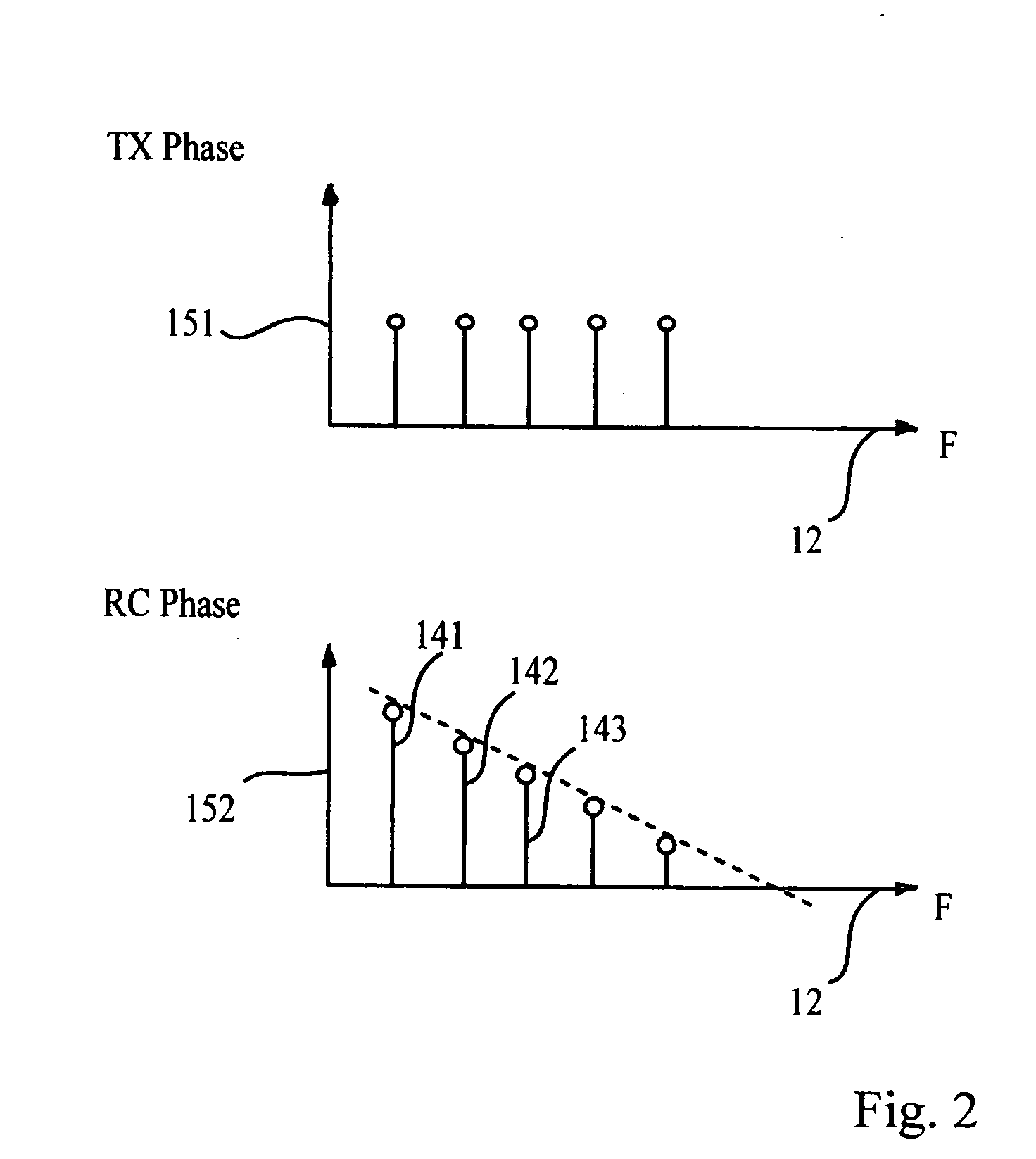
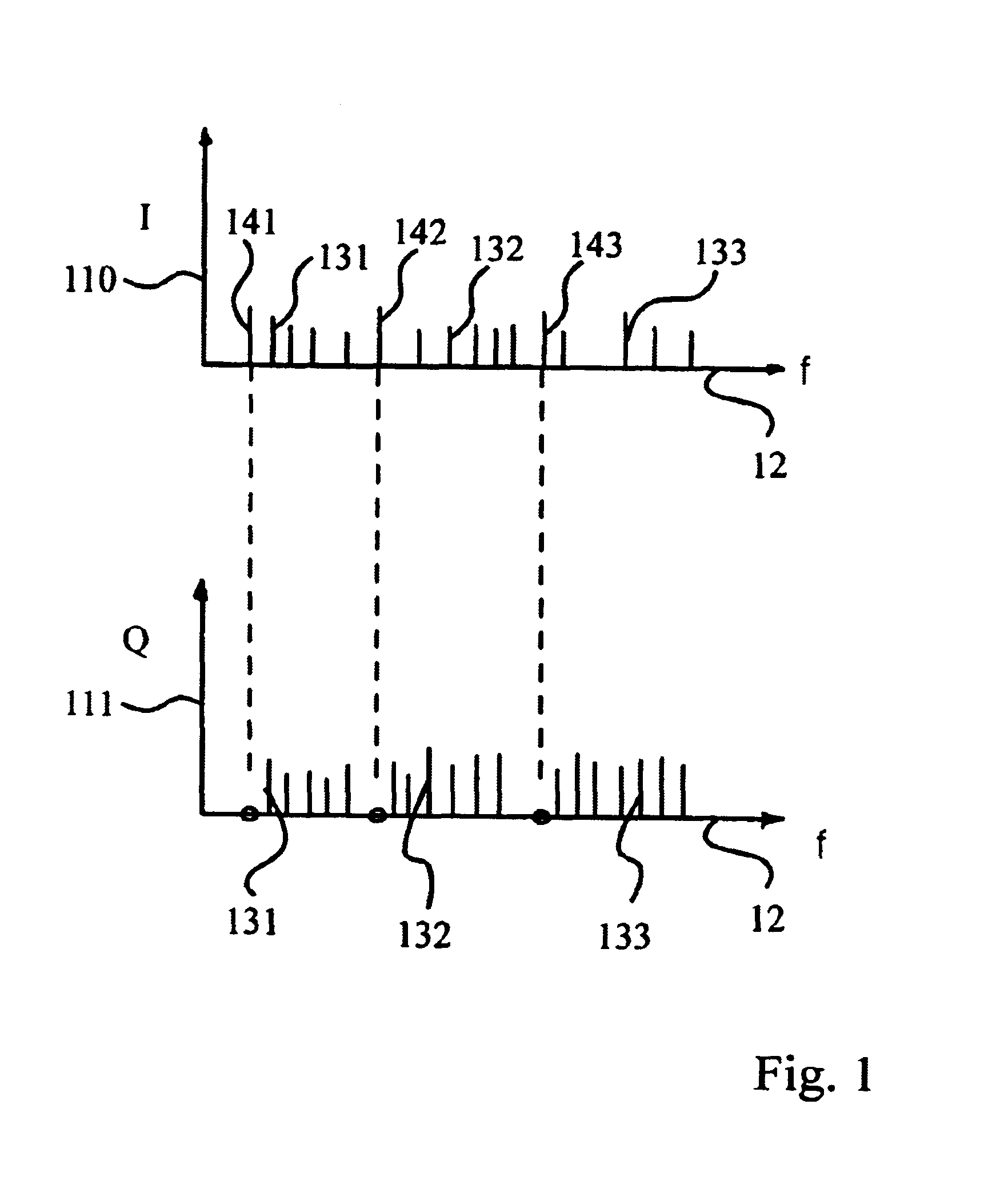
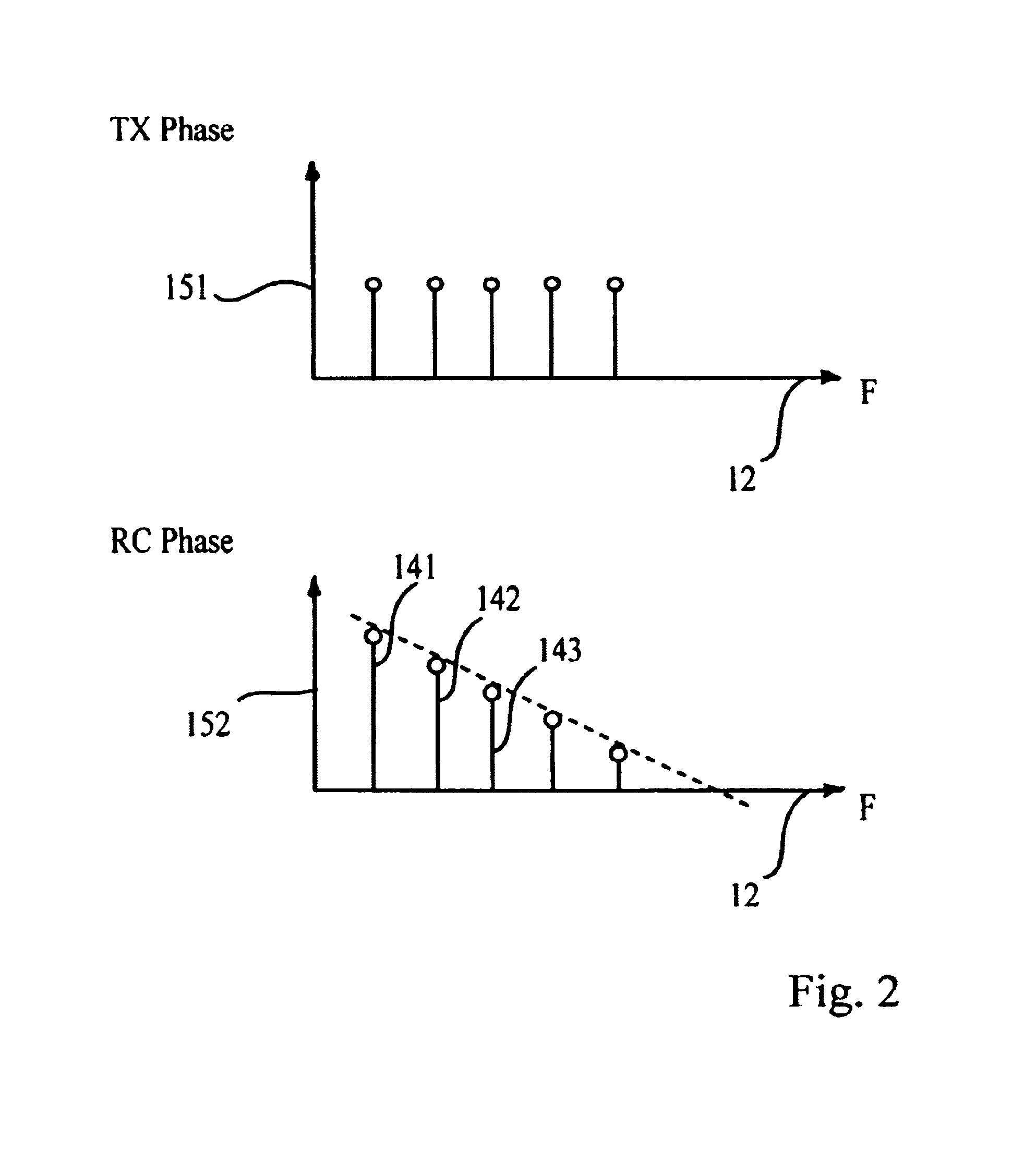
Patents
Literature
788 results about "Frequency correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
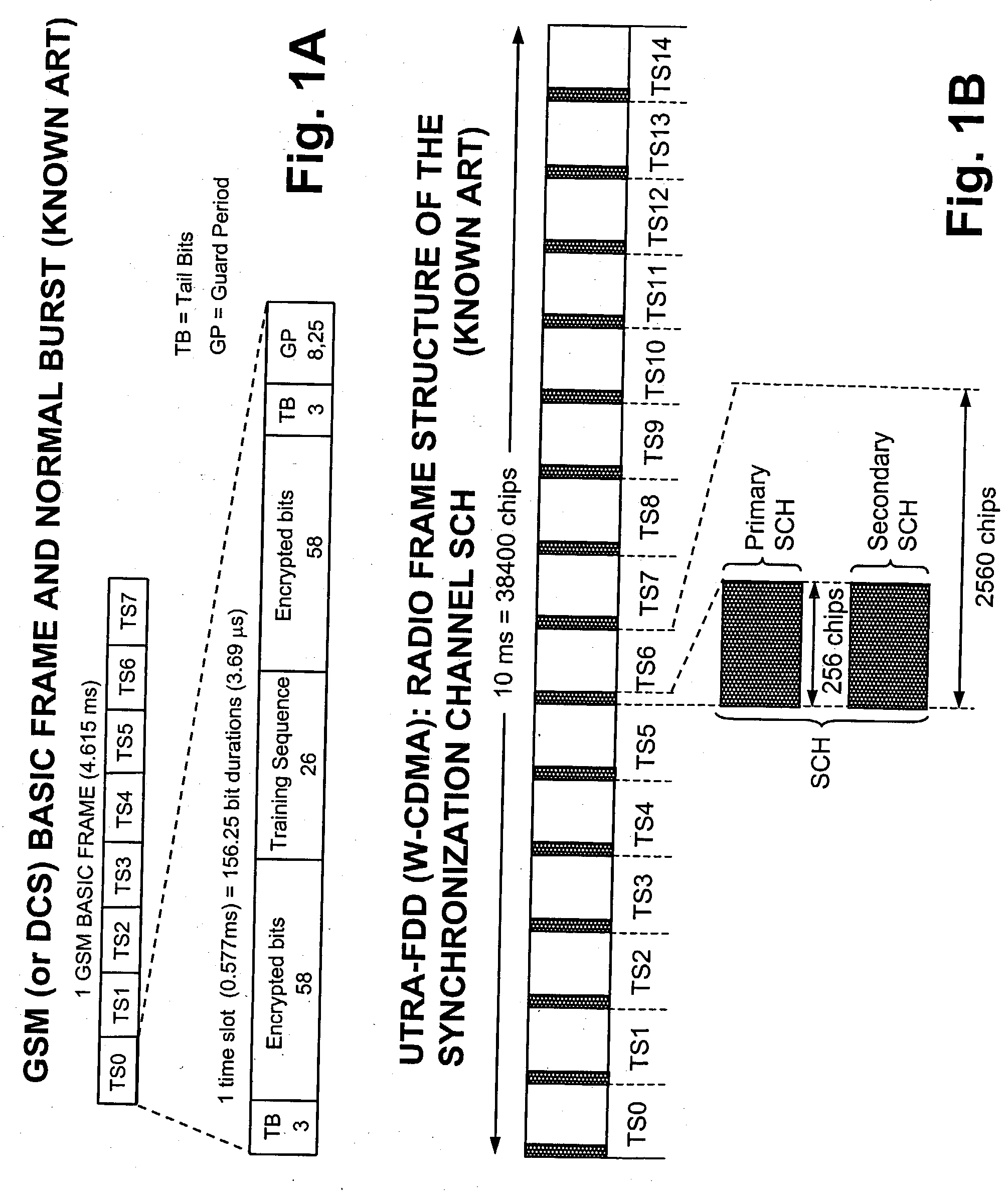
The Frequency Correction Channel is a broadcast channel used by GSM base stations. It provides a unique tone of 67.7 kHz for the Mobile Stations. This tone is used to synchronize the local clock of the mobile receiver with the base station. This is needed to correctly extract the data.
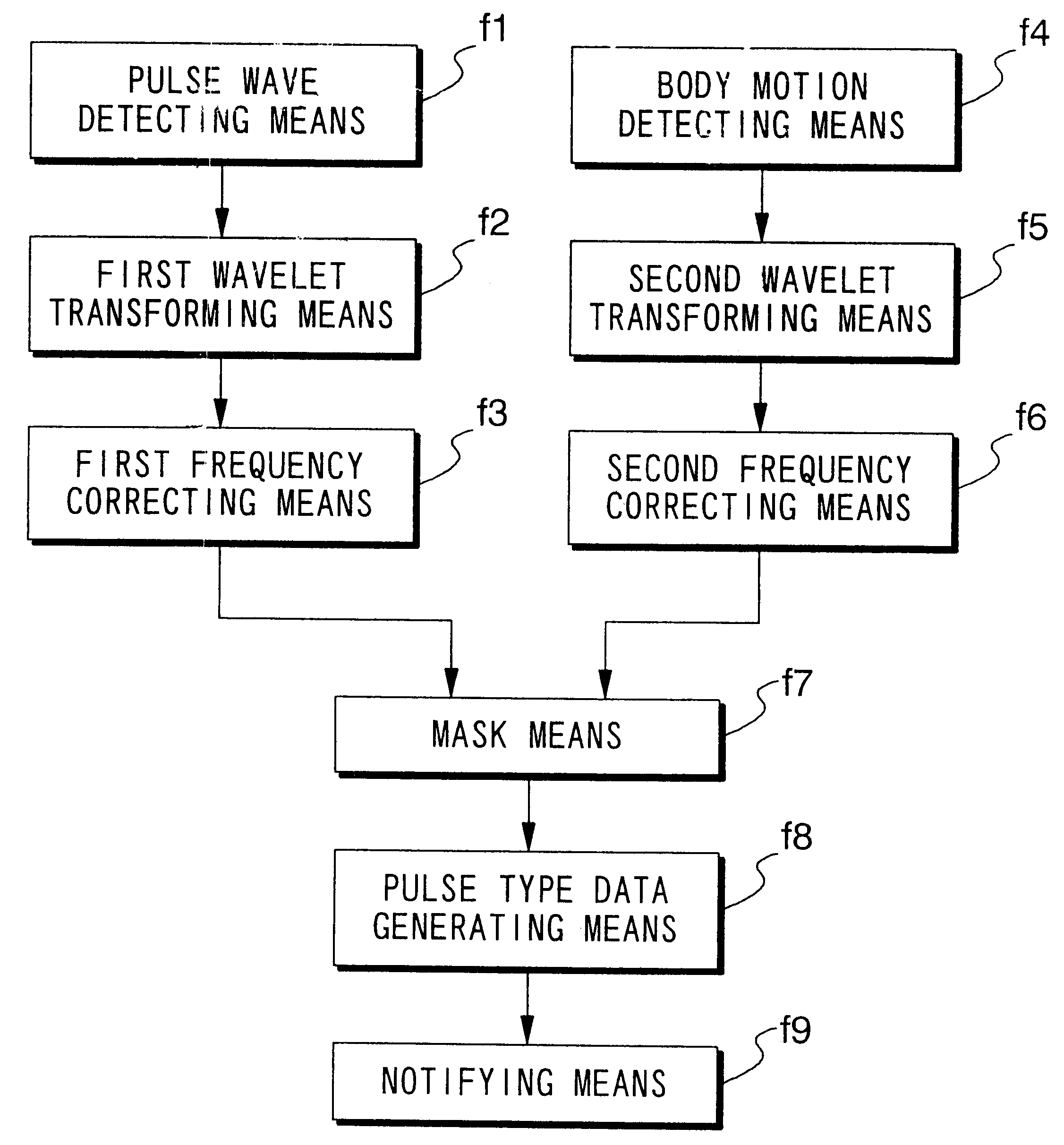
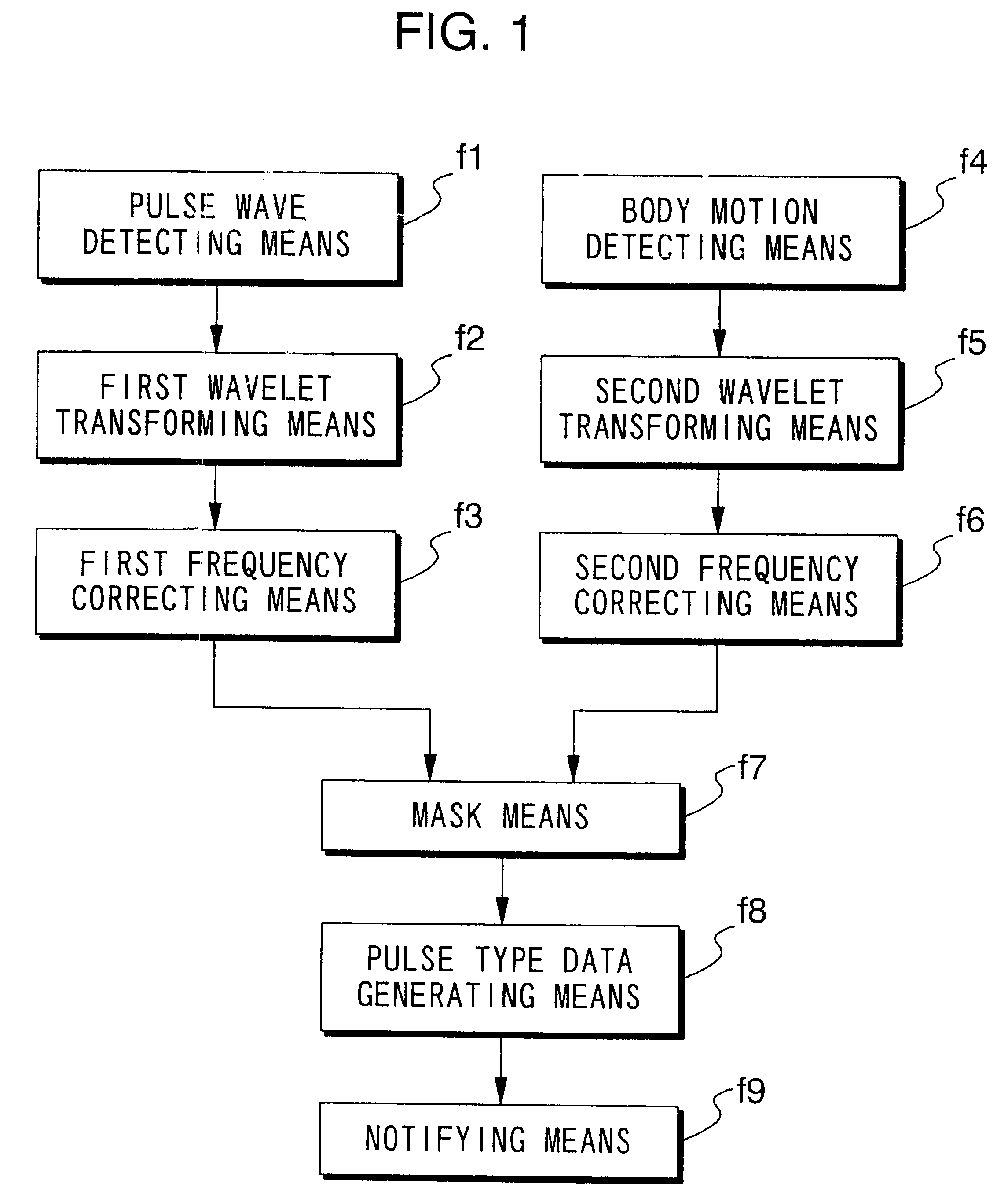
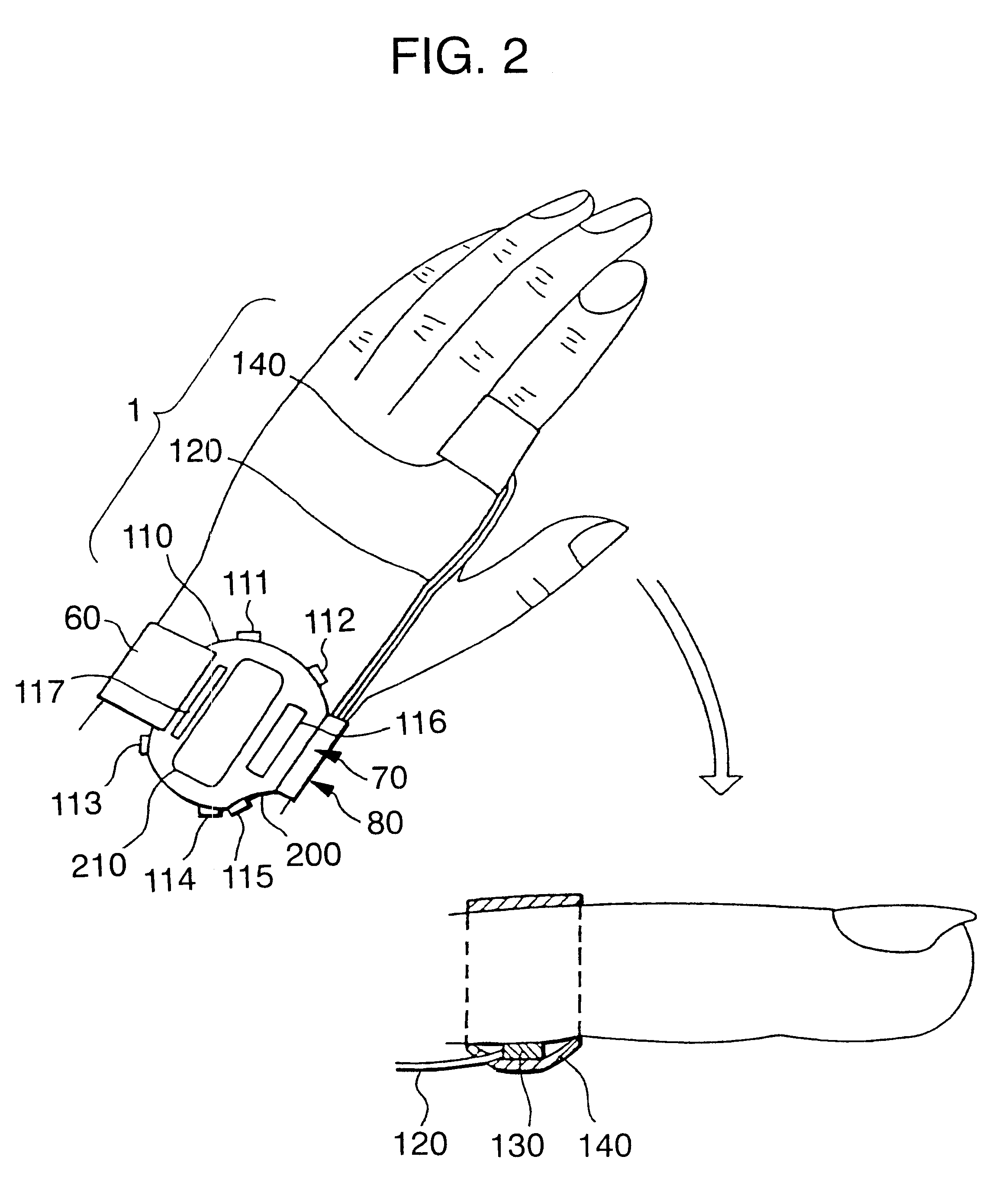
Pulse wave diagnosing device
When pulse waveform MH is detected by pulse wave detection sensor unit 130, wavelet transformer 10 performs wavelet transformation on pulse waveform MH and generates analyzed pulse wave data MKD. This analyzed pulse wave data MKD consists of a time region in which one heartbeat is divided into eighths, and the frequency region of 0-4 Hz which has been divided into eighths. Frequency corrector 11 generates corrected pulse wave data MKD' by performing frequency correction on analyzed pulse wave data MKD. Pulse type data generator 12 compares corrected pulse wave data MKD' over each frequency-time region, and generates pulse type data ZD indicating the type of pulse. Display 13 displays the pulse type for pulse waveform MH based on pulse type data ZD.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
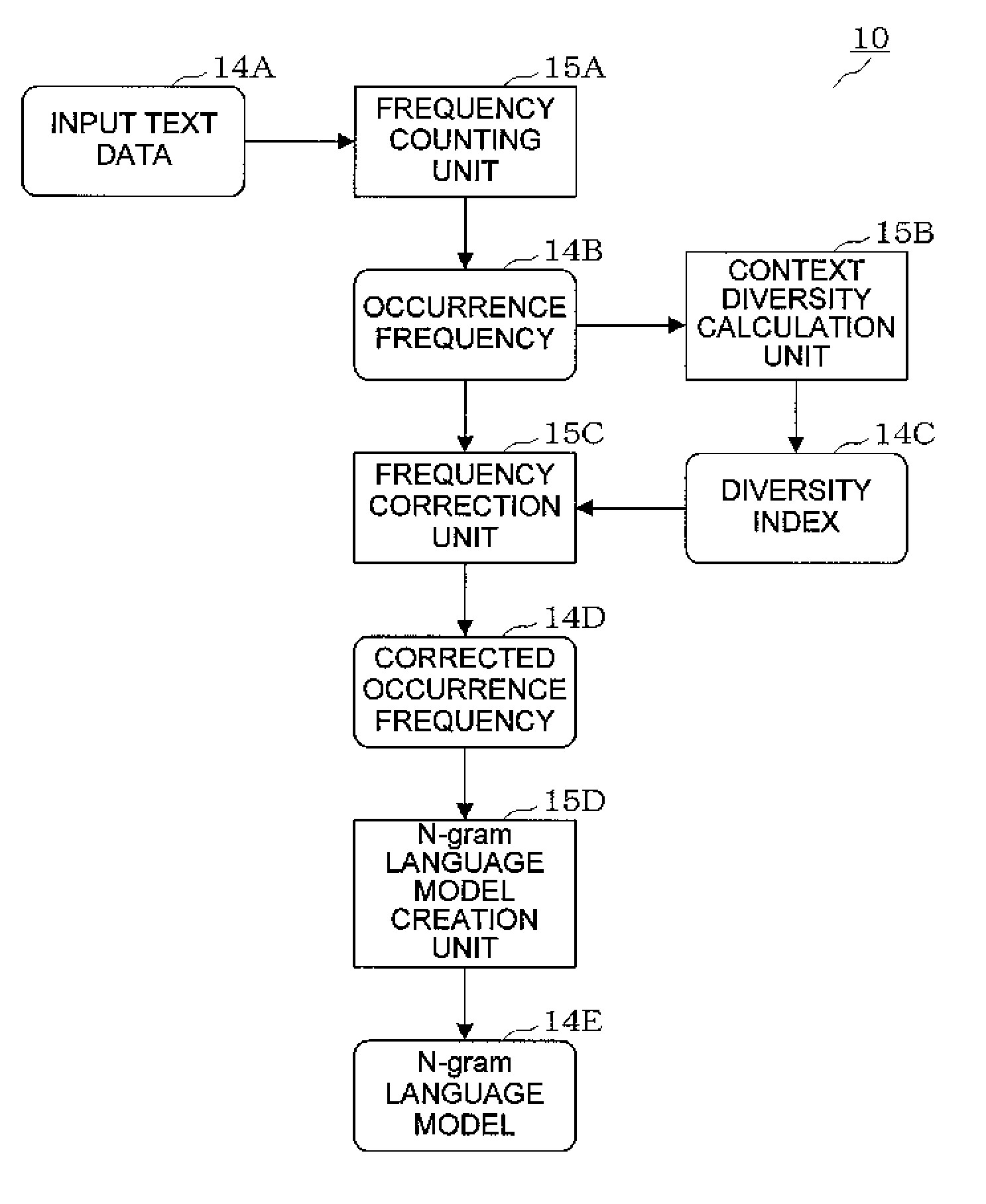
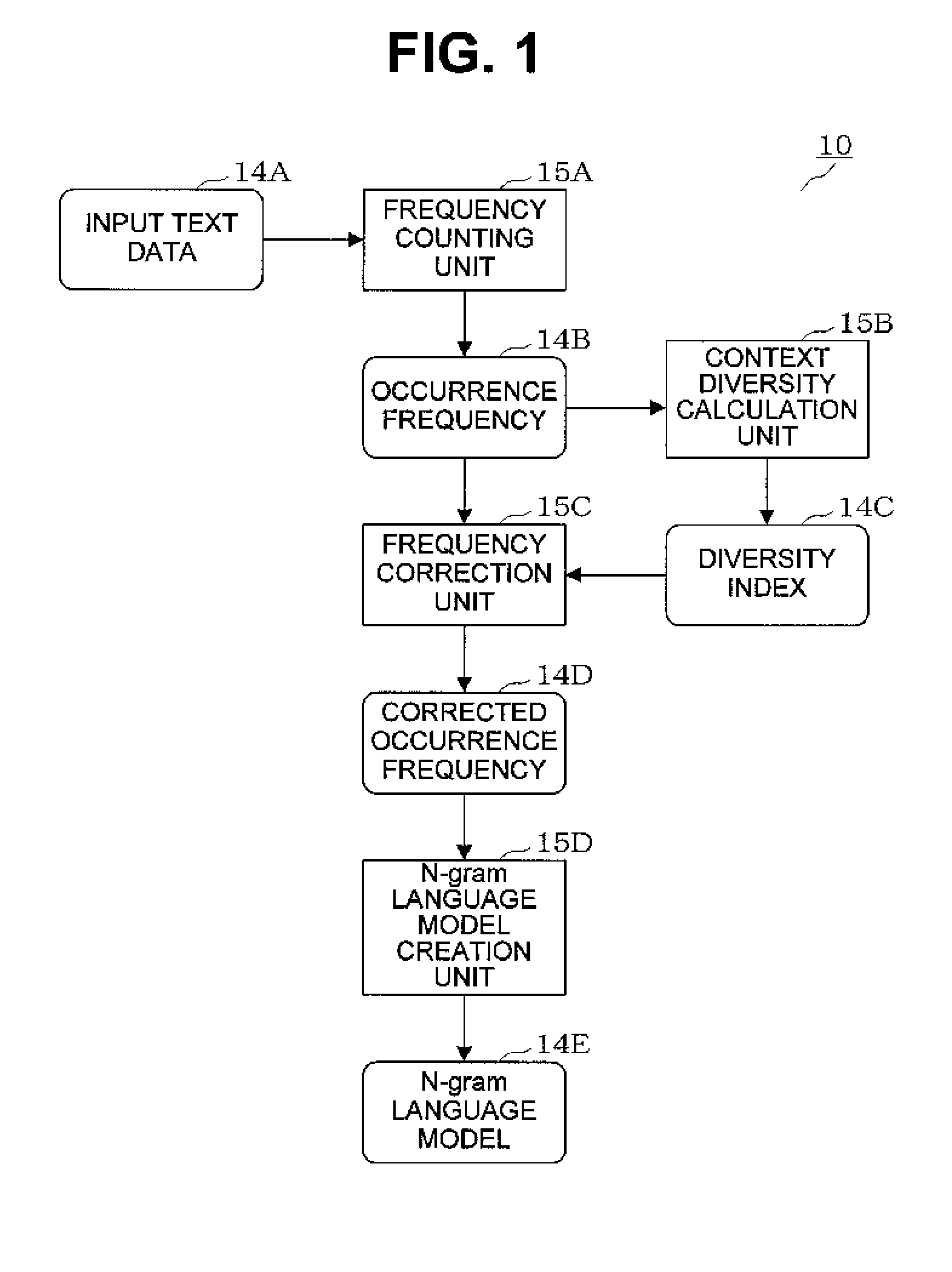
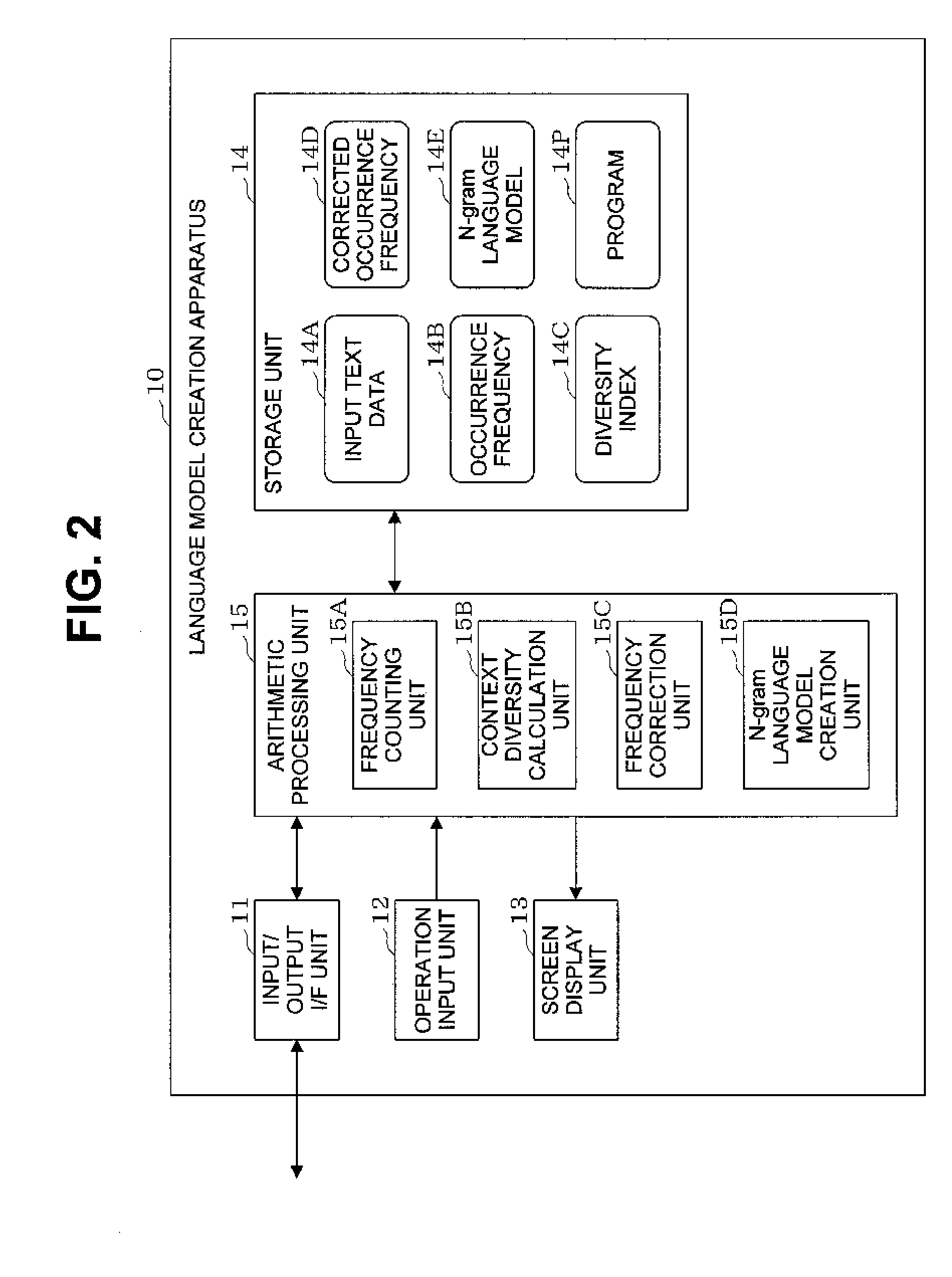
Language model creation apparatus, language model creation method, speech recognition apparatus, speech recognition method, and recording medium
InactiveUS20110161072A1Natural language translationSpeech recognitionDiversity indexContextual diversity
A frequency counting unit (15A) counts occurrence frequencies (14B) in input text data (14A) for respective words or word chains contained in the input text data (14A). A context diversity calculation unit (15B) calculates, for the respective words or word chains, diversity indices (14C) each indicating the context diversity of a word or word chain. A frequency correction unit (15C) corrects the occurrence frequencies (14B) of the respective words or word chains based on the diversity indices (14C) of the respective words or word chains. An N-gram language model creation unit (15D) creates an N-gram language model (14E) based on the corrected occurrence frequencies (14D) obtained for the respective words or word chains.
Owner:NEC CORP
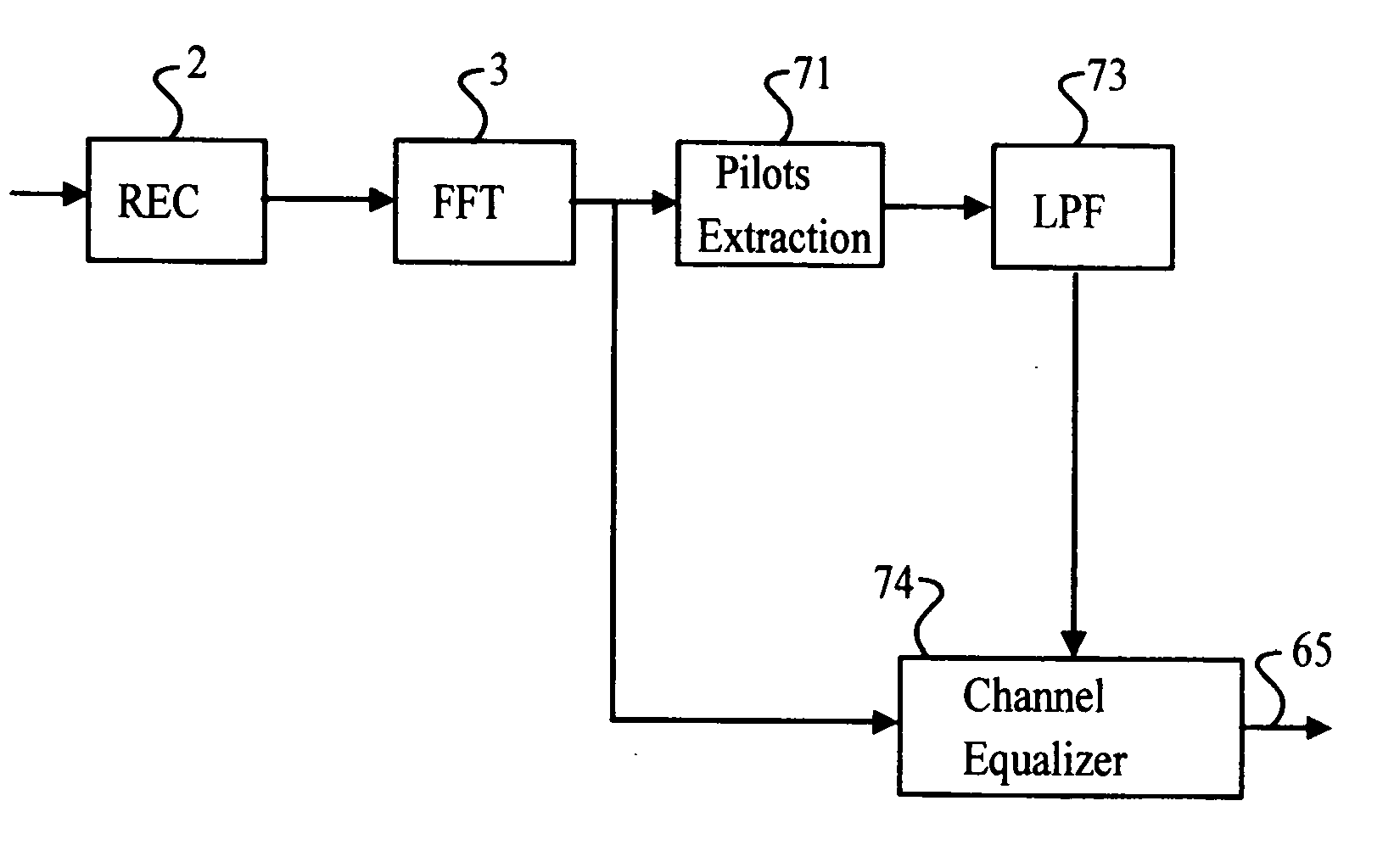
OFDM communication channel
InactiveUS20050207334A1Improve performanceFacilitate communicationTime-division multiplexChannel estimationComputer scienceDistortion
In an OFDM-based receiver, means for achieving time synchronization comprising: A. means for extracting pilot signals contained in the OFDM received signal; B. means for analyzing the pilot signals in the frequency domain and for issuing a signal indicative of a synchronization error in the received signal; C. means for correcting the synchronization error responsive to the signal indicative of the synchronization error. In an OFDM-based receiver, automatic frequency correction means in a subscriber unit comprising: A. an inner frequency correction loop for generating a LO frequency related to a frequency of a received signal; B. an outer frequency correction loop for correcting the LO frequency according to instructions received from a base station. In an OFDM-based receiver, a channel sounder comprising: A. means for extracting pilot signals contained in the OFDM received signal; B. means for analyzing the pilot signals in the frequency domain and for issuing signals indicative of a distortion in each pilot signal, wherein each of said pilot distortion signals comprises both an amplitude and a phase component; C. means for analyzing the signals indicative of a distortion in each pilot signal and for computing therefrom corrective signals for correcting distortions in the received signal.
Owner:HADAD ZION
OFDM communication channel
InactiveUS6985432B1Facilitate communicationImprove performanceFrequency-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsComputer scienceTime synchronization
In an OFDM-based receiver, a time synchronization unit comprising: A. a device for extracting pilot signals contained in the OFDM received signal; B. a device for analyzing pilot signals in the frequency domain and for issuing a signal indicative of a synchronization error in the received signal; C. a device for correcting the synchronization error, responsive to the signal indicative of the synchronization error. In an OFDM-based receiver, an automatic frequency correction device in a subscriber unit comprising: A. an inner frequency correction loop for generating a LO frequency related to a frequency of a received signal; B. an outer frequency correction loop for correcting the LO frequency according to instructions received from a base station.
Owner:ZION HADAD COMM
Low energy consumption RF telemetry control for an implantable medical device
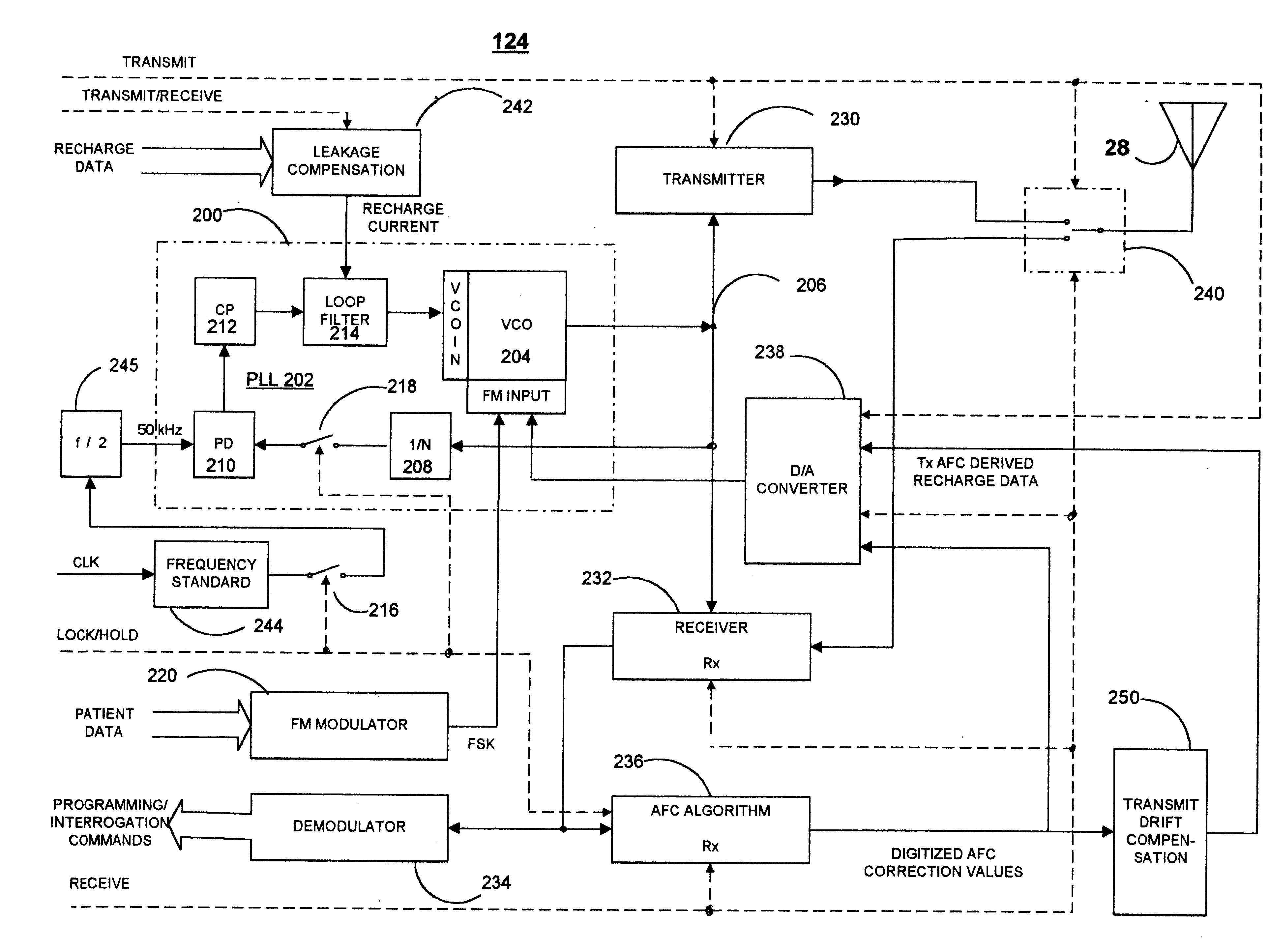
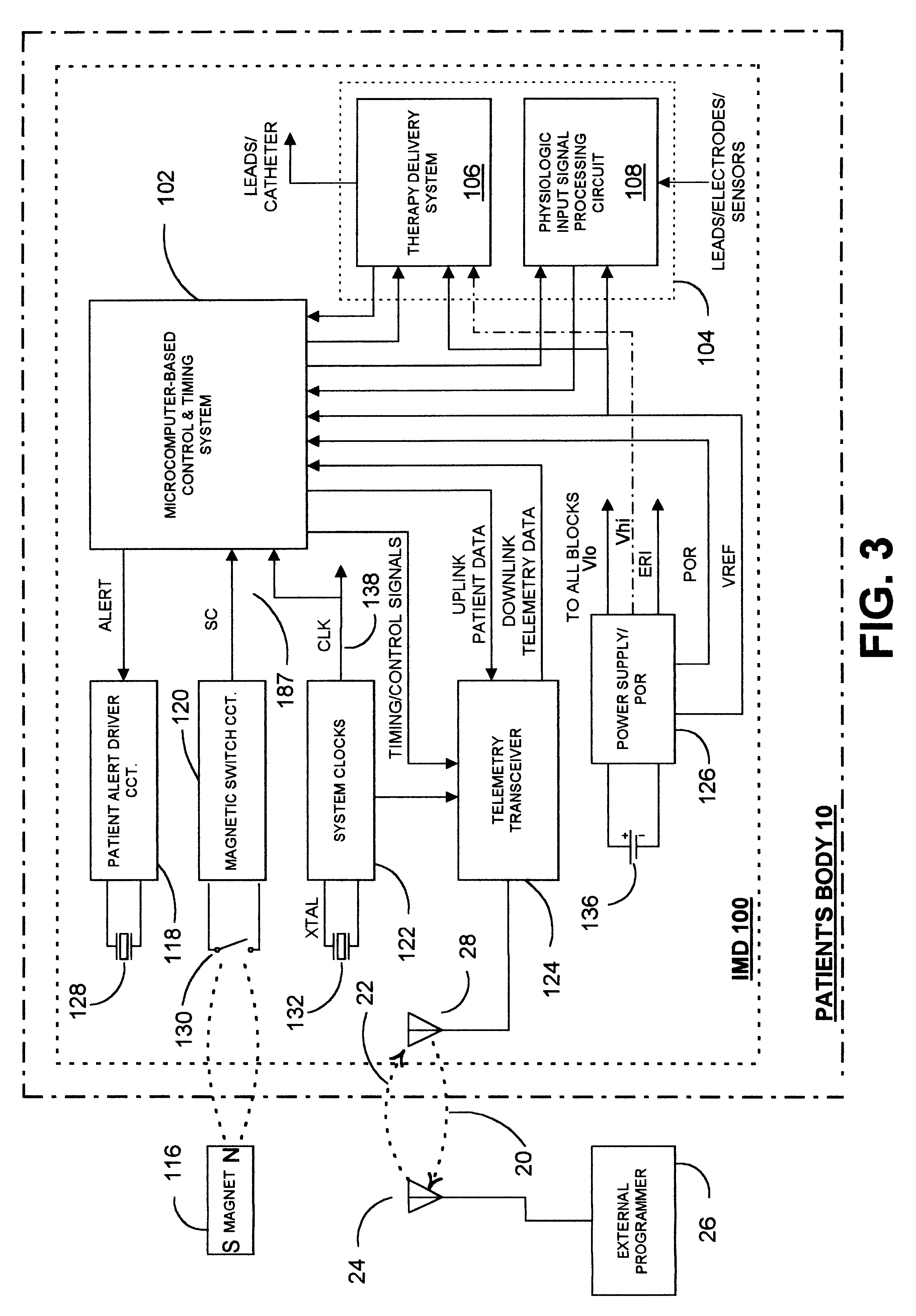
In an implantable medical device, a frequency synthesizer employed in the RF transceiver of the IMD operating system functions in a PLL LOCK mode wherein the VCO frequency is governed by the PLL and an energy saving HOLD mode wherein the PLL is not operational and the VCO generated carrier frequency can drift over time. The PLL circuit is powered up and coupled with a control voltage input and the output of the VCO to develop a frequency control voltage stored by a capacitive loop filter during initial LOCK portions of both uplink and downlink telemetry transmission time periods. A frequency modulation (FM) input of the VCO receives data bit modulation voltages that modulates the carrier frequency during uplink transmission of patient data. During the HOLD portion of a downlink telemetry transmission, an AFC algorithm is enabled and derives a frequency correction value from the difference in frequency of the constant received carrier frequency and the drifting VCO generated carrier frequency, and the frequency correction value is applied to the VCO FM input to compensate for loop filter capacitor discharge of the control voltage causing the drift. The AFC algorithm derived frequency correction value is stored in memory and is also applied during the HOLD portion of an uplink telemetry transmission to the VCO FM input to compensate for loop filter capacitor discharge of the control voltage causing the drift. In addition, a recharge current is applied to the capacitive loop filter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
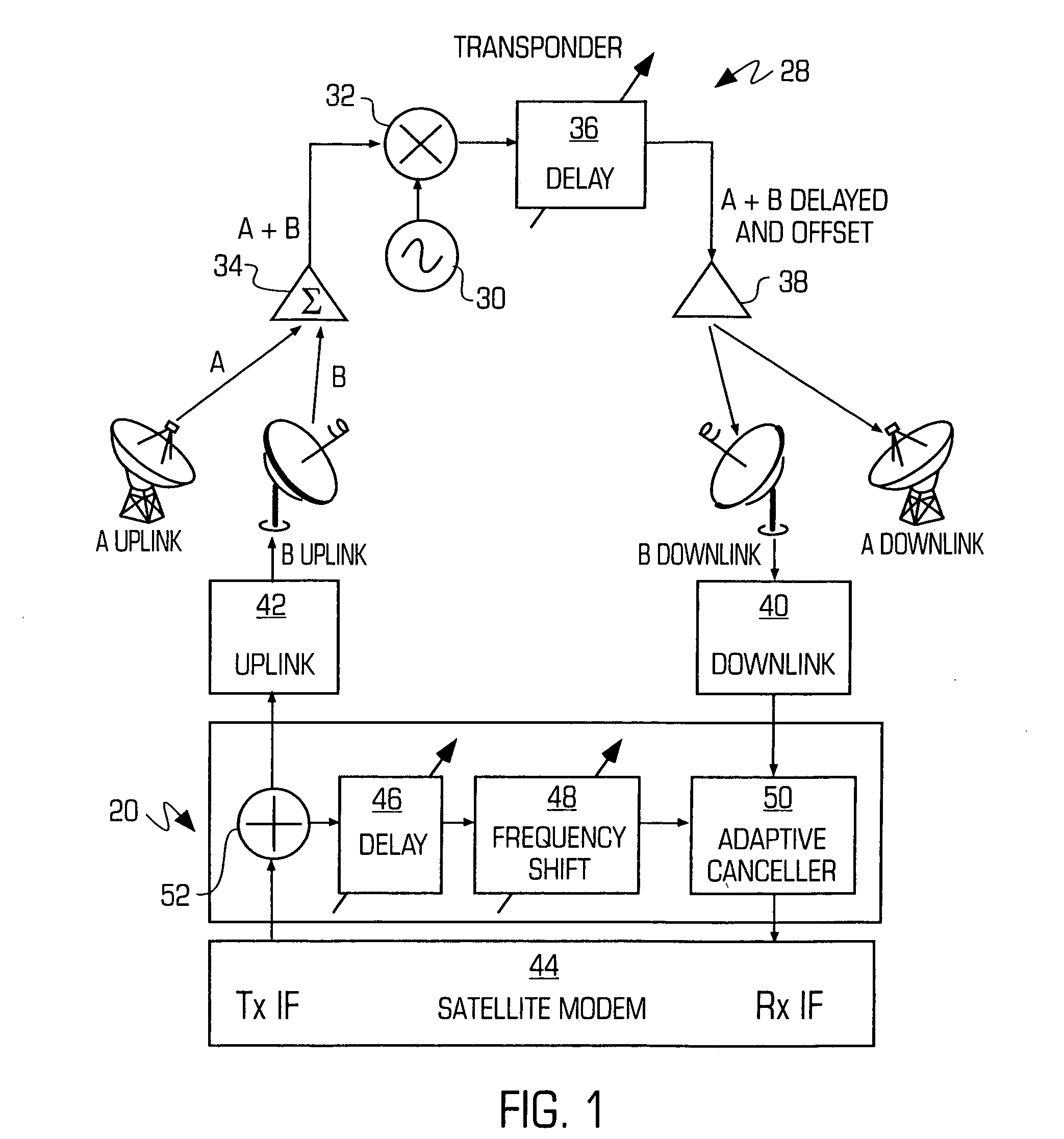
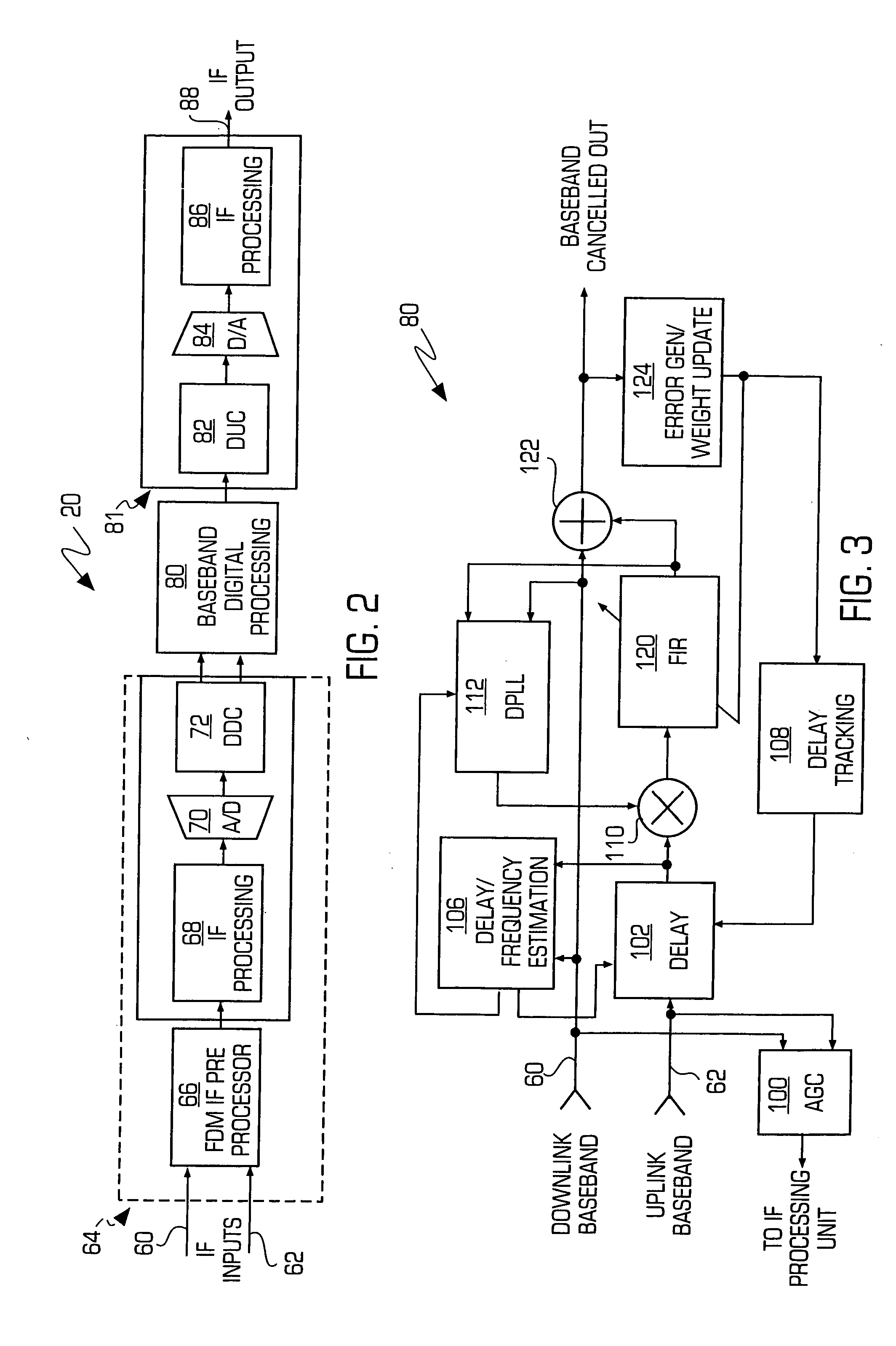
Adaptive canceller for frequency reuse systems
InactiveUS20050159128A1Easy to useHighly effectiveRadio transmissionTransmission noise suppressionFinite impulse responseAdaptive filter
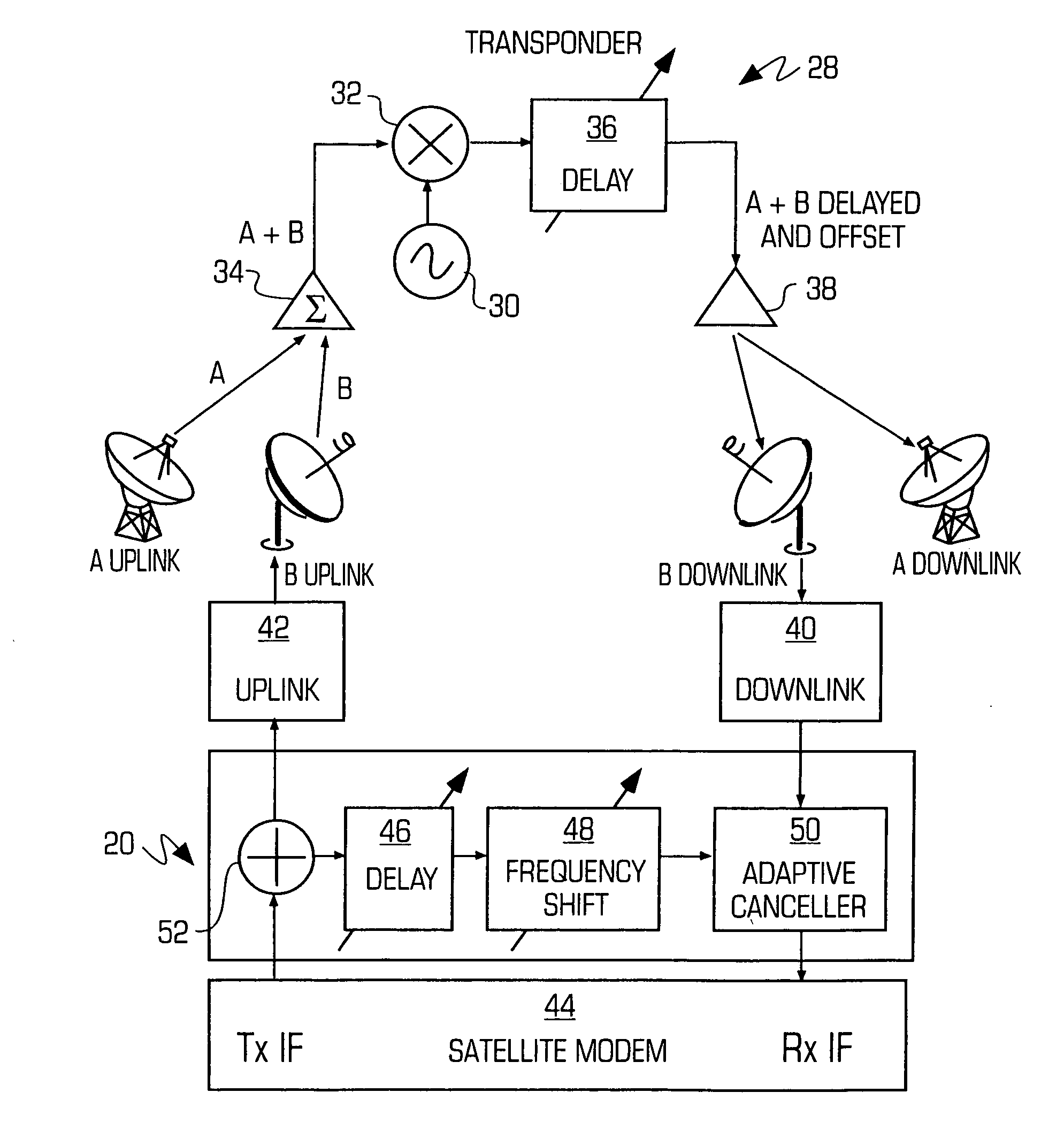
An adaptive interference canceller for canceling an interfering signal corresponding to a delayed, frequency translated, amplitude and phase offset version of a transmitted signal contained in a composite received signal relayed through a relay system such as a satellite transponder. The canceller digitally downconverts the received signal and a local replica of the transmitted signal from IF to baseband, applies a variable delay and frequency compensation to the replica as a coarse delay and frequency correction, and tracks fine delay, amplitude and phase differences using an adaptive finite impulse response filter to generate a cancellation signal corresponding to the delayed and frequency shifted version. A minimum output power process produces an error signal that drives the variable delay and adaptive filter to minimize the power in the signal of interest to maximize cancellation of the interfering signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON APPLIED SIGNAL TECH
Systems and Methods of Network Synchronization
ActiveUS20130080817A1Time-division multiplexGenerating/distributing signalsSlave clockDelay calculation
An exemplary method of synchronizing a master clock and a slave clock comprises transmitting a plurality of packets between a master device and a slave device, calculating a first skew between a first pair of the plurality of packets at the slave device and a second skew between the first pair at the master device, calculating a ratio between the first skew and the second skew, providing a slave clock frequency correction to the slave device, calculating a first packet trip delay using a time that the master device initiates sending a packet to the slave device, a time the master device receives a response from the slave device, a corrected time the slave device receives the packet, and a corrected time the slave device initiates sending the response, calculating a first offset based on the first packet trip delay, and providing the first offset to the slave device.
Owner:AVIAT U S
Wireless transmitting apparatus, wireless receiving apparatus, wireless transmission method, wireless reception method, wireless communication system, and wireless communication method
ActiveUS8248975B2Improve efficiencyAccurate performancePhase-modulated carrier systemsRadio transmissionWireless transmissionCommunications system
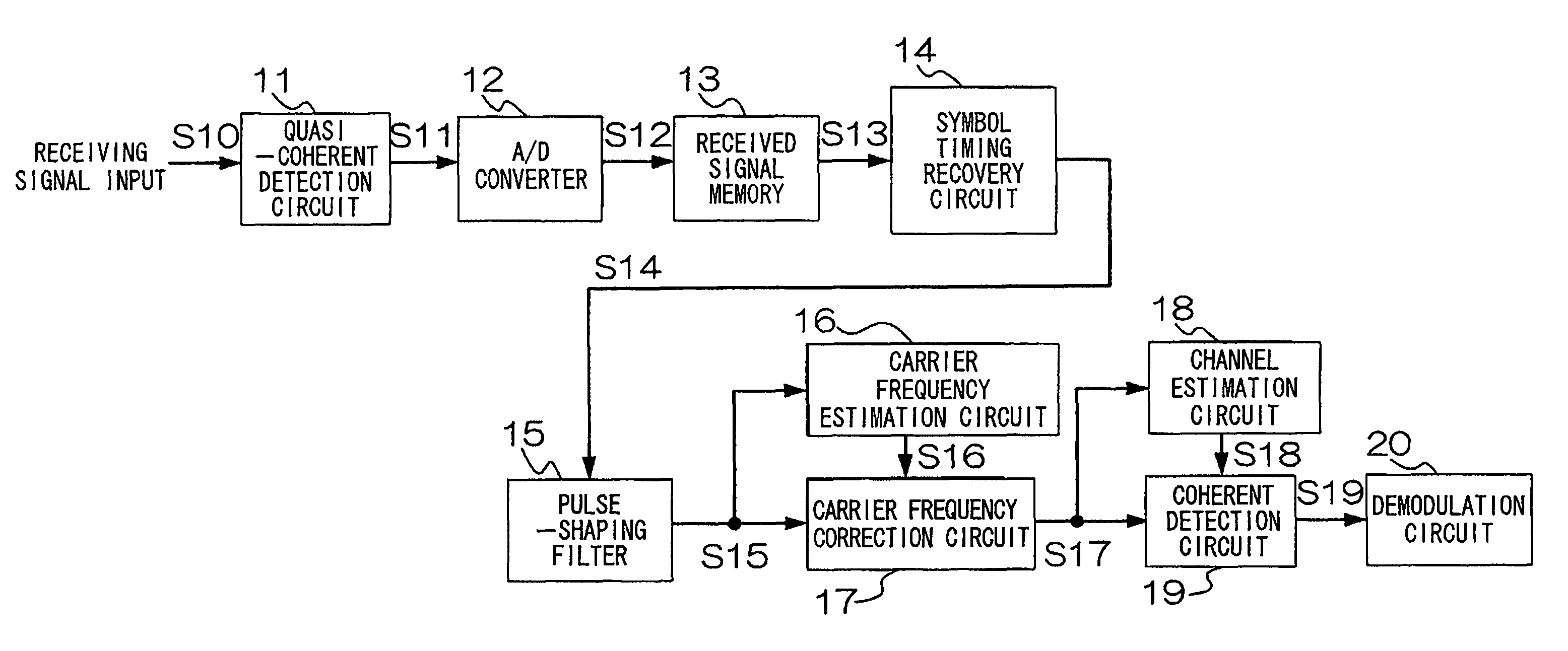
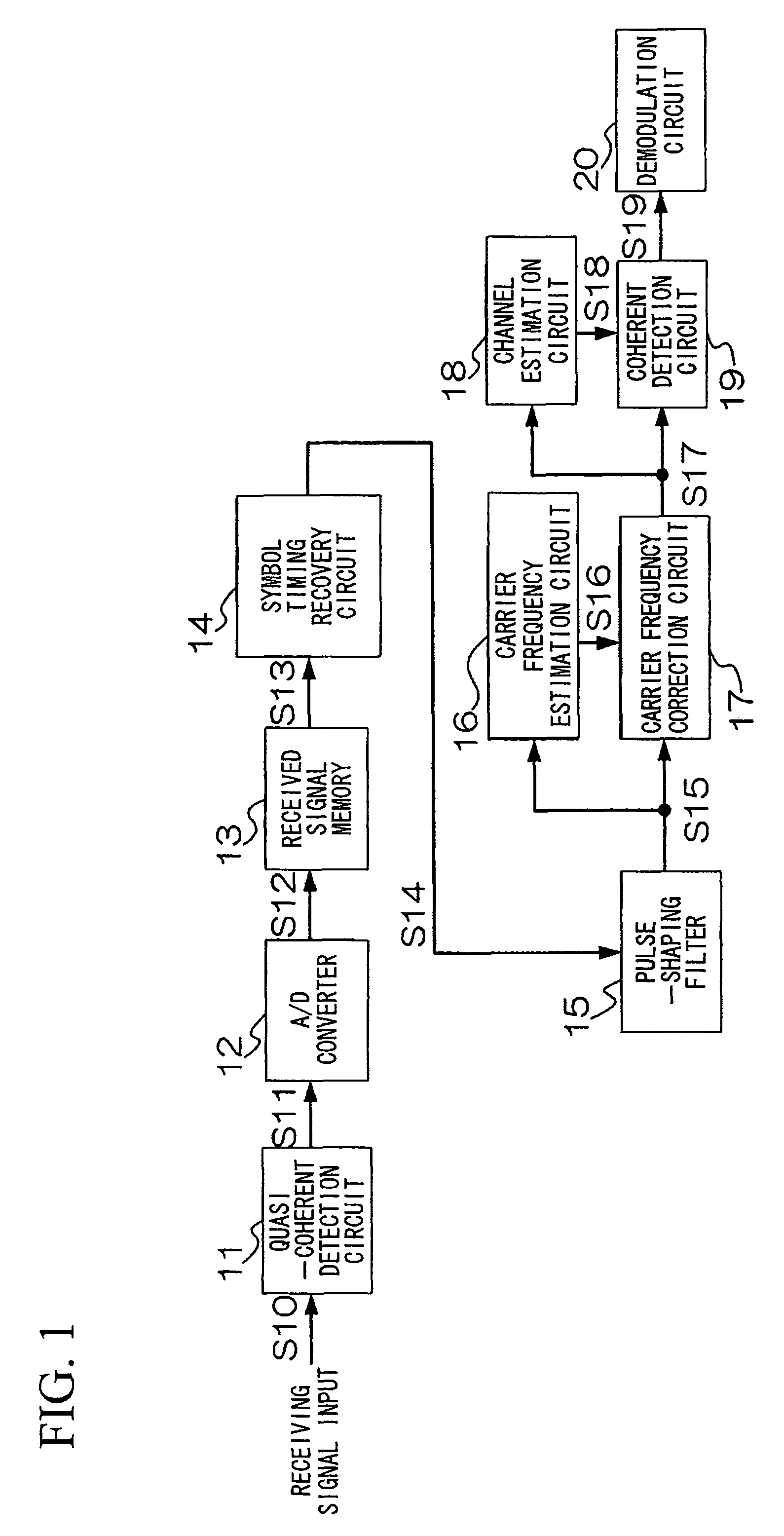
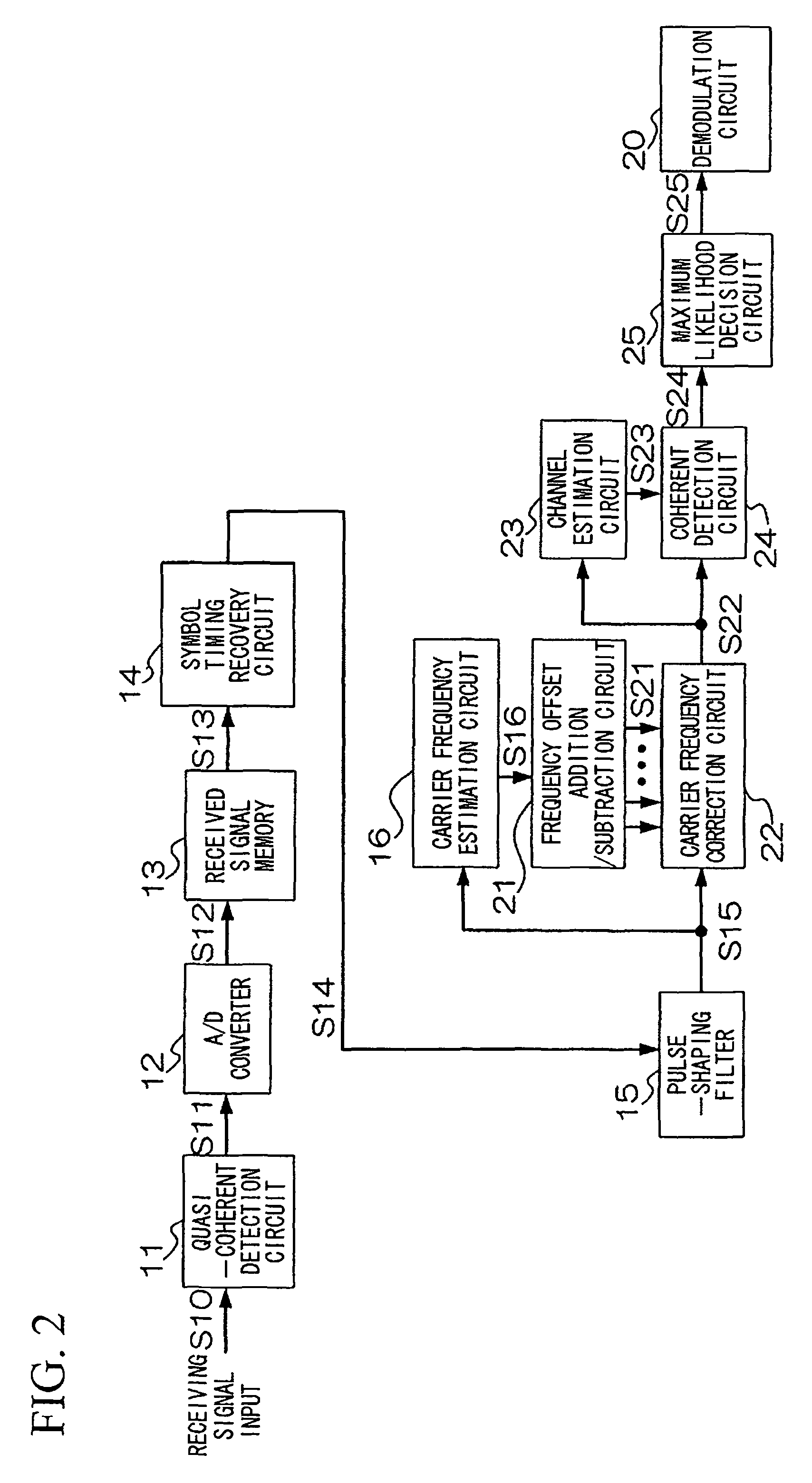
A wireless transmitting apparatus inserts a training signal into a transmission burst at fixed symbol intervals as a pilot signal, a wireless receiving apparatus performs AD conversion of a received burst signal, performs symbol timing recovery, performs frame position detection and pilot signal extraction from the received burst signal for which symbol timing was established, performs frame synchronization, and performs a carrier frequency estimation using pilot signal. A carrier frequency estimation is also performed with respect to a received burst signal for which frame synchronization was established, and channel distortion is estimated and output based on a frequency-corrected received burst signal. Channel distortion estimation is then performed with respect to a frequency-corrected received burst signal, and a data symbol sequence of the channel-compensated received burst signal is converted to a received data bit stream.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
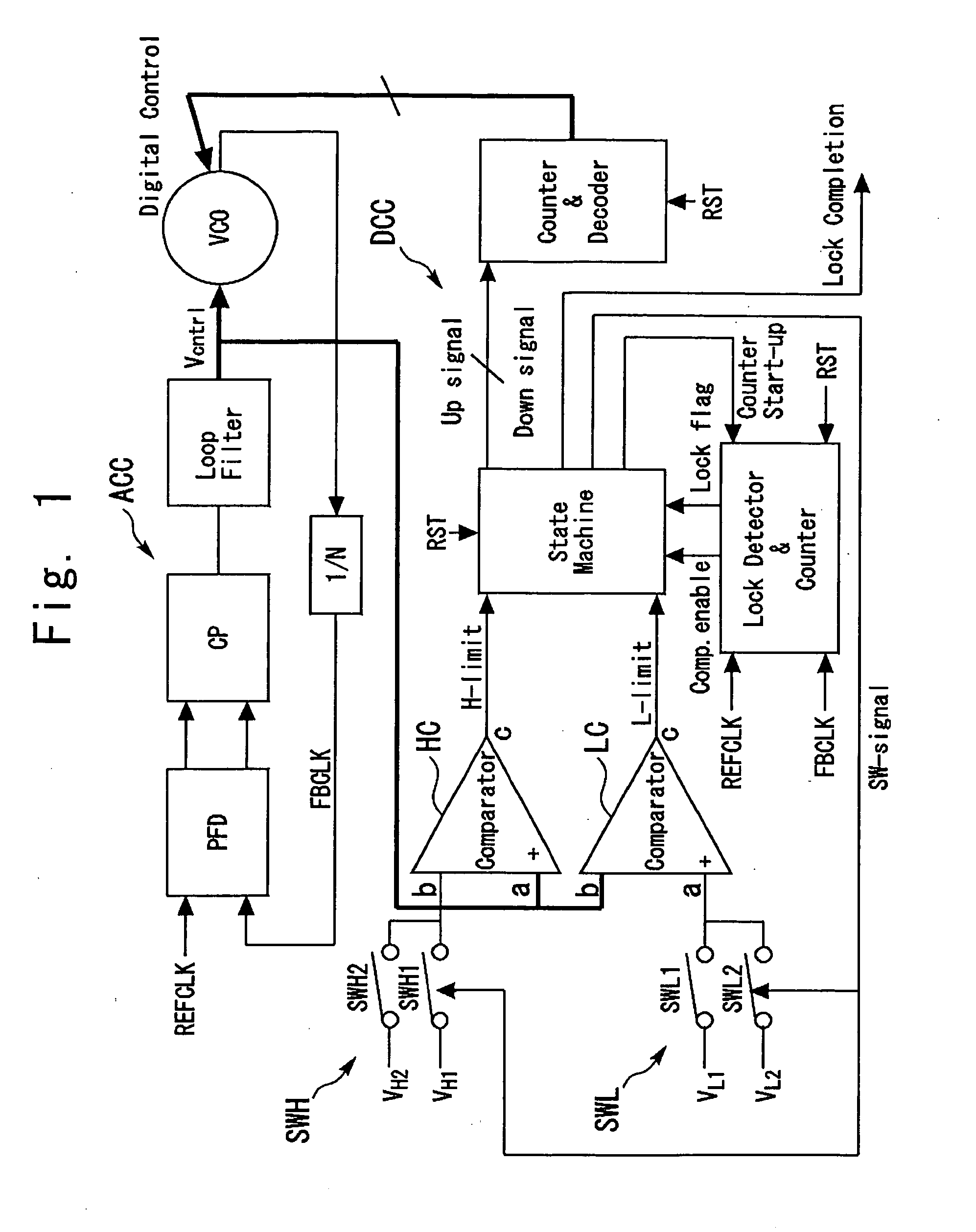
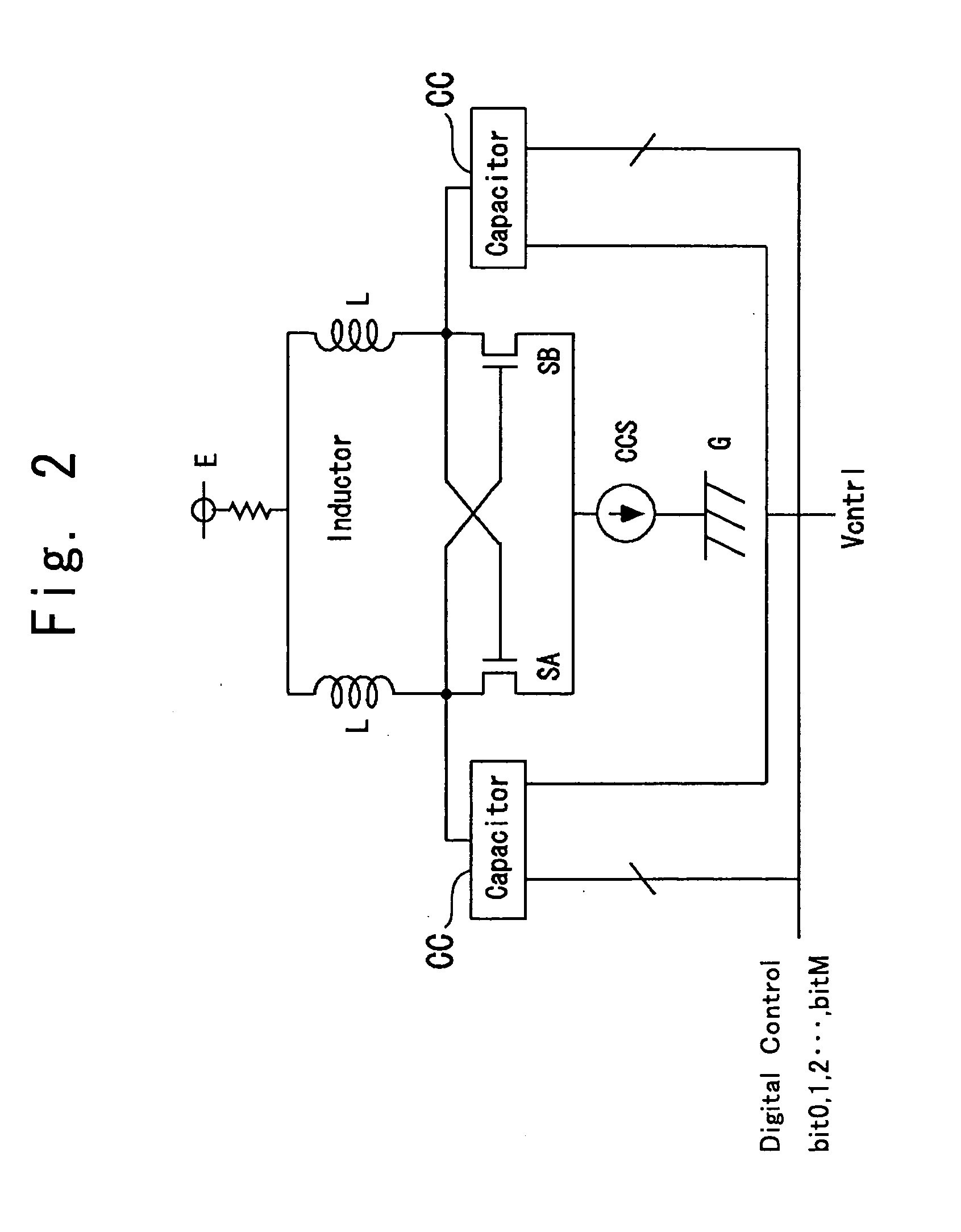
Automatic frequency correction PLL circuit
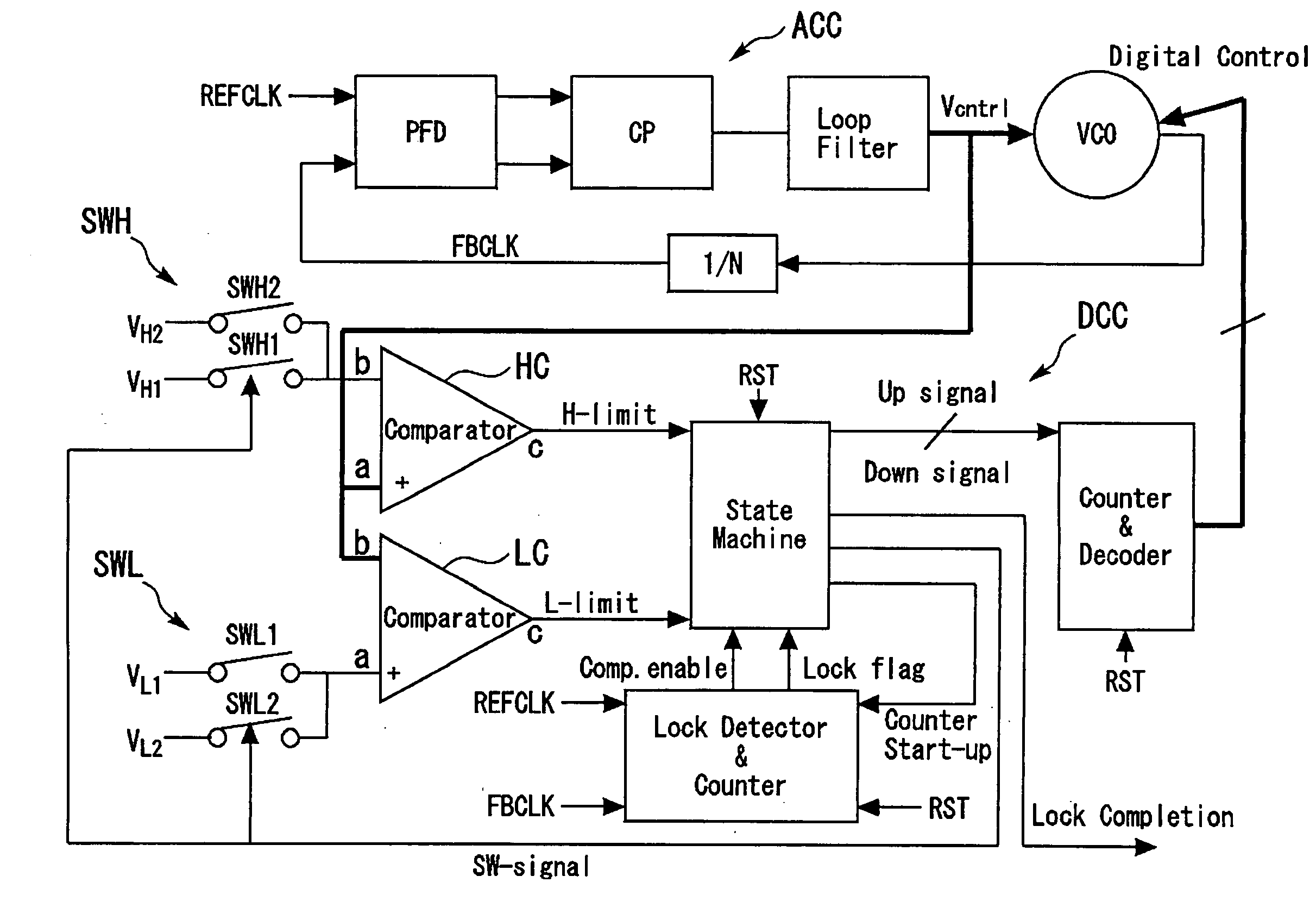
ActiveUS20050226357A1Prevent unnecessary switchingAvoid switchingPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsEngineeringComparator
An automatic frequency correction phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit includes an analog control circuit and a digital control circuit. The digital control circuit includes a High-side comparator and a Low-side comparator which receive an analog control voltage, a state monitor circuit, and a counter and decoder circuit. At least one of the High-side comparator and the Low-side comparator includes a threshold switching circuit which selectively gives a first threshold and a second threshold having different. When the analog control voltage remains between the High-side threshold and the Low-side threshold in a state in which the threshold switching circuit gives the first threshold, the threshold switching circuit switches the first threshold to the second threshold and expands the interval between the High-side threshold and the Low-side threshold.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
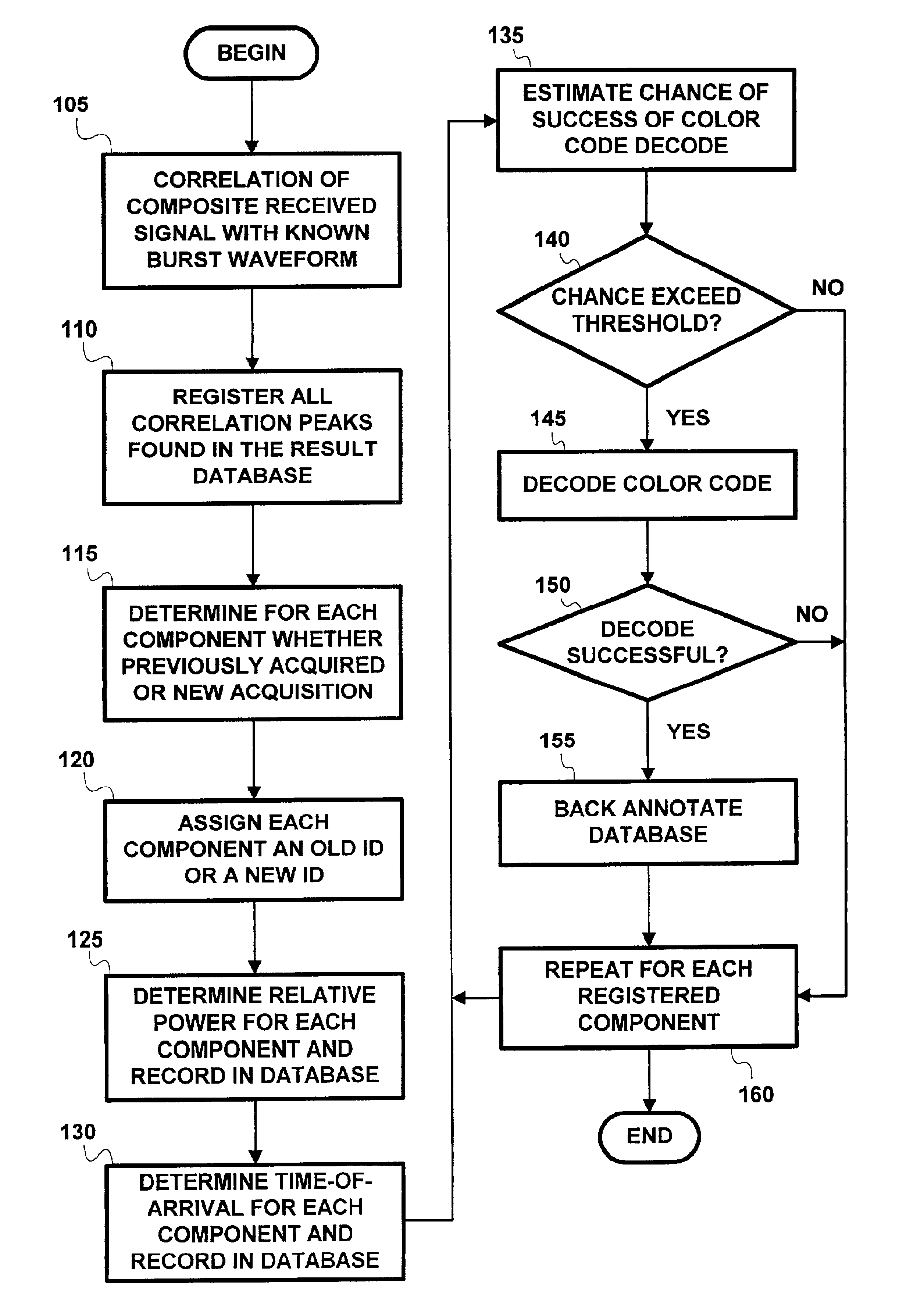
Method and apparatus for co-channel interference measurements and base station color code decoding for drive tests in TDMA, cellular, and PCS networks
InactiveUS6931235B2Improve reliabilityReduce in quantitySpatial transmit diversitySatellite radio beaconingGeolocationCo-channel interference
Co-channel interference in a wireless network is identified and quantified. Rather that using color code identification, a more reliable identification property of each co-channel component of the received composite signal is used, namely, the time of arrival of a known part of a signal. Detection and timing measurement is performed even in presence of stronger signals by focusing selectively on bursts having fixed contents (e.g., the FCCH burst used in GSM for frequency correction). The repetitive measurements of the time-of-arrival of each of the interfering components of the signal during a drive test enables determination of the geographical location of the interfering co-channel base stations.
Owner:PCTEL INC
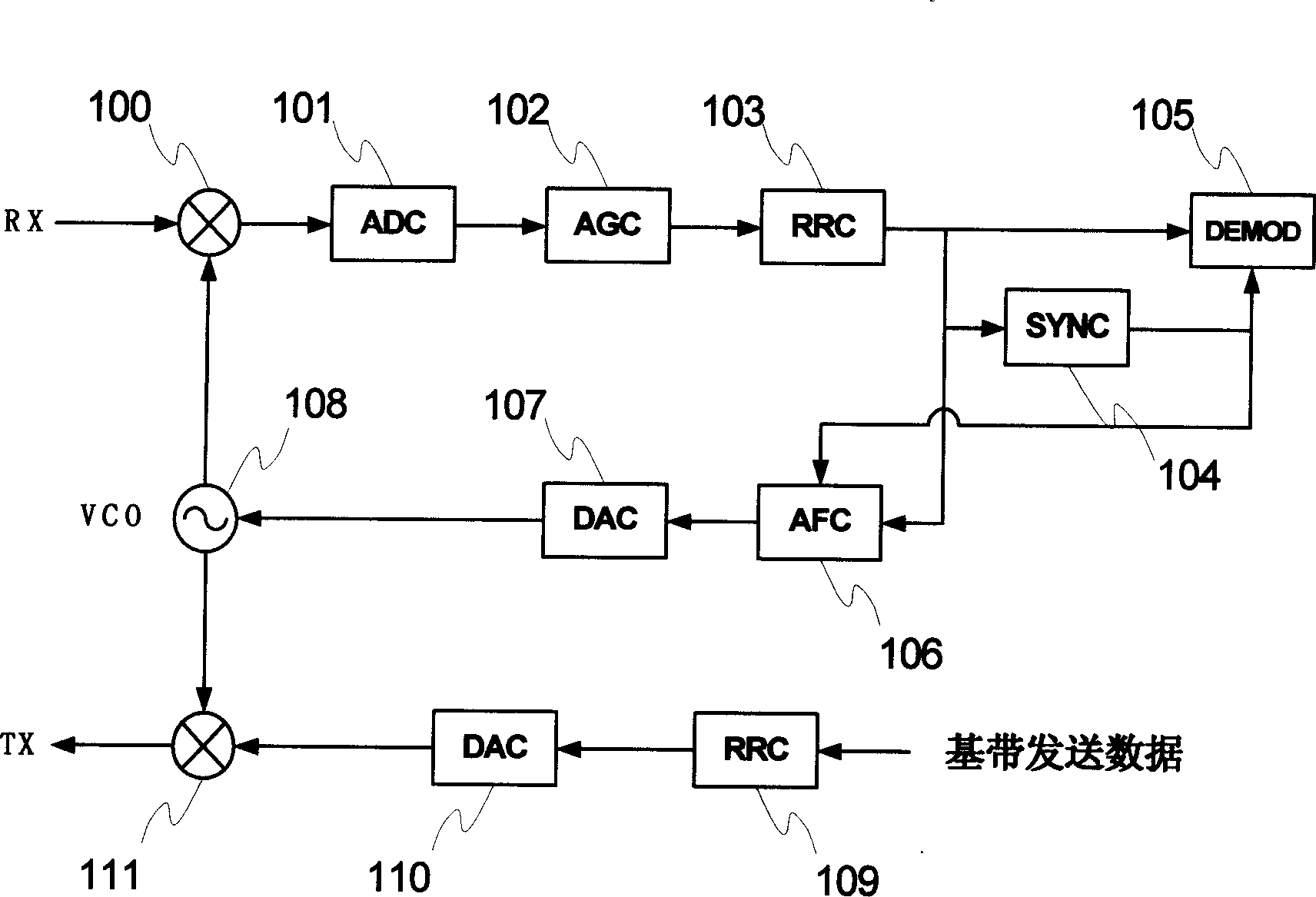
Method and arrangement for automatic frequency control in a communication system
ActiveUS20070140386A1Pulse automatic controlAutomatic frequency control detailsCommunications systemEngineering
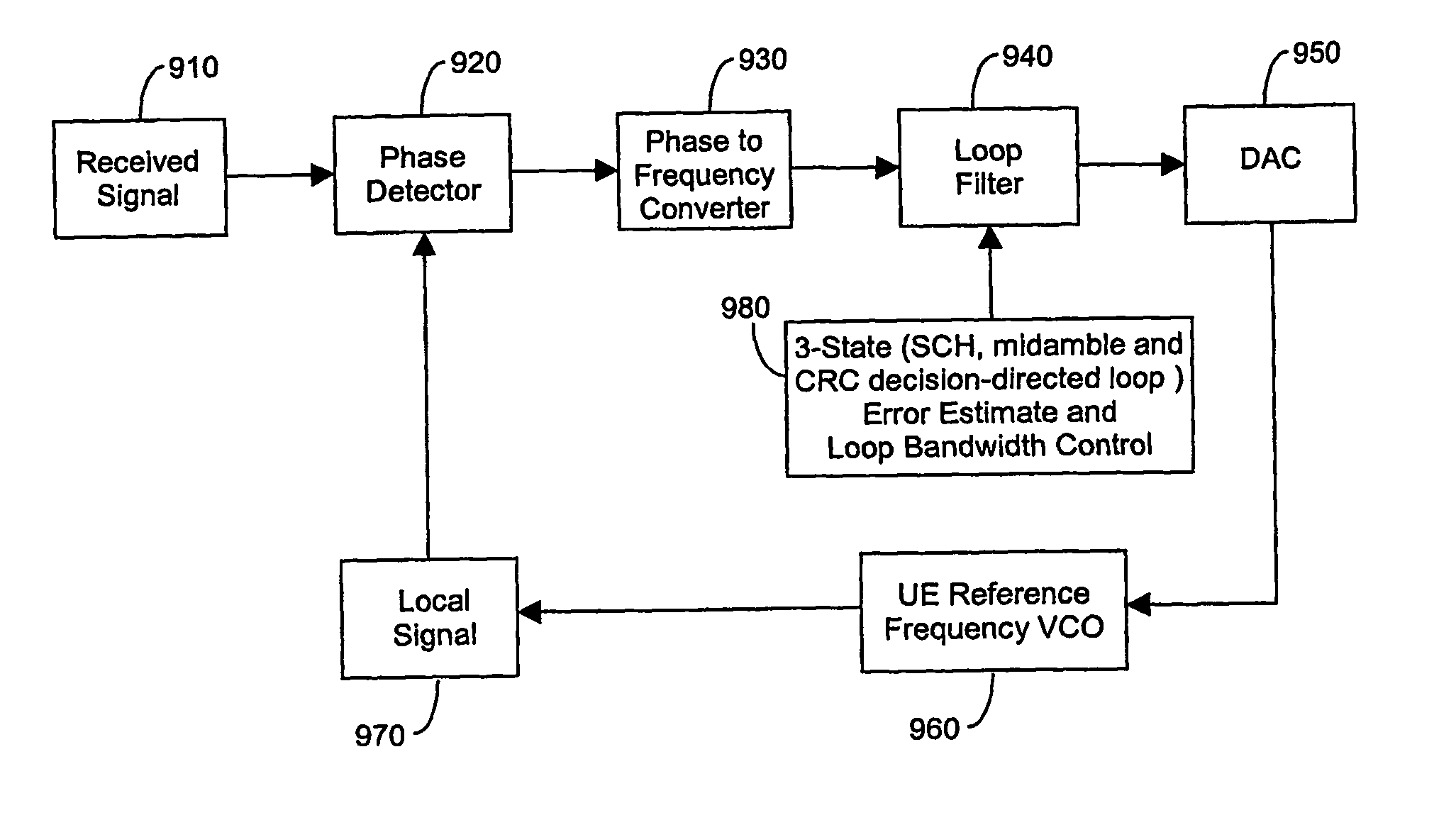
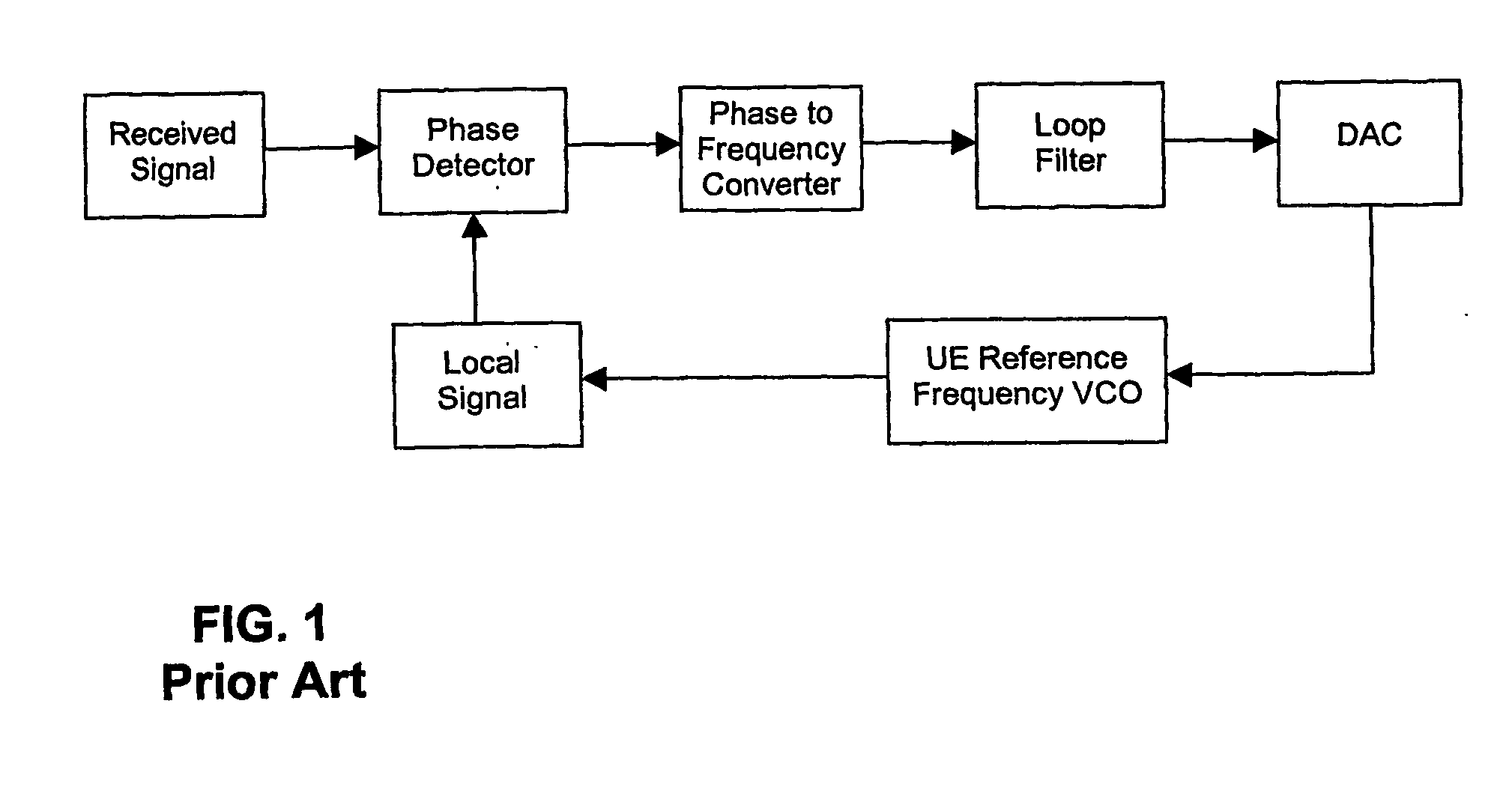
An arrangement (900), method and unit for AFC in a communication system (100) having: a frequency estimator (980) producing a decision-directed frequency estimate from a received signal; and an AFC loop receiving the decision-directed frequency estimate and performing therewith frequency control. The AFC process may use a CRC-decision directed frequency estimate as the final stage in a multi-stage AFC process (preceded by SCH- and midamble-derived frequency estimate stages), such that a verified received data sequence is used to re-construct a local copy of the ideal received data symbols expected at the output of a detector. This local copy is then correlated with the actual detector output and the results used to estimate the frequency error present on the received signal. The AFC process is inherent suited for discontinuous receive (DRX) applications. This provides the advantage of allowing required frequency correction accuracy to have minimal impact on the error rate of the received data in various channel configurations.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
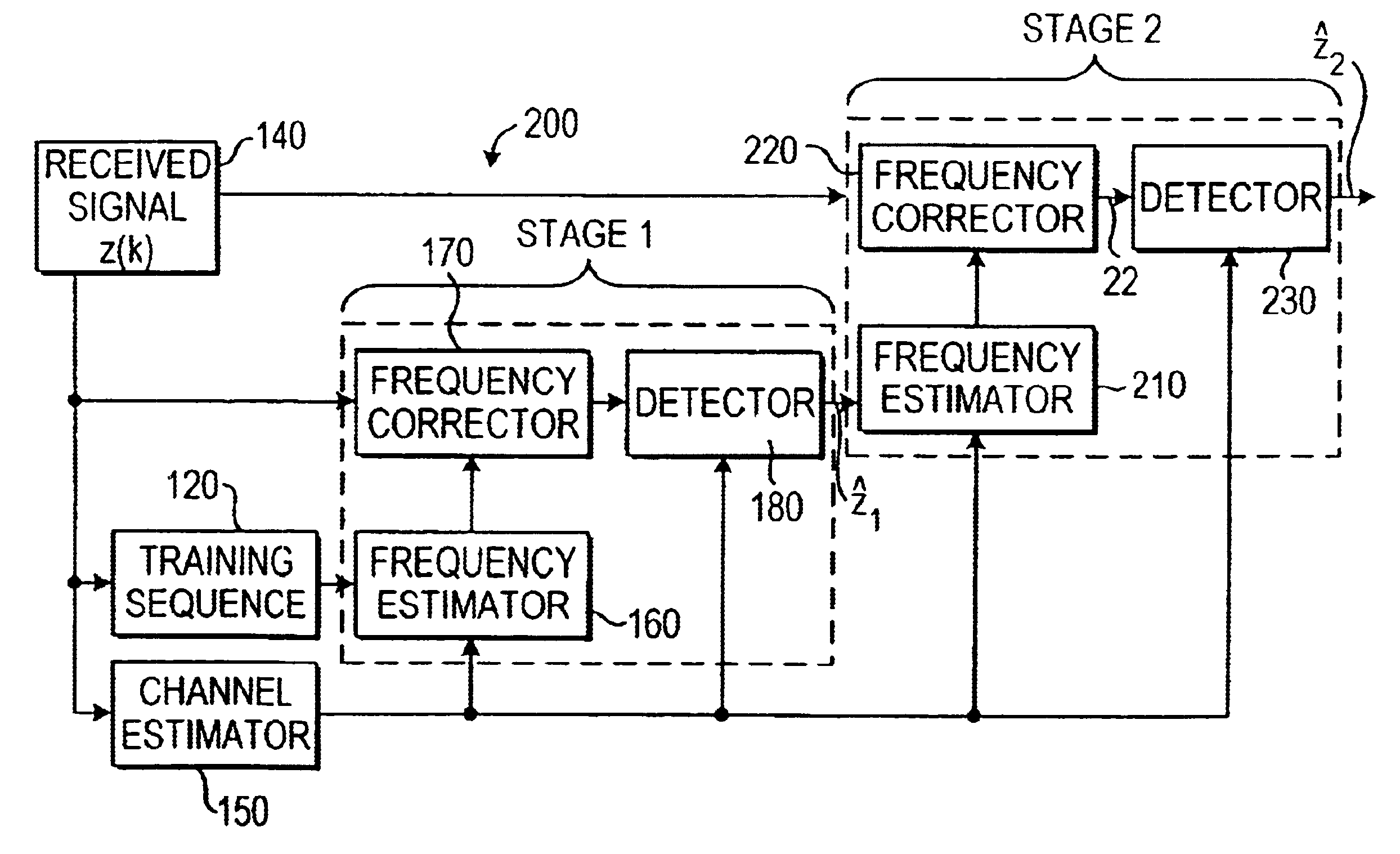
Method for automatic frequency control
A radio signal transmitted from a transmitter to a receiver of a mobile communications system, such as the GSM system, often suffers from a phenomenon known as frequency offset by which the frequency of the radio signal is changed from a first frequency to a second frequency. A method is therefore provided for automatically correcting the frequency at the receiver to restore the received radio signal to approximately the first frequency using a multistage frequency correction algorithm. The radio signal comprises a training sequence that is known to the receiver and data symbols that are not known to the receiver. In the first stage of the frequency correction, the frequency offset is coarsely estimated based on the training sequence only, and the data symbols are frequency corrected by back-rotating the received data symbols and the training sequence by the frequency offset estimate. The frequency corrected data symbols and training sequence are then input into the second stage of the frequency correction where they are used to determine a second estimate of the frequency offset that should be more accurate because the second estimate of the frequency offset is based on a larger number of symbols including symbols in the previously frequency corrected training sequence and data symbols. Using this second frequency offset estimate, the data symbols in the received radio signal are frequency corrected by back-rotating the received data symbols by the second frequency offset estimate and are output for detection.
Owner:NOKIA NETWORKS OY
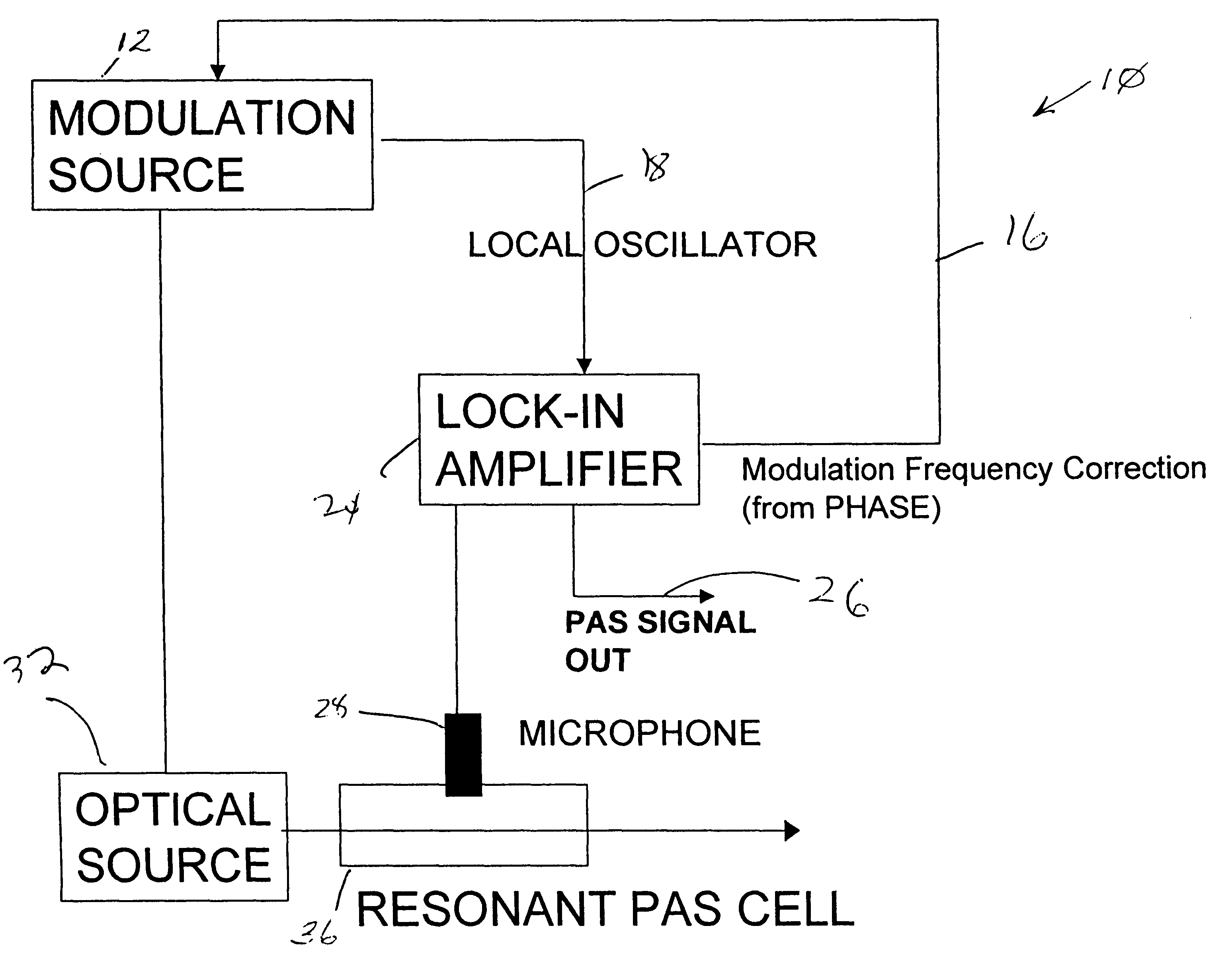
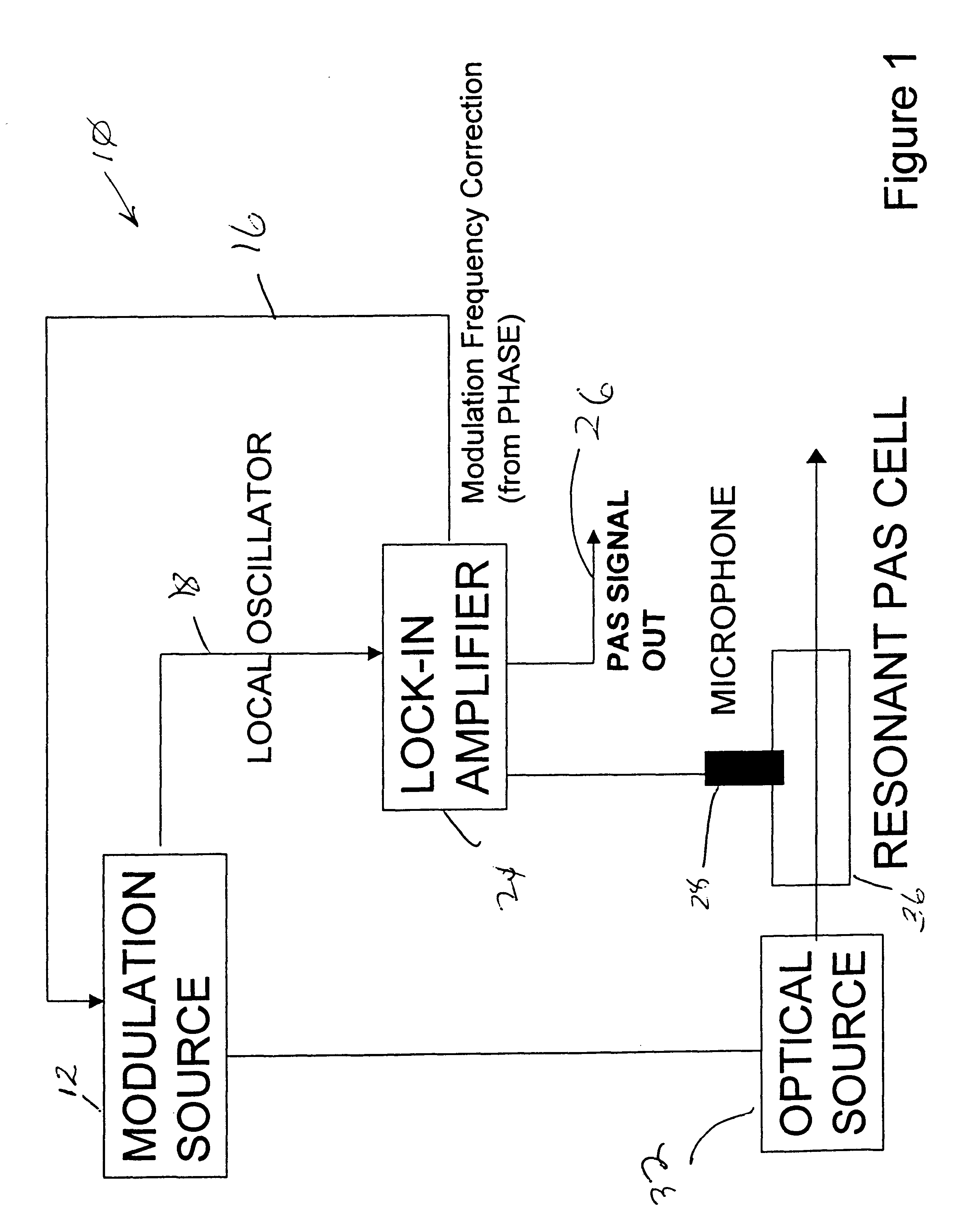
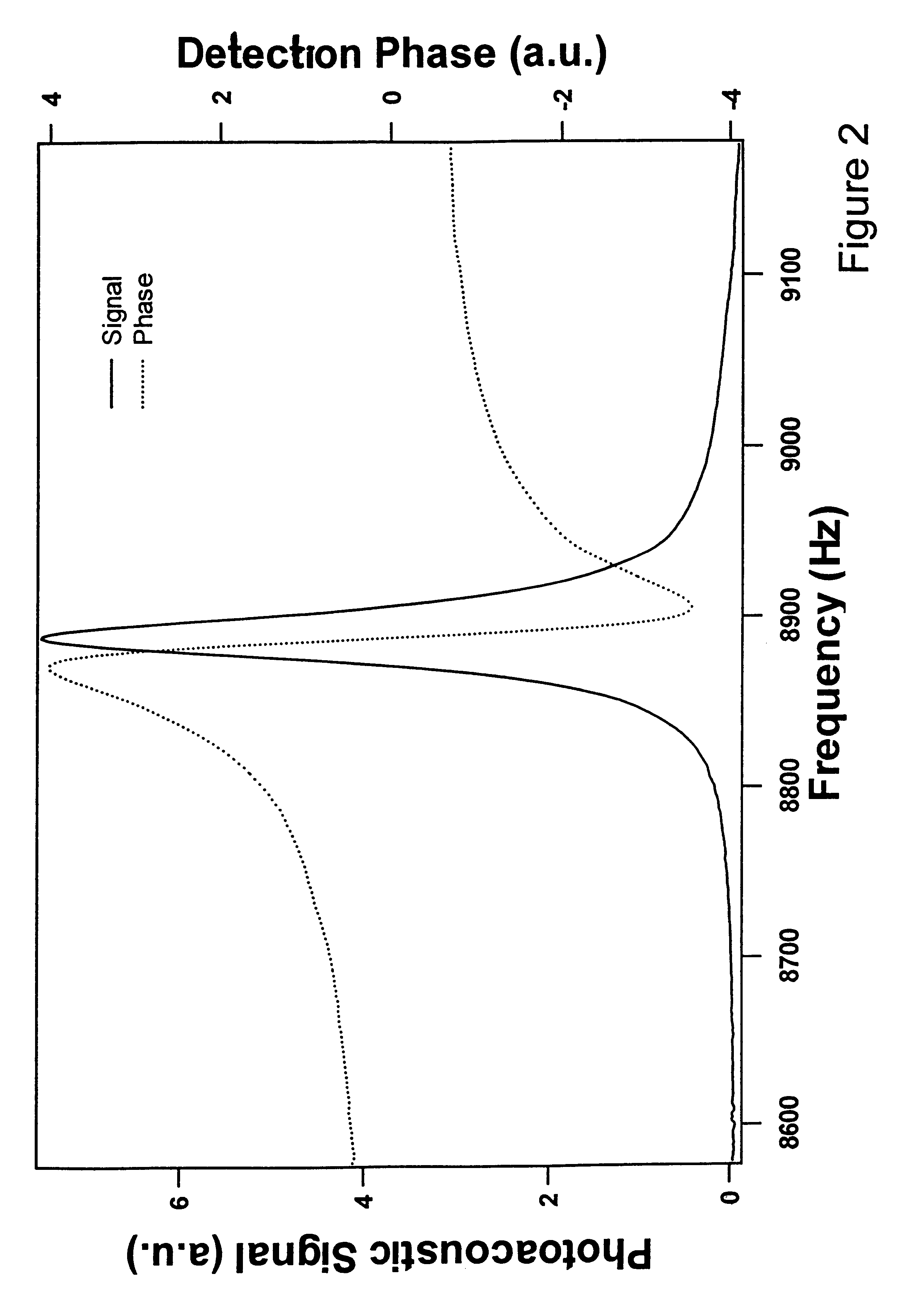
Acoustic resonance phase locked photoacoustic spectrometer
InactiveUS6608683B1High frequencyRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsSound sourcesHarmonic
A photoacoustic spectroscopy method and apparatus for maintaining an acoustic source frequency on a sample cell resonance frequency comprising: providing an acoustic source to the sample cell to generate a photoacoustic signal, the acoustic source having a source frequency; continuously measuring detection phase of the photoacoustic signal with respect to source frequency or a harmonic thereof; and employing the measured detection phase to provide magnitude and direction for correcting the source frequency to the resonance frequency.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
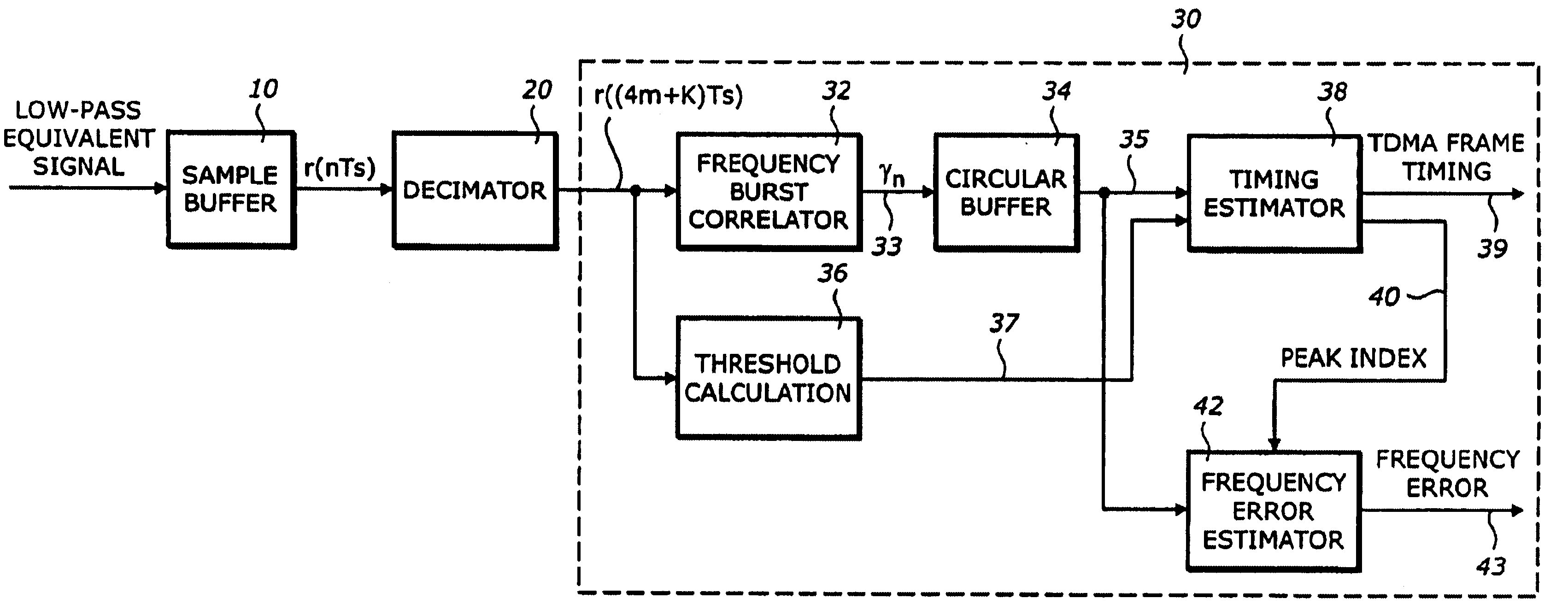
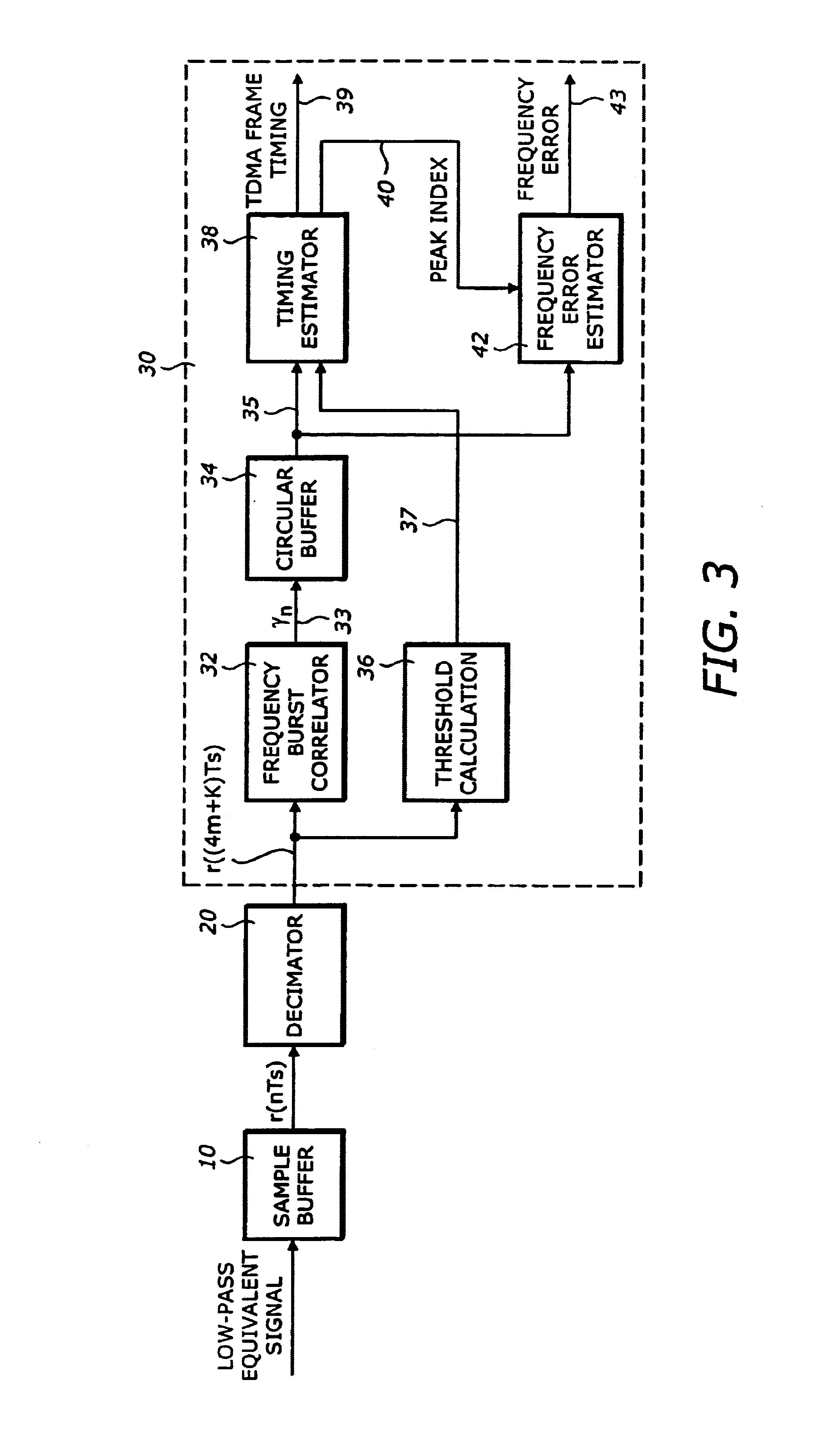
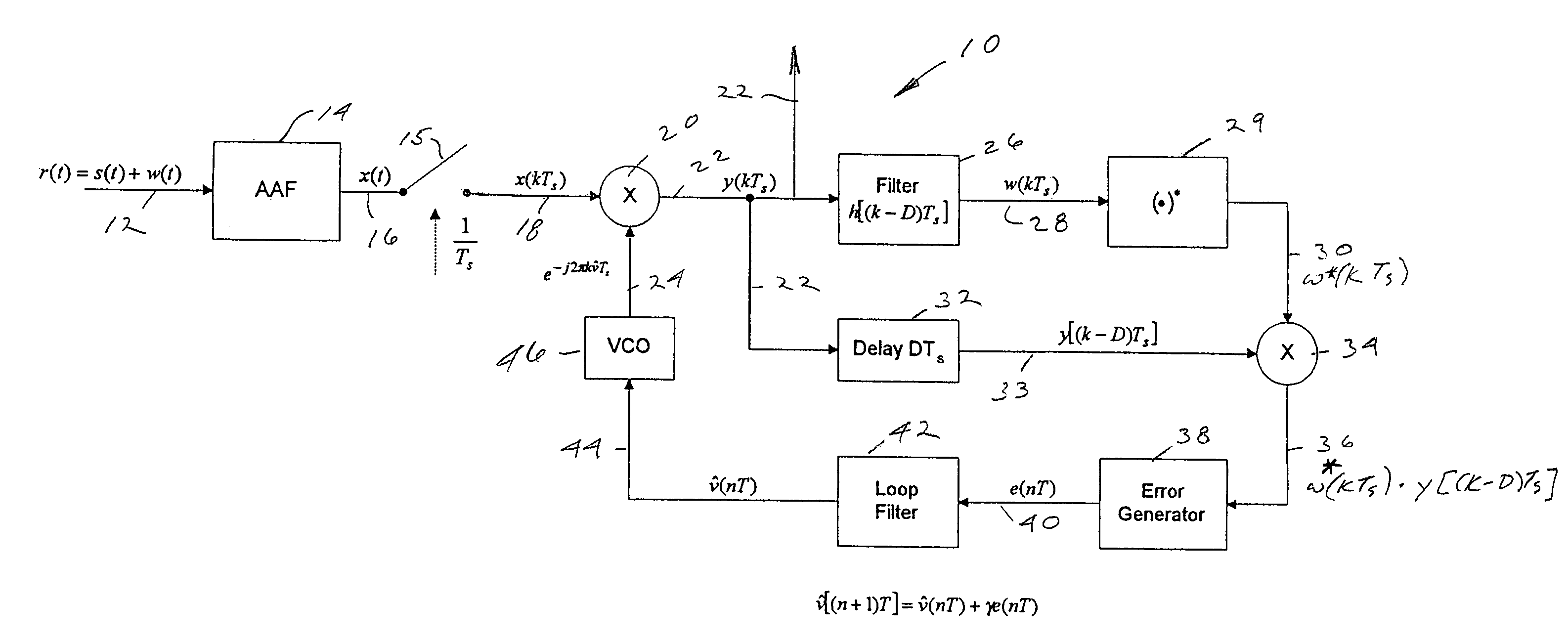
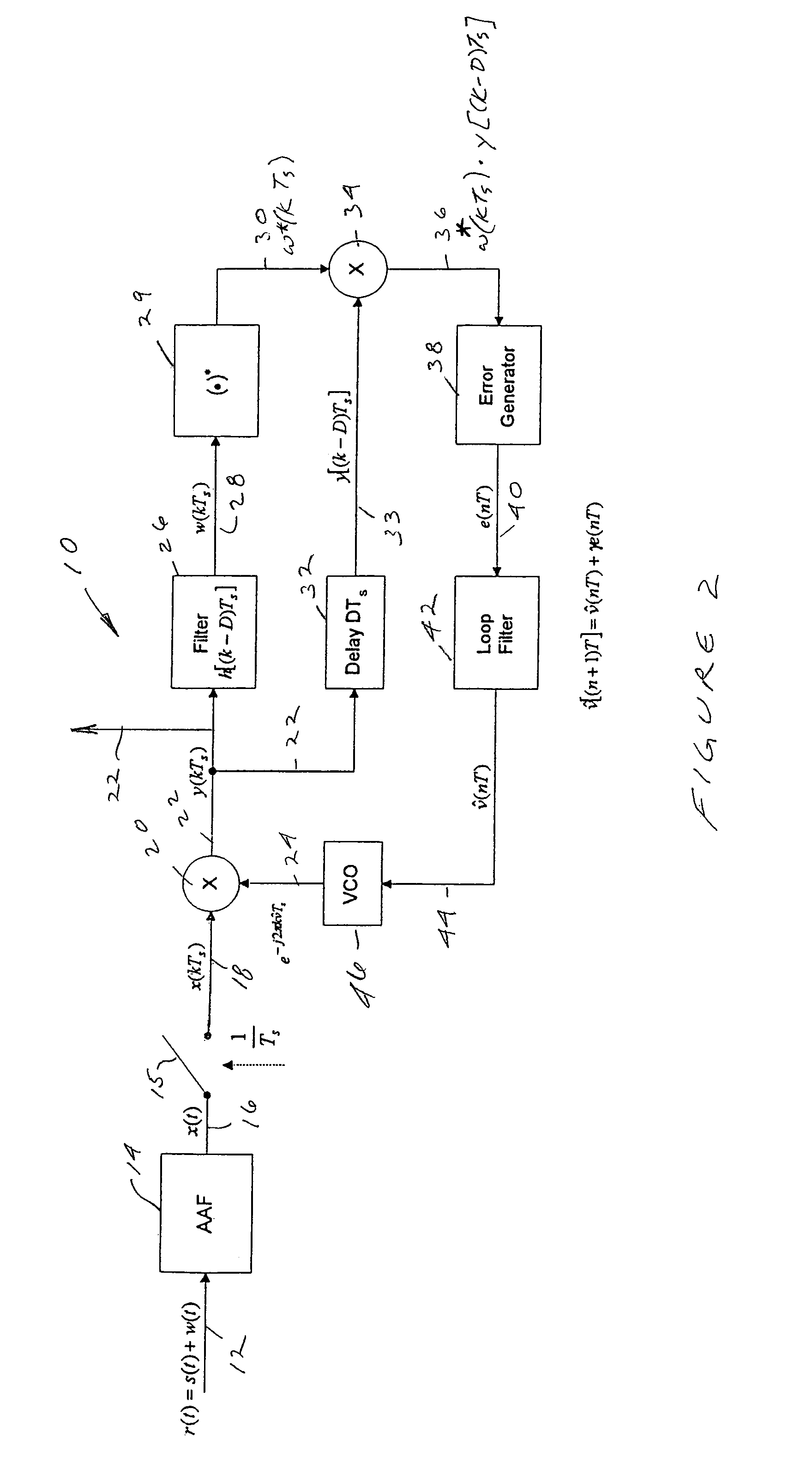
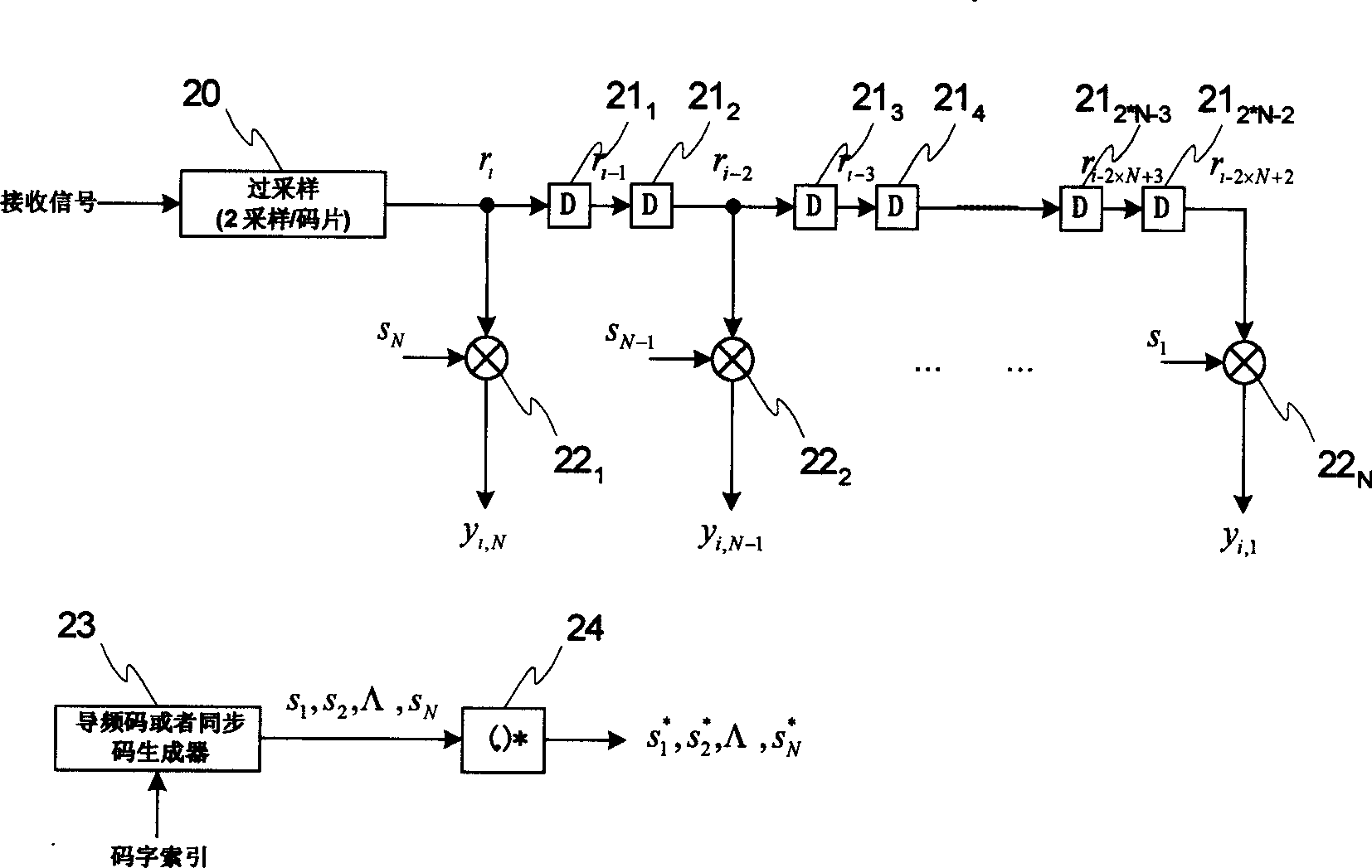
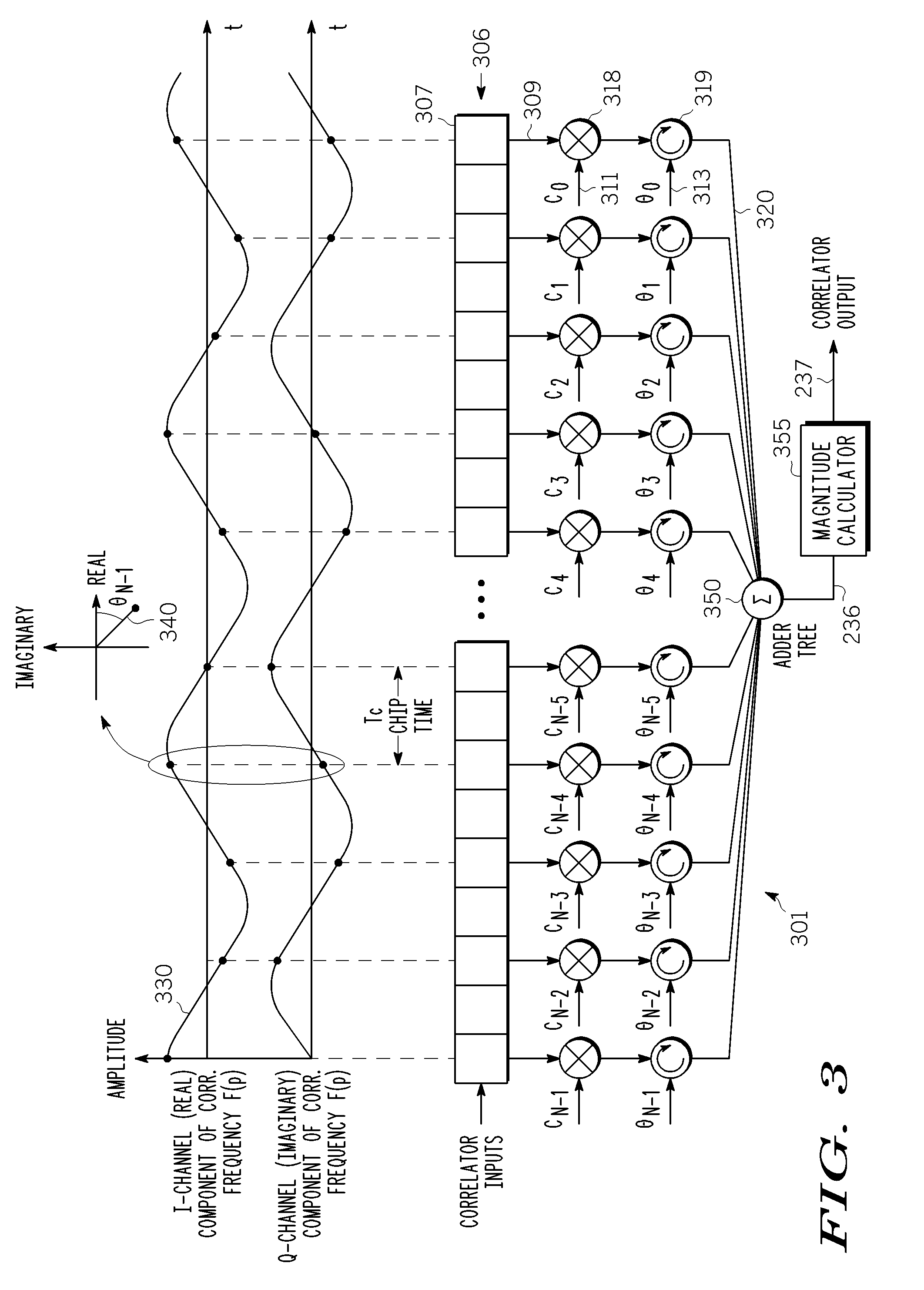
Frequency correction burst detection
A method and an apparatus for detecting a frequency correction burst embedded in a signal which includes ordered samples. The method comprises the following: (a) correlating K sequences of the ordered samples with a predetermined waveform to produce K correlation outputs, each of the K correlation outputs corresponding to one of the K sequences, having a magnitude and being associated with an order index, K being an integer, the predetermined waveform corresponding to the frequency correction burst; (b) storing the K correlation outputs in a buffer according to the order indices; and (c) estimating a parameter based on the K correlation outputs, the parameter indicating detection of the frequency correction burst. The estimated parameter includes a frequency error and an ending time of a frequency correction burst. A quality metric associated with each frequency error is also computed.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Frequency synthesizer
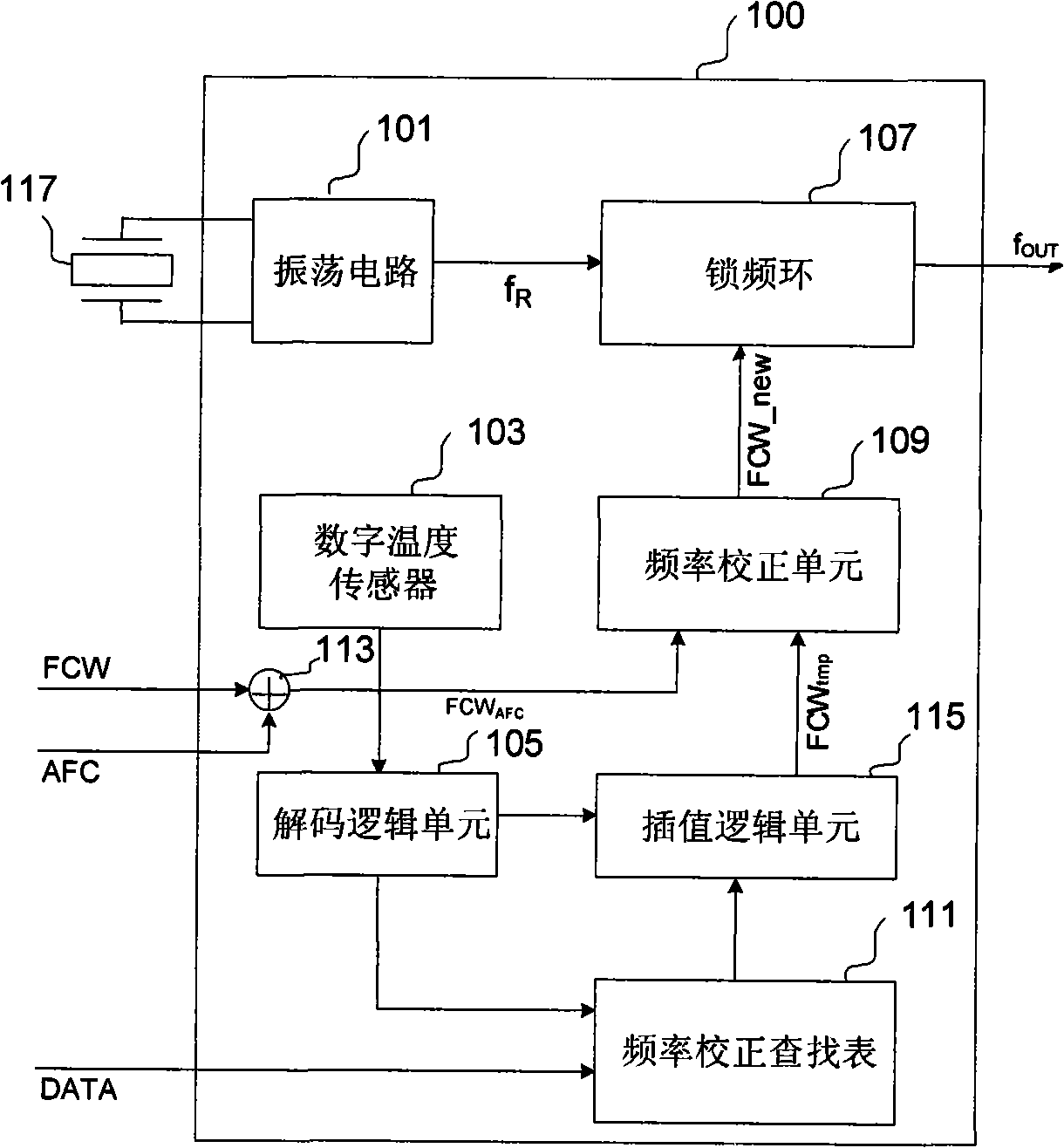
InactiveCN101272142ATo achieve temperature compensationGenerator stabilizationOscillations generatorsFrequency synthesizerFrequency modulation
The invention discloses a frequency synthesizer comprising a frequency-locked loop which runs based on the reference frequency of a crystal oscillator, a frequency correction unit and an interpolation logic unit; wherein, the frequency correction unit generates a digital frequency correction control word based on a first parameter and a second parameter; the first parameter is a combination of an automatic frequency correction word and a fixed frequency control word. The interpolation logic unit is used for generating the second parameter which expresses the temperature changing compensation; wherein, when the first parameter is a constant, the frequency-locked loop generates a fixed clock signal or when the first parameter is a binary sequence which expresses the frequency changing of a modulating signal, the frequency-locked loop generates a frequency modulating signal; temperature compensation to the frequency excursion of a reference clock can be realized by controlling the frequency correction control word.
Owner:曹秀娟
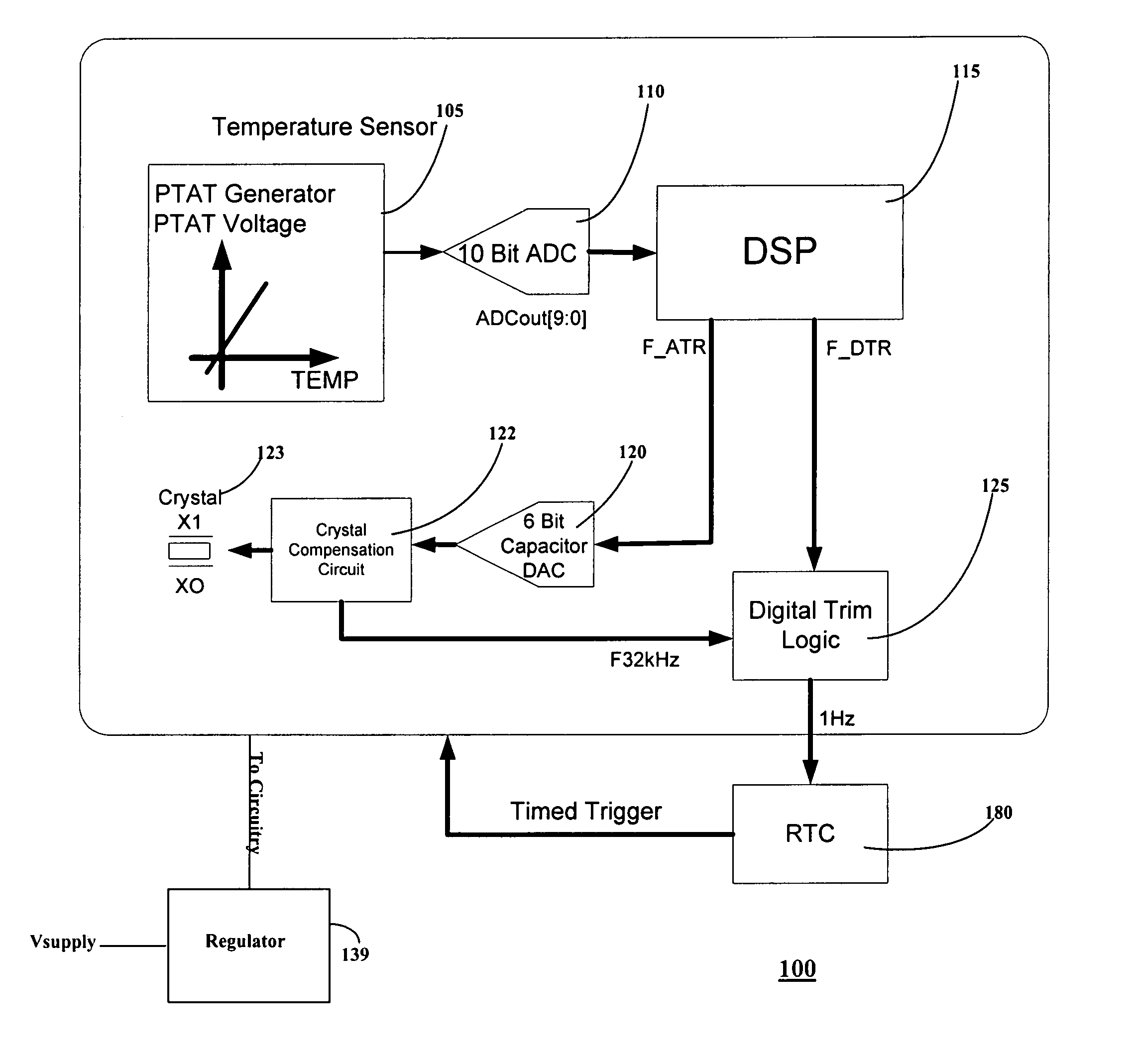
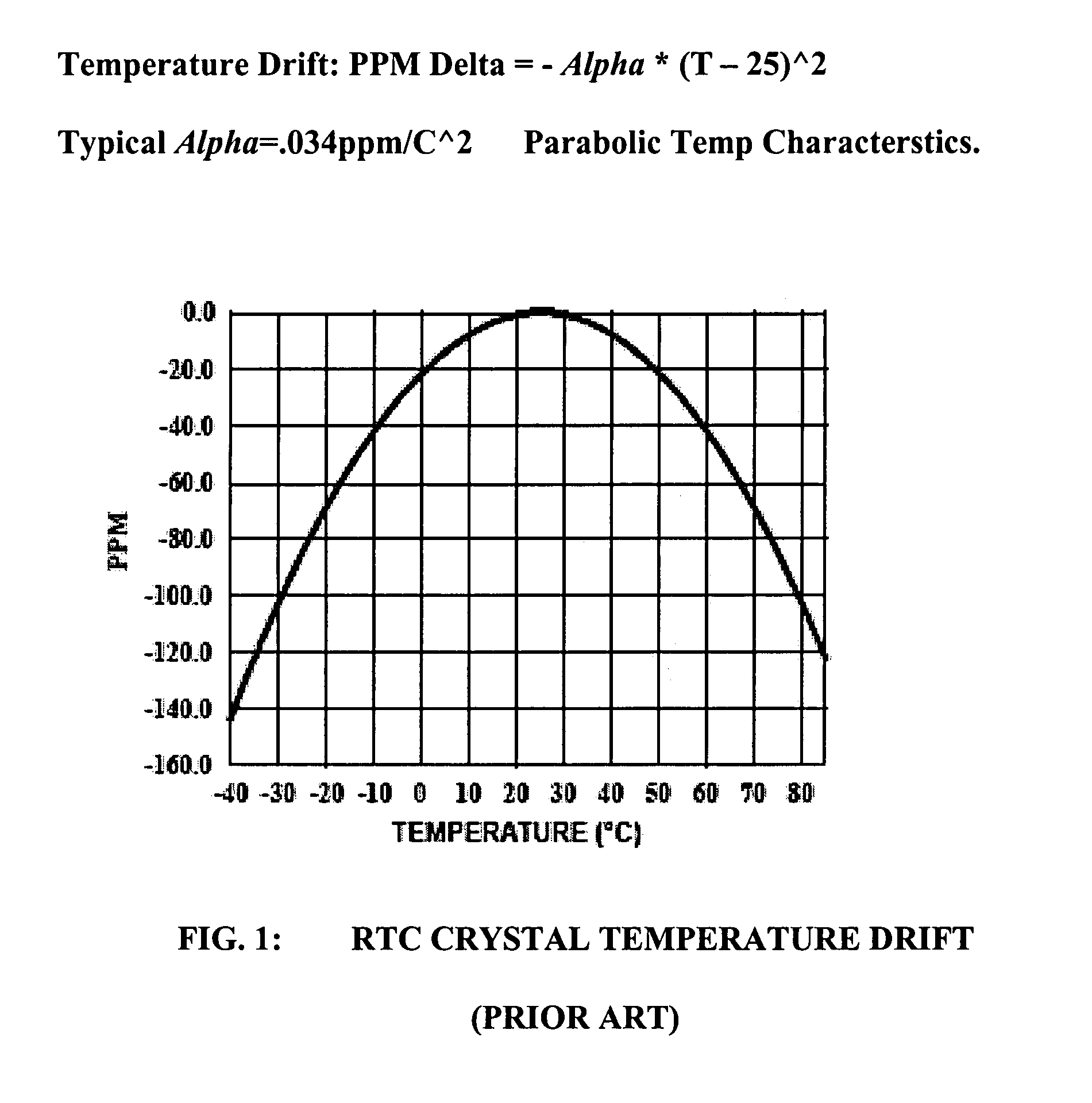
Automatic circuit and method for temperature compensation of oscillator frequency variation over temperature for a real time clock chip
ActiveUS7371005B1Low power operationFrequency stabilisation mechanismGenerator stabilizationCapacitanceReal-time clock
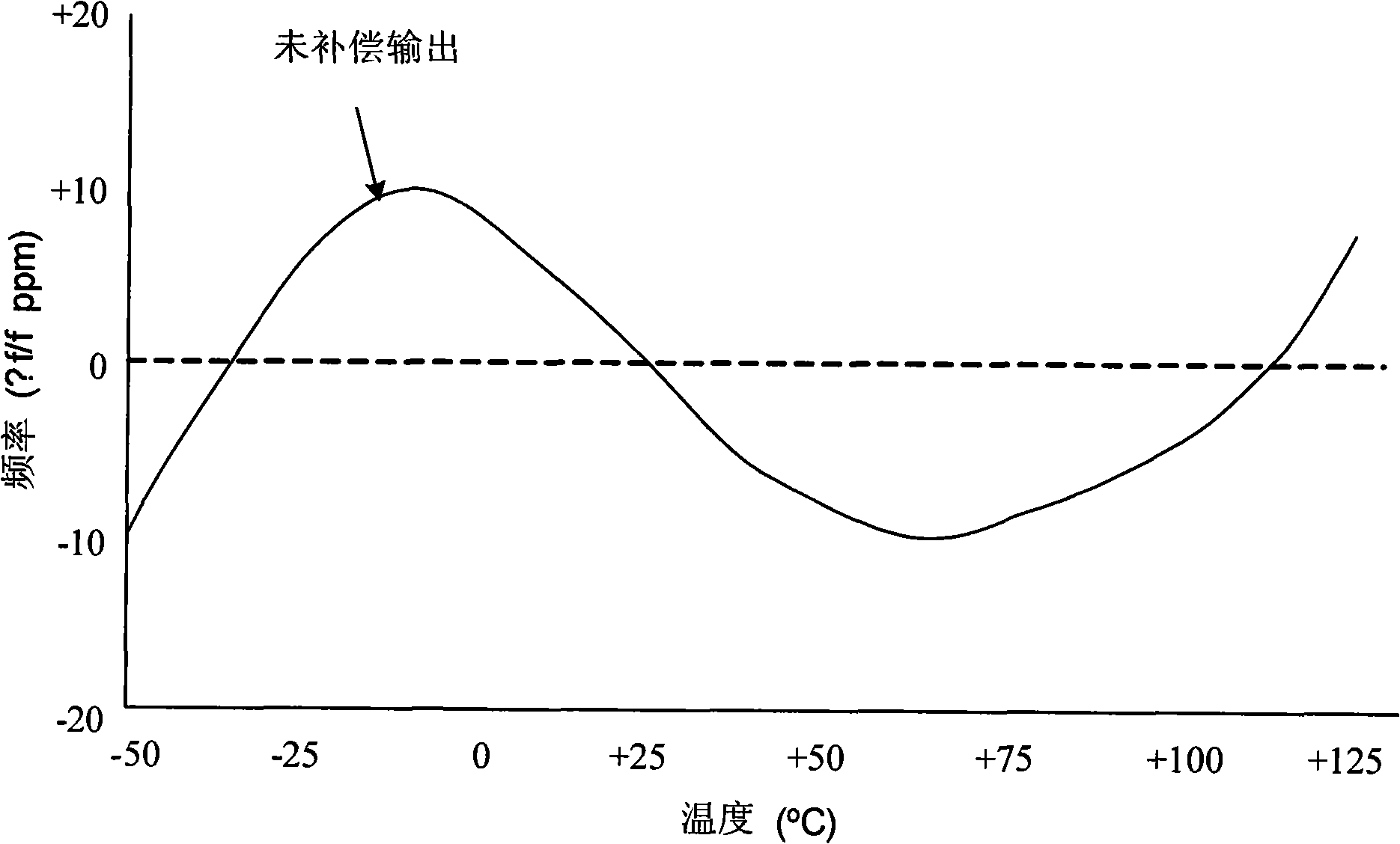
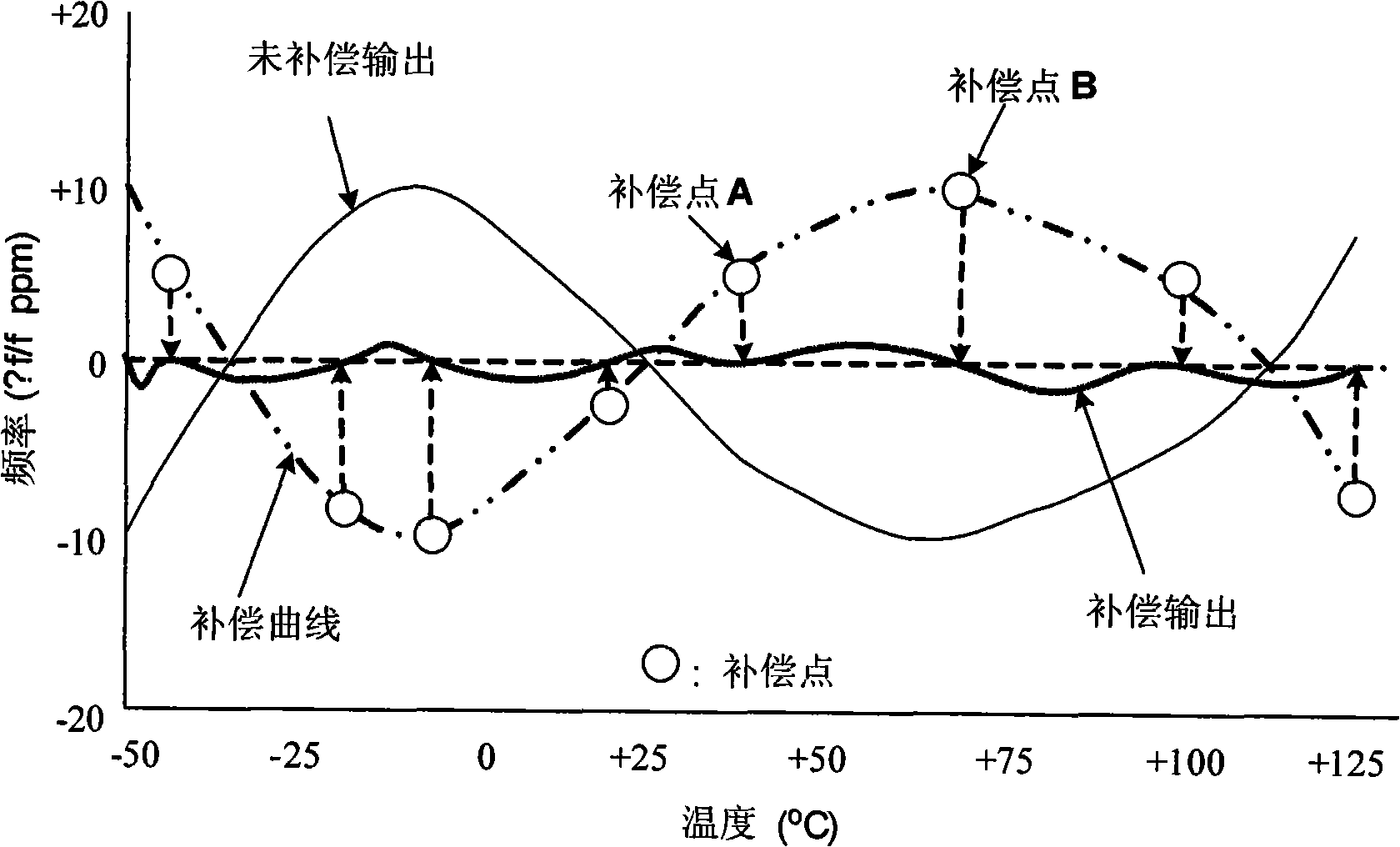
An automatic temperature compensated real-time clock (RTC) chip includes a clock portion having a crystal oscillator block including crystal compensation circuitry adapted to be coupled to a crystal. The crystal compensation circuitry includes a non-linear capacitor DAC including a plurality of load capacitors, wherein the load capacitors have respective switches which switch respective ones of the load capacitors to change a parallel resonance frequency (fp) generated by the oscillator block. The capacitor DAC is arranged so that Analog Trimming (ATR) bits received cause an arrangement of the switches to provide a non-linear change in overall load capacitance to result in a linear relationship between fp and the ATR bits. A temperature sensor block is coupled to the crystal for measuring a temperature of at least the crystal. An A / D converter is coupled to the temperature sensor for outputting a digital temperature signal representative of the temperature of the crystal. A DSP engine receives the digital temperature signal and calculates frequency correction needed to correct for frequency inaccuracy and determines a bit sequence including the ATR bits appropriate to achieve the frequency correction.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
System, method and device for implementing synchronization of micromicro honeycomb base station
InactiveCN101183898AAvoid quality problemsOne-waySynchronisation arrangementAssess restrictionHoneycombChipset
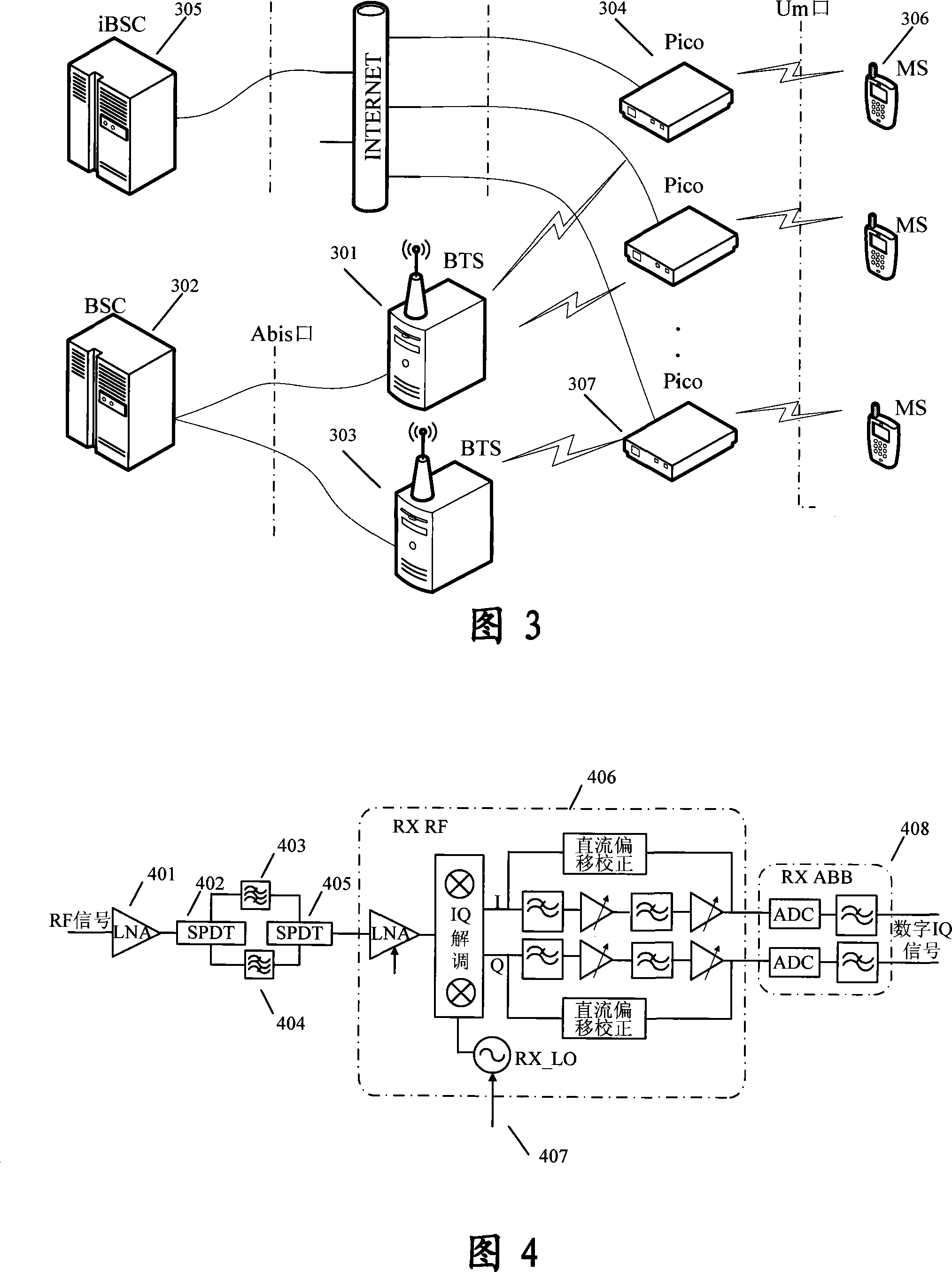
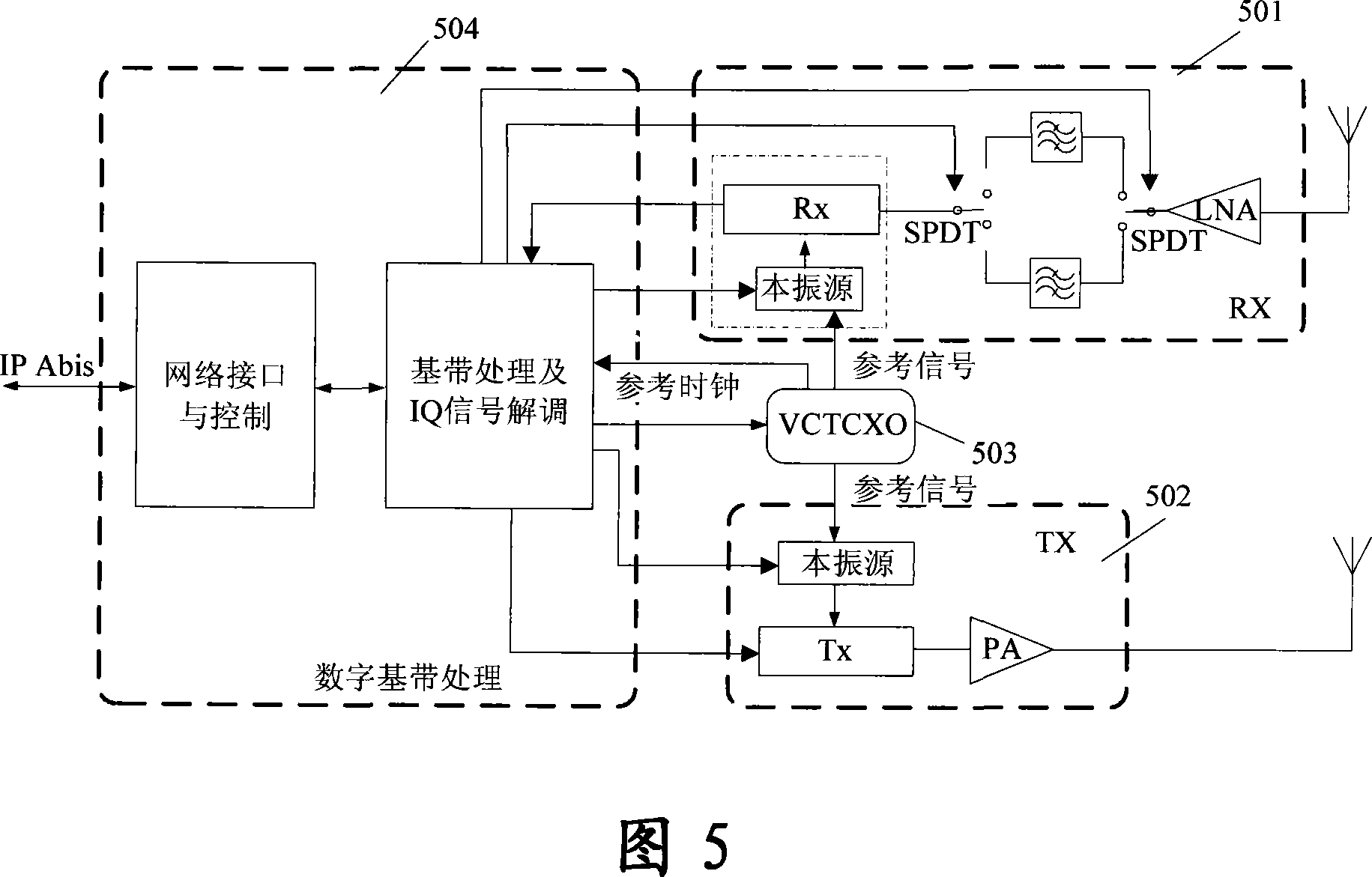
The invention relates to a system for realizing microcellular base station synchronization, which is used for the synchronization of GSM; the system comprises: BTS, BSC and Pico; wherein the master-slave synchronization method is adopted between BTSs for realizing synchronization; the hollow port Um of the BTS is adopted for Pico to realize the synchronization between Pico, i.e. the receiving channel of the Um port is used for terminal operation in synchronous receiving state to receive and search the broadcast signal channel BCH frequency points of BTS and then analyze frequency correction signal channel FCCH message so as to obtain BCH carrier timing message, according to timing message calculation and correcting the frequency deviation of local reference clock, the synchronization between Pico is realized. The invention utilizes terminal chipset to make the Pico be operated at two states of either terminal frequency band or base station frequency band, therefore no other base station functions are affected when realizing the synchronization of Pico, thereby enhancing systematic integration degree effectively and reducing systematic manufacture and maintenance cost.
Owner:ZTE CORP
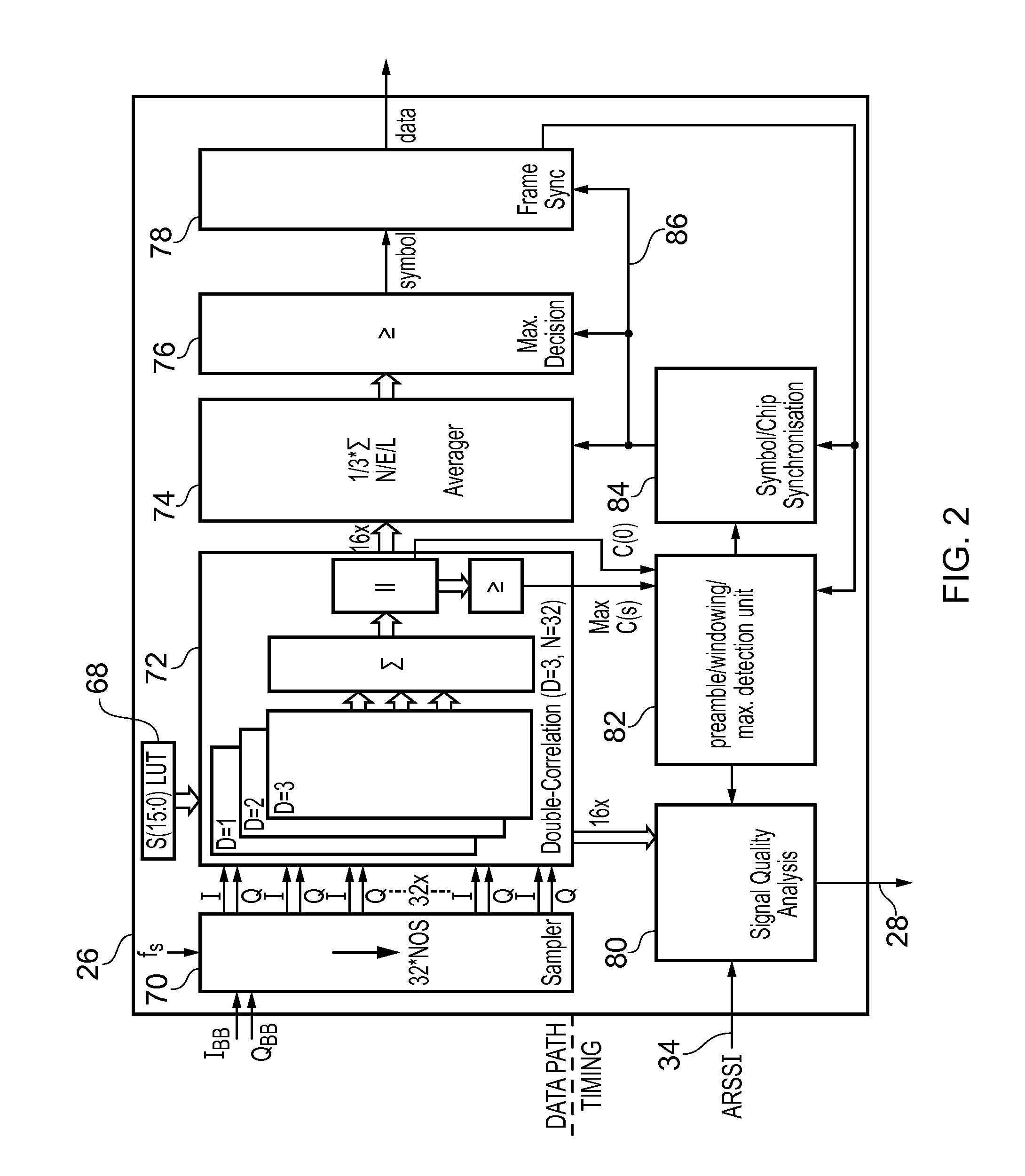
Wireless receiver
ActiveUS20110039509A1Relaxed noise requirementsLow powerPulse automatic controlRadio transmissionEngineeringAnalog-to-digital converter
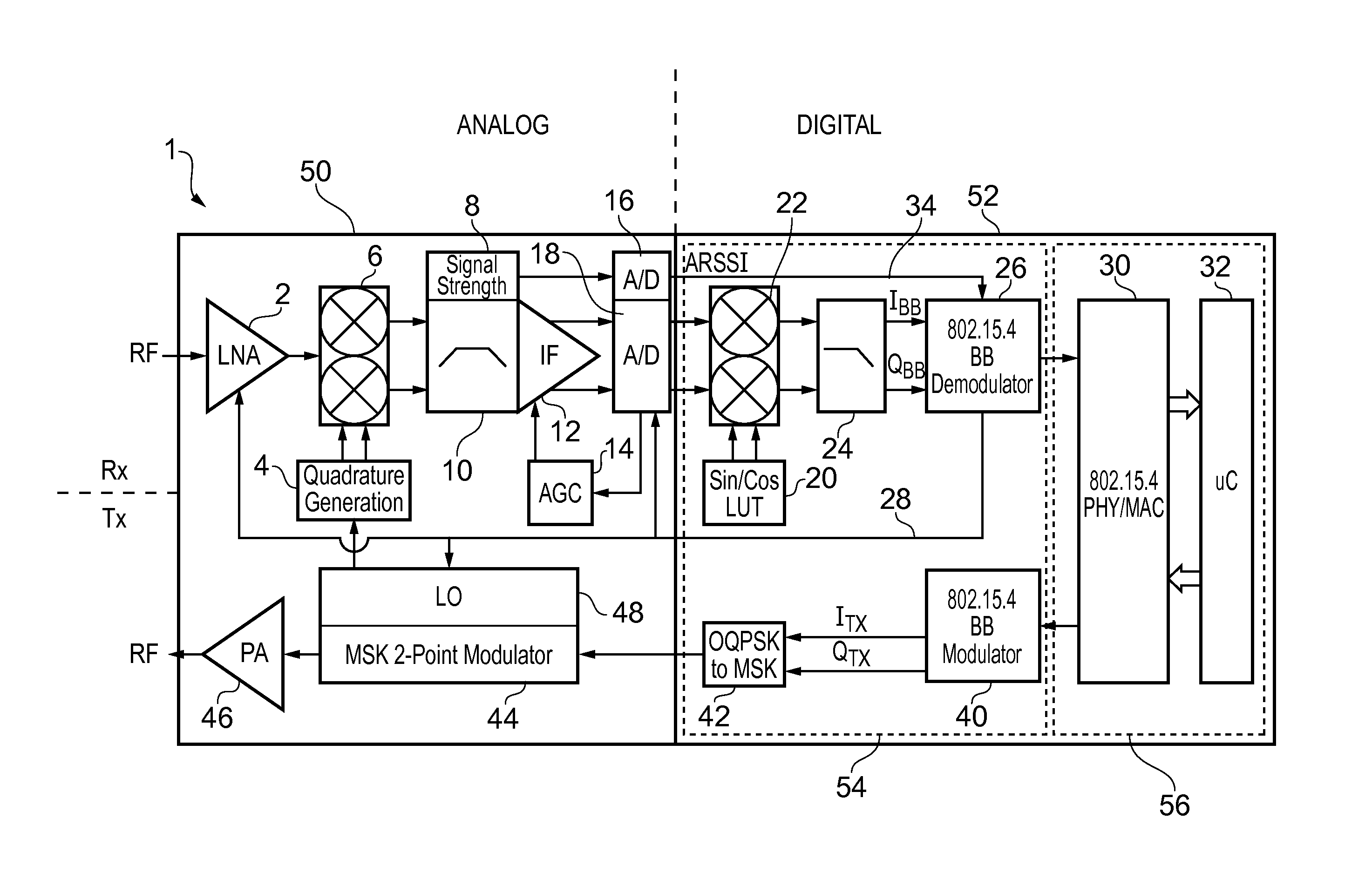
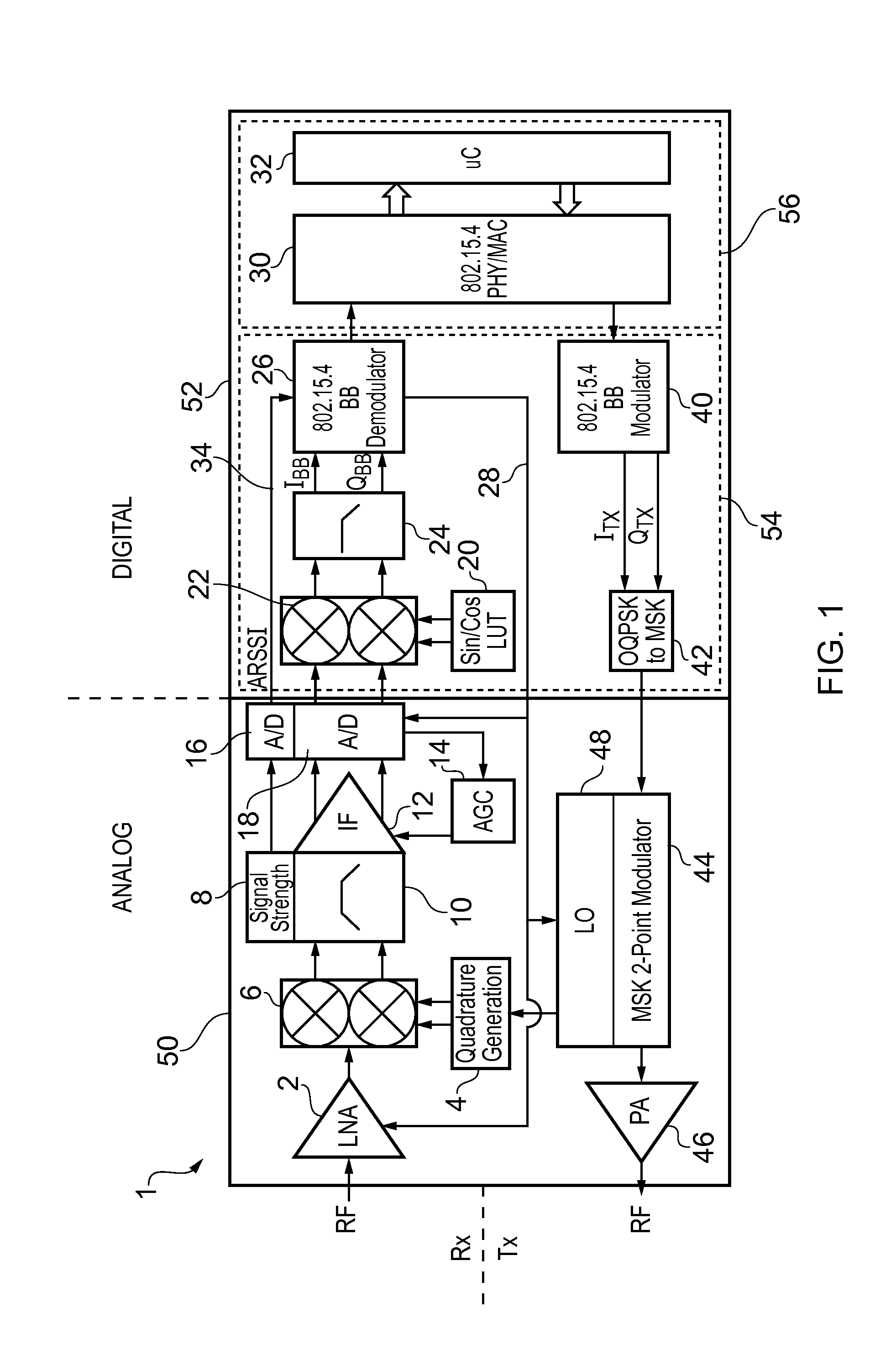
A wireless receiver designed to conform to the standard IEEE 802.15.4. The receiver comprises an analog front-end and a digital decoder. The analog components of the front end include one or more amplifiers and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The digital decoder receives the output of the ADC and demodulates it in a demodulator which is driven at an a chip frequency by an internal or external clock. The demodulator comprises a sampler operable to sample the digital signal at a sampling frequency and a correlation unit operable to process a set of bits, referred to as a chip code, in the sampled digitized signal and output therefrom a set of correlation values. The set of correlation values is an indicator of likely mapping between the chip code that has been processed and a set of possible chip codes defined according to the standard. The demodulator further comprises a symbol selection unit and a frequency correction unit. The symbol selection unit has the function of deciding which symbol has been received based on an analysis of each set of correlation values. The frequency correction unit is operable to make adjustments to the chip frequency based on the correlation values output from the correlation unit, specifically to increase or decrease the chip frequency based on a measurement of whether the maximum correlation value among each set of correlation values occurs earlier or later than predicted. This scheme has the advantage that phase and frequency compensation is done after correlation avoiding the need for coherent demodulation while at the same time not requiring the stringent specifications of a conventional non-coherent demodulation scheme.
Owner:CASCODA
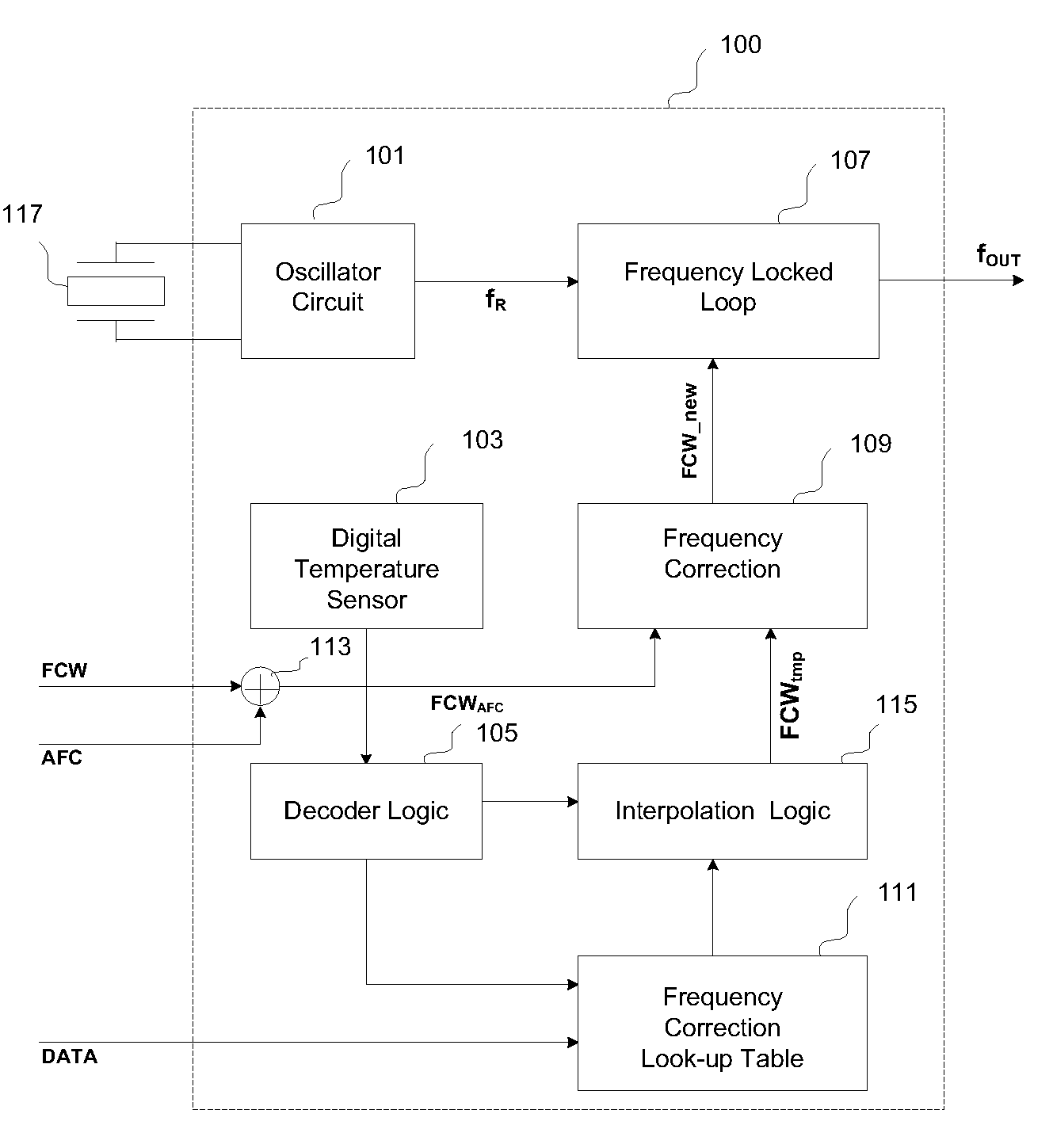
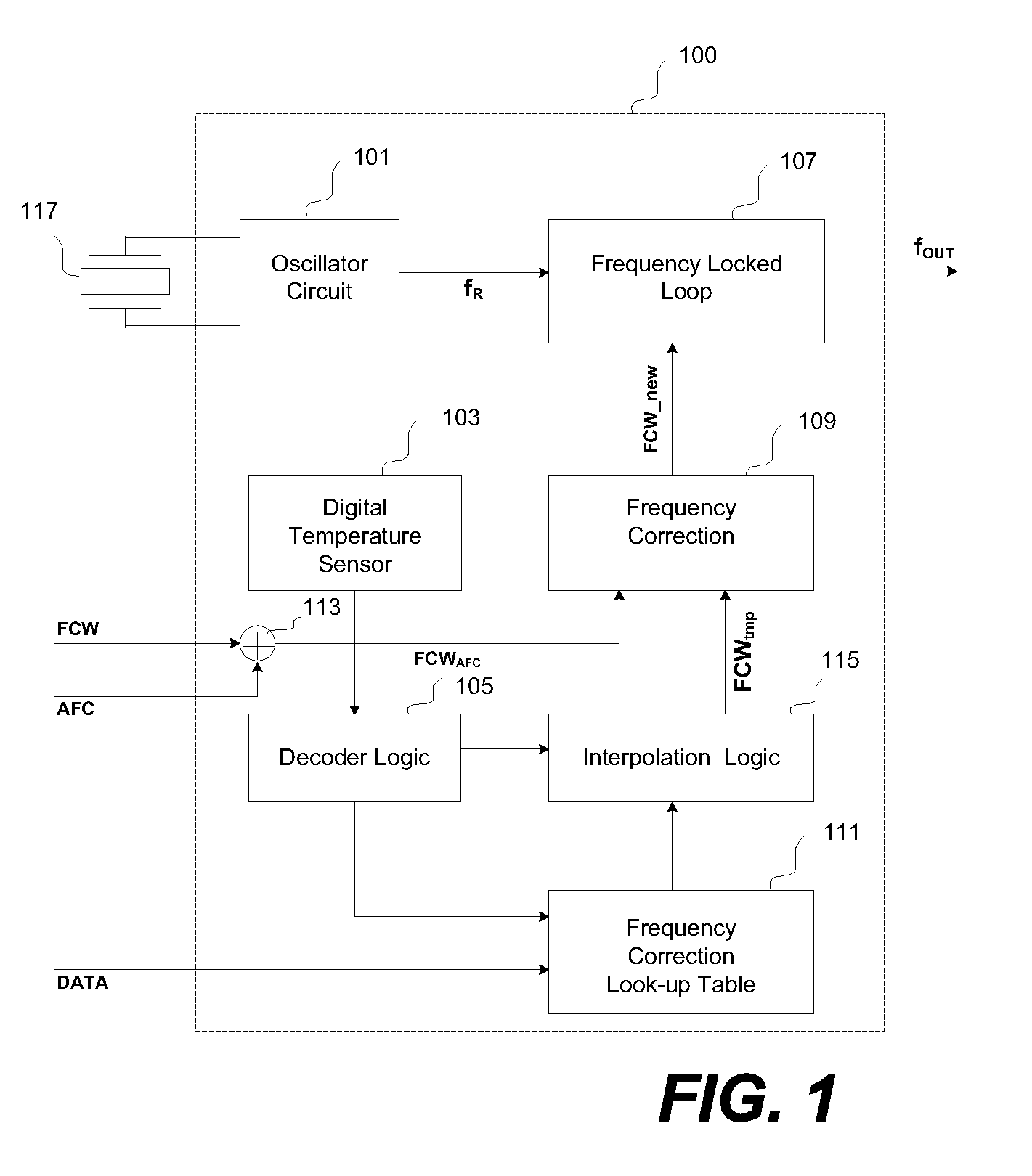
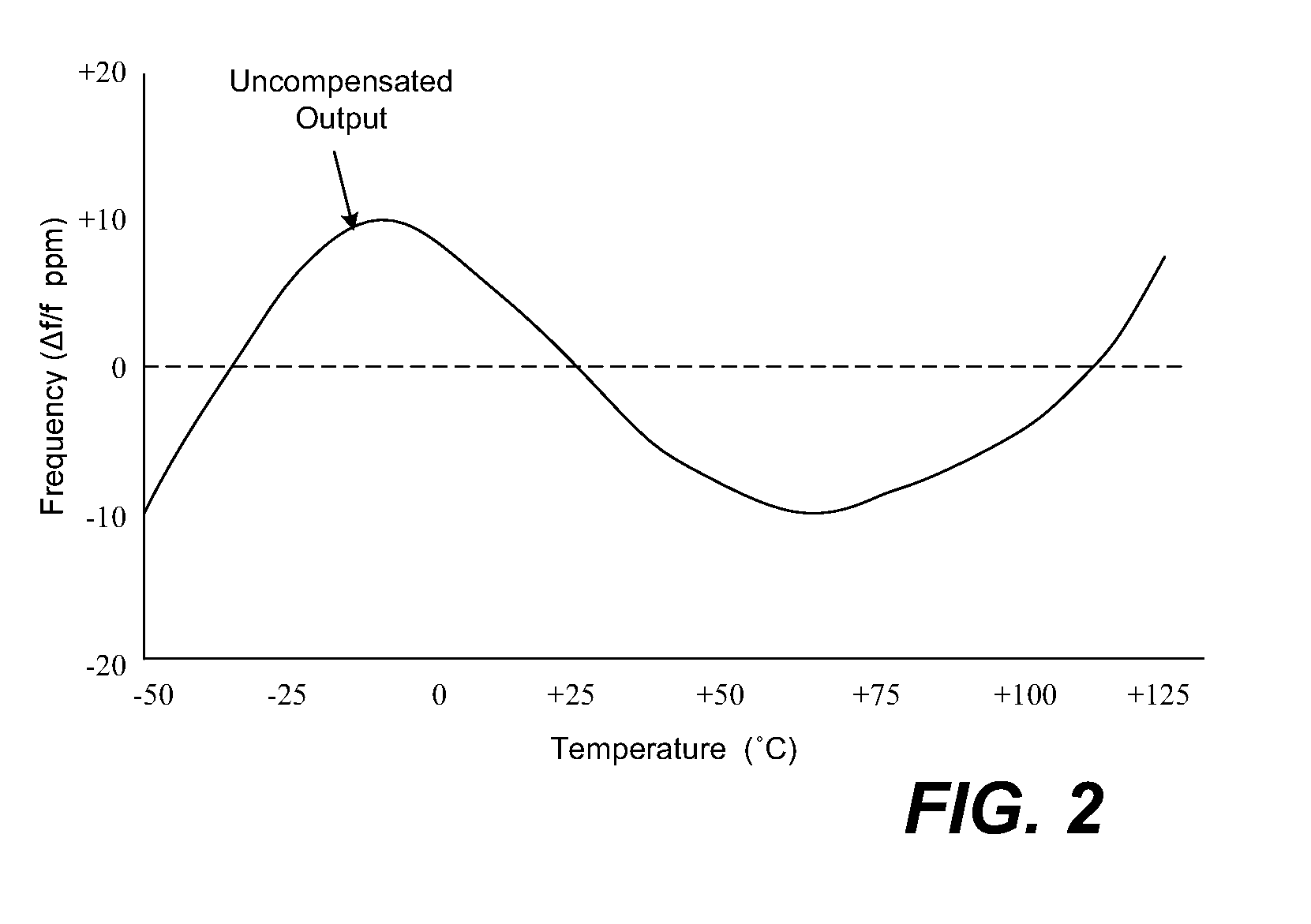
Method and apparatus for compensating temperature changes in an oscillator-based frequency synthesizer
InactiveUS7579919B1Pulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsFrequency synthesizerBase frequency
Architectures for compensating the frequency drift of an oscillator based frequency synthesizer circuit due to the change of temperature are disclosed. By applying a digitally controlled frequency word which represents the frequency difference between an output signal of a crystal oscillator and a temperature-compensated signal obtained from the output of a frequency synthesizer, the generated frequency signal is controlled so as to be temperature compensated over a wide temperature range. In one embodiment, a frequency locked loop is provided to perform functions to compensate for possible drifts in the reference signal. The frequency locked loop receives a digital frequency corrected control word based on at least a first parameter and a second parameter, wherein the first parameter is a combination of a fixed frequency control word and an automatic frequency correction word, and the second parameter is derived from an external source.
Owner:CAO WEIXUN
Frequency synchronizer
InactiveUS6947504B1Apparent advantageHigh bandwidthAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCarrier signalErrors and residuals
A frequency synchronizer system is based on the maximum likelihood criterion from estimation theory and that can achieve both frequency acquisition and frequency tracking without requiring knowledge at the receiver of the carrier's phase angle, baud timing, or a preamble consisting of known signal symbols. The synchronizer includes a processor for executing the following sequence of operations: a) initializing an estimated frequency correction factor; b) determining a corrected frequency offset value from a first product of a sample signal and the estimated frequency correction factor; c) filtering a first sample of the corrected frequency offset value to obtain a filtered corrected frequency offset value; d) imparting a delay to a second sample of the corrected frequency offset value to obtain a delayed corrected frequency offset value; e) determining a conjugate product value from a second product of the filtered corrected frequency offset value and a conjugate of the filtered corrected frequency offset value; f) determining a delay conjugate value from a third product of the delayed corrected frequency offset value and the conjugate product value; g) determining an error signal from the delay conjugate value; h) determining a frequency offset value from the error signal; and i) determining an updated value of the estimated frequency correction factor from the frequency offset value.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Automatic correcting frequency method for time-division radio communication system and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN1578485AAutomatic frequency correction is fast and accurateImprove performanceTime-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemTime delays
The automatic frequency correction method and device includes two stages of coarse frequency correction and fine frequency correction. The coarse frequency correction includes the steps of signal extraction, sliding correlation and phase deviation estimation, multiple frequency merging, creating time delay envelope, route selection, multipath merging, frequency control, etc. and corresponding modules. The fine frequency correction includes the steps of signal extraction, channel estimation and route search, route merging, frequency deviation estimation, SINR estimation, Kalman gain factor calculation, the first order loop filtering, frequency control, etc. and corresponding modules. The present invention makes it possible for the receiver to realize frequency sync in time division system fast accurately in harsh mobile communication environment.
Owner:XUANPU INDUSTRY CO LTD
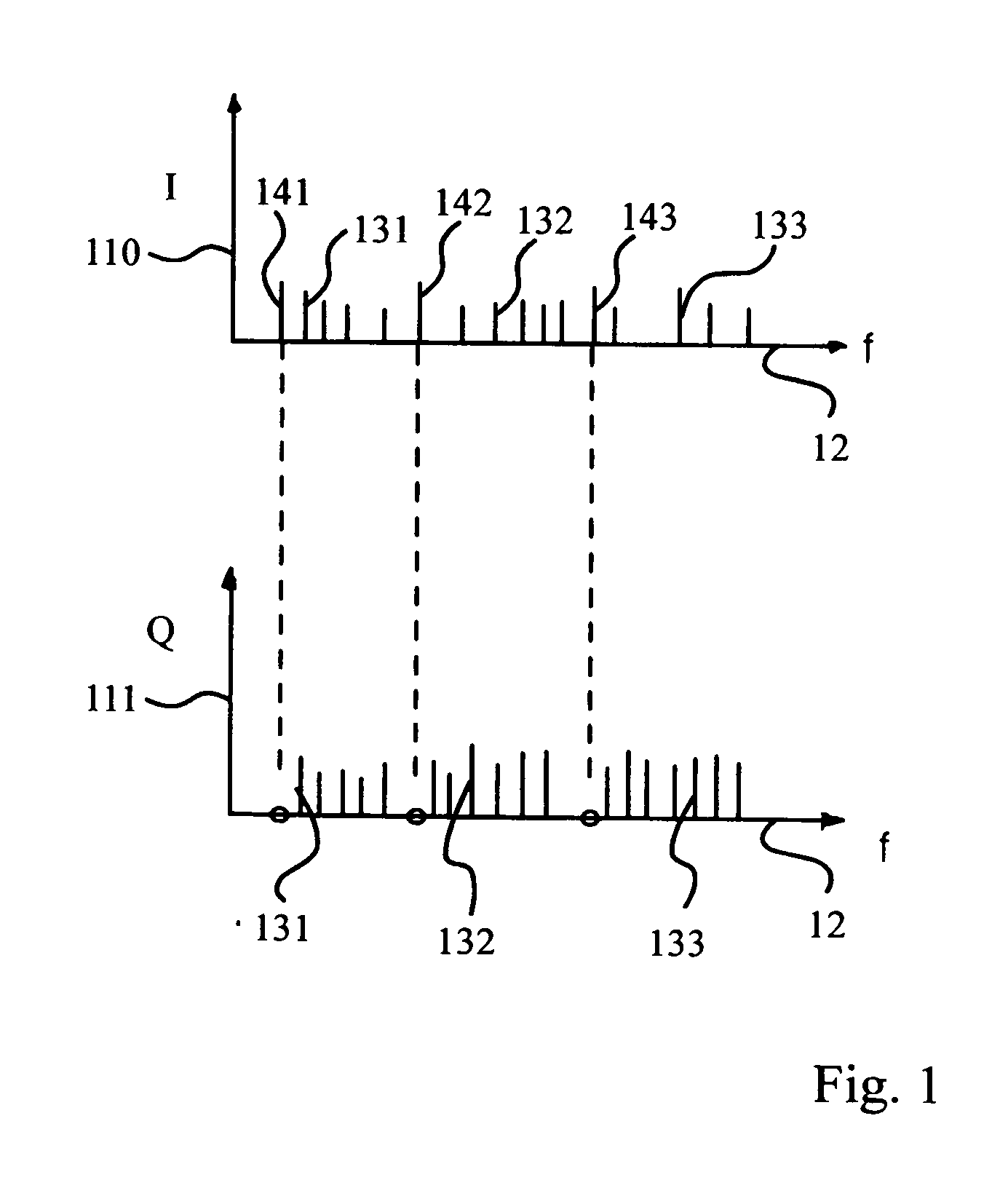
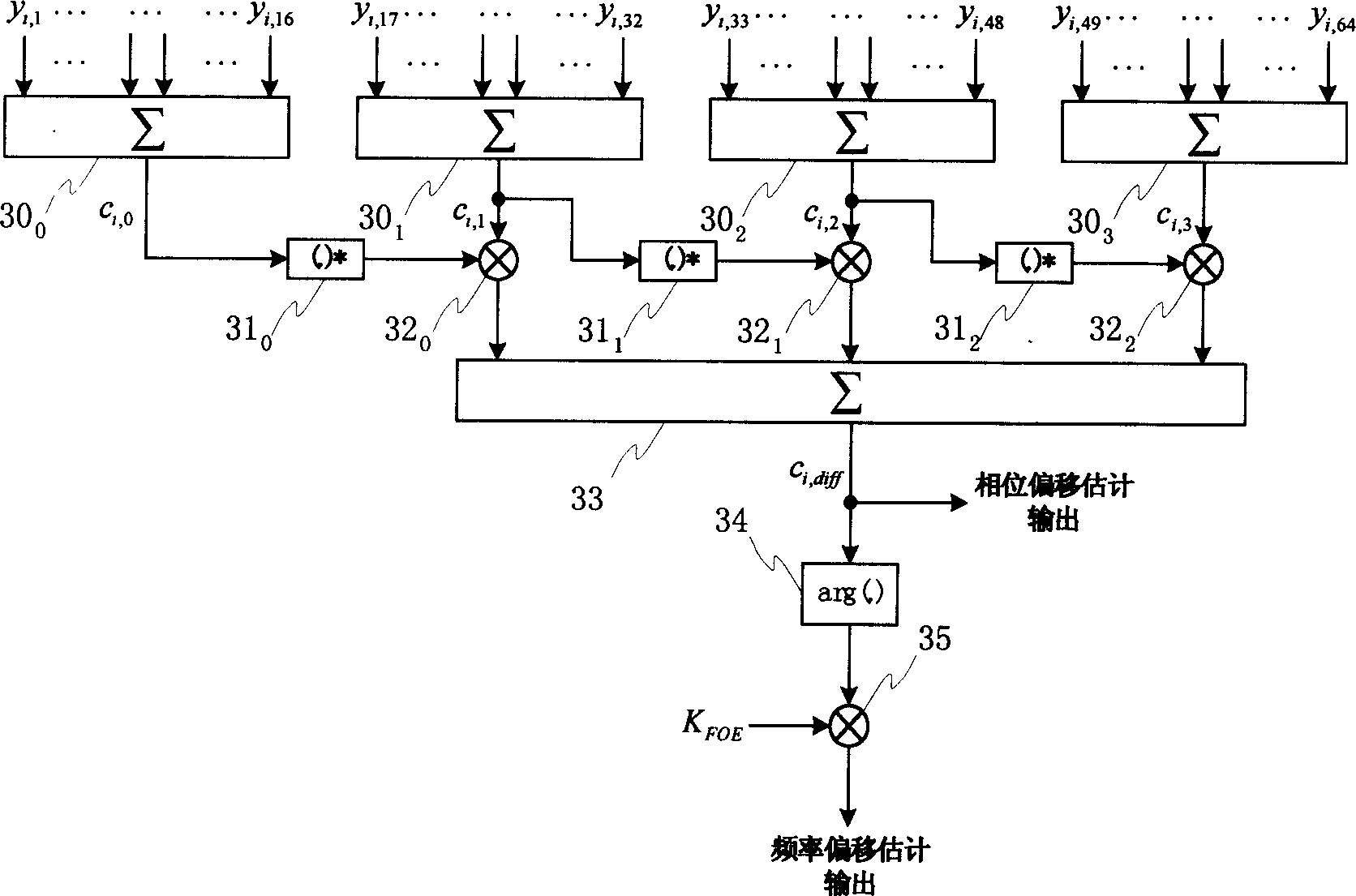
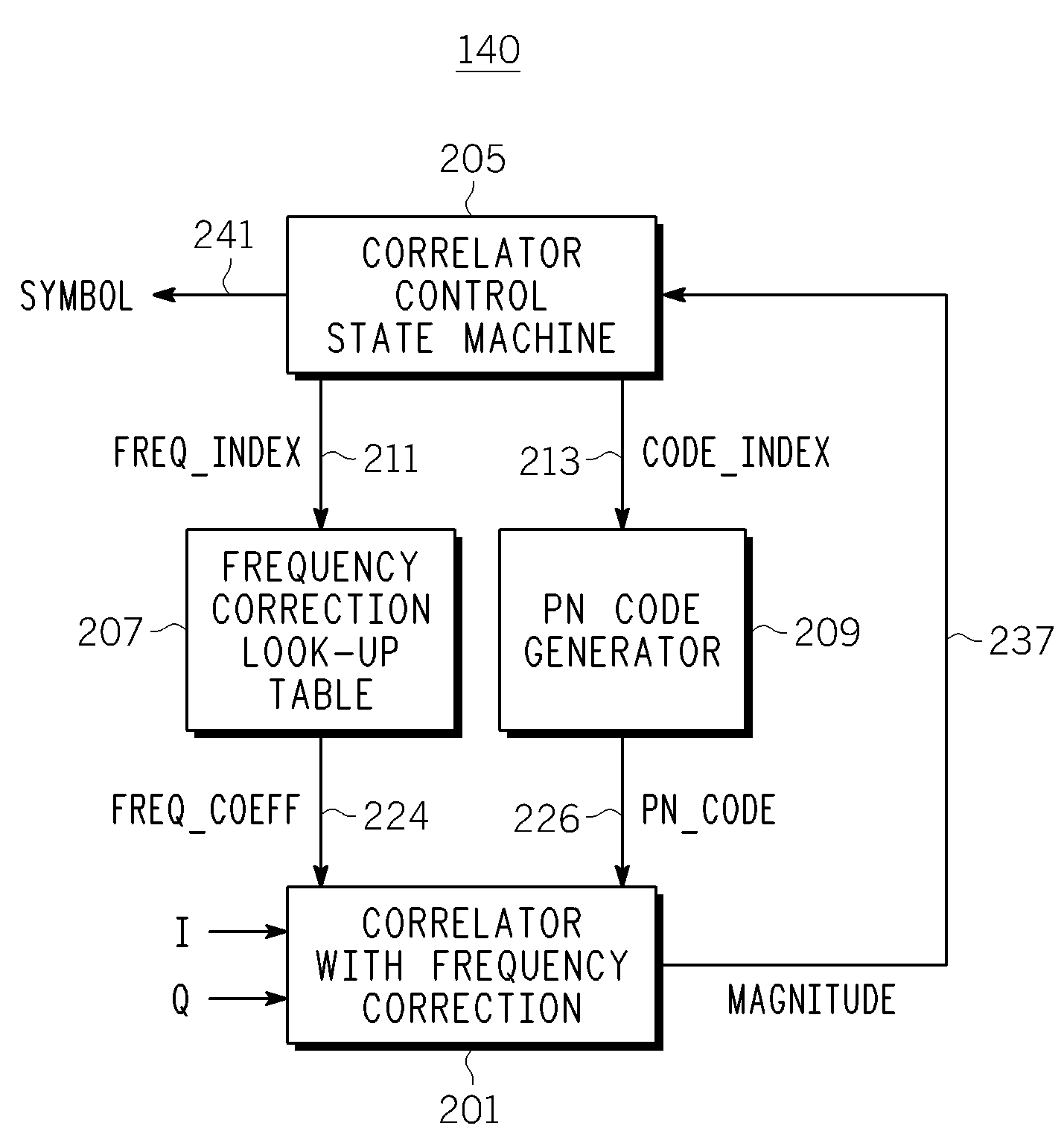
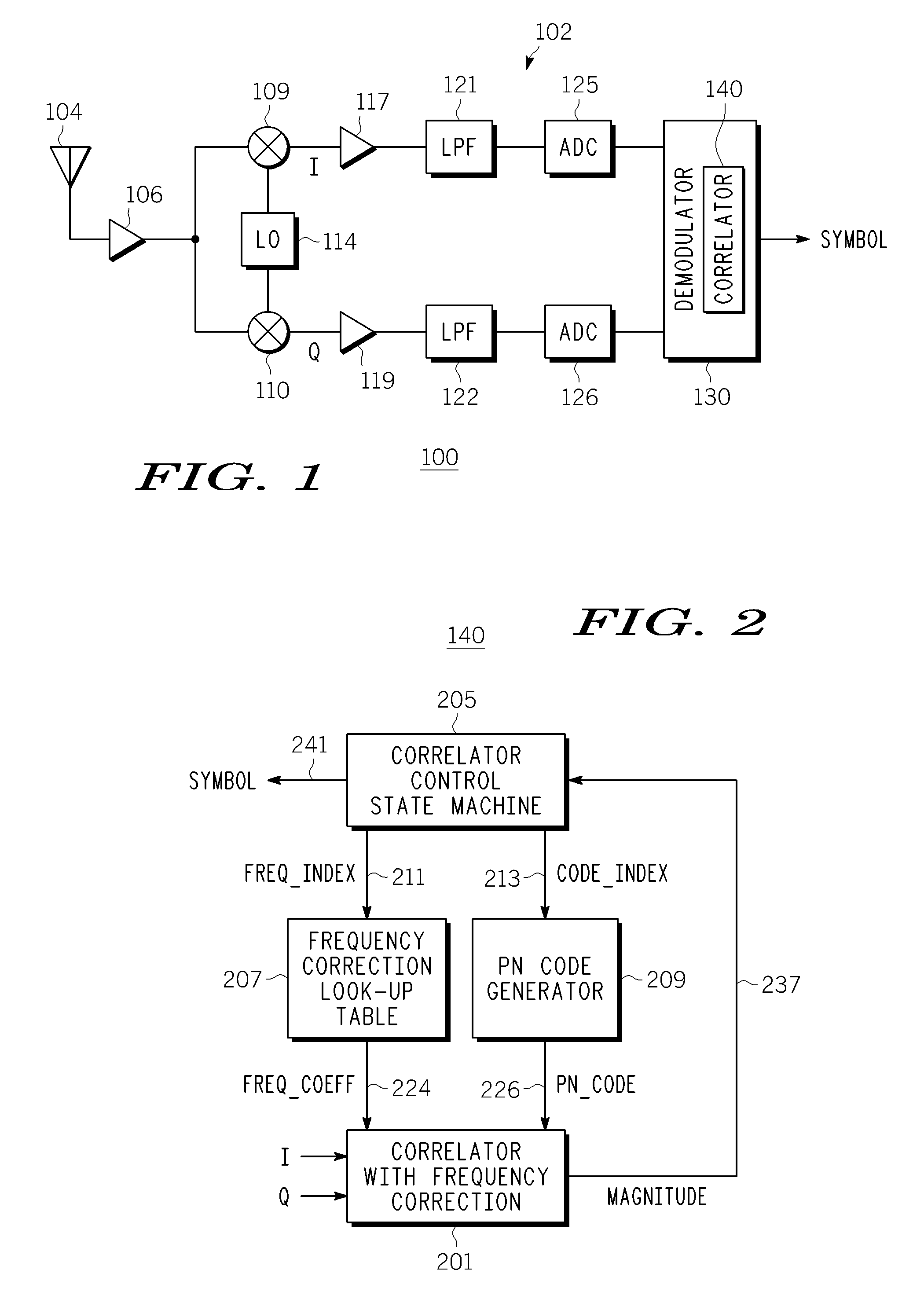
Joint de-spreading and frequency correction using a correlator
A correlator (140) for de-spreading a spread-spectrum signal includes a state machine (205), a frequency look-up table (207), a pseudorandom code generator (209), and a correlator structure (301 and 801). The spread-spectrum signal includes symbols, and each symbol includes a plurality of chips. The correlator structure includes a plurality of taps (309 and 809) at which a coordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) operation is performed to determine an offset from a nominal carrier frequency of the spread-spectrum signal and to change a phase of each chip of a received symbol, in order to correct a carrier frequency of the spread-spectrum signal while de-spreading the spread-spectrum signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
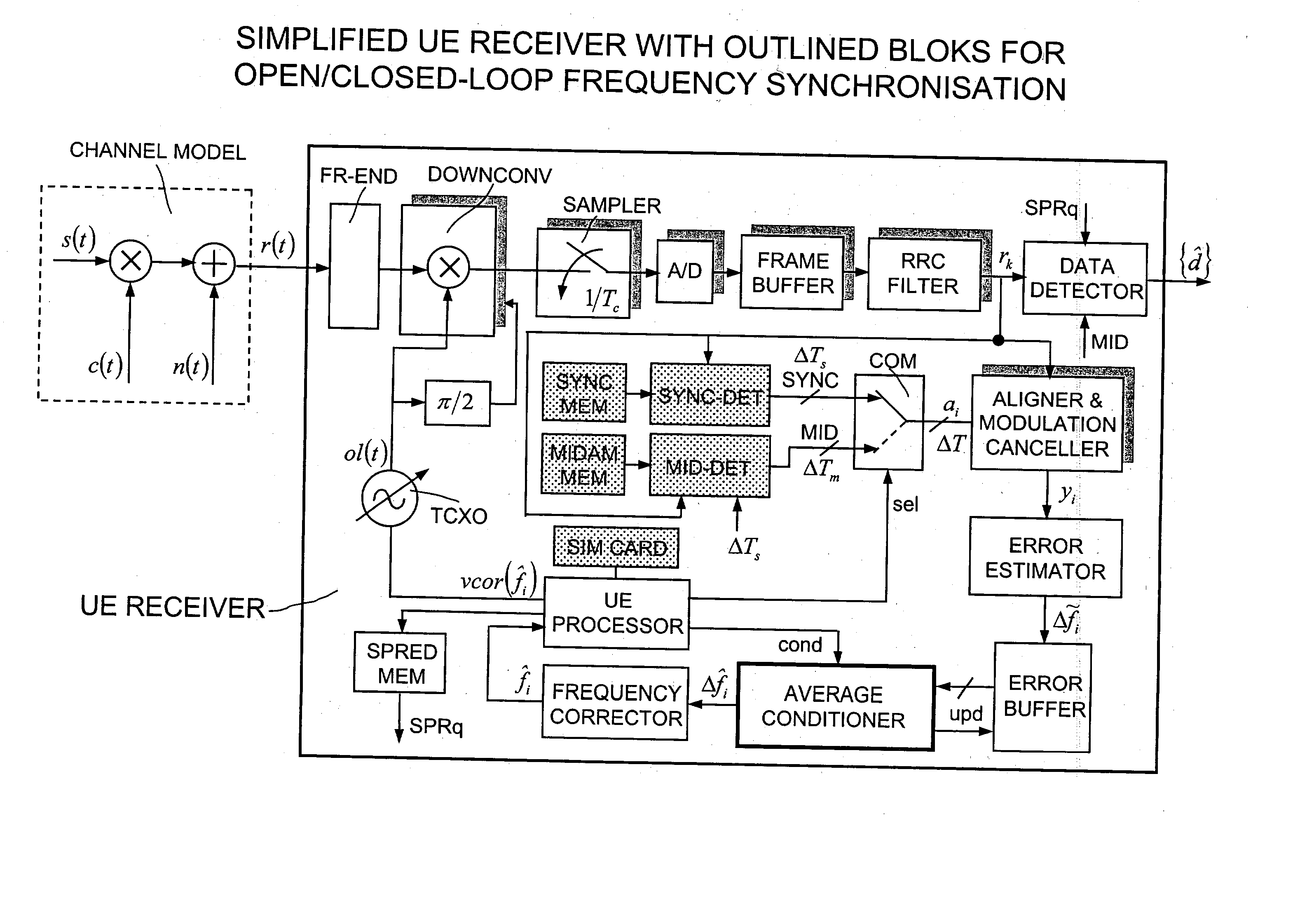
Data aided frequency synchronisation in cellular mobile equipments
InactiveUS20030181183A1Convergence can be speededOvercomes drawbackCarrier regulationRadio transmissionShift registerGreek letter sigma
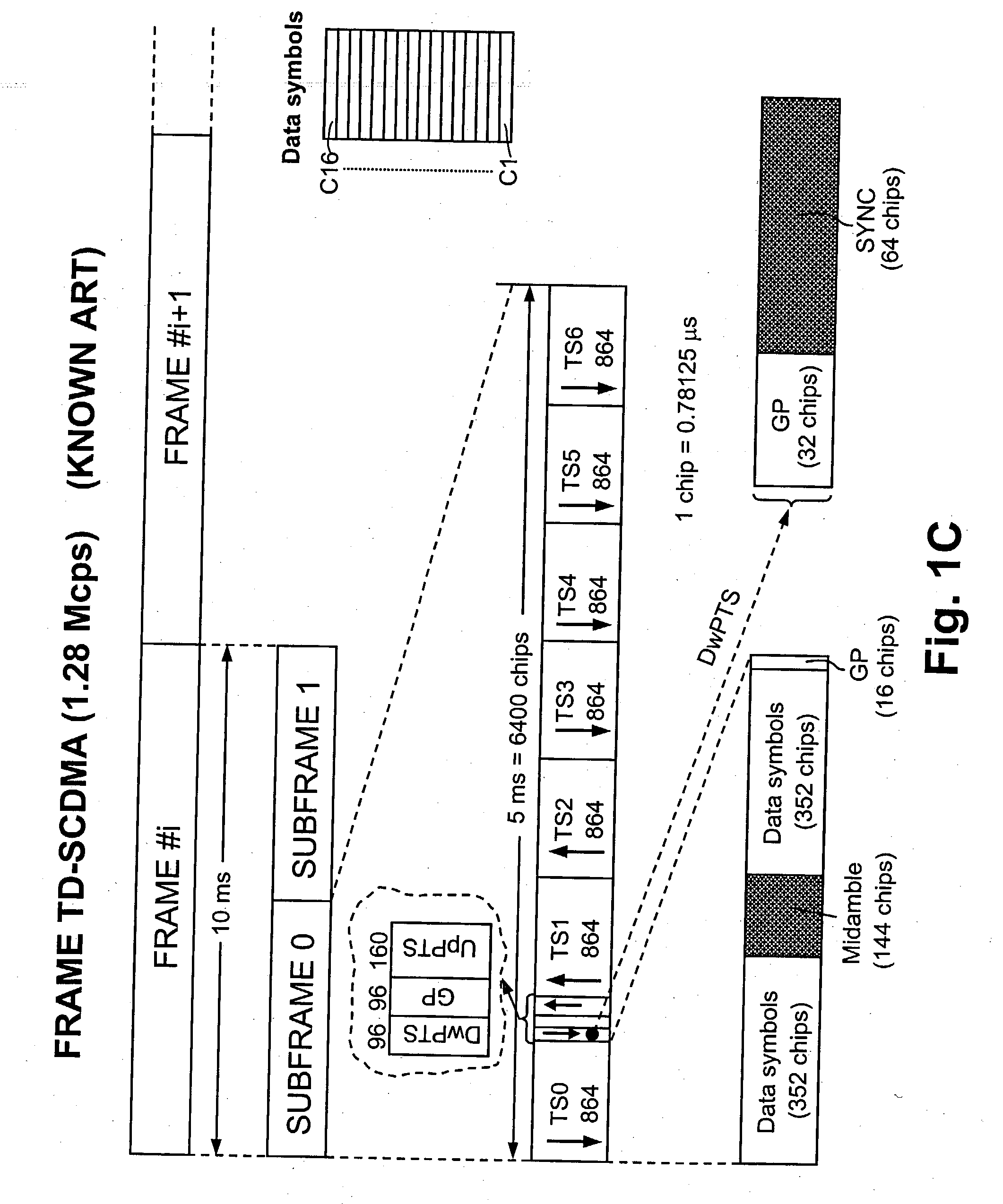
Some improvements to the conventional algorithms for data aided frequency synchronisation in cellular systems are introduced in a new method executable by the user equipments of various standards, i.e. 3GPP CDMA-TDMA, FDD mode at 3.84 Mcps, TDD mode at 3.84 Mcps, TDD mode at 1.28 Mcps; CWTS TD-SCDMA; GSM / DCS / GPRS. The method begins to obtain the suboptimal frequency errors Deltafi using a well known formula which calculates the argument of the autocorrelation over a subset of the baseband samples of the detected training sequence. The errors Deltafi are stored into a shift register L-position long and averaged to obtain an estimated frequency error Deltafi used for recursively correcting the reference frequency of the local oscillator, as: fi=fi-1+KDeltafi where K (0<=K<=1) is a weighting factor. Contrarily to the simple averaged error of the prior art, a sign criterion is used by which the average is performed on the only terms having the most recurrent algebraic sign among the stored terms Deltafi. The content of the shift register is corrected after each non-null frequency correction by subtracting K.Deltafi to all the stored terms Deltafi. Besides the frequency is corrected upon the following optional conditions, each other independents: The number of terms Deltafi having equal algebraic sign is greater than a constant alpha lower than L. The standard deviation sigma of the averaged terms Deltafi is lower than beta.sigmaold, being sigmaold the sigma of the last non-null frequency correction, and beta a constant >=1. After a minimum number gamma of iterations between two non-null frequency corrections are spent, being gamma a constant comprised between 1 and L. According to another variant the iterations of the recursive update are subdivided into an initial group with a higher K value for achieving fast convergence and a subsequent group with a lower K for achieving the required accuracy (FIG. 13).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
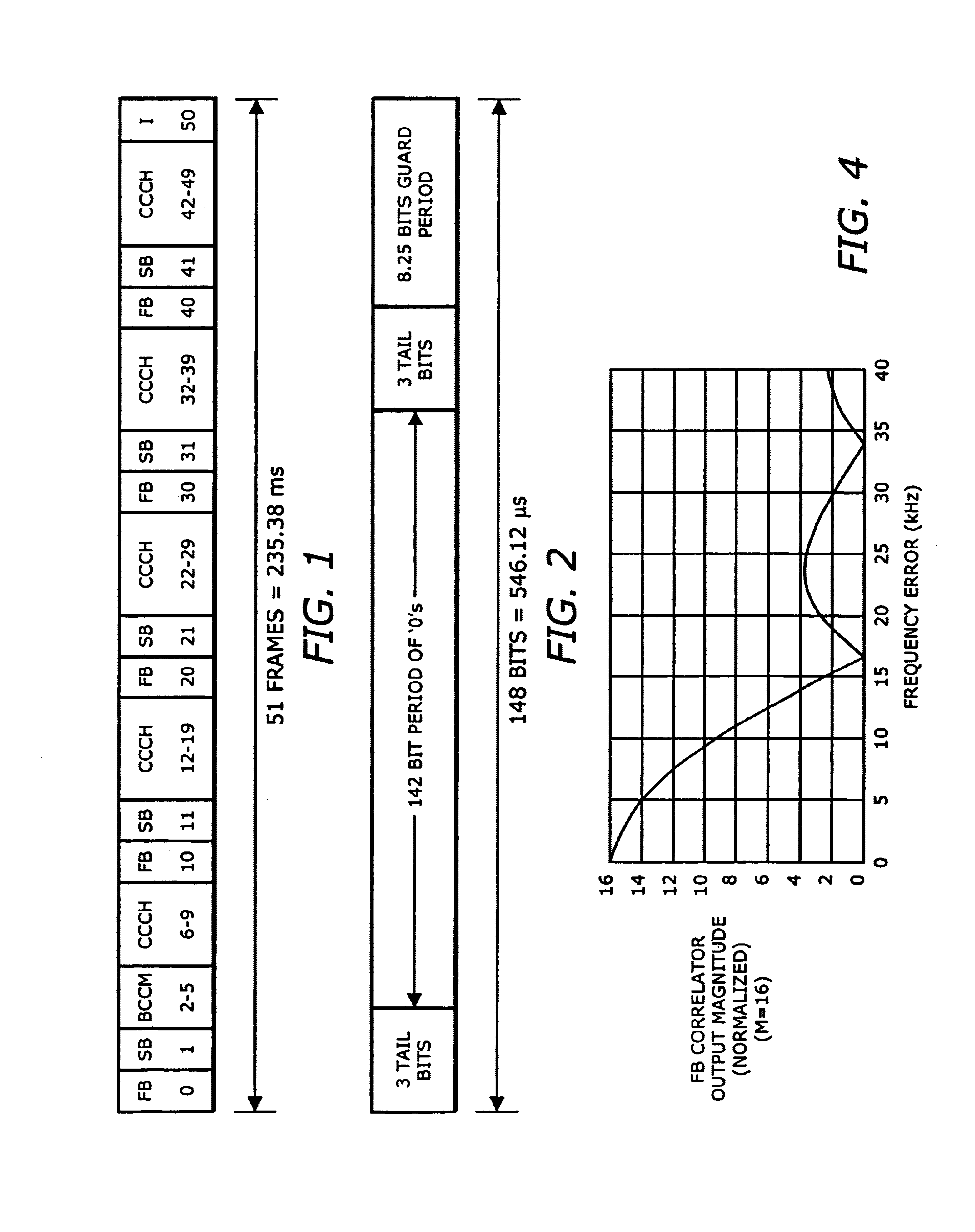
Synchronization in digital data transmission systems
InactiveUS6885693B1Successfully performedSynchronisation arrangementTransmission control/equalisingDigital dataEstimation methods
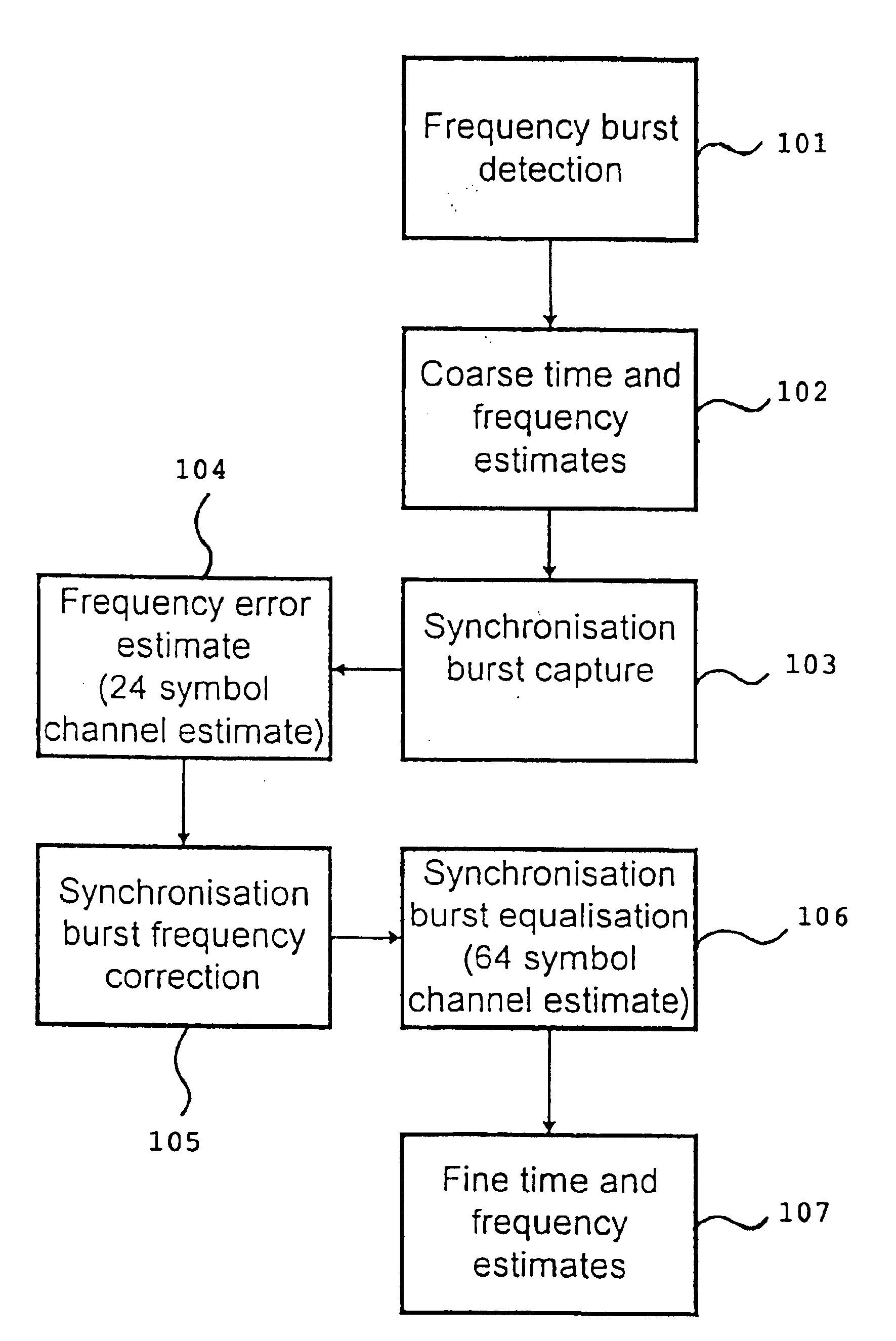
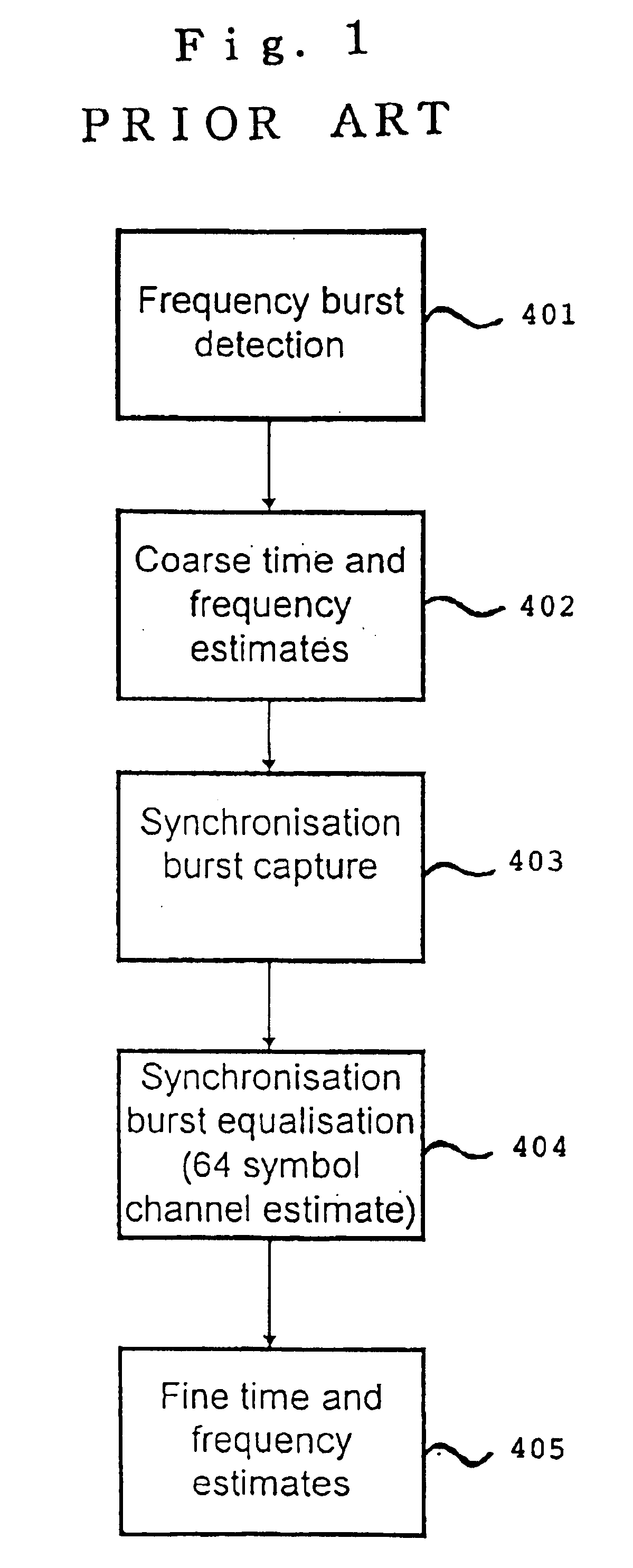
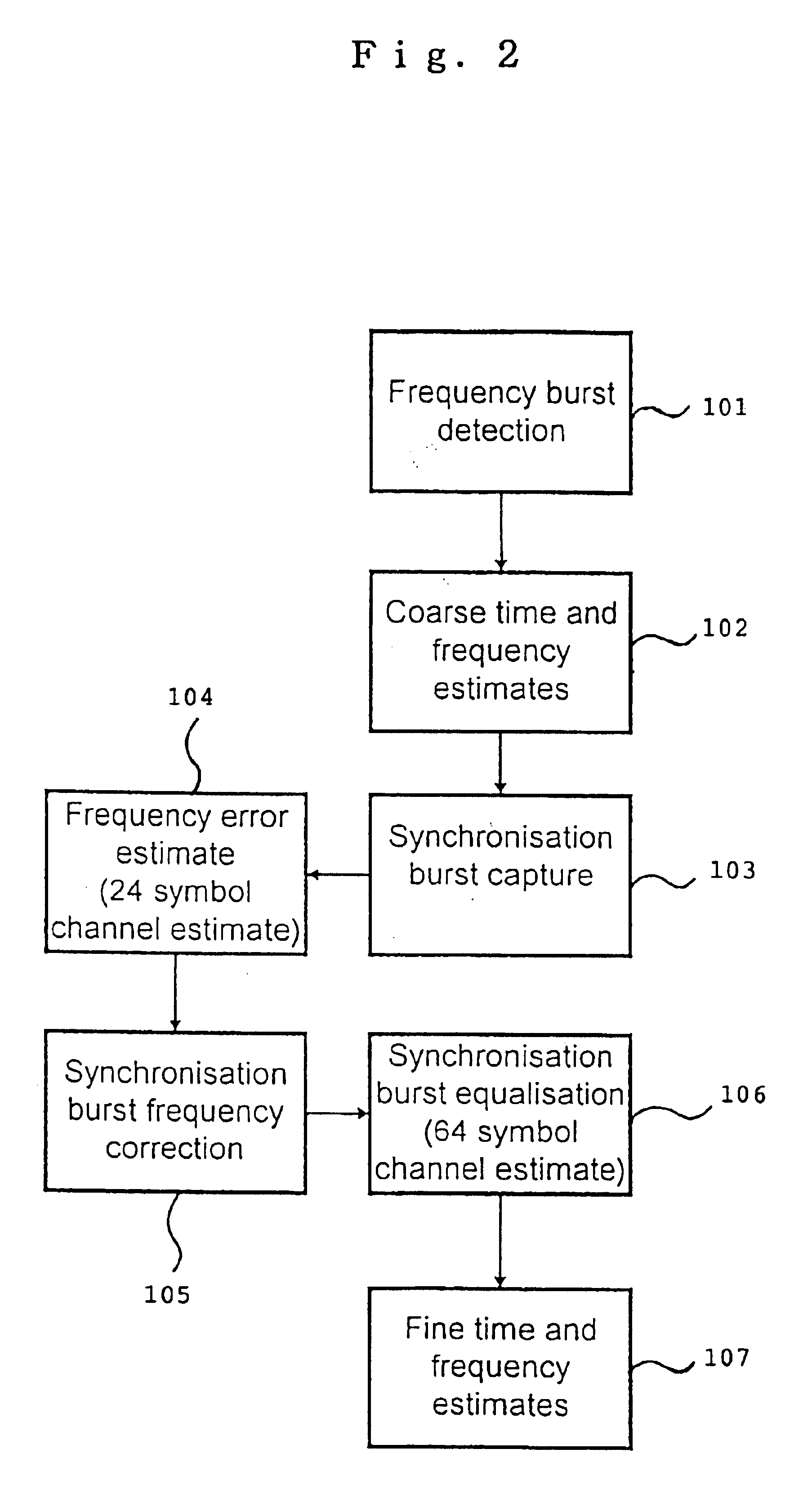
A channel estimation method for a digital telecommunication station is disclosed. A frequency correction burst is sought by scanning of the wanted channel. The frequency correction burst is used to provide coarse time and frequency synchronizations. A synchronization burst is received. Calculating the cross-correlation of the expected training sequence with the training sequence contained in said synchronous burst to obtain a channel estimate. A frequency error estimate is derived from the channel estimate, and the frequency error of the received burst is corrected in accordance with said frequency error estimate. The received synchronous burst is equalized. The frequency corrected symbols are used to refine the time and frequency synchronizations.
Owner:NEC CORP
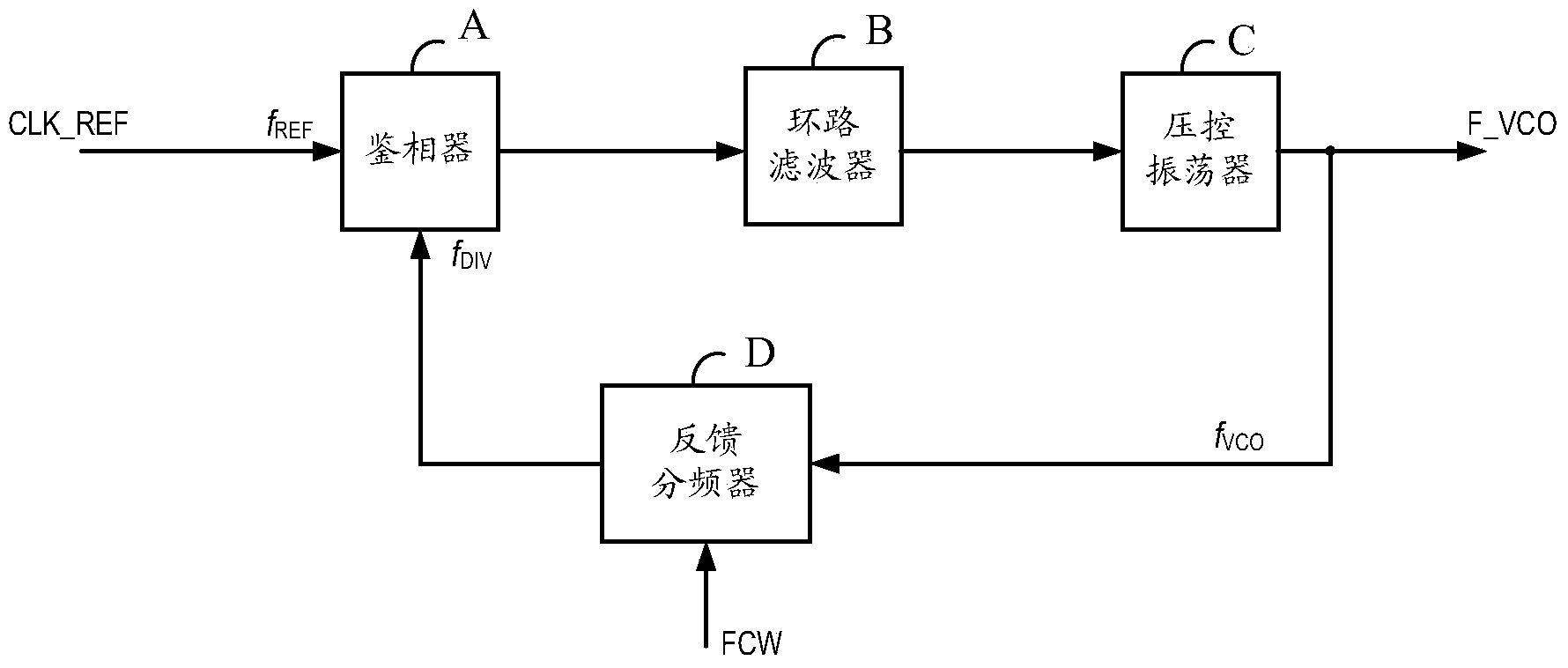
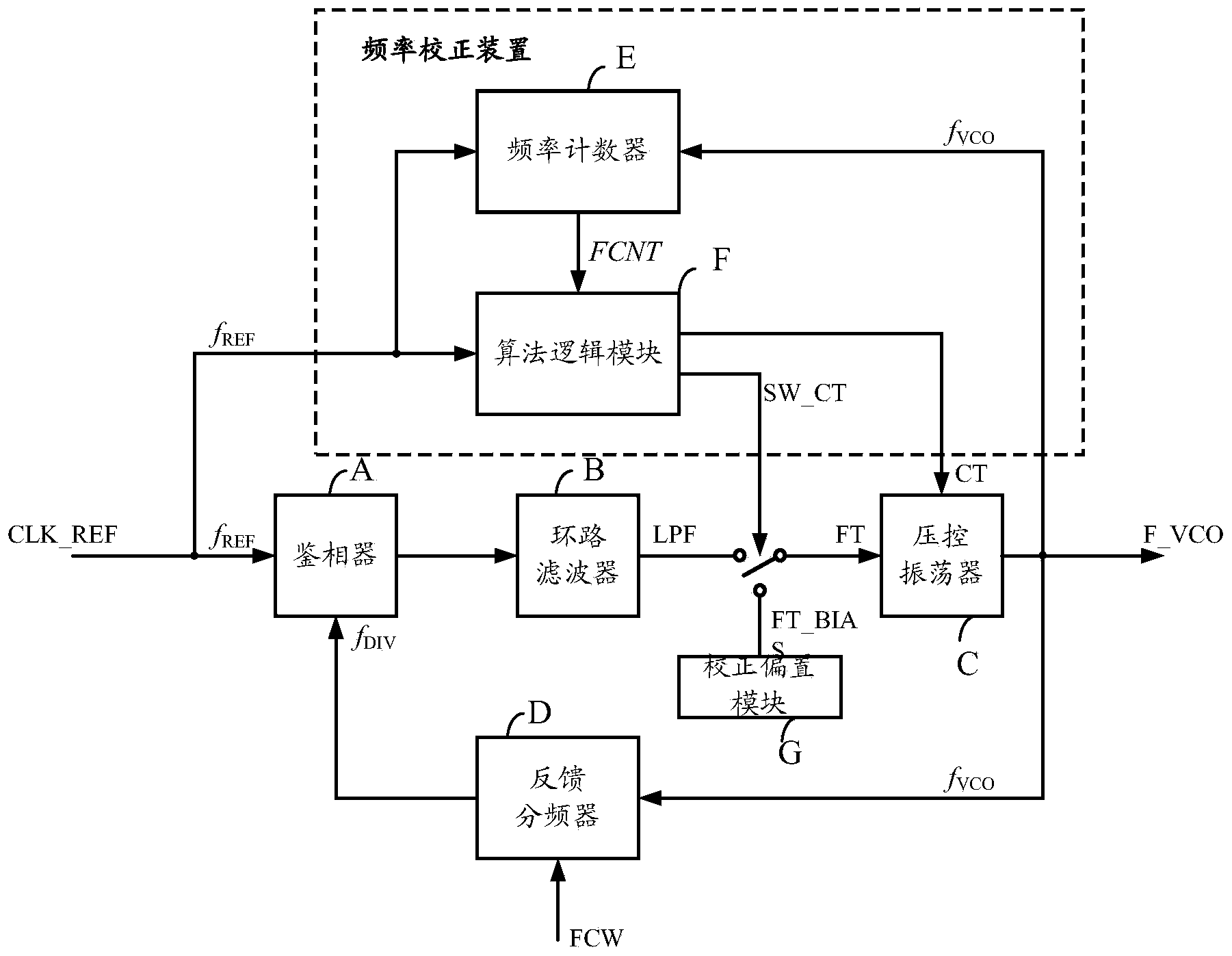
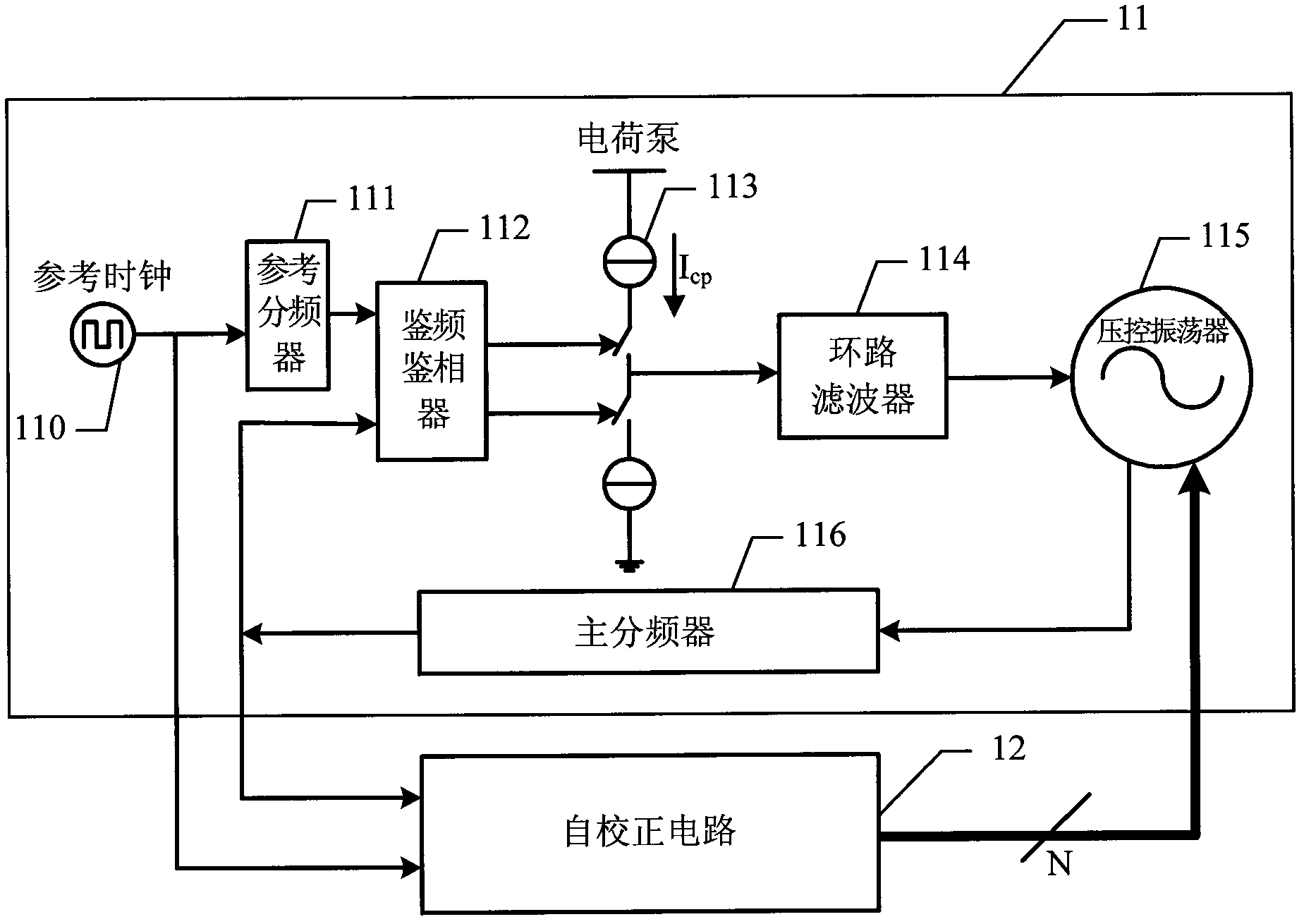
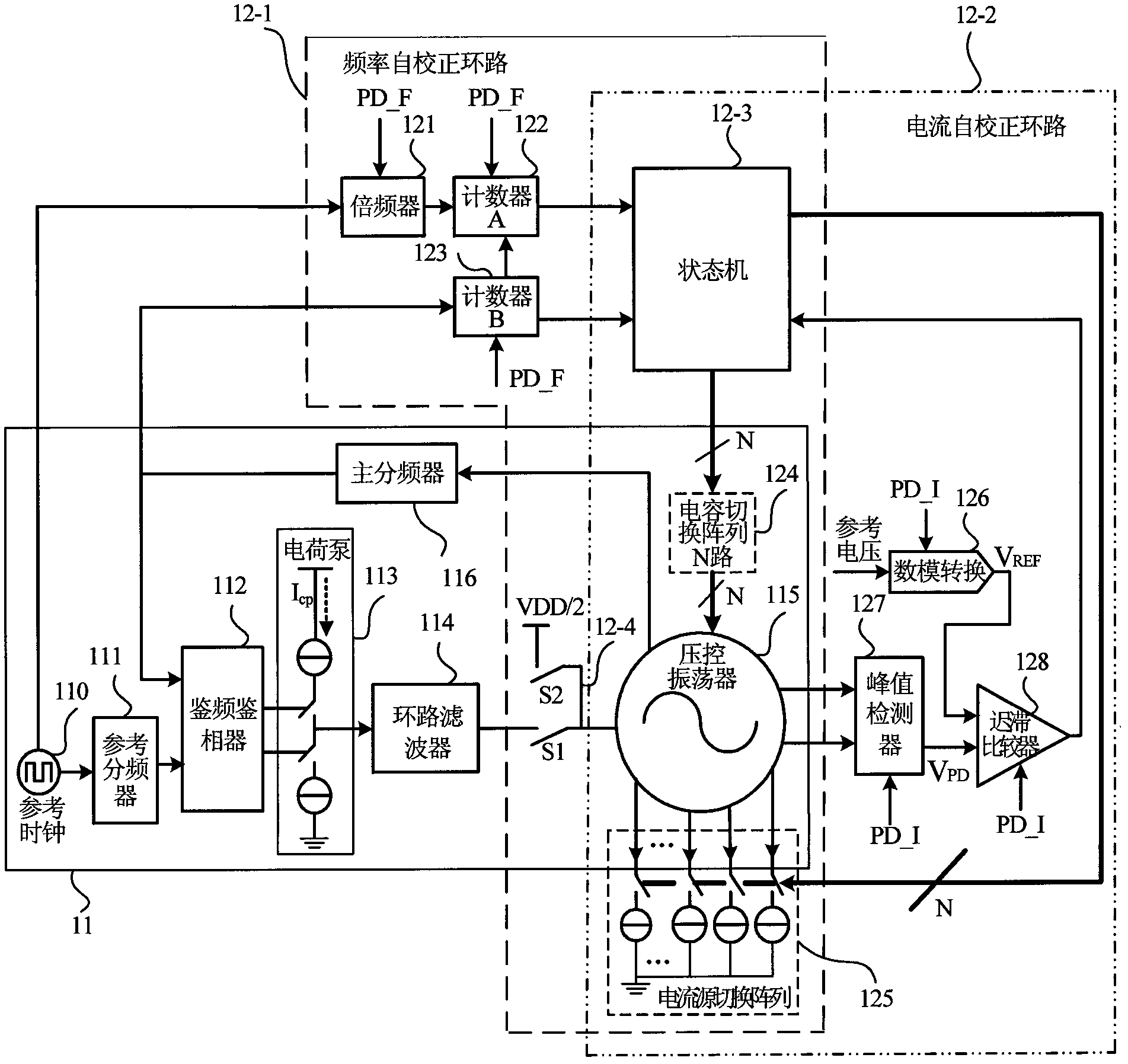
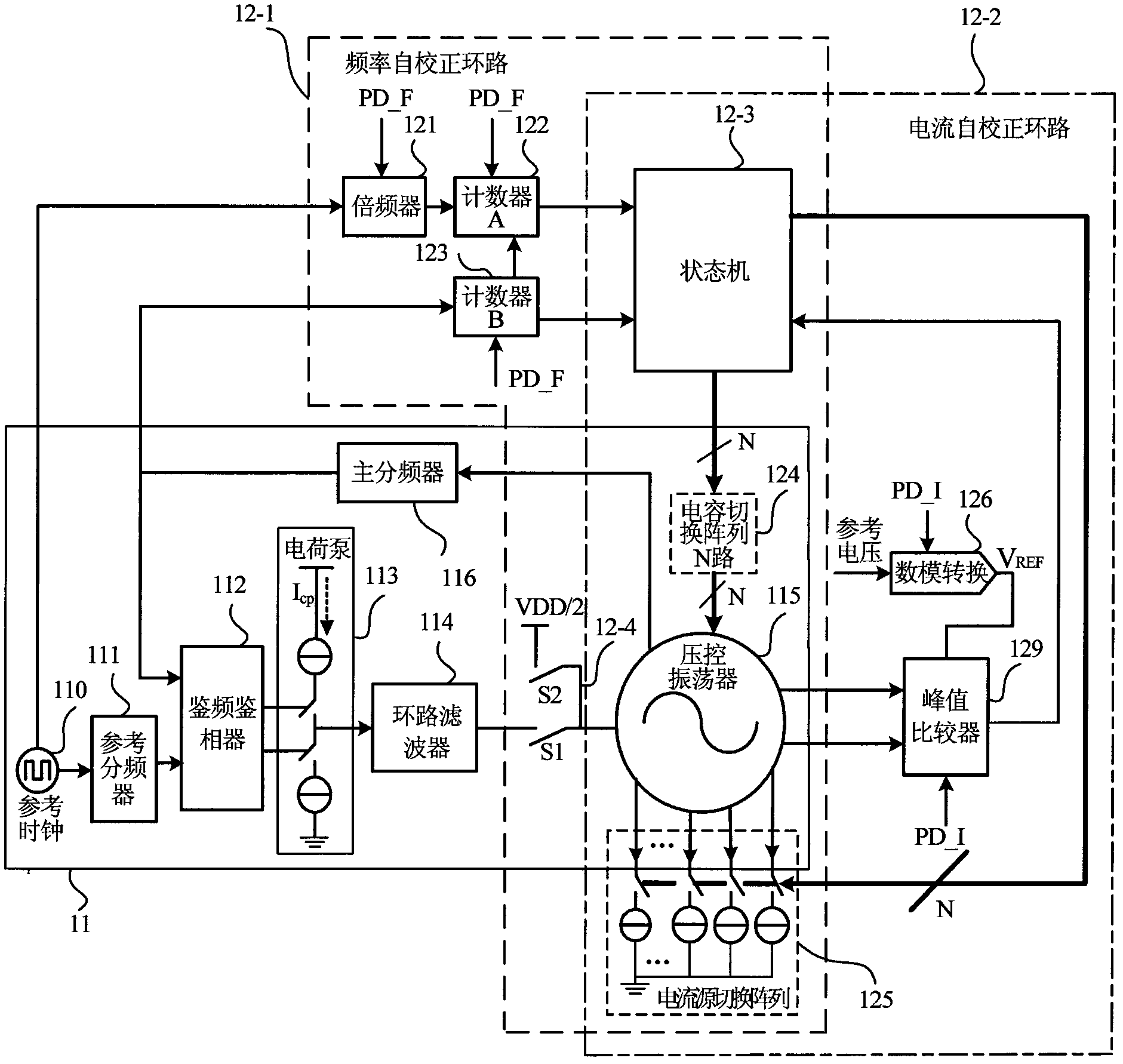
Frequency correction method and system of phase-locked loop
ActiveCN104052474AEffective control of counting timeReduce calibration timeTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringMulti bandEngineering
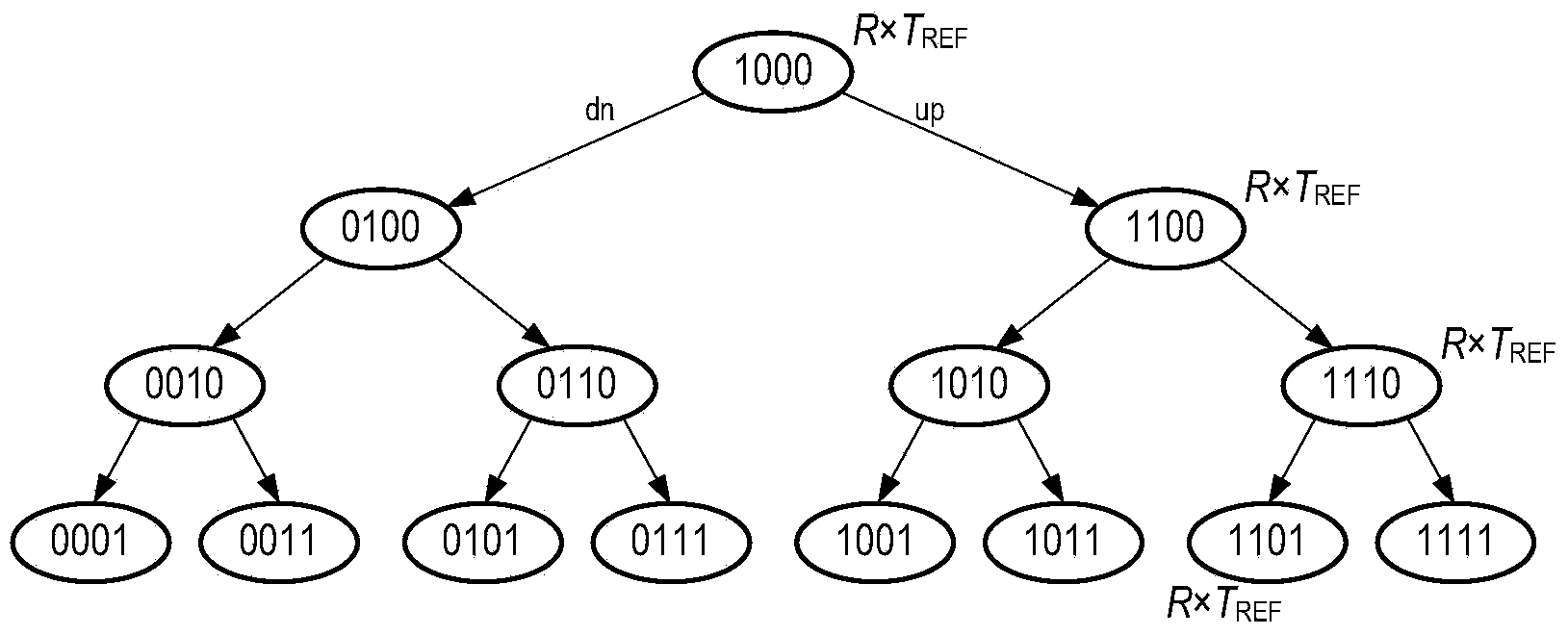
The invention provides a frequency correction method and system of a phase-locked loop. The frequency correction method and system of the phase-locked loop are applied to selection of sub-bands of multi-band voltage-controlled oscillators. The method includes the steps that in the counting time TCNT [k], frequency counting is conducted on frequency signals output by a voltage-controlled oscillator at the current working sub-band, and a frequency count value FCNT[k] is obtained, wherein the current working sub-band corresponds to a binary value of a current node in a binary search tree; the error between the FCNT [k] and a target frequency count value FCNTTARGET [k] is calculated, the absolute value of the error is compared with a predetermined value, the TCNT [k] is adjusted dynamically in value range of the TCNT [k] according to a comparison result, and a target working sub-band of the voltage-controlled oscillator is determined by combining the binary search algorithm. According to the method, the measurement error is compared with the predetermined value, and therefore whether a counting time reference is increased or not is controlled; a correct choice is made between correction time and correction accuracy, and therefore the correction time is effectively controlled; the dynamic correction method can effectively shorten the correction time on the whole.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
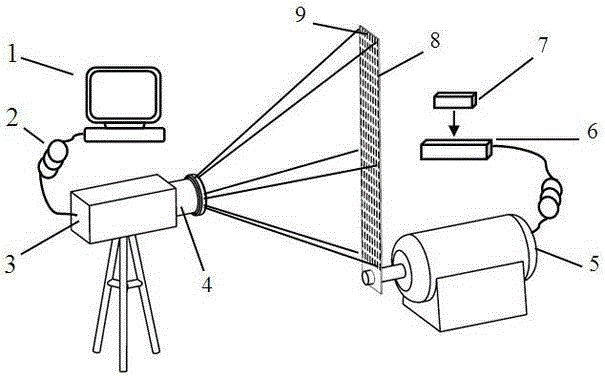
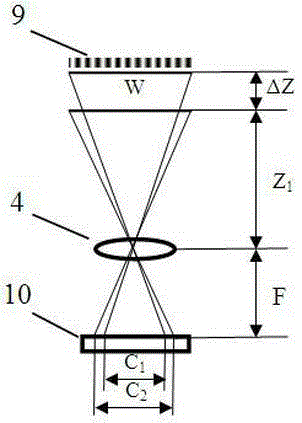
High speed multi-dimensional vibration measuring device and method based on stripe target
ActiveCN104614064AQuick measurementWith displacementSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansMeasurement deviceFourier transform on finite groups
The invention relates to a high speed multi-dimensional vibration measuring device and method based on a stripe target. The device comprises a stripe target, an imaging module, a signal control and processing module and a display module. The method includes the following steps: arranging the stripe target on a vibration structure to be measured; adopting an image module to conduct continuous imaging and recording on the stripe target; utilizing the imaging module to transmit the image of the stripe target to the signal control and processing module; utilizing the signal control and processing module to conduct Fourier transform on the stripes at the same position of the same stripe target in each frame of the image, adopting a certain peak value frequency correction method to accurate correct the peak value frequency, and then utilizing the imaging mathematical relation and the corrected peak value frequency to obtain a time domain curve with stripe target structure vibration, namely acquiring structure vibration signals through reduction; displaying an image processing result through a display module or conducting further data processing through vibration signals. By means of the device and method, vibration measurement of points, lines and faces in certain range is achieved, the measurement speed is high, and the accuracy is high.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Self-correcting frequency synthesizer capable of optimizing properties of voltage-controlled oscillator and optimizing method of self-correcting frequency synthesizer
ActiveCN102868397ALarge frequency adjustment rangeFulfil requirementsPulse automatic controlProcess deviationsMulti band
The invention discloses an optimizing method of a self-correcting frequency synthesizer capable of optimizing properties of a voltage-controlled oscillator. The method comprises the following steps that: when a chip is electrified or a channel is changed each time, a frequency self-correcting loop in a synthesizer self-correcting circuit is started firstly, and a frequency sub-wave band code necessary for the voltage-controlled oscillator is searched; secondly a current self-correcting loop in the synthesizer self-correcting circuit is started, and a current sub-wave band code that an output amplitude of the voltage-controlled oscillator achieves an appointed amplitude is searched, so that the voltage-controlled oscillator works in a minimum power consumption, a good phase noise property is obtained, and at the same time the properties of the voltage-controlled oscillator are not changed when process deviation and temperature change occur; after the accomplishment of frequency correction and current correction is judged by a state machine, a synthesizer enters into the frequency self-locking process of a phase-locked loop; and the optimization and correction process is ended. The invention further discloses the self-correcting frequency synthesizer capable of optimizing the properties of the voltage-controlled oscillator. A wider frequency adjustment range can be obtained, and good local oscillator spectrum purity is obtained through small power consumption; and the optimizing method is suitable for the self-correcting frequency synthesizer of a transceiver with low power consumption, multiple modes and multi-band frequency.
Owner:杭州中科微电子有限公司
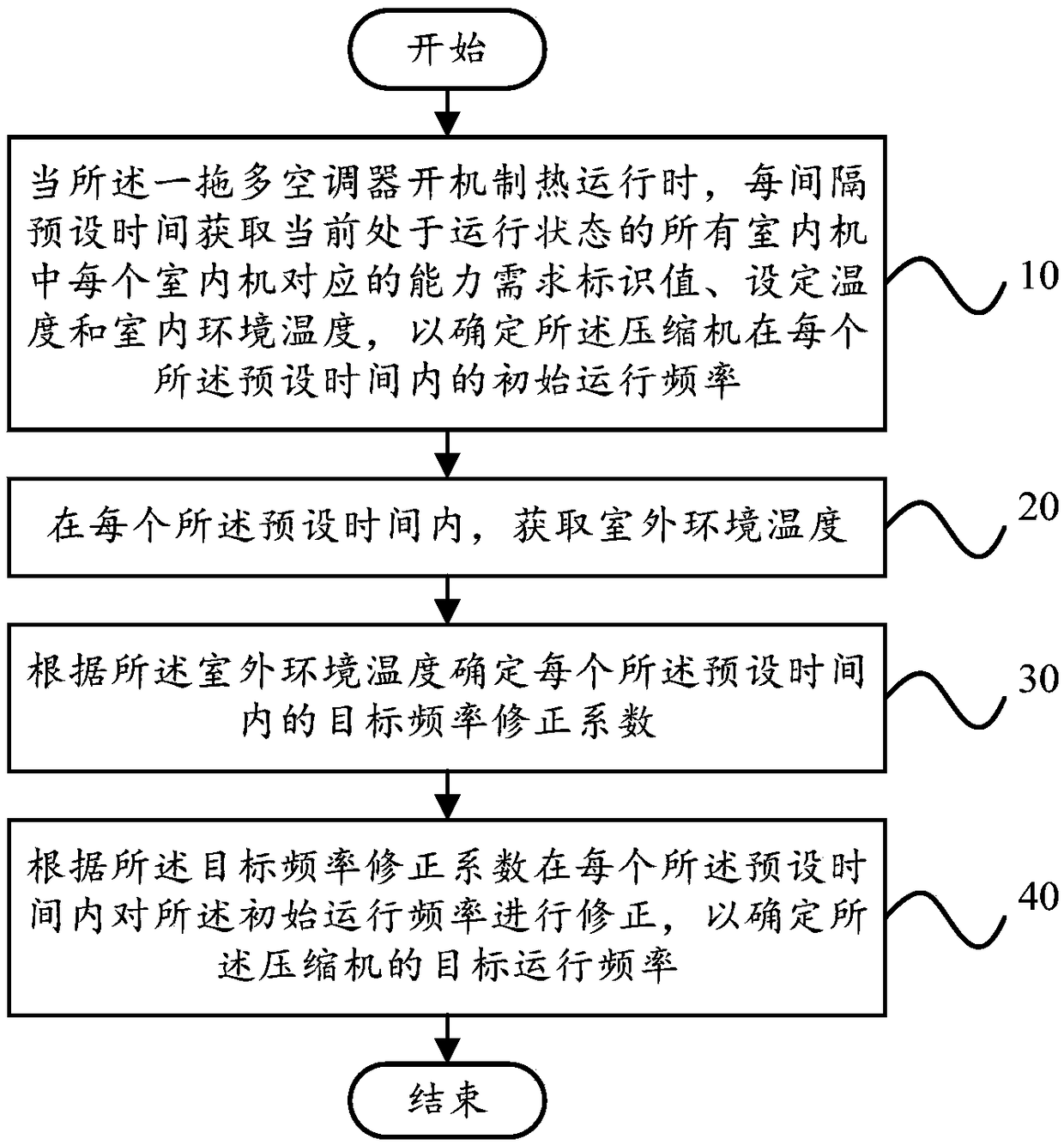
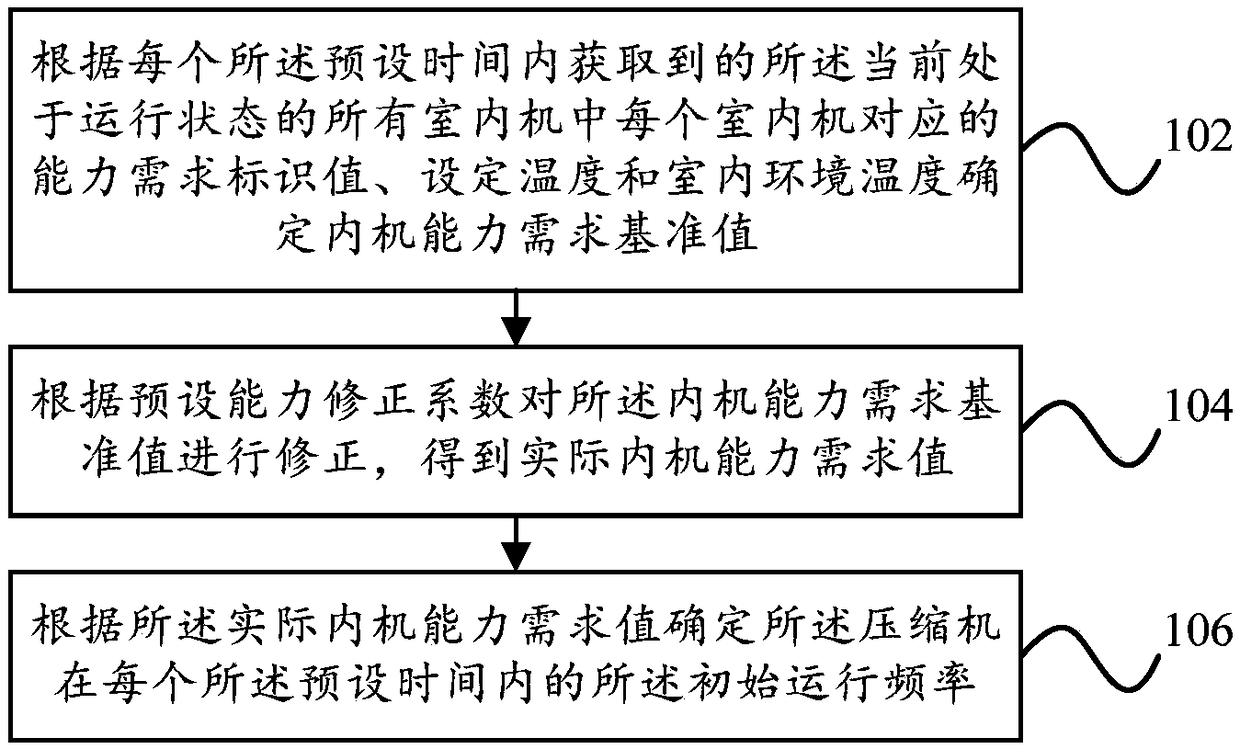
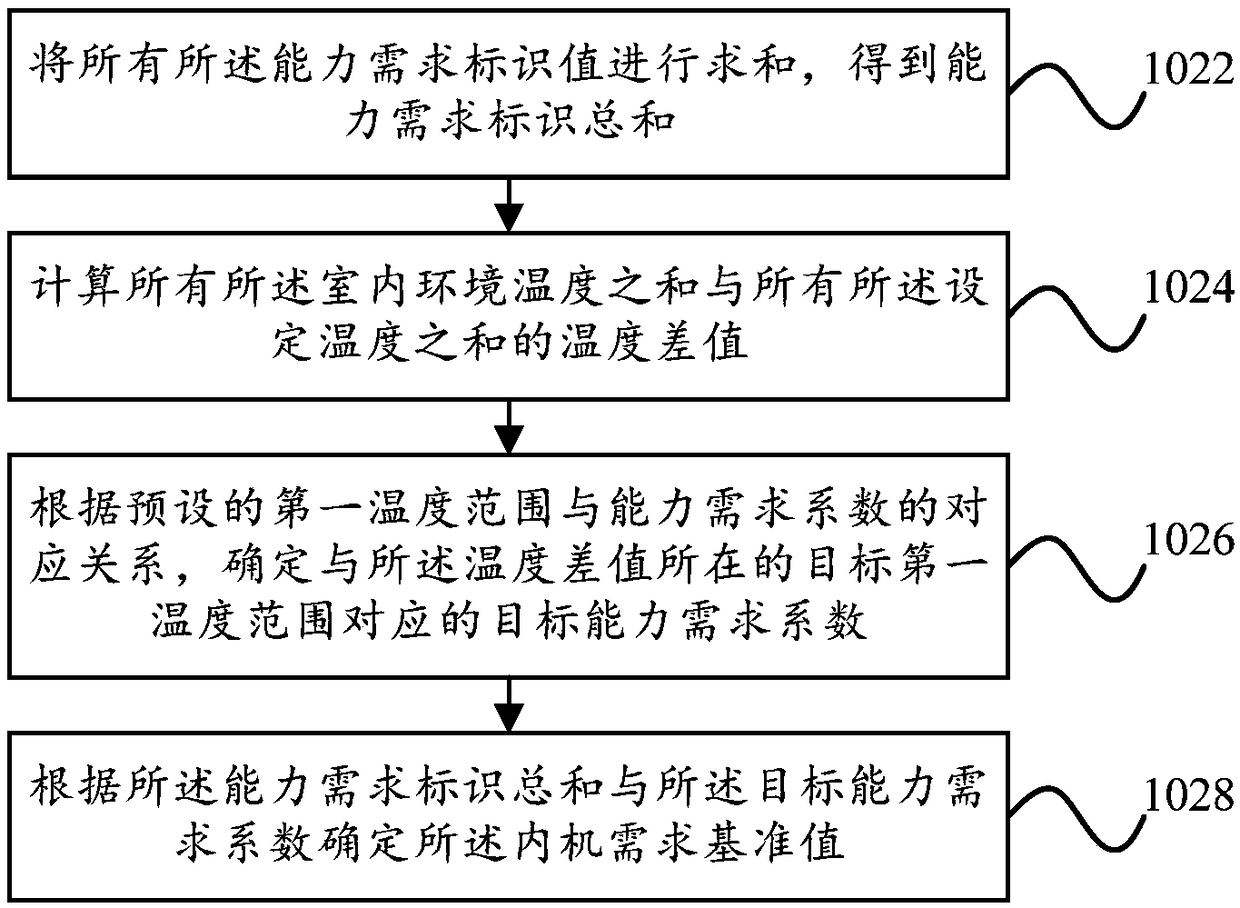
Frequency control method, frequency control device, multi-split air conditioner and storage medium
ActiveCN108592342AImprove heating effectResolve accuracyMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsOperating frequencyComputer engineering
The invention discloses a frequency control method, a frequency control device, a multi-split air conditioner and a storage medium. The frequency control method comprises the following steps that whenthe multi-split air conditioner is in the heating operation, a capability requirement identification value corresponding to each indoor unit in all indoor units in the running state, set temperatureand indoor environment temperature are acquired at interval preset time so as to determine the initial operating frequency of a compressor in each preset time; in each preset time, outdoor environmenttemperature is acquired; a target frequency correction coefficient within each preset time is determined according to the outdoor environment temperature; and the initial operation frequency within each preset time is corrected according to the target frequency correction coefficient so as to determine the target operating frequency of the compressor. According to the frequency control method, the frequency control device, the multi-split air conditioner and the storage medium, the problems that the accuracy of the tube temperature correction frequency of the middle of the indoor unit is lowand the needed time is too long are solved, and the effect of improving the heating capacity of the multi-split air conditioner is achieved.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD +1
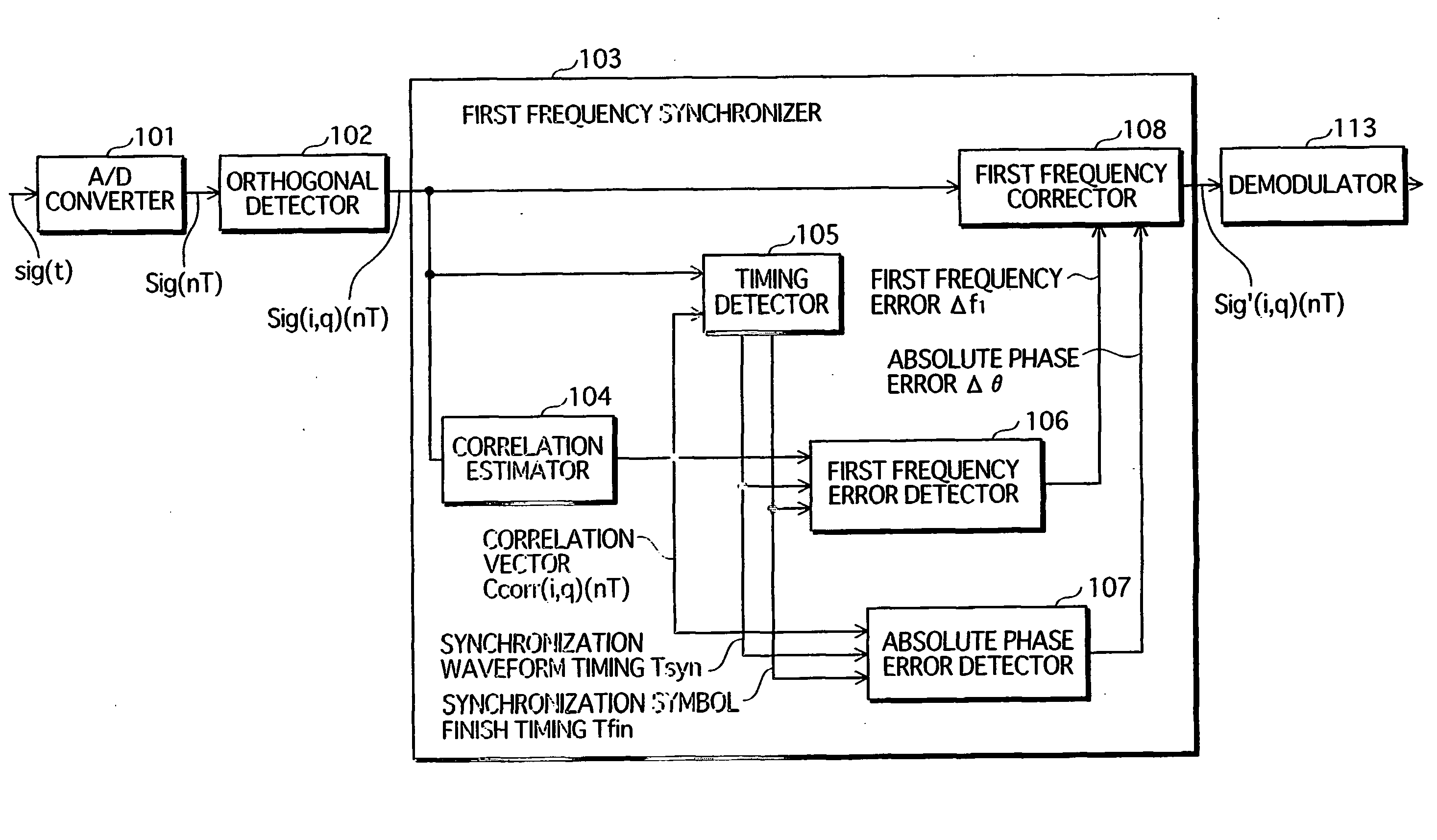
Frequency synchronization apparatus and frequency synchronization method
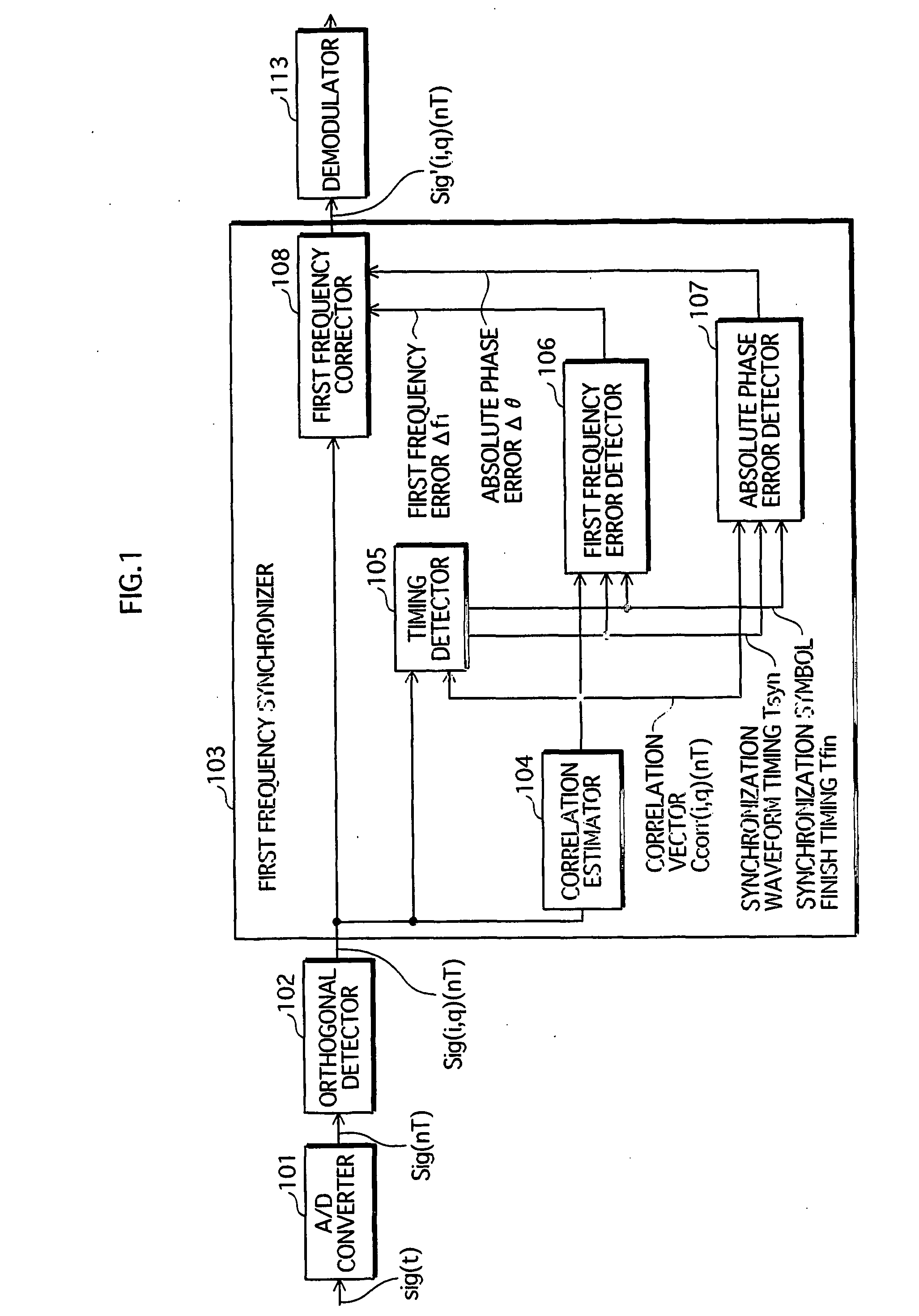
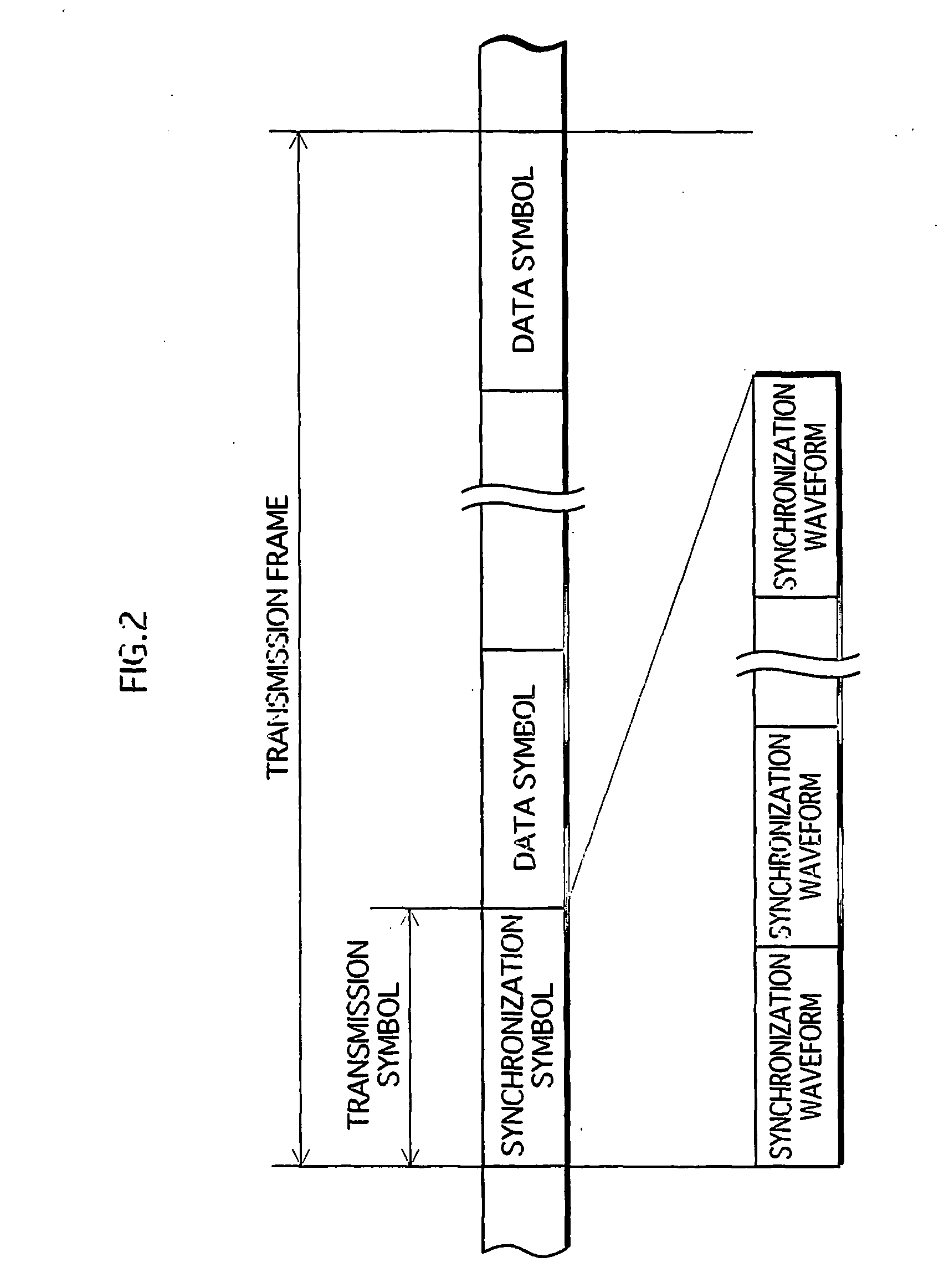
InactiveUS20060233225A1Correction errorLoss in efficiency of transmitting the synchronization signal is lowCarrier regulationSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPhase differenceWave shape
A first frequency synchronization unit (103) corresponds to the frequency synchronization apparatus of the present invention. A higher apparatus that is, for example, a wireless receiver supplies a reception signal to the first frequency synchronization unit (103) via an A / D converter (101) and an orthogonal detector (102). A synchronization symbol that includes a predetermined waveform at least twice is incorporated into the reception signal. A correlation estimator (104) generates a reference signal expressing the same waveform as the synchronization symbol, and successively finds correlation vectors between the reception signal and the reference signal. A first signal error detector (106) finds a frequency error based on an average phase difference of predetermined correlation vectors, and finds an absolute phase error based on transition of absolute phase of predetermined correlation vectors. A first frequency corrector (108) simultaneously gives the reception signal a frequency shift and phase rotation that cancel the errors.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Downlink beam forming method
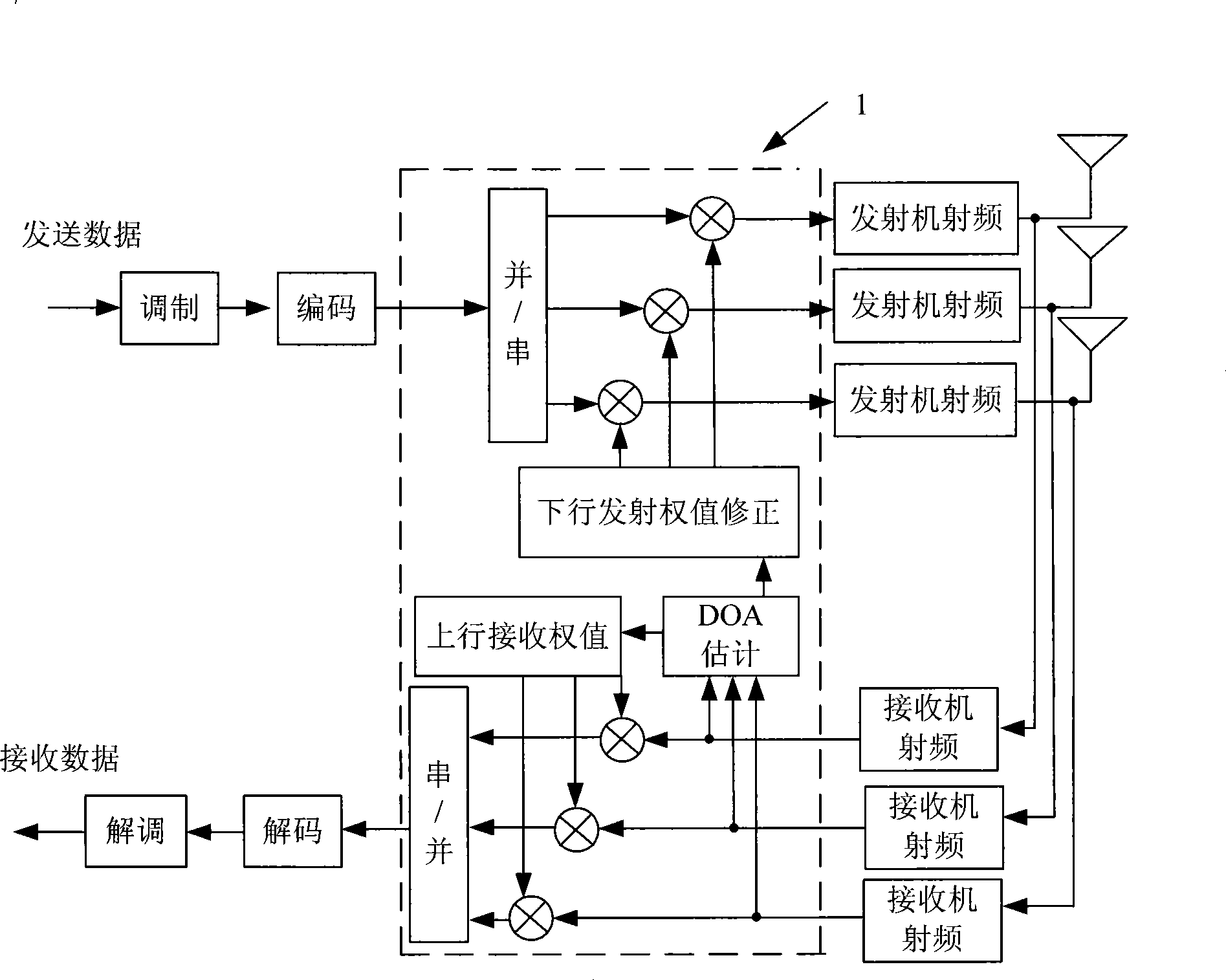
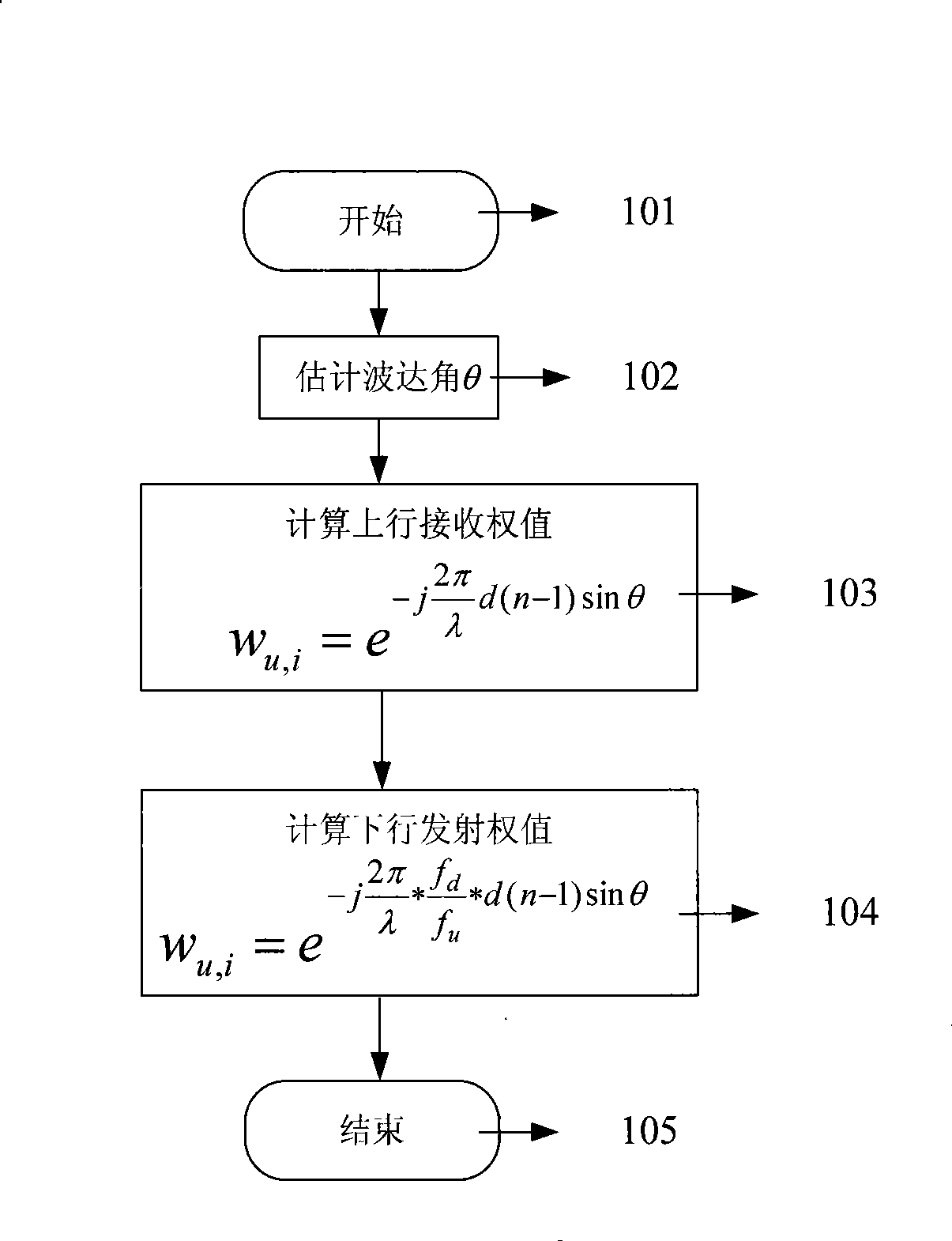
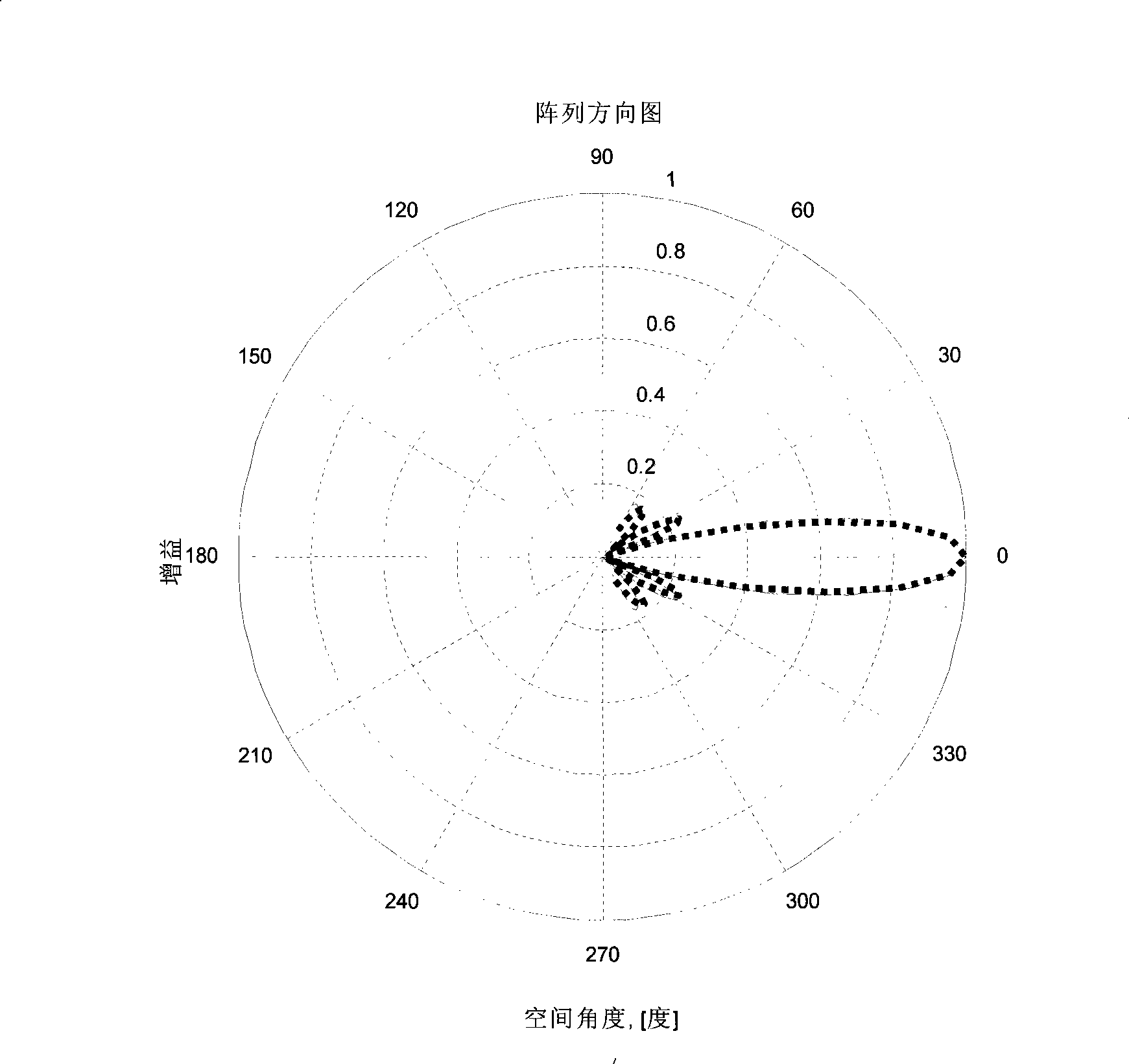
InactiveCN101364828APointing accuratelySimple structureSpatial transmit diversityComputer scienceMain lobe
The invention relates to a downlink waveform forming method, which comprises the following steps: (1.1) estimating a direction-of-arrival angle theta of a mobile terminal; and (1.2) calculating a downlink transmission weight Wd,i according to the direction-of-arrival angle theta and a frequency correction factor fd / fu and shaping, wherein the formula is shown in the chart. The method can acquire direction-of-arrival angle theta by using an uplink reference signal and can eliminate the pointing error of waveform formation caused by the difference of uplink / downlink carrier frequency in an FDD mode through the frequency correction factor fd / fu, thereby ensuring the accurate pointing direction of the main lobe of a downlink wave.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com