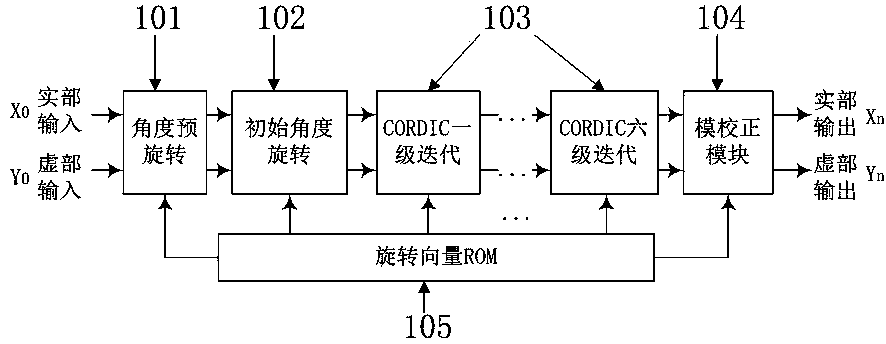
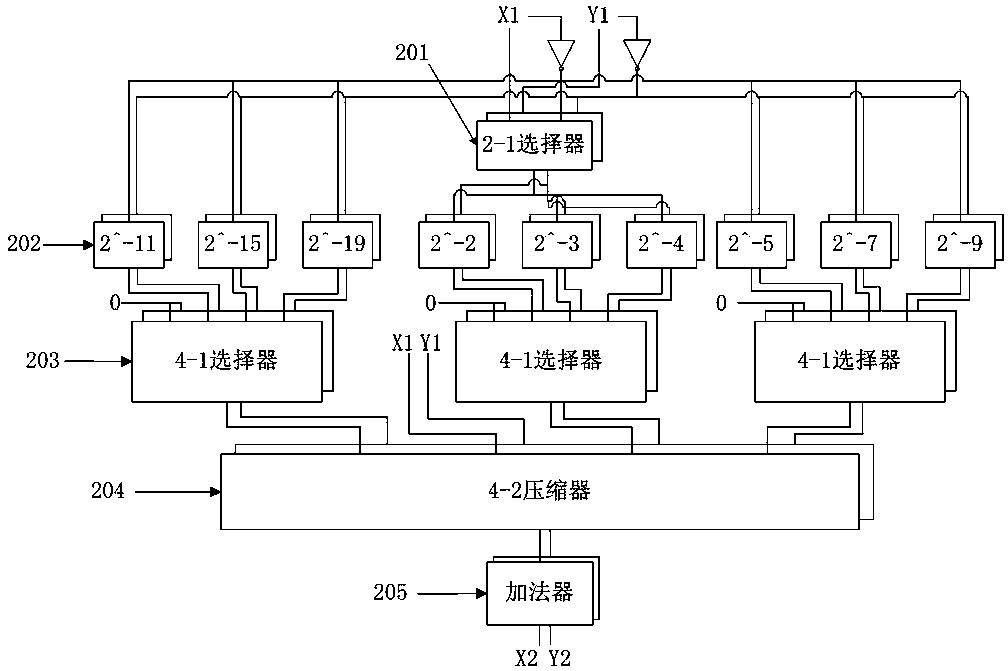
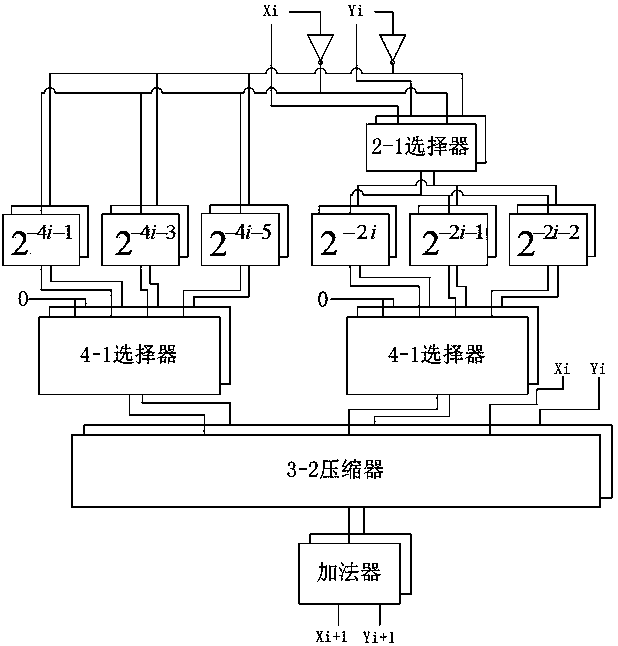
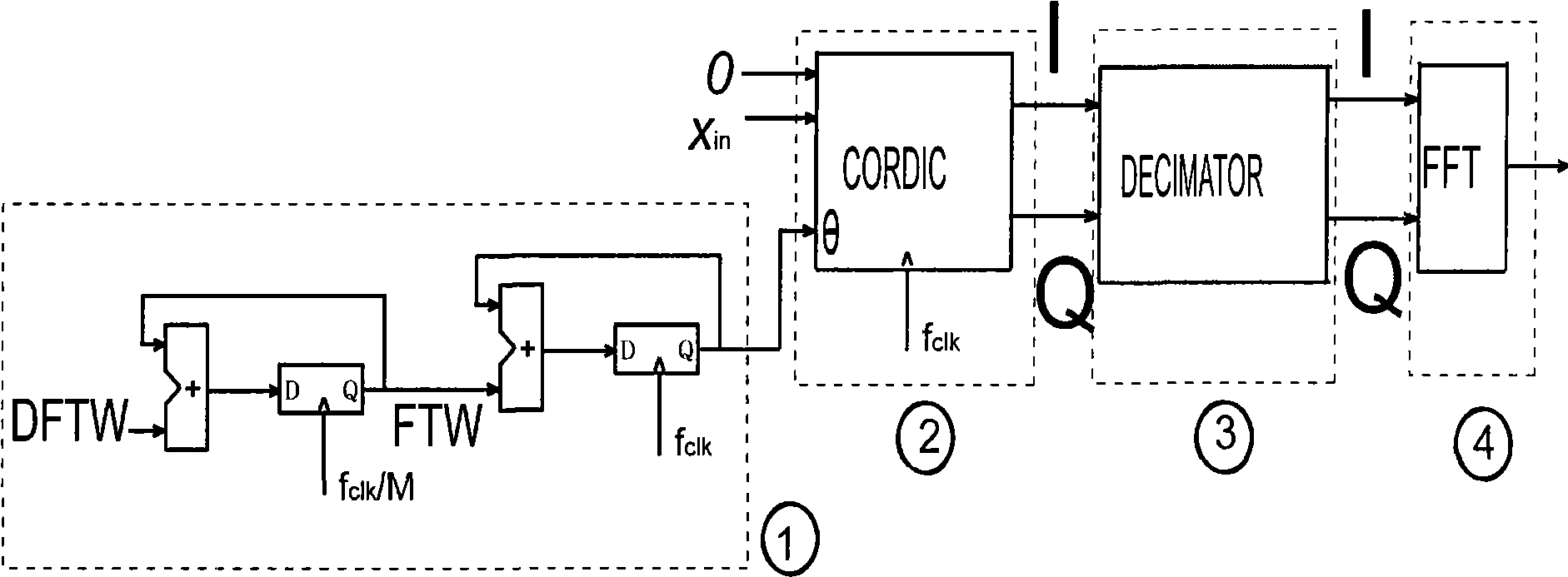
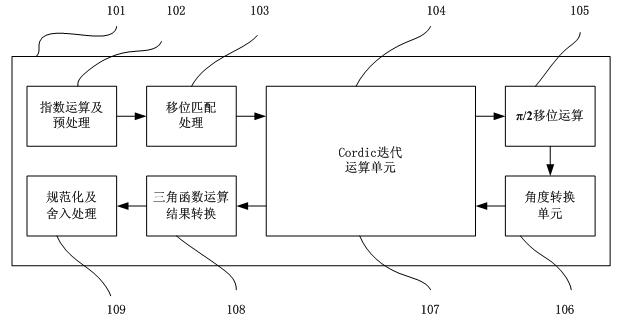
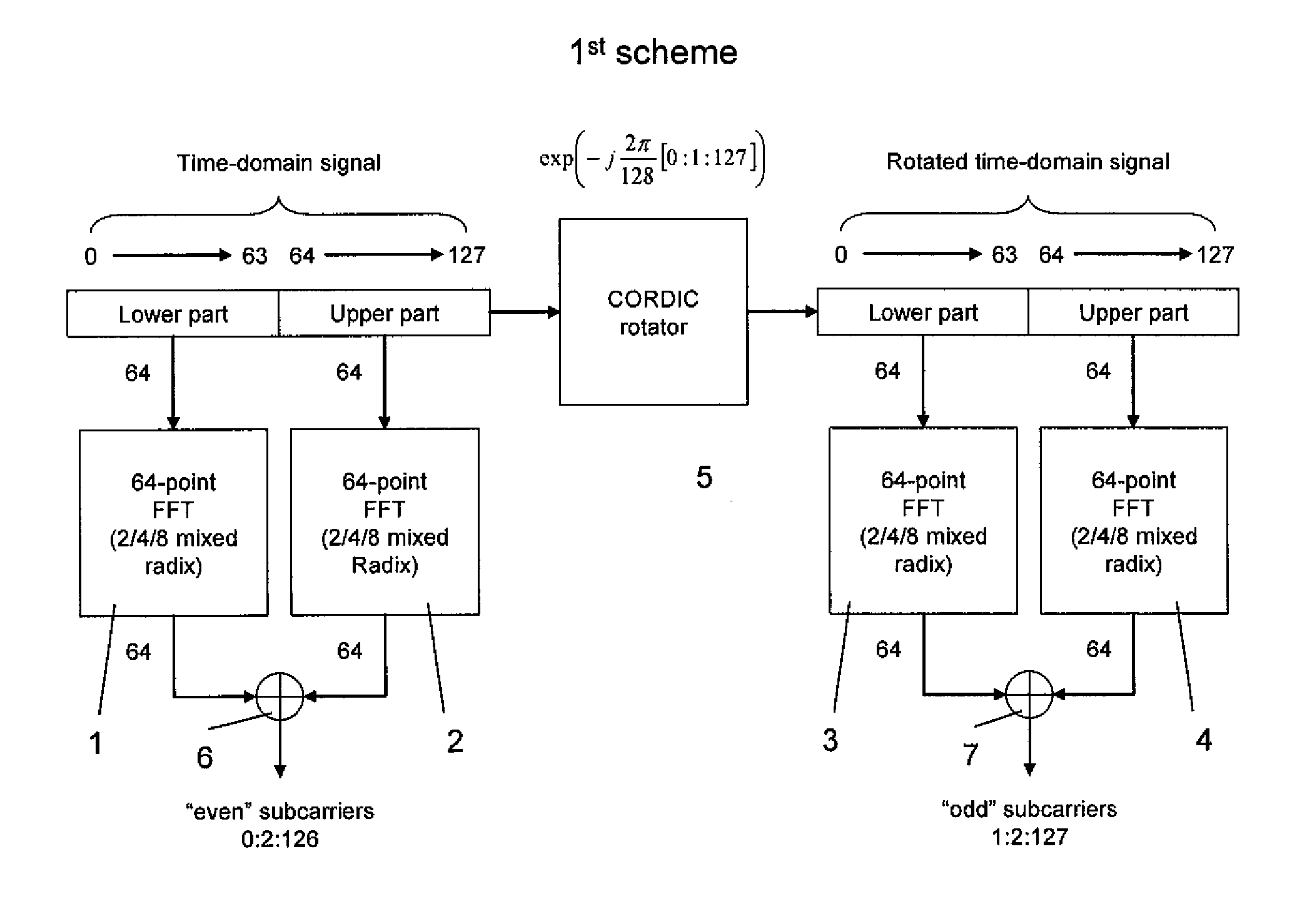
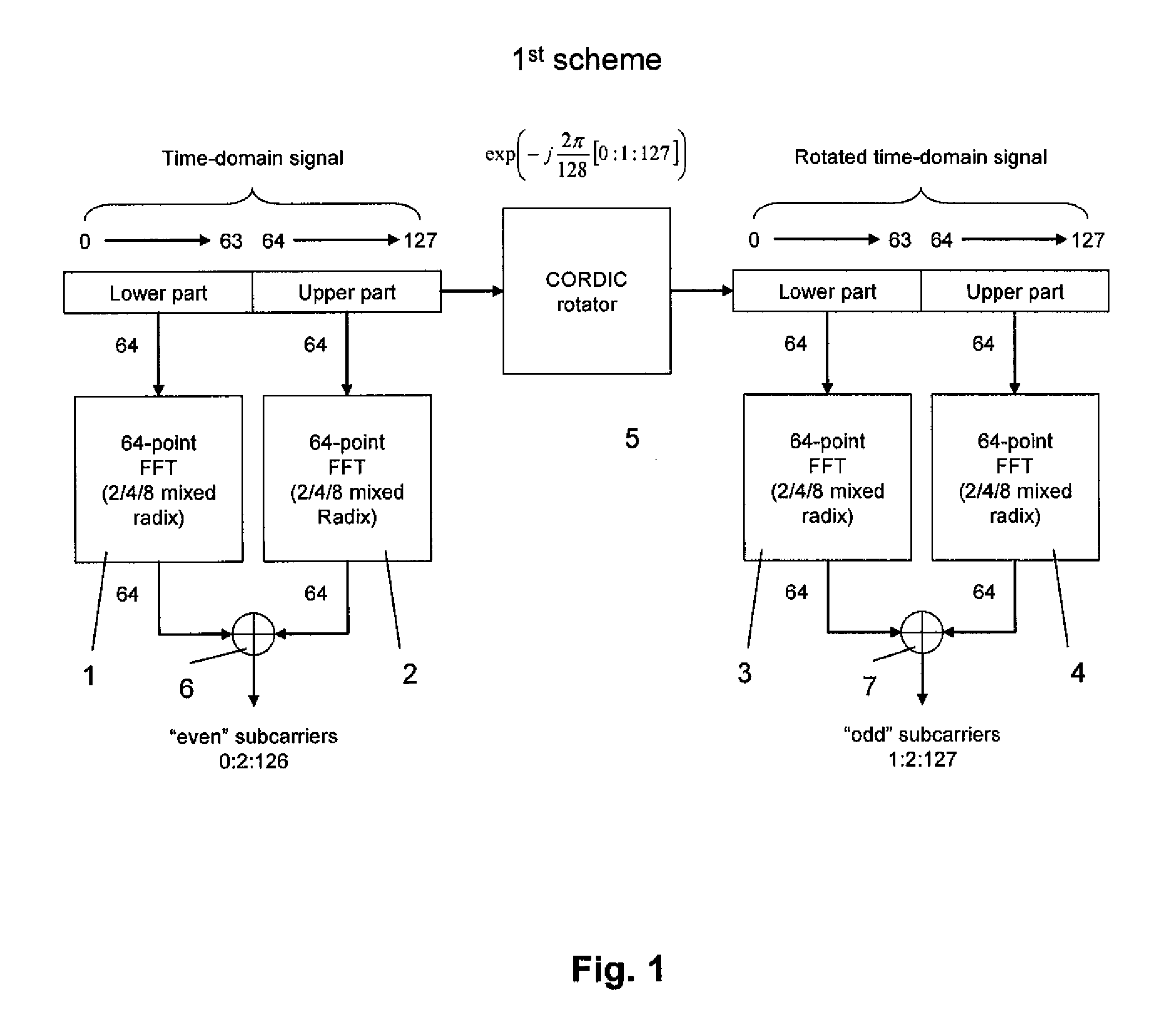
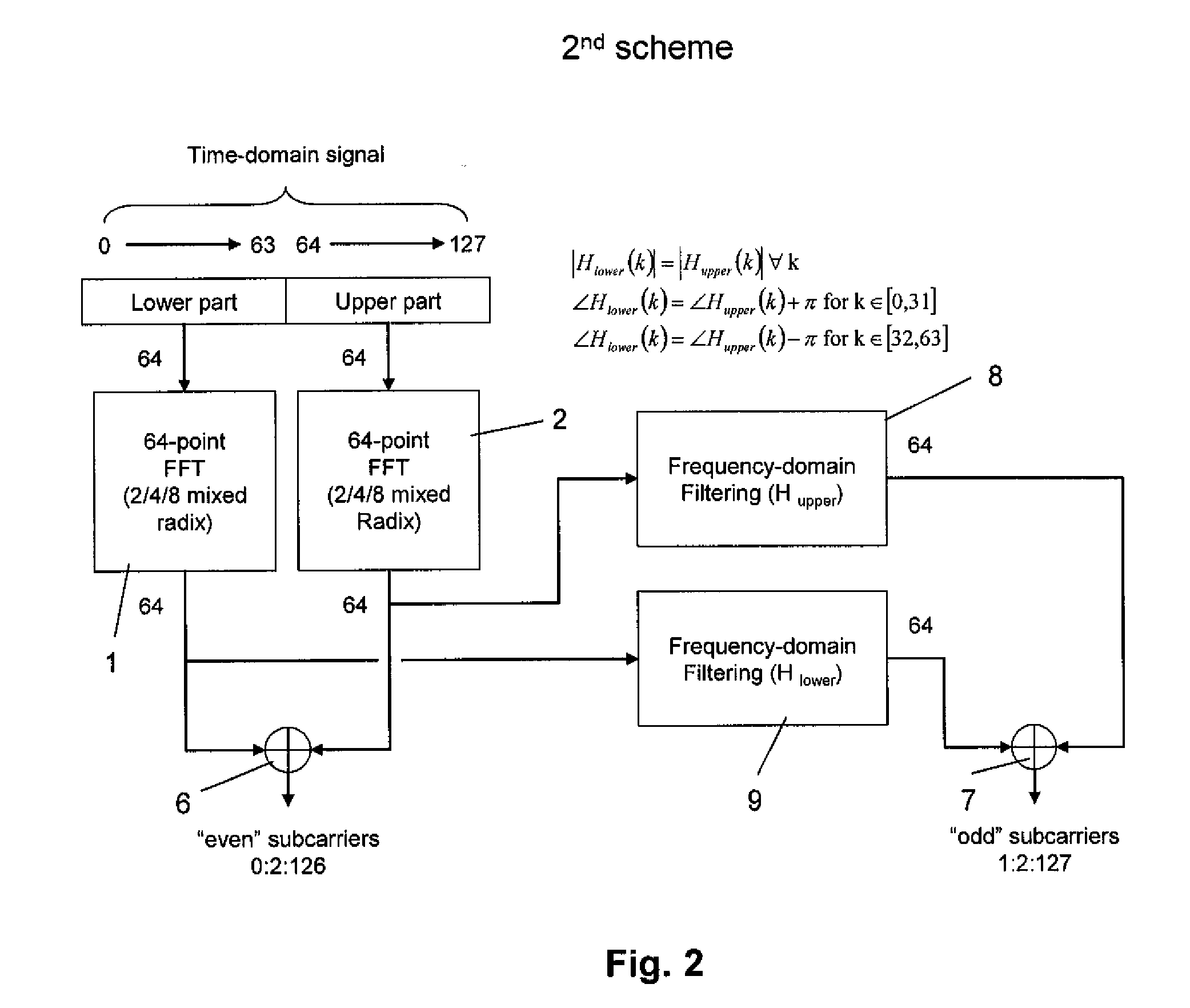
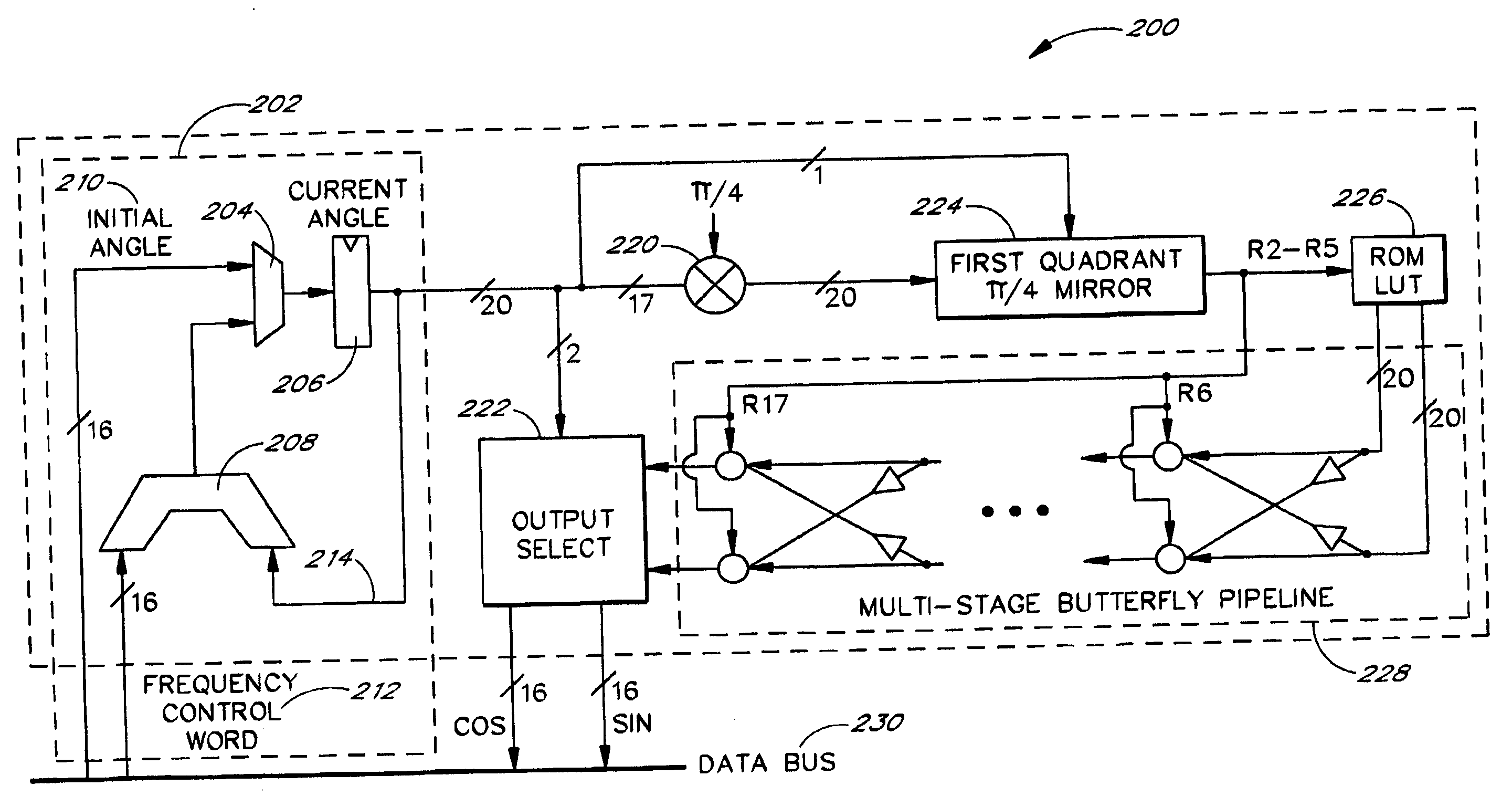
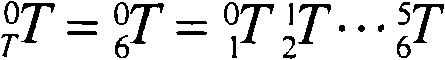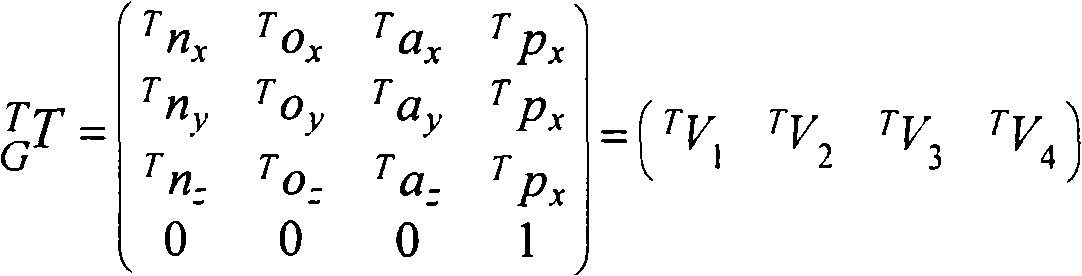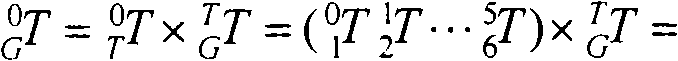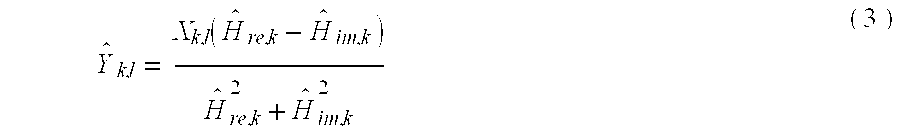Patents
Literature
111 results about "CORDIC" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
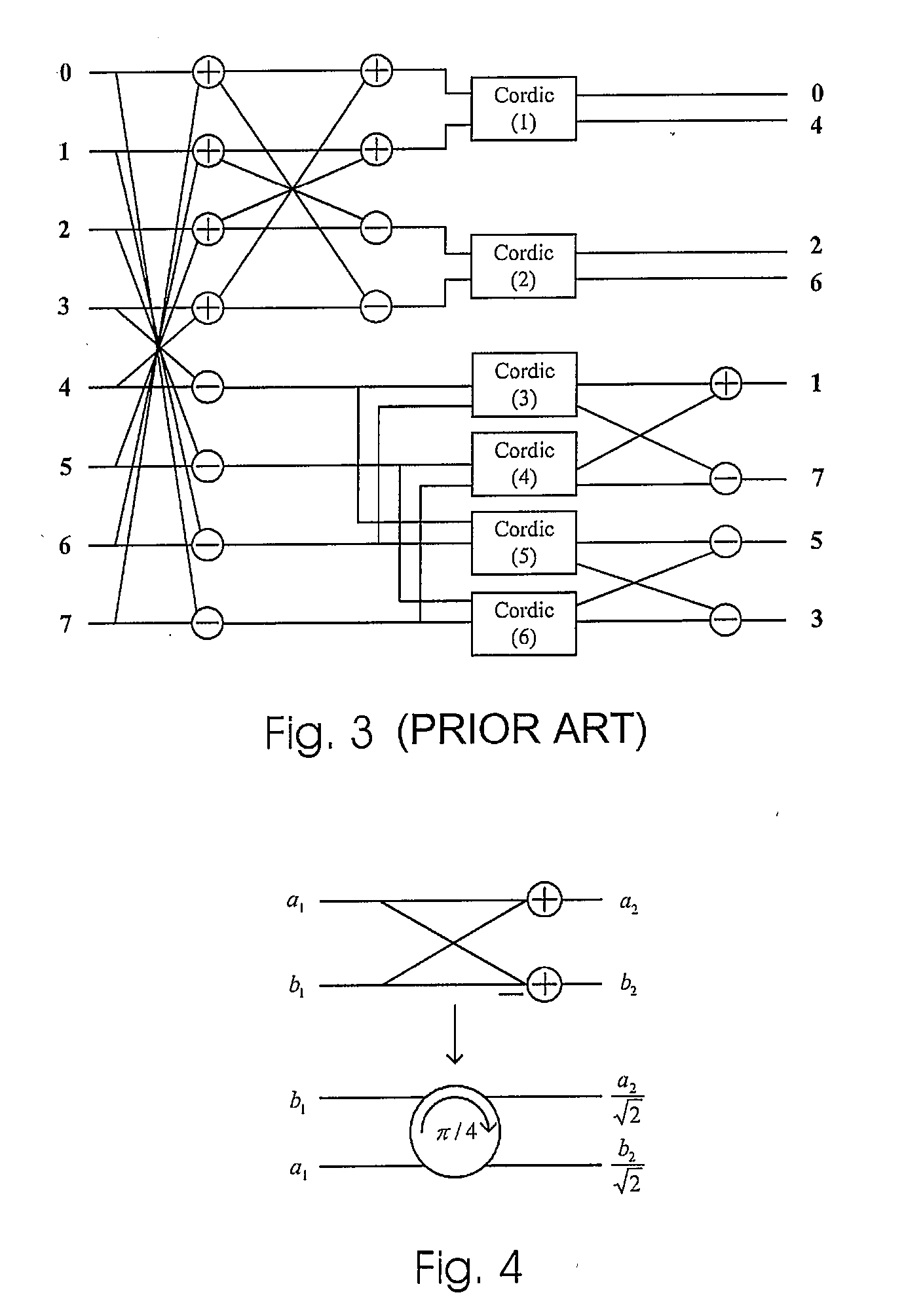
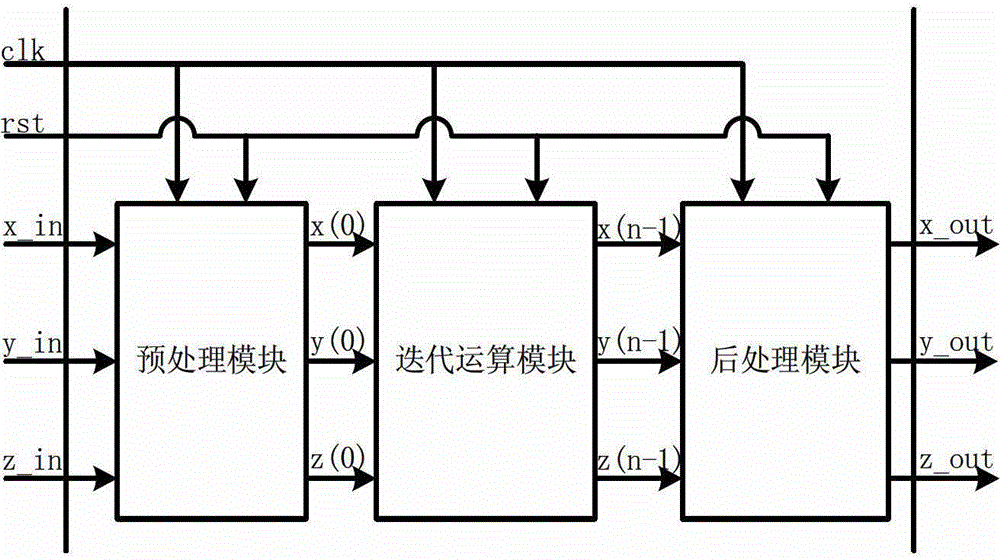
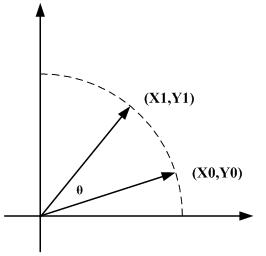
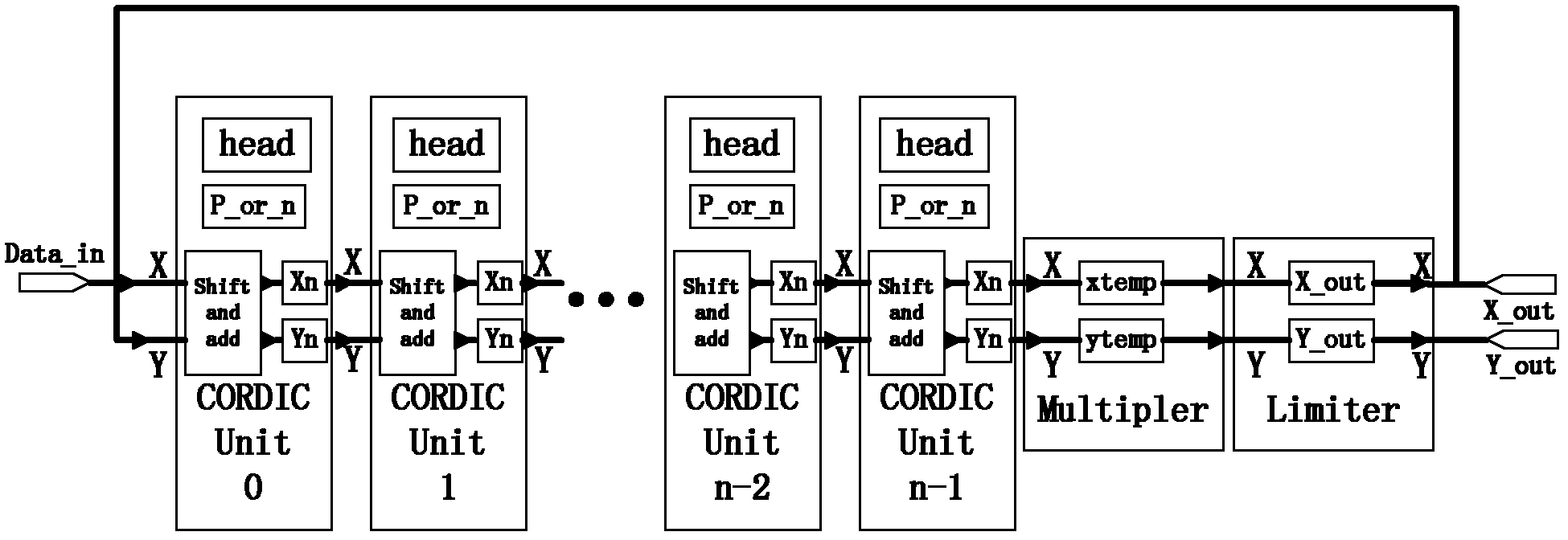
CORDIC (for COordinate Rotation DIgital Computer), also known as Volder's algorithm, is a simple and efficient algorithm to calculate hyperbolic and trigonometric functions, typically converging with one digit (or bit) per iteration. CORDIC is therefore also an example of digit-by-digit algorithms. CORDIC and closely related methods known as pseudo-multiplication and pseudo-division or factor combining are commonly used when no hardware multiplier is available (e.g. in simple microcontrollers and FPGAs), as the only operations it requires are addition, subtraction, bitshift and table lookup. As such, they belong to the class of shift-and-add algorithms.
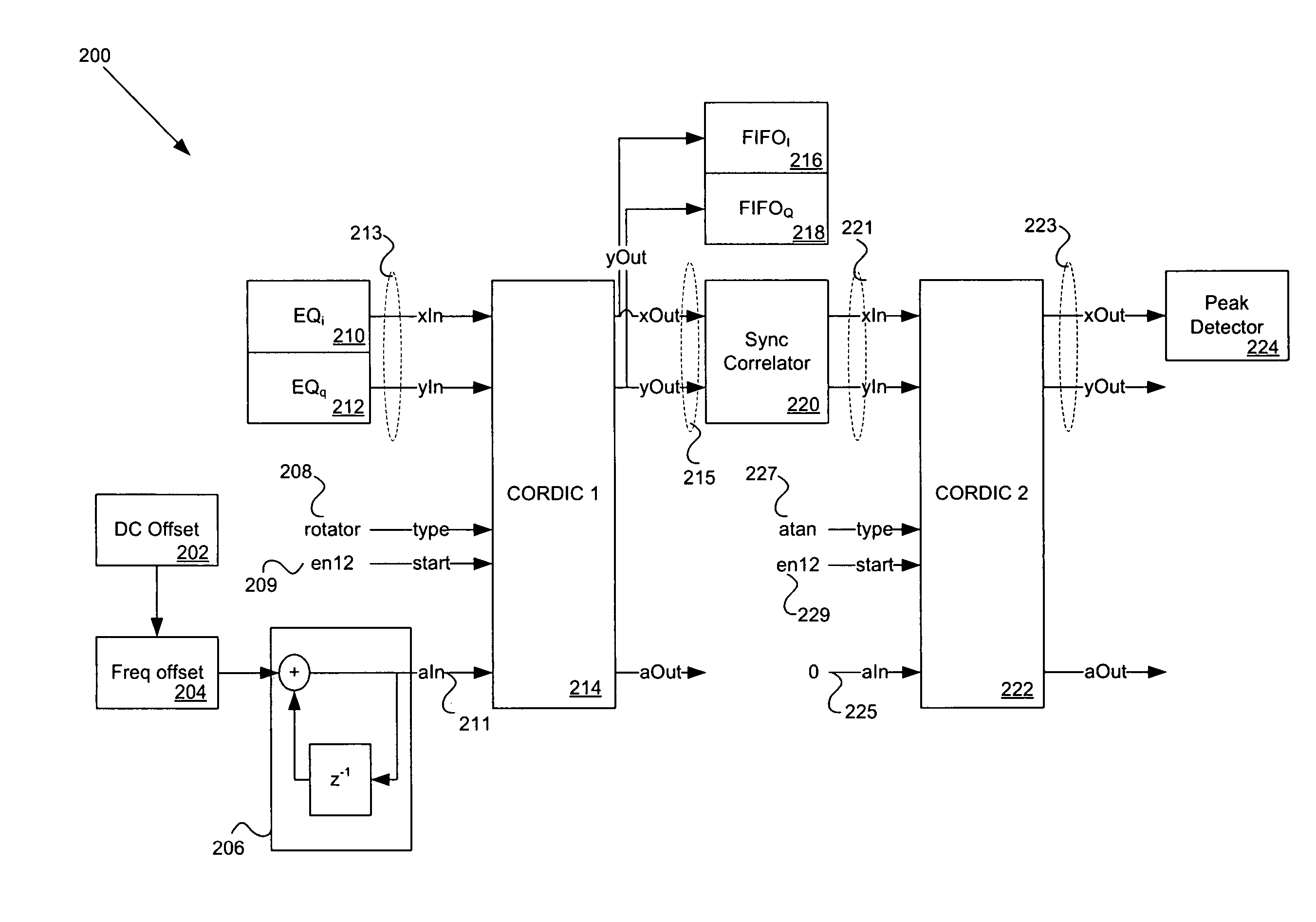
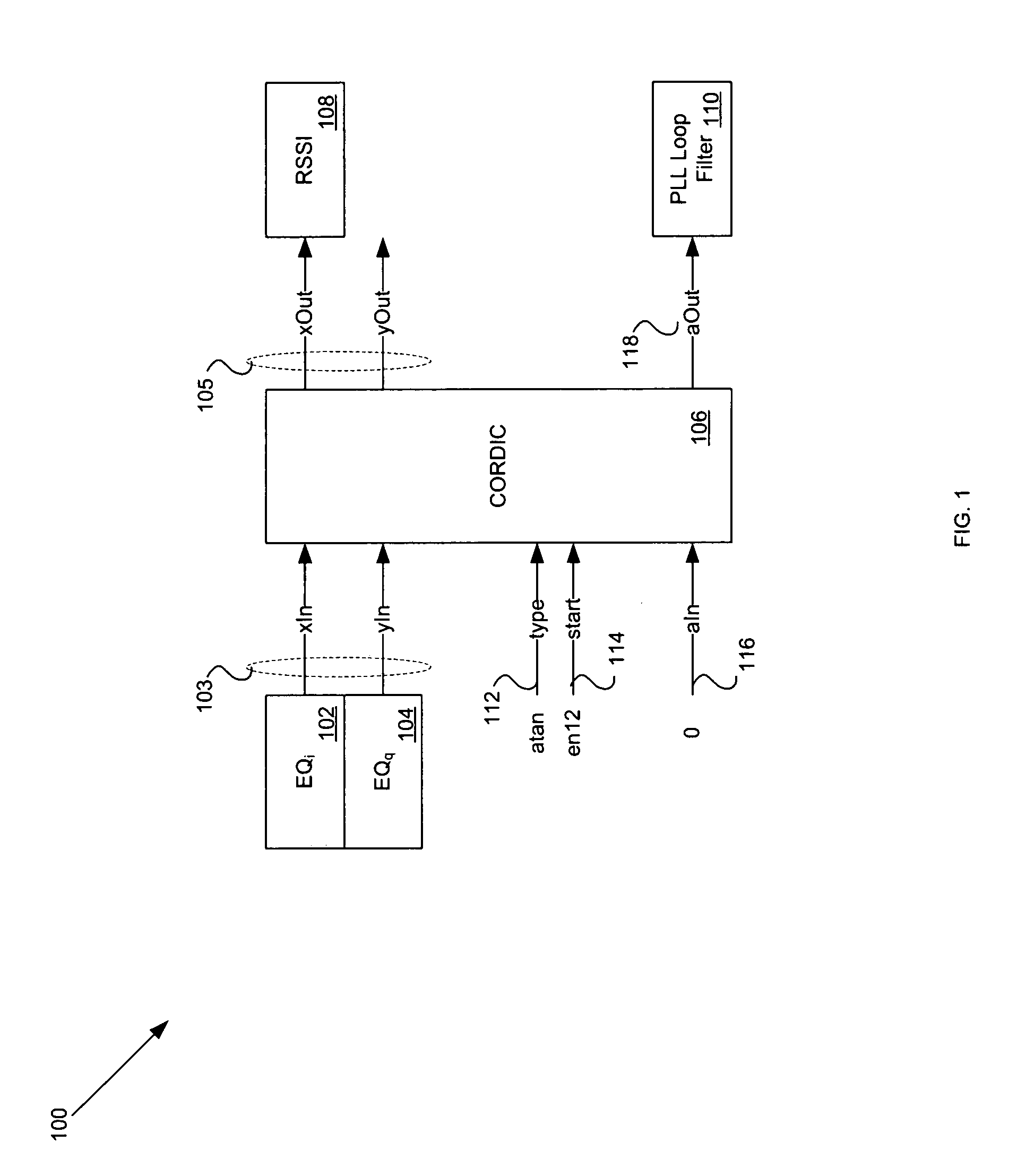
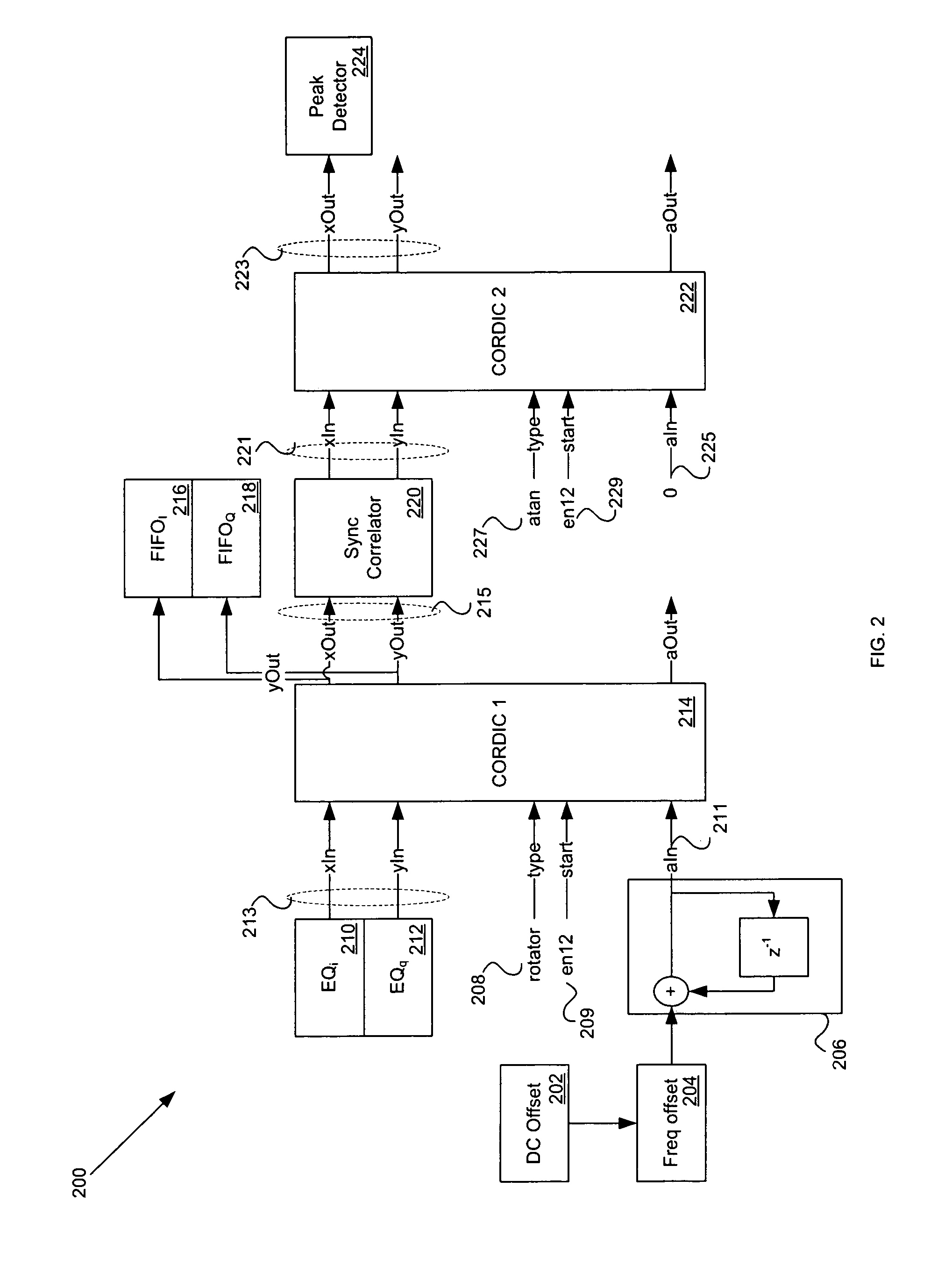
Joint de-spreading and frequency correction using a correlator
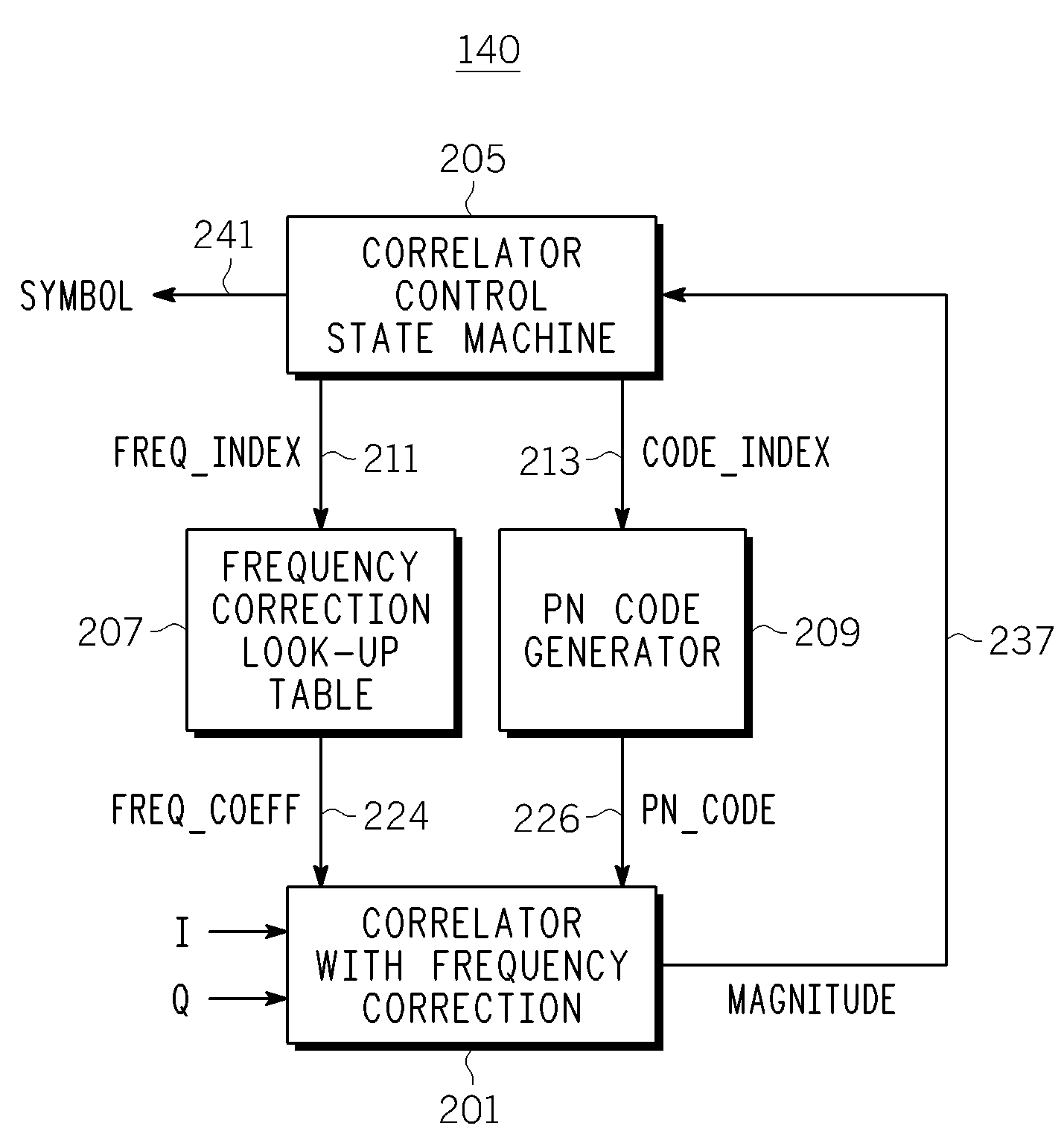
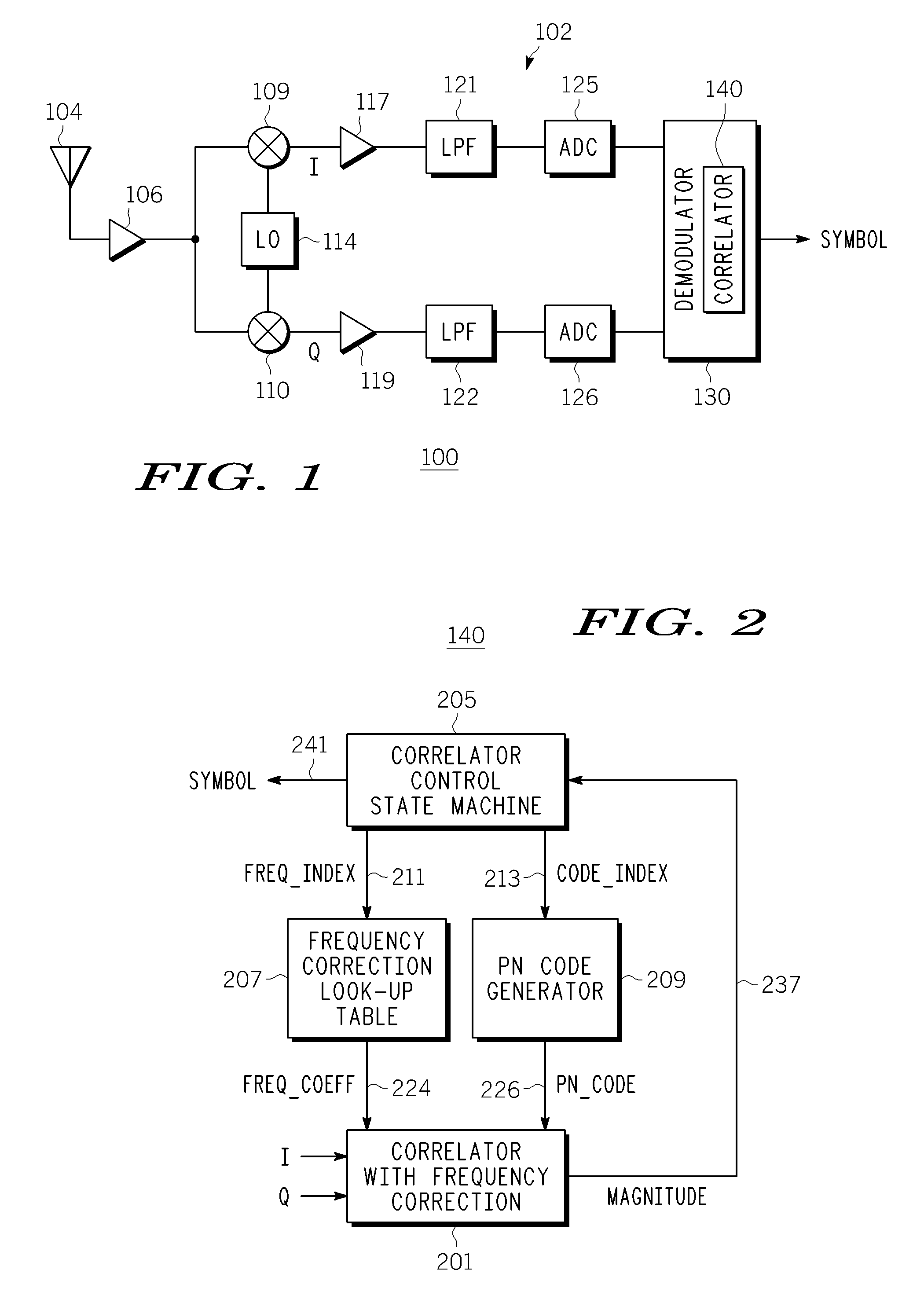
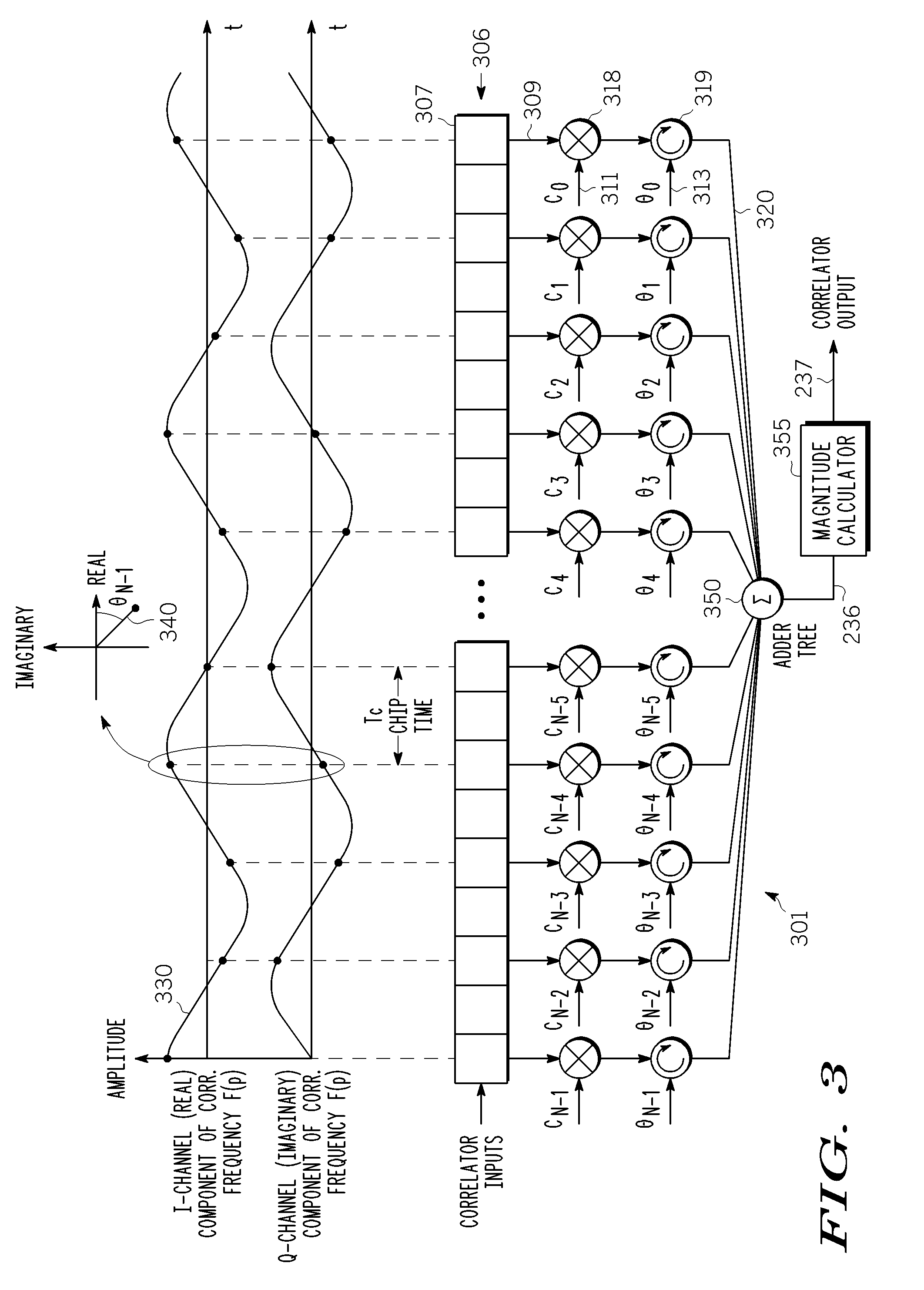
A correlator (140) for de-spreading a spread-spectrum signal includes a state machine (205), a frequency look-up table (207), a pseudorandom code generator (209), and a correlator structure (301 and 801). The spread-spectrum signal includes symbols, and each symbol includes a plurality of chips. The correlator structure includes a plurality of taps (309 and 809) at which a coordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) operation is performed to determine an offset from a nominal carrier frequency of the spread-spectrum signal and to change a phase of each chip of a received symbol, in order to correct a carrier frequency of the spread-spectrum signal while de-spreading the spread-spectrum signal.
Owner:APPLE INC
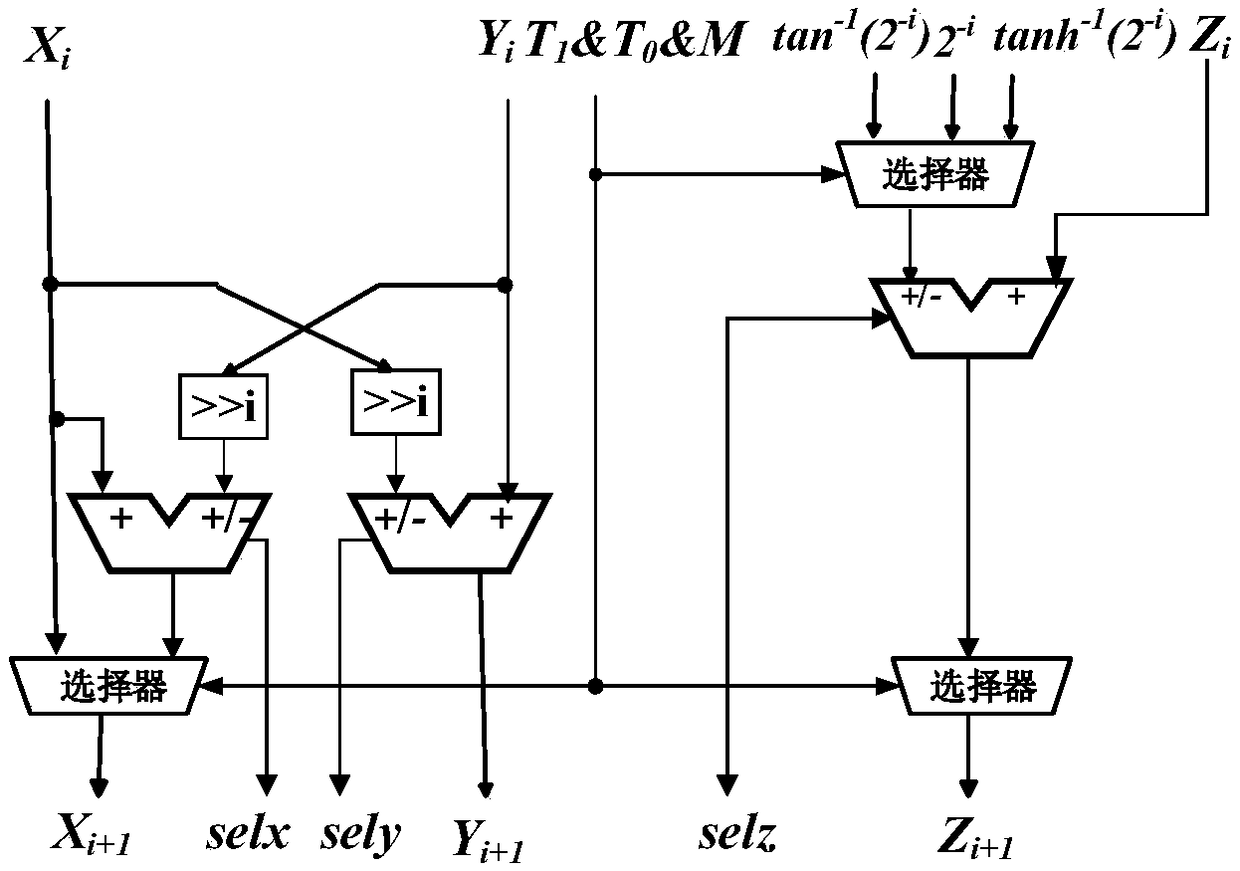
Reconfigurable floating-point operation device based on CORDIC algorithm
ActiveCN109062540AExtended region of convergenceReduce clock cyclesDigital data processing detailsReconfigurable antennaComputer module
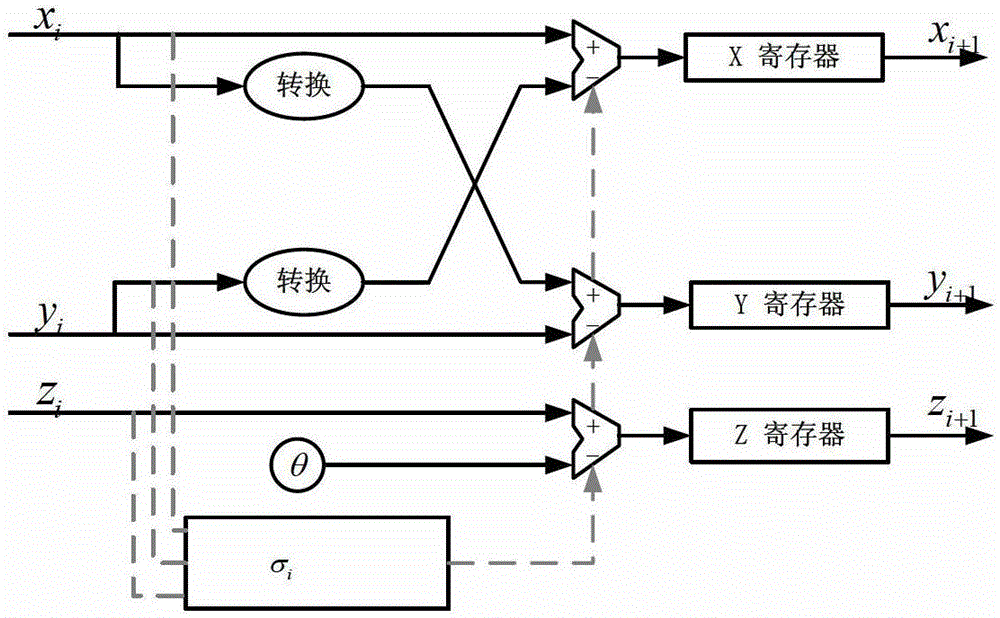
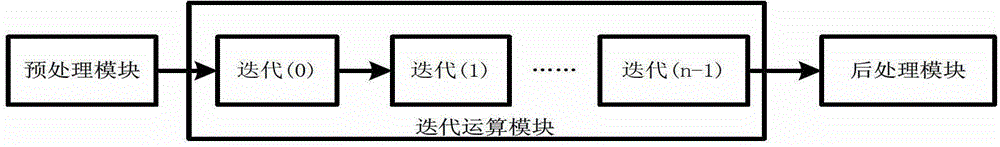
A reconfigurable floating-point arithmetic device based on CORDIC algorithm comprises a preprocessing module for completing input data from IEEE-754 standard, and maps it into the convergence region;a series-parallel hybrid reconfigurable CORDIC iterative unit module. The iterative operation part of CORDIC algorithm is composed of two parts: rotation modules A and B, wherein, the rotation moduleA is used to realize serial pipeline structure to maximize module reuse, the rotation module B is based on parallel prediction method of rotation direction and adopts tree adder structure to realize parallel structure in rotation mode; in the post-processing module, the corresponding result output is selected according to the encoded signal of the pre-processing module, and the mantissa normalization processing is completed to output the single-precision floating-point data format calculation result. The invention has the characteristics of simple principle, low delay, high precision and low hardware cost.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
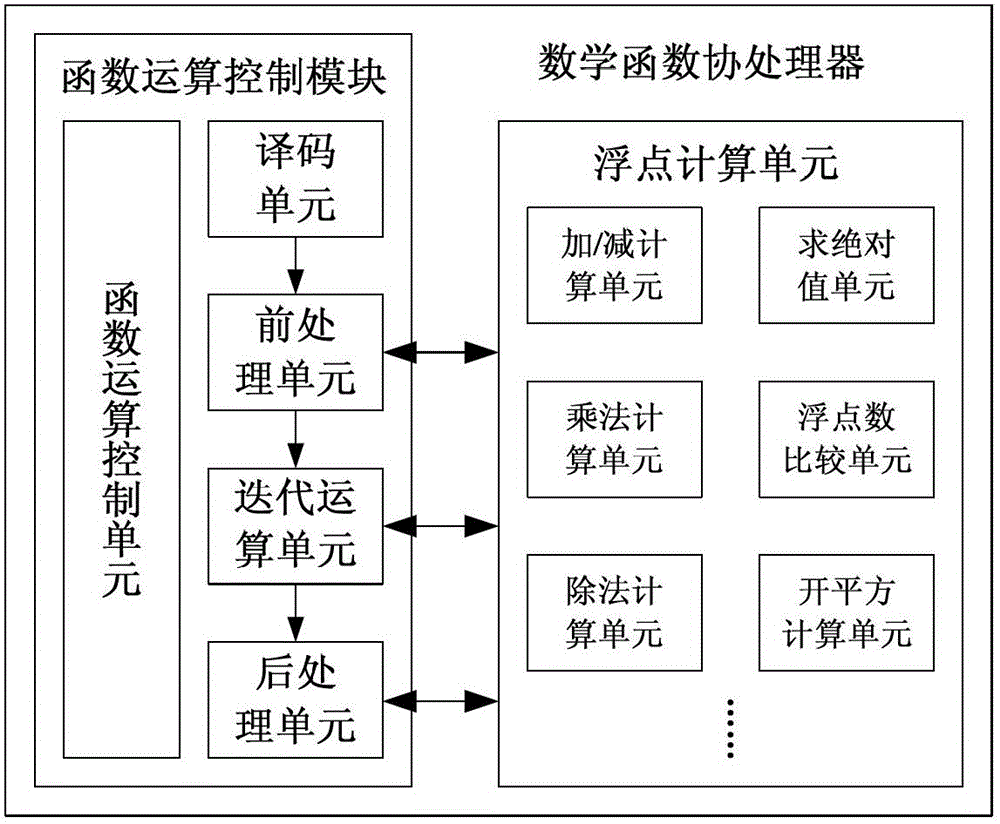
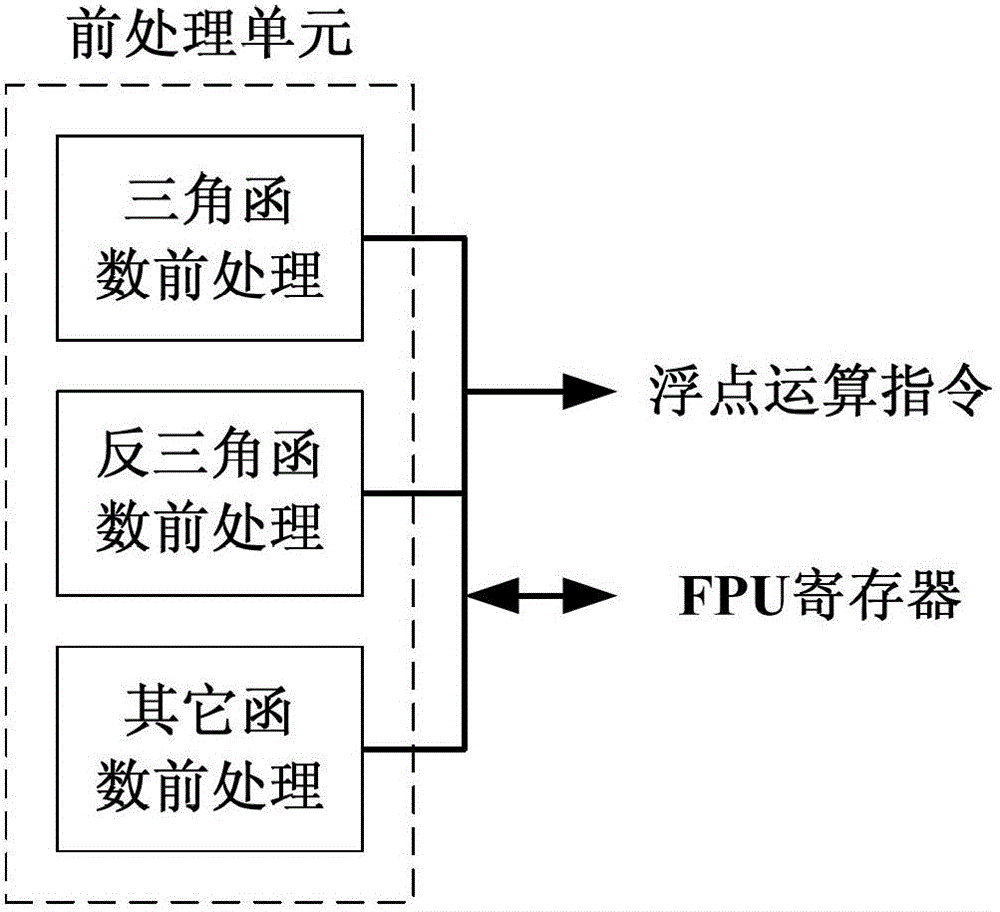
Elementary transcendental function operation method based on floating point arithmetic unit and coprocessor for method
InactiveCN102722469AThe calculation method is simple and flexibleSimple structureDigital data processing detailsComplex mathematical operationsCoprocessorSimulation
The invention provides an elementary transcendental function operation method based on a floating point arithmetic unit and a coprocessor for the method. According to the method, a coordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) algorithm is decomposed into a function operation control part and a floating point calculation part; the function operation control part is used for finishing an operation control function of the CORDIC algorithm; and the floating point calculation supports absolute value solution, addition / subtraction, multiplication, division, evolution and comparison operation of floating point number, and a general register used in the floating point calculation can be read and written by a function operation control module. A special mathematical function calculation component is redesigned as required in the conventional method, so the conventional method is complex in control and structure and high in consumption of hardware resources. By adding the function operation control module with a simple structure, transcendental function operation is realized by using the existing floating point operation instruction based on the existing floating point arithmetic unit; and the function operation control module is simple in structure and easy to implement and apply, and can support calculation of trigonometric and anti-trigonometric functions, hyperbolic function, exponential function and logarithmic function.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
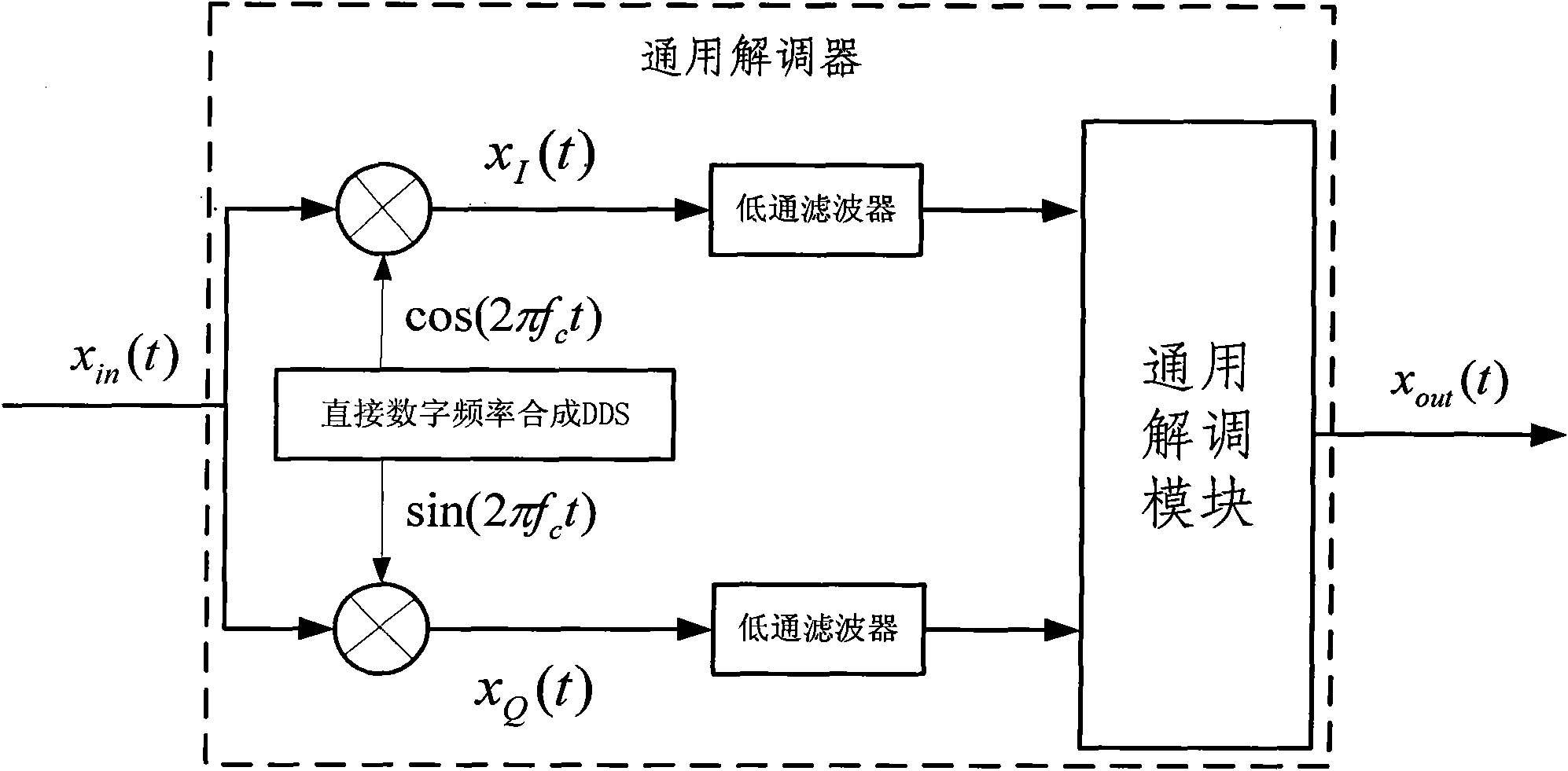
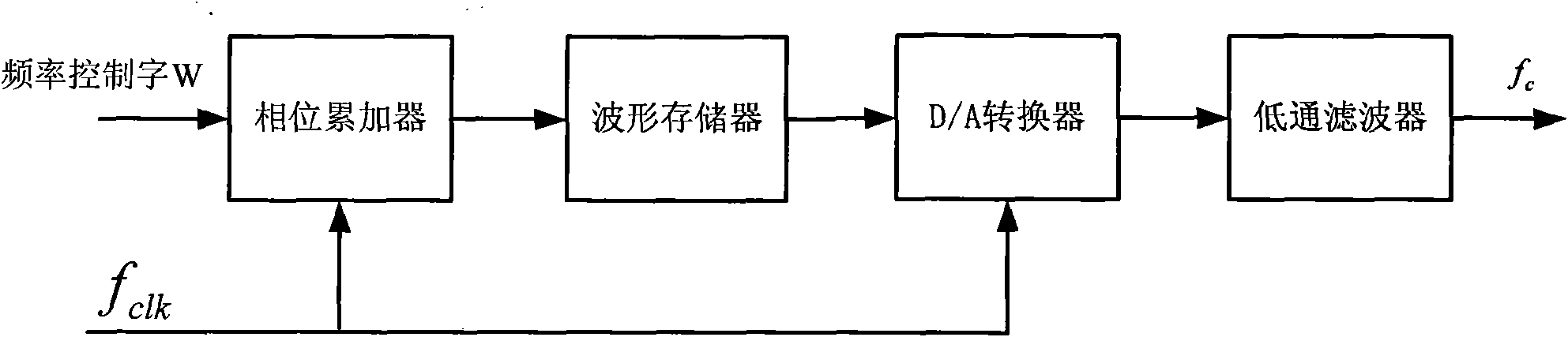
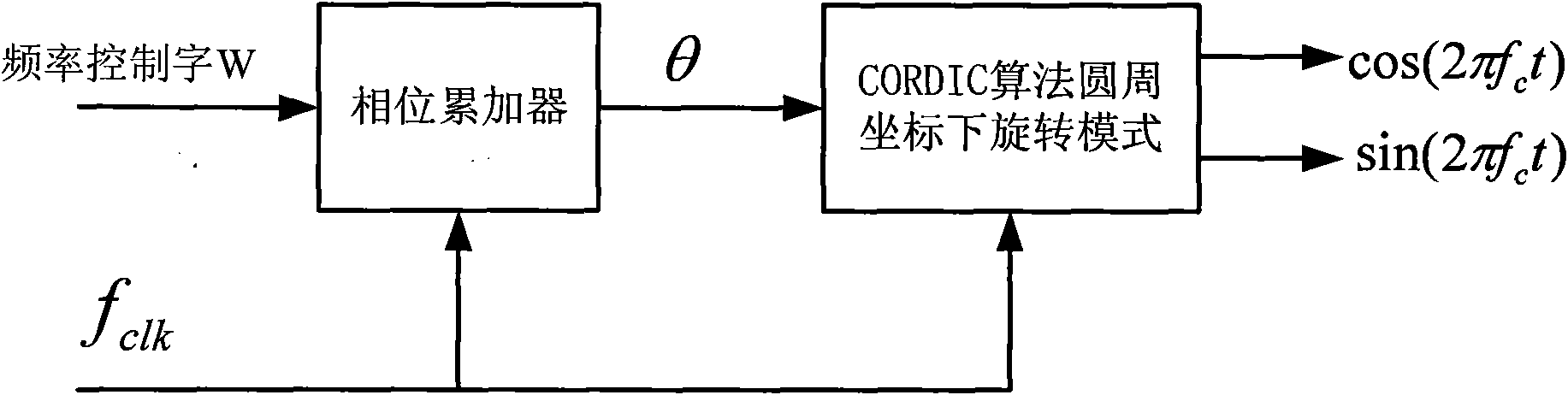
Method for realizing general demodulation of different modulating signals
InactiveCN101977176AConvergence Angle ExpandedLarge convergence angleMultiple carrier systemsLow-pass filterSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a method for realizing general demodulation of different modulating signals. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, using the direct numerical frequency synthesis method to generate two routes of local orthogonal carrier signals by expanding the rotation mode under the circumferential coordinate in the coordinated rotation digital computer (CORDIC) algorithm ofa convergence domain to synthesize equidirectional subcircuit data xI (t) and orthogonal subcircuit data xQ (t) with receiver terminal output signals; then filtering secondary harmonic components by a low pass filter; afterwards, inputting two routes of signals into a general demodulation module of the vector mode under the circumferential coordinate in the CORDIC algorithm of the convergence domain; finally, selecting a square root operation value or an arc tangent operation value according to different modulation modes to obtain demodulation information by filtering or differencing. In the invention, various modulation modes are integrated in the same hardware, so that the method has the characteristics of good flexibility and outstanding versatile performance; and meanwhile, the complex arithmetic operation is transformed into the displacement and add operation, as a result, the method can greatly reduce the complexity of hardware realization and has good carrier frequency mismatching resistance property.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
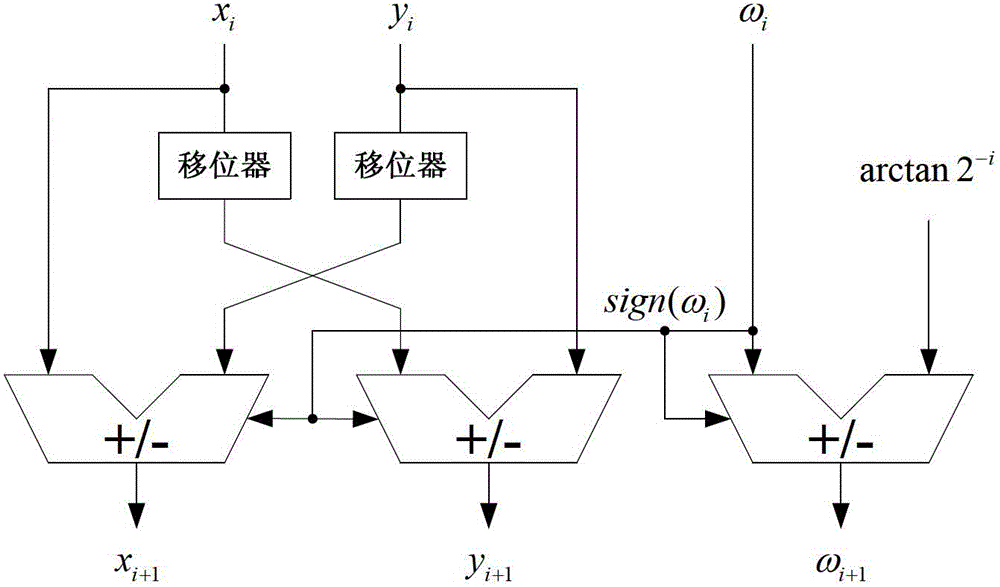
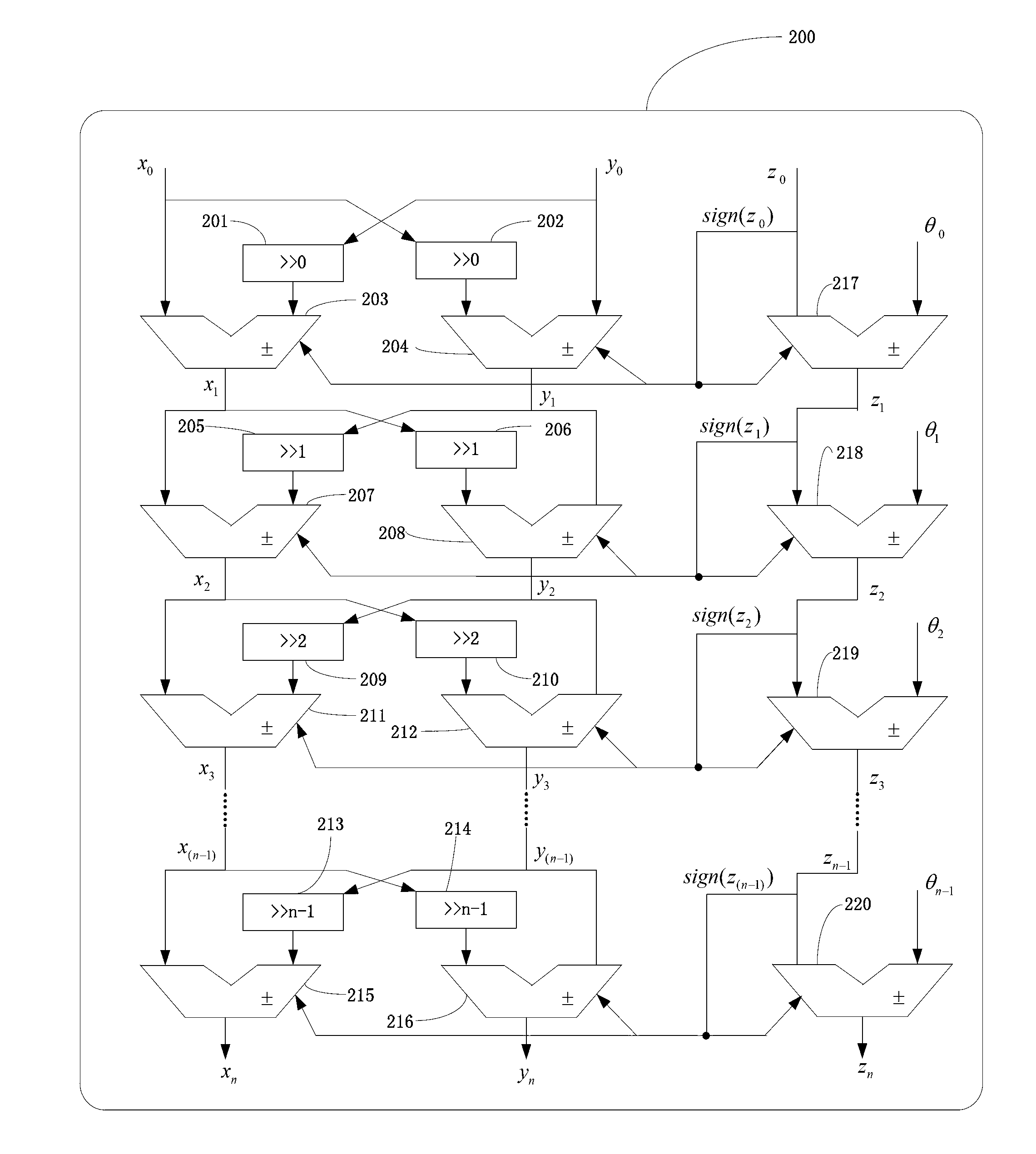
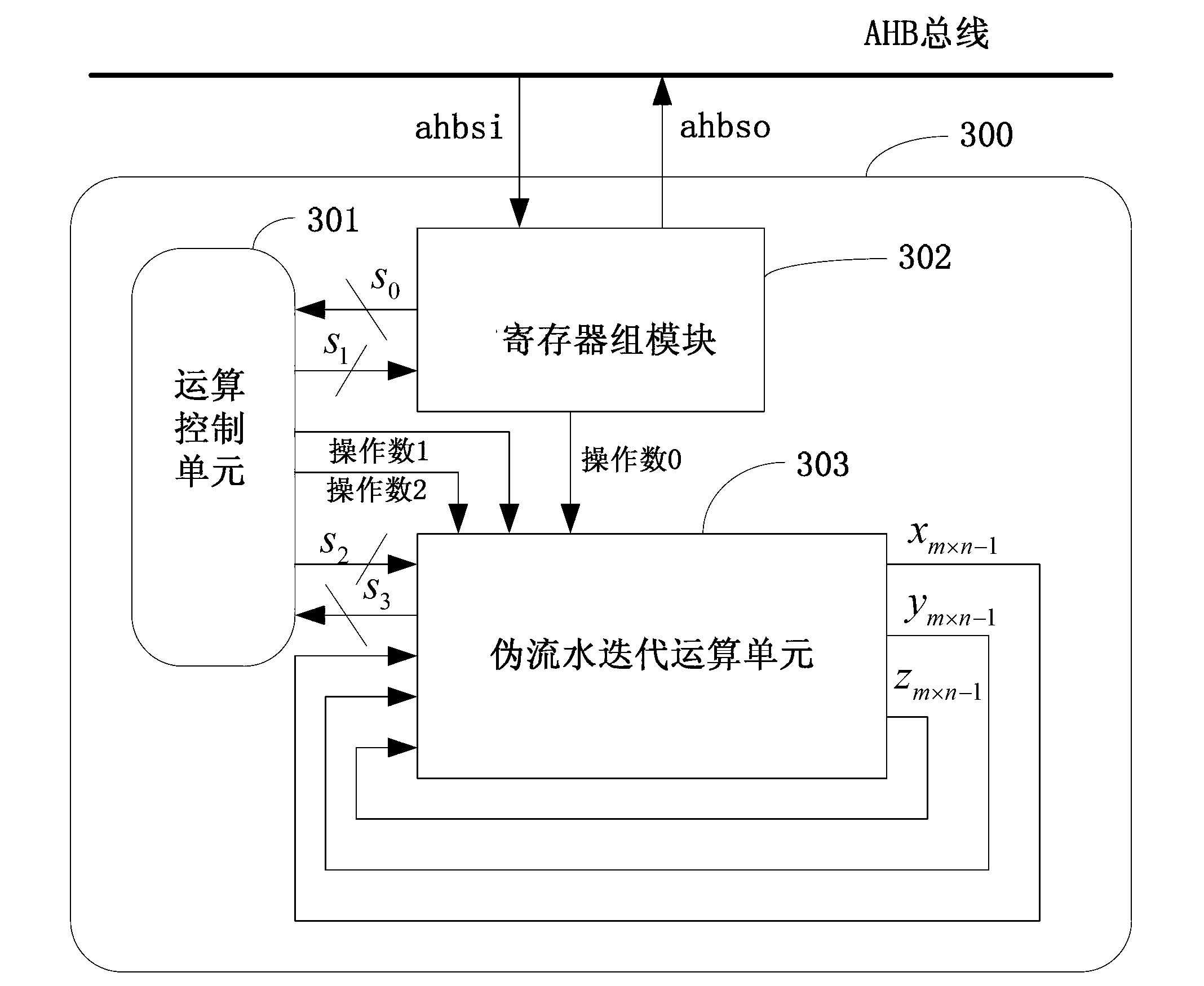
Trigonometric function arithmetic device based on combination of feedback of coordinated rotation digital computer (CORDIC) algorithm and pipeline organization
ActiveCN102981797AReduce overheadSolving technical problems at ever-increasing scaleDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerParallel computing
The invention discloses a trigonometric function arithmetic device based on combination of feedback of a coordinated rotation digital computer (CORDIC) algorithm and a pipeline organization. The trigonometric function arithmetic device comprises a register block module based on software configuration, an arithmetic control module and a fake pipeline arithmetic iteration unit. The register block module based on the software configuration comprises two kinds of registers of A and B. The arithmetic control module is responsible for connection of the arithmetic control module and the fake pipeline arithmetic iteration unit. The fake pipeline arithmetic iteration unit is composed of n levels of pipeline units used for achieving the CORDIC algorithm. According to the fake pipeline CORDIC algorithm structure based on configuration, on the premise that hardware circuit pay expenses are not increased and parallel trigonometric function computation is supported to a certain extent, trigonometric function operation without limit accuracy is achieved by means of a fake pipeline form in which outputs of the arithmetic iteration unit are continuously fed back to inputs of the arithmetic iteration unit.
Owner:NO 771 INST OF NO 9 RES INST CHINA AEROSPACE SCI & TECH
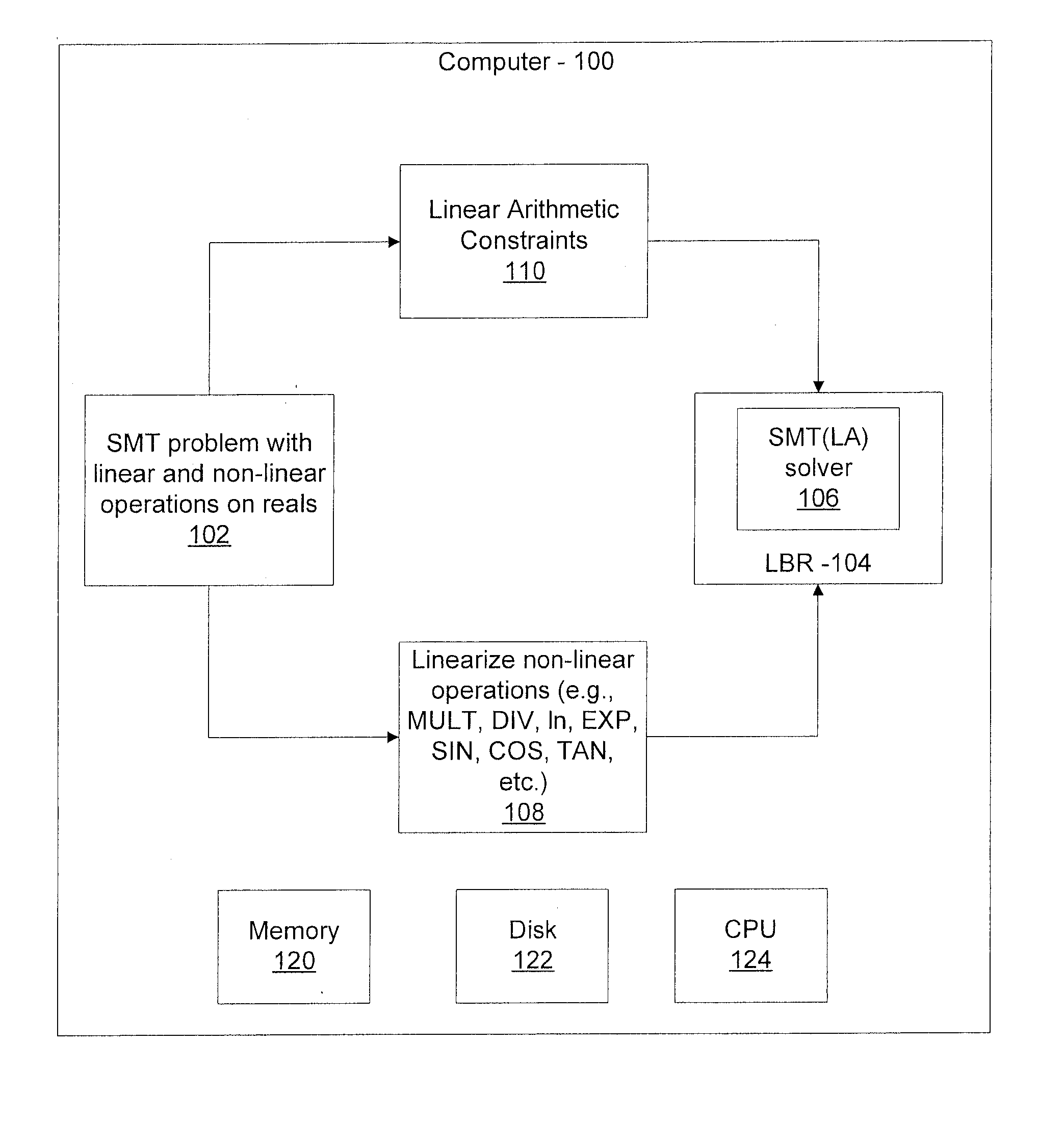
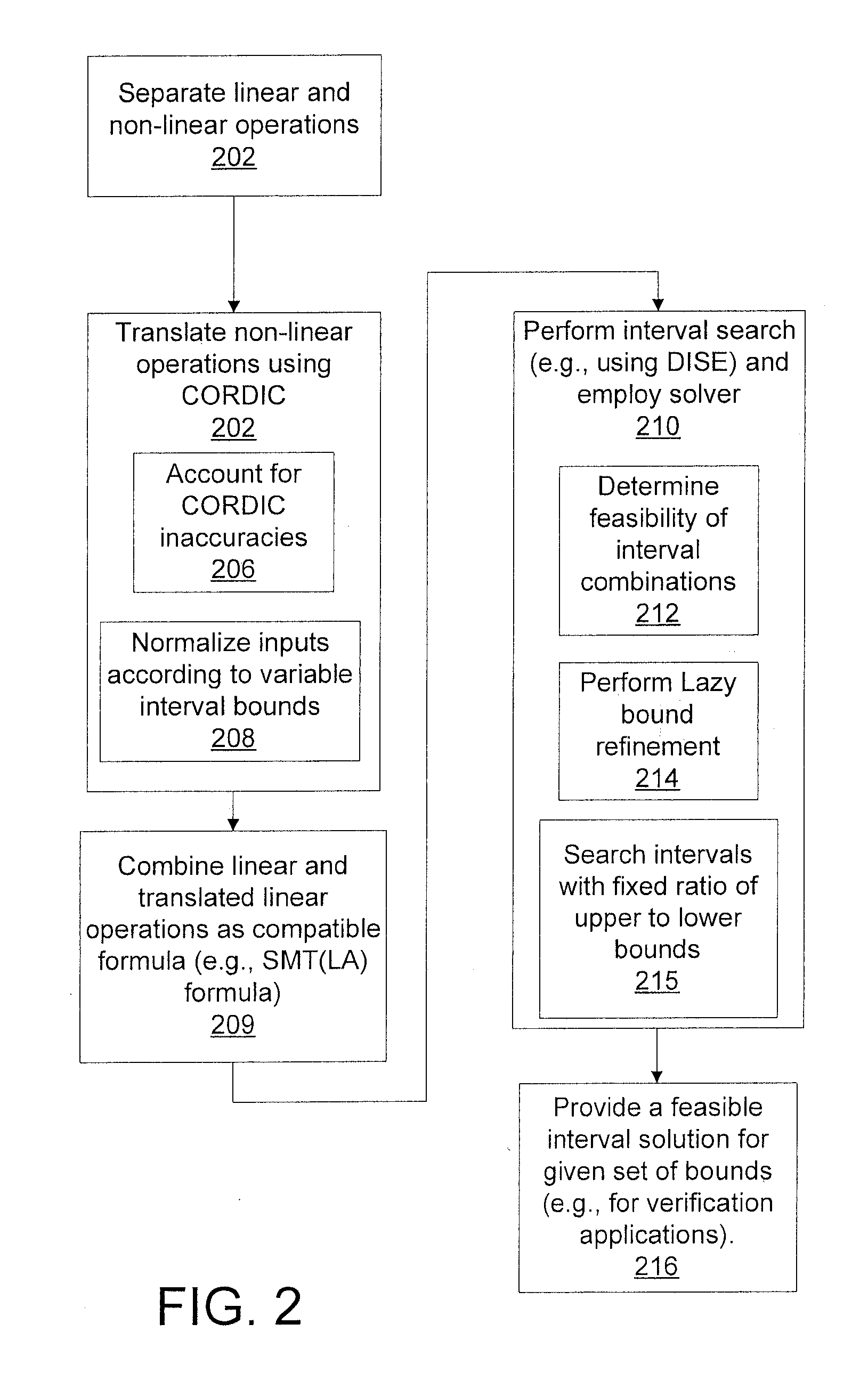
Efficient decision method for real non-linear arithmetic constraints
InactiveUS20100281086A1Digital computer detailsKnowledge representationReal arithmeticOperational transformation
A system and method for solving a decision problem having Boolean combinations of linear and non-linear operations includes translating the non-linear real operations using a COordinate Rotation DIgital Computer (CORDIC) method programmed on a computer device into linear operations maintaining a given accuracy. Linear and translated linear operations are combined into a formula. Satisfiablity of the formula is solved using a decision procedure for Boolean combinations of linear operations over integers and reals.
Owner:NEC CORP
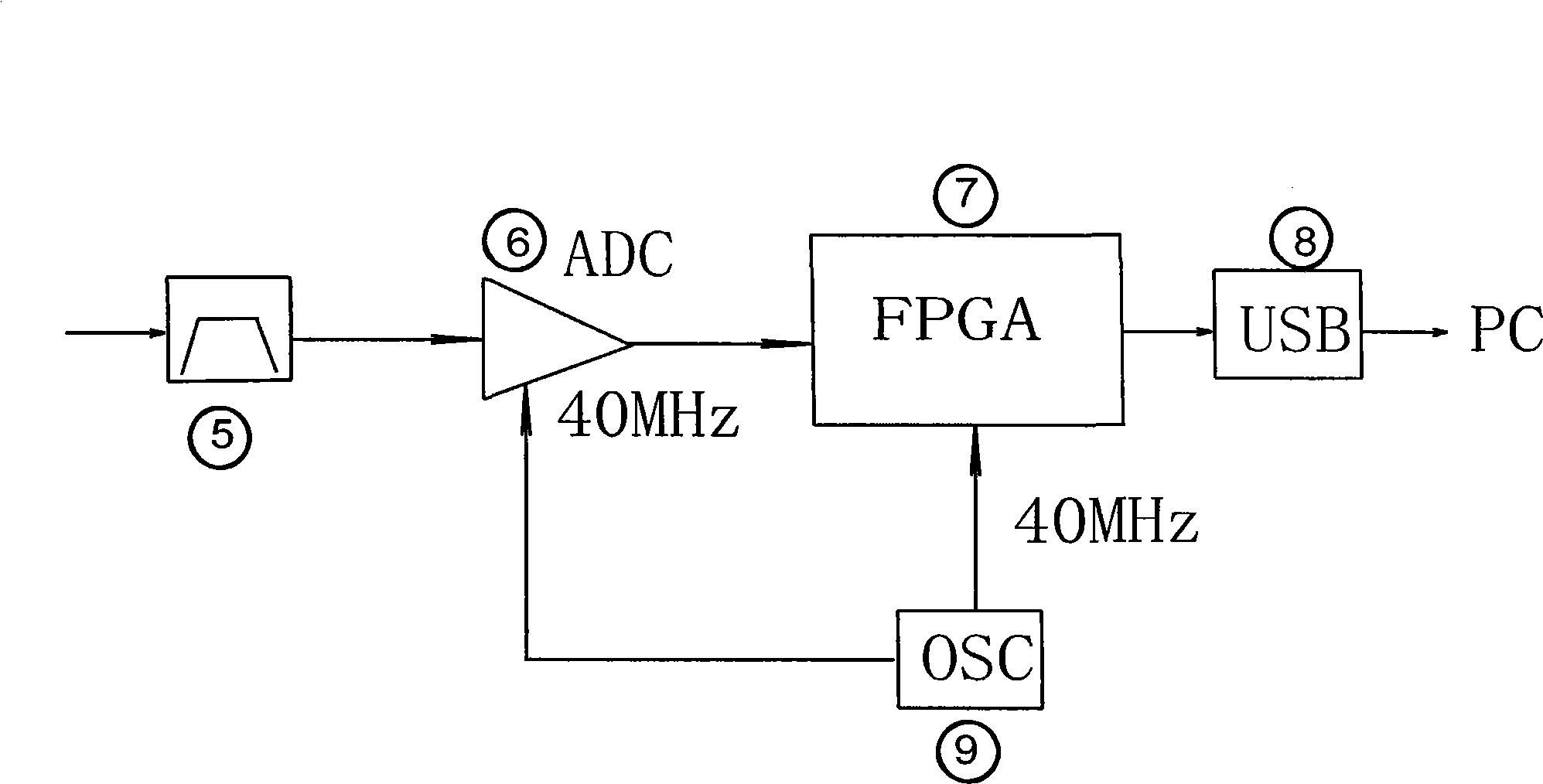
Real-time implementation of field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) design in hyperspectral imaging
A Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA) design uses a Coordinate Rotation DIgital Computer (CORDIC) algorithm that can convert a Givens rotation of a vector to a set of shift-add operations. The CORDIC algorithm can be easily implemented in hardware architecture, therefore in FPGA. Since the computation of the inverse of the data correlation matrix involves a series of Givens rotations, the utility of the CORDIC algorithm allows a causal Constrained Energy Minimization (CEM) to perform real-time processing in FPGA. An FPGA implementation of the causal CEM is described and its detailed architecture is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method and computer program therefor
InactiveCN1929470ASmall amount of calculationReduce processing latencyCode division multiplexOrthogonal multiplexCORDICImpulse response
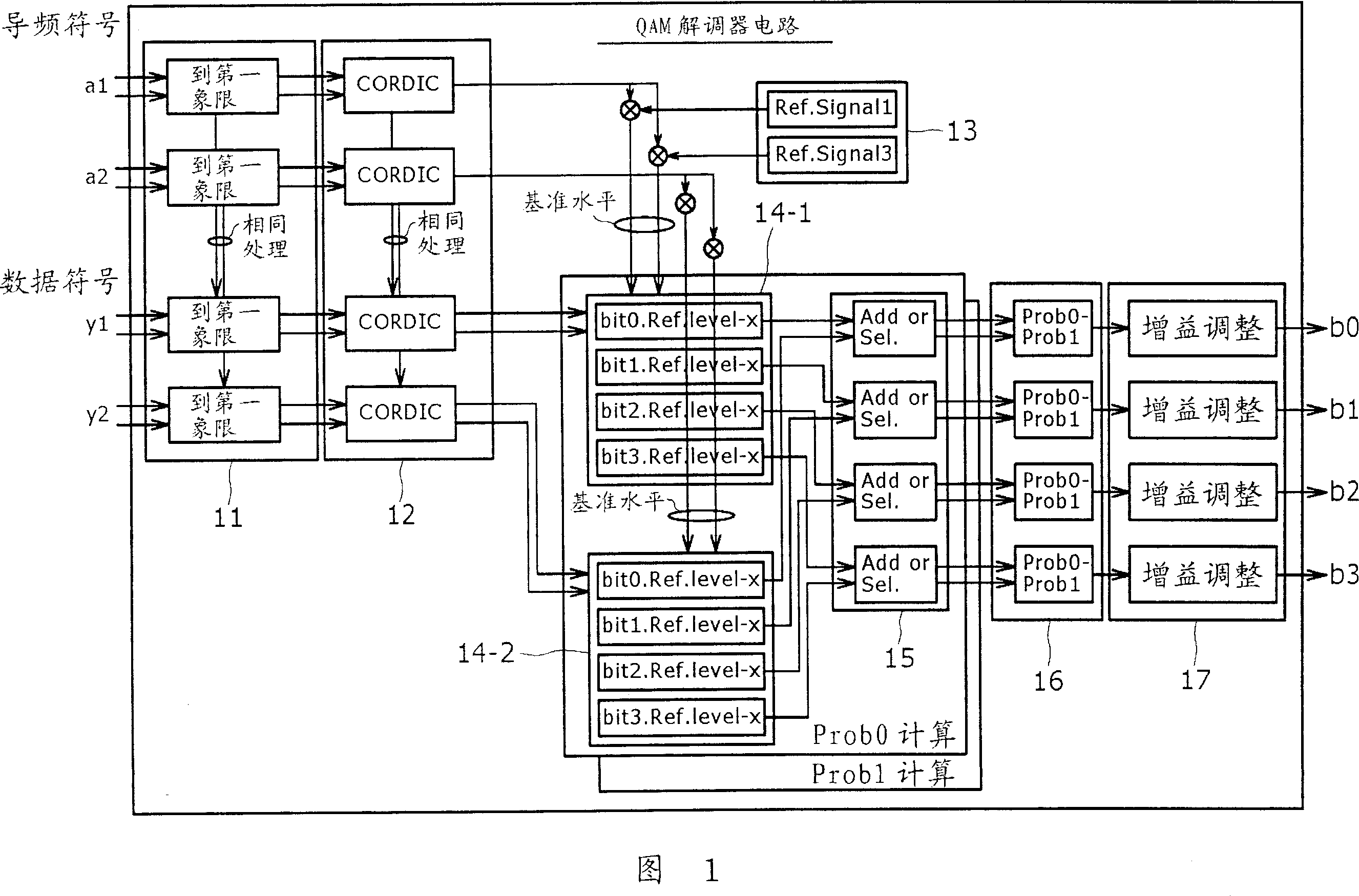
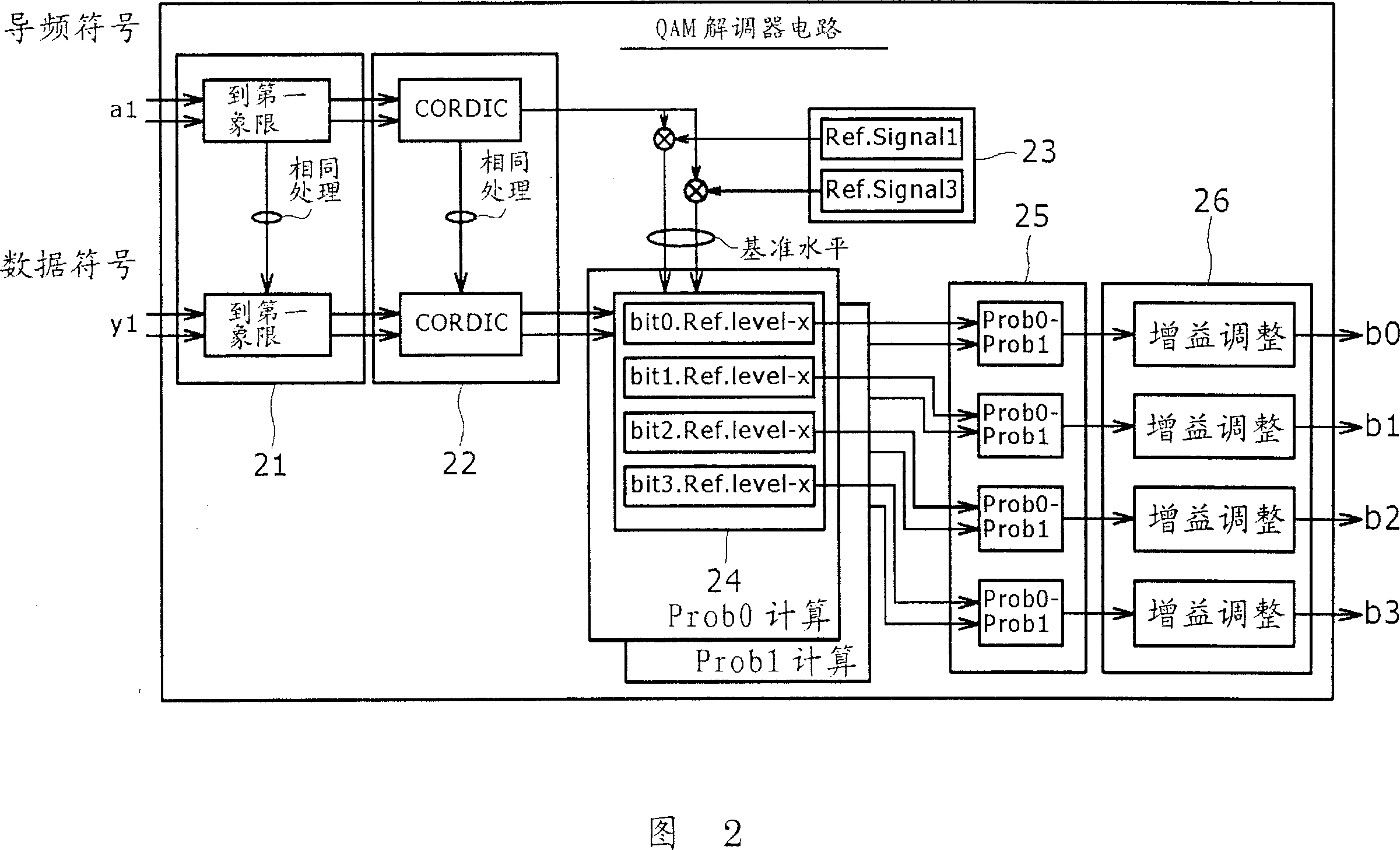
The present invention relates to a wireless communication apparatus, wireless communication method and computer program therefor. A technology for demodulating the received QAM mapping signal is provided using a known coordinate rotation digital computer performed by a complex arithmetic method i.e., CORDIC. The rotation angle for estimating the impulse response is obtained from pilot symbols and the rotation compensation of a data symbol using arc tangent are simultaneously performed. A reference symbol is set on one of the I axis and Q axis of a signal space only, thus a reference symbol closest from a reception symbol can be determined by referring to only a value of one side of the I axis or the Q axis. Since complex distance is not obtained, arithmetic processing can be simplified.
Owner:SONY CORP
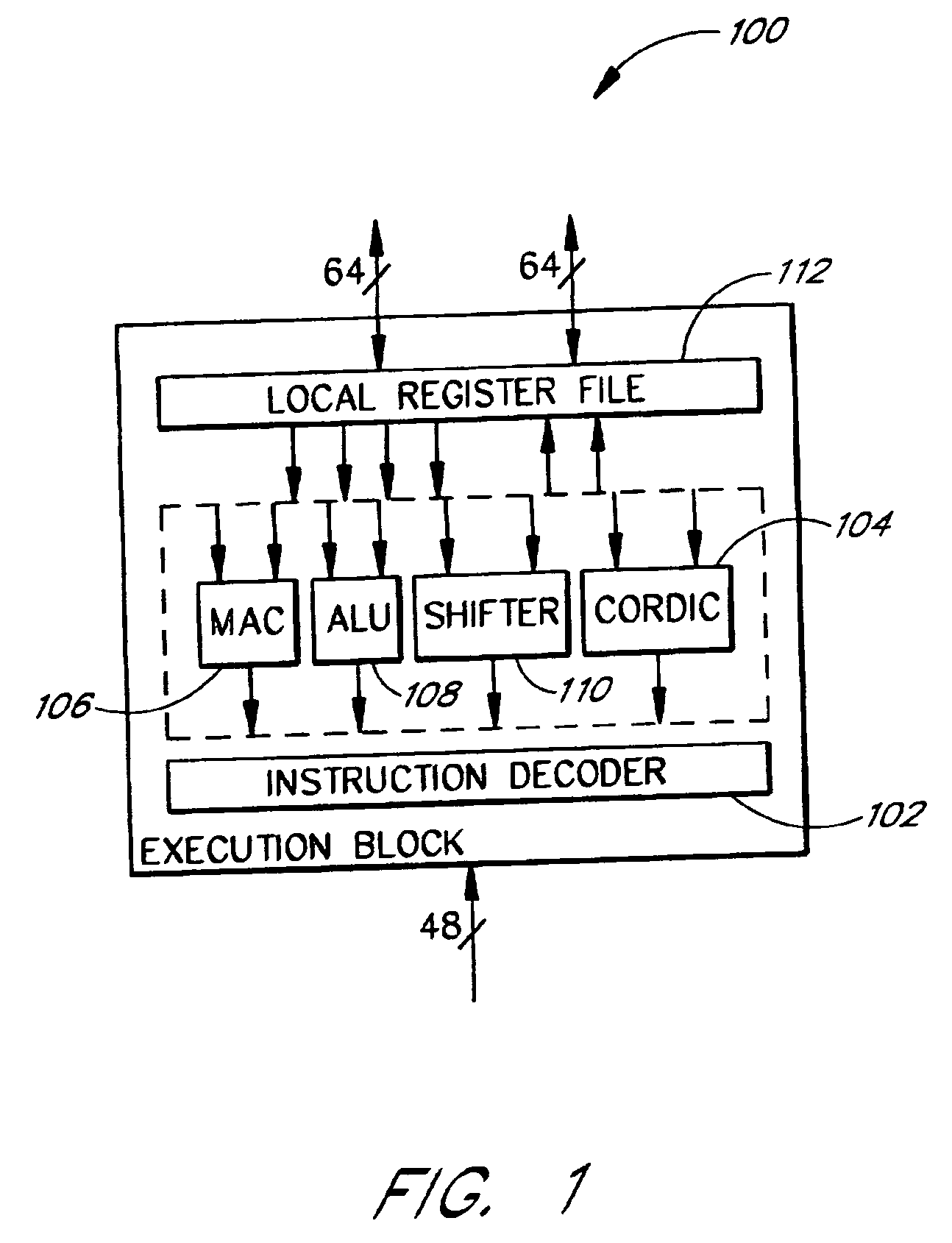
Hardware function generator support in a DSP
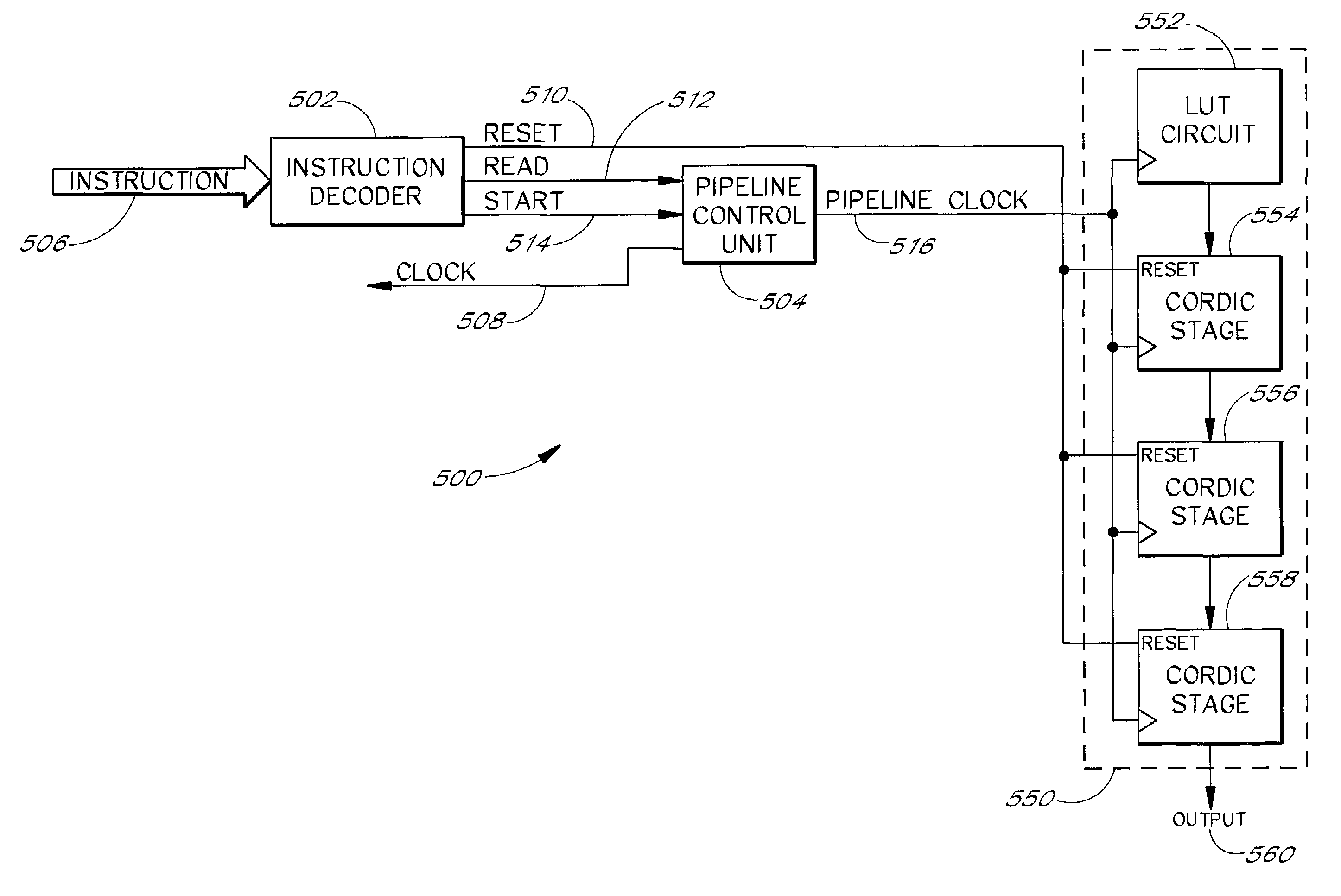
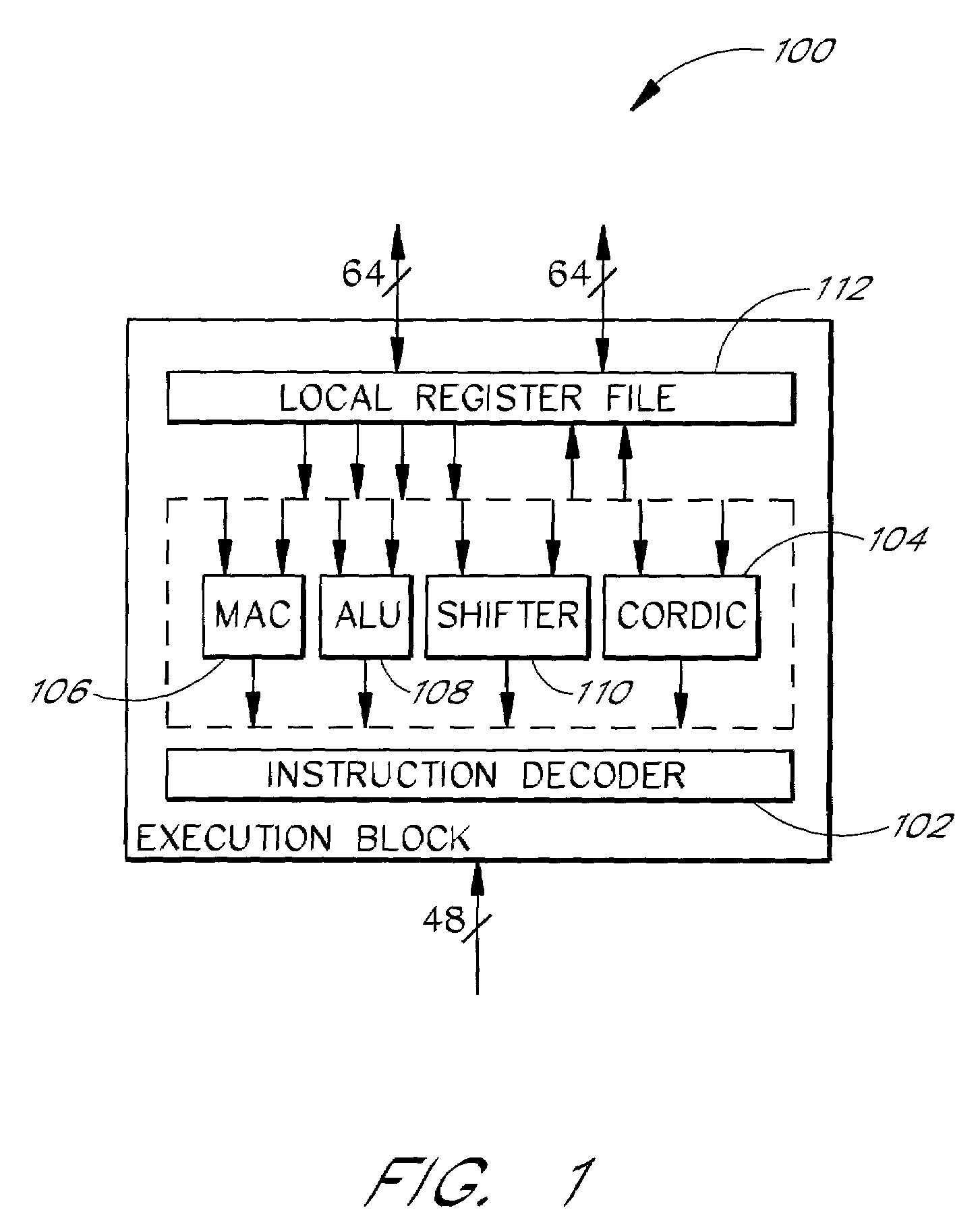
InactiveUS7031992B2Quickly and efficiently process CORDIC algorithm in pipelineLittle overheadSpeech analysisConcurrent instruction executionLine tubingParallel computing
The present invention relates to digital signal processors with an integrated module configured to compute a Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer (CORDIC) in a pipeline. The pipelined module can advantageously complete computation of one CORDIC computation for each clock pulse applied to the CORDIC module, thereby providing a CORDIC computation for each clock pulse. One embodiment advantageously computes a first portion of a computation with a lookup table and a second portion in accordance with a CORDIC algorithm. Advantageously, data in a CORDIC pipeline is automatically advanced in response to read instructions and can be automatically advanced from the beginning of the pipeline to the end of the pipeline to reinitialize the pipeline. This allows information to be retrieved from the CORDIC pipeline with relatively little overhead. The automatic starting and stopping of the CORDIC pipeline advantageously allows the retrieval of computations from efficient pipeline architectures on an as-needed basis.
Owner:QUARTICS
Method and circuit for performing cordic based loeffler discrete cosine transformation (DCT) for signal processing
InactiveUS20070250557A1Digital video signal modificationComplex mathematical operationsHand heldCORDIC
A low-power and high-quality DCT transformation based on the Cordic method is presented. The proposed Cordic based Loeffler DCT architecture only requires 38 add and 16 shift operations to carry out the DCT transformation. The complexity is almost the same as the complexity of the binDCT-C5. The simulation results show that the DCT according to the invention reduces the area and the power dissipation of the implementation compared to the original Loeffler DCT significantly. Furthermore, it only has a fraction of the power dissipation of the binDCT-C5. The major contribution of the DCT according to the invention is that it not only reduces the area and power consumption significantly, but also keeps the good transformation quality of the original Loeffler DCT. It is worth noticing that the Cordic based Loeffler DCT according to the invention is very suitable for low-power and high-quality CODECs in multimedia hand-held systems.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Six-freedom degree robot kinematics CORDIC algorithm coprocessor
InactiveCN101286115ACalculation speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital data processing detailsKinematicsCoprocessor
The invention provides a coprocessor of six DOF robot kinematics CORDIC arithmetic, which replaces the robot kinematics direct and inverse solution which can only be completed by calculating a plurality of transcendental equations, and leads the calculation process of a plurality of transcendental equations to be simplified as operations such as addition, subtraction, shift, etc., which are convenient to be realized by hardware, thus greatly improving the calculation speed of the coprocessor.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Complex multiplication unit based on modified high-radix CORDIC algorithm
InactiveCN103488459ABroaden your optionsSimplify the multiplication operationDigital data processing detailsDigital signal processingCORDIC
The invention belongs to the technical field of design of digital signal processing and integrated circuits and particularly relates to a complex multiplication unit based on a modified high-radix CORDIC algorithm. The modified high-radix CORDIC algorithm is characterized in that selection range of iterative angle of each level in CORDIC operation is further increased, and accordingly the number of required iterations is reduced and operating speed is increased while the precision is guaranteed; a method of approximate expansion of Taylor series of a cosine function is adopted, multiplication of modulus correction factors in the high-radix CORDIC algorithm is simplified, only one constant modulus correction factor exists in the hole operating process, and hardware complexity is reduced; in an application wherein a multiplier of the multiplication is preliminarily determinable, usage of a common complex multiplier can be avoided completely, hardware area of the multiplication unit and the size of a required ROM are both advantaged, and loss of computing accuracy avoided.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for pulse compression processing the linear frequency modulation signal by CORDIC
InactiveCN101499775AShorten the lengthOmit complex multiplicationMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceDigital down conversionDigital down converter
The invention discloses a method and a device used for carrying out pulse compression processing to a chirp signal by a coordinate rotations digital computer (CORDIC) arithmetic; the key point of the method is that: by arranging CORDIC, the increment of the input phase is gradually increased or reduced linearly by time; simultaneously, functions of digital down converter, digital orthogonalization and de-ramp are realized. Compared with the existing digital receiver, the internal of the digital receiver does not need memorize reference waveform; furthermore, all operations are completed by addition, reduction and replacement, thereby having extremely high efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Transcendental function device and method for realizing transcendental function utilizing same
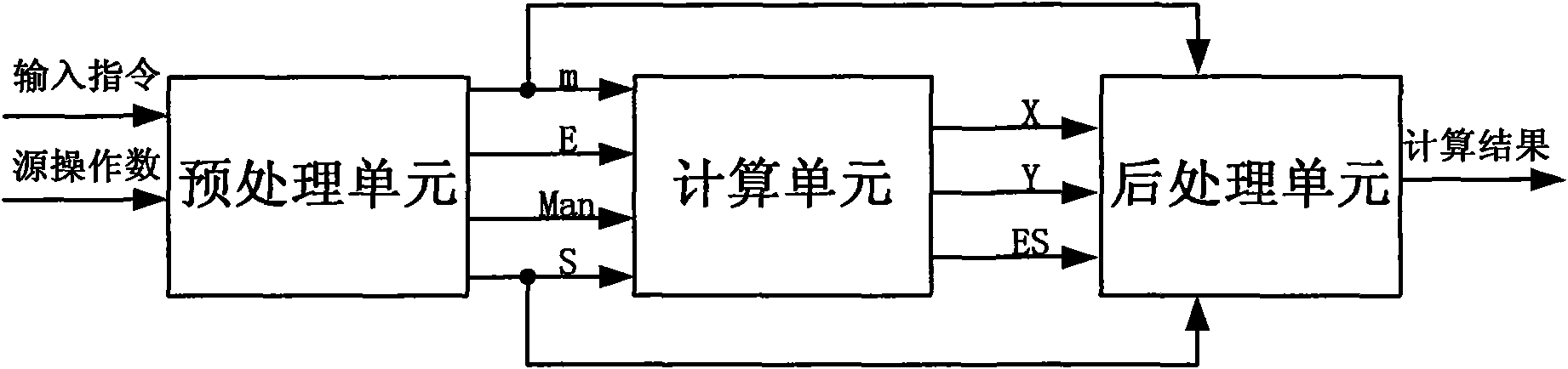
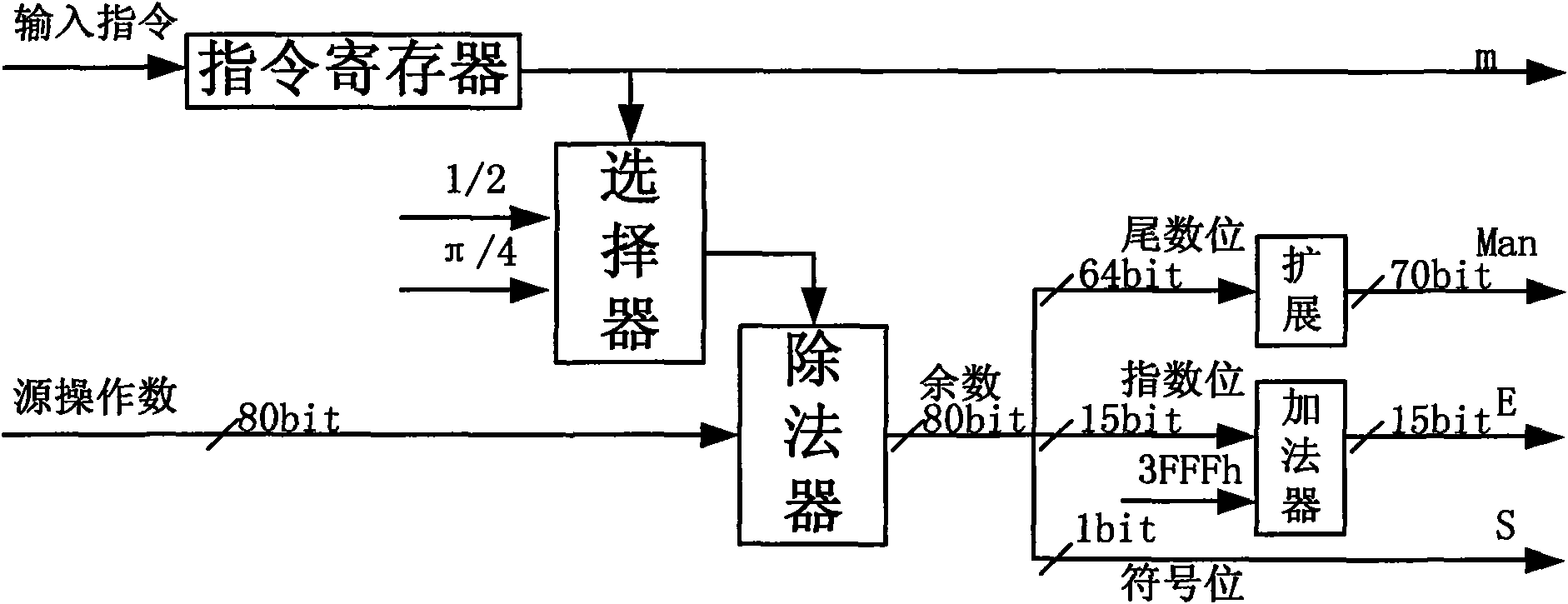
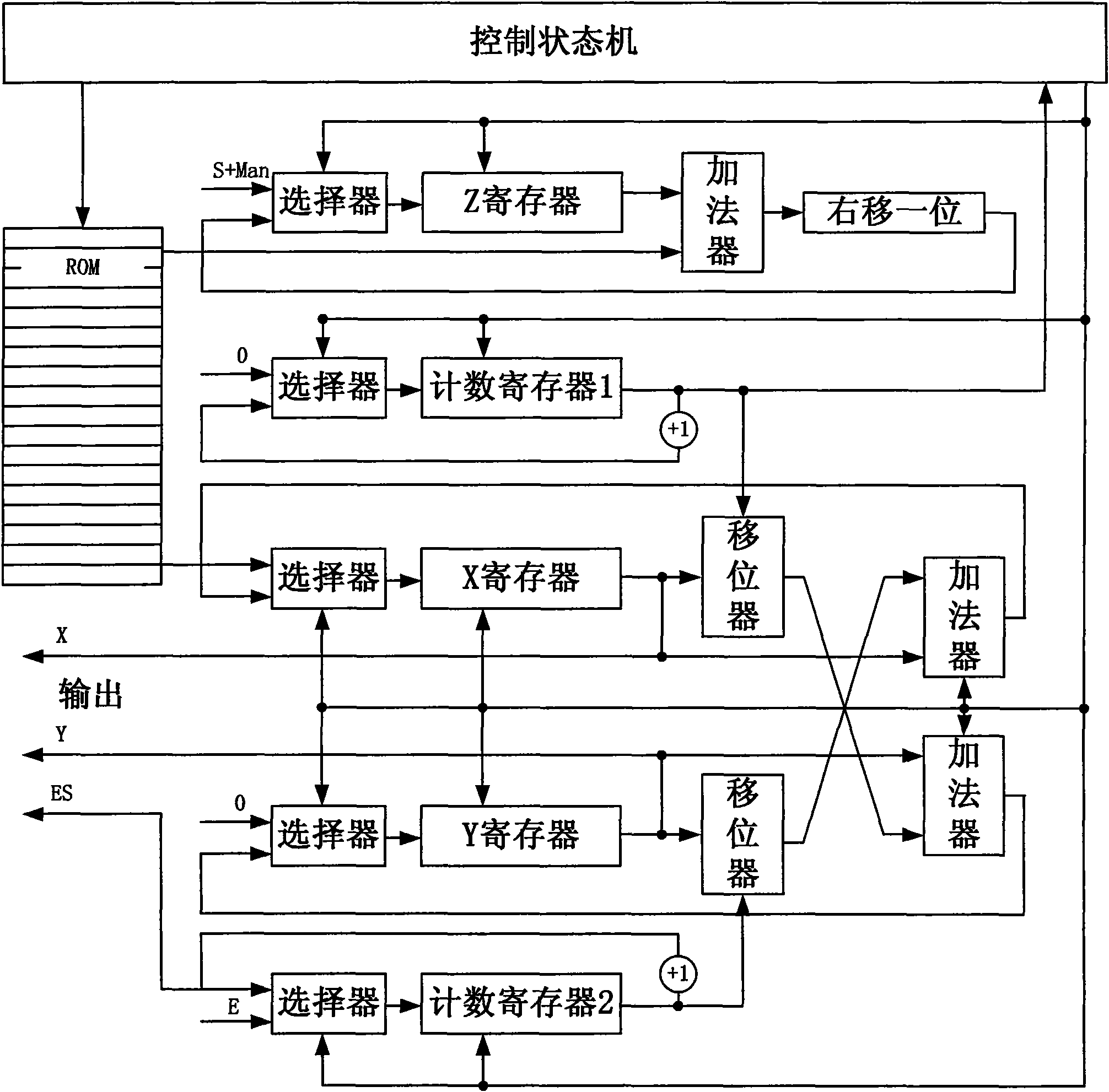
InactiveCN101630243AOvercoming processingOvercome precisionDigital data processing detailsCORDICHardware implementations
The invention discloses a transcendental function device and a method for realizing the transcendental function utilizing the same. The device comprises a preprocessing unit, a processing unit and a post-processing unit. The processing unit is composed of a counter register 1, a counter register 2, an X register and a processing passage thereof, a Y register and a processing passage thereof, a Z register and a processing passage thereof, and a control state machine. By utilizing an HPOR CORDIC device, one-one correspondence relation between indexes of a median generated in processing and a change of the counter is established, and the change of the counter register 2 represents the change of the indexes, therefore only a magnitude portion is processed to eliminate an index operation and mantissa match exponents in a floating decimal CORDIC. The device further overcomes shortcomings of large delay of the floating decimal CORDIC device and poor processing precision of a fixed point CORDIC device, and the realization price of hardware is much low.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) equalizer
InactiveUS20050157636A1Less expensiveMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexTransformerRectangular coordinates
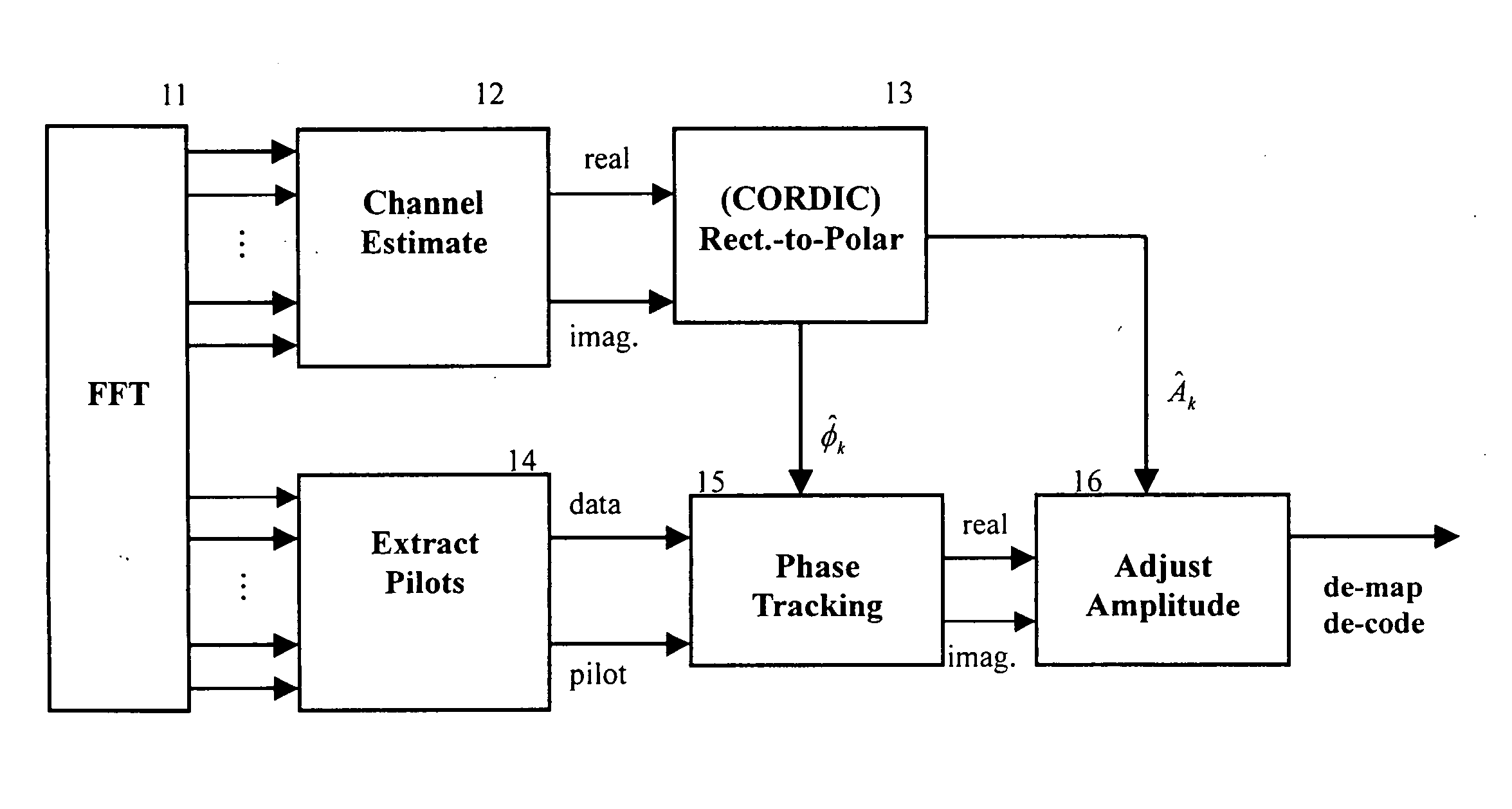
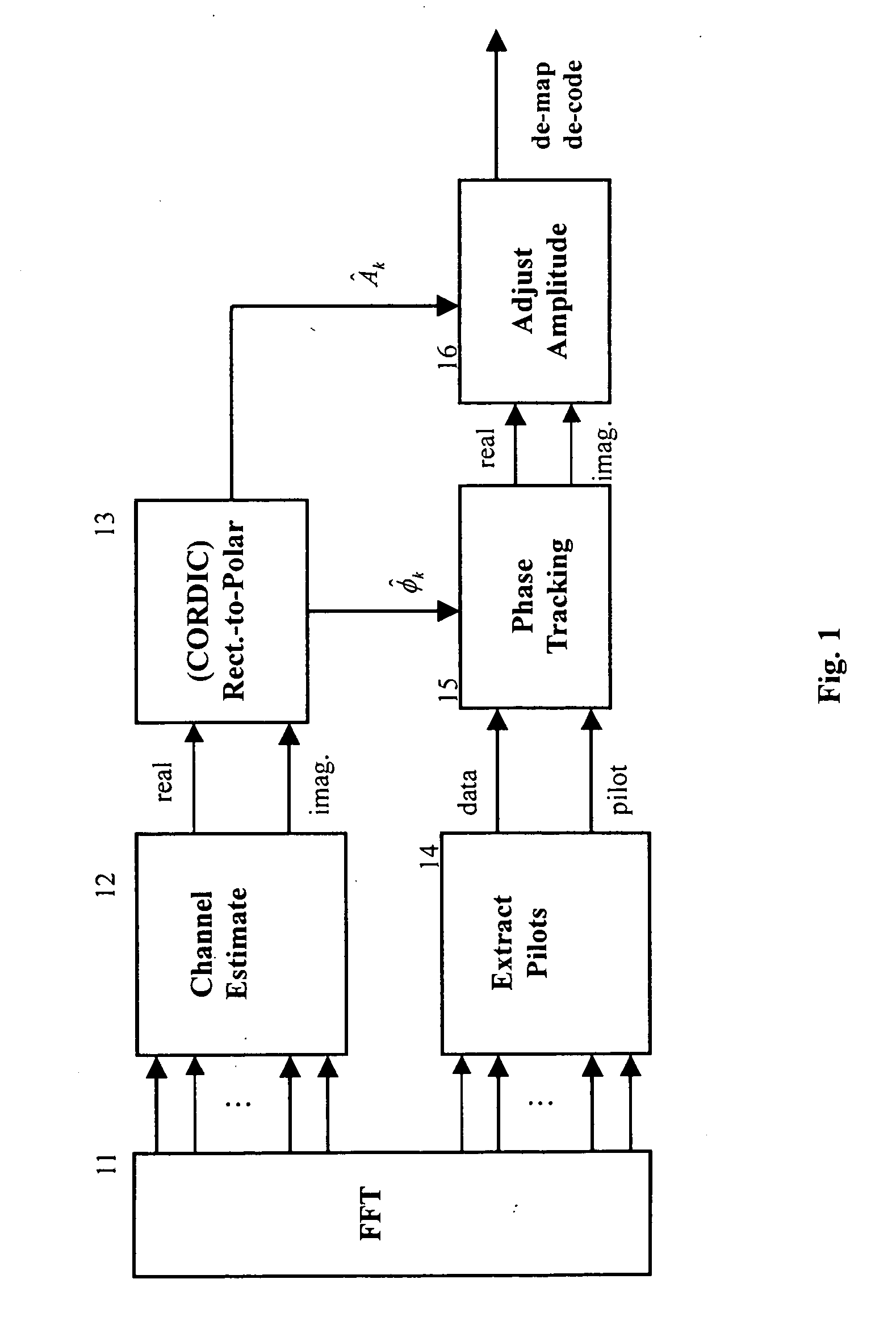
A novel and simplified orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) equalizer uses a coordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) to convert the estimated channel effects from rectangular coordinate to polar coordinate and to compensate the phase error with the same CORDIC circuit of synchronization. The OFDM equalizer comprises: a fast Fourier transformer (FFT), to conduct Fourier transformation to received signals to obtain samples of the received signals; a channel estimation circuit to estimate channel effects of a received signal as transformed by the FFT to generate a channel effect estimation value; a coordinate translator, comprising a CORDIC circuit, to translate the channel estimation value into a polar coordinate value; a pilot extractor, provided downstream to the FFT, to extract pilot signals and to track minor phase offsets of the received signal to synchronize phase of said received signal; a phase rotator to compensate phase of the received signal according to the channel estimation value and the phase tracking estimation value, to generate the real value and imaginary value of the phase compensated signal; and an amplitude adjustment circuit to adjust amplitude of the compensated signal according to the amplitude adjustment value of the channel effect estimation value of the channel estimation circuit. In the present invention, the coordinate translator and the phase rotator use the same CORDIC circuit.
Owner:KUEI ANN WEN
Method and system for reuse of CORDIC in an RF transceiver by reconfiguration in real time
InactiveUS20060093070A1Frequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverMegabit
Methods and systems for processing an RF signal are disclosed herein. Aspects of the method may comprise utilizing a single input CORDIC and a single output CORDIC for synchronizing and demodulating a received signal, wherein the received signal may comprise one or more bit rates. The received signal may comprise a one megabit per second (Mbps) signal. The single input CORDIC may be configured to operate in a rotating mode and the single output CORDIC may be configured to operate in a rotating mode and / or an arctangent (ARCTAN) mode. A rotated output of the single input CORDIC may be correlated with a phase shift keying (PSK) synchronization (sync) word and a portion of the correlated rotated output of the single input CORDIC may be buffered.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
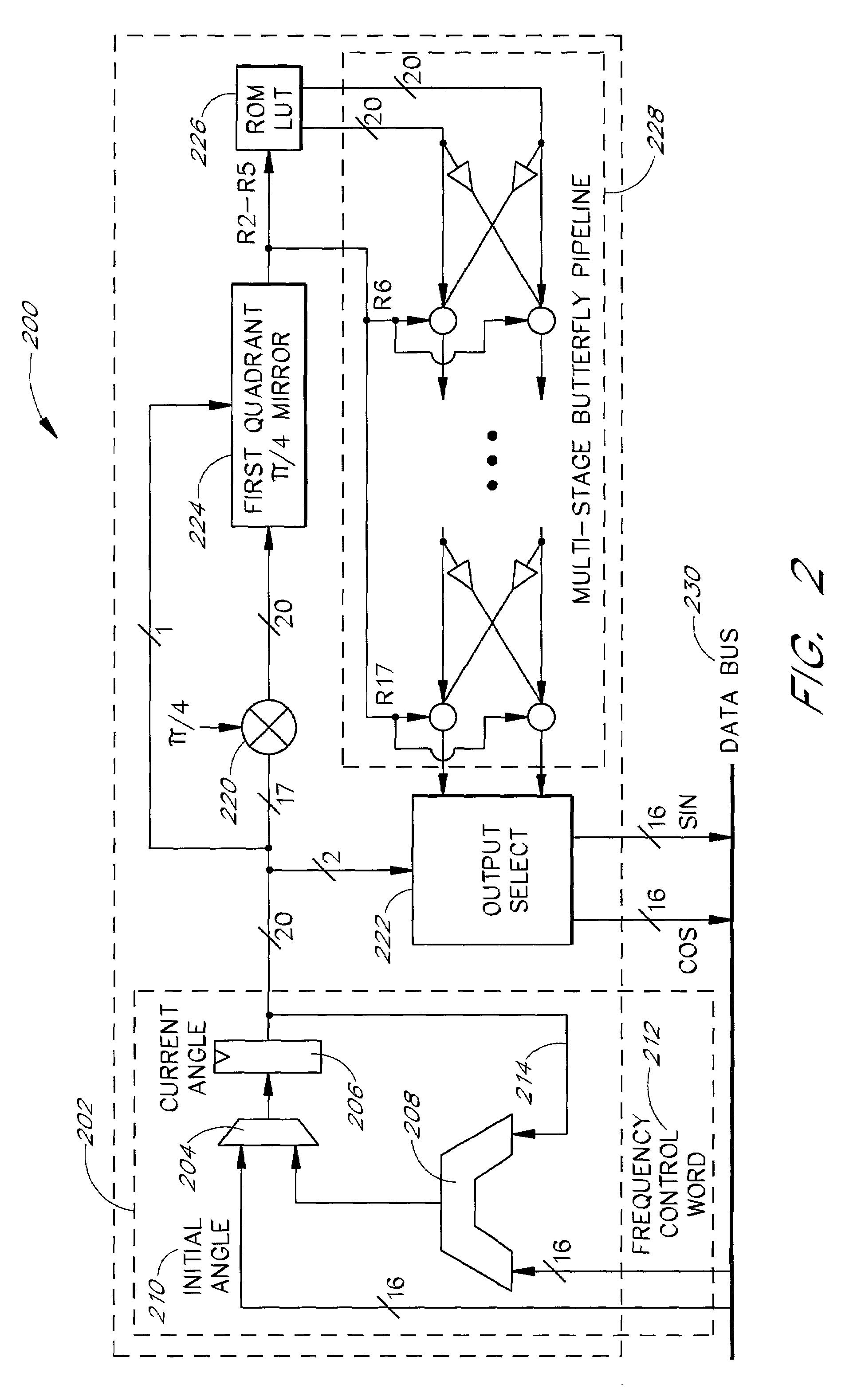
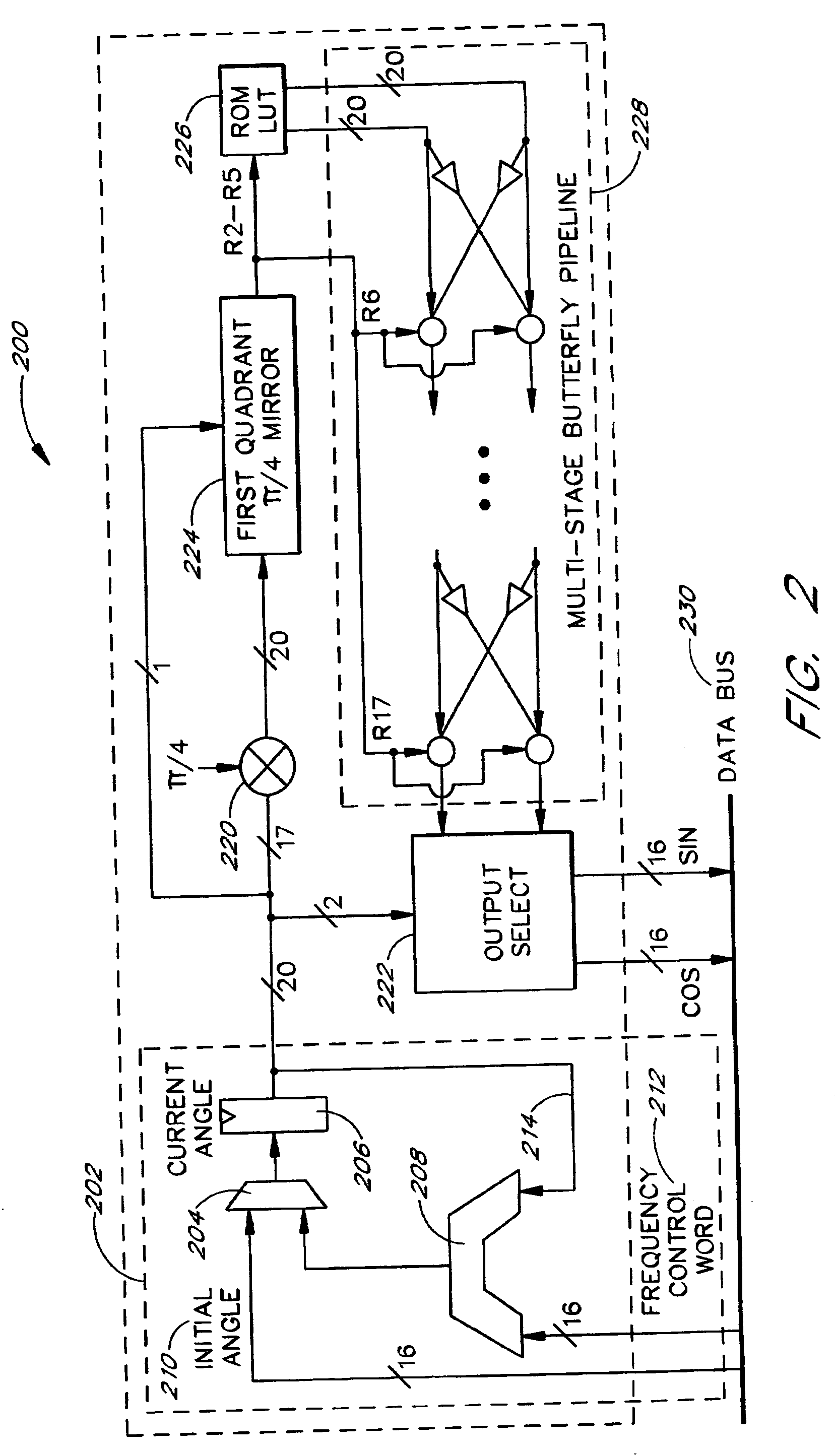
Implementation method of single-precision floating point trigonometric function covering full circumferential angle
InactiveCN103150137ASave logic resourcesIncrease working frequencyDigital data processing detailsDigital signal processingOriginal data
The invention discloses an implementation method of single-precision floating point trigonometric function covering full circumferential angle, and belongs to the field of processing of digital signal. The method comprises following steps: firstly, a preprocessing module CORDIC-PRE receives input single-precision floating point data, records the quadrant information of original data, converts the single-precision floating point data within a set angle range into high-precision floating point data, and inputs the high-precision floating point data to an iterative operation module CORDIC-CORE; secondly, the CORDIC-CORE finishes iterative operation of the CORDIC algorithm to the input data by adopting high-precision floating point operation; the result is input to a postprocessing module CORDIC-POST; thirdly, the CORDIC-POST performs quadrant recovery to sine and cosine functional values to be required to be calculated as per the quadrant information recorded in the CORDIC-PRE aiming to the input data; and the data after being recovered is converted into the precision floating point data and output. The implementation method is suitable for actual operation of CORDIC algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Trigonometric function CORDIC iteration operation coprocessor and operation processing method thereof
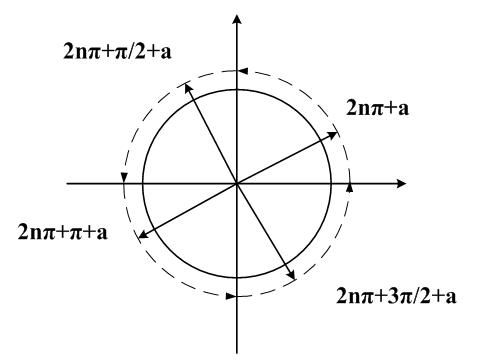
The invention relates to a trigonometric function coordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) iteration operation coprocessor. The coprocessor comprises a CORDIC iteration operation unit, an operation result output unit and an angle range conversion unit, wherein the CORDIC iteration operation unit performs CORDIC iteration operation according to an input angle and outputs an operation result to the operation result output unit; the angle range conversion unit divides the input angle by pi / 2 in the CORDIC iteration operation unit to obtain a quotient and decomposes the quotient into an m part, an n part and a p part; the quotient is 4*m+n+p, m and n are integers, n is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 3, and p is a floating-point number of less than 1; and the CORDIC iteration operation unit performs CORDIC trigonometric function iteration operation on the value of p*pi / 2. Through the technical scheme, the trigonometric function CORDIC iteration operation coprocessor supports full-angle trigonometric function operation and has higher operation efficiency.
Owner:TECHTOTOP MICROELECTRONICS
Multi-Channel Timing Recovery System
ActiveUS20090257540A1Minimum phase jitter noiseModulated-carrier systemsGeneral purpose stored program computerJitter noiseCORDIC
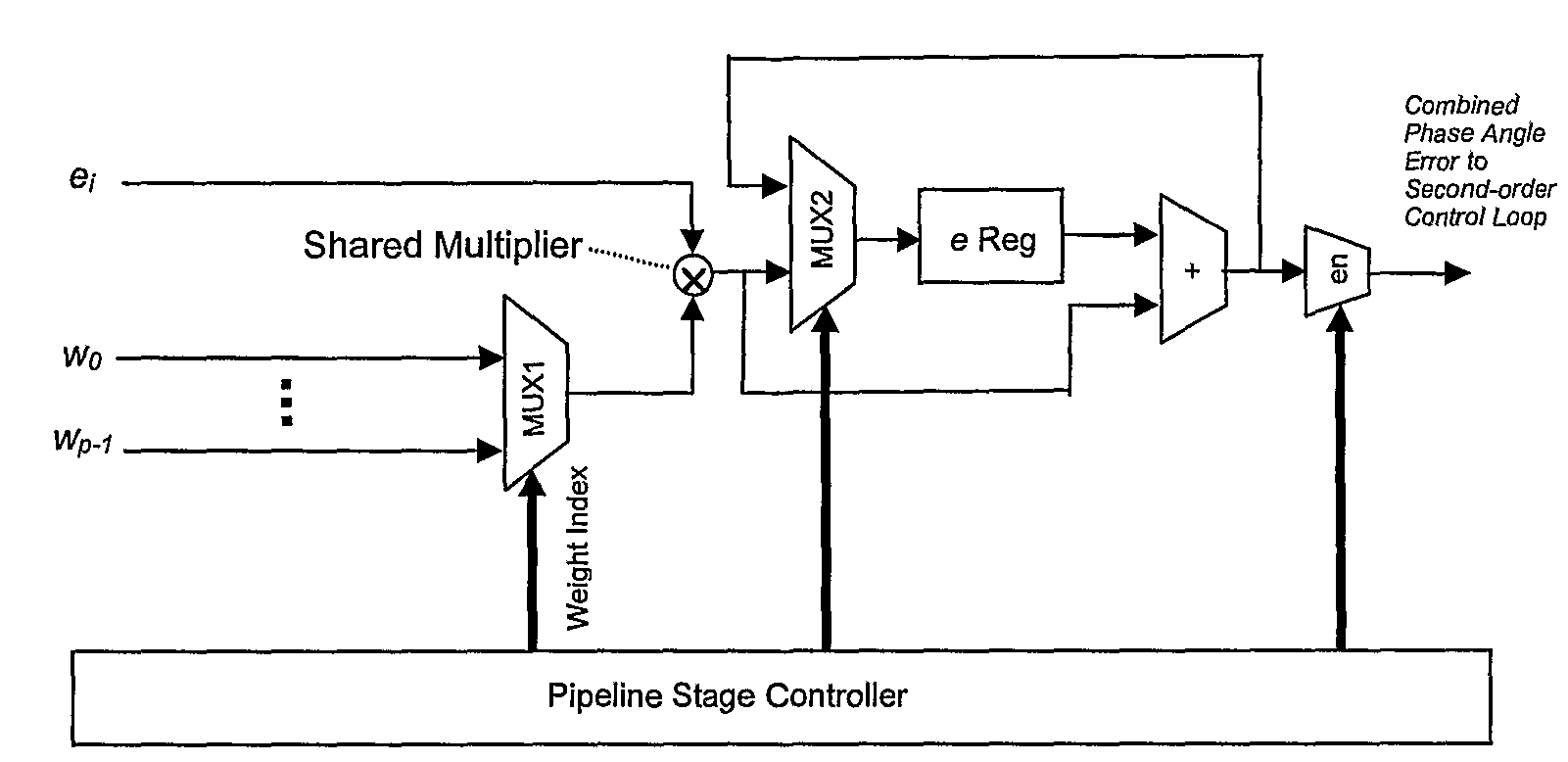
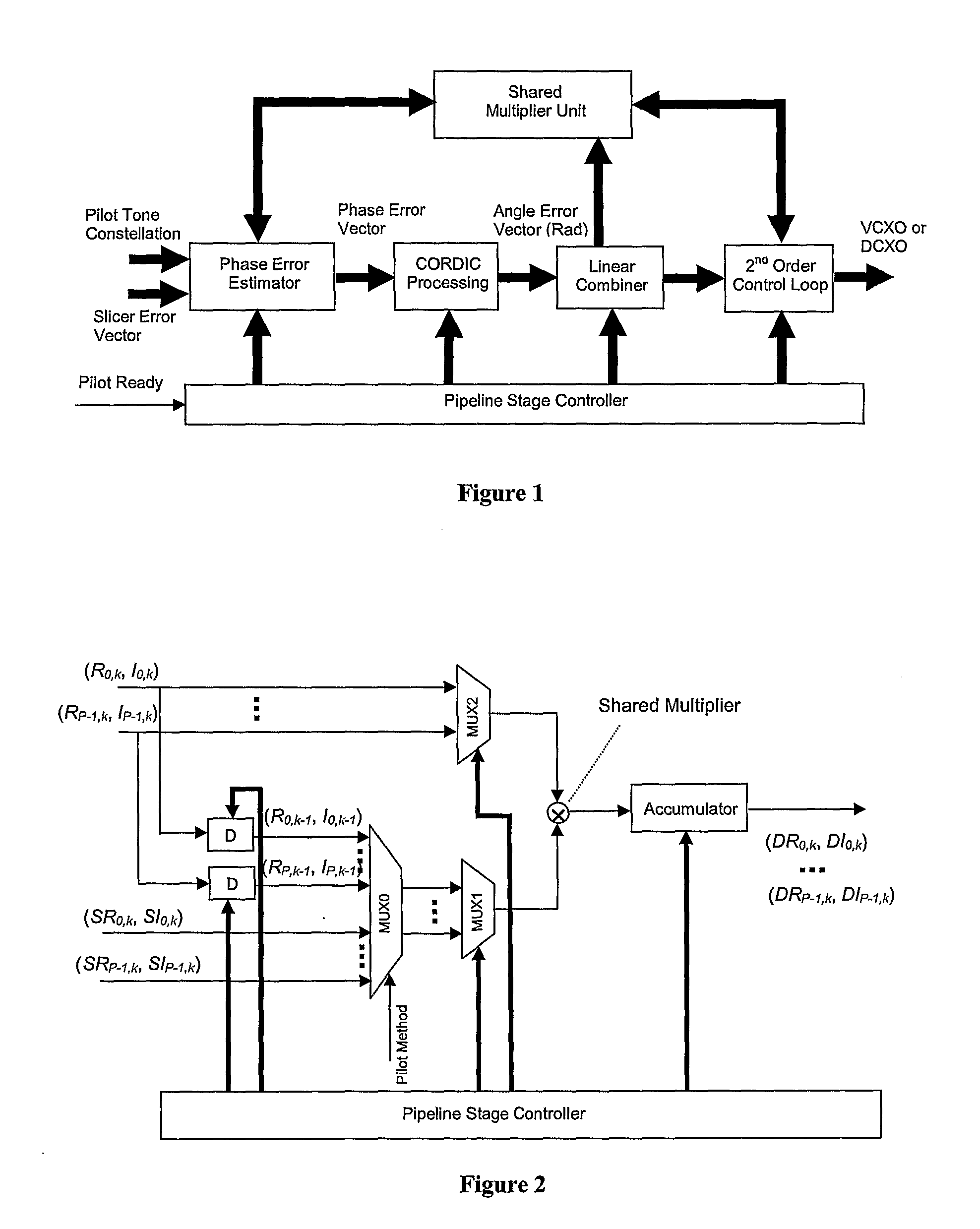
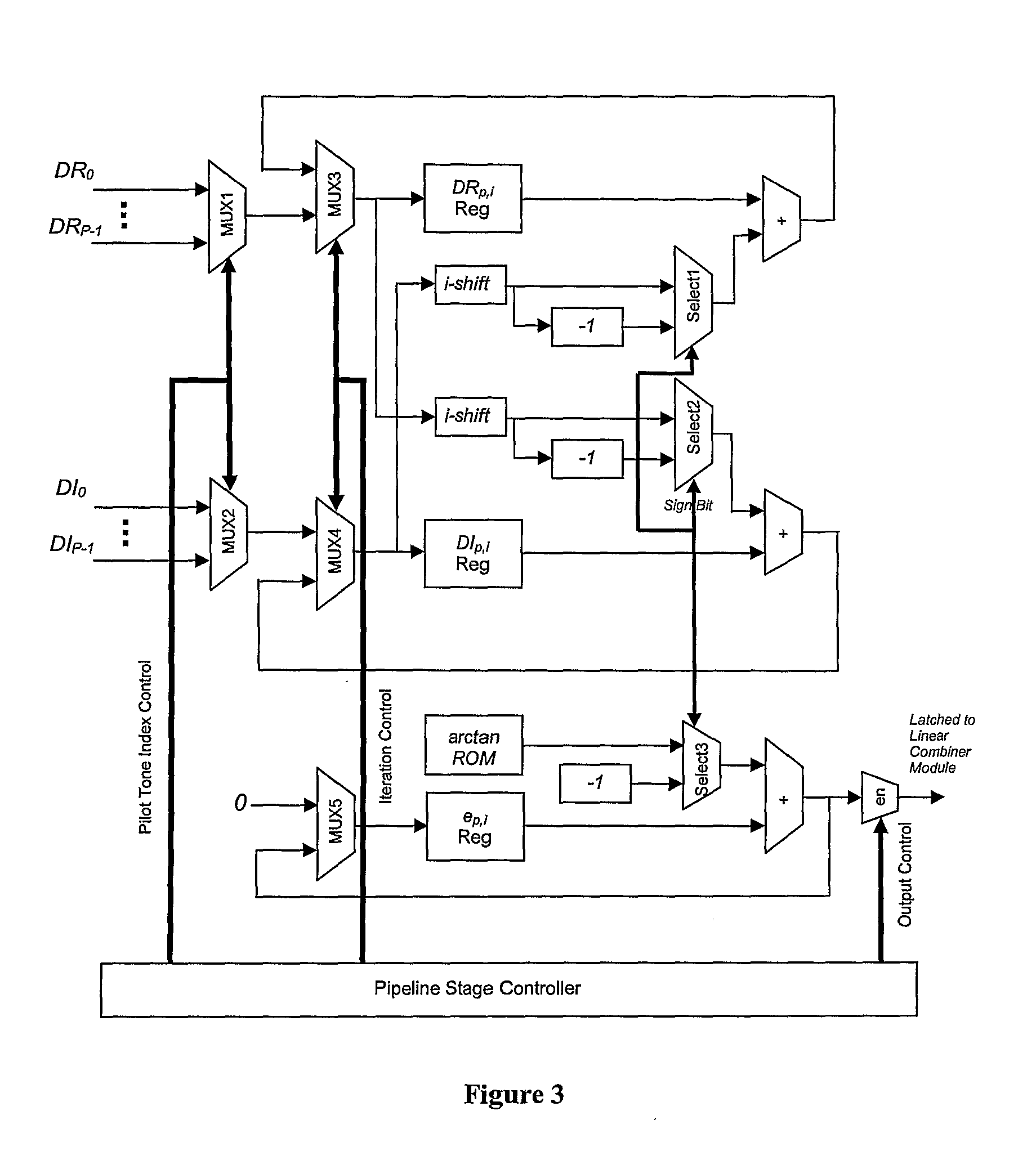
The present invention discloses a novel multi-channel timing recovery scheme that utilizes a shared CORDIC to accurately compute the phase for each tone. Then a hardware-based linear combiner module is used to reconstruct the best phase estimate from multiple phase measurements. The firmware monitors the noise variance for the pilot tones and determines the corresponding weight for each tone to ensure that the minimum phase jitter noise is achieved through the linear combiner. Then a hardware-based second-order timing recovery control loop generates the frequency reference signal for VCXO or DCXO. A single sequentially controlled multiplier is used for all multiplications in the control loop.
Owner:TRIDUCTOR TECH SUZHOU
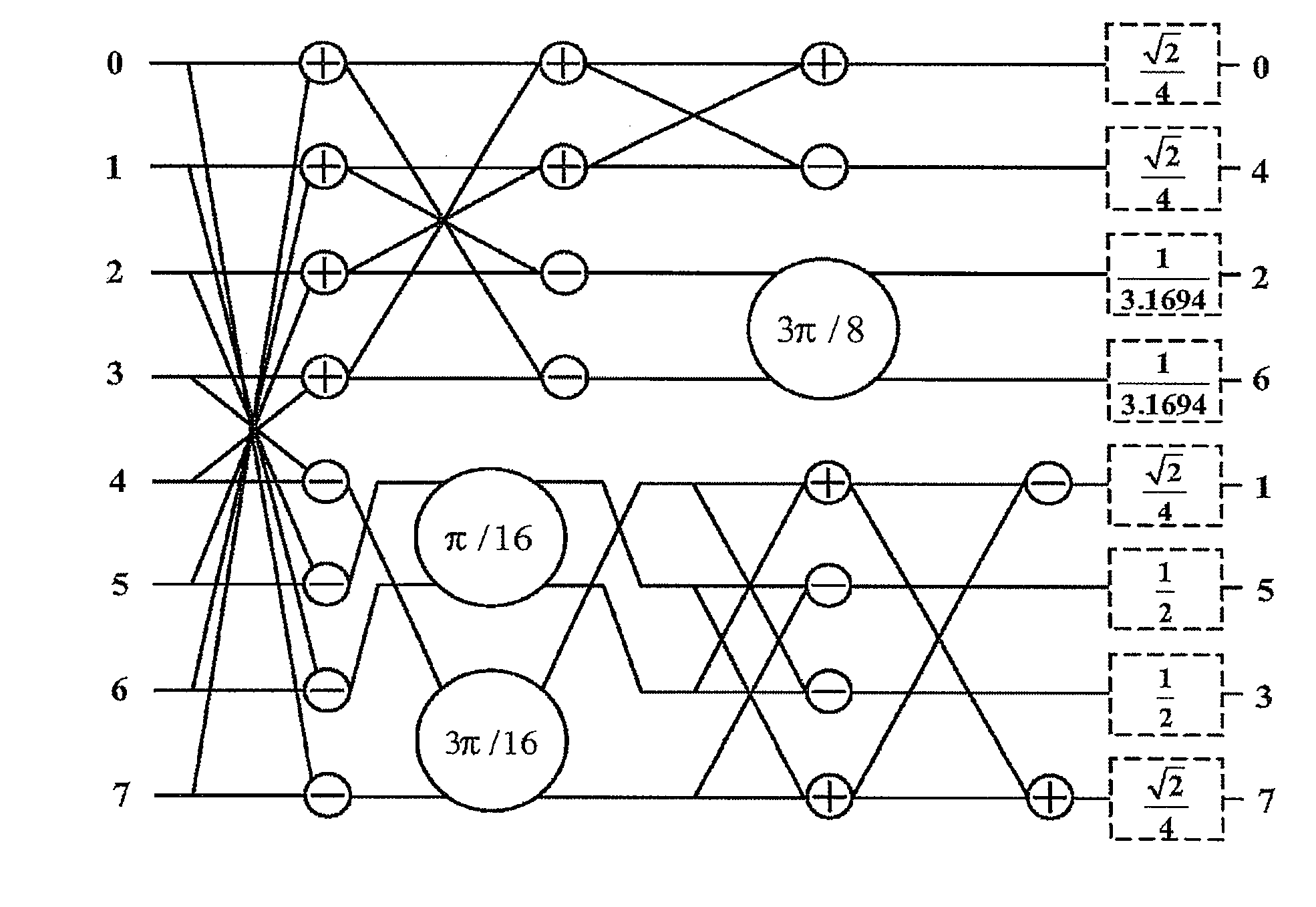
Full-pipeline floating-point trigonometric function device based on combination of CORDIC and Taylor
ActiveCN106202890AReduce power consumptionLower latencySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsCORDICLow delay
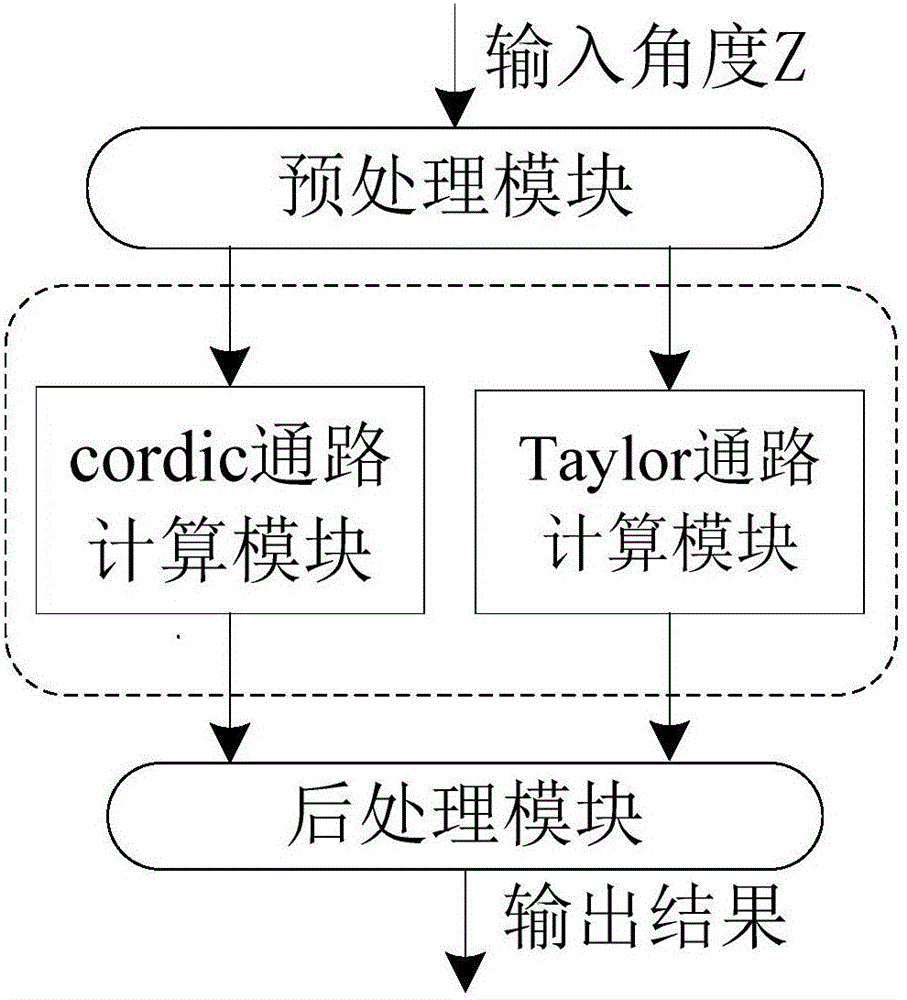
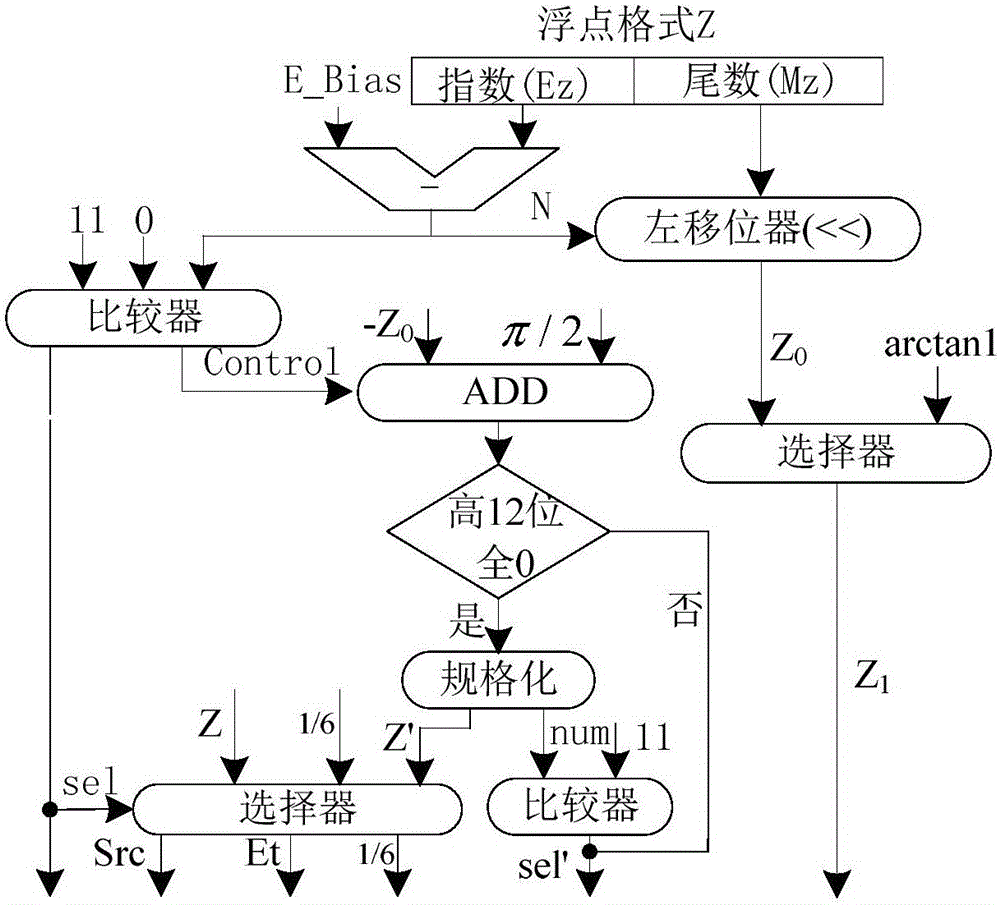
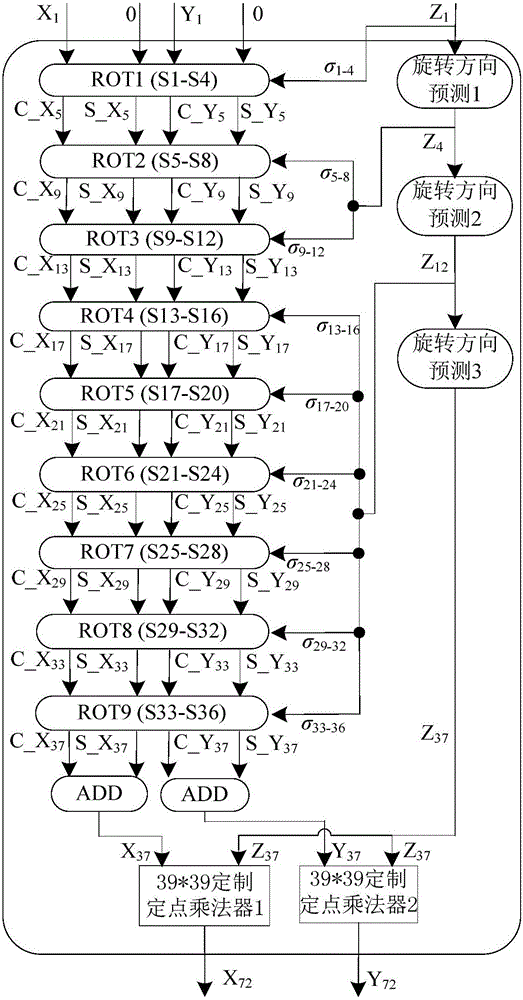
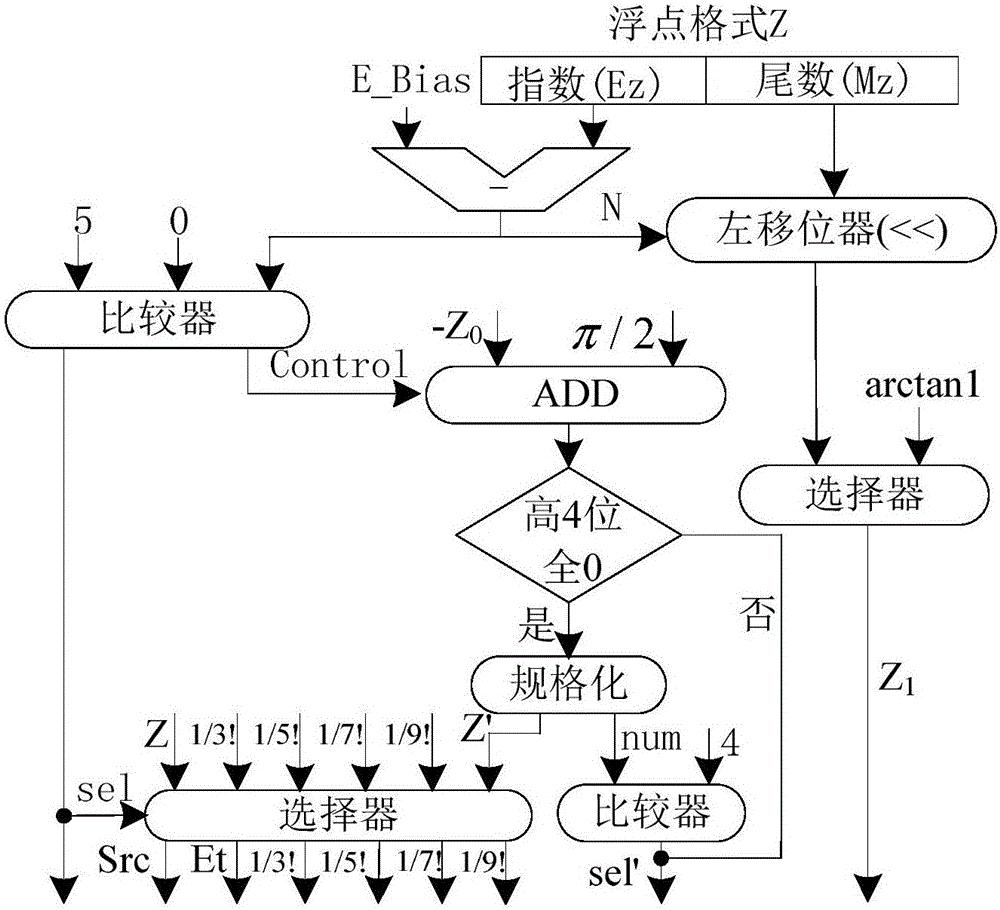
The invention discloses a full-pipeline floating-point trigonometric function device based on combination of CORDIC and Taylor algorithms. The device comprises a preprocessing module which is used for judging whether a taylor expansion algorithm is started or not according to an input angle Z and converting the input angle Z from a double-precision floating-point format into a fixed-point format; a cordic algorithm calculation path module which is used for finishing calculating sine and cosine results of the input angle Z, wherein when N is smaller than 13, obtained results are precise results and are output; a taylor algorithm calculation path module which is used for finishing calculating sine or cosine of the input angle Z, wherein only when the N is greater than or equal to 13, the taylor algorithm is selectively started; and a postprocessing module which is used for carrying out normalization processing on calculation results of the cordic algorithm and selectively outputting the sine and cosine calculation results. The device has the advantages of low delay, low error and full pipeline.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Low-overhead iteration triangular function device based on T_CORDIC (Coordinated Rotation Digital Computer) algorithm
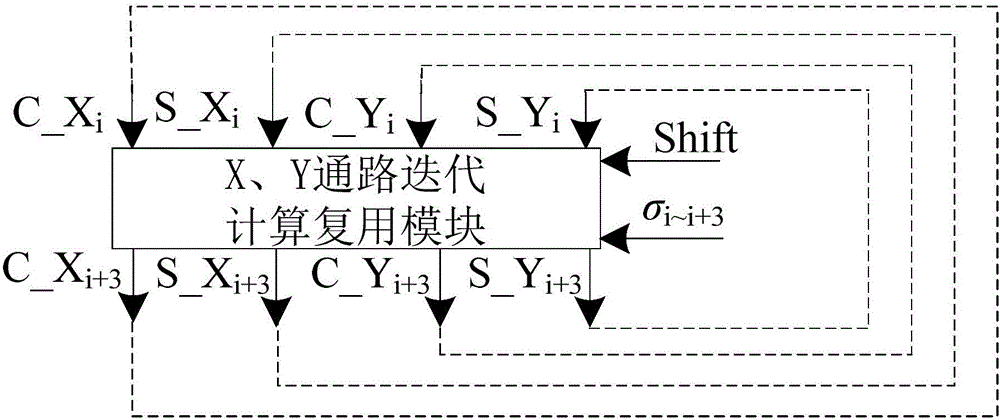
ActiveCN106155627AGuaranteed calculation accuracyGuaranteed reuseDigital data processing detailsMultiplexingTriangular function
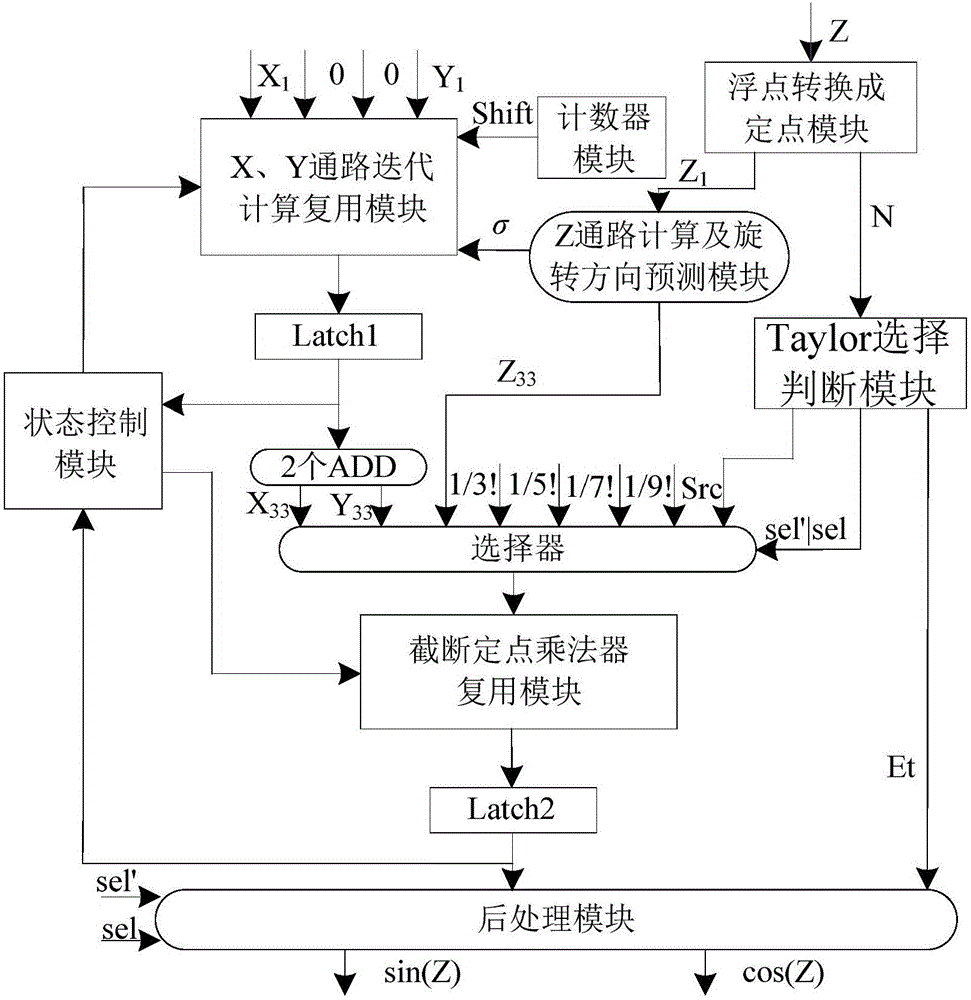
The invention provides a low-overhead iteration triangular function device based on a T_CORDIC (Coordinated Rotation Digital Computer) algorithm. The low-overhead iteration triangular function device comprises a pre-processing module, a rotary direction predication module, a CORDIC algorithm compressive iteration multiplexing module, a cut-off fixed-point multiplier multiplexing module, a state control module and a post-processing module, wherein the pre-processing module is used for finishing conversion of an input angle from a floating point format to a fixed point format of IEEE-754 standards and judging whether a Taylor algorithm is started or not; the rotary direction predication module is used for providing sign prediction on compressive iteration in the CORDIC algorithm and providing a multiplicator for parallel computing; the CORDIC algorithm compressive iteration multiplexing module is used for finishing calculation of front n / 2 times of compressive iteration in the CORDIC algorithm; the cut-off fixed-point multiplier multiplexing module is used for finishing the calculation of a Taylor expansion equation in the former period and finishing the calculation of parallel iteration in the CORDIC algorithm; the state control module is used for coordinating the multiplexing of the CORDIC algorithm compressive iteration multiplexing module and the cut-off fixed-point multiplier multiplexing module; and the post-processing module is used for selecting result output of a triangular function according to a result signal judged by the pre-processing module and converting the result to the floating point format of the IEEE-754 standards from a fixed point. The low-overhead iteration triangular function device based on the T_CORDIC algorithm has the advantages of simple principle, low delay, low errors, low overhead and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
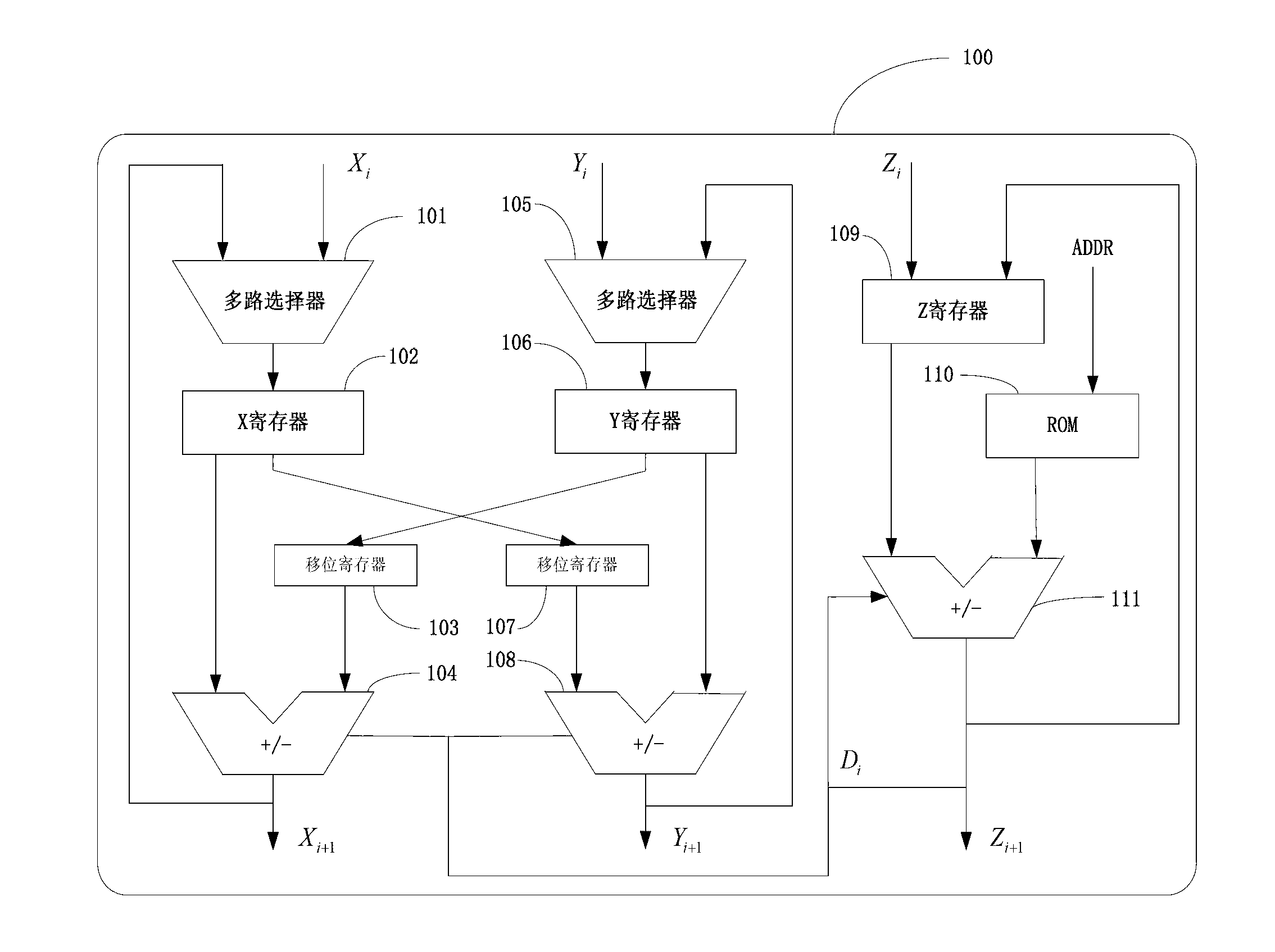
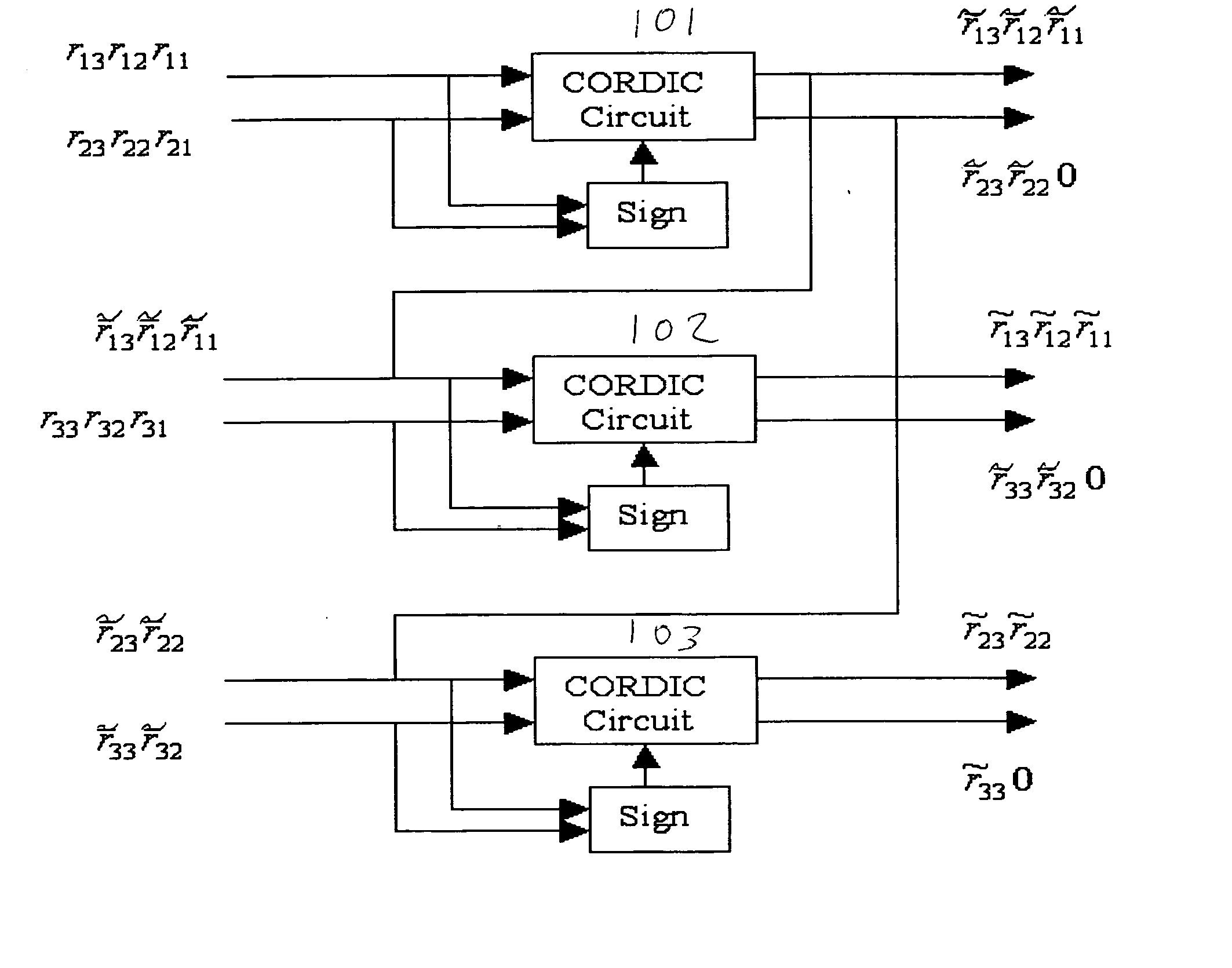
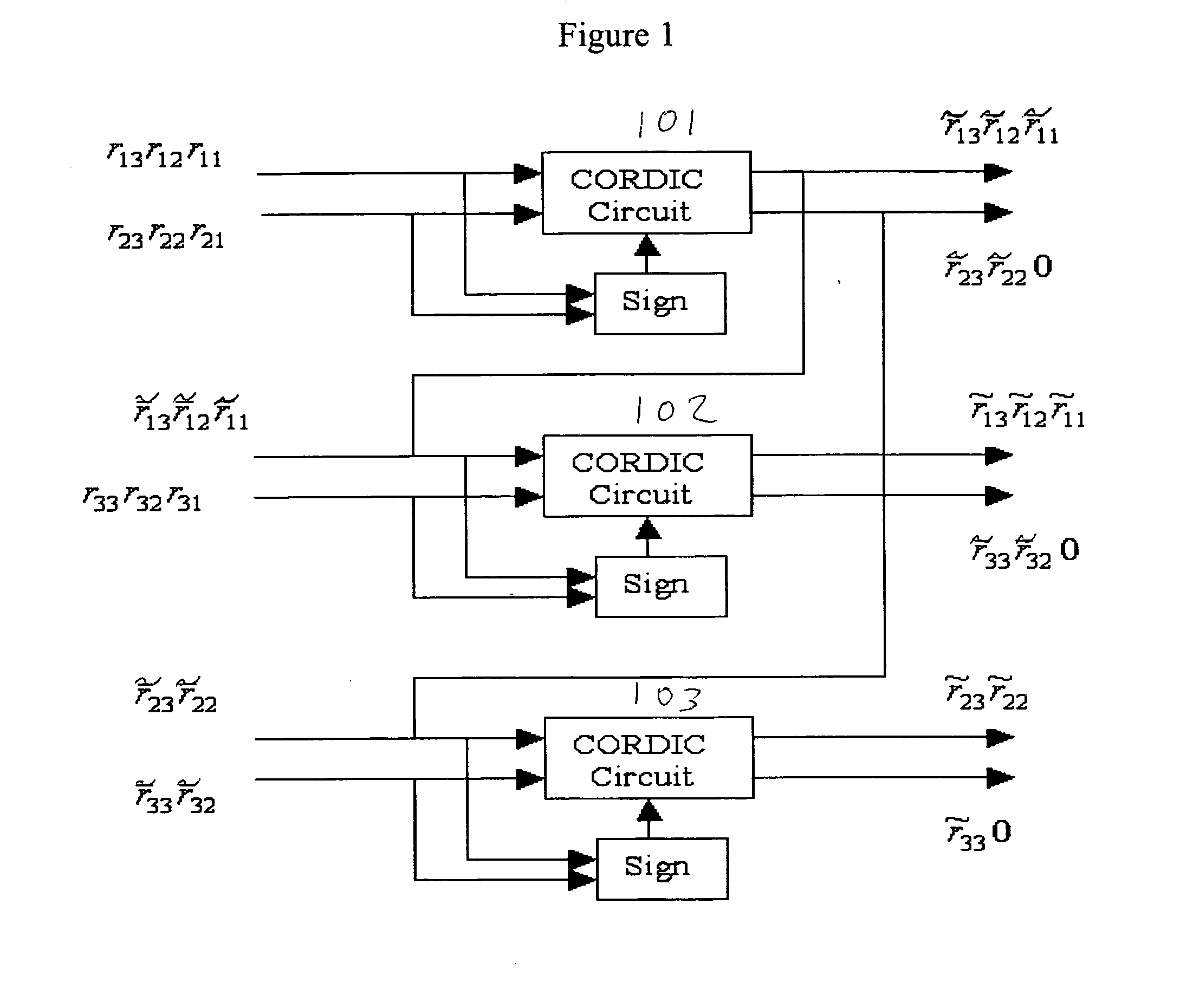
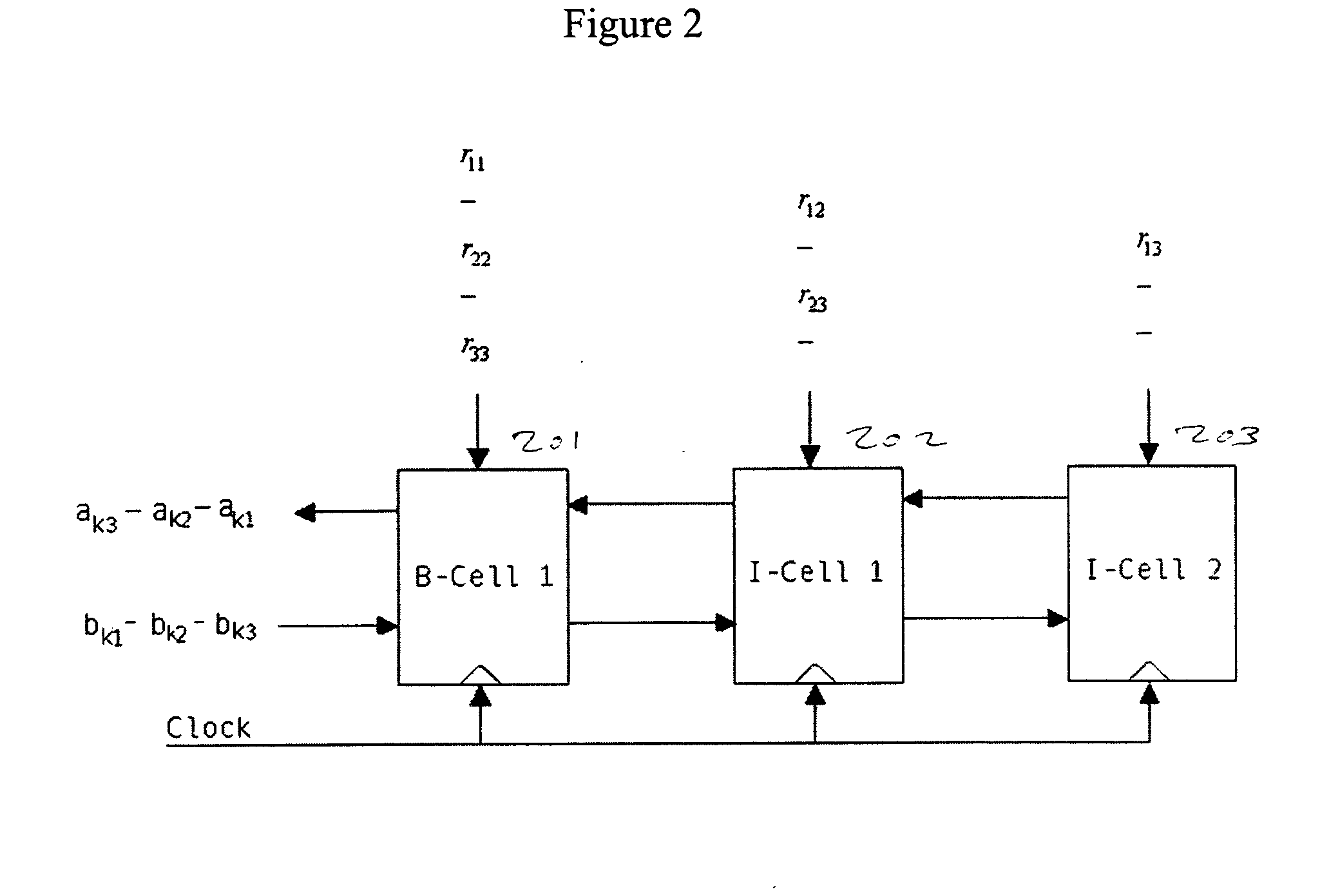
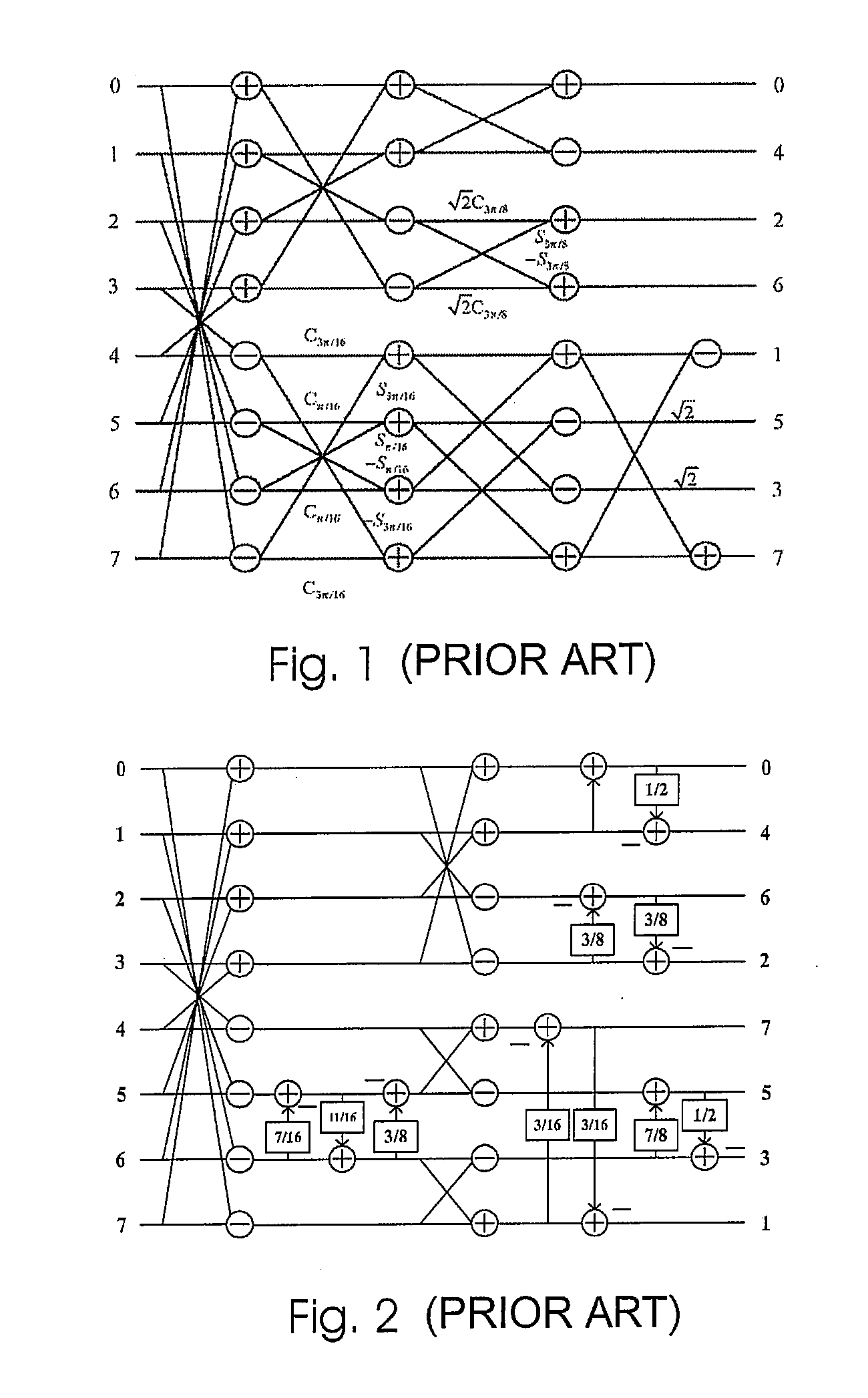
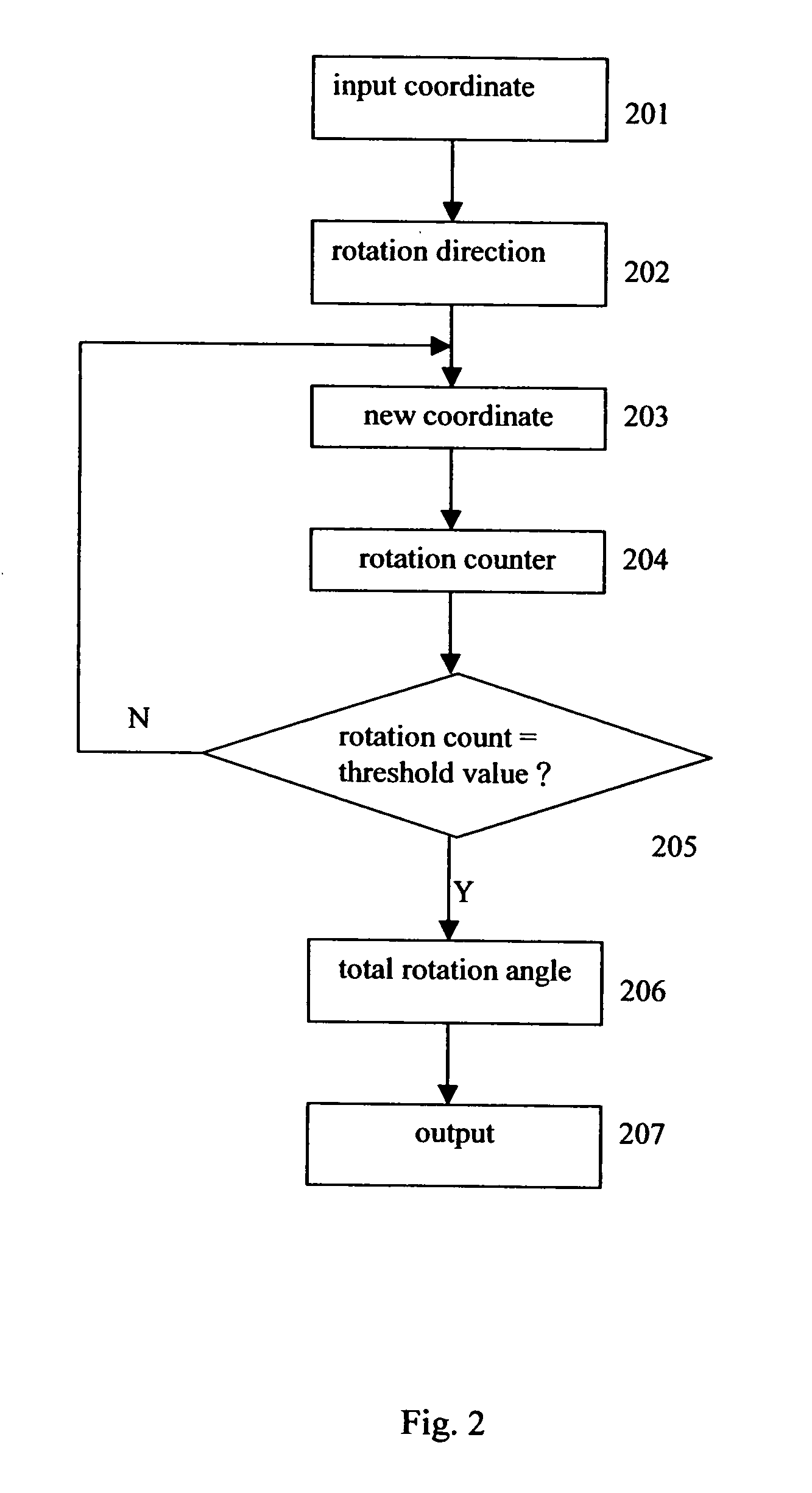
Novel CORDIC circuit
InactiveUS20050216540A1Simplify CORDIC operationHigh speedDigital data processing detailsGeometric image transformationComputer hardwareHemt circuits
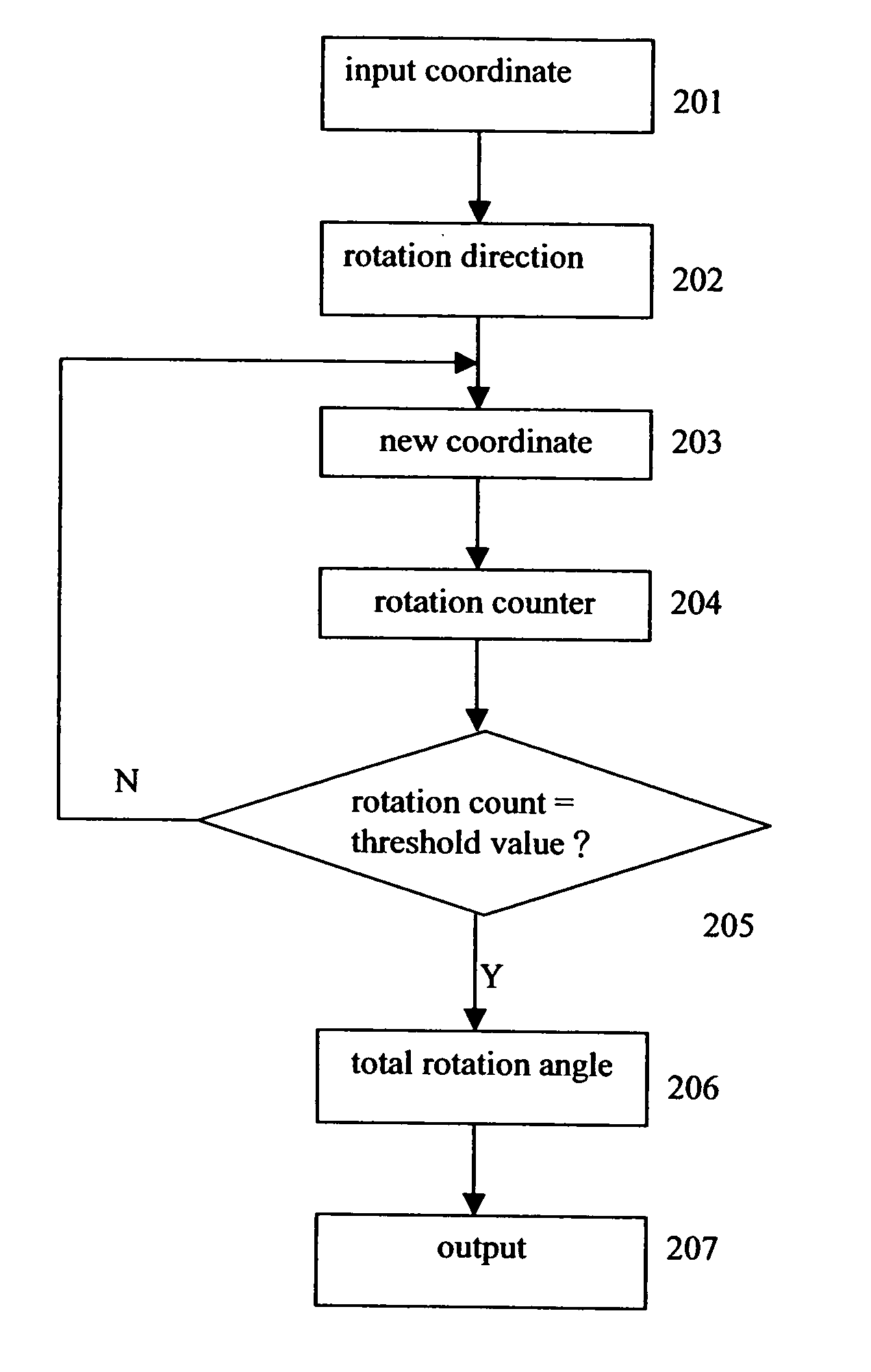
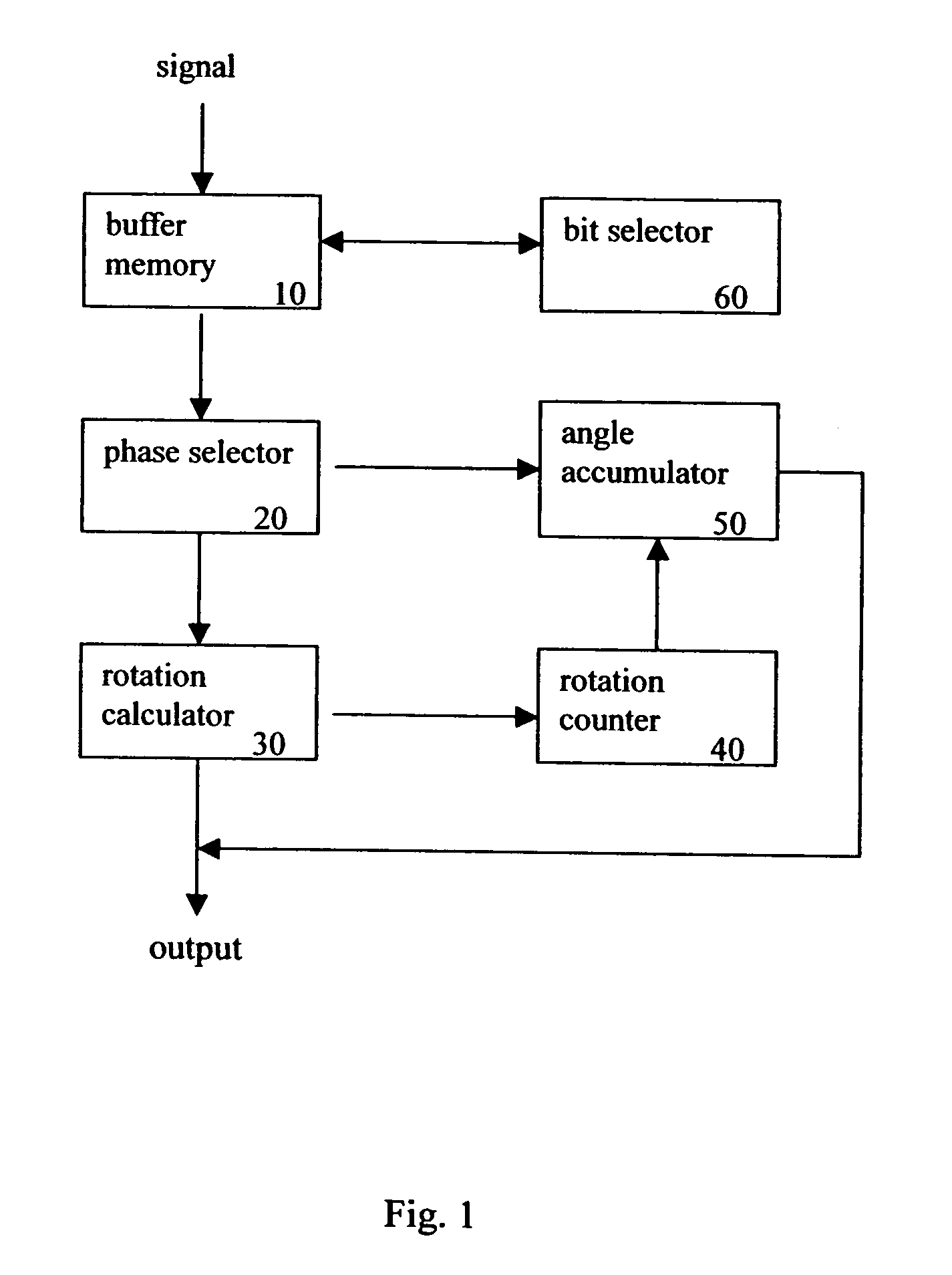
The CORDIC circuit of this invention comprises a buffer memory to record a plurality or a plurality of group of coordinate values; a phase selector to determine a rotation direction according to values recorded in said buffer memory; a rotation calculator to rotate an input coordinate for a predetermined angle and to calculate resulting coordinate value after such rotation; a rotation counter to count number of rotation being made to said input coordinate; and an angle accumulator to accumulate total rotation angle being made to said input coordinate according to value recorded by said rotation counter. The CORDIC circuit of this invention may further comprise a bit selector to shift bits of said input coordinate.
Owner:KUEI ANN WEN
Real-time implementation of field programmable gate arrays (FPGA) design in hyperspectral imaging
A Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA) design uses a Coordinate Rotation DIgital Computer (CORDIC) algorithm that can convert a Givens rotation of a vector to a set of shift-add operations. The CORDIC algorithm can be easily implemented in hardware architecture, therefore in FPGA. Since the computation of the inverse of the data correlation matrix involves a series of Givens rotations, the utility of the CORDIC algorithm allows a causal Constrained Energy Minimization (CEM) to perform real-time processing in FPGA. An FPGA implementation of the causal CEM is described and its detailed architecture is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
CORDIC algorithm-based capacitive micro-accelerometer signal detection device
InactiveCN101738495AOvercome the shortcomings of being susceptible to environmental factors such as temperatureSuppress low frequency noiseAcceleration measurementBandpass filteringDigital down converter
The invention discloses a CORDIC algorithm-based capacitive micro-accelerometer signal detection device. The device comprises a capacitive micro-accelerometer sensor, a charge amplifying module, an analogue-to-digital converter, a field programmable gate array, a first digital-to-analogue converter, an analogue bandpass filter and a second digital-to-analogue converter, wherein the capacitive micro-accelerometer sensor, the charge amplifying module, the analogue-to-digital converter, the field programmable gate array, the first digital-to-analogue converter and the analogue bandpass filter are orderly connected; and the field programmable gate array is also connected with the second digital-to-analogue converter. The CORDIC algorithm-based capacitive micro-accelerometer signal detection device can regulate the phase, the frequency, the amplitude and the like of carrier signals in real time so as to achieve good flexibility, adopts high-frequency carrier modulation to suppress low-frequency noise, such as l / f noise and the like, adopts a digital modulation mode to overcome the defect that an analogue system is easy to be influenced by environmental factors, such as temperature and the like, and can control algorithm accuracy through iteration times and a data word size.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Arithmetical logic circuit and operation method thereof
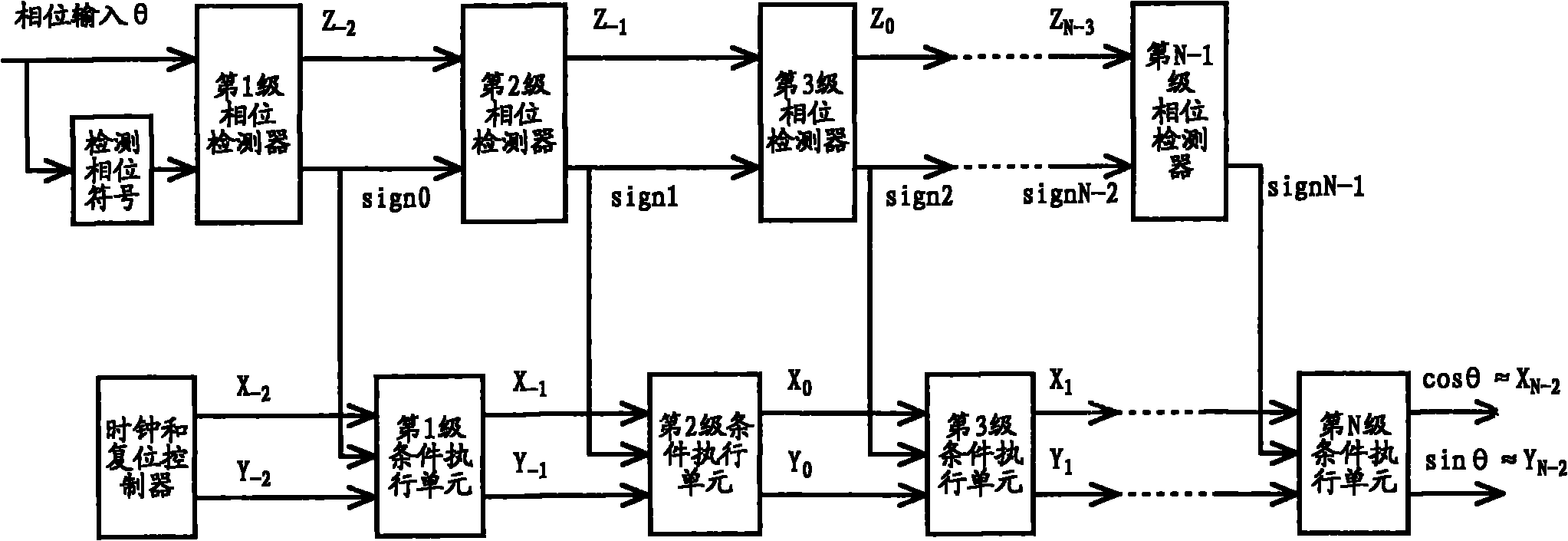
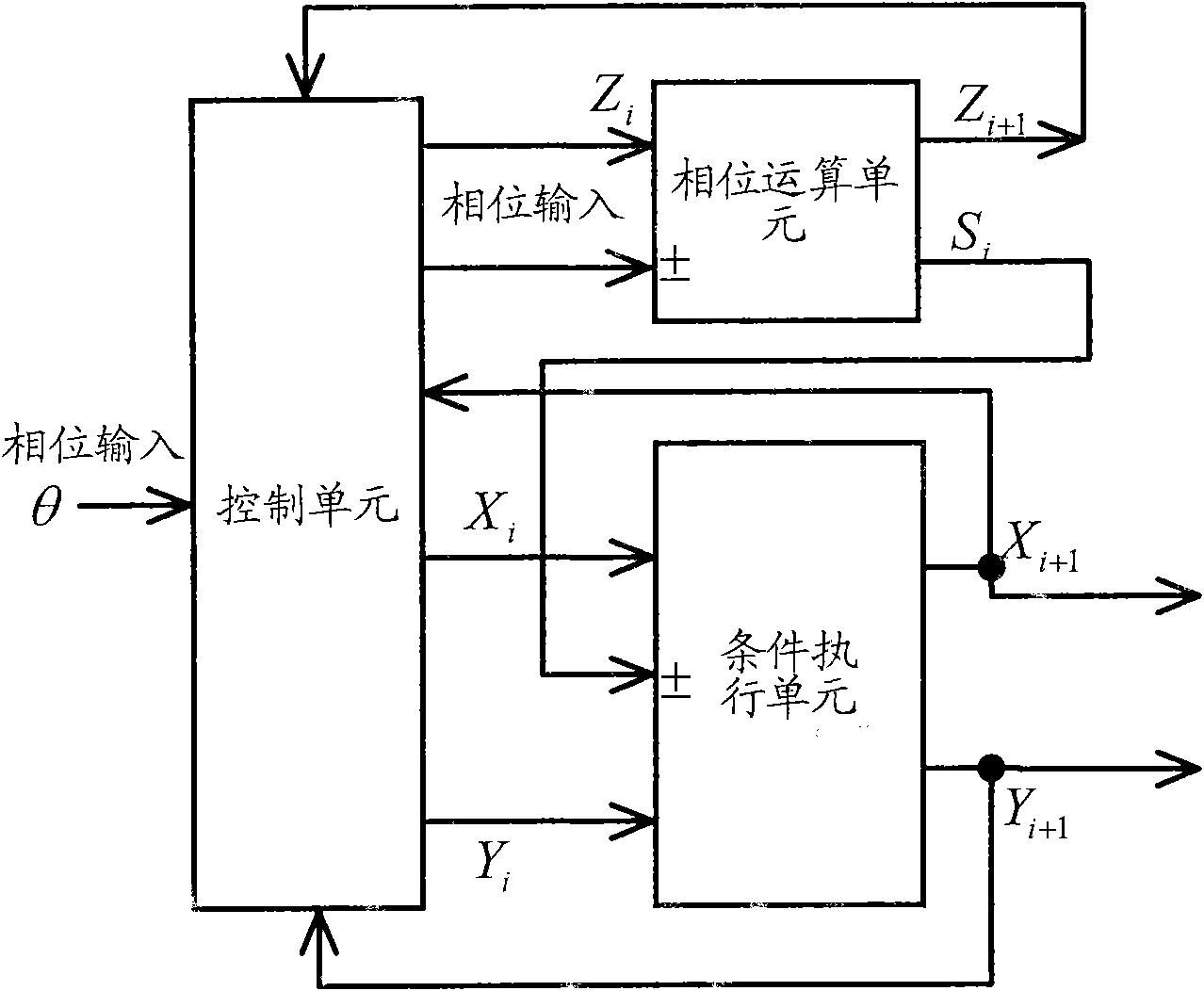
ActiveCN101997533AReduce areaImprove conditions for iteration terminationReliability increasing modificationsSpeech analysisSerializationExecution unit
The invention relates to the field of integrated circuit chips, and discloses an arithmetical logic circuit and an operation method thereof. Through the serialization design of a phase operation unit and a condition execution unit, the integrated circuit area of a coordinated rotation digital computer (CORDIC) structure for calculating a sine value and a cosine value is reduced; a serial multiplication and division circuit and a CORDIC circuit are multiplexed, so that the integrated circuit area is further reduced; in addition, the iteration termination condition in the circuit is improved, so that the operation speed is increased.
Owner:ACTIONS ZHUHAI TECH CO
Extensible QR decomposition method based on pipeline working mode
The invention provides an extensible QR decomposition method based on a pipeline working mode. A layered and cascaded structure is adopted, wherein pipeline operation is realized among layers; two lines of matrix data of each layer are subject to Givens rotation; the Givens rotation is conducted by using a coordinate rotation digital computer (CORDIC) algorithm and realized by using operations of addition and displacement; the layer number is determined by the line number or the row number of matrices; a whole QR decomposition module consists of a controller and a data processing module; a line rotation module is arranged on each layer of the data processing module; output ports of upper layers of line rotation modules are connected with input ports of lower layers of line rotation modules; the matrix data to be composed are input from an input port of the first layer of line rotation module, and sequentially flow through all the line rotation modules; and all the line rotation modules work in parallel. The scalable QR decomposition method has the advantages that hardware resources are saved; and as the iterative process of the CORDIC algorithm is split at the inner part of each layer of the data processing module, a pipeline structure is formed, the rotation operation of multiple vector groups is processed in a time sharing manner, the throughput rate is increased, and the extension is flexible.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Channel simulator and modeling method thereof
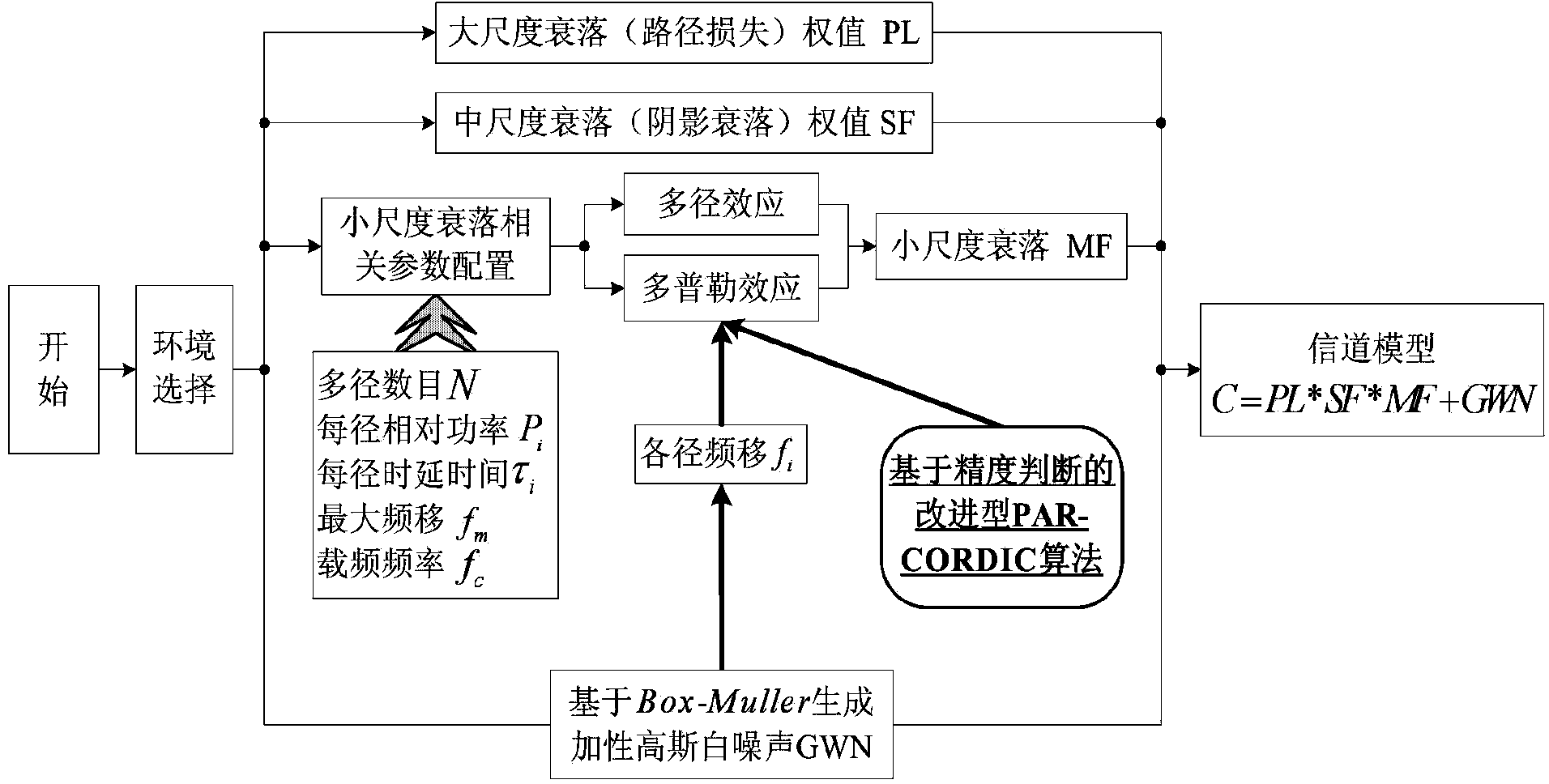
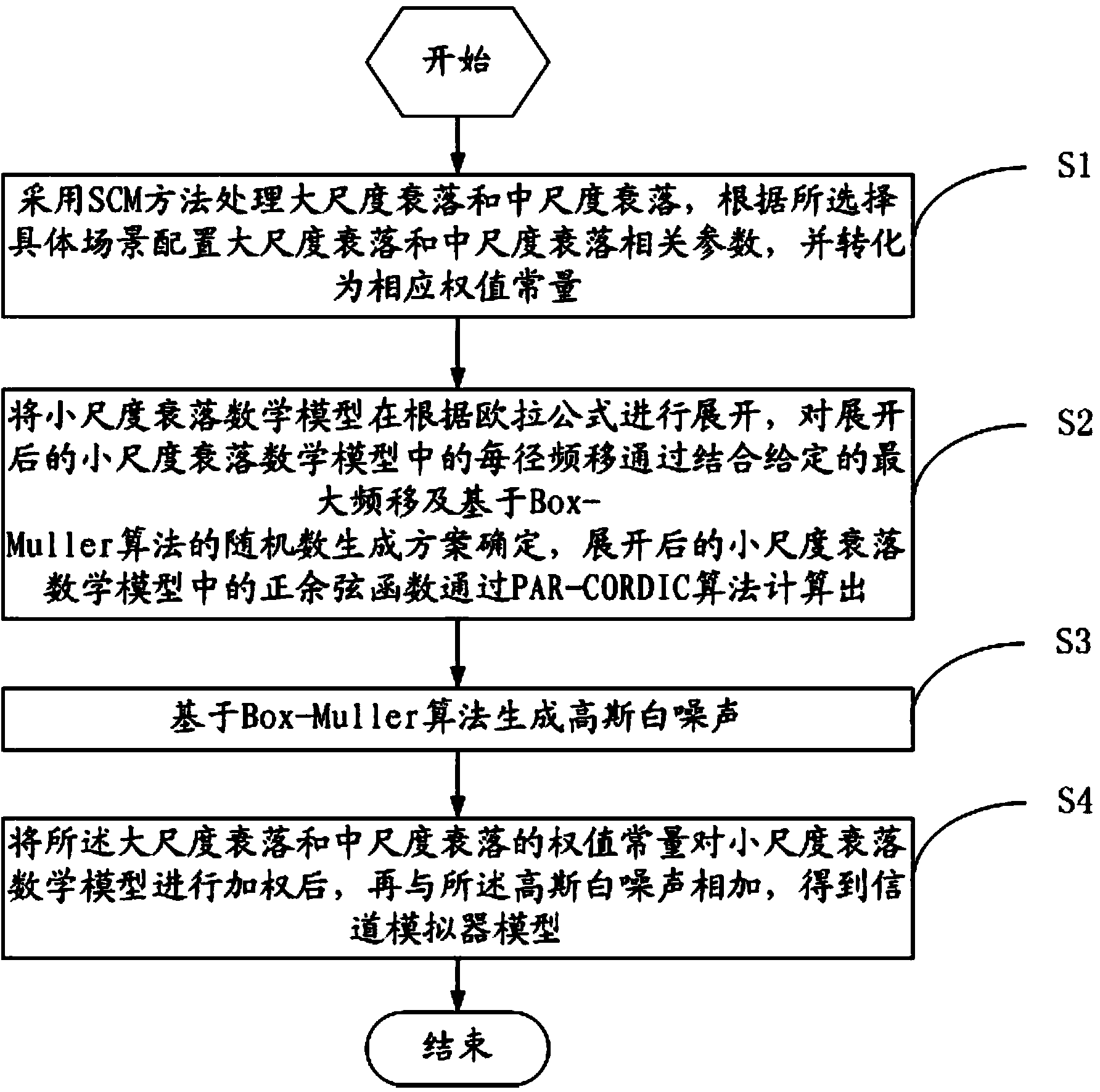
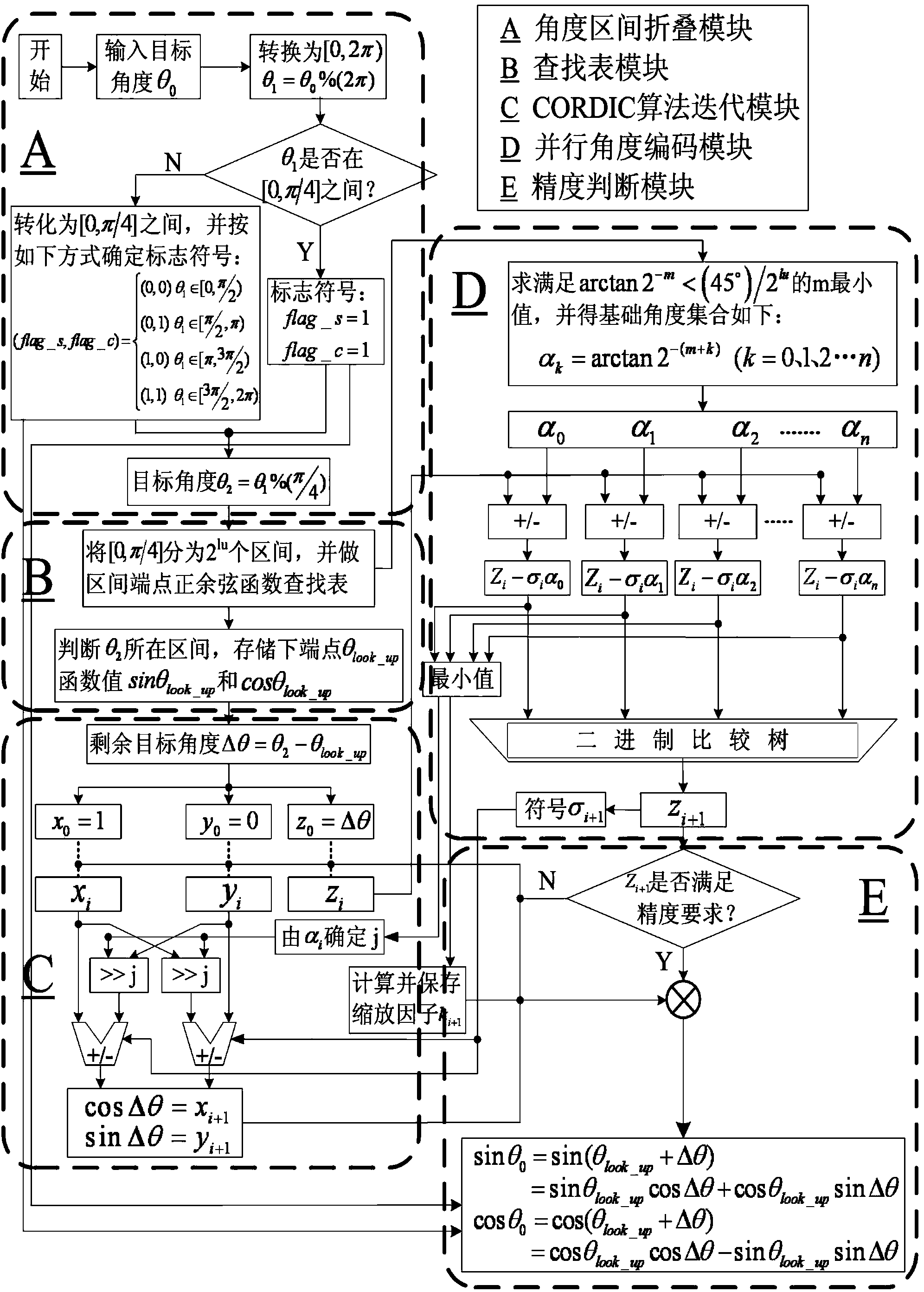
ActiveCN104038959AQuick modelingEfficient modelingWireless communicationMathematical modelResource consumption
The invention provides a channel simulator and a modeling method thereof. An SCM (space channel molding) method is used for processing large-scale fading and medium-scale fading, and correlation parameters of the large-scale fading and medium-scale fading are configured according to the selected specific scene and converted into corresponding weight constant; a small-scale fading mathematical model is expanded in accordance with the Euler's formula, the frequency shift of each path of the expanded small-scale fading mathematical model is determined by combining a given maximum frequency shift and based on a random number generation scheme of the Box-Muller algorithm, and the sine and cosine functions of the expanded small-scale fading mathematical model are calculated through the PAR-CORDIC (Coordinate Rotational Digital Computer) algorithm; Gaussian white noise is generated based on the Box-Muller algorithm; Finally, the weight constant of the large-scale fading and medium-scale fading is used for weighting the small-scale fading mathematical model and then added to the Gaussian white noise to obtain a channel simulator model. According to the channel simulator and the modeling method thereof, the modeling is quick and efficient and has the performance advantages on resource consumption, processing time and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for FFT computation
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for computing a 2N-point Fourier transform, direct or inverse, out of a 2N-sample input sequence. According to the invention, a signal processing method and apparatus is provided that makes use of an existing N-point FFT processor as well as other blocks such as a CORDIC or a filter to compute the 2N-point FFT.
Owner:NEWLOGIC TECH
Hardware function generator support in a DSP
InactiveUS20060282489A1Quickly and efficiently process CORDIC algorithmEfficient retrievalDigital data processing detailsSpeech analysisParallel computingInit
The present invention relates to digital signal processors with an integrated module configured to compute a Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer (CORDIC) in a pipeline. The pipelined module can advantageously complete computation of one CORDIC computation for each clock pulse applied to the CORDIC module, thereby providing a CORDIC computation for each clock pulse. One embodiment advantageously computes a first portion of a computation with a lookup table and a second portion in accordance with a CORDIC algorithm. Advantageously, data in a CORDIC pipeline is automatically advanced in response to read instructions and can be automatically advanced from the beginning of the pipeline to the end of the pipeline to reinitialize the pipeline. This allows information to be retrieved from the CORDIC pipeline with relatively little overhead The automatic starting and stopping of the CORDIC pipeline advantageously allows the retrieval of computations from efficient pipeline architectures on an as-needed basis.
Owner:QUARTICS
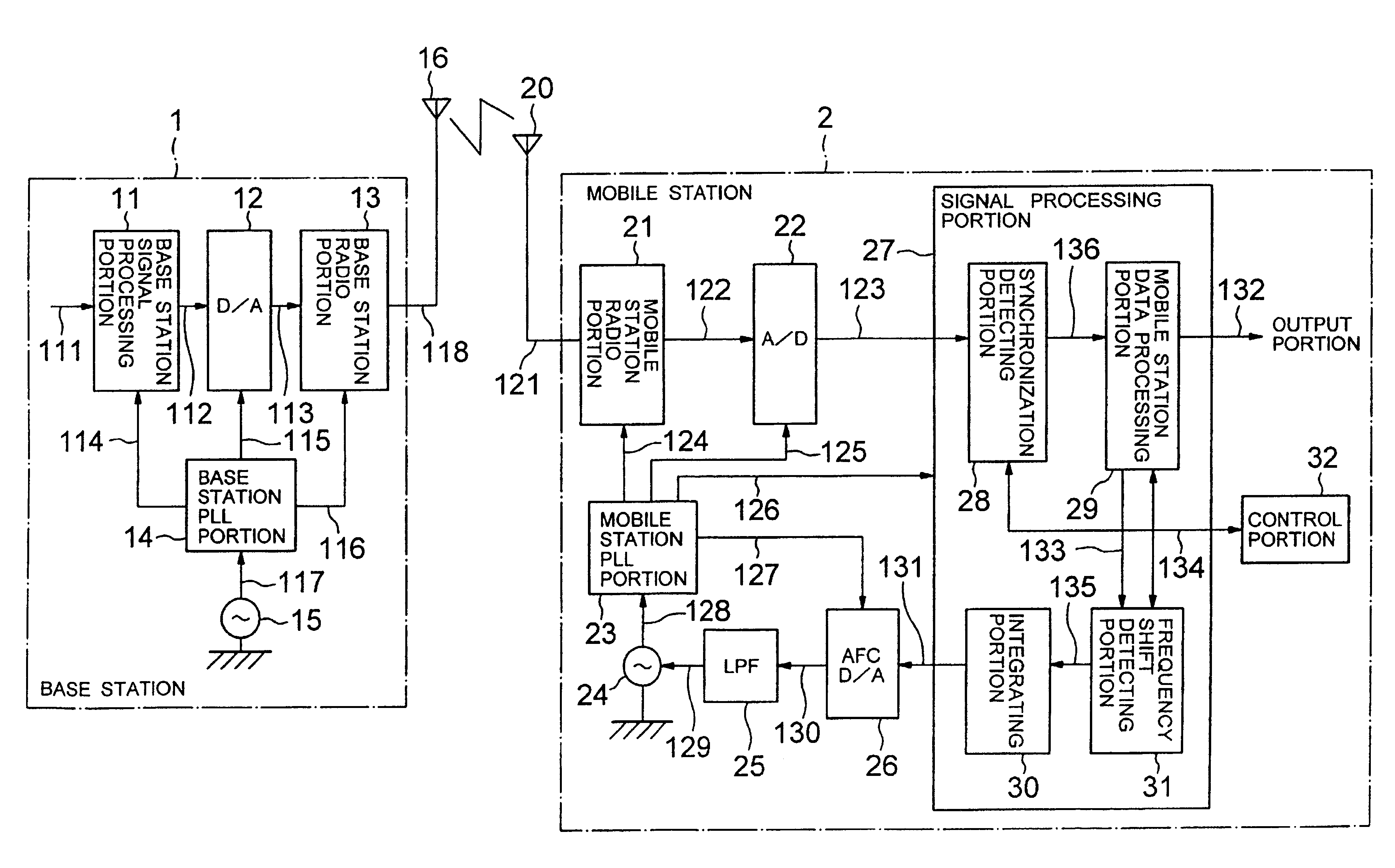
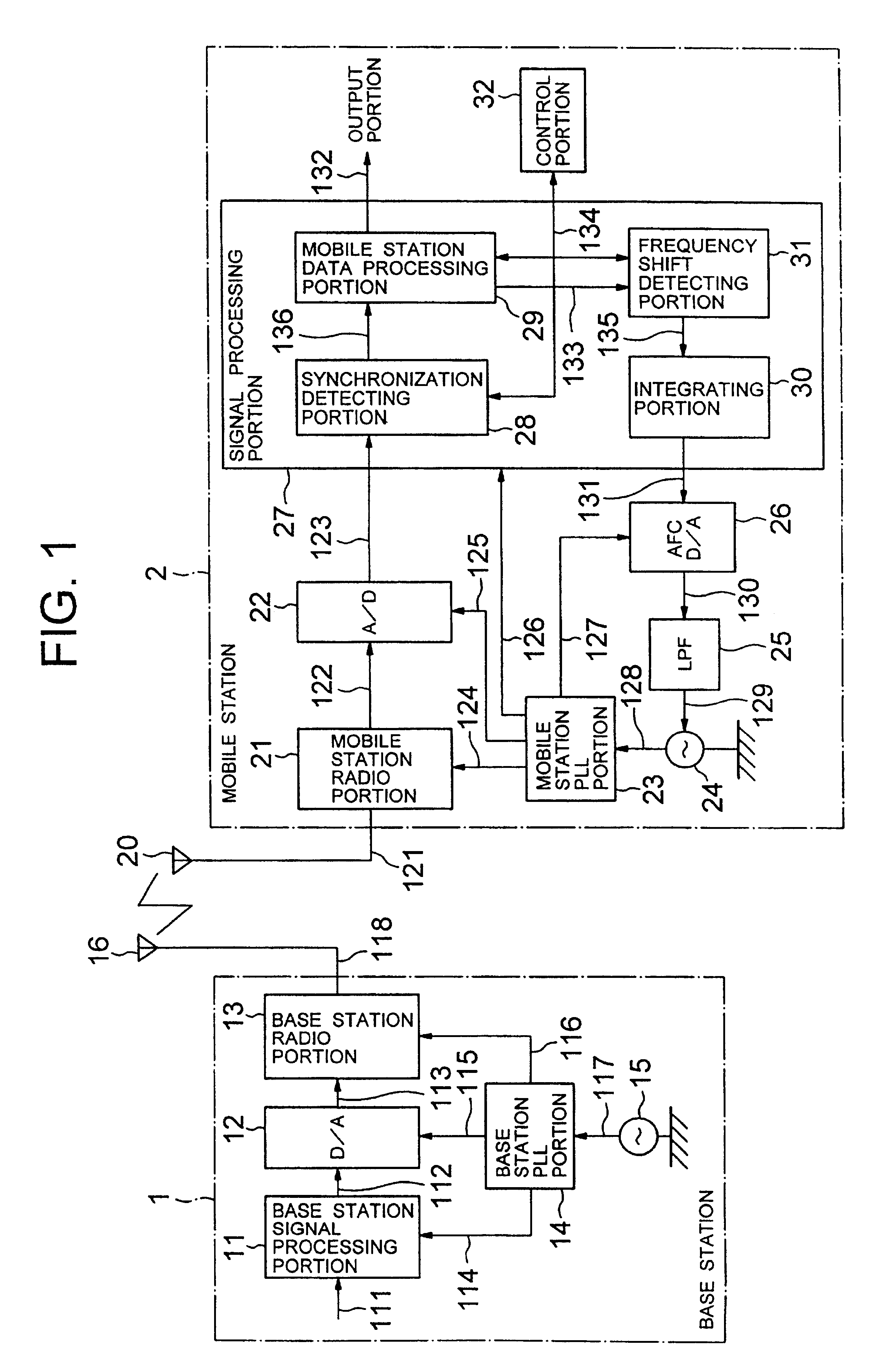
Portable radio system and portable radio equipment to be used in the same and frequency error prediction method used therefor
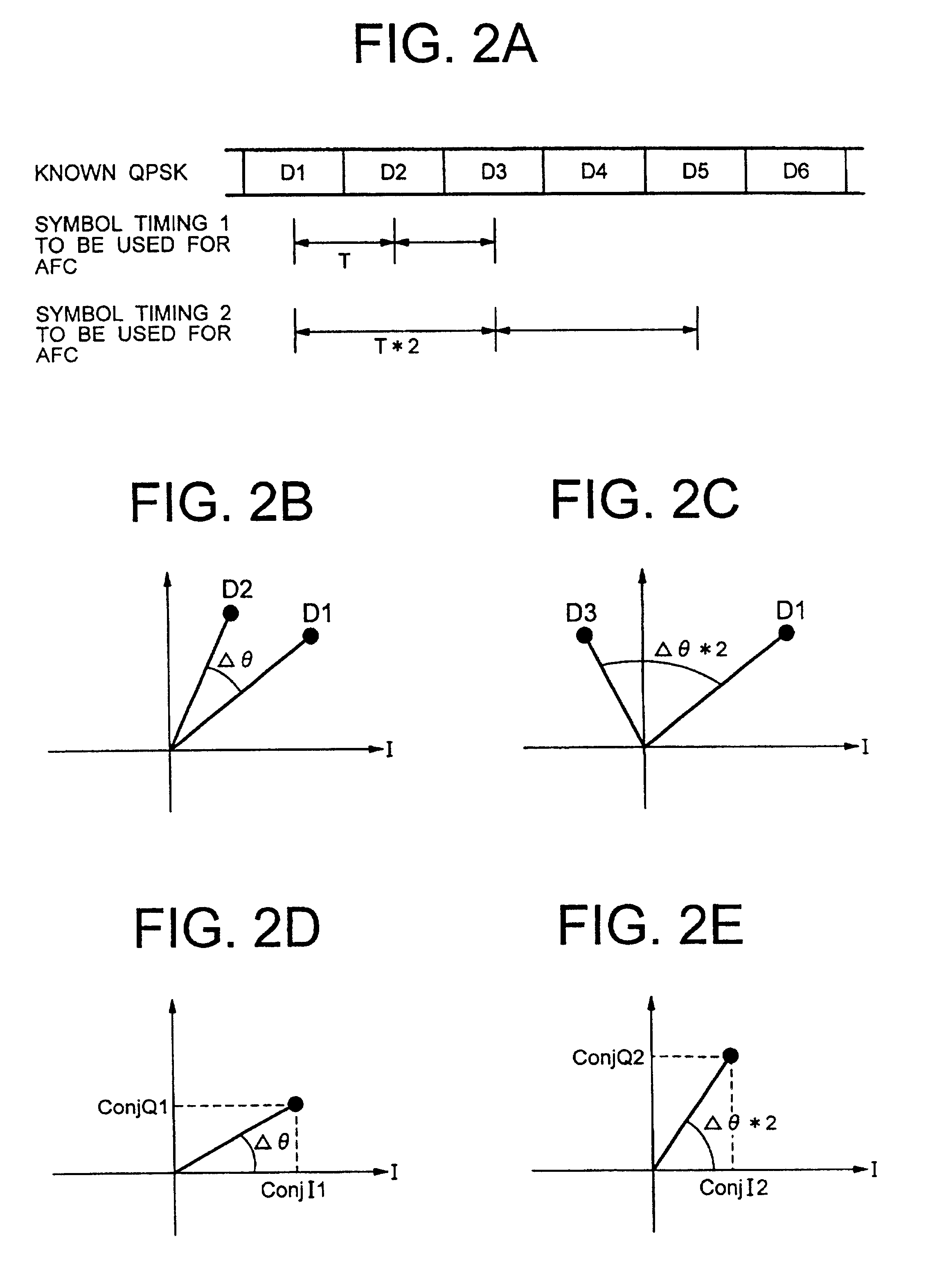
InactiveUS6891908B2Low costMakes it very inaccurateAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringRadio equipmentCORDIC
A portable radio system, a portable radio equipment to be used in the same and a frequency error prediction method can be adapted to large frequency error by making tap number smaller and frequency error smaller. The portable radio system employs an automatic frequency control for detecting a frequency shift of an internal oscillator of a portable radio equipment with reference to a received wave transmitted from a base station having higher precision of frequency and adjusting the frequency of the internal oscillator by feeding back the frequency shift to the internal oscillator. Coordinate rotation digital computation (CORDIC) is employed for calculation of arctangent in the automatic frequency control.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com