Laser microdissection and microarray analysis of breast tumors reveal estrogen receptor related genes and pathways
A technology of estrogen receptors and genes, which is applied in the field of laser microdissection and microarray analysis of breast tumors to reveal estrogen receptor-related genes and pathways, and can solve the problem of harmful gene expression data and large differences in the proportion of tumor cells, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
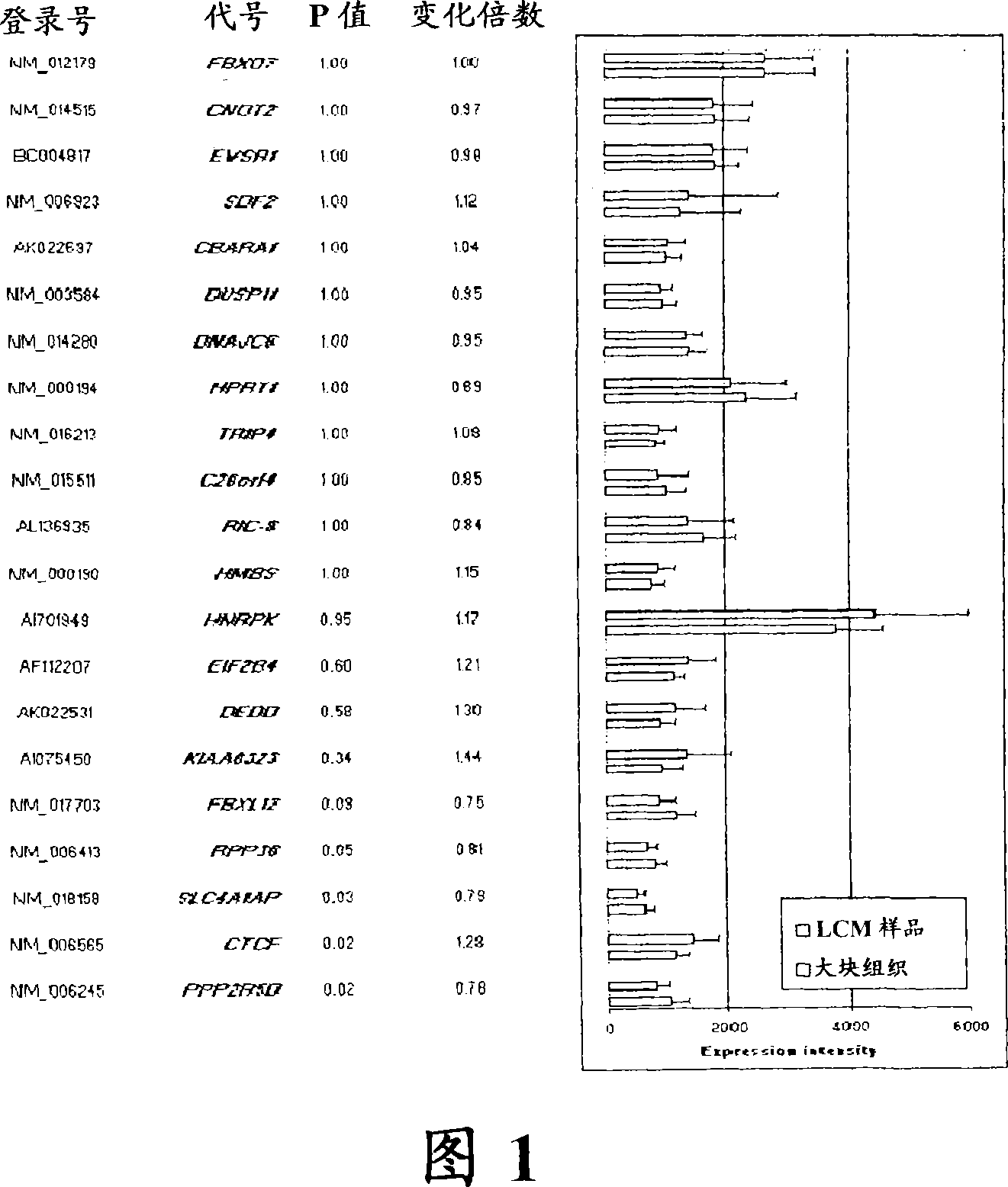
[0079] Continuity of 21 consecutively expressed genes between bulk tumor datasets and LCM-captured sample datasets Comparison of expression intensity of home genes
[0080] To gain insights into estrogen-triggered mechanisms in mammary epithelial cells, we applied the LCM technique to a cohort of 28 early-stage primary breast tumors consisting of 17 ER+ and 11 ER- tumors. Then their gene expression profiles were analyzed using Affymetrix gene chip Hul33A.
[0081]Each tumor used in this study was selected from the Erasmus Medical Center Tumor Bank in Rotterdam, The Netherlands. These tumor samples were sent to the laboratory for routine assessment of steroid hormone receptor status and thereafter stored in liquid nitrogen for preservation. Numbered tumor tissues were used in this study, which was carried out in accordance with the relevant regulations of the Dutch Federal Academy of Medical Sciences. The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Erasmus Medic...
Embodiment 2
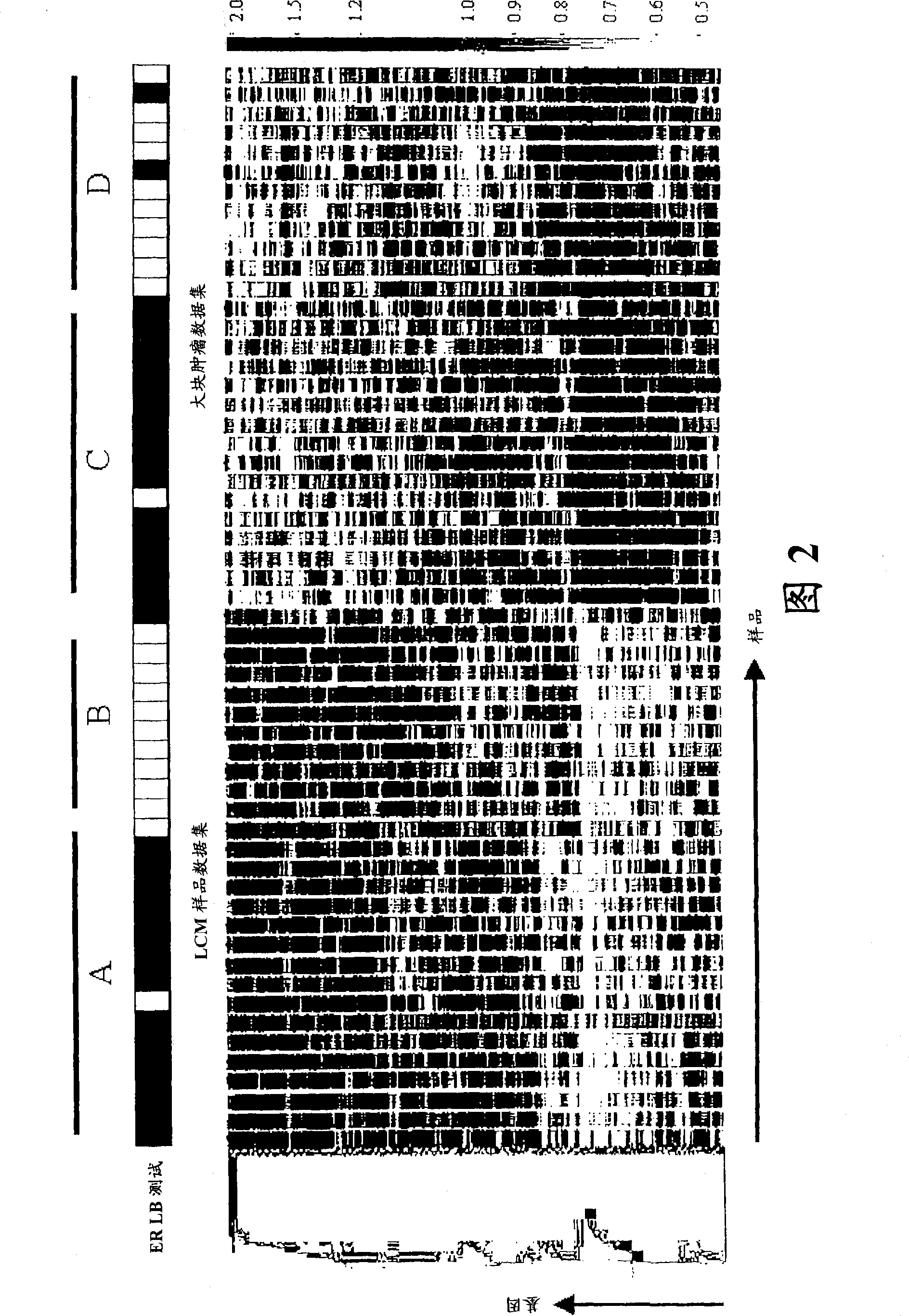
[0087] Unsupervised 2D Hierarchical Clustering of Global Gene Expression Data Using Gene Spring Software analyze
[0088] The gene expression intensities of approximately 23,000 probe sets on the Affymetrix U133A chip were first normalized using the quantile normalization method, and then the above data were filtered using the "current" expression determined by the Affymetrix MAS5.0 software. An unsupervised two-dimensional hierarchical clustering algorithm was applied to microarray data to classify individual genes on the basis of similarity in expression patterns and to cluster individual samples on the basis of similarity in global gene expression profiles. Such as figure 2 As shown, 56 samples (28 LCM samples plus 28 bulk tissues) were classified into two main groups according to the source of RNA extraction: LCM-captured tumor cells and mixed cell populations from bulk tumors . Samples in each group were further divided into two subgroups (Group A and Group B in LC...
Embodiment 3
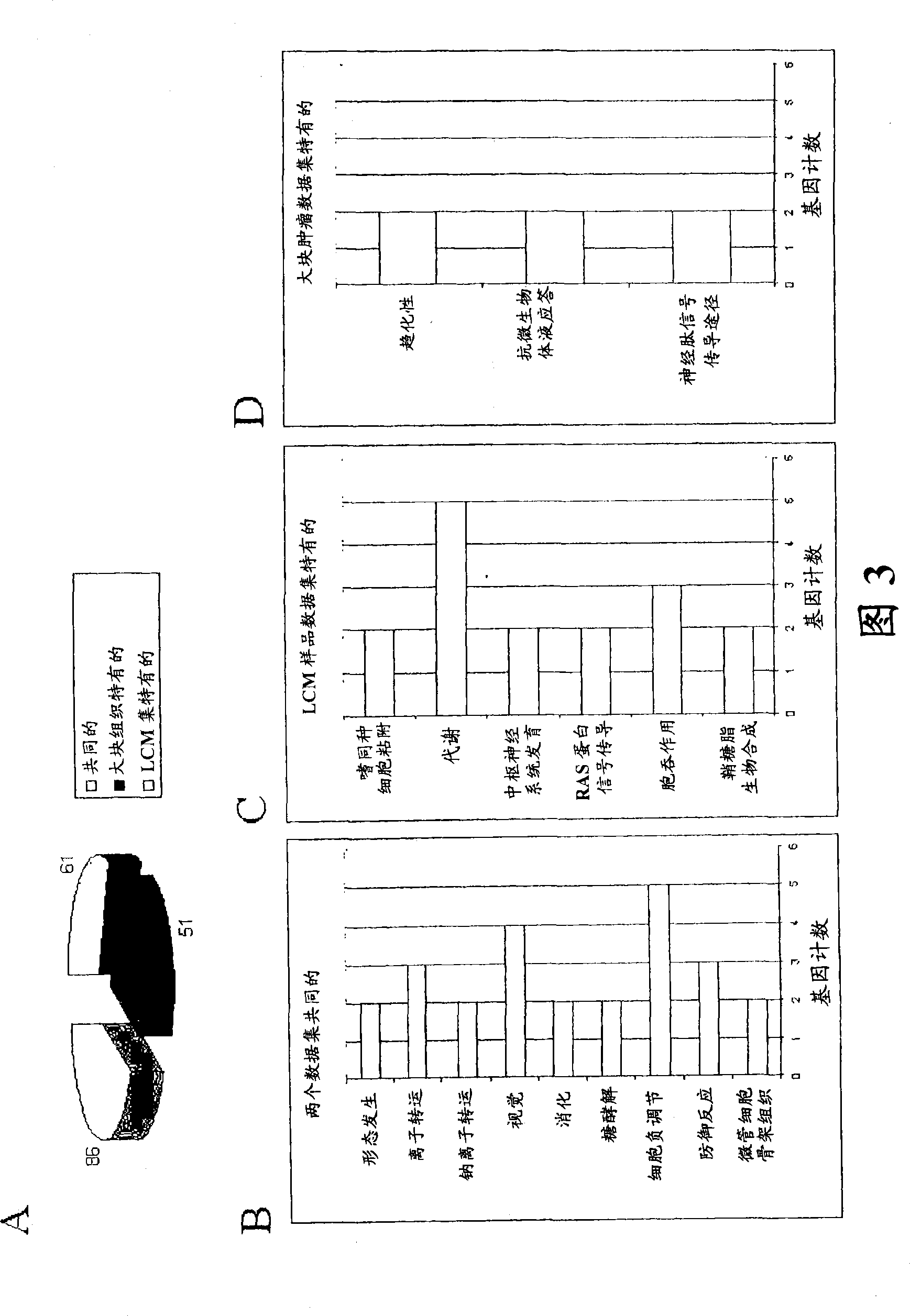
[0090] Pathway Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes Between ER+ and ER- Subgroups
[0091] To identify genes associated with ER status and pathways associated with them, we performed a t-test between each ER+ subpopulation and ER− in both datasets. Using a Bonferroni-corrected P value image 3 A; Tables 2, 3 and 4). Of the 61 common genes, 36 were relatively overexpressed and 25 were downregulated in the ER+ subgroup (Table 2). Estrogen receptor and other genes known to be involved in ER activation such as trefoil factors 1 and 3, GATA3, X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) and keratin 18 were among the upregulated genes. Sotiriou et al. (2003); Gruvberger et al. (2001); and Sun et al. (2005). On the other hand, placental cadherin (CDH3), GABRP, and secreted Frizzled-related protein-1 (SFRP1) appeared in the list of downregulated genes.
[0092] Table 2
[0093] Common genes whose expression is altered between ER+ and ER- tumors in both the LCM dataset and the bulk tumor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com