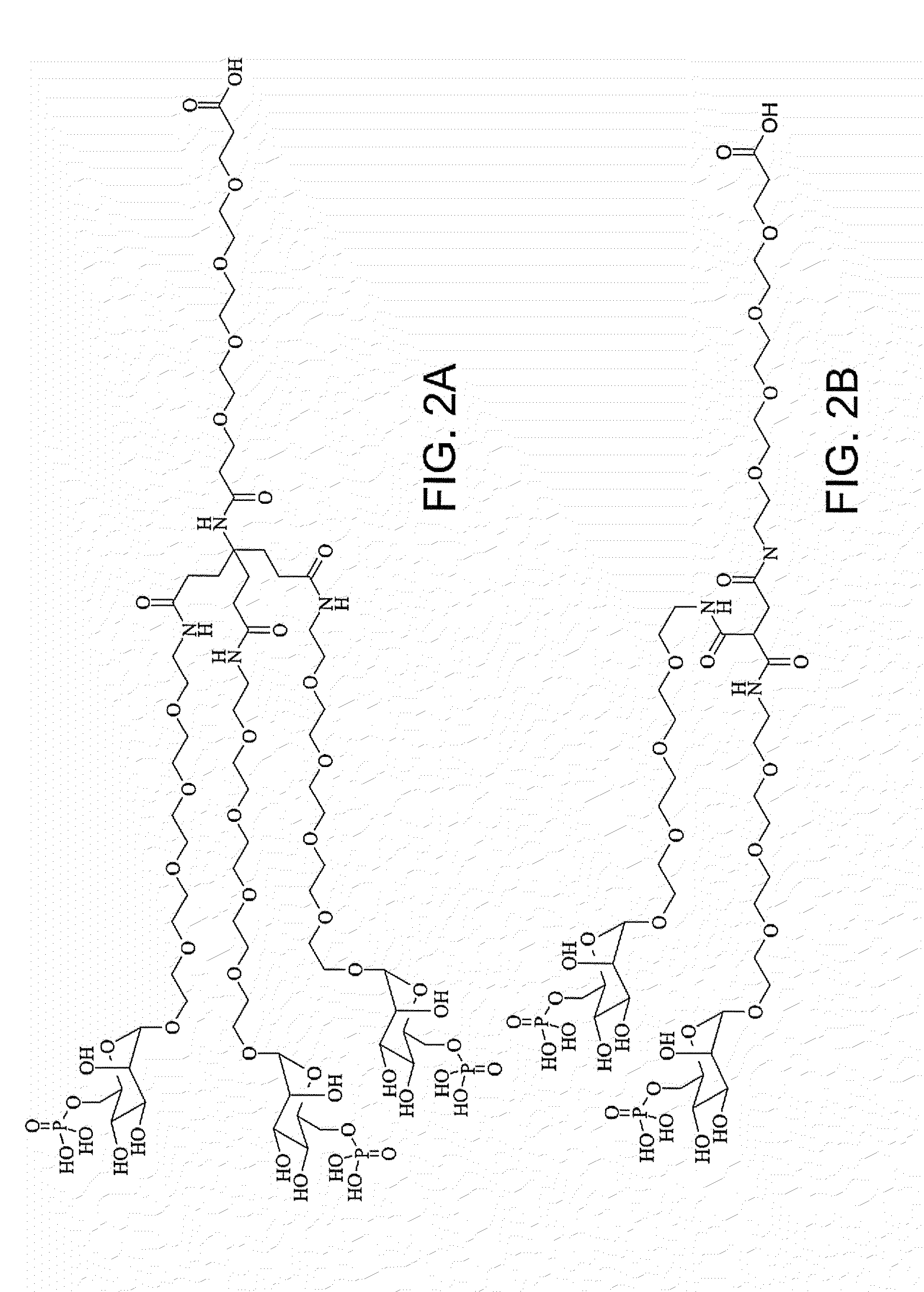
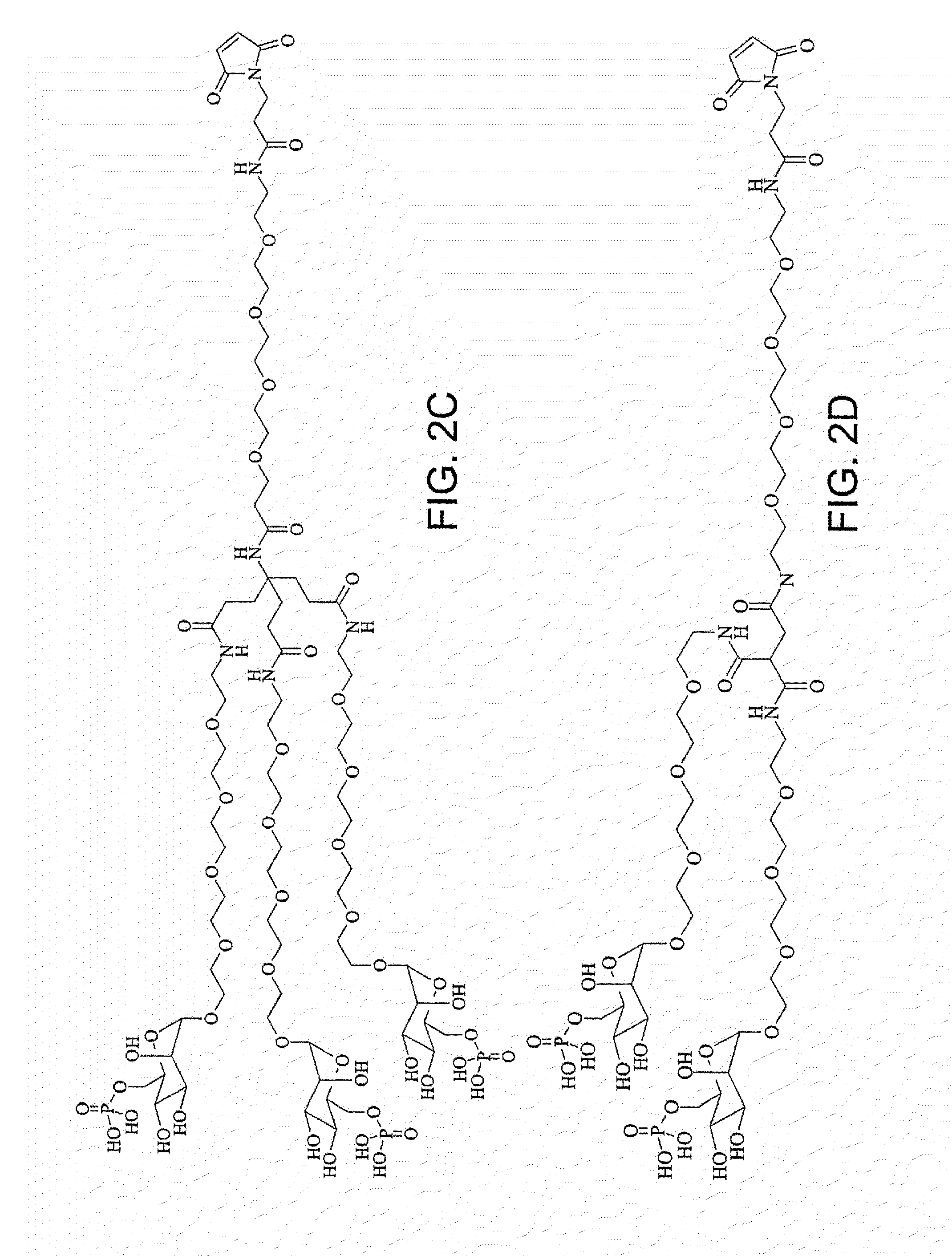
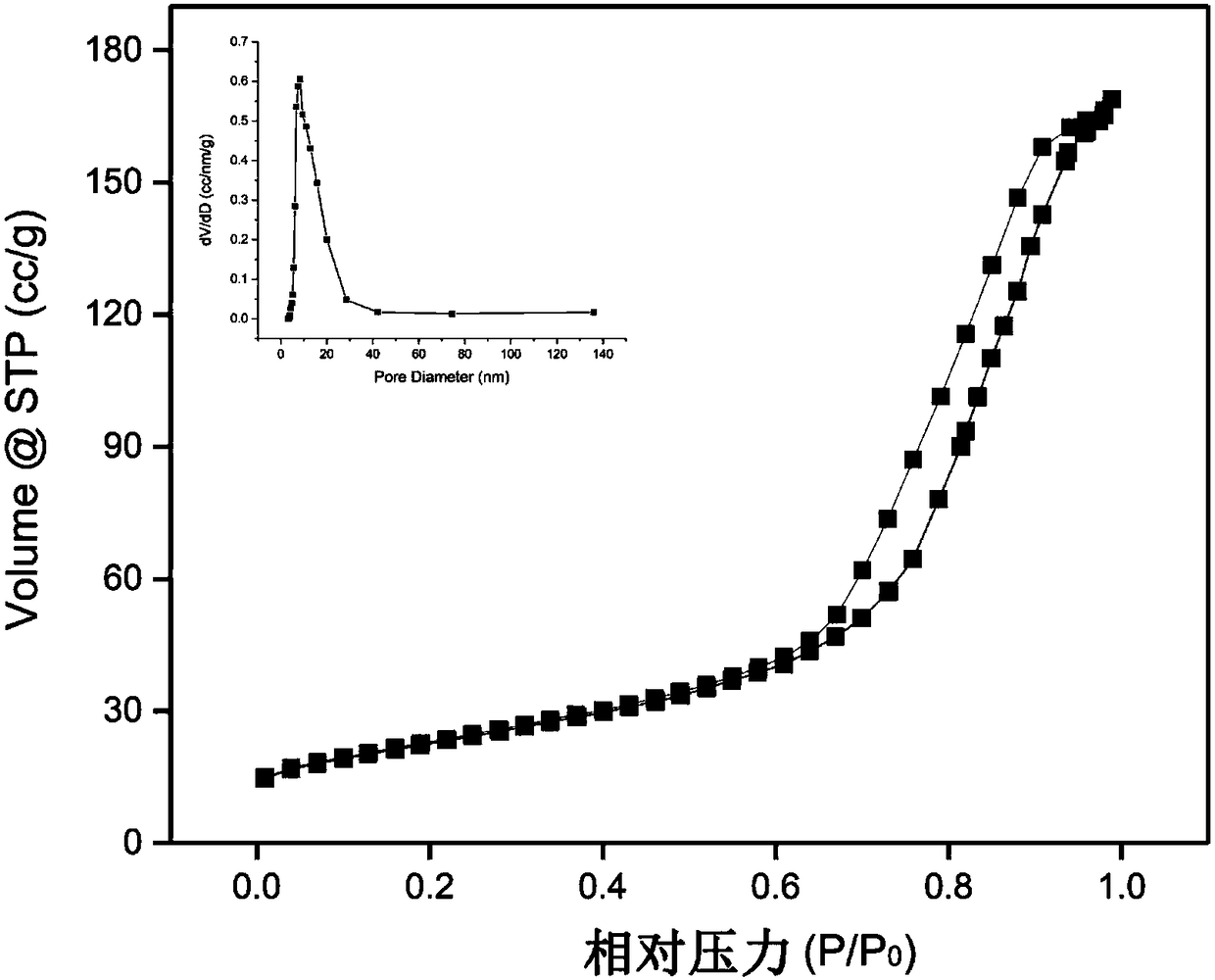
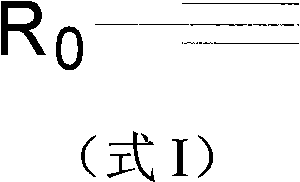Patents
Literature
147 results about "Glycosylated protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
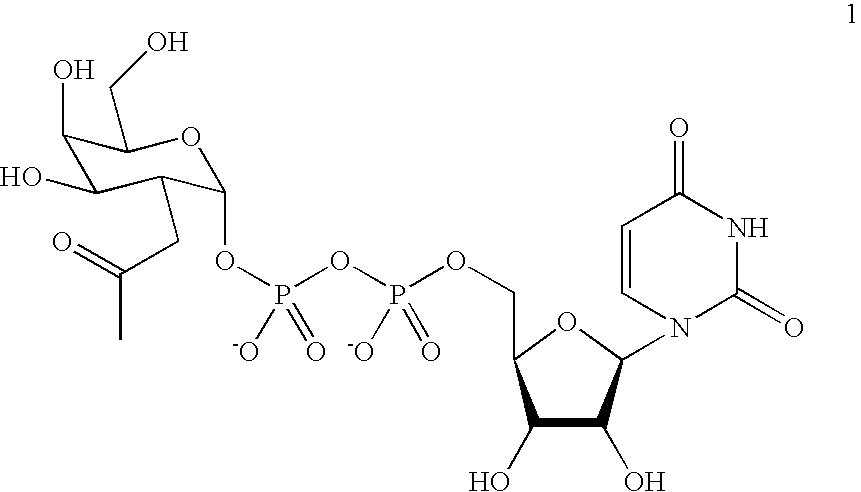
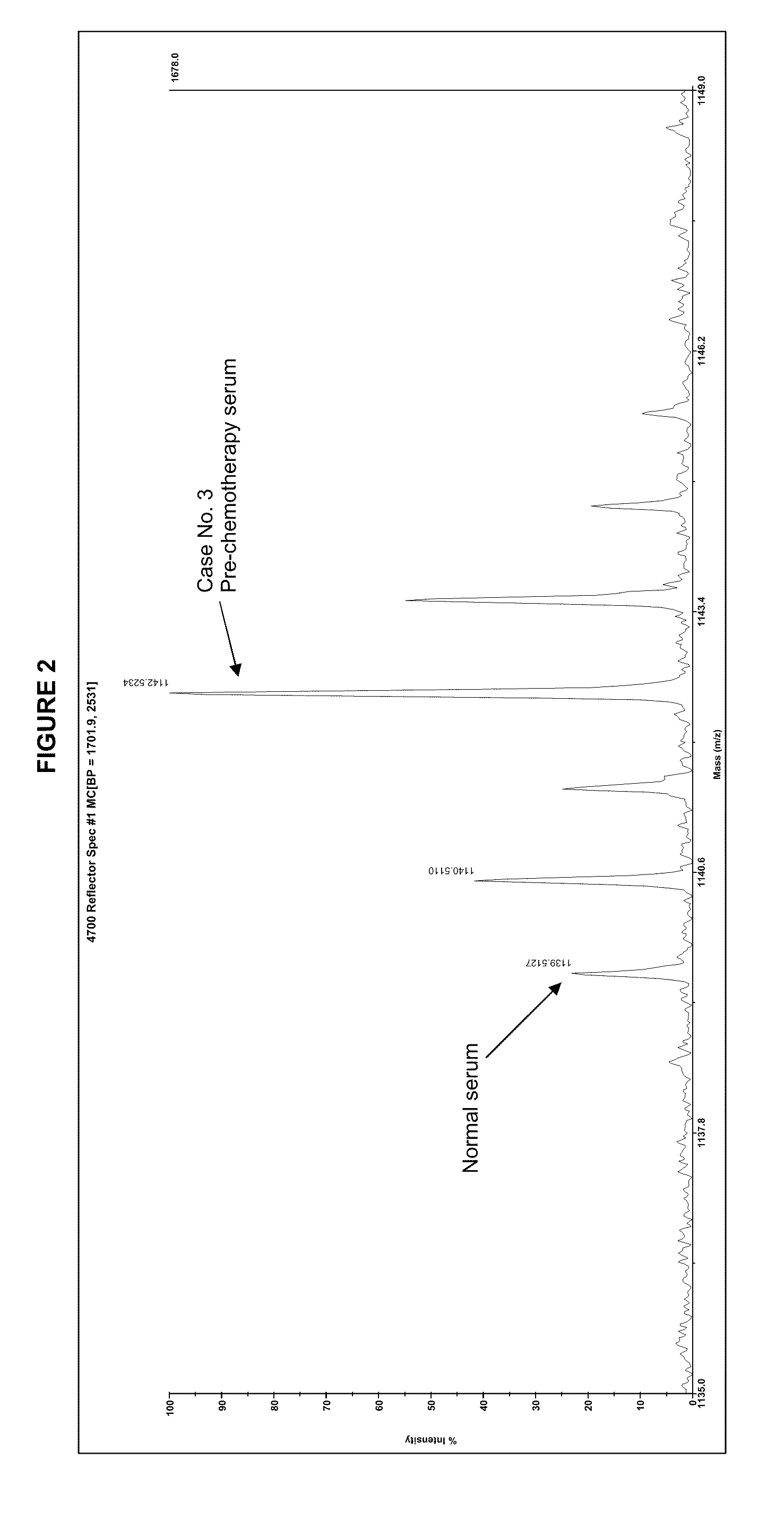
Glycosylated proteins. The glycosylated proteins include fructosamine and glycosylated hemoglobin (A1C). Fructosamine, the glycosylated protein used in veterinary medicine, is formed by nonenzymatic, irreversible binding of glucose to serum proteins, mainly albumin. 42 Rate of formation is proportional to the average BG level,...
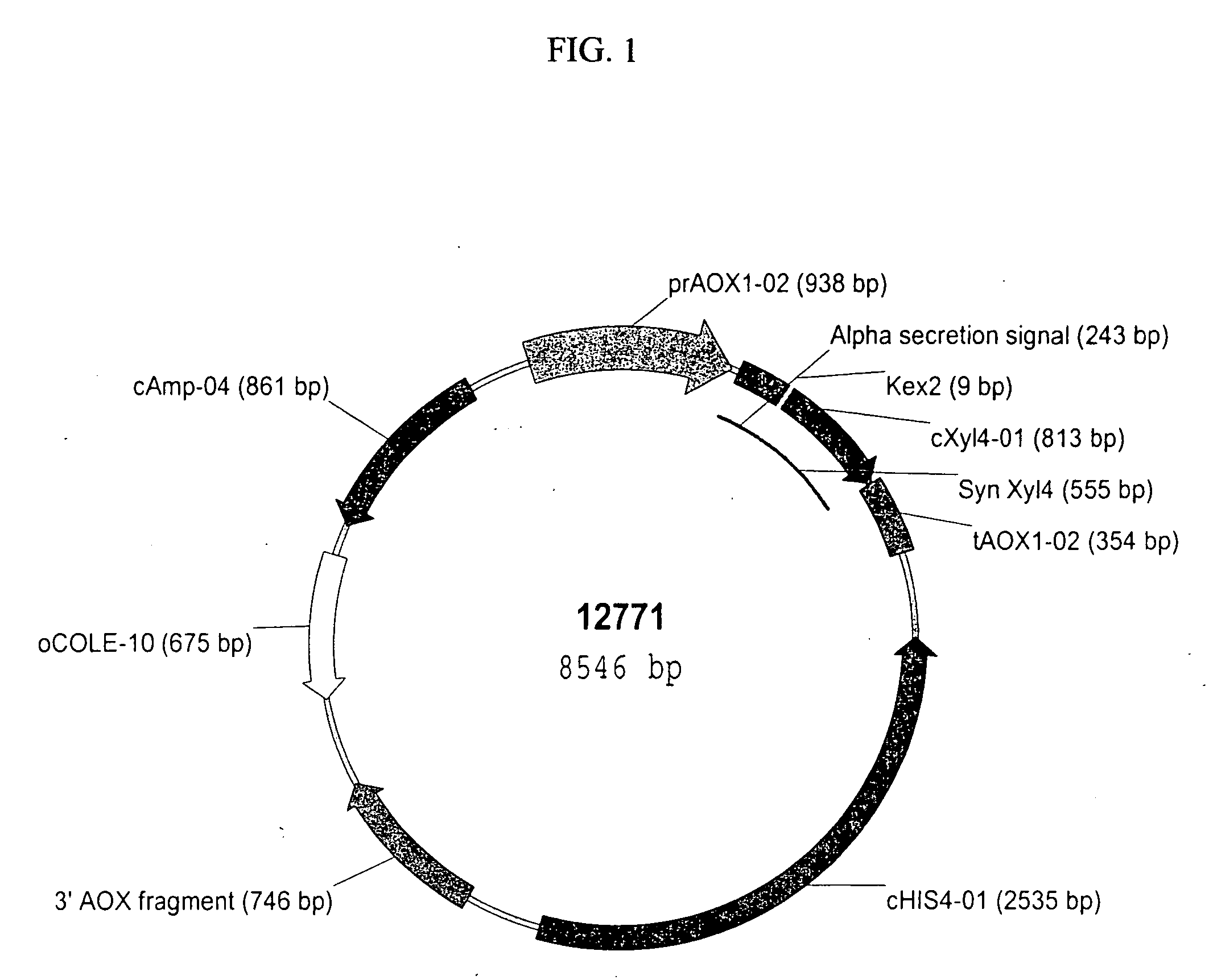
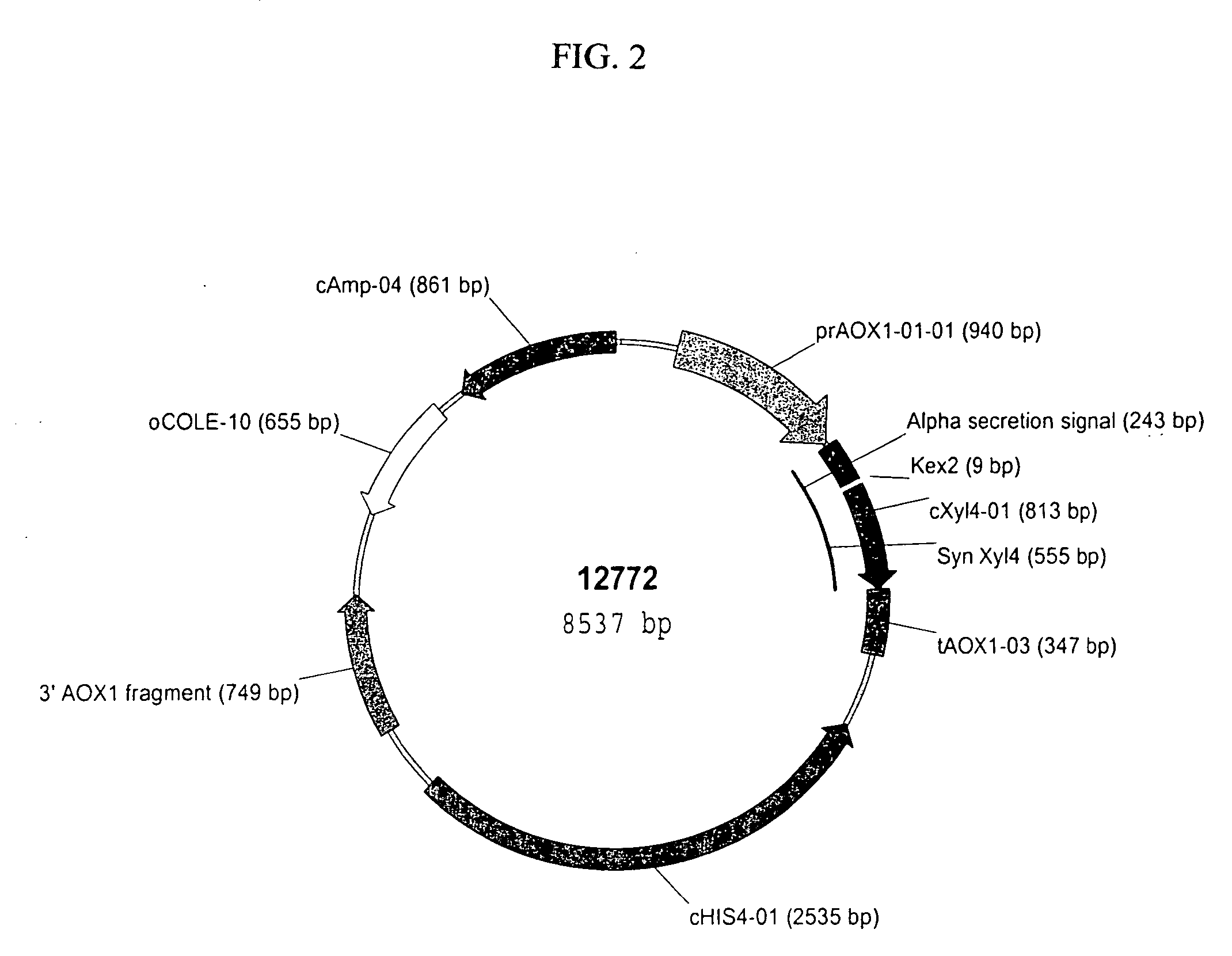
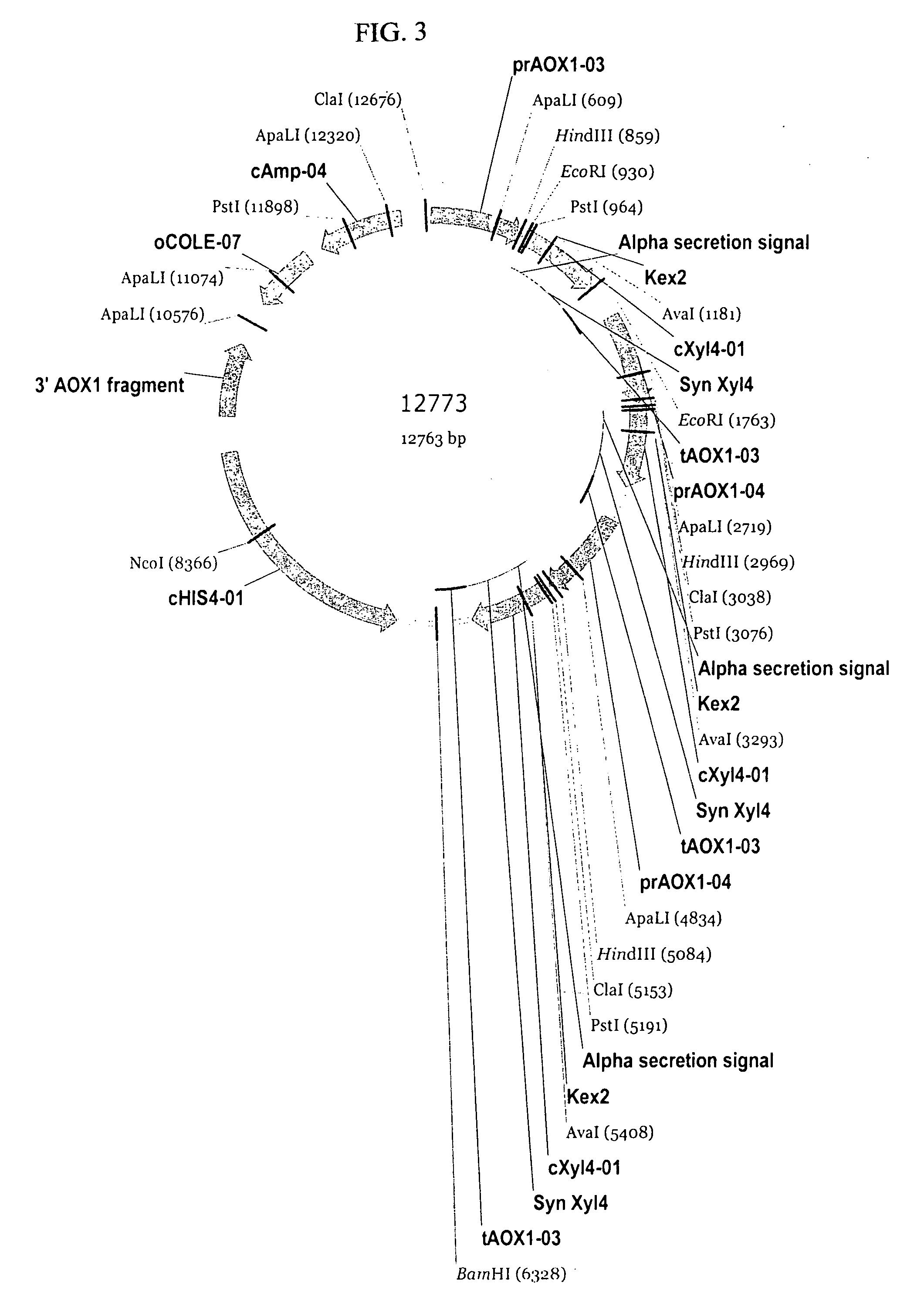
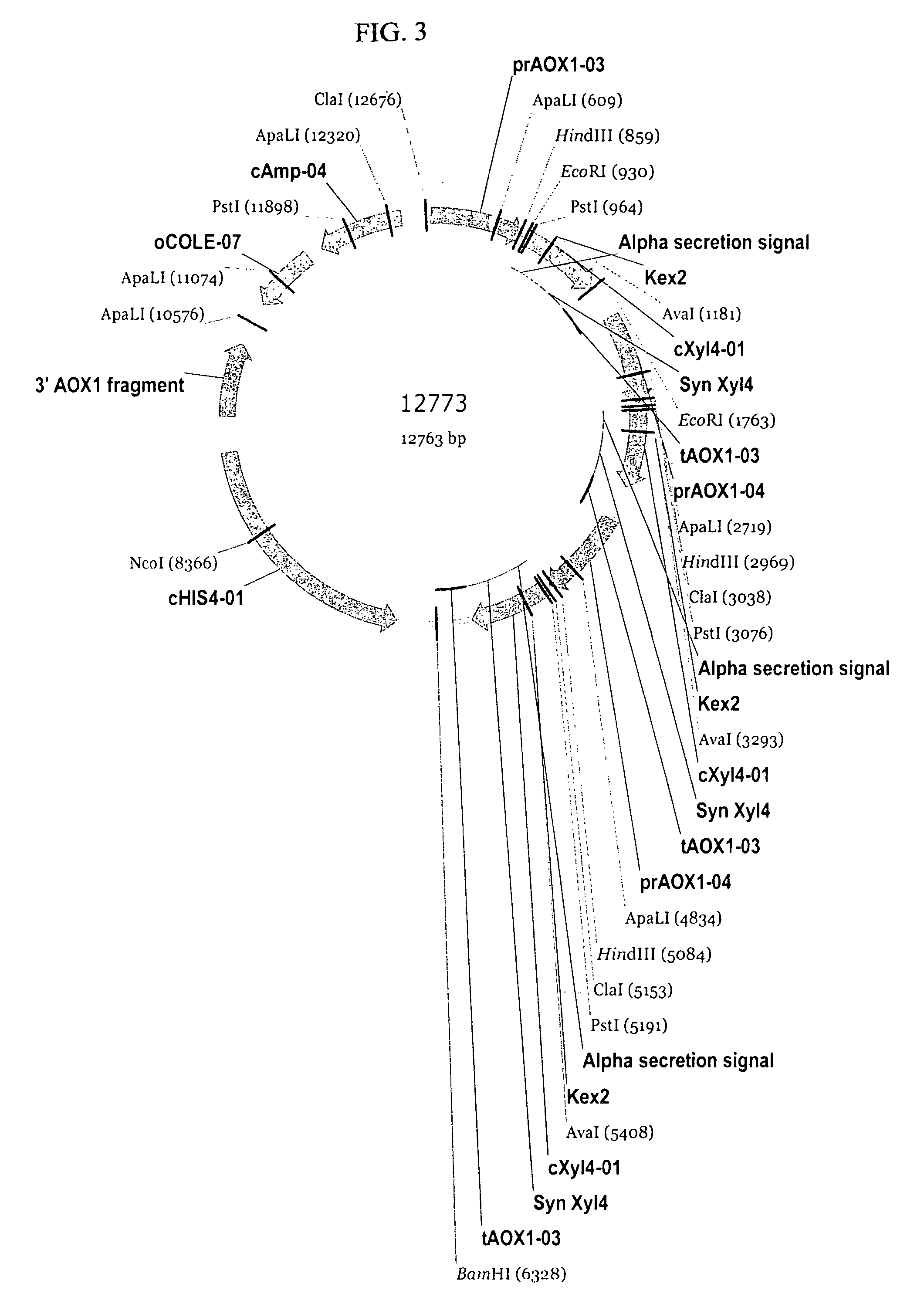
Microbially expressed xylanases and their use as feed additives and other uses
The present invention relates to codon-optimized xylanase coding sequences and the expression of xylanases in microbes and yeast. The invention further relates to using multiple copies of the xylanase expression construct for high levels of protein expression. The invention also relates to the use of xylanases as feed or food additives. The invention also relates to methods of expression of enzymes to increase thermotolerance by expressing them in organisms that glycosylate proteins compared to expression that the same enzyme without the glycosylation. Further, the invention relates to methods of preparing feed, enzyme feed additives, and methods of reducing the feed conversion ration or increasing weight gain of animals.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
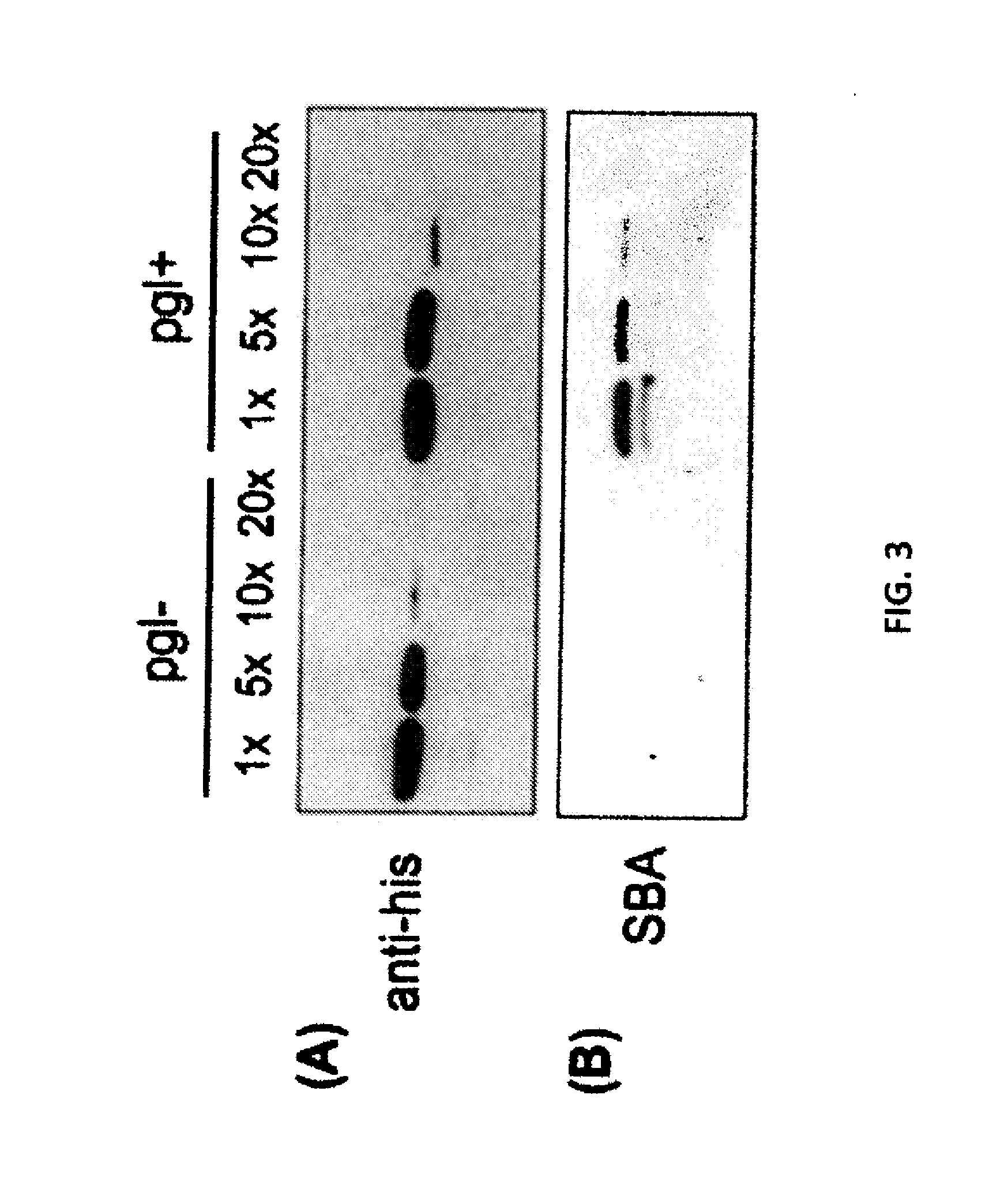
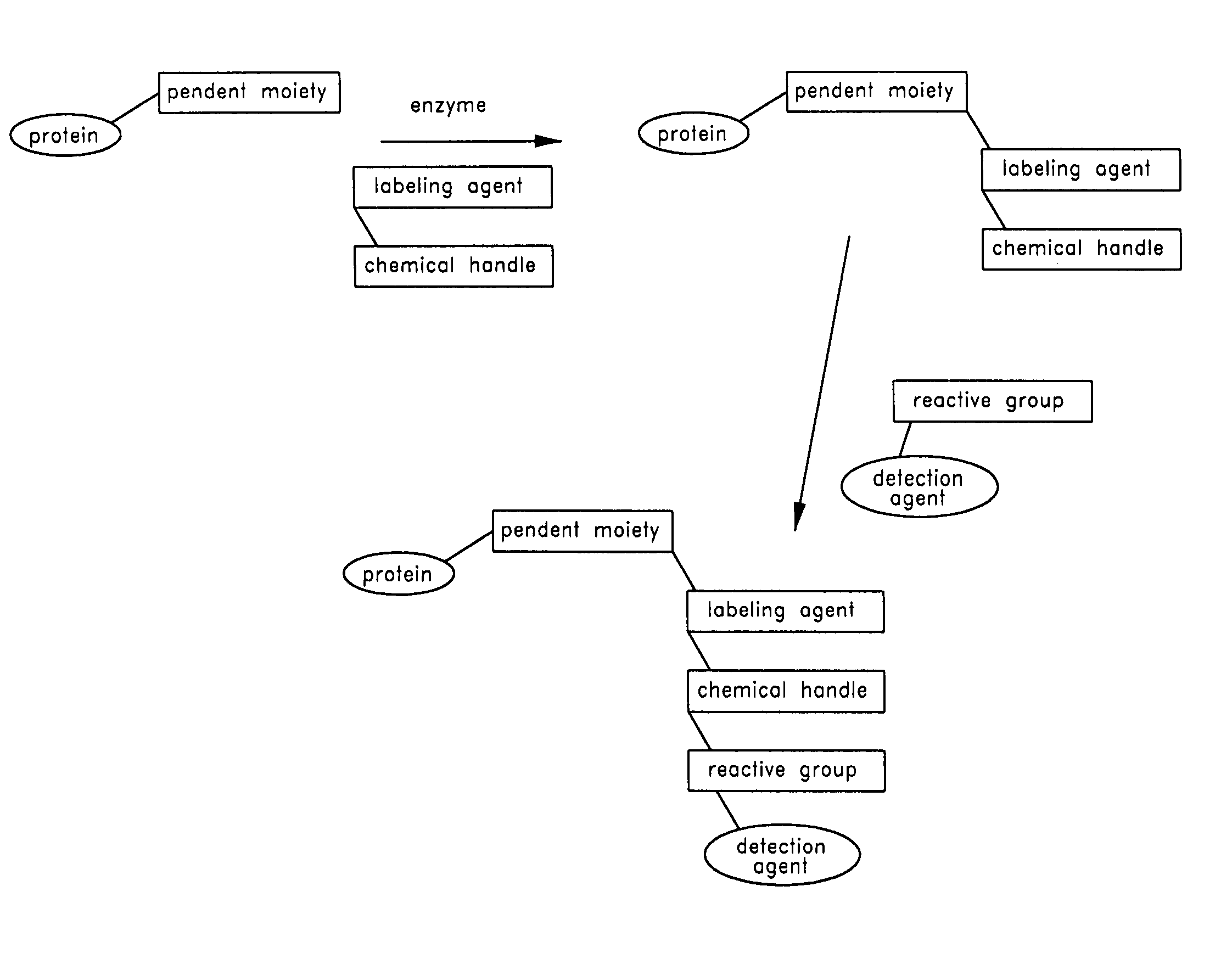
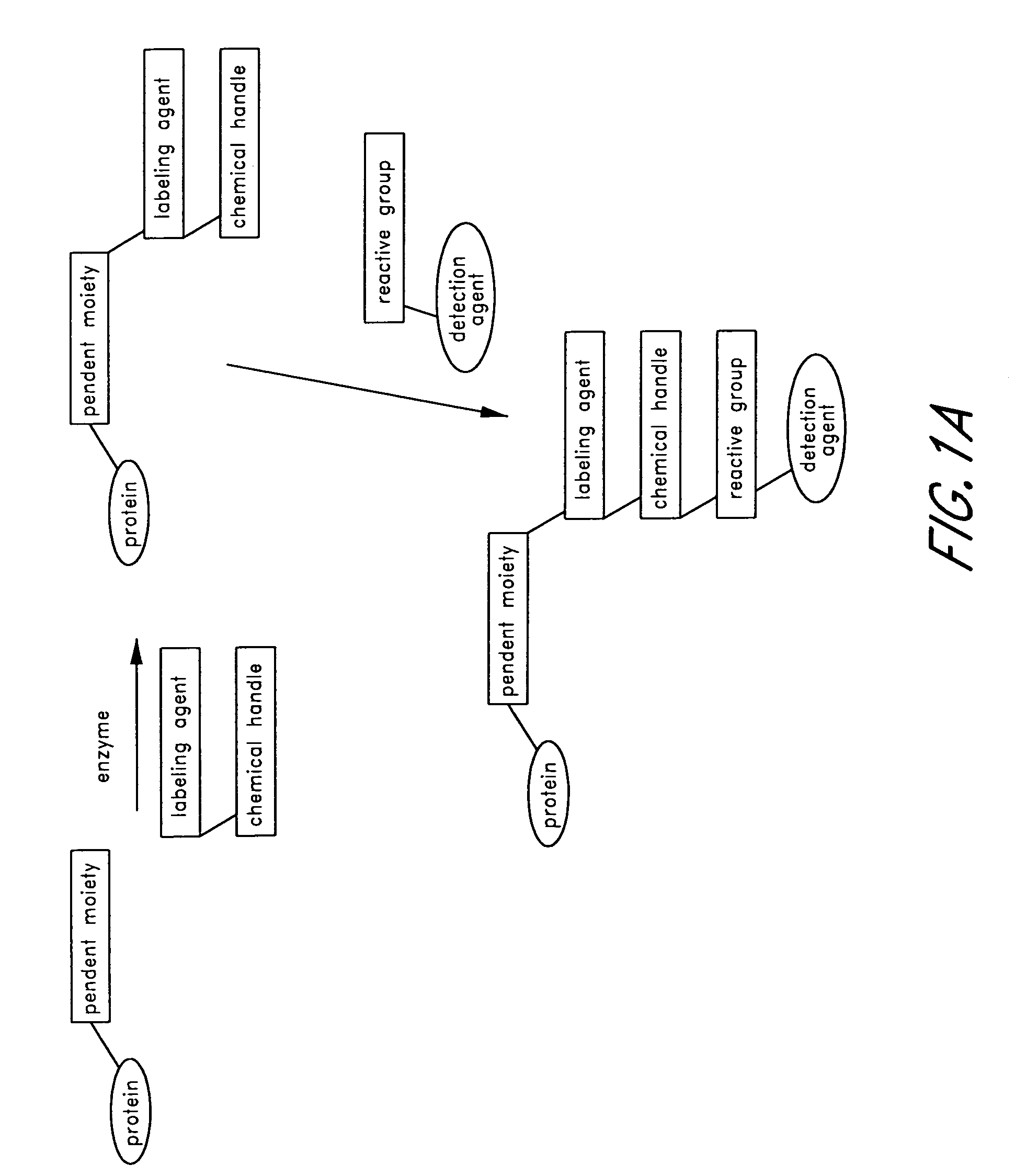
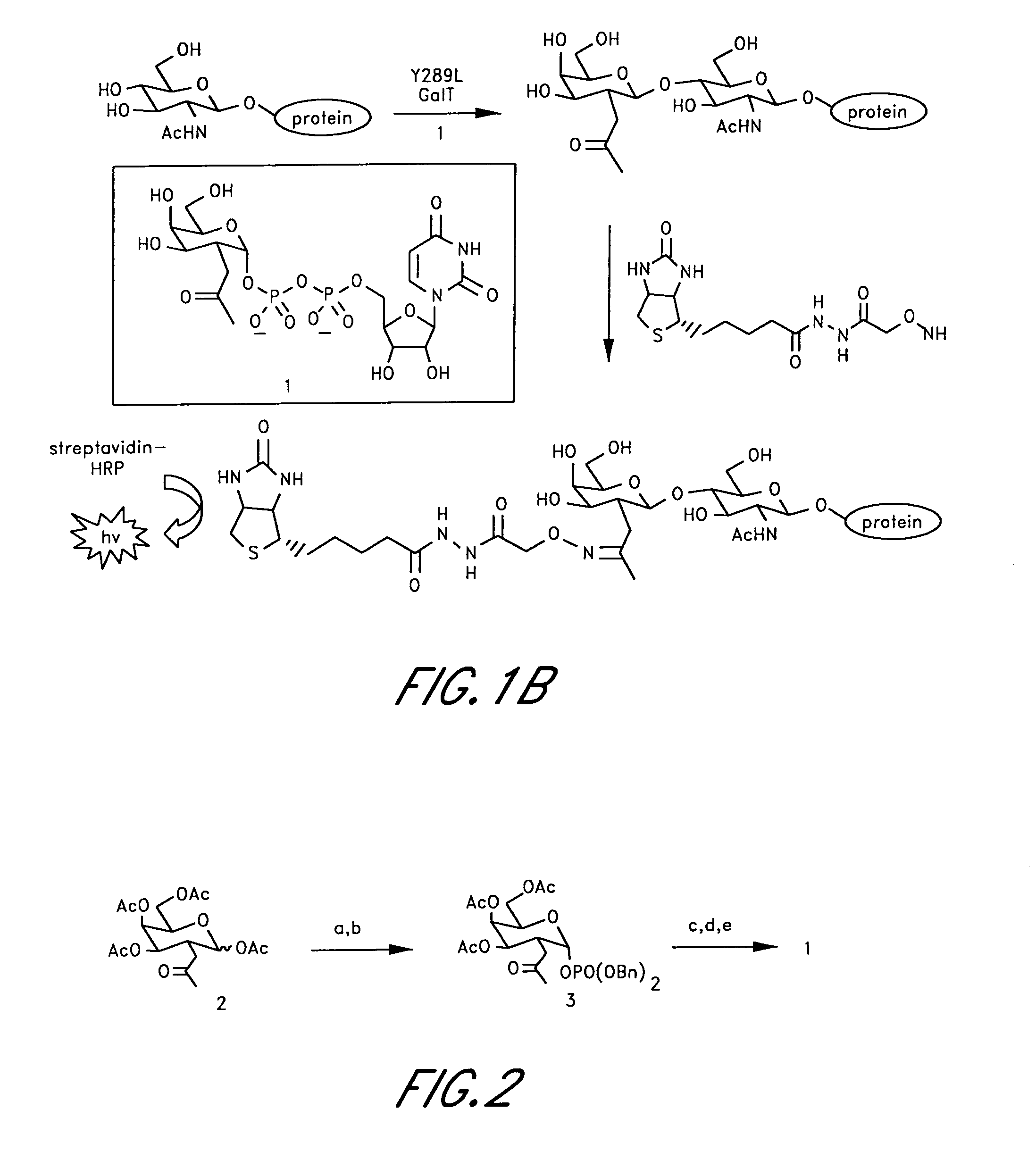
Method and compositions for the detection of protein glycosylation
ActiveUS20050130235A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPost translationalProtein insertion
The invention provides methods and compositions for the rapid and sensitive detection of post-translationally modified proteins, and particularly of those with post-translational glycosylations. The methods can be used to detect O-GlcNAc posttranslational modifications on proteins on which such modifications were undetectable using other techniques. In one embodiment, the method exploits the ability of an engineered mutant of β-1,4-galactosyltransferase to selectively transfer an unnatural ketone functionality onto O-GlcNAc glycosylated proteins. Once transferred, the ketone moiety serves as a versatile handle for the attachment of biotin, thereby enabling detection of the modified protein. The approach permits the rapid visualization of proteins that are at the limits of detection using traditional methods. Further, the preferred embodiments can be used for detection of certain disease states, such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
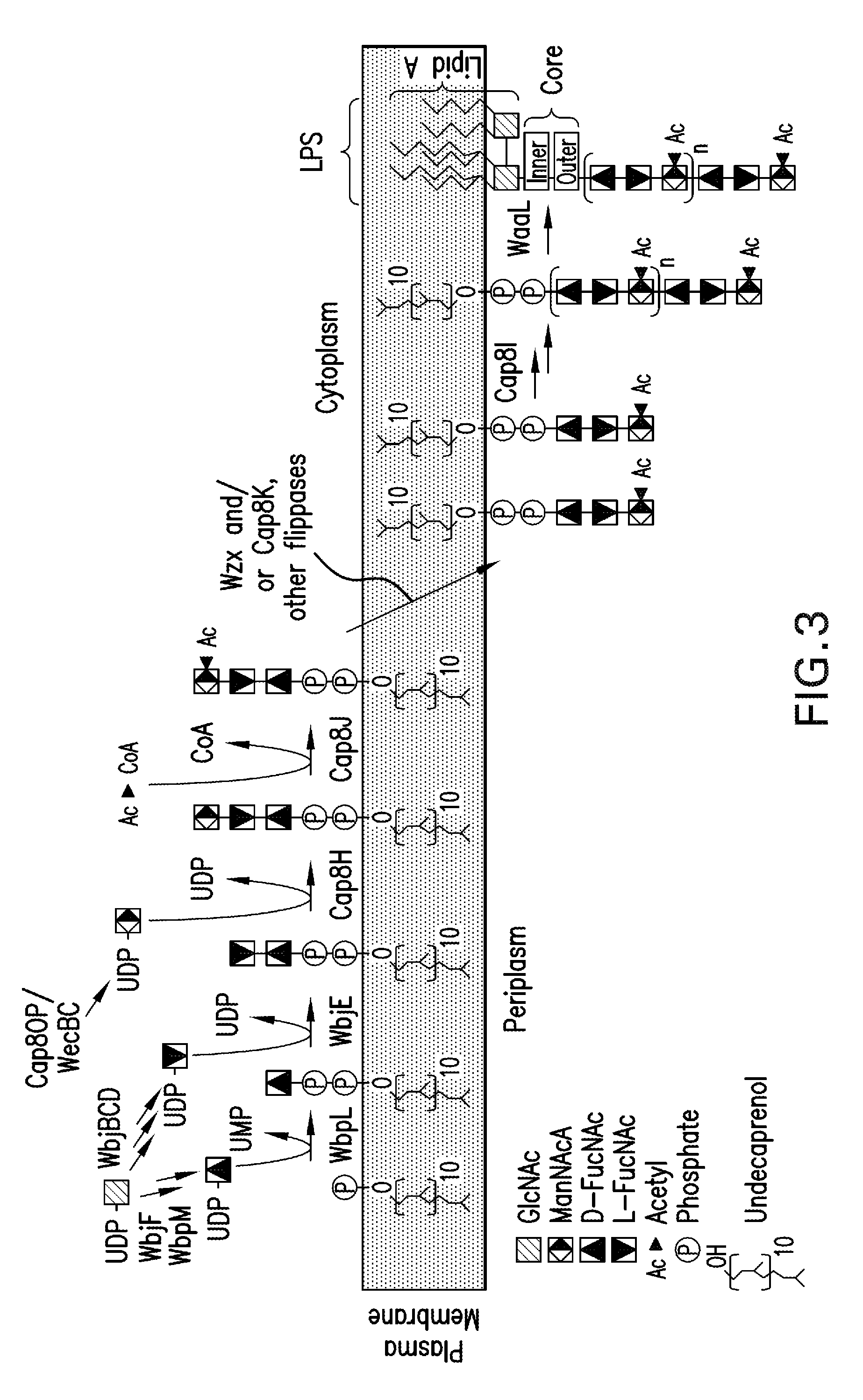
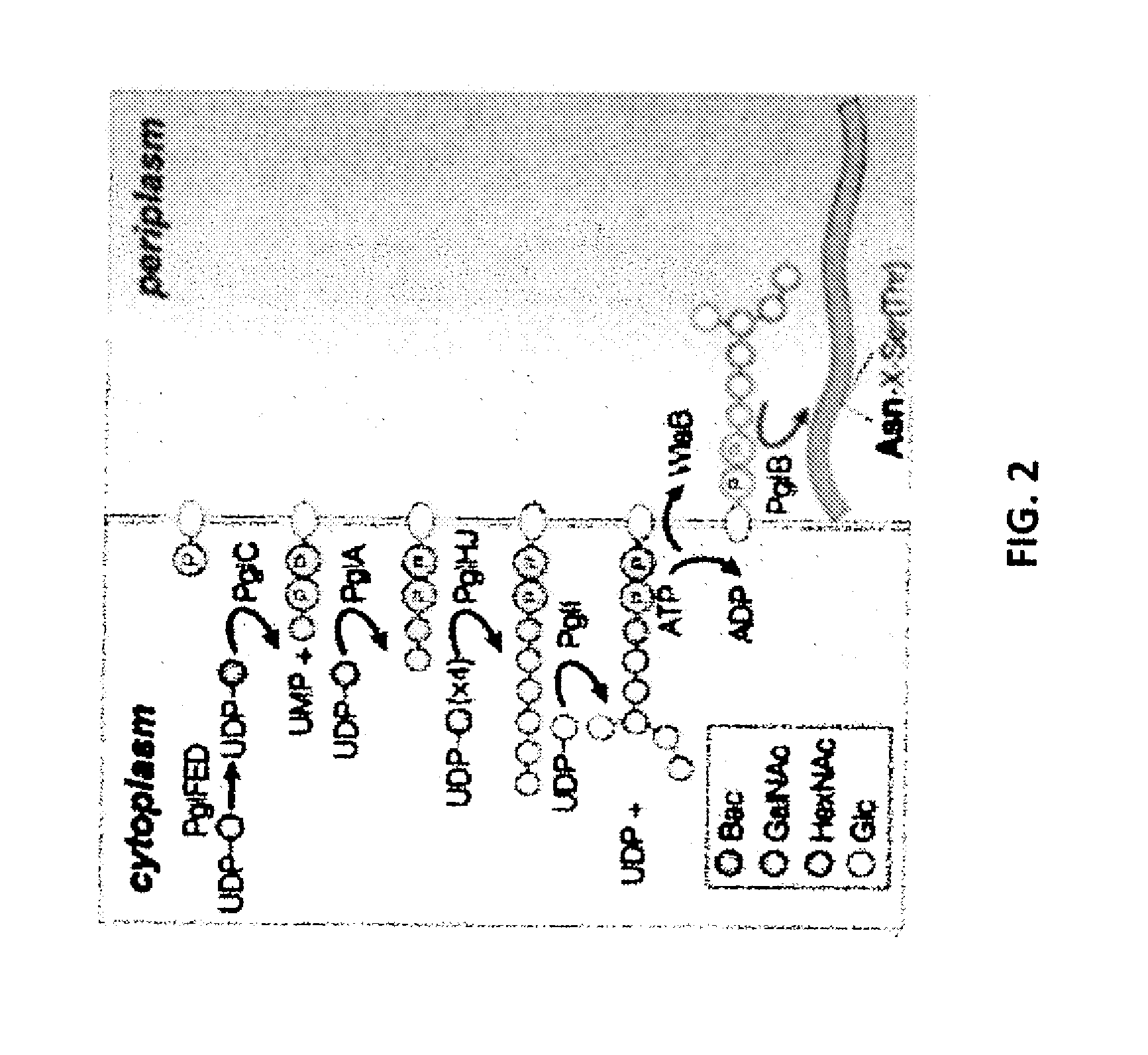
Capsular gram-positive bacteria bioconjugate vaccines
The present invention encompasses a novel S. aureus bioconjugate vaccine. More generally, the invention is directed to Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines containing a protein carrier, at least one polysaccharide such as a capsular Gram-positive polysaccharide, and, optionally, an adjuvant or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The instant invention also includes methods of producing Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines. An N-glycosylated protein is also provided that contains one or more polysaccharides such as Gram-positive polysaccharides. The invention is additionally directed to engineered prokaryotic organisms comprising nucleotide sequences encoding a glycosyltransferase of a first prokaryotic organism and a glycosyltransferase of a second prokaryotic organism. The invention further includes plasmids and prokaryotic cells transformed with plasmids encoding polysaccharides and enzymes which produce an N-glycosylated protein and / or bioconjugate vaccine. Further, the invention is directed to methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal comprising administering said bioconjugate vaccines.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Glycosylated protein expression in prokaryotes
The present invention relates to a prokaryotic host cell comprising eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity, where the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity is eukaryotic dolichyl-linked UDP-GlcNAc transferase activity and eukaryotic mannosyl-transferase activity. Also disclosed is a method of producing a glycosylated protein by providing a prokaryotic host cell comprising the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity and culturing the prokaryotic host cell under conditions effective to produce a glycosylated protein. Another aspect of the present invention pertains to a method for screening bacteria or bacteriophages by expressing one or more glycans on the surface of a bacteria, attaching a label on the one or more glycans on the surface of the bacteria or on the surface of a bacteriophage derived from the bacteria, and analyzing the label in a high-throughput format. A glycosylated antibody comprising an Fv portion which recognizes and binds to a native antigen and an Fc portion which is glycosylated at a conserved asparagine residue is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
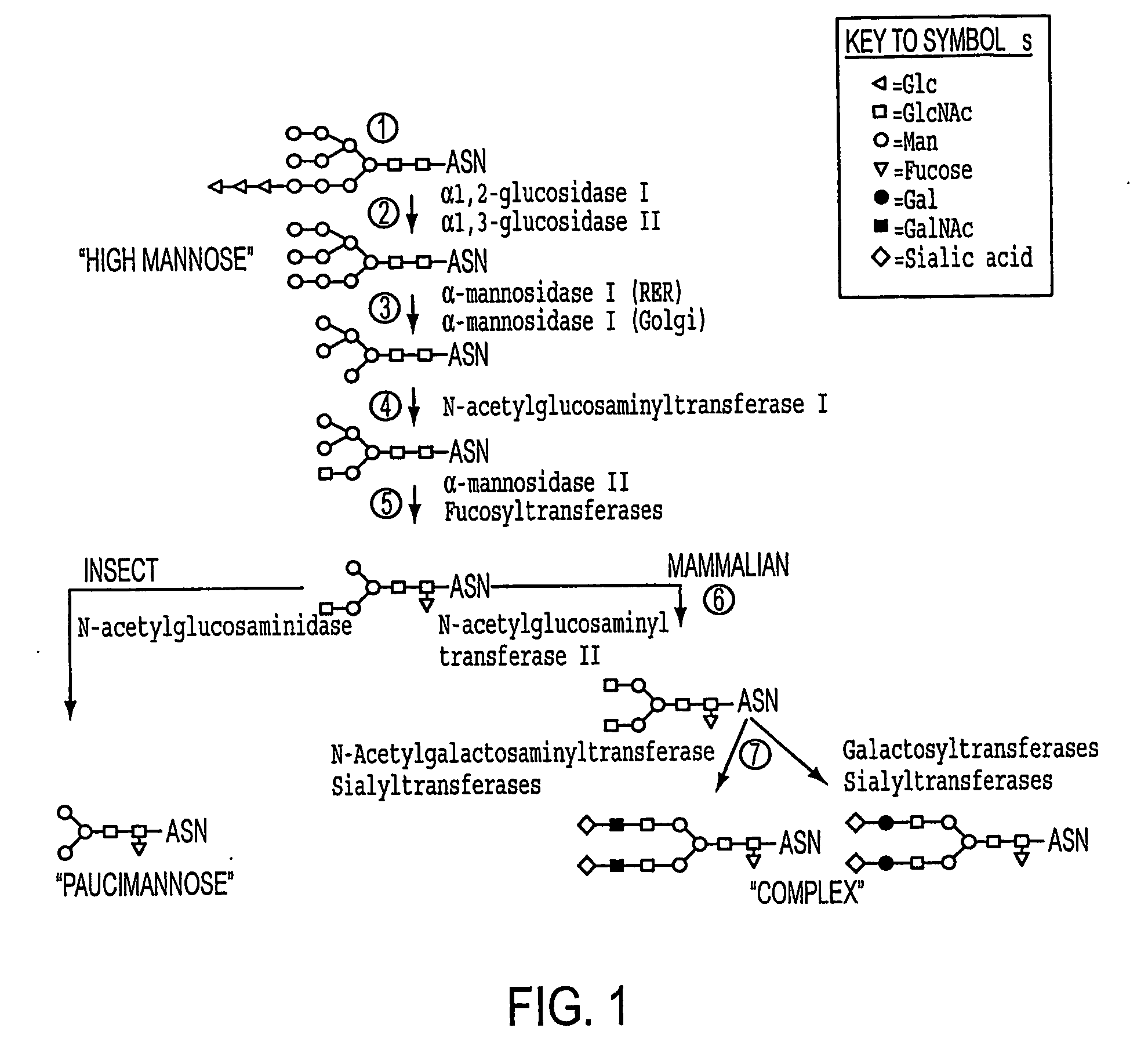
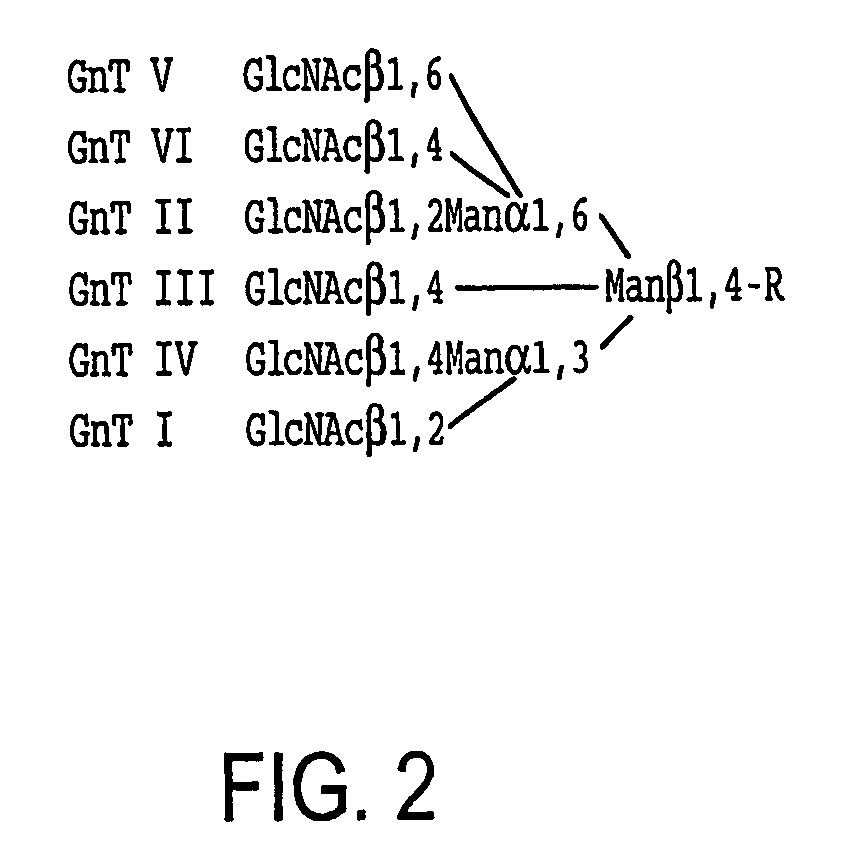
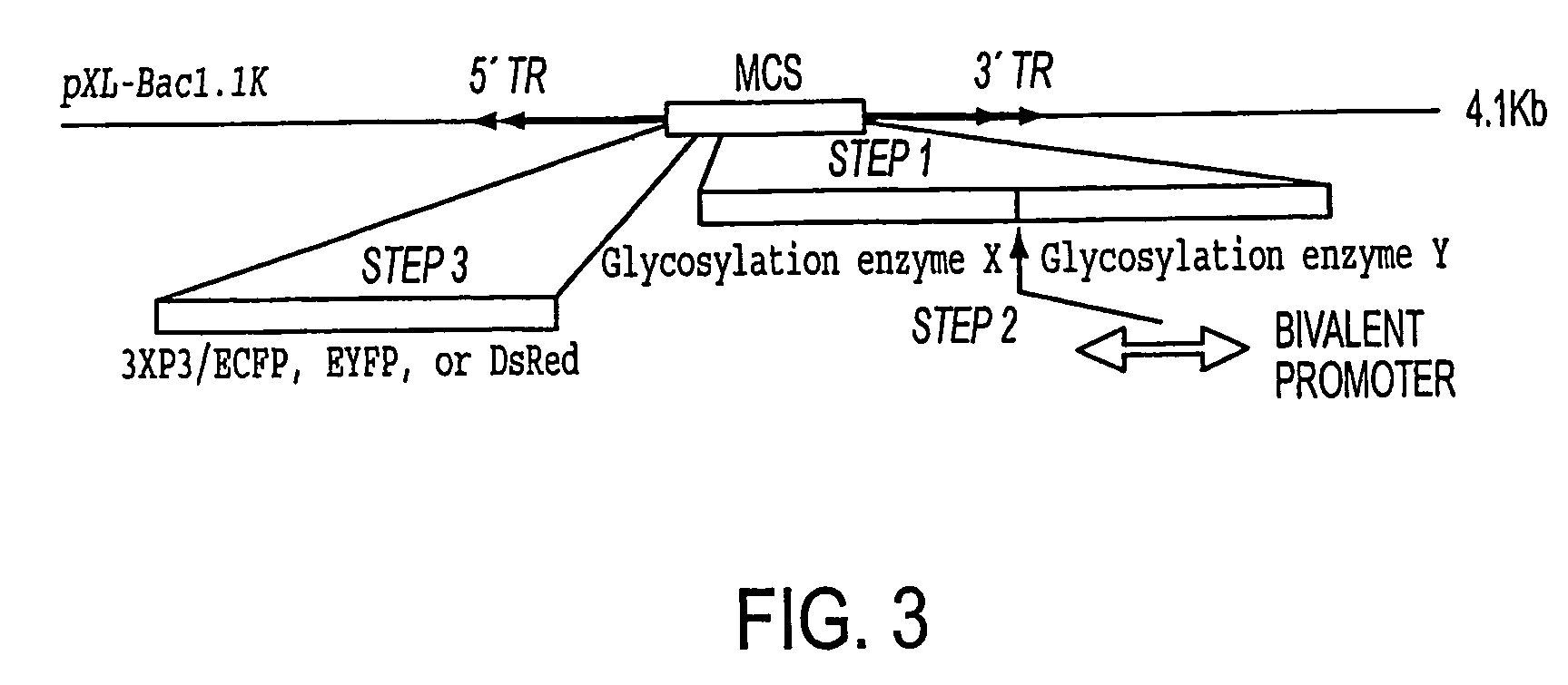
Production of human glycosylated proteins in transgenic insects
This invention relates, e.g., to transgenic insects, or progeny thereof, whose cells contain at least one genomically integrated, expressible, nucleic acid encoding two or more of a set of Nglycosylation enzymes that can glycosylate a heterologous protein with a mammalianized (e.g., humanized) glycosylation pattern. The glycosylation genes are preferably expressed in the insect cells in catalytic amounts. Also described are methods to use such a transgenic insect to produce heterologous, mammalianized polypeptides of interest.
Owner:CHESAPEAKE PERL
Method and compositions for the detection of protein glycosylation
The invention provides methods and compositions for the rapid and sensitive detection of post-translationally modified proteins, and particularly of those with post-translational glycosylations. The methods can be used to detect O-GlcNAc post-translational modifications on proteins on which such modifications were undetectable using other techniques. In one embodiment, the method exploits the ability of an engineered mutant of β-1,4-galactosyltransferase to selectively transfer an unnatural ketone functionality onto O-GlcNAc glycosylated proteins. Once transferred, the ketone moiety serves as a versatile handle for the attachment of biotin, thereby enabling detection of the modified protein. The approach permits the rapid visualization of proteins that are at the limits of detection using traditional methods. Further, the preferred embodiments can be used for detection of certain disease states, such as cancer, Alzheimer's disease, neurodegeneration, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Bioconjugates made from recombinant n-glycosylated proteins from procaryotic cells
The present invention is directed to a bioconjugate vaccine, such as an 01-bioconjugate vaccine, comprising: a protein carrier comprising a protein carrier containing at least one consensus sequence, D / E-X—N—Z—S / T, wherein X and Z may be any natural amino acid except proline; at least one antigenic polysaccharide from at least one pathogenic bacterium, linked to the protein carrier; and, optionally, an adjuvant. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to a method of producing an O1-bioconjugate in a bioreactor comprising a number steps.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Complete chemical and enzymatic treatment of phosphorylated and glycosylated proteins on protein chip arrays
InactiveUS20060269980A1Quick upgradeSimpler, more sensitive methodologiesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic digestionChemical treatment
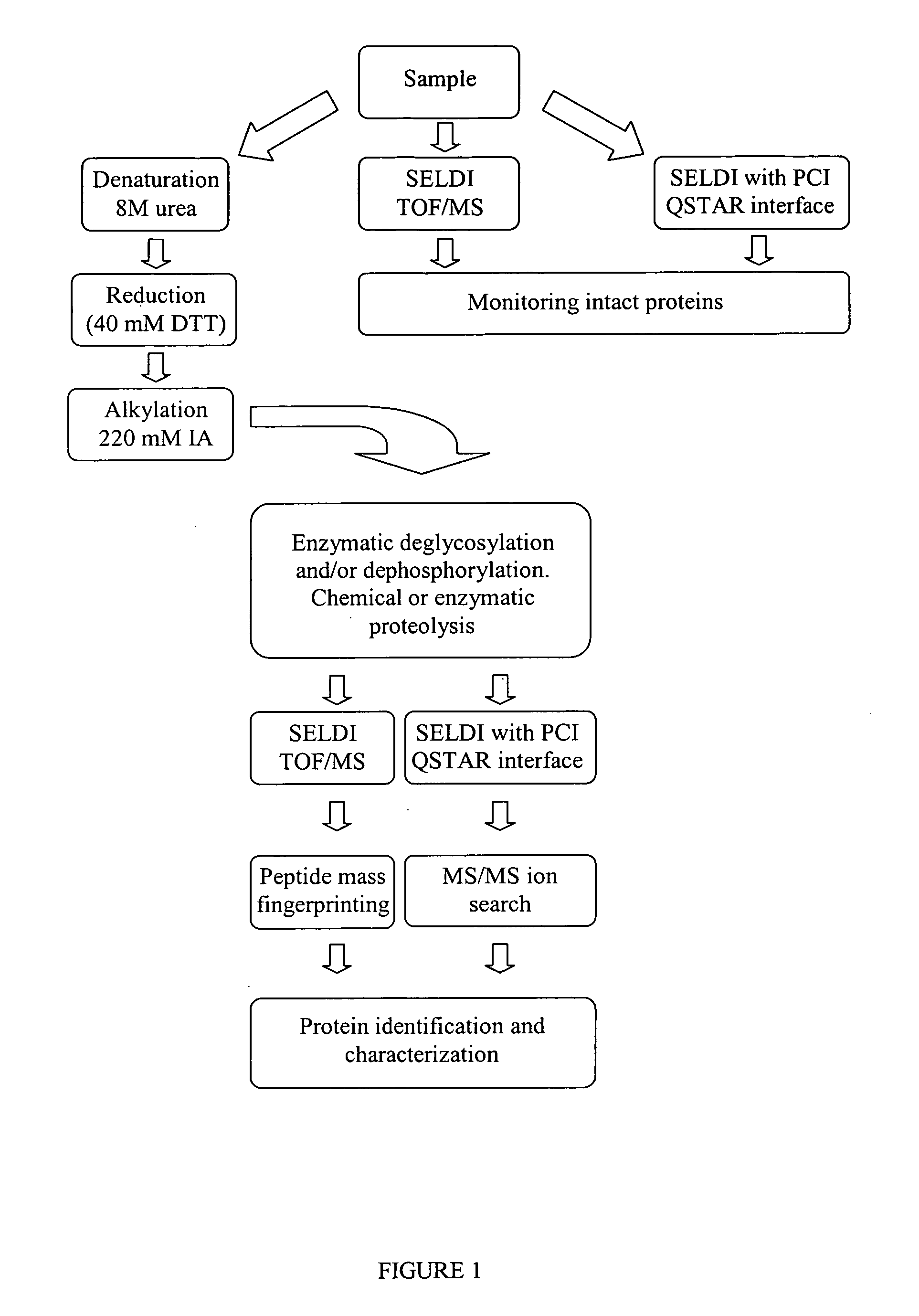
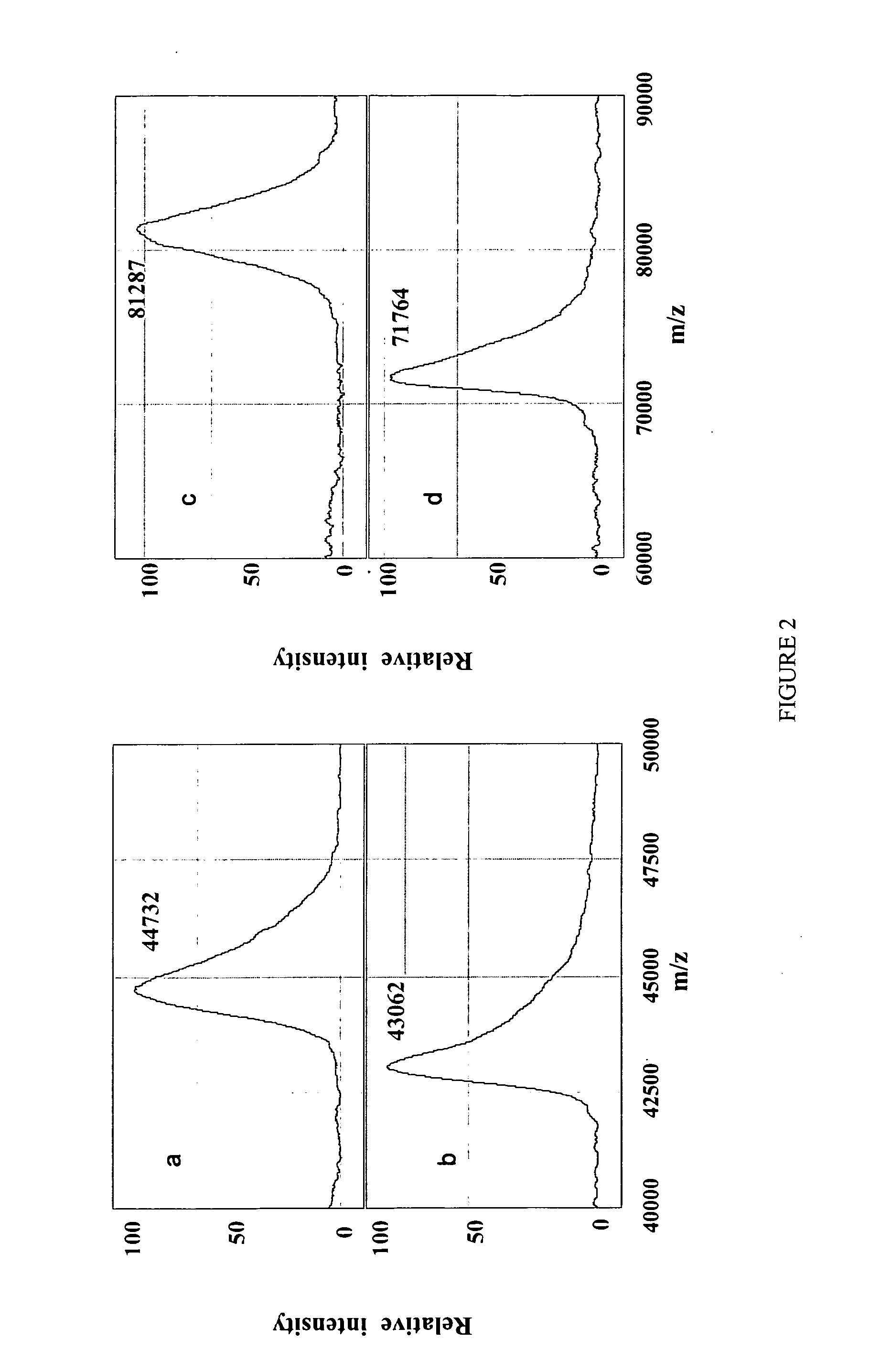
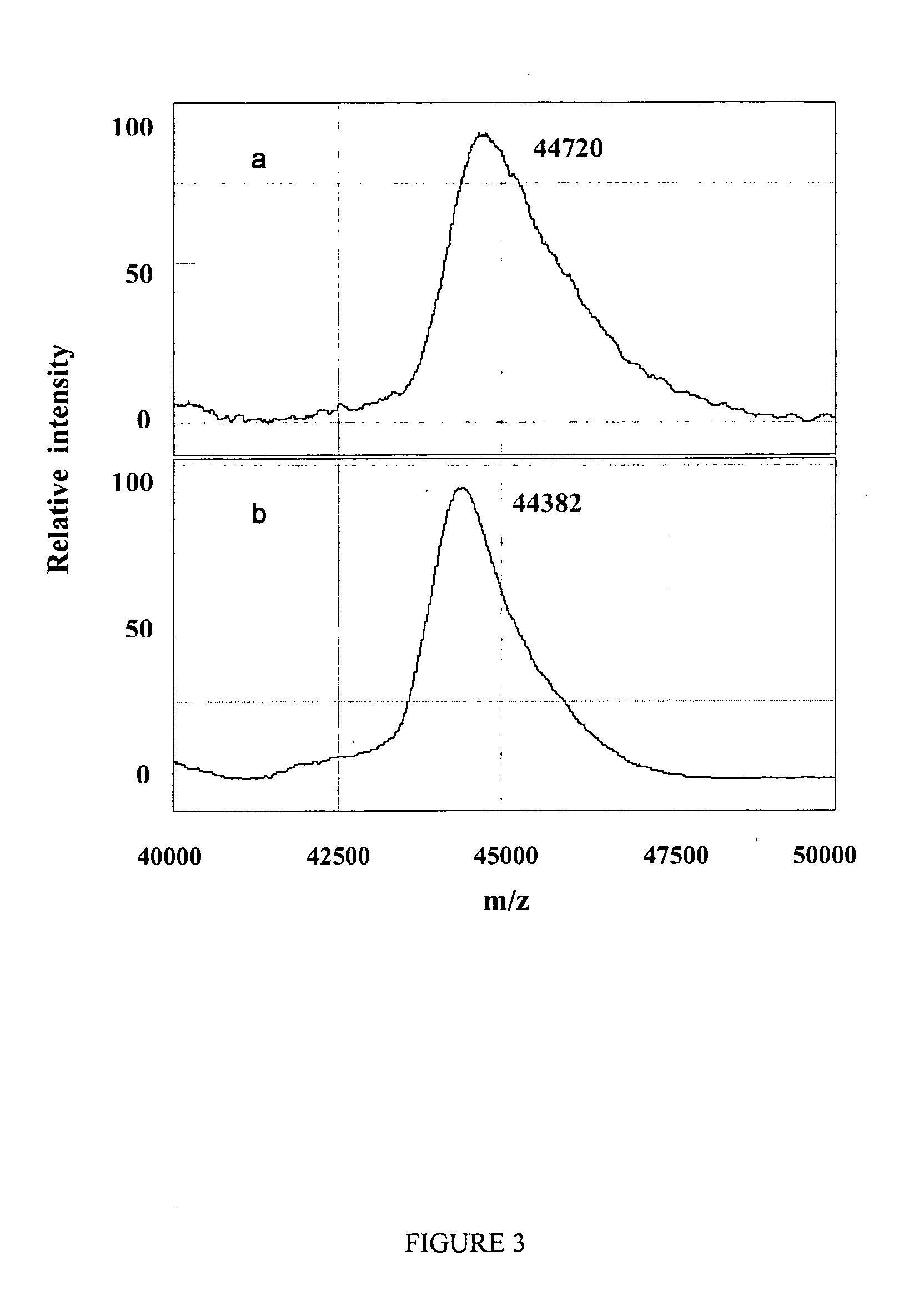
A simple and quick protocol for chemical treatment, enzymatic or chemical digestion, and subsequent identification of proteins on protein chip arrays is disclosed, together with kits therefor. The chemical treatment comprises denaturation, reduction and alkylation while enzymatic digestion encompasses deglycosylation, dephosphorylation, and digestion by various proteases. Digestion is also accomplished by various chemicals that are known to induce proteolysis. All reactions are carried out sequentially on chip. Subsequent peptide mass fingerprinting or product ion searches allow the identification of specific peptides which can be correlated to proteins. The method of the present invention can be applied to the analysis of biological samples such as urine and plasma to identify biomarkers in diseased states. The methods of the present invention allow complete on chip treatment, which can be used for rapid protein identification and structural characterization of heavily posttranslationally modified proteins.
Owner:GIBBS BERNARD F
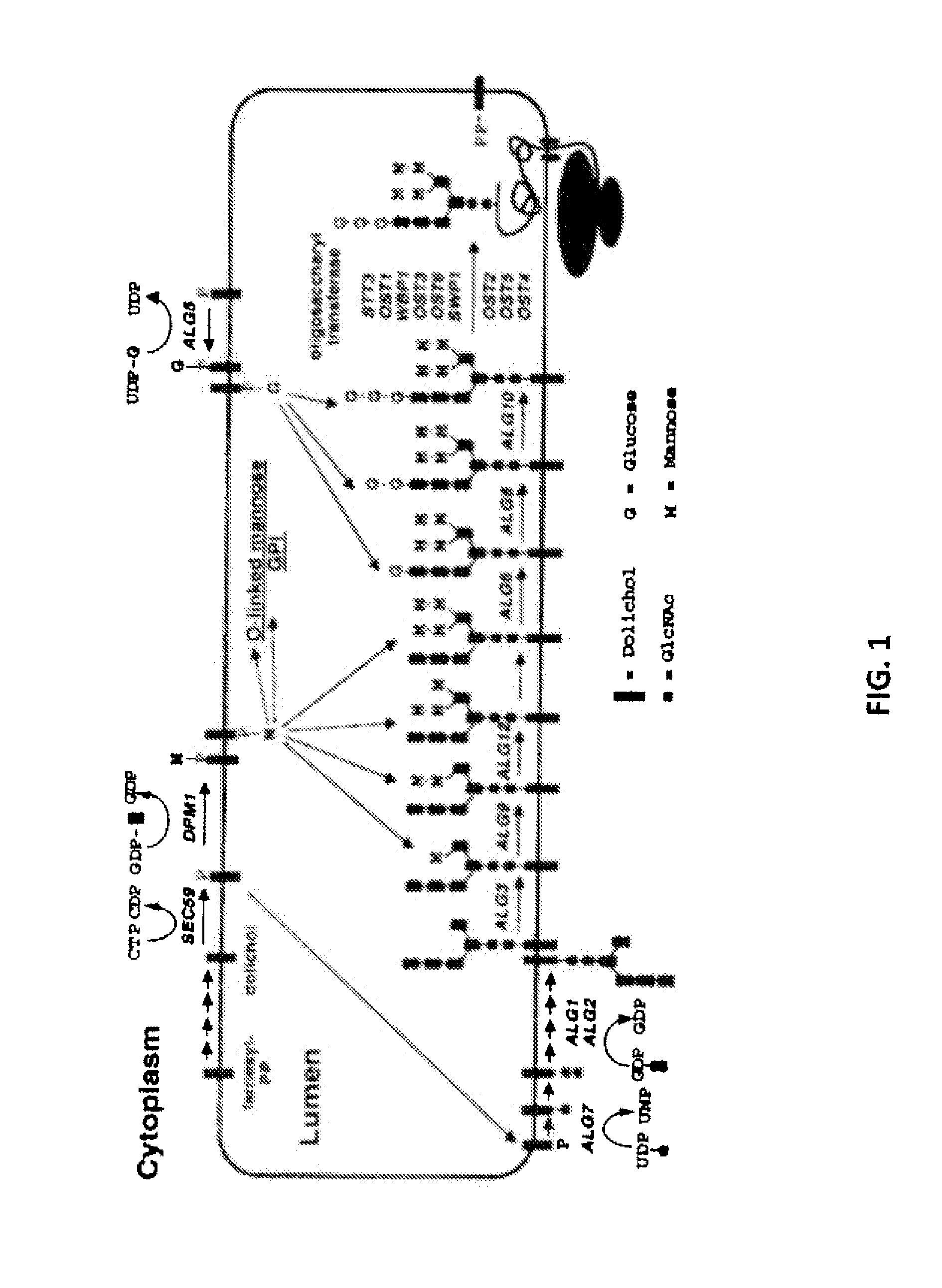
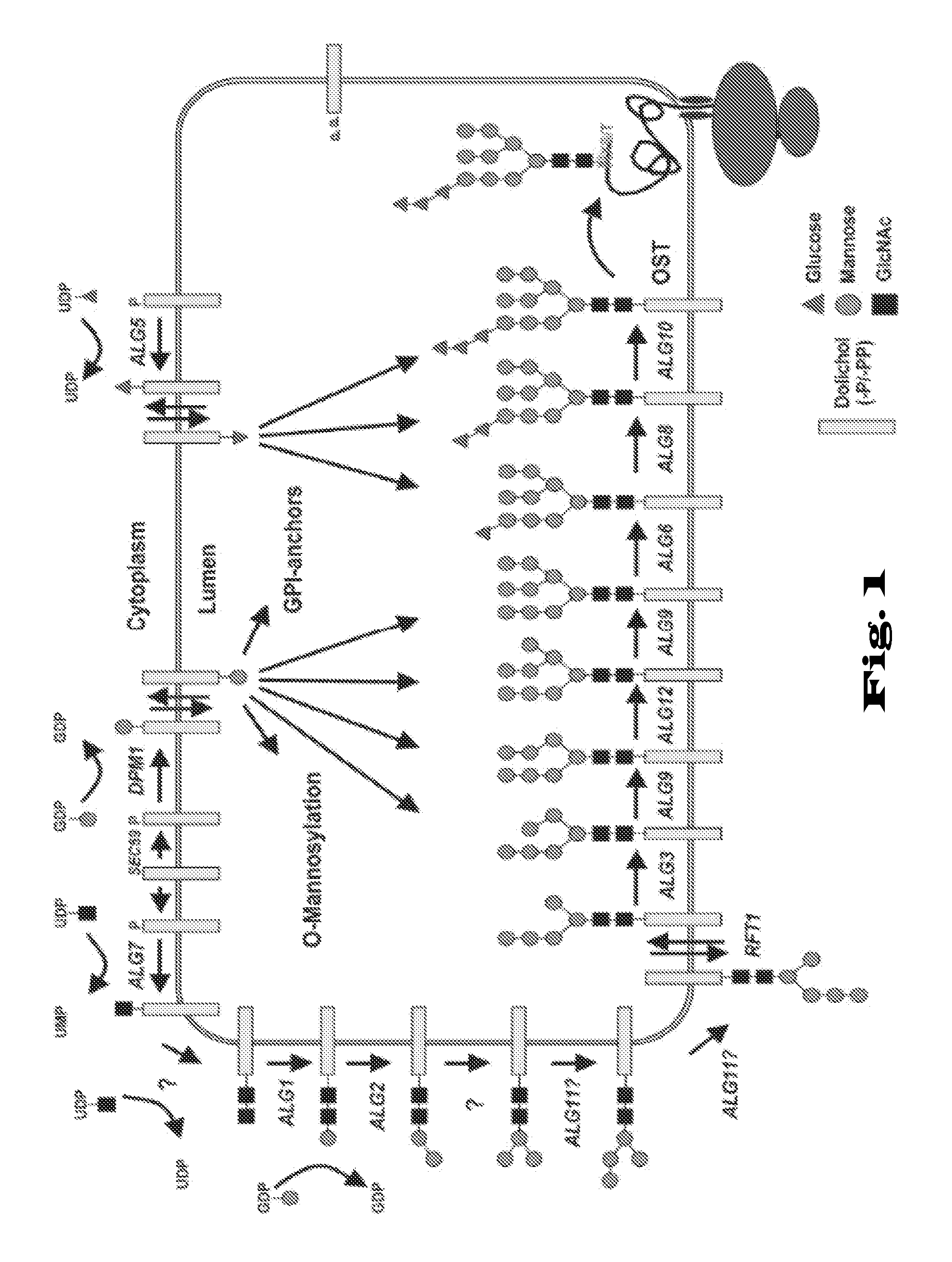
Glycosylation of proteins in host cells
InactiveUS20130040897A1Good curative effectWithout triggering unwanted side effectAnimal cellsFungiYeastTherapeutic protein
The invention provides means and methods for an improved production of glycosylated recombinant proteins in lower eukaryotes, specifically the production of human-like complex or hybrid glycosylated proteins in yeast. The invention provides genetically modified eukaryotic host cells capable of producing glycosylation optimized proteins useful as immunoglobulins and other therapeutic proteins, and provides cells capable of producing glycoproteins having glycan structures similar to glycoproteins produced in human cell. The invention further provides proteins with human-like glycan structures and novel compositions thereof producible by these modified cells.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Recombinant n-glycosylated proteins from procaryotic cells
ActiveUS20100062484A1Efficient productionBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsADAMTS ProteinsAmino acid
The present invention relates to recombinant N-glycosylated proteins, comprising one or more introduced N-glycosylated optimized amino acid sequence(s), nucleic acids encoding these proteins as well as corresponding vectors and host cells. In addition, the present invention is directed to the use of said proteins, nucleic acids, vectors and host cells for preparing medicaments. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods for producing said proteins.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Detection of glycopeptides and glycoproteins for medical diagnostics
ActiveUS20090053828A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStable Isotope LabelingMalignant lymphoma
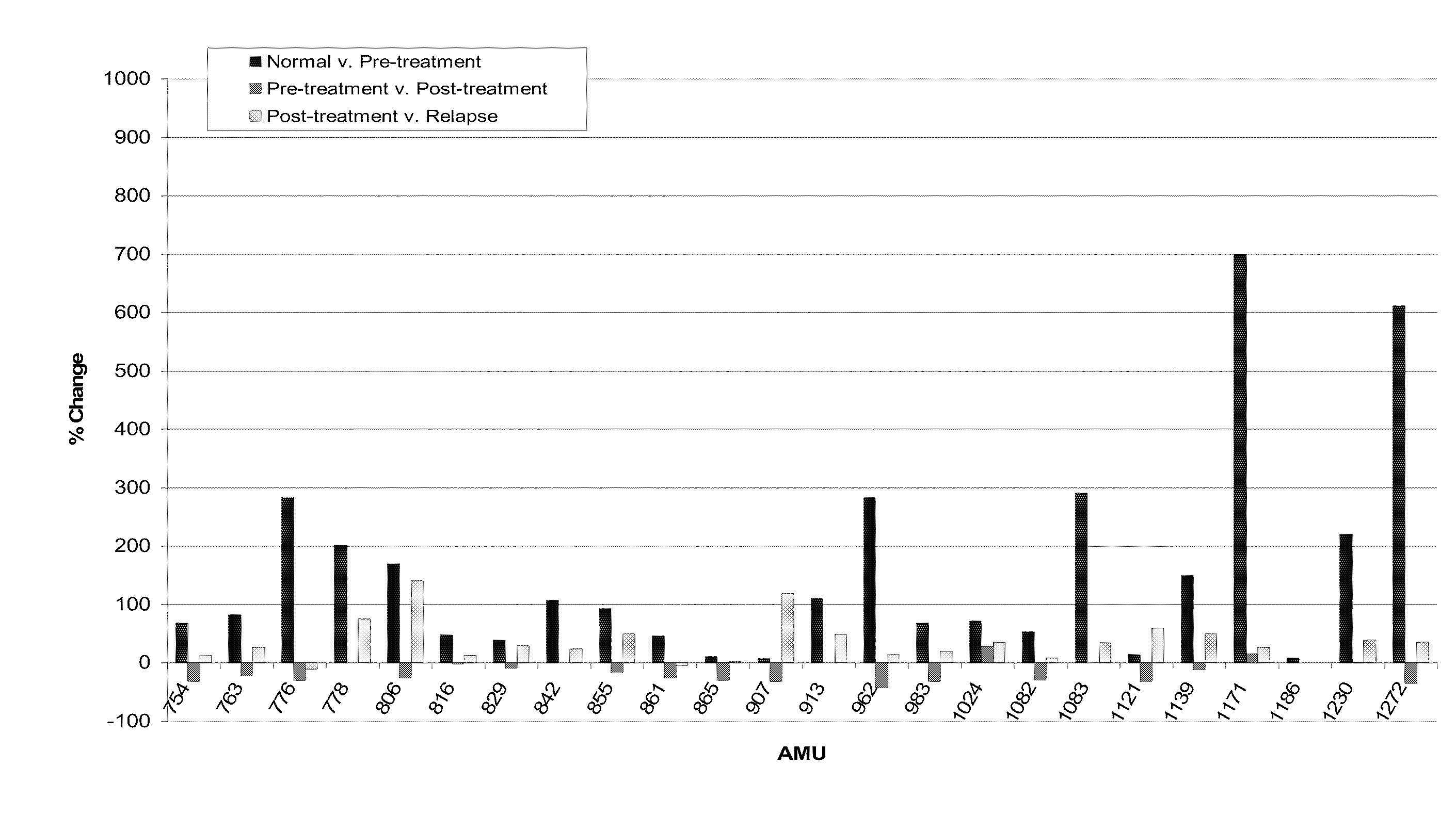
A diagnostic method for determining the absence or presence of a disease is provided. The method includes assaying the amount and / or types of glycopeptides in a sample from a subject, and comparing these to the amount and types of reference glycopeptides. The method may include the use of a stable isotope label, affinity selection, immunoaffinity chromatography, and glycoproteomics techniques, to identify and quantify changes in glycosylated peptides or glycosylated proteins associated with cancers such as malignant lymphoma or breast cancer, to monitor patient's response to therapy, and to monitor disease recurrence.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Saccharide-containing protein conjugates and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110105379A1Improve performanceSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsReagentBiomolecule
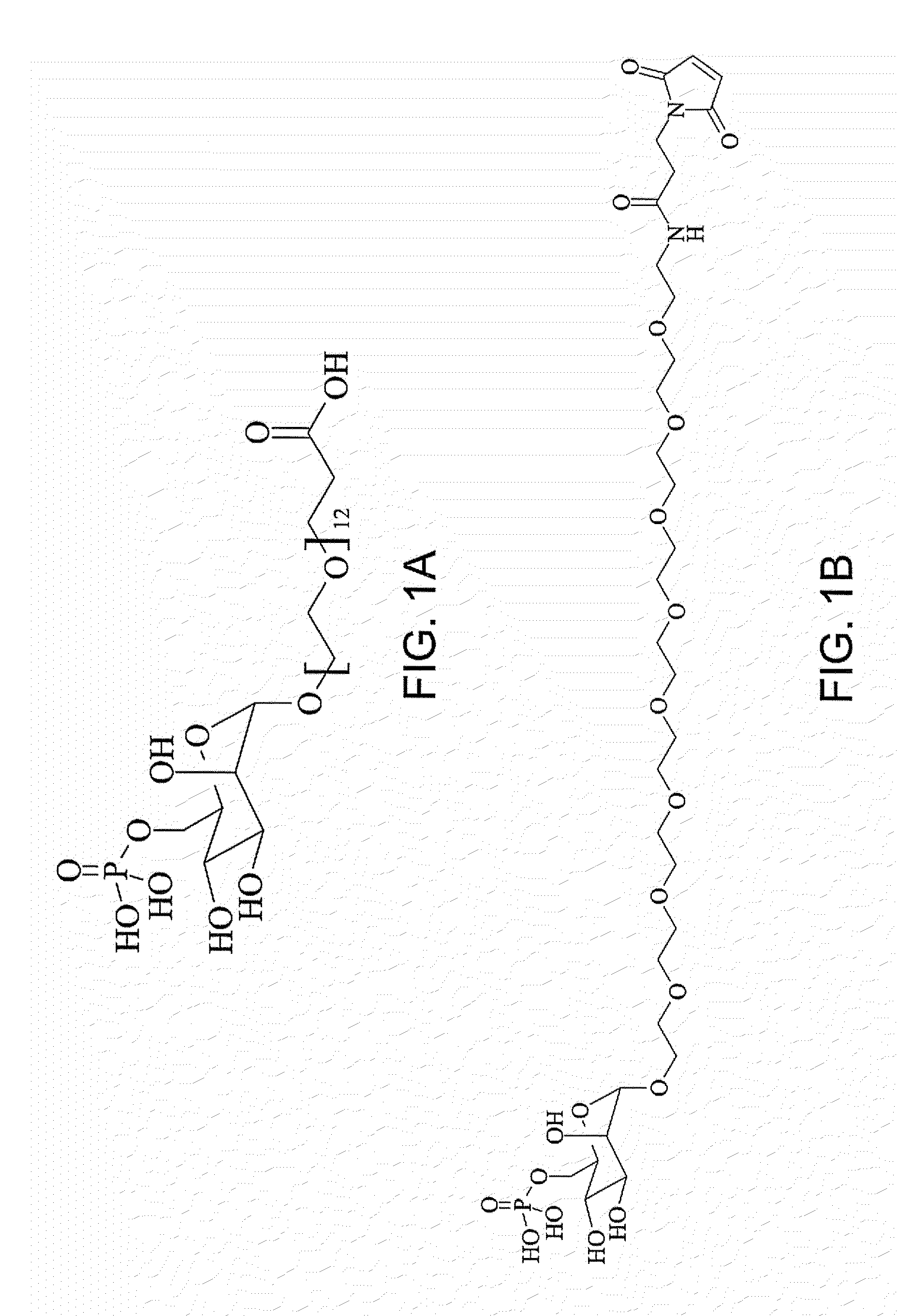
Conjugates of a saccharide and a biomolecule, covalently linked therebetween via a non-hydrophobic linker and methods of preparing same are disclosed. Also disclosed are medical uses utilizing such conjugates. Glycosylation reagents for use in preparing these conjugates are also disclosed. Glycosylated proteins, characterized by improved performance, are also disclosed.
Owner:PROTALIX
Method for specifically separating and enriching phosphorylated peptide and glycosylated peptide
ActiveCN108440641ALarge specific surface areaGood magnetic responsePeptide preparation methodsProteinPhosphorylated Peptide
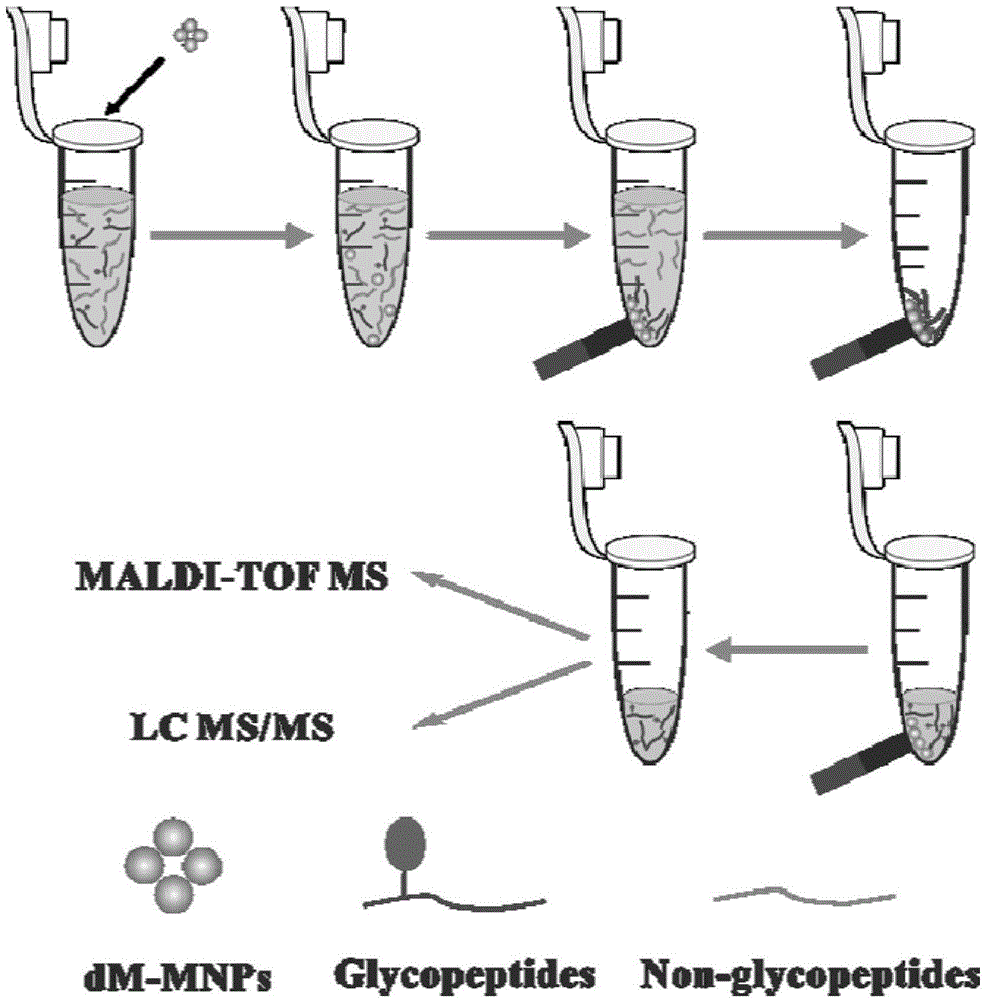
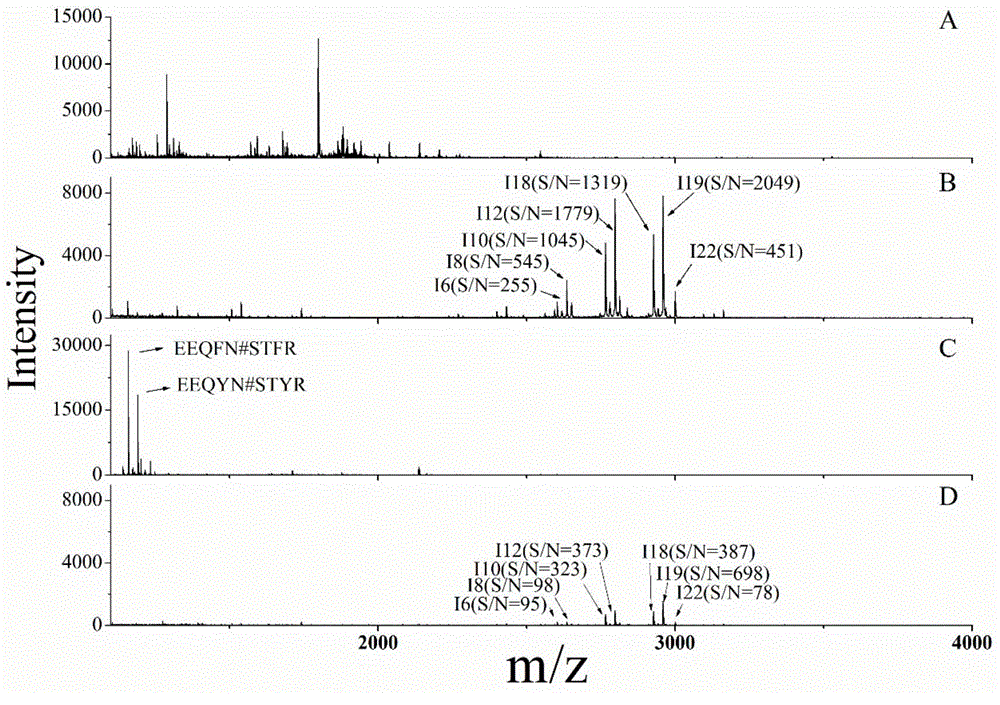
The invention provides a method for specifically separating and enriching a phosphorylated peptide and a glycosylated peptide. The method concretely comprises the following steps: preparing a dispersion from a hydrophilic magnetic meso-porous titanium dioxide material, adding the dispersion and a target phosphorylated peptide and glycosylated peptide solution into a sample introduction buffer solution, performing incubation at 37 DEG C for 30-60 min, washing a material with the sample introduction buffer solution, using ammonia water with the volume ratio of 5-20% as an elution buffer solution, performing dot targeting on the obtained eluate, and performing mass spectrometry. The method realizes the simultaneous enrichment of the low-abundance phosphorylated peptide and glycosylated peptide by controlling enriching and eluting conditions, can realize simultaneous large-scale identification of a phosphorylated protein and a glycosylated protein by MALDI-TOF MS or nano-LC-MS / MS, and hasa broad application prospect in post-translational modification proteomics.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Magnetic nano material and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105771942AImprove hydrophilicityEasy to separateOther chemical processesPreparing sample for investigationChemistryNanomaterials
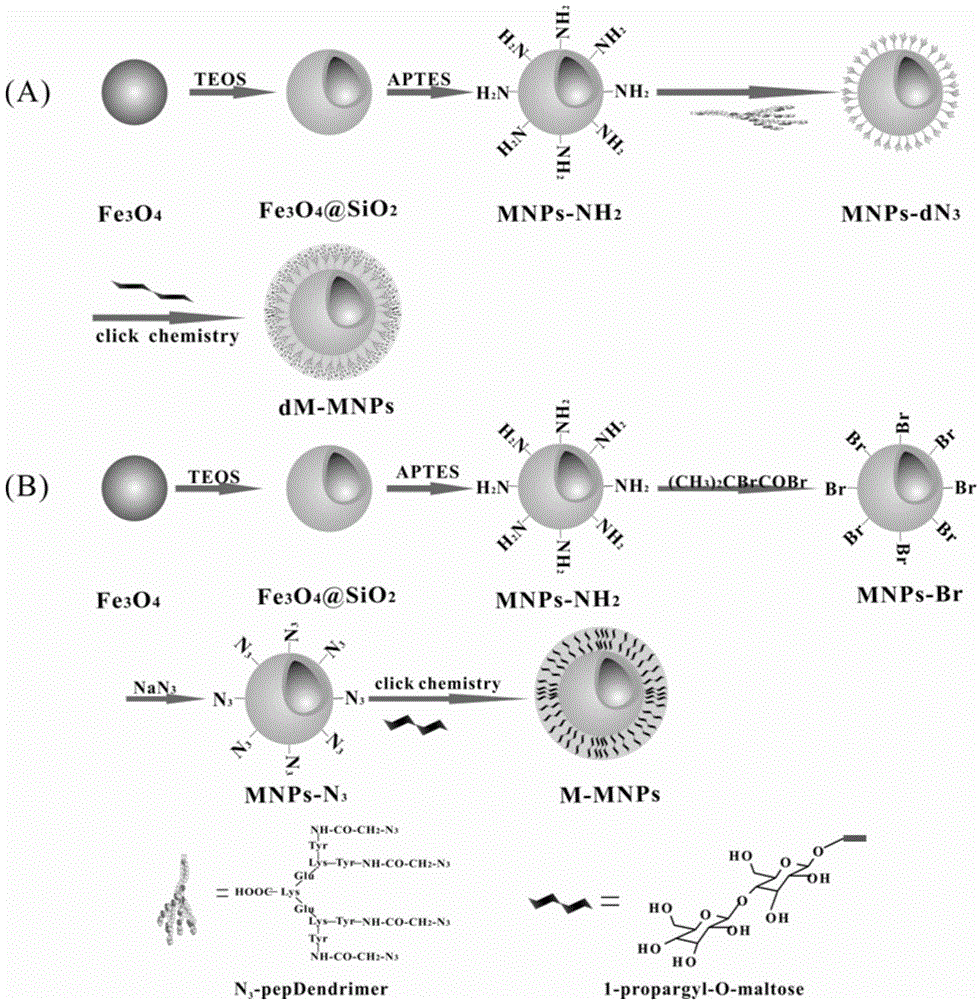
The invention relates to a pretreatment process of a glycosylated protein sample, in particular to a novel magnetic nano material for pretreatment of the glycosylated protein sample.The method comprises the steps of preparation of the magnetic nano material, subsequent modification of glycopeptide dendritic macromolecules, and enrichment of glycosylated polypeptide with the hydrophilic interaction chromatography.The method is high in sensitivity and suitable for pretreatment of glycosylated protein in a biological sample.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Glycosylation method for improving emulsification stability of collagen
InactiveCN105541998AFacilitates high emulsion stabilityImprove emulsion stabilityConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsMaillard reactionCholesterol
The invention belongs to the technical field of chitosan oligosaccharide modification of proteins, and particularly, relates to a glycosylation method for improving the emulsification stability of aquatic collagen. The aquatic collagen is subjected to glycosylation modification by adopting chitosan oligosaccharide to obtain modified glycosylated collagen; in particular, the method comprises three steps of preparation of fish skin gelatin, glycosylated protein preparation, and purification and collection; transglutaminase (TG enzyme) is used for realizing chitosan oligosaccharide modification of the collagen, functional properties (including water absorption, gelation property, thermal stability and the like) of the chitosan can be improved, the collagen is allowed to have certain physiological activities (including activities of enhancing immunity, lowering blood pressure, lowering blood sugar, reducing cholesterol and the like), moreover, the problems generated in glycosylation modification of the protein through a Maillard reaction are solved, a protein ingredient having special functional properties is developed for food industries, and a new theoretical basis and a new technical method are provided.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Electrochemistry detecting method and testing apparatus of saccharification hemoglobin content
InactiveCN101158691AEasy to combine with electrochemical analysisInexpensive combined with electrochemical analysisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingElectrochemical responseHEMOGLOBIN I
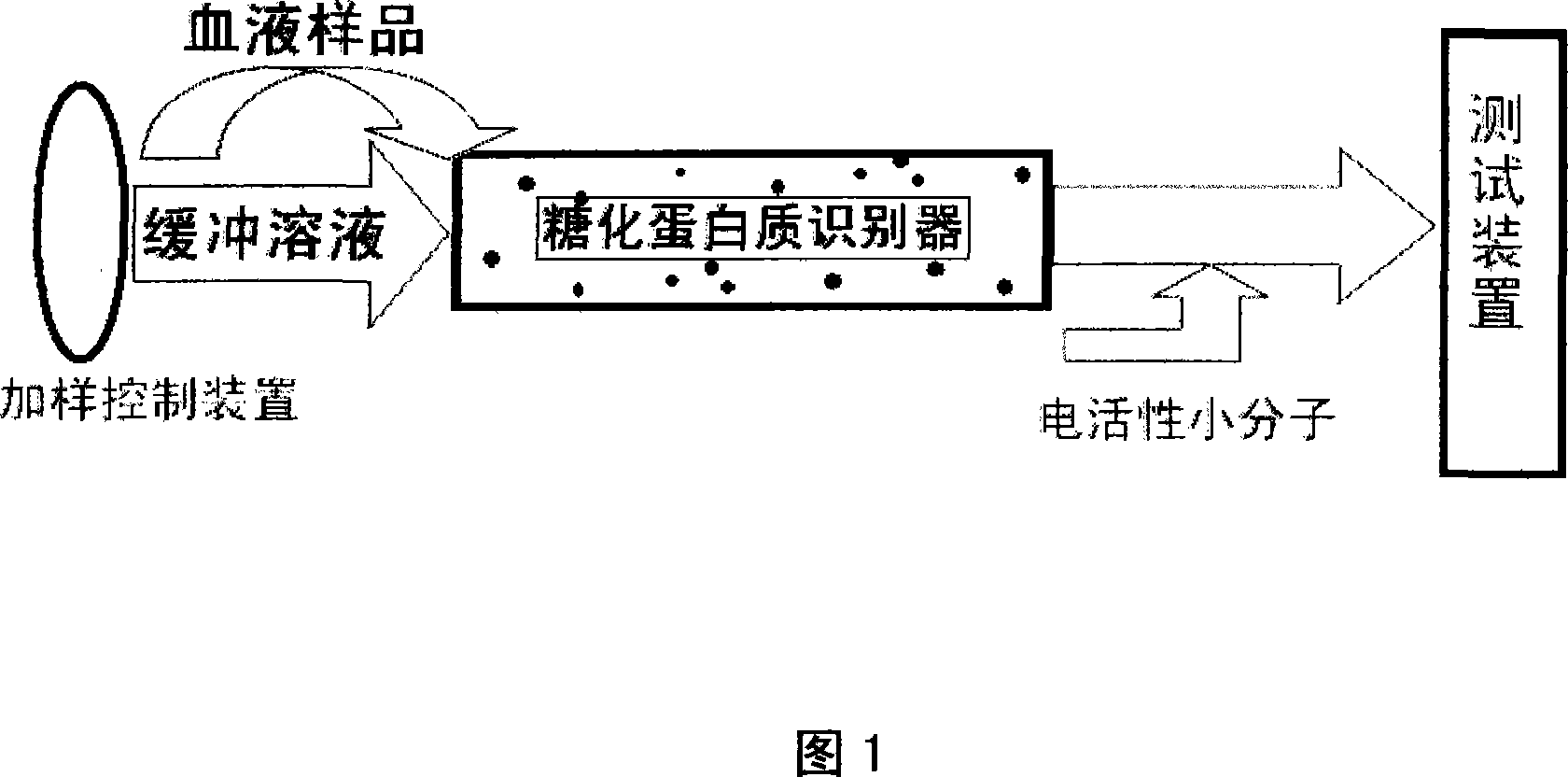
The present invention provides an electrochemical detection method for content of glycosylated hemoglobin in the blood, and is characterized in that: whole blood specimen is diluted by combined liquid ranging from 30 times to 70 times and passes through a glycosylated protein recognizer, electric activated small molecules are filled into the effluent liquid from the glycosylated protein recognizer, and electrochemical response of the liquid is detected by chemically modified electrodes after the filling, thereby obtaining the concentration of the blood glucose. The glycosylated protein recognizer is eluted by elute solvent, and the electrochemical response of the elute solvent is detected and the concentration of the glycosylated hemoglobin is obtained, thereby obtaining the content of the glycosylated hemoglobin of the sample after calculation. As the electrochemical detection is simple in operation, lower in cost and rapid in the analysis, the present invention is expected to realize the rapid determination of the clinical glycosylated hemoglobin and the rapid determination of the glycosylated hemoglobin after separation and elution.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Novel protein glycosylation grafting method
InactiveCN101906213AQuick responseOvercome the disadvantage of uneven responseFood preparationSolubilityWater soluble
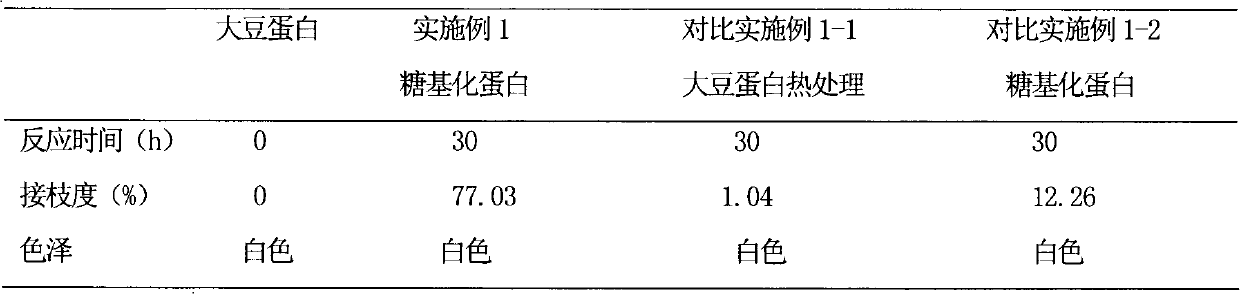
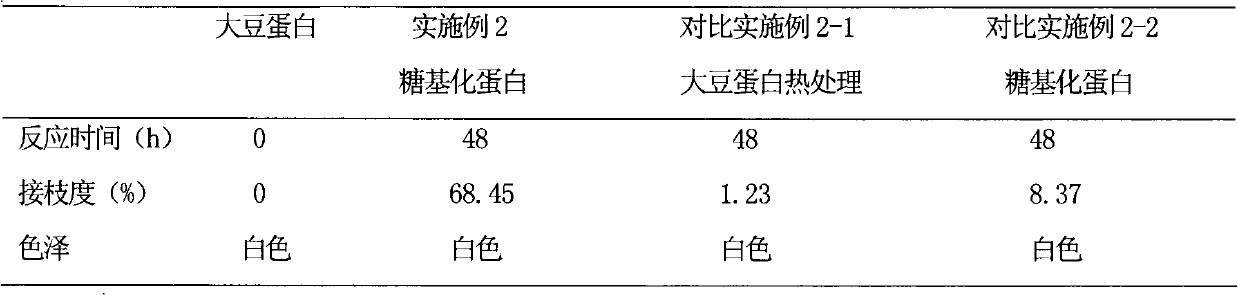
The invention discloses a novel protein glycosylation grafting method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding buffer solution into a crowding reagent and stirring the mixture to obtain solution; and (2) adding protein and glucan into the solution obtained by the step (1), stirring the mixture for 2 hours, adding NaN3 into the mixture, placing the mixture for 24 hours at the temperature of 5 DEG C, stirring the mixture for 12 to 48 hours at the temperature of between 50 and 70 DEG C again and quickly cooling the mixture to the temperature of less than 25 DEG C to obtain a glycosylation protein product. The method has the advantages of greatly improving functional characters such as water solubility, emulsibility, antioxidation and the like of a graft, along with convenientoperation and high reaction efficiency; and the product has industrial and large-scale application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Identification method for O-glycosylation peptide fragment and complete saccharide chain thereof
ActiveCN105467050AHigh sensitivityEliminate distractionsComponent separationMass spectrometryDigestion
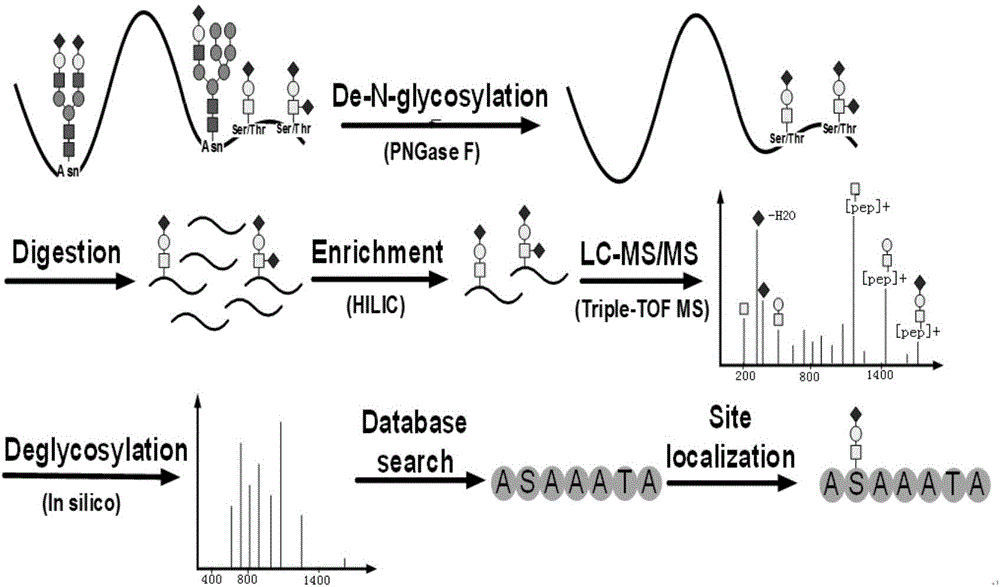
The present invention relates to an identification method for an O-glycosylation peptide fragment and a complete saccharide chain thereof. The technical process specifically comprises that a glycosylation protein sample is subjected to PNGase F digestion to remove N-glycosylation modification interference, enrichment is performed through hydrophilic interaction chromatography, and finally analysis is performed through time of flight mass spectrometer. According to the present invention, the method process has advantages of simple and rapid operation, high identification sensitivity, and the like; and the O-glycosylation peptide fragment and the complete saccharide chain thereof of the complex biological sample can be identified so as to achieve the research on the micro-uniformity of the O-glycosylation modification structure.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Glycosylated protein based on soluble soybean polysaccharides and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105669825AIncrease the degree of graftingImprove dispersion stabilityAlbumin peptidesPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingHeat stability
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing and discloses glycosylated protein based on soluble soybean polysaccharides and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps that protein and soluble soybean polysaccharides are dissolved in deionized water, a pH value is adjusted to be 6.8-7.0, a protein stock solution and a polysaccharide stock solution are obtained respectively, the protein stock solution and the polysaccharide stock solution are mixed to stay overnight and be hydrated, and a mixture is obtained through freezing drying; the mixture which is frozen dry reacts for 7-14 days in a drying device with the temperature of 60 DEG C and the humidity being 79%, reaction products are obtained and dissolved in deionized water, a pH value is adjusted to be 4.6-5.0 after stirring and mixing, a solution is centrifuged, supernatant is dried, and the glycosylated protein based on soluble soybean polysaccharides is obtained. A grafted product can effectively improve functional properties of protein nearby isoelectric points, particularly, emulsifying property, heat stability, foaming performance and the like are superior to the mixed action of protein and polysaccharides, and good market prospects are achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods and compositions for the identification of cancer markers
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the identification of cancer markers. In particular, the present invention provides methods and compositions for the identification of glycosylated proteins and protein glycosylation patterns. The present invention further provides cancer markers identified using the described methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
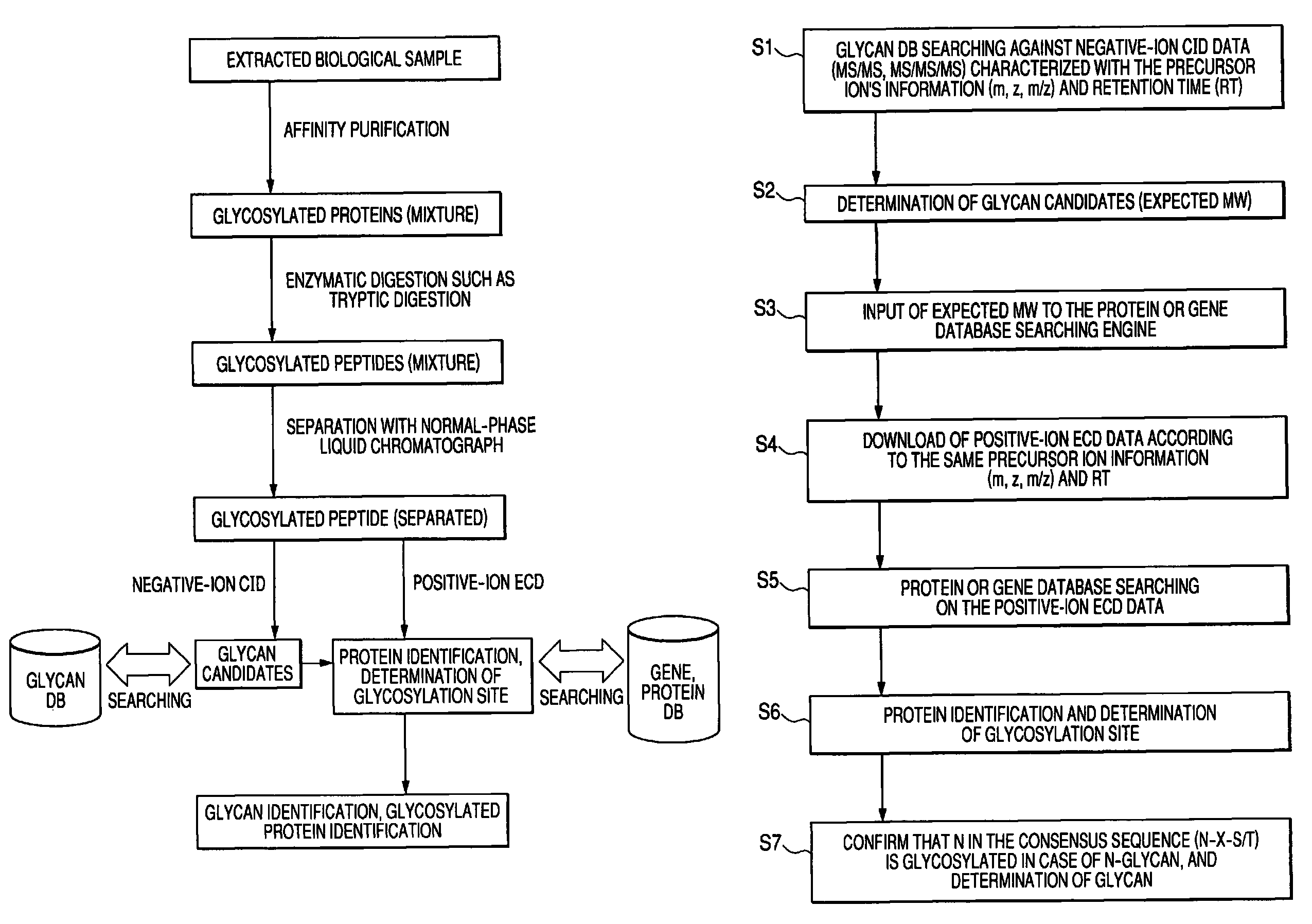
Methods and instruments for identification of glycosylated proteins and peptides
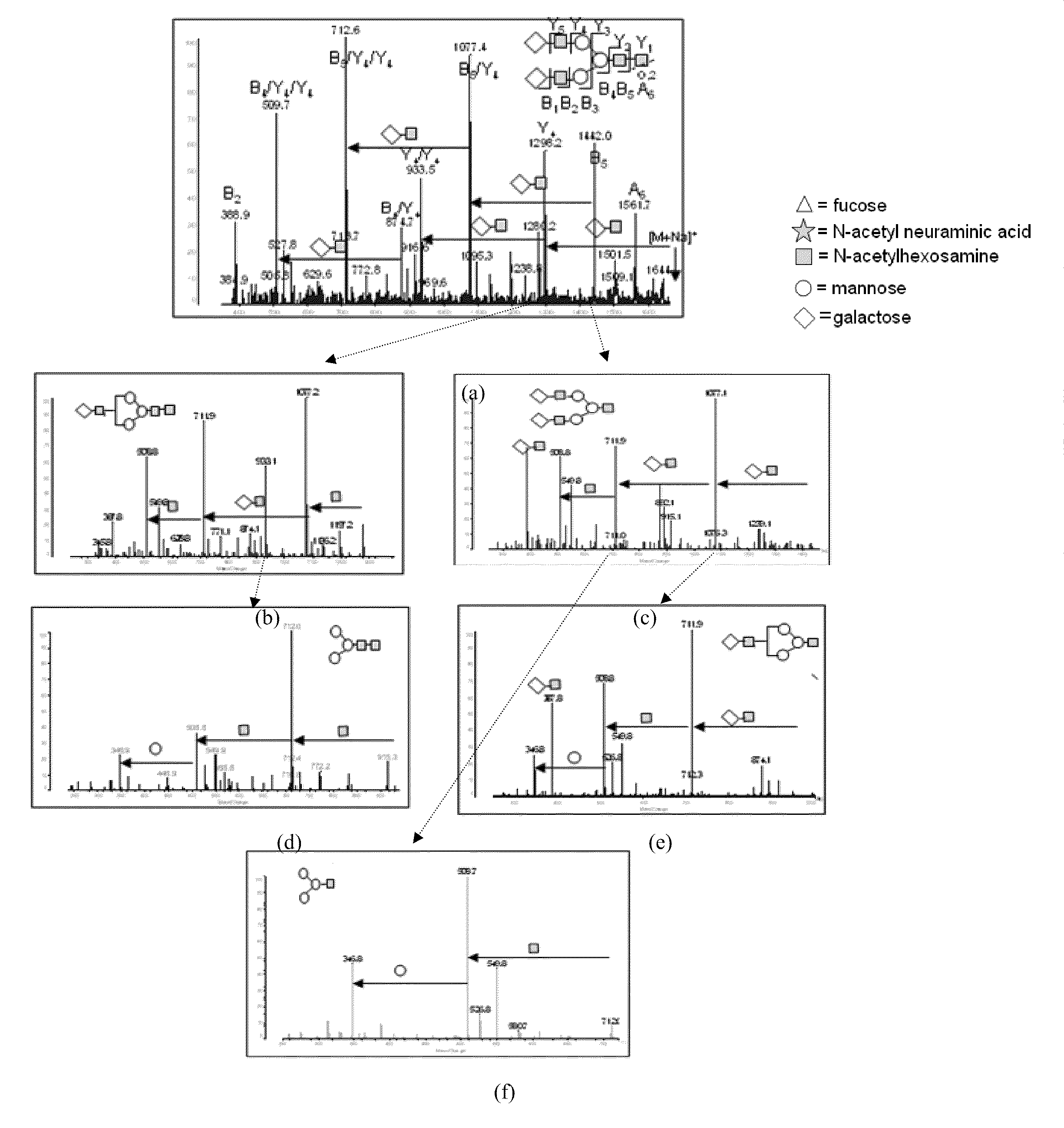
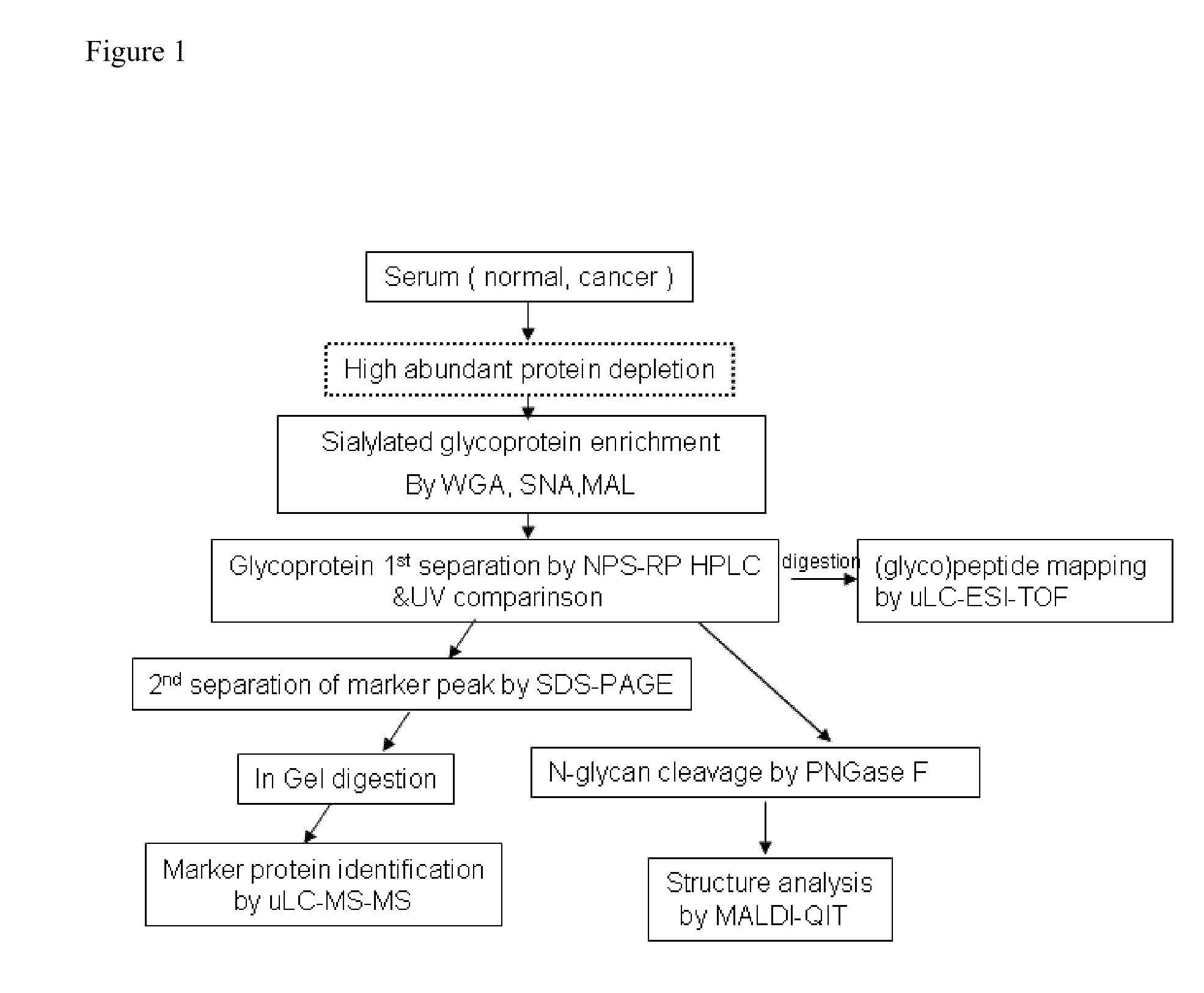
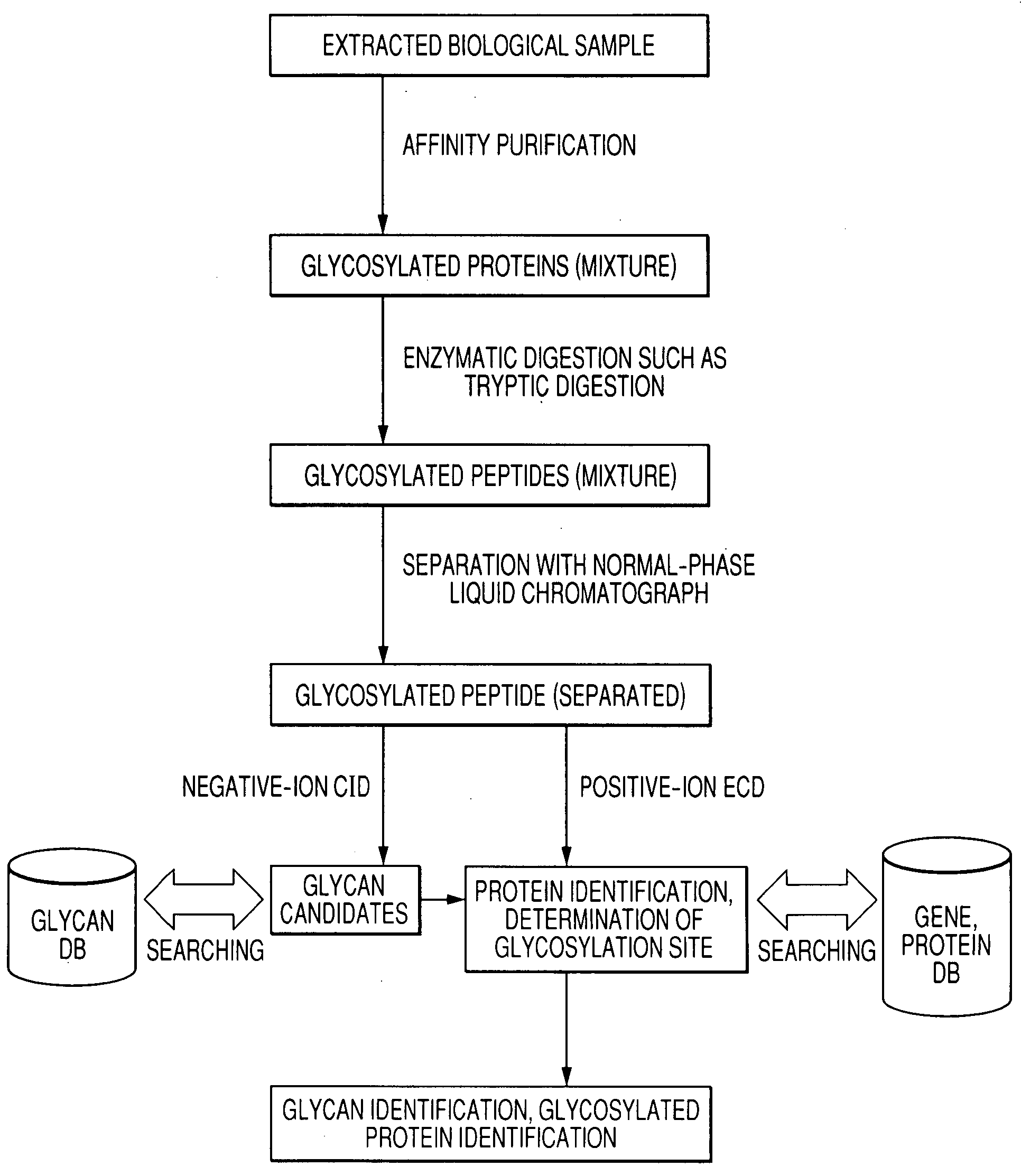
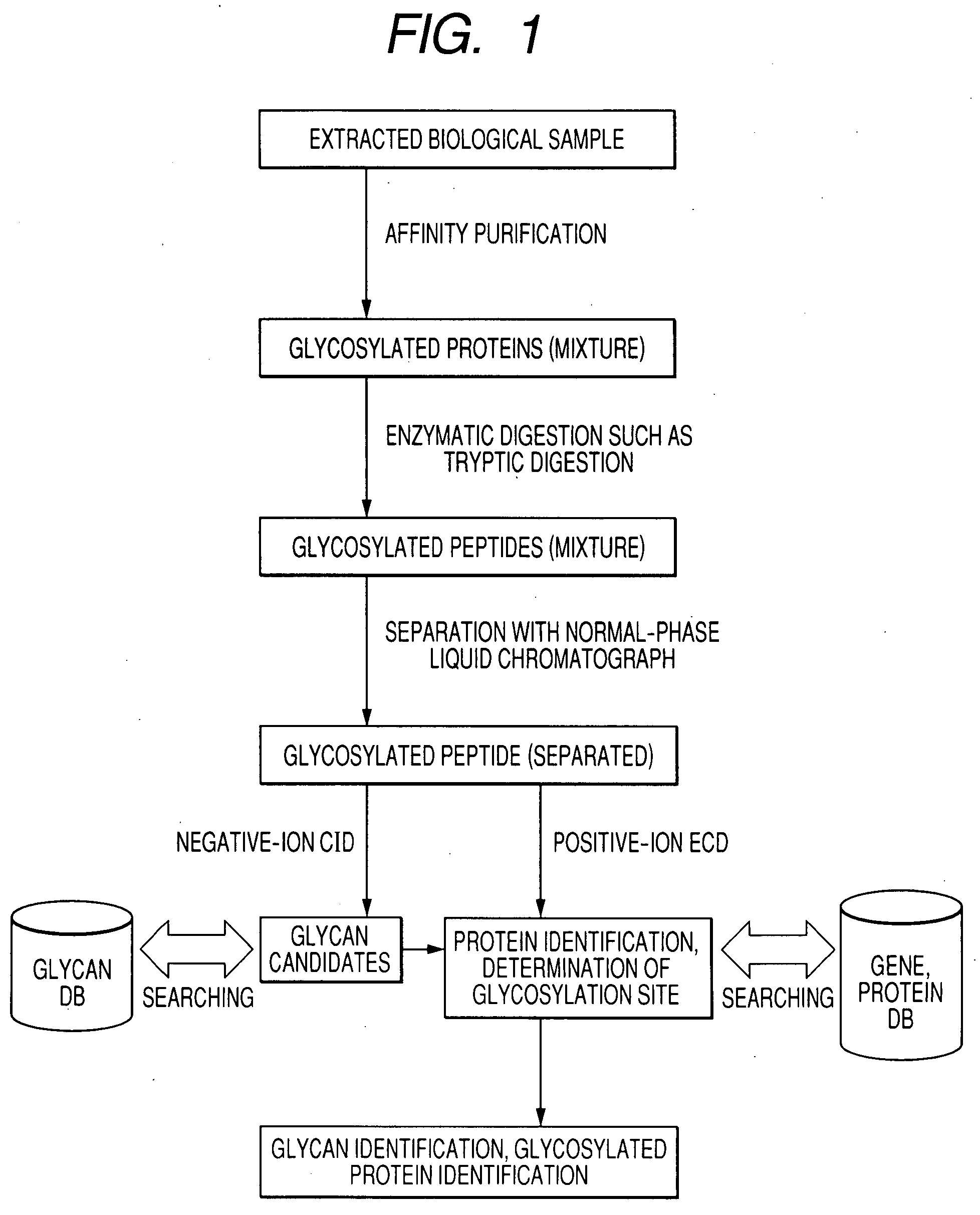
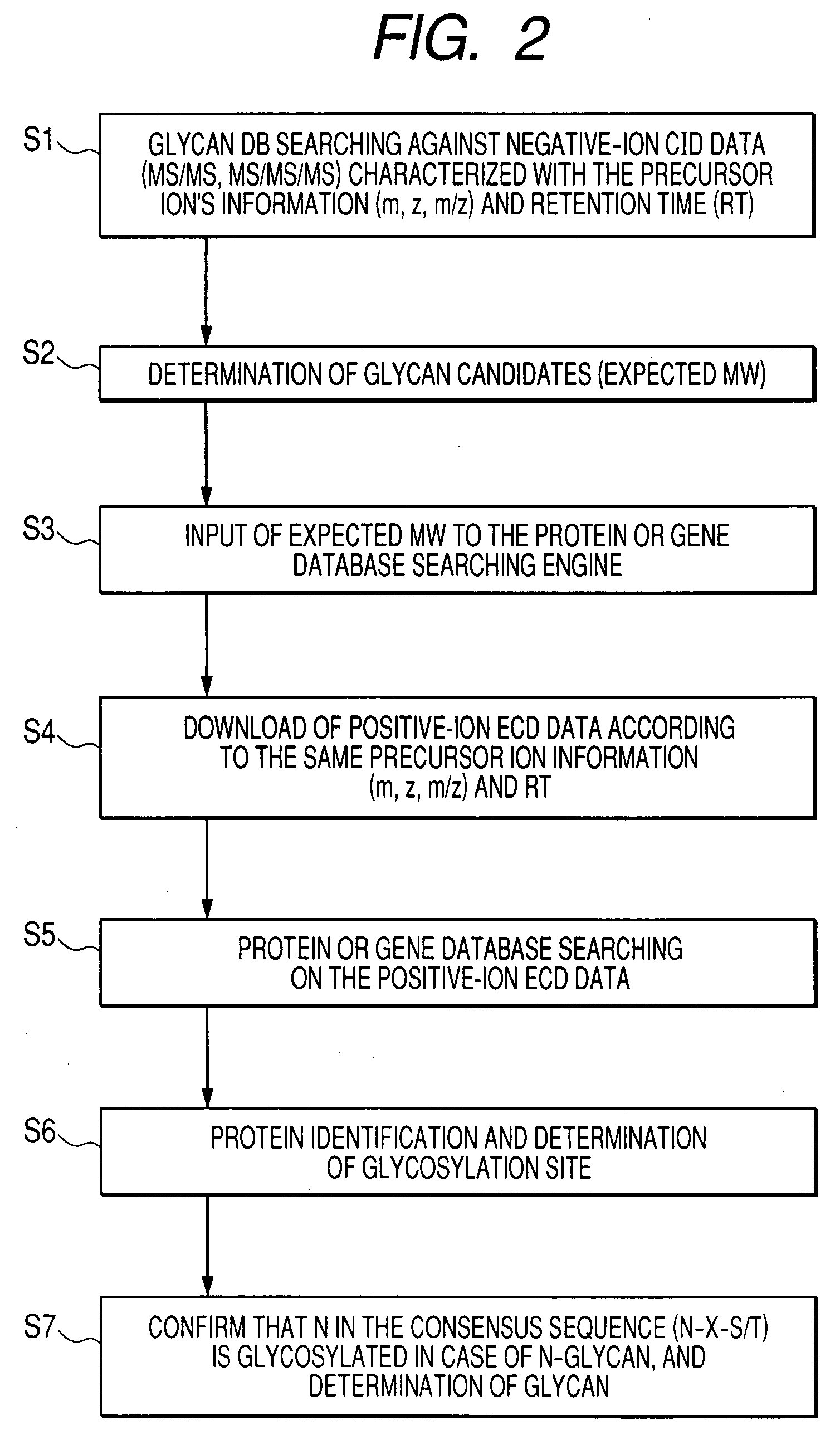
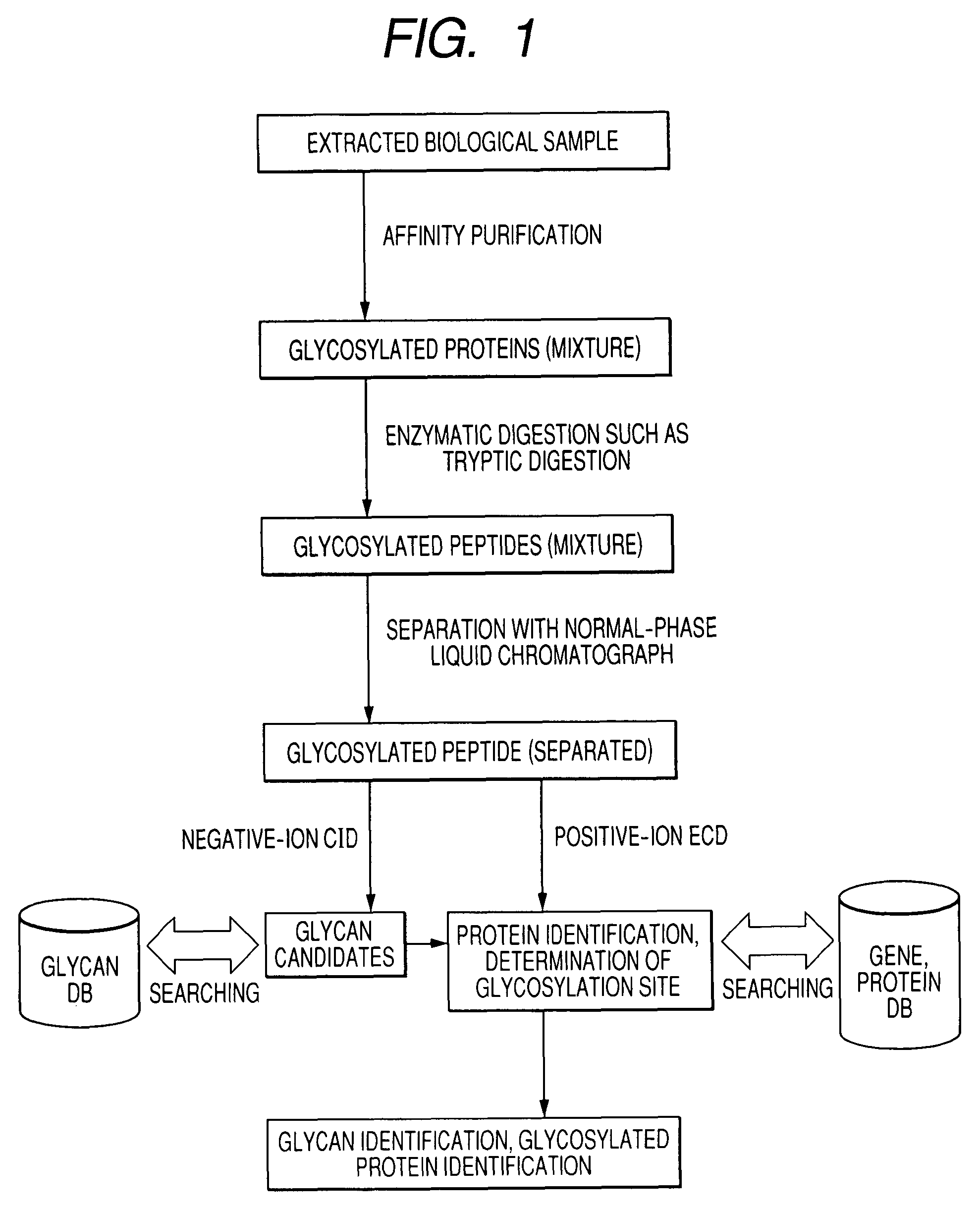
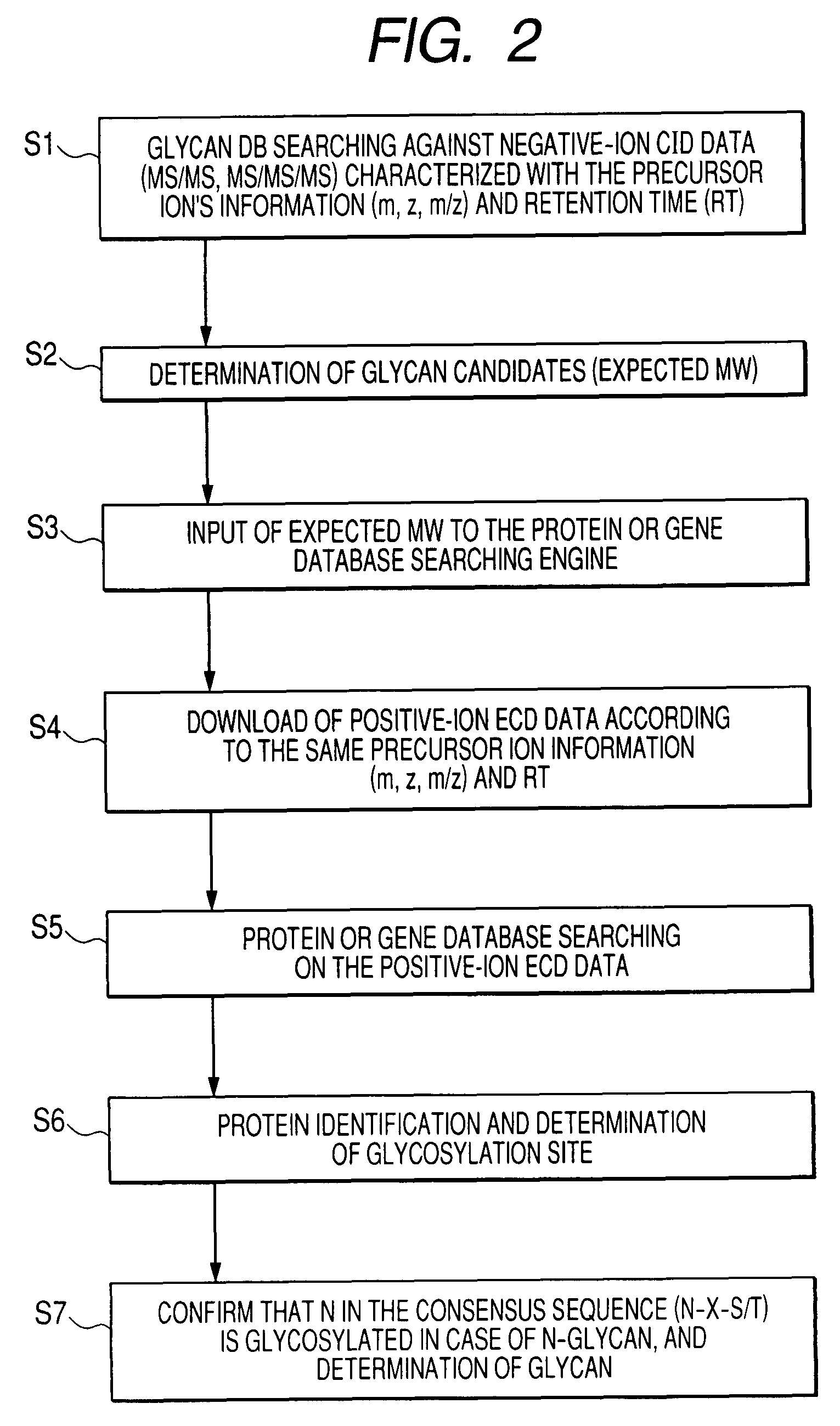
To analyze glycans and peptide sequences without liberating glycans from glycosylated peptides, a glycan structure is analyzed through negative-ion CID, in which sialic acid and fucose are resistant to elimination, and a peptide sequence is analyzed through positive-ion ECD.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Modified DNA molecule, recombinant containing the same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6936707B2Good effectImproving immunogenicityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenModified dna
There is provided a DNA molecule derived from a prokaryotic cell in which at least one of the DNA regions encoding NXB (N is asparagine, X is any amino acid other than proline, and B is serine or threonine) has been modified so that no N-glycosylation occurs during the expression in a eukaryotic cell, and since the DNA molecule has been modified at the N-glycosylation site, it produces a non-N-glycosylated protein, which thereby exhibits a high immunogenicity when, for example, it is allowed to produce, in a eukaryotic cell, an antigen protein derived from a prokaryotic cell.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Method for detecting cell glycosylation level
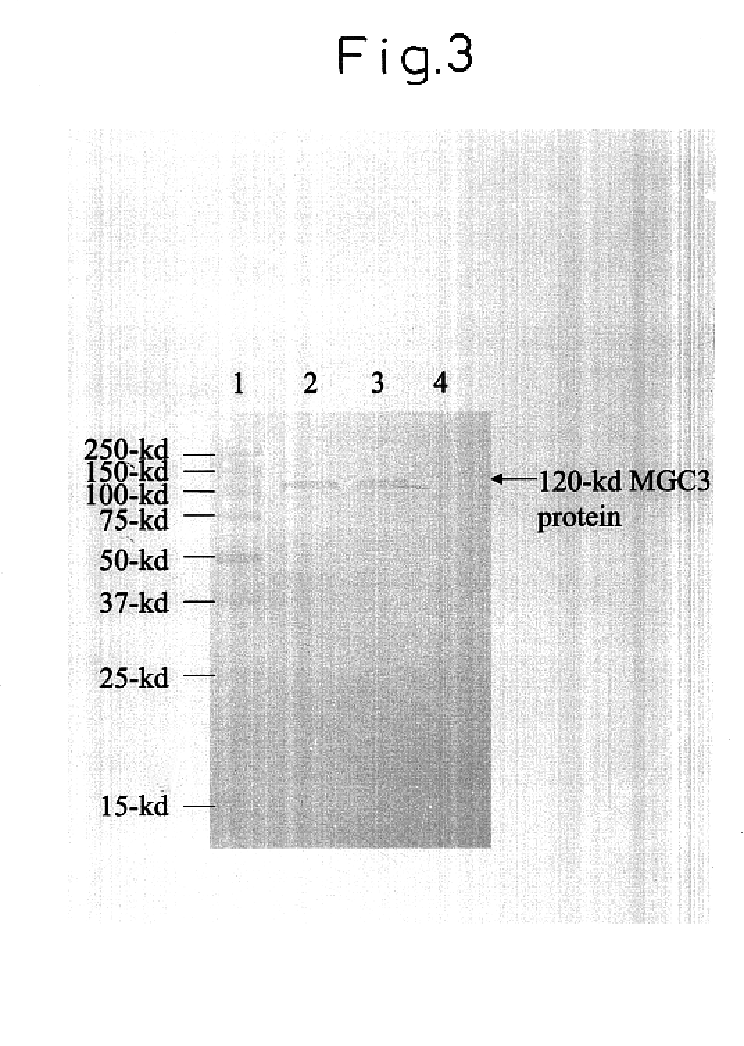
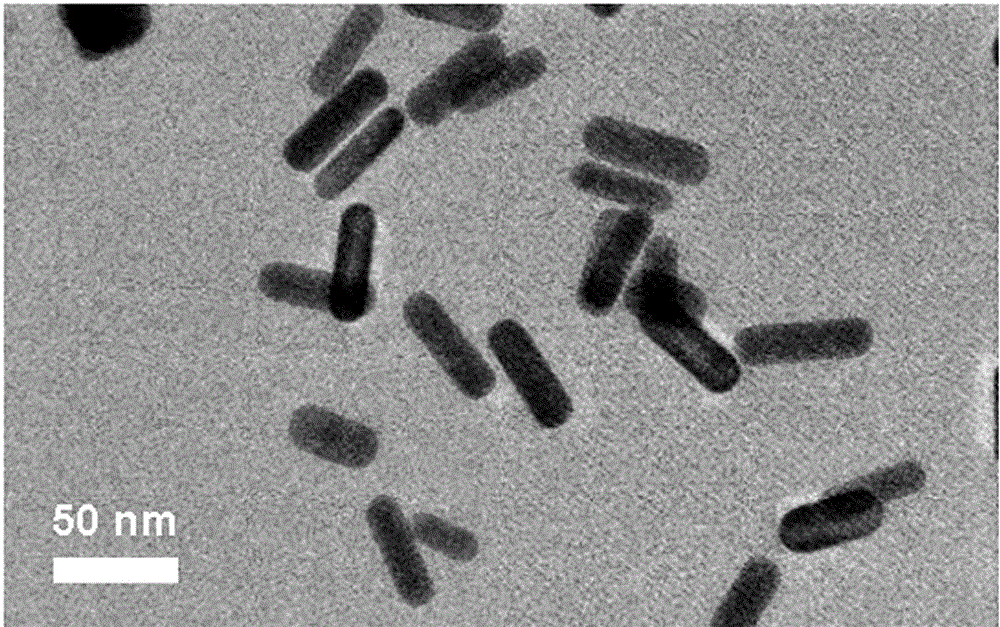
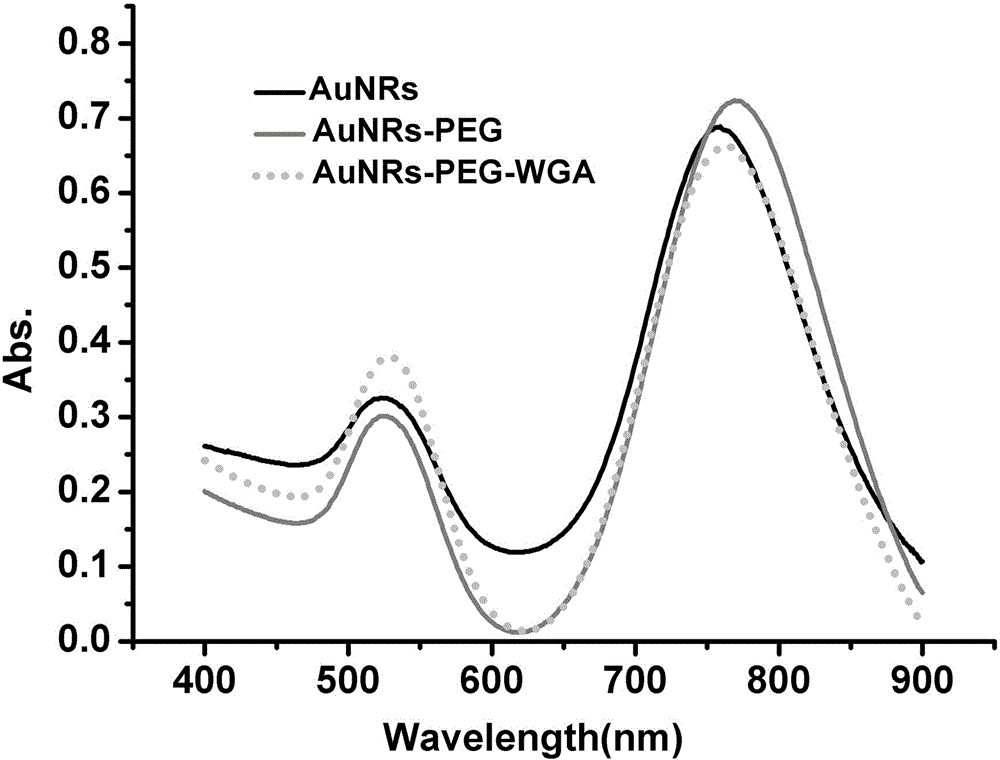
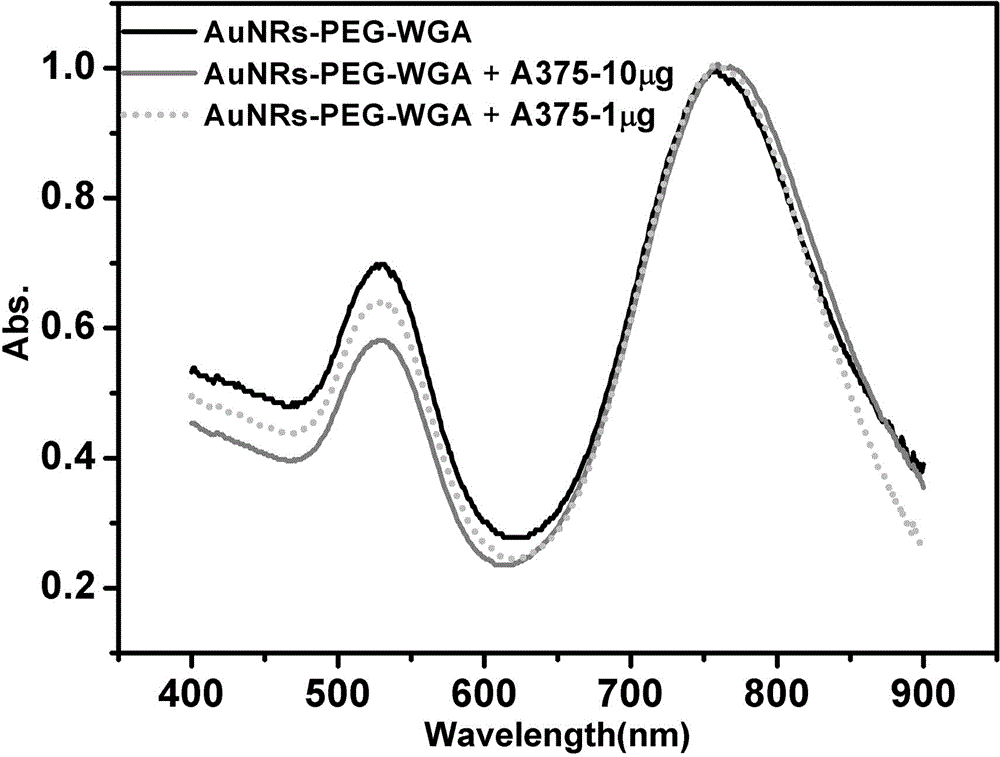
The invention provides a method for detecting cell glycosylation level by utilizing gold nano rods. The method comprises the following steps: dripping chloroauric acid into a CTAB solution, and then adding a sodium borohydride solution to prepare a seed solution; adding silver nitrate, chloroauric acid and vitamin C into the CTAB solution to prepare a growth solution; dripping the seed solution into the growth solution, and centrifuging after reaction to obtain gold nano rods; adding COOH-PEG-SH and sulfydryl malic acid into the gold nano rods for reaction to realize bio-functionalization activation of the gold nano rods so as to prepare an activated gold nano rod solution; connecting WGA agglutinin to the activated gold nano rods to obtain the activated gold nano rods provided with the WDA agglutinin and used for detecting the glycosylation level; and detecting corresponding glycosylated proteins in a cell lysis buffer by observing changes of an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Capsular gram-positive bacteria bioconjugate vaccines
The present invention encompasses a novel S. aureus bioconjugate vaccine. More generally, the invention is directed to Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines containing a protein carrier, at least one polysaccharide such as a capsular Gram-positive polysaccharide, and, optionally, an adjuvant or pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The instant invention also includes methods of producing Gram-positive and other bioconjugate vaccines. An N-glycosylated protein is also provided that contains one or more polysaccharides such as Gram-positive polysaccharides. The invention is additionally directed to engineered prokaryotic organisms comprising nucleotide sequences encoding a glycosyltransferase of a first prokaryotic organism and a glycosyltransferase of a second prokaryotic organism. The invention further includes plasmids and prokaryotic cells transformed with plasmids encoding polysaccharides and enzymes which produce an N-glycosylated protein and / or bioconjugate vaccine. Further, the invention is directed to methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal comprising administering said bioconjugate vaccines.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
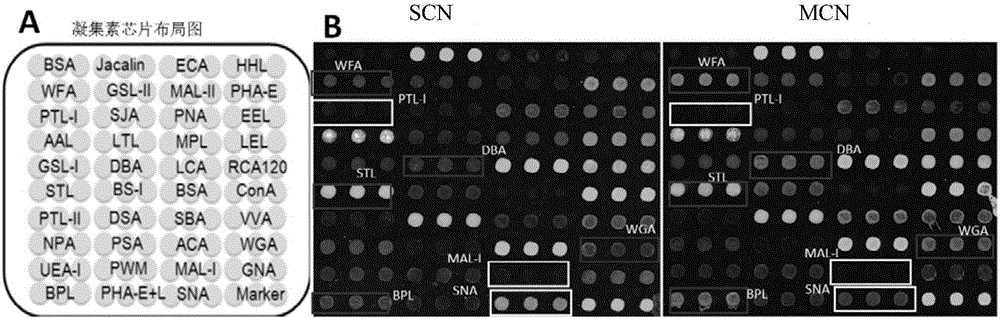
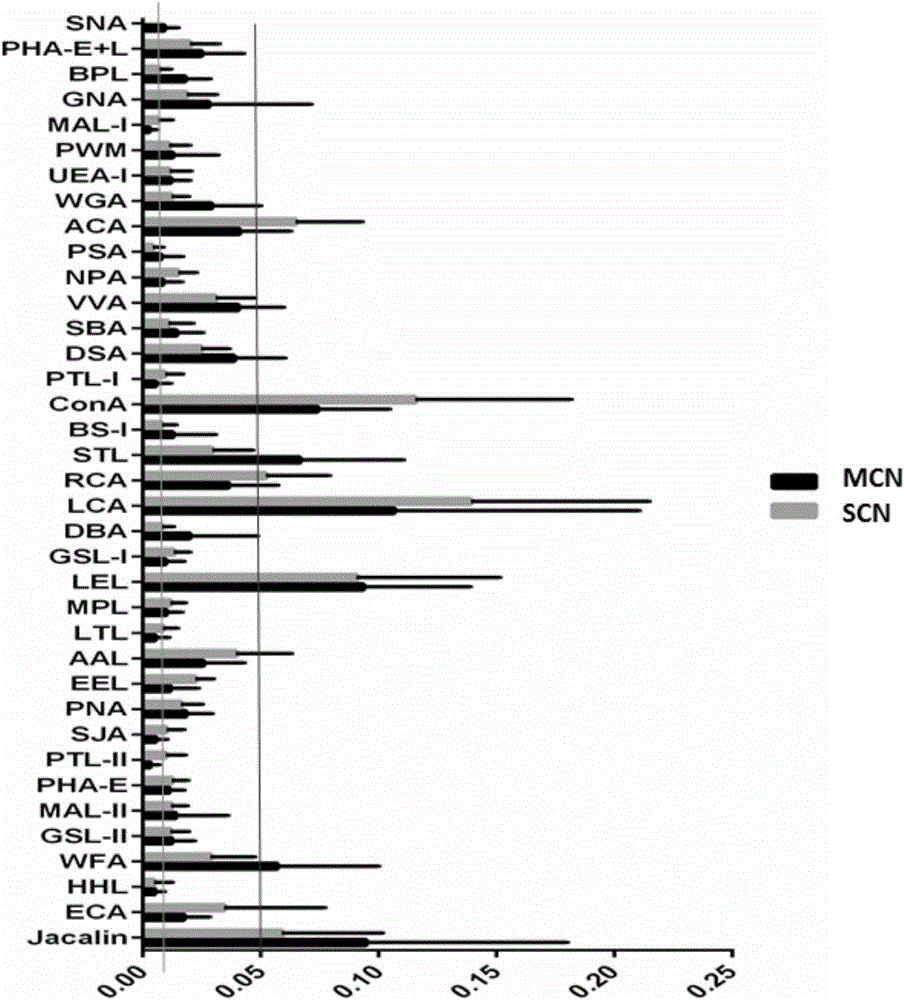
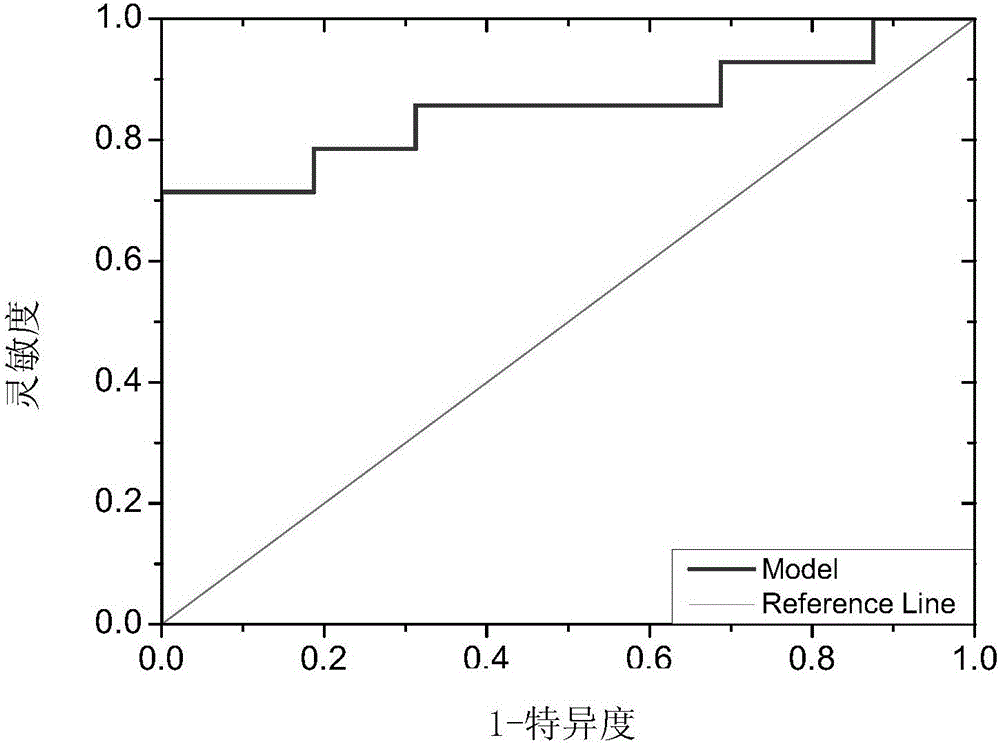
Application of lectin group recognized carbohydrate chain in distinguishing mucinous cystic neoplasm from serous cystic neoplasm
The invention discloses application of lectin group recognized carbohydrate chains in distinguishing mucinous cystic neoplasm from serous cystic neoplasm. The lectin group recognized carbohydrate chains disclosed by the invention are glycosylated protein carbohydrate chains recognized by lectin groups consisting of WGA (trticum vulgaris agglutinin), BPL (bauhinia purpurea lectin), STL (solanum tuberosum (potato) lectin), DBA (dolchos biflorus agglutinin), PTL-I (psophocarpus tetragonolobus lectin I) and MAL-I (maackia amurensis lectin I). The carbohydrate chains are different in capsula pancreatic fluid of patients suffering from mucinous cystic neoplasm and serous cystic neoplasm, the contents of the carbohydrate chains recognized by STL, WGA, BPL and DBA in the capsula pancreatic fluid of patients suffering from MCN (mucinous cystic neoplasm) are remarkably higher than those in the capsula pancreatic fluid of patients suffering from SCN (serous cystic neoplasm), the contents of the carbohydrate chains recognized by PTL-I and MAL-I in the capsula pancreatic fluid of the patients suffering from MCN are remarkably lower than those in the capsula pancreatic fluid of the patients suffering from SCN, the sensitivity of the combination of WGA and BPL in distinguishing the patients suffering from SCN from the patients suffering from MCN is 0.714, and the specificity is 1. The results show that the lectin group can be used for distinguishing the patients from SCN from the patients suffering from MCN.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Enrichment and tagging of glycosylated proteins
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Production of Non-N glycosylated protein from yeast
InactiveCN1746302AEasy constructionSimple methodFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHuman bodyGlycophorin
Production of non-glycosylated protein from yeast is carried out by constructing expression carrier containing N-glycoamidase and purposive protein gene from molecular biological technology, transferred into yeasts from electric transformation, expressing N- glycoamidase on yeast cell surface, excretory expressing purposive protein into culture medium, removing chain of glucoprotein excretory expressed from N- glycoamidase surface expressed and obtaining non-glycosylated protein. It has better expression protein activity and correct tertiary structure and no immunogenicity to human body.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Phosphorylated and/or glycosylated protein or peptide one-step enrichment modification determination method
InactiveCN101846649AIncreased Sensitivity of Mass Spectrometry InspectionsHigh Mass Spectrometry SensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPeptide preparation methodsPhosphorylationSignal gain
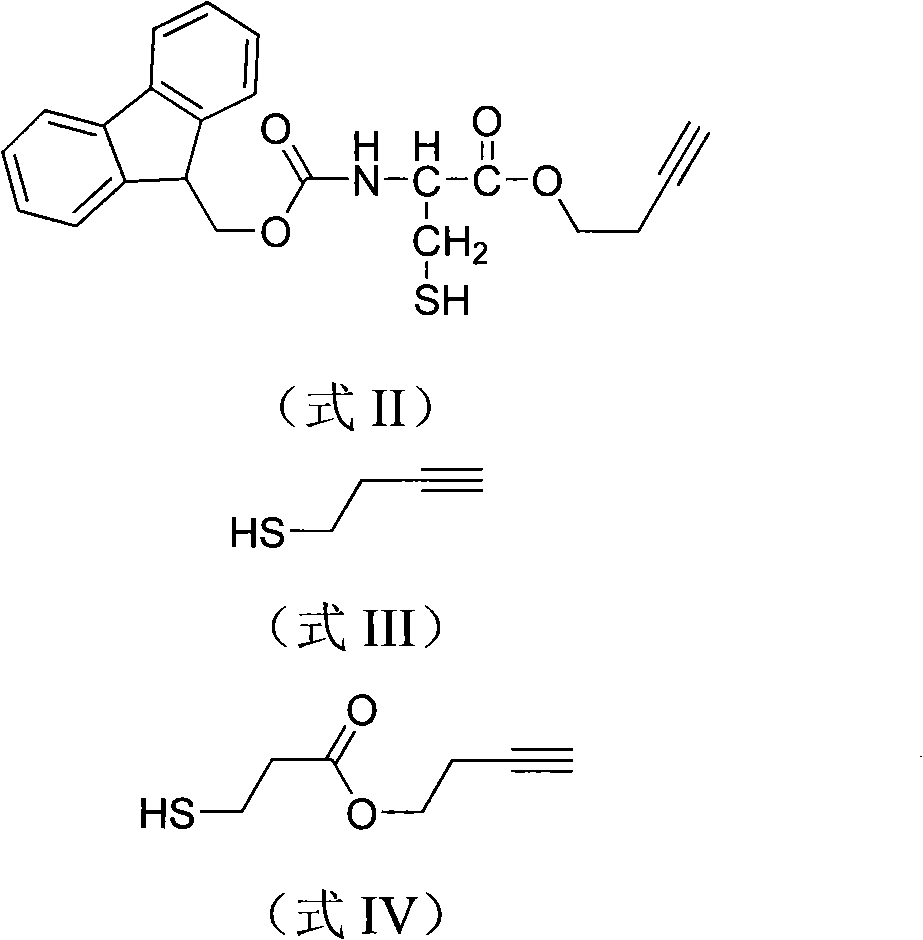
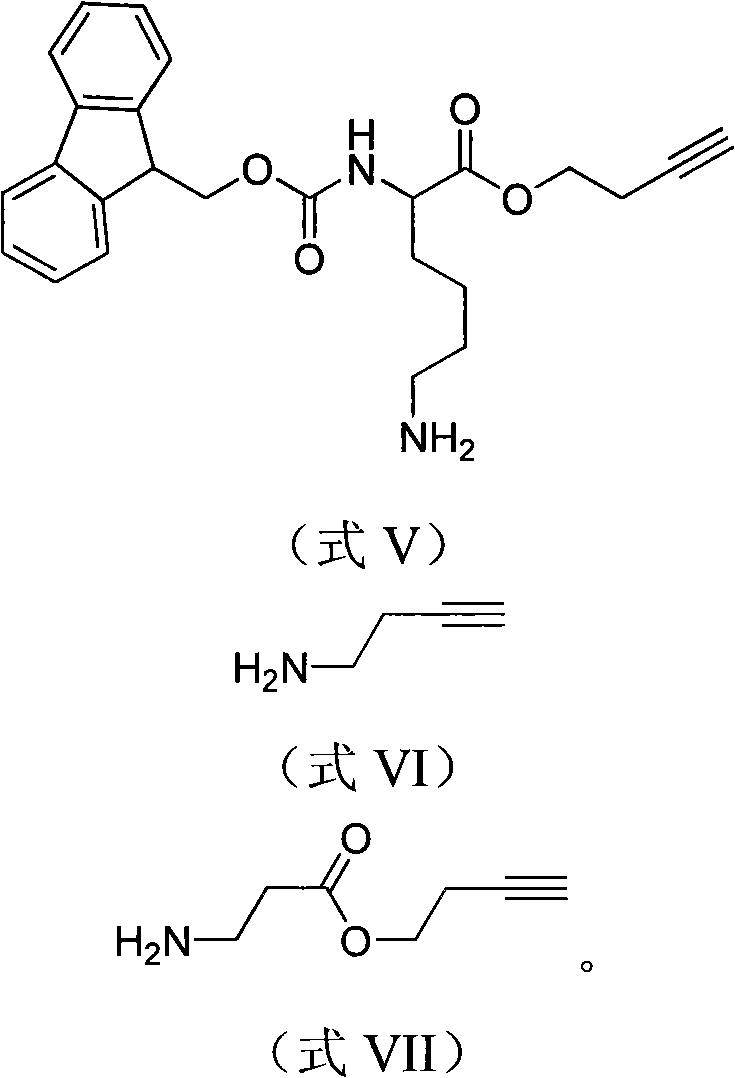
The invention discloses a phosphorylated and / or glycosylated protein or peptide one-step enrichment modification determination method. The method includes the following steps: 1) modification on end alkynyl or triazon of protein or peptide; 2) resin capturing of protein or peptide with modified end alkynyl; 3) cutting of the peptide / protein with modified alkynyl on resin. The protein or peptide enrichment modification determination method provided by the invention not only can enrich and purify the modified protein or peptide after translation but also can add one molecule segment on the protein or peptide, and the molecule segment has the functions of mass spectrum label and mass spectrum signal gain. The method has wide application prospect in the science analysis field.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods and instruments for identification of glycosylated proteins and peptides
To analyze glycans and peptide sequences without liberating glycans from glycosylated peptides, a glycan structure is analyzed through negative-ion CID, in which sialic acid and fucose are resistant to elimination, and a peptide sequence is analyzed through positive-ion ECD.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Microbially expressed xylanases and their use as feed additives and other uses
The present invention relates to codon-optimized xylanase coding sequences and the expression of xylanases in microbes and yeast. The invention further relates to using multiple copies of the xylanase expression construct for high levels of protein expression. The invention also relates to the use of xylanases as feed or food additives. The invention also relates to methods of expression of enzymes to increase thermotolerance by expressing them in organisms that glycosylate proteins compared to expression that the same enzyme without the glycosylation. Further, the invention relates to methods of preparing feed, enzyme feed additives, and methods of reducing the feed conversion ration or increasing weight gain of animals.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com