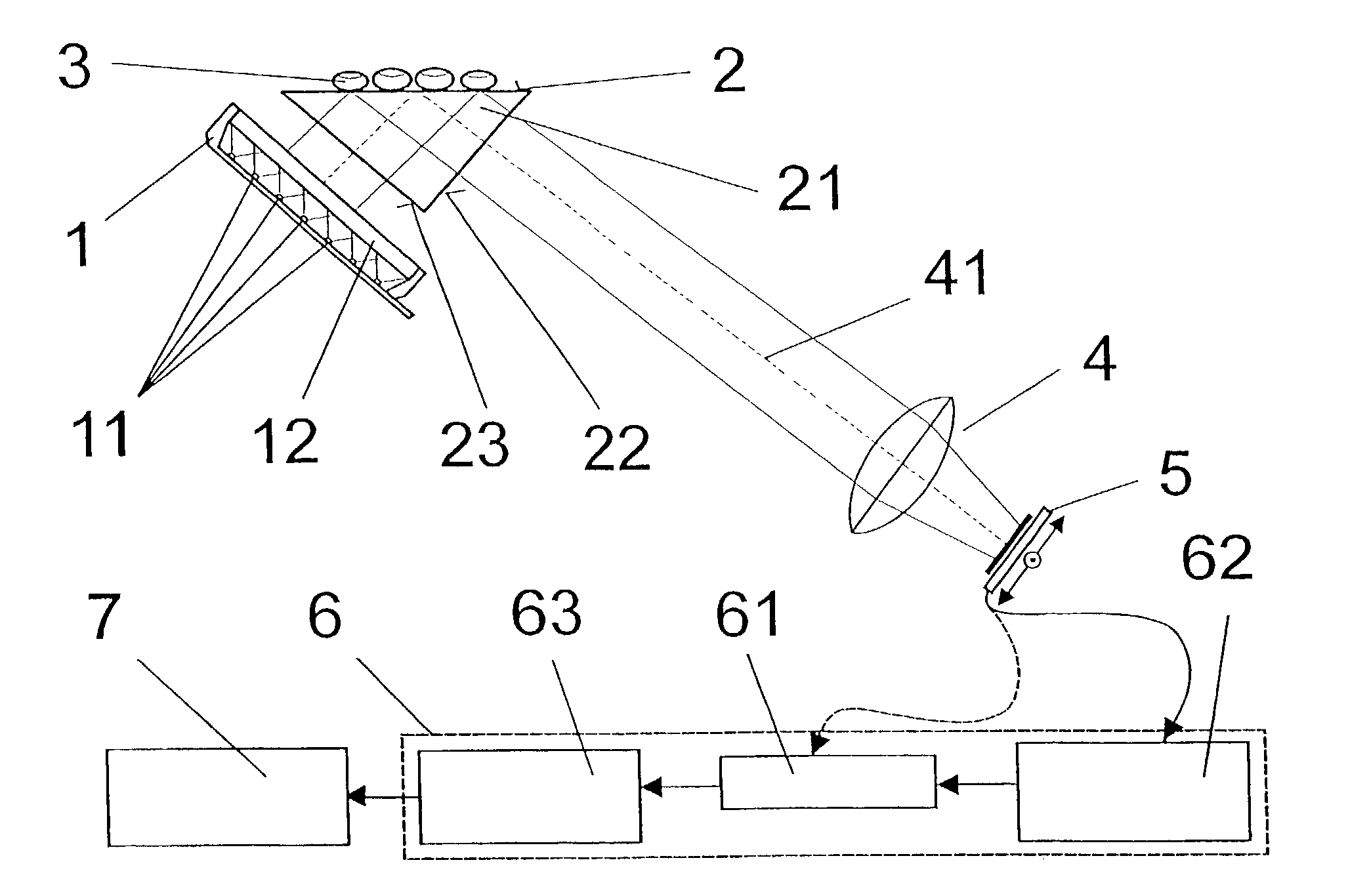
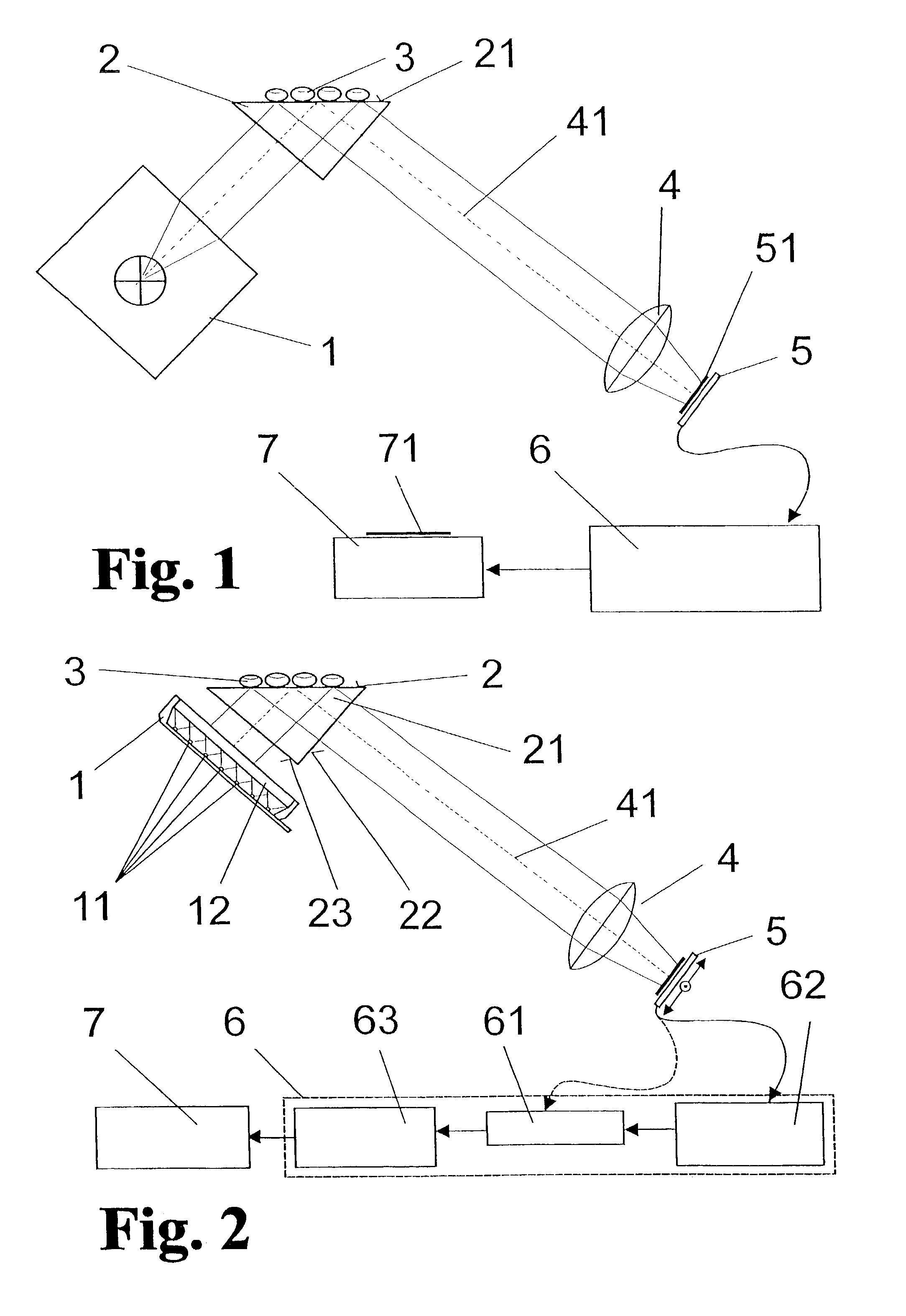
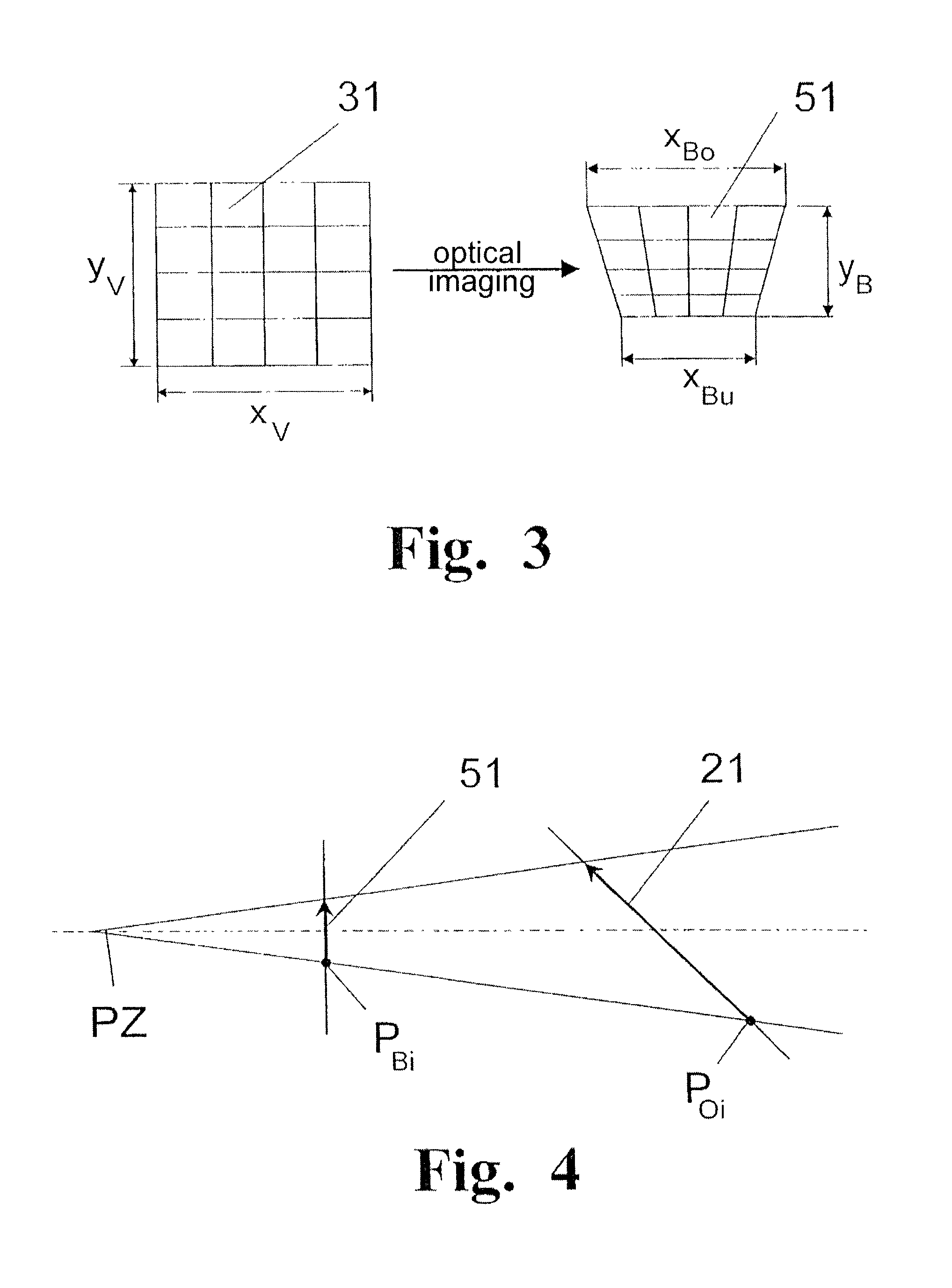
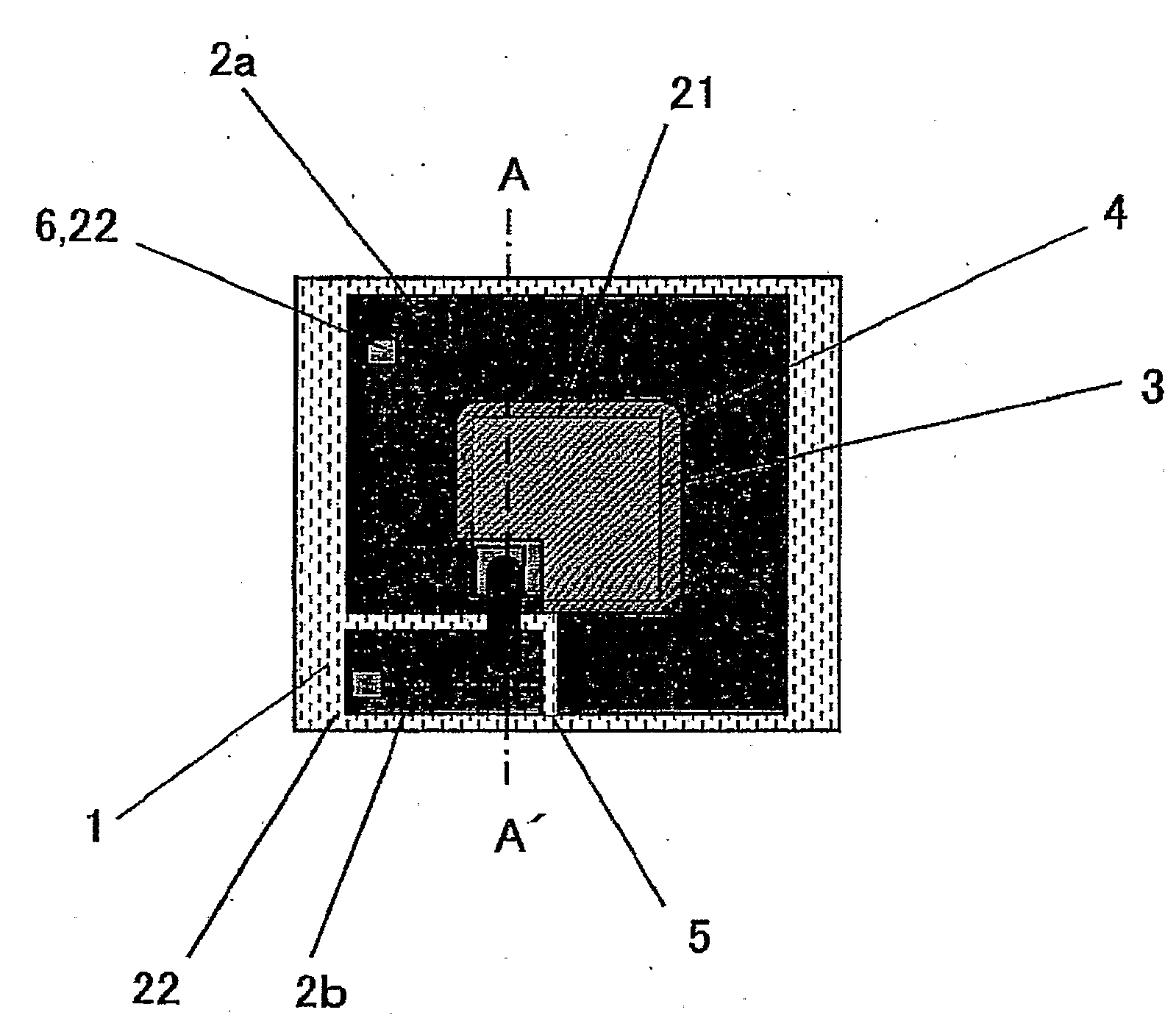
Patents
Literature
96results about How to "None is suitable for purpose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solar Panel
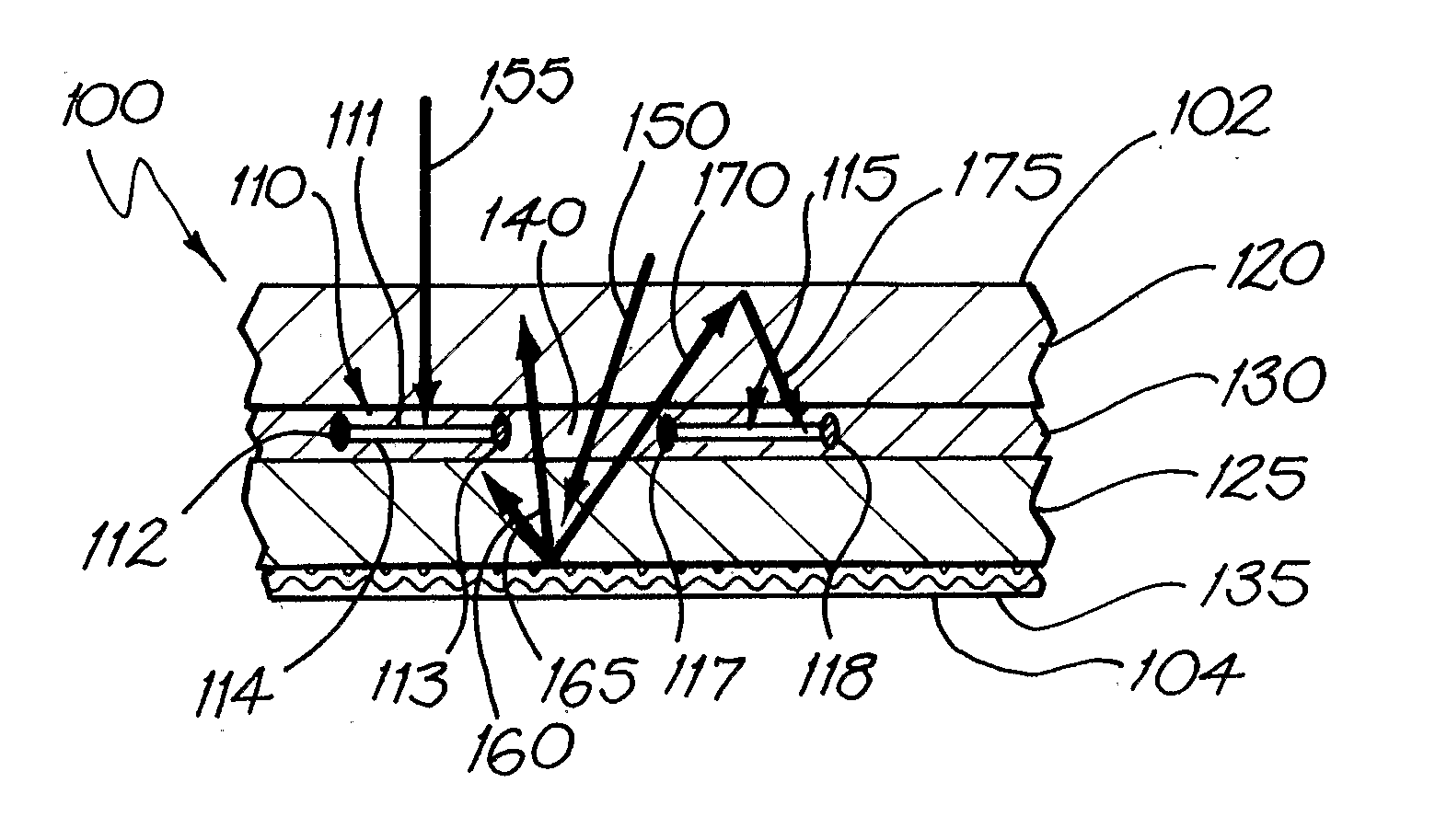
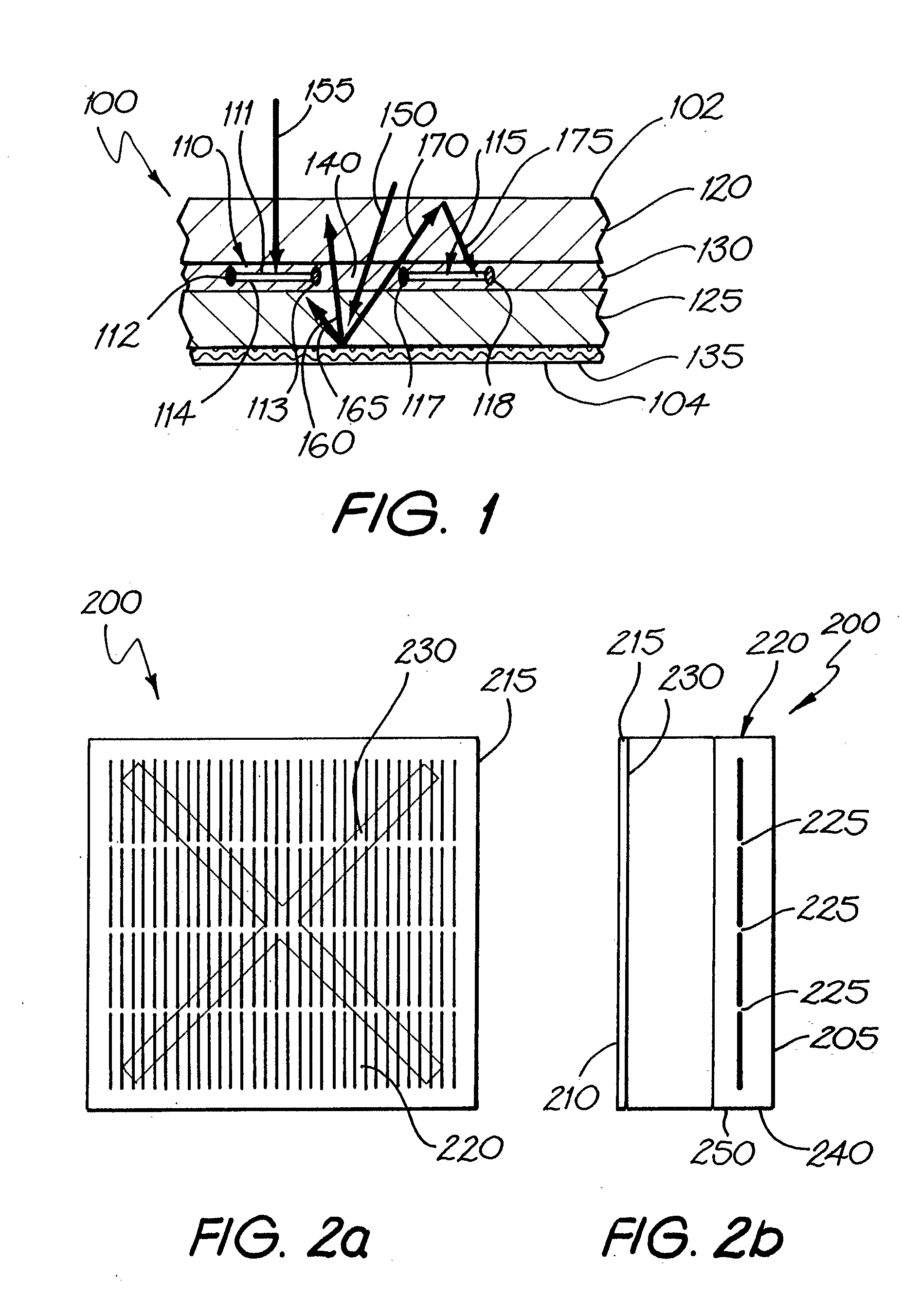
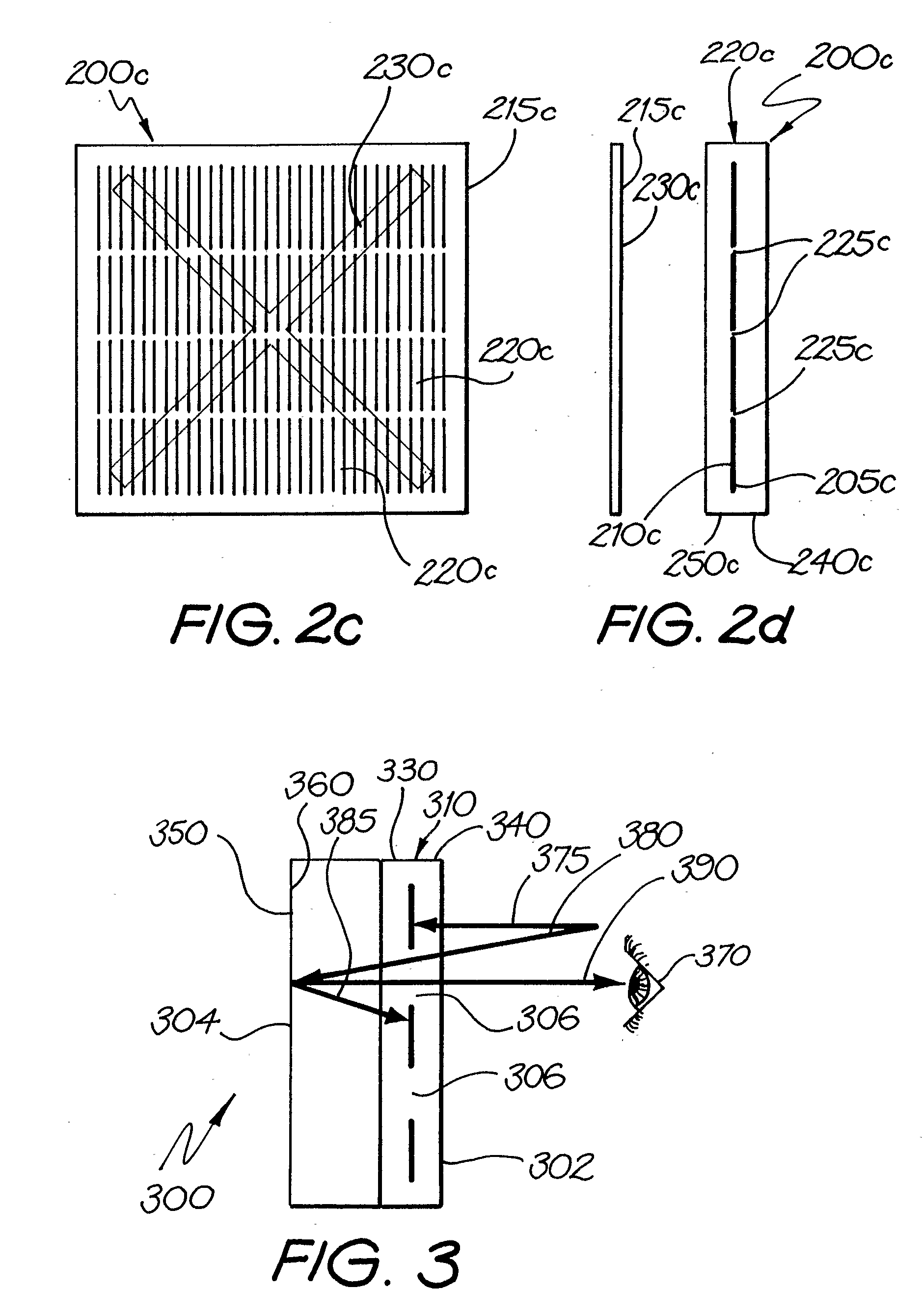
InactiveUS20070277810A1Reduce reflectivityReduce light reflectivitySolar heat devicesFinal product manufactureSolar lightEngineering
The invention provides a solar panel having a panel front and a panel back, comprising an array of solar cells and an element comprising a visually distinguishable feature. Each of the solar cells has a front and a back, wherein at least the front is capable of converting at least a portion of solar light incident thereon into electrical energy. There are spacings between at least some of the solar cells. The element comprising the visually distinguishable feature is located at at least one position selected from the group consisting of between the panel back and the panel front, on the panel front, on the panel back, at the panel front, and at the panel back, such that the visually distinguishable feature is at least partially distinguishable on viewing the panel front. The nature of the visually distinguishable feature and / or the location of the element relative to the solar cells does not completely prevent solar light incident on the panel front from being incident on at least a portion of the array.
Owner:TRANSFORM SOLAR
LED structure and luminaire for continuous disinfection
InactiveUS20170014538A1Avoid interferenceEasy to useLight source combinationsLighting elementsEffect lightWavelength conversion
A LED structure, a lighting fixture and a method of providing white light illumination. The LED structure comprises a substrate; a light emitting area defined on the substrate as a cavity; a first type of light emitting semiconductor source with bactericidal characteristics mounted in the cavity; a second type of light emitting semiconductor source mounted in the cavity with ability to excite the wavelength conversion material to generate white light; and a wavelength conversion material layer formed on top of the light emitting semiconductor sources. The invention enables disinfection by a lighting source or a luminaire visibly apparent to human as a white light source that is neither harmful to a human nor creates discomfort.
Owner:CALYXPURE INC
Narrow reactive edge treatments and method for fabrication
InactiveUS20040160367A1High isolationImprove isolationSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsSurface waveUltrasound attenuation
An electromagnetic bandgap material is electrically attached to an edge, and enables high isolation between antennas due to the attenuation of surface waves. The disclosed embodiments further provide narrow reactive edge treatments in the form of artificial magnetic conductors (AMCS) whose physical width is less than {fraction (1 / 10 of a free space wavelength for the frequency of surface currents intended to be suppressed. These embodiments still further provide several AMCs suitable for this purpose, along with several exemplary manufacturing techniques for the AMCs.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
Narrow reactive edge treatments and method for fabrication
InactiveUS6933895B2Improve isolationNone is suitable for purposeSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsUltrasound attenuationManufacturing technology
An electromagnetic bandgap material is electrically attached to an edge, and enables high isolation between antennas due to the attenuation of surface waves. The disclosed embodiments further provide narrow reactive edge treatments in the form of artificial magnetic conductors (AMCs) whose physical width is less than 1 / 10 of a free space wavelength for the frequency of surface currents intended to be suppressed. These embodiments still further provide several AMCs suitable for this purpose, along with several exemplary manufacturing techniques for the AMCs.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
Multiparticle Pharmaceutical Dosage Form for a Low-Soluble Active Substances and Method for Producing Said Pharmaceutical Dosage Form
ActiveUS20080166416A1Easy to processAffect permeabilityBiocidePowder deliveryDrug additiveActive agent
The invention relates to an oral multiparticle pharmaceutical dosage form in the form of a receptacle reducing the pH values of stomach, containing a plurality of pellets, particles, granules or agglomerates whose mean diameter ranges from 50 to 2500 μn substentially consisting of a) an internal matrix layer containing an active agent which is neither peptide or protein, nor the derivatives or conjugates thereof, a lipophilic matrix whose melting point is greater than 37° C. and a polymer with mucoadhesive effect, b) an external film coating substentially consisting of a polymer or an anionic copolymer which is optionally formulated with conventional pharmaceutical additives, wherein the active agent has a water solubility according to DAB 10, of at least 30 volume parts of water for one part by weight of the active agent and is coated with the lipophilic matrix and said active agent-containing lipophilic matrix is coated with a matrix made of a polymer with mucoadhesive effect. A method for producing the inventive multiparticle pharmaceutical dosage is also disclosed.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Holographic display screen and method for producing the screen
InactiveUS20020154349A1Large viewing angleFulfil requirementsVehicle componentsOptical elementsHolographic screenPhase grating
A transparent holographic display screen for laser projection of at least one or more monochromatic wavelengths, is constructed to selectively diffuse an incident narrow-band laser beam at a predetermined solid angle and simultaneously to pass wide-band ambient light unobstructed through the display screen. The transparent holographic display screen has at least one holographic volume phase grating which is optically coupled to or integrated with a transparent carrier plate. The holographic display screen with its volume grating is produced by illuminating a real screen as an object into a primary hologram and recording a real holographic image of said real screen into a secondary hologram.
Owner:EADS DEUT GMBH
Light-guide lights suitable for use in illuminated displays
InactiveUS7164836B2Uniform efficiencyUniform illuminationMechanical apparatusIncadescent screens/filtersOptical cavityLight guide
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
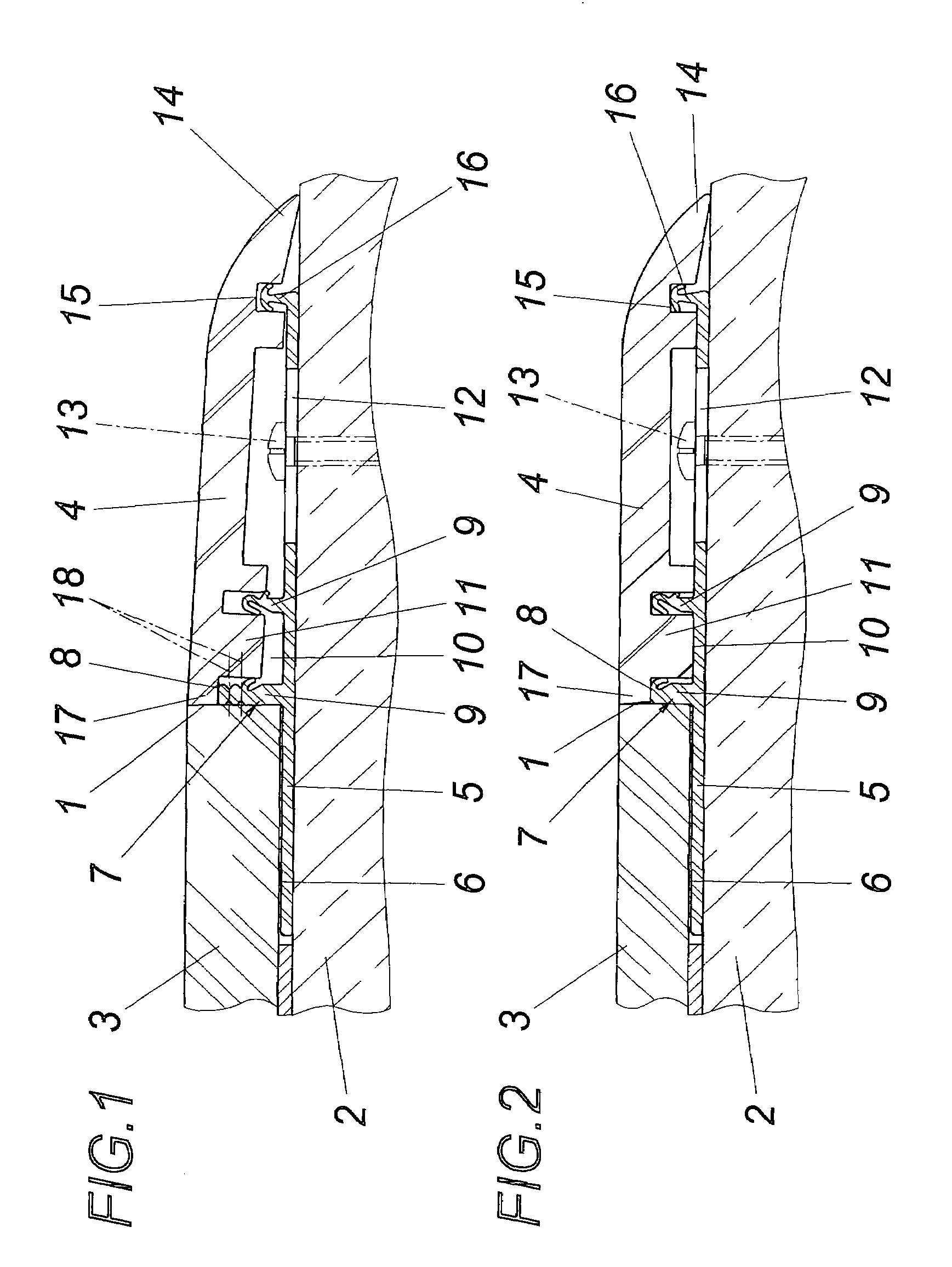
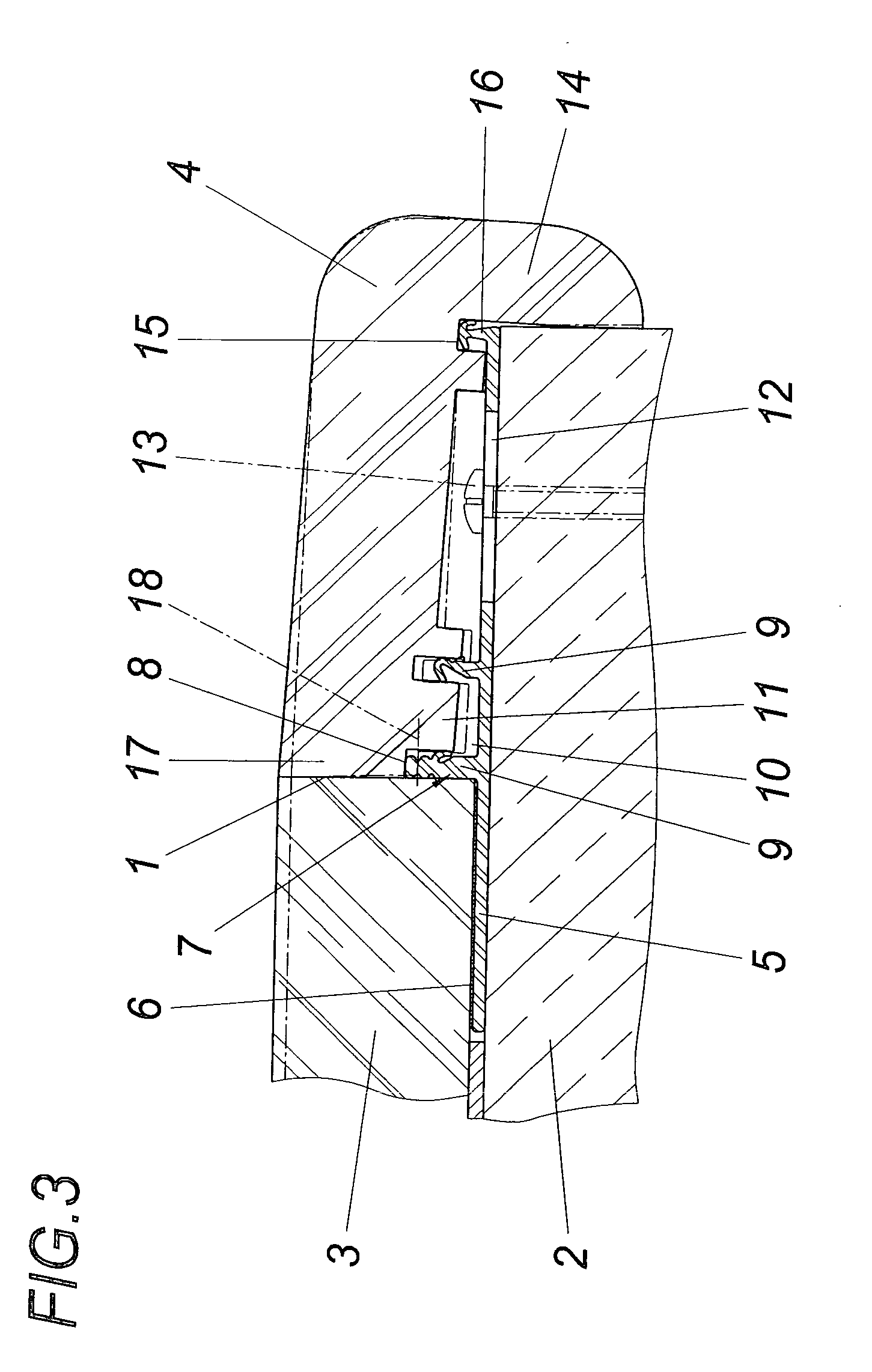
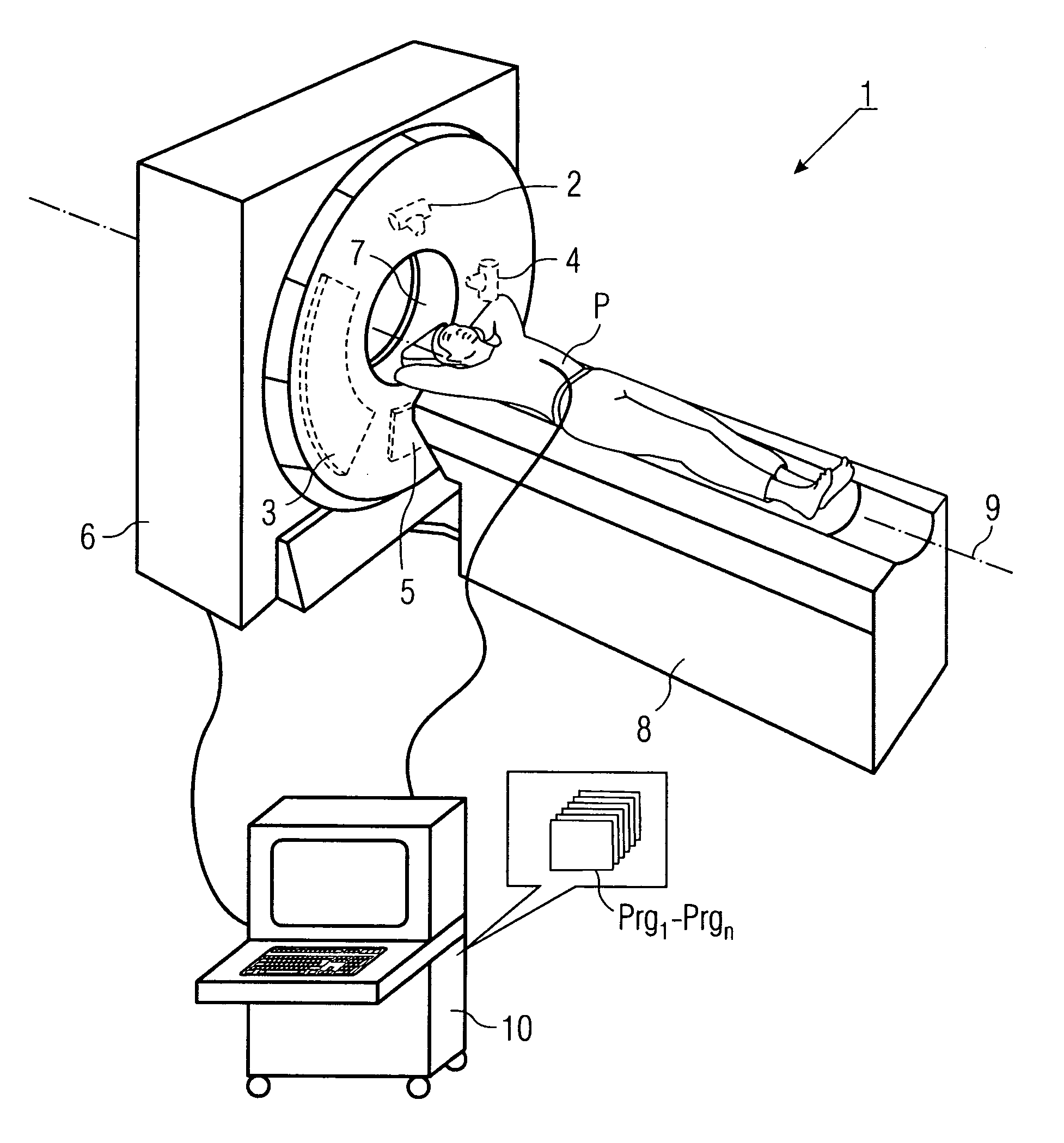
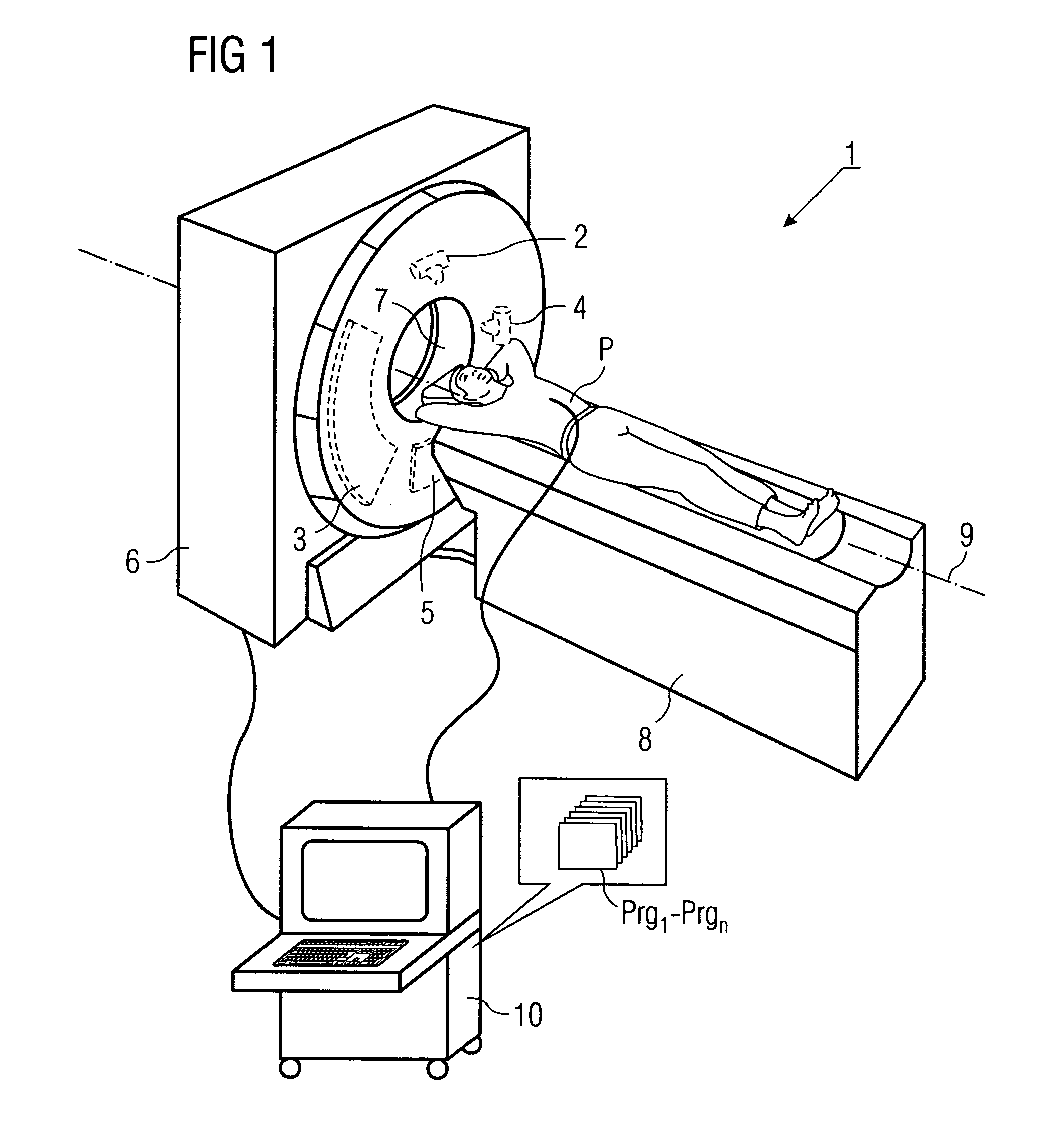
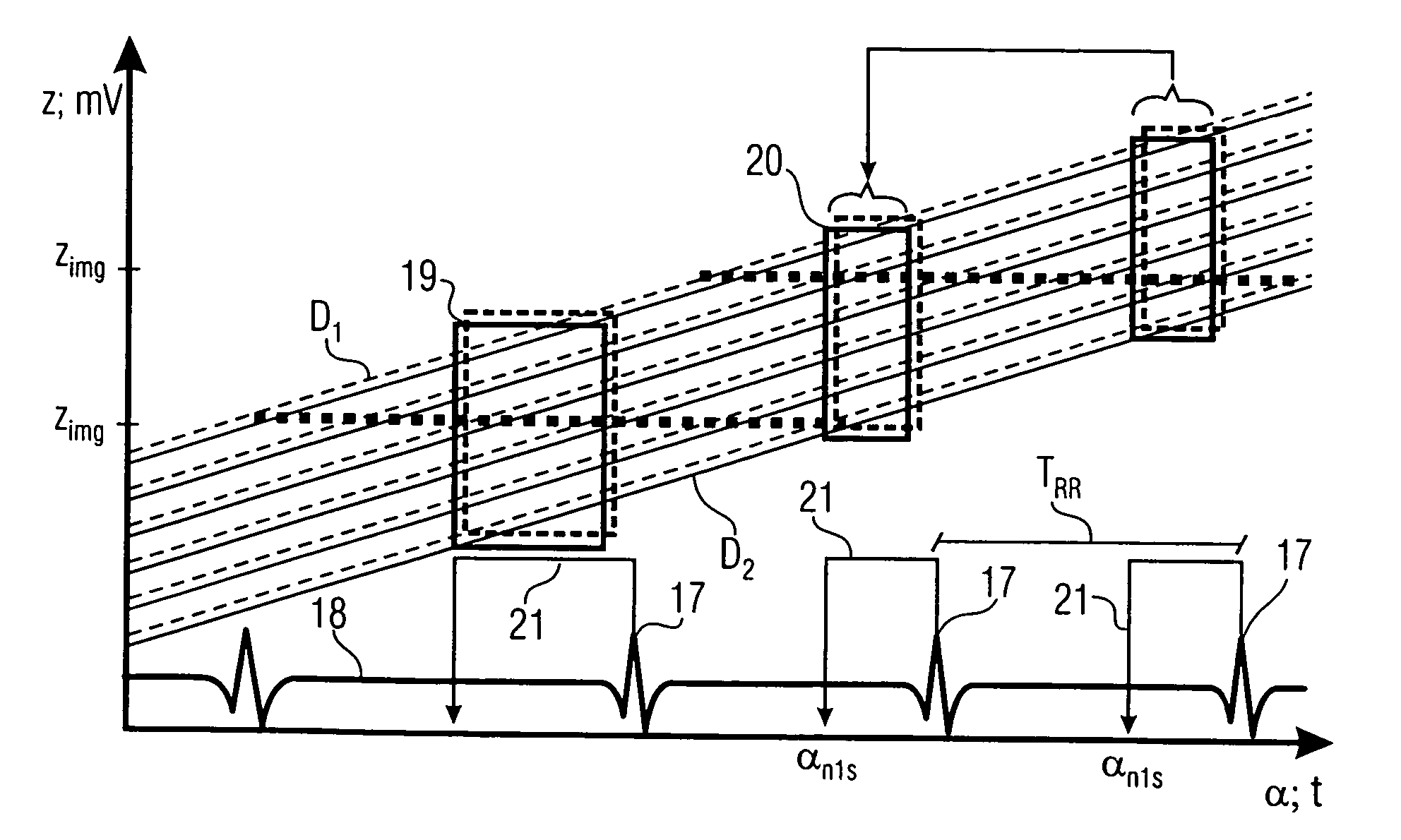
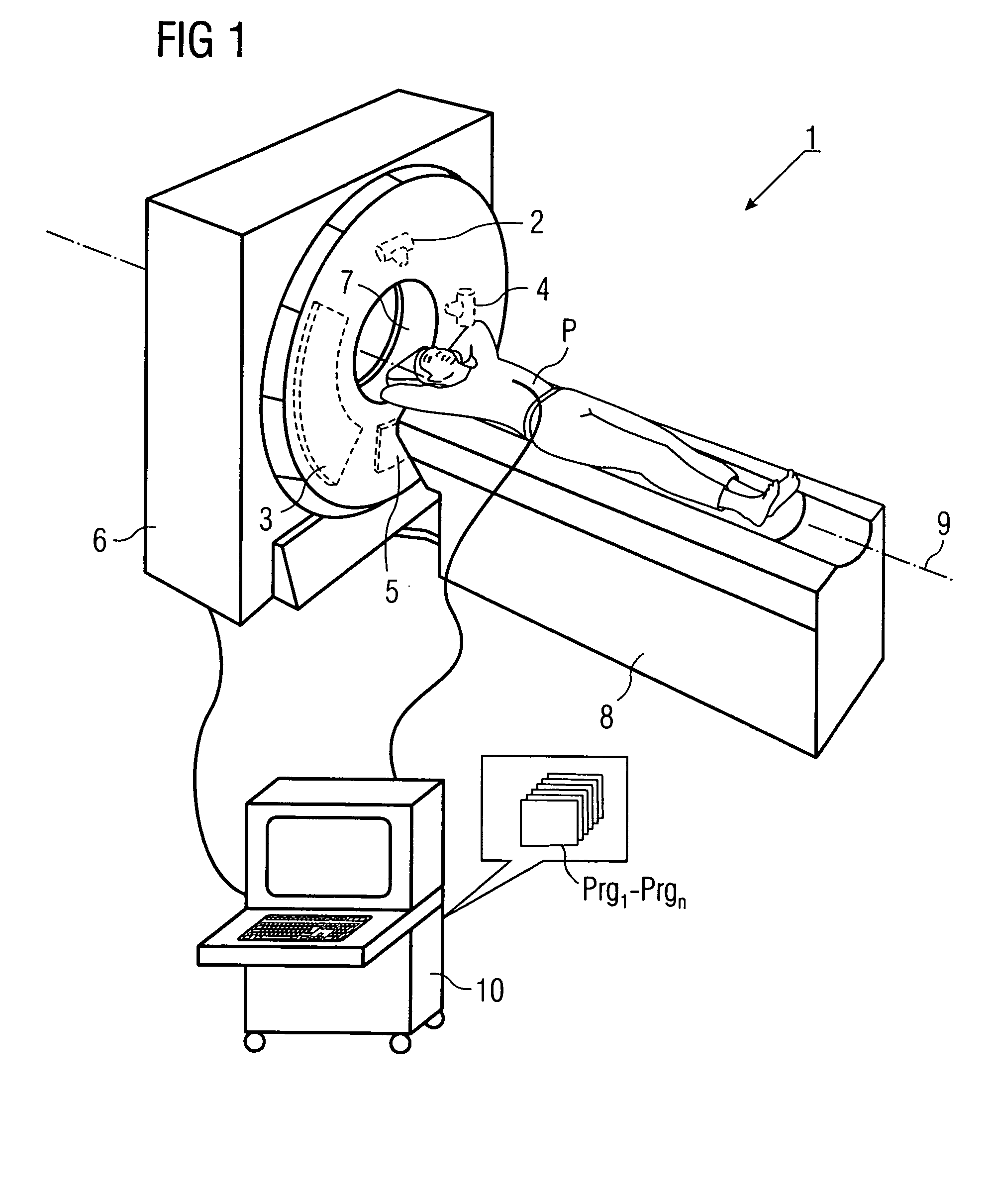
Method for production of tomographic section images of a periodically moving object with a number of focus detector combinations
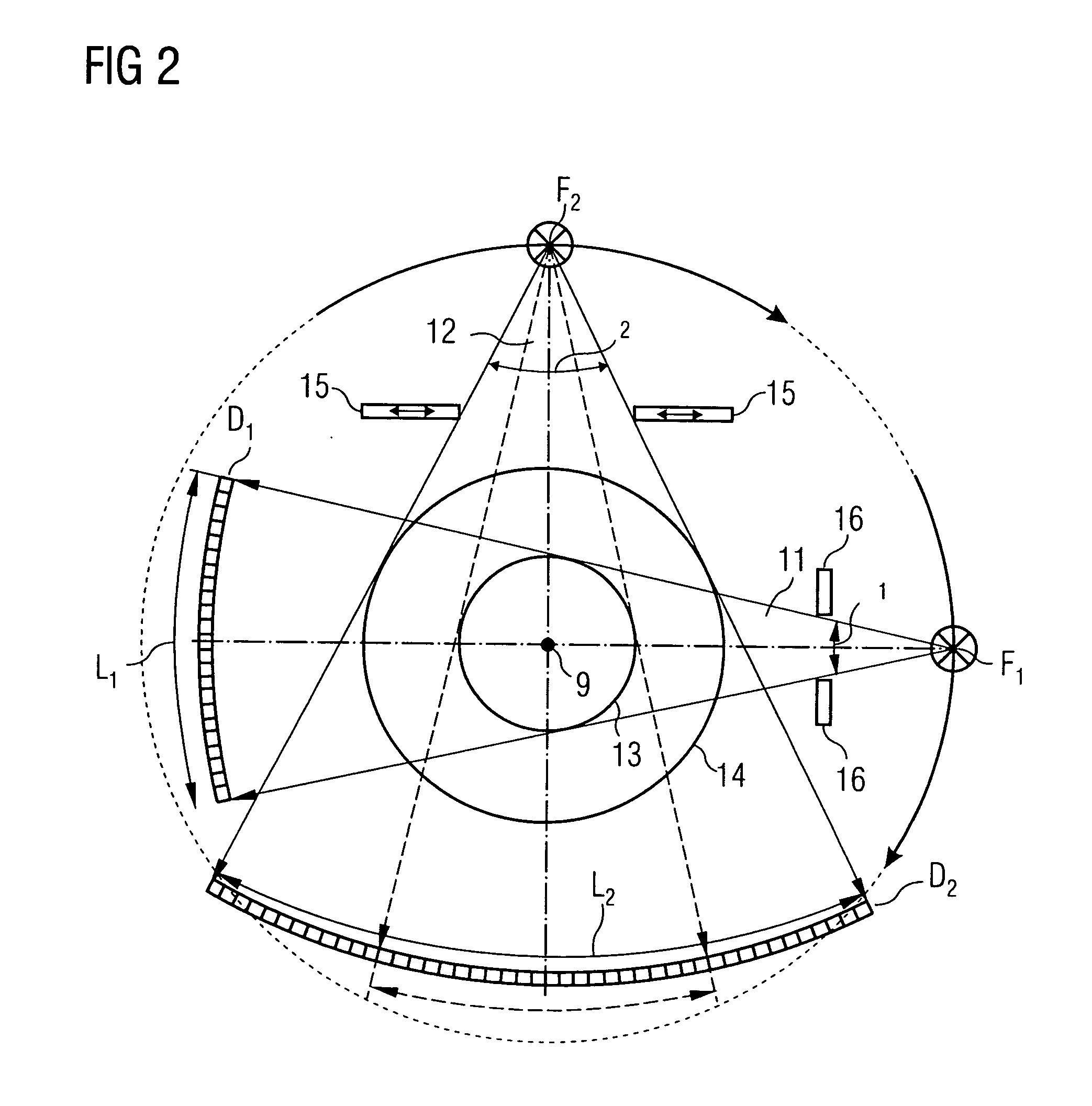
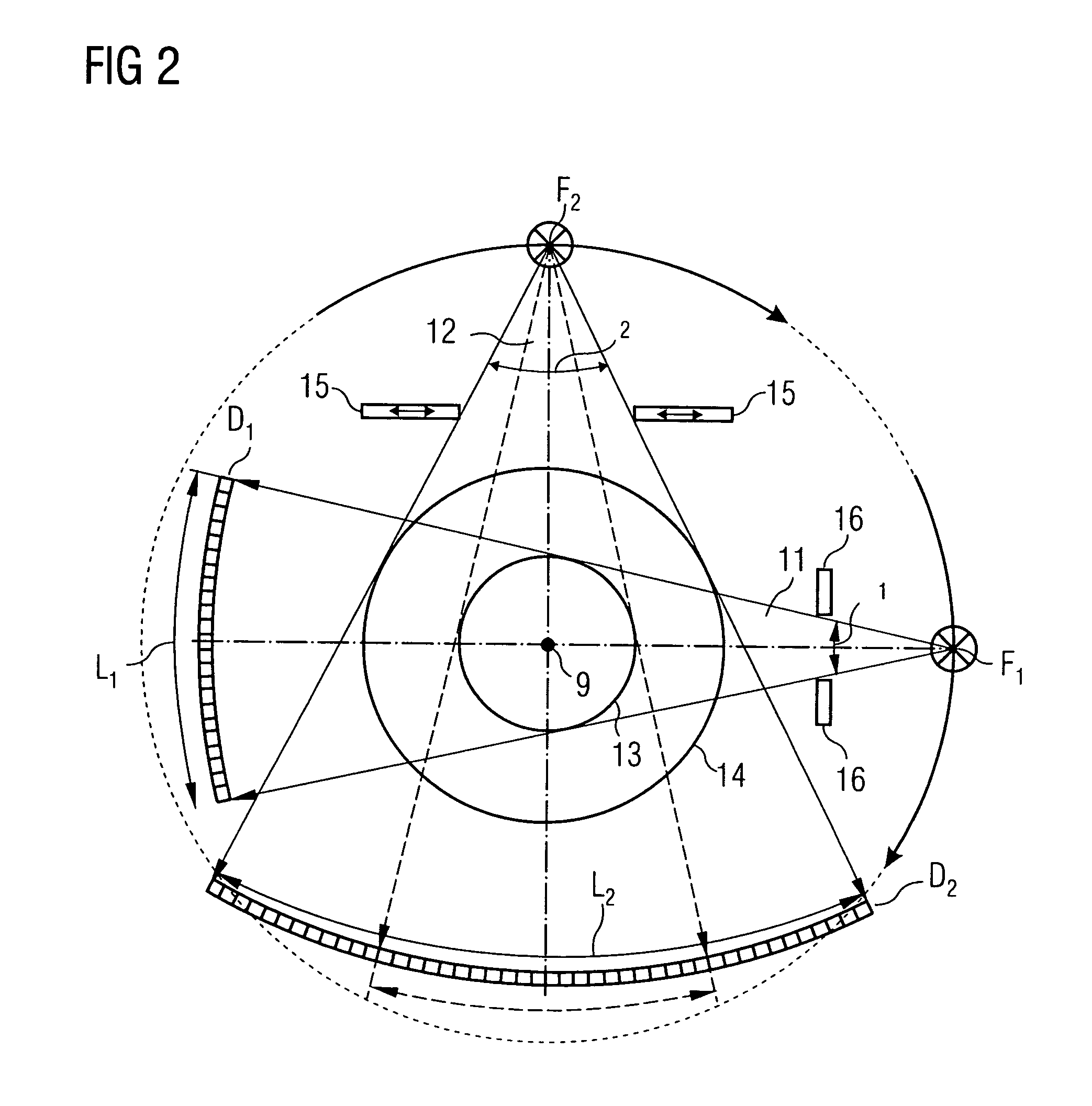
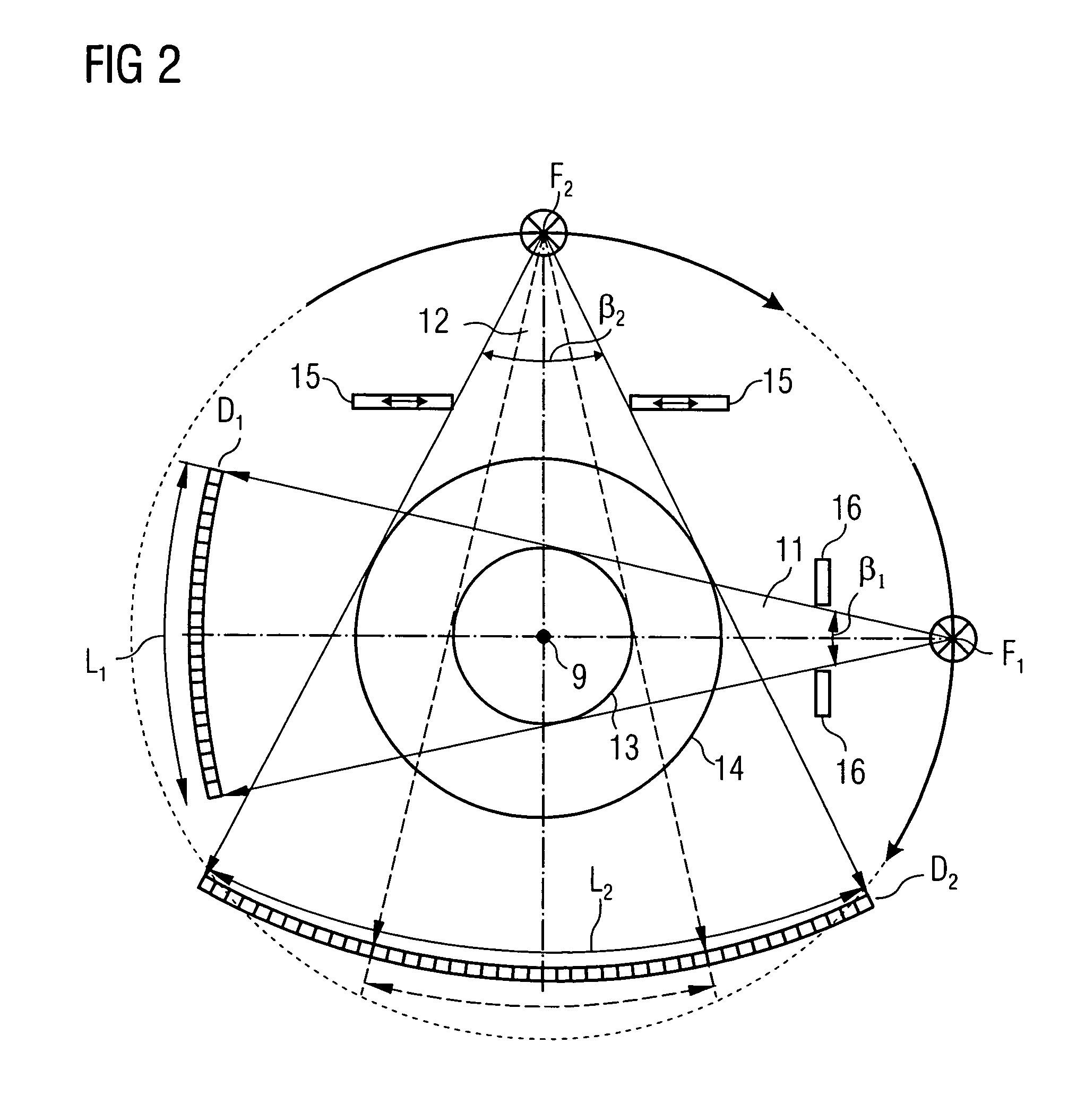
InactiveUS20050111622A1Reduce dose loadOptimize timingRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsTime correlationCt scanners
A method and CT scanner are proposed for the production of tomographic section images, in particular X-ray CT images, of a periodically moving object with periodically changing movement and rest phases. For scanning, a number of focus detector combinations with flat detectors are moved on coaxial spiral paths and movement signals from the moving object are measured at the same time in order to detect movement and rest phases. Further, the time correlation between the movement data and the detector output data stored and axial segment image stacks are then reconstructed independently of one another from sub-segments of the spiral paths using the detector output data from each detector which represent a rest phase of the moving object. Additionally, segment image stacks from the n spiral paths of the n focus detector combinations at the correct time are added up in a complementary angle form and in layers to form 180° tomography section images. The axial segment image stacks are reconstructed in a first step from double-inclined reconstruction planes. Further, in a second step, they are reformatted to produce axial segment image stacks, and detector data from a number of successive movement periods are used for this purpose.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
1,3-Benzoxazolyl derivatives as kinase inhibitors
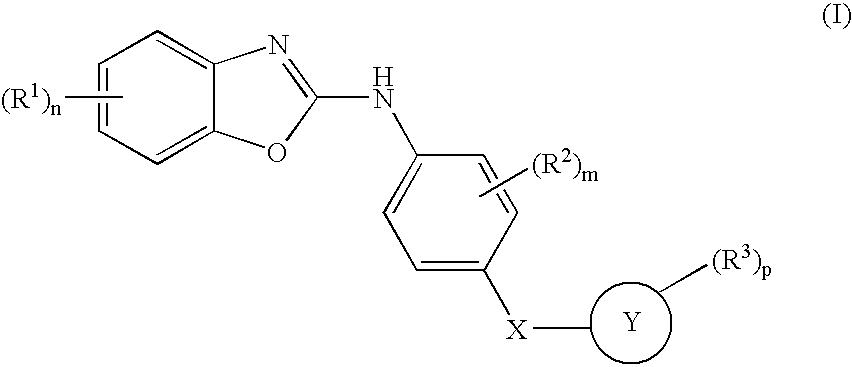
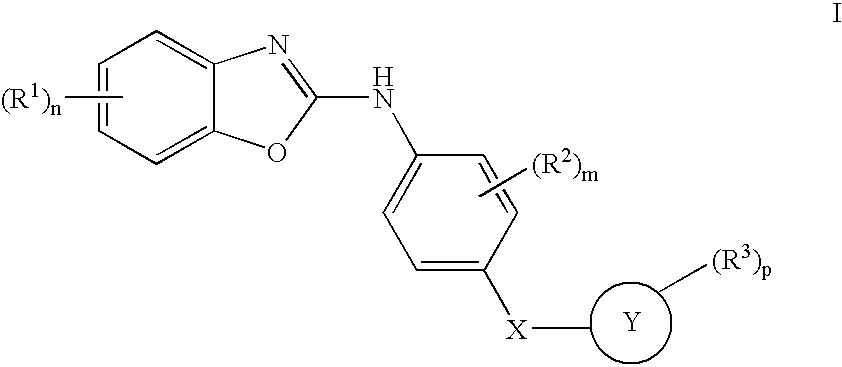
The invention relates to compounds of formula 1, the production and use thereof as a medicament for the treatment of diseases, particularly tumours and / or diseases caused, mediated or propagated by angiogenesis. The compounds of formula 1 are effective inhibitors of tyrosin kinases, particularly TIE-2 and VEGFR, and Raf-kinases. (I)
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Method and arrangement for low-distortion recording of intensity patterns occurring on a contact surface through frustrated total reflection
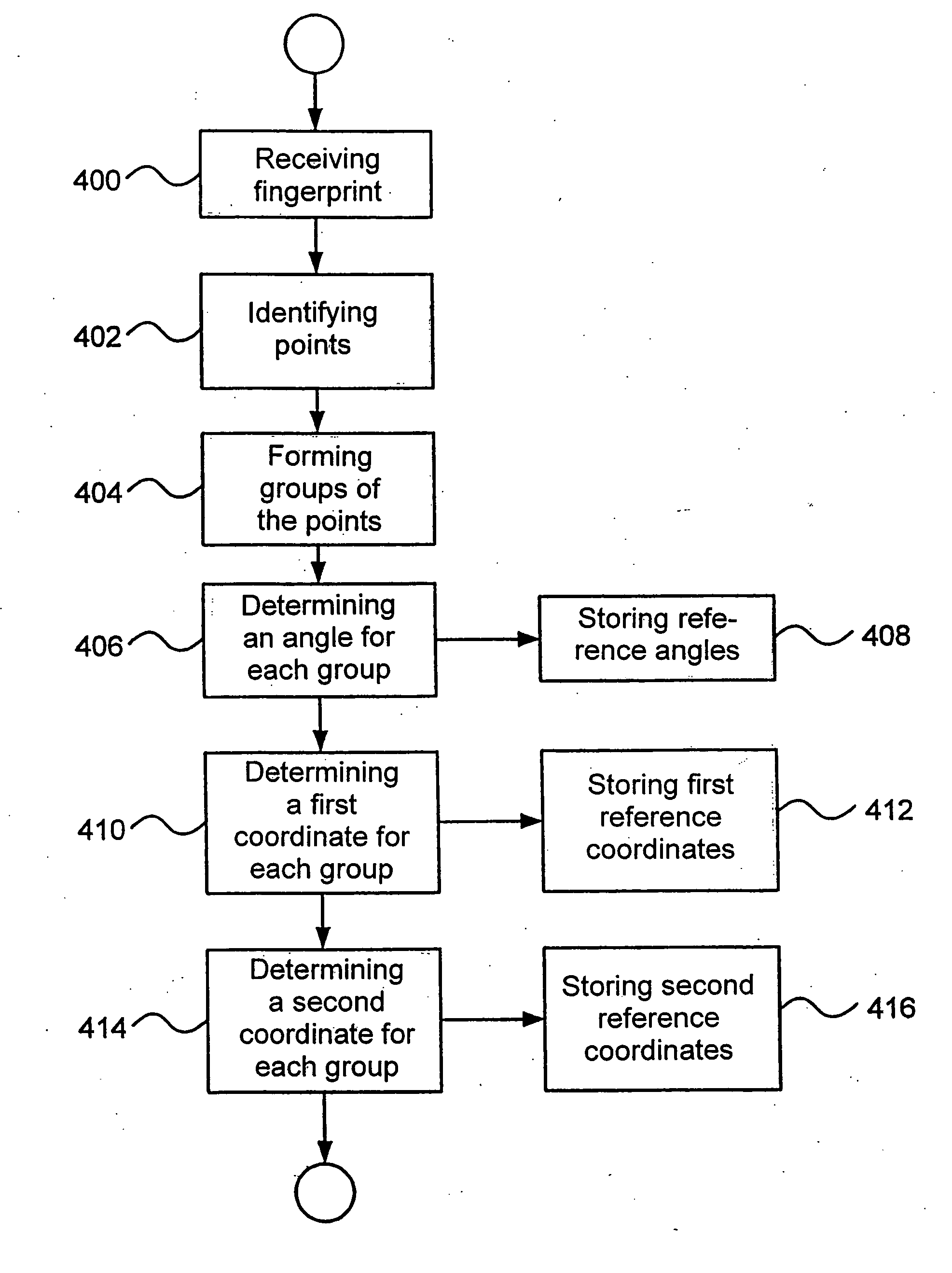
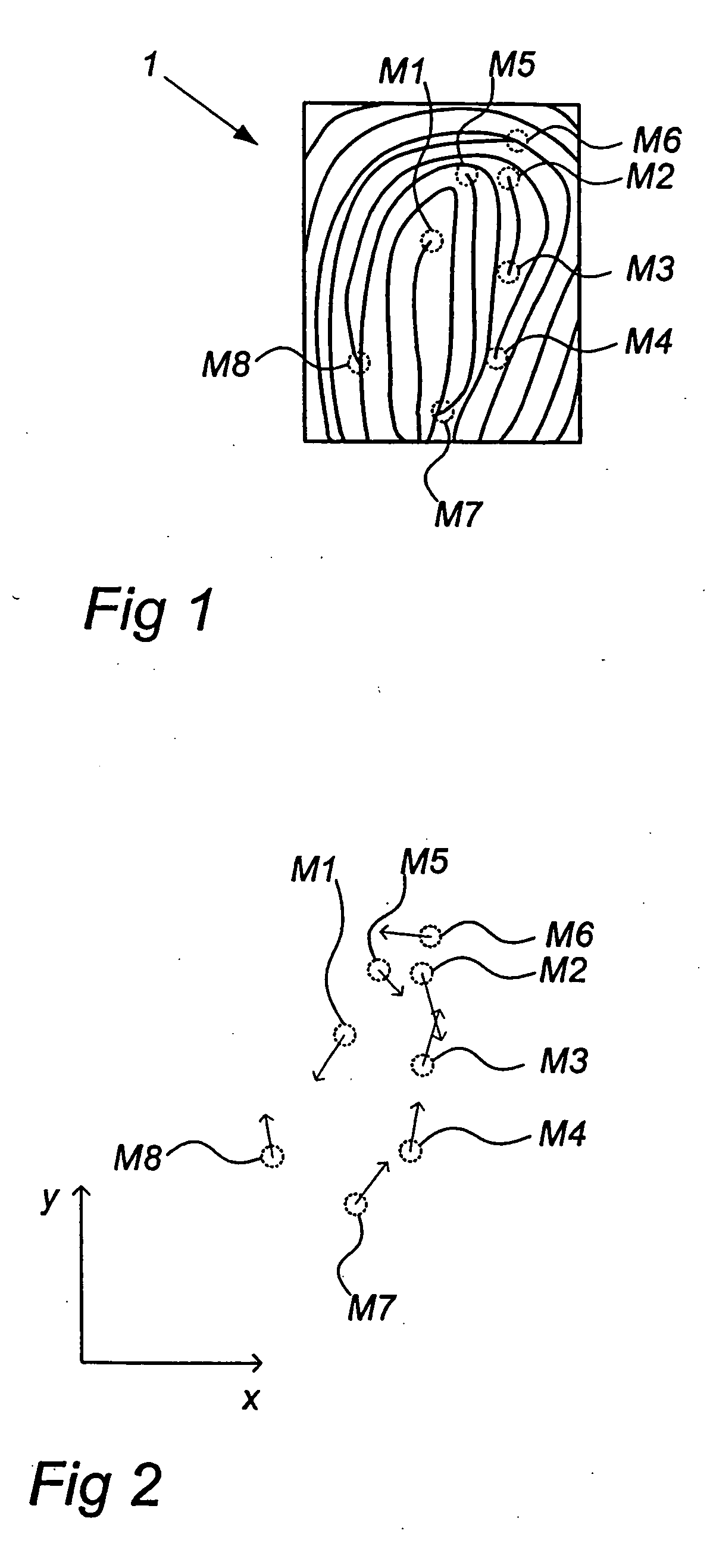
ActiveUS7130456B2Reduce distortion problemsNone is suitable for purposeGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionFingerprintImage sensor
A method and an arrangement for recording intensity patterns occurring on a contact surface by frustrated total reflection, particularly for low-distortion recording of relatively large-area fingerprints, handprints or footprints or other parts of the skin. It is an object of the invention to find a novel possibility for recording intensity patterns occurring on a support surface according to the principle of frustrated total reflection which achieves a high-resolution, low-distortion image of the intensity pattern using simple optical arrangements. This object is met, according to the invention, in that a support surface for the measurement object is illuminated homogeneously by a light source at an angle of total reflection, an image of the support surface is imaged on the image sensor as an intensity pattern only by of an imaging optical system, so that the image is imaged on the image sensor so as to be distorted but sharp in all parts of the image, and light from the light source which is totally reflected at the support surface enters parallel to the axis of the optical system, the image of the support surface is scanned by the image sensor with substantially more image elements (pixels) than those required for the desired resolution in the output-side final image of the intensity pattern, and the optoelectronically converted, trapezoidally distorted image is rectified by displacement, interpolation and averaging operations based on the generation of combined pixel data from a data surplus occurring as a result of the increased quantity of recorded pixels compared to the necessary quantity of pixels in the final image.
Owner:CROSS MATCH TECH
Semiconductor light emitting apparatus and light source apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20110090703A1Improve cooling effectSpeed up the conversion processSolid-state devicesGlobesPoint lightFluorescence
A semiconductor light emitting apparatus includes a solid-state light emitting device and a wavelength converter that converts primary light emitted by the solid-state light emitting device into secondary light at a loner-wavelength. The wavelength converter is an inorganic compact that includes a transparent wavelength conversion layer containing phosphor having a garnet crystal structure. The phosphor contains a constituent element group composed of at least one element selected from the group consisting of Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Y, La, Gd, Tb, and Lu. Part of the constituent element group is substituted by Ce3+ and the amount of Ce+ is 1 atomic % less of the entire constituent element group. As a result, a high-power and highly reliable semiconductor light emitting apparatus suitable as a point light source is provided. In addition, such a semiconductor light emitting apparatus is manufactured through a simple application of traditionally used practical technicians.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Artificial promoter libraries for selected organisms and promoters derived from such libraries
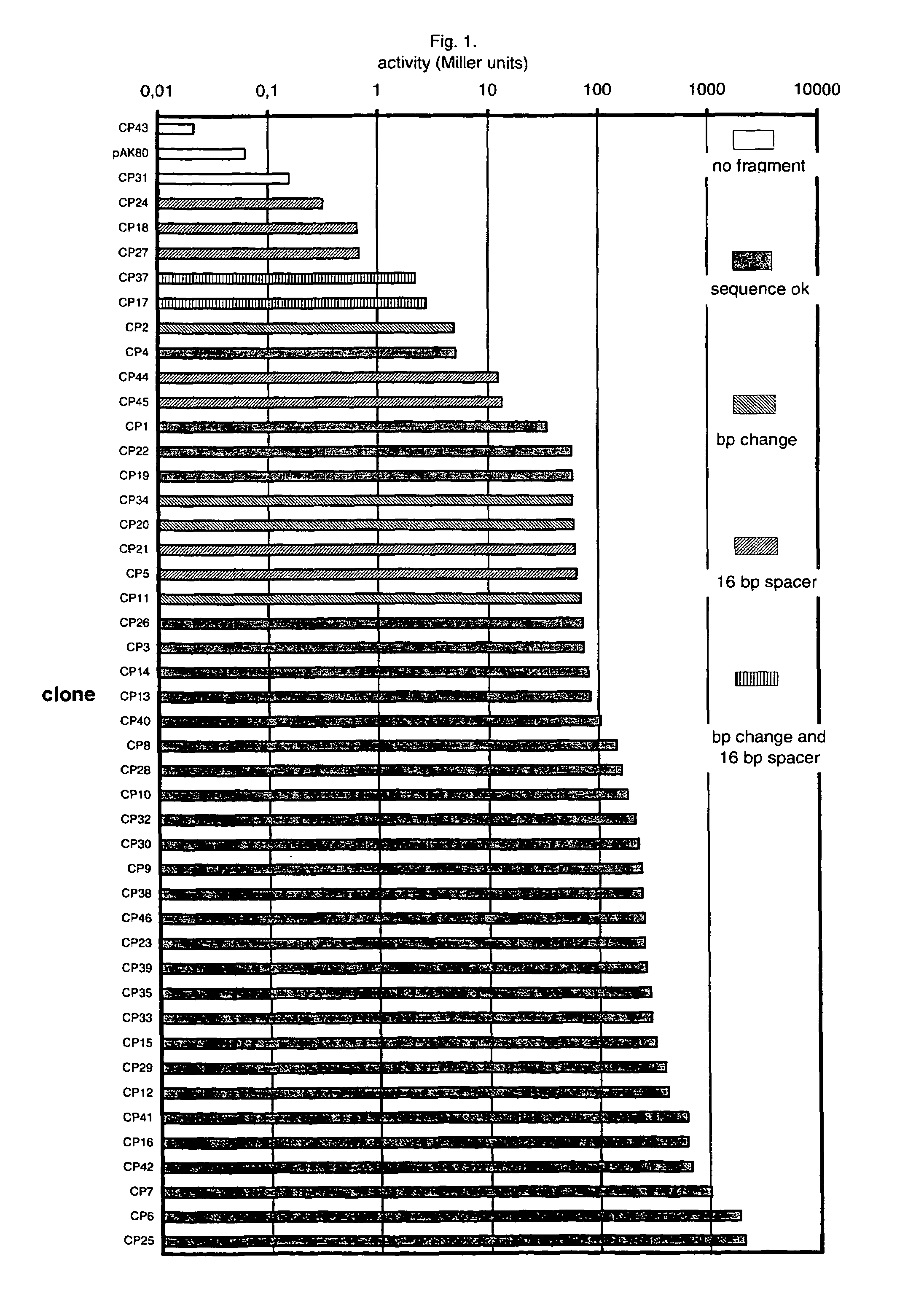
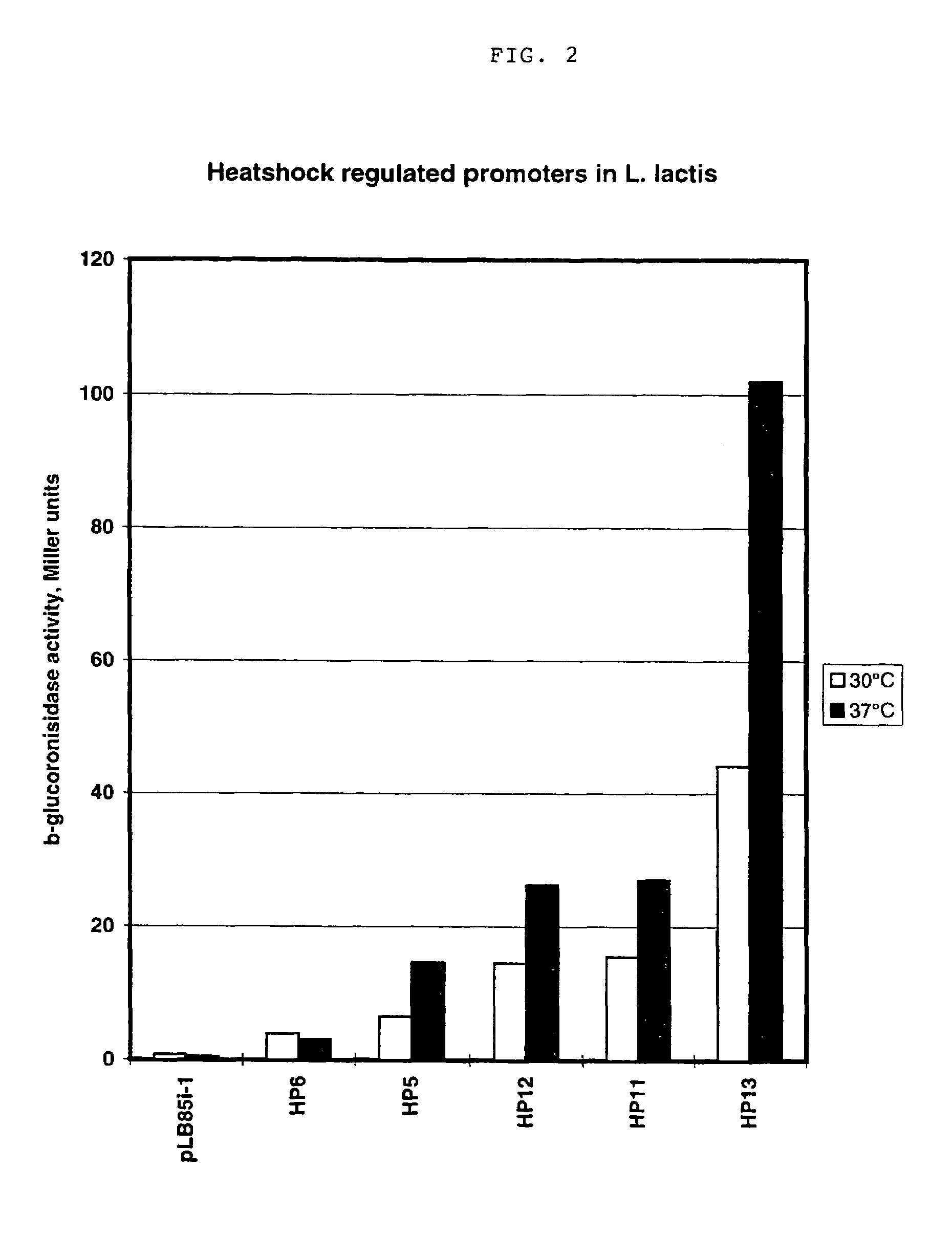
InactiveUS7199233B1Strong impactNone is suitable for purposeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleobase
An artificial promoter library (or a set of promoter sequences) for a selected organism or group of organisms is constructed as a mixture of double stranded DNA fragments, the sense strands of which comprise at least two consensus sequences of efficient promoters from said organism or group of organisms, or parts thereof comprising at least half of each, and surrounding intermediate nucleotide sequences (spacers) of variable length in which at least 7 nucleotides are selected randomly among the nucleobases A, T, C and G. The sense strands of the double stranded DNA fragments may also include a regulatory DNA sequence imparting a specific regulatory feature, such as activation by a change in the growth conditions, to the promoters of the library. Further, they may have a sequence comprising one or more recognition sites for restriction endonucleases added to one or both of their ends. The selected organism or group of organisms may be selected from prokaryotes and from eukaryotes; and in prokaryotes the consensus sequences to be retained most often will comprise the −35 signal (−35 to −30): TTGACA and the −10 signal (−12 to −7): TATAAT or parts of both comprising at least 3 conserved nucleotides of each, while in eukaryotes said consensus sequences should comprise a TATA box and at least one upstream activation sequence (UAS). Such artificial promoter libraries can be used, e.g., for optimizing the expression of specific genes in various selected organisms.
Owner:JENSEN PETER RUHDAL +1
Garment, preferably for nursing, and method for providing such
InactiveUS7430883B2Simple methodNone is suitable for purposeWeft knittingOrnamental textile articlesClosed loopEngineering
Owner:TYTEX AS
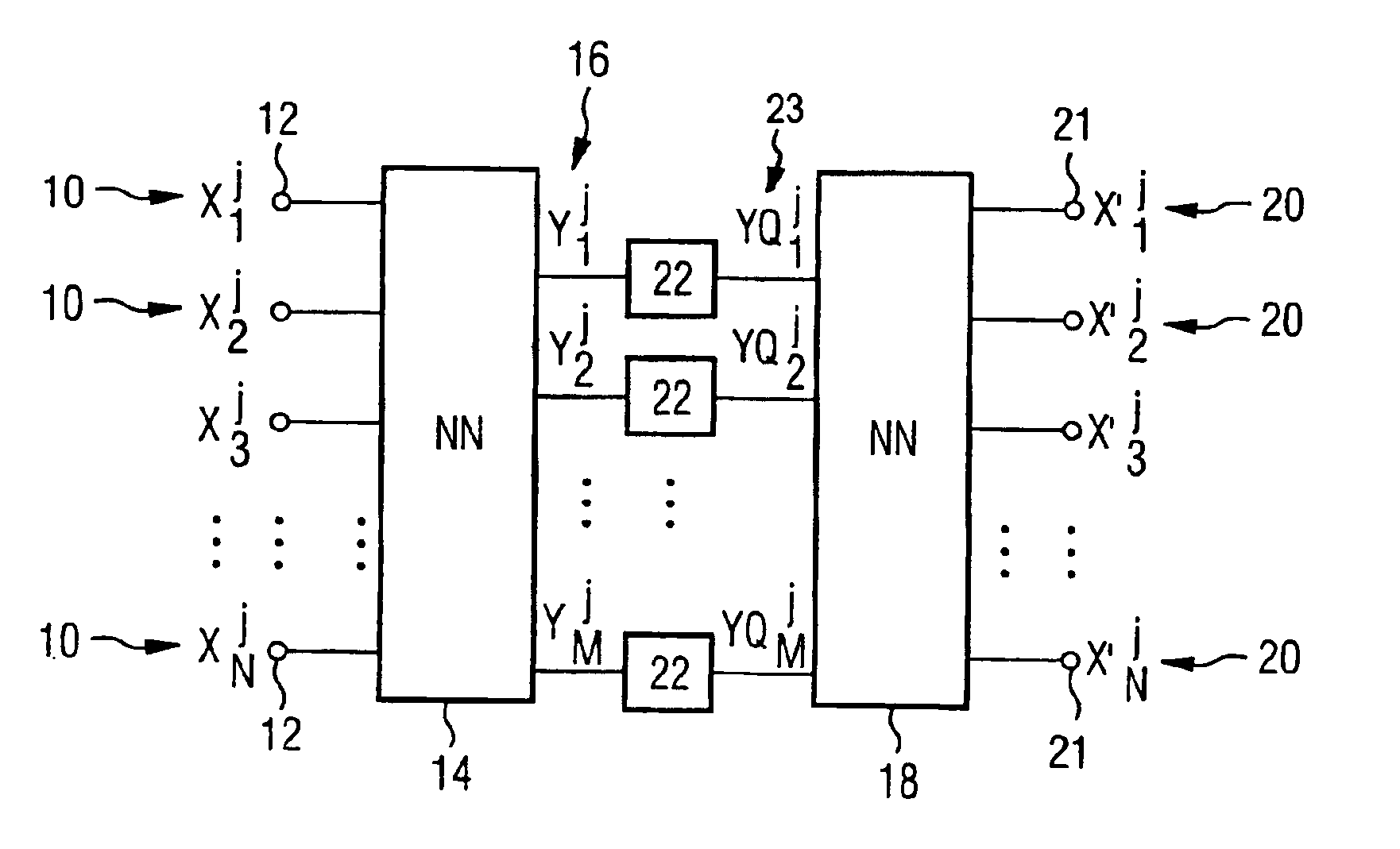
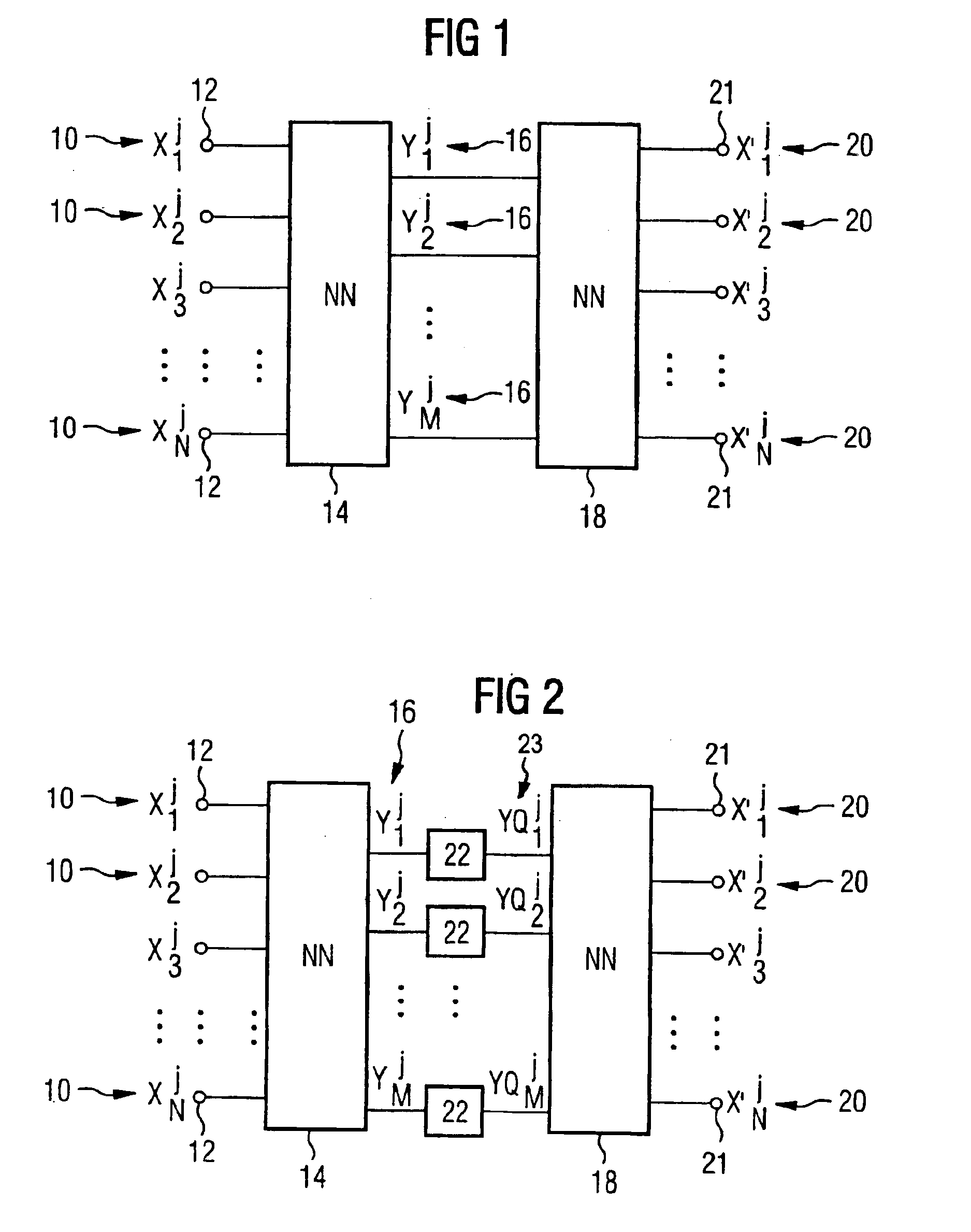
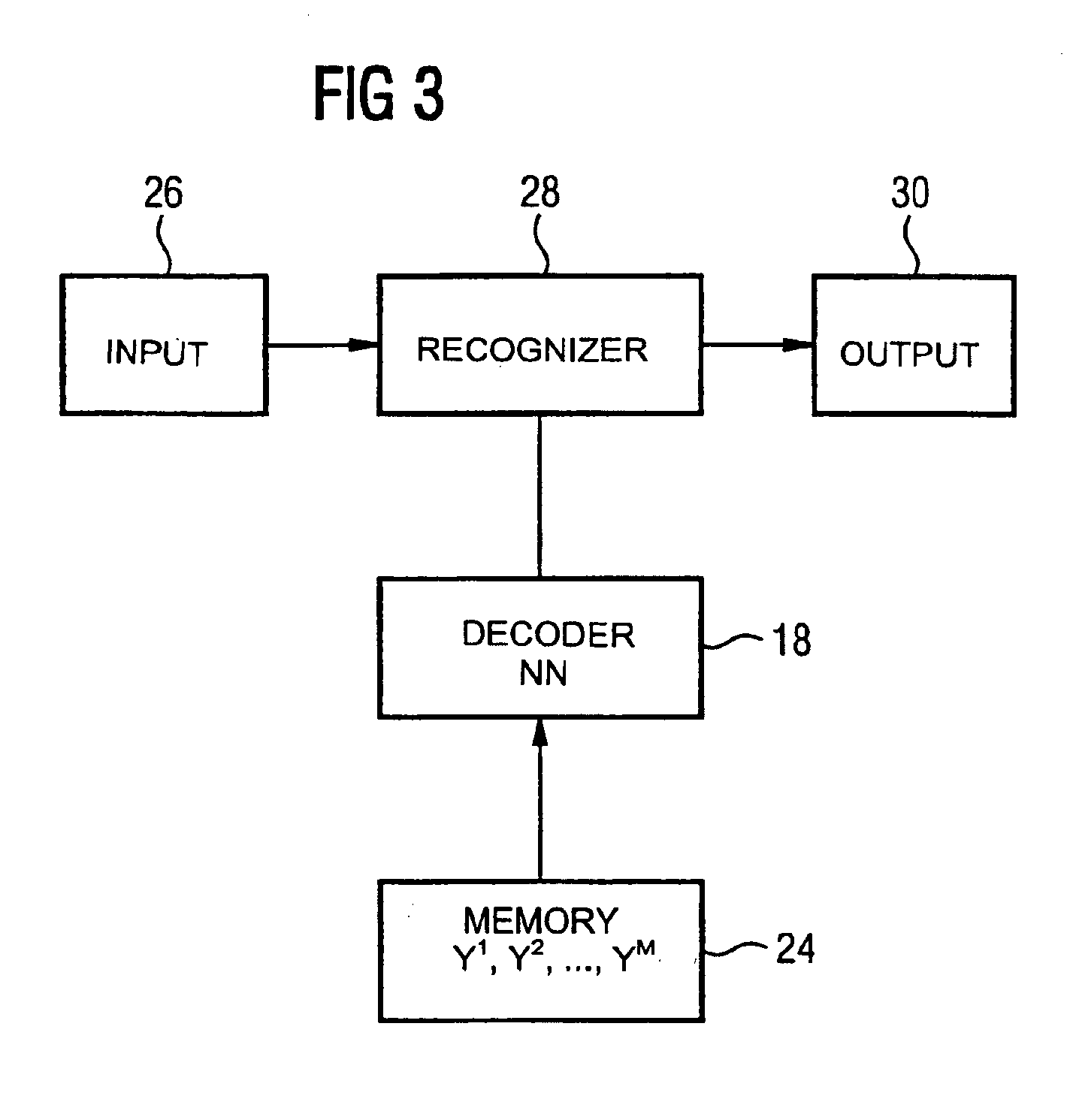
Compressing HMM prototypes
InactiveUS6907398B2Reduce storage spaceStorage space requiredDigital computer detailsCode conversionEncoderSpeech recognition
A method is described for compressing the storage space required by HMM prototypes in an electronic memory. For this purpose prescribed HMM prototypes are mapped onto compressed HMM prototypes with the aid of a neural network (encoder). These can be stored with a smaller storage space than the uncompressed HMM prototypes. A second neural network (decoder) serves to reconstruct the HMM prototypes.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG +1
Macrocyclics pyrimidines as aurora kinase inhibitors
InactiveUS8815872B2Stabilizing and improving clinical symptomInhibit tumor growthOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
Macrocyclic derivative compounds that inhibit protein kinase enzymes are disclosed along with pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and methods for synthesizing the same. Such compounds have utility in the treatment of proliferative diseases resulting from unregulated and / or disturbed kinase activity such as cancers, psoriasis, viral and bacterial infections, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
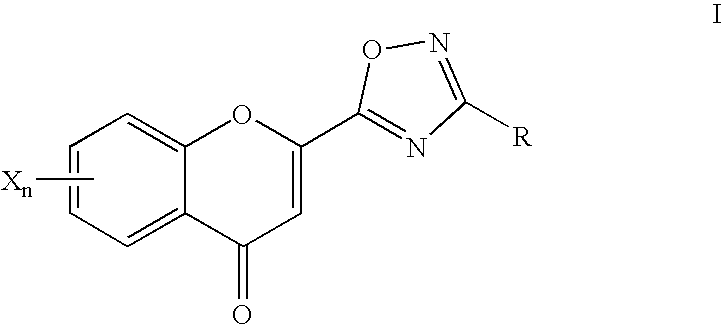
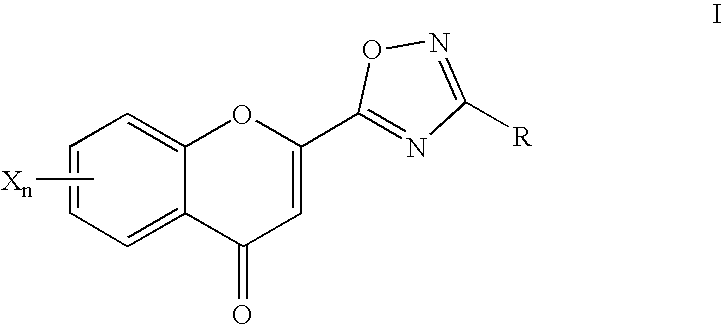
2-oxadiazolechromone derivatives
InactiveUS7354945B2Stabilising and improving clinical symptomGrowth inhibitionBiocideOrganic chemistryStress ProteinsStereochemistry
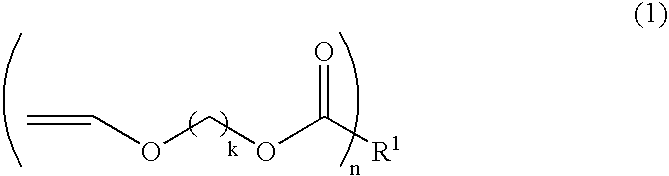
Novel compounds of the formula Iin whichR, X and n are as defined herein,are inhibitors of tyrosine kinase and can be employed for the treatment of tumours, for neuroprotection and for protection of the stress proteins of the skin.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
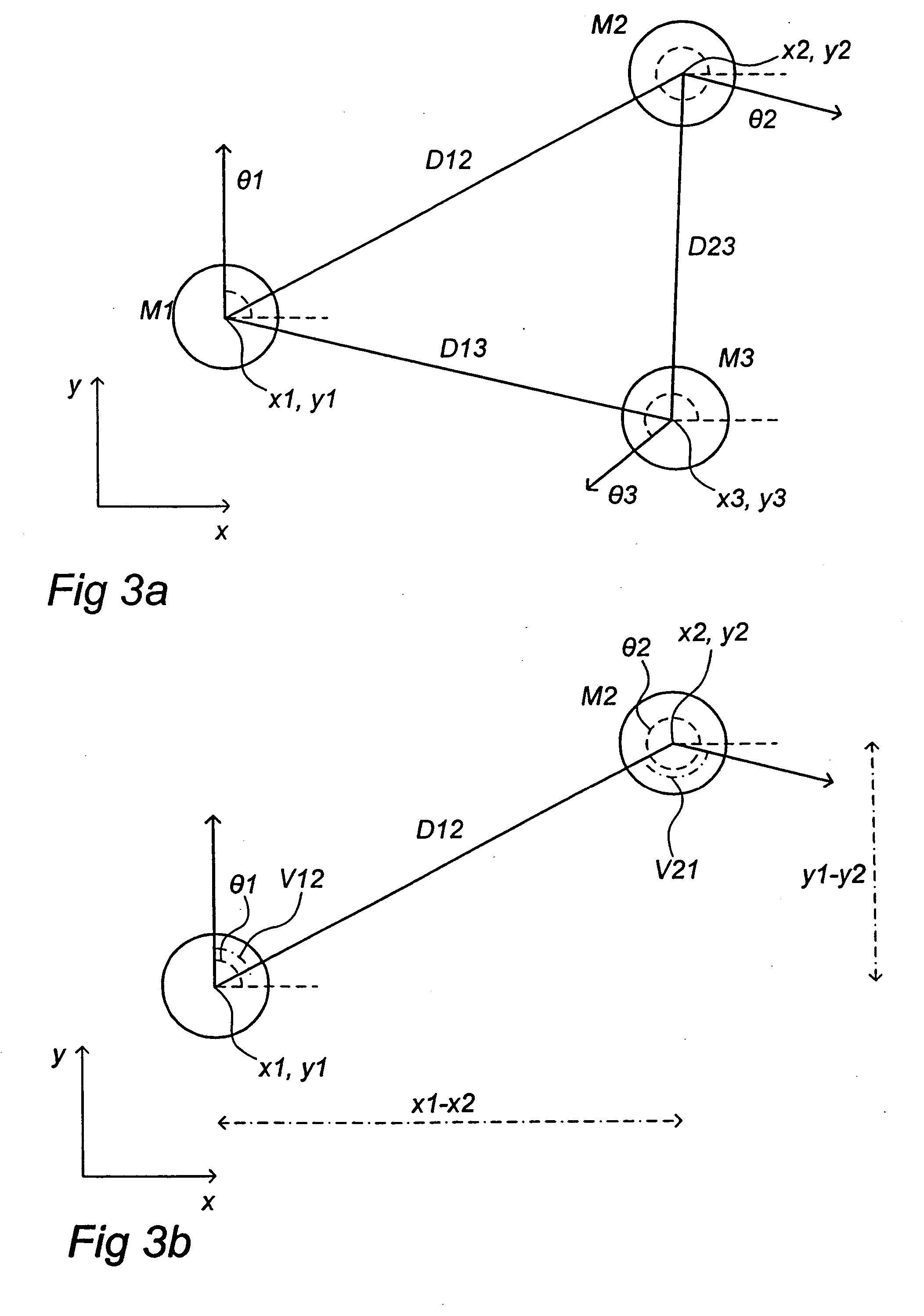
Method and device for aligning of a fingerprint
InactiveUS20070031014A1None is suitable for purposeSet become largeCharacter and pattern recognitionFingerprintComputer program
The present invention relates to methods for aligning an input fingerprint with a reference fingerprint, methods for comparing an input fingerprint with a reference fingerprint, computer program products for aligning an input fingerprint with a reference fingerprint, computer program products for comparing an input fingerprint with a reference fingerprint, devices and systems for aligning an input fingerprint with a reference fingerprint, and devices and systems for comparing an input fingerprint with a reference fingerprint.
Owner:PRECISE BIOMETRICS AB
Positive-type photosensitive resin composition and cured film manufactured therefrom
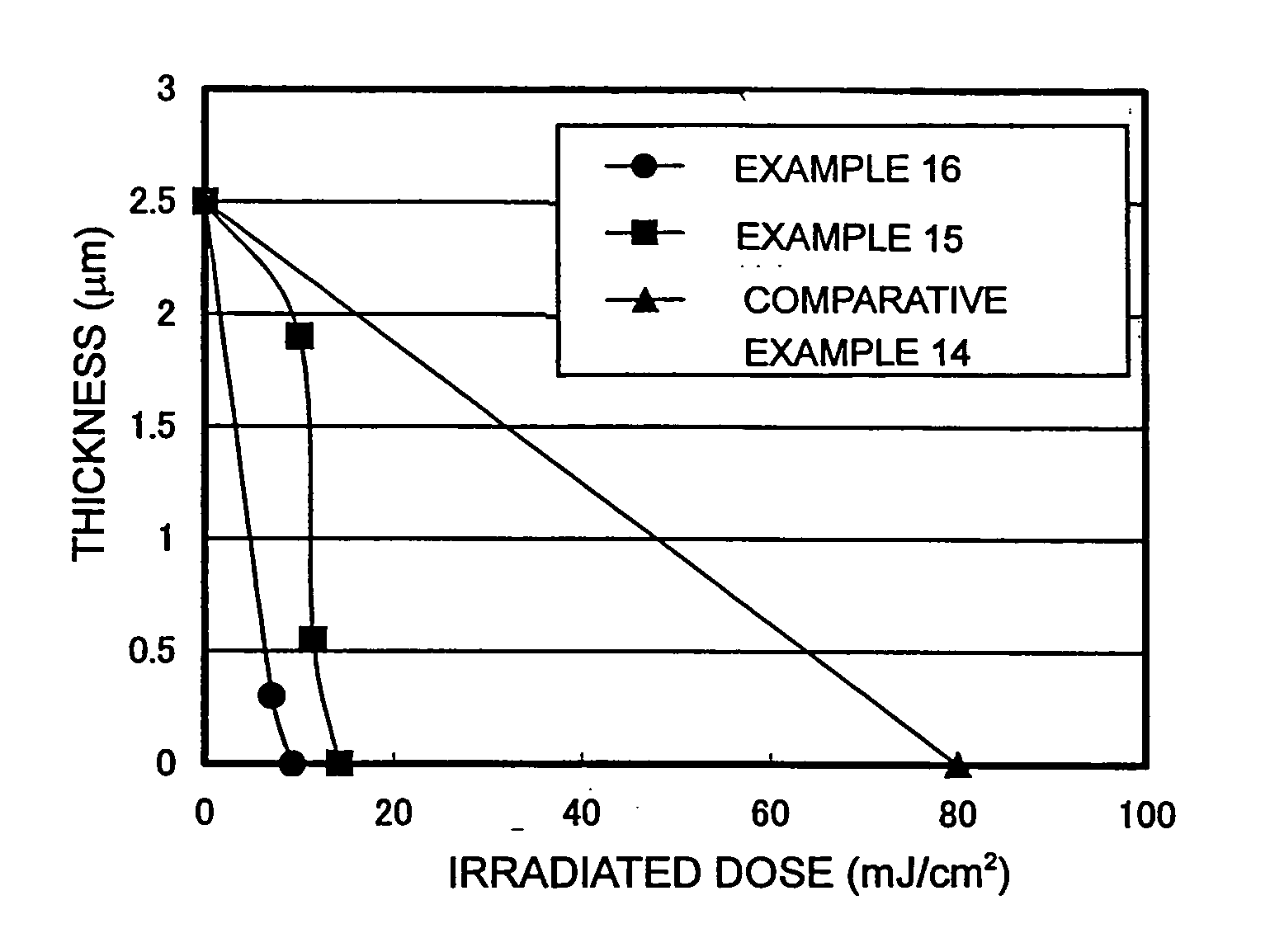
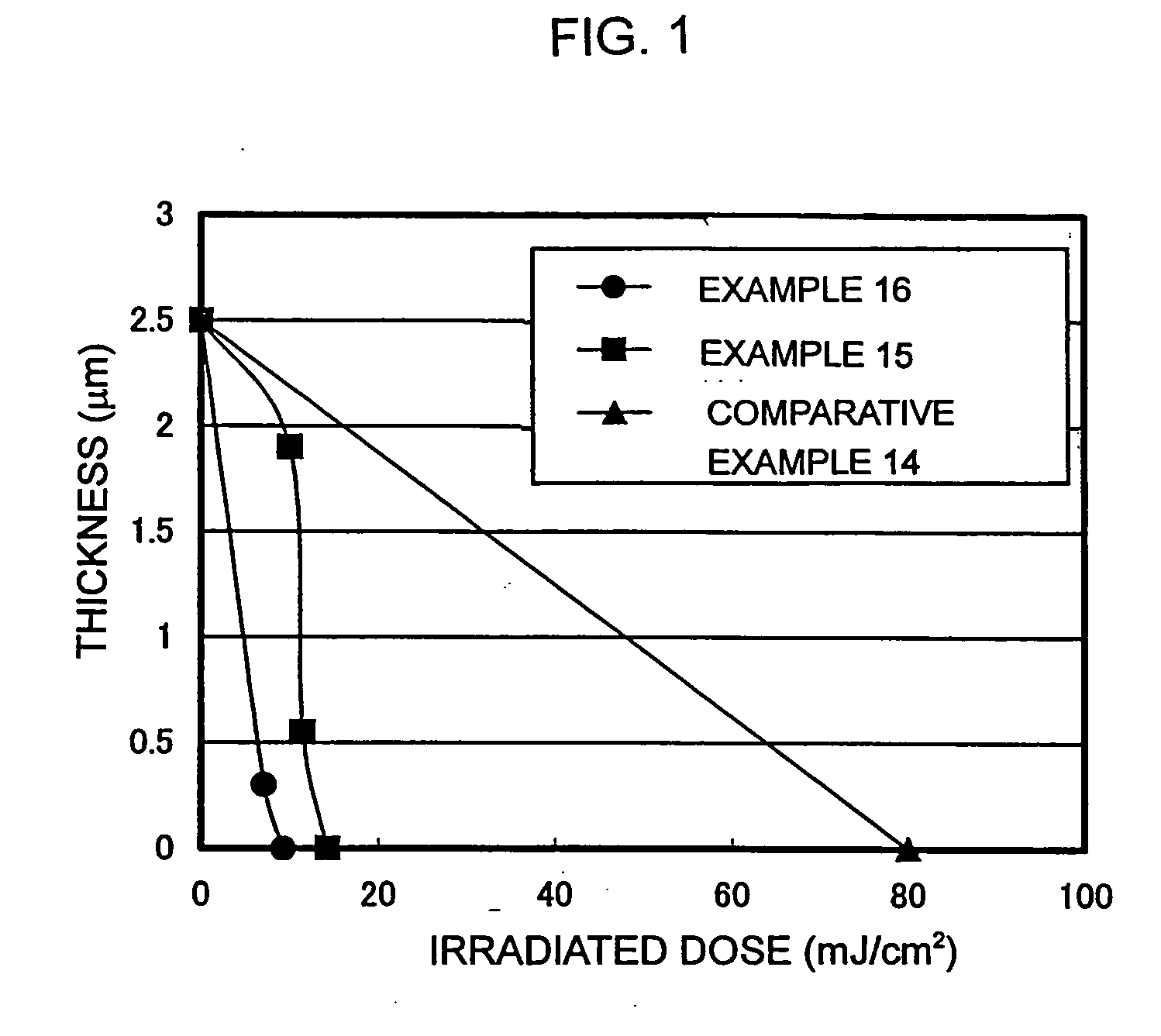
ActiveUS20070020559A1High sensitivityLittle film reductionPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsVinyl etherPolymer science
A positive-type photosensitive resin composition comprising component (A): an alkali-soluble resin having a functional group which undergoes heat crosslinking reaction with a compound of component (B), a functional group for film curing which undergoes thermoset reaction with a compound of component (C), and a number average molecular weight of 2,000 to 30,000; component (B): a compound having two or more vinyl ether groups per molecule; component (C): a compound having two or more blocked isocyanate groups per molecule; component (D): a photoacid generator; and component (E): a solvent. A production process of the positive-type photosensitive resin composition comprising mixing the above-mentioned components and maintaining the mixture at a temperature higher than room temperature. A cured film manufactured by using the positive-type photosensitive resin composition. The composition has a high sensitivity and little film reduction of unexposed part, maintains a high transmittance even after baking at a high temperature or resist stripping treatment, and cause no reduction of film thickness. Therefore, the composition provides a cured film suited as a film material for several displays.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Device for Frontal Termination of a Floor Covering
InactiveUS20090071089A1Increase the differenceSimple conditionsTreadsConstruction materialClassical mechanicsFloor covering
Owner:NEUHOFER JR FRANZ
Method for production of tomographic section images of a periodically moving object with a number of focus detector combinations
InactiveUS7039152B2Optimize timingNone is suitable for purposeRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsTime correlationCt scanners
A method and CT scanner are proposed for the production of tomographic section images, in particular X-ray CT images, of a periodically moving object with periodically changing movement and rest phases. For scanning, a number of focus detector combinations with flat detectors are moved on coaxial spiral paths and movement signals from the moving object are measured at the same time in order to detect movement and rest phases. Further, the time correlation between the movement data and the detector output data stored and axial segment image stacks are then reconstructed independently of one another from sub-segments of the spiral paths using the detector output data from each detector which represent a rest phase of the moving object. Additionally, segment image stacks from the n spiral paths of the n focus detector combinations at the correct time are added up in a complementary angle form and in layers to form 180° tomography section images. The axial segment image stacks are reconstructed in a first step from double-inclined reconstruction planes. Further, in a second step, they are reformatted to produce axial segment image stacks, and detector data from a number of successive movement periods are used for this purpose.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Light tube
InactiveUS20100110685A1Improve cooling effectNone is suitable for purposeCoupling device connectionsLighting support devicesElectricityLight pipe
A light tube including a heat sink, a light transmissive cover disposed on the heat sink, and at least one light source module is provided. A containing space is formed between the heat sink and the light transmissive cover. The light source module includes a carrier, a plurality of first light-emitting devices, a plurality of second light-emitting devices, and a plurality of non-light-emitting passive devices. The carrier is disposed on the heat sink. The first light-emitting devices are arranged on the carrier along a first straight reference line to form a first line of light-emitting devices. The second emitting devices are arranged on the carrier along a second straight reference line to form a second line of light-emitting devices. The non-light-emitting passive devices are disposed on the carrier and between the first and second lines of light-emitting devices and electrically connected to the first and the second light-emitting devices.
Owner:EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS
Garment, preferably for nursing, and method for providing such
InactiveUS20060277948A1Simple methodNone is suitable for purposeWeft knittingOrnamental textile articlesClosed loopEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for providing a nursing garment from a circular knitted fabric tube, where the nursing garment comprises a back portion and a front portion comprising breast cups completely or partly formed from at least a double layer of fabric, forming inner and outer breast cups, wherein said double layer of fabric is knitted integrally in one piece and used in an open or closed loop form, allowing knitting to be continued downwards from below the breasts. The present invention furthermore relates to a garment, preferably for use when nursing, produced by the aforementioned method.
Owner:TYTEX AS
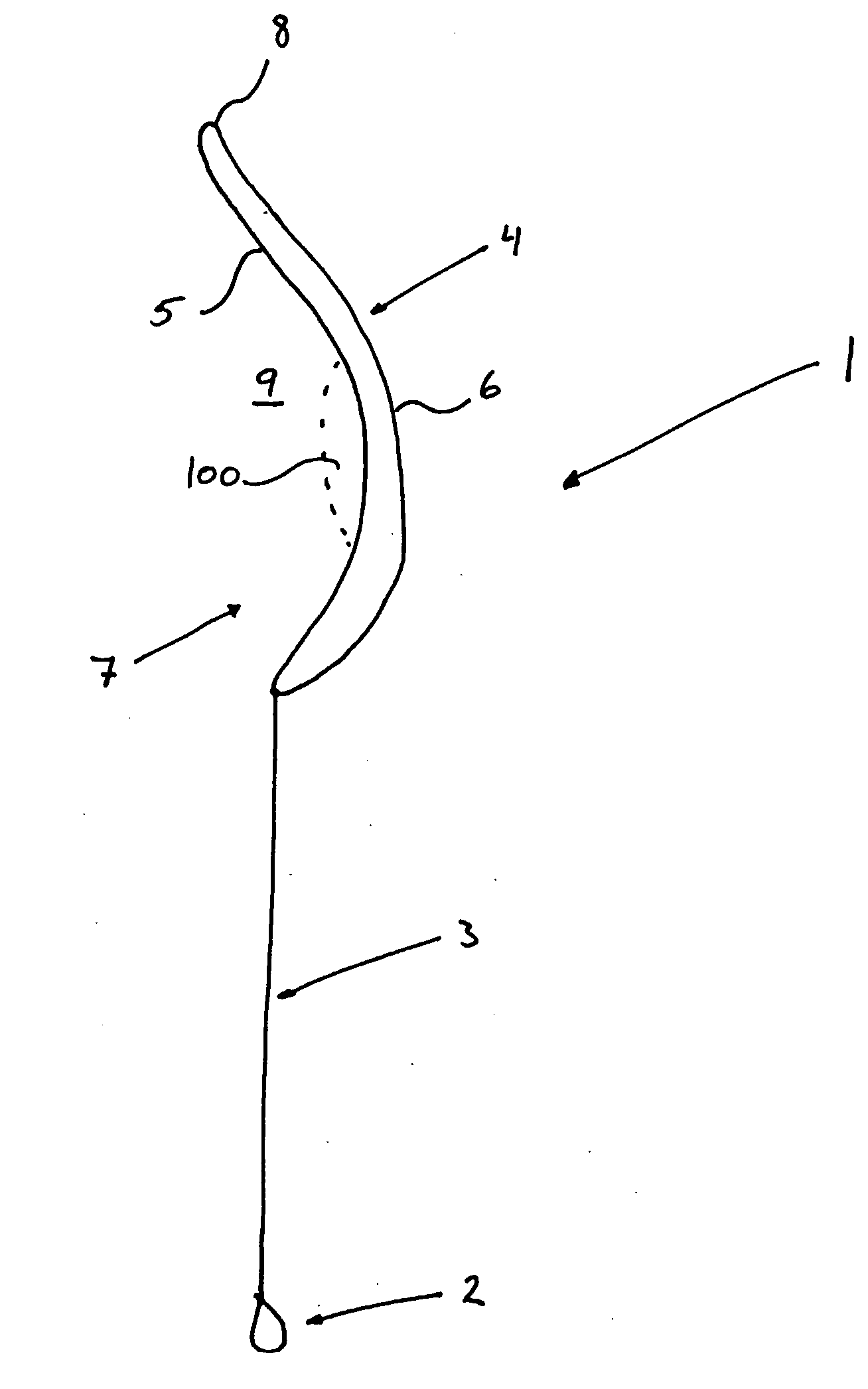
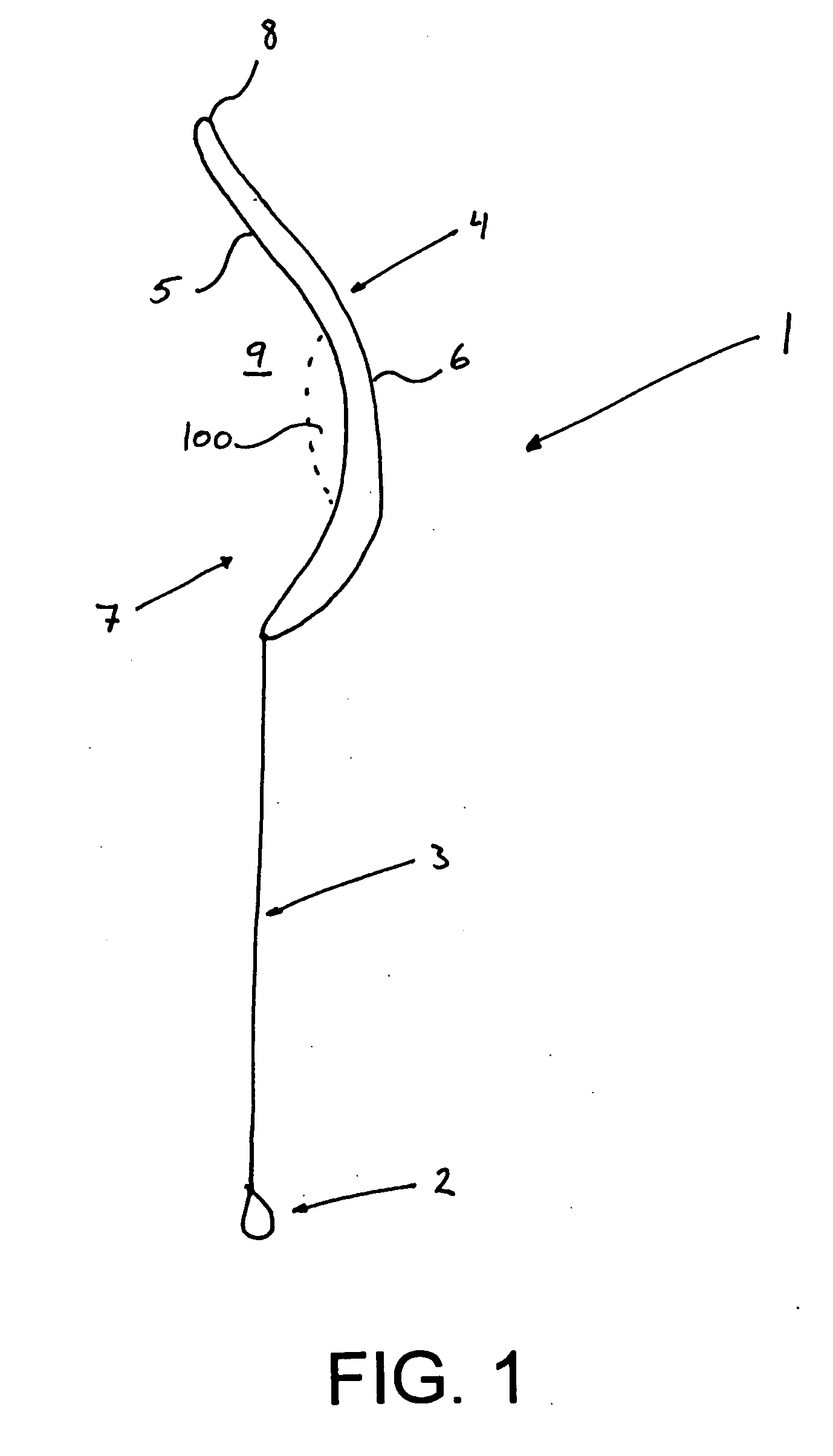
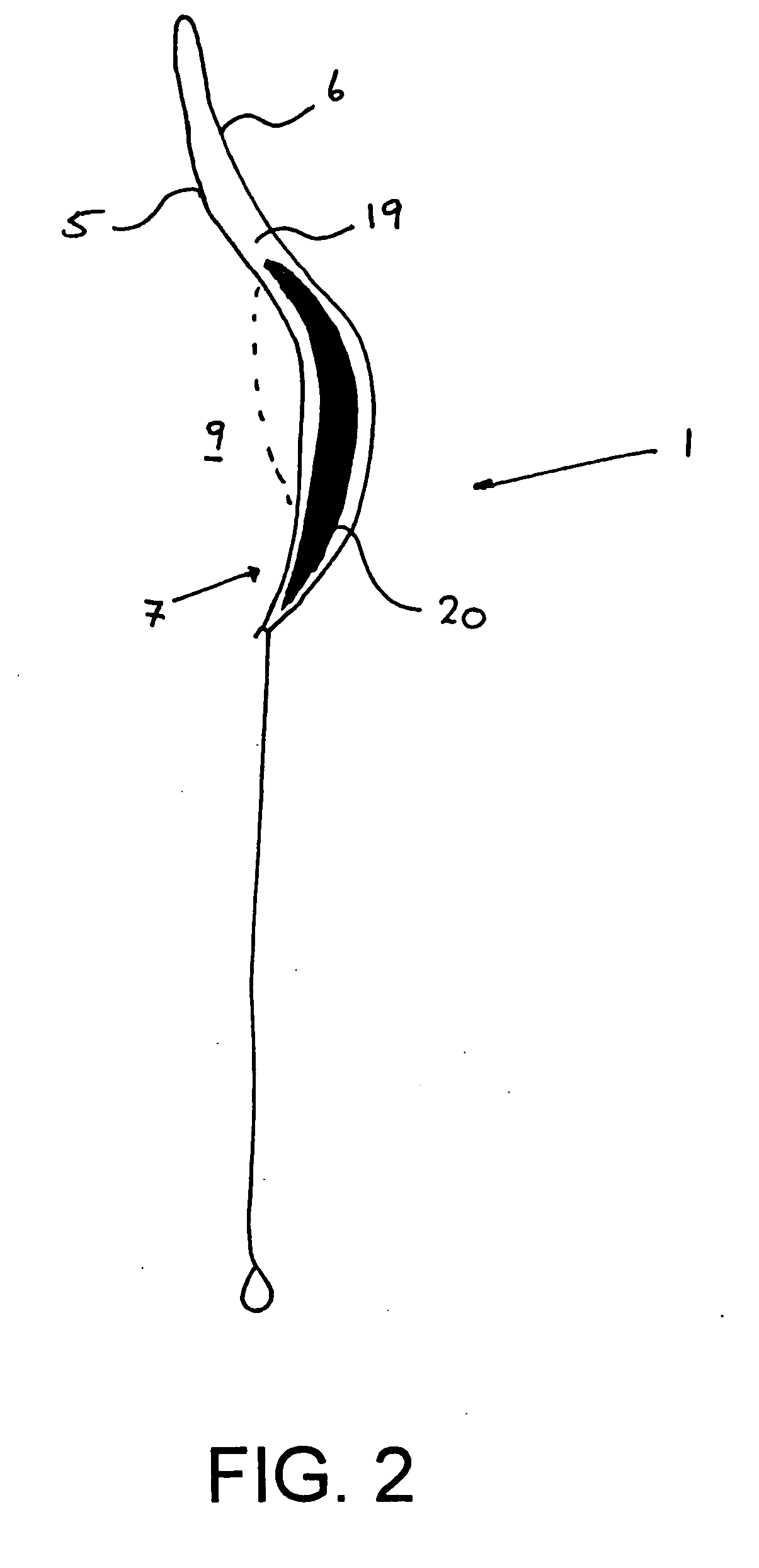
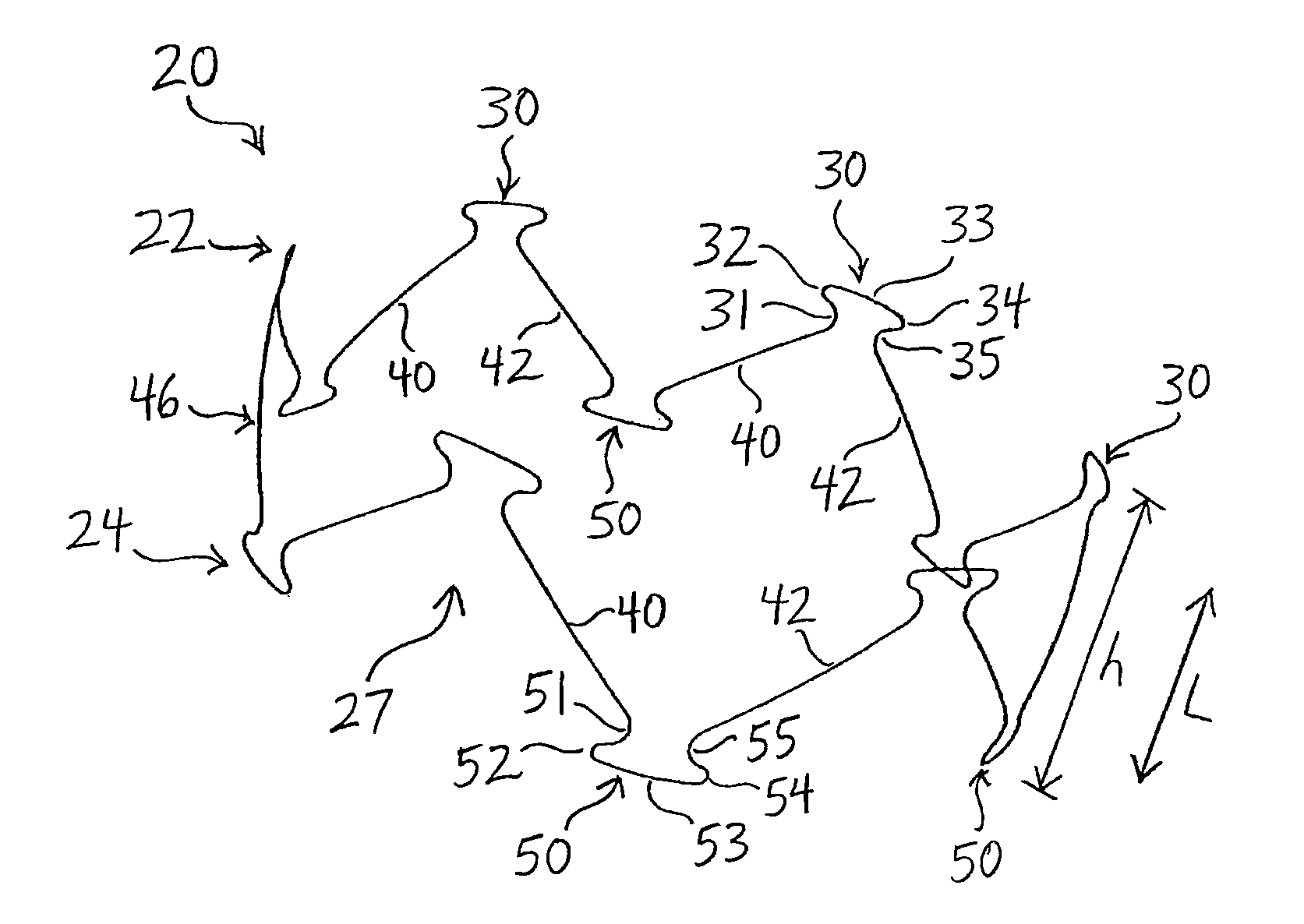
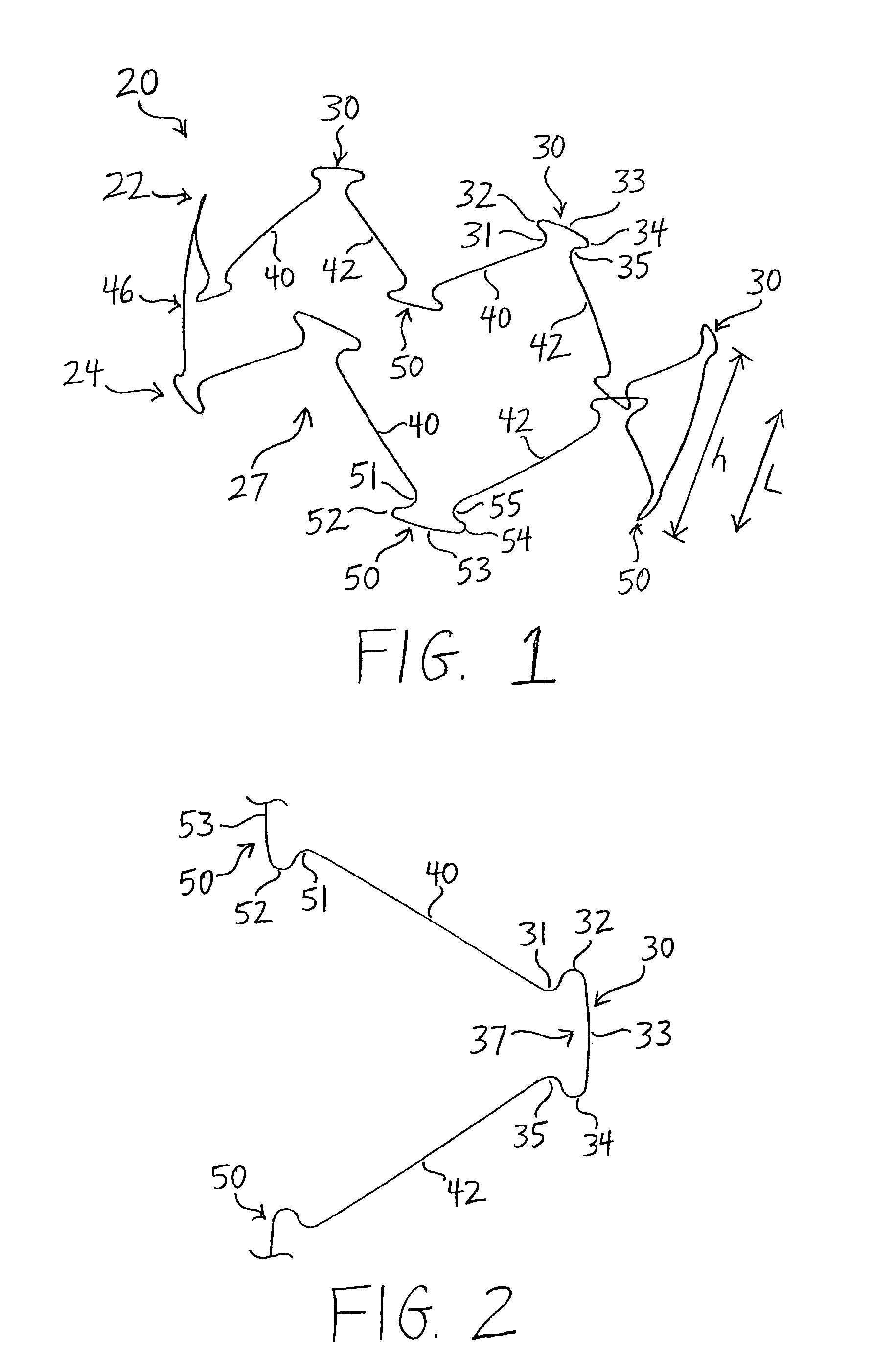
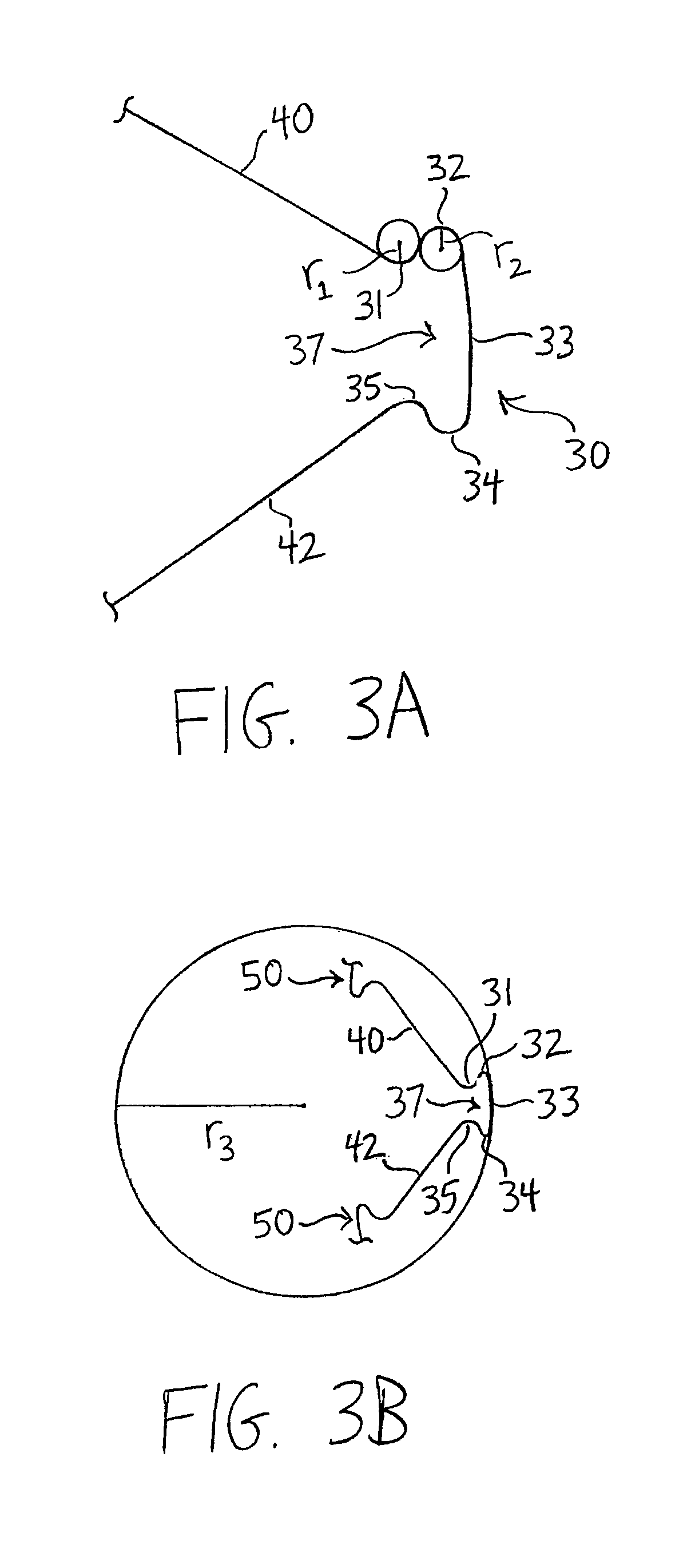
Stent having less invasive ends and improved radial force
The present invention provides a stent having less invasive ends and improved radial force. In one embodiment, the stent comprises a series of proximal apices disposed at a proximal end of the stent, a series of distal apices disposed at a distal end of the stent, and at least one angled strut segment disposed between the proximal and distal apices of the stent. At least one apex of the stent may comprise multiple curved portions. In one example, the radius of curvature of one of the curved portions is significantly greater, for example, at least 10 times greater, than each of the other radii of curvature of the apex. The curved portion having the significantly greater radius of curvature may be configured to engage a vessel wall in a less invasive manner.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Method for production of tomographic section images of a periodically moving object with a number of focus detector combinations
ActiveUS7127025B2Optimize timingNone is suitable for purposeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersImage resolution
A method is for production of tomographic section images, in particular X-ray CT images, of an at least partially periodically moving examination object with periodically changing movement and rest phases, preferably of a heart of a living being. A number of focus detector combinations are used, with the time resolution of the CT scanner being significantly increased by supplementary combination of detector data in the correct phase. On the one hand, a number of focus detector combinations which scan an examination object at the same time are used; and on the other hand a number of adjacent movement cycles of a periodically moving examination object are performed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Light-guide lights suitable for use in illuminated displays
InactiveUS20050175282A1Uniform efficiencyUniform illuminationMechanical apparatusElongate light sourcesOptical cavityLight guide
A light-guide light (1) suitable for use in illuminated displays and signs comprises a housing (3) defining an optical cavity having first and second generally parallel major faces (5, 6), and a light source (11) positioned to direct light into the optical cavity from one side. The first major face (5) comprises a material (for example, a prismatic film) having coefficients of reflection and transmission that vary with the angle at which light is incident on the material. The second major face (6) comprises a narrow-scattering reflective material having a reflectance of at least 85%, for example a highly-efficient reflective material provided with a suitable textured pattern.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method and apparatus for generating files for stereographic image display and method and apparatus for controlling stereographic image display
InactiveUS20080151044A1Without lowering displaying speedSimple structureImage analysisUsing reradiationImage synthesisComputer graphics (images)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Device for frontal termination of a floor covering
InactiveUS8266865B2Increase the differenceSimple conditionsConstruction materialStairway-like structuresButt jointFloor covering
A device is described for the frontal termination of a floating-laid floor covering (3) having a terminus profile (4) and having a fastener fitting (5) for the terminus profile (4) resting on a subfloor (2). To provide advantageous design conditions, it is suggested that the fastener fitting (5) be connected in a shear-resistant manner to the floor covering (3) and have a rest (8) for the terminus profile (4) butt-jointed on the front face (1) of the floor covering (3).
Owner:NEUHOFER JR FRANZ
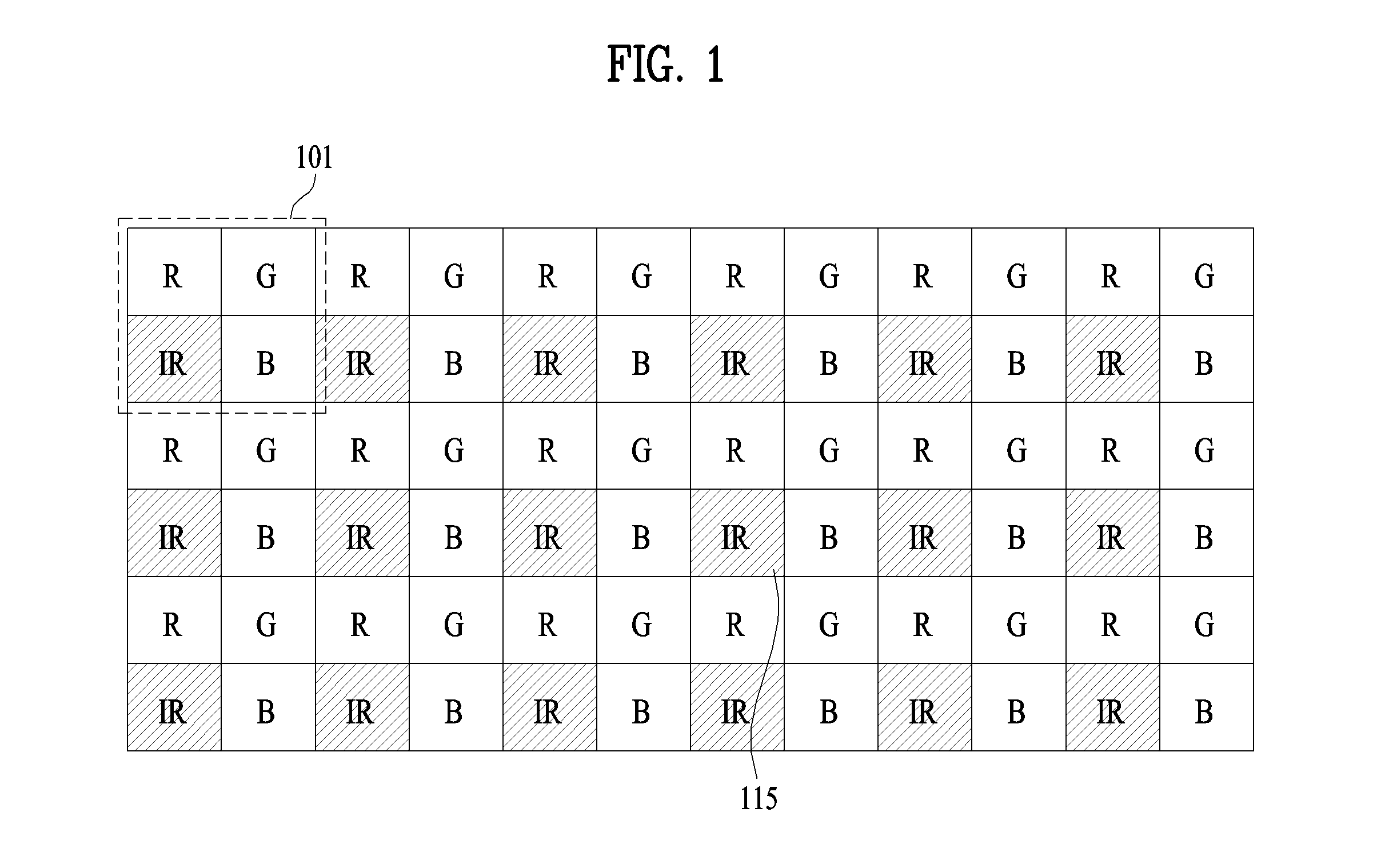
Rgb-ir sensor, and method and apparatus for obtaining 3D image by using same
ActiveUS20150312556A1None is suitable for purposeAccurate depth informationTelevision system detailsImage analysis3d imageComputer science
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Semiconductor light emitting apparatus and light source apparatus using the same
InactiveUS8459840B2Improve cooling effectSpeed up the conversion processSolid-state devicesGlobesPhosphorCrystal structure
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Butyl rubber composition and hose using same
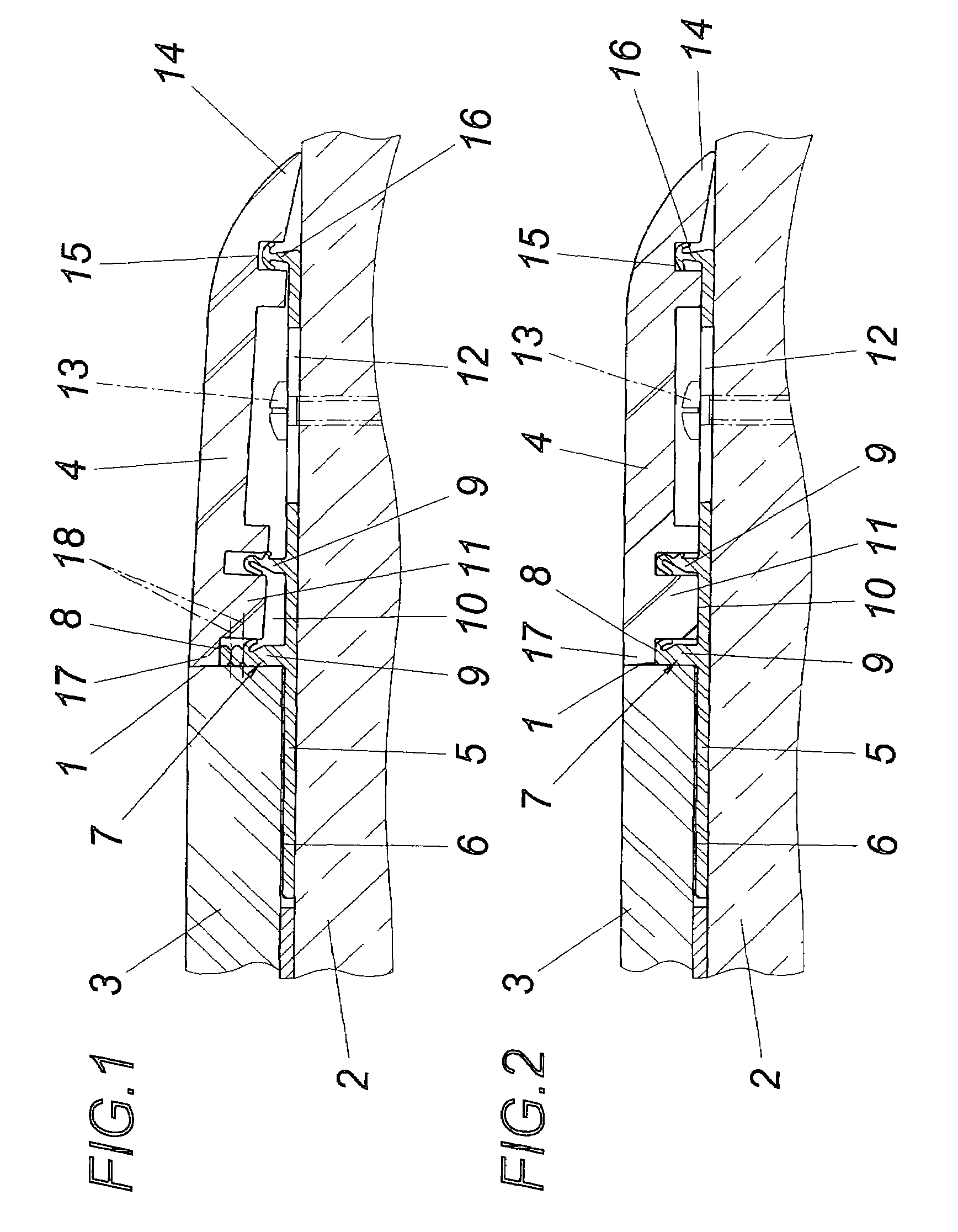
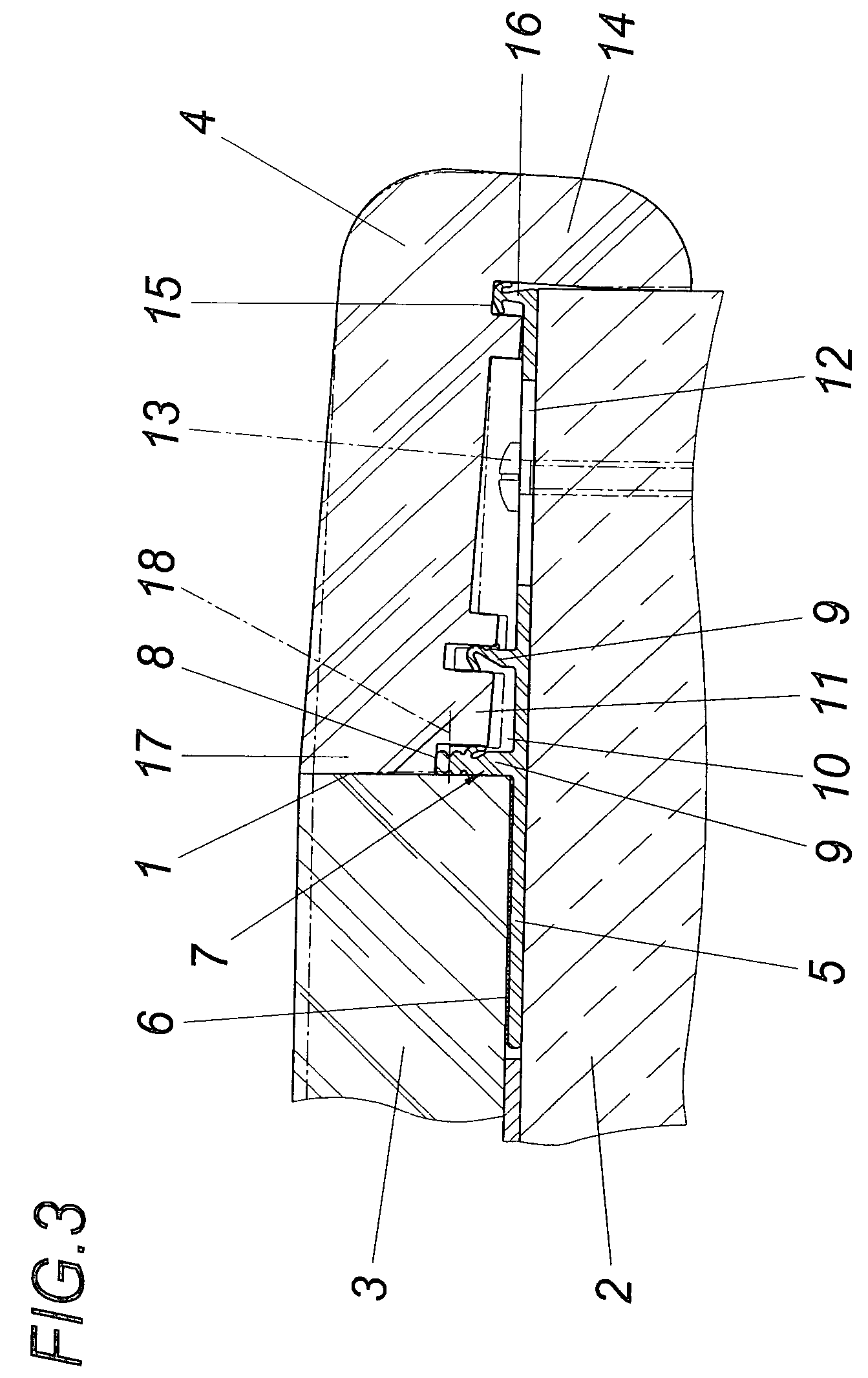
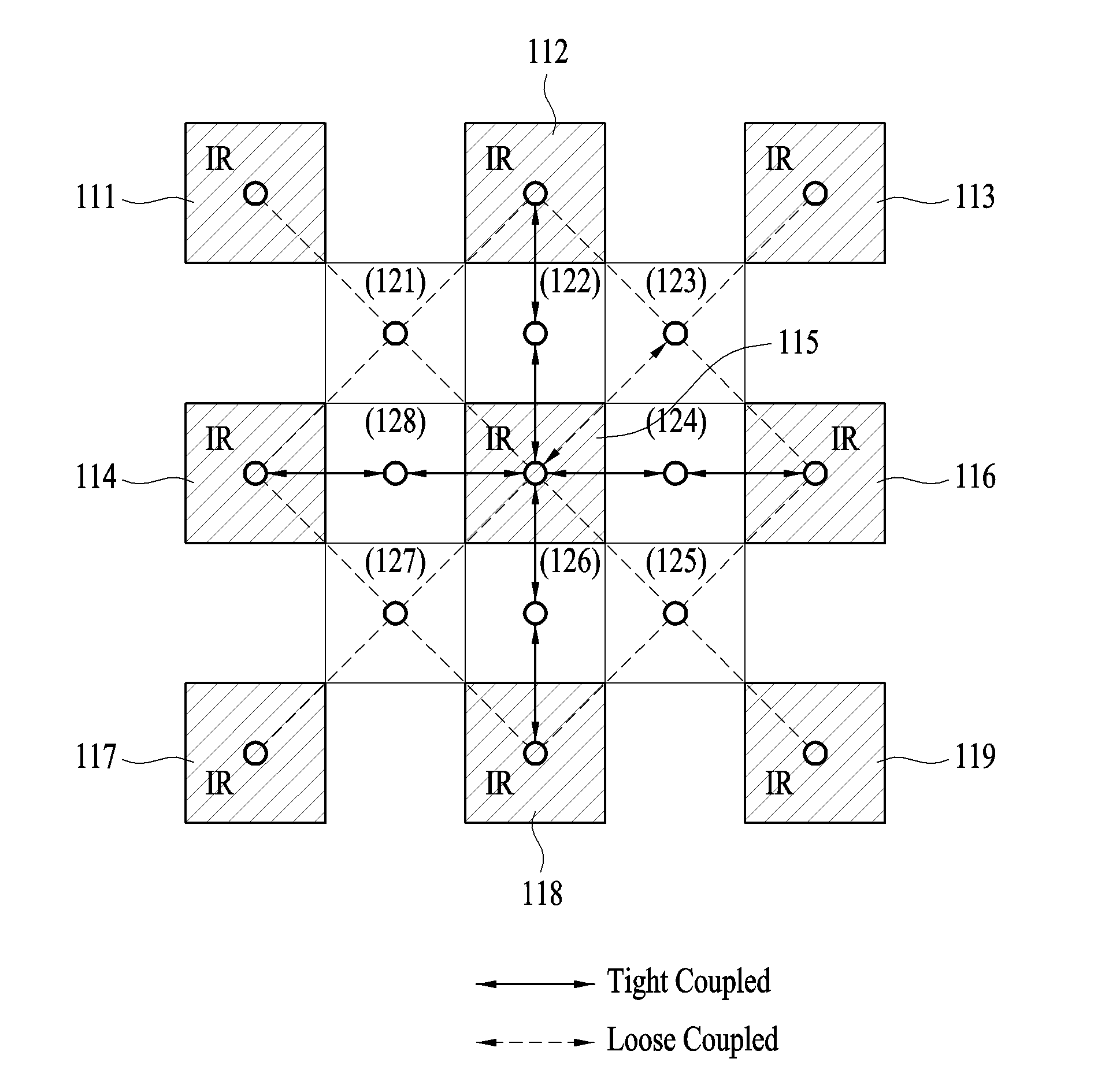
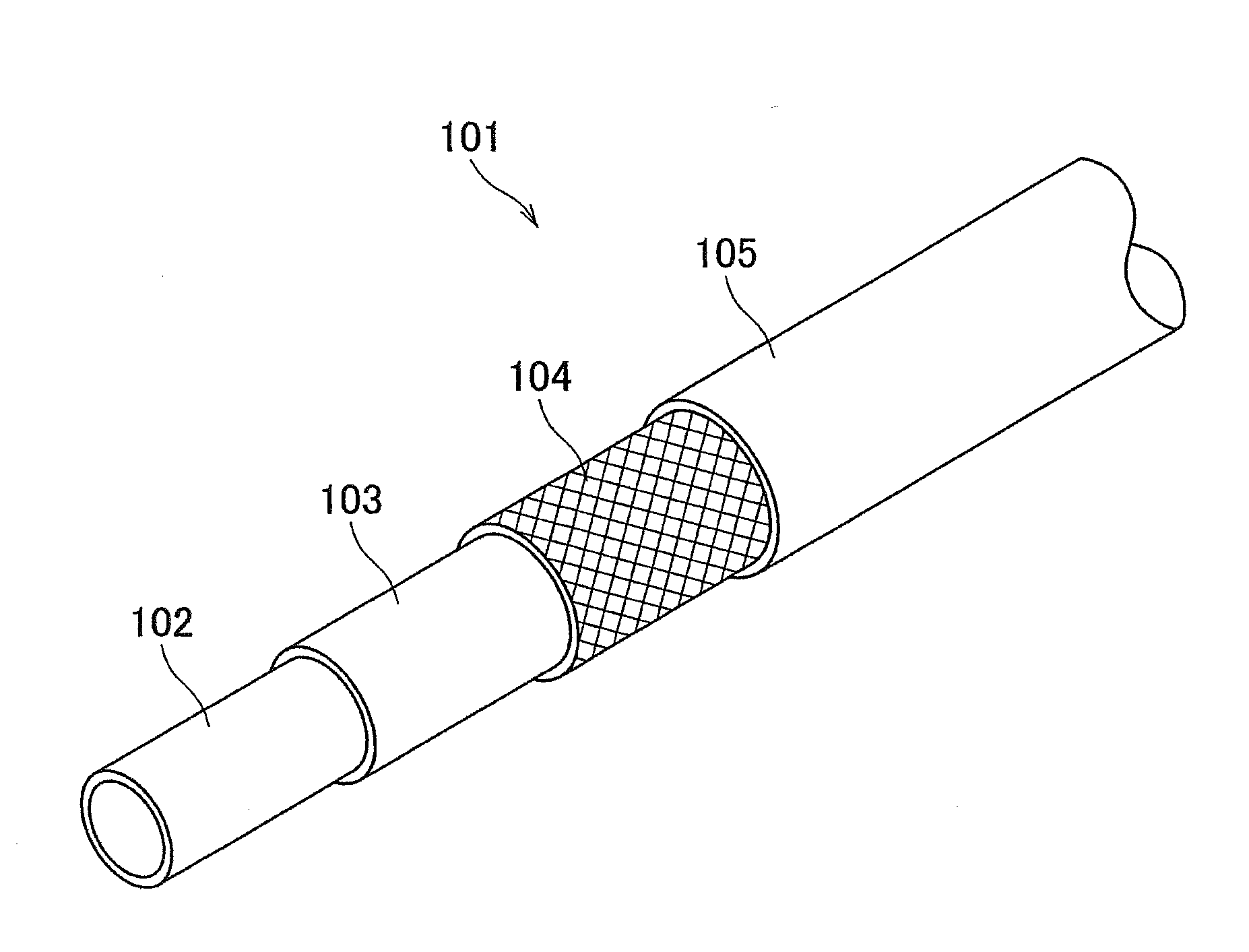
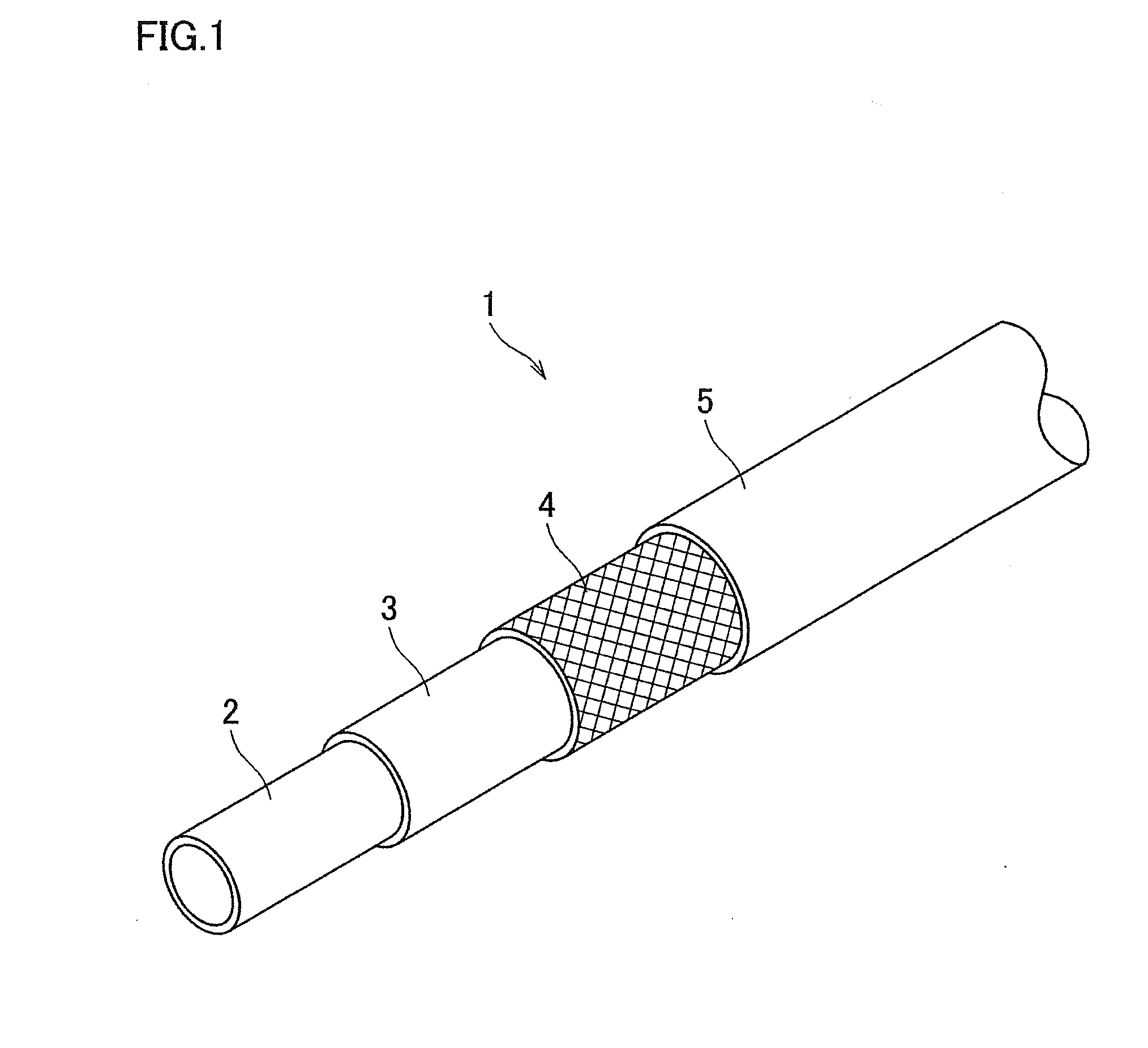
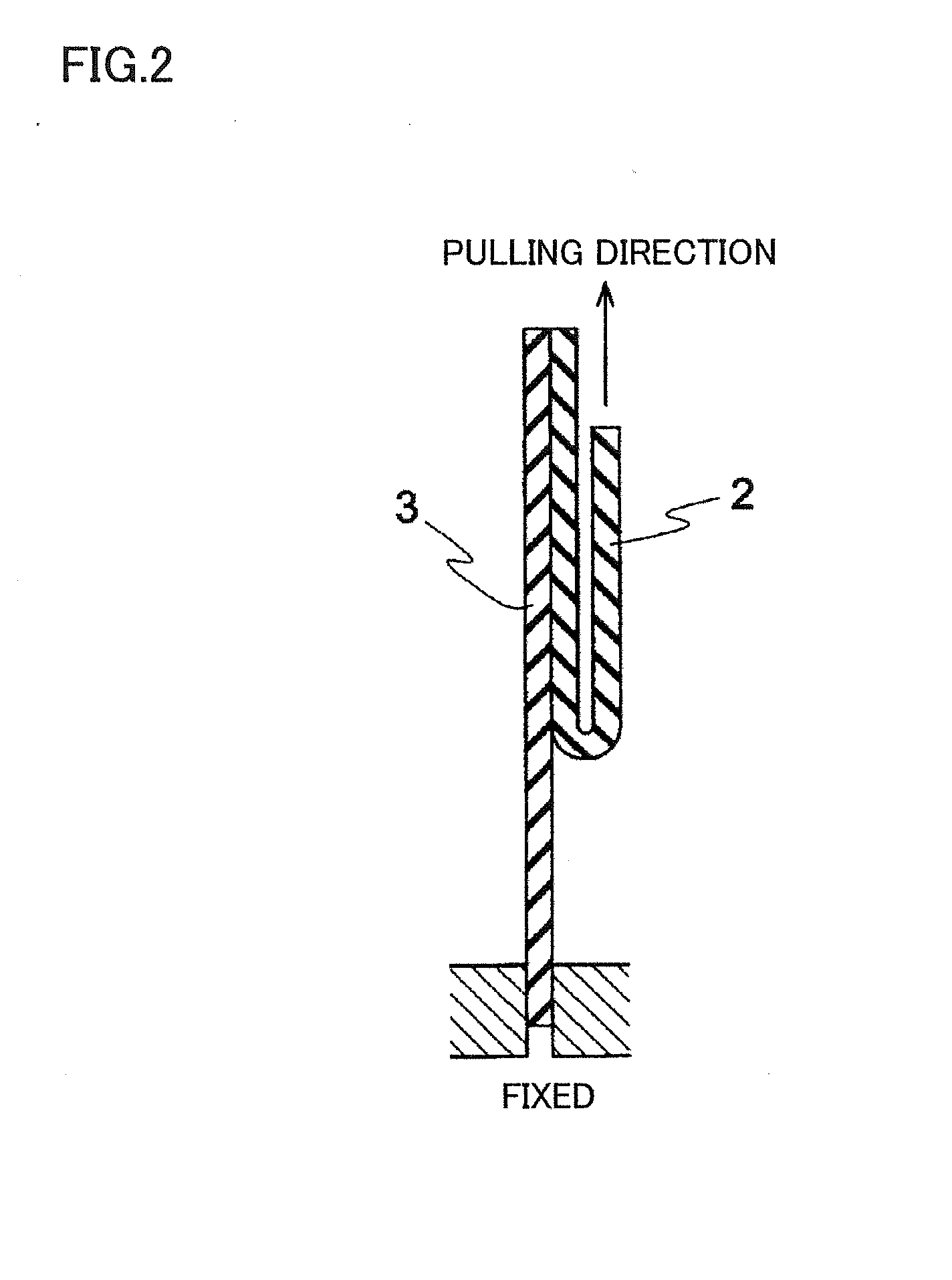
ActiveUS20150247032A1Solve the lack of adhesionImprove water resistanceCeramic shaping apparatusFlexible pipesPolymer scienceAlkylphenol
A butyl rubber composition is preferably used for an intermediate rubber layer 3 of a composite flexible hose formed by laminating, from the inner side, an innermost layer 2, intermediate rubber layer 3, fiber reinforcement layer 4, and an external rubber layer 5 in this order. The butyl rubber composition includes halogenated butyl rubber, styrene-isobutylene block copolymer, white filler, white reinforcing agent, brominated alkylphenol-formaldehyde resin, phenol resin, and methylol melamine, and 5 to 45 parts by weight of the styrene-isobutylene block copolymer is added to 100 parts by weight of the halogenated butyl rubber.
Owner:NICHIRIN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com