Patents
Literature
309 results about "Prokaryote" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A prokaryote is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό (pro) "before" and κάρυον (karyon) "nut" or "kernel". Prokaryotes are divided into two domains, Archaea and Bacteria. Species with nuclei and organelles are placed in the third domain, Eukaryota. Prokaryotes reproduce without fusion of gametes. The first living organisms are thought to have been prokaryotes.
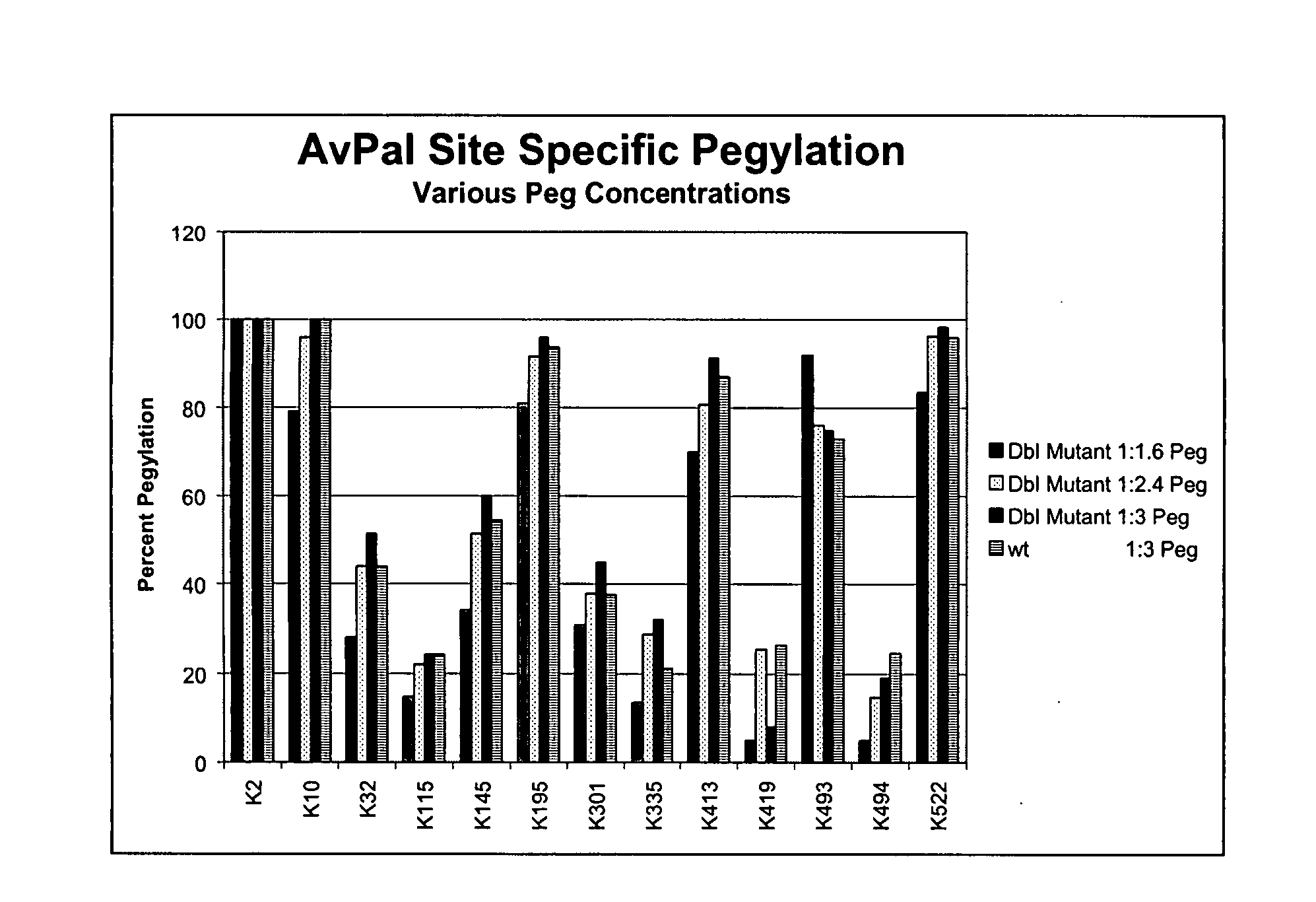
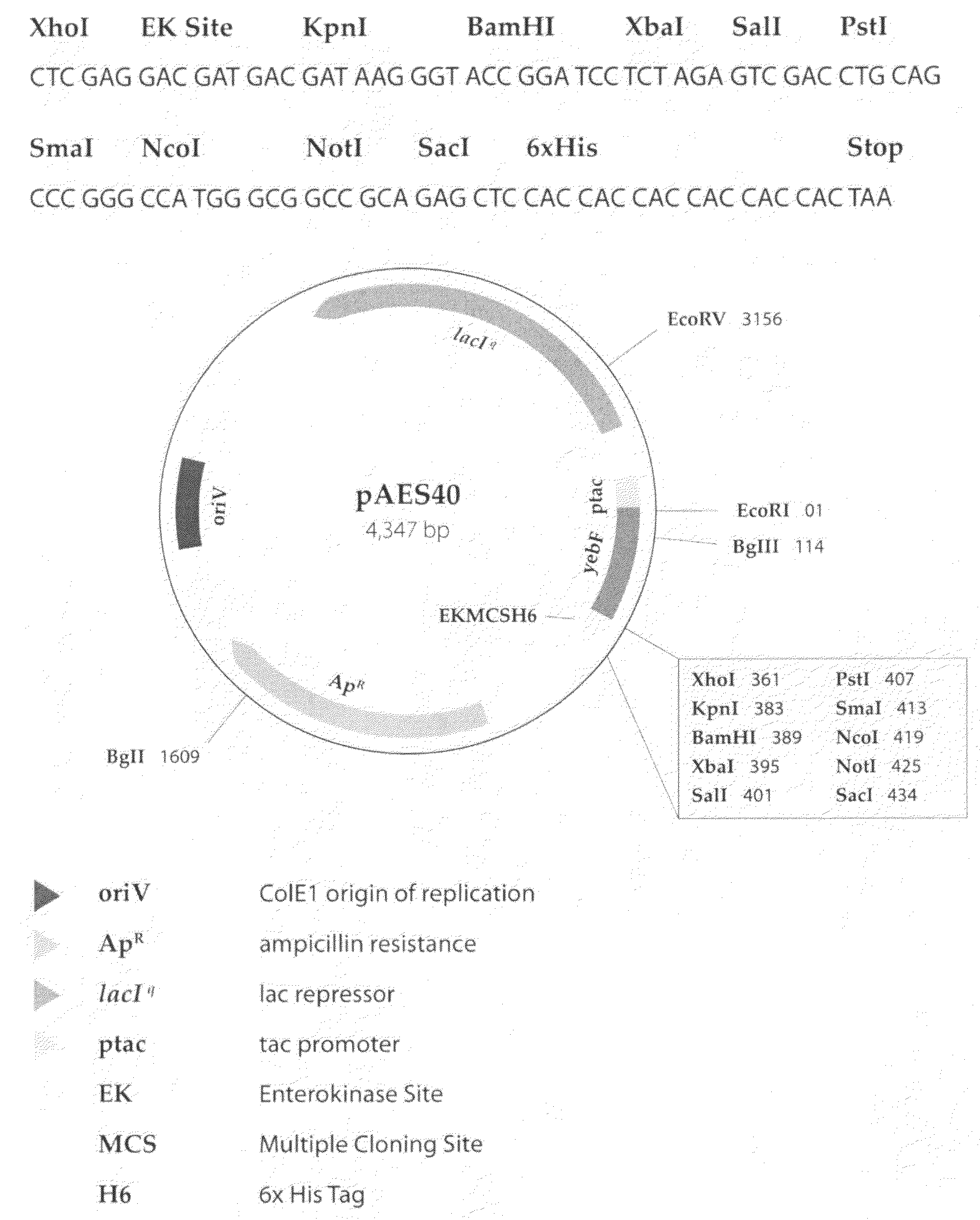
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and methods of using compositions thereof
ActiveUS7531341B1Extended half-lifeLow immunogenicityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typePAL
The present invention is directed to phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL wherein the PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity as compared to a wild-type PAL. The invention thus provides compositions of bacterial PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants and analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, and use of such compositions for therapeutic and industrial purposes.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and methods of using compositions thereof
ActiveUS20080008695A1Reduce protein aggregationReduce enzyme activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeVaccine Immunogenicity
The present invention is directed to phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL wherein the PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity and / or a reduced immunogenicity as compared to a wild-type PAL. The invention thus provides compositions of bacterial PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants and analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, and use of such compositions for therapeutic and industrial purposes.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Kits and methods for generating 5' capped RNA
InactiveUS20070281336A1Increase synthesisImprove efficiencySugar derivativesActivity regulationType specificPhosphoric acid
The present invention relates to kits and methods for efficiently generating 5′ capped RNA having a modified cap nucleotide and for use of such modified-nucleotide-capped RNA molecules. The invention is used to obtain novel compositions of such modified-nucleotide-capped RNA molecules. In particular, the present invention provides kits and methods for capping RNA using a modified cap nucleotide and a capping enzyme system, such as poxvirus capping enzyme. The present invention finds use for in vitro production of 5′-capped RNA having a modified cap nucleotide and for in vitro or in vivo production of polypeptides by in vitro or in vivo translation of such modified-nucleotide-capped RNA for a variety of research, therapeutic, and commercial applications. The invention also provides methods and kits for capturing or isolating uncapped RNA comprising primary RNA transcripts or RNA having a 5′-diphosphate, such as RNA synthesized in vitro or obtained from a biological source, including prokaryotic mRNA that is in a mixture with other prokaryotic and / or eukaryotic nucleic acids. The method for capturing modified-nucleotide-capped RNA also provides methods and kits for obtaining only type-specific or condition-specific modified-nucleotide-capped RNA by cap-dependent subtraction of that portion of the captured modified-nucleotide-capped RNA in cells of one type or condition that is the same as RNA in cells of another type or condition. The invention further provides methods and kits for using a capping enzyme system and modified cap nucleotides for labeling uncapped RNA comprising primary RNA transcripts or RNA having a 5′-diphosphate with detectable dye or enzyme moieties.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and methods of using compositions thereof
ActiveUS7534595B2High catalytic activityExtended half-lifeNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeDrug biological activity
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
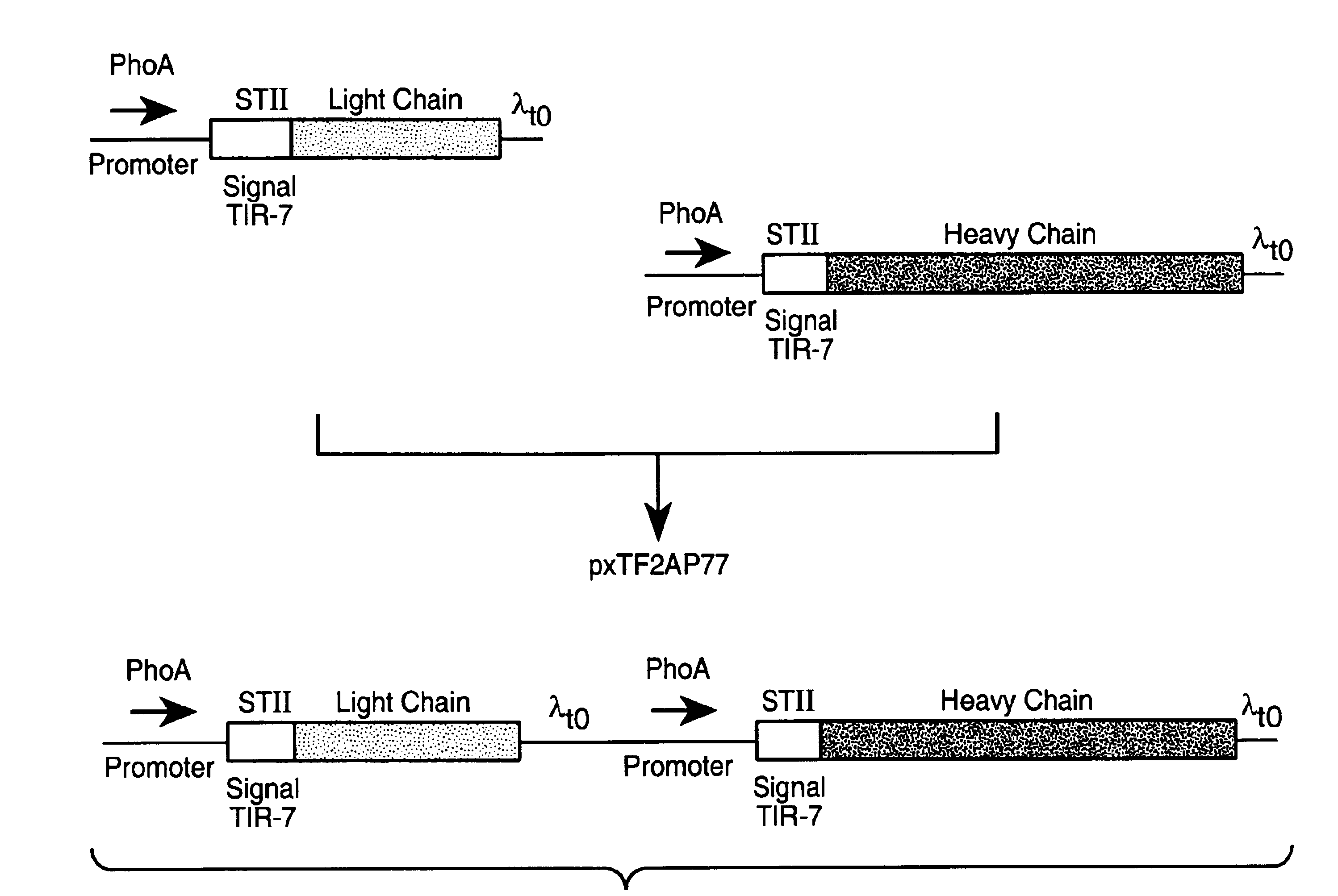
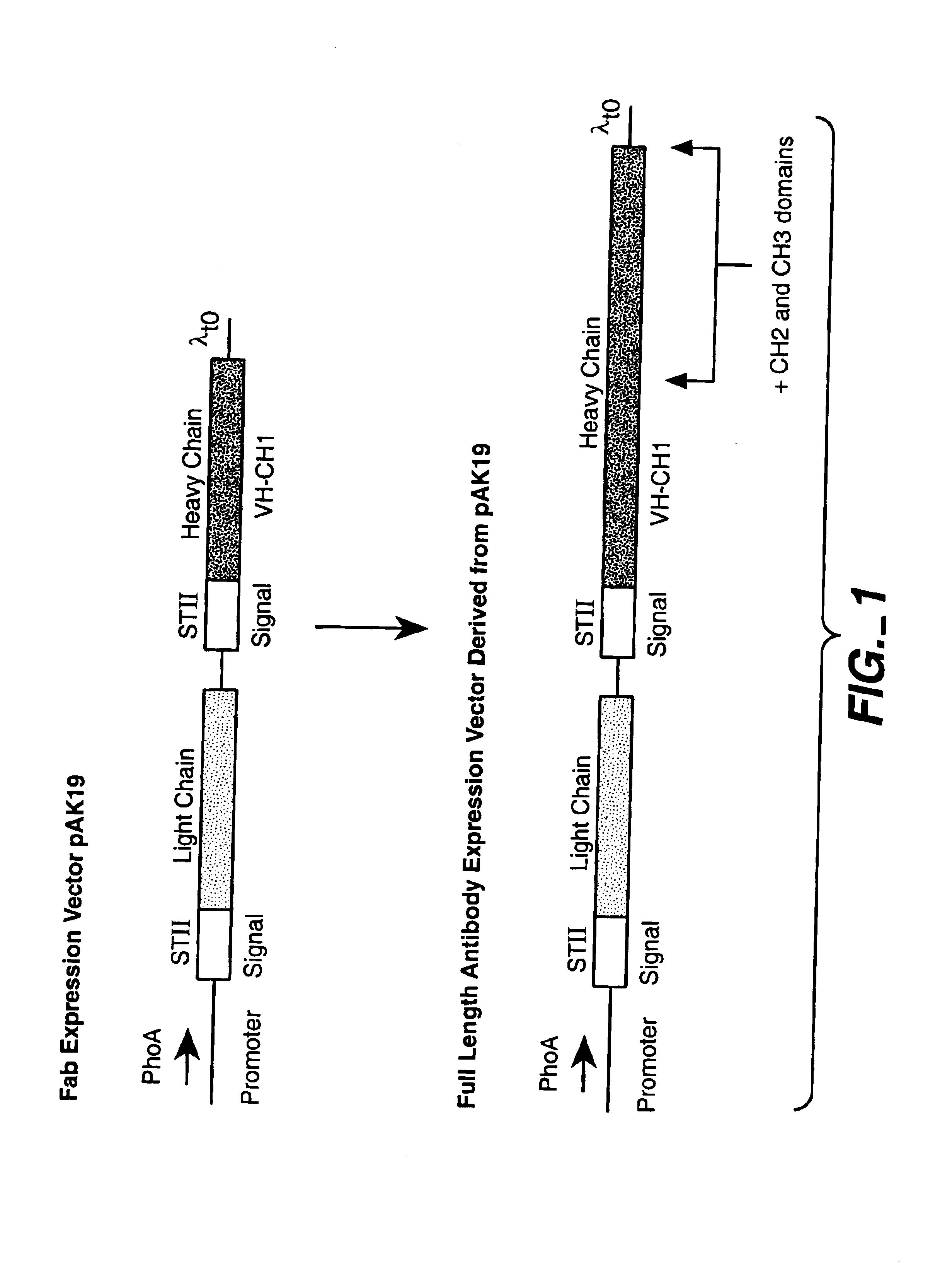
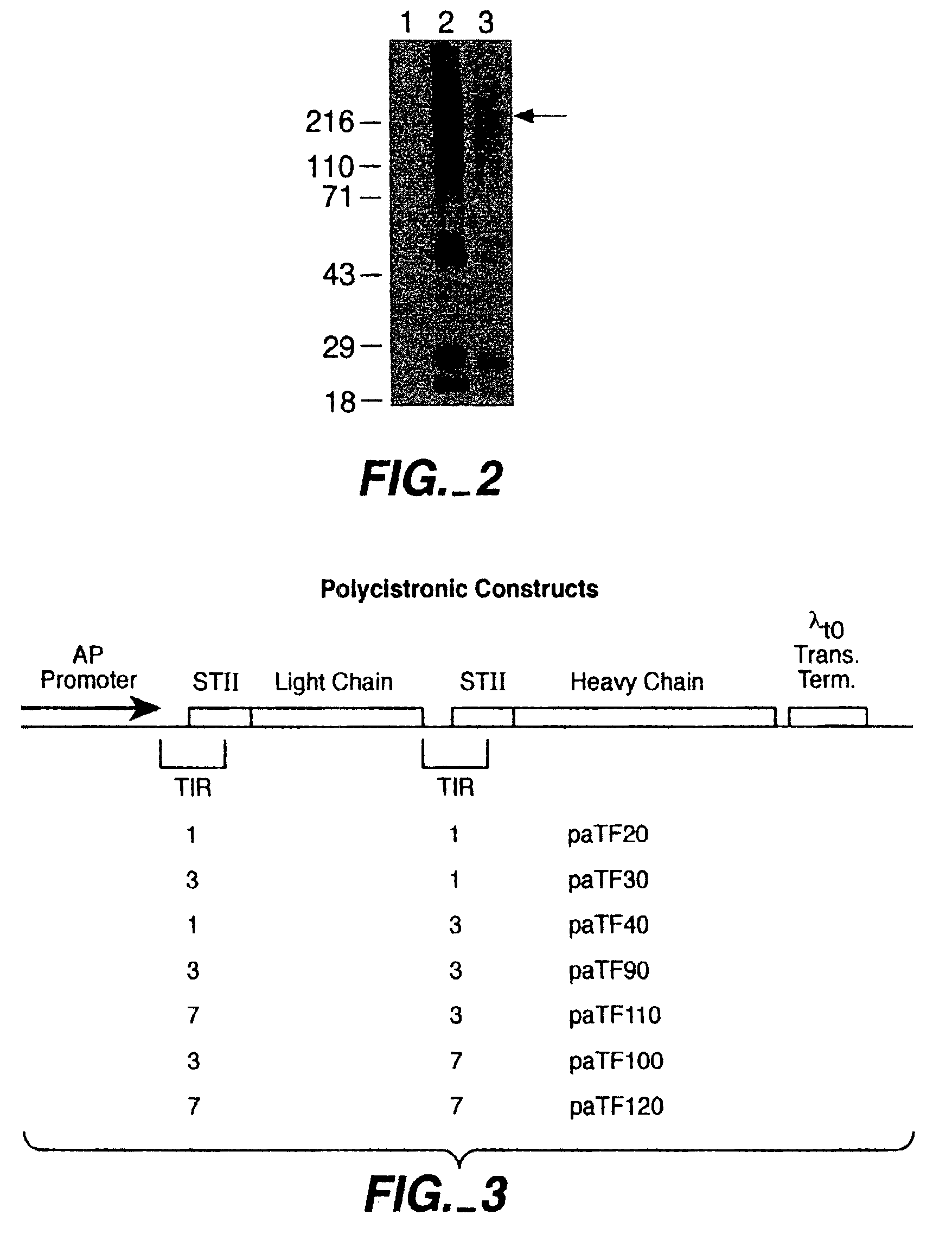
Separate-cistron contructs for secretion of aglycosylated antibodies from prokaryotes
InactiveUS6979556B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsSugar derivativesBiological studiesProkaryotic expression
The present invention provides methods and compositions for improved expression and production of recombinant antibodies in prokaryotic expression systems. Particularly contemplated are prokaryotic expression and production of full length aglycosylated antibodies. The antibody products of the invention can be used in various aspects of biological research, diagnosis and medical treatment.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and methods of treating cancer using compositions thereof
ActiveUS7537923B2High catalytic activityImprove stabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeCancer therapy
The present invention is directed to phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) variants produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity and / or a reduced immunogenicity as compared to a wild-type PAL. The invention provides compositions of prokaryotic PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants or analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, and use of such compositions for therapeutic purposes, including the treatment of cancer.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
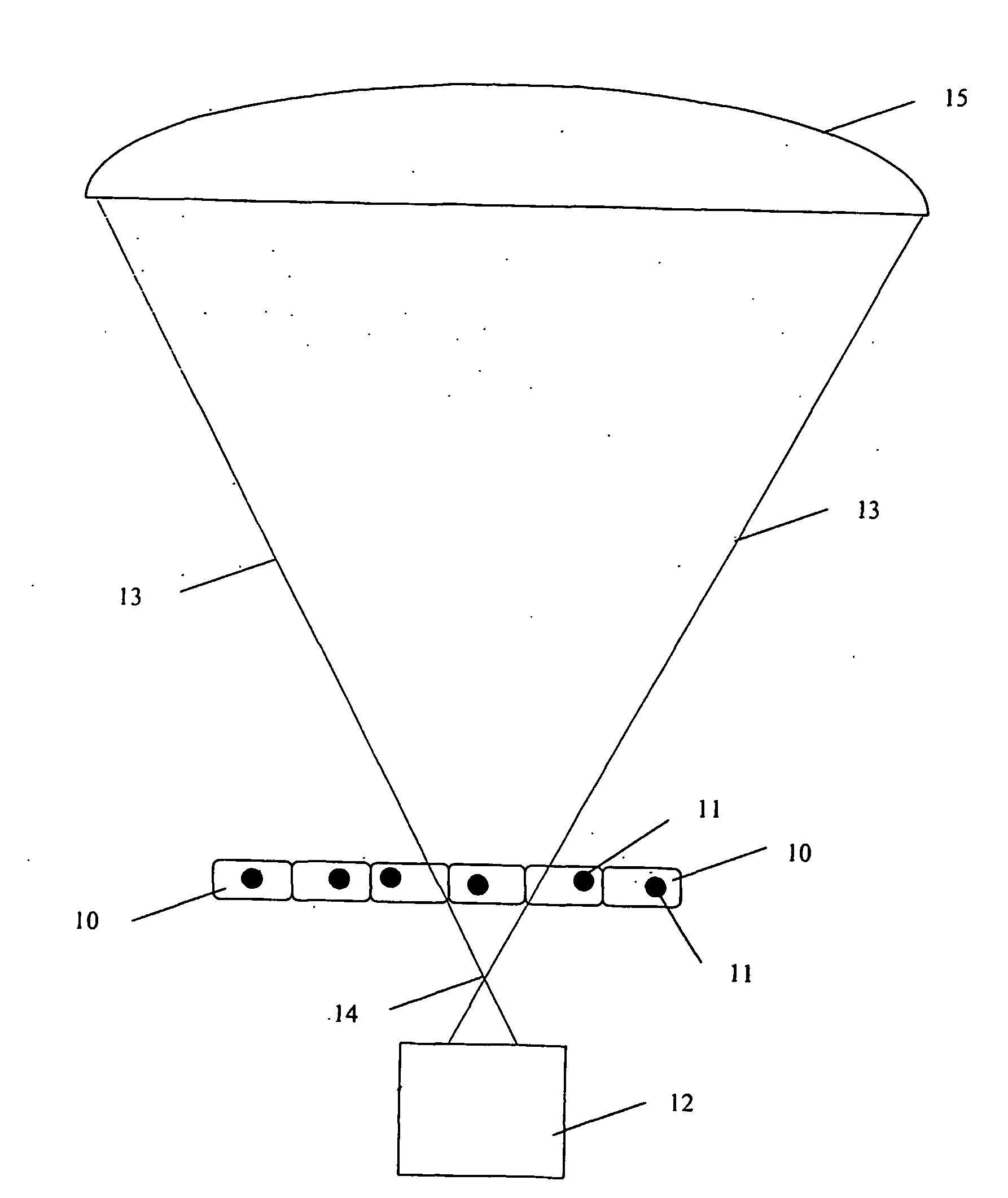
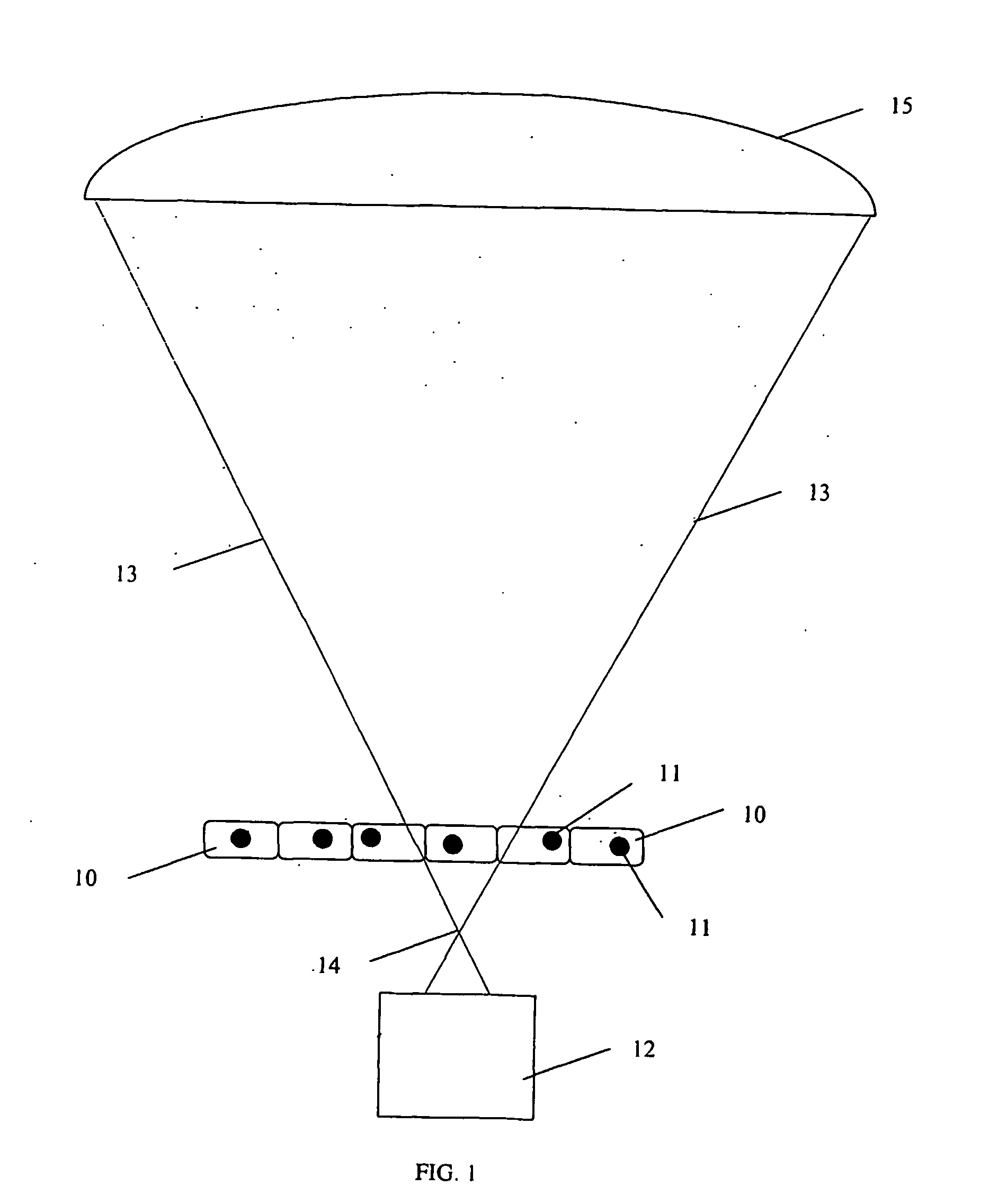
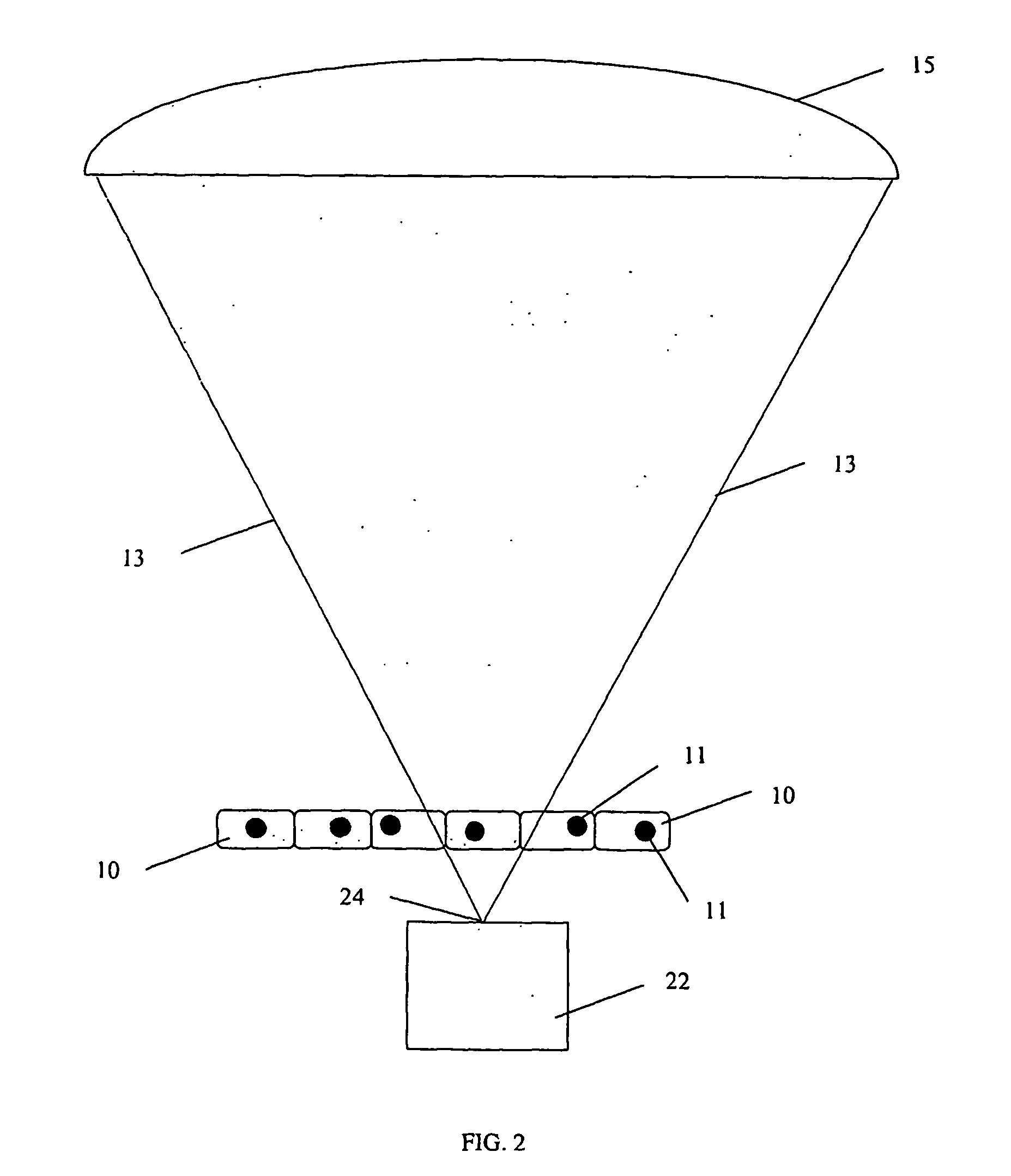
System for molecular imaging
InactiveUS20070025504A1Promote recoveryMass extinctionDiagnostics using lightMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayPhotonics
Charged and neutral particles, photons (13), photonic optics, detectors (15) and sensor arrays are used for application to molecular imaging, communication with biological organisms and monitoring and learning biological activity inside living organisms. The living organisms include among others living tissue, biological organs, cells (10), eukaryotes, prokaryotes, viruses and phages. Molecular imaging can be an effective new tool to understand the mechanisms of life and communicate, modify and control it. Techniques, methods and devices are described to achieve these aims. The probes used in molecular imaging described above will include the full spectrum of photons; charged and uncharged particles (13); chemicals; and biological probes.
Owner:TUMER TUMAY O
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase variants and methods of using compositions thereof
InactiveUS20130039898A1Effective treatmentImprove propertiesCarbon-nitrogen lyasesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeImmunogenicity
Provided herein are phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) variants produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity and / or a reduced immunogenicity as compared to a wild-type PAL. Further provided are compositions of prokaryotic PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants or analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, formulation, and use of such compositions for industrial and therapeutic purposes, e.g., treating hyperphenylalaninemia, including phenylketonuria, and other disorders, including cancer.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Human TNF receptor fusion protein
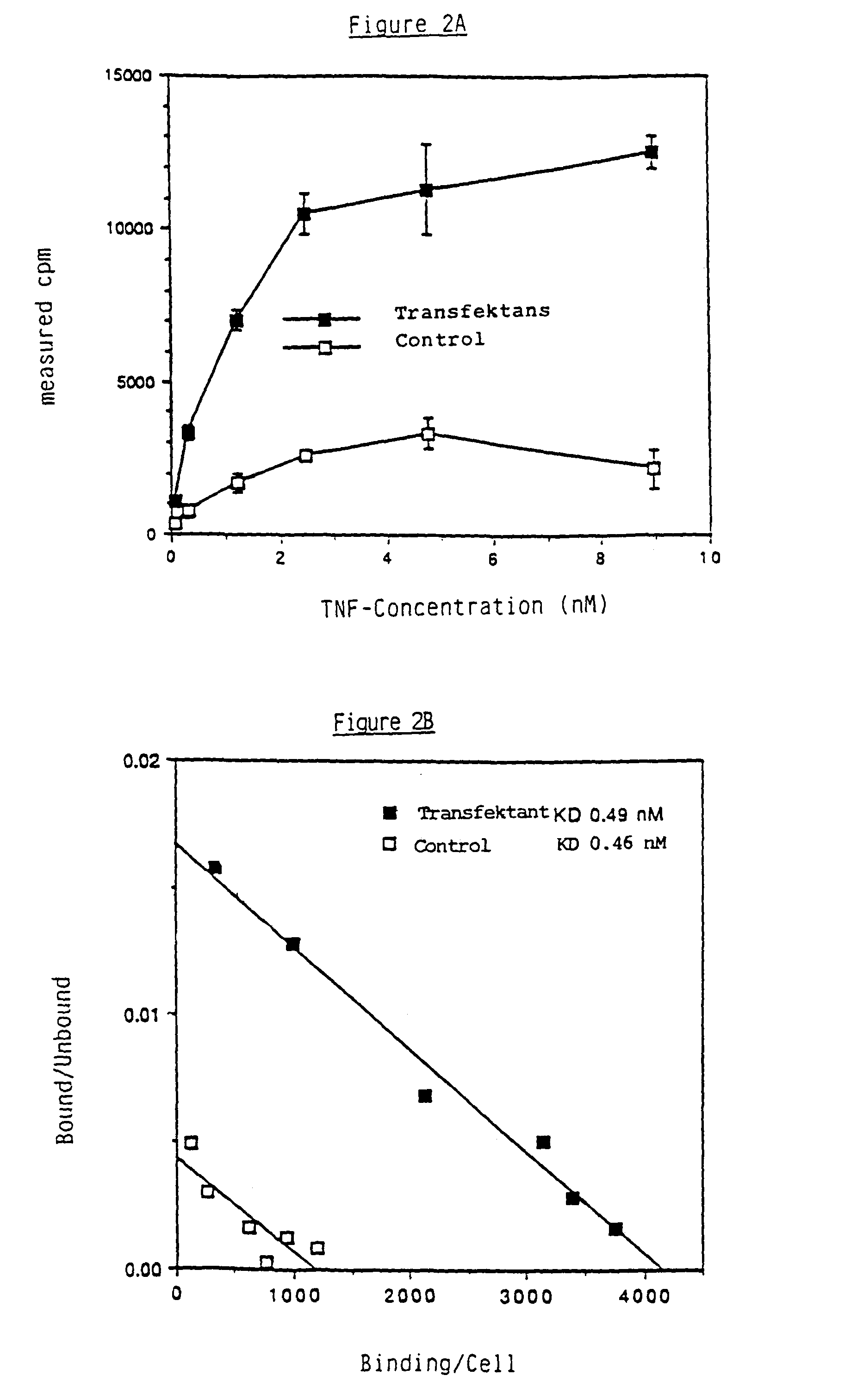
The present invention is concerned with non-soluble proteins and soluble or insoluble fragments thereof, which bind TNF, in homogeneous form, as well as their physiologically compatible salts, especially those proteins having a molecular weight of about 55 or 75 kD (non-reducing SDS-PAGE conditions), a process for the isolation of such proteins, antibodies against such proteins, DNA sequences which code for non-soluble proteins and soluble or non-soluble fragments thereof, which bind TNF, as well as those which code for proteins comprising partly of a soluble fragment, which binds TNF, and partly of all domains except the first of the constant region of the heavy chain of human immunoglobulins and the recombinant proteins coded thereby as well as a process for their manufacture using transformed pro- and eukaryotic host cells.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Secretion of antibodies without signal peptides from bacteria
The present invention is directed generally to compositions and methods for obtaining secretion of antibodies or antigen-binding antibody fragments from prokaryotes without the need for a signal peptide through making use of mutant host strains with altered secretory properties. In particular, the invention provides host cells and methods for obtaining secretion of antibodies or antigen-binding antibody fragments from bacteria without the need for a signal peptide and provides diverse libraries of antibody sequence resulting from such methods. The invention additionally provides diverse libraries.
Owner:KALOBIOS PHARMA
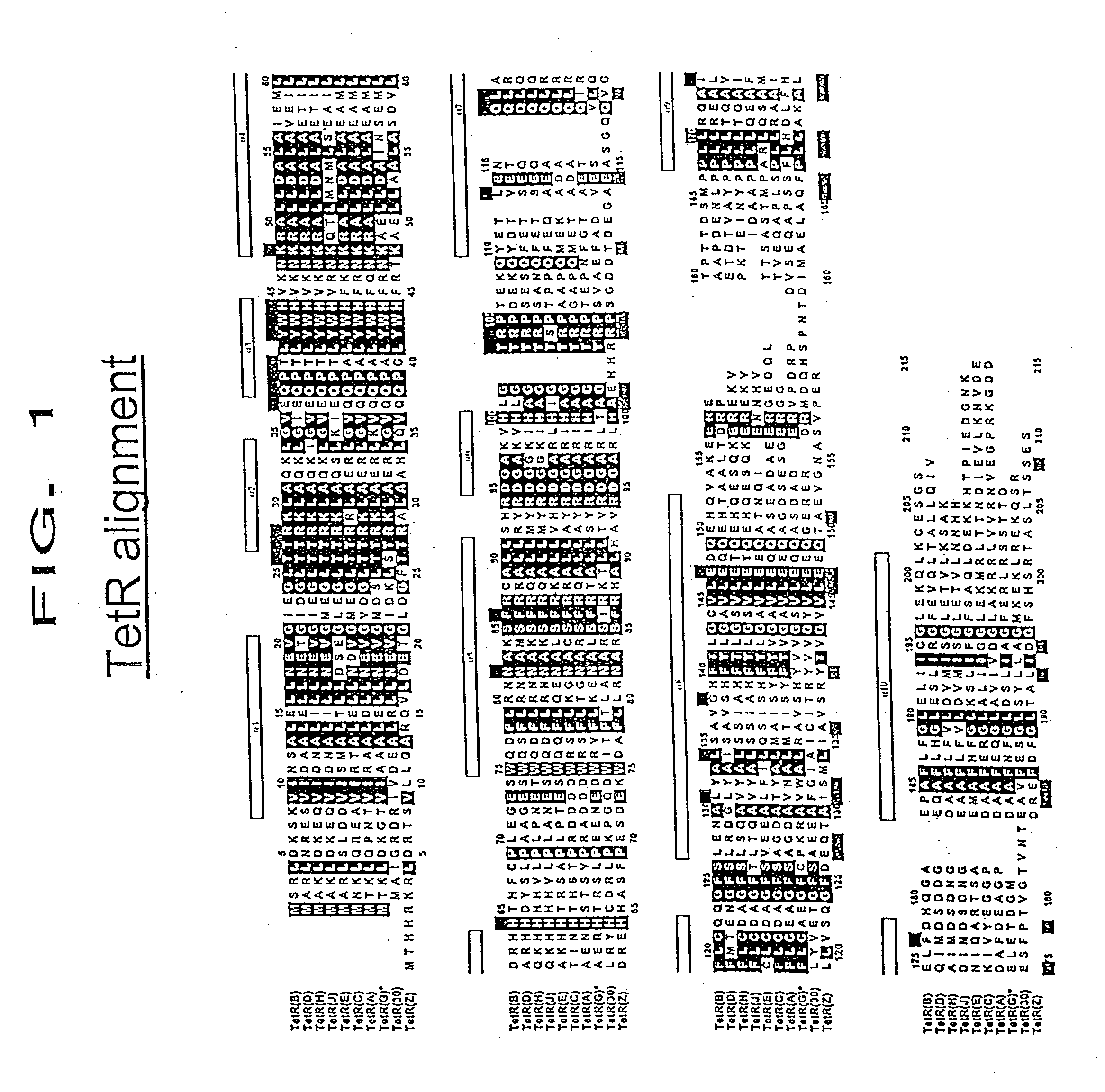
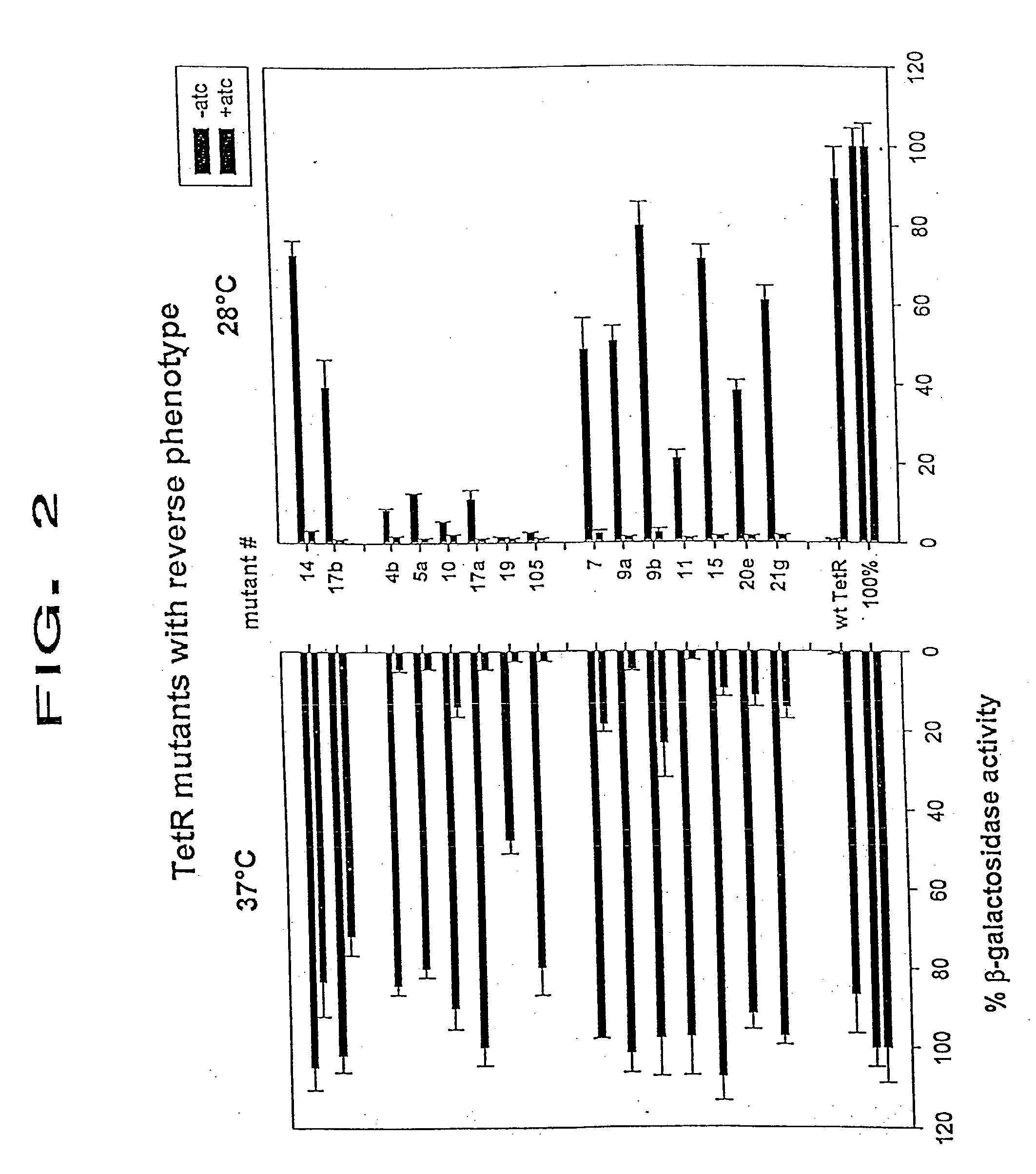
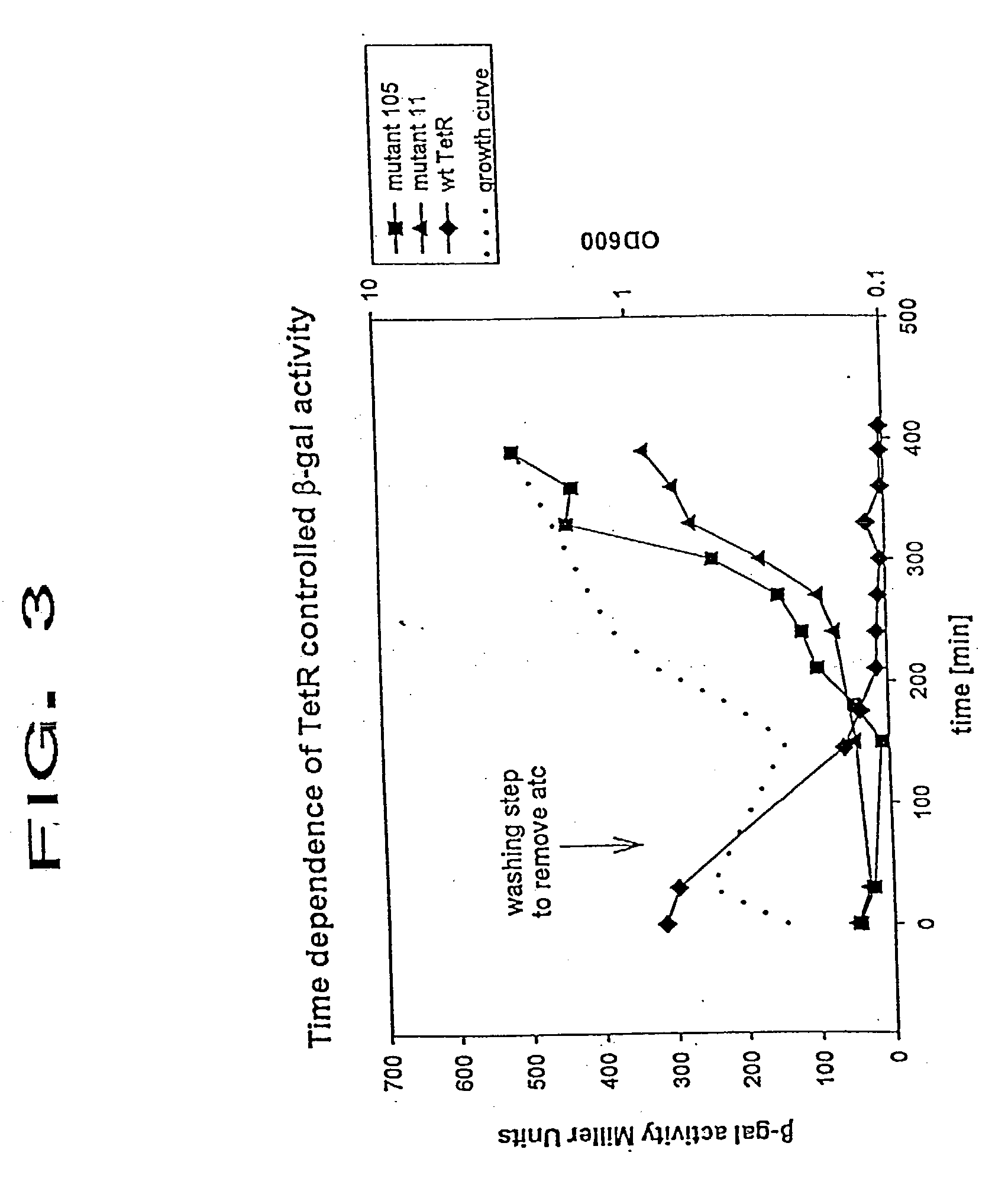
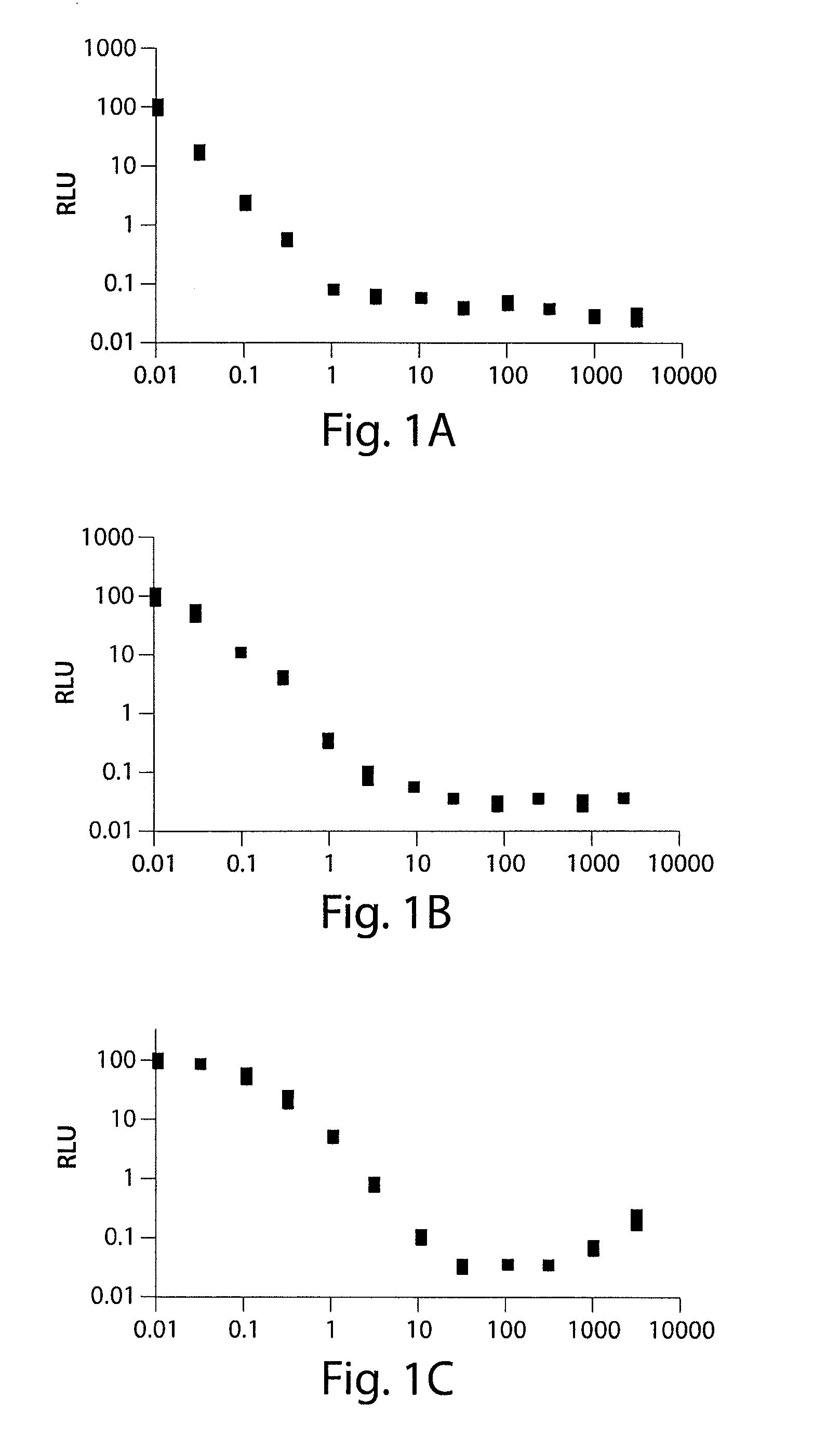
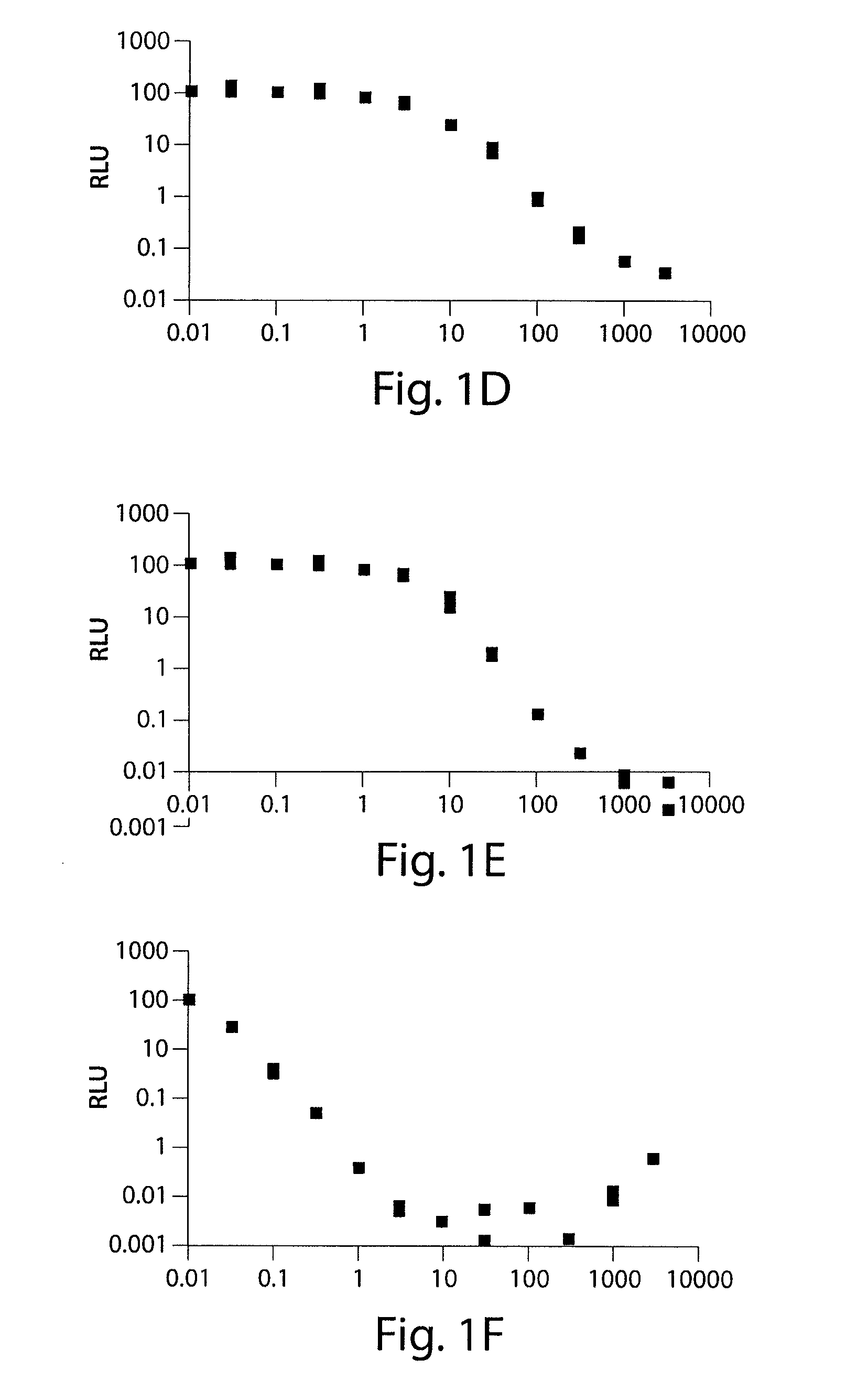
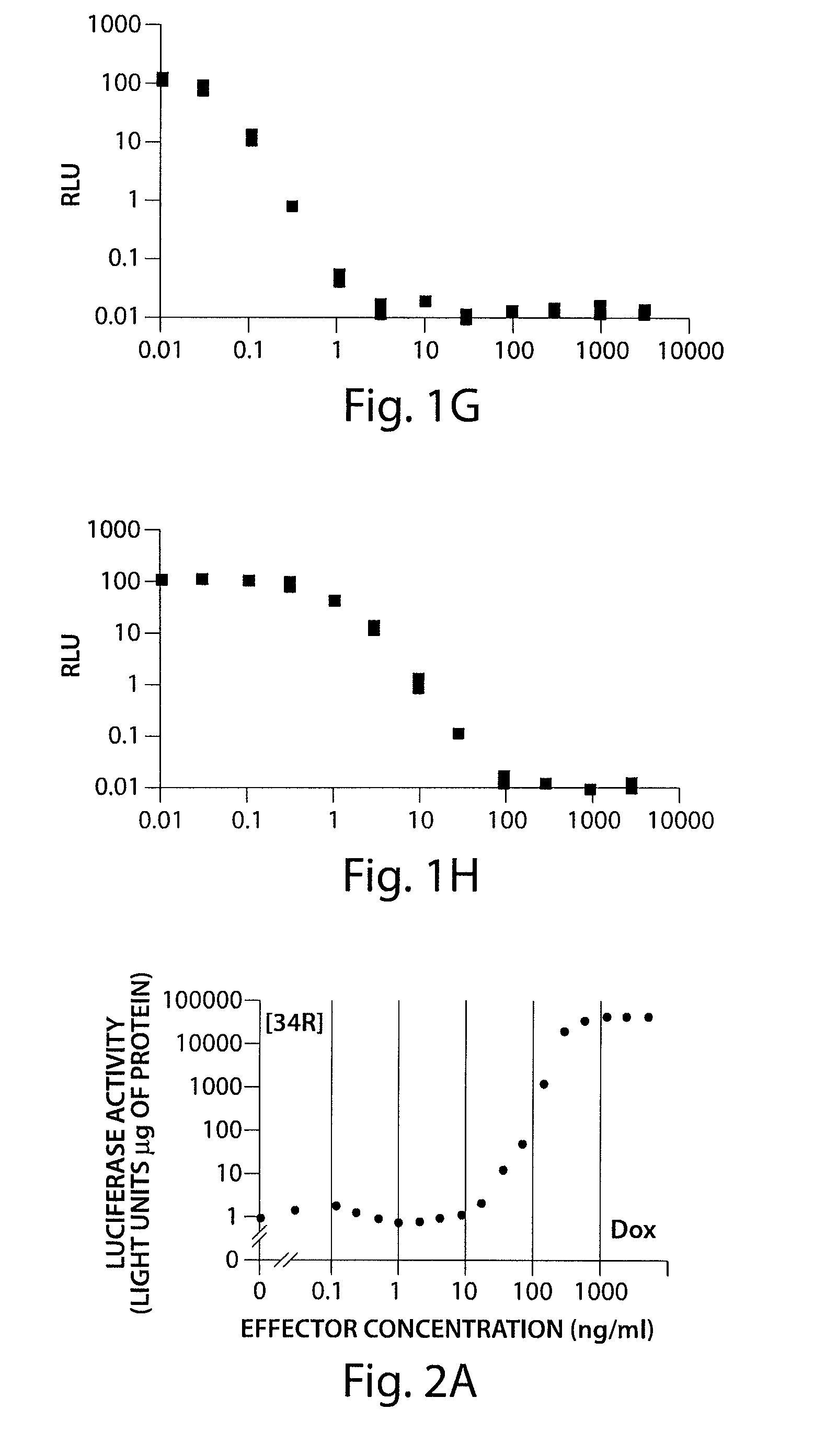
Modified tetracycline repressor protein compositions and methods of use
The present invention relates to a system for regulating gene expression in prokaryotes using modified tetracycline repressor proteins. In particular, the present invention relates to modified tetracycline repressor proteins that exhibit a "reverse" phenotype in prokaryotic organisms, nucleic acids encoding these repressor proteins, methods for identifying and preparing these proteins, and methods for using these proteins for regulating gene expression in prokaryotic organisms, in drug screening assays and for identifying non-antibiotic compounds that are specific inducers of these modified repressor proteins.
Owner:TET SYST
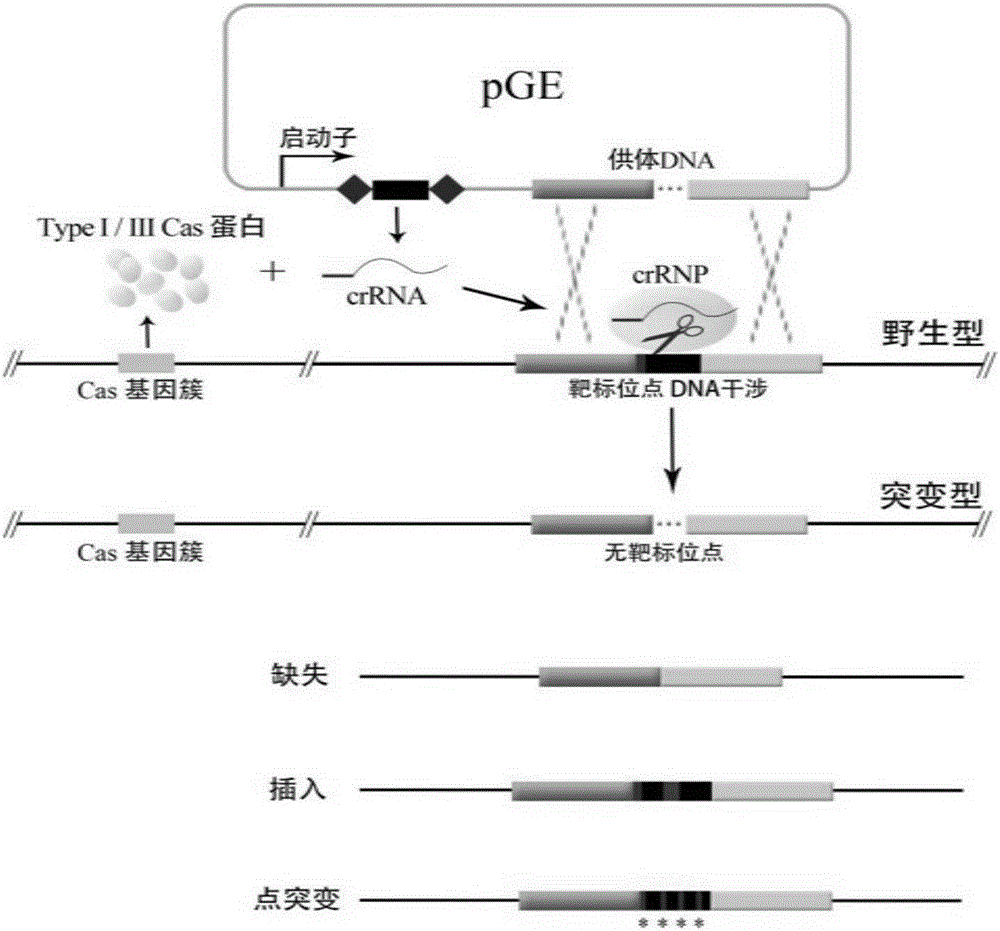
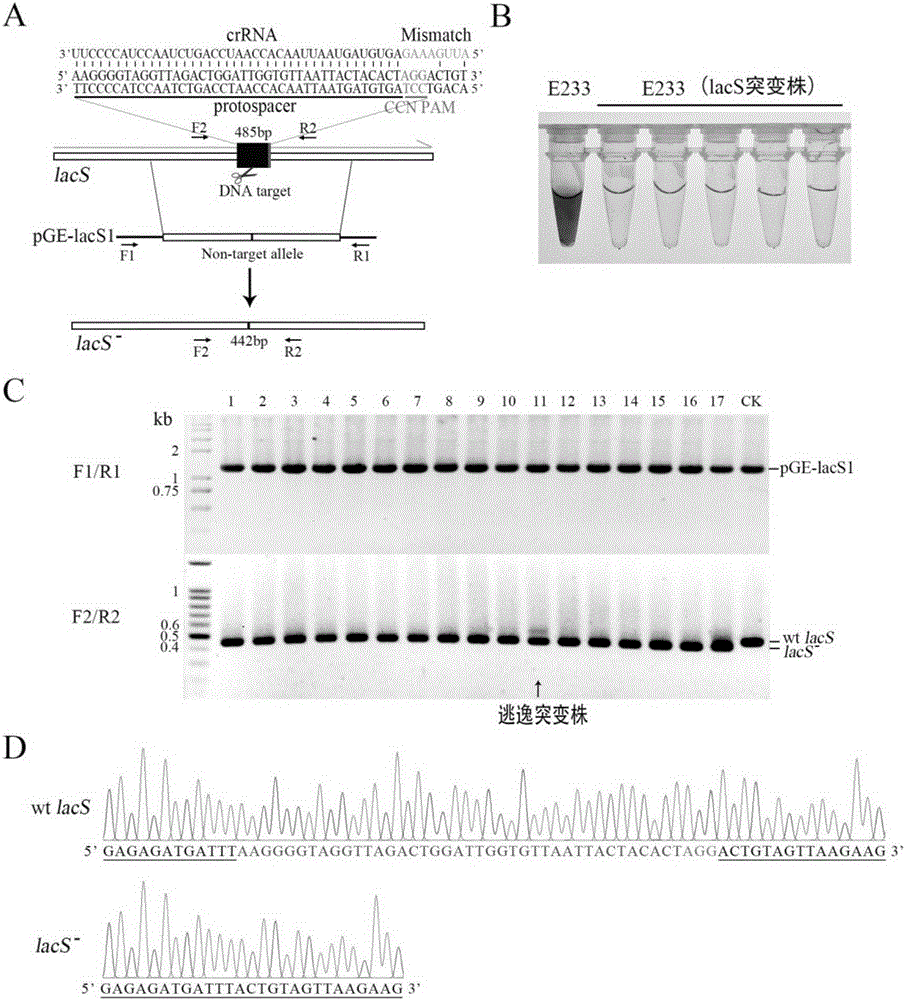
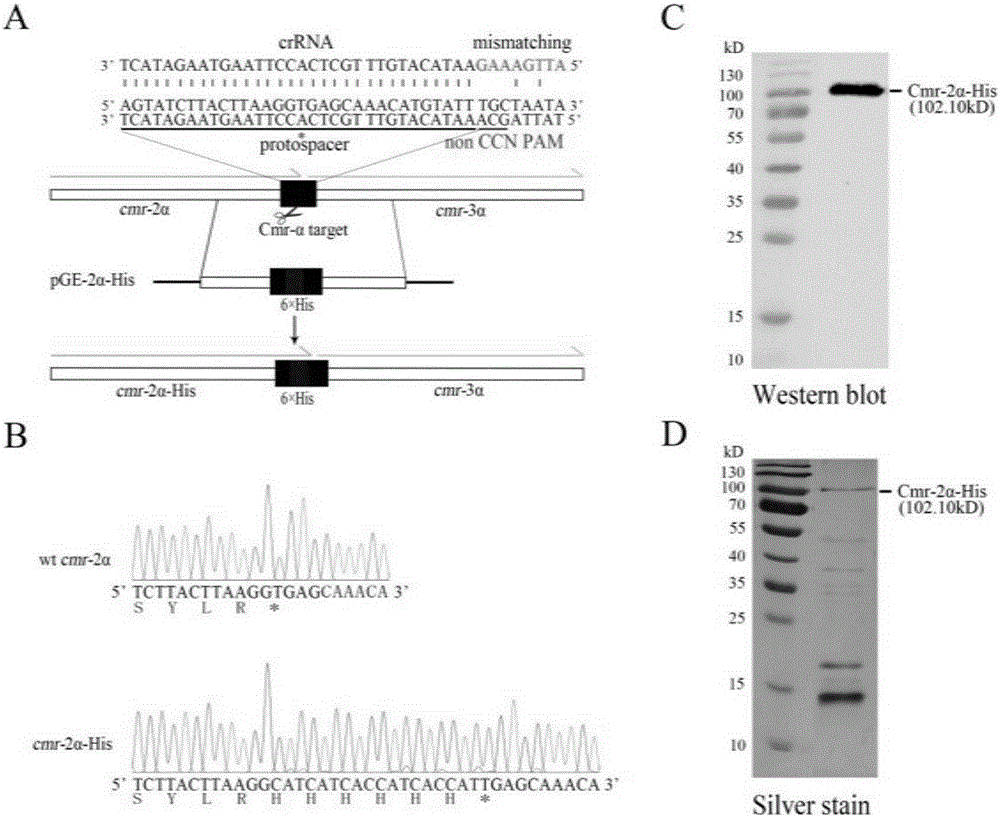
Method for editing prokaryotic genomes using endogenic CRISPR-Cas (CRISPR-associated) system
ActiveCN105331627AReduce workloadWide range of application hostsBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingWorkload
The invention relates to a method for editing prokaryotic genomes using an endogenic CRISPR-Cas (CRISPR-associated) system. An editor plasmid carrying both an artificial CRISPR cluster and a donor DNA is required to be established for the genome editing of a prokaryote containing the endogenic CRISPR-Cas system, after NDA interference is caused by the endogenic CRISPR-Cas to the genome, and the genome is edited through homologous recombination. The method has the advantages that a range of applicable hosts is wide, all bacteria and archaea containing the endogenic CRISPR-Cas being available for operation; the method is applicable to operations in various editing manners, such as deletion, insertion and point mutation; the editing efficiency is higher, screening positive rage is high, and the background is low; a flow is simple, a short period of time is required, and the workload of prokaryotic genome editing is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
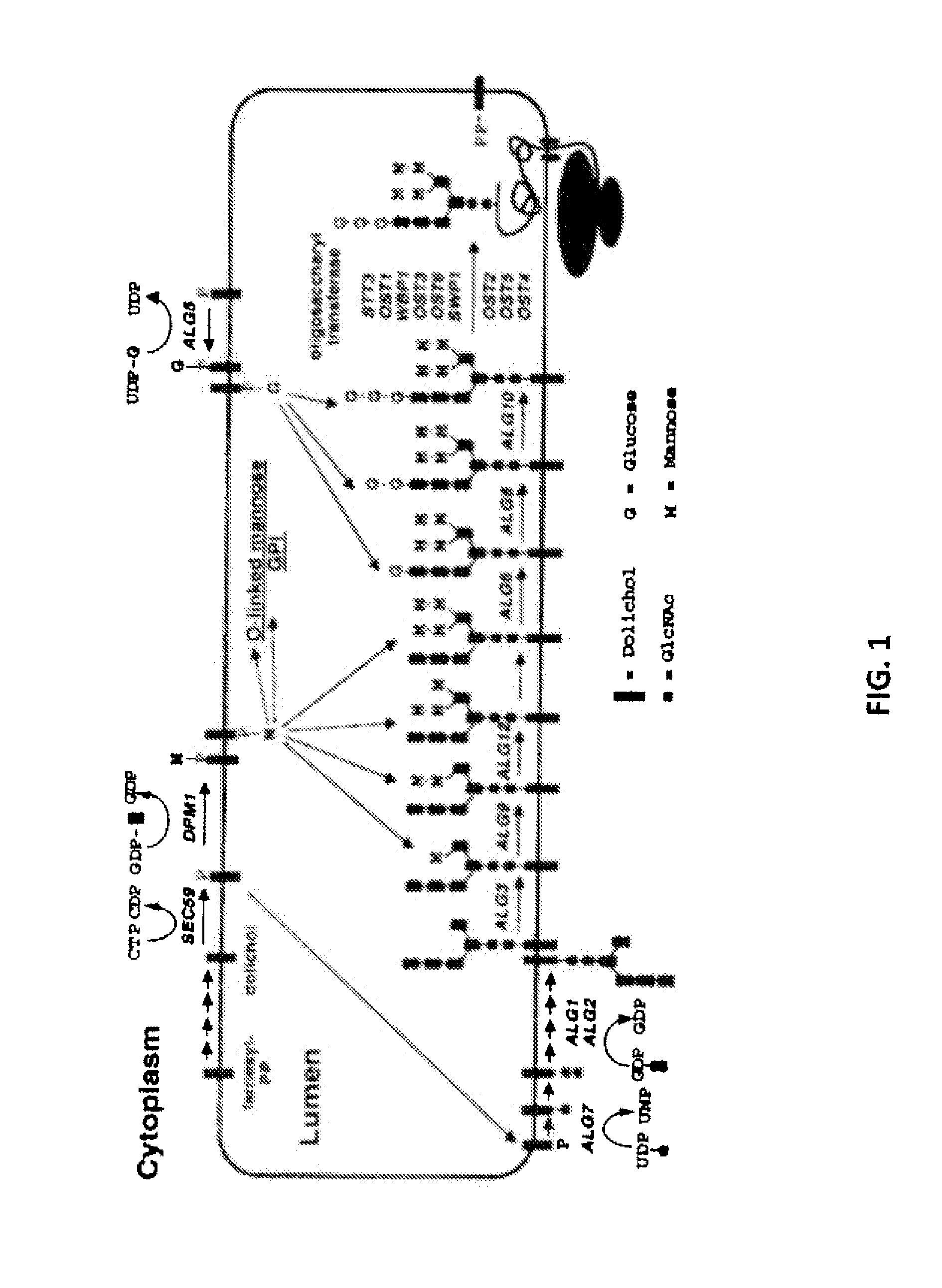
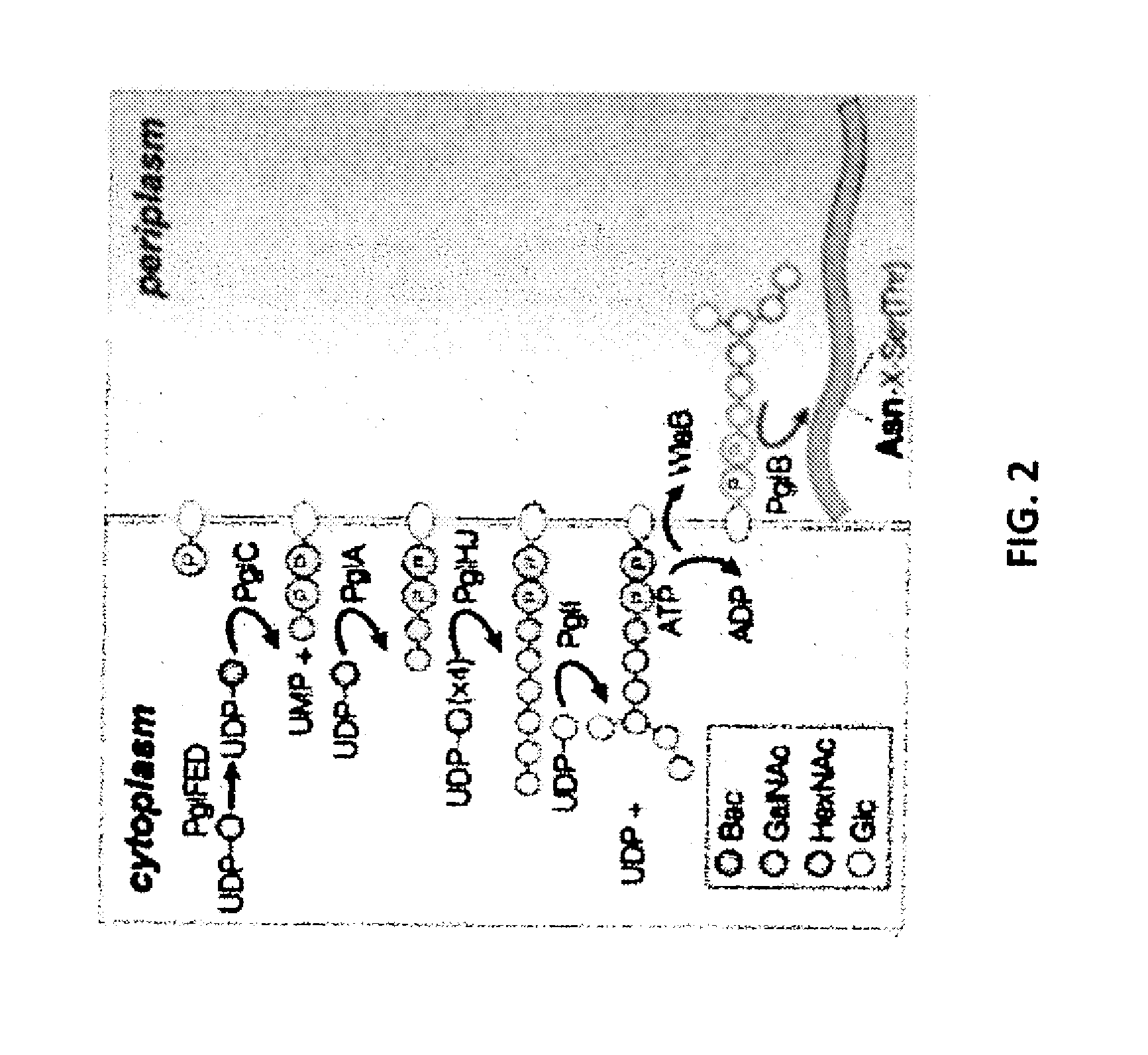
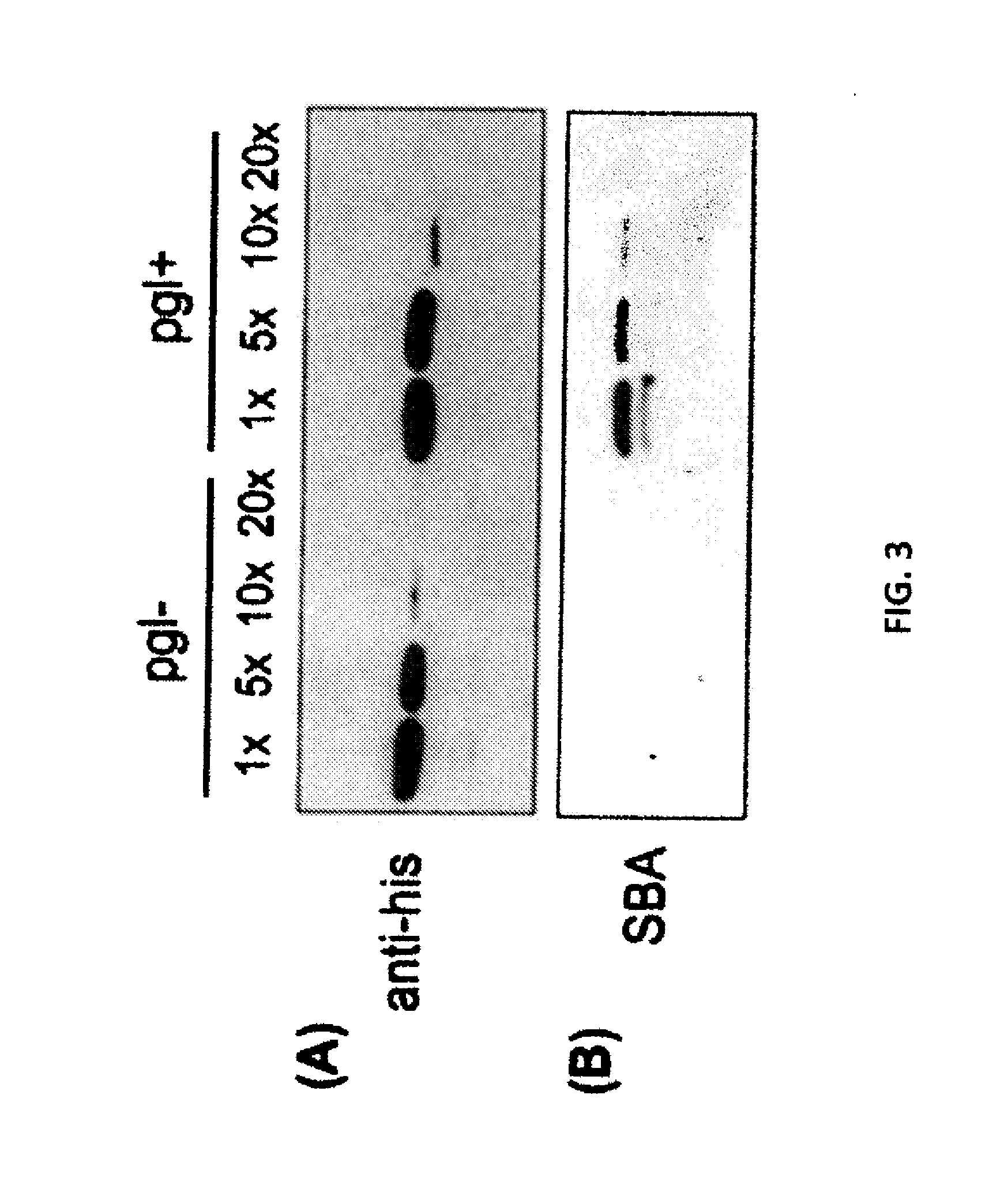
Glycosylated protein expression in prokaryotes
The present invention relates to a prokaryotic host cell comprising eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity, where the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity is eukaryotic dolichyl-linked UDP-GlcNAc transferase activity and eukaryotic mannosyl-transferase activity. Also disclosed is a method of producing a glycosylated protein by providing a prokaryotic host cell comprising the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity and culturing the prokaryotic host cell under conditions effective to produce a glycosylated protein. Another aspect of the present invention pertains to a method for screening bacteria or bacteriophages by expressing one or more glycans on the surface of a bacteria, attaching a label on the one or more glycans on the surface of the bacteria or on the surface of a bacteriophage derived from the bacteria, and analyzing the label in a high-throughput format. A glycosylated antibody comprising an Fv portion which recognizes and binds to a native antigen and an Fc portion which is glycosylated at a conserved asparagine residue is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Non-naturally occurring synthetic lytic peptides
InactiveUS6559281B1Improve the immunityImprove stabilityPeptide-nucleic acidsPeptide/protein ingredientsLytic peptideCrystallography
Non-naturally occurring lytic peptides which contain a phenylalanine residue and one or more alanine, valine and lysine residues, and optionally contain chemically masked cysteine or serine residues possess an amphipathic structure which allows them to promote cell lysis in certain pathologic organisms, and particularly in prokaryotes. Peptides having a beta-pleated sheet secondary structure and lacking cysteine residues form one embodiment of these lytic peptides.
Owner:DEMEGEN
Expression of soluble, active eukaryotic glycosyltransferases in prokaryotic organisms
Owner:RATIOPHARM GMBH
Compositions of prokaryotic phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and methods of treating cancer using compositions thereof
ActiveUS20090047265A1Great phenylalanine-converting activityLow immunogenicityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeTherapeutic intent
The present invention is directed to phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) variants produced by prokaryotes, wherein such prokaryotic PAL variant has a greater phenylalanine-converting activity and / or a reduced immunogenicity as compared to a wild-type PAL. The invention provides compositions of prokaryotic PAL and biologically active fragments, mutants, variants or analogs thereof, as well as methods for the production, purification, and use of such compositions for therapeutic purposes, including the treatment of cancer.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Method for purifying human papilloma virus advanced protein from prokaryote
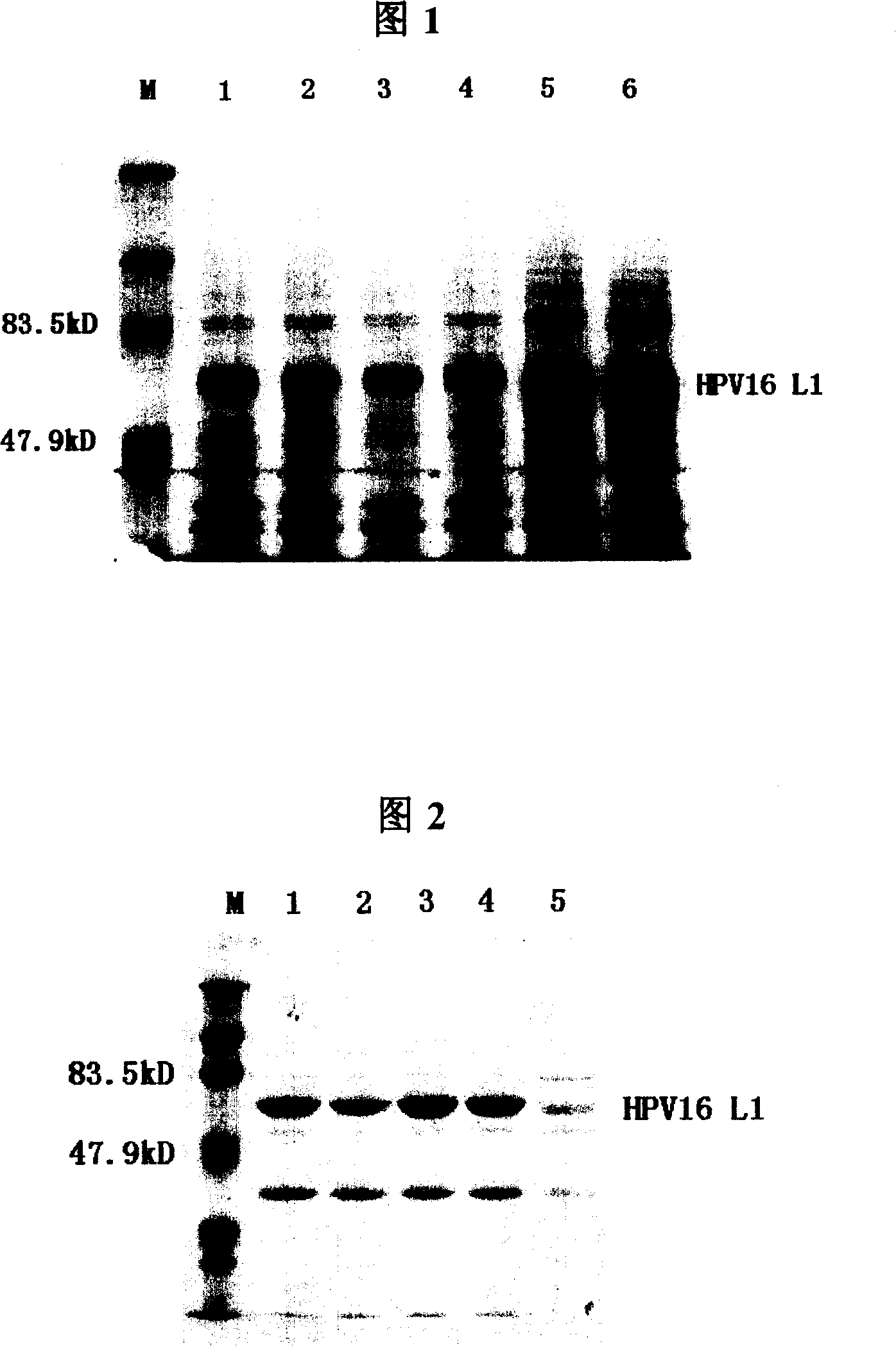
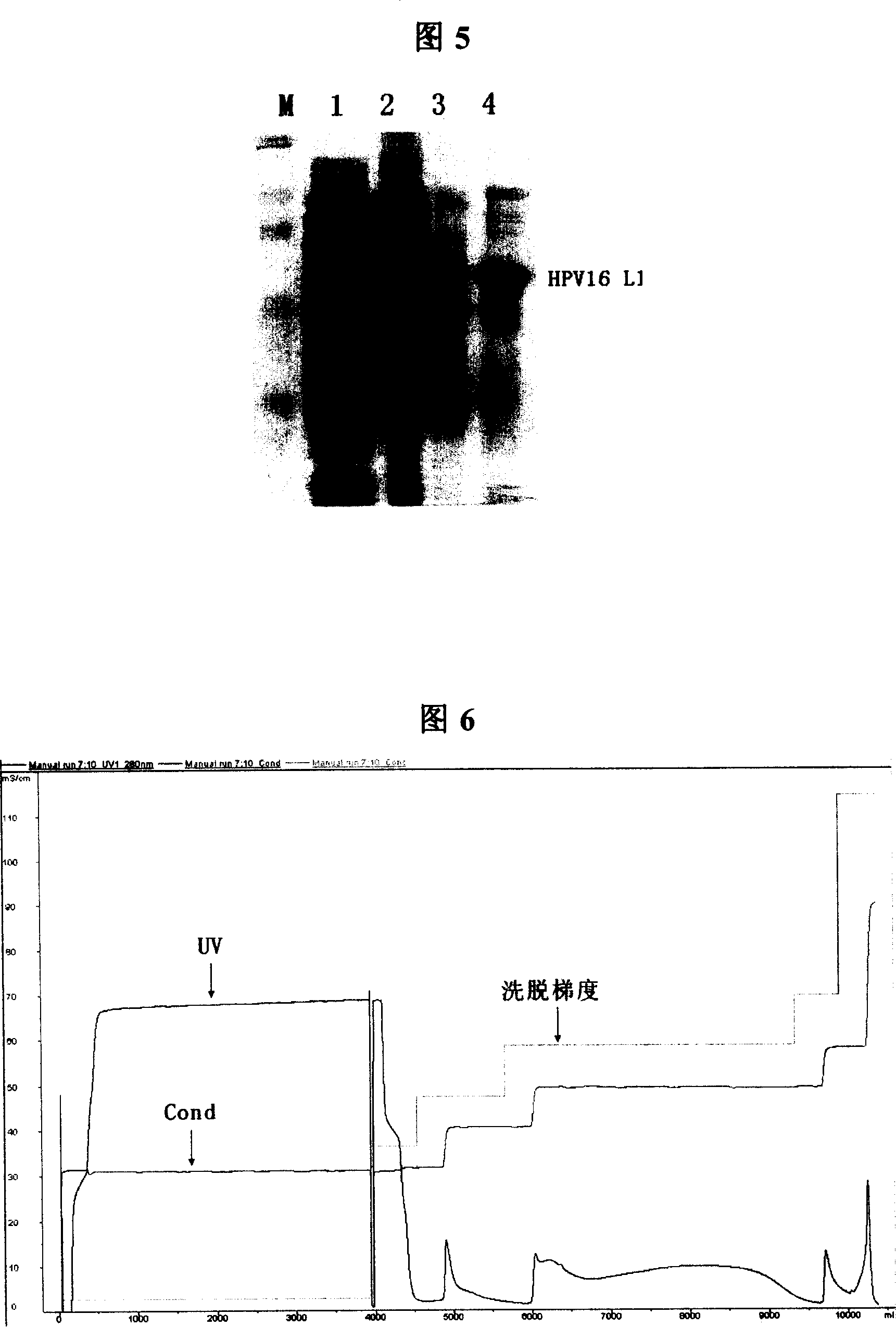
The present invention provides a purification method of human papillomavirus late protein L1 from escherichia coli. Virus-like Particles; the virus-like Particles with elctrophoresis purity more than 98 percent can be produced in a large scale through salt free precipitation, re-dissolving, ion exchange chromatography, hydrophobic interaction chromatography and renaturation of the L1 protein in the lysate supernatant of escherichia coli. With good immunogenicity, the virus particles can induce neutralizing antibodies towards homologous HPV virus, and can be used as a vaccine for preventing the infection of HPV.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Apparatus and methods for enhanced plant and lawn growth using alkane injection
Apparatus and methods are provided for introducing an alkane to a plant in order to stimulate the plant's growth. Any type of plant may be treated, including potted plants, shrubs, trees, lawns, agricultural crops and the like. In a preferred embodiment, the alkane comprises butane, but other compounds can be used, including methane, ethane and propane. The alkane may be combined with water or another liquid carrier, or plant growth-enhancing additives such as nutrients, insecticides and alkane-utilizing bacteria. To induce aerobic conditions, oxygen-containing gas such as air may be introduced along with the alkane or separately from the alkane. The introduction of alkane may enhance plant growth by increasing the indigenous microbial populations in soil, e.g. bacteria, fungi, protists, and prokaryotes, which may provide benefits such as increased nutrient uptake, faster root development, and reduced heat, drought and cold stress, resulting in enhanced plant growth.
Owner:GLOBAL BIOSCI
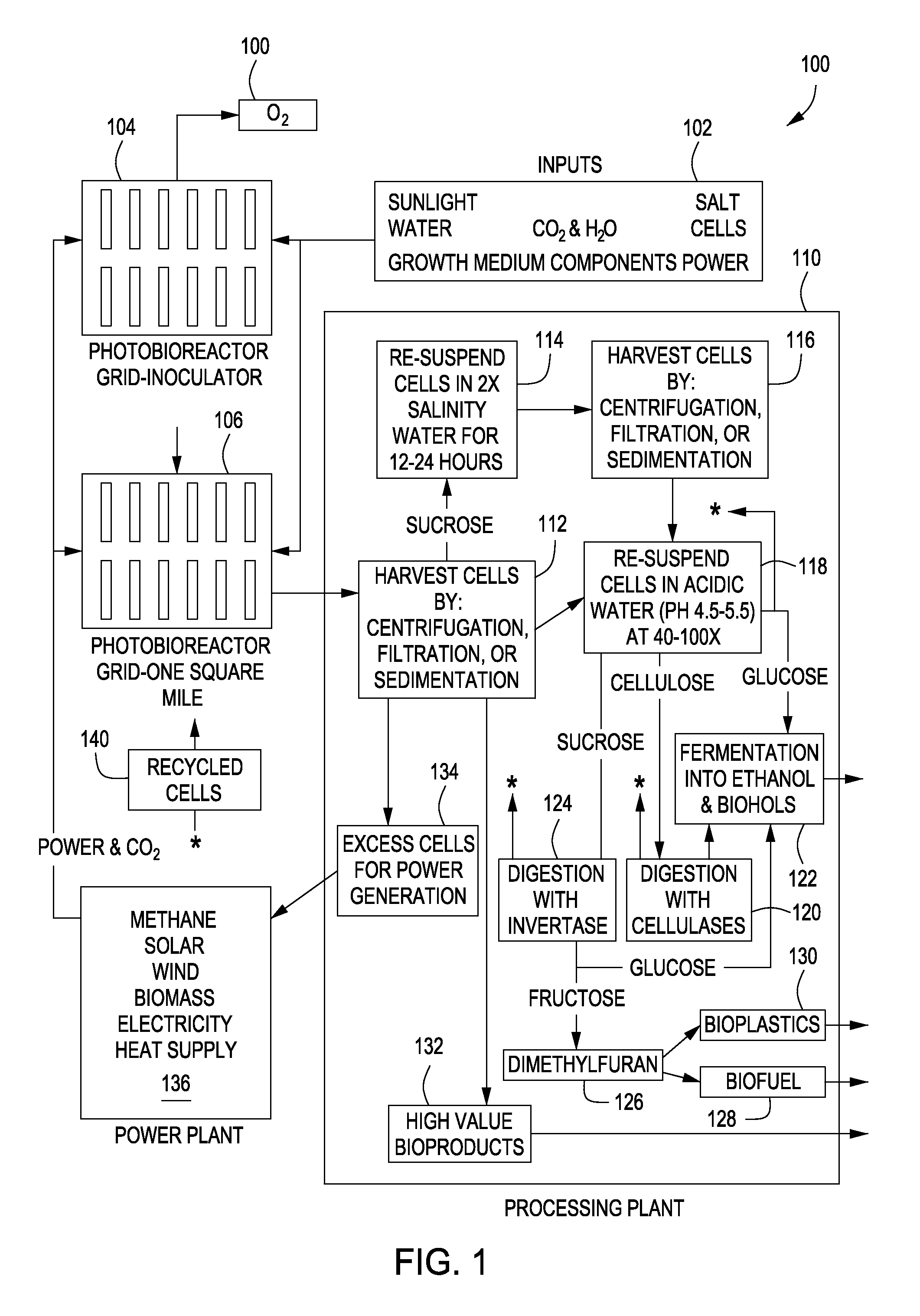
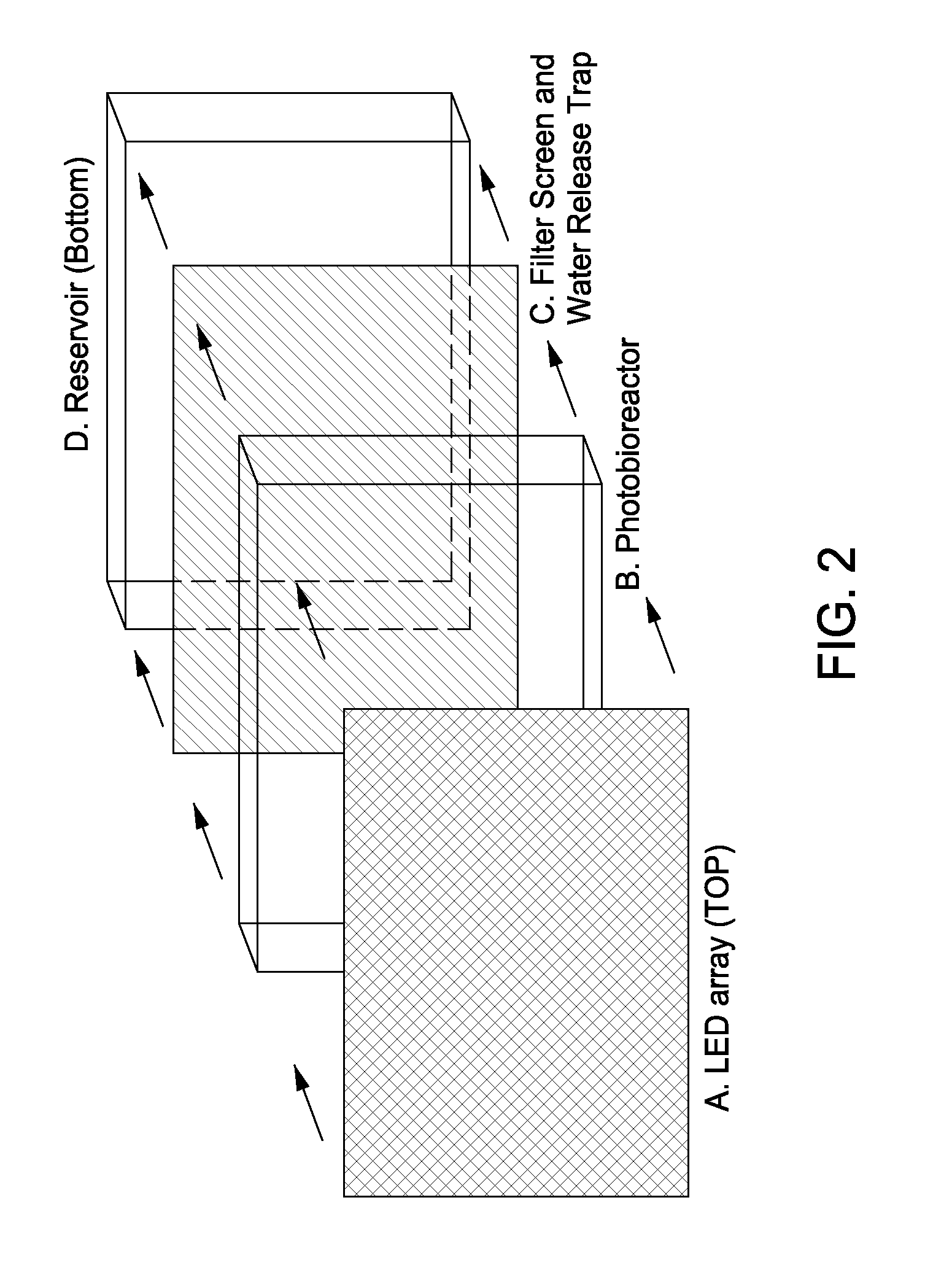
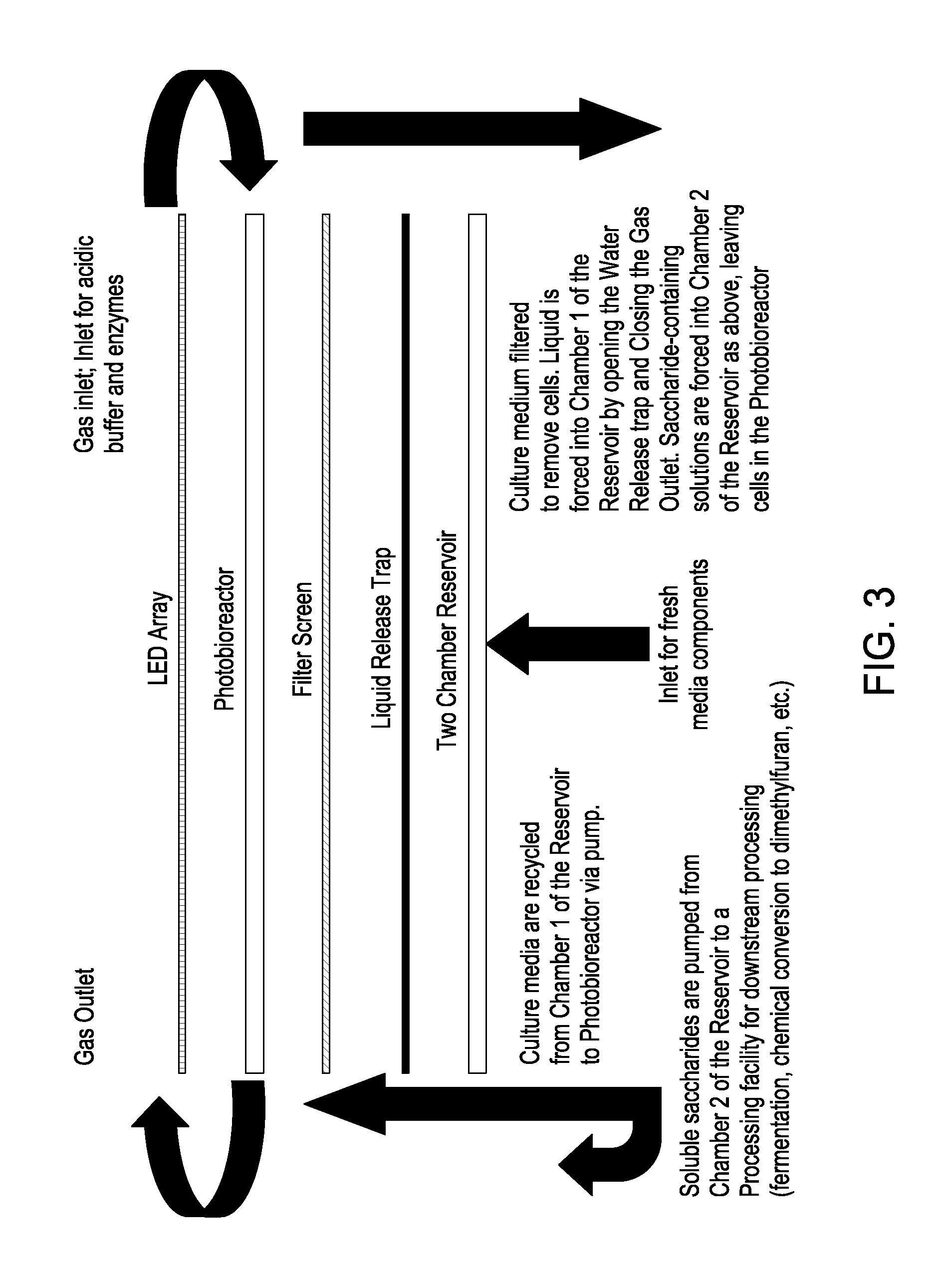
Expression of Foreign Cellulose Synthase Genes in Photosynthetic Prokaryotes (Cyanobacteria)
InactiveUS20080113413A1Large manufactureReduce crystallinityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhylum CyanobacteriaCellulose
The present invention includes compositions and methods for making and using cyanobacteria that include a portion of an exogenous cellulose operon sufficient to express cellulose. The compositions and methods of the present invention may be used as a new global crop for the manufacture of cellulose, CO2 fixation, for the production of alternative sources of conventional cellulose as well as a biofuel and precursors thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Artificial promoter libraries for selected organisms and promoters derived from such libraries
InactiveUS7199233B1Strong impactNone is suitable for purposeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleobase
An artificial promoter library (or a set of promoter sequences) for a selected organism or group of organisms is constructed as a mixture of double stranded DNA fragments, the sense strands of which comprise at least two consensus sequences of efficient promoters from said organism or group of organisms, or parts thereof comprising at least half of each, and surrounding intermediate nucleotide sequences (spacers) of variable length in which at least 7 nucleotides are selected randomly among the nucleobases A, T, C and G. The sense strands of the double stranded DNA fragments may also include a regulatory DNA sequence imparting a specific regulatory feature, such as activation by a change in the growth conditions, to the promoters of the library. Further, they may have a sequence comprising one or more recognition sites for restriction endonucleases added to one or both of their ends. The selected organism or group of organisms may be selected from prokaryotes and from eukaryotes; and in prokaryotes the consensus sequences to be retained most often will comprise the −35 signal (−35 to −30): TTGACA and the −10 signal (−12 to −7): TATAAT or parts of both comprising at least 3 conserved nucleotides of each, while in eukaryotes said consensus sequences should comprise a TATA box and at least one upstream activation sequence (UAS). Such artificial promoter libraries can be used, e.g., for optimizing the expression of specific genes in various selected organisms.
Owner:JENSEN PETER RUHDAL +1
Novel pesticidal toxins
A novel pesticidal toxin that is highly active against a wide range of lepidopteran insect pests is disclosed. The DNA encoding the pesticidal toxin can be used to transform various prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms to express the pesticidal toxin. These recombinant organisms can be used to control lepidopteran insects in various environment.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Biological species identification method based on genetic barcode
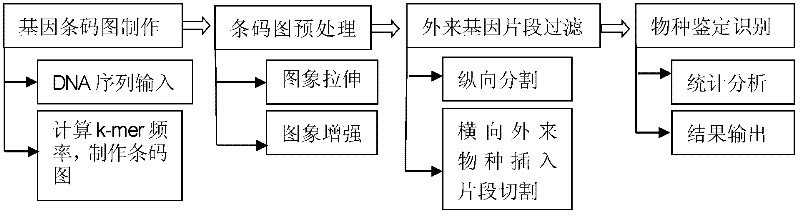
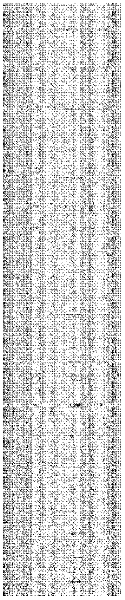
InactiveCN102332064AGenomic signature recognition at a glanceHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideBiological species
The invention discloses a biological species identification method based on a gene barcode, which comprises the following steps of: 1. the production of a gene barcode image and a gene barcode image database: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nucleotide sequences of 617 prokaryotes are downloaded from a website http: / / www. ncbi. nlm. nih. gov / , and the gene barcode image of species to be identified is produced according to the prior art; 2. the pre-processing of the gene barcode image: the gray scale of [0, L] of the gene barcode image is stretched to [0,255] by gray scale stretching, and the contrast of the gene barcode image is enhanced by gray scale enhancement; 3. the retrieval of foreign gene fragments of the gene barcode image: the longitudinal division of the gene barcode image is carried out, and the horizontal foreign gene fragments are searched; 4. species identification: the similarity quantity between the two species is determined, namely, the spatial distance between the two species is determined, and the species identification and result output are carried out according to the similarity quantity.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Methods of regulating expression of genes or of gene products using substituted tetracycline compounds
The present invention relates, at least in part, to the use of substituted tetracycline compounds for regulation of expression of nucleic acids operably linked to a tetracycline operator system. The invention pertains to compounds used in a regulatory system which utilizes components of the Tet repressor / operator / inducer system of prokaryotes to regulate gene expression in cells. Use of certain substituted tetracycline compounds, as featured in the methods of the invention, result in improved dose-response results when compared to those for e.g., tetracycline and doxycycline. Certain methods of the invention thus allow for enhanced control of the Tet repressor / operator / inducer system in regulating gene expression in cells.
Owner:MINTZ LEVIN COHN FERRIS GLOVSKY & POPEO PC
Methods for optimizing the secretion of protein in prokaryotes
Methods are provided for producing recombinant proteins by utilizing expression vectors carrying nucleic acids encoding the proteins, and secretory signal sequences to direct the secretion of the proteins to the periplasm or extracellular medium. Expression vectors which encode a fusion protein comprising a carrier protein and the protein are also provided, as are host cells transformed with the expression vectors.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
Immunoglobulin Fc libraries
Methods and composition for the screening and isolation of aglycosylated antibody Fc domain polypeptides. For example, in certain aspects methods for identifying aglycosylated Fc domains that bind to Fc receptors or preferentially bind to particular Fc receptors are described. Furthermore, the invention provides aglycosylated Fc domains that bind to Fc receptors with high affinity. Enhanced methods and media for prokaryotic based interaction screening are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Highly regulable promoter for heterologous gene expression
InactiveUS6030807APromote reproductionModulate transcriptional activityBacteriaSugar derivativesL-ArabinoseOperon gene
The invention relates to an operon encoding enzymes involved in the utilization of L-arabinose, to the promoter derived therefrom, and to expression systems utilizing the promoter. The promoter is particularly useful for expression of DNA sequences in prokaryotes because of their inducibility and repressibility of the promoter. The invention also relates to the enzymes of the operon, and antibodies thereto.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
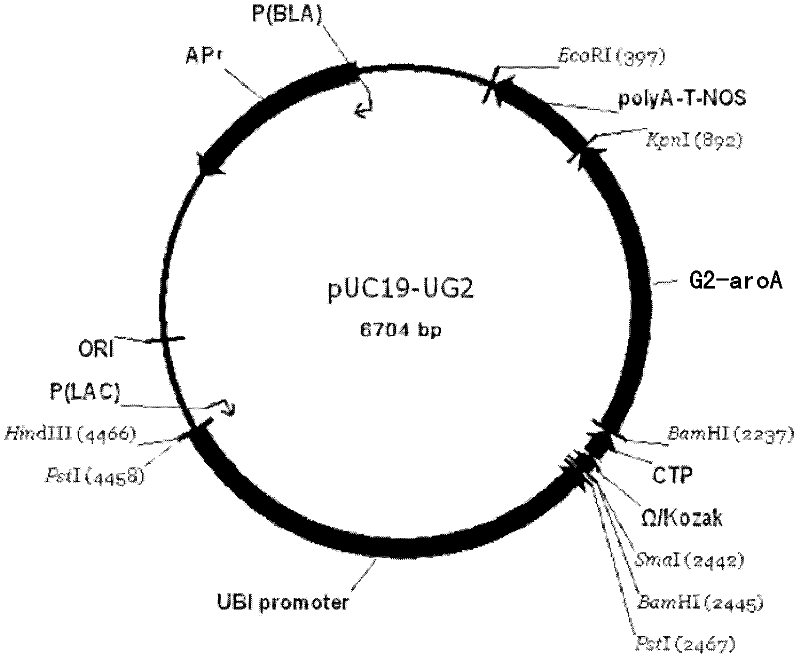
Recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment containing roundup ready gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment containing a roundup ready gene and application thereof. The recombinant DNA fragment provided by the invention comprises the following components from 1) to 3): 1) a promoter; 2) the roundup ready gene which is promoted by the promoter to be transcribed, the nucleotide sequence of the roundup ready gene is a) or b), wherein a) represents a sequence 2 in a sequence table, and b) represents a protein which has at least 98% of identity with the sequence 2 in the sequence table and is shown by a coding sequence 9; and 3) tanscription termination sequence. Compared with the transgenic corn which contains the recombinant DNA fragment in which prokaryote roundup ready gene G2-aroA is transplanted, the transgenic corn which is transplanted with the recombinant DNA fragment provided by the invention is obviously higher in the expression quantity of G2-aroA protein; and the transgenic corn is also obviously higher in the glyphosate tolerance.
Owner:BEIJING ORIGIN SEED TECH
Production and secretion of glucose in photosynthetic prokaryotes (cyanobacteria)
InactiveUS7803601B2Reduce crystallinityEasy to degradeBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesBiotechnology
The present invention includes compositions and methods for making and using an isolated cyanobacterium that includes a portion of an exogenous bacterial cellulose operon sufficient to express bacterial cellulose, whereby the cyanobacterium produces extracellular glucose. The compositions and methods of the present invention may be used as a new global crop for the manufacture of cellulose, CO2 fixation, for the production of alternative sources of conventional cellulose as well as a biofuel and precursors thereof.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
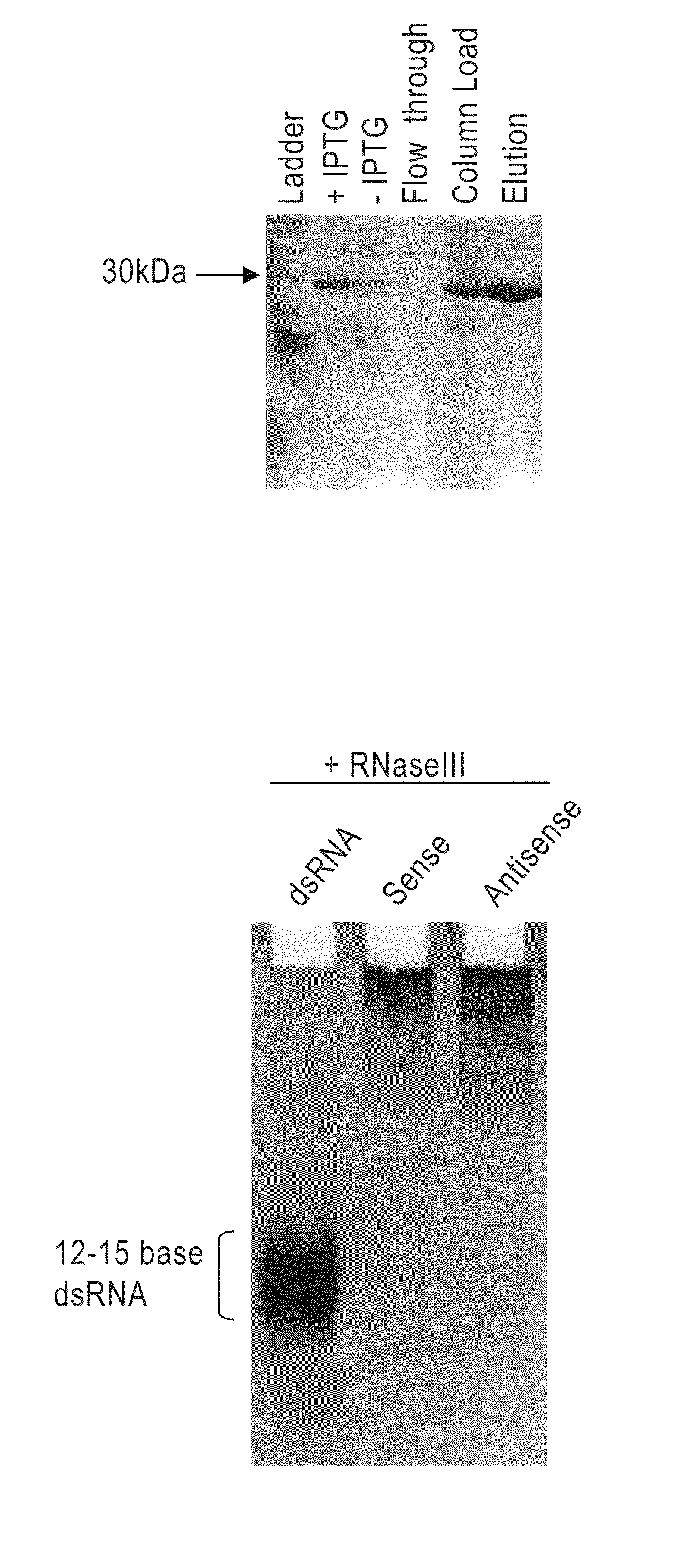
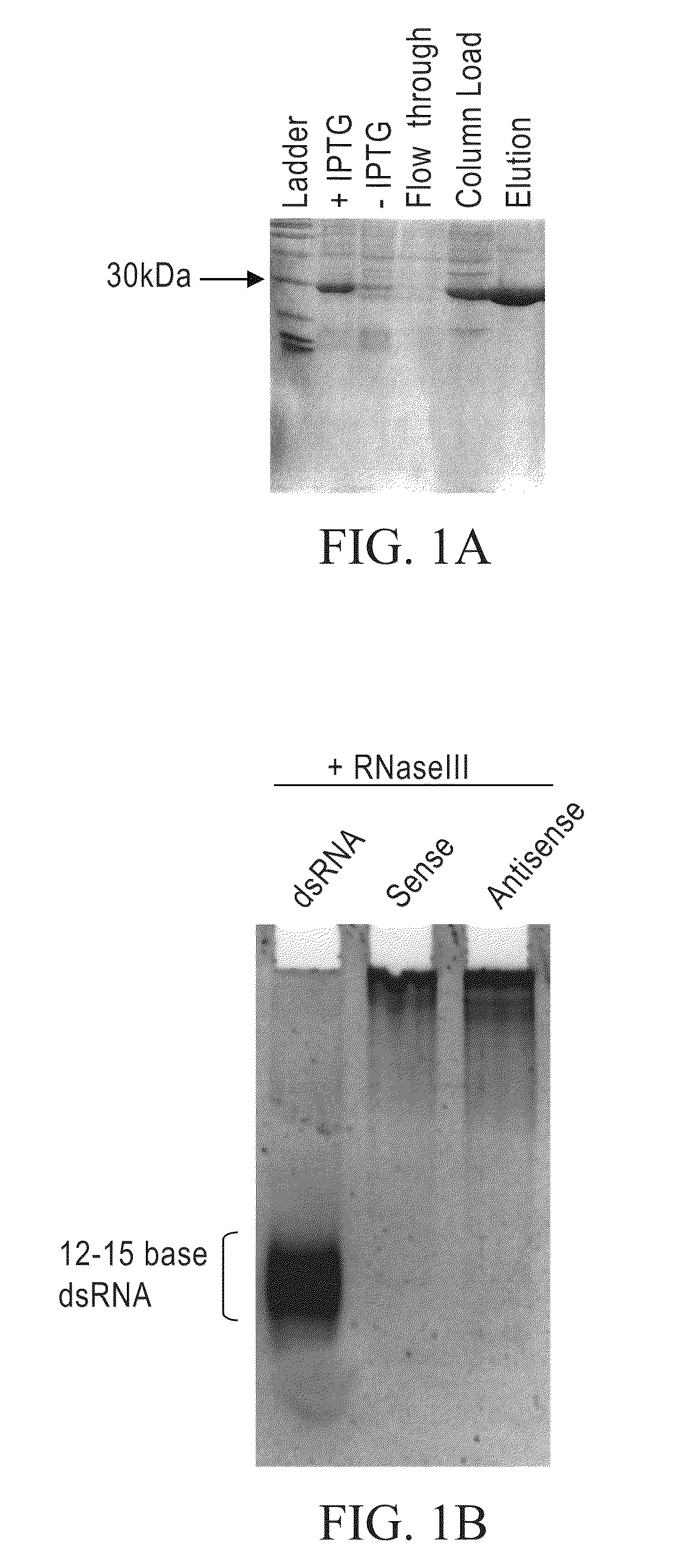
Methods and compositions relating to polypeptides with rnase iii domains that mediate RNA interference
InactiveUS20100075423A1Retain activitySugar derivativesActivity regulationRNase III activityBiochemistry
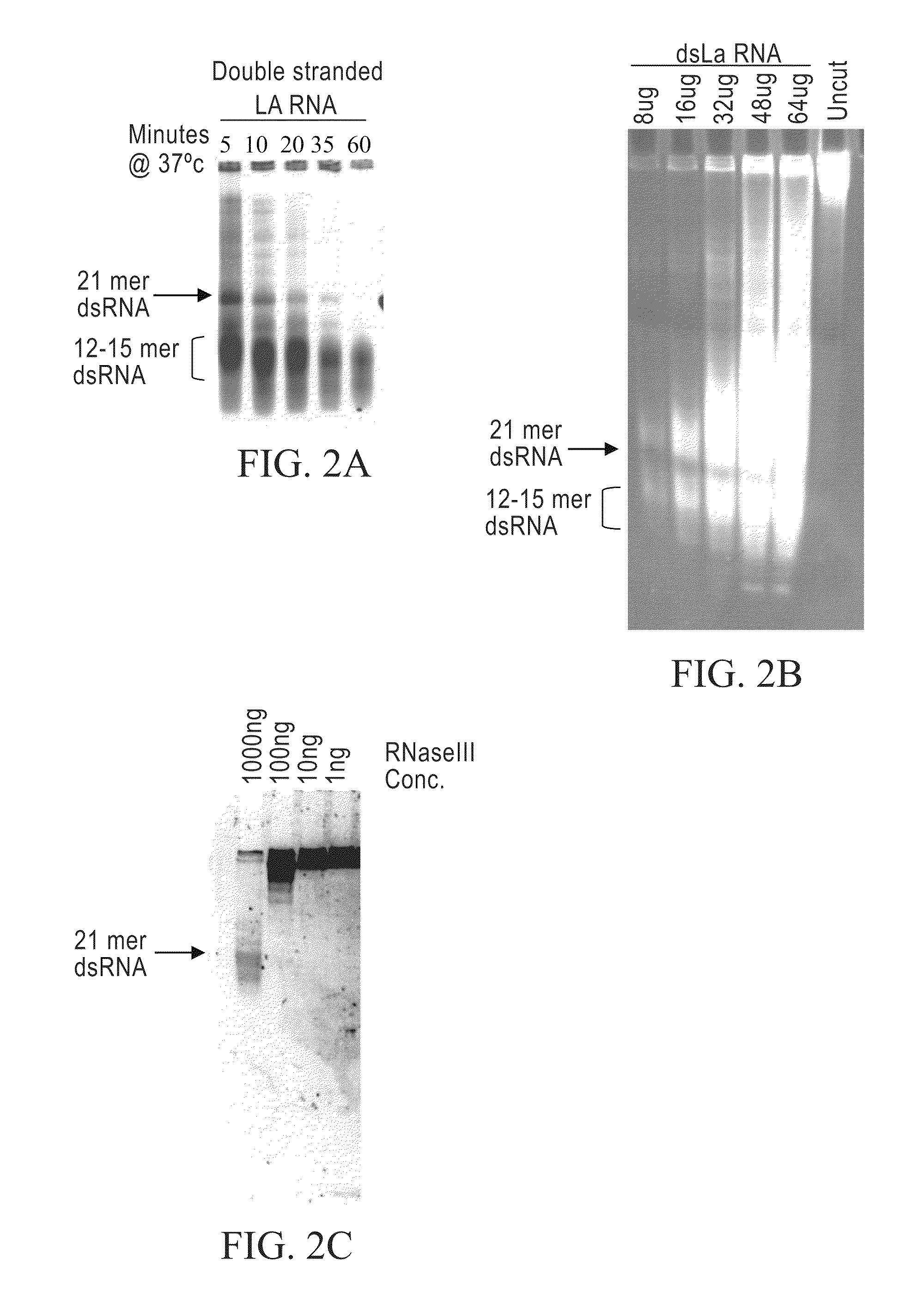
The present invention concerns methods and compositions involving RNase III and polypeptides containing RNase III domains to generate RNA capable of triggering RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) in a cell. In some embodiments, the RNase III is from a prokaryote. RNase III activity will cleave a double-stranded RNA molecule into short RNA molecules that may trigger or mediate RNAi (siRNA). Compositions of the invention include kits that include an RNase III domain-containing polypeptide. The present invention further concerns methods using polypeptides with RNase III activity for generating RNA molecules that effect RNAi, including the generation of a number of RNA molecules to the same target.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Efficient soluble expression and purification method of Abeta42 in escherichia coli
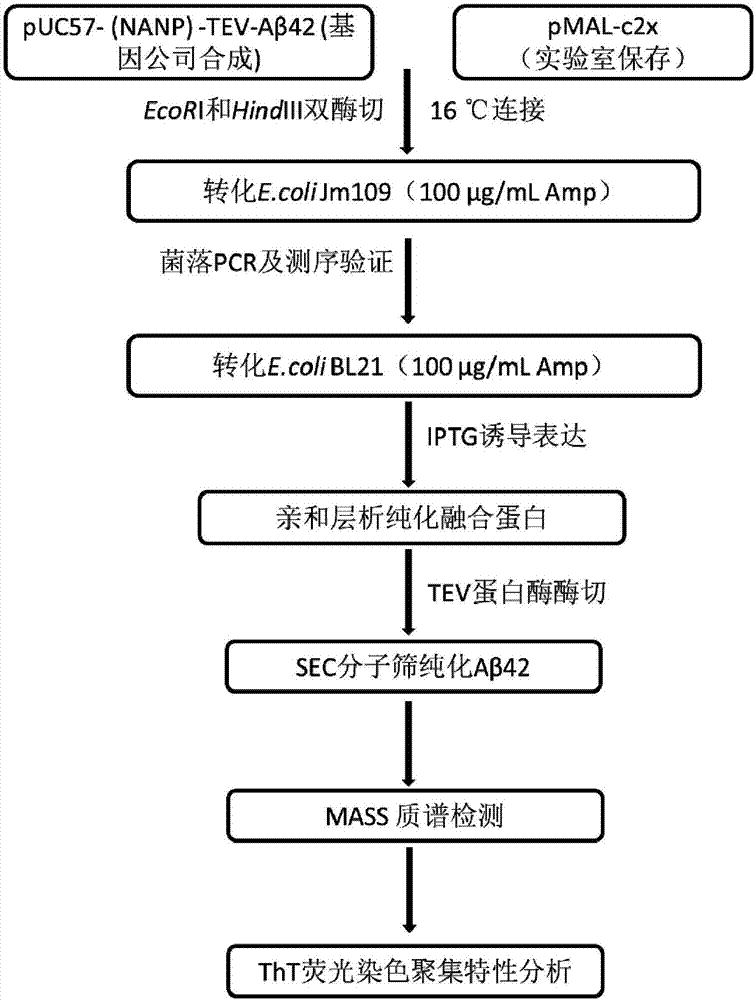
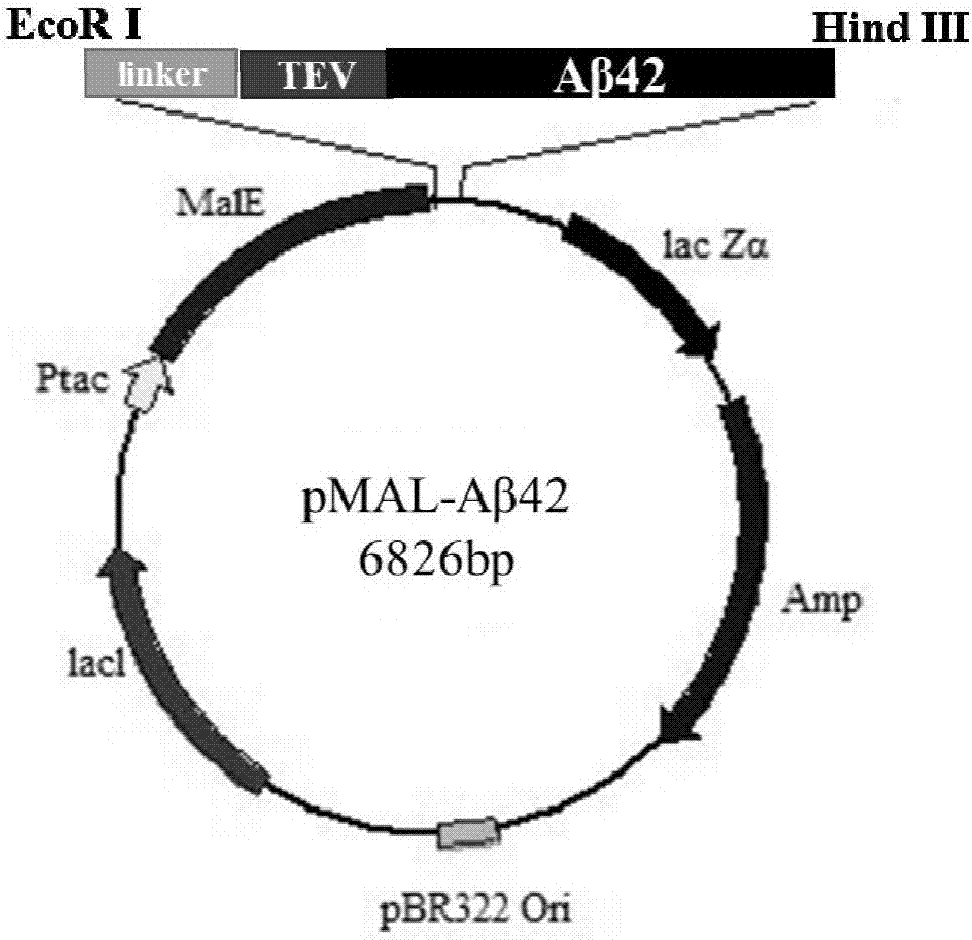
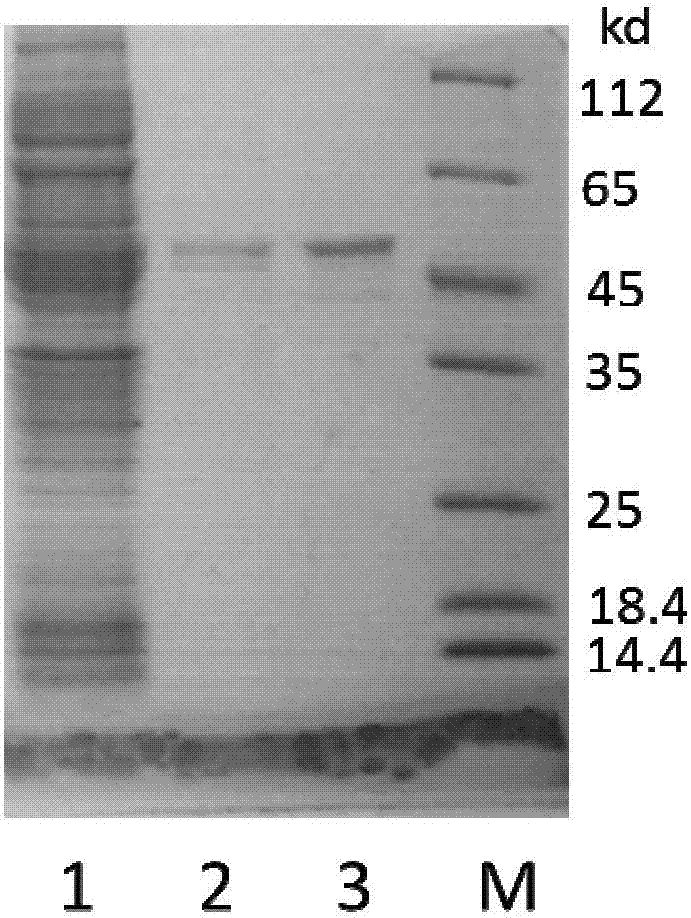
ActiveCN107245494AHigh expressionHigh purityNucleic acid vectorFusion with protease siteBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the fields of biotechnologies and genetic engineering technologies and in particular relates to an efficient soluble expression and purification method of Abeta42 in escherichia coli. An Abeta42 expression system constructed by the invention provides a construction method of an expression vector of prokaryote for soluble fusion expression of human amyloid protein Abeta42 and the expression vector is introduced into an escherichia coli expression host; target Abeta42 with high-purity bioactivity is obtained through induced expression, protein enzyme digestion, two-step purification and identification. According to the method provided by the invention, an escherichia coli expression system and fusion protein have the characteristics of high expression efficiency, large expression amount, low cost, easiness for operation and the like; an expressed Abeta42 polypeptide has the advantages of no residues, high purity, high productivity and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com