Reconfigurable floating-point operation device based on CORDIC algorithm
A floating-point calculation and algorithm technology, which is applied in calculation, instrumentation, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as limited convergence range, long algorithm delay, and unsatisfactory calculation accuracy, etc., and achieve simplified iterative calculation formulas, low delay, The effect of shortening the clock cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0028] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
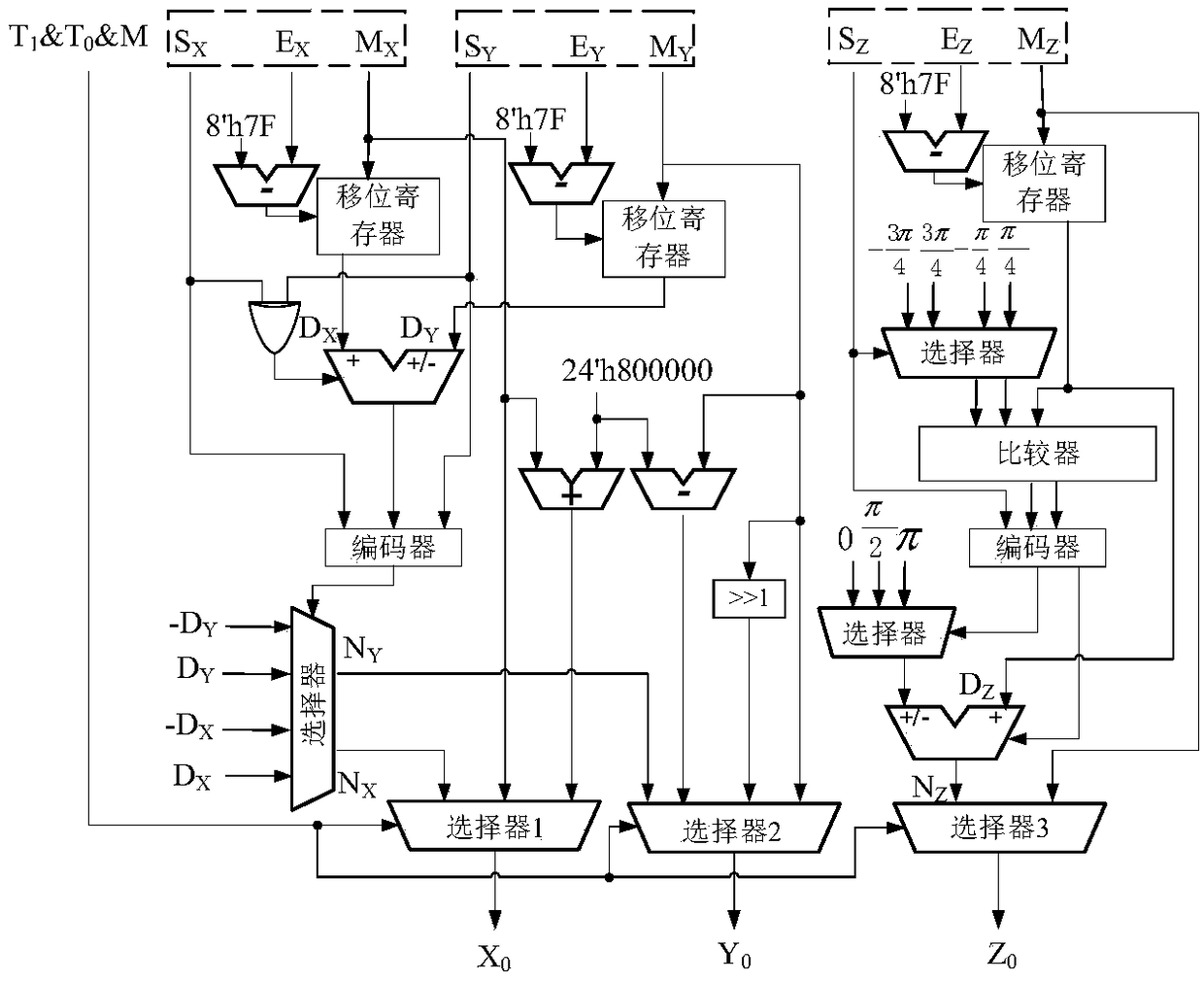
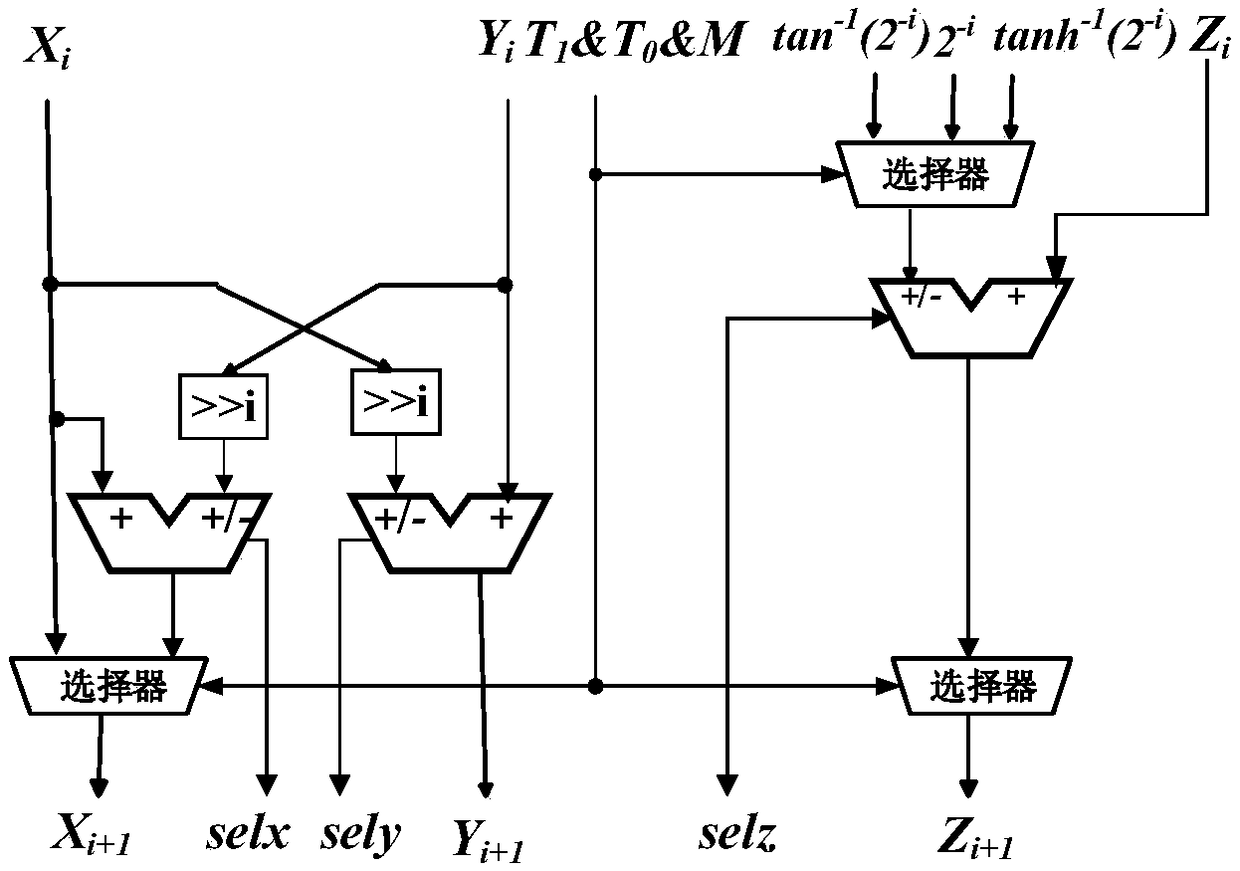
[0029] The calculation of trigonometric functions is realized in the circular coordinate system, and the calculation of the sine and cosine functions is completed in the rotation mode, and the initial value is X 0 =K 1 , Y 0 = 0, Z 0 = θ, the output is X n =cosθ,Y n =sinθ, the convergence area is -99.827°≤θ≤99.827°; the calculation of the arctangent function is completed in the vector mode, and the initial value is set to Z 0 =0, the output is Z n =tan -1 (Y 0 / X 0 ), the convergence region is -99.827°≤tan -1 (Y / X)≤99.827°.
[0030] The multiplication and division operations are implemented in the linear coordinate system, and the multiplication operation is completed in the rotation mode, and the initial value is Y 0 =0, the output is Y n =X 0 / Z 0 , the region of convergence is |z 0 |0 =0, the output is Z n =Y 0 / X ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com