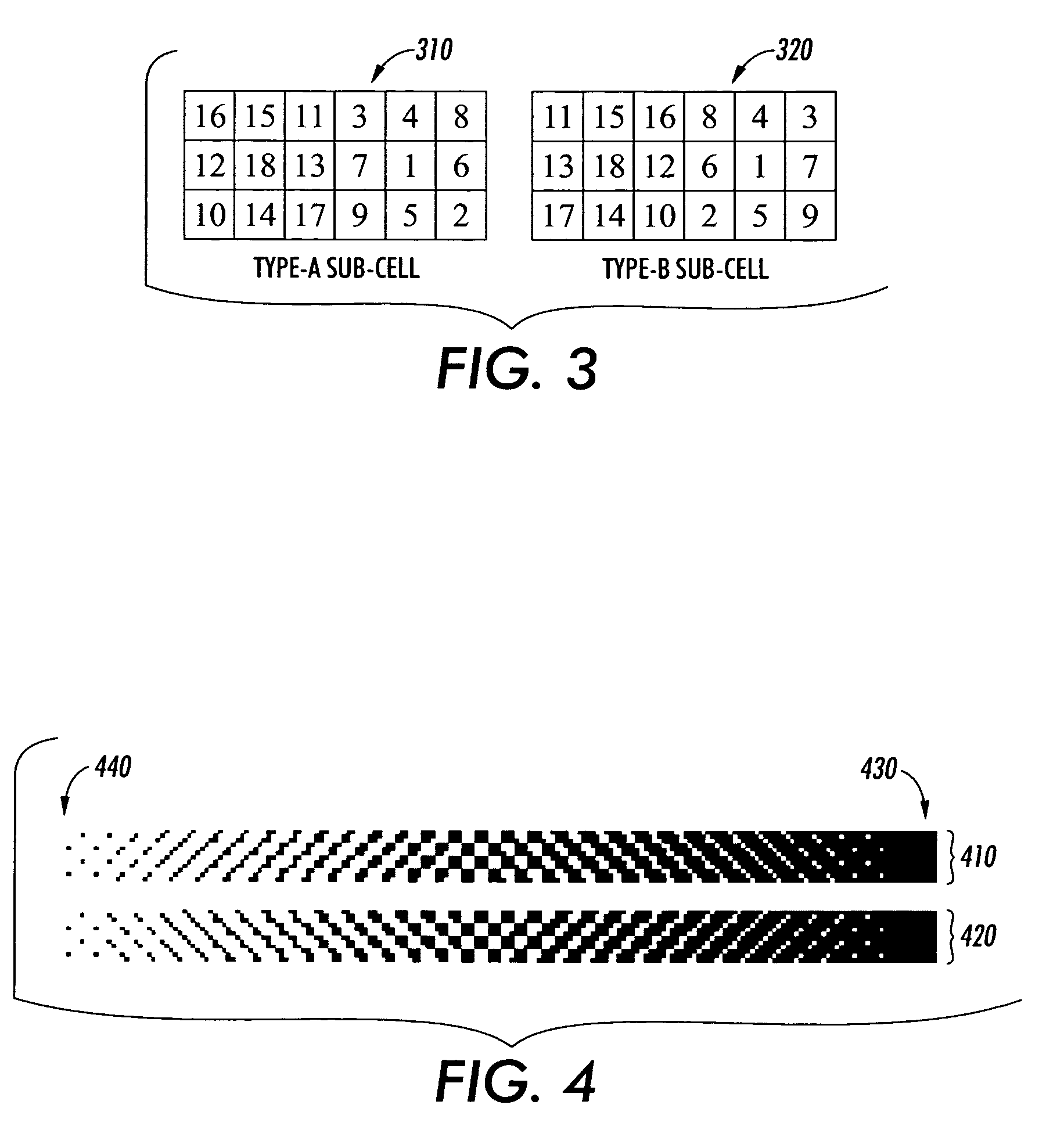
Patents
Literature
587 results about "Area coverage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coverage area is the geographic region or location in which benefits of an insurance policy may apply and be applied for the purposes of filing a valid claim. For instance, "anywhere in the world" may be the coverage area for travel health insurance.
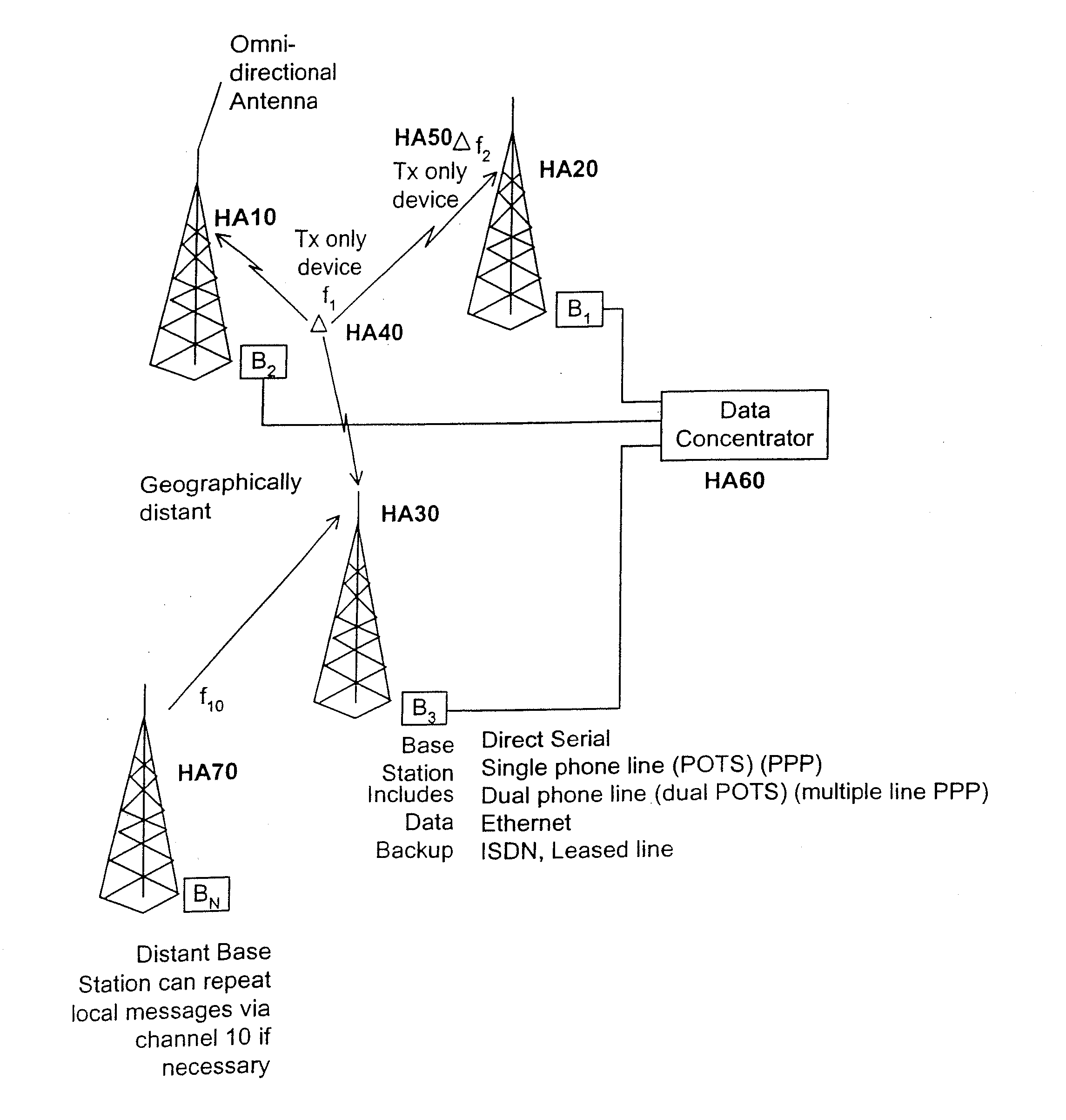
Enhanced wireless packet data communication system, method, and apparatus applicable to both wide area networks and local area networks
InactiveUS20070071114A1Conserve battery lifeReduce transmitter costPulse automatic controlDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionWide areaArea coverage
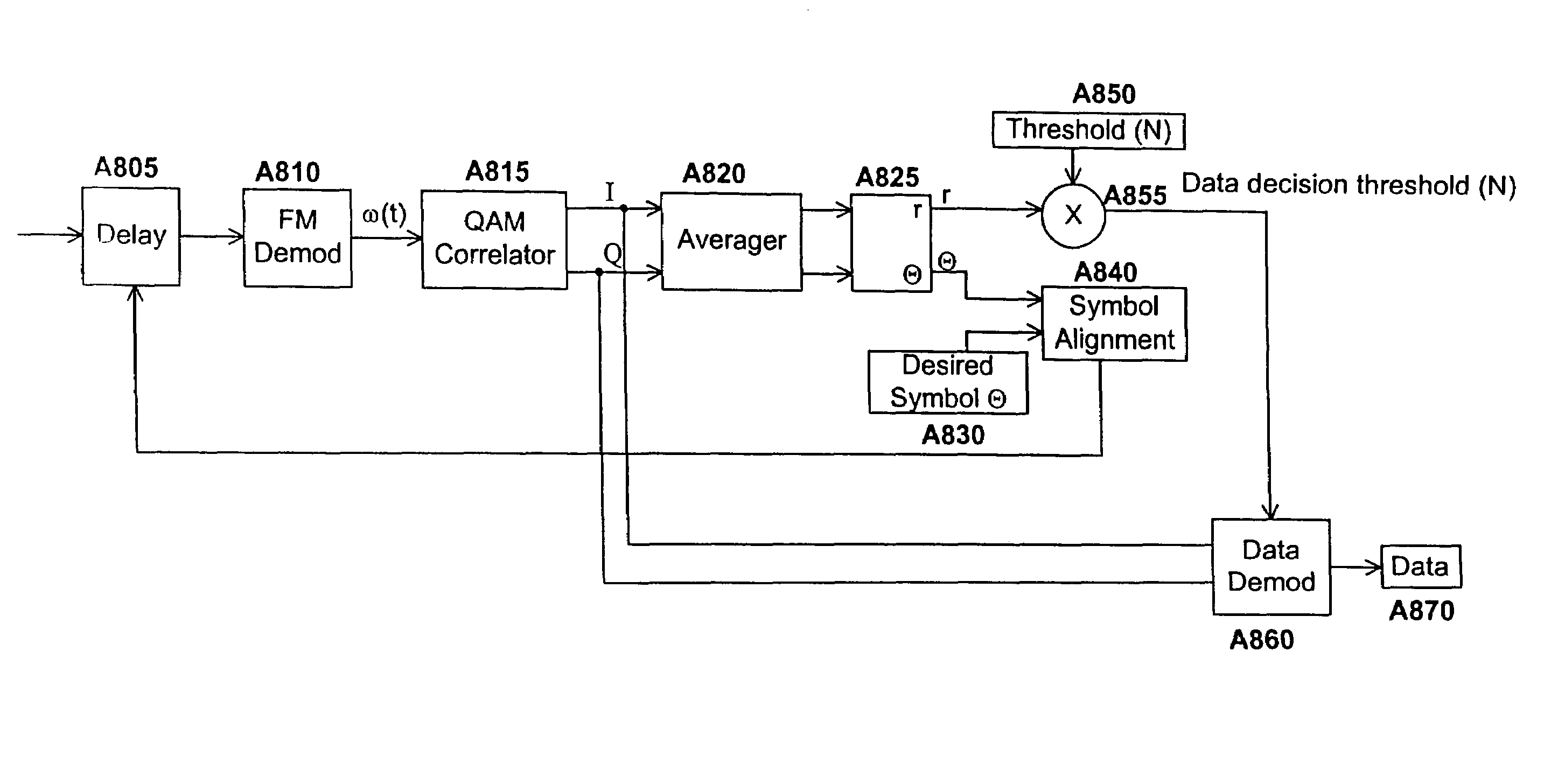
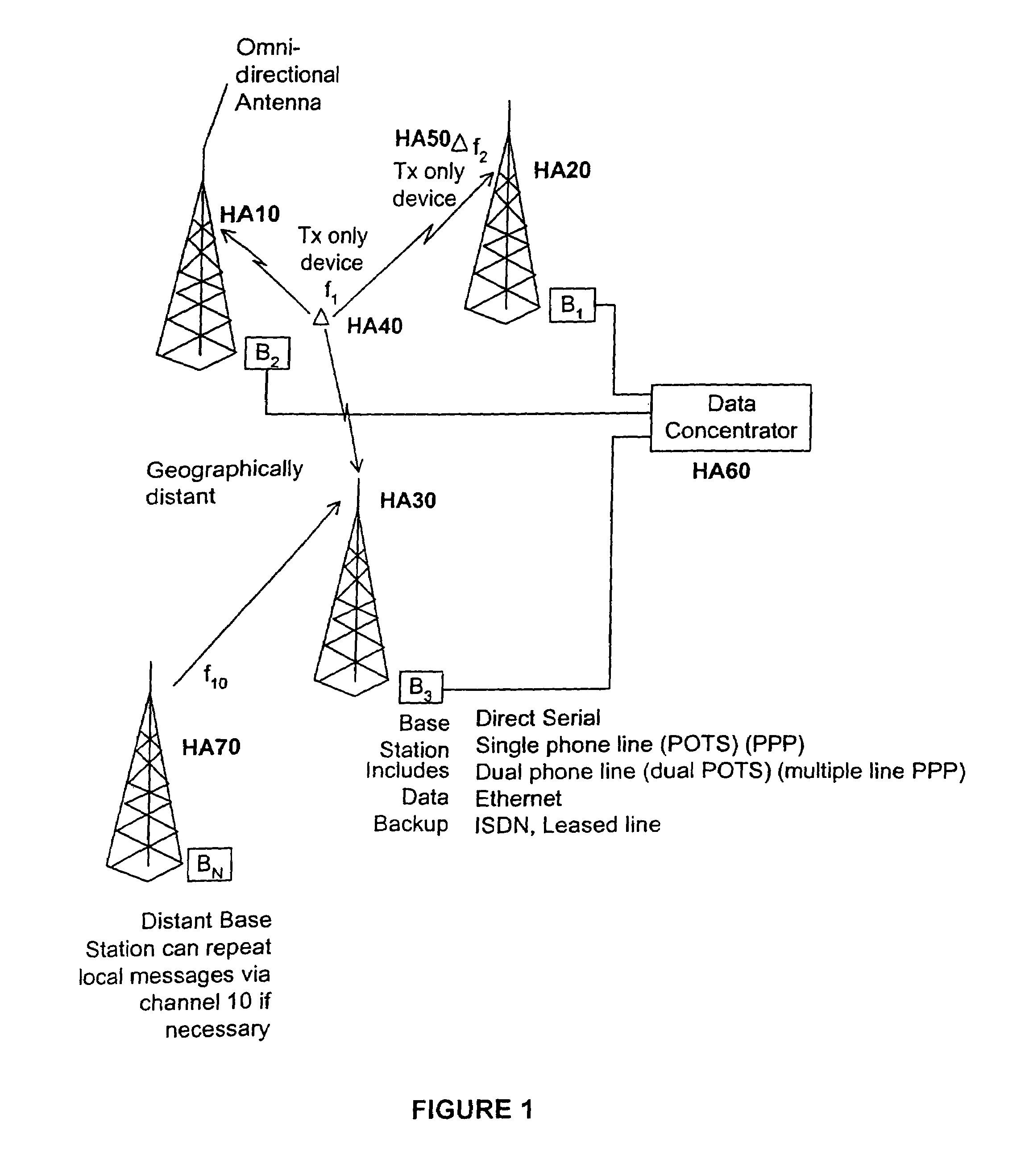
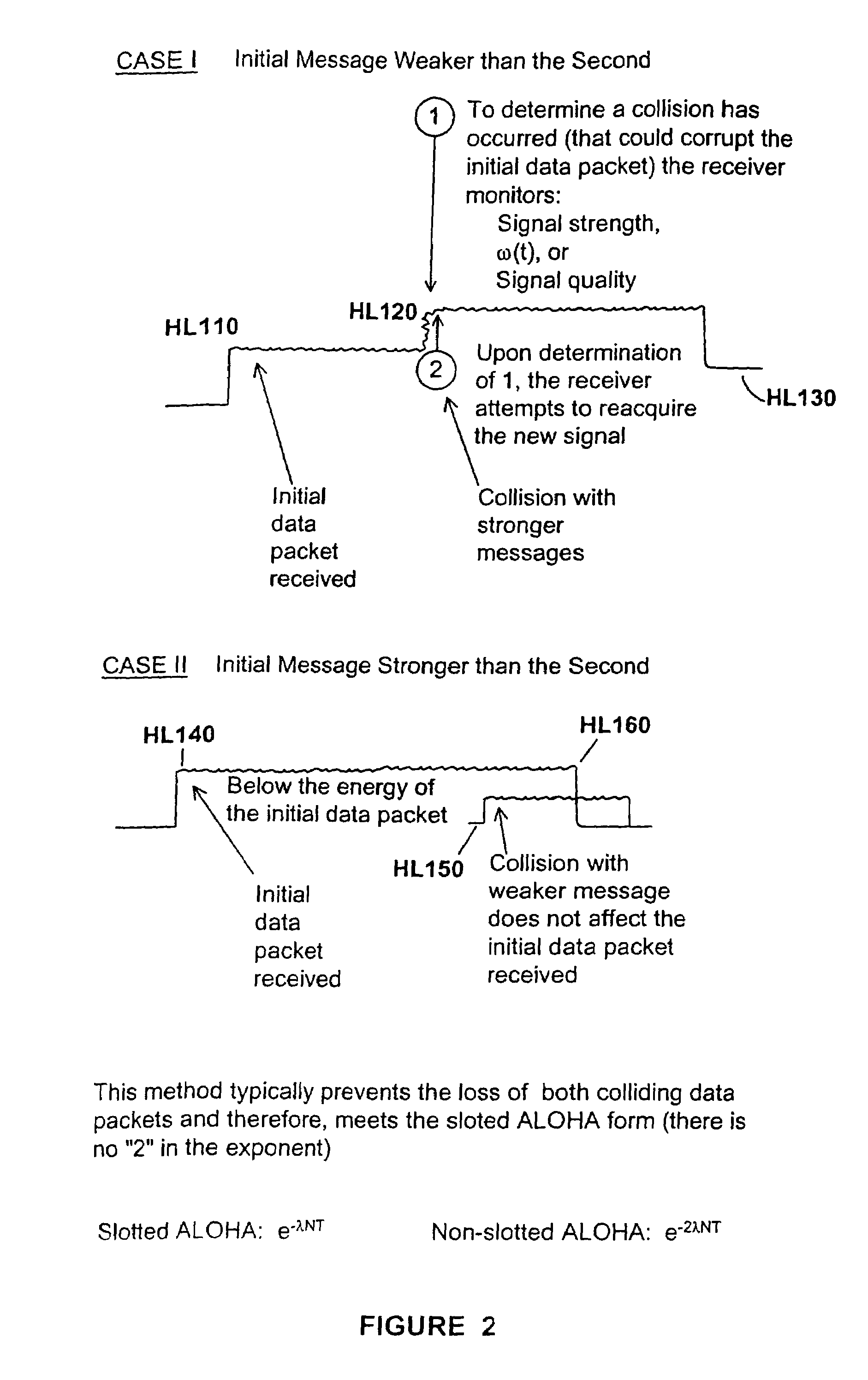
A cellular wireless packet data communication system containing transmit-only endpoint devices which transmit to receive-only base stations. The system is configured to allow for large area coverage (e.g., a metropolitan area) with far fewer number base stations than are required with conventional two-way cellular systems. The base station coverage areas are configured to overlap, allowing for reception of packets at multiple base stations. A data concentrator resolves redundantly received messages. The network is configurable as a WAN, a LAN, or a combination of the two. Novel modulation techniques (e.g., a 16QAM submodulation together with a 7FSK modulation) are used such that low cost components can be used in the transmitters and receivers while achieving outstanding probability of success performance. The endpoint devices are battery operated and accordingly, are designed for low power consumption and multi-year battery life. The system is used in a variety of applications including remote monitoring and mobile communications.
Owner:SENSUS SPECTRUM LLC
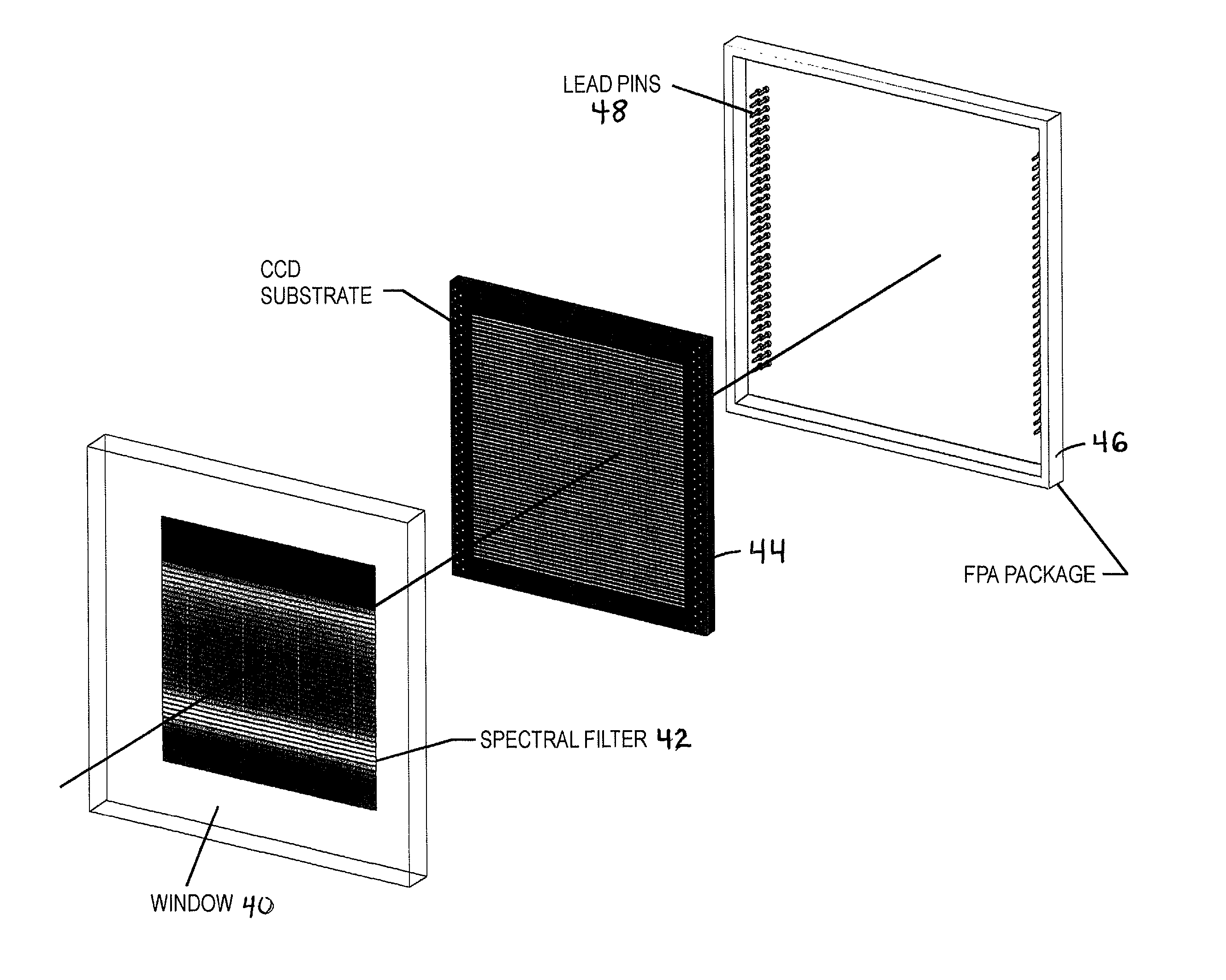
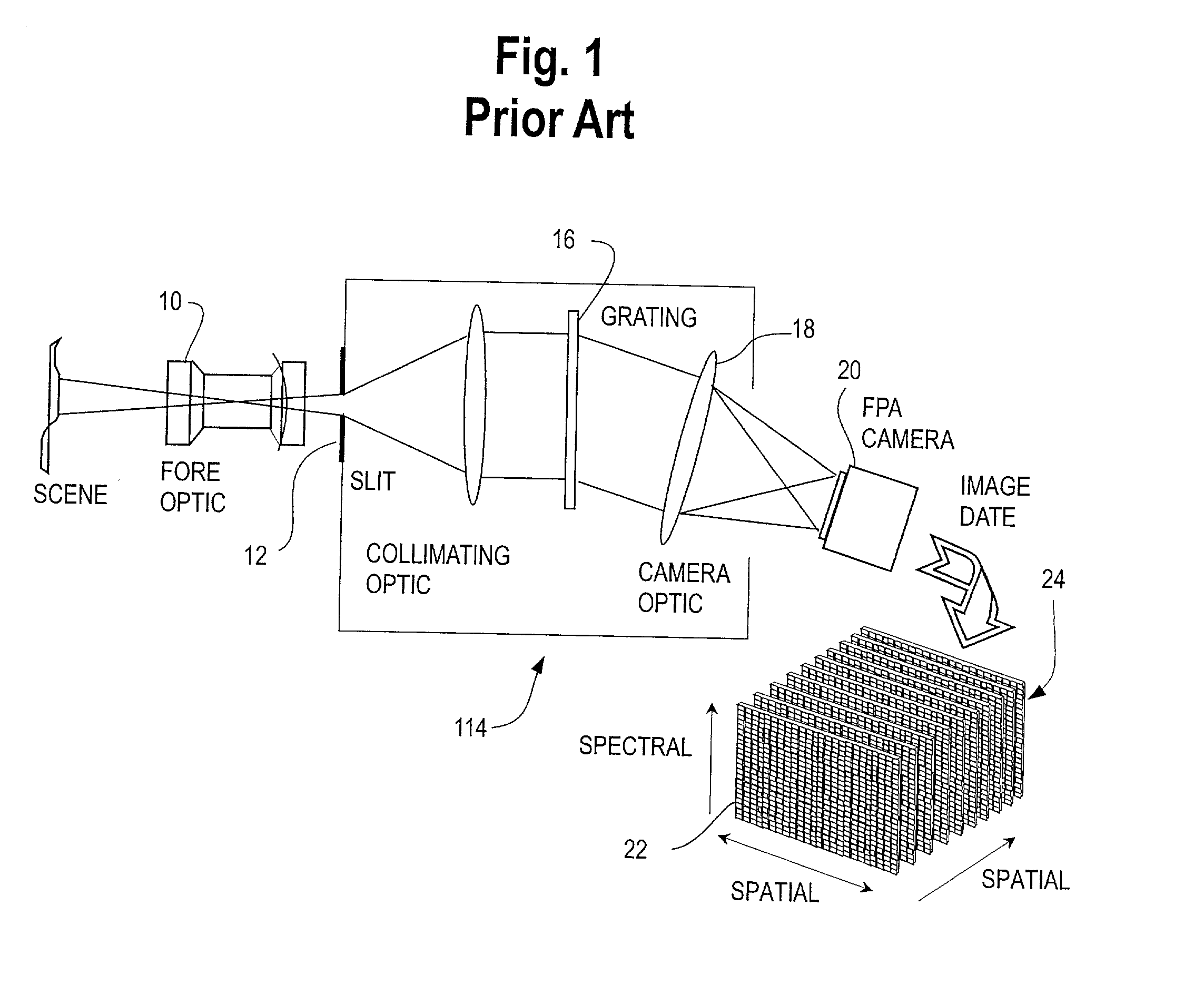
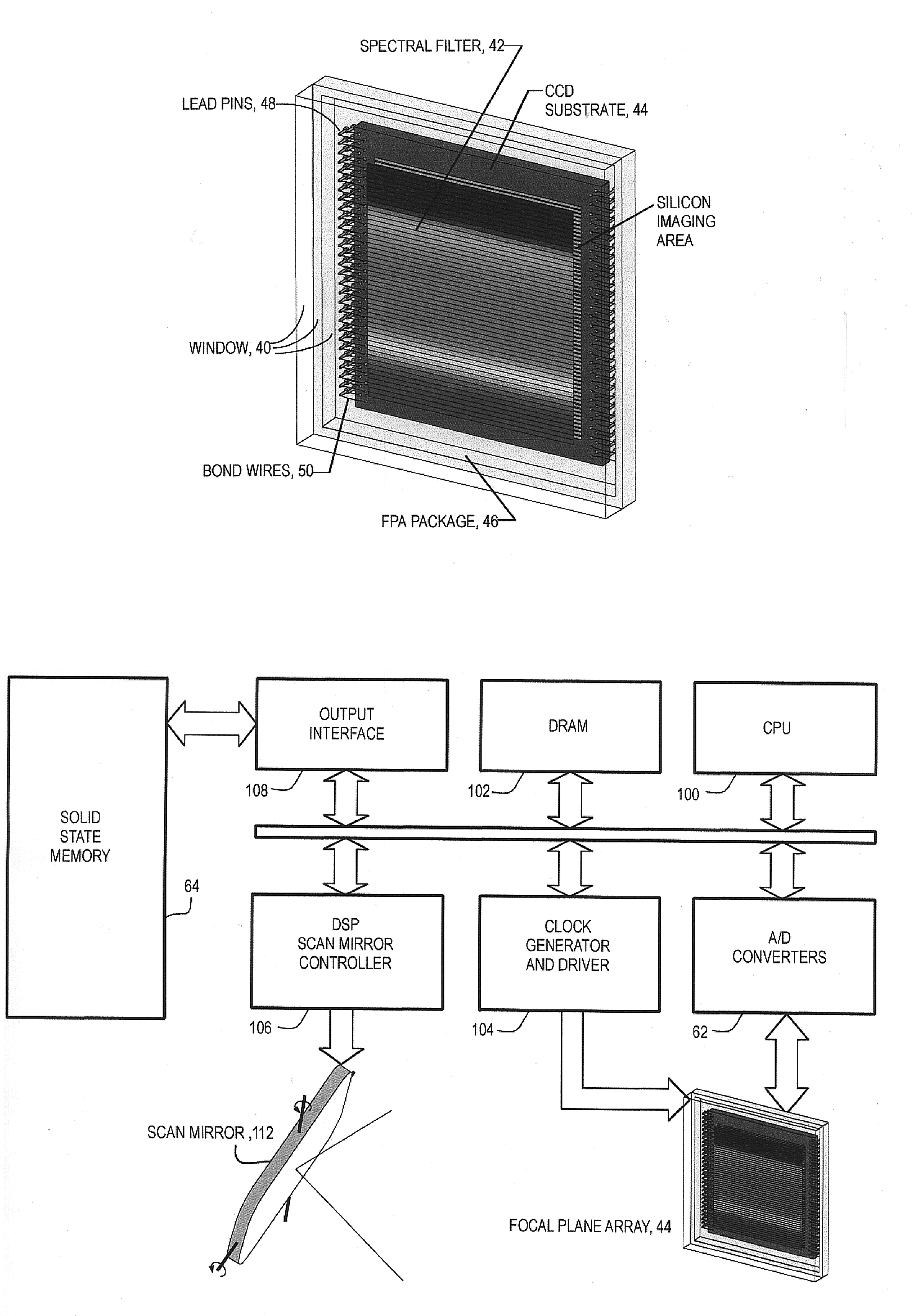
Multispectral or hyperspectral imaging system and method for tactical reconnaissance
A two-dimensional focal plane array (FPA) is divided into sub-arrays of rows and columns of pixels, each sub-array being responsive to light energy from a target object which has been separated by a spectral filter or other spectrum dividing element into a predetermined number of spectral bands. There is preferably one sub-array on the FPA for each predetermined spectral band. Each sub-array has its own read out channel to allow parallel and simultaneous readout of all sub-arrays of the array. The scene is scanned onto the array for simultaneous imaging of the terrain in many spectral bands. Time Delay and Integrate (TDI) techniques are used as a clocking mechanism within the sub-arrays to increase the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the detected image. Additionally, the TDI length (i.e., number of rows of integration during the exposure) within each sub-array is adjustable to optimize and normalize the response of the photosensitive substrate to each spectral band. The array provides for parallel and simultaneous readout of each sub-array to increase the collection rate of the spectral imagery. All of these features serve to provide a substantial improvement in the area coverage of a hyperspectral imaging system while at the same time increasing the SNR of the detected spectral image.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
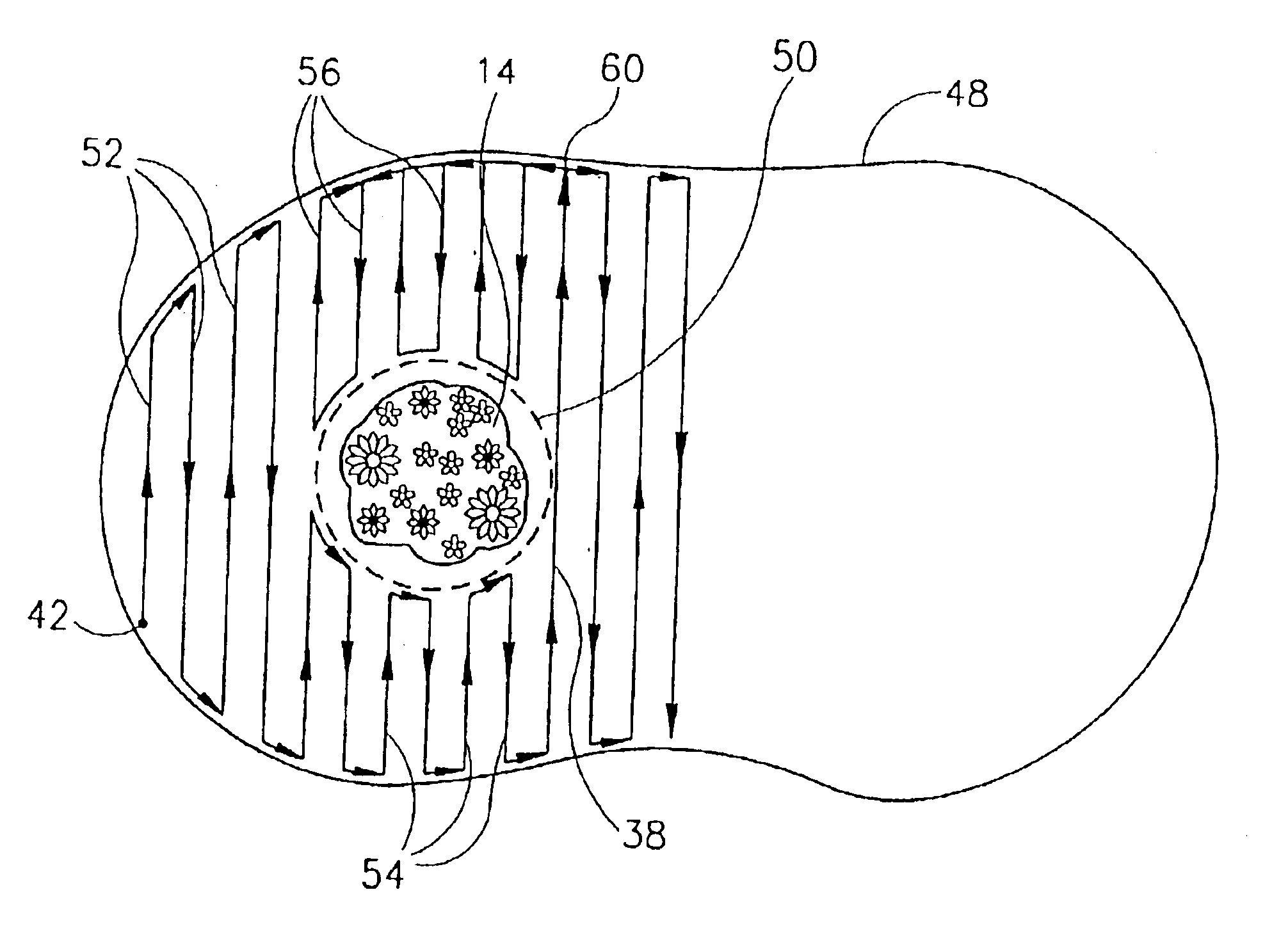
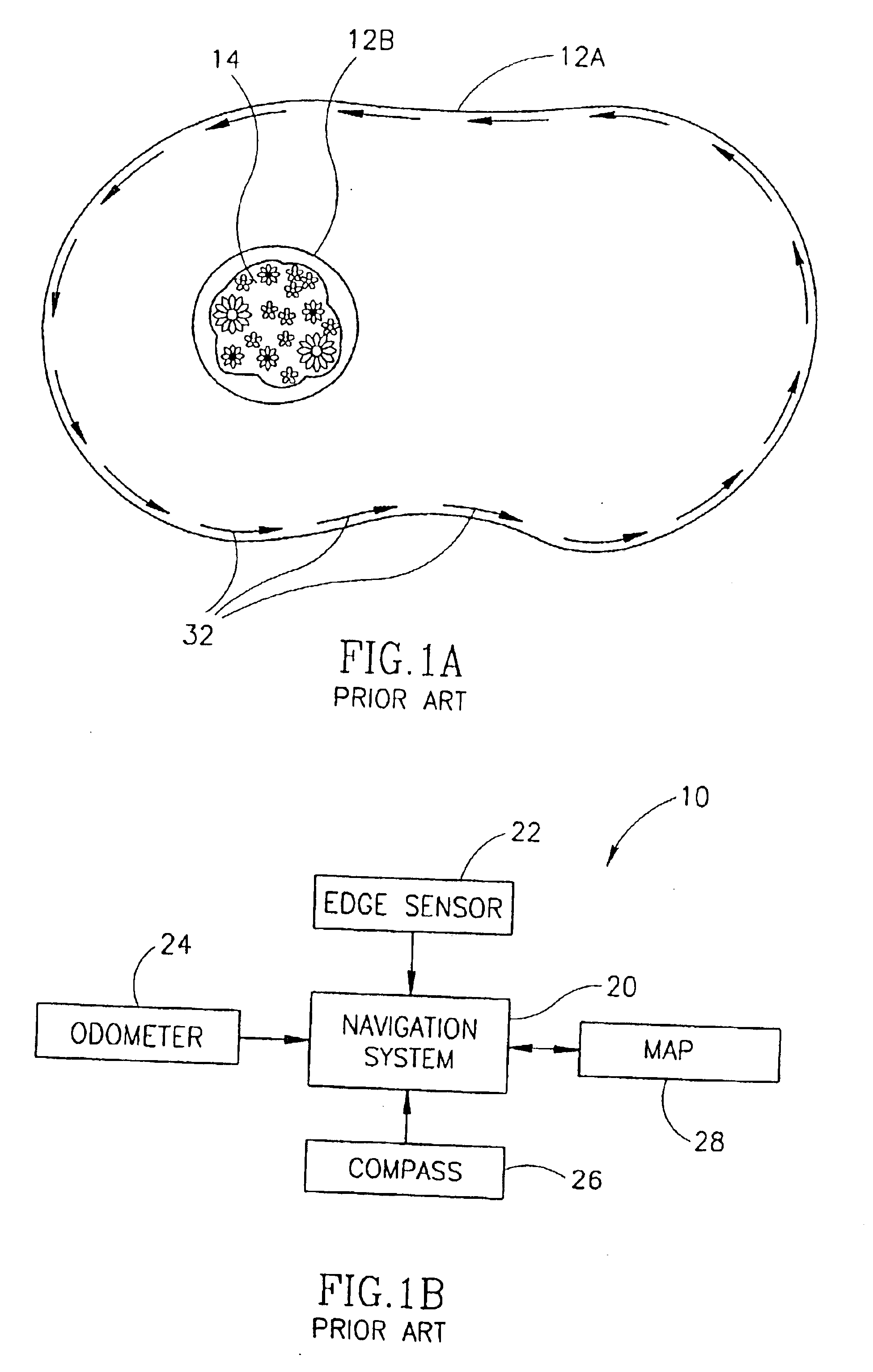
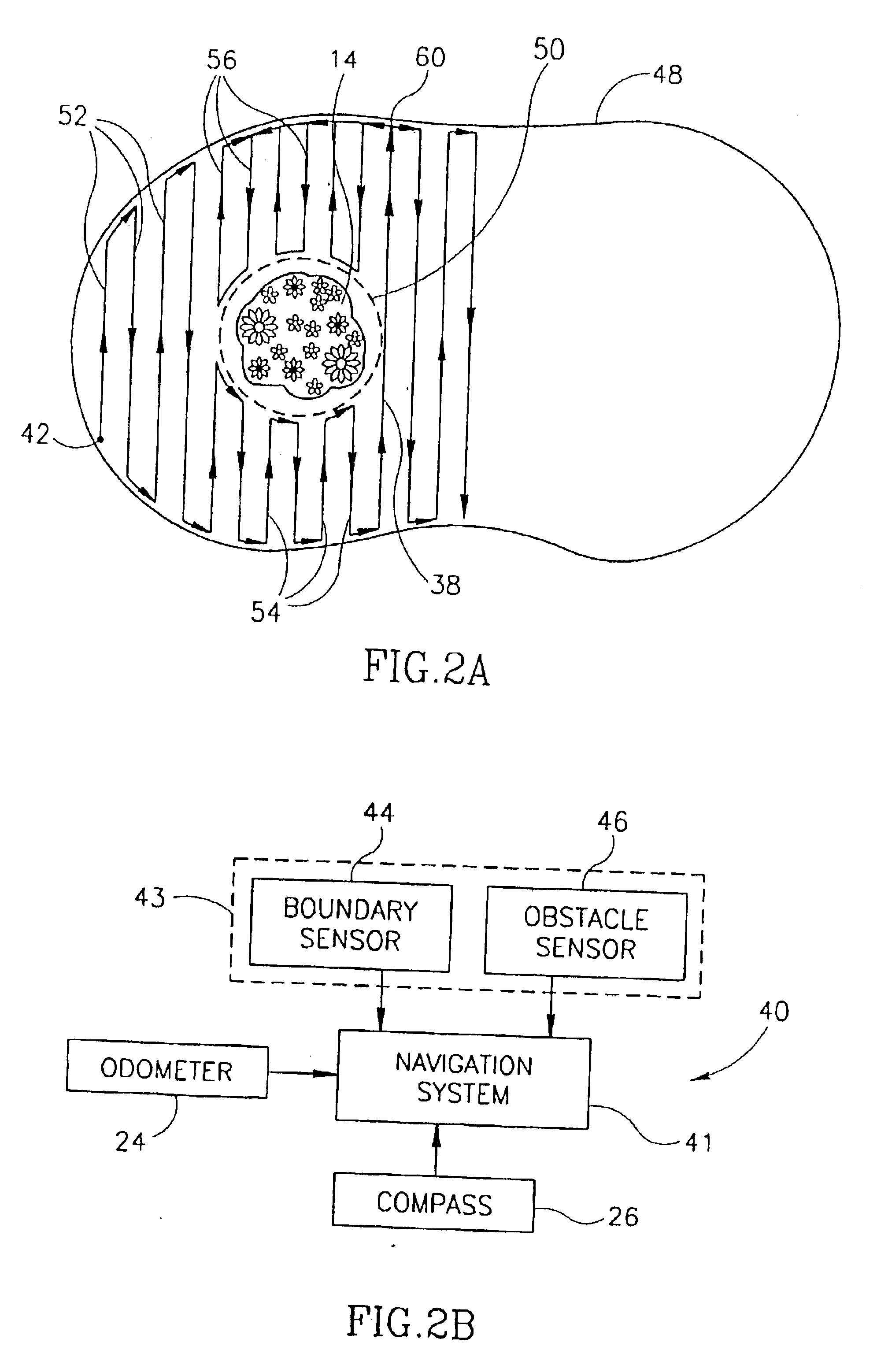
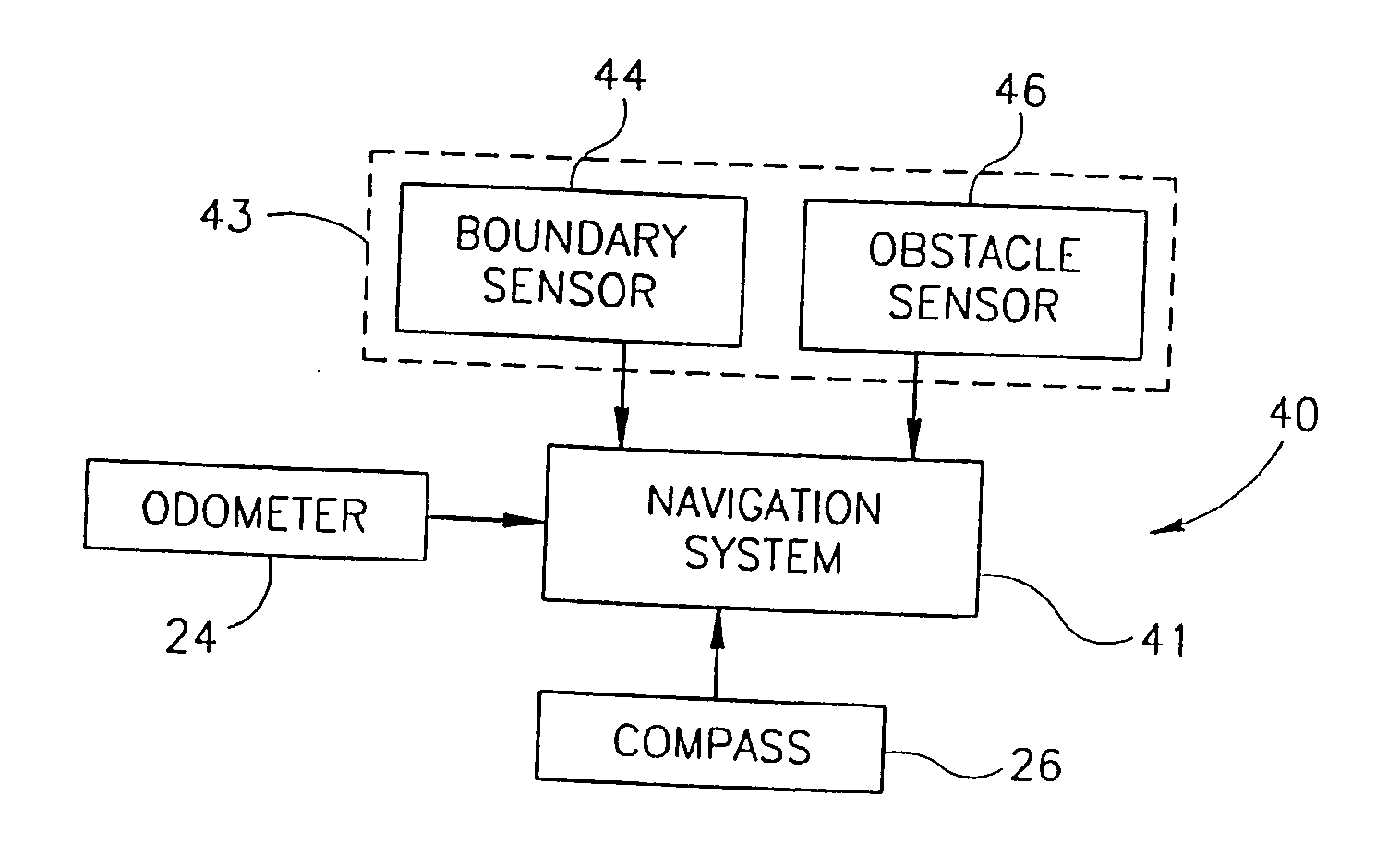
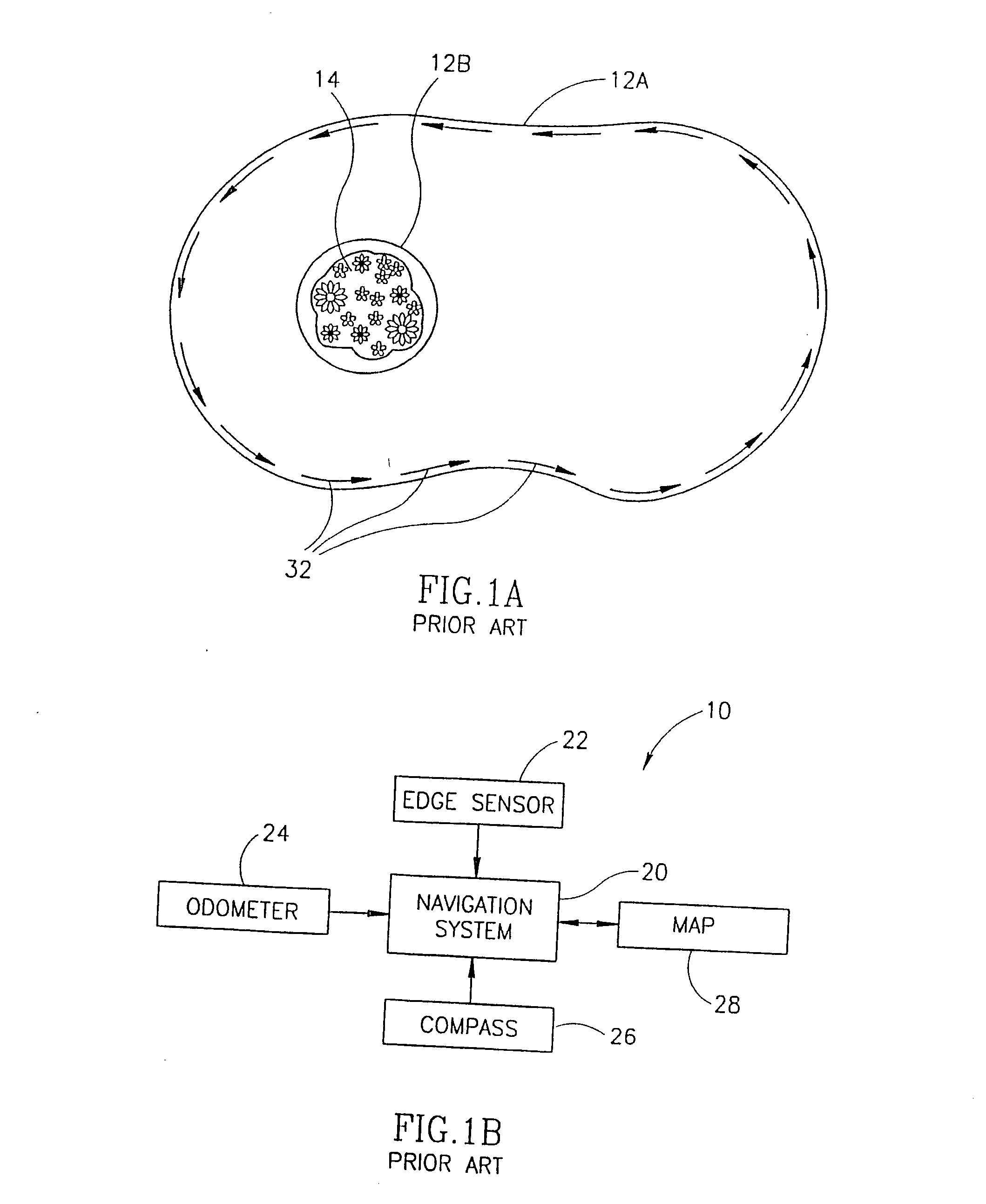
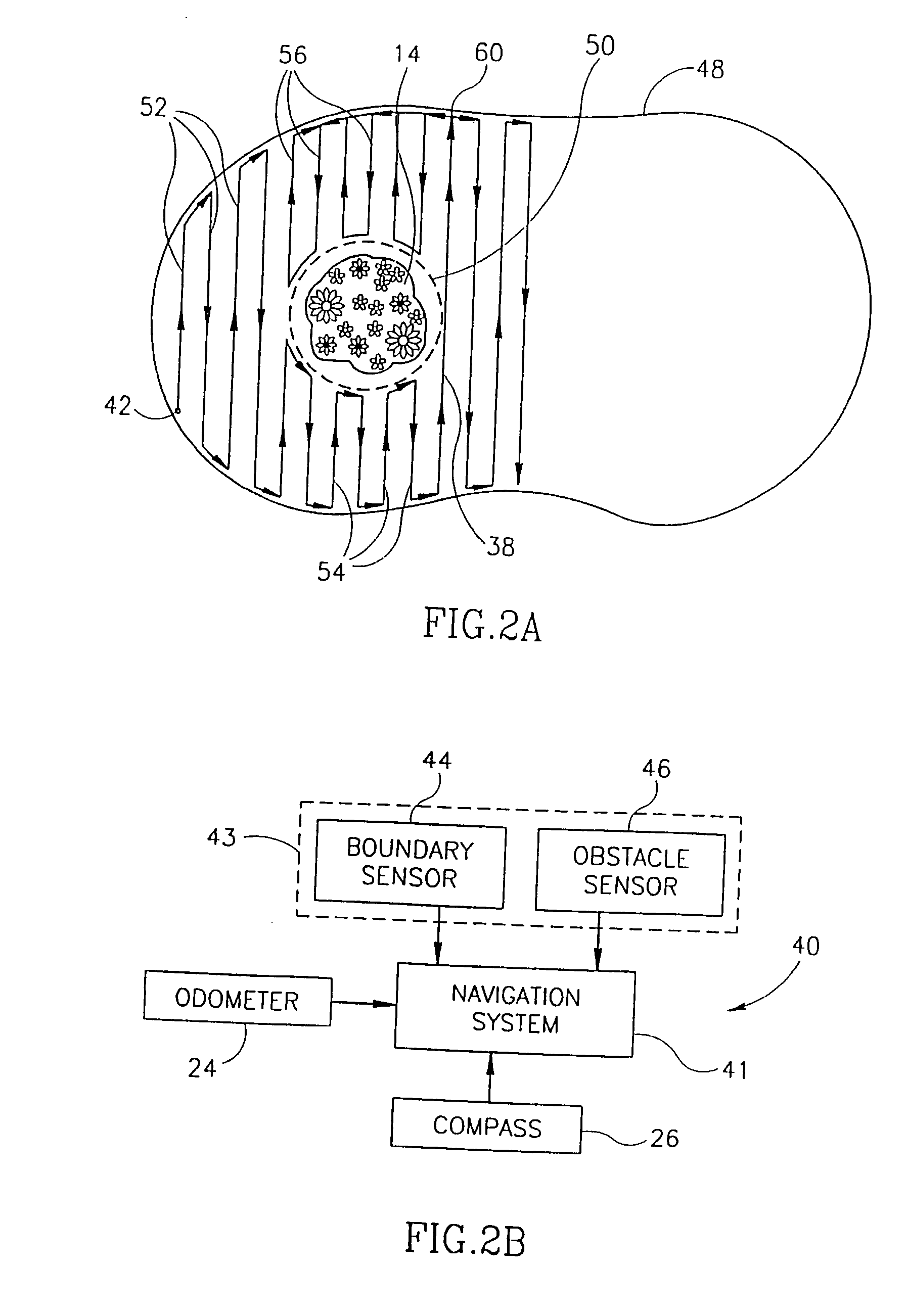
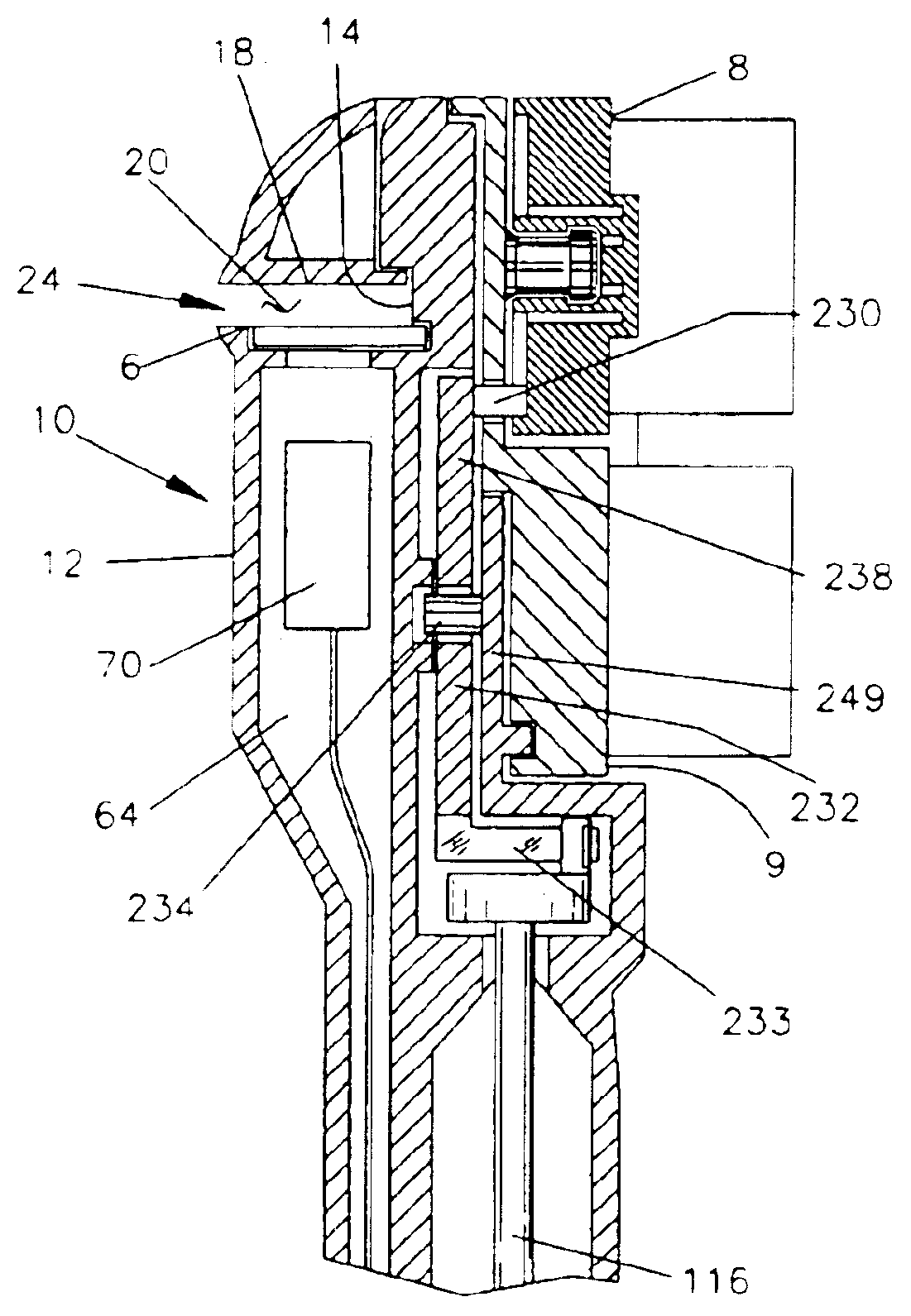
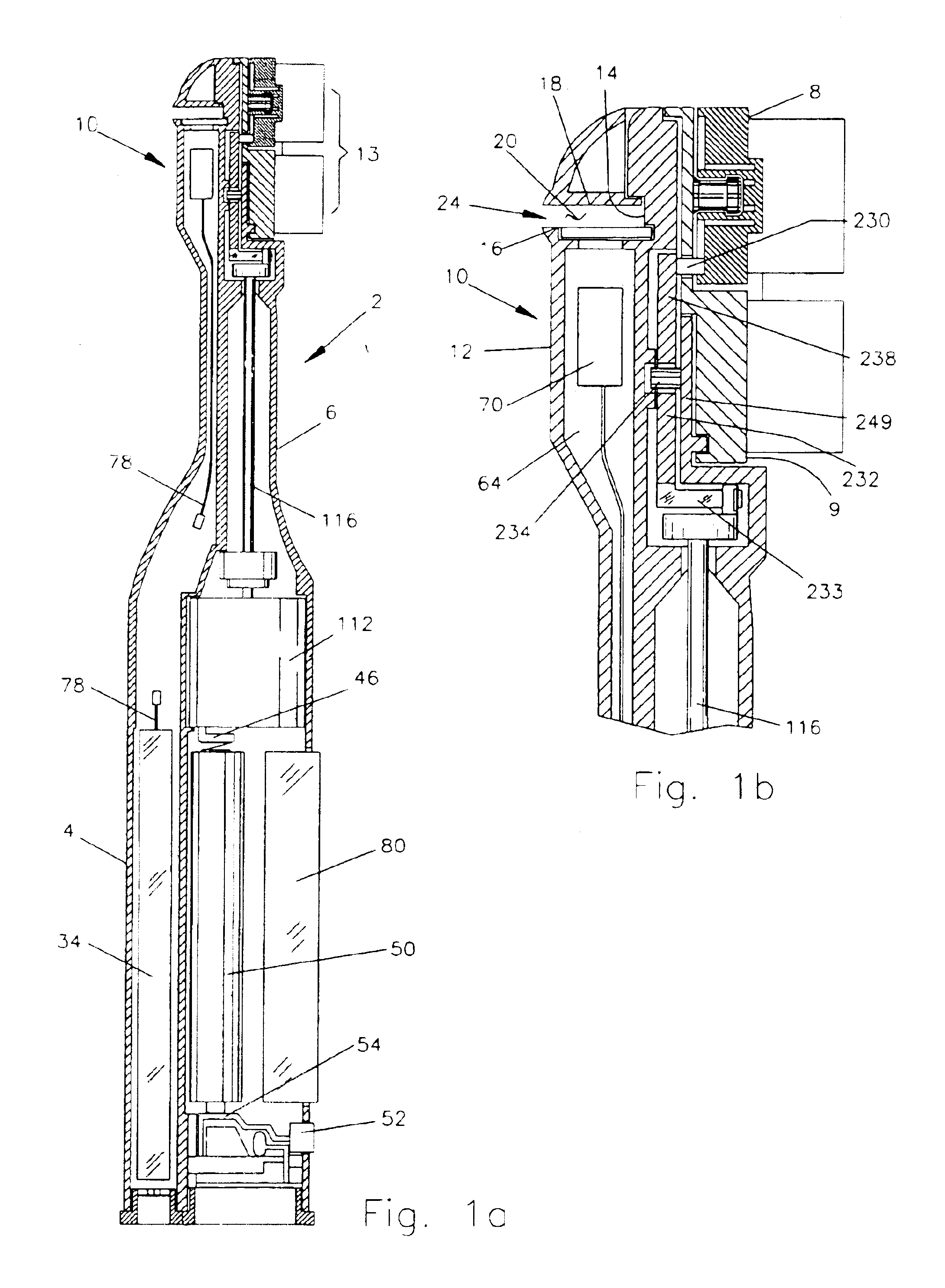
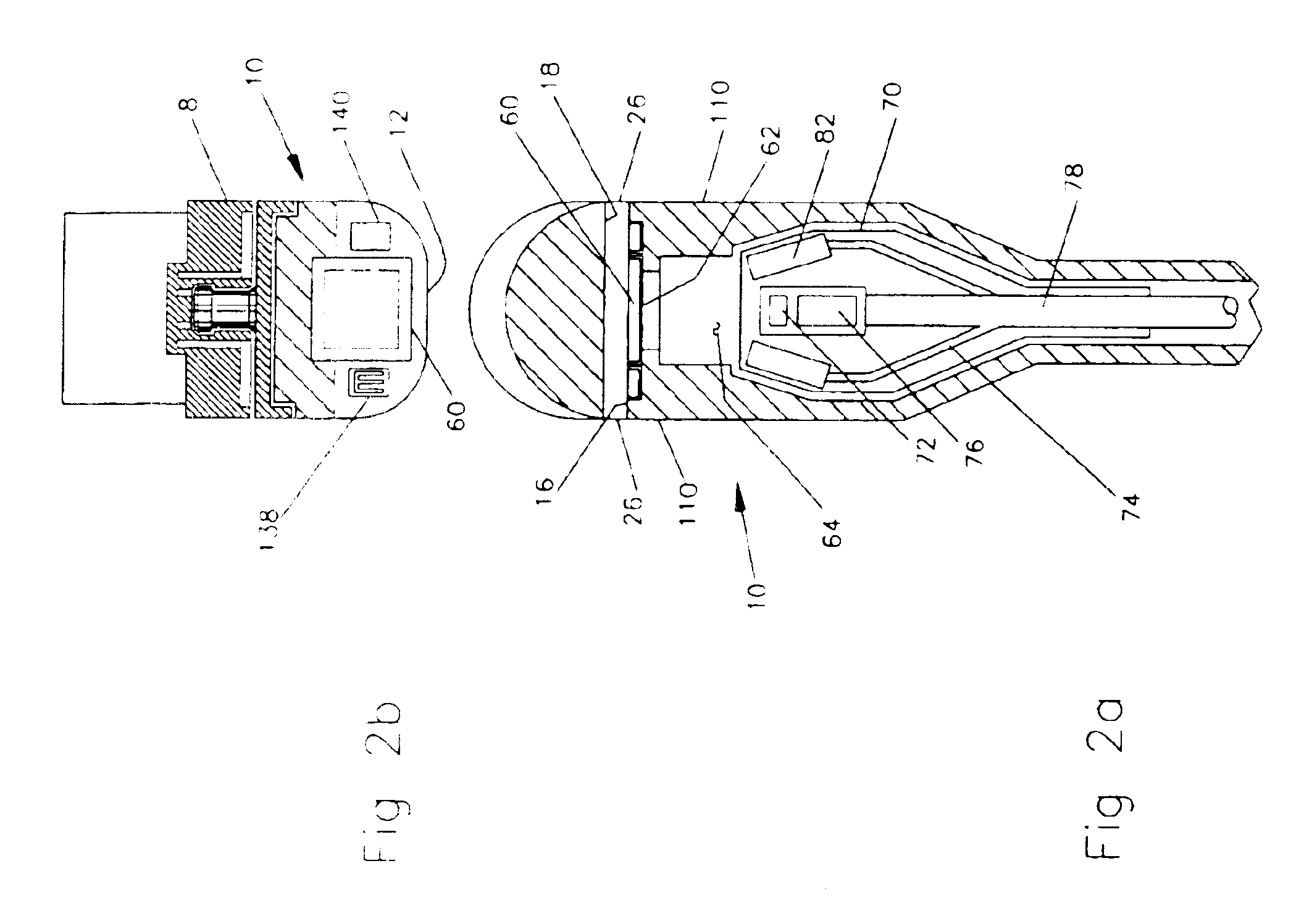
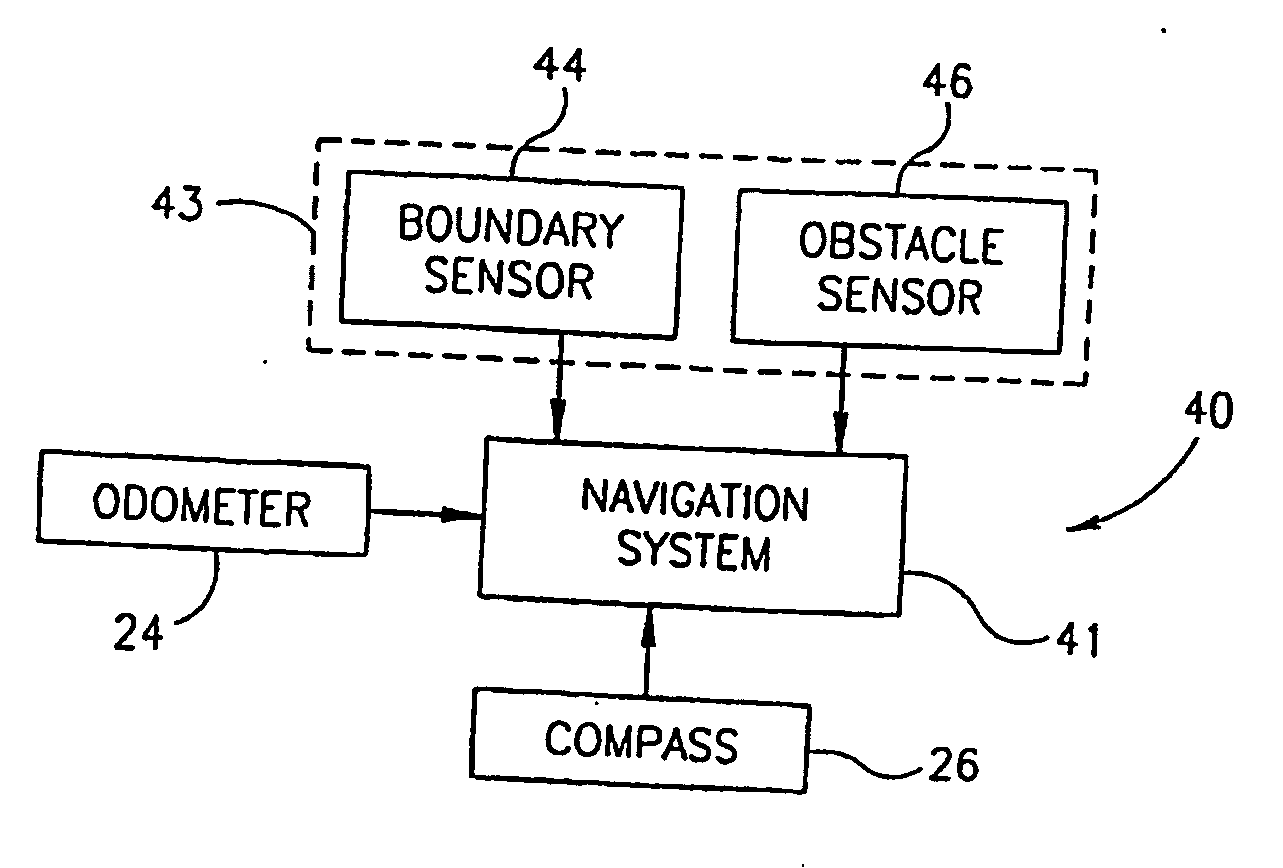
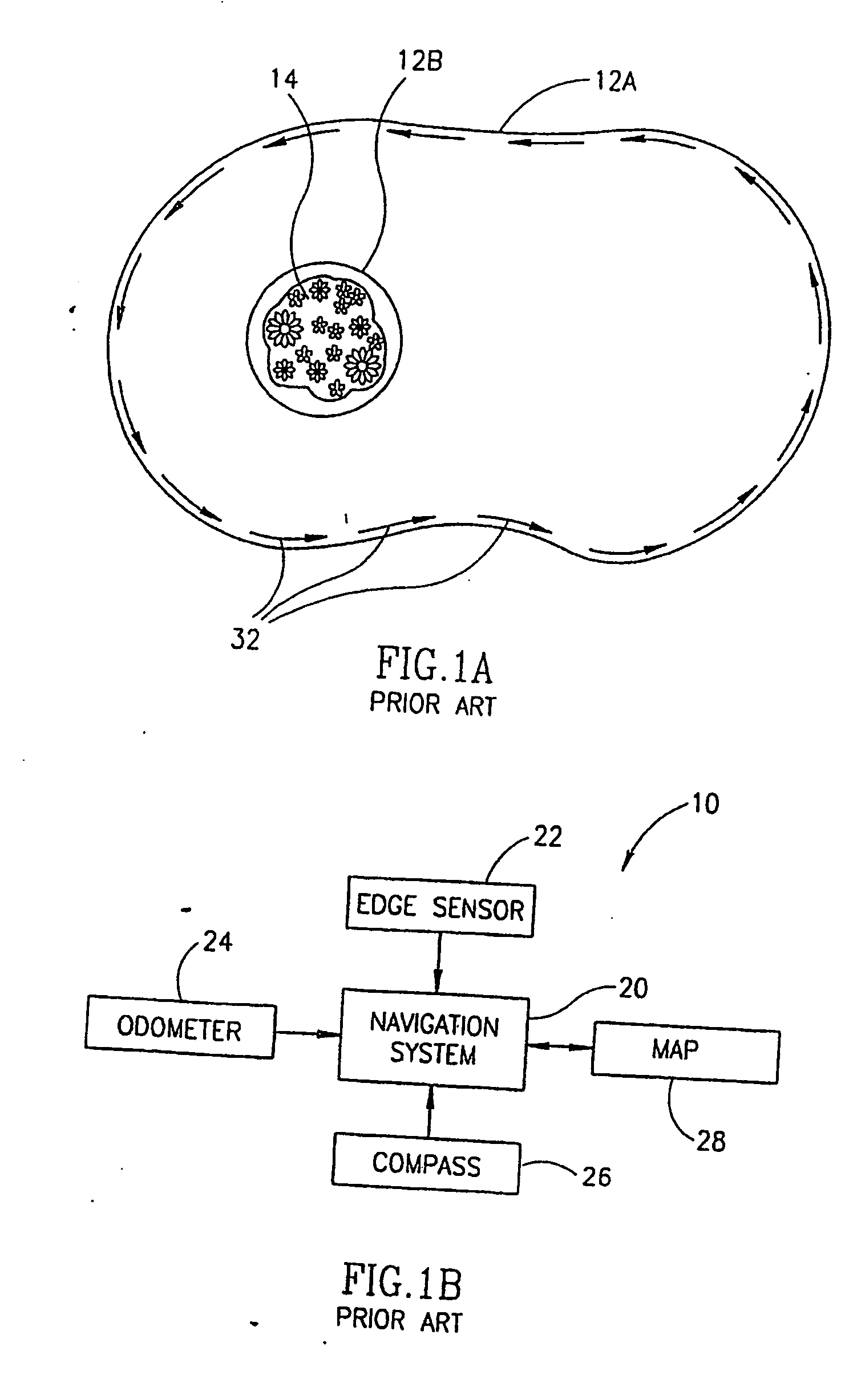
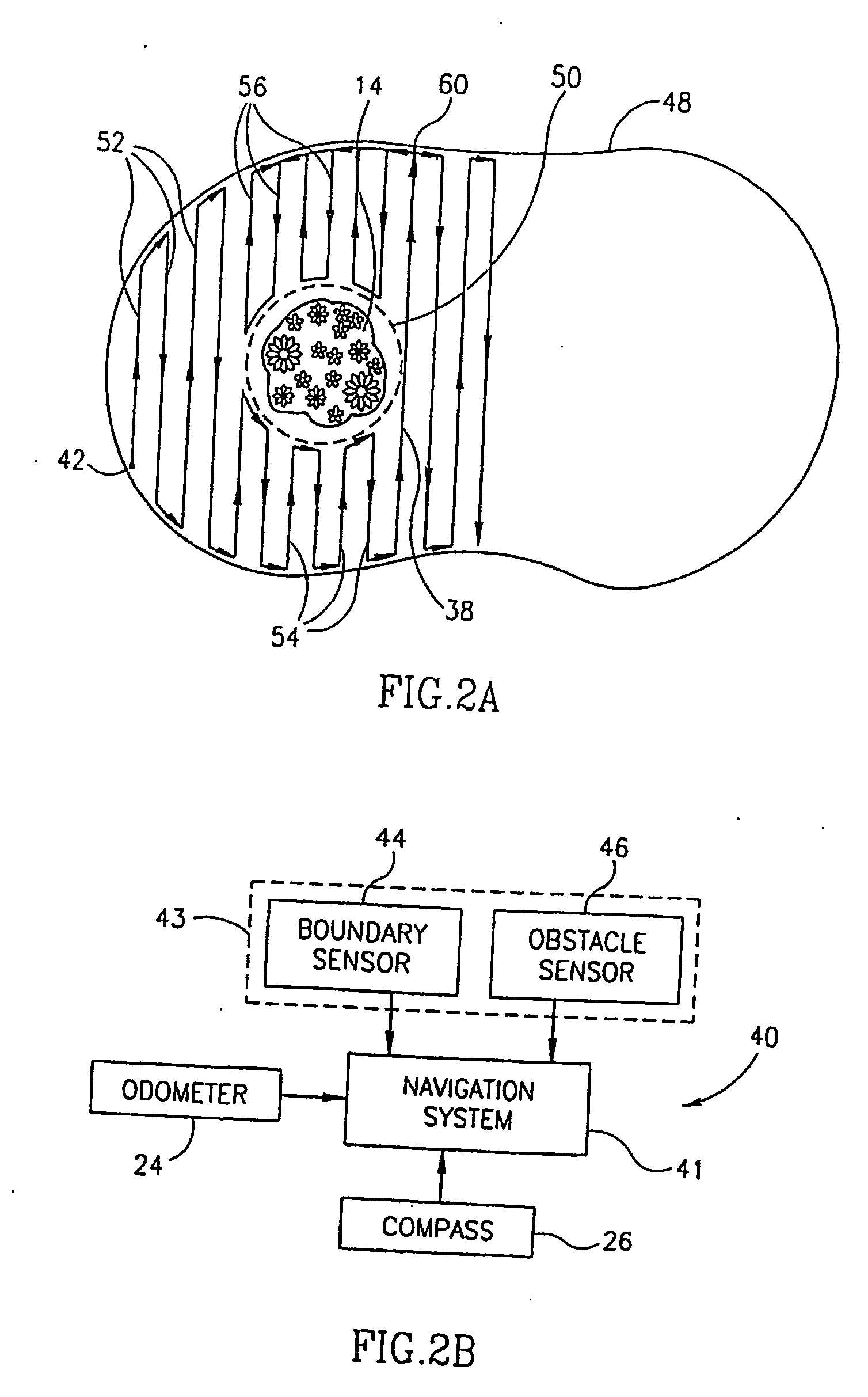
Area coverage with an autonomous robot
There is therefore provided, in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a robotic system for systematically moving about an area to be covered. The system includes at least one boundary marker (48) located along the outer edge of the area to be covered, a robot (40) with a navigation system (41) and a sensor unit (43). The navigation system (41) navigates the robot (40) in generally straight, parallel lines from an initial location and turns the robot (40) when the robot (40) encounters one of the boundary markers (48), thereby to systematically move about the area to be covered. The sensor unit (43) senses proximity to one of the at least one boundary marker (48).
Owner:MTD PRODUCTS
Coverage self-optimization method of cellular mobile communication system
ActiveCN102202330AGuaranteed service qualityIncrease profitWireless communicationSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratioMaterial resources
The invention relates to a coverage self-optimization method of a cellular mobile communication system, and is used for solving the problems of poor coverage, polluted pilot frequency and cross-area coverage. The method comprises the following steps of: measuring and reporting respective reference signal received power (RSRP) and respective signal-to-interference plus noise ratio (SINR) parameter values to a base station by each user; collecting the measurement parameter values reported by all users in a cell by the base station; judging whether the current network is in accordance with any one trigger condition of the three coverage problems; triggering a coverage self-optimization process based on dynamic adjustment on a lower dip angle of an antenna if the current network is in accordance with the condition and then adjusting the lower dip angle according to a preset scheme to solve the coverage problem; continuously adjusting an antenna azimuth angle and wave beam width or performing down-regulation on transmission power of the base station according to specific scenes and user types if the coverage requirement cannot be met within the adjustable ranges of the lower dip angle; and entering a coverage and capacity self-optimization process if the coverage problem cannot be solved by the measures. According to the method, each cell periodically initiates coverage liberalization operation for many times according to the steps so as to save manpower and material resources required by manual optimization and reduce the maintenance cost and the expenditure.
Owner:泰科系统(东莞)科技有限公司
Enhanced wireless packet data communication system, method, and apparatus applicable to both wide area networks and local area networks
InactiveUS7477694B2Improved performance characteristicsCost effectivePulse automatic controlDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionWide areaArea coverage
A cellular wireless packet data communication system containing transmit-only endpoint devices which transmit to receive-only base stations. The system is configured to allow for large area coverage (e.g., a metropolitan area) with far fewer number base stations than are required with conventional two-way cellular systems. The base station coverage areas are configured to overlap, allowing for reception of packets at multiple base stations. A data concentrator resolves redundantly received messages. The network is configurable as a WAN, a LAN, or a combination of the two. Novel modulation techniques (e.g., a 16QAM submodulation together with a 7FSK modulation) are used such that low cost components can be used in the transmitters and receivers while achieving outstanding probability of success performance. The endpoint devices are battery operated and accordingly, are designed for low power consumption and multi-year battery life. The system is used in a variety of applications including remote monitoring and mobile communications.
Owner:SENSUS SPECTRUM LLC
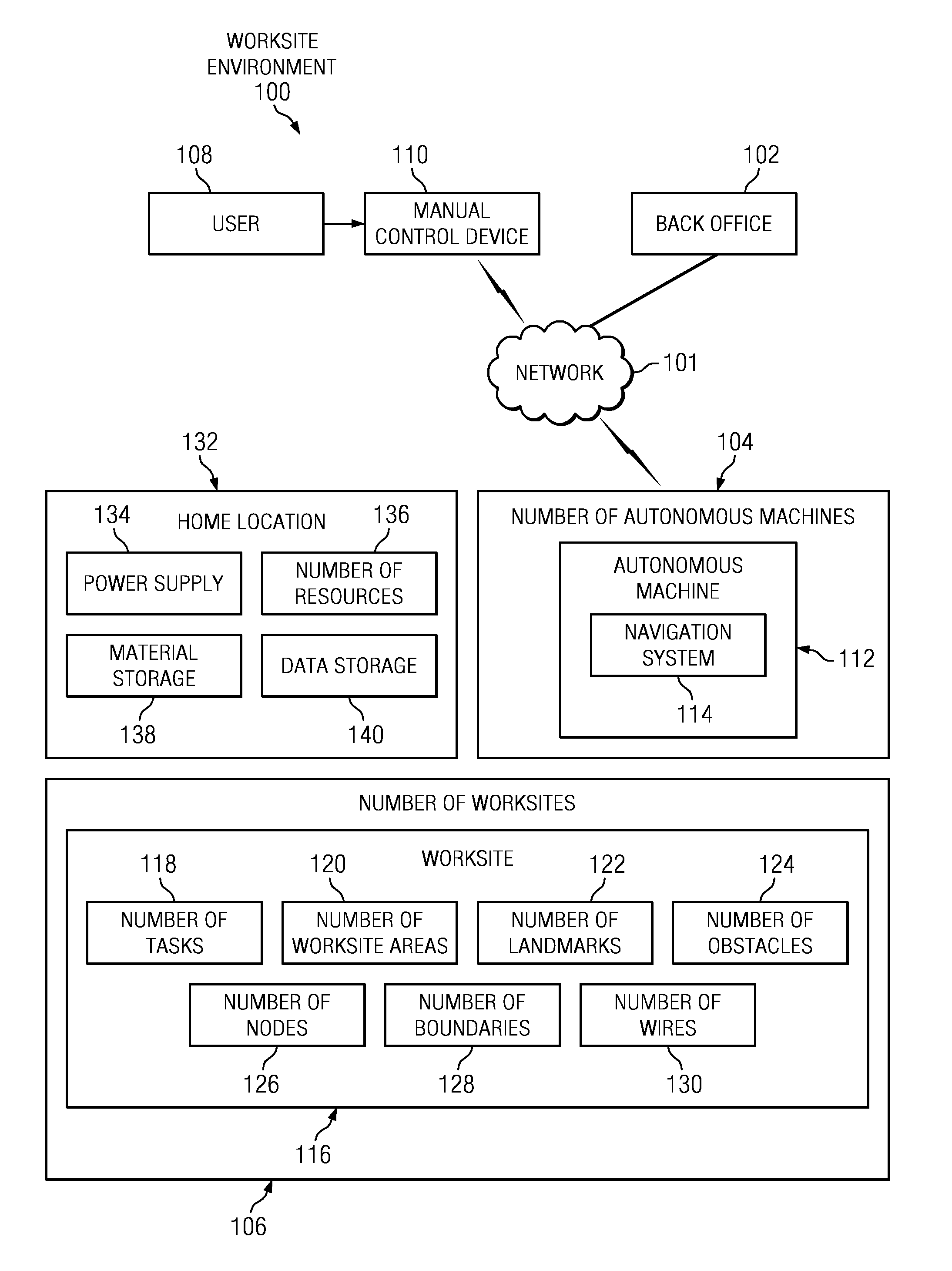
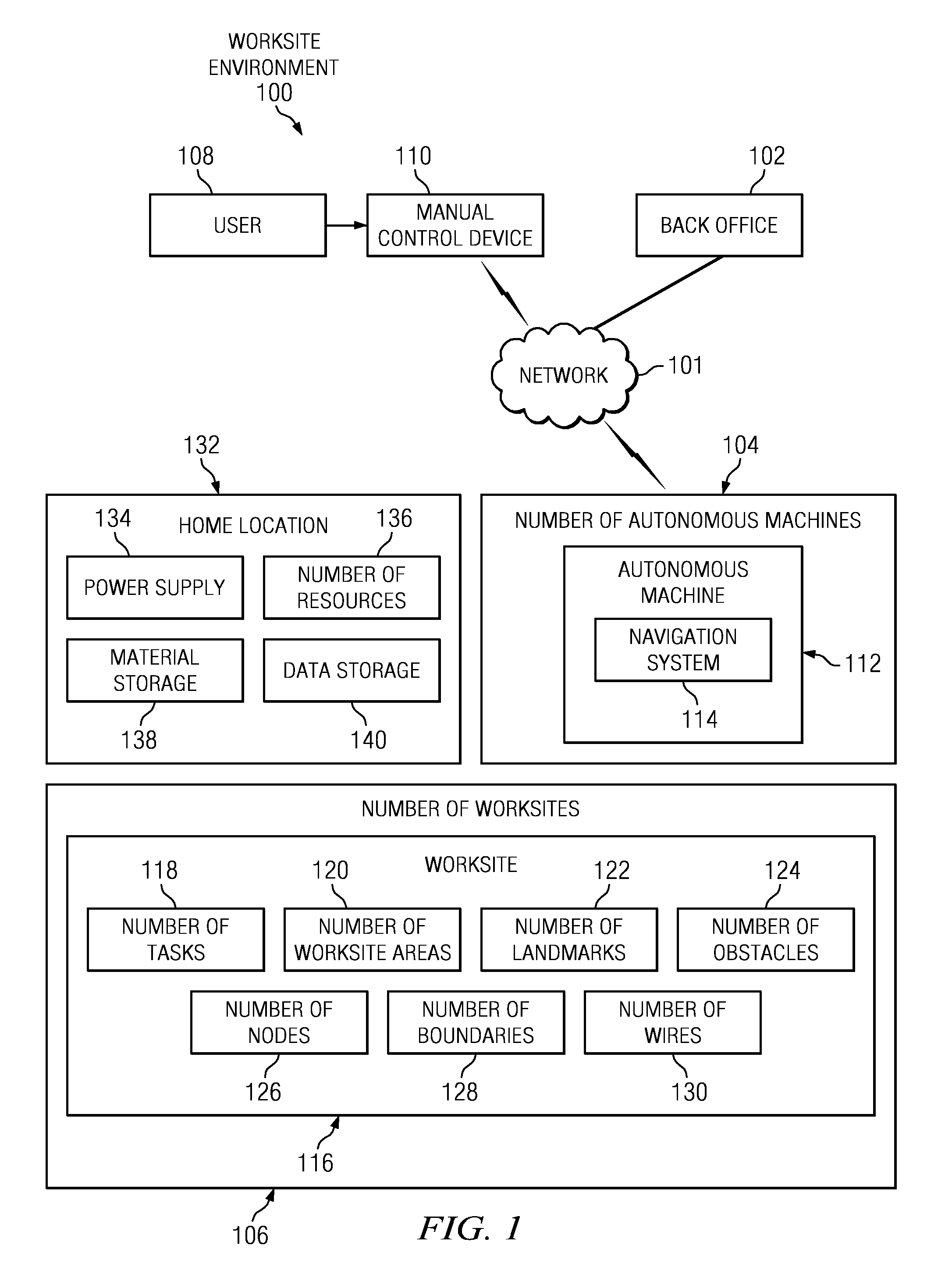
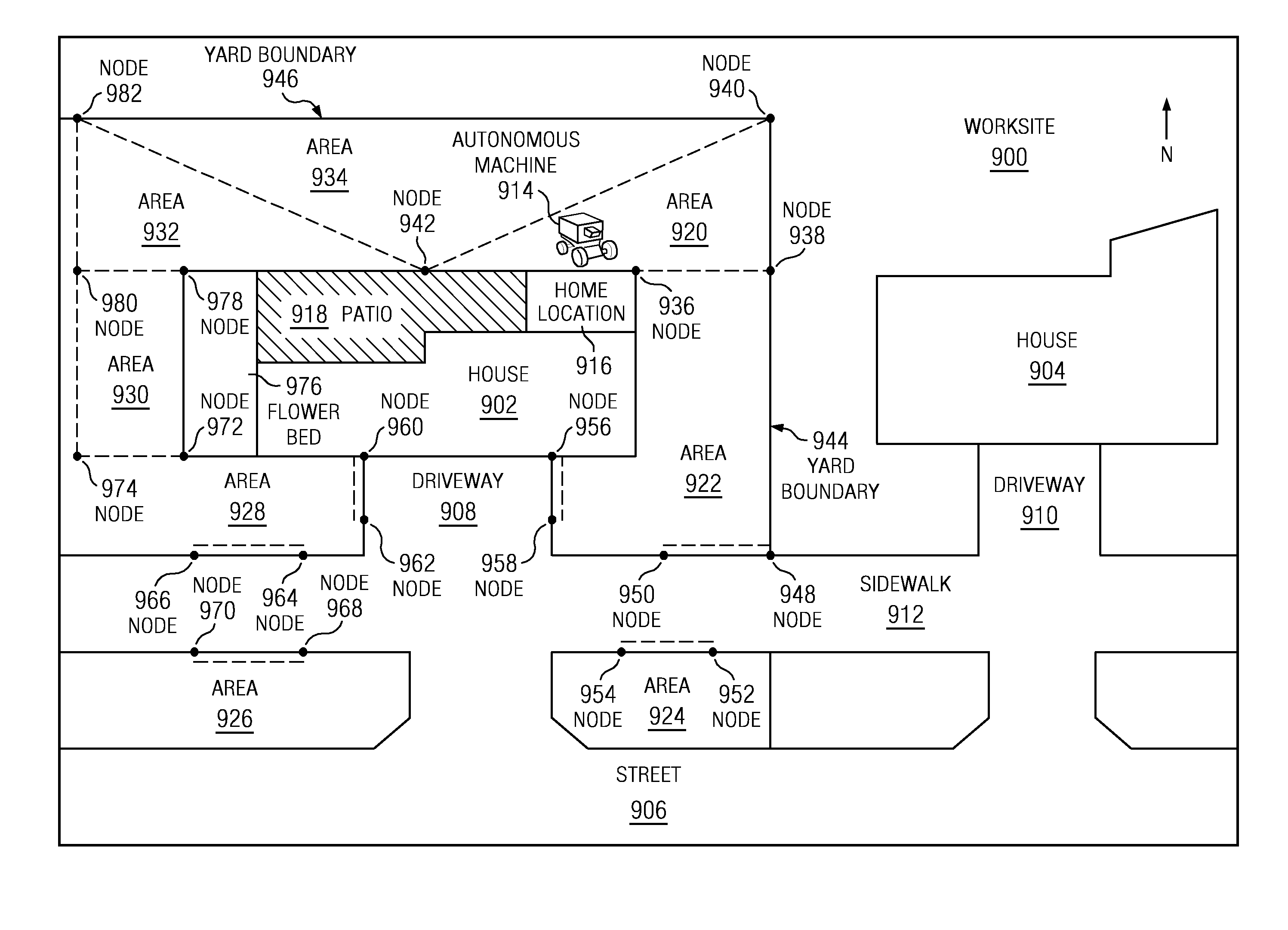
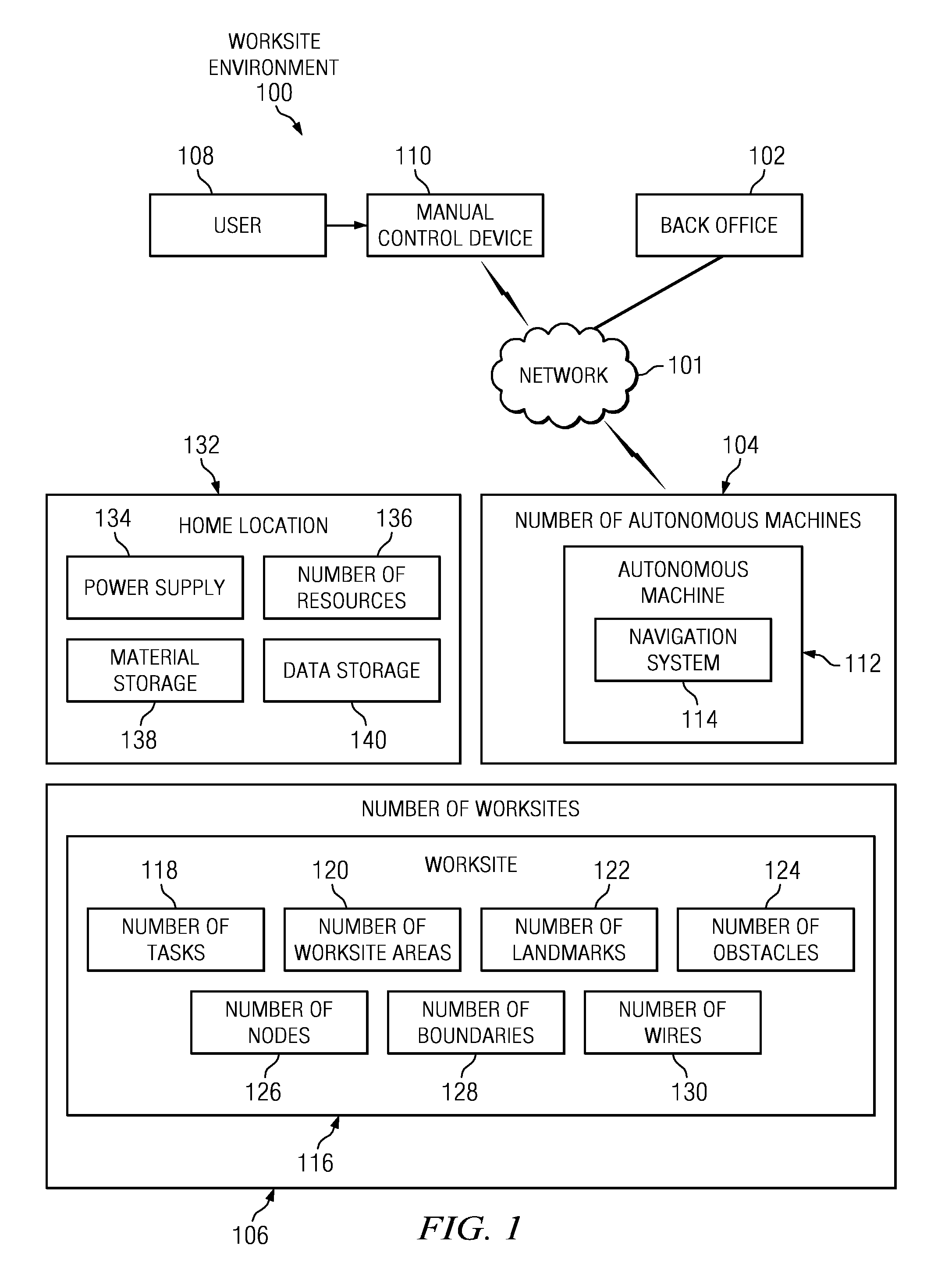
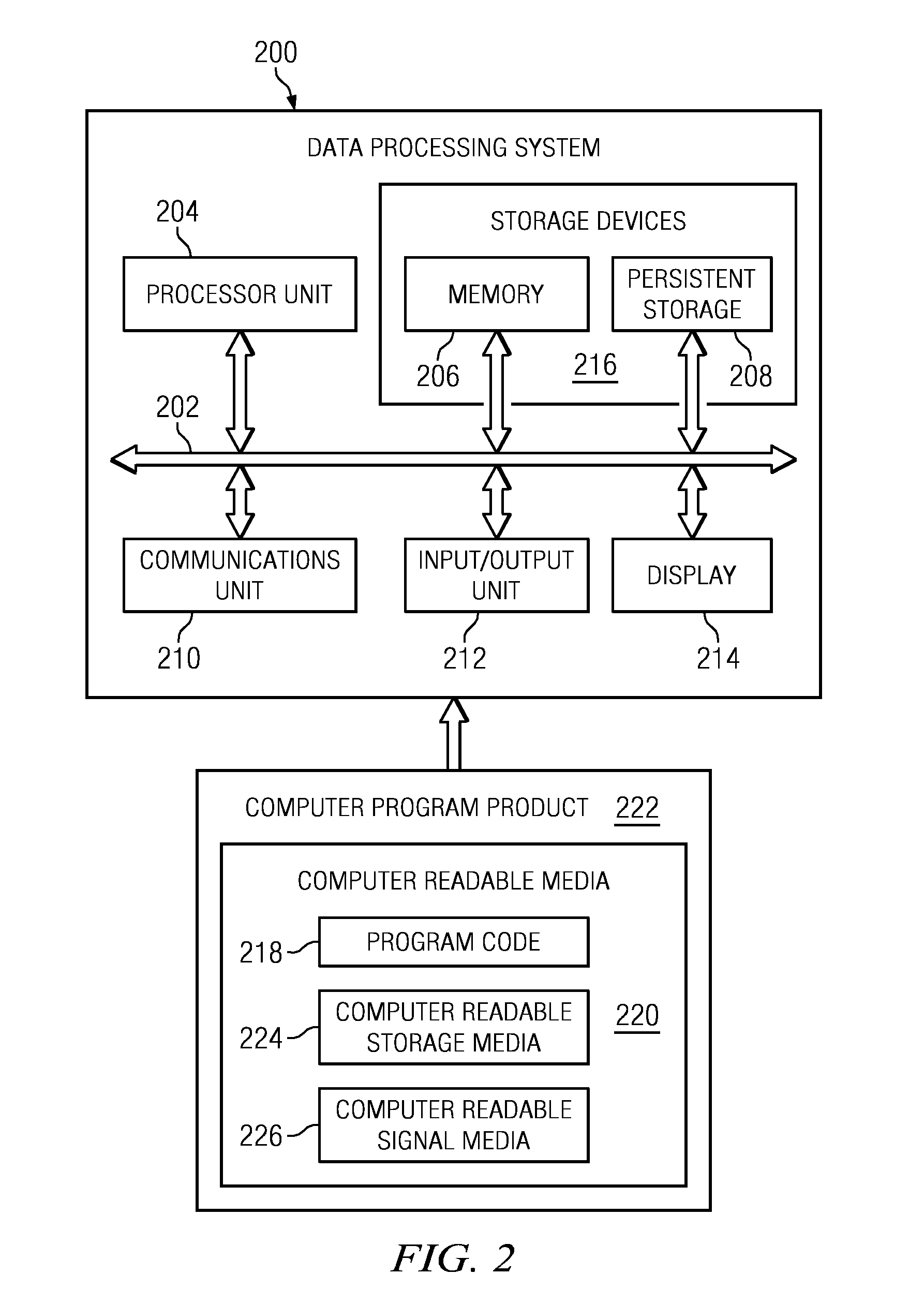
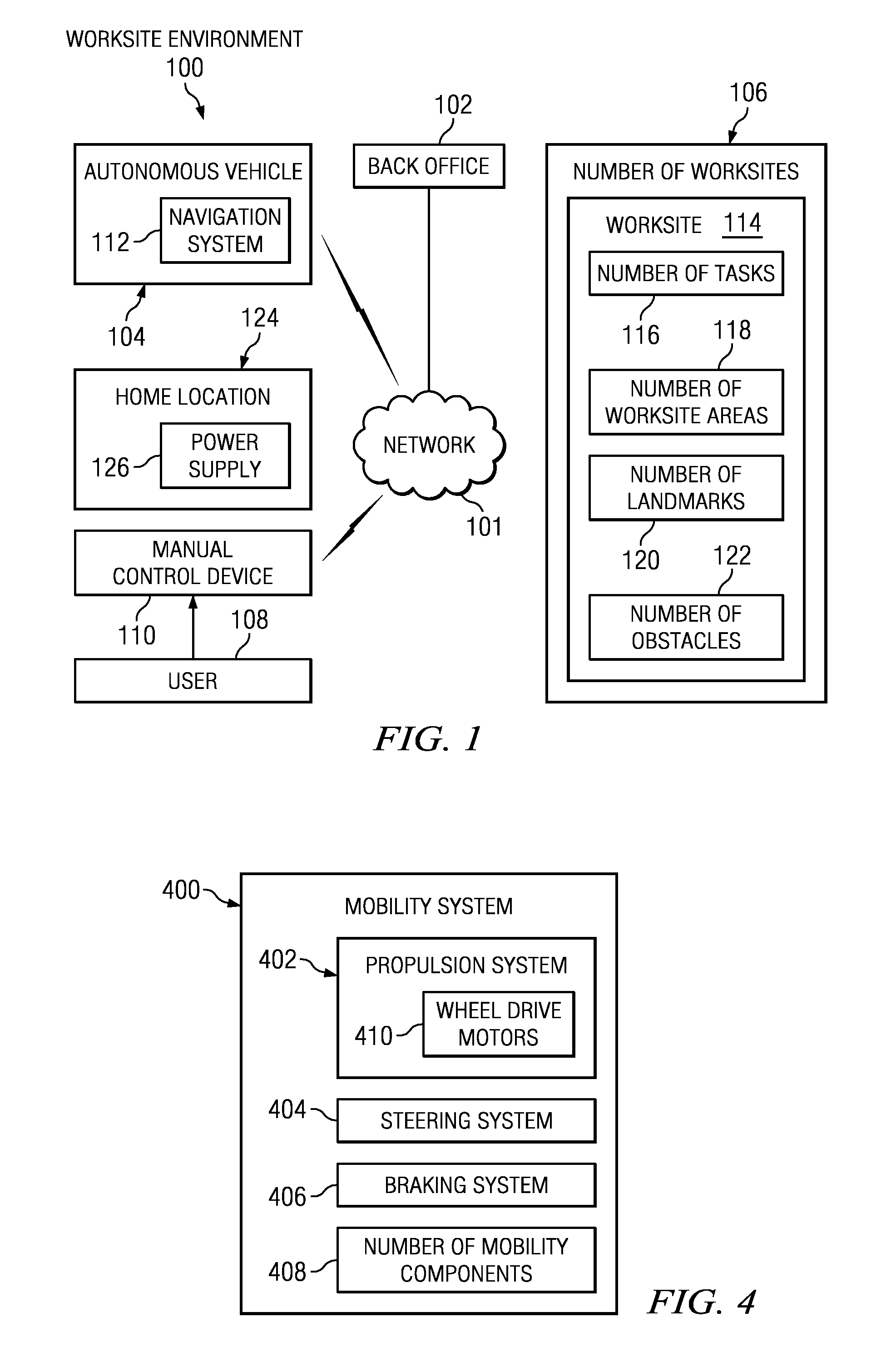
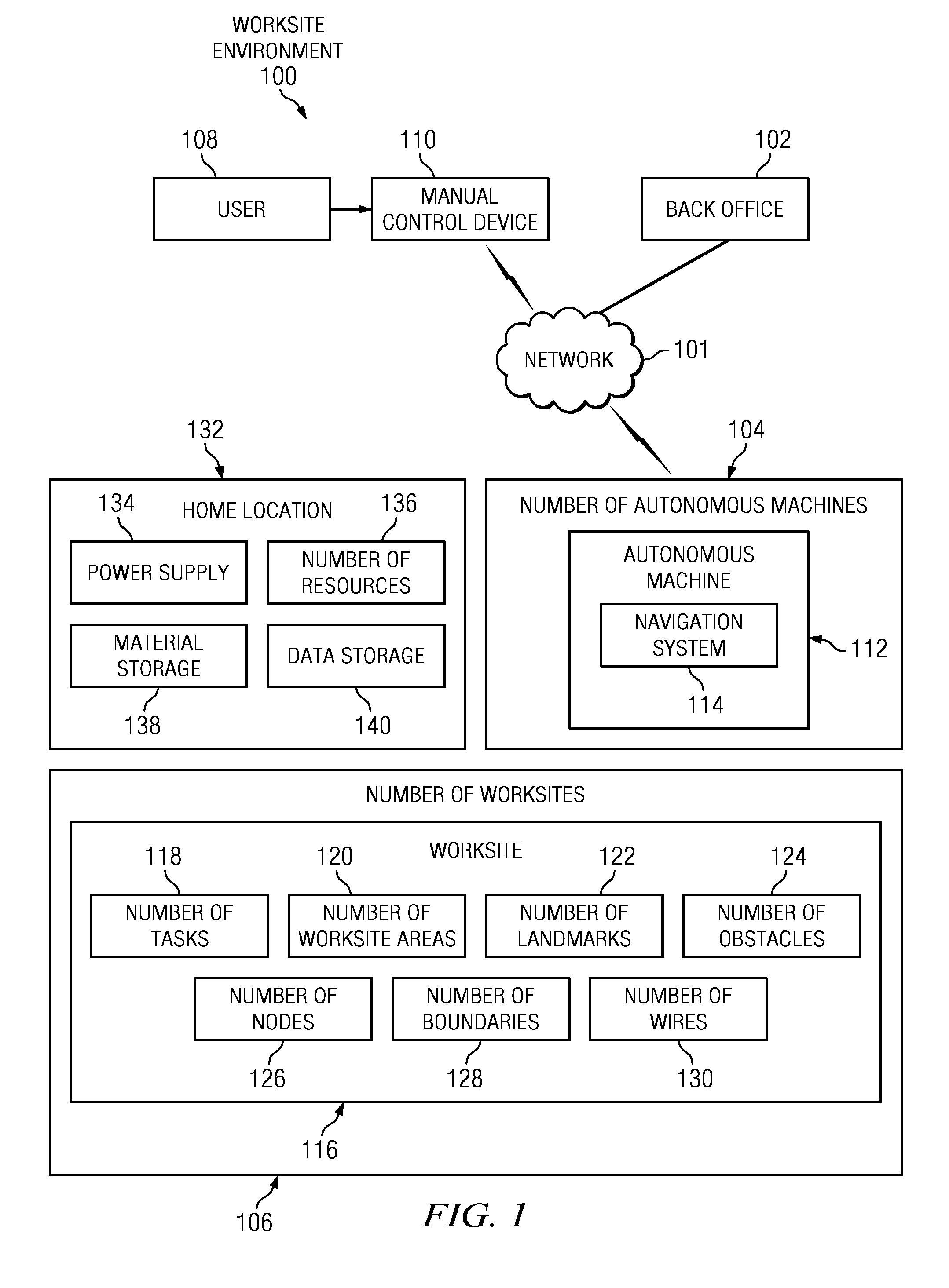
Managing autonomous machines across multiple areas
The different illustrative embodiments provide a system for autonomous machine management comprising a number of autonomous machines, a number of nodes, a performance estimation module, and a navigation system. The number of autonomous machines is configured to perform area coverage tasks in a worksite. The number of nodes is configured to define a number of worksite areas for the worksite. The performance estimation module is executed by a processor unit and configured to calculate a percentage of work completed in the number of worksite areas. The navigation system is configured to operate an autonomous machine to perform the area coverage tasks and move between the number of worksite areas.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Managing autonomous machines across multiple areas
The different illustrative embodiments provide a system for autonomous machine management comprising a number of autonomous machines, a number of nodes, a performance estimation module, and a navigation system. The number of autonomous machines is configured to perform area coverage tasks in a worksite. The number of nodes is configured to define a number of worksite areas for the worksite. The performance estimation module is executed by a processor unit and configured to calculate a percentage of work completed in the number of worksite areas. The navigation system is configured to operate an autonomous machine to perform the area coverage tasks and move between the number of worksite areas.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Area coverage with an autonomous robot
There is therefore provided, in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a robotic system for systematically moving about an area to be covered. The system includes at least one boundary marker (48) located along the outer edge of the area to be covered, a robot (40) with a navigation system (41) navigates the robot (40) in generally straight, parallel lines from an initial location and turns the robot (40) when the robot (40) encounters one of the boundary markers (48), thereby to systematically move about the are to be covered. The sensor unit (43) senses proximity to one of the at least one boundary marker (48).
Owner:MTD PRODUCTS
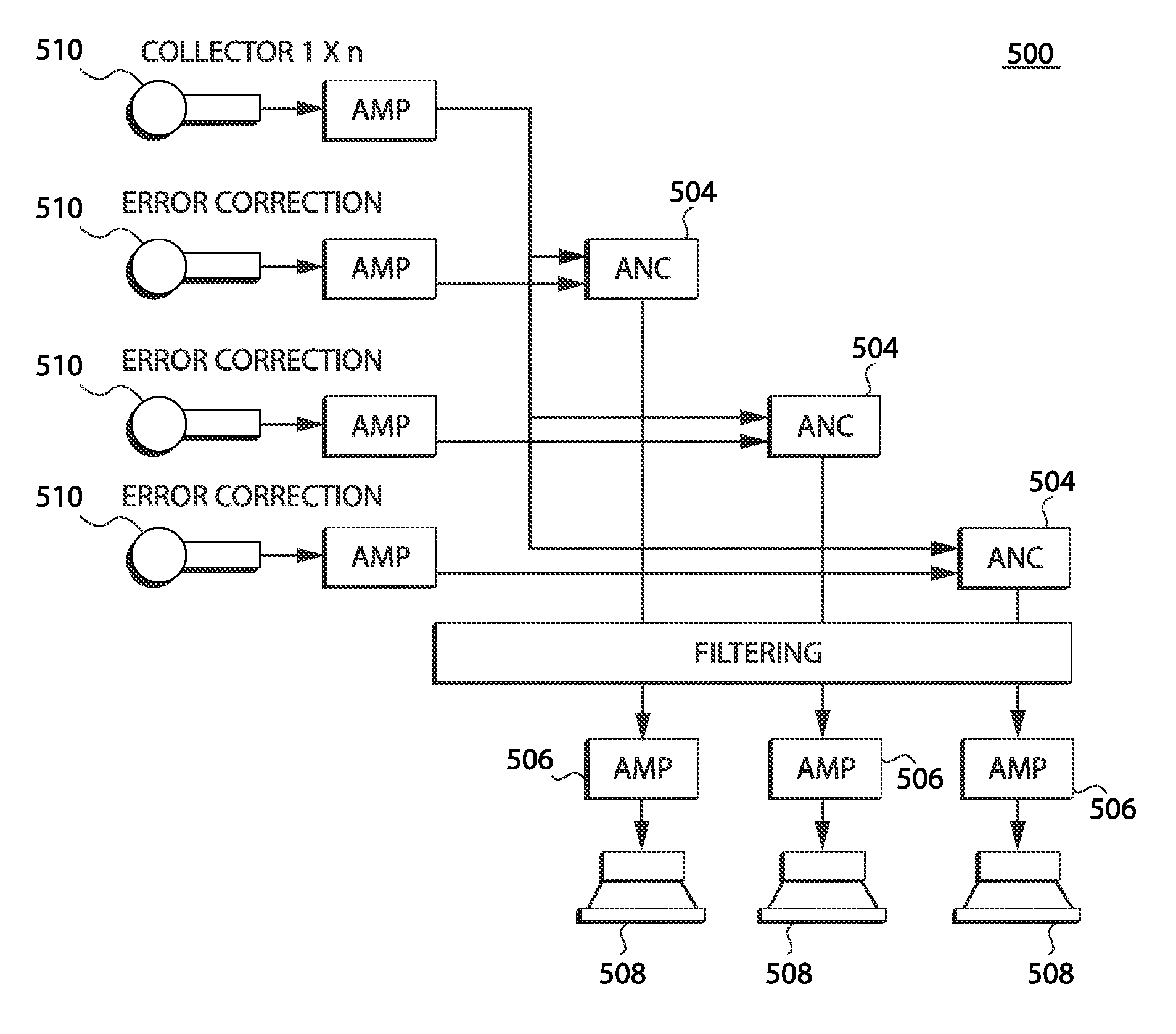
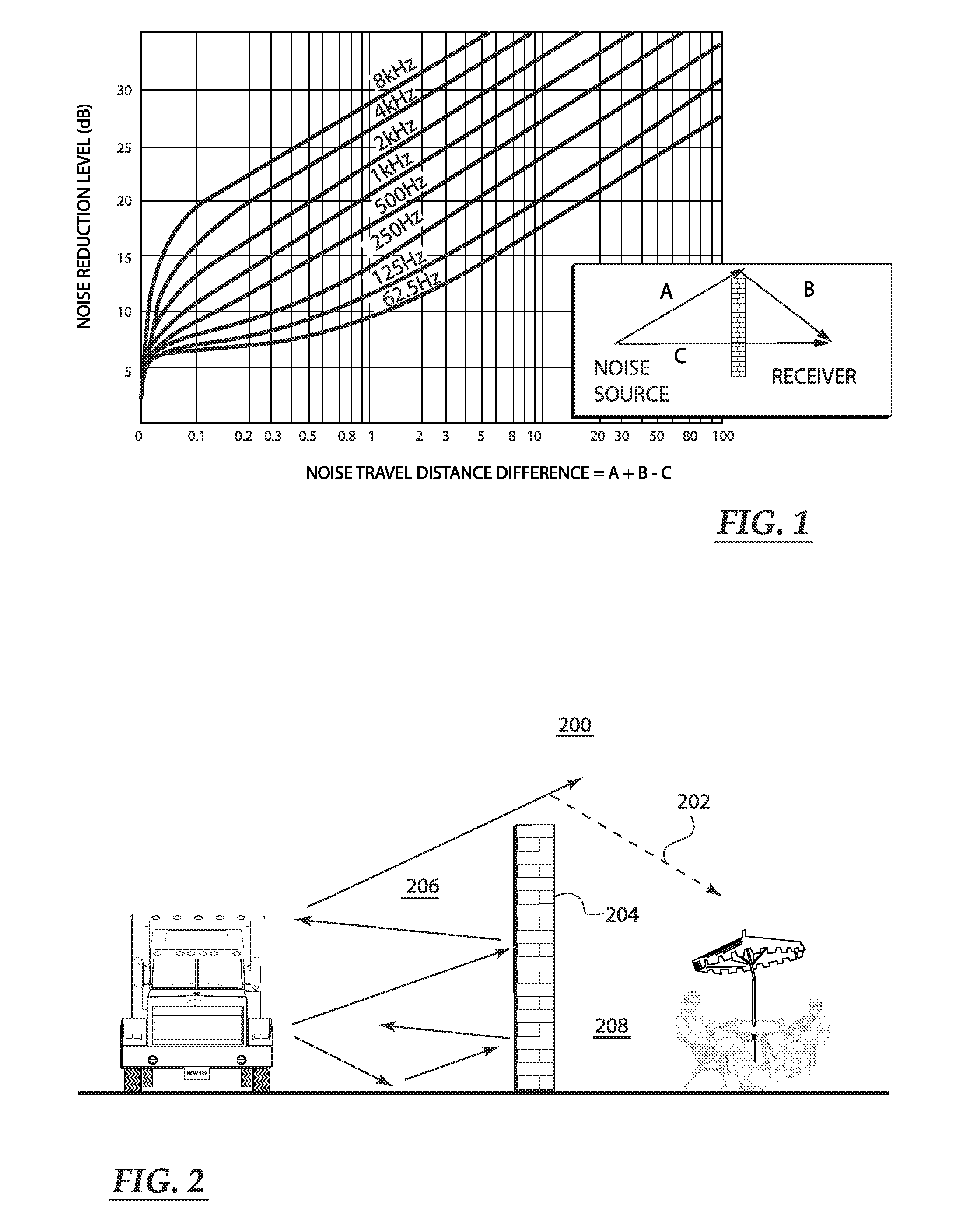
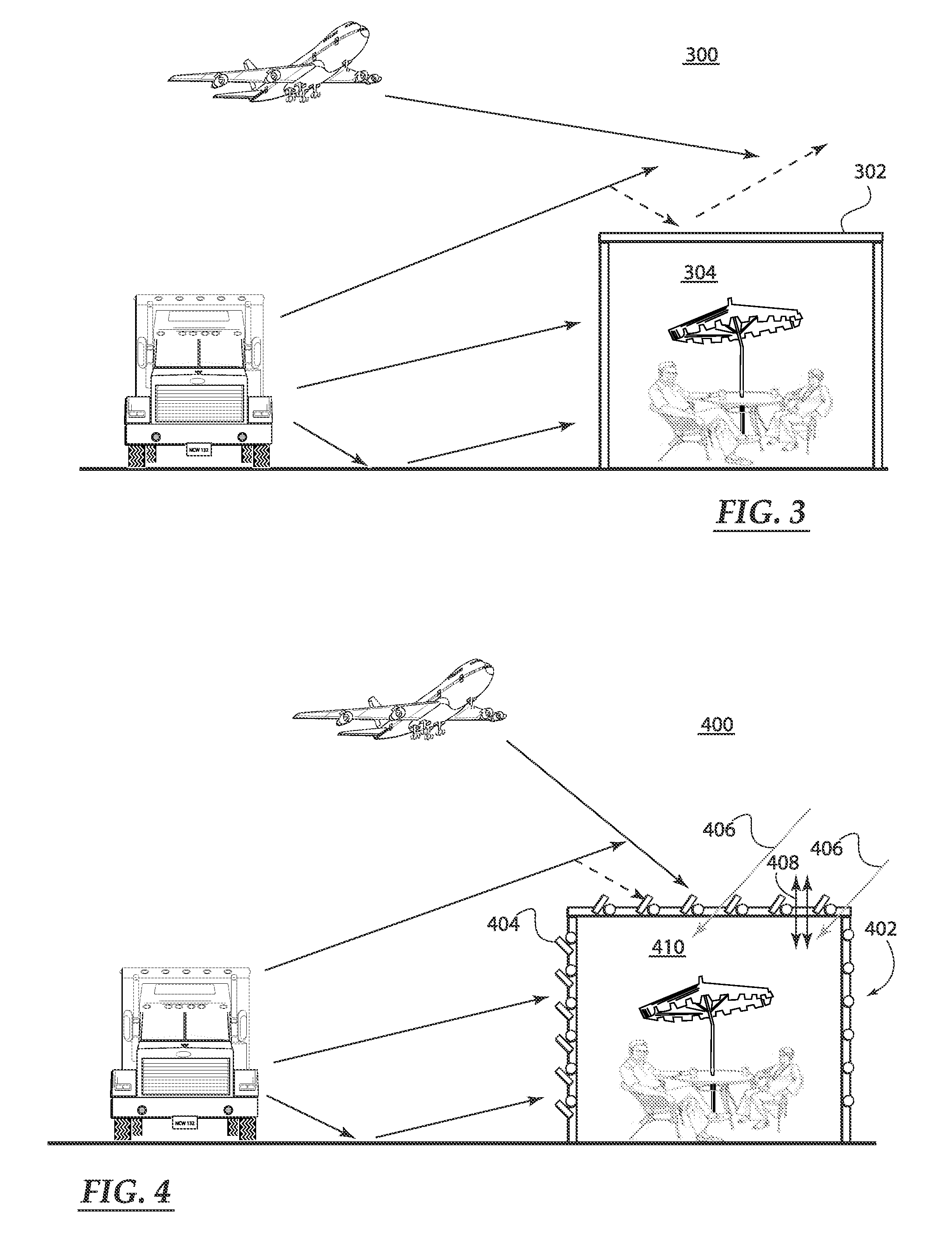
Open-air noise cancellation system for large open area coverage applications
InactiveUS20070223714A1Reduce the impactReduce the amount requiredEar treatmentNoise generationWindow shutterSystem of systems
A variety of open-air noise cancellation systems are disclosed. The systems are configured to suit the needs of the particular application, for example, an open-air sound wall installation, an open-air enclosure for a quiet area, or a window / door treatment application. A particular system may a digital-based processing architecture having a digital power amplifier that shares a common circuit board. The processing architecture receives noise signals, processes out-of-phase noise cancellation signals in response to the noise signals, and generates out-of-phase sound waves that effectively cancel low frequency components of the noise signal. One system variation utilizes passive sound absorbing blades or shutters to reduce high frequency components of the noise signal. The blades can be installed as a door or window shutter mechanism.
Owner:COMFOZONE
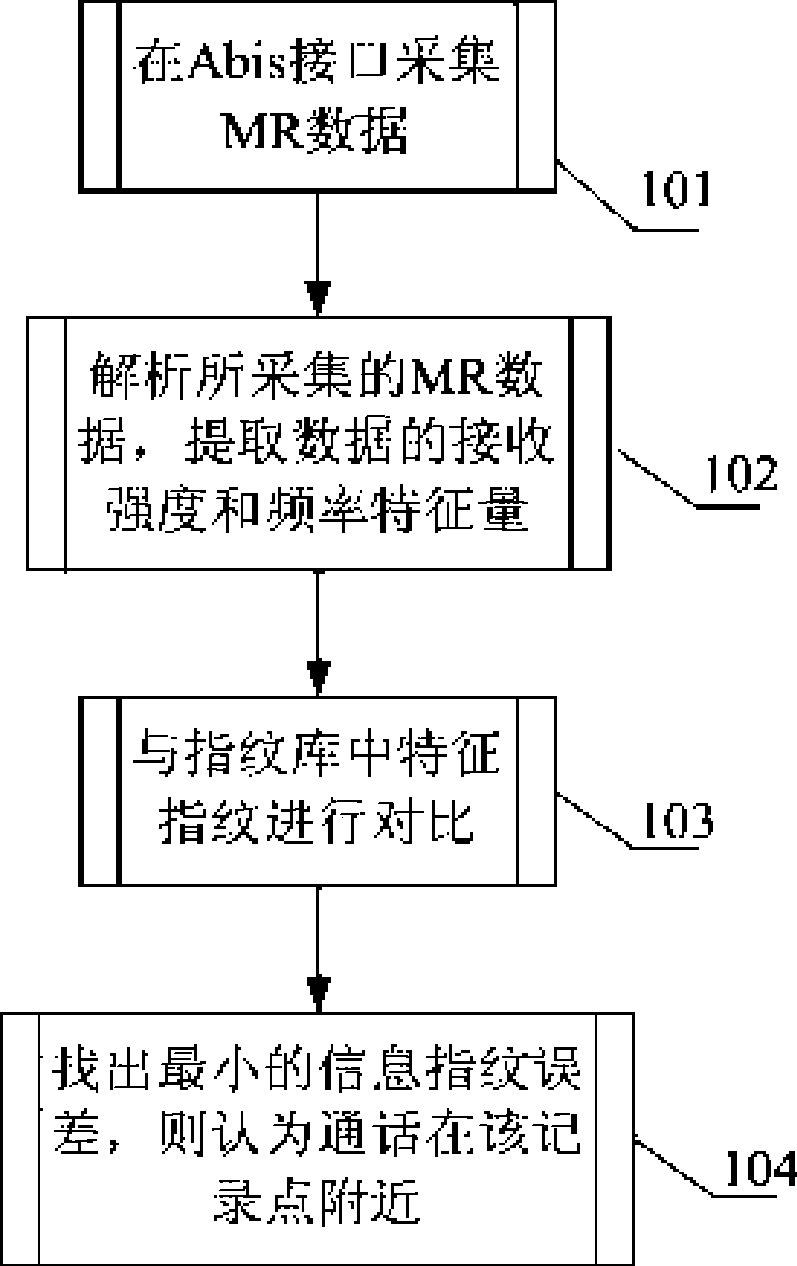
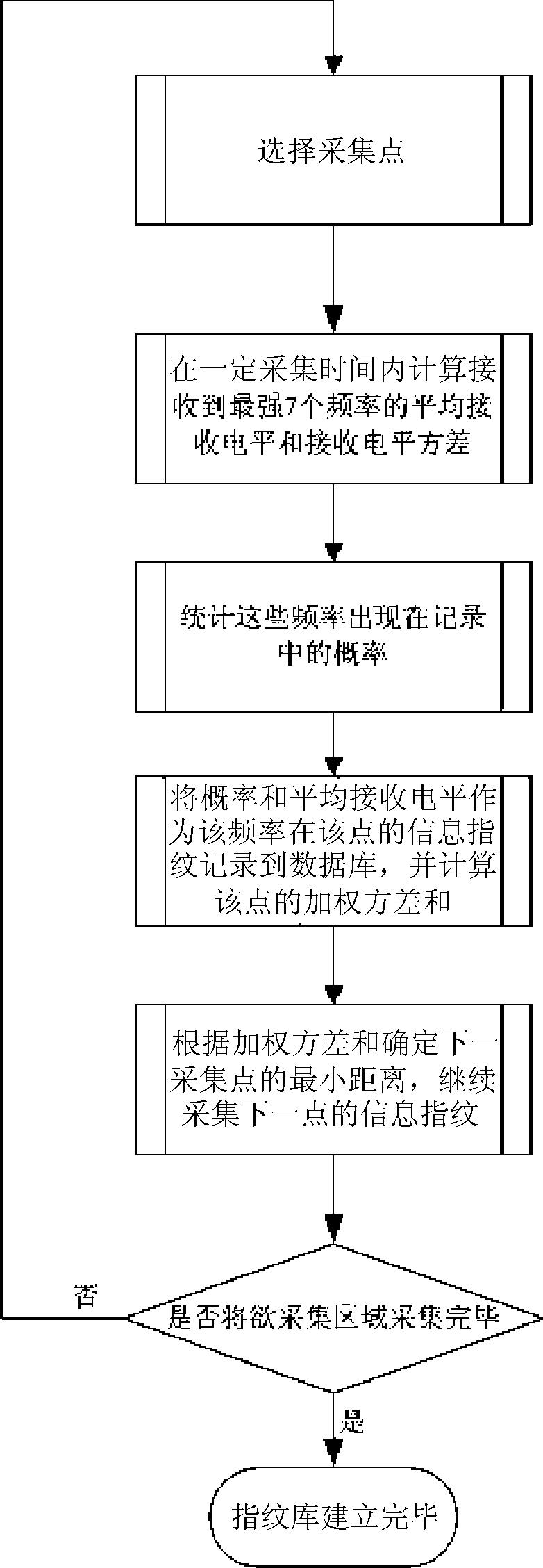
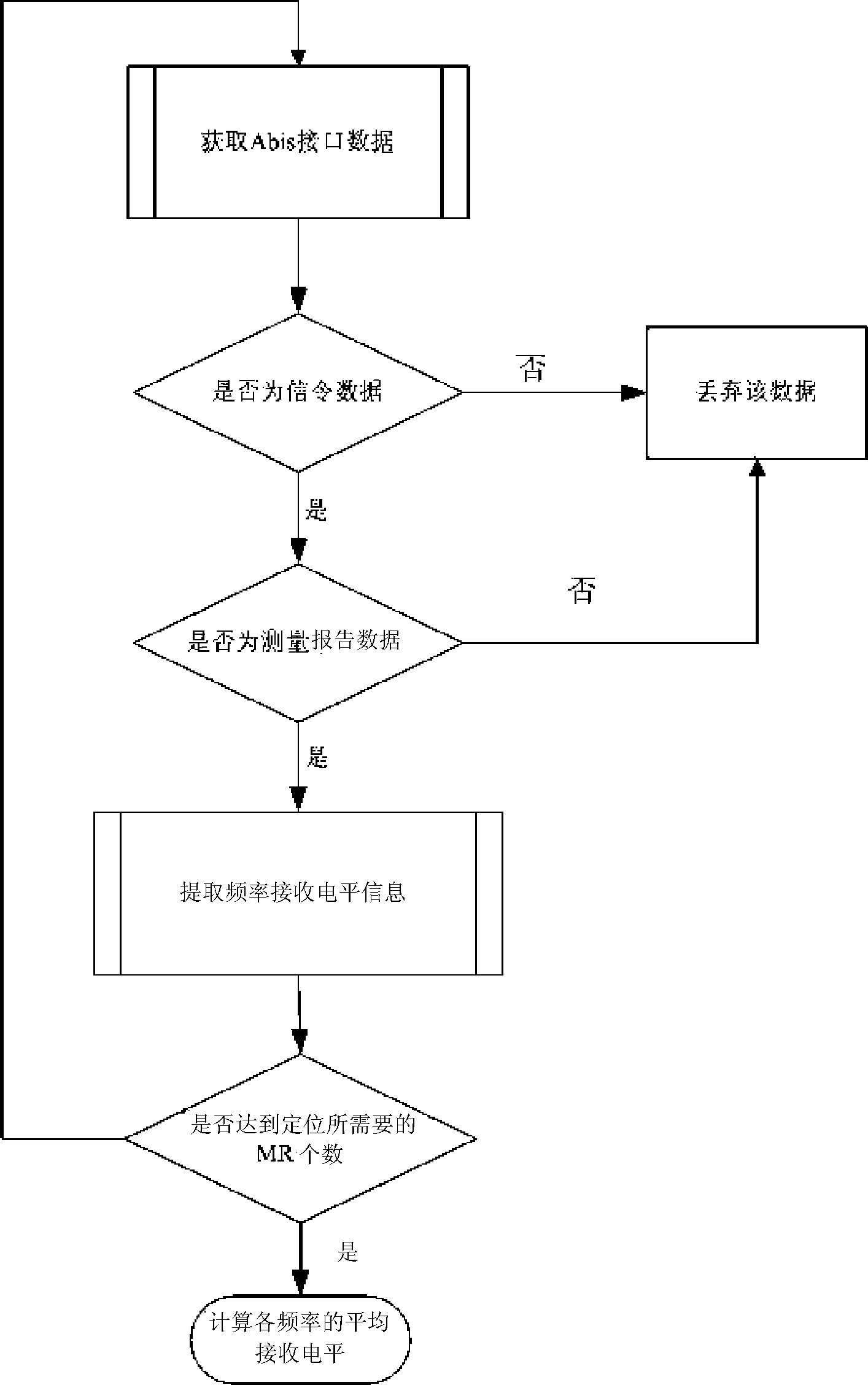
GSM network consumer positioning method based on signal receiving strength information fingerprint
InactiveCN101547506AIncrease collection workReduce the burden onWireless communicationNetwork structureGeolocation
The invention relates to GSM network positioning technical field and provides a GSM network consumer positioning method based on signal receiving strength information fingerprint, comprising following steps: step 1 establishing information fingerprint data-base in a plurality of acquisition points in a certain area coverage; step 2 intercepting the report of the consumer to the network when talking, extracting the signal receiving strength in the customer service cell and the adjacent cell; step 3 comparing the signal receiving strength and the information fingerprint errors in the information fingerprint database acquisition points, therefore, the consumer position is the geographic position where the information fingerprint error is minimum in the acquisition point. The positioning method does not change prior GSM system network structure and the consumer terminal hardware condition with low cost and positioning accuracy error less than 30 m and is suitable for positioning indoor / outdoor. The density of the acquisition points is flexibly adjusted based on the consumer actual positioning requirements.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
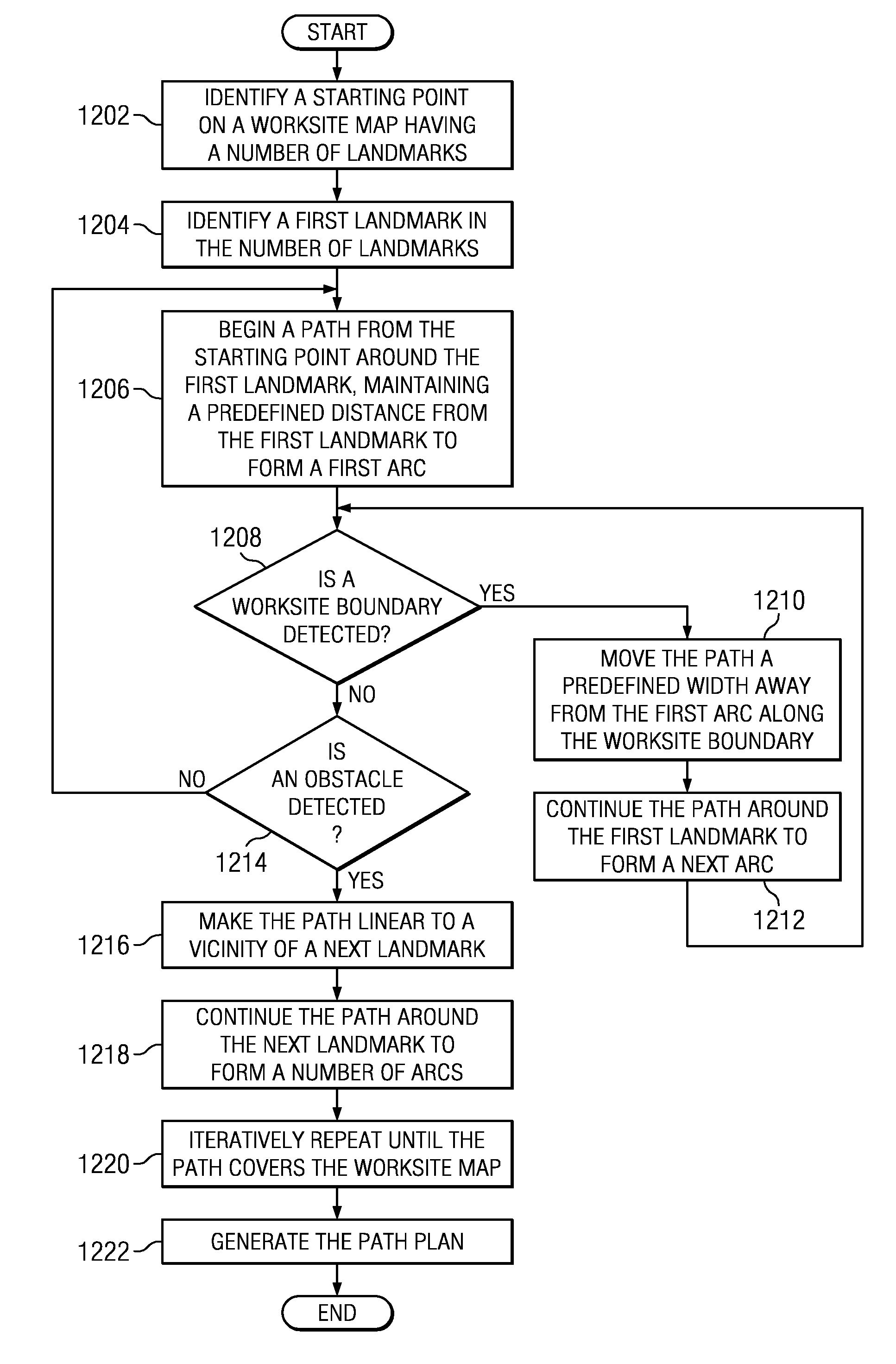
System and method for area coverage using sector decomposition
ActiveUS20110153136A1Digital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlPath planArea coverage
The different illustrative embodiments provide a method for generating an area coverage path plan using sector decomposition. A starting point is identified on a worksite map having a number of landmarks. A first landmark in the number of landmarks is identified. A path is generated around the first landmark until an obstacle is detected. In response to detecting the obstacle, the path is made linear to a next landmark. The path is generated around the next landmark.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Methods of operating arrangements of base transceiver stations in an area-covering network
InactiveUS6459900B1Reduce in quantityGuaranteed uptimeRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentCellular radioTransceiver
Owner:LITTLEFEET
Multispectral or hyperspectral imaging system and method for tactical reconnaissance
A two-dimensional focal plane array (FPA) is divided into sub-arrays of rows and columns of pixels, each sub-array being responsive to light energy from a target object which has been separated by a spectral filter or other spectrum dividing element into a predetermined number of spectral bands. There is preferably one sub-array on the FPA for each predetermined spectral band. Each sub-array has its own read out channel to allow parallel and simultaneous readout of all sub-arrays of the array. The scene is scanned onto the array for simultaneous imaging of the terrain in many spectral bands. Time Delay and Integrate (TDI) techniques are used as a clocking mechanism within the sub-arrays to increase the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the detected image. Additionally, the TDI length (i.e., number of rows of integration during the exposure) within each sub-array is adjustable to optimize and normalize the response of the photosensitive substrate to each spectral band. The array provides for parallel and simultaneous readout of each sub-array to increase the collection rate of the spectral imagery. All of these features serve to provide a substantial improvement in the area coverage of a hyperspectral imaging system while at the same time increasing the SNR of the detected spectral image.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
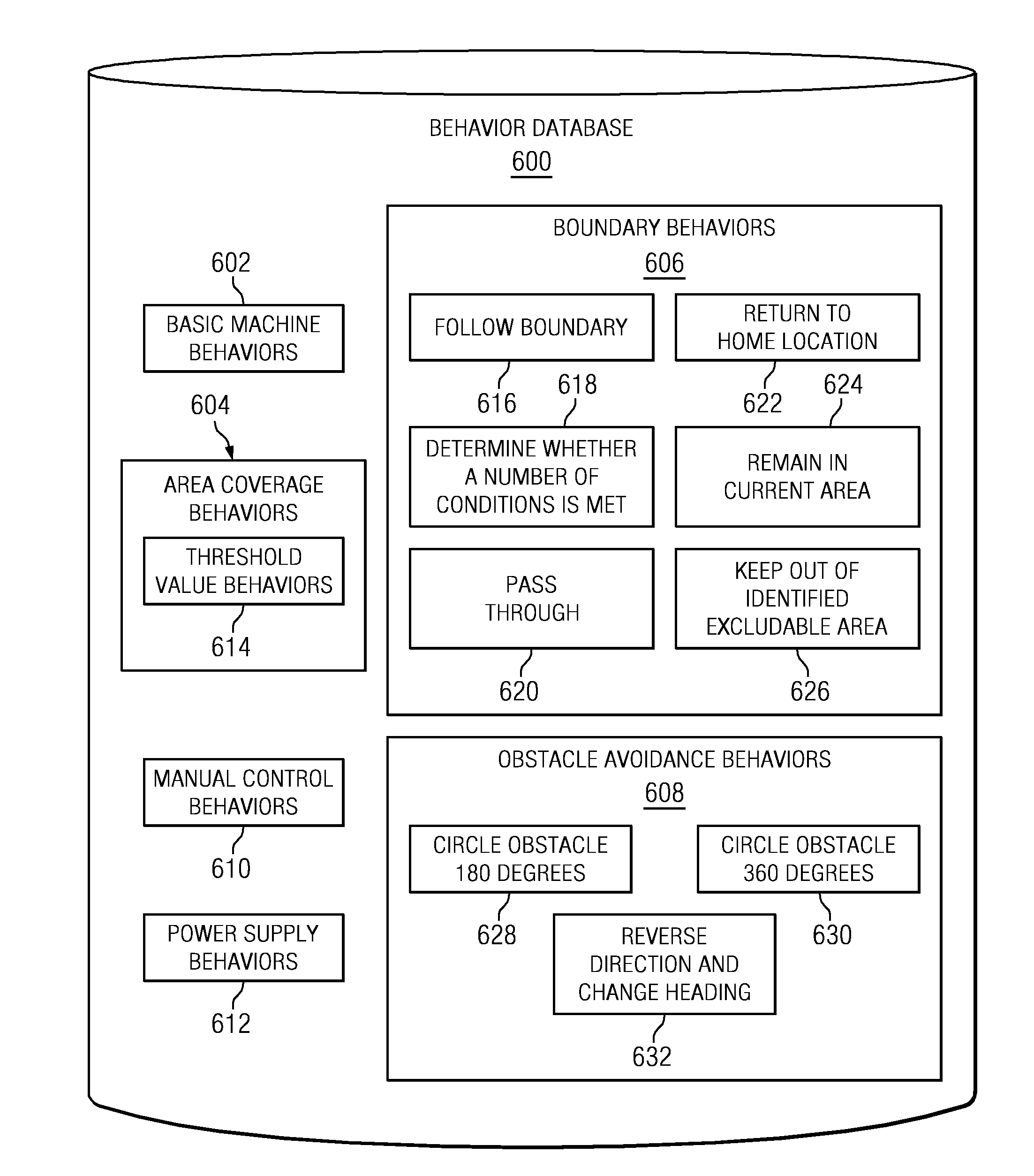
Condition based keep-out for machines
InactiveUS20110295423A1Autonomous decision making processComputer controlNavigation systemArea coverage
The different illustrative embodiments provide a system for autonomous machine management comprising a number of autonomous machines, a number of boundaries, a conditional behavior module, and a navigation system. The number of autonomous machines is configured to perform area coverage tasks in a worksite. The number of nodes is configured to define a number of worksite areas for the worksite. The conditional behavior module is executed by a processor unit and configured to determine whether a number of conditions is met for the number of worksite areas. The navigation system is configured to operate an autonomous machine to perform the area coverage tasks and move between the number of worksite areas when the number of conditions is met.
Owner:DEERE & CO
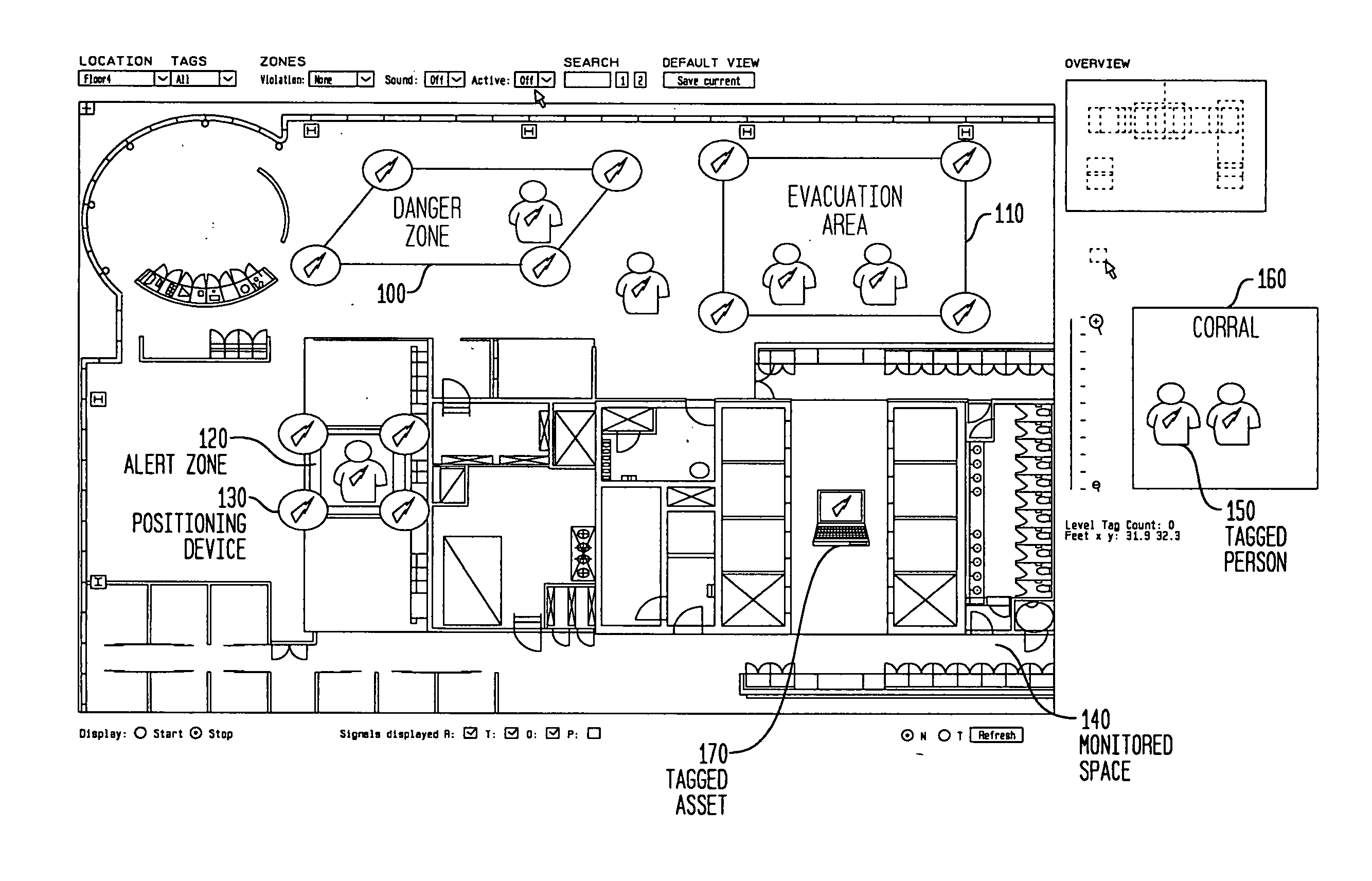
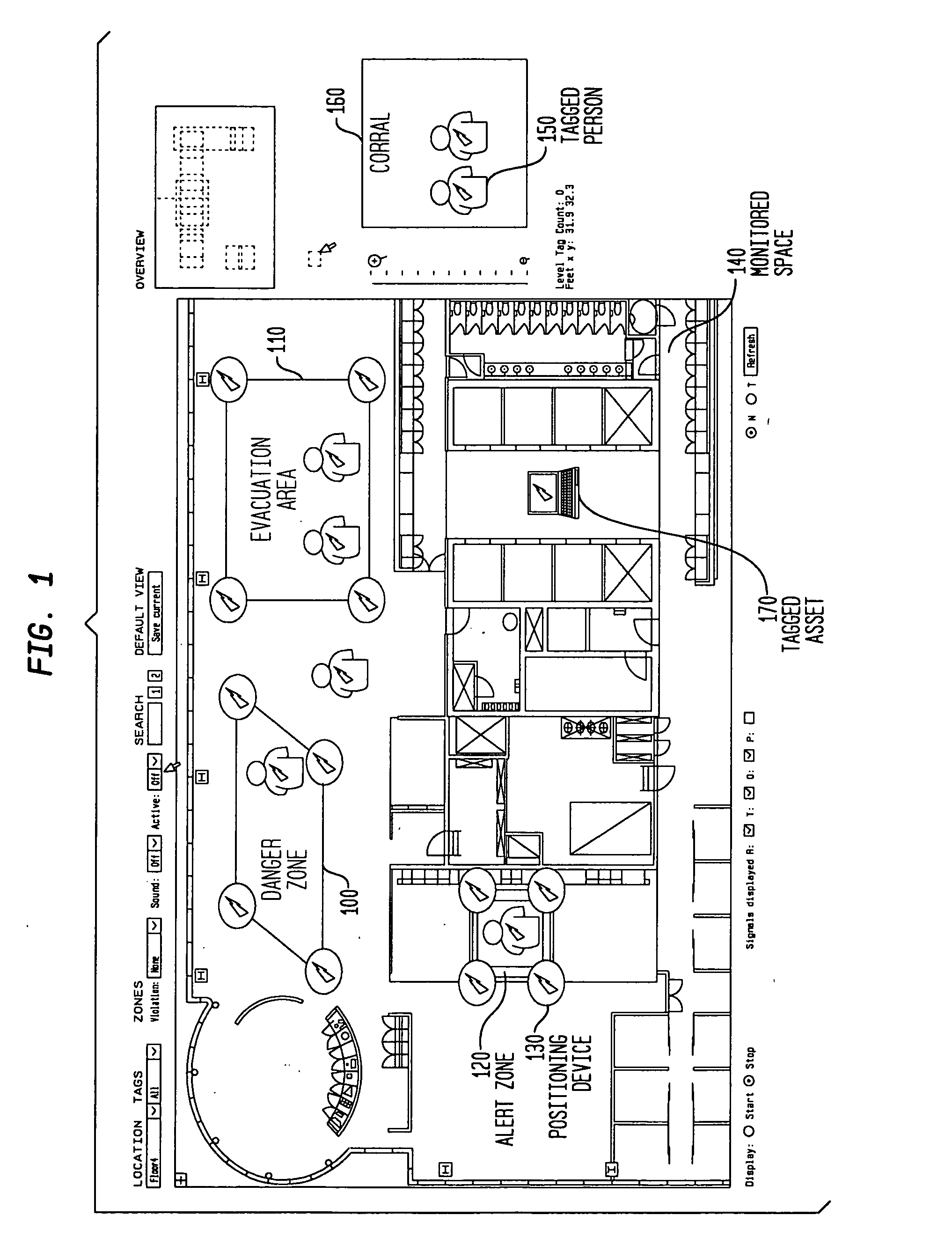
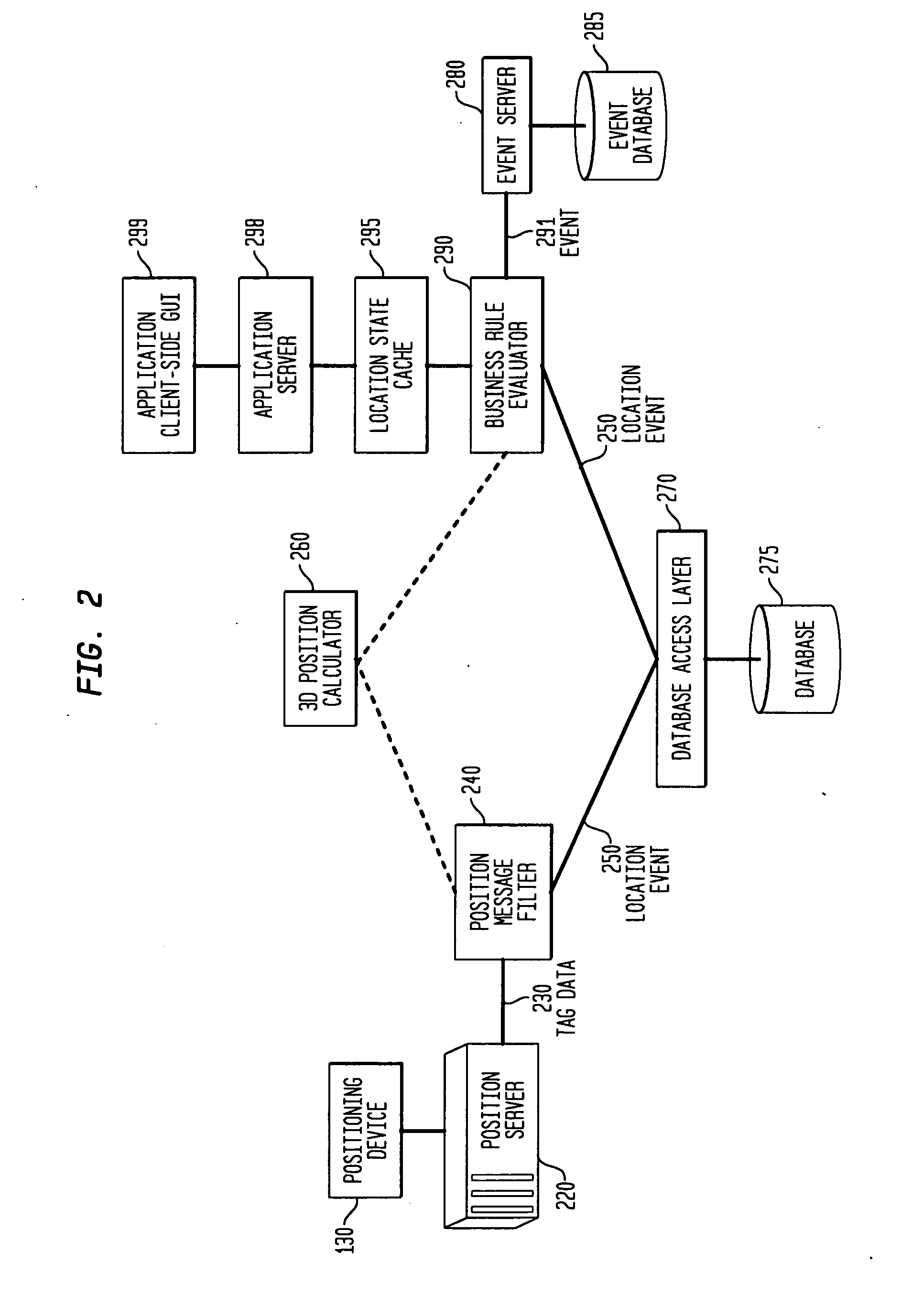
Dynamic boundary mapping using position-determination systems
InactiveUS20070188318A1Improve accuracyEliminate errorsTicket-issuing apparatusDigital data processing detailsData miningArea coverage
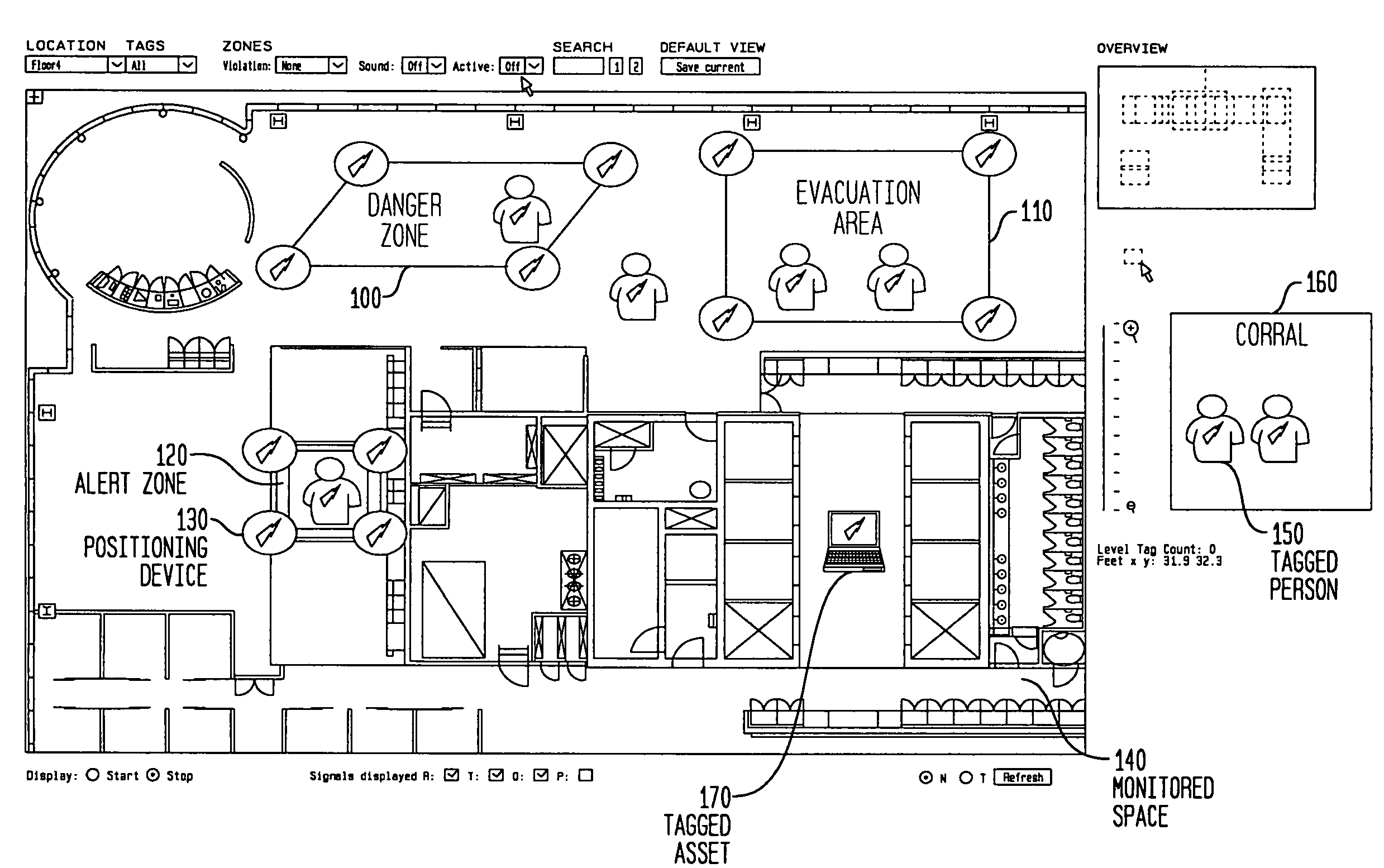
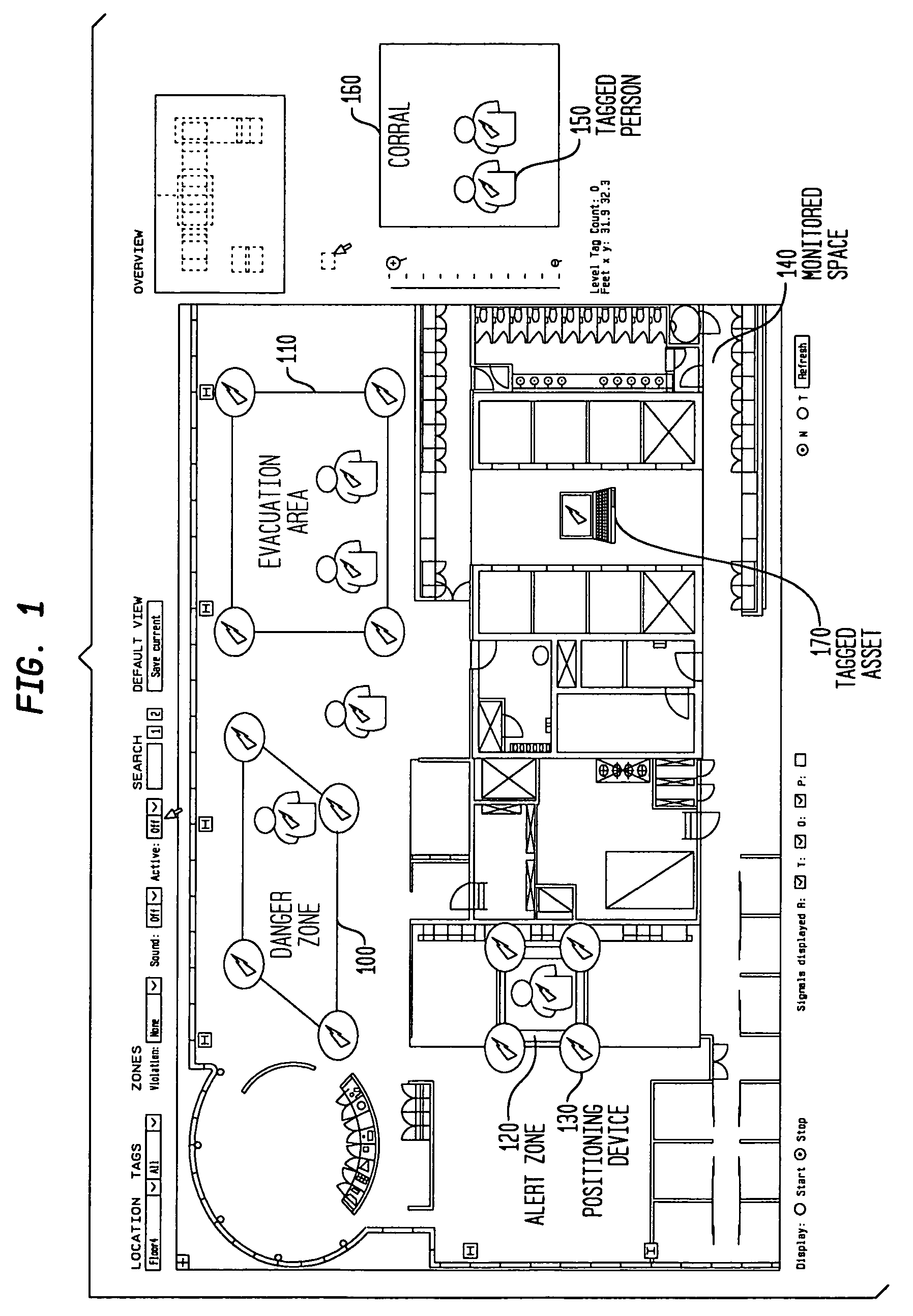
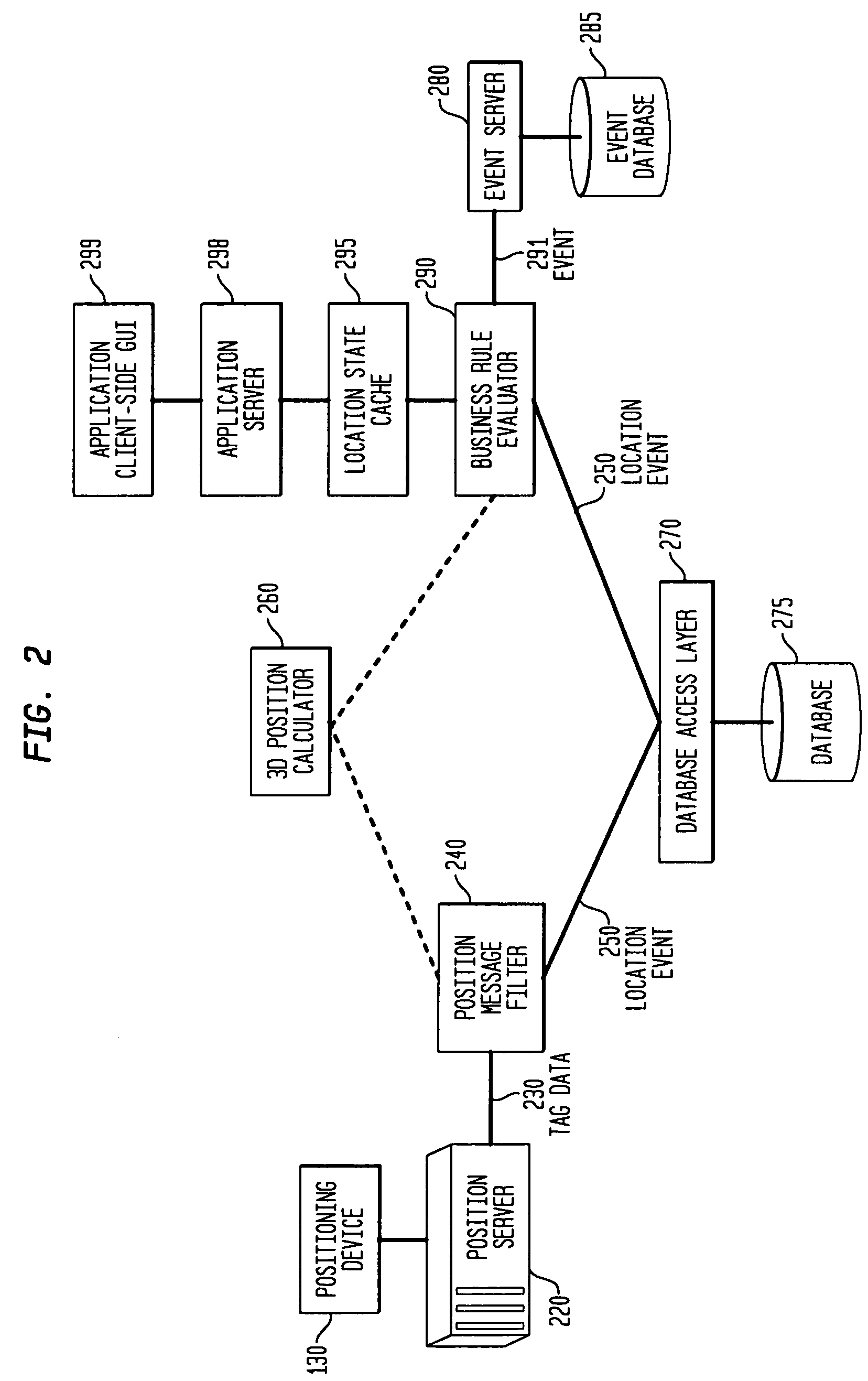
The invention provides an approach for automatic and dynamic mapping of zone boundaries for position-determination systems. The system of the present invention utilizes beacons (“position determining devices”) to identify the boundaries and limits of device area coverage (“zone”) for tracking objects with a position-determination system. Beacons, used both to identify zone boundaries and to tag assets to be tracked, are distributed within the zone. The beacon locations are then detected and displayed in the visualization application. Three or more beacons may be linked together, either manually or automatically, to establish a detection zone. Using beacons to establish detection zone boundaries eliminates guesswork and its associated errors, and produces a zone boundary that is actually valid. In an improvement over present systems, greater accuracy is assured using zone-defining beacons, because if a beacon is unintentionally placed in an area unavailable to the position-determination system, that beacon will not appear in the visualization application display, and thus will not be available to create an incorrect zone representation.
Owner:IBM CORP
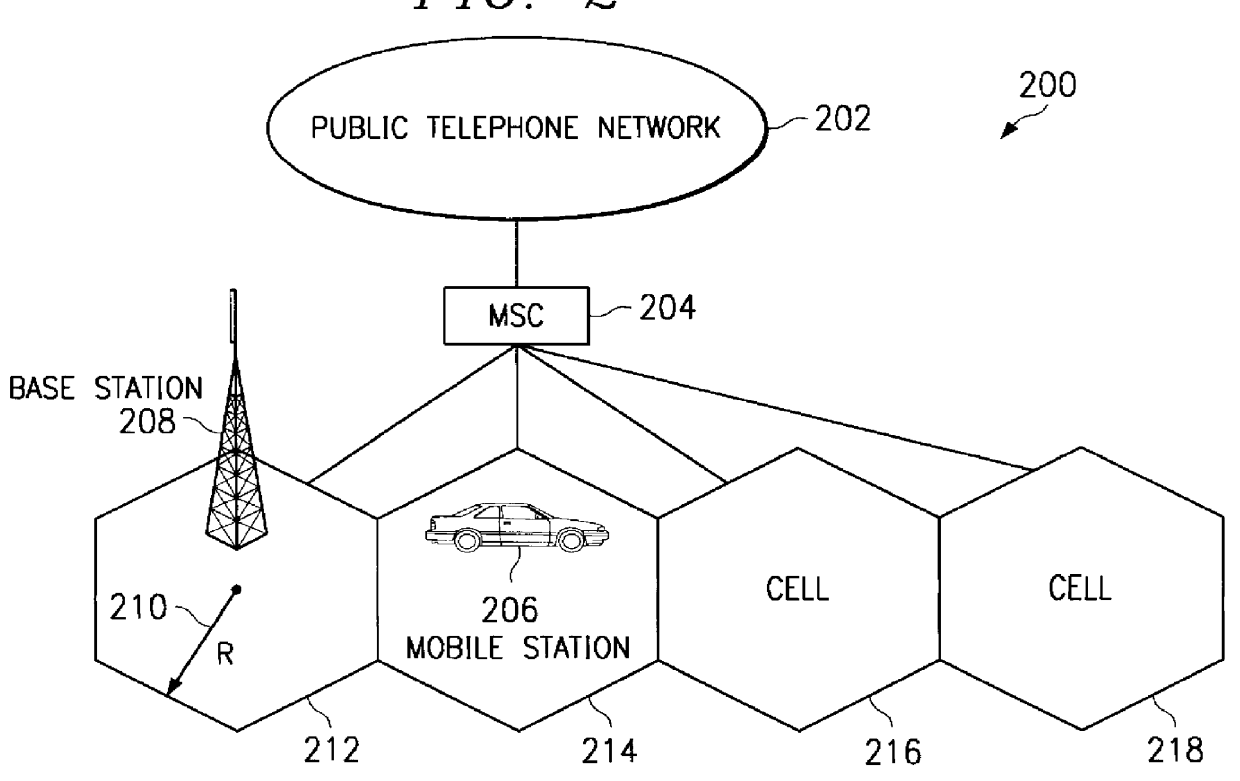
Method and apparatus for minimizing the number of samples needed to determine cell area coverage reliability in a radiotelephone system
InactiveUS6041236ARadio/inductive link selection arrangementsNetwork planningDependabilityLinear regression
A robust method for determining the boundaries of cells and the associated reliability of the RF coverage within these boundaries is presented. The invention accurately determines the average range from the base station to the cell edge from RF signal strength measurements with a linear regression approach. The accuracy of this estimate is quantified both as a range uncertainty (e.g. + / -100 meters) and as a cell coverage reliability (i.e. area / edge) through 1) simulation, 2) analysis of real data, and 3) theoretical analysis. It is shown that if the estimate of the cell radius meets the desired accuracy, then the corresponding estimates of coverage reliability (both area and edge) are more than sufficiently accurate. It is recommended that radio survey analyses incorporate this test as part of the coverage validation process.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Ultra wide band location method and system in coal mine well
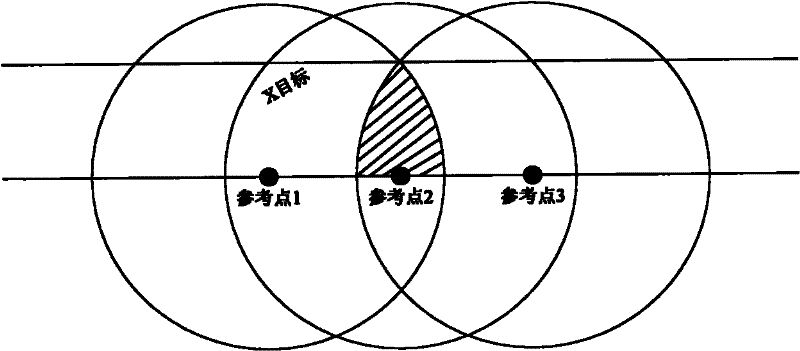
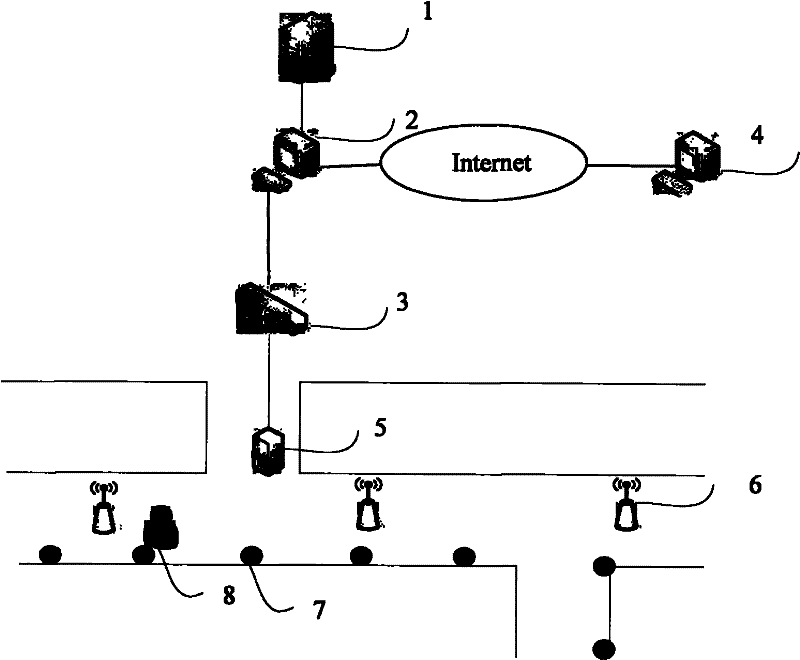
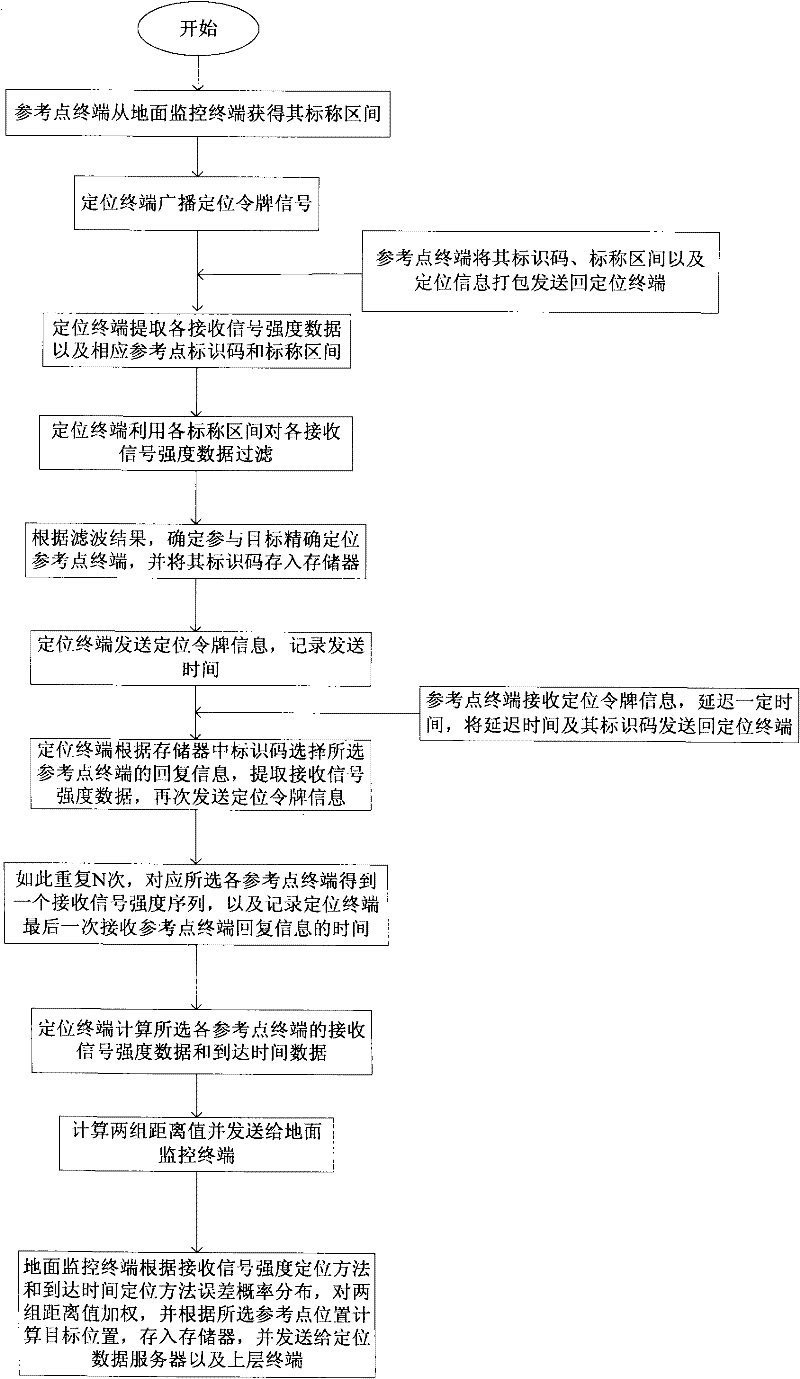
ActiveCN102213755AReduce power consumptionImprove anti-interference abilityPosition fixationTransmissionBand shapeTwo step
The invention discloses an ultra wide band location method and an ultra band location system in a coal mine well. The method is a banded cell two-step locating method and comprises the following steps of: dividing a plurality of continuously-overlapped banded locating service cells along a roadway; calculating nominal intervals of all reference points; filtering according to received signal strength (RSS) data by an object; measuring and calculating an area coverage in which the object is located; and obtaining the accurate position of the object by a hybrid location method based on cumulative average weighted processing. The system comprises an upper-layer terminal, a data locating server, a ground monitoring terminal, a switchboard, an intrinsically safe gateway, an intrinsically safe wireless relay, an intrinsically safe reference point terminal and an intrinsically safe location terminal. The ultra wide band location method and the ultra wide band location system have strong anti-reference capability, accurate location, a simple structure of system equipment and low power consumption, are more suitable for the roadway working environment, and meet the requirements of the coal mine well for specific operating environment and safety demand.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Multi-level cache architecture and cache management method for peer-to-peer name resolution protocol
InactiveUS6912622B2Efficient solutionLess resourcesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsGranularityParallel computing
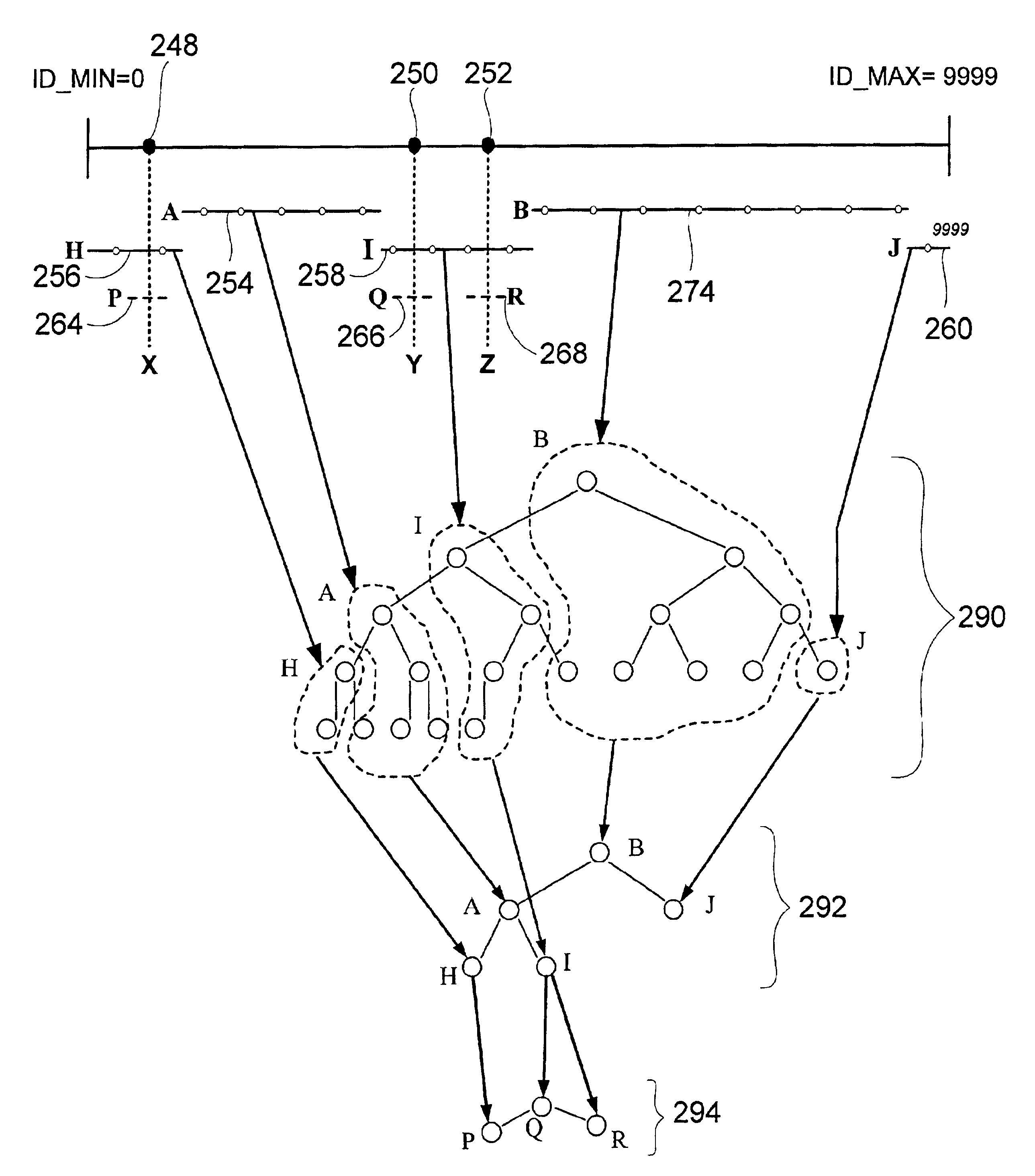
A peer-to-peer cache architecture stores peer address certificates in different cache segments according to the number of IDs being stored and their relative distance in the peer name space. The cache instantiates regions of decreased range and increased granularity as additional information from close peers is learned. In a large peer cloud where the number of instantiated IDs is not known, each succeeding cache region covers one tenth of the preceding cache region. For peers with multiple IDs registered locally, the segmented cache of the present invention combines overlapping segments of the same granularity to eliminate the duplication of information that would otherwise occur. A cache tree, an instantiated segment tree, and an uninstantiated segment tree are arranged in red-black trees to simplify the search and proper placement and instantiation of information.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
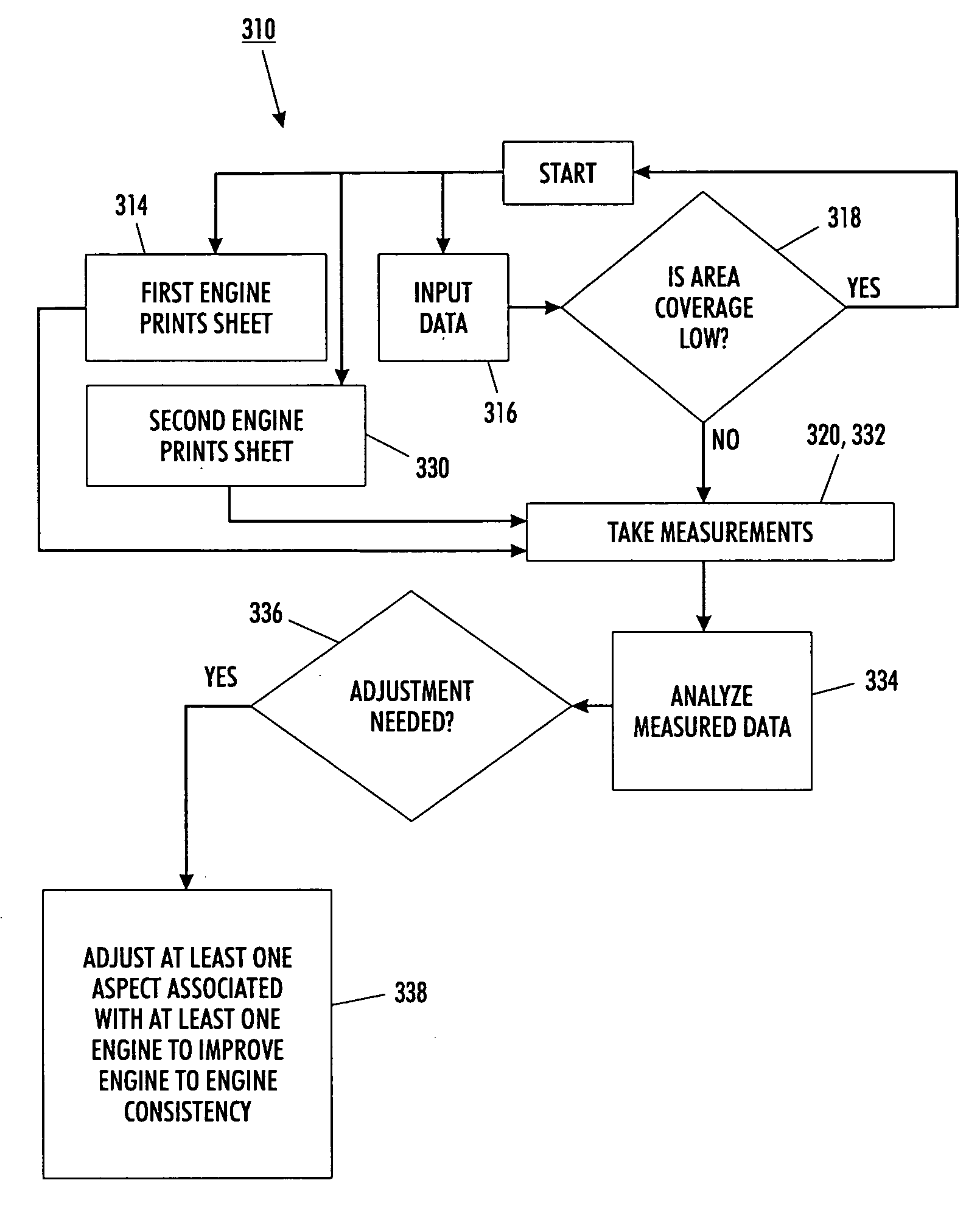
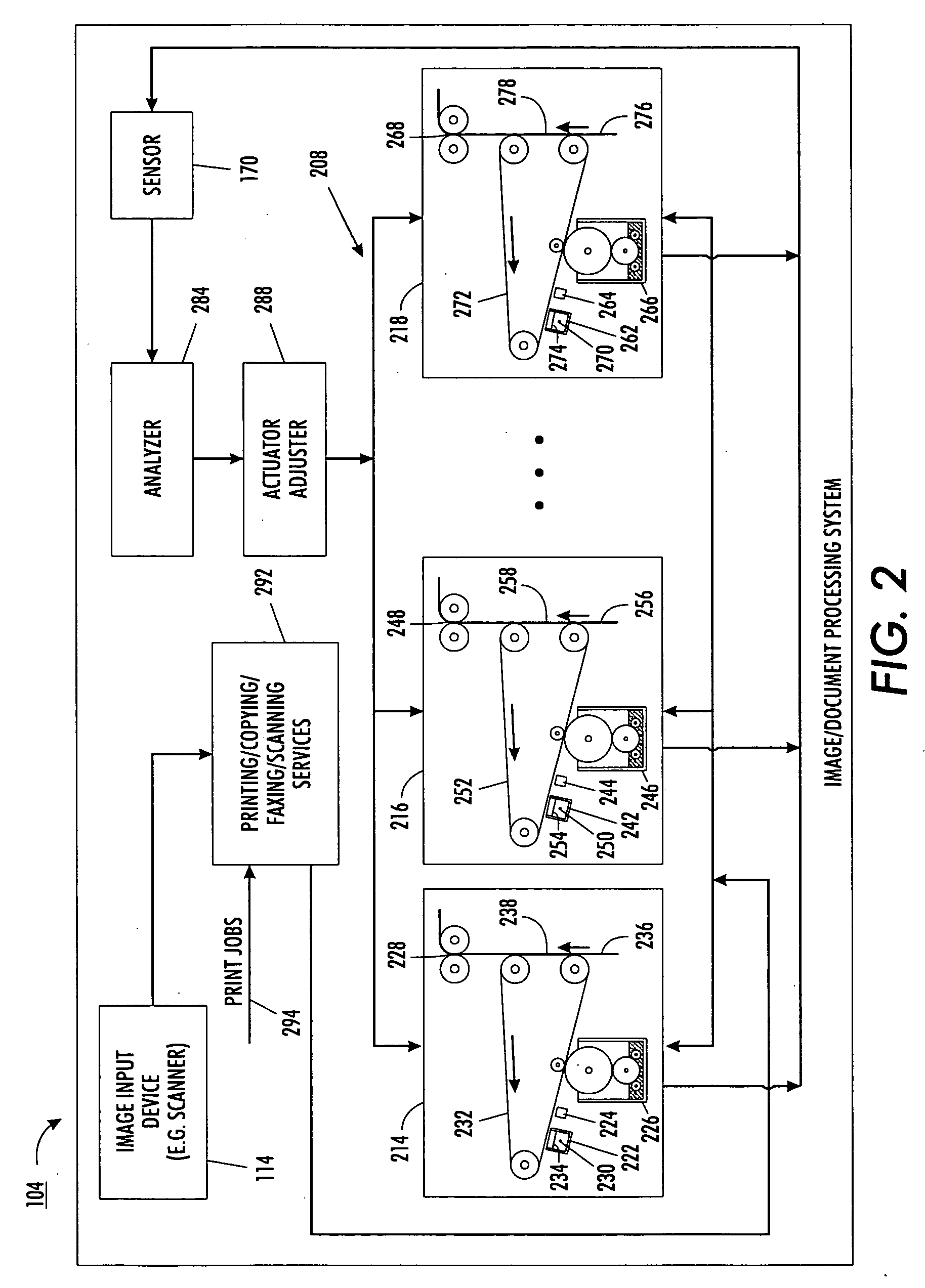
Image quality control method and apparatus for multiple marking engine systems
A full width array CCD sensor is incorporated in the media path to monitor fused pages by calculating area coverage from multiple engines in a Tightly Integrated Parallel Process (TIPP) architecture. With knowledge of the area coverage differences between print engines for a given pixel count to the ROS, a relative density difference of each engine is determined. Based on the determined relative density difference, an adjustment is calculated and applied to the engine with the largest error to match the area coverage(s) of the other engine(s).
Owner:XEROX CORP
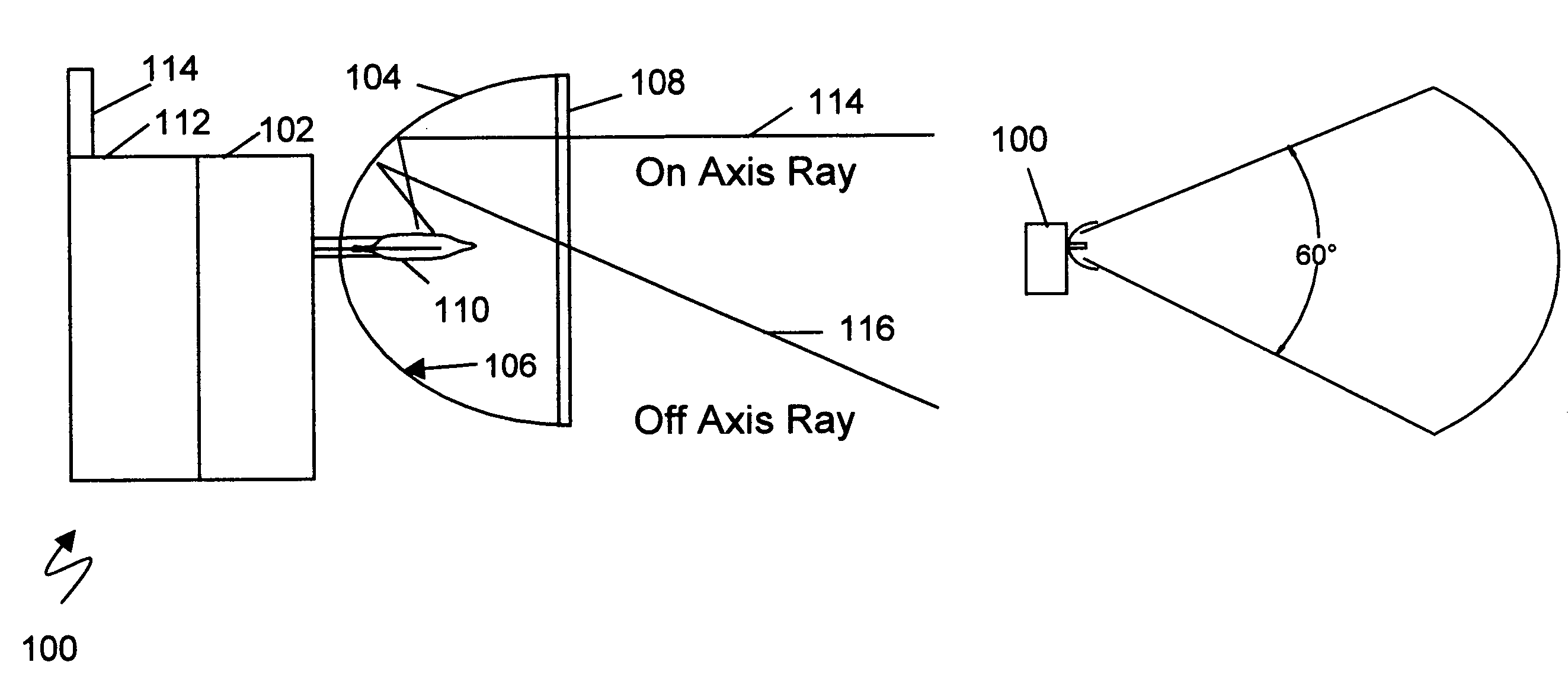
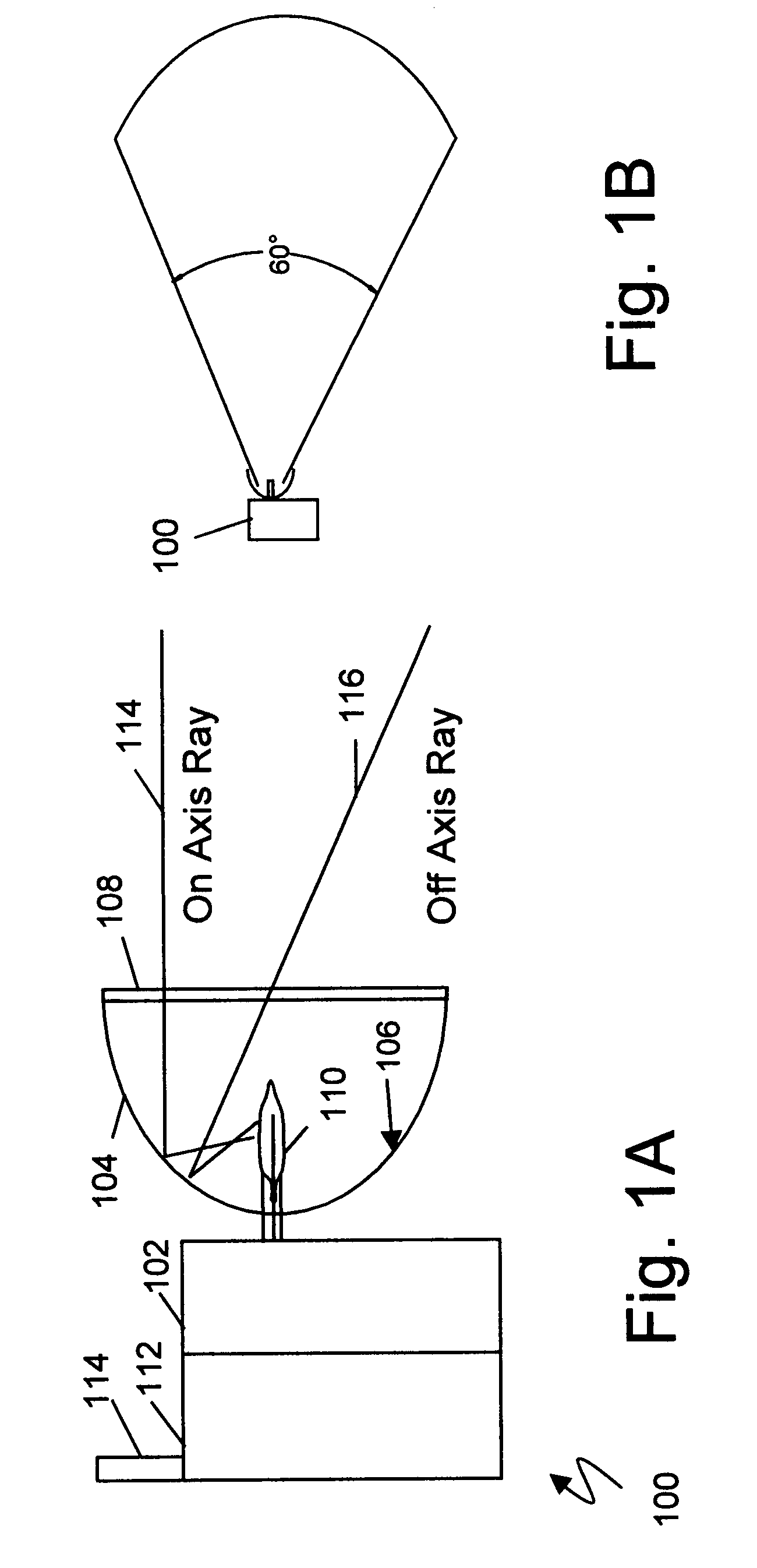
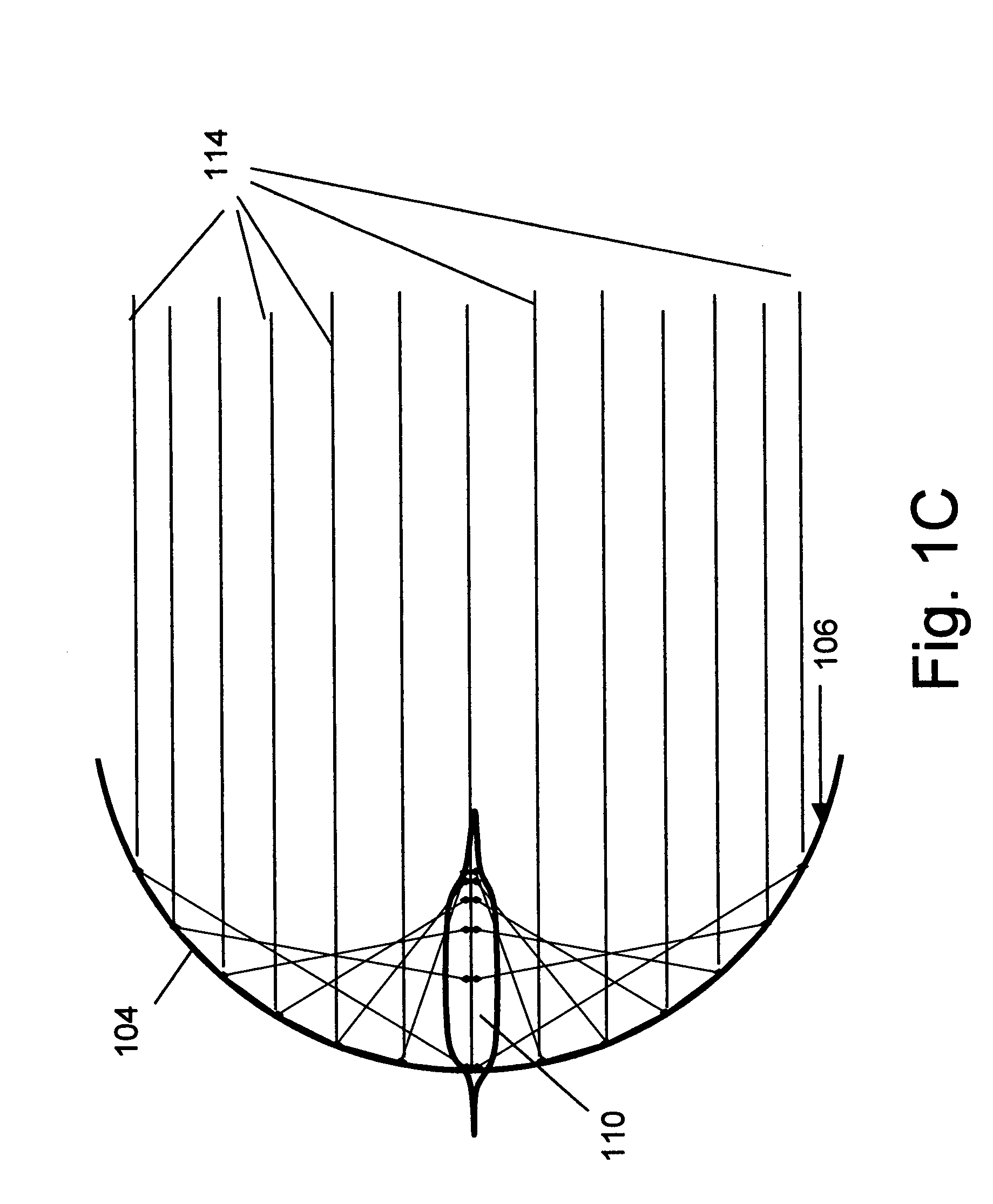
Optical flame detection system and method
ActiveUS7541938B1Improve reflectivityShort response timeRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSilicon monoxideOptoelectronics
A long range optical sensor and system for detecting the flame of forest fires or other fires while rejecting false alarms due to solar radiation is described. The sensor utilizes a collector optic that collects energy from a wide field of view and concentrates the energy onto a detector. The collector may be a non-imaging collector and may match to a non-planar sensor. In one embodiment the sensor may be arrayed to achieve larger area coverage. In another, the sensor system may be scanned to increase the encompassed viewing area. Larger areas may be covered by RF radio links or networks interconnecting multiple arrayed sensor modules. UVC reflective coatings may include enhanced aluminum with silicon dioxide, silicon monoxide, or magnesium fluoride, or high phosphorous nickel phosphorous. In one embodiment a UVC sensitive Geiger Mueller tube may be coupled to a non-imaging spherical reflective collector. A catadioptric UVC / infra-red flame sensor is disclosed. Refractive or reflective designs are considered.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Image processing system for predicting ovulation
InactiveUS6960170B2Stimulates saliva productionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSurgerySaliva sampleBristle
An image processing system for predicting ovulation using a test channel for collecting saliva sample and a miniature camera for capturing the image of the saliva at dried state for analyzing the crystalline patterns for ovulation prediction. A rotary bristle element is attached to the drive head and a notch-like test channel traverses the width of the drive head. A conductivity sensor is mounted on a wall of the test channel for detecting filling and drying of the saliva sample. An algorithm in the microprocessor analyzes the image of the dried saliva and calculates the characteristic line length of line segments of connected saliva dots. A ferning index is also defined and calculated based on the percentage of area coverage of line segments which are exceeding the threshold line length. Trend curves are established based on the daily saliva analysis in a woman's menstrual cycle for predicting days from the ovulation.
Owner:KUO YOUTI
Area coverage with an autonomous robot
There is therefore provided, in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, a robotic system for systematically moving about an area to be covered. The system includes at least one boundary marker (48) located along the outer edge of the area to be covered, a robot (40) with a navigation system (41) that navigates the robot (40) in generally straight, parallel lines from an initial location and turns the robot (40) when the robot (40) encounters one of the boundary markers (48), thereby to systematically move about the area to be covered. The sensor unit (43) senses proximity to one of the at least one boundary marker (48).
Owner:MTD PRODUCTS
Reduction of differential gloss with halftoned clear toner
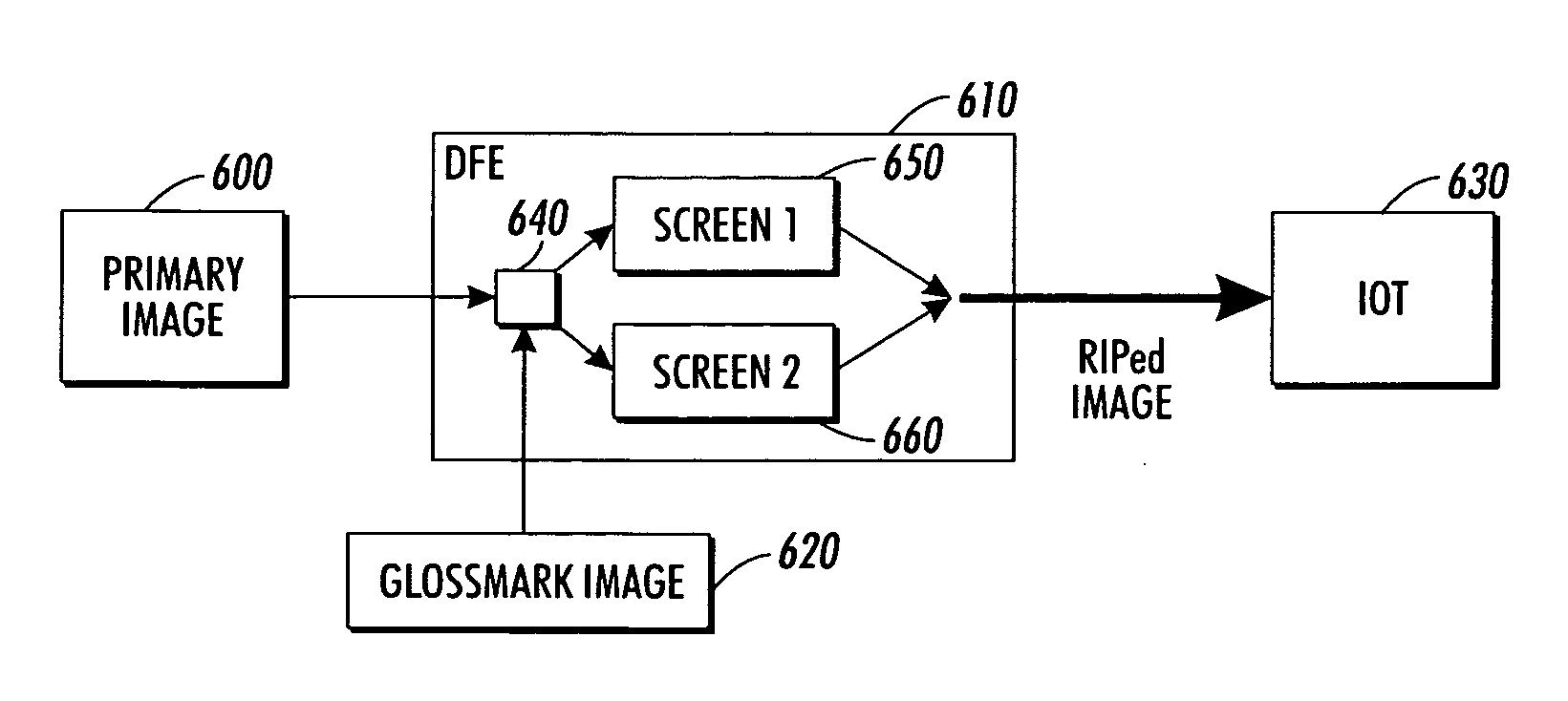
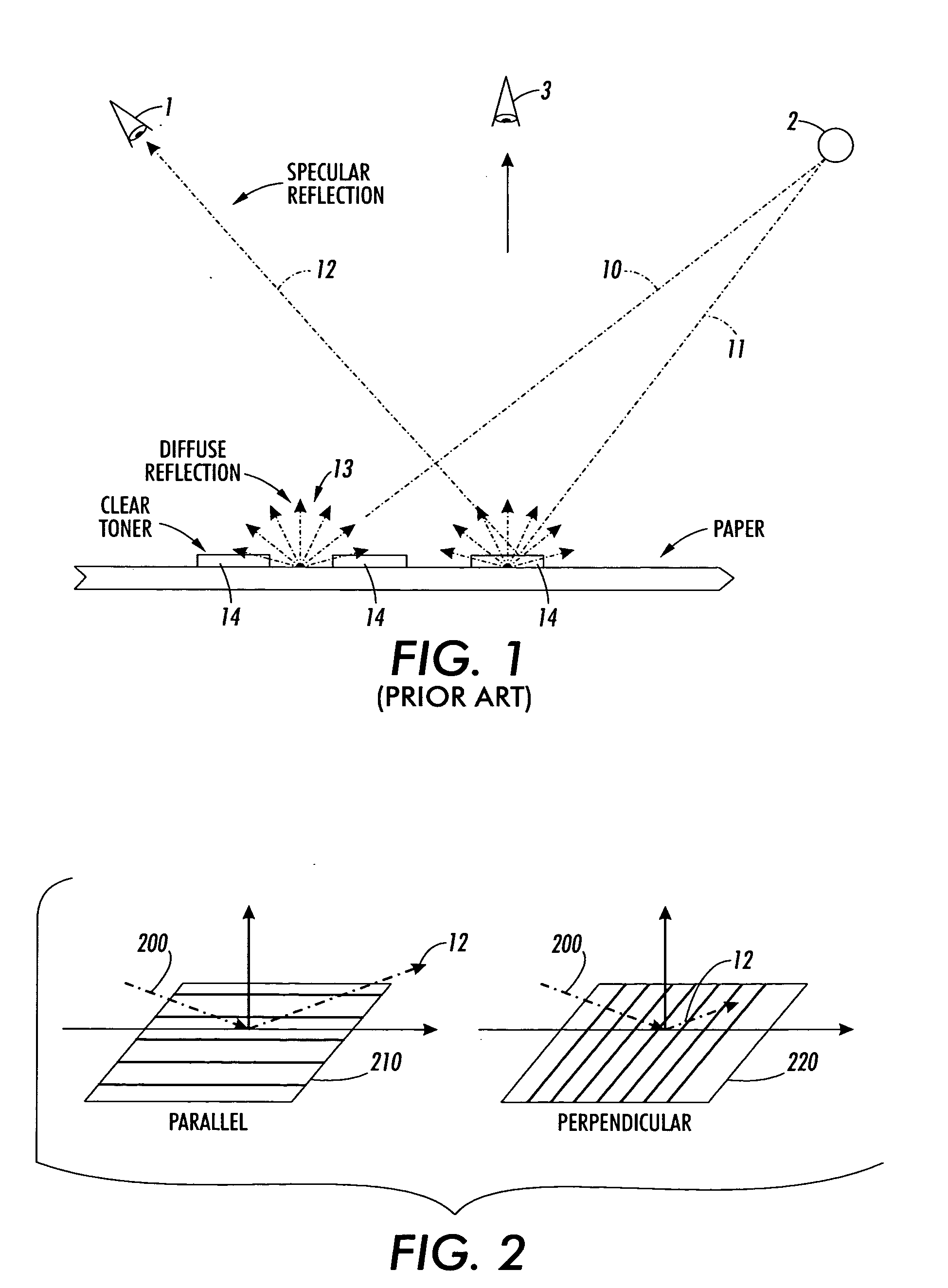
ActiveUS20060044617A1Reduce glossReduces overall image glossVisual presentation using printersPictoral communicationHueArea coverage
A method for reduction of differential gloss as found in halftone image hardcopy prints. The method comprises selecting either a single halftone or employing two halftones: a first halftone having a high apparent gloss characteristic; and a second halftone having a low apparent gloss characteristic. A determination is then made of which areas of the halftone image correspond to potentially high gloss and low gloss regions under normal printing conditions. An overlay of clear toner is applied to the hardcopy print of the halftone image. In one approach a single halftone is employed to control the physical area coverage of the applied clear toner layer so as to adjust the local gloss across for the determined regions and thereby balance the evenness of gloss across the entire hardcopy print of the halftone image. Greater physical area coverage is provided as controlled by the single halftone in low gloss regions, and corresponding less physical area coverage is provided in the low gloss regions. In a further approach two halftones are employed. The first halftone is directed to those portions of the overlaid clear toner determined as corresponding to potentially low gloss regions of the halftone image, and the second halftone is directed to those portions of the clear toner layer determined as overlaying potentially high gloss regions of the halftone image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Dynamic boundary mapping using position-determination systems
InactiveUS7443298B2Improve accuracyTicket-issuing apparatusDigital data processing detailsArea coverageData mining
The invention provides an approach for automatic and dynamic mapping of zone boundaries for position-determination systems. The system of the present invention utilizes beacons (“position determining devices”) to identify the boundaries and limits of device area coverage (“zone”) for tracking objects with a position-determination system. Beacons, used both to identify zone boundaries and to tag assets to be tracked, are distributed within the zone. The beacon locations are then detected and displayed in the visualization application. Three or more beacons may be linked together, either manually or automatically, to establish a detection zone. Using beacons to establish detection zone boundaries eliminates guesswork and its associated errors, and produces a zone boundary that is actually valid. In an improvement over present systems, greater accuracy is assured using zone-defining beacons, because if a beacon is unintentionally placed in an area unavailable to the position-determination system, that beacon will not appear in the visualization application display, and thus will not be available to create an incorrect zone representation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Printing System
InactiveUS20110096344A1Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersArea coverageComputer engineering
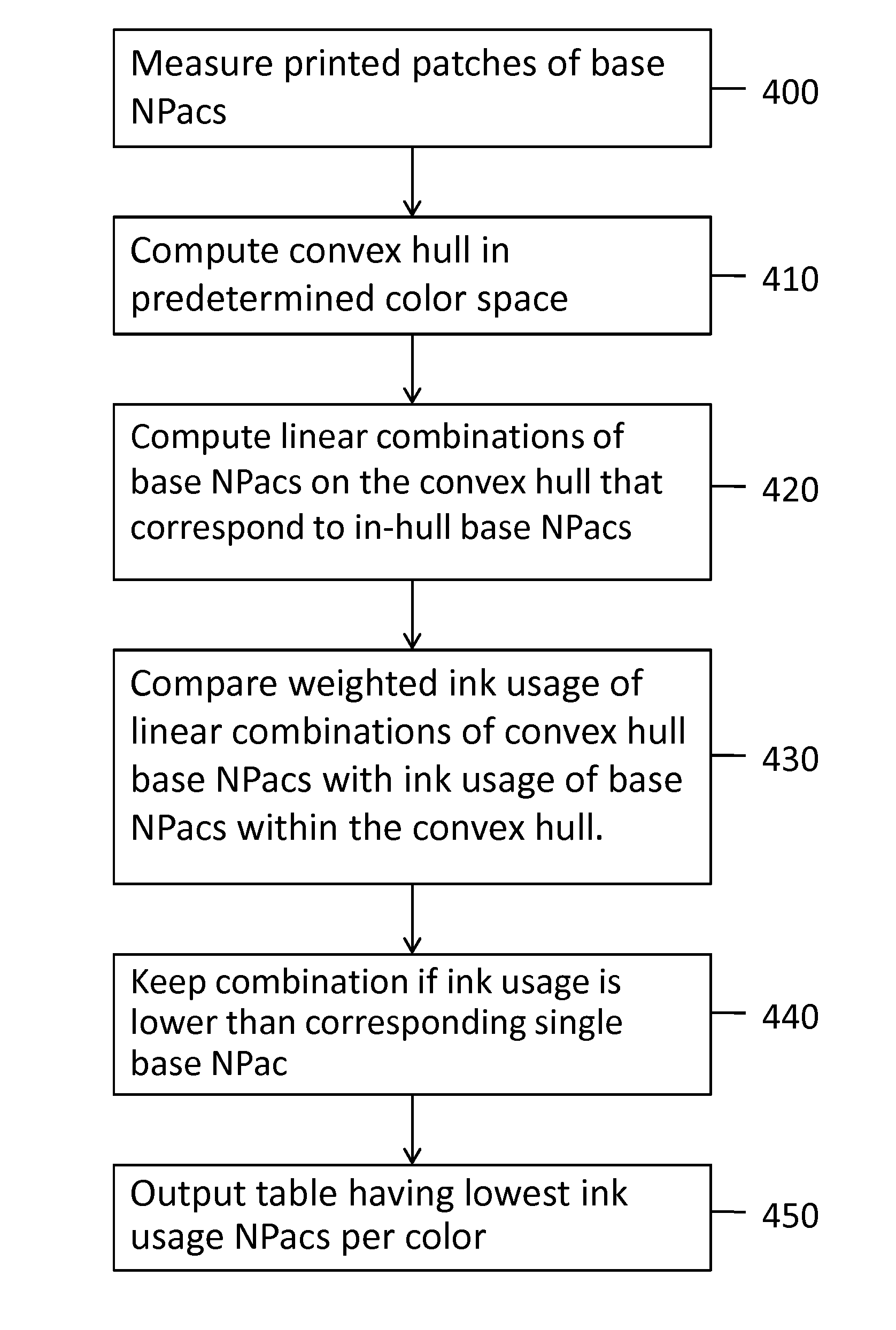
Method of computing a convex hull in a predetermined color space, comprising determining a print attribute value range pertaining to a reference print attribute value, selecting base NP (Neugebauer Primary) area coverages, comprising area coverages of single NPs and combined NPs, having print attribute values in the print attribute value range, printing and measuring patches corresponding to the base NP area coverages, computing linear combinations of the base NP area coverages, and assigning one of the base NP area coverage or the linear combination of base NP area coverages to the corresponding color, depending on which is closest to the reference print attribute value.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Digital flooring detection system
InactiveUS20070171058A1Reducing sensor resolutionLess finite resolution of location detectionBurglar alarm by pressureElectricityInterdigitated electrode
A flooring system comprising a plurality of electrode pairs in contact with a metaplastic composite material. The metaplastic material is such that it locally conducts electrical current in an area where any load is applied to the metaplastic. An electric potential is applied to one or more interdigitated electrodes located at a face of the metaplastic material in line with applied loads. Larger area coverage can be obtained either by pre-installing a subsurface layer comprising of an array of interdigitated electrodes and their trace line outputs and then covering this layer with a tiling of metaplastic material sheets that is in direct contact with the array of interdigitated electrodes, or, by directly attaching one or more interdigitated electrodes and their output trace lines to an individual sections of metaplastic material and electrically interconnecting their outputs. By applying a sufficient number of interdigitated electrodes and sheets of the metaplastic material and monitoring the electrical current flowing in each interdigitated electrode so placed, it can be determined whether and where loads are being applied to the PCC flooring material and the approximate size and shape of the load.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
Reduction of differential gloss with halftoned clear toner
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and a device for determining multi-ink color separations
A method to convert a color provided in a first color space into a color in a second color space defined by more than four colorants and a reproduction process. The method includes converting the color into a third color space, determining which of a set of gamut volumes defined in the third color space is appropriate for the color, with each point in the gamut volume achievable by an area coverage greater than zero and less than 100% of two of the colorants and an area coverage greater than zero and less than 100% of one or more darkening colorants with the remaining colorants either absent or at 100%. The method further includes carrying out any gamut mapping on the converted color so that the converted color is in the appropriate gamut volume and converting the gamut mapped color from the third color space into a set of the colorants of the second color space, such that the surface of any gamut volume with no darkening colorant is part of an umbrella surface for the N inks.
Owner:AGFA NV
Method and apparatus for determining base station wireless field strength overlay area range
ActiveCN101203015ASure easyQuick fixRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringTriangulationLongitude
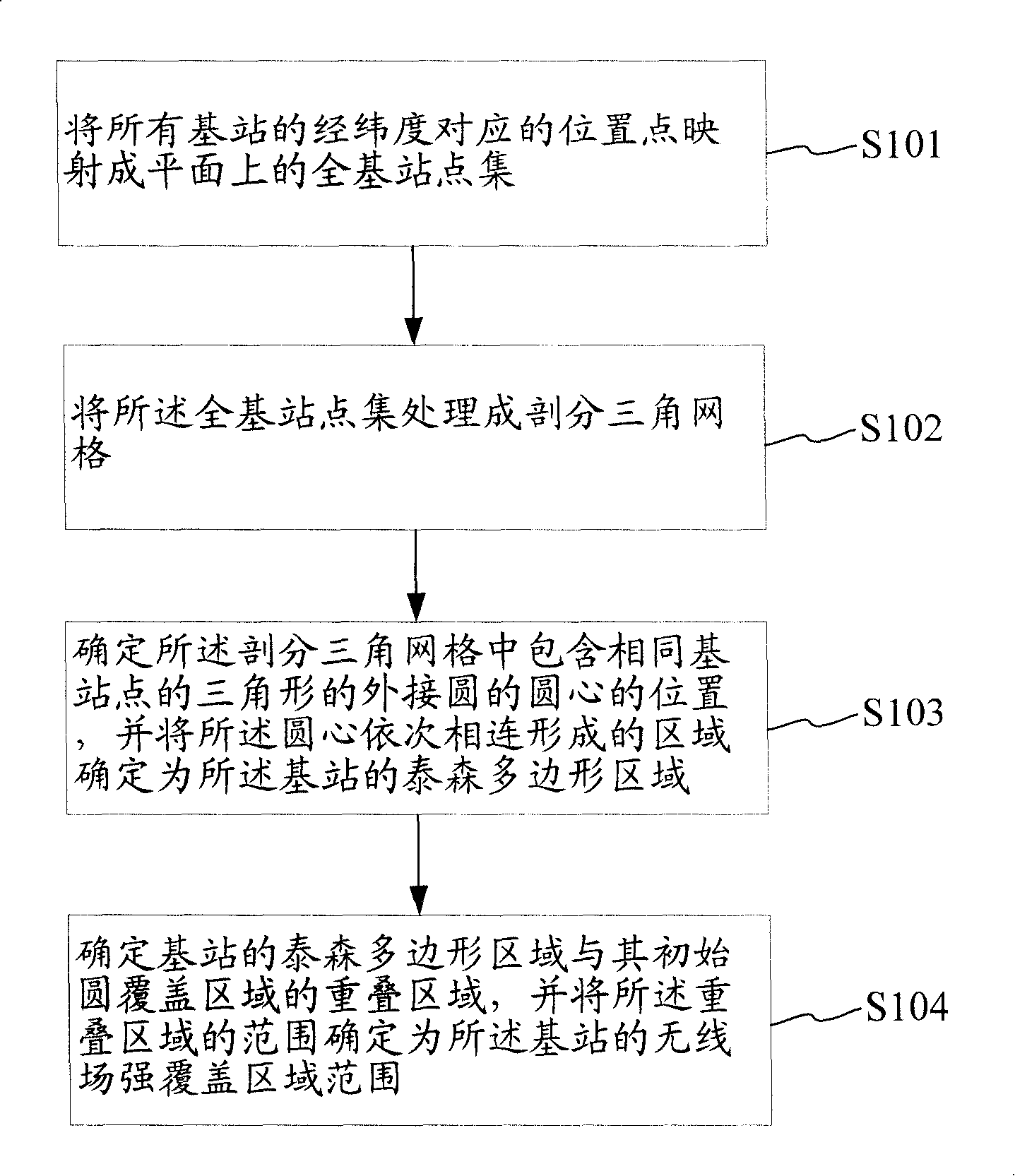
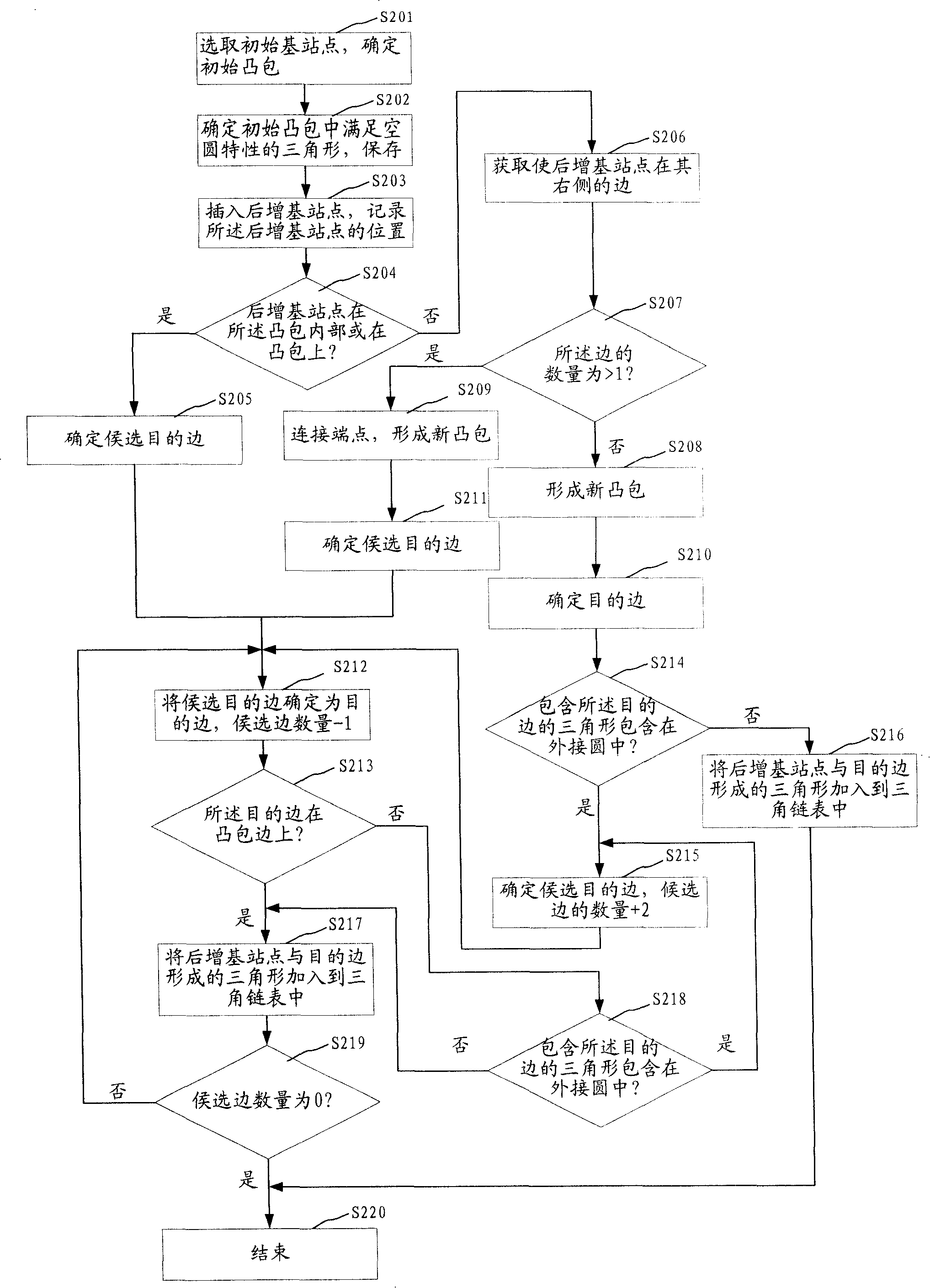
The invention discloses a method which determines the strong covering area coverage of a base station wireless field. The invention comprises the steps: location points which are corresponding to the latitudes and longitudes of all the base stations are reflected to be a whole base station point set on a plane; the whole base station point set is processed to be subdivision triangulation lattices; the circle center positions of circumcircles of the triangle, which contain the same base station point in the subdivision triangulation lattices, are determined and regions formed by the circle centers being sequentially connected with each other are determined to be a Thiessen polygon region of the base station; the overlap region of the Thiessen polygon region of the base station and the initial circle coverage region is determined and the scope of the overlap region is determined to be the scope of the strong covering area coverage of the base station wireless field. At the same time, the invention also discloses a device which determines the strong covering area coverage of the base station wireless field. By utilizing the invention, the factors of landform and physiognomy are not needed to be considered; the strong covering area coverage of the base station wireless field or a community can be simply and conveniently and fast determined.
Owner:BOCO INTER TELECOM
Method for improving soft-frequency reuse in OFDM system
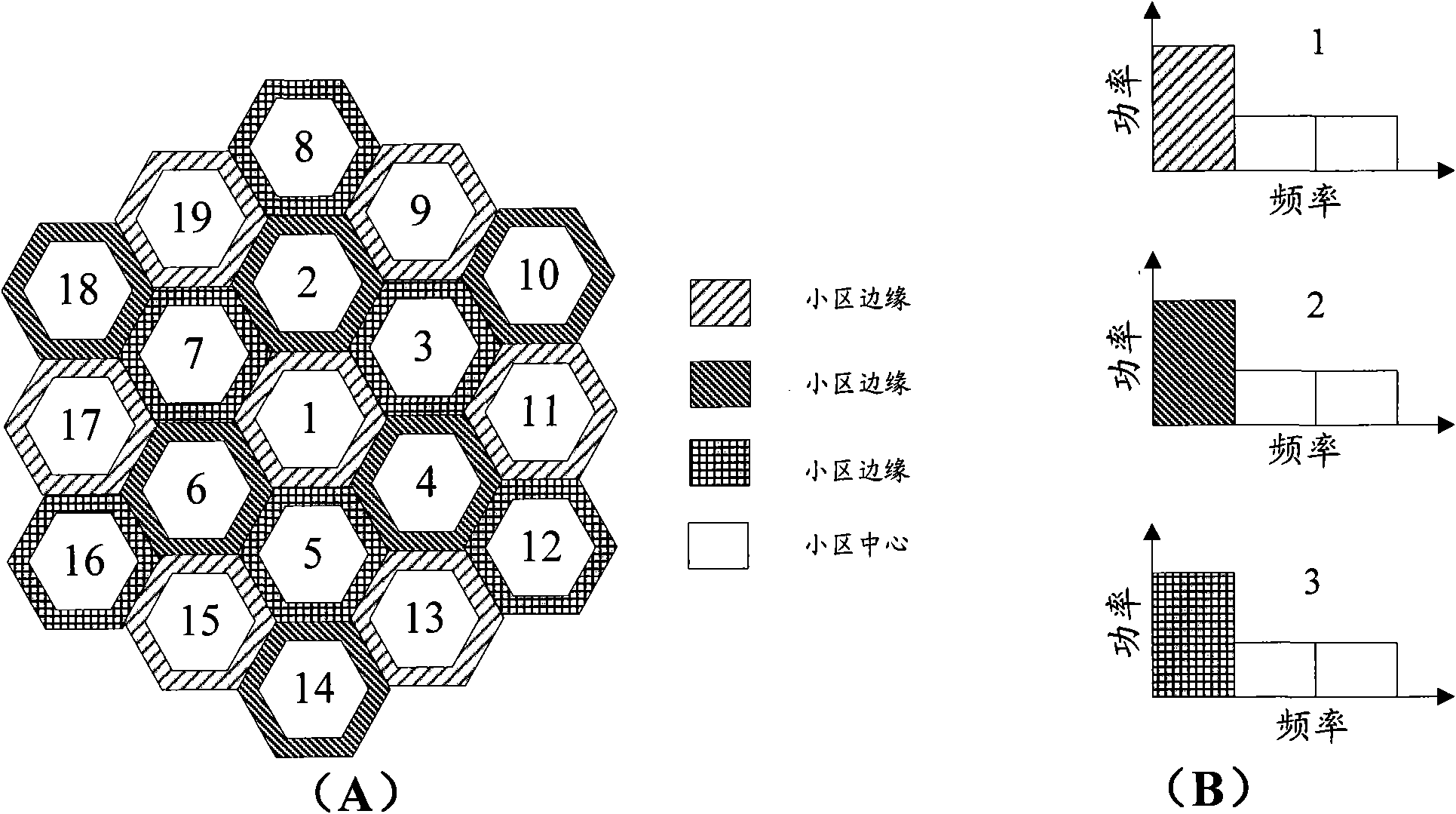
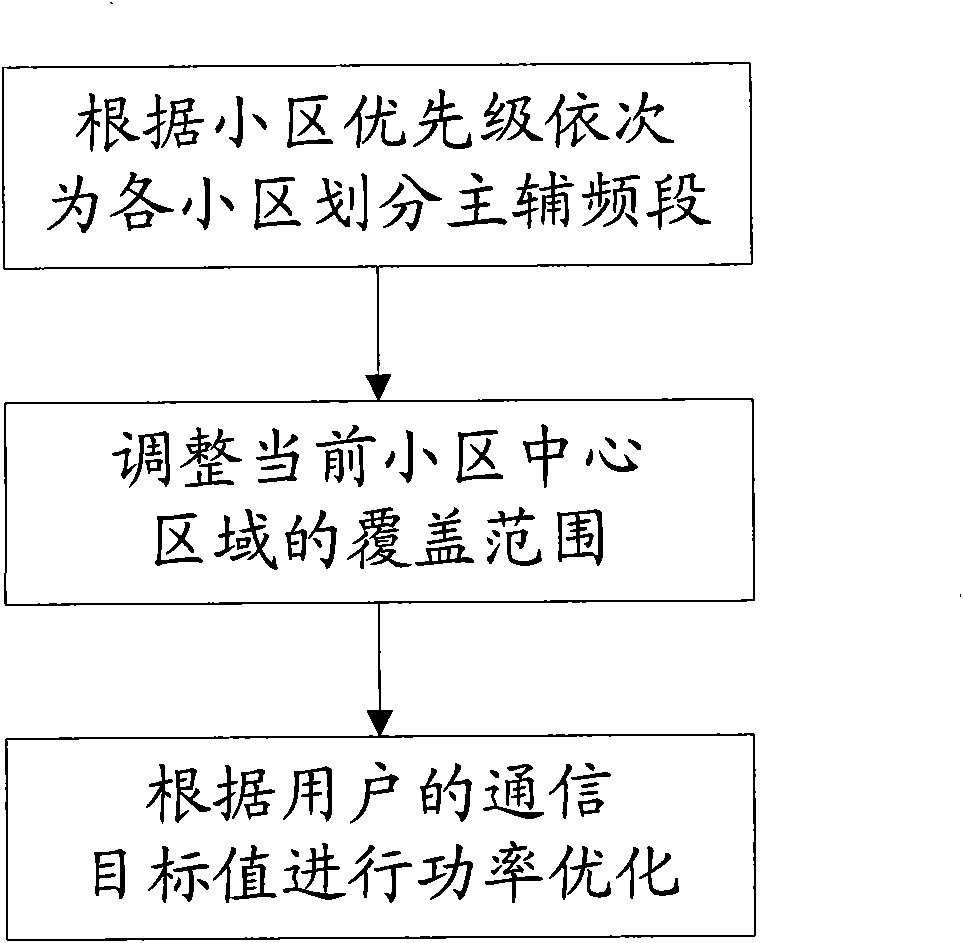
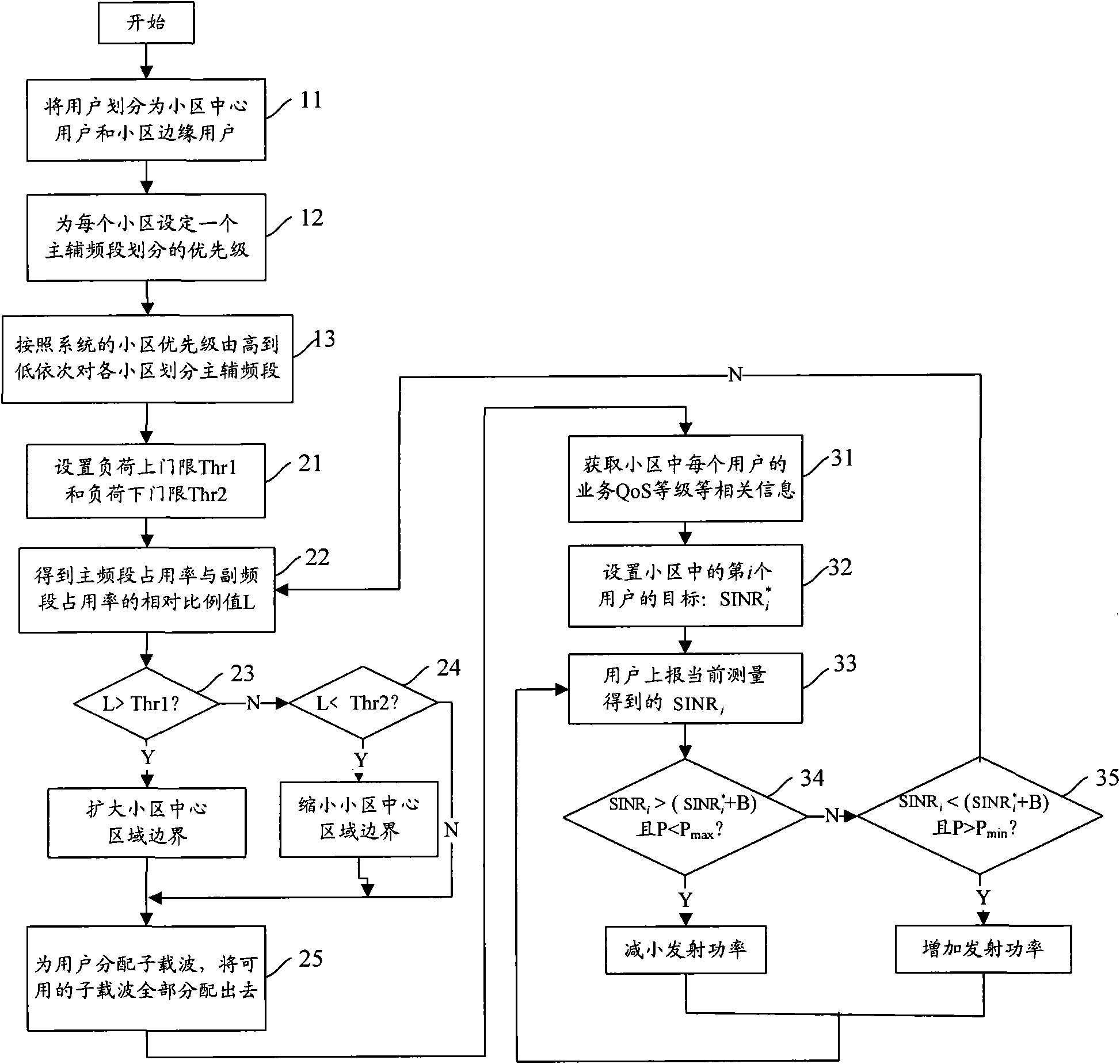
ActiveCN101600212AImprove throughputEasy to operateNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork planningQuality of serviceCurrent cell
The invention discloses a method for improving soft-frequency reuse in an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex) system. The method comprises the following operating steps: dividing main and auxiliary frequency channels for each cell according to the cell priority level in turn; adjusting the central area coverage of the current cell; carrying out the power optimization according to the communication target value of subscribers. By taking the relation between the quantities of main and auxiliary sub-carriers and the service load intensity of the central area and the edge area of the cell as a parameter, when the service distribution in the cell is not uniform, the method can adjust the central area coverage of the current cell and compromise between the main sub-carrier orthogonality of a neighbor cell and the entire frequency resource utilization rate of the cell, so as to improve the operability and availability of the soft-frequency reuse. The disturbance of the central area of the cell to the edge area thereof can be reduced by setting a communication target value for each subscriber terminal and taking the corresponding power control so that the edge throughout and total throughout of the cell can be increased on the basis that the quality of subscriber services is guaranteed.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com