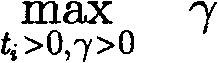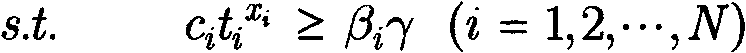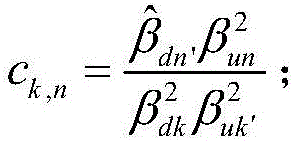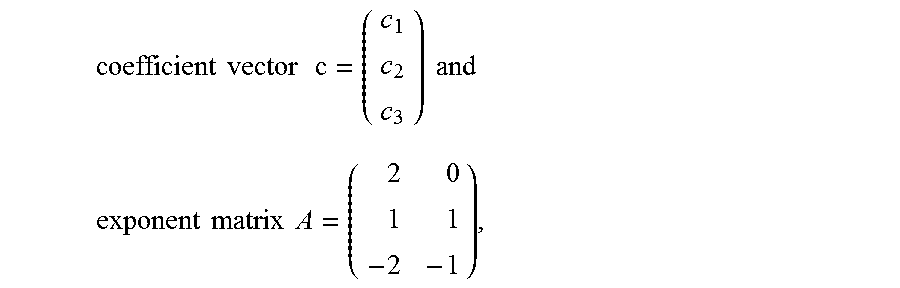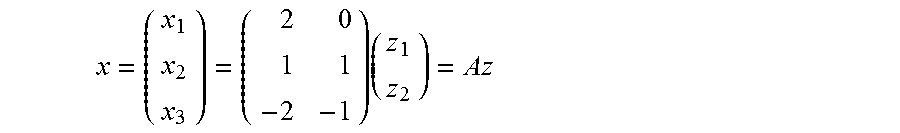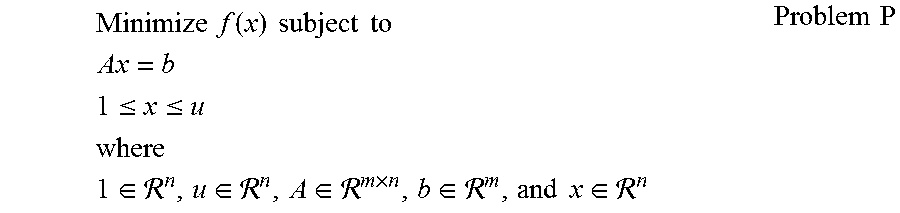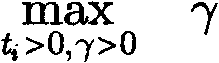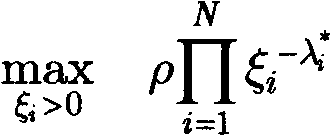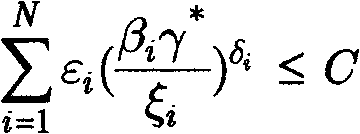Patents
Literature
47 results about "Geometric programming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A geometric program (GP) is an optimization problem of the form...
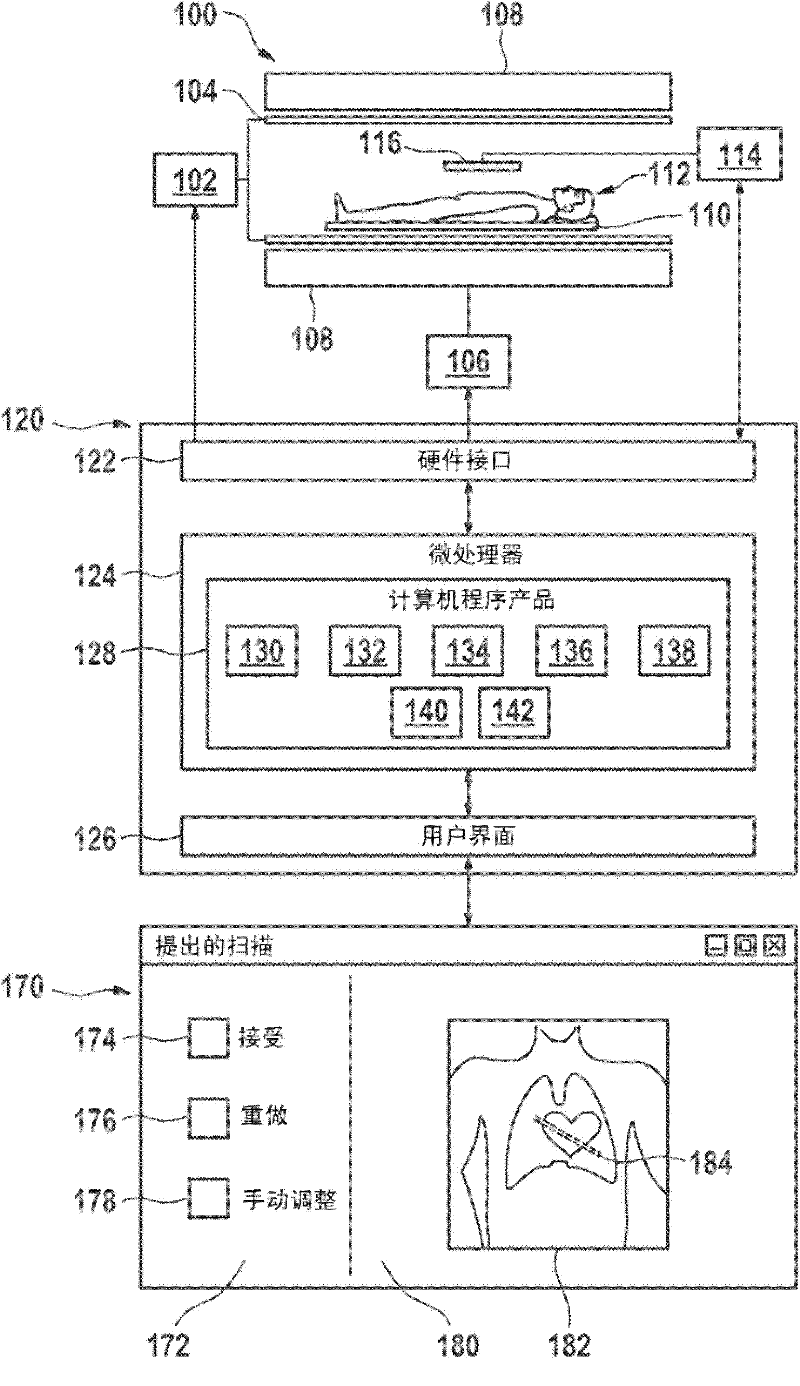
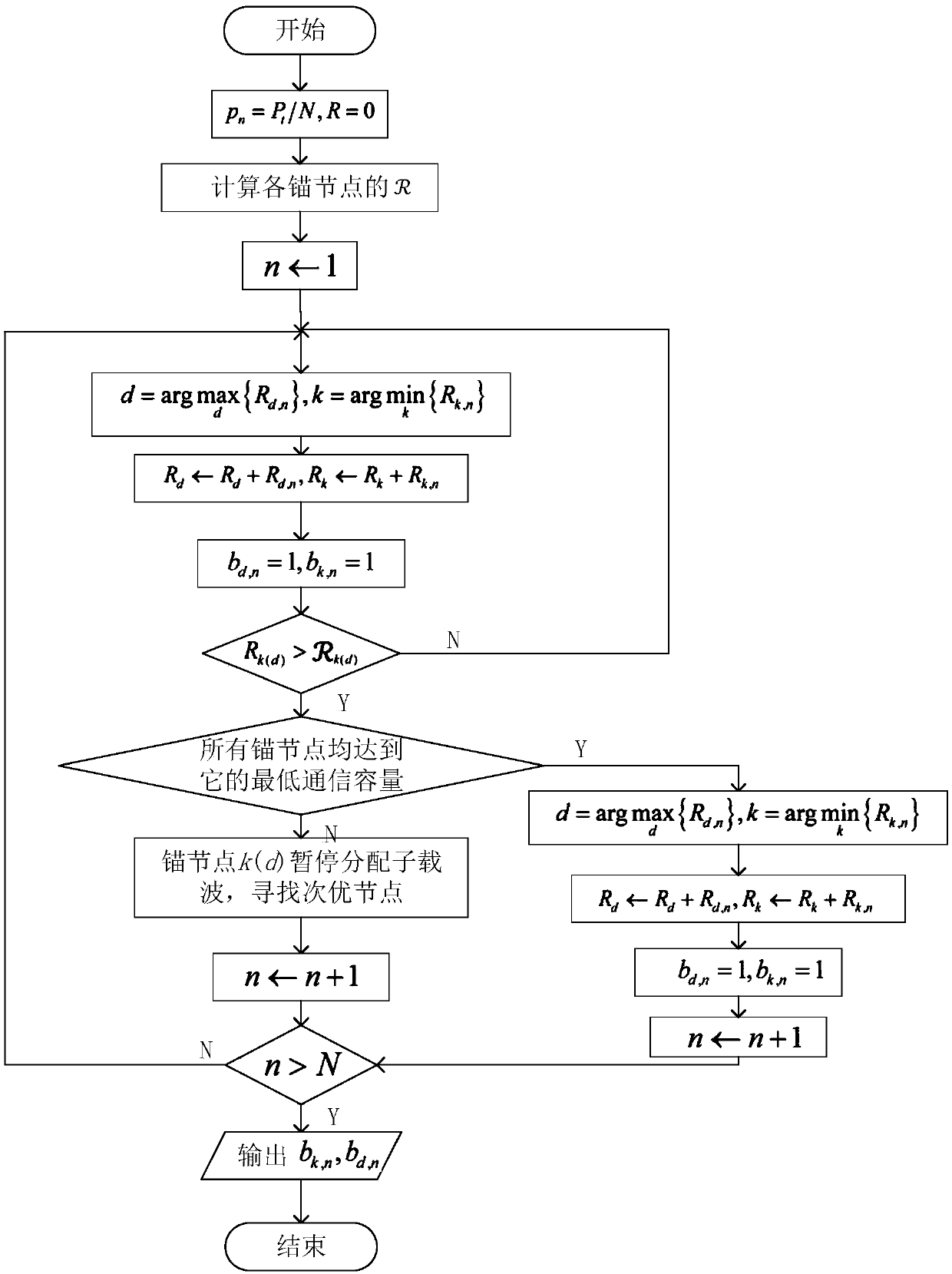
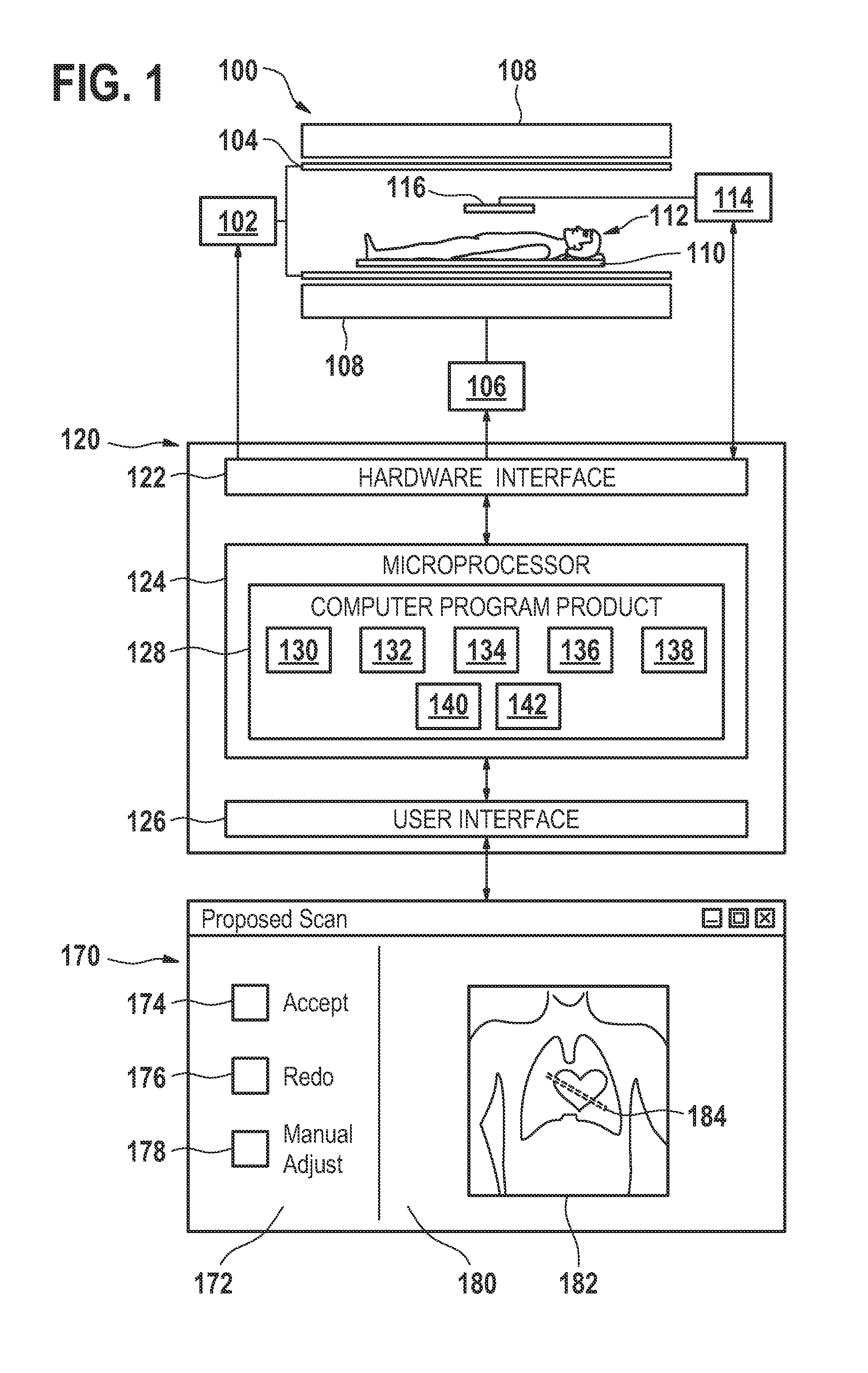
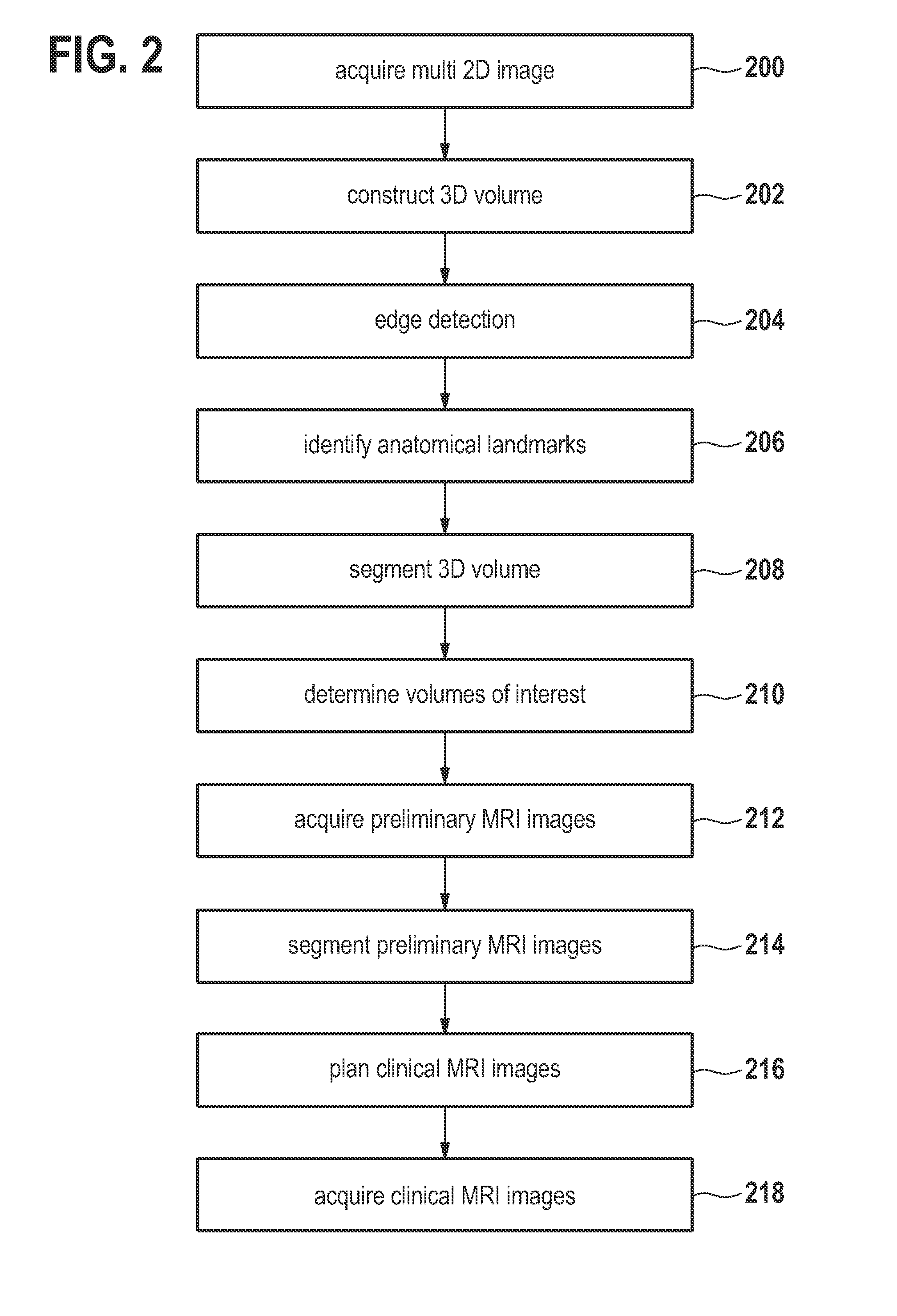
Automated sequential planning of mr scans
ActiveUS20110206260A1Quality improvementShorten the timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAnatomical landmarkGeometric programming
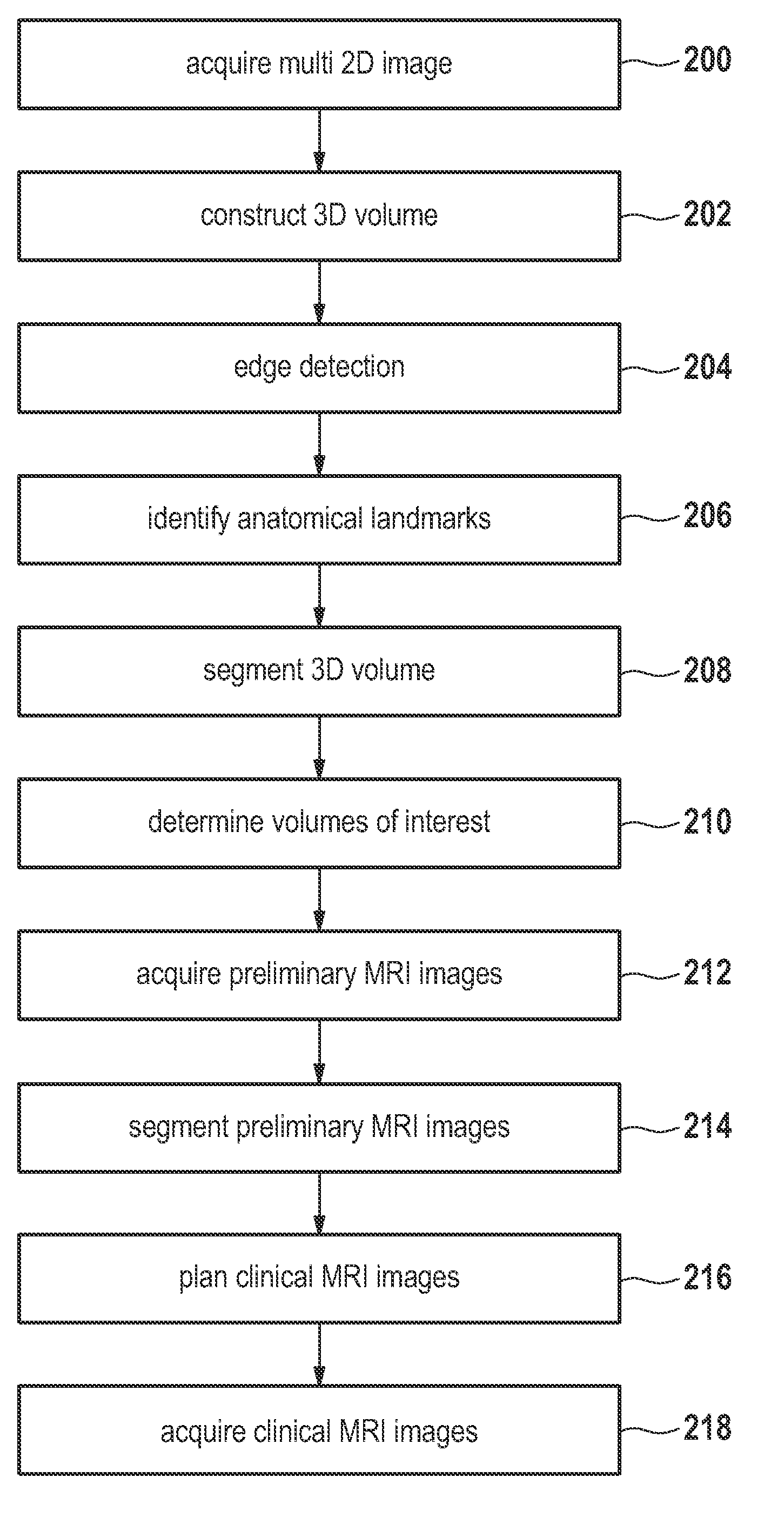
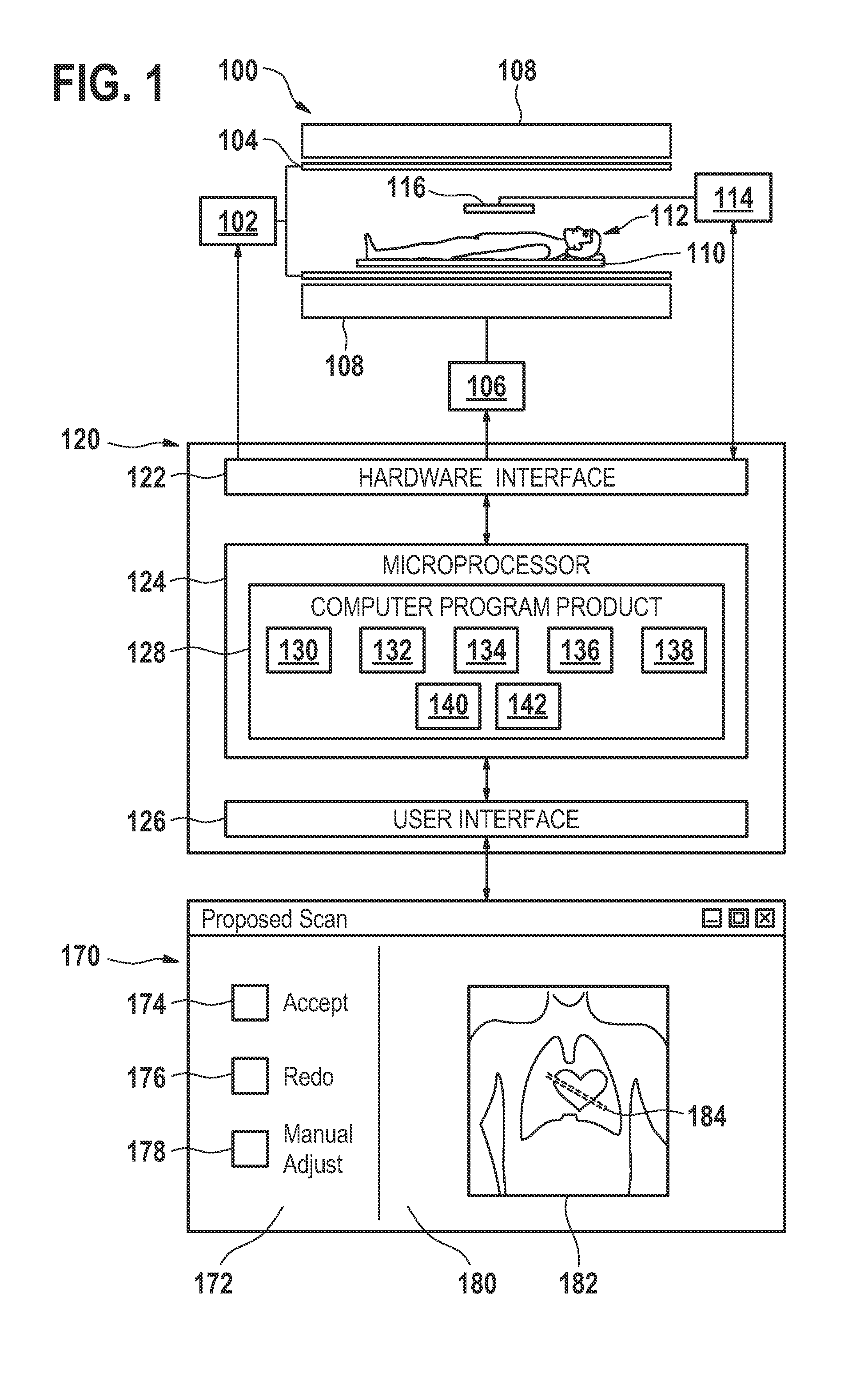
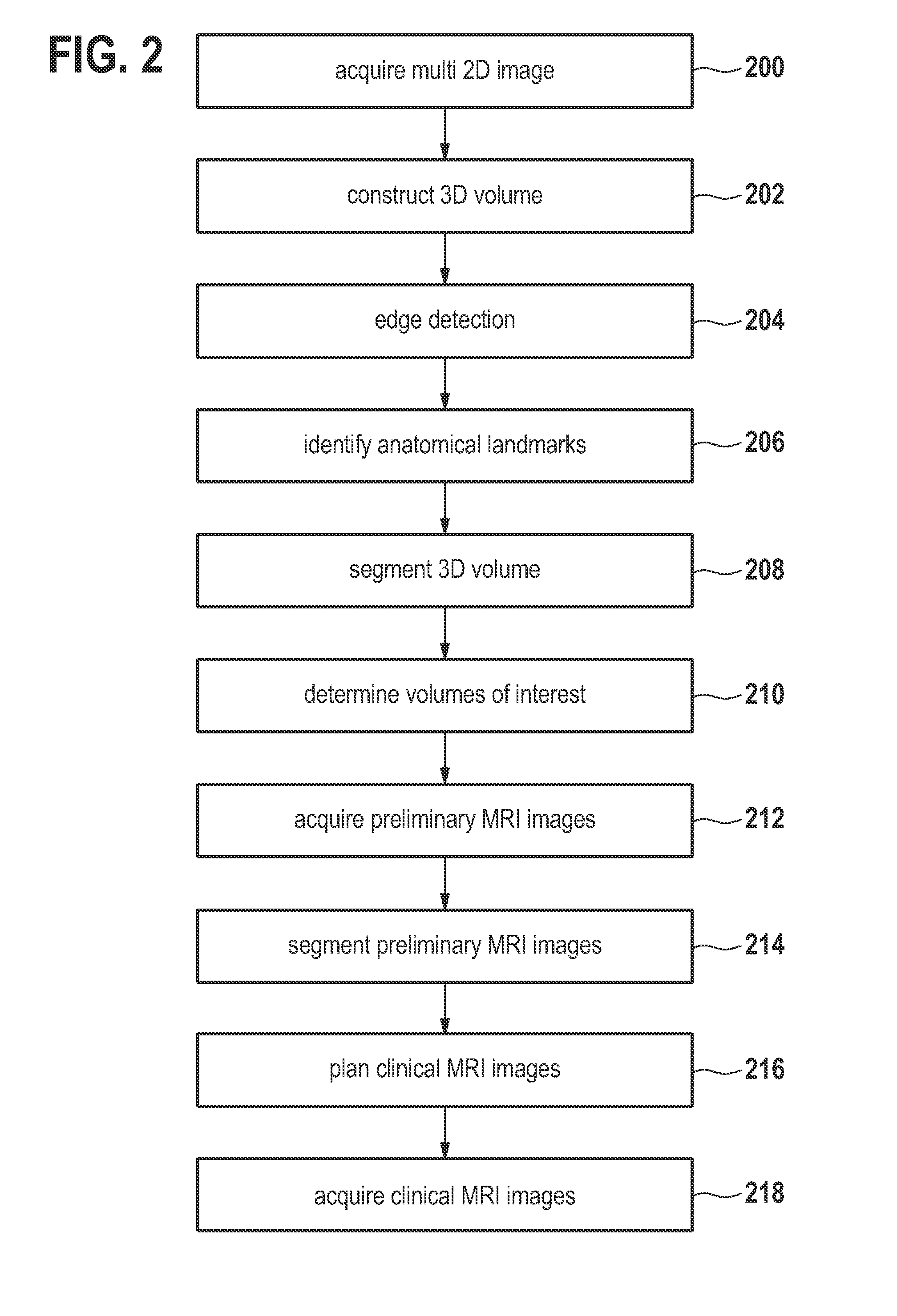
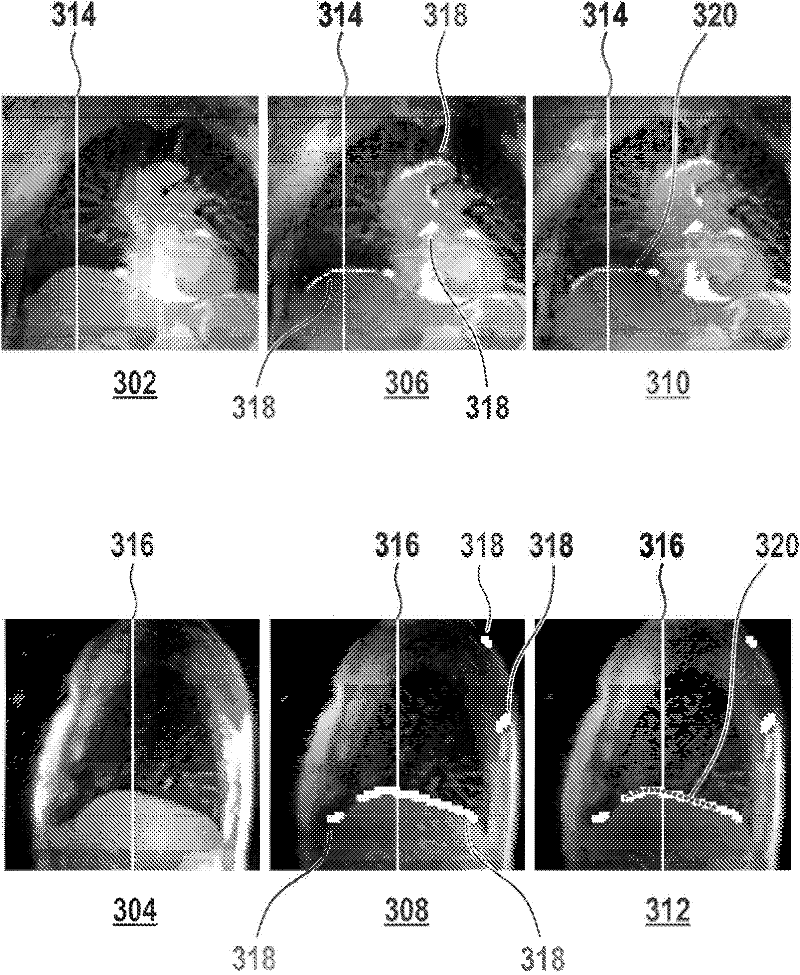
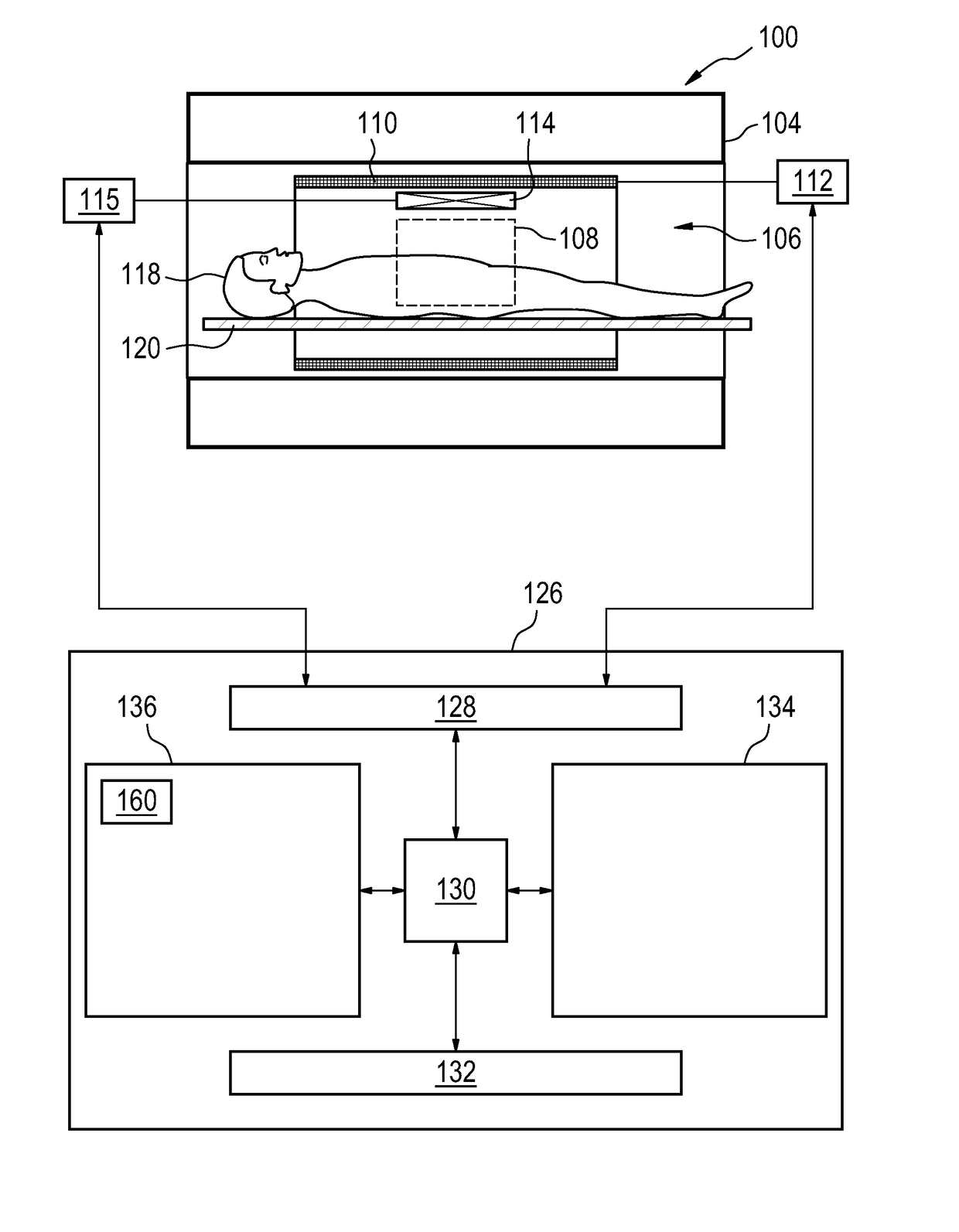
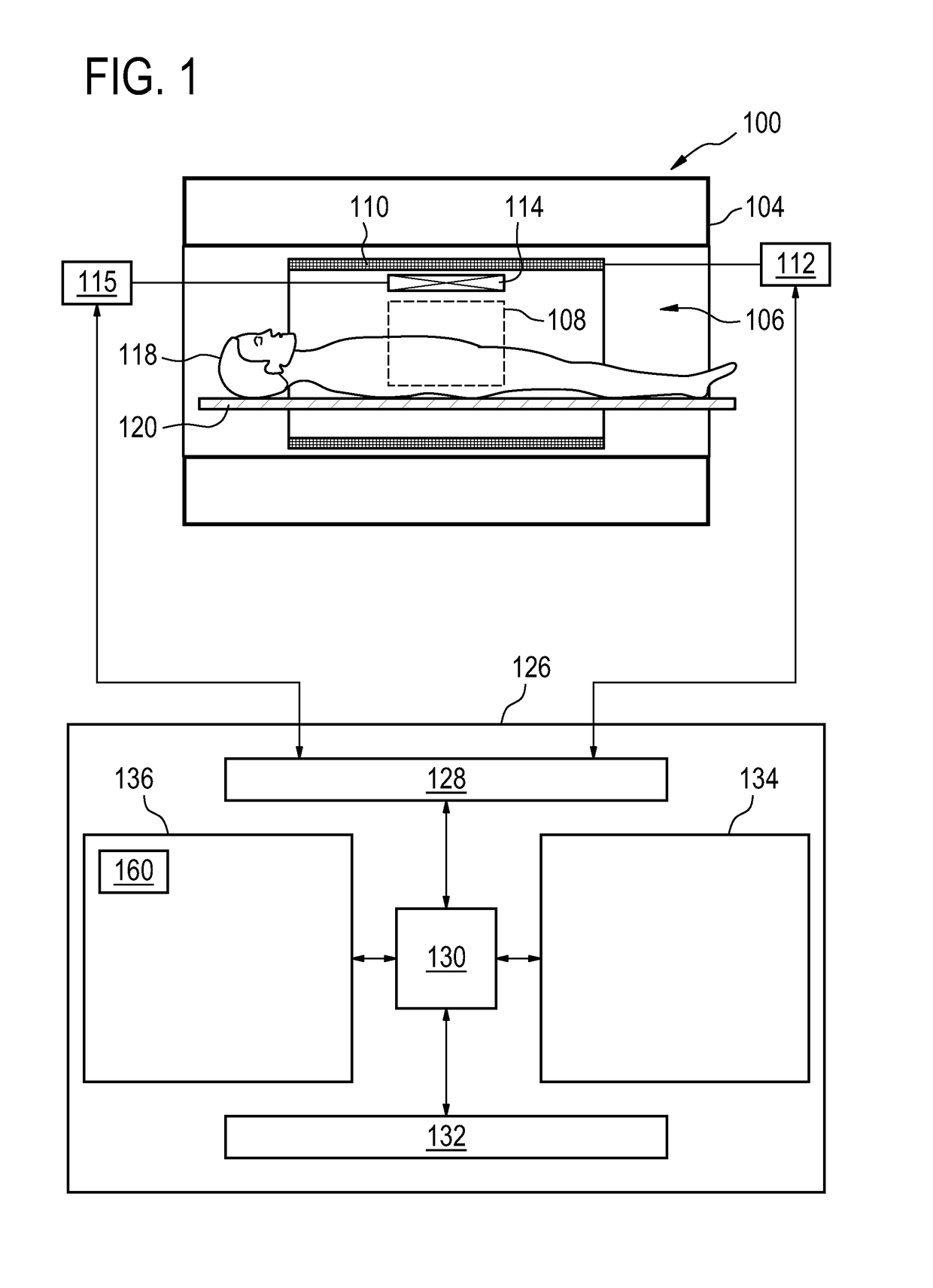
A method of acquiring at least one clinical MRI image of a subject comprising the following steps: acquiring a first survey image with a first field of view, the first survey image having a first spatial resolution,—locating a first region of interest and at least one anatomical landmarks in the first survey image, determining the position and the orientation of the first region of interest using the anatomical landmarks, the position and the orientation of the first region being used for—planning a second survey image,—acquiring the second survey image with a second field of view, the second survey image having a second spatial resolution, the second spatial resolution being higher than the first spatial resolution, generating a geometry planning for the anatomical region of interest using the second survey image,—acquiring a diagnostic image of the anatomical region of interest using the geometry planning.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
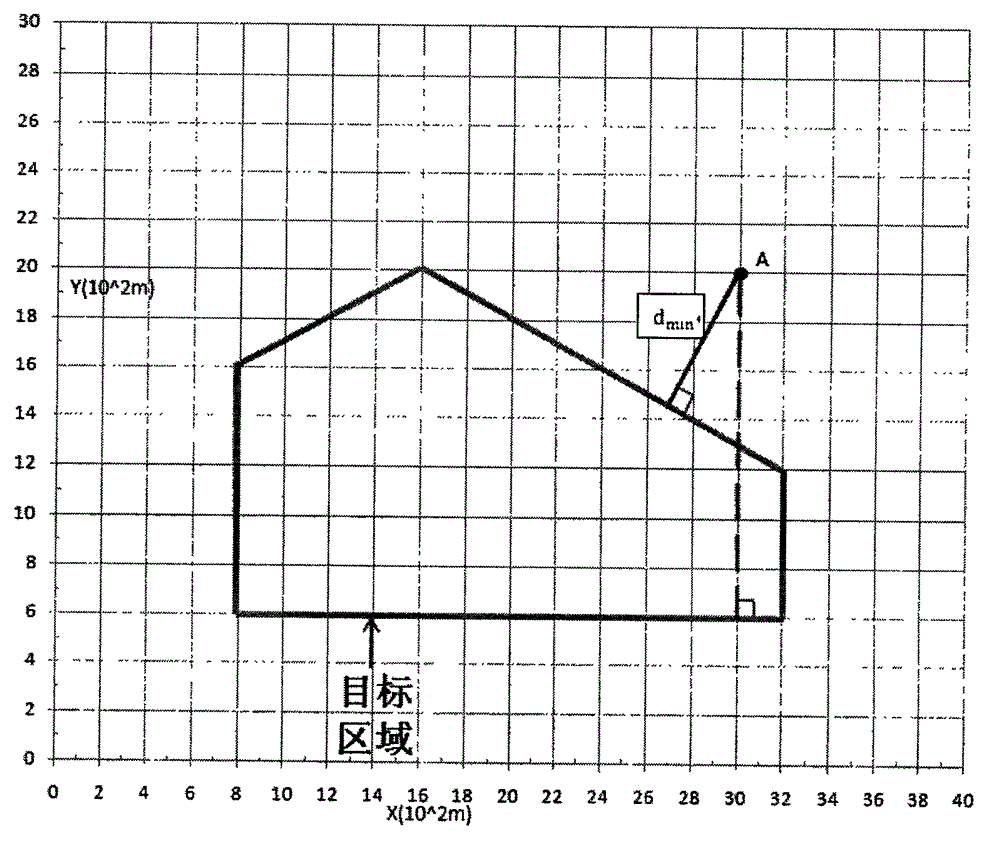
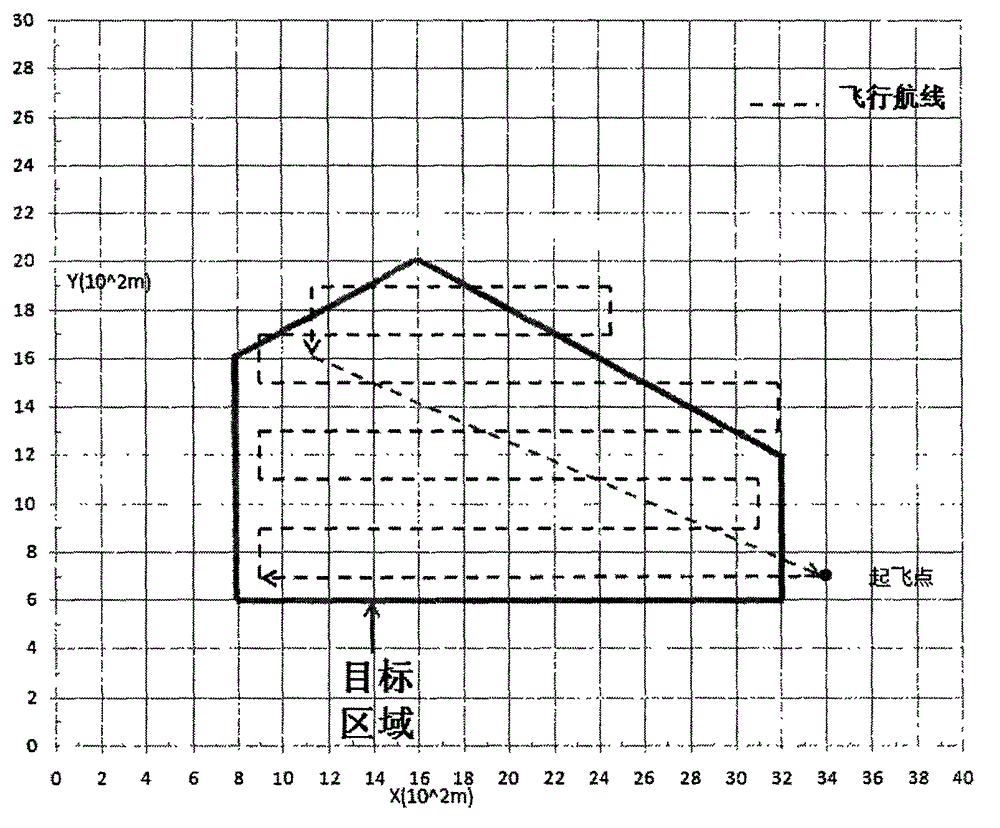
Irregular-island-based method for planning covered flight route of unmanned aerial vehicle
InactiveCN102980581ASolve the trajectory planning problemHigh standardNavigational calculation instrumentsGeometric programmingUncrewed vehicle
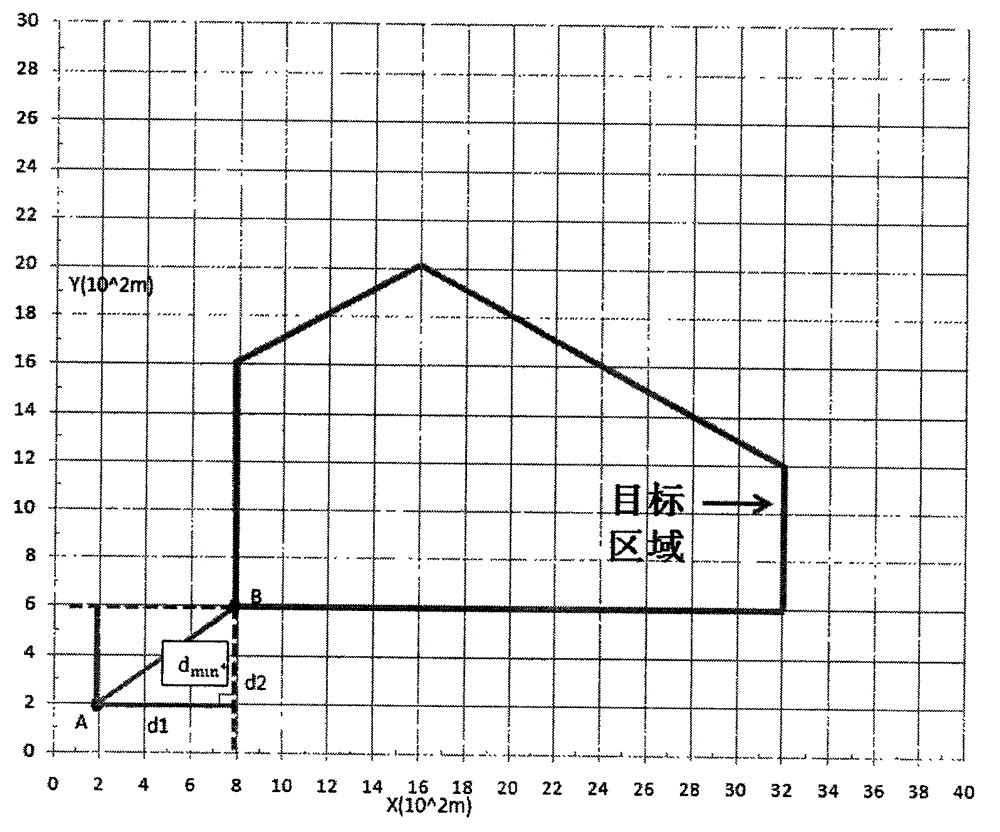
The invention provides an irregular-island-based method for planning a covered flight route of an unmanned aerial vehicle, aiming at the problem of planning an unmanned aerial vehicle flight route in an island domain. According to the method, the characteristics in island flight route traverse are sufficiently considered, i.e. the distance from a take-off point to an island is taken into consideration, particularly for an island which is relatively far away from the coast, the total journey in island flight route planning is influenced by the distance from the take-off point to the island to a large extent. in consideration of a geometric flight route programming method, the distance from the take-off point to the island and other related issues, the invention provides a new optimal circular flight route method and abandons the traditional impractical flight route planning method is abandoned; and situations such as the power of the aerial vehicle in flying are sufficiently considered in the new method. The method mainly comprises four aspects as follows: the extraction of the circumscribed polygon of the island, the calculation of the minimum span of the polygon, the calculation of the minimum distance from the take-off point to the polygon, and the design of the flight route. By utilizing the method, the combination of island monitoring and unmanned aerial vehicle flight route planning is realized, and the method particularly has a wide prospect on the aspect of offshore island monitoring.
Owner:北京中海新图科技有限公司 +1
Automated sequential planning of mr scans
ActiveCN102203630AShorten the timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsGeometric programmingAnatomical landmark
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
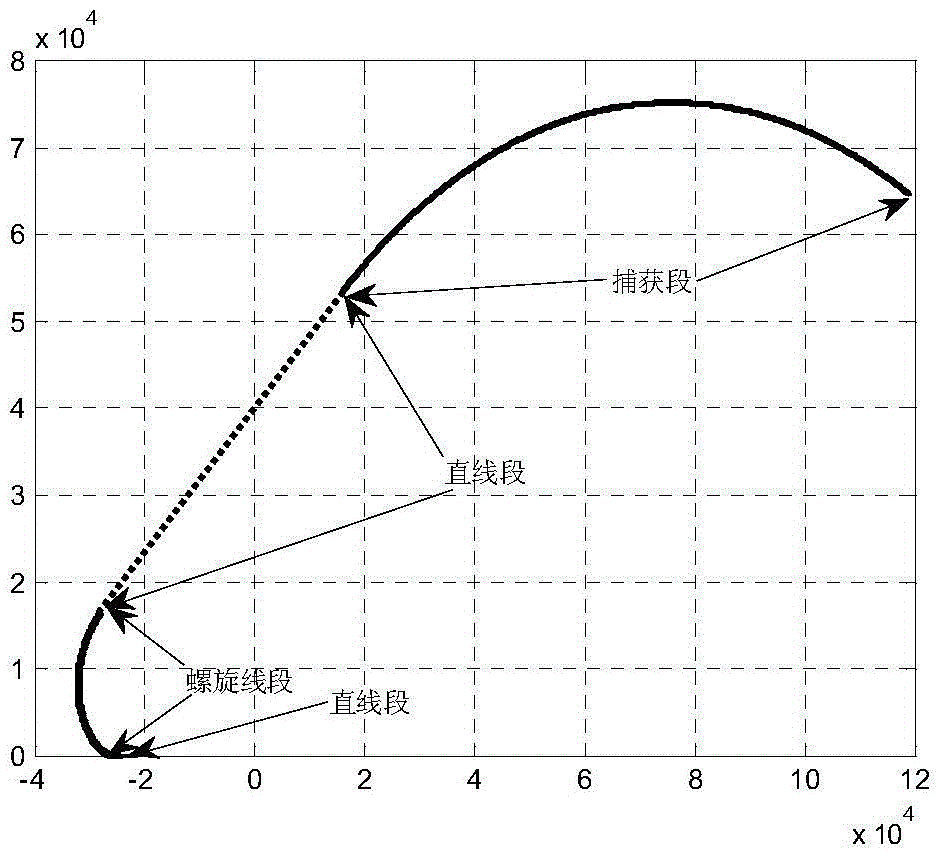
Geometric-programming-based gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method
ActiveCN104714553AReduced mobility requirementsQuick planningPosition/course control in three dimensionsGeometric programmingTrajectory planning
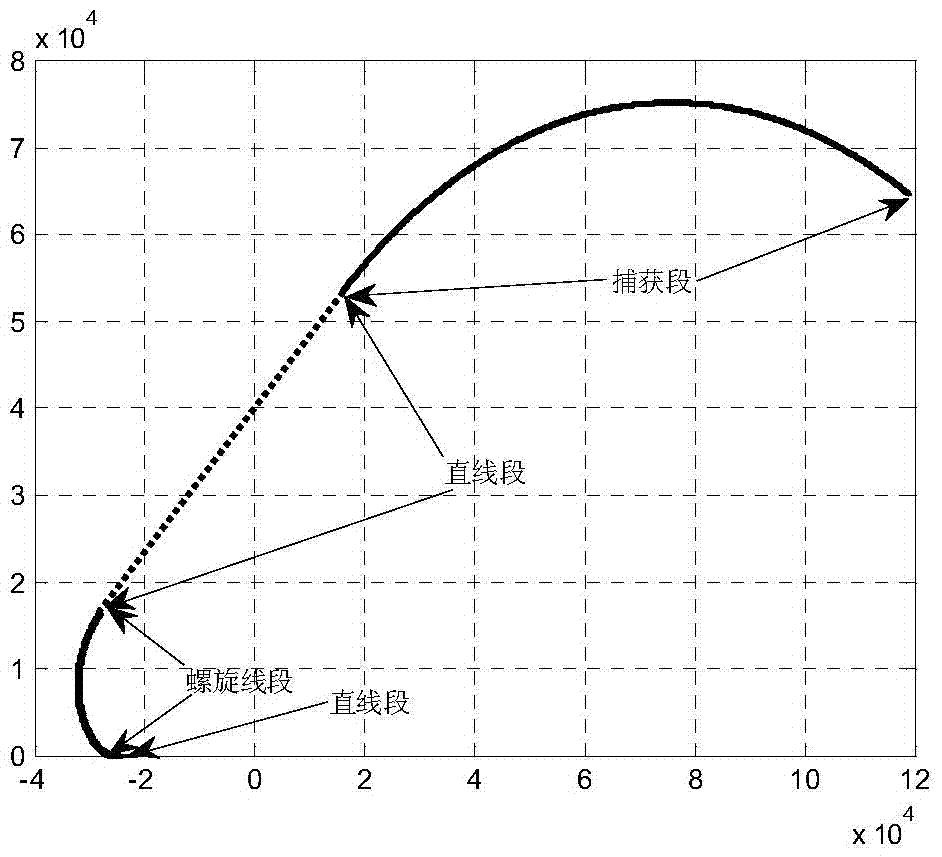
The invention discloses a geometric-programming-based gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method which is used for solving the technical problem that an existing gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, on the basis of the state of an aircraft entering a TAEM section, a geometric programming method is utilized for rapidly planning a reasonable and feasible TAEM plane trajectory; on the basis of the TAEM plane trajectory planning, height deduction is performed, and therefore a complete trajectory planning strategy is given. Due to the fact that the aircraft enters an entry of an automatic landing section in a spiral-line mode in the geographic planning process, the sudden overload change phenomenon is effectively avoided, and therefore the requirement for the aircraft maneuverability is lowered; meanwhile, during trajectory planning, the state of the aircraft at the TAEM section at the initial moment is considered, corresponding flight paths are planned in a classified mode for the entering state of the aircraft, the reasonable trajectory can be rapidly planned, the requirements for different entering directions are met, and the planning speed is high through simulation verification.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
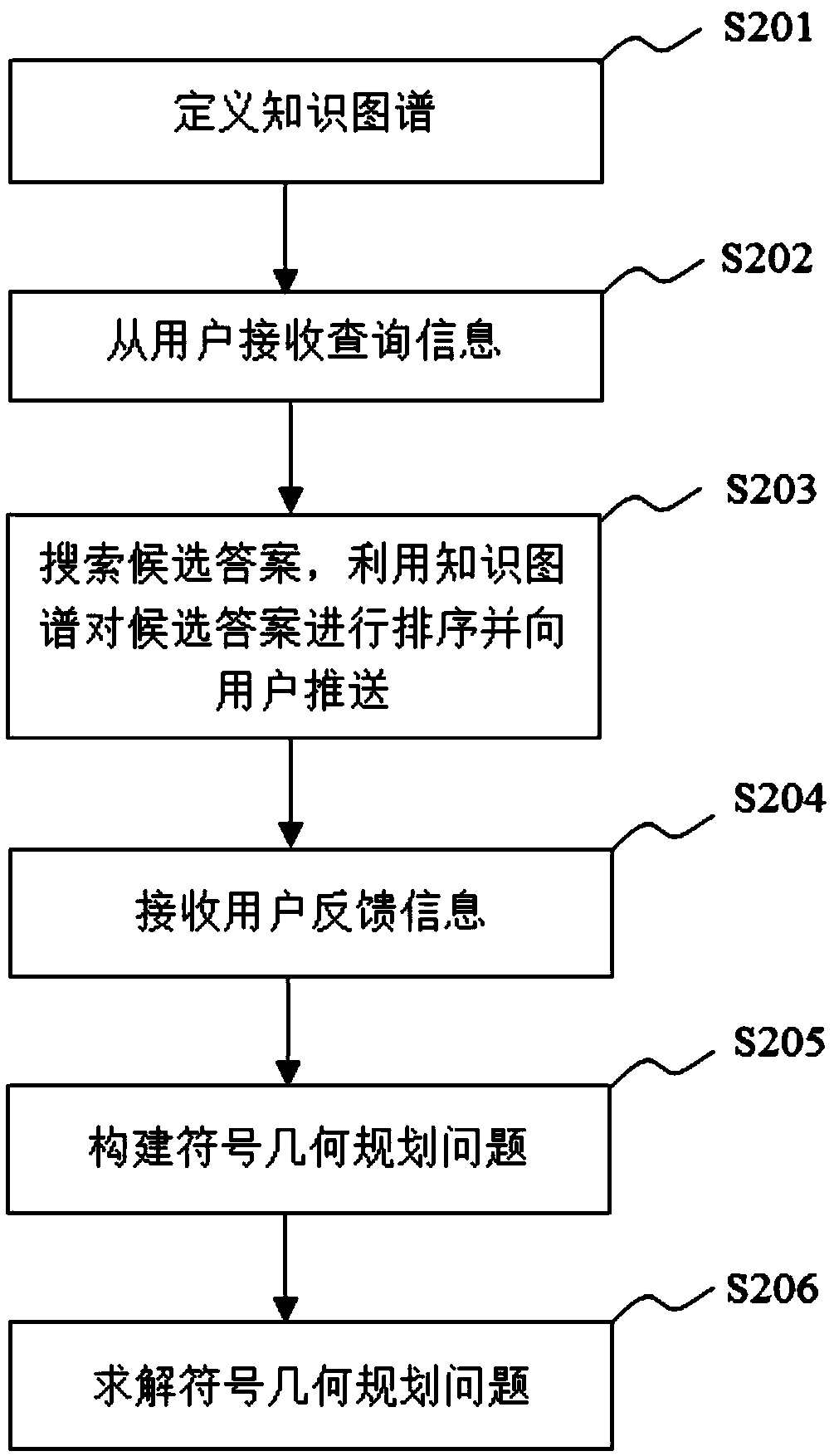
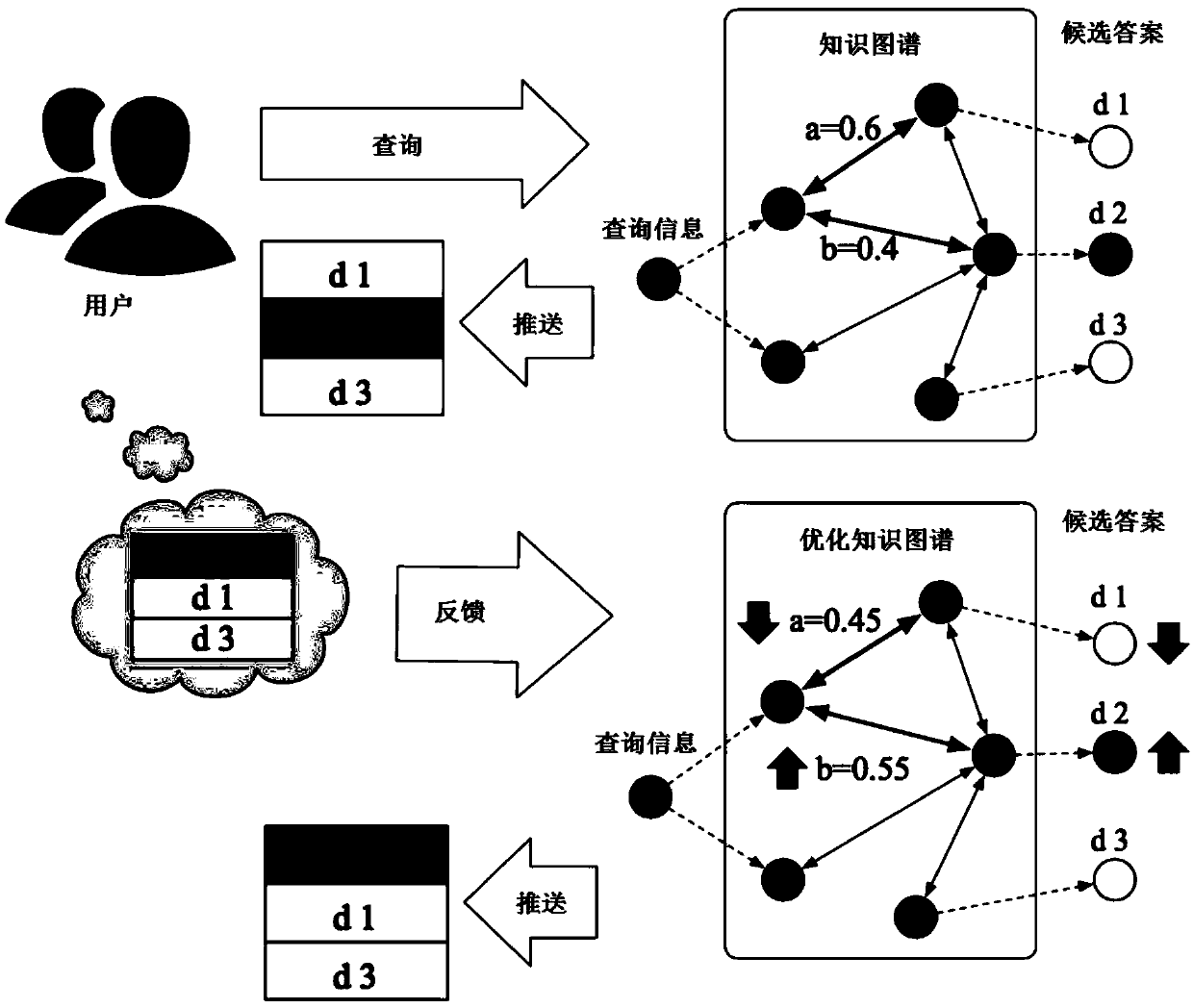
Method, device, medium, equipment and system for optimizing edge weights in knowledge map
ActiveCN108776684AQuality improvementImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsNODALGeometric programming
The invention relates to a method for optimizing edge weights in a knowledge map, comprising the following steps: defining the knowledge map, wherein the knowledge map comprises nodes, directed edgesamong the nodes and the original edge weights of the directed edges; receiving query information from a user; searching candidate answers corresponding to the query information, sorting the candidateanswers by utilizing the knowledge map, and pushing to the user; receiving feedback information on the sorted candidate answers from the user; constructing a signomial geometric programming problem, wherein a constraint function of the signomial geometric programming problem is set based on the feedback information, and a target function of the signomial geometric programming problem is an edge weight optimizing function; and solving the signomial geometric programming problem to obtain the optimized edge weights. The method provided by the invention converts an edge weight optimization problem of the knowledge map into one signomial geometric programming problem by utilizing the feedback information of the user and can efficiently and automatically improve accuracy of the edge weights andquality of the knowledge map. The invention also relates to a device, a medium, equipment and a system for optimizing the edge weights in the knowledge map.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Cognitive NOMA network stubborn resource allocation method based on energy efficiency
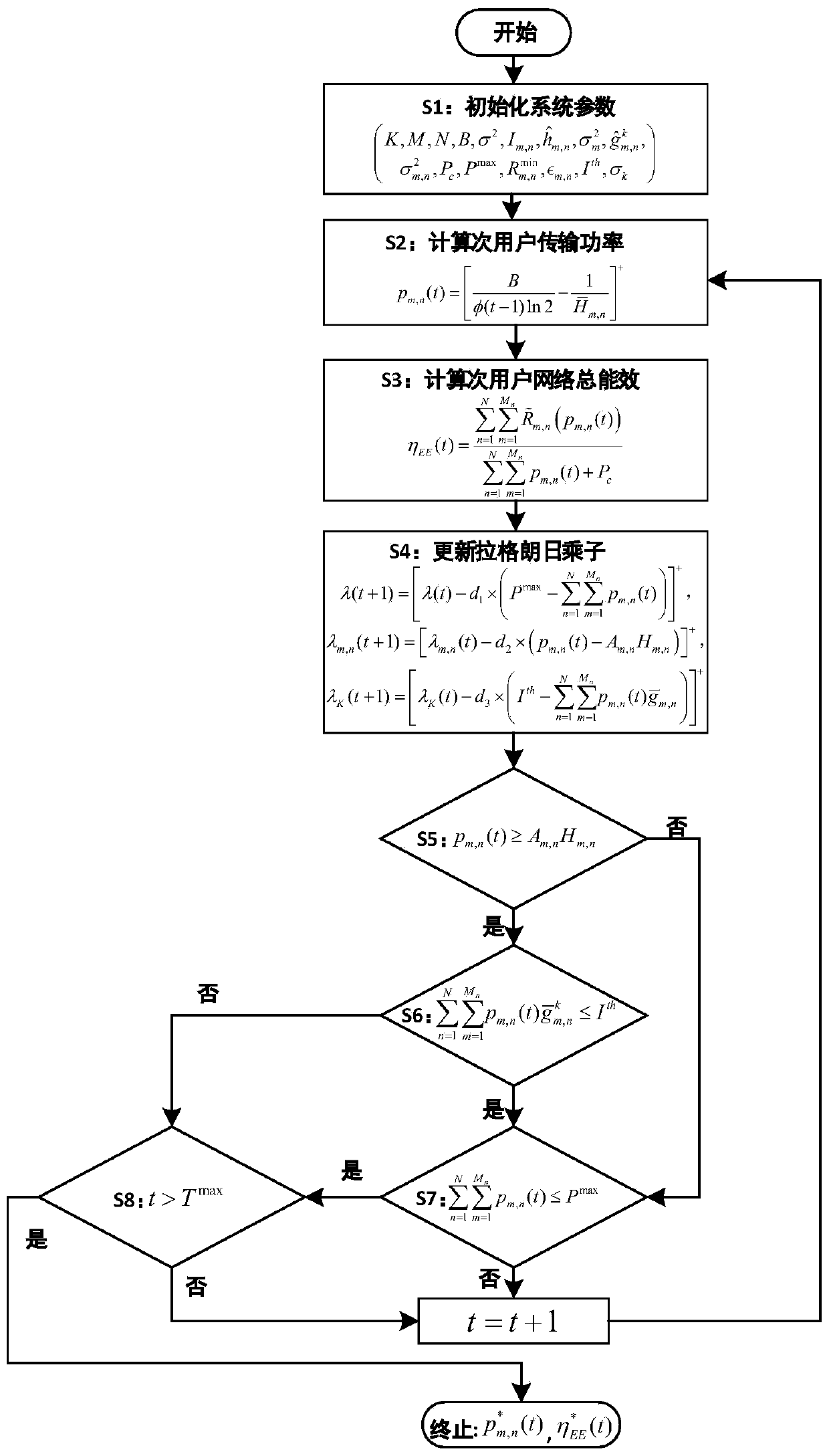
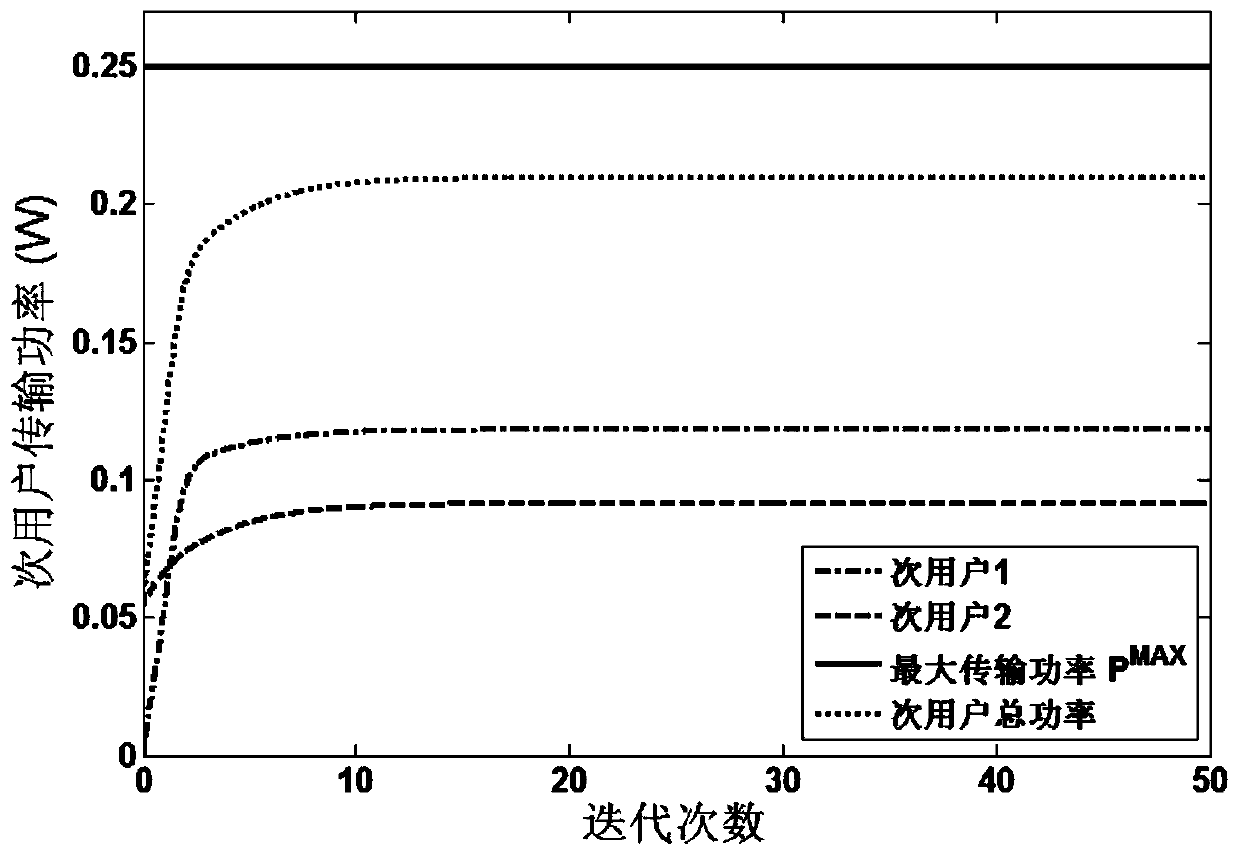
ActiveCN110417496AStubbornGuaranteed service qualityTransmission monitoringData switching networksGeometric programmingCommunications system
The invention discloses a cognitive NOMA network stubborn resource allocation method based on energy efficiency, and belongs to the technical field of resource allocation in a wireless network. Aimingat inherent randomness of a wireless communication system channel, channel parameter perturbation influence is introduced, secondary user transmitting power, interference based on outage probabilityand minimum data rate are considered as constraint conditions, secondary user network total energy efficiency is taken as an objective function, and a fractional programming problem under multiple constraint conditions is established. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, converting an original probability constraint non-convex problem into a closed geometric programming problem by utilizing continuous convex approximation and parameter transformation, then obtaining the optimal transmission power of a secondary user by adopting a Tickerbach method and a Lagrange duality method, and finally providing an optimal resource allocation method based on iteration. Simulation results show that compared with some existing methods, the method has the best stubborn performance, and meanwhile good real-time performance can be guaranteed.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Joint resource optimization method based on underwater acoustic OFDM-NOMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing-Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access) system downlink
ActiveCN109617662AEnable Adaptive CommunicationReduce time complexityTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationGeometric programmingTransmitted power
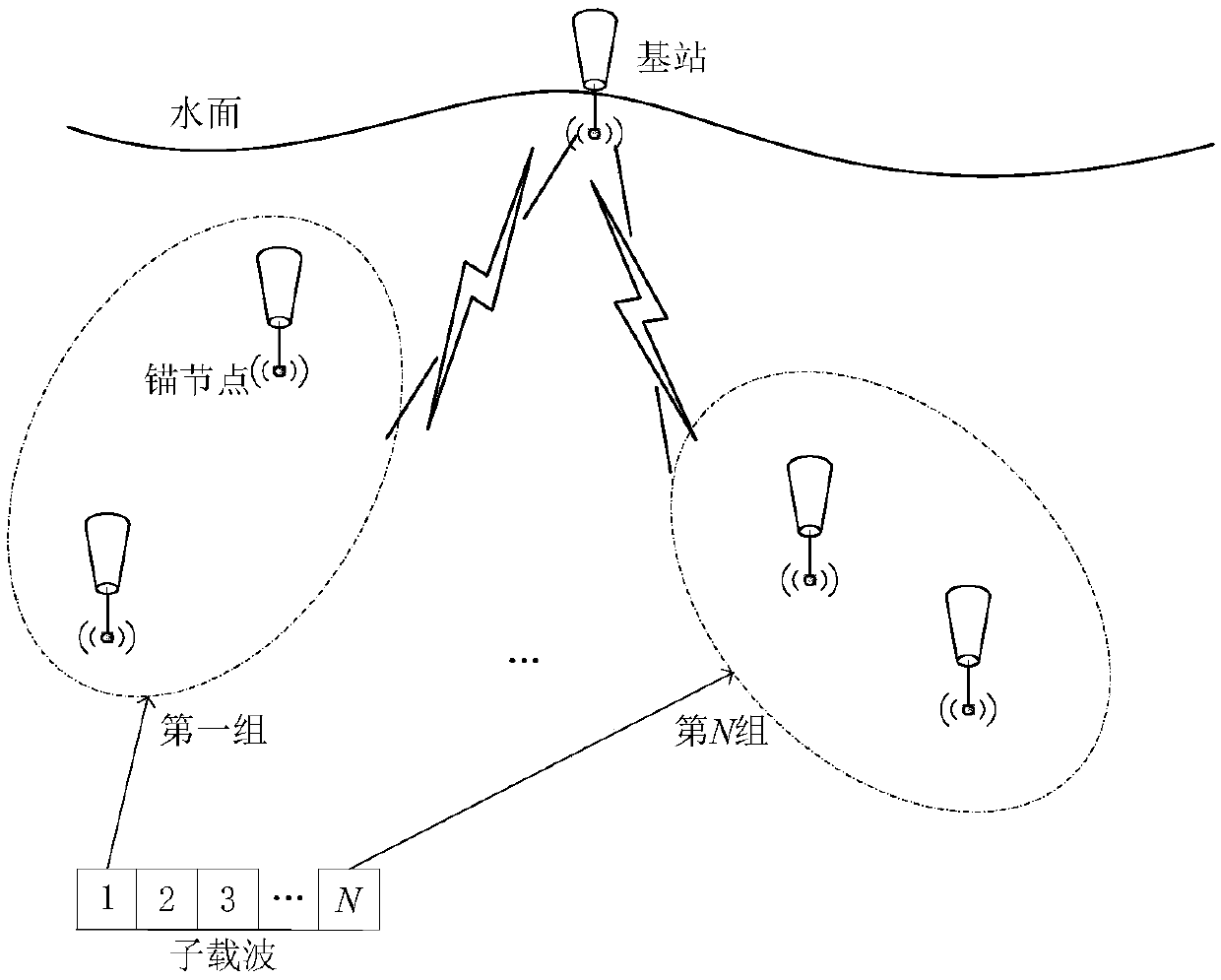
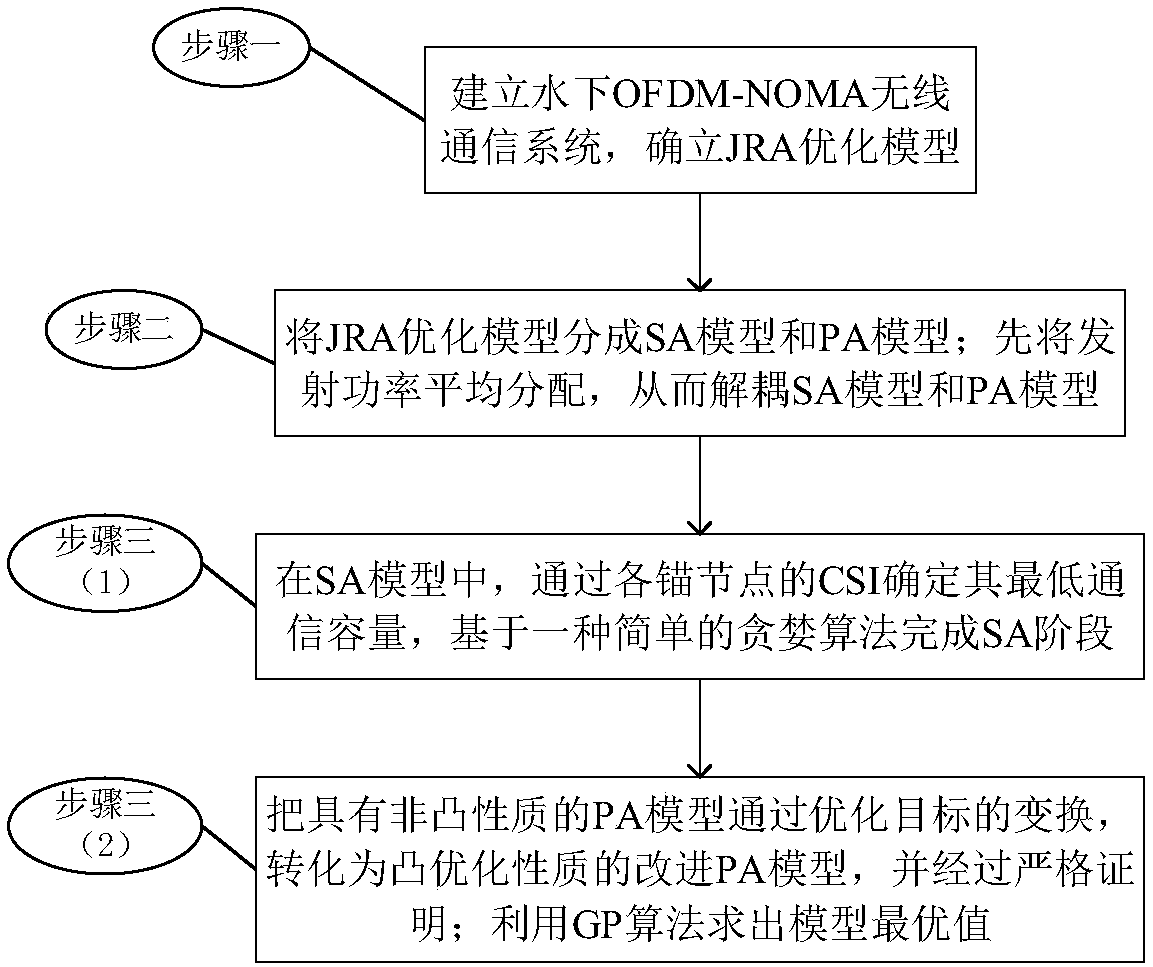
The invention provides a joint resource optimization method based on an underwater acoustic OFDM-NOMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing-Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access) system downlink and isused for solving a problem that in the prior art, no underwater non-orthogonal multiple access network resource allocation mechanism with high feasibility exists. An underwater acoustic wireless communication system based on OFDM-NOMA is established. A base station (BS) and K anchor nodes are deployed in the system. A channel information state of each anchor node is known. A constraint conditionis given. The constraint condition comprises a total transmitting power Pt of the base station and a constraint of subcarrier allocation number. A system rate sum is taken an objective function. In order to solve a joint resource optimization problem, the provided optimization problem is finished step by step. Subcarrier allocation is carried out through adoption of a greedy algorithm with relatively low algorithm complexity, so a system subcarrier allocation optimization objective is satisfied. For power allocation, an optimization objective is converted from a transmitting power to a communication rate, a power allocation model is converted into a strict convex optimization problem, and an optimum value is solved through adoption of a GP (Geometric Programming) algorithm. The method is scientific and reasonable, is low in algorithm complexity and is applicable to an underwater bad communication environment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Automated sequential planning of MR scans
ActiveUS8565505B2Reduce training requirementsEliminate errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAnatomical landmarkGeometric programming
A method of acquiring at least one clinical MRI image of a subject comprising the following steps: acquiring a first survey image with a first field of view, the first survey image having a first spatial resolution,—locating a first region of interest and at least one anatomical landmarks in the first survey image, determining the position and the orientation of the first region of interest using the anatomical landmarks, the position and the orientation of the first region being used for—planning a second survey image,—acquiring the second survey image with a second field of view, the second survey image having a second spatial resolution, the second spatial resolution being higher than the first spatial resolution, generating a geometry planning for the anatomical region of interest using the second survey image,—acquiring a diagnostic image of the anatomical region of interest using the geometry planning.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Network Bottleneck Detection Method
InactiveCN102263676AReduce loadThe result is accurateError preventionData switching networksGeometric programmingPathPing
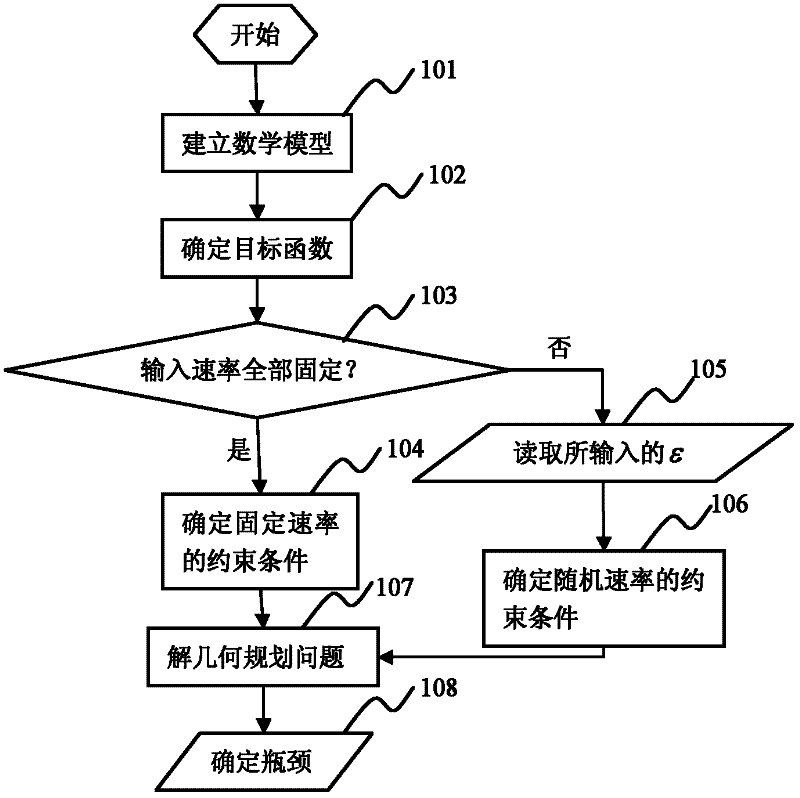
The present invention relates to the field of network technology, and discloses a network bottleneck detection method, including steps 101, establishing a mathematical model according to the network topology; 102, determining the objective function of the geometric programming problem according to the principle of network utility maximization; 103, judging all paths Whether all the input rates are fixed, if so, then execute steps 104, 107, 108 in sequence; otherwise, execute steps 105-108 in sequence; 104, determine the constraint condition of the fixed rate; 105, read the set insurance degree value ε; 106 107. Solve a geometric programming problem to obtain the packet loss rate of each link, wherein the geometric programming problem is composed of the objective function and a fixed-rate or random-rate constraint ; 108. Determine the network bottleneck according to the calculated packet loss rate of each link. The invention can improve the accuracy of network bottleneck detection, reduce network load, and improve the flexibility of network management.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
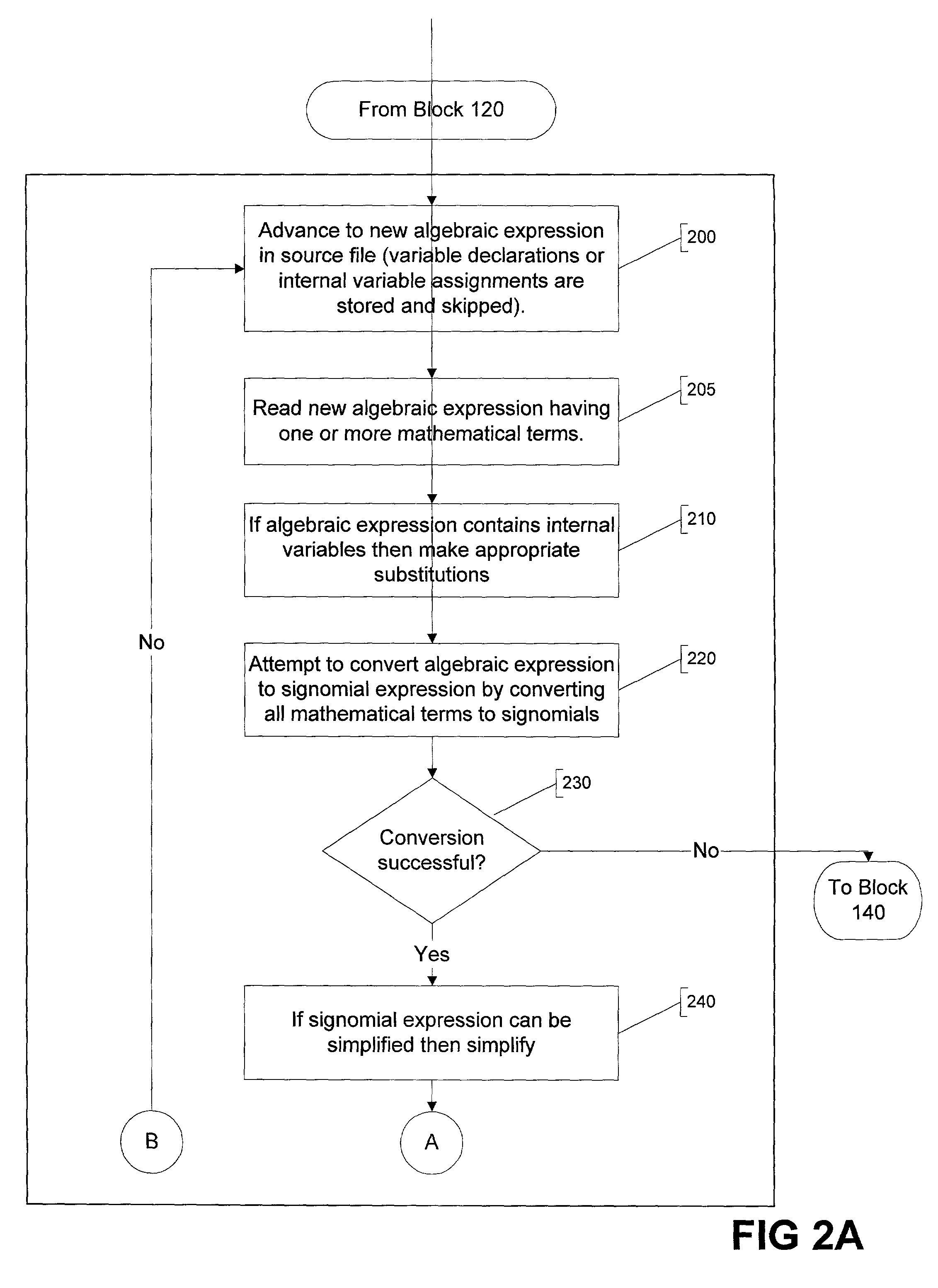
Parser for signomial and geometric programs
InactiveUS20080072215A1Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsGeometric programmingTheoretical computer science
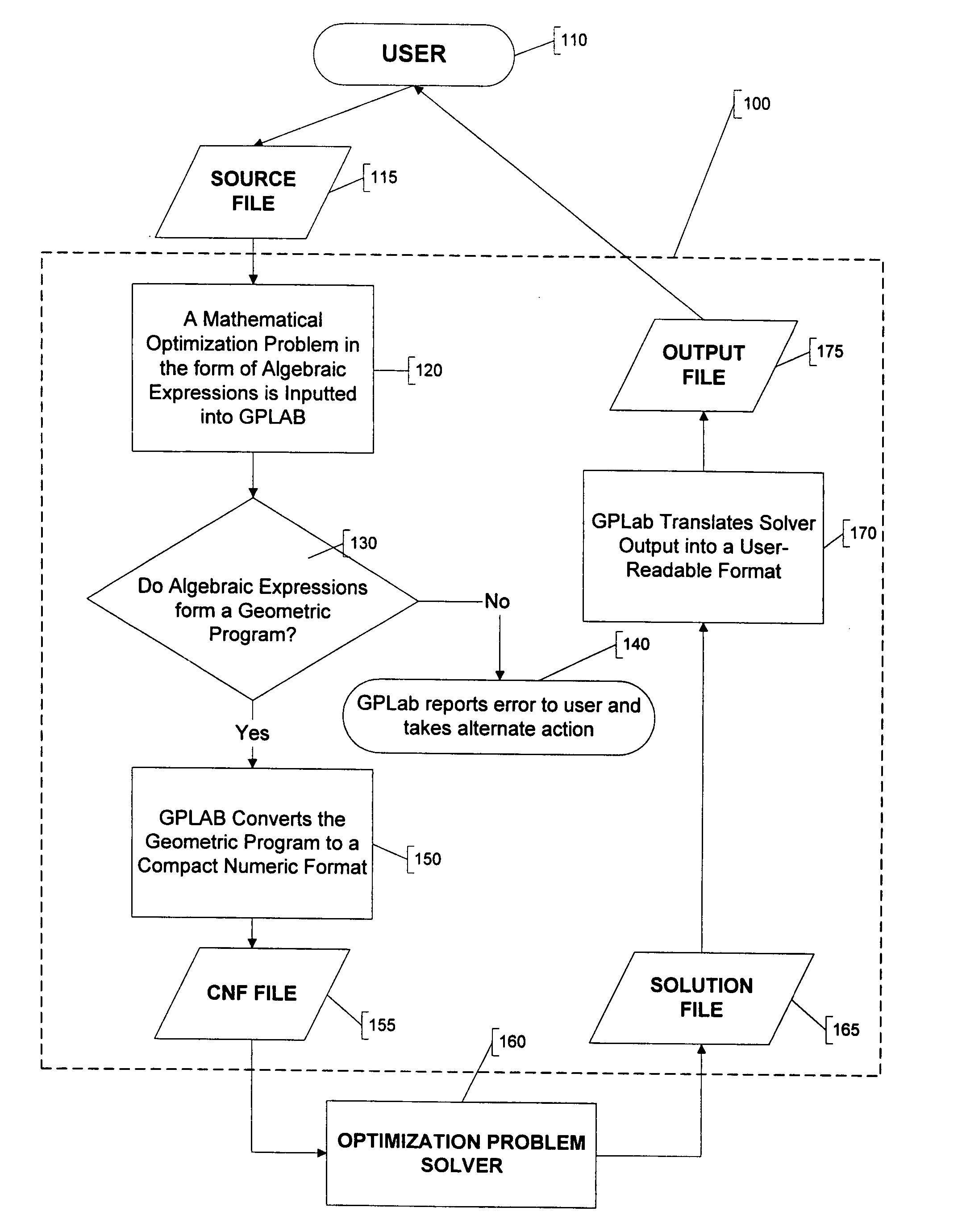
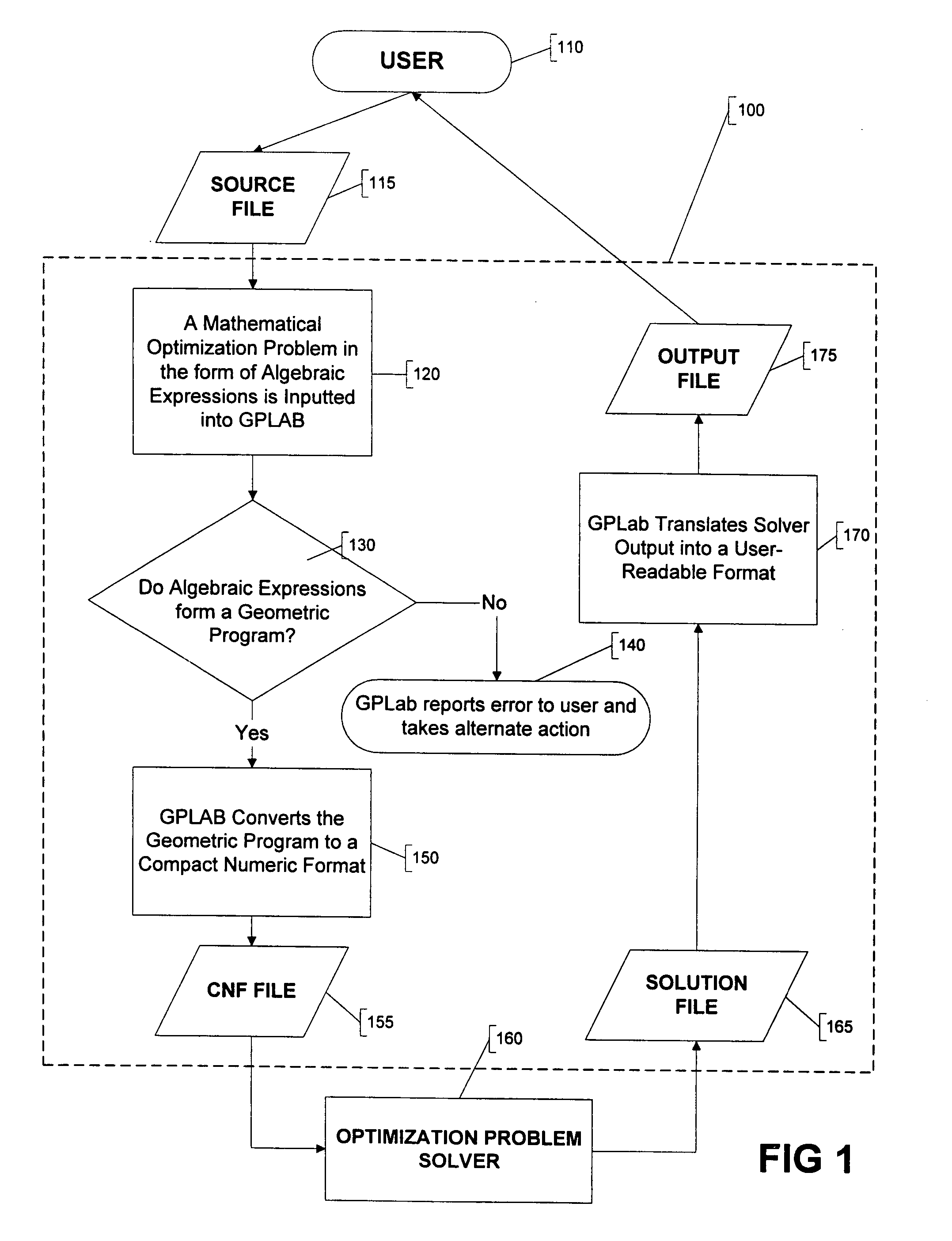
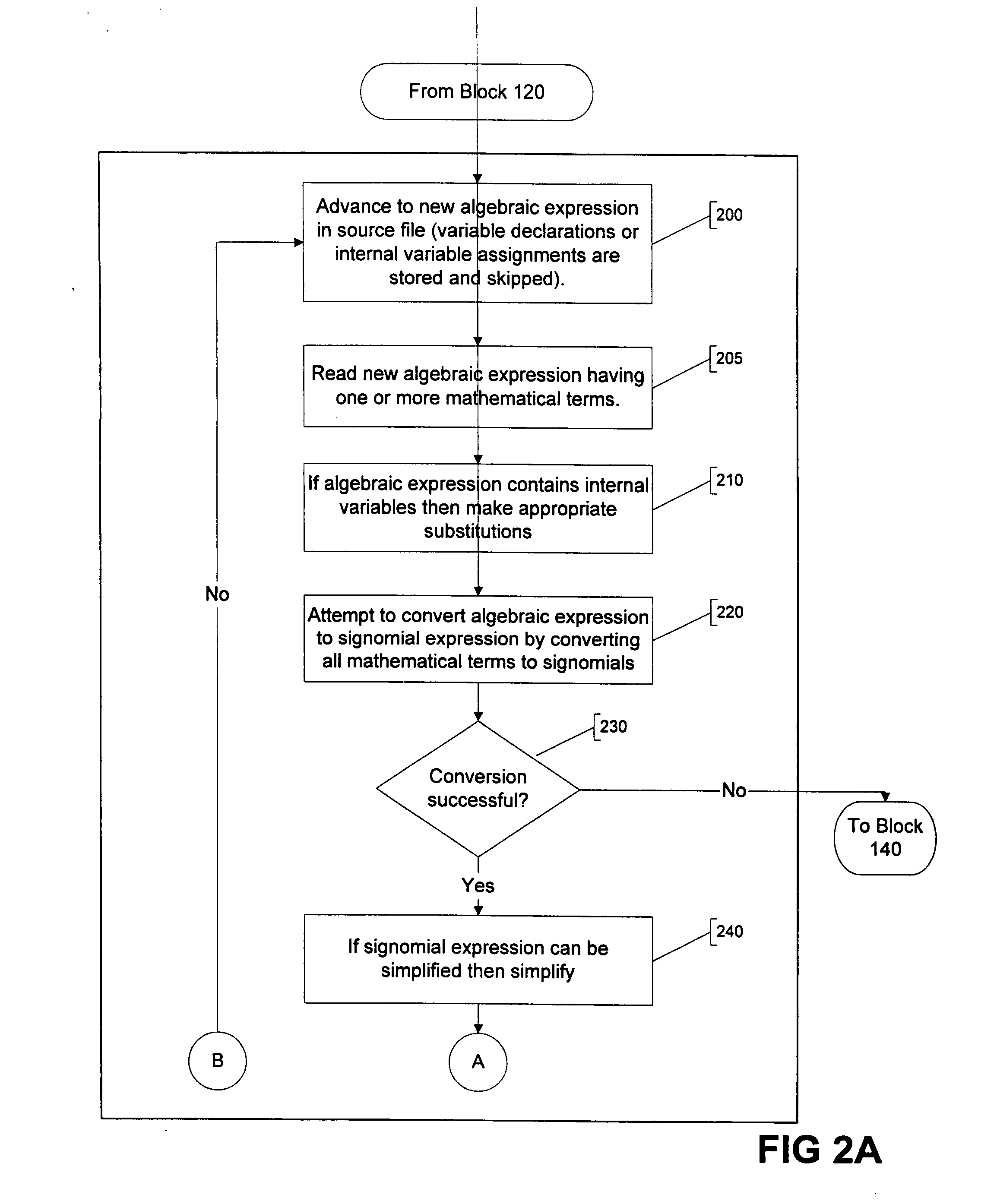
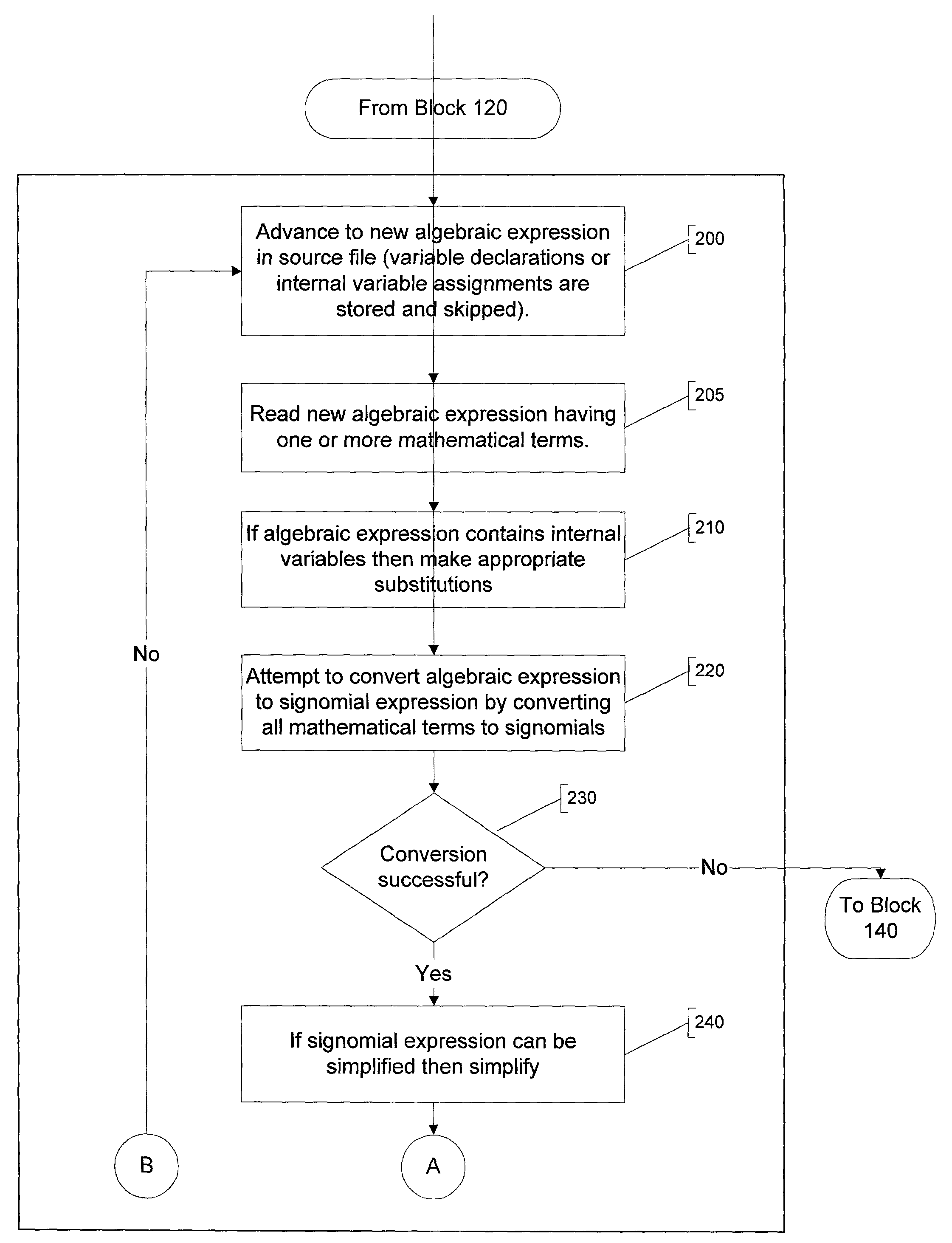
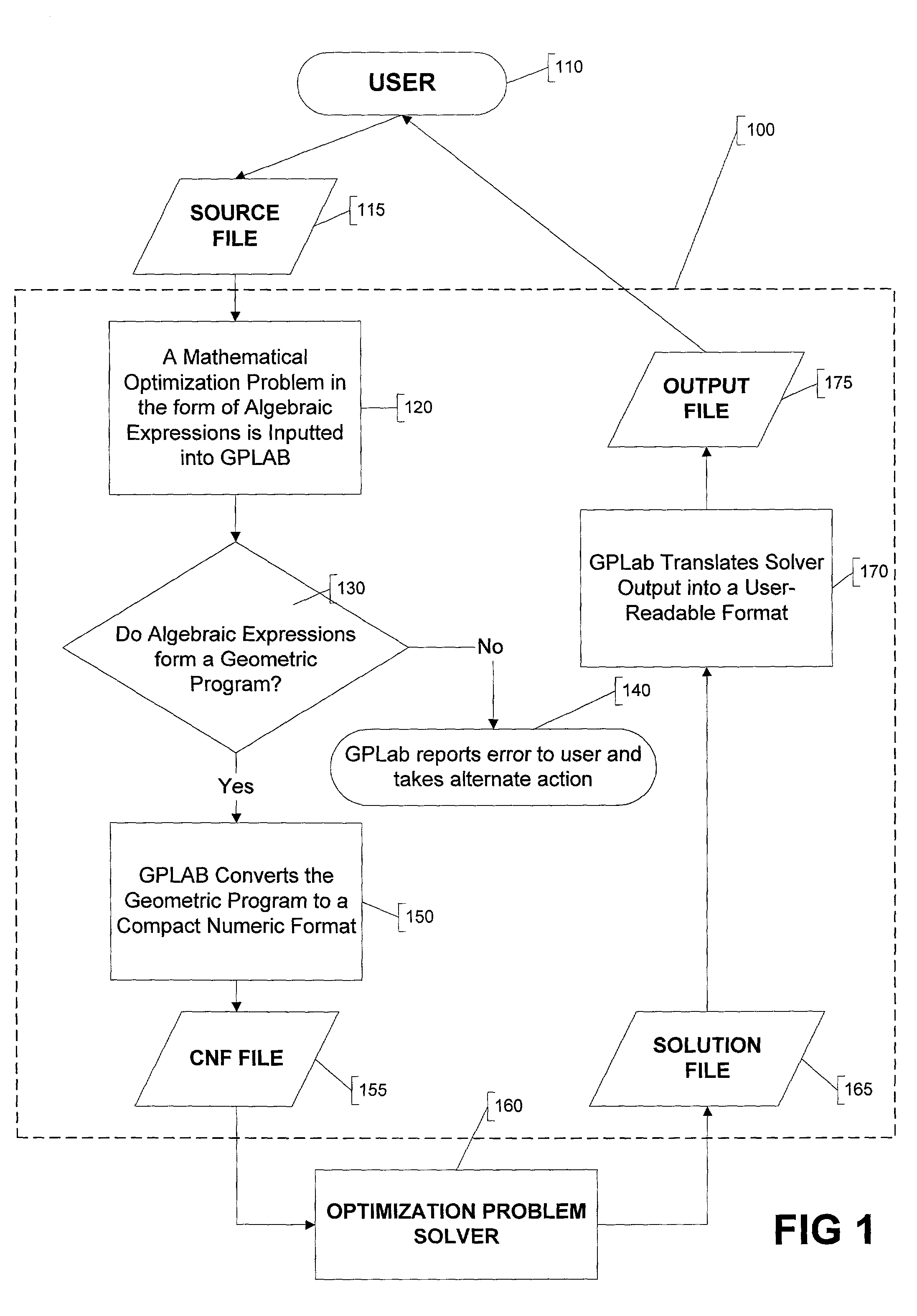
A method and apparatus for parsing signomial and geometric programs, referred to herein as “the Parser”. Signomial and Geometric programming is a unique class of mathematical problems that is useful in the study of optimization problems. The Parser is a program designed to recognize and parse both signomial and geometric programs such that they may be accepted and solved by signomial and geometric program solvers. The Parser accepts an optimization problem from a user in the form of algebraic expressions. The Parser can then identify the problem as a signomial program and can further determine if it reduces to a geometric program. If either a signomial or geometric program exists, the Parser converts the algebraic expressions to a compact numeric format that can be accepted by a computer-aided solver. In the case of a geometric program, the solver may find a global solution to the optimization problem. However, in the case of signomial program, the solver may only find a local solution. The solution found by the solver is routed back to the Parser which reports it in a user-readable format.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Parser for signomial and geometric programs
InactiveUS7299459B1Software engineeringComputation using non-denominational number representationGeometric programmingTheoretical computer science
A method and apparatus for parsing signomial and geometric programs, referred to herein as “the Parser”. Signomial and Geometric programming is a unique class of mathematical problems that is useful in the study of optimization problems. The Parser is a program designed to recognize and parse both signomial and geometric programs such that they may be accepted and solved by signomial and geometric program solvers. The Parser accepts an optimization problem from a user in the form of algebraic expressions. The Parser can then identify the problem as a signomial program and can further determine if it reduces to a geometric program. If either a signomial or geometric program exists, the Parser converts the algebraic expressions to a compact numeric format that can be accepted by a computer-aided solver. In the case of a geometric program, the solver may find a global solution to the optimization problem. However, in the case of signomial program, the solver may only find a local solution. The solution found by the solver is routed back to the Parser which reports it in a user-readable format.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
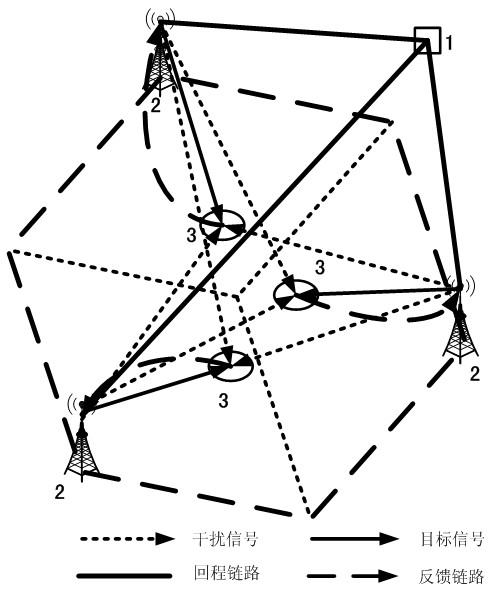
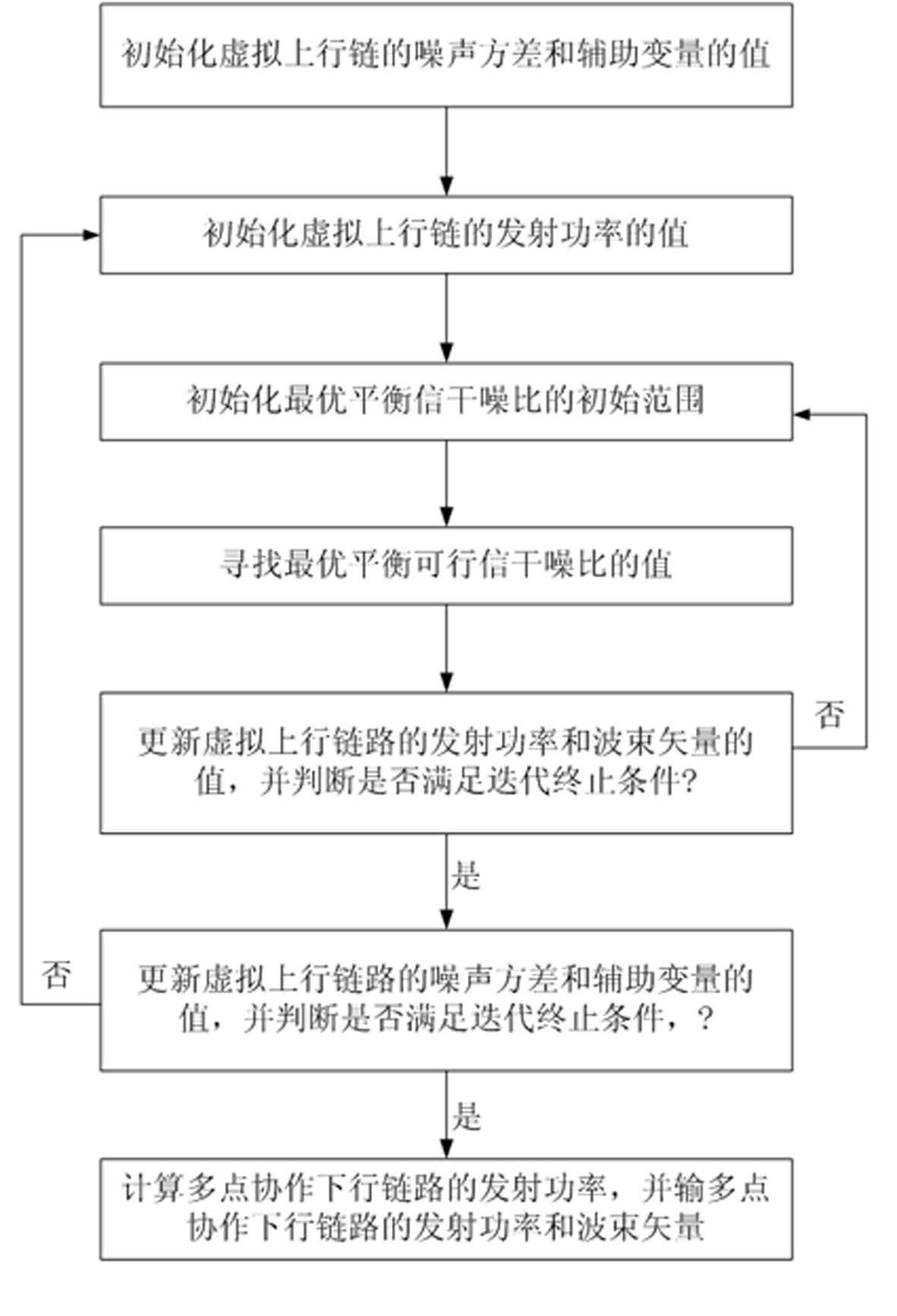
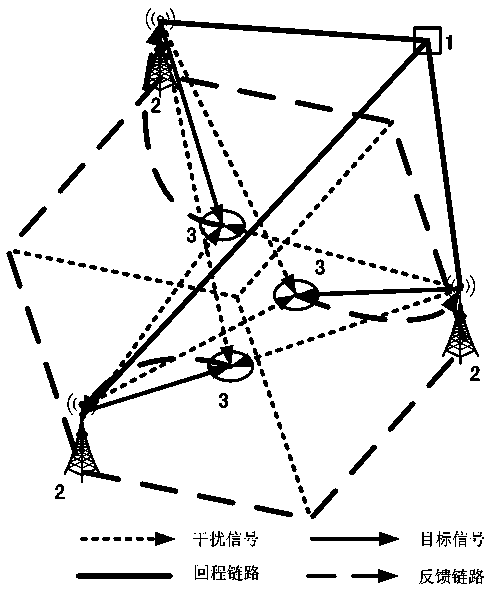
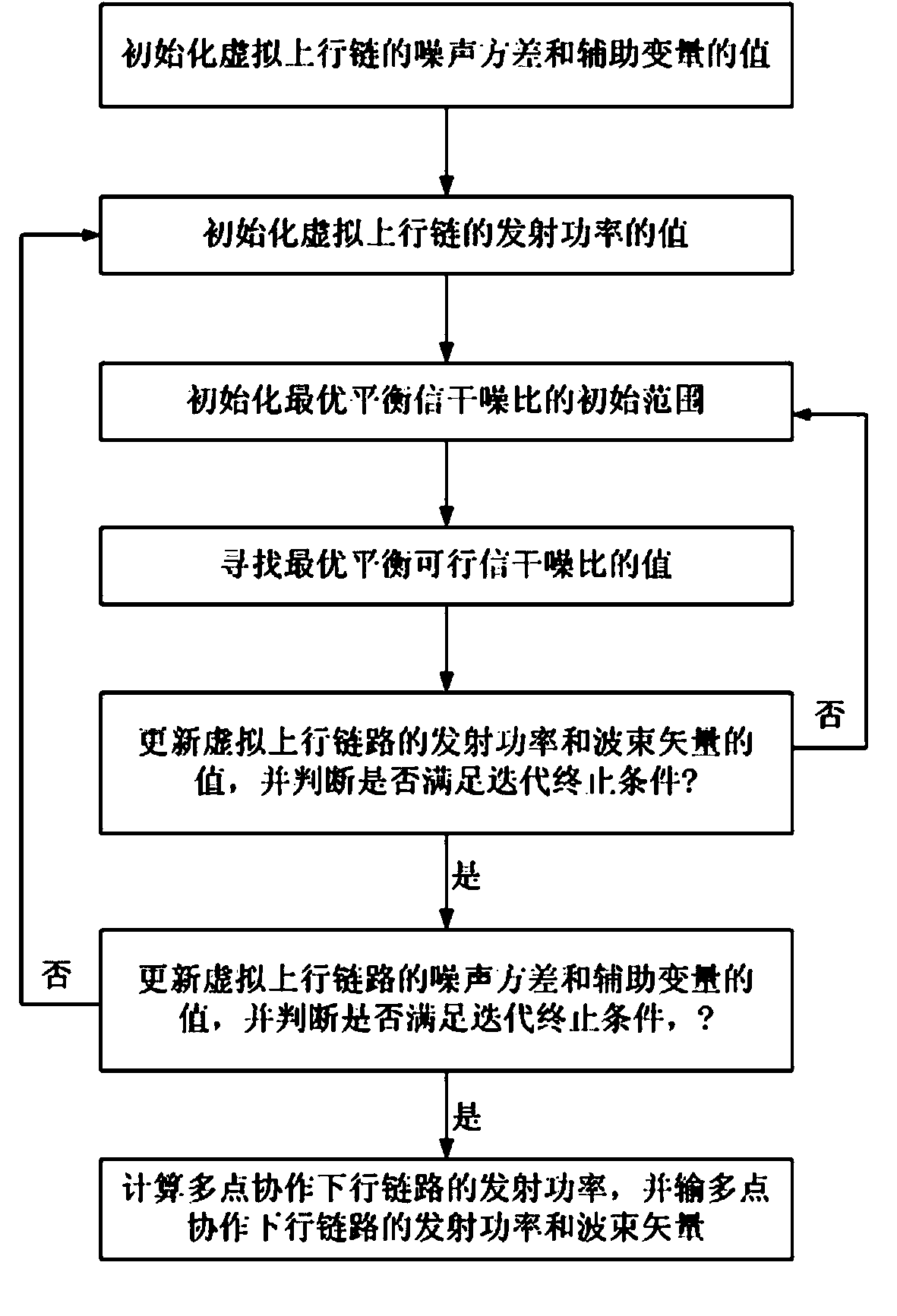
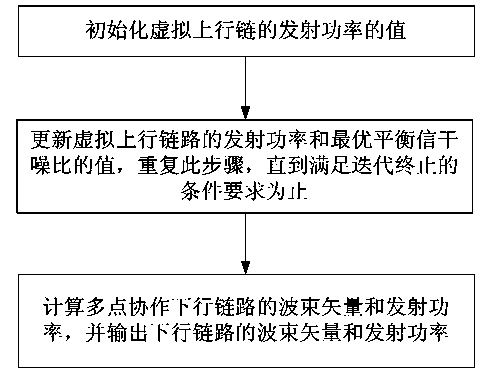
Multipoint coordinated beam forming and power allocation method for single base station power constraint
ActiveCN102355294AIncrease powerReduce consumptionPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGeometric programmingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a multipoint coordinated beam forming and power allocation method for single base station power constraint. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, transforming a multi-cell coordinated downlink minimum user signal-to-noise ratio maximization problem under the single base station power constraint into a virtual uplink optimization problem through a Lagrange duality theory; then, iteratively solving the virtual uplink optimization problem through a binary optimization method and a geometric programming optimization method, and obtaining an optimal receiving beam vector and an optimal user transmitting power of the virtual uplink; and finally, converting the solution of the virtual uplink to an optimized beam forming vector and the transmitting power of the downlink according to the duality theory. In comparison with the existing multipoint coordinated beam forming method, the method provided by the invention has obvious advantages in the aspect of speed per energy consumption and worst user speed performance, and with the method, the transmitting power can be saved by 25-30% at each base station and the impartiality among the users can be ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
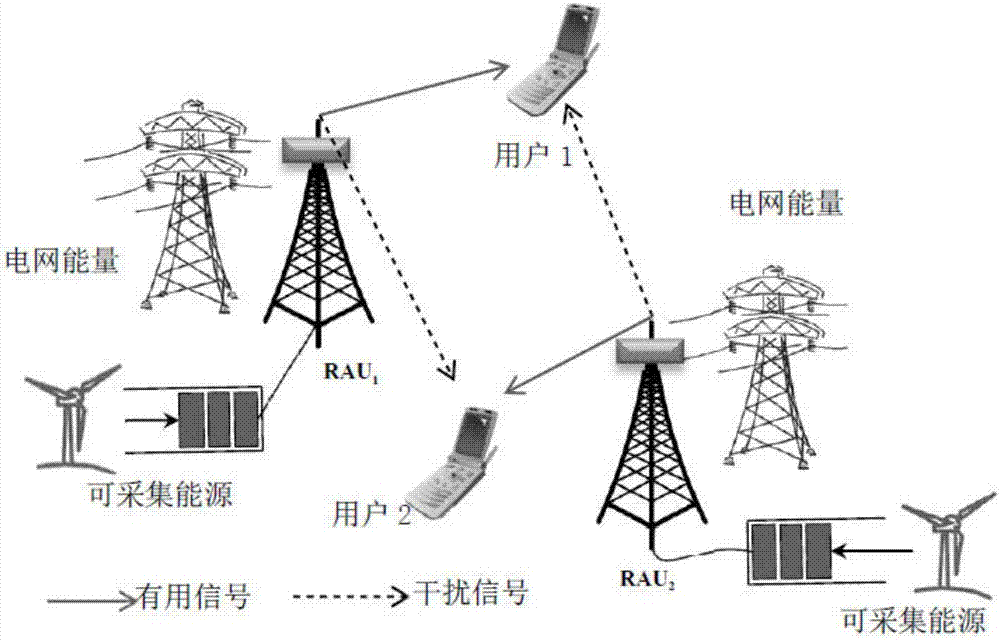
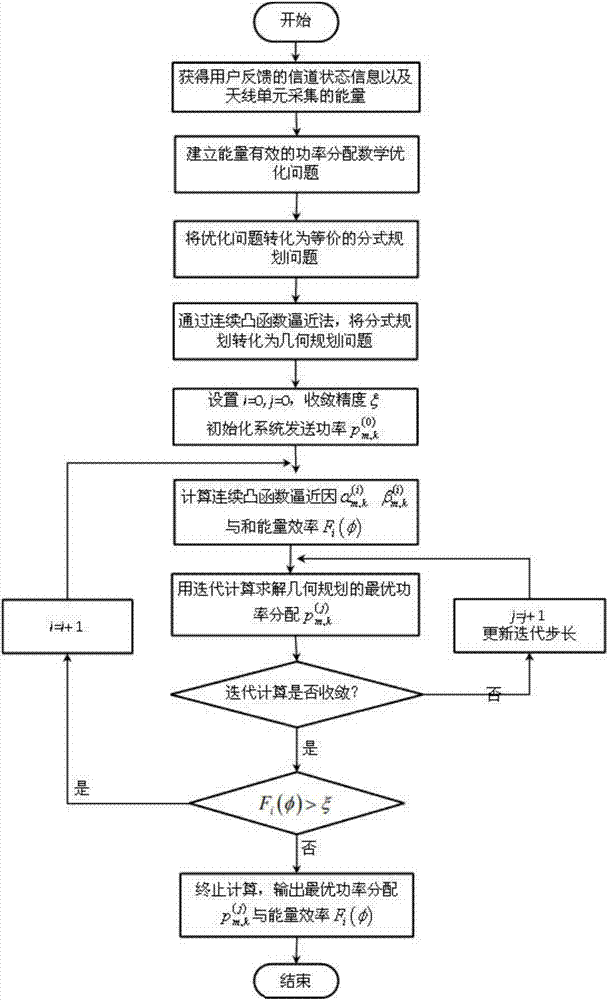
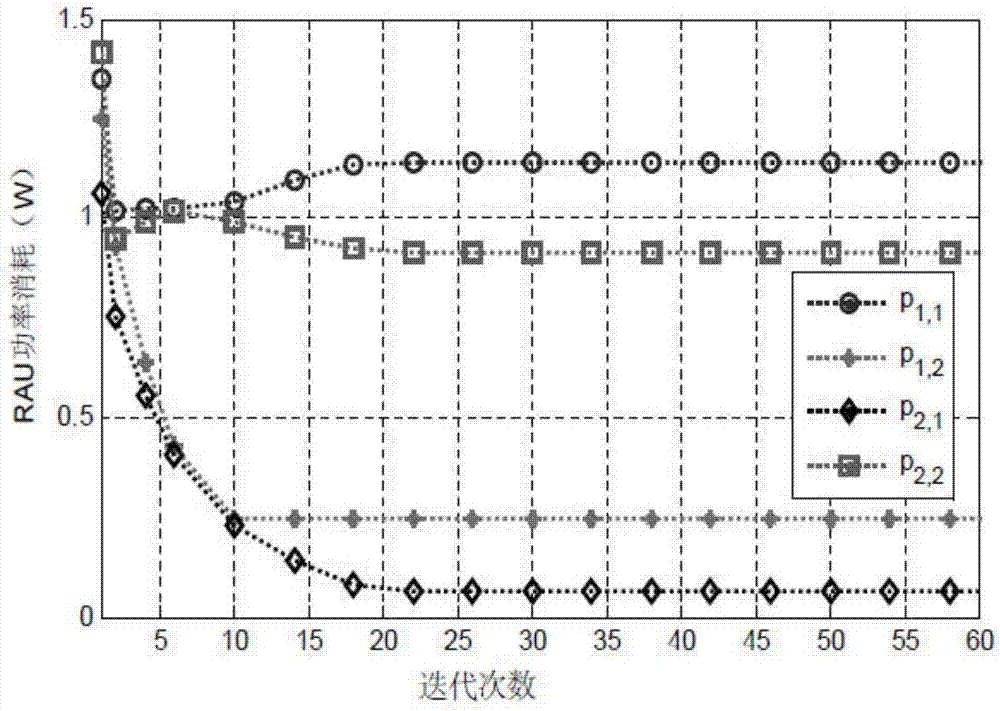
Energy-efficient power distribution method aiming at mixed energy supply distributed antenna system
ActiveCN107086885AImprove energy efficiencyPower managementRadio transmissionGeometric programmingQuality of service
The invention discloses an energy-efficient power distribution method aiming at a mixed energy supply distributed antenna system. The method comprises the following steps: combining the mains supply with the energy acquired by an antenna unit so as to serve for the distributed antenna system in a mixed energy supply way; the system preferentially uses the energy acquired by the antenna unit and takes the mains energy as the reserve capacity. In an optimal problem modelling, the system energy efficiency maximization is used as the target, the rate QoS (quality of service) demand of each user and the antenna unit power constraint are taken as the constraint condition. An optimization problem is transformed into fractional programming problem by use of the Dinkelbach, and then the fractional programming is transformed into a geometric programming problem through continuous convex function approximation, and then the power distribution of the system at the optimal energy efficiency can be obtained through the iterative computation. By considering the interference factor between the users, the energy-efficient power distribution method is not only suitable for the traditional distributed antenna system, but also suitable for the mixed supply distributed antenna system, and the energy efficiency of the distributed antenna system can be obviously improved.
Owner:上海瀚芯实业发展合伙企业(有限合伙)
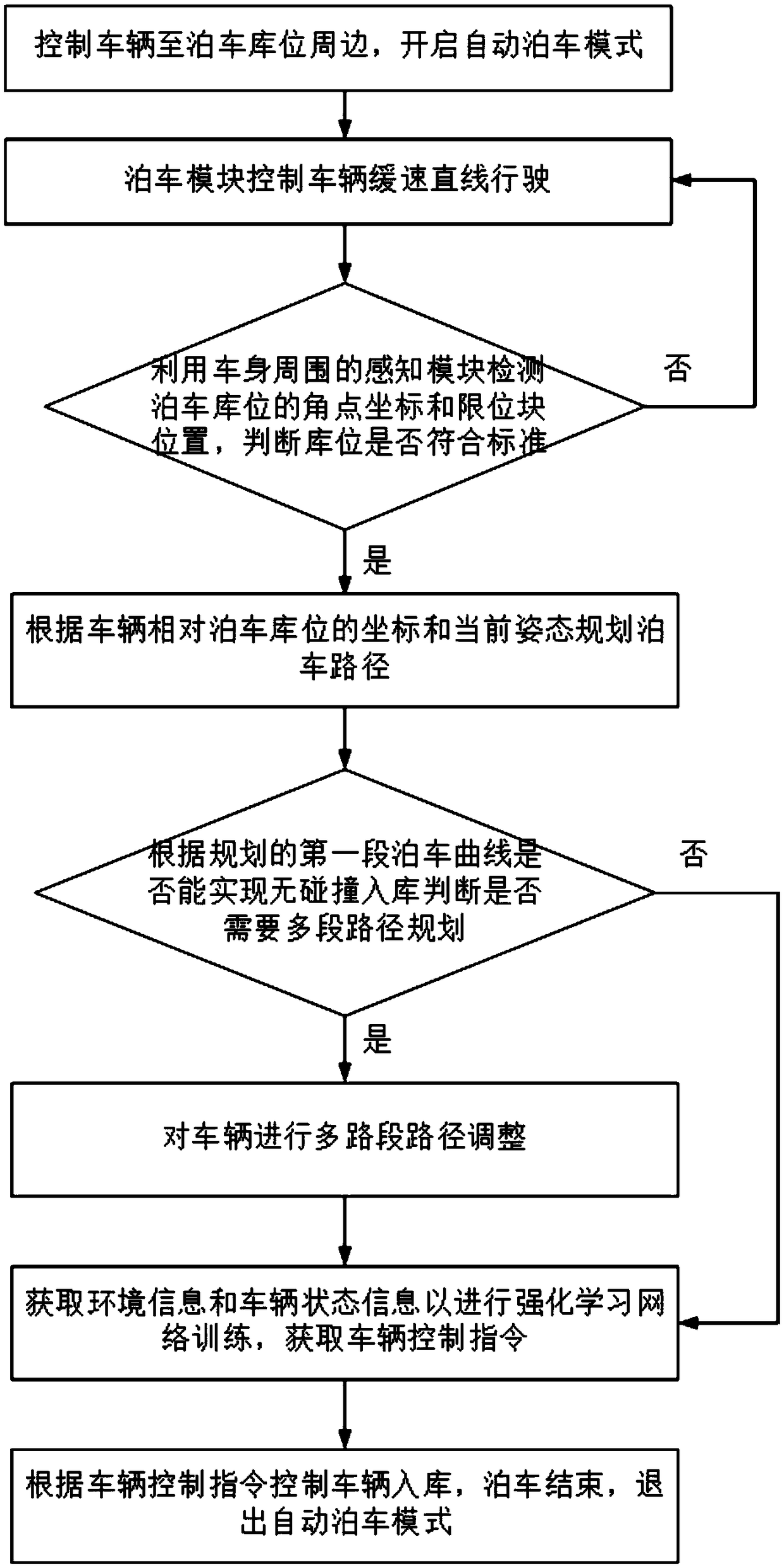
Automatic parking method and system based on geometric programming and reinforced learning
The invention relates to an automatic parking method and system based on geometric programming and reinforced learning. According to the automatic parking method, at the initial state of automatic parking, by determining a parking state, the parking trajectory is determined through geometric programming, and then is controlled through trajectory tracking and chassis control, through the stage, a vehicle can be adjusted to the pose for entering a garage at a time, and at the moment, controlling is further conducted through reinforced learning. Compared with the prior art, according to the automatic parking method, the error of trajectory planning, trajectory tracking and chassis control can be eliminated, the more ideal parking pose is achieved, and the automatic parking method can be suitable for the narrow parking environment in cities, and is high in adaptability to the environment.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
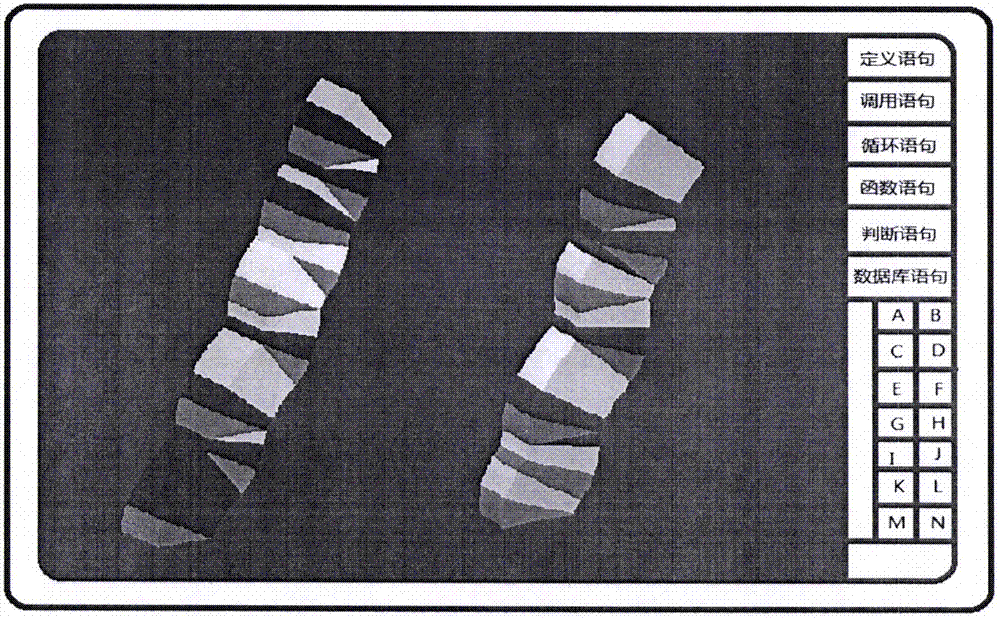
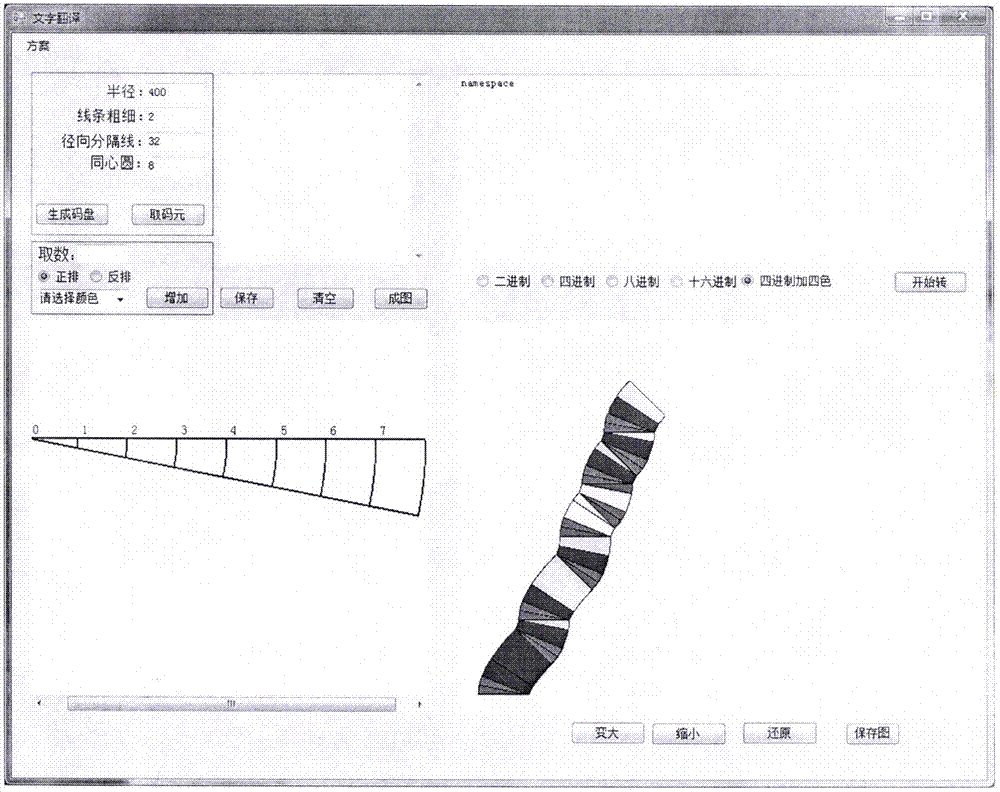
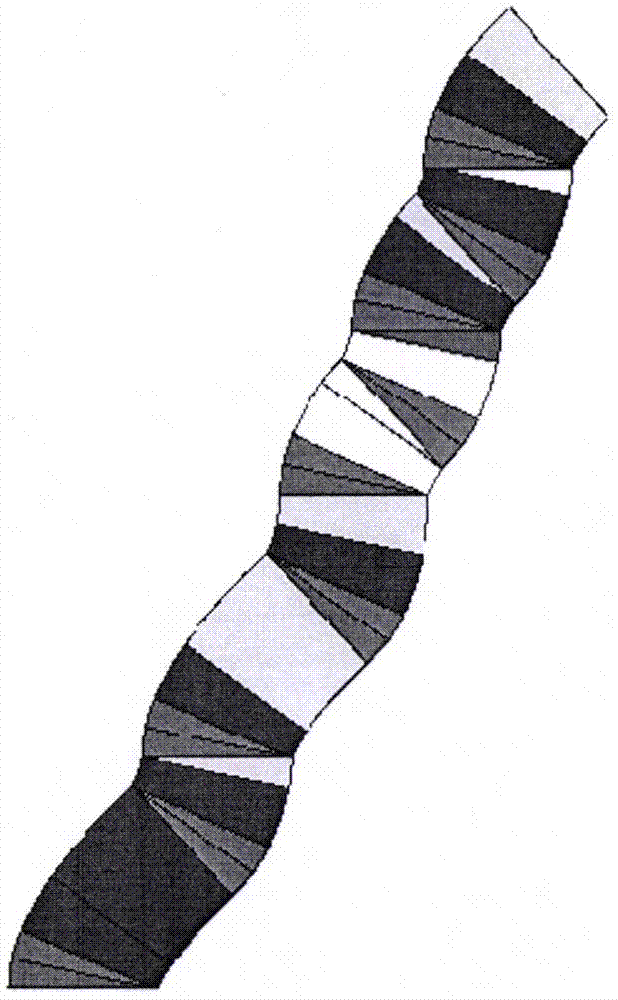
Visual three-dimensional code touch screen compiler and programming technique
ActiveCN105446747AReduce errorsImprove programming efficiencyVisual/graphical programmingCompiler constructionGeometric programmingProgram security
The invention discloses a visual three-dimensional code touch screen compiler product and its programming technique. According to the invention, visual geometric programming and three-dimensional code programming are realized; a programmer can finish programming work by one-hand or two-hand touch screen operation, therefore the workload of the programmer is greatly reduced; and the programming work is driven to humanized and intelligentized development. The built-in technologies of the new type geometric decoder and three-dimensional compiler of the invention comprise: generating a code plate and selecting a code element, coding a rule, information expression, hexadecimal number expression, conversion of digital and geometric codes, plane code to three-dimensional code, and so on; the functions of the compiler comprise: a touch screen function, program three-dimensional coding, a three-dimensional code paraphrasing function, an intelligent detection function, an automatic code storage function, an automatic connection function of three-dimensional code chains, and so on. According to the invention, the program code is converted into a shape code; a new pattern is provided for the security operation of the program; each code chain is not divided, so there is no leak for an external virus program to implant; the program is effectively prevented from being tampered and attached; and the program security is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU FIGURE CODE INFORMATION TECH LTD
Joint wireless resource allocation and power control method based on D2D communication
InactiveCN107172706AReliable transmissionLow powerPower managementQuality of serviceGeometric programming
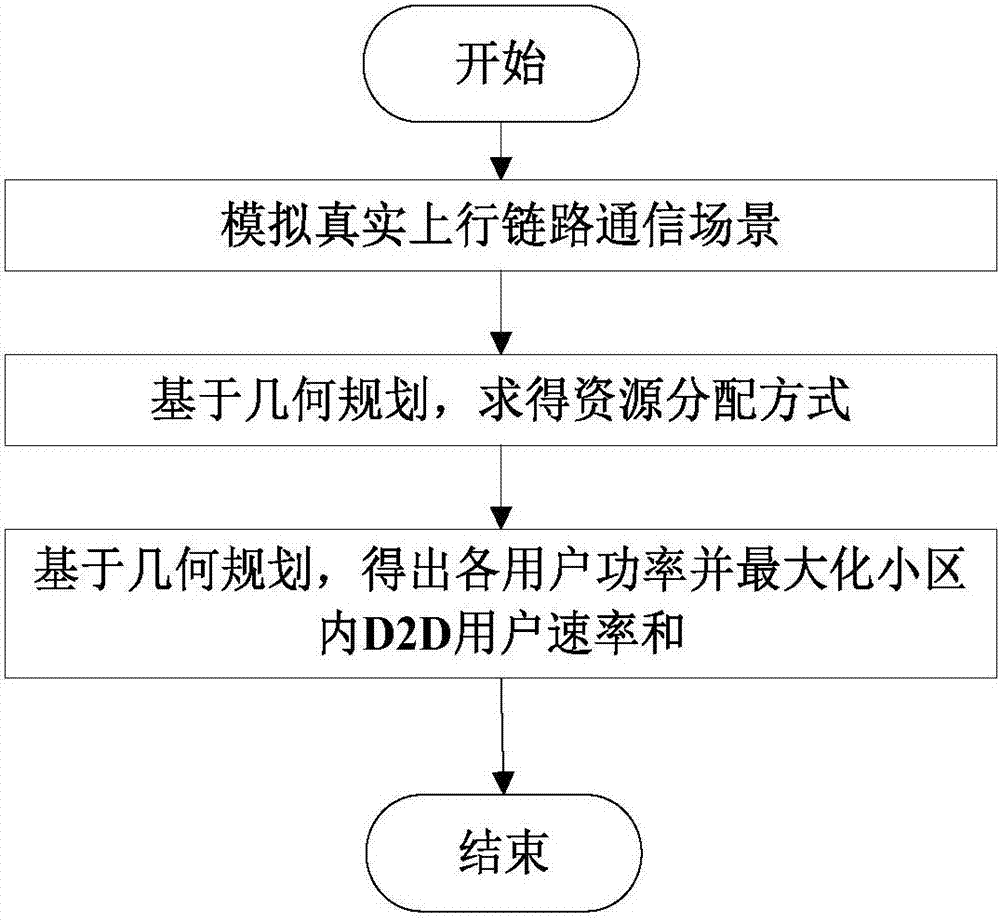
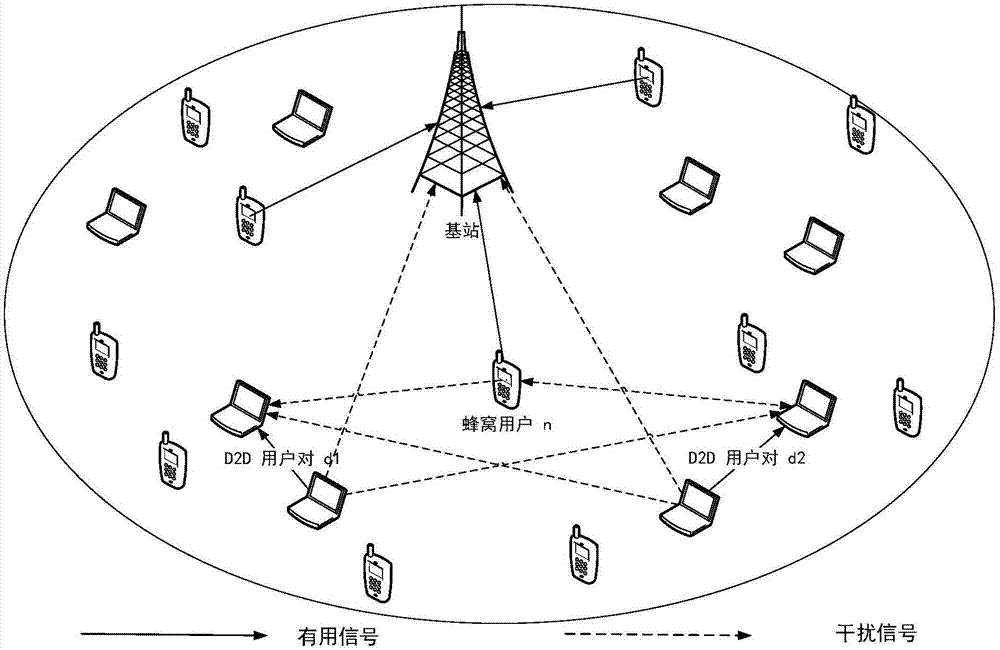
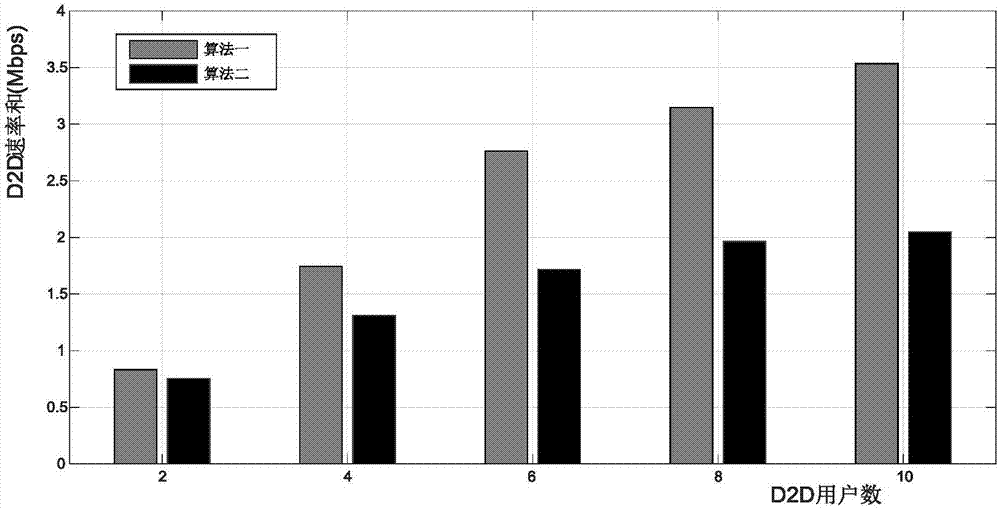
The invention discloses a joint wireless resource allocation and power control method based on D2D communication, applied to the technical field of wireless communication. A wireless resource allocation and power control algorithm based on GP (Geometric Programming) is adopted, the QoS (Quality of Service) of D2D (Device-To- Device) users and cellular users are classified in related decision making factors, the power limits of the D2D user pairs and the cellular users are comprehensively considered, and a total rate of all D2D user pairs is calculated; and the high-speed and lower-power reliable transmission in an uplink D2D communication network can be effectively satisfied.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A Regression Test Management Method for Large Scale Integrated Circuits Based on Geometric Planning
InactiveCN102289533AEffective distributionGreat functional coverageSpecial data processing applicationsGeometric programmingTime limit
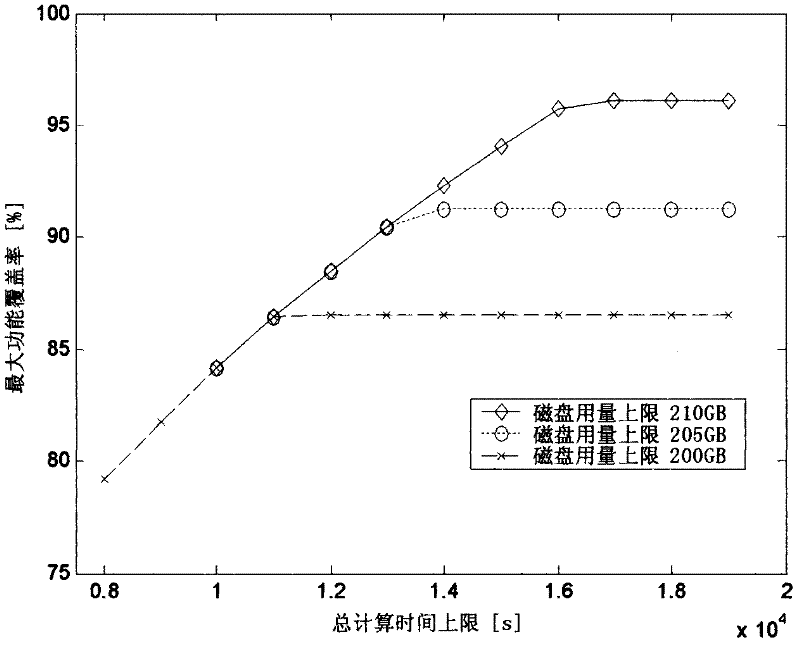
The invention discloses a method for managing the regression test of a large scale integrated (VLSI) circuit in the field of design verification and electronic design automation (EDA). According to the method, functional coverage and disk usage are modeled into the power function of time to compute a computing resource allocation solution based on a geometric programming method under the condition of limited total computing time and disk usage and obtain the optimal allocation curve of the computing resources by properly changing the total computing time limit T and the total disk usage limitS, wherein the curve is the basis for a manager to allocate computing resources for the regression test. According to the method, the efficiency of the computing resources can be maximized; the maximal function coverage can be obtained; available computing resources are effectively allocated to achieve the optimal test efficiency; the iteration of design and verification is reduced and the development period of products is shortened.
Owner:HAIMEN ZHONGDE ELECTRONICS DEV CO LTD
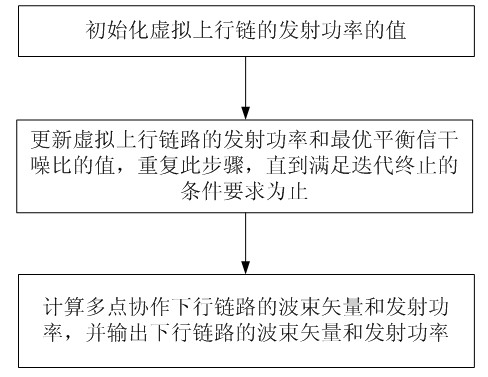
Alternative-optimization and rate-maximization multi-point cooperation wave beam forming method
InactiveCN102664665ARealize Pareto boundary solutionReduce computational complexitySpatial transmit diversityNetwork planningGeometric programmingDistribution method
The invention discloses a single base station power constraint and rate maximization multipoint cooperation wave beam forming and power distribution method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, converting sum rate maximization problem into an emission power minimization problem satisfying a minimum rate requirement; secondly, using a second-order cone programming optimization method to solve the emission power minimization problem so as to obtain an emission wave beam vector and emission power; then, taking the obtained wave beam vector as a constant, converting the sum rate maximization optimization problem into the sum rate maximization optimization problem of a single-input single-output communication network, and using a convex approximation method and a geometric programming optimization method to solve the sum rate maximization optimization problem so as to obtain the emission power of the sum rate maximization when the emission wave beam vector is given. Compared to the current sum rate maximization multipoint cooperation wave beam forming method, by using the method of the invention, calculating complexity is low and the sum rate obtained through the method of the invention approximates the optimal sum rate searched by an exhaustive method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
A Method for Optimizing Analog Integrated Circuits
InactiveCN102289549AHigh precisionWith SPICE-level accuracySpecial data processing applicationsGeometric programmingHemt circuits
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit design, in particular to an analog integrated circuit optimization method. The present invention combines a formula-based optimization method and a simulation-based optimization method: the performance parameters of the analog integrated circuit are expressed as a positive term model about the design variables, and the circuit is optimized by using the geometric programming method; in addition, the transistor-level SPICE is used The simulation results iteratively correct the normal model in the geometric programming problem to overcome the lack of accuracy of the normal model. The method optimizes the analog integrated circuit, can reach the optimization accuracy of SPICE level in a small calculation time, and solves the problem that the optimization efficiency and the optimization accuracy existing in the existing method cannot be balanced.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Flexible vector-processing algorithms for numerically solving extreme-scale, linear and non-linear, predictive and prescriptive, problems in science and engineering, on parallel-processing super computers
ActiveUS20190311306A1ForecastingConcurrent instruction executionGeometric programmingIndependent vector
A computer-implemented method for numerical solution of a geometric programming problem is described, including the computer-implemented steps of: reformulating the geometric programming problem as an equivalent generalized geometric programming optimization problem with only linear constraints, and solving the equivalent generalized geometric programming optimization problem by vector processing, including determining by computer-implemented numerical computation a solution for an unconstrained objective function whose independent vector variable is the generalized geometric programming conjugate dual of a primal decision vector variable of the geometric programming problem, and includes a variable linear combination of fixed vectors enabling the vector processing. Also described are computer-readable storage devices, computer program products, and computer systems for such numerical solution methodology.
Owner:ELMOR LEE PETERSON & MIRIAM MEARS PETERSON TRUSTEES OF THE ELMOR & MIRIAM PETERSON JOINT TRUST DATED OCTOBER 5 2023
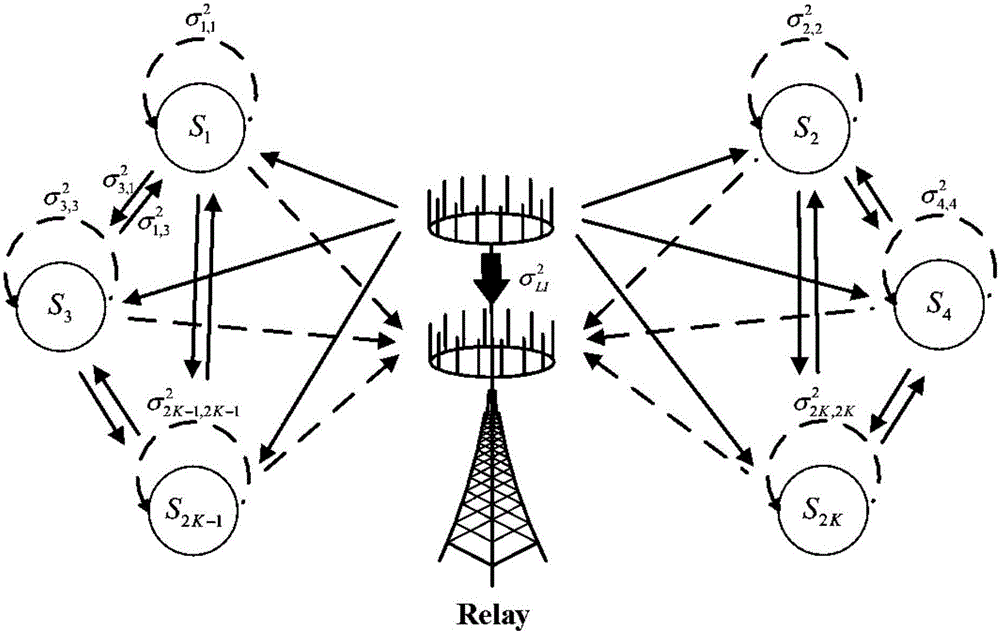
Power optimizing method for two-way full-duplex MIMO (massive multiple input multiple output) antenna relay system
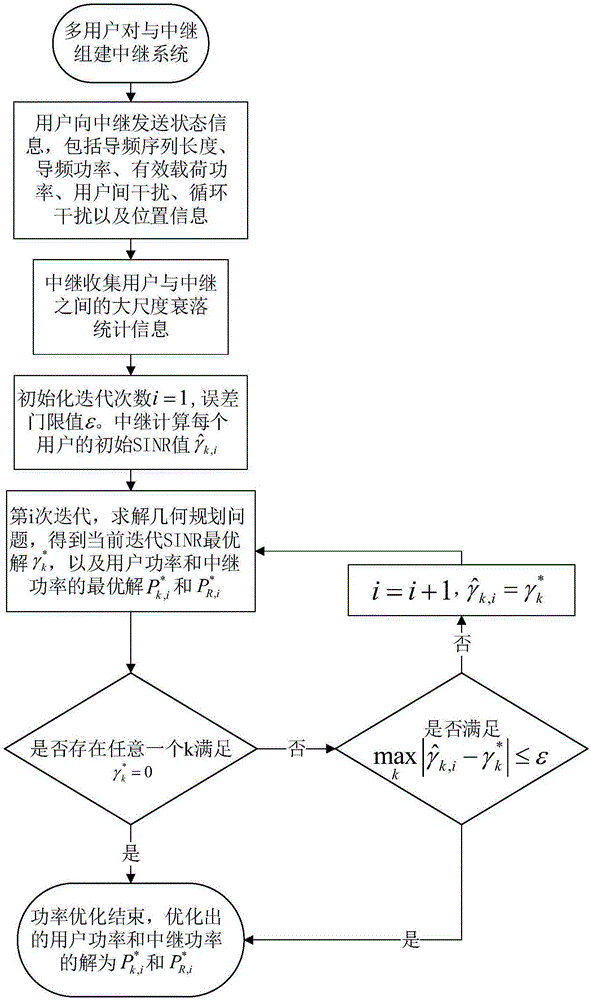
ActiveCN105871438AReduce the number of calculationsReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityHigh level techniquesGeometric programmingSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
The invention provides a power optimizing method for a two-way full-duplex MIMO (massive multiple input multiple output) antenna relay system. The method comprises the steps as follows: step 1, establishing the two-way full-duplex MIMO antenna relay system; step 2, sending state information to a relay through all user terminals; step 3, collecting statistical information of large-scale fading between all users and the relay through the relay; step 4, setting the number of iterations, and calculating initial SINR (signal to interference plus noise ratio) of each user; step 5, solving a geometric programming problem about the SINR, user power and relay power to obtain optimal solutions of the user power and relay power in the geometric programming problem; step 6, performing zero determining; step 7, performing convergence determining; step 8, automatically adding 1 to the number of iterations, setting an initial SINR value of the next iteration, and returning to execute the step 5; step 9, ending power optimization. The method has the advantages of reducing the complexity and power consumption of the system and greatly improving the accessibility and rate of the system by adopting the priori statistical information of large-scale fading.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Flexible vector-processing algorithms for numerically solving extreme-scale, linear and non-linear, predictive and prescriptive, problems in science and engineering, on parallel-processing super computers
A computer-implemented method for numerical solution of a geometric programming problem is described, including the computer-implemented steps of: reformulating the geometric programming problem as an equivalent generalized geometric programming optimization problem with only linear constraints, and solving the equivalent generalized geometric programming optimization problem by vector processing, including determining by computer-implemented numerical computation a solution for an unconstrained objective function whose independent vector variable is the generalized geometric programming conjugate dual of a primal decision vector variable of the geometric programming problem, and includes a variable linear combination of fixed vectors enabling the vector processing. Also described are computer-readable storage devices, computer program products, and computer systems for such numerical solution methodology.
Owner:PETERSON ELMOR L
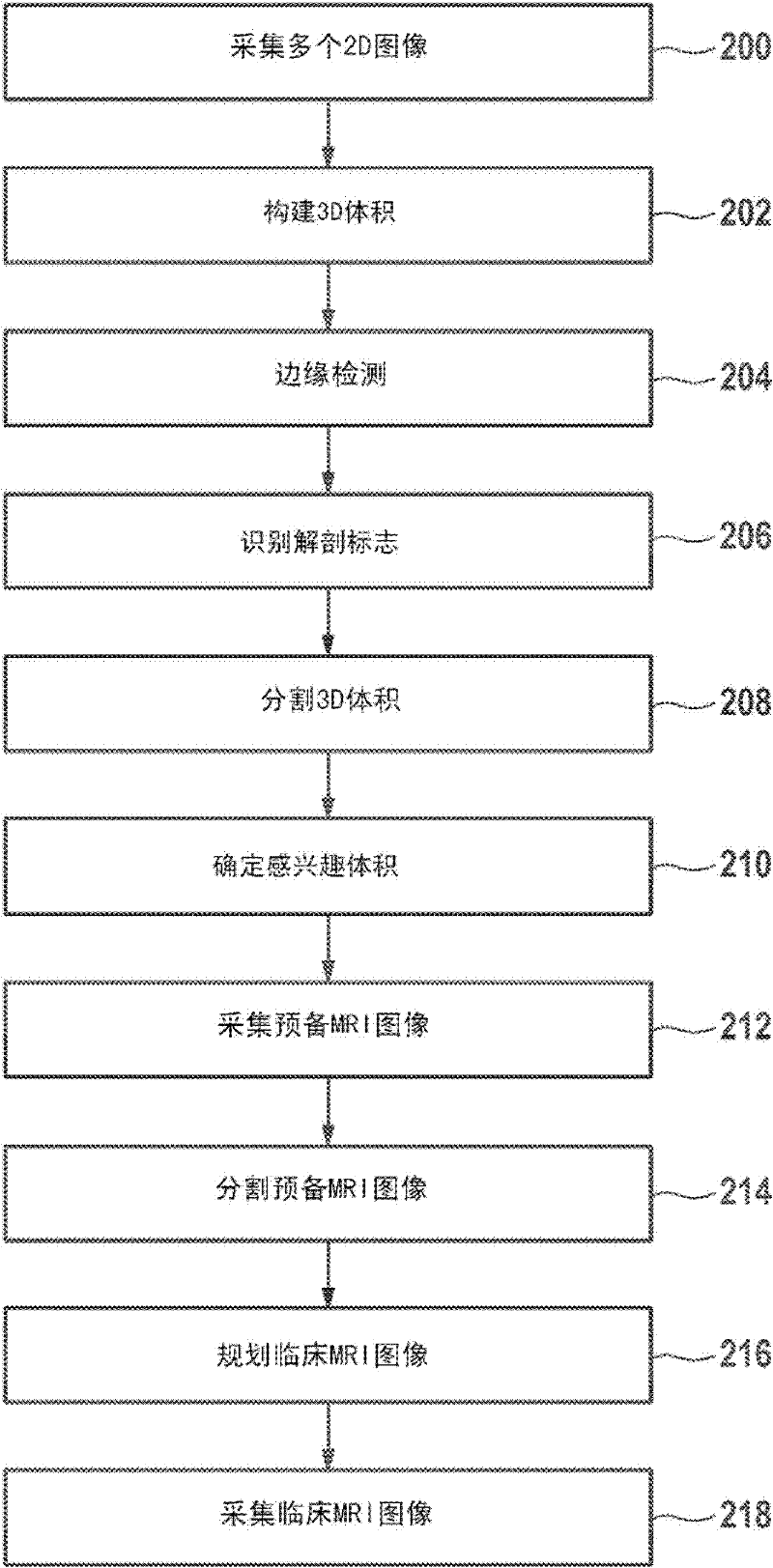
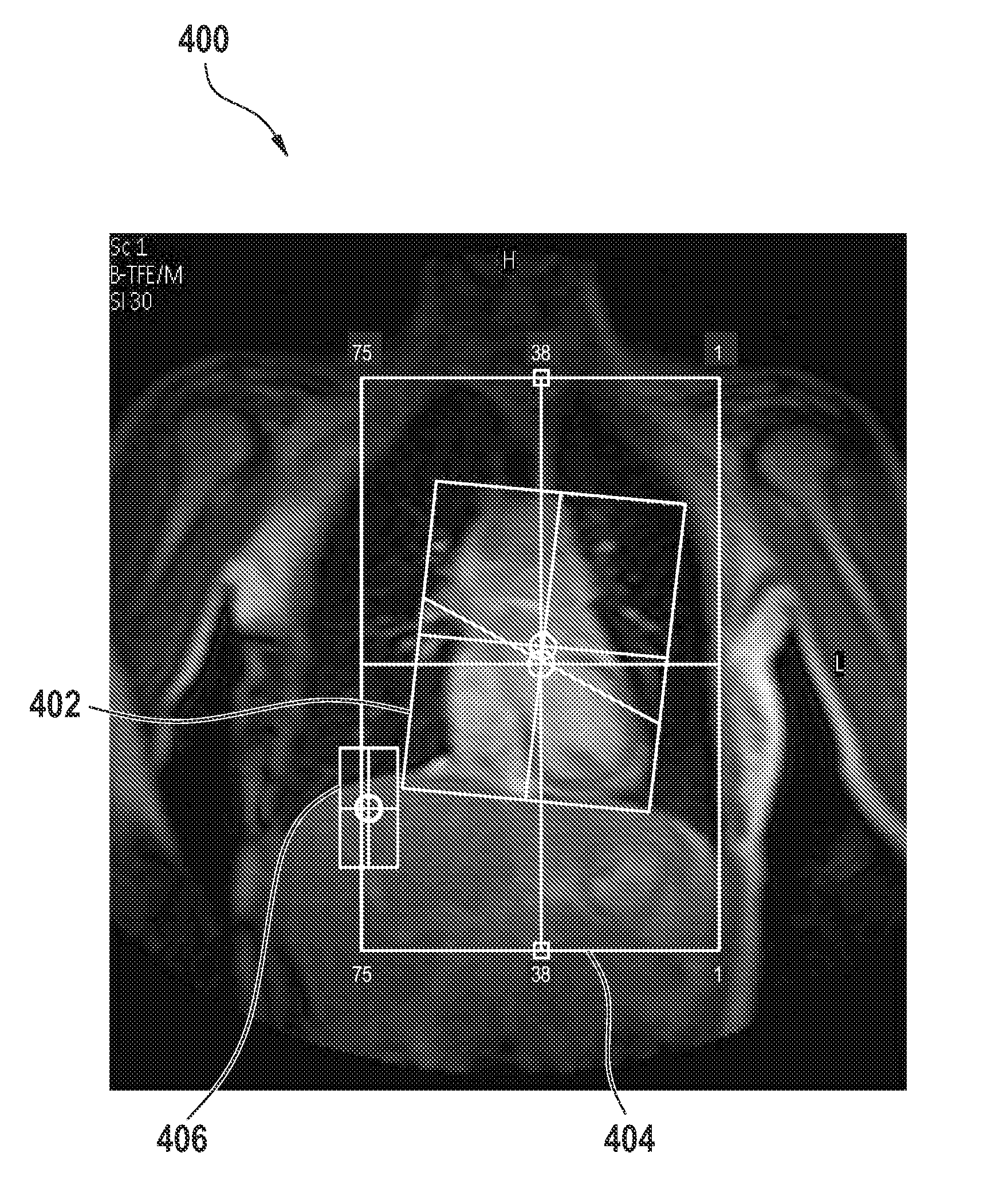
Scan geometry planning method for MRI or ct
InactiveUS20180045800A1Facilitate communicationImprove accuracyComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringGeometric programmingBody volume
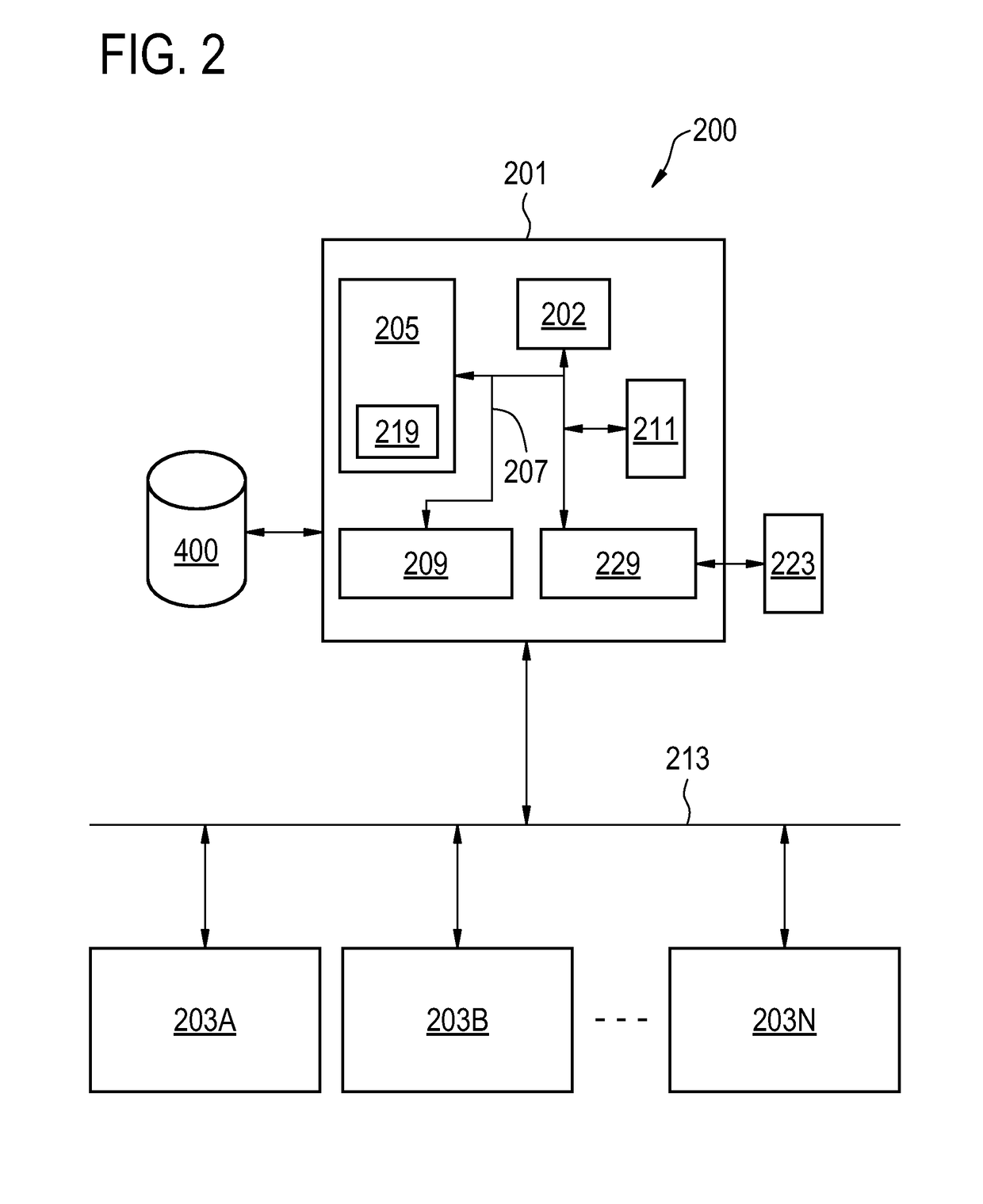
The present invention relates to a method for scan geometry planning. The method comprises: providing at least one scanning imaging system (203A-N, 100) coupled to a computer server (201); controlling the server (201) to communicate with the at least one scanning imaging system (203A-N); building a database (400) from image data obtained from the at least one scanning imaging system, wherein the image data indicates scan 5 geometries in association with respective reference images acquired using the scan geometries; receiving at the server (201) a scan geometry request from a scanning imaging system (203A) of the at least one scanning imaging system, the request being indicative of a survey image, wherein the survey image is obtained during a calibration scan by imaging a patient by the requesting scanning imaging system (203A); comparing the survey image with 10 the reference images; sending the requesting scanning imaging system data indicative of a scan geometry associated with a reference image of the reference images that matches the survey image; controlling the requesting scanning imaging system (203A) to acquire imaging data during a clinical scan of the body volume using one of the submitted scan geometry and a modified scan geometry that results from the modification of the submitted scan geometry 15 at the requesting scanning imaging system; controlling the requesting scanning imaging system (203A) to send the modified scan geometry to the server (201) in case the modified scan geometry is used for the acquiring of imaging data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Multipoint coordinated beam forming and power allocation method for single base station power constraint
ActiveCN102355294BIncrease powerReduce consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementGeometric programmingTransmitted power
The invention discloses a multipoint coordinated beam forming and power allocation method for single base station power constraint. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, transforming a multi-cell coordinated downlink minimum user signal-to-noise ratio maximization problem under the single base station power constraint into a virtual uplink optimization problem through a Lagrange duality theory; then, iteratively solving the virtual uplink optimization problem through a binary optimization method and a geometric programming optimization method, and obtaining an optimal receiving beam vector and an optimal user transmitting power of the virtual uplink; and finally, converting the solution of the virtual uplink to an optimized beam forming vector and the transmitting power of the downlink according to the duality theory. In comparison with the existing multipoint coordinated beam forming method, the method provided by the invention has obvious advantages in the aspect of speed per energy consumption and worst user speed performance, and with the method, the transmitting power can be saved by 25-30% at each base station and the impartiality among the users can be ensured.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
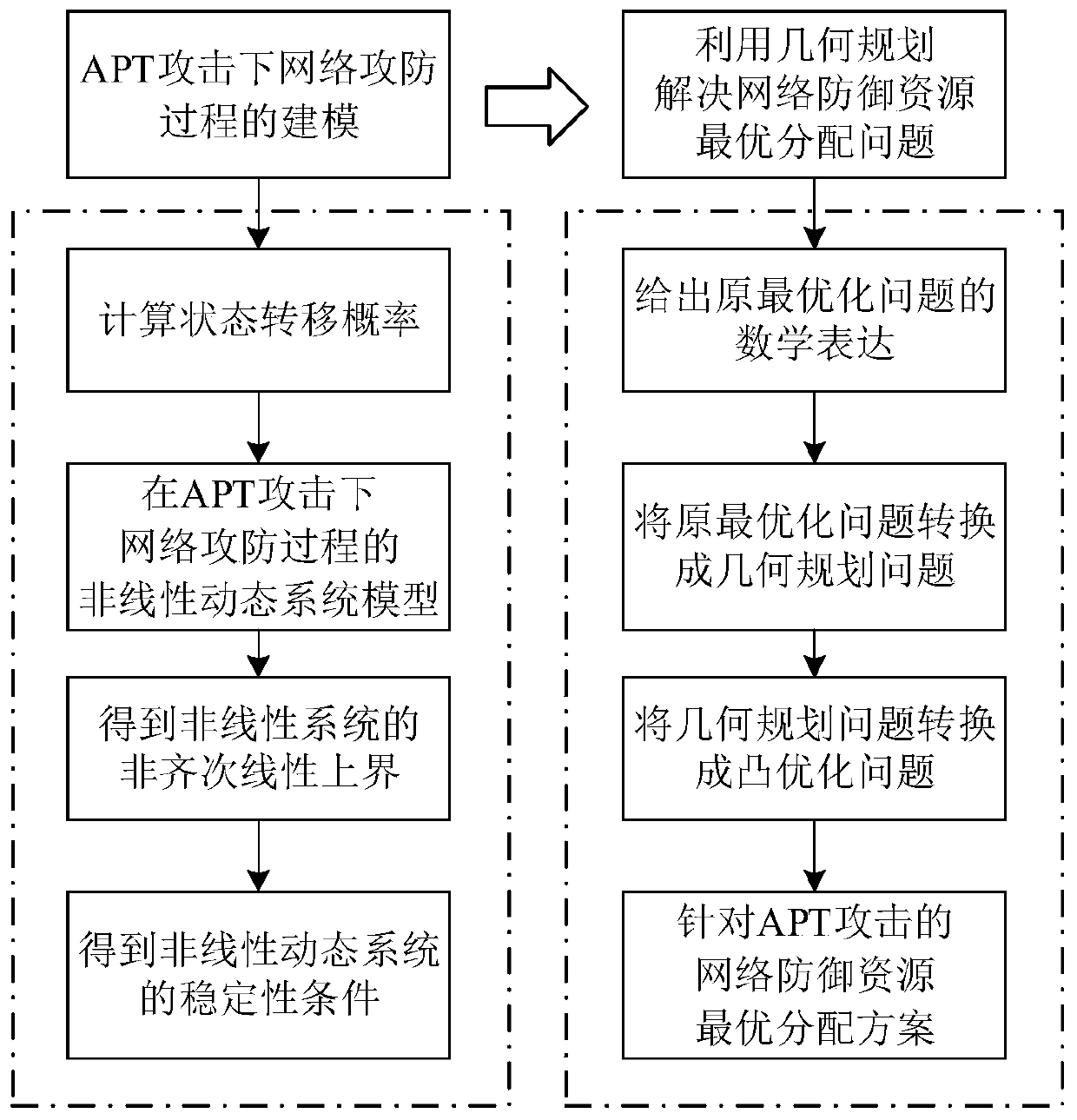
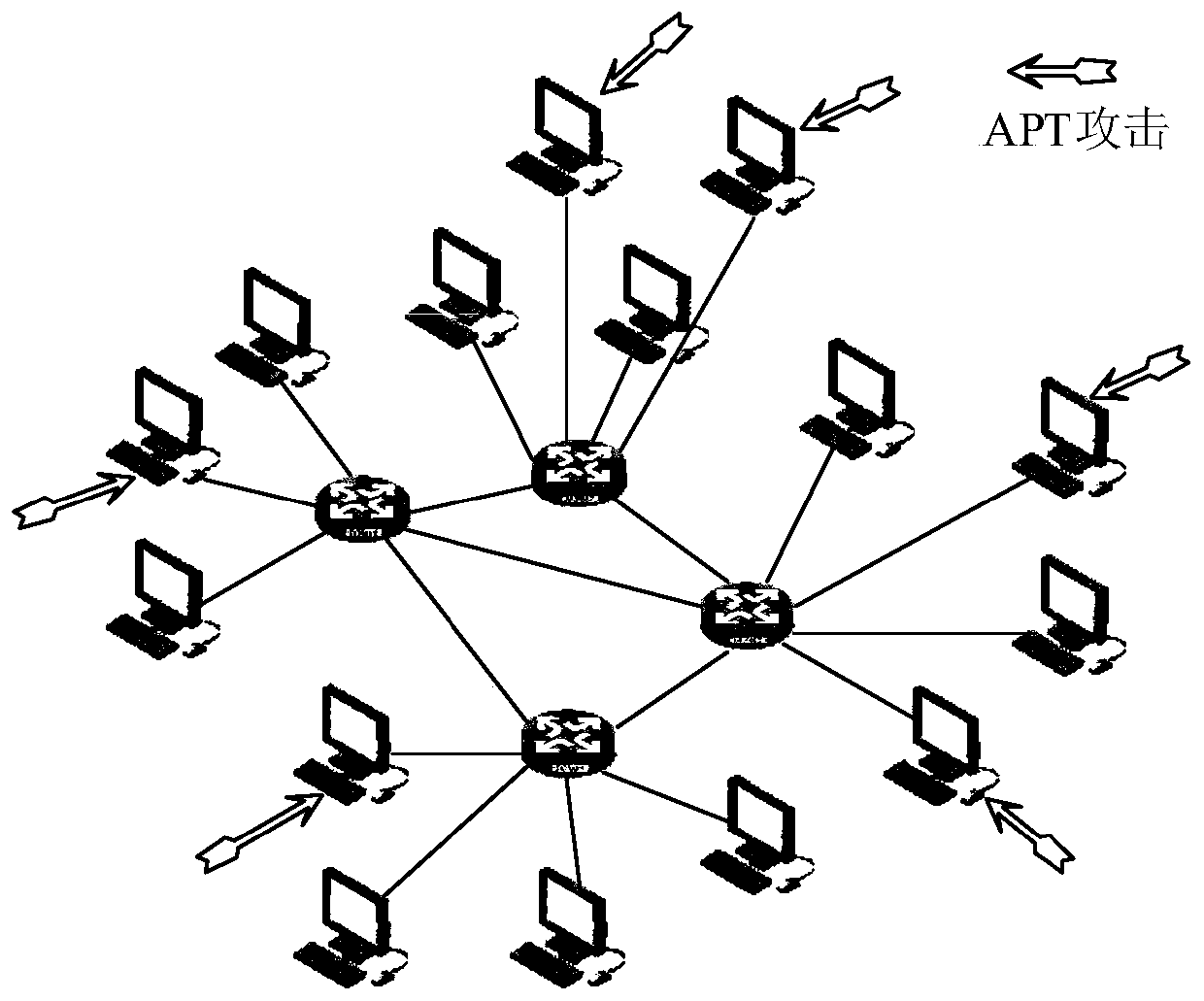
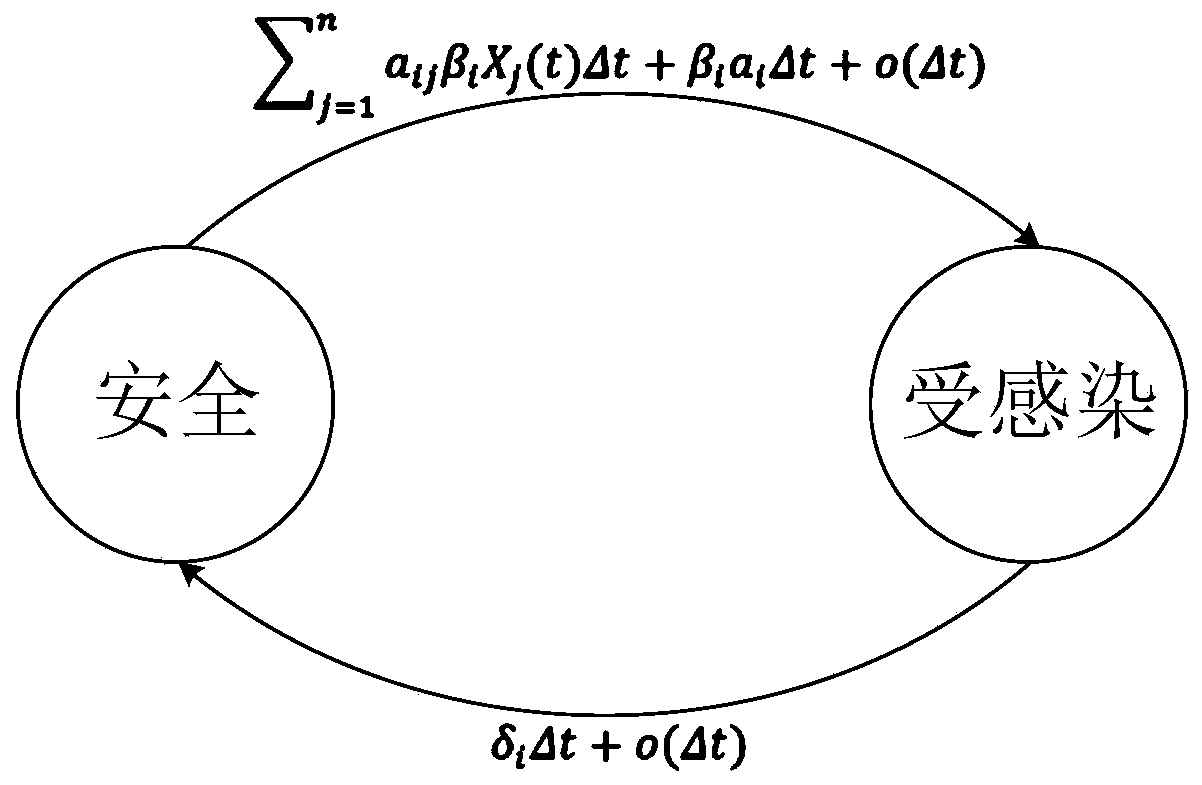
Network defense resource optimal allocation method for advanced persistent threats
ActiveCN110365713ARealize the purpose of defending against APT attacksReduce lossesData switching networksGeometric programmingNetworked system
The invention discloses a network defense resource optimal allocation method for advanced persistent threats. The method comprises the following steps: modeling a network attack and defense process ofthe advanced persistent threats by using a time-varying dynamic system theory; and calculating the number of prevention resources and recovery resources needing to be allocated to each network node by utilizing a modeling result and combining a geometric programming method, so that the effectiveness of the defense resources is maximized. According to the method, when the network system is subjected to the APT attack, the optimal network defense resource allocation scheme can be adopted to defend the APT attack as soon as possible under the condition of giving a certain defense resource, so that the loss generated by the APT attack is minimized, and the aim of defending the APT attack by the network system is fulfilled.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Manpower cost management method for large-scale integrated circuit testing
ActiveCN102799516AEfficient use ofHas polynomial time complexitySoftware testing/debuggingRegression testingGeometric programming
The invention belongs to the electronic design automation field of large-scale integrated circuit design verification, and particularly relates to a manpower cost management method for the large-scale integrated circuit testing. According to the method, as the condition of the contradictory problem between the restricted manpower cost and an operation of pursuing the acute maximal functional coverage rate index in a testing process, and the problem that how to distribute quantitative indexes (improved in each test) by managers are solved, the optimum utilization of the manpower cost can be achieved is realized, and the functional coverage rate of testing can be quickly up to the maximum value. According to the method, the functional coverage rate and the disk dosage are set as a power function of time in an information modeling mode, and based on a geometric programming method, the optimal solution gamma* of the maximal functional coverage rate and the sensitivity of gamma* to the constraint that Beta i (i = 1, 2,..., N) is greater than or equal to Beta i gamma*0 and is less than or equal to 1 is obtained, wherein the N refers to the number of regression testing; then, the manpower cost of each test is set as a power function of improved quantitative indexes in a modeling mode; and finally, the optimal manpower resource management problem is transformed into a geometric programming problem, thereby obtaining the optimal quantitative index required to be improved in each test and the optimal value of the maximal functional coverage rate after the improvement.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for solving complementary geometric programming problem based on NOMA technology
The invention provides a method for solving a complementary geometric programming problem based on an NOMA technology. The method comprises the steps: carrying out continuous convex approximation in an infinite iteration mode, so that a non-convex problem can be converted into a convex optimization problem in each iteration; calculating the absolute value of the difference value with the last result; when the difference value is smaller than a certain value, acquiring the optimal solution of complementary geometric programming under the precision. A new solution is provided for the non-convexproblem with high complexity in a communication system.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Trajectory planning method for terminal energy management of glide vehicle based on geometric programming
ActiveCN104714553BReduced mobility requirementsQuick planningPosition/course control in three dimensionsGeometric programmingEngineering
The invention discloses a geometric-programming-based gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method which is used for solving the technical problem that an existing gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, on the basis of the state of an aircraft entering a TAEM section, a geometric programming method is utilized for rapidly planning a reasonable and feasible TAEM plane trajectory; on the basis of the TAEM plane trajectory planning, height deduction is performed, and therefore a complete trajectory planning strategy is given. Due to the fact that the aircraft enters an entry of an automatic landing section in a spiral-line mode in the geographic planning process, the sudden overload change phenomenon is effectively avoided, and therefore the requirement for the aircraft maneuverability is lowered; meanwhile, during trajectory planning, the state of the aircraft at the TAEM section at the initial moment is considered, corresponding flight paths are planned in a classified mode for the entering state of the aircraft, the reasonable trajectory can be rapidly planned, the requirements for different entering directions are met, and the planning speed is high through simulation verification.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
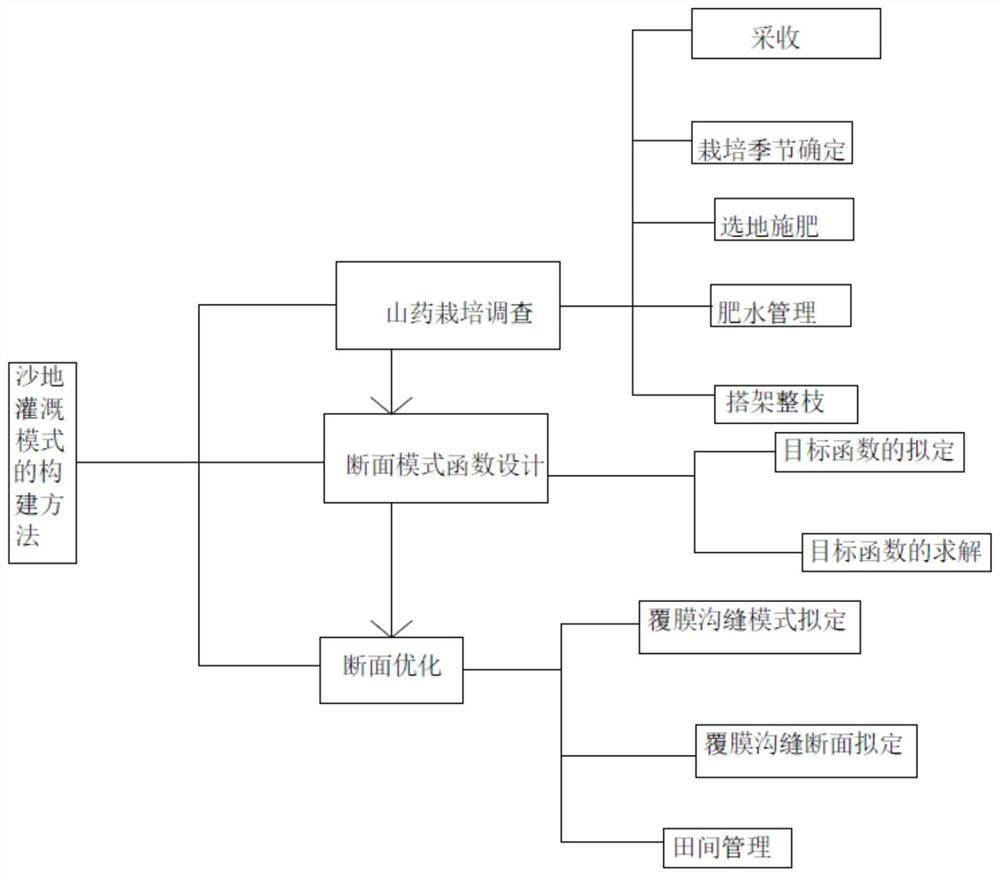
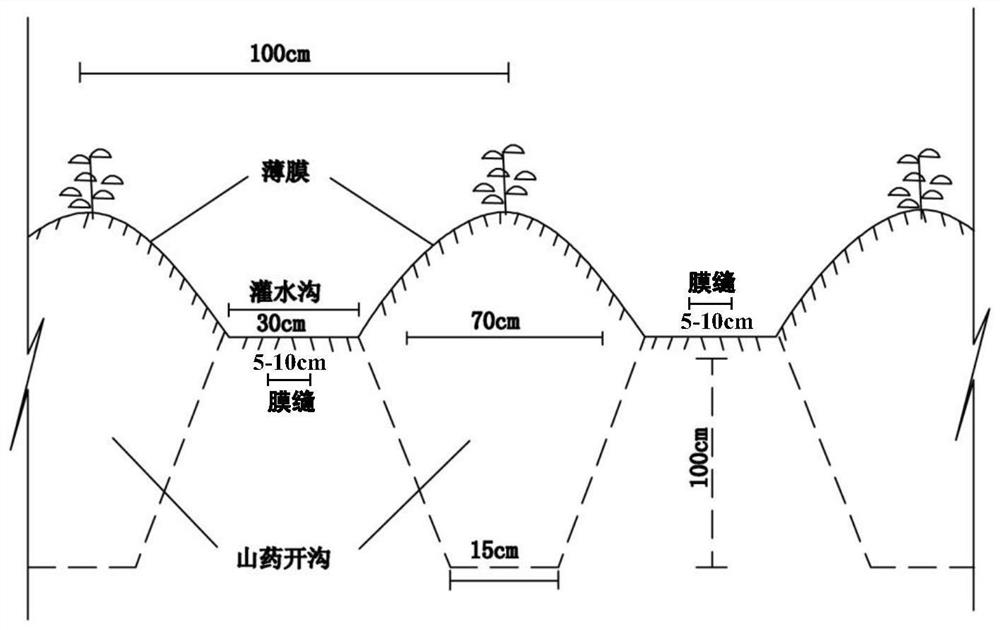
A construction method of sandy yam irrigation mode
ActiveCN112434424BScientific and reasonable designMeet normal water needsClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationGeometric programmingAgricultural engineering
The invention relates to a method for constructing a yam irrigation mode in sandy land, including yam cultivation investigation, yam ditch irrigation section mode function design, and yam ditch irrigation section optimization. Among them, the work process of yam cultivation technology investigation is the determination of cultivation season, site selection and fertilization, fertilizer and water management, erection and pruning and harvesting; yam ditch irrigation section mode function design According to the geometric programming method, the objective function model is constructed to increase the income, and the construction suitable for sandy land is constructed. The objective function of the geometric planning of furrow irrigation of Chinese yam is solved according to the corresponding constraints. Experiments have proved that the invention has strong functionality, simple, effective, low-cost technology, and significant benefits of increasing income and reducing disasters, and can be widely used in sandy yam planting areas.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
A Power Control Method Based on Outage Probability and Geometric Programming
ActiveCN113382465BReduce consumptionMinimize expected valuePower managementHigh level techniquesGeometric programmingControl theory
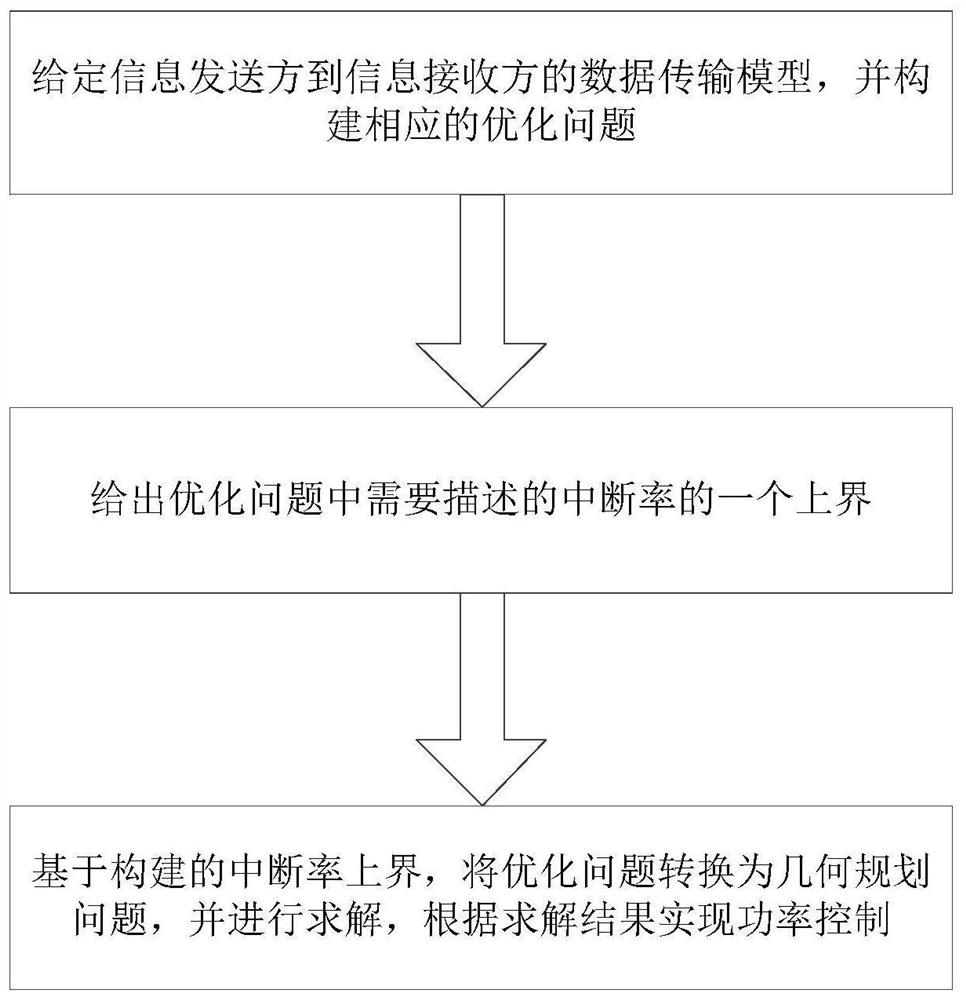
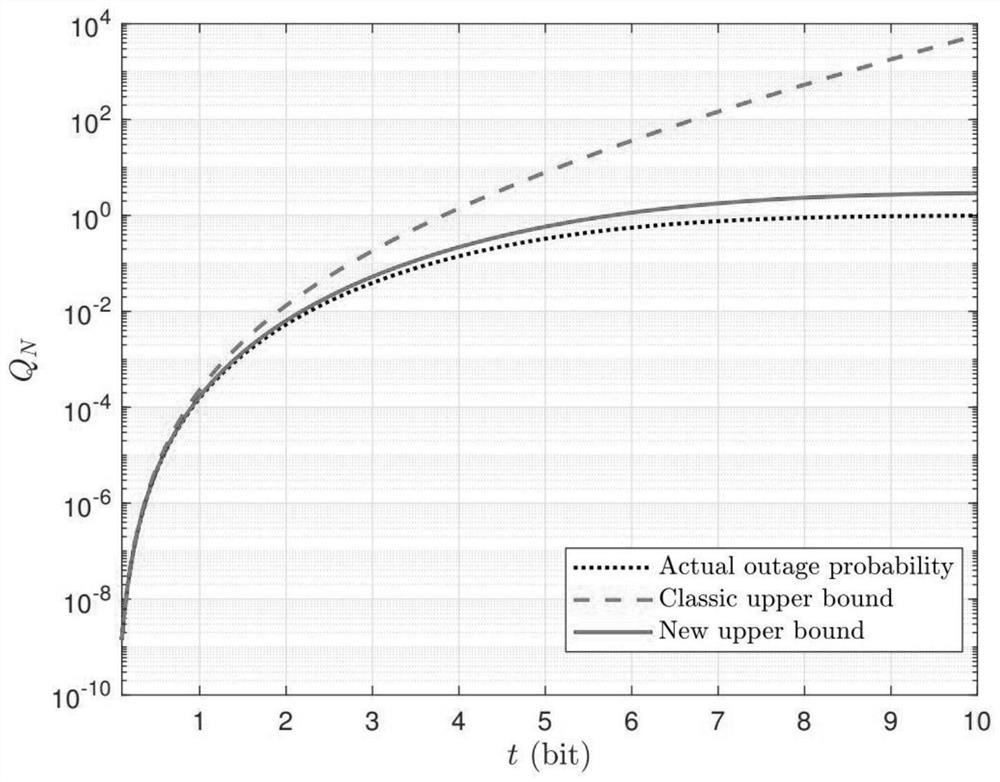
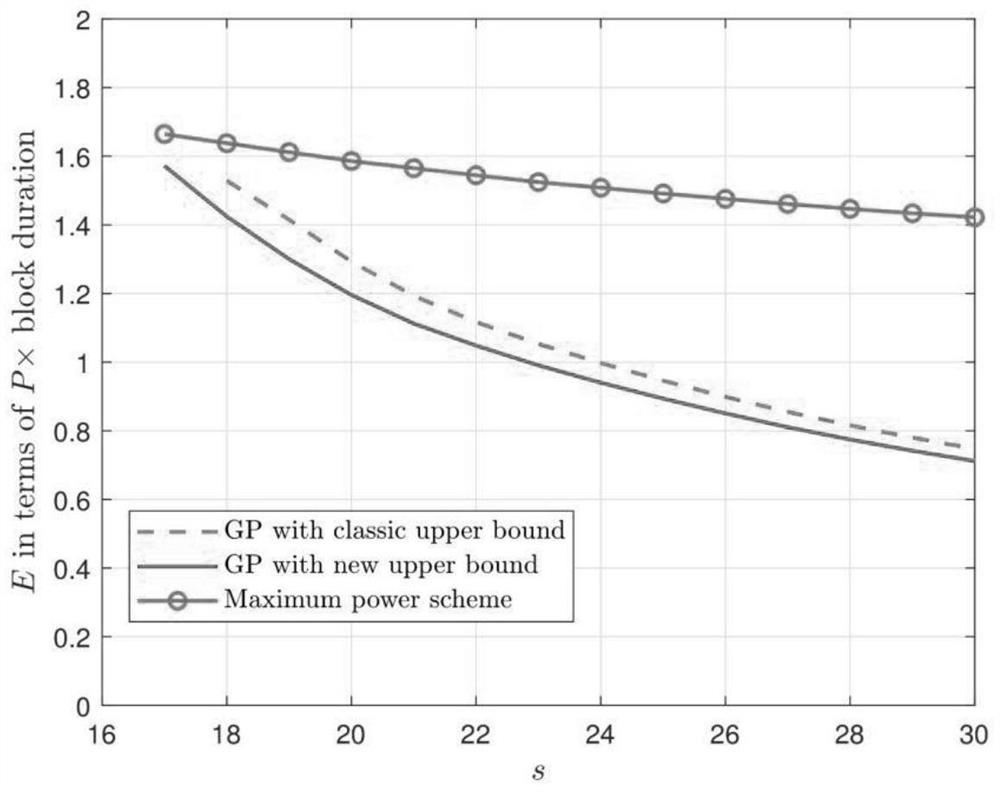
The invention discloses a power control method based on outage probability and geometric programming, comprising the following steps: S1. Given a data transmission model from an information sender to an information receiver, and constructing a corresponding optimization problem; S2. Giving an optimization problem An upper bound of the outage rate that needs to be described in ; S3. Based on the upper bound of the outage rate constructed, the optimization problem is converted into a geometric programming problem and solved, and power control is realized according to the solution result. The power control method based on outage probability and geometric programming disclosed in the present invention adopts an upper bound of the outage rate closer to reality, allowing stricter average transmission delay restrictions, and the GP algorithm solves the power, and performs power control according to the solution result, which can Minimize the expected value of the power of each block, thereby reducing the total transmission power and reducing energy consumption.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIV OF HONG KONG SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com