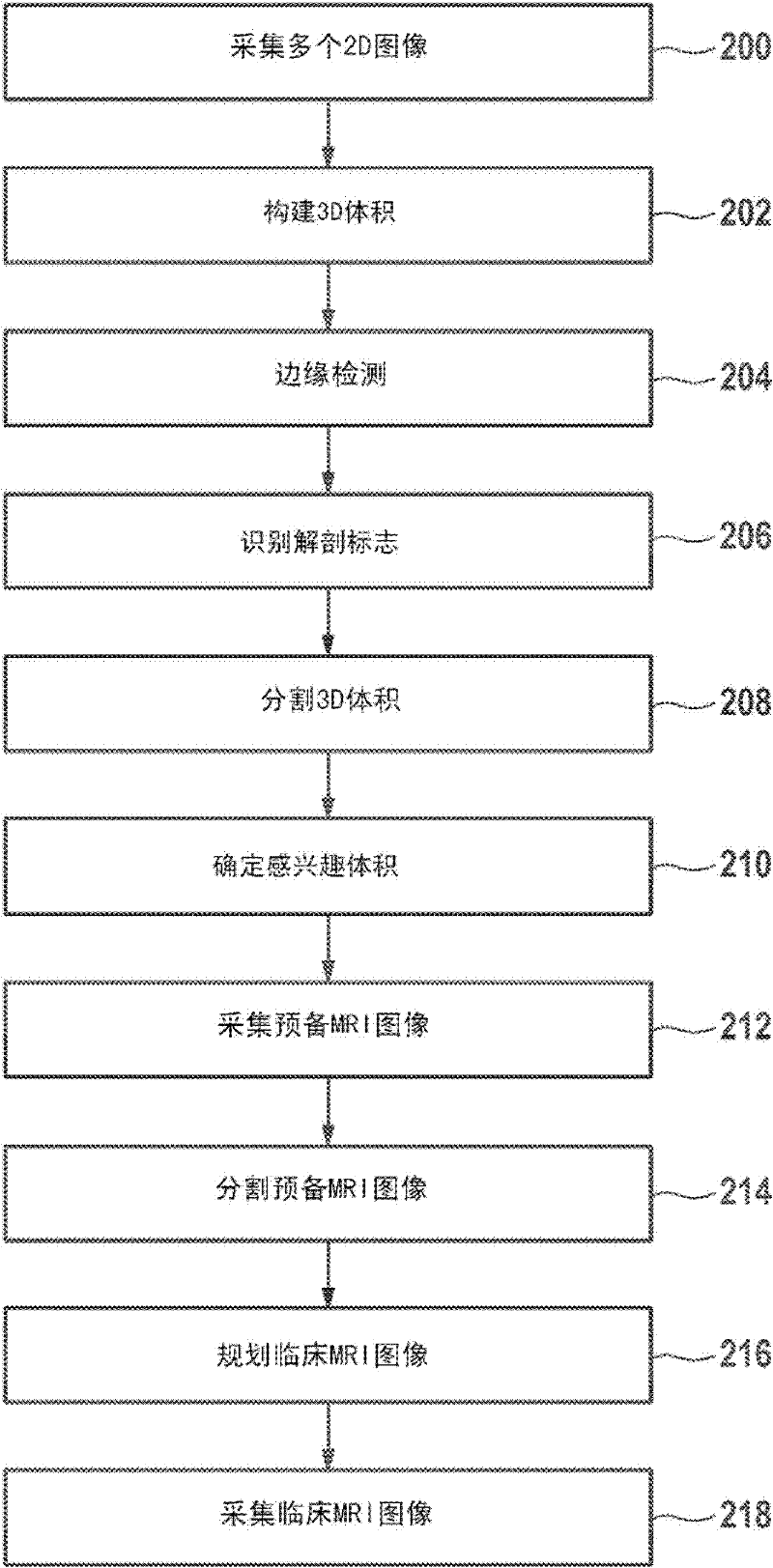
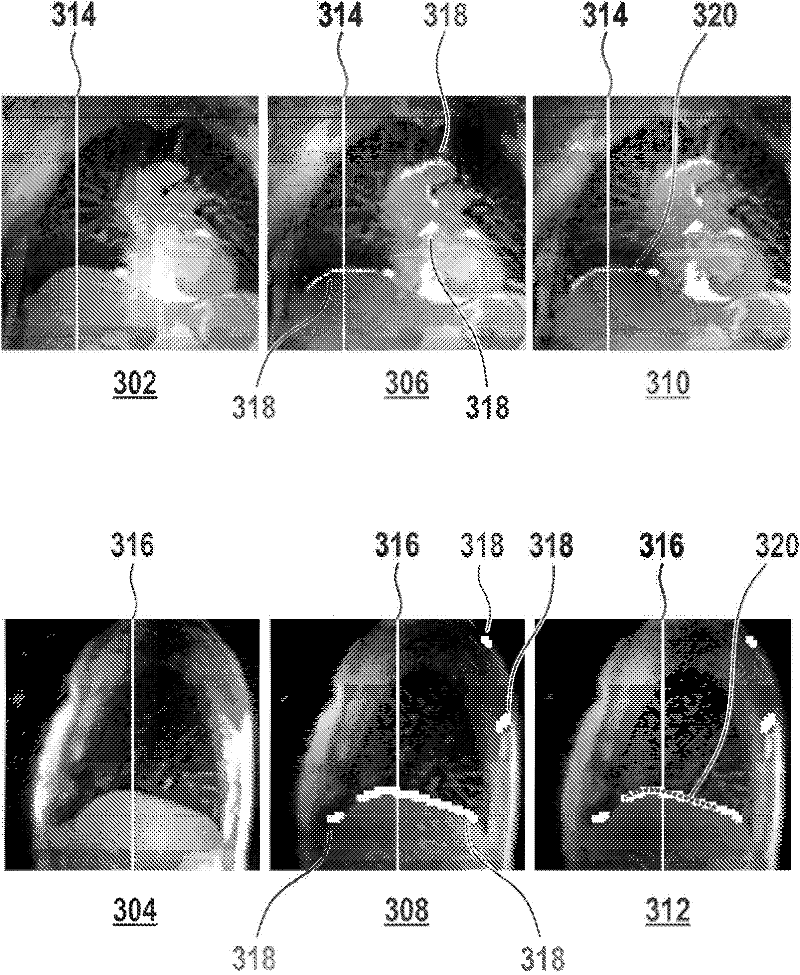
Automated sequential planning of mr scans
一种规划、规划数据的技术,应用在磁共振测量、仪器、测量装置等方向,能够解决很难临床MRI图像再现性、临床图像不同质量水平、增加患者花费等问题,达到减少培训要求、消除操作者误差、避免变化性的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
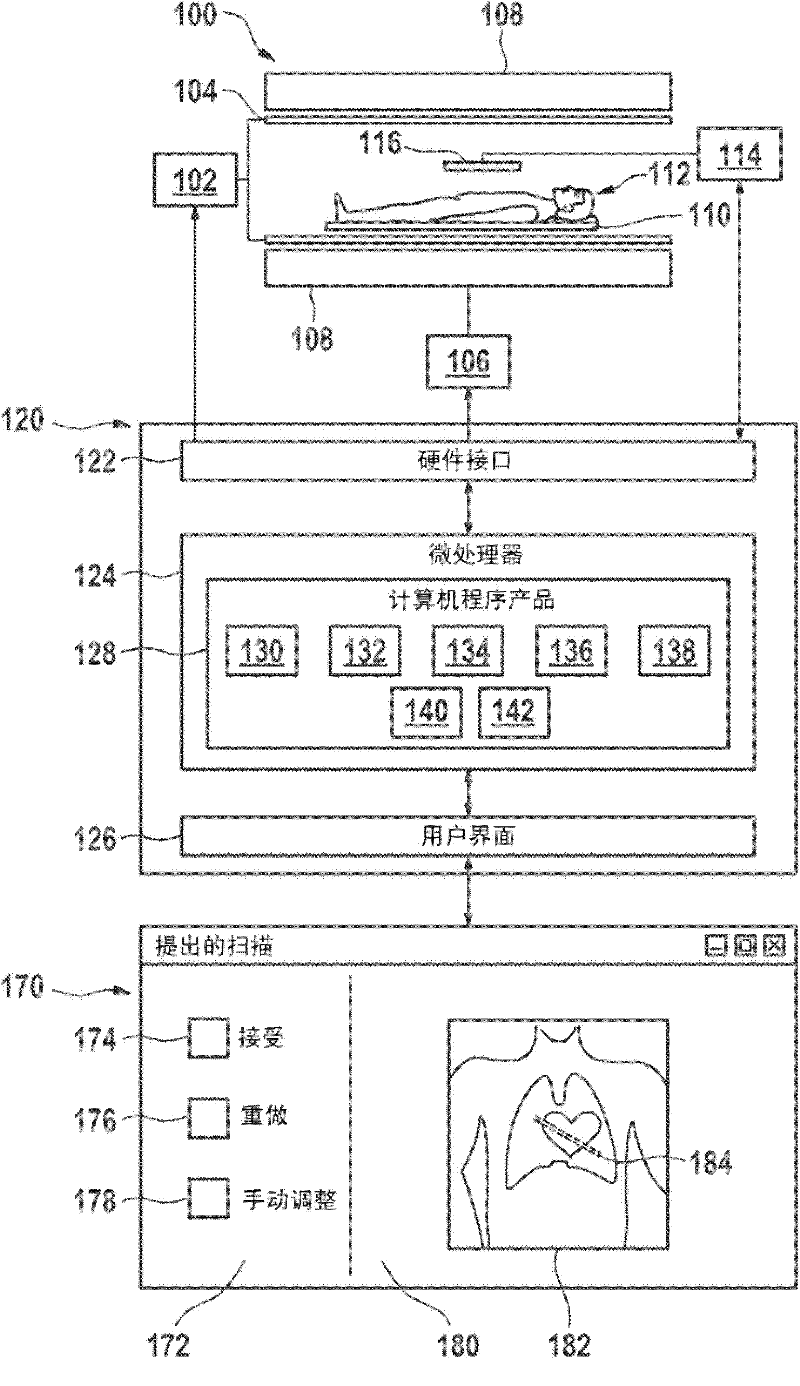
[0039] figure 1 An embodiment of an MRI scanner 100 capable of implementing embodiments of the invention is shown. There is a static magnet 108 that produces a large magnetic field, also referred to as BO, that is capable of aligning nuclear spins in a patient 112 or other subject with the BO field. A patient 112 is seated on a support 110 within the bore of the magnet. Gradient coils 104 are also located within the bore of the magnet and enable adjustment of the magnetic field. The transceiver coil 116 is adjacent to the volume of the patient 112 being imaged. This coil transmits and receives RF signals. In transmit mode, the coil generates an RF signal that produces a localized perturbation of the magnetic field for manipulating the orientation of the patient's 112 core spins. In receive mode, the phased array transceiver coils 116 receive RF signals caused by the rotation of the nuclear spins in the B0 field. The function of the transceiver coil can very generally be d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com