QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) linked molecular marker for controlling corn female parent haploidy production and application thereof
A technology of molecular markers and female parents, which is applied in the field of corn genetics and molecular biology, can solve the problems of low induction rate, high haploid induction rate, and inequity, so as to improve induction efficiency, reduce blindness, and accelerate engineering The effect of the application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example
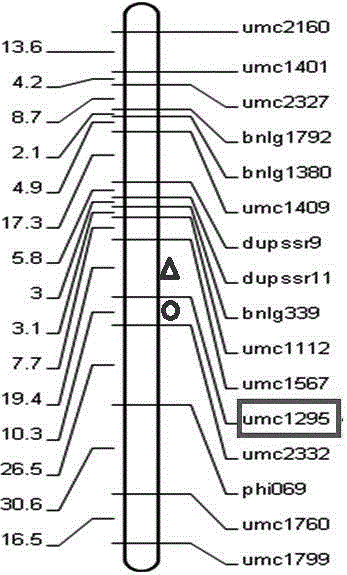
[0023] Experimental Example: Discovery of Molecular Markers Linked to QTLs Produced by Maternal Haploids
[0024] 1. Preparation of F 2 Progeny plant
[0025] Zheng 58, a maize inbred line with low inducibility of parthenogenesis, was used as parent 1 (P 1 ) and maize inbred line K22 with higher parthenogenetic inducibility as parent 2 (P 2 ) for hybridization, the resulting hybrid seed is F 1 Substituting the seed, the F 1 The plant obtained by sowing the seeds is F 1 Generation plants, the F 1 The generation plants are selfed, and the seeds obtained are F 2 generation seeds.
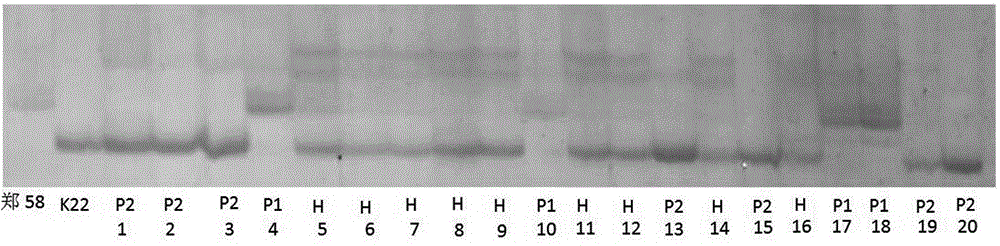
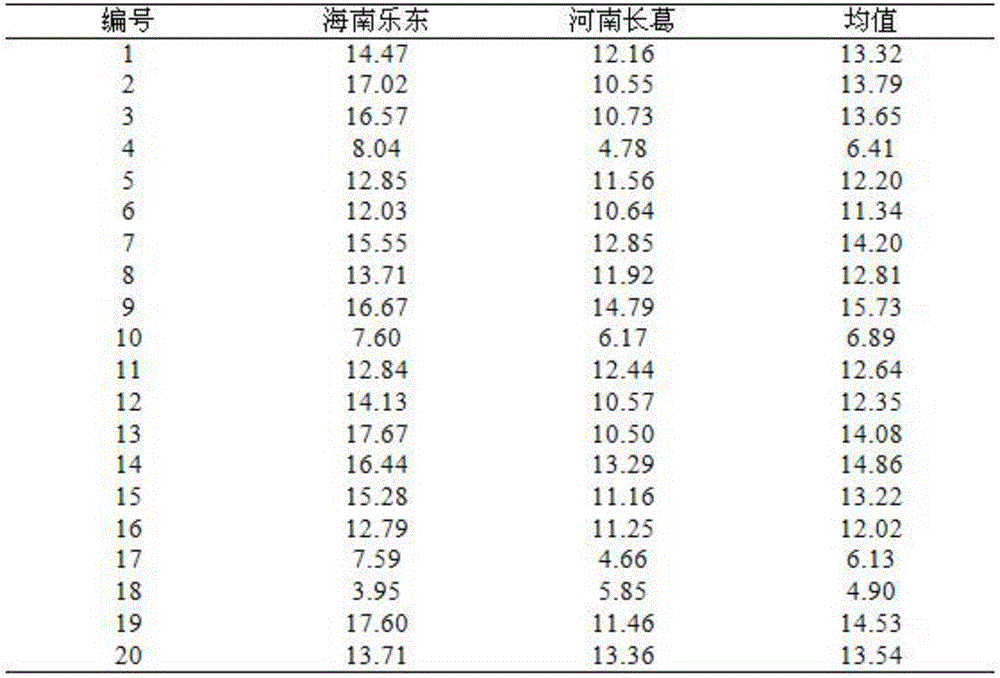
[0026] 2. Corn F 2:3 The construction of the haploid trait identification population of the family group and the statistics of the maternal haploid frequency take parent 1, parent 2 and F 2 A small amount of leaves at the seedling stage (after the stage of 5 true leaves) of a single plant of the generation population, using the rapid extraction method of genomic DNA of maize, extracts the geno...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com