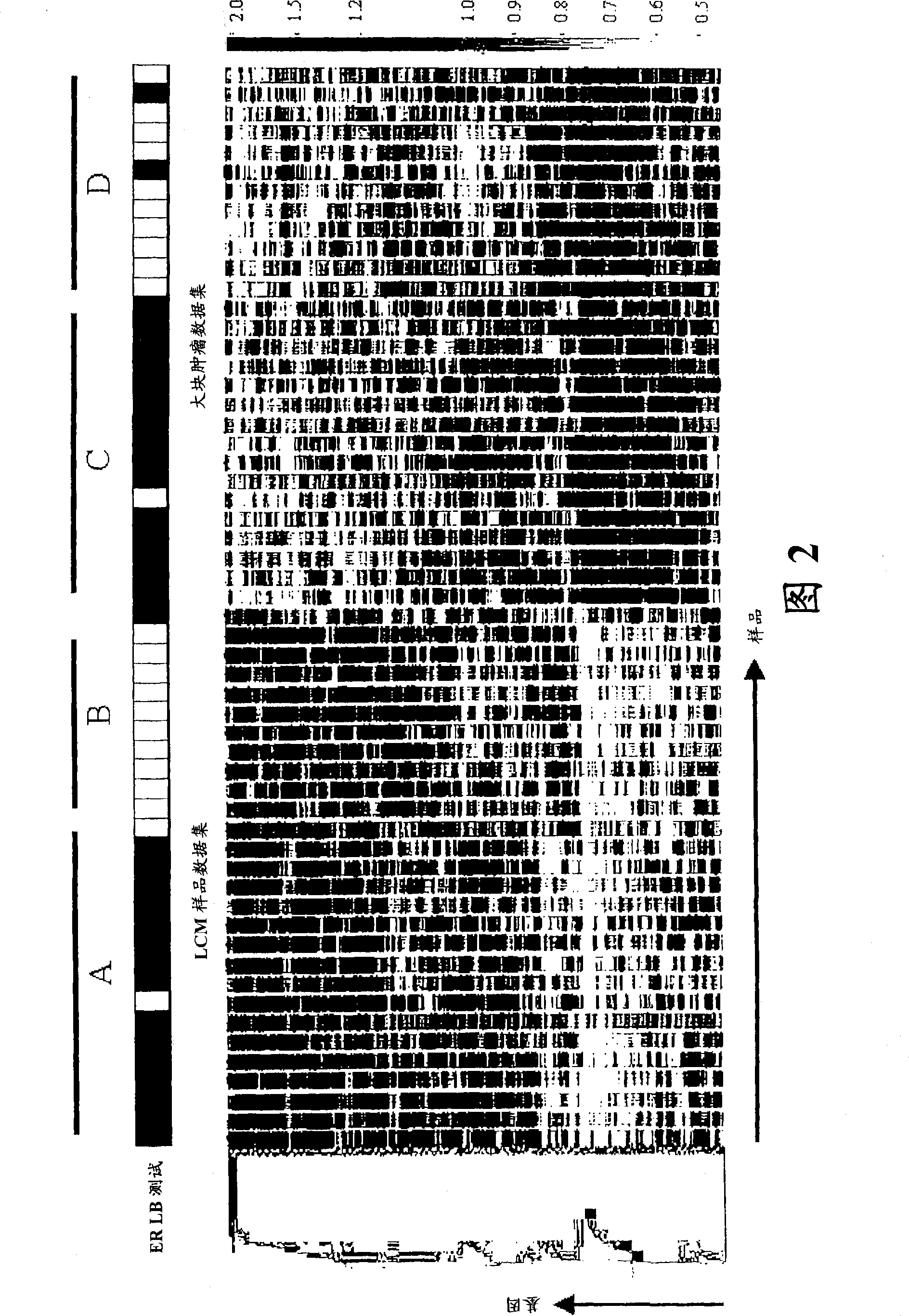
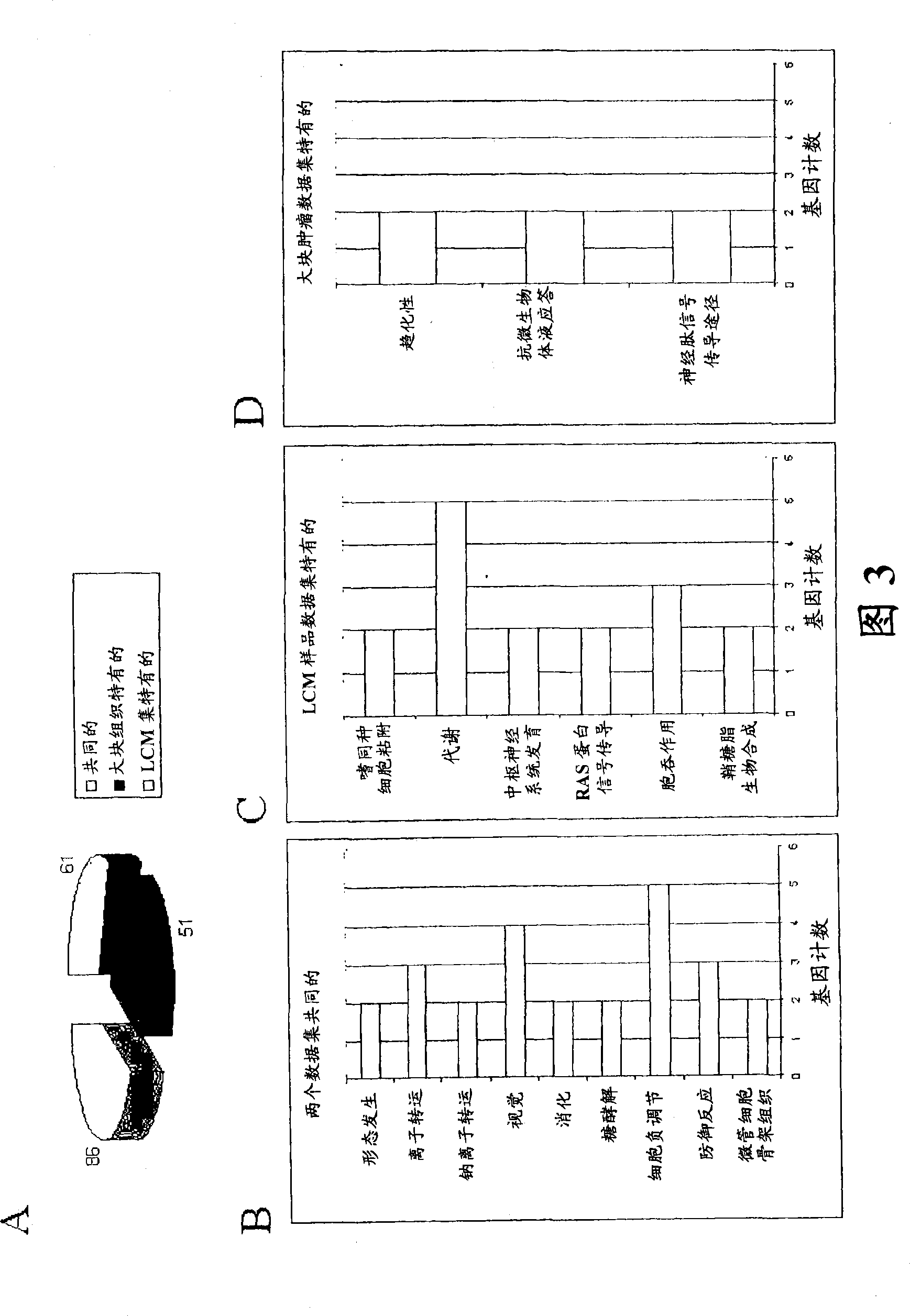
About 70% to 80% of breast cancers express estrogen receptor-a (ERa), and estrogens play important roles in the development and growth of hormone-dependent tumors. Together with lymph node metastasis, tumor size and histological grade, ER status is considered one of the prognostic factors in breast cancer, and an indicator for hormonal treatment. 147 genes and 112 genes with significant P- value and having significant differential expression between ER+ and ER- tumors were identified from the LCM data set and bulk tissue data set, respectively. 61 genes were found to be common in both data sets, while 85 genes were unique to the LCM data set and 51 genes were present only in the bulk tumor data set. Pathway analysis with the 85 genes using Gene Ontology suggested that genes involved in endocytosis, ceramide generation, Ras / ERK / Ark cascade, and JAT- STAT pathway may play roles related to ER. The gene profiling with LCM-captured tumpr cells provides a unique approach to characterize and study epithelial tumor cells and to gain an insight into signaling pathways associated with ER.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
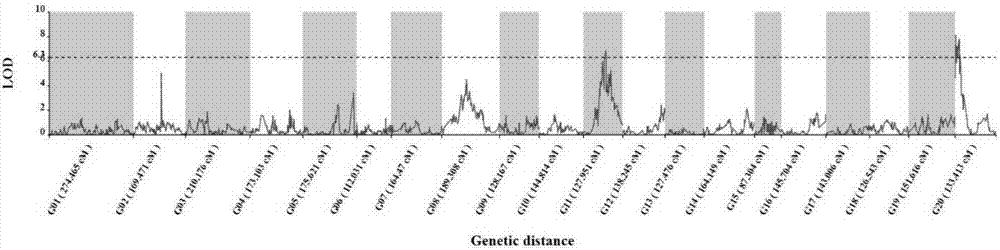
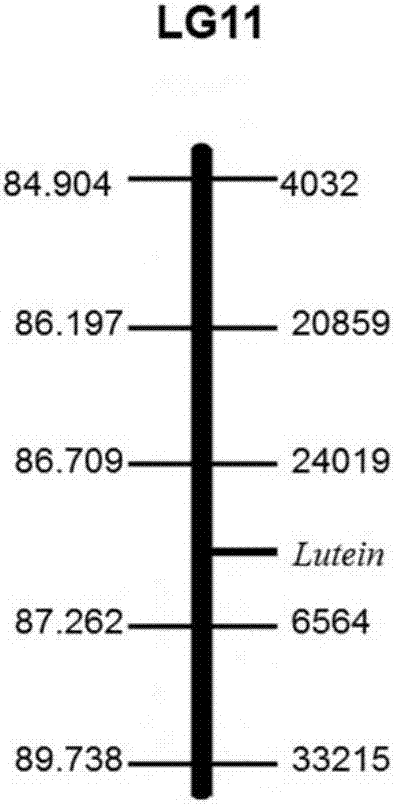
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) molecular markers closely linked to pumpkin lutein content major QTL (quantitative trait loci) and application of SNP molecular markers
ActiveCN107142315AShorten the timeHigh contribution rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene mappingLutein
The invention discloses SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) molecular markers closely linked to pumpkin lutein content major QTL (quantitative trait loci) and application of the SNP molecular markers. The molecular markers are positioned on a Chinese pumpkin No. 11 linkage group and are respectively located on two sides of a lutein gene, wherein the molecular marker 6564 comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 or the homologous SNP sequence of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1; the molecular marker 24019 comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2 or the homologous SNP sequence of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The SNP molecular markers have the advantages that the positioned QTL is significantly correlated to quantitative traits (p<0.05) and is high in contribution rate, the explanation probability of the molecular marker 6564 is 15.2%, the explanation probability of the molecular marker 24019 is 15.6%, and pumpkin lutein content can be predicted through the two molecular markers; dCAPS (derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences) amplification primers designed according to the molecular markers can be applied to pumpkin variety improvement molecular marker assisted selection in a simple, fast and high-throughput manner, molecular marker assisted selection technical support is provided for the early identification and screening of pumpkin lutein content traits, and the time of traditional gene mapping is shortened greatly at the same time.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker, primers and method for estimating left-end length of N introgressed segment of tobacco
ActiveCN105200052AReduce the burden onReduce outputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene mappingNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a molecular marker, primers and a method for estimating the left-end length of an N introgressed segment of tobacco. The molecular marker is a sequence represented as Seq ID No.1 or Seq ID No2. According to estimating method, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed by adopting a GL4.06 primer pair and a GL3.50 primer pair as the primers and adopting to-be-detected N introgressed segment containing tobacco genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template, then electrophoresis detection is performed, and if a DNA segment with the corresponding size is obtained through amplification, the N introgressed segment of detected tobacco is as long as a disease-resistant control material Samsun NN in the molecular marker position; if the DNA segment with the corresponding size is not obtained through amplification, the N introgressed segment of the detected tobacco is shorter than the disease-resistant control material Samsun NN in the molecular marker position. The method can be simply, conveniently and rapidly applied to anti-TMV (tobacco mosaic virus) gene mapping of the tobacco and TMV-resistant tobacco variety breeding in a high-throughput manner, and reduction of linkage redundancy with the N gene is facilitated.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Molecular marker, primers and method for estimating right-end length of N introgressed segment of tobacco
ActiveCN105200149AReduce the burden onReduce outputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNicotiana tabacumTobacco mosaic virus
The invention relates to a molecular marker, primers and a method for estimating the right-end length of an N introgressed segment of tobacco. The molecular marker is a sequence represented as Seq ID No.1 or Seq ID No2. According to estimating method, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed by adopting a TN5.51 primer pair and a TN5.34 primer pair as the primers and adopting to-be-detected N introgressed segment containing tobacco genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template, then electrophoresis detection is performed, and if a DNA segment with the corresponding size is obtained through amplification, the N introgressed segment of detected tobacco is as long as a disease-resistant control material Coker176 in the molecular marker position; if the DNA segment with the corresponding size is not obtained through amplification, the N introgressed segment of the detected tobacco is shorter than the disease-resistant control material Coker176 in the molecular marker position. The method can be simply, conveniently and rapidly applied to anti-TMV (tobacco mosaic virus) gene mapping of the tobacco and anti-TMV tobacco variety breeding in a high-throughput manner, and reduction of linkage redundancy with the N gene is facilitated.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Method for gene mapping from genotype and phenotype data
InactiveUS20050250098A1Model-free and computationally effectiveOvercomes drawbackMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGene mappingGenetic linkage disequilibrium
A method for gene mapping from genotype and phenotype data utilizes linkage disequilibrium between genetic markers mi, which are polymorphic nucleic acid or protein sequences or strings of single-nucleotide polymorphisms deriving from a chromosomal region. All marker patterns P that satisfy a certain pattern evaluation function e(P) are searched from the data, each marker mi of the data is scored by a marker score and the location of the gene is predicted as a function of the scores s(mi) of all the markers mi in the data.
Owner:LICENTIA OY
Physalis angulata cpSSR-labeled primer developed based on chloroplast genome sequence and its application
ActiveCN110195123AAdd raw dataEvaluate polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene mappingGenetic diversity
The invention discloses a Physalis angulata cpSSR-labeled primer developed based on a chloroplast genome sequence and its application. The primer pair SEQ ID NO. 1 to SEQ ID NO. 60 is based on the development of the Physalis angulata chloroplast genome sequence, based on the sequencing of the chloroplast genome, a large amount of sequence information is analyzed, and then cpSSR site screening andcpSSR-labeled primer design are carried out. The patent overcomes the problem of low efficiency, long cycle and high cost of traditional SSR marker development, and fills the blank of the current cpSSR labeling information of Physalis angulata. The polymorphism and applicability of the cpSSR-labeled primer are evaluated by screening cpSSR primers and genetic diversity analysis. The cpSSR polymorphism-labeled primer provided in the patent lays the foundation for the study of genetic diversity evaluation, germplasm identification, importance gene mapping and molecular marker-assisted breeding ofPhysalis angulata.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker SIsv1363 closely linked with Setaria italica L. Beauv. leaf color gene
InactiveCN102690811AImprove throughputEasy to set upMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGene mappingGenomic DNA
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, relates to a molecular marker and especially relates to a molecular marker SIsv1363 closely linked with a Setaria italica L. Beauv. leaf color gene. The molecular marker SIsv1363 has a sequence shown in the Seq ID NO.1. The invention also relates to primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv1363, a use of the molecular marker SIsv1363 and the primers in Setaria italica L. Beauv. leaf color gene mapping or Setaria italica L. Beauv. genetic breeding, and a Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding method. The molecular marker SIsv1363 links a genomic DNA sequence and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. leaf color gene, and is conducive to establishment of a Setaria italica L. Beauv. molecular marker auxiliary breeding system. A genetic close linkage distance between the molecular marker SIsv1363 and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. leaf color gene is 0.15cM. In Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding practices and resource and variety identification, the simple, fast and high throughput utilization of the molecular marker SIsv1363 and the primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv1363 can be realized.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
Molecular marker SIsv0067 closely linked with Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene
InactiveCN102690812AEasy to set upImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGene mappingAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, relates to a molecular marker and especially relates to a molecular marker SIsv0067 closely linked with a Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene. The molecular marker SIsv0067 has a sequence shown in the Seq ID NO.1. The invention also relates to primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv0067, a use of the molecular marker SIsv0067 and the primers in Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene mapping or Setaria italica L. Beauv. genetic breeding, and a Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding method. The molecular marker SIsv0067 links a genomic DNA sequence and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene, and is conducive to establishment of a Setaria italica L. Beauv. molecular marker auxiliary breeding system. A genetic close linkage distance between the molecular marker SIsv0067 and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene is 3cM. In Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding practices and resource and variety identification, the simple, fast and high throughput utilization of the molecular marker SIsv0067 and the primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv0067 can be realized.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
Molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN108220467ASpeed up the breeding processEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene mappingNucleotide sequencing
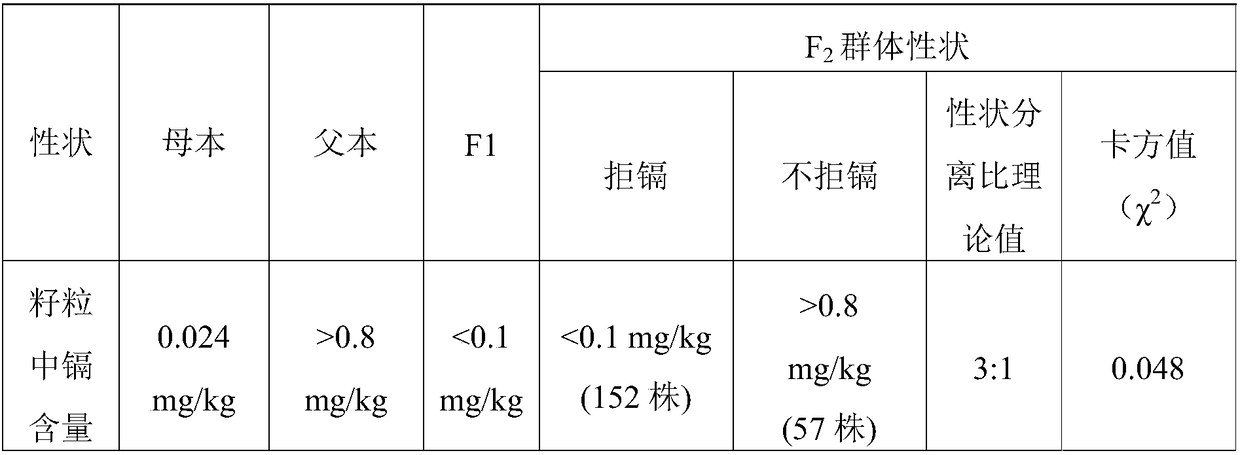
The invention discloses a molecular marker and application thereof. The molecular marker shows insertion / deletion length polymorphism of a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:3. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention is tightly associated with cadmium repelling character of rice and can be effectively used for gene mapping and detection of the cadmium repelling character of the rice aswell as assistant breeding of the molecular marker of the rice.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST +3
Molecular marker method of cucumber spire etiolation gene
ActiveCN106957897AAccurate genetic lociEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGene mapping
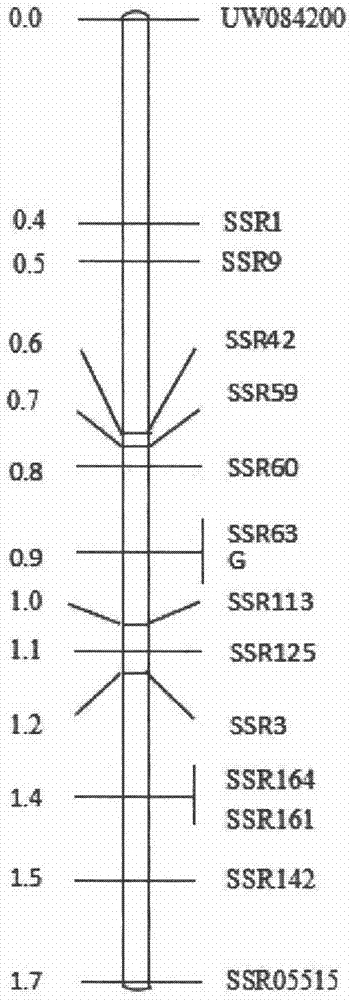
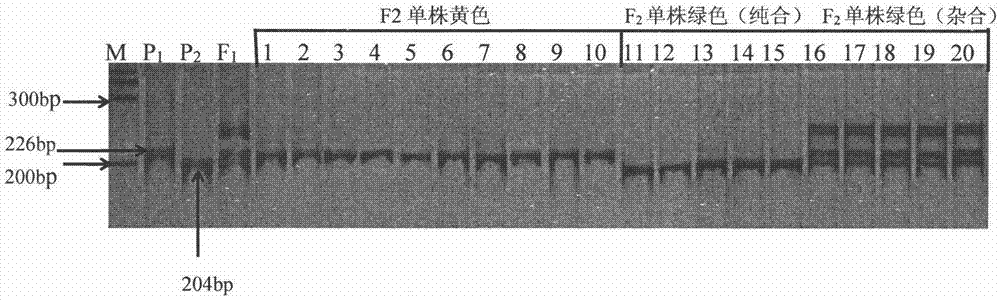
The invention discloses a molecular marker method of cucumber spire etiolation gene linking, belonging to the biotechnical field. A molecular marker SSR63 closely linked to the cucumber spire etiolation gene is disclosed for the first time, the forward and reverse primers of the marker are respectively: 5'GCTTCATCCTGTGGCGT3' and 5'CCAGTCATGGGTTTGTTGGA3'. In F2 constructed from spire cucumbers and green-leaf cucumbers, 226bp products can be amplified from the primers SSR63F / SSR63R inspire etiolation strain, 204bp product or product containing both 204bp and 226bp strips can be amplified in green-leaf strain, and all the products can be closely linked with vyl. The molecular marker closely linked with cucumber spire etiolation gene vyl can be used for cucumber spire etiolation gene mapping or molecular marker-assisted breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
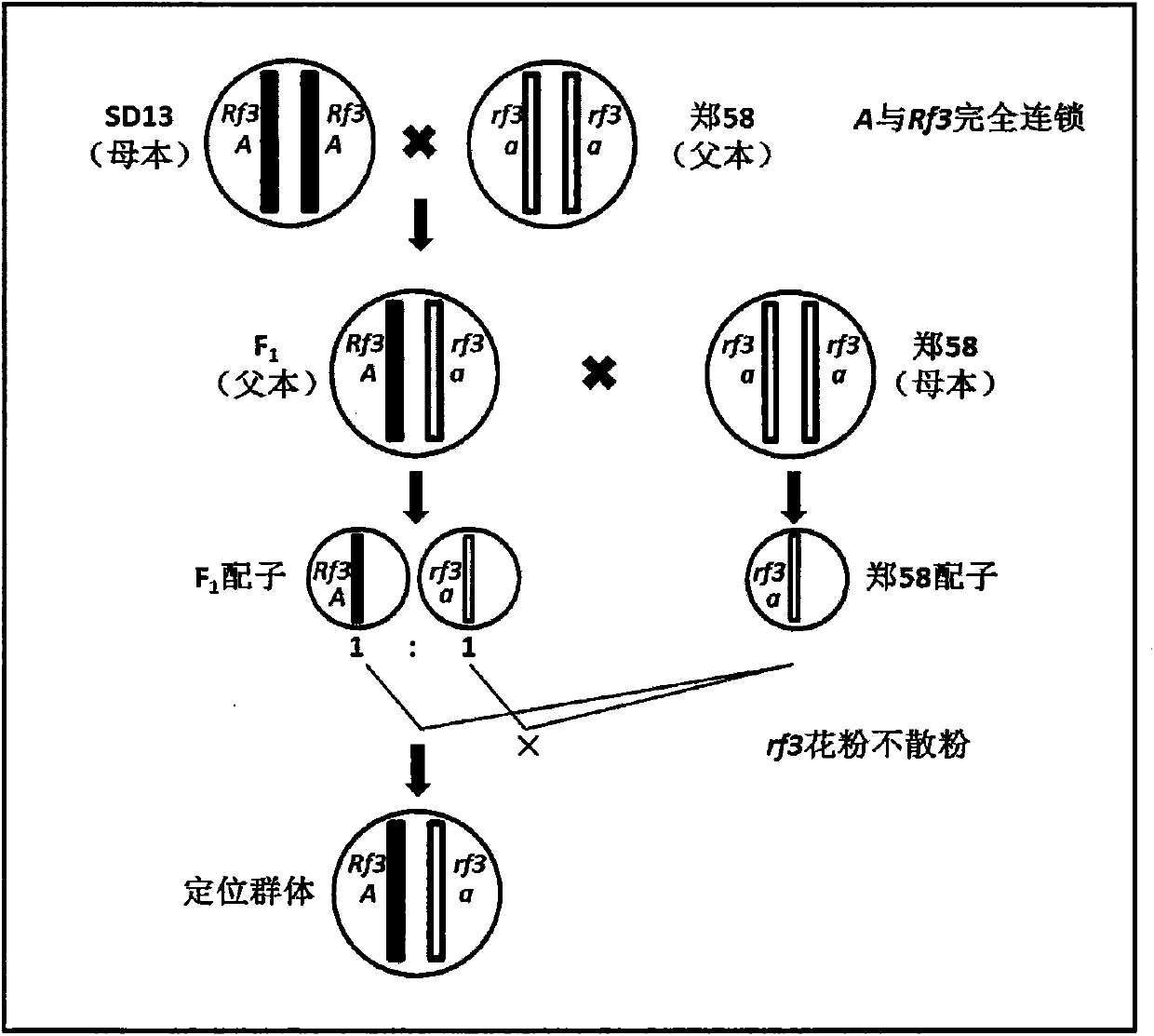
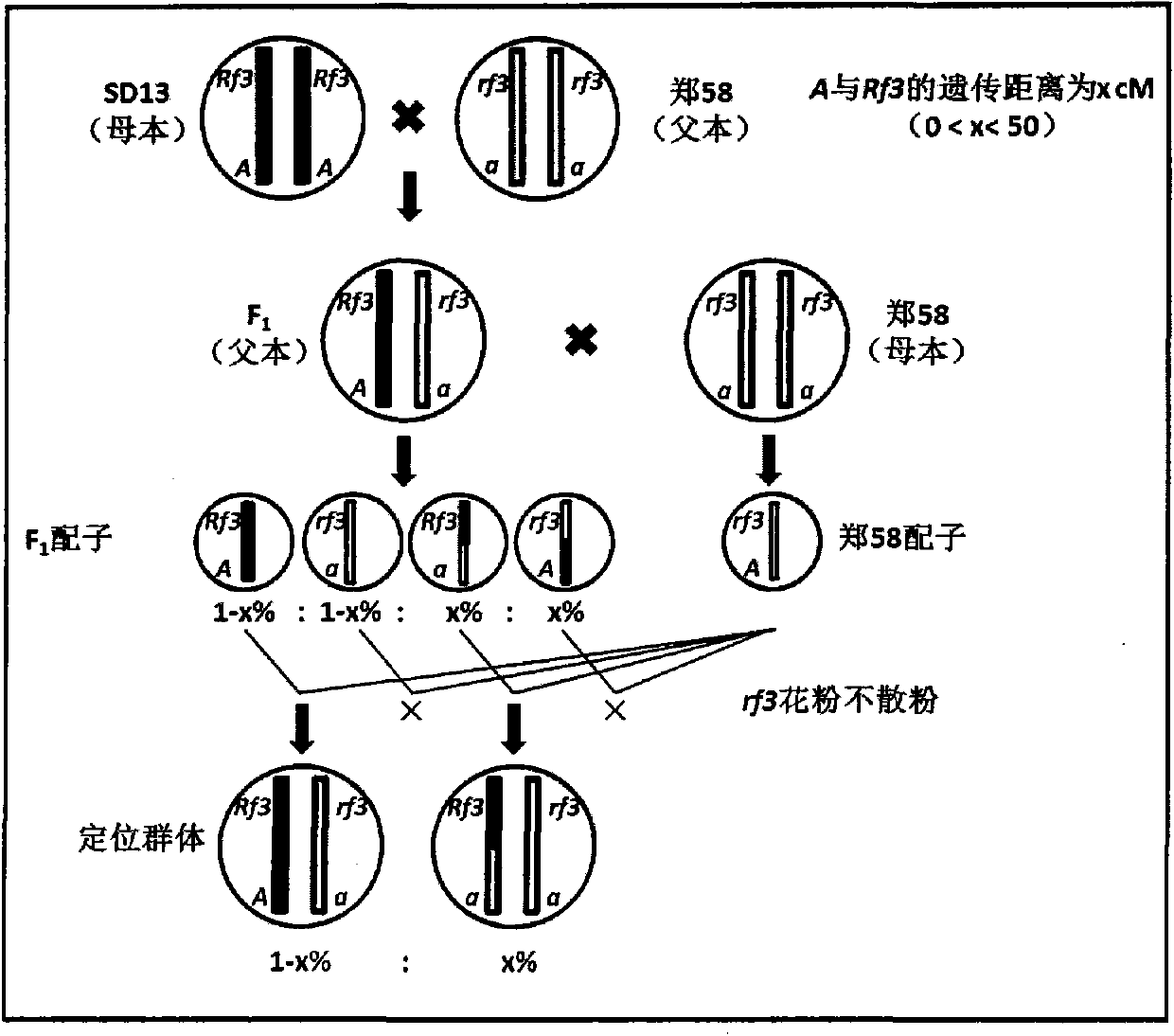
New method for mapping corn S-type cytoplasm male sterility fertility restoring gene Rf3
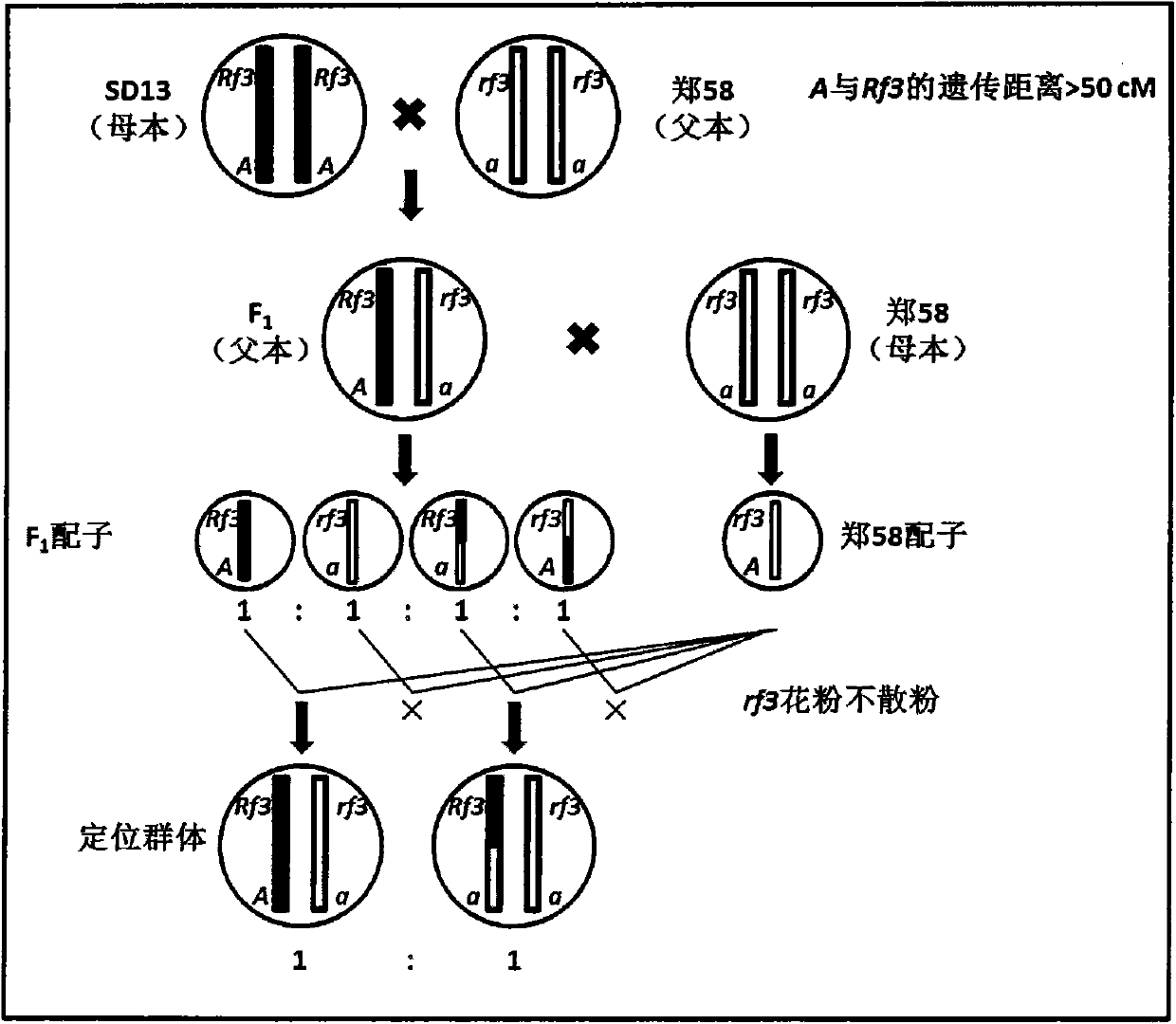
InactiveCN103416297AAvoid positioning deviationSave human effortMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationGene mappingPhenotypic trait
The invention belongs to the technical field of corn gene mapping, in particular to a new method for mapping a corn S-type cytoplasm male sterility fertility restoring gene Rf3. According to a conventional method for mapping a qualitative character gene, a backcross or selfing population is constructed, the gene type of an individual is inferred through phenotype identification, molecular marker detection is performed, and the position of the gene is determined through two-point and three-point tests. When the Rf3 gene is mapped with the conventional method, the phenotype identification is affected by human and environmental factors easily, the workload is large and the size of the population to be mapped is limited. The mapping method aims to overcome the defects of the conventional method for mapping the Rf3 gene and does not need the phenotype identification. The new method is characterized in that due to the fact that the gene type of the utilized population to be mapped is already known, the phenotype does not need to be identified, a large population can be constructed, and enough recombined individuals can be found in one generation to fine map the Rf3 gene. The method for mapping the Rf3 gene is effective and promotes three-line sterility seed production by the utilization of the Rf3 gene in production.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene mapping expression vector for detecting plant autophagy phenomenon and application
InactiveCN105441470AEasy and accurate positioningPrecise positioningFluorescence/phosphorescenceVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceLaser scanning
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to construction of a gene vector for detecting a cell autophagy phenomenon. A protein of an Atg8 gene mapping expression vector is expressed in a suspension cell after being fused with a green fluorescence protein (GFP), and subcellular localization is performed by detecting the position of a fused protein through a laser scanning confocal microscope. Through a simple, convenient and accurate method for locating in living cells, a reference basis is laid for the research of the molecular mechanism of the tobacco cell autophagy phenomenon.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
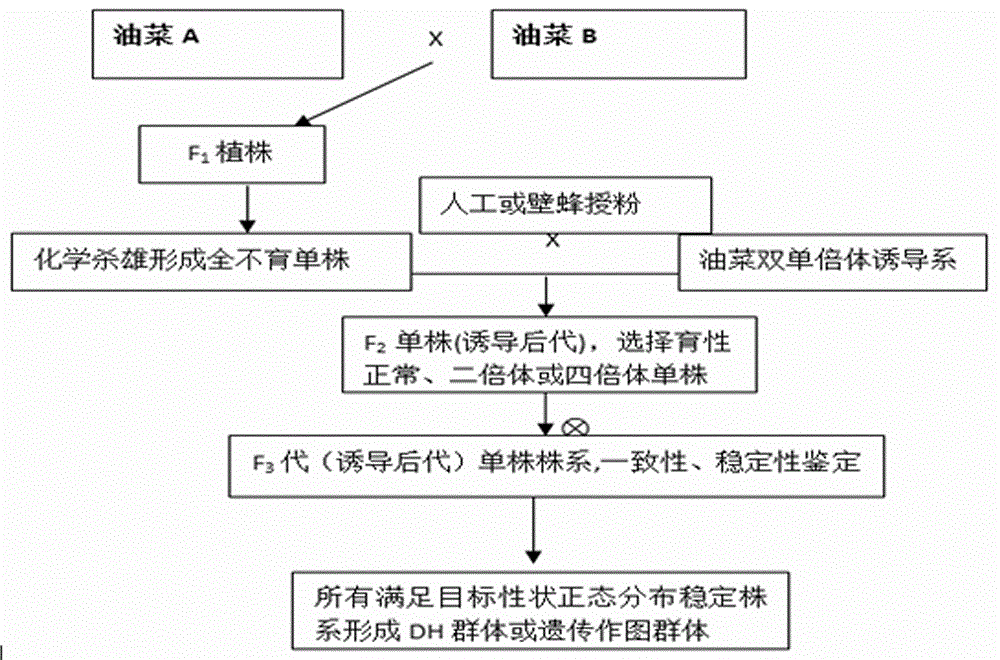
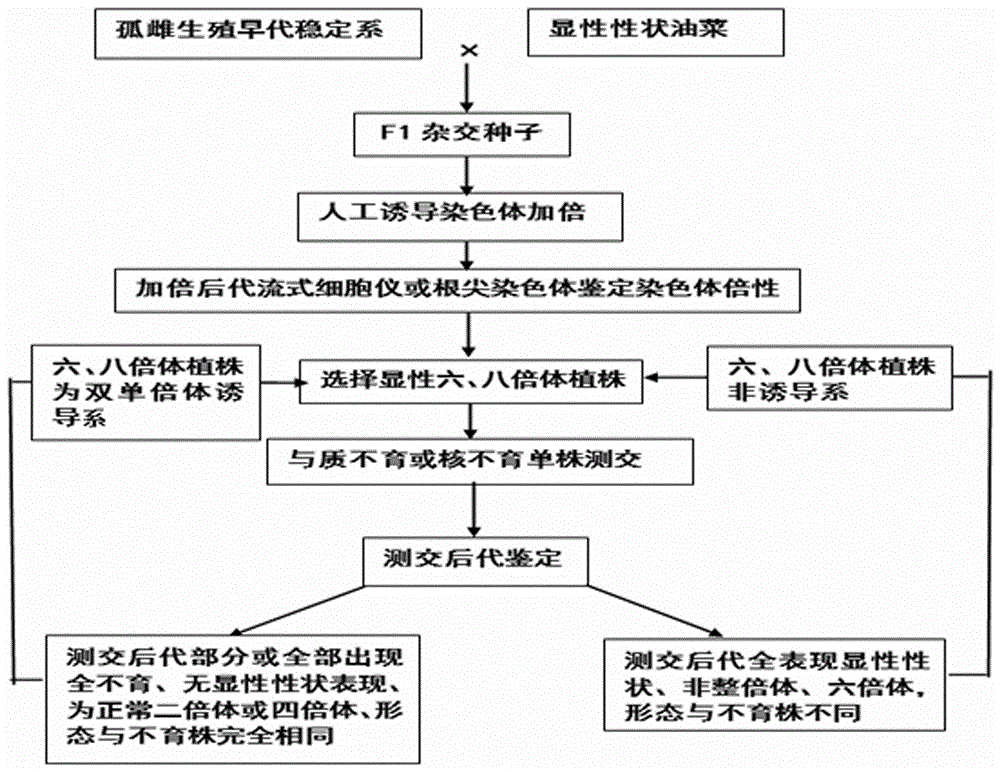
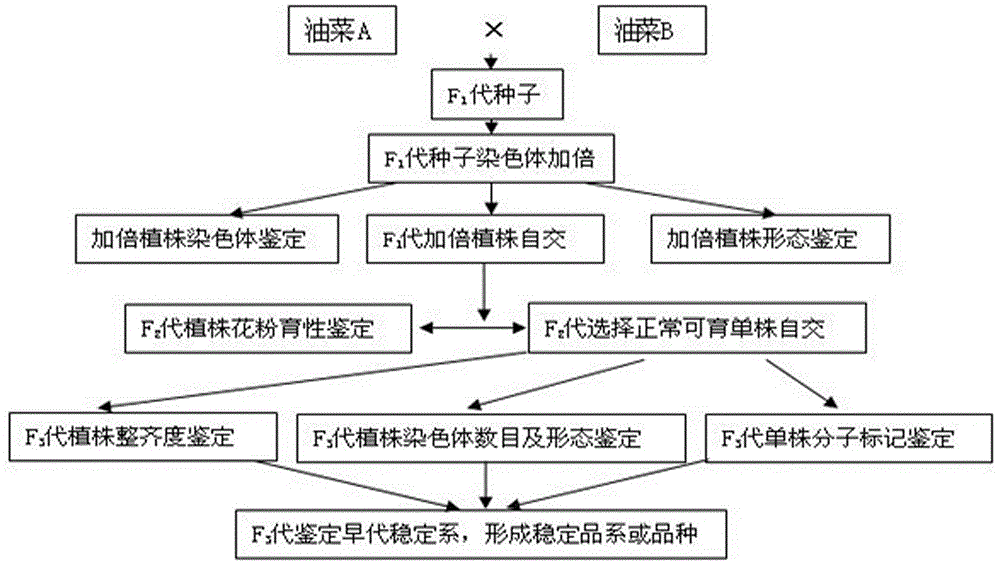
Method for creating rape genetic-stability group through rape doubled haploid inducible system in large scale
ActiveCN106069719ASimple methodEasy to masterMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissue cultureGene mappingF1 generation
The invention provides a method for creating a rape genetic-stability group through a rape doubled haploid inducible system in large scale. The method comprises the steps: 1), according to research requirements, selecting and breeding an objective trait; 2), according to the objective trait, selecting and breeding two parent materials with relatively large objective trait difference; 3), enabling the two parent materials to be hybridized; 4), pollinating parent hybridized F1 generation by using the rape doubled haploid inducible system; 5), discriminating induced progeny genetic stability; 6), performing induced progeny objective trait research to form the genetic-stability group. The method provided by the invention can be applied to three cultivated species of rapes, including cabbage type rapes (2n=38), turnip type rapes (2n=20) and mustard type rapes (2n=36), can obtain rapid (three-generation) large-scale genetic-stability DH (double haploid) groups, has a remarkable facilitation function to rape fundamental research, particularly application of genetic mapping groups to gene mapping, gene fine mapping and QTL analysis, shortens the cycle of rape fundamental research, and reduces the labor and material investments.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data
InactiveUS20050064408A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsGene mappingGenetic linkage disequilibrium
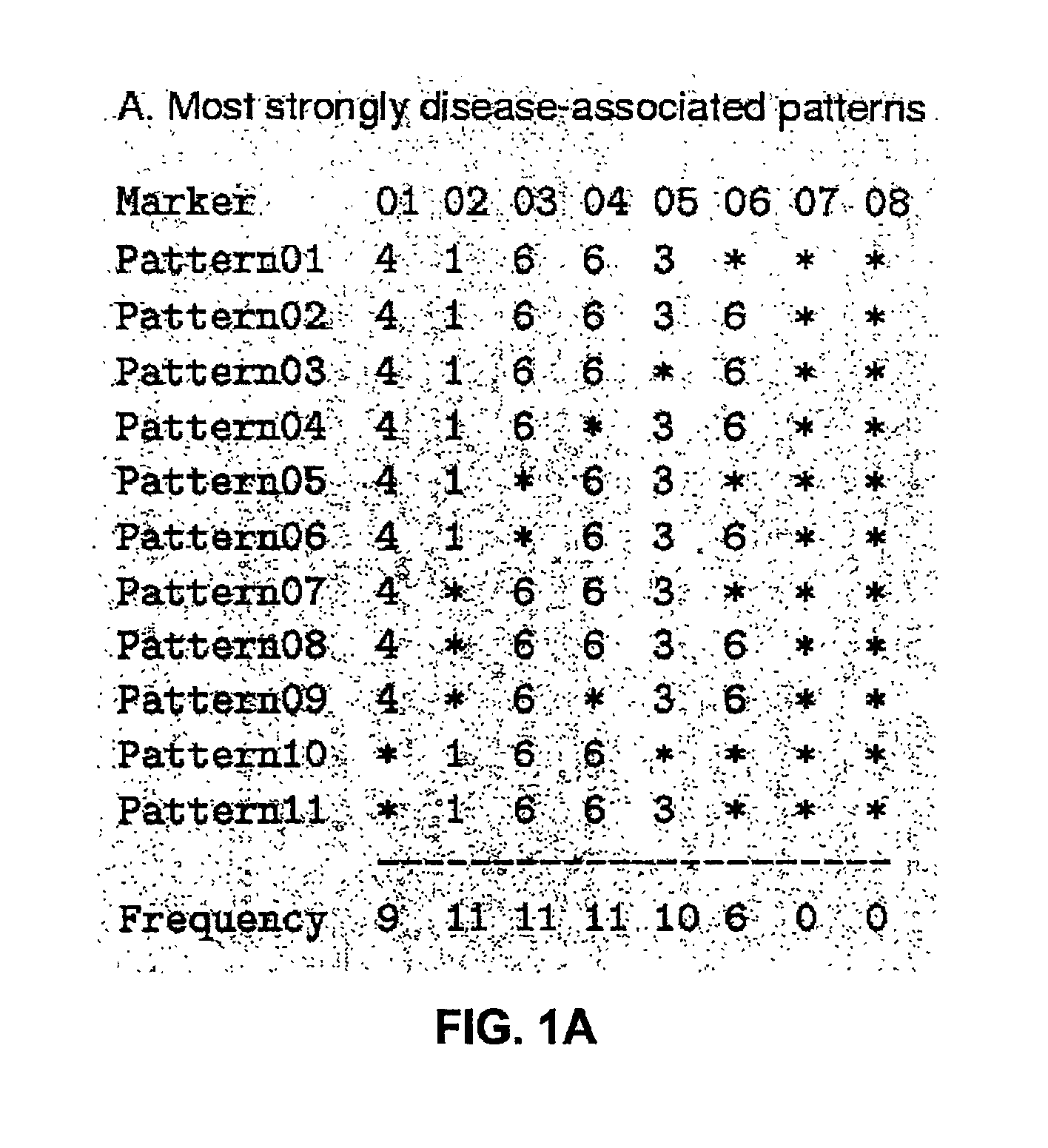
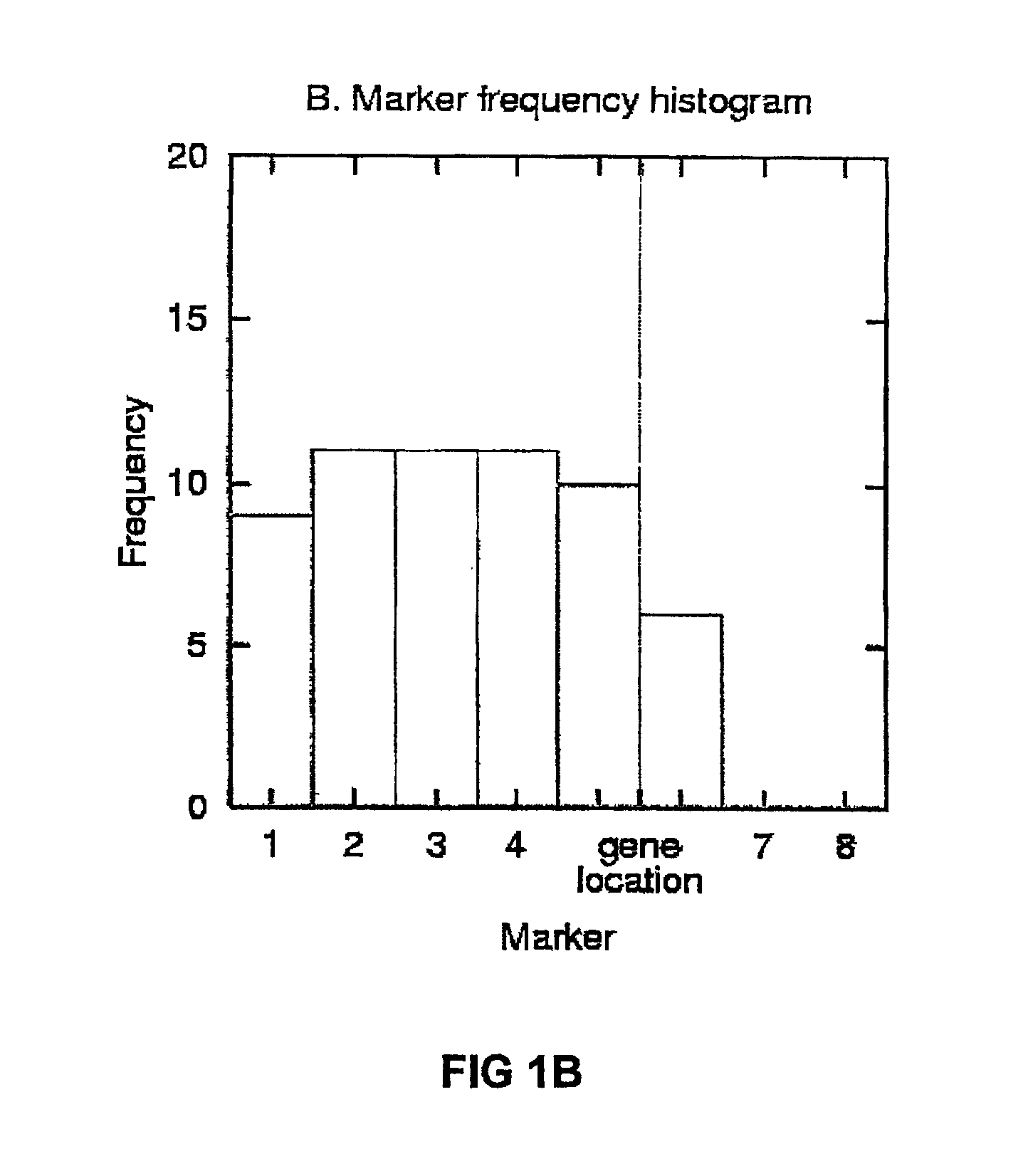
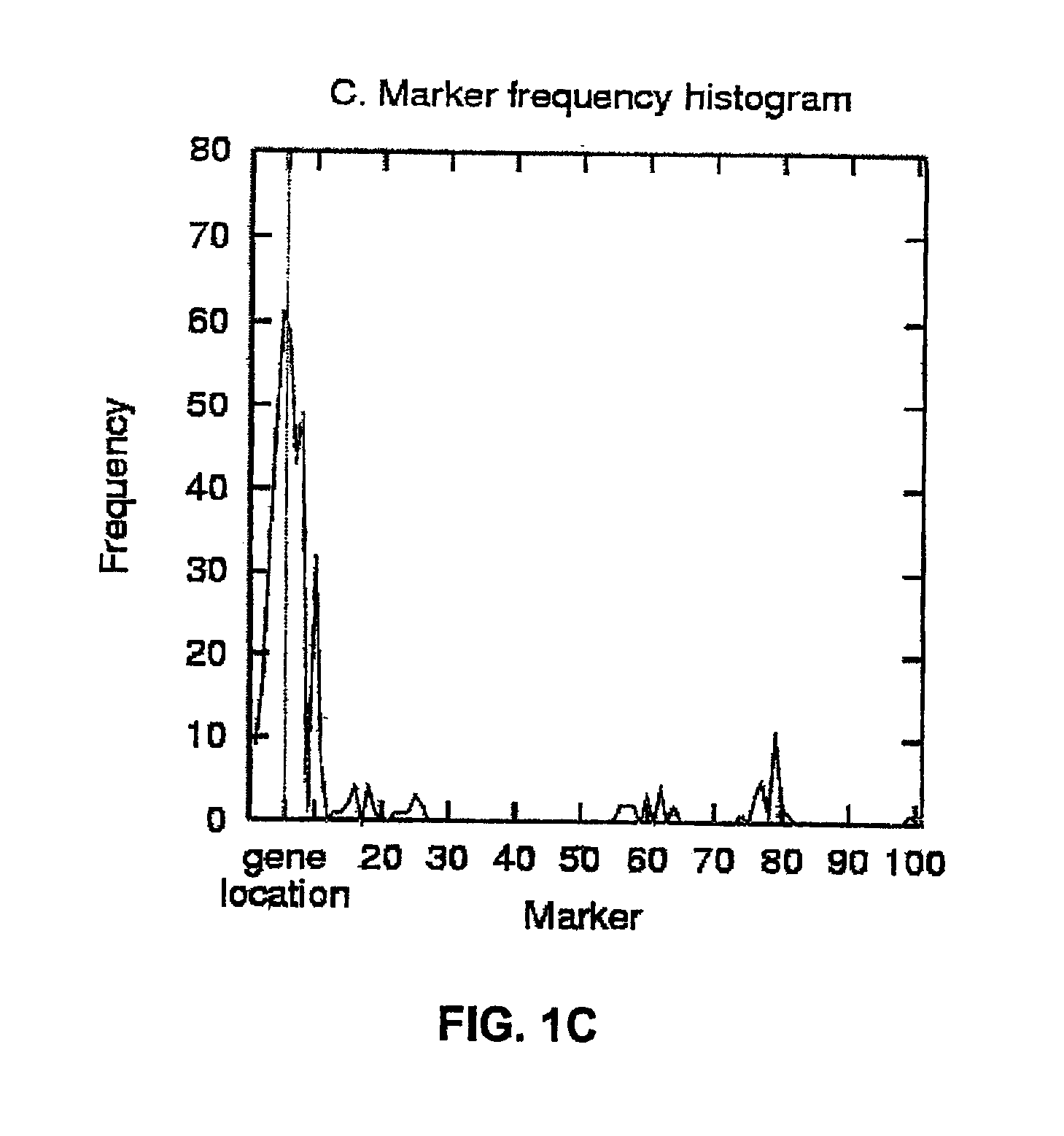
The present invention relates to a method for gene mapping from chromosome and phenotype data, which utilizes linkage disequilibrium between genetic markers mi, which are polymorphic nucleic acid or protein sequences or strings of single-nucleotide polymorphisms deriving from a chromosomal region. The method according to the invention is based on discovering and assessing tree-like patterns in genetic marker data. It extracts, essentially in the form of substrings and prefix trees, information about the historical recombinations in the population. This infor-mation is used to locate fragments potentially inherited from a common diseased founder, and to map the disease gene into the most likely such fragment. The method measures for each chromosomal location the disequilibrium of the prefix tree of marker strings starting from the location, to assess the distribution of disease-associated chromosomes.
Owner:LICENTIA OY
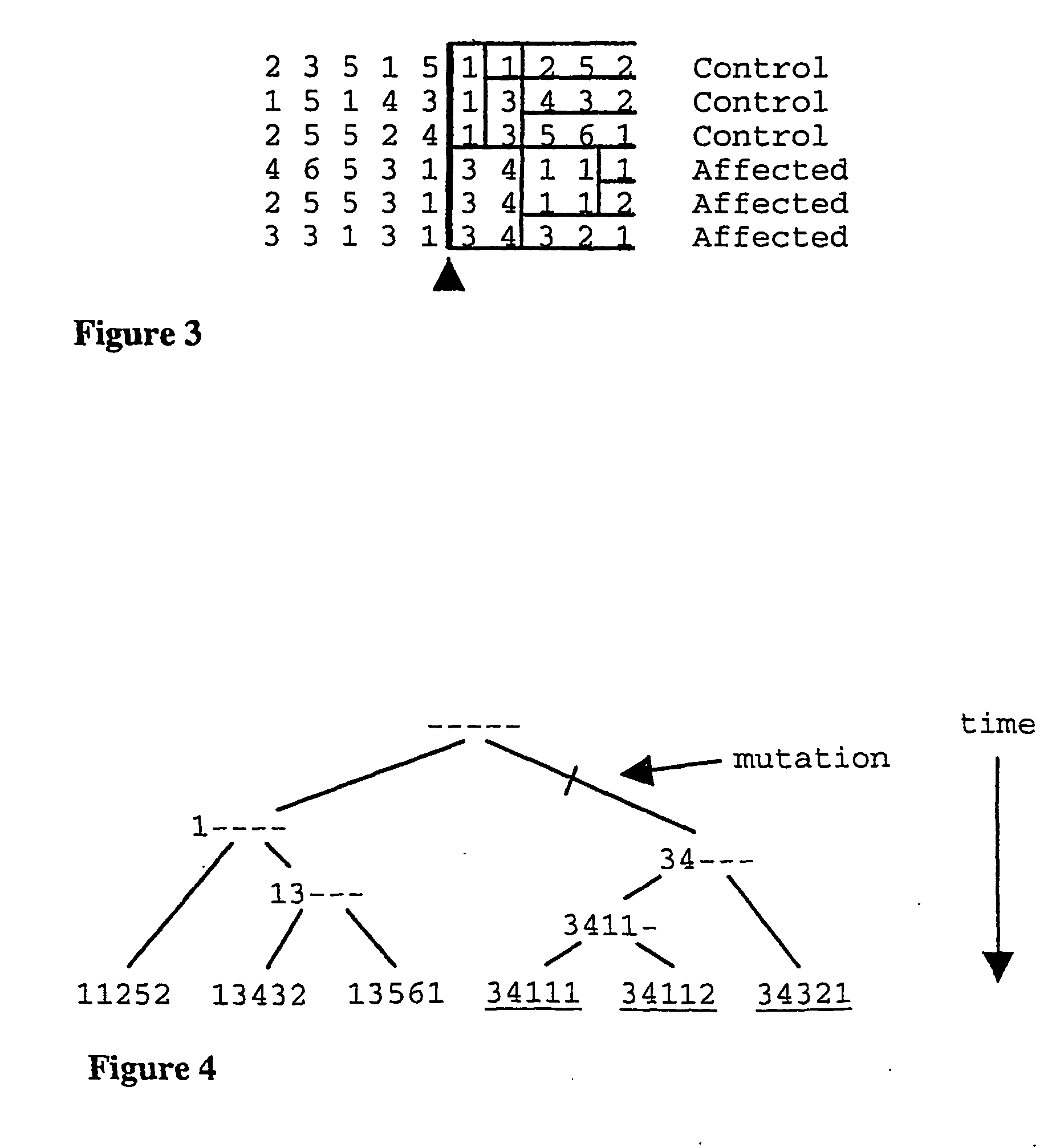
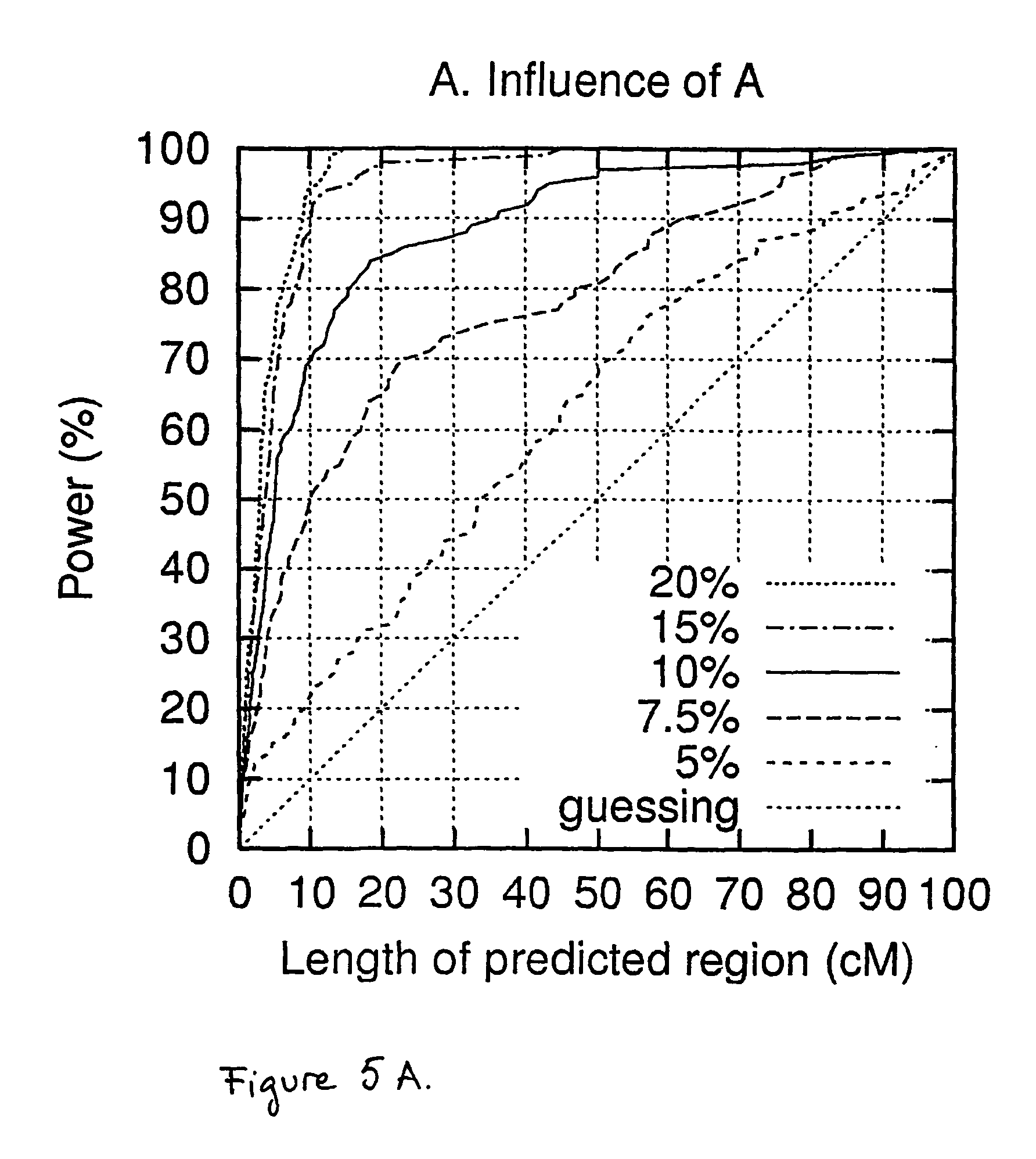
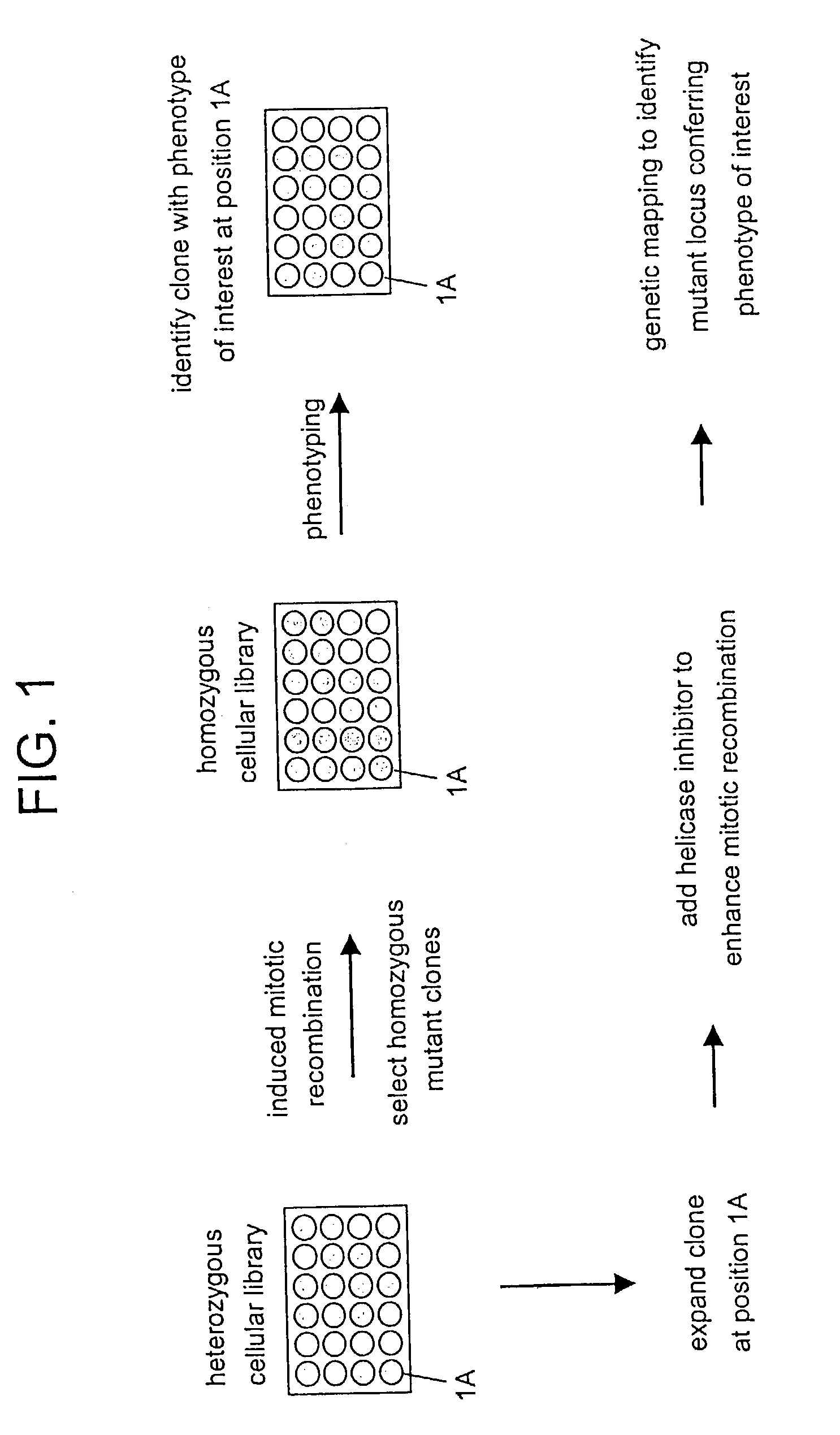
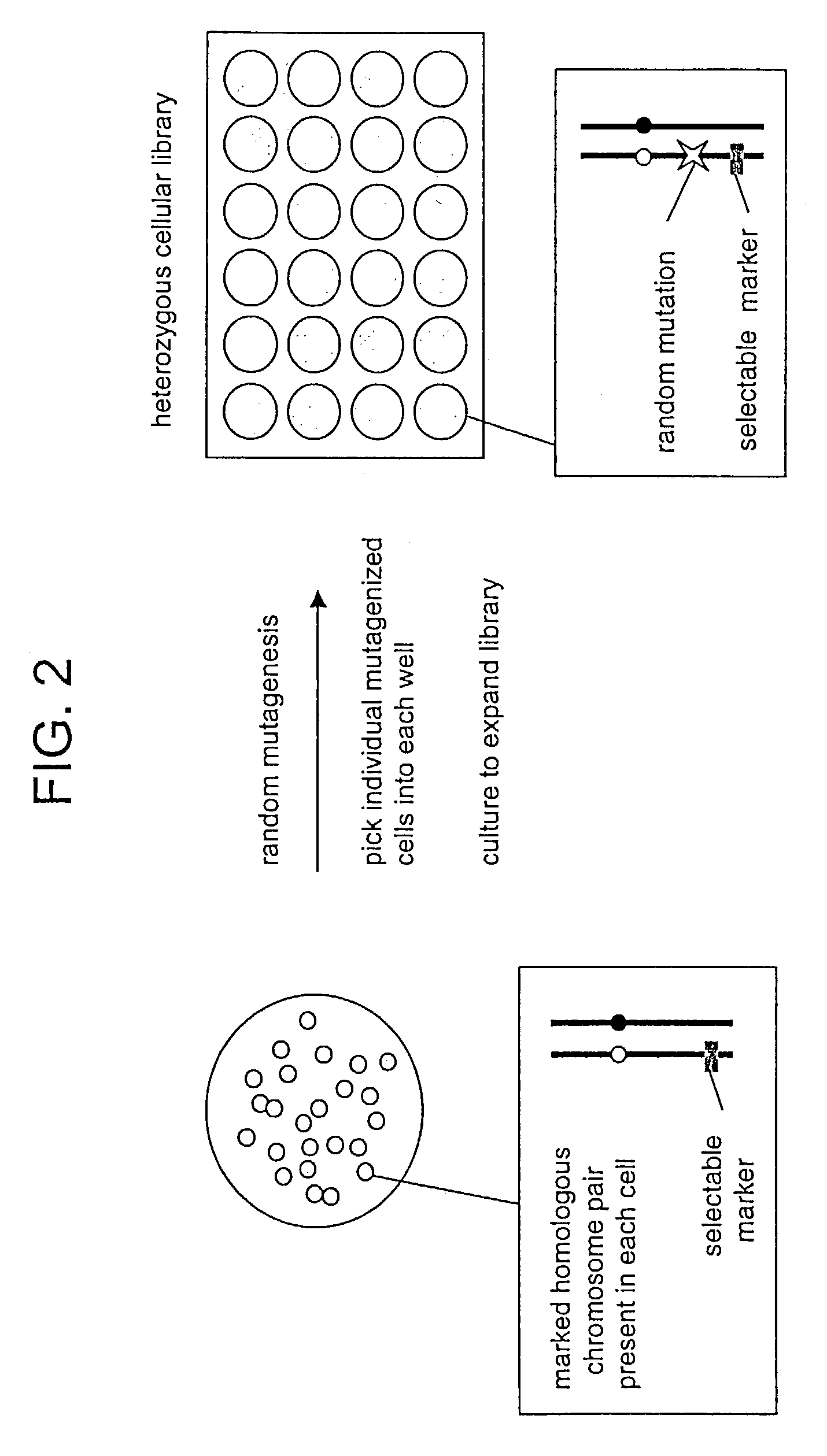
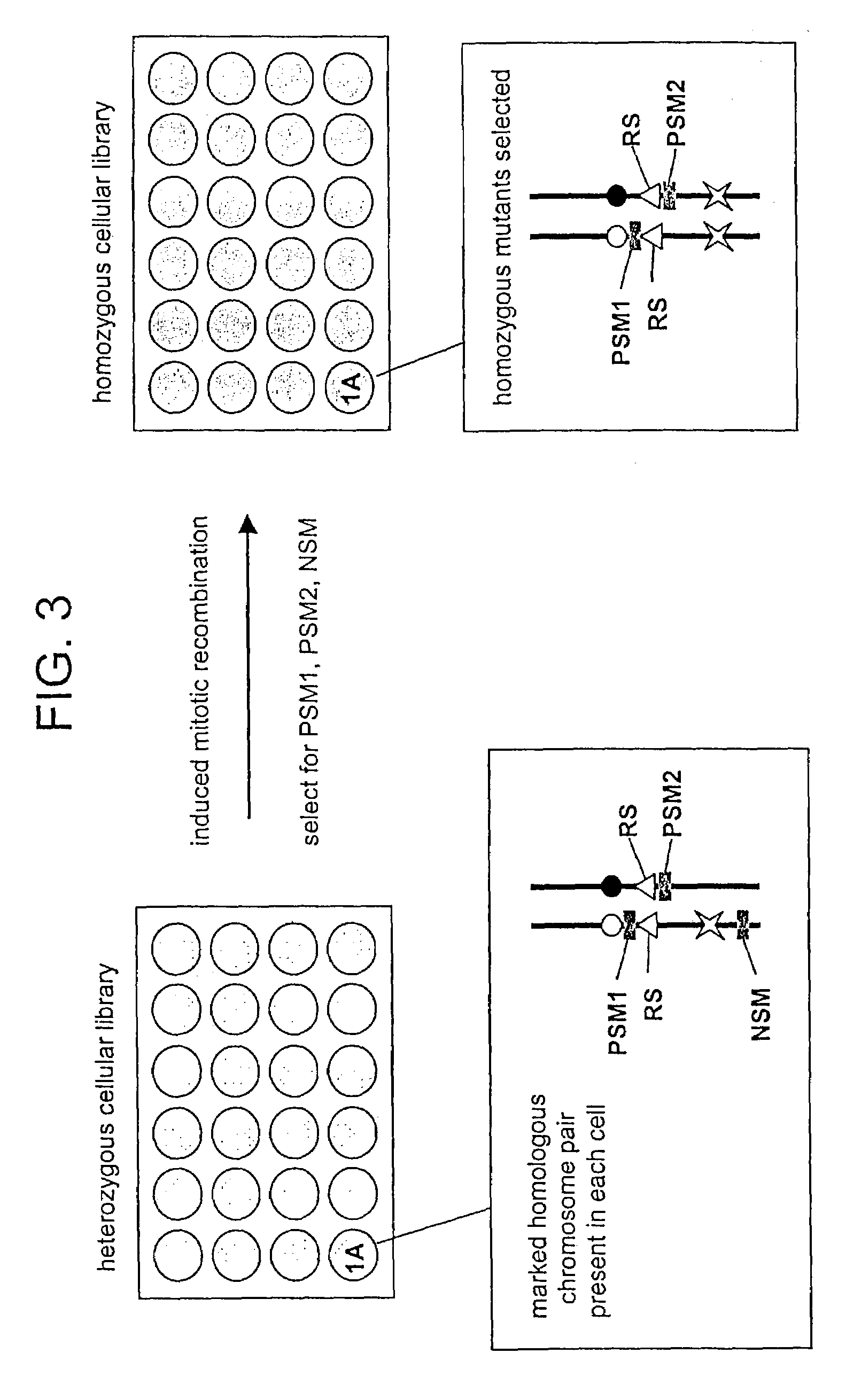
In Vitro mutagenesis, phenotyping, and gene mapping
Cellular libraries useful for in vitro phenotyping and gene mapping. In a representative approach, a method for preparing a homozygous cellular library includes the steps of providing a heterozygous cellular library comprising a plurality of isolated parent cells; inducing site-specific mitotic recombination in the plurality of isolated parent cells; culturing the plurality of isolated parent cells, whereby a population of daughter cells is produced; and selecting daughter cells comprising a homozygous genetic modification, whereby a homozygous cellular library is prepared.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Molecular marker SIsv0832 closely linked with Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene
InactiveCN102690818AEasy to set upImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGene mappingAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, relates to a molecular marker and especially relates to a molecular marker SIsv0832 closely linked with a Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene. The molecular marker SIsv0832 has a sequence shown in the Seq ID NO.1. The invention also relates to primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv0832, a use of the molecular marker SIsv0832 and the primers in Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene mapping or Setaria italica L. Beauv. genetic breeding, and a Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding method. The molecular marker SIsv0832 links a genomic DNA sequence and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene, and is conducive to establishment of a Setaria italica L. Beauv. molecular marker assistant breeding system. A genetic close linkage distance between the molecular marker SIsv0832 and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. heading stage gene is 3.5cM. In Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding practices and resource and variety identification, the simple, fast and high throughput utilization of the molecular marker SIsv0832 and the primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv0832 can be realized.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
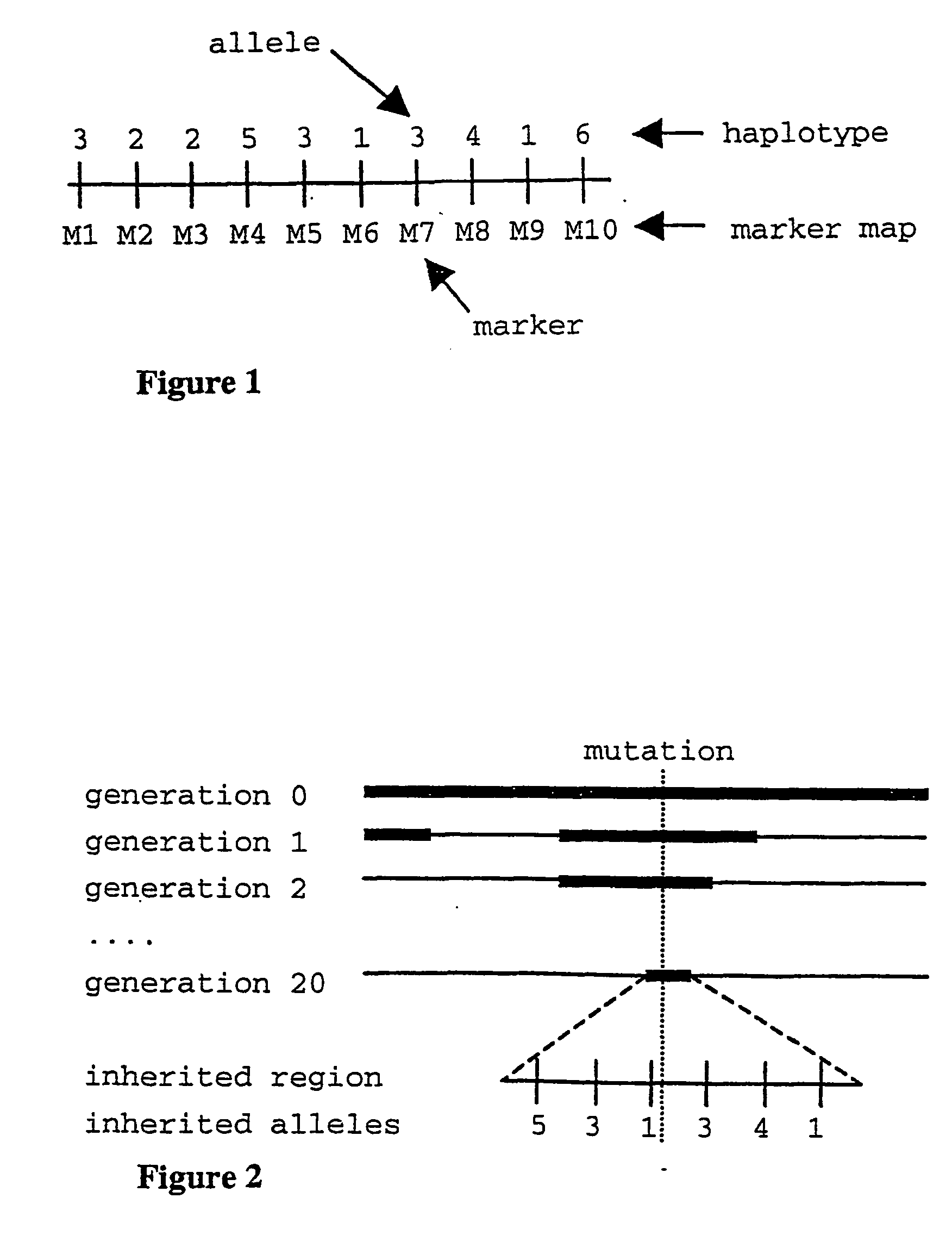
In situ methods for gene mapping and haplotyping
The present invention is directed to in situ methods for providing a definitive haplotype of a subject. The haplotype information generated by the methods described herein is more accurate than that provided by prior art methods that only give an inferred haplotype. Accordingly, in one aspect the present invention provides an in situ method for obtaining genetic information for a polyploid subject, the method including the steps of obtaining a biological sample from the subject, the sample containing: (i) at least one paternally-derived DNA molecule, and / or (ii) at least one maternally-derived DNA molecule, analyzing any one or more of the paternally- or maternally-derived DNA molecules for nucleotide sequence information, wherein the step of analyzing determines whether any two DNA markers are present in cis on one chromosome, or in trans across two sister chromosomes. Use of in situ methods such as FISH allows for the provision of phase-specific information on DNA markers without recourse to methods for physically separating sister chromosomes. Applicants propose that method eliminates the problem of incorrect or misleading inferences concerning the phase of two or more loci within a haplotype, and allows for revelation of two or more participatory genes within a haplotype, uncomplicated by differences in modes of inheritance.
Owner:HAPLOMIC TECH
Quantitative screening method for embrittling special rice
InactiveCN104969783ARealize quantitative detectionLabor savingHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyGene mapping
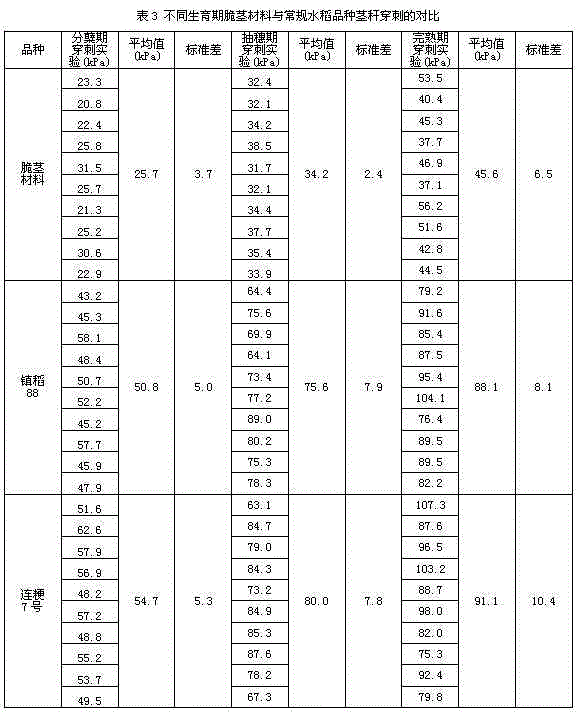
The invention provides a quantitative screening method for embrittling special rice. According to the quantitative screening method, a specific embrittlement treatment method and a detection method are adopted to to-be-screened materials for detection, and accurate numerical indices are obtained by identifying detection organs and parts with the notable difference degree and detection periods among the to-be-screened materials, ultimately realizing notable and accurate quantitative screening of the phenotypic difference degree among embrittling special rice. The problems of embrittling stalk gene mapping of embrittling special rice breeding and inaccuracy in embrittlement phenotypic difference degree screening in multiple genes pyramiding breeding are solved, thereby greatly saving manpower and cost of molecular detection, and realizing accurate quantitative screening of the embrittling special rice.
Owner:YIELEAD RICE IND
Gene mapping integration and expression system and application thereof
ActiveCN106978416AMicroencapsulation basedMicroinjection basedGene mappingSite-specific recombination
The invention relates to a gene mapping integration and expression system and application thereof. Particularly, the invention relates to integration and high-efficiency expression of a nucleic acid constructor at a specific site in a transgenic sheep genome, wherein the nucleic acid constructor contains a homologous arm sequence combined with a chromosome region, a site-specific recombination sequence, an exogenous gene expression cassette and a selection marker gene expression cassette. By delivering the constructor into a host cell, mapping integration and expression of a target gene in a host cell genome can be achieved, a transgenic cell can be obtained, and transgenic sheep expressing the target gene can be obtained with the transgenic cell as a donor cell. By means of the site-specific recombination technique, expression of other specific exogenous genes and genetic modification of a transgene can be achieved in somatic cells of the transgenic sheep.
Owner:SHANGHAI TRANSGENIC RES CENT
Molecular marker SIsv0701 closely linked with Setaria italica L. Beauv. seta color gene
InactiveCN102690813AImprove throughputEasy to set upMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGene mappingGenetics
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, relates to a molecular marker and especially relates to a molecular marker SIsv0701 closely linked with a Setaria italica L. Beauv. seta color gene. The molecular marker SIsv0701 has a sequence shown in the Seq ID NO.1. The invention also relates to primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv0701, a use of the molecular marker SIsv0701 and the primers in Setaria italica L. Beauv. seta color gene mapping or Setaria italica L. Beauv. genetic breeding, and a Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding method. The molecular marker SIsv0701 links a genomic DNA sequence and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. seta color gene, and is conducive to establishment of a Setaria italica L. Beauv. molecular marker auxiliary breeding system. A genetic close linkage distance between the molecular marker SIsv0701 and the Setaria italica L. Beauv. seta color gene is 1.2cM. In Setaria italica L. Beauv. breeding practices and resource and variety identification, the simple, fast and high throughput utilization of the molecular marker SIsv0701 and the primers for amplification of the molecular marker SIsv0701 can be realized.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com