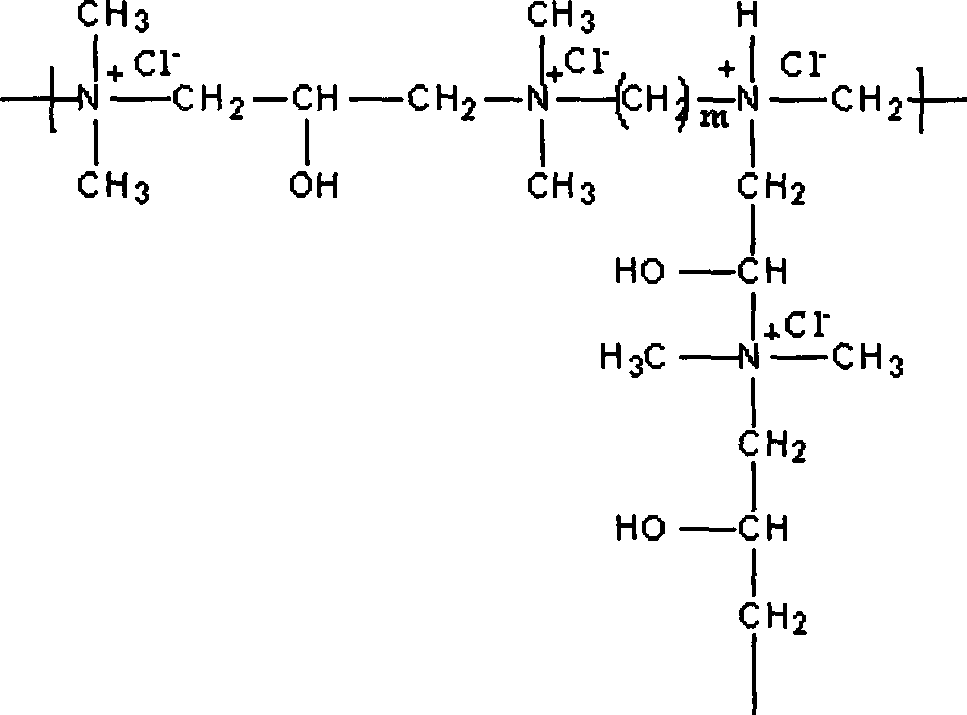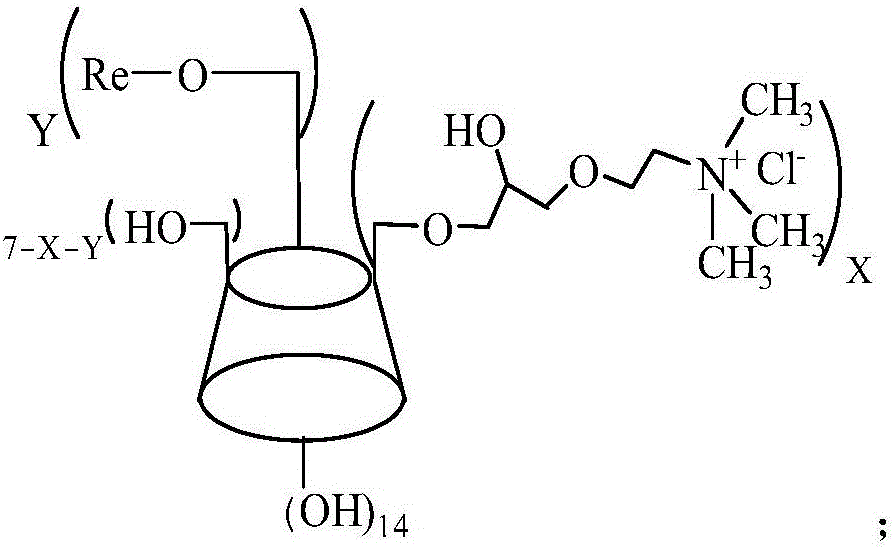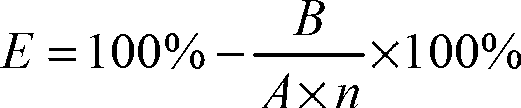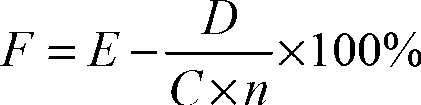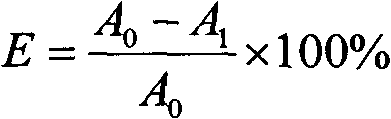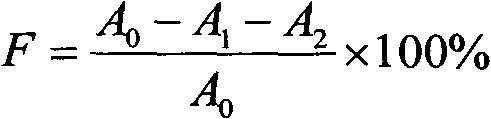Patents
Literature
441 results about "Salt free" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
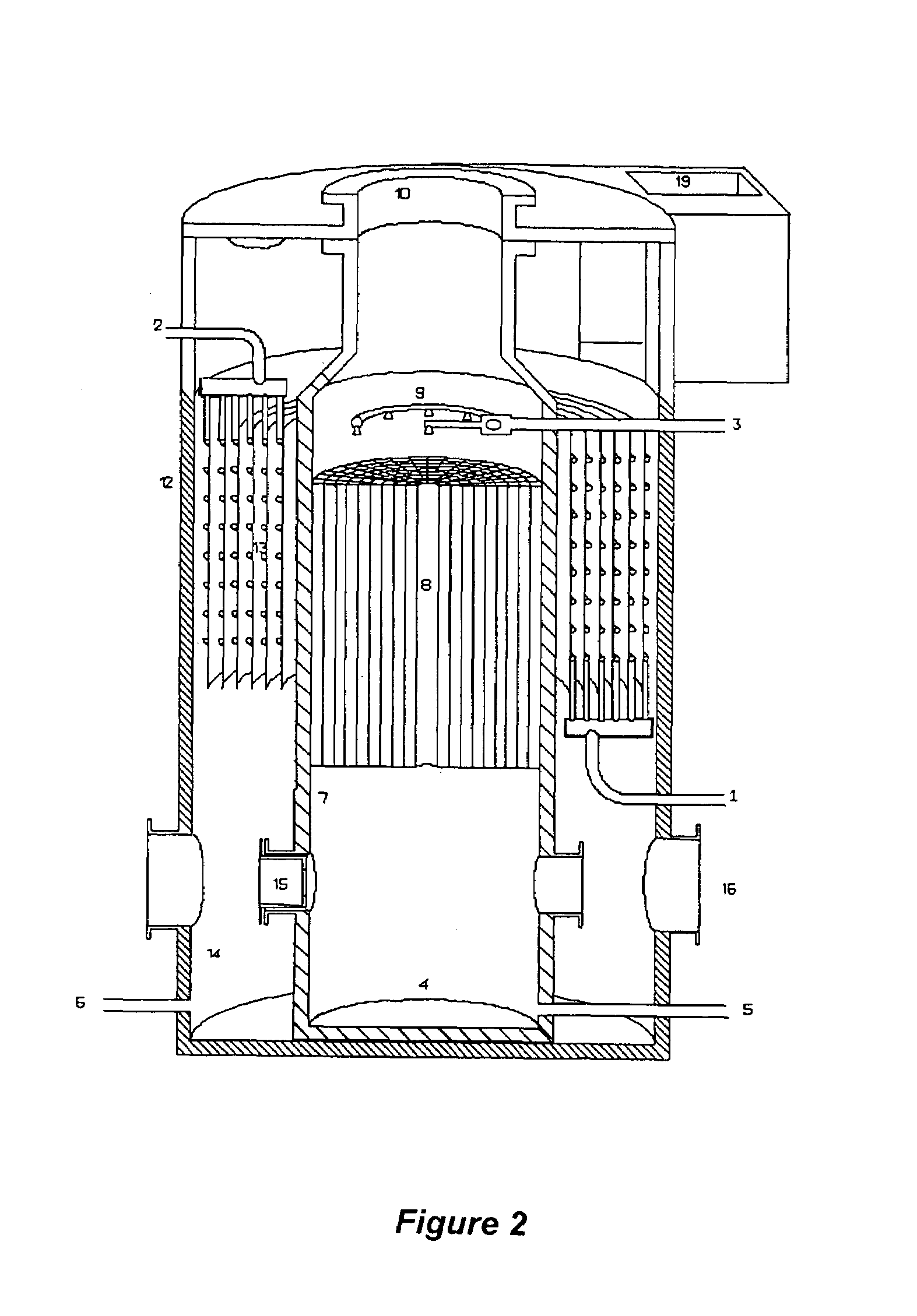
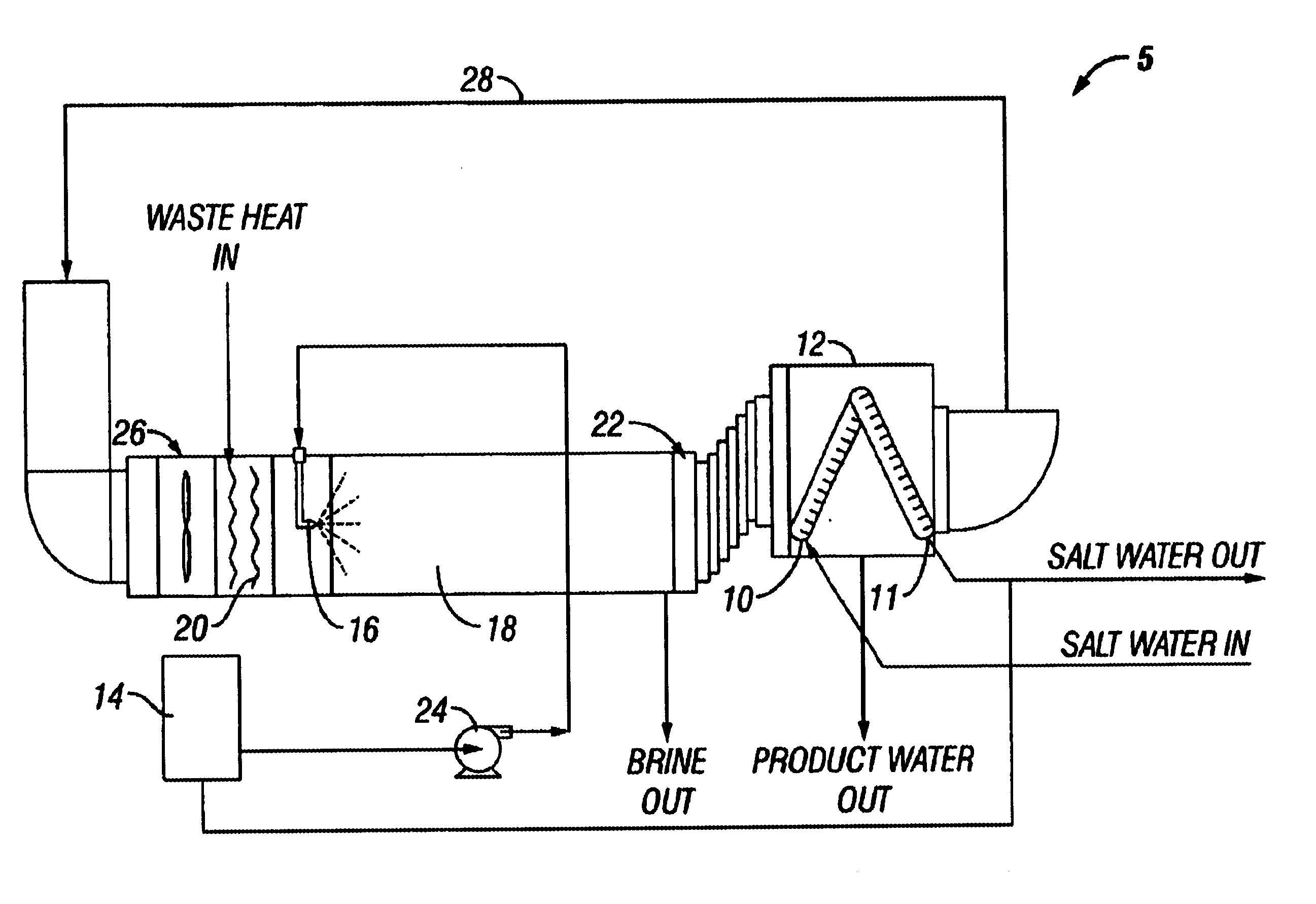
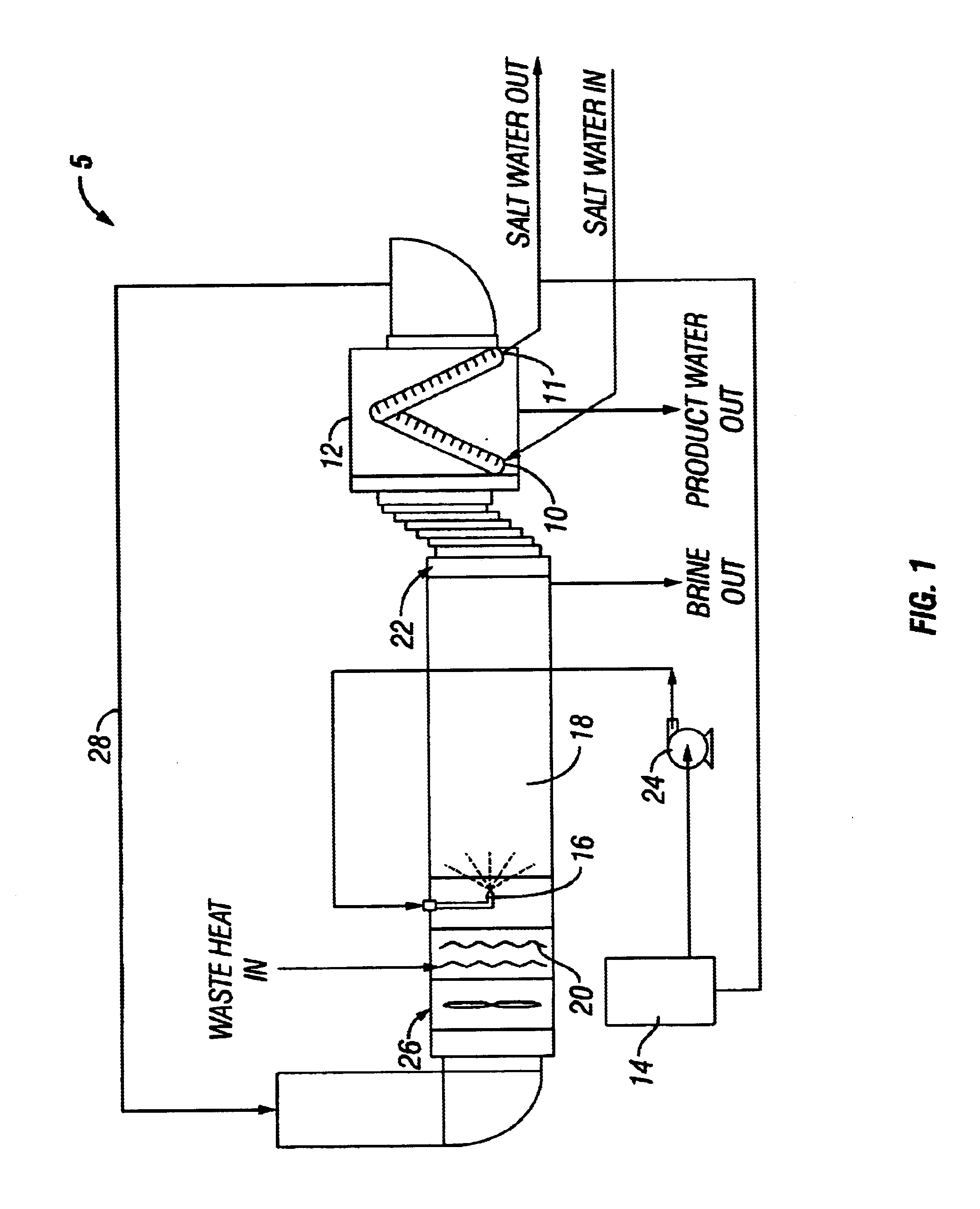
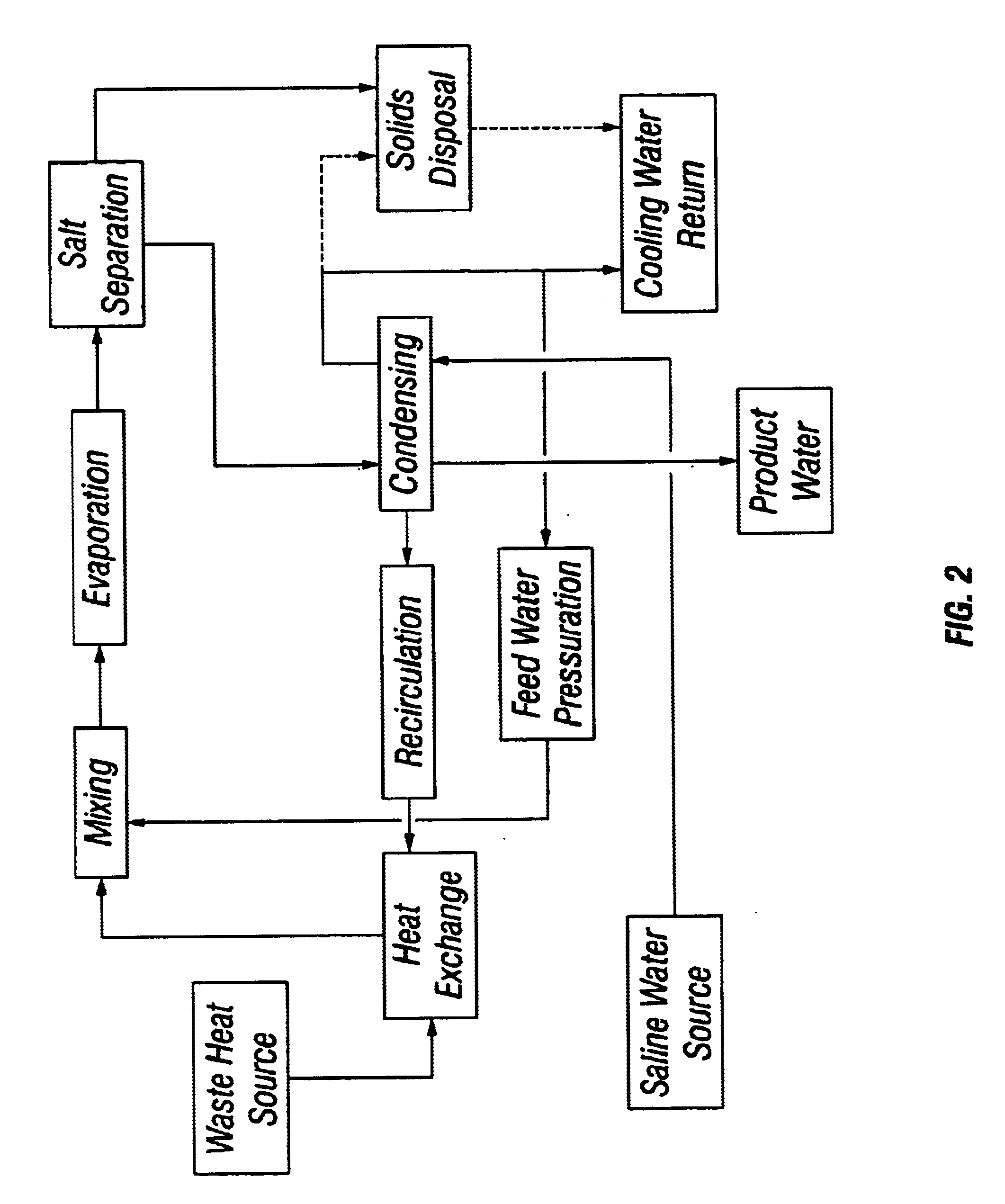
Apparatus and method for thermal desalination based on pressurized formation and evaporation of droplets
A method for removing dissolved solids, particularly salts, from water. An apparatus for performing the inventive method is disclosed. The aqueous solution to be treated, for example sea water, is atomized using special non-pneumatic nozzles, and sprayed into an evaporation chamber through which air, heated by waste heat, is blown. The micro-droplets undergo rapid evaporation in the chamber, resulting in the separation of the salt solids from the vapor phase of the water. The mixture of suspended solids and water vapor is filtered to remove and collect the salts, and the water vapor is condensed to collect the salt-free water.
Owner:AQUASONICS RSE INC
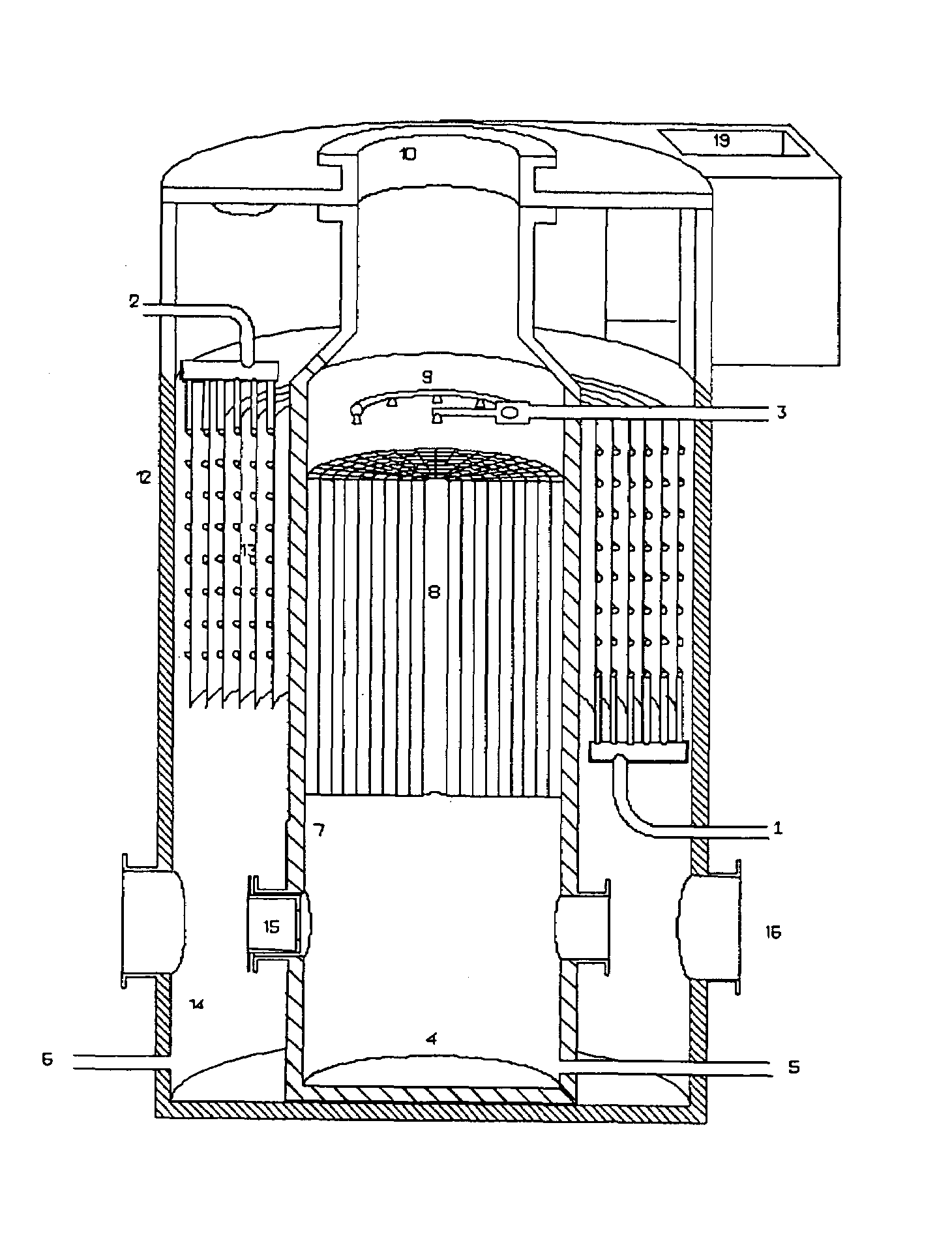
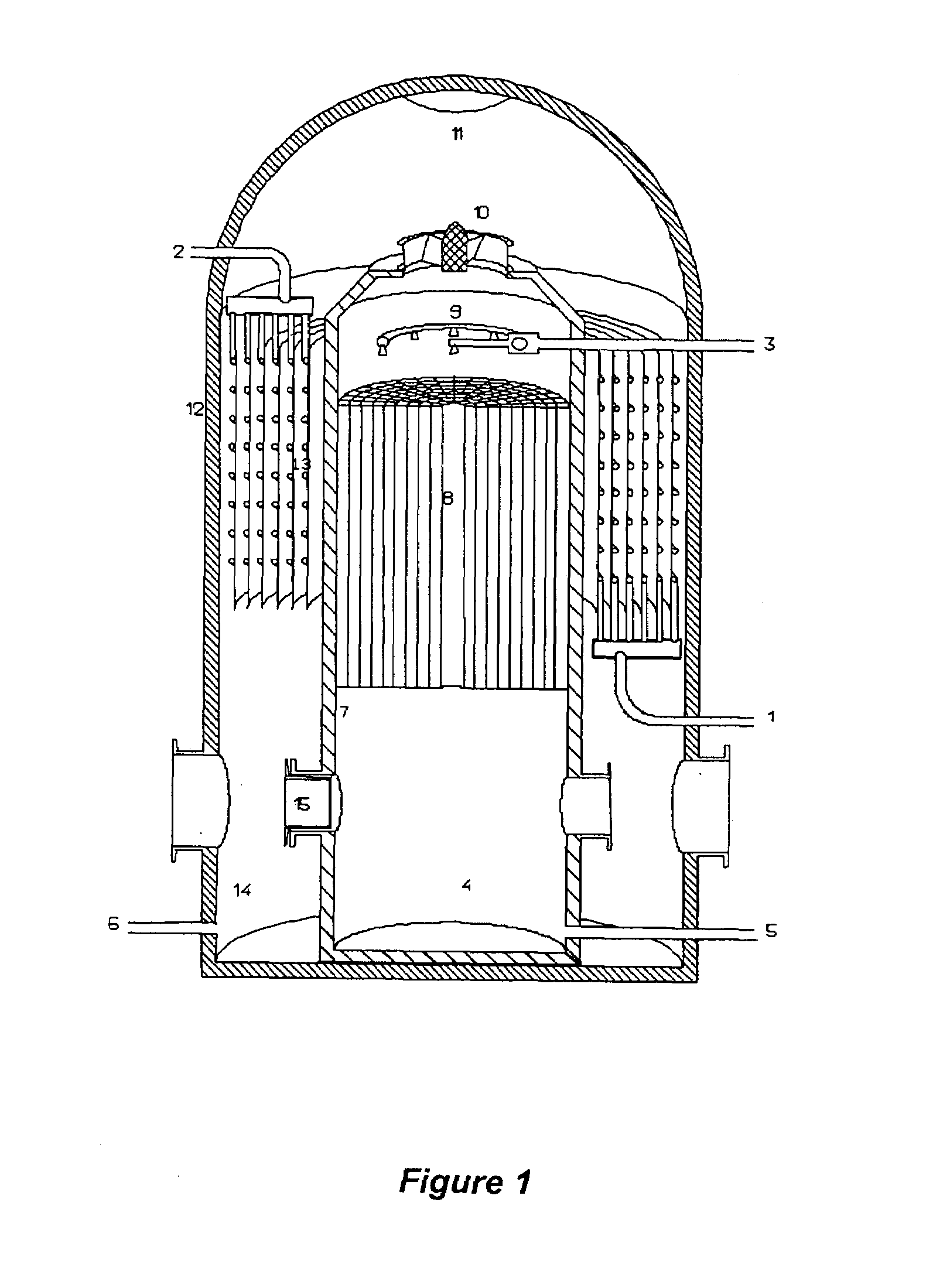
Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation
ActiveUS20110044824A1Reduce excessive wasteMaximizing membrane efficiencyFlexible member pumpsServomotorsHigh concentrationConcentration ratio
A method and apparatus for renewable power generation utilizes the chemical potential dissimilarity between solutions of differing ionic formulations. A train is formed by a sequentially ordered set of a plurality of cells in which each successive cell is related to the preceding cell. Each cell has pumping means and hydro-power generation turbine means to form a closed hydraulic loop configured for specified volumetric and flow capacity. Adjacent cells share semipermeable membranes. Each cell is charged with a brine of specified ionizable inorganic salt quantity and type with the brine being cycled in a controlled concentration-pressure loop, with each of the cells operating at progressively increasing concentration and osmotic pressure ratio. A continuous and constant flow rate of substantially salt-free permeate flux is maintained across each cell, the flux being osmotically induced from low salt concentration water being fed at the first cell in the train and exiting at the last cell along with the discarded high concentration water brine. The salt-free permeate flux is continuously induced, in symbiotic mode, through the shared membranes, driven by the chemical influence of concentration potential field bounded by water of low to no salt concentration on one end of the train and by brine of high salt concentration on the other end of the train with sufficient concentration difference to provide driving force for said plurality of cells, while maintaining adequate concentration difference between adjacent cells to enhance osmosis function, as well as defining a concentration ratio within each cell to ensure a net positive power generation.
Owner:KELADA MAHER ISAAC
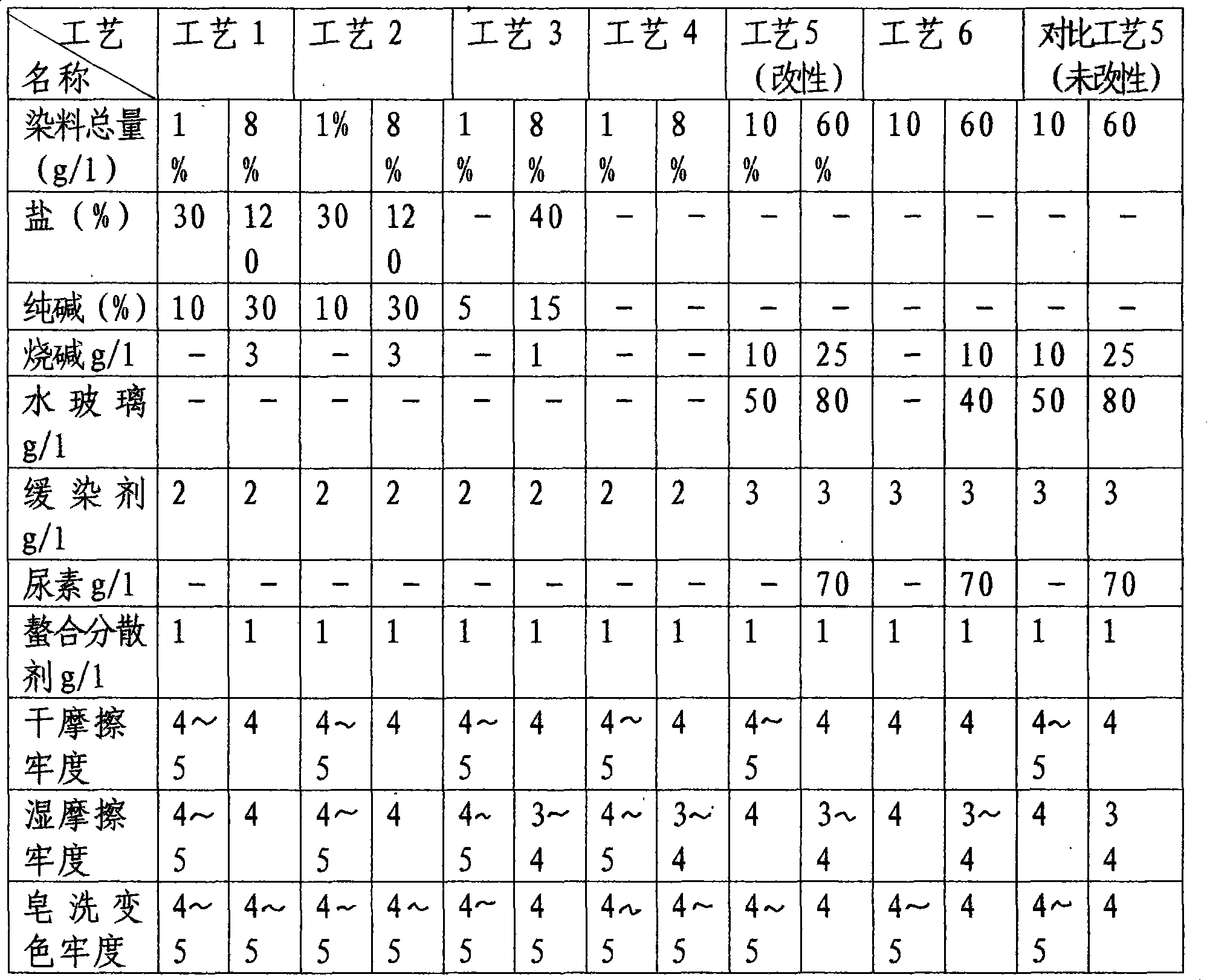
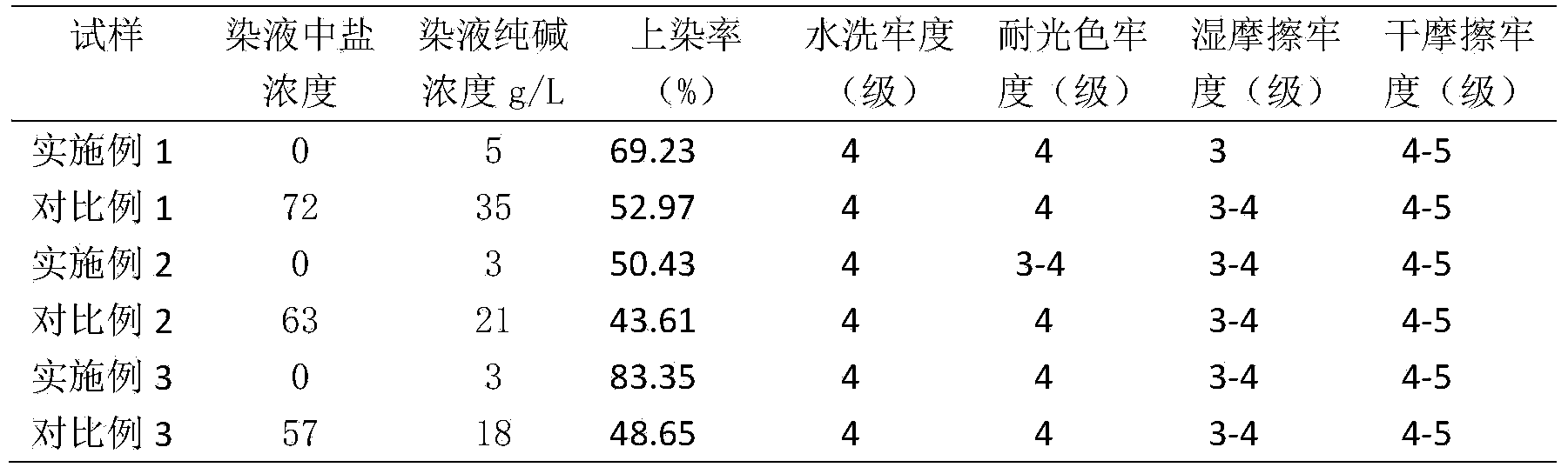
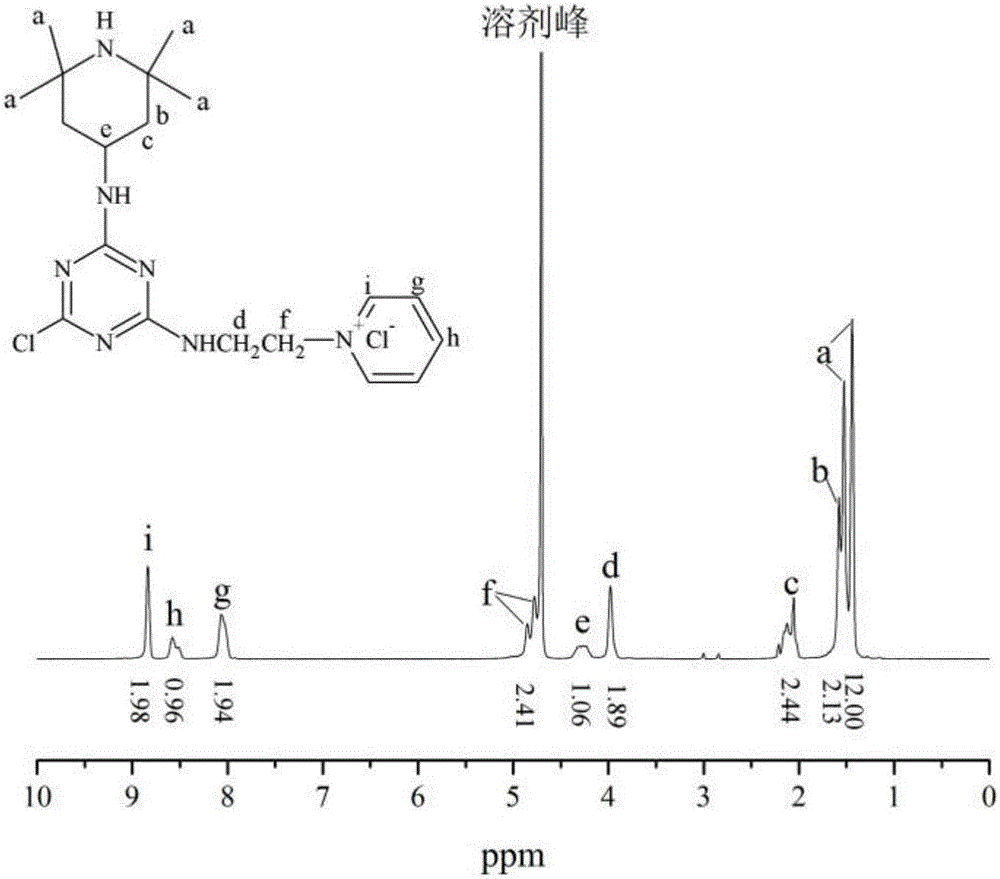
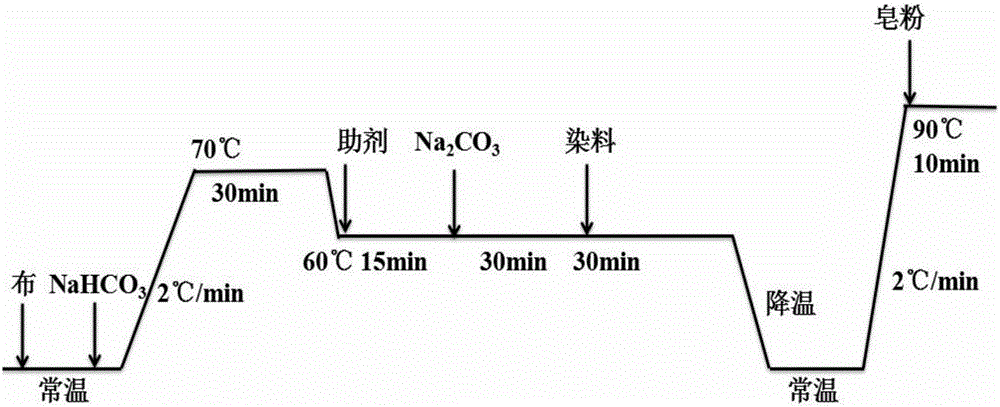
Ecological low-salt dyeing and finishing agent for reactive dyes and preparation method and applications thereof
The invention discloses an ecological low-salt dyeing and finishing agent for reactive dyes, which comprises a crosslinking cationic modifier A and a branched cationic modifier B, wherein the weight ratio of the crosslinking cationic modifier A to the branched cationic modifier B is (30-50): 50. The ecological low-salt dyeing and finishing agent for reactive dyes disclosed by the invention has the advantages that in the process of treating cotton fibers by using the crosslinking cationic modifier and the branched cationic modifier, the inner portions and surfaces of the fibers can be modified through cationization, therefore, the utilization rate of reactive dyes can be improved, and the dye-uptake rate and fixation rate of cotton fabrics are significantly higher than those in conventional dyeing; salt-free low-alkali dyeing even salt-free alkali-free dyeing can be achieved, and dyeing wastewater can be recycled for secondary utilization; and the color fastness to washing and the color fastness to rubbing are consistent with those of conventional cotton fabrics.
Owner:南通曙光染织有限公司
Salt free dyeing with reactive dye
The invention provides a reactive dye salt-free dyeing process for cotton fiber, which comprises the following steps of pre-treatment, modified treatment, dyeing, post-treatment and so on. The modified treatment is that a copolymer of poly epichlorohydrin and polyamine used for cotton fiber is pretreated and cleaned under high temperature and alkali conditions before a special reactive dye used for a leveling agent is added to dye the cotton fiber, and the dyeing process is completed under salt-free, alkali-free or low-alkali conditions, thereby improving dyeing and fixing rate of the dye. The reactive dye salt-free dyeing process simplifies the prior dyeing process, is simple and easy to understand for operators, reduces influences of human operation factors on dyeing process and dyeing quality, and lowers production cost and sewage treatment cost overall.
Owner:胡红湘
Salt-free pad steam continuous dyeing method for active dye
InactiveCN101200859AFor quick replacementGood reproducibilityDyeing processLiquid/gas/vapor textile treatmentTextile printerSalt free
The present invention relates to a continuous saltless pad-steam dyeing method with reactive dyes, which belongs to the novel technical field of textile printing and dyeing. After being singed, desized, boiled, bleached and mercerized, the half-finished product of cellulosic fibre woven fabric is dyed in the process of the continuous dyeing technique of padding, steam fixation, water washing, soaping, water washing and drying by the reactive dyes. The half-finished product of the preprocessed cellulosic fibre woven fabric is produced by pad dyeing, steaming and water washing, wherein, dyeing solution is composed of M reactive dyes, leveling agent, fixation alkali agent and water, and the mixture ratio is as follows: M reactive dyes: 0.01 percent to 10 percent, leveling agent: 0.1 percent to 0.2 percent, fixation alkali agent: 1.5 percent to 4 percent, and water: balance. The method is different from the conventional continuous dyeing technique of padding, drying, padding and steaming, which uses reactive dyes, and also different from the shortened wet-steaming technique with reactive dyes. On the conventional continuous padding machine, the novel method can fulfill the whole process of reactive dyeing without a hot-air padding machine and only with a developing and soaping range, thus greatly saving energy and reducing cost.
Owner:SHANXI CAIJIA PRINTING & DYEING
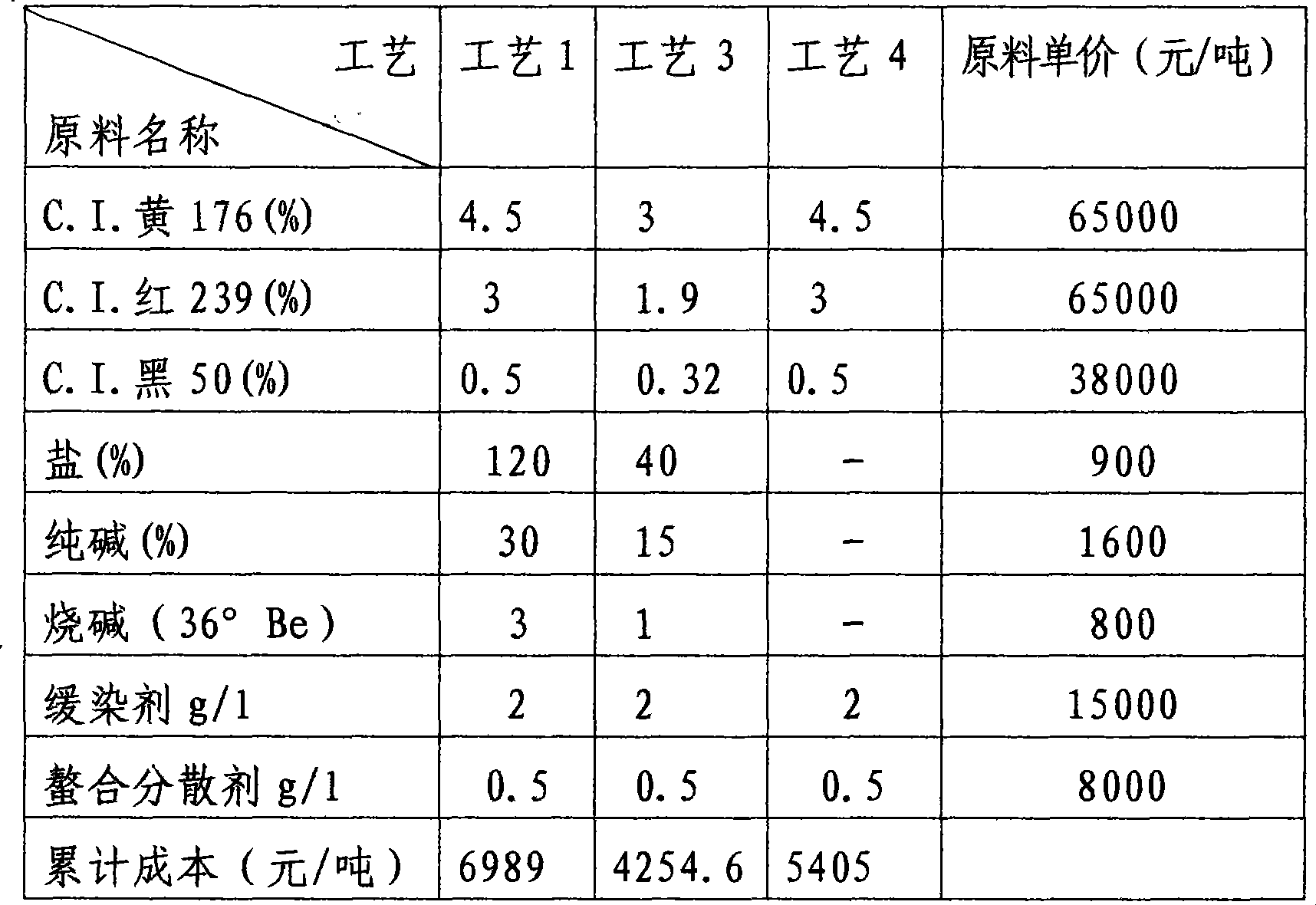
Recovery method of highly pure lactic acid and alkyl lactate
InactiveUS20120142945A1Efficient separationRecovering highly pure lactic acid more economicallyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationLiquid productRecovery method
A method for recovery of highly pure alkyl lactate and lactic acid is provided, which includes a step 1 for producing source liquid comprising lactic acid or ammonium lactate; a step 2 for dehydrating the source liquid product of step 1; a step 3 for producing liquid mixture by sequentially adding and stirring alcohol and acid solution to the dehydrated source liquid; a step 4 for separating and removing ammonium salt precipitation from the liquid mixture of step 3; a step 5 for producing alkyl lactate from ammonium salt-free liquid mixture by esterification reaction; and a step 6 for separating alcohol and alkyl lactate by distillation from the mixture of step 5.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
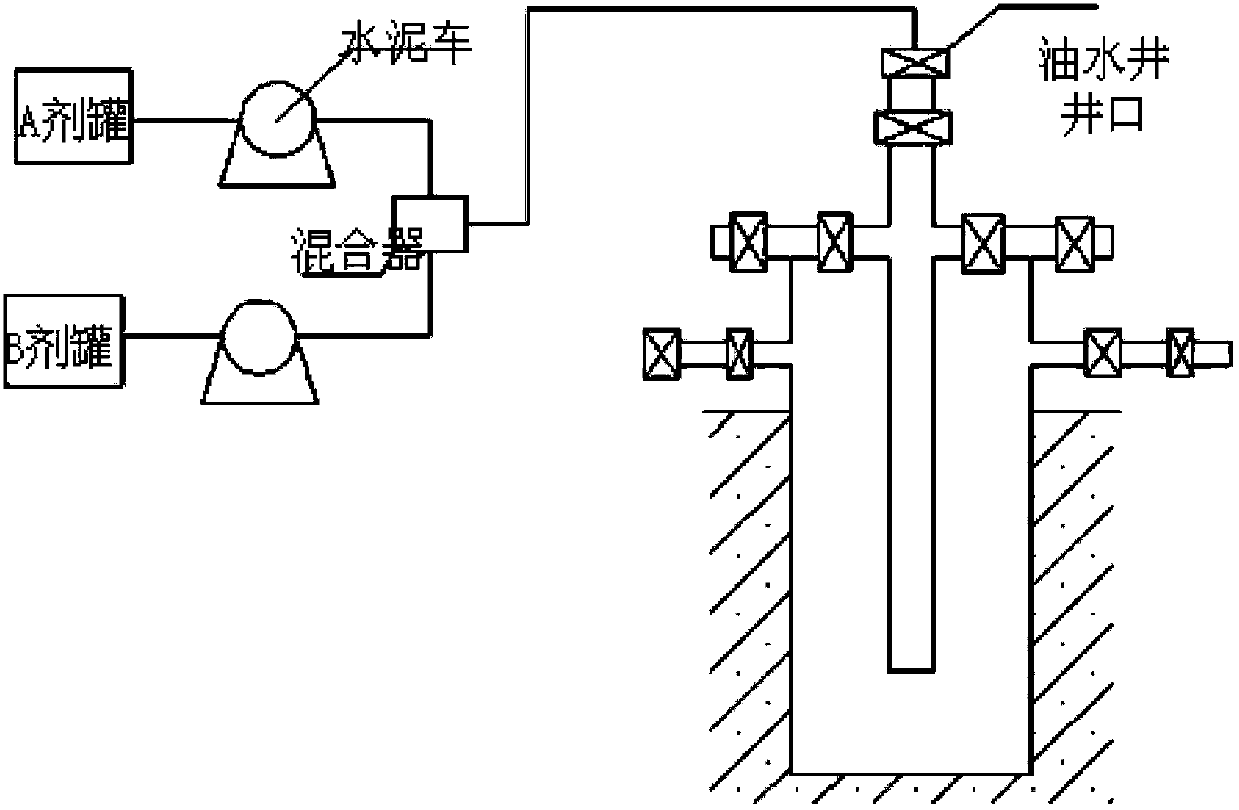
Self-generating foam blocking removal agent for oil-water well and blocking removal process
The invention relates to a self-generating foam blocking removal agent for an oil-water well and a blocking removal process. The foam blocking removal agent is composed of an agent formula A and an agent formula B, wherein the agent formula A is composed of inorganic acid, organic acid, quinoline quaternary ammonium salt, alkynol, iodine salt, imidazoline acetate, polyethenoxy ether sulfonic acid, dodecyl trimethyl quaternary ammonium salt and clear water; and the agent formula B is composed of carbonate, peroxide, fluorosurfactant, salt-free imidazoline, ferric ion stabilizer, foam stabilizer and clear water. The blocking removal process comprises the following steps: injecting a certain amount of prepad fluid through a cementing truck; then, injecting the agent A through one cementing truck and the agent B through another cementing truck; after the injection of the agent A and the agent B is finished, injecting displacement fluid; then injecting clear water; and shutting in the well, and then performing flowback or directly transferring into production. According to the invention, based on the synergic effect between the surfactants, the injected blocking removal agent has blocking removal effect and simultaneously has profile control and displacement effect for an injection well; and the injected blocking removal agent has blocking removal effect and simultaneously has foam huff and puff effect on an oil well.
Owner:陕西一诺油气工程技术服务有限公司
Processing method of salt-free dyeing through activated dye
InactiveCN102899929AIncrease the adsorption rateImprove adsorption capacityDyeing processInorganic saltsOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a processing method of salt-free dyeing through activated dye, which includes the steps of: (1), acid pickling and enzyme washing of cotton fabric after the pretreatment of scouring and bleaching; (2) mixing water with organic solvent at volume ratio of (1:4)-(1:9) to form a mixed solution, and then adjusting the pH value of the mixed solution; and (3)dyeing the pretreated cotton fabric in 20-30 DEG C activated dye by using the mixed solution, then carrying out water scrubbing, acid pickling, soaping, hot-water scrubbing, color fixing and softening on the dyed cotton fabric, and finally recovering the solvent. With the processing method, the adsorption rate and the equilibrium adsorption amount of the activated dye are improved, and environmental and ecological problems caused when large quantity of inorganic salt is used are completely solved. In the dyeing process, the input of inorganic salt is omitted, so the operational techniques and the labor intensity in the dyeing process are effectively simplified and the production cost is reduced. Through a solvent recovery system, the solvent contained in the dyeing residue of the hydrosolvent is recovered for cycle use. Therefore, the recovery and the recycling of the resource are realized, the production cost is saved and the pollution to the environment is alleviated.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
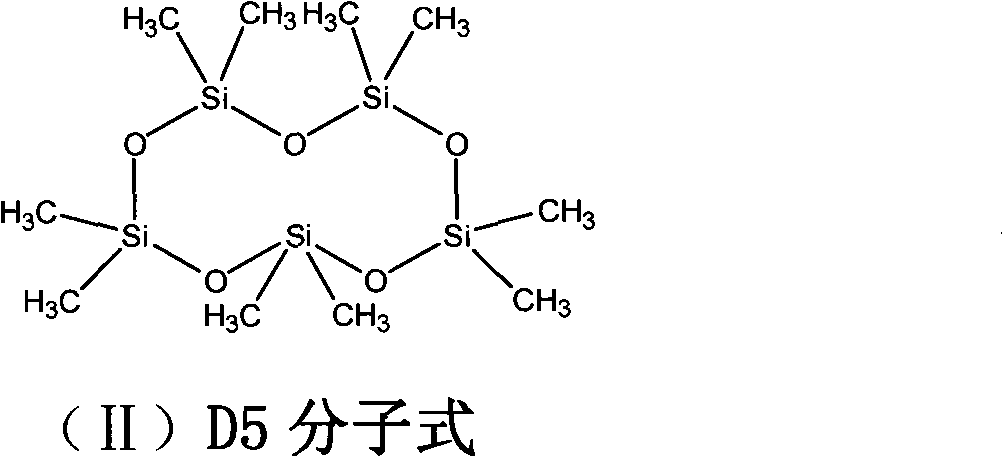
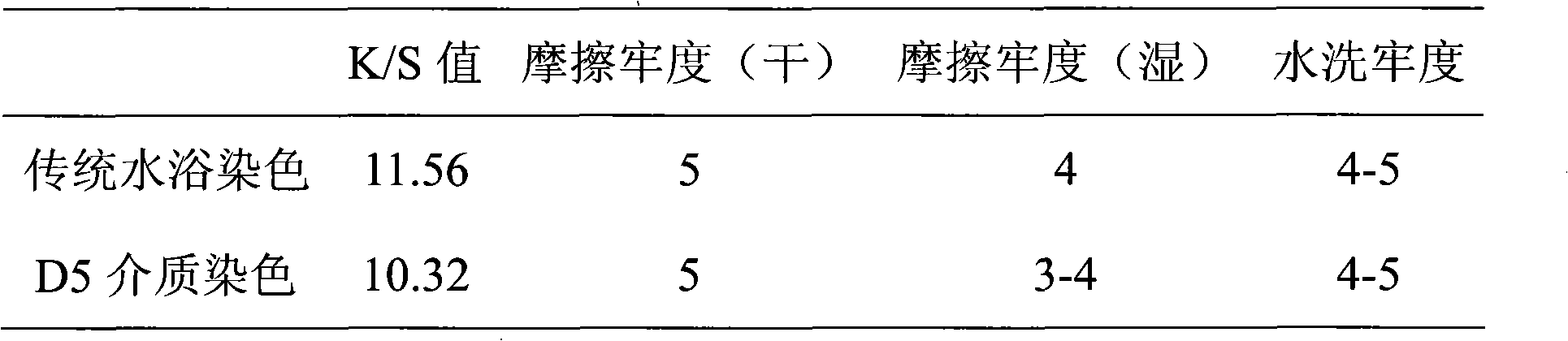
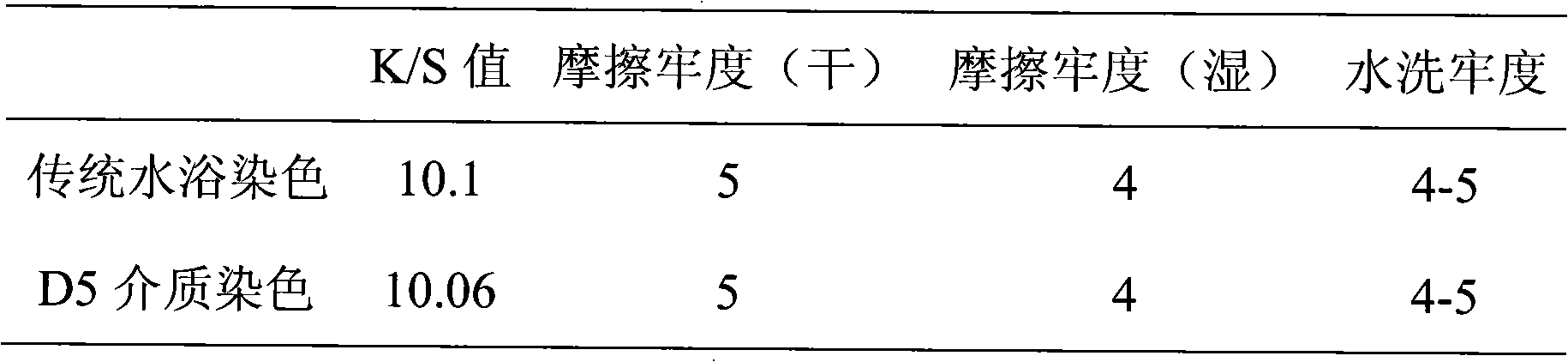
New dyeing method of active dye taking methylsiloxane as medium
The invention discloses a new dyeing method of an active dye taking methylsiloxane as a medium. In the invention, a non-aqueous medium is adopted, which can rapidly close to a fiber surface under the condition of not adding electrolyte for accelerating dye completely, thereby obviously improving adsorption rate and equilibrium adsorption capacity of the active dye, improving fixation rate of the dyeing, completely avoiding the problems of environment and zoology caused by using a large number of inorganic salts, and realizing salt-free dyeing of the active dye in a real meaning. The medium adopted by the invention can be used repeatedly, thereby reducing environmental pollution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV +1
Method for preparing stevioside
Owner:DAMIN FOODSTUFF ZHANGZHOU CO LTD
A kind general multi-purpose foam fire-extinguishing agent
InactiveCN101125243ASimple production processReduce water consumptionFire extinguisherSalt freeAlkyl polyglycoside
The invention relates to an A popular type multifunctional foam fire extinguishing agent, which mainly consists of a protecting colloid consisting of microlite chitin, sesbania gum and hydroxyethyl cellulose; vesicant consisting of polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol sodium sulfate, alkyl polysaccharide glycoside, salt free imidazoline and hydrocarbon surface active agent; burn resisting film forming agent consisting of silicone surface active agent, fluorocarbon surface active agent and fluorocarbon silicone surface active agent; flame retardant comprising one or a plurality of condensed phosphate, borax and boric acid; addition agent consisting of short chain alcohol and ether and metal salt; osmotic agent which is high efficient osmotic agent BS or rapid osmotic agent T; and water margin. Being applicable for the prior various foam fire extinguishing devices, the fire extinguishing agent not only can put out the polar and non-polar A, B fires, but also can effectively put out the polar and non-polar mixture fires with any ratio with little fire extinguishing agent and water. The invention has the advantages of simple processing technique, no special facility, low cost and no environmental pollution in production and usage.
Owner:只茂海
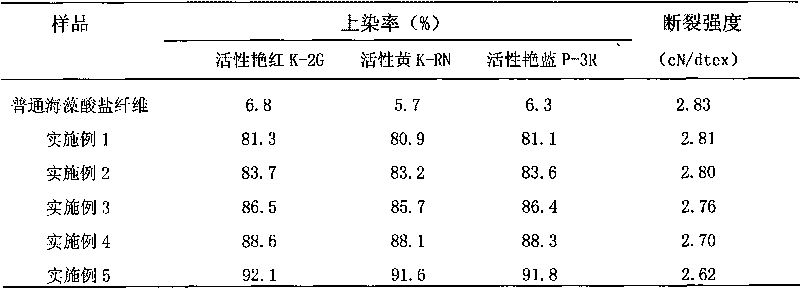
Manufacturing method of stainable alginate fibers
ActiveCN101736440AAchieve dyeingMeet diverse needsAlginate artificial filamentsWet spinning methodsColour fastnessState of art
The invention disclose a manufacturing method of stainable alginate fibers, which comprises the following steps of: adding a water-soluble dendrimers compound into a alginate fiber spinning solution, and solidifying, drafting, water washing and post-processing by adopting wet spinning equipment and technology to obtain the alginate fibers with excellent staining property, wherein the content of dendrimers in the alginate fibers is 1-10 percent. Compared with a traditional alginate fiber production technology, the invention has the advantages that the prepared alginate fibers can be applied to direct dyes and active dyes under a salt-free condition to realize staining and have higher dye uptake rate which generally reaches above 80 percent and is 10-15 times that of the alginate fibers produced by the traditional technology. In addition, the alginate fibers prepared by the invention has better color fastness and particularly excellent wet-processing fastness which reaches above grade 4.
Owner:QINGDAO TIANYI GROUP
Dyeing method adopting activated dye with high fixation rate
The invention relates to a dyeing method adopting an activated dye with a high fixation rate. The dyeing method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, a water / organic solvent co-solvent system is adopted to enable the activated dye to dye cotton fabrics; after dyeing is completed, the water content on the fabrics is reduced through changing dye bath or evaporation; organic alkali and inorganic alkali are added for fixation for a certain period at a certain temperature; and after the fixation is completed, the fabrics are subjected to washing, soaping, washing and drying. The technical scheme adopted by the invention has a simple technology, convenience in operation and no special requirement for dye and equipment, large-scale production can be performed by conventional equipment, the solvent is easy to recycle, and salt-free and low-alkaline dyeing can be achieved; and meanwhile, hydrolysis of the dye on the fabrics can be reduced, so that the dye can be fixed on fibers, the environmental pollution and the production cost are reduced, and the dyeing method has wide application prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
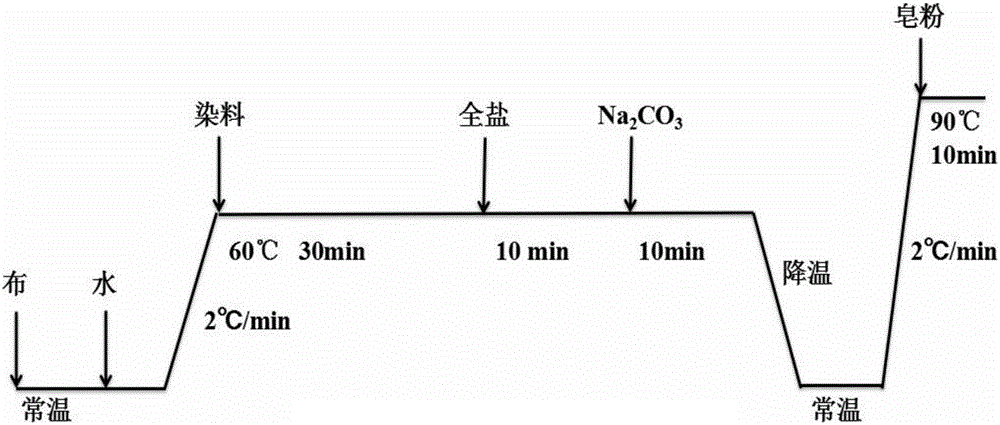
Method for cation modification and salt-free dyeing of cellulose fiber fabric
ActiveCN104233866AImprove permeabilityImprove uniformityDyeing processVegetal fibresRing dyeingSalt free
The invention discloses a method for cation modification and salt-free dyeing of a cellulose fiber fabric. The method comprises the steps as follows: preparing a high-polymer cation modifier aqueous solution with soft water, adding the cellulose fiber fabric, then adding NaOH, exerting pressure, heating the solution for a thermostatic reaction, performing cooling and pressure relief, discharging the modifying solution, and performing washing to obtain a cation-modified fabric; placing the cation-modified fabric in a dyeing machine, adding the soft water, sequentially dissolving reactive dye and sodium carbonate with return water, injecting the reactive dye and the sodium carbonate into the dyeing machine, heating the dyeing machine to the dyeing temperature, keeping the temperature, discharging a residual dyeing solution, and dehydrating and drying the fabric after a washing-soaping-washing process to obtain the salt-free low-alkaline dyed fabric. With the adoption of the method, salt-free low-alkali dyeing is realized, the problems of dyeing defects, color sinking and ring dyeing as well as reduction of the color fastness when cellulose fiber fabrics modified by high-polymer cation modifiers are dyed with reactive dyes are solved, a leveling agent is not required to be added during dyeing, the sodium carbonate and the dye can be added into a dyeing vat simultaneously, the sodium carbonate is not required to be added repeatedly during dyeing, and the dyeing operation is simple and easy to control.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
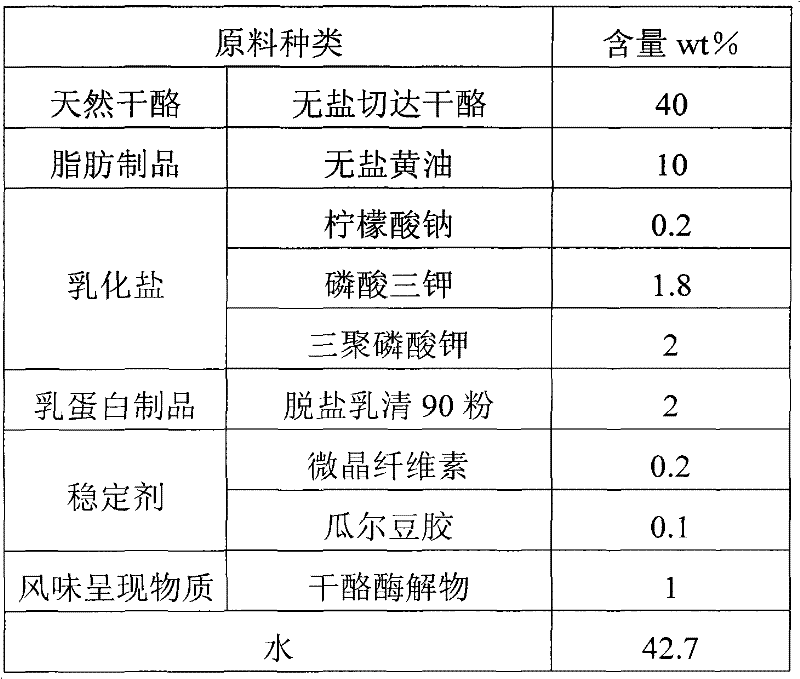
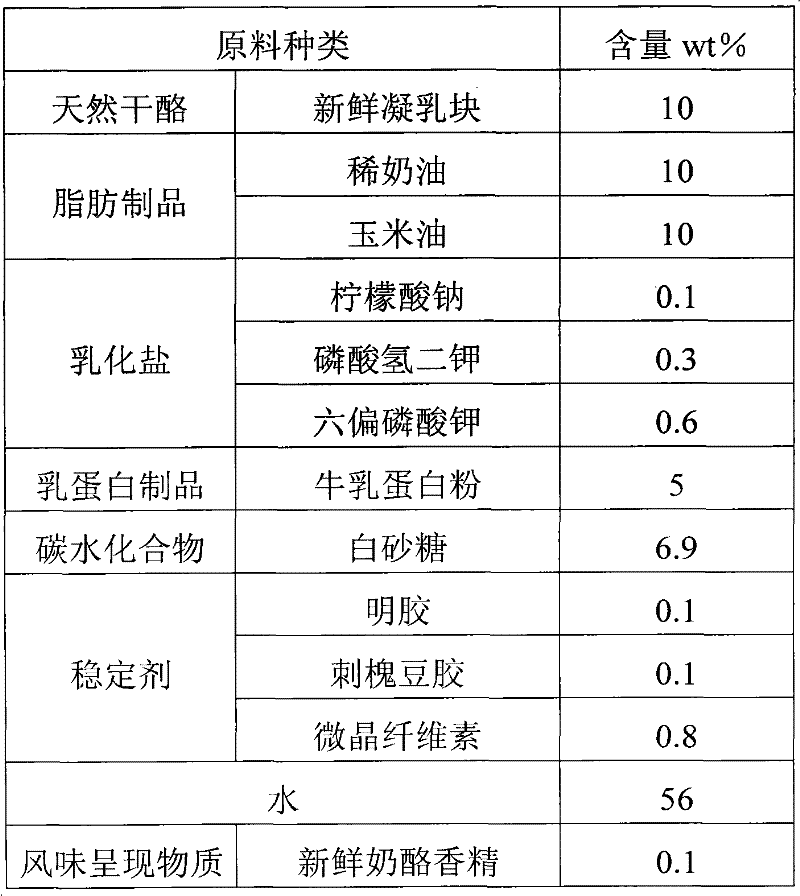
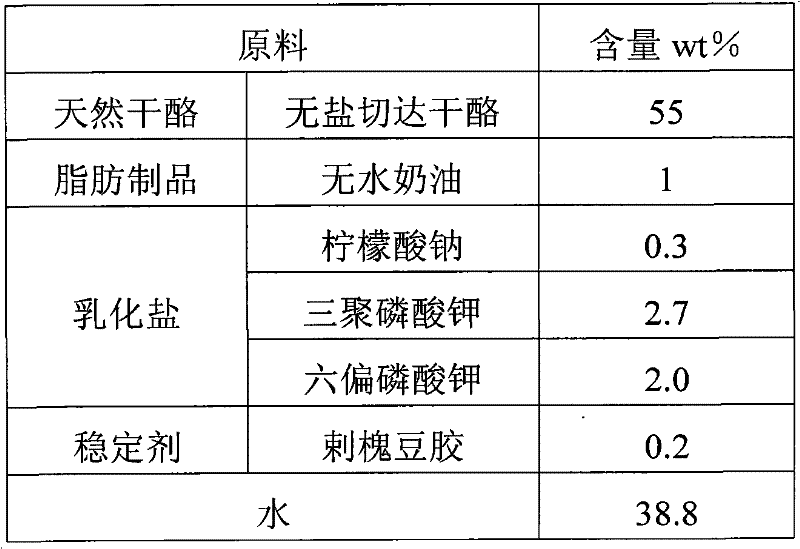
Spread processed cheese and method for preparing same
The invention discloses spread processed cheese and a method for preparing the same. The processed cheese comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 10 to 55 percent of natural cheese, 1 to 5 percent of emulsifying salt, 1 to 40 percent of fat product, 0.2 to 1.0 percent of stabilizer and 21 to 56 percent of water, wherein the natural cheese is the fresh curd and / or salt-free cheese; the emulsifying salt is prepared by mixing sodium citrate and potassium phosphate in a mass ratio of 1:9-1:19; the sodium content of the fat product is less than or equal to 60mg / 100g; and the stabilizer can be one or more of glutin, guar gum, microcrystalline cellulose, locust bean gum and modified starch. The spread processed cheese has good taste and texture compared with the conventionalspread processed cheese, and the content of sodium ions is lower than 120mg / 100g, which is 40 to 80 percent less than that of the common cheese; and the spread processed cheese meets the low-sodium food standard and has a stable state and good flavor, tissue and taste. In addition, the preparation method is simple, and easy to implement.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
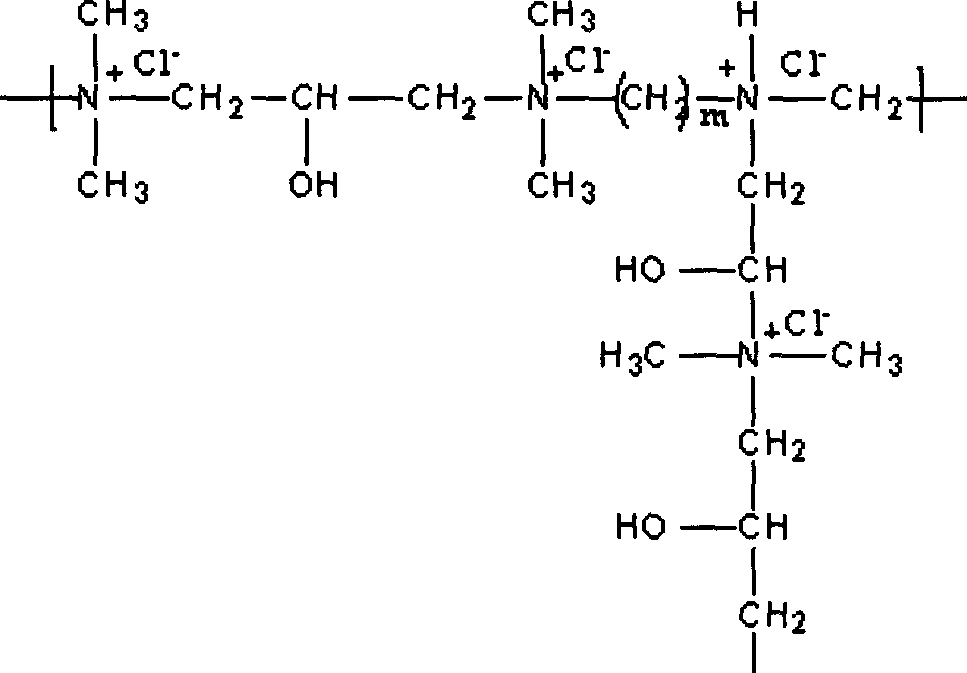
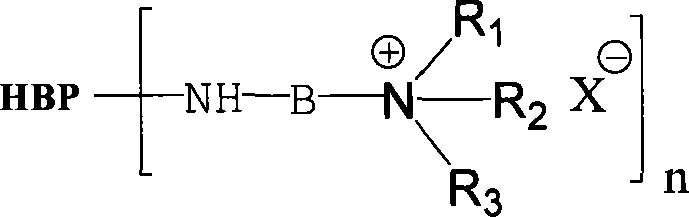
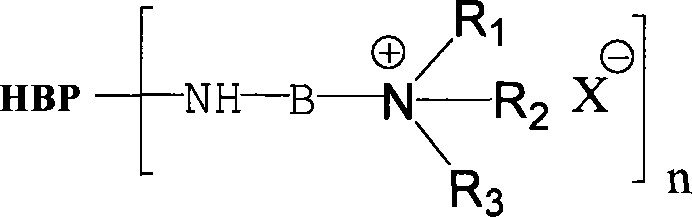
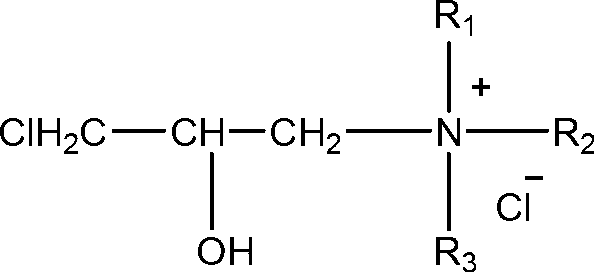
Amine-terminated hyperbranced compound quaternary ammonium salt and preparation method thereof
The present invention discloses amino end hyper-branched compound quaternary ammonium salt and the preparation method, pertaining to the art of macromolecular material technology. The method adopts the amino end hyper-branched compound as the matrix for quaternary ammoniation of the amido on the surface or grafting the quaternary ammonium salt, thus obtaining the polymerized quaternary ammonium salt. The preparation method is that the amino end hyper-branched compound is dissolved in deionized water and then a certain amount of quaternary ammoniation reagent is added; after being even mixed, the polymerized quaternary ammonium salt with characteristics of the hyper-branched compound and the polycation. The present invention has the advantages that the synthetic process is simple, the synthetic cost is relatively low, the product can be applied to cation modification of cellulose fiber and protein fiber, salt-free dyeing of active dyestuff, direct dyestuff, acid dyestuff, acid mordant dyestuff, etc., and the antiseptic performance and anti-UV performance of the fabric is enhanced. At the same time, the present invention is applied to sewage treatment agent, antibacterial agent, surface active agent, functional material forebody, medical carrier, etc.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for dyeing reactive dye by one-step method without salt
InactiveCN101532259AReduce consumptionImprove the shortcomings of dyeing batch productionDyeing processFiberSalt free
The invention relates to a method for dyeing a reactive dye by one-step method without salt. The method comprises two-dip-one-dry or three-dip-one-dry process, wherein dye solution used for dipping and drying consists of 15 to 25g / l of dye and 1g / l of an alkaline agent; pickup is between 55 and 60 percent; then, the dyeing solution is subjected to steaming, washing, hot water washing and drying. The method has a simple dyeing process, does not have special requirement on the dye, does not relate to modification of fibers and application of salt-free dye cross linker; preliminary drying and cylinder drying are saved, and consumption of heat energy is greatly reduced; compared with a cold pad-batch dyeing process, the defects of cold pad-batch clearance production is improved, efficiency is improved, and defects of water spots, stains and hard hand feel are overcome.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
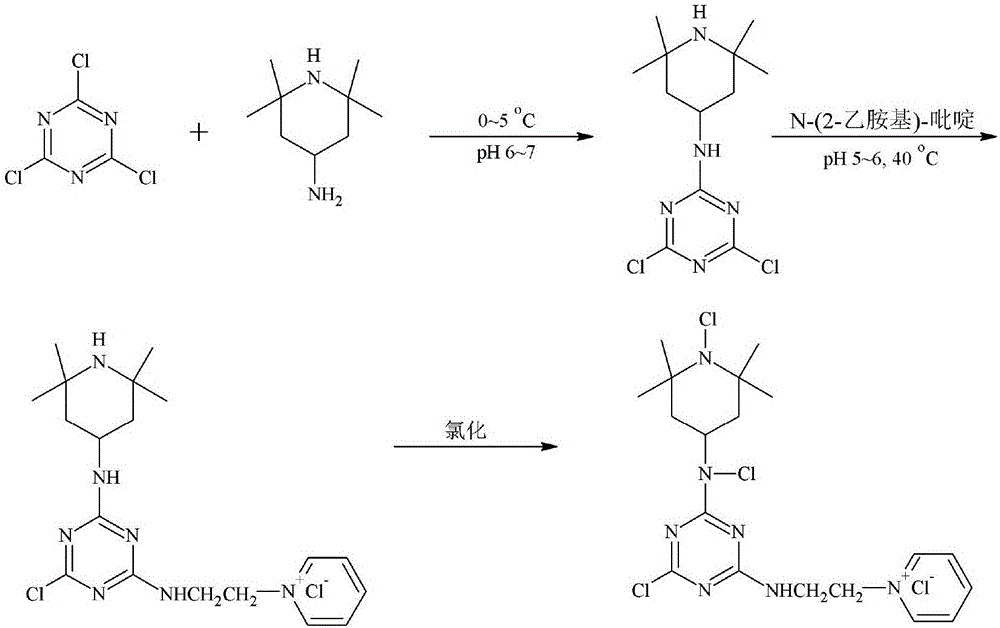
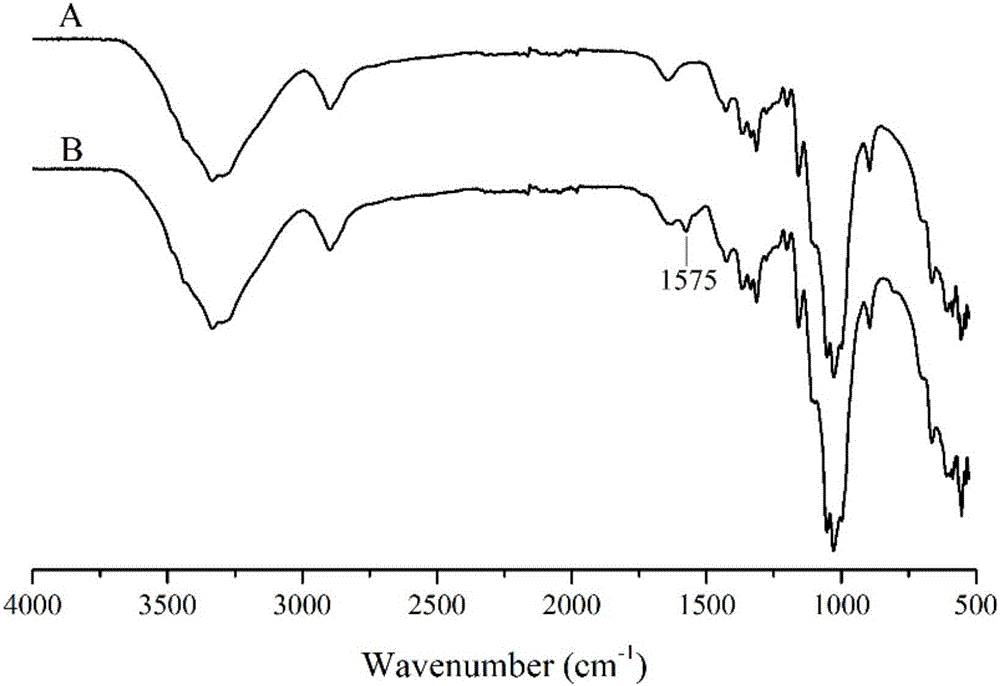
Triazine quaternary ammonium salt halamine antibacterial agent and preparation method thereof, and salt-free antibacterial finishing method
The invention provides a triazine quaternary ammonium salt halamine antibacterial agent. The triazine quaternary ammonium salt halamine antibacterial agent is a compound with a structure as shown in a formula (I) in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) dropwise adding an organic solution of 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidylamine into an aqueous or organic solution of cyanuric chloride or cyanuric fluoride, and carrying out a reaction for 1 to 4 h; (2) pouring an aqueous solution of chlorinated N-(2-ethylamino)-pyridine into the reaction solution, carrying out a reaction for 2 to 6 h, dropwise adding an acid-binding agent in the whole process of the reaction, and allowing the pH value of the reaction solution to be 5.0 to 8.0; (3) after the reaction is completed, carrying out filtering, purifying and drying so as to obtain a triazine quaternary ammonium salt halamine antibacterial precursor; and (4) placing the triazine quaternary ammonium salt halamine antibacterial precursor into a halogenated solution, carrying out standing at room temperature for 0.5 to 1.5 h, and after completion of standing, carrying out filtering and drying so as to obtain a quaternary ammonium salt halamine antibacterial agent product. The triazine quaternary ammonium salt halamine antibacterial agent provided by the invention is a salt-free reaction-type halamine antibacterial agent with excellent antibacterial properties and good precursor water-solubility.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Reactive dye salt-free dying process of cotton fabric
InactiveCN103526606APlay a protective effectImprove dyeing effectDyeing processGraft reactionSalt free
The invention relates to a reactive dye salt-free dying process of cotton fabric. The reactive dye salt-free dying process of the cotton fabric comprises the following steps: (1) performing grafting reaction on glycidol trimethyl ammonium chloride and an amino-terminated hyperbranched compound to obtain amino-terminated hyperbranched compound quaternary ammonium salt; (2) placing the cotton fabric in the solution of the amino-terminated hyperbranched compound quaternary ammonium salt, performing dipping treatment at 20 to 90 DEG C for 20 to 80 minutes, taking out the cotton fabric and completely washing the cotton fabric for later use; (3) placing the modified cotton fabric into reactive dye and dyeing at normal temperature; and (4) washing after dyeing is finished, adding soap flakes of 3 g / L, performing soap boiling at 90 to 100 DEG C for 5 to 10 minutes and airing. The reactive dye salt-free dying process of the cotton fabric has the benefits that after the cotton fabric is modified, the dyeing property is obviously improved, the dyeing ratio is increased, the amount of dyeing waste water is reduced, and the environment is protected. Compared with the unmodified cotton fabric subjected to traditional salt dyeing, the cotton fabric has higher K / S value and achieves better effects on color fastness to rubbing and color fastness to washing.
Owner:KUNSHAN P&X GARMENTS
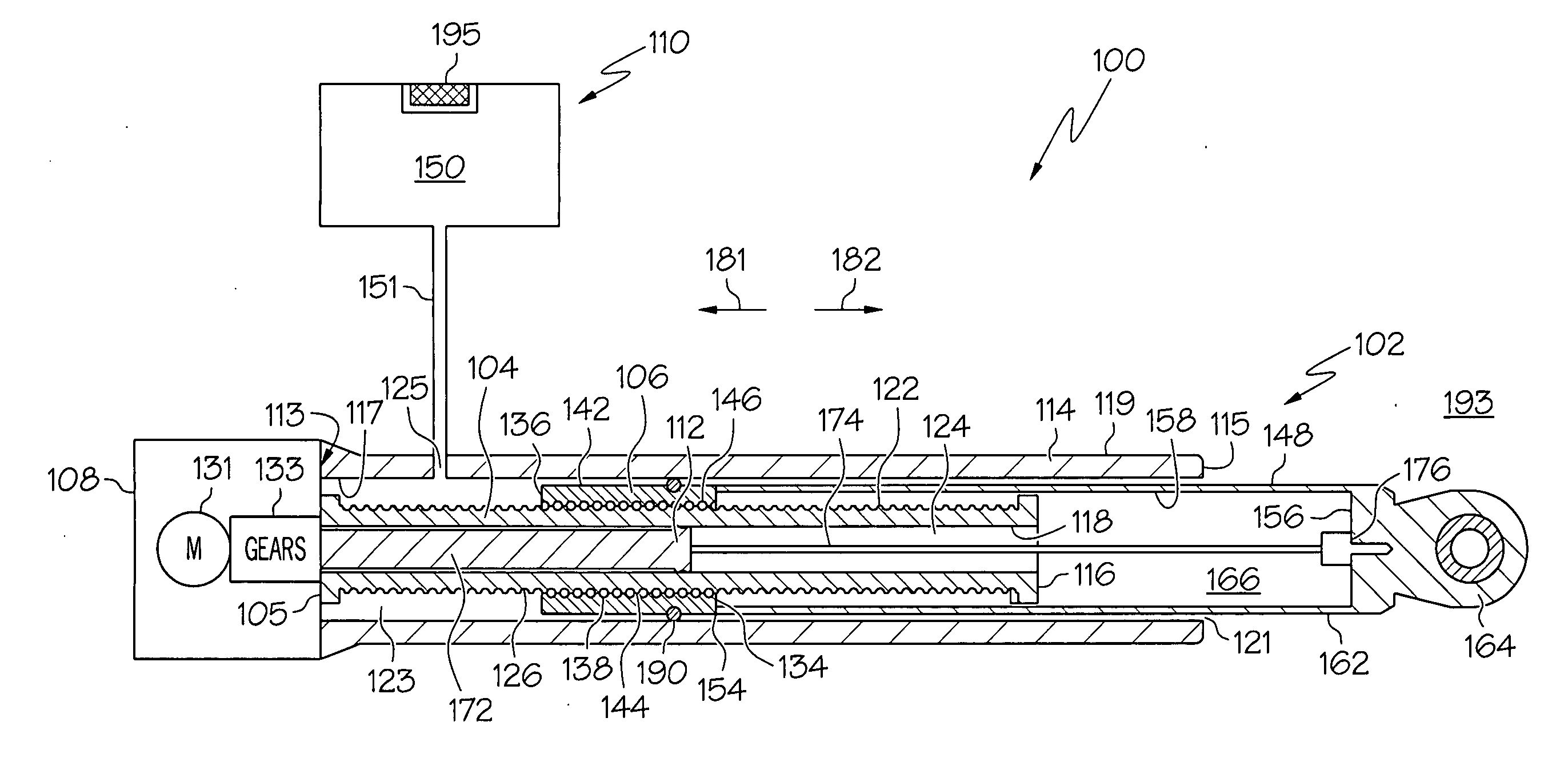
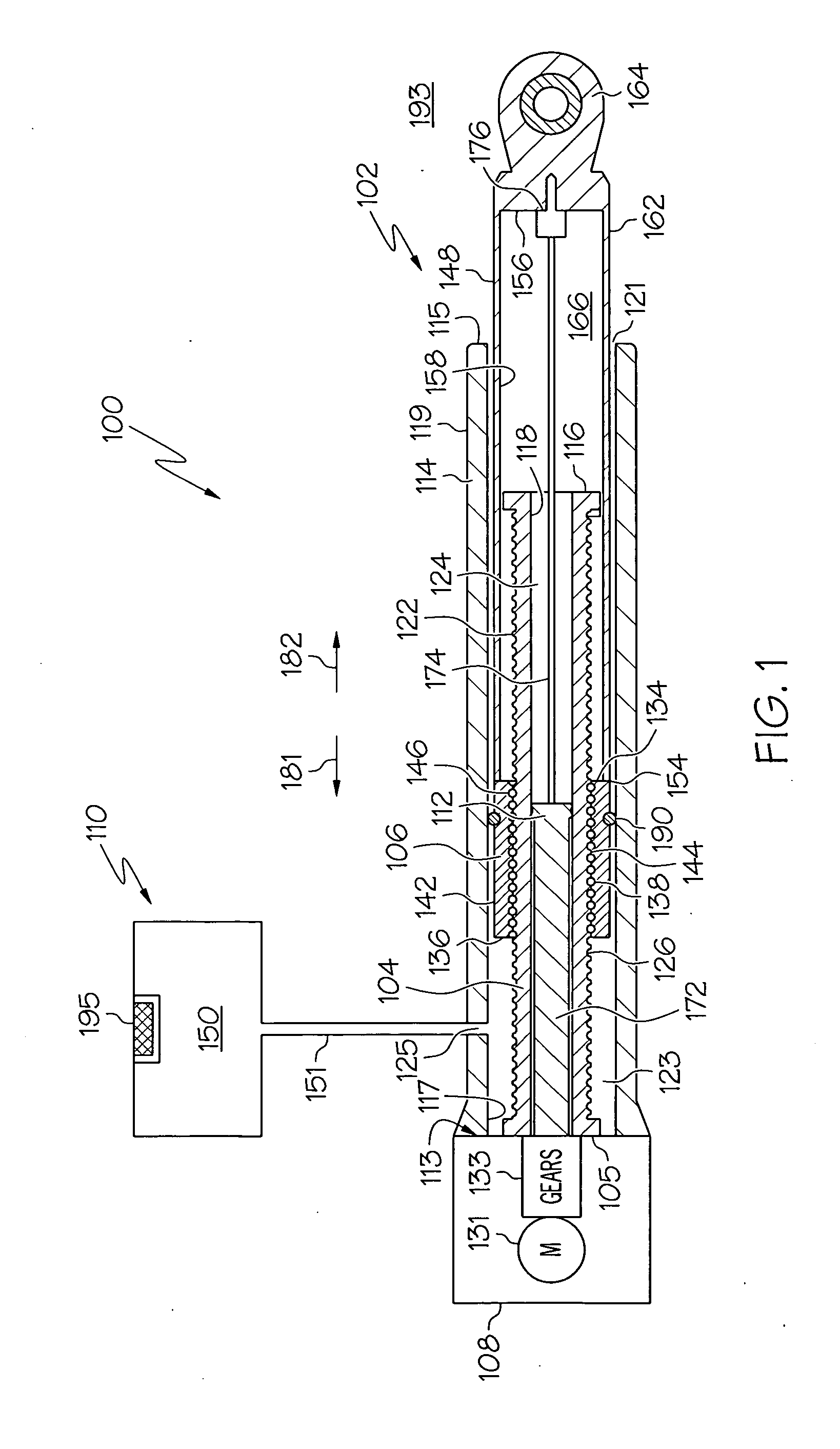
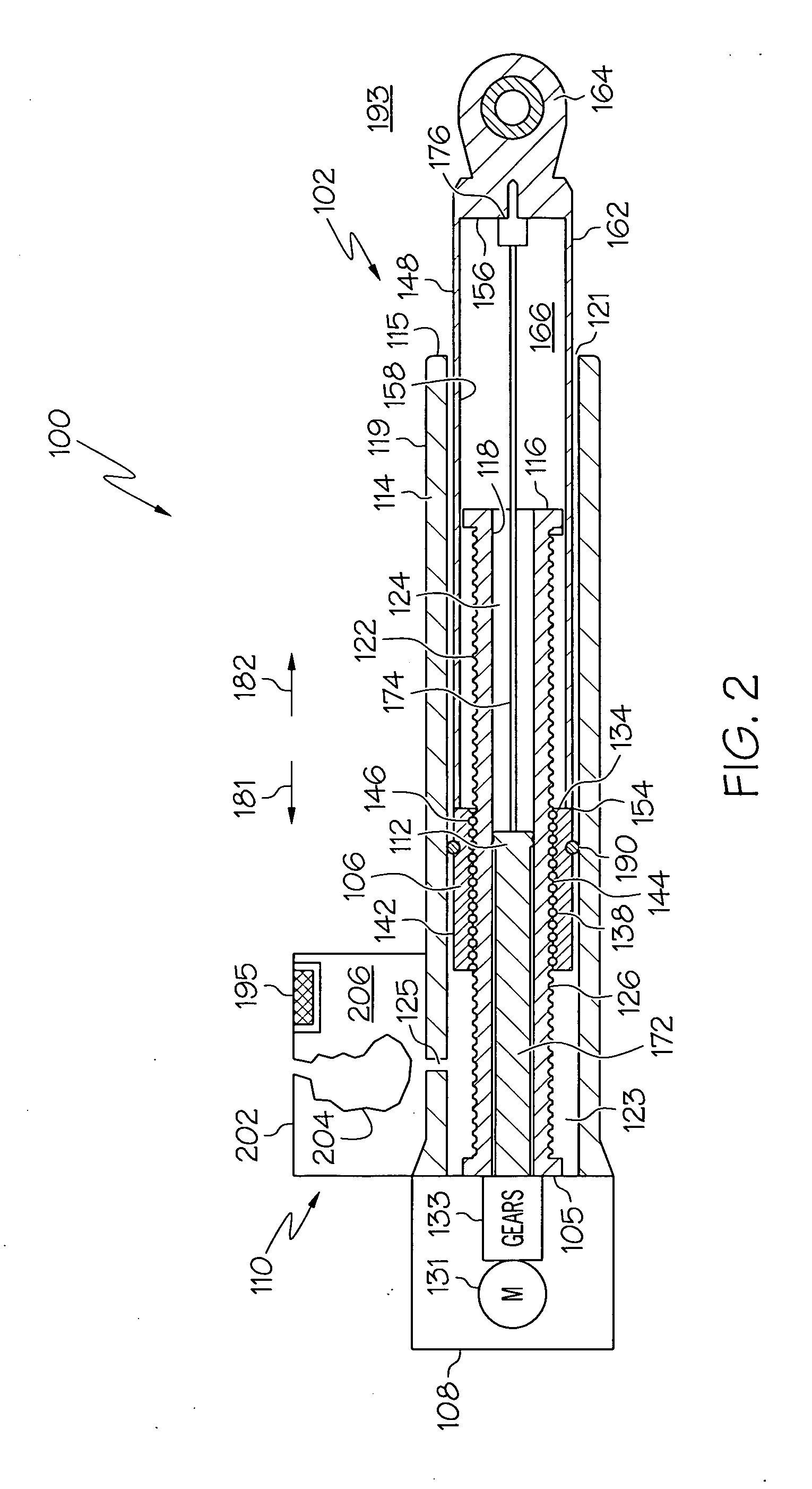
Electromechanical linear actuator including an environmental control and air management system
An actuator that at least inhibits the deleterious effects of corrosive fluids, such as salt-laden air, does not rely on relatively expensive materials. At least a portion of the actuator housing is sealed from the surrounding salt-laden air, and is in fluid communication with an air reservoir that includes a supply of relatively salt-free, or substantially salt-free, air. The actuator is configured to exchange air between the air reservoir and the actuator housing, thereby at least substantially inhibiting the ingress of salt-laden air into much of the actuator.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Low-salt and multi-strain segmented fermentation process for fermented soya beans
InactiveCN103535634AIncrease aromaIncrease contentMulti-step food processesFood preparationFlavorMicroorganism
The invention provides a low-salt and multi-strain segmented fermentation process for fermented soya beans. The low-salt and multi-strain segmented fermentation process comprises the following steps: selecting soy beans; immersing; cooking; inoculating and carrying out starter propagation; carrying out primary fermentation; inoculating a yeast and carrying out secondary fermentation to obtain a finished product. With the adoption of the low-salt and multi-strain segmented fermentation process, a process method for carrying out segmented fermentation after the starter propagation and adding microorganisms to increase the aroma is applied to the fermentation production of the fermented soya bean; pure strains are used for carrying out the starter propagation so as to improve the protease activity of a bean starter; the salt-free health-insulation fermentation is used for improving the content of amino acid nitrogen and shortening the time spent on the primary fermentation; in the secondary fermentation process, zygosaccharomyces rouxii is added to increase the aroma of the fermented soya beans and shorten the secondary fermentation time; a product not only has the unique aroma of the fermented soya beans, but also has the rich mellow flavor, sauce flavor and ester flavor; the mass percentage of the amino acid nitrogen of the product reaches 0.81g / 100g and the mass percentage of the salt of the product is about 8g / 100g and is reduced by more than 47.78% when being compared with that of conventional fermented soya beans (more than 12%); the fermentation time lasts for 19 days and is shortened by 3-6 days.
Owner:GUIZHOU SHUIXIANGZI FOOD CO LTD
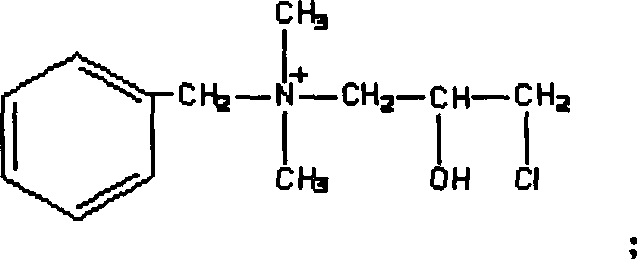
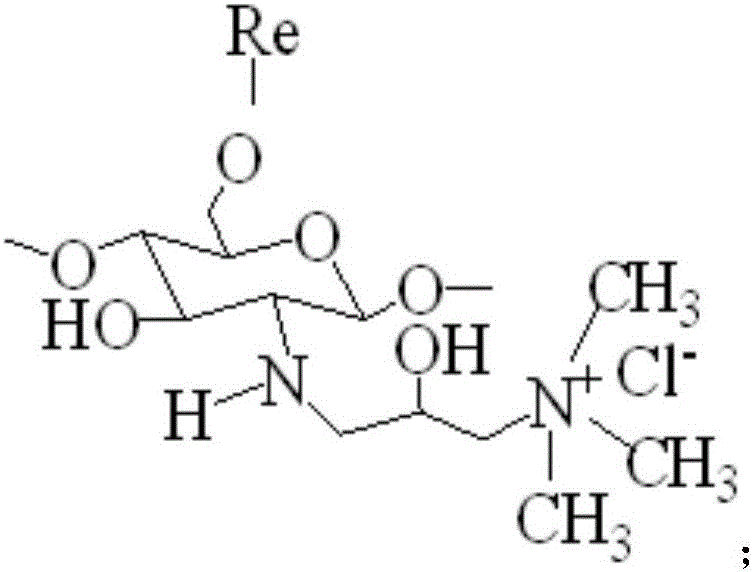
Reactive beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to reactive beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The reactive beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt is synthesized through two steps, namely, step 1, taking beta-cyclodextrin, choline chloride and epoxy chloropropane as raw materials to be subjected a ring opening substitution reaction to generate beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt; step 2, taking the beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt and a compound as raw materials to be subjected to a substitution reaction to generate the reactive beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt. The reactive beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt has no toxic or side effect; when being used for salt-free dyeing of an active dyestuff of cotton fabric, the reactive beta-cyclodextrin quaternary ammonium salt has relatively good dyeing effect; the pollution to the environment by salt in wastewater is reduced and treatment pressure of dyeing and finishing wastewater is alleviated; the dyed fabric has relatively good dyeing effect; the dyeing rate of the active dyestuff is 65 percent to 85 percent and the color fixation rate is 55 percent to 70 percent; the dry rubbing fastness is more than grade 4 and the wet rubbing fastness is more than grade 3.
Owner:那坡同益新丝绸科技实业有限公司
Cellulosic fiber fabric reactive dye salt-free deep-color dyeing method
InactiveCN103074766AReduce repulsionTo achieve the purpose of salt-free dyeingDyeing processVegetal fibresThermal insulationSalt free
The invention relates to a cellulosic fiber fabric reactive dye salt-free deep-color dyeing method, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a modifier aqueous solution, increasing the temperature to 60-80 DEG C, adding a test sample, stirring, adding sodium hydroxide, stirring, washing and drying to obtain a modifier test sample; and (2) adding a reactive dye and a levelling agent, increasing the temperature to 60-80 DEG C, adding the modifier test sample, dyeing for 20-30 minutes in a stirring manner, adding substitution alkali, dyeing for 30-45 minutes in a stirring and thermal insulation manner, decreasing the temperature to the room temperature, soaping, washing and oven drying. According to the invention, the modifier is used for modifying cellulosic fibers, so that the repulsive force between dye anions and fibers can be reduced, the purpose of fabric reactive dye salt-free dyeing can be achieved, the method is simple and convenient to operate, the effect is obvious, no additional equipment is required, and the cost is controllable.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Method for carrying out salt-free dyeing on un-scoured and unbleached cotton textile by reactive dyes
The invention relates to a method for carrying out salt-free dyeing on an un-scoured and unbleached cotton textile by reactive dyes and belongs to the technical field of textile printing, dyeing and finishing. According to the method, the un-scoured and unbleached cotton textile is pre-swelled in a pre-swelling liquid which is formed by mixing a high-proportion alcohol-type organic solvent and a small amount of water, and the pre-swelled cotton textile is dyed by a dyeing liquid which is formed by mixing a high-proportion alcohol-type organic solvent, water and dyes, the wettability and the dyeability of the un-scoured and unbleached cotton textile can be effectively enhanced, and the pre-treating work processes of scouring and bleaching the cotton textile are reduced. The method can effectively enhance the dye-uptake rate, the color fixation rate, the dyeing effect and the color fastness of the reactive dyes onto the un-scoured and unbleached cotton textile, can completely meet production requirements, does not need salt, and is simple in technology, high in feasibility and easy for industrialization; the use amount of water is reduced greatly; besides, the alcohol-type organic solvents can be recycled, so that the method is little in pollution, low in cost, clean, energy-saving, safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV +1
Reactive dye salt-free dyeing method
The invention relates to a reactive dye salt-free dyeing method which comprises the following steps of: soaking pre-swelled cotton fabric into reactive dye liquor, heating up to a primary dyeing temperature of 40-100 DEG C and keeping the temperature for 0-20 minutes, adding an organic solvent, heating up to a dyeing temperature of 60-100 DEG C and keeping the temperature for 0-20 minutes, adding soda ash, heating up to a fixation temperature of 40-100 DEG C and keeping the temperature for 30-60 minutes, cooling to room temperature, and carrying out washing, soaping and washing on the cotton fabric. The method is simple and easy to industrialize, is capable of obtaining dye-uptake and fixation rate higher than a traditional reactive dye dyeing process, has relatively good leveling property and is capable of realizing salt-free low-alkaline dyeing.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Ammonium-salt-free plating assistant agent used for hot dip galvanizing and technical methods for preparation and use thereof
ActiveCN101575692AGood drying temperatureReduce generationHot-dipping/immersion processesSalt freePhosphate
The invention provides an ammonium-salt-free plating assistant agent used for hot dip galvanizing and technical methods for preparation and use thereof, belonging to the technical field of the surface plating technique of steel and iron materials. The technical proposal is as follows: the aqueous solution of the plating assistant agent has the following components of zinc chloride, sodium chloride, a nonionic surface active agent (cocinic acid alkanolamide, fatty acid alkanolamide or alkanolamide phosphate ester) and a perfluoro-carbon type surface active agent with the respective proportion in sequence of 80 to 350g / L, 30 to 100g / L, 2 to 4g / L and 0.1 to 2g / L, and the balance of water. When the plating assistant agent is used for hot dip plating: the steel and iron product after oil and dust removing is dipped into the ammonium-salt-free plating assistant agent for plating assistant treatment firstly, the temperature is controlled to be in the range of 40 to 80 DEG C, then drying or baking is carried out at the temperature of 40 to 140 DEG C so as to lead the surface of the product to be adhered with a layer of even plating assistant film, and then the obtained product is dipped into molten zinc for hot dip plating. The invention has the advantages that the plating assistant agent is not added with ammonium salt, thus being capable of greatly reducing the generation of dusts when in hot dip plating, reducing pollution to environment and improving working environment.
Owner:CHANGSHU FENGFAN POWER EQUIP +1
Salt-free dyeing method of vinyl sulphone type reactive dye for cotton fiber
The invention relates to a salt-free dyeing method of vinyl sulphone type reactive dye for cotton fiber, mainly comprising the steps of modifying cotton fiber, dyeing the cotton fiber and the like. The modifying treatment is realized by the steps of: soaking and rolling the cotton fiber by a solution containing acrylamide respectively for two times, and then soaking in a sodium hypochlorite solution to perform Hoffman degradation. The modified cotton fiber is dyed by the vinyl sulphone type reactive dye under a salt-free condition; and therefore, the dyeing rate and the color fixing rate of the dye are improved. By use of the salt-free dyeing method, the content of inorganic salts in dyeing wastewater is reduced, benefit is brought for environment protection, a cotton fiber modifying process can be combined with a chlorine blanching process, the production process is simple and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Wild vegetable instant food and processing method thereof
InactiveCN102696998AMeet the needs of food all year roundSimple methodFood preparationMonosodium glutamateSaline water
The invention discloses wild vegetable instant food and a processing method thereof. The processing method comprises the following steps of blanching fresh and cleaned edible wild vegetable such as Chinese toon sprout, bamboo shoots or pteridium aquilinum in water with the temperature of 80 DEG C for 2-3 minutes; rapidly cooling after fishing out; draining; soaking with saline for 3-5 days; rinsing with water to be salt-free; dehydrating to be with moisture content of 40-45 percent; chopping wild vegetables into sections or sectional slices; stirring and mixing with a mixed seasoning comprising fresh ginger particles, white sugar, chilli powder, sichuanese pepper powder, table salt and monosodium glutamate; splashing the wild vegetables with boiling vegetable oil; metering and packaging according to 50-200g; vacuumizing; and sterilizing. The food is cooked green vegetable food, is stored at room temperature, can keep original flavor and fresh and tender taste of fresh wild vegetables within a year, and can be eaten after a bag is opened. The method is simple, the processing production period is short, the production cost is low, and the wild vegetable resources of a mountainous area can be fully utilized.
Owner:镇巴县长兴实业有限责任公司
Installation used to obtain salt-free sea water at a low temperature with continuous operation and enthalpy recovery
InactiveUS7381310B2Low costReduce energy consumptionGeneral water supply conservationAuxillariesWater desalinationSalt free
Owner:HERNANDEZ HERNANDEZ MARIA FERNANDO +1
Reactive chitosan quaternary ammonium salt, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a reactive chitosan quaternary ammonium salt, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out Friedel-Crafts reaction on chitosan and 2,3-epoxy propyl-trimethyl ammonium chloride to generate N-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan, and carrying out substitution reaction on the N-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chloride chitosan and a compound to generate the reactive chitosan quaternary ammonium salt. The reactive chitosan quaternary ammonium salt is an aid for reactive dye cotton fabric salt-free dyeing, is soluble in water, and has the advantages of no toxic or side effect and favorable environment friendliness. When being used for reactive dye salt-free dyeing of cotton fabrics, the reactive chitosan quaternary ammonium salt has favorable dyeing effects, reduces the environmental pollution of salts in wastewater, and greatly lowers the dye printing production cost. When the reactive chitosan quaternary ammonium salt is used in the dyeing process to obtain the cotton fabric, the dye-uptake rate of the reactive dye is 70-85%. The fixation rate is 47-55%, the dry fastness to rubbing is greater than Grade 4, and the wet fastness to rubbing is greater than Grade 3.
Owner:WUYI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00000.png)
![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00001.png)
![Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation Induced symbiotic osmosis [iso] for salinity power generation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b4b27964-7dda-4348-9317-116c9790f6a1/US20110044824A1-20110224-D00002.png)