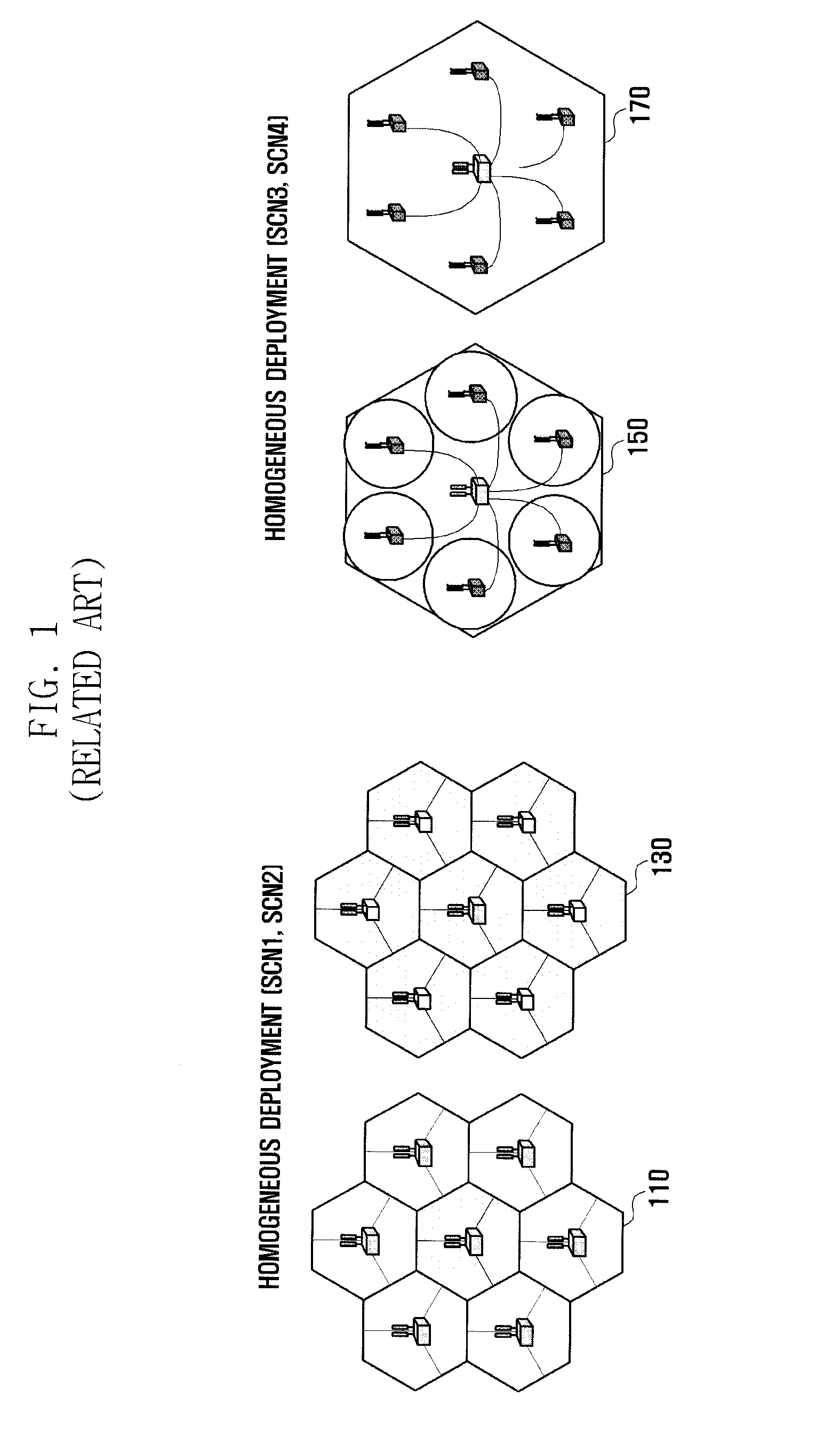
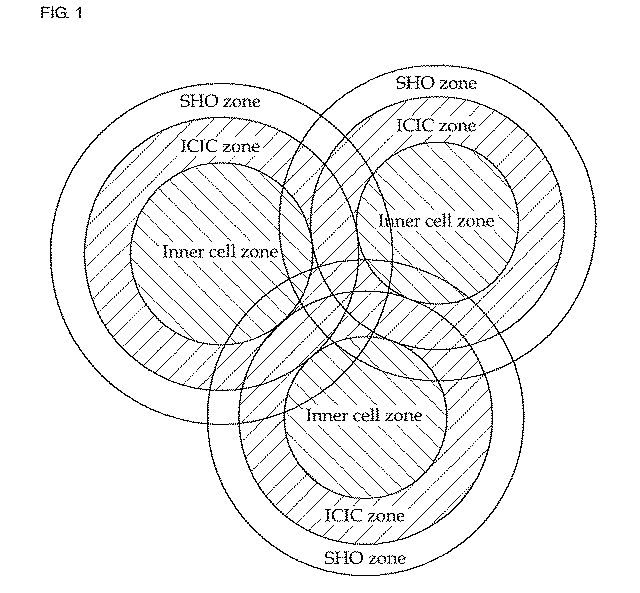
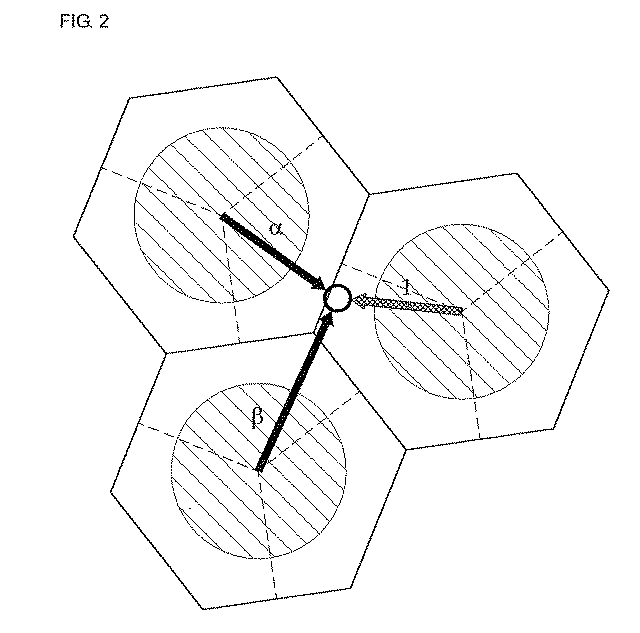
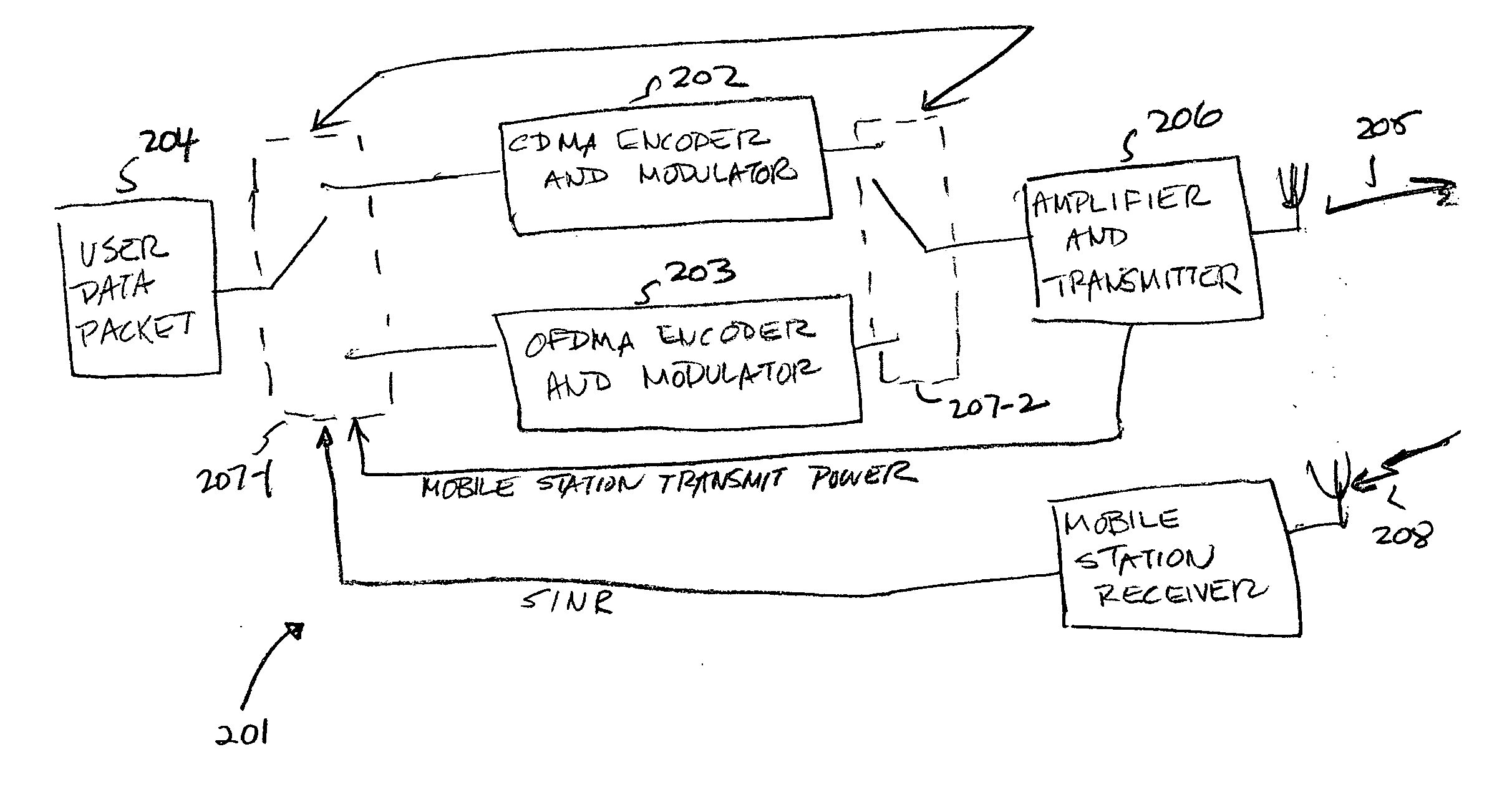
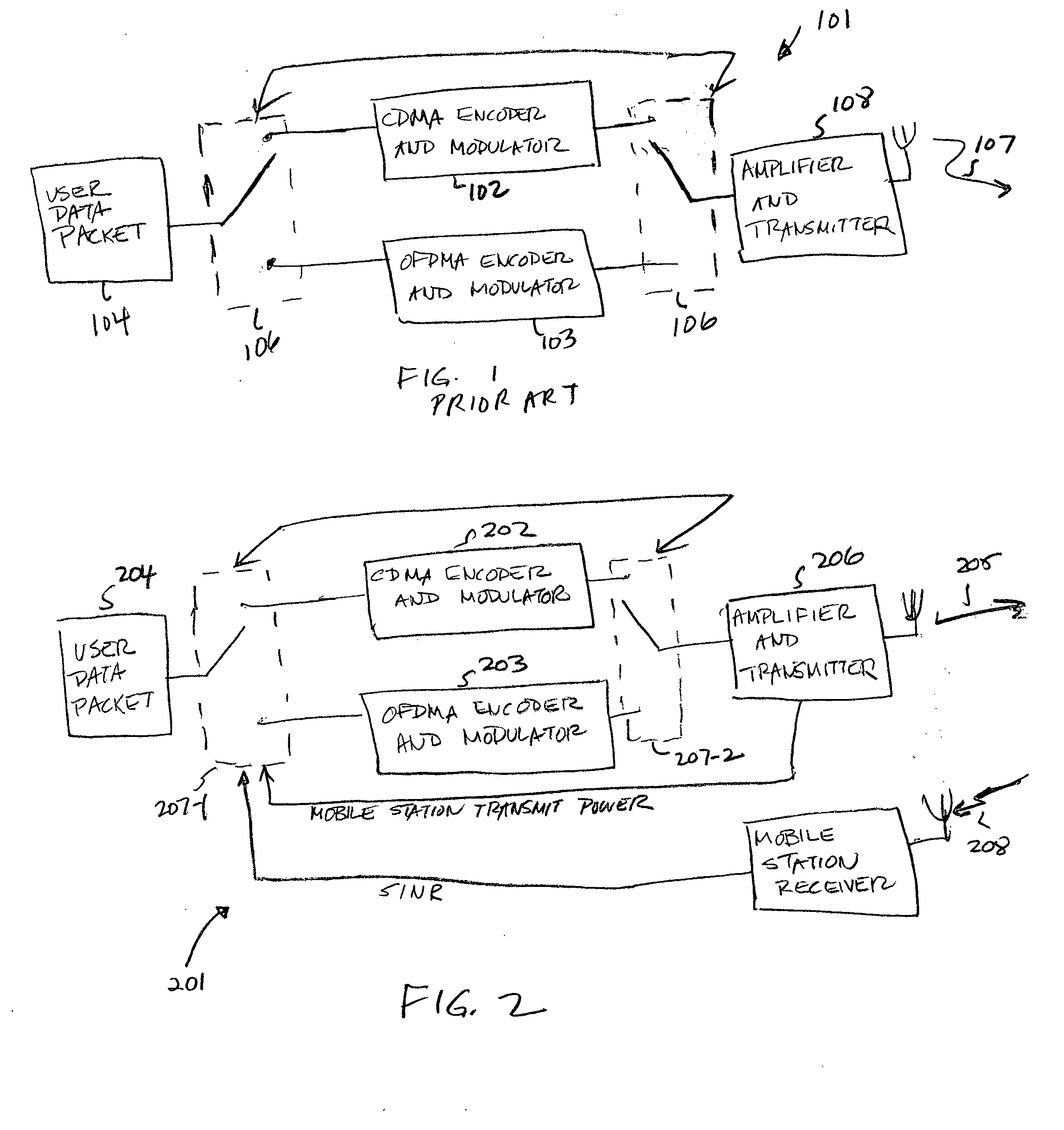
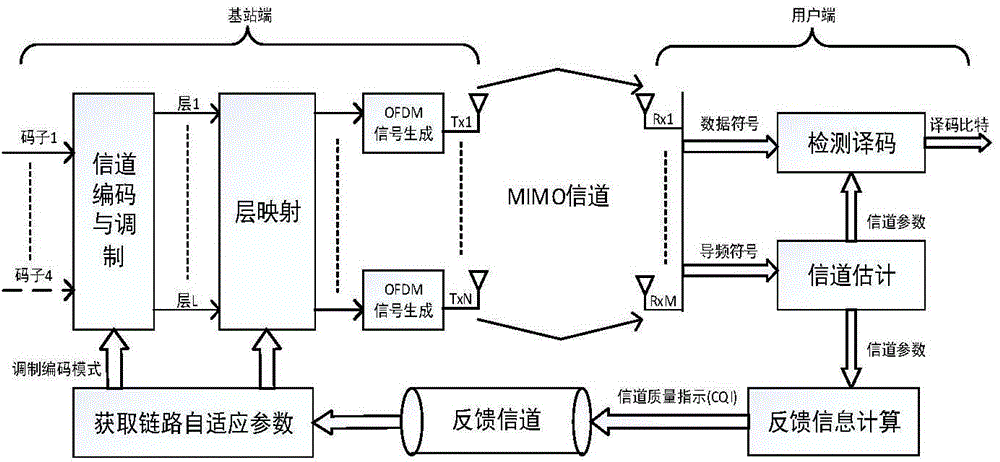
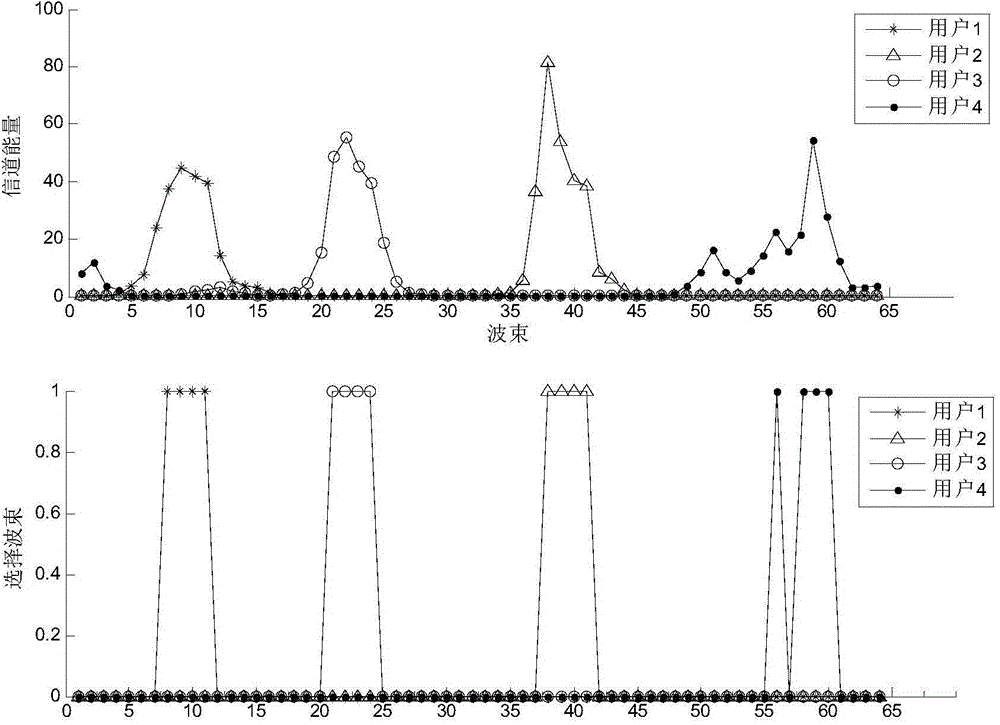
Patents
Literature
630 results about "Signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
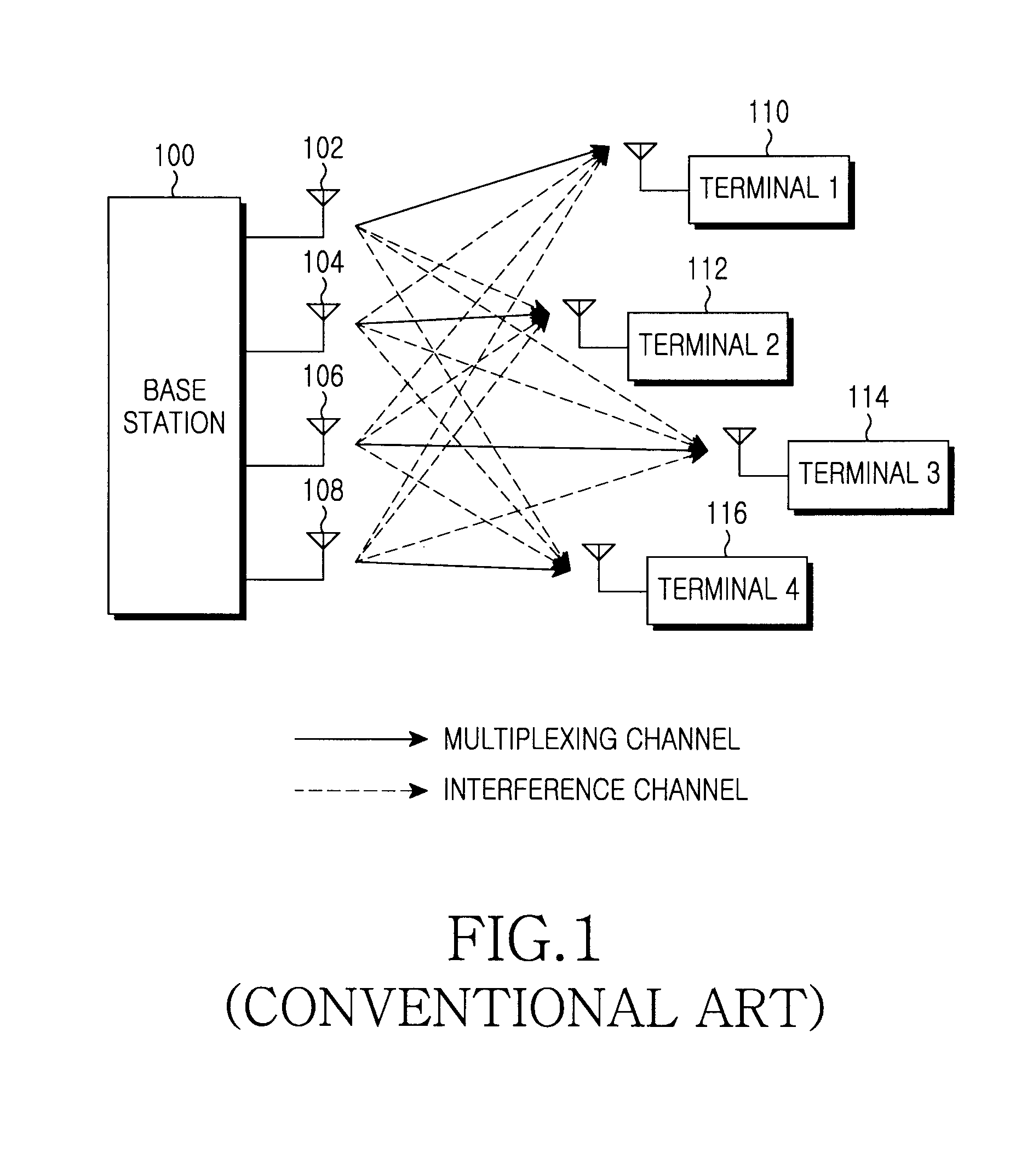
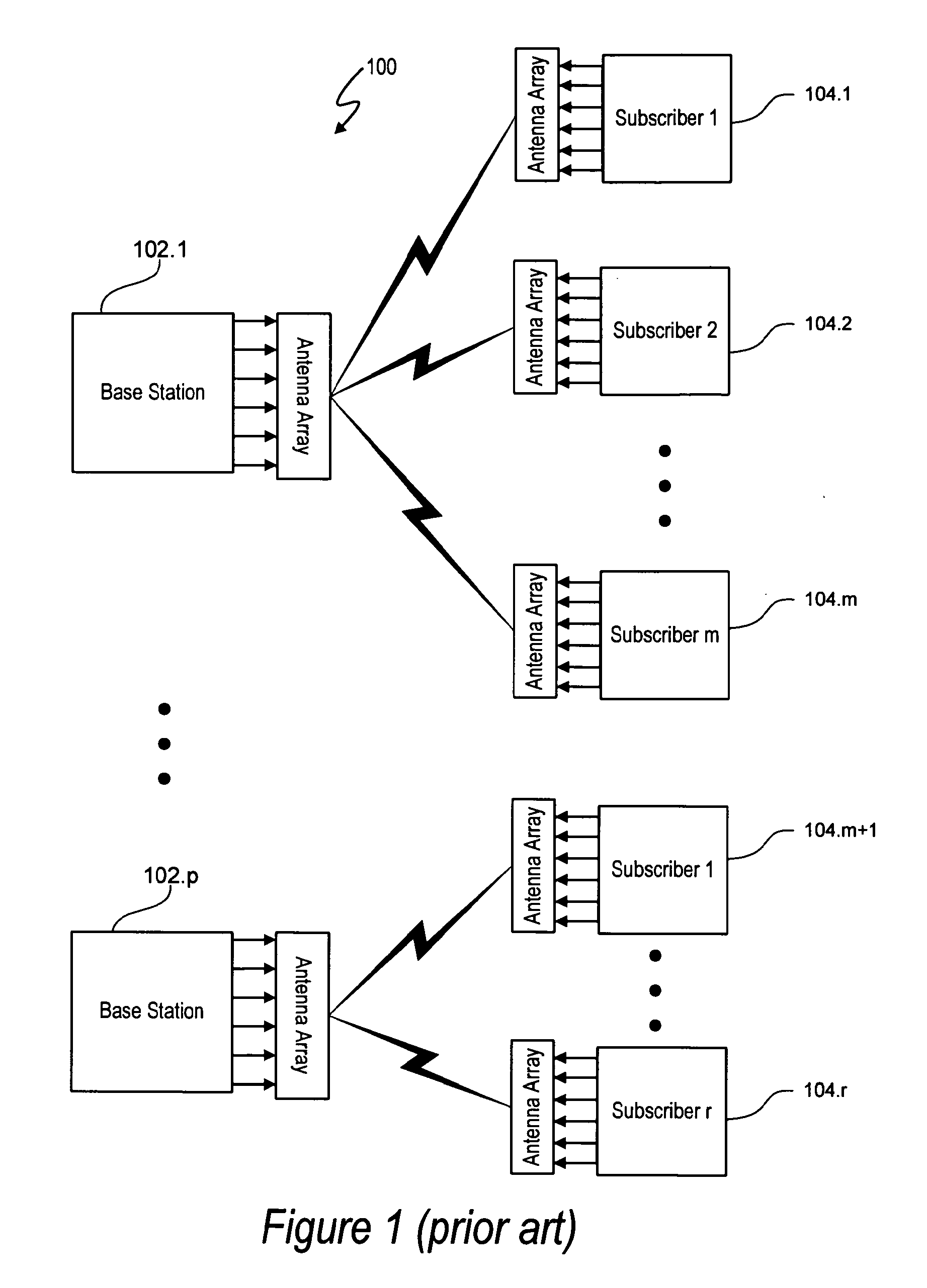
In information theory and telecommunication engineering, the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) (also known as the signal-to-noise-plus-interference ratio (SNIR)) is a quantity used to give theoretical upper bounds on channel capacity (or the rate of information transfer) in wireless communication systems such as networks. Analogous to the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) used often in wired communications systems, the SINR is defined as the power of a certain signal of interest divided by the sum of the interference power (from all the other interfering signals) and the power of some background noise. If the power of noise term is zero, then the SINR reduces to the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR). Conversely, zero interference reduces the SINR to the SNR, which is used less often when developing mathematical models of wireless networks such as cellular networks.
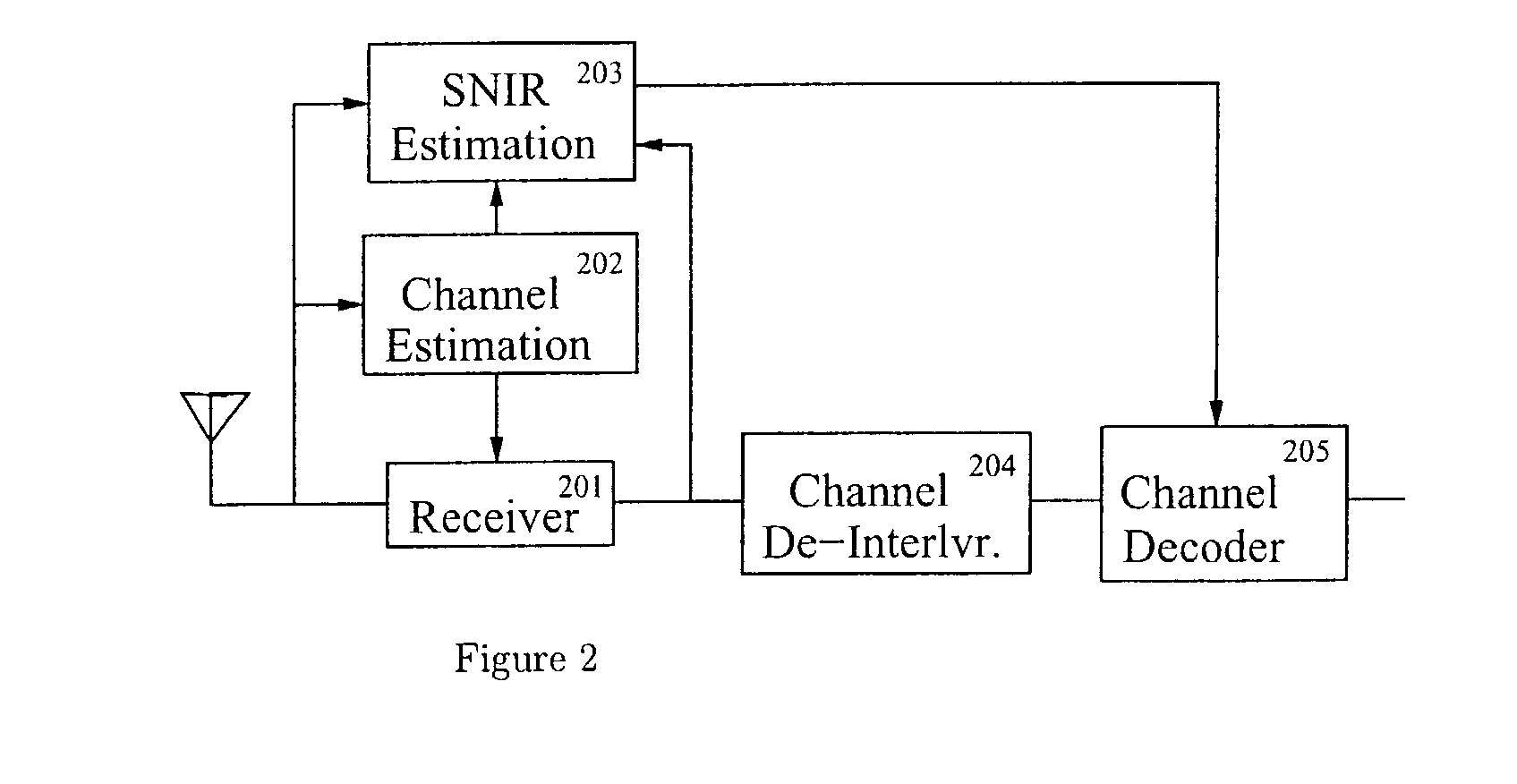
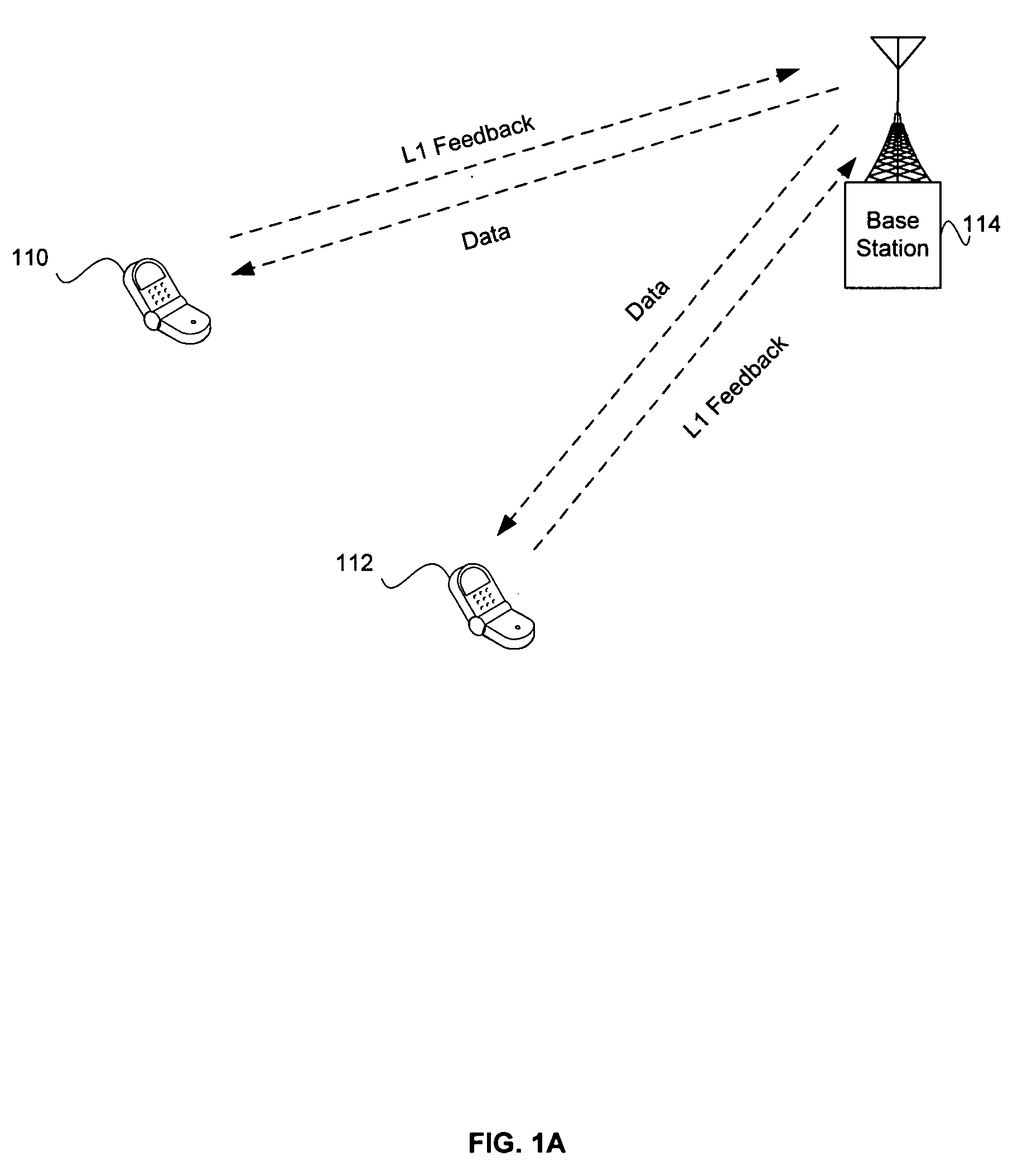
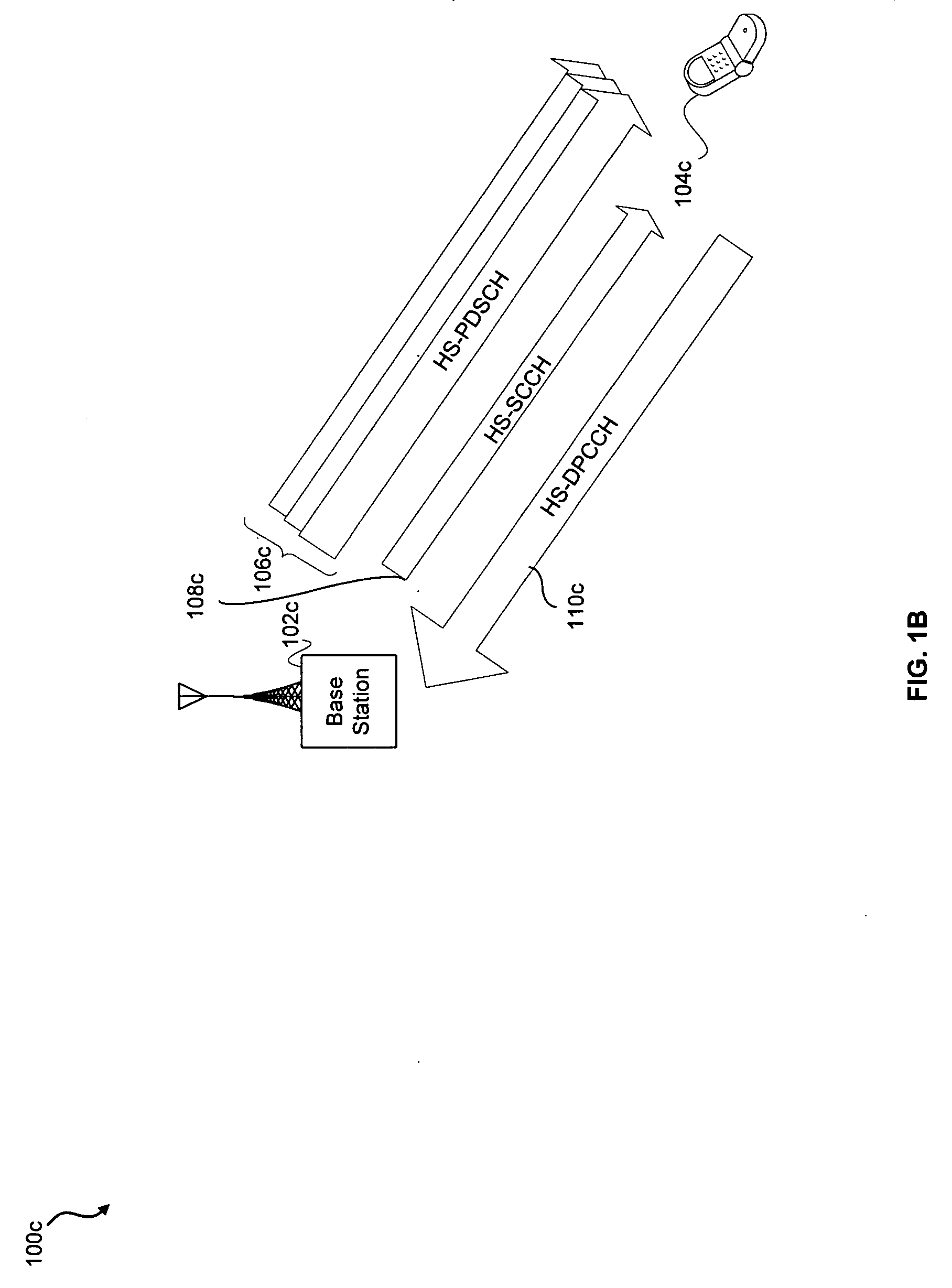
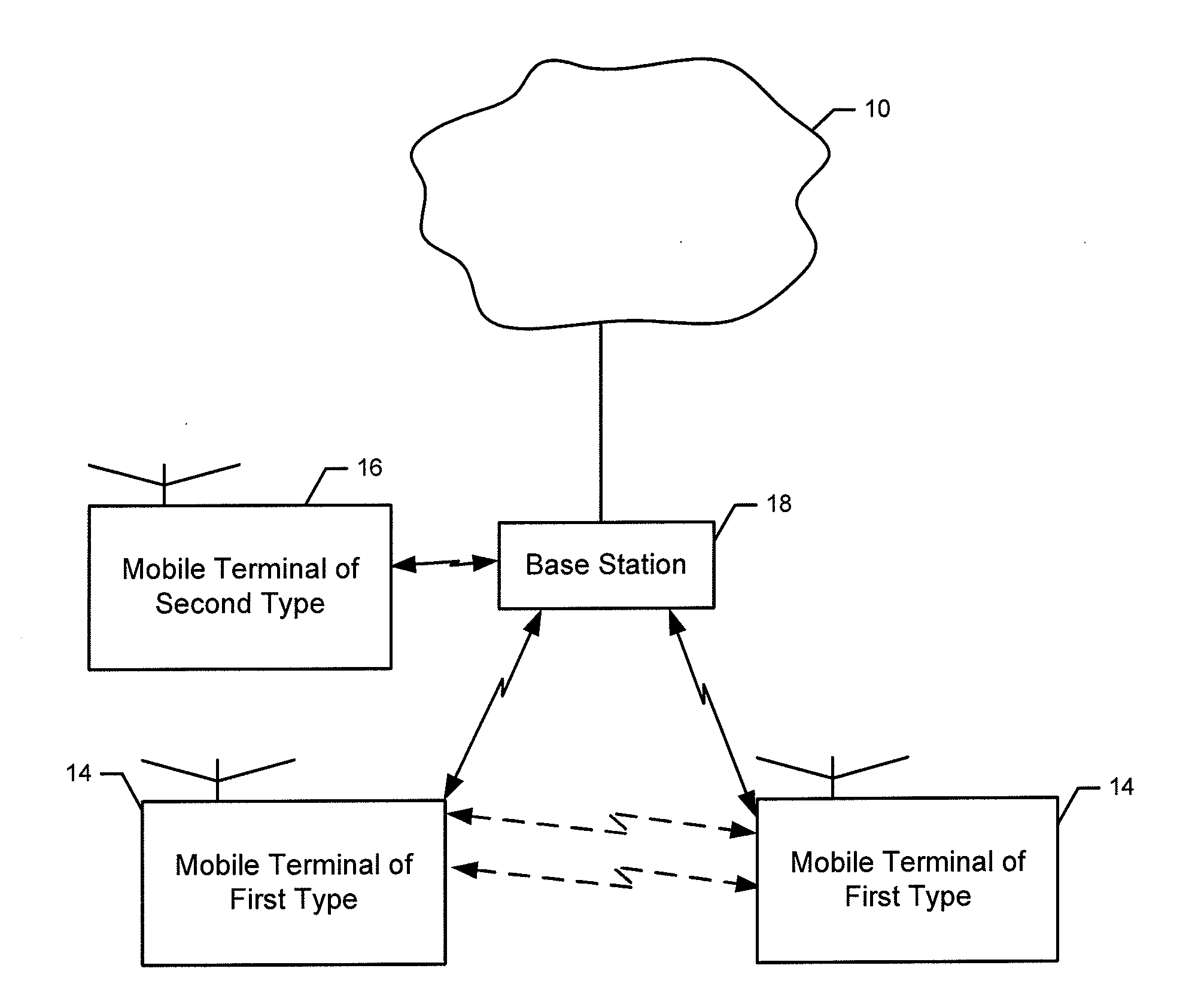
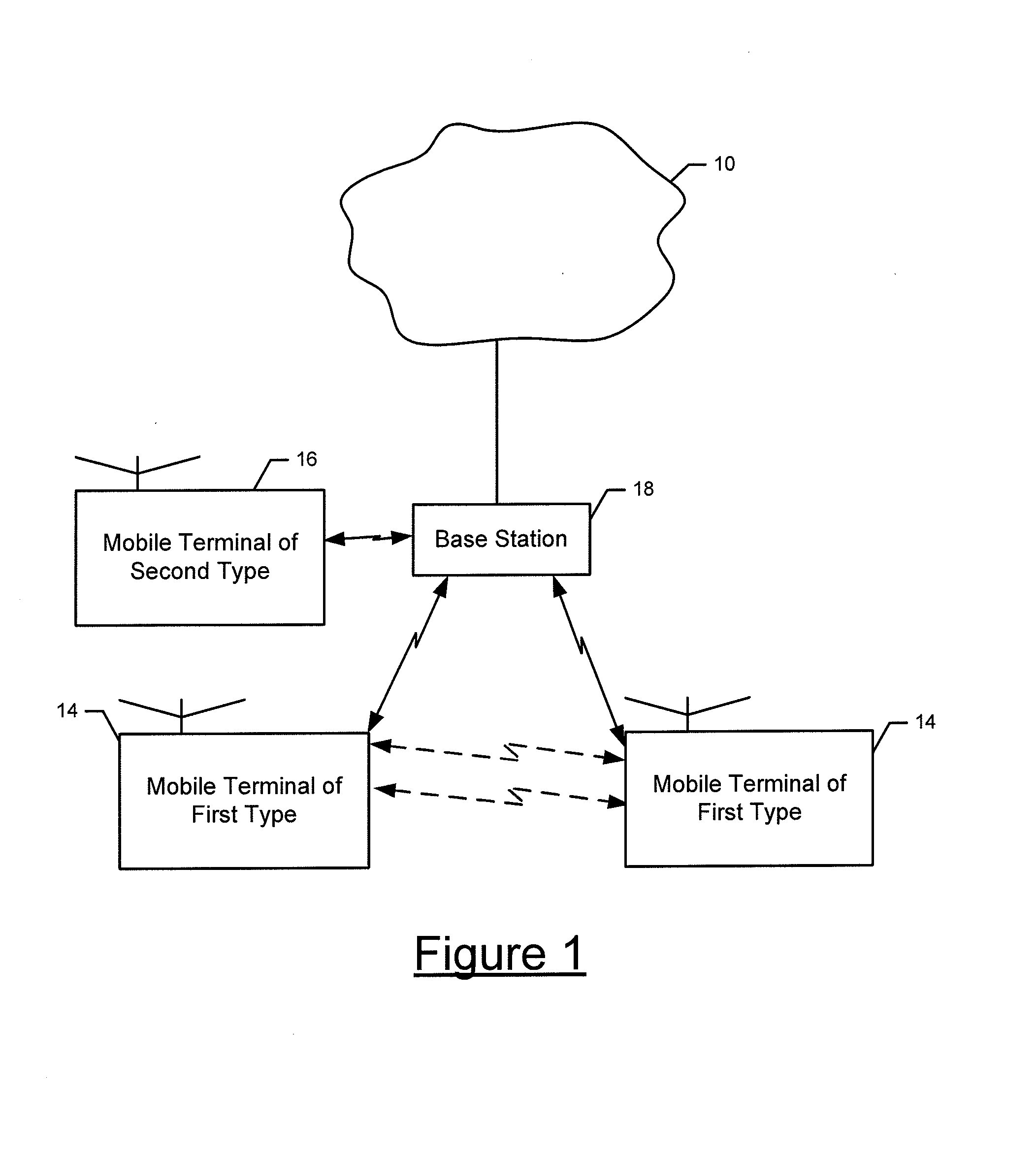
Method and system for performing distributed outer loop power control in wireless communication networks
InactiveUS20090093267A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce signal to noise ratioPower managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioReceiver front end
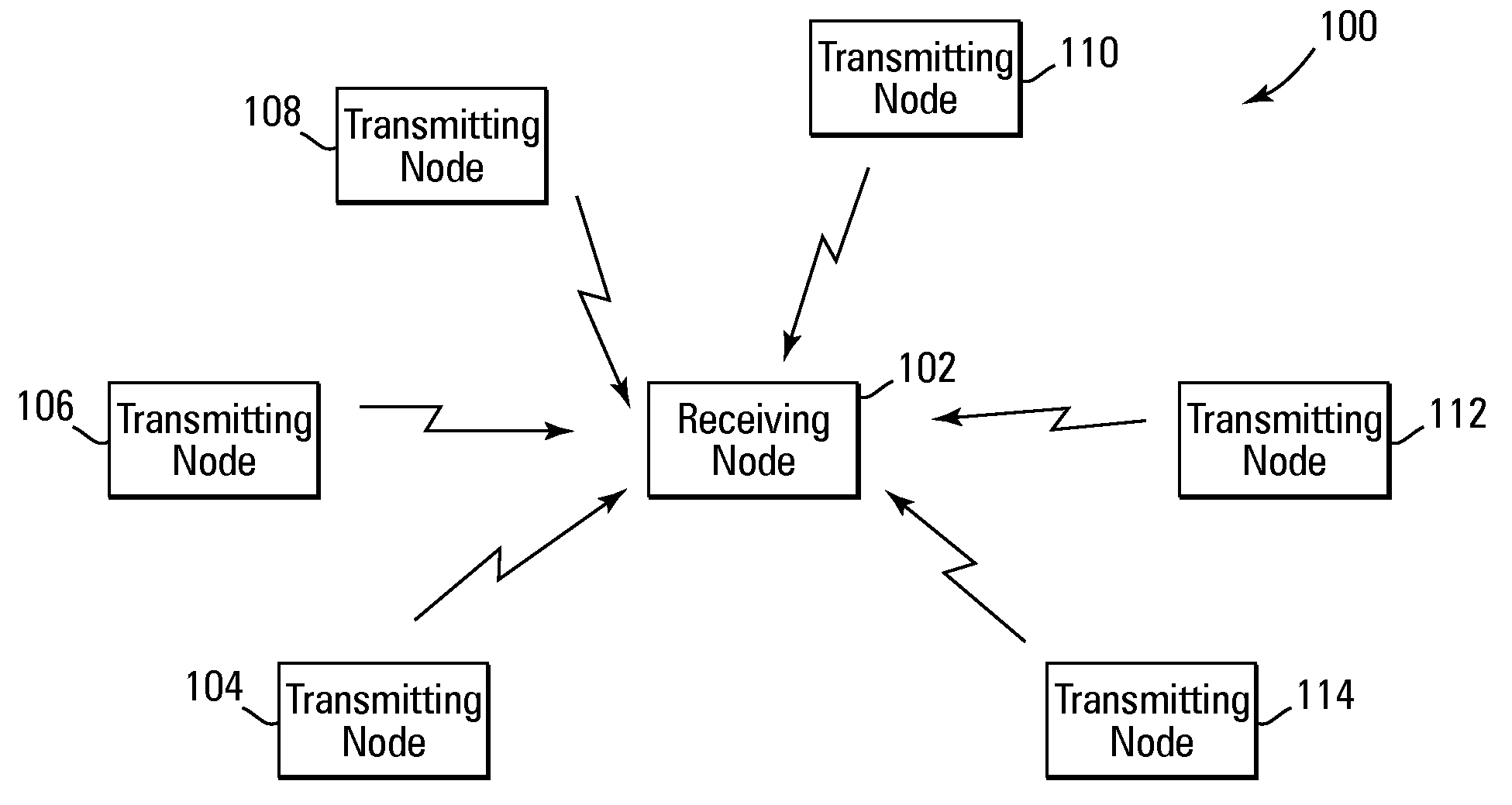
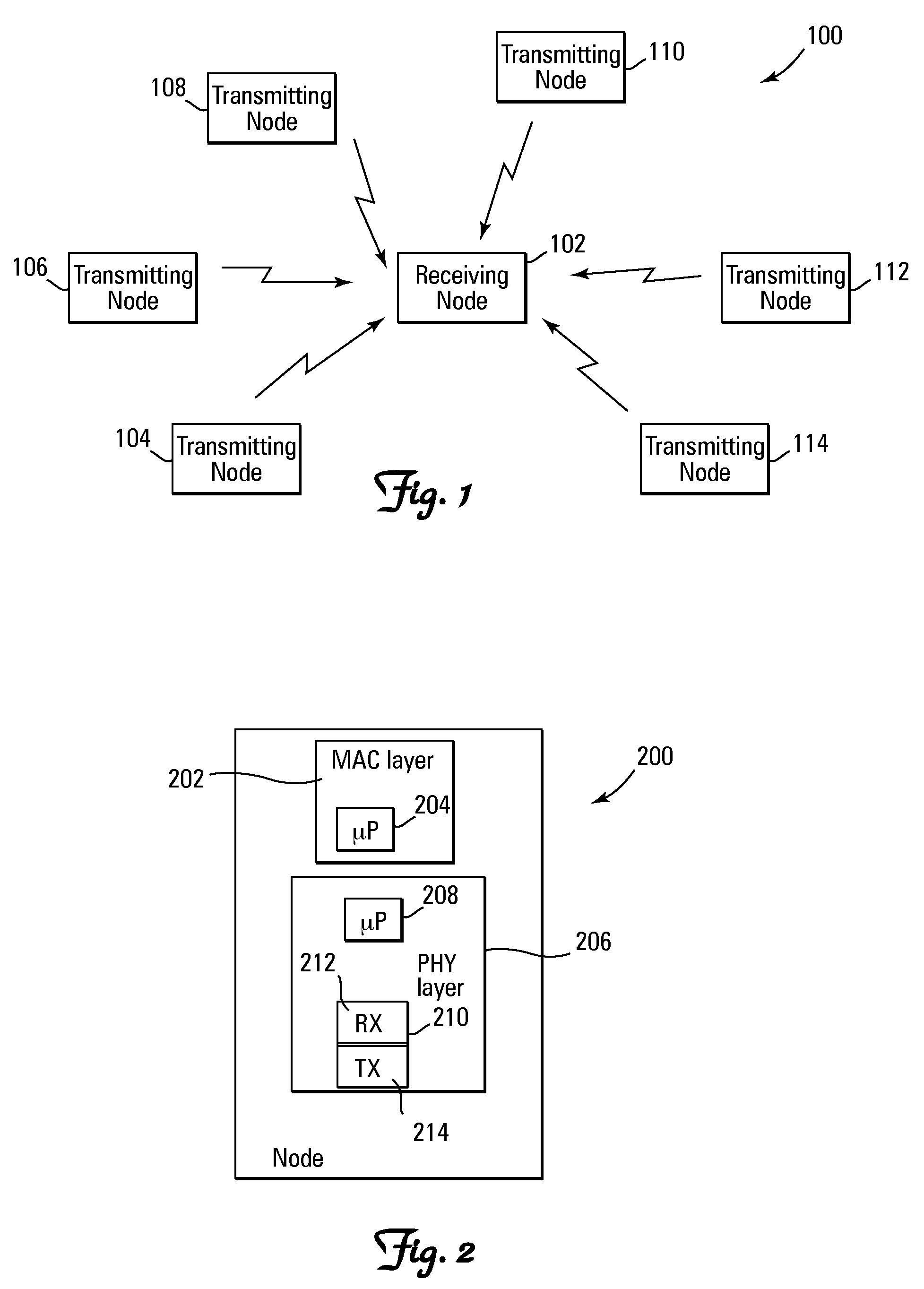
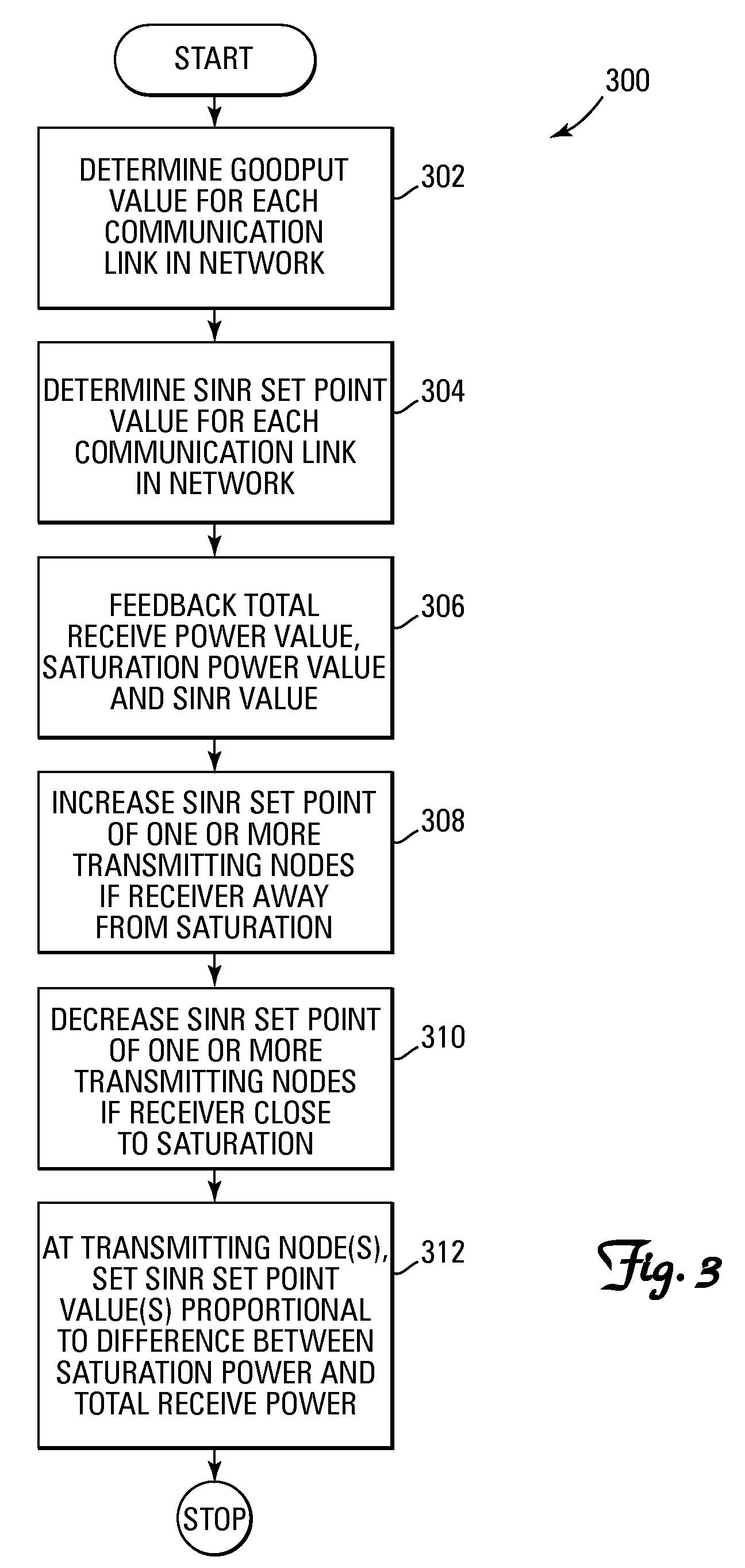
A method and system for performing distributed outer loop power control in a wireless communication network are disclosed. The method includes the steps of determining a transmit power for a plurality of transmitting nodes such that signals sent from each of the transmitting nodes are received at a receiver associated with a receiving node at a predetermined signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR) set point, increasing the SINR at the receiving node of one or more transmitting nodes of the plurality of transmitting nodes if a saturation value for a front end of the receiver associated with the receiving node is not near a predetermined saturation value, and decreasing the SINR at the receiving node of the one or more transmitting nodes of the plurality of transmitting nodes if the saturation value for the front end of the receiver associated with the receiving node is near the predetermined saturation value.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
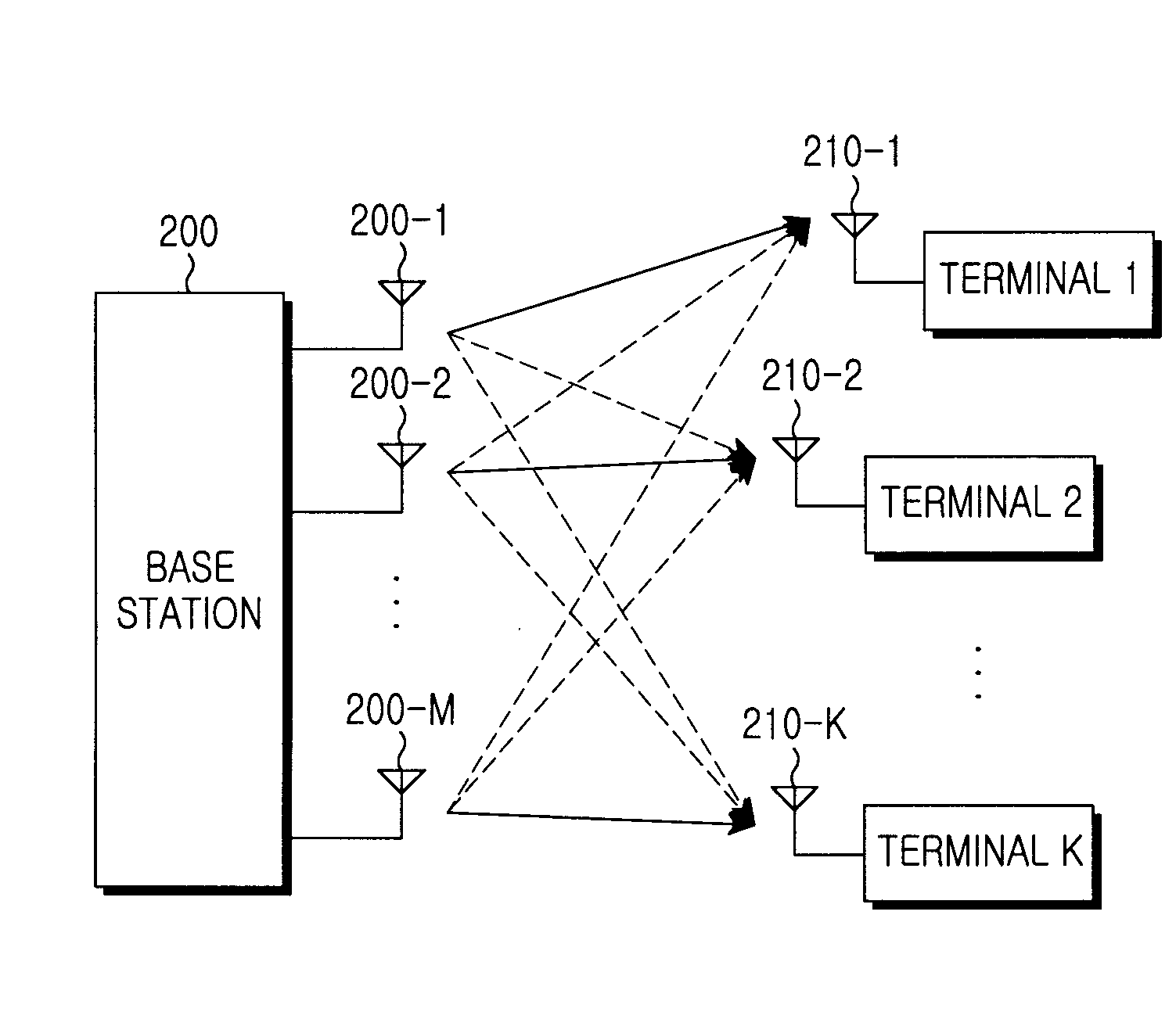
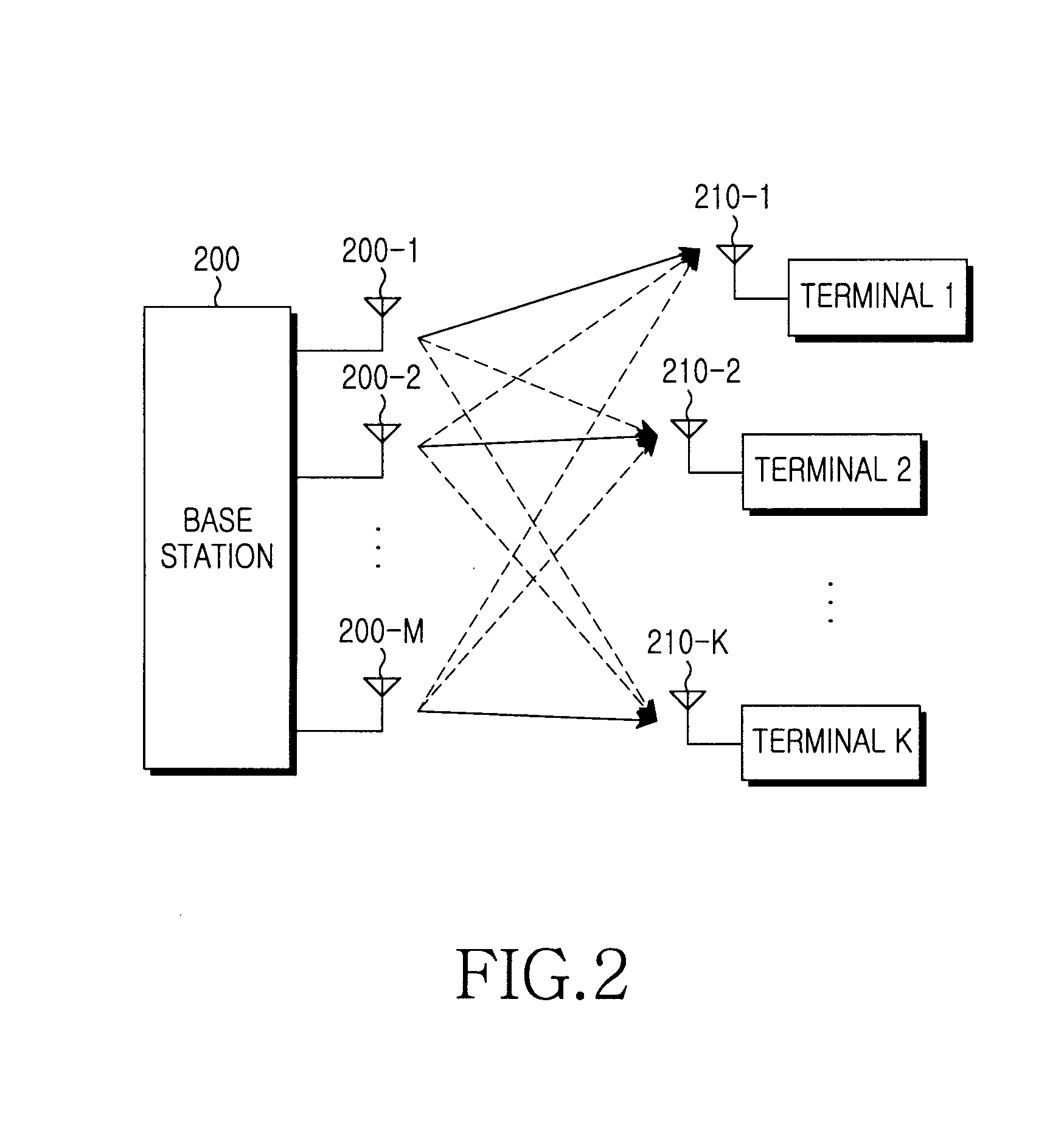
Coverage self-optimization method of cellular mobile communication system
ActiveCN102202330AGuaranteed service qualityIncrease profitWireless communicationSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioMaterial resources
The invention relates to a coverage self-optimization method of a cellular mobile communication system, and is used for solving the problems of poor coverage, polluted pilot frequency and cross-area coverage. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring and reporting respective reference signal received power (RSRP) and respective signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR) parameter values to a base station by each user; collecting the measurement parameter values reported by all users in a cell by the base station; judging whether the current network is in accordance with any one trigger condition of the three coverage problems; triggering a coverage self-optimization process based on dynamic adjustment on a lower dip angle of an antenna if the current network is in accordance with the condition and then adjusting the lower dip angle according to a preset scheme to solve the coverage problem; continuously adjusting an antenna azimuth angle and wave beam width or performing down-regulation on transmission power of the base station according to specific scenes and user types if the coverage requirement cannot be met within the adjustable ranges of the lower dip angle; and entering a coverage and capacity self-optimization process if the coverage problem cannot be solved by the measures. According to the method, each cell periodically initiates coverage liberalization operation for many times according to the steps so as to save manpower and material resources required by manual optimization and reduce the maintenance cost and the expenditure.
Owner:泰科系统(东莞)科技有限公司
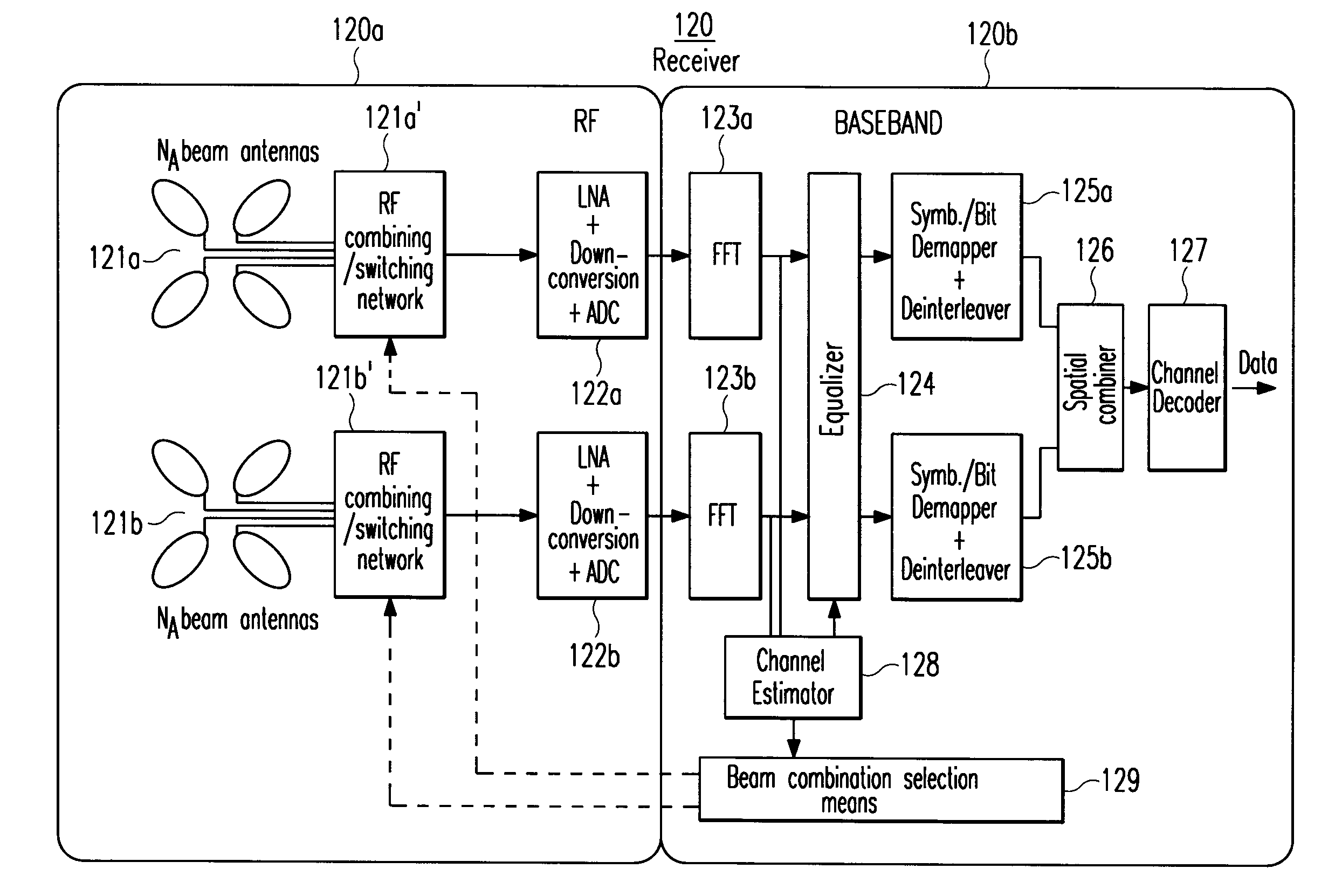
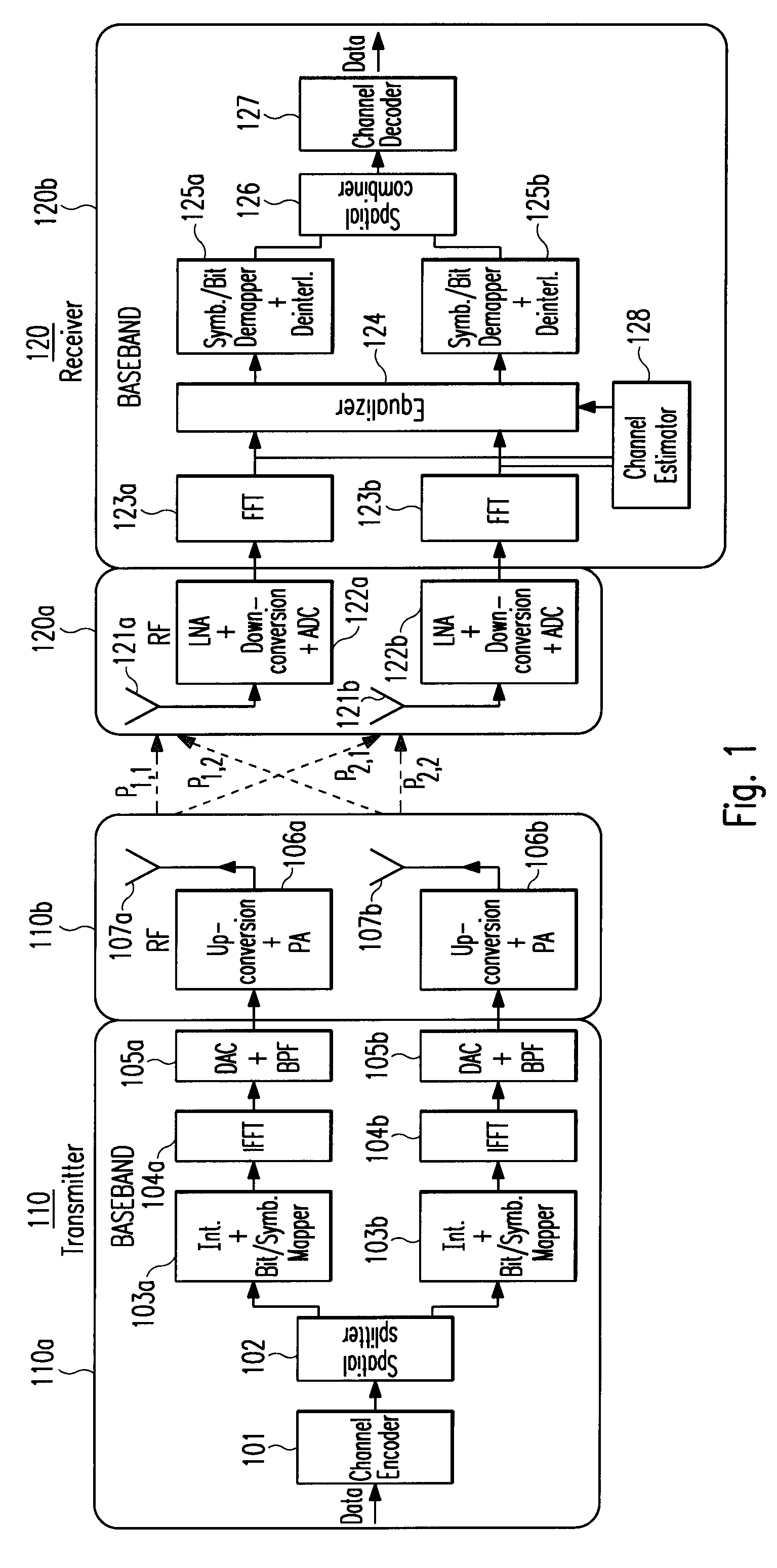
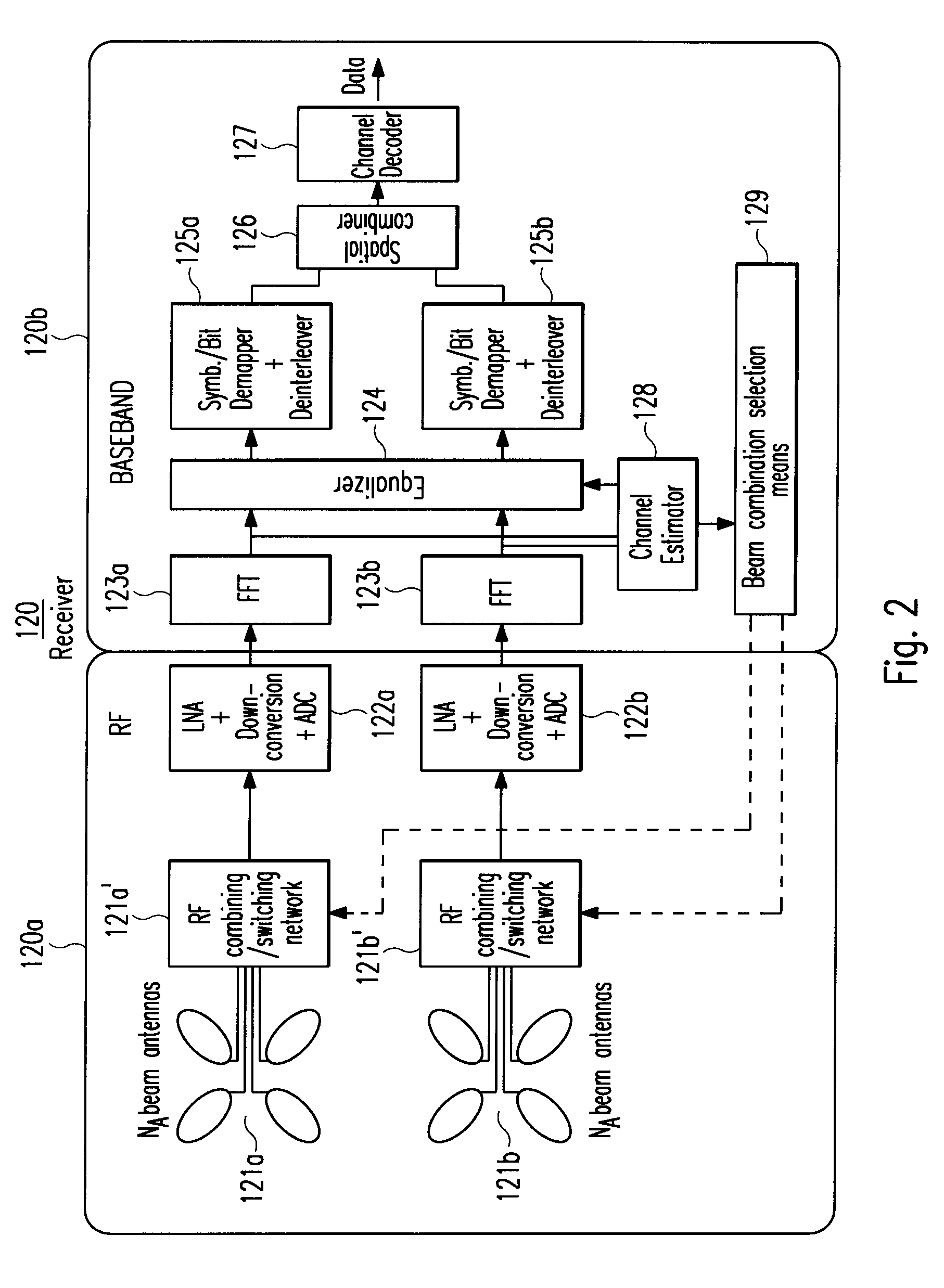
Multiple-input multiple-output spatial multiplexing system with dynamic antenna beam combination selection capability
ActiveUS20070230639A1Maximized ratioMinimizing correlation coefficientPolarisation/directional diversityMultiplex communicationAmplitude responseSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
The present invention generally relates to the field of wireless communication systems. It particularly refers to a spatial diversity transmitter (110) and a spatial diversity receiver (120) in a wireless multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) spatial multiplexing system as well as a corresponding method for wirelessly transmitting and receiving modulated RF signals via multiple wireless signal propagation paths (Pl) of a multipath fading channel in a way that correlation between the MEMO channel components are reduced and / or the signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) is increased which hence result in an improved bit error rate (BER) or packet error rate (PER) performance of said wireless MIMO spatial multiplexing system. On the receiver side, for example, this is achieved by controlling at least one antenna switching and / or combining means (121a′+b′) to select a specific combination of different fixed beam antennas (121a+b) from each receiver-resident antenna array. According to the invention, said selection is based on estimated values of the channel impulse responses (hl(τl, t)) for said signal propagation paths (Pl). An antenna beam selection control means (129) is configured for selecting a specific antenna beam combination so as to maximize the average signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratios ( γl) of RF signals (rl(τl, t, φl)) received via said multiple wireless signal propagation paths (Pl) and / or to minimize the correlation coefficients (ρr<sub2>l1< / sub2>r<sub2>l2< / sub2>(t)) indicating the correlations of different pairs of these RF signals (rl1(τl1, t, φl1) and rl2(τl2, t, φl2)).Thereby, each fixed beam antenna (121a+b) of the receiver-resident antenna arrays has a distinct radiation pattern with a different beam center and / or beam width in the azimuth and / or elevation plane, wherein a superposition of all these radiation patterns may cover all possible azimuthal (φ) and / or elevational angles of arrival (θ) of an RF signal (s(t)).For compensating detected multipath fades in the channel amplitude response (|Hl(f, t)|) of at least one signal propagation path (Pl) between the spatial diversity transmitter (110) and the spatial diversity receiver (120), a receiver-resident channel estimation and / or equalization circuitry (124, 128) is applied.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
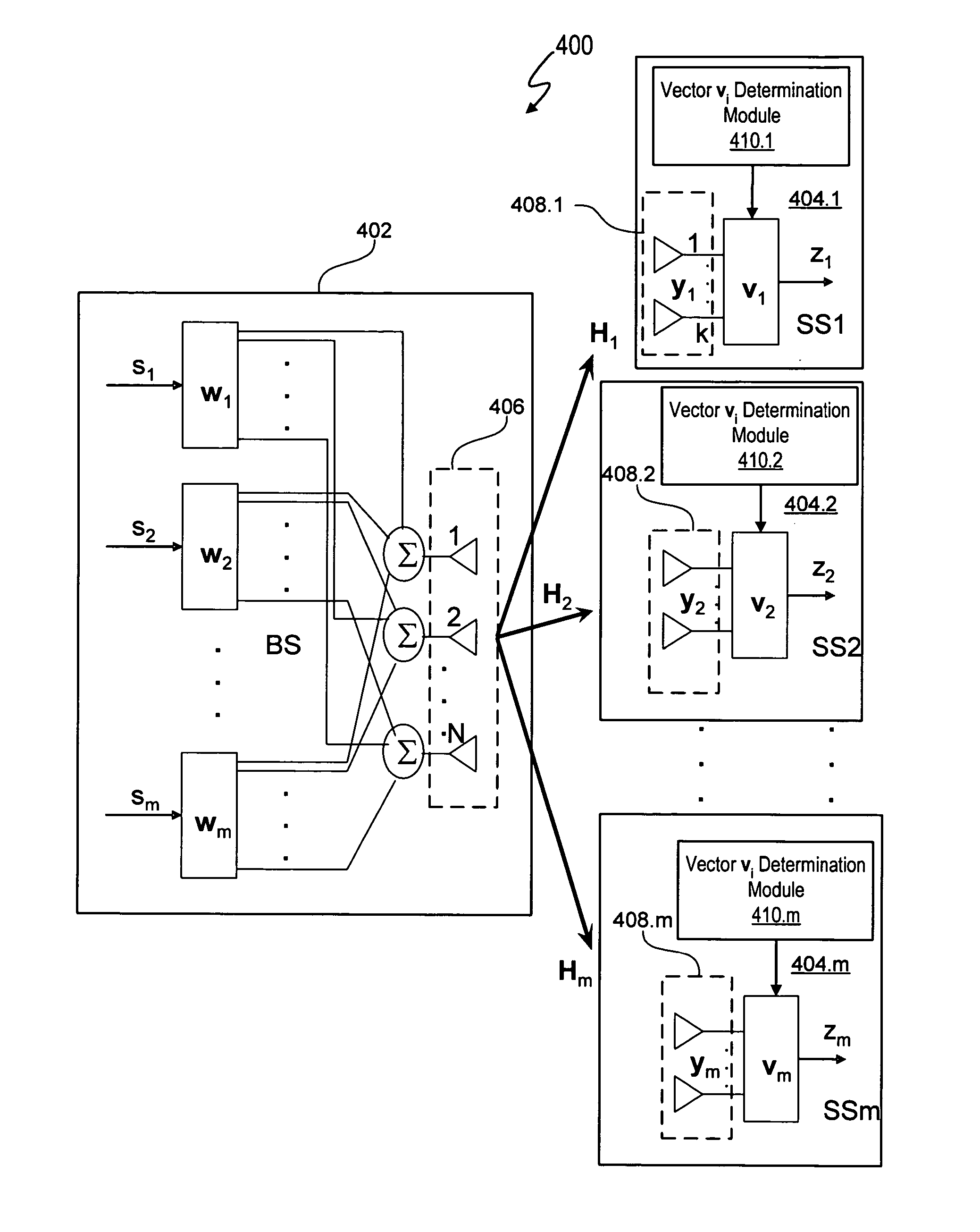
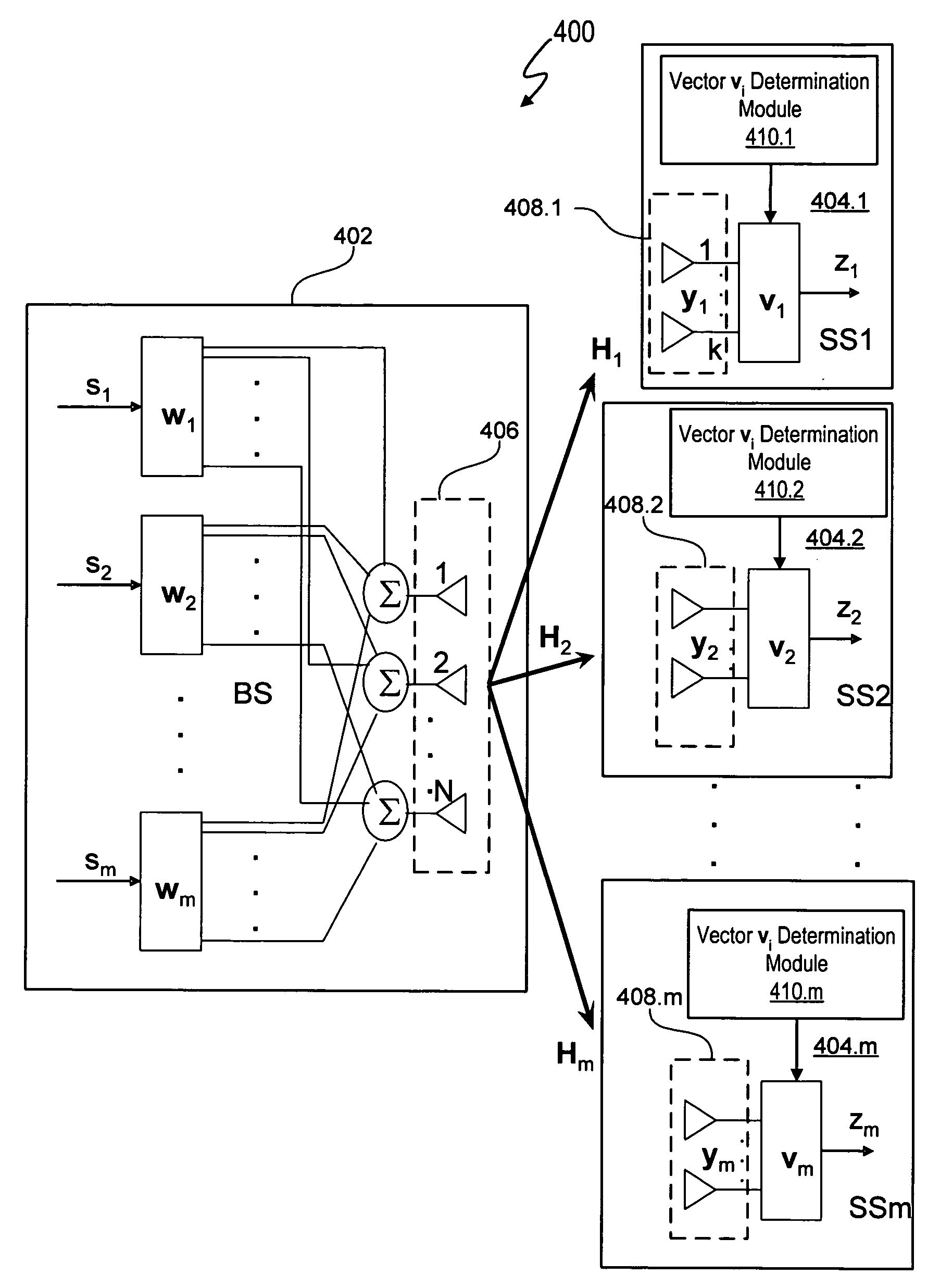
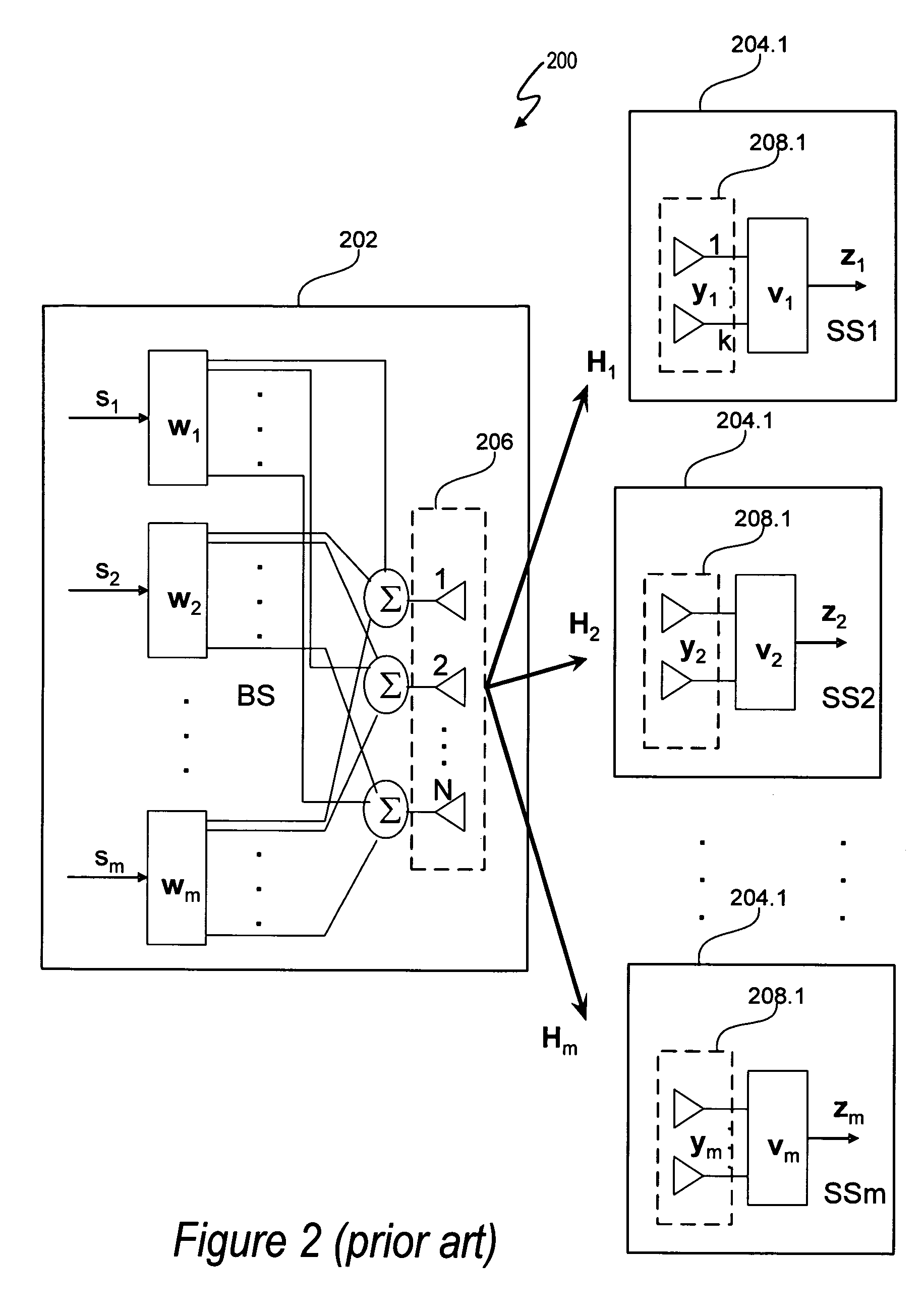
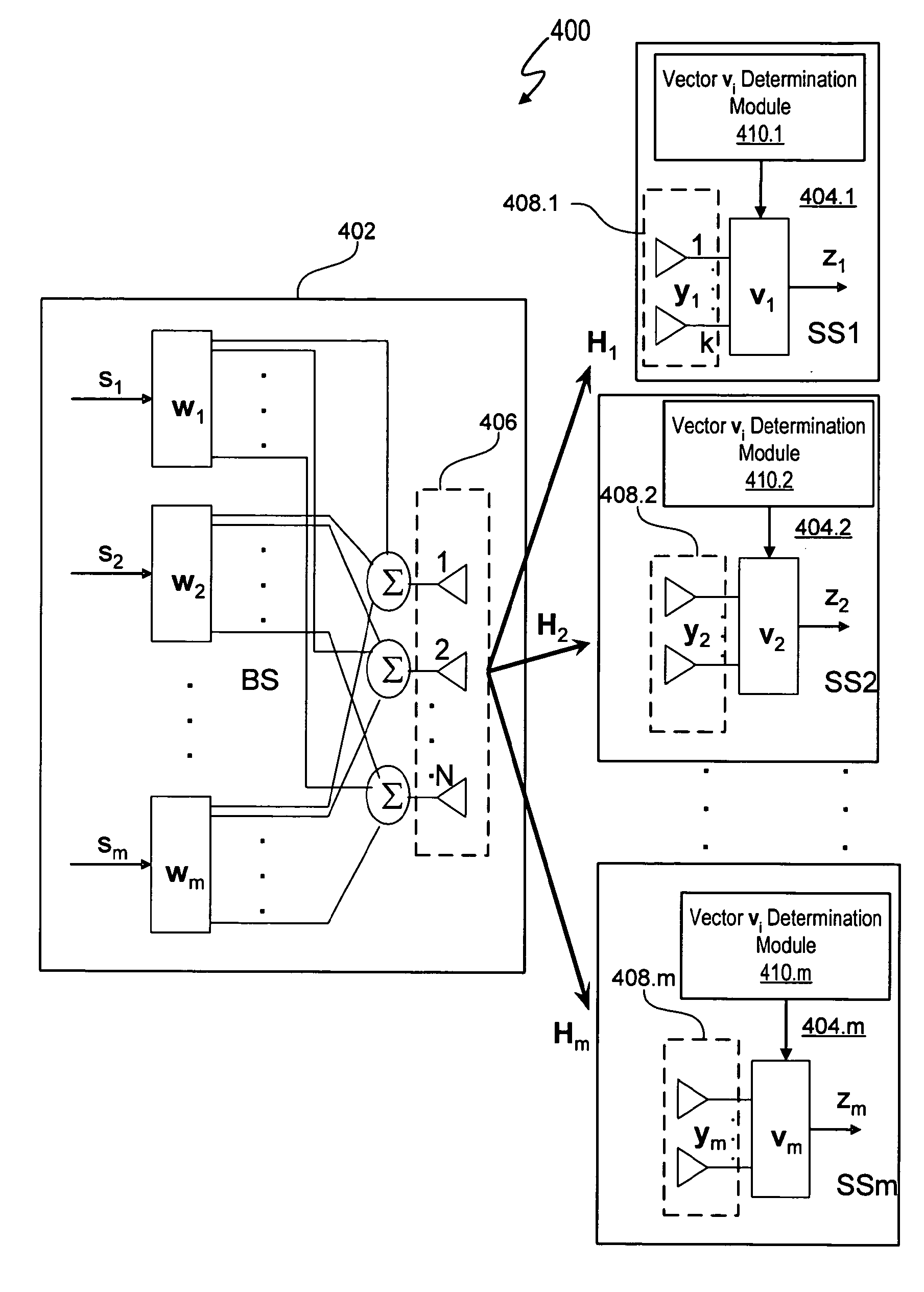
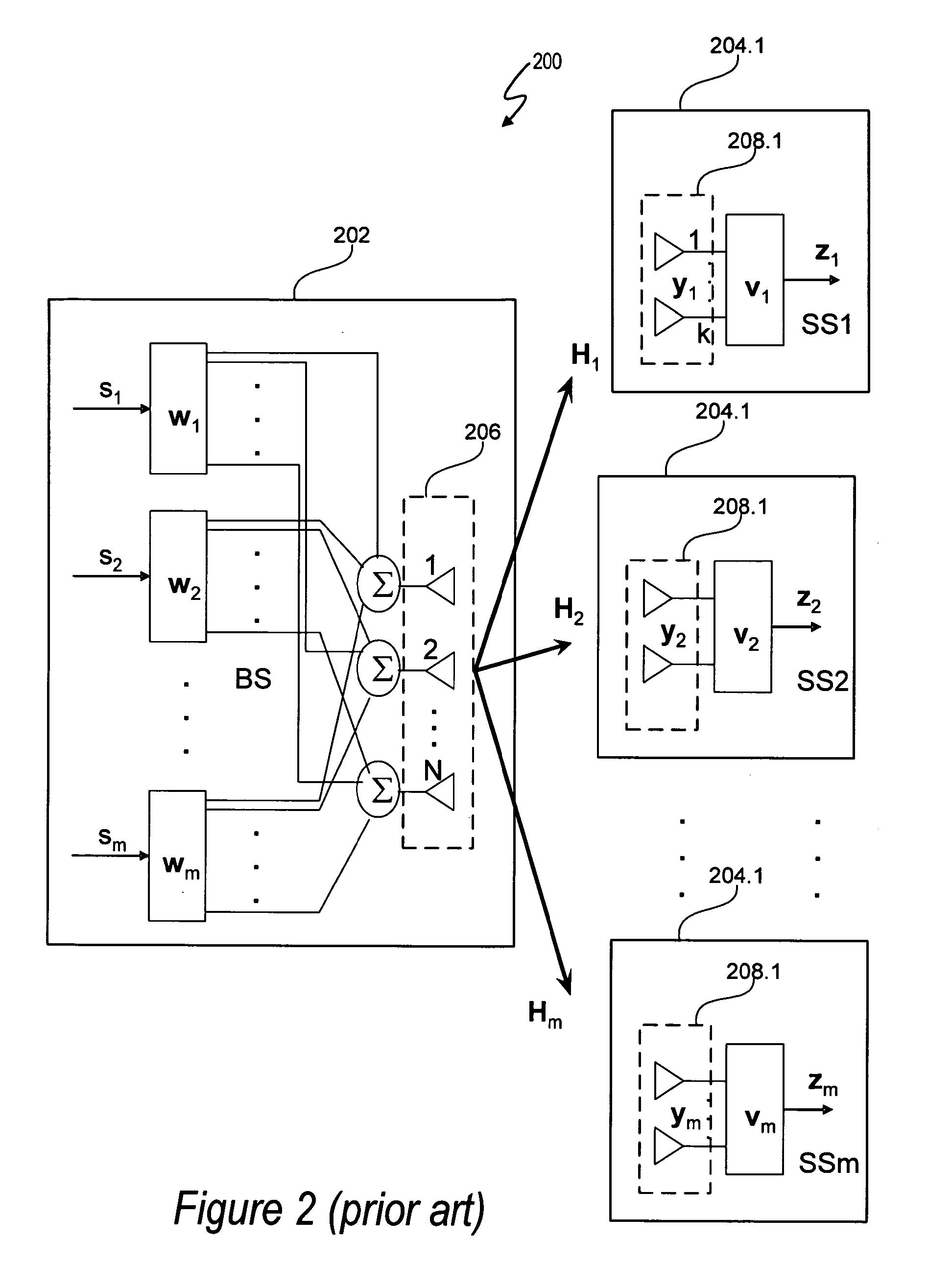
Beamforming for non-collaborative, space division multiple access systems
ActiveUS20070092019A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsBaseband systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A wireless communication system noncollaborative, multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) system determines subscriber station combining and weighting vectors that yield a high average signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR). Each subscriber station independently transmits information to a base station that allows the base station to determine a weight vector wi for each subscriber station using the determined combining vector of the subscriber station. The ith combining vector corresponds to a right singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between a base station and the ith subscriber station. Each subscriber station transmits signals using a weight vector vi, which corresponds to a left singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between the ith subscriber station and the base station. The base station uses the weight vector wi to determine the signal transmitted by the ith subscriber station.
Owner:APPLE INC
High data rate closed loop MIMO scheme combining transmit diversity and data multiplexing
InactiveUS7181167B2Improve wireless communication performanceSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentMultiplexingCommunications system
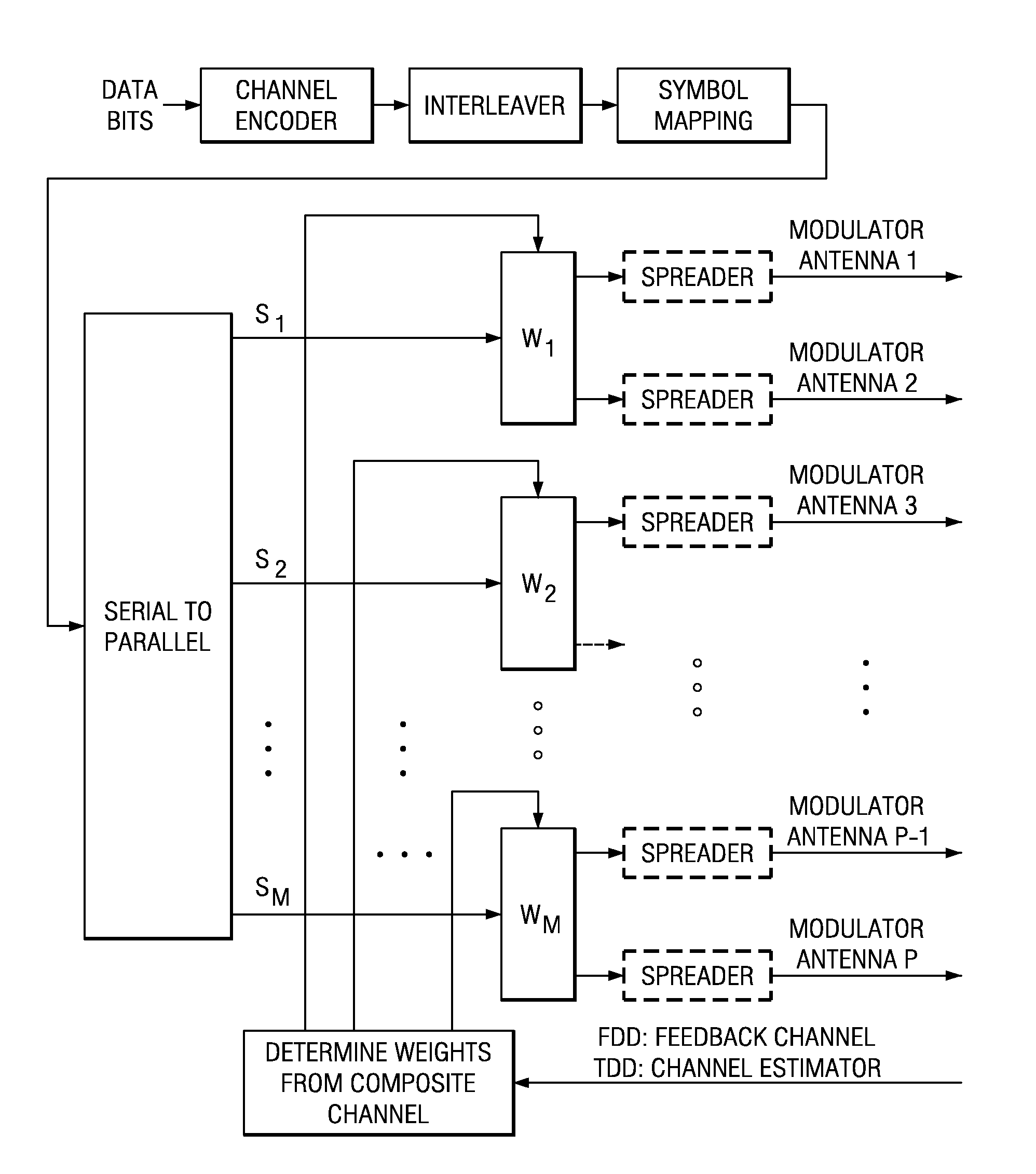
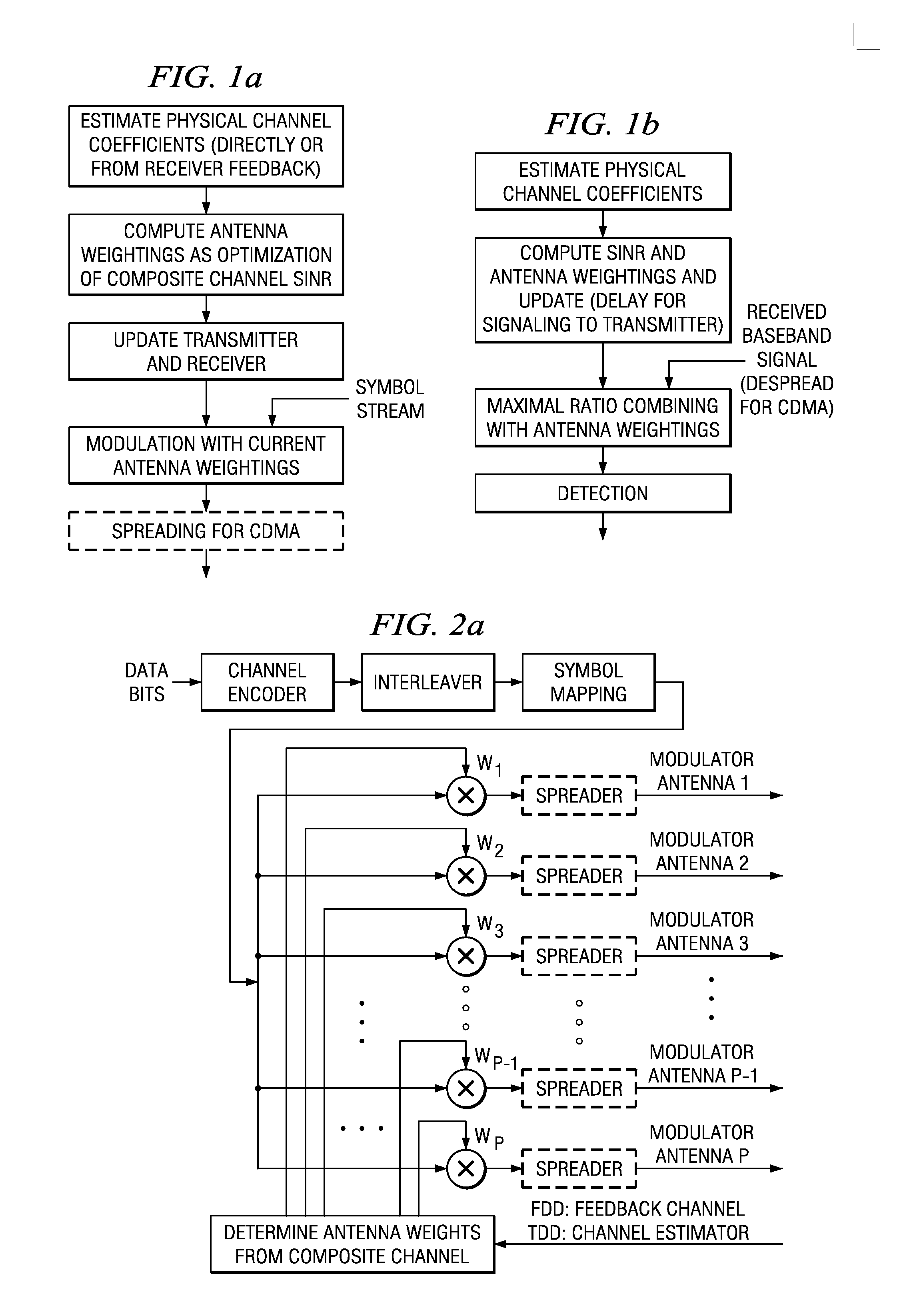
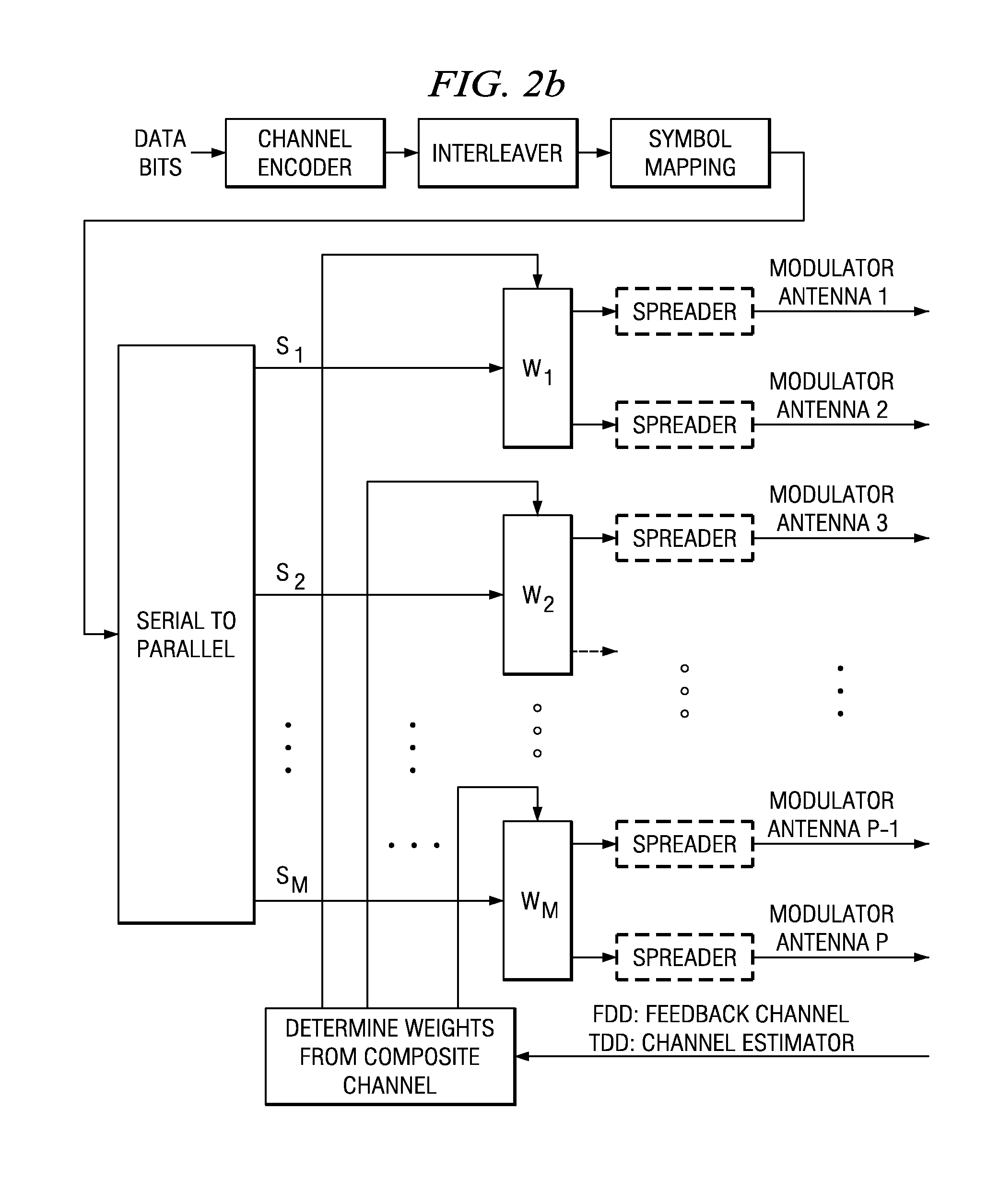
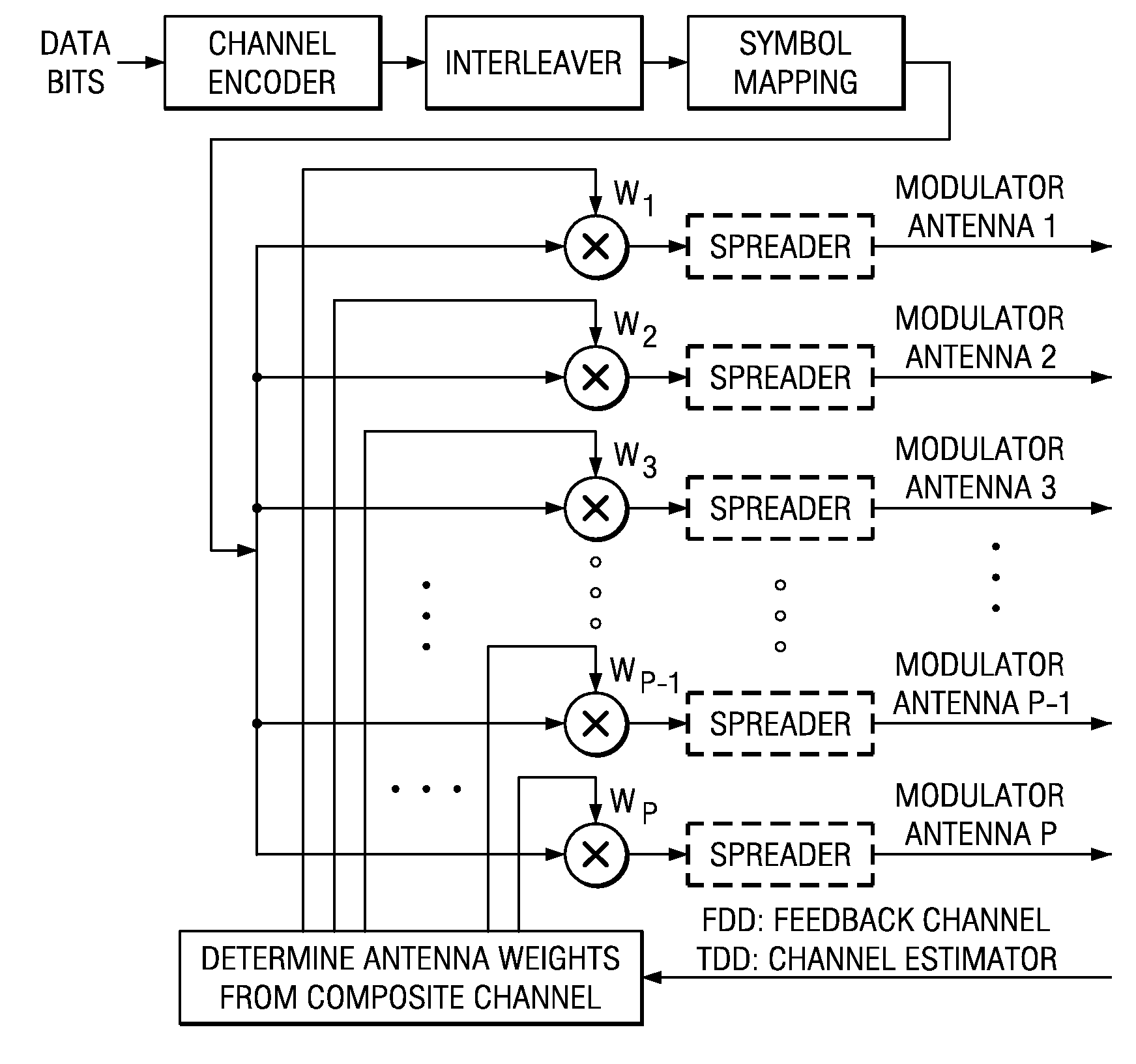
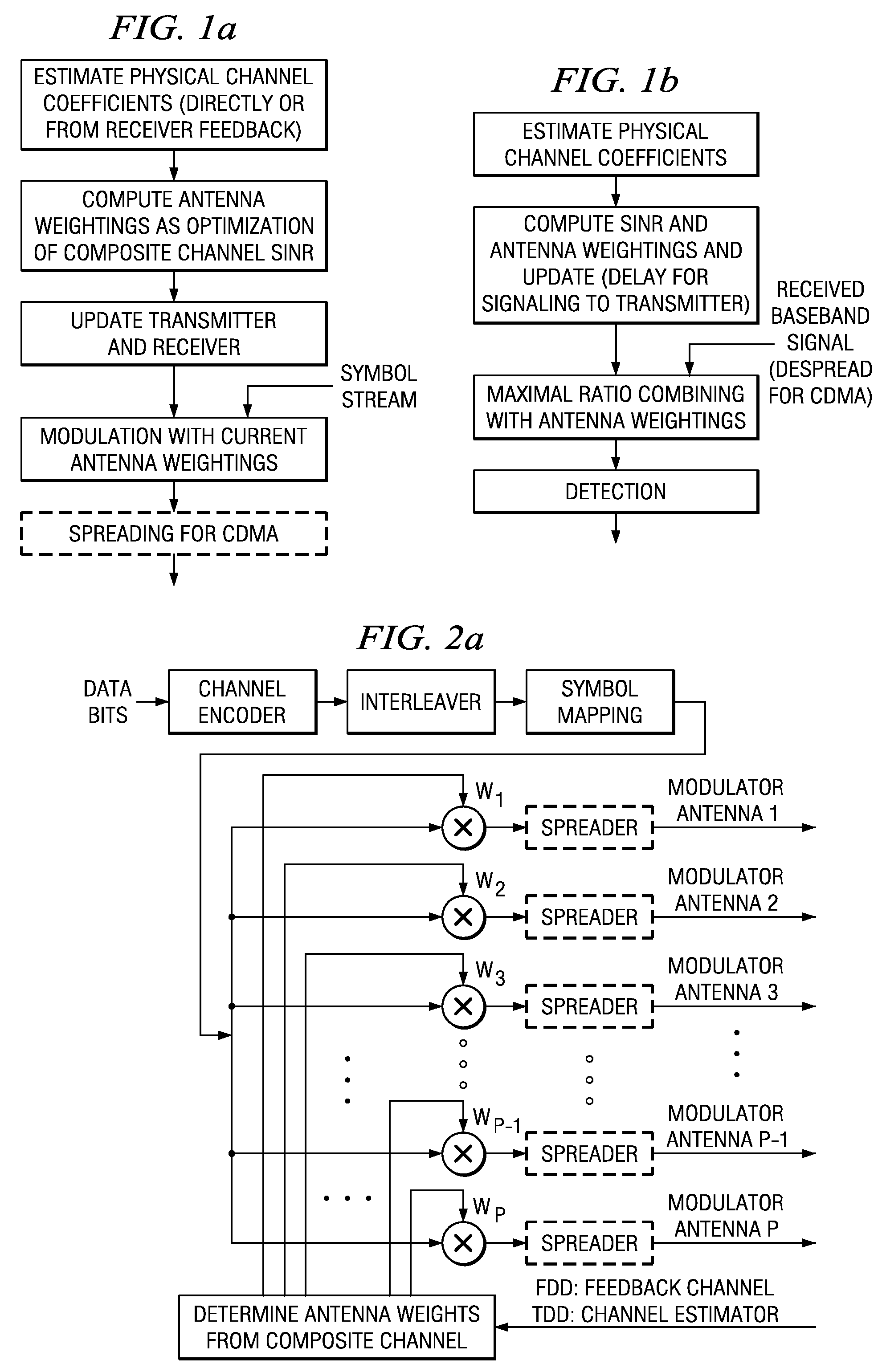
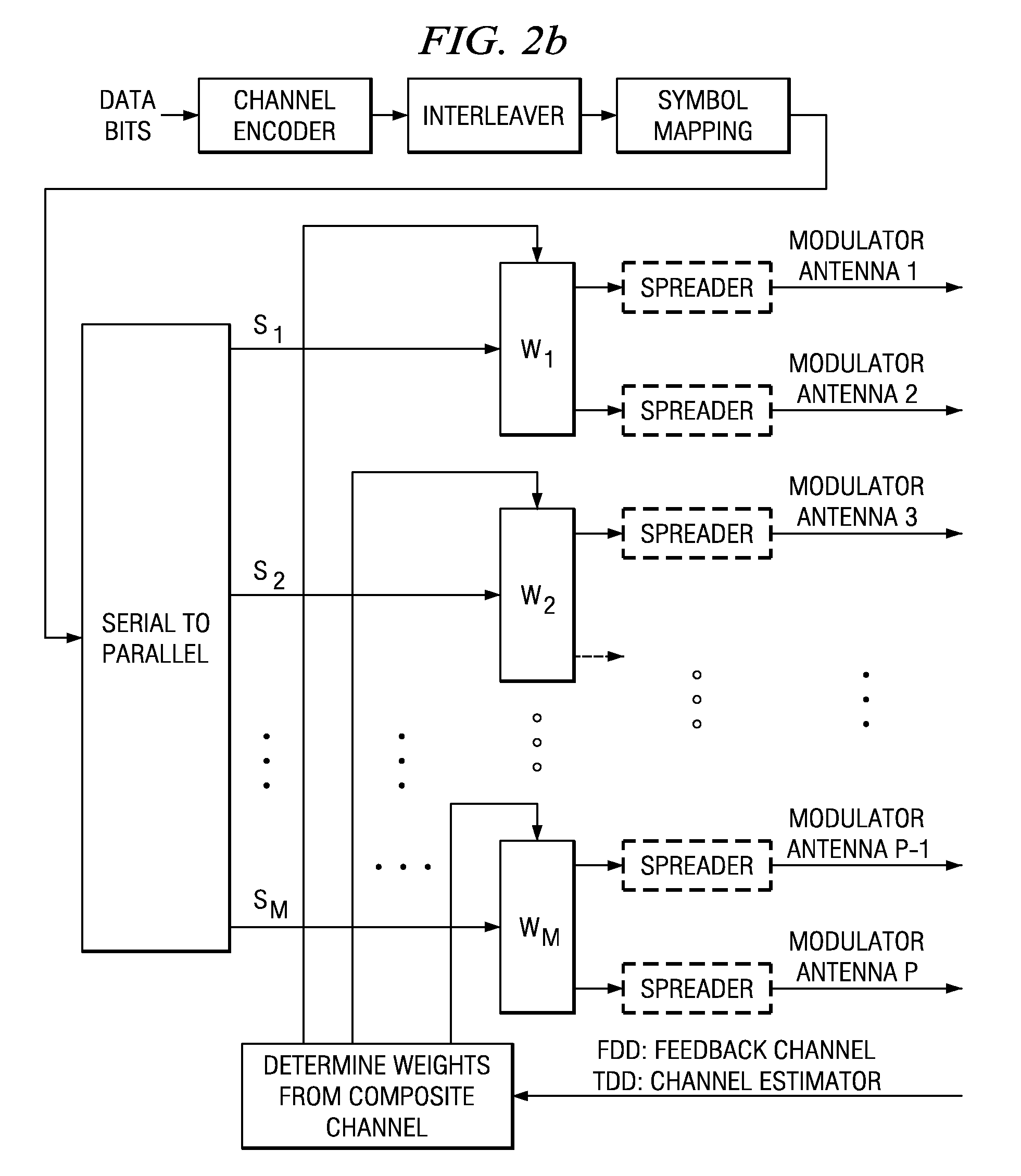
Closed loop multiple-antenna wireless communications system with antenna weights determined by maximizing a composite channel signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio minimum. Multiplexed symbol streams over subsets of antennas enhance throughput.
Owner:INTEL CORP
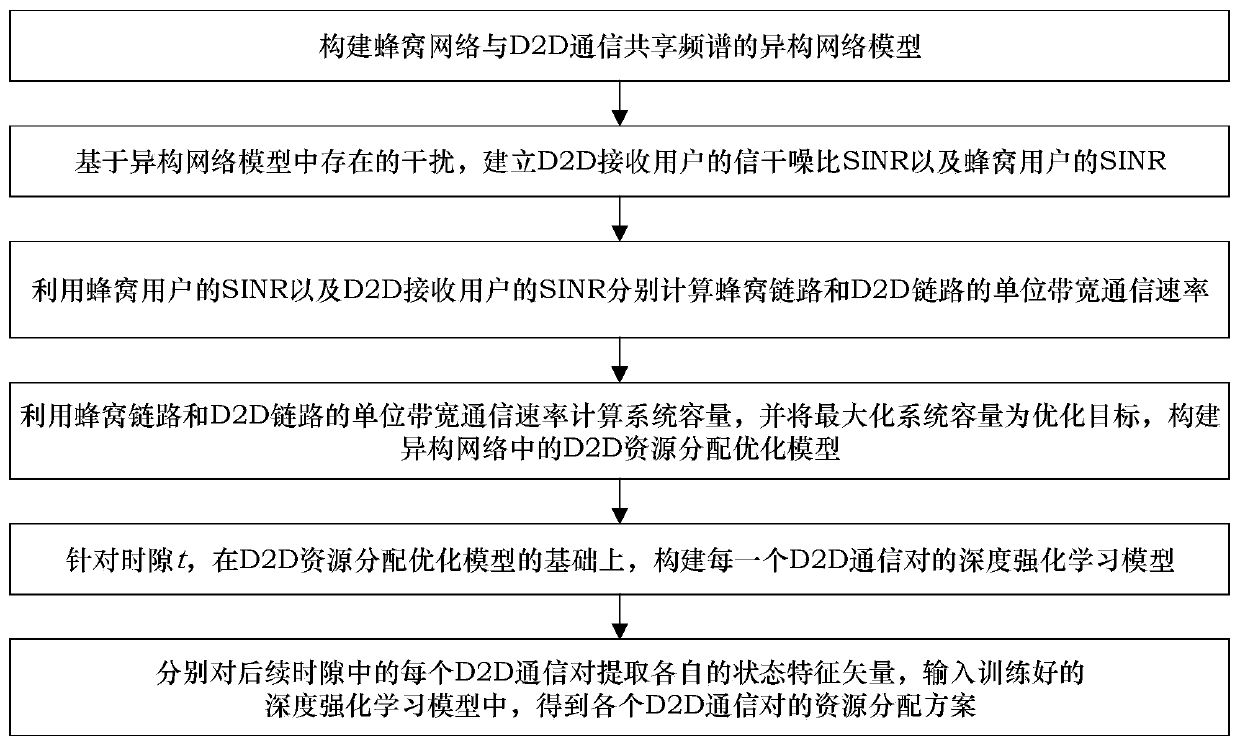
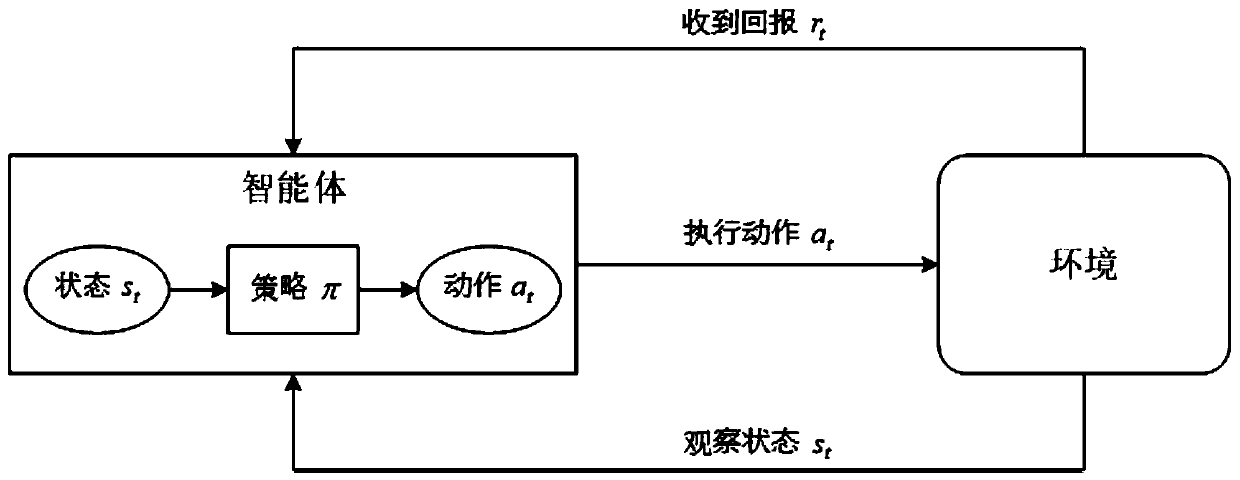
A D2D resource allocation method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning
ActiveCN109729528AOptimize transmit powerGuaranteed communication qualityConnection managementHigh level techniquesSystem capacityFrequency spectrum
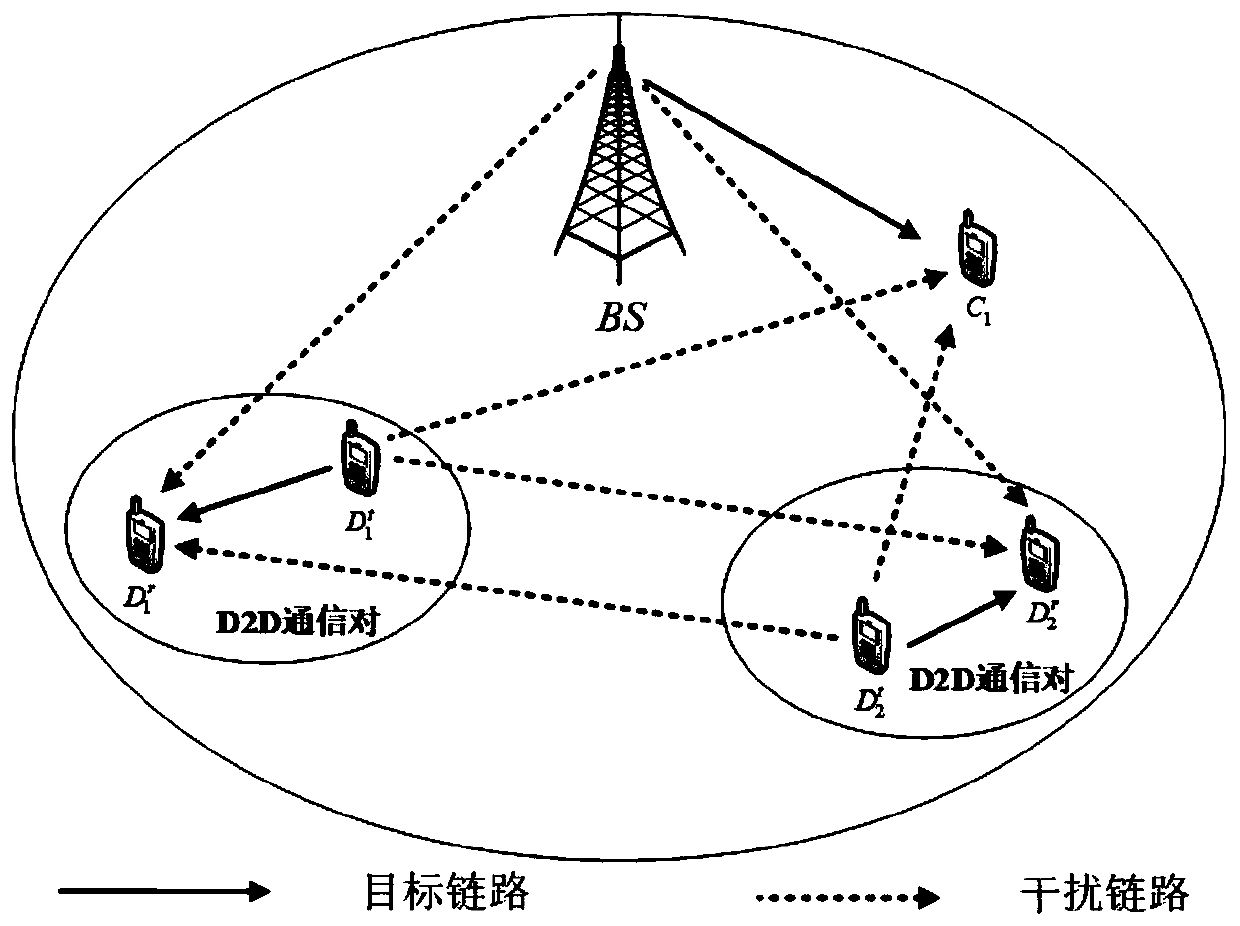
The invention discloses a D2D resource allocation method based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning, and belongs to the field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps:firstly, constructing a heterogeneous network model of a cellular network and D2D communication shared spectrum; establishing a signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) of a D2D receiving userand an SINR of a cellular user based on the existing interference, respectively calculating unit bandwidth communication rates of a cellular link and a D2D link, and constructing a D2D resource allocation optimization model in a heterogeneous network by taking the maximum system capacity as an optimization target; For the time slot t, constructing a deep reinforcement learning model of each D2D communication pair on the basis of the D2D resource allocation optimization model; And respectively extracting respective state feature vectors from each D2D communication pair in the subsequent time slot, and inputting the state feature vectors into the trained deep reinforcement learning model to obtain a resource allocation scheme of each D2D communication pair. According to the invention, spectrum allocation and transmission power are optimized, the system capacity is maximized, and a low-complexity resource allocation algorithm is provided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
High Data Rate Closed Loop MIMO Scheme Combining Transmit Diversity and Data Multiplexing
InactiveUS20060291581A1Improve wireless communication performanceSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentMultiplexingCommunications system
Closed loop multiple-antenna wireless communications system with antenna weights determined by maximizing a composite channel signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio minimum. Multiplexed symbol streams over subsets of antennas enhance throughput.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for scheduling multiple users in a communication system
ActiveUS20080219194A1Maximize diversityMaximize throughputBroadcast transmission systemsRadio transmissionCommunications systemGroup scheduling
A method and apparatus for scheduling multiuser terminals in a communication system is provided. A receiver receives feedback information from a plurality of user terminals. A user grouping unit selects terminals having a maximum Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) among terminals having the same beam index and beam subset index, from among the plurality of user terminals, and generates terminal groups using the selected terminals, each terminal group including terminals having the same beam subset index. A group scheduling unit calculates a throughput of each of the terminal groups to determine which terminal group has the maximum throughput. A random precoding unit generates random beam vectors corresponding to terminals included in the terminal group determined to have the maximum throughput, and transmits data for user terminals, included in the terminal group determined to have the maximum throughput, over the generated random beam vectors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Beamforming for non-collaborative, space division multiple access systems
ActiveUS7602837B2Diversity/multi-antenna systemsBaseband systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A wireless communication system noncollaborative, multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) system determines subscriber station combining and weighting vectors that yield a high average signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR). Each subscriber station independently transmits information to a base station that allows the base station to determine a weight vector wi for each subscriber station using the determined combining vector of the subscriber station. The ith combining vector corresponds to a right singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between a base station and the ith subscriber station. Each subscriber station transmits signals using a weight vector vi, which corresponds to a left singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between the ith subscriber station and the base station. The base station uses the weight vector wi to determine the signal transmitted by the ith subscriber station.
Owner:APPLE INC
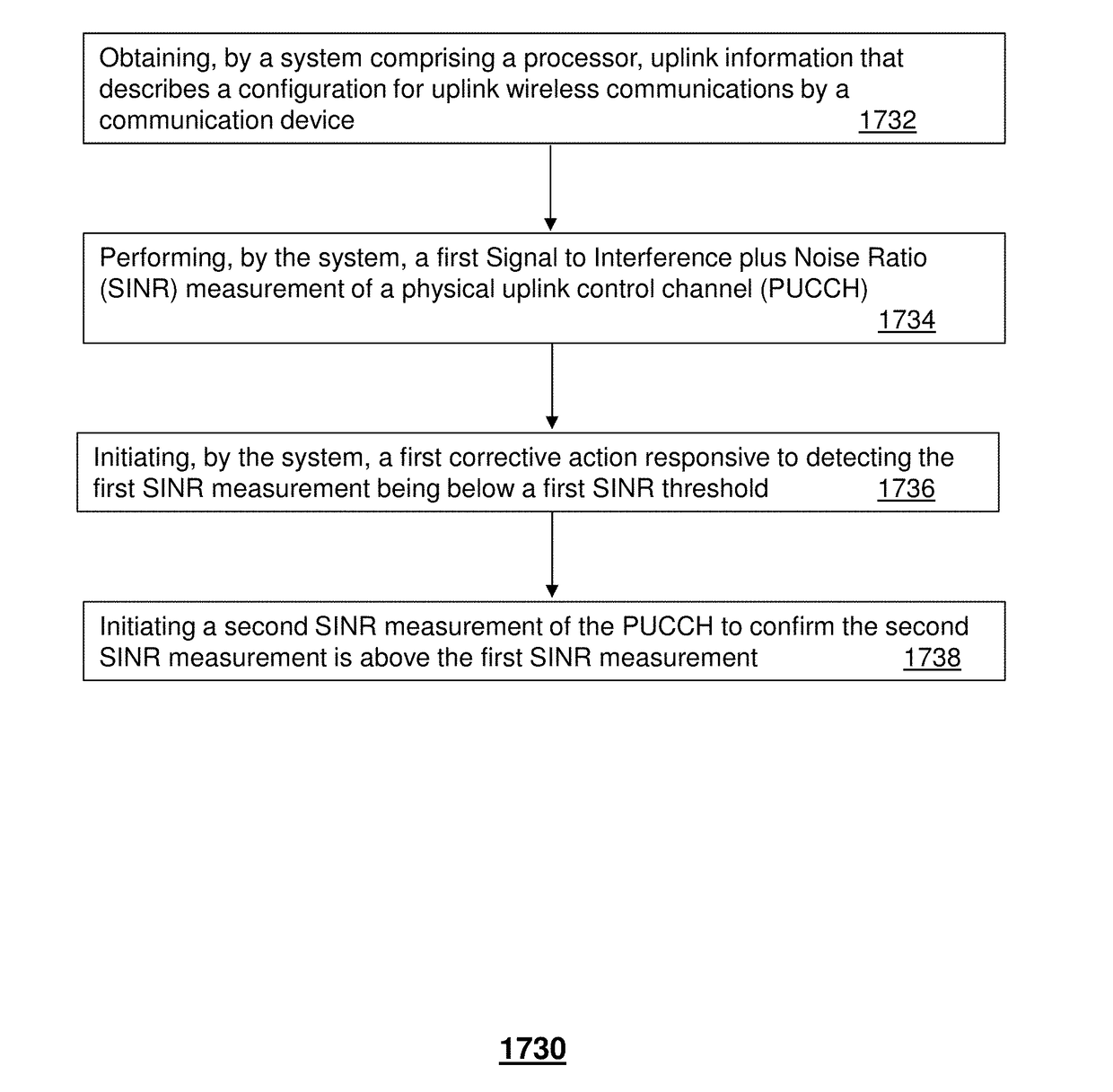
Managing interference in control channels and methods thereof
ActiveUS20180294932A1Transmission path divisionCriteria allocationTelecommunicationsSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A system that incorporates aspects of the subject disclosure may perform operations including, for example, obtaining uplink information that describes a configuration for uplink wireless communications by a communication device, wherein the uplink information comprises a first assignment of a first resource block to the communication device for transport of control information as a physical uplink control channel (PUCCH); performing a first Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) measurement of the PUCCH; initiating a first corrective action responsive to detecting the first SINR measurement being below a first SINR threshold; and initiating a second SINR measurement of the PUCCH to confirm the second SINR measurement is above the first SINR measurement. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPERCONDUCTOR CORP
Channel code decoding for the CDMA forward link
InactiveUS6996385B2Improve error correction performanceImprove estimation accuracyError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorBaseband system detailsSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioTelephone network
Channel coding is used on the forward link of a CDMA cellular telephone network to allow the CDMA mobile channel decoder to perform error correction. On a wireless link, channel code performance is improved by providing the channel decoder with an estimate of the reliability of each received symbol. This reliability information is typically the ratio of desired signal energy to interference plus noise variance at the channel decoder input. This invention improves CDMA mobile channel decoder performance using a new technique for calculating more accurate estimates of the signal to interference plus noise ratio at the input of the mobile channel decoder.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
Beamforming for Non-Collaborative, Space Division Multiple Access Systems
ActiveUS20090190688A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsBaseband systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A wireless communication system noncollaborative, multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) space division multiple access (SDMA) system determines subscriber station combining and weighting vectors that yield a high average signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR). Each subscriber station independently transmits information to a base station that allows the base station to determine a weight vector wi for each subscriber station using the determined combining vector of the subscriber station. The ith combining vector corresponds to a right singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between a base station and the ith subscriber station. Each subscriber station transmits signals using a weight vector vi, which corresponds to a left singular vector corresponding to a maximum singular value of a channel matrix between the ith subscriber station and the base station. The base station uses the weight vector wi to determine the signal transmitted by the ith subscriber station.
Owner:APPLE INC
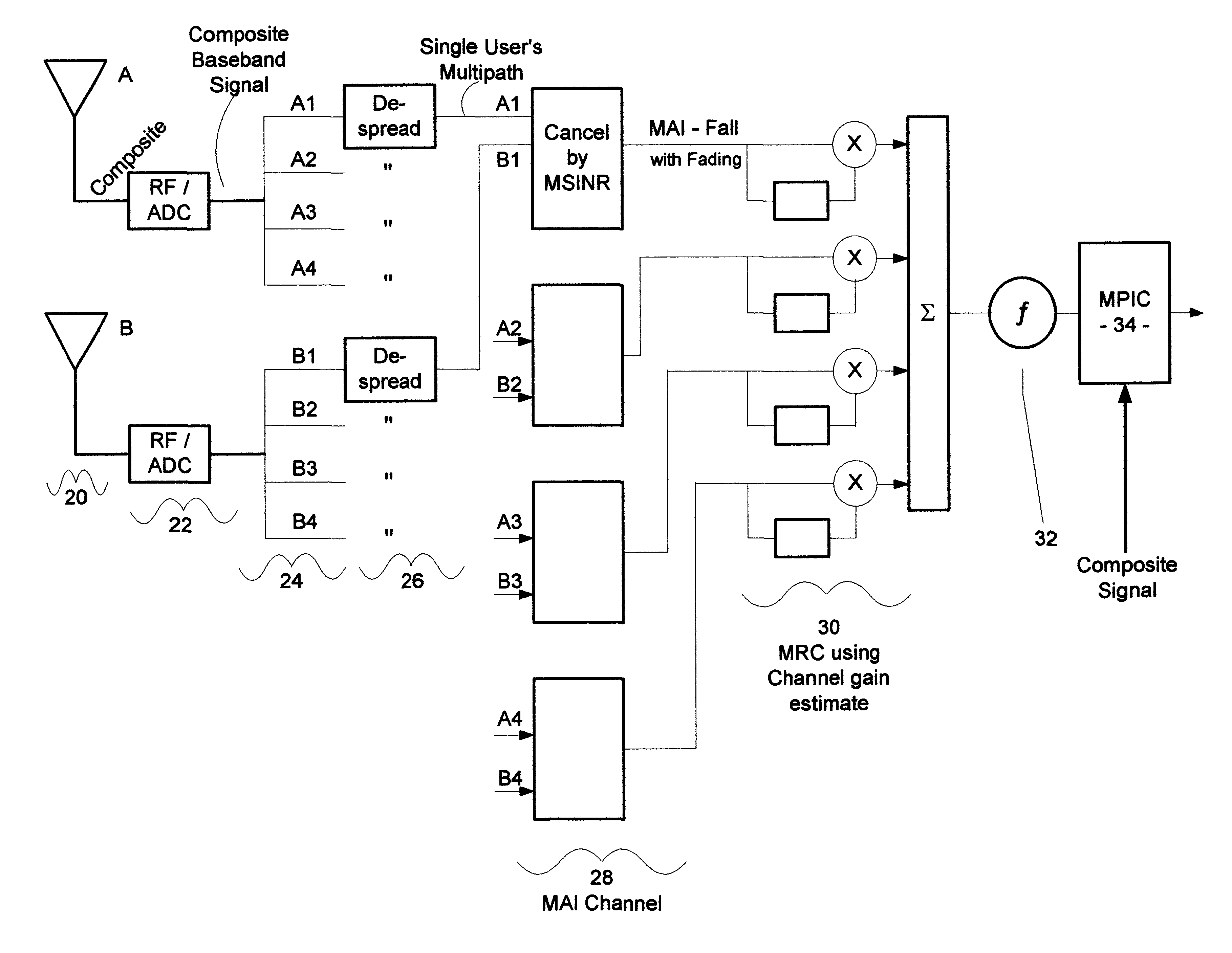
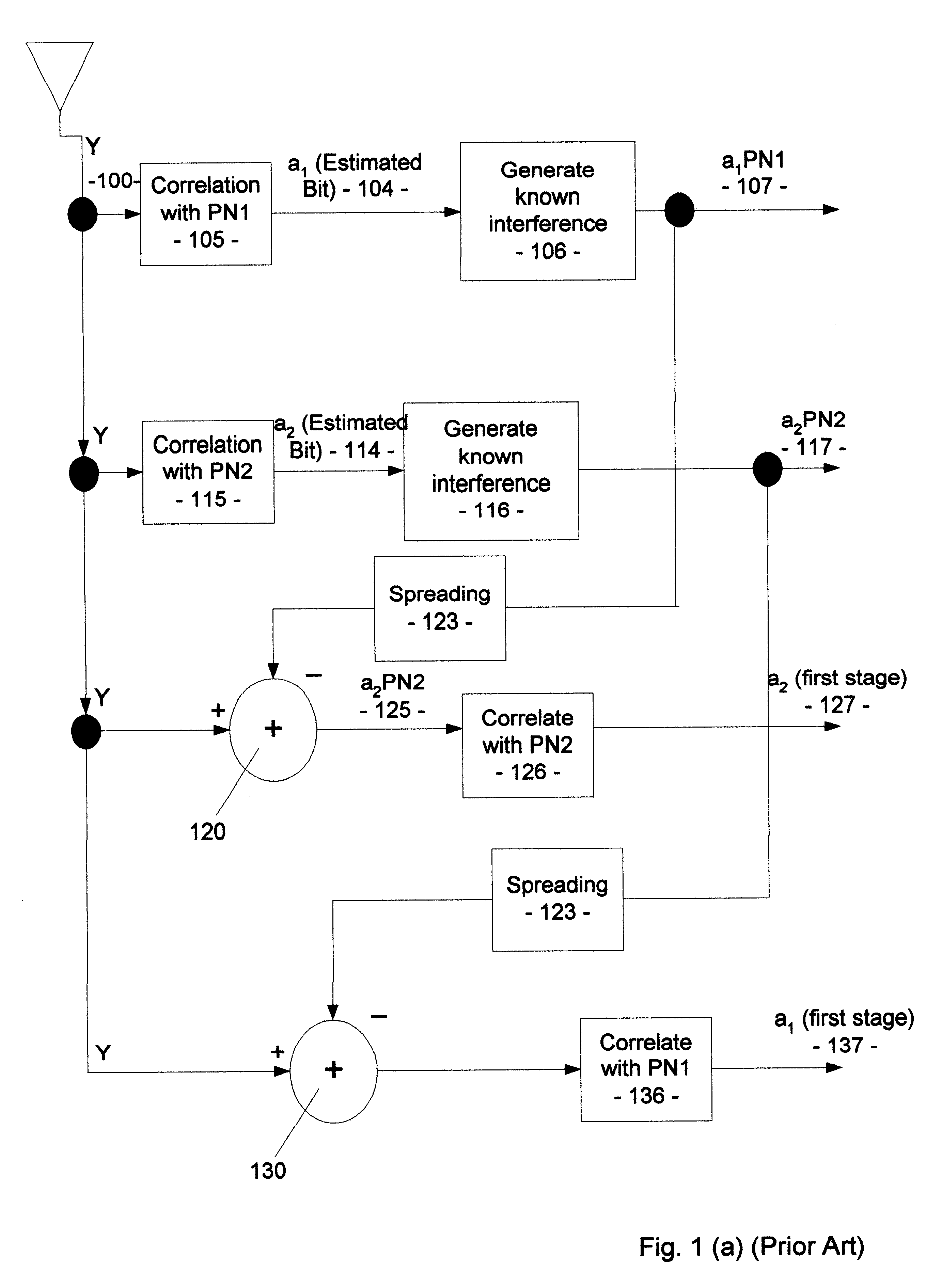
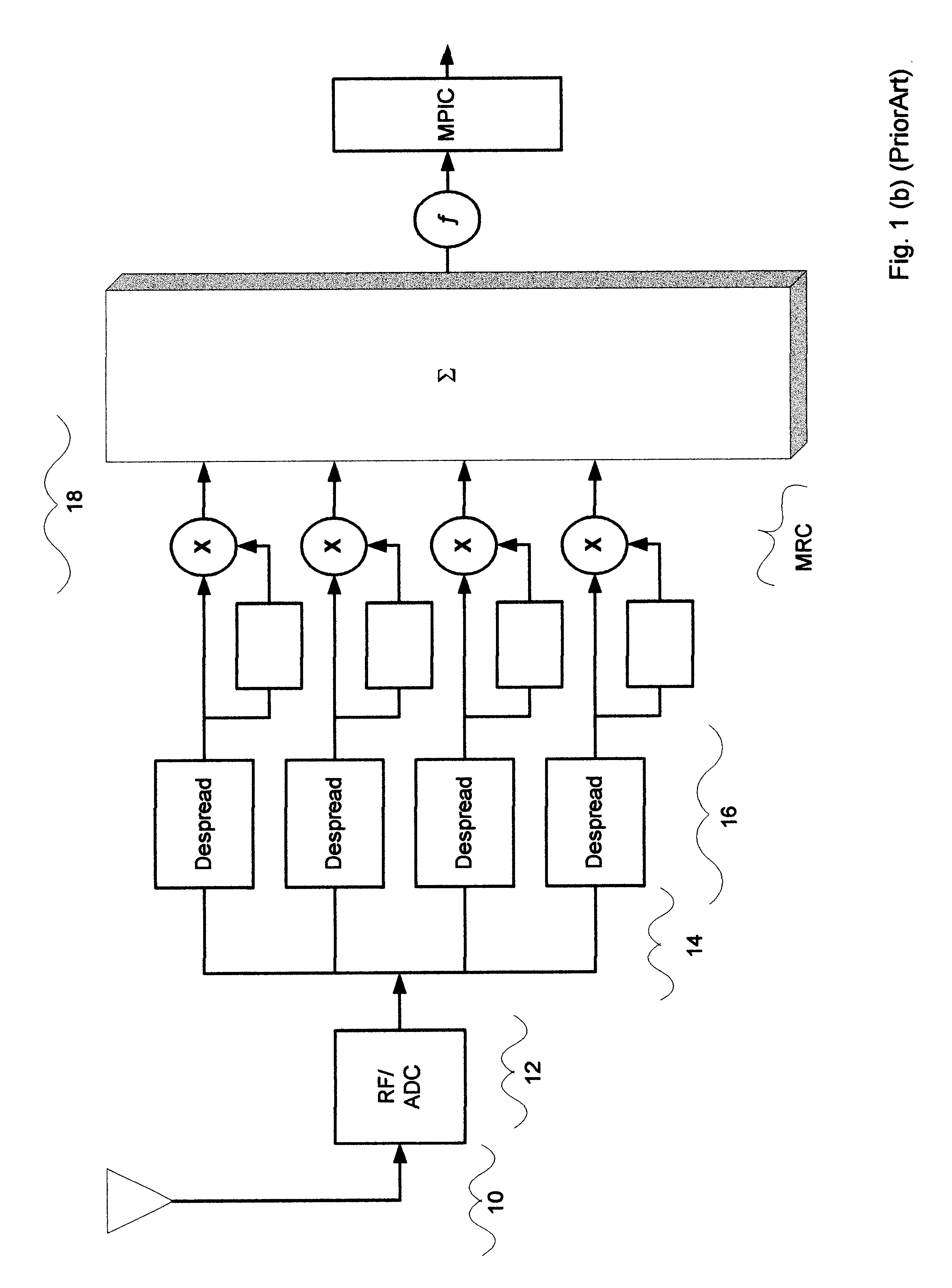
Method and system for canceling multiple access interference in CDMA wireless communication system
InactiveUS6882678B2Reduce distractionsMaximize signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioCode division multiplexSecret communicationCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A receiver for the third-generation (“3G”) CDMA wireless system is disclosed. The receiver is adapted to mitigate the correlated interference by adaptive antenna process which will maximize the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio. After the mitigation of correlated interference from first step space process, the second step is to counter fading with MRC which is optimum after the mitigation of correlated interference. After these first two steps of interference mitigation by adaptive antennas and fading compensation through MRC, the decision signal for the first stage of MPIC will have the strongest desired part and least interference compared to any MPIC available. As can be appreciated, the first stage BER of the present receiver will be the lowest. Then, this low BER will result in a more accurate MAI regeneration, which will further cause a lower BER for the next stage and any subsequent stages. Therefore, the BER of the receiver of the present invention is more likely to converge to the BER of a single user, i.e. MAI-free, faster than those in the conventional systems. In other words, for a given BER requirement, the receiver of the present invention will take the least number of iterations to achieve.
Owner:CHIBO CAPITAL
Coordinated communication method and apparatus
ActiveUS20130231125A1Improve communication performanceSite diversityReceivers monitoringCommunications systemSounding reference signal
A method and an apparatus of a coordinator forming a coordinated communication system for enhancing cell edge terminal throughput are provided. The method includes receiving information on Sound Reference Signal (SRS) reception power at a terminal for respective cells of a scheduler belonging to the coordinator from the scheduler, generating terminal distinction information for indicating whether a terminal is a cell edge terminal based on the SRS reception power information or Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) estimated from the SRS reception power information, generating interference relationship information between terminals and cells based on the SRS reception power information or estimated SINR, and transmitting the terminal distinction information and interference relationship information to the scheduler.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for determining joint transmission cells
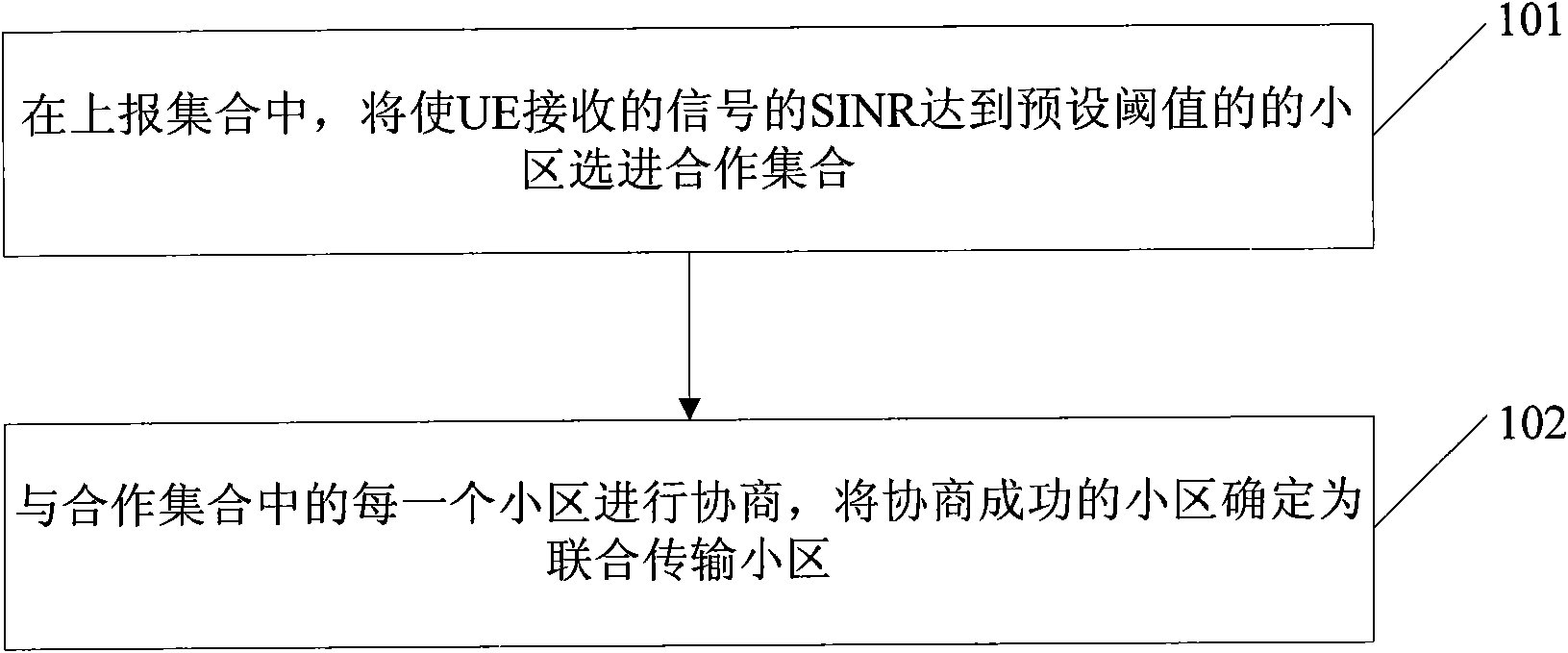
ActiveCN101938299ASpatial transmit diversityBroadcast service distributionSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioEngineering
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for determining joint transmission cells, belonging to the field of network communication. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring the signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) of a signal received by user equipment (UE) according to the channel status information (CSI) of each cell in a report set sent by the UE, and selecting the cells with the SINR reaching a preset threshold into a cooperation set; and negotiating with each cell in the cooperation set, and determining the cells successfully negotiated as the joint transmission cells. The device comprises a selection module and a negotiation module. The technical scheme provided by the embodiment can be used for predicting transmission interference from surrounding cells so as to ensure that sufficient SINR is provided to the UE.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
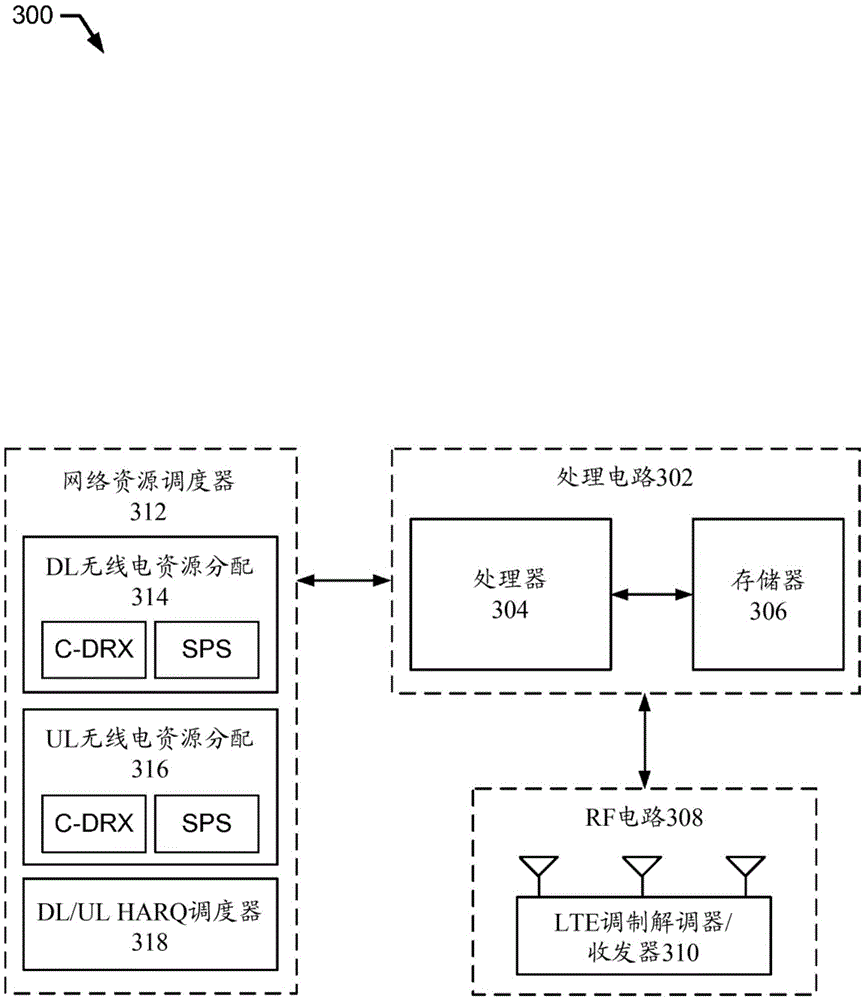
Delayed and bundled retransmissions for low bandwidth applications
ActiveCN105580445APower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioControl channel
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for performing delayed hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) communications in the downlink (DL) to reduce power consumption for a user equipment (UE) during a connected mode discontinuous reception (C-DRX) cycle. An enhanced NodeB can be configured to monitor a physical uplink control channel (PUCCH) for DL HARQ information to determine when the PUCCH contains a negative acknowledgement (NACK) message, and in response to determining that the PUCCH contains a NACK message, the eNodeB can wait until a next C DRX ON duration to transmit a HARQ DL retransmission. The eNodeB can also determine whether or not to bundle the HARQ DL retransmission in consecutive transmission time intervals, based on a signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) associated with the UE.
Owner:APPLE INC
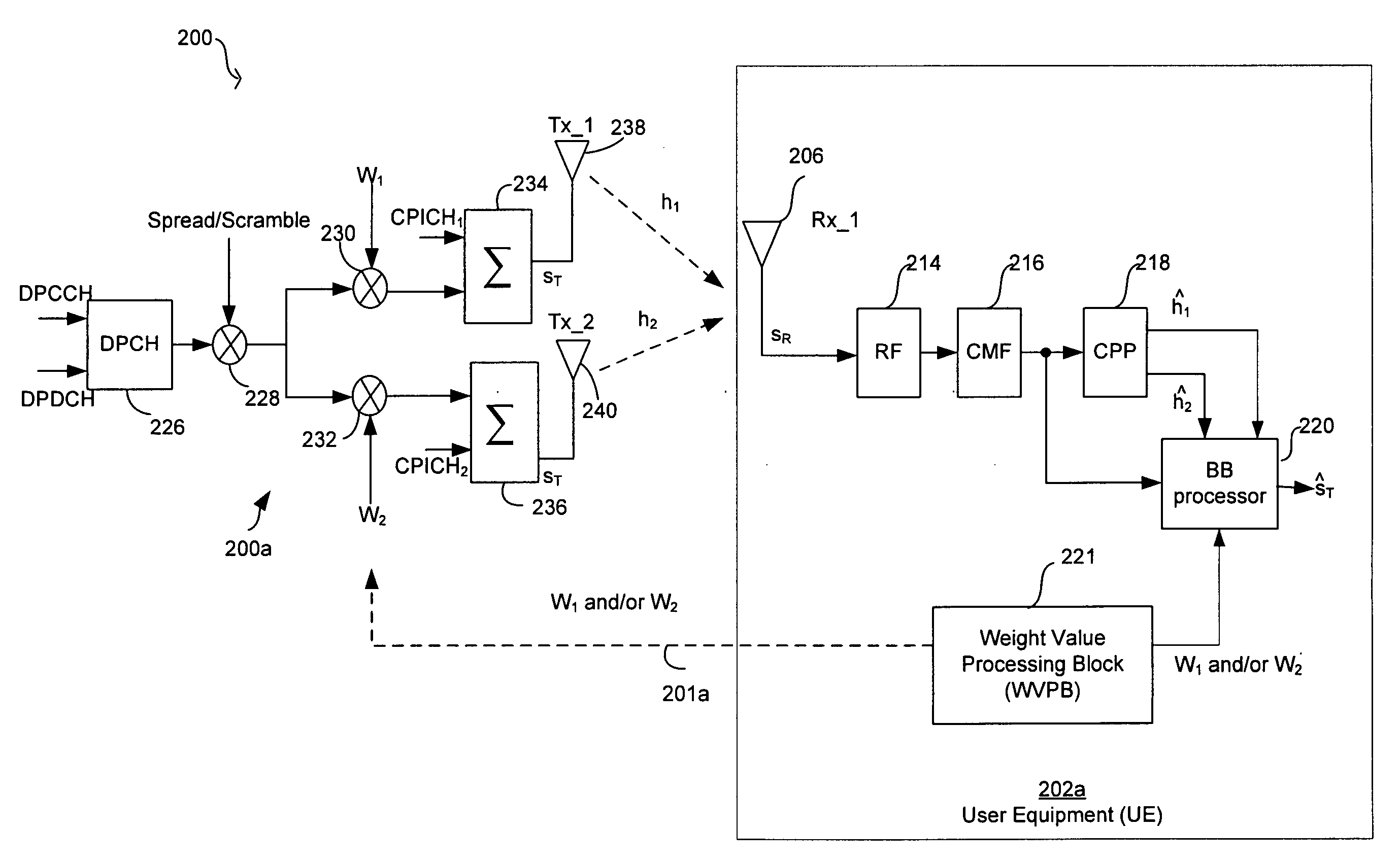
Method and apparatus to improve closed loop transmit diversity modes performance via interference suppression in a WCDMA network equipped with a rake receiver
ActiveUS20070280147A1Improve closed loop transmit diversity mode performancePolarisation/directional diversitySubstation equipmentCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
Methods and systems for processing signals in a wireless communication system are disclosed. Aspects of the method may include calculating at a receiver, a plurality of signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) values for a wireless signal, which is received from a transmitter, based on a corresponding plurality of weight values. A maximum one of the calculated plurality of SINR values may be determined. At least one weight value including one of the corresponding plurality of weight values may be fed back to the transmitter. The at least one weight value including one of the corresponding plurality of weight values may be associated with the determined maximum one of the calculated plurality of SINR values. The at least one weight value including one of the corresponding plurality of weight values may be communicated to the transmitter via at least one downlink communication channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
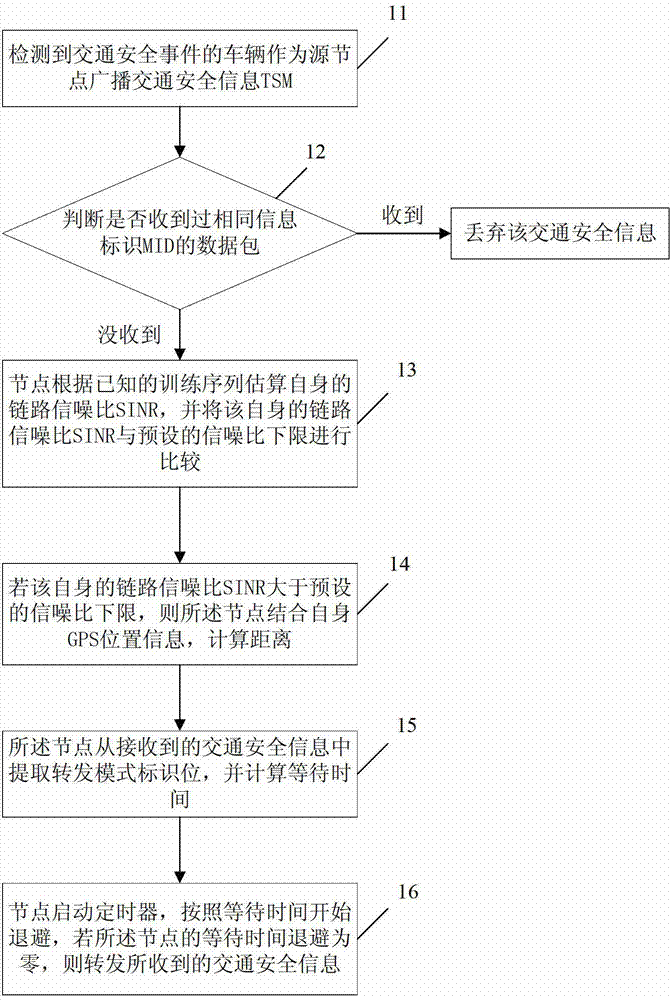
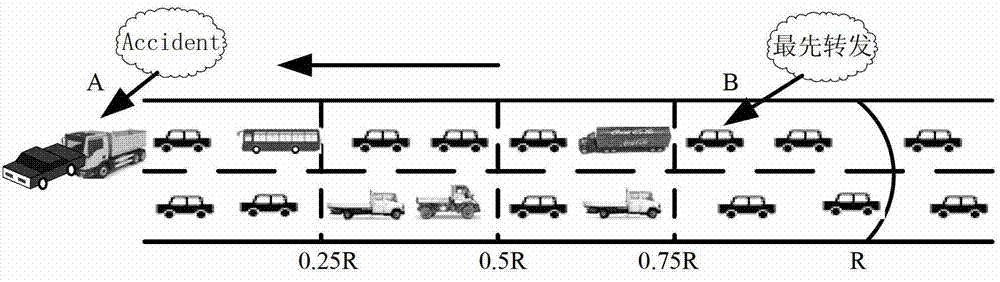
Traffic safety management (TSM) information multihop broadcasting method
InactiveCN102883274AImprove reliabilityReduce forwarding collision problemBroadcast service distributionSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioNetwork packet
The invention discloses a traffic safety management (TSM) information multihop broadcasting method. The method comprises the following steps of: detecting a traffic safety event vehicle to serve as a source node to broadcast TSM information; calculating a reference waiting time slot Tn of a highway section in which a node is positioned by the node which receives the TSM information according to a weight factor, namely the distance between the node and the source node, dynamically regulating additional forwarding waiting time Delta n according to an estimated value of link quality signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR), and calculating and acquiring waiting time tn of the node for transmitting a message; and when the waiting time tn is reduced to zero, immediately broadcasting request traffic forward (RTF), after a previous forwarding node receives the RTF, determining a single relay node to transmit a data packet, and immediately forwarding the received TSM information after the node receives the RTF. By the method, link quality information is combined, data forwarding reliability is fully guaranteed, the phenomenon of forwarding collision between multiple nodes in the same highway section is reduced at the same time, and the link load and data redundancy in a media access control (MAC) layer are effectively reduced based on an RTF / authorized traffic forward (ATF) forwarding confirmation mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
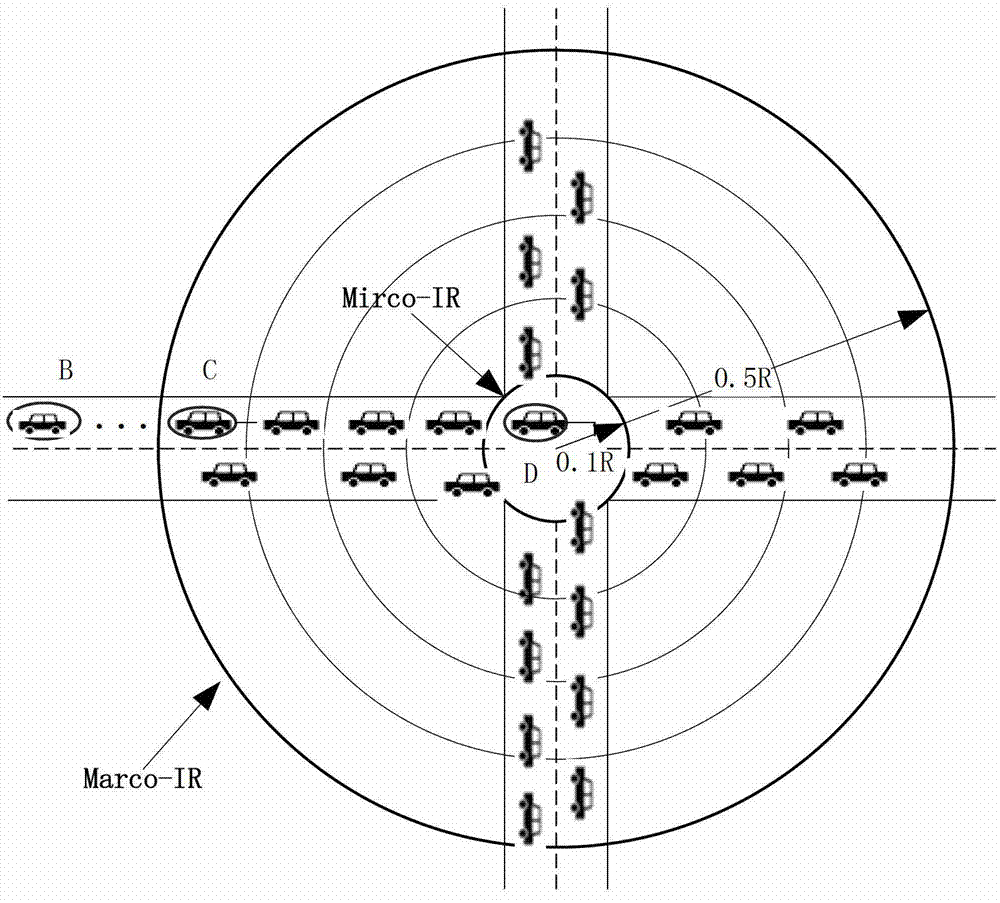
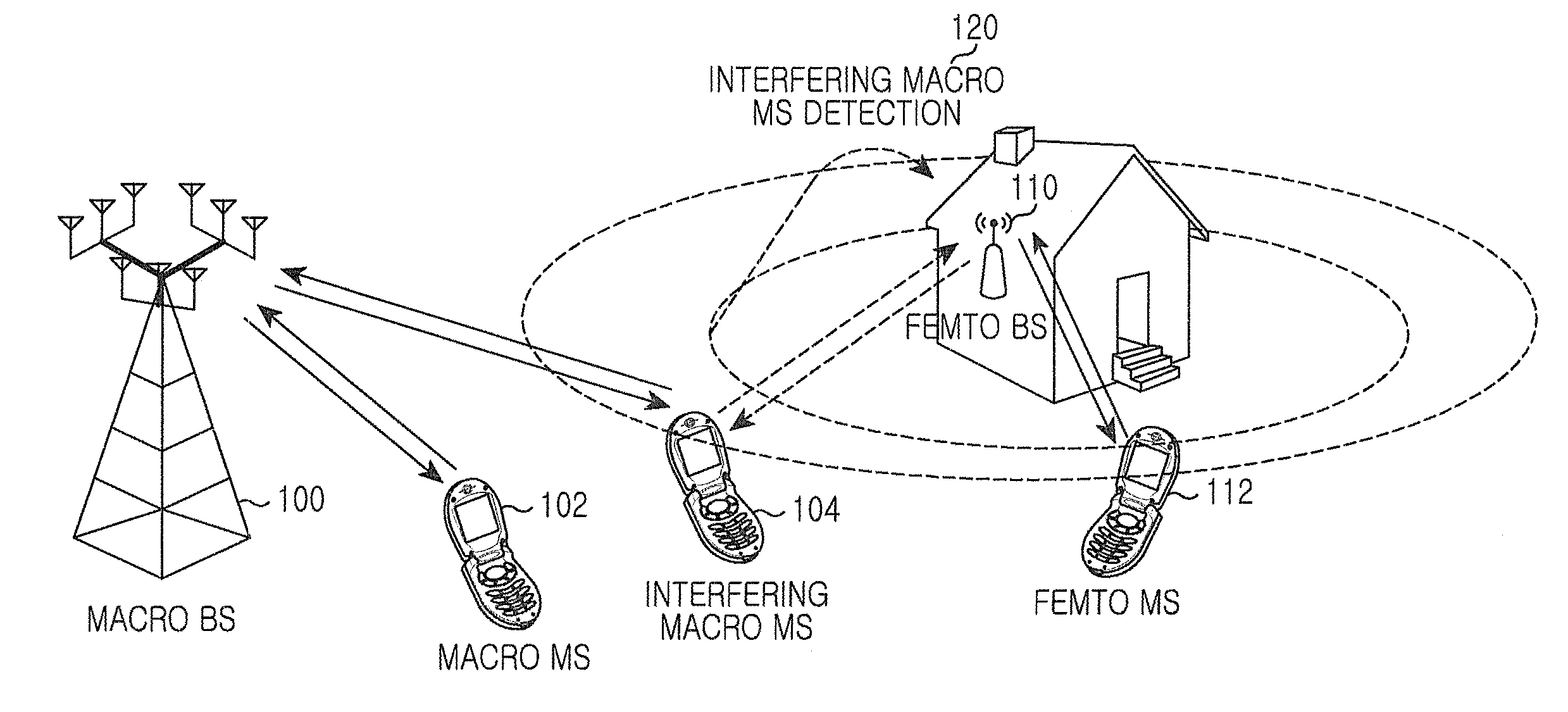
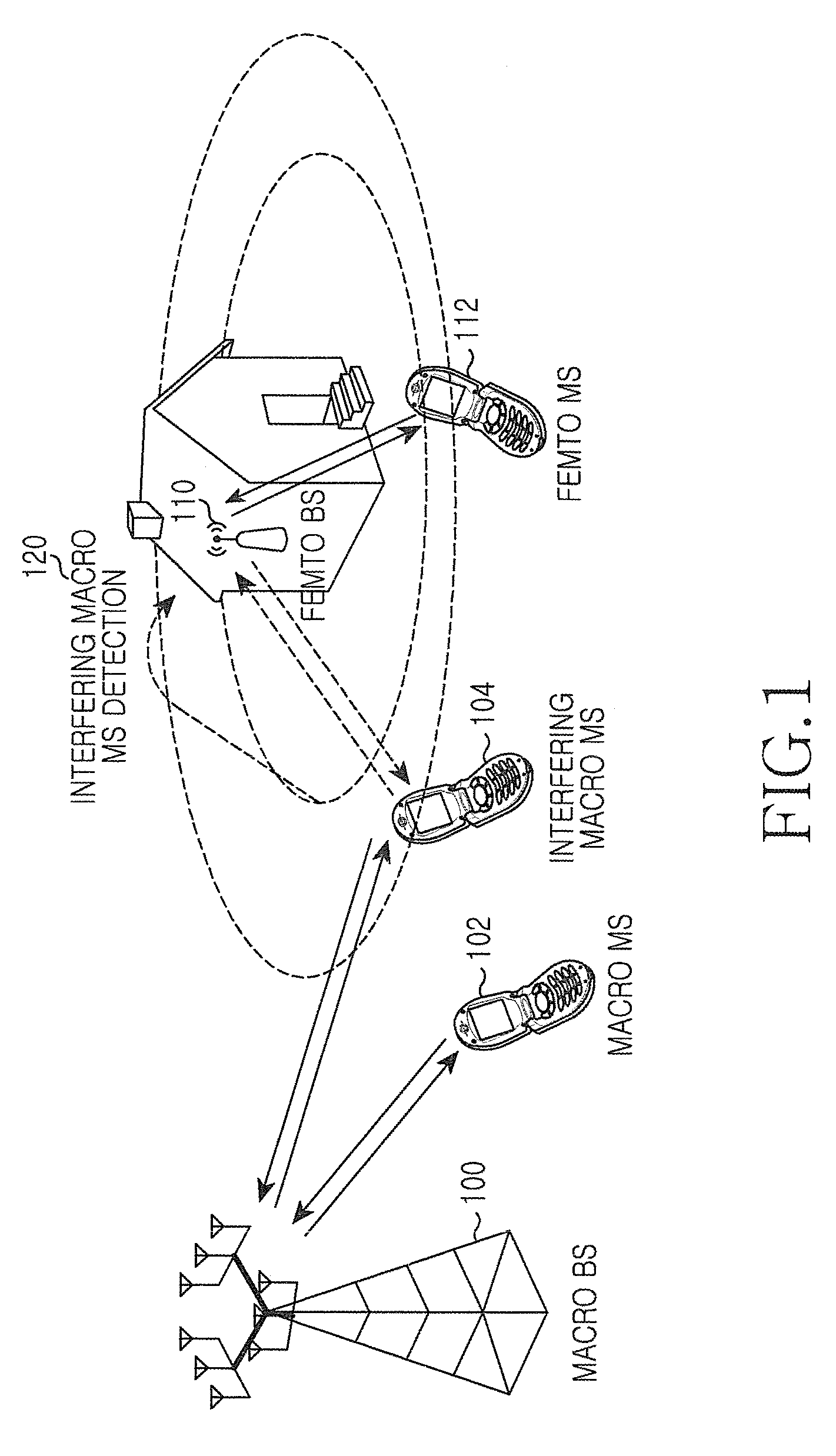
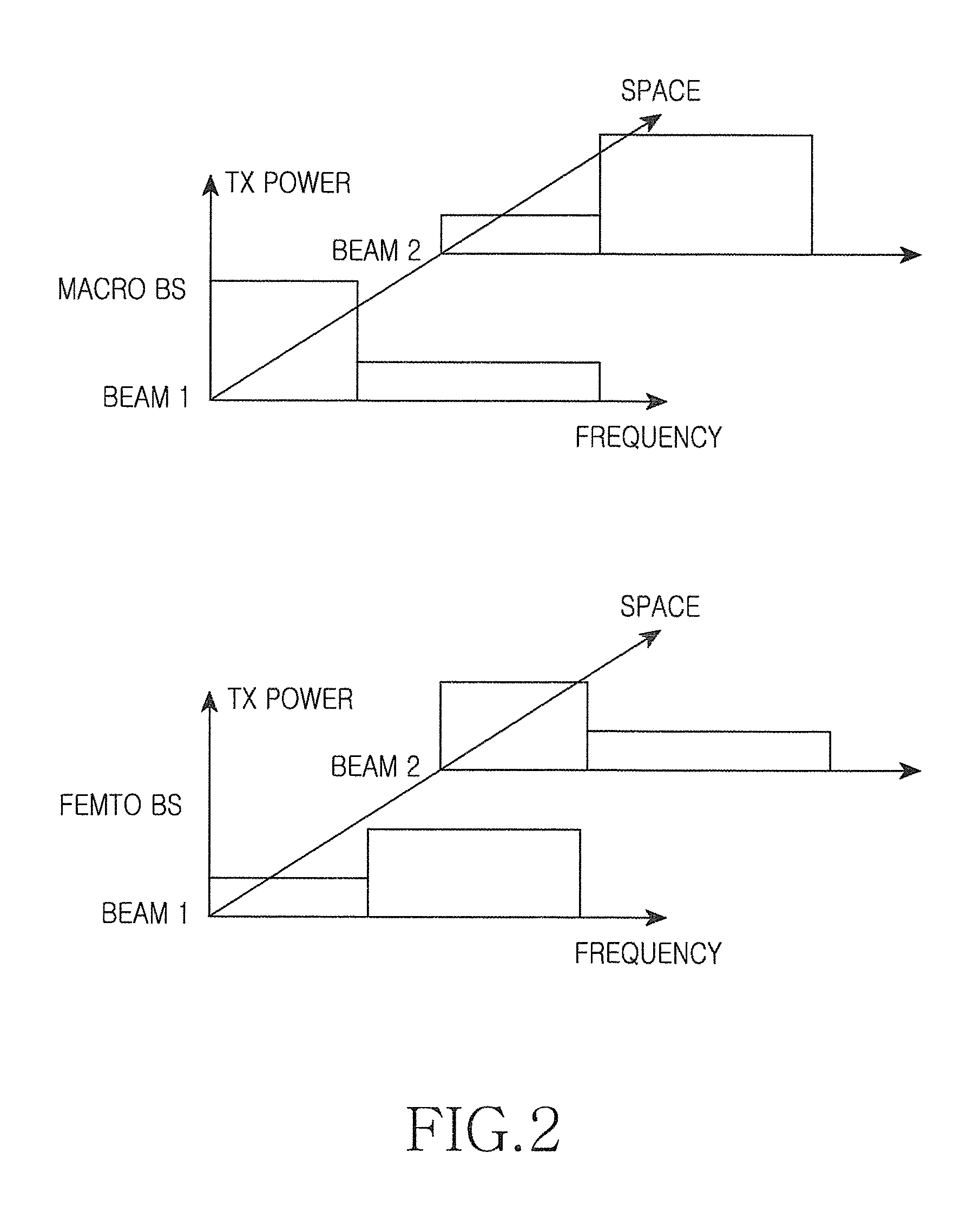
Method and apparatus for interference mitigation in heterogeneous network using beamforming
InactiveUS20120190378A1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementChannel powerSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
A method and apparatus provide interference mitigation in a heterogeneous network using beamforming. In the method, a macro Mobile Station (MS) receives a broadcast message including a Precoding Matrix Index (PMI) set restricted in a macro cell, measures a Signal-to-Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) and a channel power from an adjacent femto Base Station (BS) and calculates a PMI, determines whether to request a dedicated frequency resource for a macro MS on the basis of the measured SINR, the channel power from the adjacent femto BS, and the calculated PMI, and requests the dedicated frequency resource for the macro MS from a macro BS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for facilitating packet scheduling for a hybrid communication network
InactiveUS20130016666A1Convenient ArrangementWireless commuication servicesSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioPacket scheduling
Methods, apparatus and computer program products facilitate scheduling in a hybrid communication network with mobile devices of the first type such as device-to-device (D2D) mobile terminals and second type of mobile terminals such as cellular terminals. A scheduling activity factor is calculated based at least in part on a total number of both mobile devices of the first type and second type of mobile terminals, which is sent to at least one first type of mobile terminal. After signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) information is received from the at least one first type of mobile terminal after transmission of the scheduling activity factor, the first type of mobile terminal may be scheduled separately from second type of mobile terminals, based at least in part on the SINR information which is utilized to establish a predefined or determined threshold.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for effective multi-cell interference control service
ActiveUS20100159972A1Solve co-channel interferenceSite diversityTransmission monitoringQuality of serviceSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
There are provided a method and apparatus for an effective multi-cell interference control service, to make it possible for users located at a cell boundary to dynamically select a suitable interference control technique by monitoring interference information collected by user terminals and network conditions of a serving base station and adjacent base stations to solve co-channel interference by adjacent cell users.The apparatus for a multi-cell interference control service comprises: a user terminal for requesting interference control from a BS (base station); and a serving BS for requesting the interference control from an adjacent BS, wherein the user terminal comprises: an SINR (signal to interference plus noise ratio) measurement unit for sensing interference level of an adjacent cell; a collaboration determination unit for determining whether to collaborate with the adjacent BS, considering a user QoS (quality of service); a collaboration gain determination unit for requesting multi-cell interference control, considering interference control gain; and a collaboration request signal transmission unit for requesting collaboration with the adjacent BS from the serving BS, and wherein the serving BS comprises: a collaboration gain information collection unit for collecting collaboration gain information of the user terminal; an inter-cell signal control unit for requesting inter-cell interference control; and a service start determination unit for determining whether to start an interference control service with a collaborating adjacent cell.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
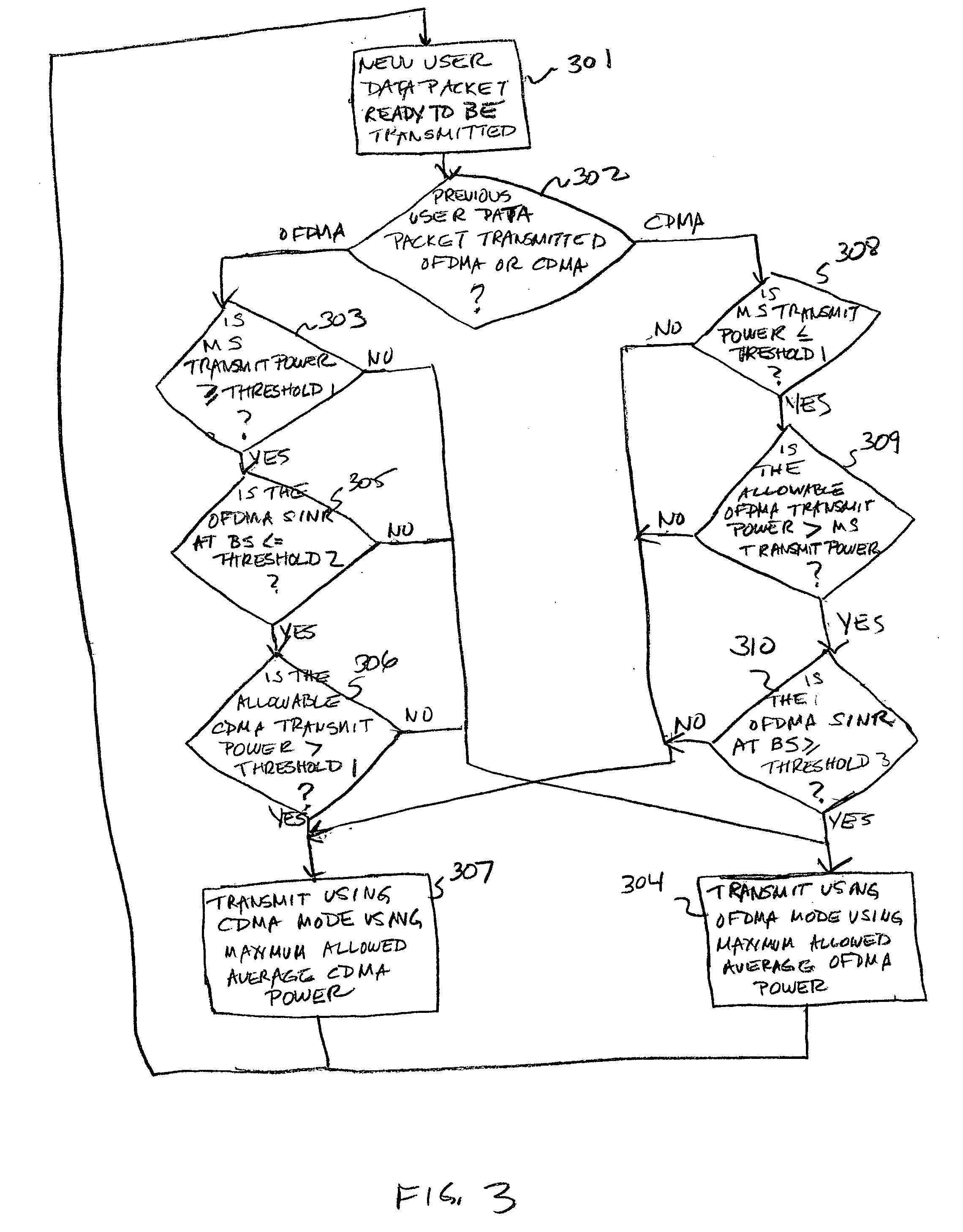
Method of switching modes of uplink transmission in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20080013476A1Optimal data rateMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemUplink transmission
A hybrid multi-mode mobile station makes a decision either to encode and modulate a new user data packet using the same OFDMA or pre-coded CDMA mode used for the last retransmission of a previous packet or to switch modes based on inputs of a measured average transmission power of the previous packet and a Signal-to-Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR) as determined from measurements made by the base station and either directly reported to the mobile station or calculated by the mobile station from measurements made by the base station that are reported back to the mobile station.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
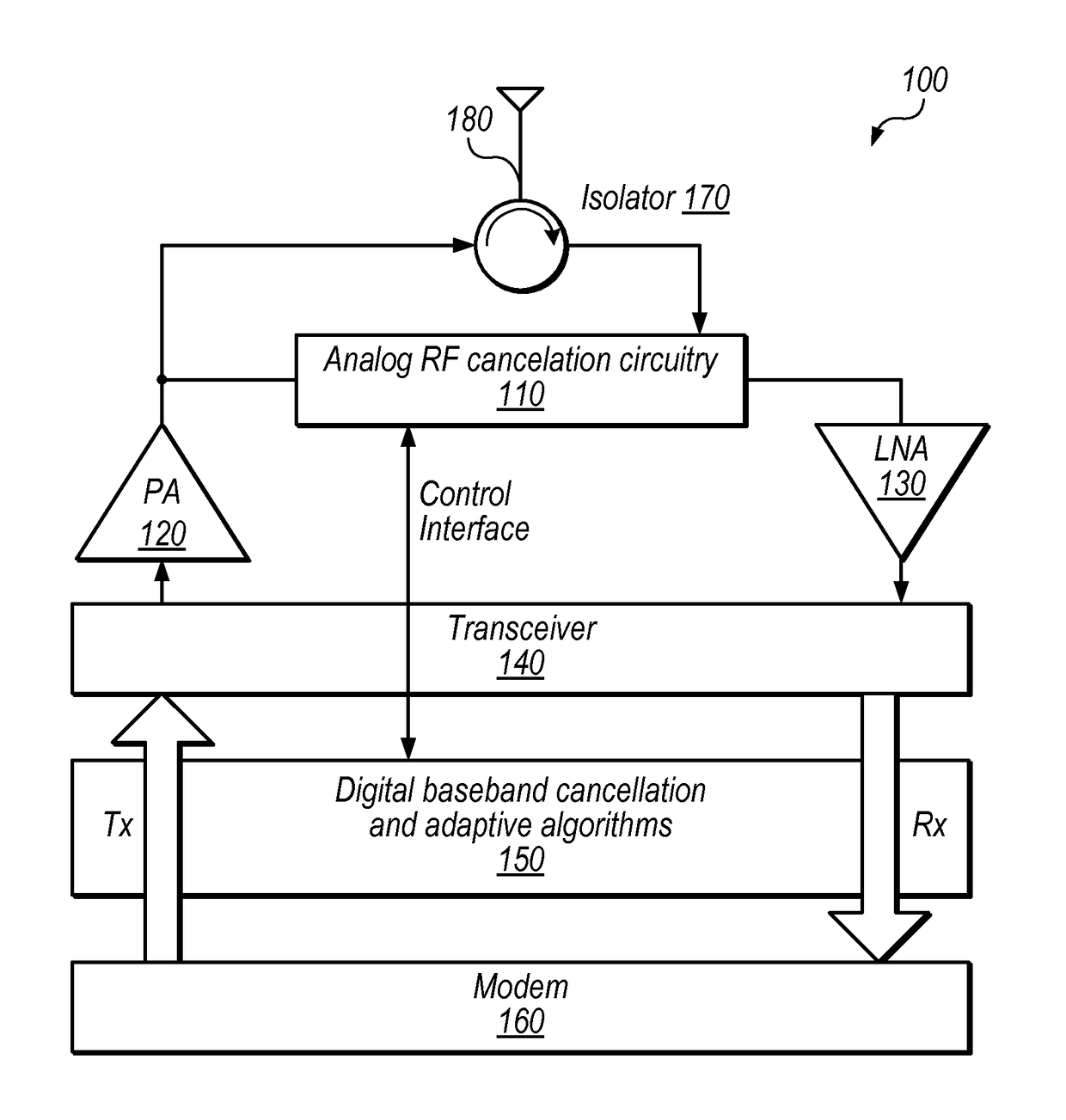
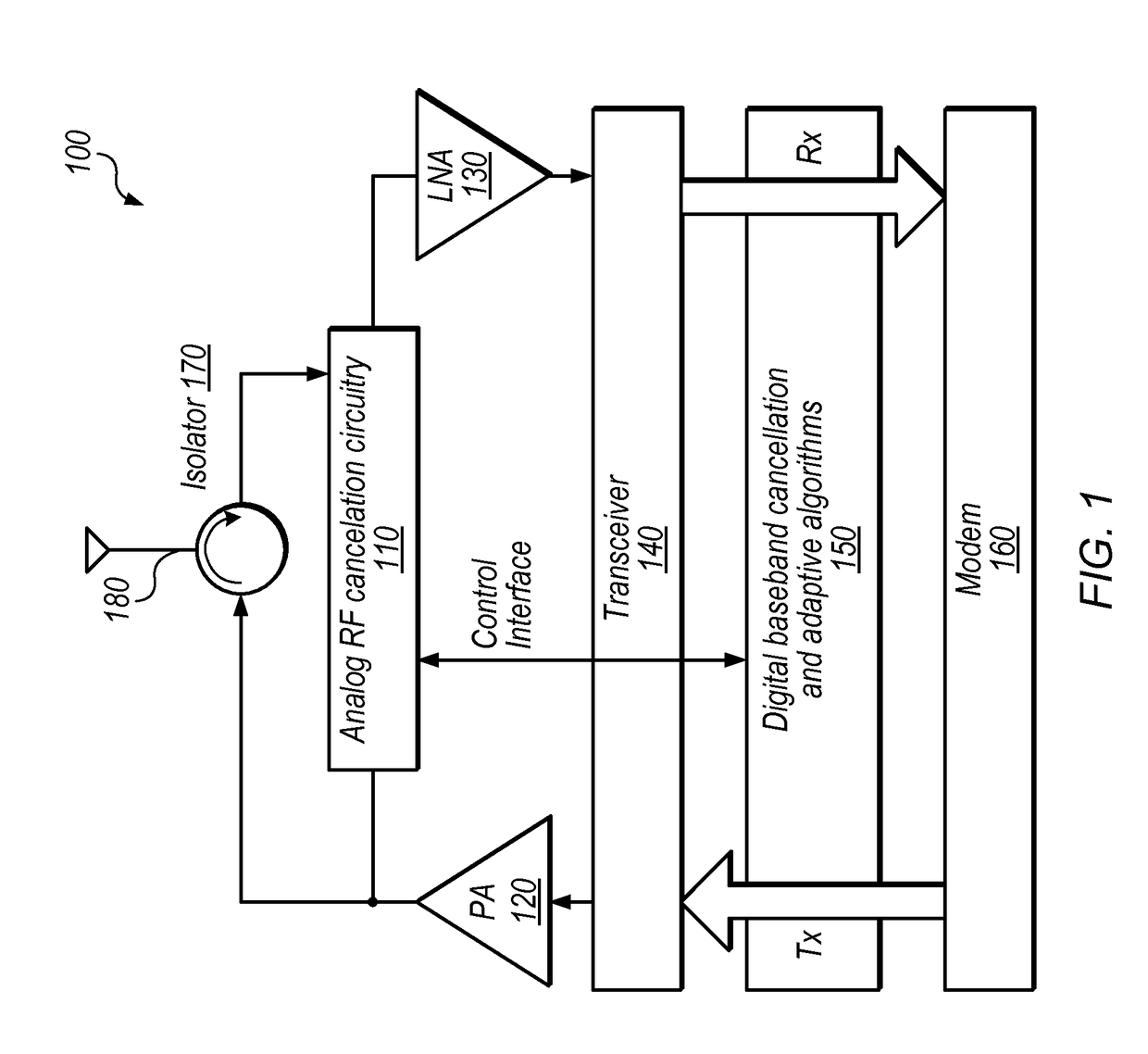
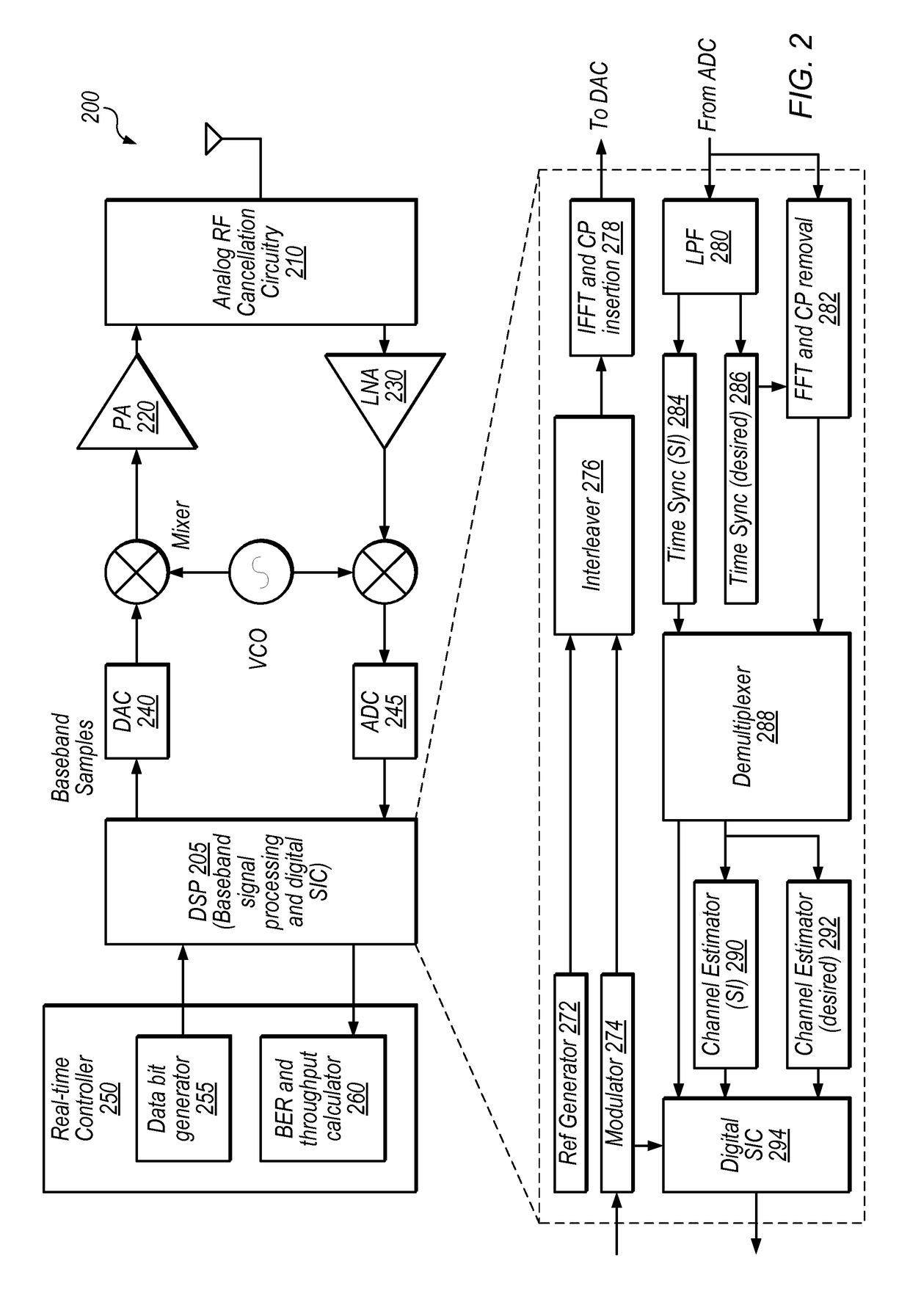
Channel Quality Reporting for Full-Duplex Radio
ActiveUS20170141886A1Criteria allocationSignalling characterisationSelf interferenceTransmitted power
Techniques are disclosed relating to channel quality reporting for full-duplex (FD) wireless communications. In some embodiments an apparatus (e.g., a mobile device) is configured to receive a reference signal in a wireless communication and determine an effective signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) for FD communications based on a measured SINR of the reference signal and one or more self-interference cancelation levels. The apparatus may determine the one or more self-interference cancelation levels based on the transmit power of signals transmitted by the apparatus and residual power after SIC. The SIC levels may include both analog and digital SIC levels, which may be separately determined. One or more modulation and coding schemes may be determined based on the effective SINR. In some embodiments, multiple effective SINRs are determined for multiple different transmission modulation orders used by the apparatus.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
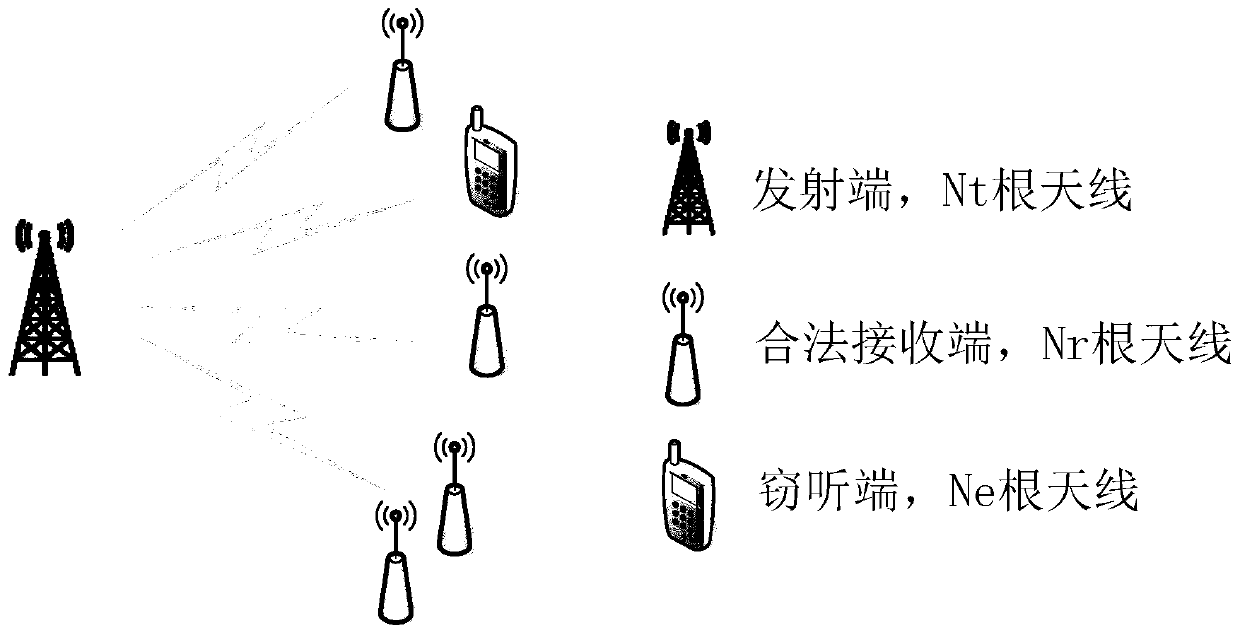
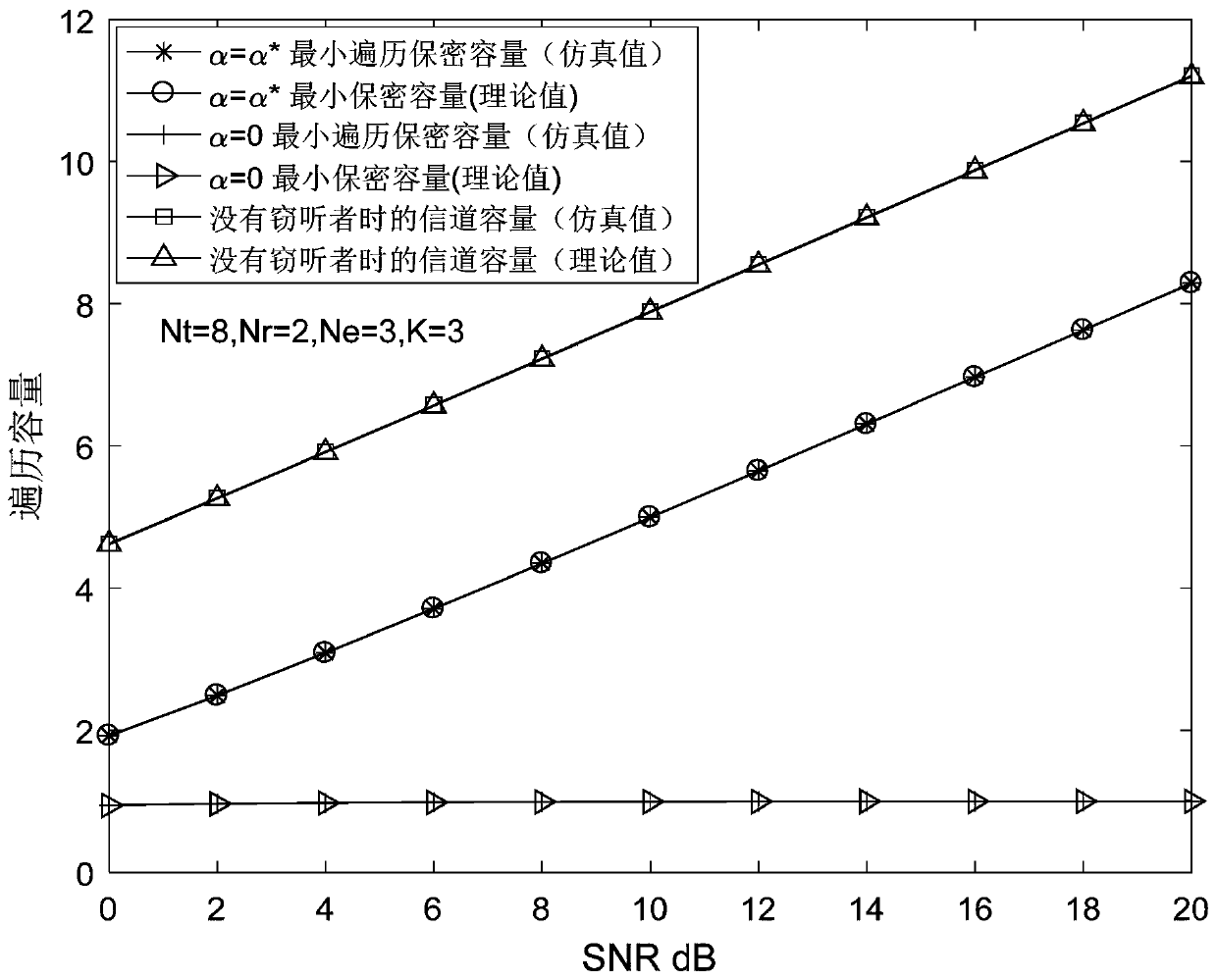
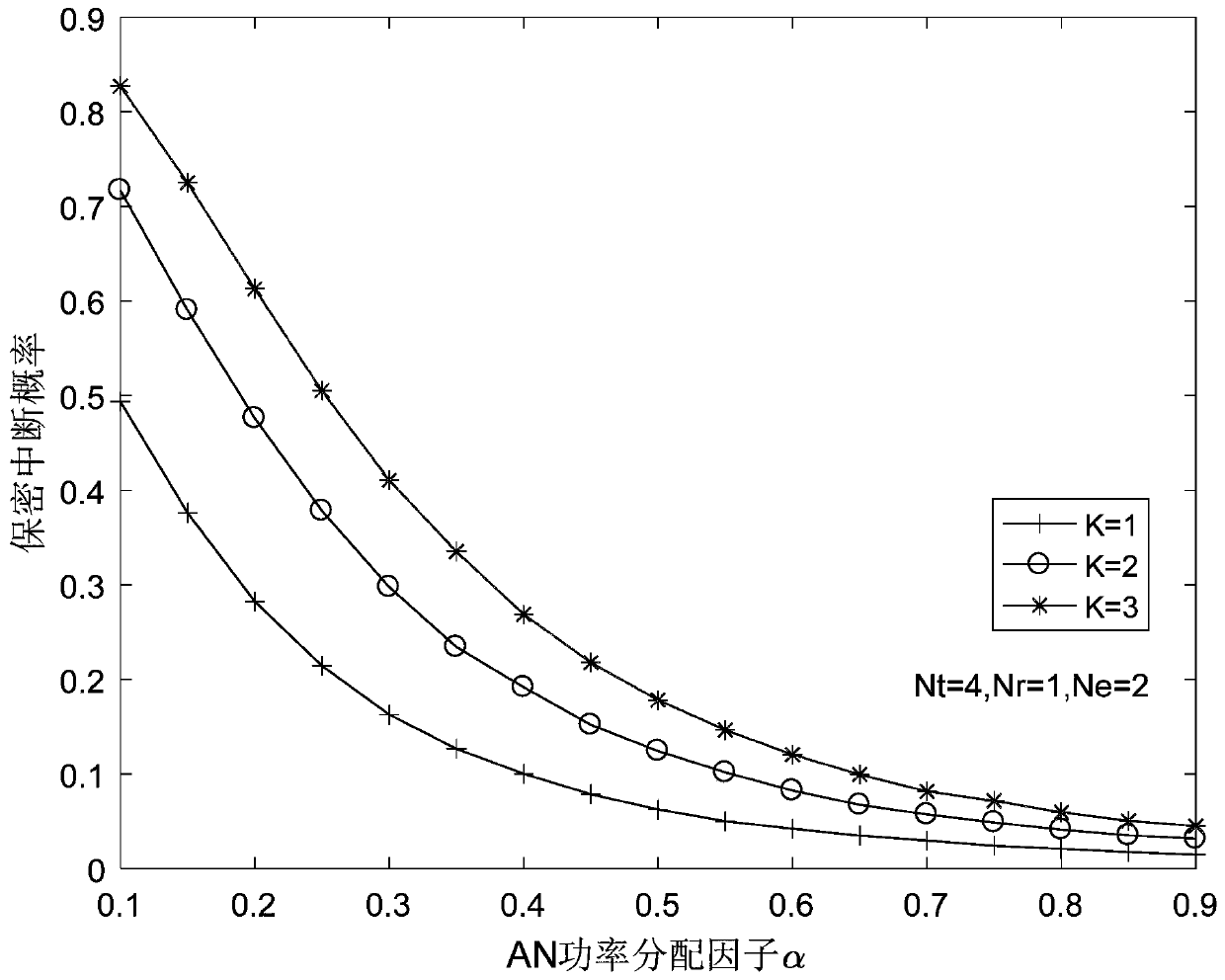
A physical layer safety method based on artificial noise power distribution
ActiveCN109861783AImprove security featuresSmall secrecy break probabilityPower managementSecret communicationCommunications systemSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
The invention discloses a physical layer safety method based on artificial noise power distribution, and relates to a physical layer safety method. The objective of the invention is to solve the problems of high confidentiality interruption probability and poor confidentiality in an existing broadcasting system. The method comprises the following steps: 1, transmitting a signal by a transmitting end; 2, calculating a received signal reaching the kth legal receiver end and a received signal reaching the eavesdropper end; 3, calculating the signal to interference plus noise ratio of the kth legal receiver and the signal to interference plus noise ratio of the eavesdropper; 4, calculating the instantaneous confidentiality capacity of the kth legal receiver; 5, calculating an optimal artificial noise power distribution factor; and 6, calculating the confidentiality interruption probability according to different artificial noise power factors, and drawing a change curve of the confidentiality interruption probability along with the artificial noise power distribution factor to obtain the artificial noise power distribution factor meeting the requirements. The invention is applied to the field of physical layer security of a wireless broadcast communication system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Self-adaptive transmission method of large-scale MIMO downlink
ActiveCN104702324AAdaptive transport implementationImprove reliabilitySpatial transmit diversityMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumResource element
The invention provides a self-adaptive transmission method of a large-scale MIMO downlink. The self-adaptive transmission method of the large-scale MIMO downlink comprises the following steps: firstly, utilizing a stronger correlation of a large-scale MIMO spatial channel to transform the spatial channel into a beam domain through a DFT transformation; in the beam domain, utilizing a maximum system and rate as a criterion to select uses communicate simultaneously, and assigning an optimal transmission beam for each user, thereby determining a transport layer number and a pre-coding matrix for each user; then, by taking inter-user interferences into consideration, calculating a MMSE balanced posterior signal to interference plus noise ratio on each resource element of each transport layer for each user; and then, acquiring an equivalent signal to interference plus noise ratio for each user by an equivalent signal to noise ratio mapping; finally, on the premise that a word error rate of the transmission is ensured, by each client, to be lower than a given value, determining and feeding back a channel quality indicator of each codon, aiming at maximizing the system throughput. By the self-adaptive transmission method of the large-scale MIMO downlink, the reliability of a large-scale MIMO wireless transmission is increased; and an excellent system spectral efficiency is acquired while the system word error rate is ensured to be lower than the given value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
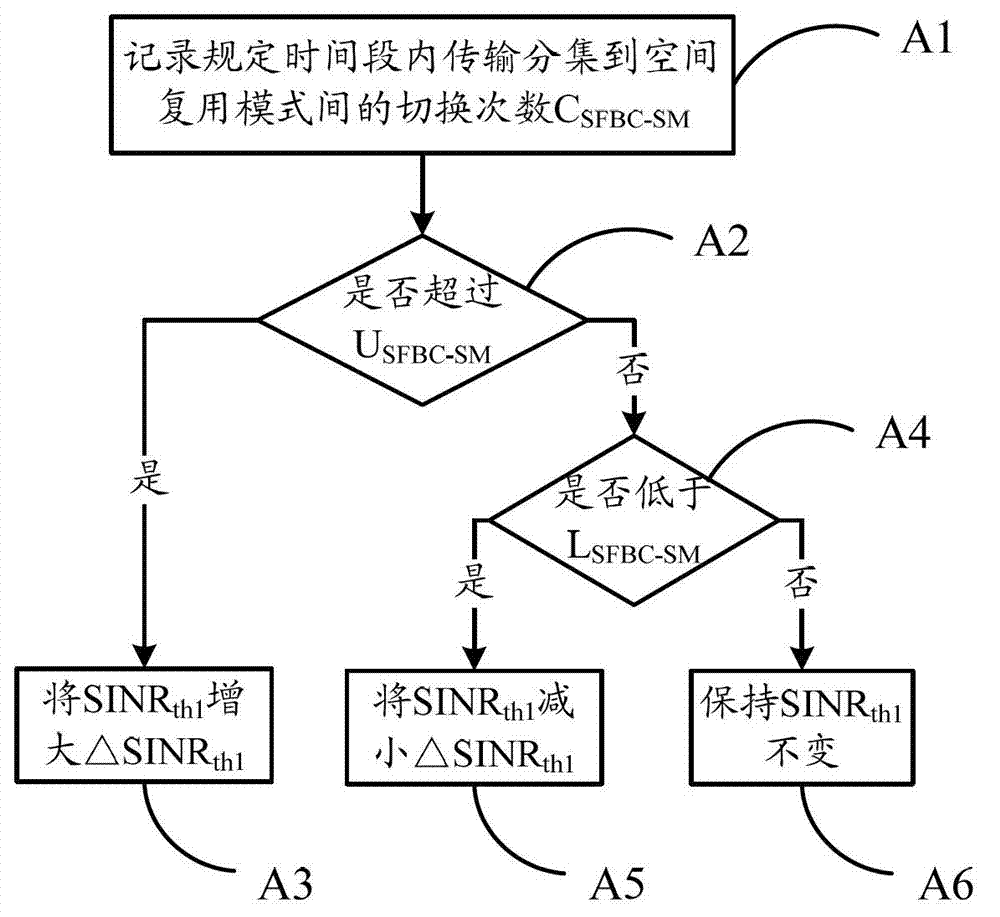
Self-adapting switching method and device of transmission mode of LTE (Long Term Evolution) multi-antenna system
InactiveCN103179619ASimple structureReduce complexityWireless communicationSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioGeolocation
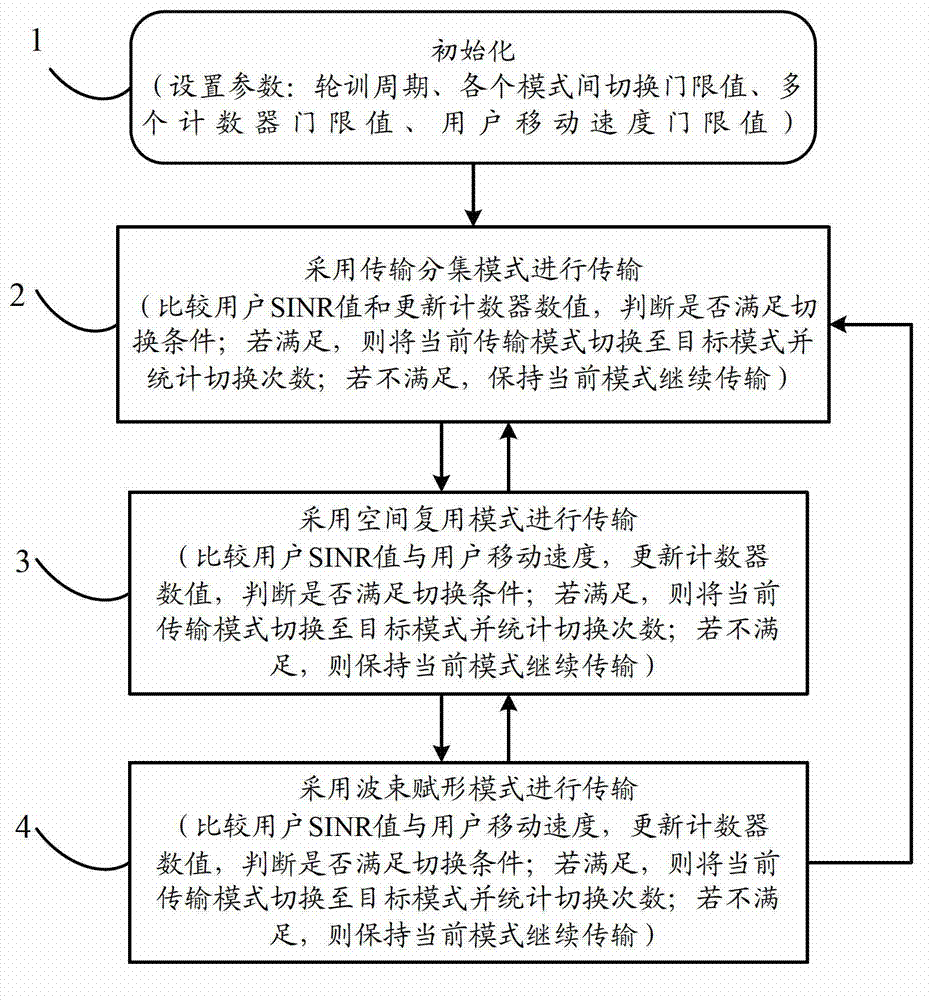
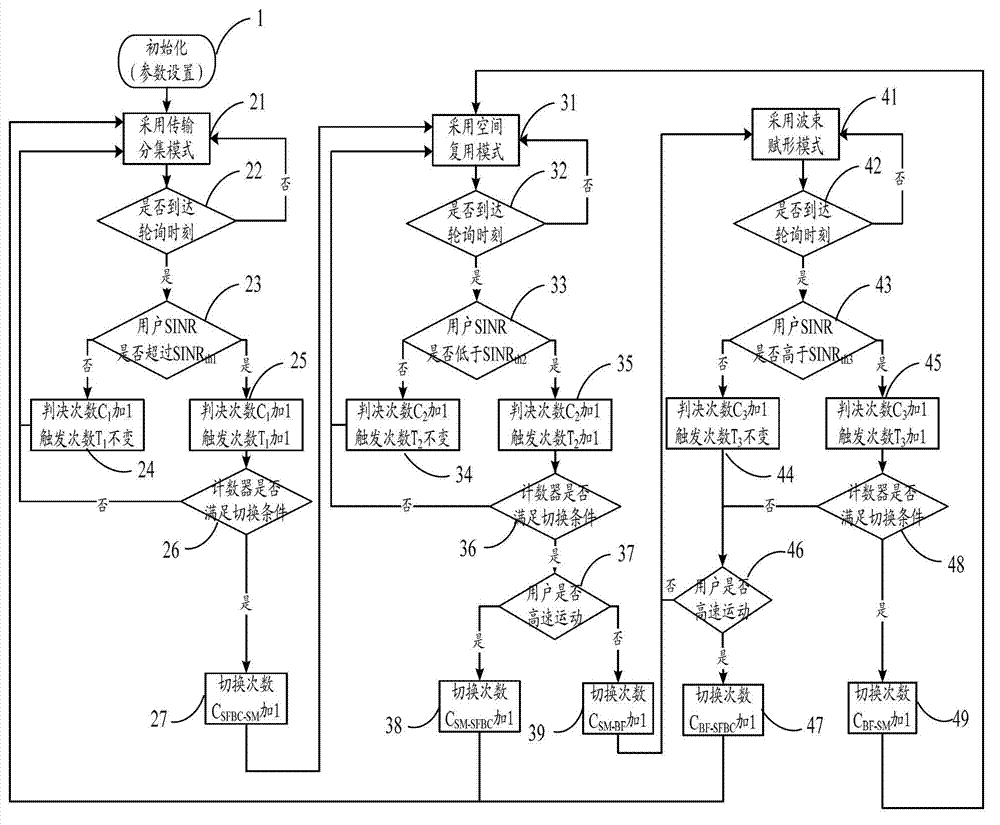
The invention relates to a self-adapting switching method of a transmission mode of an LTE (Long Term Evolution) multi-antenna system, and the self-adapting switching method comprises the following steps that: a base station sets an appropriate transmission mode in a self-adapting way for a user by taking the SINR (Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio), the movement speed and the geographic position of the user as judgment conditions. The self-adapting switching method comprises the following operation steps of: firstly initially determining multiple parameters, namely a polling period needed by transmission mode switching, a mode switching threshold value, a counter threshold value and a user movement speed threshold value; then determining transmitting data of an acquiescent transmission diversity mode; then calculating an SINR value according to CQI (Channel Quality Indicator) fed back by the user, and comparing the SINR value with a predetermined switching threshold; updating corresponding judgment time and triggering time counters; judging whether a mode switching condition is met or not; and switching a current mode into an ideal target mode, or continuously keeping the current mode to carry out data transmission. The self-adapting switching method disclosed by the invention can be used for regulating the mode switching threshold value and the user movement speed threshold value in real time by counting switching times within set time, thereby realizing the effective balance of network transmission efficiency and timeliness in the switching process.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
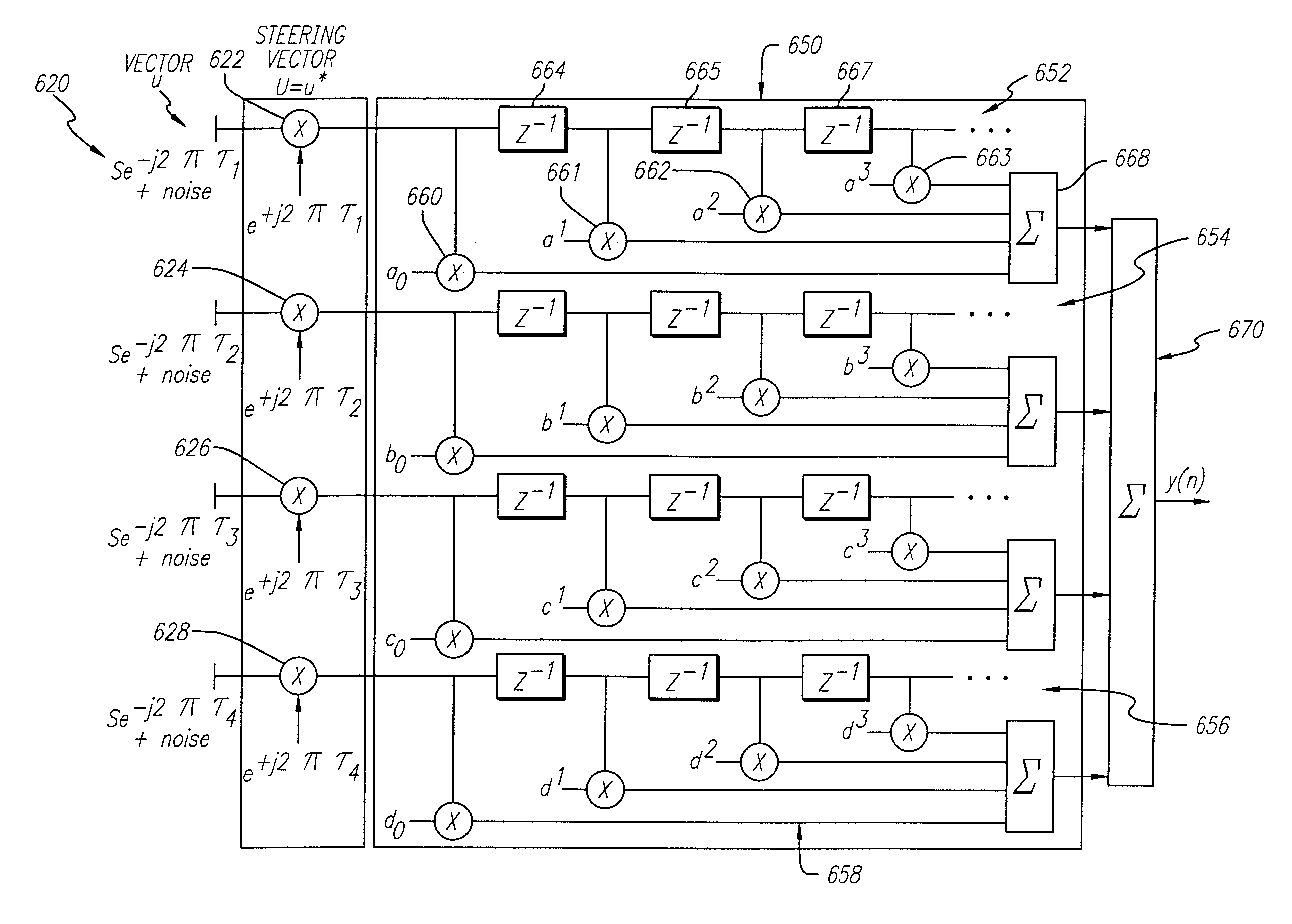
Beamforming and interference cancellation system using general purpose filter architecture
InactiveUS6317467B1Multiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityGeneral purposeInterference cancelation
A beamforming system including a multiplier stage for providing a plurality of steered signal terms, each term being a product of an input signal term and a steering signal term. A filter multiplies the steered signal terms by a plurality of respective filter weights to provide a plurality of weighted products. The weighted products are summed to provide an output beam directionally responsive to the steering signal. A microprocessor provides the steering signal terms and the filter weights in response to the input signal and / or user input. In the preferred embodiment, the filter is a reconfigurable, general purpose matched filter configured to multiply a plurality of delayed representations of a respective one of the steered signal terms by a plurality of the weights to provide a plurality of intermediate weighted product terms. The filter further includes a summing circuit for accumulating the intermediate weighted product terms to provide a respective one of the plurality of weighted products. The inventive beamforming system cancels unwanted interference, while forming a beam to allow a desired signal to be received with a maximum signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR). Through a data-capture RAM, the system allows interference samples to be collected and passed to a microprocessor to calculate the optimum filter weights. The received beam may be steered to any desired direction to form an optimal space-time adaptive matched filter.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
An uplink adaptive coding and modulation method and a base station for realizing the method
InactiveCN102281119APrevent frequent changesSolve the fluctuation problem of uplink throughputChannel coding adaptationAdaptation strategy characterisationCurrent channelSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
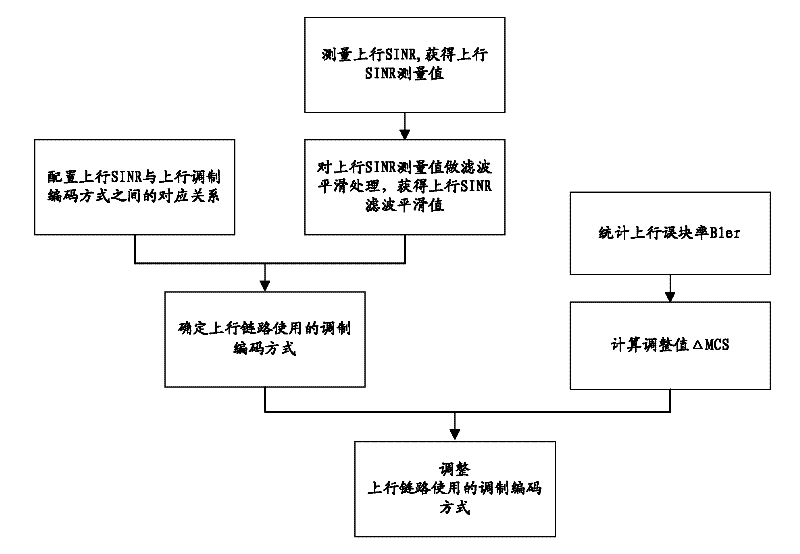
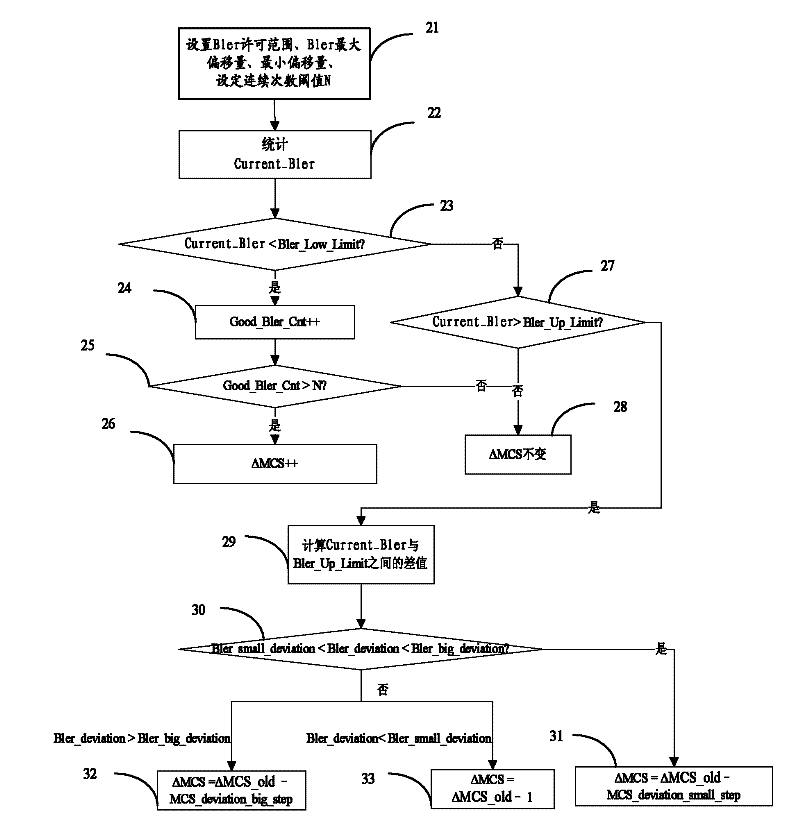
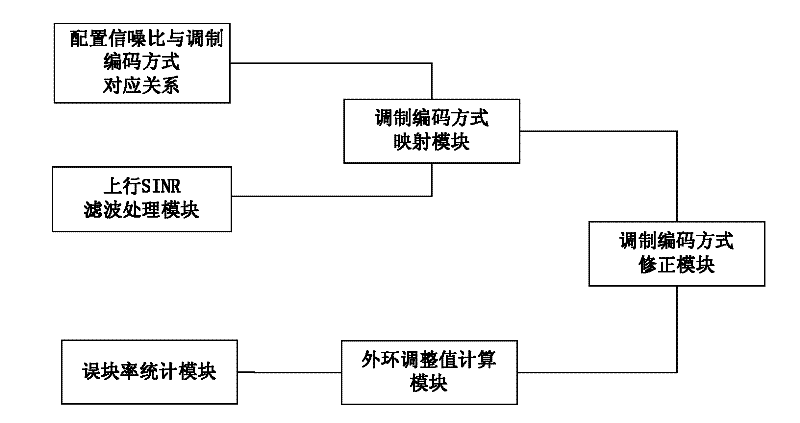
The invention discloses an uplink adaptive modulation and coding method and a base station implementing the method, wherein the method includes: the base station locally configures the corresponding relationship between uplink Signal to Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR) and uplink Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS), measures uplink SINR to obtain the uplink SINR measurement value, performs filtering and smoothing processing on the SINR measurement value and history SINR filtering values to obtain uplink SINR smoothing filtered value, and determines the MCS adopted by the uplink based on the uplink SINR smoothing filtered value and the corresponding relationship. Through the invention, the dependence on the corresponding relationship between the uplink SINR and the MCS is reduced, and the current channel conditions can be reflected more in real, responses can be made quickly and stability and reliability of the system can be effectively guaranteed.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Adaptive HARQ for Half Duplex Operation for Battery and Antenna Constrained Devices
ActiveUS20160112162A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCriteria allocationTelecommunicationsProcess support
A user equipment (UE) implements improved communication methods which enable uplink (UL) transmissions consistent with an UL timeline. The UE may have a transmit duty cycle and may transmit acknowledge / negative acknowledge messages to a base station according to the transmit duty cycle. Additionally, the UE may be configured to determine signal-to-interference-plus noise ratio (SINR) between the UE and the base station and compare SINR to a threshold. The UE may transmit redundancy versions of data in consecutive sub-frames with a duty cycle of two transmissions per X+1 sub-frames if SINR is equal or above the threshold and redundancy versions using a duty cycle of one transmission per X sub-frames if SINR is below the threshold. Further, the UE may be configured to communicate a number of UL HARQ processes supported by the UE, receive first information in a first sub-frame, and send second information X sub-frames after the first sub-frame.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method, apparatus and equipment for sending and receiving data of MIMO system
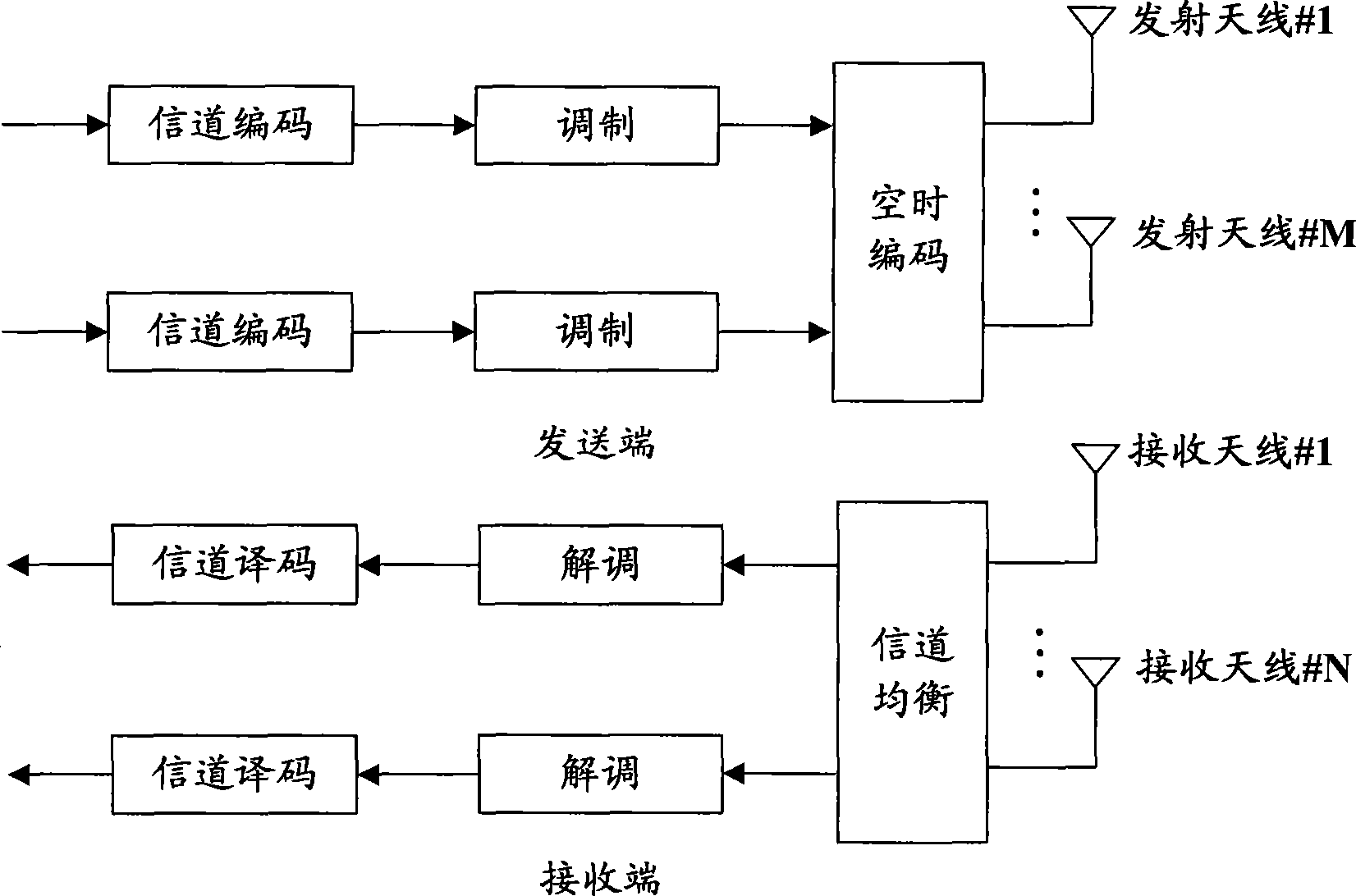
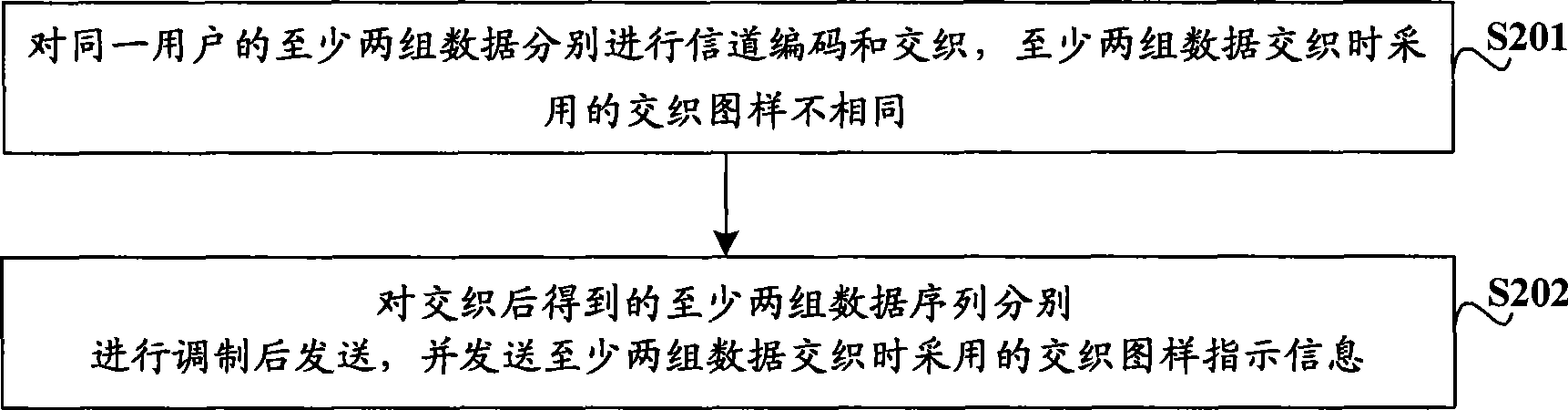
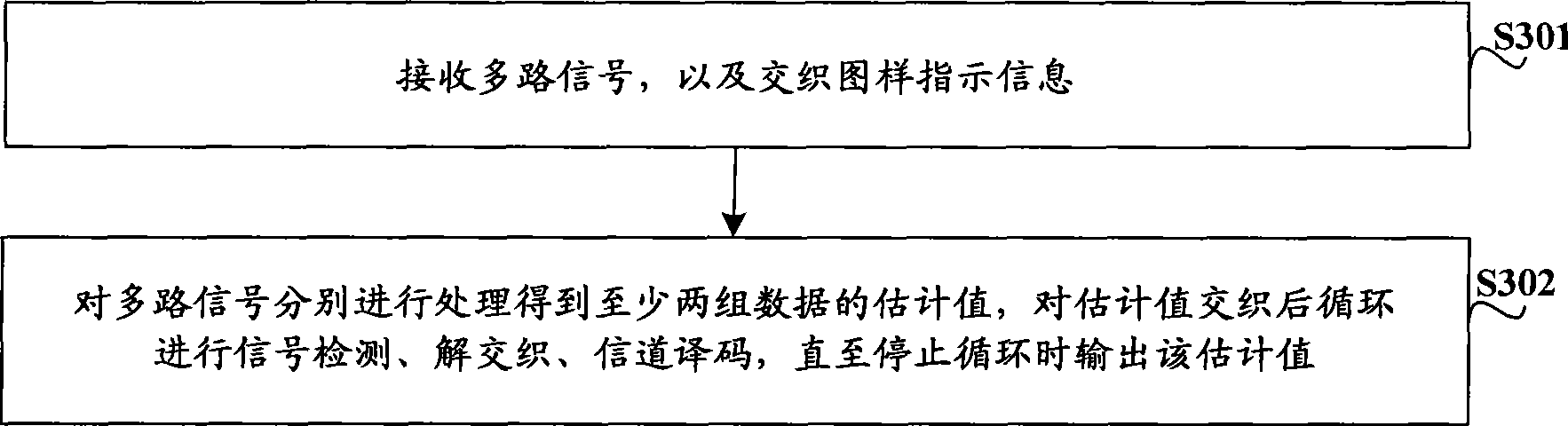
InactiveCN101437007AImprove performanceEasy to detectDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsMulti inputSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
The invention relates to the technical field of mobile communication, in particular to data sending technology for a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) system and corresponding data receiving technology. The embodiment of the invention provides a data sending method, a corresponding data receiving method, a corresponding data receiving device and corresponding data receiving equipment for the MIMO system, and is used for increasing the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio of received signals of the MIMO system and improving the performance of the system. The data sending method for the MIMO system comprises the following steps: at least two groups of data of the same user are subjected to channel coding and interweaving respectively, and interweaving patterns adopted when the data are interwoven are not same; two data sequences obtained after the interweaving are modulated respectively and then are sent, and interweaving pattern indication information adopted when the data are interwoven is sent.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com