Patents
Literature
222 results about "Signomial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
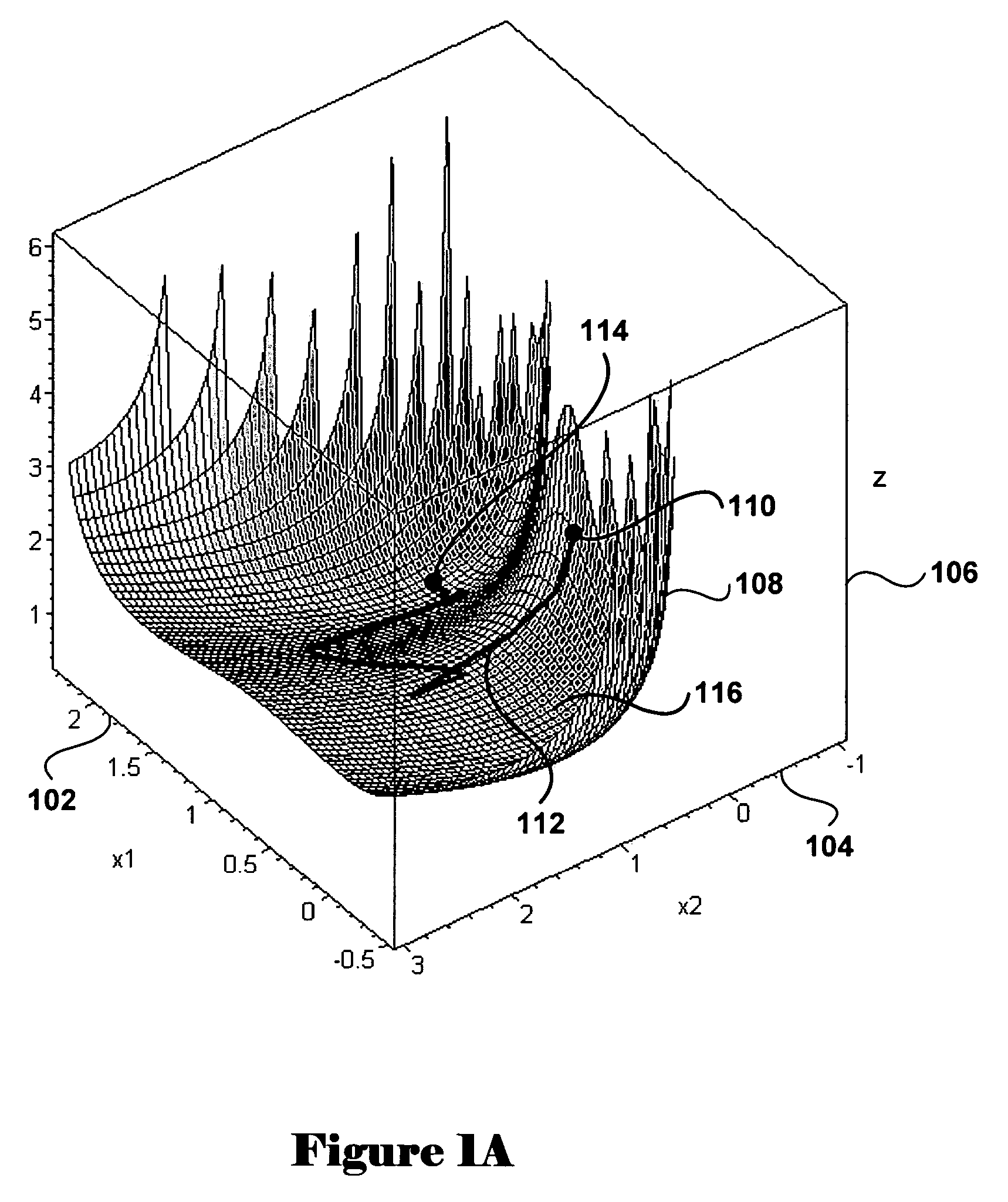
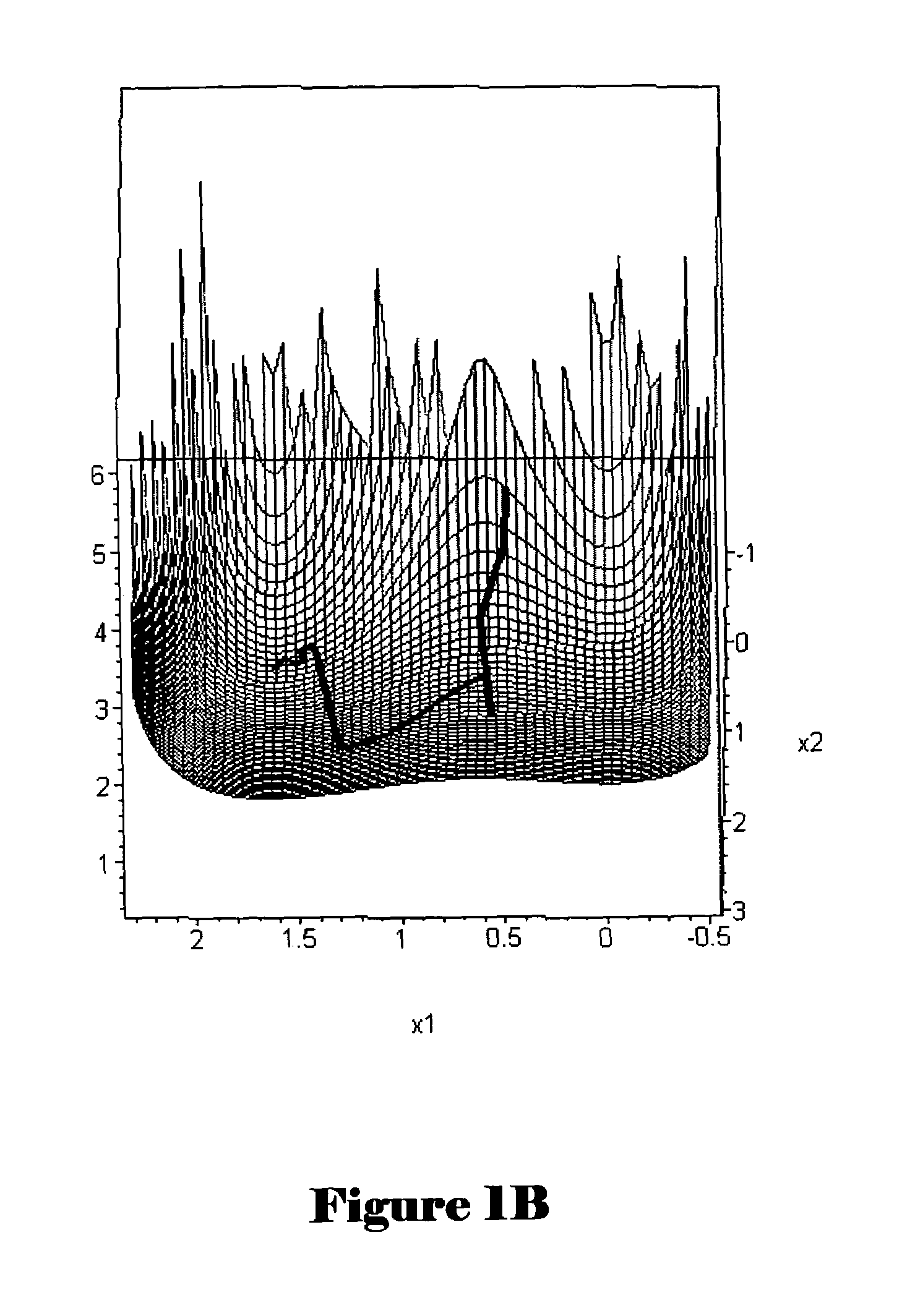
A signomial is an algebraic function of one or more independent variables. It is perhaps most easily thought of as an algebraic extension of multivariable polynomials—an extension that permits exponents to be arbitrary real numbers (rather than just non-negative integers) while requiring the independent variables to be strictly positive (so that division by zero and other inappropriate algebraic operations are not encountered).
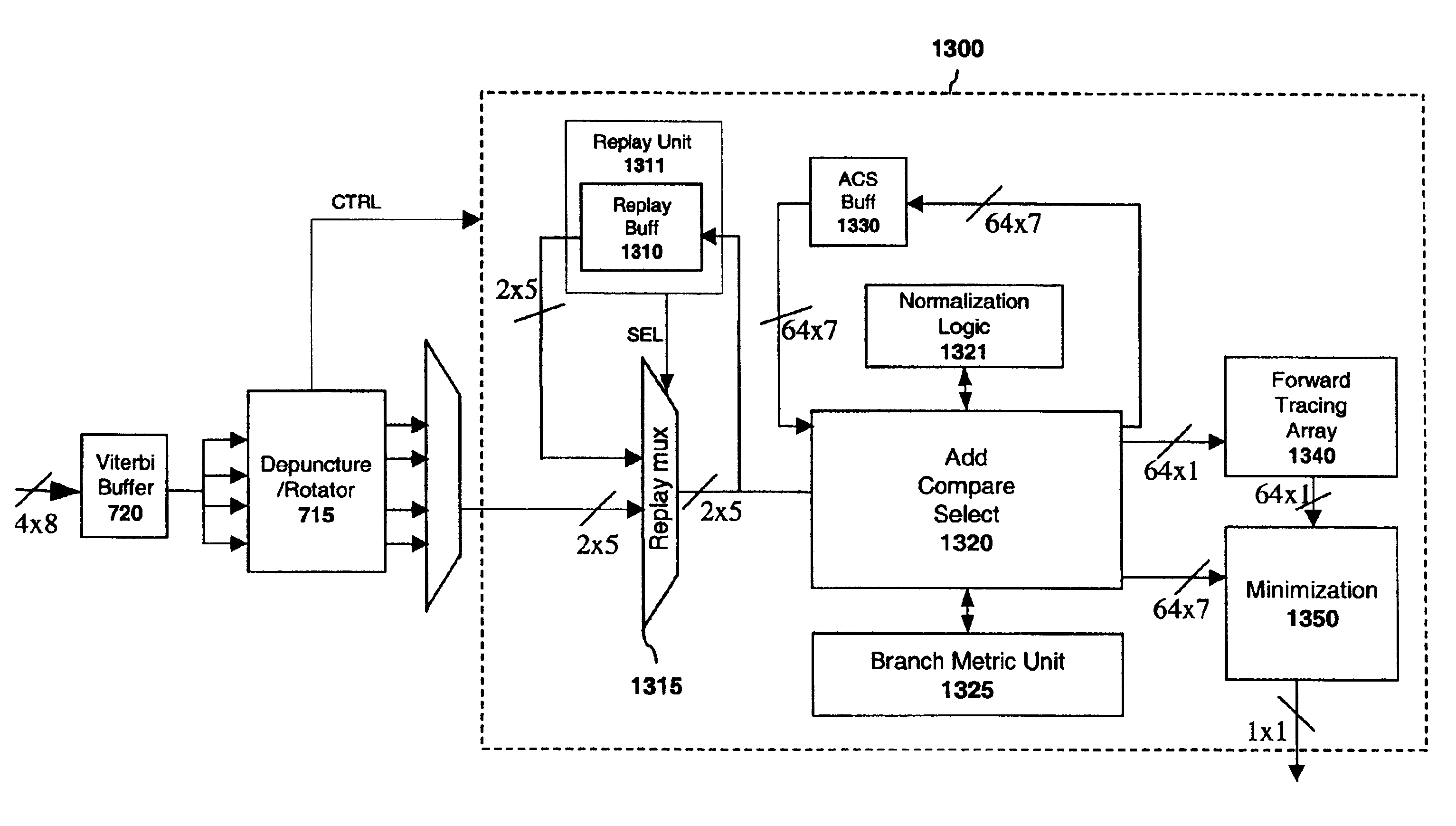
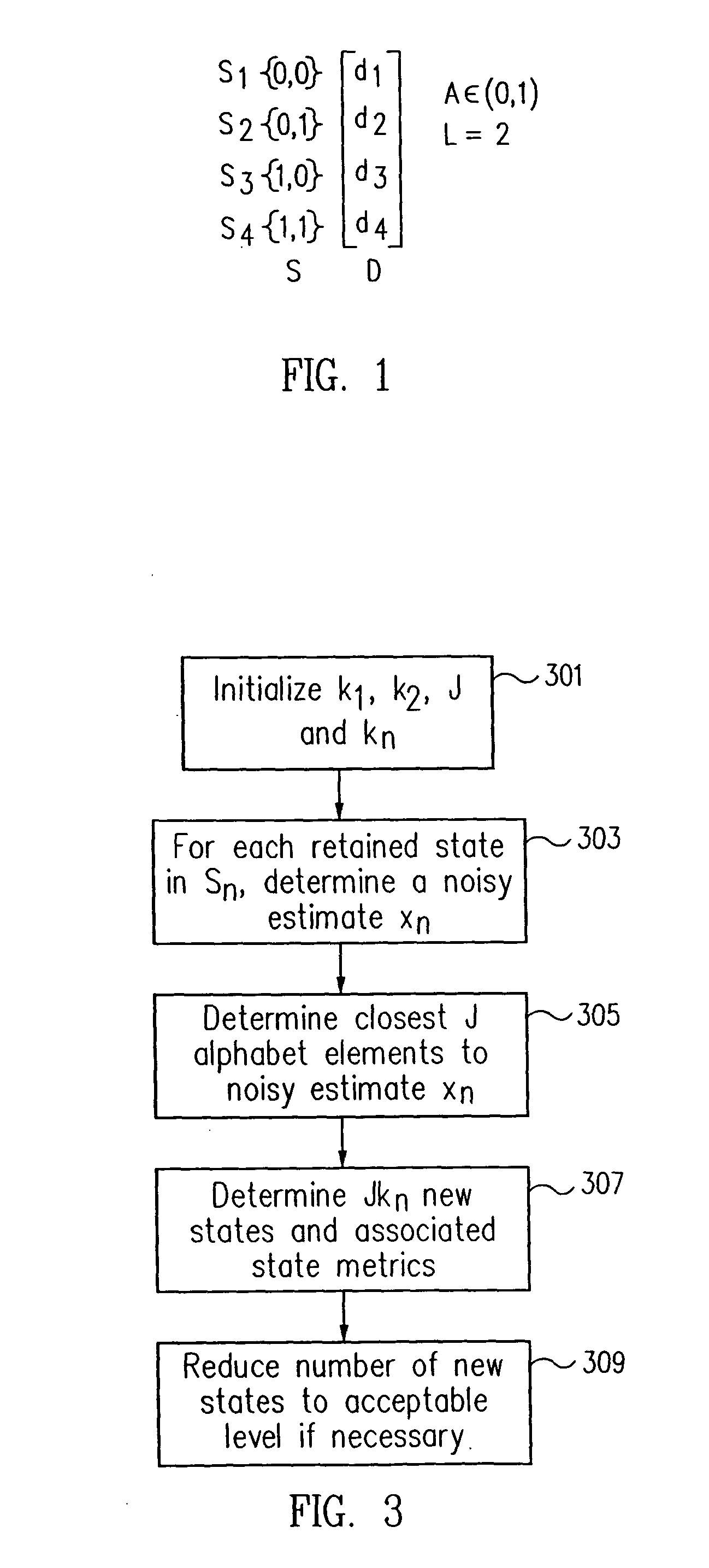
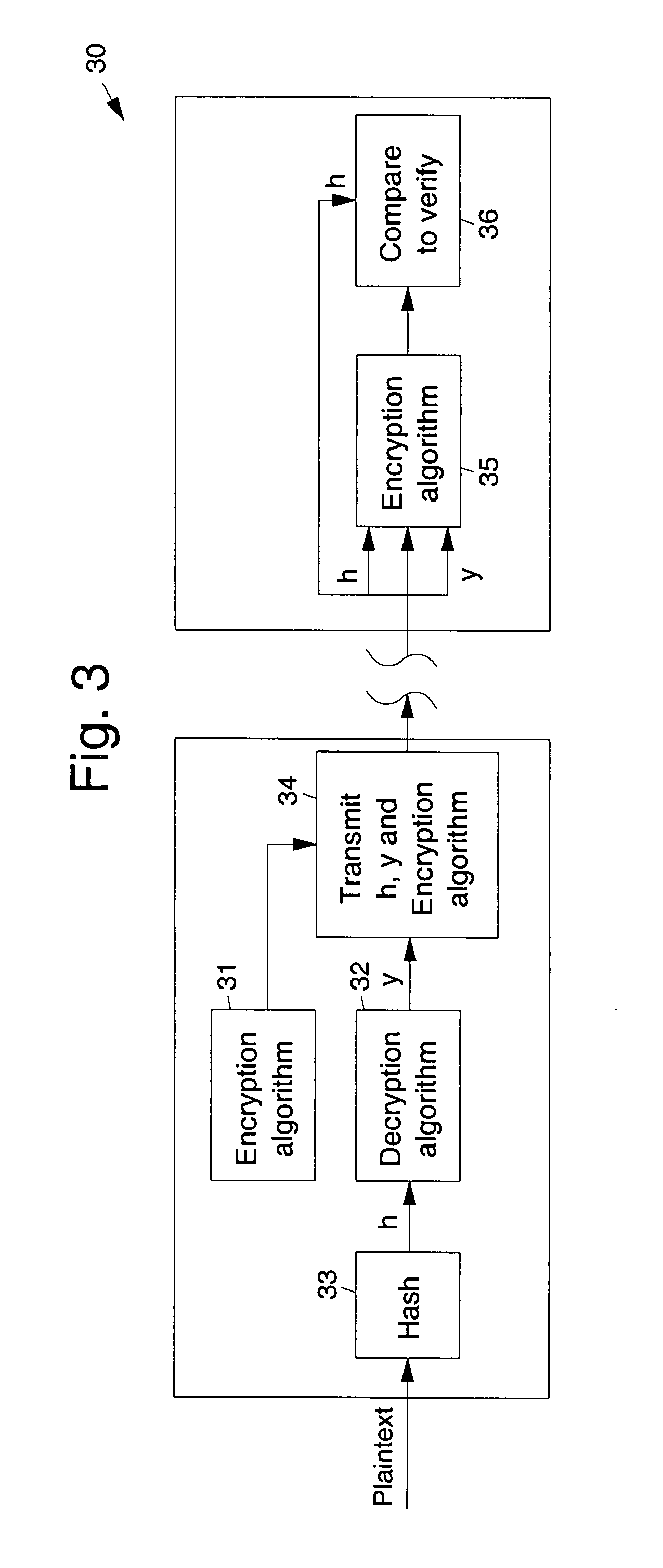
Apparatus and method for saturating decoder values
InactiveUS7073118B2Television system detailsData representation error detection/correctionSign bitSignomial
In one embodiment of the invention, during add-compare-select computations, the output of the adders is guaranteed to be a positive value because the only time normalization logic subtracts a normalization amount is when all accumulators are greater than the normalization amount. As such, the detection of overflow is greatly simplified. Overflow in the add-compare-select unit may be indicated simply by the value of the most significant bit (“MSB”) (i.e., the sign bit) of the result. If the MSB of the result of the adder is set then, in one embodiment, the output of the adder gets forced the maximum possible value given the number of bits. For example, this value will be forced to 7h7f if the value is represented by 7-bits. That is to say, if an overflow is detected, then the accumulator is saturated to the maximum value.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Data processing apparatus and method
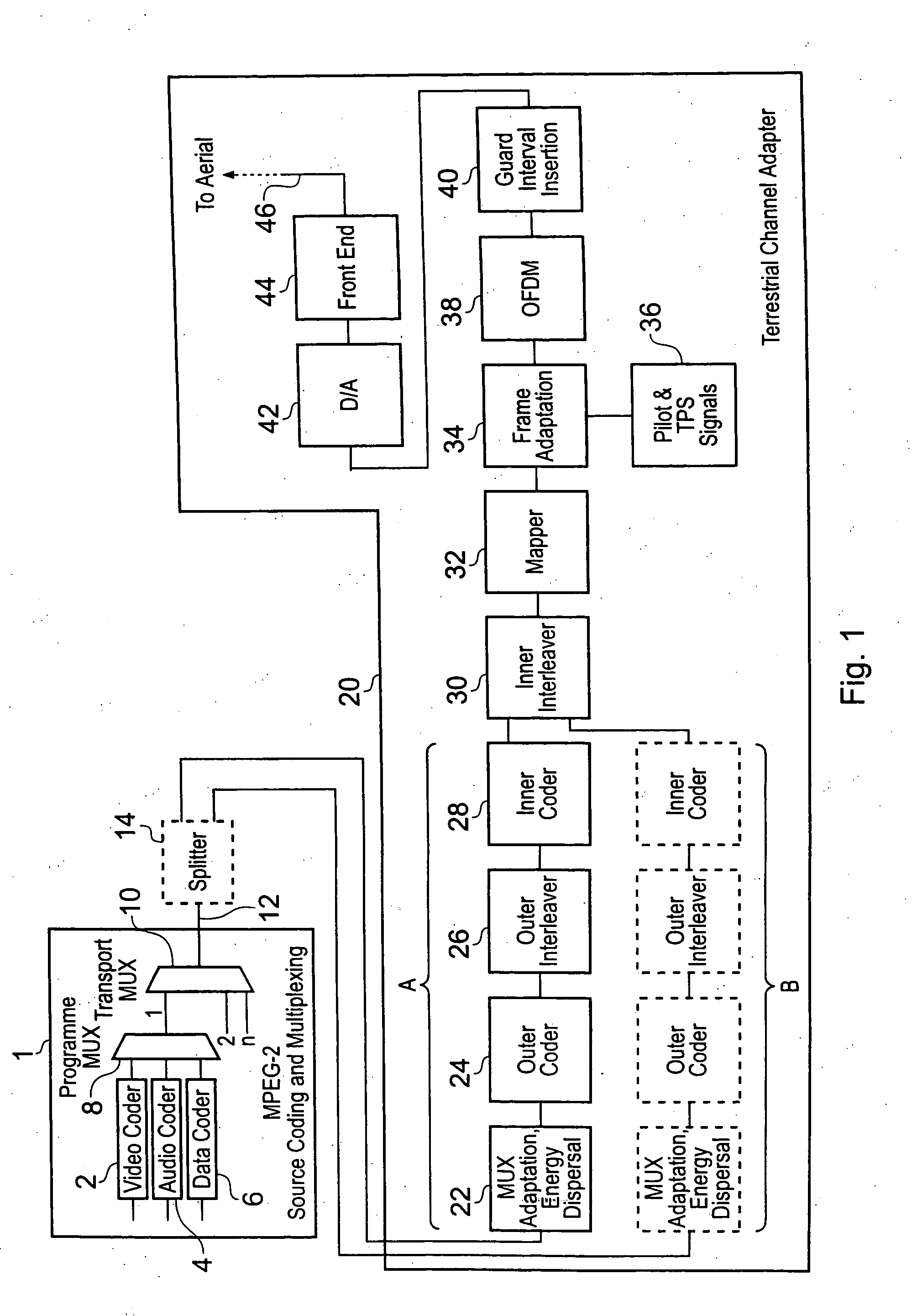
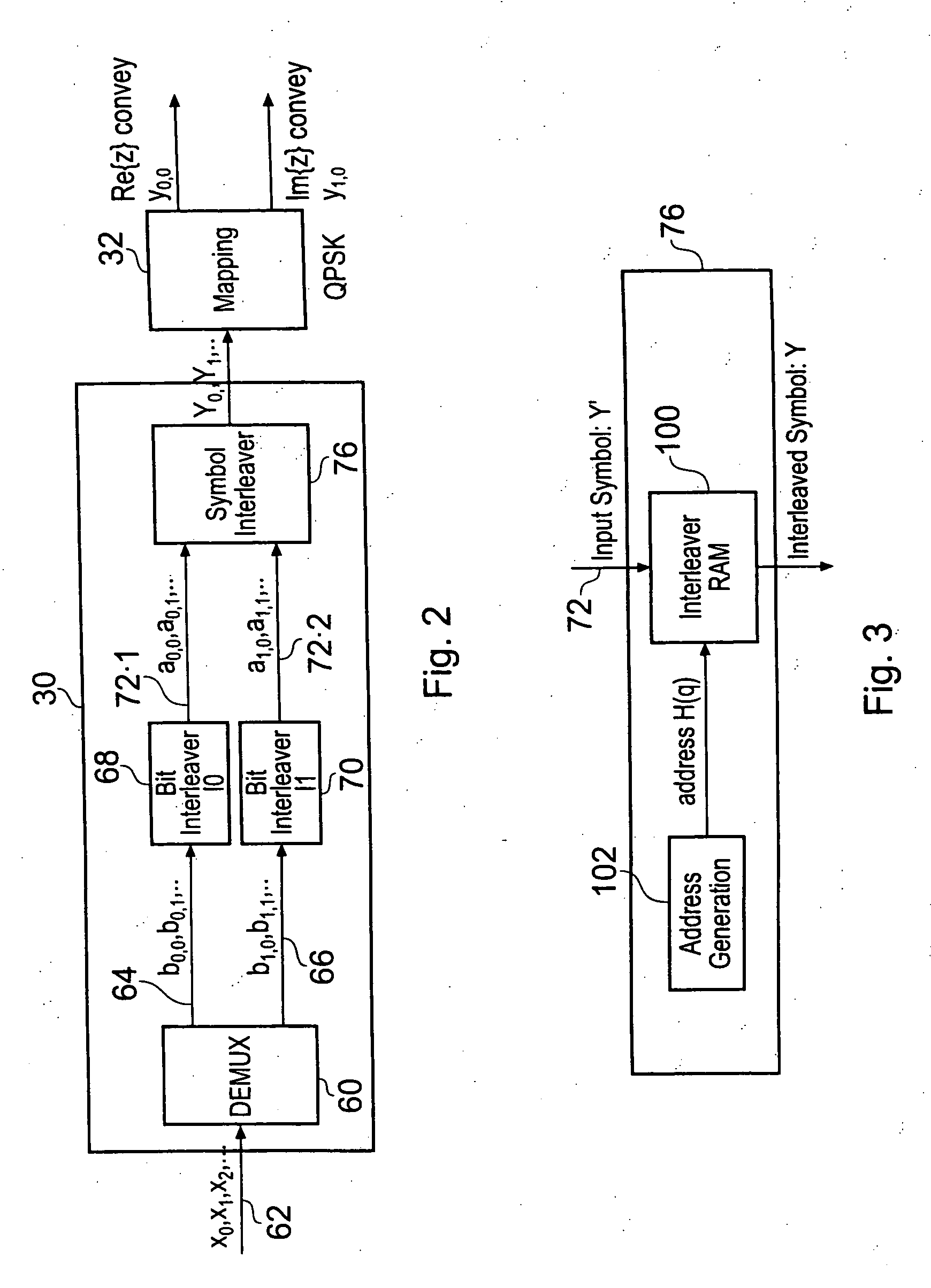
ActiveUS20040246888A1Easy to receiveTrack time variationTelevision system detailsCode conversionCarrier signalAddress generator
A data processing apparatus maps input symbols to be communicated onto a predetermined number of carrier signals of an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) symbol. The data processor includes an interleaver memory which reads-in the predetermined number of data symbols for mapping onto the OFDM carrier signals. The interleaver memory reads-out the data symbols on to the OFDM carriers to effect the mapping, the read-out being in a different order than the read-in, the order being determined from a set of addresses, with the effect that the data symbols are interleaved on to the carrier signals. The set of addresses are generated from an address generator which comprises a linear feedback shift register and a permutation circuit. In order to provide a 4 k mode for an OFDM modulated system such as a Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) standard such as DVB-Terrestrial (DVB-T) or DVB-Handheld (DVB-H) standards, a generator polynomial for the linear feedback shift register of Ri'[10]=Ri-1'[0]⊕Ri-1'[2] is provided with a permutation order which has been established by simulation analysis to optimise communication performance via typical radio channels.
Owner:SONY EUROPE BV
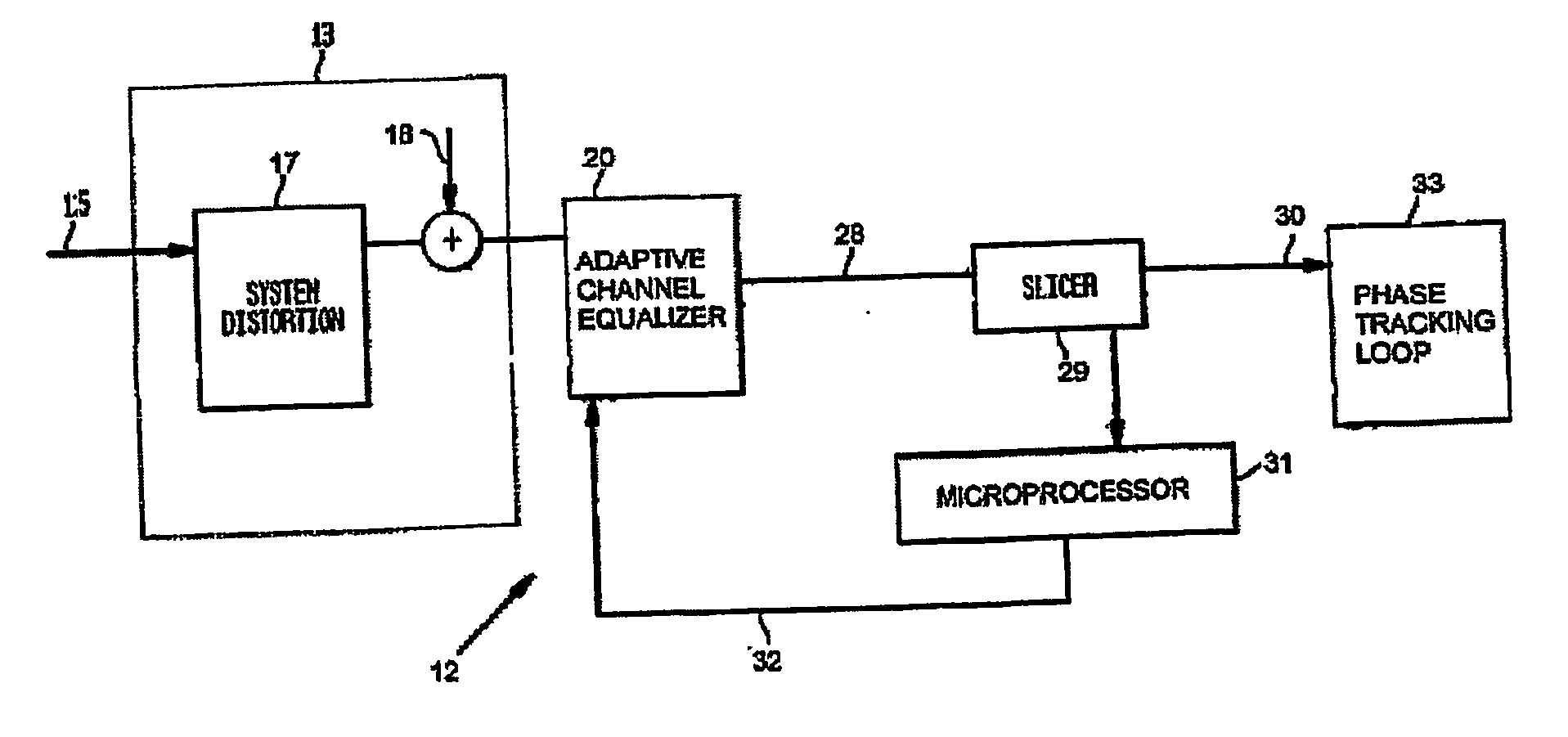
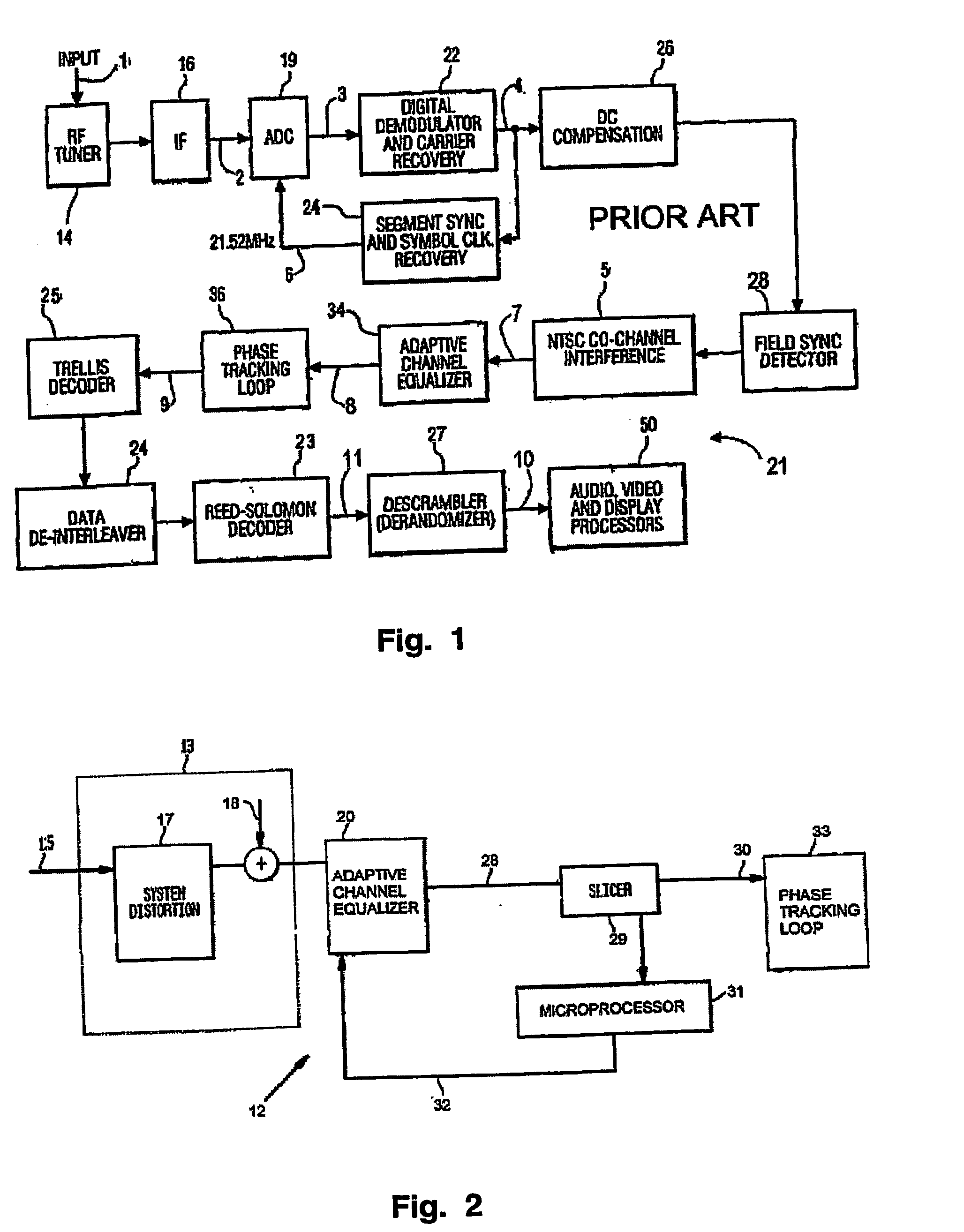
Equalizer status monitor
InactiveUS20050175080A1Reduce complexityThe testing process is simpleTelevision system detailsMultiple-port networksEngineeringSelf adaptive
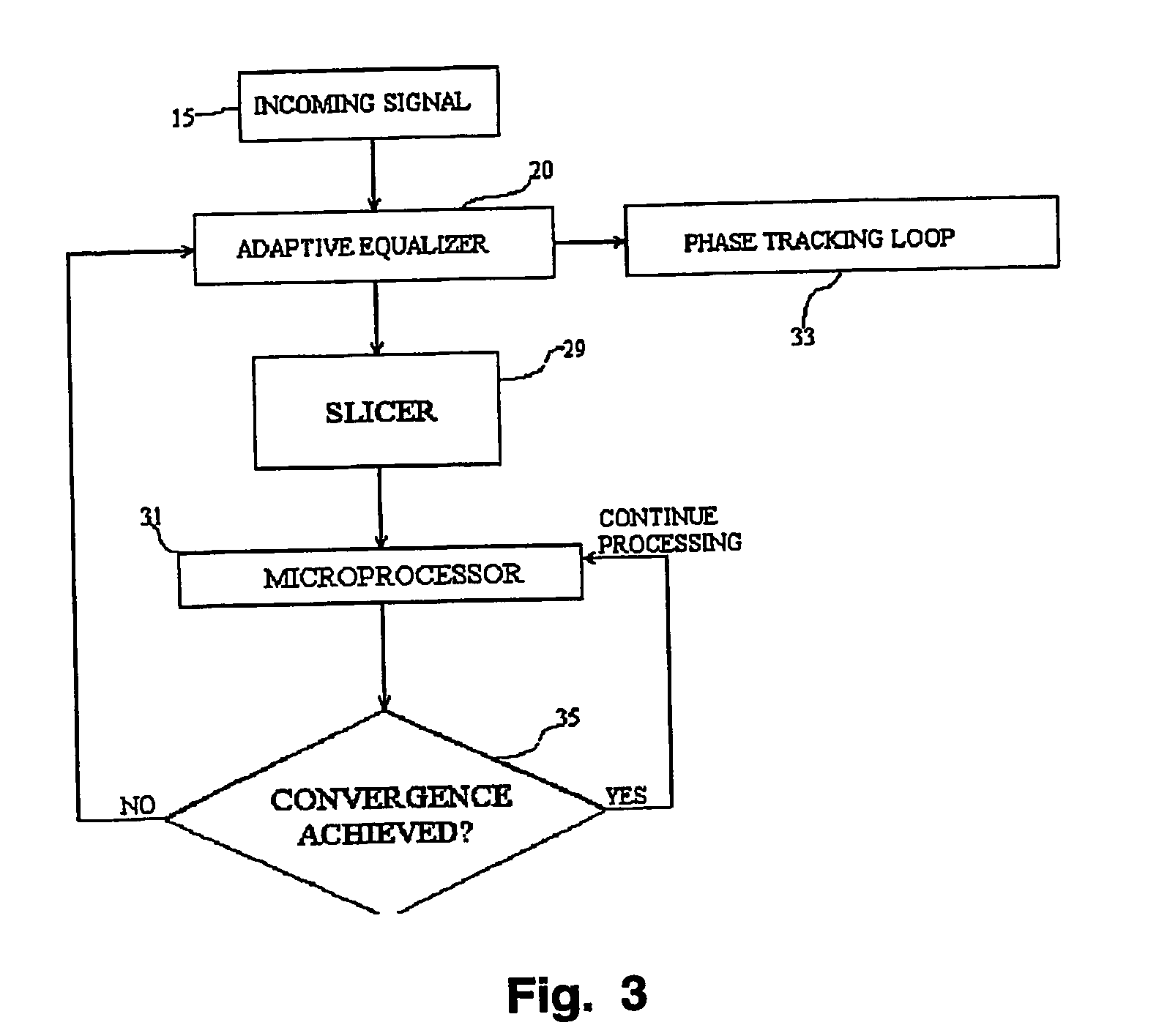
A system for monitoring the output of an adaptive channel equalizer in order to determine if convergence has been achieved. A slicer samples data from the equalizer during a predetermined period. The output data from the slicer is forwarded to a microprocessor in order to apply a test standard to the slicer data. For example, if one of every possible transmitted symbol is detected by the microprocessor, convergence is assumed to have occurred. If the test criterion is not met, a reset signal is sent to the equalizer.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
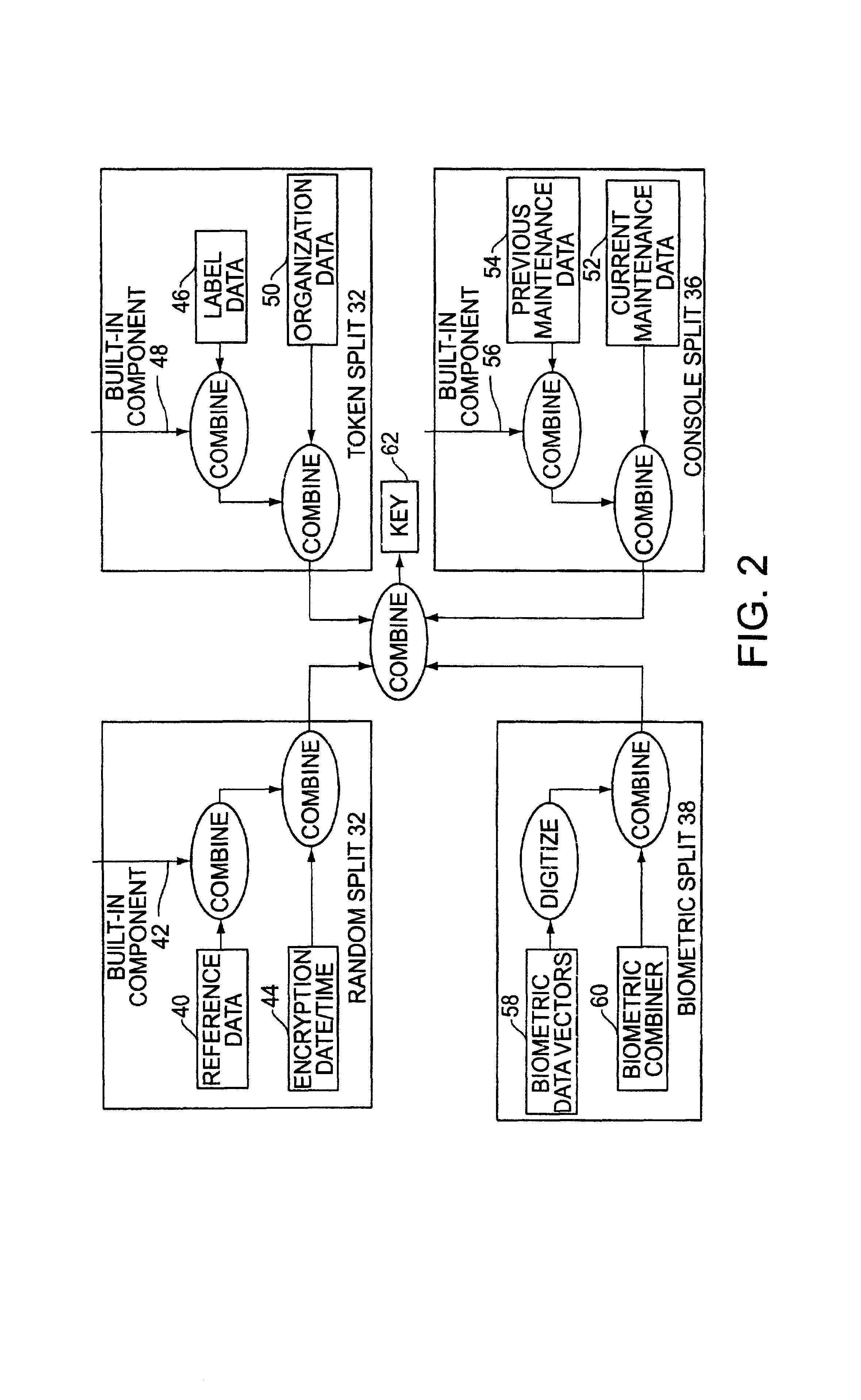
Cryptographic key split combiner
InactiveUS6542608B2Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesBiometric dataLabeled data
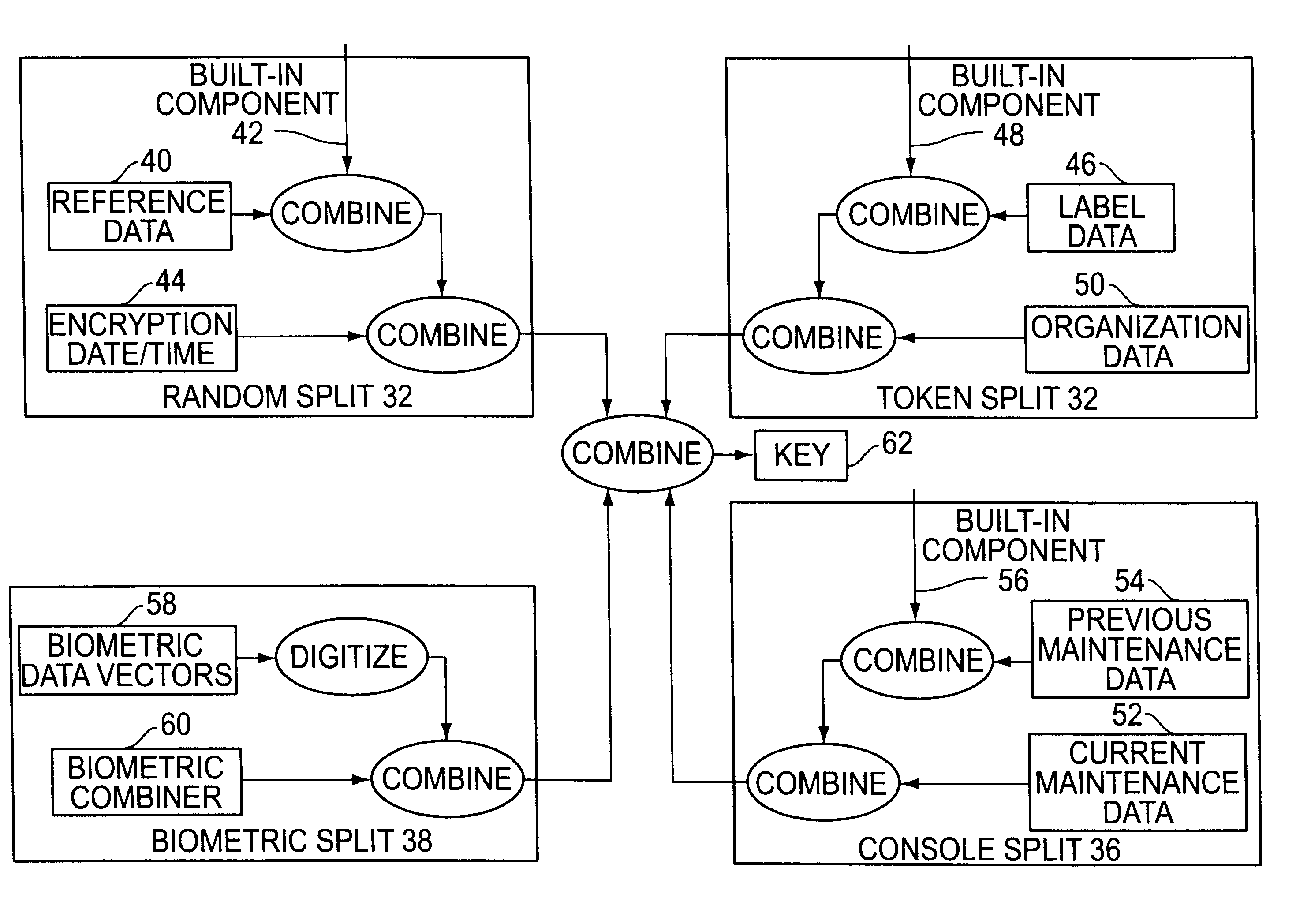
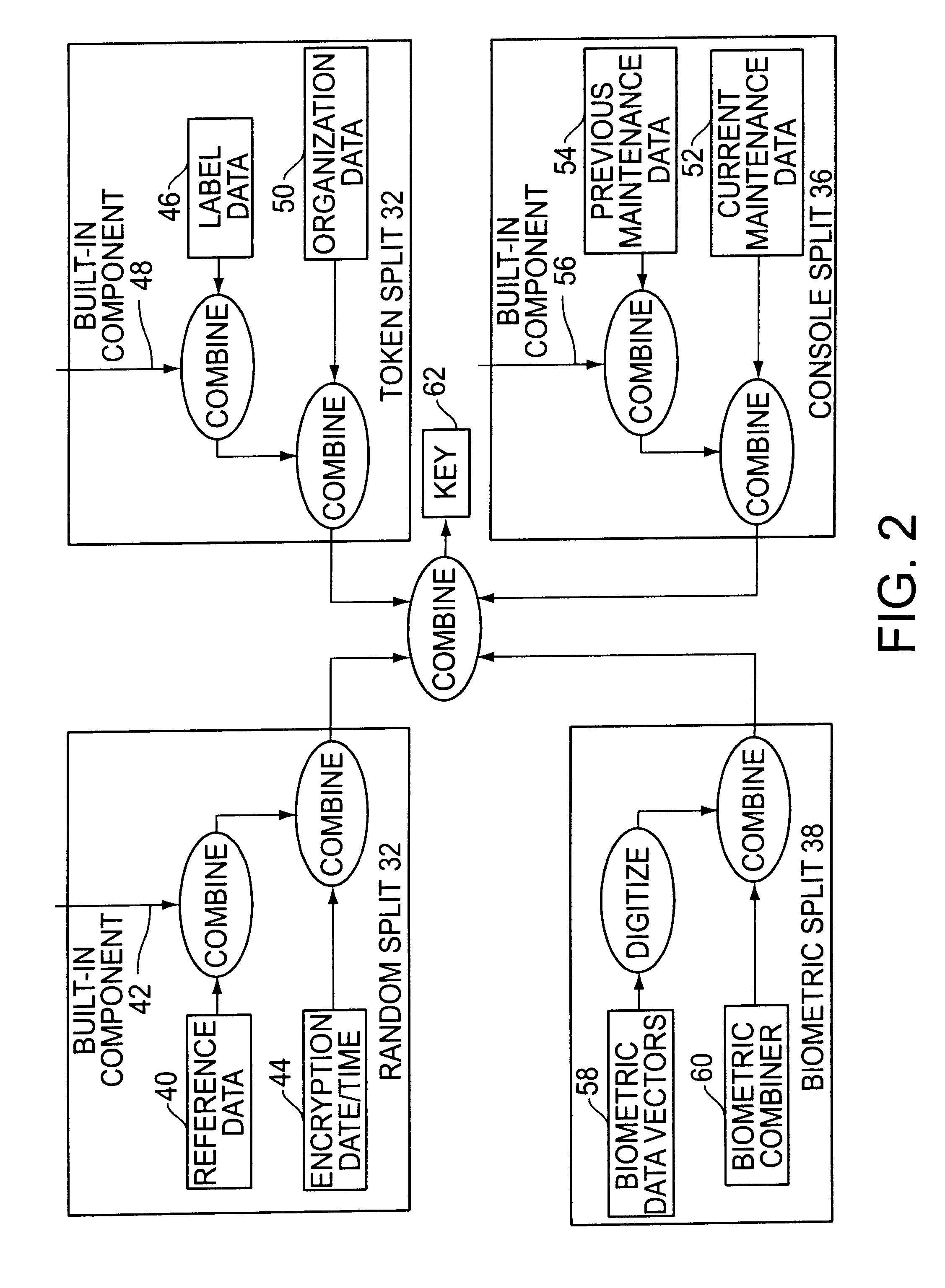
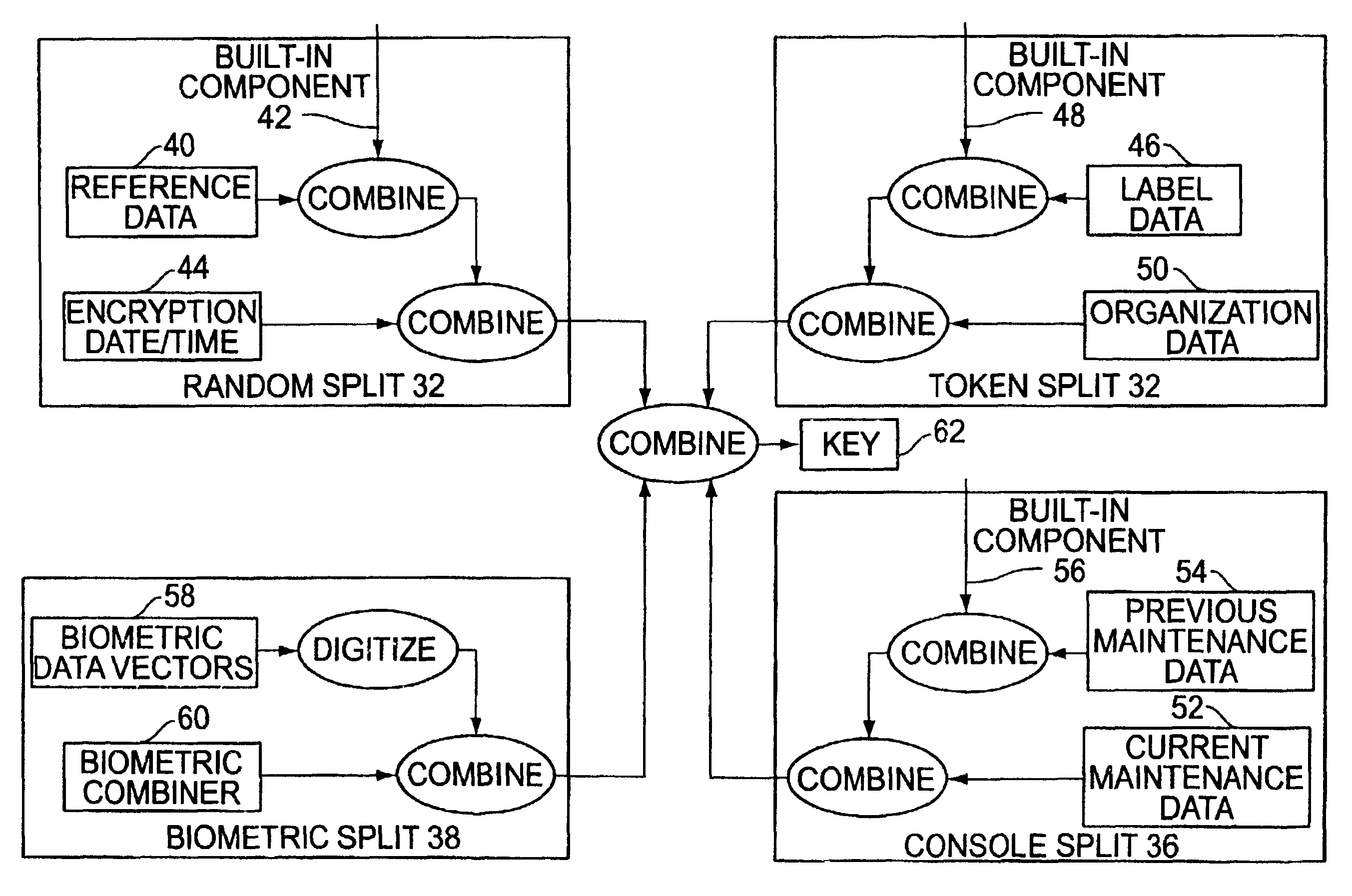
A cryptographic key split combiner, which includes a number of key split generators for generating cryptographic key splits and a key split randomizer for randomizing the cryptographic key splits to produce a cryptographic key, and a process for forming cryptographic keys. Each of the key split generators generates key splits from seed data. The key split generators may include a random split generator for generating a random key split based on reference data. Other key split generators may include a token split generator for generating a token key split based on label data, a console split generator for generating a console key split based on maintenance data, and a biometric split generator for generating a biometric key split based on biometric data. All splits may further be based on static data, which may be updated, for example by modifying a prime number divisor of the static data. The label data may be read from a storage medium, and may include user authorization data. The resulting cryptographic key may be, for example, a stream of symbols, at least one symbol block, or a key matrix.
Owner:TECSEC
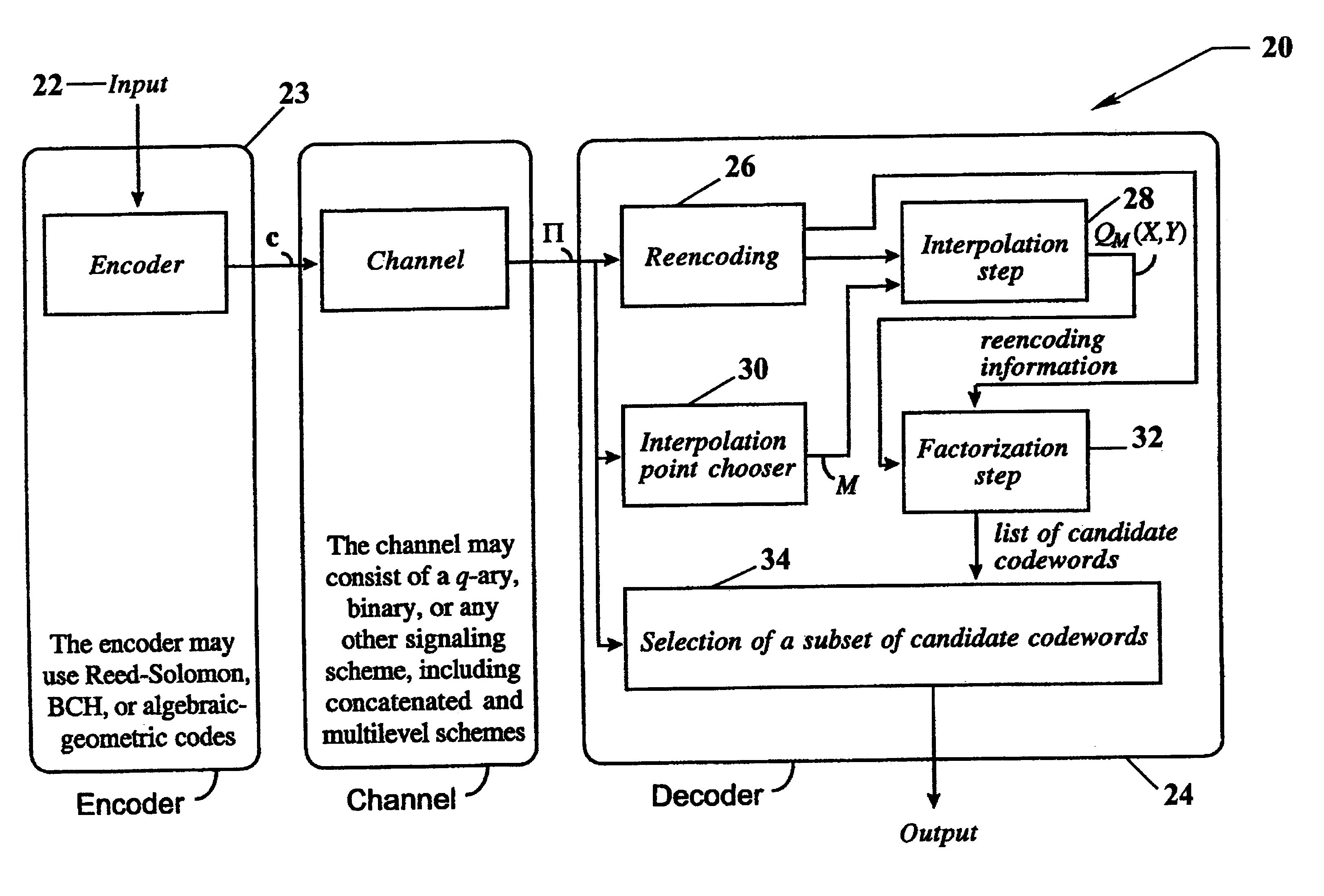
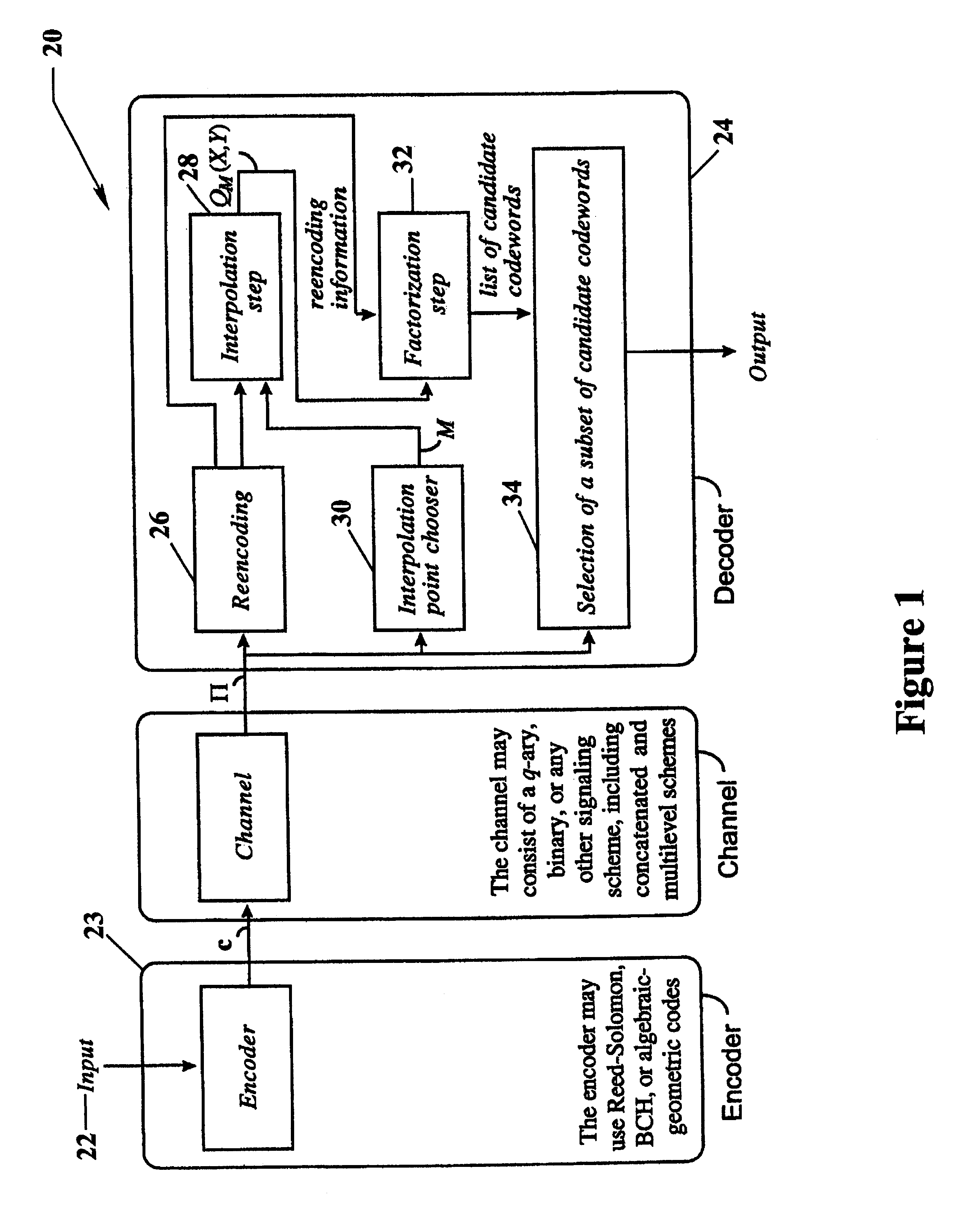
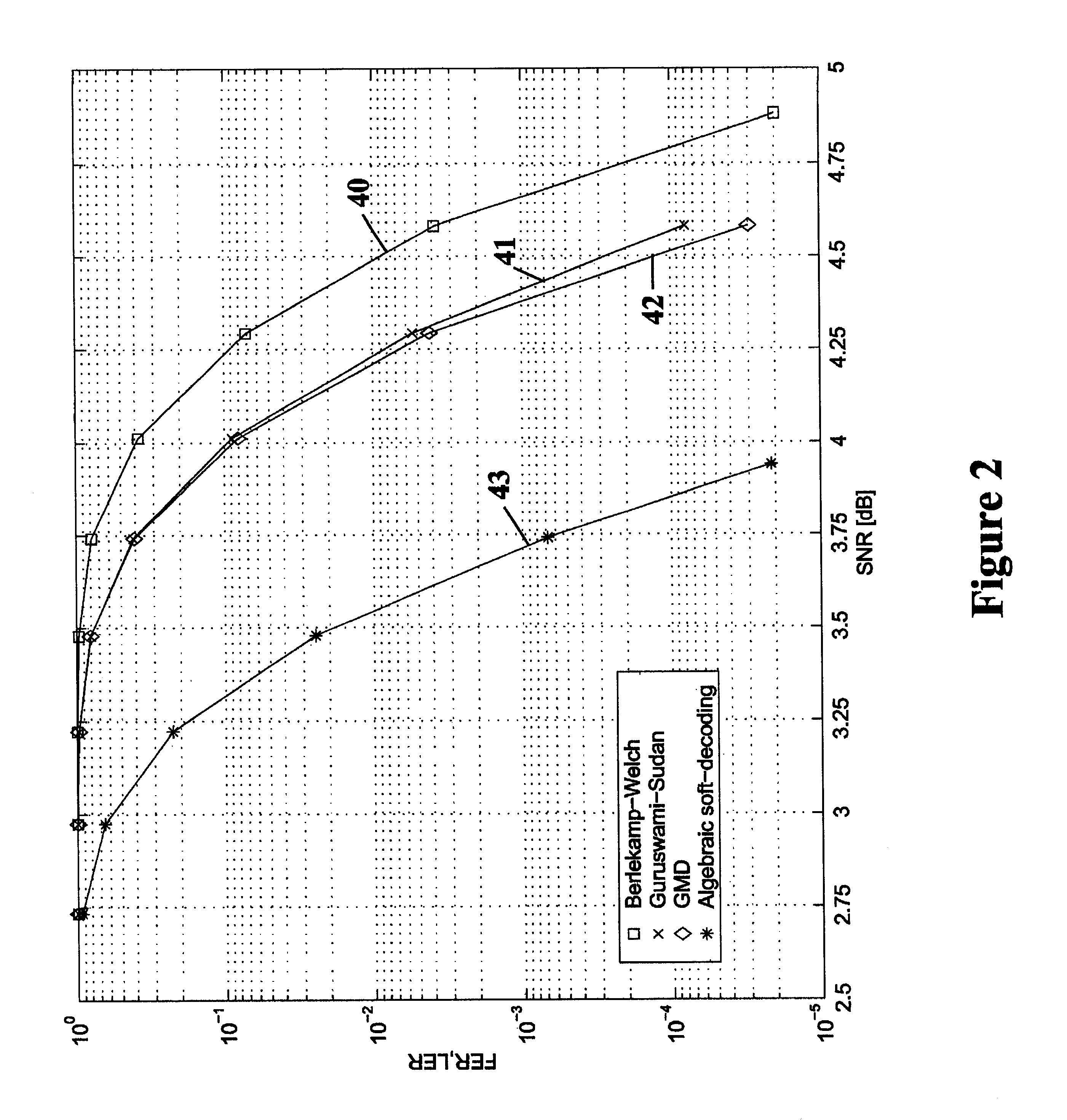
Algebraic soft decoding of reed-solomon codes
InactiveUS6634007B1Maximizes the expected scoreMaximizing the expected scoreOther decoding techniquesAlgebraic geometric codesDecoding methodsRound complexity
An algorithmic soft-decision decoding method for Reed-Solomon codes proceeds as follows. Given the reliability matrix Pi showing the probability that a code symbol of a particular value was transmitted at each position, computing a multiplicity matrix M which determines the interpolation points and their multiplicities. Given this multiplicity matrix M, soft interpolation is performed to find the non-trivial polynomial Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y) of the lowest (weighted) degree whose zeros and their multiplicities are as specified by the matrix M. Given this non-trivial polynomial Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y), all factors of Q<HIL><PDAT>M< / SB><PDAT>(X,Y) of type Y-f(X) are found, where f(X) is a polynomial in X whose degree is less than the dimension k of the Reed-Solomon code. Given these polynomials f(X), a codeword is reconstructed from each of them, and the most likely of these codewords selected as the output of the algorithm. The algorithmic method is algebraic, operates in polynomial time, and significantly outperforms conventional hard-decision decoding, generalized minimum distance decoding, and Guruswami-Sudan decoding of Reed-Solomon codes. By varying the total number of interpolation points recorded in the multiplicity matrix M, the complexity of decoding can be adjusted in real time to any feasible level of performance. The algorithmic method extends to algebraic soft-decision decoding of Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem codes and algebraic-geometry codes.< / PTEXT>
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
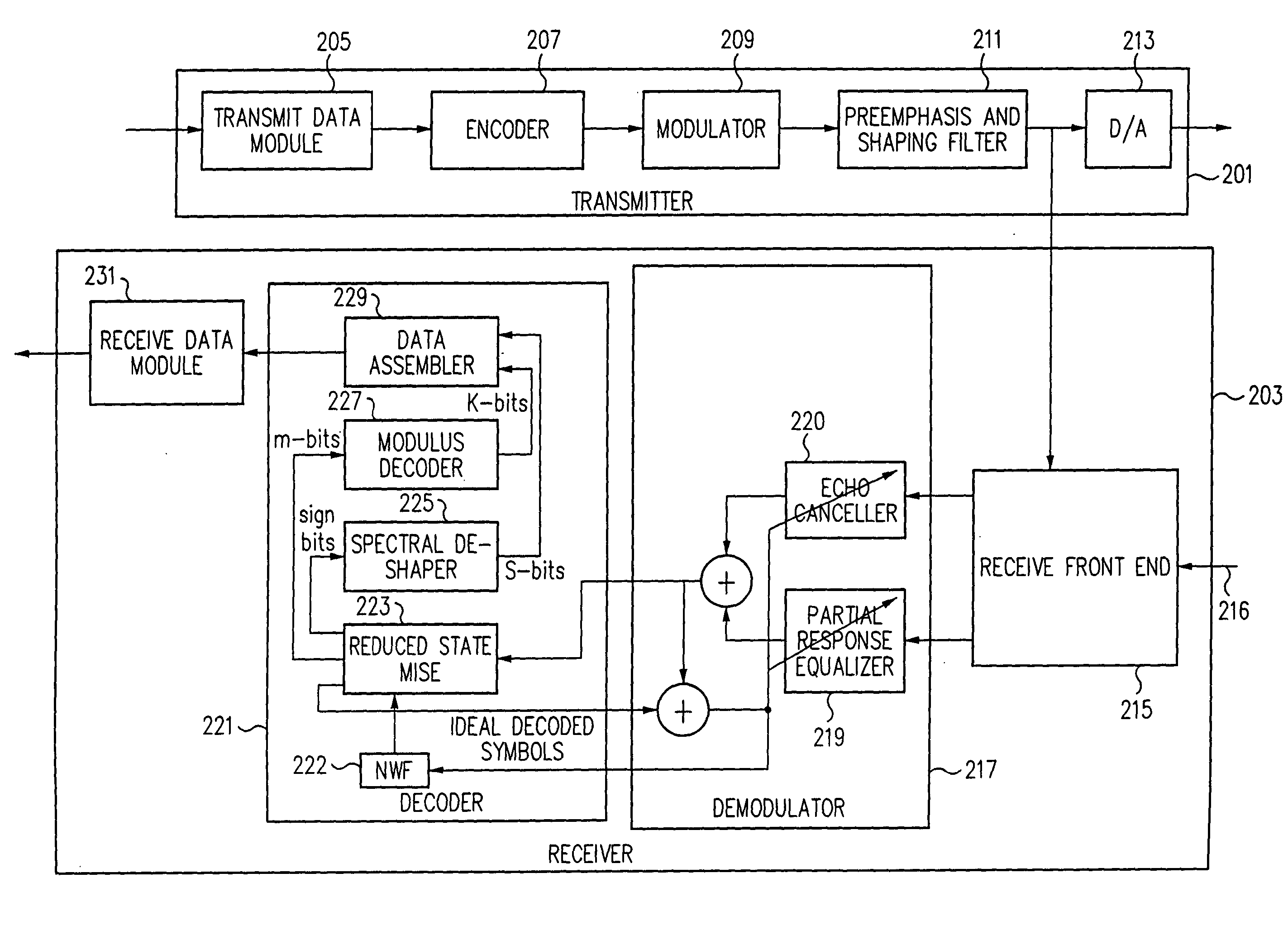
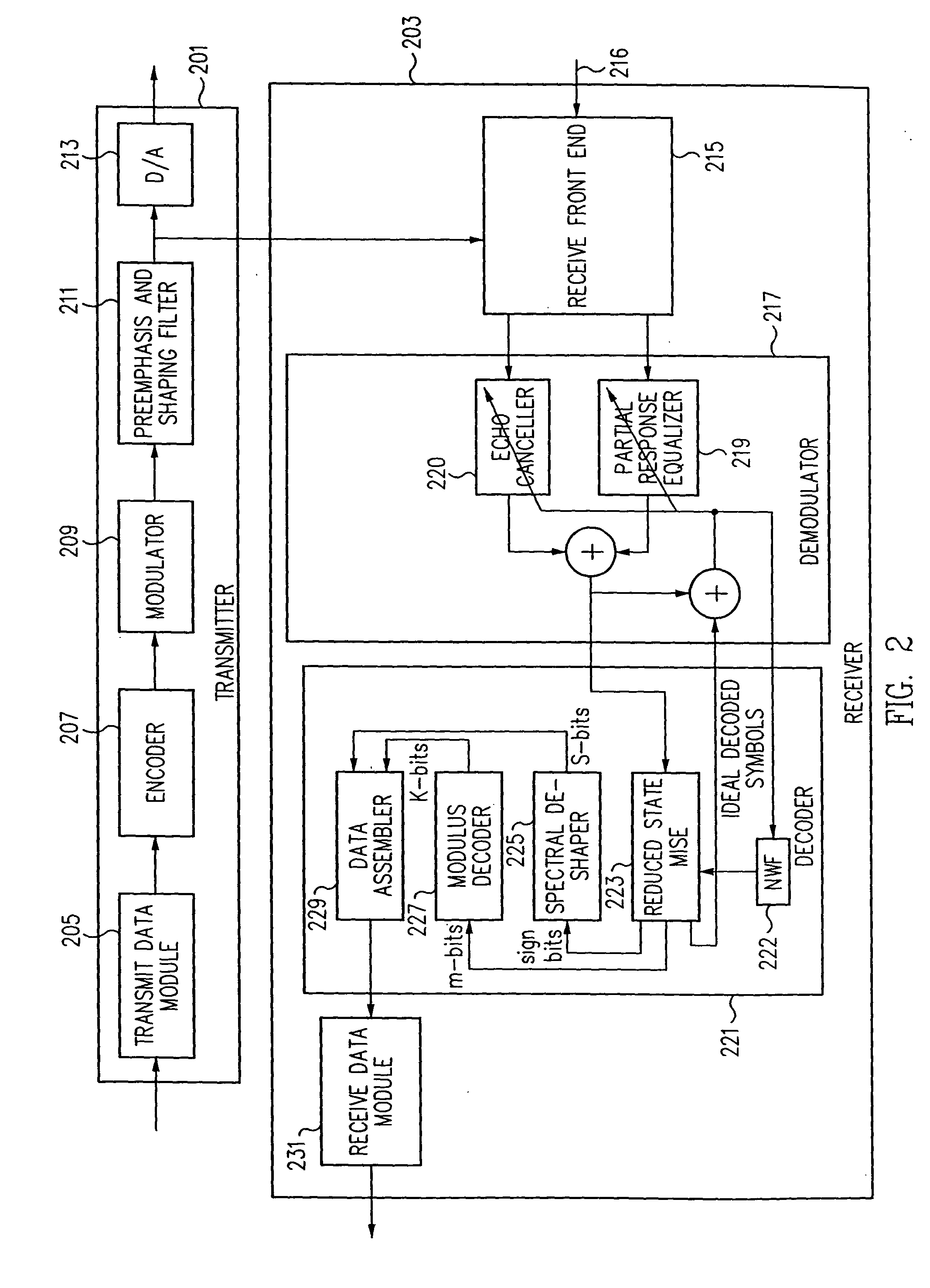
Efficient partial response equalization
InactiveUS20040037374A1Other decoding techniquesAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsUltrasound attenuationState dependent
A reduced state maximum likelihood sequence estimator allows the use of improved equalization techniques that provides greatly improved performance for channels with severe attenuation and spectral nulls. The reduced state maximum likelihood sequence estimator retains kn states of a total number of K states, kn<K, with each retained state having an associated state metric. (J)(kn) new states are determined based on kn previous states and a most recently received sample, using J transitions, J being a less than L, where L is a size of a symbol alphabet. (J)(kn) new state metrics are determined which are respectively associated with each new state. The new state metrics are compared to a threshold and those states whose metric does not exceed the threshold are retained. The reduced complexity of the MLSE allows for the use of partial response equalizers, e.g., a partial response class V (PRV) equalizer. The number of retained states kn varies according to an adaptive threshold which limits the number of retained states between a lower bound and an upper bound. The threshold may be determined according to the metric of the most likely state of the retained states and a selected one of a plurality of transition metrics associated with the most likely state metric.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
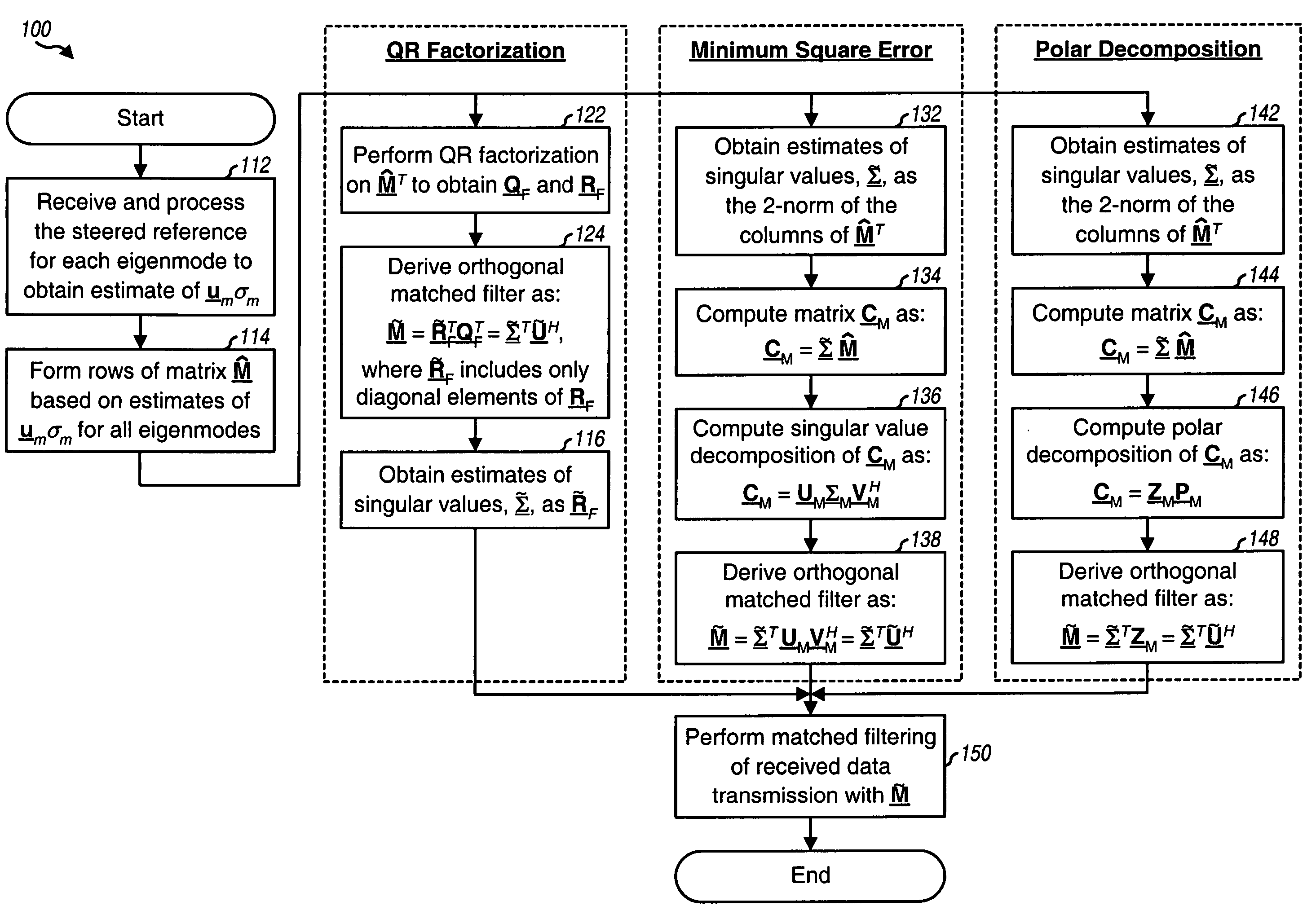
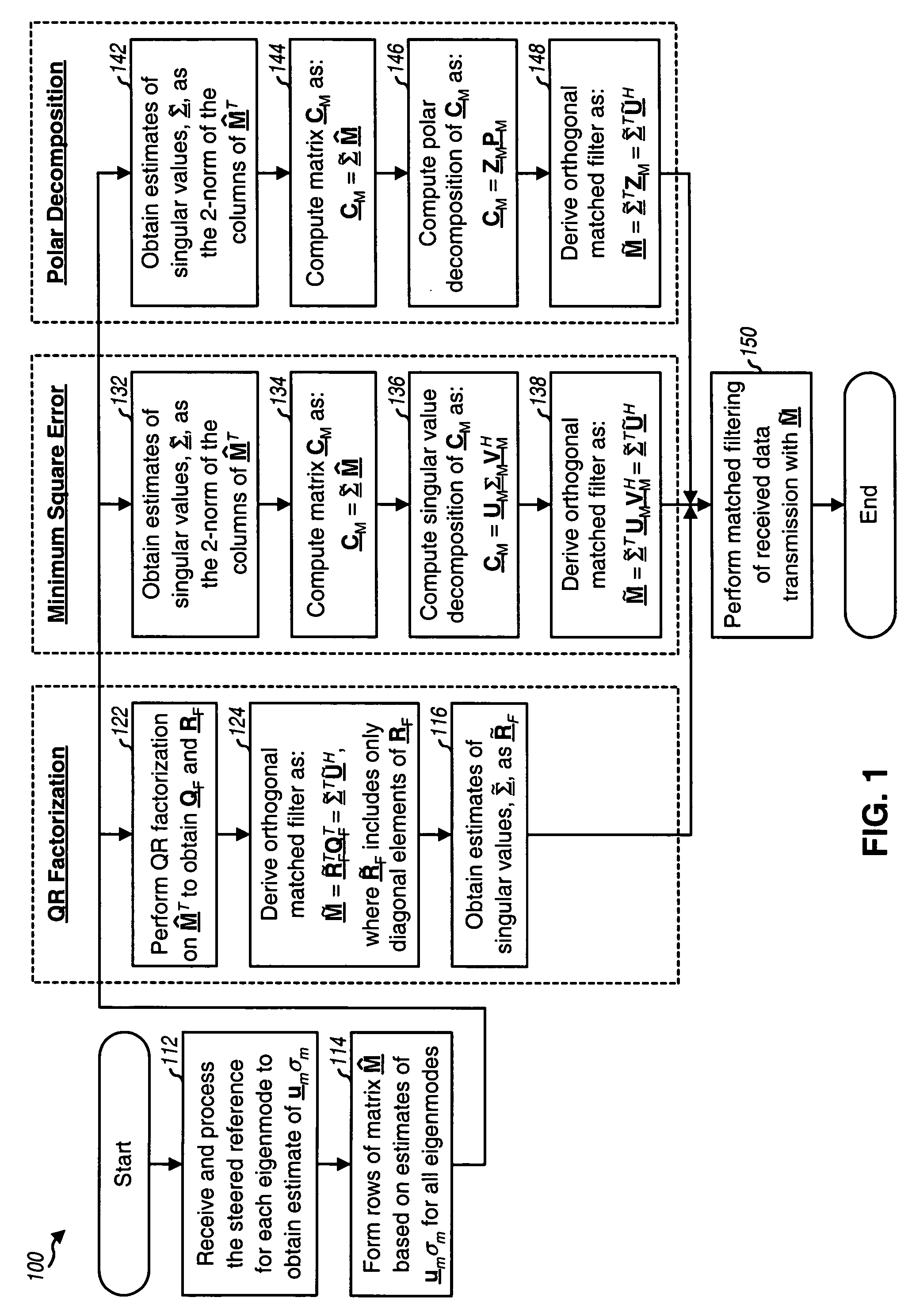
Derivation of eigenvectors for spatial processing in MIMO communication systems
Techniques for deriving eigenvectors based on steered reference and used for spatial processing. A steered reference is a pilot transmission on one eigenmode of a MIMO channel per symbol period using a steering vector for that eigenmode. The steered reference is used to estimate both a matrix Σ of singular values and a matrix U of left eigenvectors of a channel response matrix H. A matrix Ũ with orthogonalized columns may be derived based on the estimates of Σ and U, e.g., using QR factorization, minimum square error computation, or polar decomposition. The estimates of Σ and U (or the estimate of Σ and the matrix Ũ) may be used for matched filtering of data transmission received via a first link. The estimate of U or the matrix Ũ may also be used for spatial processing of data transmission on a second link (for reciprocal first and second links).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus using coordinate interleaving to increase diversity in a MIMO system
InactiveUS20060034381A1Increase diversityPolarisation/directional diversityPhase-modulated carrier systemsAs elementEngineering
A method to increase diversity in MIMO fading channels interleaves coordinates of complex symbol(s) in a transmission frame after encoding and modulating. Specifically, an input signal is encoded and modulated into a codeword, jointly across at least two pipes, said pipes having space, time, frequency, or other nature, wherein the codeword spans a frame and is defined as at least one complex symbol whose complex values are all those to be transmitted during all channel uses covered by the frame. Each of the complex symbols have a first and second coordinate. After modulating, which may be combined with encoding in a signal space encoder, the coordinates are interleaved. In modulation, the complex symbols (typically two dimensional) may arise as elements of a multidimensional (typically greater than two dimensions) signal constellation, in which case those multidimensional constellation coordinates are the ones that are interleaved in the frame. The frame carrying the interleaved coordinates is transmitted by the first and at least second antennas, possible opposed sub-frames of the overall frame being transmitted separately by opposed antennas. A coset selector is used in some embodiments to maximize a minimum Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between coordinates within a coset to control diversity and / or coding gain. In some embodiments, the operation of the encoder and modulator is such as to maximize a minimum coordinate-wise Hamming distance, and / or a minimum Euclidean distance, between allowable codewords, and / or to provide additional structure for the allowable codewords. A method, transmitter, system, and mobile station are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Distribution matching for probabilistic constellation shaping with an arbitrary input/output alphabet
ActiveUS20190149242A1Small sizeHigh likelihoodModulated-carrier systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsBinary alphabetSymbol of a differential operator
Consistent with the present disclosure, an encoder circuit is provided at a transmit side of an optical fiber link that maps an input sequence of bits of fixed length k a sequence of symbols of a codeword of length n, such that the symbols of the codeword define a predetermined transmission probability distribution. Preferably, each symbol of the codeword is generated during a corresponding clock cycle, such that after n clock cycles, a complete codeword corresponding to the input bit sequence is output. On a receive end of the link, a decoder is provided that outputs the k-bit sequence every n clock cycles. Accordingly, buffers need not be provided at the output of the encoder and the input of the decoder, such that processing of the input sequence, codewords, and output sequence may be achieved efficiently without large buffers and complicated circuitry. Moreover, the input sequence, with any binary alphabet may be matched to a desired output distribution with any arbitrary alphabet. Accordingly, probabilistic constellation shaping may be achieved over constellations of arbitrary size. In addition, relatively long codewords, may be encoded and decoded with the apparatus and method disclosed herein. Accordingly, for a fixed SNR a higher SE (more bits per symbol) can be achieved. Alternatively, for a fixed SE, a lower SNR may be sufficient. Moreover, the resulting SE may be finely tailored to a particular optical link SNR to provide data transmission rates that are higher than the low order modulation formats that would otherwise be employed for optical signals carried by such links.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Digital equalizing method and radio communication receiver implementing said method
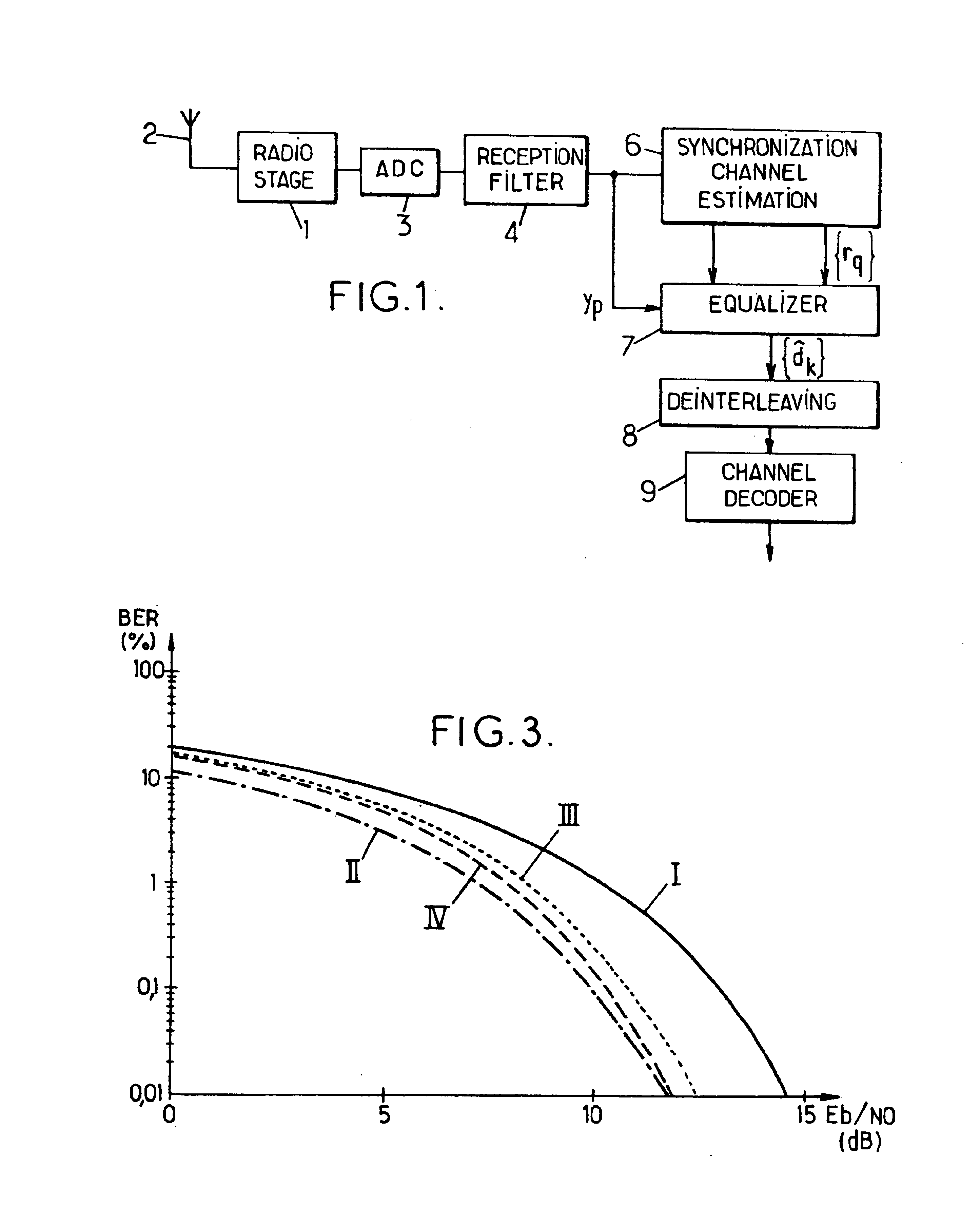
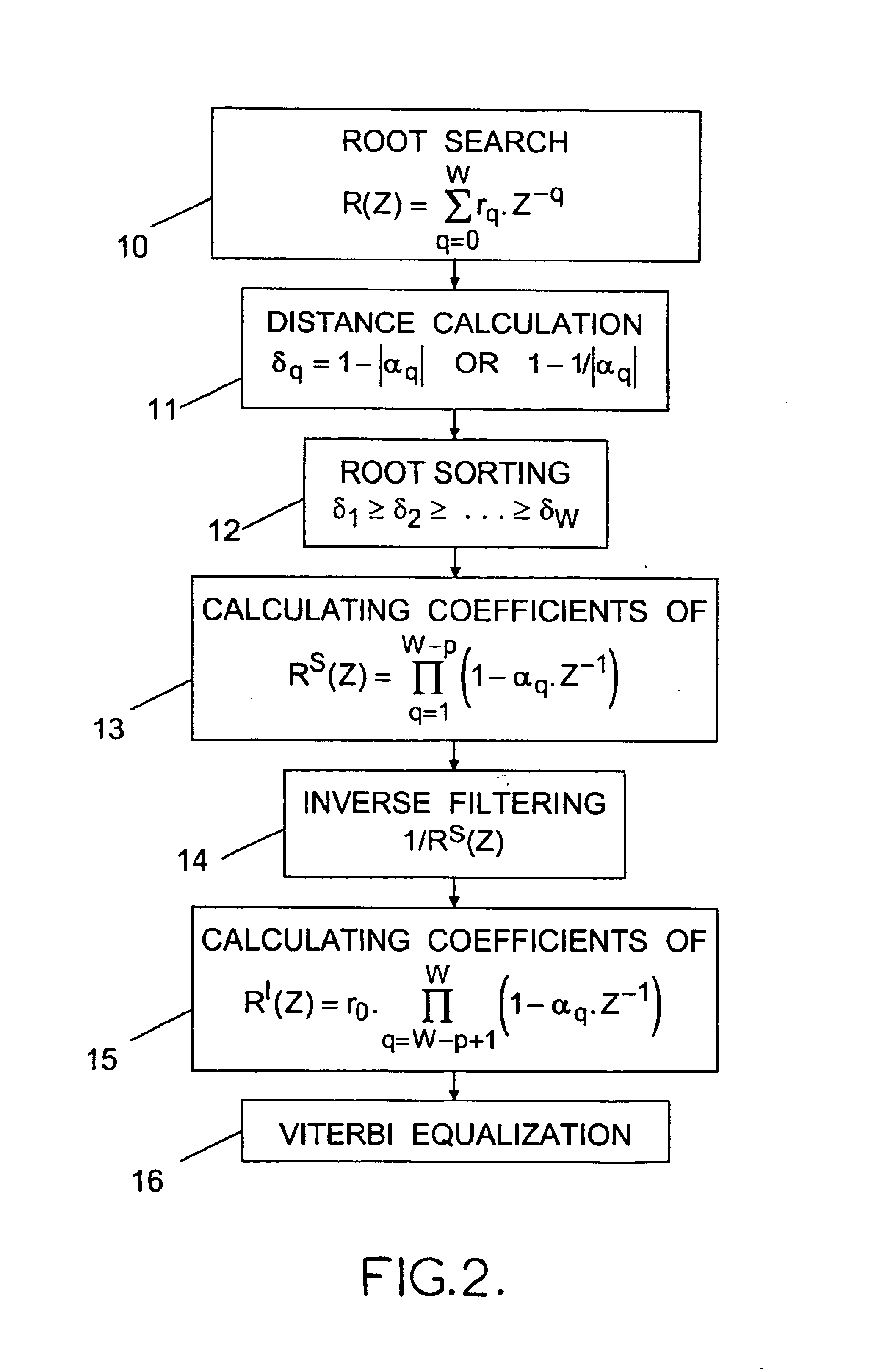
InactiveUS6850562B1Increase valueSolution value is not highMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationChannel impulse responsePartition of unity
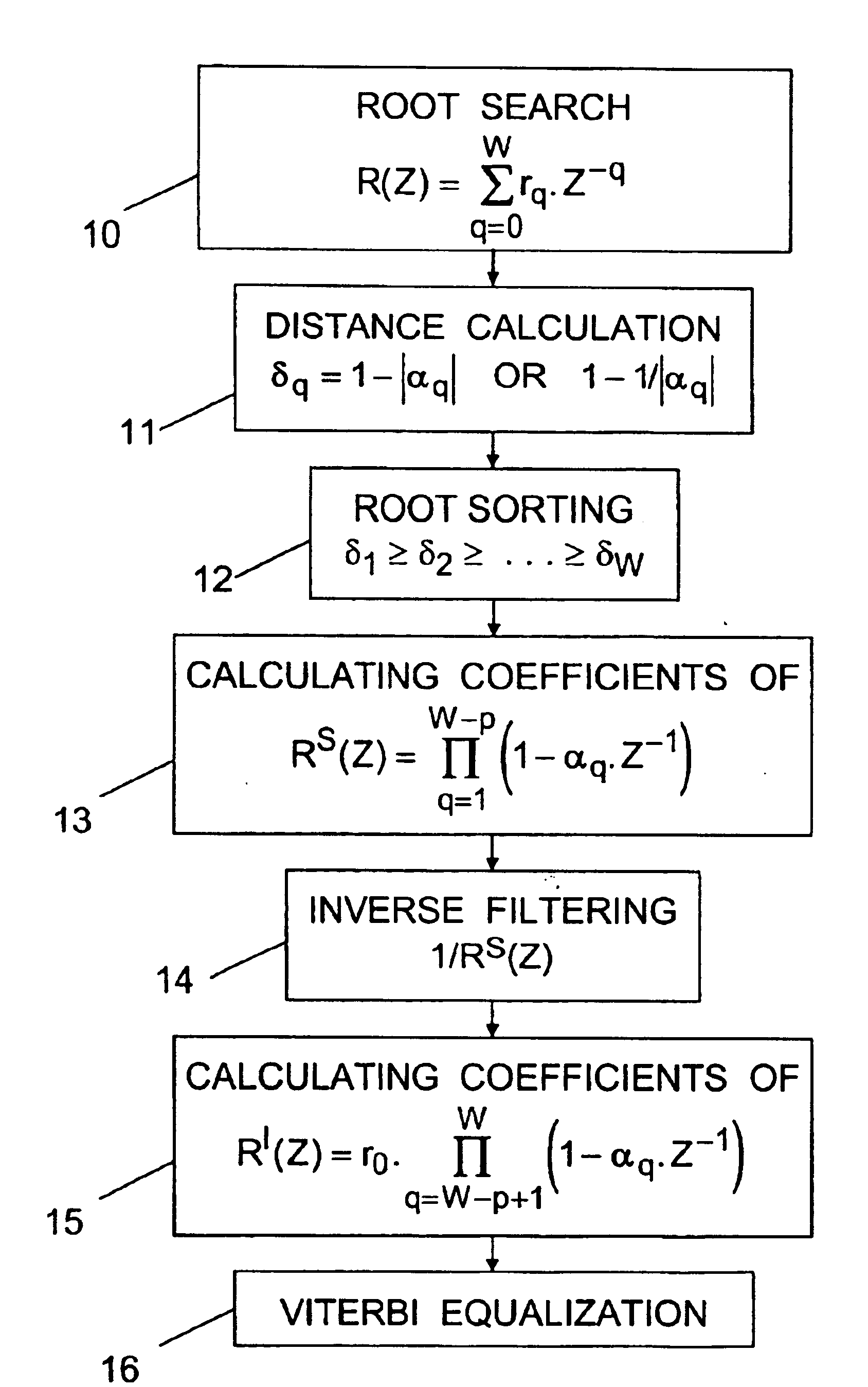
For processing samples of a signal received via a channel represented by an impulse response of W−1 coefficients, the method comprises: determining the W roots of the Z-transform of the channel impulse response; producing an intermediate signal by equalizing the received signal by a zero-forcing method or the like based on an impulse response whose Z-transform is a Z−1 polynomial of degree W-p having as roots those of the W roots which are furthest from the unit circle of the complex plane; and then obtaining estimations of the transmitted signal symbols by applying a Viterbi-type equalization method or the like based on an impulse response whose Z-transform is a Z−1 polynomial of degree p having as roots those of the W roots which are nearest to the unit circle.
Owner:APPLE INC
Asymmetric cryptosystem employing paraunitary matrices
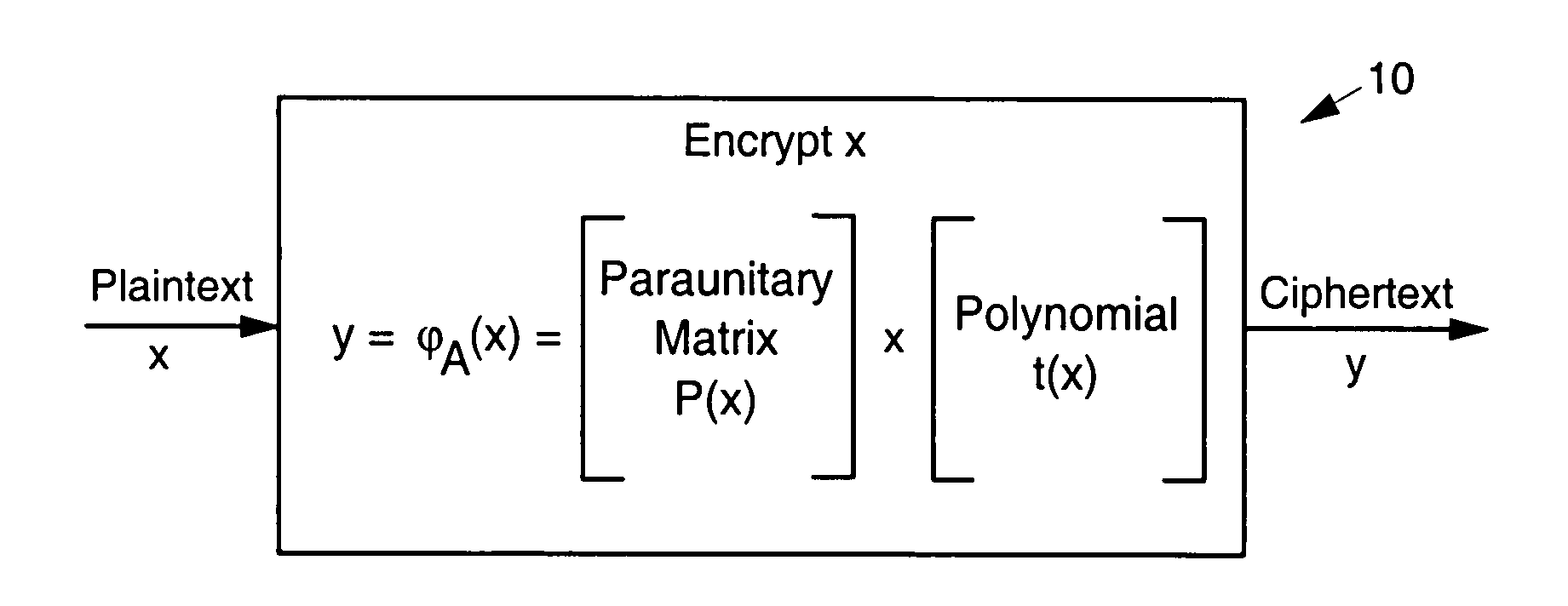
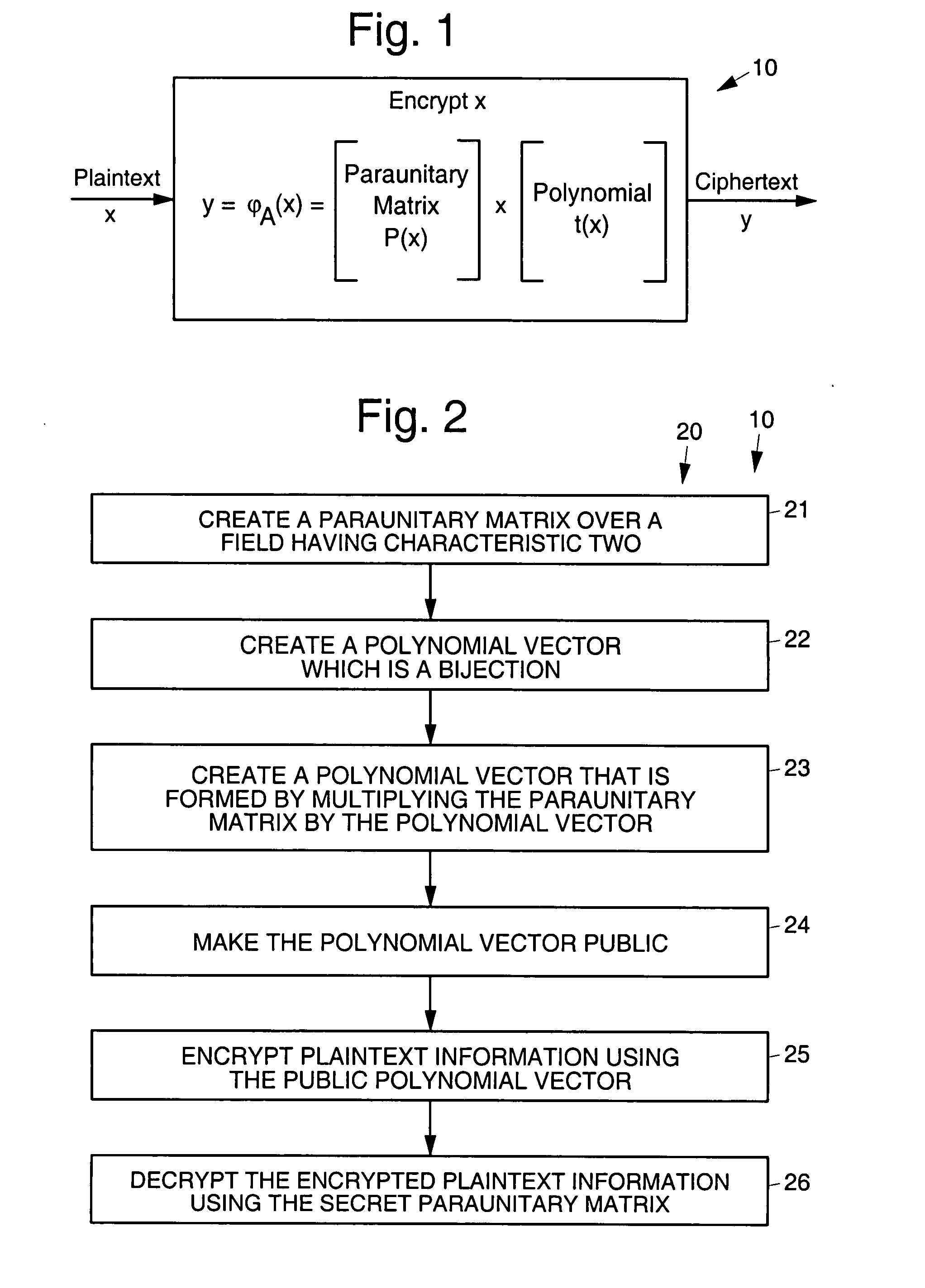
InactiveUS20090010428A1Public key for secure communicationSecret communicationNon symmetricCiphertext
Disclosed are multivariate paraunitary asymmetric cryptographic systems and methods that are based on paraunitary matrices. An algebraic approach is employed in designing the multivariate cryptographic systems and methods. The cryptographic systems and methods are based on formulating a general system of multivariate polynomial equations by paraunitary matrices. These matrices are a family of invertible polynomial matrices that can be completely parameterized and efficiently generated by primitive building blocks. Using a general formulation that involves paraunitary matrices, a one-way function is designed that operates over the fields of characteristic two. To include a trapdoor, approximations are made to the paraunitary matrix. The result is a trapdoor one-way function that is efficient to evaluate, but hard to invert unless secret information about the trapdoor is known. An exemplary implementation operates on the finite field GF(256). In this example, the message block includes 16 to 32 symbols from GF(256), i.e., the block size n is an integer between 16 and 32. The ciphertext block takes its elements from the same field and has at least 10 extra symbols.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
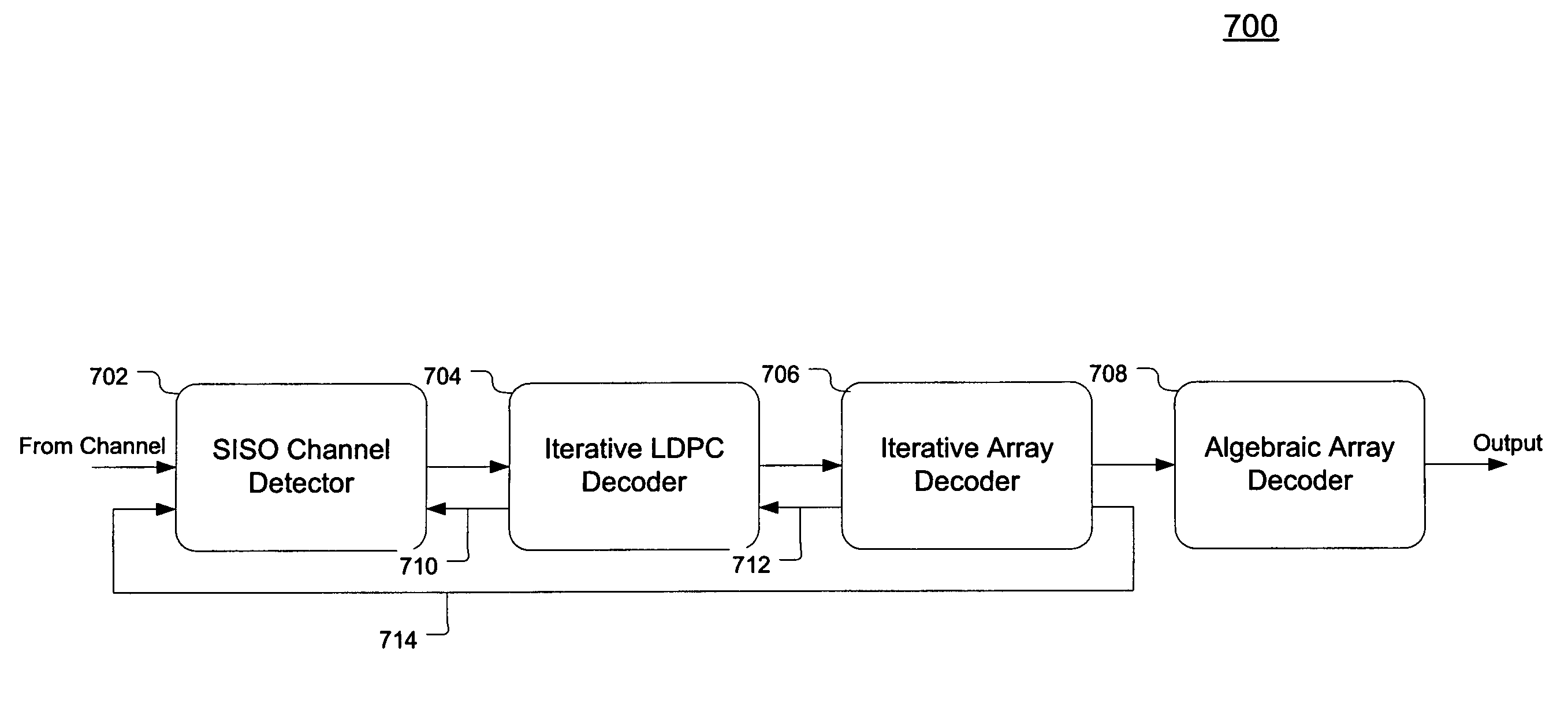
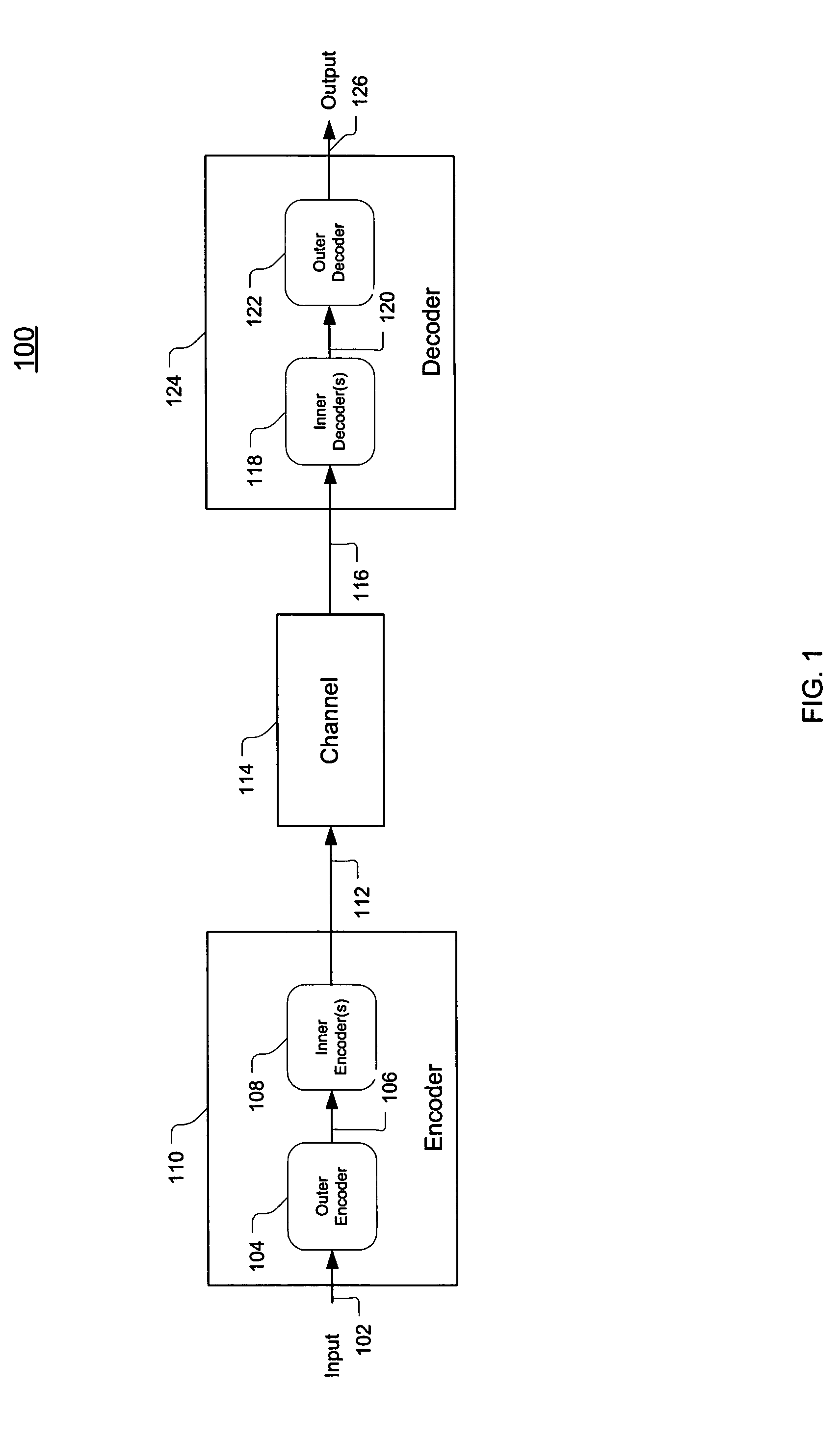
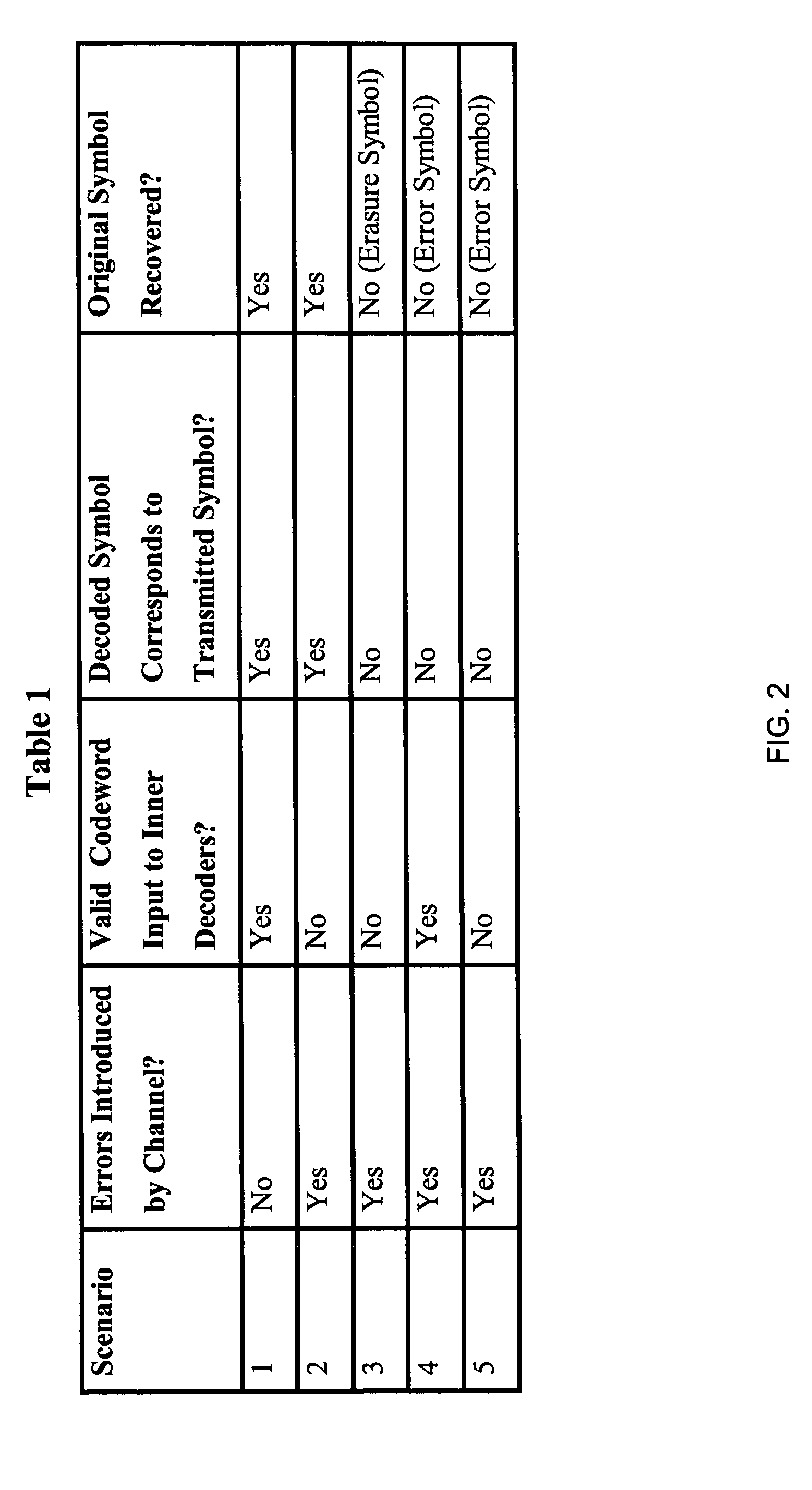
Concatenated iterative and algebraic coding
An apparatus for error-correction encoding information includes, in one embodiment, an outer encode that generates algebraically decodable data, the outer encoder operatively coupled to one or more inner encoders that generate iteratively decodable data. The outer encoder is adapted to encode a group of (q−r) original data symbols using r code symbols to produce q outer-encoded symbols, wherein the coding gain of the outer encoder provides for the correction of up to x symbol errors and (r−2x) symbol erasures where r is an integer greater than zero and x is an integer such that0≤x<r2.The one or more iterative EC-inner encoders are adapted to inner encode each of the q outer-encoded symbols or combinations of several outer-encoded symbols independently of the others, wherein each symbol is encoded with h additional code bits.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Four-dimensional polynomial model for depth estimation based on two-picture matching
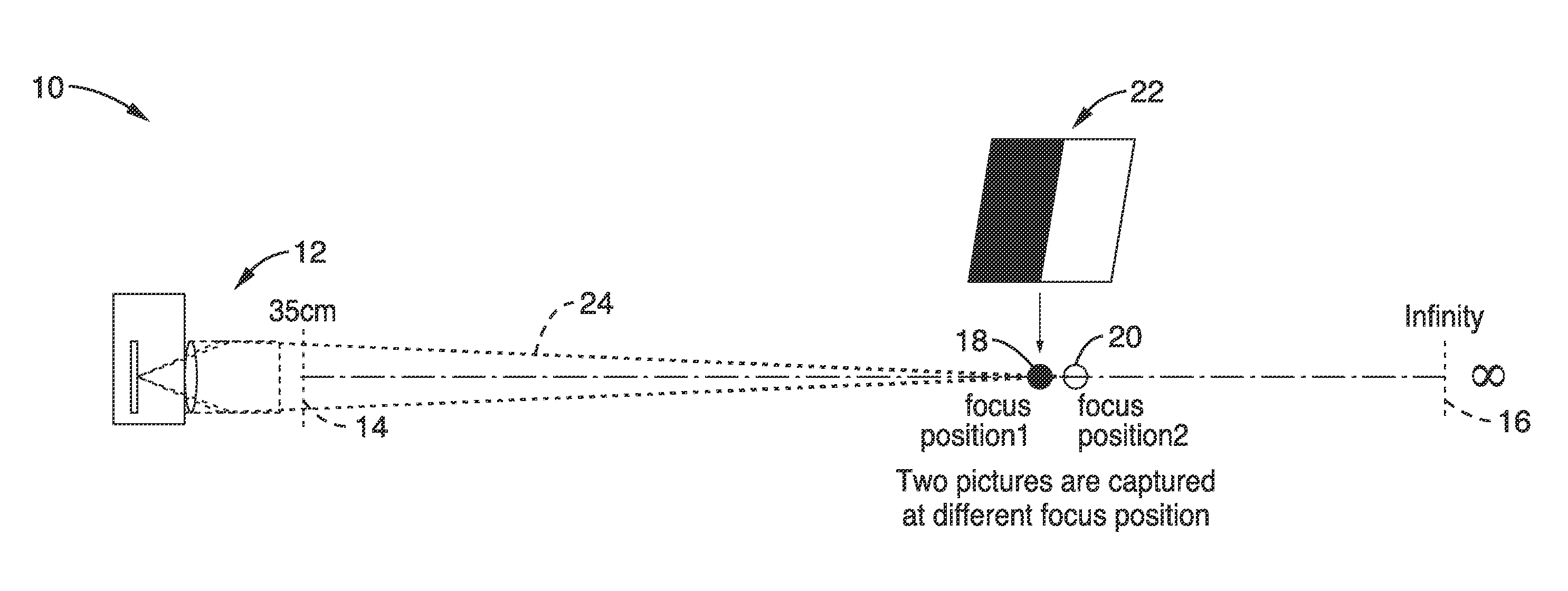
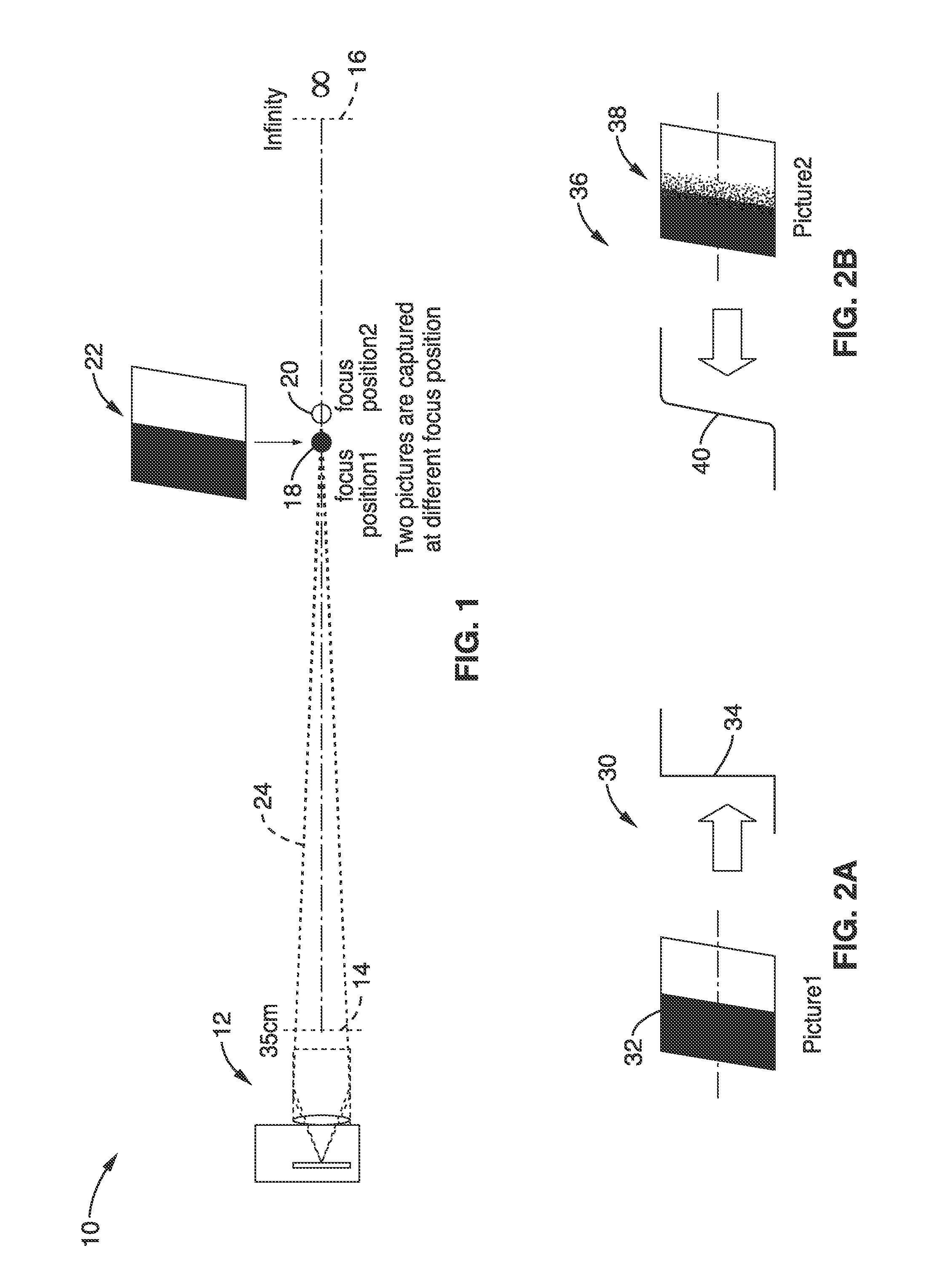
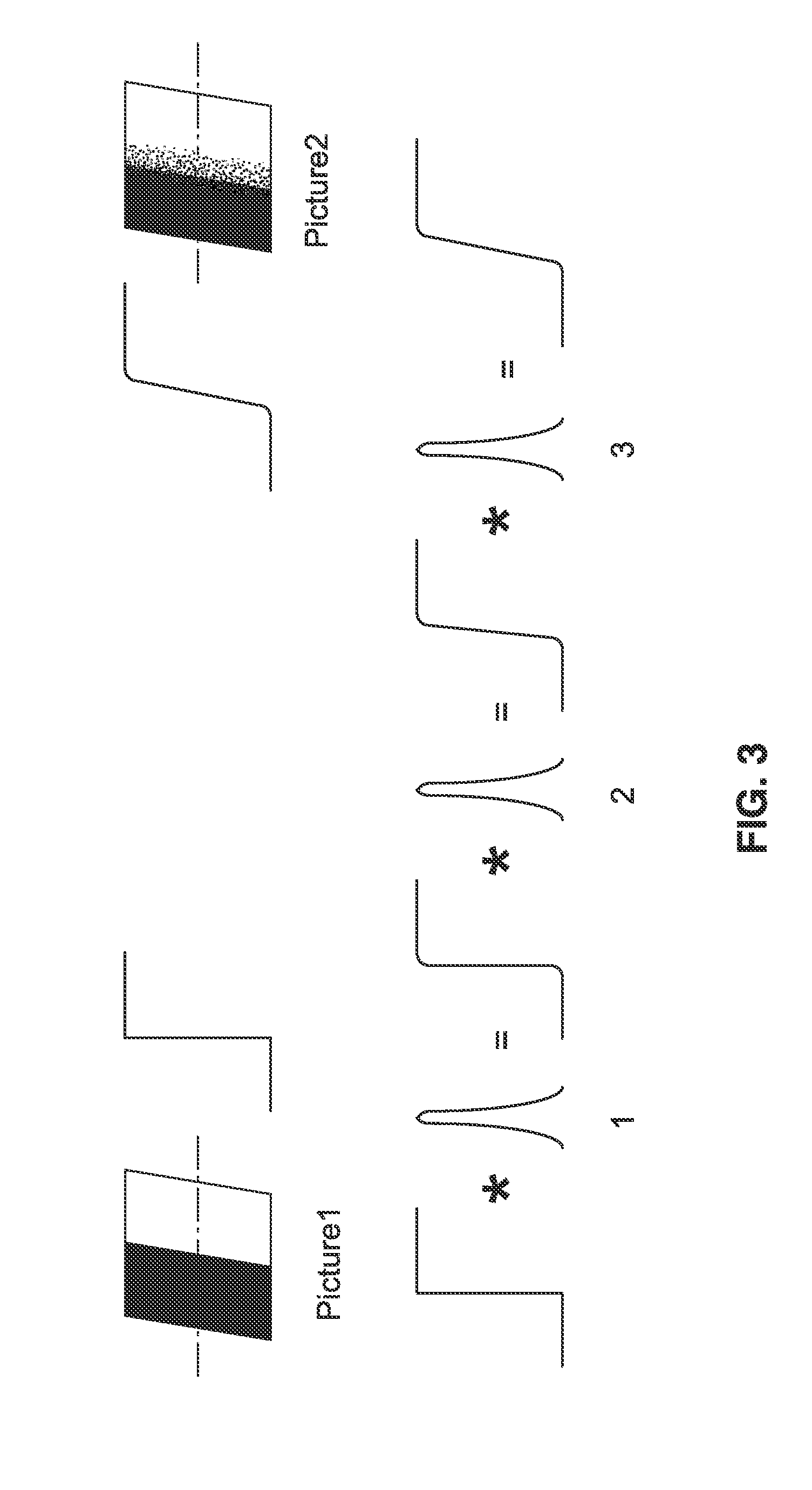
ActiveUS20110249173A1Accurate estimateAccurately renderedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFocal positionComputer science
Camera depth estimation is performed in response to picture matching based on blur difference computed between images captured at different focal positions. A blur difference model is stored in the camera based on characterization of the camera with a series of matching curves in which blur difference varies depending on the focal length, aperture, subject distance, and lens focus position. A four-dimensional polynomial model is created to fit the matching curves for use in estimating subject distance. During operation, images are captured for use in estimating subject distance. Motion compensation is applied and blur difference is determined. Blur difference is utilized in the polynomial model to estimate subject distance. Subject distance estimates can be output or utilized within an auto focus process to provide accurate focus adjustments.
Owner:SONY CORP
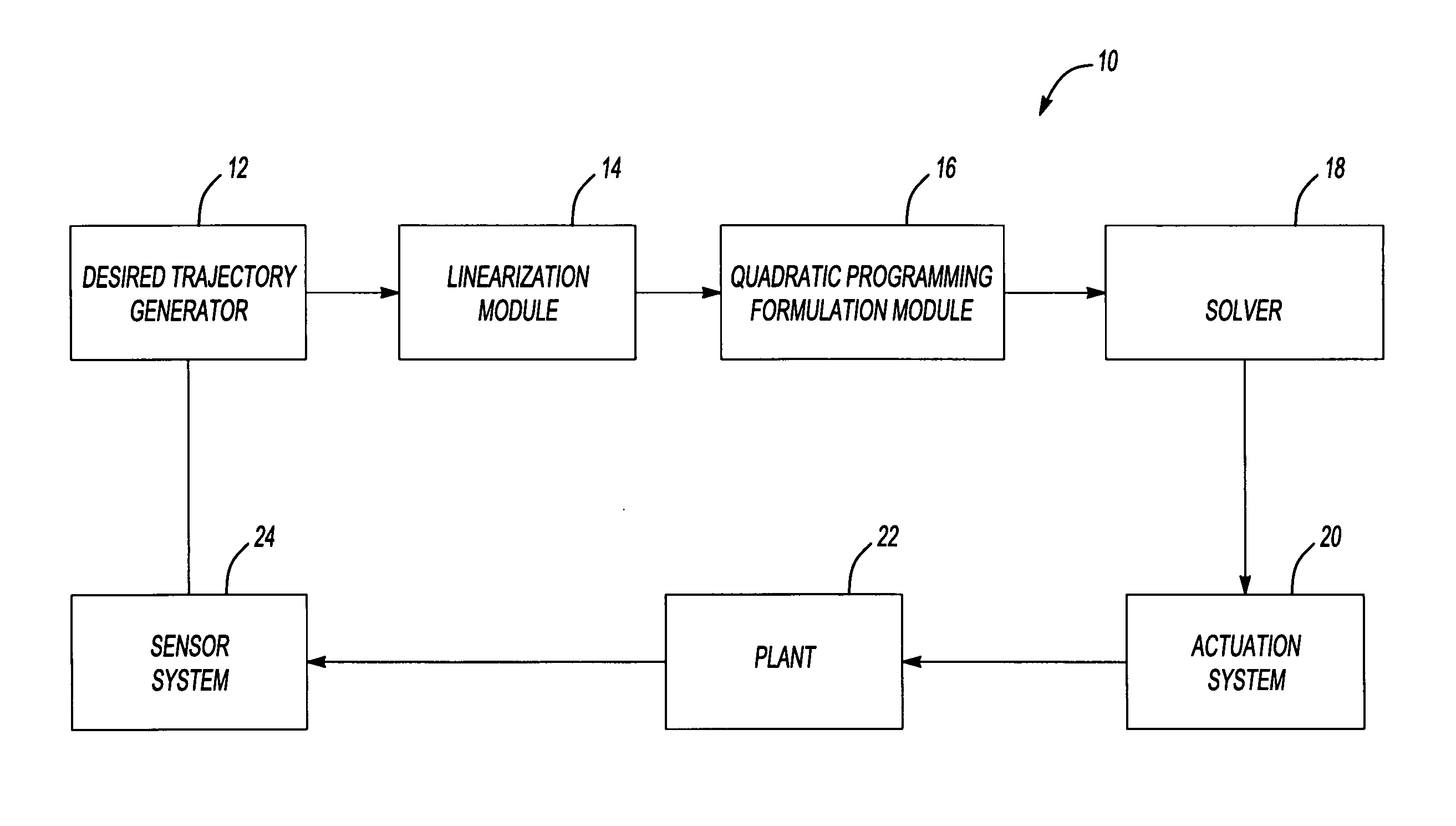
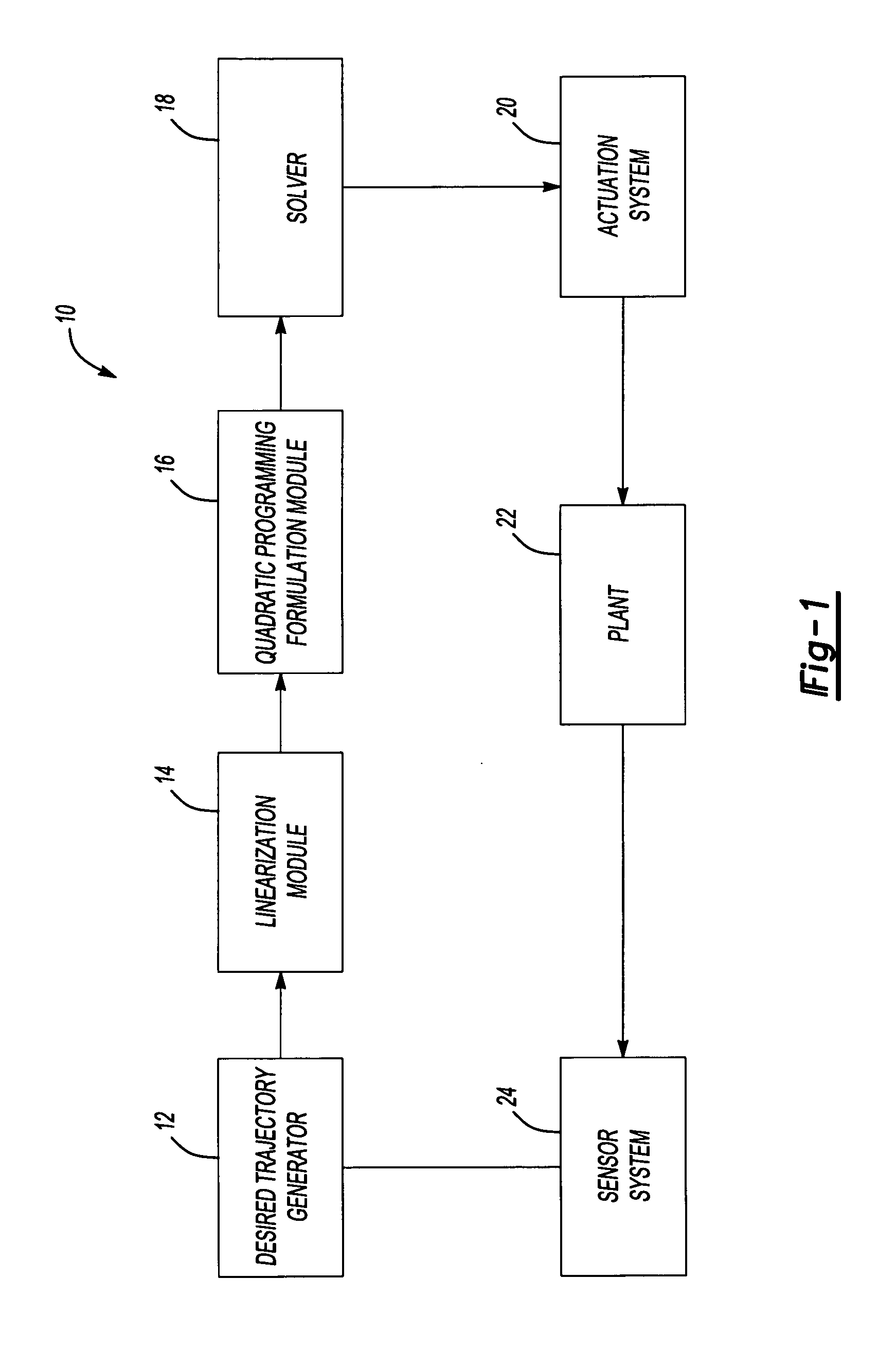
Method and system for optimization of general problems
InactiveUS7072723B2Adaptive controlComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmSymbol of a differential operator
Owner:CLEARSIGHT SYST
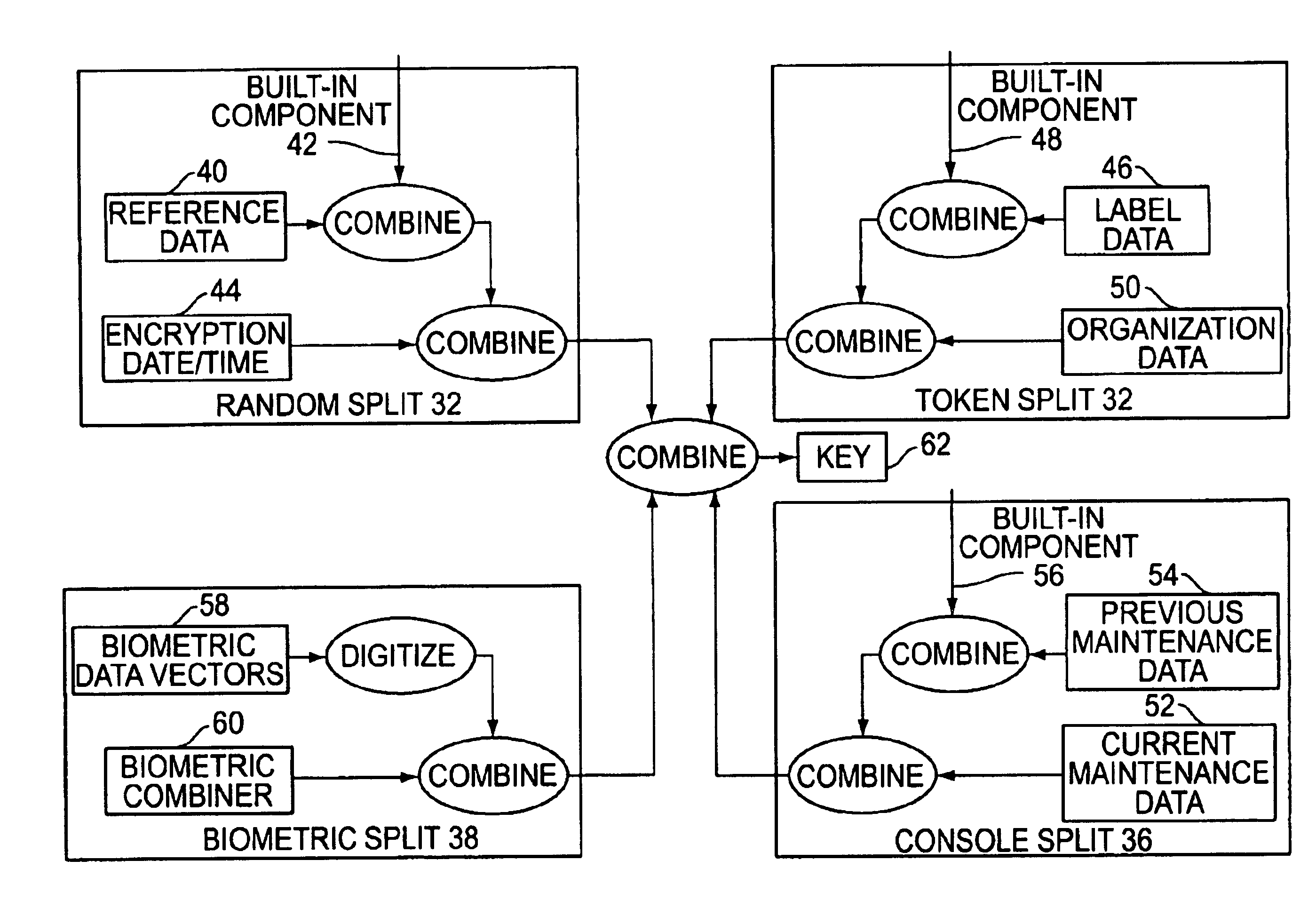
Cryptographic key split combiner
InactiveUS7212632B2Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesBiometric dataLabeled data
A cryptographic key split combiner, which includes a number of key split generators for generating cryptographic key splits and a key split randomizer for randomizing the cryptographic key splits to produce a cryptographic key, and a process for forming cryptographic keys. Each of the key split generators generates key splits from seed data. The key split generators may include a random split generator for generating a random key split based on reference data. Other key split generators may include a token split generator for generating a token key split based on label data, a console split generator for generating a console key split based on maintenance data, and a biometric split generator for generating a biometric key split based on biometric data. All splits may further be based on static data, which may be updated, for example by modifying a prime number divisor of the static data. The label data may be read from a storage medium, and may include user authorization data. The resulting cryptographic key may be, for example, a stream of symbols, at least one symbol block, or a key matrix.
Owner:TECSEC
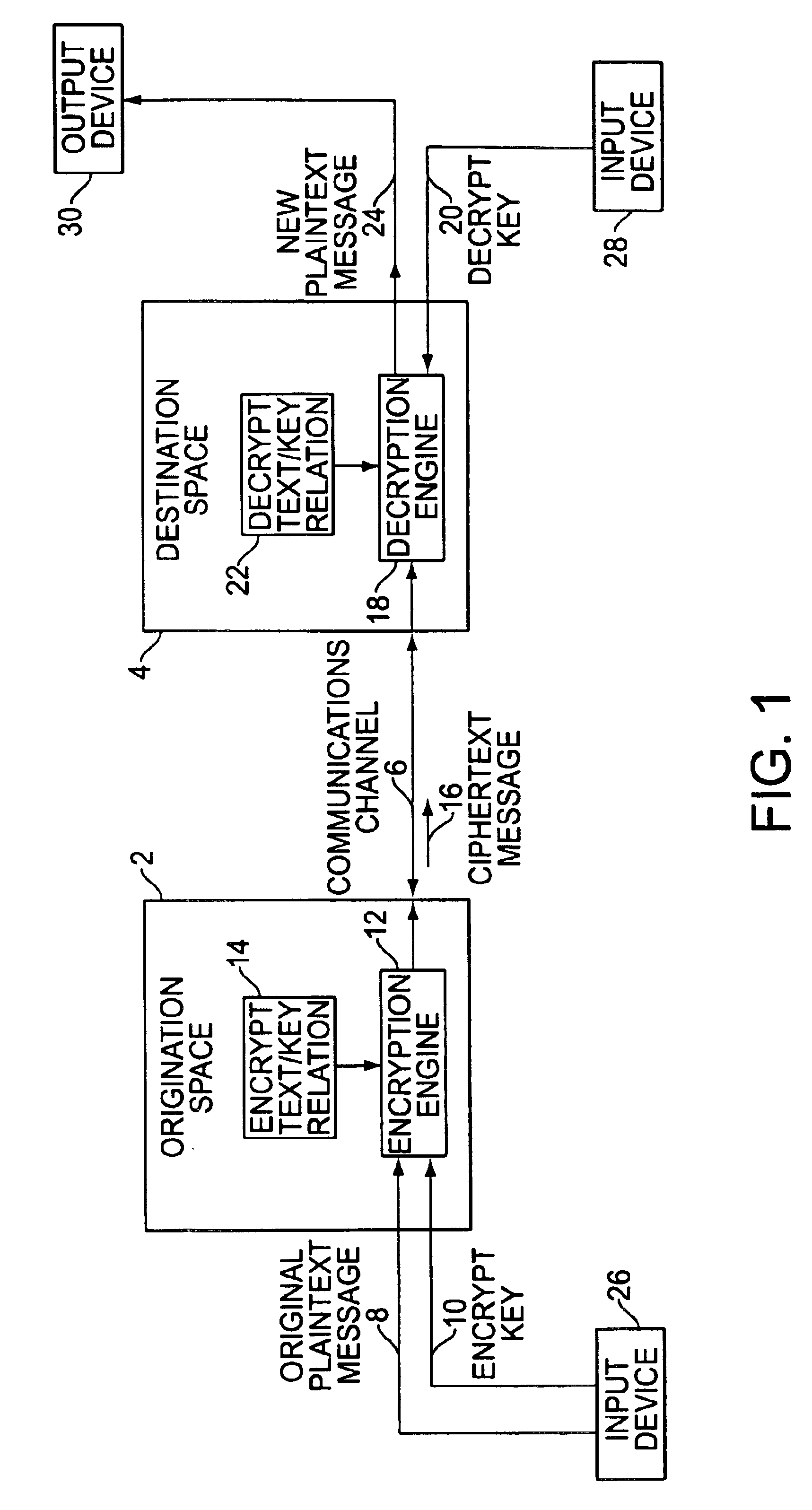
Cryptographic key split combiner
InactiveUS6885747B1Key distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsBiometric dataLabeled data
A cryptographic key split combiner, which includes a number of key split generators for generating cryptographic key splits and a key split randomizer for randomizing the cryptographic key splits to produce a cryptographic key, and a process for forming cryptographic keys. Each of the key split generators generates key splits from seed data. The key split generators may include a random split generator for generating a random key split based on reference data. Other key split generators may include a token split generator for generating a token key split based on label data, a console split generator for generating a console key split based on maintenance data, and a biometric split generator for generating a biometric key split based on biometric data. All splits may further be based on static data, which may be updated, for example by modifying a prime number divisor of the static data. The label data may be read from a storage medium, and may include user authorization data. The resulting cryptographic key may be, for example, a stream of symbols, at least one symbol block, or a key matrix.
Owner:TECSEC
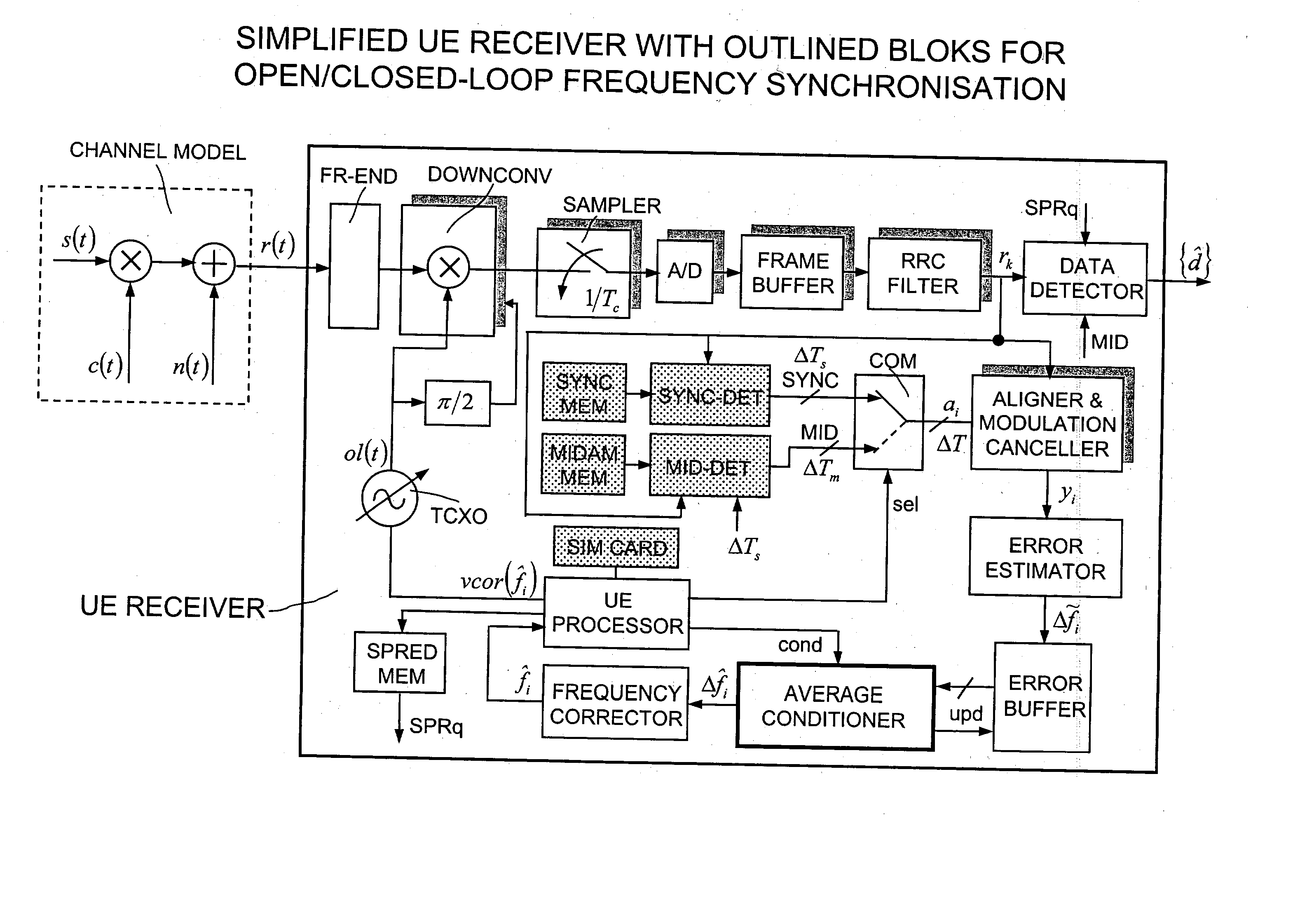
Data aided frequency synchronisation in cellular mobile equipments
InactiveUS20030181183A1Convergence can be speededOvercomes drawbackCarrier regulationRadio transmissionShift registerGreek letter sigma
Some improvements to the conventional algorithms for data aided frequency synchronisation in cellular systems are introduced in a new method executable by the user equipments of various standards, i.e. 3GPP CDMA-TDMA, FDD mode at 3.84 Mcps, TDD mode at 3.84 Mcps, TDD mode at 1.28 Mcps; CWTS TD-SCDMA; GSM / DCS / GPRS. The method begins to obtain the suboptimal frequency errors Deltafi using a well known formula which calculates the argument of the autocorrelation over a subset of the baseband samples of the detected training sequence. The errors Deltafi are stored into a shift register L-position long and averaged to obtain an estimated frequency error Deltafi used for recursively correcting the reference frequency of the local oscillator, as: fi=fi-1+KDeltafi where K (0<=K<=1) is a weighting factor. Contrarily to the simple averaged error of the prior art, a sign criterion is used by which the average is performed on the only terms having the most recurrent algebraic sign among the stored terms Deltafi. The content of the shift register is corrected after each non-null frequency correction by subtracting K.Deltafi to all the stored terms Deltafi. Besides the frequency is corrected upon the following optional conditions, each other independents: The number of terms Deltafi having equal algebraic sign is greater than a constant alpha lower than L. The standard deviation sigma of the averaged terms Deltafi is lower than beta.sigmaold, being sigmaold the sigma of the last non-null frequency correction, and beta a constant >=1. After a minimum number gamma of iterations between two non-null frequency corrections are spent, being gamma a constant comprised between 1 and L. According to another variant the iterations of the recursive update are subdivided into an initial group with a higher K value for achieving fast convergence and a subsequent group with a lower K for achieving the required accuracy (FIG. 13).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Receiver, transmitter-receiver, and communication method
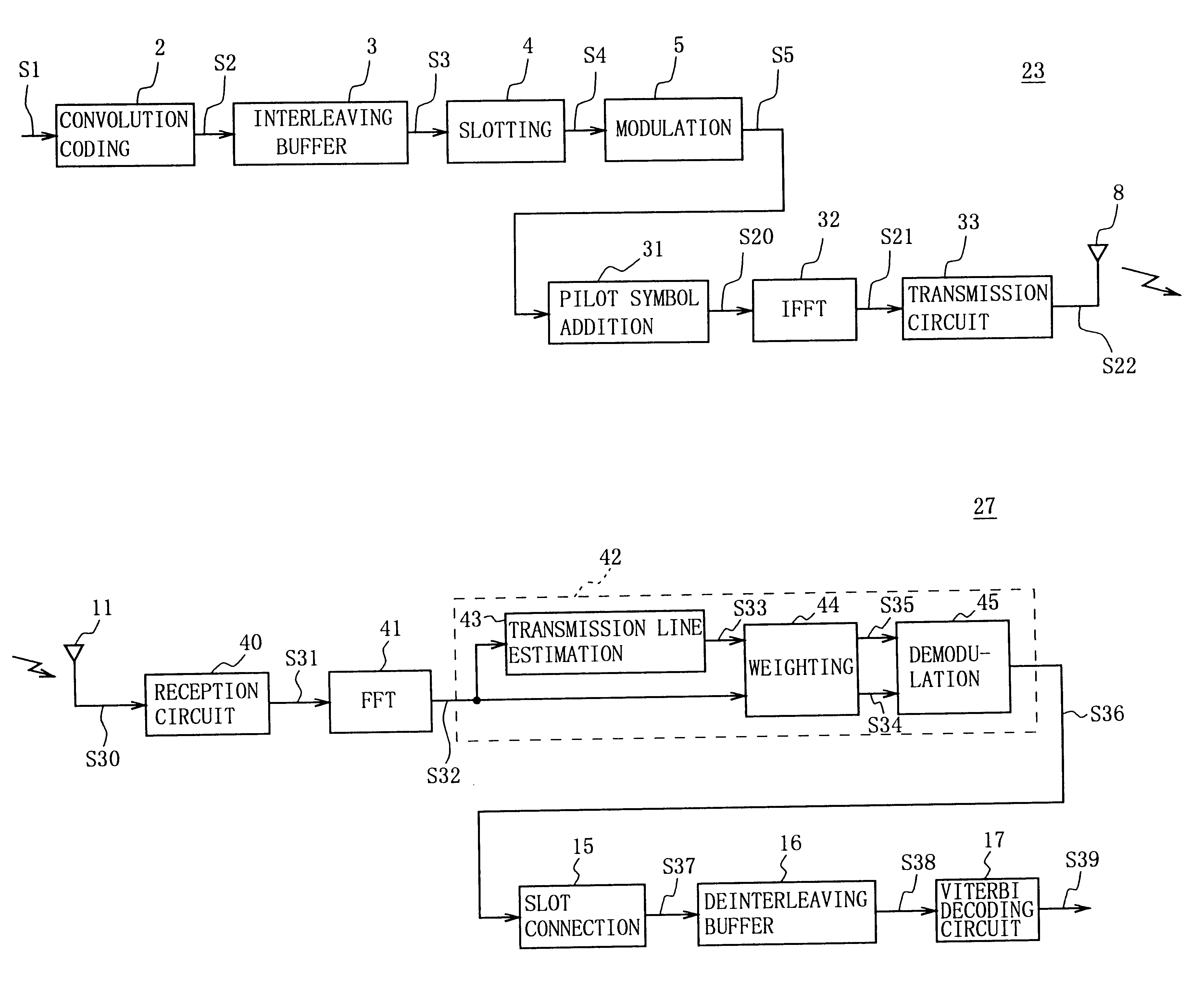
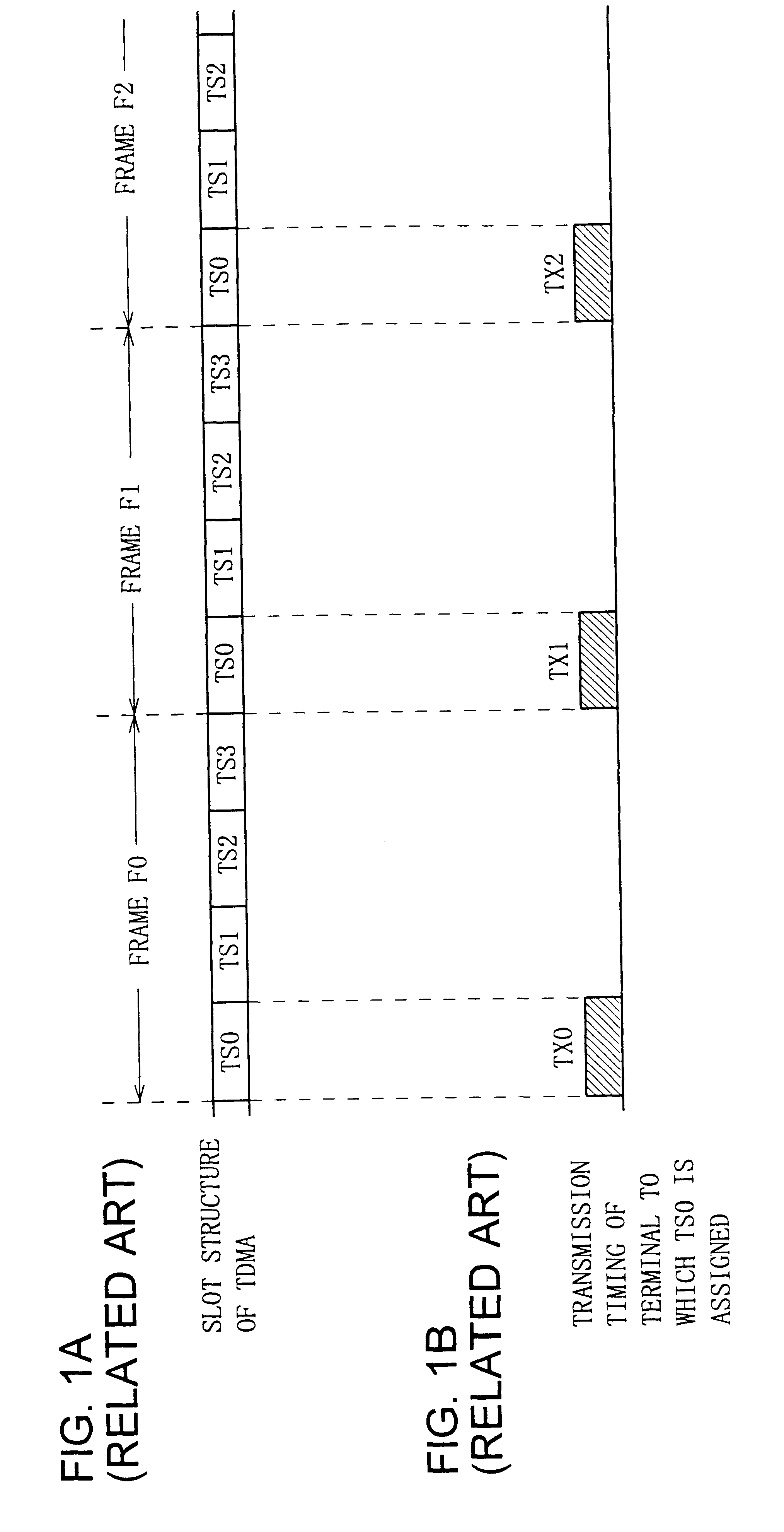
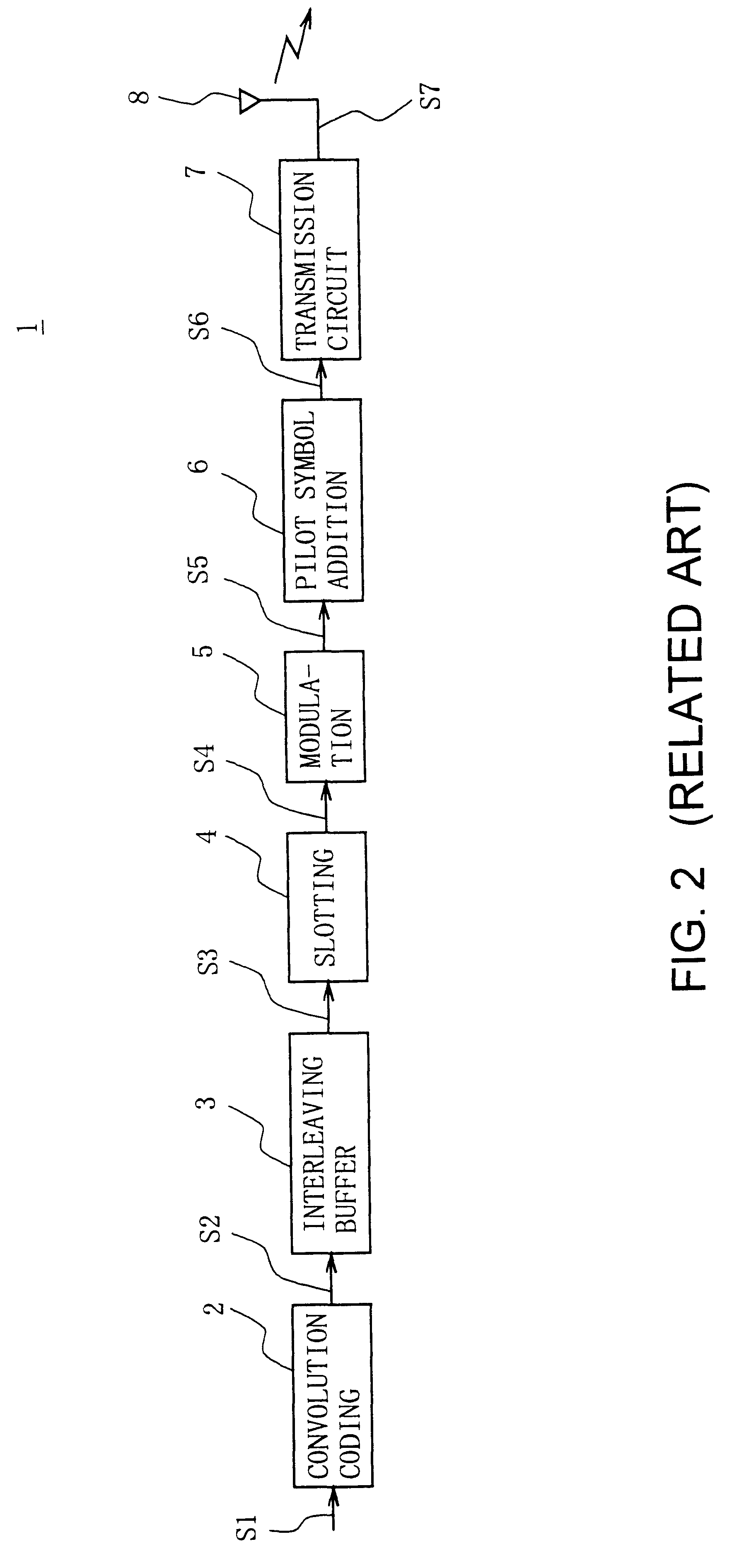
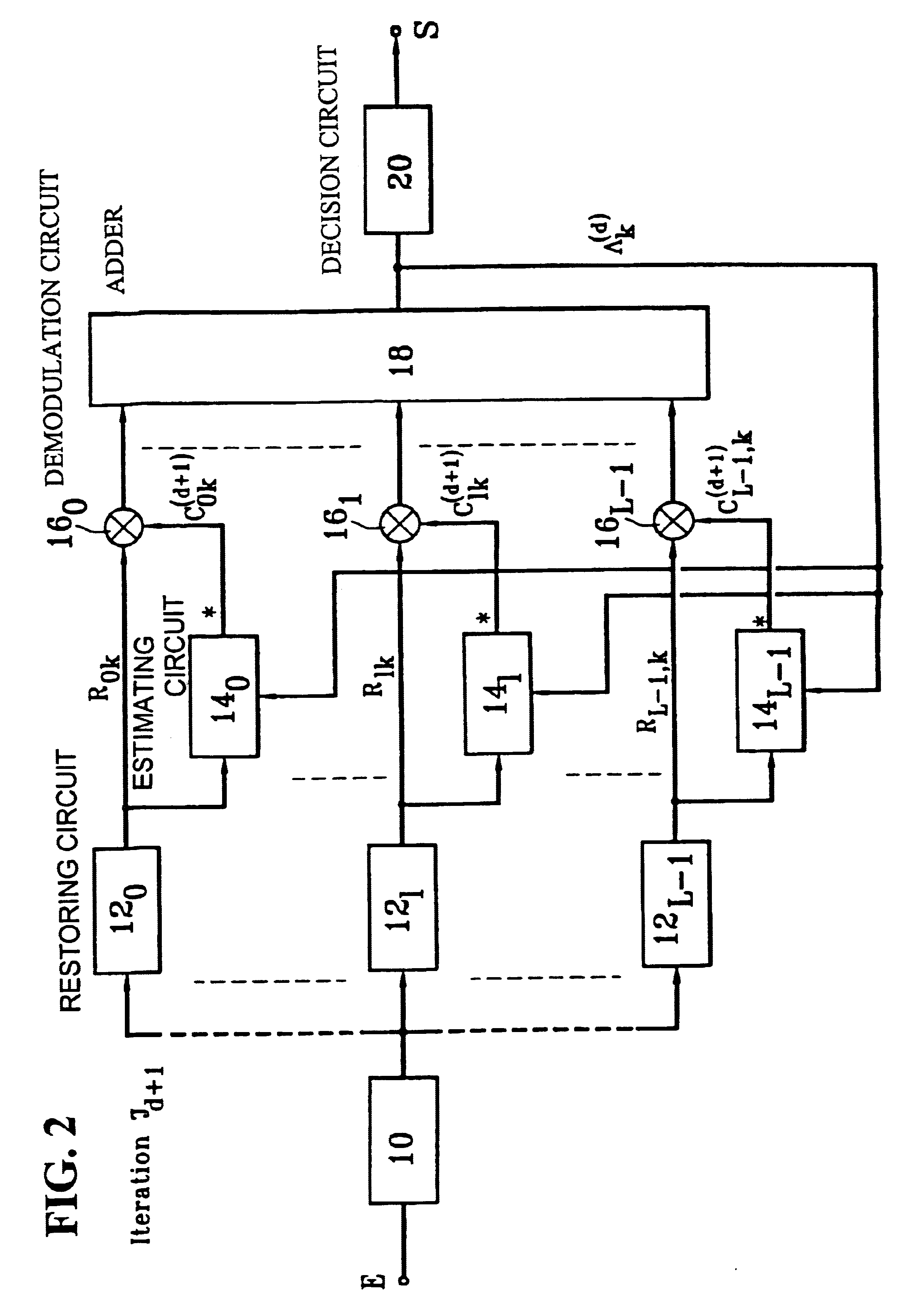
InactiveUS6243423B1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionSignomialComputer science
A receiver restores a transmitted information bit series accurately by performing maximum-likelihood series estimation. The operation of the receiver includes estimating characteristics of a transmission line for each symbol based on the amplitude and phases of pilot symbols which are extracted from reception symbol groups, calculating weighting factors showing the reliability of the transmission line in symbols based on the estimation result and the reception symbol groups, multiplying each symbol of information symbol groups which are extracted from the reception symbol groups by the weighting factors to reflect the transmission-line reliability in symbols, and restoring an information bit series by applying maximum-likelihood series estimation to coded bit groups restored from the information symbol groups on which the reliability is reflected.
Owner:SONY CORP
Carrier-phase-based relative positioning device
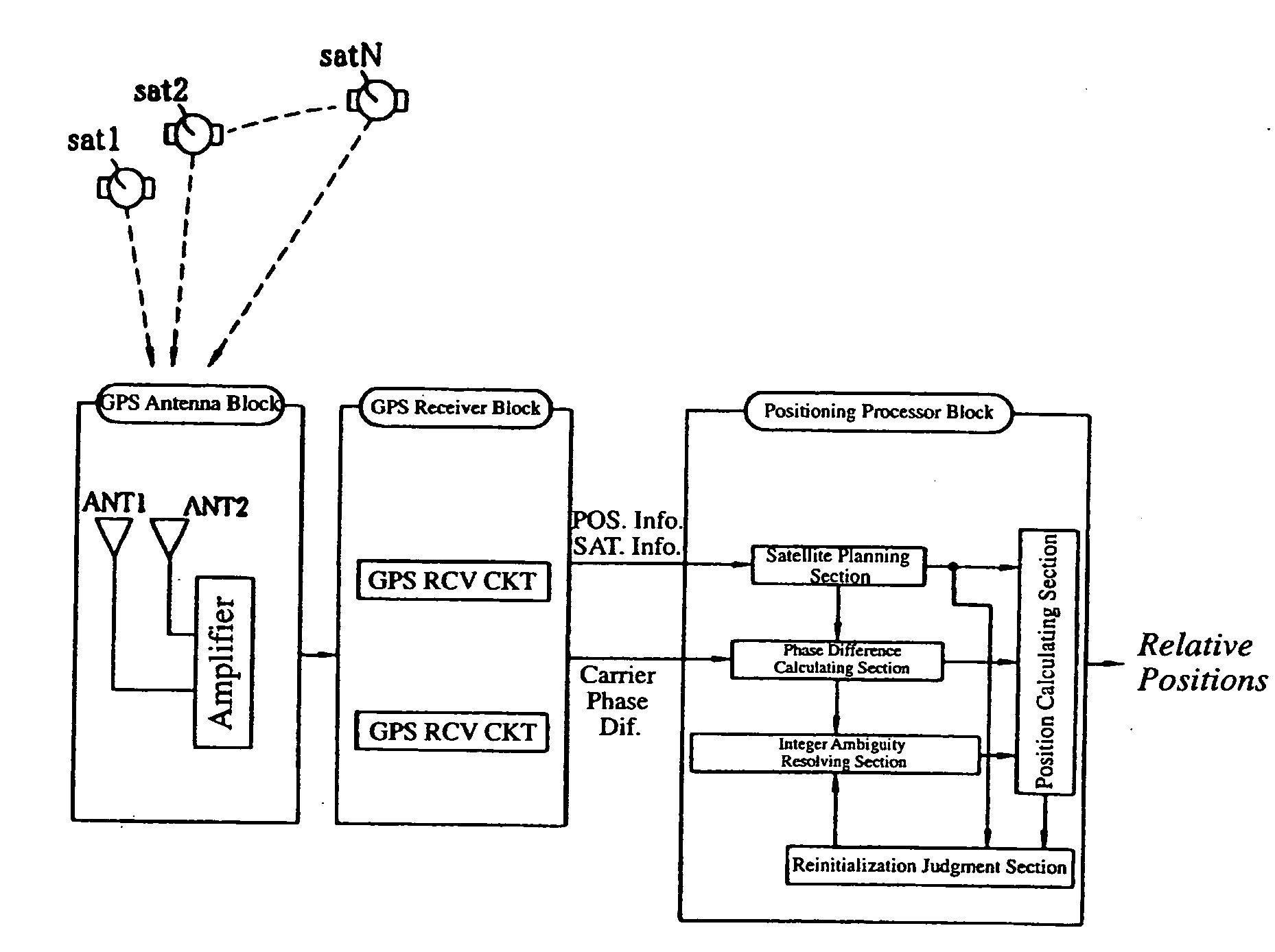
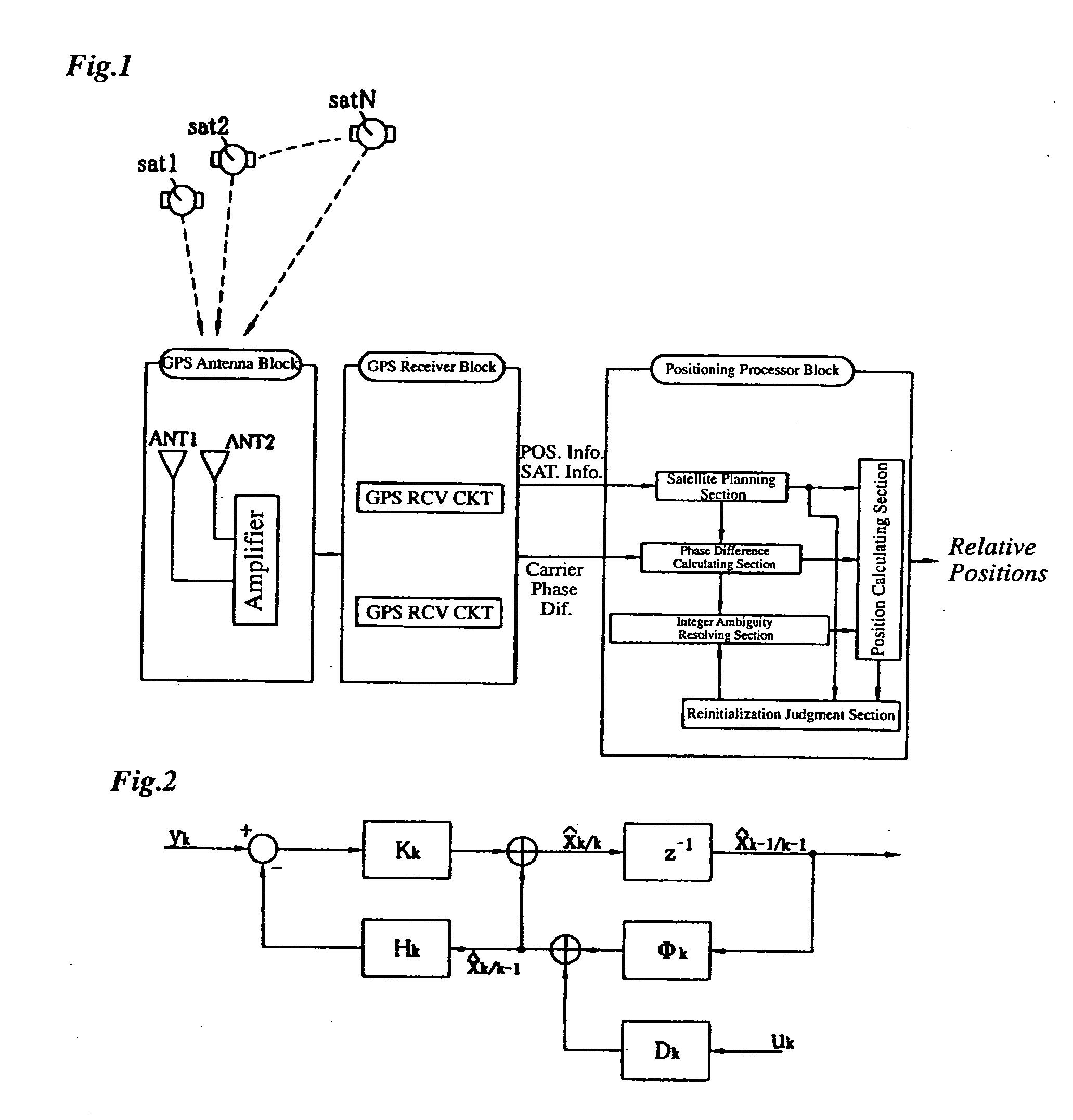
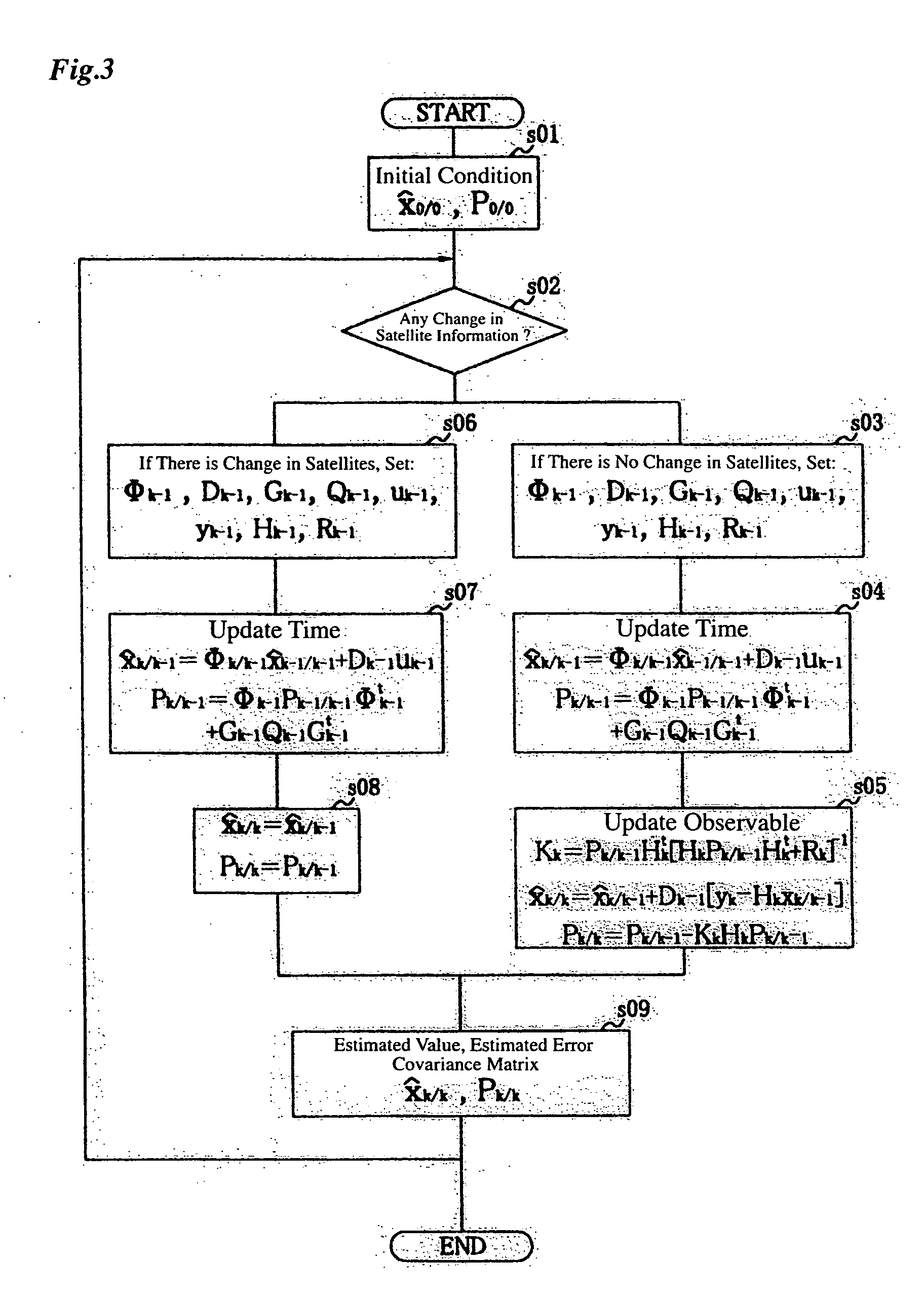
InactiveUS20040145518A1Quick fixEasily and uninterruptedly estimate integer ambiguityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterDouble phase
A carrier-phase-based relative positioning device employs a signal processing method which makes it possible to continue estimation of integer ambiguity values even when the number of positioning satellites has changed, determine an integer ambiguity value by efficiently verifying the integer ambiguities in a short time, and calculate a baseline vector. The positioning device includes an integer ambiguity resolving section which determines integer ambiguities of single or double phase differences using a Kalman filter and lambda notation. The Kalman filter is used to calculate estimated values of floating ambiguities and the lambda notation is used to calculate estimated values of the integer ambiguities based on the floating ambiguities. A candidate of a potentially true integer ambiguity that is considered most reliable is determined through various verification processes. When the number of positioning satellites has increased or decreased, or when a reference satellite has been switched, a floating ambiguity after the change in satellite information is estimated from a baseline vector estimated before the change.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
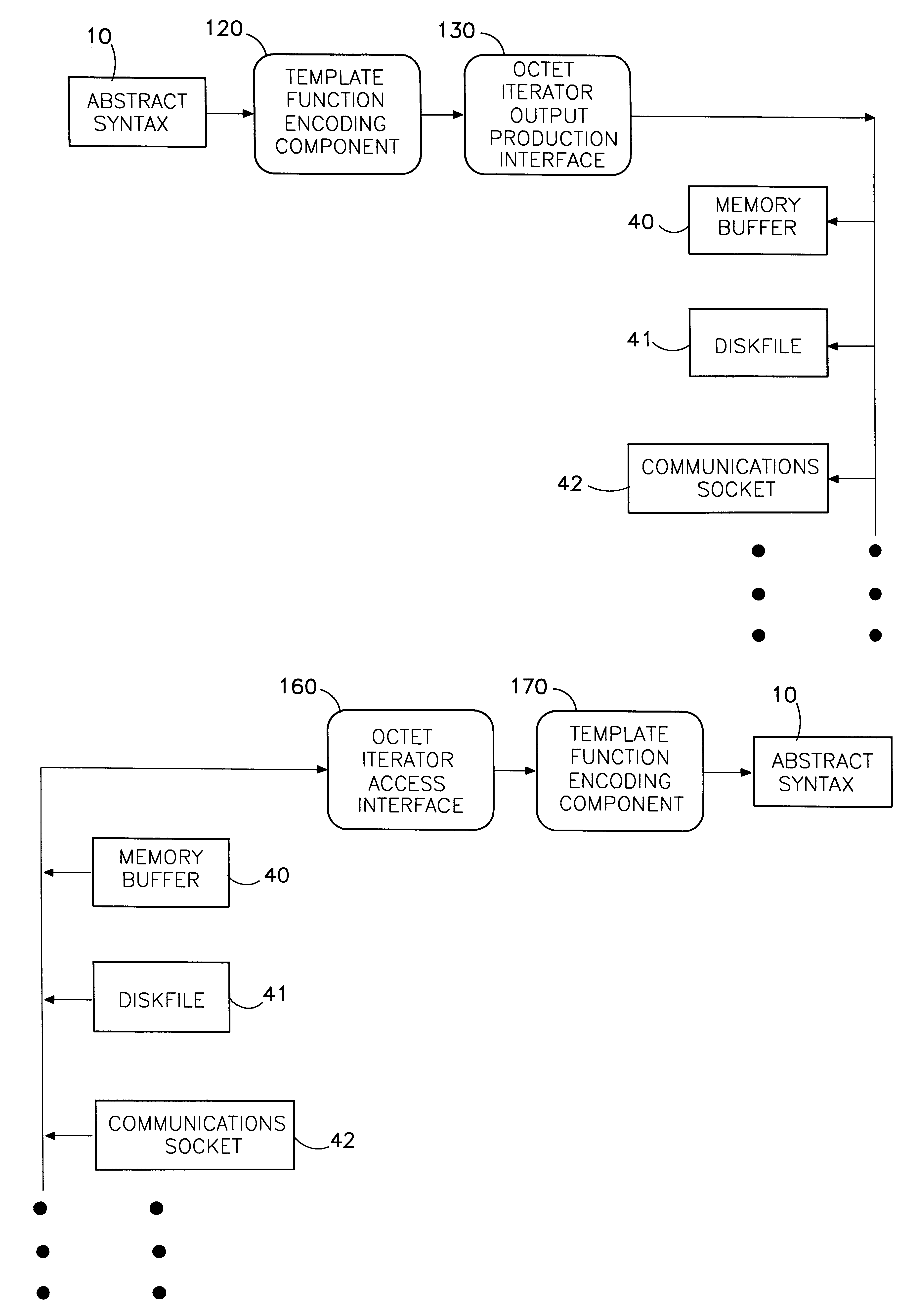
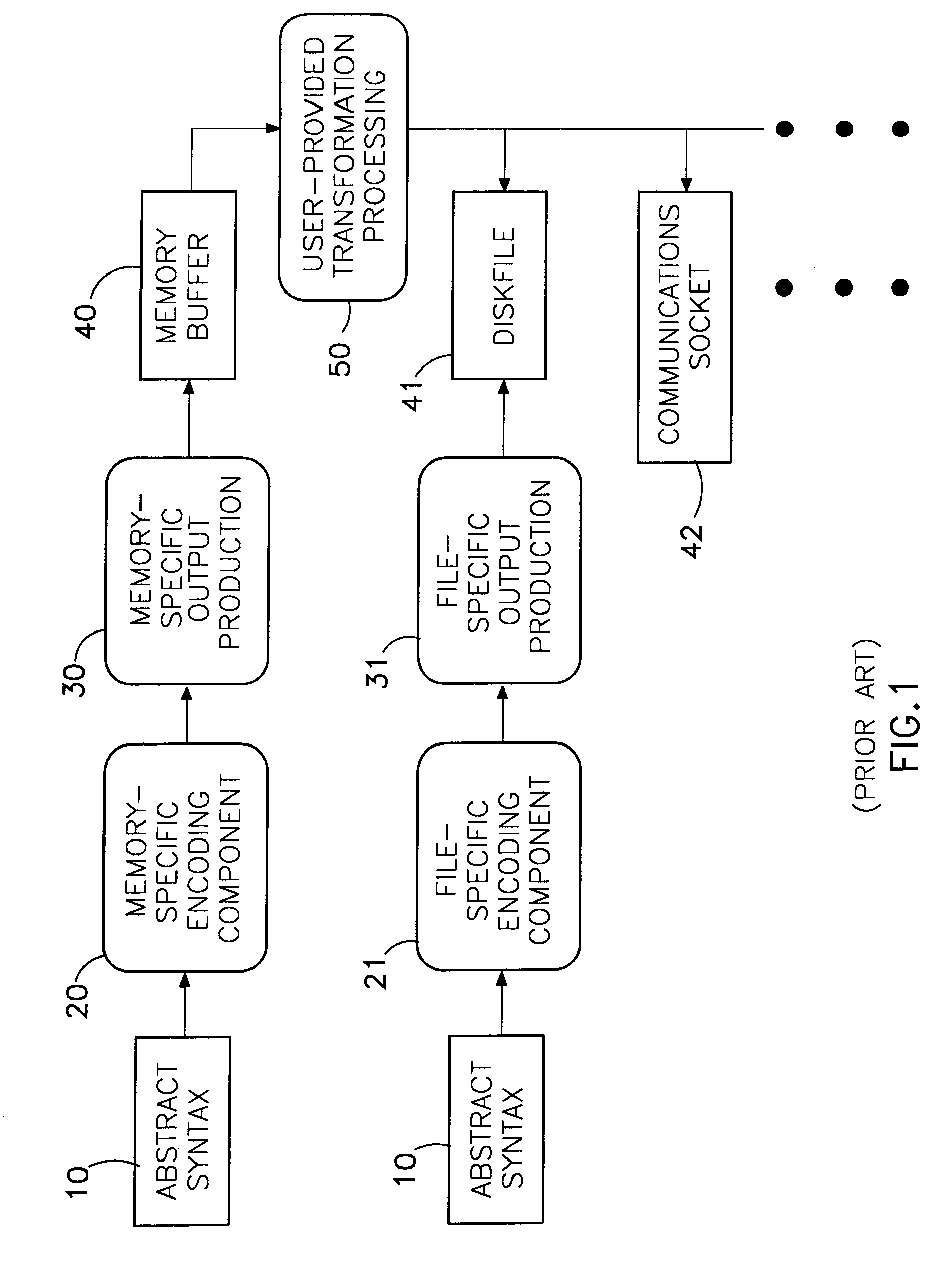
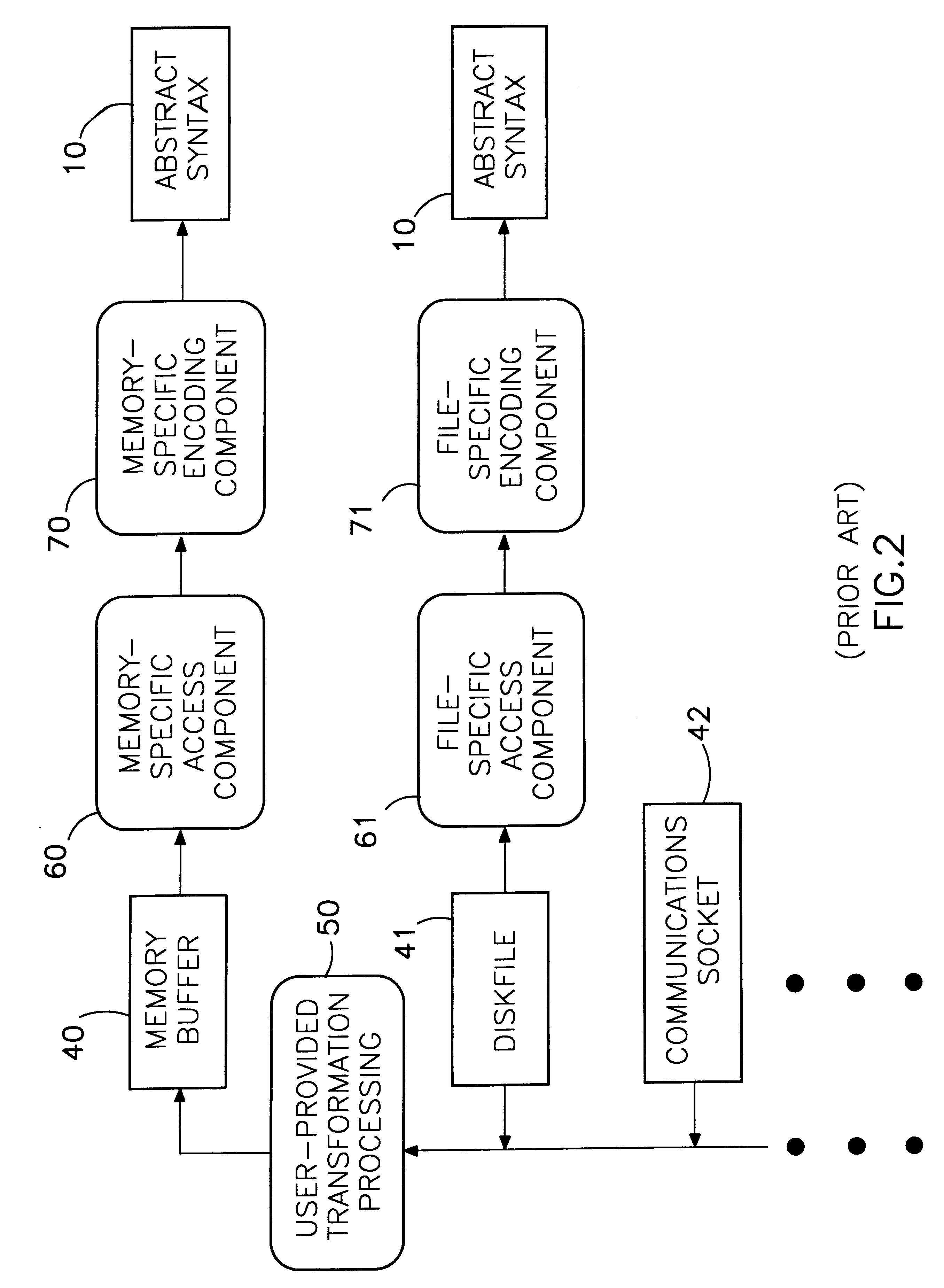
Octet iterator template interface for protocol transfer syntax coding services
InactiveUS6256778B1Minimal requirementSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsIteratorOpen Systems Interconnection
A method is disclosed that allows the concise implementation of one protocol encoding / decoding device for syntax conversion between an abstract data syntax and a transfer syntax presented in an open-ended variety of input / output / storage mediums, including, but not limited to random-access memory, disk files, communications sockets, buffer lists, and other static or dynamically-extensible storage structures. The abstract syntax is described using the Abstract Syntax Notation One standard and presented in a higher-level object-oriented programming language such as C++. The transfer syntax is specified by standardized encoding rules and results in a stream of octets (unsigned 8-bit characters) suitable for communication transport using the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) protocol model. The result of encoding (which is also the input for decoding) is called a protocol data unit (PDU). For different applications, it may be useful to present the PDU using various input / output or storage mediums such as listed above. The disclosed method employs a template function parameterized on an octet output iterator interface to provide an ASN.1 encoding mechanism, and a corresponding template function parameterized on an octet input iterator interface to provide an ASN.1 decoding mechanism, both independent of the medium in which the PDU is presented.
Owner:OLIVER CHRISTOPHER
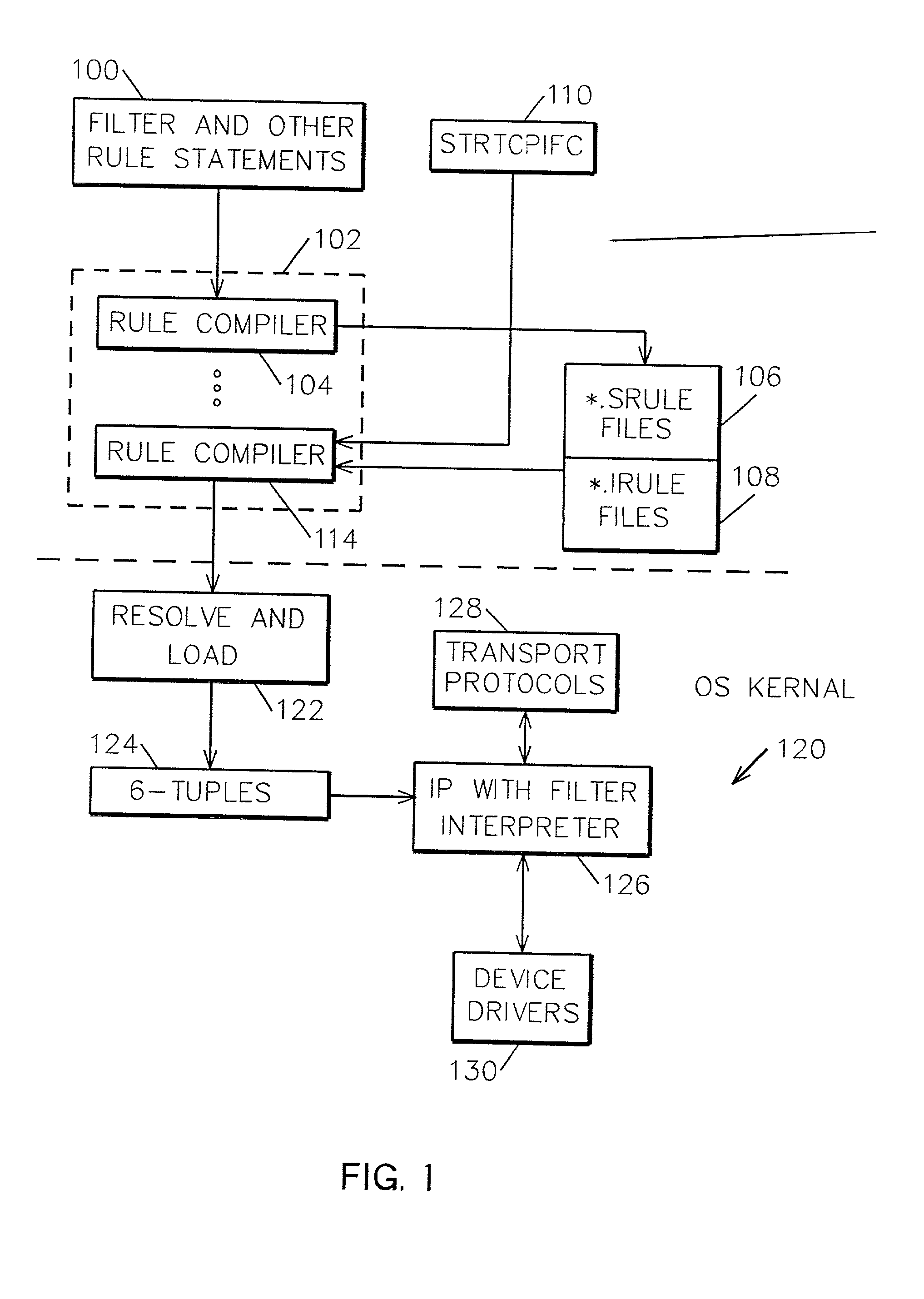
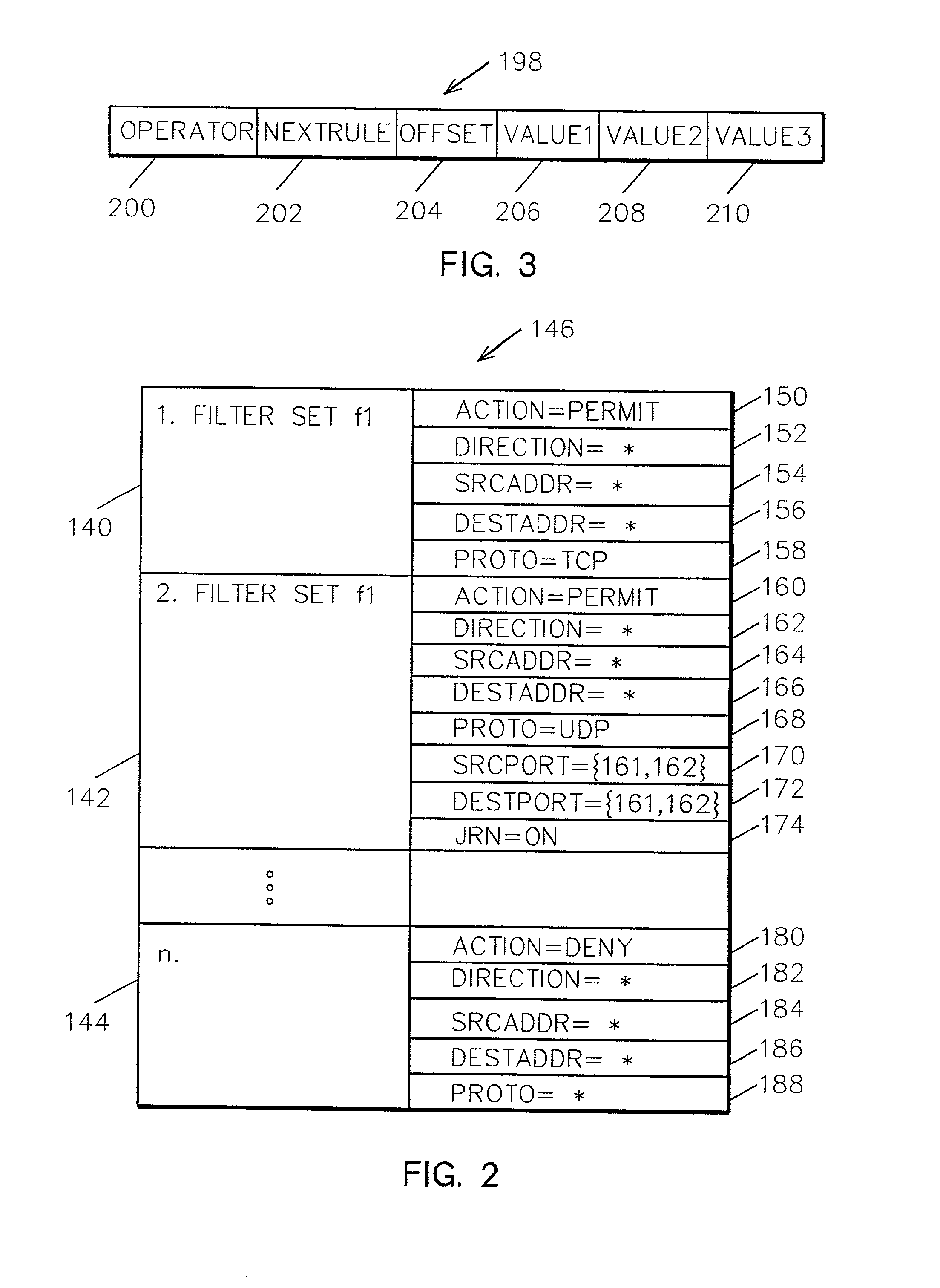
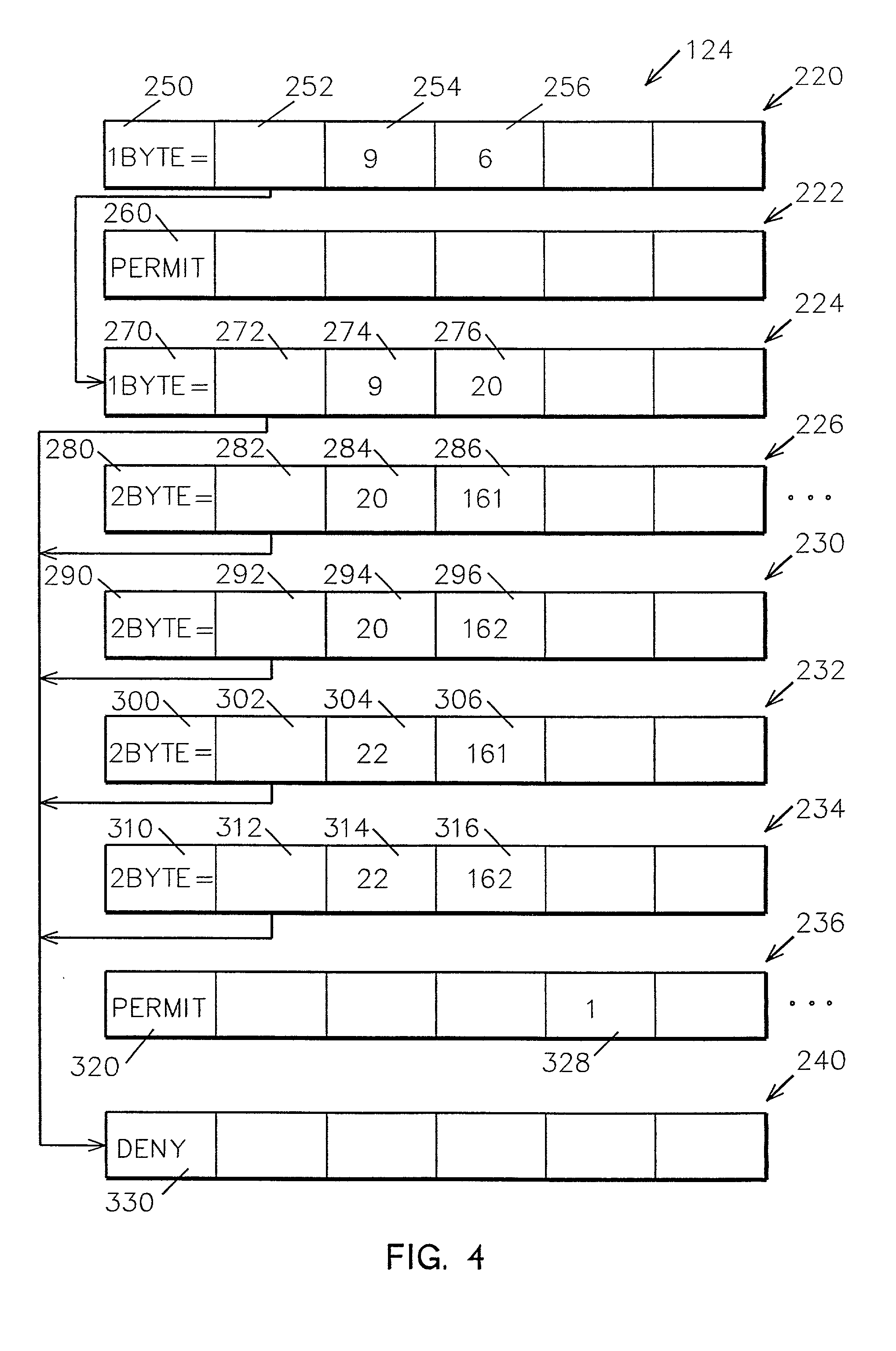
System and method for very fast IP packet filtering
InactiveUS20010000193A1Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsOperational systemFiltering rules
Small, optimized sequences of binary 6-tuples representing filter rules achieve very fast IP packet filtering. Filtering IP packets received from a caller at the physical interface to an operating system kernal is accomplished by processing FILTER rule statements entered by a user in a rules file to generate 6-tuple filtering rules, each of the 6-tuple filtering rules including an operator index; resolving relative and symbolic indexes in these 6-tuples filtering rules to form resolved filtering rules and loading the resolved filtering rules to the operating system kernal; and interpreting the resolved filtering rules for each IP packet received at the physical interface.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Bitwise adaptive encoding using prefix prediction
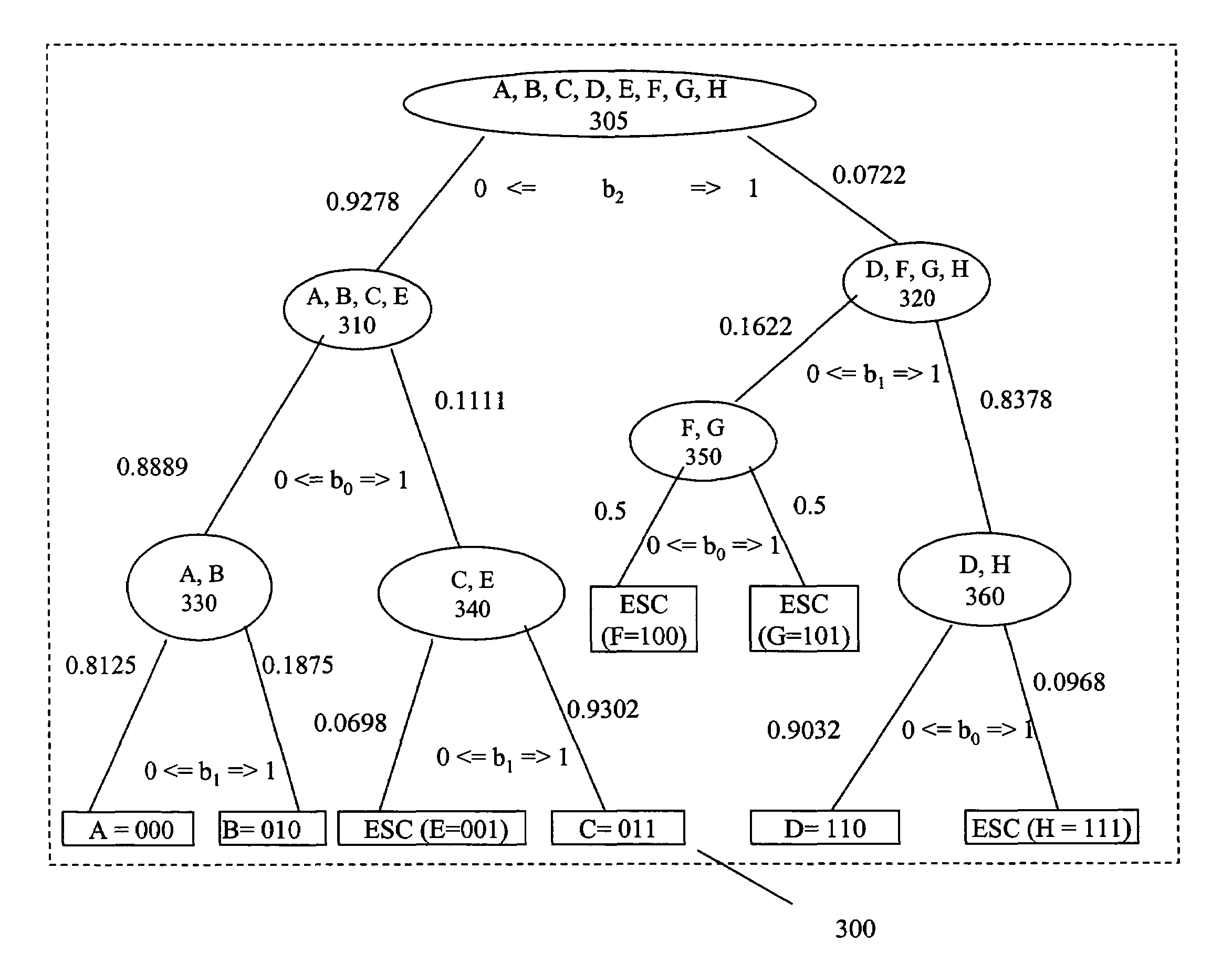
InactiveUS7274671B2Effective evaluationEfficiently encodeCode conversionData switching by path configurationAdaptive encodingAssessment data
A technique is presented for compressing data which leverages the frequency of an escape symbol for better compression. The prefix of a data string is evaluated and the probability of all characters that might succeed it is predicted in tabular form. Symbols are designated “Hit” or “Miss” based upon whether they are in the table. A binary tree is generated by partitioning nodes into Zero and One groups based on a single bit value. A partition bit is chosen to maximize the difference of probability sums of Hit symbols in Zero and One groups, with exceptions for partitions having non Hit symbols in one of the groups. A probability value is assigned to each branch, based on the probabilities of Hit and Miss symbols. Encoding or decoding a symbol is facilitated by encoding or decoding the branch probabilities on the shortest path from the root to the leaf node containing the symbol using arithmetic encoding or decoding method.
Owner:BOLY MEDIA COMM
Iterative rake receiver and corresponding reception process
InactiveUS6674740B1Code division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsDecision circuitFrequency spectrum
A CDMA radiocommunication signals receiver for receiving signals obtained from spectrum symbols spread using pseudo-random sequences and having been propagated along a number of paths. The receiver includes a filter configured to restore L unspread signals for each symbol, corresponding to L different paths, a calculating circuit configured to calculate L estimates of the L different paths, and a demodulator configured to process each of the L unspread signals using the corresponding L estimates to obtain L path contributions. Also included is an adder configured to form a sum of the L path contributions and for outputting an estimate of a received symbol, and a decision circuit configured to make a decision about a value of the received symbol based on a value of the estimate of the received symbol output by the adder. Further, the receiver processes blocks of N symbols, each block having data symbols and control symbols, each symbol being identified by a rank k that it occupies in the block, where k varies from 0 to N-1. Also, for each path identified by an index l, where l varies from 0 to L-1, and for each block, the receiver considers a vector Cl with N components that characterizes the path during the block, and the receiver defines a vector base BK, vectors of the vector base BK being N eigenvectors of the matrix E [ClCl<.T>], each vector Cl being decomposed in the vector base, where decomposition coefficients denoted GlK form independent random Gaussian variables. In addition, coefficients GlK, define a vector Gl with N components for each path l, and the calculating circuit estimates each vector Gl, using an iterative process based on EM estimation-maximization algorithm based on a maximum a posteriori probability criterion.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
System and method for solving equality-constrained quadratic program while honoring degenerate constraints
InactiveUS20060282178A1Improve accuracyIncreased complexityAdaptive controlMatrix decompositionAlgorithm
A system and method more accurately solves equality-constrained a quadratic program without significantly increasing computational load. The solver can be used to iteratively determine the solution to a general quadratic program via an active set method. The algorithm determines which of the equality constraints are binding and which constraints are not. The non-binding constraints are dropped from the active set and the objective function improved. The non-binding constraints are identified based upon the signs of the Lagrange multipliers of the equality constraints. The algorithm determines the optimization variables and the Lagrange multipliers independently of one another based upon a single matrix factorization.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Elliptic polynomial cryptography with multi y-coordinates embedding
InactiveUS20060029221A1Reduce complexitySame level of securityPublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputation complexityCryptosystem
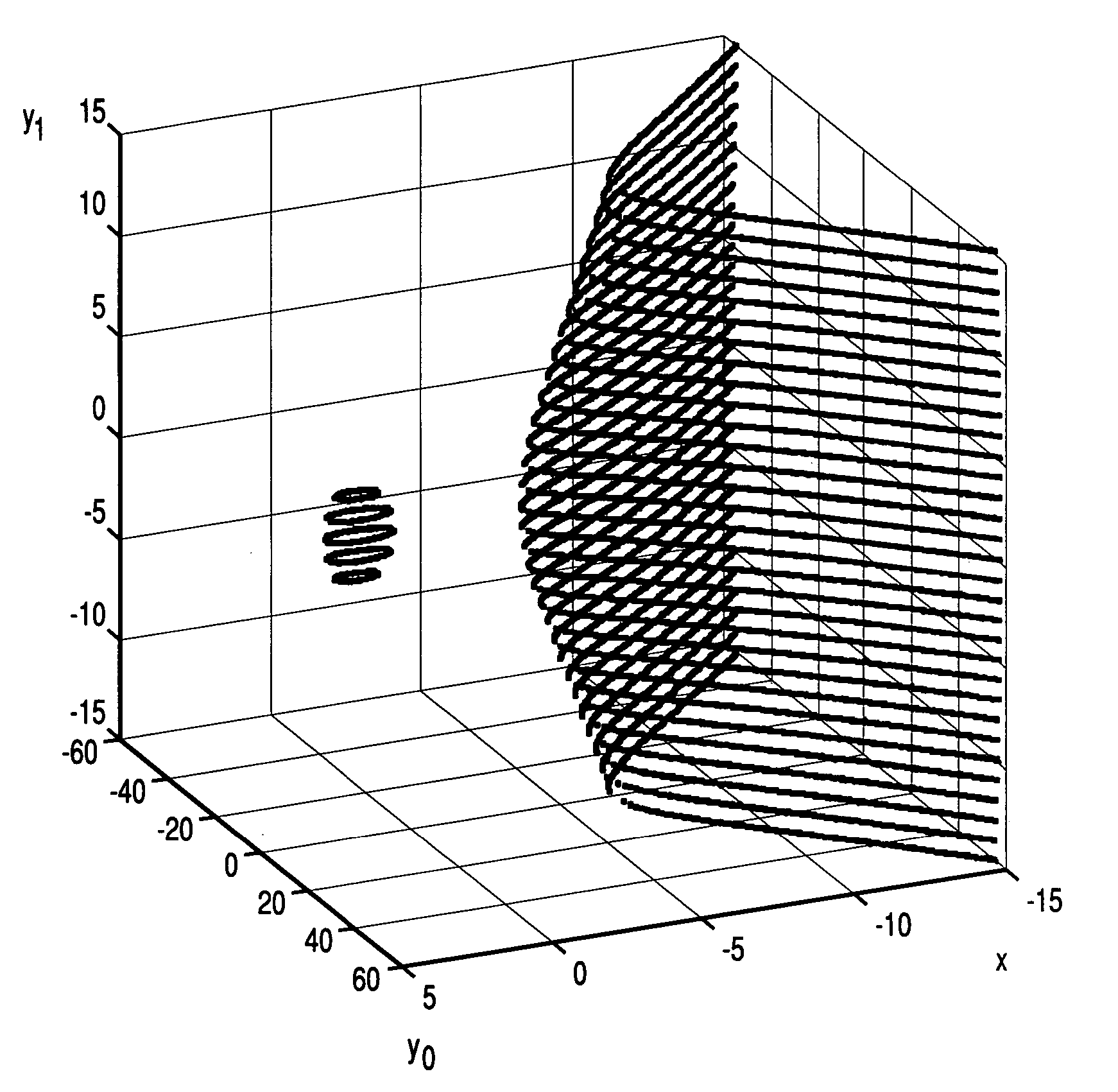
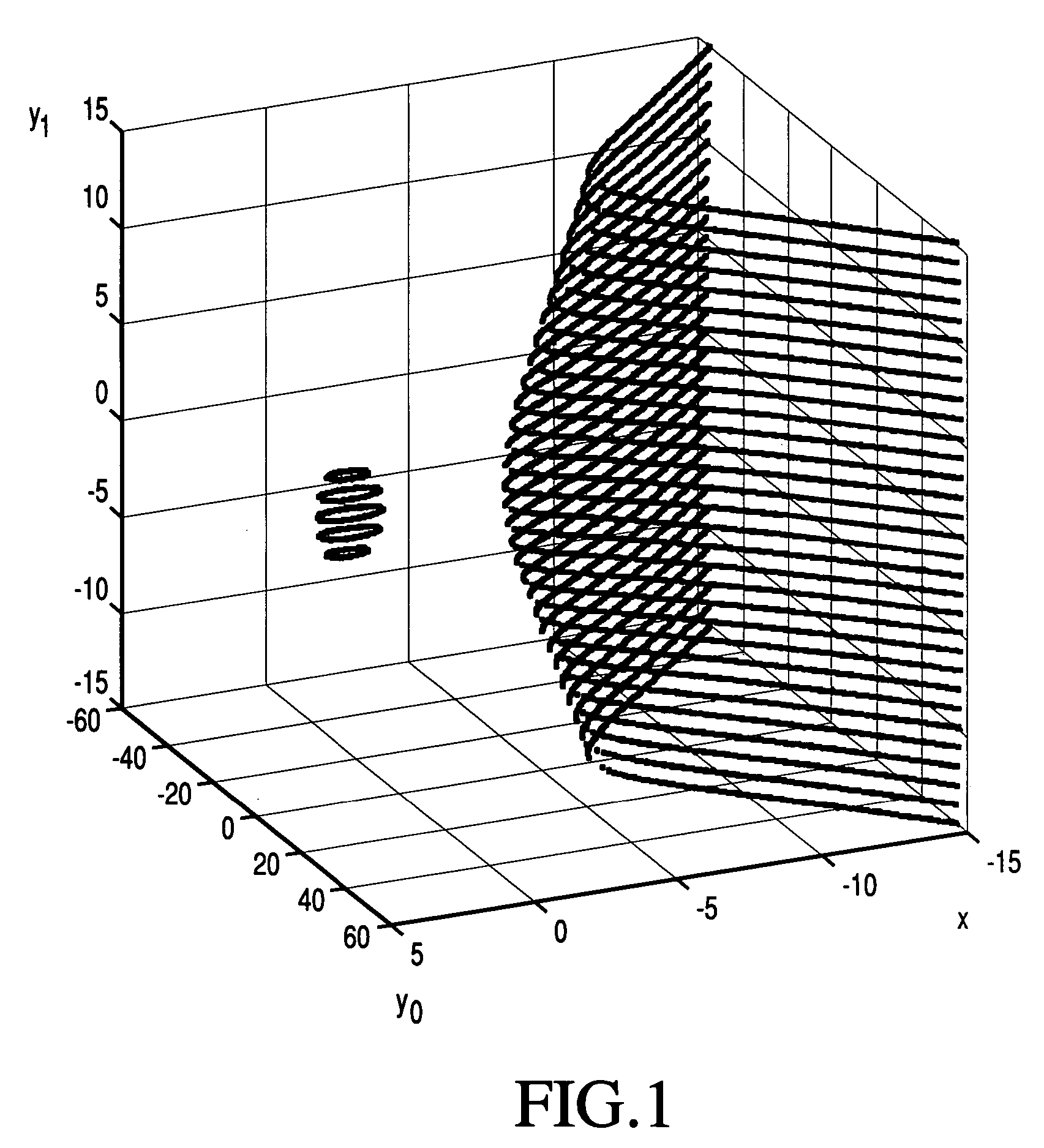
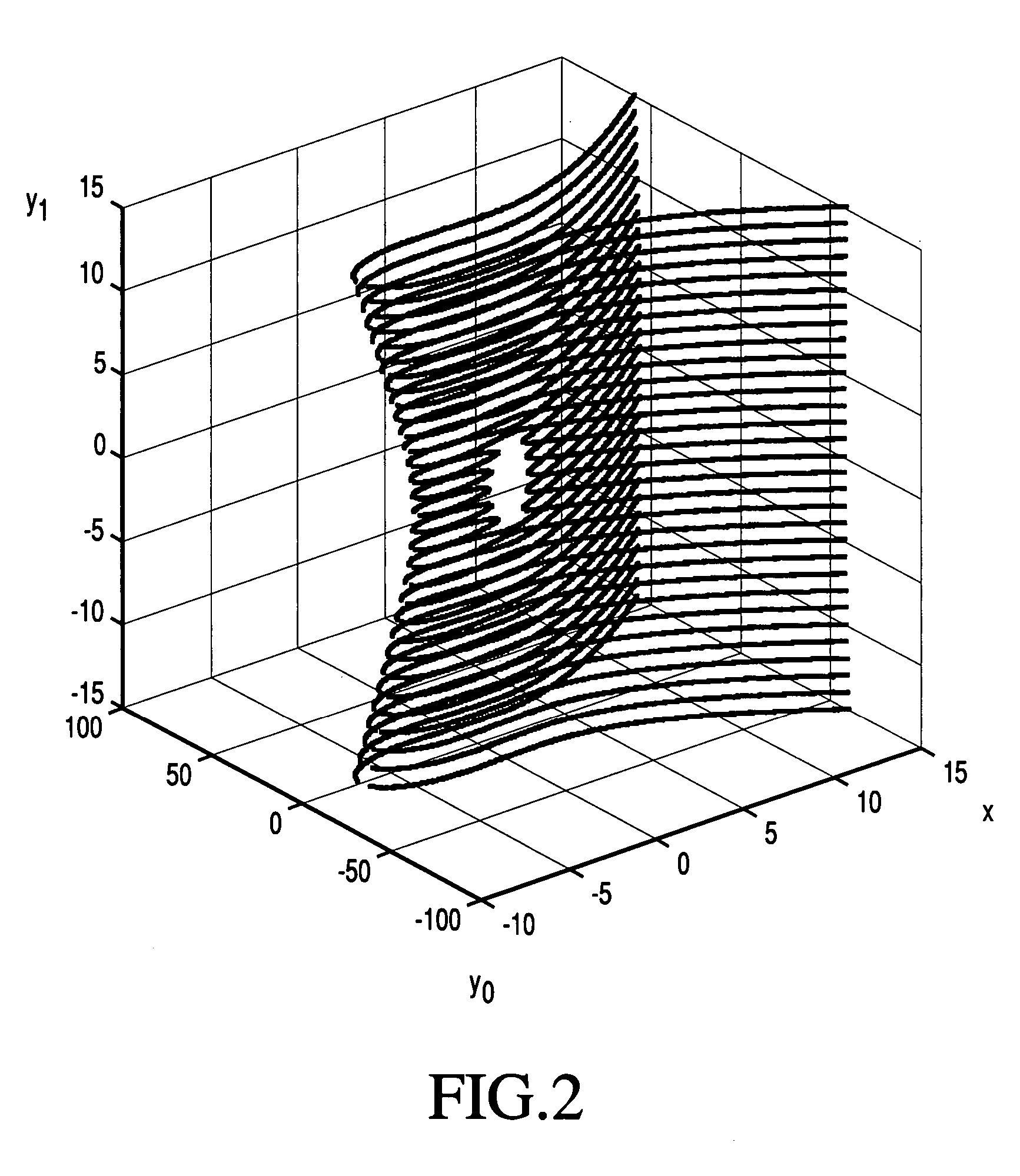
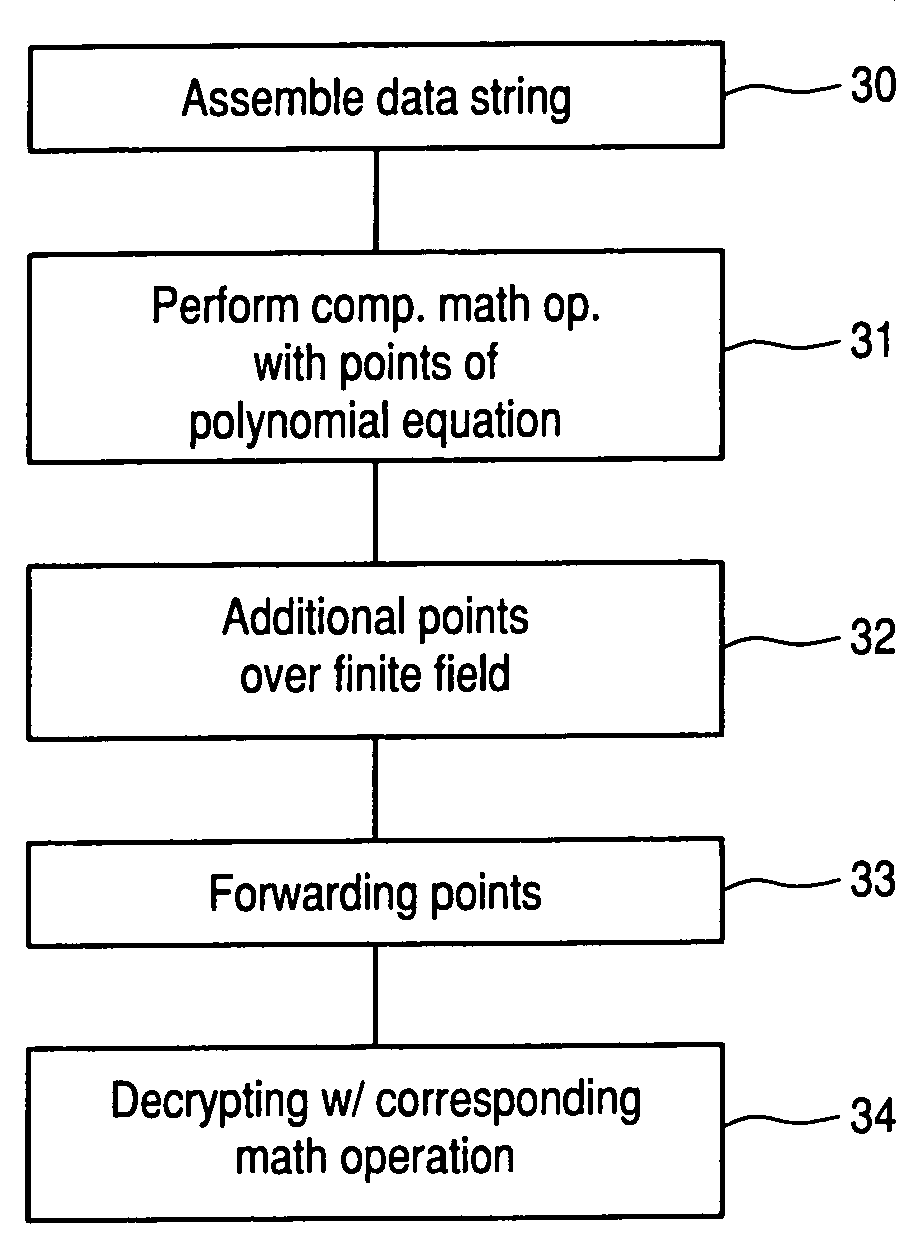
Given a set of elliptic points that satisfy an elliptic polynomial equation defined over a finite field, F, which requires N-bits to represent its elements, a new method of cryptographic encryption and decryption is presented which uses more than one quadratic variable that are termed y-coordinates to obtain an elliptic polynomial equation with multi y-coordinates instead of one y-coordinate. The additional y-coordinates are used to embed extra message data bits. A ny-fold increase in the number of embedded message data bits in a single elliptic point can be achieved with the improved method when using ny additional y-coordinates. The reason is that the number of points that satisfy an elliptic polynomial equation defined over F(p) and which can be used in the corresponding cryptosystem is increased by a factor of (#F)ny, where # denotes the size of a field. The use of the additional y-coordinates can be used to reduce computational complexity. Alternatively, this can be used to increase security by making the bit positions where data bits are embedded known only to the sender and receiver. Also, it can be used as a countermeasure by randomizing the bit positions where data bits are embedded.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Elliptic polynomial cryptography with multi x-coordinates embedding
InactiveUS7483533B2Increase the number ofData augmentationDigital data processing detailsPublic key for secure communicationComputation complexityCountermeasure
Given a set of elliptic points that satisfy an elliptic polynomial equation defined over a finite field F which requires N-bits to represent its elements, a method of cryptographic encryption and decryption is presented which uses more than one cubic variable that are termed x-coordinates to obtain an elliptic polynomial equation with multi x-coordinates instead of one x-coordinate. The additional nx x-coordinates are used to embed extra message data bits. A nx-fold increase in the number of embedded message data bits in a single elliptic point can be achieved with the improved method. The reason is that the number of points that satisfy an elliptic polynomial equation defined over F and which can be used in the corresponding cryptosystem is increased by a factor of (#F)nx, where # denotes the size of a field. The use of additional x-coordinates can be used to reduce computational complexity. Alternatively, this can be used to increase security by making the bit positions where data bits are embedded known only to the sender and receiver. Also, it can be used as a countermeasure by randomizing the bit positions where data bits are embedded.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
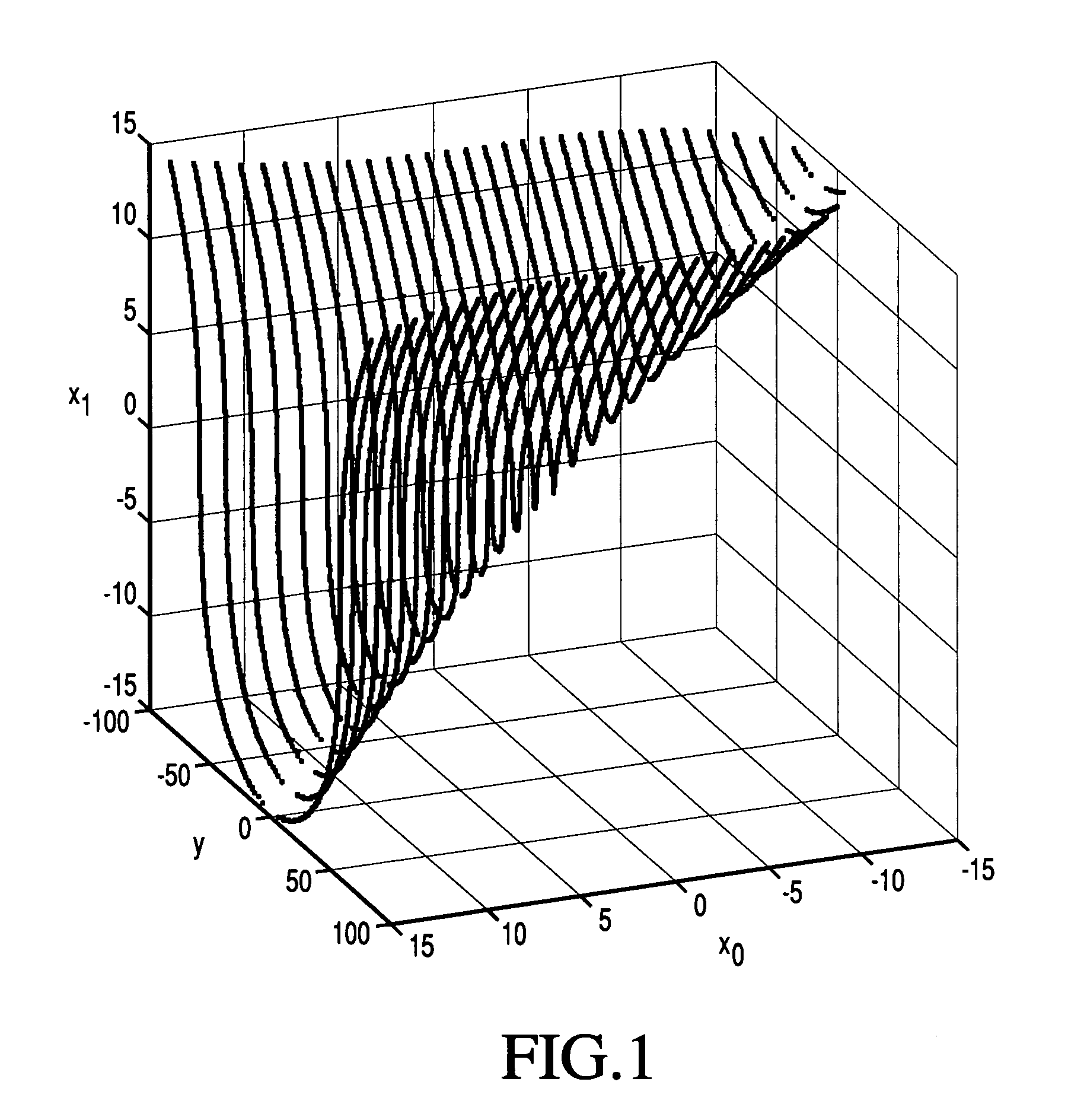
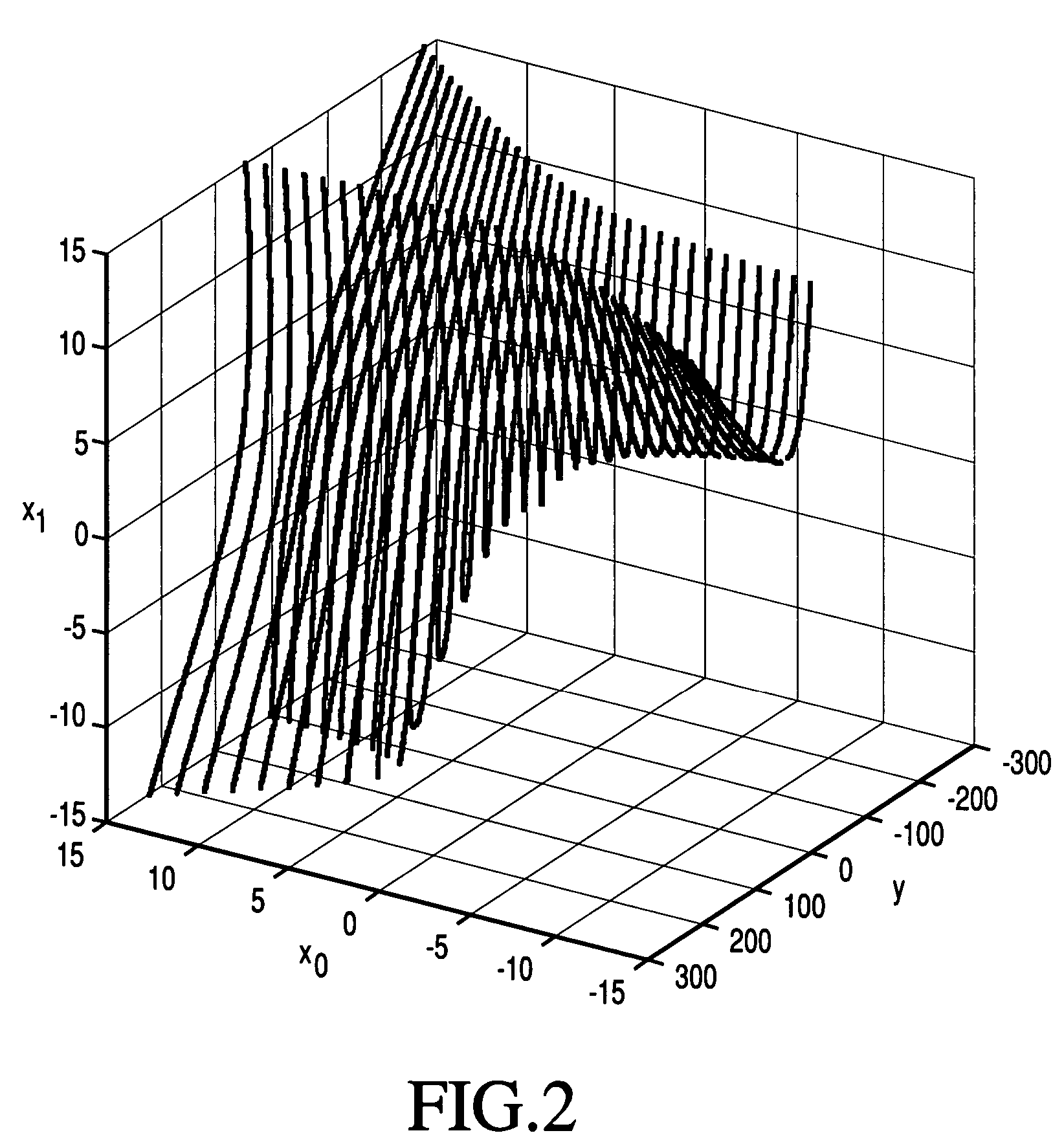
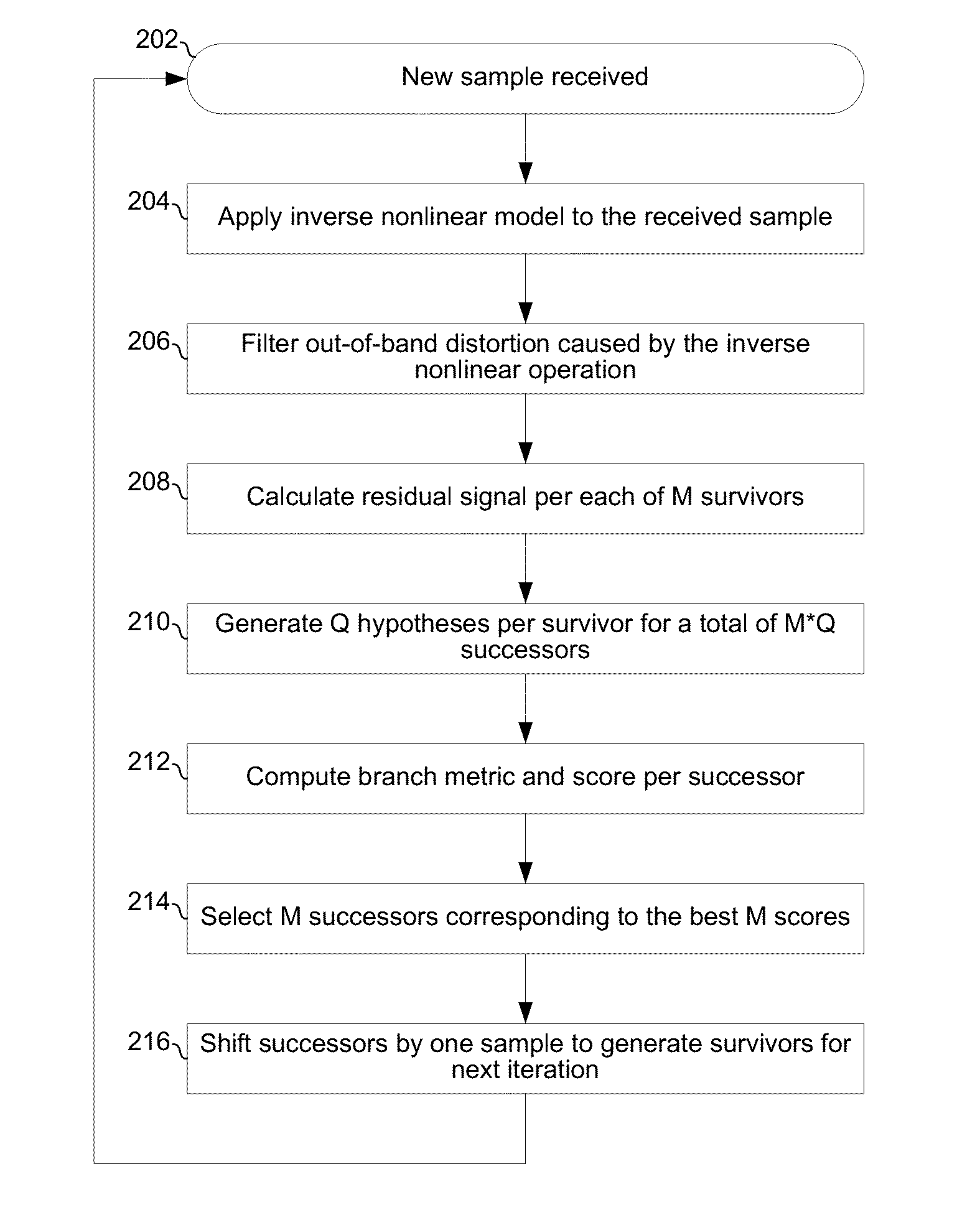
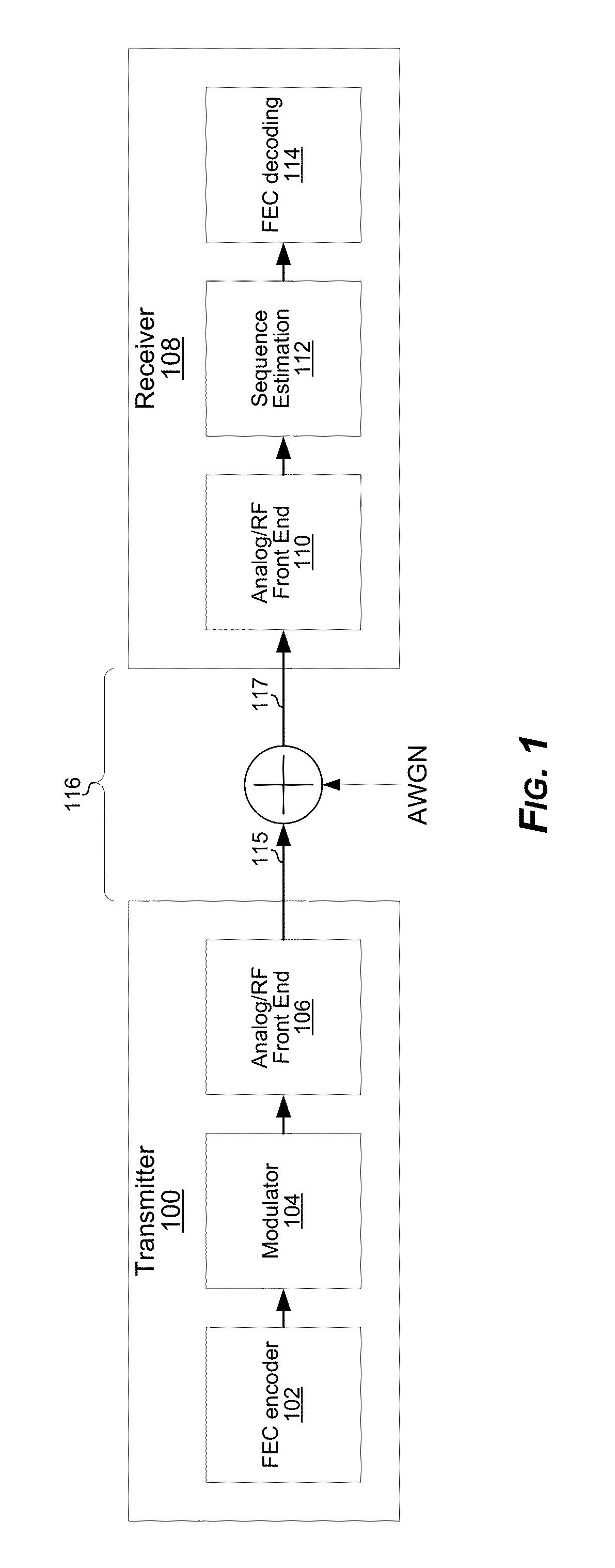
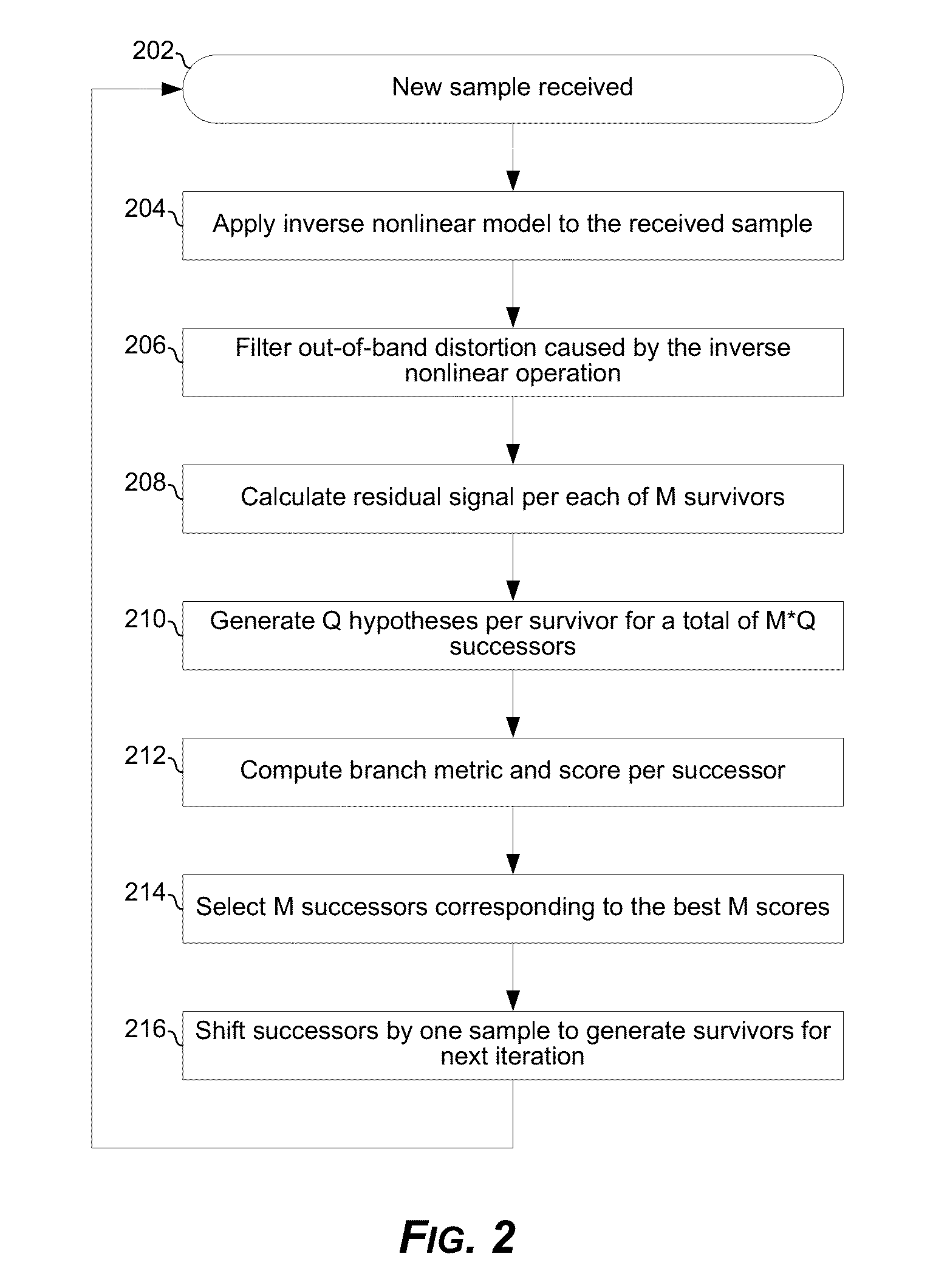
Hypotheses generation based on multidimensional slicing
A receiver is configured to receive a sample of an inter-symbol correlated (ISC) signal, the sample corresponding to a time instant when phase and / or amplitude of the ISC signal is a result of correlation among a plurality of symbols of a transmitted symbol sequence. The receiver may linearize the sample of the ISC signal. The receiver may calculate a residual signal value based on the linearized sample of the ISC signal. The receiver may generate an estimate of one or more of said plurality of symbols based on the residual signal value. The linearization may comprise applying an estimate of an inverse of a non-linear model. The non-linear model may be a model of nonlinearity experienced by the ISC signal in a transmitter from which the ISC signal originated, in a channel through which the ISC signal passed en route to the receiver, and / or in a front-end of the receiver.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Code static detection method
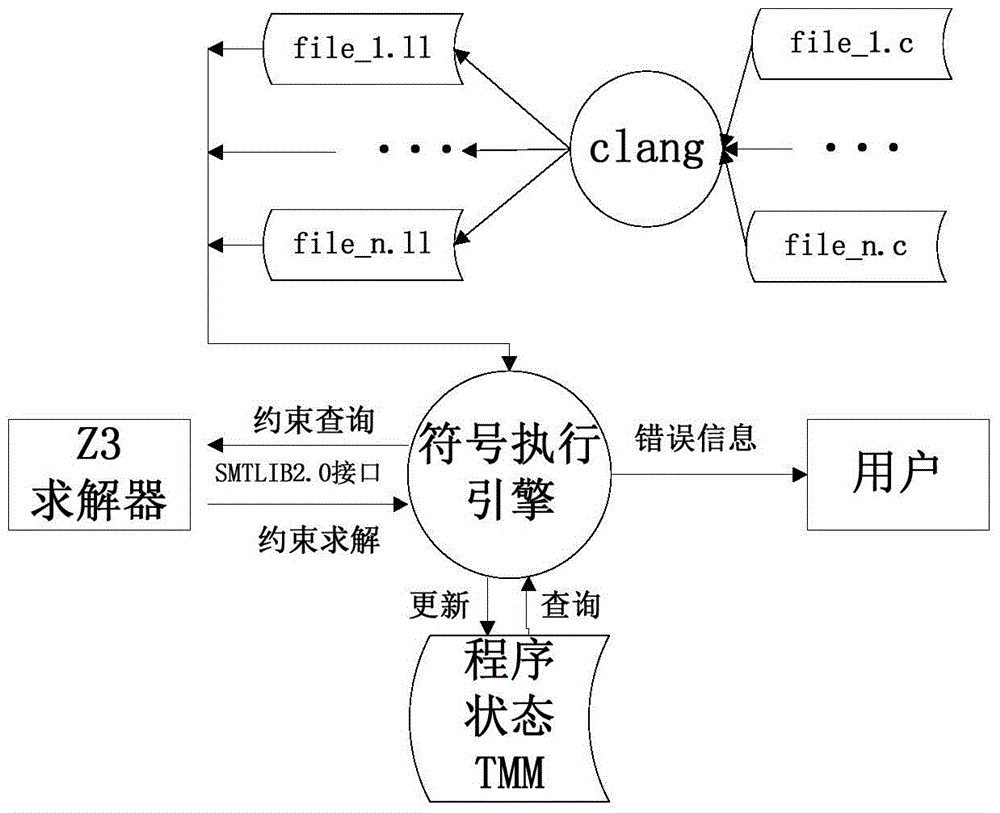
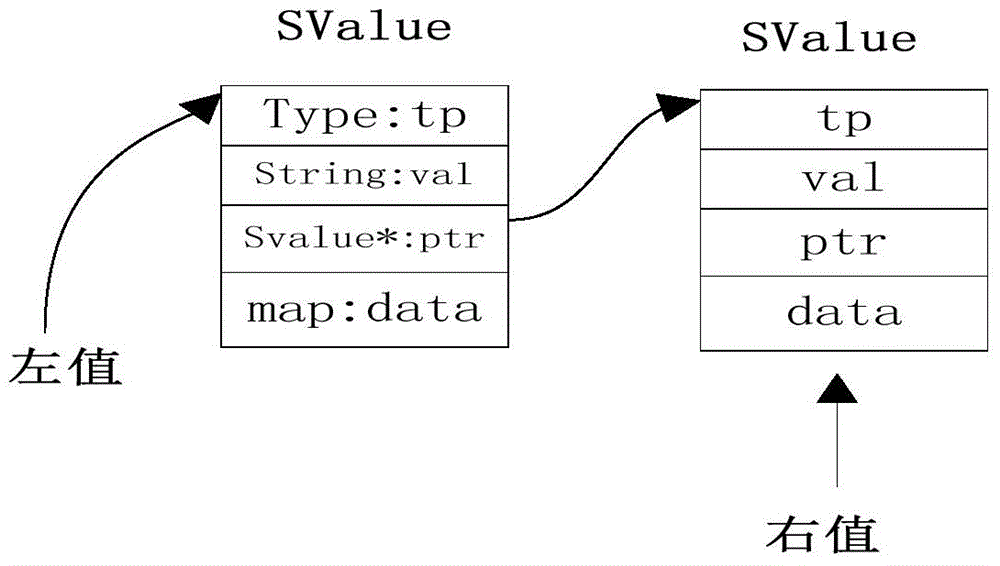
ActiveCN104965788AEnable cross-language analysisRealize analysisSoftware testing/debuggingArray data structureSource code
The invention discloses a code static detection method, particularly relates to an LLVM IR (low level virtual machine intermediate representation) based symbol execution algorithm in the technical field of utilization of initial values of variable symbols of given programs, and solves the problems of single supported language and incapability of better processing pointers and aliases for a static detection method in the prior art and the problems in detecting potential program bugs and the like. The method comprises the steps of: (1) obtaining a source code, and preprocessing and converting the source code into an LLVM assembly program; (2) simulating interpretive execution of the LLVM assembly program obtained by conversion by applying the symbol execution algorithm, and recording the symbol value of each variable in different paths and the constraint conditions of each path; and (3) according to the recorded symbol value of each variable in different paths and constraint conditions of each path, calling an SMT (satisfiability modulo theories) solver Z3 to check whether the symbol value of the variable meets the path constraint and the bug constraint, and judging whether the program has potential bugs. The method is applied to array bound overflow, division by zero and null pointer dereference.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
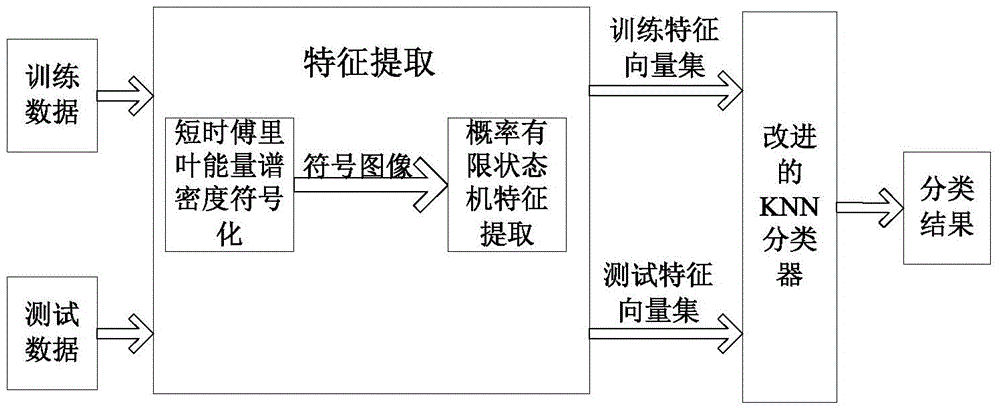
Bearing fault diagnosis method based on symbolic probabilistic finite state machine
ActiveCN104931263AImprove stabilityImprove practicalityMachine bearings testingFeature vectorFeature extraction
The invention discloses a bearing fault diagnosis method based on a symbolic probabilistic finite state machine. The method comprises the steps that a one-dimensional time series with concentrated training data is converted to a two-dimensional symbol matrix; a probabilistic finite state machine model is constructed for the two-dimensional symbol matrix; an extracted left feature vector is used as a feature value to represent an original bearing signal; and finally an improved K- nearest neighbor classification (KNN) algorithm is used to learn the left feature vector of a bearing signal of a known failure category. For a bearing signal to be diagnosed, the same feature extraction method is used, and then the improved KNN algorithm is used to realize fault diagnosis. According to the invention, a K-means clustering method is used to improve the traditional K- nearest neighbor classification algorithm, and the computation efficiency and the fault diagnosis effect of the bearing diagnosis algorithm are improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
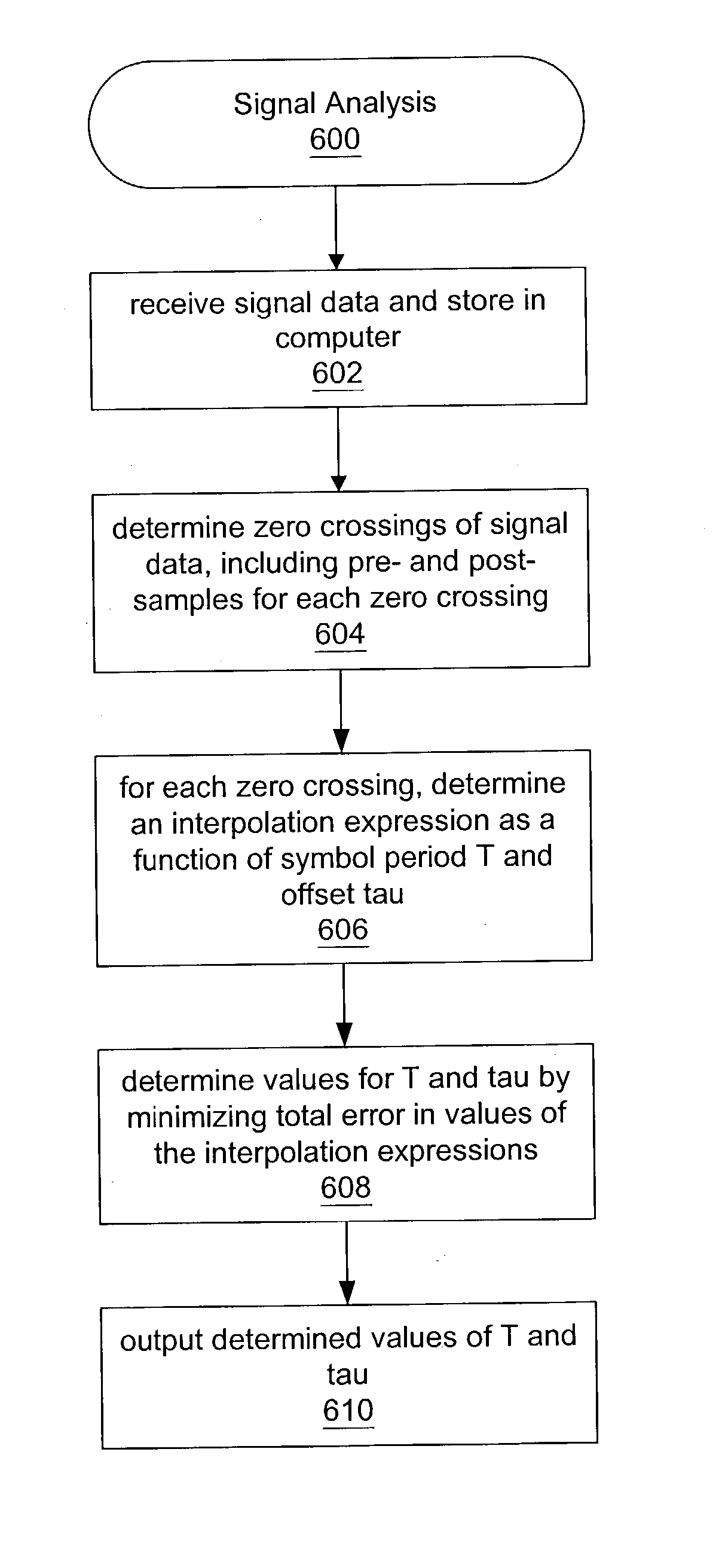
Zero crossing method of symbol rate and timing estimation
ActiveUS20040131113A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionAlgorithmSymbol of a differential operator
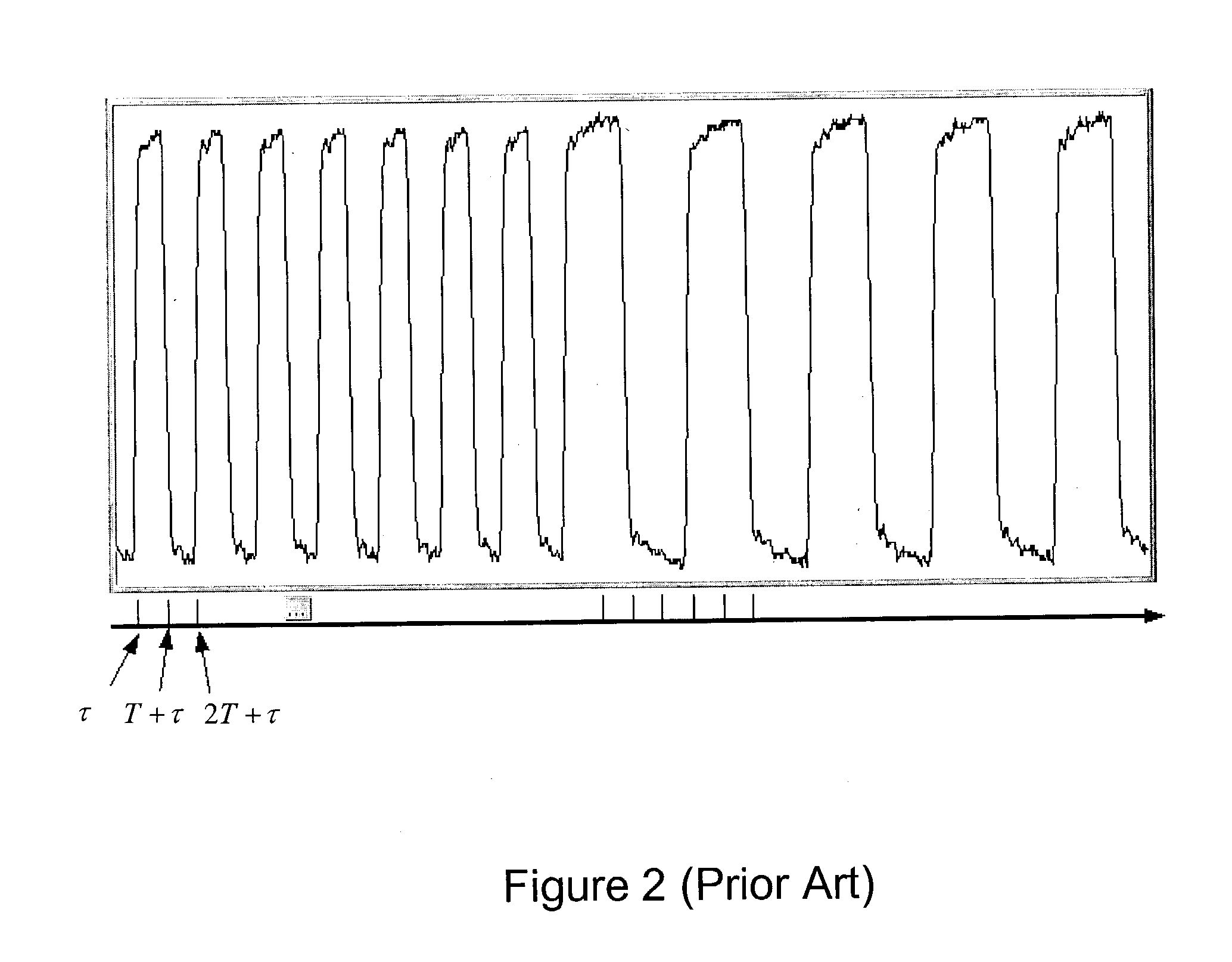
System and method for analyzing communication signals. A digital signal comprising multiple samples is received, representing a plurality of binary symbols. Zero crossings of the signal are determined, each comprising a respective first sample immediately preceding the zero crossing and a respective second sample immediately following the zero crossing. Per zero crossing, an error expression is determined interpolating between the first and second samples as a function of estimated period T and estimated offset tau of the signal. Based on the error expressions, values of T and tau are determined using a linear fit that minimizes a total error of values of the error expressions. T and tau are usable in analyzing the signal, e.g., each zero crossing corresponds to a respective symbol represented by a respective segment of the signal. The segments are overlaid based on T and tau, forming an eye diagram usable to analyze the signal.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com